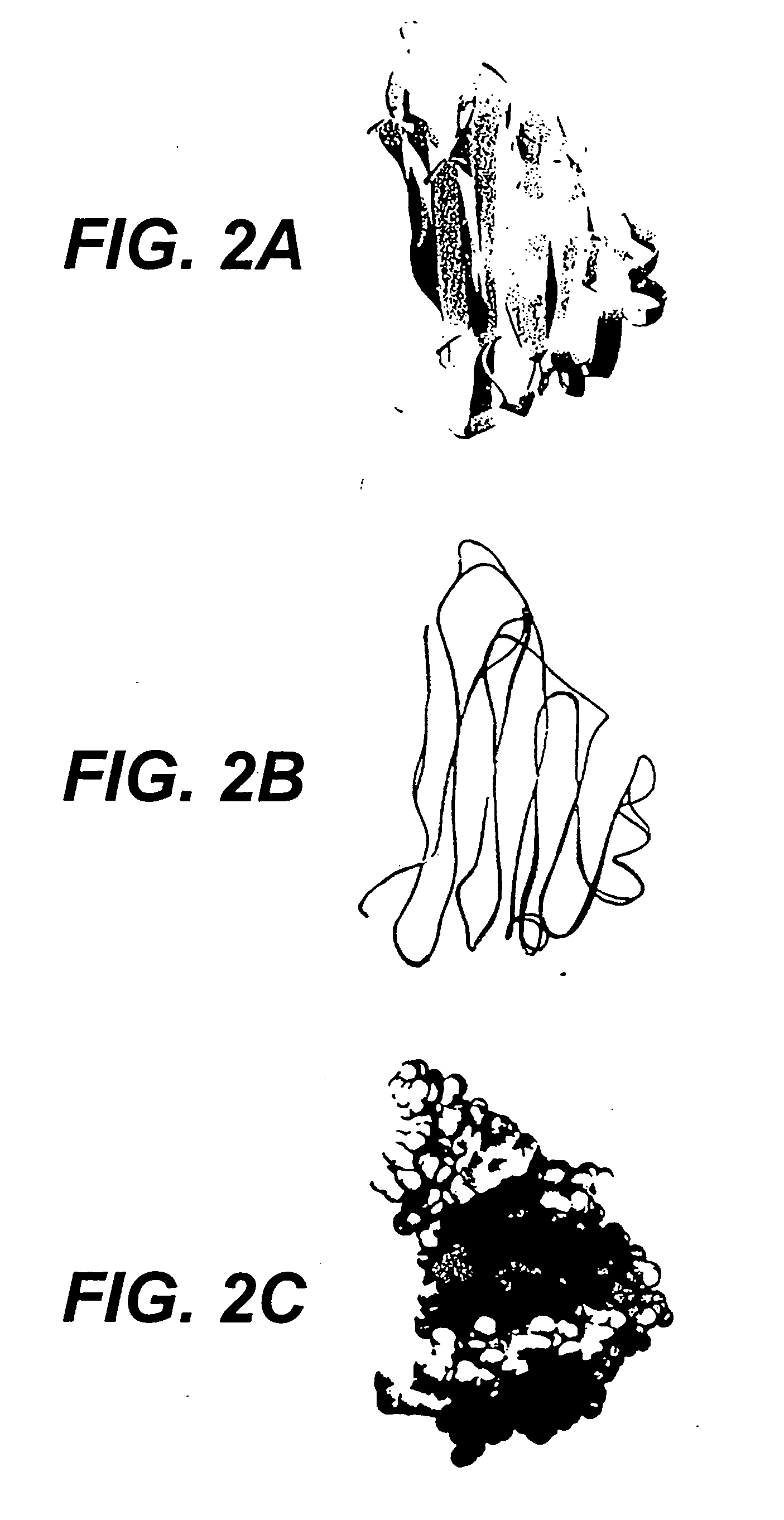
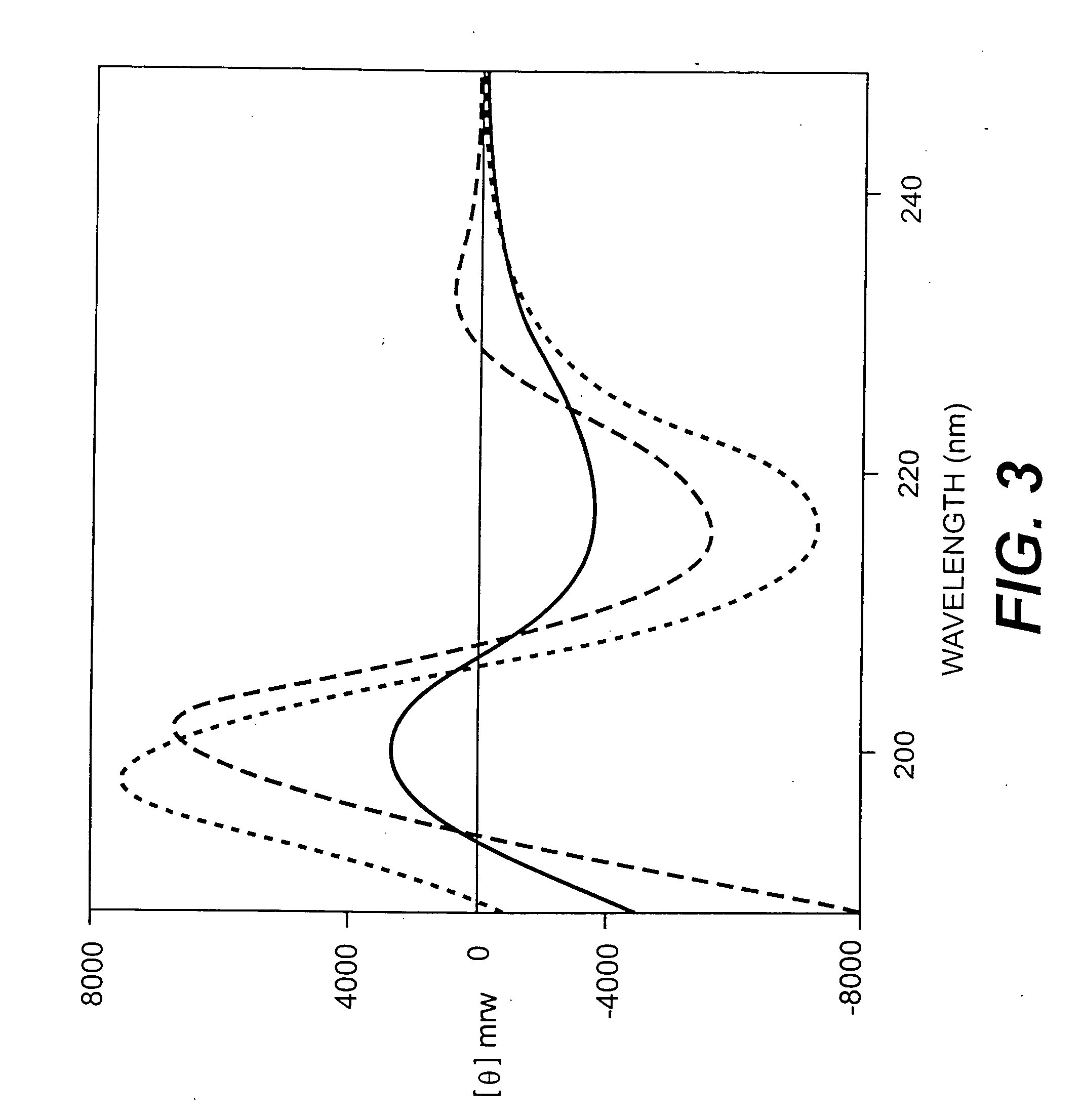
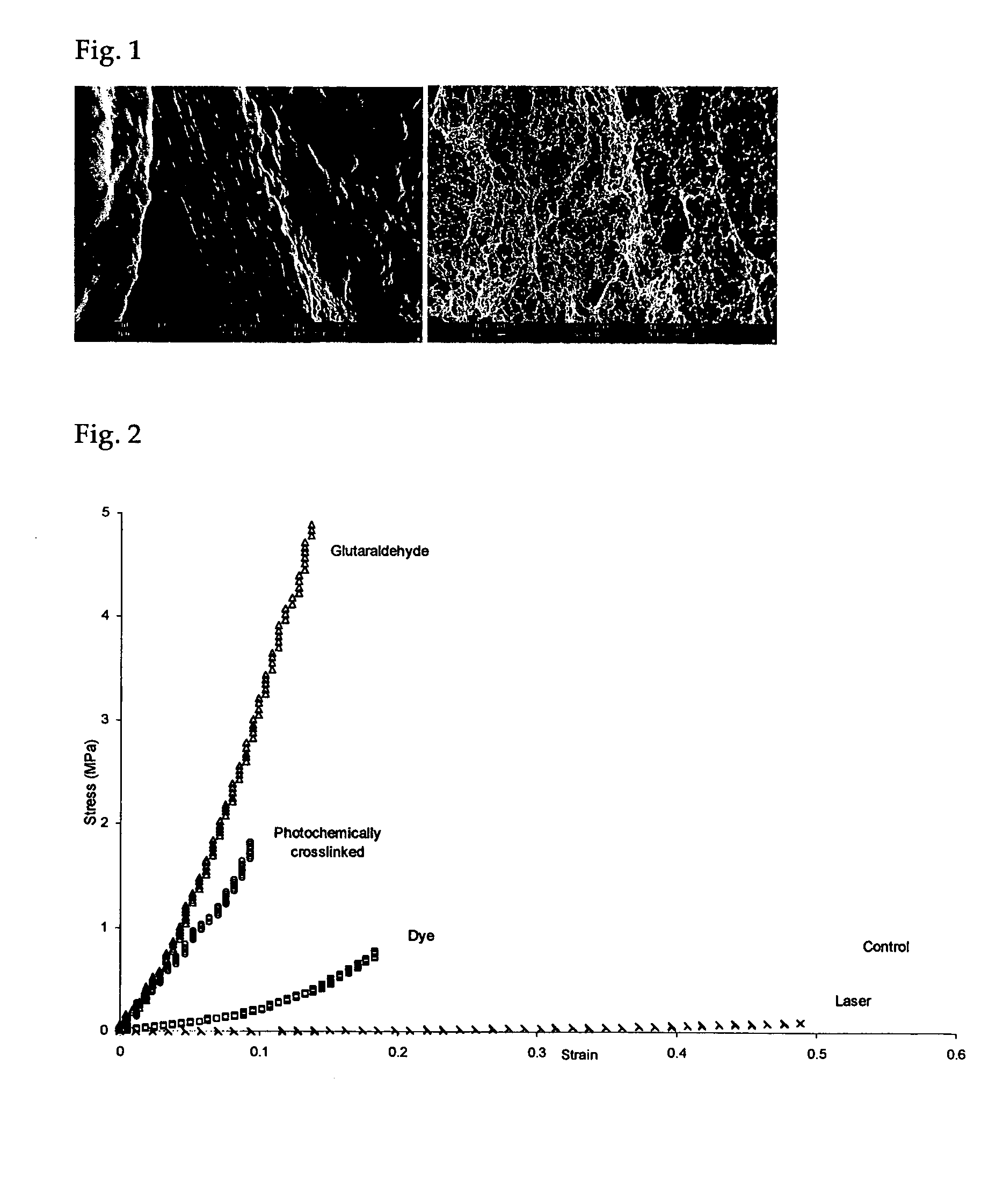
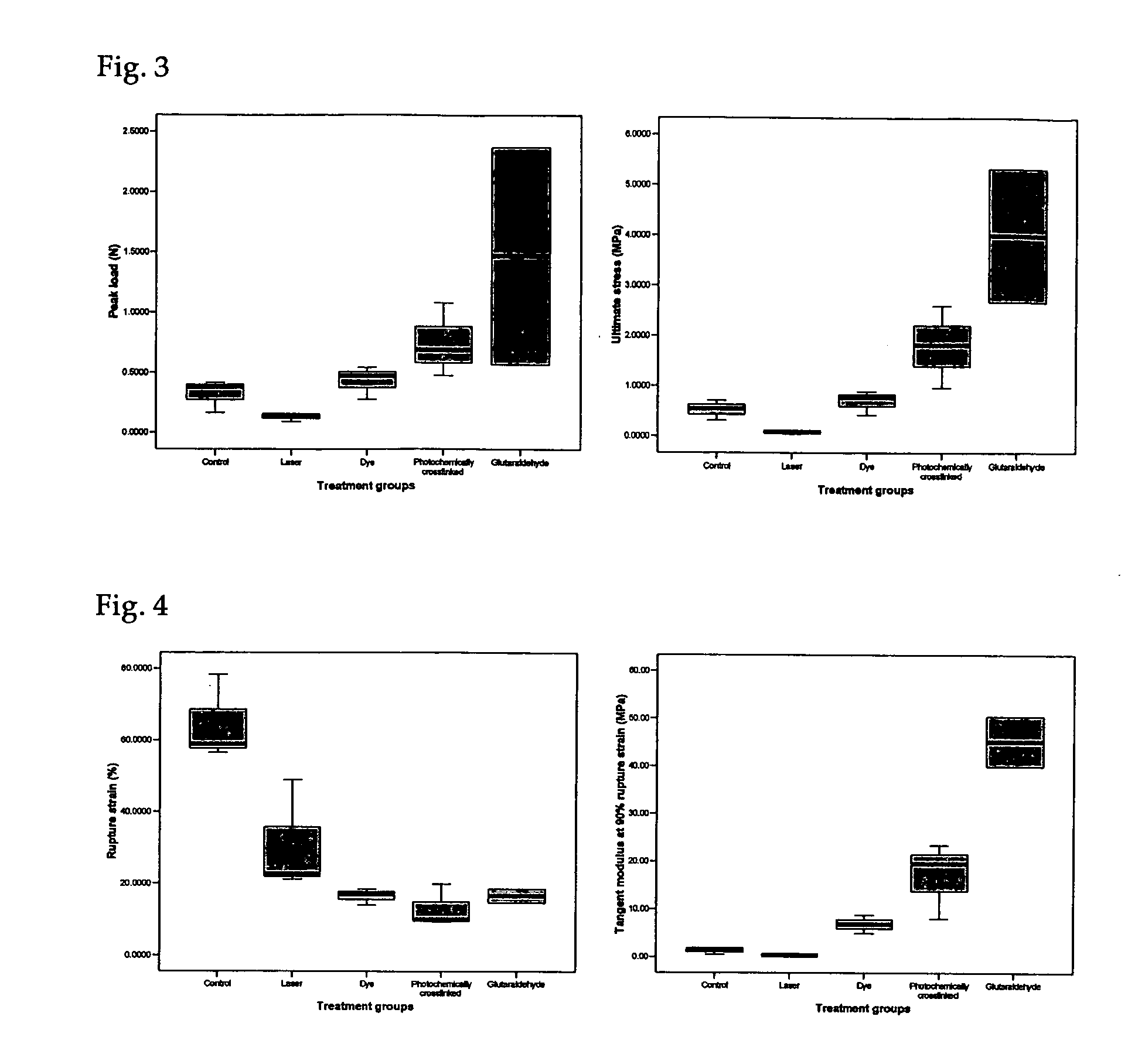
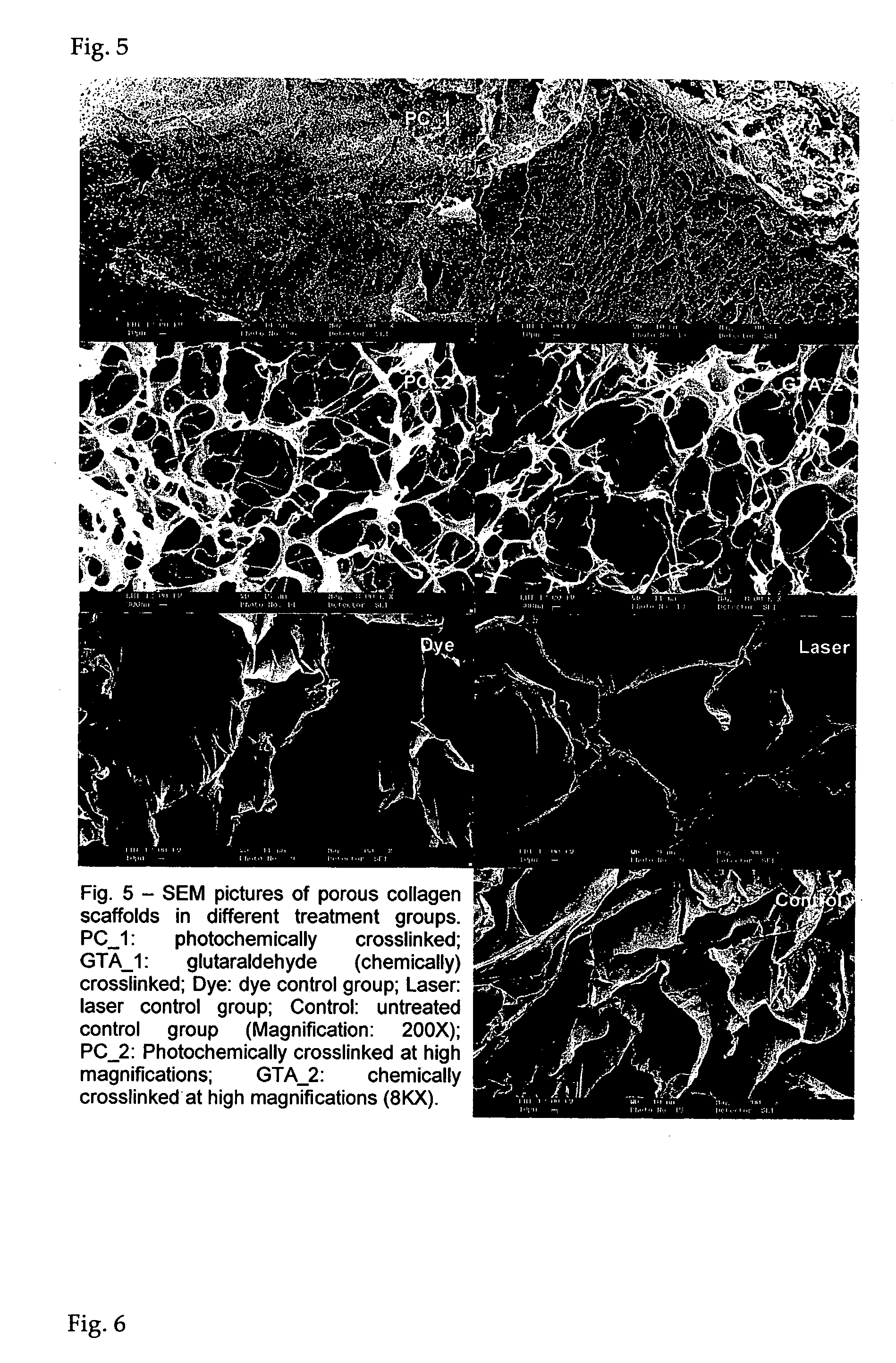
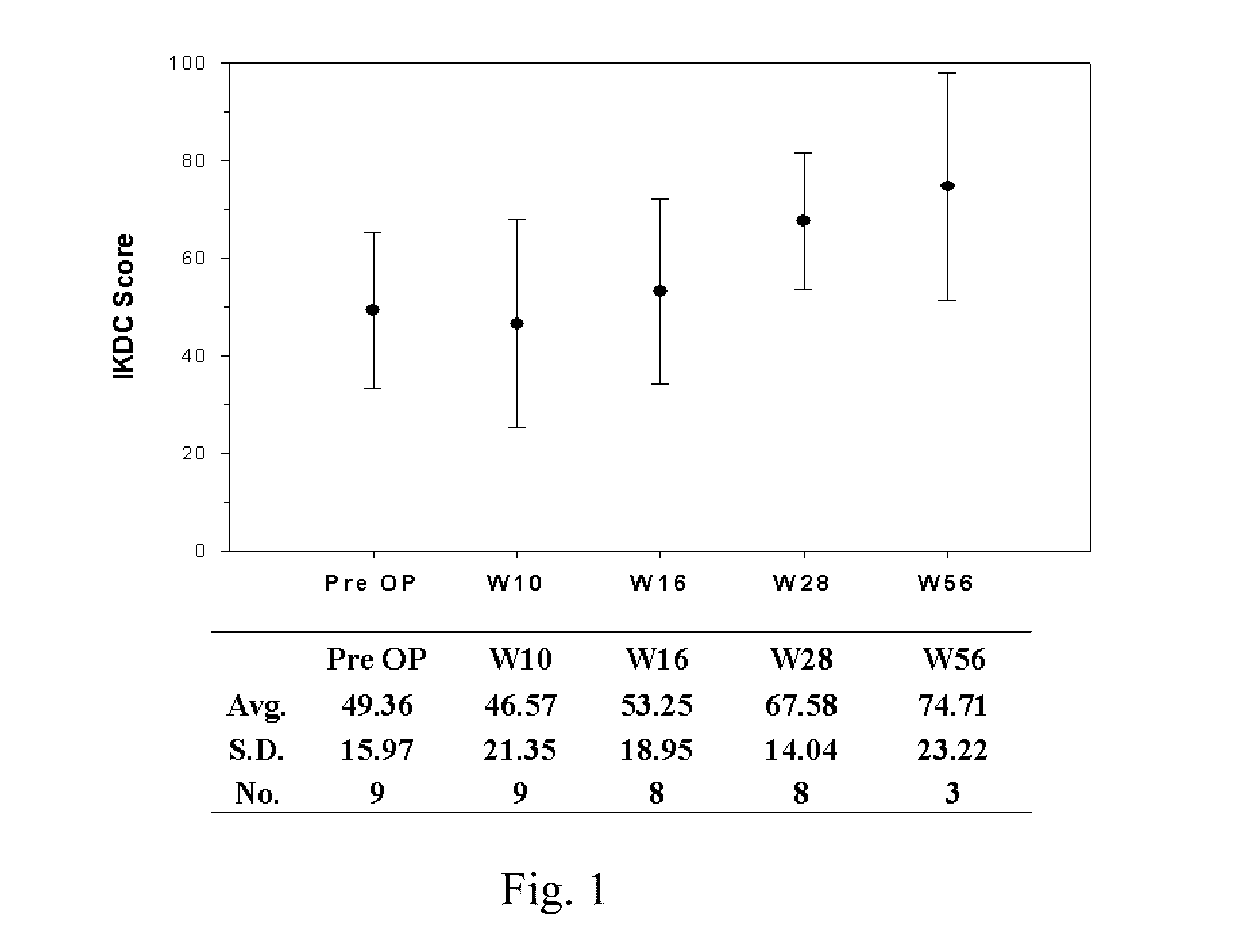
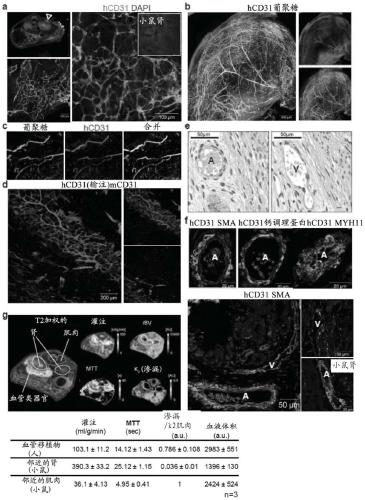
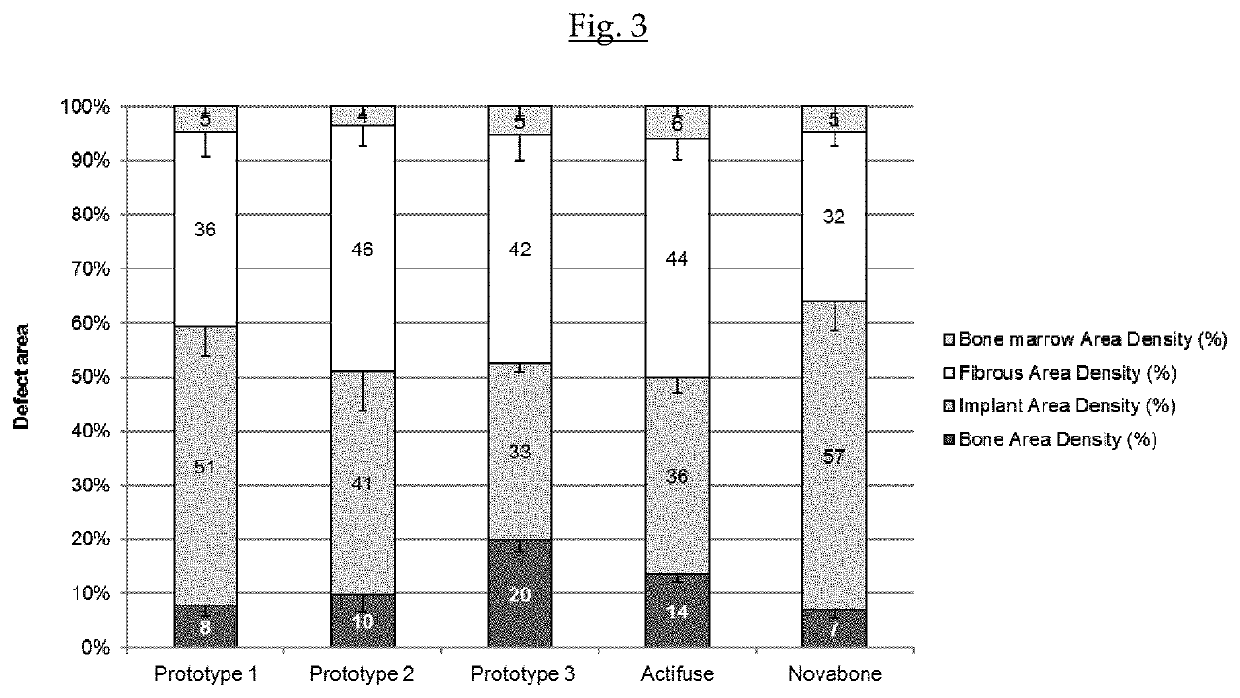
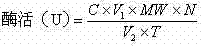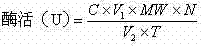Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Collagen substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Some cells adhere directly to collagen substrates, while others utilize glycoproteins (i.e., serum fibronectin or that produced by the cells) to bind to collagen.2 In both situations, cultured cells are exposed to an environment which includes the major proteins found in the in vivo interstitial matrix.
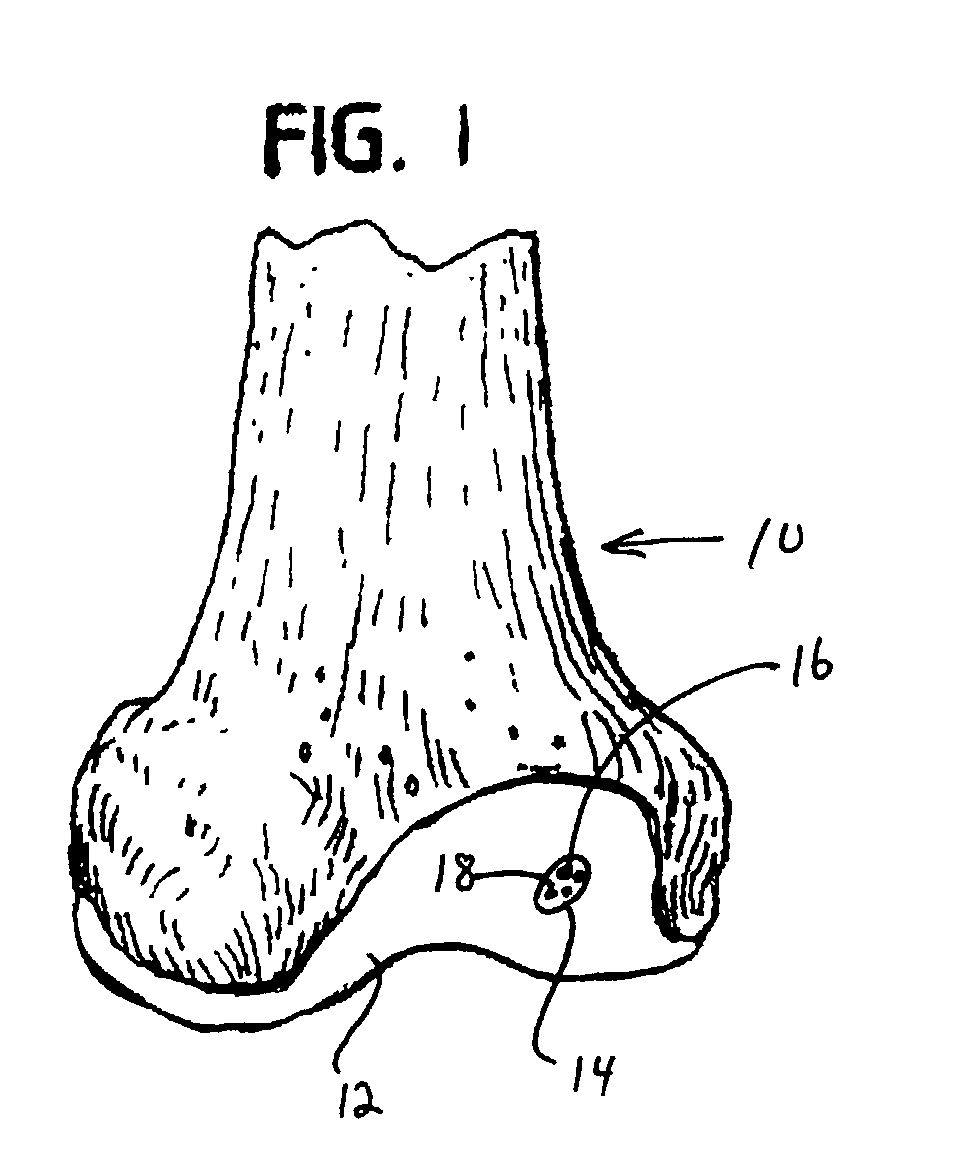
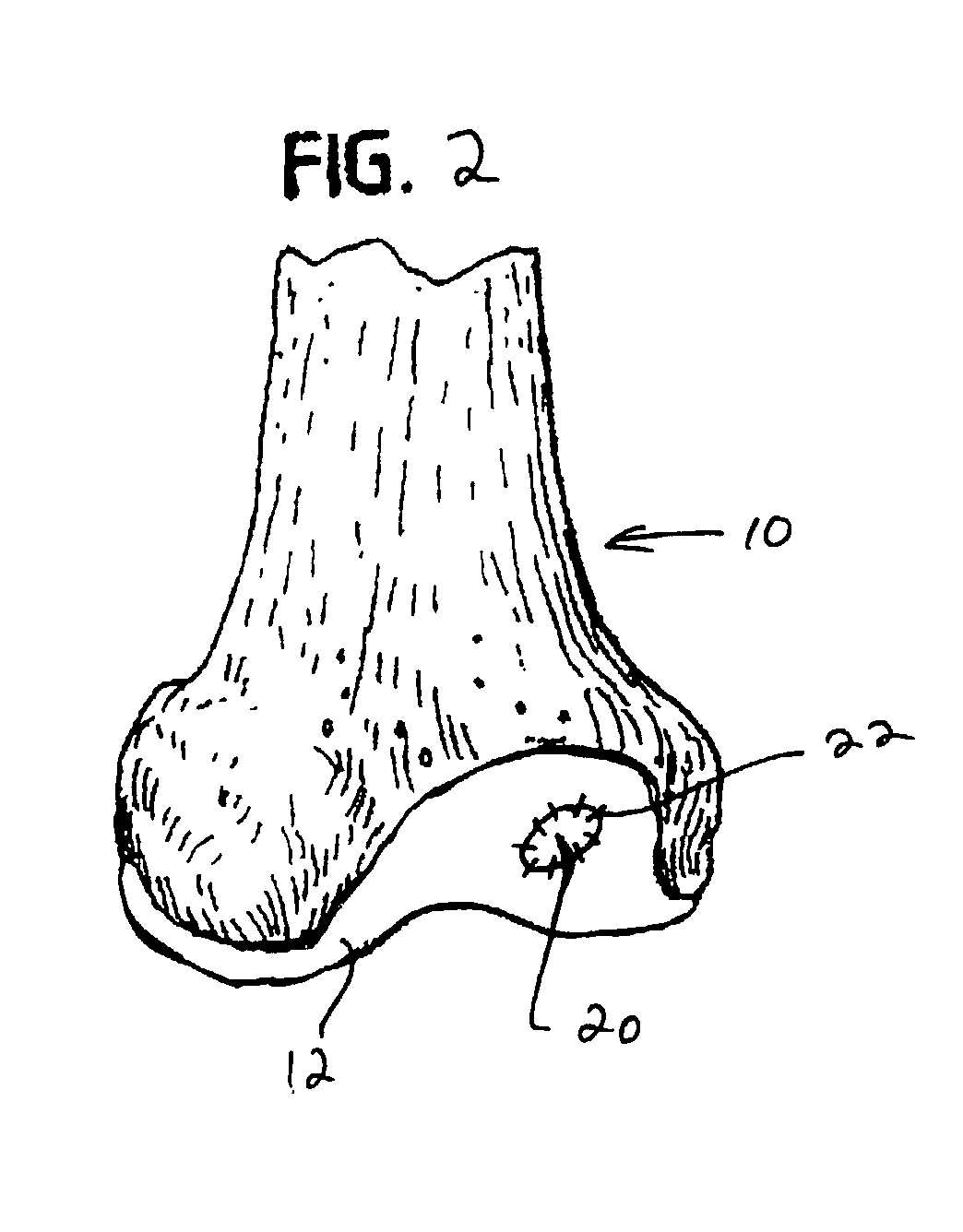
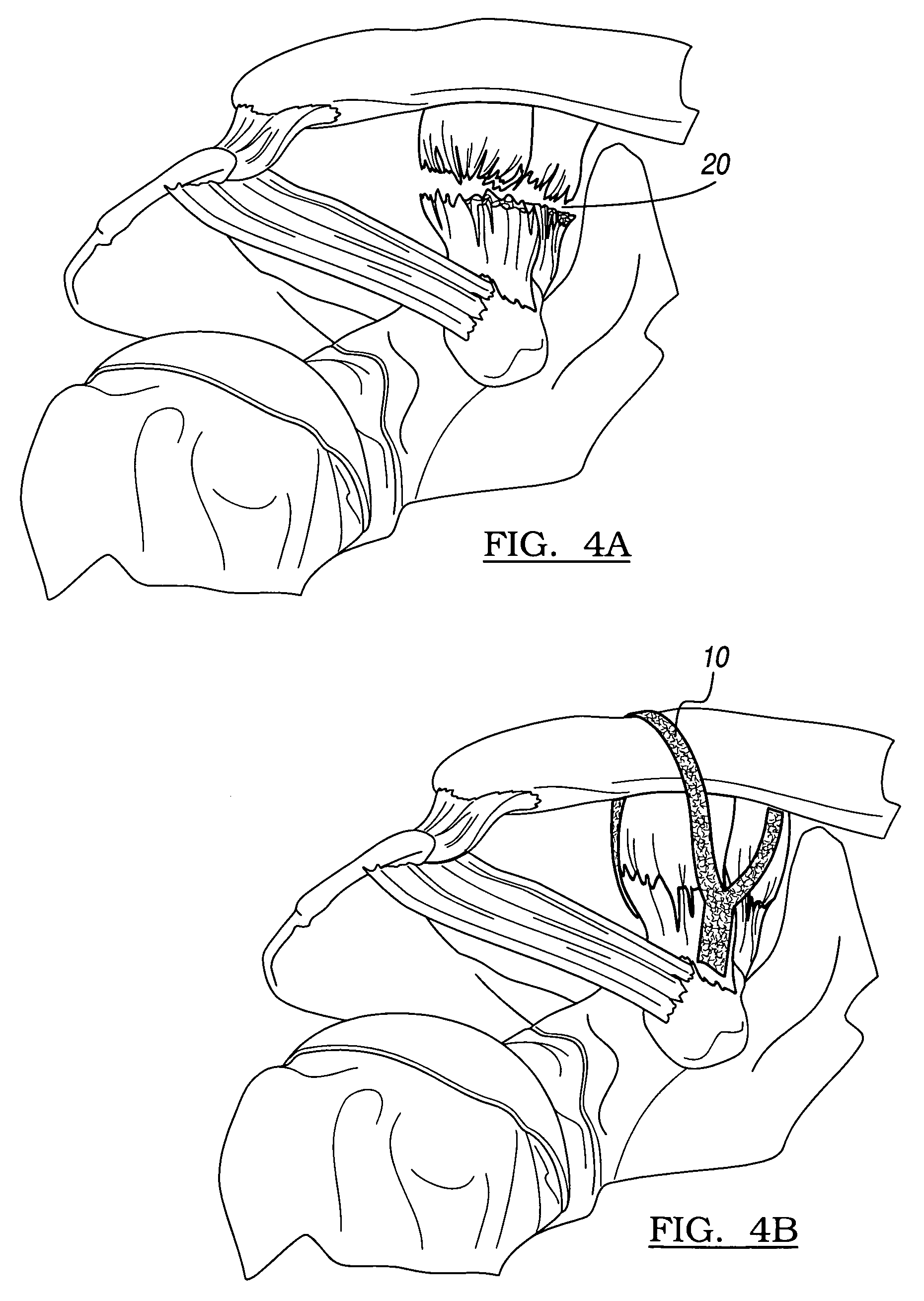
Collagen carrier of therapeutic genetic material, and method
InactiveUS20030039695A1Powder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsGenetic MaterialsNucleic acid sequencing
A collagen matrix material is charged with a cell growth-promoting derived nucleic acid sequence. The nucleic acid sequence-charged collagen matrix material may be utilized in a method of promoting regeneration of surface cartilage of a joint. In the method, an area of injury is covered with the nucleic acid sequence-charged collagen matrix material, the collagen matrix material is fixed over the area to be treated, and the area is allowed to heal.
Owner:ED GEISTLICH SOHNE FUR CHEM IND
Composite collagen material and method of forming same
A felt for repairing soft tissue defects comprising a membranous collagen substrate and a bioresorbable fiber felted onto the collagen substrate. Methods of preparing a felt and methods of repairing soft tissue damage with a felt are also provided.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Degradation-Stabilised, Biocompatible Collagen Matrices
ActiveUS20120165264A1Increased denaturingHigh outlayBiocideCosmetic preparationsBasic researchHaemostatic agent
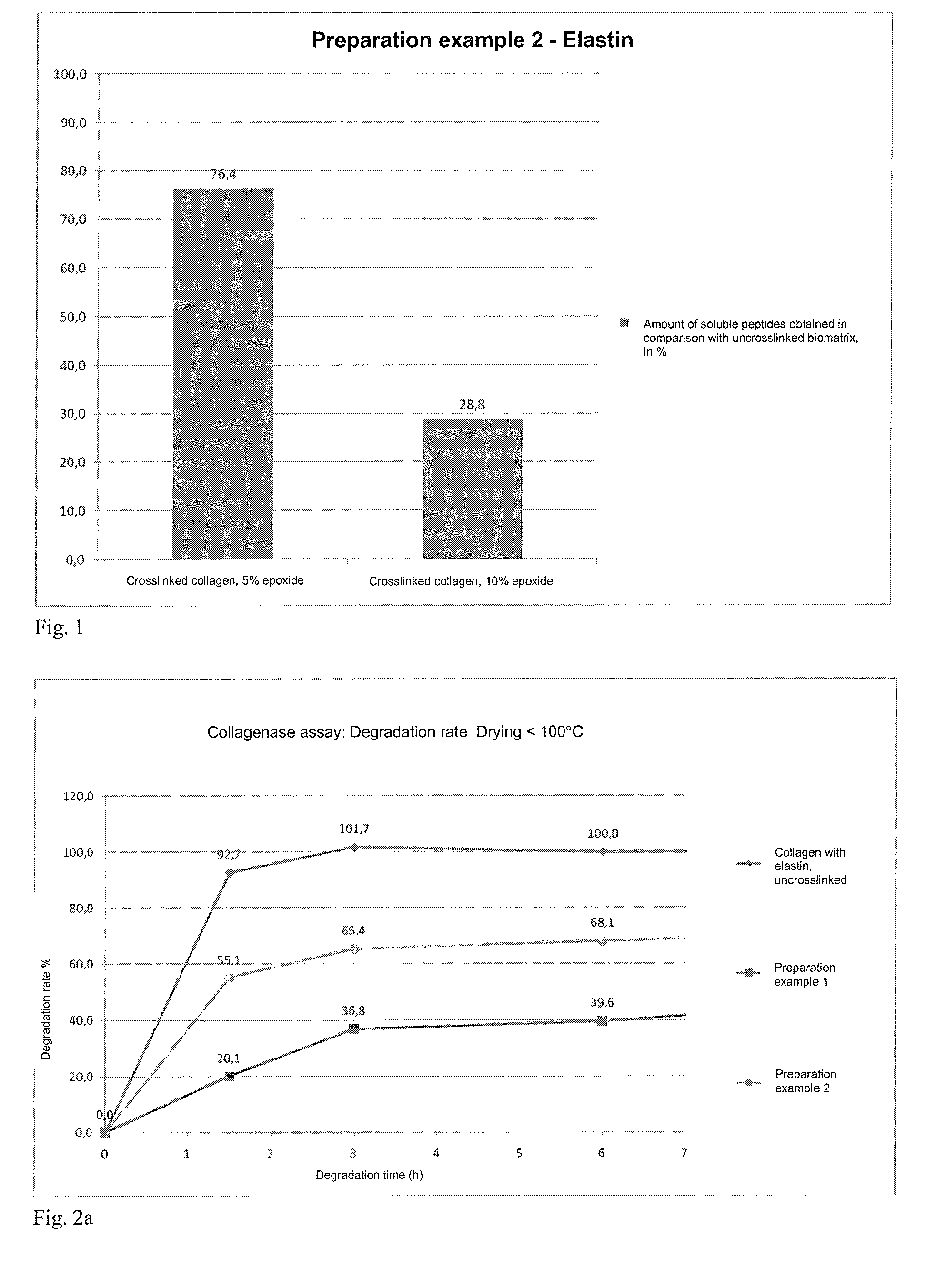
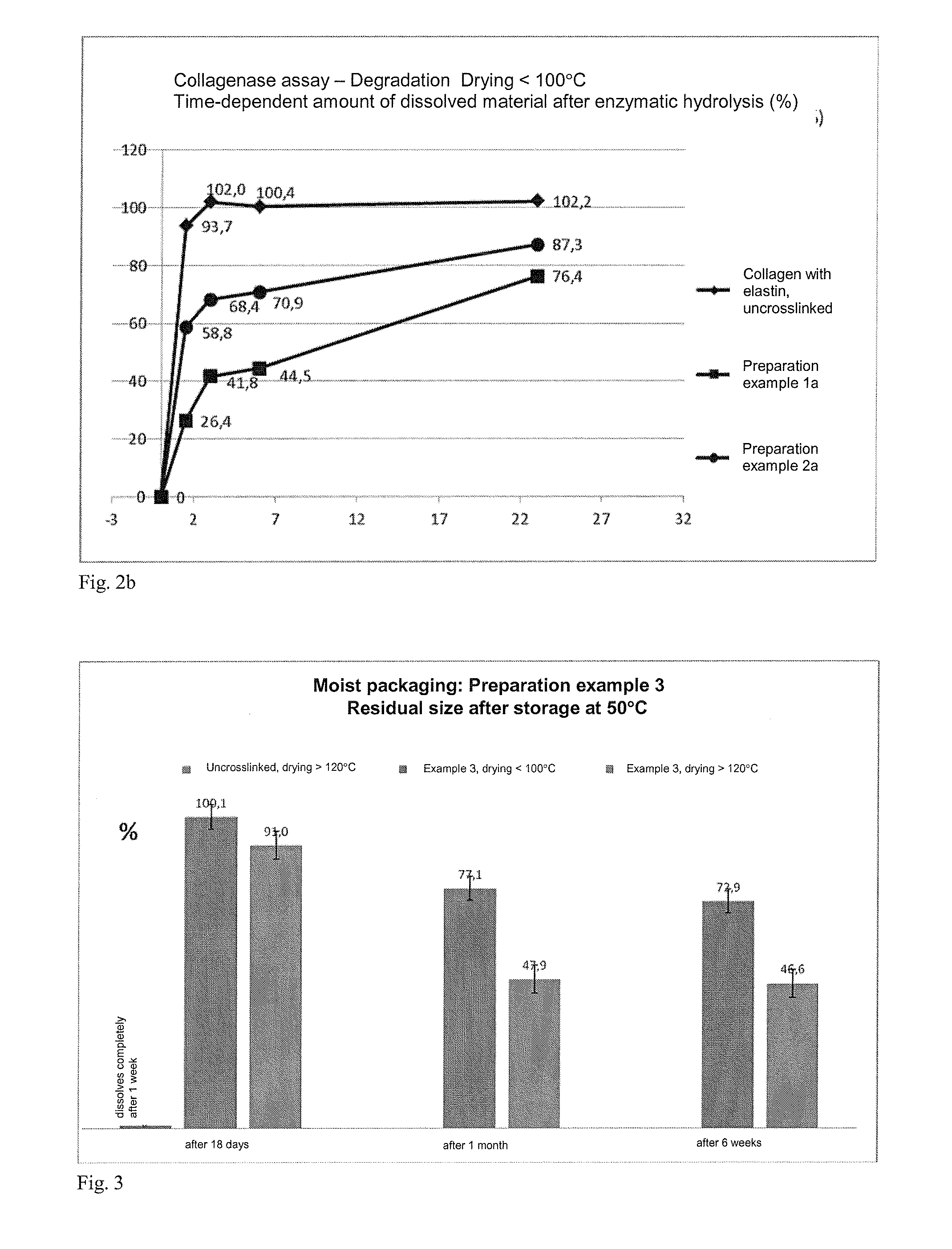
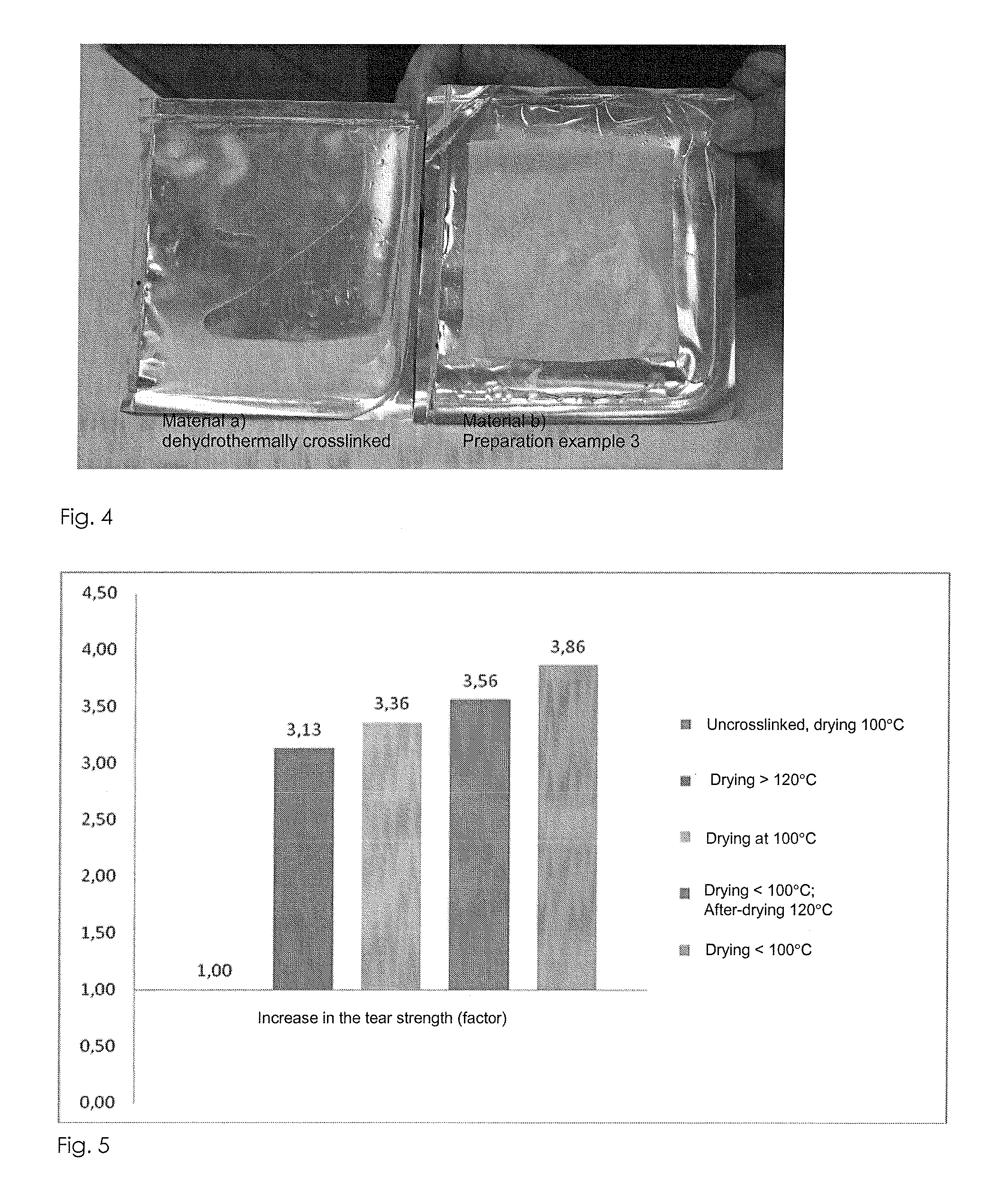
The present invention relates to degradation-stabilised, biocompatible collagen matrices which are distinguished in particular by the fact that they contain soluble collagen and peptide constituents, to processes for the preparation of such collagen matrices, which processes include in particular chemical crosslinking with an epoxy-functional crosslinking agent, and to the use of the collagen matrices according to the invention as a cosmetic or pharmaceutical agent, in particular for topical use, and as a wound treatment agent, as an implant or as a haemostatic agent in humans or animals, and as a scaffold for cell population in the biotechnology, basic research and tissue engineering field.
Owner:MEDSKIN SOLUTIONS DR SUWELACK AG
Collagen-binding proteins from Enterococcal bacteria
InactiveUS20050180986A1Inhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCell-Extracellular MatrixBinding site
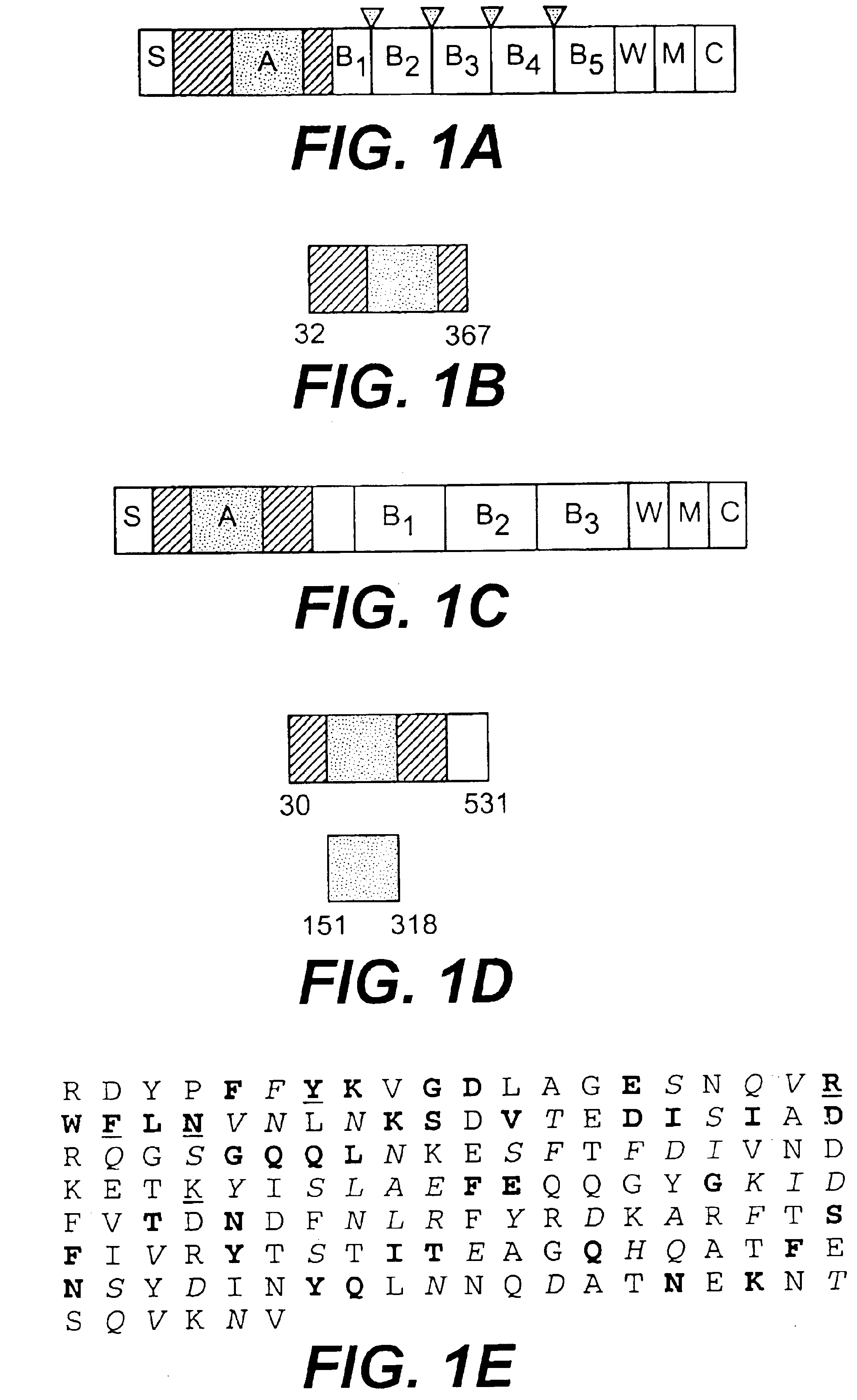
A collagen-binding MSCRAMM entitled Ace from enterococcal bacteria is provided which was homologous to the ligand-binding region of Cna, the collagen-binding MSCRAMM from Staphylococcus aureus, and which can be utilized to inhibit adhesion of enterococcal bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins. The N-terminal region of Ace contained a region (residues 174-319), or A domain, contains several 47-residue tandem repeat units between the collagen-binding site and cell wall-associated regions. The Ace protein can be utilized in methods of preventing and / or treating enterococcal infection, and in addition, antibodies raised against Ace, or its A domain, can be used to effectively inhibit the adhesion of enterococcal cells to a collagen substrate.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Photochemically crosslinked collagen scaffolds and methods for their preparation
ActiveUS20060099268A1High strengthImprove thermal stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCollagen scaffoldCollagenan
A method for producing collagen-based scaffolds with improved characteristics, which broadens the usage of collagen in tissue engineering and the products so produced are described. The method comprises reconstitution of three-dimensional collagen matrices from collagen monomer solution and crosslinking the matrix with a light source in the presence of a photosensitizing reagent. The crosslinked products can be in any shape and form and used in the dry or wet state, for applications including but not limited to tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Porated cartilage products
This invention provides porated cartilage products, methods of producing porated cartilage products, and methods of treating subjects by administering cartilage products. Optionally, the cartilage products are sized, porated, and digested to provide a flexible cartilage product. Optionally, the cartilage products comprise viable chondrocytes, bioactive factors such as chondrogenic factors, and a collagen type II matrix. Optionally, the cartilage products are non-immunogenic.
Owner:OSIRIS THERAPEUTICS
Surgical grafts for repairing chondral defects
An implant containing a collagen matrix embedded with chondrocyte-like cells, its use in repairing a chondral defect, and a method of preparing the implant.
Owner:KARTIGEN BIOMEDICINE INC
Collagen-binding proteins from enterococcal bacteria
InactiveUS6908994B1Avoid stickingInhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesCell-Extracellular MatrixBinding site
A collagen-binding MSCRAMM entitled Ace from enterococcal bacteria is provided which was homologous to the ligand-binding region of Cna, the collagen-binding MSCRAMM from Staphylococcus aureus, and which can be utilized in a similar manner as other collagen-binding MSCRAMMs to inhibit adhesion of enterococcal bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins. The N-terminal region of Ace contained a region (residues 174-319), or A domain, which appears to be equivalent to the minimal ligand-binding region of the collagen-binding protein Cna (Cna 151-318), and contains several 47-residue tandem repeat units, called B domain repeat units, between the collagen-binding site and cell wall-associated regions. The Ace protein of the invention can thus be utilized in methods of preventing and / or treating enterococcal infection, and in addition, antibodies raised against Ace, or its A domain, can be used to effectively inhibit the adhesion of enterococcal cells to a collagen substrate. The Ace protein of the present invention is thus a functional collagen-binding MSCRAMM and can be utilized to treat or prevent invention in the same manner as other isolated MSCRAMMs have been utilized, namely in methods of treating or preventing infections and diseases caused by enterococcal bacteria.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
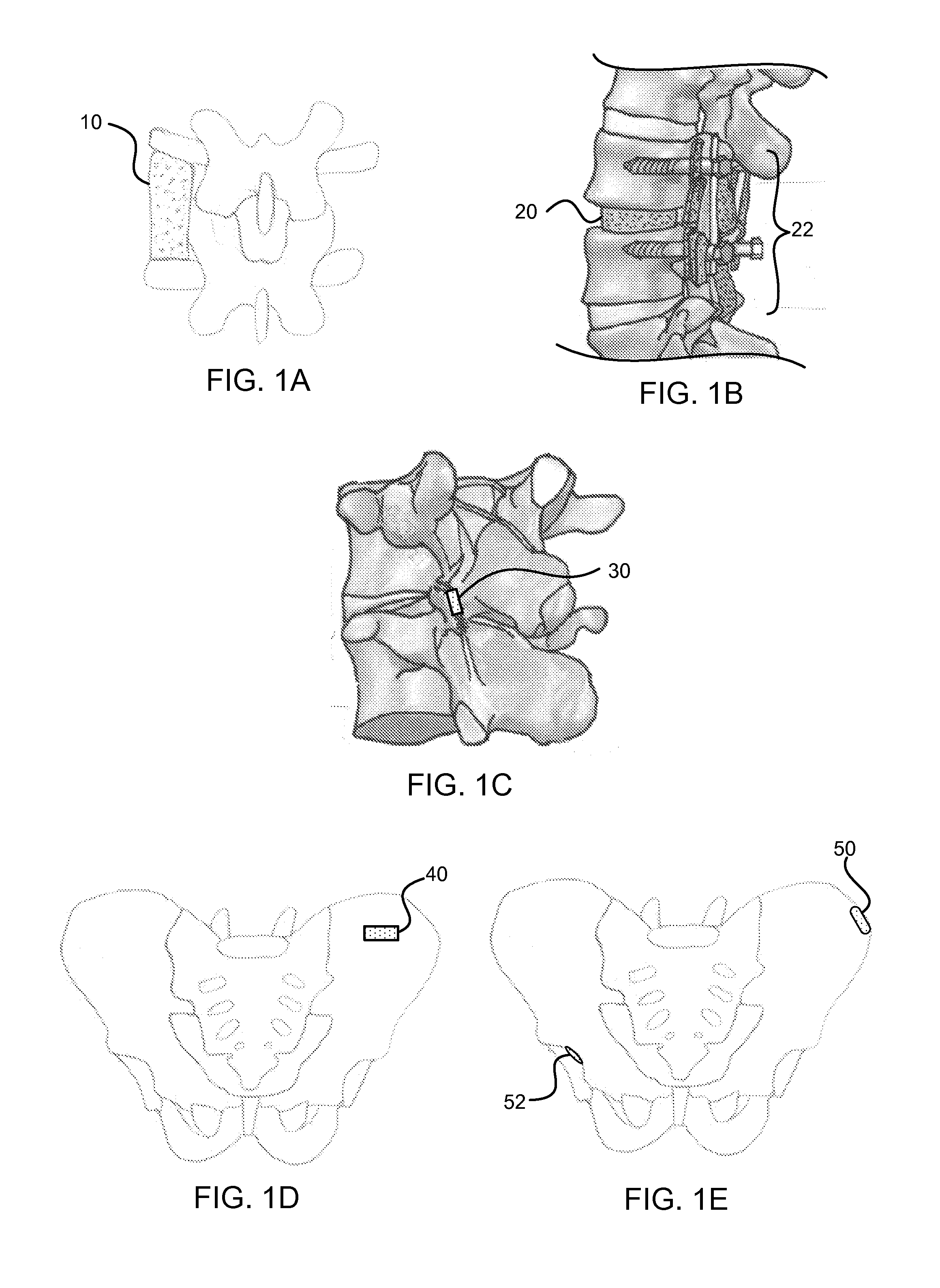
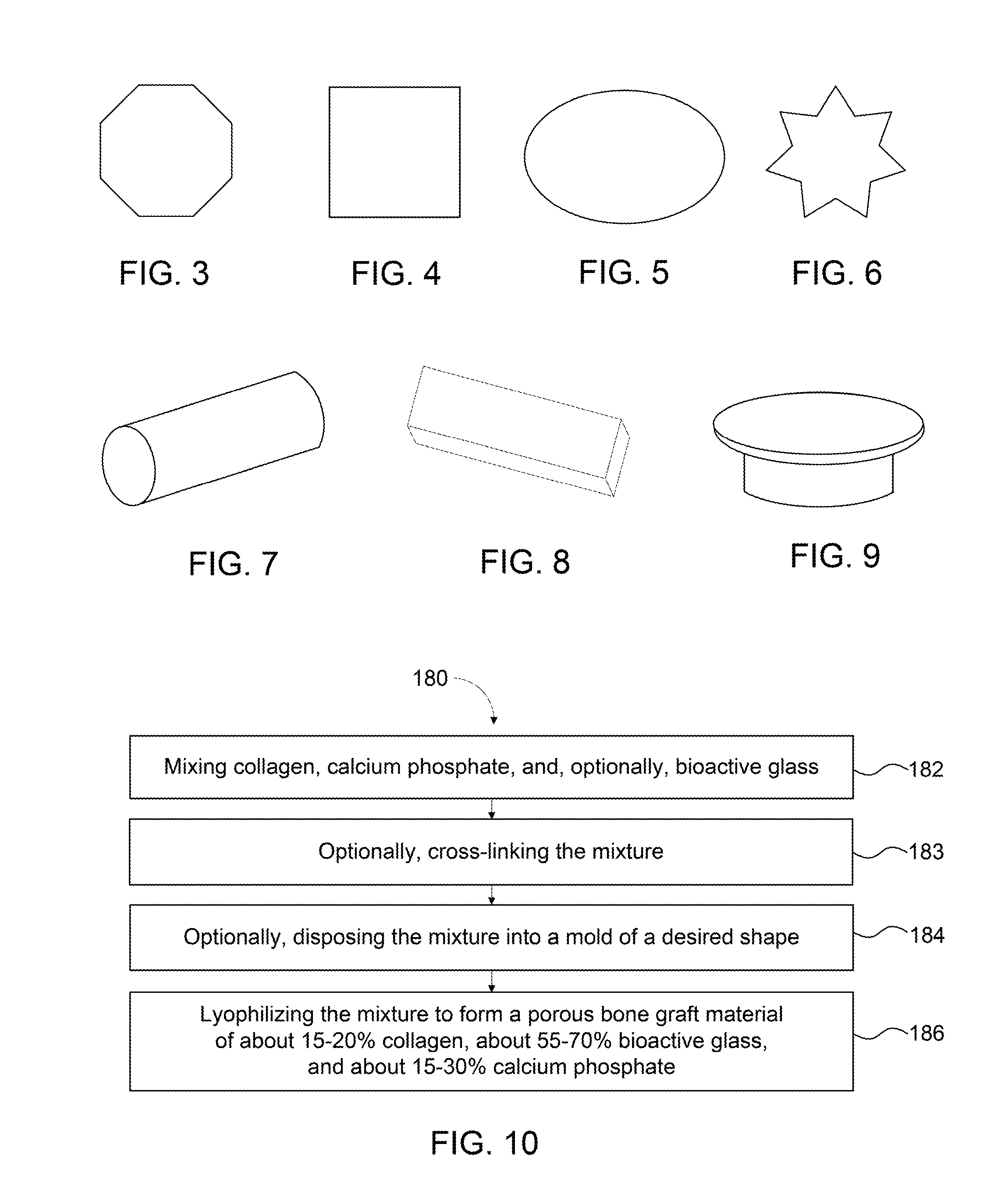
Bone graft materials and methods
Compositions, materials, methods and kits for bone grafting are described. In some embodiments, a bone graft composition includes about 15% to about 20% by weight collagen, about 55% to about 70% by weight bioactive glass, and about 15% to about 30% by weight a calcium phosphate. The bioactive glass and the calcium phosphate together are about 80% to about 85% by weight of the bone graft composition. In some embodiments, a bone graft composition includes a collagen matrix and a plurality of bioactive glass particulates dispersed throughout the collagen matrix. The collagen matrix is about 20% to about 60% by weight of the bone graft composition, and the bioactive glass is about 40% to about 80% of the bone graft composition. In some embodiments, a majority of the bioactive glass particulates are about 53 μm to about 425 μm in size.
Owner:BIOVENTUS
Determination method of enzyme activity of collagenase
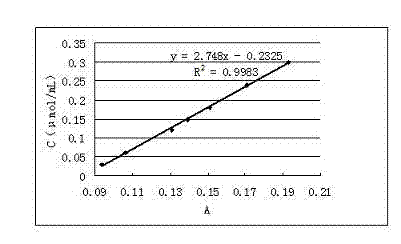
ActiveCN102809541AEliminate distractionsStable contentColor/spectral properties measurementsHydroxyprolineEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a determination method of enzyme activity of collagenase, and aims to solve the problems of non-uniform enzyme activity detection standard and poor data consistency existing in the prior art. The determination method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a reagent; (2) preparing hydroxyproline gradient samples; (3) determining the hydroxyproline gradient samples, drawing a C-A standard curve according to a determined absorbance A and hydroxyproline gradient sample concentration C and fitting a standard curve formula; (4) preparing enzymatic hydrolysate to be determined: adding insoluble collagen or gelatin serving as a collagen substrate into an enzyme solution to be determined for enzymatic hydrolysis, centrifuging to obtain supernatant, and diluting the supernatant to prepare the enzymatic hydrolysate to be determined; (5) preparing a blank solution; (6) determining the enzyme activity and determining the absorbance A of the enzymatic hydrolysate to be determined according to the operation conditions of the step (3); (7) calculating the hydroxyproline concentration in the enzymatic hydrolysate to be determined; and (8) calculating the enzyme activity of the collagenase. The determination method has the characteristics of uniform enzyme activity detection standard, capability of solving the problem of substrate difference, high measuring accuracy and consistent enzyme activity data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Three dimensional cell culture
InactiveCN101448932ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingSupport matrixIn vitro growth
The present invention describes method for culturing preadipocytes isolated ex vivo, the method including introducing preadipocytes into a three dimensional support matrix, and allowing the cells to differentiate in vitro into adipocytes within the support matrix. The matrix may be a collagen matrix. The method may be used for investigating the development of stem cells, or for investigating the response of adipocytes to stimuli. The method provides a system whereby adipocytes with biological properties resembling those in vivo can be grown in vitro.
Owner:THE OPEN UNIV
Medical beta phase tricalcium phosphate/collagen cmposite material and its preparing method
InactiveCN1647826AComponent distribution is evenGood biocompatibilityProsthesisBeta phaseRestorative material
The medical composite beta-tricalcium phosphate / collagen material consists of nano level beta-tricalcium phosphate in 50-67 wt% and collagen 33-50 wt%. Through in-situ complexing of collagen and beta-tricalcium phosphate, nanometer level beta-tricalcium phosphate powder is deposited on collagen substrate, and under the action of glutaraldehyde, the composite material has raised mechanical strength. The composite beta-tricalcium phosphate / collagen material of the present invention has homogeneous components, close combination, excellent biocompatibility, proper pore size and other features, and is suitable for use as the medical bone repairing material.
Owner:翁文剑 +7
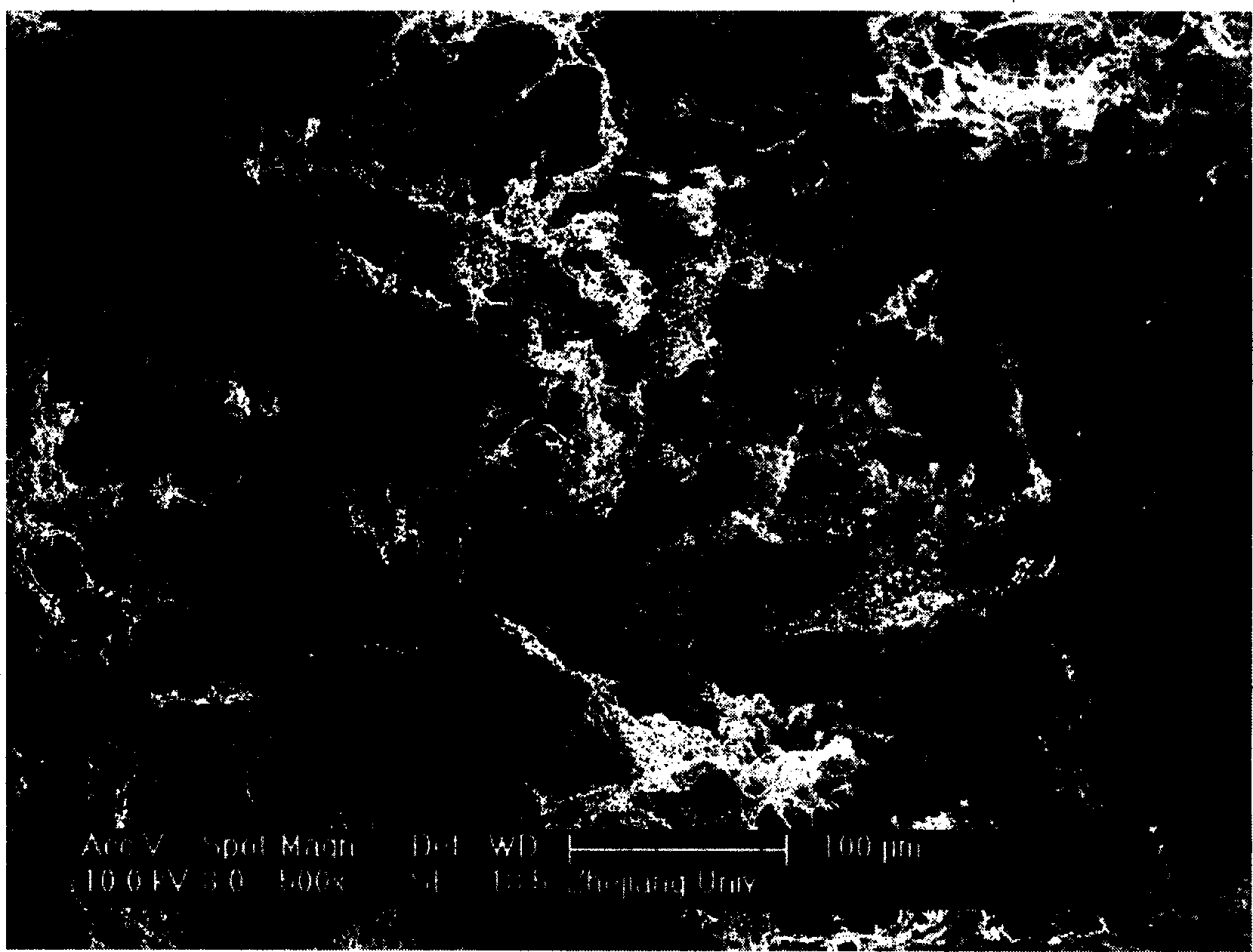
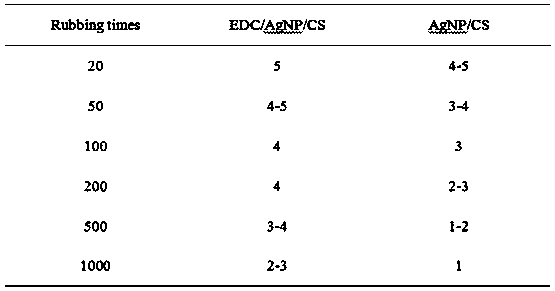
Stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107899077AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove stabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsBacterial AdhesionsAqueous solution
The invention provides a preparation method of a stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a chitosan water solution is used for soaking a collagen substrate; then, water washing is performed to remove uncombined chitosan, wherein the molecular weight of the chitosan is 50 thousand to 500 thousand; (2) a nano-silver water solution is usedfor soaking the matter obtained in the step (1); then, water washing is performed to remove uncombined nano-silver; (3) an EDC and NHS mixed solution is used for soaking the matter obtained in the step (2); then, water washing is performed; next, drying is performed to obtain the stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating. The obtained compound antibacterial coating has three kinds of antibacterial functions of resisting the bacterial adhesion, releasing bactericides for sterilization and realizing contact sterilization; the antibacterial performance is excellent; meanwhile, the compound antibacterial coating also has excellent stability, is applicable to various kinds of complicated environment and is particularly applicable to medical instrument surface anti-bacterium.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
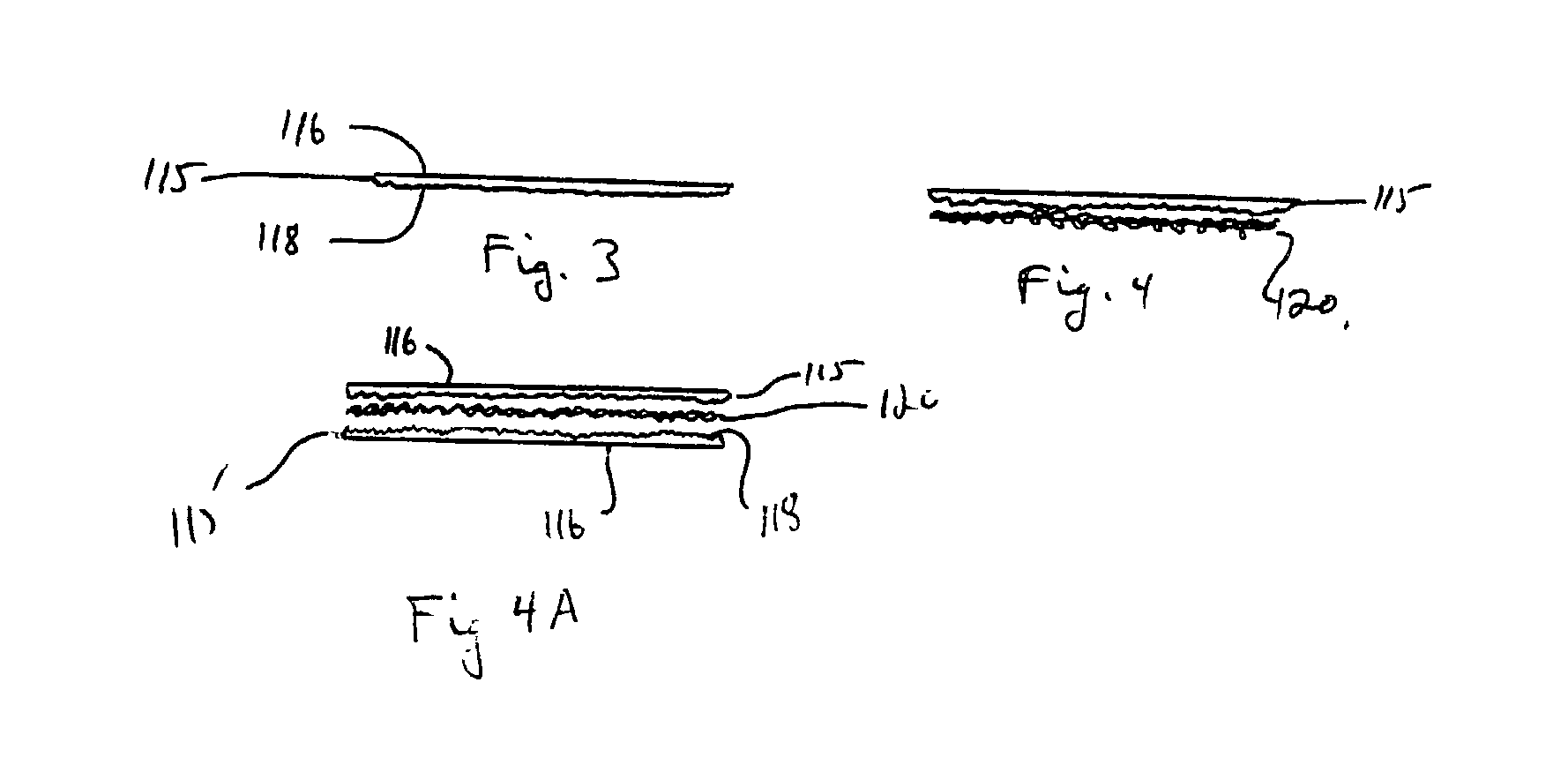
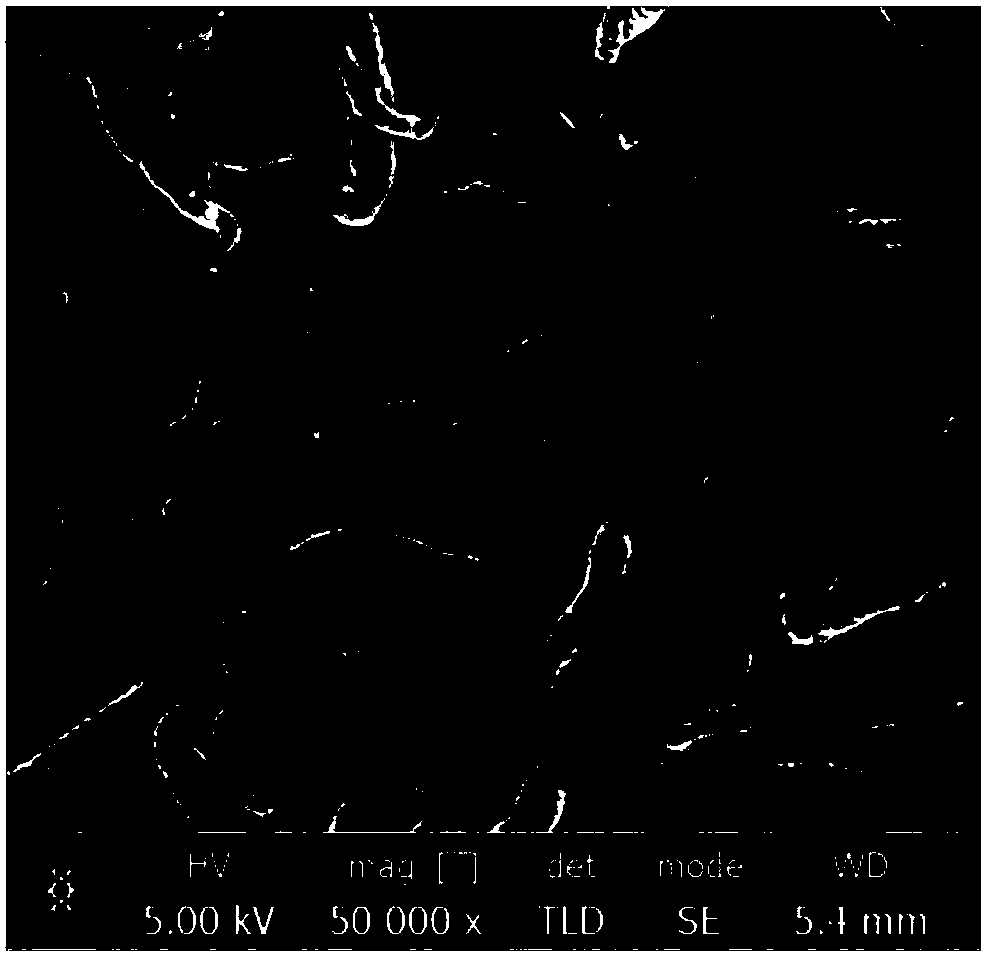
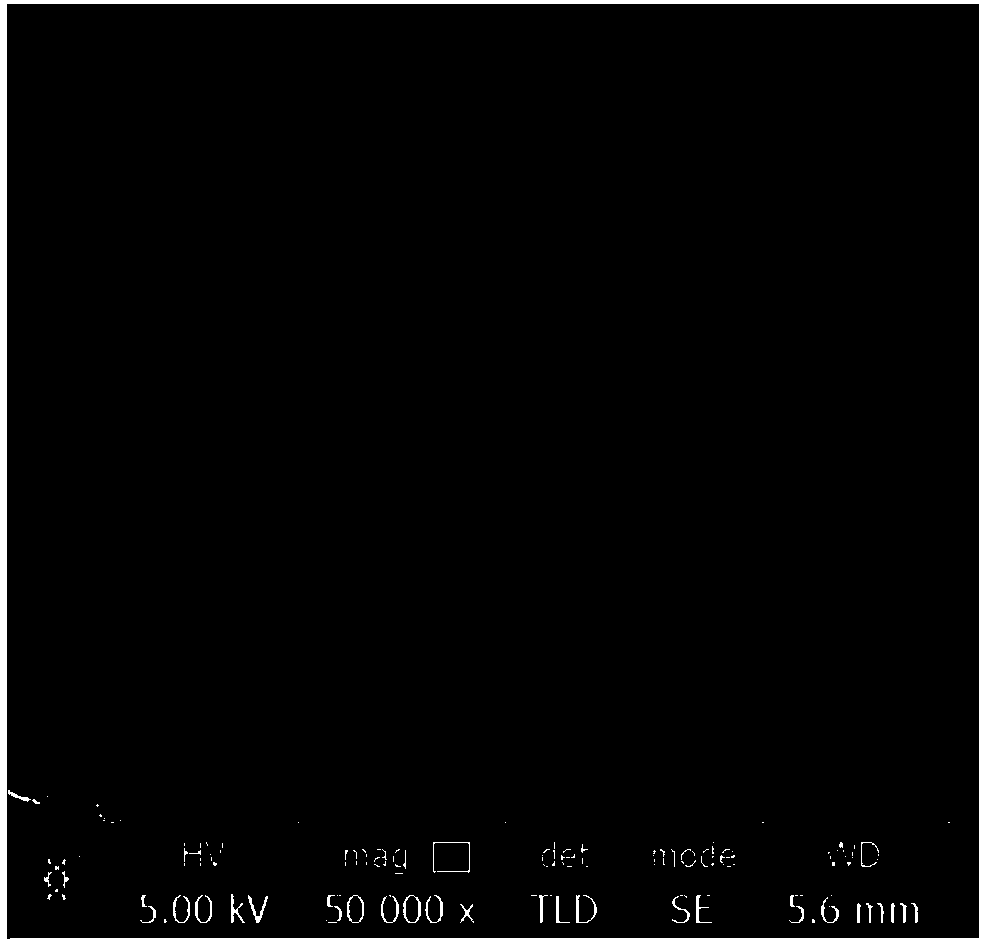
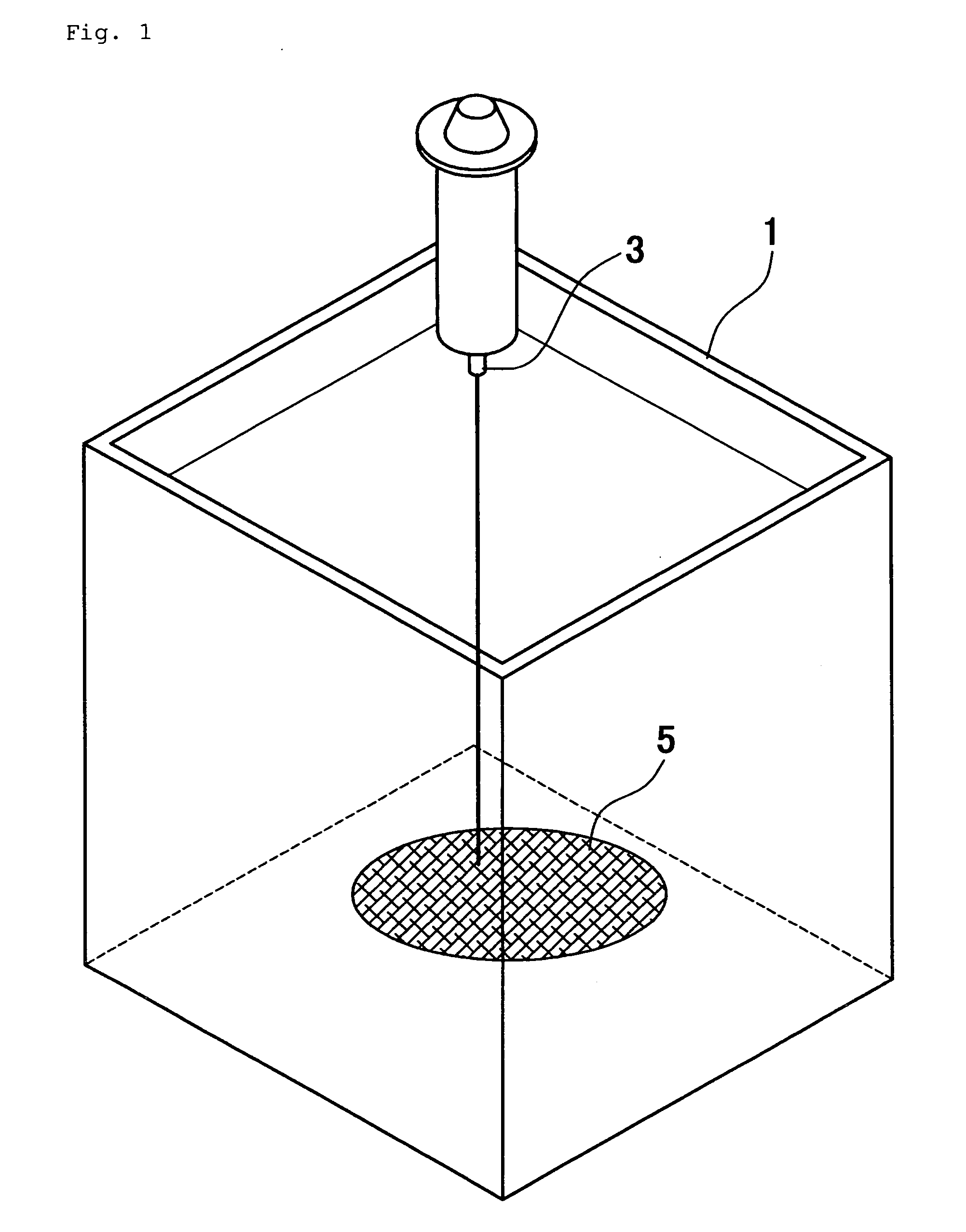
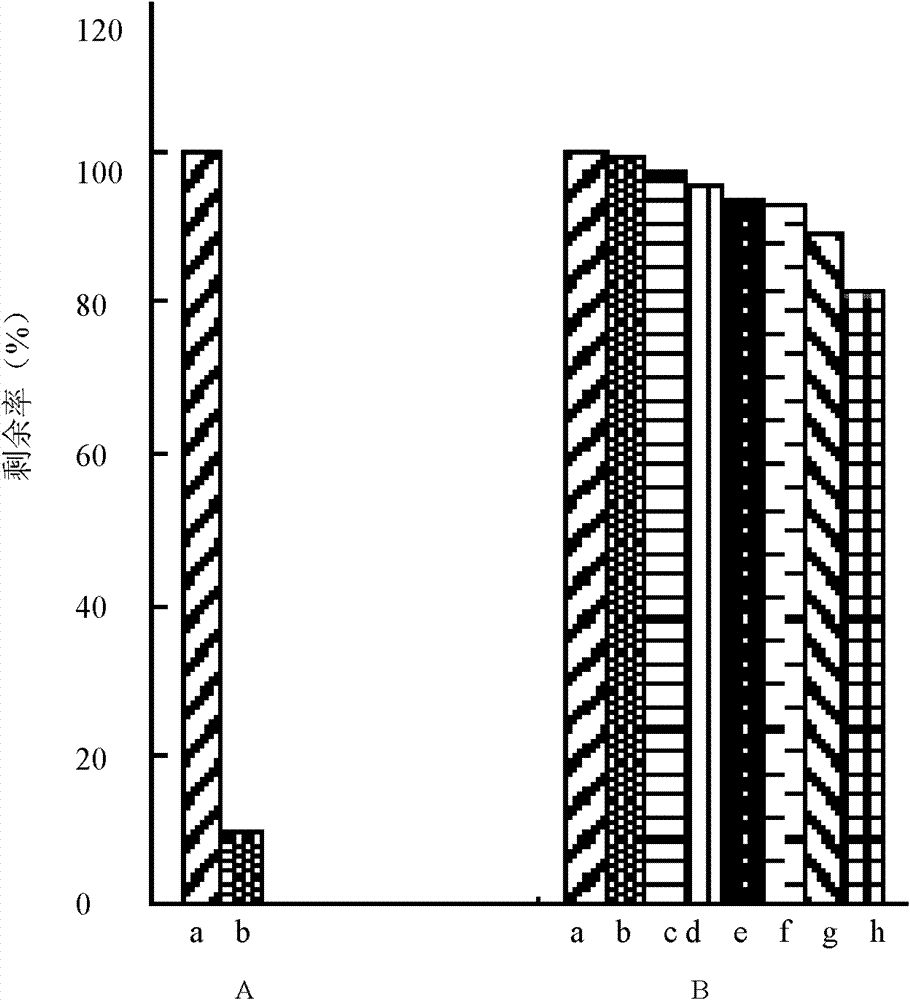
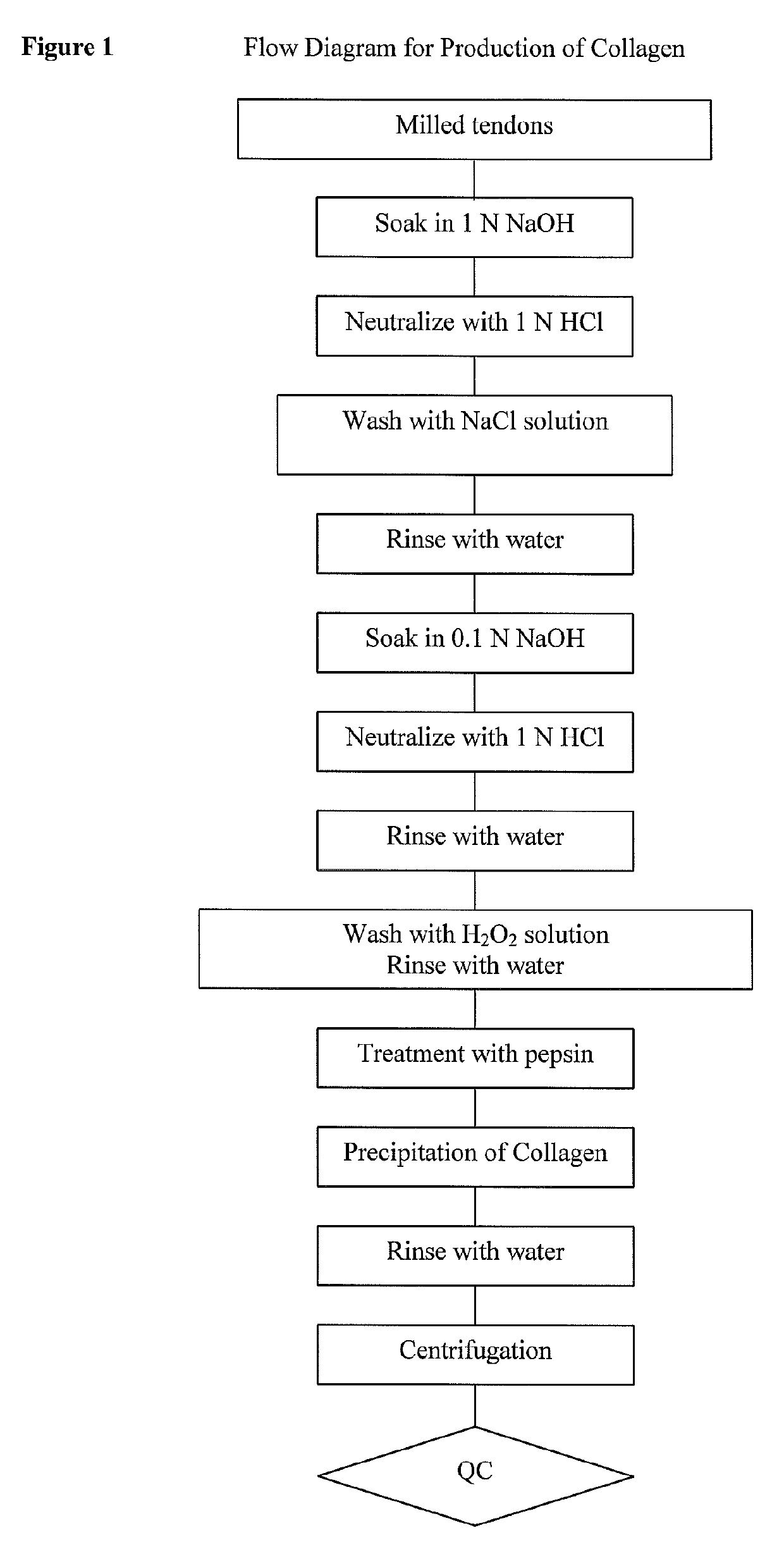
Collagen substrate, method of manufacturing the same, and method of using the same
InactiveUS20070009585A1Easy to getFlexible deformationSynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsLiving bodyCollagen matrices
In order to provide a substrate for medical applications, which may be freely elastically deformed depending on a shape of a defective portion or hemostasis portion in a living body, is biocompatible and suitable for tissue regeneration or cell proliferation, or hemostasis, and can be easily manufactured. A collagen substrate of the present invention includes a three-dimensional mesh formed of spun collagen filaments. Preferably, the collagen substrate of the present invention includes cotton formed of spun collagen filaments.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Application of collagen matrix as tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveCN102772822AImprove mechanical propertiesControl degradation rateProsthesisAcetic acidFreeze-drying
The invention discloses novel application of a collagen matrix as a tissue engineering scaffold. The collagen matrix comprises the following substances expressed in mass parts: 50 to 90 of collagen, 8 to 48 of chitosan and 0.5 to 5 of glycerin. A preparation method for the collagen matrix comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving collagen in an acetic acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.01 to 0.1% to prepare a collagen solution with a concentration of 1 to 3%; 2) dissolving chitosan in the acetic acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.01 to 0.1% to prepare a chitosan solution with a concentration of 1 to 3%; 3) mixing the collagen solution, the chitosan solution (in terms of dry weight) and glycerin according to a mass ratio of 50-90: 8-48: 0.5-5 and carrying out freeze drying at a temperature of -80 DEG C to -10 DEG C for 1 to 5 d so as to obtain a spongy material; 4) immobilizing the spongy material with an aldehyde cross-linking agent at a temperature of 40 to 50 DEG C for 20 to 100 min; and 5) rinsing the spongy material with an aqueous solution of glycerin and drying the spongy material in vacuum so as to obtain the collagen matrix. According to results of cell culture experiments, the collagen matrix provided by the invention can promote cell growth and can be used as a tissue engineering scaffold.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
Neural Progenitor Cell Differentiation
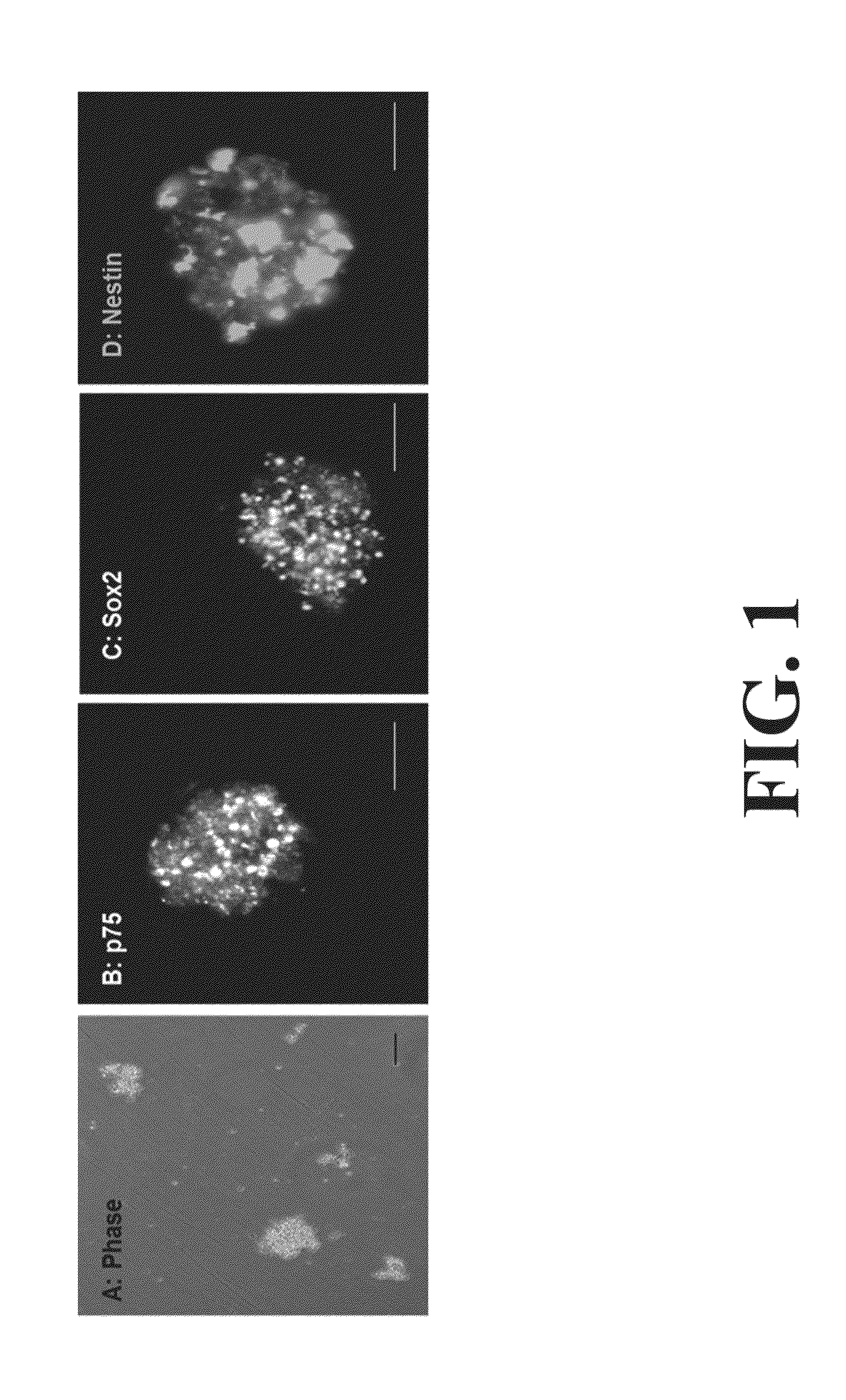
ActiveUS20140271905A1Restore motor functionEffective amountNervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseProgenitor
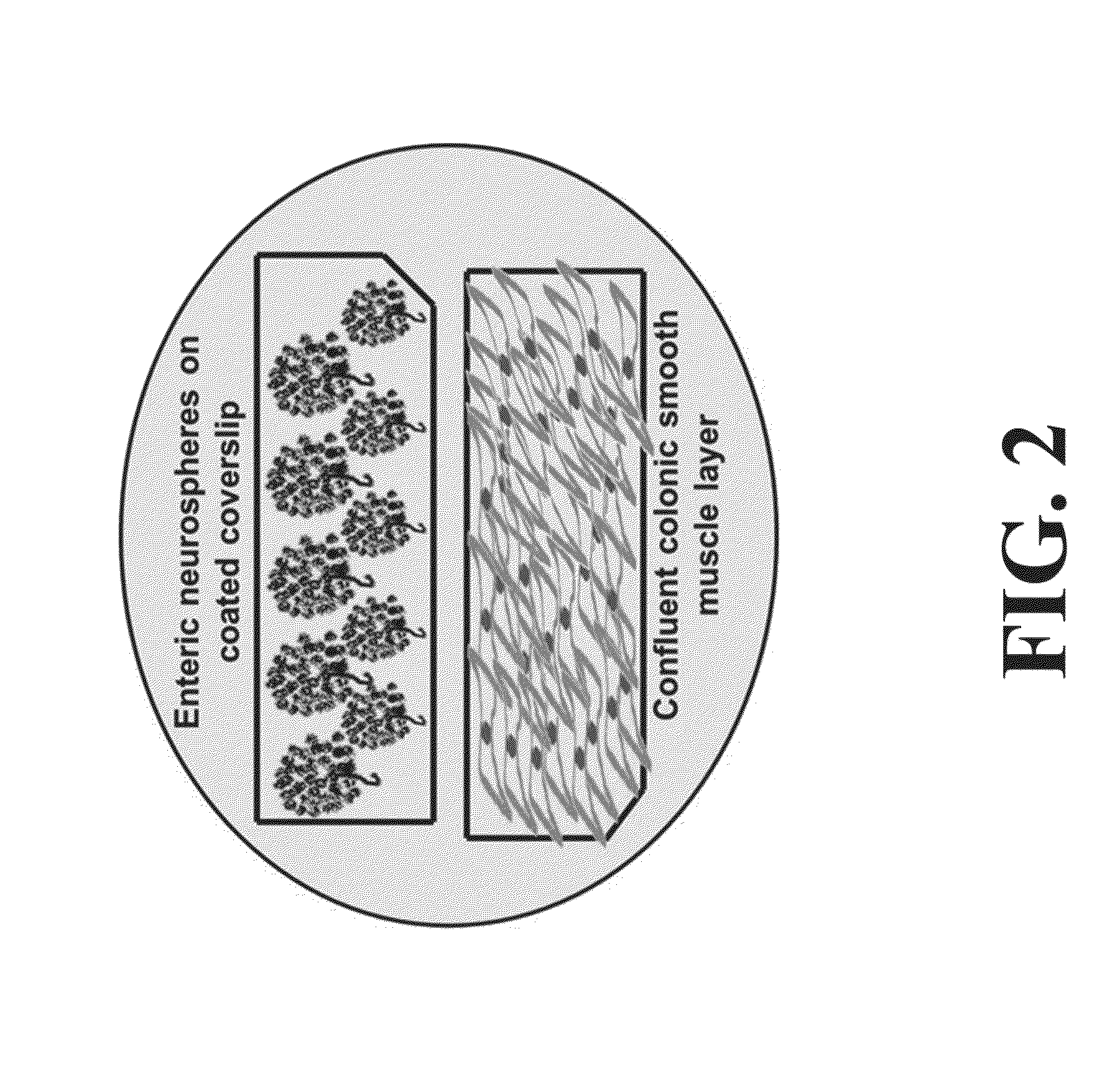
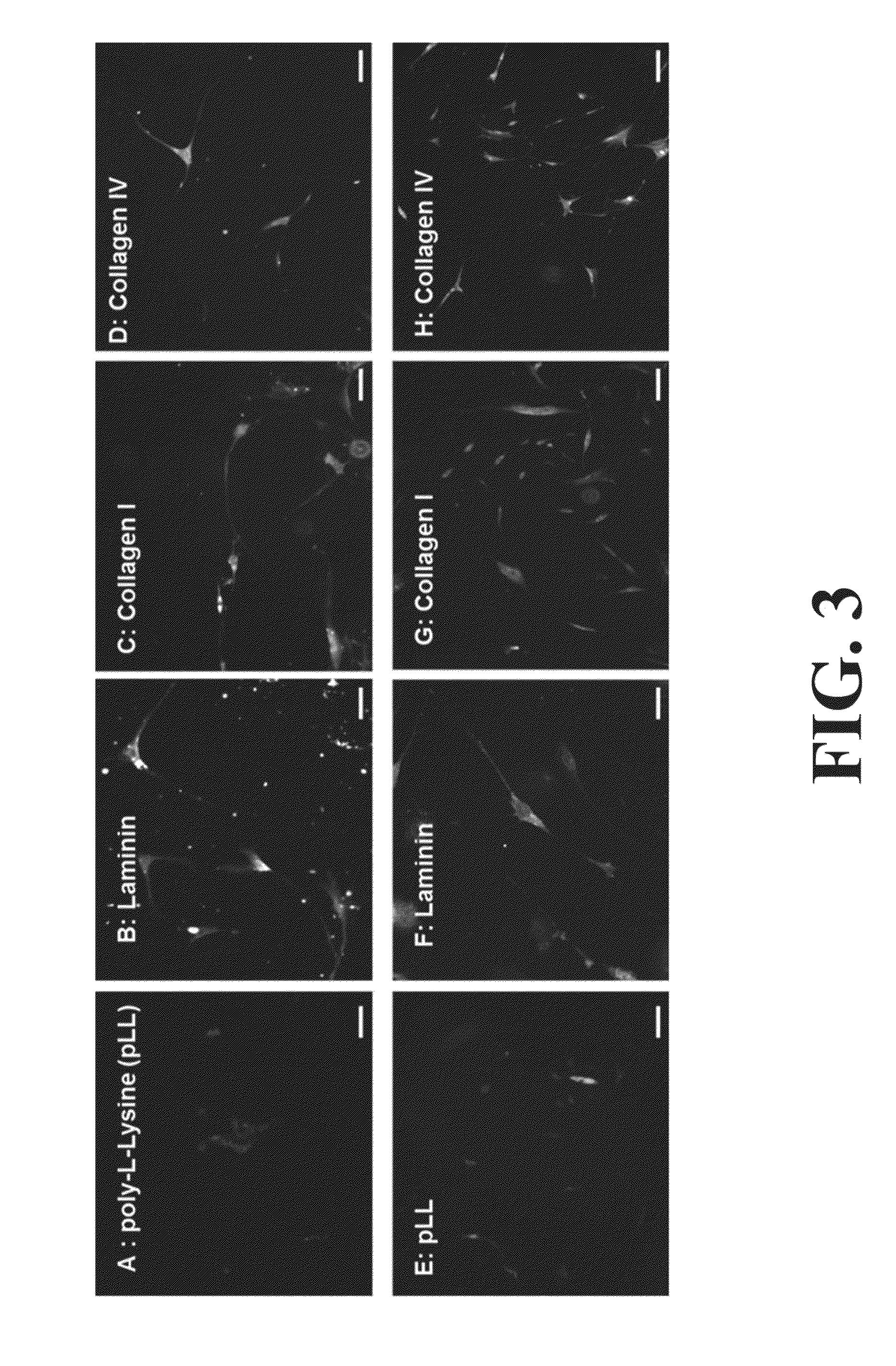
Differentiation and stability of neural stem cells can be enhanced by in vitro or in vivo culturing with one or more extracellular matrix (ECM) compositions, such as collagen I, IV, laminin and / or a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. In one aspect of the invention, adult mammalian enteric neuronal progenitor cells can be induced to differentiate on various substrates derived from components or combinations of neural ECM compositions. Collagen I and IV supported neuronal differentiation and extensive glial differentiation individually and in combination. Addition of laminin or heparan sulfate to collagen substrates unexpectedly improved neuronal differentiation, increasing neuron number, branching of neuronal processes, and initiation of neuronal network formation. In another aspect, neuronal subtype differentiation was affected by varying ECM compositions in hydrogels overlaid on intestinal smooth muscle sheets. The matrix compositions of the present invention can be used to tissue engineer transplantable innervated GI smooth muscle constructs to remedy aganglionic disorders.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Calcium fluoride collagen micro-fiber composite and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106567151AAchieve internal mineralizationPromote growthMonocomponent protein artificial filamentArtifical filament manufactureProtein solutionProtein fiber
The invention relates to a calcium fluoride collagen micro-fiber composite and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of: (1) adding collagen protein fiber powder to an acetic acid solution to prepare a collagen protein solution, and uniformly coating a surface of a substrate with the collagen protein solution and diffusing the collagen protein solution with ammonia water to produce a collagen substrate; (2) uniformly mixing and stirring sodium fluoride, sodium chloride and water to prepare a solution A, uniformly mixing and stirring calcium chloride, a polyacrylic acid solution, 4-hydroxyethyl piperazine ethanesulfonic acid and water to obtain a solution B, slowly adding the solution A dropwise to the solution B and regulating the pH of the system to prepare a calcium fluoride precursor solution; and (3) soaking the collagen substrate in the calcium fluoride precursor solution for mineralization to prepare the calcium fluoride collagen micro-fiber composite. The method for producing the calcium fluoride collagen micro-fiber composite is carried out through internal mineralization of the collagen micro-fibers at normal temperature and under normal pressure, thereby achieving internal mineralization of the collagen micro-fibers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Blood vessel organoid, methods of producing and using said organoids
The present invention relates to a method of generating an artificial blood vessel organoid, comprising providing stem cells capable of vascular differentiation, stimulating mesoderm differentiation in said stem cells, stimulating vascular differentiation in said stem cells, developing a cell aggregate from said stem cells, embedding said cell aggregates in a collagenous 3D matrix and stimulatingvascular differentiation of the aggregate in said collagenous 3D matrix; organoids obtainable from said method, uses of said methods and organoids in manipulation and screening studied and kits for performing the methods.
Owner:IMBA INSTITUT FUR MOLEKULARE BIOTECH
Controllable-degradation lacrimal passage suppository and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a controllable-degradation lacrimal passage suppository and a preparation method thereof. The lacrimal passage suppository is a novel slippage-preventing absorbable lacrimal passage suppository having multiple shapes and multiple degradation times and obtained with a cross-linked collagen matrix as a main raw material and through homogenization, freeze-drying molding and other processing steps. The multiple designed shapes not only all can be convenient to implant in surgery, but also can effectively prevent slippage; in addition, after implantation, the lacrimal passage suppository is swelled due to absorption of water, so that the stability of the product after implantation is more ensured, and the security is extremely high. In addition, with a specific micro-pore structure of the product, epiphora and other complications appearing after the product is implanted can be avoided. The method is simple in process and strong in operability. The prepared product can effectively relieve or treat xerophthalmia.
Owner:SHAANXI BOYU REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane, and making method and application thereof
ActiveCN104368043AFlat surfaceSimple preparation processProsthesisSodium bicarbonateCartilage lesion
The invention discloses a making method of a collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane. The method comprises the following steps: 1, shearing a raw material pork leg tendon, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis, centrifuging, filtering, and dissolving to obtain an I type collagen solution; 2, neutralizing the I type collagen solution obtained in step 1 by using a 1M sodium bicarbonate solution; 3, pouring the neutralized I type collagen solution obtained in step 2 into a die, and drying at 30-40DEG C for 35-54h to form an I type collagen matrix membrane in the die; and 4, immersing the I type collagen matrix membrane obtained in step 3 in a 20-200[mu]g / mL parathyroid hormone related peptide solution, and incubating at 30-40DEG C for 0.5-2h to obtain the parathyroid hormone related peptide compounded I type collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane. The invention also discloses the collagen matrix cartilage repairing membrane and an application thereof. The cartilage repairing membrane has certain adhesiveness to injured surfaces of cartilage, and is suitable for repairing cartilage injuries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINGYUE BIOTECH
Preparation method of regional function specific clinical periodontal defect repair module
The invention provides a preparation method of a regional function specific clinical periodontal defect repair module. The module comprises an alveolar bone regeneration functional domain, a periodontal ligament regeneration functional domain and a barrier membrane functional domain. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, carrying out 3D printing on the personalized magnesium-doped wollastonite alveolar bone regeneration functional domain according to clinical alveolar bone defects; and taking MNBG-modified improved PCL / gelatin electrospun membrane as the periodontal ligament regeneration functional domain and Si-HPMC / MA-CMCS hydrogel formed by photocuring as the barrier membrane functional domain, and integrating the alveolar bone regeneration functional domain, the periodontal ligament regeneration functional domain and the barrier membrane functional domain. Imitation periodontal fiber guide structure design and MNBG modification of the periodontal ligament regeneration functional domain provide guidance and support for secretion and integration of collagen matrixes, and MNBG modification can induce proliferation and vertical migration of periodontal ligament fibroblasts, so that vertical increment of periodontal ligament tissue in a defect area is improved, the regeneration of a periodontal tissue complex is promoted, the determinacy of periodontal tissue regeneration is improved, and the technical sensitivity of a periodontal regeneration operation is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cell-collagen-silica composites and methods of making and using the same
PendingUS20180141996A1Efficient and cost-effectiveConnective tissue peptidesVertebrate cellsFiberSilicic acid
Soluble, self-assembling collagens derived from tissues are extensively characterized such that one can predict and customize the final collagen-fibril matrix with respect to fibril microstructure (i.e., fibril density, interfibril branching), viscoelasticity and proteolytic degradability. As shown herein these matrices template and direct the deposition of mesoporous silica at the level of individual collagen fibrils. The fibril density, silicic acid concentration, and time of exposure to silicifying solution were varied and the resulting hybrid materials were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy, and rheology. Microstructural properties of the collagen-fibril template are preserved in the silica surface of hybrid materials. Results for three different collagen fibril densities, corresponding to shear storage moduli of 200 Pa, 1000 Pa, and 1600 Pa, indicate that increased fibril density increases the absolute amount of templated silica when all other silica synthesis conditions are kept constant. The mechanical properties of the hybrid material are dominated by the presence of the silica coating rather than the starting collagen matrix stiffness.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for preparing collagen substrate material for oral cavity by using biological bone
ActiveCN112807490ARich sourcesReduce the induced inflammatory responseTissue regenerationProsthesisImmune rejectionBone material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a collagen substrate material for an oral cavity by using biological bone. The method comprises the steps of cutting young bovine bone or swine bone, then, carrying out treatments such as virus removing, defatting, deproteinization, decalcification, cell removing and endotoxin removing, then, carrying out freeze-drying, and then, shearing the bone into required specifications. The whole process is simple, the production cycle is short, and thus, large-scale mass production is facilitated. According to the method, the young bovine bone or swine bone is selected as a raw material and is rich in source, degradation-induced inflammatory reactions are reduced, and clearing is easy, so that immunological rejections caused after human body implantation are avoided. Moreover, the young bovine bone and swine bone materials have good porosity and pore size channels and are similar to human bones in porosity, a human body microenvironment is simulated, crawling passing of seed cells such as osteoblasts is facilitated, healing of soft tissue can be excellently promoted, and the osteogenesis capability is relatively good. Furthermore, chemical reagents of all treatment steps are spin-dried in a long running water state and washed off, the speed is high, and the washing is thorough and residual-free, so that the safety of use of the product is further guaranteed.
Owner:西岭(镇江)医疗科技有限公司
Drug delivery device for providing local analgesia, local anesthesia or nerve blockage
ActiveUSRE47826E1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmide active ingredientsAmino estersFibrillar collagen
The invention relates to a drug delivery device for providing local analgesia, local anesthesia or nerve blockade at a site in a human or animal in need thereof, the device comprising a fibrillar collagen matrix; and at least one drug substance selected from the group consisting of amino amide anesthetics, amino ester anesthetics and mixtures thereof, the at least one drug substance being substantially homogeneously dispersed in the collagen matrix, and the at least one drug substance being present in an amount sufficient to provide a duration of local analgesia, local anesthesia or nerve blockade which lasts for at least about one day after administration.
Owner:INNOCOLL PHARMACEUTICALS LTD
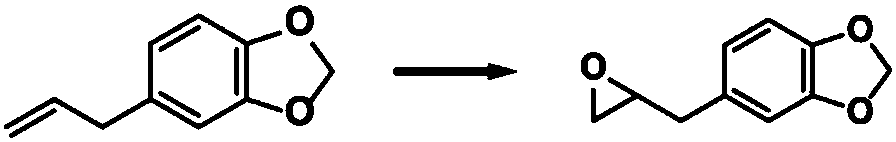
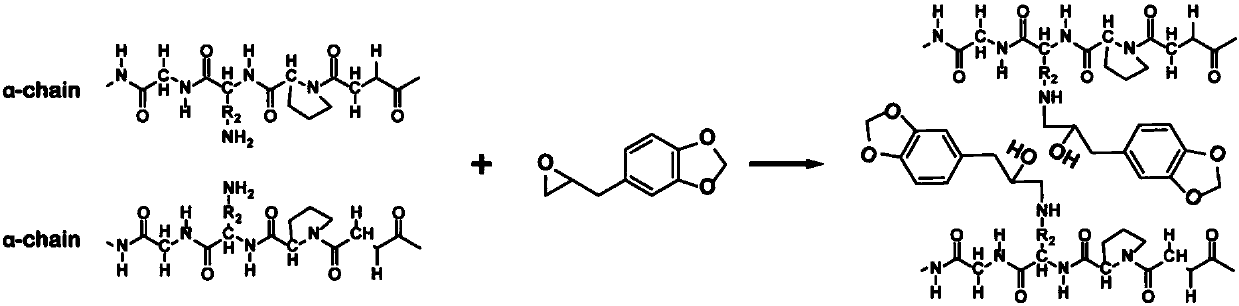
Antibacterial collagen preparation method based on epoxidation modification of safrole
ActiveCN107903322ARetention of antimicrobial activityDoes not affect the domainConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsEpoxySide chain
The invention discloses an antibacterial collagen preparation method based on epoxidation modification of safrole. According to the method, safrole is modified with a weak epoxidation reagent, and themodified safrole is covalently introduced into collagen by using the covalent reaction between the epoxy group and the amino group on the side chain of the collagen macromolecule, such that the collagen substrate has good antibacterial activity. According to the present invention, the collagen material obtained by using the modification method has the long-lasting antibacterial function, whereinthe three-stranded spiral structure of the collagen substrate cannot be destroyed, and the inherent biocompatibility can be completely retained, such that the application prospect in the collagen-based biomedical material field is broad.
Owner:YIBIN UNIV
Collagen matrix or granulate blend of bone substitute material
ActiveUS20200390939A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBiphasic calcium phosphateCalcium pidolate
Collagen matrix granulate blend, and process for making and using a collagen matrix or granulate blend including collagen and particles of a biphasic calcium phosphate / hydroxyapatite (CAP / HAP) bone substitute material having a sintered CAP core and having its total external surface covered by at least one closed epitactically grown layer of nanocrystalline HAP deposited on the external surface of the sintered CAP core, whereby the epitactically grown nanocrystals have the same size and morphology as human bone mineral, wherein the closed epitactically grown layer of nanocrystalline HAP is transformed from the CAP on the external surface of the sintered CAP core has a non-homogeneous external surface comprising individual clusters of flat crystal platelets consisting of epitactically grown HAP nanocrystals and coarse areas between the individual clusters, whereby the percentage of the coarse areas between the individual clusters as measured by SEM is at least 20% of the total surface.
Owner:GEISTLICH PHARMA
Method of culturing proliferative hepatocytes
The present invention relates to a method of culturing animal cells, preferably primary hepatocytes, comprising a first step of culturing the animal cells in non-adherent culture vessel, preferably alow or ultra-low attachment culture vessel, a second step of embedding the animal cells in a collagen matrix or in a gelatin matrix, and a third step of culturing the animal cells embedded in the collagen matrix or in the gelatin matrix, thereby obtaining 3D animal cell structures comprising proliferative animal cells, preferably spheroids comprising proliferative primary hepatocytes. The invention also relates to a spheroid comprising proliferative primary hepatocytes and the uses thereof for engineering an artificial liver model or an artificial liver organ, and for assessing in vitro the liver toxicity, genotoxicity and / or the effects of a drug or a compound.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
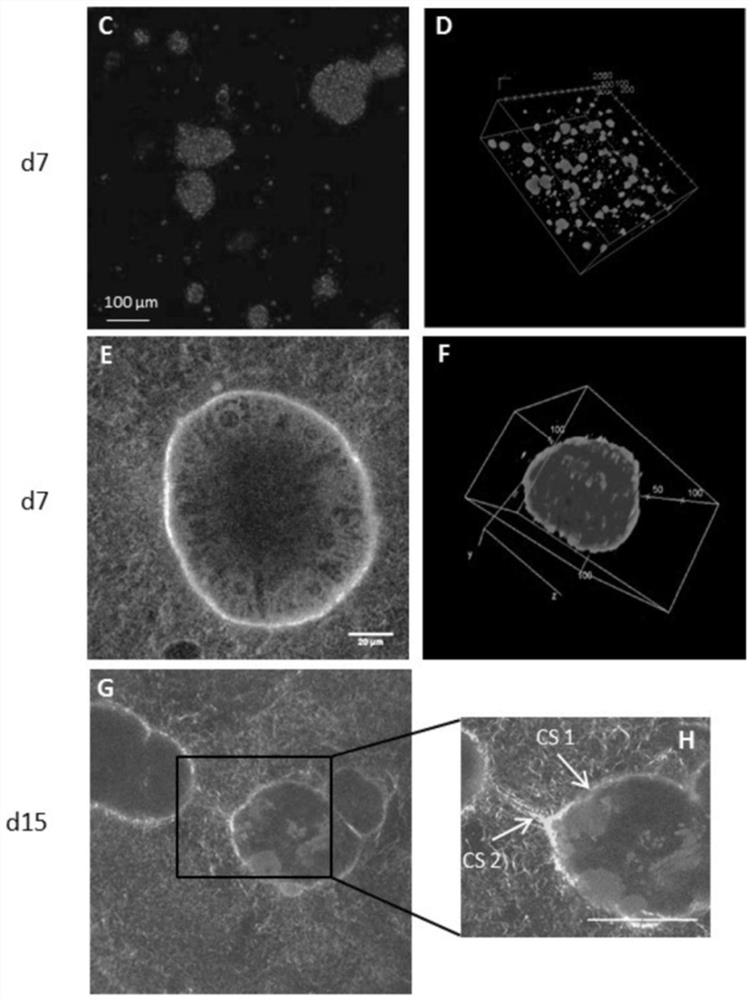
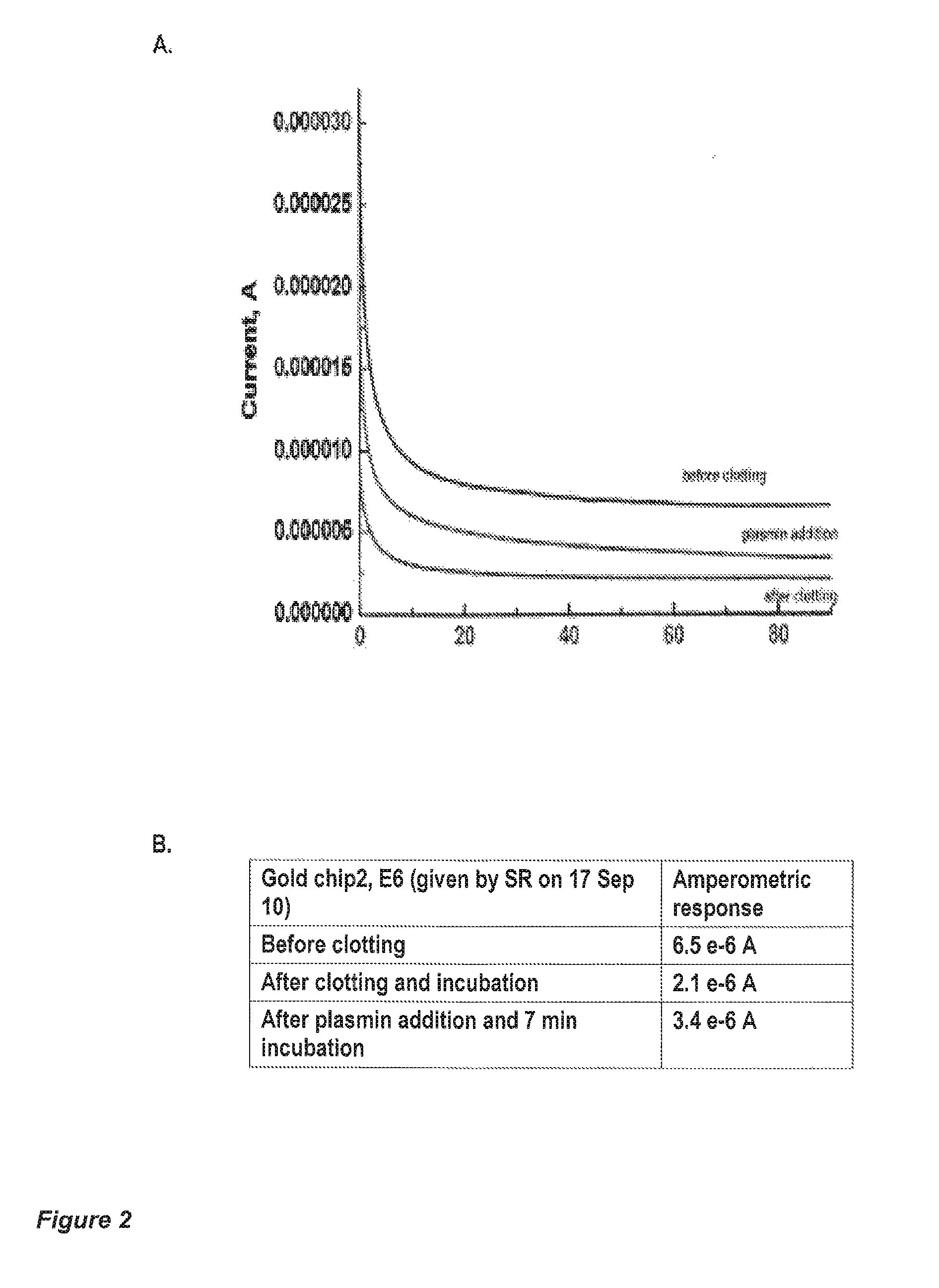
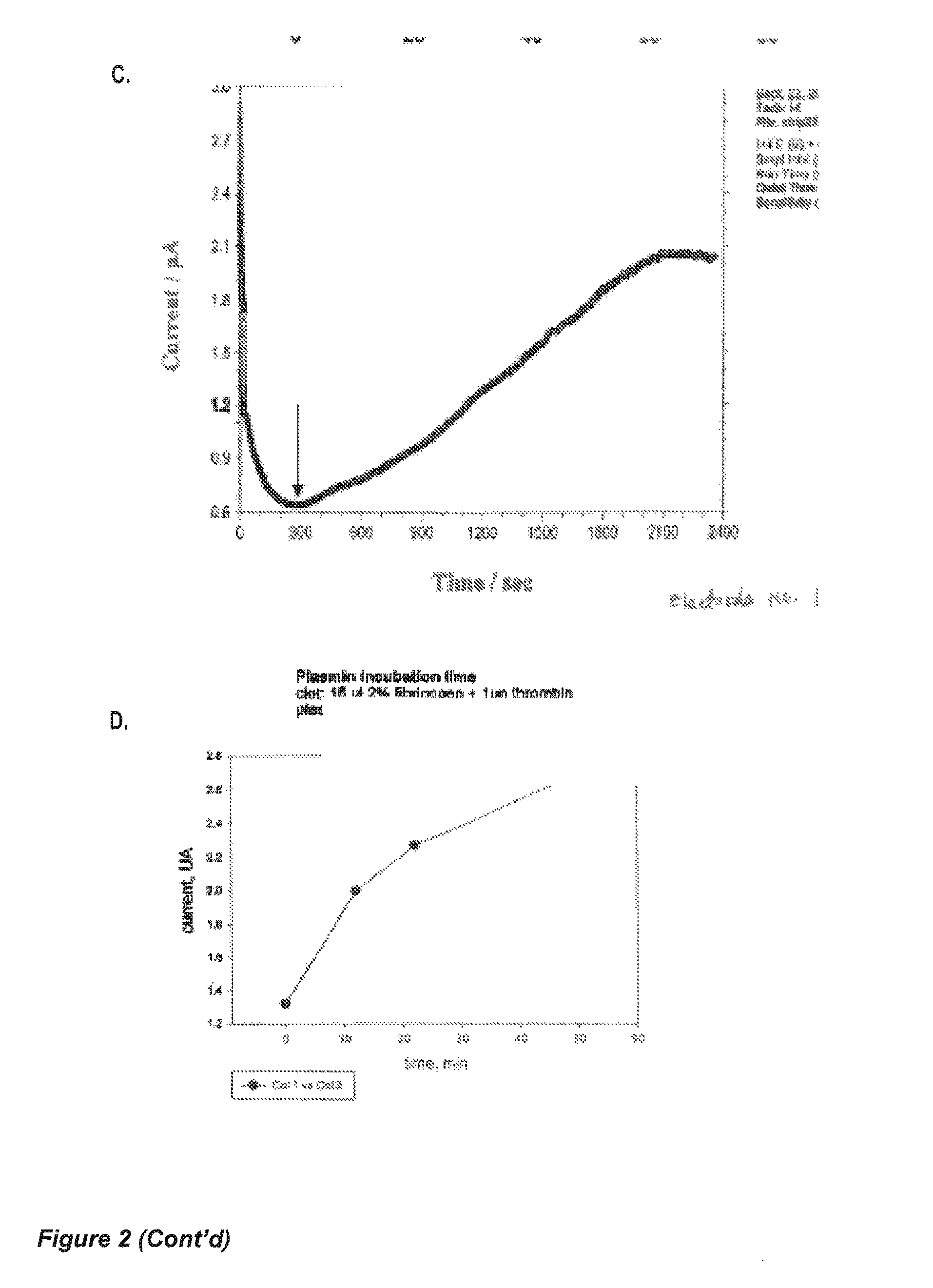
System and method for detecting and monitoring proteolysis of protein matrices
InactiveUS9453833B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Apparatus and methods are provided for detecting and monitoring proteolysis of protein matrices such as fibrin clots, extracellular matrix and collagen matrix. The apparatus and methods involve in general the measurement of diffusion-limited electrochemical currents generated by an electroactive species or elactomer in a synthetic protein matrix. The apparatus and methods are applied in various embodiments to detect and monitor the proteolytic activities of a sample, and more specifically fibrinolytic activities and collagenase activities of a sample. The apparatus and methods are utilized generally in the monitoring and diagnostics of cardiovascular, cerebralvascular, and oncology conditions.
Owner:DIGITAL DIAGNOSTICS PTY LTD +1
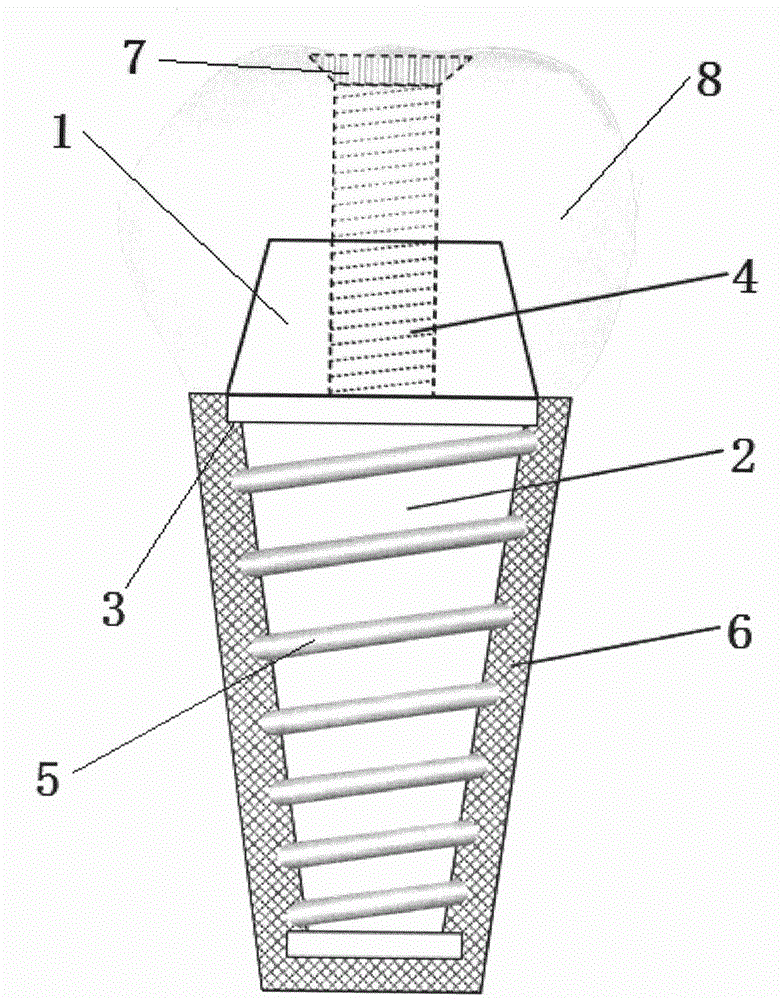
Method for manufacturing immediately implanted tooth with periodontal bioactivity
ActiveCN104523341AImprove boot activityGood biocompatibilityDental implantsCoatingsTitaniumTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an immediately implanted tooth with periodontal bioactivity. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a pure titanium or titanium alloy implant core; (2) preparing self-curing calcium-magnesium phosphate powder; (3) preparing a collagen solution; (4) preparing an artificially synthesized P substance polypeptide; (5) preparing an SP crosslinking collagen substance; (6) mixing and stirring the calcium-magnesium phosphate powder and the SP crosslinking collagen substrate to prepare bioactive paste; (7) coating the root part of the implant core with the bioactive paste, pressurizing, curing and lyophilizing to prepare an artificial tooth root with periodontal bioactivity; (8) connecting the crown part of the implant core to an artificial tooth crown suitable for the tooth-missing appearance to obtain the immediately implanted tooth. According to the method, the artificial tooth root with a bionic cementum structure is constructed, so that the prepared implant tooth has partial life signs of a natural transplanted tooth, has spontaneous periodontal curing bioactivity, can be immediately implanted after a tooth is extracted, and can be used for remarkably shortening the tooth repairing time and improving the implant success rate.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
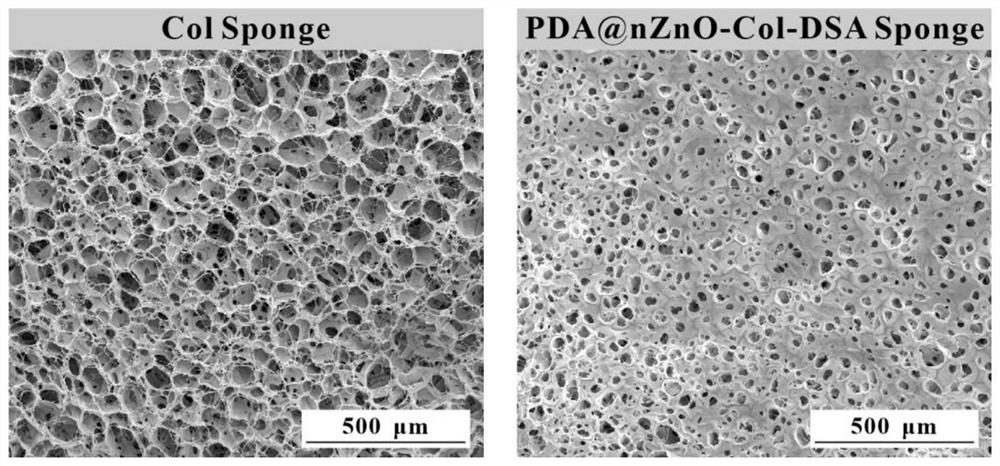
Nano-zinc oxide/collagen-based antibacterial dressing and preparation method thereof
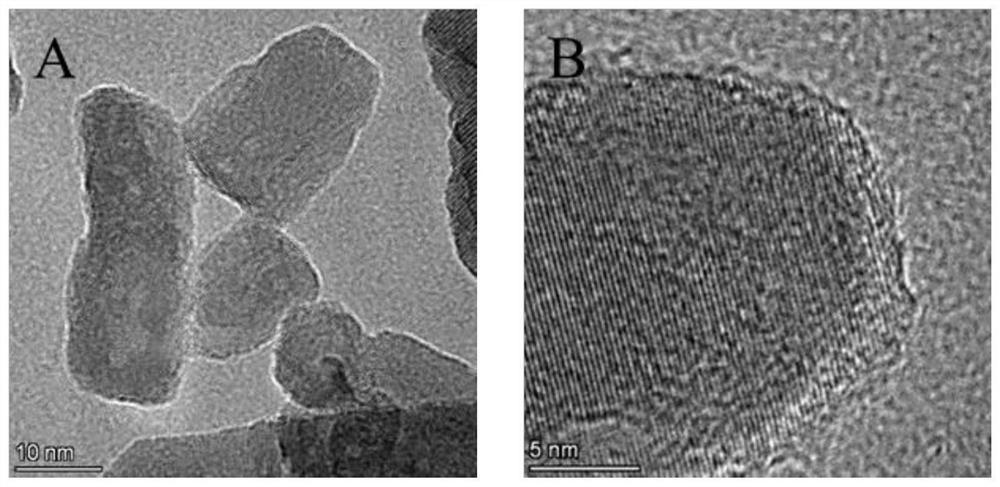
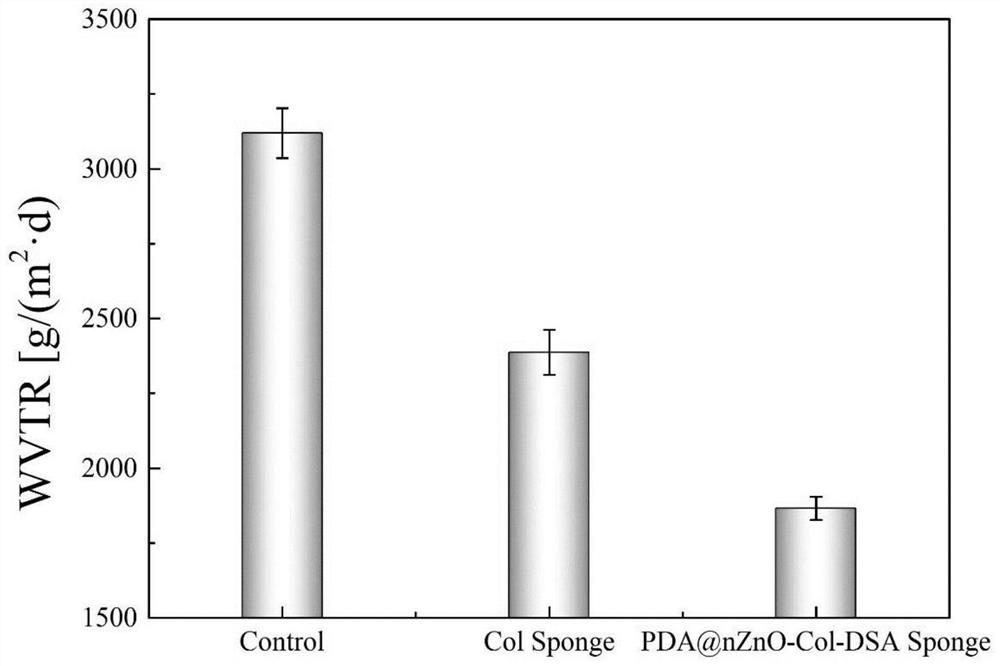
ActiveCN113577362AReduce usagePrevent the occurrenceAbsorbent padsBandagesWound dressingFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a nano zinc oxide / collagen-based antibacterial dressing and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing nano-zinc oxide by adopting a hydrothermal method, forming a wrapping layer on the surface of the nano-zinc oxide through dopamine auto-polymerization, and then grafting the nano-zinc oxide to a collagen molecular chain under the catalytic action of EDC / NHS to prepare a modified collagen solution. The soaking the modified collagen sponge prepared by freeze drying in a dialdehyde polysaccharide solution, and freeze-drying to obtain the nano-zinc oxide / collagen-based antibacterial dressing. Nano-zinc oxide is uniformly introduced into a collagen matrix in a chemical grafting manner, and collagen is modified by chemical crosslinking of dialdehyde polysaccharide serving as a natural polymer aldehyde crosslinking agent, so that the collagen-based antibacterial dressing with relatively high mechanical strength, good biocompatibility and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity is prepared; The invention has a good application prospect in the field of medical wound dressings.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com