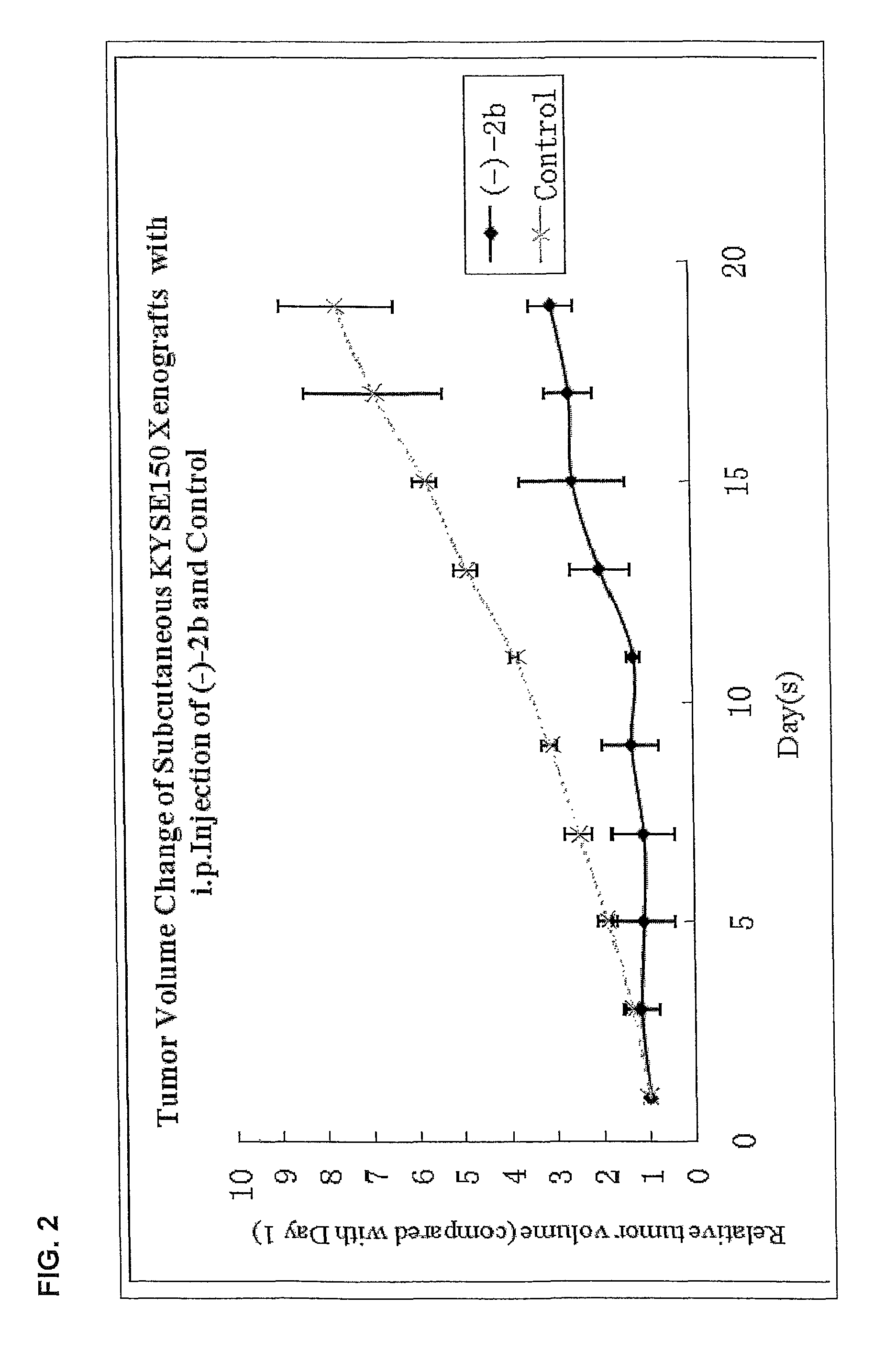
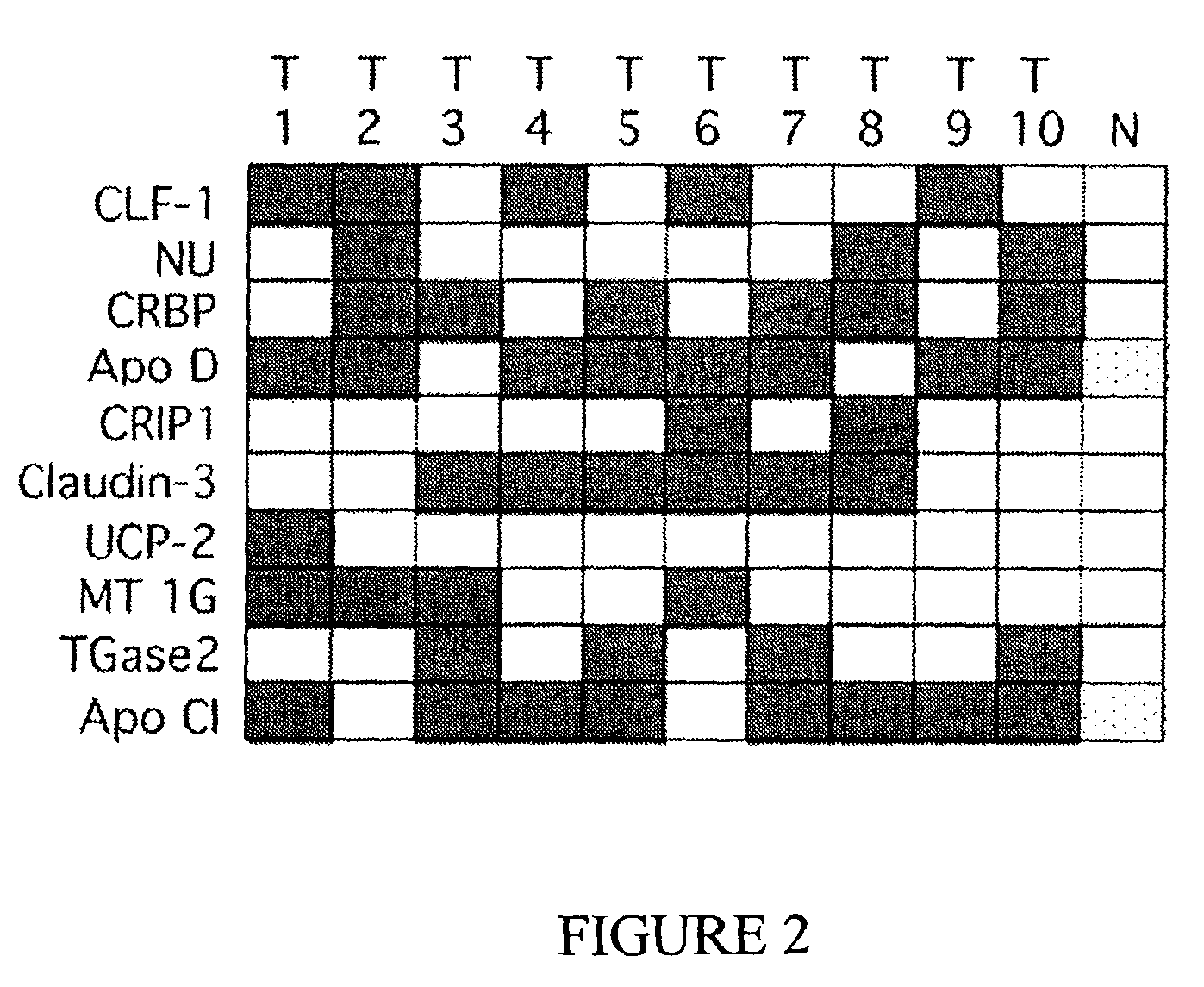
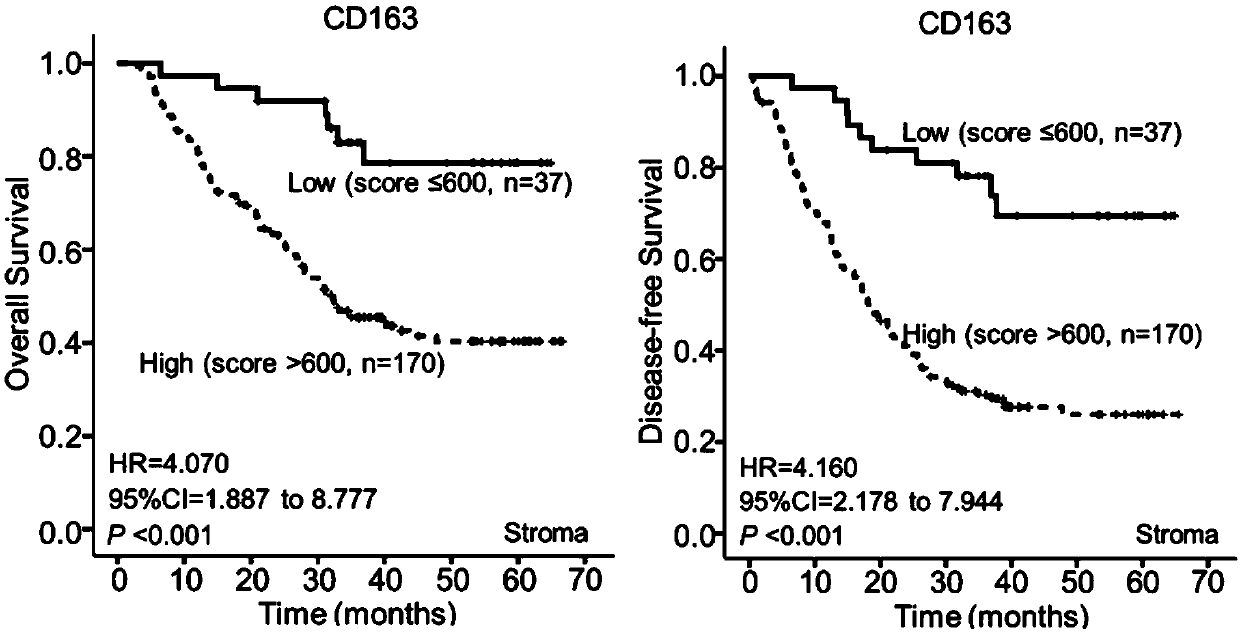
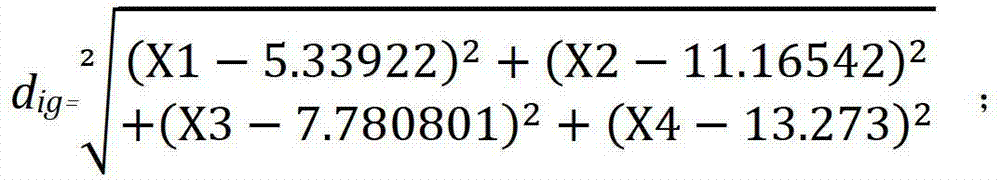Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
228 results about "Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
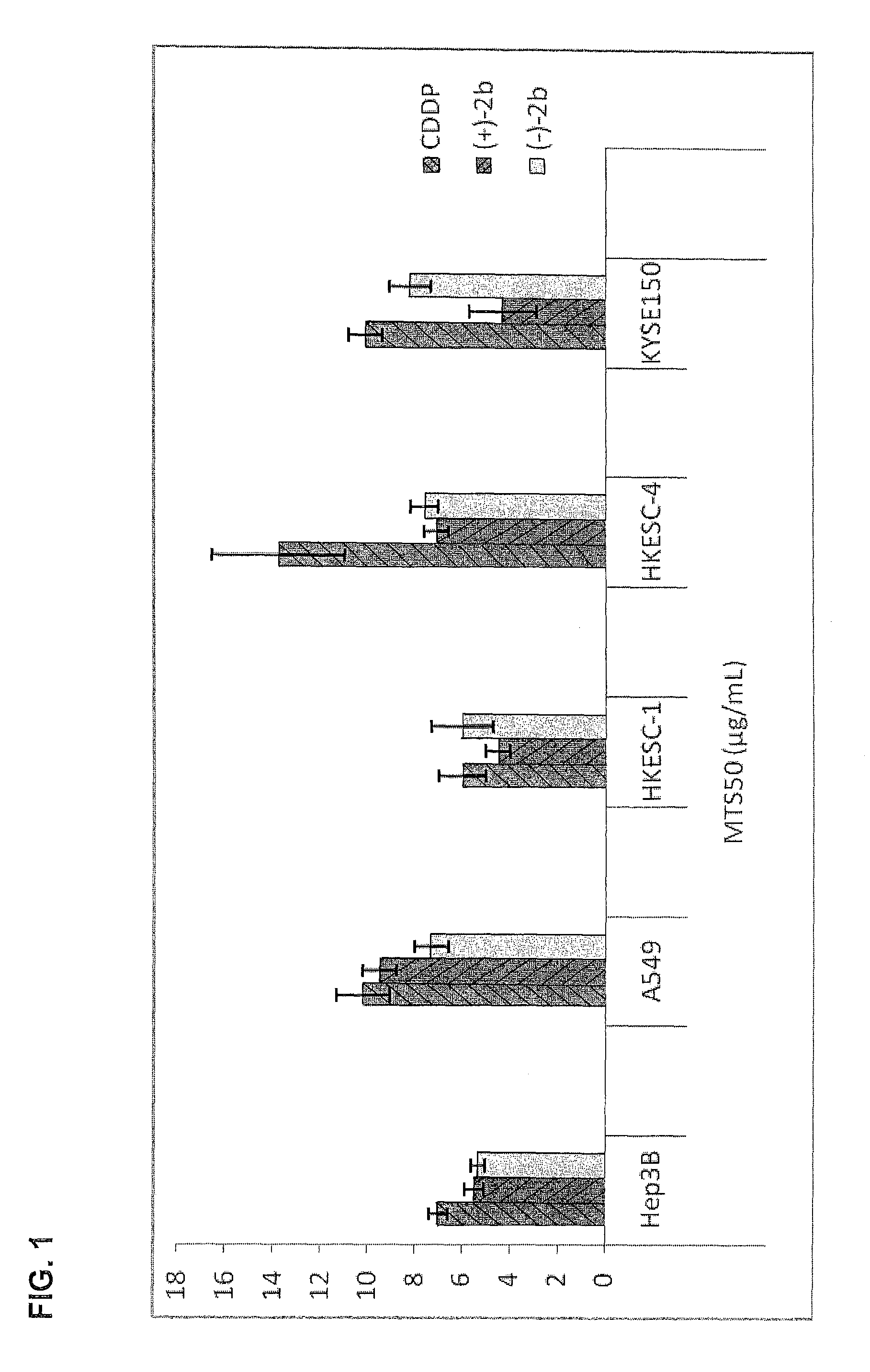
Quinoline derivatives as Anti-cancer agents
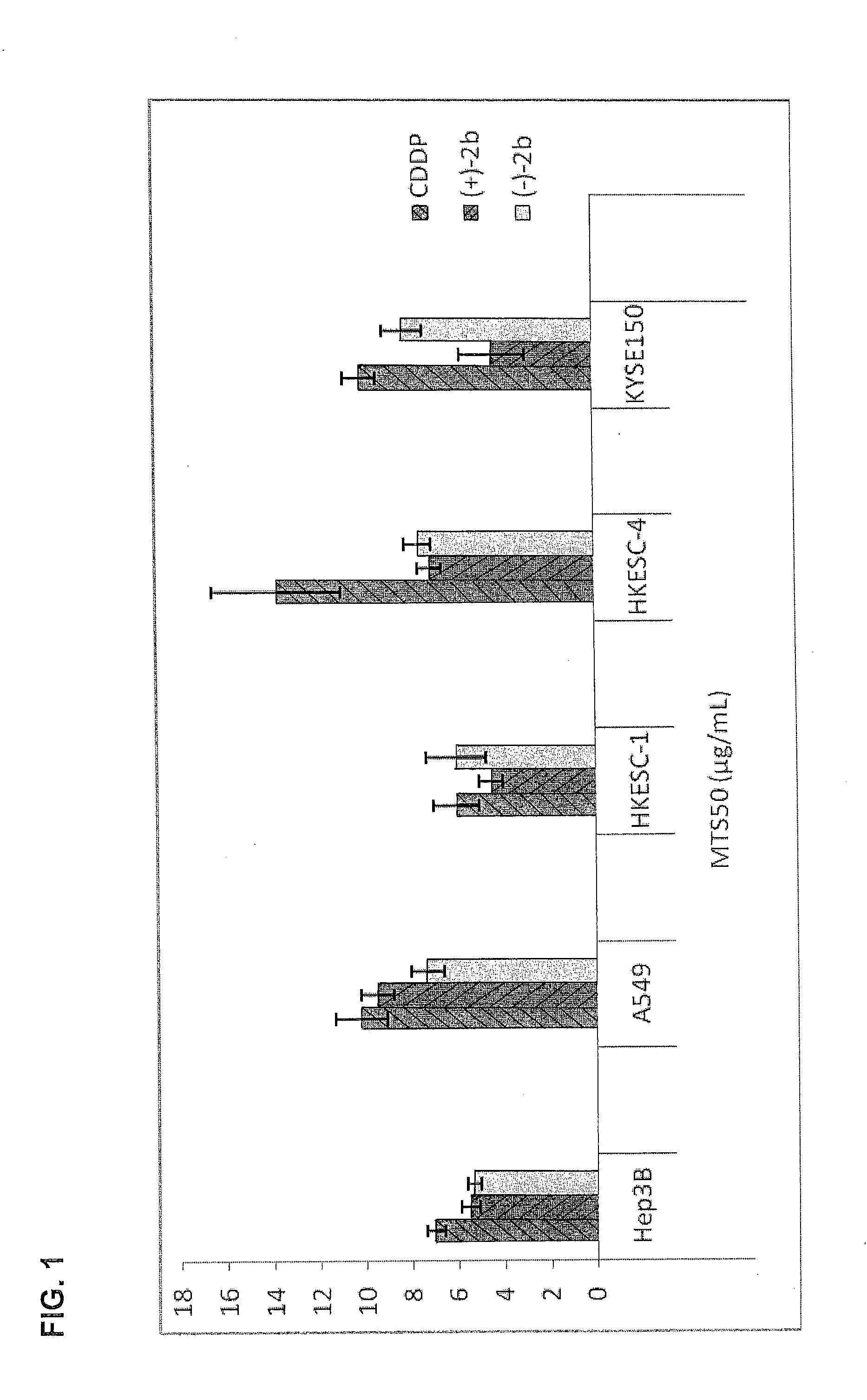
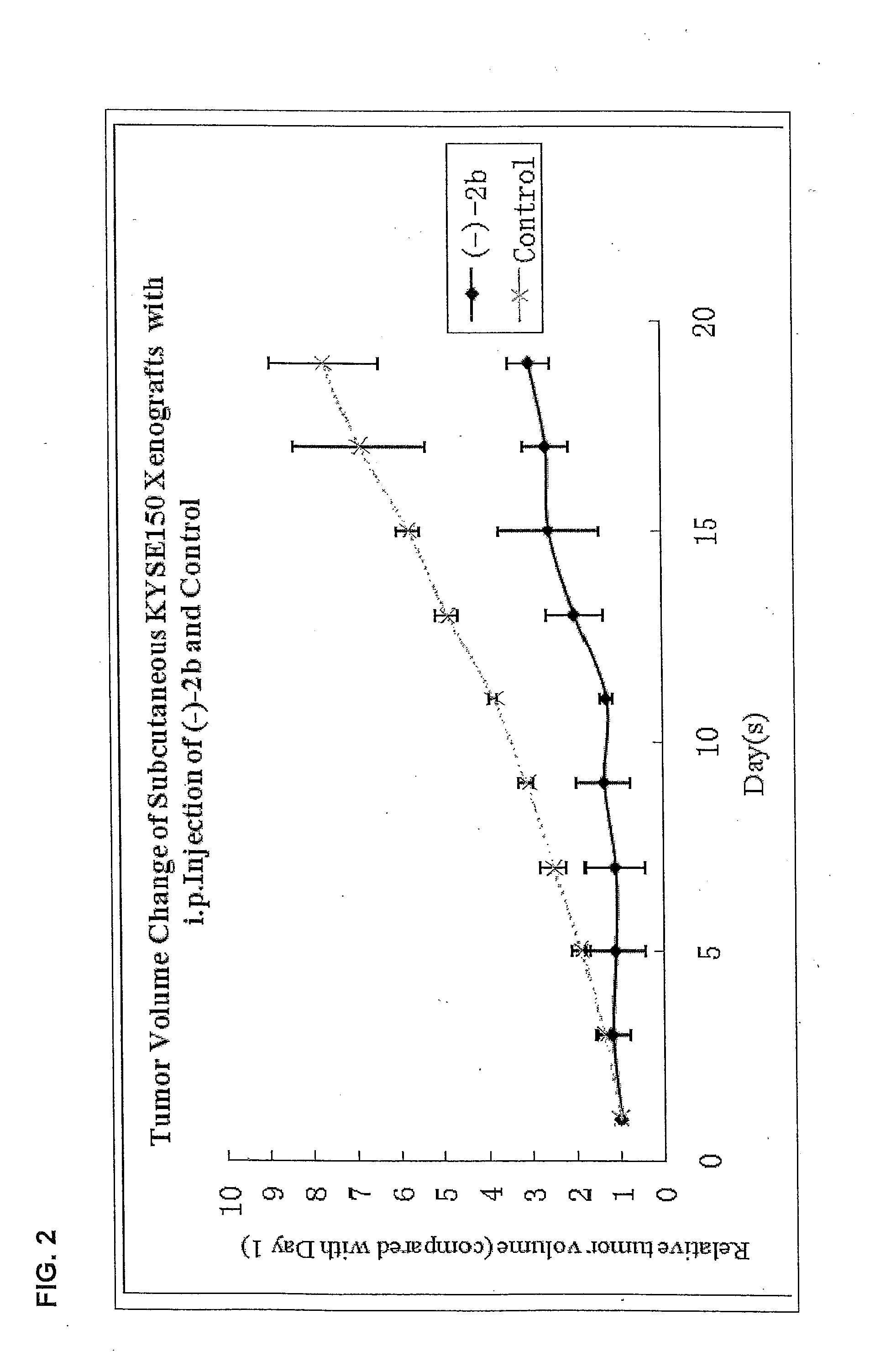
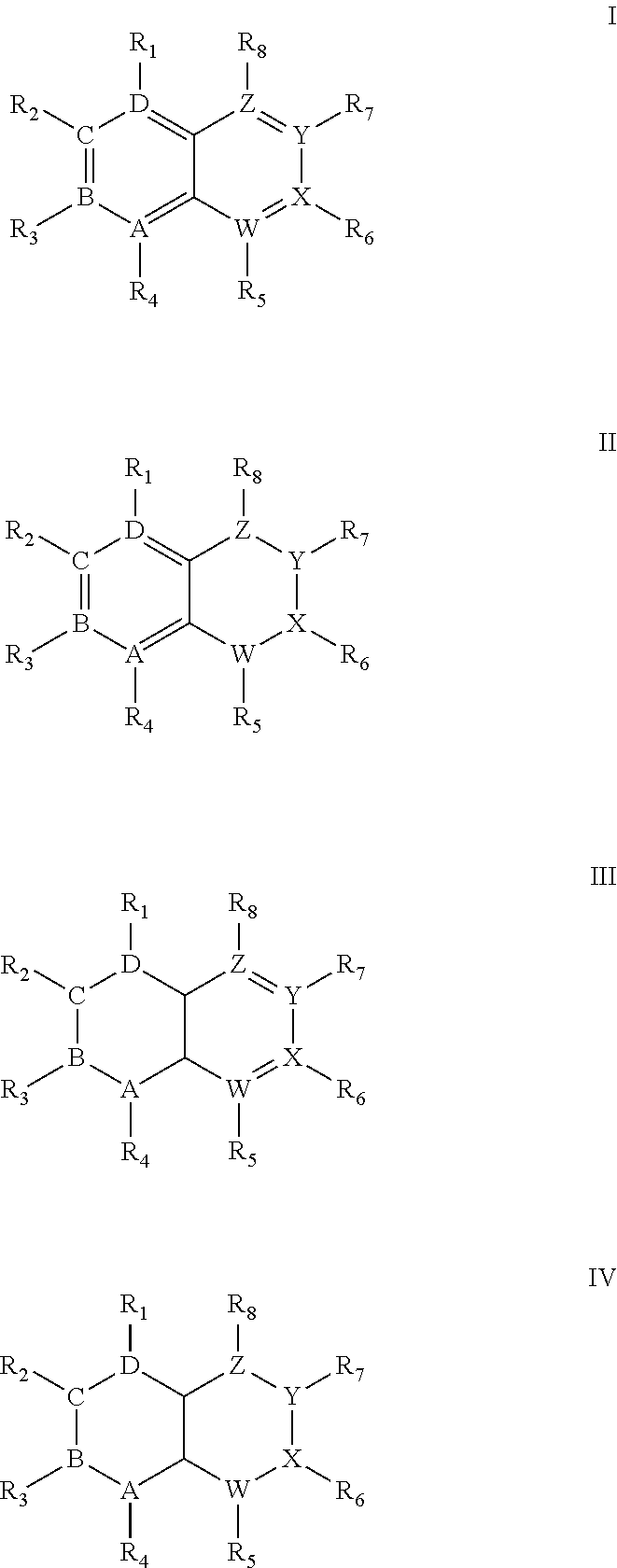
Quinoline derivatives showing anticancer activities against cancer cell lines of hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B), lung carcinoma (A549), esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (HKESC-1, HKESC-4 and KYSE150). The quinoline derivatives have a backbone structure of the following formulas:
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Protein chip for detecting esophageal squamous carcinoma marker and kit box of protein chip
The invention discloses a high-throughput multi-index protein chip for screening esophageal squamous carcinoma specific protein markers, and discloses a kit supporting the use. 55 types of esophageal squamous carcinoma differential proteins in the serum or blood plasma are selected and used as the esophageal squamous carcinoma protein markers and protein contrast prepare the protein chip; and the protein chip comprises a substrate, protein detection indicators and a contrast detection indicator coating, wherein the protein detection indicators are distributed as arrays on the substrate. Detection liquid of a supplementary experiment reagent is filled in the kit. By adopting the protein chip, the protein profiles of three types of people, namely, normal people, people subjected to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma precancerous lesions, and people subjected to the esophageal squamous carcinoma, can be determined; and means are provided for screening the esophageal squamous carcinoma in the early stage, diagnosing in mid stage and late stage, as well as monitoring the state of illness.
Owner:JIANGSU YUANHUA BIO TECH
Methods of cytodiagnostic staging of neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveUS7258987B2Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEpitheliumSquamous Carcinomas
Methods of diagnosing whether an epithelial tissue is an abnormal tissue by determining an expression pattern for PML in the epithelial tissue; determining an expression pattern for nuclear bodies in the epithelial tissue; determining SUMO-1 colocalization and comparing the expression pattern for PML and the expression pattern for nuclear bodies with a control are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for diagnosing whether a subject has mild dysplasia, moderate dysplasia, Type A severe dysplasia, Type B severe dysplasia, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, or poorly-differentiated cervical squamous cell carcinoma, by determining an expression pattern for PML, an expression pattern for nuclear bodies, and SUMO-1 colocalization and determining whether the sample is consistent with expression patterns expected for mild dysplasia, moderate dysplasia, Type A severe dysplasia, Type B severe dysplasia, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, or poorly-differentiated cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for distinguishing between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveUS20070264644A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLung squamous cell carcinomaCXCL13
The present invention is a method distinguishing between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. In particular, a 10-gene classifier has been identified which can be used to distinguish between primary squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. These genes include CXCL13, COL6A2, SFTPB, KRT14, TSPYL5, TMP3, KLK10, MMP1, GAS1, and MYH2. A panel of one or more of these genes, or proteins encoded thereby, can be used for early diagnosis and selection of an appropriate therapeutic treatment.
Owner:WISTAR INST THE A CORP OF PA +1
Application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor strain CH-H-1
The invention relates to an application of an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor strain CH-H-1 in a mammal for producing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. The primary tumor strain CH-H-1 disclosed by the invention can realize multiple passages through NOD / SCID mice, has significance for solving the bottleneck that the current treatment of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma can not avoid distant metastasis, and is an ideal object for fundamental research on the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and clinical early application.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Product for performing assisted prediction on postoperative survival time length of esophageal squamous carcinoma patient
ActiveCN103243161AGood conditionAccurate and Effective TreatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsMedicineEffective treatment
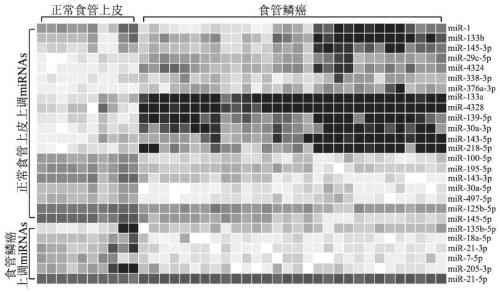
The invention discloses a product for performing assisted prediction on postoperative survival time length of an esophageal squamous carcinoma patient. The product comprises substances for detecting 178 miRNA expression quantity substances comprising hsa-miR-218-5p, hsa-miR-142-3p, hsa-miR-150-5p and hsa-miR-205-5p, and records a carrier with the diagnostic criteria and functional expressions as follows: if 0.94dig is less than dip, the postoperative survival time of the esophageal squamous carcinoma patient to be tested is more than 5 years, and if the 0.94dig is more than or equal to dip, the postoperative survival time of the esophageal squamous carcinoma patient to be tested is less than 5 years. After the result of the postoperative survival time of the esophageal squamous carcinoma patient is predicted by using the product, more accurate and effective treatment is adopted, and the patient condition can be effectively improved. In addition, the medicine which influences the expression quantities of hsa-miR-218-5p, hsa-miR-142-3p, hsa-miR-150-5p and hsa-miR-205-5p can be used for treating the esophageal squamous carcinoma.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
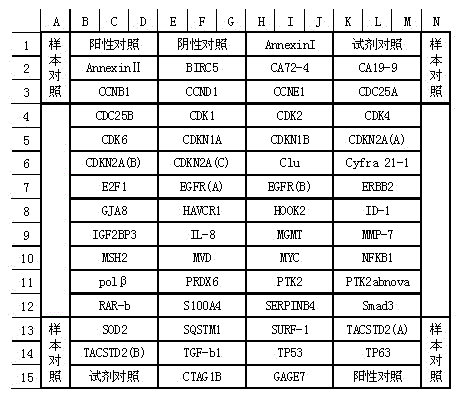
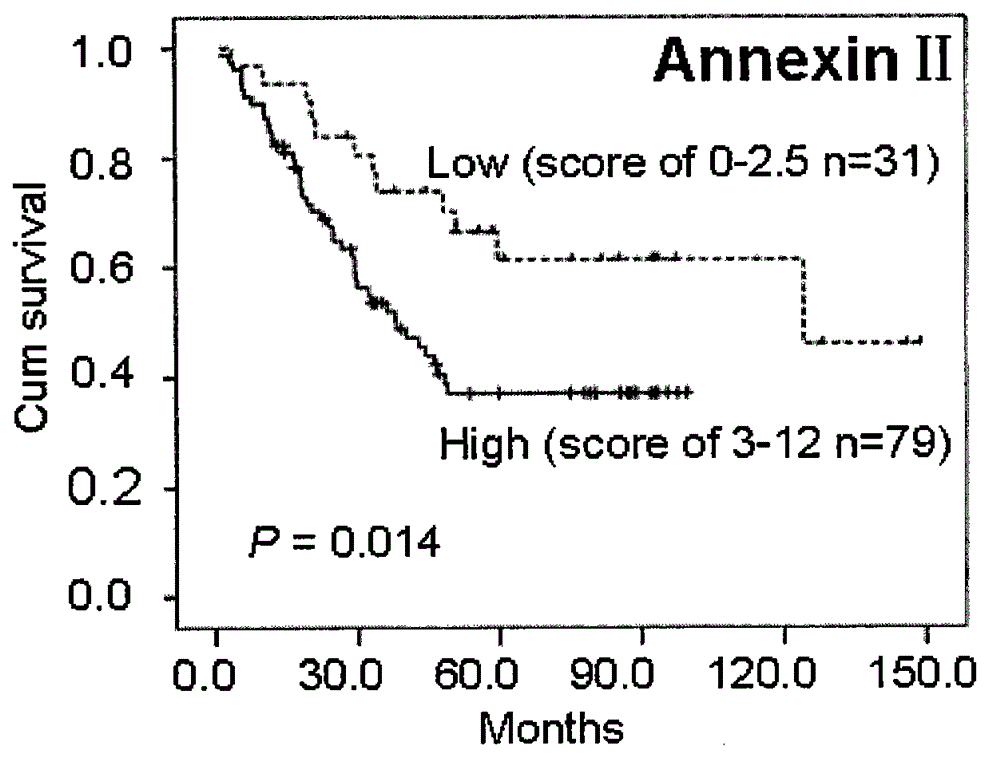
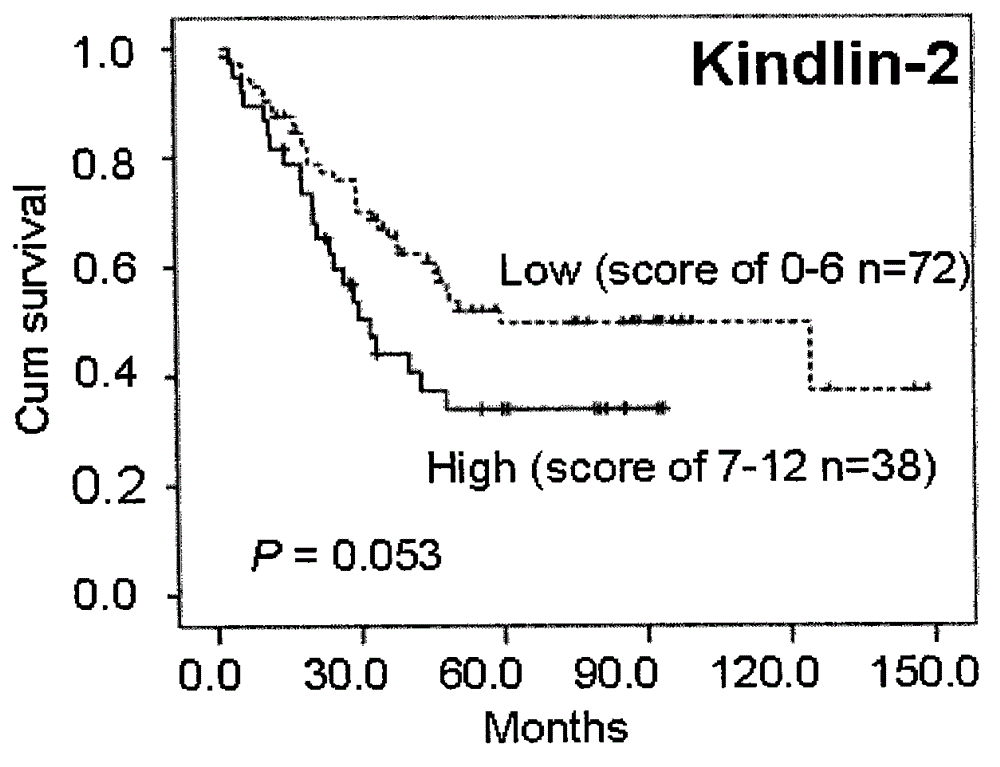
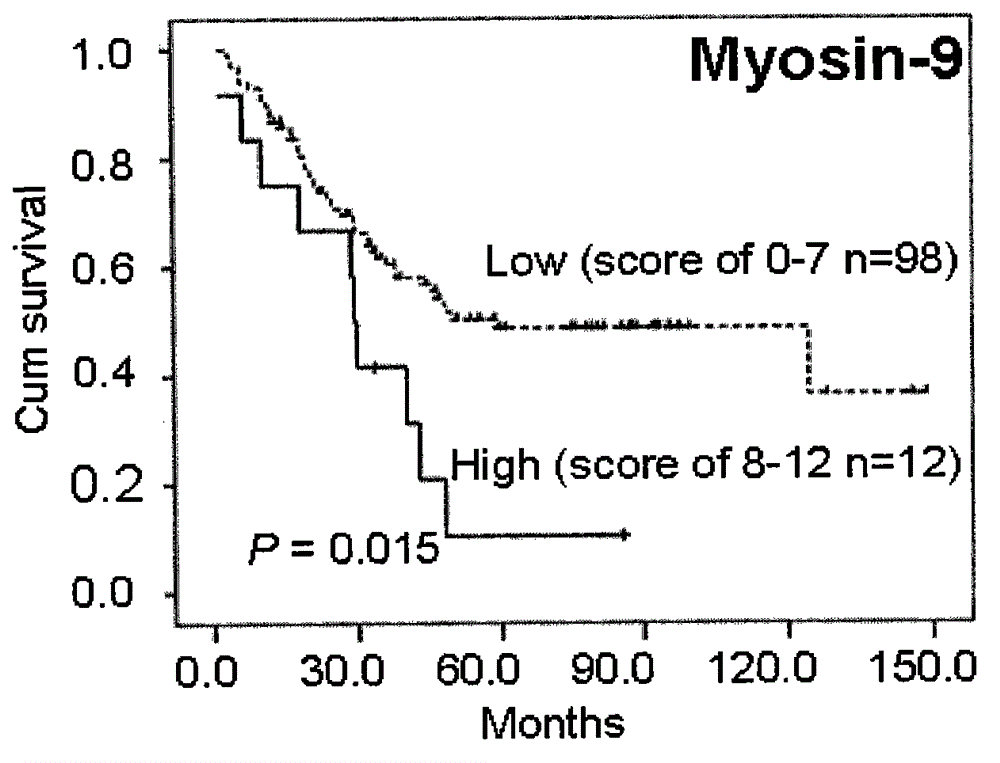
Kit integrating three proteins such as Kindlin-2, Myosin-9 and Annexin II for prognosis evaluation of patient suffering from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
The invention aims to provide a reagent capable of detecting the expression condition of a target protein in a paraffin-embedded tissue, and particularly provides a kit used for evaluating the prognosis information of a patient suffering from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The kit comprises antibodies of the three target proteins, namely Annexin II, Kindlin-2 and Myosin-9, and further comprises goat serum, 0.01 M citrate repair liquid, 3% H2O2, a Polymer reinforcing agent, a Polymer, a DAB color reagent and a PBS solution. The kit can be used for evaluating the prognosis of the patient; compared with the international TNM staging, the kit is simpler and easier to use, and higher in both sensitivity and specificity, and is more suitable for the prognosis evaluation of Chinese suffering from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Autoantibody joint detection ELISA kit for early screening of esophageal squamous carcinoma
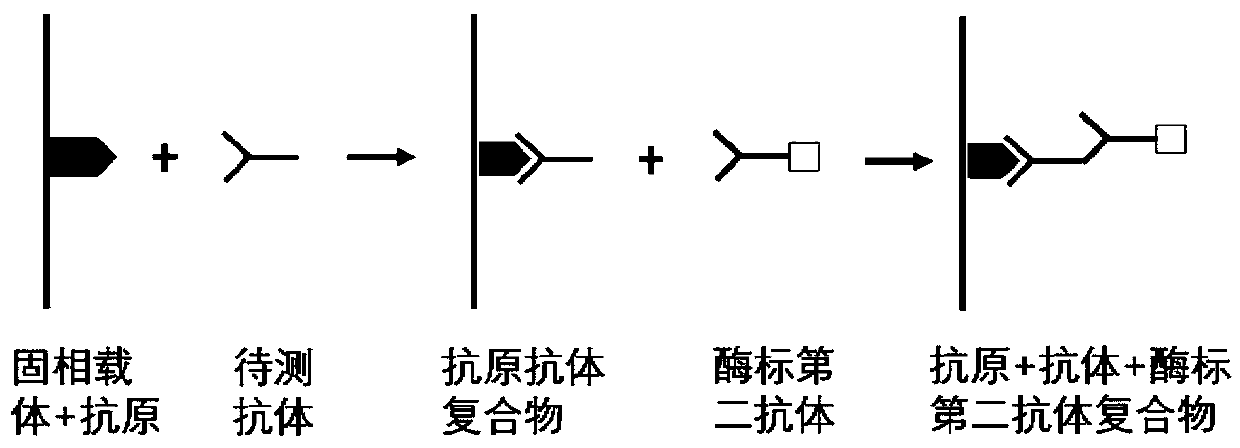
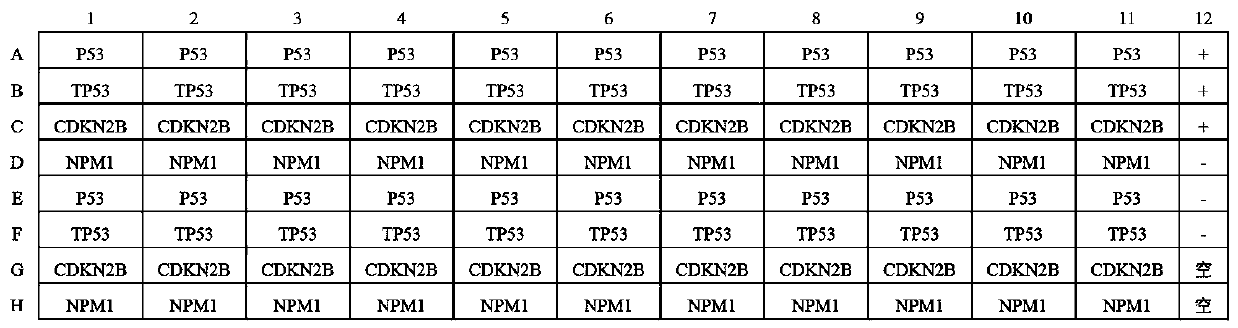
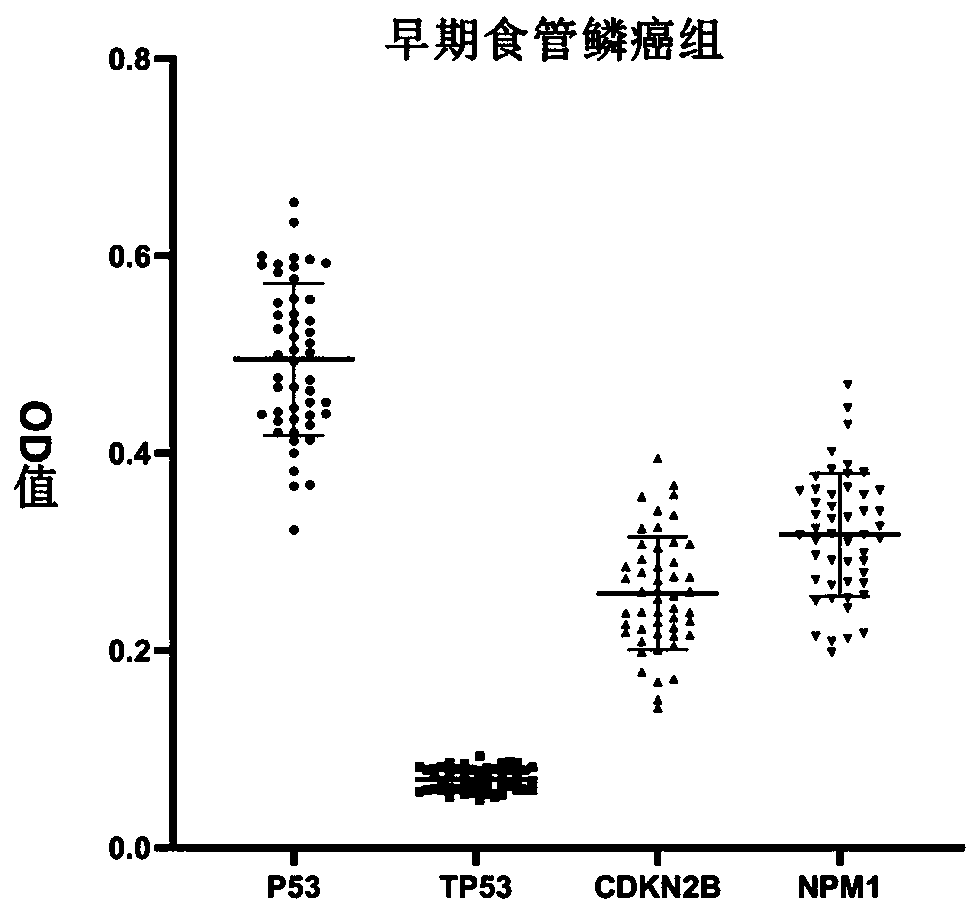
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical oncology, and particularly discloses an autoantibody joint detection ELISA kit for early screening of esophageal squamous carcinoma. The kit comprises a solid-phase carrier and a tumor-associated antigen coated on the solid-phase carrier, wherein the tumor-associated antigen consists of P53, TP53, CDKN2B and NPM1. Furthermore, the kit comprises sample diluent, a second antibody, second antibody diluent, positive control serum, negative control serum, developing solution, stop solution and washing solution. The ELISA kit is capable of effectively detecting the esophageal squamous carcinoma, especially the early esophageal squamous carcinoma, has detection sensitivity up to 88.8% and specificity up to 86.3%, can be used for the large-scale screening of asymptomatic groups in high-risk areas of the esophageal squamous carcinoma, and is beneficial for the esophageal squamous carcinoma screening and early discovery of the asymptomatichigh-risk groups.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
MiRNA combination used for detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof
InactiveCN101851682AEasy to useRelieve painMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell CarcinomaPathology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology, and discloses a miRNA combination used for detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof. The miRNA combination comprises miR-22, miR-127-3p, miR-148b and miR-223, and the miRNA combination can further comprise one or more of miR-10a, miR-100 and miR-133a. A kit comprises a probe combination of the miRNAs. The miRNA combination and the probe combination thereof provided by the invention can be used for detecting the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and can be used as a diagnosis marker for improving the accuracy of detection, improving the insuperable low specificity and low sensitivity, caused by individual difference, of a single marker, and improving a clinical detectable rate remarkably by combining other detection indicators and clinical symptoms of a patient, so the miRNA combination and the probe combination thereof become an effective means for early diagnosis of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Due to the adoption of the miRNA combination, a noninvasive serological test is adopted so as to bring convenience to clinical promotion.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A +1
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and application thereof
ActiveCN109342727AGood distinctionIncreased sensitivityDisease diagnosisStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell CarcinomaAutoantibody production
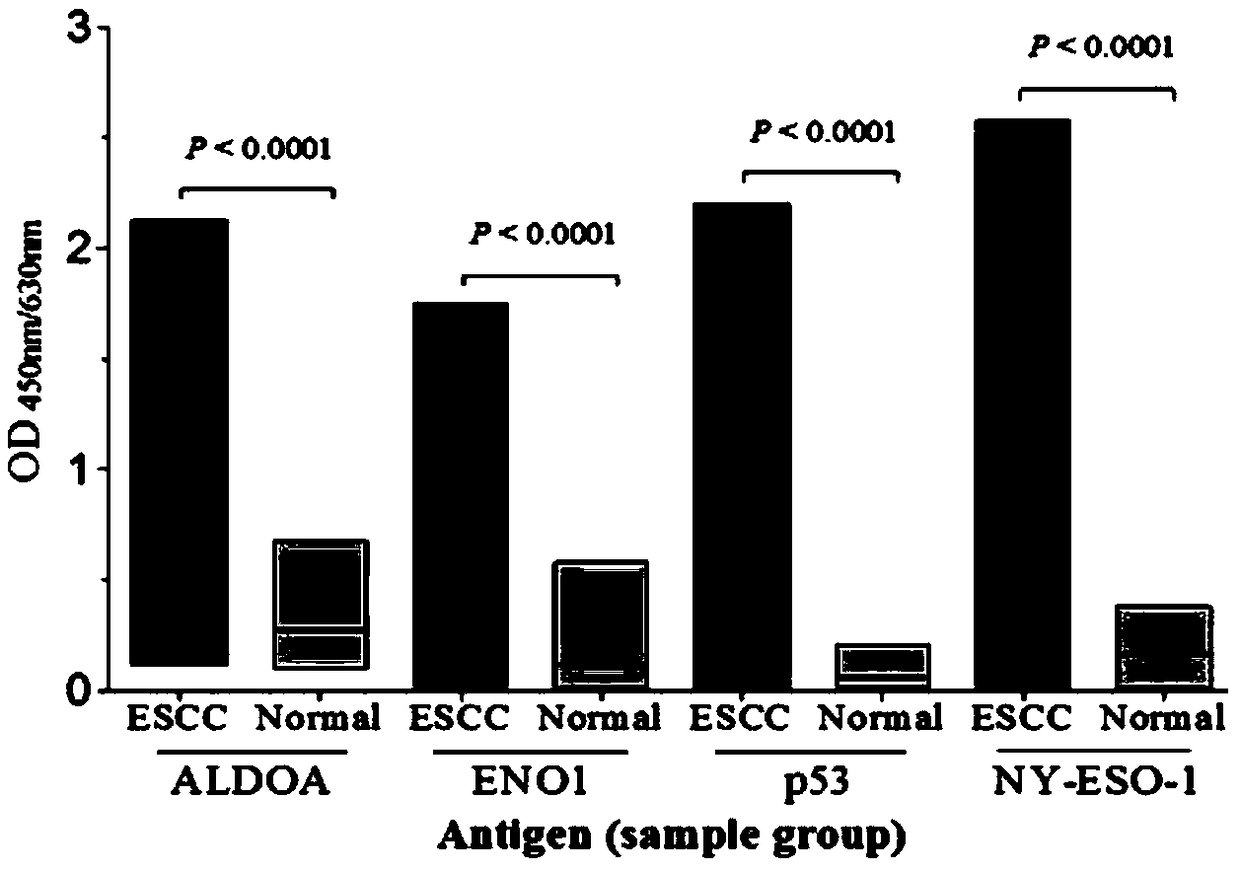
The invention relates to an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and an application thereof. The molecular model mainly comprises an ALDOA autoantibody, an ENO1 autoantibody, a p53 autoantibody, and an NY-ESO-1 autoantibody, and can be used for preparing a kit for distinguishing esophageal squamous carcinoma patients and healthy medical examiners. The kit for detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients mainly comprises recombinant ALDOAD protein, recombinant ENO1 protein, recombinant p53 protein, and recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein. According to the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma autoantibody molecular marker model and the application thereof, the ENO1 autoantibody is found to be elevated in serum level in the esophageal squamous carcinoma patients for the first time, and is jointly detected with the ALDOA autoantibody, the p53 autoantibody, and the NY-ESO-1 autoantibody for distinguishing the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients andthe healthy medical examiners, and has a better distinguishing effect than a single index detection; and in addition, the detection method adopted by the invention is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay indirect method, is simple and convenient to implement, has good sensitivity and specificity, and is a method which is mature and reliable and can be widely used in base layer hospitals.
Owner:汕头市颂美恩生物科技有限公司
Microfluid system used for detecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and application thereof
The invention discloses a microfluid system used for detecting CTCs of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The microfluid system is prepared through the following steps: 1, preparation of a microfluid pipeline system which is divided into two or more parallel microfluid channels from an inlet, wherein the microfluid channels are provided with a plurality of fishbone structures; 2, etching of a silicon nanowire substrate; 3, surface modification and biotin bio-functionalization of silicon nanowires; and 4, modification of the silicon nanowire substrate and assembling of a PDMS microfluid chip. In use of the system, cells of a to-be-detected sample and 200 [mu]L of a PBS solution of biotin-modified p-EpCAM and p-cKit are subjected to co-incubation for 1 h, and then a co-incubation product is injected into the microfluid system for detection. The microfluid system provided by the invention can recognize and bind to CTCs with extremely low content, and is applicable to traditional immunofluorescence dyeing; obtained detection results and phenotypic analysis results can be subjected to further specific release; so purification of CTCs is realized, and the purity of CTCs is improved so as to meet requirements of gene detection limits.
Owner:无锡准因生物科技有限公司
Function of HOXD-AS1 in diagnosis and treatment of esophageal squamous carcinoma
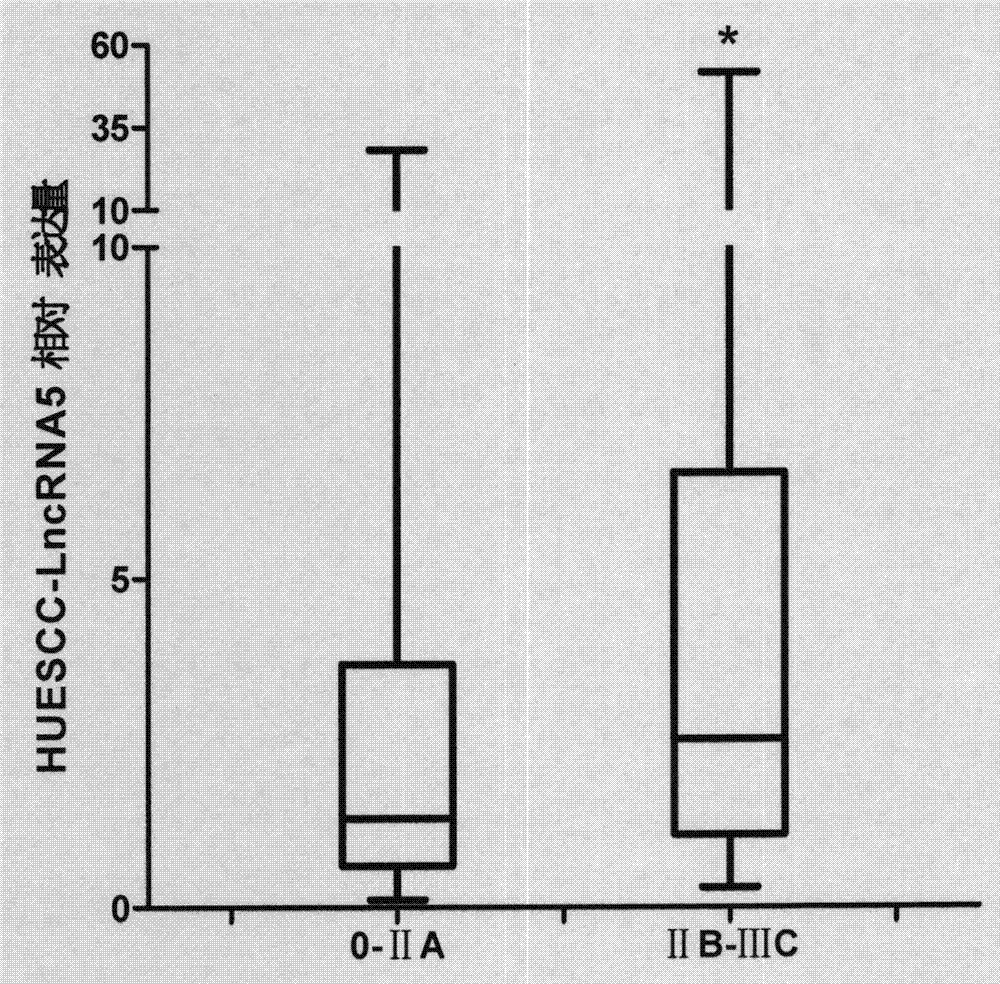
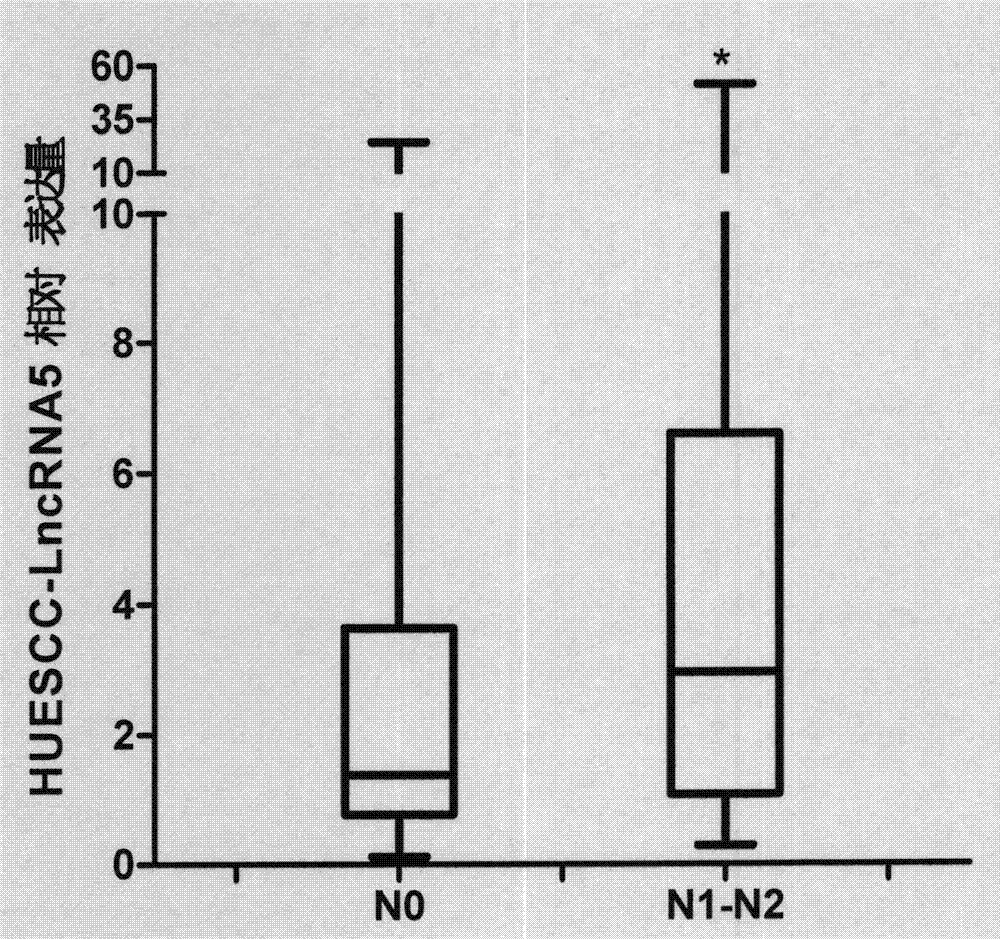
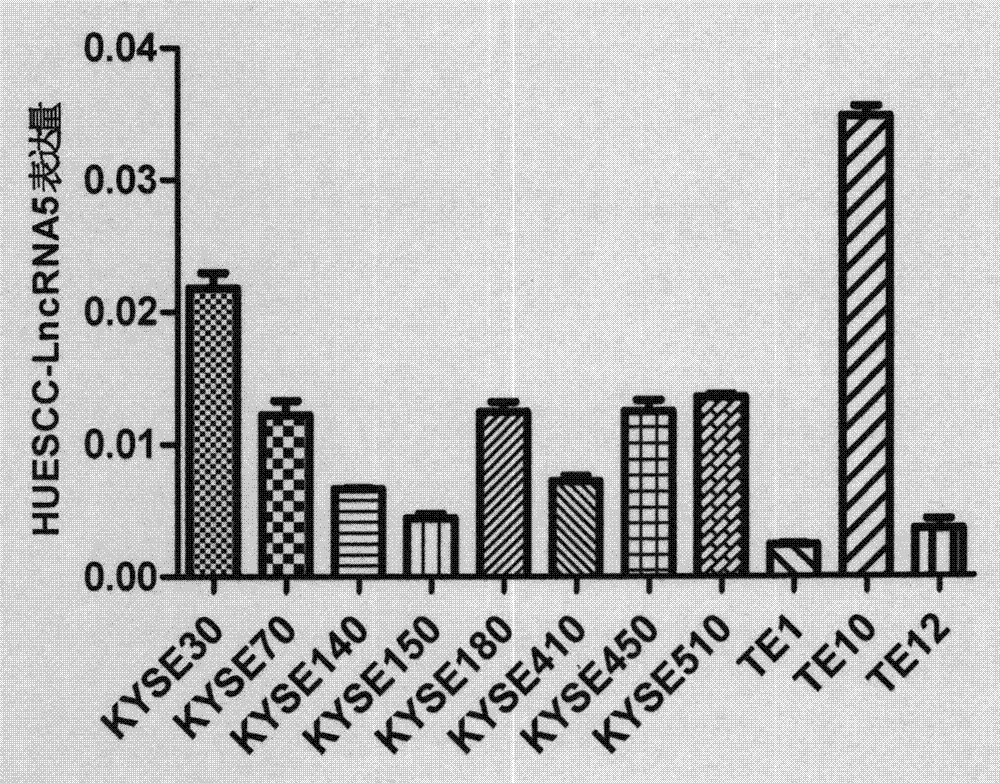
The invention discloses a function of HOXD-AS1 in diagnosis and treatment of esophageal squamous carcinoma and relates to discovery, detection and application of long-chain noncoding RNA. According to the sequences of the long-chain noncoding RNA, a specific real-time quantitative PCR primer is designed and synthesized; a real-time quantitative PCR preparation is utilized to detect the expression level of the long-chain noncoding RNA in a clinical case specimen of the esophageal squamous carcinoma, and results show that the expression of the long-chain noncoding RNA in the esophageal squamous carcinoma is remarkably up-regulated and the expression level of the long-chain noncoding RNA is highly associated with both clinical stages and pathological N stages of an esophageal squamous carcinoma patient. The specific detection sequences disclosed by the invention are expected to be used for preparing the preparation for auxiliary diagnosis, curative effect prediction or prognosis judgment of the esophageal squamous carcinoma. In addition, two siRNA sequences for specifically knocking down the expression of the long-chain noncoding RNA are designed and synthesized; an experiment proves that after the expression level of the long-chain noncoding RNA is specifically knocked down in a human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell strain, the quantity of migrated tumor cells is remarkably reduced; therefore the siRNA sequences disclosed by the invention is also expected to be used as a molecular targeting treatment tool for inhibiting the cell migration rate of the esophageal squamous carcinoma.
Owner:江苏万成生物医学研究院有限公司
Cancer lesion detection and diagnosis system for early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of narrow-band endoscopic image
ActiveCN112102256AAccurate detectionAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic systemEndoscopic image
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and particularly relates to a cancer lesion detection and diagnosis system for early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of a narrow-band endoscopic image. The system comprises a feature extraction backbone network, a feature pyramid, a region candidate network, a region of interest pooling unit and a cancer focus classification network, and a system for visualization on a narrow-band imaging endoscope image. The backbone network is used for extracting a feature map of an input image; the feature pyramid is used for fusing features of different scales; the region candidate network proposes a possible lesion region; the region of interest pooling unit pools the features to a suspected lesion area; the cancer lesion classification network classifies the cancer lesions; and finally, a narrow-band imaging endoscopic image is visualised, and frame selection marking is carried out on the cancer lesions by using different colors. The image of the narrow-band imaging endoscope is input into the network model, the cancer focus of the early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma existing in the image is detected and diagnosed, the diagnosis efficiency can be effectively improved, and a doctor is assisted in obtaining higher diagnosis precision.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
ALDOA autoantibody andapplications thereof in diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveCN105277709ABiological testingStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell CarcinomaAutoantibody production
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and medical technology, and relates to a marker ALDOA autoantibody for distinguishing between esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients and normal persons, and a detection method and applications thereof. In the invention, the serum proteome research technology is adopted to identify a new marker ALDOA autoantibody for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Purified ALDOA proteins are subjected to ELISA analysis for detecting expression level of the ALDOA autoantibody in serums of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients and normal persons, and the results indicate that the level of the ALDOA autoantibody in the serum of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients is obviously higher than that of the normal persons. The ALDOA autoantibody of the invention can serve as the marker of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and can be used in the diagnosis of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:汕头大学医学院附属肿瘤医院 +2
Marker for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis and application of marker
ActiveCN109897899ARealize individualized treatmentImprove treatmentHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementLife qualitySquamous Carcinomas
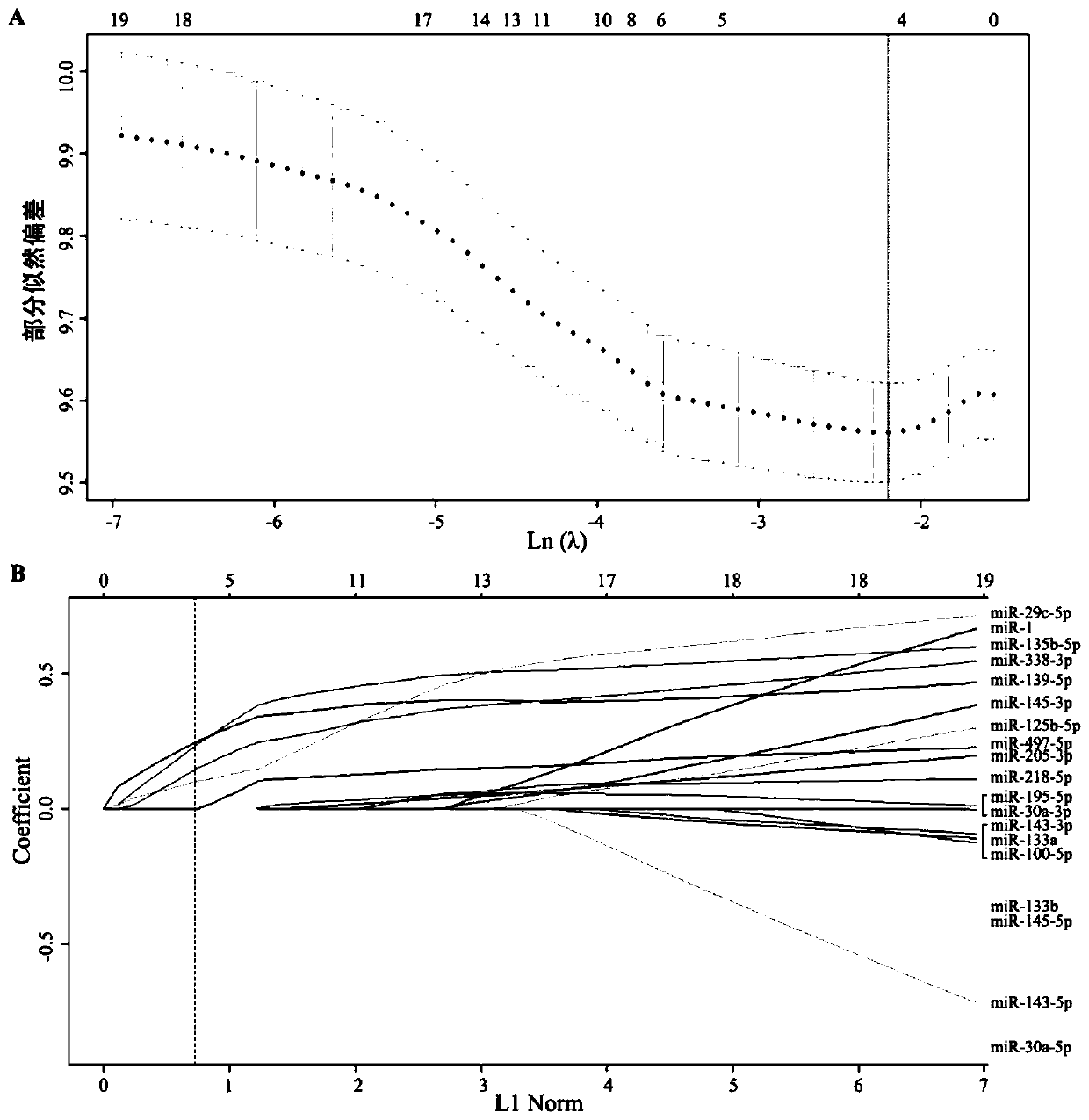
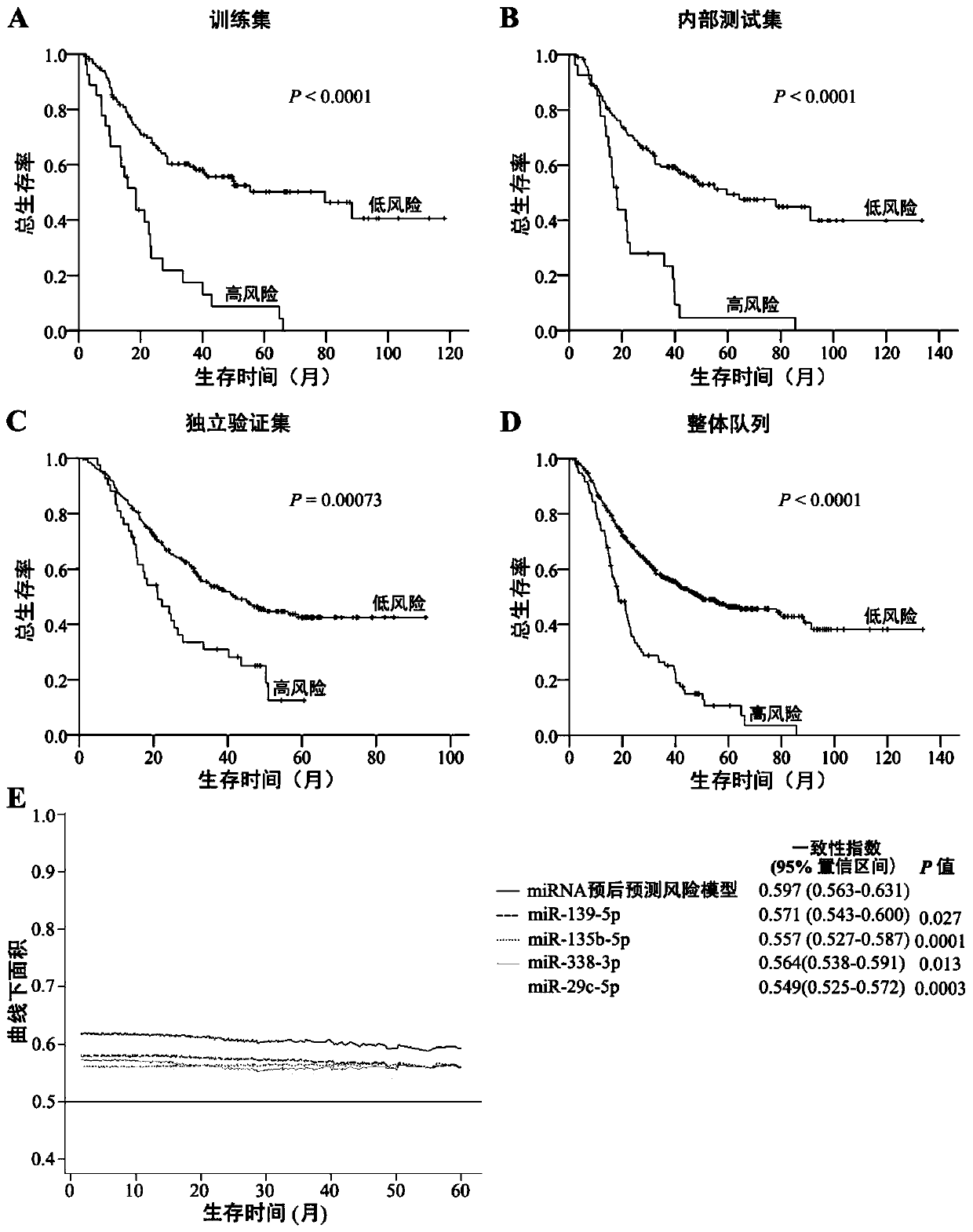
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering and tumor markers, in particular to a marker for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis and an application of the marker. The marker is a combined marker consisting of one or more of miR-135b-5p, miR-139-5p, miR-29c-5p and miR-338-3p, and locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis is predicted by detecting expression levels of the four miRNA in tumor tissue and performing calculation according to a formula (0.4690*miR-135b-5p expression level)+(0.3839*miR-139-5p expression level)+(0.1733*miR-29c-5p expression level)+(0.3368*miR-338-3p expression level). The combined marker has the advantages of good stability and high sensitivity and specificity and can more accurately and more valuably evaluateprognosis of patients than traditional clinical pathological factors such as TNM (tumor-node-metastasis) staging and the like. On one hand, the molecular marker related to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis is provided, on the other hand, an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis prediction model is established, so that individual treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma isrealized, the comprehensive treatment level of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is improved, the life quality of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients is improved, and the lifetime of theesophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients is prolonged.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Kit used for aided prediction on postoperative survival time of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
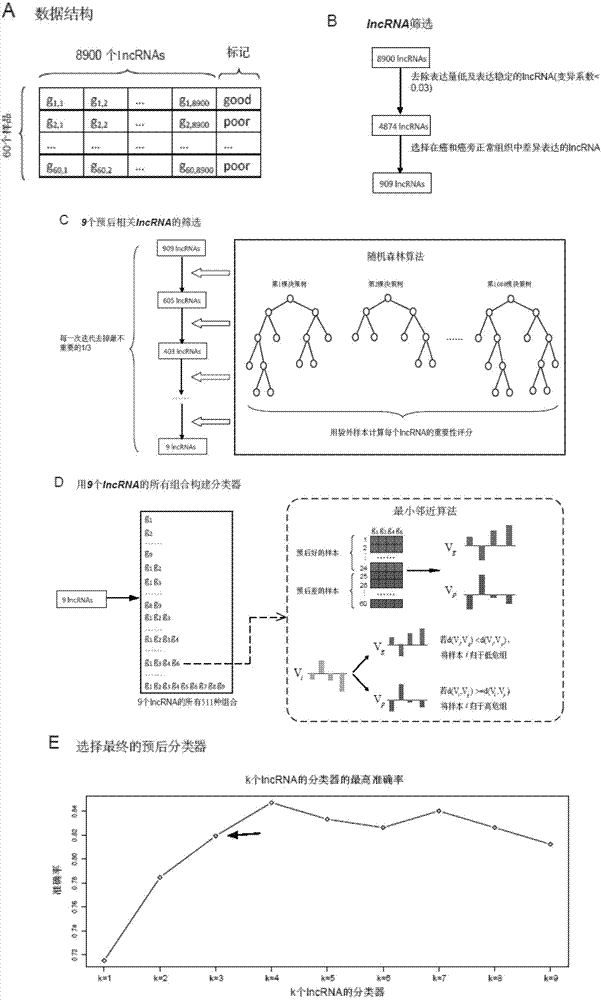
The invention discloses a kit used for aided prediction on postoperative survival time of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients. The kit comprises a substance used for detecting lncRNA 1 expression quantity, a substance used for detecting lncRNA 2 expression quantity, and a substance used for detecting lncRNA 3 expression quantity; the sequence of lncRNA 1 is represented by sequence 1 in a sequence table; the sequence of lncRNA 2 is represented by sequence 2 in the sequence table; and the sequence of lncRNA 3 is represented by sequence 3 in the sequence table. A plurality of ESCC patients are investigated; expression characteristics of lncRNA in cancer tissue and near cancer normal tissue are analyzed; it is observed that expression profile of a plurality of lncRNA in cancer tissue is obviously different from that of near cancer normal tissue; a model is established based on three lncRNA relative expression quantity; and the model can be used for aided prediction on postoperative survival time of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
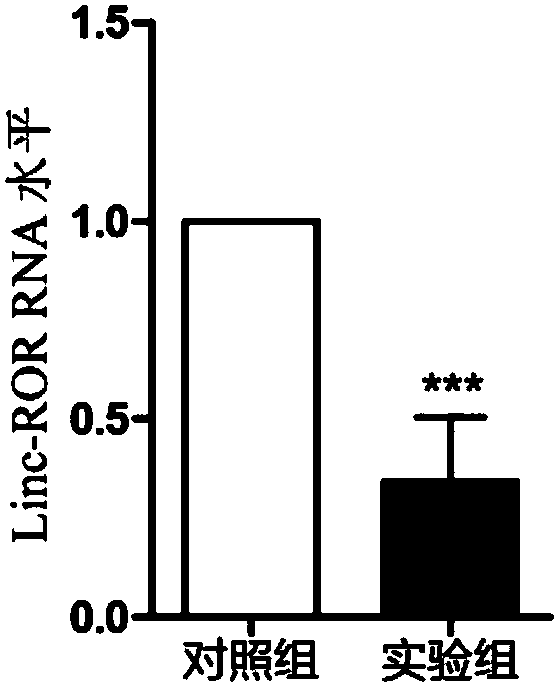
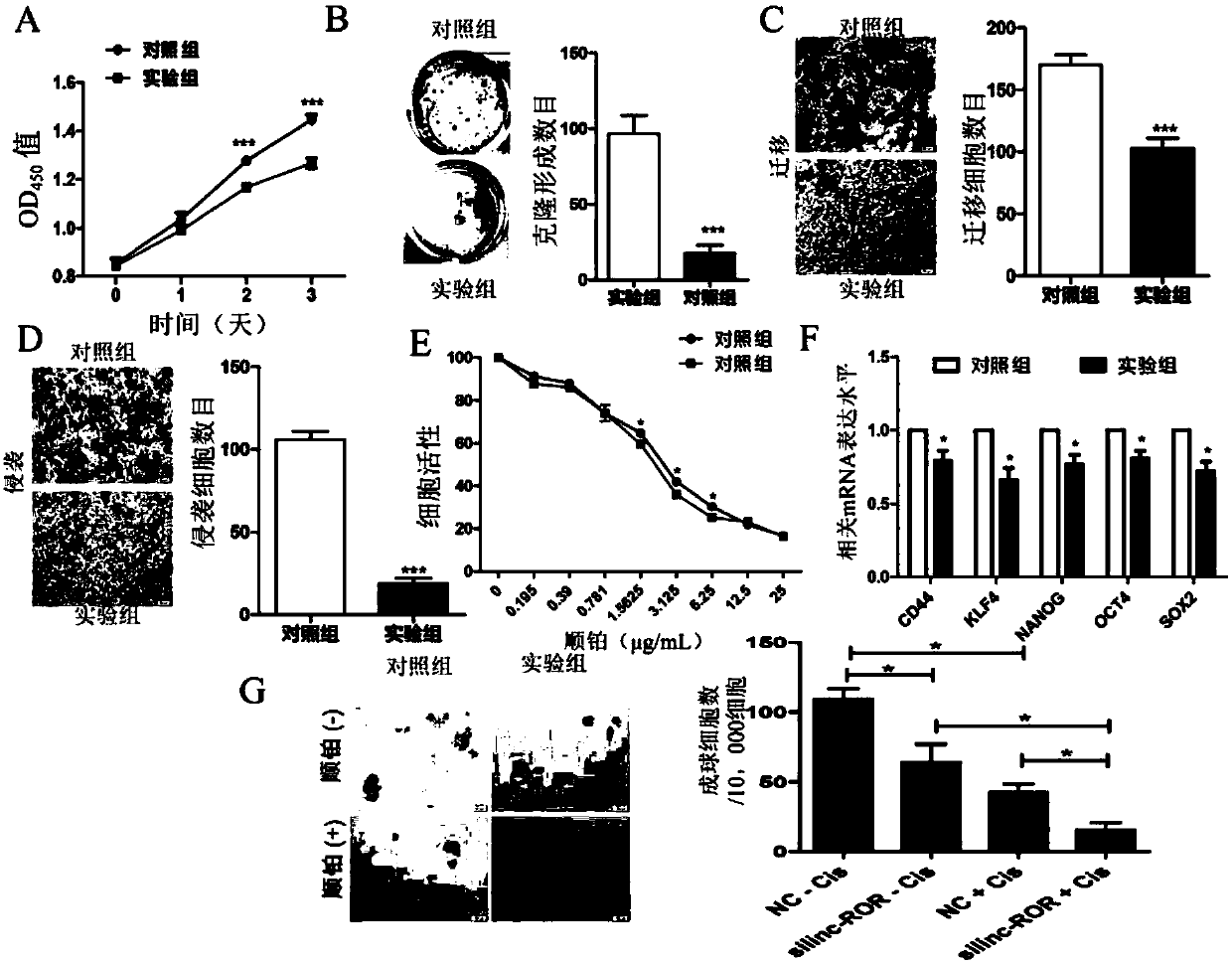
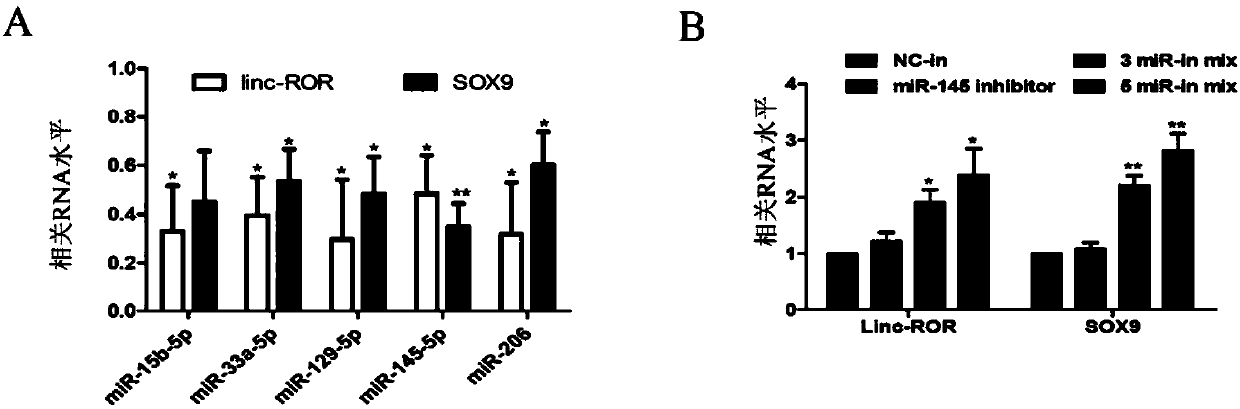
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA-ROR
InactiveCN107760685APrevent proliferationSuppress drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMir 145 5pInvasion and migration
The invention discloses application of long-chain non-coding RNA-ROR, in particular to application of a substance used for detecting linc-ROR and a substance used for inhibiting expression and / or functions of linc-ROR in preparation of products used for assisting diagnosis and treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma respectively. Experiments show that inhibition of linc-ROR expression can inhibit proliferation, invasion, migration and drug resistance of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells and tumor stem cell-like characteristics and plays an important role in occurrence and development ofesophageal squamous carcinoma. Meanwhile, multiple microRNAs include has-miR-15b-5p, has-miR-33a-5p, has-miR-129-5p, has-miR-145-5p and has-miR-206 and can be targeted to linc-ROR. The invention provides a new target used for diagnosing and treating the esophageal squamous carcinoma, and a linc-ROR gene can be taken as a new target marker and used for preparing a new product used for diagnosing and / or treating the esophageal squamous carcinoma. The application disclosed by the invention has important clinical significance in improvement of diagnosis and treatment level of the esophageal squamous carcinoma.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Quinoline derivatives as anti-cancer agents
Quinoline derivatives showing anticancer activities against cancer cell lines of hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B), lung carcinoma (A549), esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (HKESC-1, HKESC-4 and KYSE150). The quinoline derivatives have a backbone structure of the following formulas:
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor line CH-H-2
InactiveCN102766600AStable traitsHigh metastatic potentialTumor/cancer cellsPrimary tumorBasic research
The invention relates to an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor line CH-H-2 which is used in mammals to produce esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. The primary tumor line CH-H-2 can be passed by NOD / SCID mice for multiple times, is significant in solving the inevitable bottleneck problem of distant metastasis in the current esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treatment, and is an ideal object for the basic research and clinical early application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Long-chain non-coding RNA LINC01419 molecular marker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof
InactiveCN108588220AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIndividualized treatment5 aza cdr
The invention discloses a long-chain non-coding RNA marker for assisting diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The long-chain non-coding RNA is LINC01419, the expression amount of the long-chain non-coding RNA is detected and can be used for auxiliary diagnosis or prediction of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and the methylation status of a GSTP1 gene is monitored to predict the sensitivity of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to 5-FU chemotherapy. The expression level of a LINC01419 gene can be detected by an RT-PCR, real-time quantitative PCR, immunoassay, in situ hybridization, a chip or a high-throughput sequencing platform. The invention further discloses application of a methyltransferase inhibitor 5-Aza-CdR to regulate the expression of the long-chainnon-coding RNA LINC01419 and response to the 5-FU, and application of an inhibitor medicine including the long-chain non-coding RNA LINC01419 in treatment of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The molecular marker of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is provided, a theoretical basis for mechanism research and clinical individualized treatment of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma isprovided, and by monitoring the overexpression of the LINC01419 in the ESCC, a new treatment strategy for the clinical treatment of the ESCC can be provided.
Owner:汕头大学医学院附属肿瘤医院
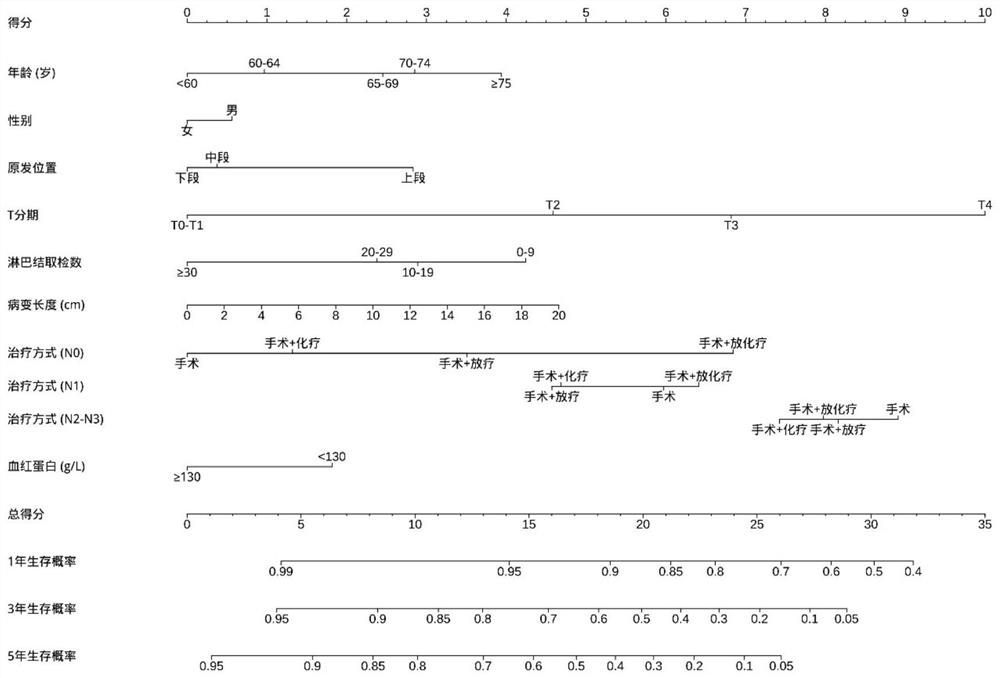
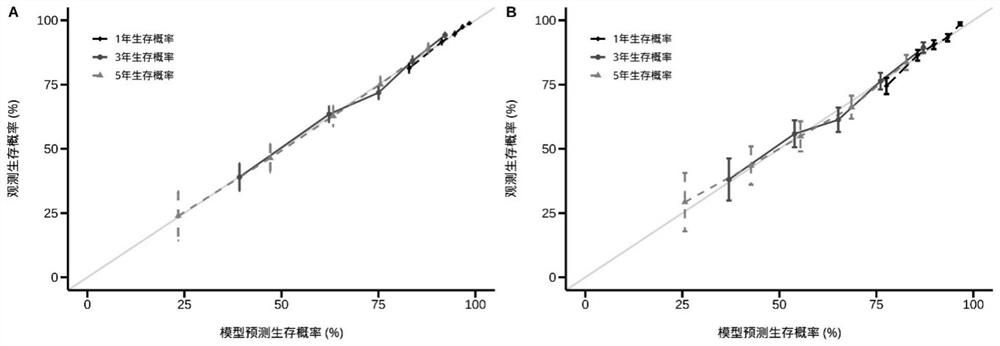
Lasso-based esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient risk prediction column diagram model establishment method
ActiveCN112635056AFeature variable foundImprove performanceMedical data miningHealth-index calculationOncologyRisk groups
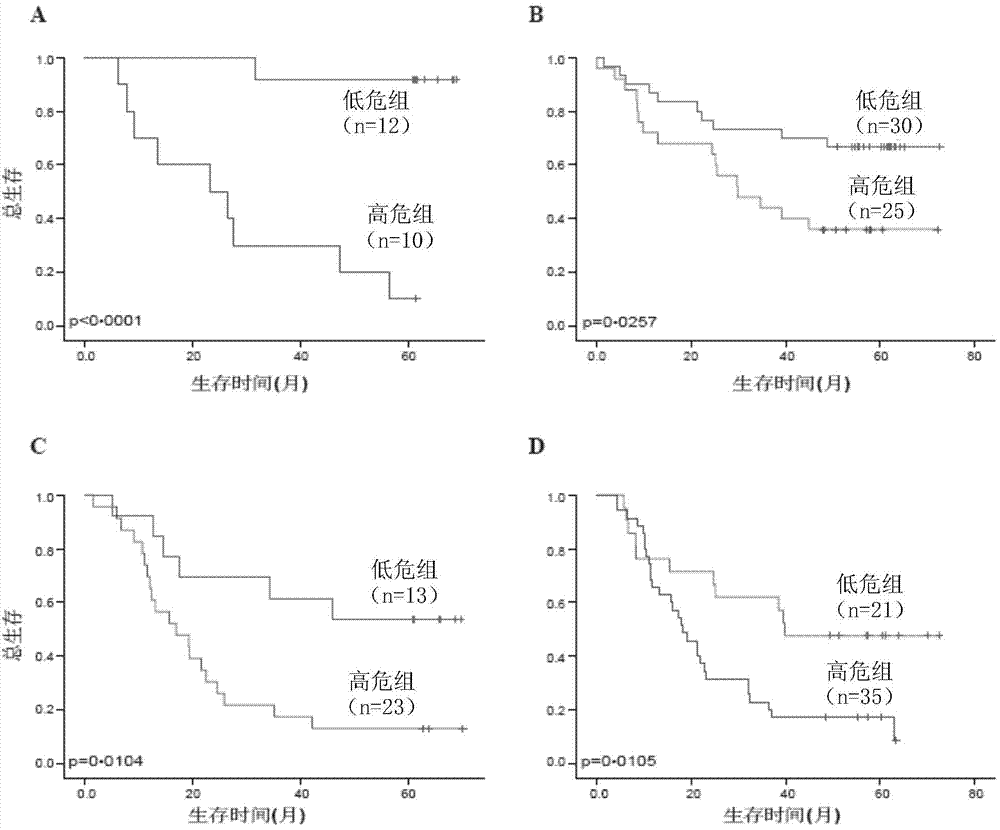
The invention provides a Lasso-based esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient risk prediction column diagram model establishment method, which is used for evaluating the postoperative survival risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting clinical data of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients, analyzing the clinical data by utilizing single-factor Cox, Lasso and multi-factor Cox regression analysis methods to obtain important characteristic variables, and establishing probability prediction models with different characteristic dimensions; secondly, selecting a probability prediction model with better performance and establishing a postoperative risk prediction column diagram model of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient; and finally, dividing the patients into a high-risk group and a low-risk group according to the postoperative risk prediction column diagram model of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients, and verifying the reliability and effectiveness of model classification through a KM survival curve analysis method. According to the method, the postoperative survival risk of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient can be accurately predicted, reference is better provided for treatment of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient, and meanwhile the risk prediction cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Esophageal squamous carcinoma radical postoperative patient prognosis prediction model construction method and device
PendingCN113270188AConducive to survivalAccurateMedical simulationMedical data miningParanasal Sinus CarcinomaPatient characteristics
The invention discloses an esophageal squamous carcinoma radical postoperative patient prognosis prediction model construction method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining clinical diagnosis and treatment data and follow-up visit survival data, carrying out multi-factor Cox regression analysis on patient characteristic variables, tumor pathology characteristic variables, treatment condition variables and test index variables according to follow-up visit survival data, carrying out variable screening by utilizing a step-by-step back algorithm and an Akaike information criterion, and carrying out variable screening on the screened candidate variables again to obtain modeling variables; and performing multi-factor Cox regression analysis on modeling variables and interaction items of every two modeling variables to construct a prognosis prediction model of a patient after the esophageal squamous carcinoma radical operation, wherein the prediction variables comprise age, gender, tumor primary position, T stage, lymph node detection number, tumor size, preoperative hemoglobin level and N stage treatment mode interaction items. According to the method, the prediction accuracy can be improved, the optimal benefit group of different treatment schemes is defined, and the prognosis evaluation precision of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is realized.
Owner:BEIJING CANCER HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL
Detection and application of long non-coding RNA having substantial expression decrease in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveCN103952478AHigh sensitivityQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCurative effectRNA Sequence
The invention relates to long non-coding RNA and application thereof. According to a sequence of the long non-coding RNA, specific qRT-PCR (Quantitative Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers and probes are designed and synthesized and reagents used for esophageal carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis or curative effect prediction are prepared. The qRT-PCR reagents are utilized for detecting the expression level of the long non-coding RNA in specimens of esophageal carcinoma clinical cases and a substantial decrease of the long non-coding RNS expression is found in esophageal carcinoma. The long non-coding RNA can be applied to preparing reagents used for esophageal carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis, curative effect prediction or prognosis judgment.
Owner:NANJING FIRST HOSPITAL
Medicine for inhibiting proliferation of esophageal cancer cells
InactiveCN108187050AImprove tolerancePromote proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cell linesCisplatin
The invention discloses a medicine for inhibiting proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. The roles of SOX9 in the occurrence and development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and a downstream molecular mechanism regulated by the SOX9 are researched from the view of tumor stem cells by detecting clinical specimens and establishing an in vitro cell model and an in vivo mouse model; experiments proves that the SOX9 is highly expressed in the tissues of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and in esophageal cancer stem cell balls, and can promote the proliferation and self-renewal of a cell line of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, the formation of tumor stem cell balls, the growth of transplantation tumor in nude mice, and the tolerance to chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin. The invention provides a theoretical basis and an experimental basis for further clarifying the occurrence and development mechanism and targeted treatment of esophageal cancer.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Application of NFI transcription factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN107904307AAssess the degree of differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisOvarian Squamous Cell CarcinomaTissue Differentiation
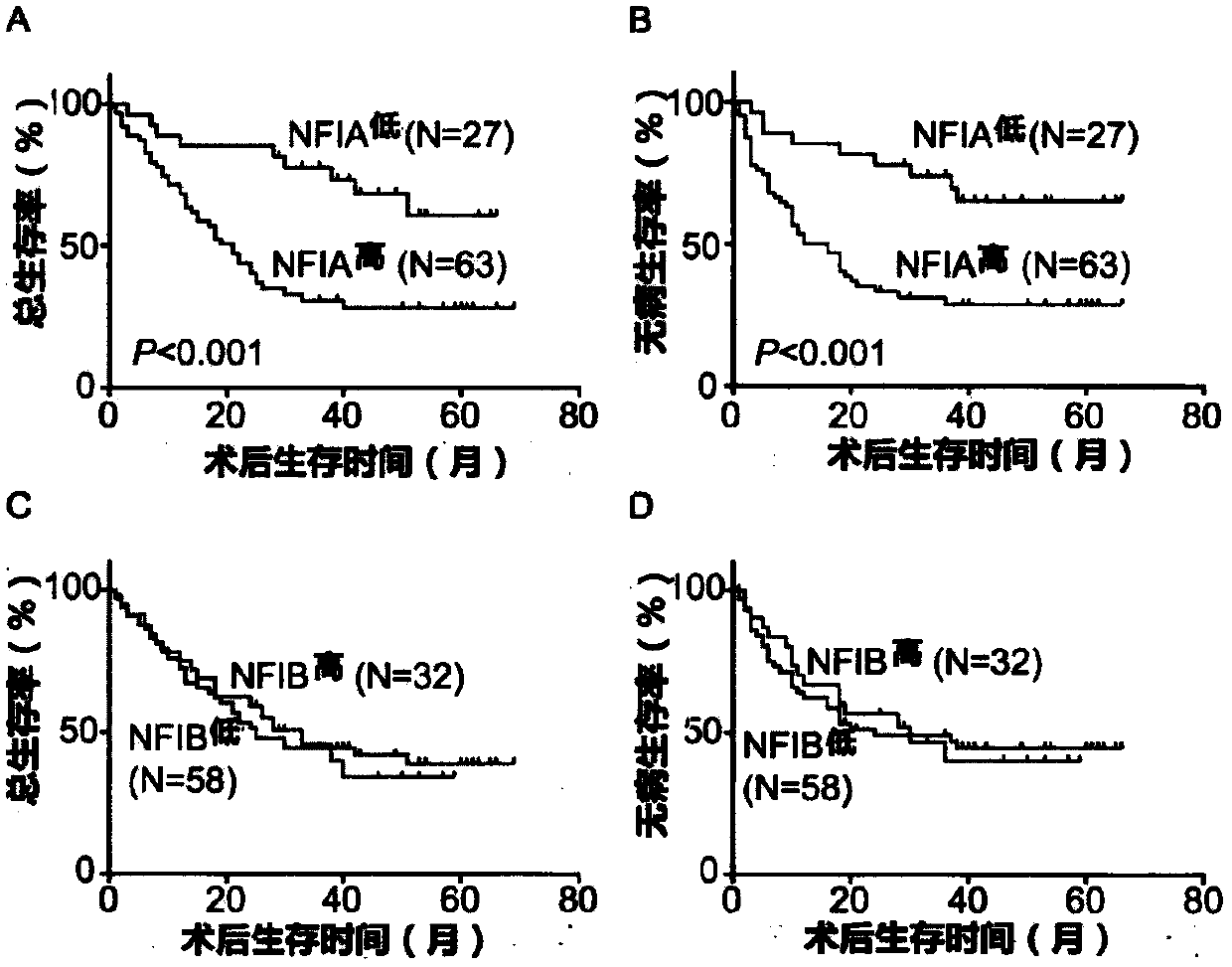
The invention discloses the application of NFI transcription factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and particularly relates to the application of a transcription factor NFIB in the diagnosisof esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the application of a transcription factor NFIA in evaluating the differentiation degree, TNM staging and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thelevel of the NFI transcription factors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is detected and analyzed by the immunohistochemical technique, it is found that patients with high expression of NFIA havea low tumor differentiation degree, a high TNM stage and poor prognosis, and high expression of NFIB corresponds to a low esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue differentiation degree, in this way,a new way is provided for the diagnosis and prognosis judgment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and a reference is provided for clinicians to analyze the condition of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Application of ZNF750 in screening targeted medicine for treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveCN109652545AStable knockout of proliferative abilityStable knockout invasionMicrobiological testing/measurementOvarian Squamous Cell CarcinomaGenes mutation
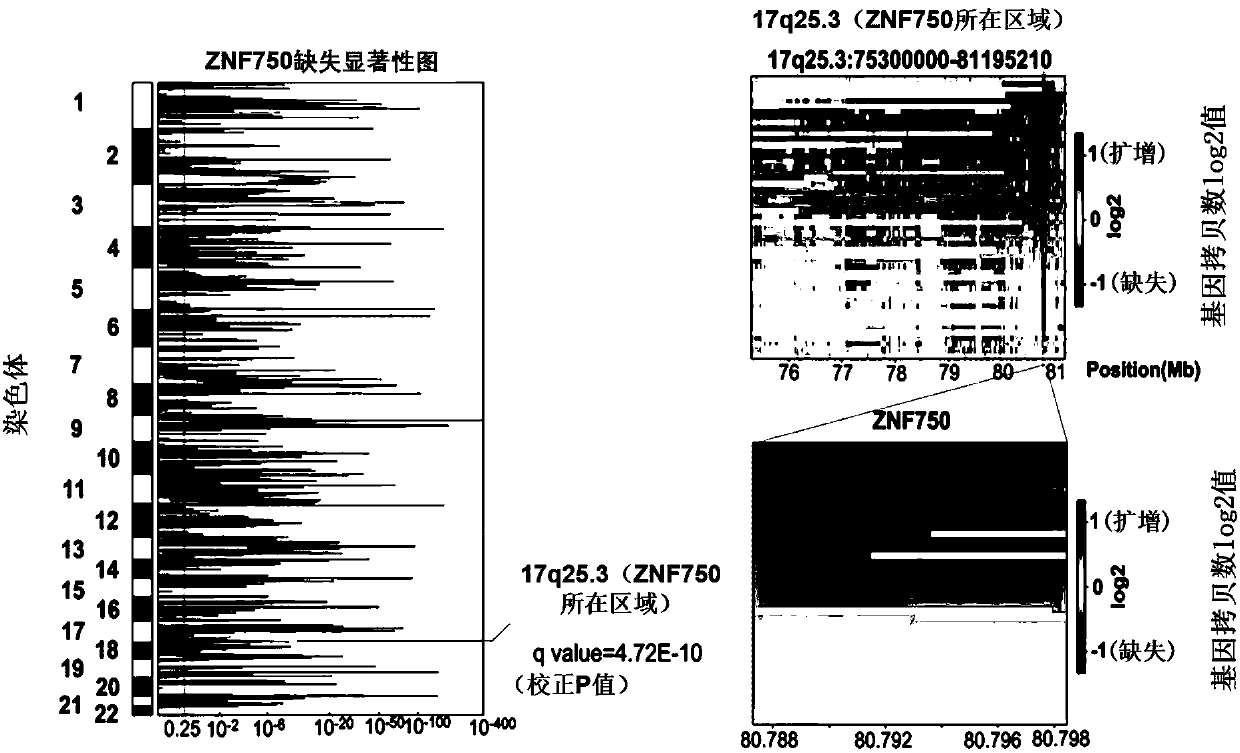
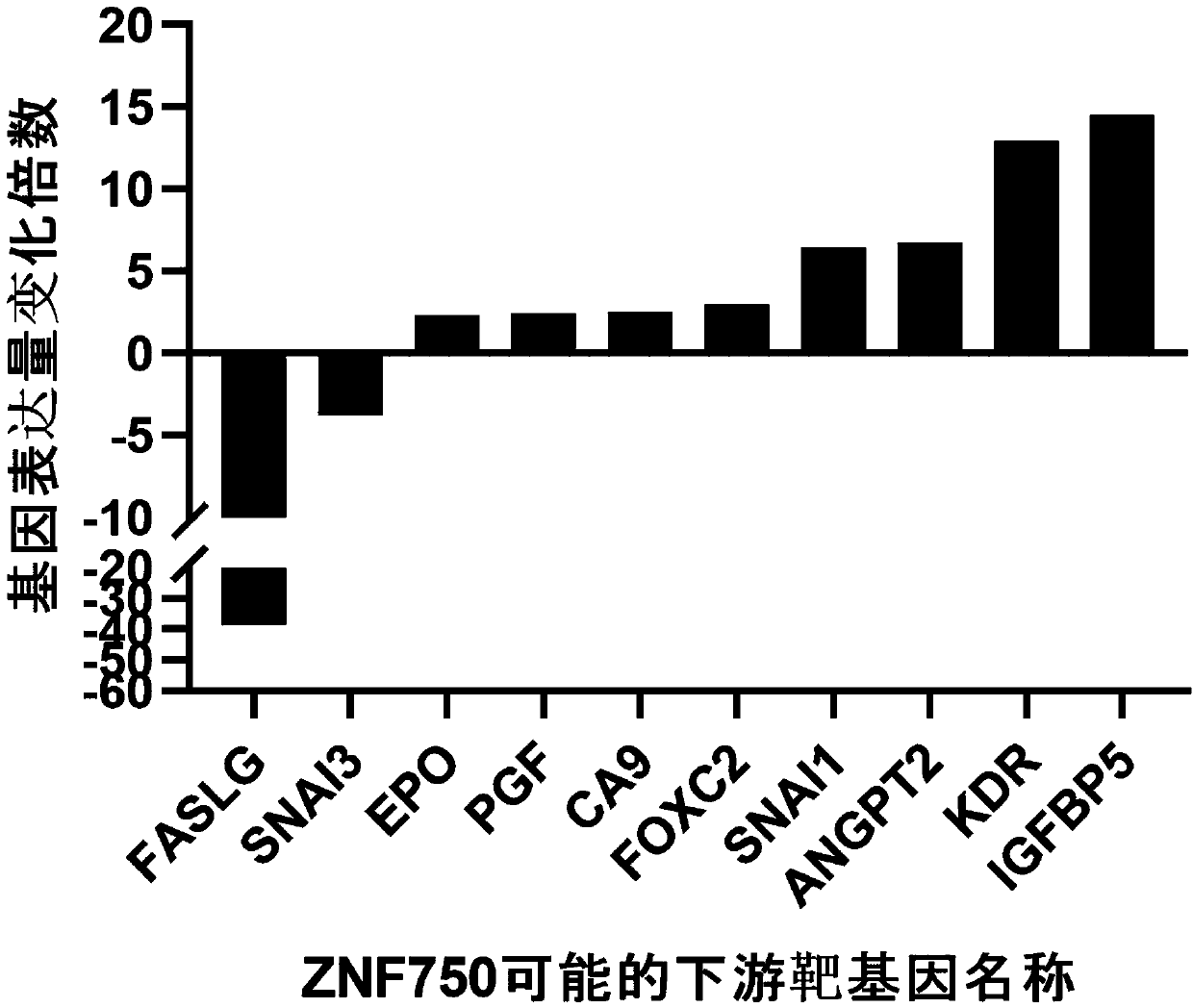
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicine, provides an application of ZNF750 in screening a targeted medicine for treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, provides a novel target for blocking the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells or inhibiting the change of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells, and provides a treatment clue for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with ZNF750 variation. The invention provides the application of ZNF750 in screening the targeted medicine for treating the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with ZNF750 gene mutation, deletion, inactivation variation or ZNF750 low expression. The targeted medicine treats the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting or blocking angiogenesis-related gene expression of a downstream target gene of ZNF750. The detection of ZNF750 mutation can divide the patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma into two groups of mutant type and wild type, and the medicine targeted to KDR can provide effective treatment selection for the patients with ZNF750 inactivation variationand improve the clinical prognosis.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Early molecular diagnosis marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and application of marker
ActiveCN107519193AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOncologyMolecular diagnostics
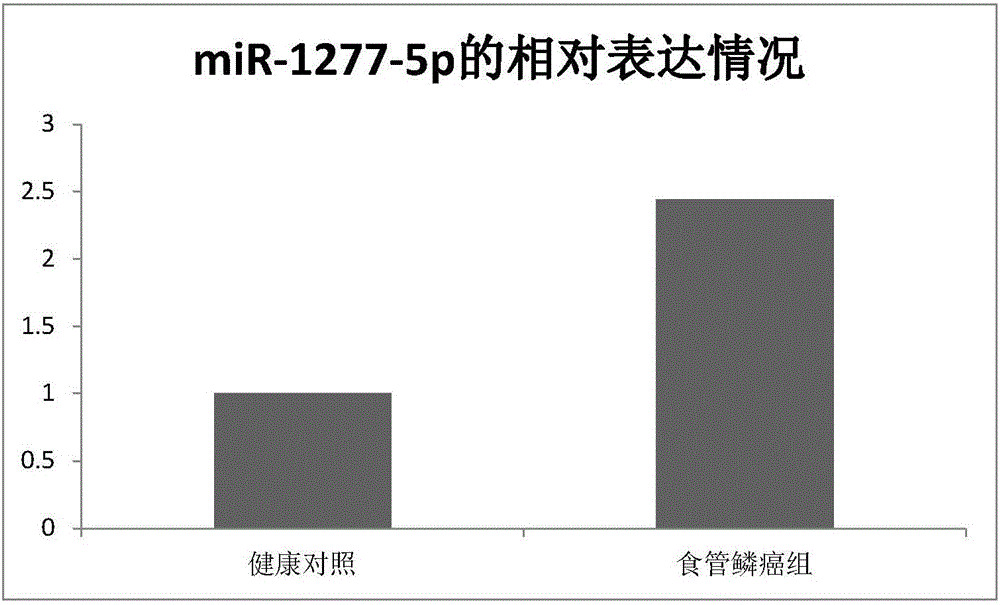
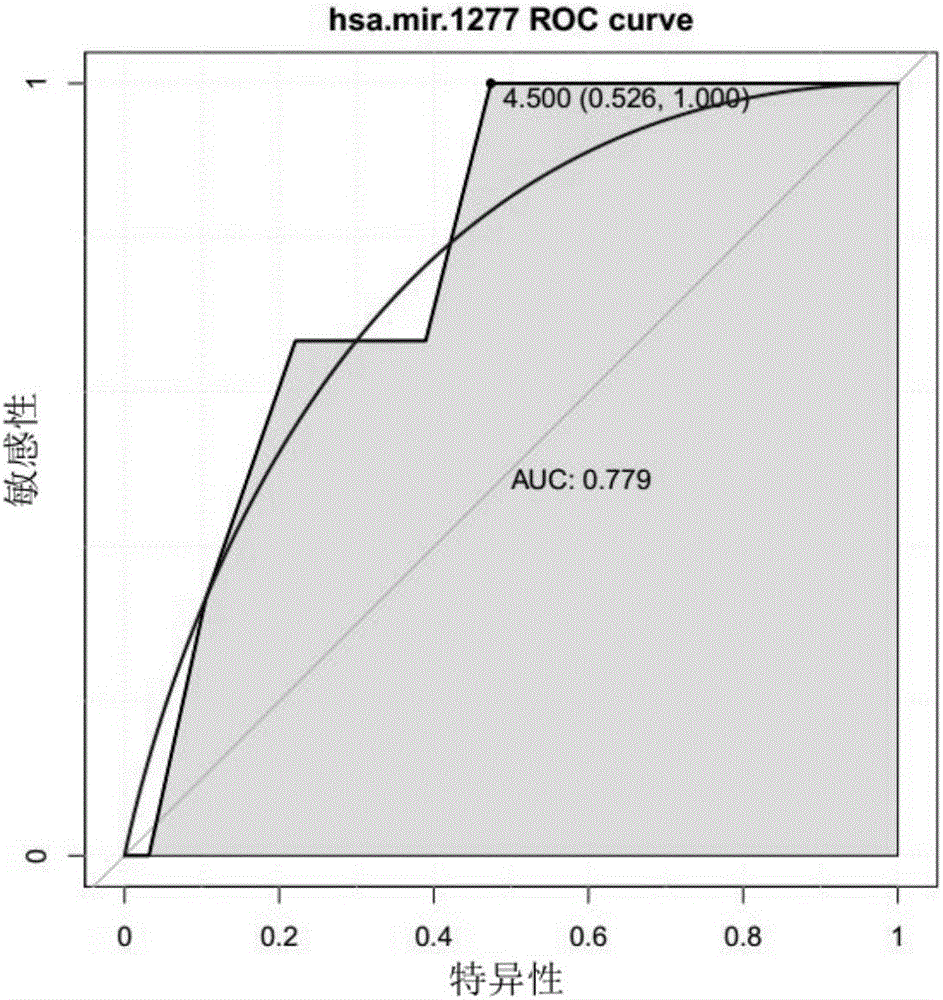
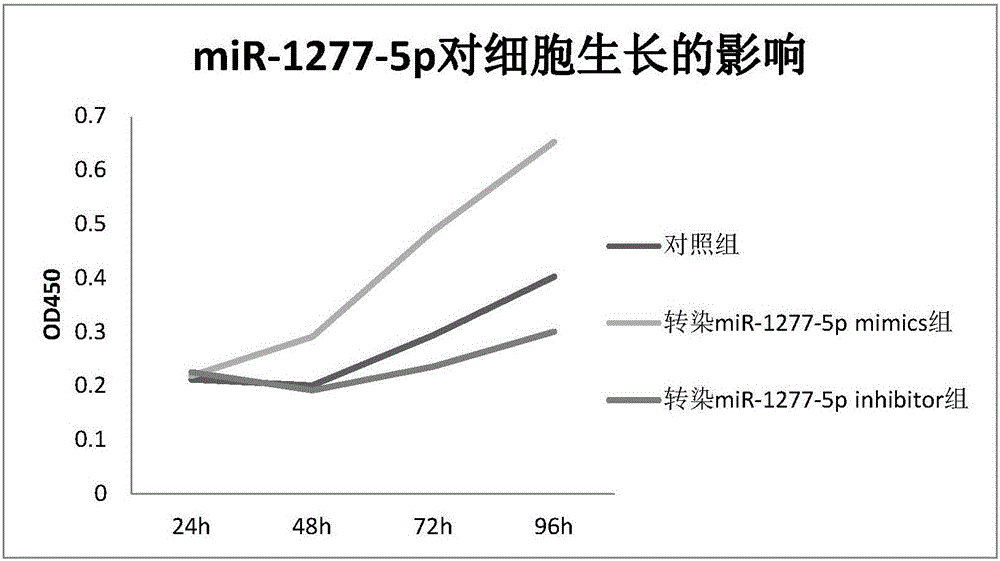
The invention relates to an early molecular diagnosis marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and an application of the marker. Parts of patients suffering from early esophageal squamous carcinoma may lose the best treatment opportunity due to indefinite diagnosis caused by the existing diagnostic technique level of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, more accurate indexes are required for supplement, and a molecular biology method for researching and identifying effective molecule markers is a key means for assisting existing clinical diagnosis, clinical intervention guide and precancerous warning. The provided early molecular diagnosis marker mir-1277 for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and mature miRNA provide a potential basis for accurate diagnosis of clinical esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and have important actual application value.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
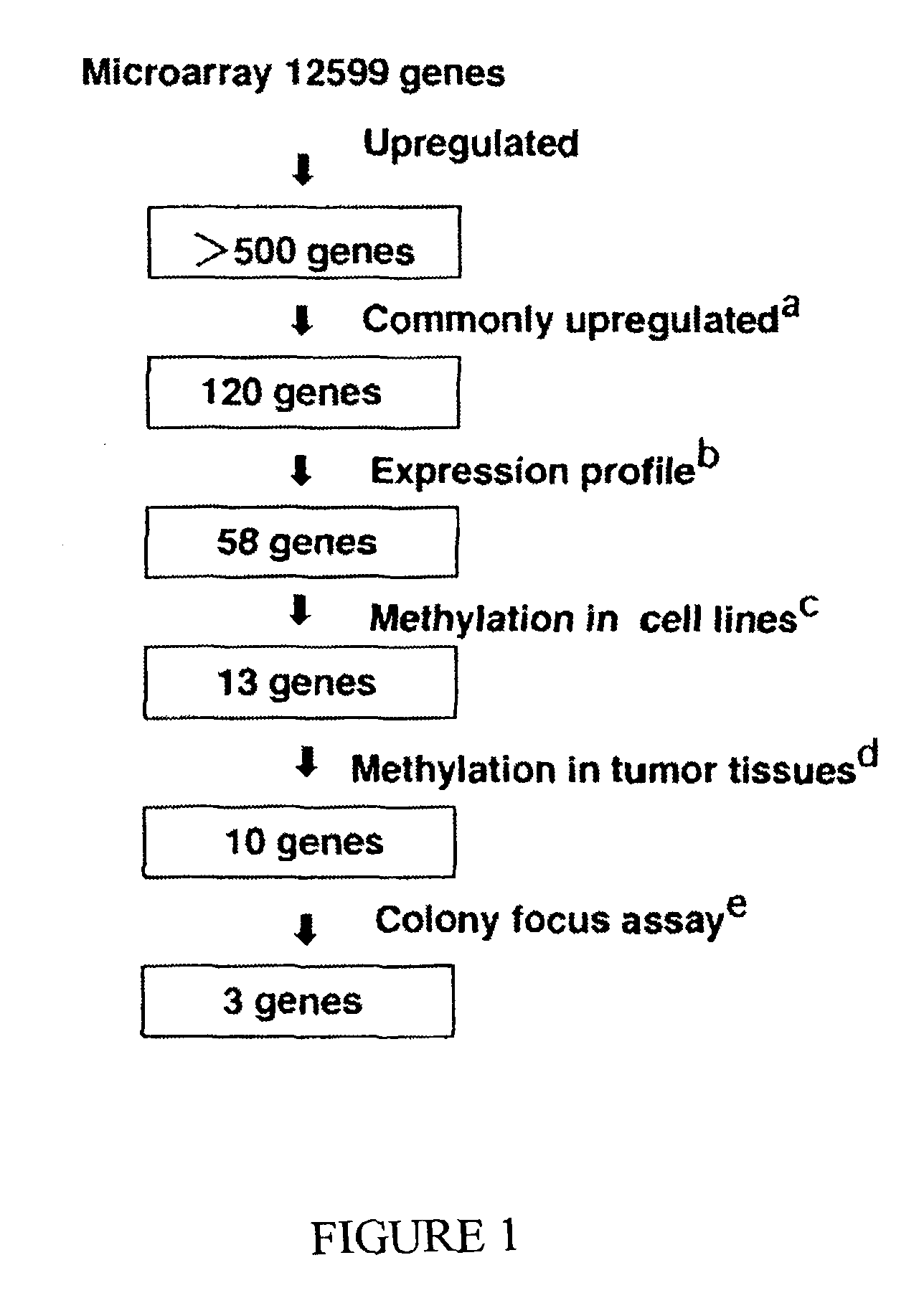
Genomic screen for epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes
Methods of genomic screening to identify epigenetically silenced genes, including epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes are provided. Also provided are methods of detecting a cancer, for example, an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, as are methods of treating a subject having such a cancer.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Application of combined metabolism biomarker for diagnosing esophageal squamous carcinoma and kit
PendingCN112858551AHigh diagnostic sensitivityEffective diagnosisComponent separationMetaboliteOncology
The invention relates to novel application of small molecule metabolites, namely hypoxanthine, 2-ketoisocaproic acid, glutamic acid and aspartic acid, in a serum sample as combined markers in preparation of a kit for distinguishing patients with esophageal squamous carcinoma and esophageal epithelial atypical hyperplasia in subjects. The invention further relates to a kit for detecting patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in subjects. The relative concentration of the combined markers in serum samples from the subjects is detected, the variables P of the combined marker are calculated based on a linear regression equation, and whether the subjects suffer from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or not is judged based on a determined threshold value. The kit can realize high-sensitivity and high-efficiency detection of several metabolites involved in the invention, and has the advantages of low detection cost and good repeatability. The kit can be applied to clinical auxiliary diagnosis of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, has the advantages of high diagnosis sensitivity and capability of effectively distinguishing the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from precancerous lesions, and has a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma microenvironmental cell marker molecular model and application thereof
ActiveCN109541209ASensitiveWith characteristicsMaterial analysisAdjuvantStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The invention relates to an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma microenvironmental cell marker molecular model and application thereof. The molecular model mainly comprises a-SMA+ (invasive frontier) fibroblasts, CD163+ (interstitial) macrophages, CD117+ (protogenic layer) mastocytes and CD117+ (invasion frontier) mastocytes. The molecular model can be used to predict the prognosis of patients withesophageal squamous carcinoma and group adjuvant treatment sensitivity groups. A kit mainly includes an anti-CD117 protein antibody, an anti-CD163 protein antibody and an anti-a-SMA protein antibody.According to the invention, the combination of three molecules combined with histopathological features predicts patients' prognosis, which has a higher predictive effect than single index detectionand clearly distinguishes patients with esophageal squamous carcinoma adjuvant treatment sensitivity; an immune tissue chemical hypersensitivity two-step method on which the molecular model is based is a mature and reliable method which can be widely used in primary hospitals; and compared with international TNM staging, the molecular model has a higher predictive effect, and is simpler, easier, more sensitive and more specific.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com