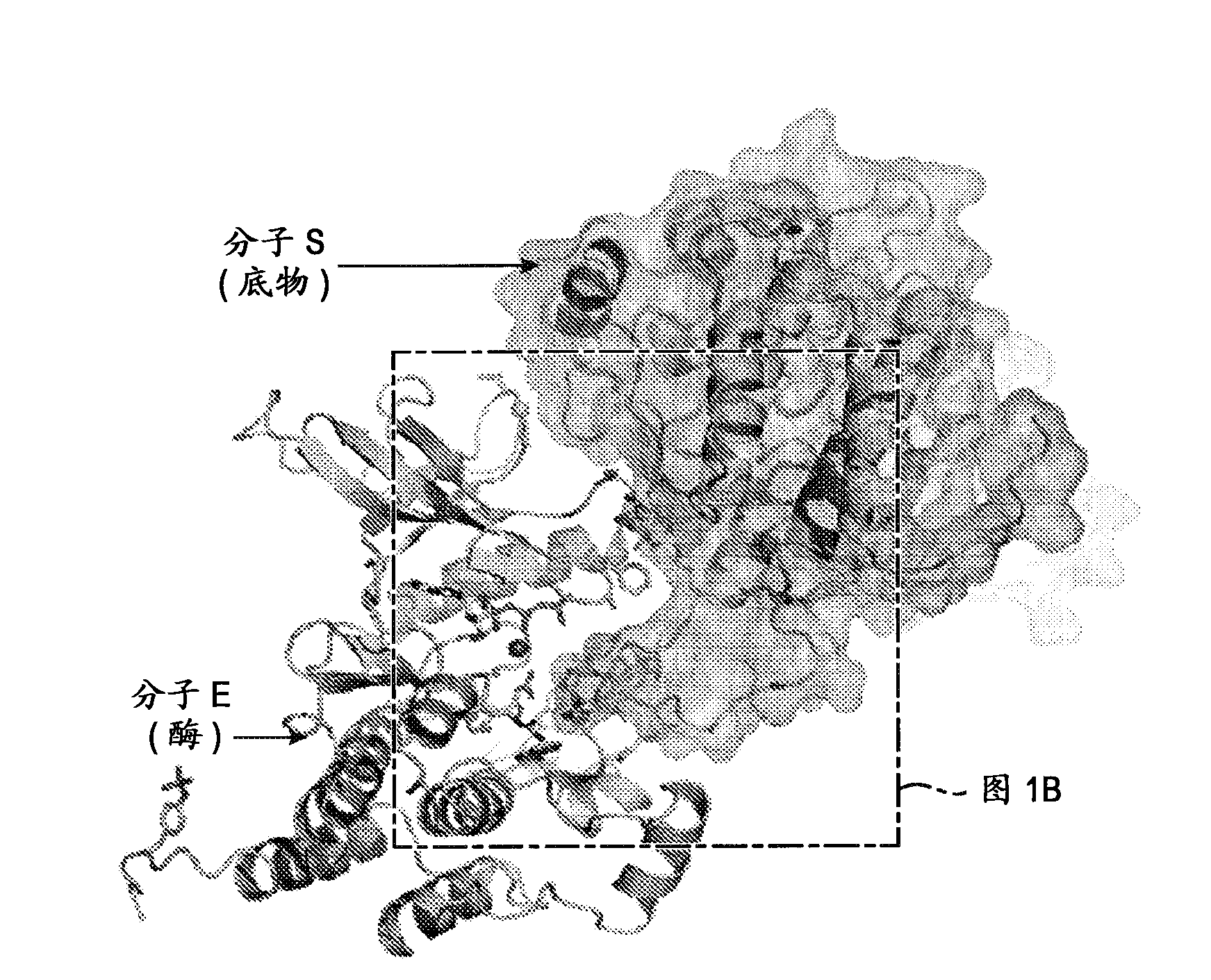
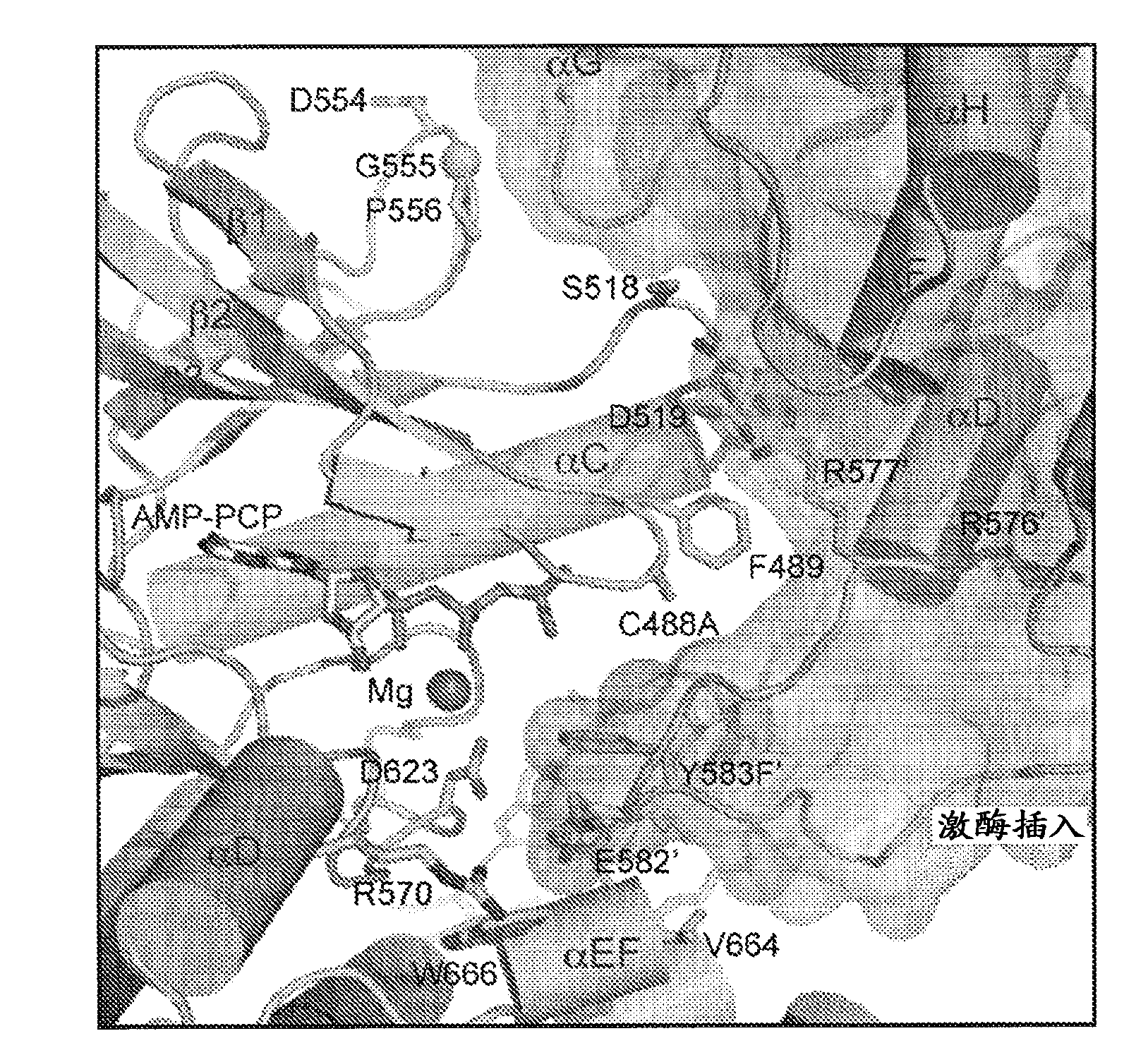
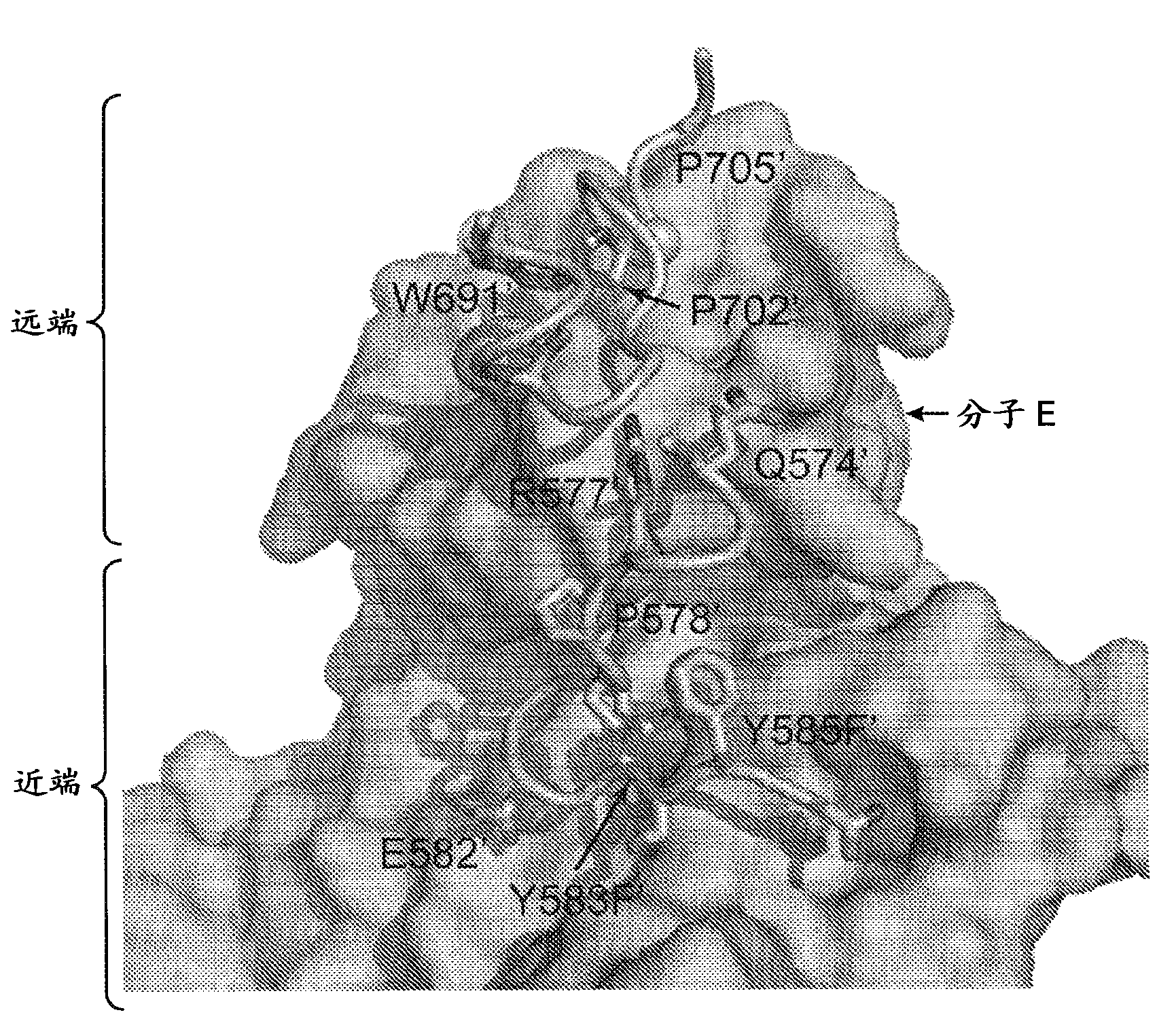
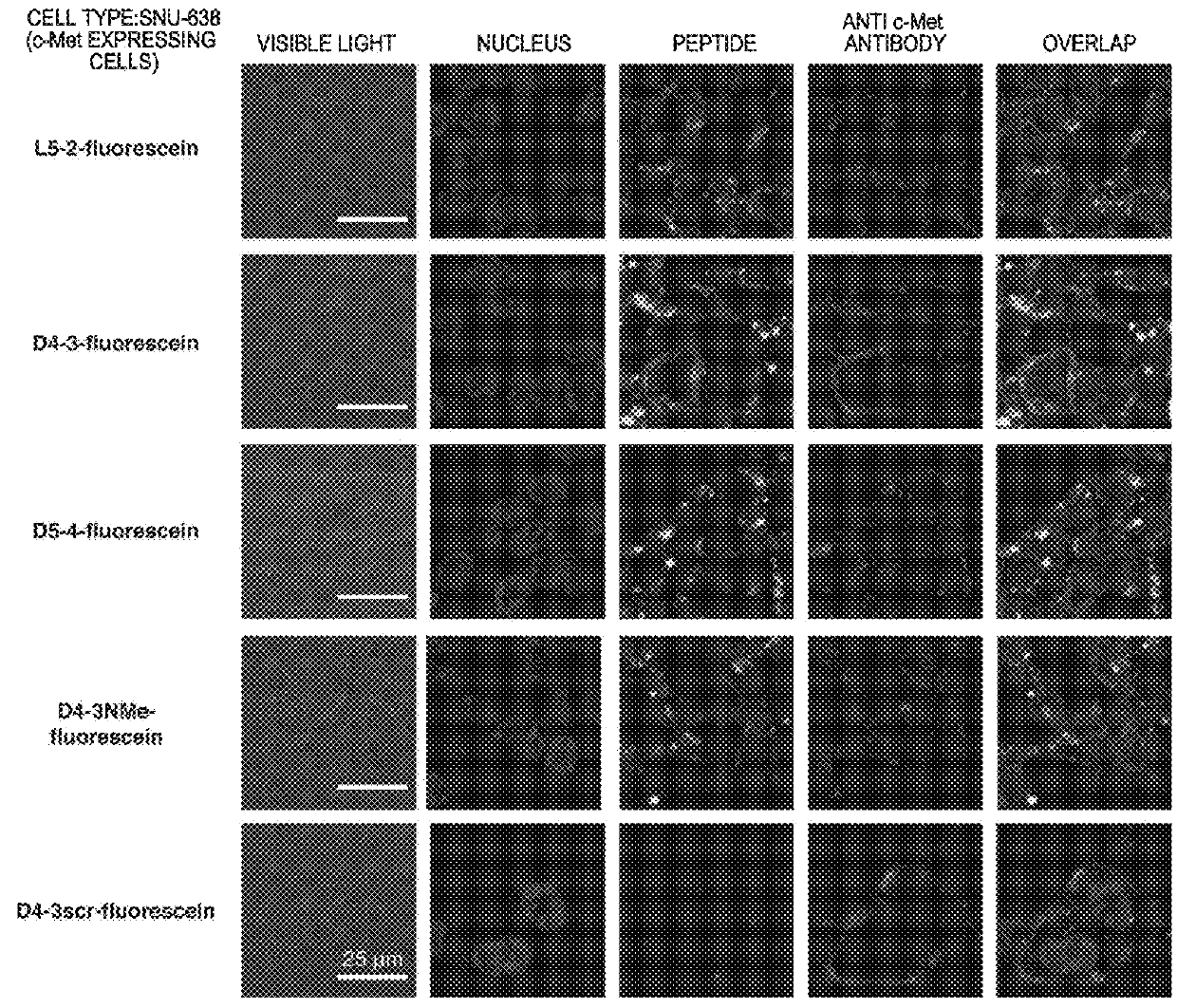
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Autophosphorylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Autophosphorylation is a type of post-translational modification of proteins. It is generally defined as the phosphorylation of the kinase by itself. In eukaryotes, this process occurs by the addition of a phosphate group to serine, threonine or tyrosine residues within protein kinases, normally to regulate the catalytic activity. Autophosphorylation may occur when a kinases' own active site catalyzes the phosphorylation reaction (cis autophosphorylation), or when another kinase of the same type provides the active site that carries out the chemistry (trans autophosphorylation). The latter often occurs when kinase molecules dimerize. In general, the phosphate groups introduced are gamma phosphates from nucleoside triphosphates, most commonly ATP.
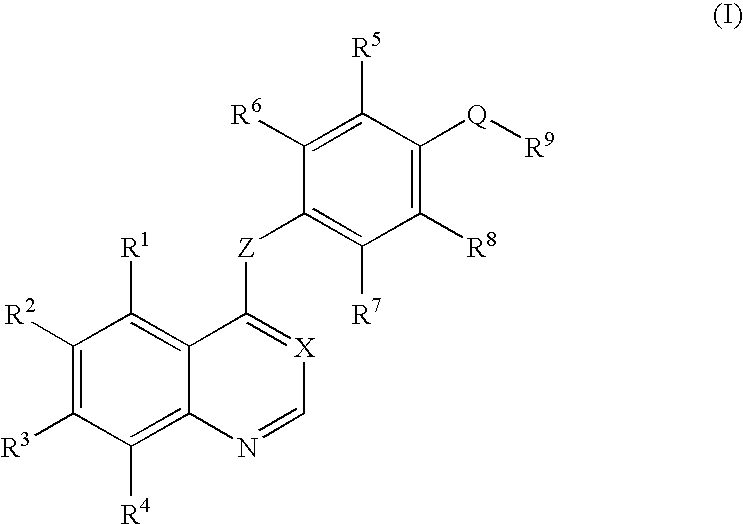
Quinoline or quinazoline derivatives inhibiting auto-phosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptors
InactiveUS20050049264A1Antitumor activityGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellHalogen
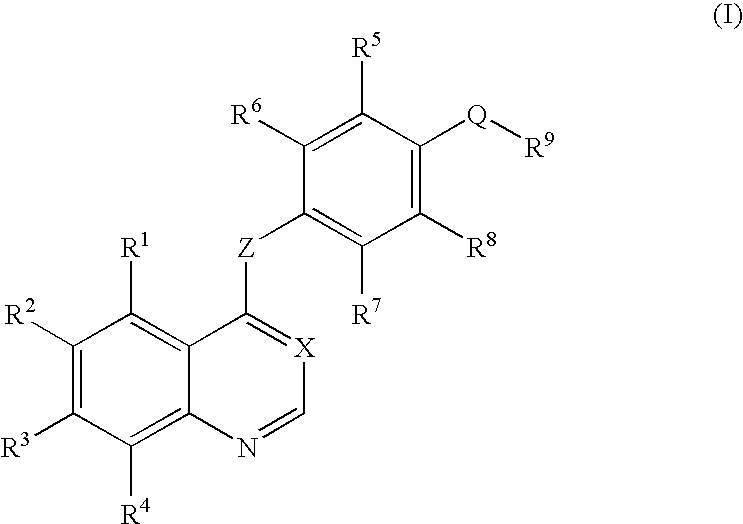
An objective of the present invention is to provide novel compounds which have inhibitory activity against autophosphorylation of an FGF receptor family and, when orally or intraveneously administered, can suppress the growth of cancer cells. The compounds of the present invention are represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof: wherein X represents CH or N; Z represents O or S; Q represents NR10, CR11R2, carbonyl, O, S(═O)m, wherein m is 0 to 2, or urea; R1 to R3 each independently represent H, OH, halogen, nitro, amino, alkyl, alkoxy or the like in which the alkyl and alkoxy groups are optionally substituted; R4 represents H; R5 to R8 each independently represent H, halogen, alkyl, or alkoxy; and R9 represents an optionally substituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic group.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
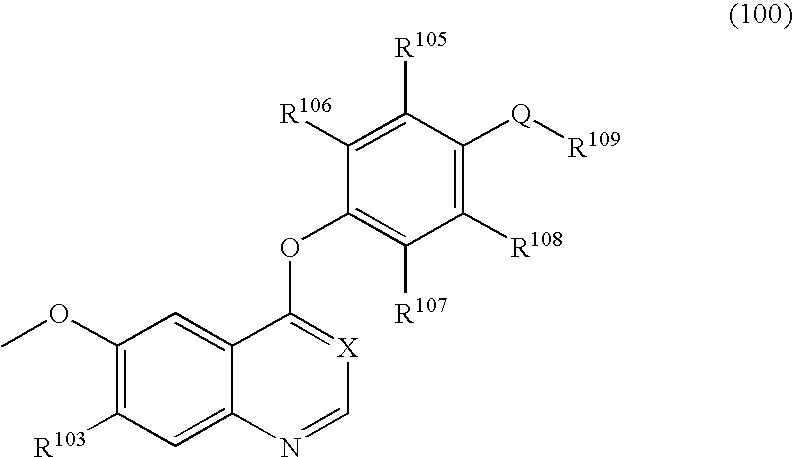
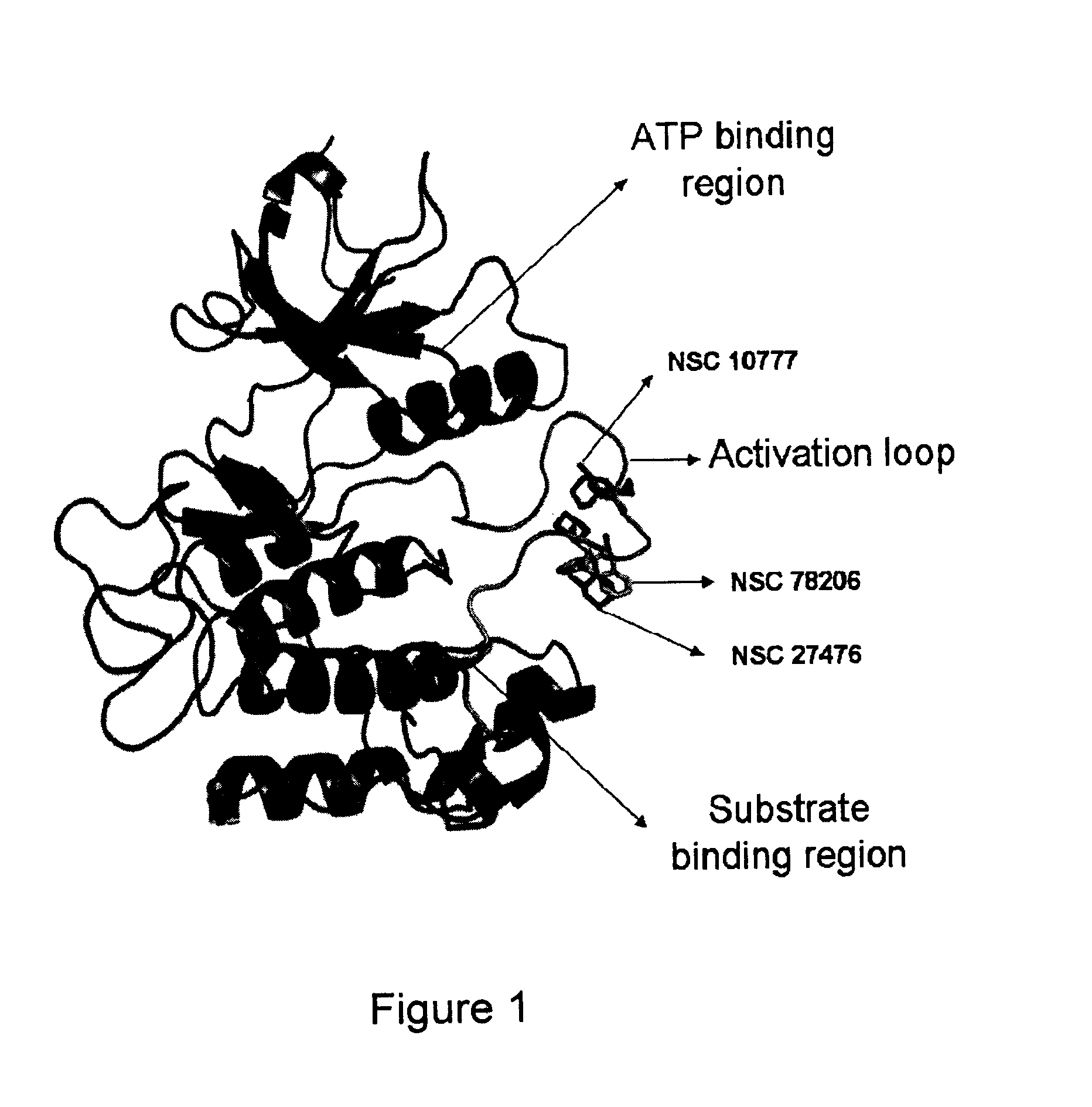
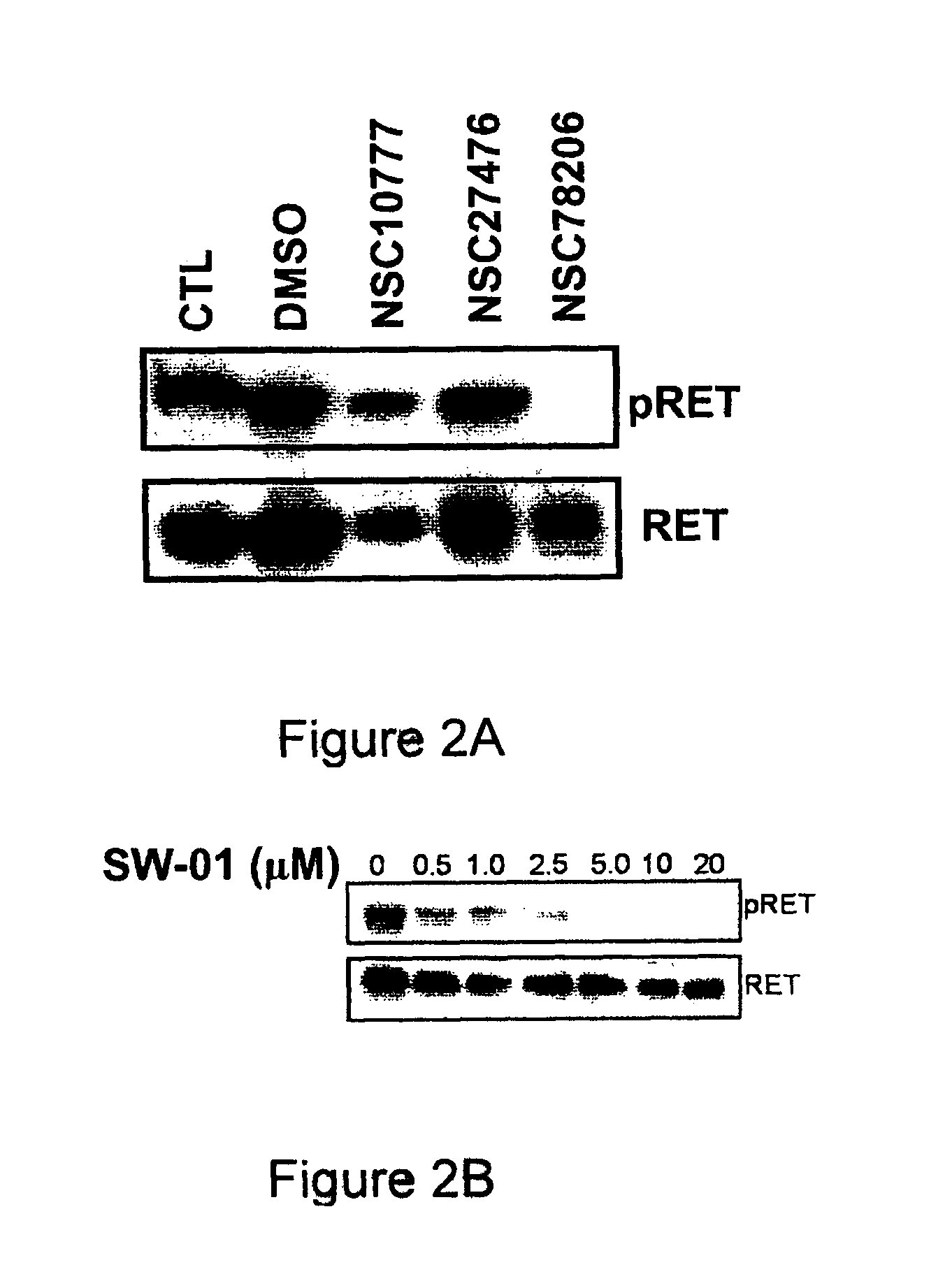
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising RET inhibitors and methods for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS8629135B2Reduce transferGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic compound preparationCancer preventionAutophosphorylation
Owner:SINGH VINAY K +2
Quinoline or quinazoline derivatives inhibiting auto-phosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptors
InactiveUS7495104B2Antitumor activityGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellAutophosphorylation
An objective of the present invention is to provide novel compounds which have inhibitory activity against autophosphorylation of an FGF receptor family and, when orally or intraveneously administered, can suppress the growth of cancer cells. The compounds of the present invention are represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof:wherein X represents CH or N; Z represents O or S; Q represents NR10, CR11R2, carbonyl, O, S(═O)m, wherein m is 0 to 2, or urea; R1 to R3 each independently represent H, OH, halogen, nitro, amino, alkyl, alkoxy or the like in which the alkyl and alkoxy groups are optionally substituted; R4 represents H; R5 to R8 each independently represent H, halogen, alkyl, or alkoxy; and R9 represents an optionally substituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic group.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising RET Inhibitors and Methods for the Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20110201598A1Inhibit tumor growthReduce transferBiocideOrganic compound preparationCancer preventionPancreas Cancers
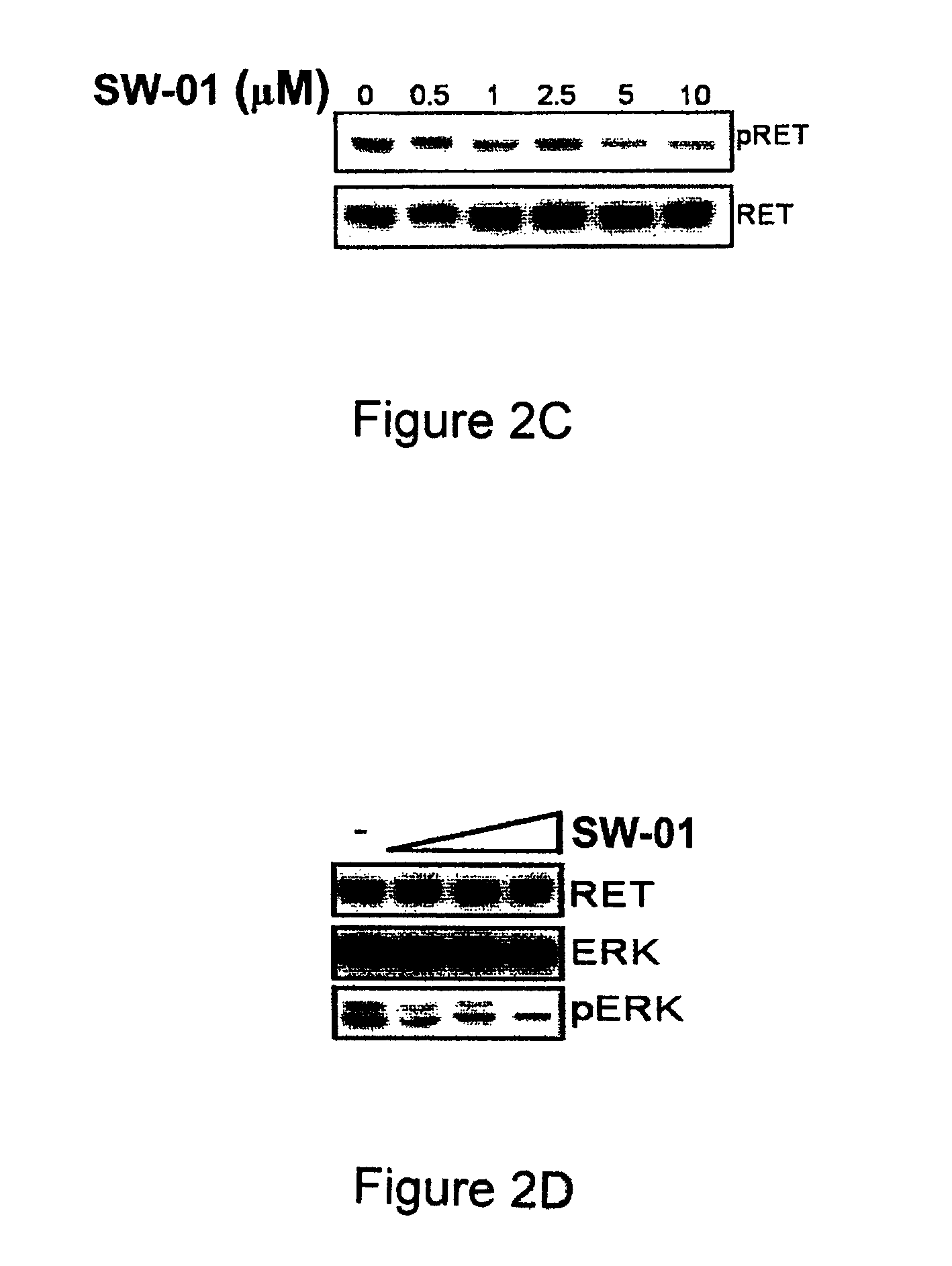
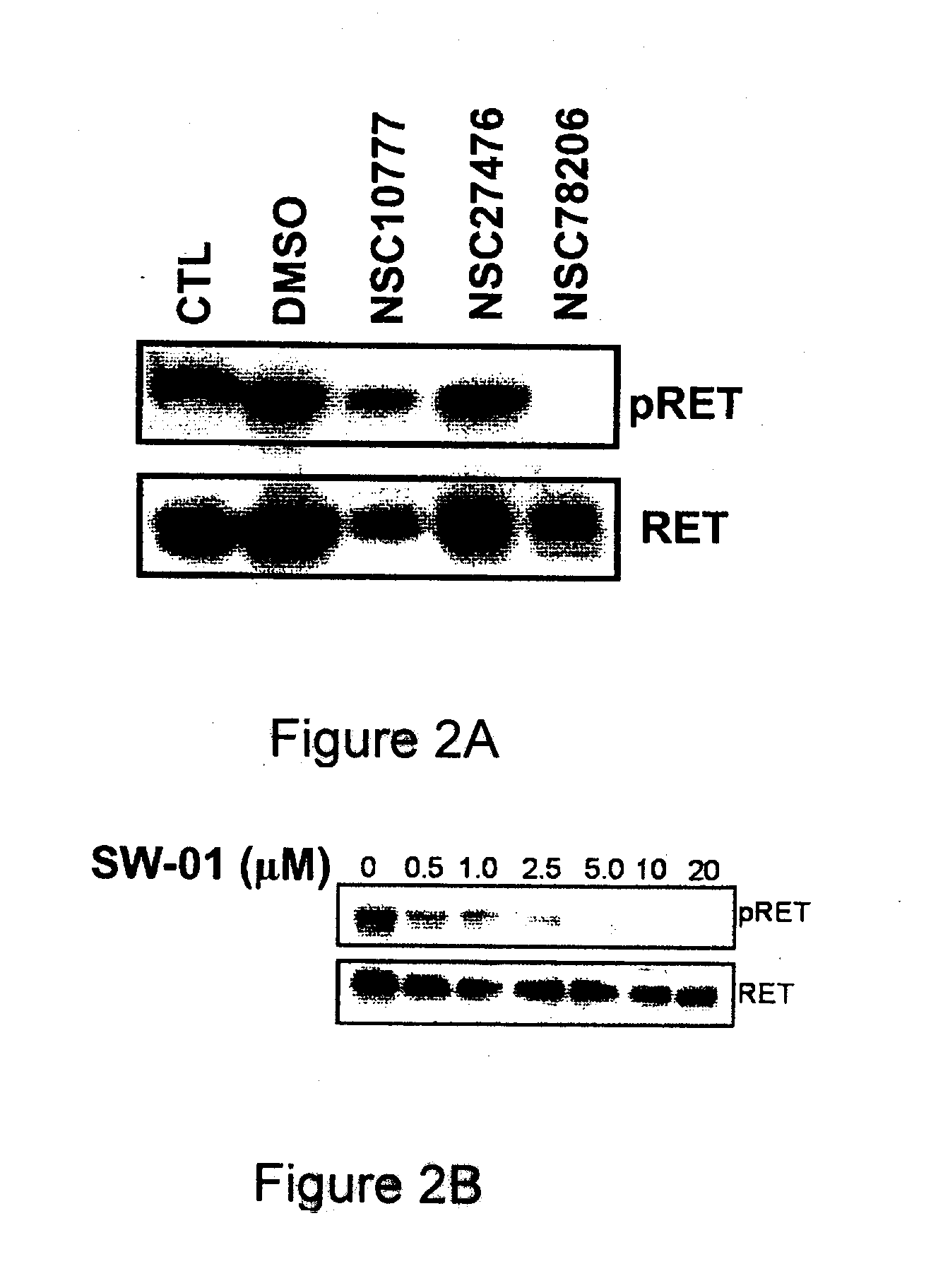
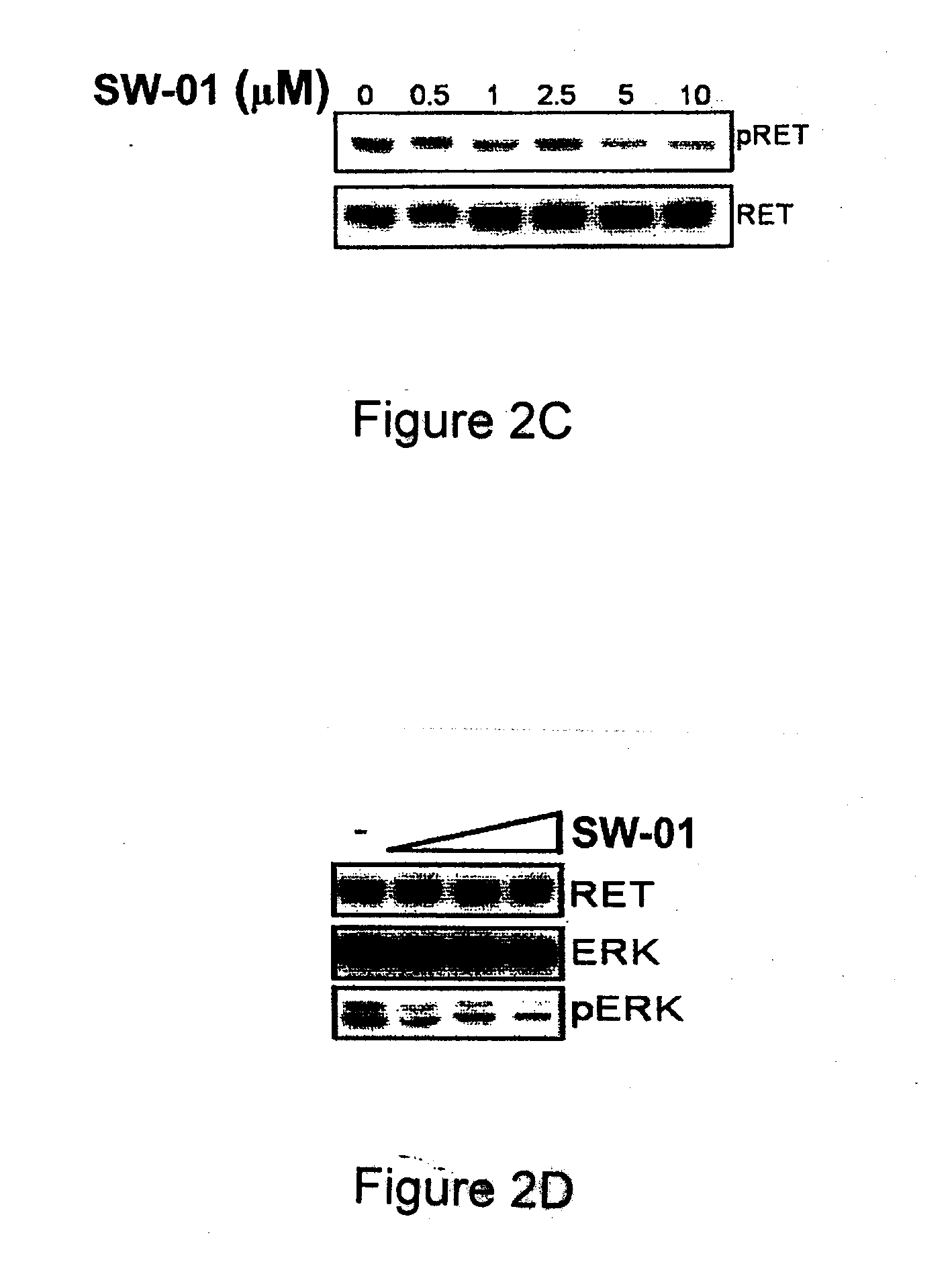
A class of compounds useful in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating or preventing cancer is described. The compounds' ability to inhibit RET kinase is quantified, i.e., their respective RET IC50 and EC50 values are described. One such compound, known as cyclobenzaprine and herein as SW-01, has been identified as RET-specific with an IC50 of 300 nM. SW-01 inhibits RET autophosphorylation and blocks the growth and transformation of thyroid cancer cell lines. It has been further tested in pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and SCLC cell lines. The compounds show utility for inhibition of survival and proliferation of tumour cells.
Owner:SINGH VINAY K +2
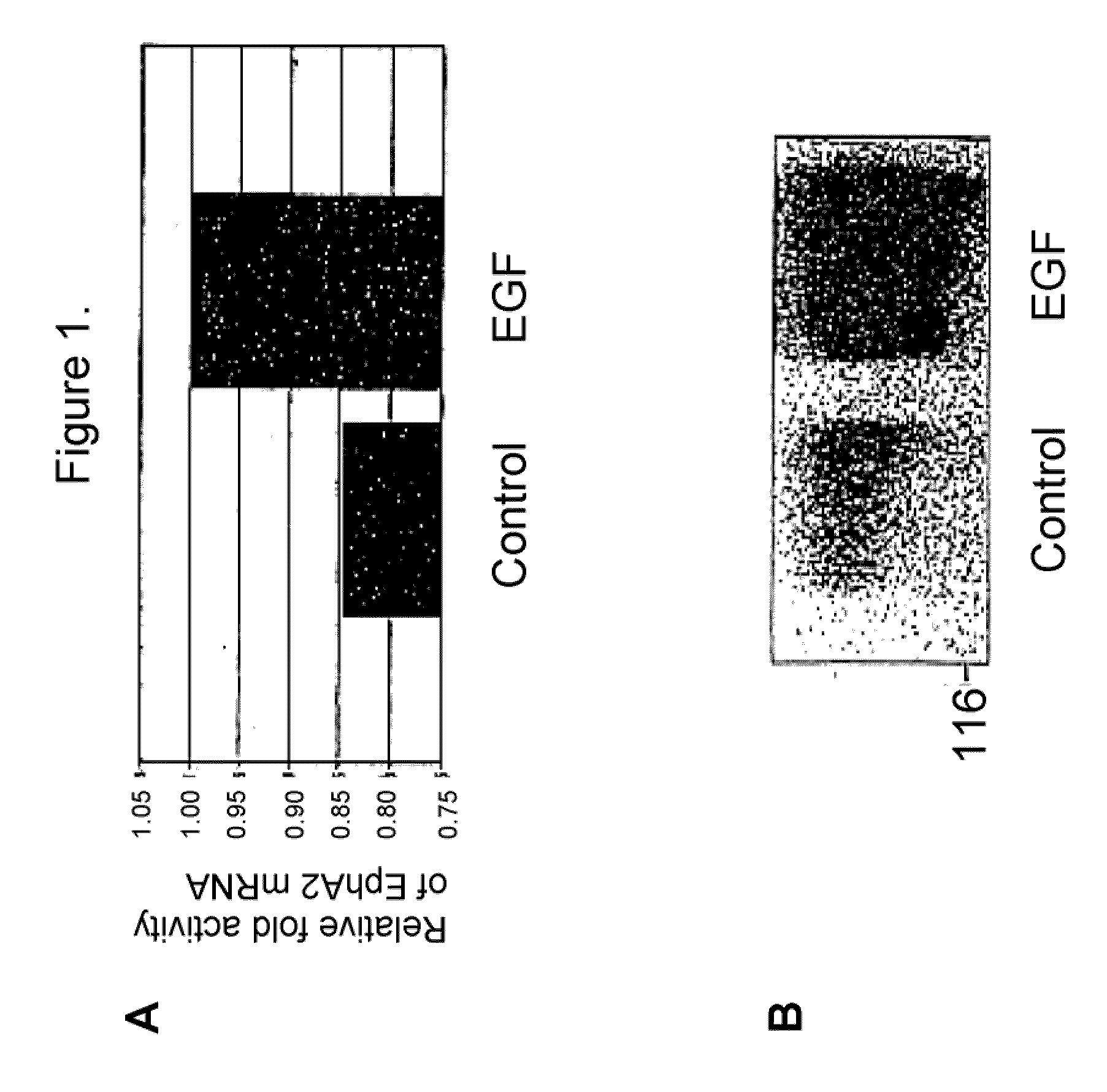
EphA2, hypoproliferative cell disorders and epithelial and endothelial reconstitution
InactiveUS20050049176A1Convenient treatmentReduces and avoids unwanted effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticCell layerInflammatory Bowel Diseases
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of a hypoproliferative cell disorder, especially those disorders relating to the destruction, shedding, or inadequate proliferation of epithelial and / or endothelial cells, particularly interstitial cystitis (IC) and lesions associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more agents that are antagonists of EphA2. In certain embodiments, the EphA2 antagonistic agent of the invention decreases EphA2-endogenous ligand binding, upregulates EphA2 gene expression and / or translation, increases EphA2 protein stability or protein accumulation, decreases EphA2 cytoplasmic tail phosphorylation, promotes EphA2 kinase activity (other than autophosphorylation or ligand-mediated EphA2 signaling), increases proliferation of EphA2 expressing cells, increases survival of EphA2 expressing cells, and / or maintains / reconstitutes epithelial and / or endothelial cell layer integrity. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antagonistic agents of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for therapy for a hypoproliferative cell disorder. Diagnostic methods and methods for screening for therapeutically useful agents are also provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Polynucleotides encoding GFRα3
InactiveUS7026138B1Facilitating identification and characterizationEasy to detectSugar derivativesTissue cultureNucleotideReceptor activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences, including expressed sequence tags (ESTs), oligonucleotide probes, polypeptides, vectors and host cells expressing, and immunoadhesions and antibodies to mammalian GFRα3, a novel α-subunit receptor of the GDNF (i.e. GFR) receptor family. It further relates to an assay for measuring activation of an α-subunit receptor by detecting tyrosine kinase receptor activation (i.e., autophosphorylation) or other activities related to ligand-induced α-subunit receptor homo-dimerization or homo-oligomerization.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
GFRalpha3 and its uses
InactiveUS20060216289A1Facilitating identification and characterizationEasy to detectFungiSenses disorderAutophosphorylationReceptor activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences, including expressed sequence tags (ESTs), oligonucleotide probes, polypeptides, vectors and host cells expressing, and immunoadhesions and antibodies to mammalian GFRα3, a novel α-subunit receptor of the GDNF (i.e. GFR) receptor family. It further relates to an assay for measuring activation of an α-subunit receptor by detecting tyrosine kinase receptor activation (i.e., autophosphorylation) or other activities related to ligand-induced α-subunit receptor homo-dimerization or homo-oligomerization.
Owner:DE SAUVAGE FREDERIC +3
Enantioselective biotransformation for preparation of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor intermediates
Owner:AGOURON PHARMA INC
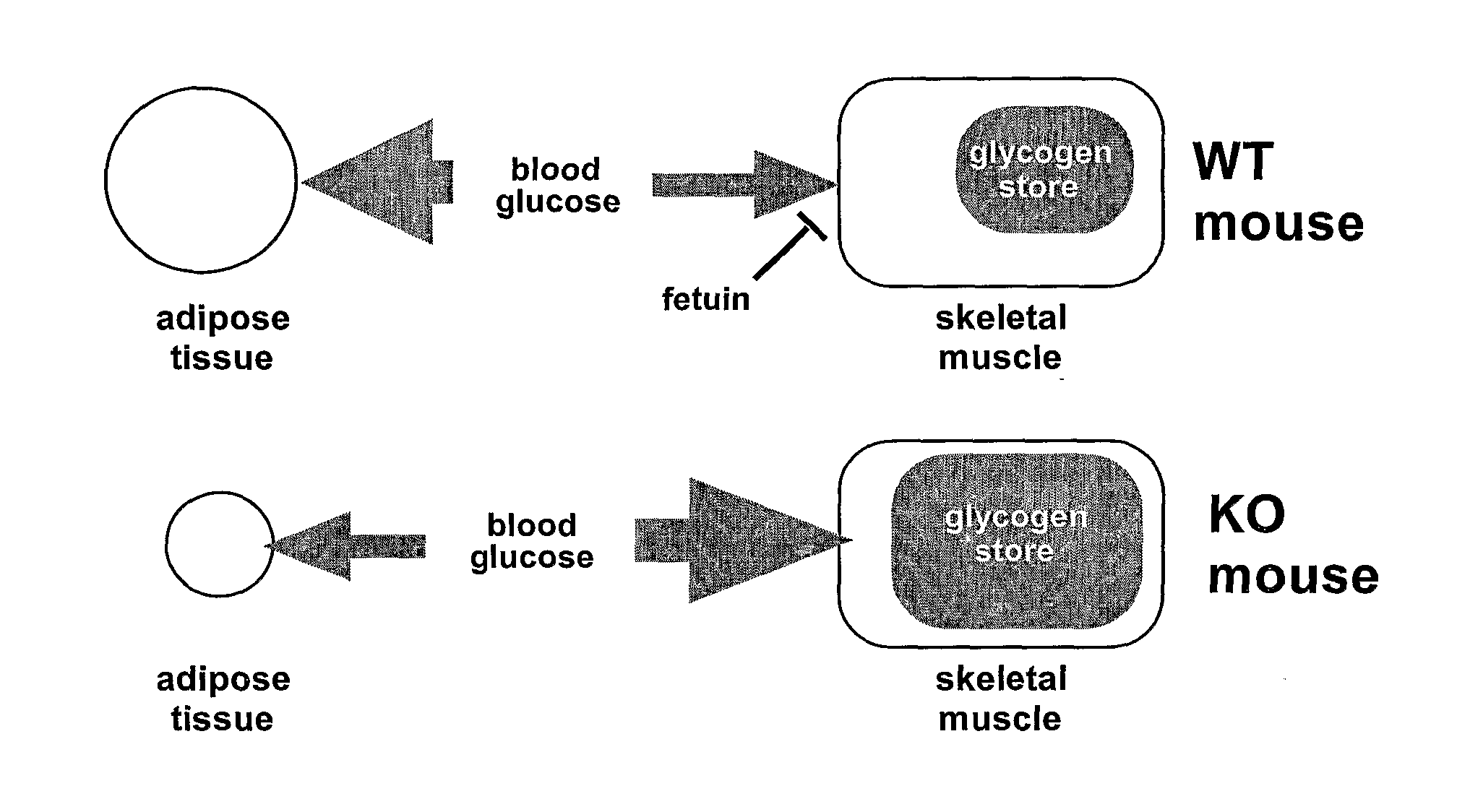
Inhibition of alpha-2 hs glycoprotein (AHSG/fetuin) in obesity and insulin control of glucose homeostasis
InactiveUS20080050372A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreased basalPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlpha-2-HS-glycoproteinAnti-CEA Antibody
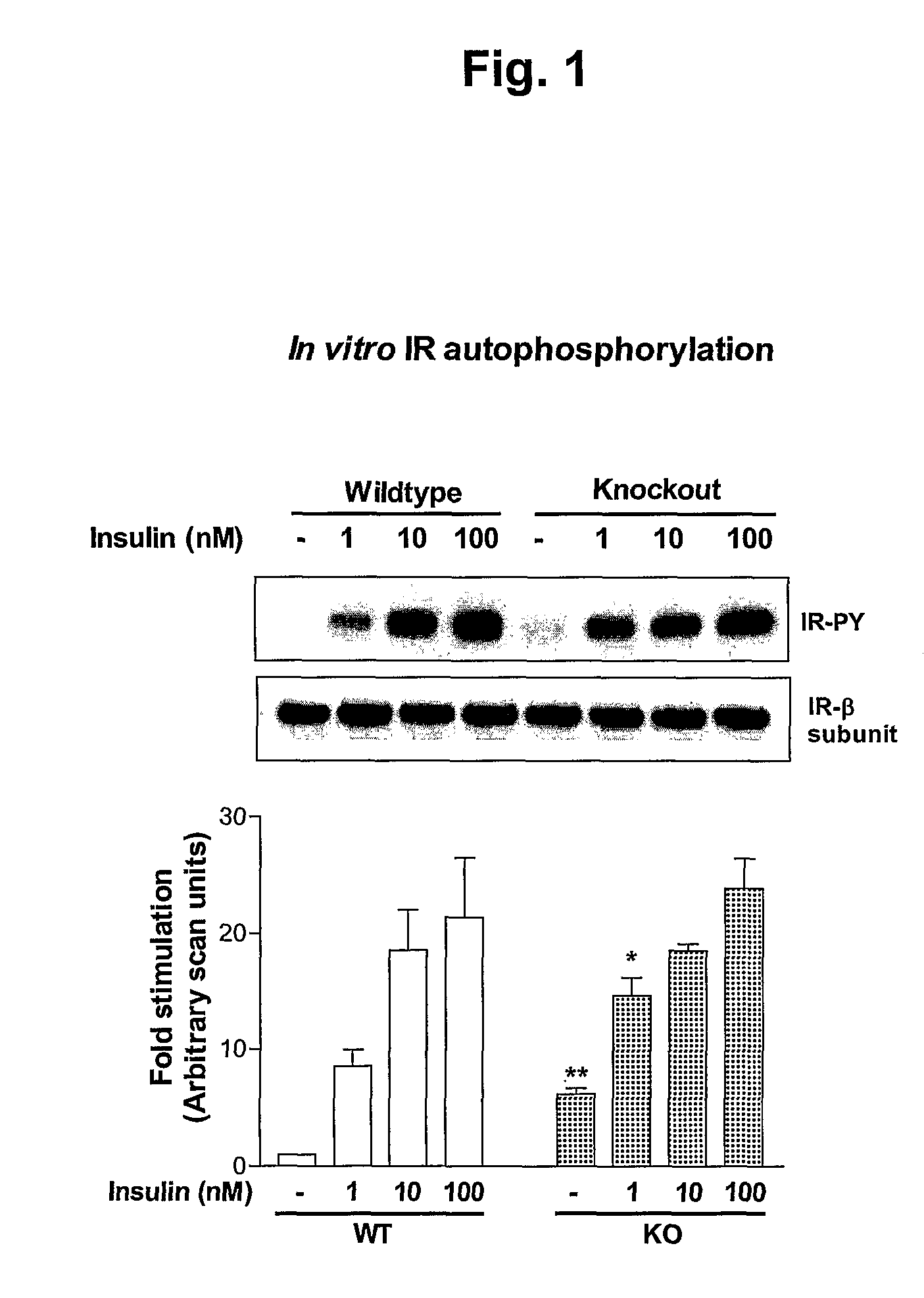
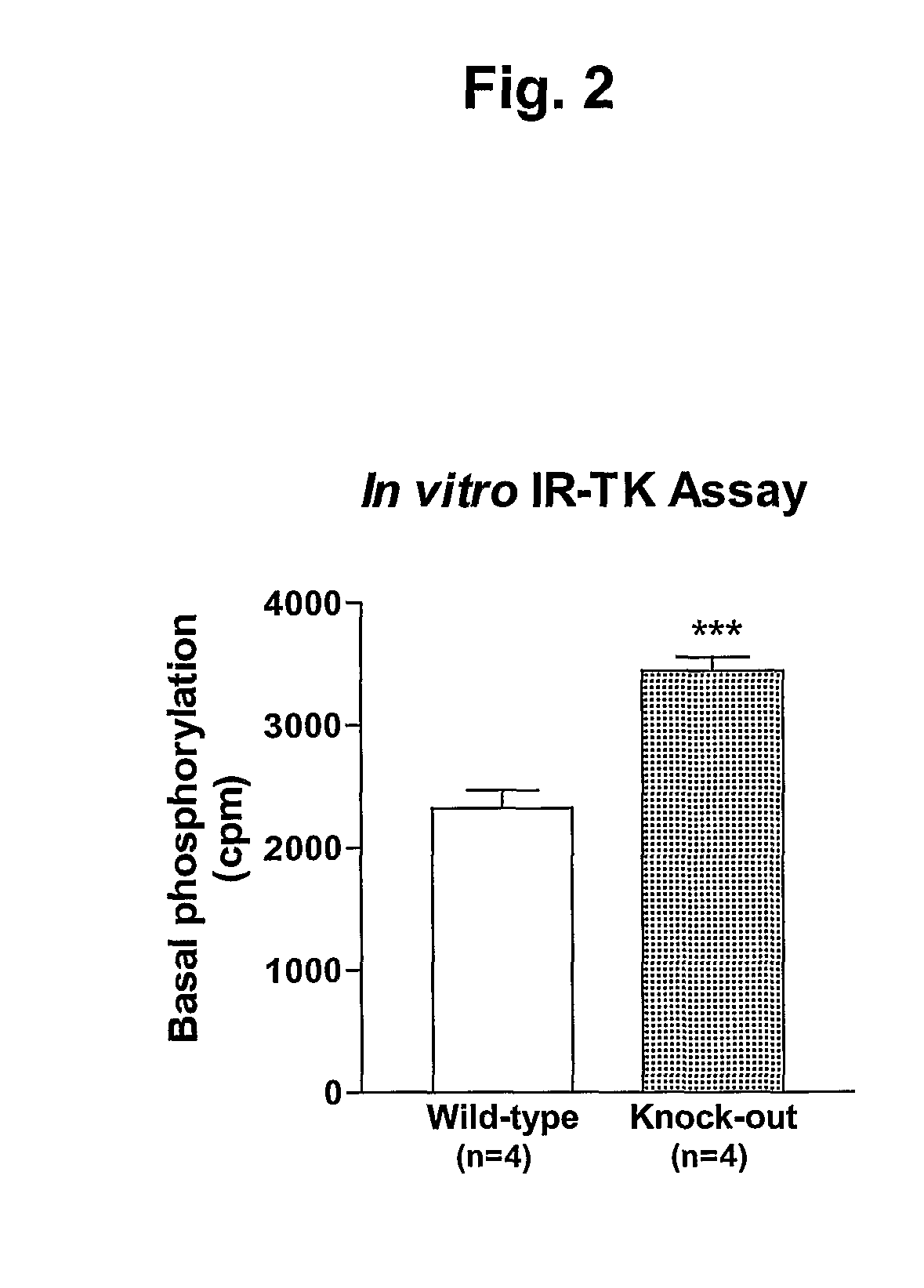
α2-Heremans Schmid Glycoprotein (AHSG) inhibits insulin-induced autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor (IR) and IR-tyroskine kinase (TK) activity; genetic ablation of the Ahsg gene enhances insulin signal transduction and increase whole-body insulin sensitivity. Therefor, AHSG and its gene(s) are useful targets for agents that inhibit the development or progression of Type II diabetes or any disease or disorder associated with increased insulin resistance. Provided herein is a method for inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG protein in a cell using compounds that inhibit phosphorylation of AHSG. Also disclosed is a method of augmenting the phosphorylation or IR-TK activity in a liver or muscle cell by providing a compound that lowers the amount of active AHSG or inhibits the biological activity of AHSG. Such effects may be achieved by delivering an antisense nucleic acid construct that hybridizes with AHSG encoding DNA. This invention includes a method (a) treating a subject that is susceptible to, or suffers from, obesity and insulin resistance or (b) increasing insulin sensitivity, and thereby preventing or treating insulin resistance in the subject. The method comprises lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG in the subject, preferably in liver or muscle, by using AHSG antisense constructs or an anti-AHSG antibody. In a subject eating a high fat diet, the effect on body weight gain and / or insulin resistance is diminished, and total body fat content is lowered, by lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the action of the AHSG in the subject using the agents noted above.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Quinoline and quinazoline derivatives and drugs containing the same
InactiveUS20060211717A1Low level of side effectLow level of effectBiocideOrganic chemistryEccentric hypertrophyDisease
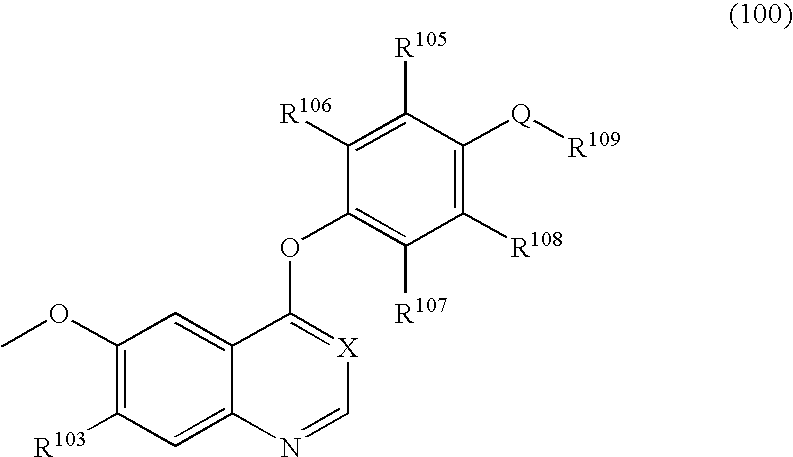
There are provided compounds which can be used in the treatment of diseases mediated by the autophosphorylation of a PDGF receptor, specifically, compounds which can inhibit neointima formation hypertrophy. The compounds are those represented by formula (I) or pharmacologically acceptable salts or solvates thereof: wherein R1 and R2 represent hydrogen, alkyl or the like; R3, R4, R5, and R6 represent hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, alkoxy or the like; R11 and R12 represent hydrogen, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl or the like; and A represents any one of formulae (i) to (x), provided that compounds wherein R3, R4, R5 and R6 represent hydrogen and A represents group (v) wherein u is 0 (zero) and R19 represents phenyl optionally substituted by halogen, alkyl, or alkoxy are excluded.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA
Application and research method of atopaxar hydrobromide as novel JAK-STAT3 signal path inhibitor
ActiveCN110393718ANo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrobromideRNA extraction
The invention relates to an application of atopaxar hydrobromide as a novel JAK-STAT3 signal channel inhibitor. The atopaxar hydrobromide can be used for inhibiting STAT3 activity and STAT3 downstreamgene expression to control cell proliferation; the atopaxar hydrobromide has an inhibition effect on STAT3 activation induced by cytokines and JAKs self-phosphorylation; in computer molecular simulation, the atopaxar hydrobromide can be combined with an SH2 structural domain of STAT3 and has very high affinity with a JAK kinase JH1 structural domain; and the atopaxar hydrobromide can horizontallyinhibit the tumor cell growth. A research method of the atopaxar hydrobromide as a novel JAK-STAT3 signal pathway inhibitor comprises the following steps: cell culturing; protein extraction; western-Blot; RNA extraction; RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and fluorescent quantitative PCR; luciferase activity analysis; cell viability analysis; cell cycle detection by flow cytometry; cell apoptosis detection by flow cytometry; nude mouse transplantation tumor experiments; computer molecular dynamics simulation docking analysis; and data calculation and processing. The invention lays a foundation for further cell cycle detection and subsequent research and development of novel small molecule drugs.
Owner:QINGDAO MARINE BIOPHARMACEUTICAL RES INST +1
Enantioselective biotransformation for preparation of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor intermediates
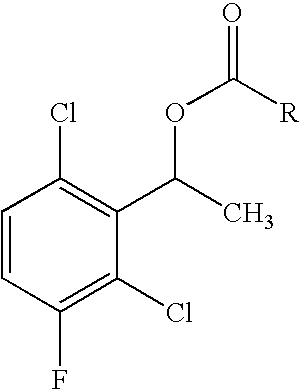
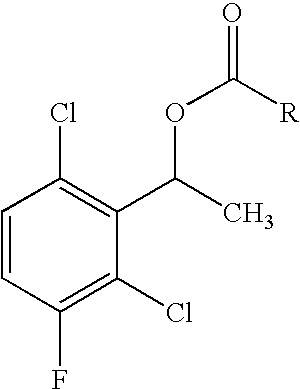
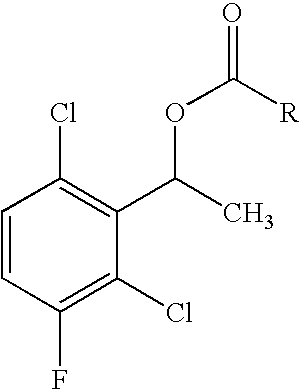
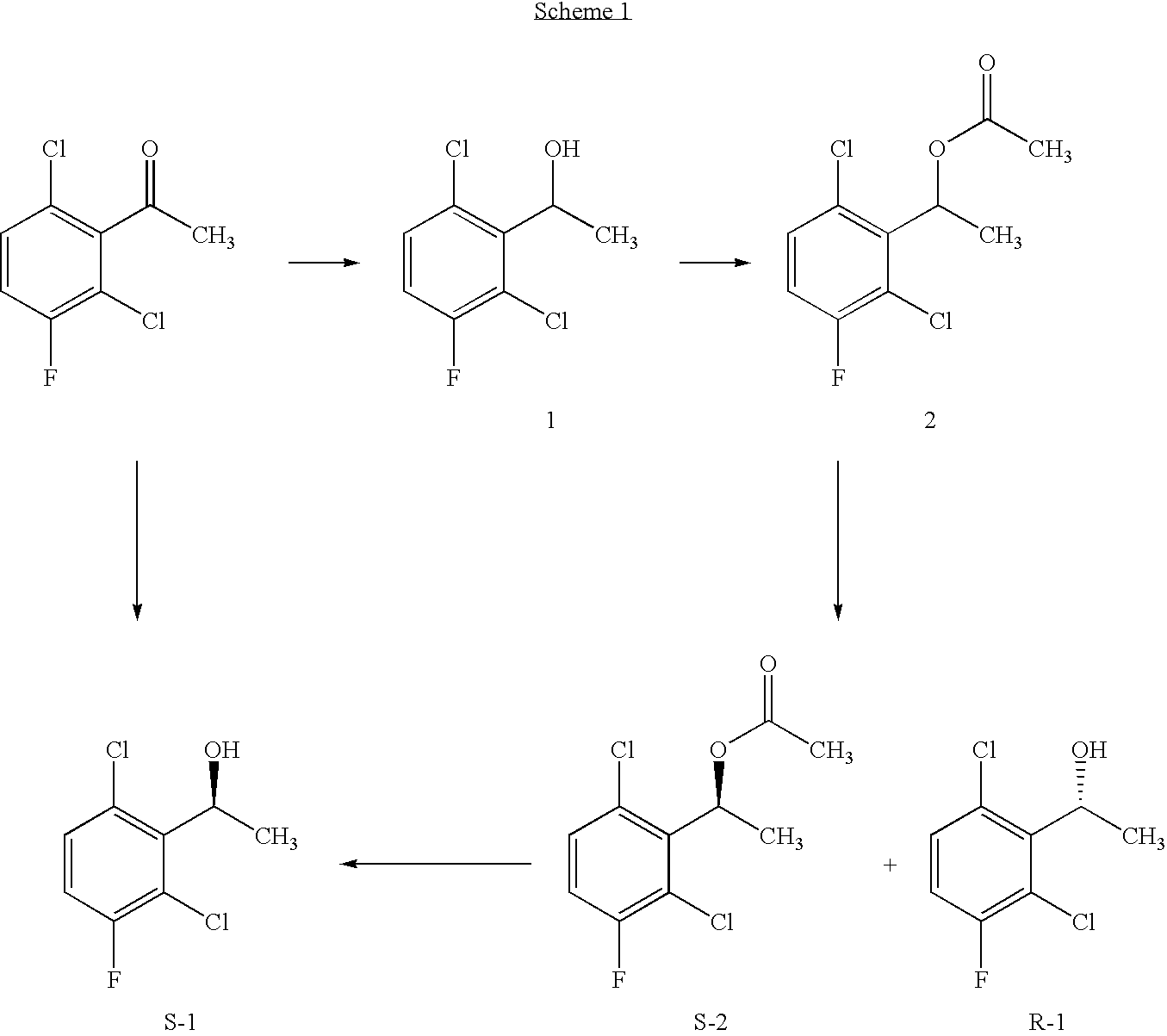
The invention relates to biocatalytic methods for preparing enantiomerically pure stereoisomers of 1-(2,6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethanol. Disclosed are methods of preparation of the desired (S)-enantiomer, which methods are based on a combination of enzymatic resolution, chemical esterification and chemical hydrolysis with inversion of 1-(2,6-dichloro-3-fluorophenyl)ethyl esters or stereoselective bio-reduction of 2,6-dichloro-3-fluoro-acetophenone with a biocatalyst such as an enzyme or a microorganism. The chiral (S)-enantiomer can be used in the synthesis of certain enantiomerically enriched, ether linked 2-aminopyridine compounds that potently inhibit auto-phosphorylation of human heptocyte growth factor receptor.
Owner:AGOURON PHARMA INC
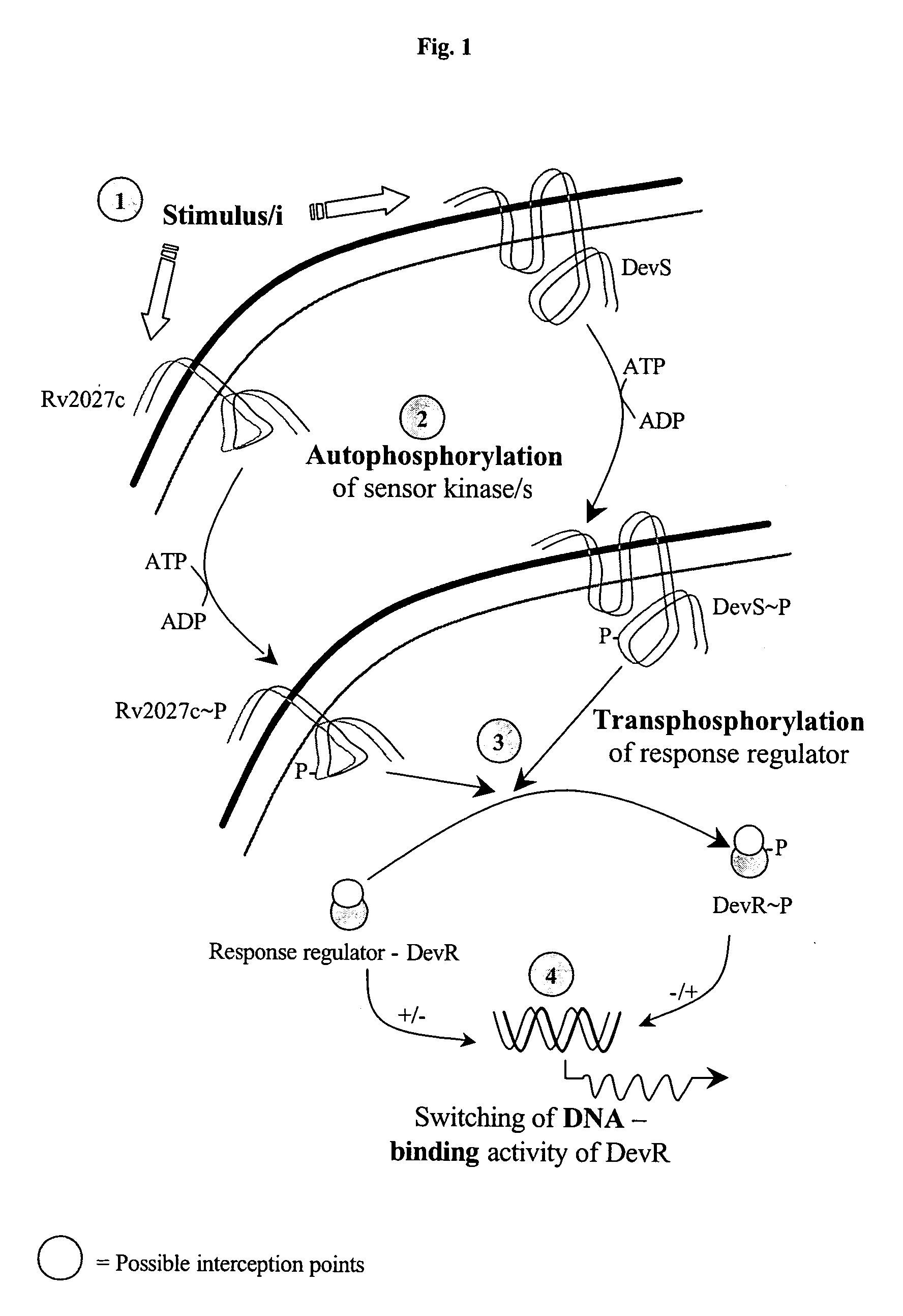
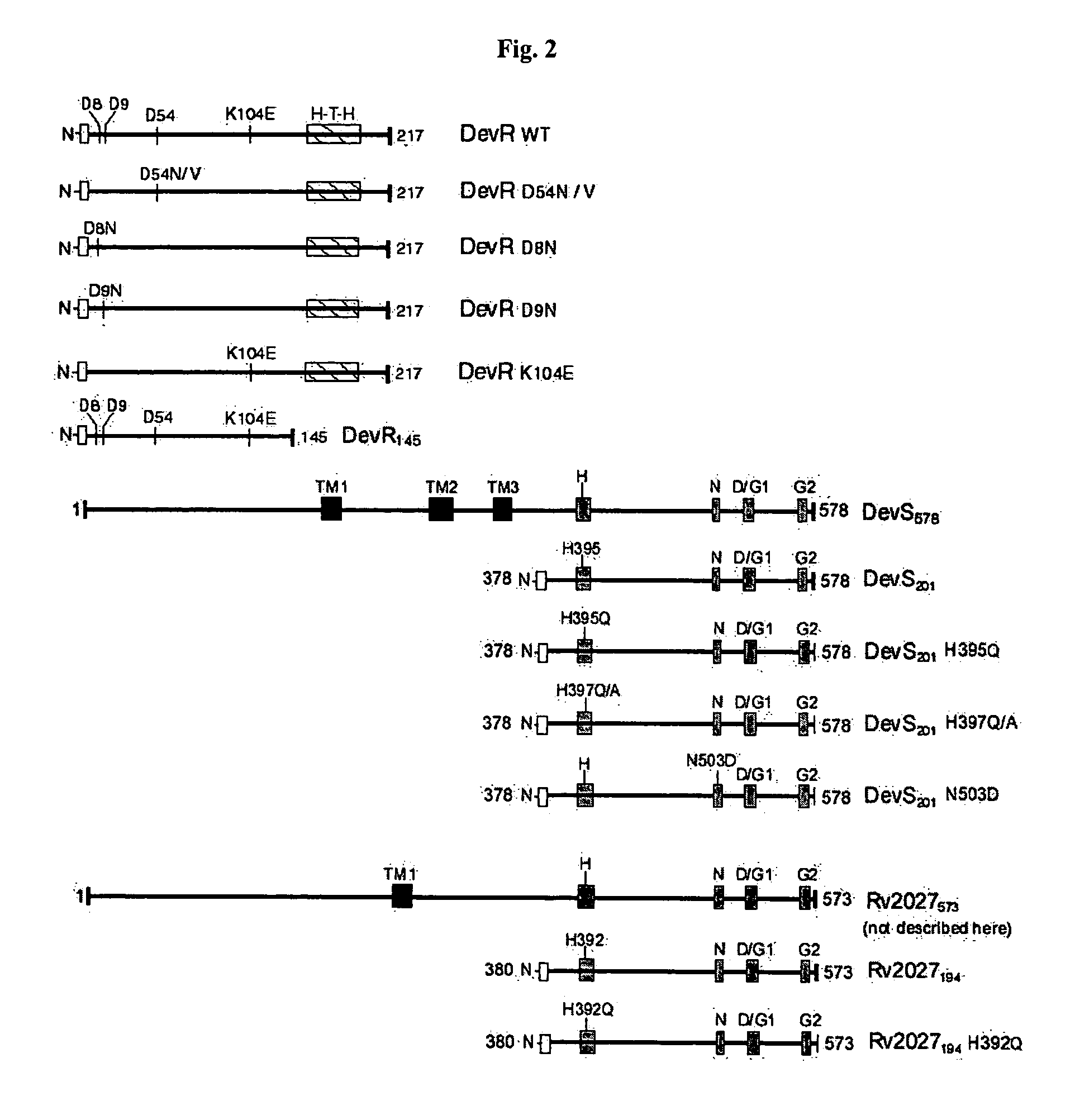
Screening method for developing drugs against pathogenic microbes having two-component system
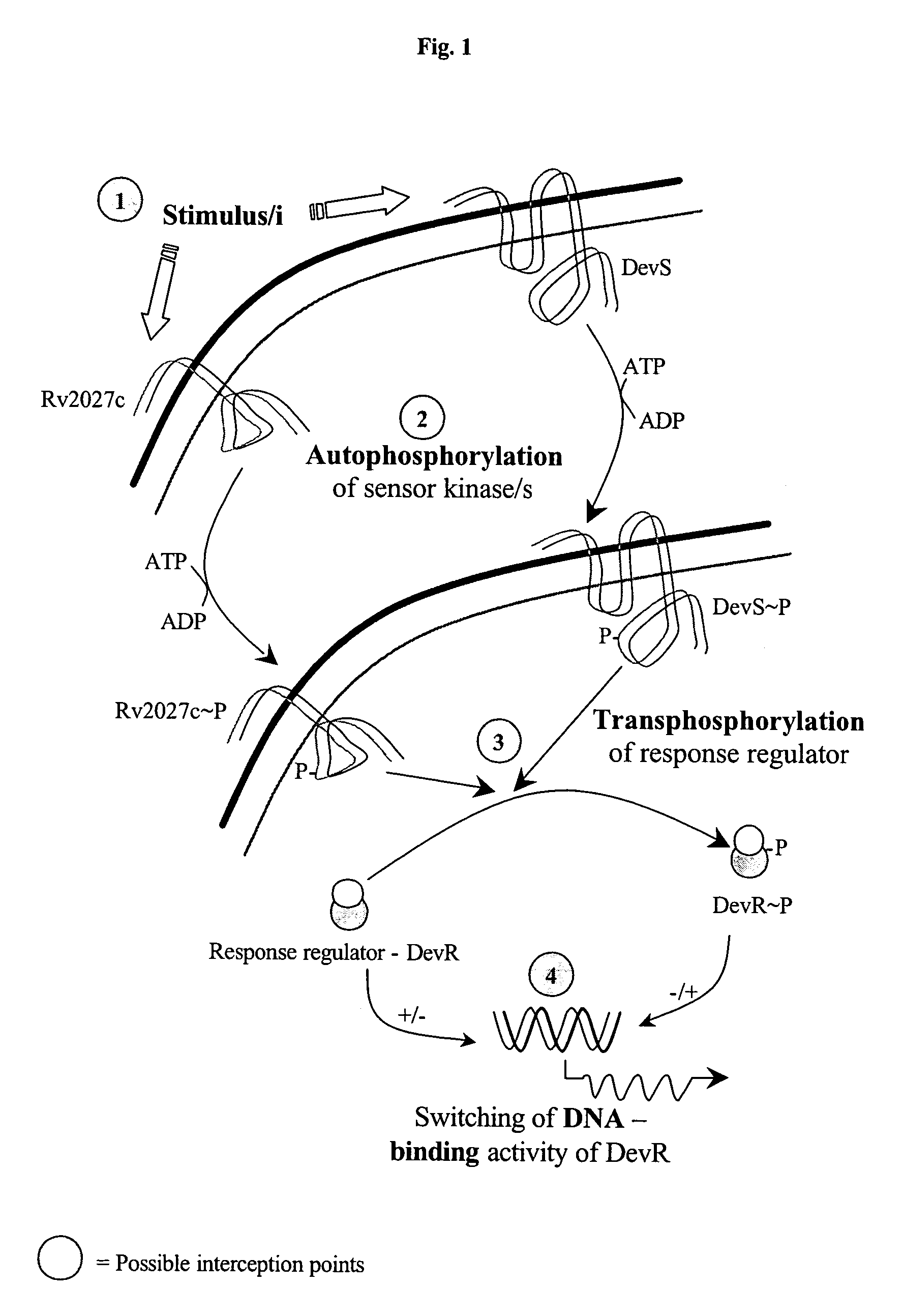
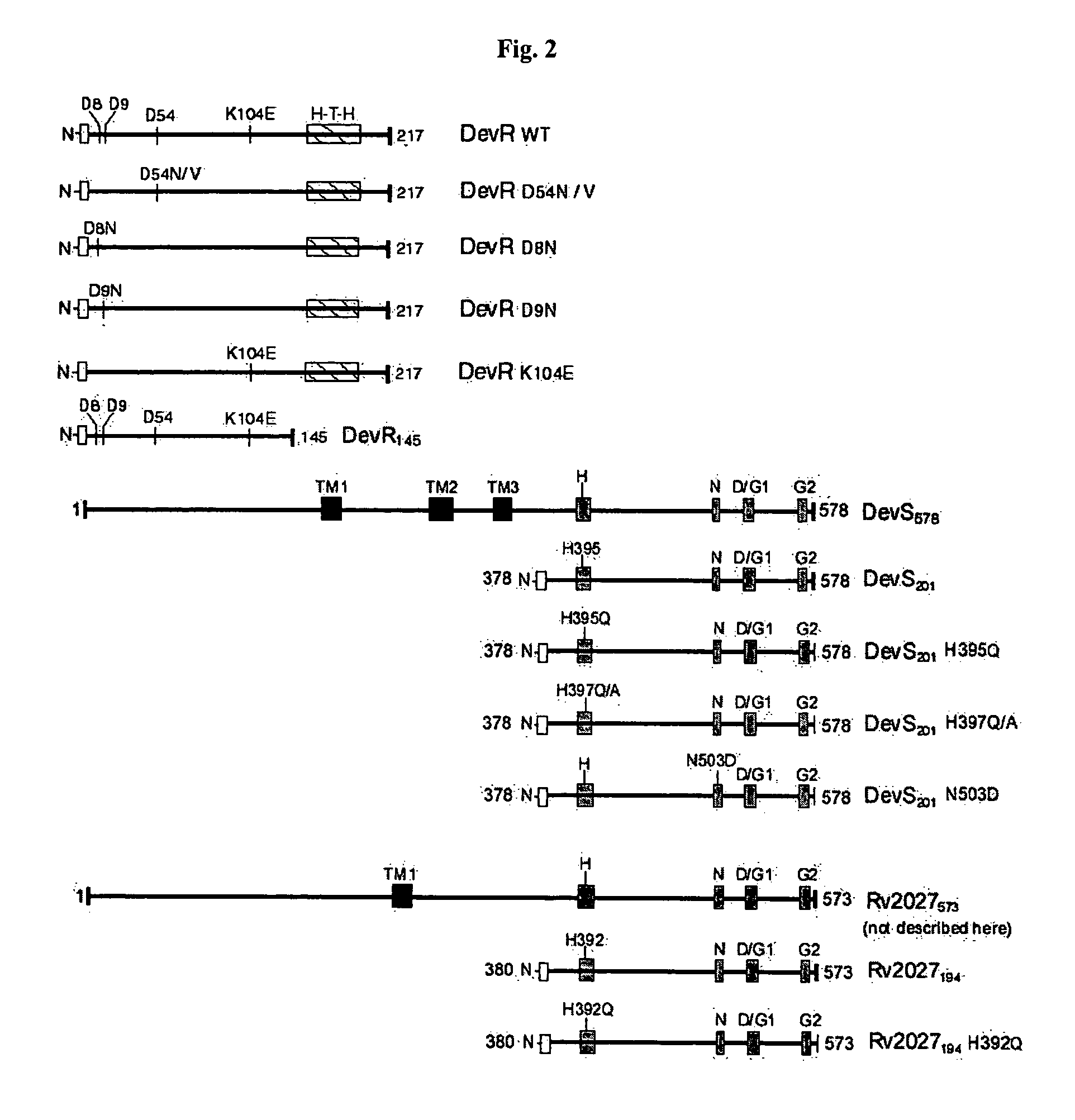
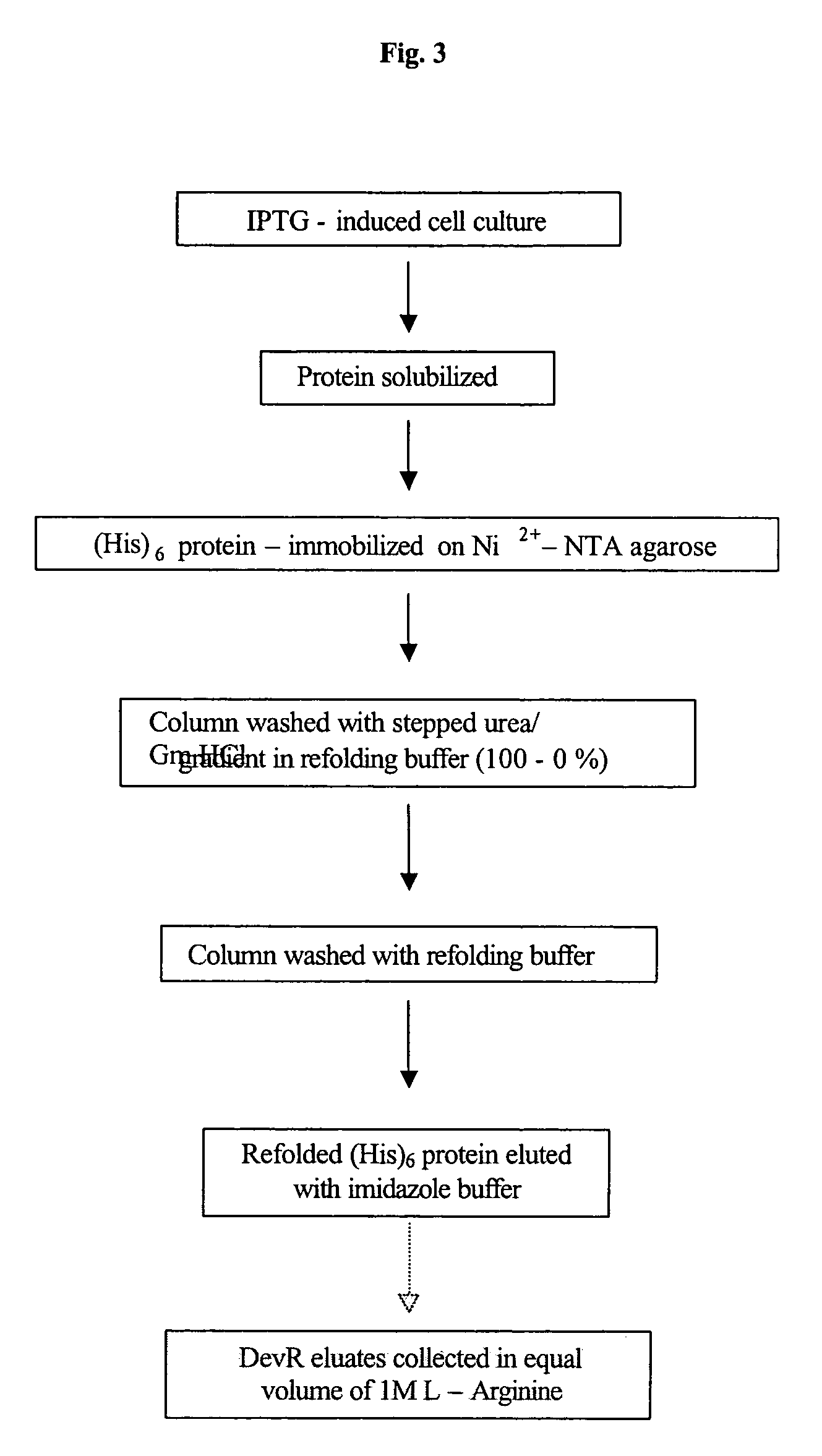
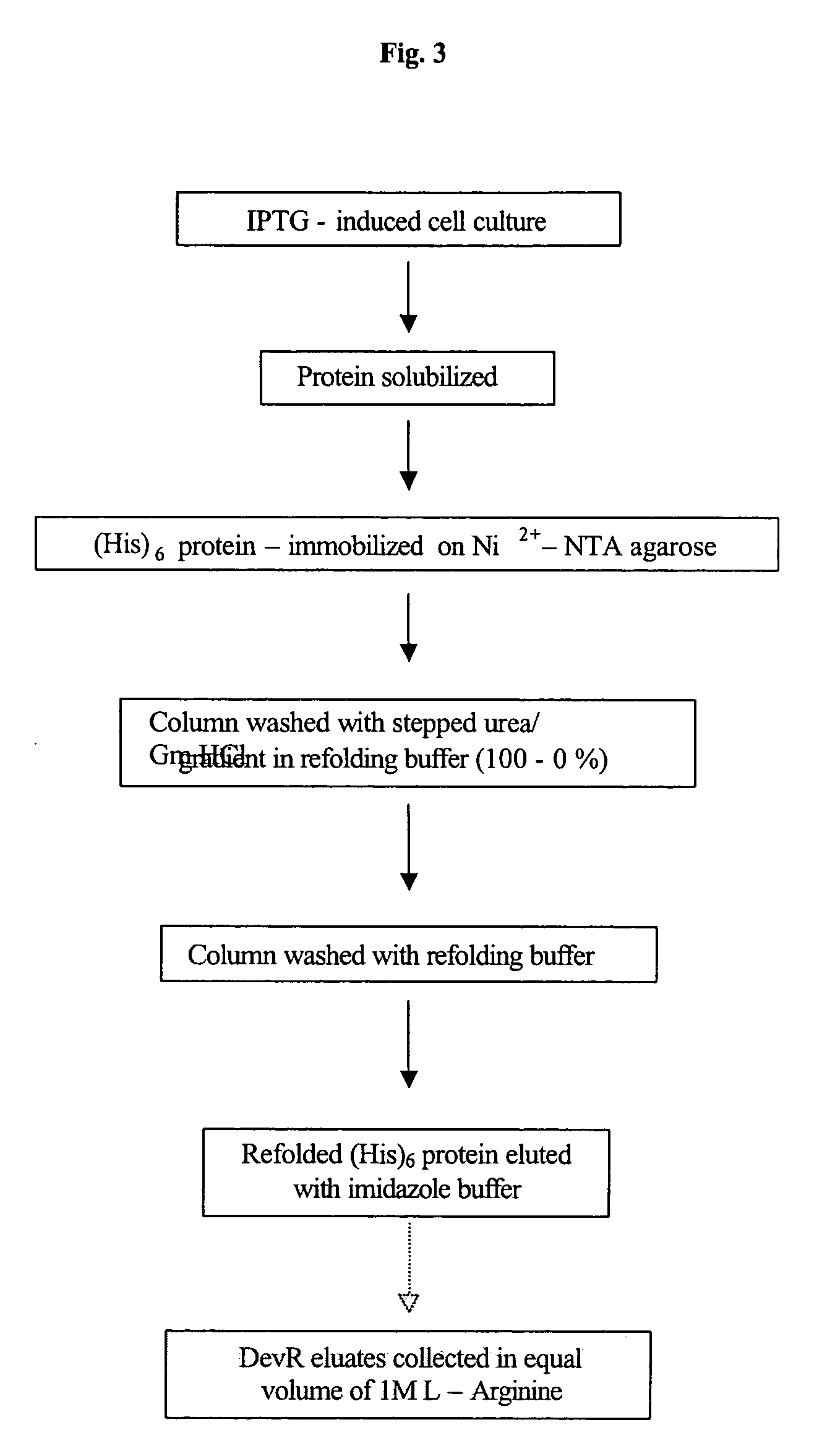
The present invention relates to a package of screening methods for developing drugs against pathogenic microbes having two-component system of DevR-DevS and / or DevR-Rv2027c and its homologues, said method comprising steps of over-expressing DevR, DevS, and Rv2027c and their single domain derivatives including mutant variant proteins, autophosphorylating DevS, and Rv2027c proteins and thereafter, phosphotransfering to DevR and its derivatives in SDS-PAGE or High-throughput format in the presence of a test compound, and determining the drug-potential of the test compound, wherein the potential of the drug is inversely proportional to (i) the degree of autophosphorylation of DevS and Rv2027c, (ii). the degree of phosphotransfer-based dephosphorylation of DevR and / its single domain derivative, and (iii). the degree of dephosphorylation of phosphorylated species of DevS and Rv2027c and / their single domain derivatives, and a method of treatment, and a composition thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Inhibitors of autophosphorylation protein kinases
InactiveUS7189694B2Inhibit enzymatic functionShuts down functioning pathwayPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticADAMTS ProteinsTyrosine
The subject invention concerns peptide molecules that specifically inhibit the enzymatic function of tyrosine kinases, including the JAK and EGF receptor (EGFR) family of kinases, to autophosphorylate, i.e., to transfer a phosphate group from ATP to an amino acid in the kinase. Phosphorylation of proteins is the most fundamental method for signal transduction among proteins in a cell. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation activities inhibits the enzyme's signaling and shuts down the functioning pathways originating from the enzyme. The JAK2 and EGFR tyrosine kinases are involved in both inflammatory disorders and cancer. In these disorders, the tyrosine kinases can often be activated in an uncontrolled fashion. The subject application also concerns antibodies that bind to a tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation site. The subject invention also concerns pharmaceutically acceptable formulations of the subject peptides and antibodies, and methods for treating inflammatory and oncological disorders by inhibiting tyrosine kinase signaling in these situations by administering a peptide or antibody of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Trophinin-Binding Peptides and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20080200369A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBinding peptideAutophosphorylation
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods useful for promoting sperm motility, promoting embryonic stem cell formation, promoting trophoblast formation, or promoting neuronal growth. The compositions and methods are based on peptide sequences that bind trophinin, inhibit bystin-mediated arrest of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor, and promotes EGF receptor autophosphorylation.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INST
Epha2 and hyperproliferative cell disorders
InactiveUS20090162933A1Promote migrationIncrease secretionSenses disorderDigestive systemCell phenotypeDisease
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of a non-neoplastic hyperproliferative cell or excessive cell accumulation disorders, particularly those involving hyperproliferation of epithelial or endothelial cells. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more EphA2 agonistic agents that bind to EphA2 and increase EphA2 cytoplasmic tail phosphorylation and / or increase EphA2 autophosphorylation, in cells which EphA2 has been agonized. In another embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more EphA2 agonistic agents that bind to EphA2 and reduce EphA2 activity (other than autophosphorylation). In another embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise administration of an effective amount of one or more EphA2 agonistic agents that bind to EphA2 and decrease a pathology-causing cell phenotype (e.g., a pathology-causing epithelial cell phenotype or a pathology-causing endothelial cell phenotype). In another embodiment, the methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more EphA2 agonistic agents that are EphA2 antibodies that bind to EphA2 with a very low Koff rate. In preferred embodiments, agents of the invention are monoclonal antibodies. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 agonistic agents of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful in therapy for non-neoplastic hyperproliferative cell or excessive cell accumulation disorders.
Owner:KIENER PETER A +3
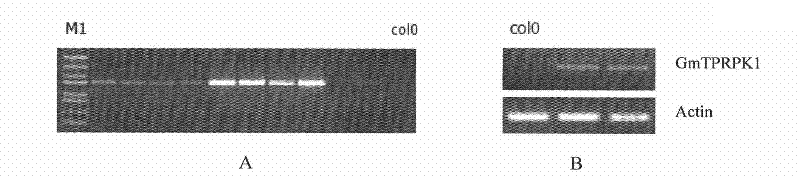
Plant stress tolerance related protein GmTPRPK1, encoding gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102234319AIncrease resistanceIncrease the distributionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAutophosphorylation
The invention discloses a plant stress tolerance related protein GmTPRPK1, an encoding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is (a) or (b): (a) the protein is composed of an amino acid sequence represented by a sequence 1 in a sequence listing; and (b) the protein which is related to the plant stress tolerance, derived from the sequence 1, and obtained through substituting and / or deleting and / or adding to the amino acid sequence of the sequence 1 by one or some amino acid residues. The GmTPRPK1 expresses under the induction of drought, high salt, ABA,ethylene and the like, and the expression of the GmTPRPK1 is inhibited under the low temperature threat. The GmTPRPK1 can enhance the resistance of a plant to high salt and drought, and the growth ofroots. The GmTPRPK1 allows autophosphorylation to be carried out, and can be positioned on nucleuses and cell membranes, and the distribution range is large. The GmTPRPK1 of the present invention lays the foundation for artificially controlling the expression of the anti-stress and stress resistance related gene, and plays an important role in breeding plant varieties with strengthened anti-stress and stress resistance.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
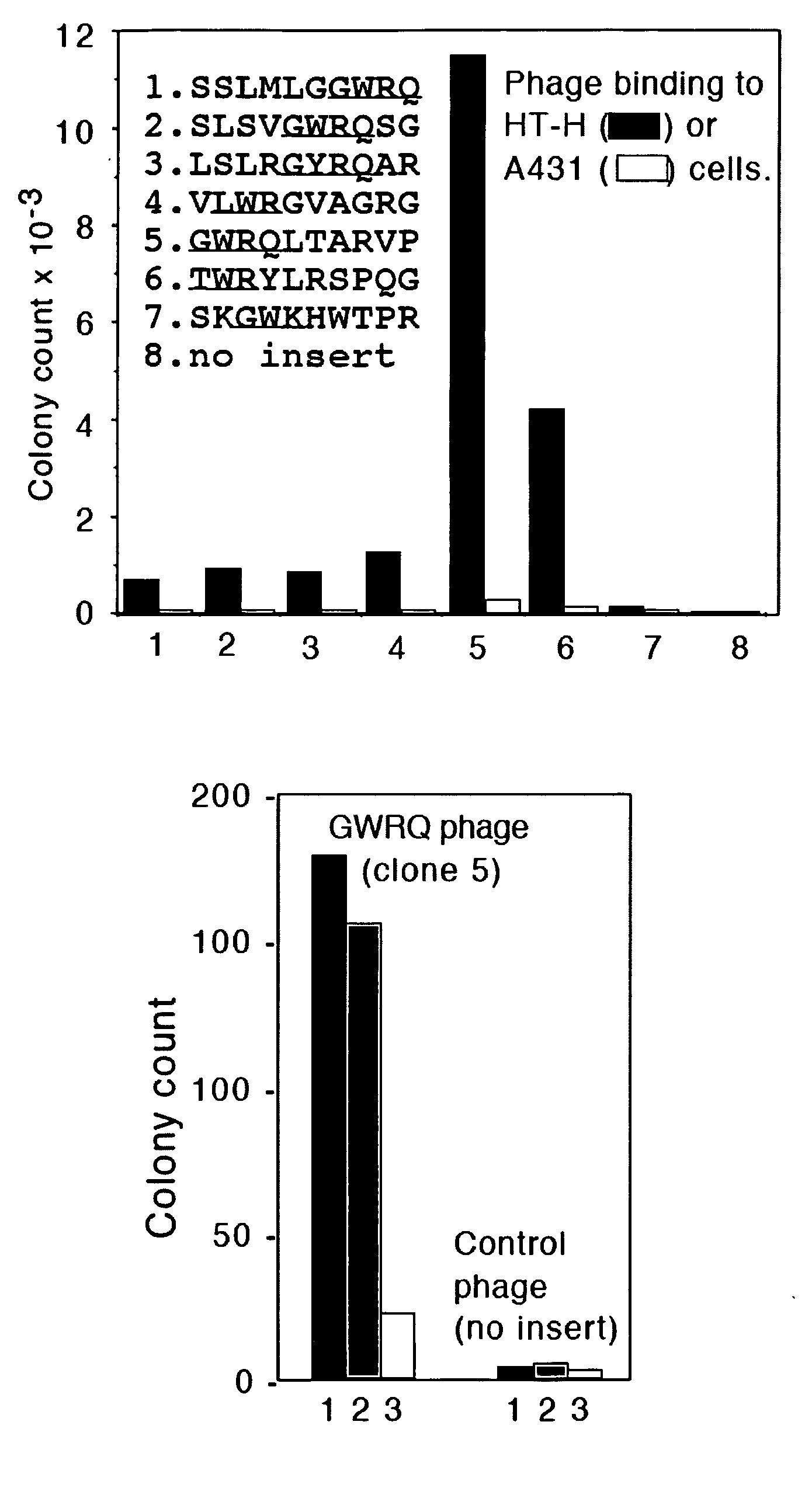
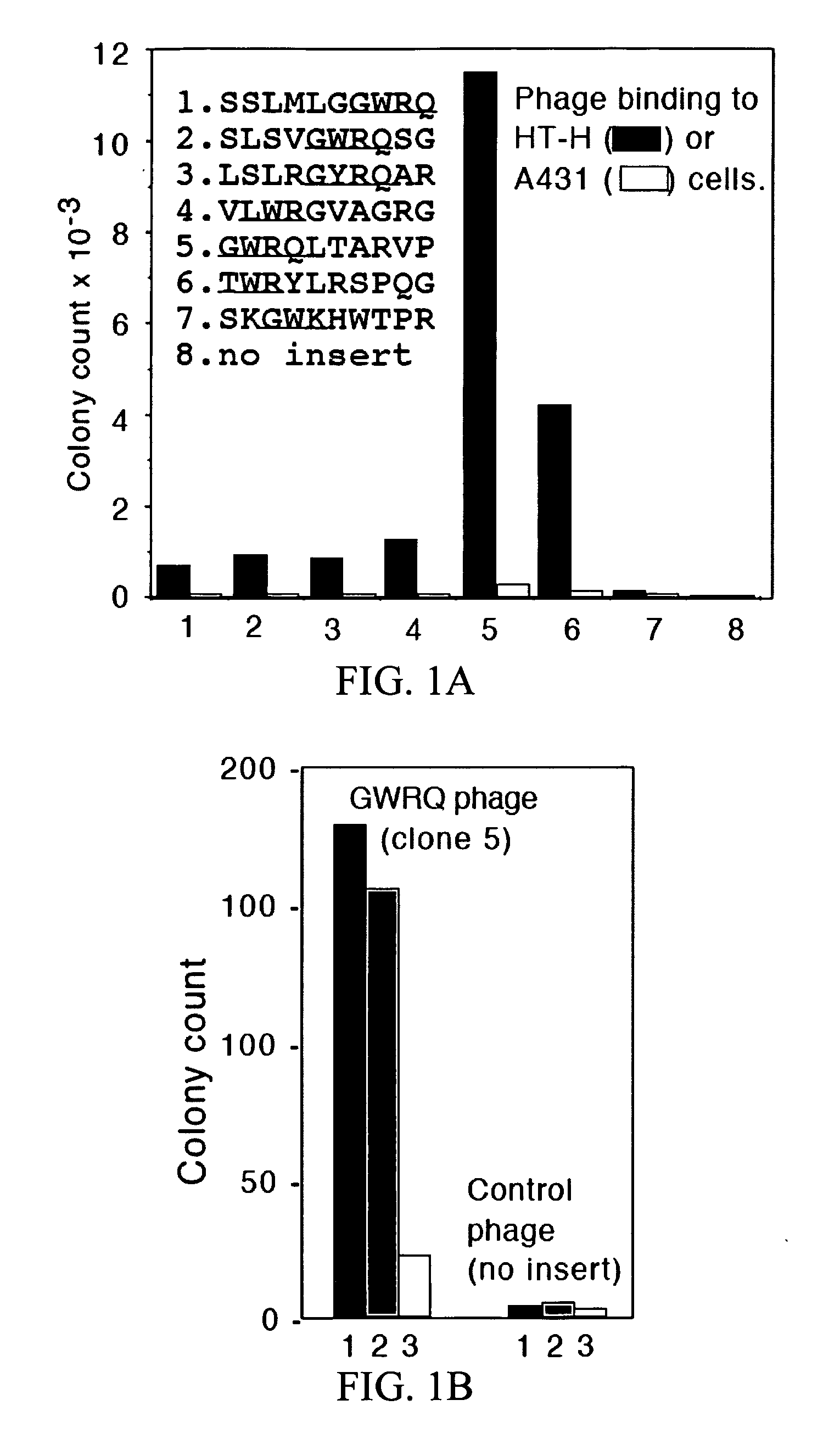
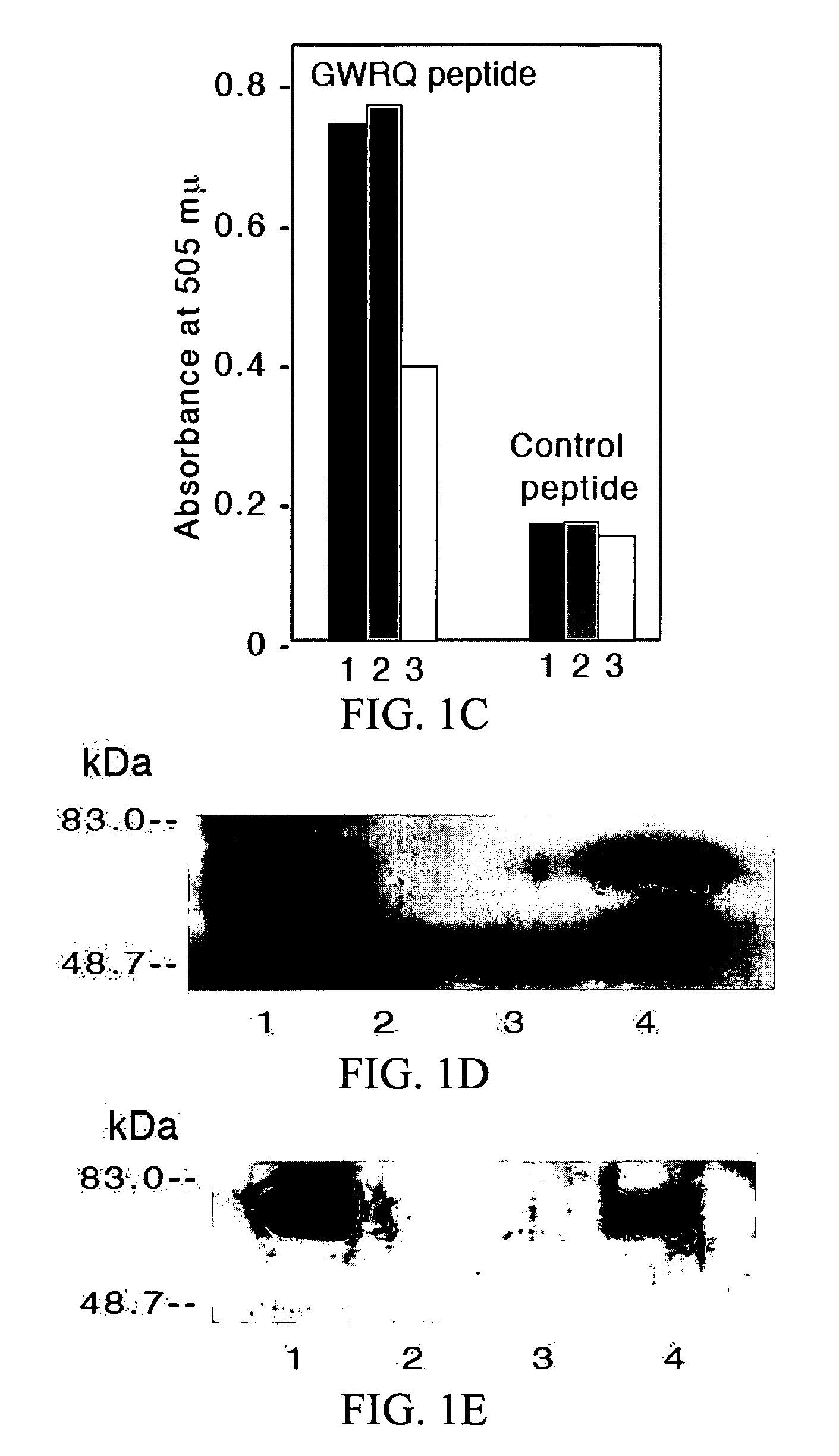
Targeted peptide of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and application thereof
InactiveCN102993272ASmall molecular weightEasy to synthesizePeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsLipid formationSmall peptide
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and relates to a targeted peptide of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the application thereof. The design of the invention comes from small peptides of EY1068ING (sequence (SEQ) identity (ID) NO:1), PDY1148QQD (SEQ ID NO:2) and AEY1173LR(SEQ ID NO:3) of main self-phosphorylation acting site of EGFR. The peptide is used for modifying nanometer lipid carriers which comprise solid-state lipid material, lipid-state oil, fat-soluble emulsifier, polyethylene glycol (PEG) modified lipid, water-soluble emulsifier and additive. The peptide has the following characteristics: (1) the obtained polypeptide has small molecular weight, convenient synthesis, low cost, high affinity with EGFR and strong specificity; (2) the obtained small peptides has good EGFR targeting and can be used for constructing the carriers for targeted therapy of tumor with high expression of EGFR.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
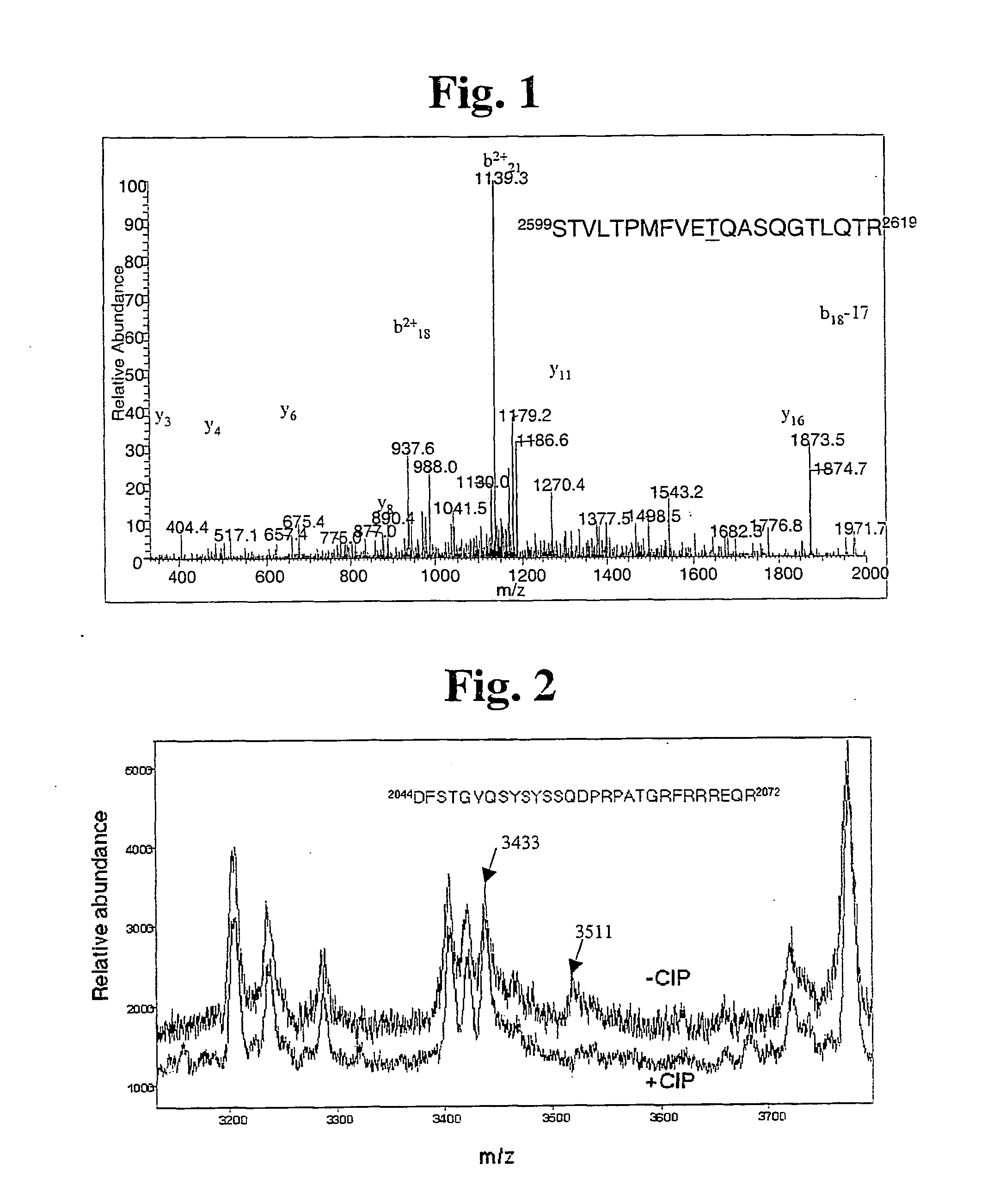
Dna dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit phosphorylation sites and antibodies thereto
InactiveUS20050176935A1Enhance cell viabilityMonitor effectivenessPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCancer cellAutophosphorylation
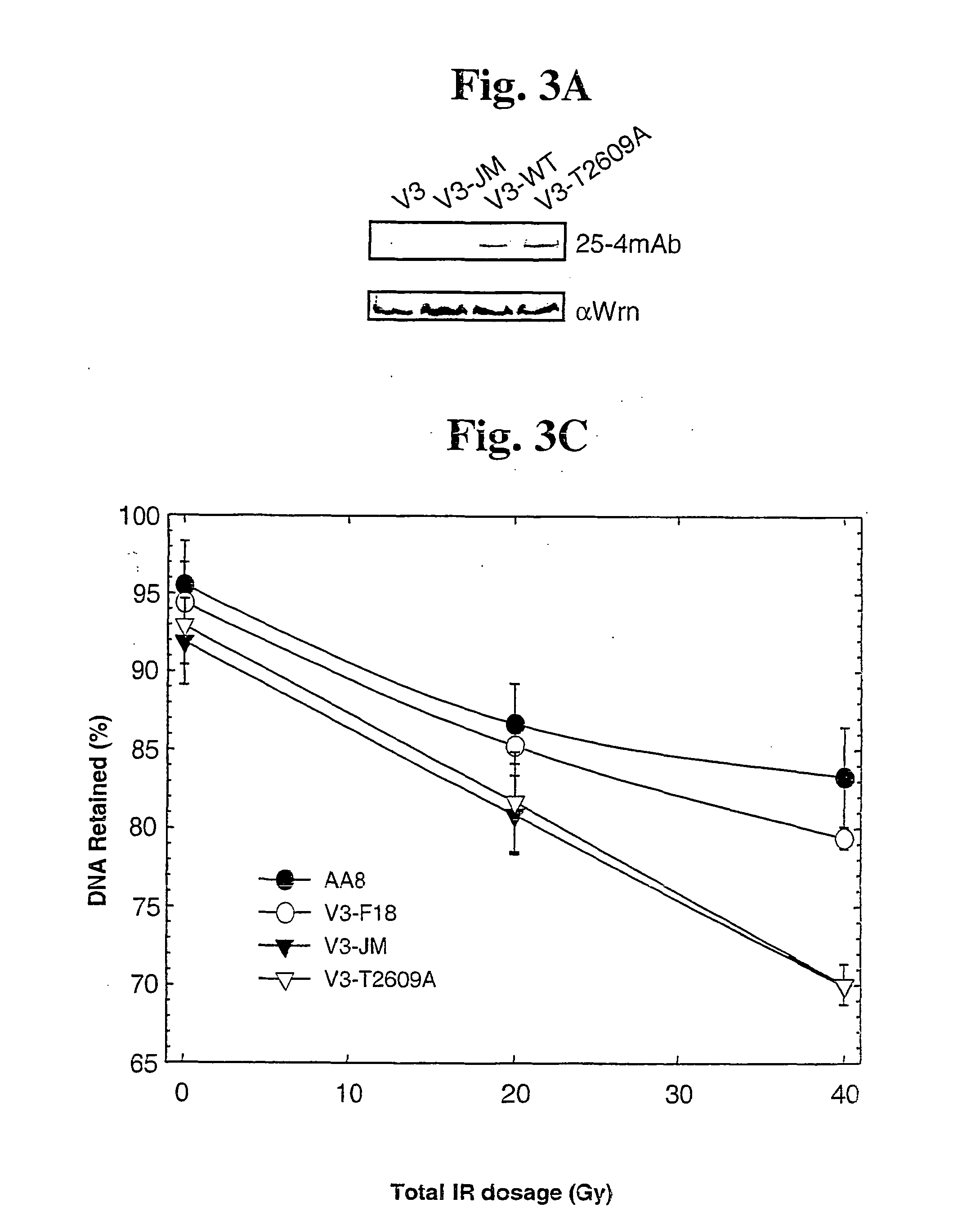
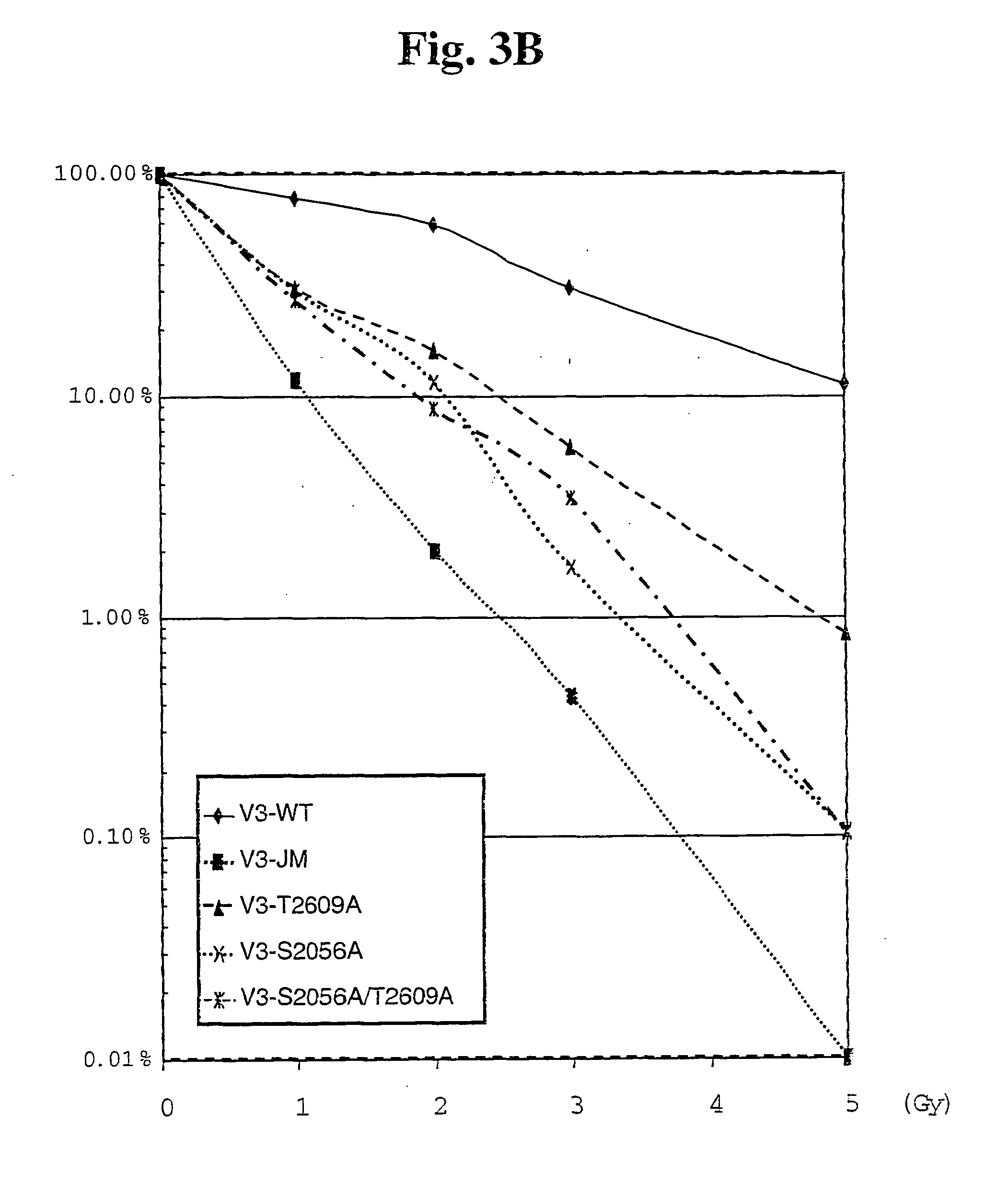
The identification and use of two major DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation sites. Threonine (T) 2609 and Serine (S) 2056, including antibodies specific for phosphorylated T2609 and 52056. Peptides and polynucleotides encoding same, that feature these two sites of phosphorylation. The antibodies do not bind to the unphosphorylated DNA-PKcs protein or peptide, thus providing diagnostic tools to monitor the effectiveness of treatments which target the DNA repair pathway of cancer cells, and the ability to intervene or inhibit in phosphorylation of T2609 or 52056, either through application of a drug or an antibody, to increase the radiosensitivity of cancer cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
C-Met Protein Agonist
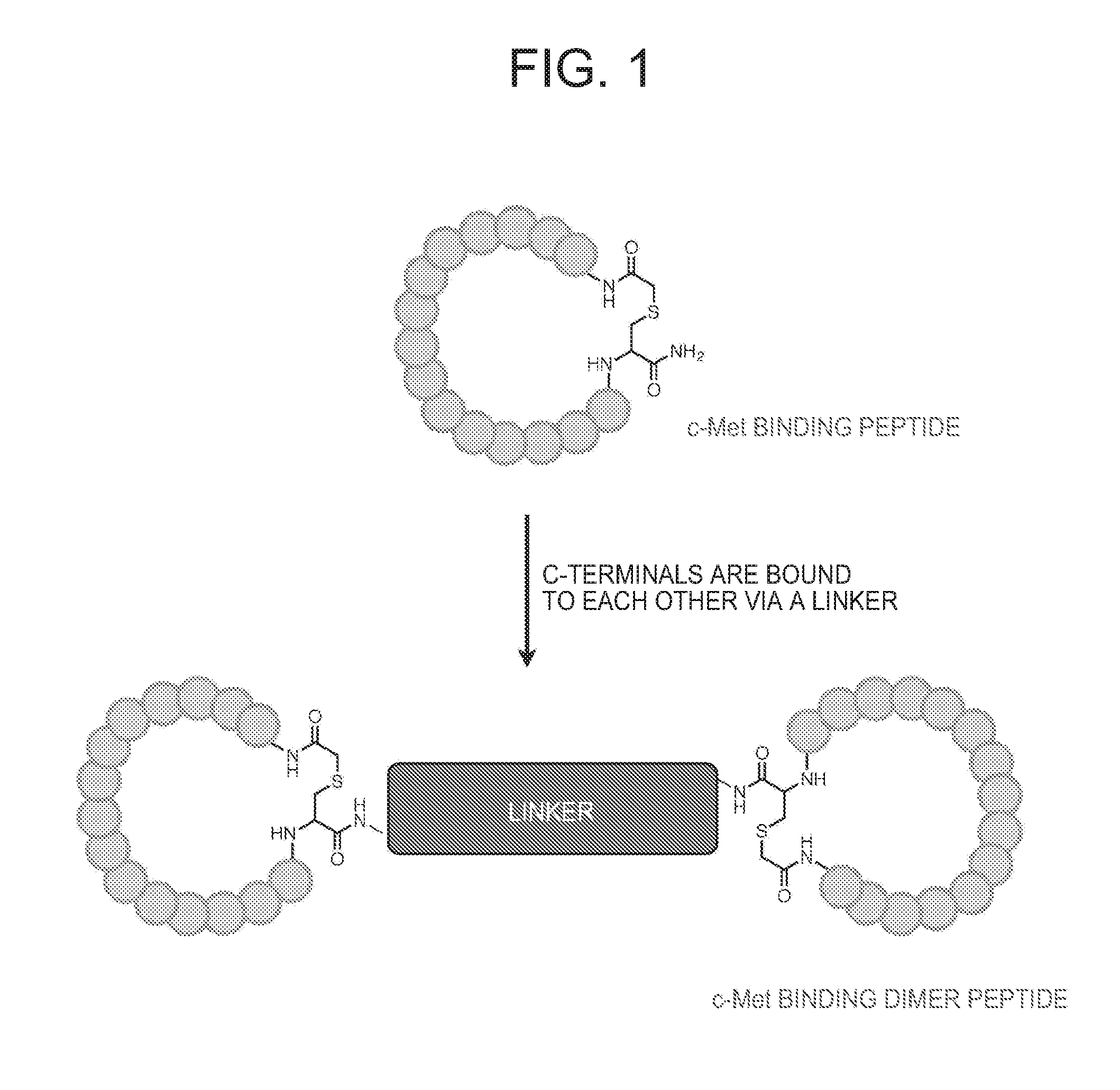
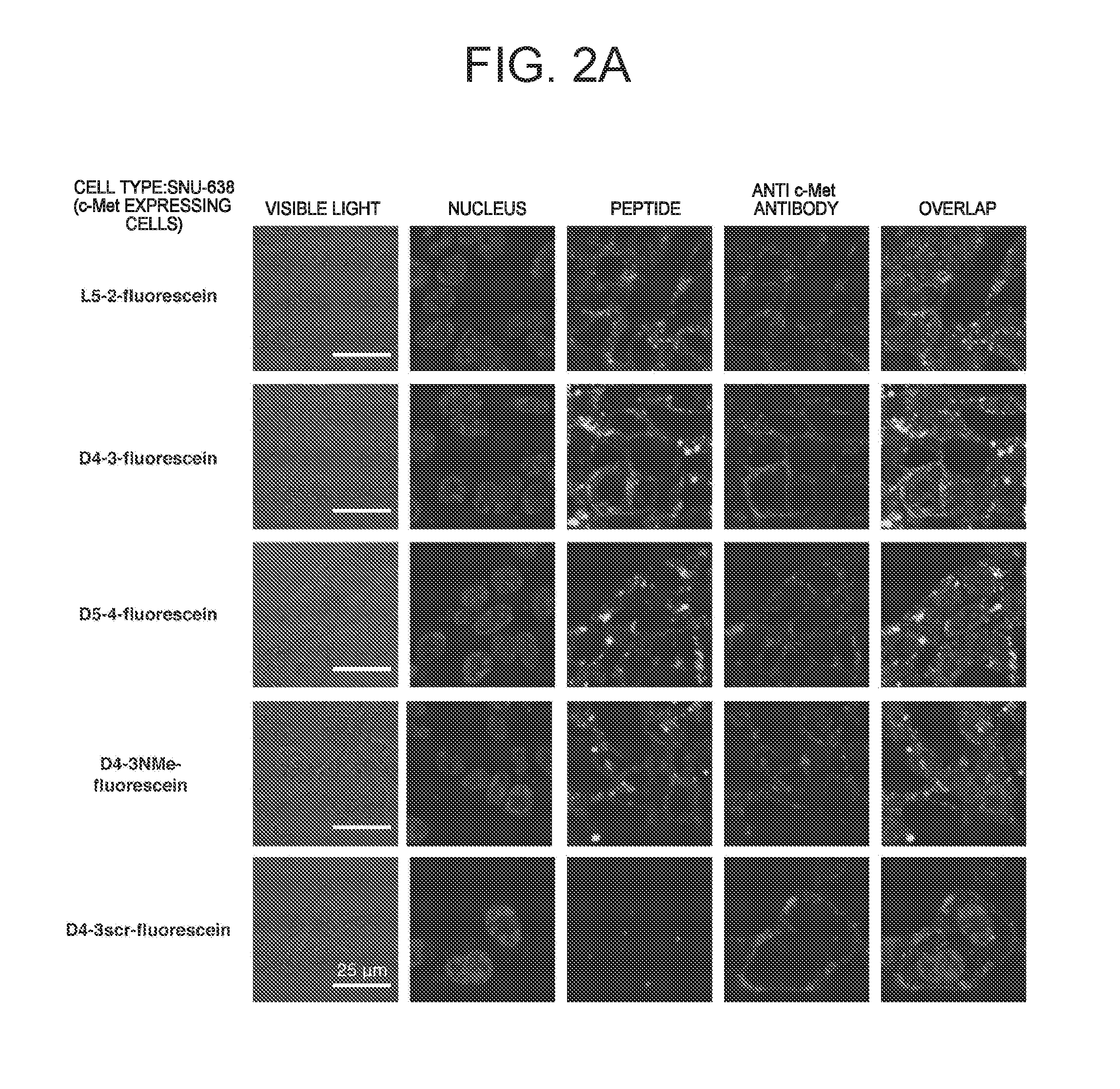
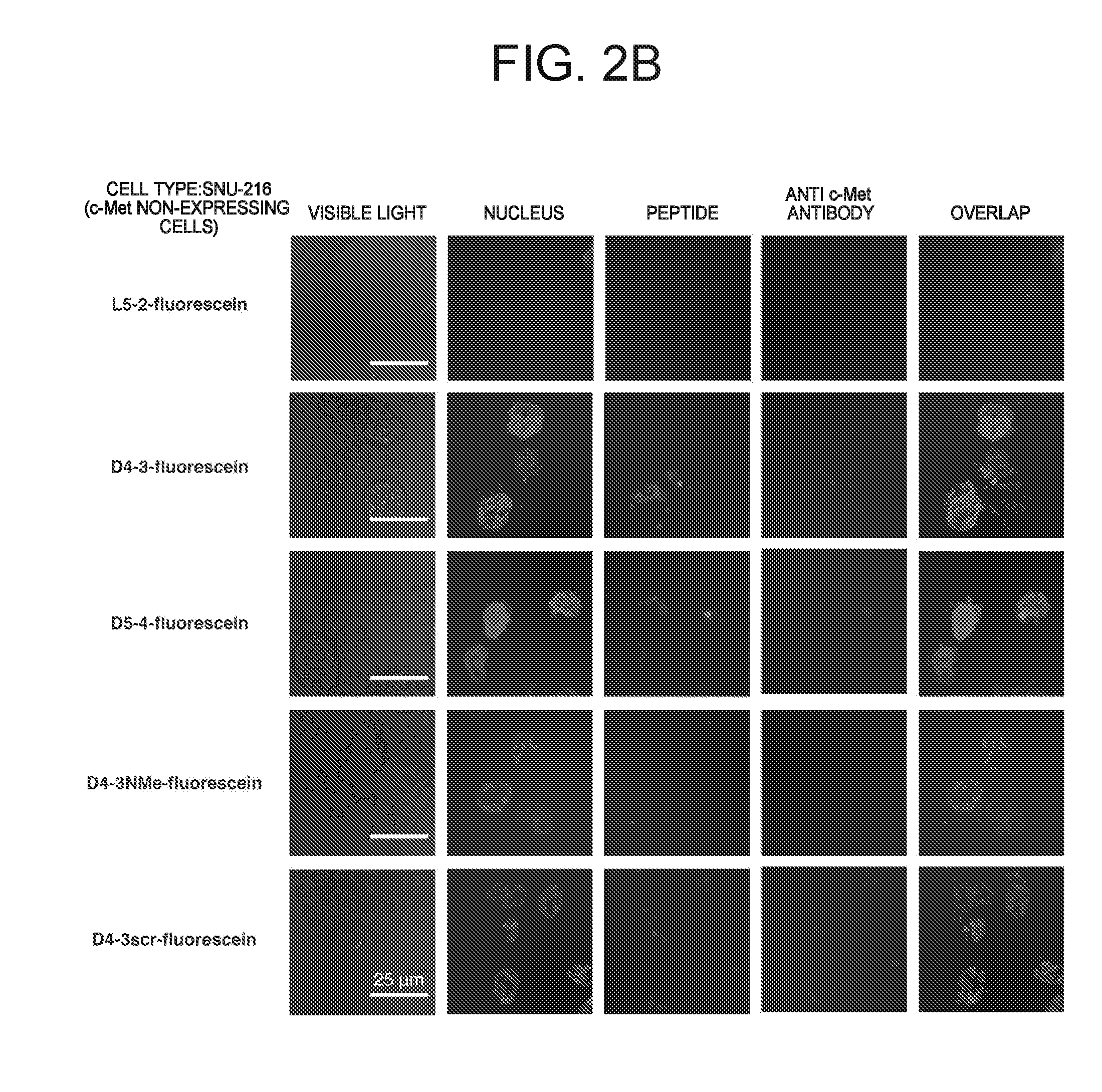
ActiveUS20160237119A1Promote cell growth cellPromote cell cell migrationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsC-MetAutophosphorylation
Object of the present invention is to provide a peptide functioning as a c-Met agonist. The present invention provides a peptide complex comprising two or more peptides that bind to a c-Met protein and a linker that links the two or more peptides to one another. Such a peptide complex promotes autophosphorylation of the c-Met protein and induces cell growth.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Methods of Screening for Janus Kinase 3 Interacting Compounds
The present invention provides a method for screening compounds for their ability to inhibit autophosphorylation of Janus kinase 3 in the absence of any additional substrate. The present invention also provides a method for screening compounds that bind to Janus kinase 3 domains other than the kinase domain, to identify synthetic or natural compounds including biomolecules, that modulate Janus kinase 3 activity. This invention also describes a multi-component screening kit composed of purified recombinant Janus kinase 3 proteins and recombinant phosphorylated Janus kinase 3 fusion proteins including, one or more phosphorylated or non-phosphorylated domain-deleted Janus kinase 3 fusion proteins.
Owner:KUMAR NARENDRA +1
GFRalpha3 and its uses
InactiveUS20050221330A1Easy to detectEasy to identifyFungiSenses disorderAutophosphorylationReceptor activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences, including expressed sequence tags (ESTs), oligonucleotide probes, polypeptides, vectors and host cells expressing, and immunoadhesions and antibodies to mammalian GFRα3, a novel α-subunit receptor of the GDNF (i.e. GFR) receptor family. It further relates to an assay for measuring activation of an α-subunit receptor by detecting tyrosine kinase receptor activation (i.e., autophosphorylation) or other activities related to ligand-induced α-subunit receptor homo-dimerization or homo-oligomerization.
Owner:DE SAUVAGE FREDERIC +3
Screening method for developing drugs against pathogenic microbes having two-component system
The present invention relates to a package of screening methods for developing drugs against pathogenic microbes having two-component system of DevR-DevS and / or DevR-Rv2027c and its homologues, said method comprising steps of over-expressing DevR, DevS, and Rv2027c and their single domain derivatives including mutant variant proteins, autophosphorylating DevS, and Rv2027c proteins and thereafter, phosphotransfering to DevR and its derivatives in SDS-PAGE or High-throughput format in the presence of a test compound, and determining the drug-potential of the test compound, wherein the potential of the drug is inversely proportional to (i) the degree of autophosphorylation of DevS and Rv2027c, (ii). the degree of phosphotransfer-based dephosphorylation of DevR and / its single domain derivative, and (iii). the degree of dephosphorylation of phosphorylated species of DevS and Rv2027c and / their single domain derivatives, and a method of treatment, and a composition thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for Measuring Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation
InactiveUS20080206800A1Quality improvementSpecificity efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAutophosphorylationKinase inhibition
Method, kit and composition for measuring the autophosphorylation of one or more tyrosine kinases in presence of a kinase inhibitor compared to the absence of said kinase inhibitor for kinase specificity profiling of kinase inhibitors.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
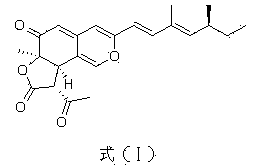
Application of compound Ochrephilone in preparing anti-tuberculosis medicine
InactiveCN103735542AHas clinical application prospectsHas potentialAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTuberculosis mycobacteriumThreonine
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and in particular relates to application of a compound Ochrephilone in preparing an anti-tuberculosis medicine. The compound Ochrephilone belongs to the family of natural toxins. Researches discover than the compound Ochrephilone has autophosphorylation activity of mycobacterium tuberculosis serine / serine-threonine kinase G, so that the Ochrephilone can be used for preparing a new anti-tuberculosis medicine by using mycobacterium tuberculosis serine / serine-threonine kinase G as a target.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for measuring tyrosine kinase phosphorylation
InactiveUS7981633B2Quality improvementSpecificity efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsAutophosphorylationO-phospho-L-tyrosine
The present invention relates to methods for measuring the autophosphorylation of one or more tyrosine kinases and use of such methods in profiling kinase inhibitors and activators. As a representative example, the method comprises inducing kinase autophosphorylation activity in cells in presence and in absence of a kinase inhibitor, lysing the cells, capturing the tyrosine kinase in the cell lysate by adding a plurality of tyrosine kinase specific binding proteins which are associated with unique dyes, adding a phosphotyrosine specific antibody tagged with a marker which is distinguishable from the unique dyes, and identifying the autophosphorylated tyrosine kinase by detecting the unique dye and the marker. Alternately, the tyrosine kinases themselves could be coupled to the unique dyes. The present invention also relates to kits and compositions for carrying out the above-described methods.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
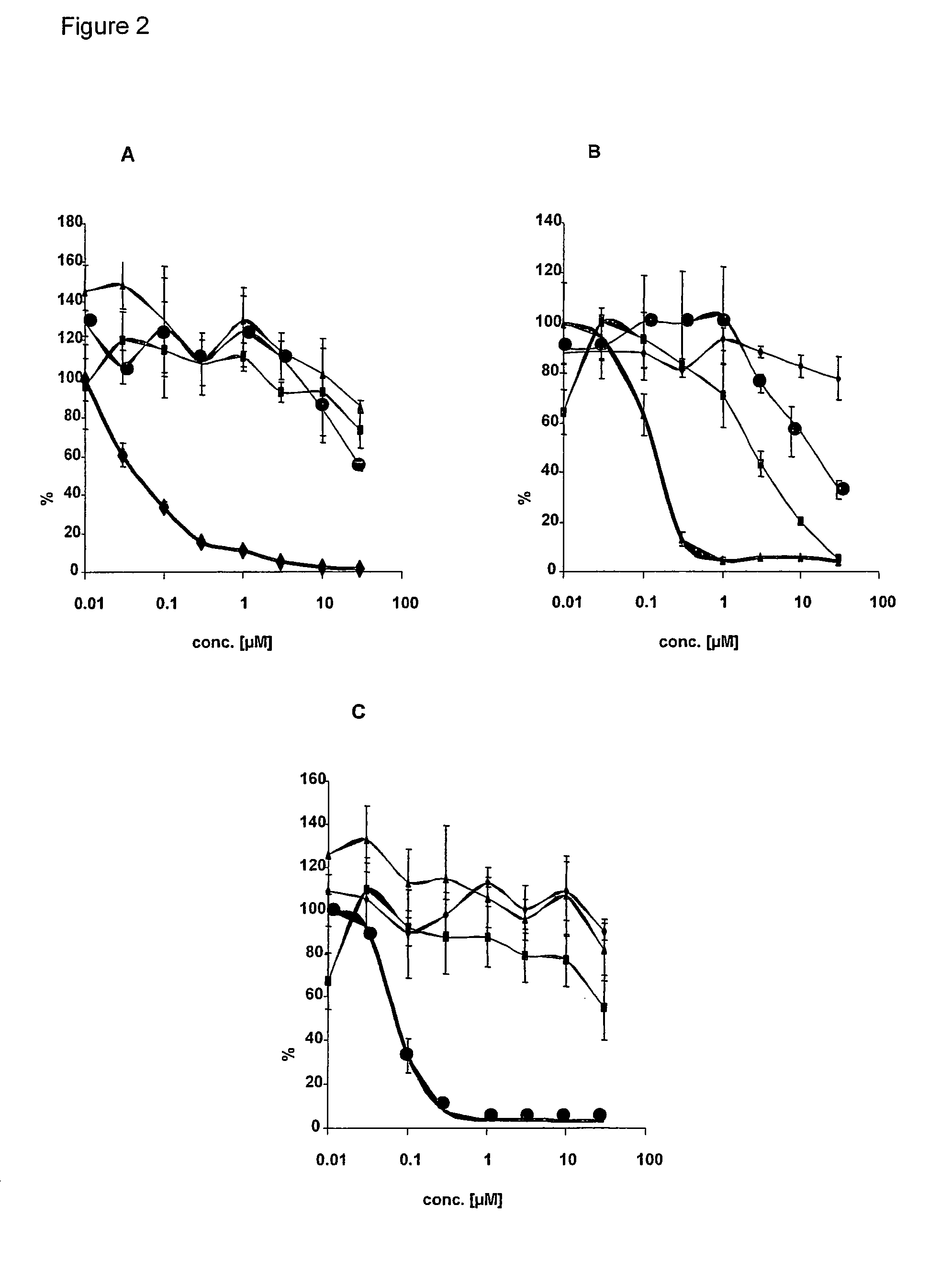
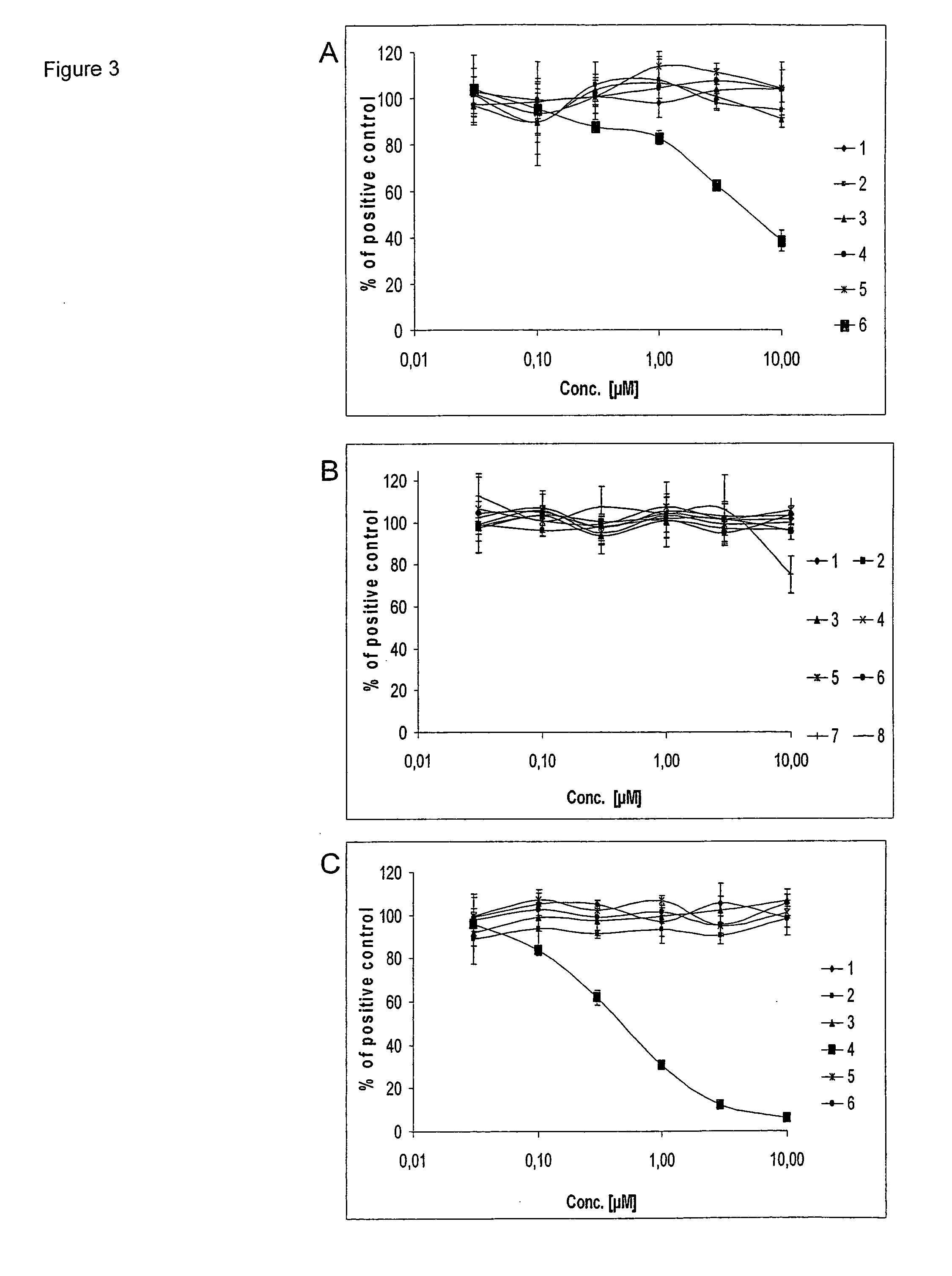
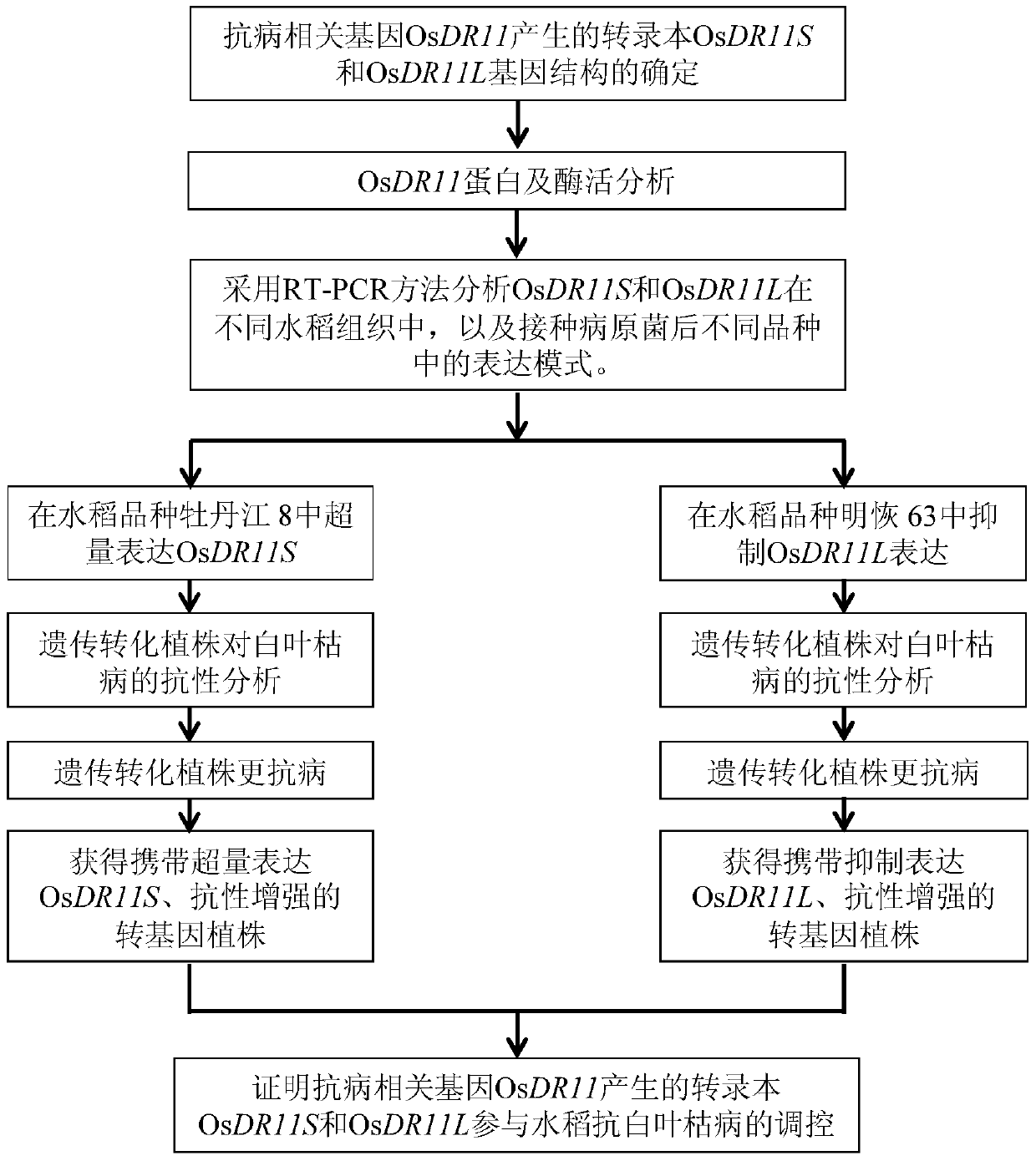
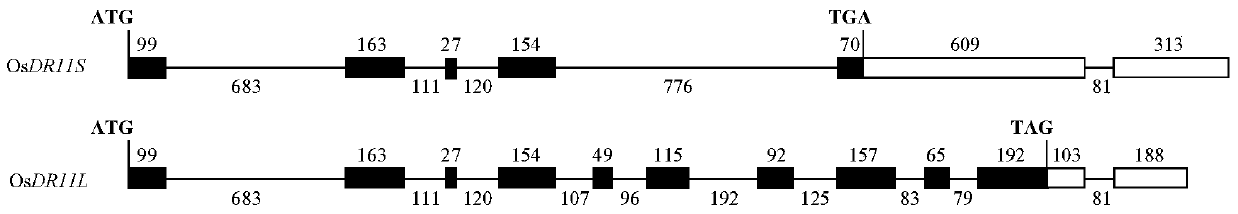
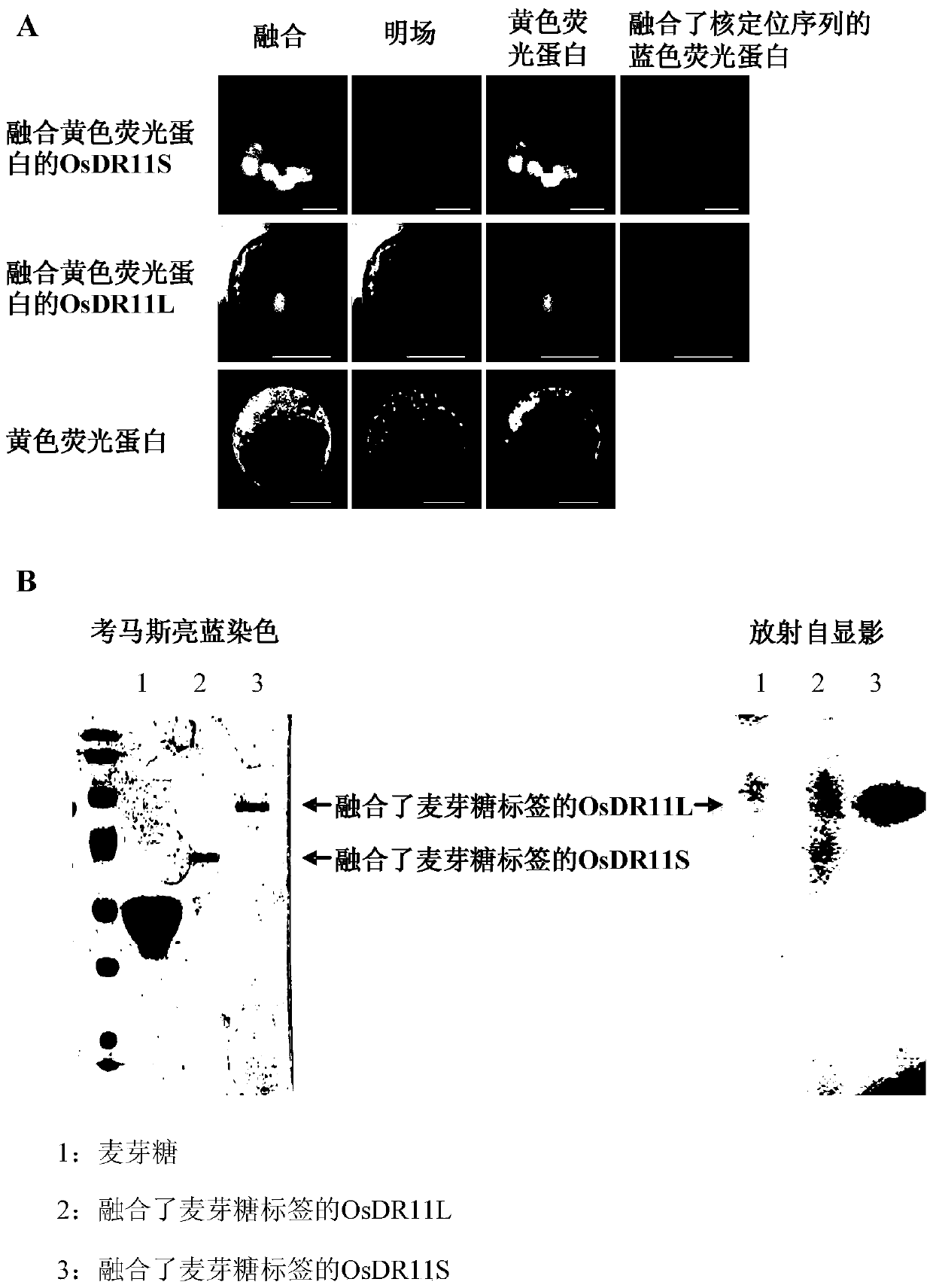
Rice disease resistance-related gene osdr11 and its application in rice disease resistance
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to identification and functional verification of two transcripts (OsDR11S and OsDR11L) produced by rice disease resistance-related gene OsDR11 due to different selective splicing patterns. The OsDR11 gene codes LAMMER protein kinase, OsDR11S has no autophosphorylation activity, and OsDR11L has autophosphorylation activity. The genes are used for controlling rice to resist diseases caused by xanthomonas oryzae, and the bacterial blight resistance abilities of transgenic rice plants for over expression of OsDR11S and transgenic rice plants for inhibiting OsDR11L expression are remarkably improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
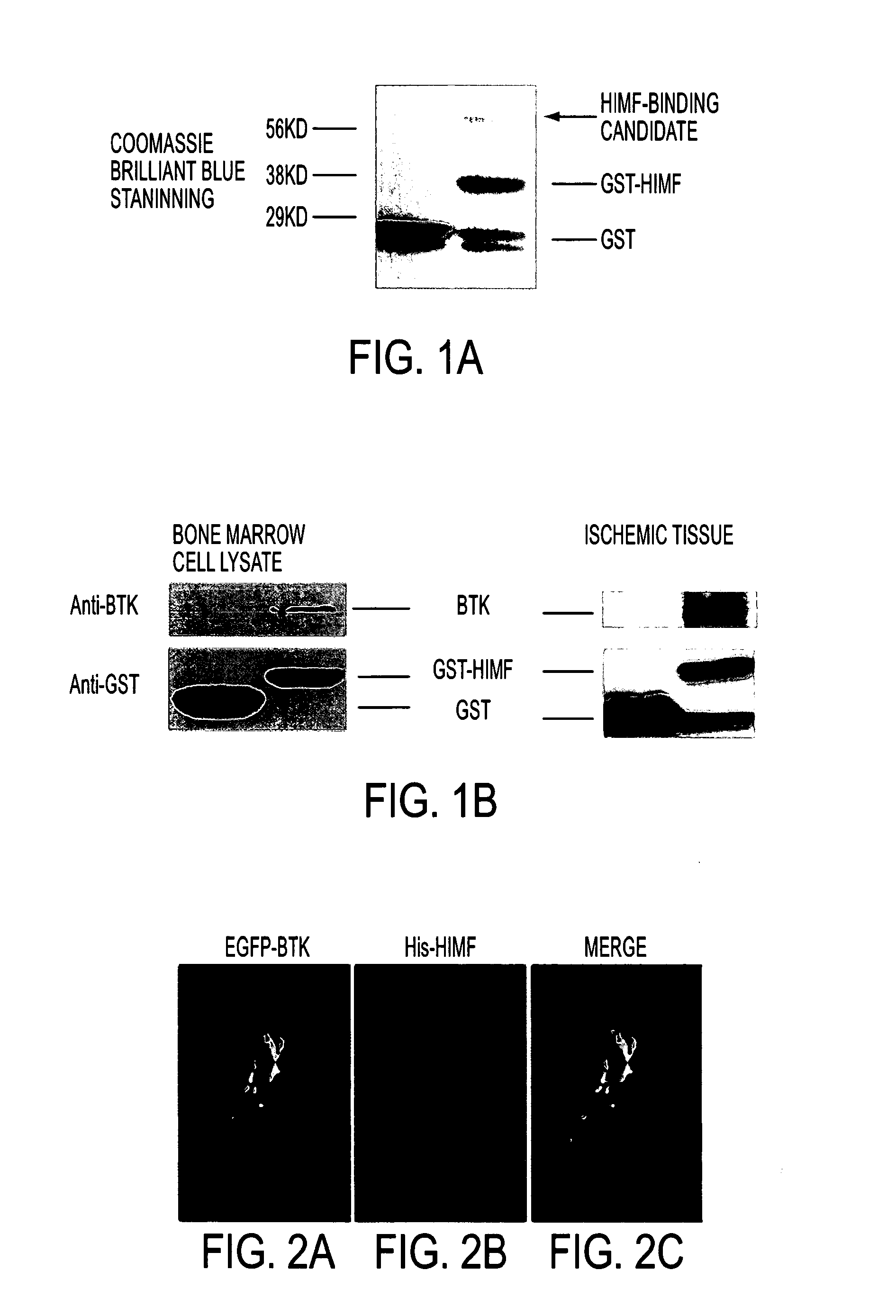
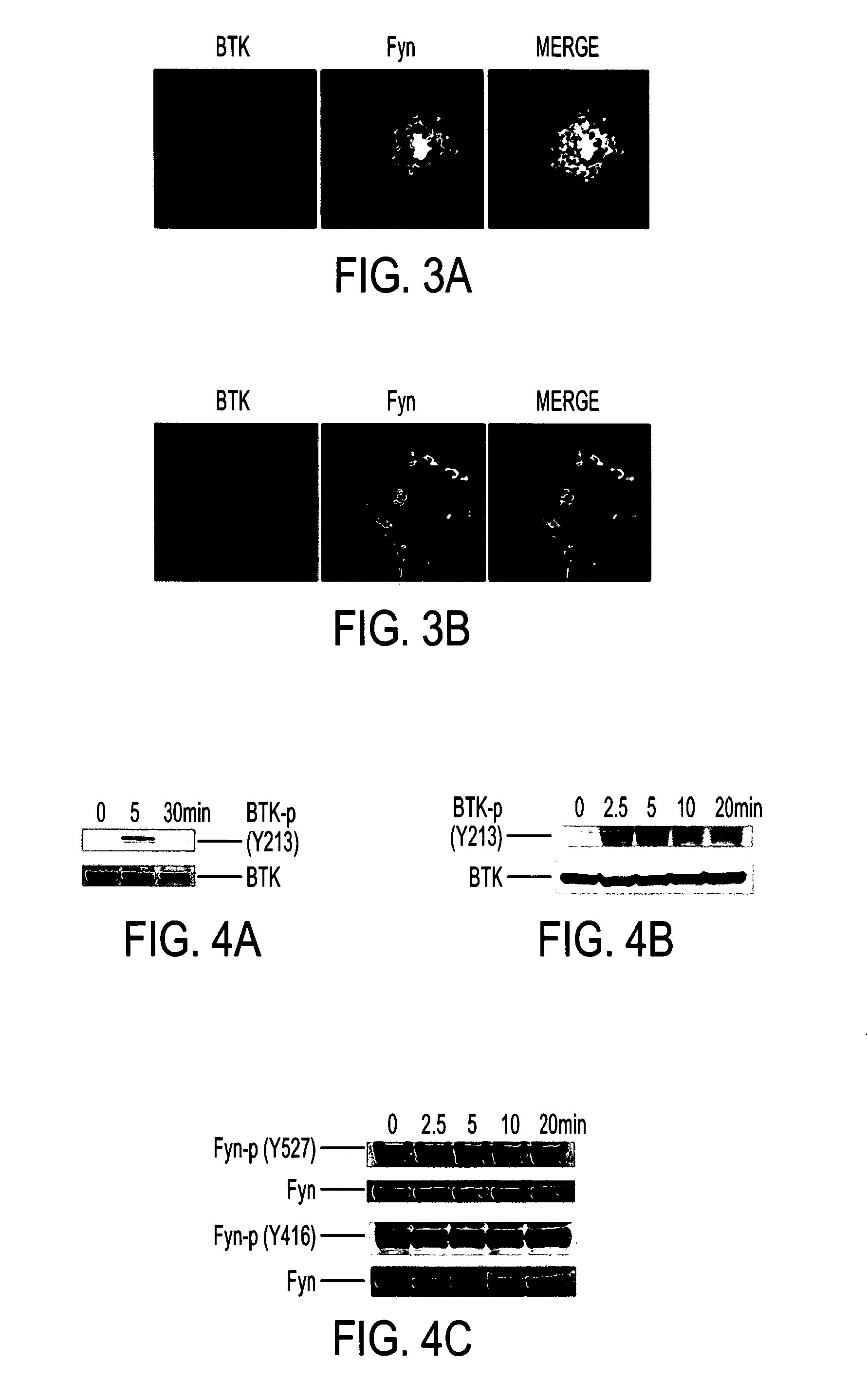
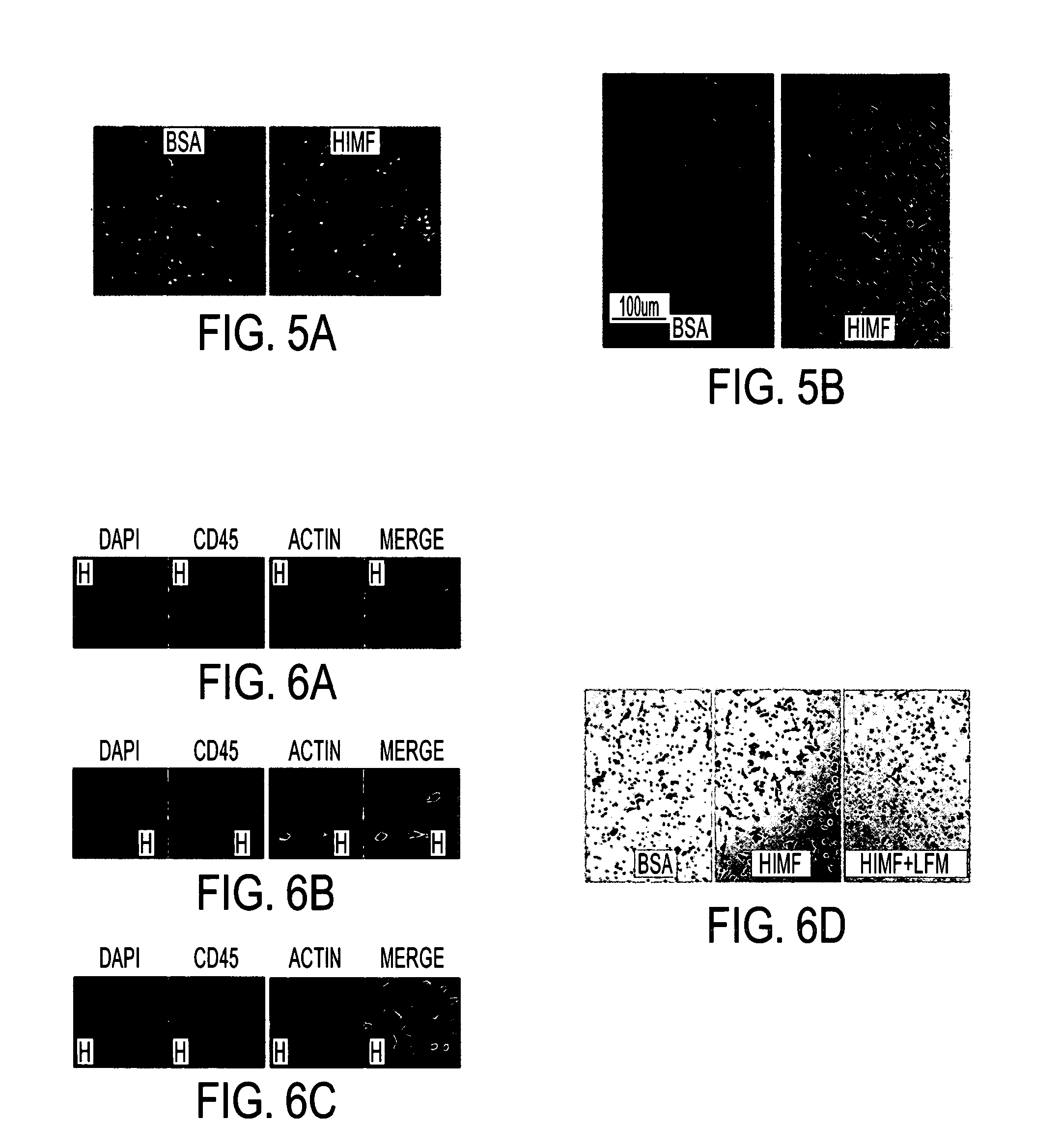
Himf and btk in pulmonary, cardiac and inflammation disorders
Hypoxia induced mitogenic factor (HIMF) is a member of the “found in inflammatory zone” (FIZZ) / resistin family of proteins and has potent mitogenic, angiogenic, and vasoconstrictive effects in the lung vasculature. The receptor / binding partners for this family of proteins have been largely unknown. We identified Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a functional HIMF binding partner through GST-HIMF pull-downs and mass spectrometry. Using primary cultured HIMF-stimulated murine bone marrow cells, we demonstrated that BTK was recruited to the leading edge of the cells. We also demonstrated that BTK and the closely related tyrosine kinase Fyn, colocalized at the growth cone process in these cells. HIMF stimulation induced BTK autophosphorylation, which peaked at 2.5 minutes. A transwell migration assay showed that treatment with recombinant murine HIMF induced migration of primary cultured bone marrow cells, which was completely blocked by the BTK inhibitor, LFM-A13. In vivo studies, using the rat hindlimb ischemia model, revealed that HIMF can stimulate angiogenesis in the hypoxic tissue probably through inducing the migration of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) to areas of active angiogenesis. Our results indicate that HIMF may acts as a chemotactic molecule in stimulating the migration of leukocytes / EPCs from bone marrow to targeted tissues through activation of the BTK pathway.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases (rtk) and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides moieties that bind to the asymmetric contact interface of a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), wherein the moieties inhibit ligand induced trans autophosphorylation of the RTK. The present invention also provides methods of treating or preventing an RTK-associated disease and methods for identifying moieties that bind to an asymmetric contact interface of an RTK.
Owner:YALE UNIV
c-Met protein agonist
ActiveUS9994616B2Promote growthEasy to migratePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsC-MetAutophosphorylation
A peptide functioning as a c-Met agonist is described. A peptide complex comprising two or more peptides that bind to a c-Met protein and a linker that links the two or more peptides to one another is described. Such a peptide complex promotes autophosphorylation of the c-Met protein and induces cell growth.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com