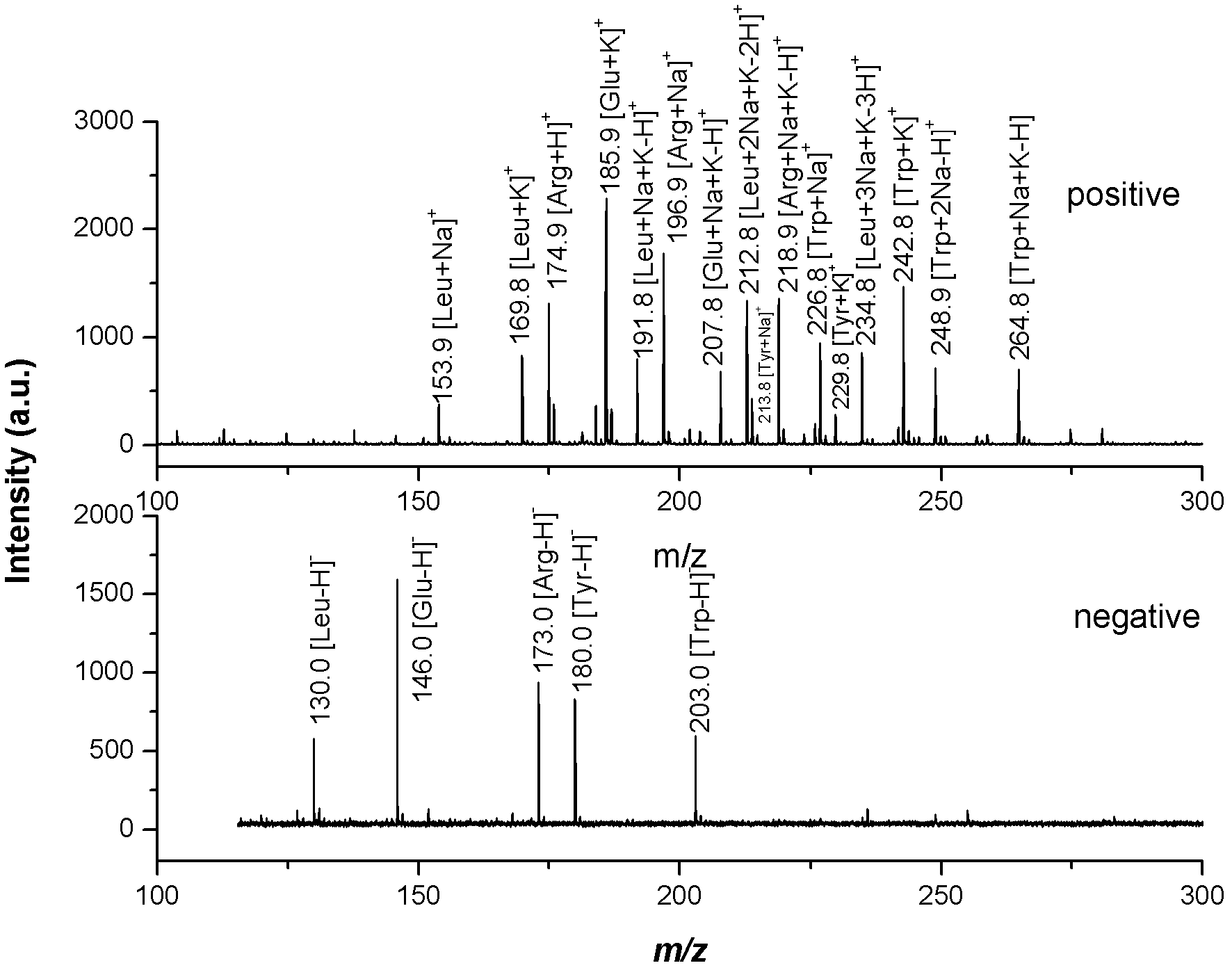
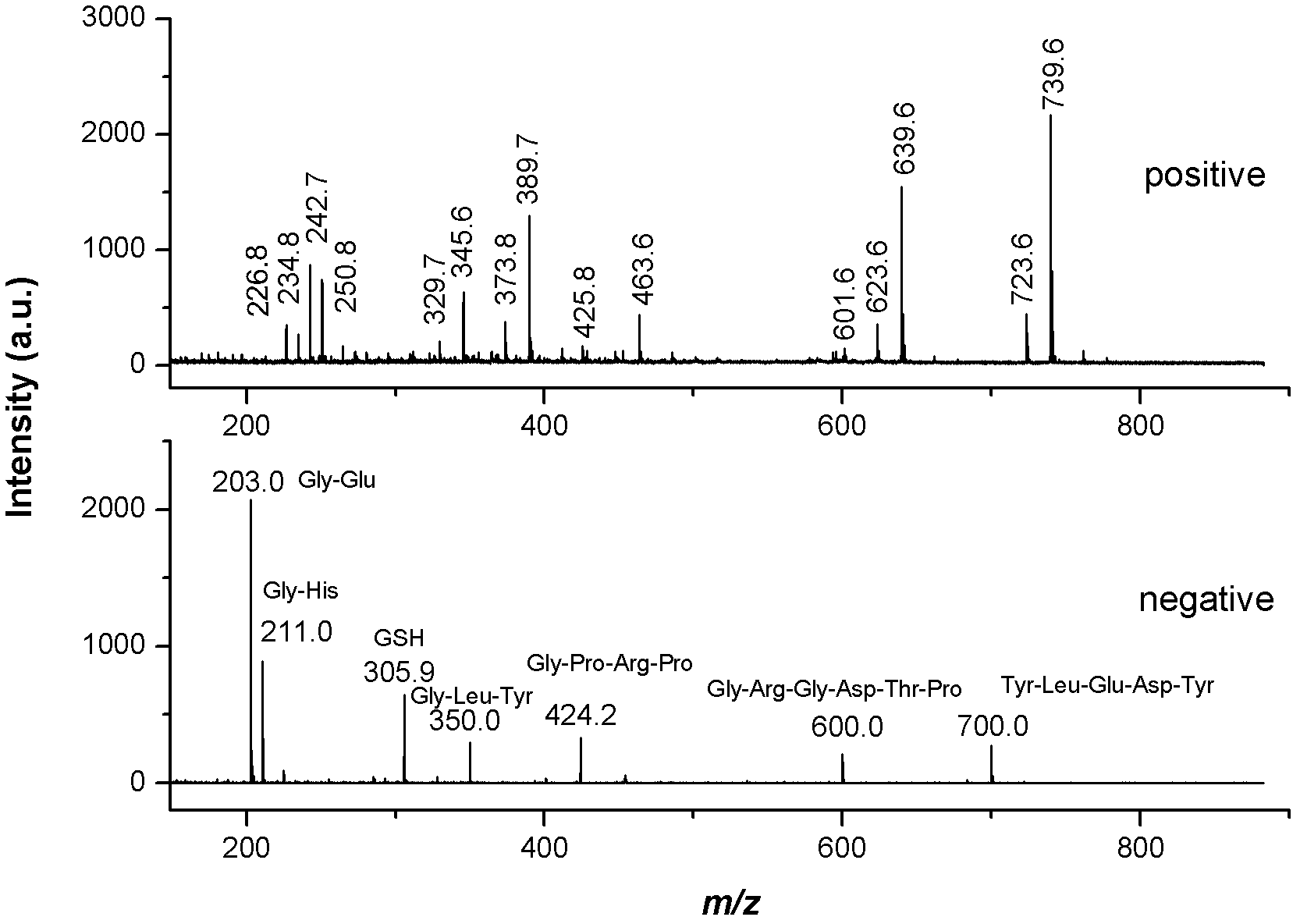
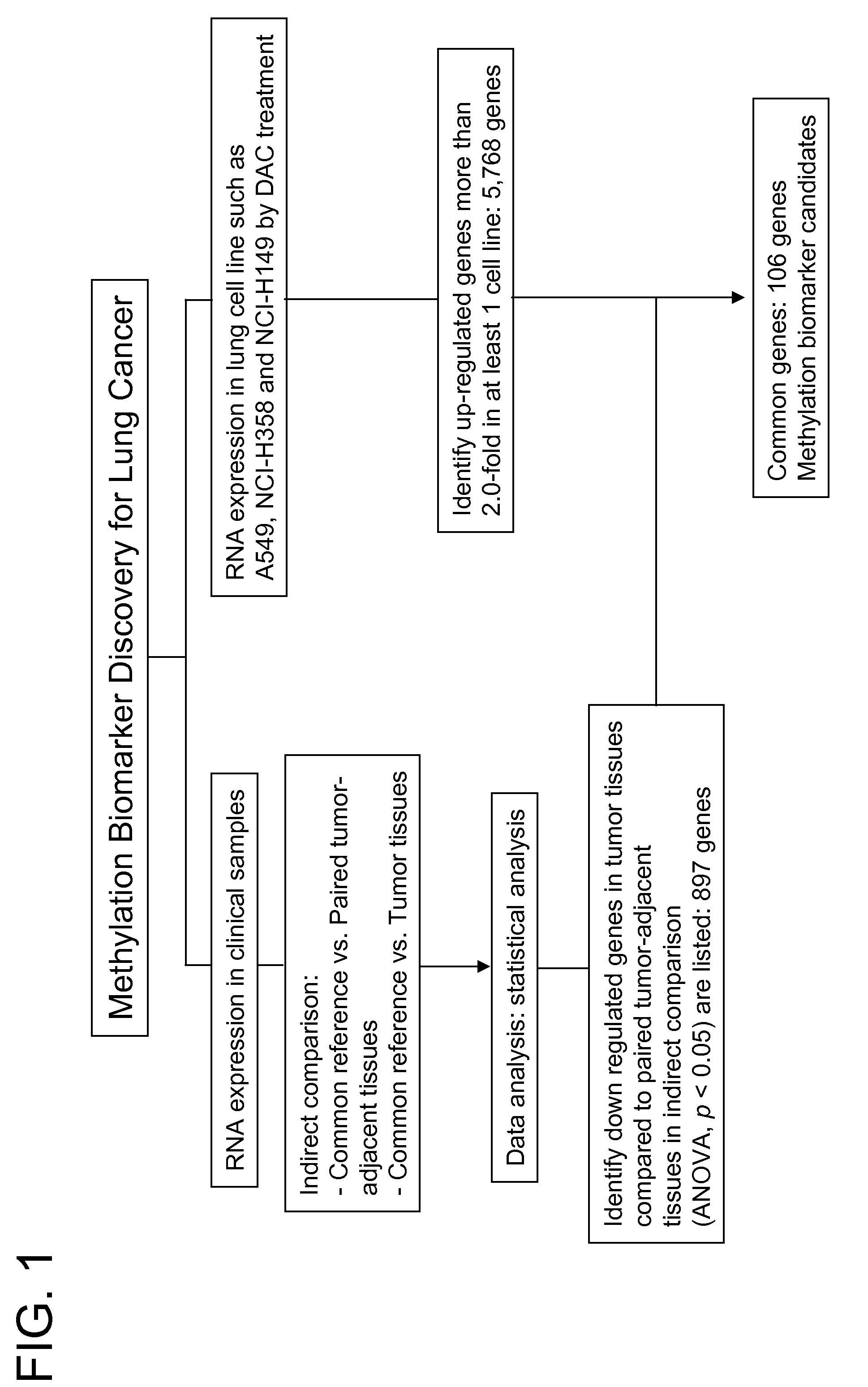
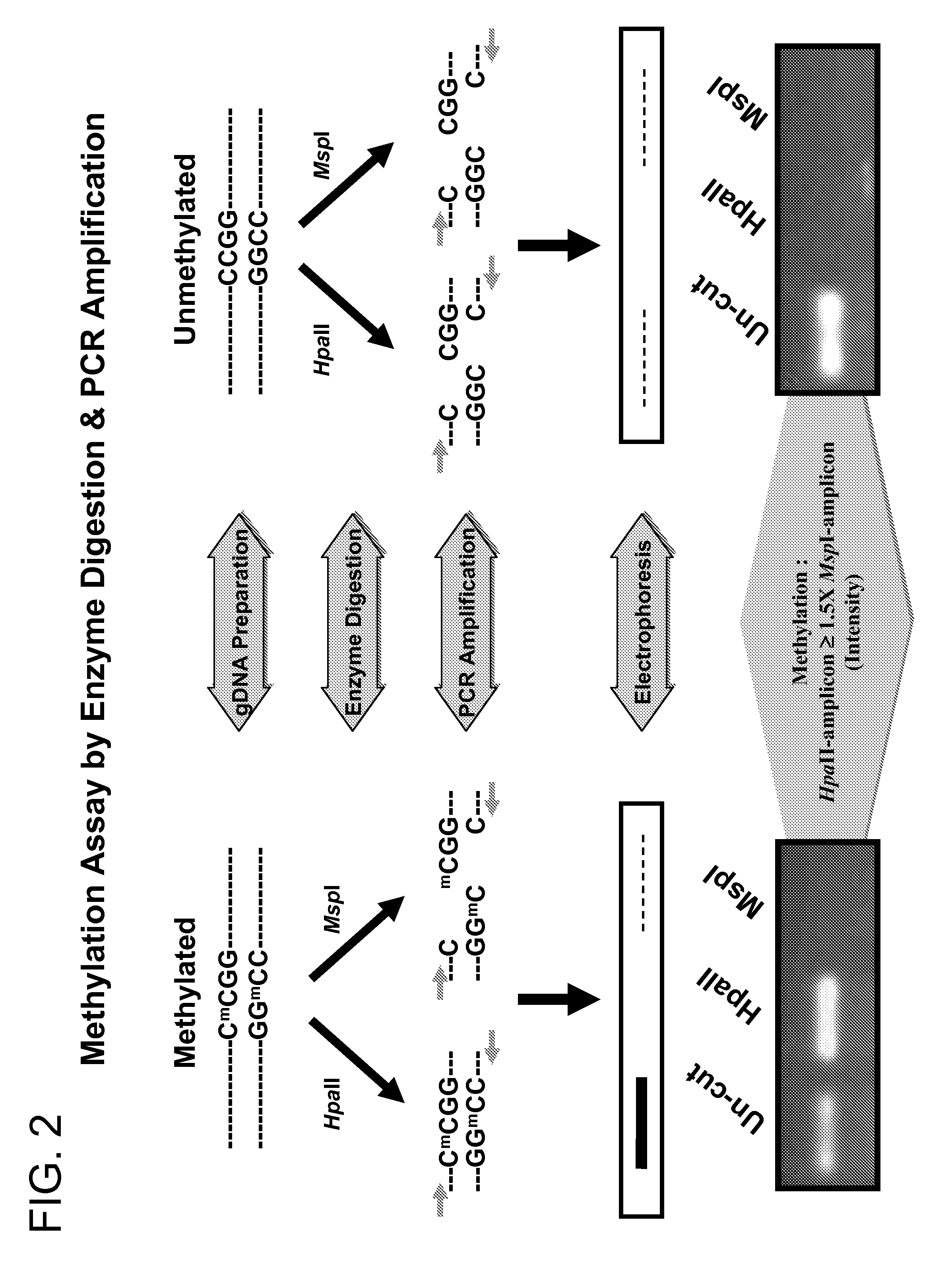
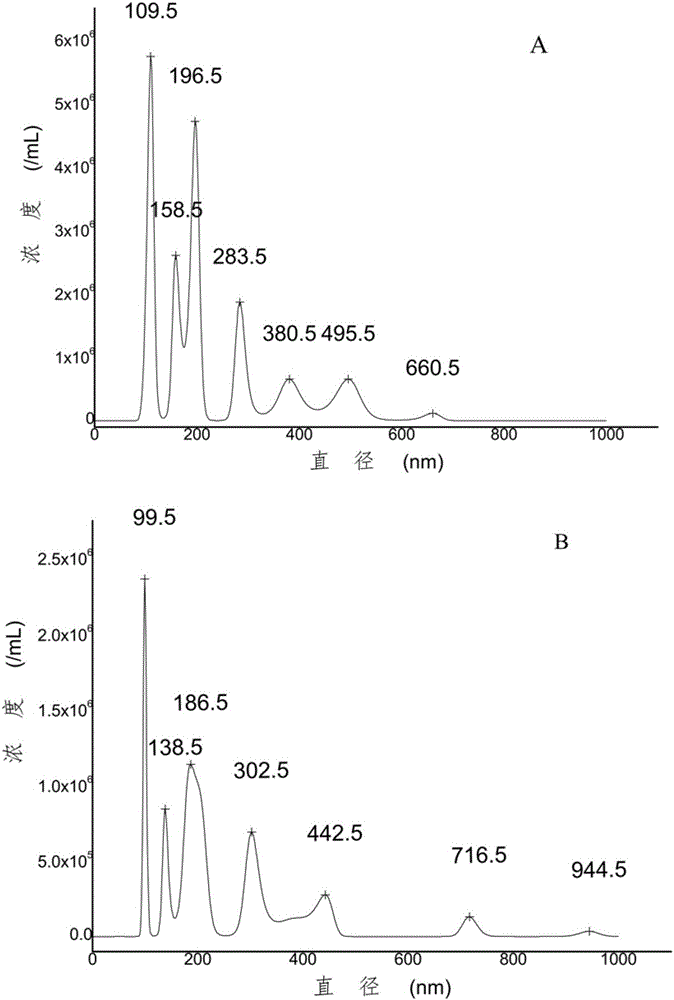
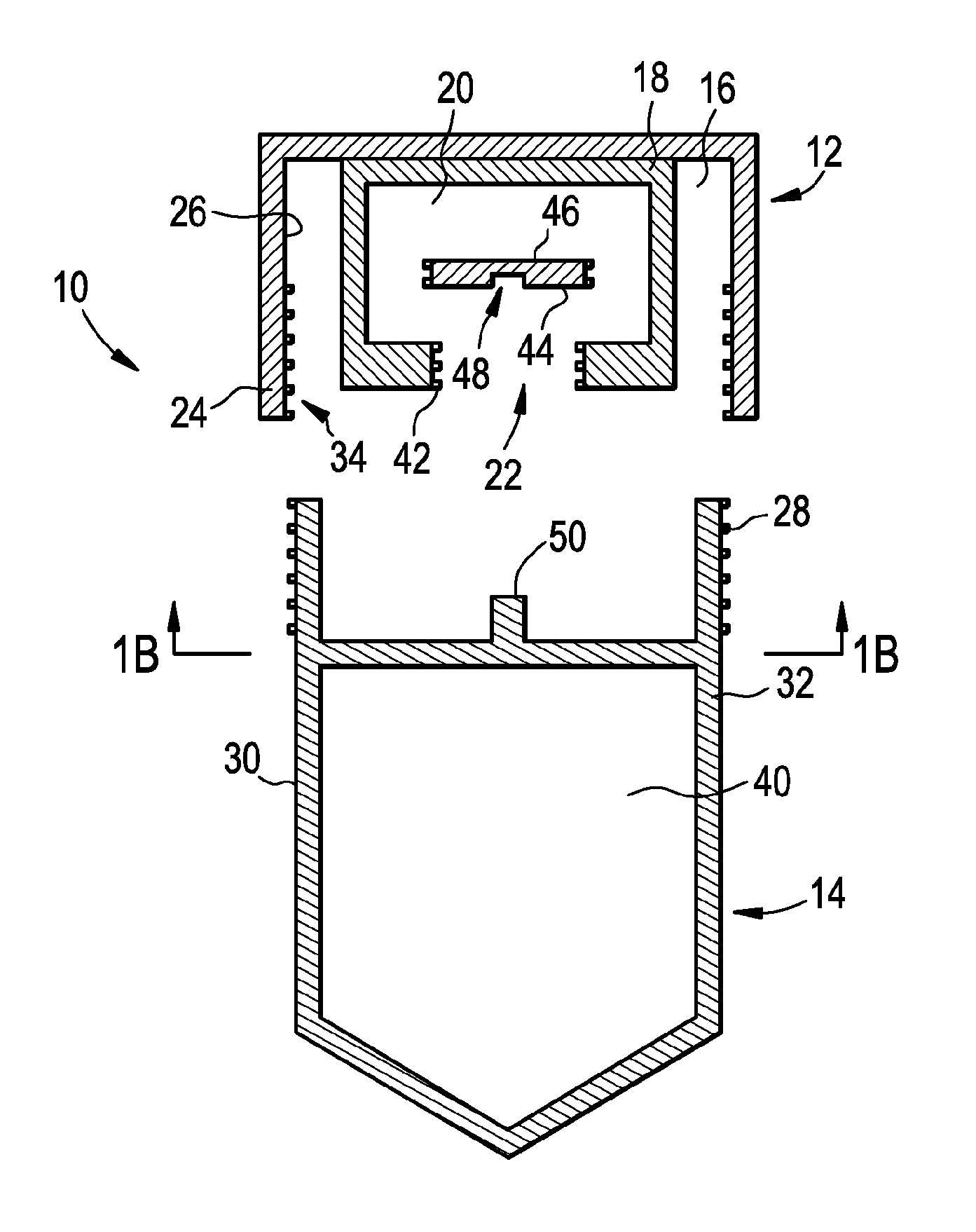
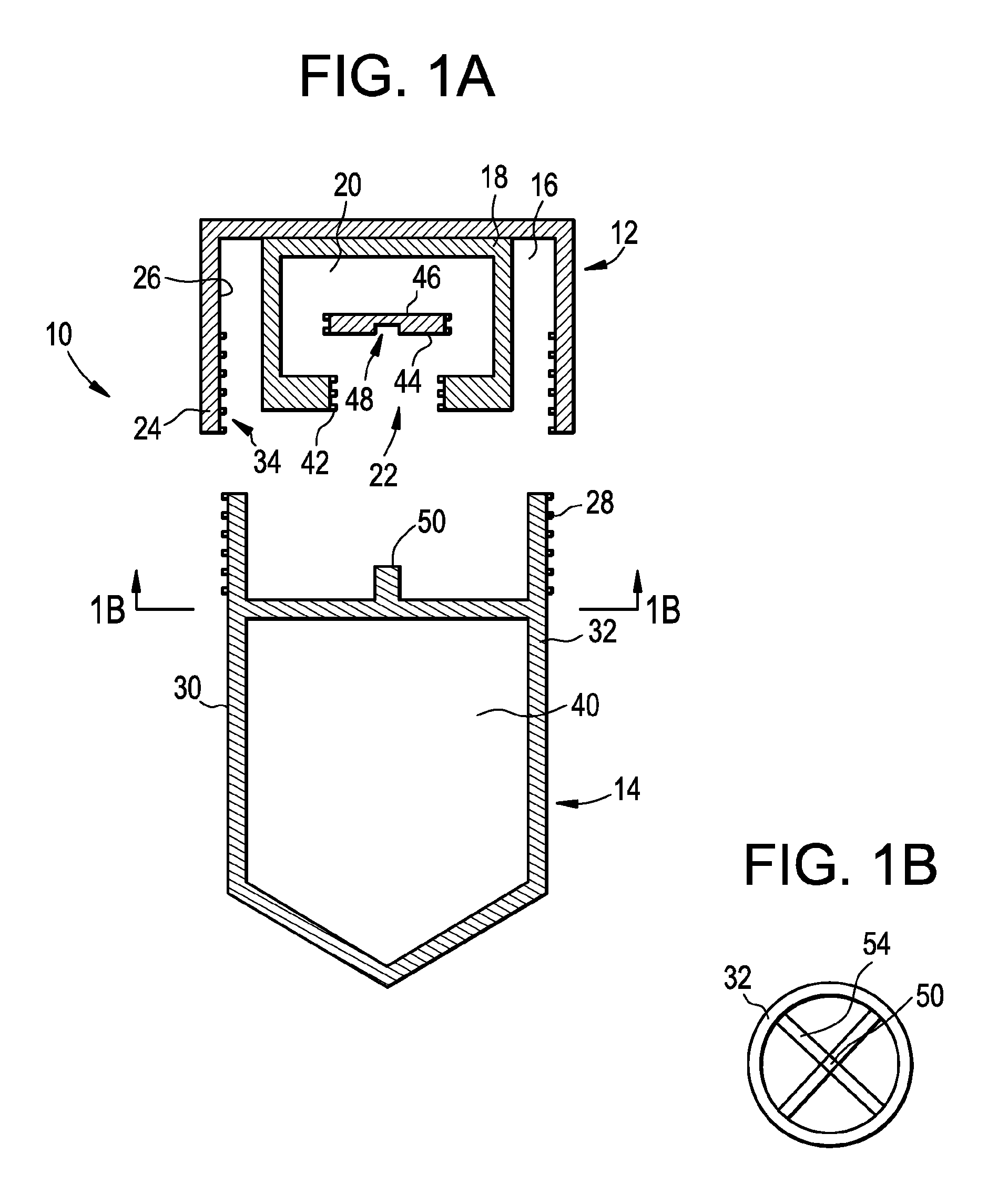
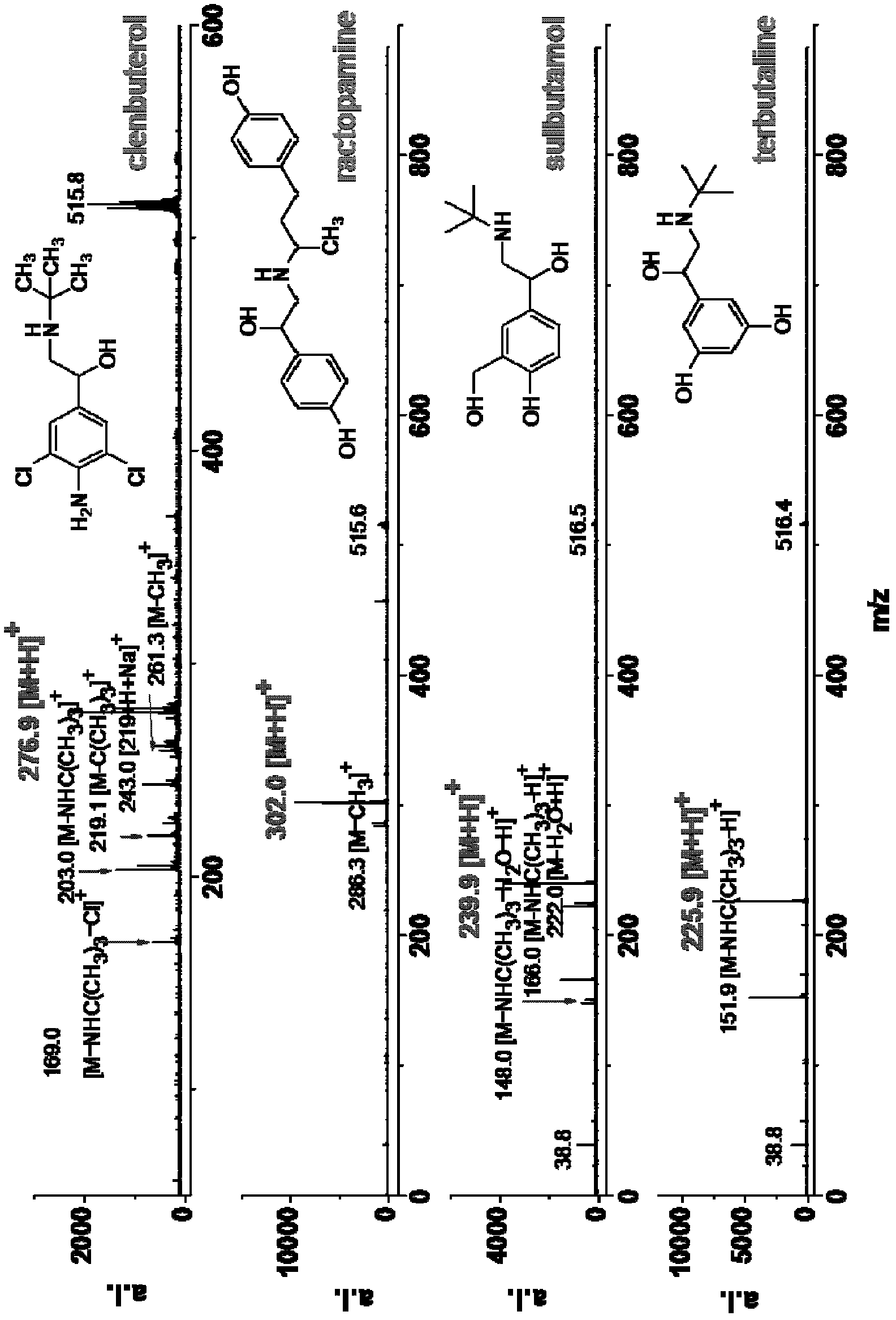
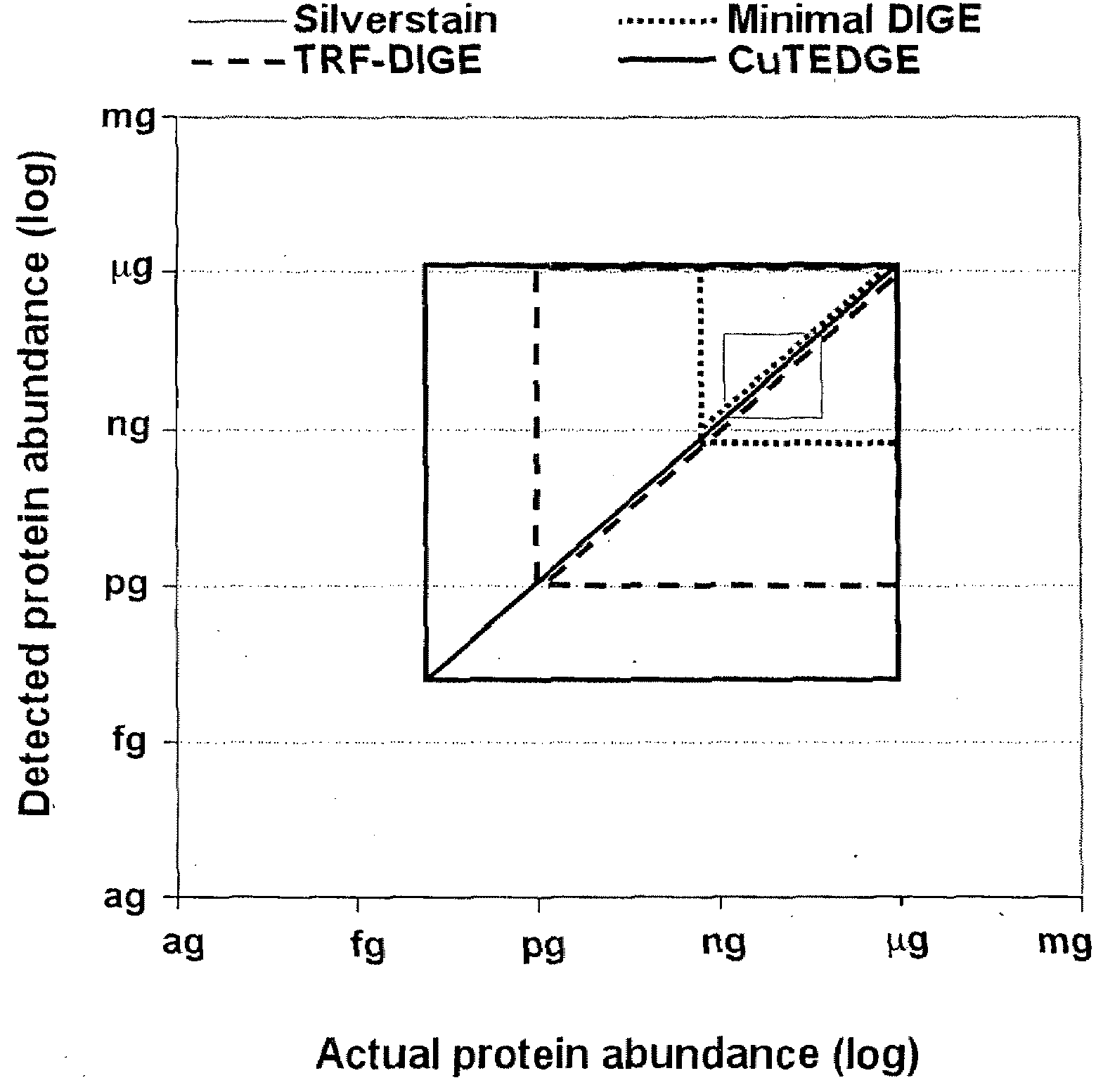
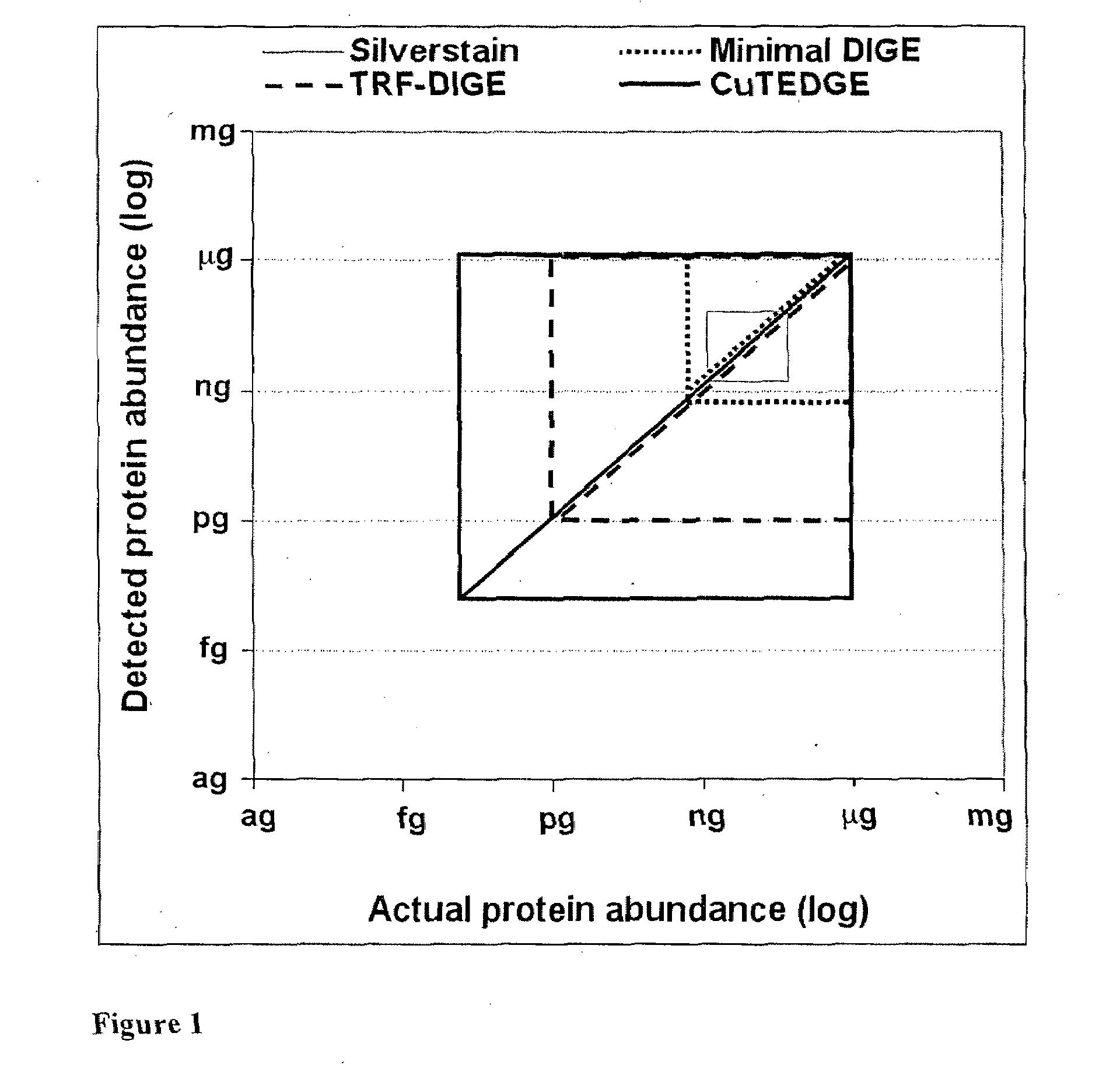
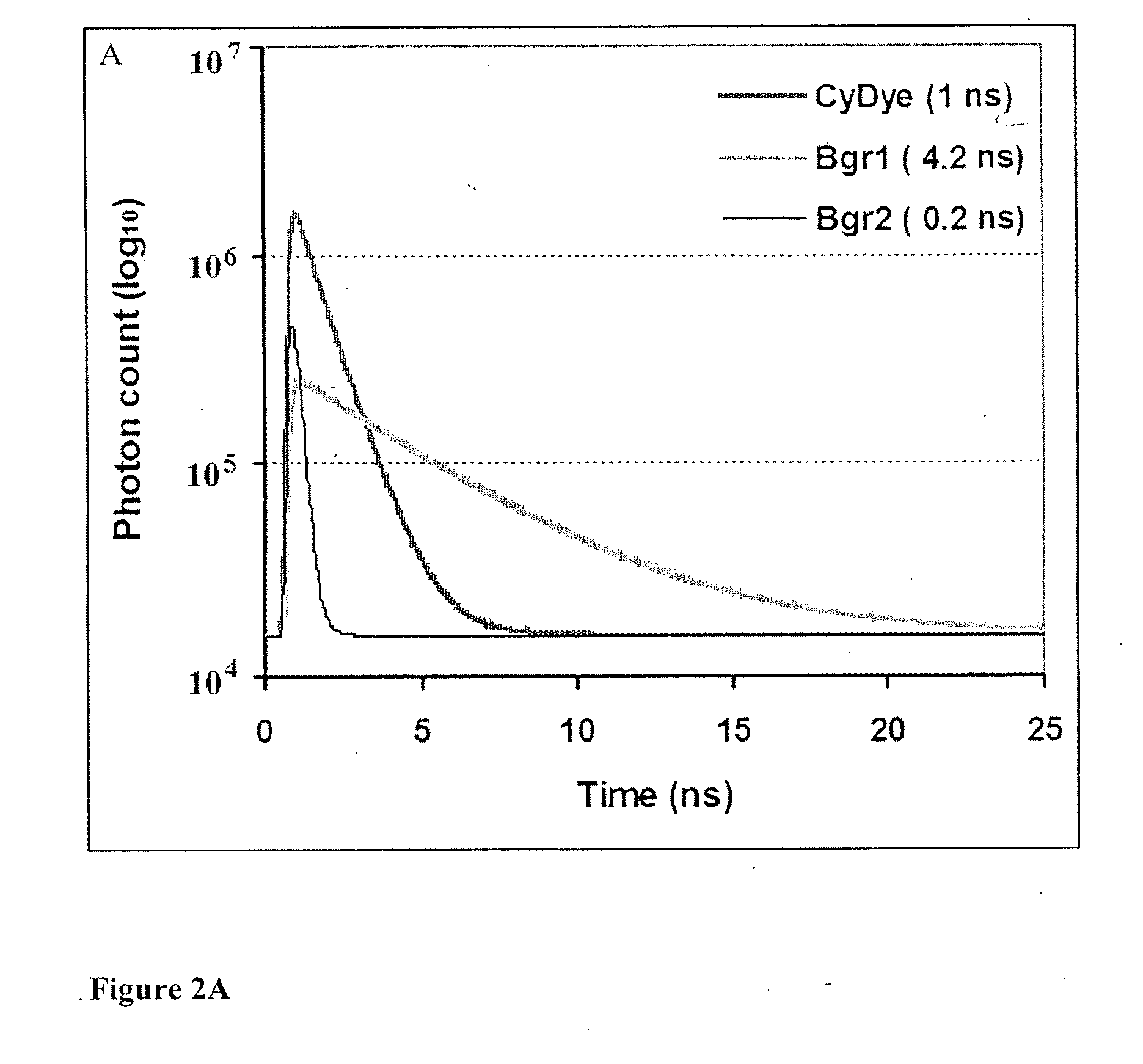
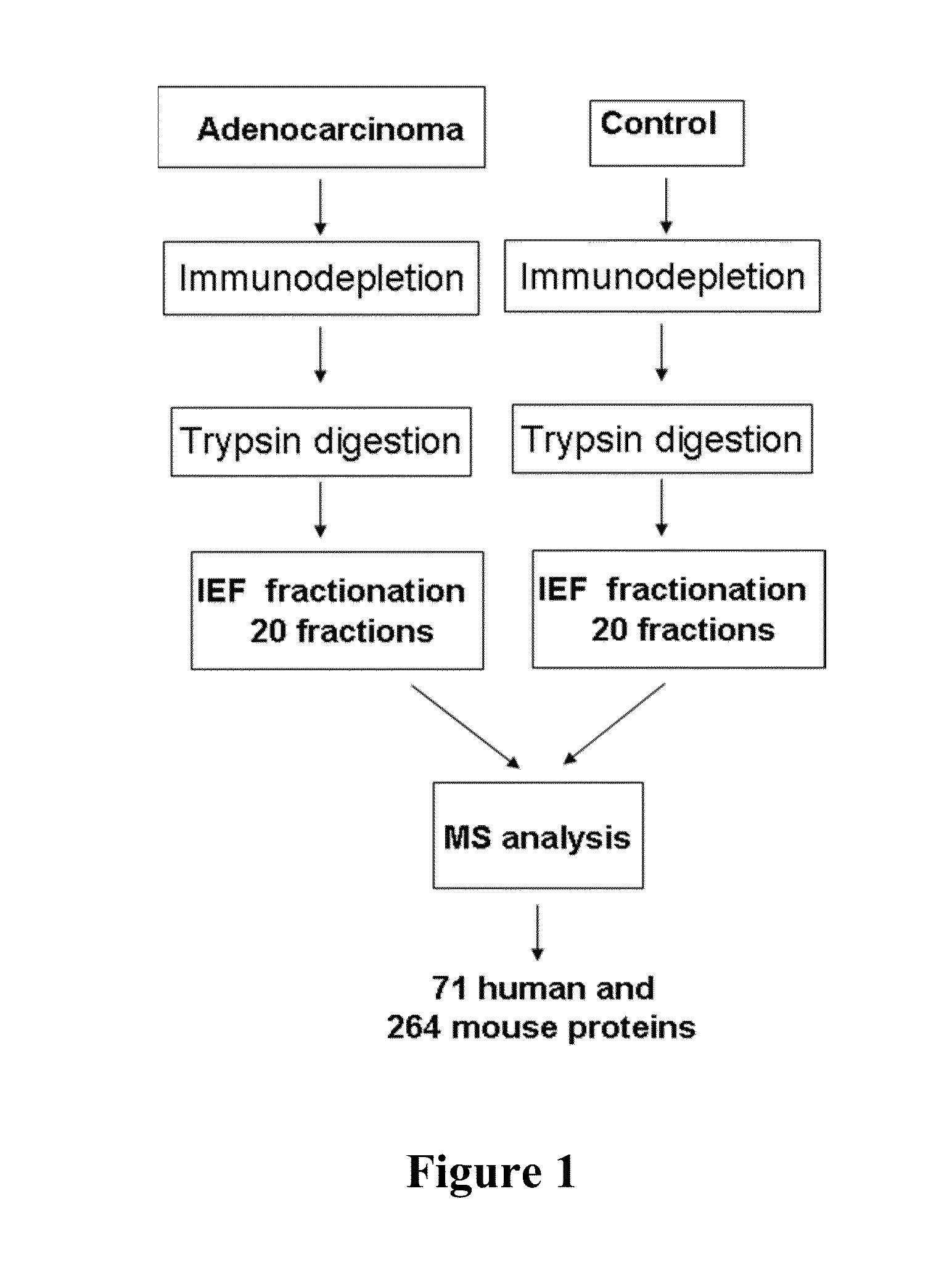
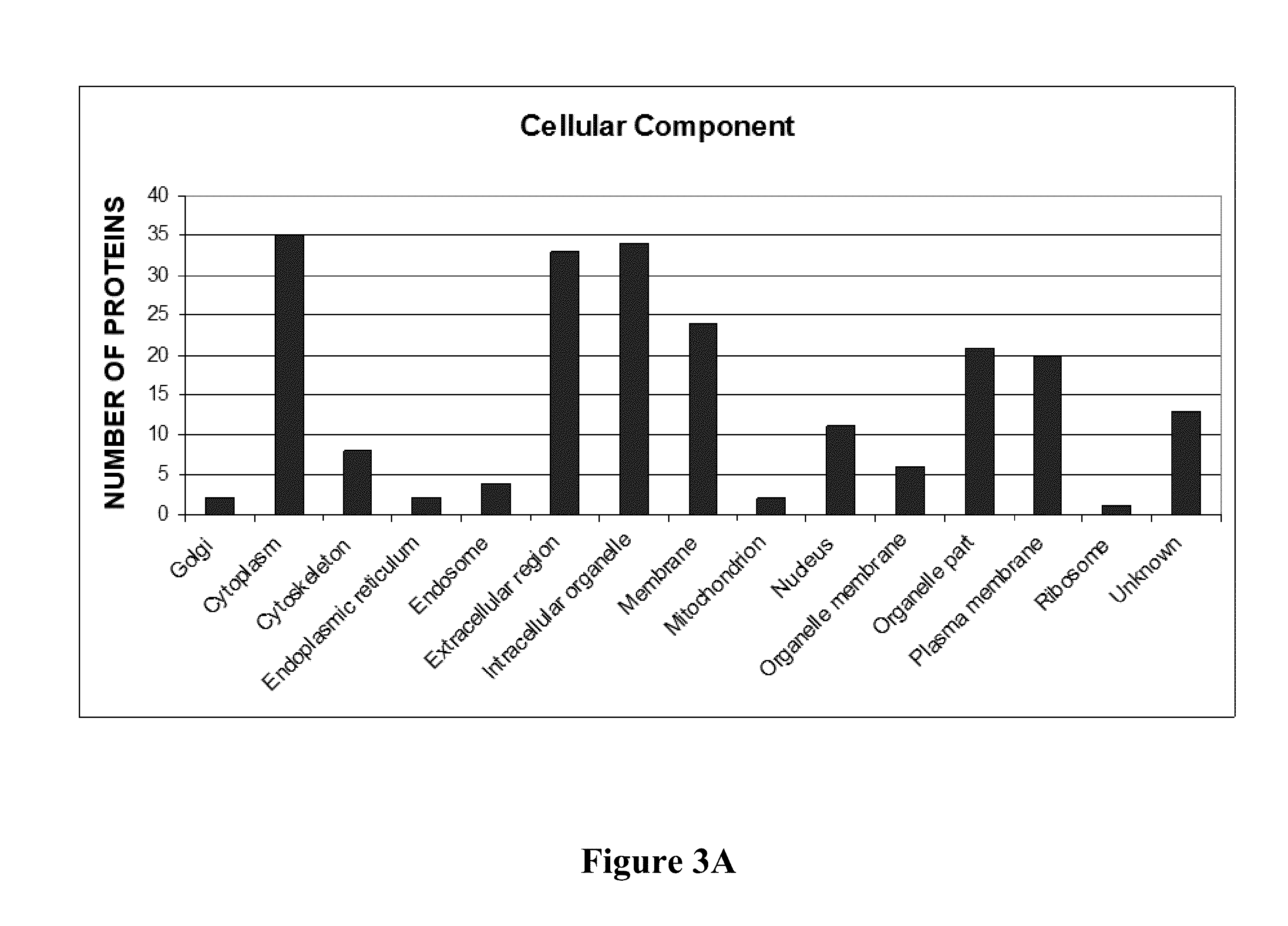
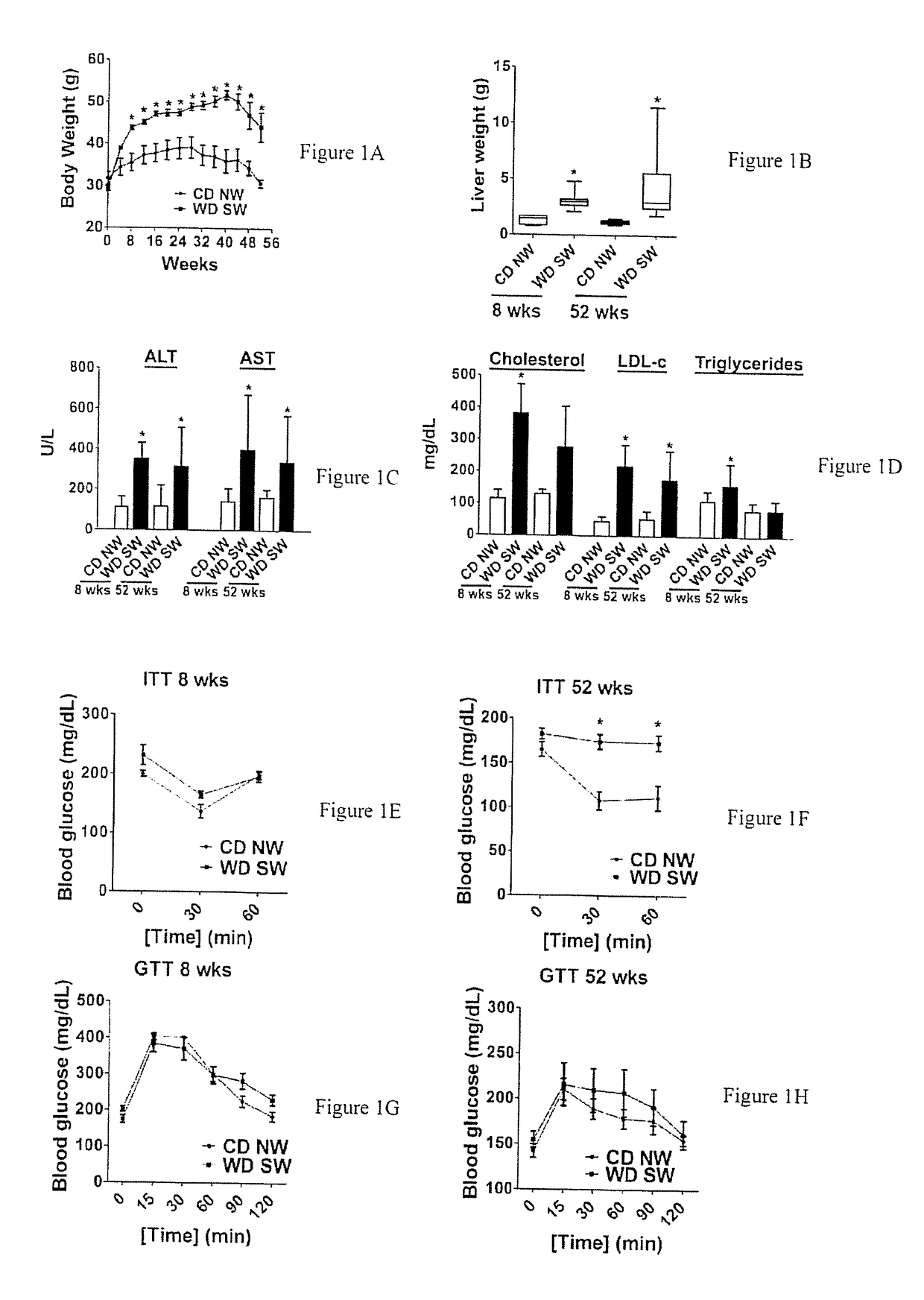
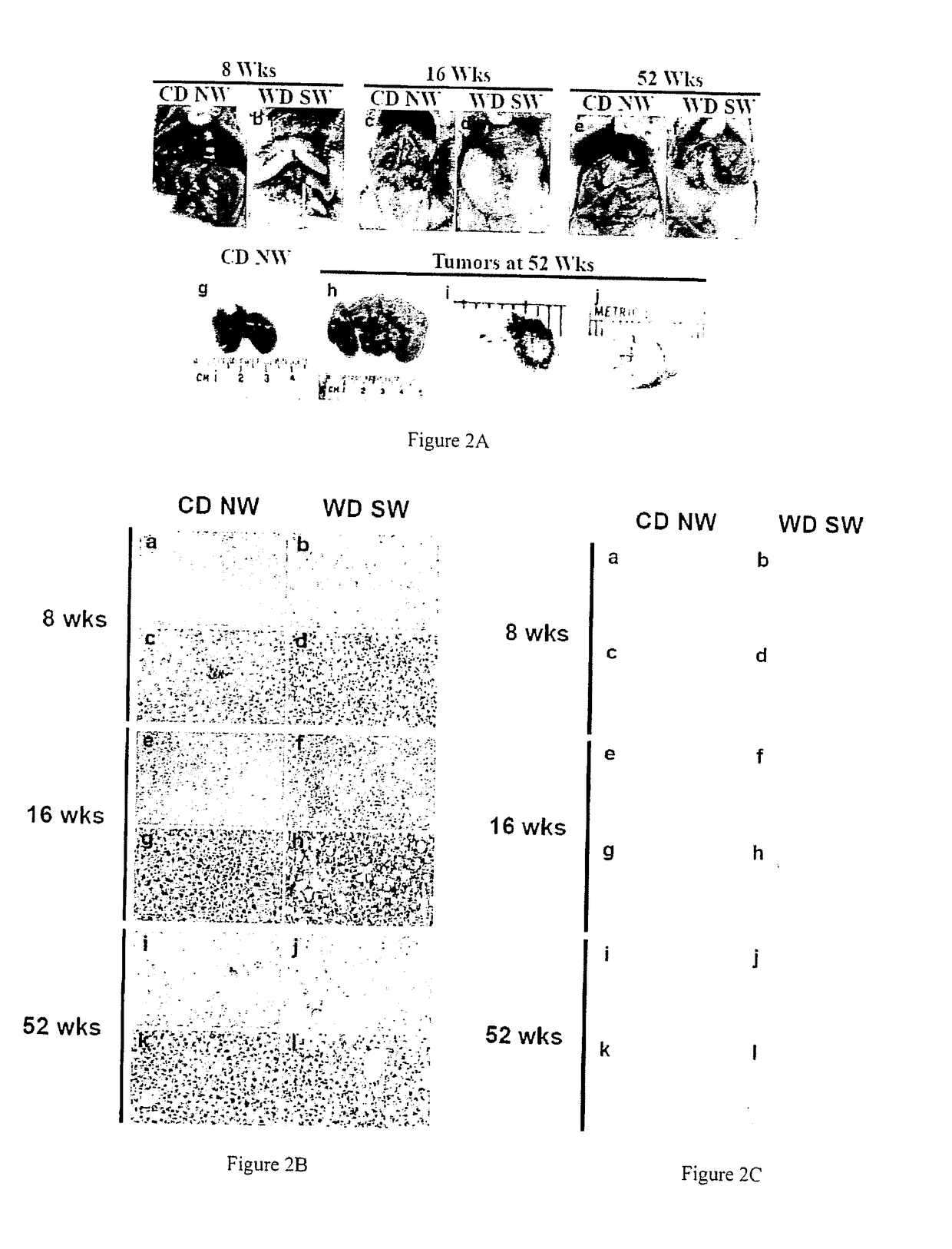
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Biomarker discovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biomarker discovery is a medical term describing the process by which biomarkers are discovered. Many commonly used blood tests in medicine are biomarkers. There is interest in biomarker discovery on the part of the pharmaceutical industry; blood-test or other biomarkers could serve as intermediate markers of disease in clinical trials, and as possible drug targets.
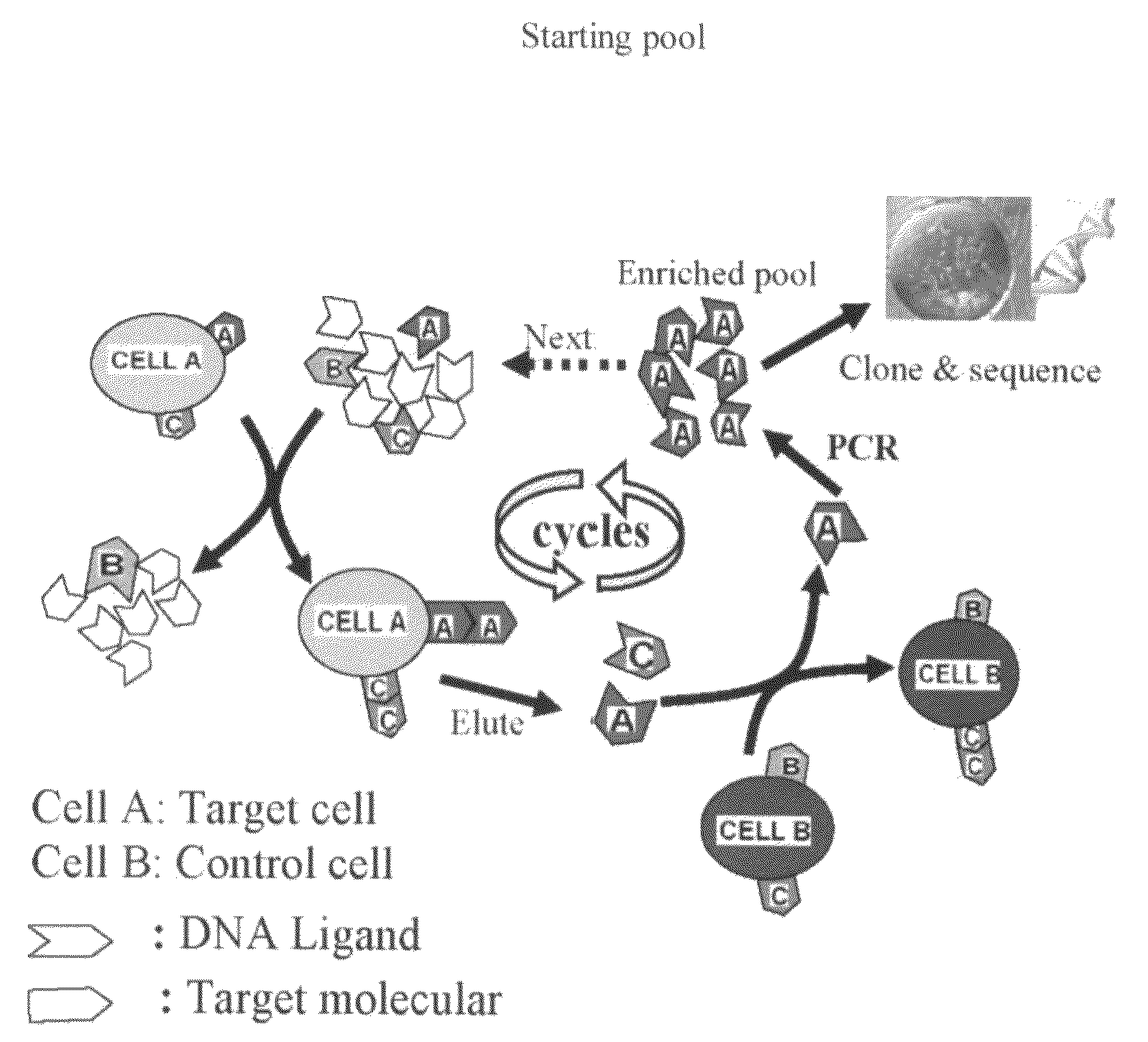
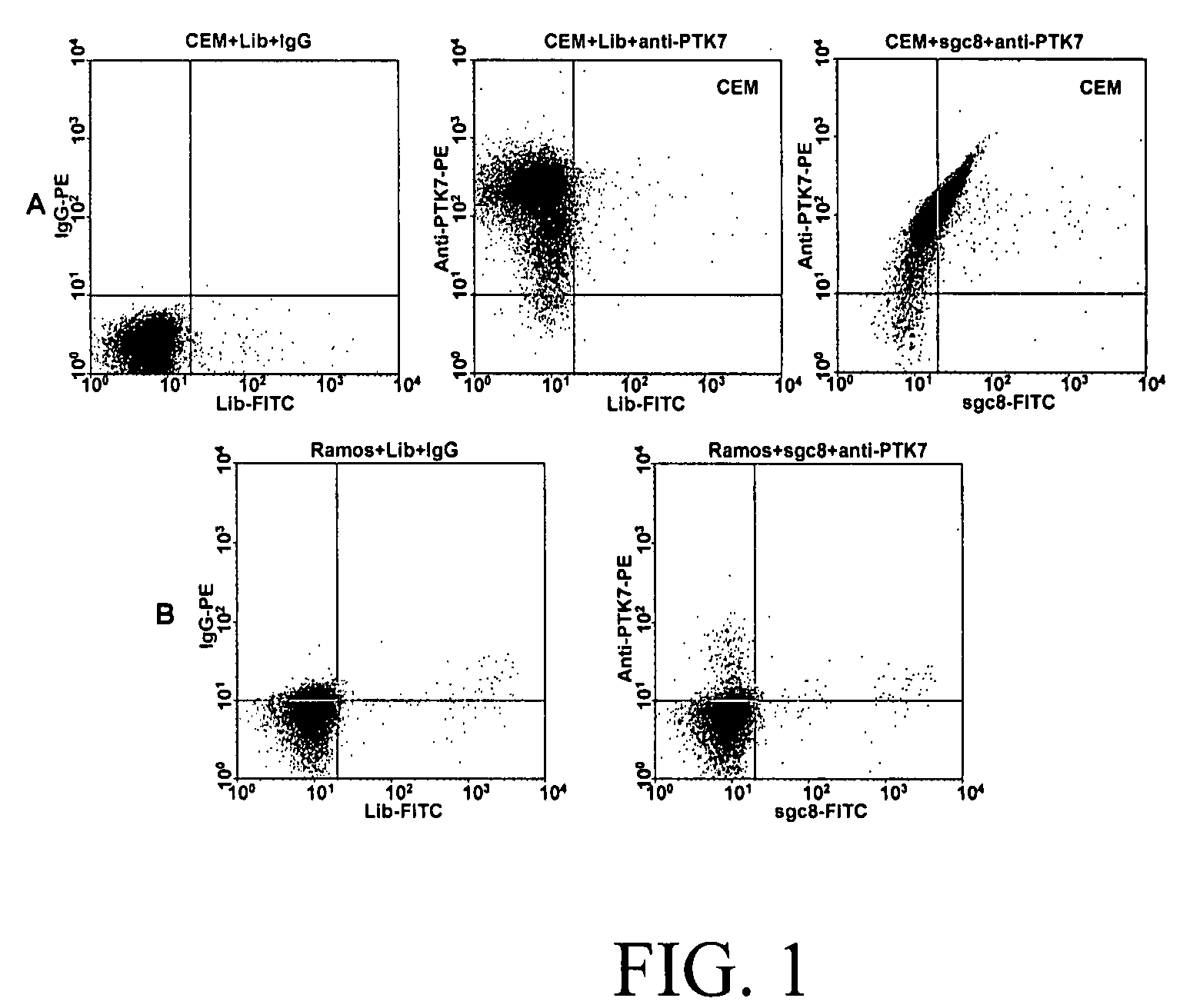
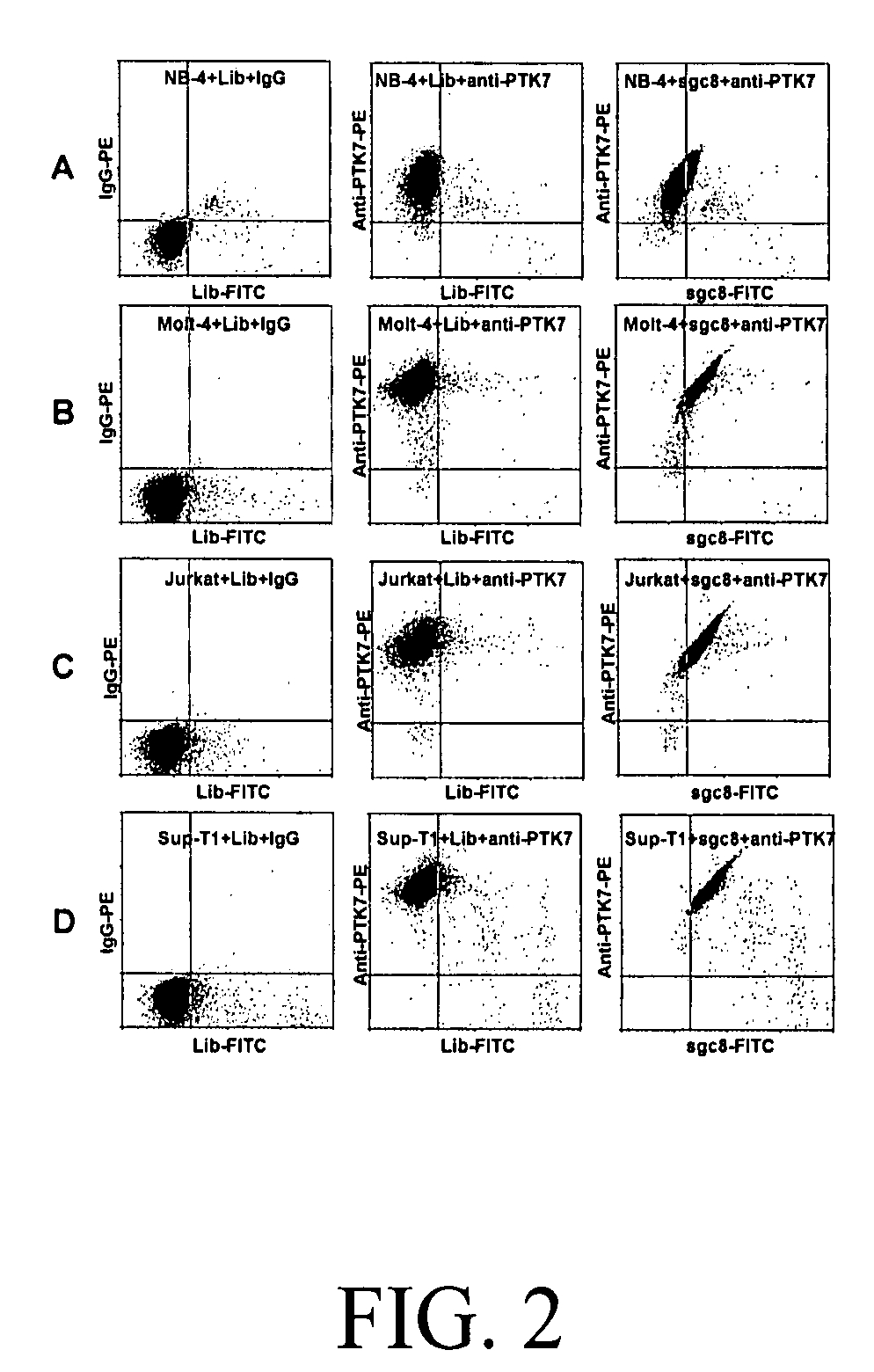
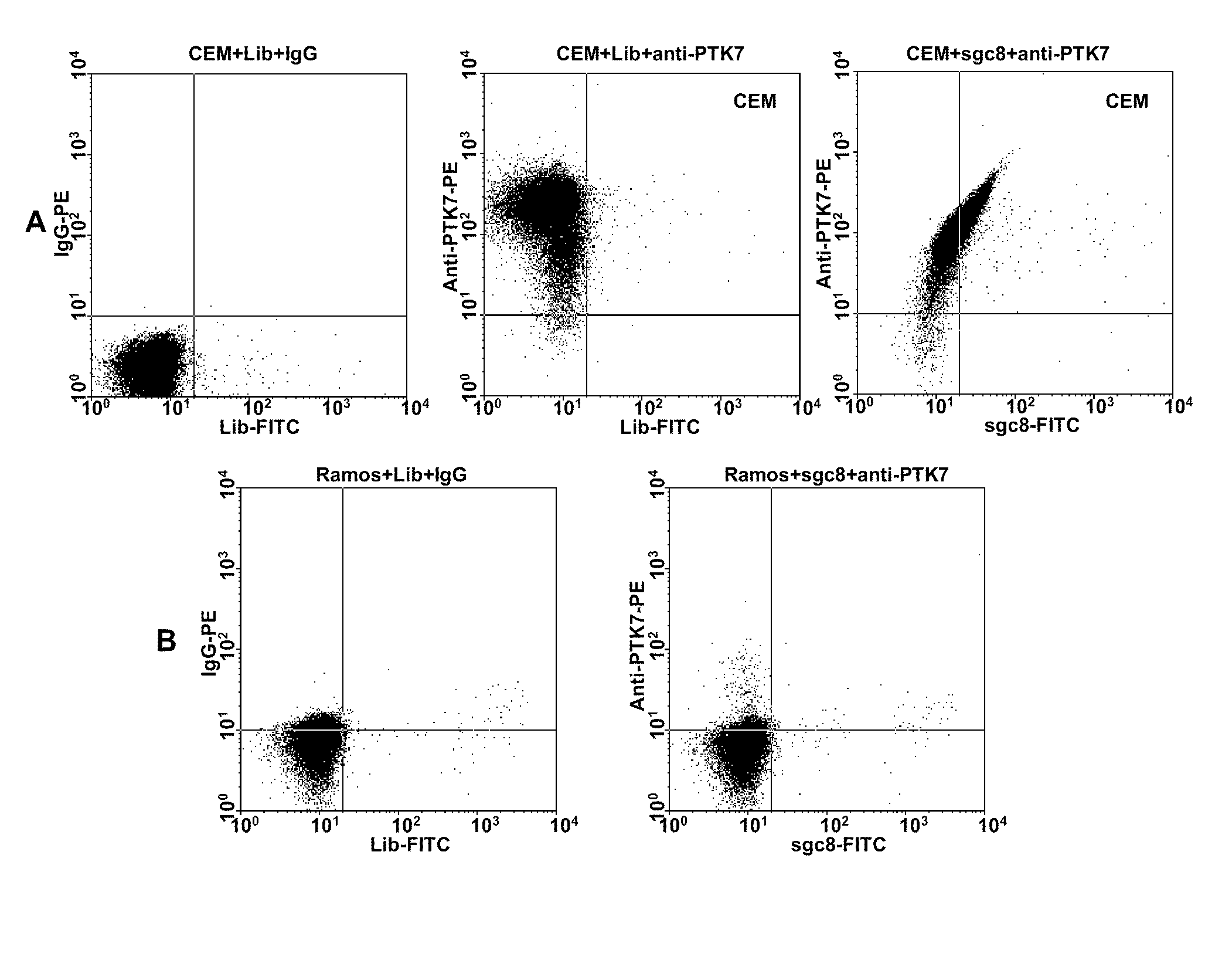
Aptamer-based methods for identifying cellular biomarkers
InactiveUS20090117549A1Easy to fixEasy to synthesizeElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesBiotin-streptavidin complexCancer cell
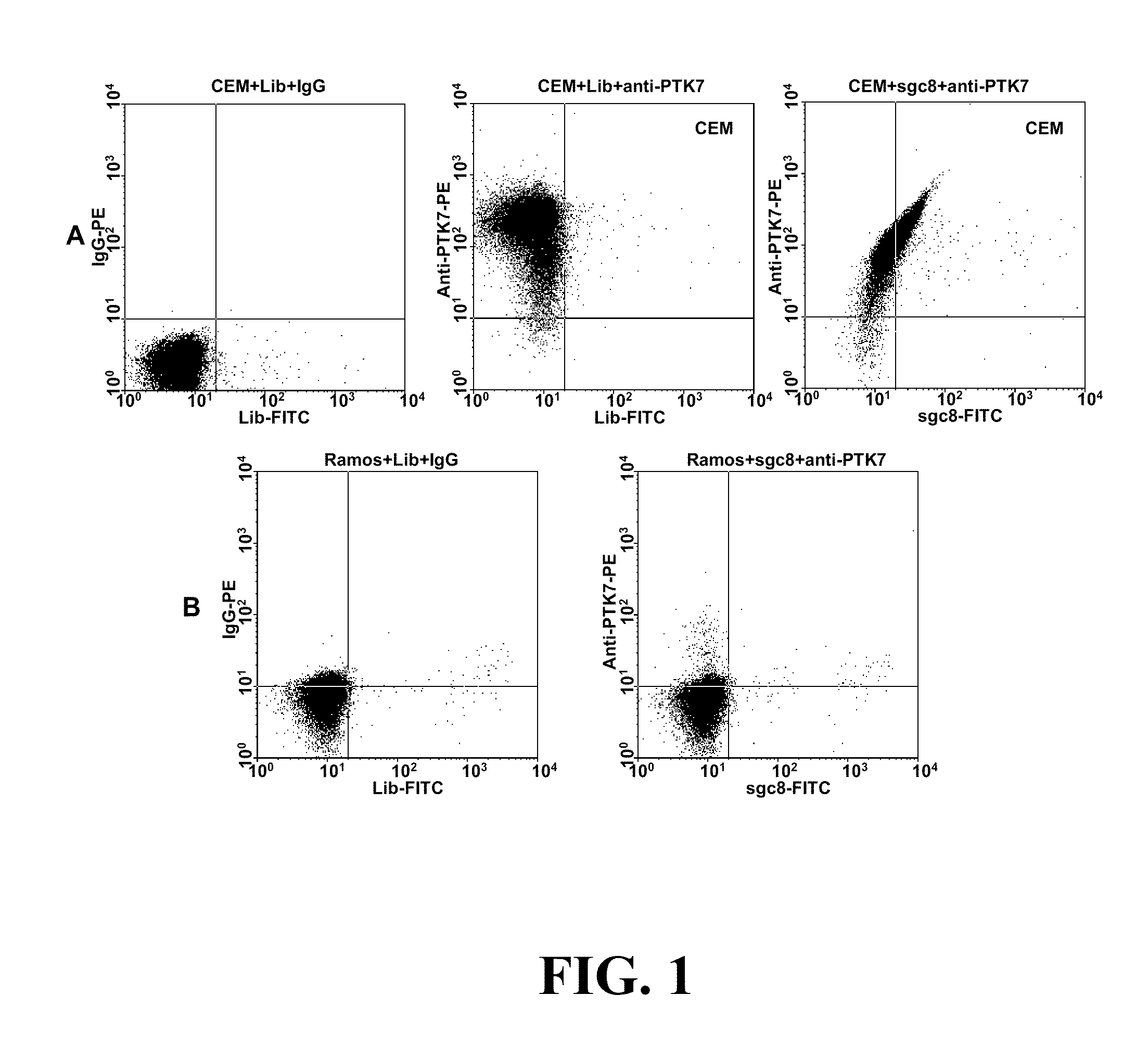
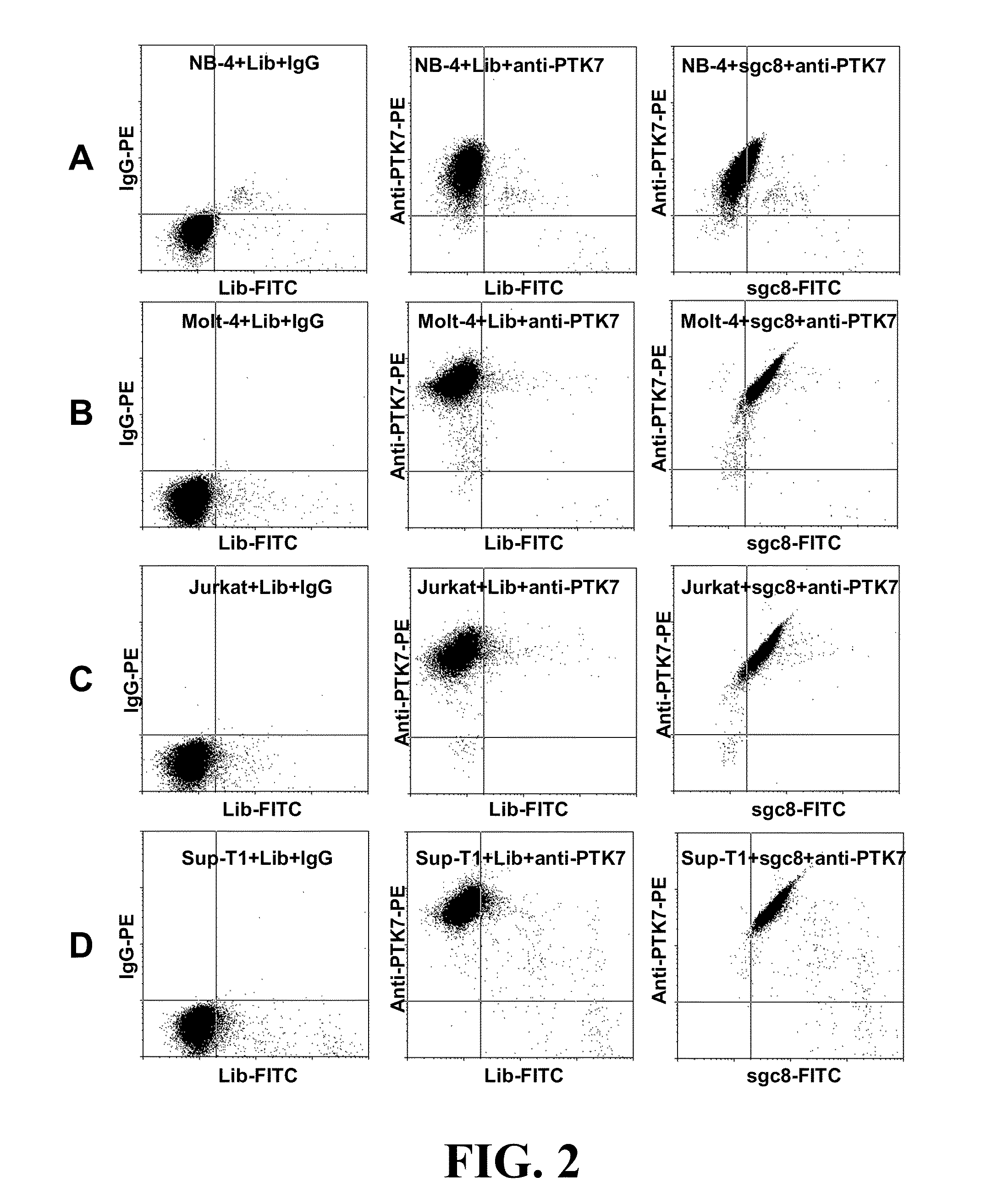
In this invention, a biomarker discovery method has been developed using specific biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and magnetic streptavidin beads. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotide ligands are firstly generated by whole-cell based SELEX technique. Such ligands can recognize target cells with high affinity and specificity and can distinguish cells that are closely related to target cells even in patient samples. The targets of these oligonucleotide ligands are significant biomarkers for certain cells. These important biomarkers can be captured by forming complexes with biotin-labeled oligonucleotide ligands and collecting the complexes using magnetic streptavidin beads, whereupon the captured biomarkers are analyzed to identify the biomarkers. Analysis of biomarkers include HPLC-Mass Spectroscopy analysis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, flow cytometry, and the like. The identified biomarkers can be used for pathological diagnosis and therapeutic applications. Using the disclosed methods, highly specific biomarkers of any kinds of cells, in particular cancer cells, can easily be identified without prior knowledge of the existence of such biomarkers.
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
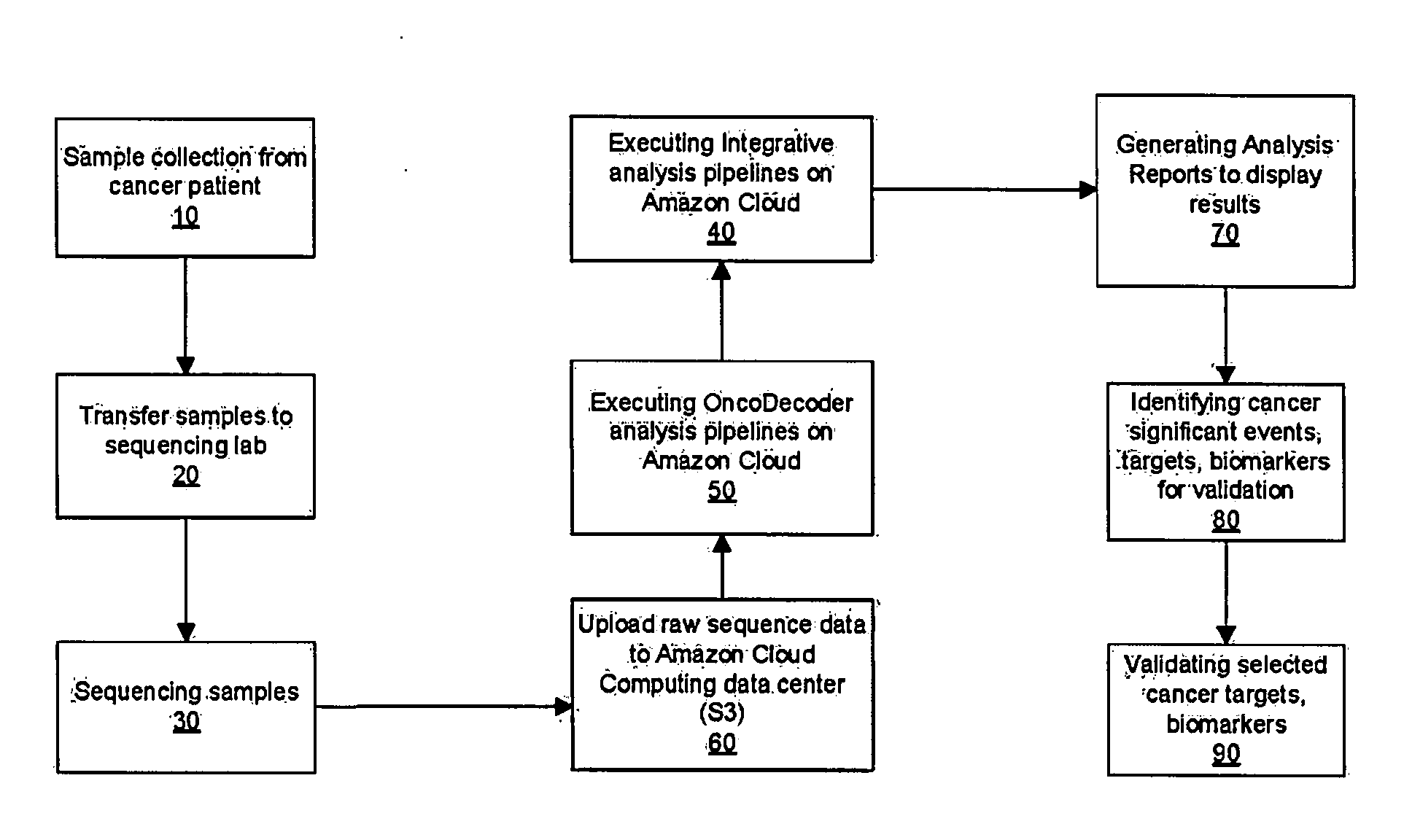
Systems and methods for cancer-specific drug targets and biomarkers discovery
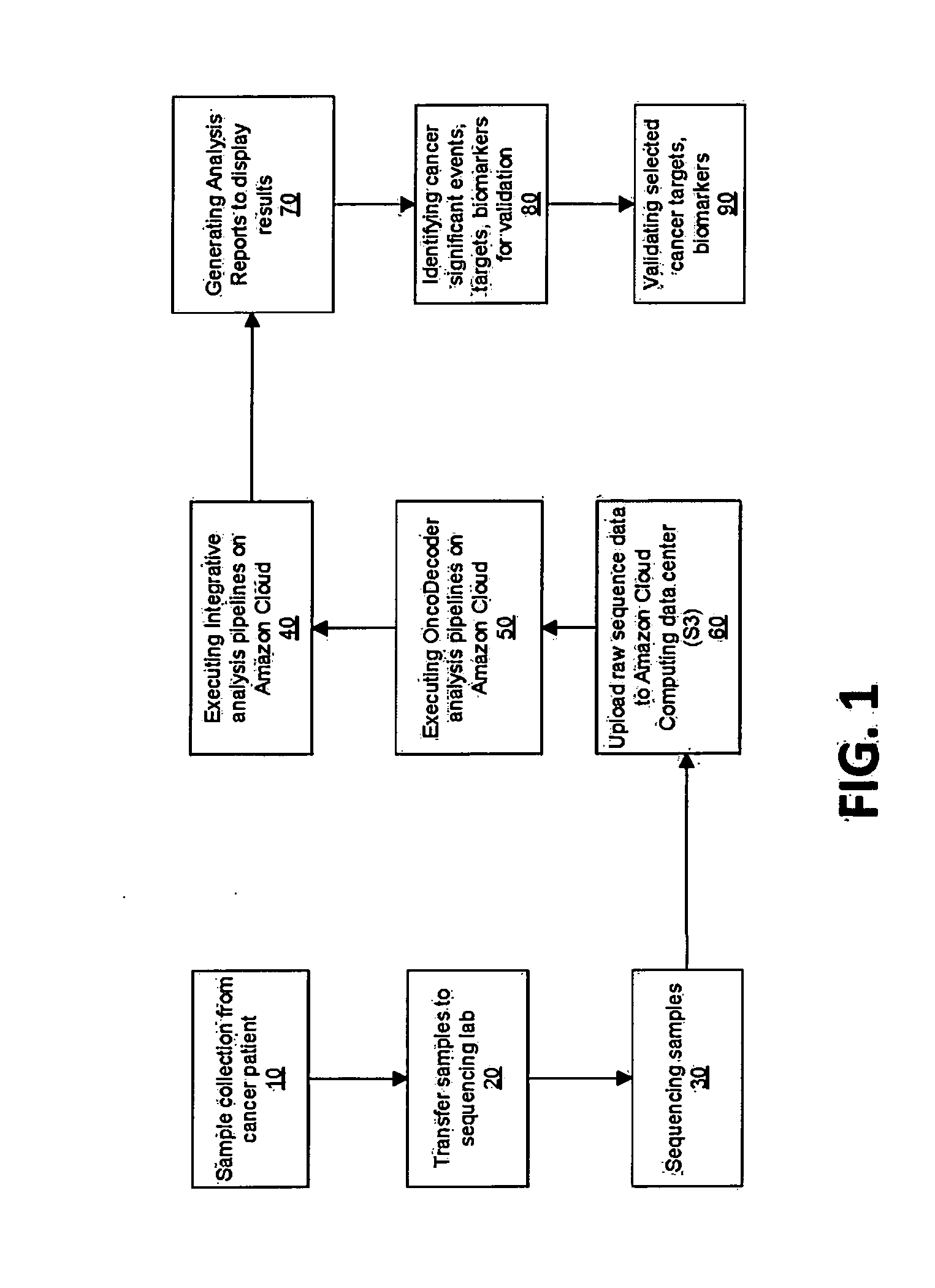
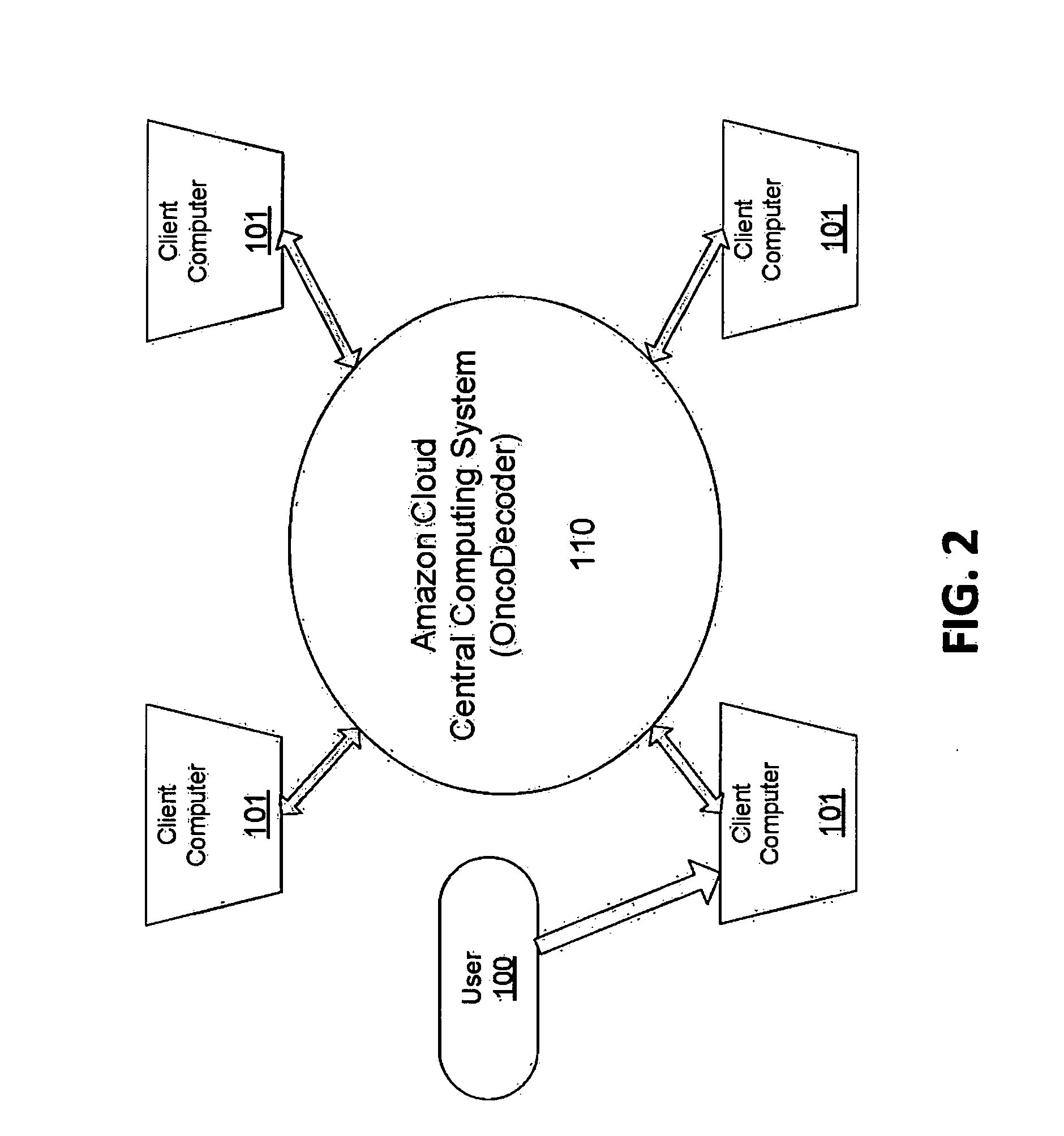
InactiveUS20130184999A1Improve throughputMinimal hardware requirementProteomicsGenomicsHuman cancerBiomarker discovery
The present invention provides users with cloud-based high throughput computing system for integrative analyses of next generation sequencing genomic data, such that human cancer biomarkers and drug targets can be accurately and quickly identified. Advantageously, the present invention harness a comprehensive systematic analysis pipelines for all types of next generation sequencing genomic data, advanced genomic variants calling algorithms and modeling, variant data correlation and integration, and identification of cancer specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Thus, the present invention will aid users so that less of their time and efforts are required in order to obtain precisely the desired information for which they are analyzing.
Owner:DING YAN
Analysis of transcriptomic data using similarity based modeling
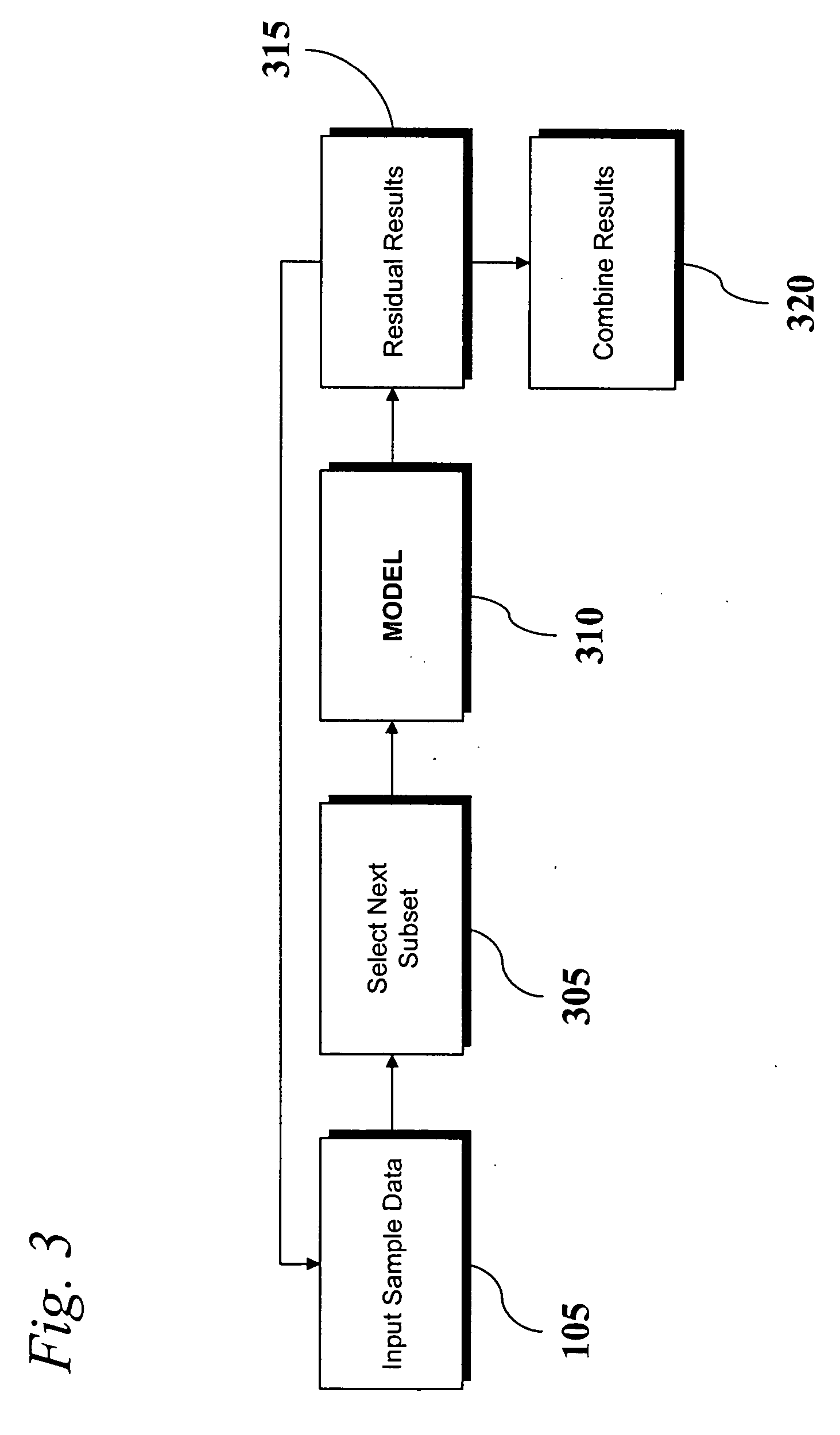
InactiveUS20060293859A1Classification capability can be extendedSmall and fast computing footprintBiostatisticsBiological testingBiomarker discoveryModelling analysis
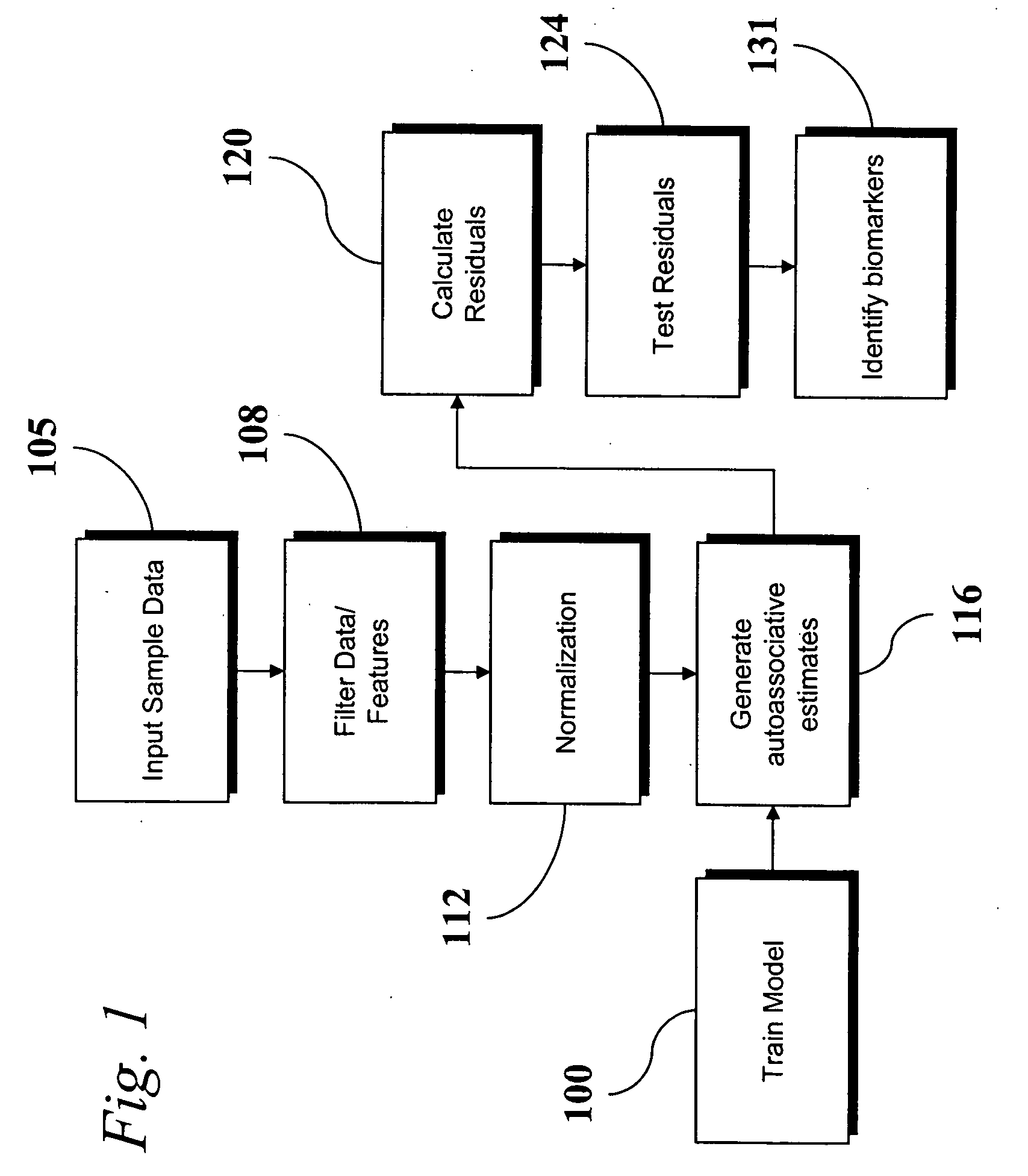
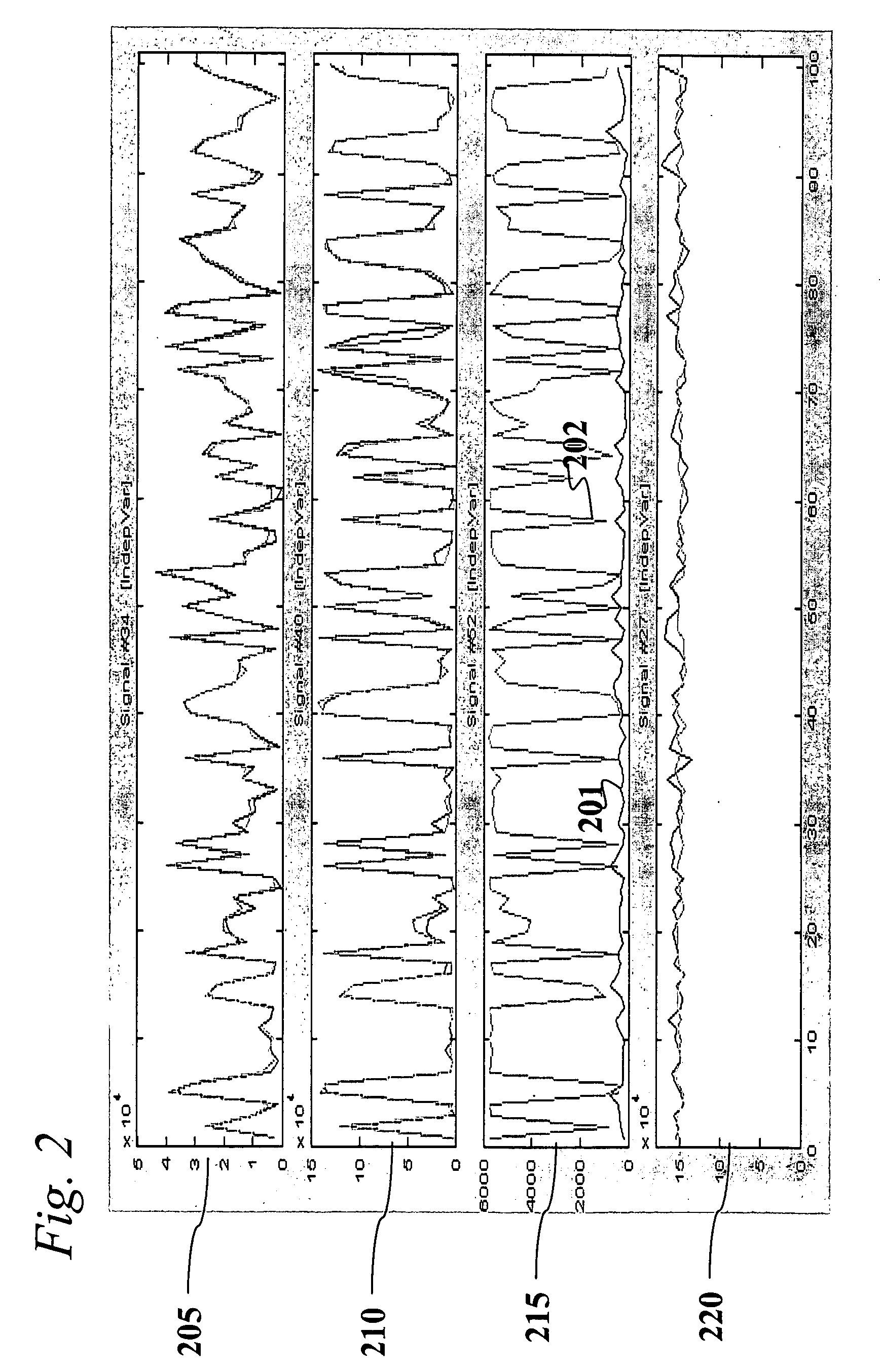
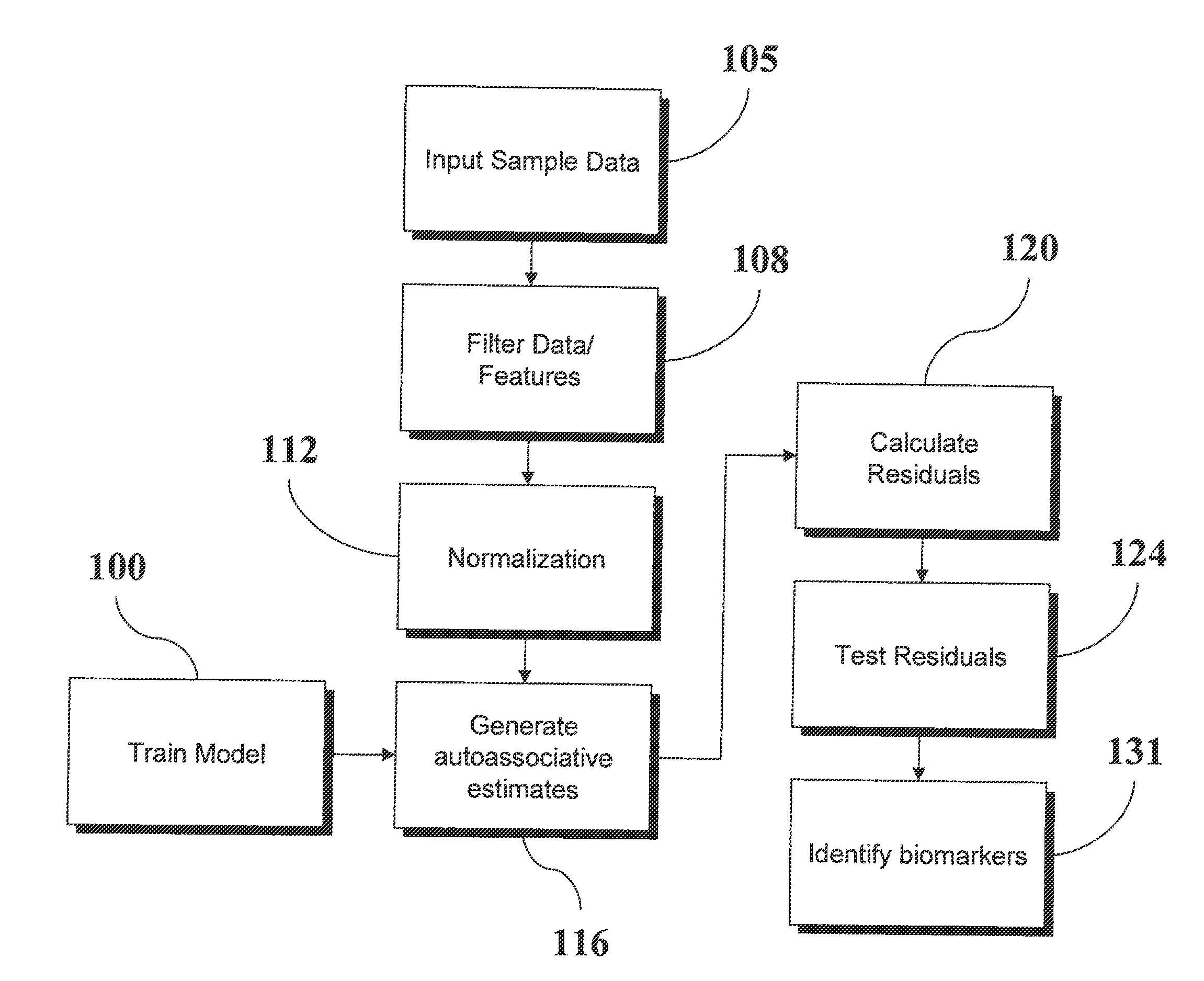
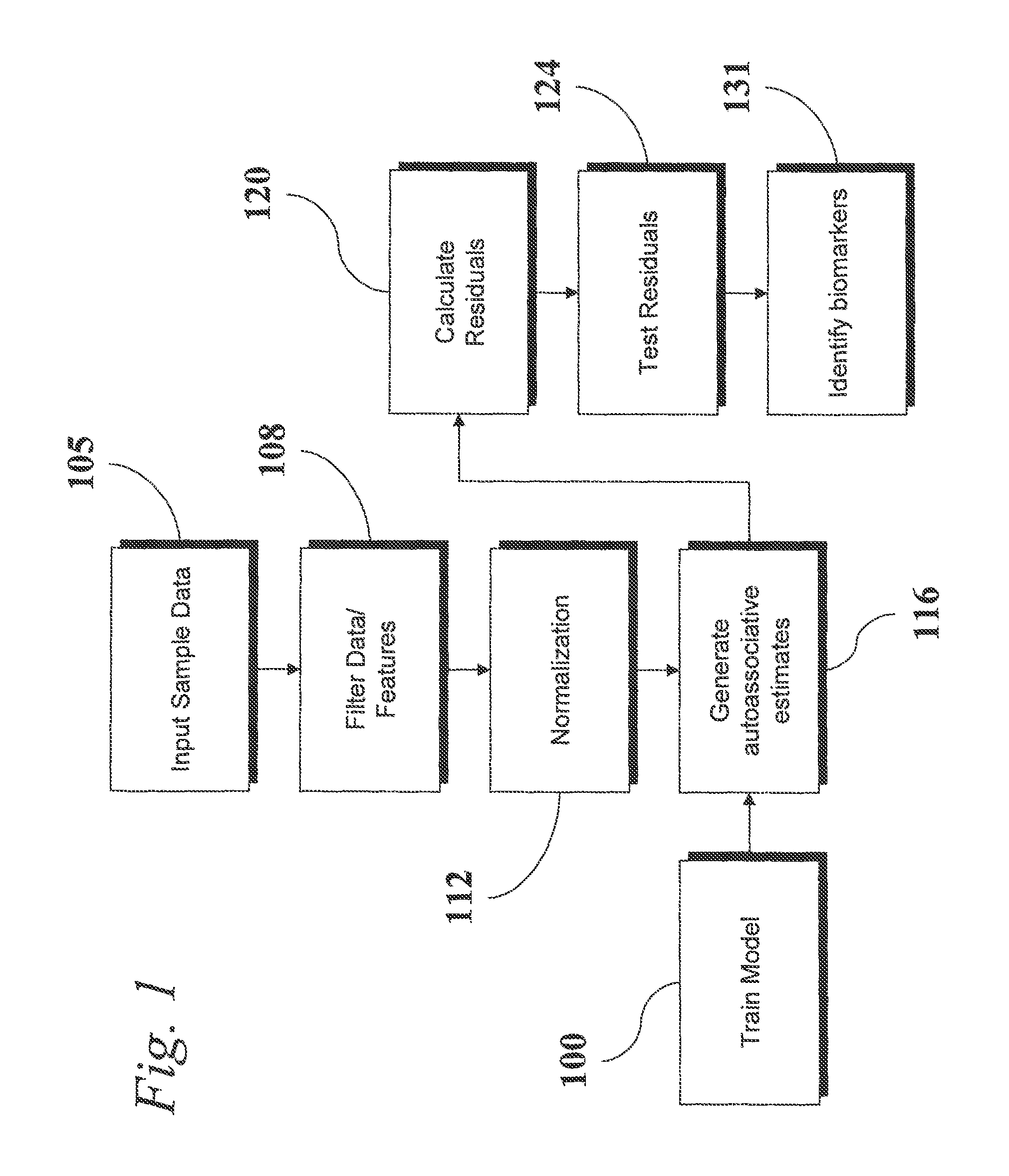
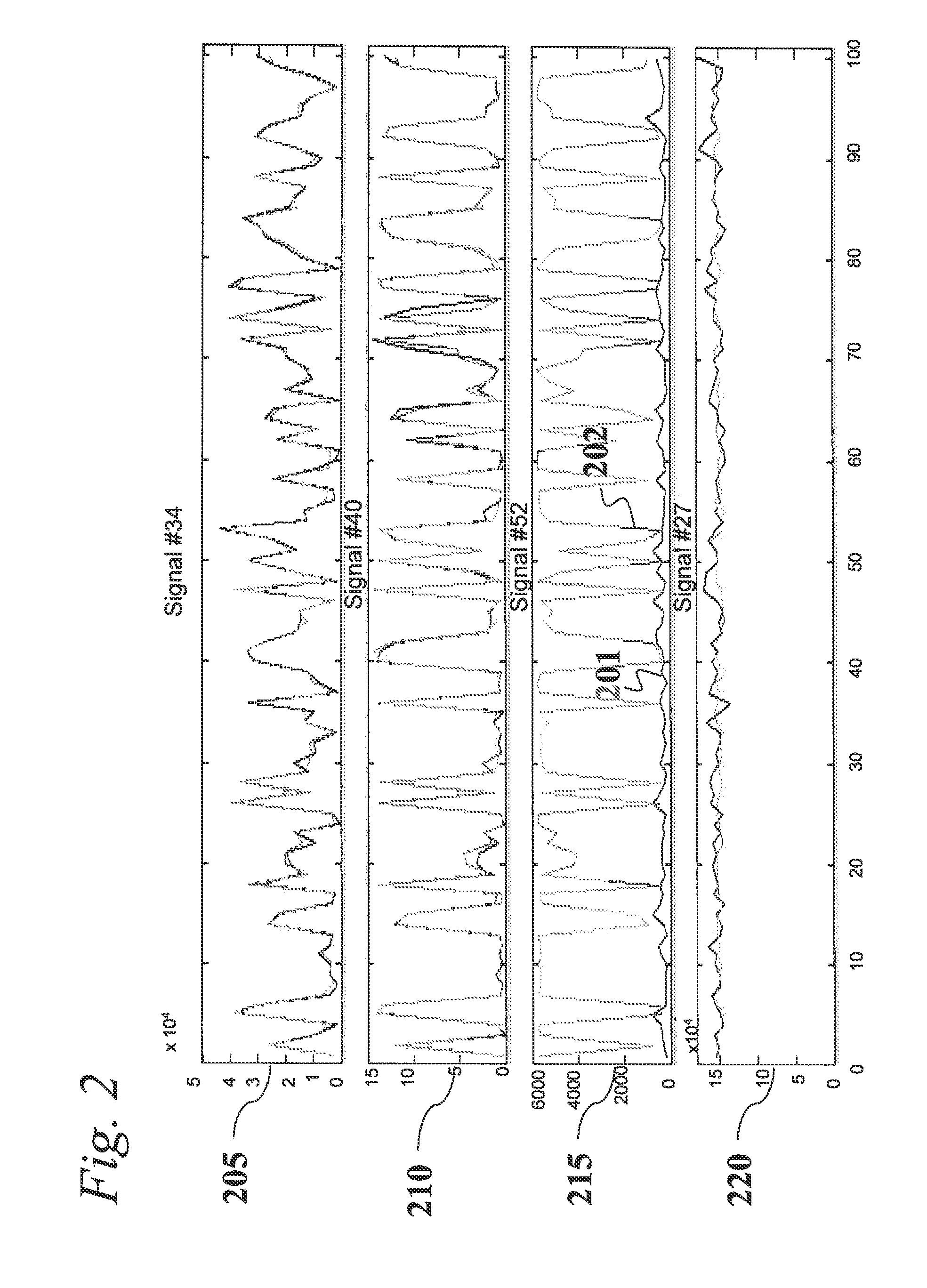
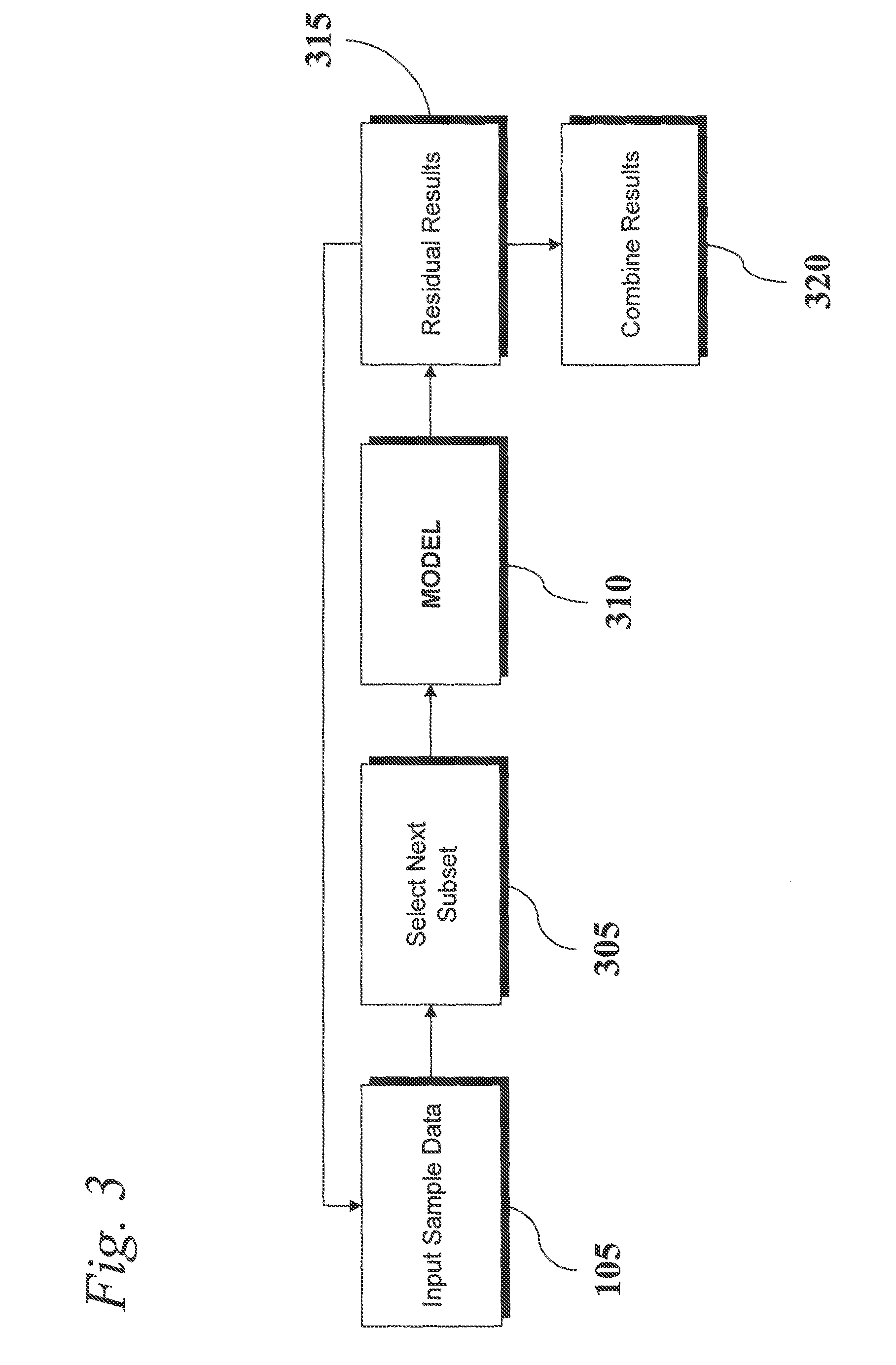
An analytic apparatus and method is provided for diagnosis, prognosis and biomarker discovery using transcriptome data such as mRNA expression levels from microarrays, proteomic data, and metabolomic data. The invention provides for model-based analysis, especially using kernel-based models, and more particularly similarity-based models. Model-derived residuals advantageously provide a unique new tool for insights into disease mechanisms. Localization of models provides for improved model efficacy. The invention is capable of extracting useful information heretofore unavailable by other methods, relating to dynamics in cellular gene regulation, regulatory networks, biological pathways and metabolism.
Owner:VENTURE GAIN L L C
Computer based system for predicting treatment outcomes
InactiveUS20130041683A1Simple systemPotential for errorData processing applicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationBiomarker discovery
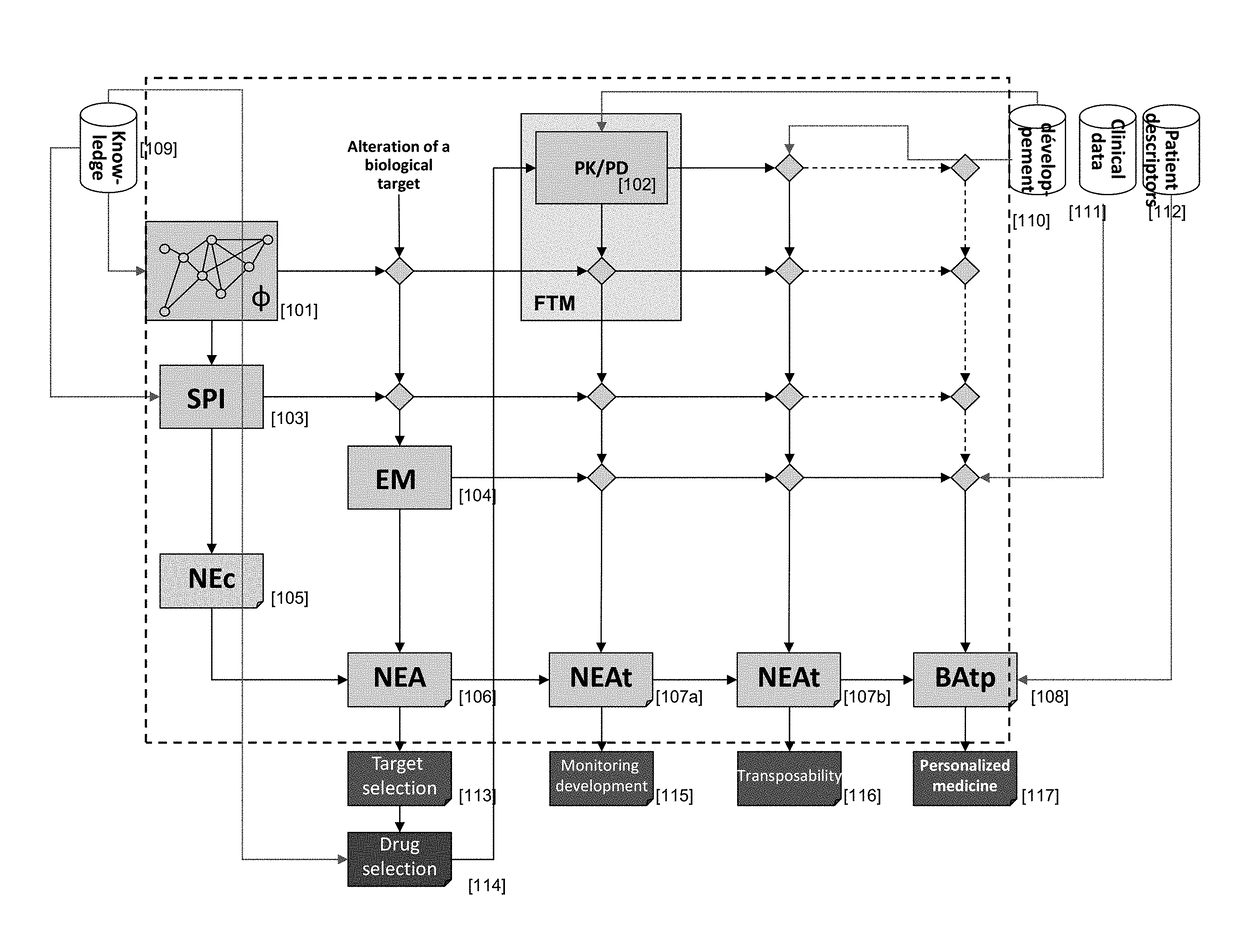
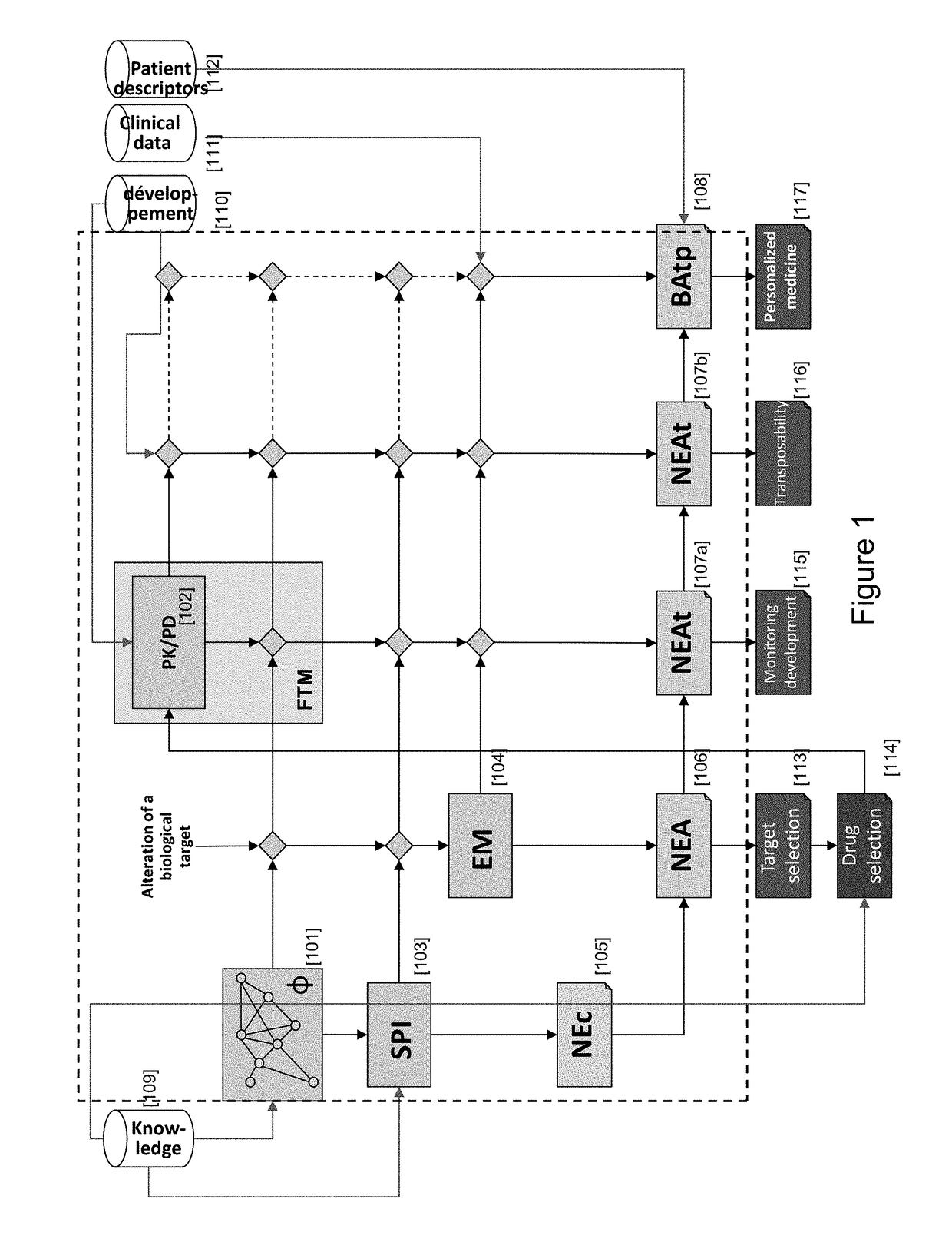
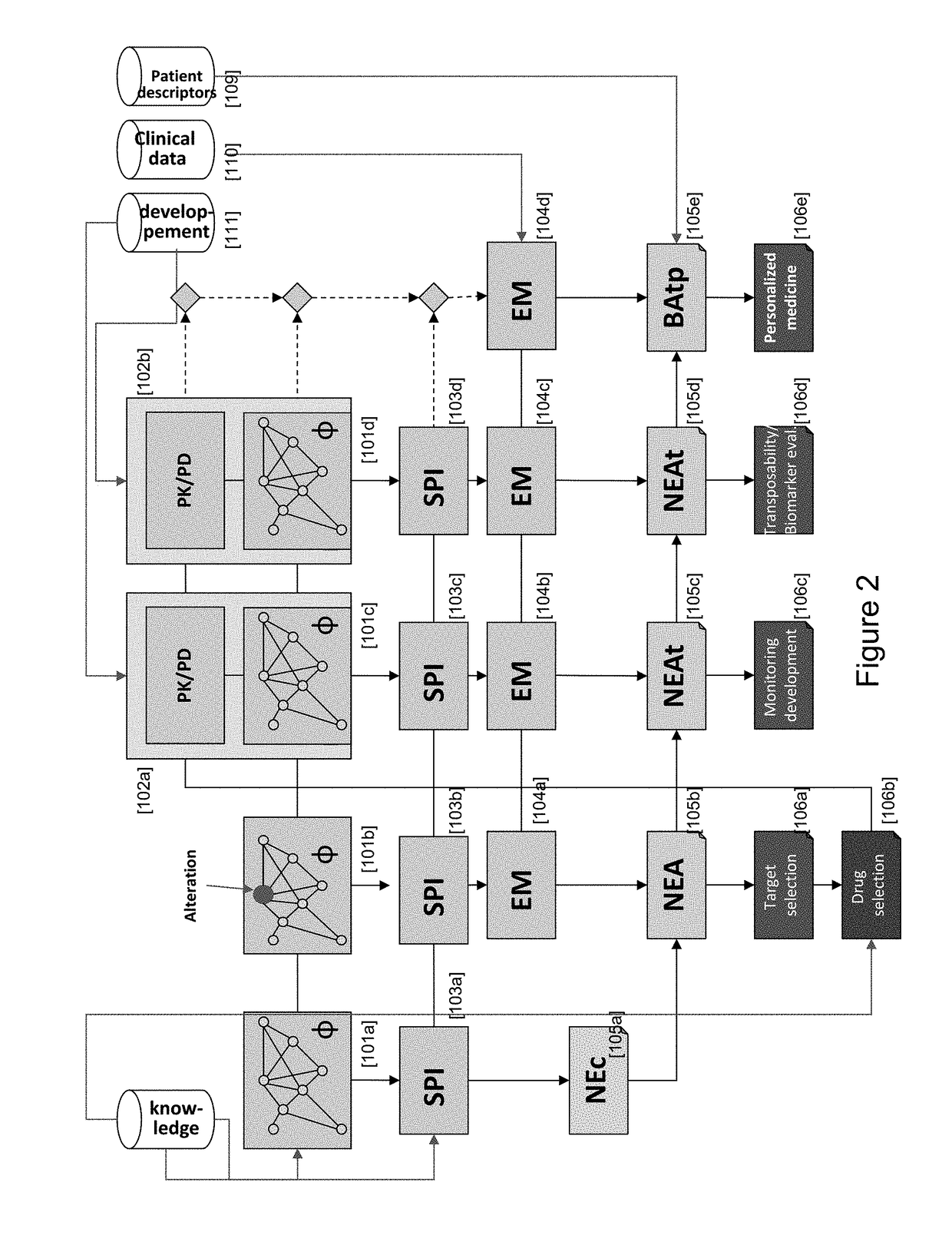
This invention relates to computer systems for conducting drug and biomarker discovery, drug development, and personalized medicine, and more generally managing healthcare, and in particular to a system and method for predicting the therapeutic value of a treatment to an individual. The treatment is associated with a function that describes, in a population of individuals, the benefit from a treatment, generally in terms of occurrence of a medical event under treatment, as a function of the risk (e.g., the occurrence of the medical event) without said treatment.
Owner:NOVADISCOVERY +1
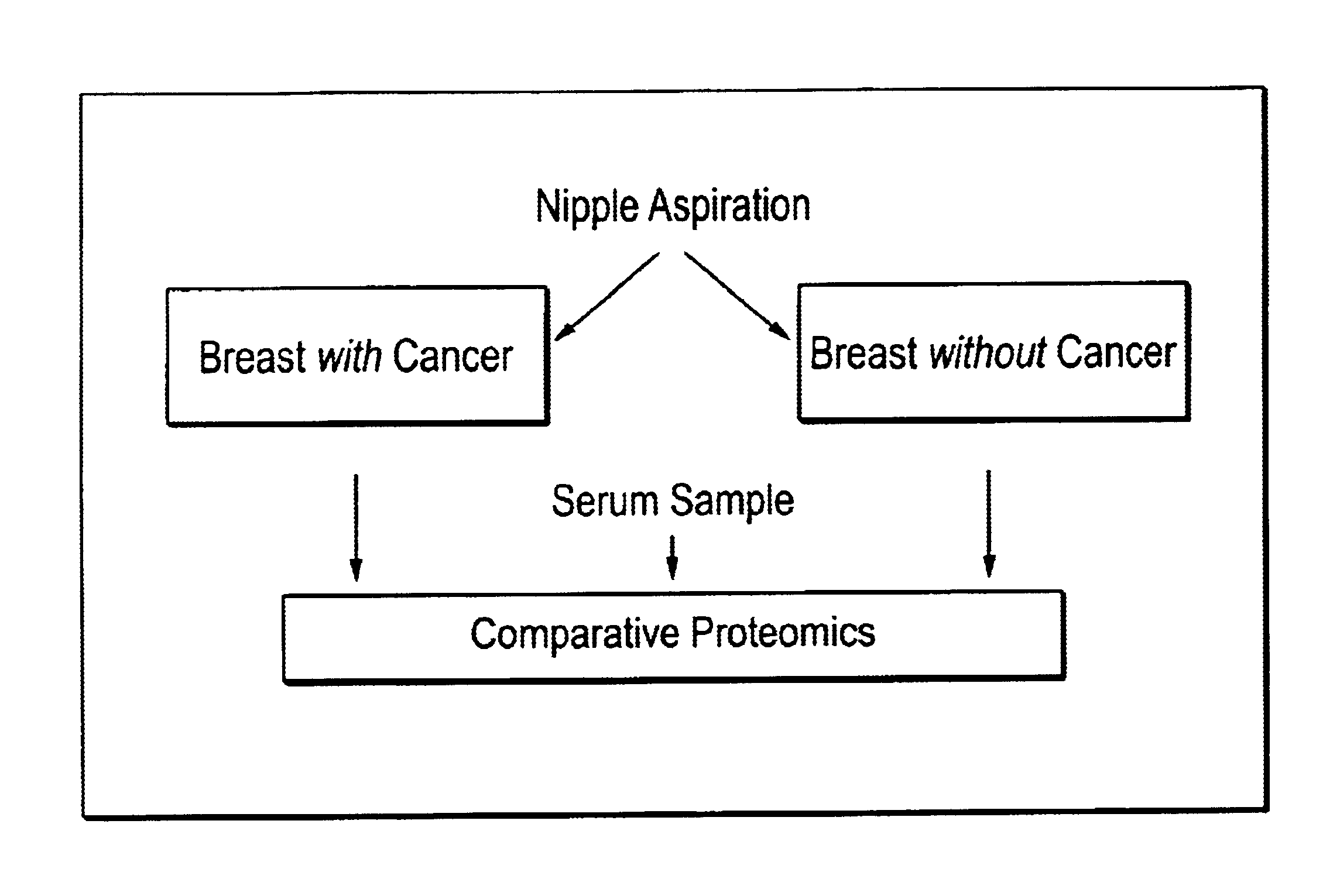
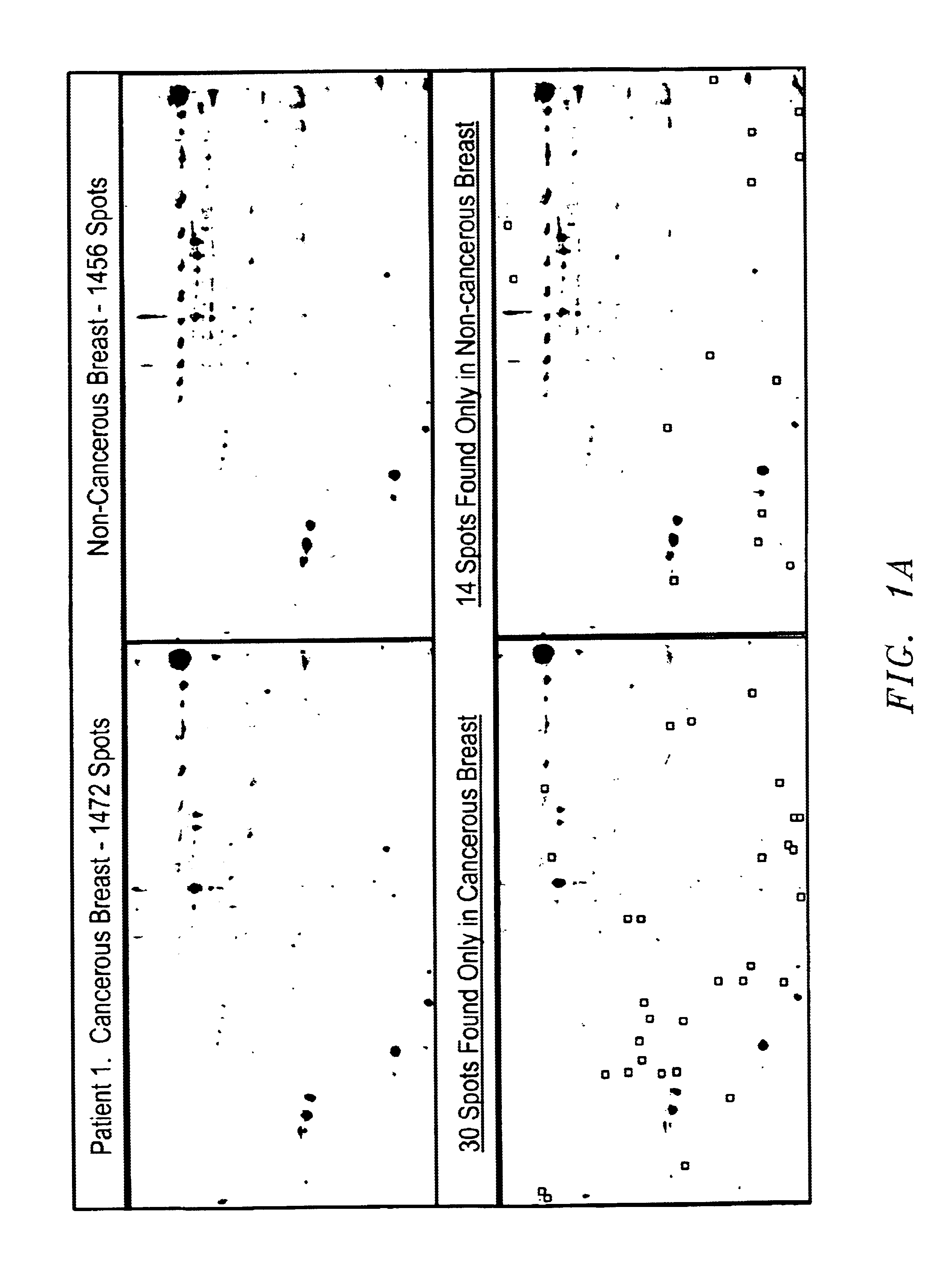
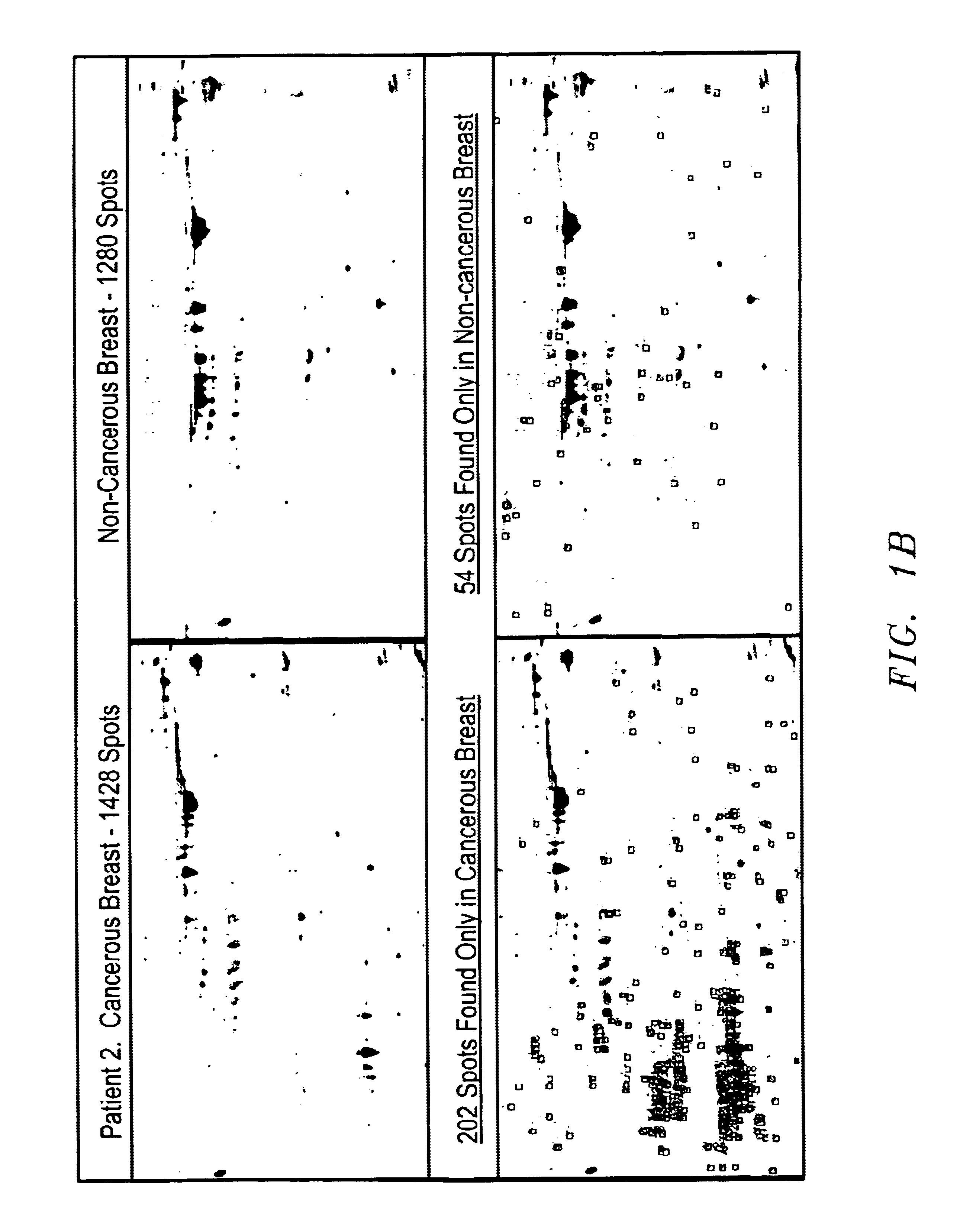
Methods and compositions for detection of breast cancer
Systematic comparisons of breast ductal fluid samples obtained by nipple aspiration from women with unilateral breast cancer revealed significant differences in ductal fluid protein expression between the breast with cancer and the breast without cancer in each patient. This study demonstrates that breast ductal fluid contains over 1000 separate protein species and suggests that ductal fluids from breast cancer patients may be useful for high-throughput biomarker discovery.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix
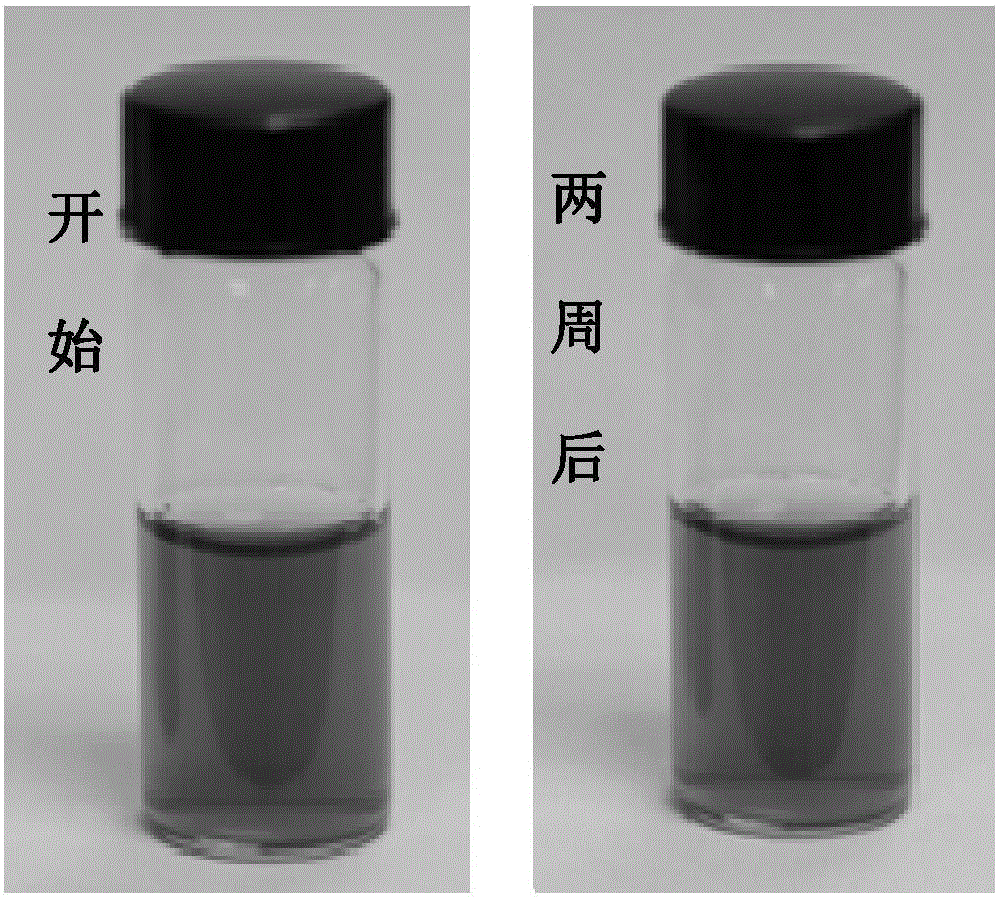
InactiveCN102645481AOvercoming the inability to efficiently analyze small molecule samplesReduce processing requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectroscopyBiomarker discovery
The invention discloses application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as a matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix. The carbon spots serve as an analysis method of the MALDI matrix and are suitable to mass spectrum analysis for the micromolecules with the m / z between 150-1000. Suitable molecule types comprise amino acid, polypeptide, beta-exhilarant, fatty acid, polymer and the like. When the method is used for detecting the molecule with the m / z between 150-1000, background peaks hardly exist to produce background interference. The method can be effectively used in the fields of organic and biomass spectrometry, spectrometry imaging, protein spectroscopy, metabonomics, biomarker discovery, environment analysis and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
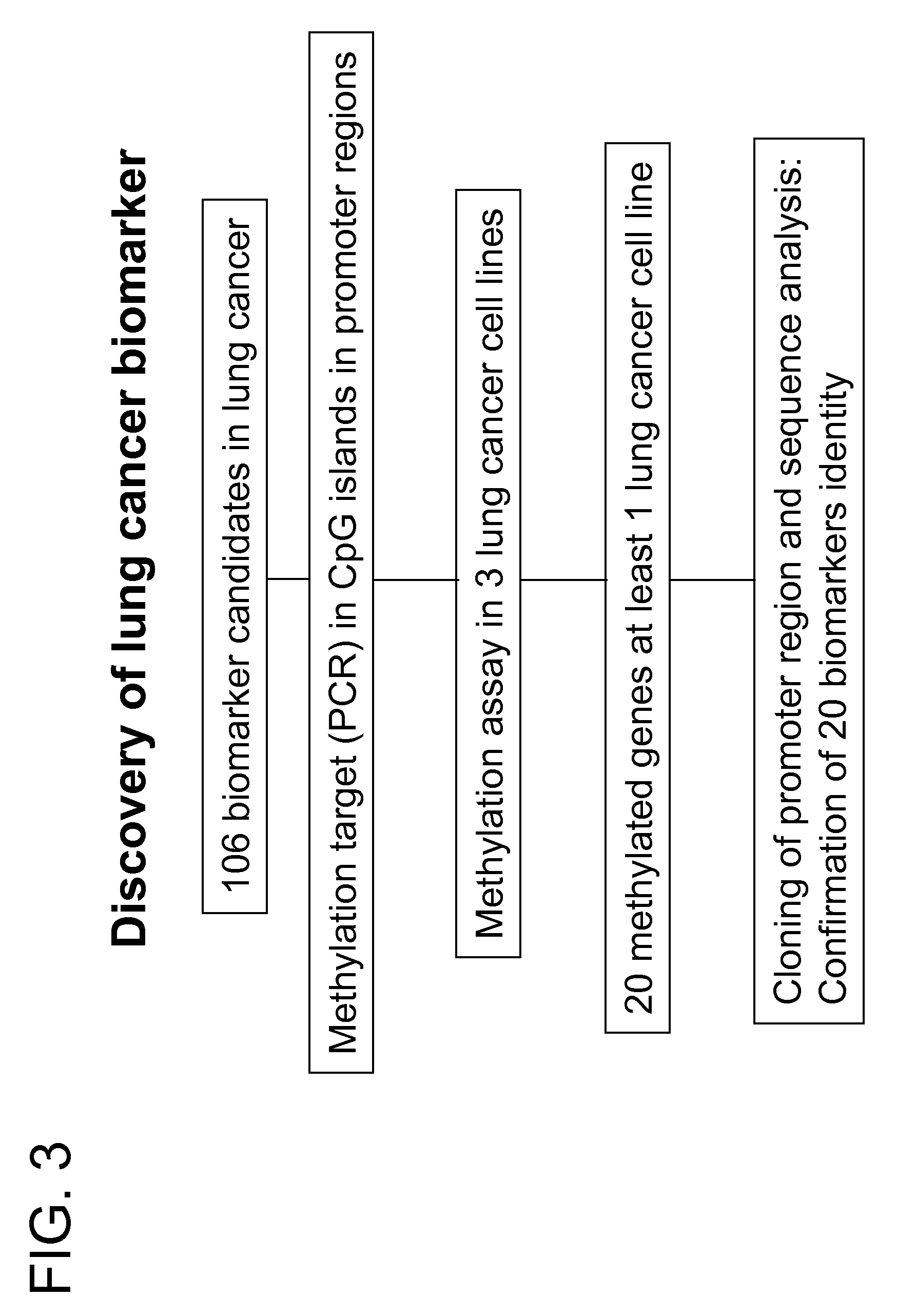
Lung cancer biomarker discovery
InactiveUS20070264659A1Early detectionAccurate diagnostic systemMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker discoveryOncology
Owner:GENOMICTREE
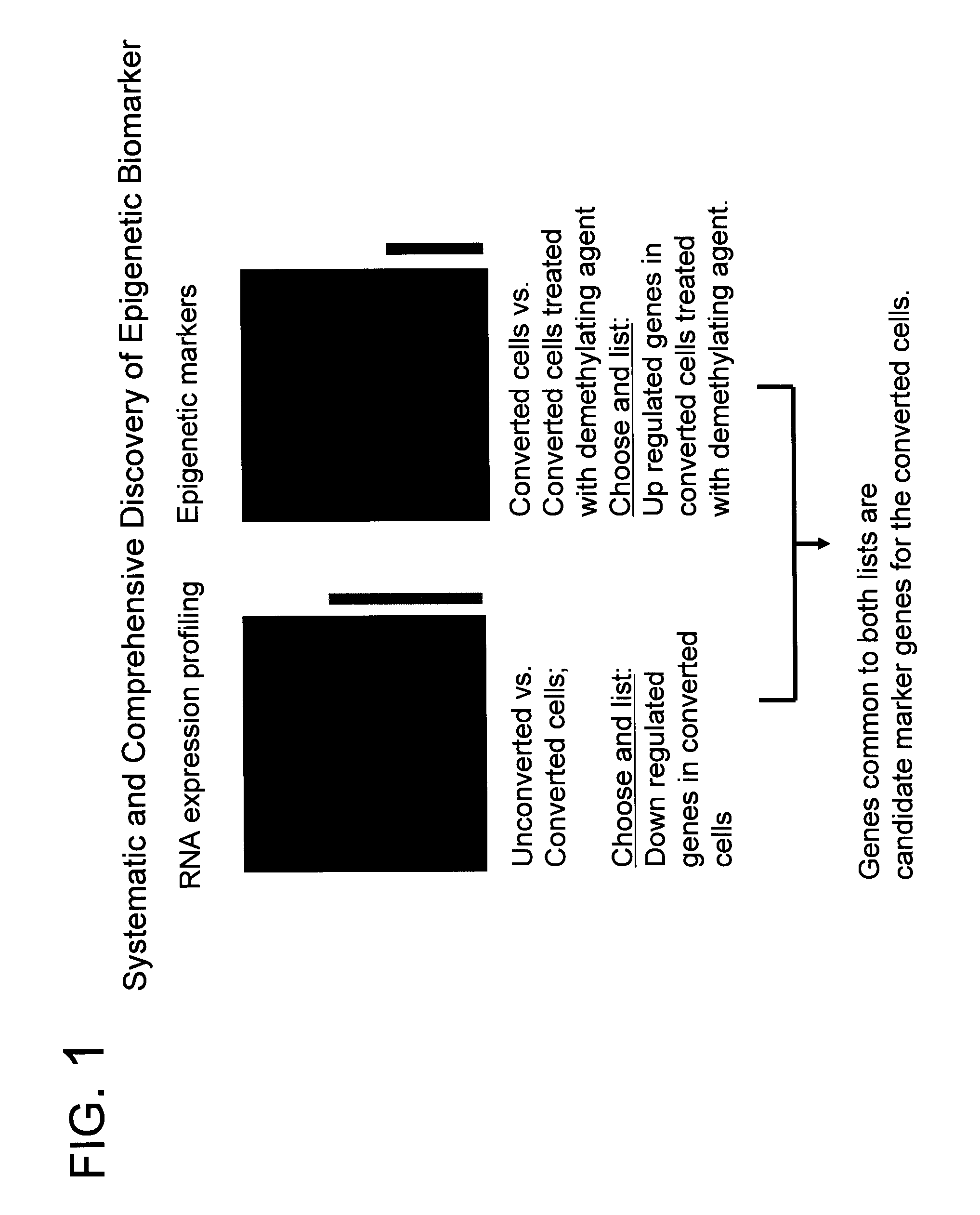
System for biomarker discovery
InactiveUS20060211009A1Early detectionAccurate diagnostic systemSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransformation cellBiologic marker
The present application discloses a method for discovering a methylation marker gene for the conversion of a cell comprising: (i) comparing converted and unconverted cell gene expression content to identify a gene that is present in greater abundance in the unconverted cell; (ii) treating a converted cell with a demethylating agent and comparing its gene expression content with gene expression content of an untreated converted cell to identify a gene that is present in greater abundance in the cell treated with the demethylating agent; and (iii) identifying a gene that is common to the identified genes in steps (i) and (ii), wherein the common identified gene is the methylation marker gene.
Owner:GENOMICTREE
Analysis of Transcriptomic Data Using Similarity Based Modeling
ActiveUS20110093244A1Small footprintFast data processingBiostatisticsComputation using non-denominational number representationBiomarker discoveryOrganism
An analytic apparatus and method is provided for diagnosis, prognosis and biomarker discovery using transcriptome data such as mRNA expression levels from microarrays, proteomic data, and metabolomic data. The invention provides for model-based analysis, especially using kernel-based models, and more particularly similarity-based models. Model-derived residuals advantageously provide a unique new tool for insights into disease mechanisms. Localization of models provides for improved model efficacy. The invention is capable of extracting useful information heretofore unavailable by other methods, relating to dynamics in cellular gene regulation, regulatory networks, biological pathways and metabolism.
Owner:PHYSIQ
Application of molybdenum disulfide/nanosilver composite serving as matrix to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry
ActiveCN105929017AThe synthesis method is simpleOvercoming Matrix Background Interference ProblemsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiomarker discoveryMass spectrometry imaging
The invention discloses application of a molybdenum disulfide / nanosilver composite serving as a matrix to MALDI (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization) time of flight mass spectrometry. Few-layer molybdenum disulfide is prepared according to an improved chemical lithium ion intercalation and exfoliation method, on the basis of which the molybdenum disulfide / nanosilver composite is prepared through in-situ reduction of silver nitrate. An analysis method taking molybdenum disulfide / nanosilver composite as an MALDI matrix is applicable to mass spectrometry of micromolecules with molecular weight smaller than 1000 and suitable for molecules of amino acids, oligopeptides, fatty acids, alkaloids, hormones, antibiotics, antibacterial drugs, anticancer drugs and the like. Matrix background interference is avoided when the method is adopted for detection of molecules with a mass-to-charge ratio (m / z) smaller than 1000. The method can be effectively applied to fields of organic and biomass spectrometry, imaging mass spectrometry, protein mass spectrometry, metabonomics, biomarker discovery, environmental analysis and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
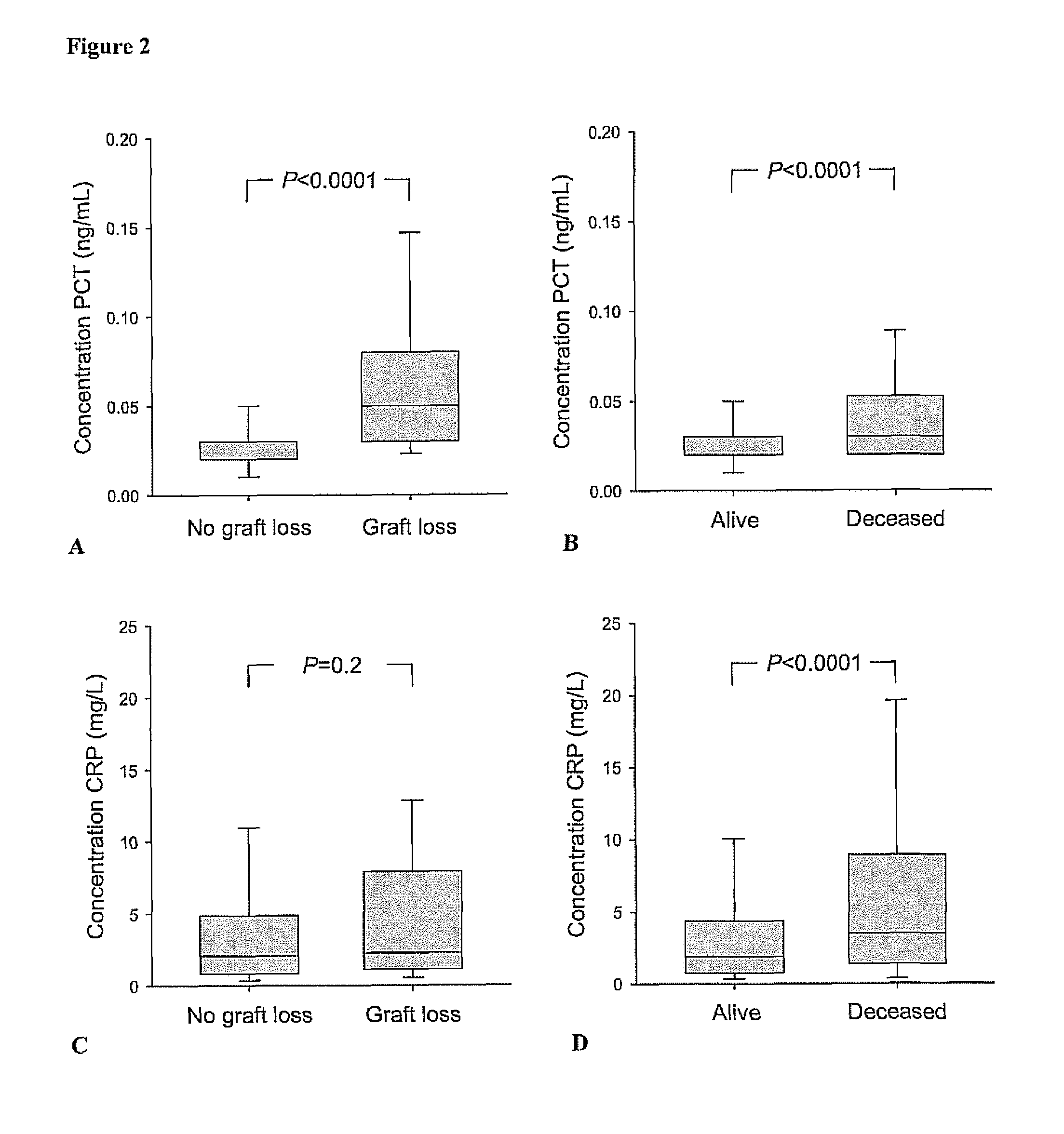
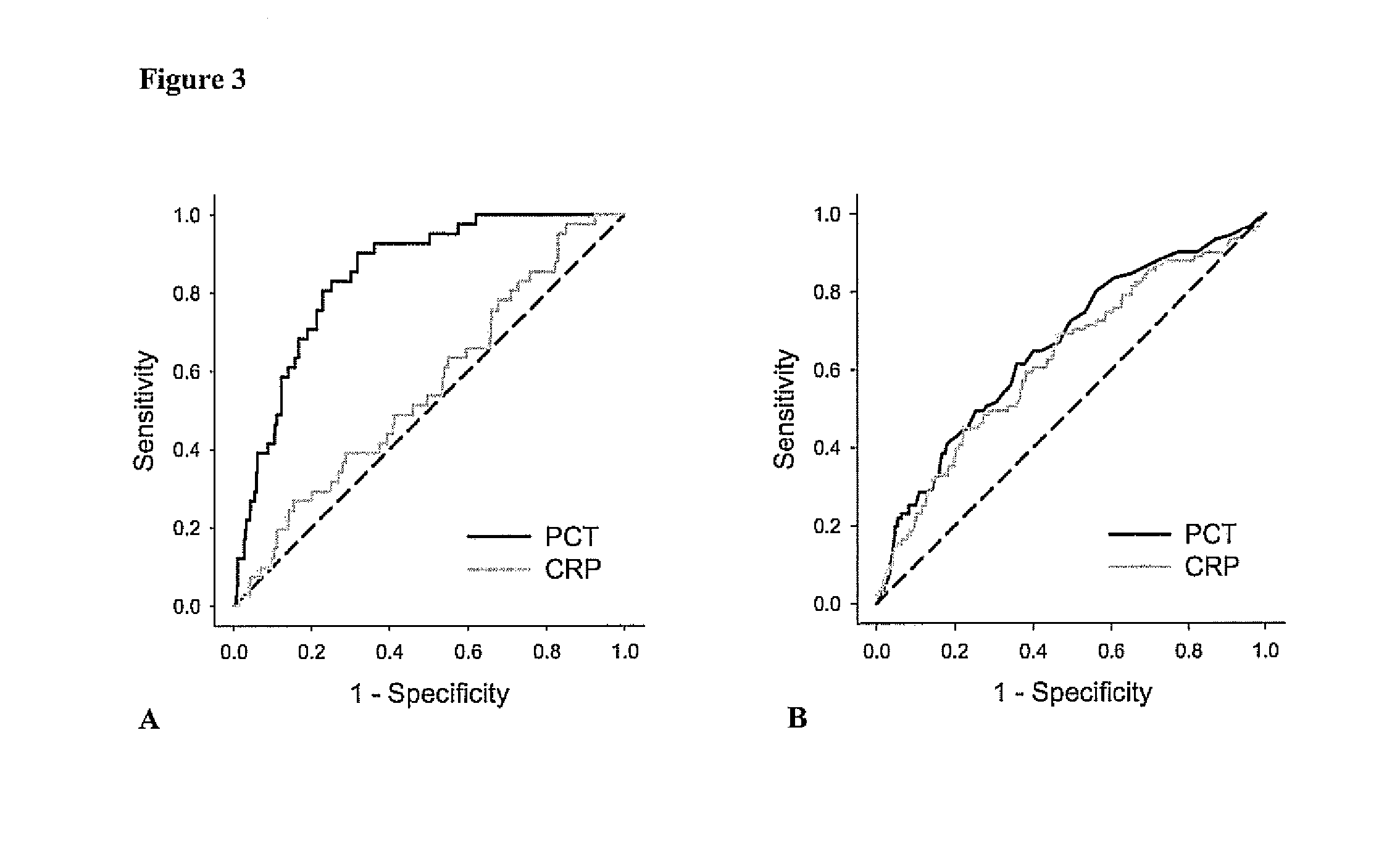
Marker for graft failure and mortality
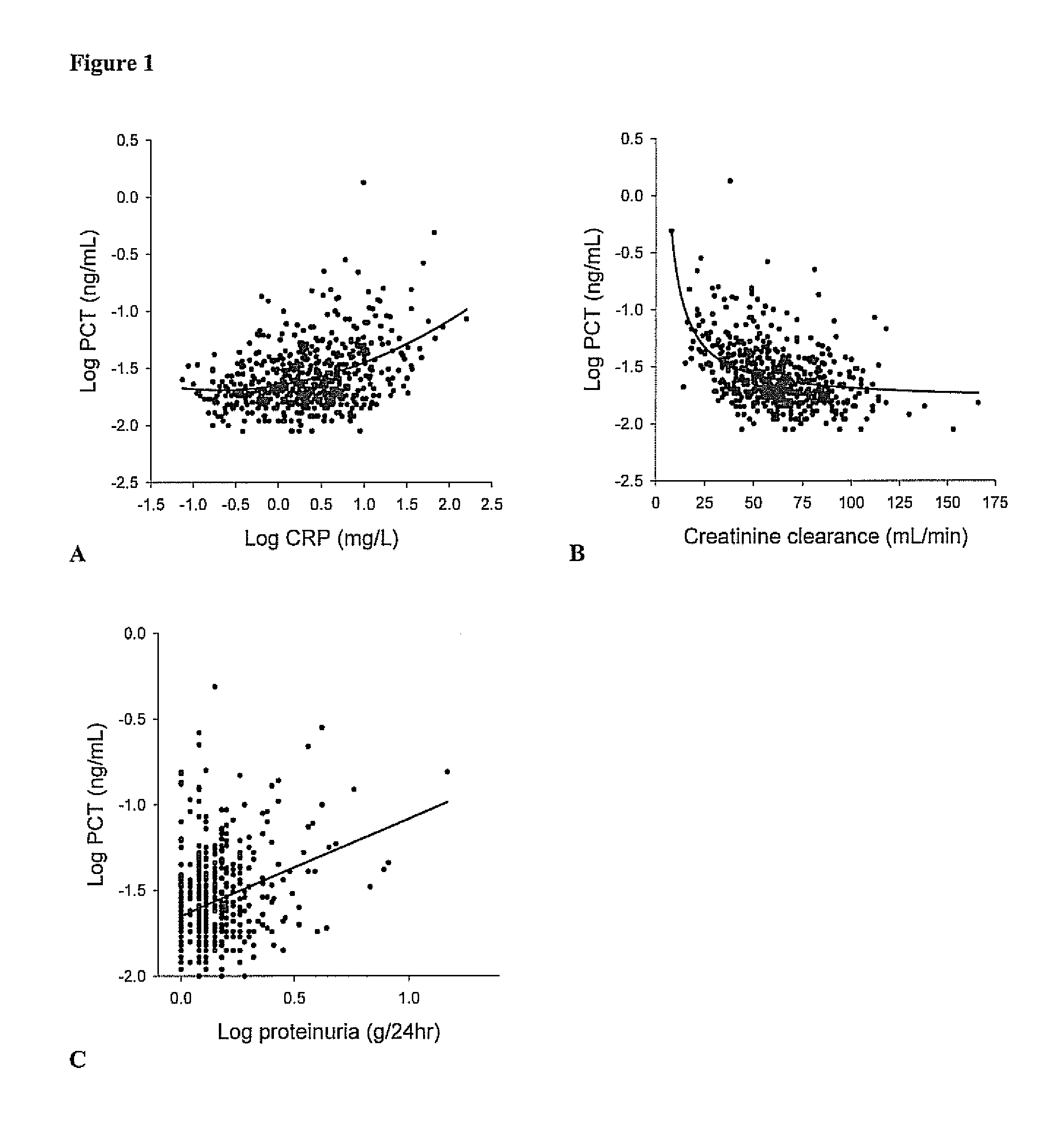
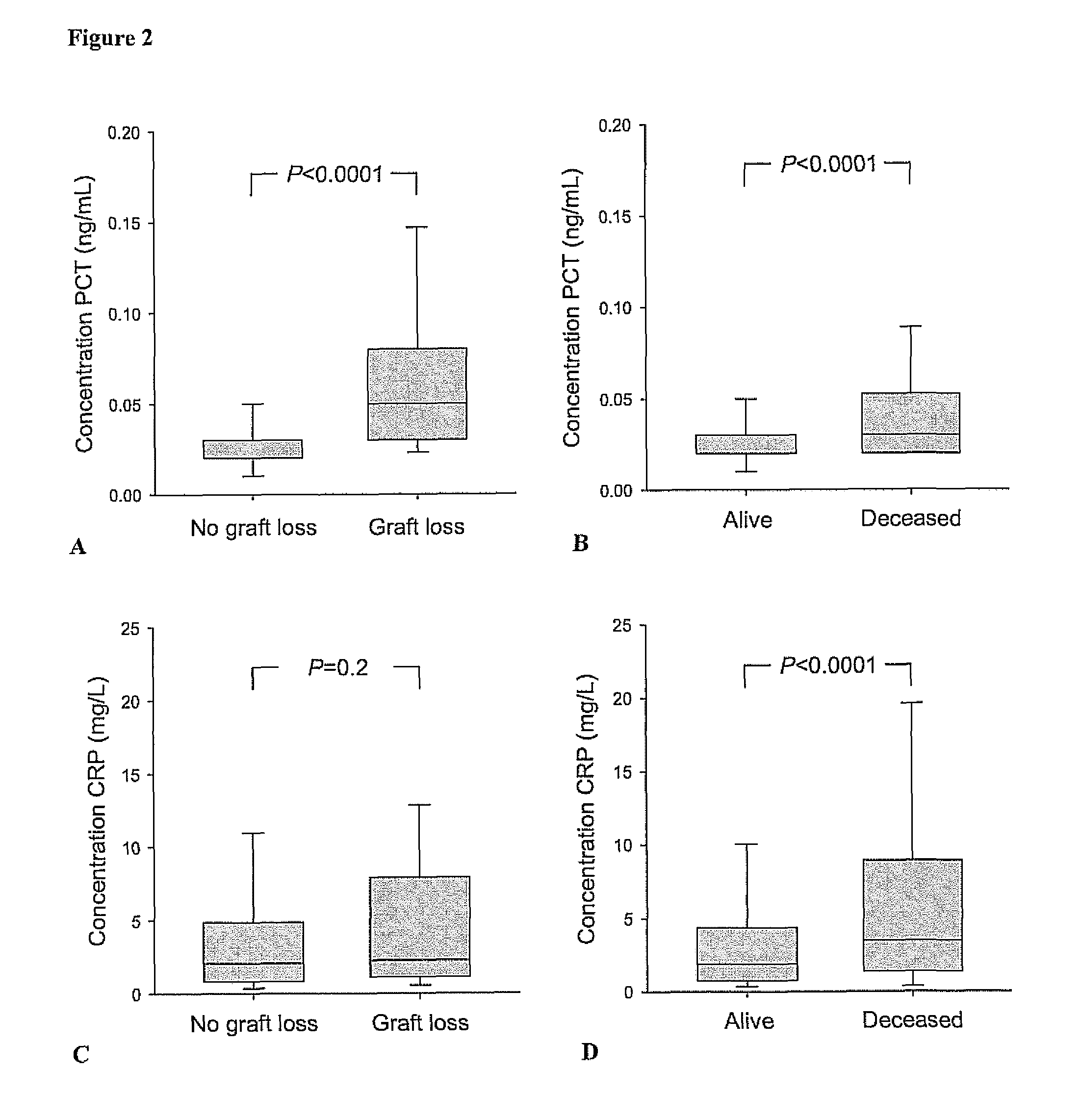
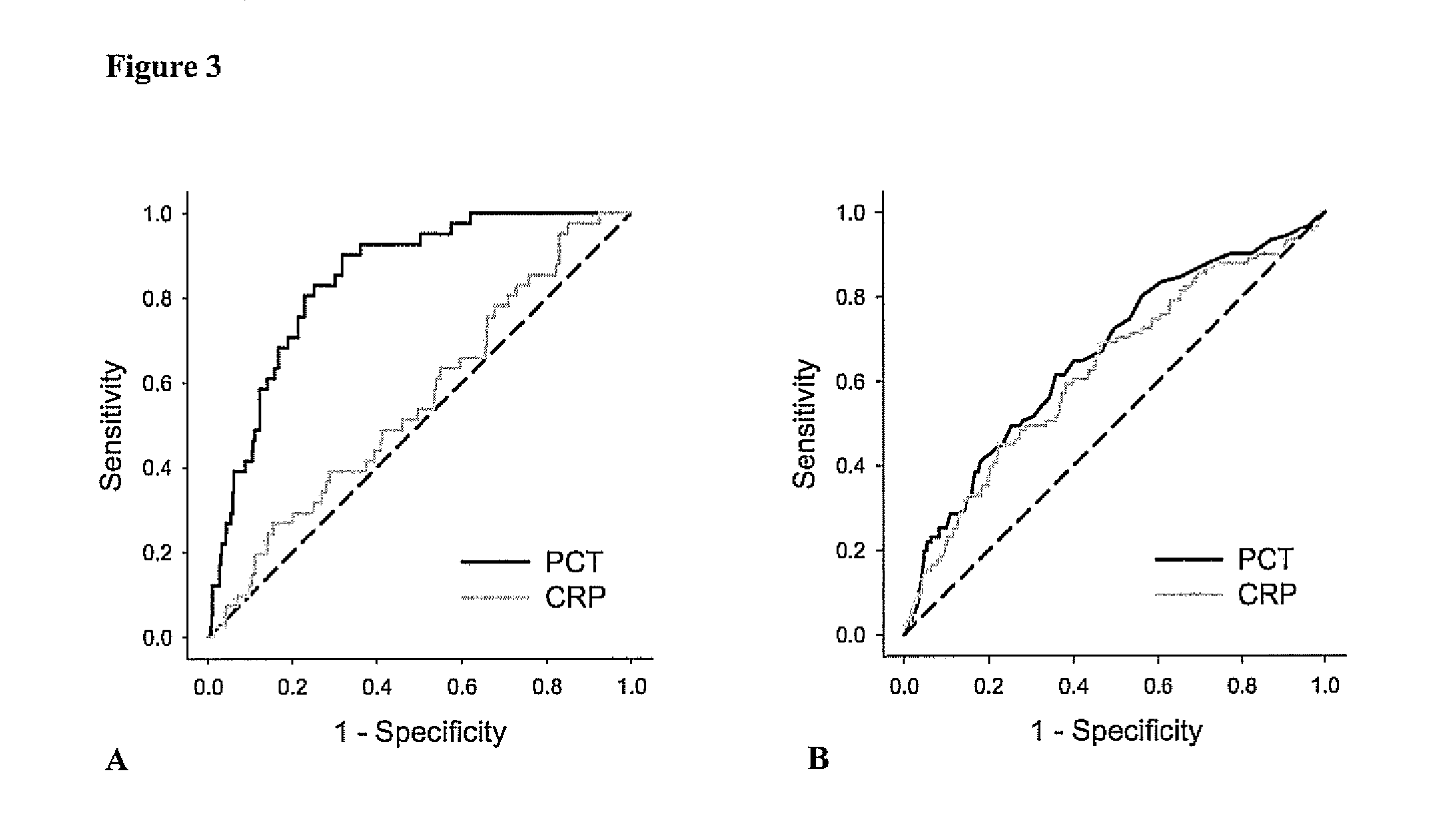
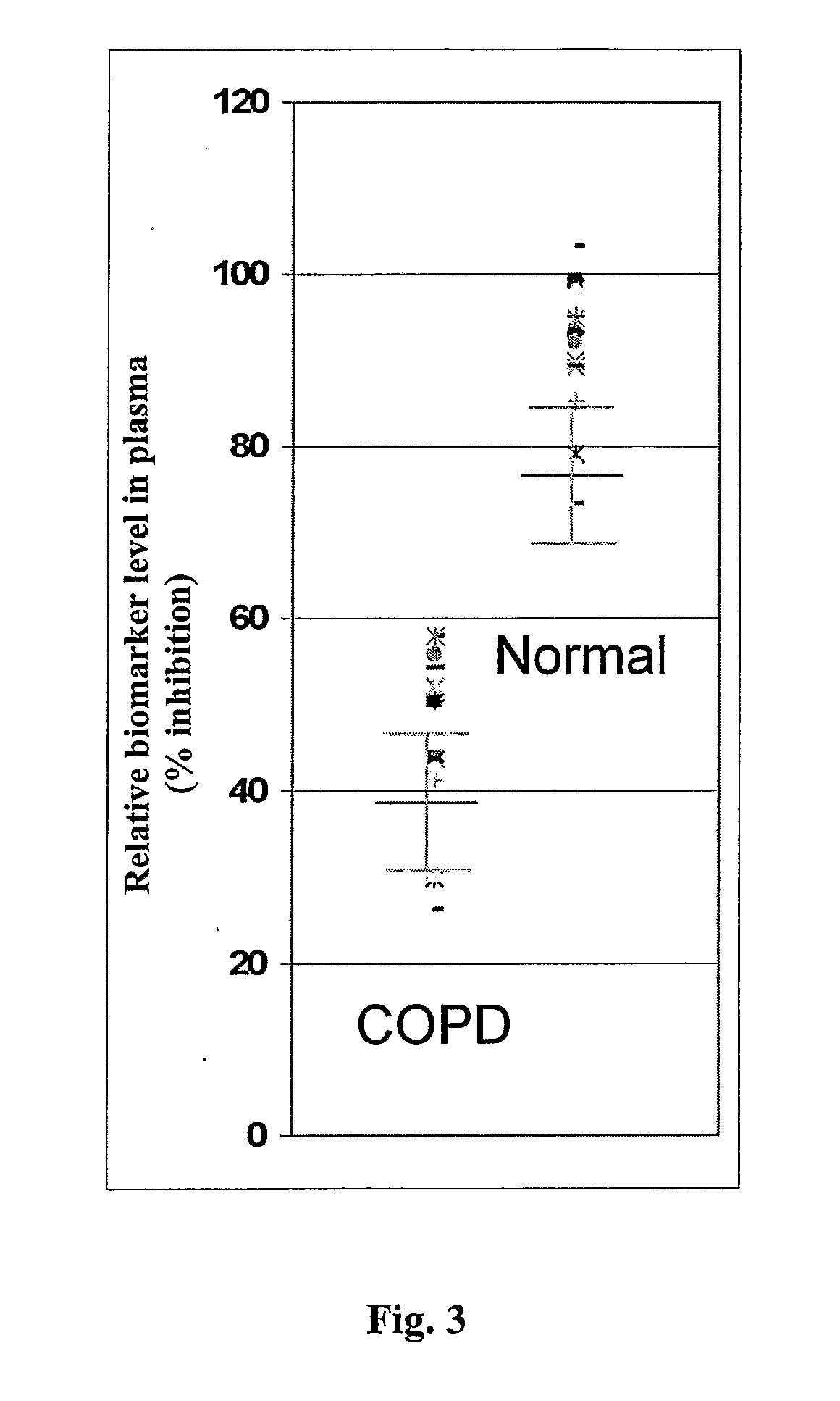
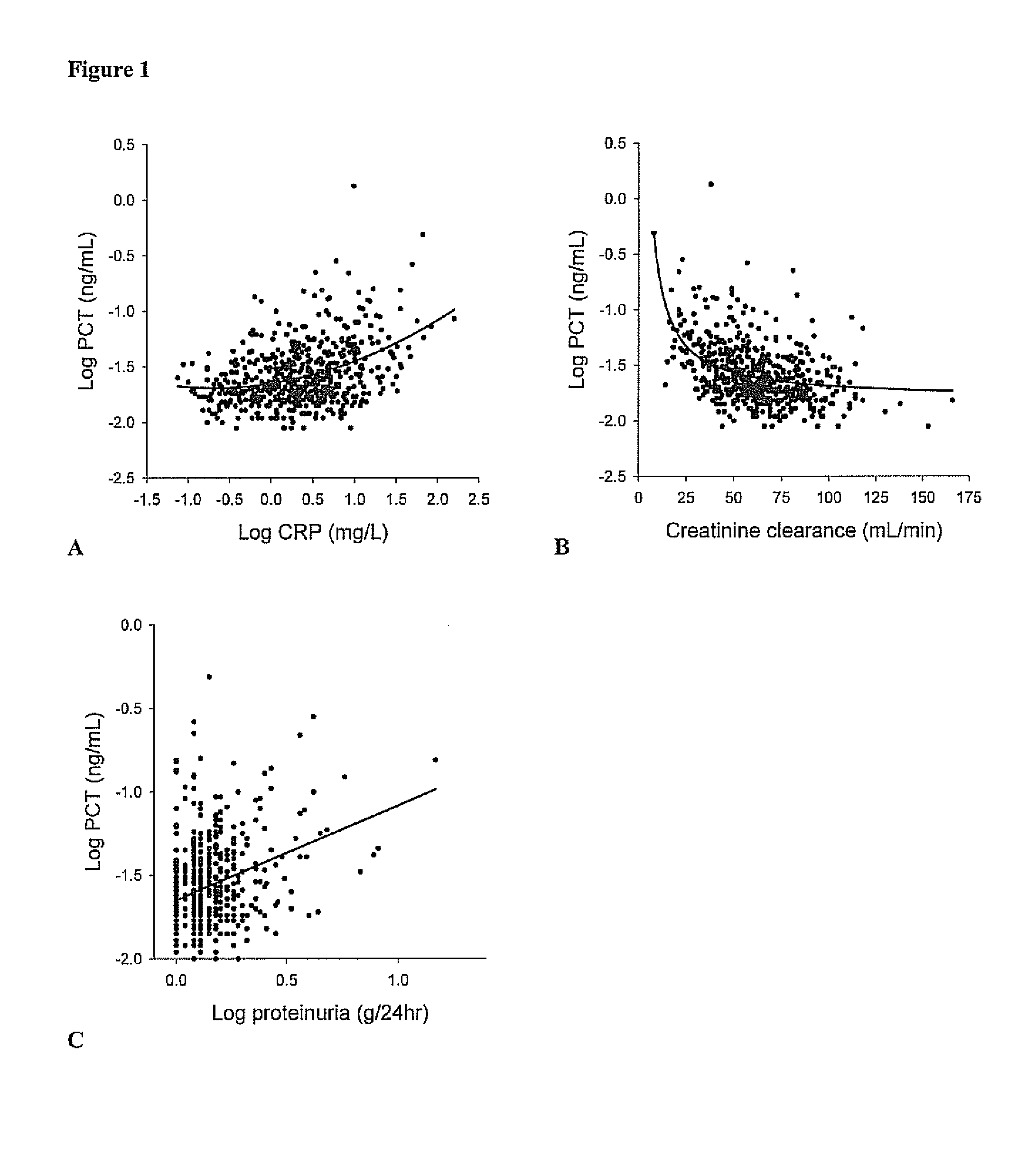
ActiveUS8889366B2Lower levelAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsOrgan transplantationMortality rate
Subject of the present invention is a biomarker for graft failure and / or mortality after organ transplantation. Procalcitonin was found to be a useful marker for the prediction or risk stratification for graft failure and / or mortality of a subject who has received an organ transplant and monitoring and therapy guidance of such subject.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Methods for fractionating and processing microparticles from biological samples and using them for biomarker discovery
InactiveUS20130052647A1Efficient trappingEfficiently provideFatty acids production/refiningMicroorganismsCell freeFractionation
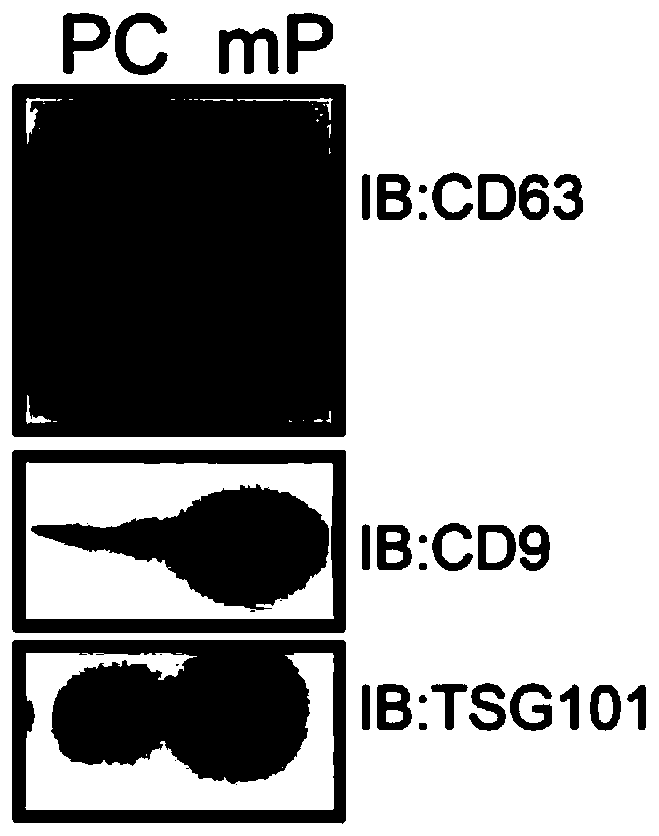
Described herein are methods, devices, and compositions for fractionation and processing of microparticles from biological samples, and to methods for obtaining and using the microparticles for biomarker discovery. Biological samples include cell-free fluids, for example blood plasma, blood serum, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and saliva, as well as conditioned media. Conditioned media is the liquid growth media used to propagate cells in vitro. Purification of microparticles from cell-free fluids is challenging, typically accomplished by prolonged ultracentrifugation. Described herein is an alternative method for efficiently harvesting and processing microparticles from cell-free fluids and from conditioned media. Embodiments described herein relate to use of the microparticles and their contents recovered from conditioned media derived from propagation of human and animal cells, as a source of biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of diseases and pathological conditions.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Monoclonal antibody based biomarker discovery and development platform
InactiveUS20070172887A1Low and no diffusion limitationRapid and high throughputCompound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAnalyte
A method or platform for monoclonal antibody based biomarker discovery is disclosed. The method according to the invention provides for the integration of analyte collection, hybridoma screening and nanovolume integrated mass spectrometry (NVIMS) to achieve a robust screening system that is capable, for example, of cutting 4-6 years off of the classical biomarker discovery and development process. The invention provides a platform for the rapid, high-throughput production, isolation and characterization of, e.g., disease specific biomarkers together with highly specific monoclonal antibodies. The method of the invention has a variety of applications such as, but not limited to, drug testing, biohazard applications, ecological applications, physiological applications and / or pathology screening applications. The method of the invention is also capable of being performed or used as or with a high-throughput screening process or system of the invention.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Extracting method of extracellular vesicles and kit
PendingCN109825472ALow costIncrease throughputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellular vesicleBasic research
The invention relates to the technical field of biological separation and extraction, in particular to an extracting method of extracellular vesicles. The method comprises the steps that a biologicalsample is provided; the biological sample is in contact with a capturing surface at least twice on the condition that impurities in the biological sample are partially or wholly reserved on the capturing surface, wherein the impurities are partial or whole other substances except the extracellular vesicles in the biological sample, and the capturing surface comprises an inner surface and / or outersurface of a spherical-particle porous material; when the impurities are partially or wholly reserved on the surface of a capture, breakthrough liquid is extracted liquid containing the extracellularvesicles; or the breakthrough liquid is further concentrated. By means of the method, the epicyte vesicles can be quickly separated and purified, the separation operation is simple, the single use cost is low, the separated sample in high in purity, the bioactivity of the sample is kept good, and the extracting method is applied to fundamental research in the aspects of biomarker discovery, biotherapy and the like and industrial production.
Owner:易春 +2
Preparation method of saliva extracellular vesicles and application of saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis
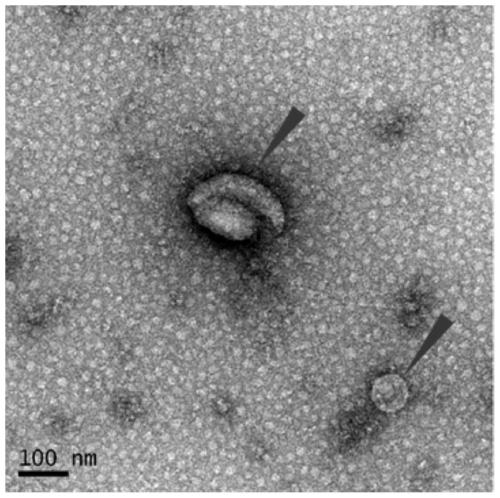
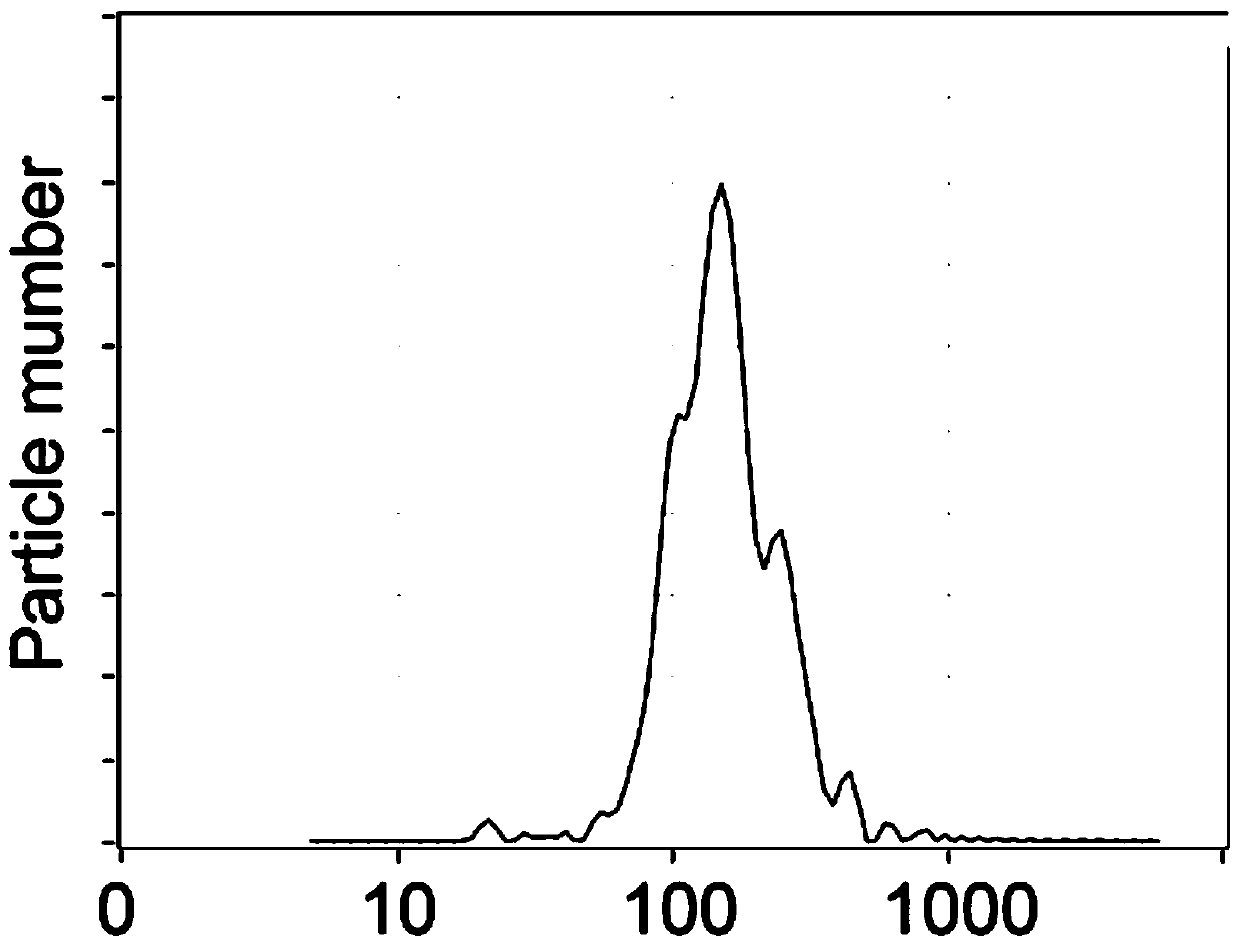
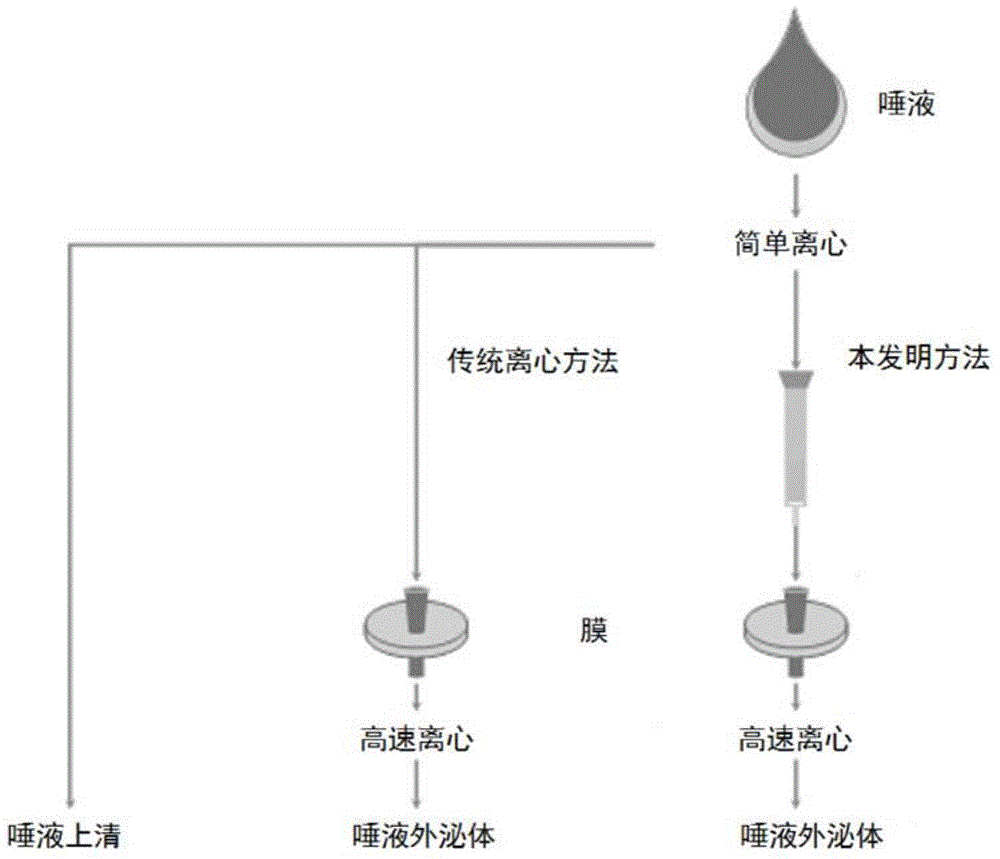
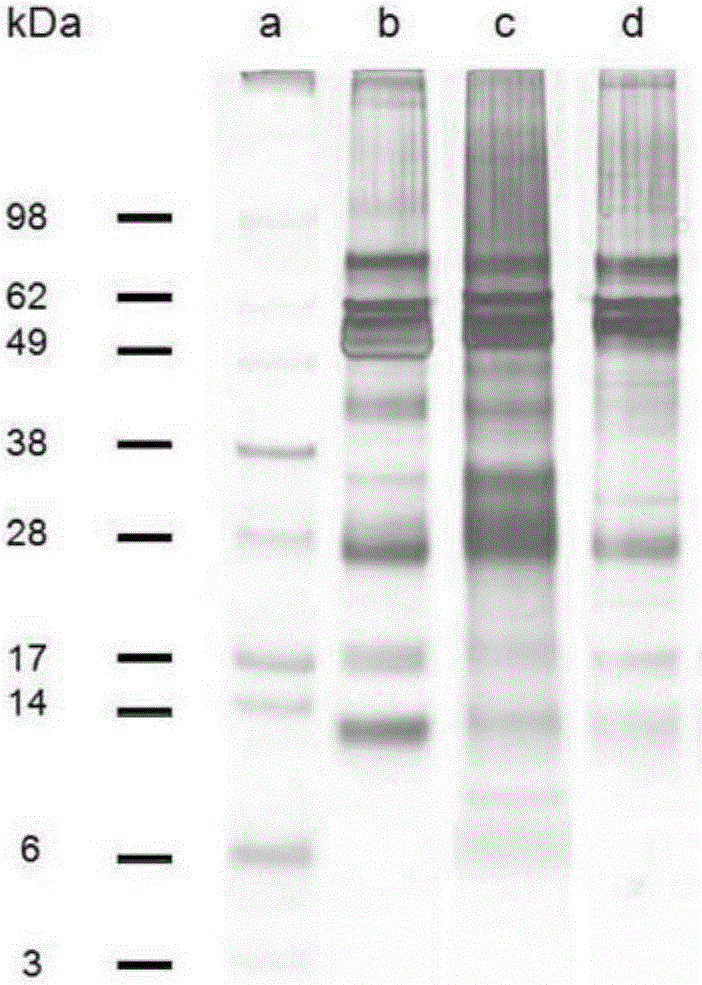
ActiveCN105675774AEasy to operateHigh recovery rateComponent separationSaliva sampleBiomarker discovery
The invention discloses a preparation method of saliva extracellular vesicles and application of the saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis.The preparation method includes the steps of removing high-abundance proteins from saliva samples, filtering out mucoproteins, separating and extracting the extracellular vesicles, characterizing the obtained extracellular vesicles, extracting extracellular vesicle proteins, identifying the extracellular vesicle proteins and applying the extracellular vesicle proteins to lung cancer biomarker discovery.Currently, a normalized saliva extracellular vesicle preparation technology is absent, and high-abundance protein interference and background impurity interference, existing in existing preparation technologies, result in shortcomings of low extracellular vesicle recovery rate, fewer identified proteins and the like, so that true extracellular vesicle proteomics information can be reflected difficultly.The preparation method of the saliva extracellular vesicles and application of the saliva extracellular vesicles to molecular diagnosis have the advantages that saliva of healthy adult volunteers and lung cancer patients is taken as the samples, and an affinity chromatography and membrane separation combined technology is adopted, so that after the high-abundance proteins and the mucoproteins of the saliva are removed, the extracellular vesicles in the saliva are extracted centrifugally, proteomes of the extracellular vesicles are analyzed and more extracellular vesicle proteins are identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device for sample collection
ActiveUS9442046B2Improve securityCell dissociation methodsWithdrawing sample devicesHazardous substanceBiomarker discovery
The disclosure relates to devices, solutions and methods for collecting and processing samples of bodily fluids containing cells (as well as embodiments for the collection, and processing and / or analysis of other fluids including toxic and / or hazardous substances / fluids). In addition, the disclosure relates generally to function genomic studies and to the isolation and preservation of cells from saliva and other bodily fluids (e.g., urine), for cellular analysis. With respect to devices for collection of bodily fluids, some embodiments include two mating bodies, a cap and a tube (for example), where, in some embodiments, the cap includes a closed interior space for holding a sample preservative solution and mates with the tube to constitute the (closed) sample collection device. Upon mating, the preservation solution flows into the closed interior space to preserve cells in the bodily fluid. The tube is configured to receive a donor sample of bodily fluid (e.g., saliva, urine), which can then be subjected to processing to extract a plurality of cells. The plurality of cells can be further processed to isolate one and / or another cell type therefrom. The plurality of cells, as well as the isolated cell type(s), can be analyzed for functional genomic and epigenetic studies, as well as biomarker discovery.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Computer based system for predicting treatment outcomes
InactiveUS20180039726A1Simple systemPotential for errorBiostatisticsSystems biologyPersonalizationComputerized system
Owner:NOVADISCOVERY
Marker for graft failure and mortality
ActiveUS20110171750A1Lower levelDisease diagnosisBiological testingOrgan transplantationMortality rate
Subject of the present invention is a biomarker for graft failure and / or mortality after organ transplantation. Procalcitonin was found to be a useful marker for the prediction or risk stratification for graft failure and / or mortality of a subject who has received an organ transplant and monitoring and therapy guidance of such subject.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Combinatorial multidomain mesoporous chips and a method for fractionation, stabilization, and storage of biomolecules
ActiveUS20110065207A1High protein recoveryLow protein amountElectrolysis componentsSamplingFractionationTherapeutic effect
A new fractionation device shows desirable features for exploratory screening and biomarker discovery. The constituent MSCs may be tailored for desired pore sizes and surface properties and for the sequestration and enrichment of extremely low abundant protein and peptides in desired ranges of the mass / charge spectrum. The MSCs are effective in yielding reproducible extracts from complex biological samples as small as 10 μl in a time as short as 30 minutes. They are inexpensive to manufacture, and allow for scaled up production to attain the simultaneous processing of a large number of samples. The MSCs are multiplexed, label-free diagnostic tools with the potential of biological recognition moiety modification for enhanced specificity. The MSCs may store, protect and stabilize biological fluids, enabling the simplified and cost-effective collection and transportation of clinical samples. The MSC-based device may serve as a diagnostic tool to complement histopathology, imaging, and other conventional clinical techniques. The MSCs mediated identification of disease-specific protein signatures may help in the selection of personalized therapeutic combinations, in the real-time assessment of therapeutic efficacy and toxicity, and in the rational modulation of therapy based on the changes in the protein networks associated with the prognosis and the drug resistance of the disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Analysis of transcriptomic data using similarity based modeling
ActiveUS8515680B2Small footprintFast data processingSugar derivativesDigital data processing detailsBiomarker discoveryModelling analysis
An analytic apparatus and method is provided for diagnosis, prognosis and biomarker discovery using transcriptome data such as mRNA expression levels from microarrays, proteomic data, and metabolomic data. The invention provides for model-based analysis, especially using kernel-based models, and more particularly similarity-based models. Model-derived residuals advantageously provide a unique new tool for insights into disease mechanisms. Localization of models provides for improved model efficacy. The invention is capable of extracting useful information heretofore unavailable by other methods, relating to dynamics in cellular gene regulation, regulatory networks, biological pathways and metabolism.
Owner:PROLAIO INC
Aptamer-based methods for identifying cellular biomarkers
InactiveUS20110124015A1Easy to fixEasy to synthesizeElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesBiotin-streptavidin complexAptamer
Owner:TAN WEIHONG +1
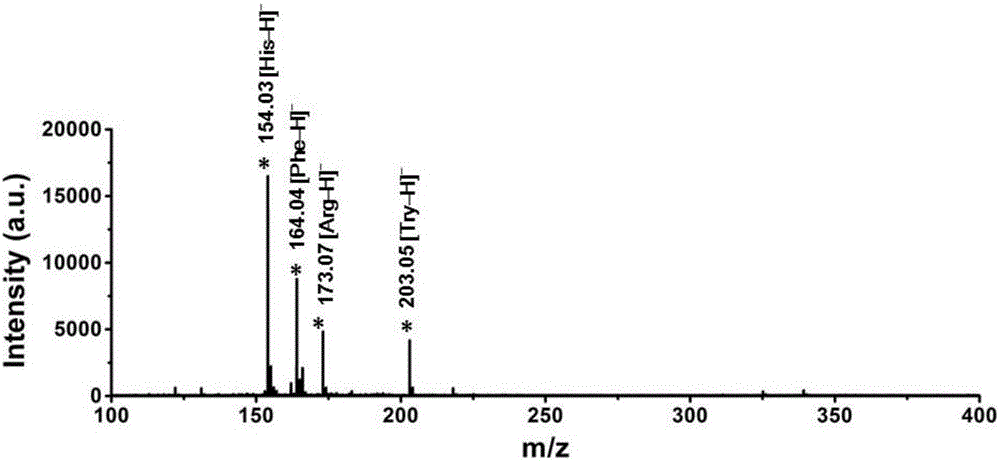
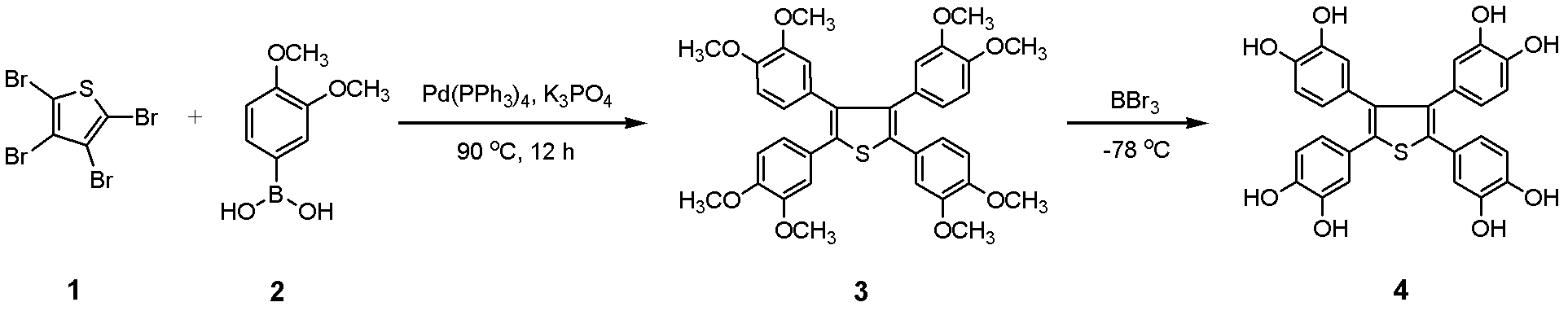
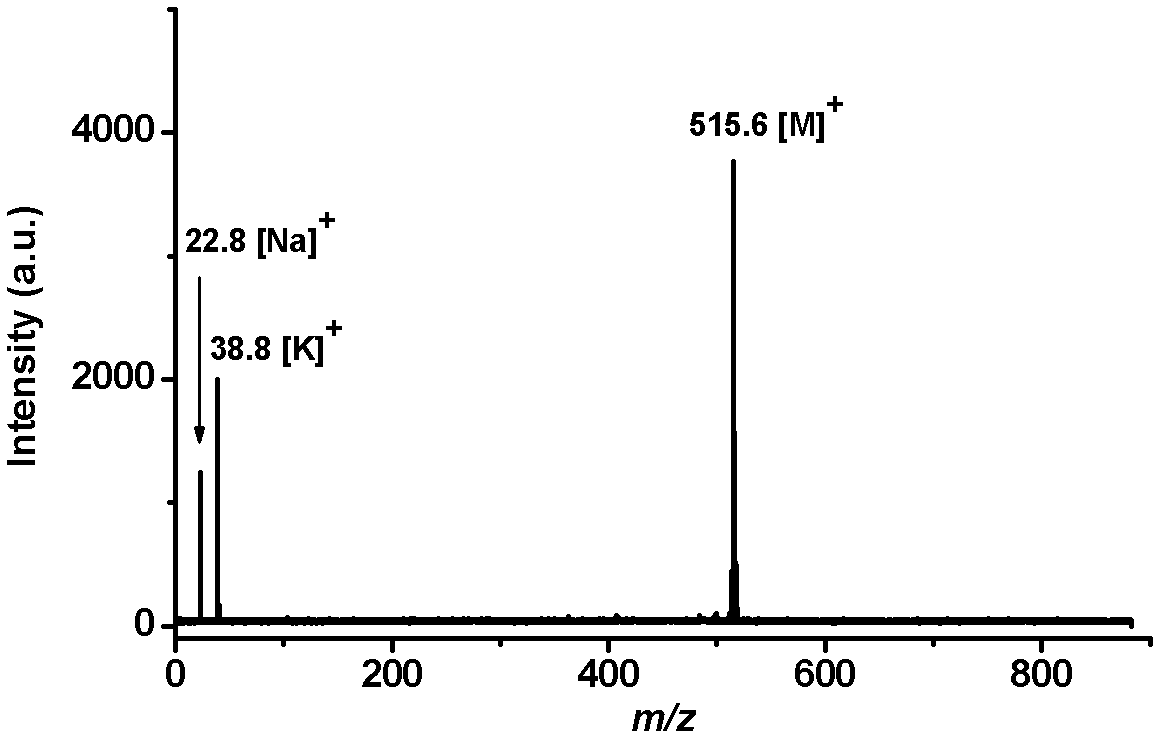
2,3,4,5,-tetra(3',4'-dihydroxyl phenyl)thiophene and application thereof as MALDI (matrix assisted laser desorption ionization) matrix in analyzing small molecules
ActiveCN102603707ANo background distractionsOvercoming the inability to efficiently analyze small molecule samplesOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectroscopyPurine
The invention discloses 2,3,4,5,-tetra(3',4'-dihydroxyl phenyl)thiophene and application of 2,3,4,5,-tetra(3',4'-dihydroxyl phenyl)thiophene as an MALDI (matrix assisted laser desorption ionization) matrix in analyzing small molecules. The analysis method using 2,3,4,5,-tetra(3',4'-dihydroxyl phenyl)thiophene as the MALDI matrix is suitable for performing mass spectrum analysis on the small molecules with m / z being less than 1000. And adaptive molecule varieties comprise amine matters such as amino acids, vitamins, excitants, caffeine, urea, dopamine, melamine, aniline, purines and pyrimidines, etc., wherein background interference is not produced because of only a few fixed background peaks when the method is used for detecting the molecules with m / z being less than 1000. The method for preparing 2,3,4,5,-tetra(3',4'-dihydroxyl phenyl)thiophene provided by the invention can be effectively applied to fields such as the organic and biological mass spectrum, the mass spectrum imaging, the protein spectroscopy, the metabonomics, the biomarker discovery, the environment analysis and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
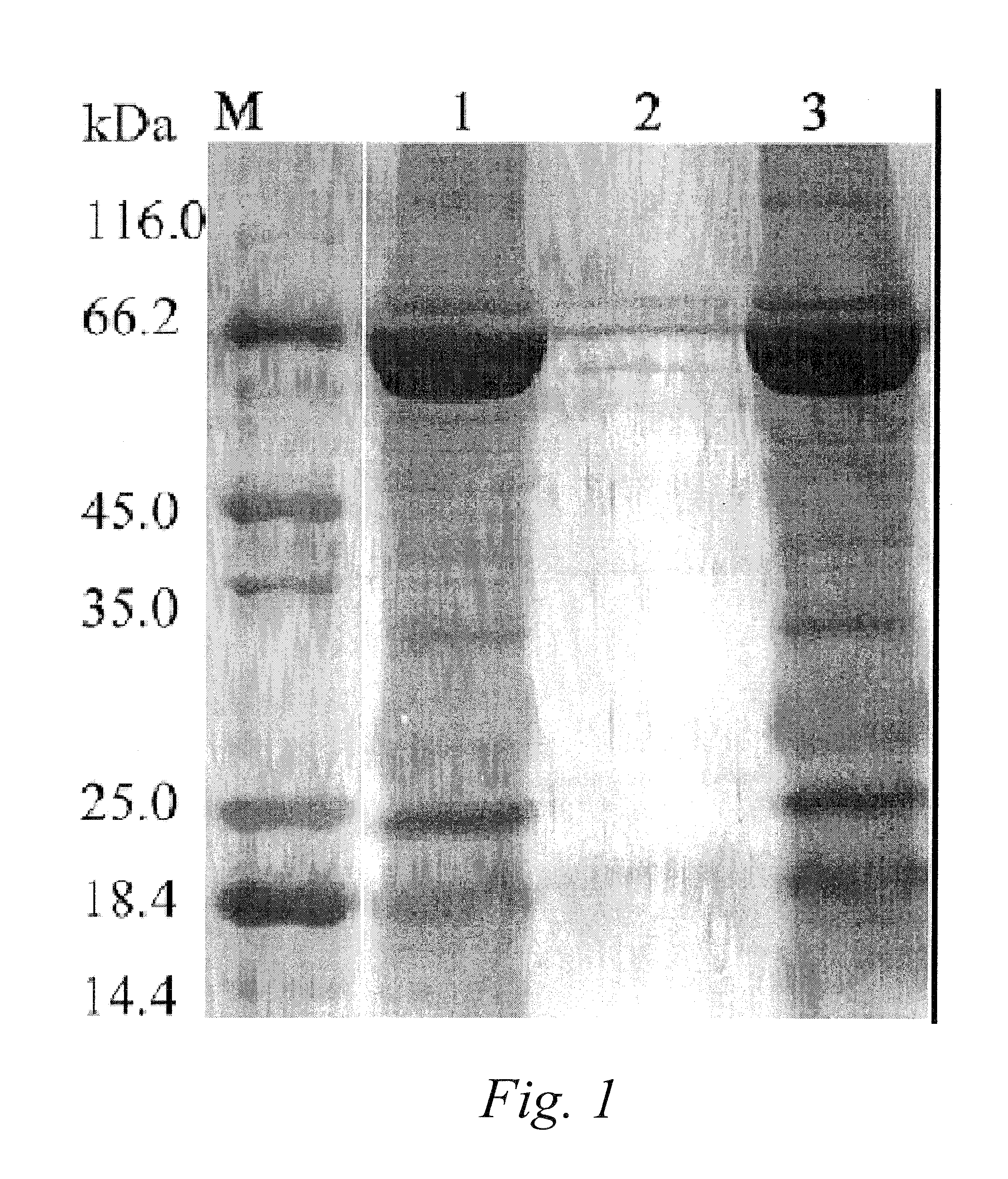
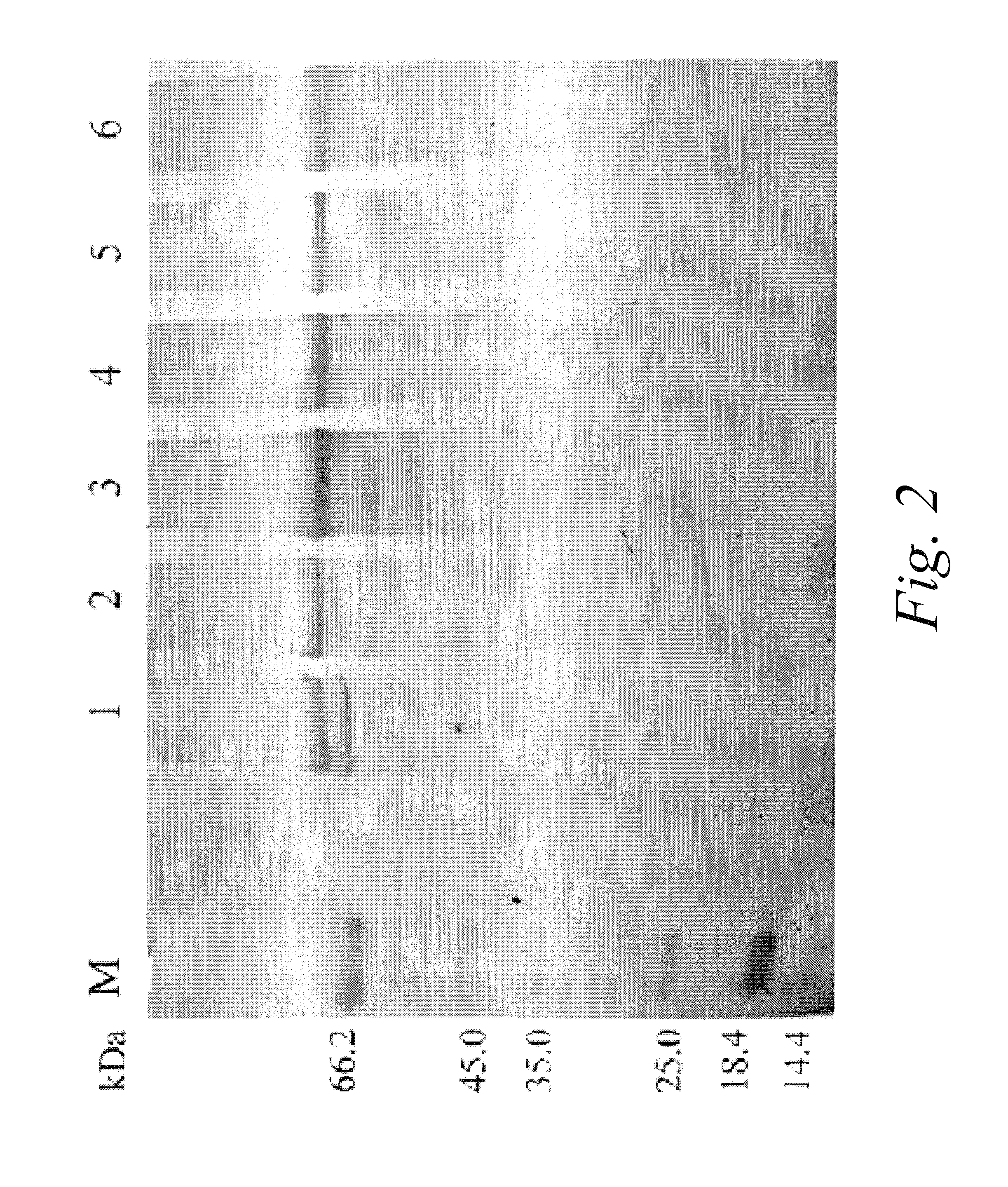
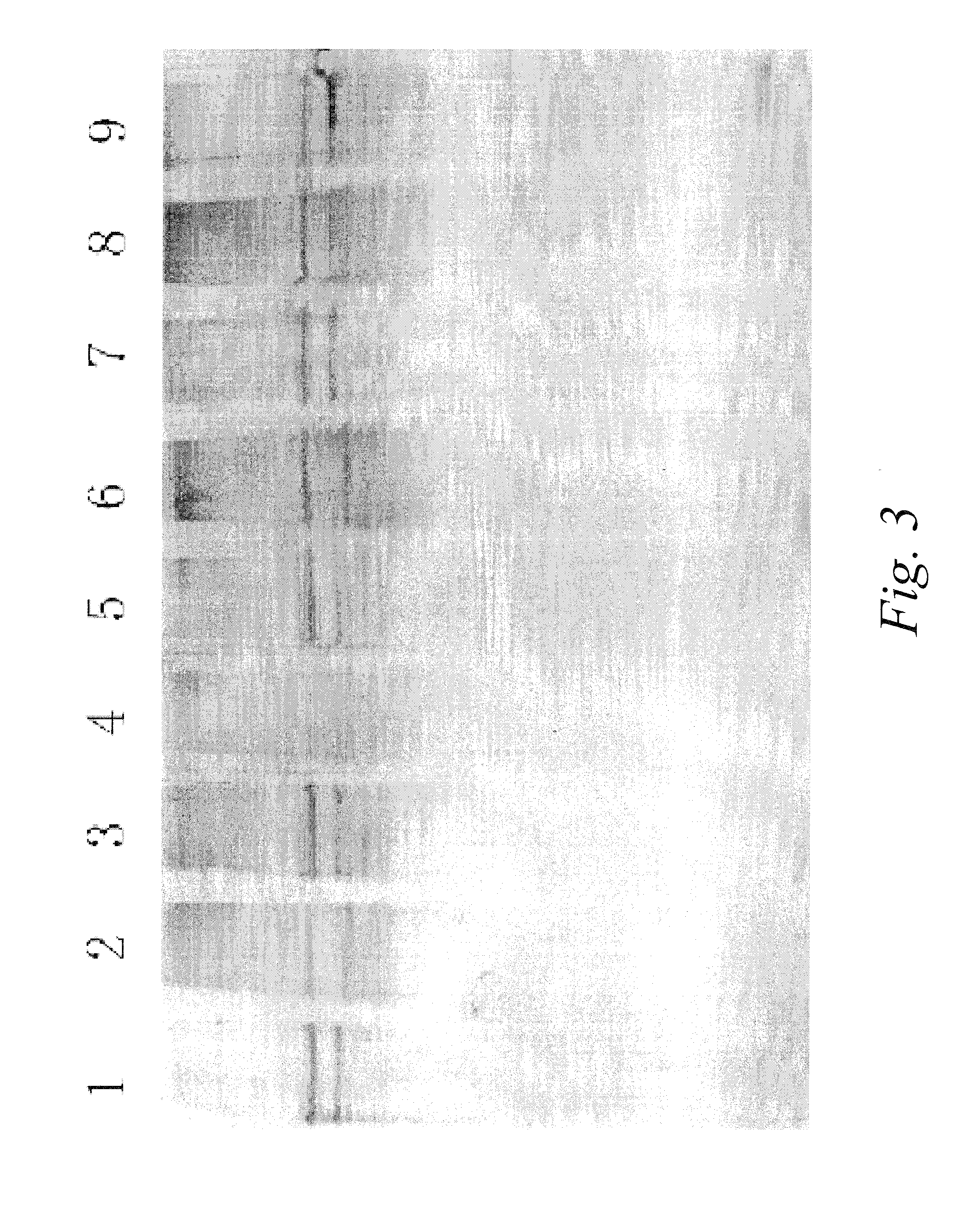
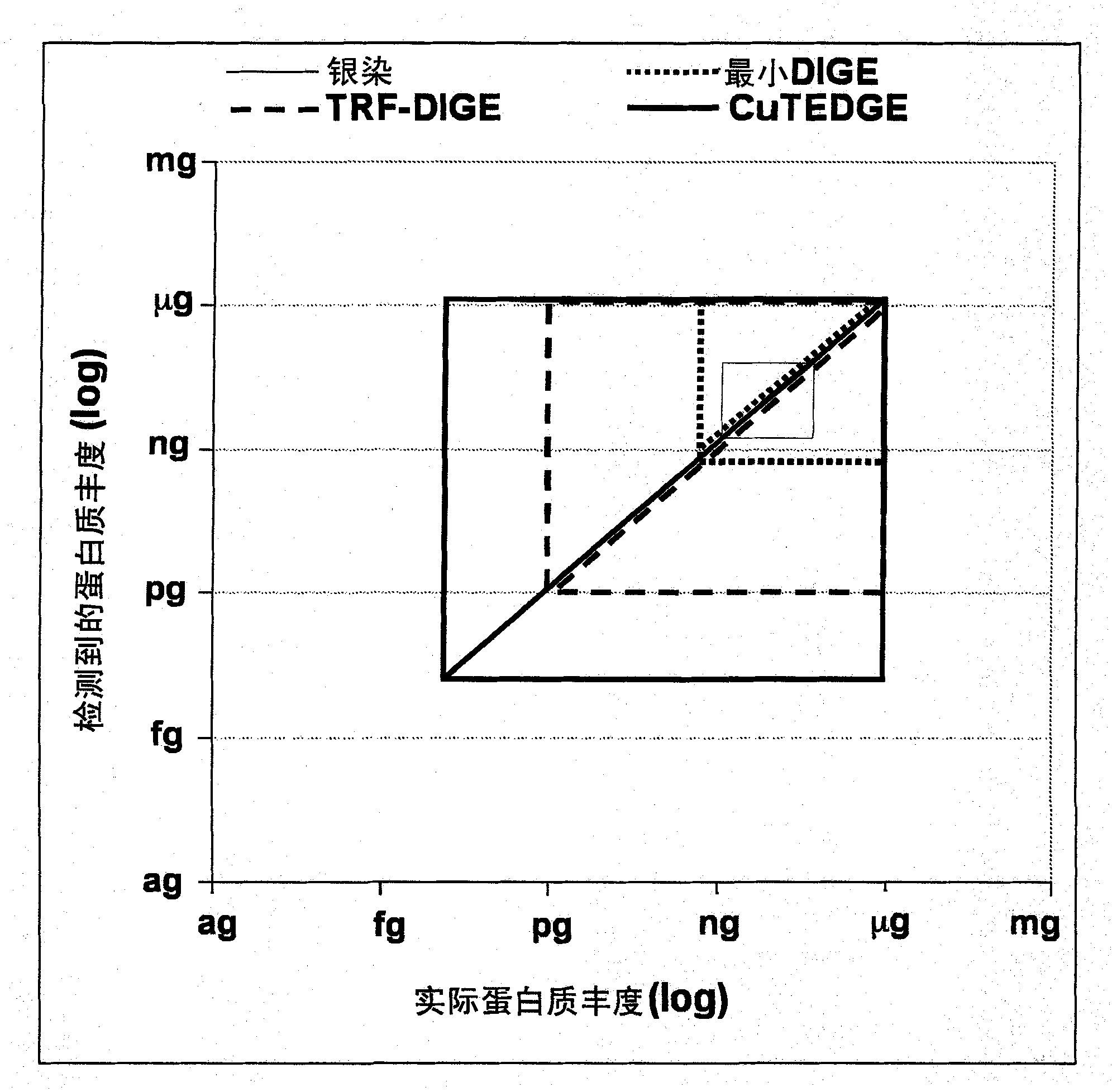
Cumulative time-resolved emission two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
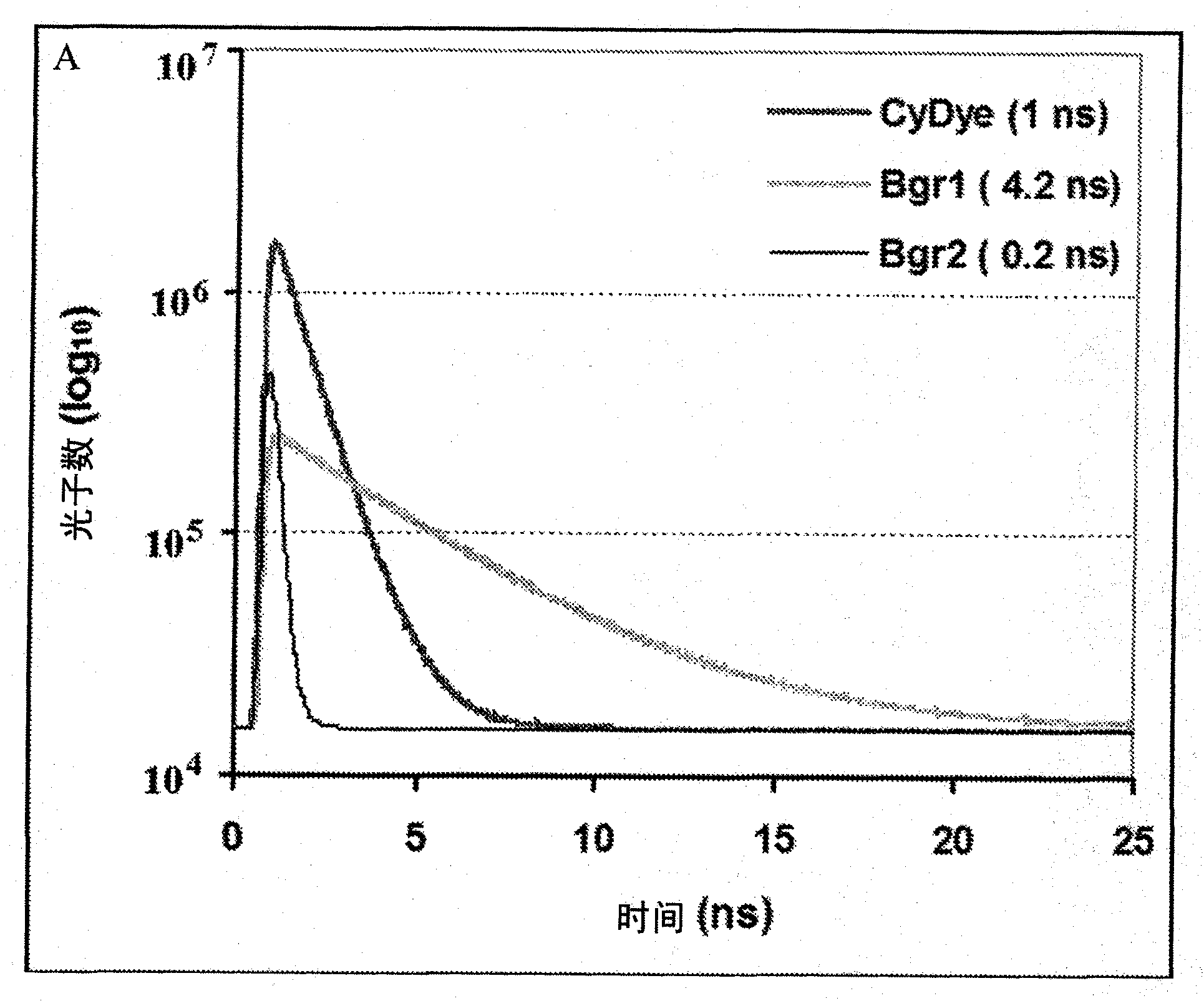
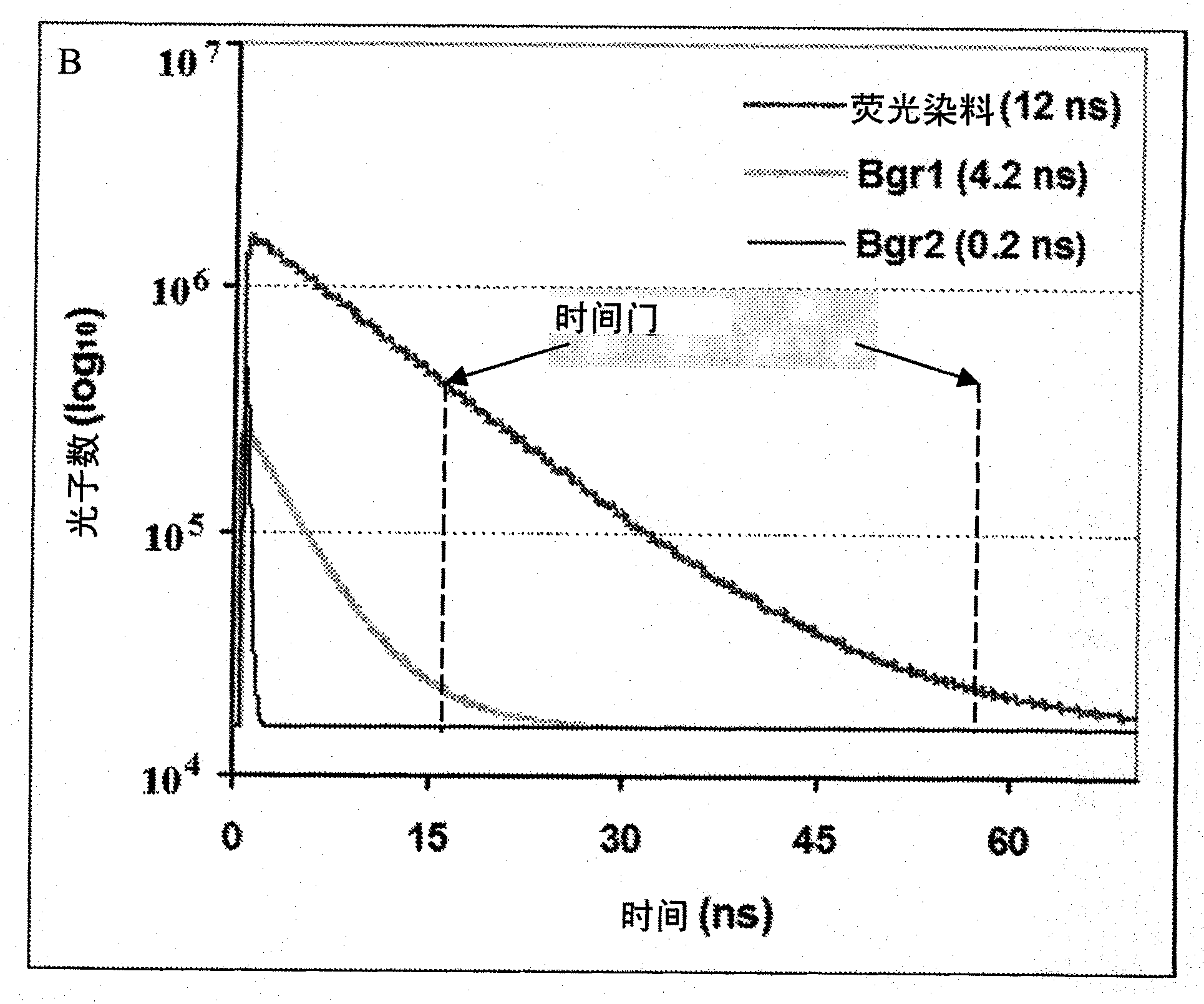
ActiveUS20090316992A1Increased experimental varianceReduce needMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansProtein detectionBiomarker discovery
A new instrumental design is provided for in-gel detection and quantification of proteins. This new platform, called Cumulative Time-resolved Emission 2-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis, utilizes differences in fluorescent lifetime imaging to differentiate between fluorescence from specific protein labels and non-specific background fluorescence, resulting in a drastic improvement in both sensitivity and dynamic range compared to existing technology. The platform is primarily for image acquisition of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, but is also applicable to protein detection in one-dimensional gel systems as well as proteins electroblotted to e.g. PVDF membranes. Given the increase in sensitivity of detection and dynamic range of up to 5-6 orders of magnitude compared to existing approaches, the described invention represents a technological leap in the detection of low abundance cellular proteins, which is desperately needed in the field of biomarker discovery.
Owner:HIKARI BIO AB
Process for differential polypeptides detection and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110020836A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineTest sample
Provided herein is an affinity media and the construction and use thereof. The affinity media may be used, for example, for the detection of differential proteins / peptides by depletion of proteins / peptides similar to those in a control sample from a test sample in the search for biologically and pathologically important proteins / peptides. The detected differential proteins / peptides provide vital information for biomarker discovery, drug target discovery, and personalized medicine and treatment.
Owner:LI RONGXIU
Cumulative time-resolved emission two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
ActiveCN102037352AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansProtein detectionBiomarker discovery
A new instrumental design is provided for in-gel detection and quantification of proteins. This new platform, called Cumulative Time-resolved Emission 2-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis, utilizes differences in fluorescent lifetime imaging to differentiate between fluorescence from specific protein labels and non-specific background fluorescence, resulting in a drastic improvement in both sensitivity and dynamic range compared to existing technology. The platform is primarily for image acquisition of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, but is also applicable to protein detection in one-dimensional gel systems as well as proteins electroblotted to e.g. PVDF membranes. Given the increase in sensitivity of detection and dynamic range of up to 5-6 orders of magnitude compared to existing approaches, the described invention represents a technological leap in the detection of low abundance cellular proteins, which is desperately needed in the field of biomarker discovery.
Owner:HIKARI BIO AB
Combinatorial multidomain mesoporous chips and a method for fractionation, stabilization, and storage of biomolecules
A new fractionation device shows desirable features for exploratory screening and biomarker discovery. The constituent MSCs may be tailored for desired pore sizes and surface properties and for the sequestration and enrichment of extremely low abundant protein and peptides in desired ranges of the mass / charge spectrum. The MSCs are effective in yielding reproducible extracts from complex biological samples as small as 10 μl in a time as short as 30 minutes. They are inexpensive to manufacture, and allow for scaled up production to attain the simultaneous processing of a large number of samples. The MSCs are multiplexed, label-free diagnostic tools with the potential of biological recognition moiety modification for enhanced specificity. The MSCs may store, protect and stabilize biological fluids, enabling the simplified and cost-effective collection and transportation of clinical samples. The MSC-based device may serve as a diagnostic tool to complement histopathology, imaging, and other conventional clinical techniques. The MSCs mediated identification of disease-specific protein signatures may help in the selection of personalized therapeutic combinations, in the real-time assessment of therapeutic efficacy and toxicity, and in the rational modulation of therapy based on the changes in the protein networks associated with the prognosis and the drug resistance of the disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
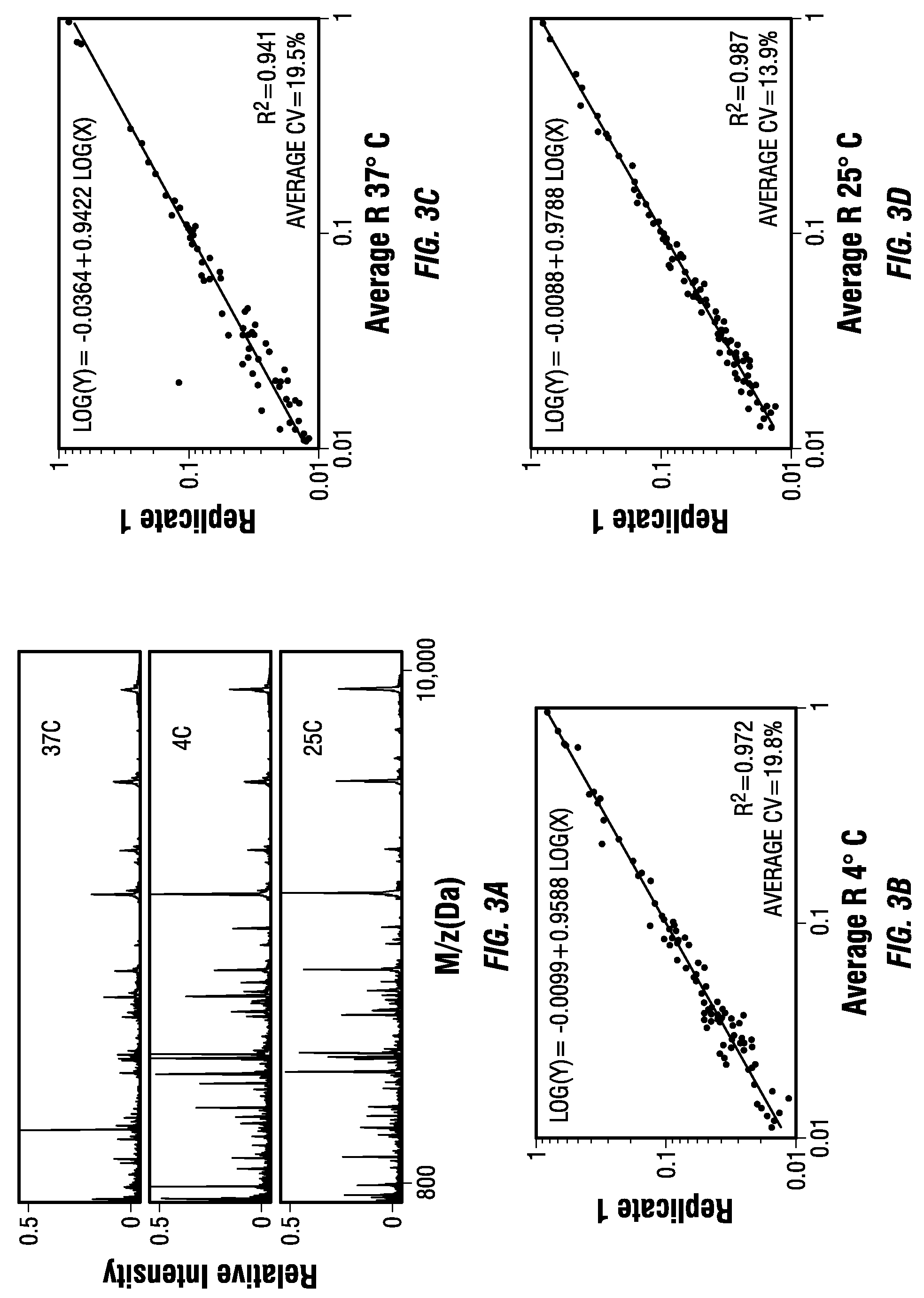
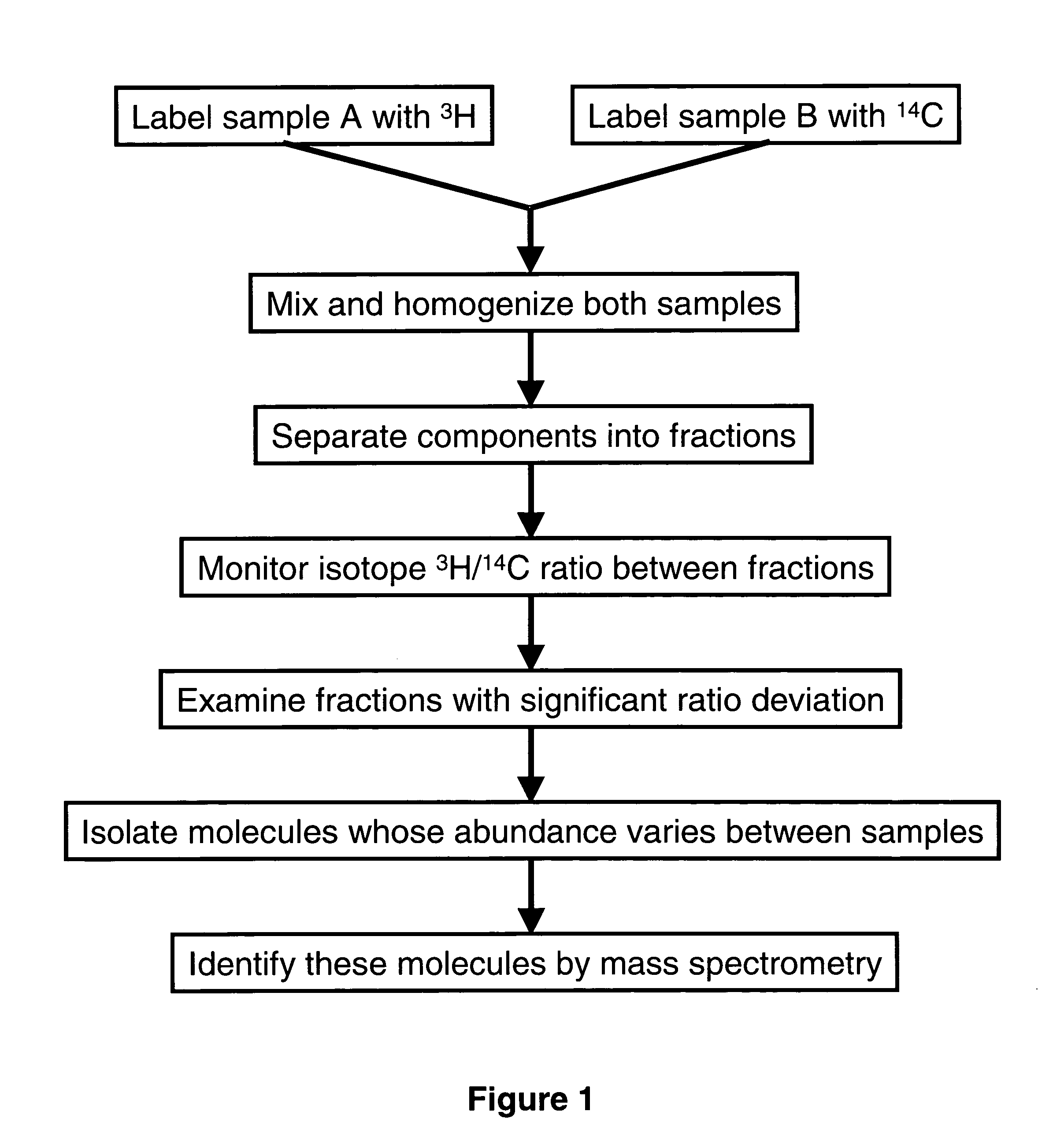
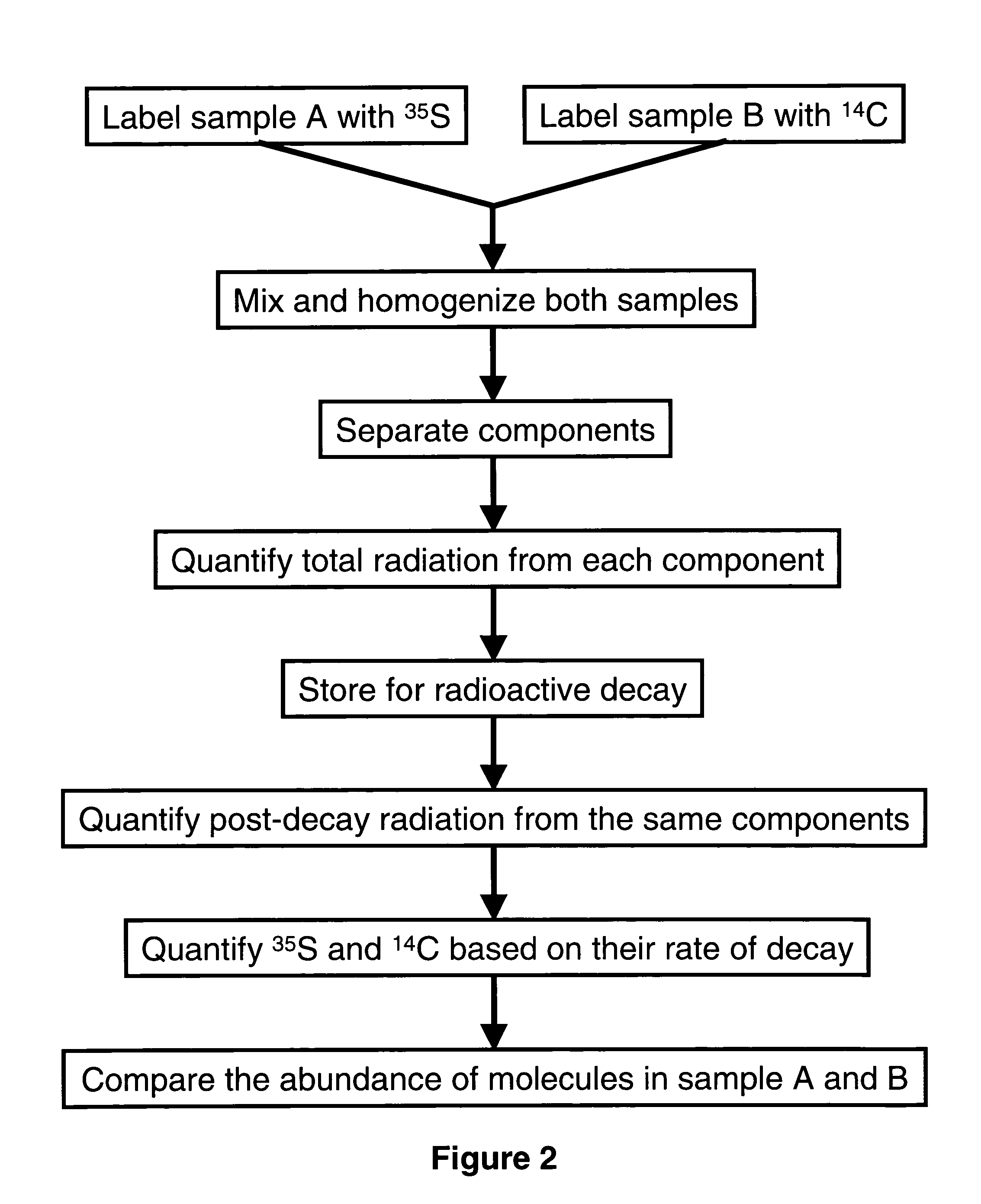
Radioactive multiplexing analytical methods for biomarkers discovery
ActiveUS20060084065A1Low costShorten the timeComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsHalf-life
A novel analytical method involves labeling samples with different radioactive labeling agents, mixing and subjecting the mixture to any separation technique, and then differentially detecting and quantifying subcomponents from each sample for comparison. The novel technique exploits the differences in radiation energy or half-life between isotopes to make differential detection and quantification of labels possible. Detailed methods for differential detection and quantification are also described as well as the construction and application of hardware and software to enable and enhance such a process. This method is useful in finding molecular differences between two samples in differential proteomics, phosphor-proteomics, glycomics, metabolomics, transcriptomics, genomics and diagnostic applications.
Owner:PROTEOMYX
Method of cancer diagnosis, progression and response to therapy using a primary xenograft mouse model for cancer serum biomarker discovery
A method of determining disease diagnosis, progression and response to therapy through the use of xenograft animal models for determining cancer biomarkers is presented. In use, a tumor from a patient is transplanted into an animal model such as a mouse. Expression levels of biomarkers for a disease are assessed in the serum of the animal model. A personalized gene expression profile or biomarker gene signature may be obtained from the expression levels of the biomarkers which can be used to determine disease recurrence, progression and response to therapy.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
A mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and uses thereof
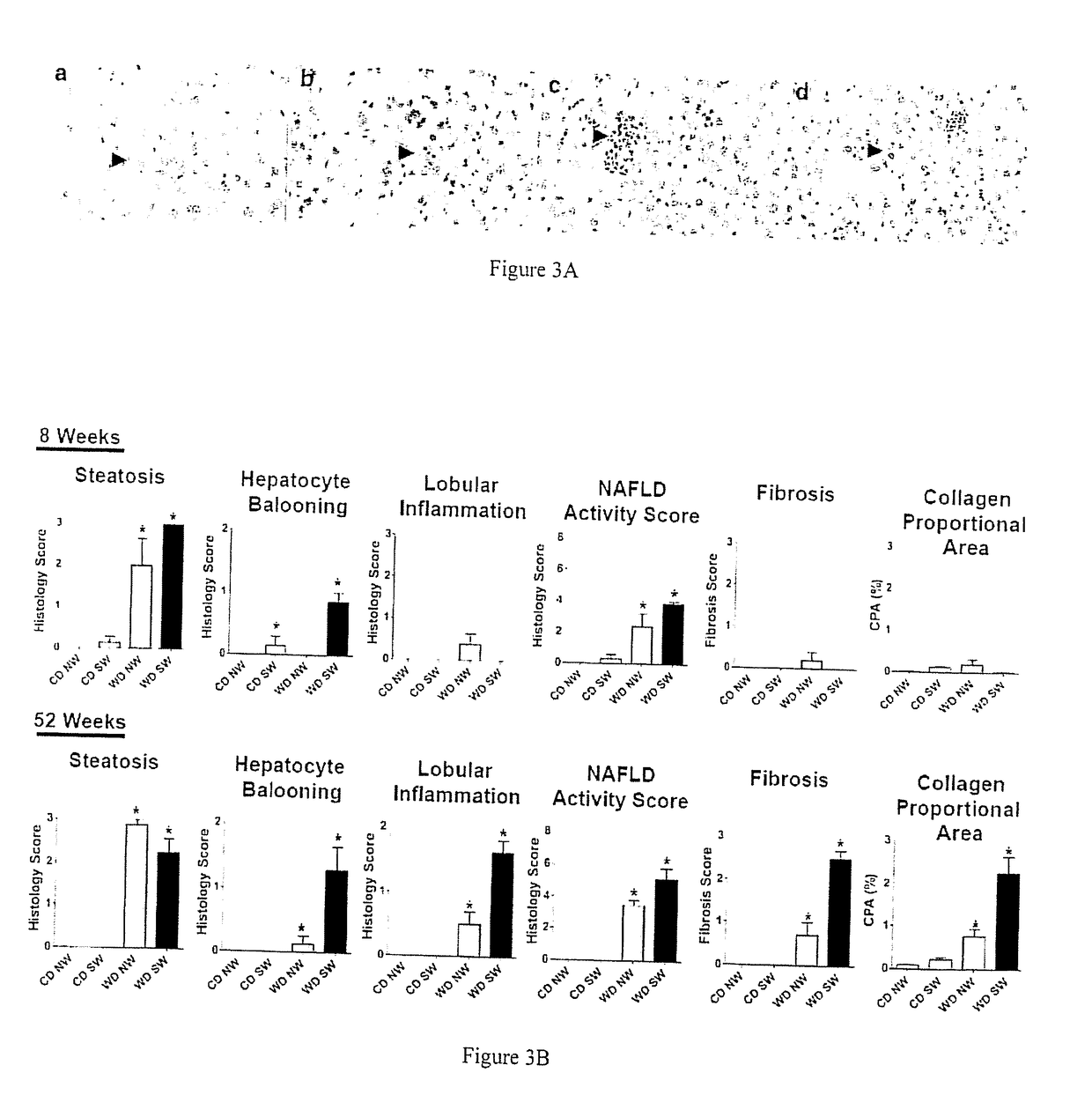
An isogenic murine animal model for liver disease resulting from a Western (high fat, high sugar) diet is provided. This phenotypically and genotypically stable model sequentially develops steatosis (4-8 weeks), steatohepatitis (12-16 weeks), progressive fibrosis (16 week onwards) and spontaneous HCC (32-52 weeks), but only when fed a diet high in fat and sugar. The mice also develop obesity, insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, and the mouse hepatic transcriptome is concordant with the human NASH transcriptome at early and late time points, including activation of lipogenic, inflammatory and apoptotic signaling. The mouse HCC gene signature resembles S1 and S2 human HCC subclasses. This simple model of NASH and HCC that mirrors the development of human disease in terms of its triggers, serology, phenotype, histology, transcriptome and outcomes has utility in new target discovery, biomarker discovery, diagnostic test development, and screening and development of drugs for the corresponding liver conditions.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Method of cancer diagnosis, progression and response to therapy using a primary xenograft mouse model for cancer serum biomarker discovery
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com