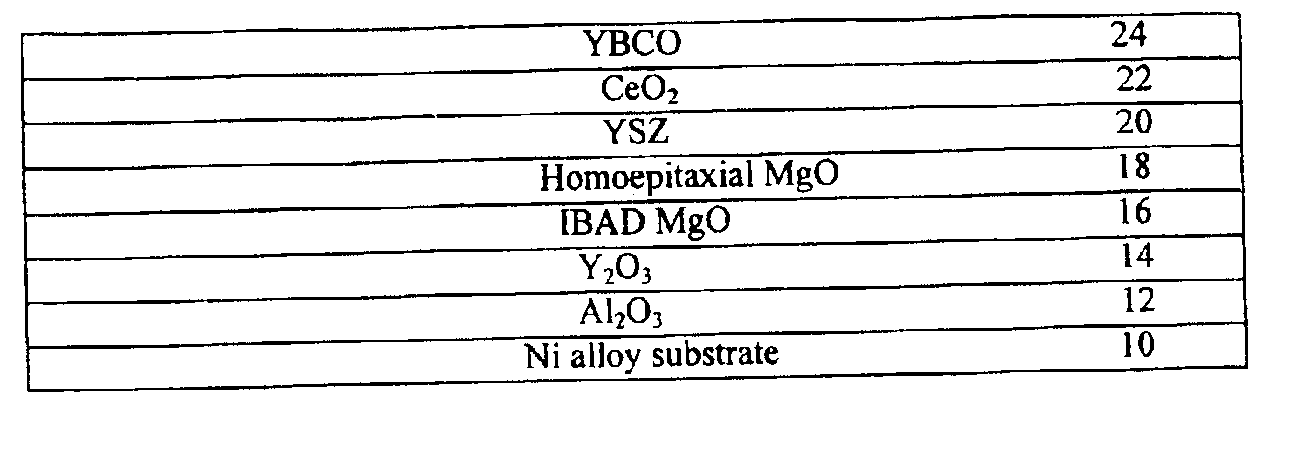Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
844 results about "High-temperature superconductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-Tc or HTS) are materials that behave as superconductors at unusually high temperatures. The first high-Tc superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller, who were awarded the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials".
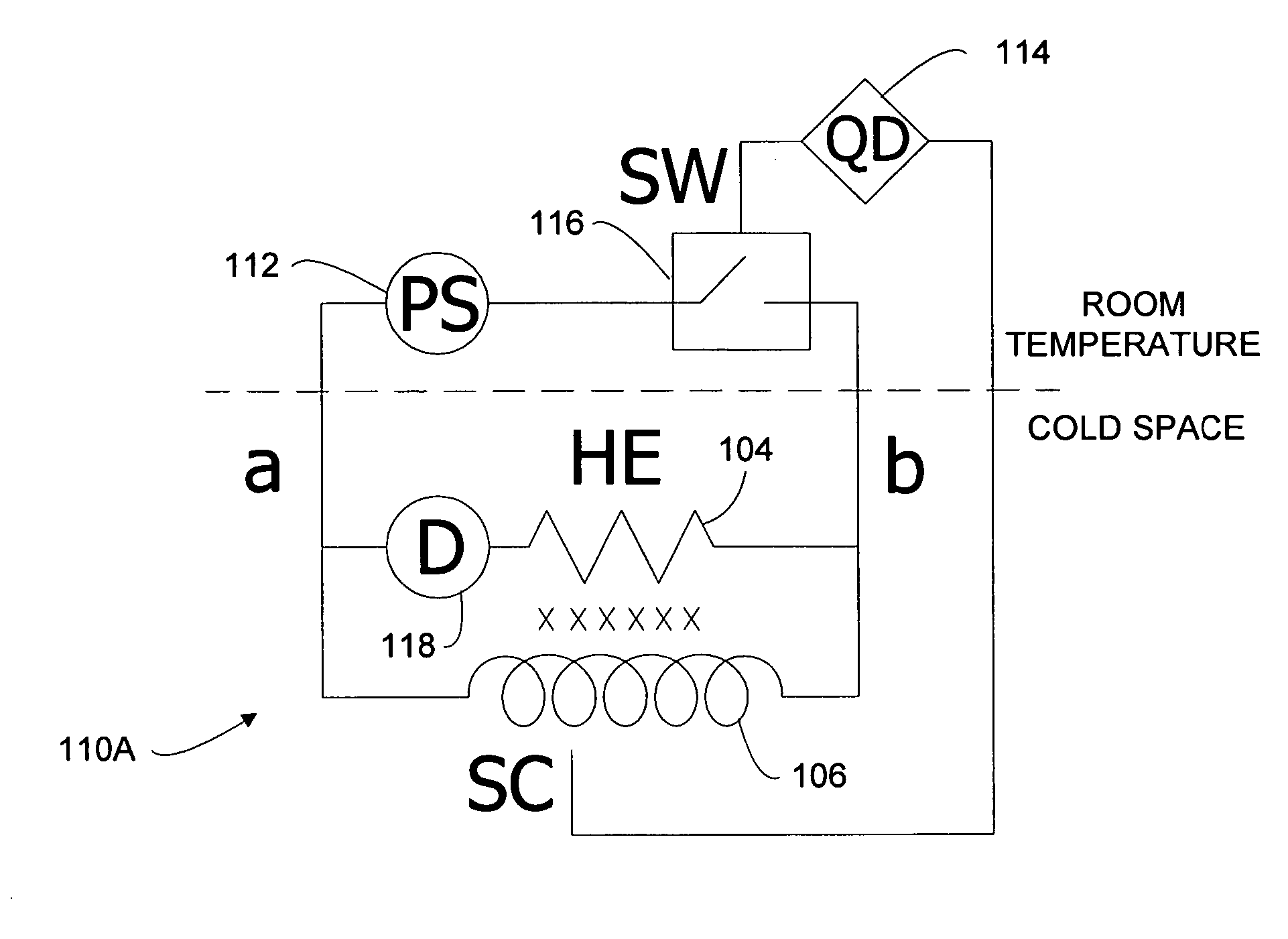
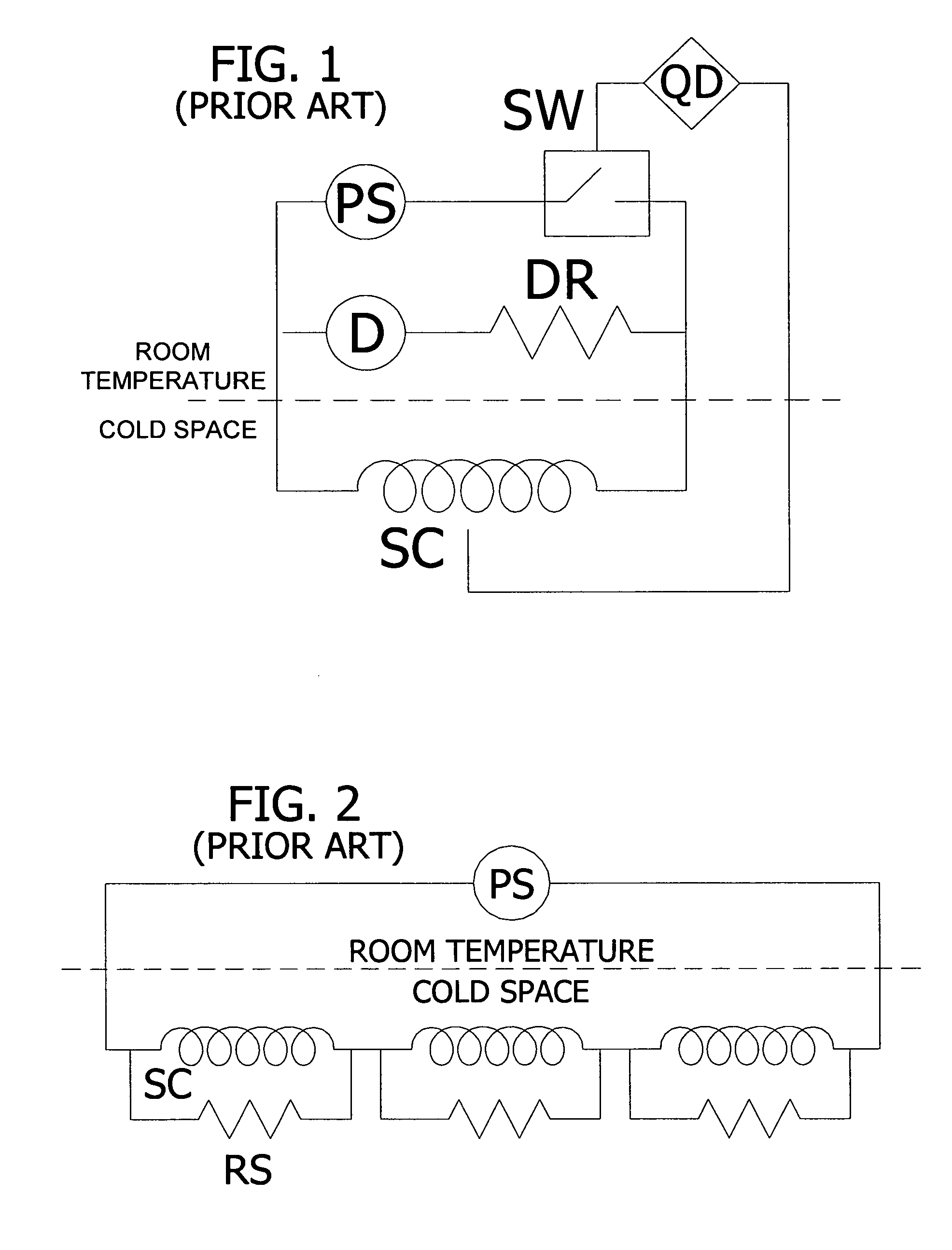
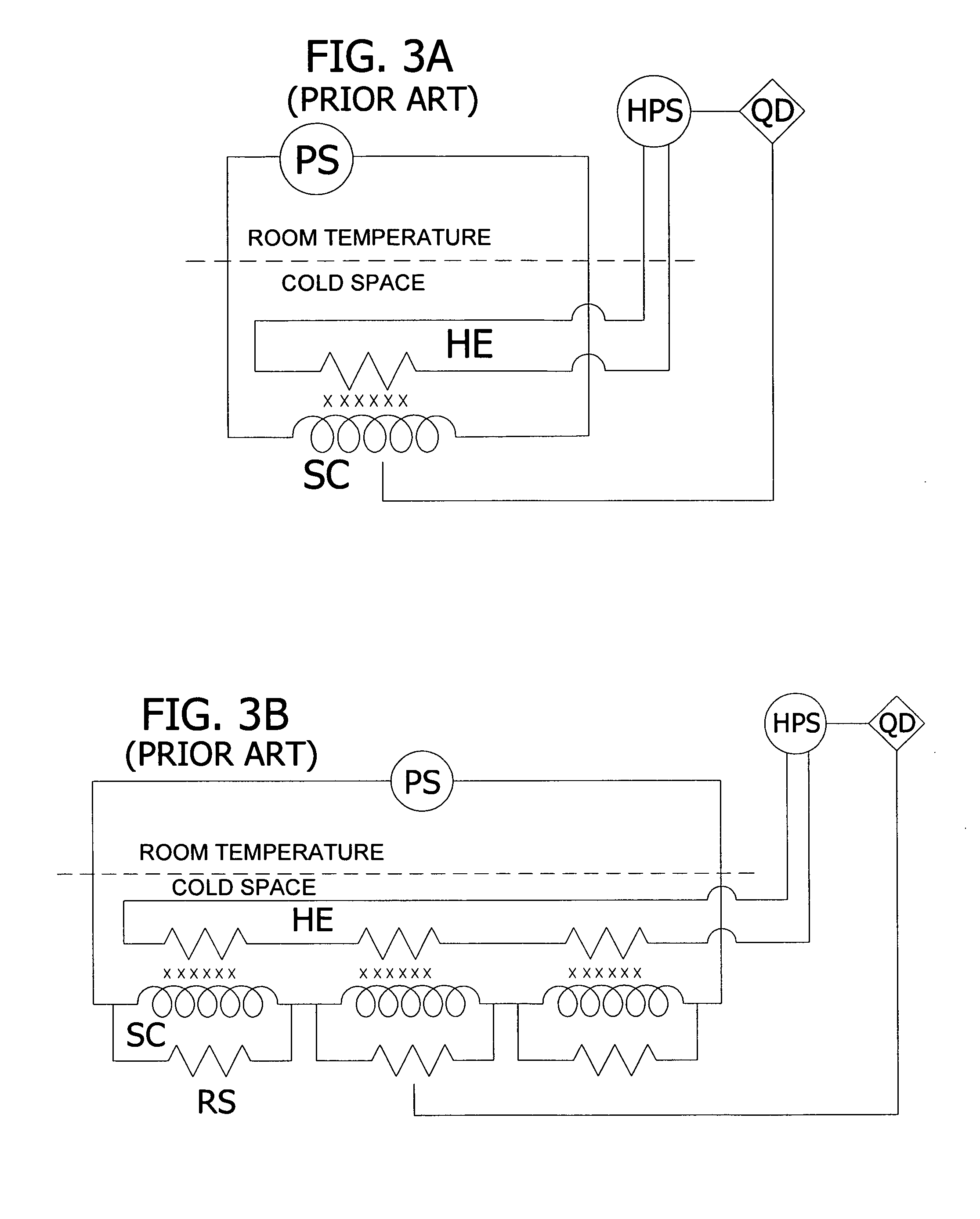
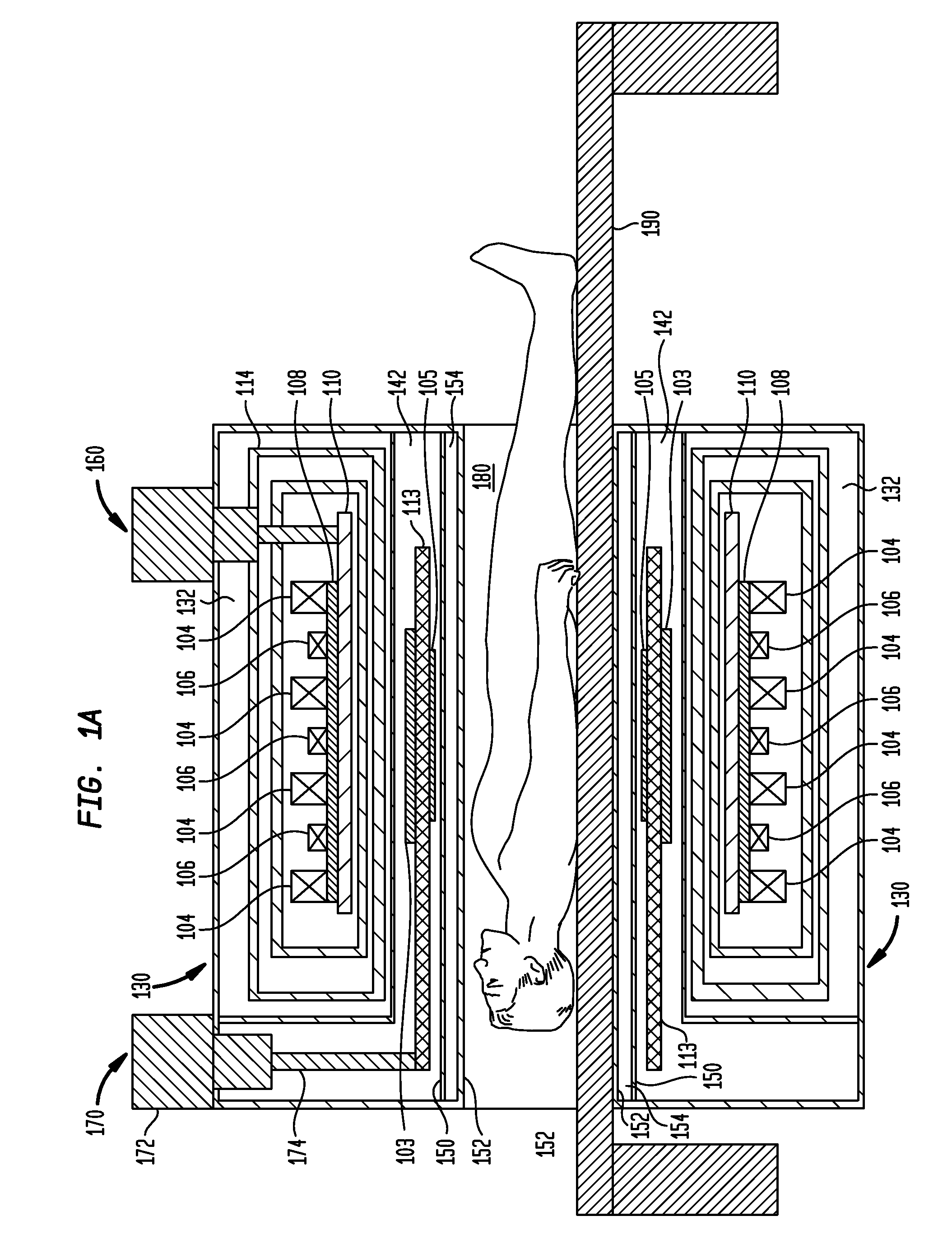
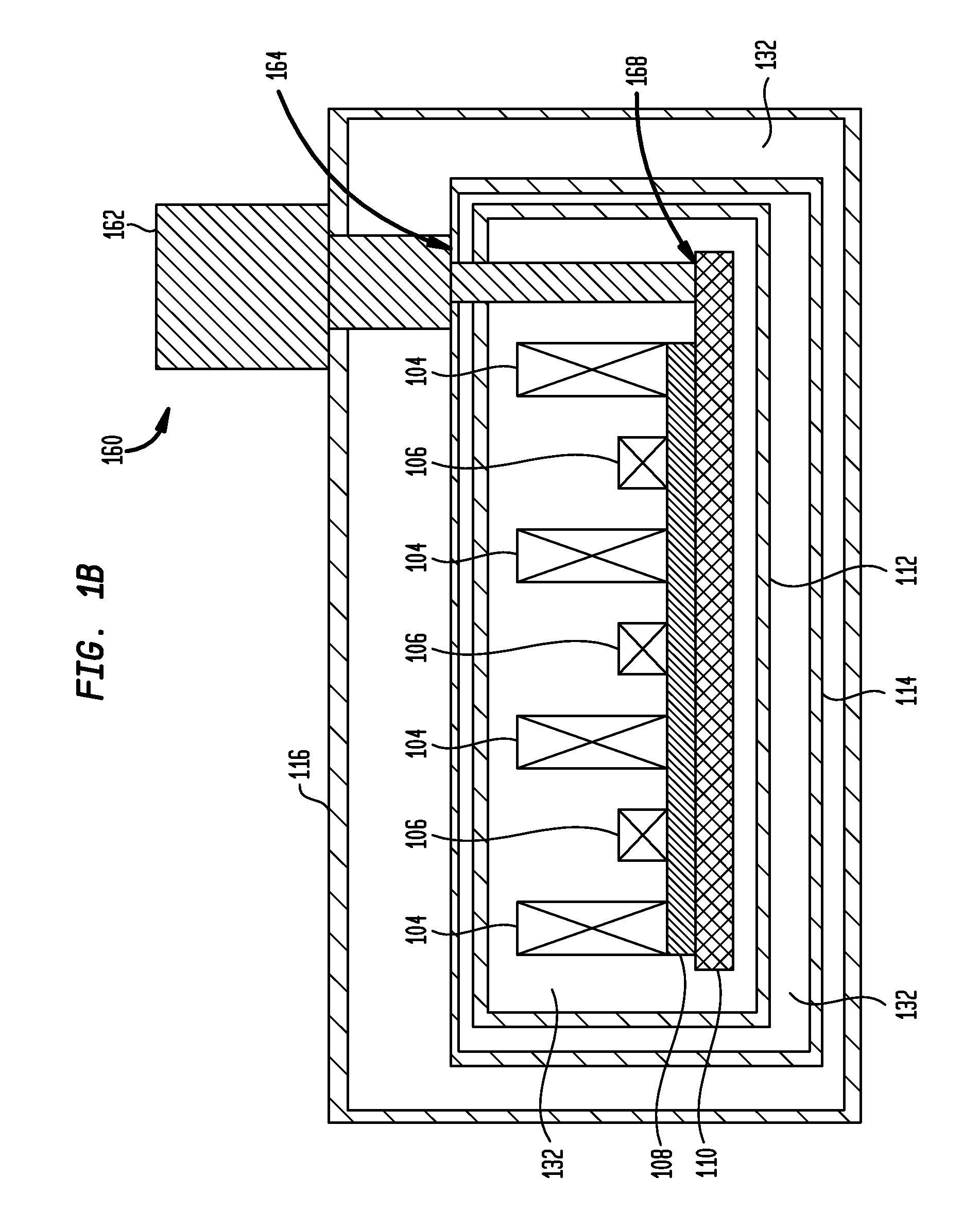
Quench protection of HTS superconducting magnets
InactiveUS20060291112A1Improved active protectionEffective quench protectionTransformers/inductances coolingSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh-temperature superconductivitySuperconducting Coils
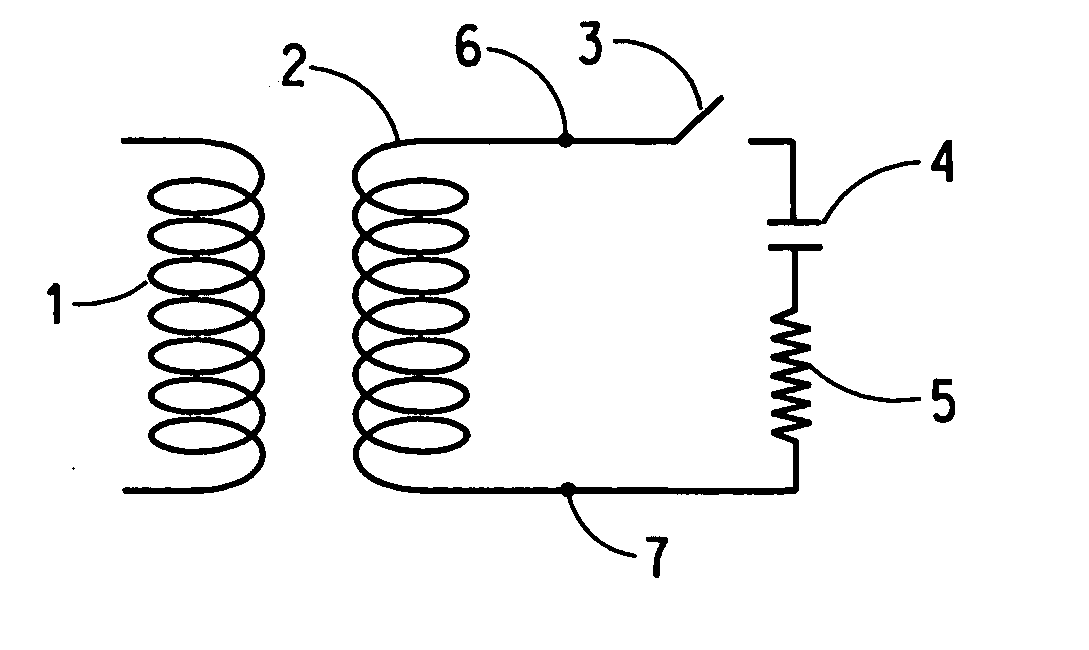
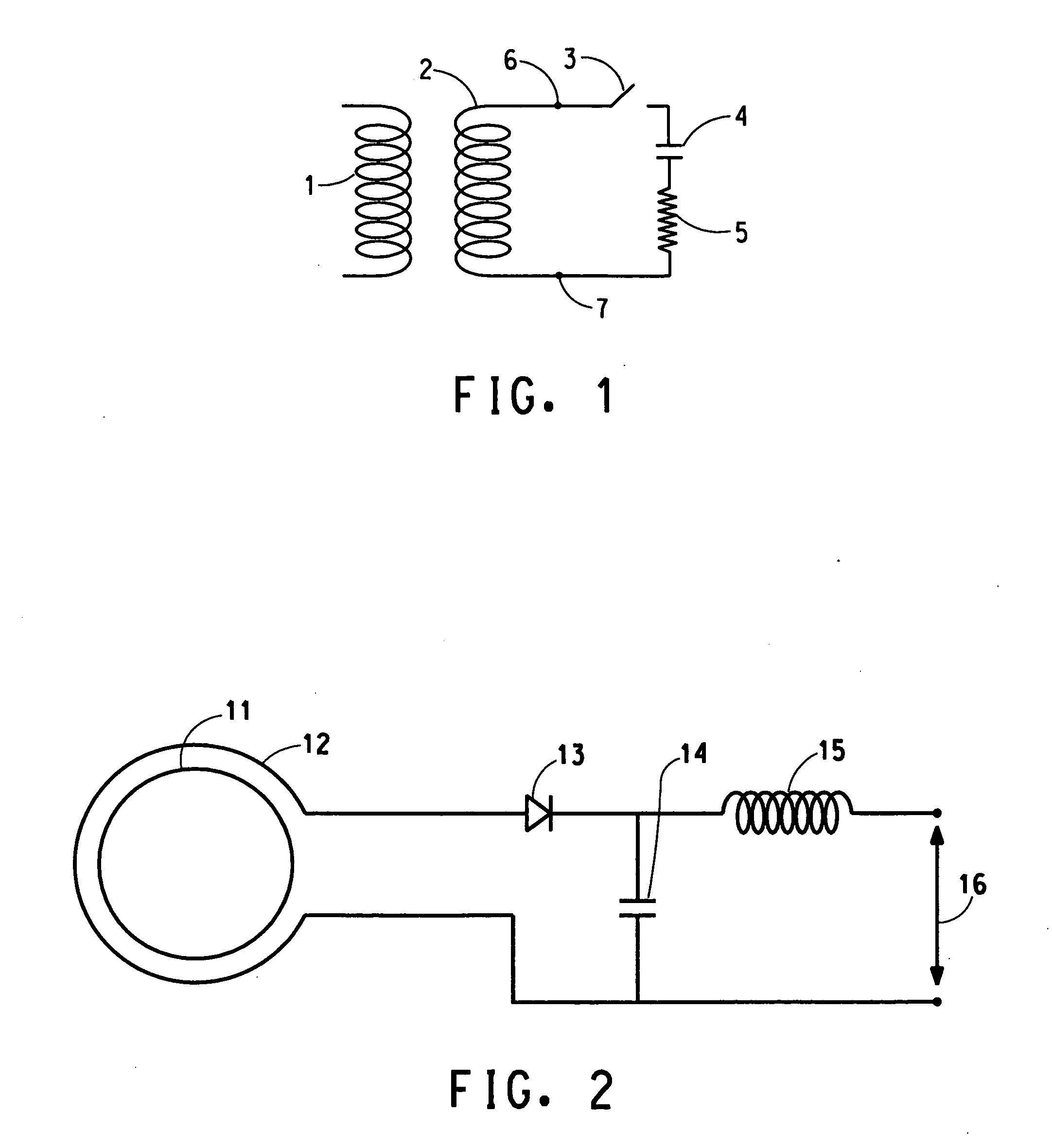
A method of constructing a superconducting coil. The method includes embedding a plurality of heater elements throughout a superconducting coil. The heater elements are positioned according to a predetermined distribution and substantially in thermal contact with the coil for heating the coil in response to a quench condition. Other aspects of the invention involve an active protection circuit and a high temperature superconductor magnet that includes such an active protection circuit for internally dissipating stored magnetic energy in the event of a quench.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
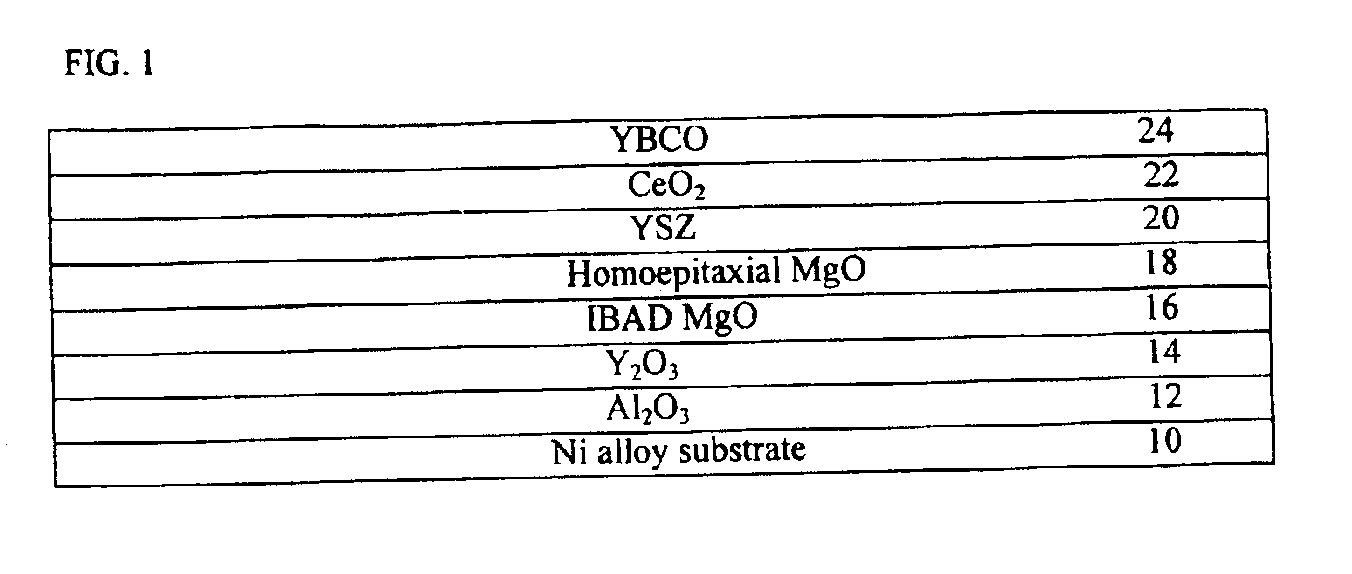
High temperature superconducting thick films
InactiveUS6933065B2Polycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHigh-temperature superconductivityNitrogen oxide
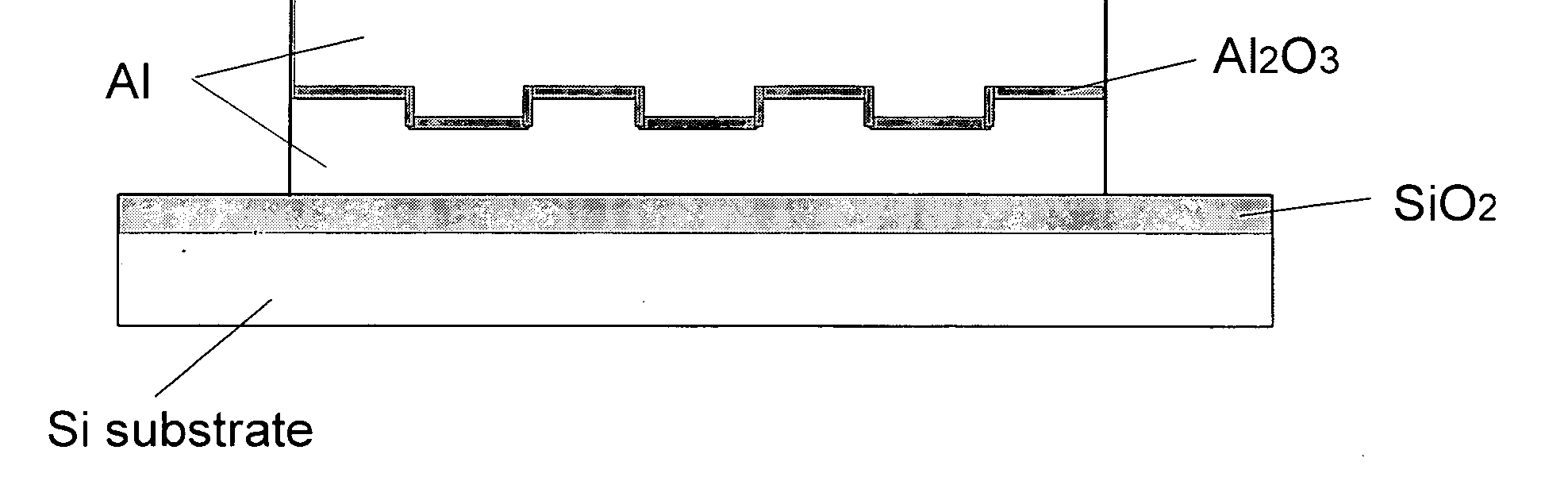
An article including a substrate, a layer of an inert oxide material upon the surface of the substrate, (generally the inert oxide material layer has a smooth surface, i.e., a RMS roughness of less than about 2 nm), a layer of an amorphous oxide or oxynitride material upon the inert oxide material layer, a layer of an oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure upon the amorphous oxide material layer is provided together with additional layers such as at least one layer of a buffer material upon the oriented cubic oxide material layer or a HTS top-layer of YBCO directly upon the oriented cubic oxide material layer. With a HTS top-layer of YBCO upon at least one layer of a buffer material in such an article, Jc's of 1.4×106 A / cm2 have been demonstrated with projected Ic's of 210 Amperes across a sample 1 cm wide.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method of forming a multifilament ac tolerant conductor with striated stabilizer, articles related to the same, and devices incorporating the same
ActiveUS20090131262A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Testing apparatus for high temperature, superconducting, magnetic suspension and dynamic performance and testing method with the same
InactiveCN1963421AForce measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCircular discMagnetic rotation
This invention relates to high temperature super conductive magnetic float dynamic test device, wherein, the bottom socket motor drives stainless steel disc and its top ring high temperature superconductive float cargo magnetic rotation; the bottom L shape shell top has been loaded with cylinder to drive down supportive rack for sliding along rack; the supportive rack is loaded with motor cylinder along supportive rack down level movement; upper and middle slide boards are fixed with sensor test level guide force; middle board and its down slide board can slide for vertical sliding.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High temperature superconducting wires and coils
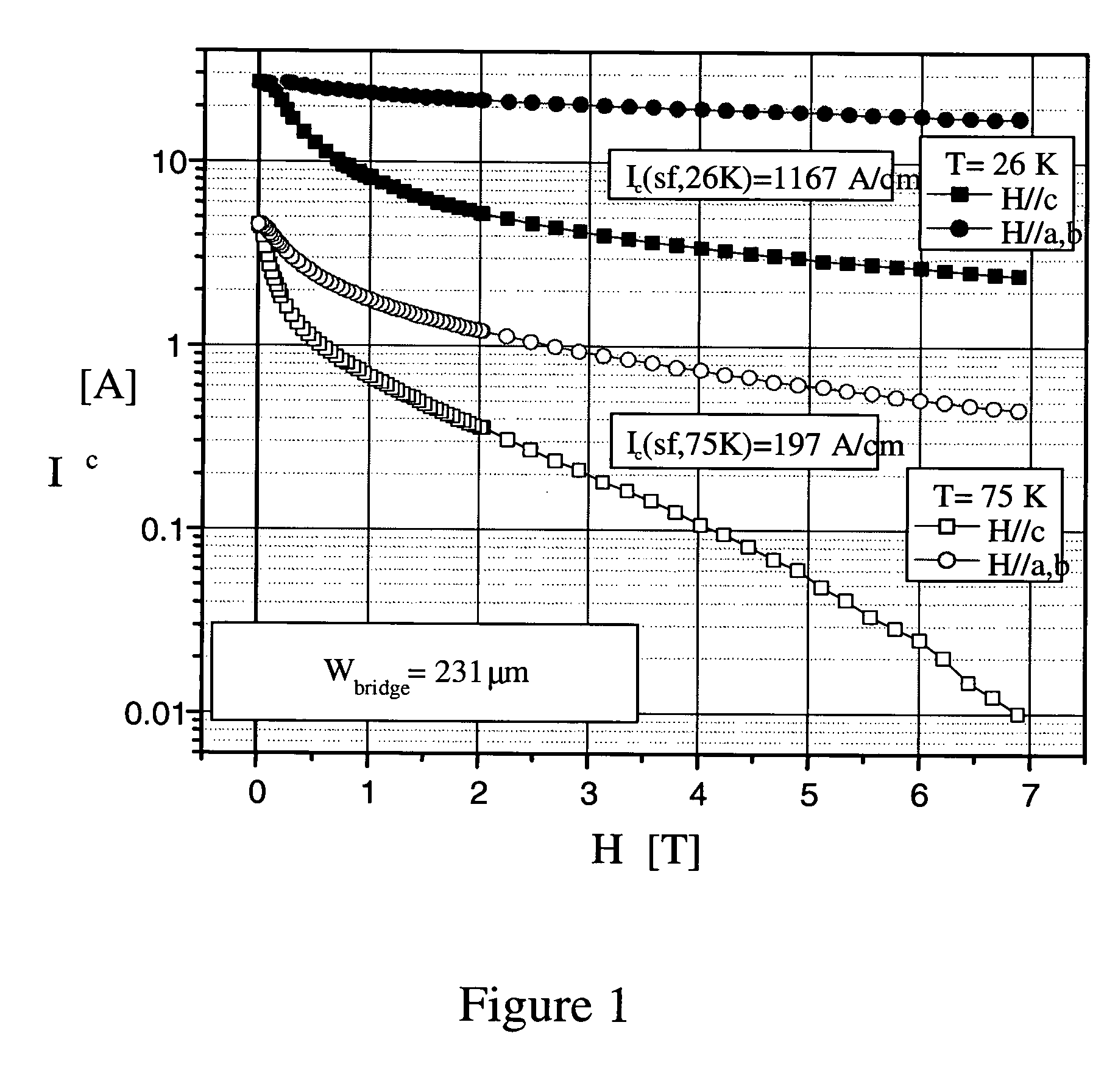
ActiveUS20070111893A1Enhance critical current densityHigh densitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetsElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
A superconducting wire includes first and second superconducting layers disposed on one or more substrates in stacked relationship, the first superconducting layer comprising a high temperature superconducting oxide of a first composition and the second superconducting layer comprising a high temperature superconducting layer of a second composition, wherein the first and second compositions are different. The first superconductor layer optionally includes a high temperature superconductor composition selected to provide enhanced critical current (Ic(c)) in the presence of magnetic fields perpendicular to surface of the superconducting layer (H / / c). The second superconductor layer optionally includes a high temperature superconductor composition selected to provide enhanced critical current (Ic) in the presence of magnetic fields parallel to surface of the superconducting layer (H / / ab).
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
High power superconductive circuits and method of construction thereof
InactiveUS6041245AReduce current densityHigh Power Handling CapabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesMicrowaveHigh-temperature superconductivity
A high power high temperature superconductive circuit for use in various microwave devices including filters, dielectric resonator filters, multiplexers, transmission lines, delay lines, hybrids and beam-forming networks has thin gold films deposited either on a substrate or on top of the high temperature superconductive film. Alternatively, other metal films can be used or a plurality of dielectric films can be used or a dielectric constant gradient substrate can be used. The use of these materials in a part or parts of a microwave circuit reduces the current density in those parts compared to the level of current density if only high temperature superconductive film is used. This increases the power handling capability of the circuit.
Owner:COM DEV LTD
Cold end of heavy current lead out wire made from high-temperature superconductor, and low resistance connector of superconducting transmission line
InactiveCN1873847ASave cooling capacityLess investmentSuperconducting magnets/coilsEngineeringSuperconducting transmission lines
The disclosed adaptor between cold junction of leading wire in heavy current of high-temperature superconductor and low resistance of superconducting transmission line includes structure: welding piles of high-temperature superconductor arranged in spaces to outer wall of support tube made from stainless steel in low thermal conductance; welding warm end in piles of high-temperature superconductor to transition piece of copper; through braze welding, cold end in piles is joined to NbTi / Cu superconducting line; cross winding NbTi / Cu line on inner copper tube sheathed inside outer copper tube; cooling superconducting line and copper connector by using liquid helium between inner and outer copper tubes. Features are: simple structure, suitable to connection under 20kA. In the invention, resistance of adaptor is lowered as 1.4-4.6n ohm. In supercritical quantity of helium flow 4g / s, all loss of 6 pieces of adaptor and 12 pieces of butt end of transmission line is less than 0.1Mpa.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of fabrication of high temperature superconductors based on new mechanism of electron-electron interaction
InactiveUS20070108437A1Dissimilar materials junction devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh-temperature superconductivitySingle crystal
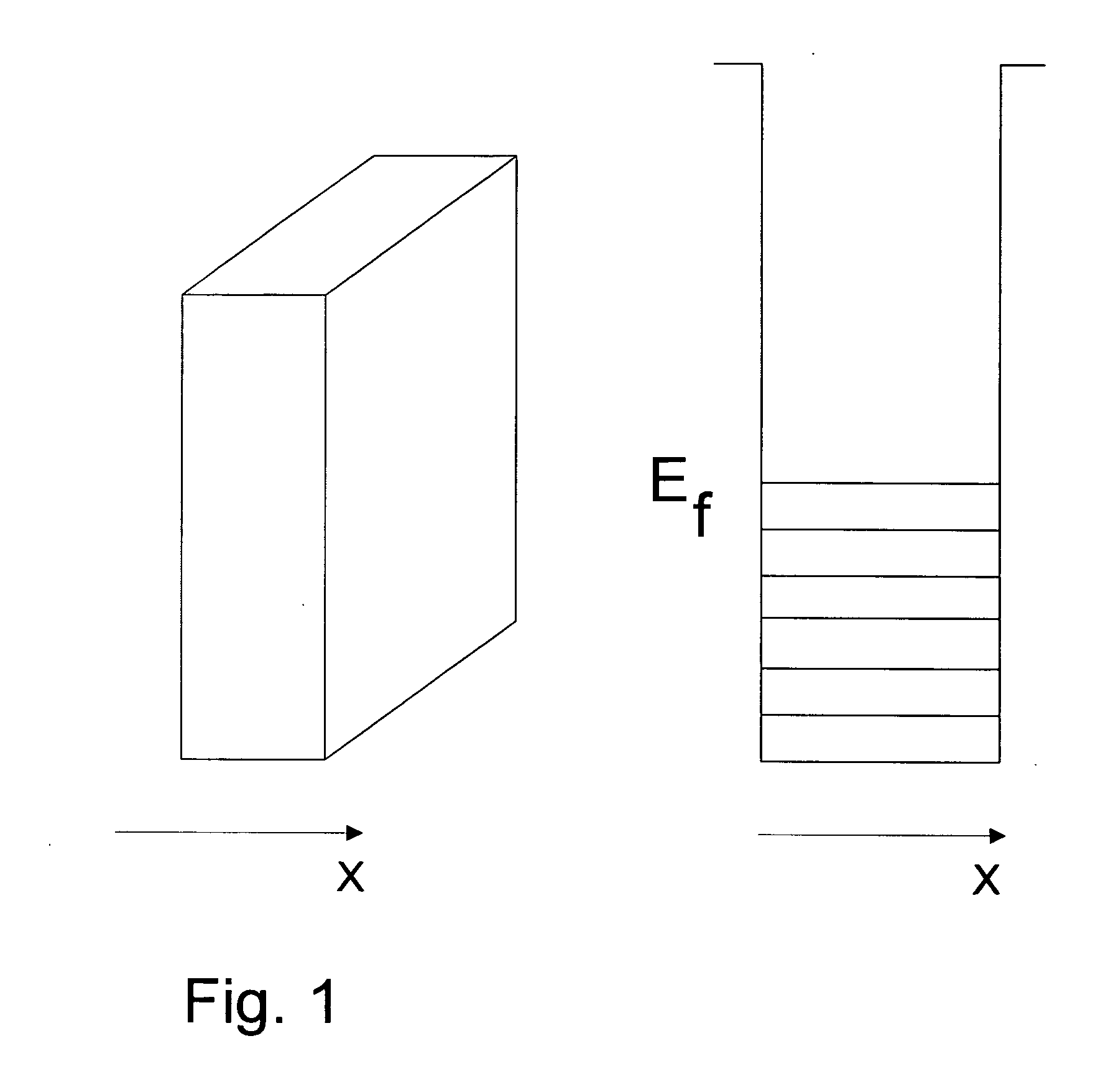
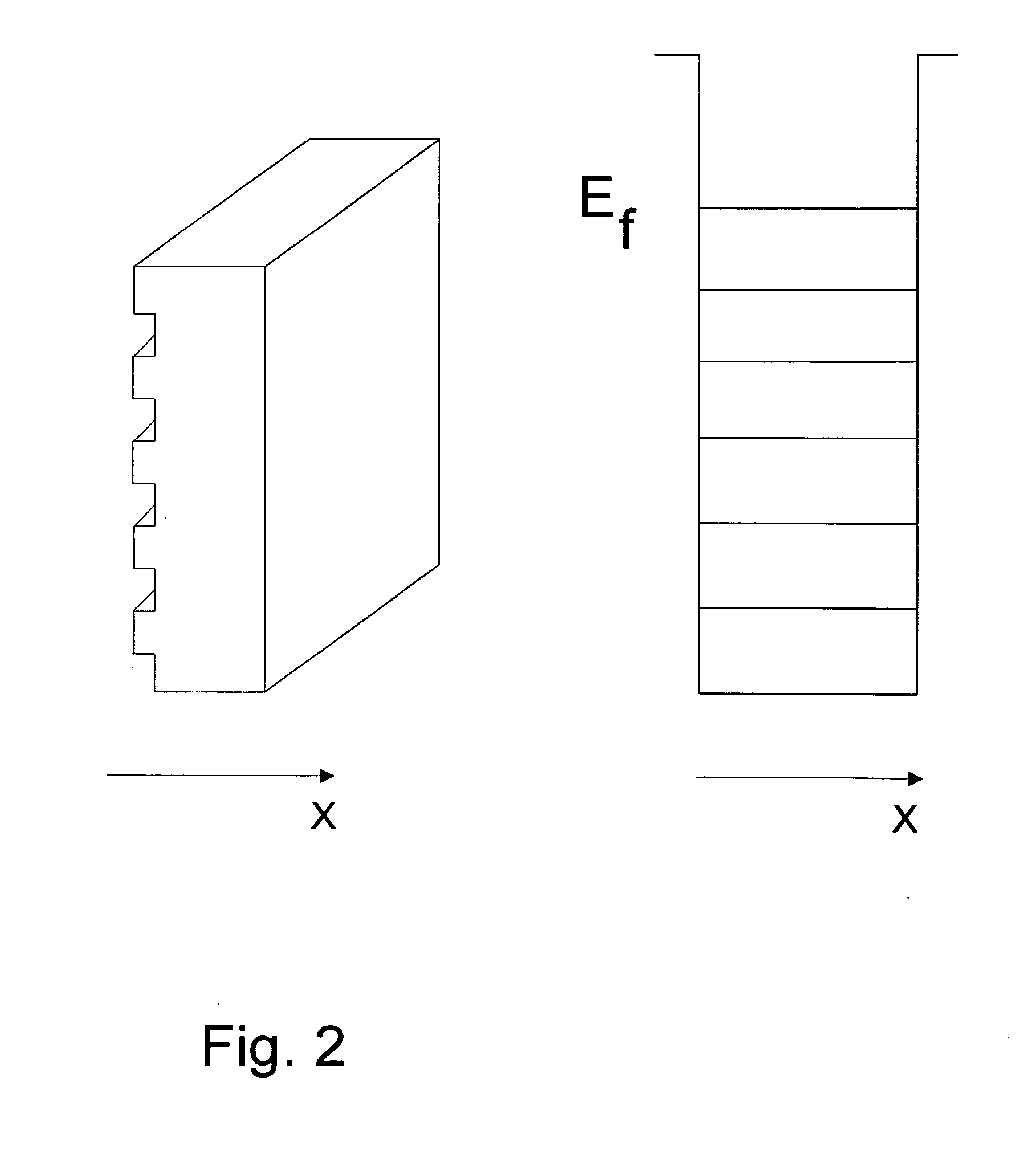
The present invention is a superconducting tunnel junction comprising two thin films characterized in that the thin films have an indented surface facing each other and are separated by an insulator layer. Typically, the depth of the indents is in the range of 5 to 10 nm, the width of the indents is in the range of 50 to 200 nm, the thickness of the insulator layer is in the range of 1 to 3 nm, and the thickness of the films is less than electron mean free path of a material comprising said films, and is typically in the range of 50 to 100 nm. Preferably the films are single crystal films or amorphous films.
Owner:TAVKHELIDZE AVTO
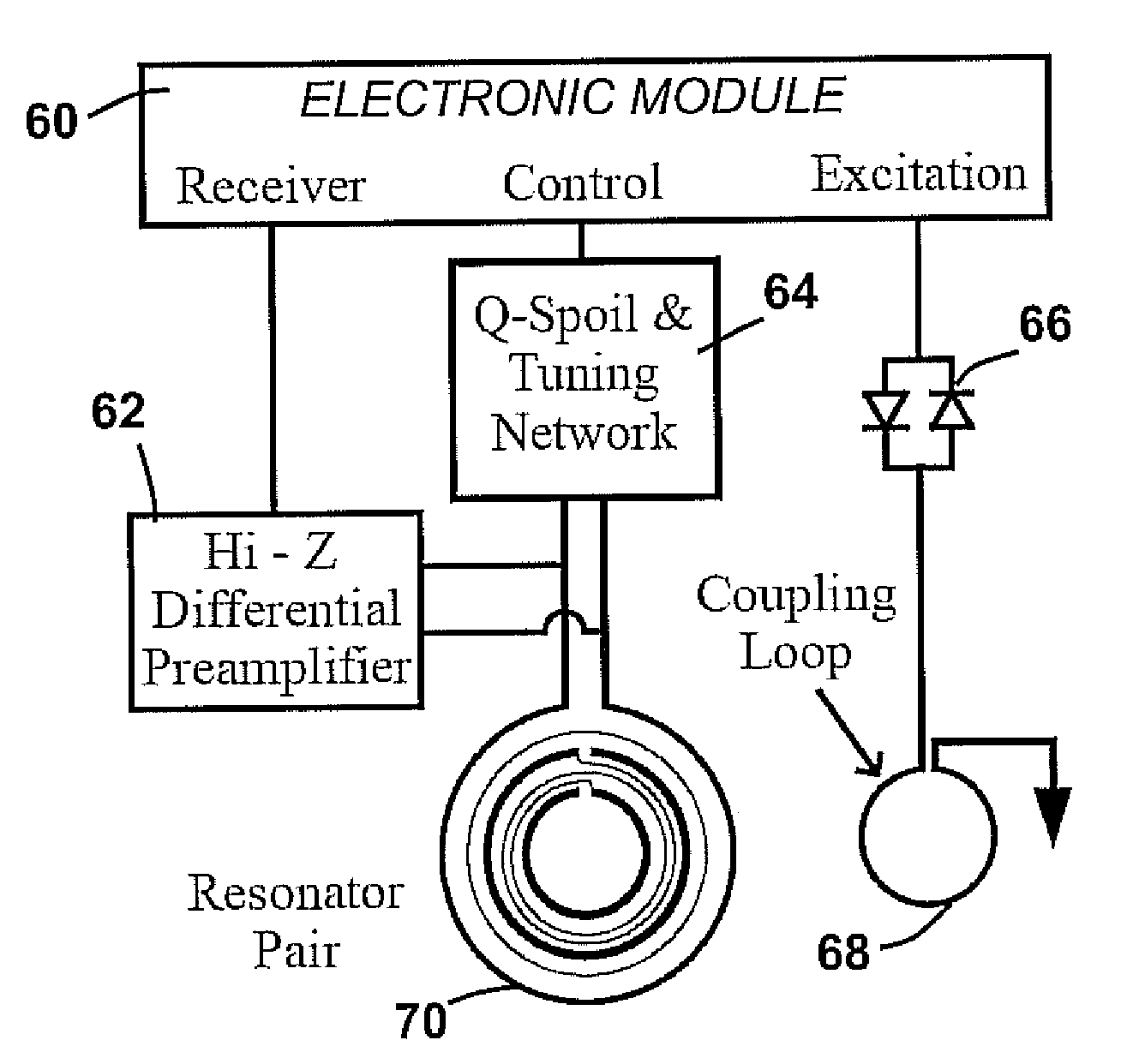
Detecting quadrupole resonance signals using high temperature superconducting resonators
InactiveUS7511500B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceAnalyteHigh-temperature superconductivity
Narrowband quadrupole resonance (QR) probes were developed from thin-film high-temperature superconducting (HTS) resonators. The QR probes are useful in analyte-detection systems, in particular for the detection of nitrogen-containing compounds. Embodiments of the invention provide greater than an order of magnitude improvement in sensitivity and the ability to reject RF interference sources located outside the pass-band of a superconducting QR probe. Methods and apparatus are described for analyte detection and resonance frequency adjustment.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Multifilament Superconductor Having Reduced AC Losses and Method for Forming the Same
ActiveUS20110319271A1CoatingsCable/conductor manufactureHigh-temperature superconductivityMaterials science
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC +1
High temperature superconductor tape RF coil for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS6943550B2Decorative surface effectsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentHigh-temperature superconductivityEtching
A HTS RF coil is disclosed having at least a factor of three improvement in the SNR over a comparable copper coil and at least a factor of six improvement in Q over a comparable copper coil. A commercially available HTS tape is formed into a loop. High-Q capacitors are soldered across the loop ends. The silver sheath covering the tape is removed through chemical etching. The coil is placed in a holder for mechanical support and protection and covered with a cover having through holes enabling the coolant to directly contact the HTS coil.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF +1
Measuring device of high-temperature superconductive suspension tiny force
InactiveCN102853954AMeet the test requirementsIsolate connection interferenceApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityMeasurement device
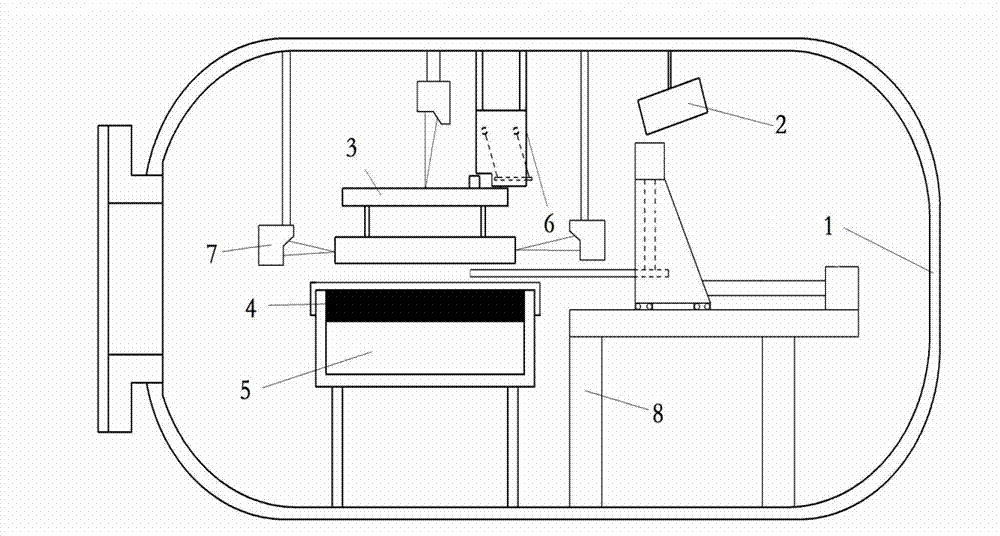
The invention discloses a measuring device of a high-temperature superconductive suspension tiny force. The measuring device comprises a vacuum cabin, a high-speed camera, a permanent magnet platform, a superconductor platform, a low temperature system, a calibration firing pin, a charge coupled device (CCD) laser speed detector and a floating mechanism; different firing calibration forces are provided through a calibration firing pin structure; then four configured CCD laser displacement sensors respectively obtain the vibration data along the vertical direction and the horizontal direction of a permanent magnet platform corresponding to different calibration forces, thereby forming an one-to-one corresponding relationship of the calibration force and the permanent magnet platform movement. When the tiny thrust of an electric thruster is acted on the permanent magnet platform, the CCD laser displacement sensor can obtain the vibration properties on the vertical and horizontal directions of the permanent magnet platform; then the tiny thrust of the electric thruster can be calculated according to the obtained one-to-one corresponding relationship of the calibration force and the permanent magnet platform movement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for joining second-generation high-temperature superconducting wires by melting diffusion
InactiveCN101971273ALower eutectic pointSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsHigh-temperature superconductivityHot Temperature
The present invention relates to a welding method for a second generation high temperature superconducting wire including a substrate, a buffer layer, a superconductor layer, and a stabilizing material layer, wherein parts of the stabilizing material layers contained in two strands of the second generation high temperature superconducting wire are removed, the superconductor layers of two strands of the second generation high temperature superconducting wire exposed by the removal of the stabilizing material layer abut each other and are heated to the melting point of the superconductor layer to melt-diffuse the abutting superconductor layers and weld two strands of the second generation high temperature superconducting wire together. Subsequently, the welded portion is oxygenation-annealed under an oxygen atmosphere to recover superconducting properties of the second high temperature superconducting wire. The above-described configuration of the present invention enables superconductor layers to directly abut each other and to be melt-diffused without using a mediator, thus producing a wire having a full length with a rare junction resistance as compared to a normal conduction junction method. Specifically, the present invention brings a partial oxygen pressure to a nearly vacuum state to lower the melting point, thereby enabling junction processes to be performed without melting a stabilizing material layer containing silver (Ag).
Owner:K·约恩
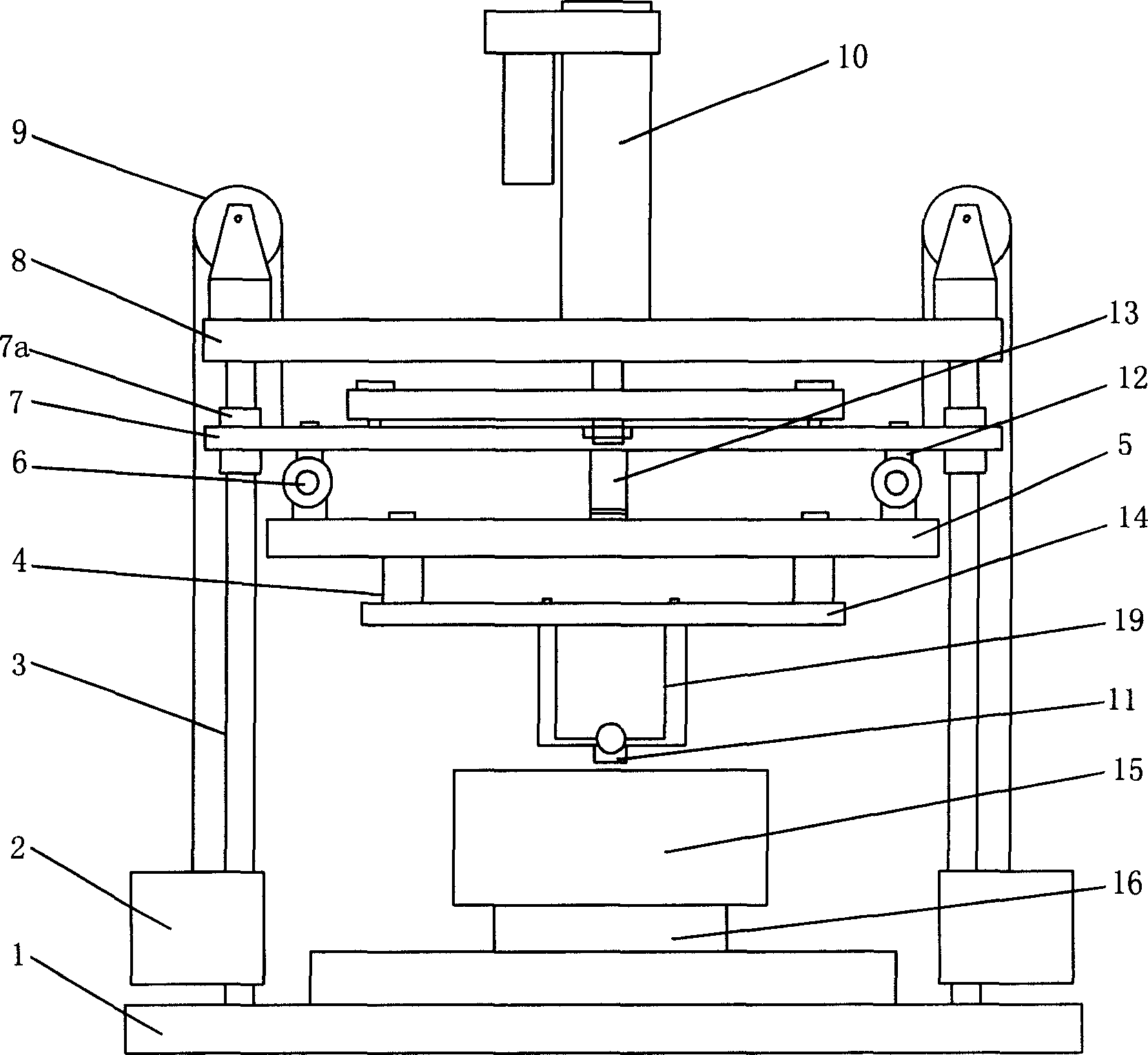
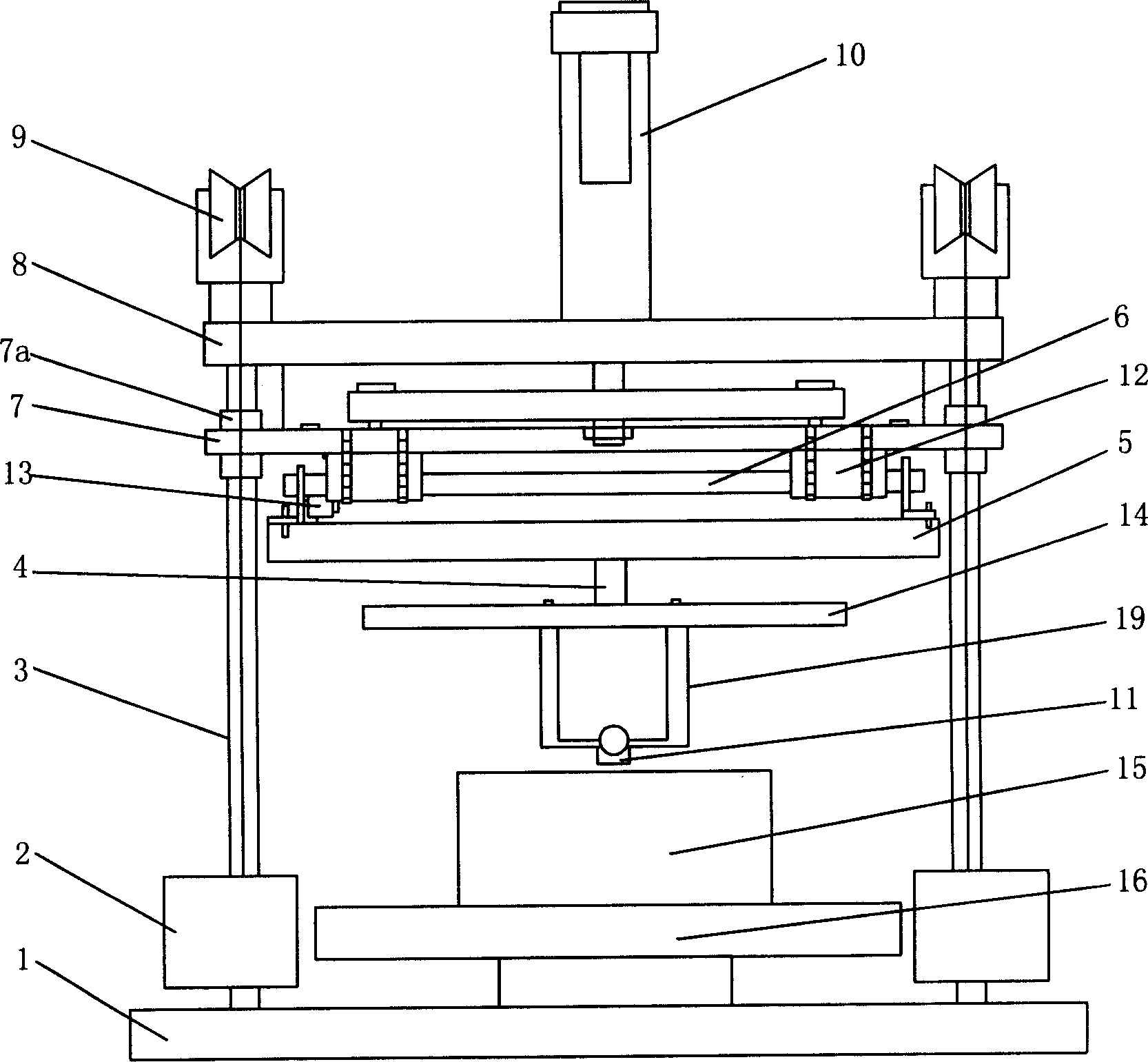
Testing device of magnetic suspension of high-temperature superconductor, and testing method for using the device
InactiveCN1916654AOvercome vertical forceOvercome the defect that the guidance ability cannot be measured at the same timeForce measurementMagnetic property measurementsHigh-temperature superconductivityEngineering
A device used to test magnetic suspension performance of high temperature superconductive block consists of planar two-dimensional accurate positioner, support frame, sliding base, guiding screw, base cover, sliding jacket of guiding screw, guiding force and vertical force transducers, hanging plate, mechanism for hang sample and computer. It is featured as fixing electric cylinder on beam plate, connecting screw to sliding base by passing screw through beam plate in order to let said device detect out relation of vertical force or guiding force to displacement and time as well as magnetic rigidity of vertical force or guiding force.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High-temperature superconductive cable insulation electrical characteristic test device
ActiveCN101387672ABreakdown field strengthEasy to useElectrical testingMachines/enginesHigh-temperature superconductivityThermal insulation
The invention provides a ultra-high temperature superconductive cable insulation electric character tester, comprising a low temperature pressure thermal insulation controller provided with a cover board, a hole at the center of the cover board, an insulation sleeve penetrating through the hole, a vacuum connector mounted on the cover board, a connecting tube for filling liquid nitrogen and a connecting tube for adding pressure which are mounted on the cover board, a test electrode in the low temperature pressure insulation container, and a conductive bar in the insulation sleeve, of which the upper end is connected with high voltage and the lower end is connected with the high voltage end of the test electrode. The ultra-high temperature superconductive cable insulation electric character tester can improve the electric property of the insulation material of a high temperature superconductive cable, under low temperature liquid nitrogen temperature, having simple operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INT SUPERCONDUCTION TECH CO LTD
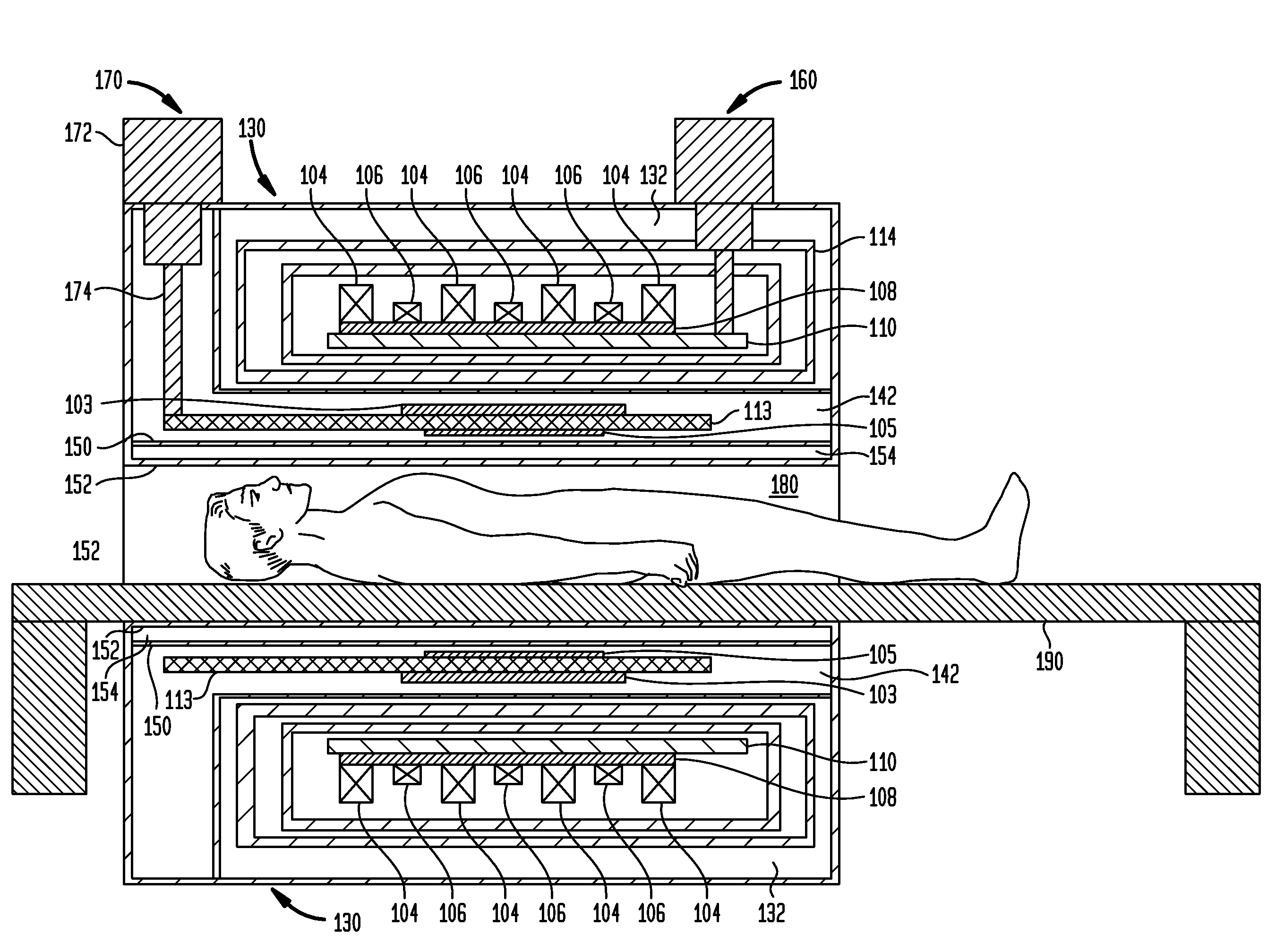
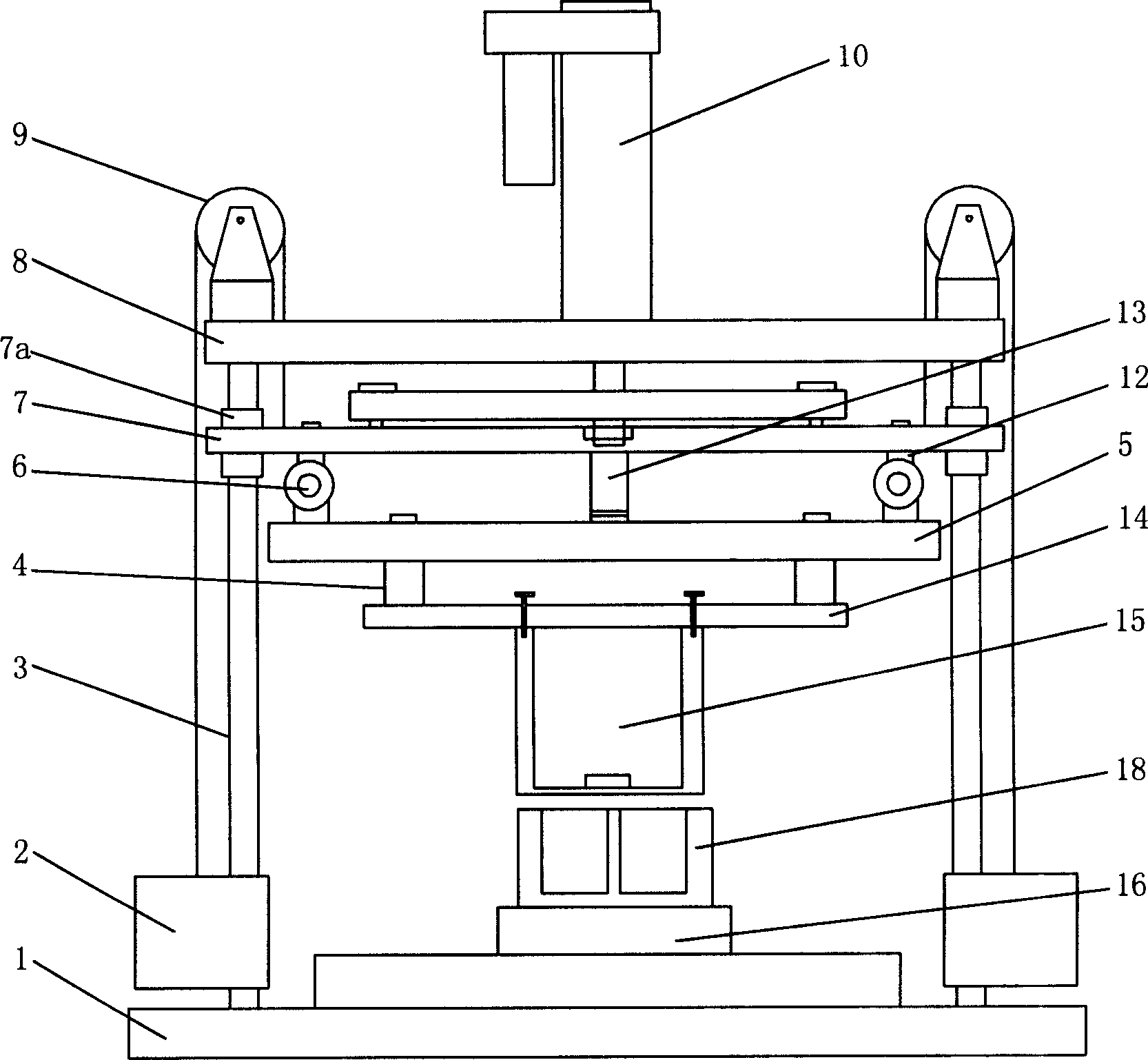
Compact isocentric gantry
A gantry for administering proton beam therapy with improvements which reduce the size, weight, costs and radiation beam loss associated with proton beam therapy systems currently commercially available. The gantry utilizes achromatic superconducting multi-function electromagnet systems wherein the magnets can include dipoles and quadrupoles. The achromatic properties of the rampable magnet systems allow for ease of transmission of the beam whose energy is rapidly changed through a large range of different energies without changing of the strength of the magnetic fields or dipole settings. The magnets may be made with either low or high temperature superconductors. The gantry design further integrates beam scanning but keeps the gantry isocentric. A much greater fraction of the beam can be transmitted through the gantry than with current art, thereby reducing radiation shielding requirements and the demand put on the accelerator to produce large quantities of proton beam.
Owner:PRONOVA SOLUTIONS
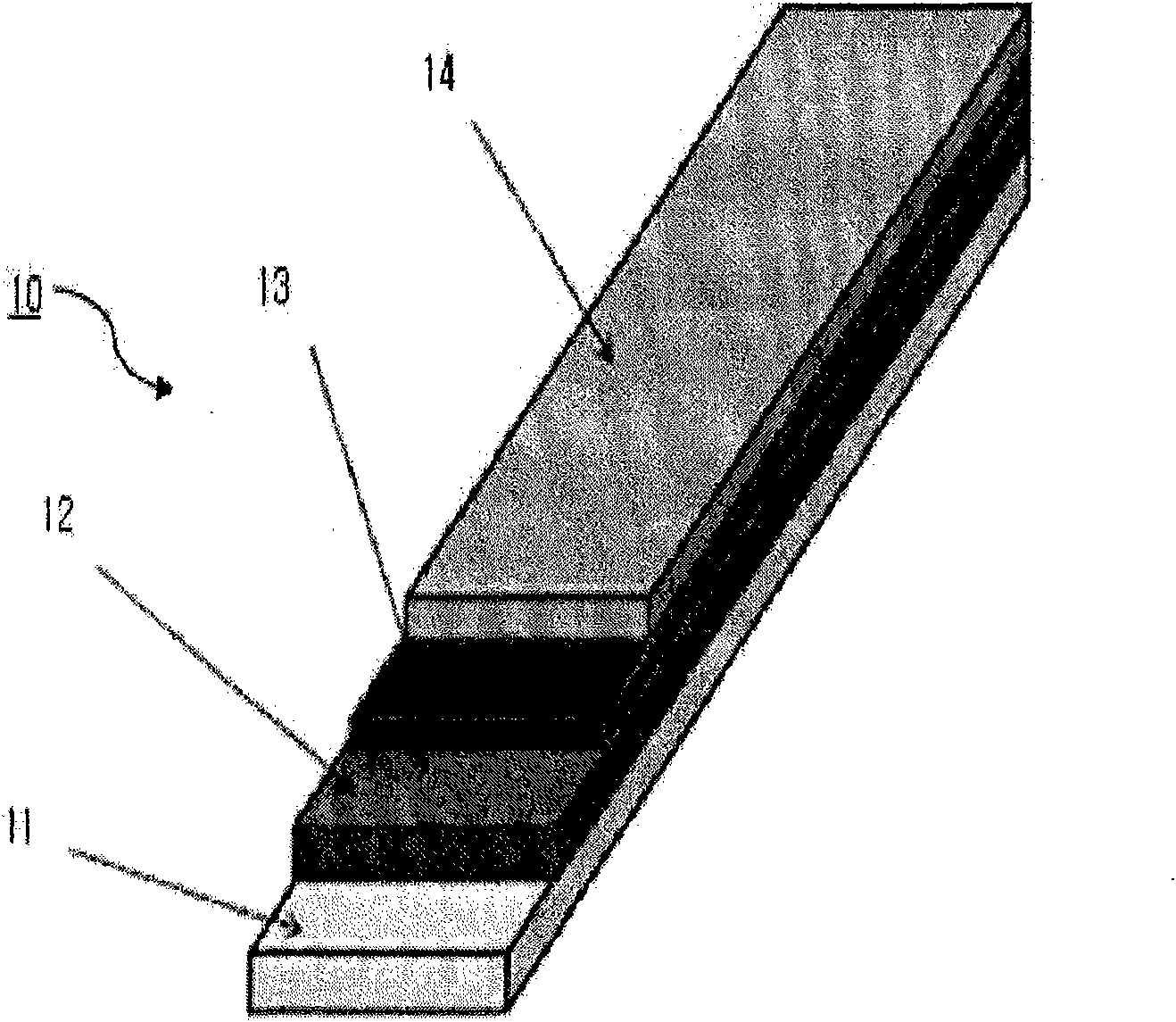
Segmented superconducting tape having reduced AC losses and method of making
ActiveUS20070191202A1Reduce AC-lossReducing AC losses in such tapesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
A superconducting tape having reduced AC losses. The tape has a high temperature superconductor layer that is segmented. Disruptive strips, formed in one of the tape substrate, a buffer layer, and the superconducting layer create parallel discontinuities in the superconducting layer that separate the current-carrying elements of the superconducting layer into strips or filament-like structures. Segmentation of the current-carrying elements has the effect of reducing AC current losses. Methods of making such a superconducting tape and reducing AC losses in such tapes are also disclosed.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization
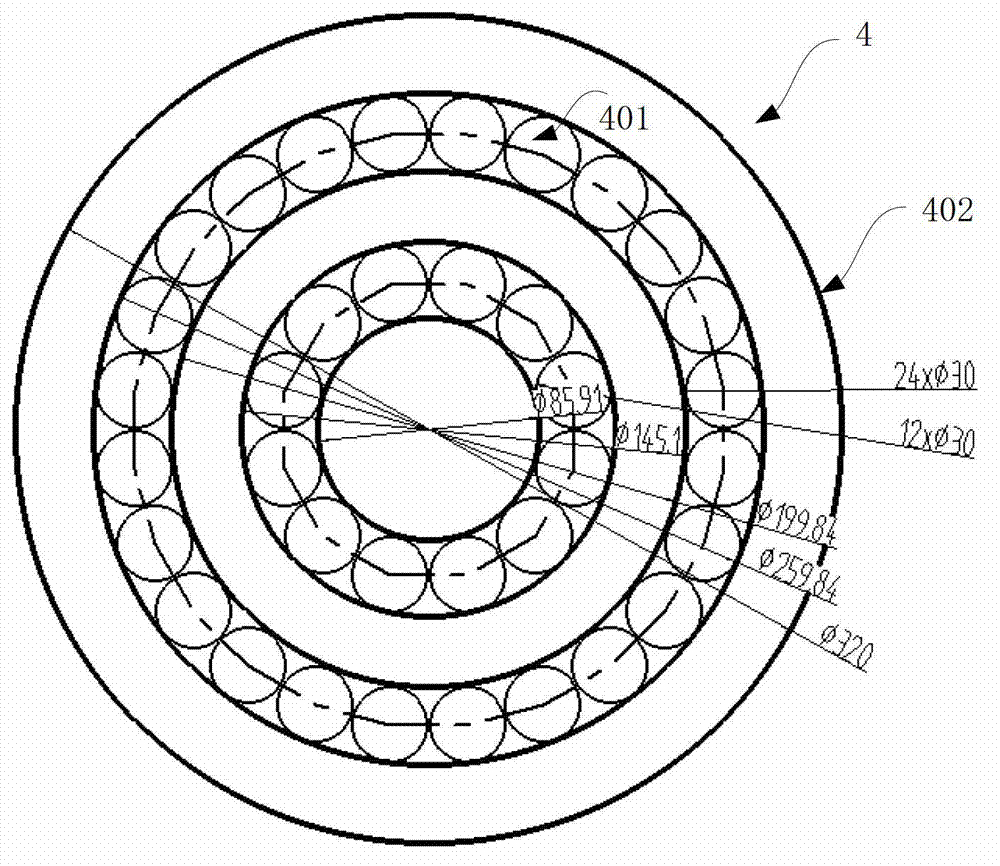
ActiveCN102545725AReduce volatilityNon-pressured vesselsRefrigeration devicesLevitationHigh-temperature superconductivity
A super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization comprises a low temperature container (1), a refrigerating machine (2), a refrigerated screen (3), a liquid helium container (4), a super-conduction rotor (5), a levitation coil (6), a rotor cavity (7), an infusion tube (8), a condenser (12) and a polar axis displacement sensor (13). Heat generated by a current lead wire of the levitation coil (6) after the levitation coil (6) is powered on cannot be transmitted into the liquid helium container (4) through a room temperature current lead wire connector (9), a high temperature super-conduction current lead wire connector (10) and a low temperature super-conduction current lead wire connector (11), so that volatilization of liquid helium in the liquid helium container (4) is reduced. Helium in the condenser (12) is refrigerated through the refrigerating machine (2) to be liquefied so that zero volatilization of liquid helium in the liquid helium container (4) is achieved. The super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization does not need to be infused with liquid helium for many times and can independently run for a long period.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
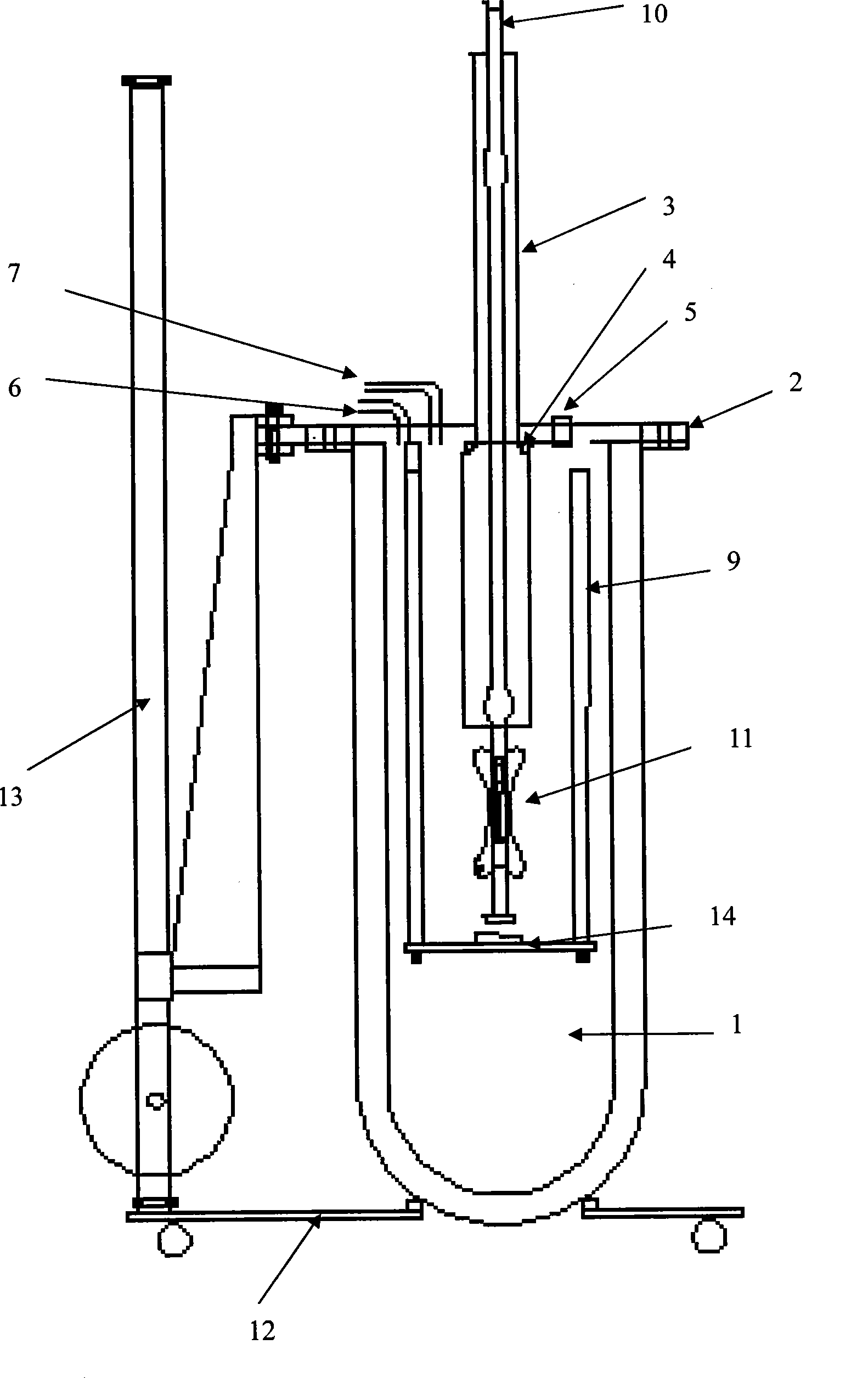
Evacuated tube transport system with improved cooling for superconductive elements
InactiveUS20140261055A1Reduce constructionLow costRailway tunnelsRailway componentsHigh-temperature superconductivityTransport system
A High Temperature Superconductor Maglev (HTSM) for Evacuated Tube Transport (ETT) with a magnetic levitation structure for ETT capsule vehicles traveling in an evacuated tube. At least one ETT capsule travels within an evacuated tube, an upper and a lower cryostat respectively mount at the top and bottom of said ETT capsule along the length thereof, at least a plurality of superconductor levitation force elements divided between said upper and lower cryostats. The levitation force being spread over the length of capsule, however substantially concentrated in a compact cross-sectional area. At least a pair of permanent magnetic elements mounted at the top and bottom of the evacuated tube to cooperate with the superconductor elements to levitate the capsule.
Owner:OSTER DARYL
Prepn process of high temperature superconductive Ni-W alloy
The present invention belongs to the field of technology of preparing rough base belt for high temperature superconductive coating and superconductive film. The preparation process of the ppi includes the following steps: discharge plasma sintering the mixture inside mold comprising Ni powder and W powder of purity over 99.9 % and granularity of 3-6 micron; maintaining at 800-1200 deg.c and 30-80 MPa for 0-10 min; cold rolling Ni-W plate at room temperature in the gate deformation of 5-15 % and total deformation over 97 %; re-crystallizing and annealing in the atmosphere of Ar with mixed H2 in 4 vol%, at temperature of 900-1300 deg.c and with annealing time of 0.5-3 hr. The said process is simple and fast, and the obtained polycrystalline Ni-W belt is used in depositing high temperature superconductive YBCO film.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Low temperature superconducting assembly with low joint resistance for high temperature superconducting current lead cold end
InactiveCN101694908ASatisfy <1 nano-oh requirementSuperconducting magnets/coilsConnection contact member materialElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh-temperature superconductivity
The invention discloses a low temperature superconducting assembly with low joint resistance for a high temperature superconducting current lead cold end. The resistance of a 40-70kA high temperature superconducting super current lead of which the lower end is connected with a low temperature superconducting bus must be as low as 1 nano-ohm. A rectangular section niobium-titanium / copper superconducting wire or a high conductivity copper material and a paired box type joint structure connected with the superconducting bus are adopted in the low temperature superconducting assembly. Tests prove that the joint resistance of the low temperature superconducting assembly and a high temperature superconducting assembly can be as low as 0.5 nano-ohm, and the joint resistance of the superconducting bus is lower than 1 nano-ohm. The low temperature superconducting assembly is a middle result for developing super current leads of an international thermonuclear fusion test reactor and has the characteristics of novel conception and low manufacturing cost.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Decoupling high temperature superconductor sensor arrays in nuclear quadrupole resonance detection systems
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Q-damping of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system
InactiveUS20060082368A1Useful in detectionMaterial analysis by using resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
The use of a high temperature superconductor single loop or coil in the Q-damping circuit for a high temperature superconductor transmit, receive, or transmit and receive self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance system results in improved performance of the nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Superconducting coil quench detection method
InactiveCN101126787AImprove reliabilityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical testingHigh-temperature superconductivityThermodynamics
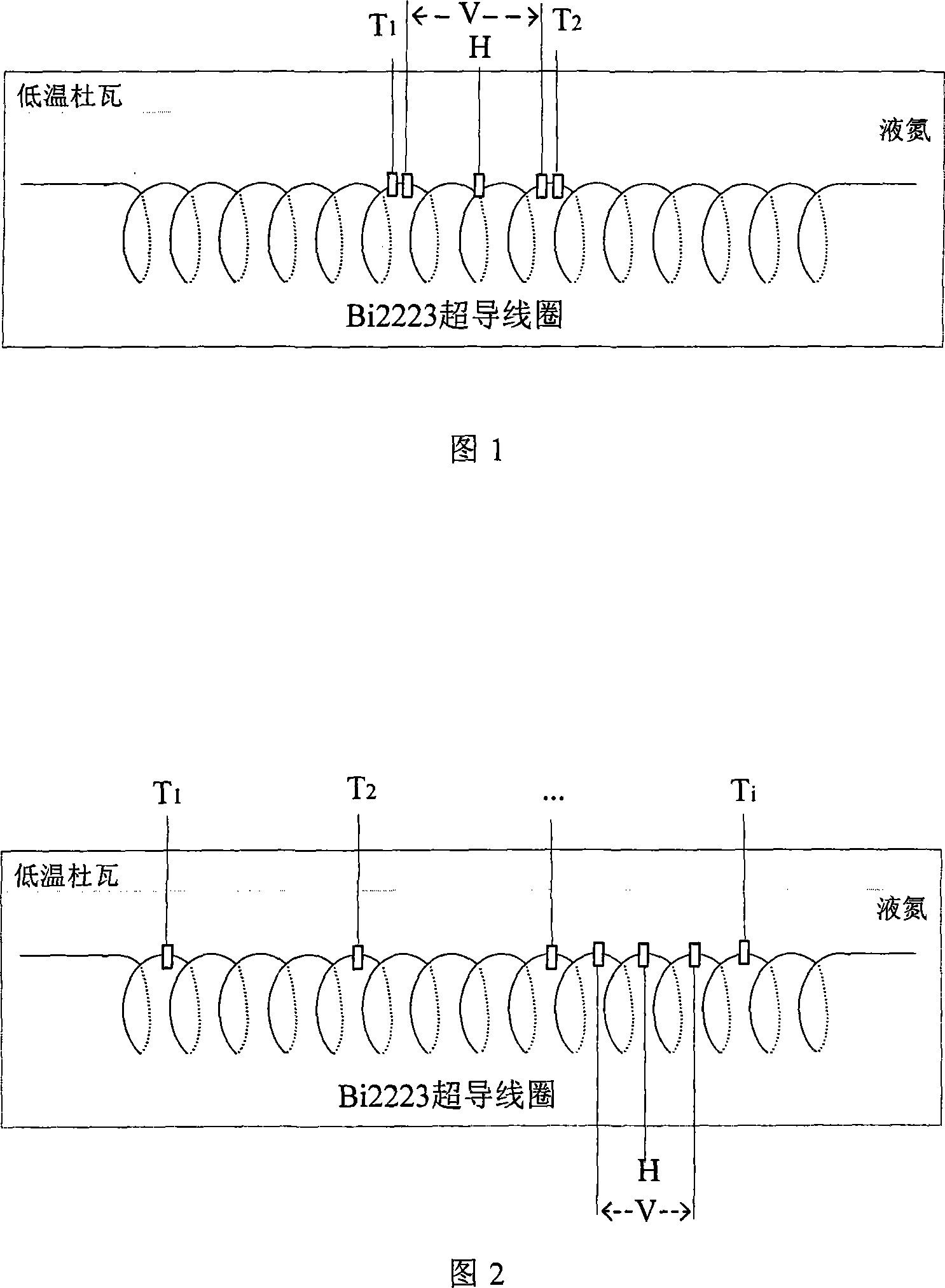
The utility model relates to a quench detecting method of superconducting coils, which is characterized in detecting the temperature of superconducting coil winding at real time; a quench detecting value (temperature rising rate) is acquired by the means that the difference value on adjacent temperature in time is divided by time interval of temperature detection. By comparing the temperature rising rate with the threshold value of the temperature rising rate, the coil quench can be judged if the temperature rising rate exceeds the threshold valve. The determination method on the threshold value of the temperature rising rate is to detect the voltage and the temperature near the quench point at the same time in the process of detecting quench on the superconducting coil and to transform the temperature into the temperature rising rate. When the voltage rises to 1MuV / cm, coil quenches and the mean value of the temperature rising rate on both side of quench point is the threshold value of the temperature rising rate. The utility model is closer to the essence of physical phenomenon and has the advantages of fast detecting speed and high sensitivity. The utility model is applicable for low temperature superconducting (NbTi, Nb3Sn, MgB2) coils and high temperature superconducting (Bi2223, YBCO) coils.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Q-damping of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadropole detection system
InactiveUS20050140371A1Television system detailsSelective content distributionElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
The use of a bias controlled diode in the Q-damping circuit of a high temperature superconductor transmit, receive, or transmit and receive self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system results in improved performance. The diode is operated with a forward bias such that the diode is resistive with a resistance of about 10 to about 1000 ohms.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
High Temperature Interfacial Superconductivity
InactiveUS20090137398A1Raise the superconducting transition temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsHigh-temperature superconductivityTunnel junction
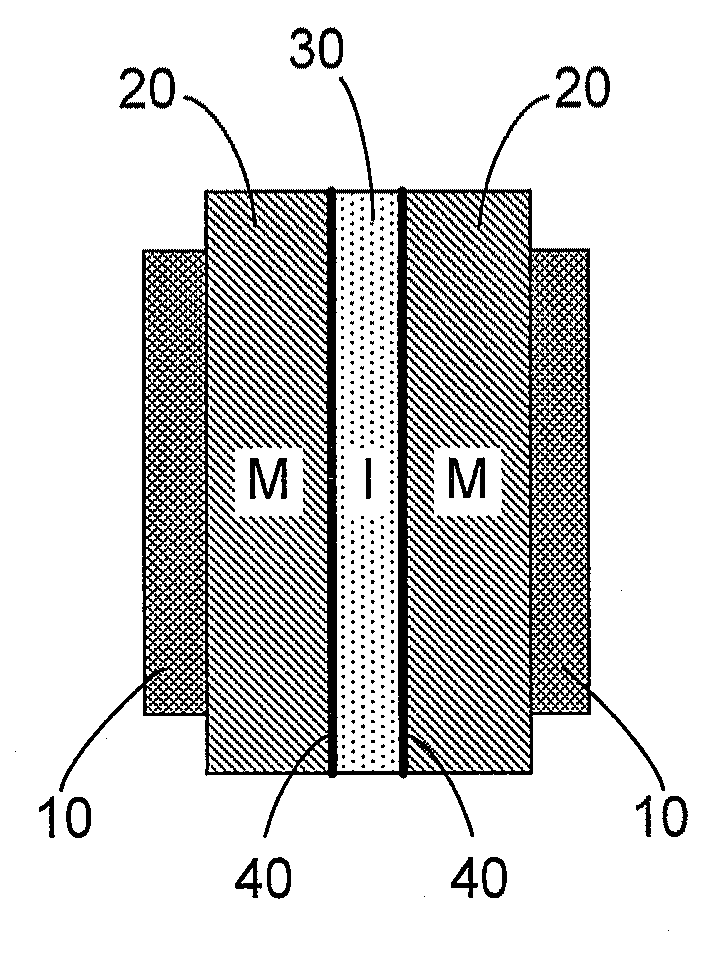
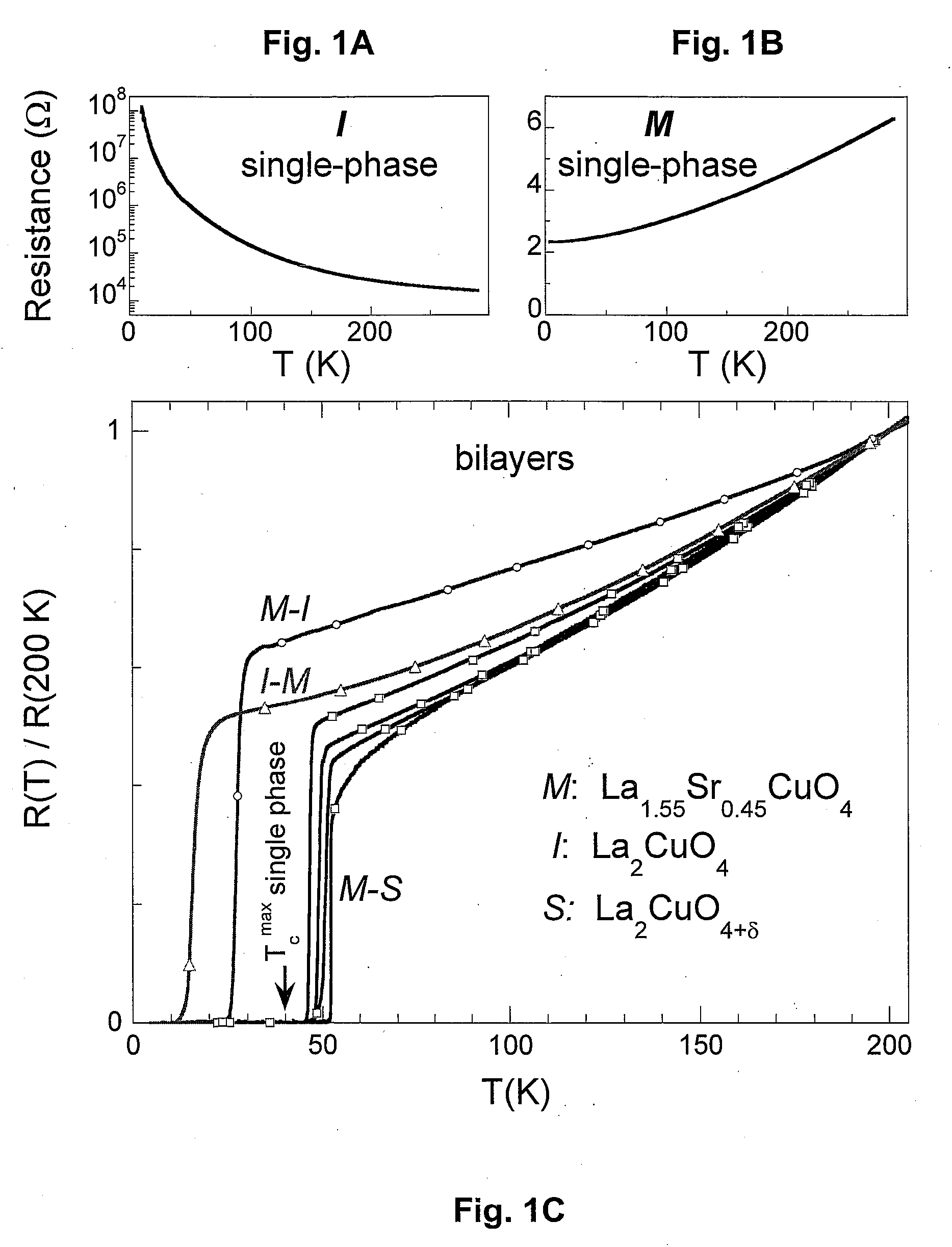
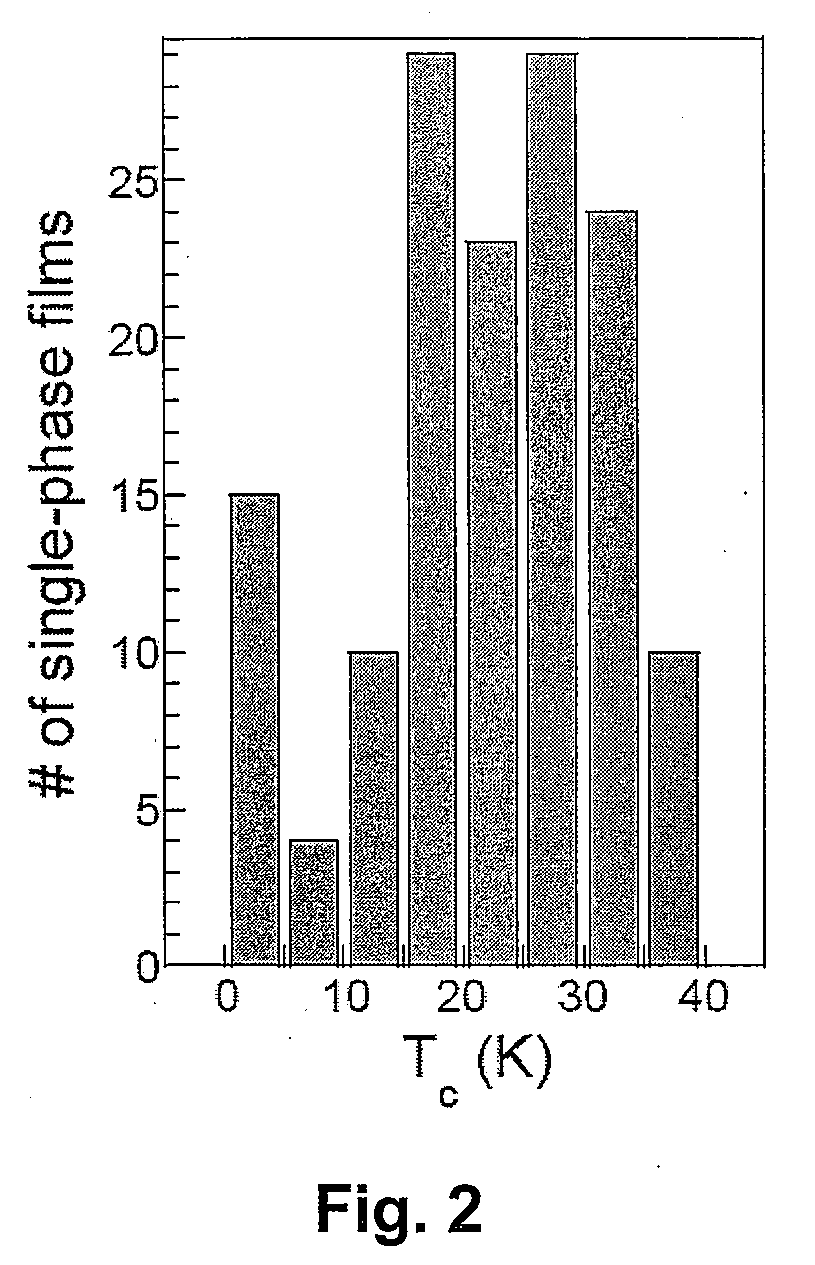
High-temperature superconductivity confined to nanometer-scale interfaces has been a long standing goal because of potential applications in electronic devices. The spontaneous formation of a superconducting interface in bilayers consisting of an insulator (La2CuO4) and a metal (La1−xSrxCuO4), neither of which is superconducting per se, is described. Depending upon the layering sequence of the bilayers, Tc may be either ˜15 K or ˜30 K. This highly robust phenomenon is confined to within 2-3 nm around the interface. After exposing the bilayer to ozone, Tc exceeds 50 K and this enhanced superconductivity is also shown to originate from a 1 to 2 unit cell thick interfacial layer. The results demonstrate that engineering artificial heterostructures provides a novel, unconventional way to fabricate stable, quasi two-dimensional high Tc phases and to significantly enhance superconducting properties in other superconductors. The superconducting interface may be implemented, for example, in SIS tunnel junctions or a SuFET.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
High-temperature superconducting low-temperature helium self-circulation cooling system
ActiveCN103606430ARealize self-circulationSimplify operating proceduresCompression machinesSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh-temperature superconductivitySuperconducting Coils
The invention discloses a high-temperature superconducting low-temperature helium self-circulation cooling system. Vertical temperature and density differences of low-temperature helium in the system allow natural convective circulation to form, and the problems that the superconducting magnet used in the direct cooling manner of a small refrigerator is poor in cooling effect and the necessary application of expensive low-temperature helium pumps in forced convective circulation cooling causes high cost are solved. After the system stabilizes, operating pressure is low; the safety problem is solved. A superconducting magnet and a current lead form a whole which can be lifted in or out of magnet mounting space and which is convenient to demount, mount and change; cooling medium helium has controllable temperature, and conditions for the study on performances of high-temperature superconducting magnets at specific temperature are provided.
Owner:VACREE TECH +1
Design method for coaxial bidirectional transmission direct-current high-temperature superconducting cable body
InactiveCN101404193AReduce lossLoss hasSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectric power systemDc current
The invention relates to a design method used for transmitting DC high-temperature superconducting cable body coaxially and bidirectionally, belonging to the field of power system transmission and transformation; the design method comprises the steps as follows: according to the mechanical characteristic and the radius of enwinding framework of the superconducting strips, parameters of the superconducting cable body such as the enwinding helix angle and the enwinding pitch are determined; the magnetic field distribution of all layers of superconducting cable body are determined according to the operation current, thus determining the critical current on all layers of the cable; according to the critical current and the operation redundancy, iterative calculation is carried out for operation current and the magnetic field, thus finally gaining the critical current, best operation current, enwinding layer number and number of the cables. The designed superconducting cable body increases no enwinding process difficulty and achieves bidirectional transmission of DC current; the utilization ratio of the superconducting strip critical current reaches more than 90%; the quantity and low-temperature heat loss of the superconducting cable low-temperature container are respectively reduced by half. The design method has the advantages of large transmission capability, no loss, compact structure, certain current limiting capability, stable mechanical structure, self-shielding, no electromagnetic interference and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
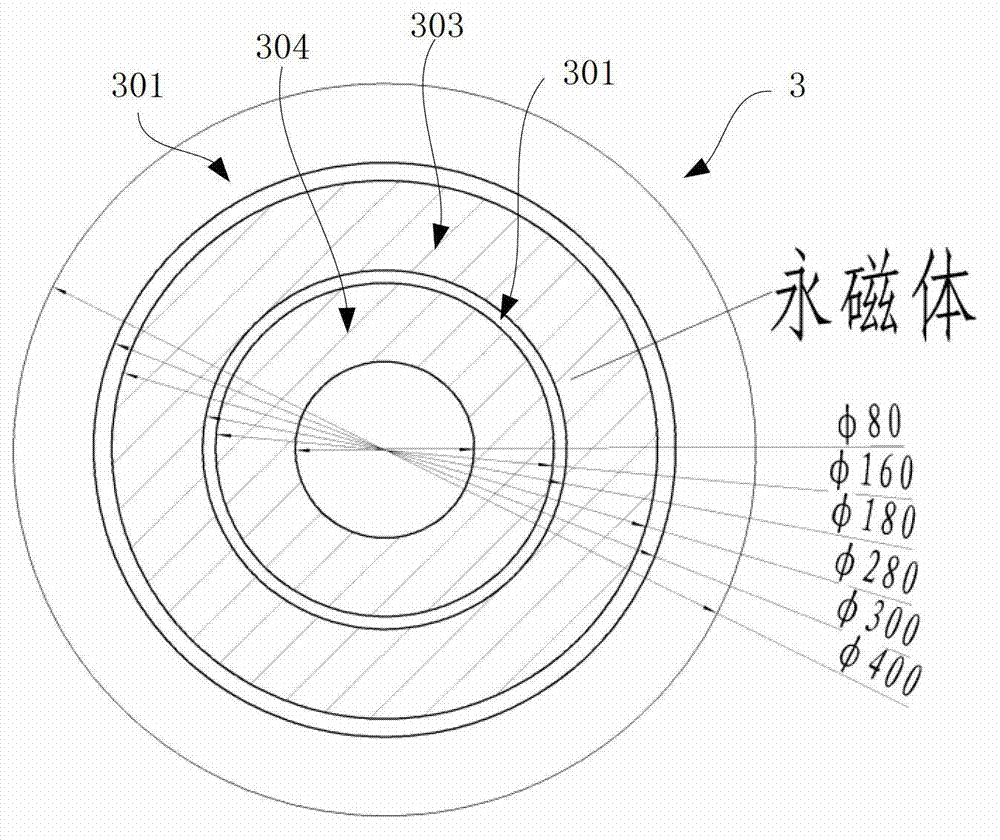
High-field superconducting magnet system with wide separation gaps
ActiveCN101728051AReduce distanceIncrease profitSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh-temperature superconductivityCold shield
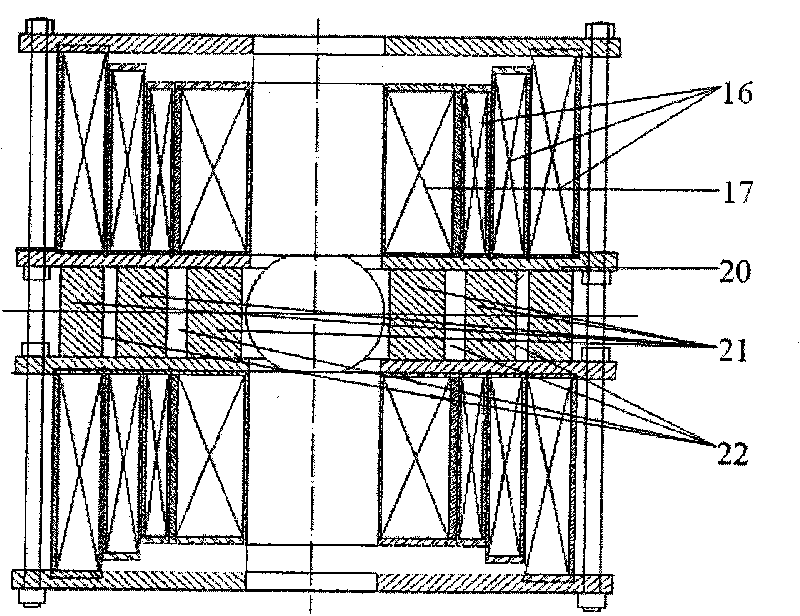
The invention discloses a high-field superconducting magnet system with wide separation gaps. Superconducting coils of the system comprise a low-temperature superconducting coil (16) and a high-temperature superconducting coil (17). The superconducting coils are connected with a cold shield (3) and a flange (2) of a low-temperature container through a support pull rod (8), and are supported in the low-temperature container integrally. A thermoswitch (7) is connected with a primary cold head and a secondary cold head of a refrigerating machine (1), and the secondary cold head is connected with magnet-reinforcing support flanges (10) arranged at two ends of the low-temperature and high-temperature superconducting coils through a cold-guiding belt (5). The superconducting magnet system is provided with a horizontal room-temperature hole (12) and a vertical room-temperature hole (15); an outer cold shield (11) of the horizontal room-temperature hole is used for preventing heat radiation of the horizontal room-temperature hole (12) to the superconducting coils. A separation support frame (9) separates the low-temperature superconducting coil (16) and the high-temperature superconducting coil (17) into two parts, so when the superconducting magnets are integrated into a whole, a two-dimensional room-temperature space is contained in the integrated superconducting magnets.
Owner:中科磁控(北京)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com