Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Superconductor classification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Superconductors can be classified in accordance with several criteria that depend on physical properties, current understanding, how expensive is cooling them or their material.
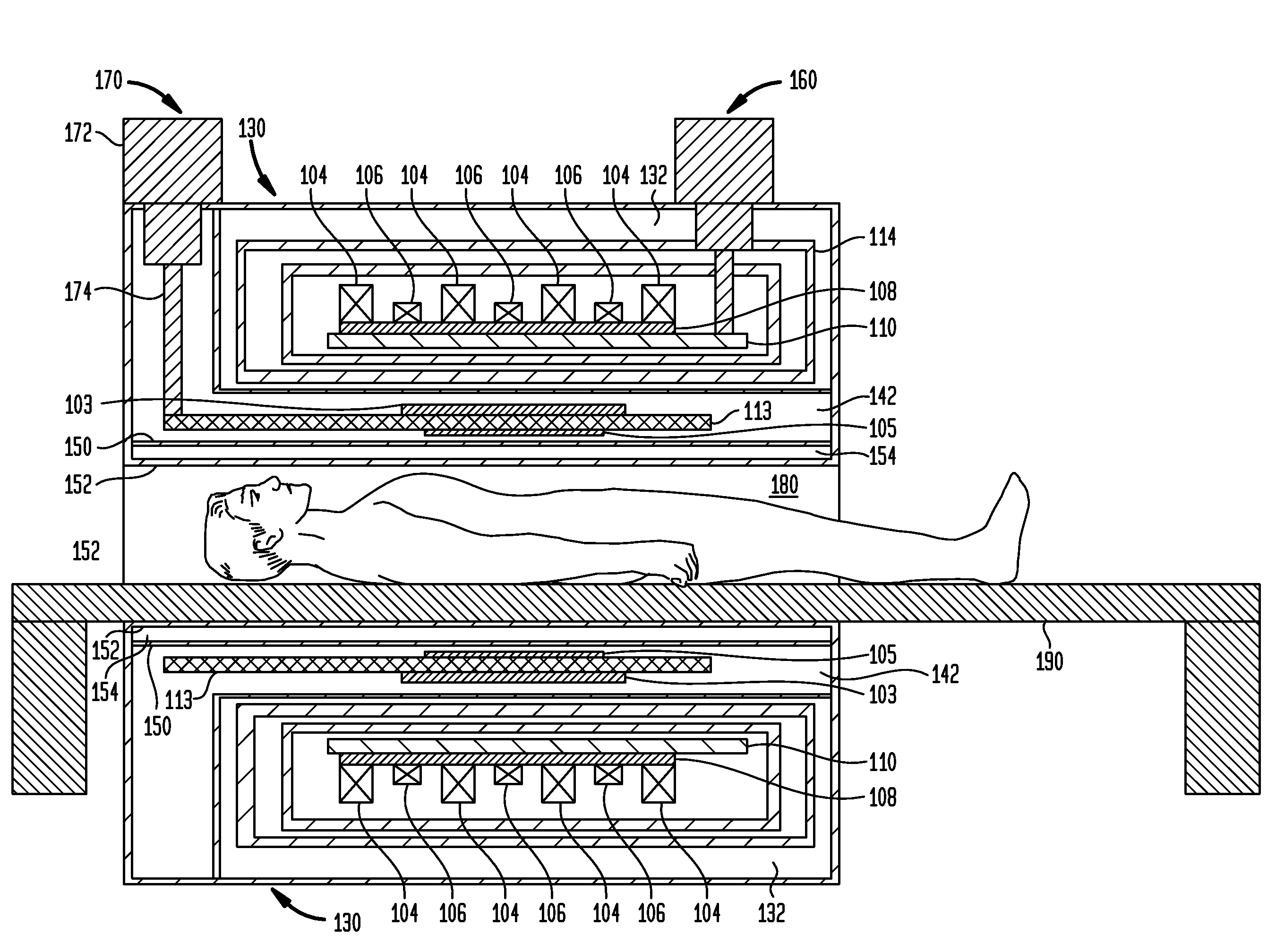
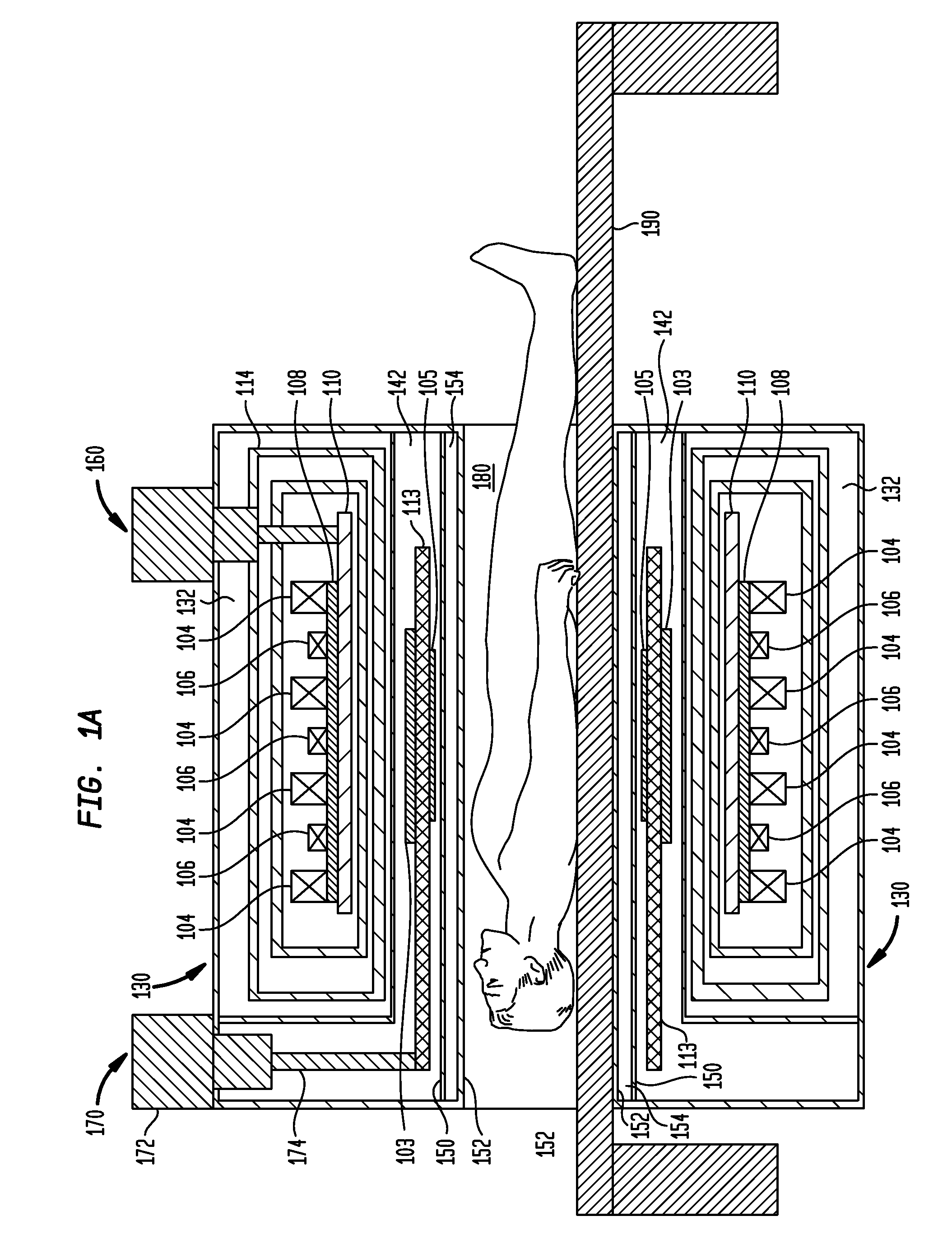
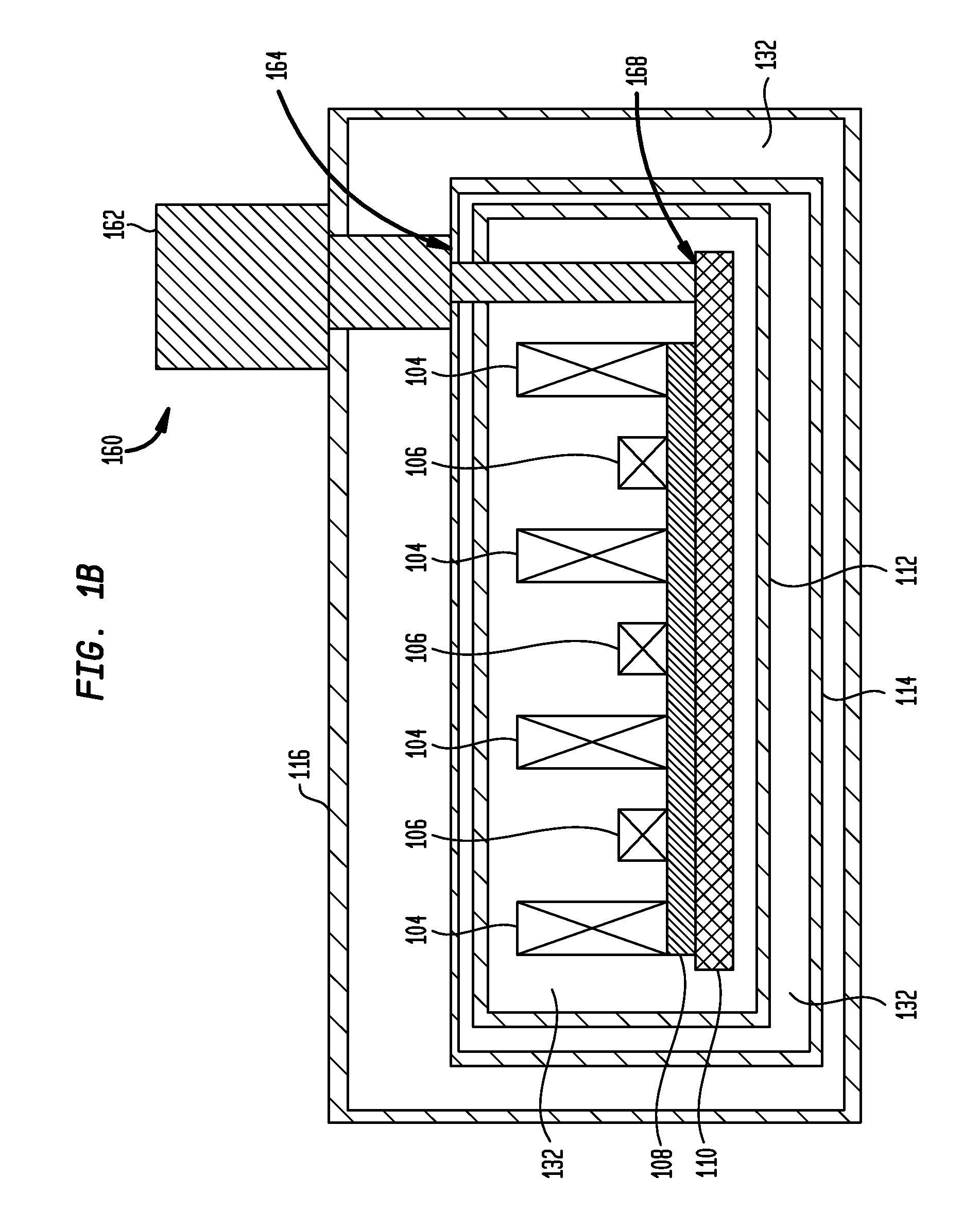
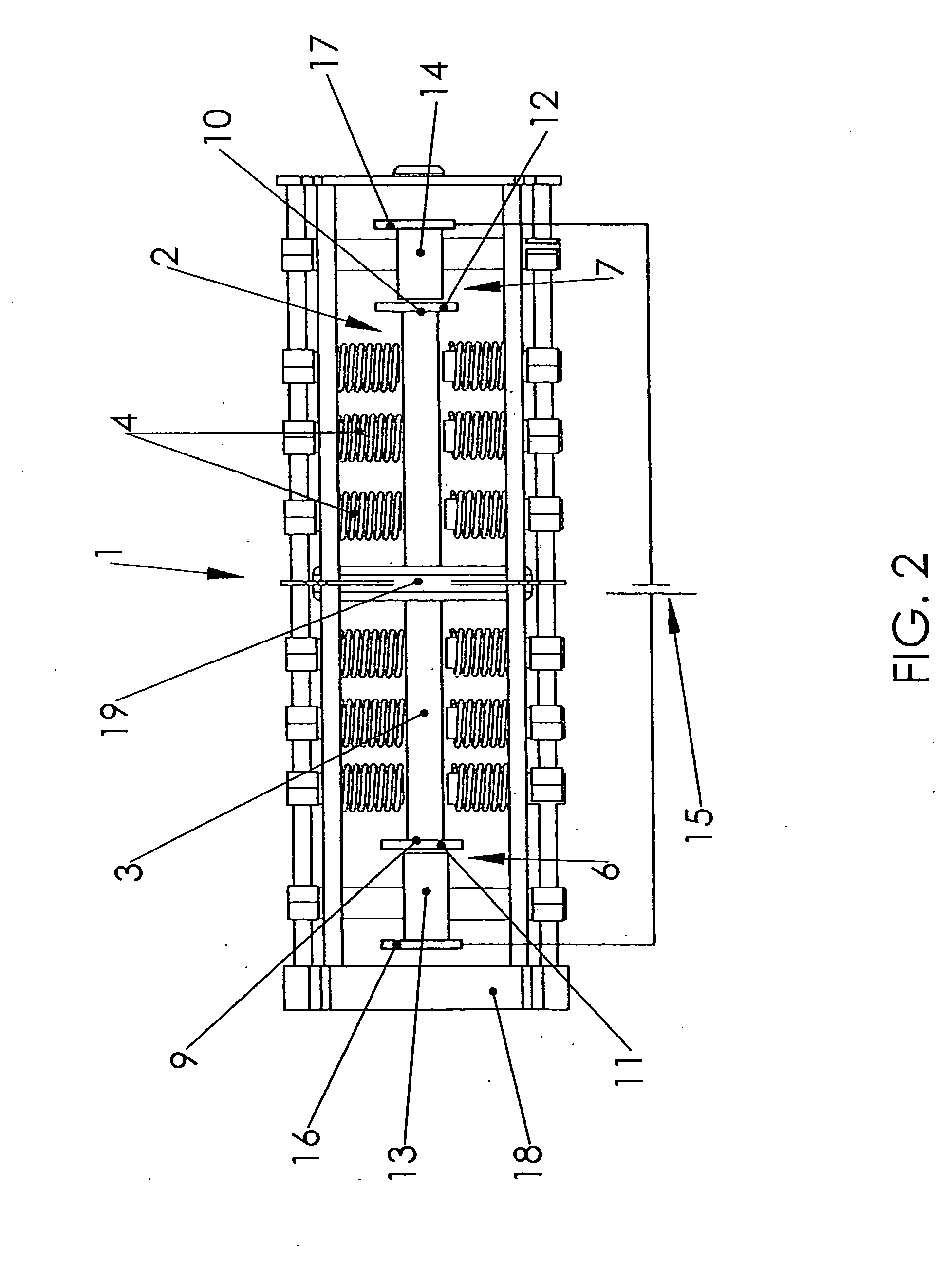
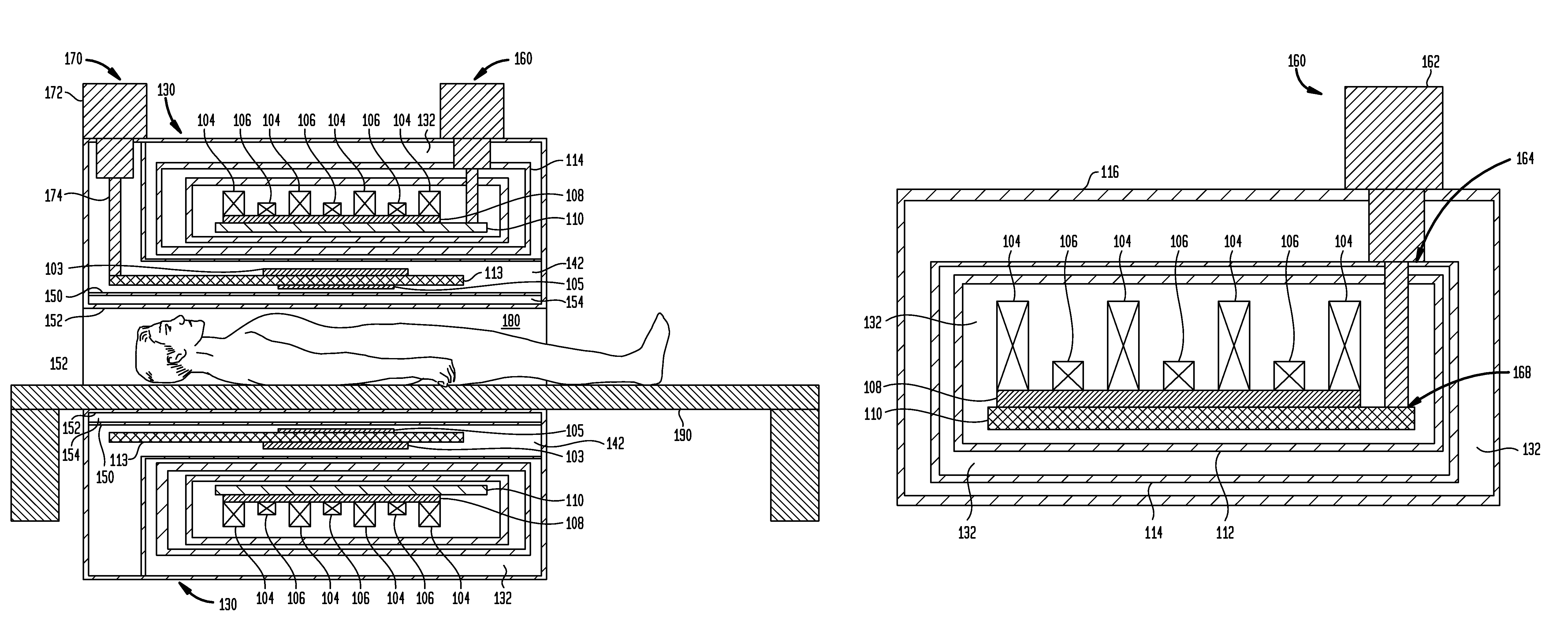
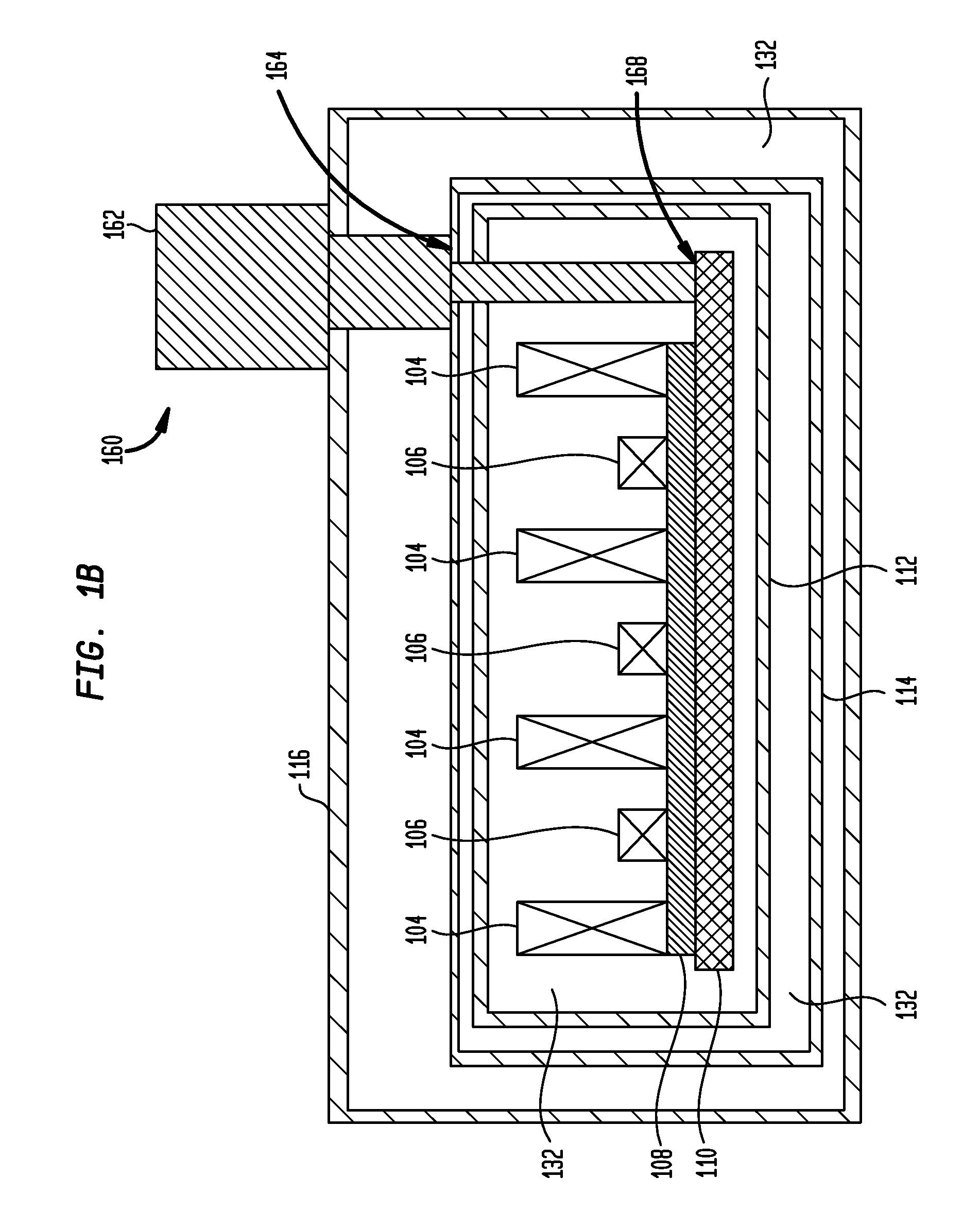
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Advanced process flow for quantum memory devices and josephson junctions with heterogeneous integration
ActiveUS9455391B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectTrapping
A process for constructing a superconducting Josephson-based nonvolatile quantum memory device comprising: sequentially depositing on a silicon substrate a thermal oxide buffer layer, a superconductor bottom-electrode thin film, and an oxide isolation layer; patterning an active window having dimensions smaller that 10 nanometers in the oxide isolation layer; then sequentially depositing a bottom tunnel oxide layer, a charge-trapping layer, a top cap, and a top superconductor electrode layer; defining an active region by dry etching down to the oxide isolation layer while protecting the active region from etch chemistry; depositing a device passivation layer; defining and patterning vias from a top of the device passivation layer to the superconductor bottom-electrode thin film and to the top superconductor electrode of the active region; and depositing metal interconnect into the vias.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Superconductors and methods for making such superconductors
InactiveUS20050173679A1Simple manufacturing processInexpensive mass productionConductive materialOrganic conductorsElectrical conductorVolumetric Mass Density
This invention concerns an improvement of the supercurrent carrying capabilities, i.e. the increase of critical current densities, of polycrystalline superconductor structures, especially of high-Tc superconductors fabricated with a coated conductor technique to provide superconducting layers containing flat grains. A superconductor with superior critical current density is obtained by joining, i.e. pressing or otherwise bringing into intensive facial contact, preferably superconducting contact, two or more such superconducting layers.
Owner:MANNHART JOCHEN DIETER +4
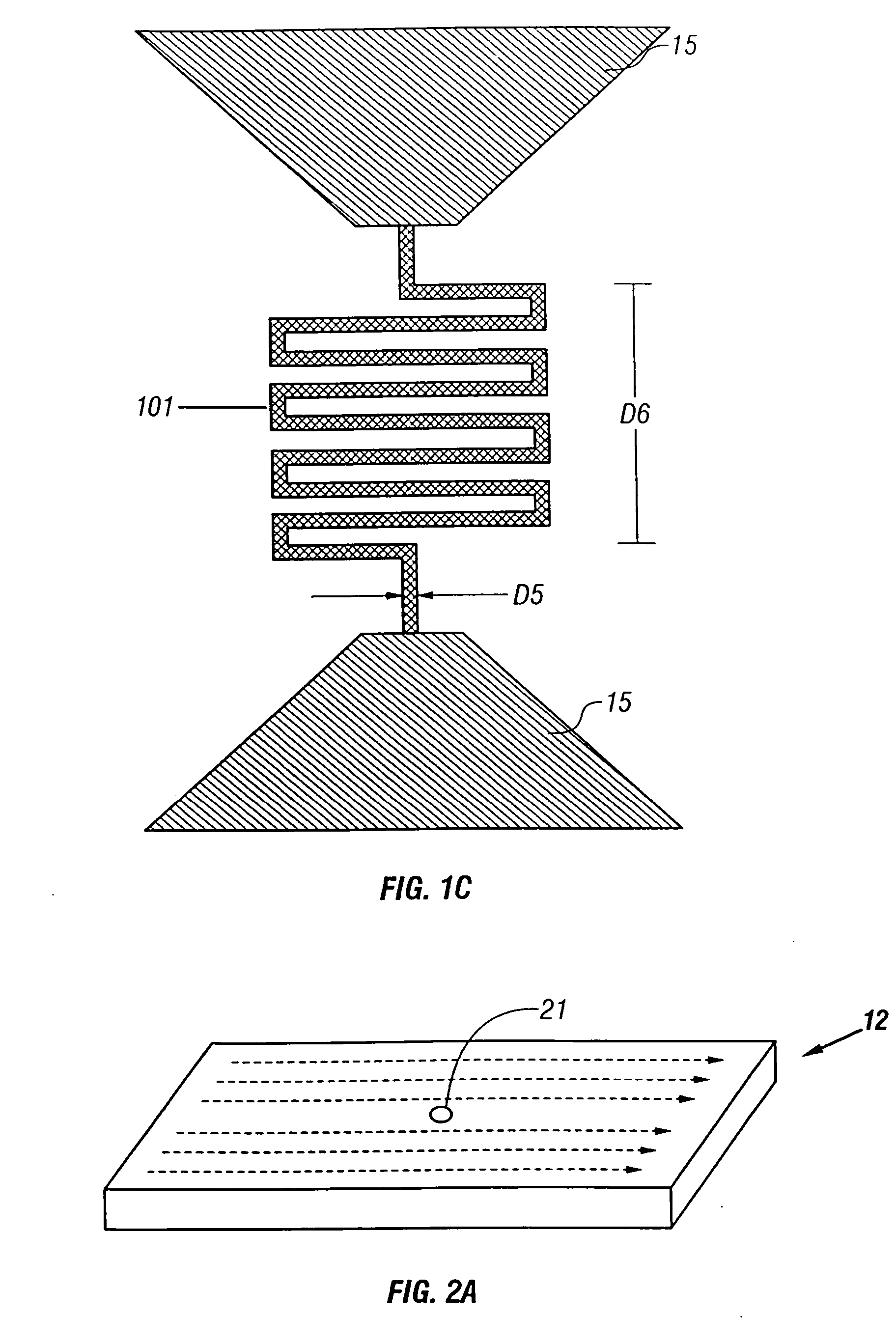
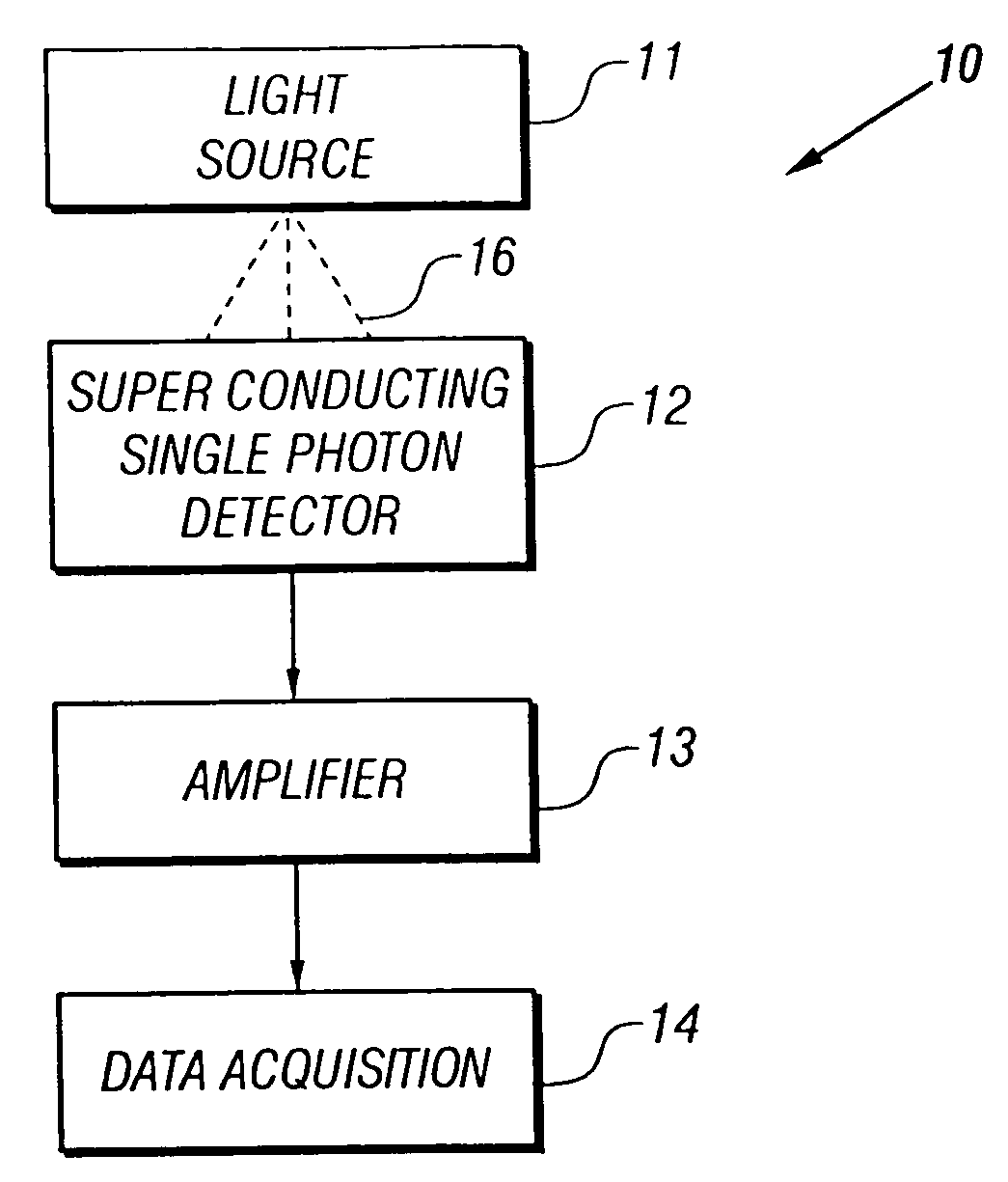
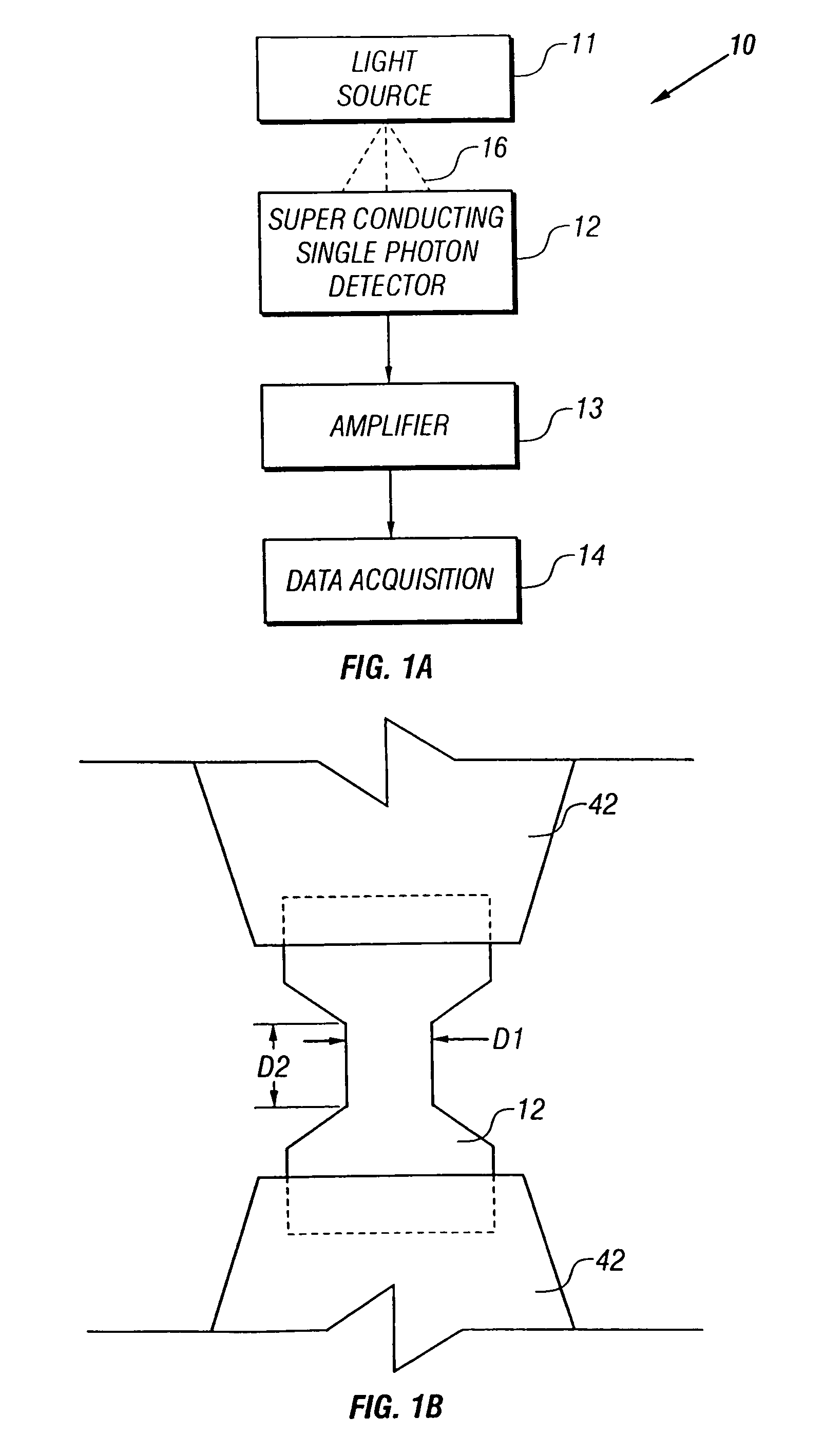
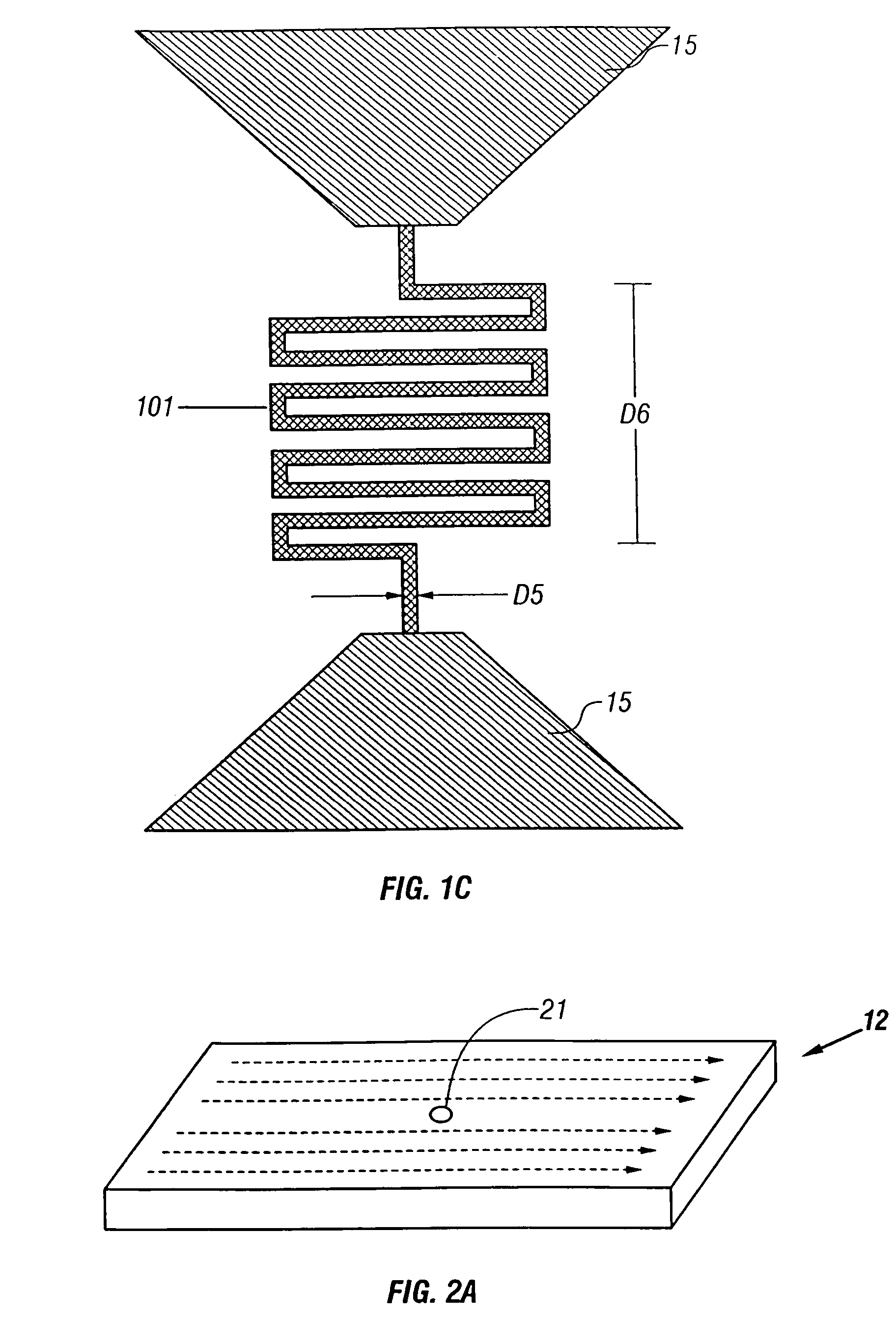
Superconducting single photon detector
InactiveUS20050051726A1Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease surface areaSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDevice materialSuperconductor classification
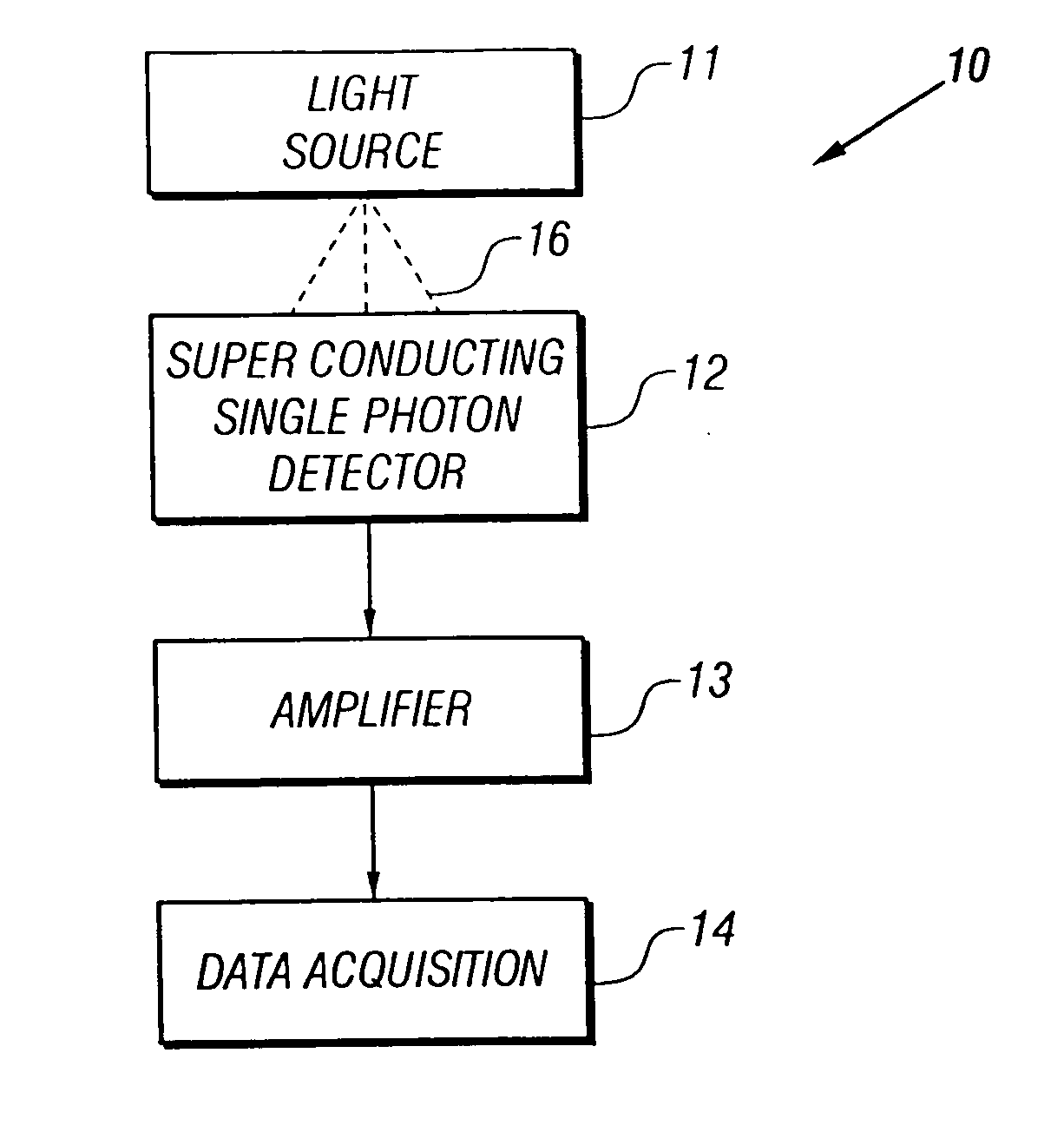
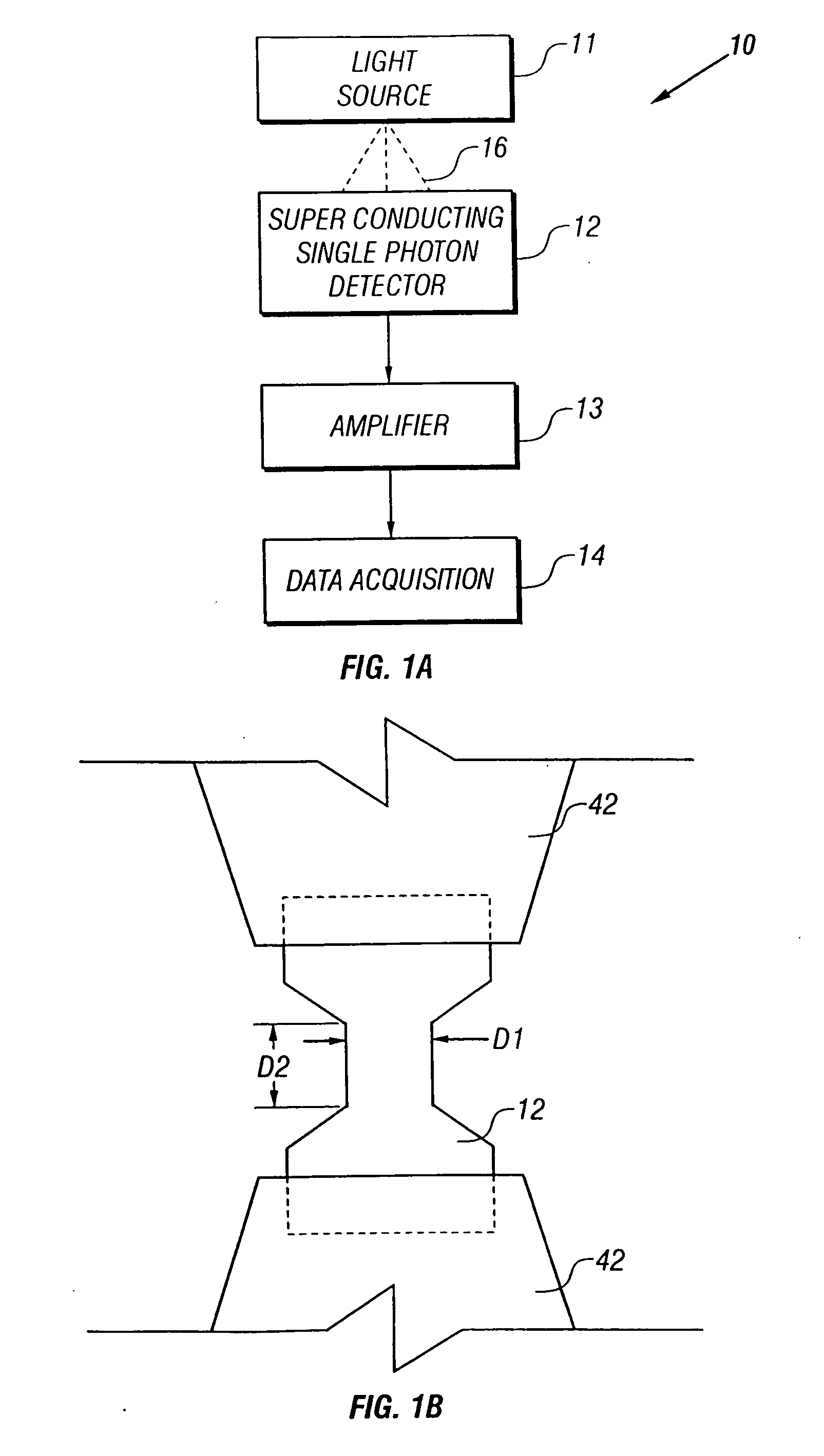
A single-photon detector includes a superconductor strip biased near its critical current. The superconductor strip provides a discernible output signal upon absorption of a single incident photon. In one example, the superconductor is a strip of NbN (niobium nitride). In another example, the superconductor strip meanders to increase its probability of receiving a photon from a light source. The single-photon detector is suitable for a variety of applications including free-space and satellite communications, quantum communications, quantum cryptography, weak luminescence, and semiconductor device testing.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
Superconducting single photon detector
InactiveUS7049593B2Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease surface areaRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesSuperconductor classificationLuminescence
A single-photon detector includes a superconductor strip biased near its critical current. The superconductor strip provides a discernible output signal upon absorption of a single incident photon. In one example, the superconductor is a strip of NbN (niobium nitride). In another example, the superconductor strip meanders to increase its probability of receiving a photon from a light source. The single-photon detector is suitable for a variety of applications including free-space and satellite communications, quantum communications, quantum cryptography, weak luminescence, and semiconductor device testing.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
Magnetic field and electrical current visualization system
InactiveUS6934068B2Improve imaging effectLarge spacingNon-linear opticsFilm researchSuperconductor classification
Magnetic field and / or electrical current imaging systems utilizing magneto-optical indicator films (MOIF) based on magneto-optical material with in-plane single easy axis type of magnetic anisotropy provide improved magnetic field resolution and dynamic range with the use of specific illumination conditions. Methods that provide the two-dimensional distribution of the external magnetic field vectors are disclosed together with the methods of extraction of said information. The visualizing systems offer high spatial resolution and / or high magnetic field resolution combined with fast sampling rates and the capability of performing large-area imaging. The applications of such systems include nondestructive testing and damage assessment in metal structures via magnetic materials or induced currents, integrated circuit testing and quality control, general magnetic material and thin film research, permanent magnet quality control, superconductor research and many others.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Superconducting integrated circuit technology using iron-arsenic compounds
A new family of superconducting materials with critical temperature up to 55 K have recently been discovered, comprising a crystal structure with atomic layers of iron and arsenic alternating with atomic layers of rare-earth oxide or alkaline earth. The present invention identifies structures for integrated circuit elements (including Josephson junctions) in these and related materials. These superconducting circuit elements will operate at a higher temperature than low-temperature superconductors such as niobium, and may be easier to manufacture than prior-art high-temperature superconductors based on copper-oxides.
Owner:HYPRES
Phonon maser
InactiveUS20080020935A1Inexpensive and quick and safeReduce sending costsExcitation process/apparatusSolid masersMaserSingle crystal
A phonon maser is comprised of a resonant cavity, a superconductive gain medium, and pumping means. The resonant cavity is comprised of highly reflective means and partially reflective means. The superconductive gain medium is an elongated superconductor, which may be a crystalline high-temperature ceramic superconductor or a single-crystal superconductor. The pumping means provide electromagnetic energy for the superconductive gain medium in order to form and then excite Cooper pairs. Trapped in the resonant cavity and amplified by the population inversion, the resonating bundles of superposed free phonons eventually break through the partially reflective means and enter the vacuum of space in a collimated, coherent, and all-penetrating beam of bundles of superposed guest phonons. This beam changes properties of the ambient space, including its gravitational energy.
Owner:VOLFSON BORIS
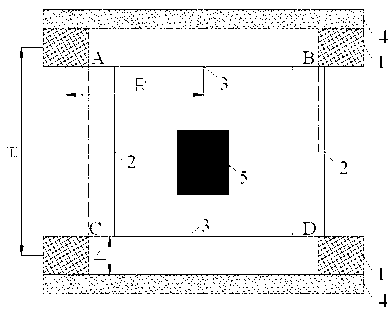
Gravitational field simulation device and method for geotechnical engineering model test
ActiveCN102841129AEasy to testSolve the problem that the force of the rock and soil mass cannot be truly reflectedMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic tension forceModel sample
The invention relates to a gravitational field simulation device and method for geotechnical engineering model test, belonging to the geotechnical engineering test device and method. According to the characteristic that magnetic force is applied to the materials with similar magneto-sensitive properties in the magnetic field, the magnetic field is used to simulate the gravitational field needed by the model test. A test device formed by combing a permanent magnet or superconductor with an energized coil is used to generate magnetic field intensity which is distributed linearly along the direction of the gravitational field, the minimum magnetic field intensity is enough to subject the materials with similar magneto-sensitive properties to saturation magnetization, and the magnetic field intensity which is distributed linearly can ensure that the magnetic force which has the same direction as the gravitational field and is adjustable in size can be applied to the materials with similar magneto-sensitive properties, thus the gravitational state needed by the model test can be obtained. The gravitational field simulation device and method have the advantages that: the stable magnetic field which is distributed linearly can be generated, the stable constant magnetic force can be applied to the materials with similar magneto-sensitive properties, and the gravitational field needed by the model sample made of the materials with similar magneto-sensitive properties can be simulated by the gravitational field. The gravitational field simulation device is simple, easy and convenient to test, and low in cost, and has high strong operability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
NMR spectrometer
InactiveUS20080231277A1Lower resistanceSuppress interferenceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a highly-sensitive nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer which achieves a high Q factor using a superconductor, and concurrently which is provided with a probe antenna maintaining the magnetic homogeneity of the static magnetic field in a sample space. An antenna coil is fabricated by using a wire having a superconducting layer formed on the surface of a metal wire.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Superconductor magnetic resonance imaging system and method (super-MRI)
ActiveUS8253416B2Magnetic measurementsMachines/enginesMagnetic field gradientHigh-temperature superconductivity
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Superconducting dot/anti-dot flux qubit based on time-reversal symmetry breaking effects
InactiveUS20020130313A1Overcome effectSuppresses decoherence processQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMagnetic force microscopeSuperconductor classification
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a dot of superconductive material, where the superconductor possesses a dominant order parameter with a non-zero angular momentum and a sub-dominant order parameter that can have any pairing symmetry. Alternately a solid-state quantum computing structure includes an anti-dot, which is a region in a superconductor where the order parameter is suppressed. In either embodiment of the invention, circulating persistent currents are generated via time-reversal symmetry breaking effects in the boundaries between superconducting and insulating materials. These effects cause the ground state for the supercurrent circulating near the qubit to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents store quantum information, which creates the basis of qubits for quantum computing. Writing to the qubits and universal single qubit operations may be performed via the application of magnetic fields. Read-out of the information may be performed using a SQUID microscope or a magnetic force microscope.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
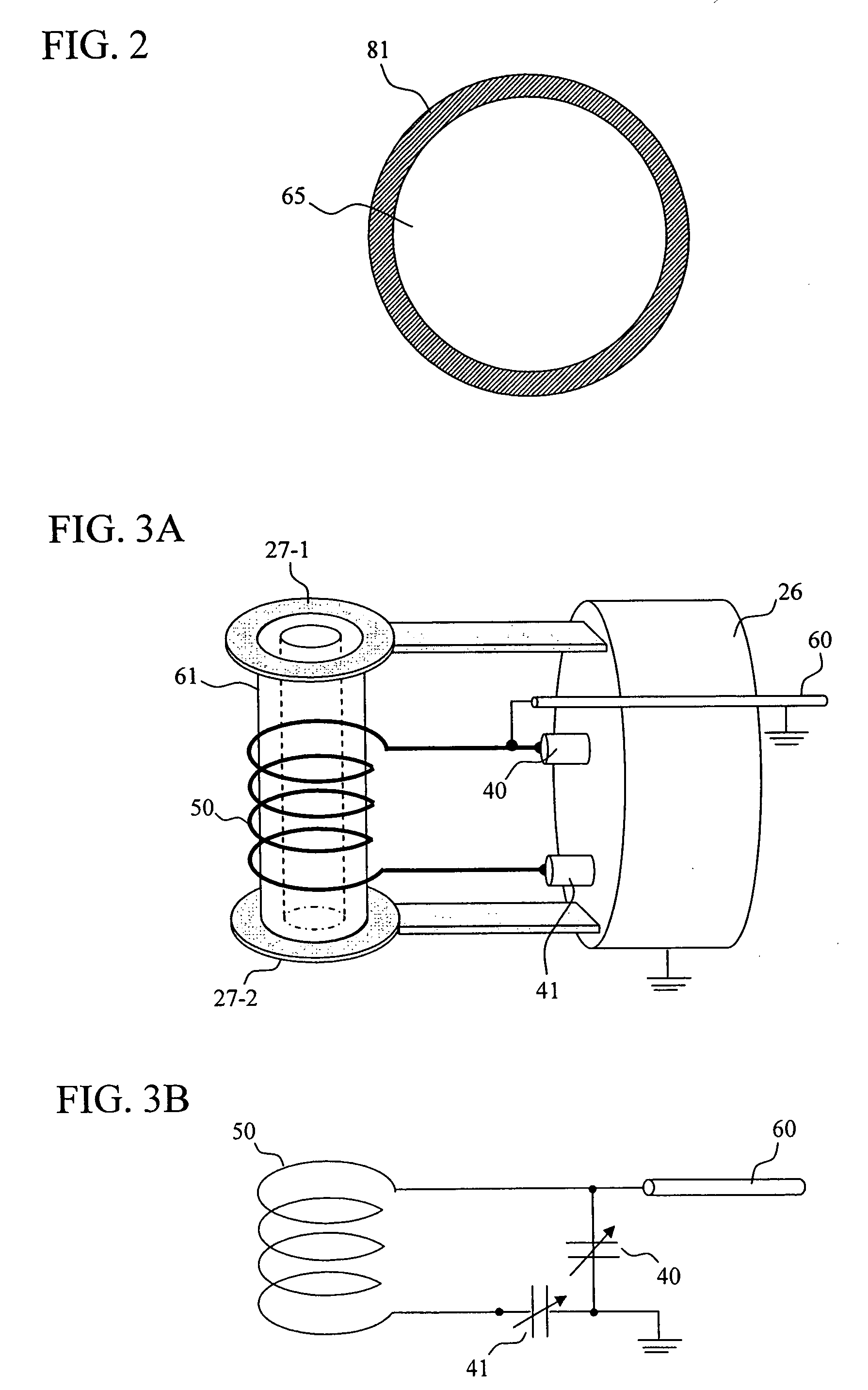
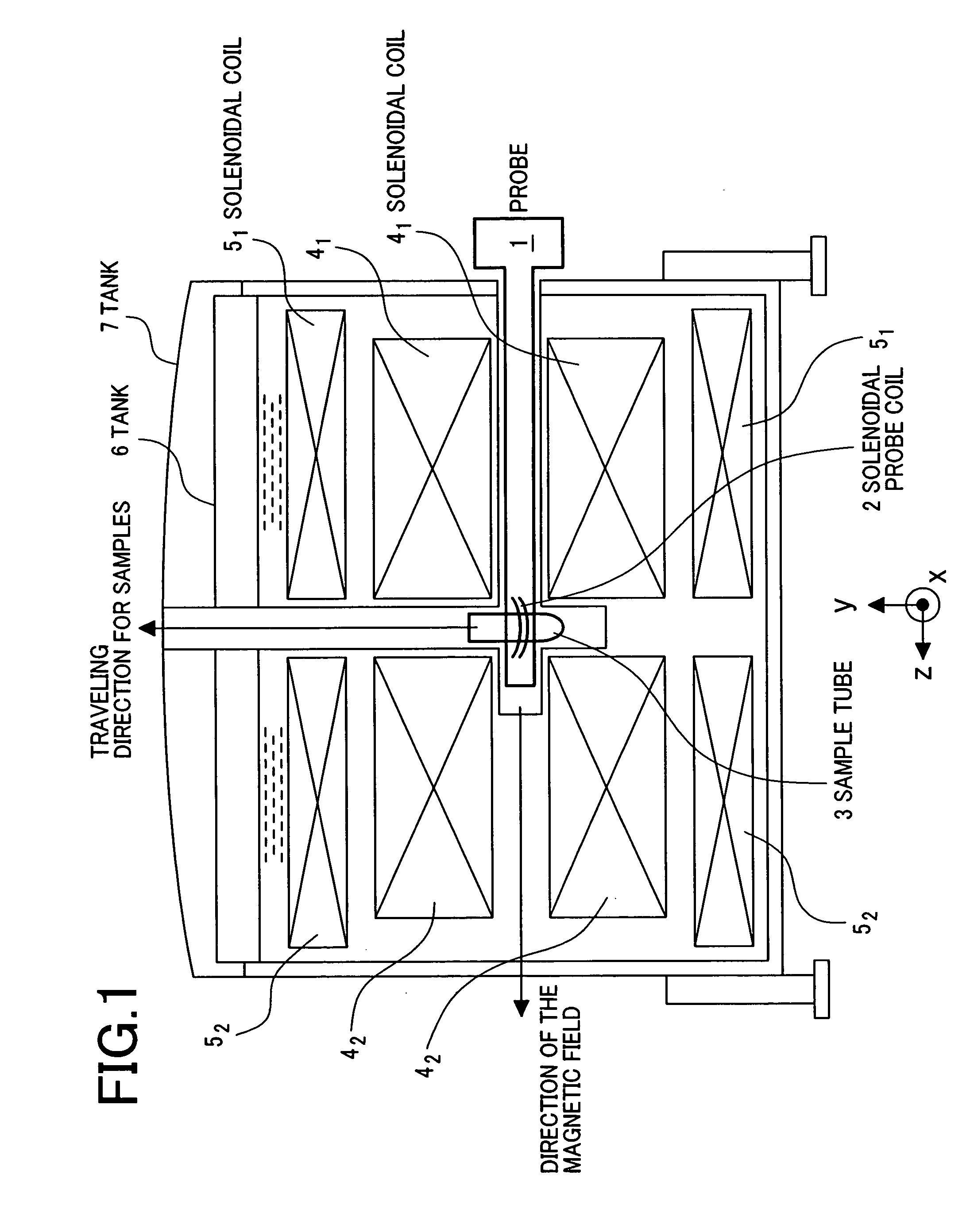
Nuclear magnetic resonance probe coil
InactiveUS7164269B2High quality factorUniform magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
A solenoid-type probe coil wherein superconductive thin film is used, whose quality factor is high, and which is put in an uniform magnetic field and occupies a small space is provided. For that purpose, the coil is made by piling up, in generally parallel, two or more substrates on which superconductive film is formed and connecting superconductors and normal-metal thin films through capacitance or low contact resistance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Machinery windings of yttrium barium copper oxide and related coated conductor
InactiveUS7566684B1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsDeferred-action cellsYttrium barium copper oxideElectrical conductor
A superconductor coating inclusive, tape-like electrical conductor and windings using such conductor for magnets and electrical machines, etc. The described windings are suited for inclusion of successor superconductor materials such as yttrium barium copper oxide wherein magnetic flux related losses can potentially be excessive and preclude successful machine operation. Winding orientation and configuration of the conductor in an alternating current machine for lower losses are disclosed along with methods and apparatus for achieving the desired windings. Windings intended for differing locations within a machine of this type are made possible by the invention. Equations relating to magnetic losses incurred in such windings are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Terahertz signal detection device
InactiveCN103090977AHigh sensitivityImprove job stabilityPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSuperconductor classificationMetal thin film
The invention discloses a terahertz signal detection device which comprises an integrated chip. A low-temperature semiconductor reading circuit and a superconductor detector are simultaneously arranged on the integrated chip, the low-temperature semiconductor reading circuit and the superconductor detector are mutually communicated, and the superconductor detector is used for detecting a terahertz signal. The terahertz signal detection device can not only reduce system noise, and improve sensitivity, working stability and operation speed of a superconductor terahertz direct detector, but also facilitates designing and manufacturing of an imaging system of a terahertz two-dimensional detection array based on a multichannel reading circuit. The terahertz signal detection device can integrate a superconductor component and a semiconductor component on the same chip, and can easily achieve metal thin film wire leading through micromachining technology. Due to the fact that an integration level is improved, a bonding pad is greatly reduced, and therefore, the aims that noise is reduced and systematic operation speed is improved are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
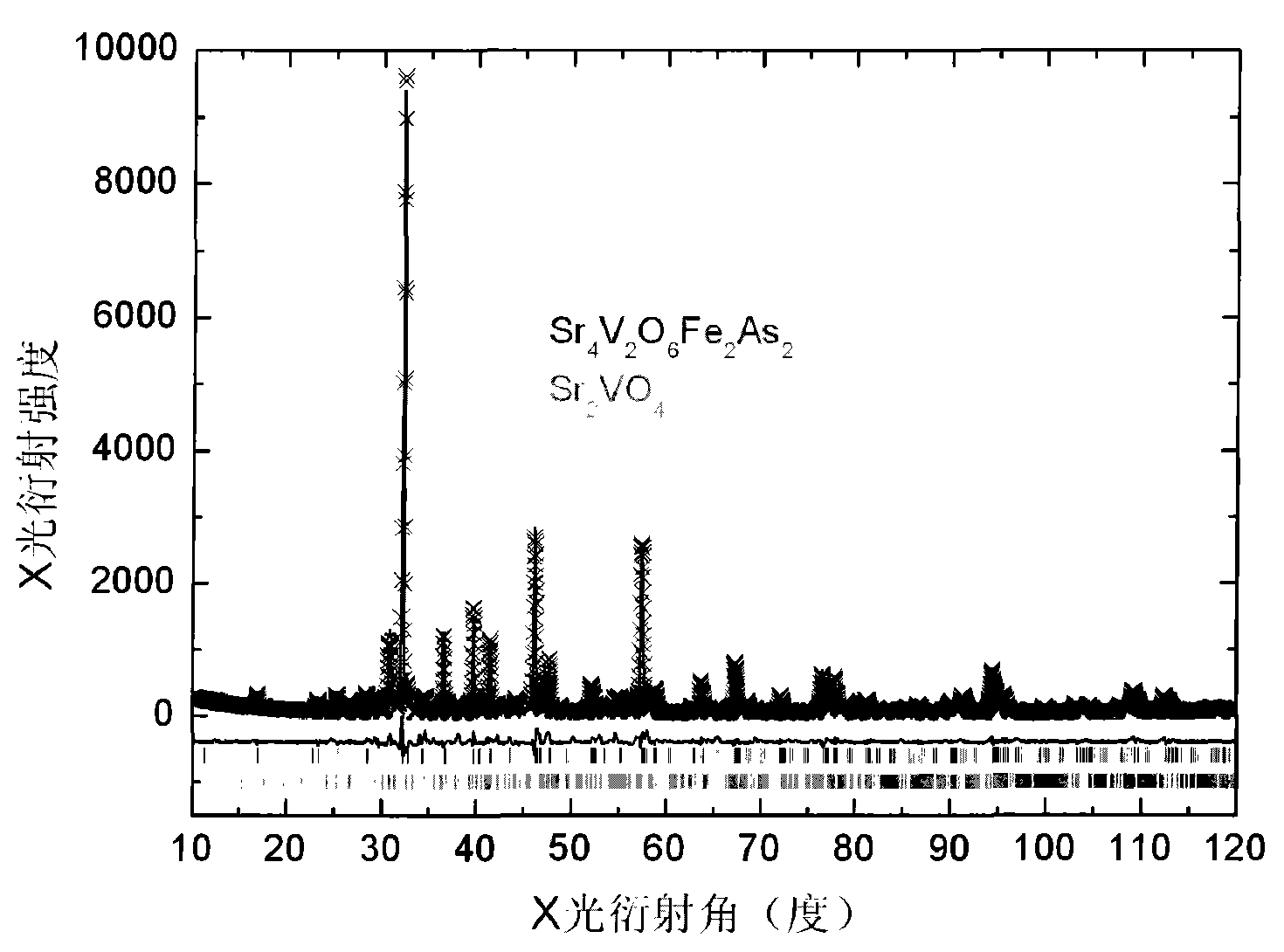
Perovskite structure-based single-phase iron-based superconductive material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101993247AGood superconducting stabilityHigh critical fieldChemical reactionSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention relates to a perovskite structure-based single-phase iron-based superconductive material and a preparation method thereof. The material has a two-dimensional laminar structure, and the composition is shown by the formula of Sr4V2O6Fe2As2. The preparation method of the material comprises the following steps of: preparing a SrAs precursor sample and an FeAs precursor sample; mixing the precursors, Sr0, V2O3, Fe and the like by using a solid-state chemical reaction method; and reacting at a high temperature to directly synthesize a perovskite layer-based iron-based superconductive material. Compared with other known iron-based superconductors, the material has higher bidimensionality. The material has electronic carrier characteristics, carrier concentration of 1,020 to 1,022 / cm<3> and superconductive transformation temperature of about 40K. An upper critical magnetic field of the material at a low temperature is estimated to be greater than 250 teslas, so that the material is probably applied to superconductive power transmission, strong magnetic field generation and the like. In addition, the material can also be used in a superconductive filter and the like. The preparation method is simple.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for measuring the neuro-magnetic field from a human brain and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20050272996A1Preventing trapping of geomagnetismReduce adverse effectsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringRelative displacementLow noise
The present invention provides a low-noise MEG apparatus of high sensitivity. A MEG apparatus using a magnetic shield of high critical temperature superconductor is set on the floor of a building via mechanical vibration suppressor supports to prevent appearance of noise signals. Also, the apparatus is equipped with means for preventing any relative displacement between the SQUID magnetic sensors and the magnetic shield of high critical temperature superconductor, thereby not letting an inevitable mechanical vibration of least strength produce any variable components of the trapped static magnetic field, which the SQUID magnetic sensors could be sensitive to.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Superconducting devices by optimization of the superconductor's local critical current
ActiveUS20160042841A1Increase the critical currentReduce AC-lossSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetsCondensed matter physicsCritical current
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for producing superconducting devices and to superconducting devices. The method comprises determining one or more regions of reduced critical current density in the superconducting device and modifying the critical current density in the one or more regions of reduced critical current density, so as to increase the overall critical current or to decrease the overall AC losses of the superconducting device. The modifying comprises modifying the amount and / or distribution of the superconducting material in the one or more regions of reduced critical current density; and / or modifying the chemical composition of the superconducting material in the one or more regions of reduced critical current density; and / or decreasing the cooling temperature in the one or more regions of reduced critical current density. A superconducting device formed according to such method can also be provided.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
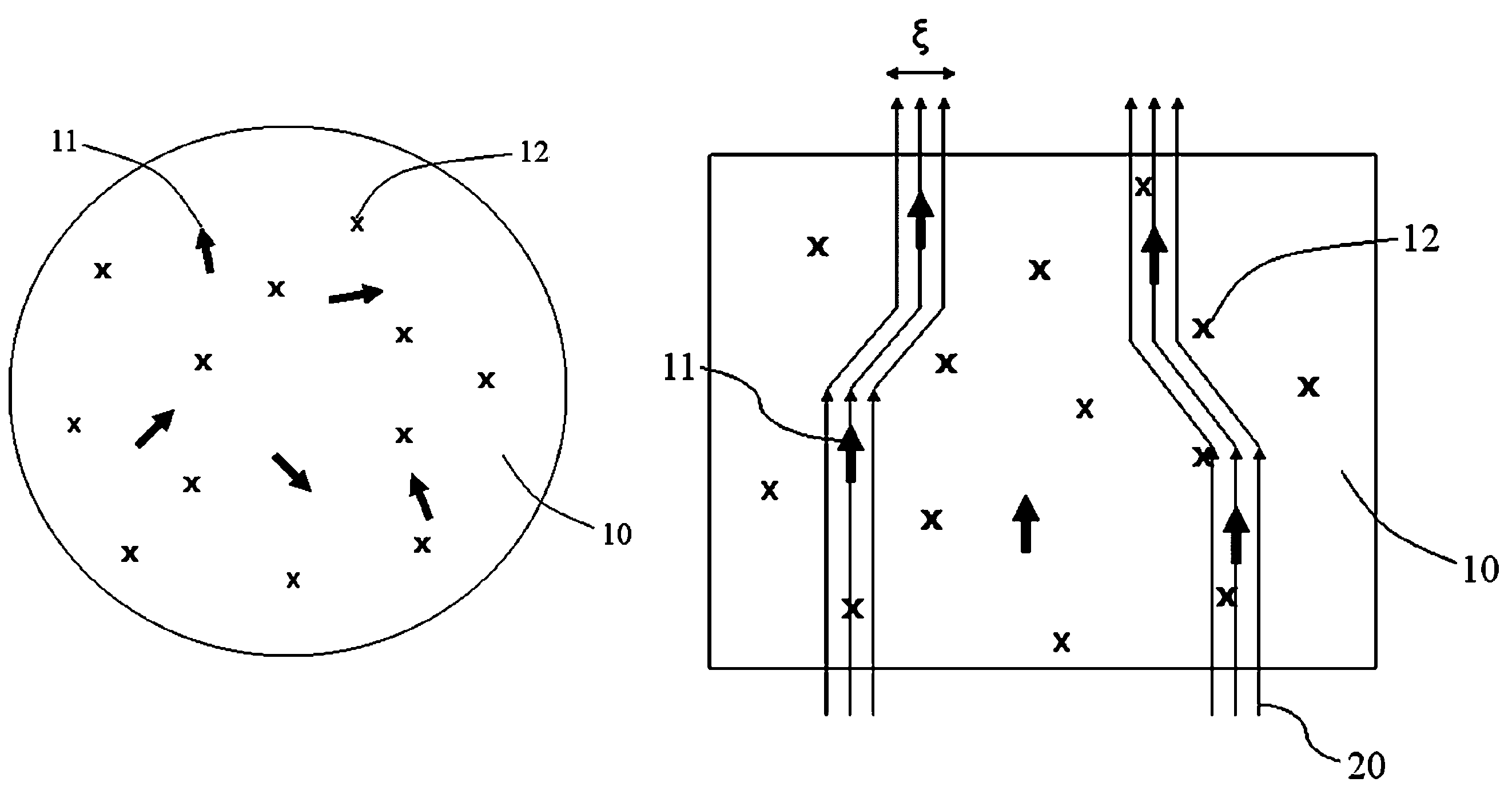
Superconducting NMR resonators with macroscopically homogeneous superconductor distribution
InactiveUS6605945B2Minimal influenceGood compensationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorResonance
An NMR resonator for receiving RF signals at desired resonance frequencies from a measuring sample in a volume under investigation disposed about a coordinate origin (x,y,z=0), with a means for producing a homogeneous magnetic field B.sub.0 in the direction of a z axis, wherein superconducting conductor structures are disposed between z=-.vertline.z.sub.1.vertline. and z=+.vertline.z.sub.2.vertline. on a surface which is translation-invariant (=z-invariant) in the z direction at a radial separation from the measuring sample, is characterized in that a compensation arrangement is additionally provided on the z-invariant surface, which extends to values of at least +.vertline.z.sub.2.vertline.+0.5.vertline.r.vertline.>z> -.vertline.z.sub.1.vertline.-0.5.vertline.r.vertline., wherein .vertline.r.vertline. is the minimum separation between the measuring sample and the compensation arrangement, wherein the compensation arrangement comprises further superconducting conductor structures which are RF-decoupled from the RF resonator, with the conductor structures of the compensation arrangement and of the RF resonator being composed of individual surface sections ("Z-structures") which comprise superconducting structures and are disposed in the z-invariant surface to each extend along the entire length in the z direction of the conductor structures of the compensation arrangement and of the RF resonator, those superconducting structures being disposed such that decomposition of the surface of the Z structures into a plurality of small equally sized surface elements and application of a homogeneous test magnetic field along the surface normal of each surface element for all surface elements which differ only with respect to their z position, induces a magnetic dipole moment of the same strength. In this manner, the disturbing influence caused by magnetization of the superconductor is very well compensated for.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Generation of electric oscillations by continuous, supercooled superconductors under a voltage
InactiveUS20060097809A1Increase output powerLess brittleOscillations generatorsSmall amplitudeSuperconductor classification
The essence of the invention is the use of supercooled superconductors for generation of high-frequency electric oscillations. The superconductor is supercooled, i.e. in the normal phase at a temperature lower than the critical transition temperature for superconductivity, under an applied electric energy source. In such non equilibrium conditions the superconductor can have negative differential conductivity which can be used as an active medium in generators of electric ( current and voltage) oscillations. Such generators can be used in the superconducing electronics. Oscillation can be modulated by the change of bias voltage, electrostatic doping by a gate electrode, or by light. When small amplitude oscillations are stabilized near to the critical temperature the generator can be used as a bolometer. The supercooled superconductors can be used also as transistors and frequency mixers. The negative differential conductivity of superconductor is created by the excess conductivity of fluctuation Cooper pairs. This behavior is predicted by the solution of the Boltzmann kinetic equation of the metastable in the normal phase Cooper pairs. Boltzmann equation for fluctuation Cooper pairs is derived as a state-of-the-art application of the microscopic theory of superconductivity.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
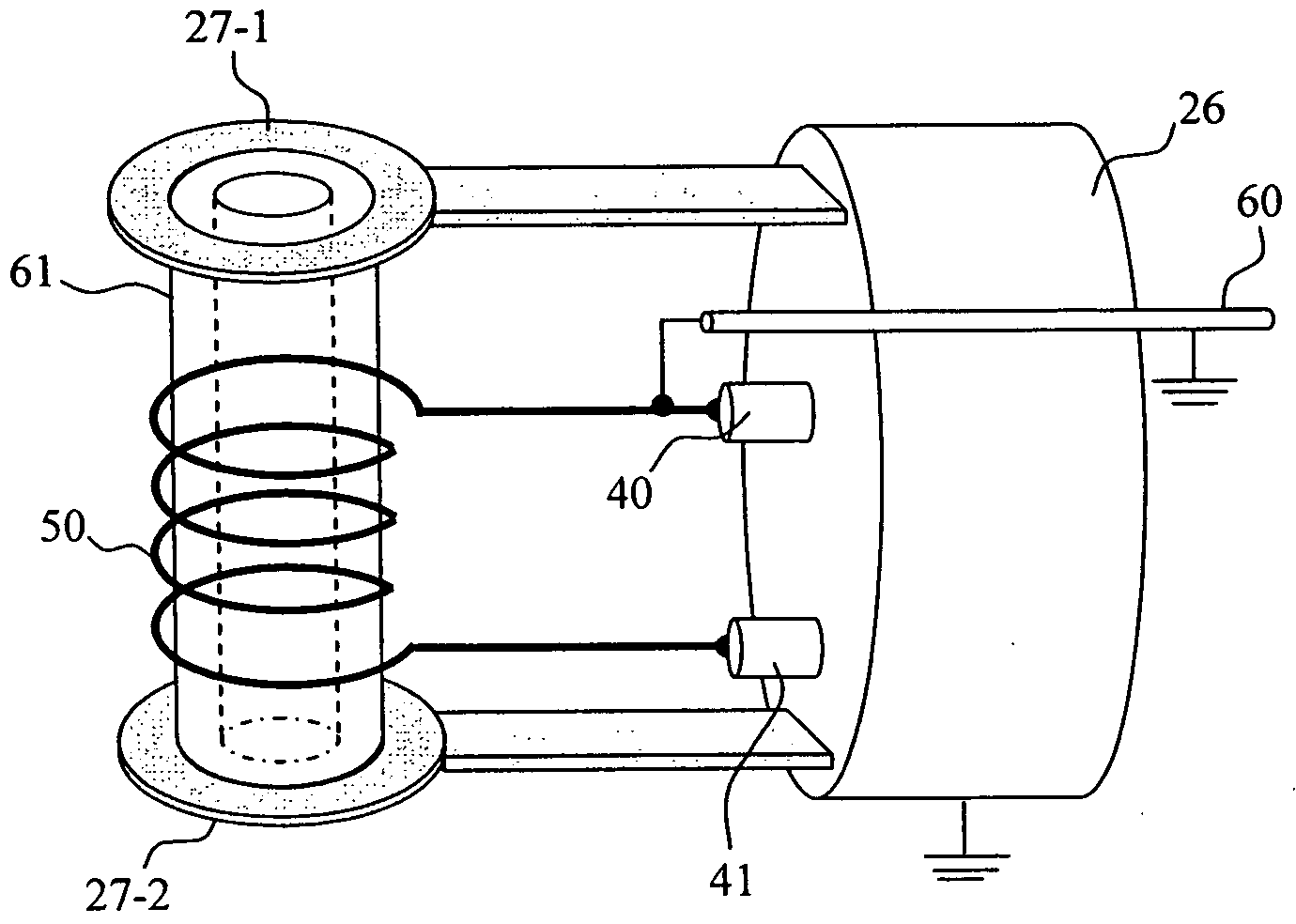
Multi-point testing system for dynamic surface magnetic field and thermal distribution of superconductor
InactiveCN102359905AImprove detection accuracySolve fundamental key issuesMaterial thermal conductivityTesting foodCopperTops mode
The invention discloses a multi-point testing system for the dynamic surface magnetic field and thermal distribution of a superconductor, which comprises a bracket consisting of a horizontally-arranged copper support plate and a vertically-arranged copper support bar; a vibration exciter, an aluminum tray and a superconductor testing device are sequentially arranged on the copper support plate in a bottom-top mode; and a height-adjustable aluminium beam, a permanent magnet hung on the aluminum beam and a permanent magnet fixed bolt for fixing the permanent magnet on the aluminium beam are horizontally arranged on the copper support bar. By using the multi-point testing system for the dynamic surface magnetic field and thermal distribution of a superconductor disclosed by the invention, the defects in the prior art that a deformation measuring sensor is poor in adaptability, poor in validity of measured data, poor in measurement accuracy, low in detection precision and the like can be overcome, thereby achieving the advantages that a deformation measuring sensor is good in adaptability, good in validity of measured data, good in measurement accuracy and high in detection precision.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Nuclear magnetic resonance probe coil
InactiveUS20060119359A1High quality factorSpace minimizationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
A solenoid-type probe coil wherein superconductive thin film is used, whose quality factor is high, and which is put in an uniform magnetic field and occupies a small space is provided. For that purpose, the coil is made by piling up, in generally parallel, two or more substrates on which superconductive film is formed and connecting superconductors and normal-metal thin films through capacitance or low contact resistance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for acquiring alternating-current loss of three-dimensional asymmetric structure high-temperature superconducting magnet
ActiveCN109884402AEffective calculationSmall amount of calculationResistance/reactance/impedenceNonlinear resistorNon symmetric
The invention discloses a method for acquiring alternating-current loss of a three-dimensional asymmetric structure high-temperature superconducting magnet, wherein a three-dimensional finite elementanalytical model is built according to the structure of the superconducting magnet, the magnetic field intensity of a superconducting domain is calculated and extracted, the magnetic field intensity as a Dirichlet boundary condition is loaded to a local equivalent two-dimensional model so as to realize effective calculation of the alternating-current loss of the superconducting winding. Accordingto the method in the invention, the technical problem that when the alternating current loss of the three-dimensional asymmetric high-temperature superconducting magnet is calculated, normal solutioncannot be achieved due to too high degree of freedom of the model; meanwhile, according to the method proposed by the invention, the nonlinear resistance characteristic of a superconductor and the nonlinear BH magnetization characteristic of a ferromagnetic material can be fully considered, and the method has important significance in evaluating the alternating-current loss during design of the actual engineering superconducting magnet.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Modularization reconfigurable method and device based on superconductive magnetic flux pinning connection
InactiveCN103023389AEasy to controlEasy to implementMagnetic holding devicesFlux pinningElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a modularization reconfigurable method based on superconductive magnetic flux pinning connection and a simulation device applying the method. Particularly, interaction of an II-type high-temperature superconductor with a magnet and the characteristic of controllable magnetic field direction and size are utilized to establish reconfiguration of the modularization structure in a manner of establishing a superconductive magnetic flux pinning connecting interface. The magnetic flux pinning characteristic of the high-temperature superconductor in a superconducting state is fully utilized, the superconductive magnetic flux pinning connecting interface configured under the characteristic has certain rigidity and dampness and can be compared as connection by a spring having certain rigidity, and the superconductor can naturally enter the superconductive state in a space environment so that the reconfigurable method provides brand new developing idea for in-orbit assembly of a modularized spacecraft and has broad application prospect in the field of novel spacecraft development.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Superconductor with enhanced high magnetic field properties, manufacturing method thereof, and MRI apparatus comprising the same
ActiveUS7791343B2Enhanced pinningHigh propertyMagnetic measurementsSuperconductor detailsElectric power transmissionNon magnetic
A superconductor exemplarily described herein includes a superconducting material containing magnetic impurities and non-magnetic disorders formed in the superconducting material. The superconductor described herein is suitable for use in magnet applications and power transmission.
Owner:CUTTING EDGE SUPERCONDUCTORS INC
Device for measuring electric current density of superconductor with Campbell method
InactiveCN103926454ADetermining the Magnetic Field Penetration DepthCurrent density measurementsMagnetic measurementsControl system
The invention discloses a device for measuring the electric current density of a superconductor with the Campbell method. According to the technical scheme, the device for measuring the electric current density of the superconductor with the Campbell method is mainly formed by a detection device and an output signal processing and storage device. The detection device comprises a detection coil and a reference coil. The output signal processing and storage device comprises a tuning circuit, a voltmeter and a computer, the computer is provided with an auxiliary measuring and control system and used for recording and analyzing data, and electric signals formed in the detection coil and the reference coil are tuned through the external tuning circuit to be sent to the voltmeter and the computer. According to the device, flux changes in the coils are represented through the voltage, the magnetic field penetration depth of the superconductor is accordingly determined, the slope of the relation between the magnetic field penetration depth and the magnetic induction intensity is solved to obtain the superconductivity critical current density, effective signals generated by a sample are detected through the two coils, the accuracy and the reliability are achieved, and the Campbell magnetic measurement current theory is achieved through an enforceable measurement tool.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
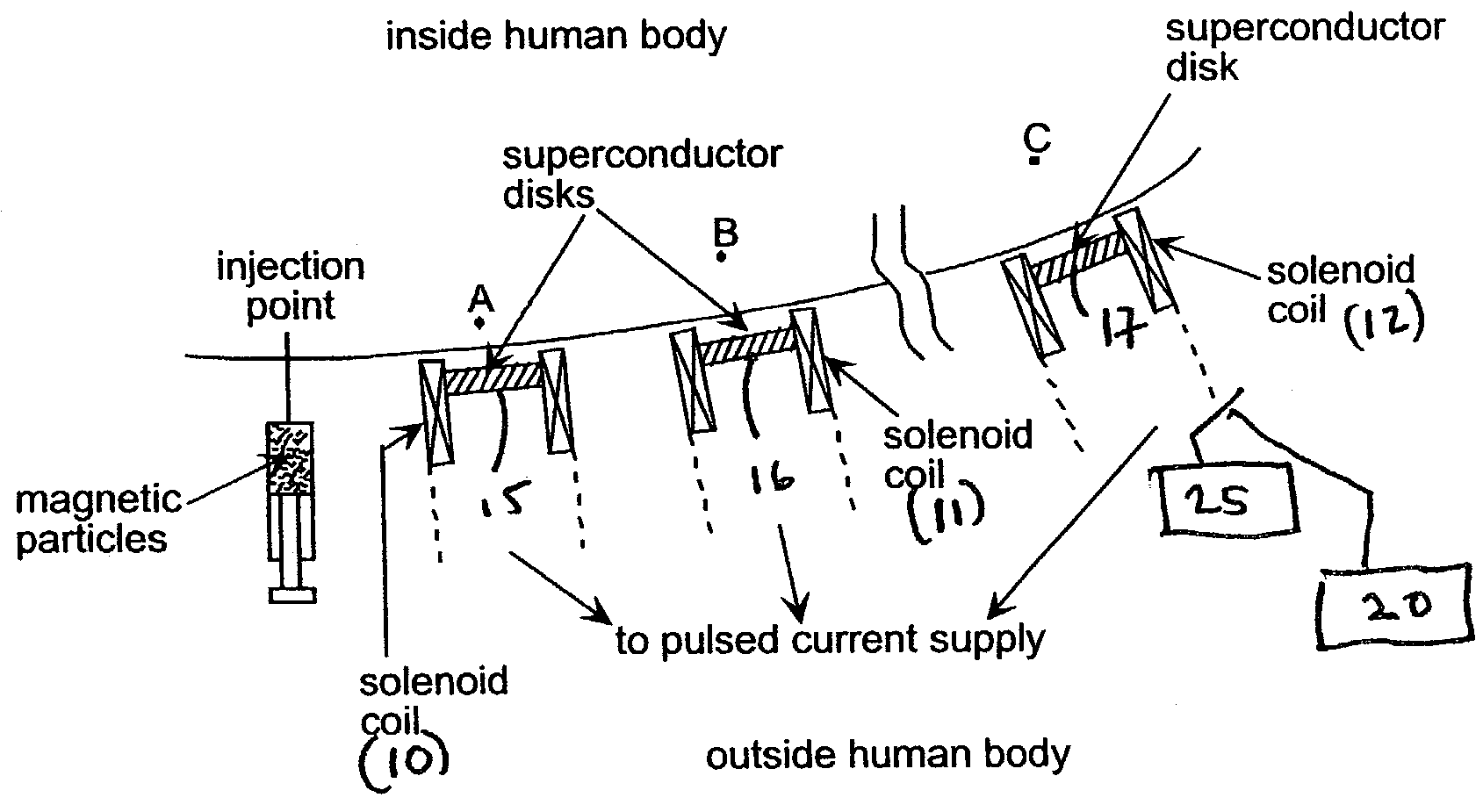
Superconducting magnetic control system for manipulation of particulate matter and magnetic probes in medical and industrial applications
A system and method of controlling movement of magnetic material with at least first and second high temperature superconductors at spaced locations. A plurality of solenoids are associated with the superconductors to induce a persistent currents in preselected high temperature superconductors establishing a plurality of magnetic fields in response to pulsed currents introduced to one or more of the solenoids. Control mechanism in communication with said solenoids and / or said high temperature superconductors are used to demagnetize selected ones of the high temperature superconductors to reduce the magnetic fields substantially to zero. Magnetic material is moved between magnetic fields by establishing the presence thereof and thereafter reducing magnetic fields substantially to zero and establishing magnetic fields in other superconductors arranged in a predetermined configuration.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method for testing a superconductor under increased current load in a series-produced and actively shielded superconducting NMR magnet
ActiveUS7368911B2Increase loadTemporal field stability of the magnet coil configurationSuperconductive properties measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesCurrent loadInductance
A method for testing a new superconducting wire involves charging an actively shielded magnet coil configuration which comprises a first partial region which can be superconductingly short-circuited using an additional switch. A superconductor to be tested under increased current load is used in this first partial region, thereby preventing superconductor in the second partial region from being subjected to this increased current load. Operating currents are determined for both partial regions that have the desired excess current in the first partial region, with the overall field B0 only slightly differing from the standard operating field of the magnet coil configuration. The operating currents are adjusted through initial charging of the overall magnet coil configuration, thereby taking into consideration the inductive coupling between the partial regions and after closing of the additional switch, by continued charging or discharging in the second partial region only. The method permits inexpensive testing of a superconductor in a series-produced NMR magnet under NMR conditions.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Superconducting dot/Anti-dot flux qubit based on time-reversal symmetry breaking effects
InactiveUS20020130315A1Overcome effectSuppresses decoherence processQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMagnetic force microscopeSuperconductor classification
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a dot of superconductive material, where the superconductor possesses a dominant order parameter with a non-zero angular momentum and a sub-dominant order parameter that can have any pairing symmetry. Alternately a solid-state quantum computing structure includes an anti-dot, which is a region in a superconductor where the order parameter is suppressed. In either embodiment of the invention, circulating persistent currents are generated via time-reversal symmetry breaking effects in the boundaries between superconducting and insulating materials. These effects cause the ground state for the supercurrent circulating near the qubit to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents store quantum information, which creates the basis of qubits for quantum computing. Writing to the qubits and universal single qubit operations may be performed via the application of magnetic fields. Read-out of the information may be performed using a SQUID microscope or a magnetic force microscope.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method of making a superconductive oxide body
InactiveUS6291402B1High fracture loadImprove toughnessSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorCuprate
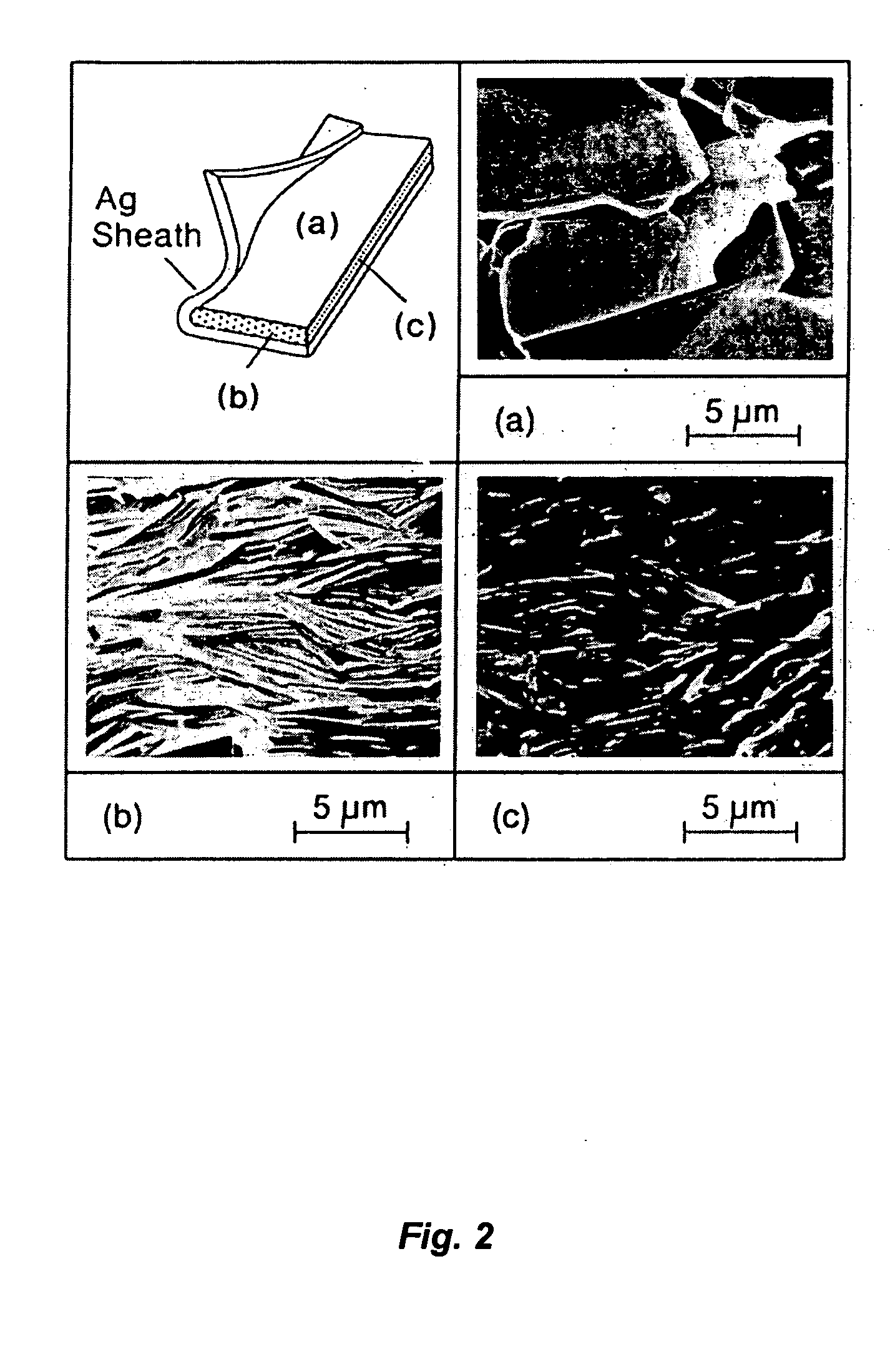
Some mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties of high Tc superconductors such as (Ba, Y) cuprates can be substantially improved by the dispersal of an appropriate metal in the superconductive body. For instance, mixing Ag particles with superconductive powder of nominal composition Ba2YCu3O7 and processing the mixture in the conventional manner can produce superconductive bodies having Tc of about 93 K and substantially greater fracture strength and normal state electrical and thermal conductivity than otherwise identical bodies that do not contain Ag particles.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com