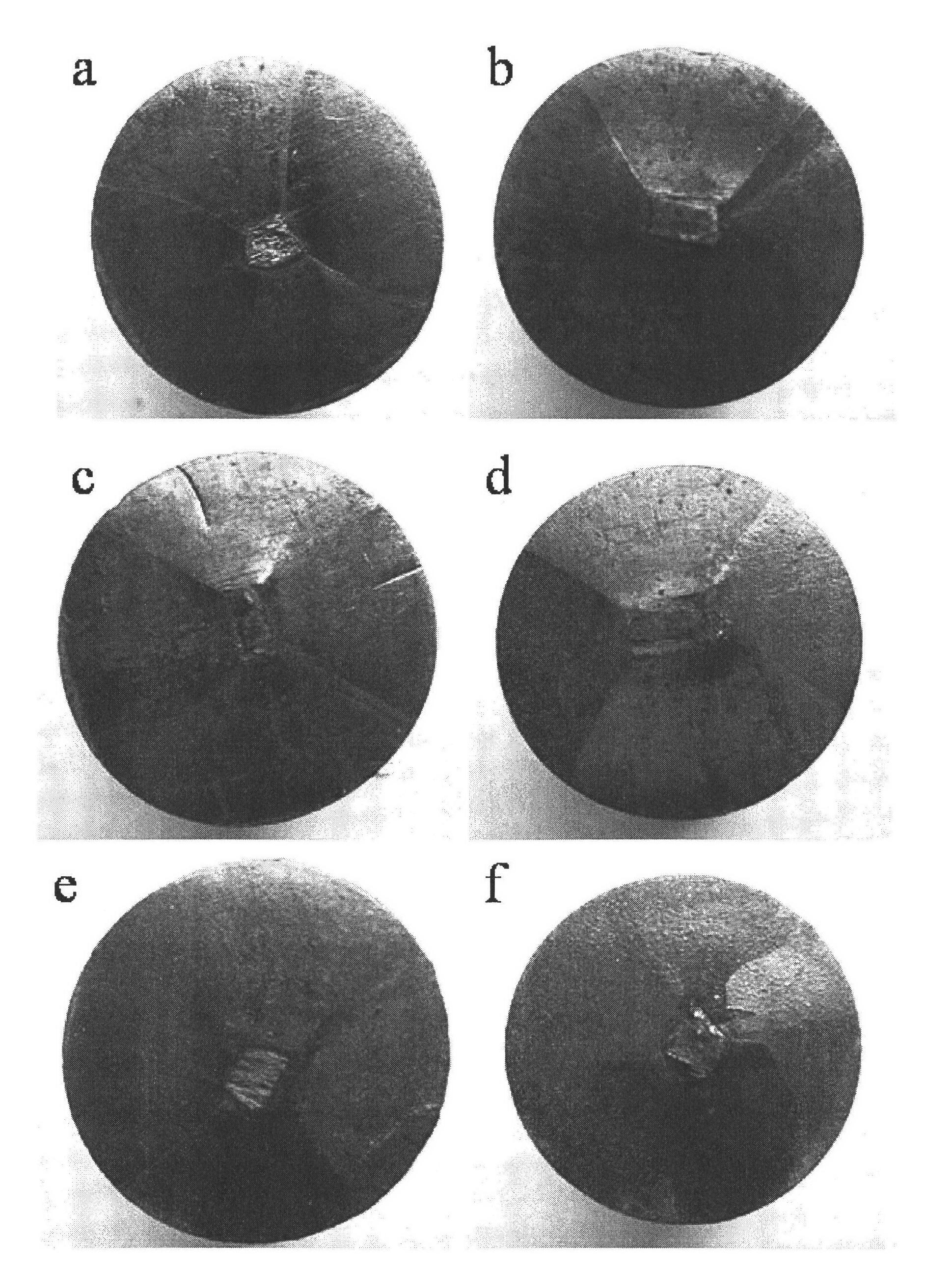
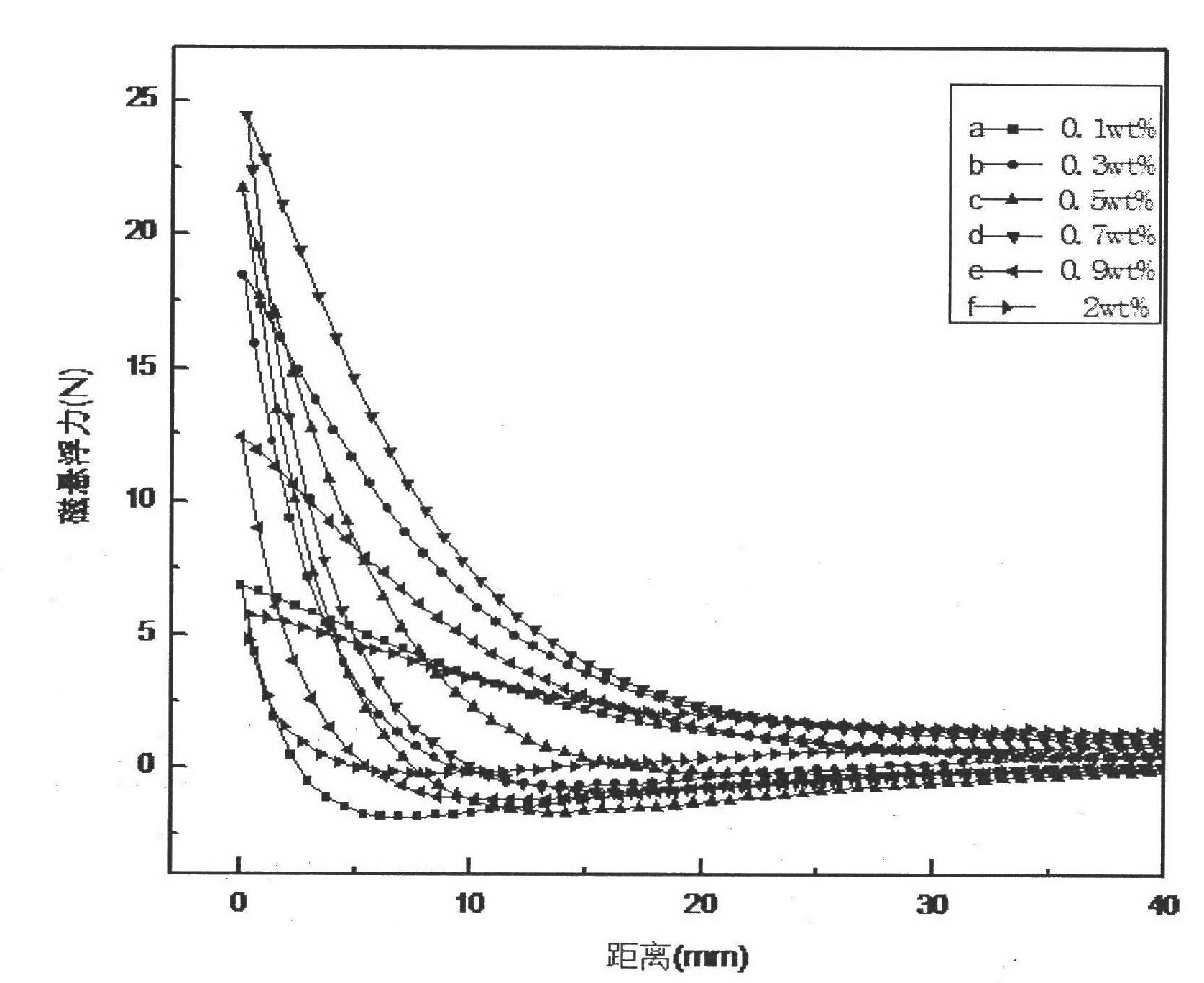
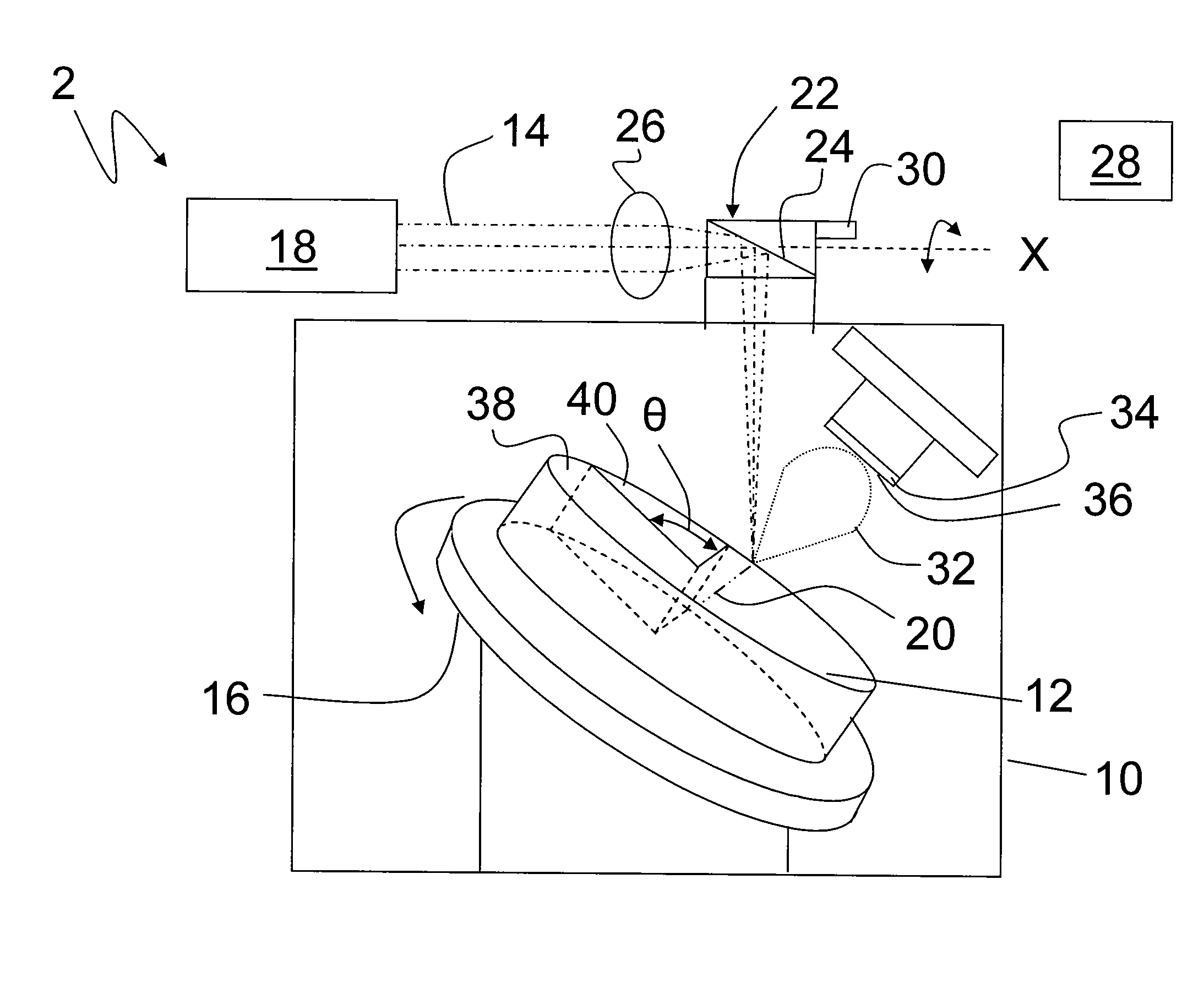
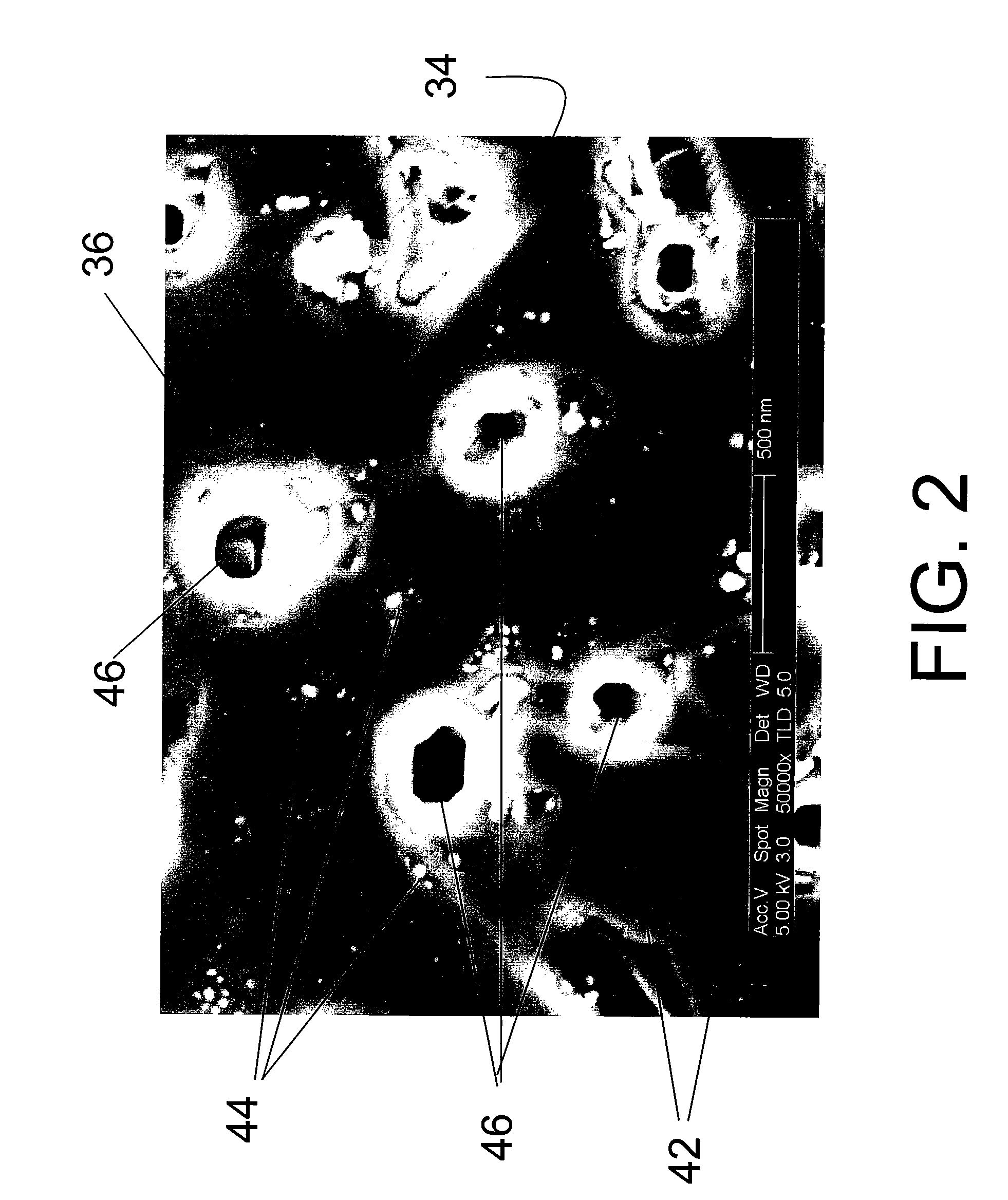
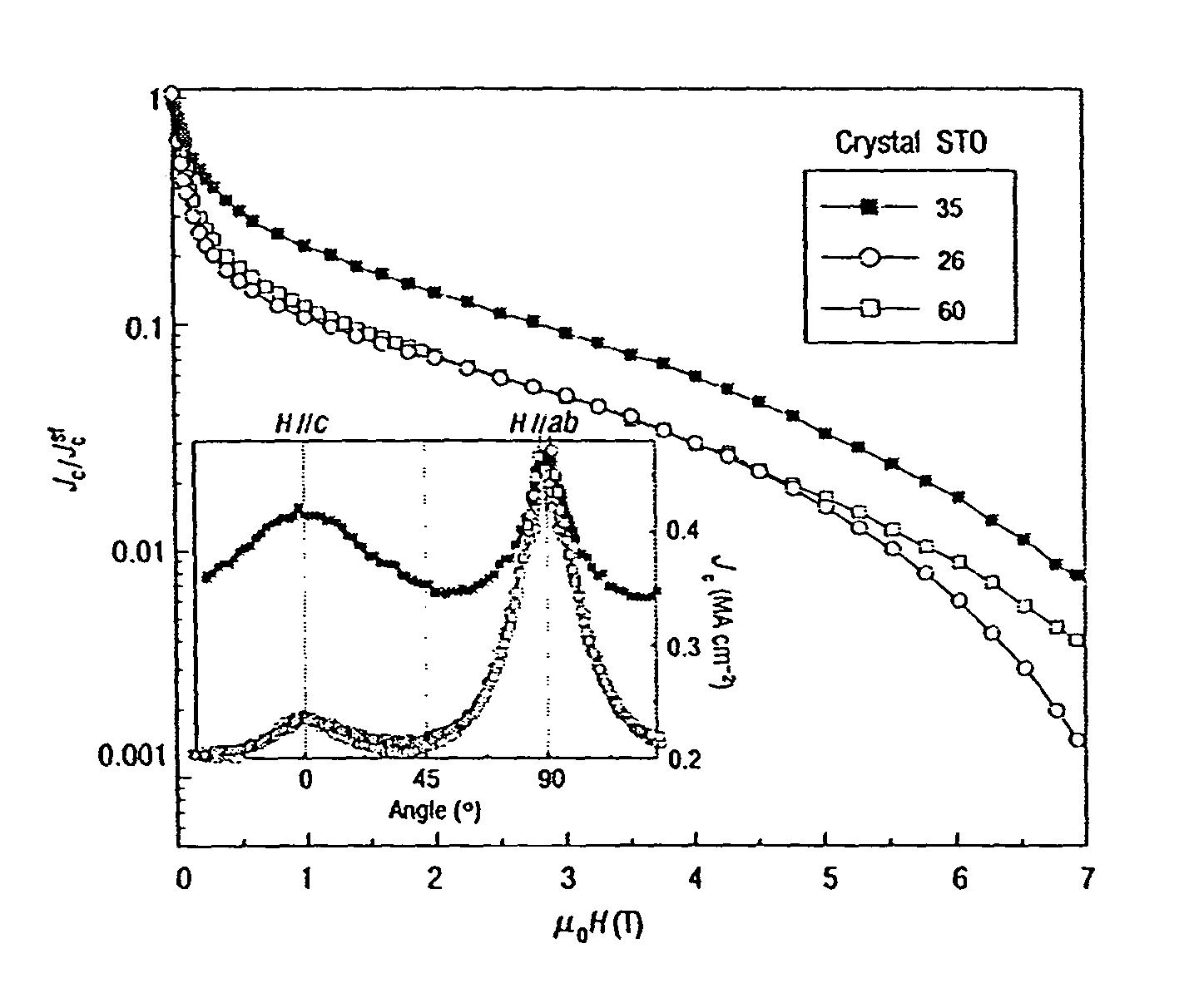
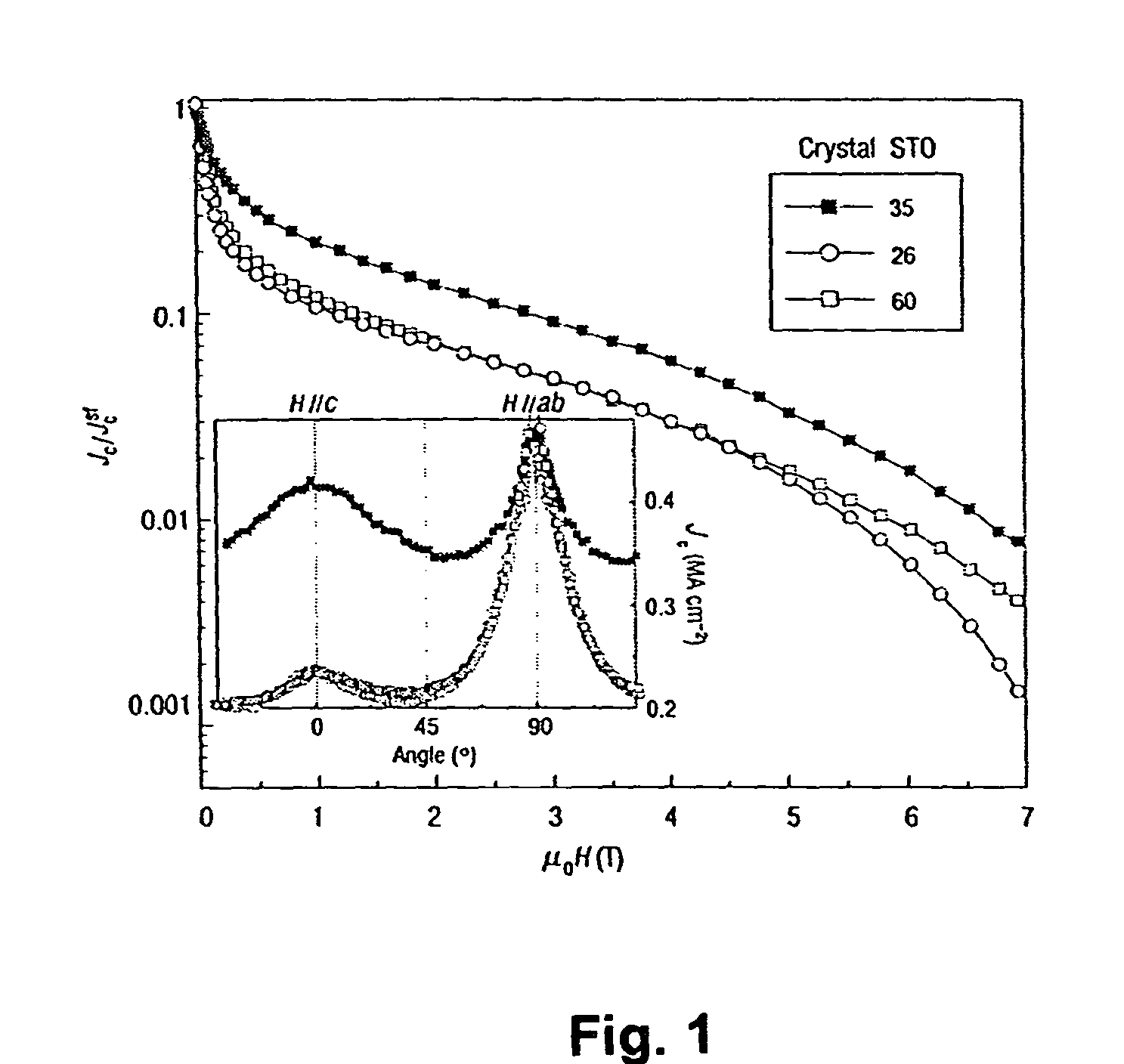
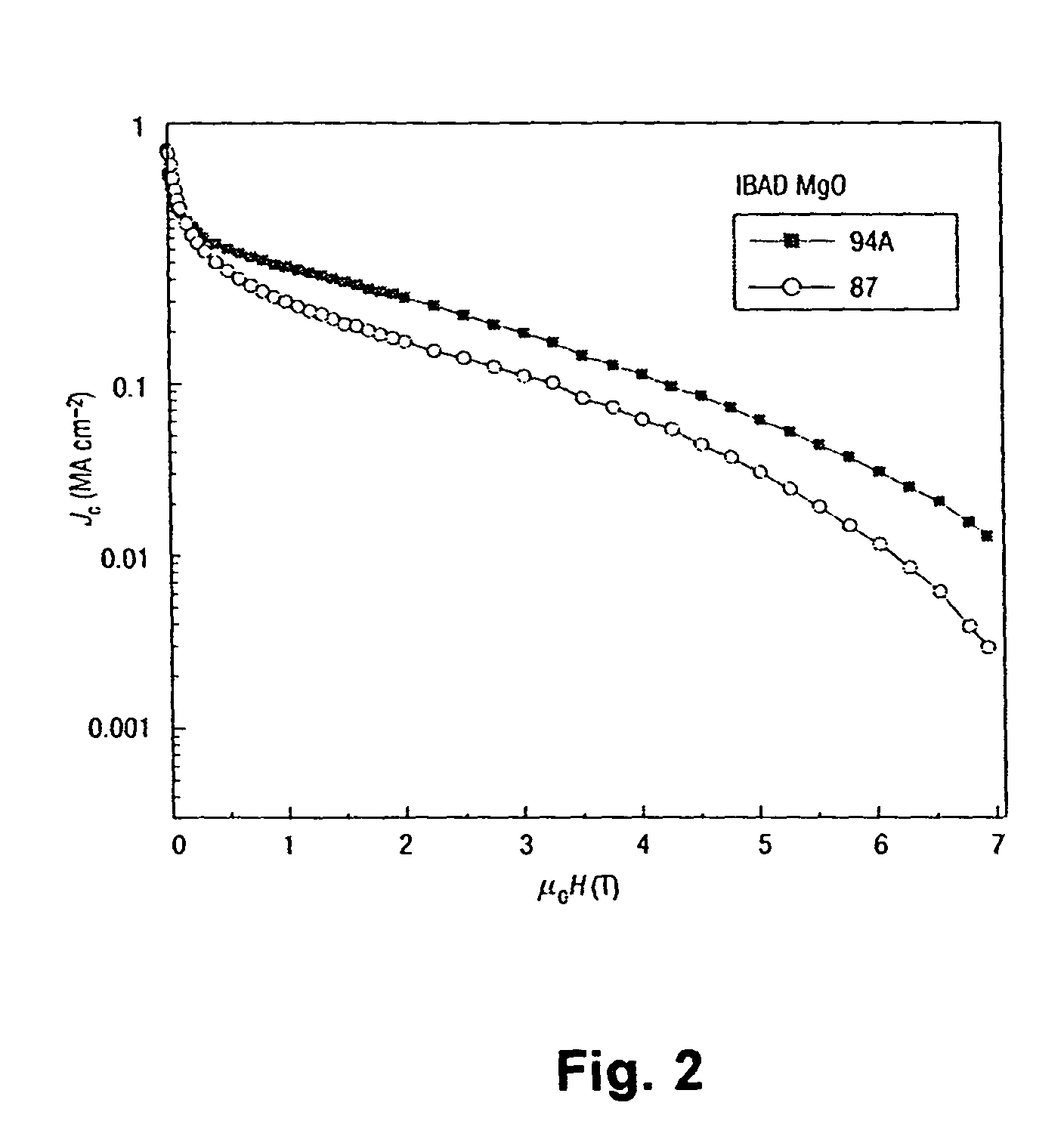
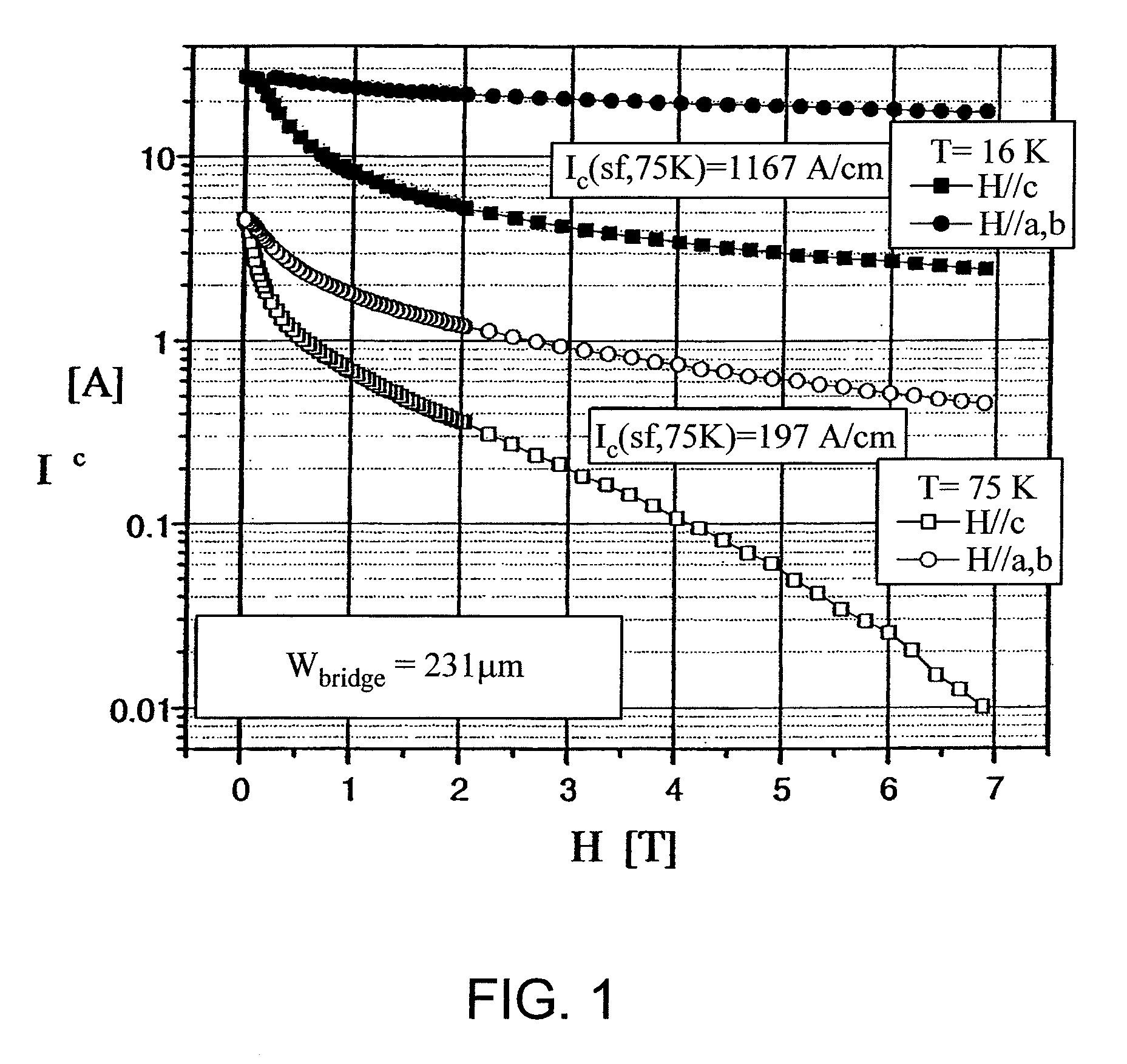
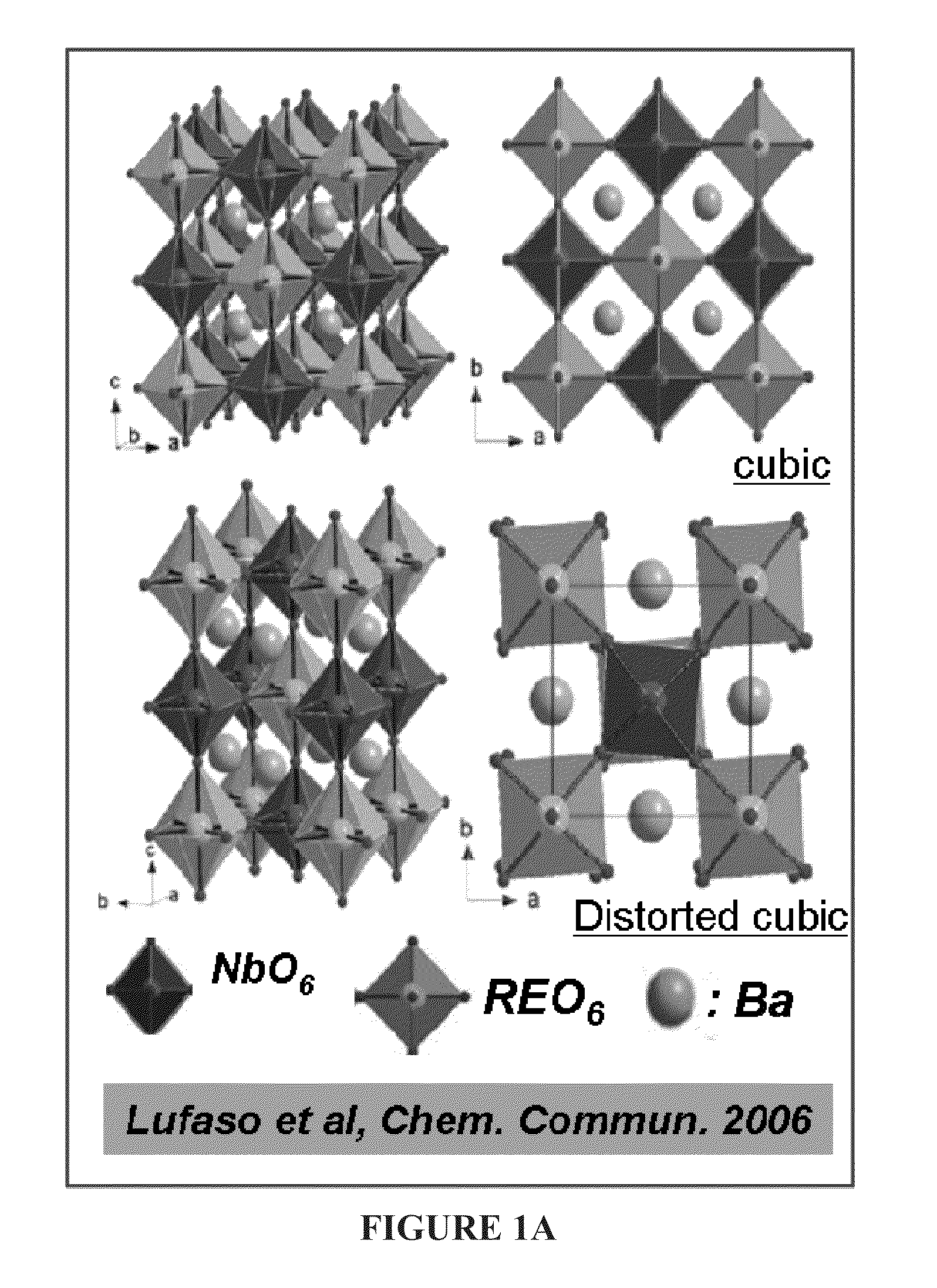
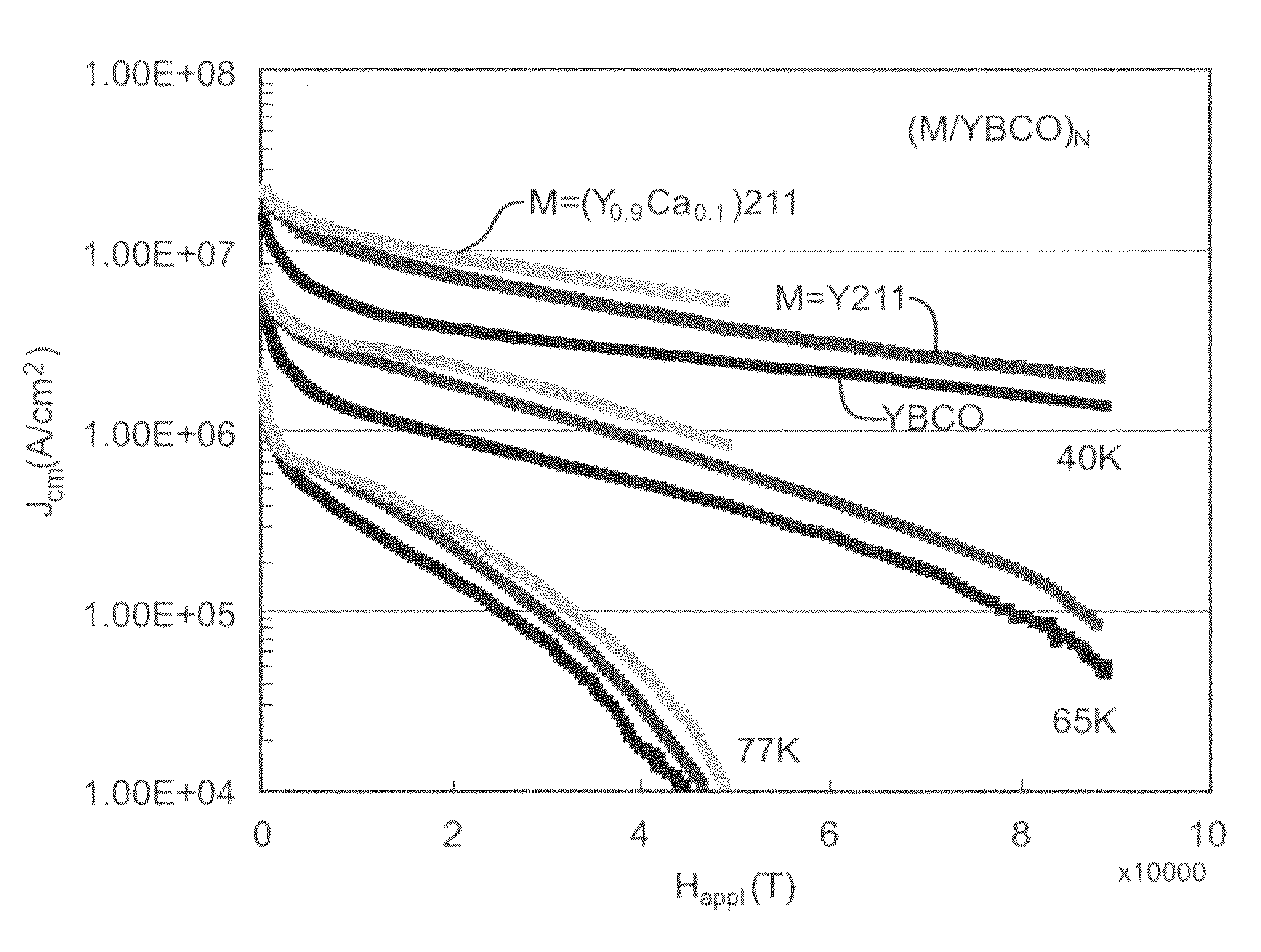
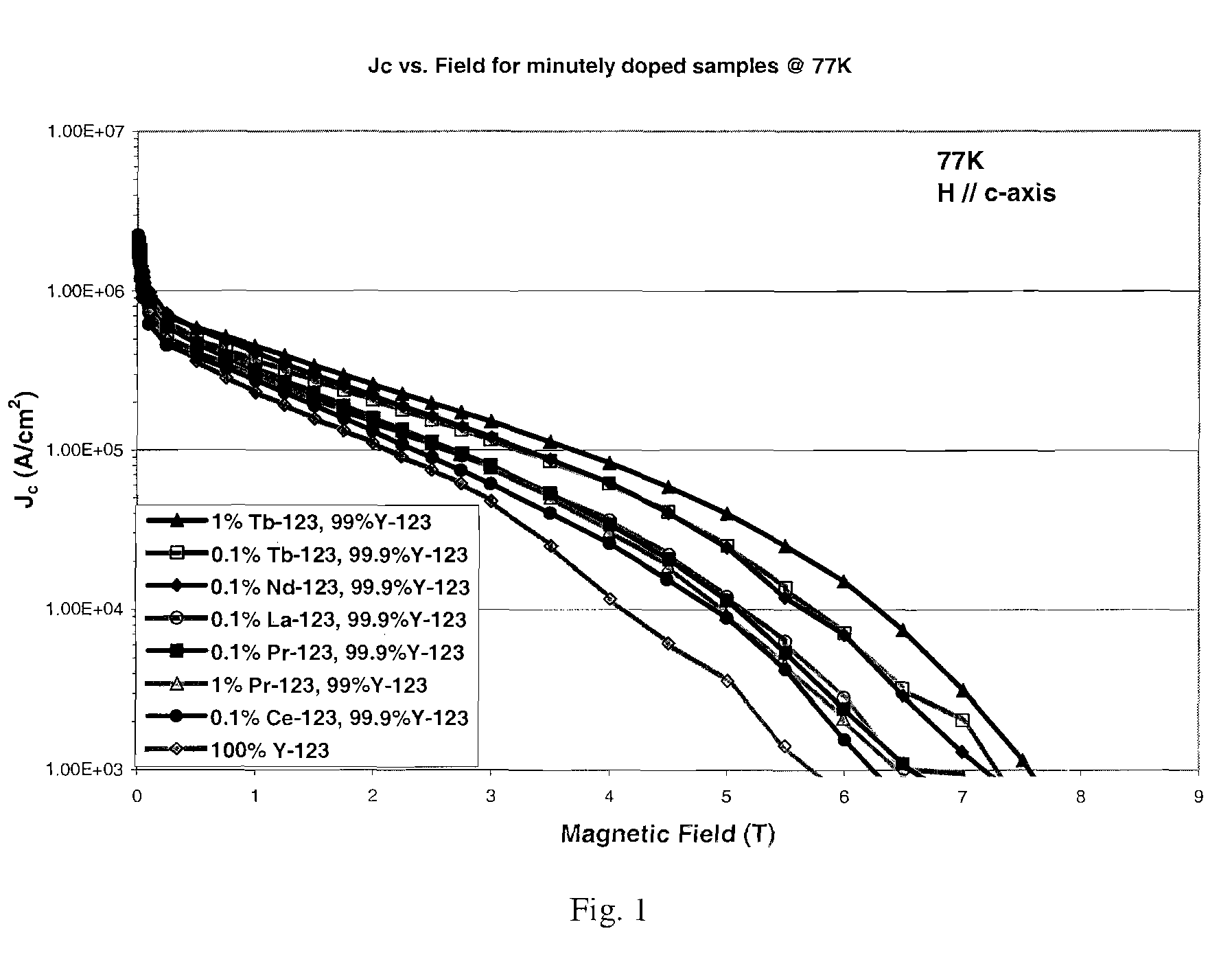
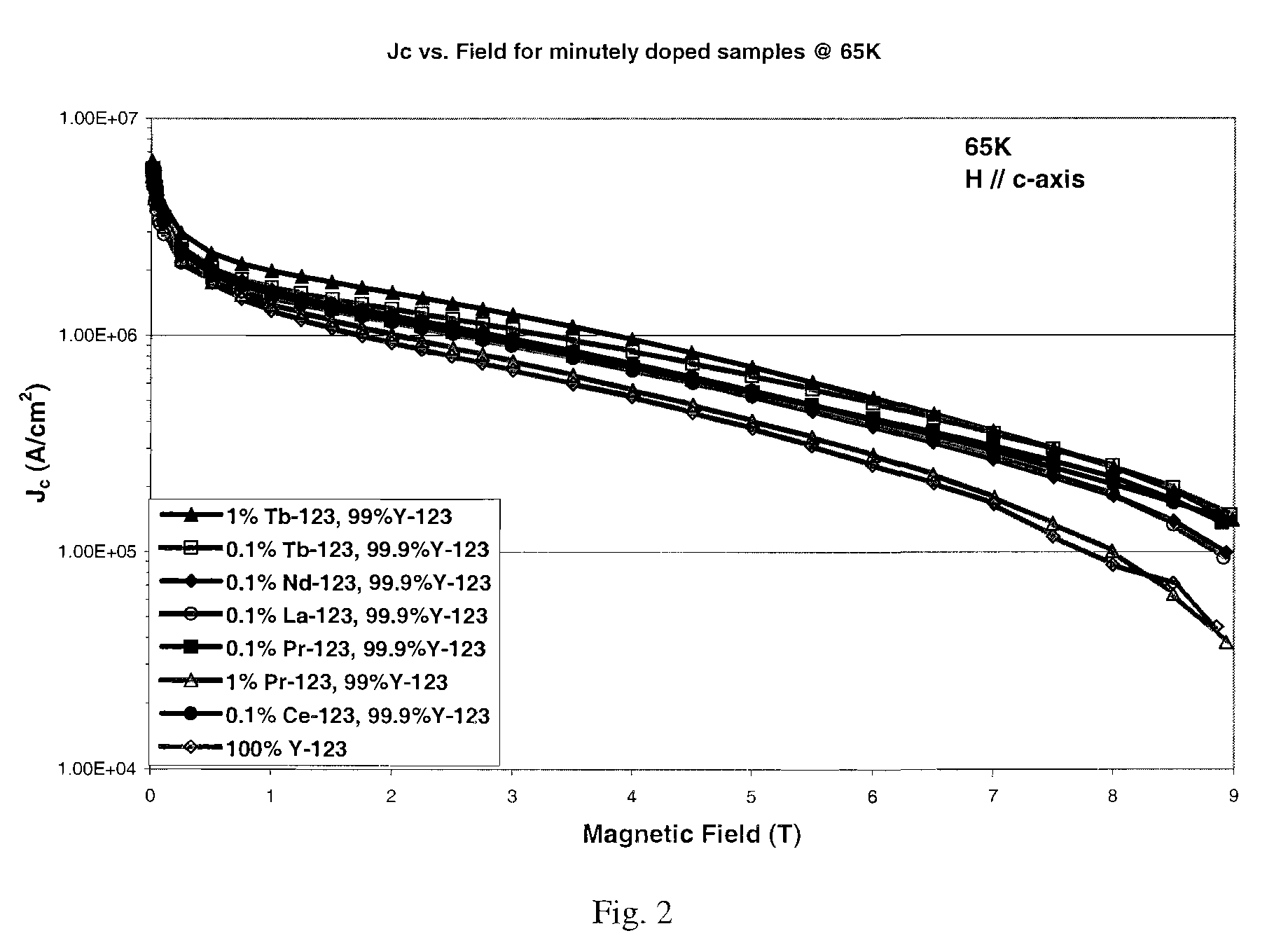
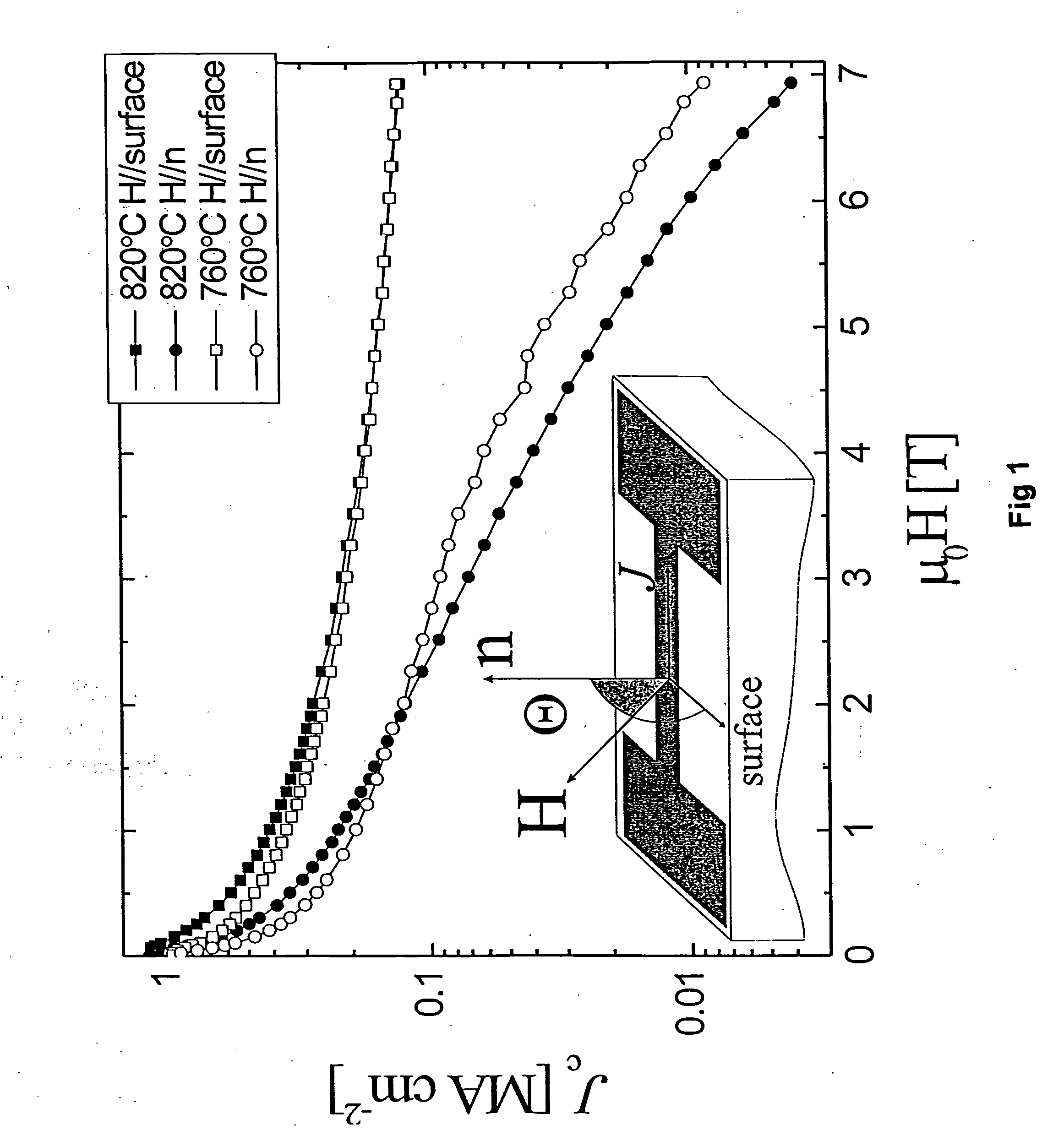
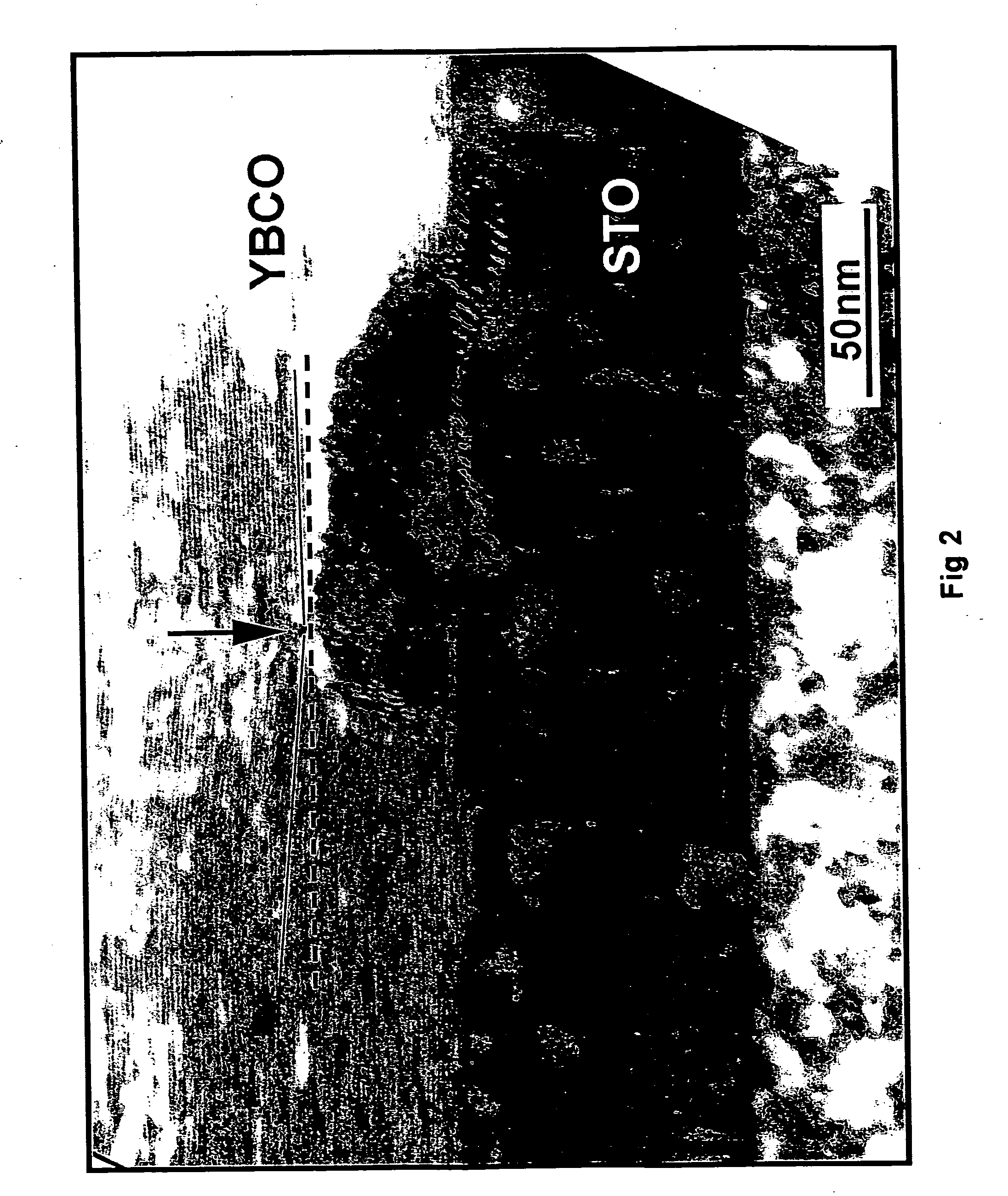
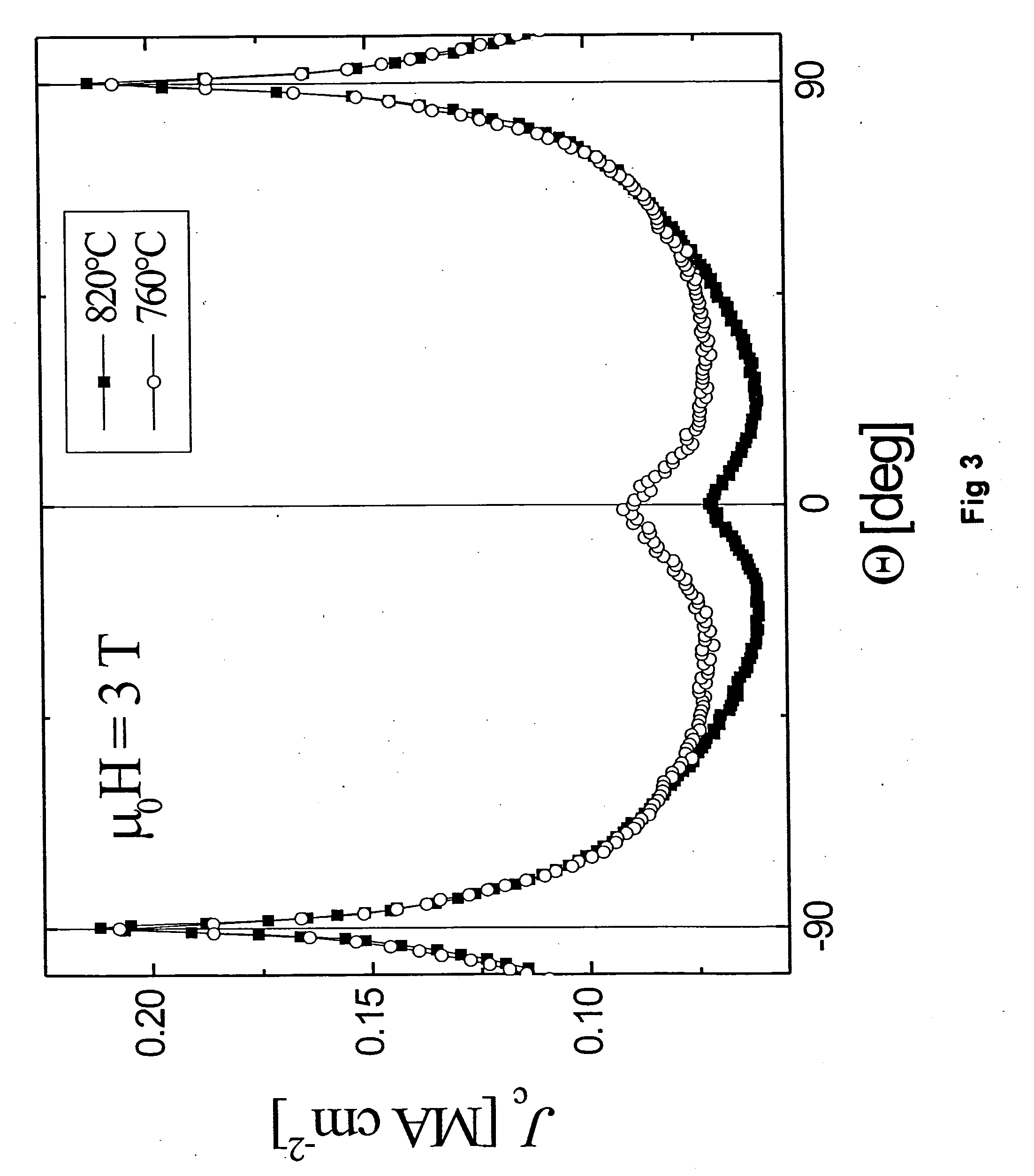
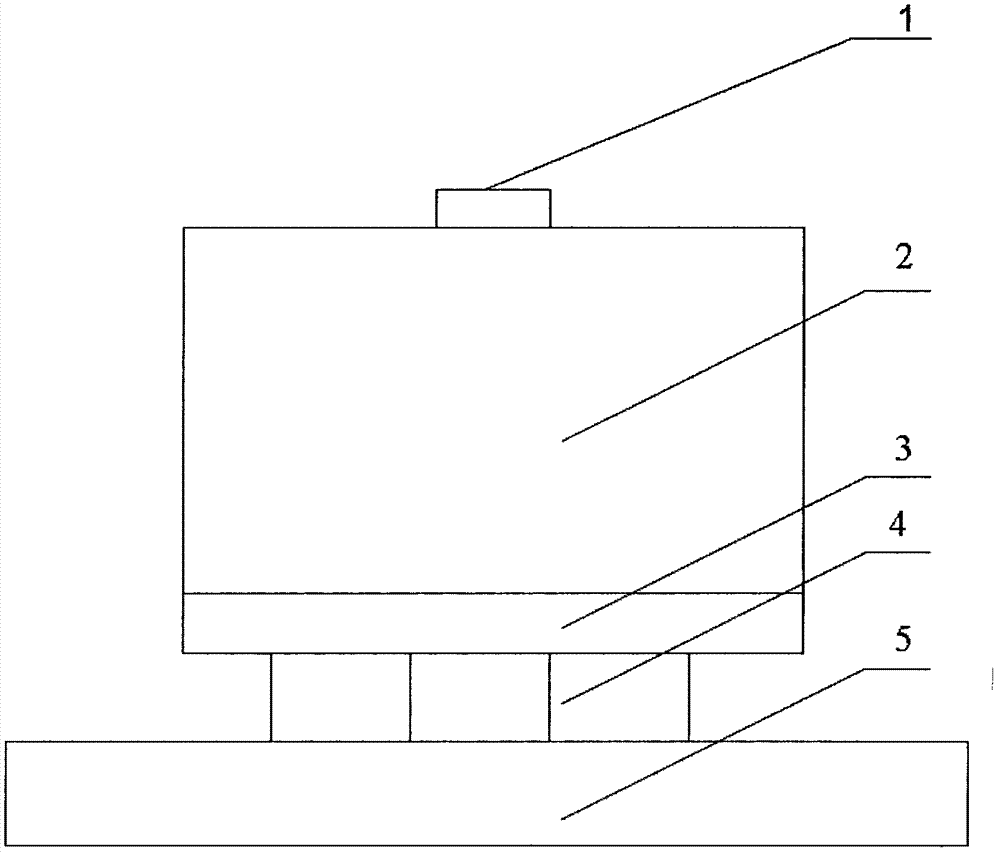
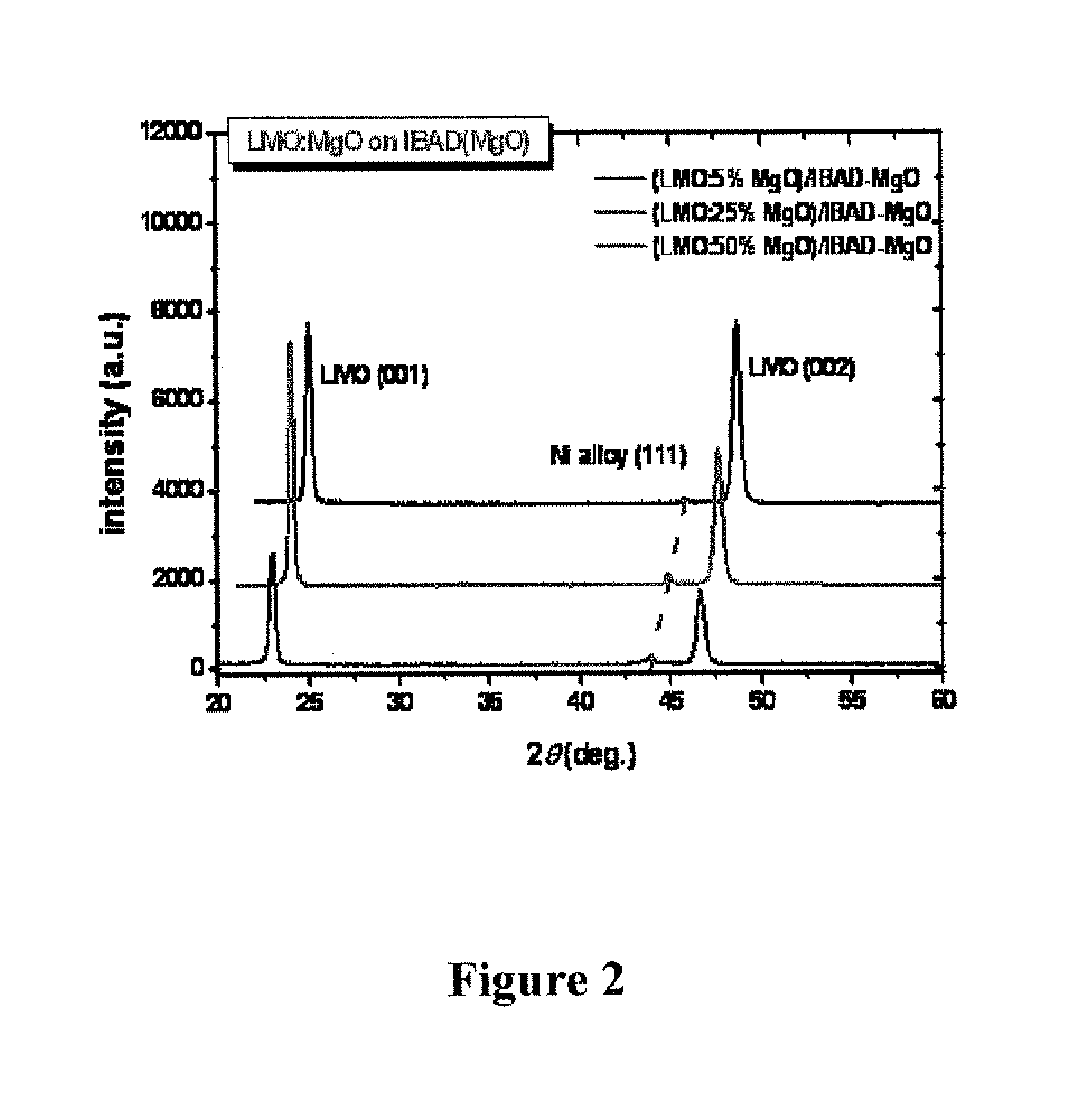
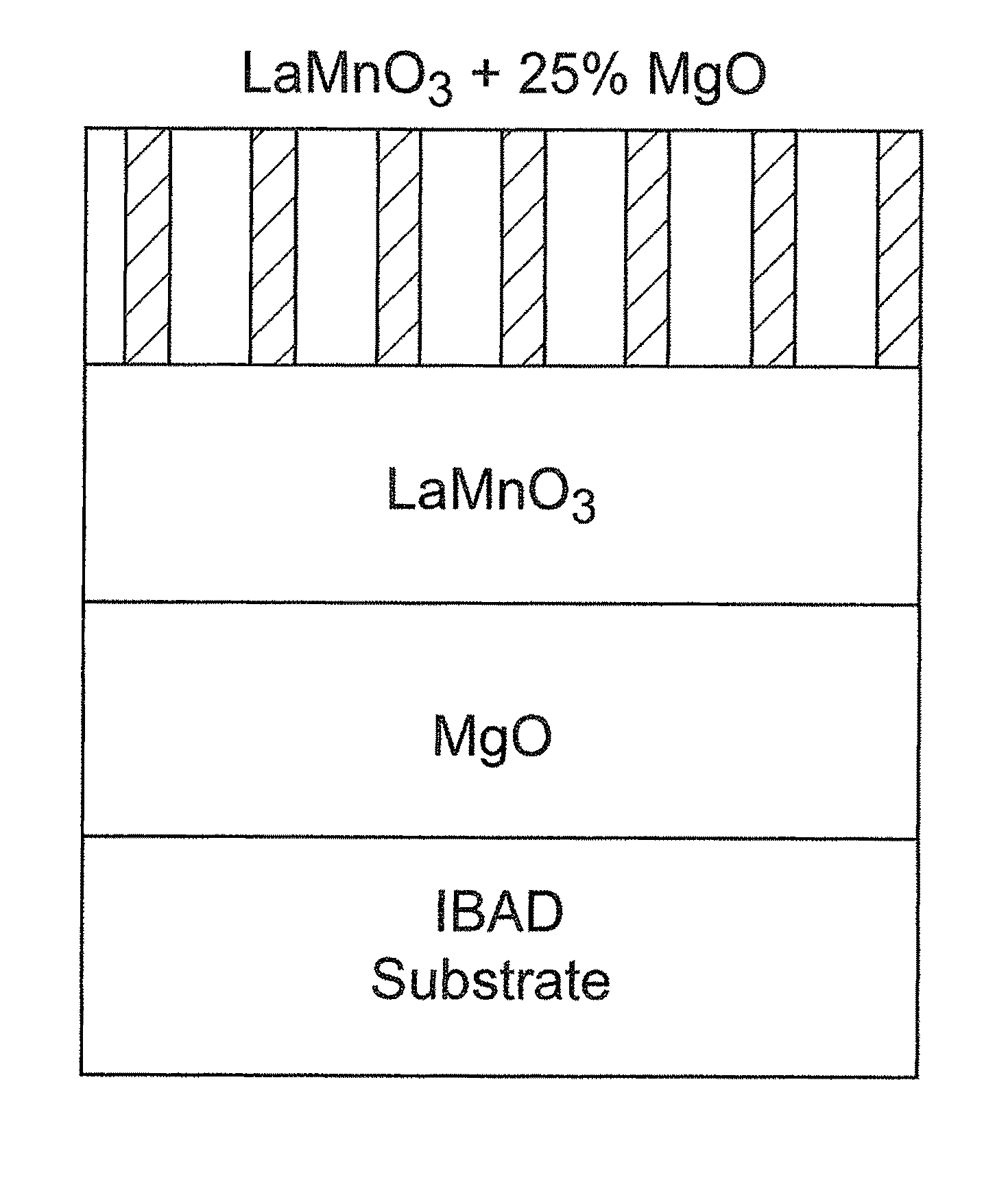
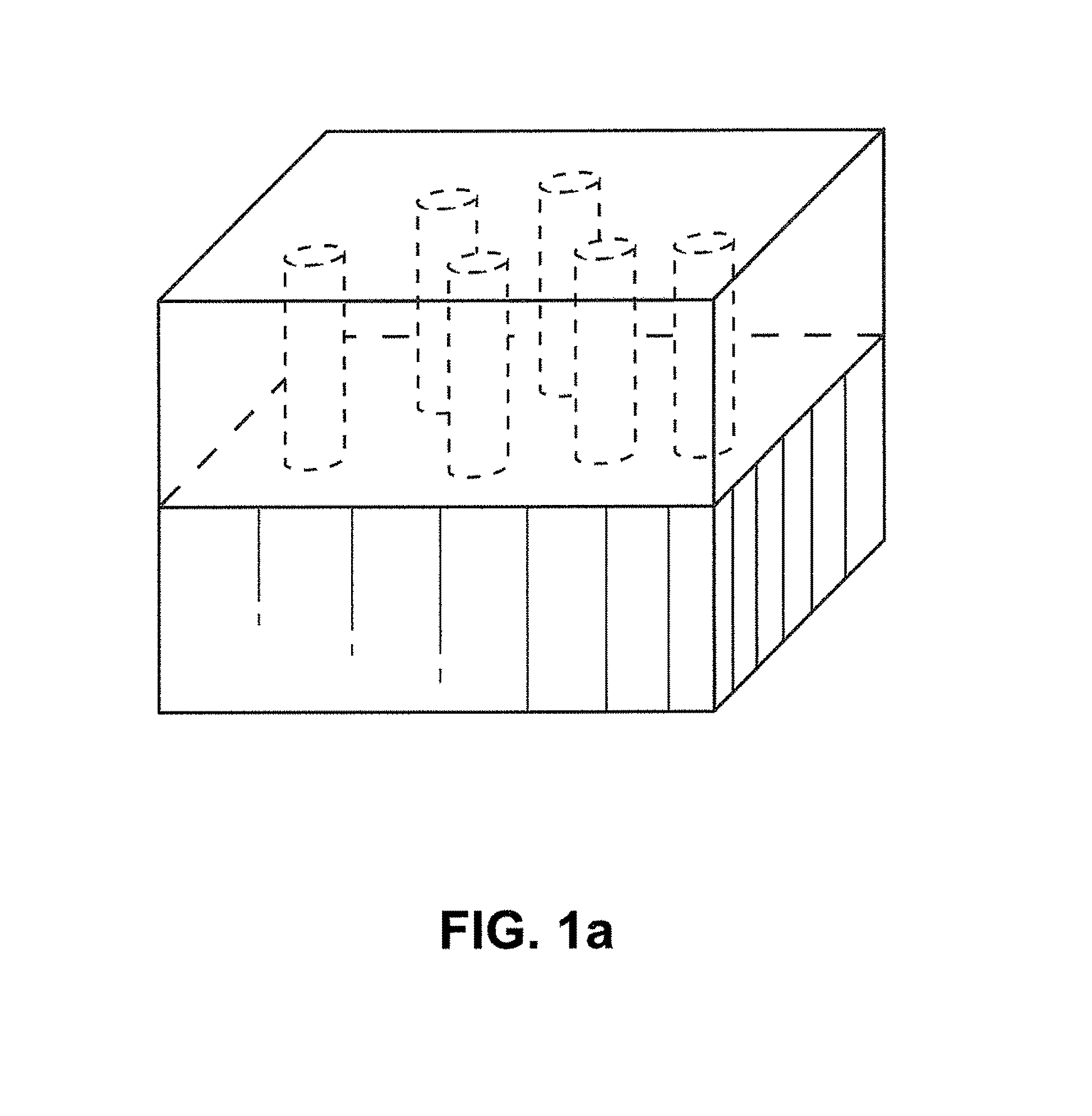
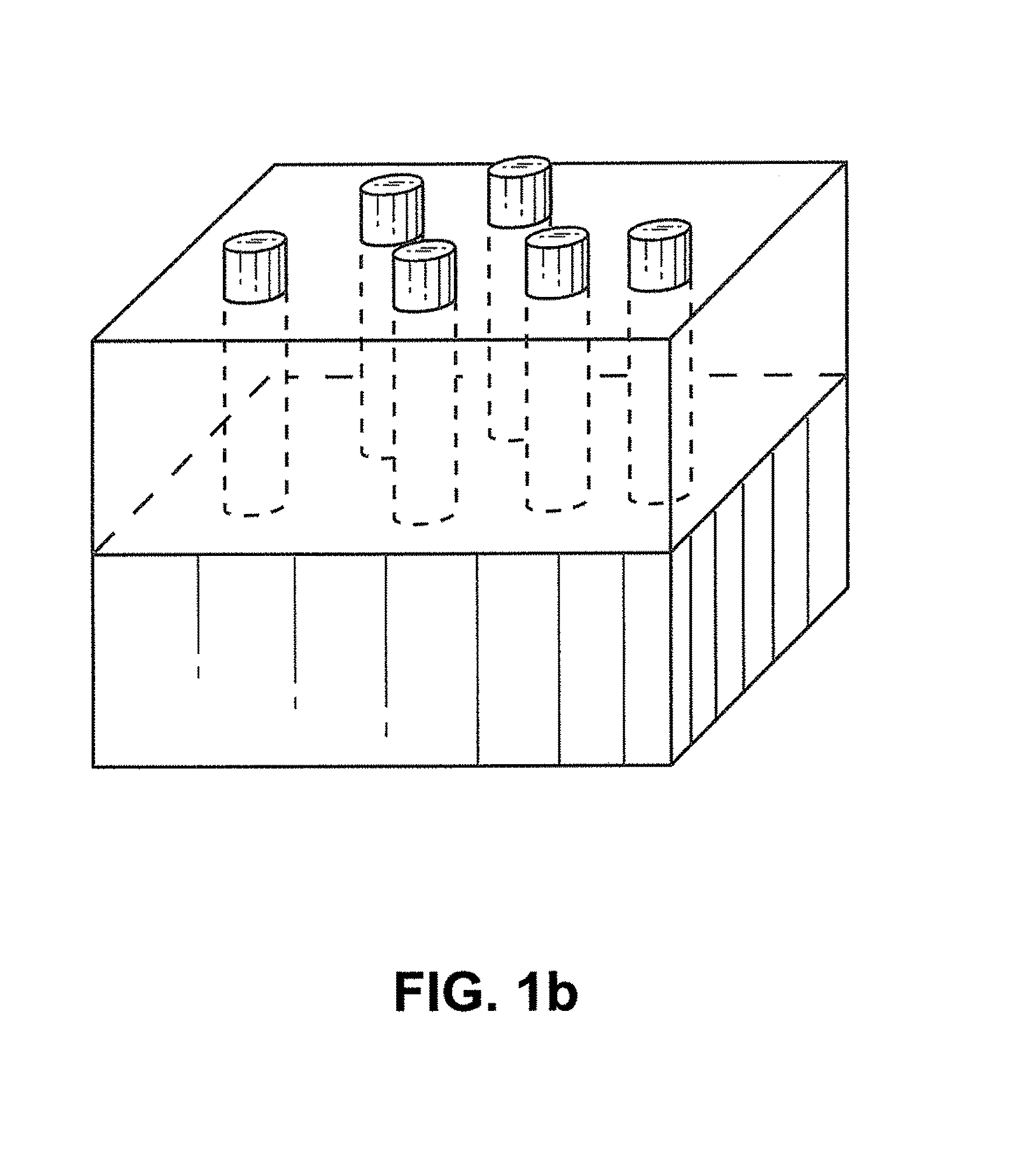
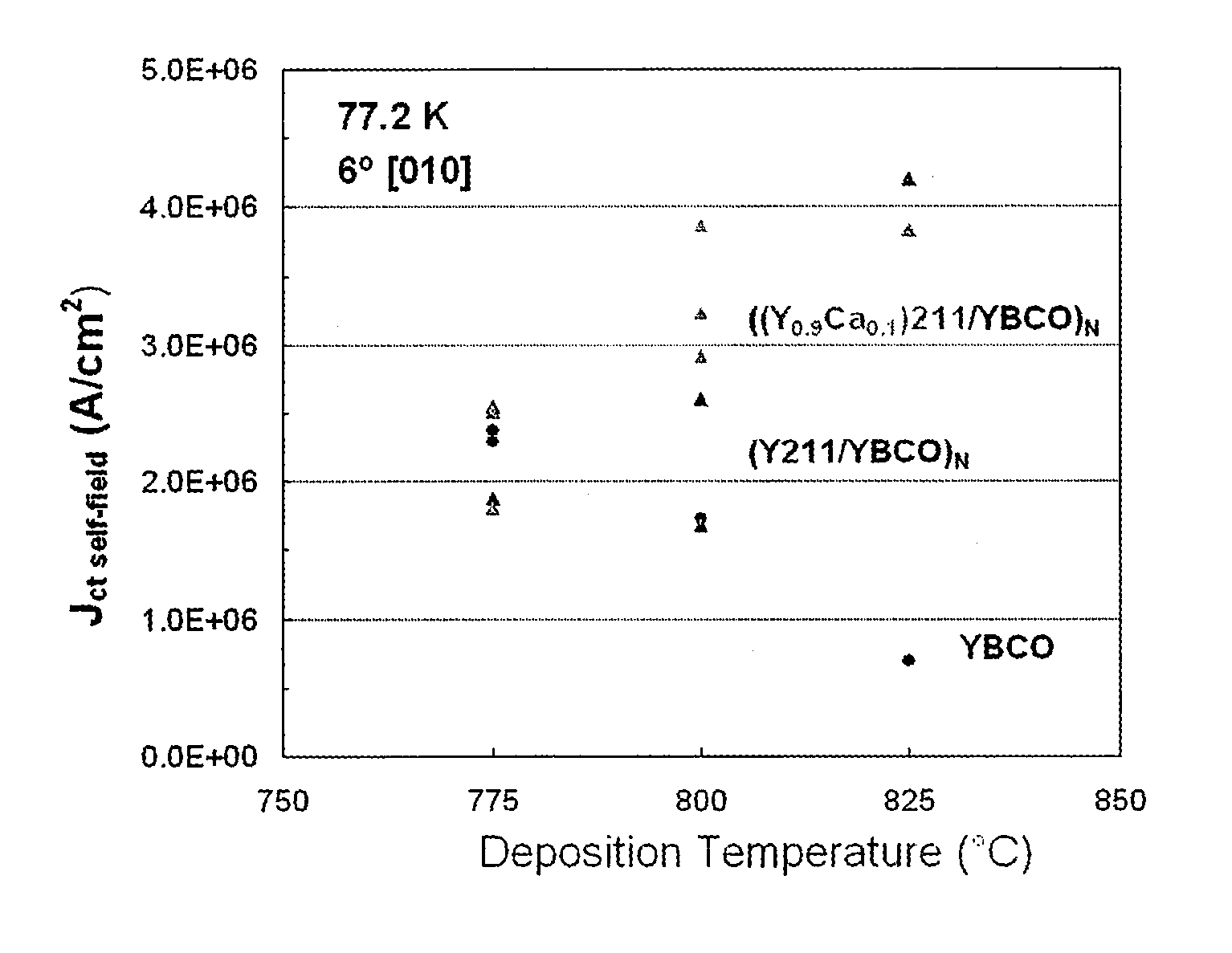
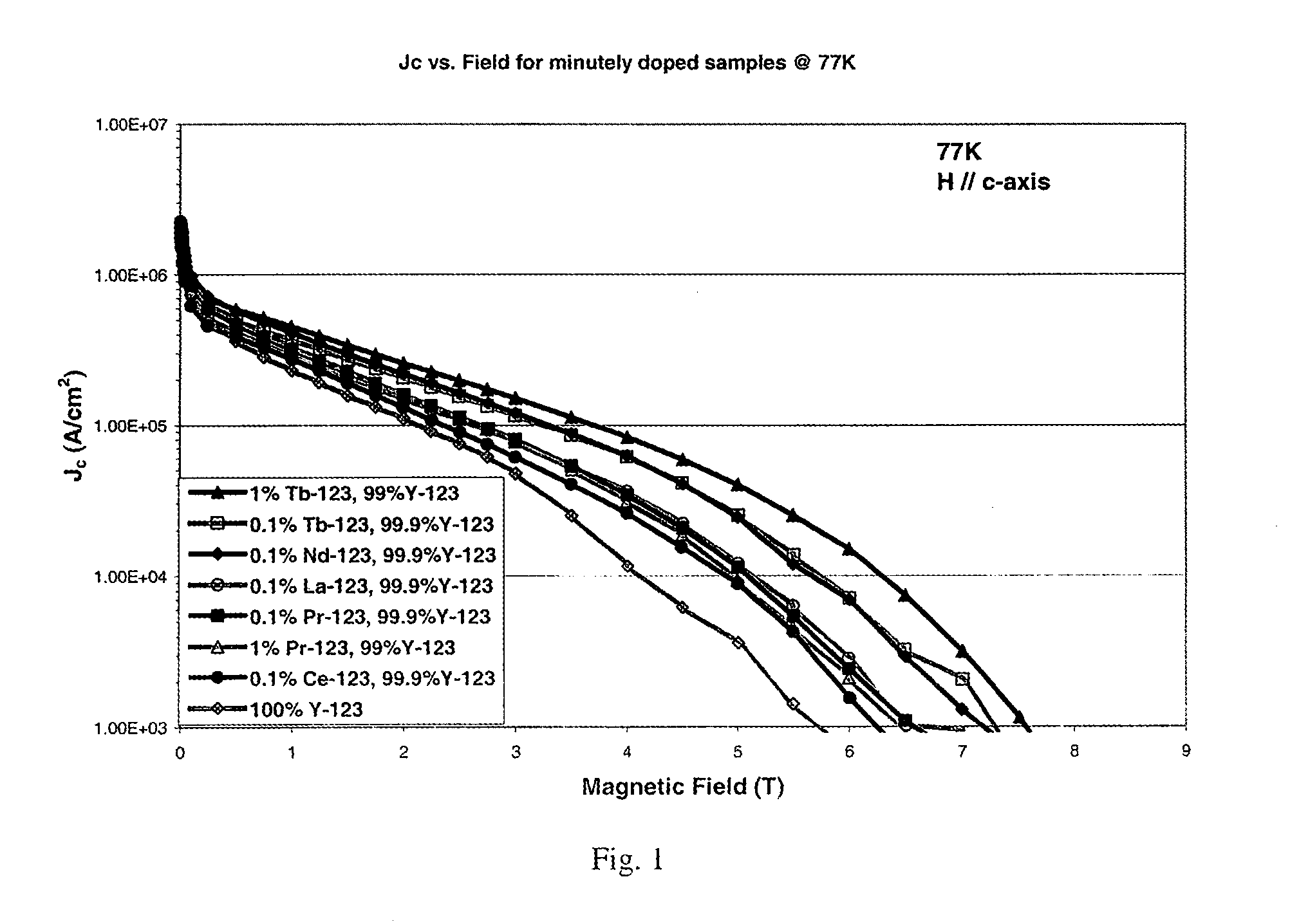
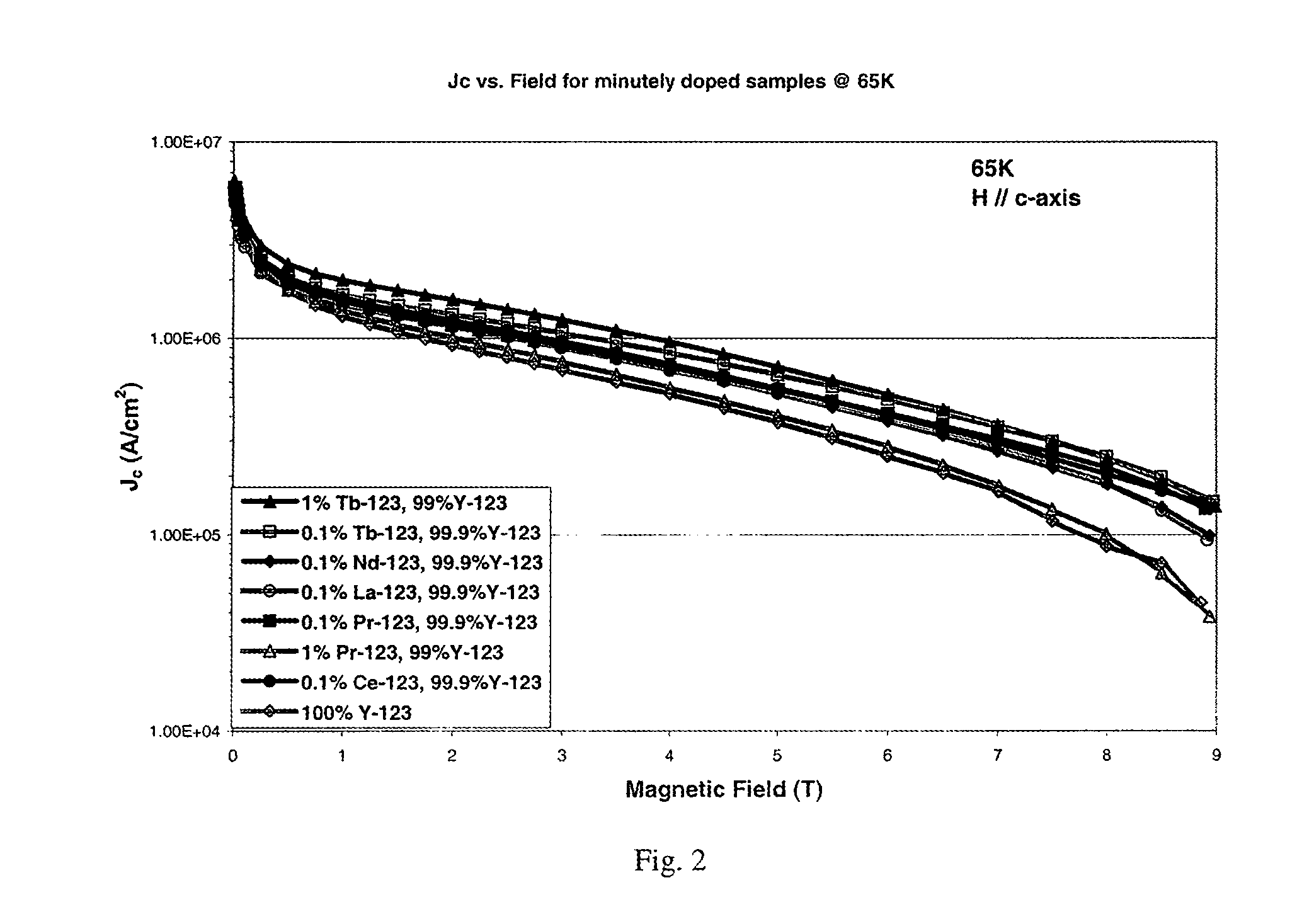
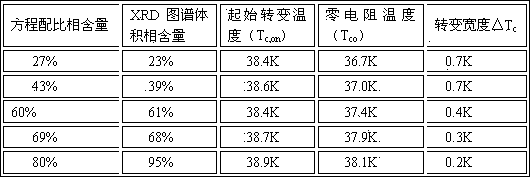
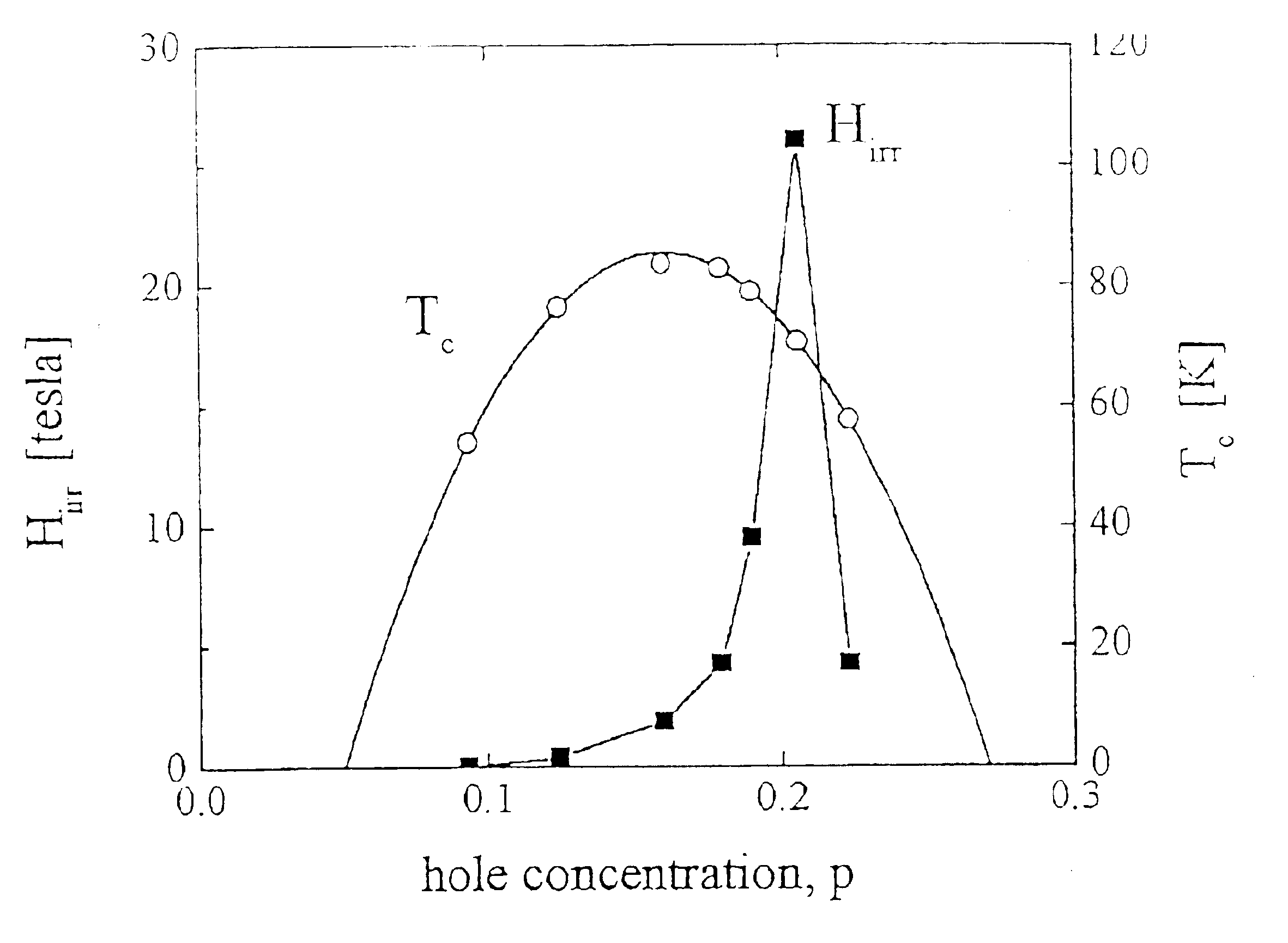Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Flux pinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flux pinning is the phenomenon where a superconductor is pinned in space above a magnet. The superconductor must be a type-II superconductor because type-I superconductors cannot be penetrated by magnetic fields. The act of magnetic penetration is what makes flux pinning possible. At higher magnetic fields (above Hc1 and below Hc2) the superconductor allows magnetic flux to enter in quantized packets surrounded by a superconducting current vortex (see Quantum vortex). These sites of penetration are known as flux tubes. The number of flux tubes per unit area is proportional to the magnetic field with a constant of proportionality equal to the magnetic flux quantum. On a simple 76 millimeter diameter, 1-micrometer thick disk, next to a magnetic field of 28 kA/m, there are approximately 100 billion flux tubes that hold 70,000 times the superconductor's weight. At lower temperatures the flux tubes are pinned in place and cannot move. This pinning is what holds the superconductor in place thereby allowing it to levitate. This phenomenon is closely related to the Meissner effect, though with one crucial difference — the Meissner effect shields the superconductor from all magnetic fields causing repulsion, unlike the pinned state of the superconductor disk which pins flux, and the superconductor in place.
Oxide films with nanodot flux pinning centers
InactiveUS20050159298A1Increasing critical current densitySimple and versatileMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsNanodotRare-earth element
A method for producing a thin film includes disposing a precursor solution onto a substrate to form a precursor film. The precursor solution contains precursor components to a rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide including a salt of a rare earth element, a salt of an alkaline earth metal, and a salt of a transition metal in one or more solvents, wherein at least one of the salts is a fluoride-containing salt. The precursor solution also contains an additive component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of forming a second phase nanoparticle, either alone or in combination with one or more of the precursor components of the precursor solution or a dopant component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of substituting for an element of the rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide, and treating the precursor film to form an intermediate metal oxyfluoride including the rare earth, the alkaline earth metal, the transition metal and the additive metal or dopant metal of the precursor solution.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Preparation method of single domain yttrium barium copper oxide superconductor
ActiveCN102534787ASimple processImproved Flux Pinning PerformancePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsFlux pinningYttrium barium copper oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a single domain yttrium barium copper oxide superconductor; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing Y2BaCuO5 precursor powder and liquid phase source powder, pressing a Y2BaCuO5 precursor block, a liquid phase block and a supporting bock, preparing a green body, growing a single domain yttrium barium copper oxide block in an infiltration manner, and carrying out oxygen permeation processing. A second phase nanoparticle Y2Ba4CuBiOx / Y2Ba4CuMOx (M is Bi or W) is successfully introduced for forming a flux pinning center by adopting a top seed crystal infiltration growing method and adding a metallic oxide (Bi2O3 powder and WO3 powder) for doping, thereby the powder preparation technology is simplified, the experimental period is shortened, the experiment cost is reduced, and the flux pinning capacity of the superconductor is increased. Y2O3 is used for preparing the supporting block which stably supports two briquettes above the supporting block in the slow cold growing process of an yttrium barium copper oxide block so as to prevent liquid phase from running off. The preparation method can be used for preparing the yttrium barium copper oxide superconductor and can also be used for preparing high-temperature superconductors of other series such as Gd, Sm, Nd, Eu and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Enhanced pinning in YBCO films with BaZrO3 nanoparticles
ActiveUS20060025310A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningHigh temperature superconducting
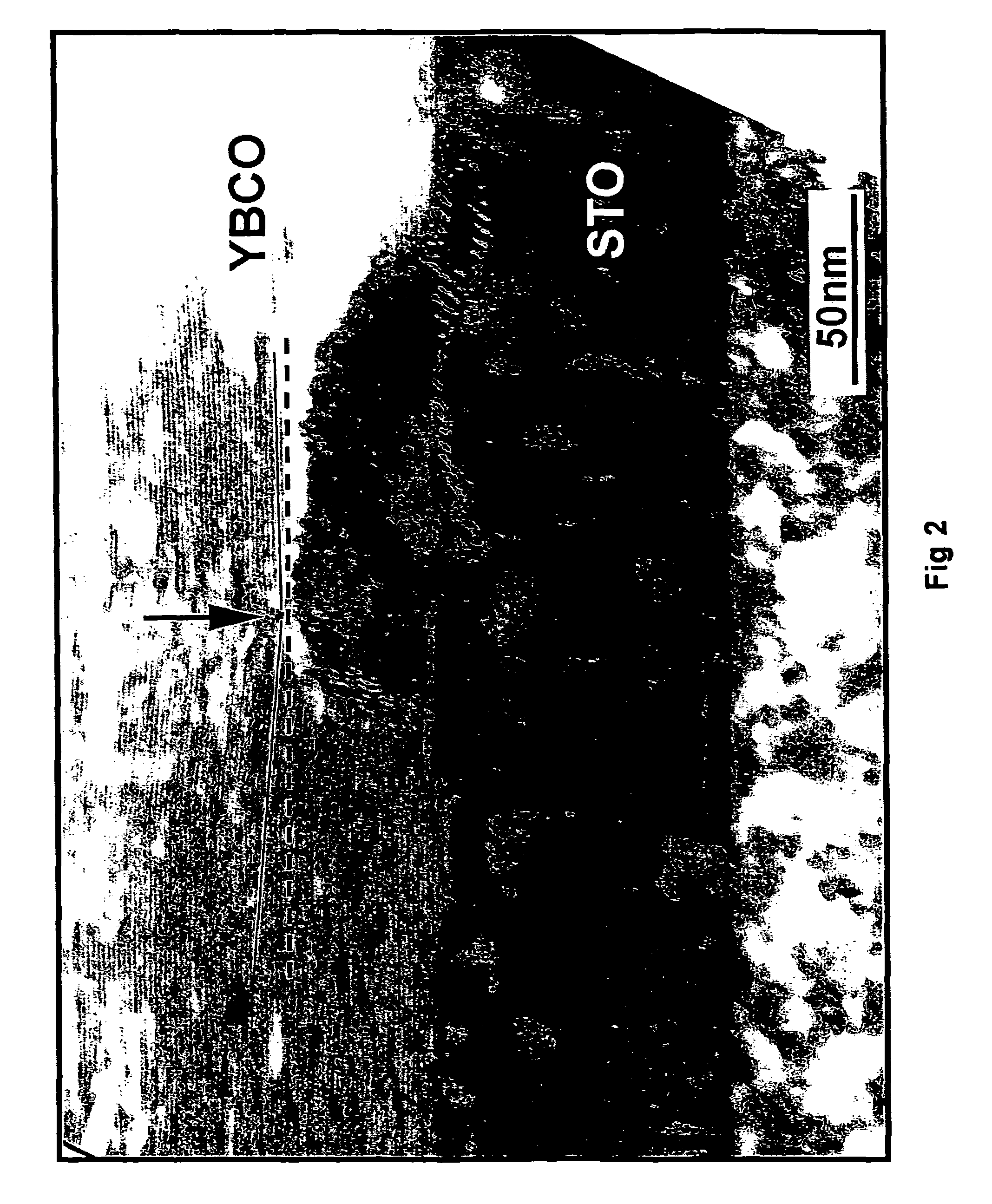
A process and composition of matter are provided and involve flux pinning in thin films of high temperature superconductive oxides such as YBCO by inclusion of particles including barium and a group 4 or group 5 metal, such as zirconium, in the thin film.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
FLUX PINNING ENHANCEMENTS IN SUPERCONDUCTIVE REBa2CU3O7-x (REBCO) FILMS AND METHOD OF FORMING THEREOF
ActiveUS20070129255A1Avoid adverse reactionsSeparationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesFlux pinning
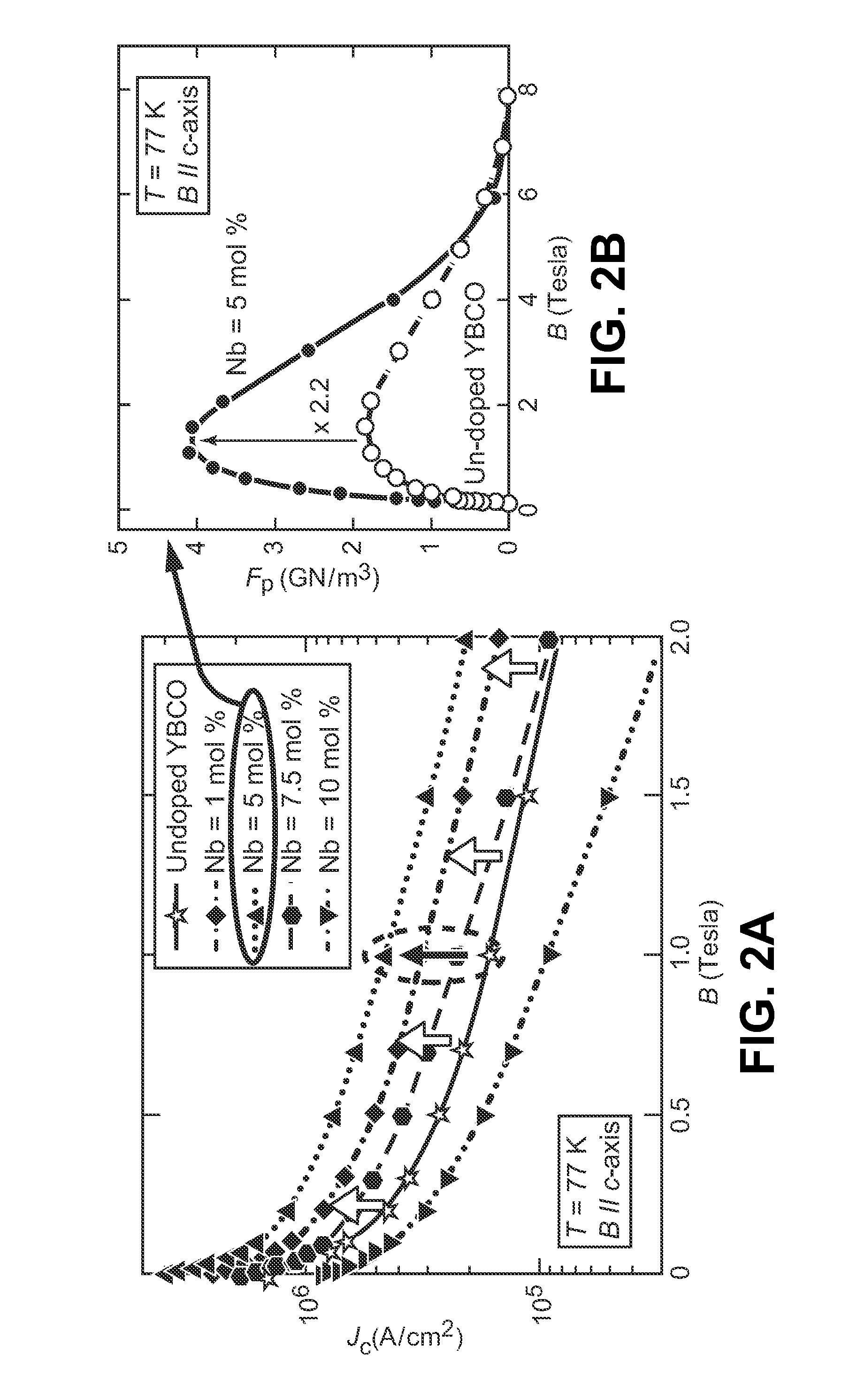
Nanometer-sized non-superconducting particulates in superconductive REBCO films, where RE is a rare earth metal, for flux pinning enhancement and a method of forming are disclosed. A target with a second phase material sector portion and a superconductive material portion is used in a pulse laser deposition process to form films on substrates according to the present invention. The films consist of 10-20 nm-sized precipitates. In a 0.5 μm thick film, a transport critical current density (Jc)>3 MA / cm2 at 77K in self-field was measured. In one embodiment, magnetization Jc at 77 K and 65K showed significant improvements in a composite YBCO films with fine precipitates produced according to the present invention as compared to non-doped (standard) YBCO films (>10 times increase at 9 T, 65 K).
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
Enhanced pinning in YBCO films with BaZrO3 nanoparticles
ActiveUS7737087B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningHigh temperature superconducting
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Oxide films with nanodot flux pinning centers
InactiveUS20100048406A1Increasing critical current densitySimple and versatileMaterial nanotechnologySuperconductors/hyperconductorsNanodotRare-earth element
A method for producing a thin film includes disposing a precursor solution onto a substrate to form a precursor film. The precursor solution contains precursor components to a rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide including a salt of a rare earth element, a salt of an alkaline earth metal, and a salt of a transition metal in one or more solvents, wherein at least one of the salts is a fluoride-containing salt. The precursor solution also contains an additive component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of forming a second phase nanoparticle, either alone or in combination with one or more of the precursor components of the precursor solution or a dopant component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of substituting for an element of the rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide, and treating the precursor film to form an intermediate metal oxyfluoride including the rare earth, the alkaline earth metal, the transition metal and the additive metal or dopant metal of the precursor solution.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Nb-DOPED PEROVSKITE FLUX PINNING OF REBCO BASED SUPERCONDUCTORS BY MOCVD
InactiveUS20120035056A1Layered productsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningDopant
A method of making a superconducting article that involves using MOCVD to deposit onto a uniaxially or biaxially textured surface an epitaxial layer that includes a superconducting material such as REBa2Cu3O7 and a secondary phase comprising at least one dopant, the dopant including Nb, Ta and / or V, or combinations thereof.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for improving performance of high temperature superconductors within a magnetic field
InactiveUS7642222B1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningParticulates
The present invention provides articles including a base substrate including a layer of an oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure layer thereon; and, a buffer layer upon the oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure layer, the buffer layer having an outwardly facing surface with a surface morphology including particulate outgrowths of from 10 nm to 500 run in size at the surface, such particulate outgrowths serving as flux pinning centers whereby the article maintains higher performance within magnetic fields than similar articles without the necessary density of such outgrowths.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Flux pinning enhancements in superconductive REBa2CU3O7-x (REBCO) films and method of forming thereof
ActiveUS7687436B2Avoid adverse reactionsSeparationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesMagnetization
Nanometer-sized non-superconducting particulates in superconductive REBCO films, where RE is a rare earth metal, for flux pinning enhancement and a method of forming are disclosed. A target with a second phase material sector portion and a superconductive material portion is used in a pulse laser deposition process to form films on substrates according to the present invention. The films consist of 10-20 nm-sized precipitates. In a 0.5 μm thick film, a transport critical current density (Jc)>3 MA / cm2 at 77K in self-field was measured. In one embodiment, magnetization Jc at 77 K and 65K showed significant improvements in a composite YBCO films with fine precipitates produced according to the present invention as compared to non-doped (standard) YBCO films (>10 times increase at 9 T, 65 K).
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Superconductive Article with Prefabricated Nanostructure for Improved Flux Pinning
ActiveUS20110028328A1Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFlux pinningHigh-temperature superconductivity
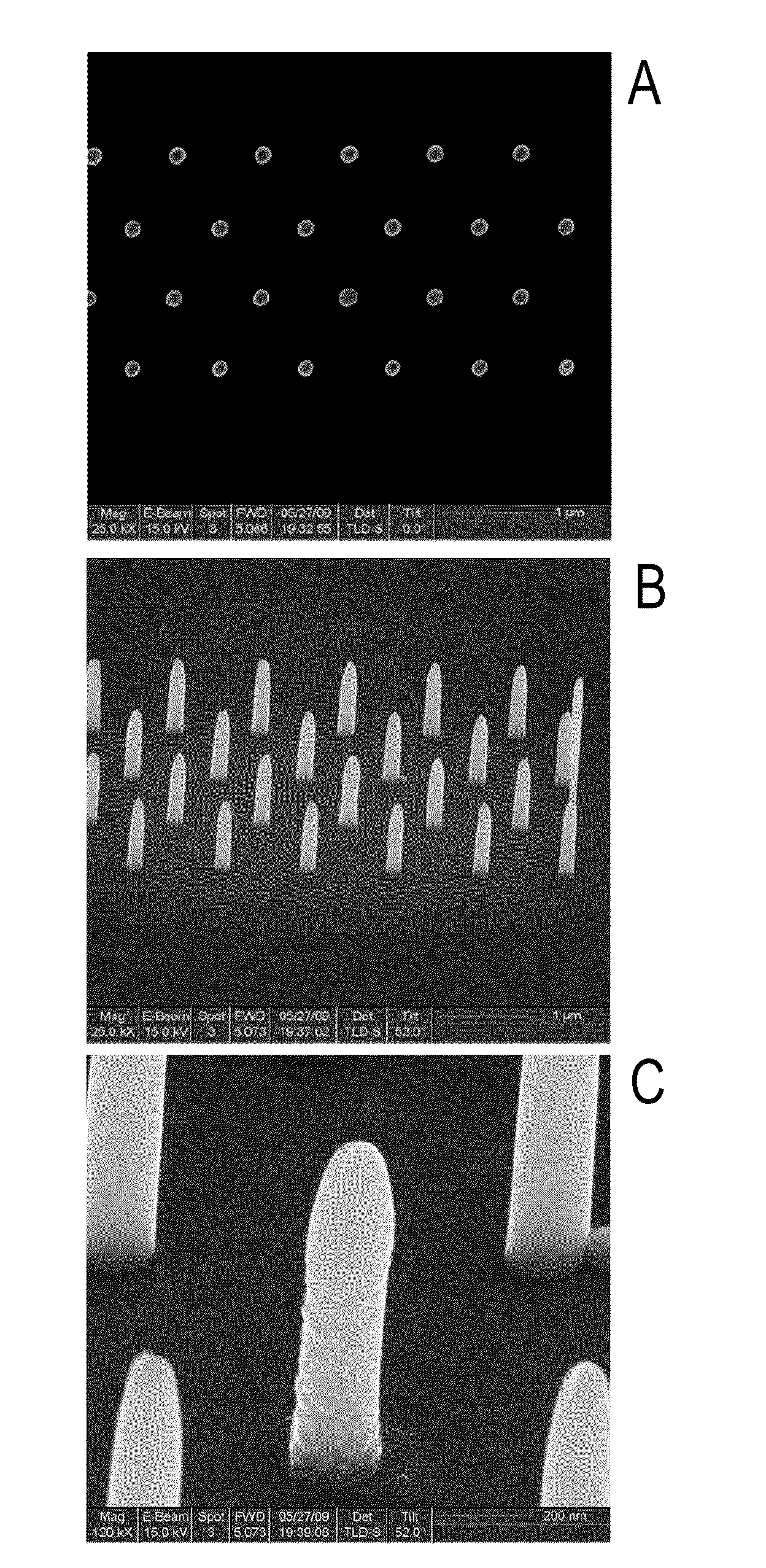
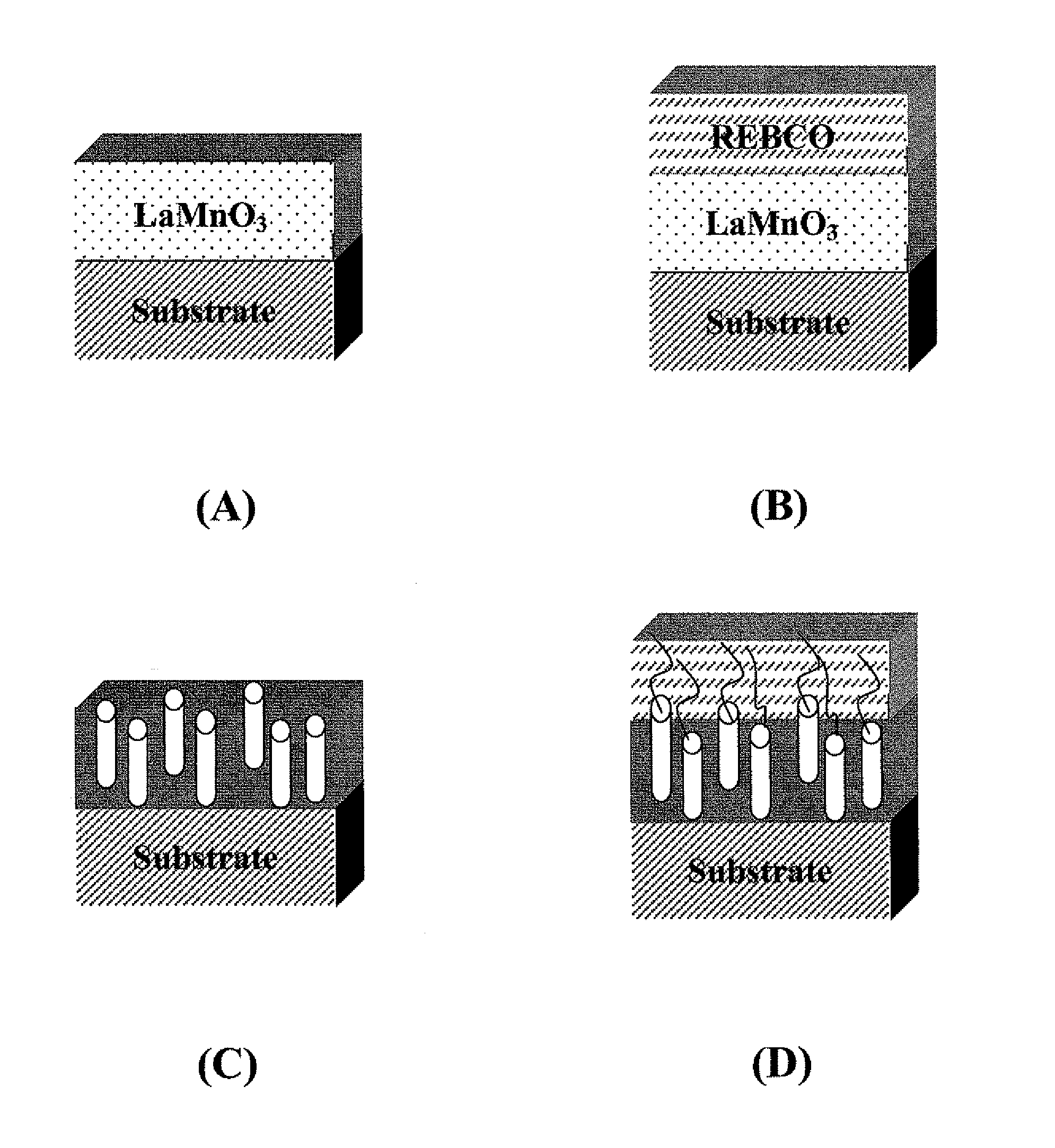
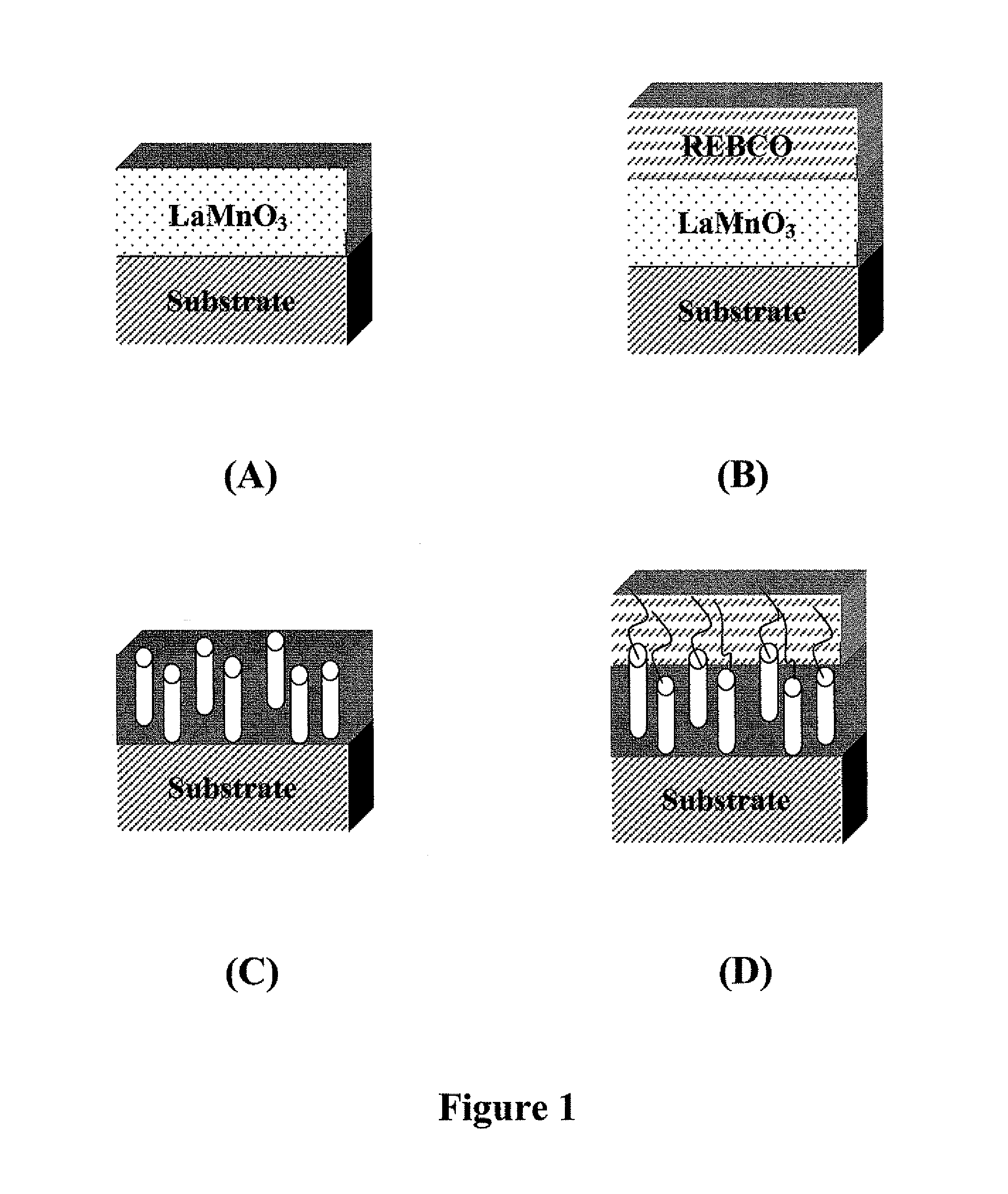
A superconducting article comprises a substrate, a buffer layer overlying the substrate, and a high-temperature superconducting (HTS) layer overlying the buffer layer. The HTS layer includes a plurality of nanorods. A method of forming a superconducting article comprises providing a substrate, depositing a buffer layer overlying the substrate; forming a nanodot array overlying the buffer layer; depositing an array of nanorods nucleated on the nanodot array; and depositing a high-temperature superconducting (HTS) layer around the array of nanorods and overlying the buffer layer.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Re-type oxide superconducting wire and process for producing the same
ActiveUS8326387B2Little dependenceAngular dependenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningComposite substrate
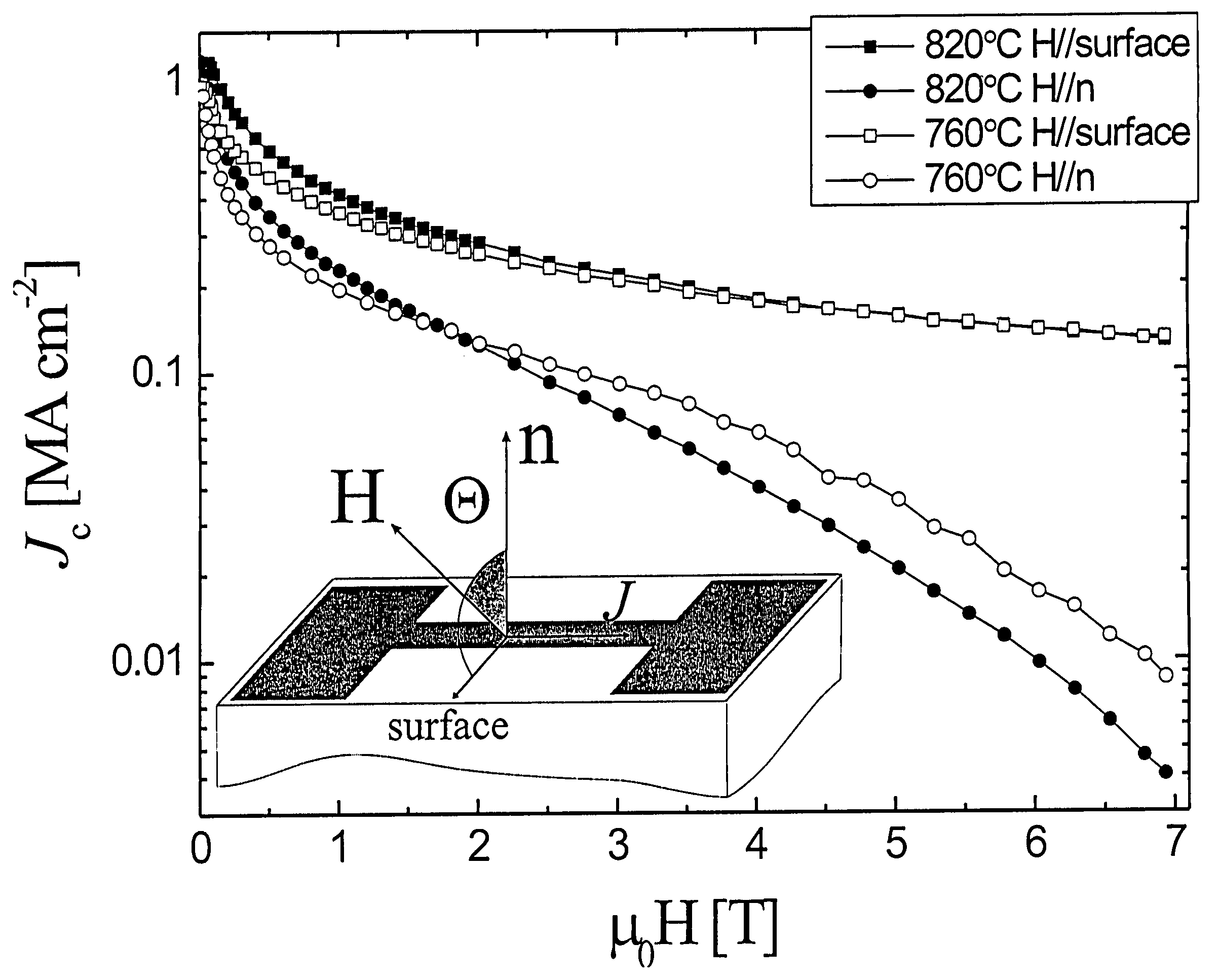
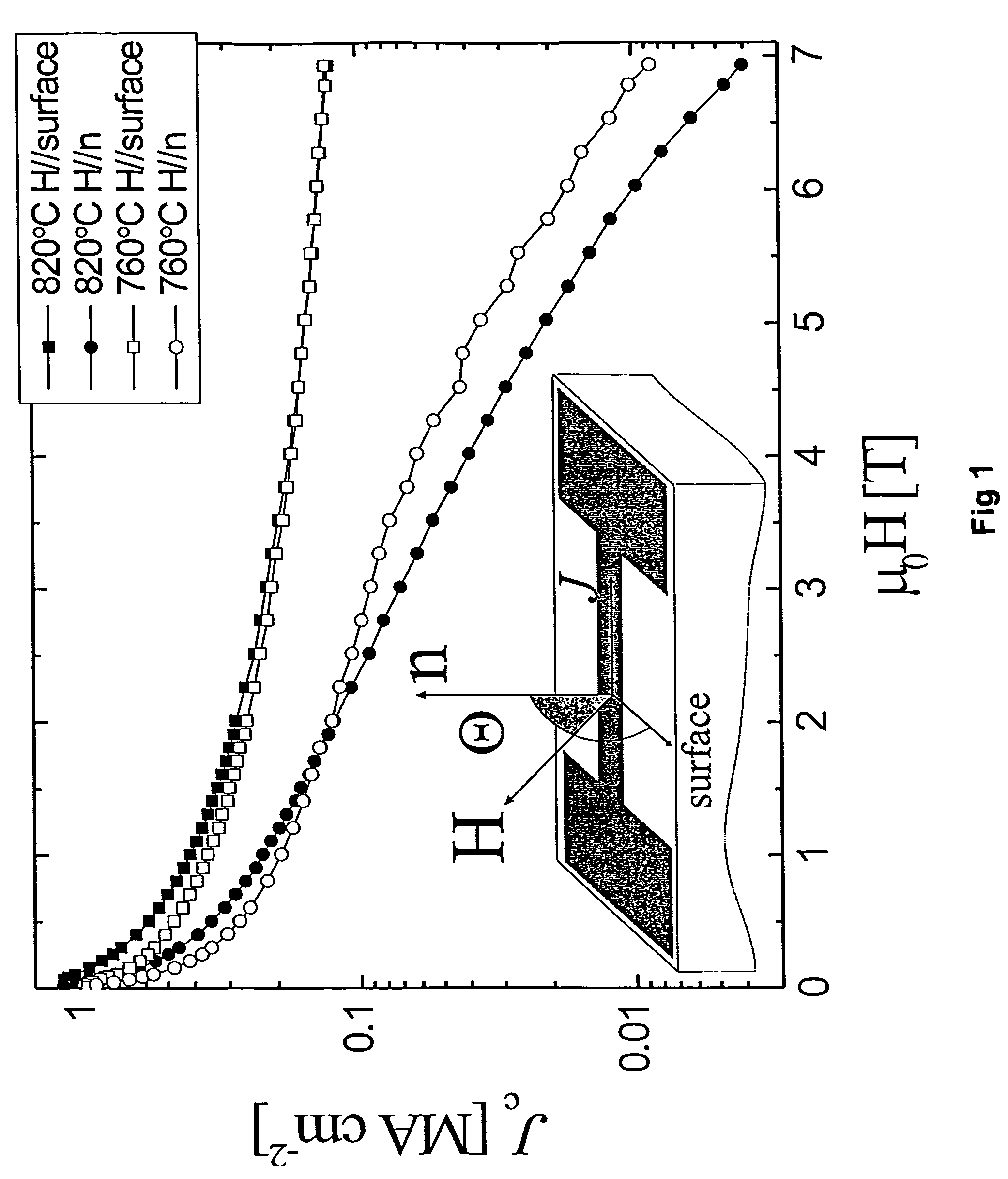
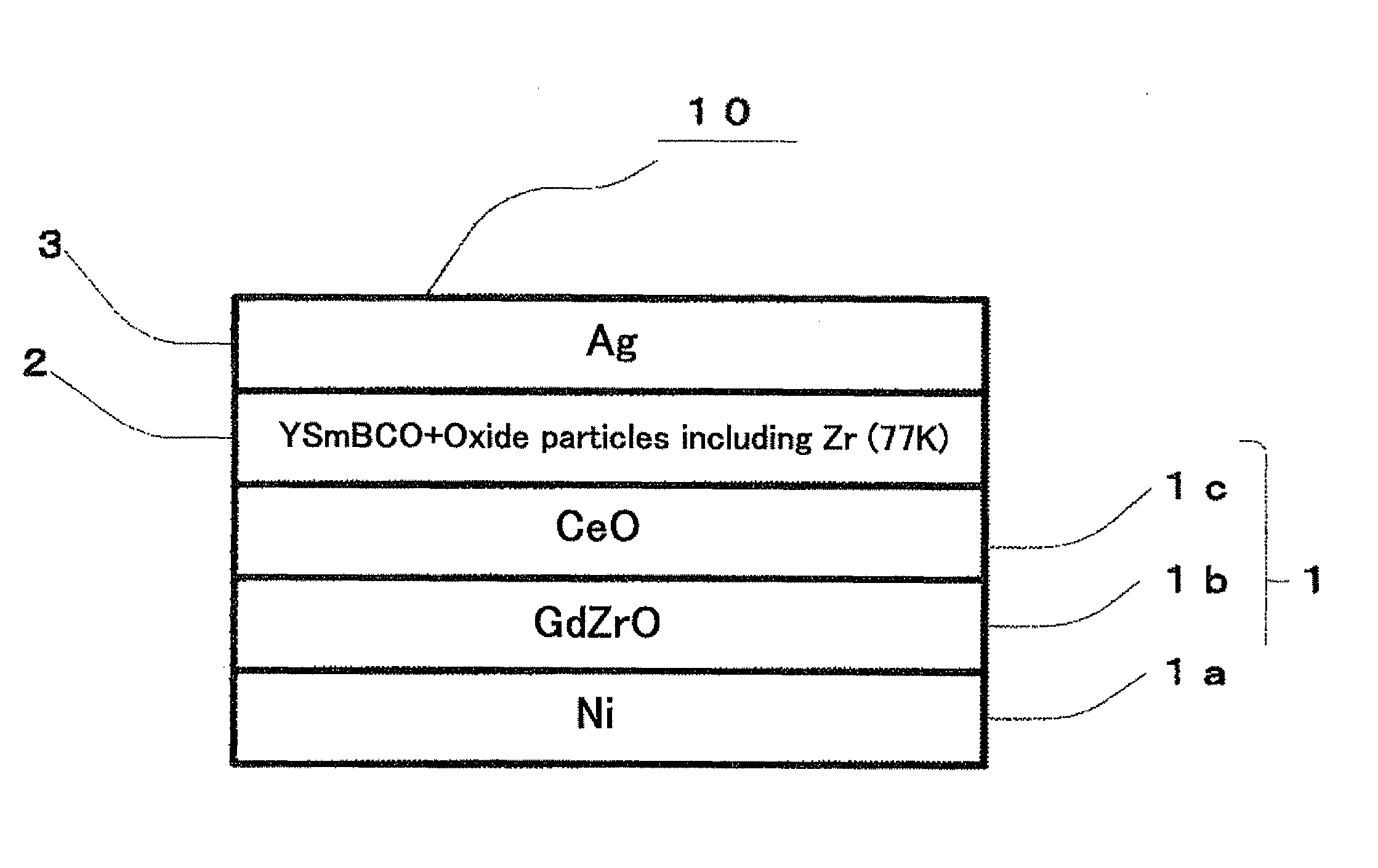
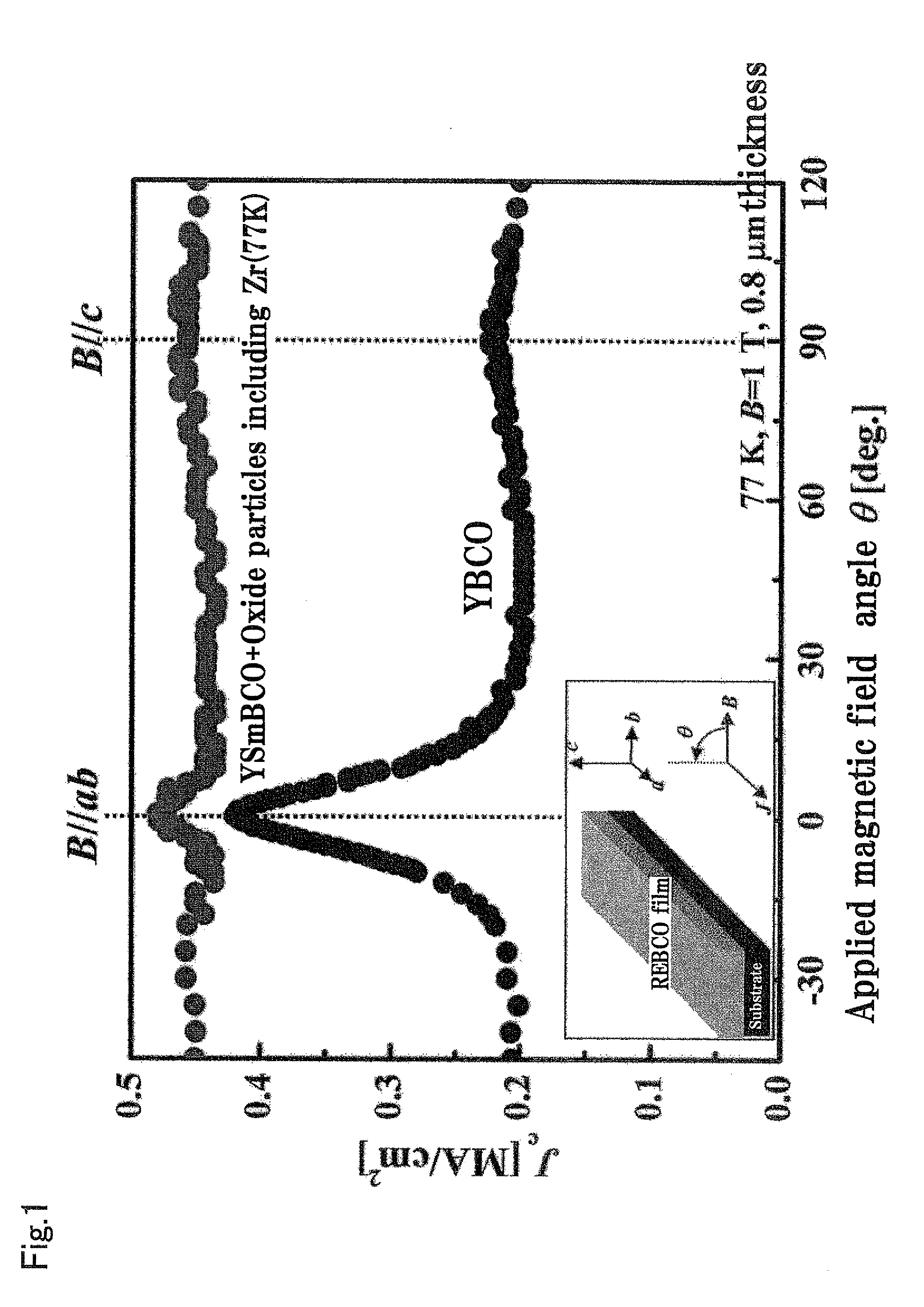
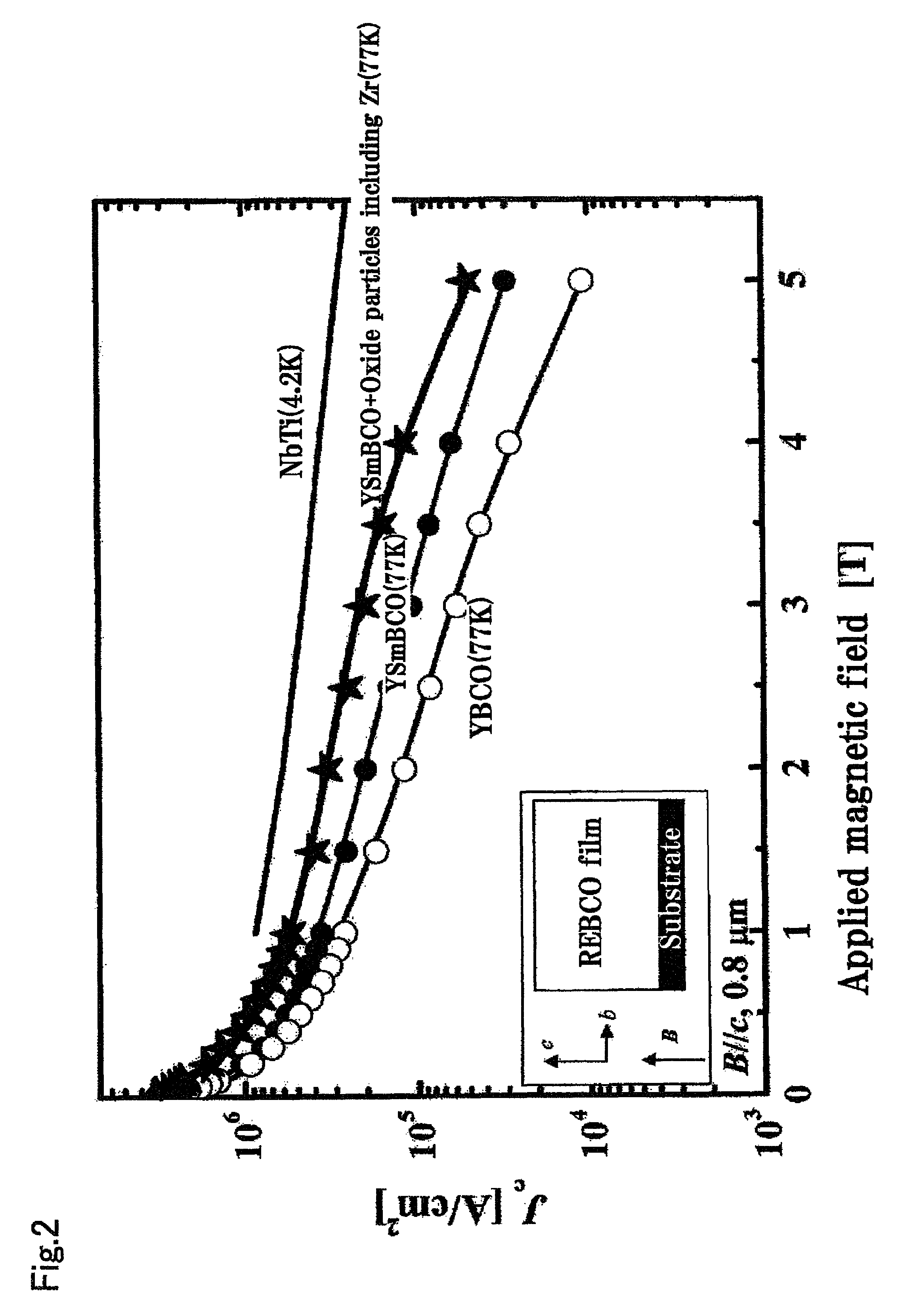
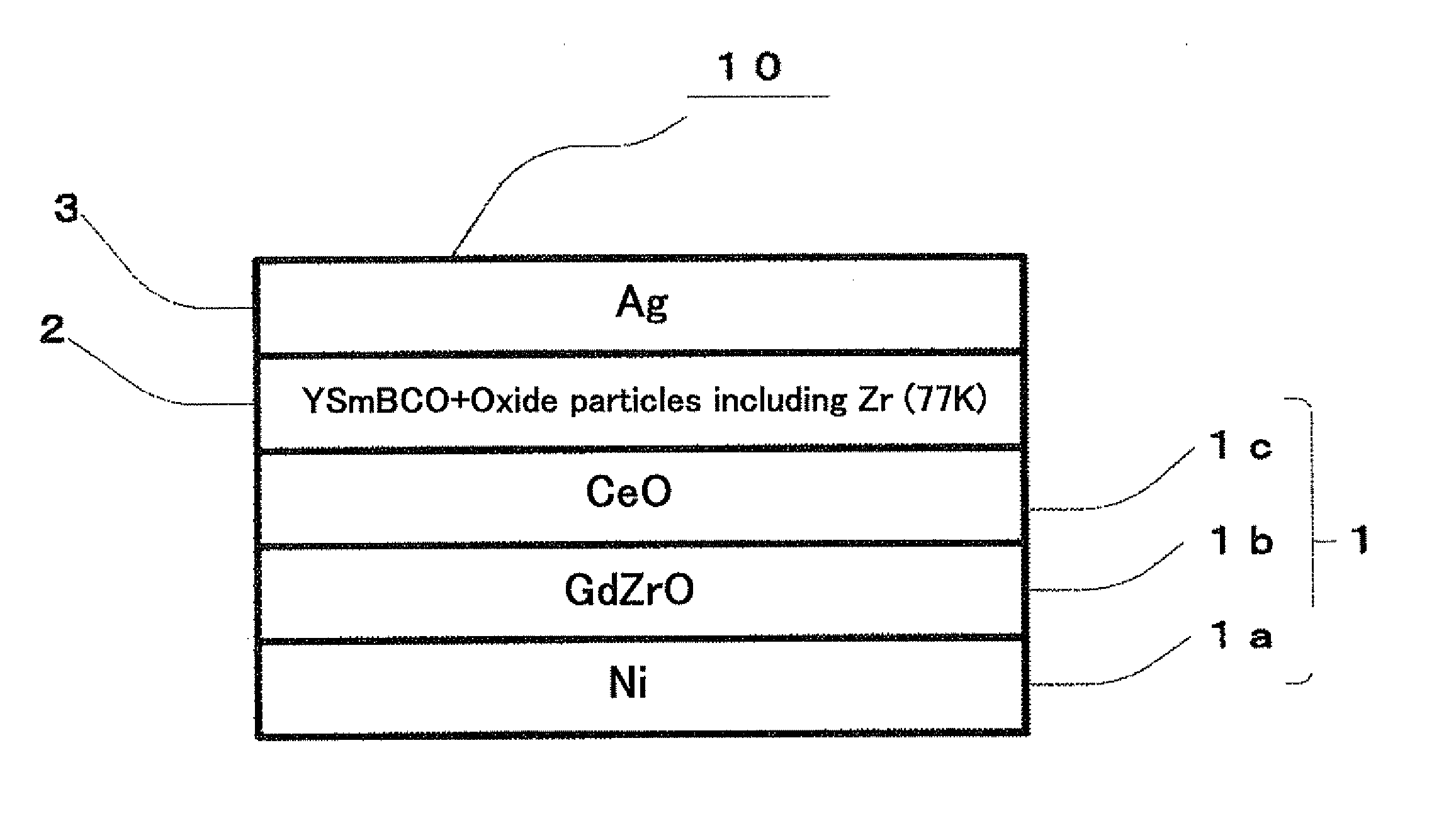
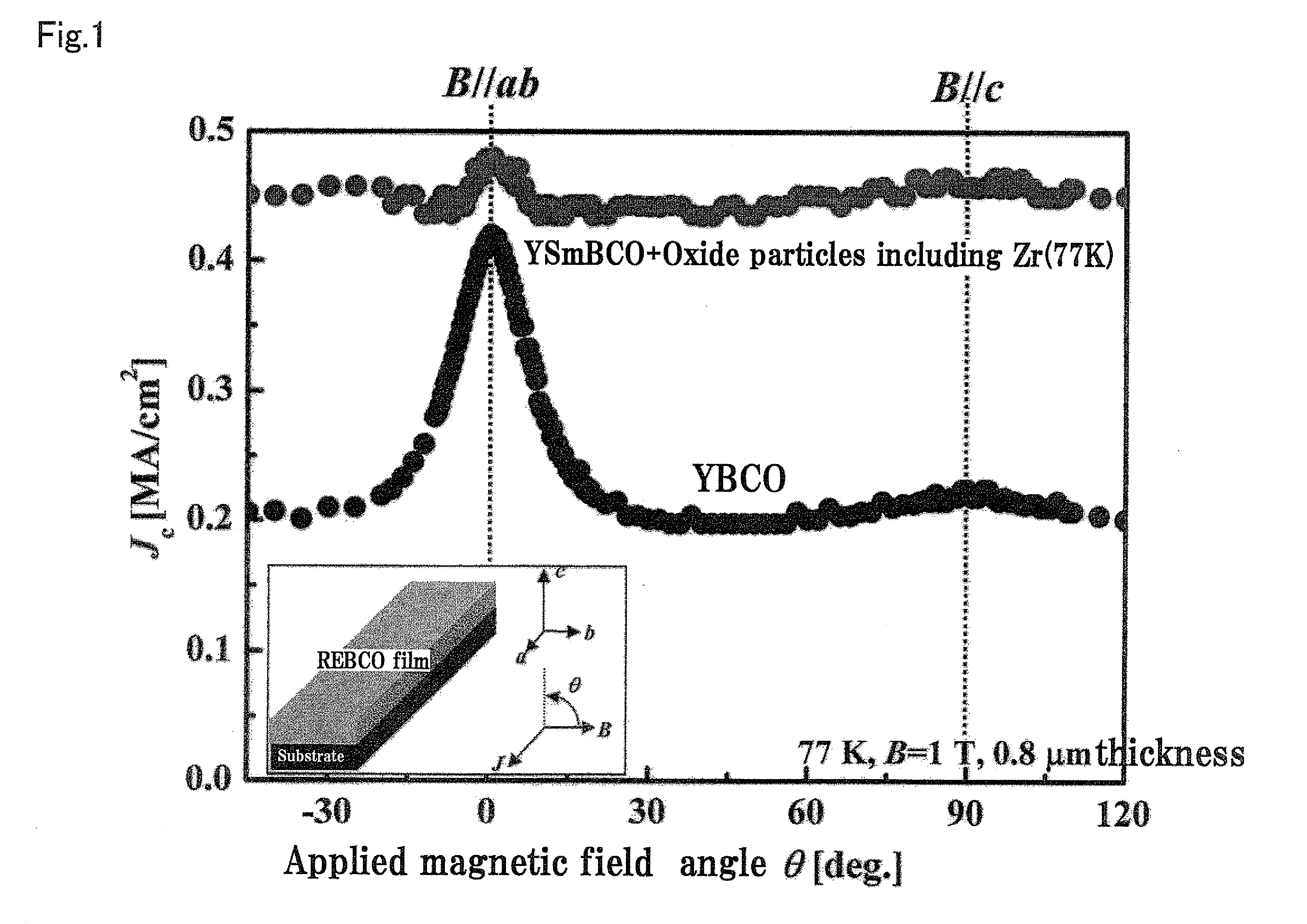
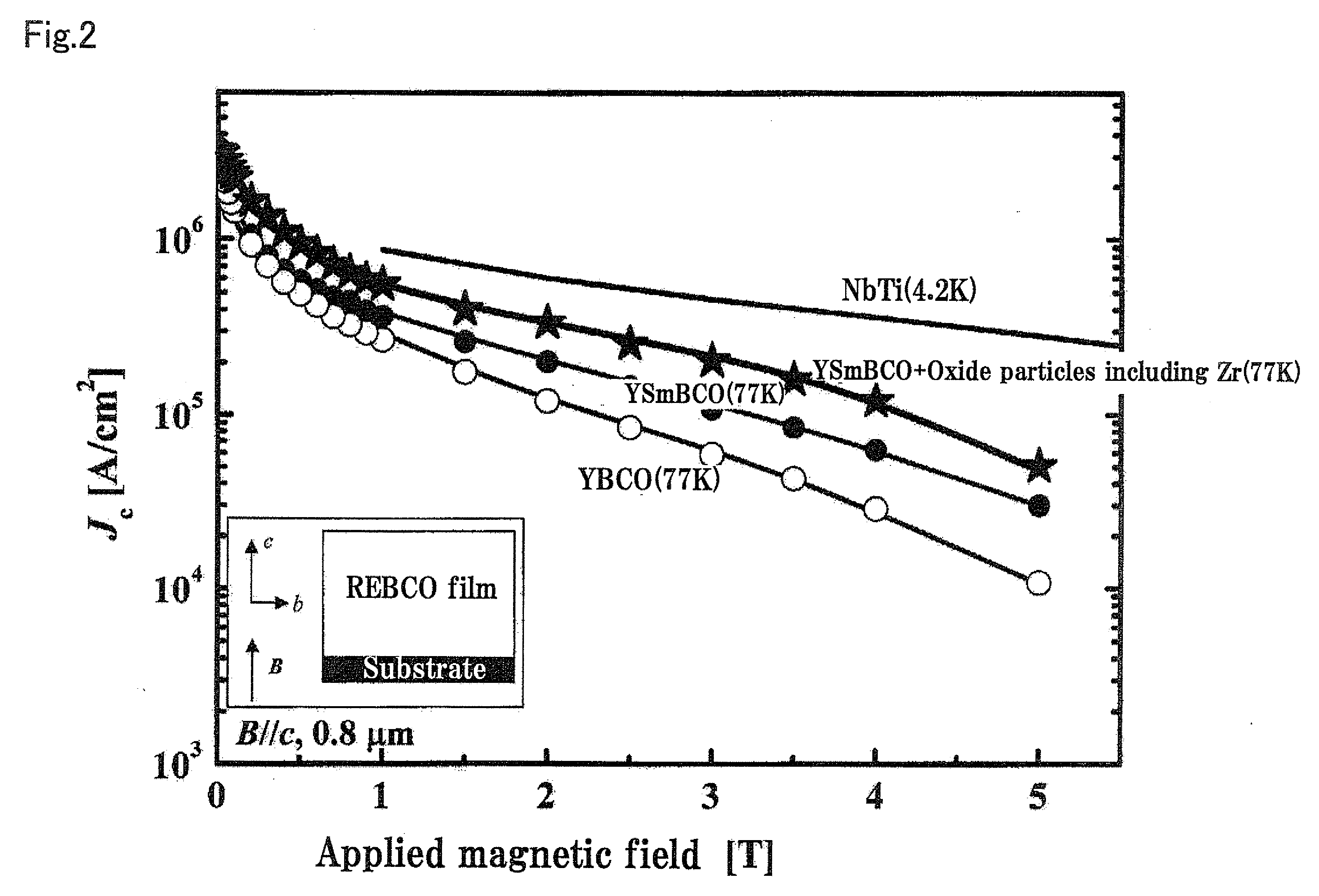
A RE-type oxide superconducting wire having excellent angular dependence for magnetic field of Jc is obtained by finely dispersing magnetic flux pinning centers into a superconductor. A mixed solution which comprises a metal-organic complex solution including a metal element which composes a RE-type oxide superconductor whose Ba content is reduced and a metal-organic complex solution including at least one or more kinds of metals which are selected from Zr, Ce, Sn, or Ti which has a larger affinity for Ba is coated onto an intermediate layer of a composite substrate, and the assembly is then calcined to disperse artificially and finely oxide particles (magnetic flux pinning centers) including Zr. Thus, the angular dependence for magnetic field (Jc,min / Jc,max) of Jc can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SWCC SHOWA CABLE SYST CO LTD
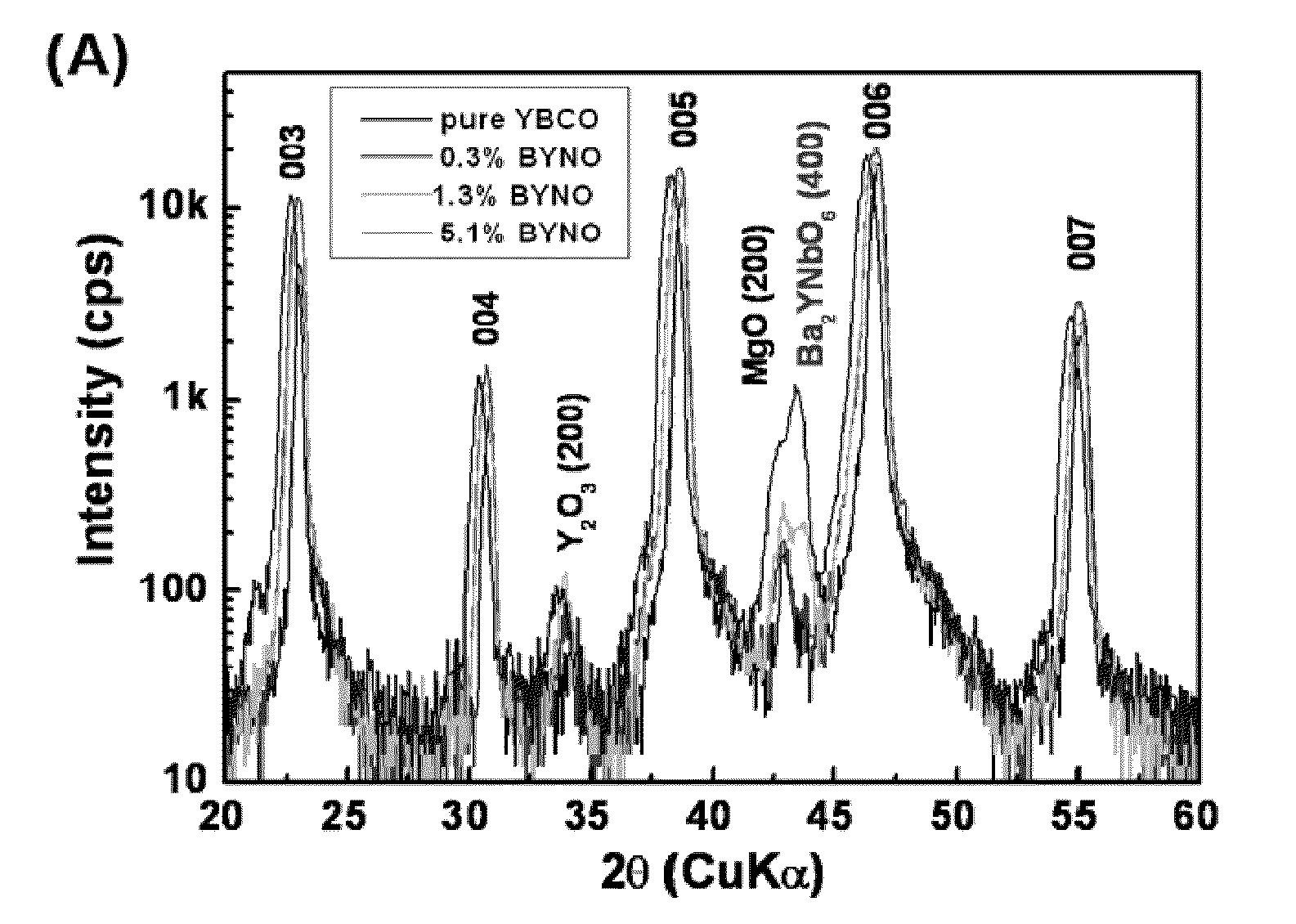
CRITICAL CURRENT DENSITY ENHANCEMENT VIA INCORPORATION OF NANOSCALE Ba2(Y,RE)NbO6 IN REBCO FILMS
A superconducting article includes a substrate having a biaxially textured surface, and an epitaxial biaxially textured superconducting film supported by the substrate. The epitaxial superconducting film includes particles of Ba2RENbO6 and is characterized by a critical current density higher than 1 MA / cm2 at 77K, self-field. In one embodiment the particles are assembled into columns. The particles and nanocolumns of Ba2RENbO6 defects enhance flux pinning which results in improved critical current densities of the superconducting films. Methods of making superconducting films with Ba2RENbO6 defects are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Flux pinning of cuprate superconductors with nanoparticles
ActiveUS8383552B1Enhanced flux pinningReduce material costsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingDopantFlux pinning
The present invention provides a method of making a high temperature superconductor having a doped, nanoparticulate pinning structure. The method includes providing a nanoparticulate pinning material, providing a cuprate material, doping the nanoparticulate pinning material with a dopant to form a doped nanoparticulate material, depositing a layer of the cuprate material on a substrate, and depositing a layer of the doped nanoparticulate material on the layer of cuprate material. The invention also provides a high temperature superconductor (HTS) having a doped, nanoparticulate pinning structure including a plurality of layers of a cuprate material and a plurality of layers of a doped nanoparticulate pinning material. At least one layer of the doped nanoparticulate pinning material is stacked between two layers of the cuprate material.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE US SEC THE
Low-temperature fast powder sintering method for superconductive MgB2 nano particle
InactiveCN101186306AUniform sizeEasy to prepareSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesFlux pinningRoom temperature
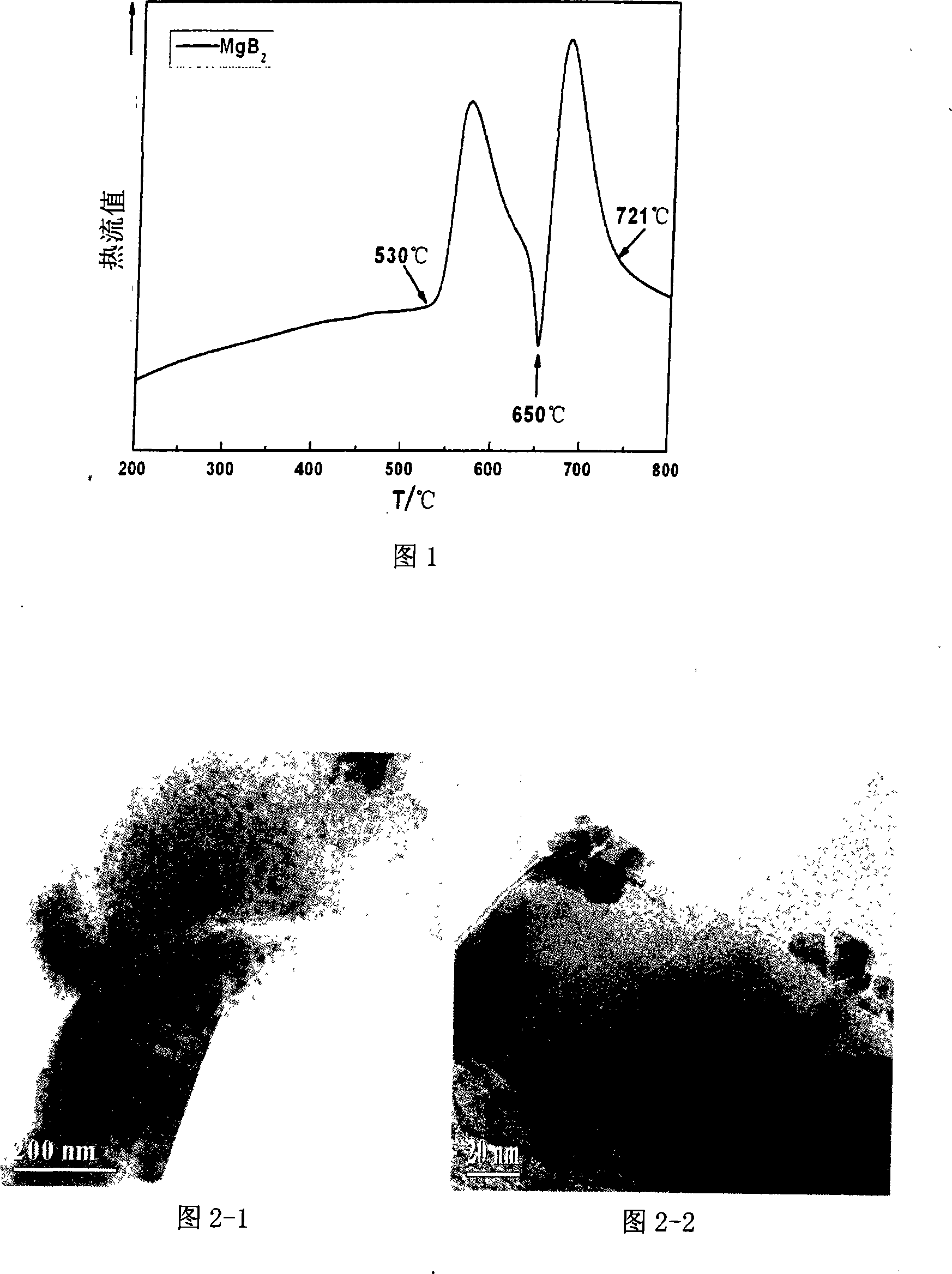
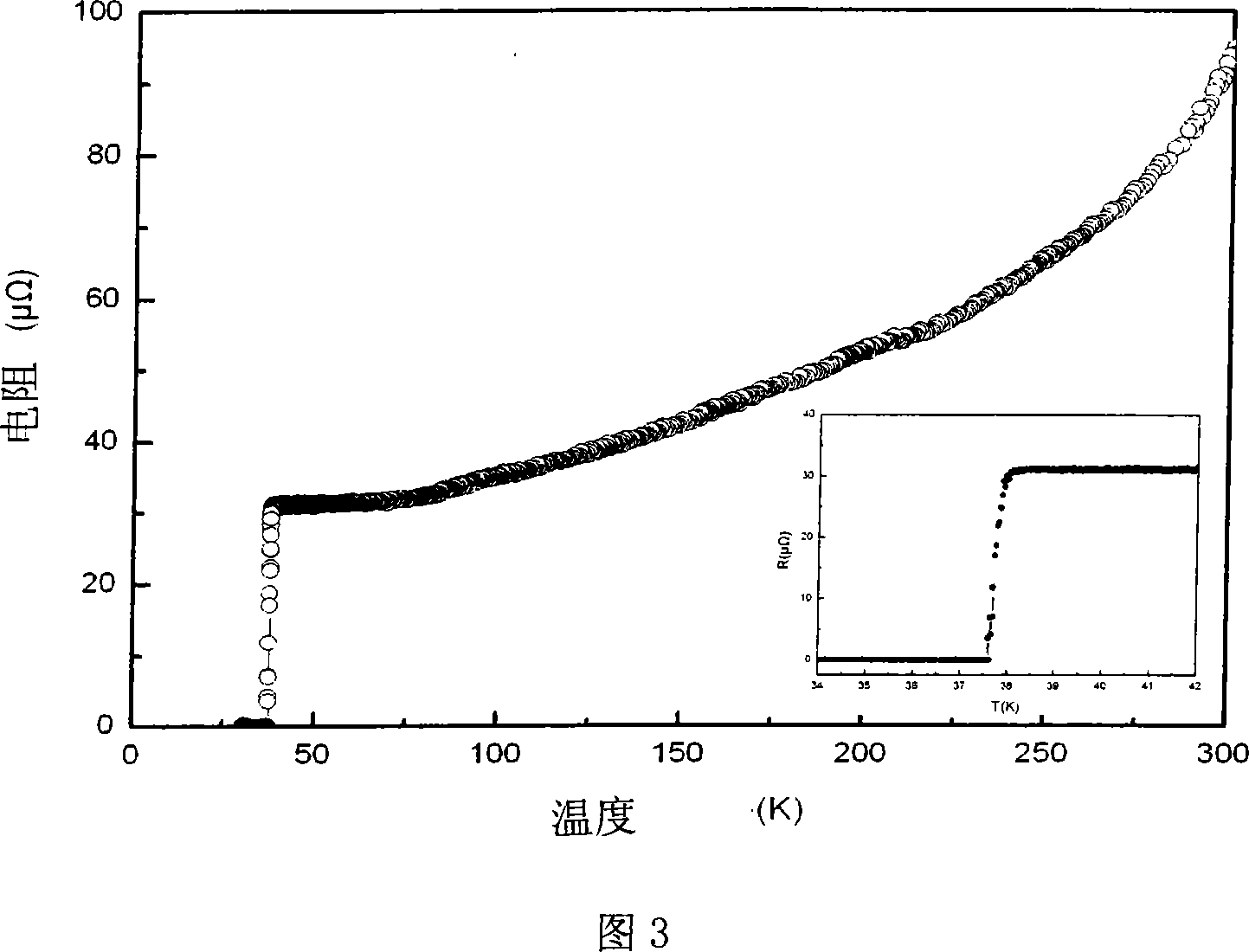
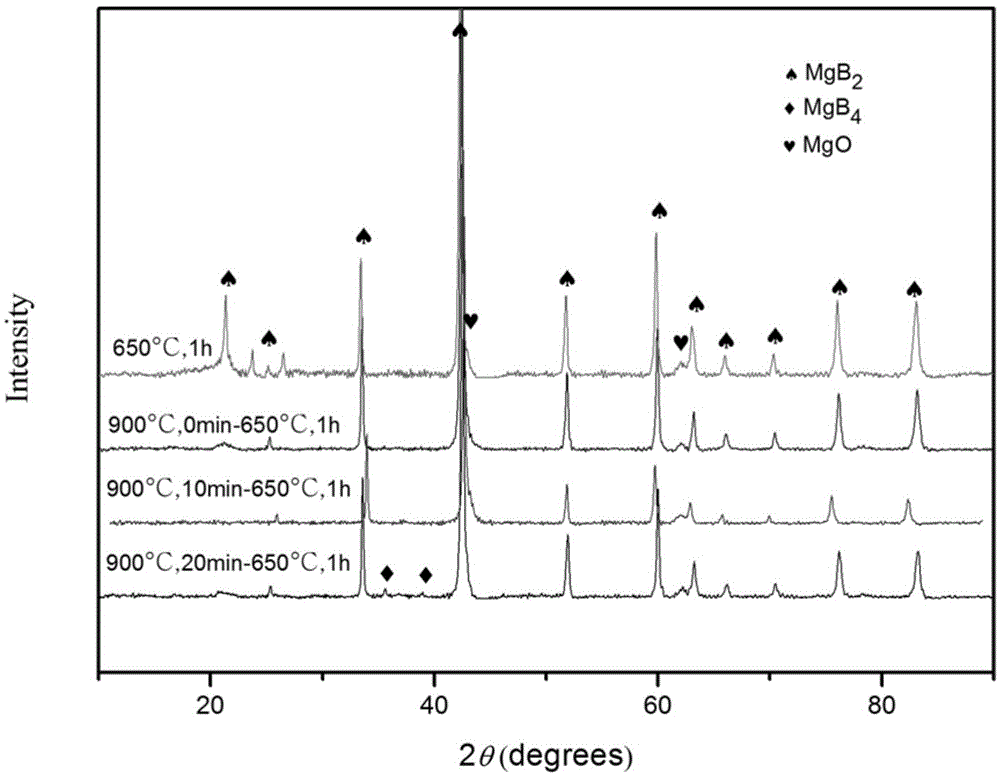
The invention discloses a low-temperature fast powder sintering method for a superconduct nano-particle MgB2, which comprises the steps: magnesium powder and amorphous boron are mixed according to atomic ratio: Mg:B is equal to 1-1.5:2, then the compound is grinded for 0.3 to 2 hours and is pressed into block under the pressure of 2-7MPa; the block is added into a heating device and is added with argon, and the temperature raises to 980K - 1010K at the speed of 20 - 40K / min, then the temperature lowers to room temperature at the speed of 40 - 50K / min, and the superconduct nano-particle MgB2 is made. The diameter of MgB2 of the invention is about 10 to 20nm; Tc value is up to 38.5K, when the MgB2 nano particles are used for measuring superconducting transition temperature, which can not only maintain superconducting transition temperature close to theoretical value, but also be taken as the center of flux pinning, thereby enhancing critical current density.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method for MgB2 based composite element doped cryogenic conductor
ActiveCN101343184AIncrease the critical current densityImproved Flux PinningSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesFlux pinningHydrogen
The invention provides a preparation method of an MgB2 matrix composite element doped superconductor, and the preparation process comprises: firstly mixing dried magnesium powder, boron powder and Ti3SiC2 powder fully according to a certain proportion for 1 to 2 hours, and molding the mixed powder by compression; then putting the mixture into a vacuum annealing furnace, and preserving the heat of the furnace for 1 to 10 hours at a temperature of between 700DEG C and 1000DEG C under the protection of a gas mixture of pure argon gas or argon gas and hydrogen; and finally cooling the mixture to the room temperature, so as to prepare the MgB2 matrix composite element doped superconductor with high critical current density. The adoption of the MgB2 matrix superconductor prepared by the preparation method can introduce the second phase particle as an effective pinning center while changing the crystal structure of the MgB2 matrix superconductor, and the acquired MgB2 matrix superconductor has high critical current density in the background magnetic field of over 3-Tesla, and can realize the low-cost preparation of the MgB2 matrix superconductive material, and effectively improve the flux pinning of the MgB2 matrix superconductor.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Superconductor films with improved flux pinning and reduced ac losses
InactiveUS20100081574A1Increased flux pinningReduce AC-lossSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningChemistry
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
High critical current density MgB2-base super conductor and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1812000AIncrease the critical current densityImproved Flux PinningSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsFlux pinningRoom temperature
This invention relaters to a high critical current density superconductor of MgB2 base and its manufacturing method characterizing that C, Zr and other compounds are dispersed in said superconductor with MgB2 as the base, during the preparation, first of all, dried Mg, B, Zr and carbon powder in proportion are mixed fully for 1-2 hours to be formed then to be put in a vacuum annealing furnace to keep the temperature for 1-10 hours to be protected by Ar or mixed gas of Ar and H under 740-760deg.C to be cooled to room temperature to get a superconductor with MgB2 base of high critical current density.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Re-type oxide superconducting wire and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20110124508A1Angular dependenceReduce concentrationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningComposite substrate
A RE-type oxide superconducting wire having excellent angular dependence for magnetic field of Jc is obtained by finely dispersing magnetic flux pinning centers into a superconductor. A mixed solution which comprises a metal-organic complex solution including a metal element which composes a RE-type oxide superconductor whose Ba content is reduced and a metal-organic complex solution including at least one or more kinds of metals which are selected from Zr, Ce, Sn, or Ti which has a larger affinity for Ba is coated onto an intermediate layer of a composite substrate, and the assembly is then calcined to disperse artificially and finely oxide particles (magnetic flux pinning centers) including Zr. Thus, the angular dependence for magnetic field (Jc,min / Jc,max) of Jc can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SHOWA ELECTRIC WIRE & CABLE CO
Modularization reconfigurable method and device based on superconductive magnetic flux pinning connection
InactiveCN103023389AEasy to controlEasy to implementMagnetic holding devicesFlux pinningElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a modularization reconfigurable method based on superconductive magnetic flux pinning connection and a simulation device applying the method. Particularly, interaction of an II-type high-temperature superconductor with a magnet and the characteristic of controllable magnetic field direction and size are utilized to establish reconfiguration of the modularization structure in a manner of establishing a superconductive magnetic flux pinning connecting interface. The magnetic flux pinning characteristic of the high-temperature superconductor in a superconducting state is fully utilized, the superconductive magnetic flux pinning connecting interface configured under the characteristic has certain rigidity and dampness and can be compared as connection by a spring having certain rigidity, and the superconductor can naturally enter the superconductive state in a space environment so that the reconfigurable method provides brand new developing idea for in-orbit assembly of a modularized spacecraft and has broad application prospect in the field of novel spacecraft development.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for improving performance of high temperature superconductors within a magnetic field
InactiveUS20100022397A1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsParticulatesFlux pinning
The present invention provides articles including a base substrate including a layer of an oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure layer thereon; and, a buffer layer upon the oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure layer, the buffer layer having an outwardly facing surface with a surface morphology including particulate outgrowths of from 10 nm to 500 run in size at the surface, such particulate outgrowths serving as flux pinning centers whereby the article maintains higher performance within magnetic fields than similar articles without the necessary density of such outgrowths.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Preparation method of monodomain yttrium barium copper oxide superconducting bulk material
ActiveCN102534787BSimple processImproved Flux Pinning PerformancePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsFlux pinningYttrium barium copper oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a single domain yttrium barium copper oxide superconductor; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing Y2BaCuO5 precursor powder and liquid phase source powder, pressing a Y2BaCuO5 precursor block, a liquid phase block and a supporting bock, preparing a green body, growing a single domain yttrium barium copper oxide block in an infiltration manner, and carrying out oxygen permeation processing. A second phase nanoparticle Y2Ba4CuBiOx / Y2Ba4CuMOx (M is Bi or W) is successfully introduced for forming a flux pinning center by adopting a top seed crystal infiltration growing method and adding a metallic oxide (Bi2O3 powder and WO3 powder) for doping, thereby the powder preparation technology is simplified, the experimental period is shortened, the experiment cost is reduced, and the flux pinning capacity of the superconductor is increased. Y2O3 is used for preparing the supporting block which stably supports two briquettes above the supporting block in the slow cold growing process of an yttrium barium copper oxide block so as to prevent liquid phase from running off. The preparation method can be used for preparing the yttrium barium copper oxide superconductor and can also be used for preparing high-temperature superconductors of other series such as Gd, Sm, Nd, Eu and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
CRITICAL CURRENT DENSITY ENHANCEMENT VIA INCORPORATION OF NANOSCALE Ba2(Y,RE)TaO6 IN REBCO FILMS
A superconducting article includes a substrate having a biaxially textured surface, and an epitaxial biaxially textured superconducting film supported by the substrate. The epitaxial superconducting film includes particles of Ba2RETaO6 and is characterized by a critical current density higher than 1 MA / cm2 at 77K, self-field. In one embodiment the particles are assembled into columns. The particles and nanocolumns of Ba2RETaO6 defects enhance flux pinning which results in improved critical current densities of the superconducting films. Methods of making superconducting films with Ba2RETaO6 defects are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
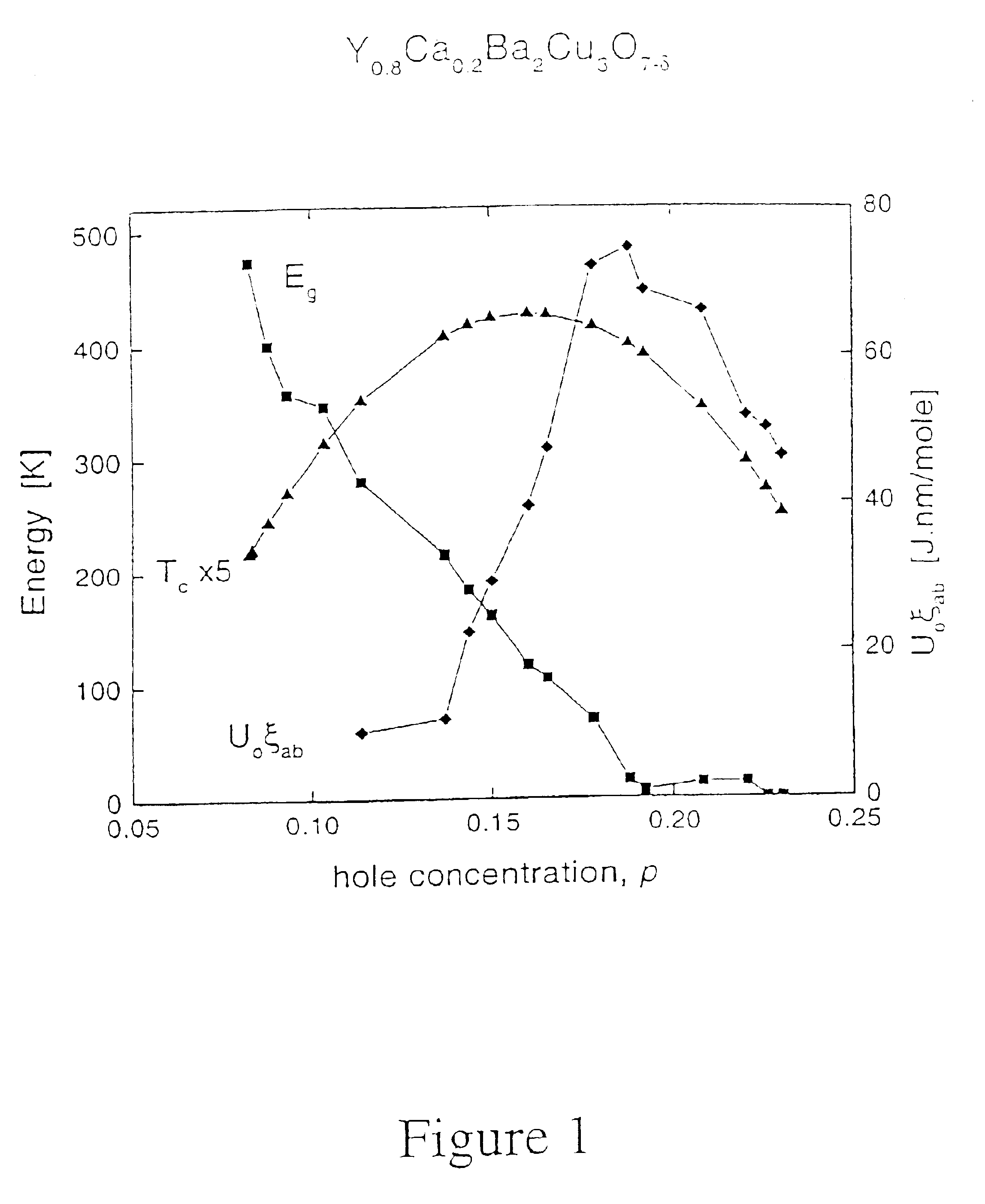
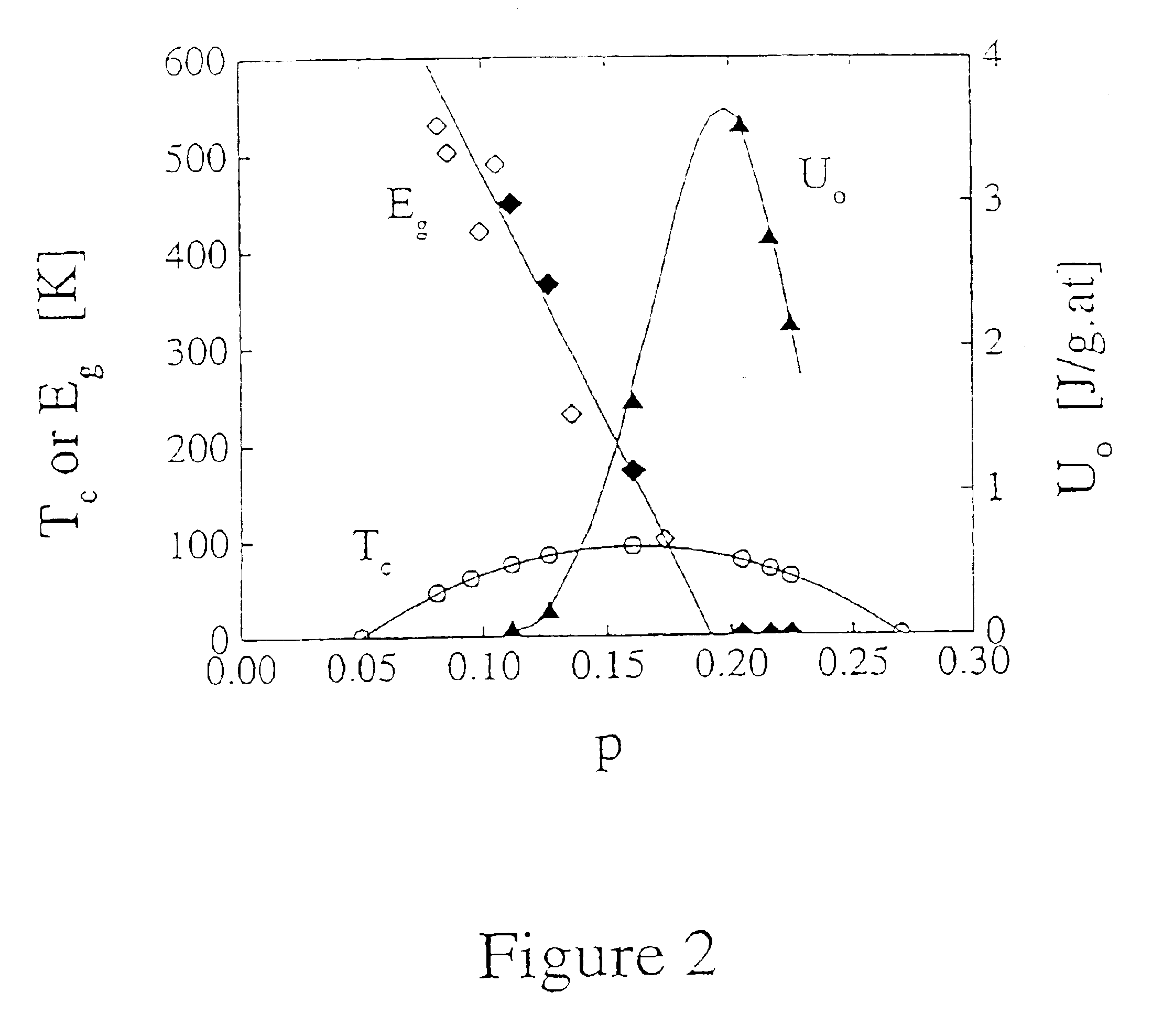
Critical doping in high-Tc superconductors for maximal flux pinning and critical currents
InactiveUS6784138B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsFlux pinningHigh-temperature superconductivity
A method for maximising critical current density (Jc) of high temperature superconducting cuprate materials (HTSC) which comprises controlling the doping state or hole concentration of the materials to be higher than the doping state or hole concentration of the material that provides a maximum superconducting transition temperature (Tc), and to lie at about a value where the normal-state pseudogap reduces to a minimum. Jc is maximised1 at hole concentration p≈0.19. HTSC compounds are also claimed.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Method for increasing superconducting critical current density of ex-situ magnesium diboride block through self reaction
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for producing microstructured templates and their use in providing pinning enhancements in superconducting films deposited thereon
ActiveUS8486864B2Increased flux pinningReduced AC lossesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingFlux pinningSurface layer
The present invention relates to a method for producing a phase-separated layer useful as a flux pinning substrate for a superconducting film, wherein the method includes subjecting at least a first and a second target material to a sputtering deposition technique in order that a phase-separated layer is deposited epitaxially on a primary substrate containing an ordered surface layer. The invention is also directed to a method for producing a superconducting tape containing pinning defects therein by depositing a superconducting film on a phase-separated layer produced by the method described above.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Magnetic suspension display platform
PendingCN107319840AGuaranteed suspension stabilityFurniture partsMagnetic bearingsFlux pinningHigh temperature superconducting
The invention discloses a magnetic suspension display platform, and belongs to the technical field of the magnetic suspension. The magnetic suspension display platform comprises a first platform and a second platform. The first platform comprises a high temperature superconductor array and a matched low temperature device thereof, such as a Dewar. The second platform comprises multiple sub-platforms. Each sub-platform has a magnet array formed by multiple magnets. The first platform and the second platform can form the horizontal suspension coordination of the vertical corresponding through the flux pinning force between the magnetic array and the high temperature superconductor array, and the magnetic force balance coordination is formed between the neighboring sub-platforms. The first platform and the second platform of the magnetic suspension display platform are made of a high temperature superconductivity material and a permanent magnet material (or a superconducting coil), the magnetic suspension coordination between two platforms can be realized by using the flux pinning force, and the magnetic force balance between multiple sub-platforms of the second platform formed by multiple magnets can be realized, so the whole suspension stability of the magnetic suspension display platform is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Superconductor films with improved flux pinning and reduced AC losses
InactiveUS7919435B2Simple and inexpensiveIncreased flux pinningSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsFlux pinningChemistry
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Flux pinning of cuprate superconductors with nanoparticles
InactiveUS8623788B1Enhanced flux pinningLow costSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric discharge heatingFlux pinningDopant
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
In-situ preparation method of magnesium borate-magnesium oxide multiphase superconducting material with different superconducting phase contents
InactiveCN103848626ASolve the quench problemSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFlux pinningSuperconducting fault current limiters
The invention discloses an in-situ preparation method of a magnesium borate-magnesium oxide multiphase superconducting material with different superconducting phase contents. According to the method, an MgB2-MgO multiphase superconductor adjustable and controllable in the superconducting phase content in situ is prepared in vacuum through taking boron (B), magnesium (Mg) and diboron trioxide (B2O3) as raw materials. The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnesium diboride (MgB2) multiphase superconducting material adjustable and controllable in the superconducting phase content in situ. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and has the advantages that the wide-range in-situ adjustment and control of the superconducting phase content of an MgB2 multiphase superconductor can be realized and key techniques and base materials are provided for studying the magnesium borate superconducting weak connection property, the flux pinning behavior, the resistor type magnesium borate superconducting fault current limiter (SCFCL) and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing Nb3Sn containing silicon and carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing Nb3Sn containing silicon and carbon, comprising the following steps of uniformly mixing Nb powder, Sn powder and nanometer Si / N / C powder in the molar ratio of (0.8-0.975): (1.8-1.95): (0.025-0.2), obtaining a superconducting material after sintering or forging, putting the superconducting material in a vacuum furnace, introducing argon after vacuumizing, holding the temperature for 1.5-3h at the temperature of 500-800 DEG C and finally obtaining the Nb3Sn superconducting material containing the silicon element and the carbon element. The obtained Nb3Sn superconducting material has the capability of high flux pinning.
Owner:JIANGSU WINAD LIGHTING TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com