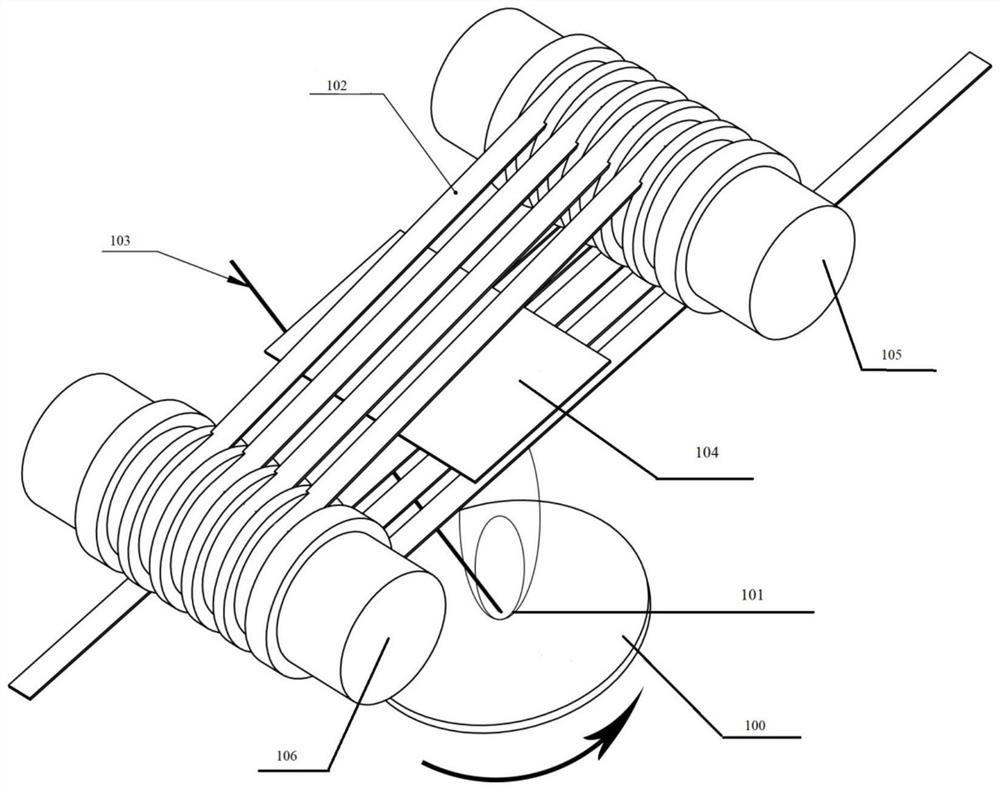
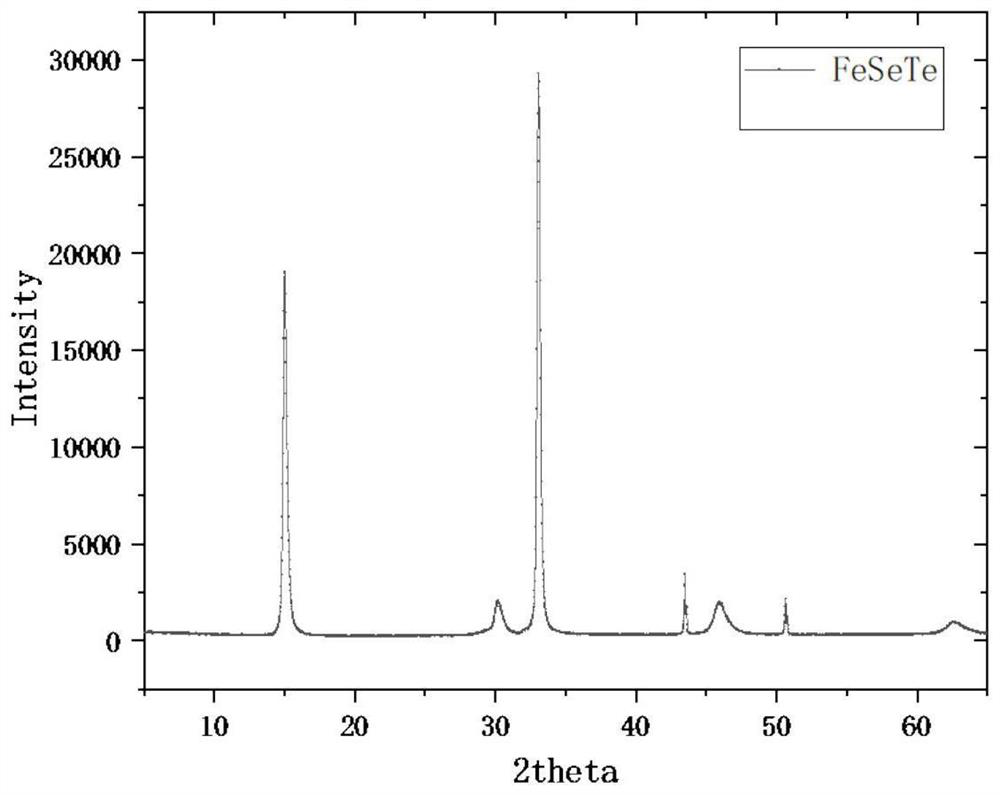
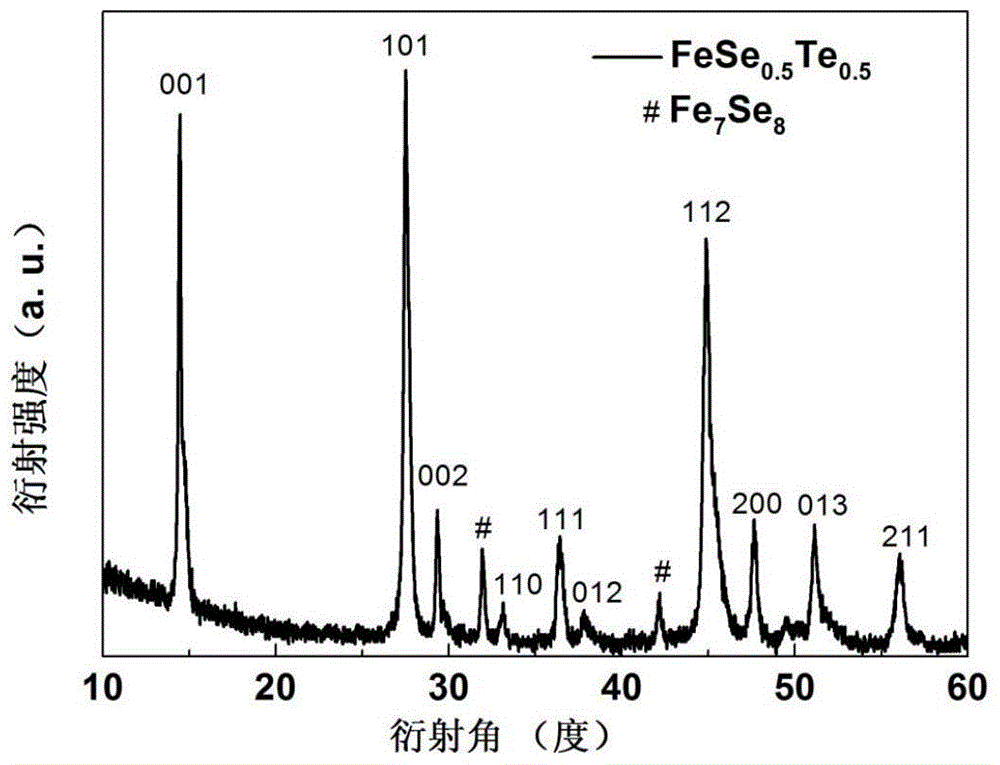
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Raise the superconducting transition temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
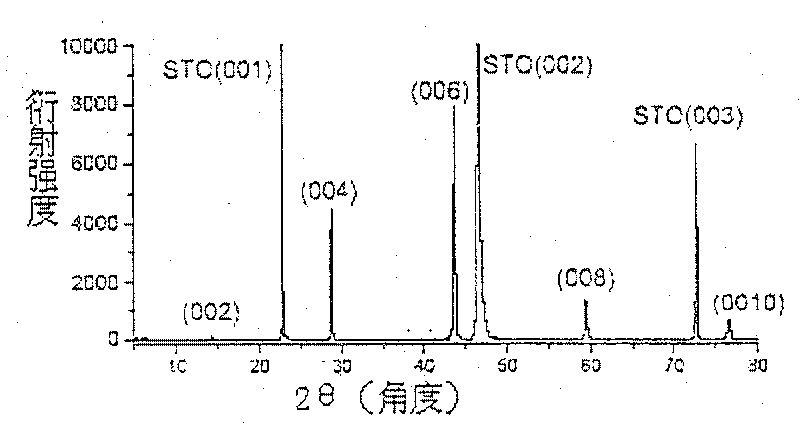
High Temperature Interfacial Superconductivity
InactiveUS20090137398A1Raise the superconducting transition temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsHigh-temperature superconductivityTunnel junction
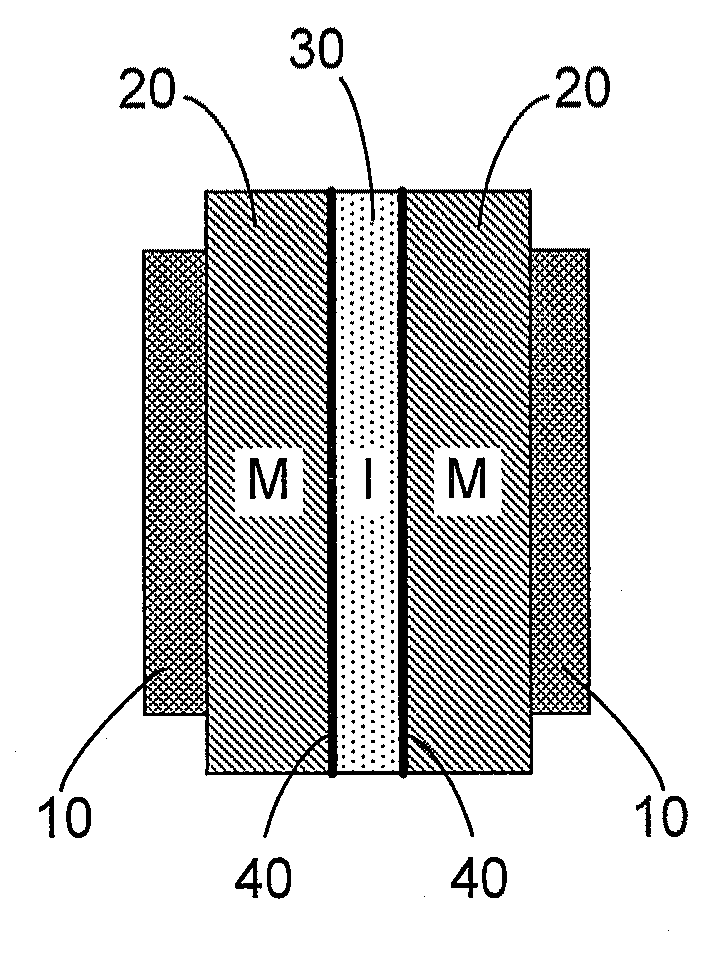
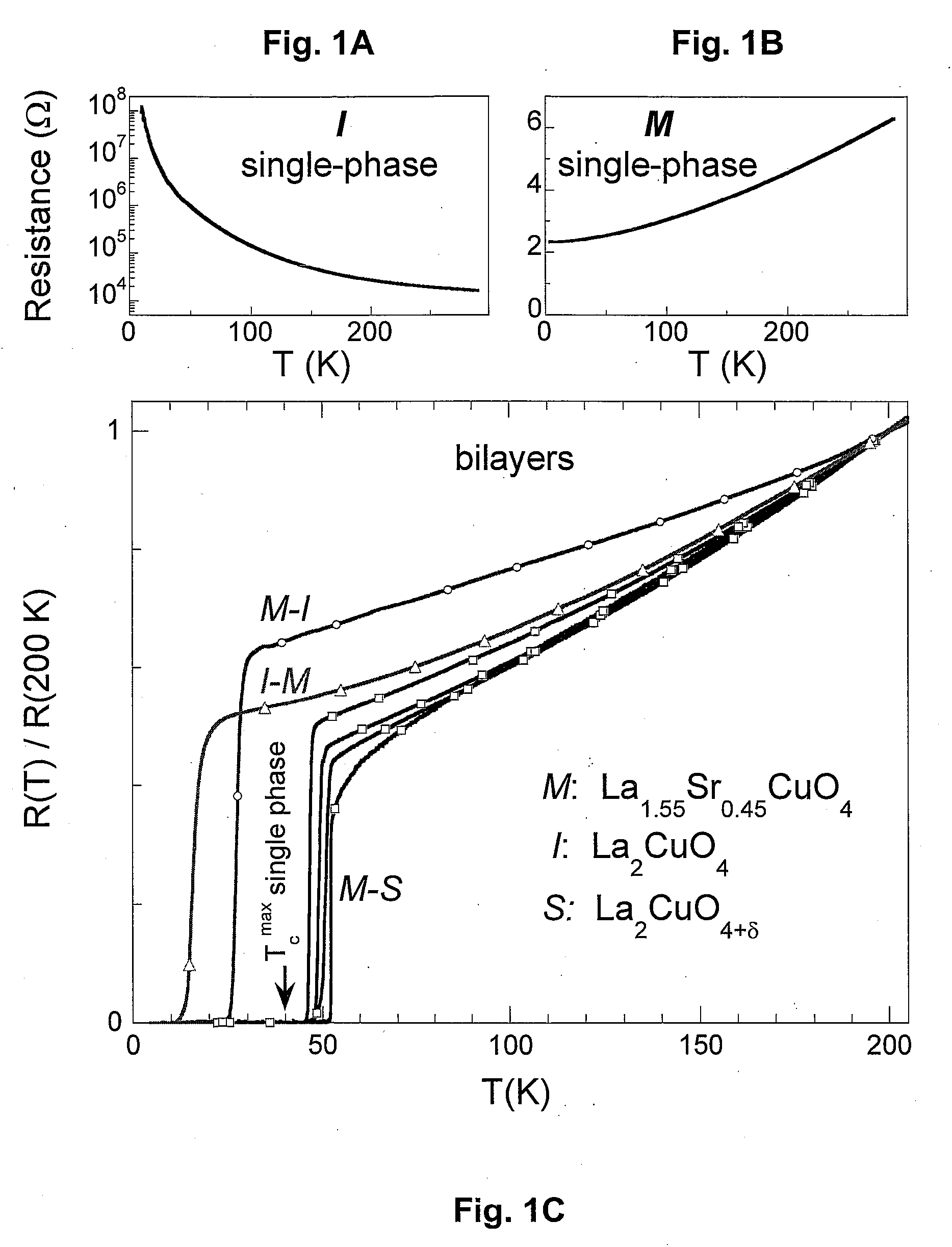
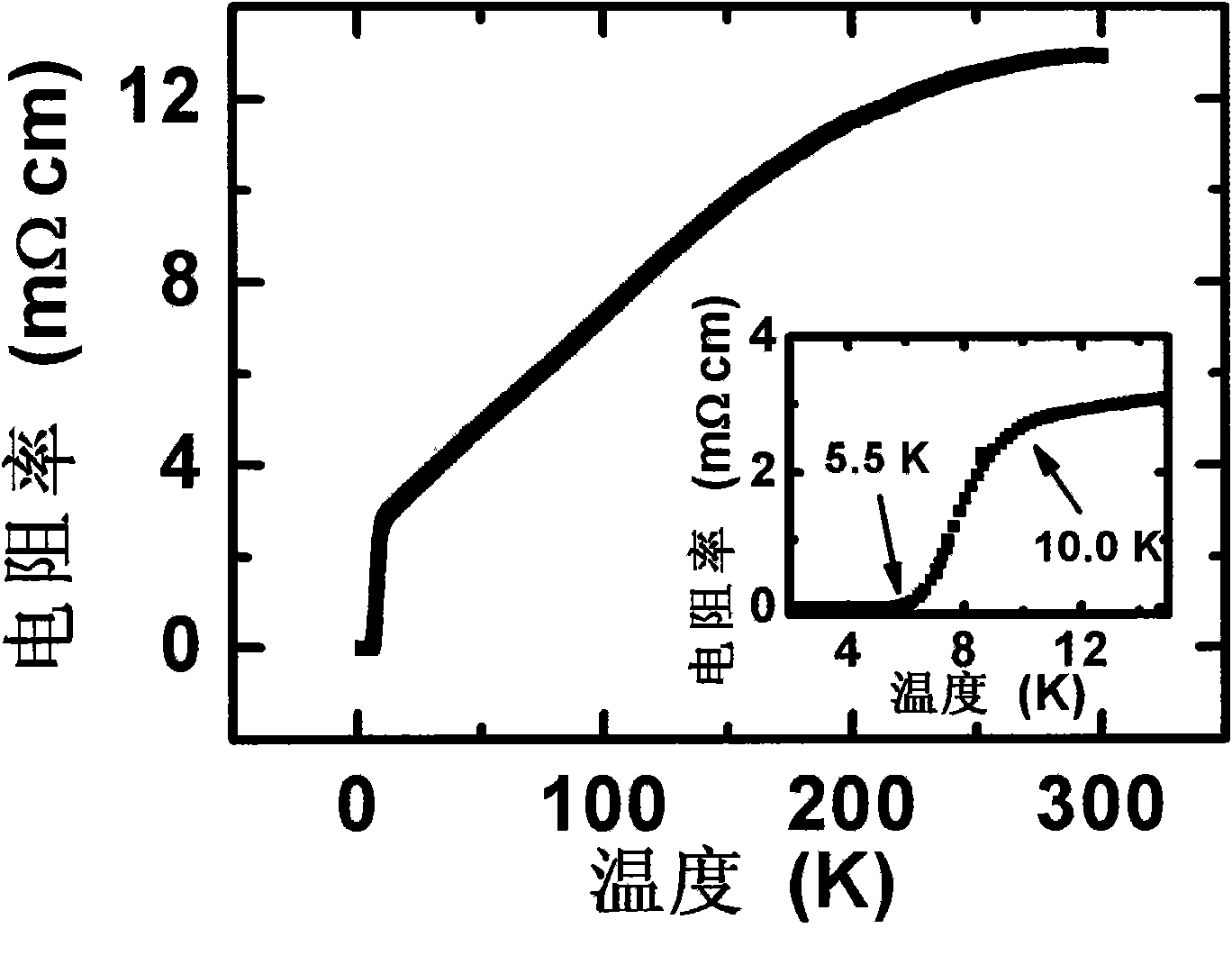
High-temperature superconductivity confined to nanometer-scale interfaces has been a long standing goal because of potential applications in electronic devices. The spontaneous formation of a superconducting interface in bilayers consisting of an insulator (La2CuO4) and a metal (La1−xSrxCuO4), neither of which is superconducting per se, is described. Depending upon the layering sequence of the bilayers, Tc may be either ˜15 K or ˜30 K. This highly robust phenomenon is confined to within 2-3 nm around the interface. After exposing the bilayer to ozone, Tc exceeds 50 K and this enhanced superconductivity is also shown to originate from a 1 to 2 unit cell thick interfacial layer. The results demonstrate that engineering artificial heterostructures provides a novel, unconventional way to fabricate stable, quasi two-dimensional high Tc phases and to significantly enhance superconducting properties in other superconductors. The superconducting interface may be implemented, for example, in SIS tunnel junctions or a SuFET.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
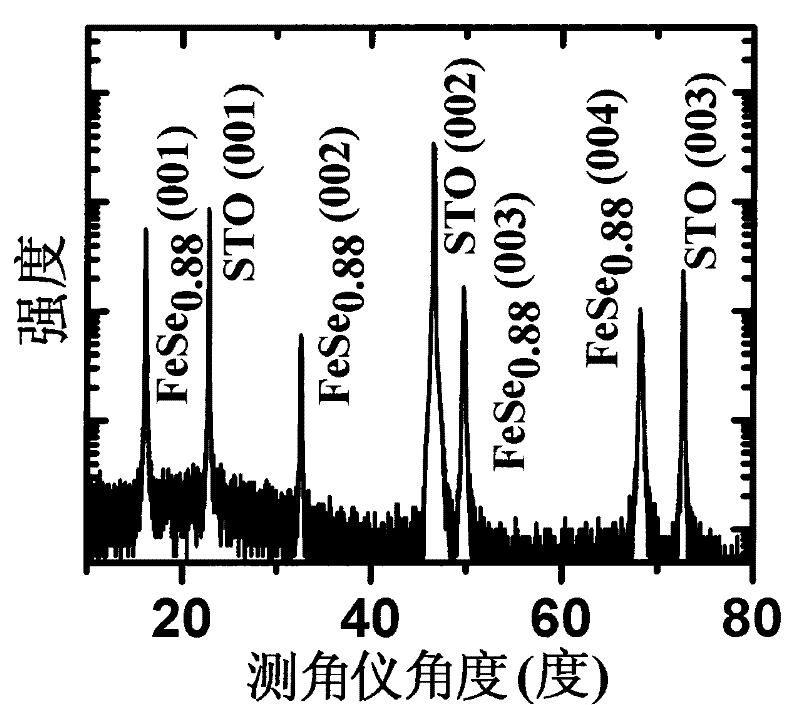
Preparation method of epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film and prepared epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film
ActiveCN101867012AQuality improvementRaise the superconducting transition temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOptoelectronicsGreek letter alpha
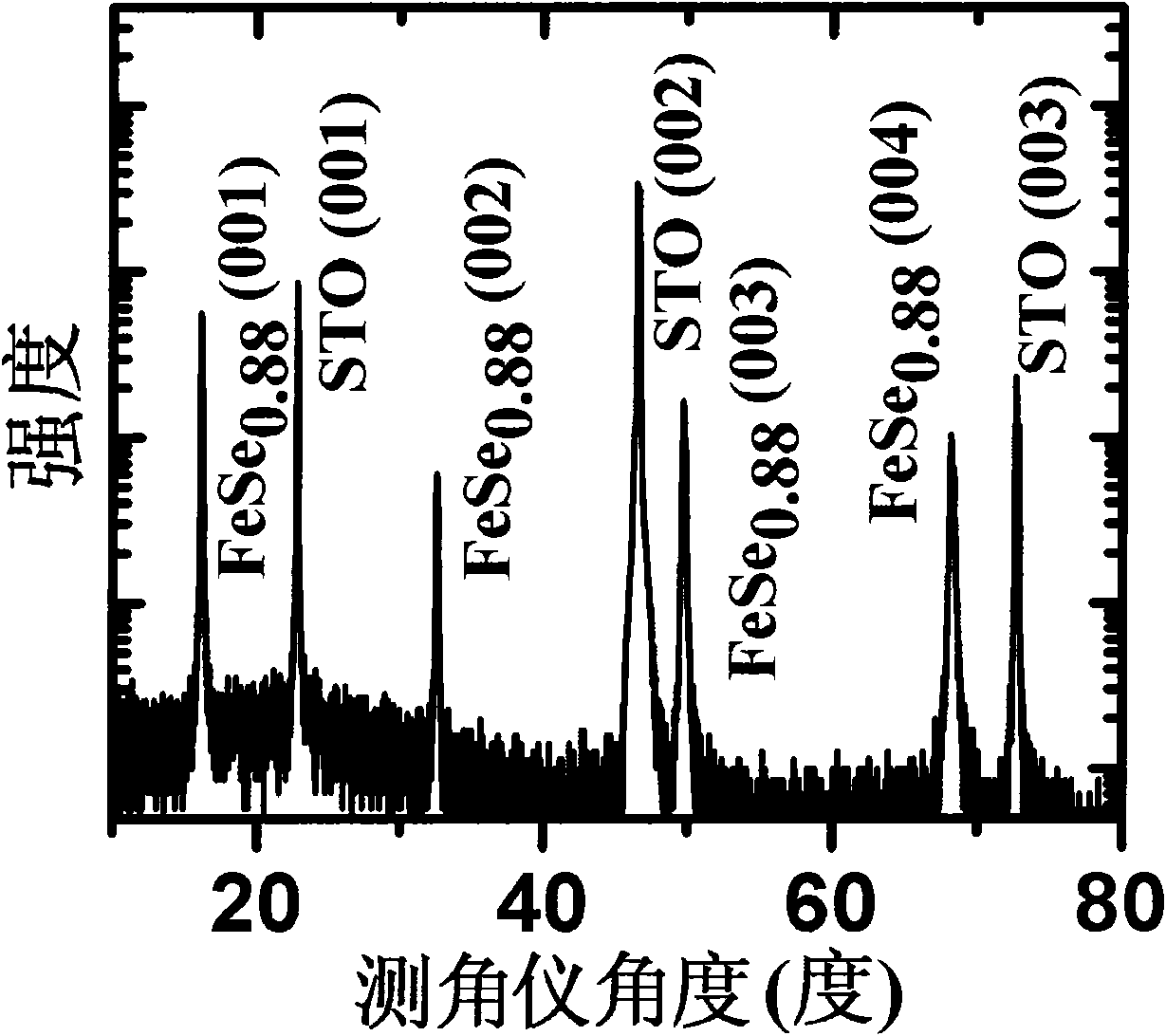
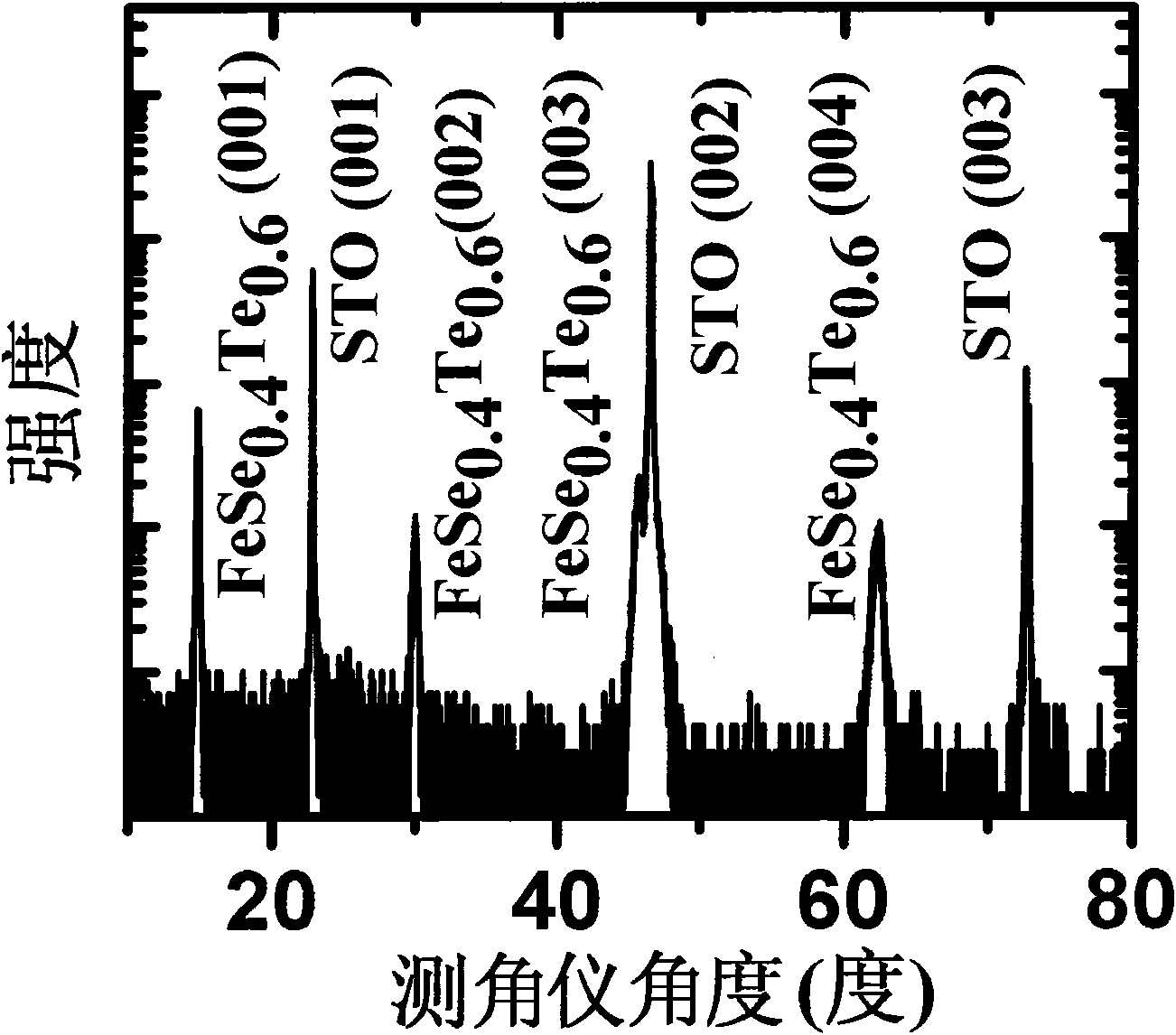
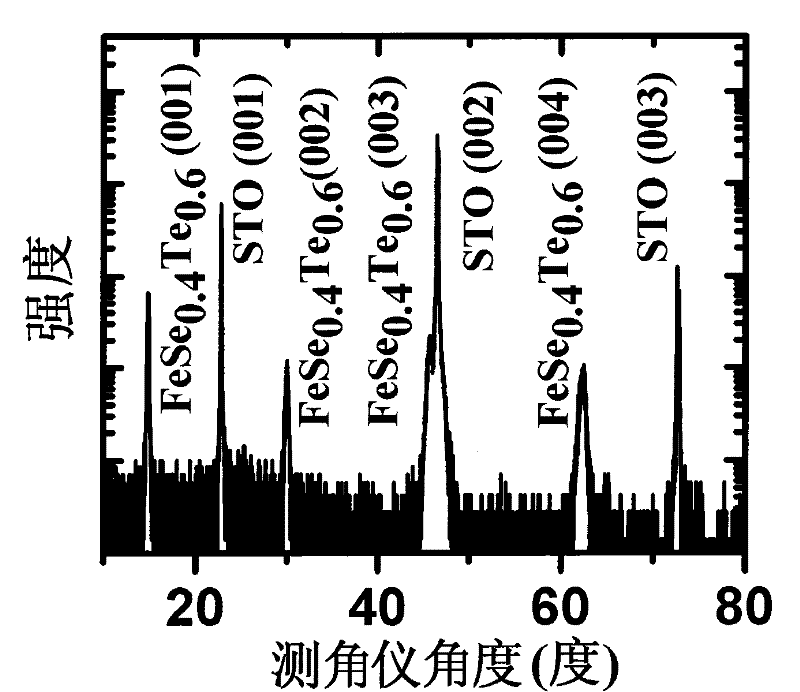
The invention provides a preparation method of an epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film, comprising the following steps: a) preparing a target material needed by the epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film, placing the target material into a vacuum cavity of a pulse laser deposition system, wherein the target material is FeSex or FeSe(1-y)Tey target material, x is more than or equal to 0.80 and is less than or equal to 1.0, y is more than 0 and is less than or equal to 1.0; b) preparing a substrate, fixing the substrate on a substrate platform, and placing the substrate platform into the vacuum cavity of the pulse laser deposition system; c) heating the substrate platform and further heating the substrate; and d) utilizing a pulse laser deposition method to grow the thin film on the substrate. The invention also provides a single-alpha-phase and c-oriented epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film prepared according to the method.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving superconducting performance of Sn-added FeSe1/2Te1/2 superconductor
ActiveCN104445097APromote formationSimple manufacturing methodSelenium/tellurium compundsRoom temperatureSuperconducting transition temperature
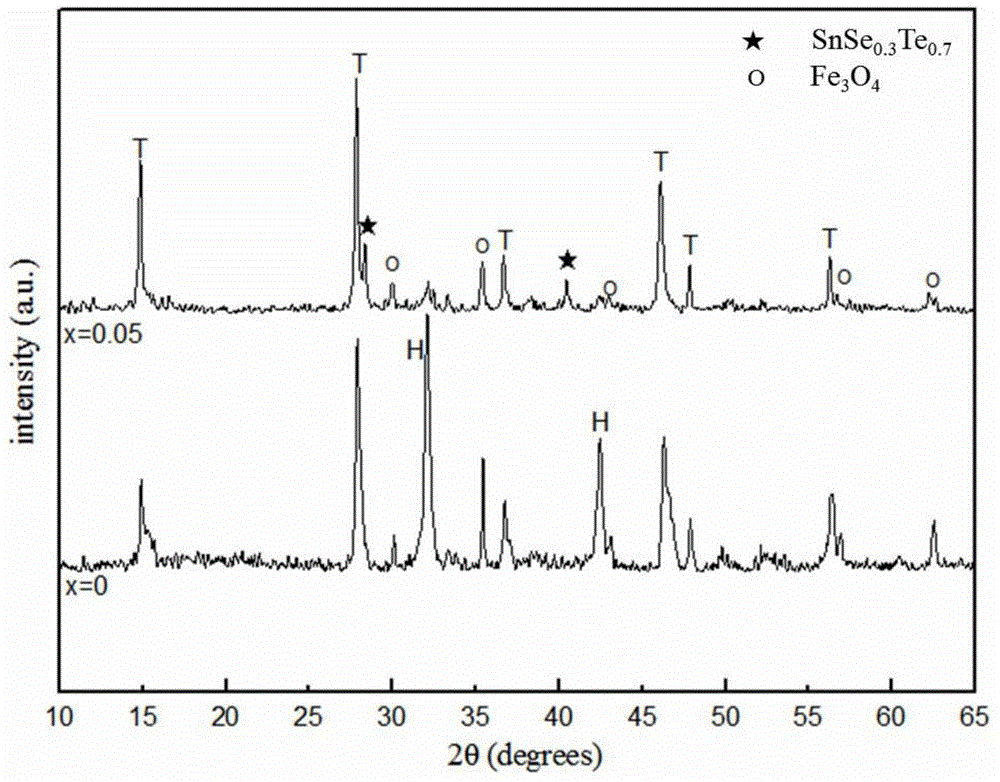
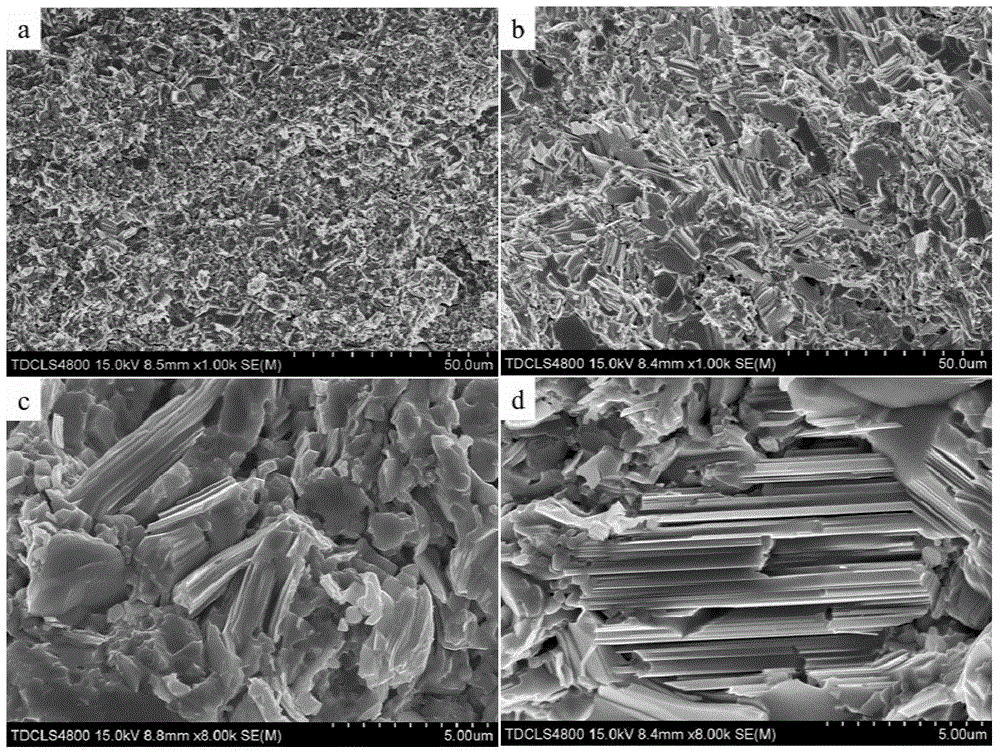
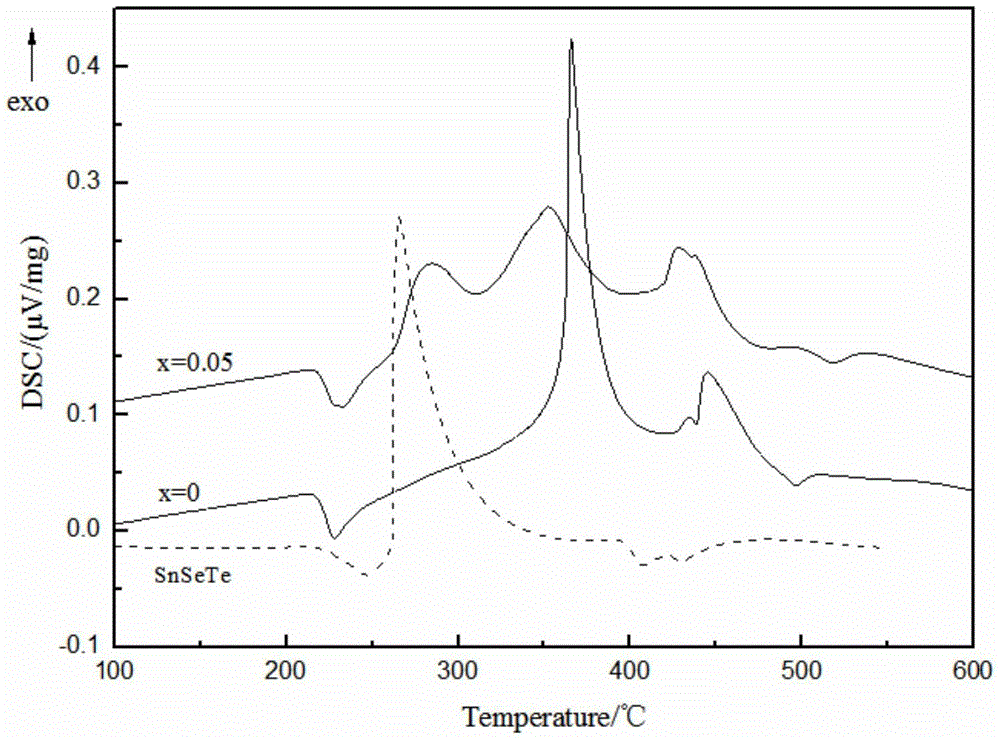
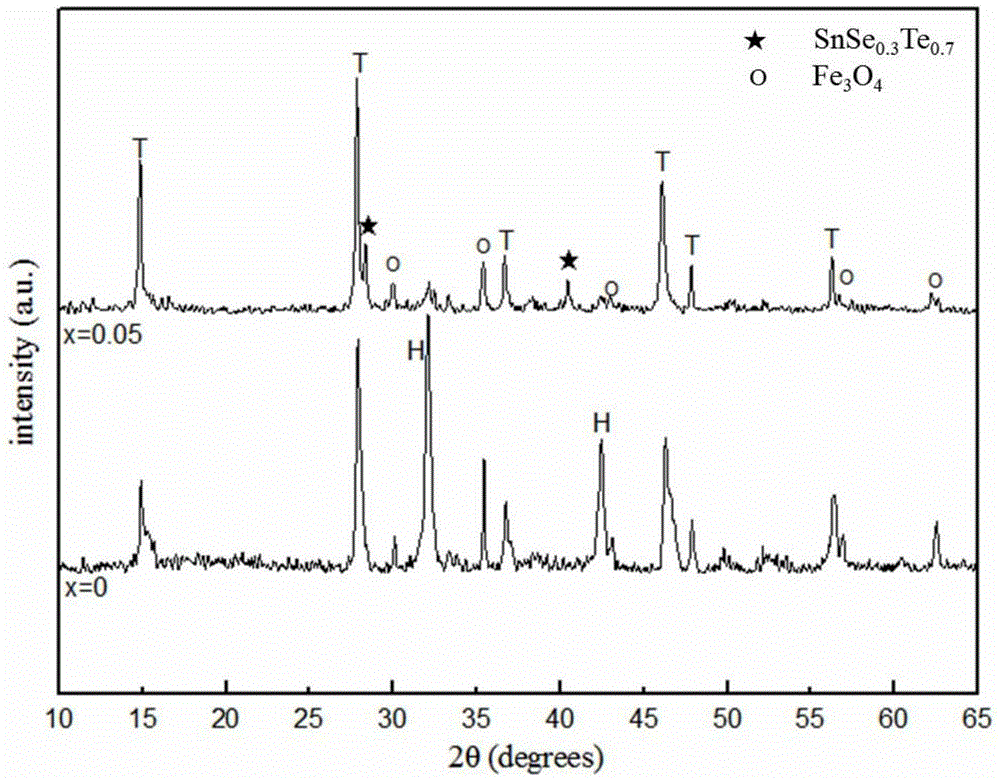
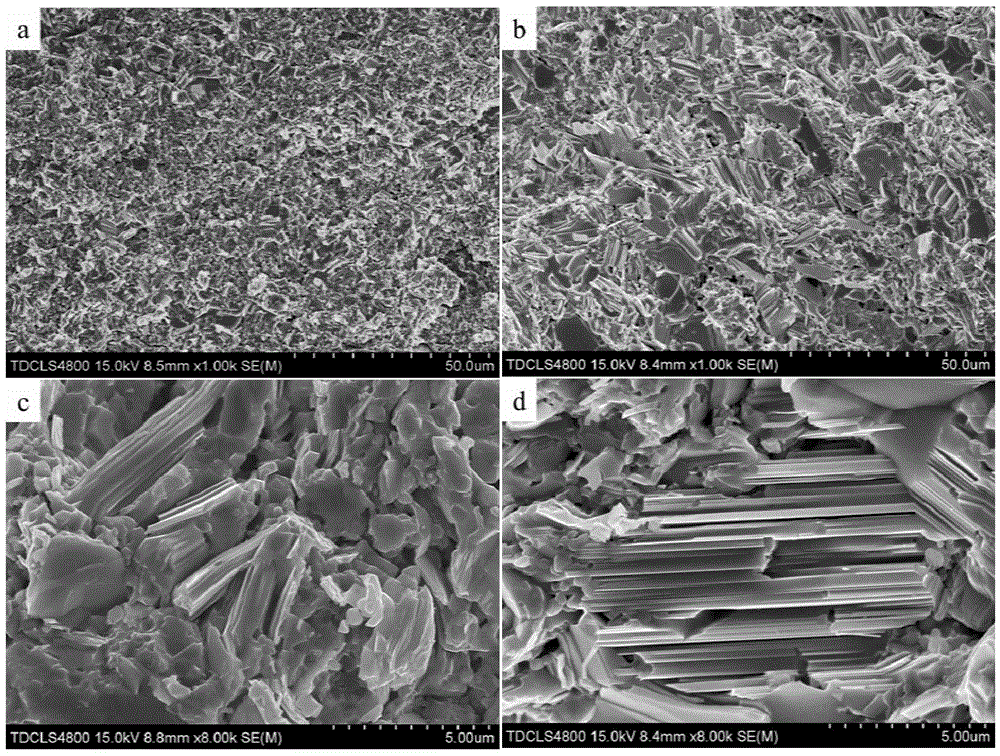
The invention relates to a method for improving the superconducting performance of a Sn-added FeSe0.5Te0.5 superconductor. The method comprises the steps of mixing Sn powder and FeSe0.5Te0.5 powder in a weight ratio of 0.05: 1, and sufficiently grinding the mixture in an agate mortar for 20-30 minutes; and then preparing into a flake under the pressure of 6-8MPa, finally putting the flake into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter, heating to 600 DEG C under the protection of flowing high-purity argon, preserving the heat for 5-10 hours, and cooling to room temperature. A fact that a Sn-Se-Te liquid phase generated by reaction between Sn and FeSe0.5Te0.5 can accelerate the transformation from a non-superconducting phase to a superconducting phase is discovered for the first time and is favorable for forming a superconducting laminar structure so that the superconducting transition temperature of the structure is finally significantly improved, thus providing an important clue for optimizing a preparation process of an iron-based superconductor, illuminating an iron-based superconducting mechanism and promoting the development of the superconducting theory.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing MgB2 superconductive material
InactiveCN1569633ASimple manufacturing processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesCrucibleFree cooling
The invention relates to a process for preparing MgB2 superconducting material which comprises the steps of, grinding B2O3 and Mg powder under the protection of oinert gas, loading the grinded raw material into ceramic crucible, sintering the crucible in vacuum pit furnace, naturally cooling down to room temperature in vacuum or under the inert gas protection status.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for improving transformation temperature of apical oxygen doping high temperature superconductor
InactiveCN101229980ARaise the superconducting transition temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorMetallurgy
The invention relates to a novel method for increasing superconducting transition temperature Tc, in particular to a method for increasing the superconducting transition temperature Tc by using vertex angel oxygen in sequence. In the invention, a precursor method and a high temperature and high pressure method are used for synthesizing a high temperature superconductor of Sr2CuO3+Delta (Delta is more than zero and less than 1) with a single phase; the material refers to a p-typed high temperature superconductor with a single layer of CuO2 plane and a simple structure and the vertex angle oxygen partly occupied; the high temperature superconductor after synthesized under high temperature is treated thermally with the temperature of the thermal treatment of 50 DEG C to 500 DEG C and the time of the thermal treatment is 0.5 hour to 30 hours. The vertex angle is ordered, the Tc of Sr2CuO3+Delta after synthesized under high pressure increases from 30 to 75 K to 90 to 100 K after thermal treatment in low temperature. The method can be applicable to other systems and can be taken as a new path for developing a higher Tc superconducting material.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel quasi-two-dimensional Ru-doped tellurium-containing superconducting material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110615412AEasy to makeLow requirements for preparation conditionsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsManufacturing technologyTe element
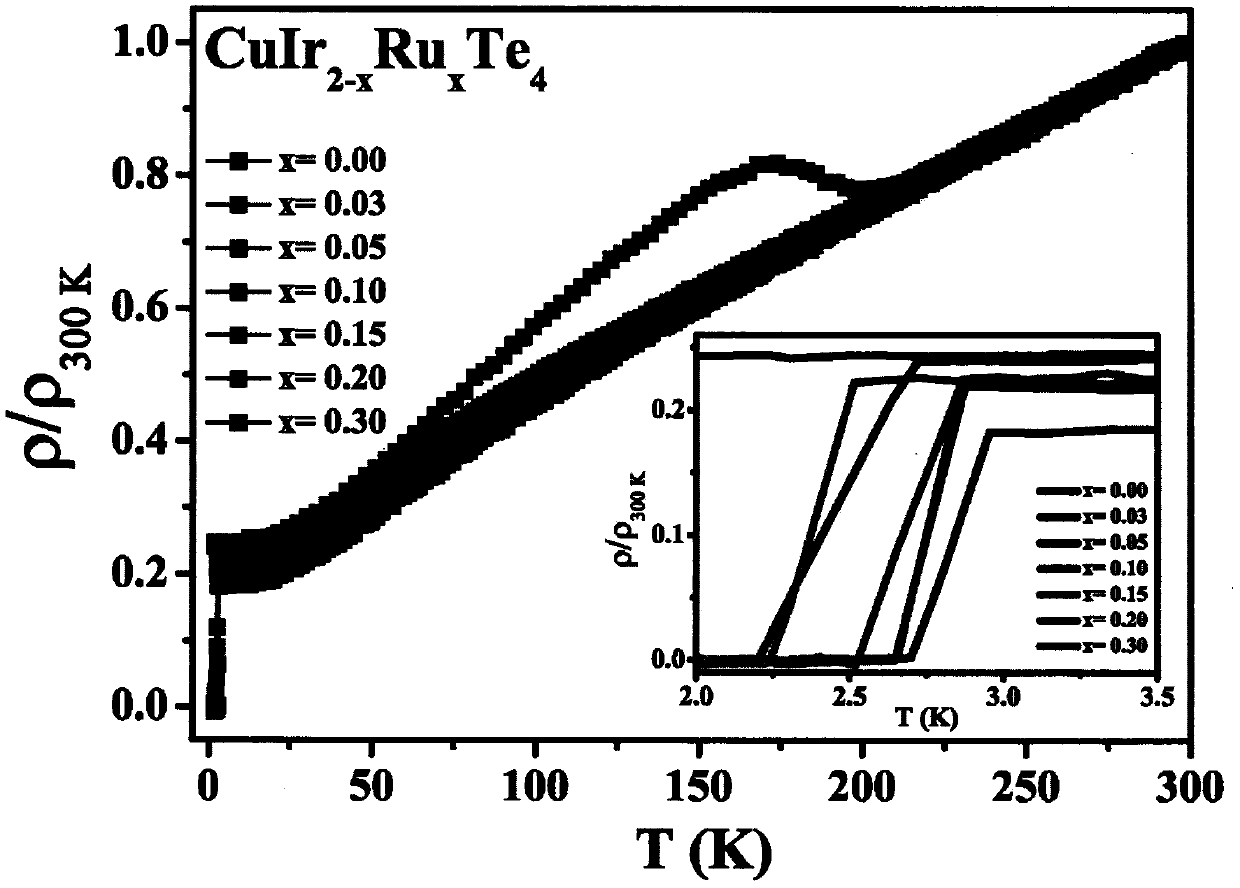
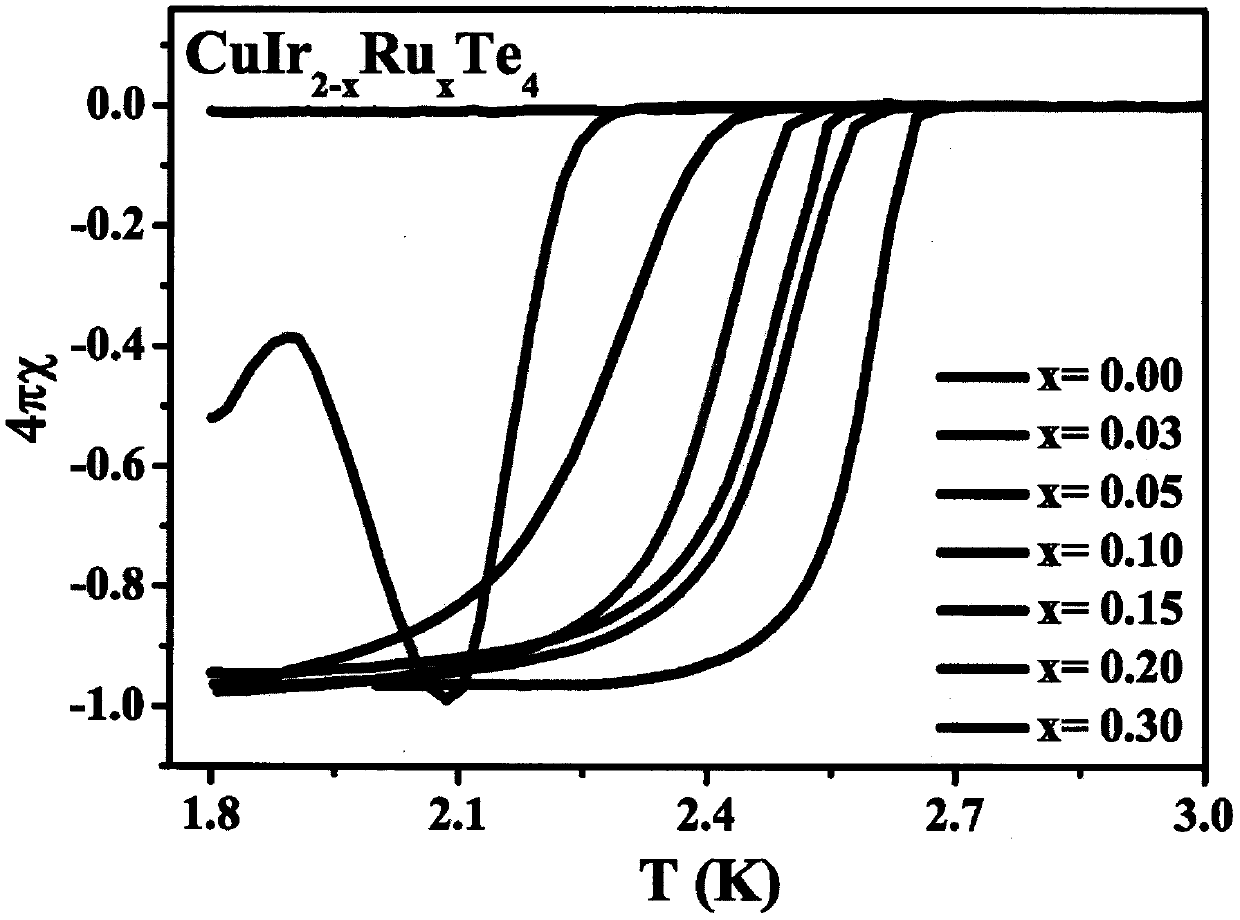
The invention relates to a series of superconducting materials with the chemical general formula of CuIr<2-x>RuxTe4 (0.03 < = x < = 0.3) and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technicalfield of functional material manufacturing. The preparation method is of a traditional high-temperature solid-phase process. The method comprises the following steps: according to a corresponding stoichiometric ratio, fully grinding elemental Cu, ir, Ru and Te, vaccumizing and sealing a quartz tube, then vaccumizing the quartz tube and sealing the quartz tube at high temperature, and finally sintering the sealed quartz tube filled with raw materials in a furnace at 850 DEG C for 4 days to obtain polycrystalline powder of the CuIr<2-x>RuxTe4 (0.03 < = x < = 0.3). Physical properties are testedthrough a comprehensive physical property testing system (PPMS) is used for determining the superconductivity of the target product by measuring the physical properties such as conductivity, magneticproperties and heat capacity of the target product. This is the first reported Ru doped tellurium-containing AB2X4 type (A, B = metal ion, and X = O, S, Se, Te) series superconductor. By synthesizingthe compound, the application range of the AB2X4 type compound can be widened, so that the AB2X4 type compound has a huge application prospect in the aspects of electric power, communication, high-tech equipment, military equipment and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
MgB2-based superconductor doped with heterogeneous phases of topological illuminants and preparation method of superconductor
InactiveCN108383531AChange superconductivityRaise the superconducting transition temperatureLuminescent compositionsDopantSuperconducting transition temperature
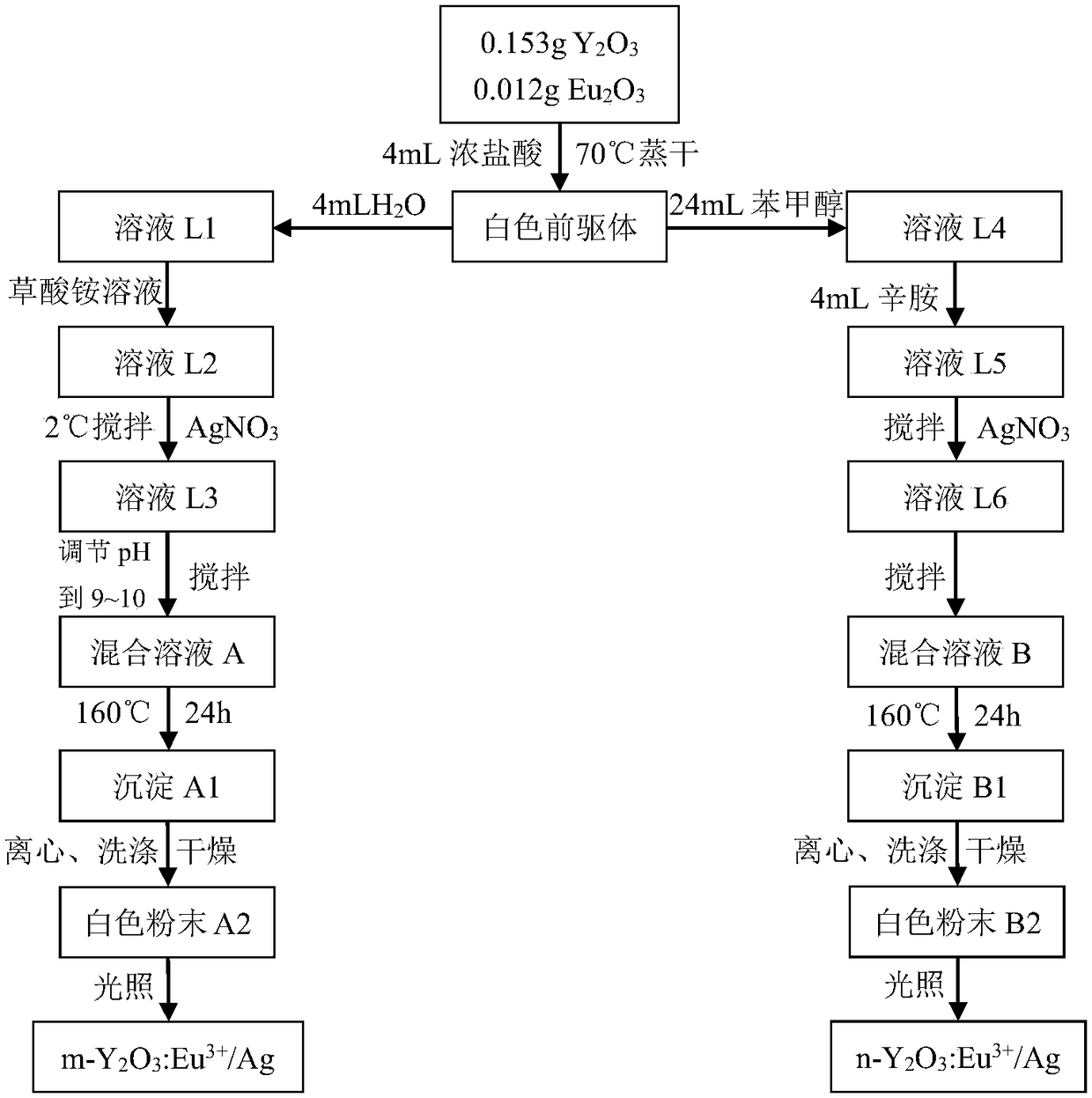
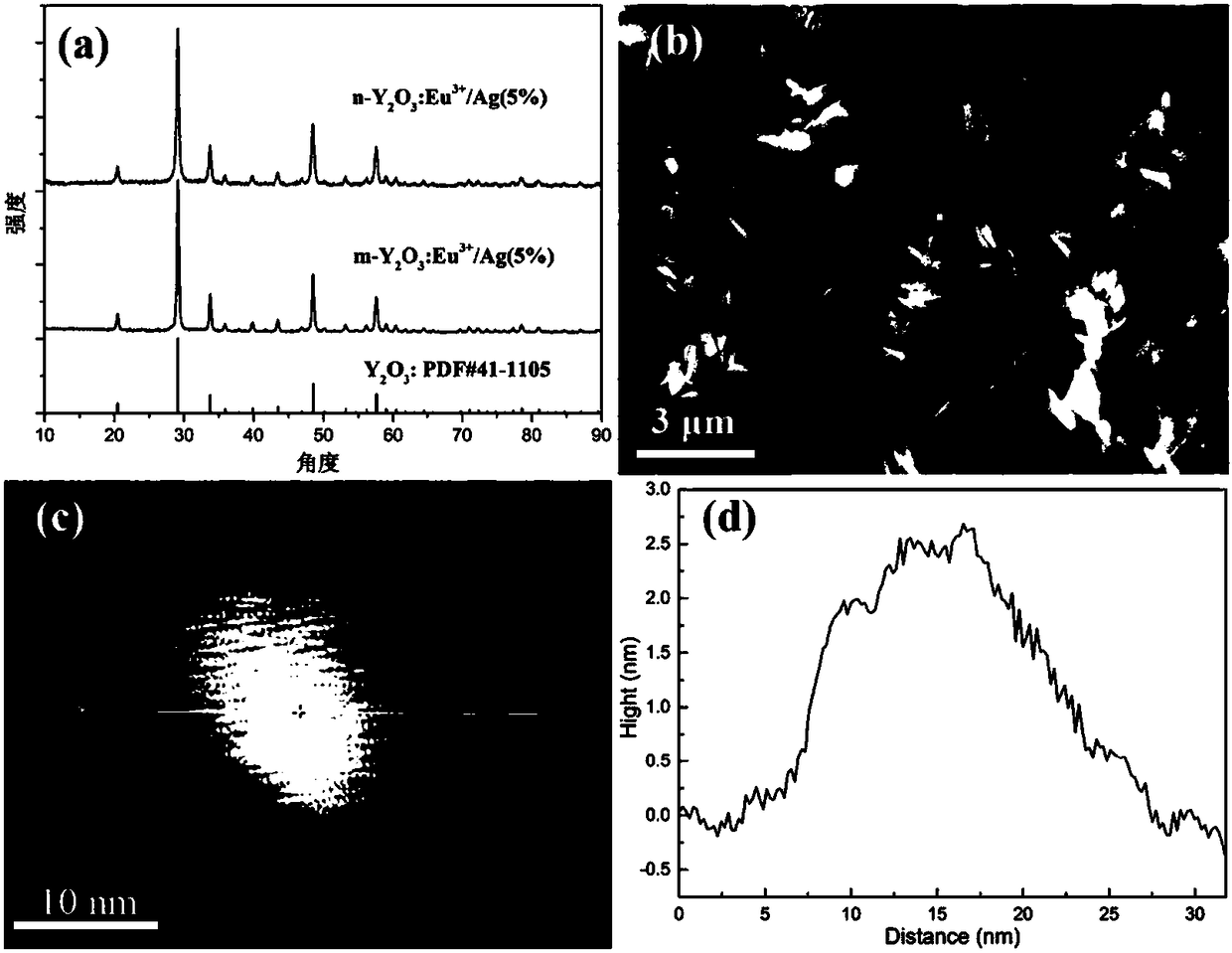
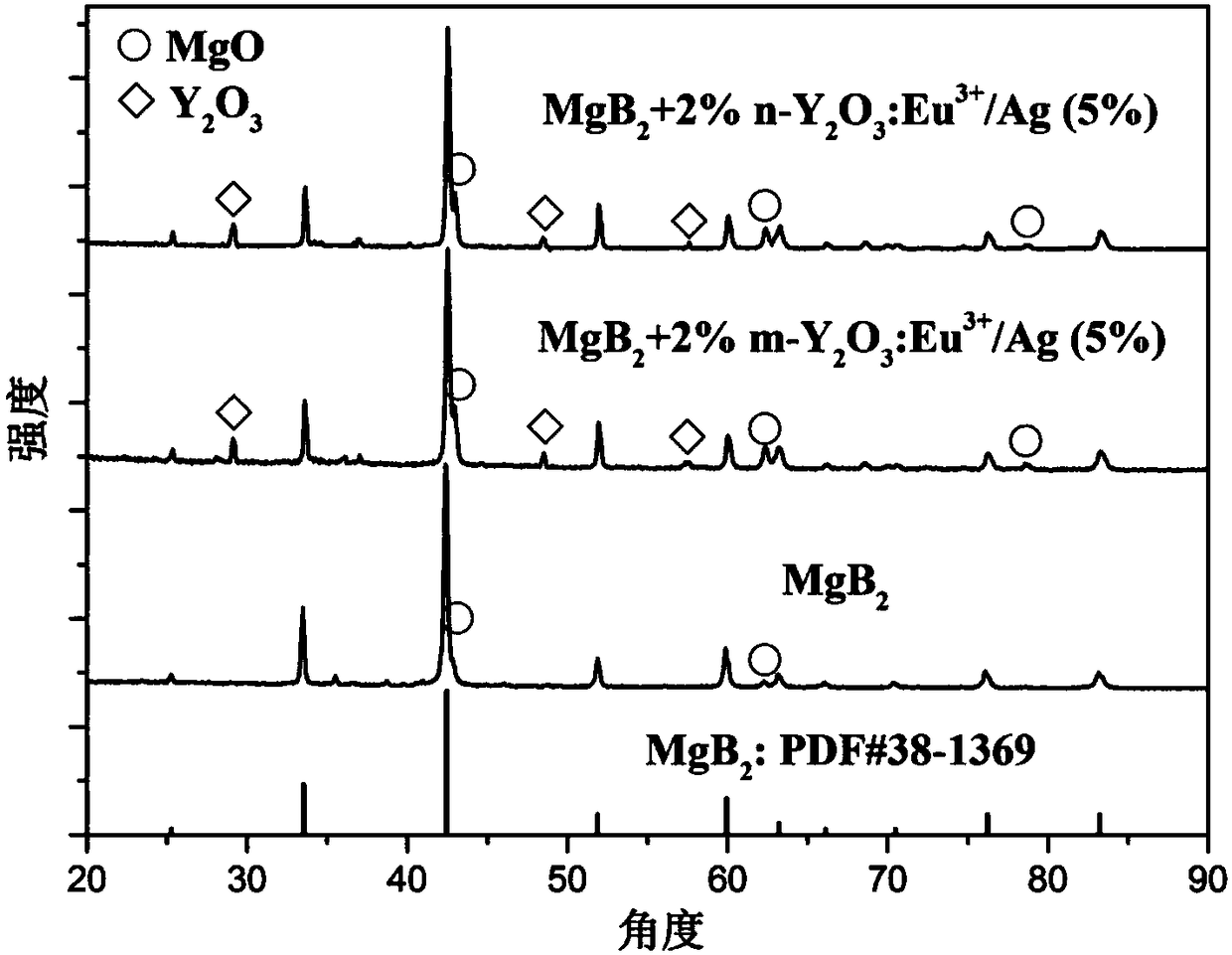
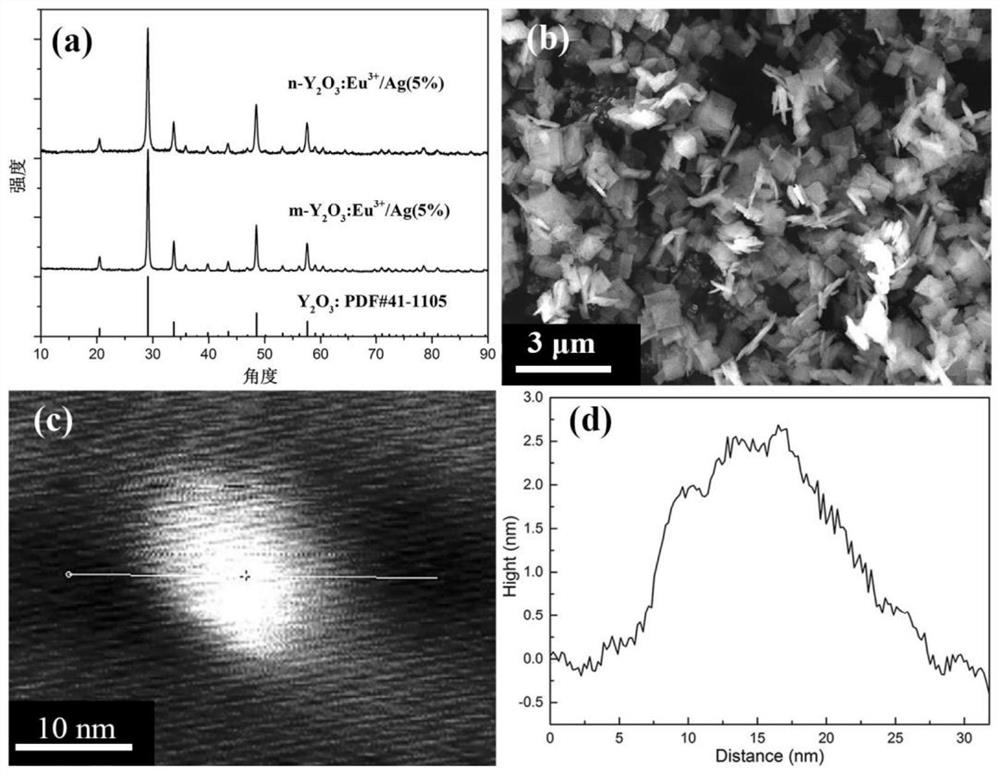
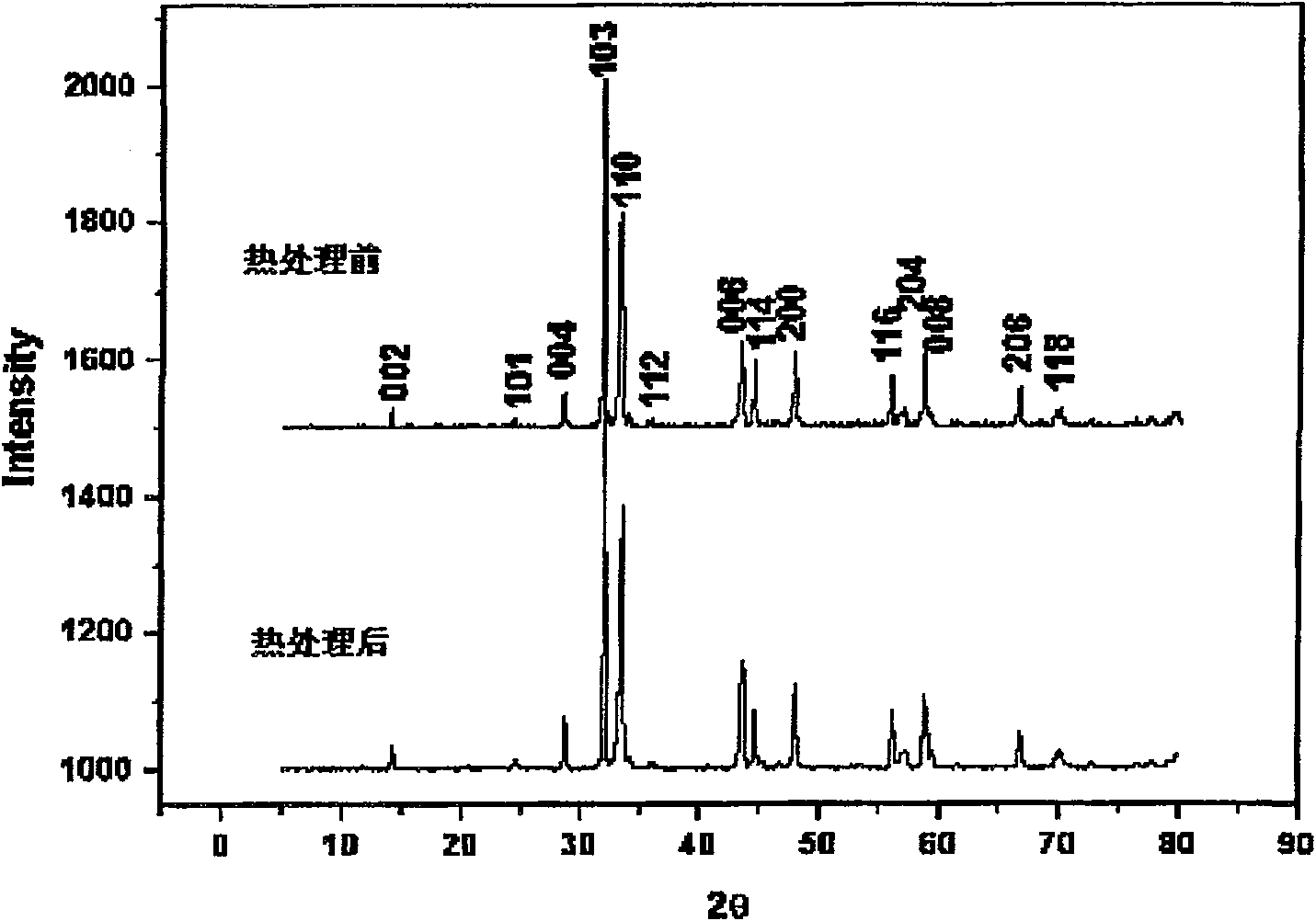
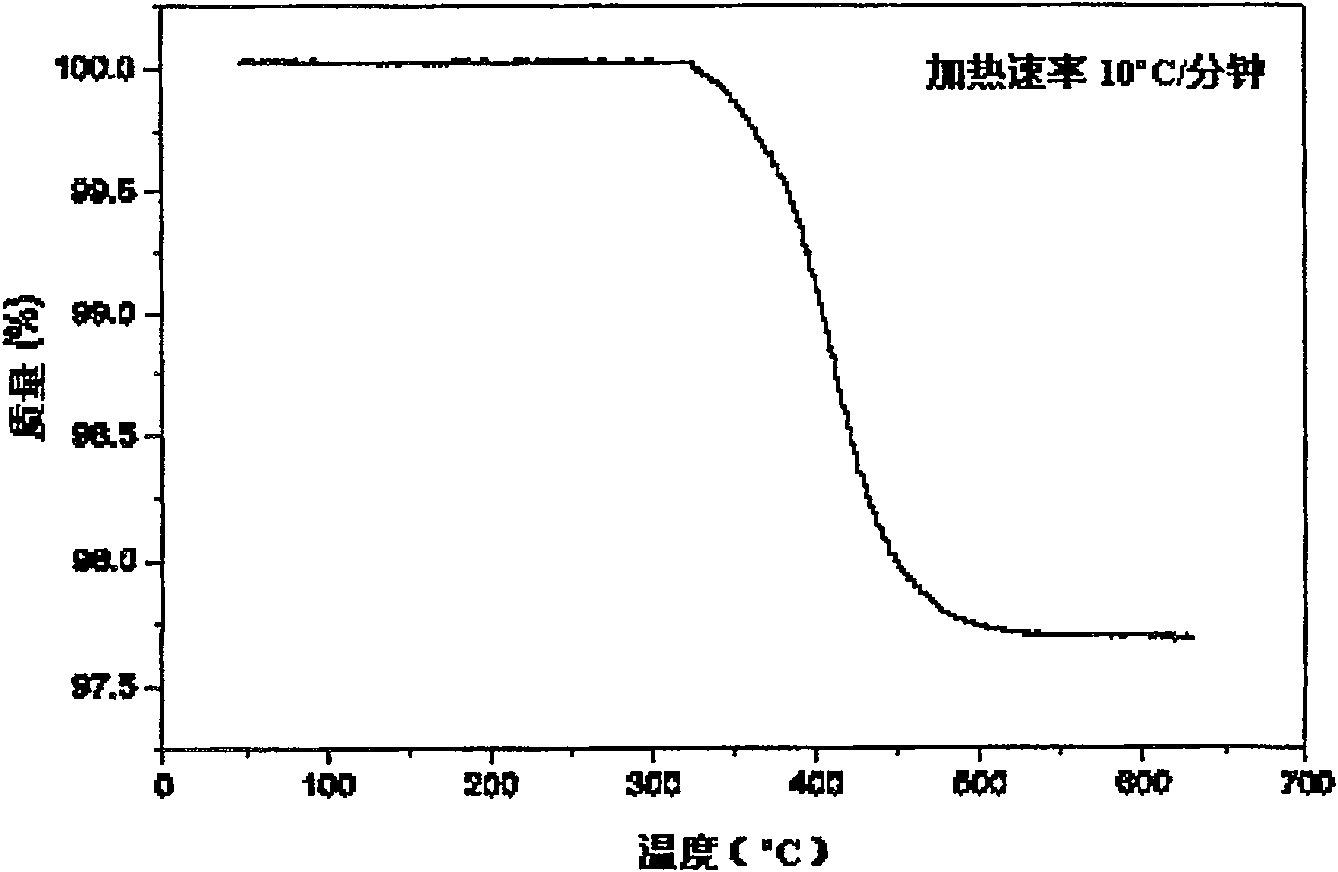
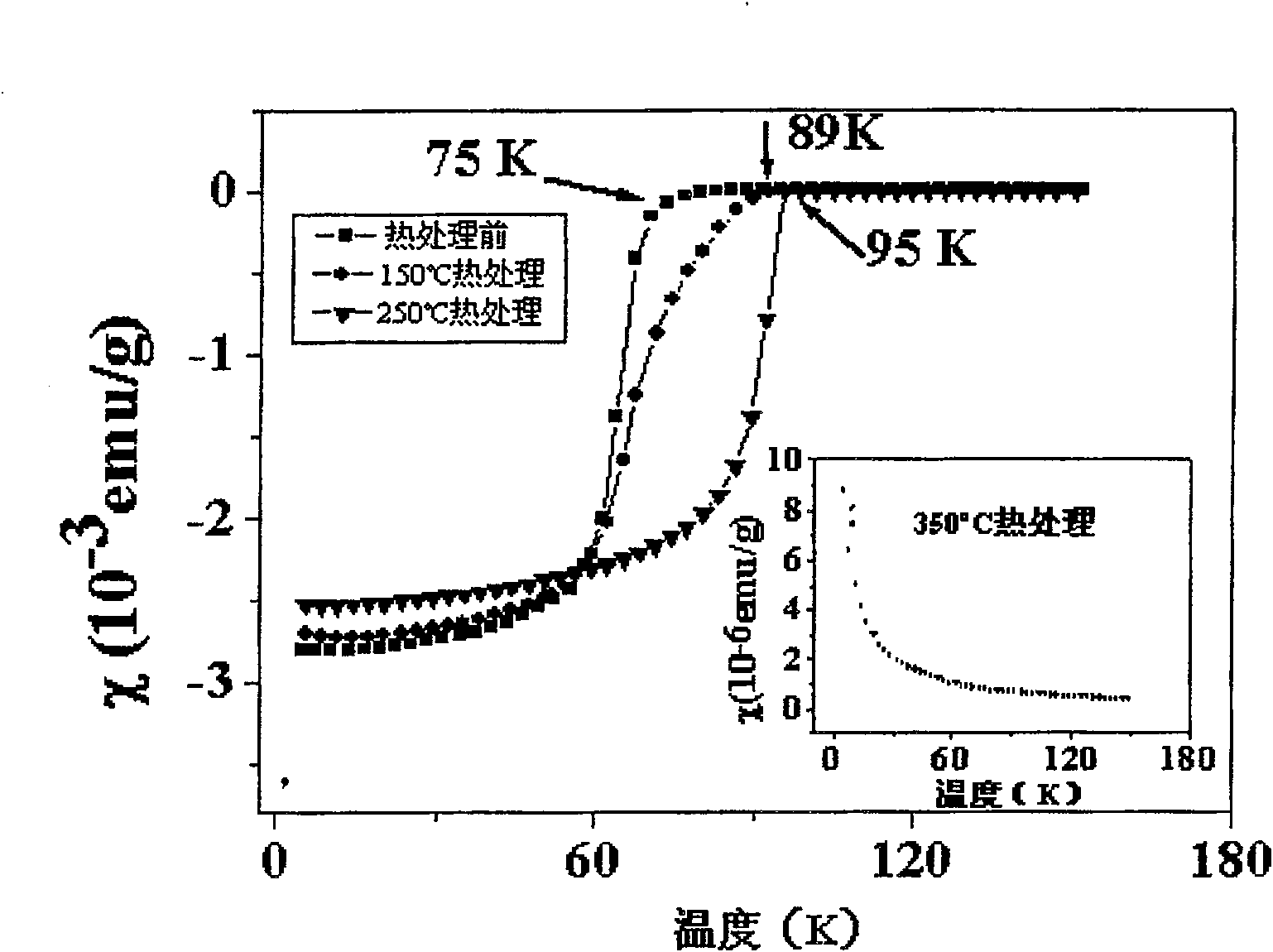
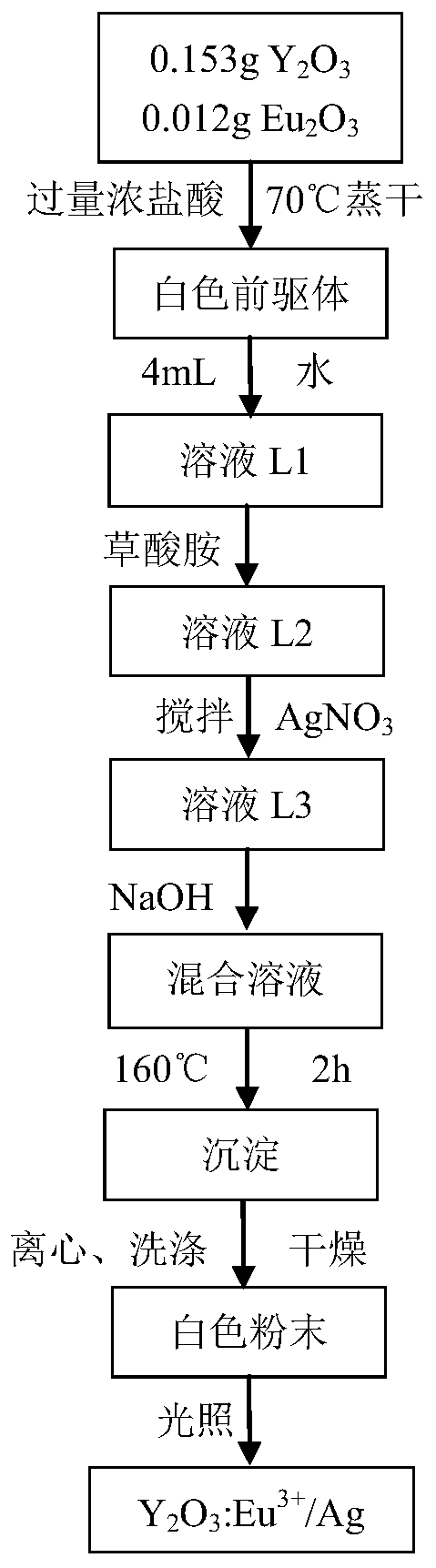
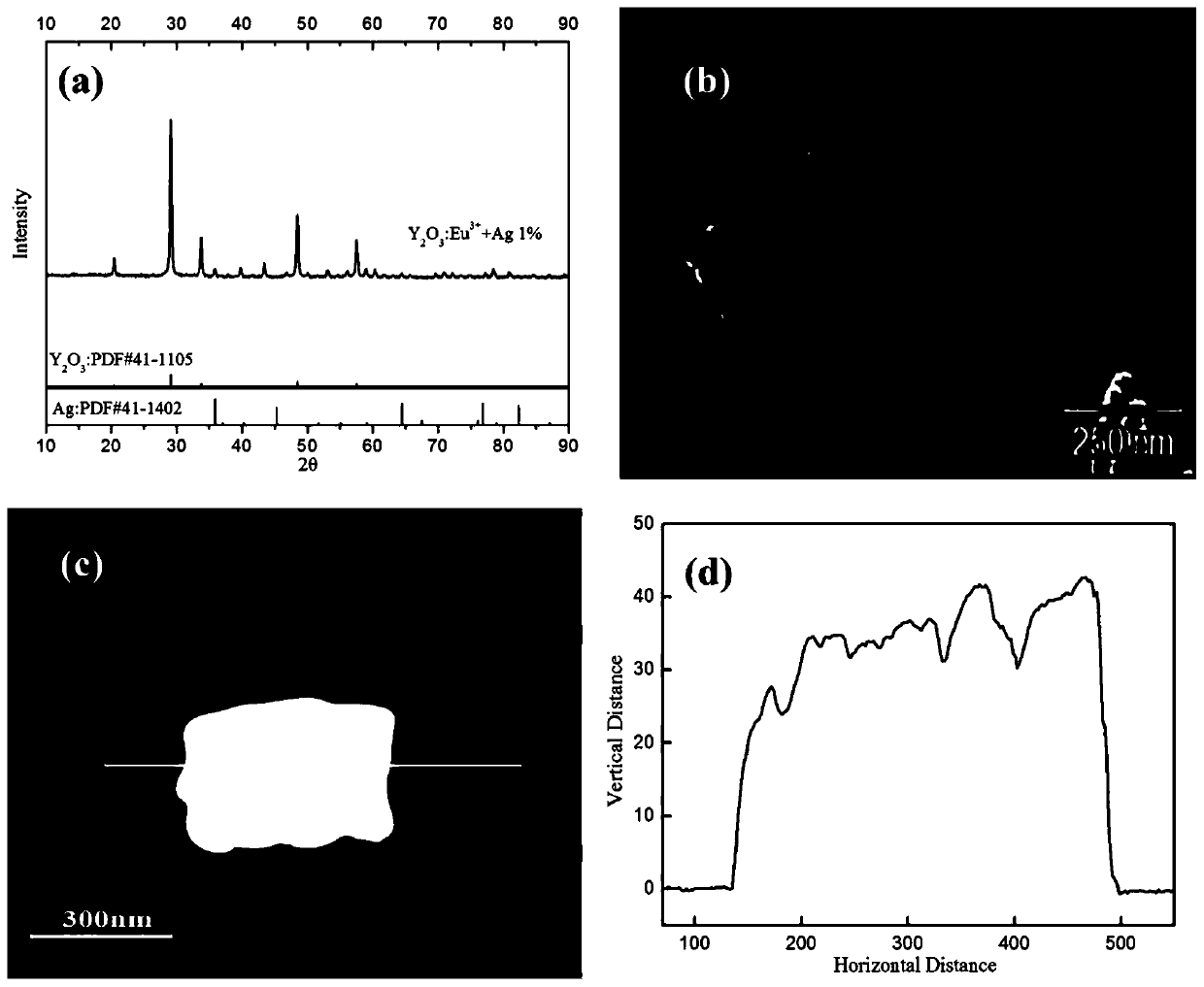
The invention relates to a MgB2-based superconductor doped with heterogeneous phases of topological illuminants and a preparation method of the superconductor. The topological illuminants are used fordoping to change the superconducting transition temperature of the MgB2-based superconductor. A hydrothermal method is adopted for preparing the three topological illuminants including the micrometersheet m-Y2O3:Eu3+ / Ag, the nanosheet n-Y2O3:Eu3+ / Ag and the nanosheet n-Y2O3:Eu3+ / AgCl. A heterotopic doping method is used for preparing the MgB2-based superconductor doped with the heterogeneous phases of the topological illuminants. The change of the superconducting transition temperature of a doped sample is studied by changing the size of dopants, the content of Ag, the mass fraction of the dopants and the like. It is found in experiments that when n-Y2O3:Eu3+ / AgCl is used as the dopant and the doping concentration is 1%, the transition temperature of the doped MgB2-based superconductor is higher than that of a corresponding pure MgB2 sample.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Superconducting nanowire single photon detector and method of obtaining such detector
PendingCN112531101AEasy to packImprove applicabilitySuperconductor detailsNanoopticsNanowirePhoton detection
The present invention relates to a superconducting nanowire single photon detector comprising a superconducting nanowire configured and arranged for incidence of photons on a region of the superconducting nanowire and for forming a local non-superconducting region or hot spot on the region. The superconducting nanowire is made of a high Tc cuprate superconductor material having a superconducting critical temperature above 77K. The invention also relates to a method of obtaining a superconducting nanowire single photon detector of the invention.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE CIENCIES FOT NIQUES
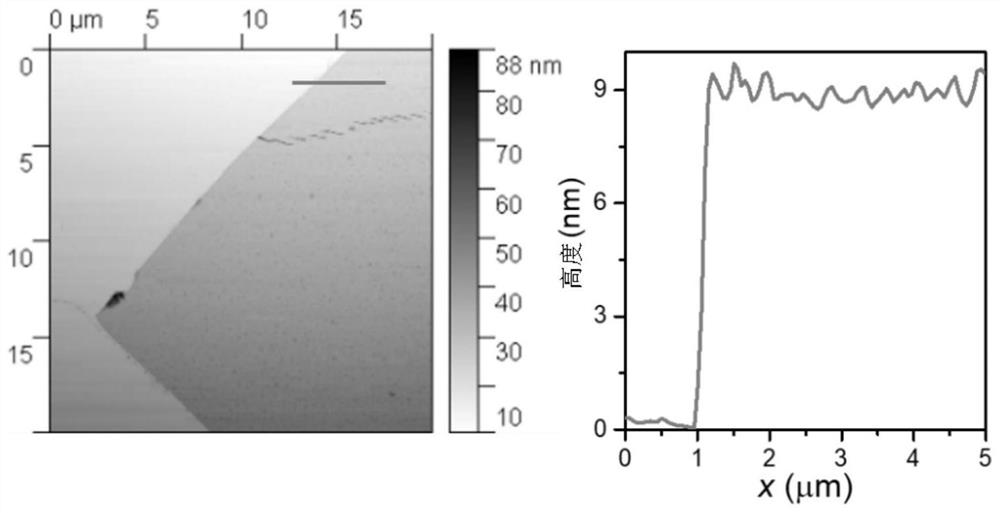
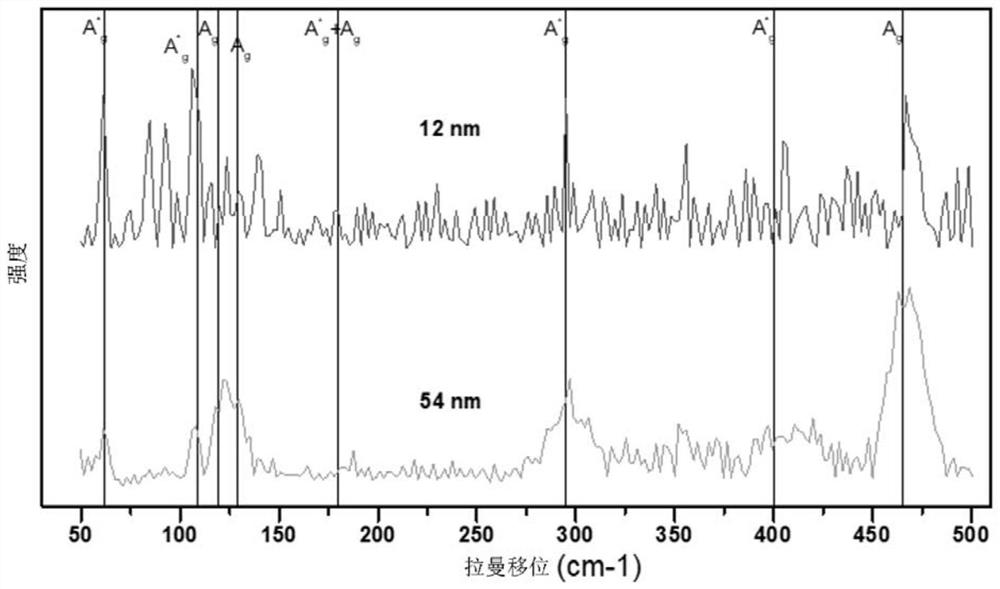
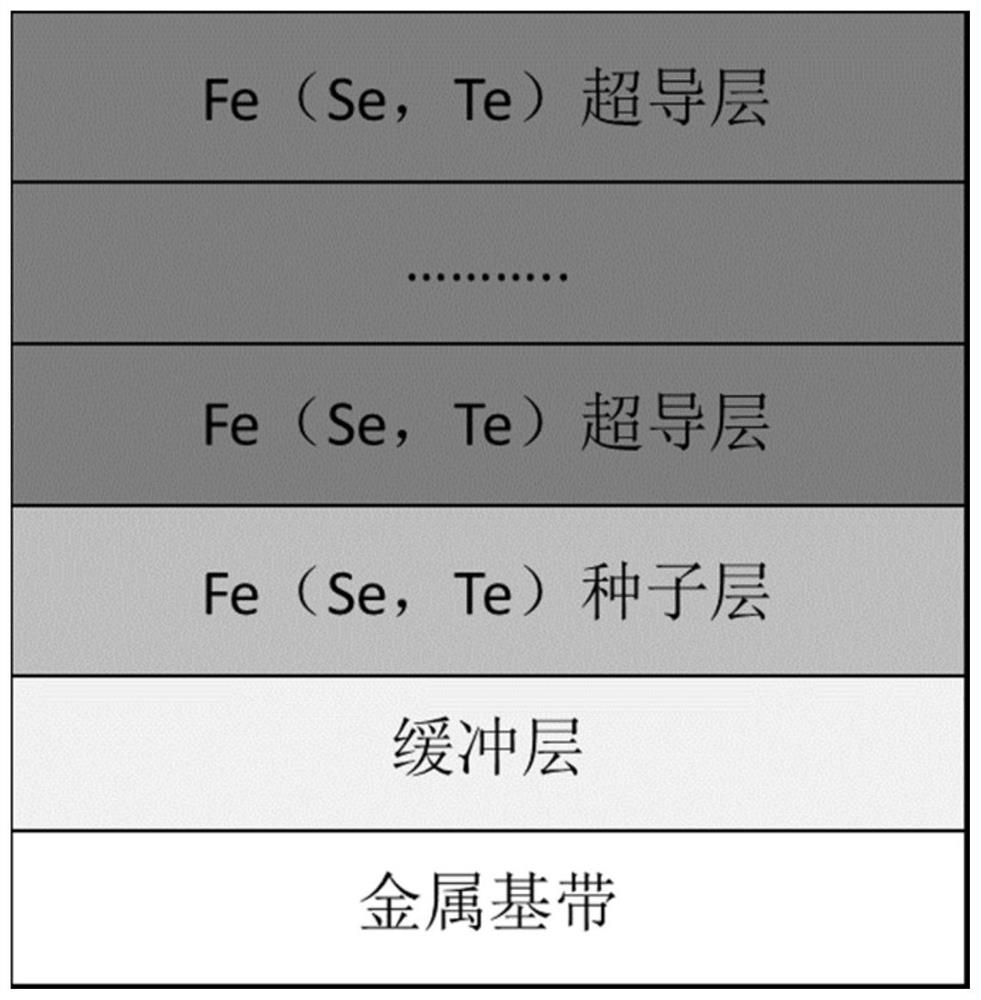
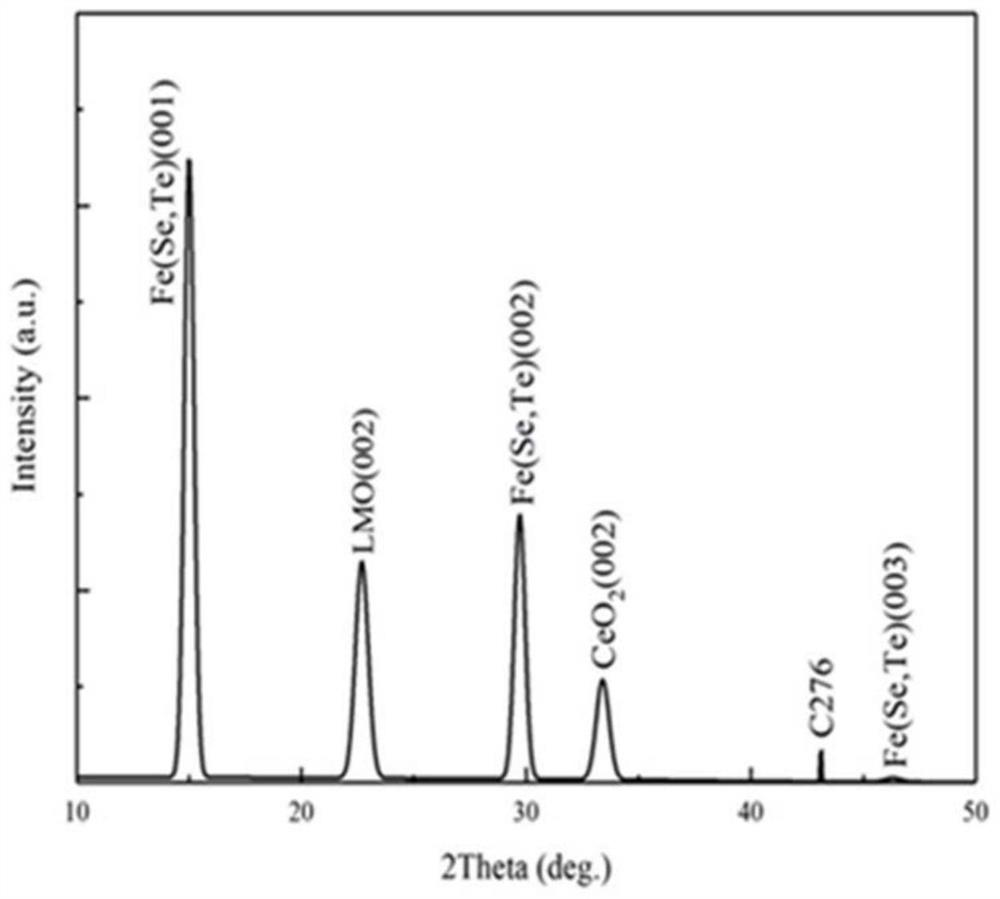
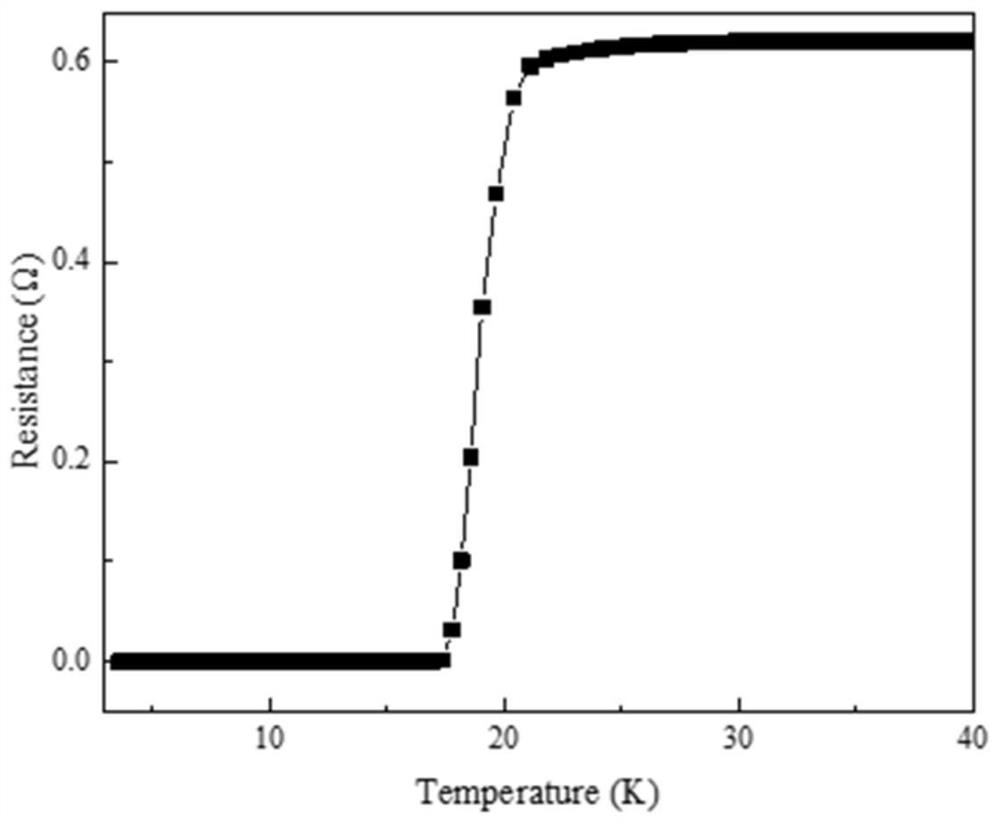
Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114318242AIncrease the critical currentRaise the superconducting transition temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSelf fieldSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention relates to a Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film and a preparation method and application thereof, and the preparation method of the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film comprises the following steps: depositing a Fe (Se, Te) seed layer on a metal base band plated with a buffer layer by adopting a multi-channel pulse laser deposition method, and then depositing a plurality of Fe (Se, Te) superconducting layers on the Fe (Se, Te) seed layer. Compared with the prior art, the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film prepared by the method has pure C-axis orientation, high superconducting transition temperature, high critical current and high critical current density, and under 4.2 K and self field, the critical current is greater than 300A, and the critical current density is as high as 2.3 MA / cm < 2 >; the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film provided by the invention has high critical current and critical current density in a self field and a magnetic field, can meet high-intensity magnetic field application, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film and prepared epitaxial iron-based superconducting thin film
ActiveCN101867012BQuality improvementRaise the superconducting transition temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOptoelectronicsVacuum chamber
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polystyrene colloidal sphere and niobium film composite heterostructure superconducting material and preparation method
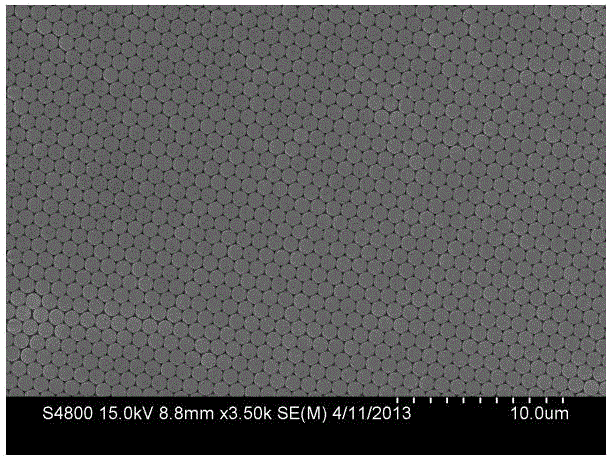
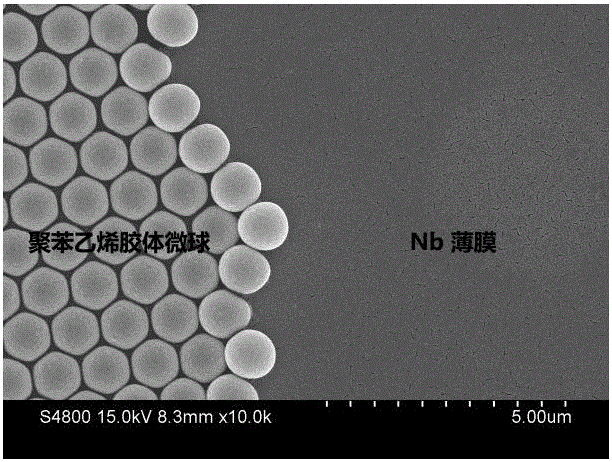
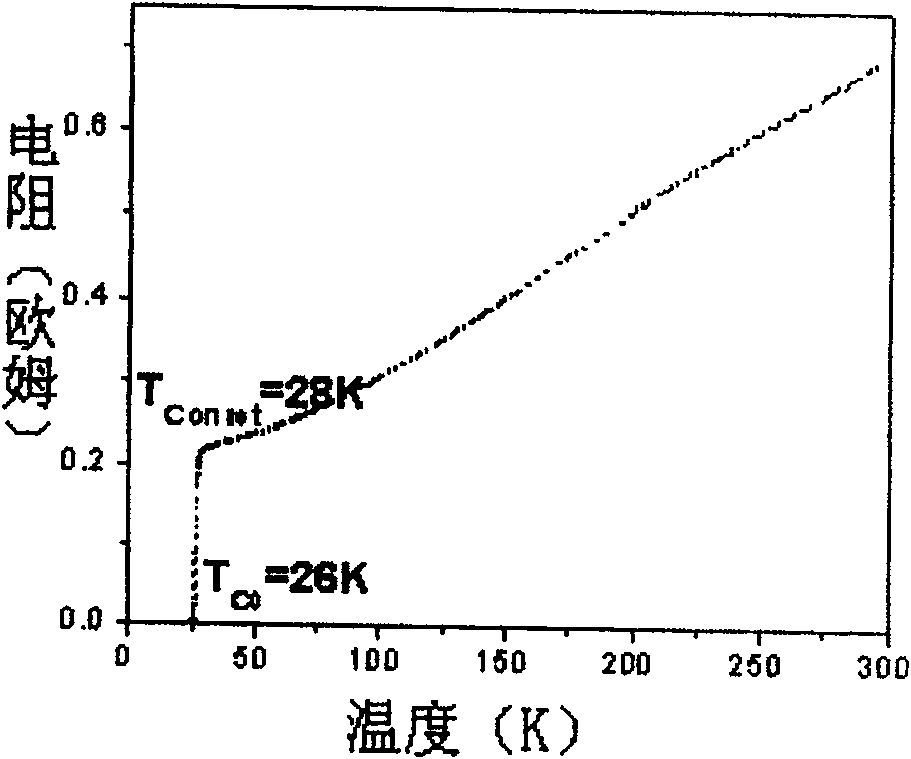
InactiveCN105990512BSimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologySuperconductor detailsHeterojunctionMicrosphere
The invention discloses a composite heterostructure superconducting material of polystyrene colloidal spheres and niobium films, comprising a substrate, a niobium film and a polystyrene colloid hexagonal array film, the niobium film is located on the substrate, and the polystyrene hexagonal array film The film is covered on the niobium film; the polystyrene hexagonal array film includes a plurality of polystyrene colloidal microspheres, and each polystyrene colloidal microsphere is closely arranged in a single layer to form a hexagonal array. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the superconducting material. In the present invention, polystyrene colloidal microspheres and niobium superconducting thin film materials are constructed as heterostructure nanostructure materials, and the critical temperature of superconducting transition is regulated by changing the contact area of colloidal spheres and niobium substrates, thereby improving the superconductivity of niobium thin films. The conduction transition temperature Tconset, the material preparation process is simple, and the required equipment is less, which greatly reduces the preparation cost of the superconducting material and is conducive to popularization and application.
Owner:李志刚 +1
The method of adding fese1/2te1/2 to superconductor with sn to improve superconductivity
ActiveCN104445097BPromote formationSimple manufacturing methodSelenium/tellurium compundsRoom temperatureSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention relates to a method for improving the superconducting performance of a Sn-added FeSe0.5Te0.5 superconductor. The method comprises the steps of mixing Sn powder and FeSe0.5Te0.5 powder in a weight ratio of 0.05: 1, and sufficiently grinding the mixture in an agate mortar for 20-30 minutes; and then preparing into a flake under the pressure of 6-8MPa, finally putting the flake into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter, heating to 600 DEG C under the protection of flowing high-purity argon, preserving the heat for 5-10 hours, and cooling to room temperature. A fact that a Sn-Se-Te liquid phase generated by reaction between Sn and FeSe0.5Te0.5 can accelerate the transformation from a non-superconducting phase to a superconducting phase is discovered for the first time and is favorable for forming a superconducting laminar structure so that the superconducting transition temperature of the structure is finally significantly improved, thus providing an important clue for optimizing a preparation process of an iron-based superconductor, illuminating an iron-based superconducting mechanism and promoting the development of the superconducting theory.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
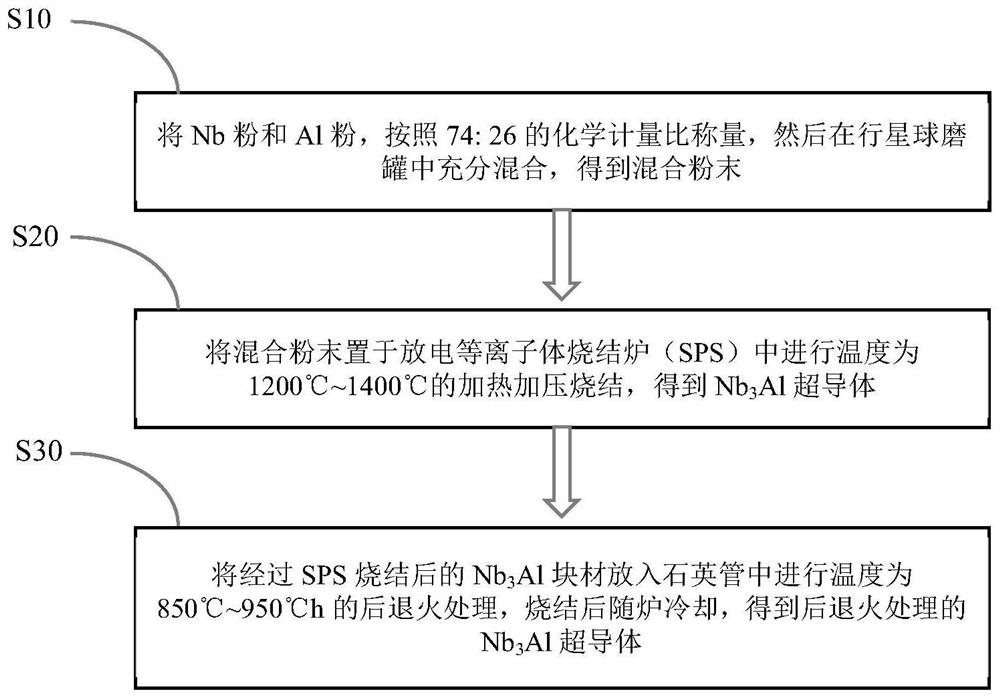
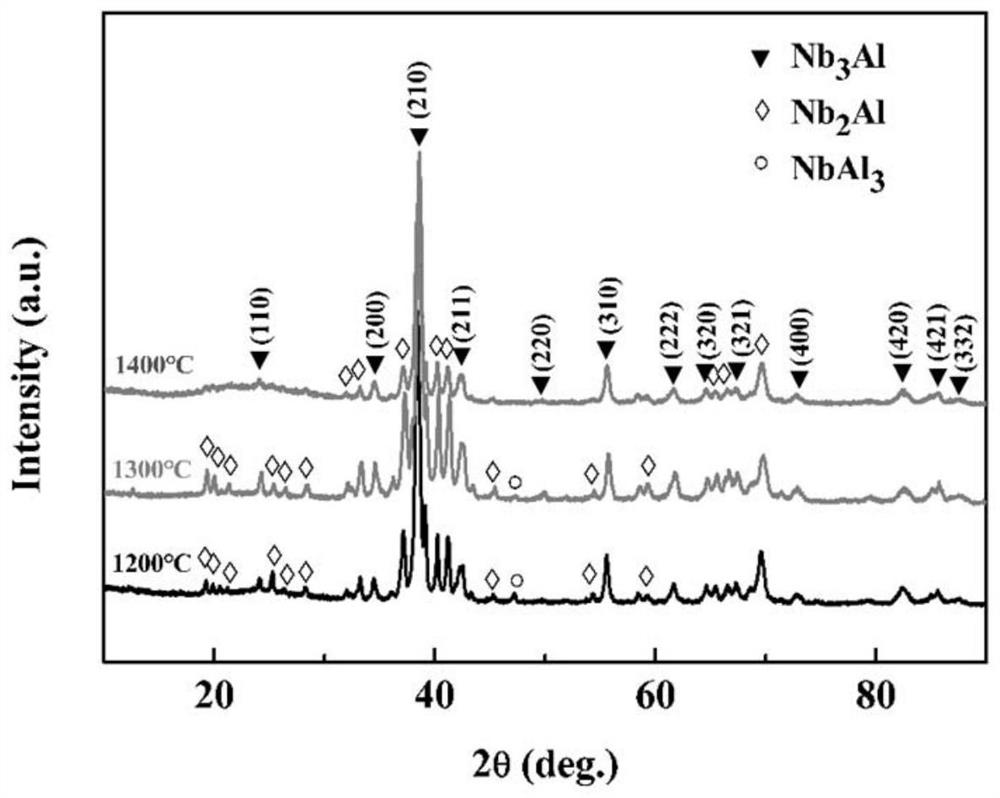
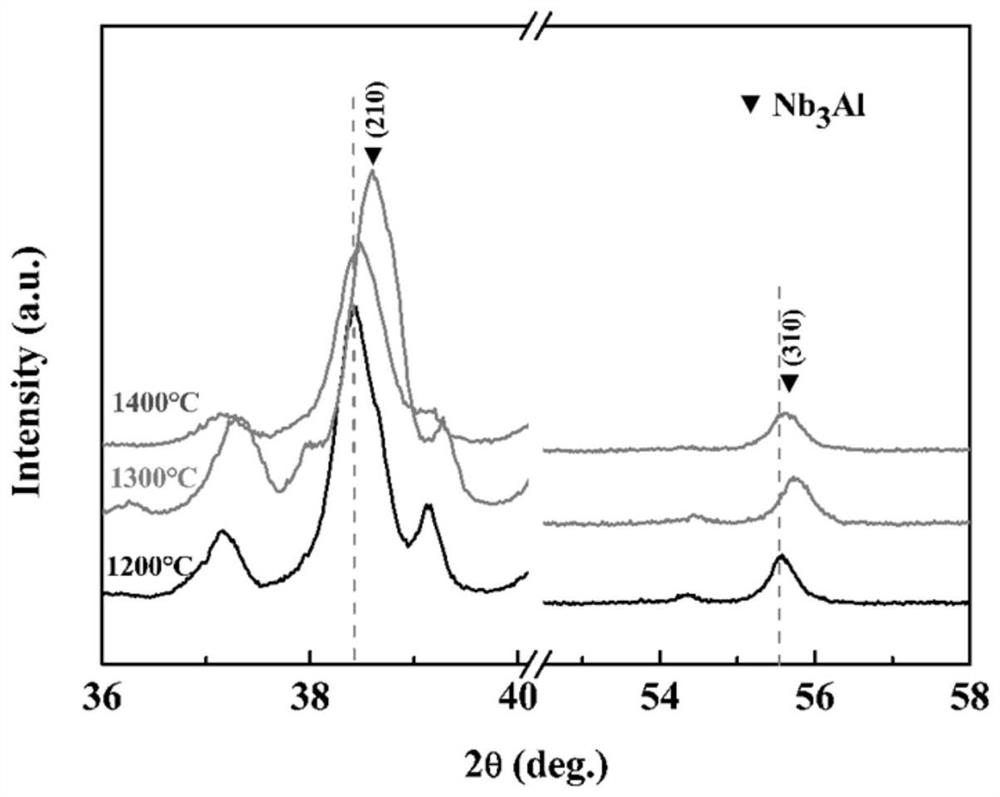
A rapid preparation of nb 3 al superconductor method
ActiveCN114182123BFirmly connectedImprove compactnessSuperconductor elements usageAl powderBall mill
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Topological luminophore heterogeneously doped mgb 2 Base superconductor and its preparation method
InactiveCN108383531BChange superconductivityRaise the superconducting transition temperatureLuminescent compositionsDopantLuminophore
The invention relates to MgB doped with a heterogeneous phase of a topological light emitter 2 Based superconductor and its preparation method, using topological emitter doping to change MgB 2 The superconducting transition temperature of the base superconductor. The present invention adopts hydrothermal method to prepare three kinds of topological illuminants: micron sheet m-Y 2 O 3 :Eu 3+ / Ag, nanosheet n‑Y 2 O 3 :Eu 3+ / Ag and n-Y 2 O 3 :Eu 3+ / AgCl. Heterogeneous phase-doped MgB prepared by ex-situ doping 2 base superconductor. By changing the size of the dopant, the content of Ag and the mass fraction of the dopant, the change of the superconducting transition temperature of the doped sample was studied. In experiments, it was found that when using n‑Y 2 O 3 :Eu 3+ / AgCl as the dopant, and when the doping concentration is 1%, the doped MgB 2 The transition temperature of the base superconductor is higher than that of the corresponding pure MgB 2 sample.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for improving transformation temperature of apical oxygen doping high temperature superconductor
InactiveCN100575309CRaise the superconducting transition temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorMetallurgy
The invention relates to a novel method for increasing superconducting transition temperature Tc, in particular to a method for increasing the superconducting transition temperature Tc by using vertex angel oxygen in sequence. In the invention, a precursor method and a high temperature and high pressure method are used for synthesizing a high temperature superconductor of Sr2CuO3+Delta (Delta is more than zero and less than 1) with a single phase; the material refers to a p-typed high temperature superconductor with a single layer of CuO2 plane and a simple structure and the vertex angle oxygen partly occupied; the high temperature superconductor after synthesized under high temperature is treated thermally with the temperature of the thermal treatment of 50 DEG C to 500 DEG C and the time of the thermal treatment is 0.5 hour to 30 hours. The vertex angle is ordered, the Tc of Sr2CuO3+Delta after synthesized under high pressure increases from 30 to 75 K to 90 to 100 K after thermal treatment in low temperature. The method can be applicable to other systems and can be taken as a new path for developing a higher Tc superconducting material.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of preparing electron type high-temperature superconductor lanthanum cerium cuprum oxygen film
InactiveCN101206935BLow costReduced vacuum requirementsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingCeriumOxygen
The invention provides a method for preparing an electron-doped high-temperature superconductor La2-xCexCuO4 film. Direct current magnetron sputtering equipment is used, and the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, according to La2-xCexCuO4 and the compounding ratio that 0.08 is less than or equal to x and x is less than or equal to 0.16, a solid phase reaction method is adopted to prepare a La2-xCexCuO4 ceramic target, and then the ceramic target is arranged on the target seat of a reaction chamber; secondly, substrate choice: SrTiO3, MgO or LaAlO3 is chosen, washed to be clean and then put on a heating stage in the reaction chamber, and the reaction chamber is closed; thirdly, the reaction chamber is vacuumized till the vacuum of a back side is superior to 2.0*10<-4>Pa; fourthly, the substrate is heated to 600-800 DEG C; fifthly, a reacting gas is charged in the reaction chamber; sixthly, the surface of the La2-xCexCuO4 ceramic target is pre-sputtered; seventhly, the heating stage is moved to the target position, and the La2-xCexCuO4 film begins to be prepared on the substrate; eighthly, after the reaction is ended, the reacting gas is stopped to be charged, the vacuum is pumped till the vacuum degree is superior to 2*10<-4> Pa, then the temperature of the substrate with La2-xCexCuO4 film prepared is dropped to the annealing temperature, and the annealing is performed; ninthly, the substrate with La2-xCexCuO4 film prepared is naturally cooled to the room temperature.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing magnesium diboride superconducting wire or strip by electron beam annealing
ActiveCN104882533BReduce oxidationReduce the chance of decompositionSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentChemical reactionMagnesium diboride
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnesium diboride superconducting wire or strip by electron beam annealing. The method adopts electron beam to anneal the unphased MgB2 wire or strip precursor prepared by in-situ powder sleeve method in vacuum. Annealing, within the annealing time of several seconds to several minutes, the magnesium-boron mixed powder in the wire or strip precursor undergoes a chemical reaction to finally generate magnesium diboride superconducting wire or strip. Electron beam parameters and annealing time are determined according to different wire or strip precursor thickness and annealing temperature requirements during annealing, and the annealing of different diameter wires or strips is completed by precisely controlling the electron beam acceleration voltage, beam current and annealing time. The magnesium diboride superconducting wire or strip prepared by the invention has stable properties, fine and uniform crystal grains, uniform phase formation, and a transition temperature higher than 37K.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
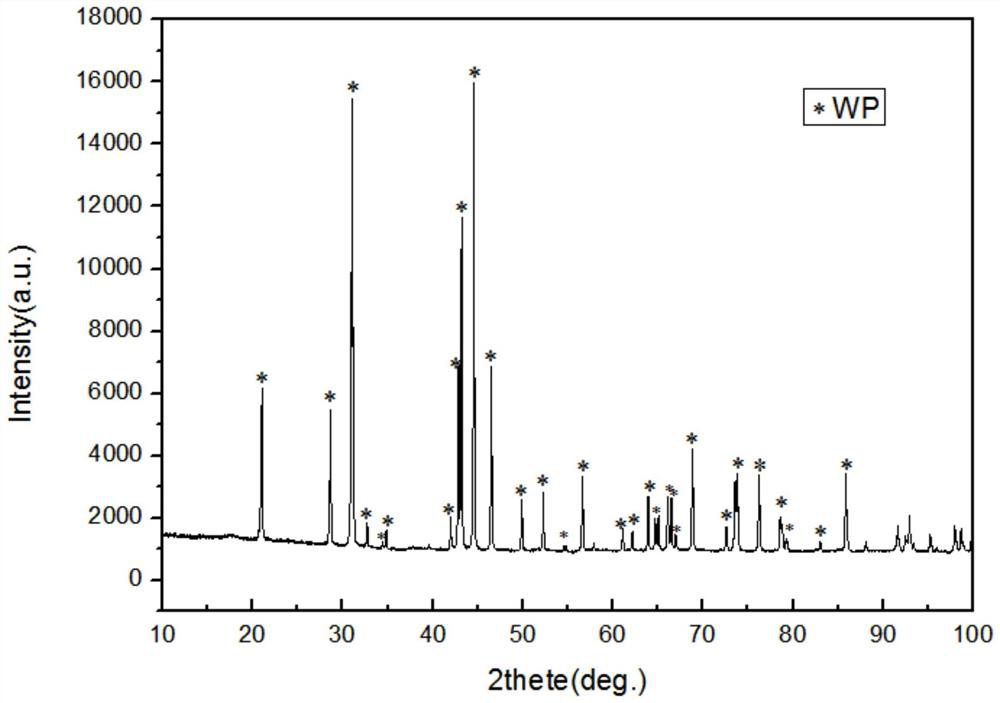
High temperature and high pressure preparation of a conventional superconductor material tungsten phosphide (wp)
ActiveCN110499529BImprove yieldLow costPolycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHigh densitySynthetic materials
The invention discloses a high temperature and high pressure synthesis method of conventional superconductor material tungsten phosphide (WP) crystal. The invention mainly relates to a WP crystal having catalytic performance and superconducting performance, and belongs to the field of conventional superconducting materials. Mix tungsten powder and red phosphorus powder according to the molar ratio of 1:1 to 1:4, grind and mix them evenly. Synthetic WP material. For the first time, the present invention uses a high temperature and high pressure method to prepare WP sintered blocks and large-size single crystals with superconducting properties, which have the characteristics of high crystallinity, high density, stable structure, environmental friendliness, low cost, and high synthesis efficiency. . Because of its simple preparation process and great application potential, it can be used as HDS&HDN catalytic materials, and it is also the first superconductor in the phosphide series with MnP structure, which has played a good role in the research of other materials in the phosphide series.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
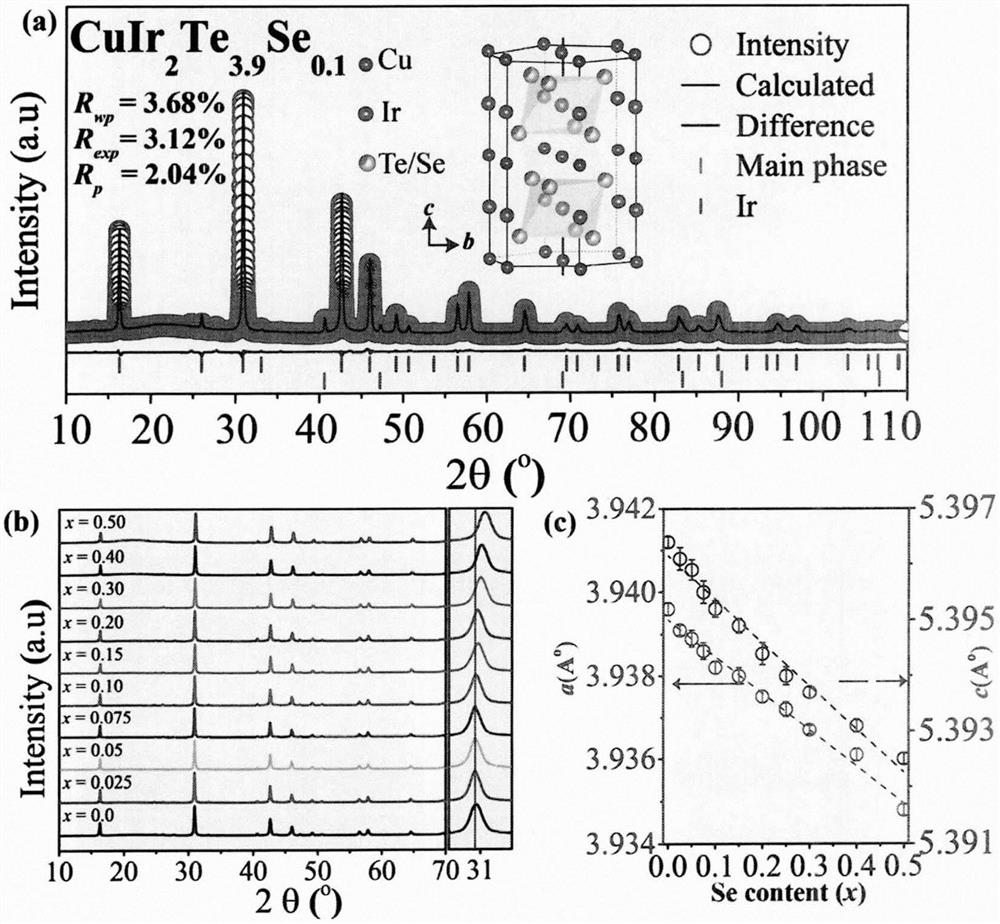
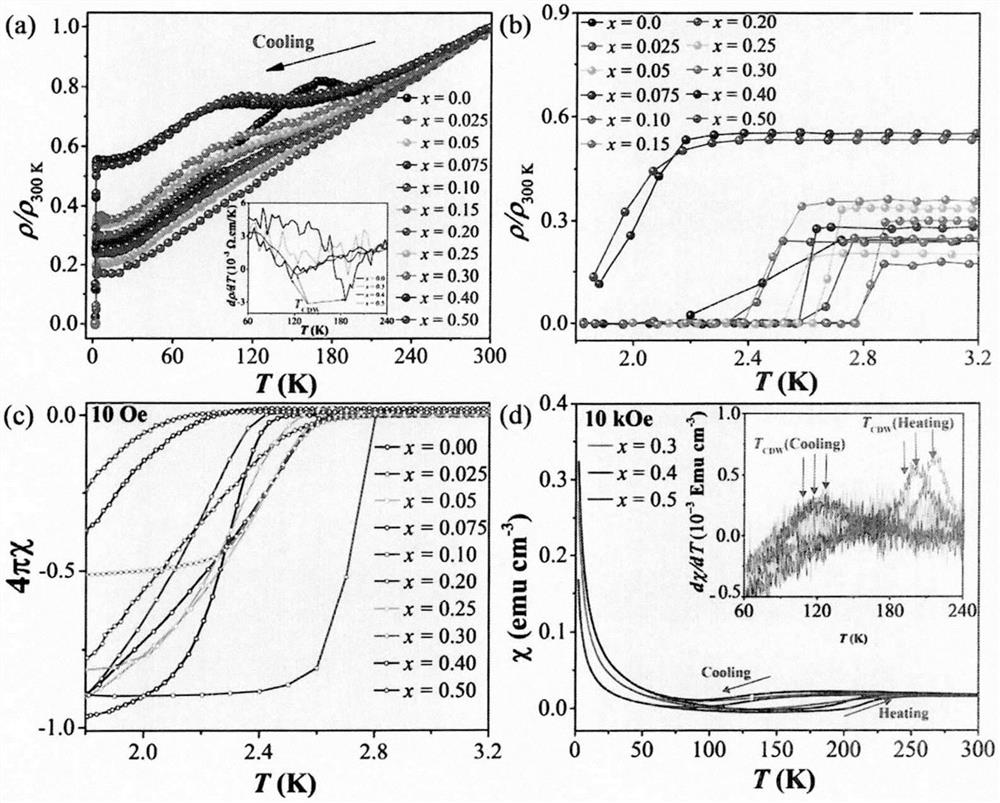
Novel quasi-two-dimensional selenium-doped tellurium-containing superconducting material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113371686AEasy to manufactureLow equipment requirementsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsSuperconducting magnets/coilsSeleniumPowder
The invention relates to a novel quasi-two-dimensional selenium-doped tellurium-containing superconducting material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of functional material manufacturing, wherein the chemical general formula of the novel quasi-two-dimensional selenium doped tellurium-containing superconducting material is CuIr2Te4-xSex (x is greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than or equal to 0.5). According to the invention, a traditional high-temperature solid phase method is used, high-purity Cu, Ir, Te and Se powder (the purity is larger than or equal to 99.9%) with corresponding stoichiometric ratios are fully ground and then placed in a quartz tube, then vacuumizing and sealing are conducted, the sealed quartz tube containing raw materials is placed in a furnace, sintering is conducted for 120 h at a temperature of 850 DEG C to obtain CuIr2Te4-xSex (x is larger than or equal to 0.0 and smaller than or equal to 0.5) polycrystalline powder, the polycrystalline powder is tabletted after complete grinding, a flaky sample is placed into a vacuum sealed quartz tube, and sintering is performed at 850 DEG C for 240 hours to obtain a flaky CuIr2Te4-xSex (x is greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than or equal to 0.5) sample; and a comprehensive physical performance test system (PPMS) is used, and low-temperature performance of physical properties such as conductivity, magnetic property, specific heat capacity and the like of a sample is measured to finally determine that the target product has superconductivity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
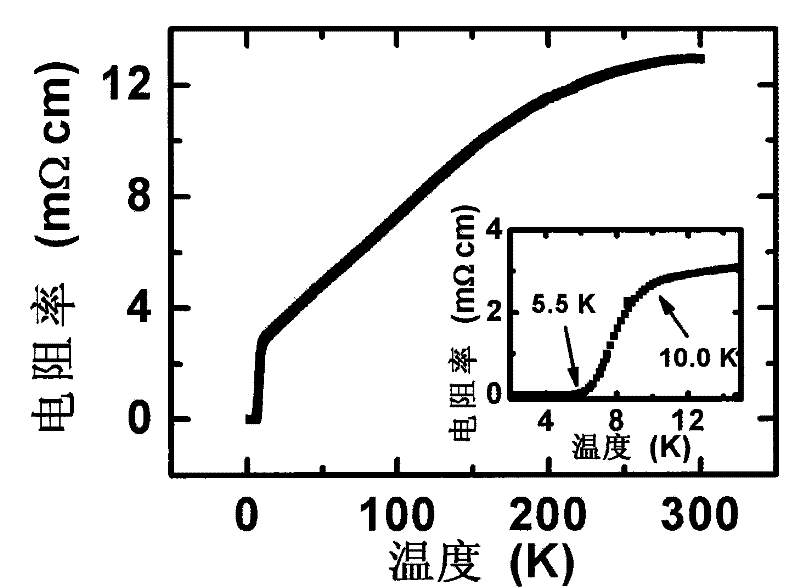
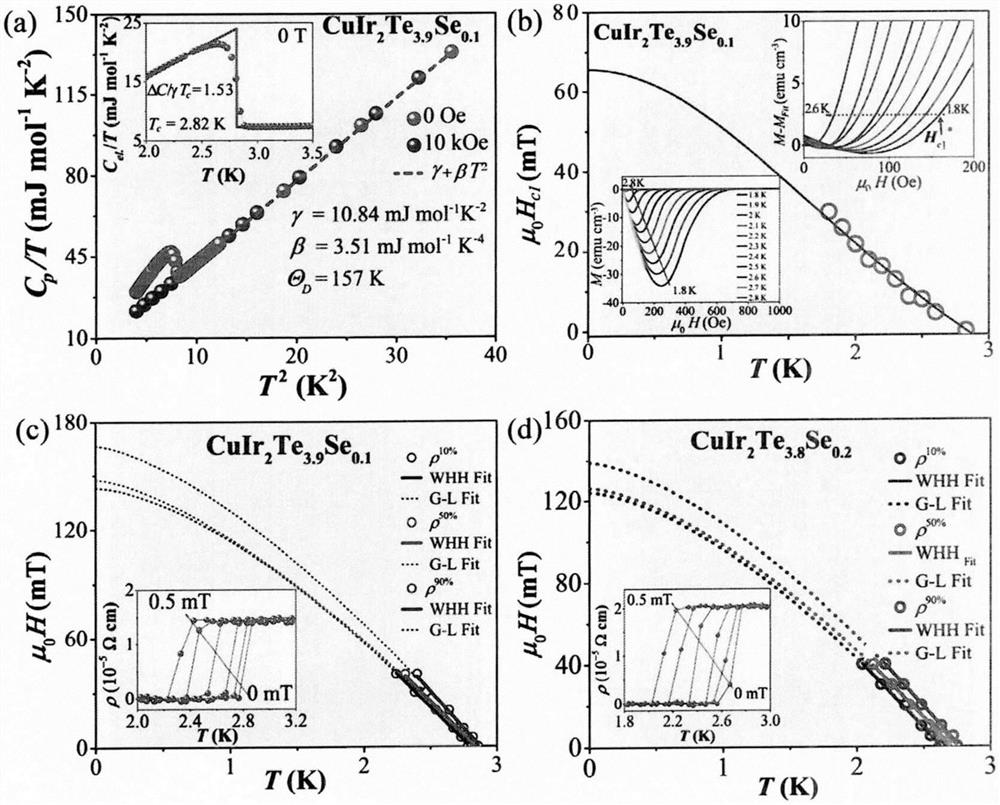
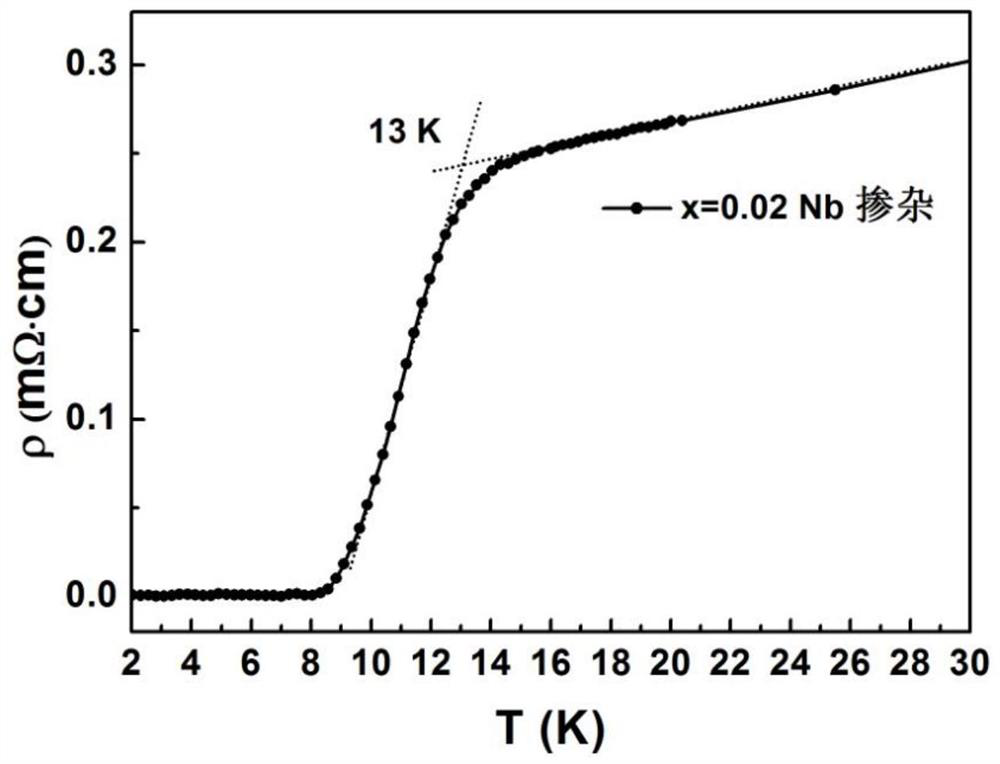
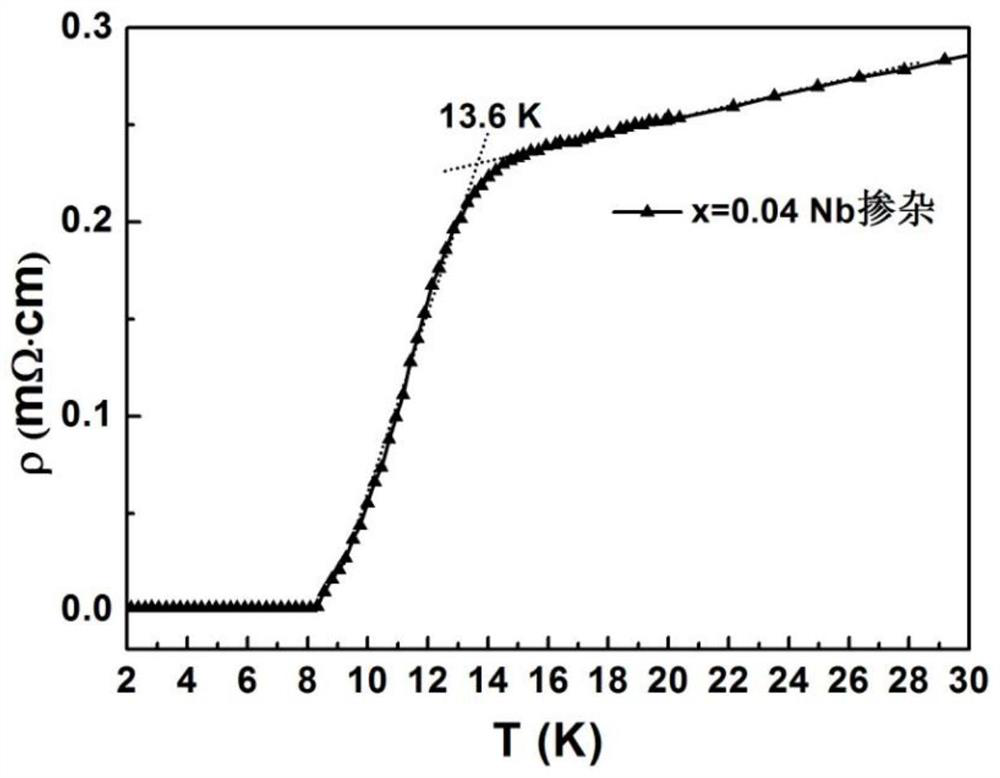
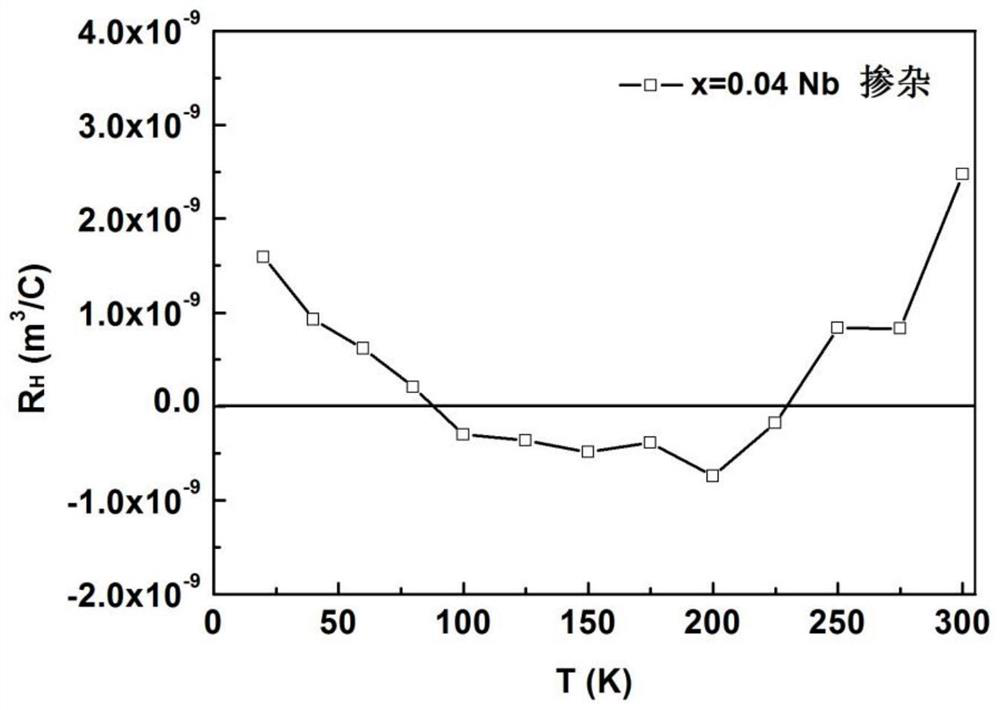
A method of niobium doping to increase the superconducting transition temperature of iron selenium
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing MgB2 superconductive material
InactiveCN1264749CSimple manufacturing processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesCrucibleFree cooling
The invention relates to a process for preparing MgB2 superconducting material which comprises the steps of, grinding B2O3 and Mg powder under the protection of oinert gas, loading the grinded raw material into ceramic crucible, sintering the crucible in vacuum pit furnace, naturally cooling down to room temperature in vacuum or under the inert gas protection status.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
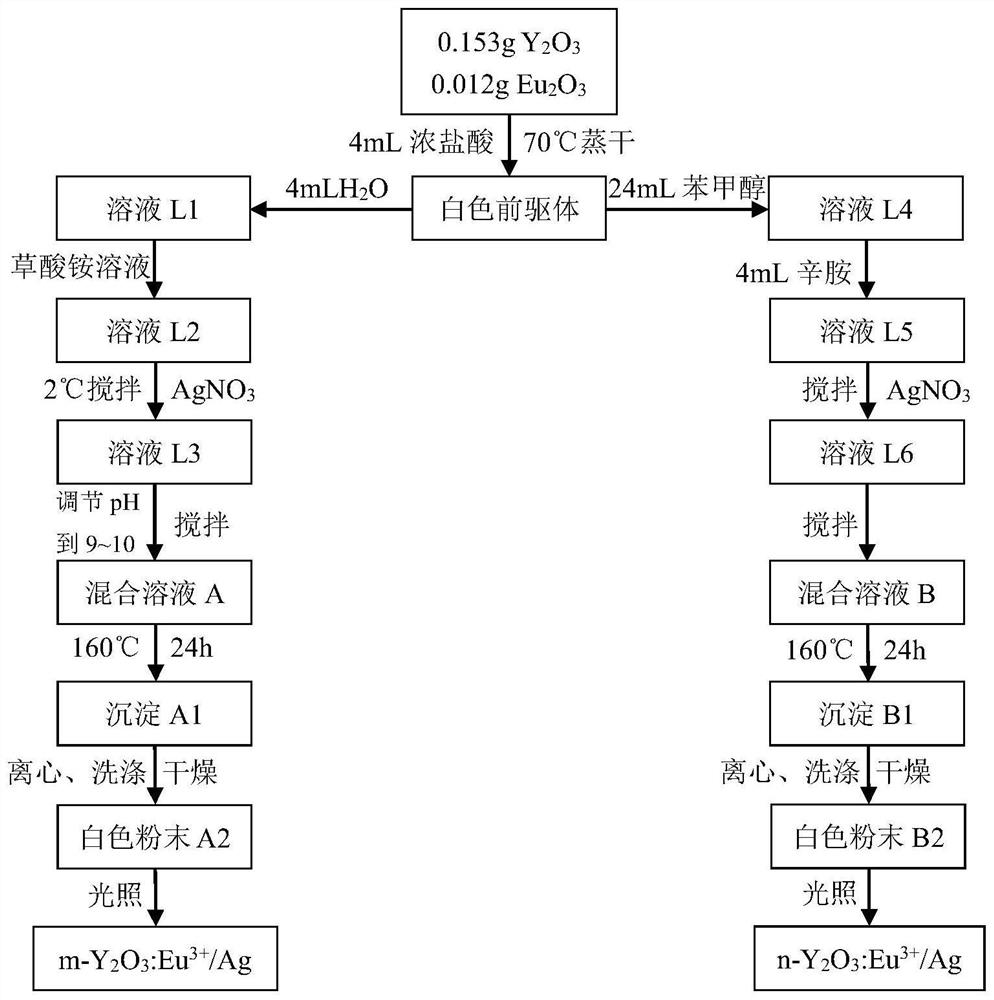
Topological illuminator heterogeneous phase doped Bi(Pb)-Sr-Ca-Cu-O metasuperconductor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109942290AImproved superconducting transition temperatureRaise the superconducting transition temperatureLuminescent compositionsSolid phasesElectric field
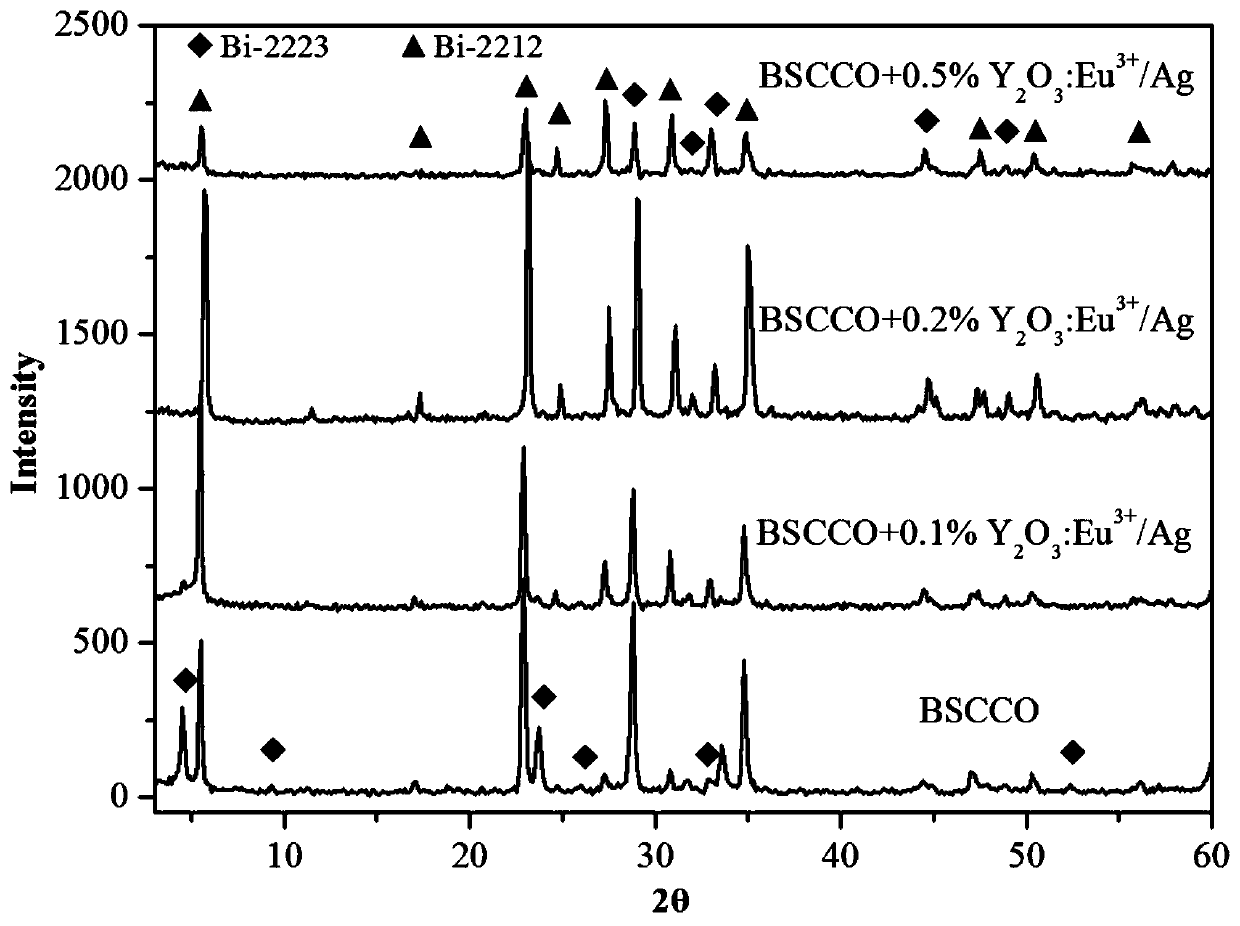
The invention relates to a topological illuminator heterogeneous phase doped Bi(Pb)-Sr-Ca-Cu-O intelligent metasuperconductor and a preparation method thereof. The superconducting transition temperature of a Bi(Pb)-Sr-Ca-Cu-O superconductor is improved by utilizing topological illuminator doping. A Y2O3:Eu<3+> / Ag topological illuminator having 1 percent by mass of Ag is prepared by adopting a hydrothermal method, and the topological illuminator heterogeneous phase doped Bi(Pb)-Sr-Ca-Cu-O superconductor is prepared by adopting a solid-phase sintering method. Under the effect of an external electric field, the superconducting transition temperature of a Y2O3:Eu<3+> / Ag topological illuminator heterogeneous phase is excited to perform electroluminescence, and the superconducting transition temperature of a Bi(Pb)-Sr-Ca-Cu-O superconductor is influenced through electroluminescence. Changes of the superconducting transition temperature of a doped sample is studied by changing the mass percentage of a doping agent. Experiments discover that the superconducting transition temperature of a doped sample is higher than that of a pure sample.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Novel indium-containing transition metal telluride superconducting material and preparation method thereof
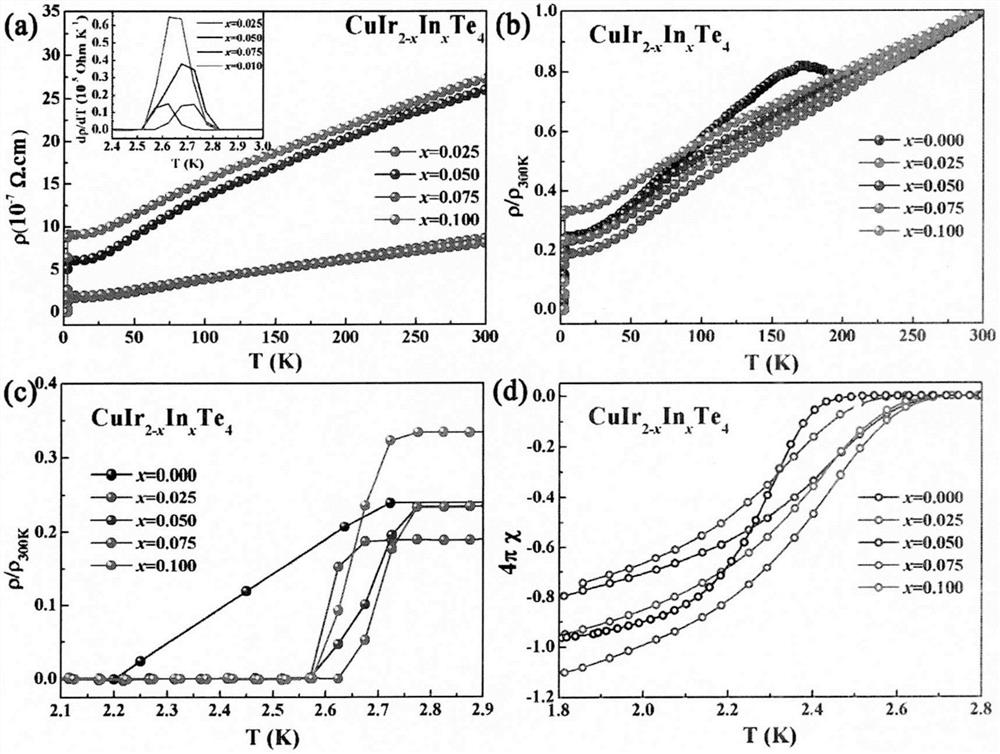
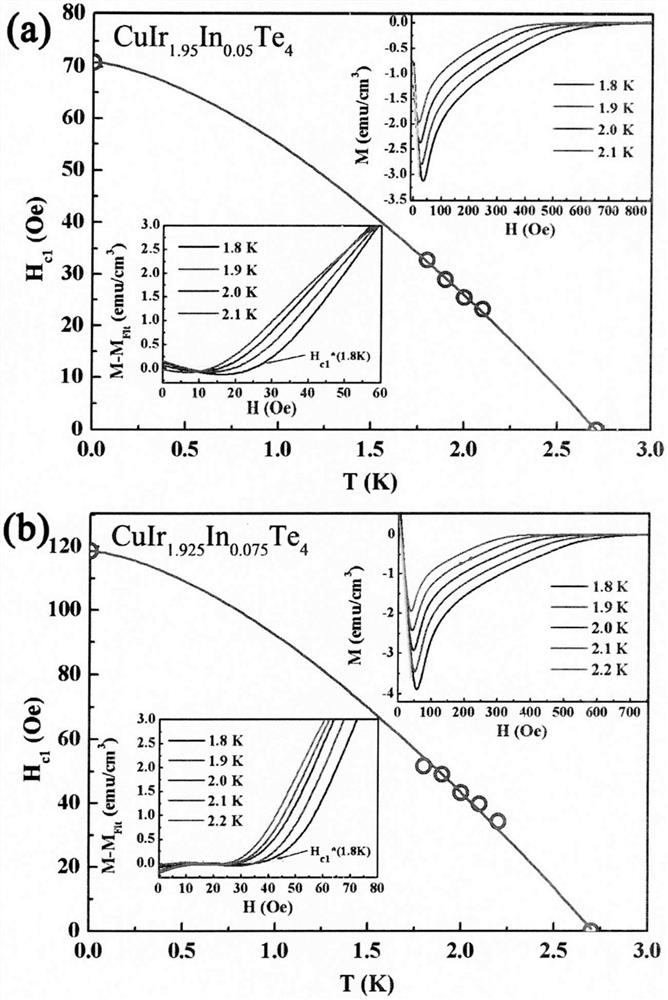
PendingCN113371685AEasy to makeLow requirements for preparation conditionsSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsIndiumCritical magnetic field
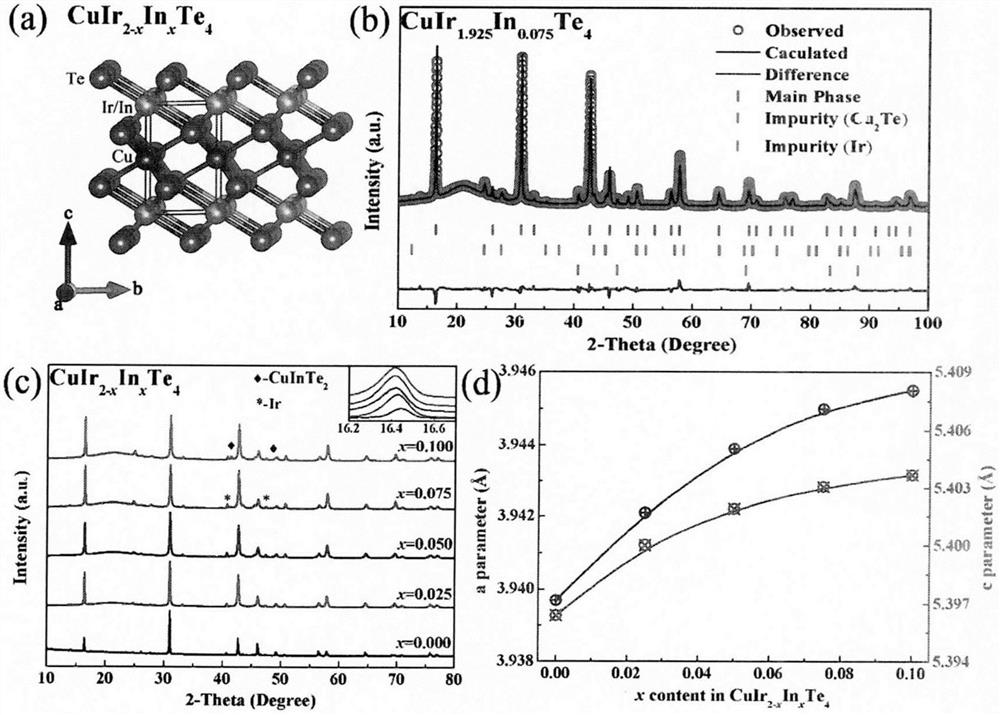
The invention relates to a novel indium-containing transition metal telluride superconducting material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of quantum function material manufacturing. The preparation method is a traditional high-temperature solid-phase method and comprises the following steps: fully grinding Cu, Ir, In and Te according to corresponding stoichiometric ratios, vacuumizing, sealing in a quartz tube, putting the sealed quartz tube filled with raw materials into a furnace, and sintering at 800 DEG C for 120 hours to obtain CuIr2-xInxTe4 (x is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.1) polycrystalline powder. According to the invention, the physical properties of the material are tested through a comprehensive physical property test system (PPMS), and the superconducting physical properties of a target material are deeply investigated by measuring the physical properties such as conductivity, magnetic properties, upper and lower critical magnetic fields and the like of the material; the novel quasi-two-dimensional indium-doped transition metal tellurium compound superconducting material is reported for the first time; and by synthesizing the compound superconducting material, a new member is added for the family of transition metal sulfide superconducting materials, and people are helped to understand the physical properties of high-temperature copper-based or iron-based superconducting.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
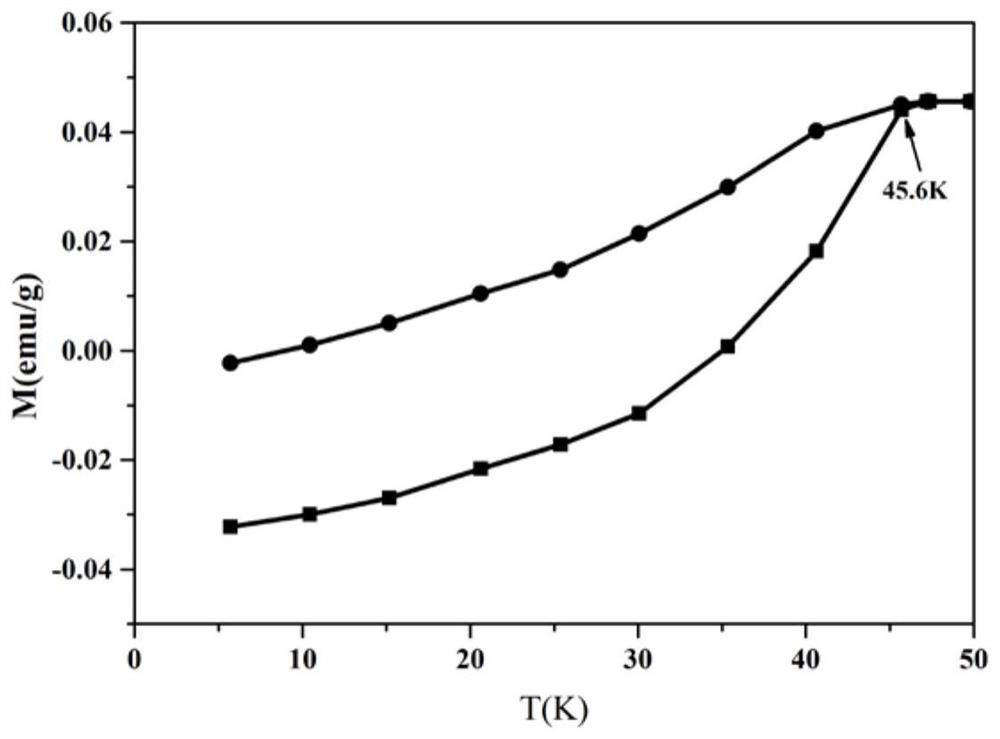
Iron-based superconducting new material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112002485AImprove superconductivityRaise the superconducting transition temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsOrganic chemistry methodsIron powderChloride
The invention discloses a novel iron-based superconducting material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of iron-based superconducting materials. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps: preparing FeSe powder from iron powder and selenium powder, putting the FeSe powder, cesium chloride and a sodium citrate solution into a container, then, adding 4-tert-butyl pyridine into a container, fully mixing all the components, sealing, performing ultrasonic treatment, pouring the mixed reaction solution into a reaction kettle, sealing, putting the obtained product into a drying oven, heating, cooling the product to room temperature, grinding the product to obtain Cs0.77Na0.23(C9H13N)0.18Fe2Se2 powder, then putting the powder into the drying oven, performing annealing treatment, and taking out the powder to obtain the Cs0.77Na0.23(C9H13N)0.18 Fe2Se2 iron-based superconducting new material. The iron-based superconducting new material has a relatively high superconducting transition temperature.
Owner:嘉兴市爵拓科技有限公司
Polystyrene colloidal sphere and niobium film composite heterogeneous structure superconducting material and preparation method
InactiveCN105990512ASimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologySuperconductor detailsMicrosphereNiobium
The invention discloses a polystyrene colloidal sphere and niobium film composite heterogeneous structure superconducting material, which comprises a substrate, a niobium film and a polystyrene colloidal hexagonal array film, wherein the niobium film is located on the substrate, and the polystyrene colloidal hexagonal array film coats the niobium film; the polystyrene colloidal hexagonal array film comprises multiple polystyrene colloidal microspheres; and single layers of the polystyrene colloidal microspheres are tightly arranged to form the hexagonal array. The invention also discloses a method of preparing the superconducting material. The polystyrene colloidal microspheres and the niobium superconducting film material are constructed into a heterogeneous structure nanostructure material; through changing the contact area between the colloidal spheres and the niobium substrate, the critical temperature for superconducting transition is regulated, the superconducting transition temperature Tc<onset> for the niobium film is thus improved; and the material preparation process is simple, needed devices are few, the superconducting material preparation cost is greatly reduced, and popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:李志刚 +1
Method for preparing electronic high temperature superconductor lanthanum-cerium-copper oxide films
InactiveCN100593583CLow costReduced vacuum requirementsVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCeriumFree cooling
The present invention provides a method of preparing electron type high-temperature superconductor LCCO film, using pulse laser sedimentary equipment. The present invention comprises the following steps that: firstly, according to the ratio of La2-xCexCuO4, wherein, x is more than or equal to 0.08, and less than or equal to 0.16, a LCCO ceramic target material is prepared by adopting the solid state reaction method and arranged on a target seat of a reaction chamber; secondly, a substrate is selected; SrTiO3, MgO or LaAlO3 is selected, cleaned and put onto a heating table inside the reaction chamber, and then the reaction chamber is closed; thirdly, the reaction chamber is vacuumized till the back bottom vacuum is superior to 2.0x10-4Pa; fourthly, the substrate is heated to 675-800 DEG C by a heater; fifthly, reaction gas is pumped into the reaction chamber; sixthly, the surface of the LCCO ceramic target material is cleaned; seventhly, the LCCO ceramic target material is heated to besublimated, and then a LCCO film is initially prepared on the substrate; eighthly, after reaction is over, the reaction gas is stopped from being pumped into the reaction chamber, and the reaction chamber is vacuumized till the vacuum is superior to 2x10-4Pa; then the substrate with the prepared LCCO film is cooled to be at annealing temperature for annealing; finally the substrate with the prepared LCCO film is naturally cooled to be at room temperature.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of metal-based superconducting tape and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112981326BLess componentsSimple structureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingThin membraneSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention belongs to the technical field of superconductors, and in particular relates to a metal-based superconducting tape and a preparation method thereof. A method for preparing a metal-based superconducting tape, comprising the following steps: 1) using a pulsed laser deposition method to form a thin film on the surface of the metal-based tape; in the pulsed laser deposition method, using Fe (1‑x) Se y Te (1‑y) Target or Fe (1+x) Se y Te (1‑y) A target material, wherein 0≤x≤0.1, 0.1≤y≤0.9; 2) depositing a protective layer on the surface of the thin film by a magnetron sputtering method. The iron-based superconducting tape can be rapidly and continuously prepared by the method of the invention, and the prepared superconducting tape has good C-axis orientation, smooth surface, high superconducting transition temperature and high critical current density.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
A rapid preparation of high-quality fese 0.5 te 0.5 Superconducting polycrystalline method
ActiveCN104649236BSimple preparation processNo need to waste manpowerSelenium/tellurium compundsRoom temperatureFree cooling
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
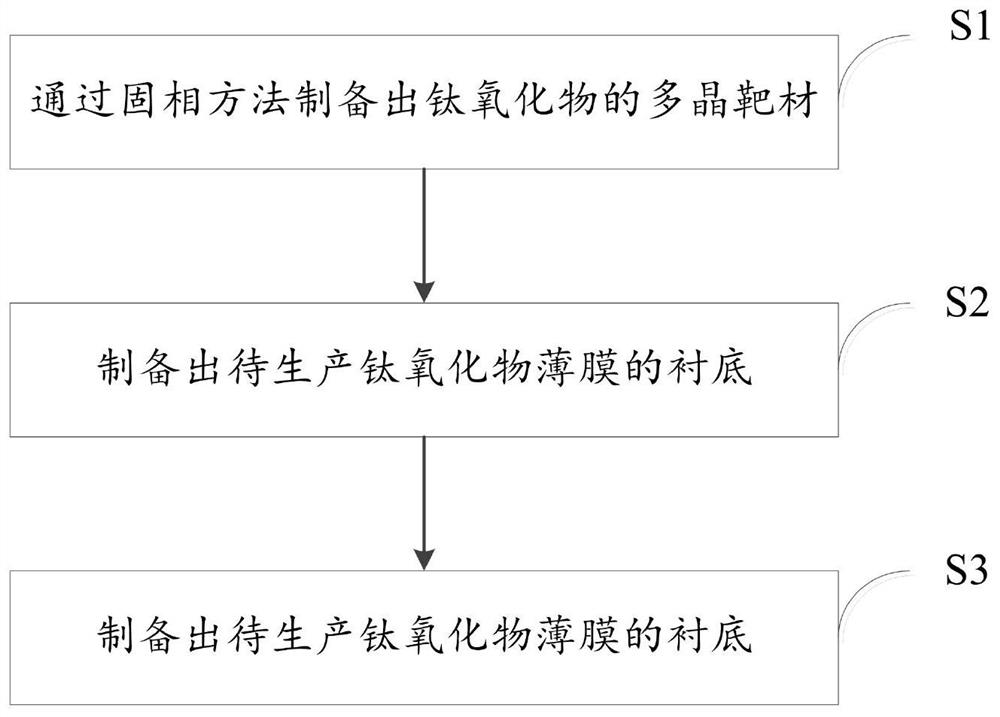
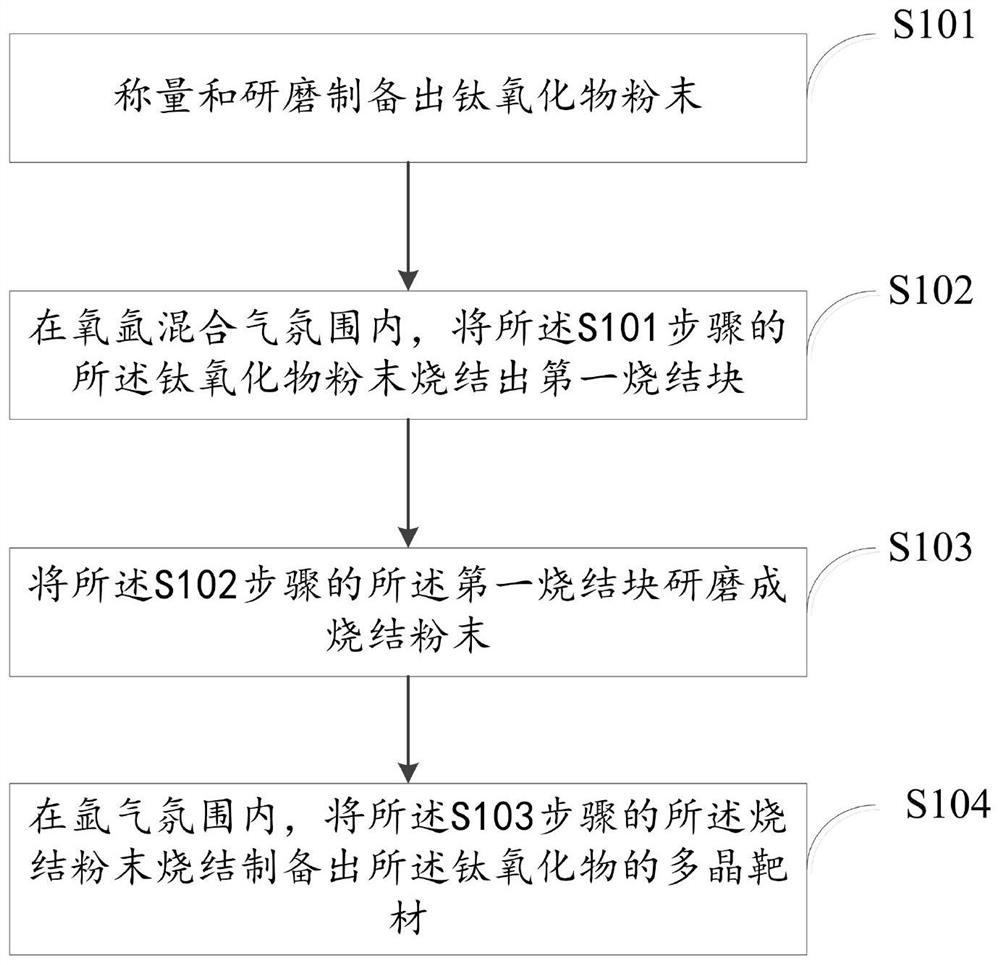
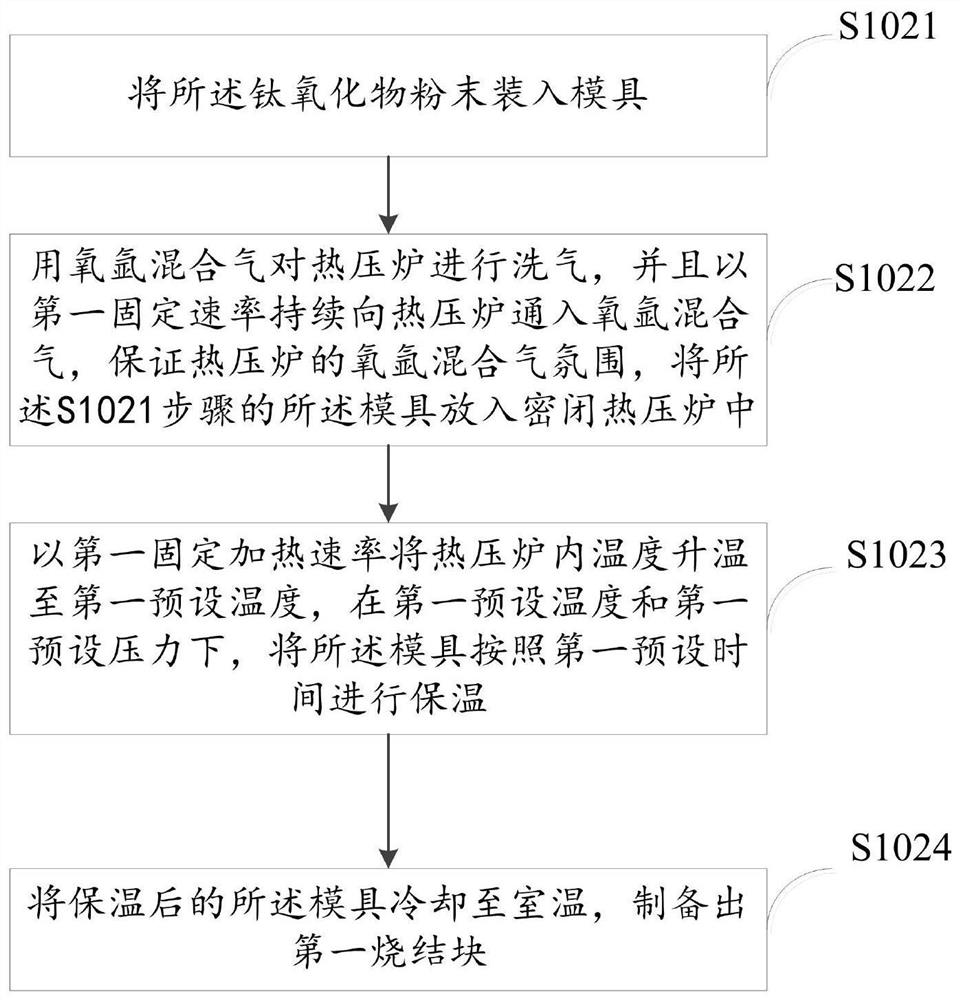
Preparation method of titanium oxide superconducting thin film
ActiveCN112824555ASimple growth processAvoid oxygen contentPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateMetallurgyMaterial synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of material synthesis, in particular to a preparation method of a titanium oxide superconducting thin film. The method comprises the steps that S1, a polycrystalline target material of titanium oxide is prepared through a solid phase method; S2, a substrate of the titanium oxide superconducting thin film to be produced is prepared; and S3, the target material in the step S1 is subjected to ablation through a pulse laser deposition system, the target material obtained after ablation extends on the substrate in the step S2, and the titanium oxide superconducting thin film is prepared. According to the method, the titanium oxide superconducting thin film material can be prepared without controlling oxygen partial pressure in the growth process, the growth process of the titanium oxide superconducting thin film material is simplified, and the superconducting transition temperature is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving FeSe superconducting transition temperature by adding Mg
ActiveCN103360073BSynthetic sintering technology is simple and easyPromote practical progressSuperconductor detailsRoom temperatureSuperconducting transition temperature
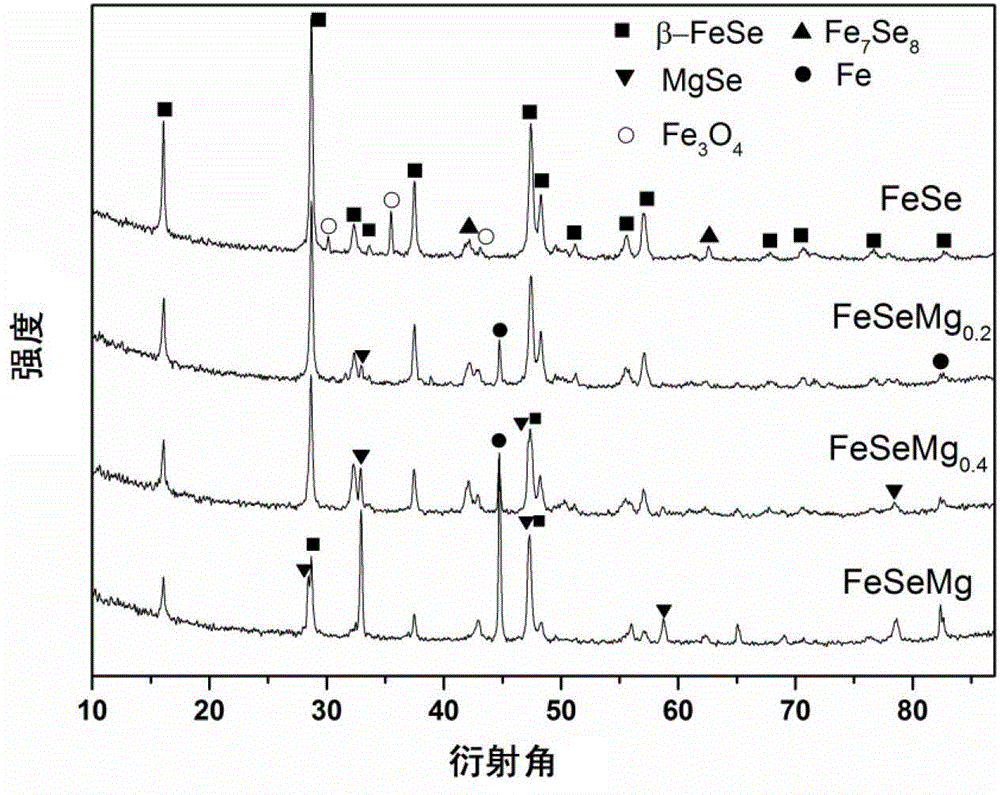
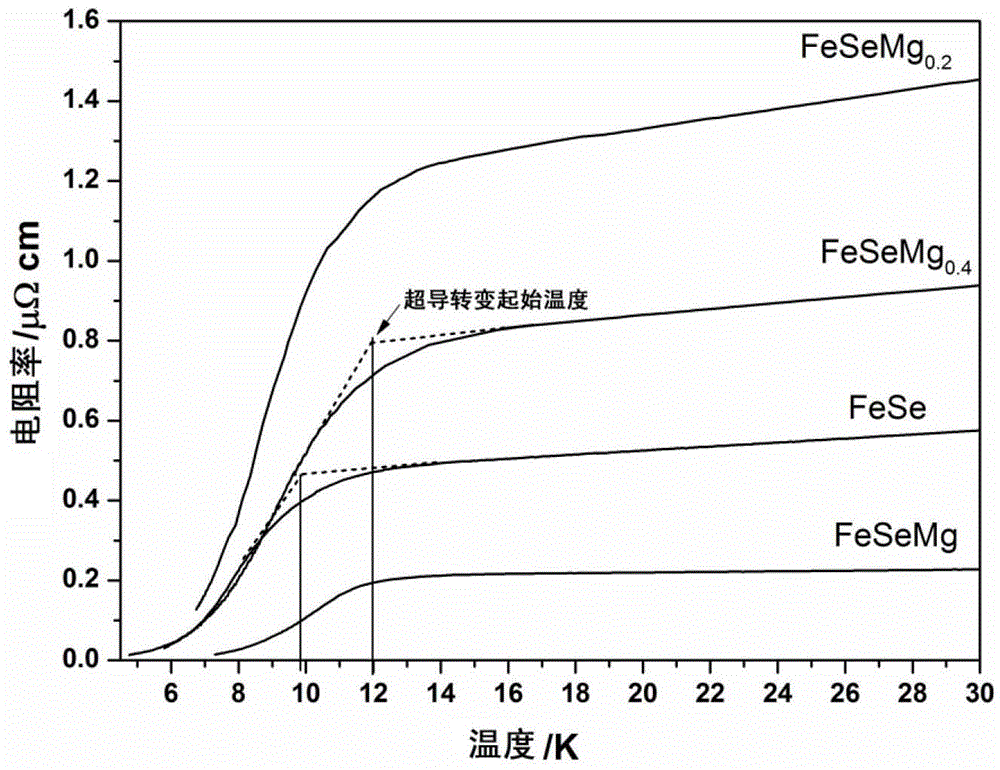
The invention relates to a method for adding Mg to increase the superconducting transition temperature of FeSe; grinding Fe powder and Se powder in an agate mortar or planetary ball mill according to the atomic ratio of Fe:Se=1:0.90~1.05, and then pressing them into thin flakes , put it into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter or tubular sintering furnace, keep sintering at 600-700°C for 18-48 hours, and then cool down to room temperature. The sintered FeSe block was ground into powder again. Grind Mg powder and FeSe powder in an agate mortar or ball mill according to an atomic ratio of 0.2 to 1:1, press into thin slices, and put them into a high-temperature differential scanning calorimeter or tube sintering furnace for sintering at 700 to 800°C. Allow 0.5 to 1 hour to cool down to room temperature. MgSe coexists with unreacted FeSe, which affects the lattice constant of FeSe, increasing its superconducting transition temperature from 9.8K to 12.1K, an increase of more than 20%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com