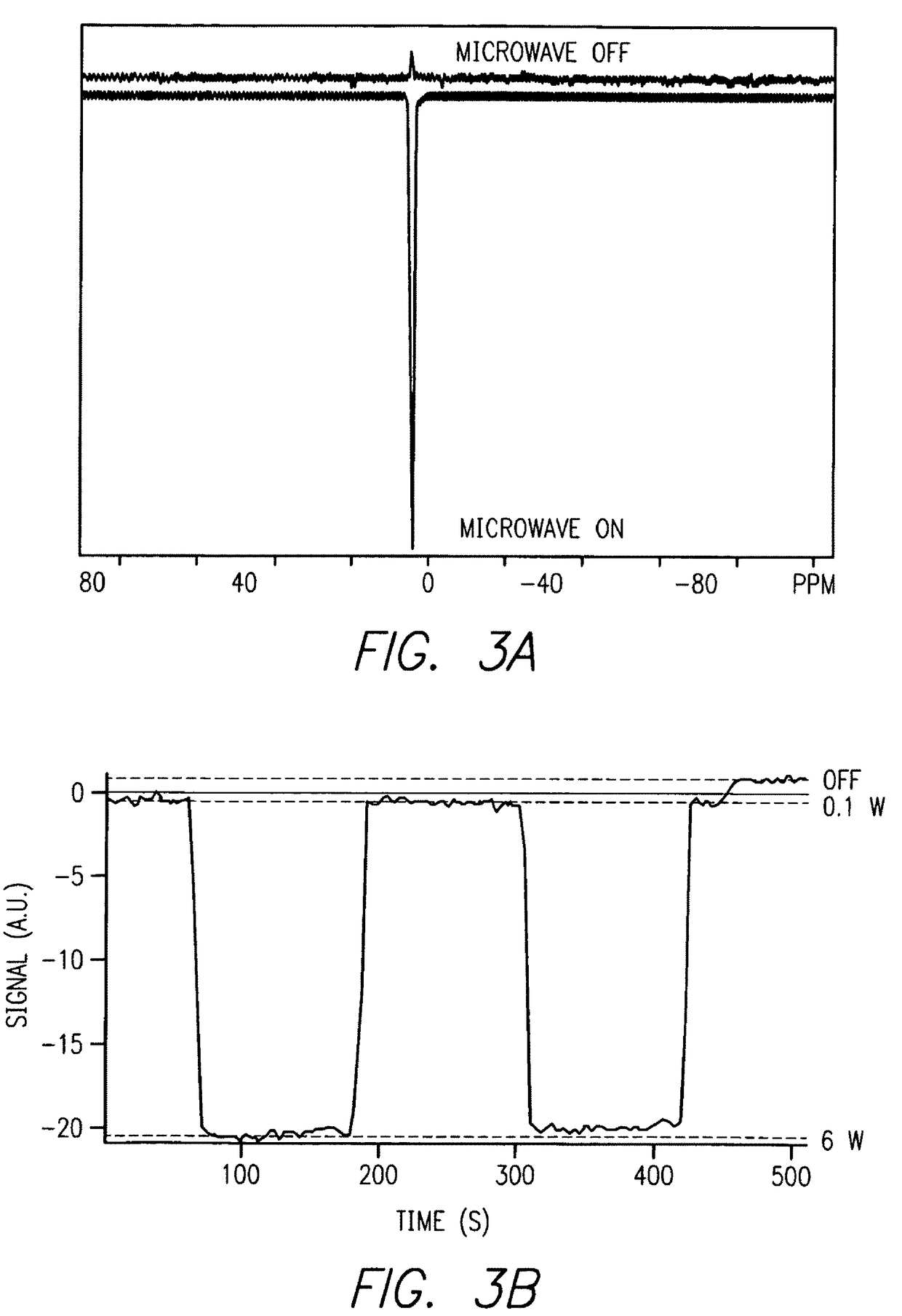
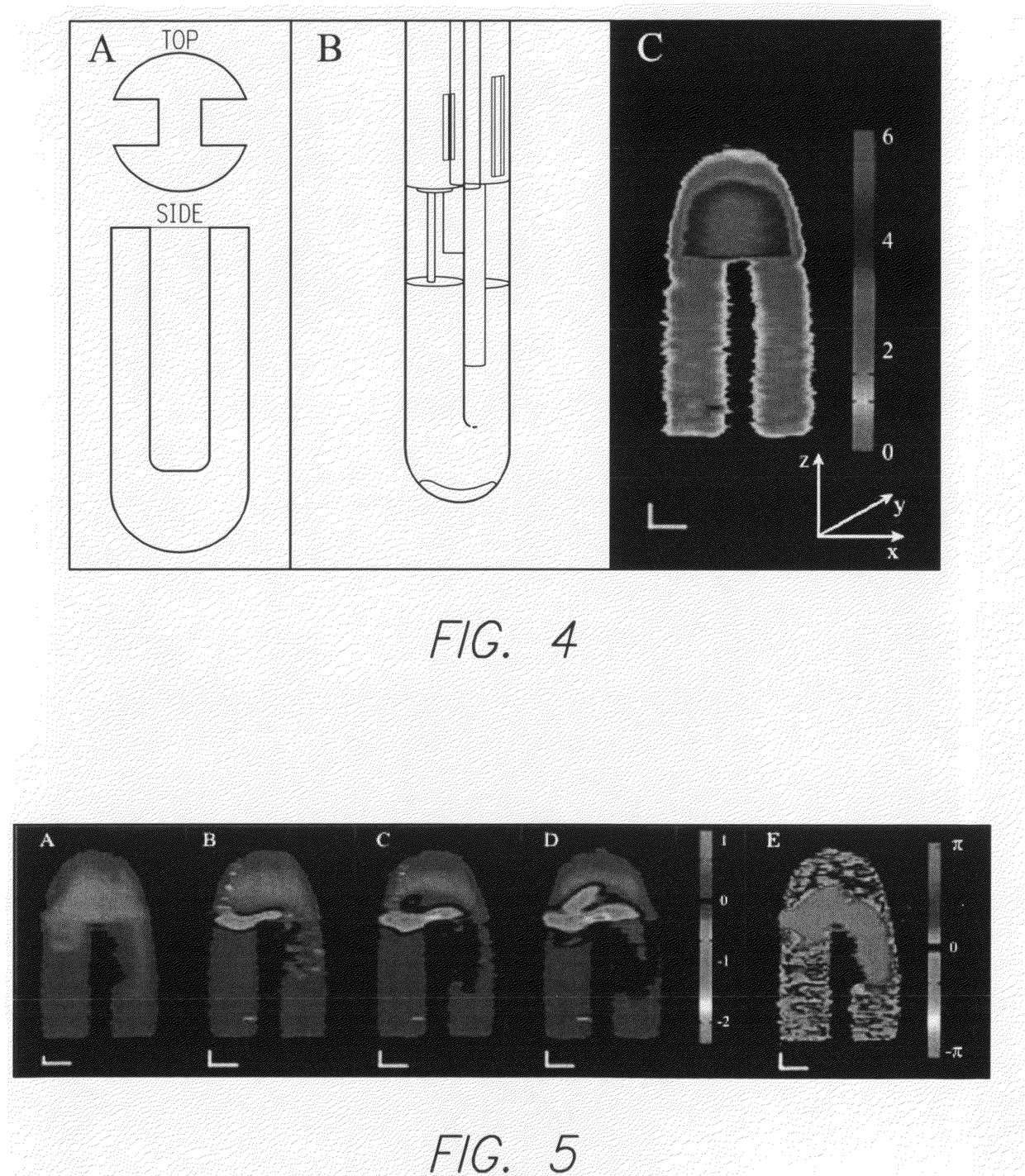
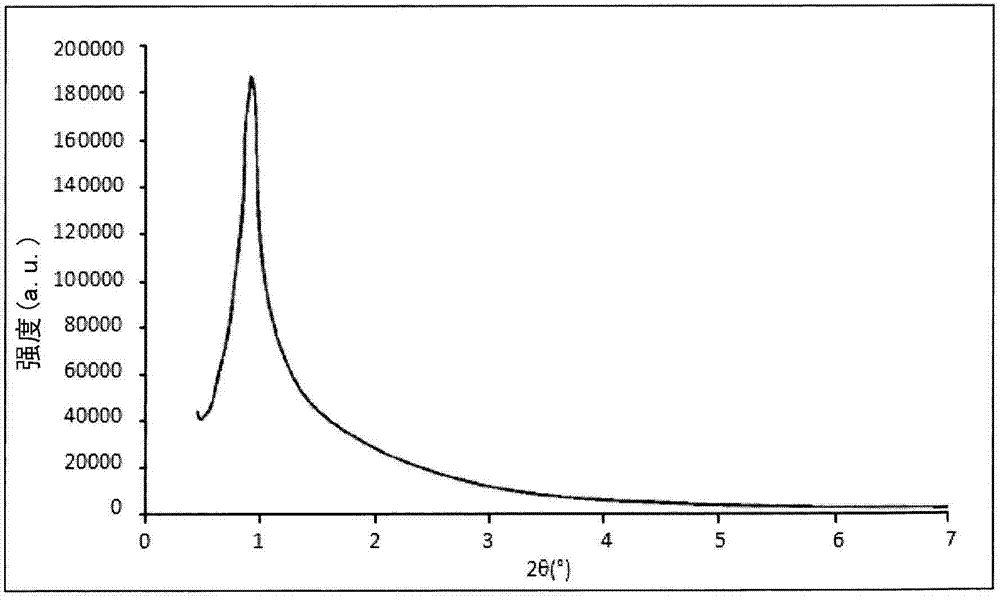
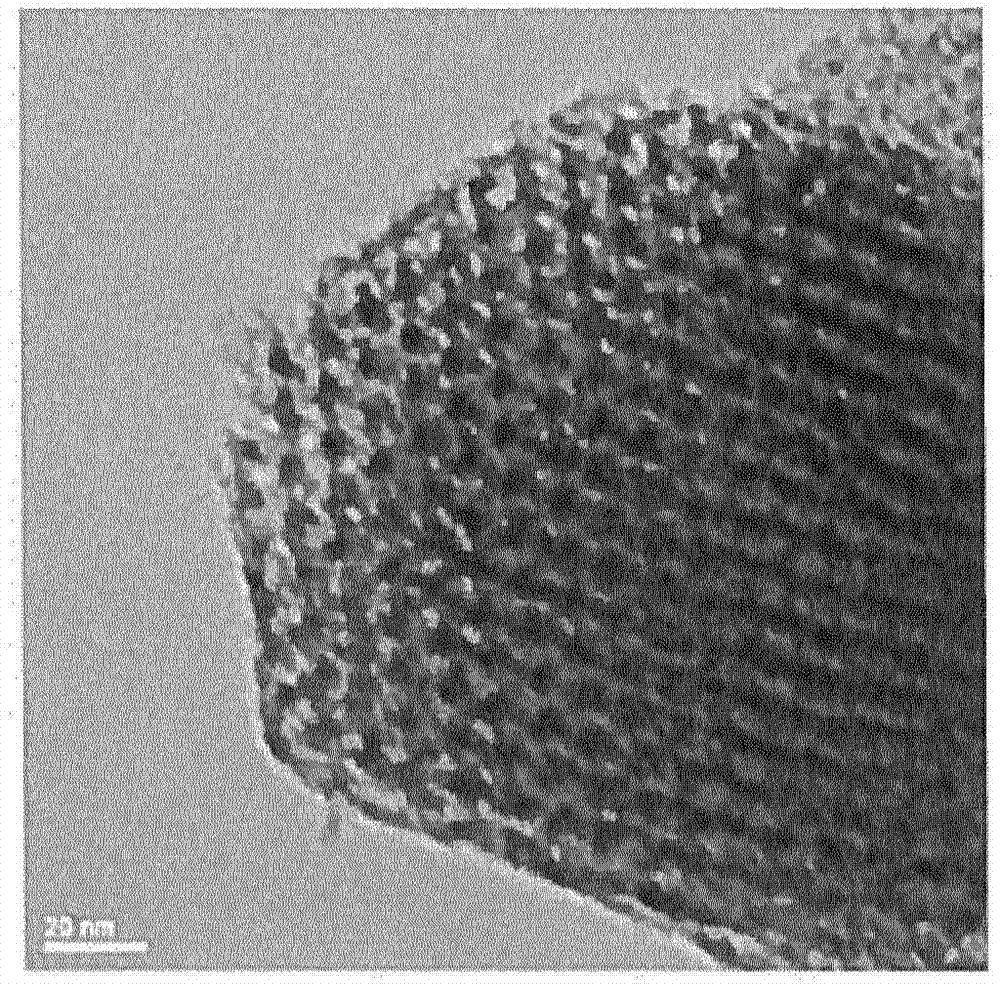
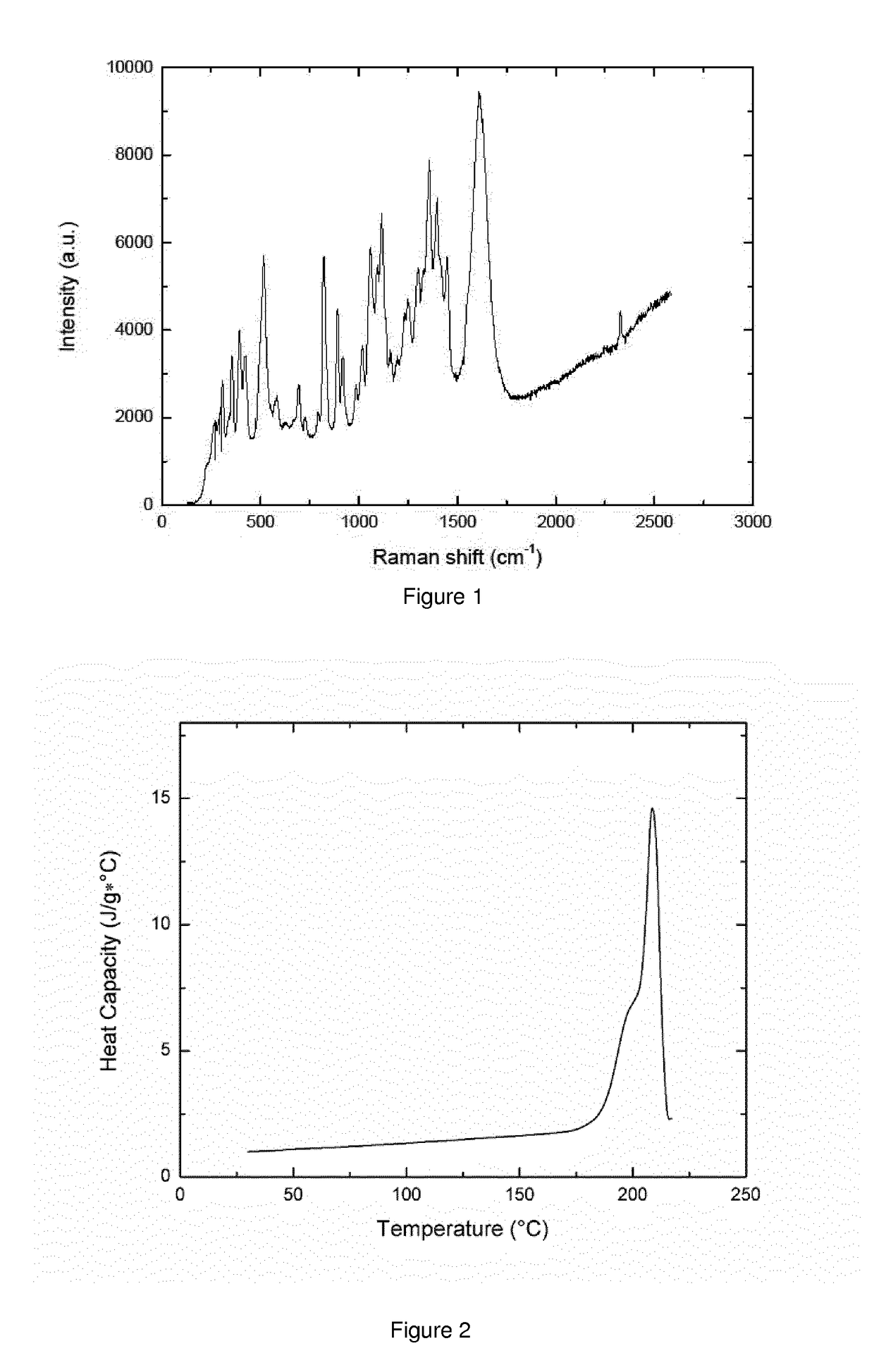
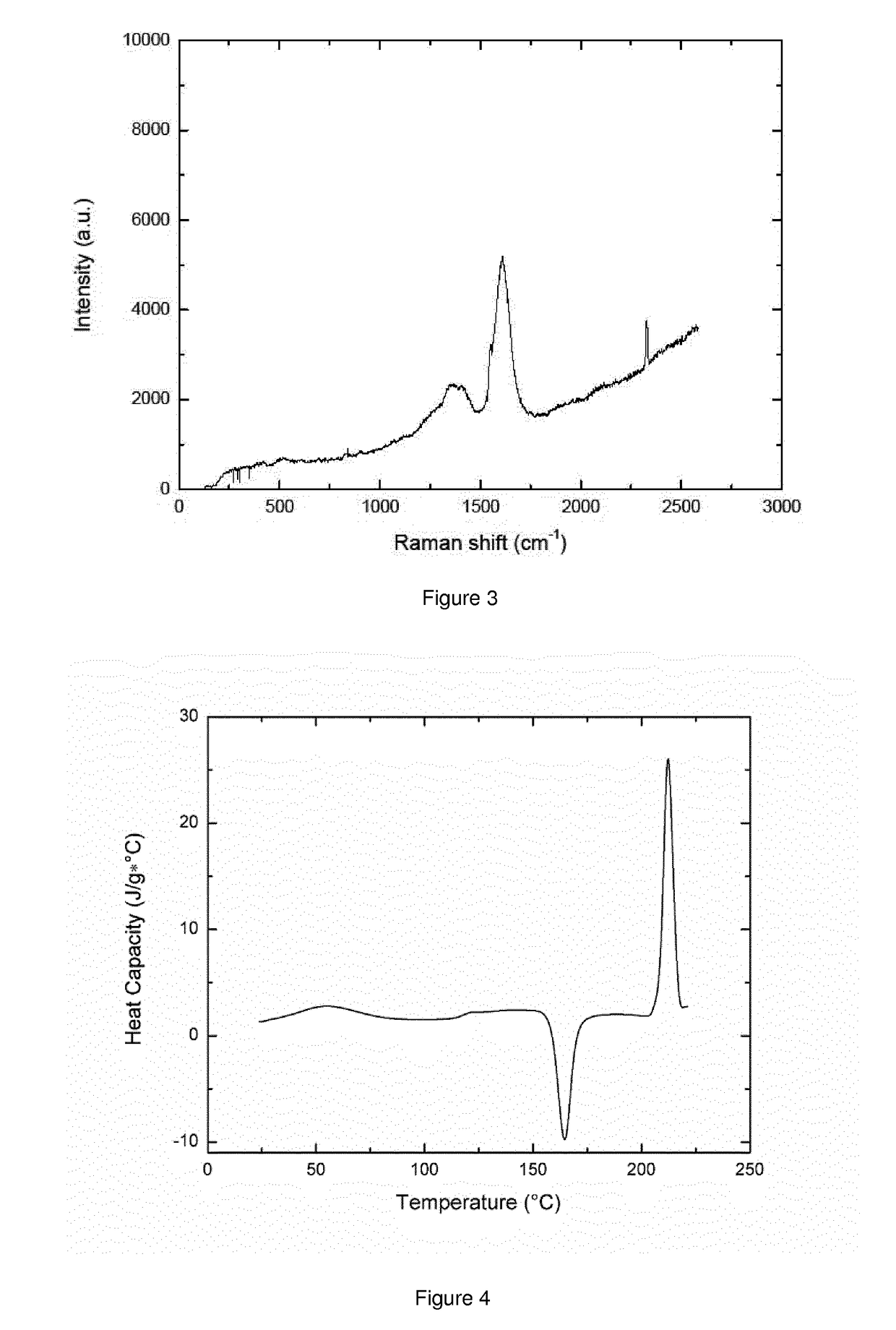
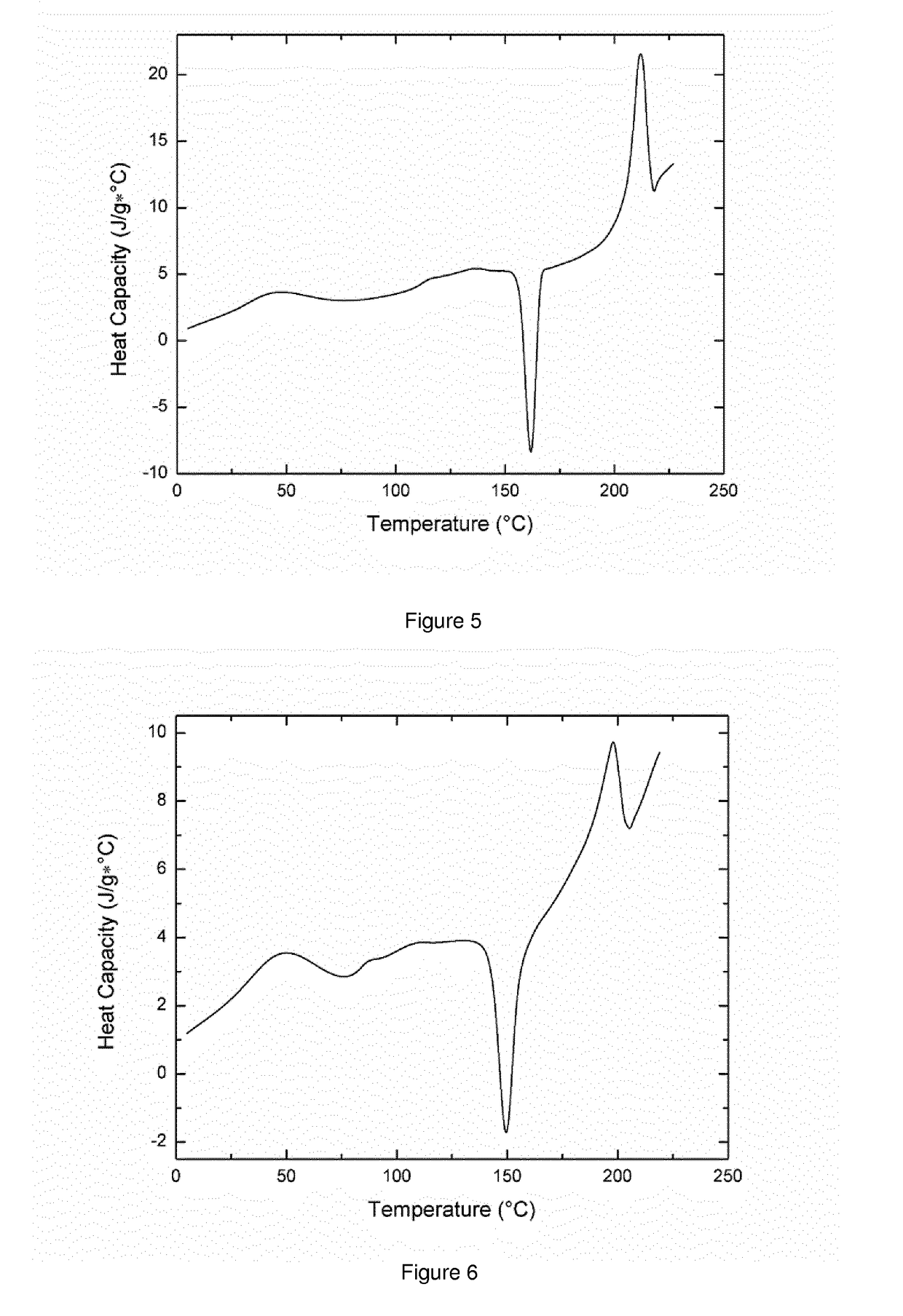
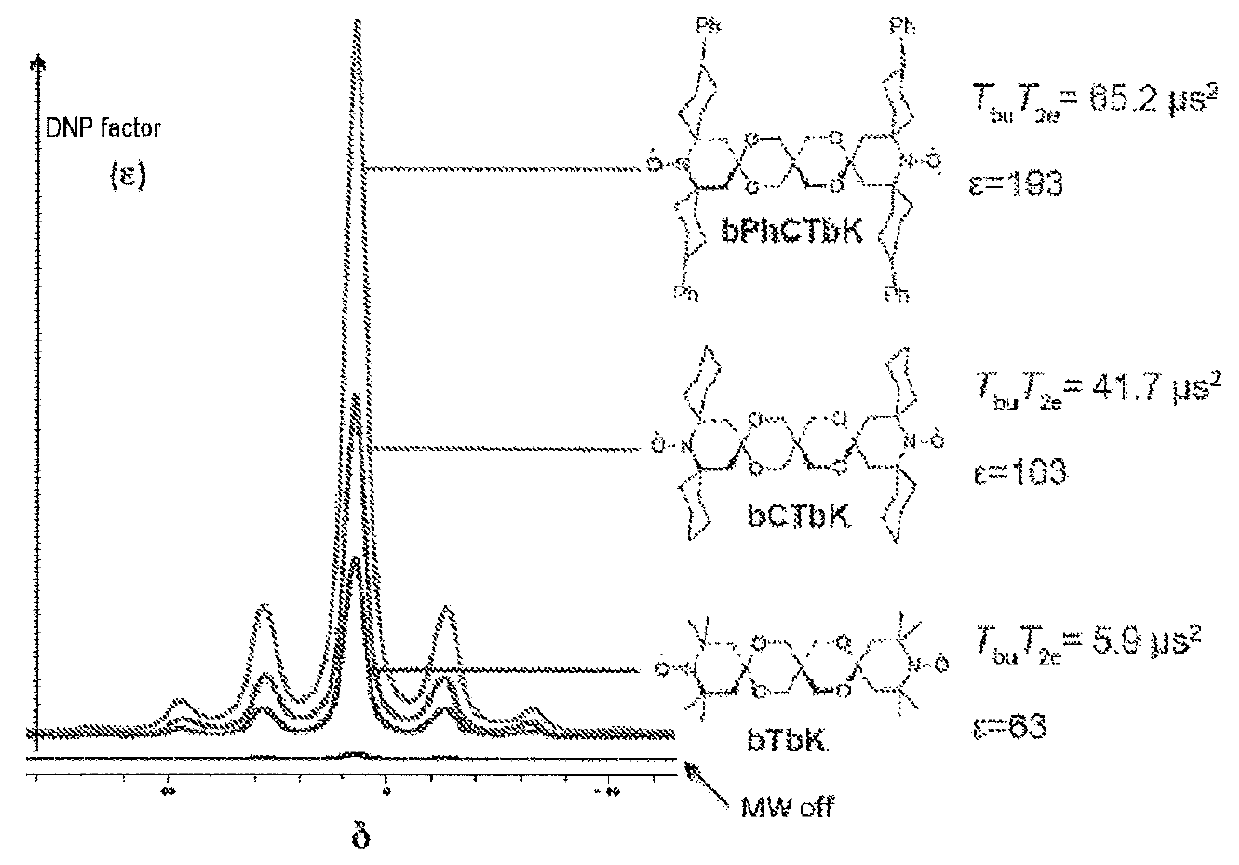
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Dynamic nuclear polarisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agents: water soluble carbon-13 enriched fullerene and carbon nanotubes for use with dynamic nuclear polarization
InactiveUS20070025918A1Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingNanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringDynamic nuclear polarisationCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to carbon-13 enriched fullerene and carbon nanotube (CNT) compositions for improved magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”). The invention also relates to a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) method of MRI utilizing the carbon-13 enriched fullerene and CNTs of the invention.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
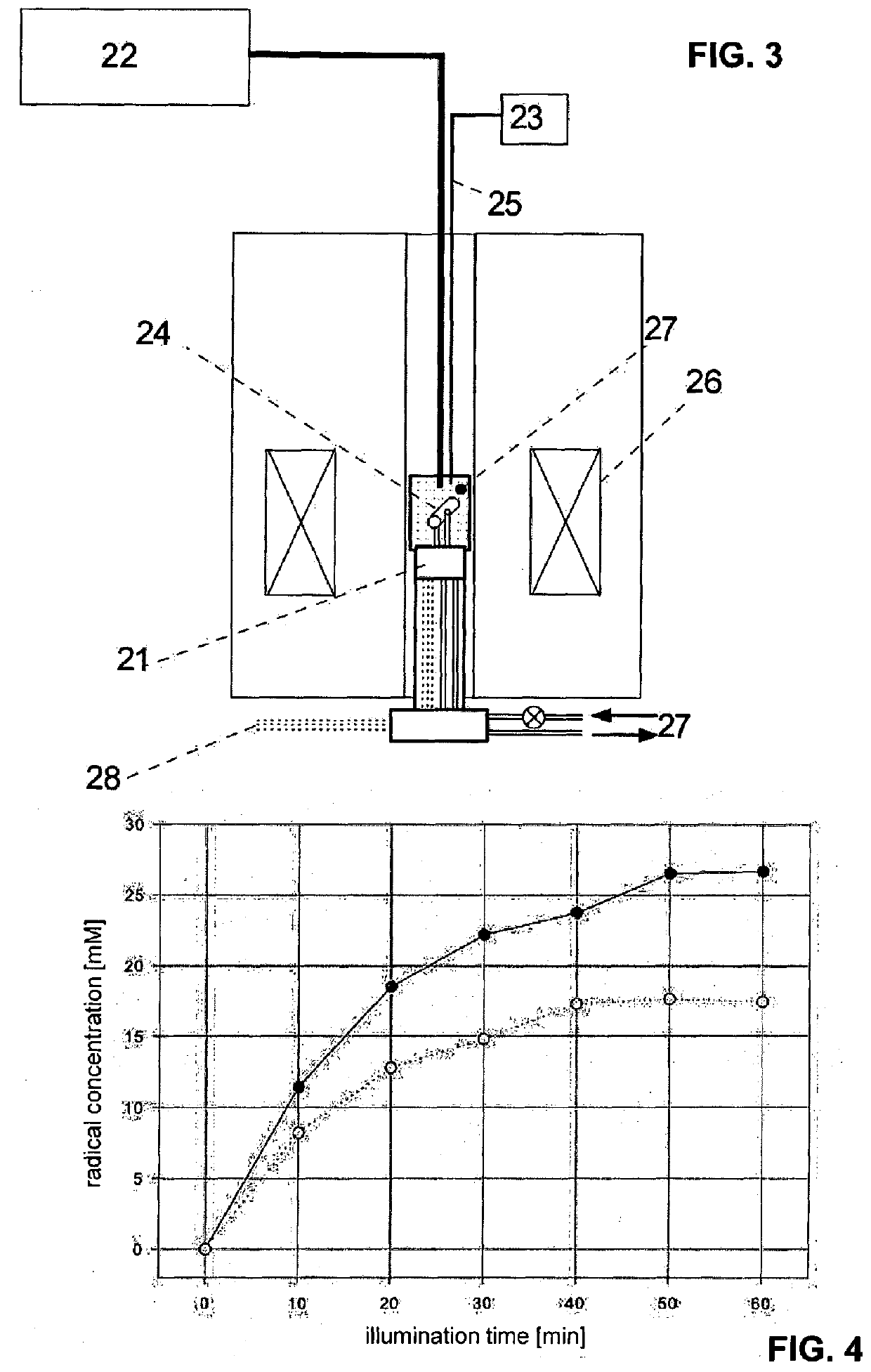
Method for the generation of radicals for dynamic nuclear polarization and uses thereof for nmr, mrs and MRI
ActiveUS20160033590A1Increased polarizationImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUltravioletElectromagnetic radiation
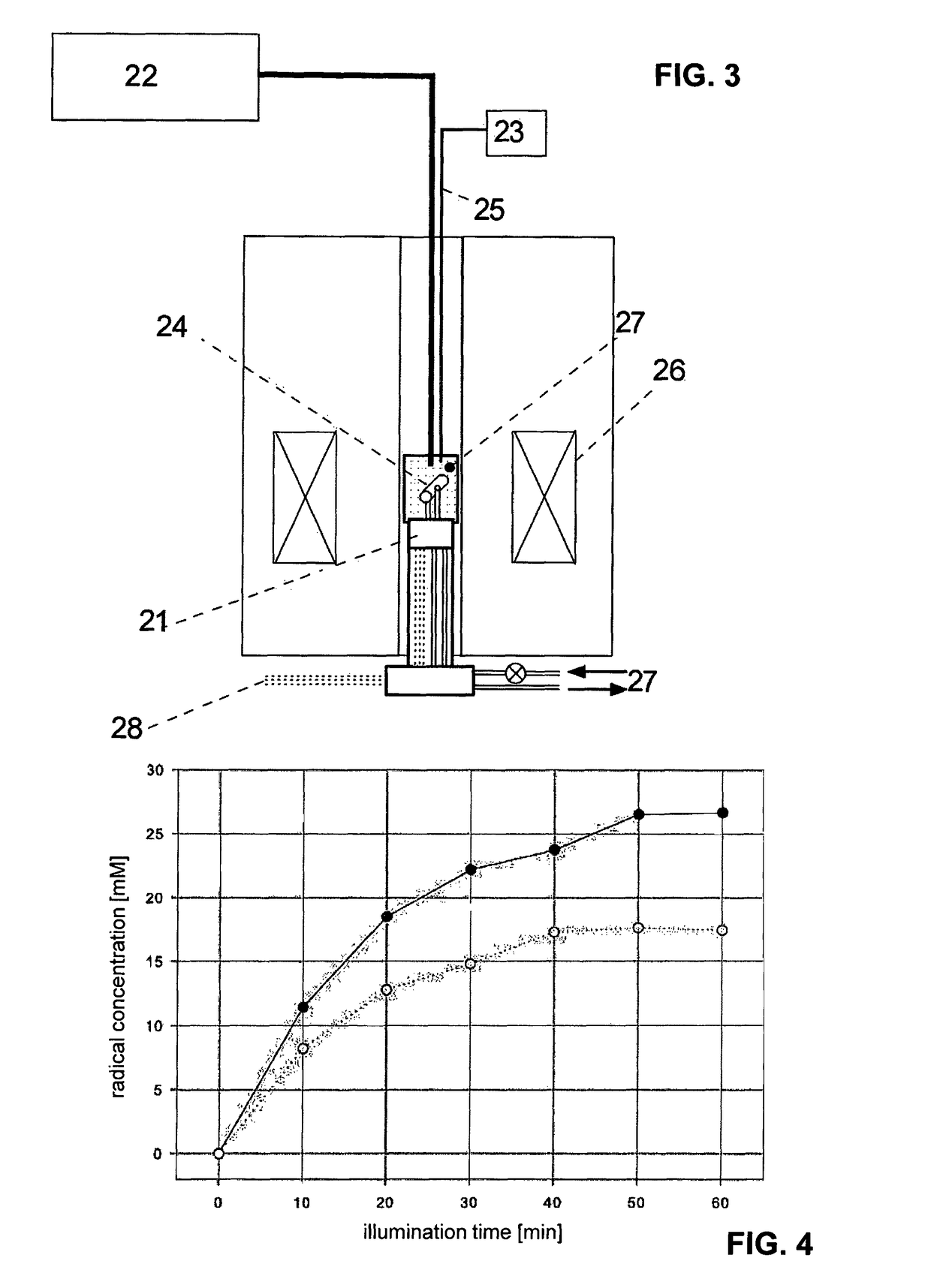
A method for the preparation of a sample comprising highly polarized nuclear spins is proposed, comprising at least the following steps:a) provision of molecules with 1,2-dione structural units and / or molecules with 2,5-diene-1,4-dione structural units in the solid state;b) generation of radicals from these molecules by photo induced electron transfer by a first electromagnetic irradiation in the visible or ultraviolet frequency range in the solid state;c) dynamic nuclear polarization in the presence of a magnetic field in the solid state by applying a second electromagnetic irradiation with a frequency adapted to transfer spin polarization from the electrons to the nuclear spins leading to a highly polarized state thereof. Furthermore uses of correspondingly prepared samples for NMR, MRS and MRI experiments are proposed.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS20150008917A1Low costReduce complexityMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) NMR apparatus comprises (i) a cooling unit, configured to cool a sample in a capillary, (b) a DNP polarization unit configured to polarize the sample in the capillary, (c) a stripline-based NMR detector comprising a stripline for NMR analysis of the sample in the capillary, (d) a transport unit configured to guide the capillary from the DNP polarization unit to the stripline of stripline-based NMR detector; and (e) a heating unit configured to heat the sample in the capillary before analysis of the sample by the stripline-based NMR detector. Fast (1D-3D) NMR measurements with high resolution may be obtained.
Owner:STICHTING KATHOLIEKE UNIV
Imaging agents and methods of use thereof
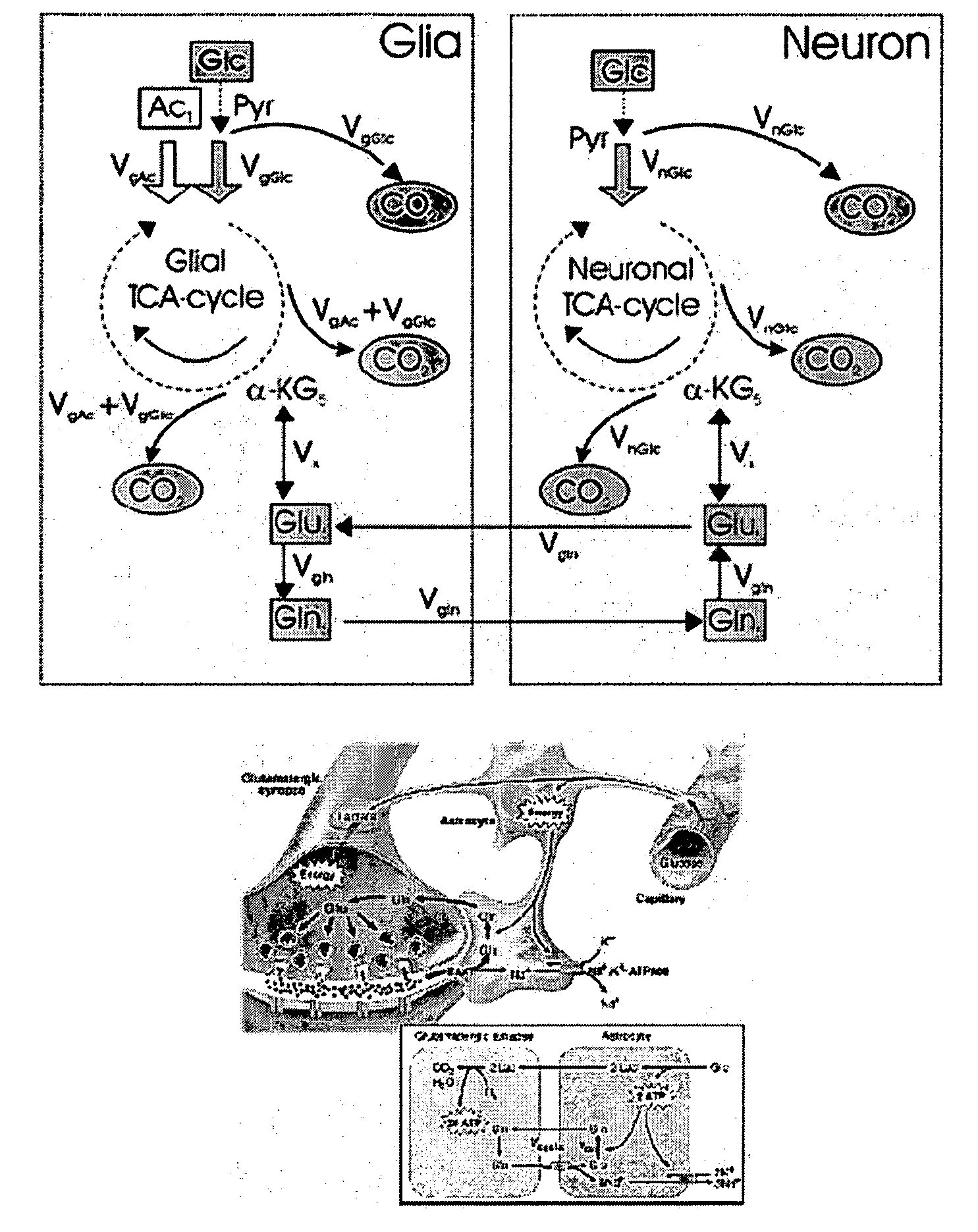
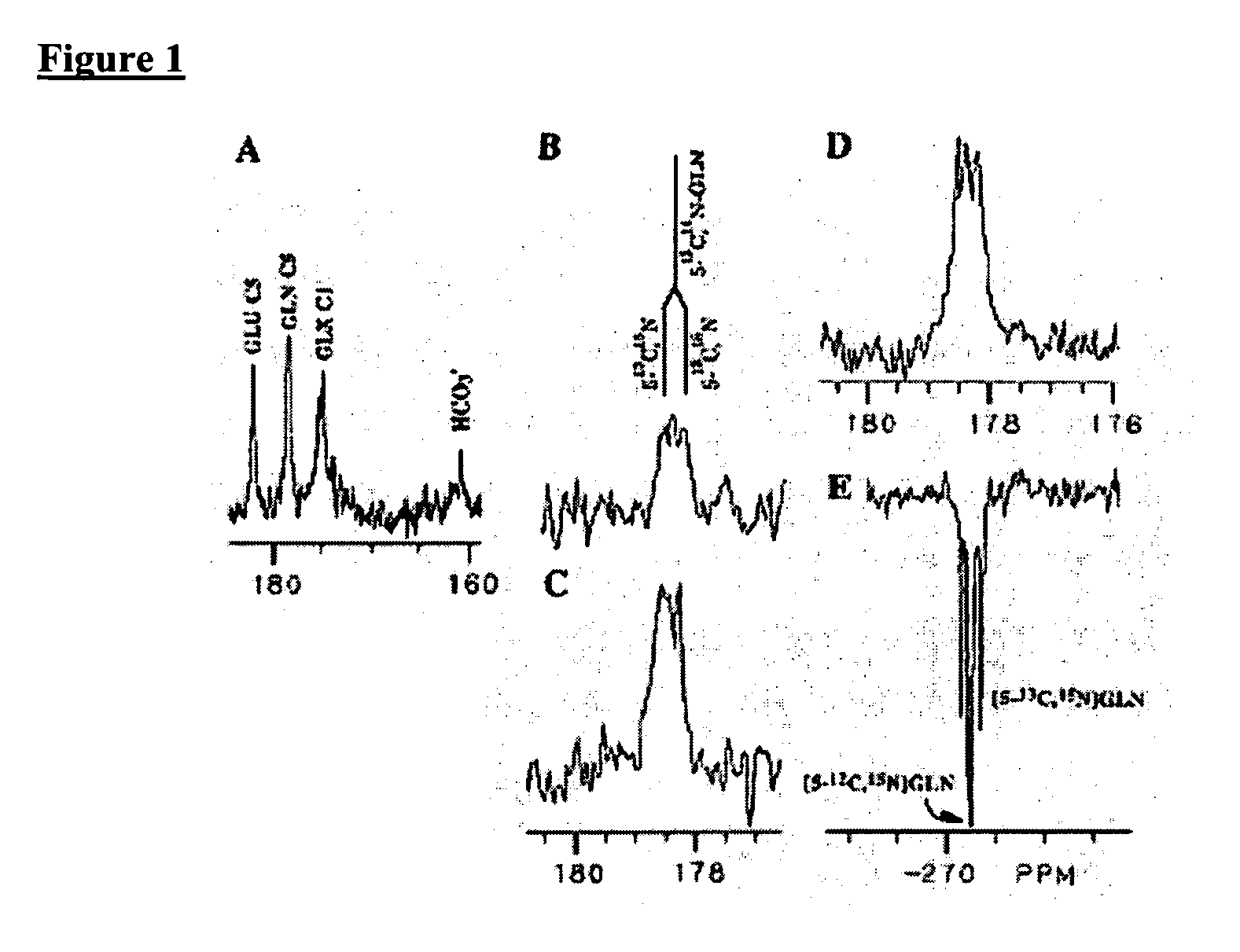
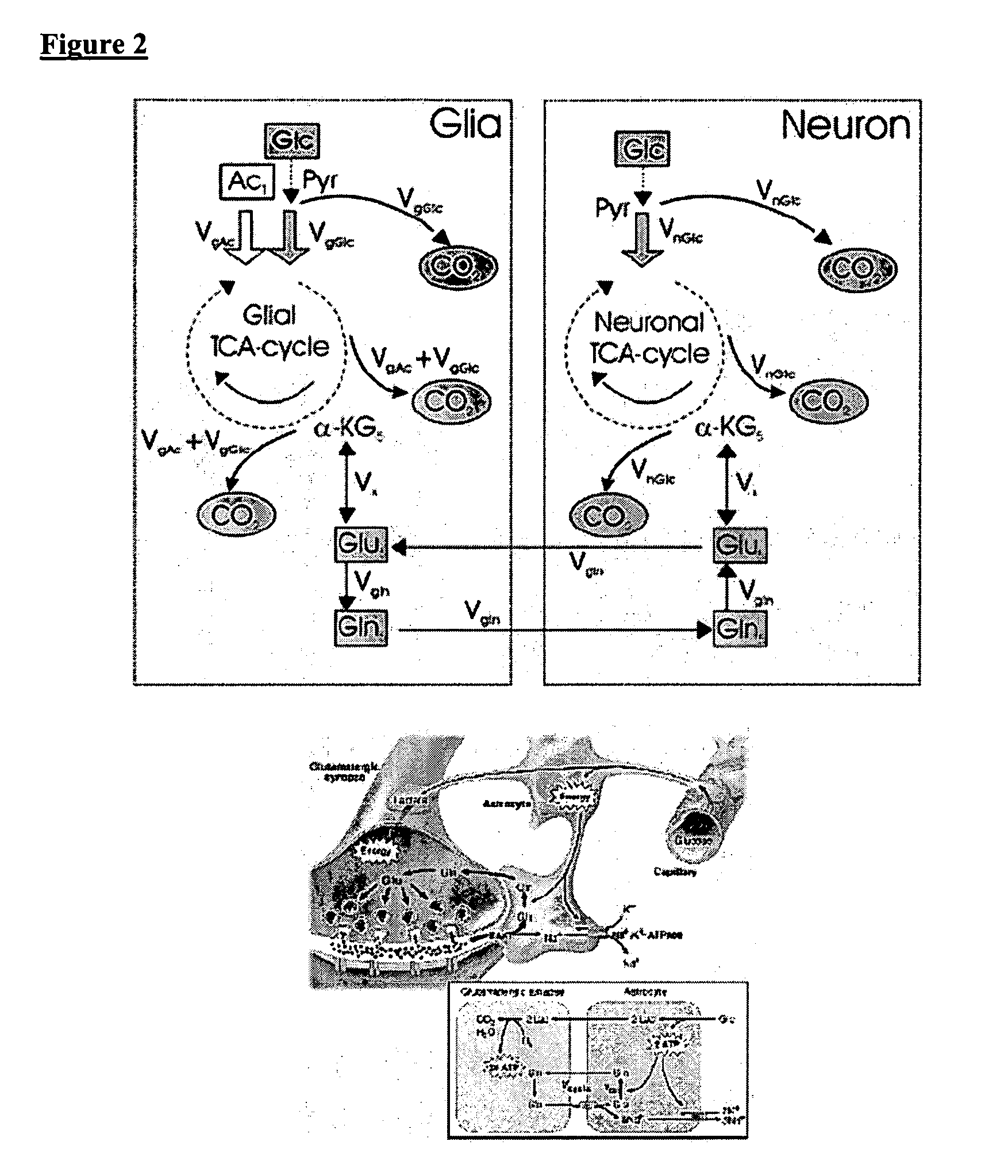
Compositions and methods useful in connection with magnetic resonance imaging are provided. Metabolites hyperpolarized by dynamic nuclear polarization are used as reporter molecules in nuclear magnetic resonance (“NMR”) spectroscopy to study metabolic pathways and diagnose disease states. The reporter molecules include hyperpolarized glutamine and hyperpolarized acetate. The invention includes the reporter molecules, compositions including the reporter molecules in pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, methods for studying metabolic pathways that include introducing one or more of the reporter molecules to a mammalian subject and imaging a target substance using NMR spectroscopy, and kits useful in studying metabolic pathways that incorporate one or more of the reporter molecules and instructions for their use.
Owner:HUNTINGTON MEDICAL RES INST
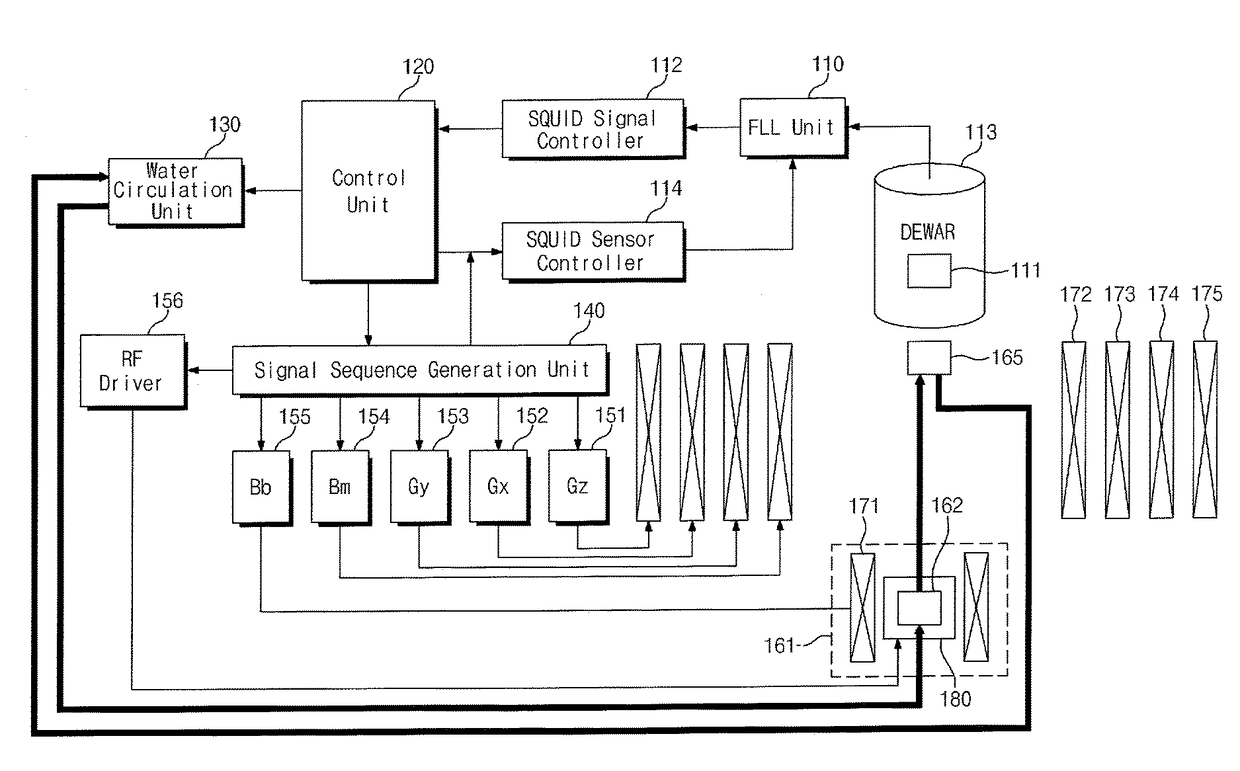
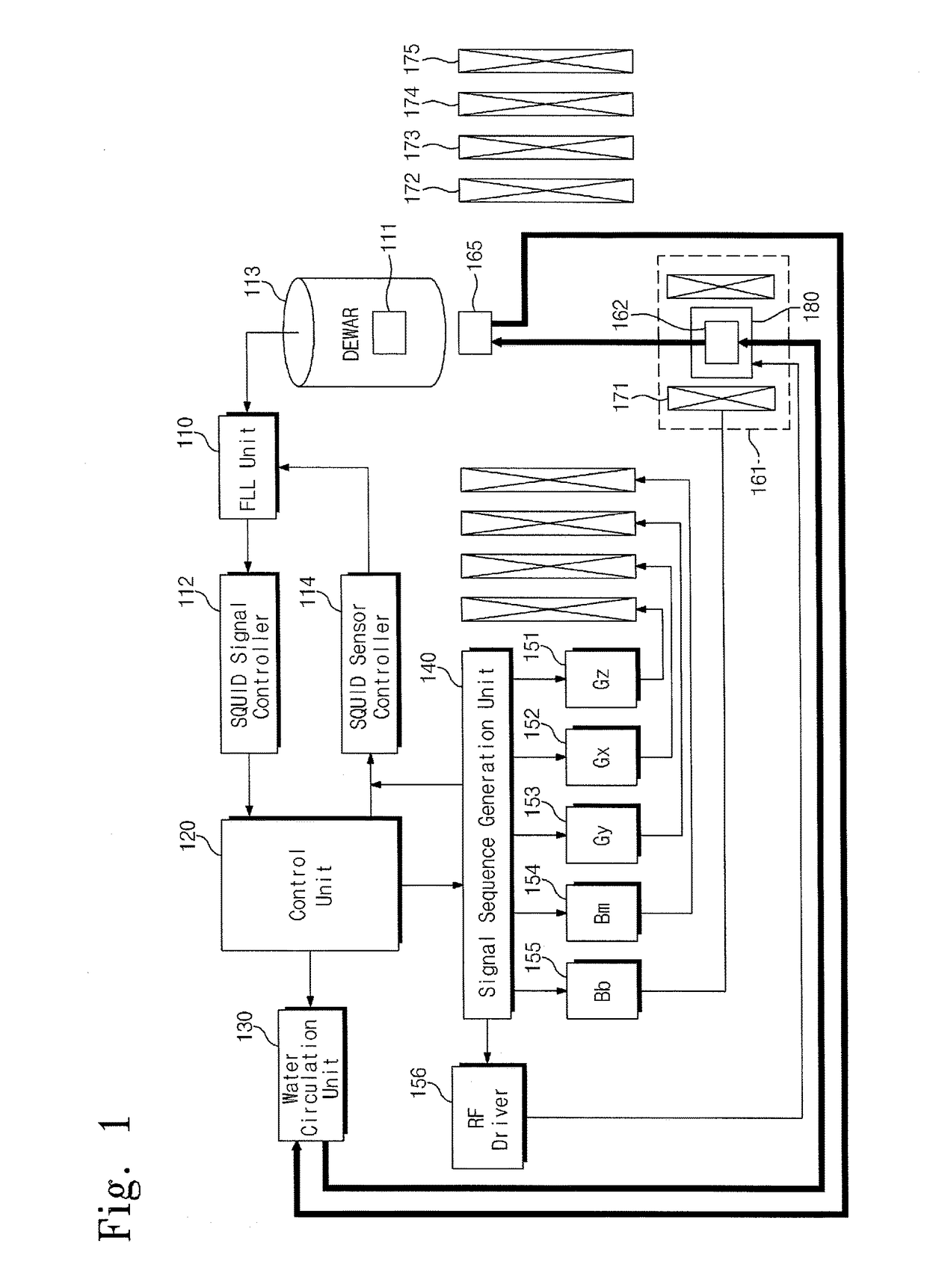
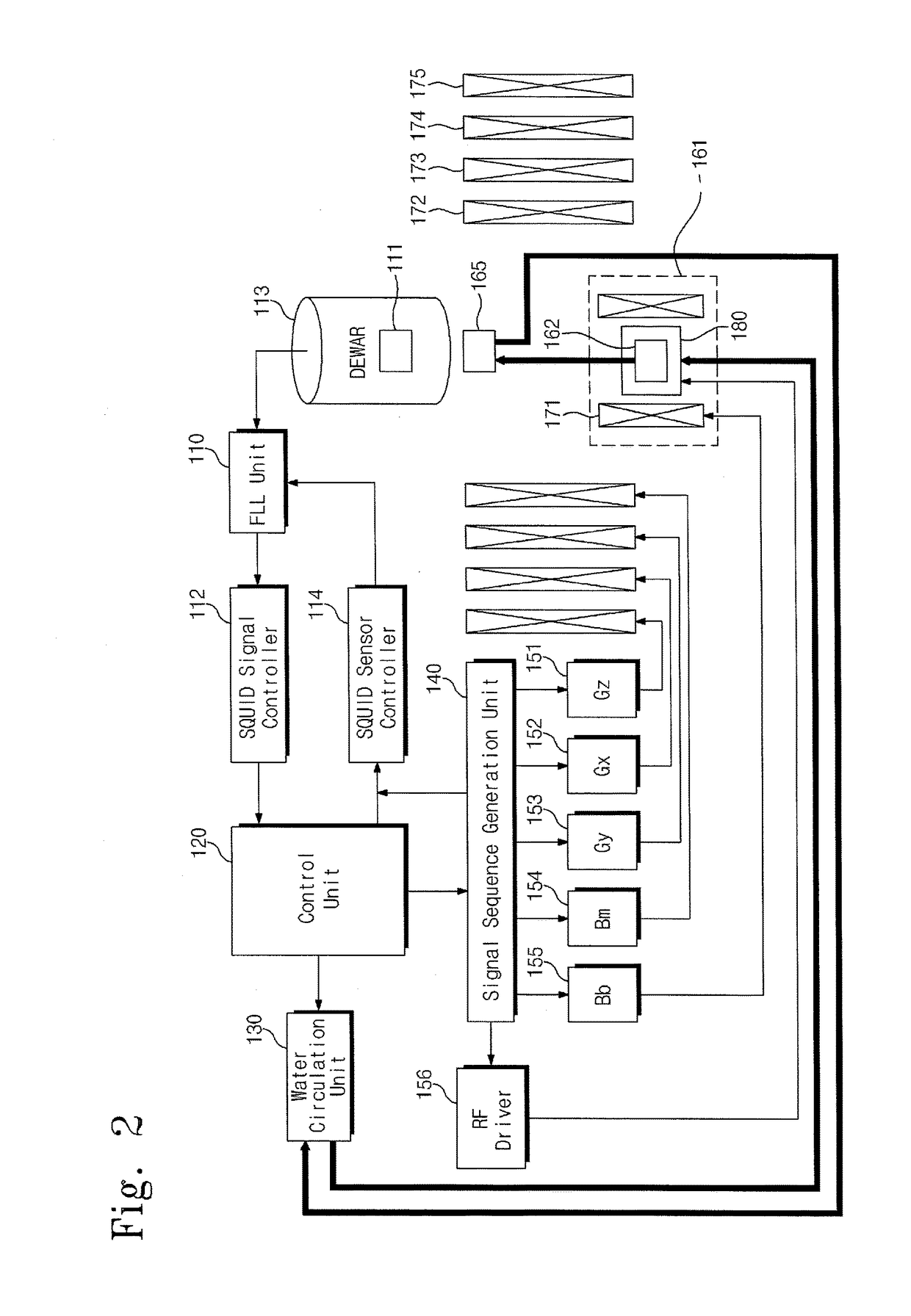
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance method
ActiveUS20130278265A1Measurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringWater useHydrogen atom
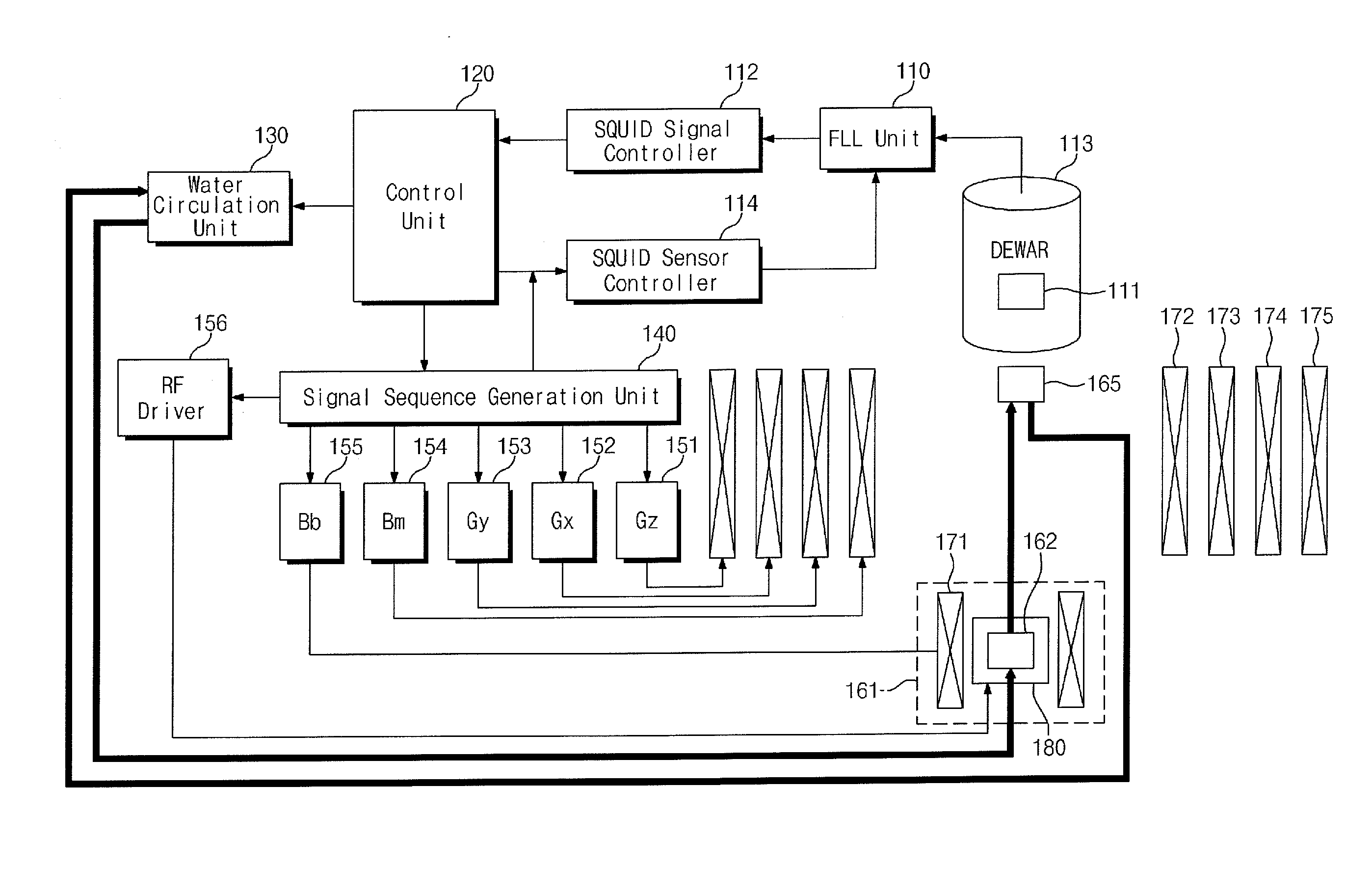
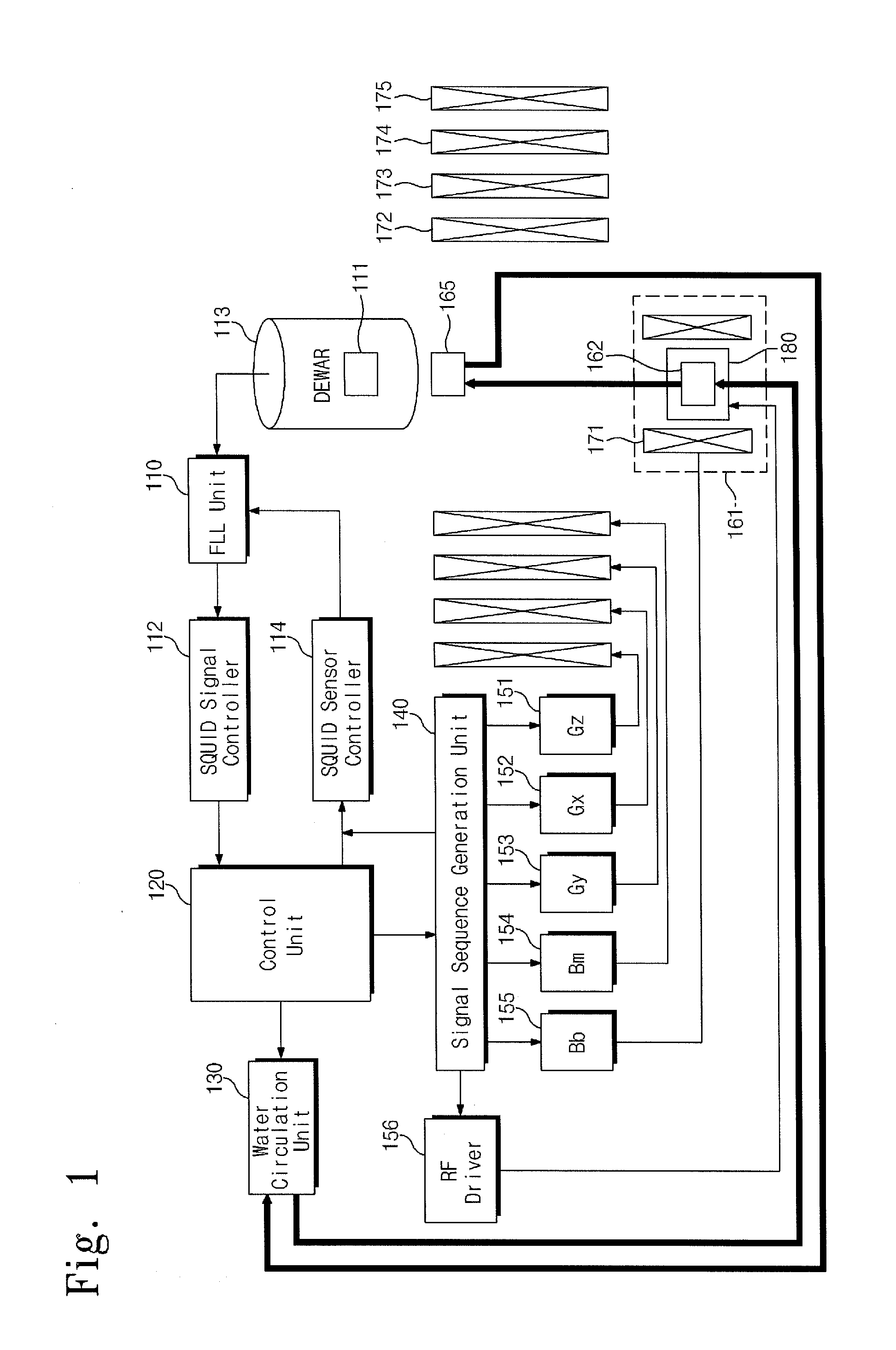
Provided are a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device and a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance method. The low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device includes a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) amplification unit to amplify the nuclear polarization of hydrogen atoms of water using a DNP-possible substance (DNP substance) to provide the amplified nuclear polarization to a measurement target, a sensor unit to measure a magnetic resonance signal of the measurement target using a SQUID sensor or an optically-pumped atomic magnetometer, and a measurement field coil to apply a measurement field to the measurement target. The DNP amplification unit is separated from the measurement target, the sensor unit, and the measurement field coil.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Parallel magnetic resonance method based on dynamical nuclear polarization multinuclear simultaneous enhancement
ActiveCN105717153AEnhanced signalGet mutual relationshipAnalysis using double resonanceProton NMRMulti dimensional
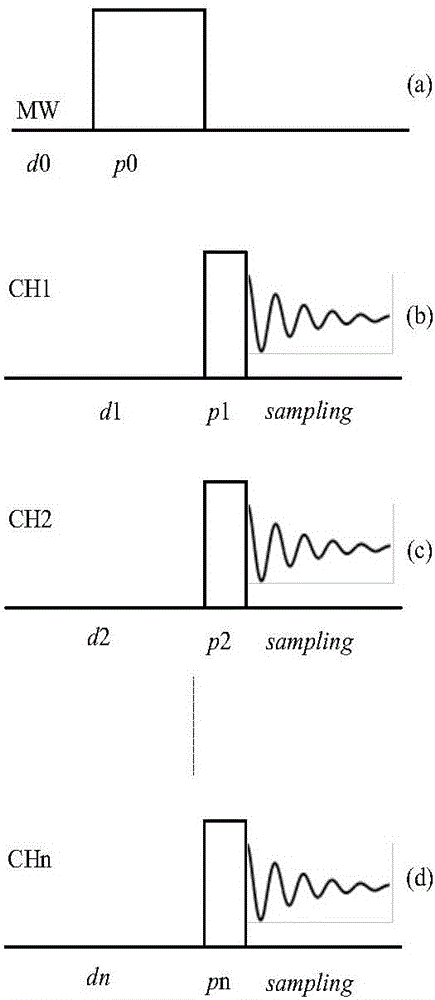
The invention discloses a parallel magnetic resonance method based on dynamical nuclear polarization multinuclear simultaneous enhancement. An electronic-nuclear spin system is located in a magnetic field with the strength of B0; the electronic-nuclear spin system is irradiated through microwaves; microwave irradiation is stopped; nuclear magnetic resonance pulses are applied; enhancement signals of atomic nucleuses corresponding to all channels are collected; enhancement spectrograms or images are reestablished and obtained. Under the condition of saturated electrons, signal enhancement of multiple atomic nucleuses can be obtained at the same time. The mutual relation between different atomic nucleuses and electrons and the mutual relation between the atomic nucleuses can be obtained at the same time. Under the condition of a single saturated electron, enhancement images of different atomic nucleuses can be obtained at the same time, and the two-dimensional and multi-dimensional spectrograms of different atomic nucleuses can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance of water under ambient conditions
InactiveUS7906962B2Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingMeasurements using double resonanceDrug compositionsProton NMRRadio frequency
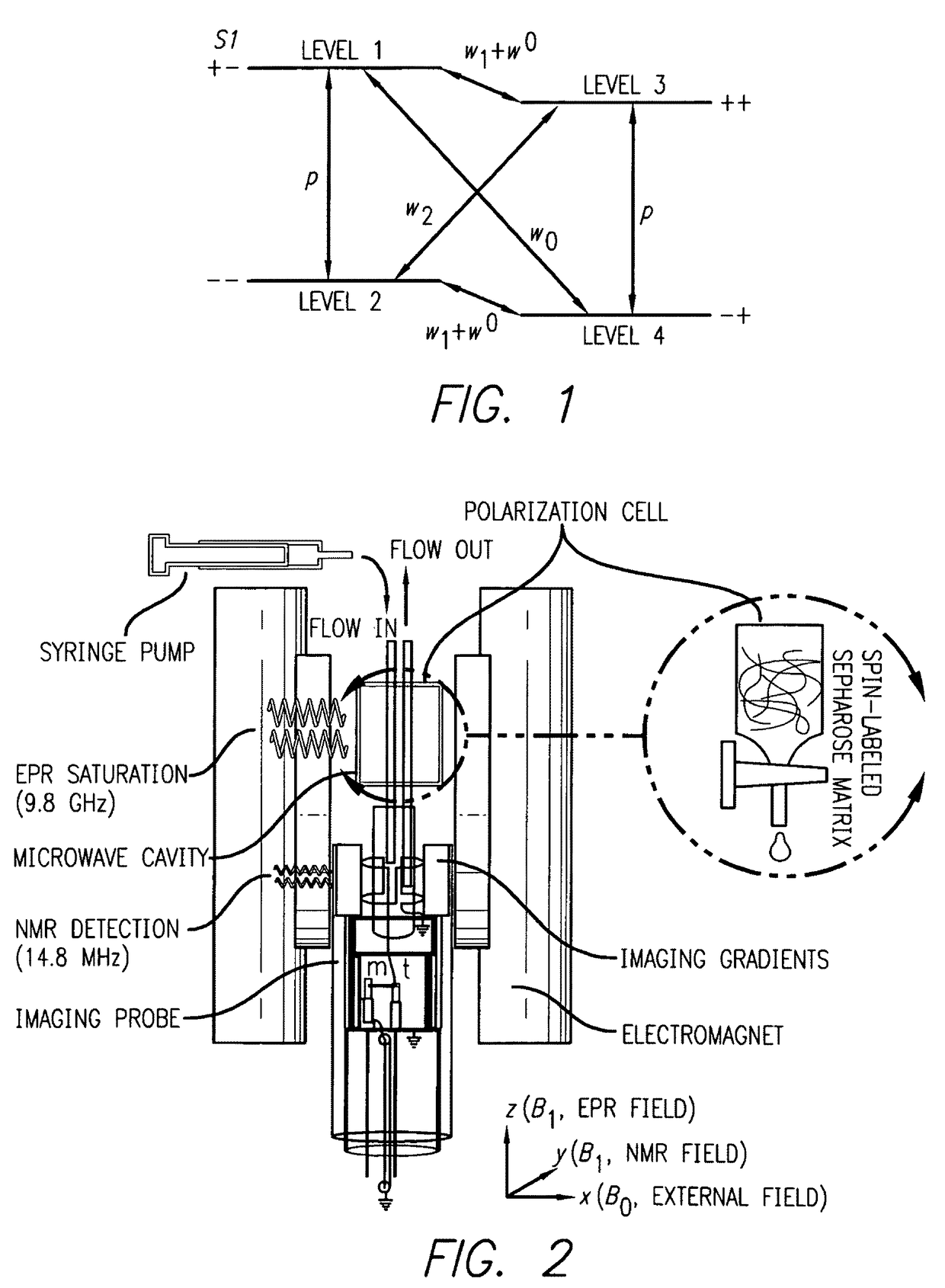
A method and apparatus are provided for treating hydrated material in a fluid that contains water in which a stable nitroxide is attached to the hydrated material. A dynamic nuclear polarization process (DNP) is conducted on the hydrated material whereby to hyperpolarize the water. A polarization cell contains the hydrated material to obtain hyperpolarized water free from the nitroxide. The dynamic nuclear polarization process is conducted using components comprising a tunable, solid state high power X-band driver and an X-band resonator for microwave transmission to the hydrated material. The components can also include a radio-frequency nuclear magnetic resonance probe, a permanent magnet formed to receive the hydrated material, a portable nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and an electron spin resonance detector. The components can be sized to be portable, and include electrical input and output and a lap-size hard-case with access to the electrical input and output.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Porous and structured materials for dynamic nuclear polarization, process for their preparation and NMR analysis method
InactiveCN104520727AMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMagnetic variable regulationRegular distributionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention concerns materials consisting in a porous and structured network, this network being at least in part formed by Si atoms, or Si atoms and metal atoms, linked to each other's via siloxy bonds, the amount of radical ranging from 0.50 to 0.03 mmol of radical per gram of material, and in that the network is formed with a sol-gel step using an organosilane for the introduction of the organic molecules allowing their regular distribution within the porous structured material. The invention also concern a process for the preparation of such material and a method of analysis by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) of an analyte wherein it uses dynamic nuclear polarization generated with a material according to the invention.
Owner:UNIV CLAUDE BERNARD LYON 1 +2
Method of improving magnetic resonance sensitivity
InactiveUS20100201362A1High sensitivityIncrease heightMeasurements using double resonanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Dynamic nuclear polarisation
We describe a method for use in enhancing MRI signals and increasing the sensitivity of NMR spectroscopy. The method involves the use of dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) in which the polarizing agents are sequestered at the interface between two phases a sample phase, and a polarizing phase in such a way that the polarizing agent can be easily removed from the sample prior to analysis. The method produces much efficiency for sample manipulation, and the polarization process. In at least one embodiment the hyper-polarization can be repeated so as to allow the accumulation of spectra of the same material for further increasing the signal to noise ratio. The method also allows a discernment of which peaks in an NMR spectrum of a mixture belong to each individual component.
Owner:HOLMAN III BRUCE
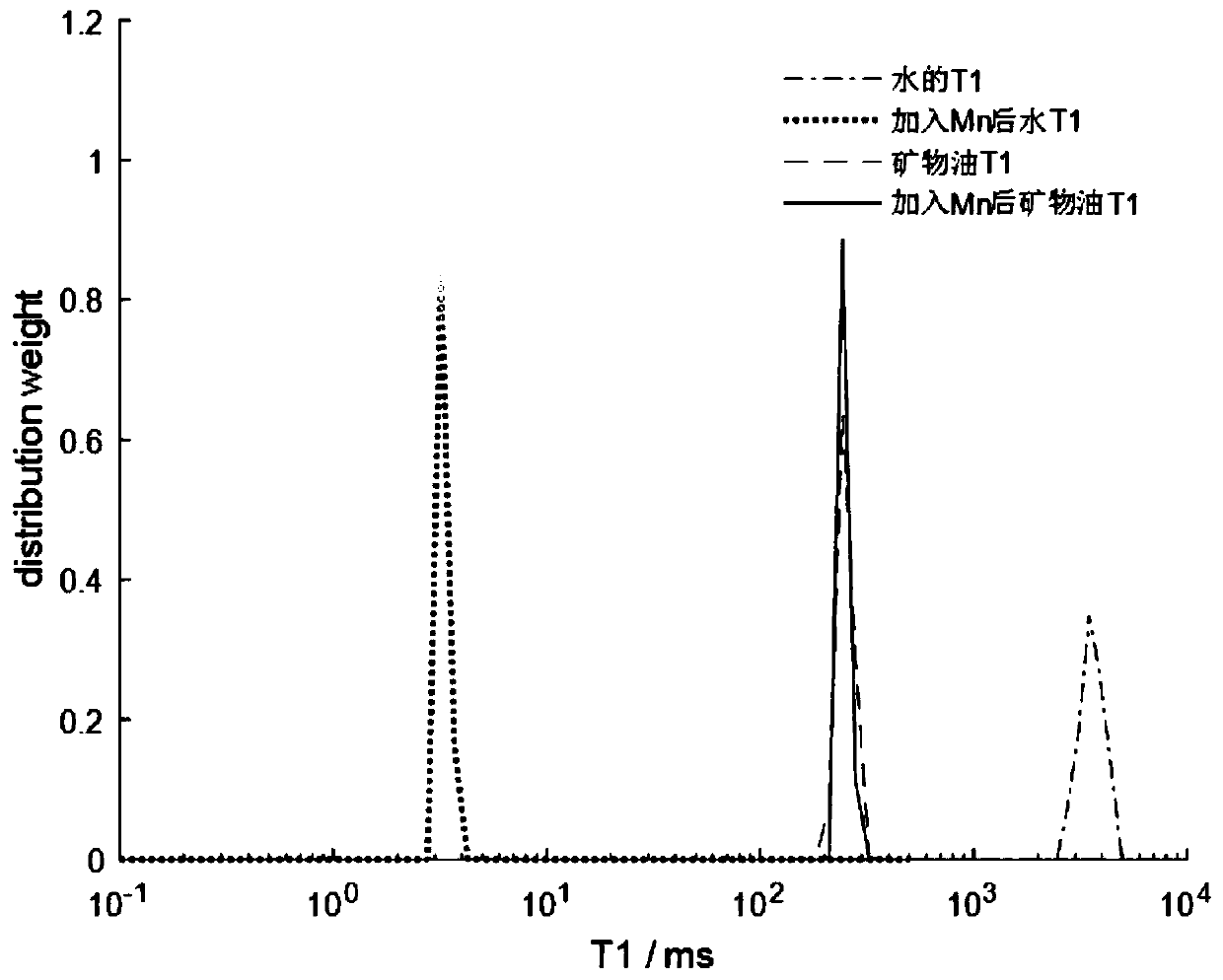
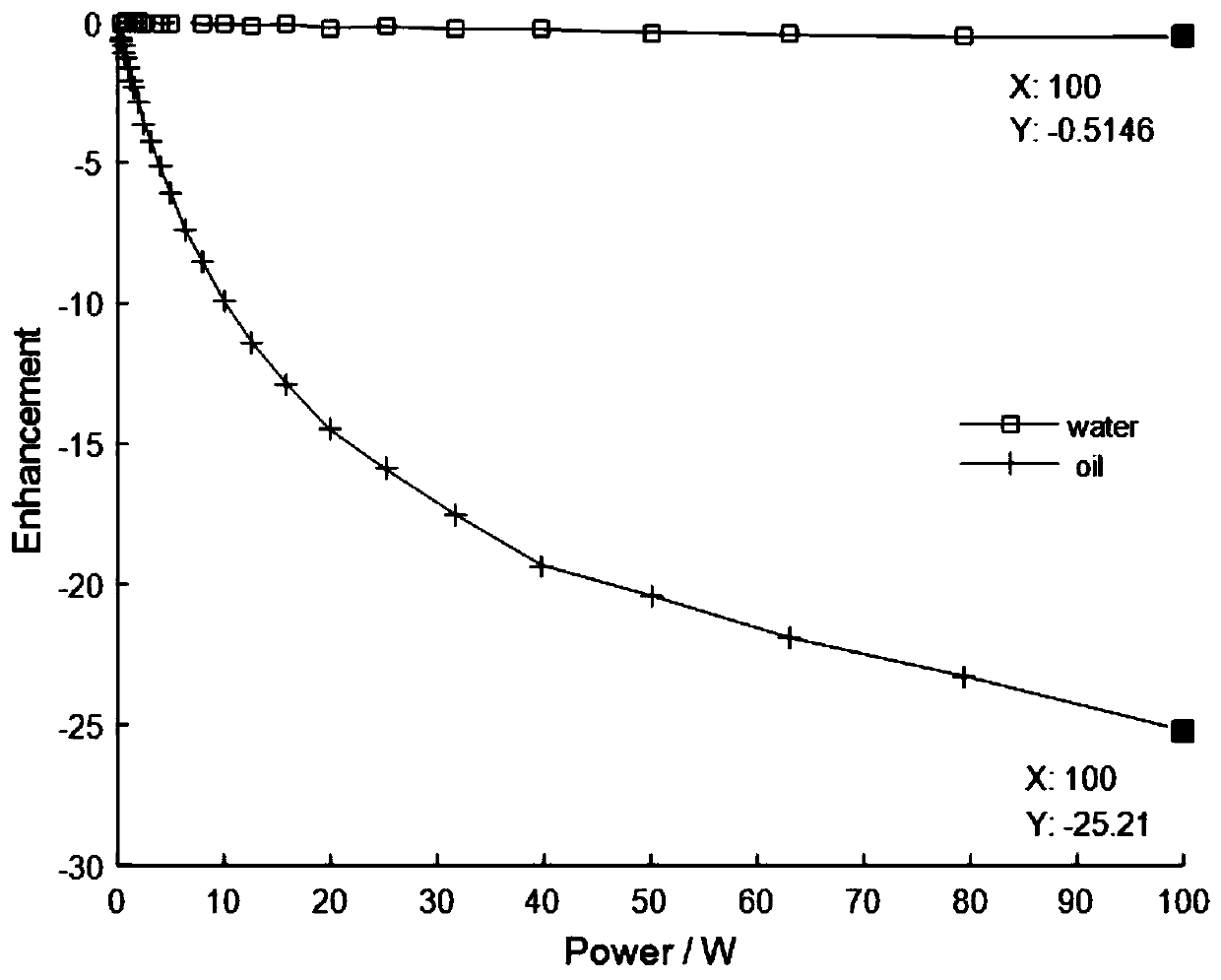
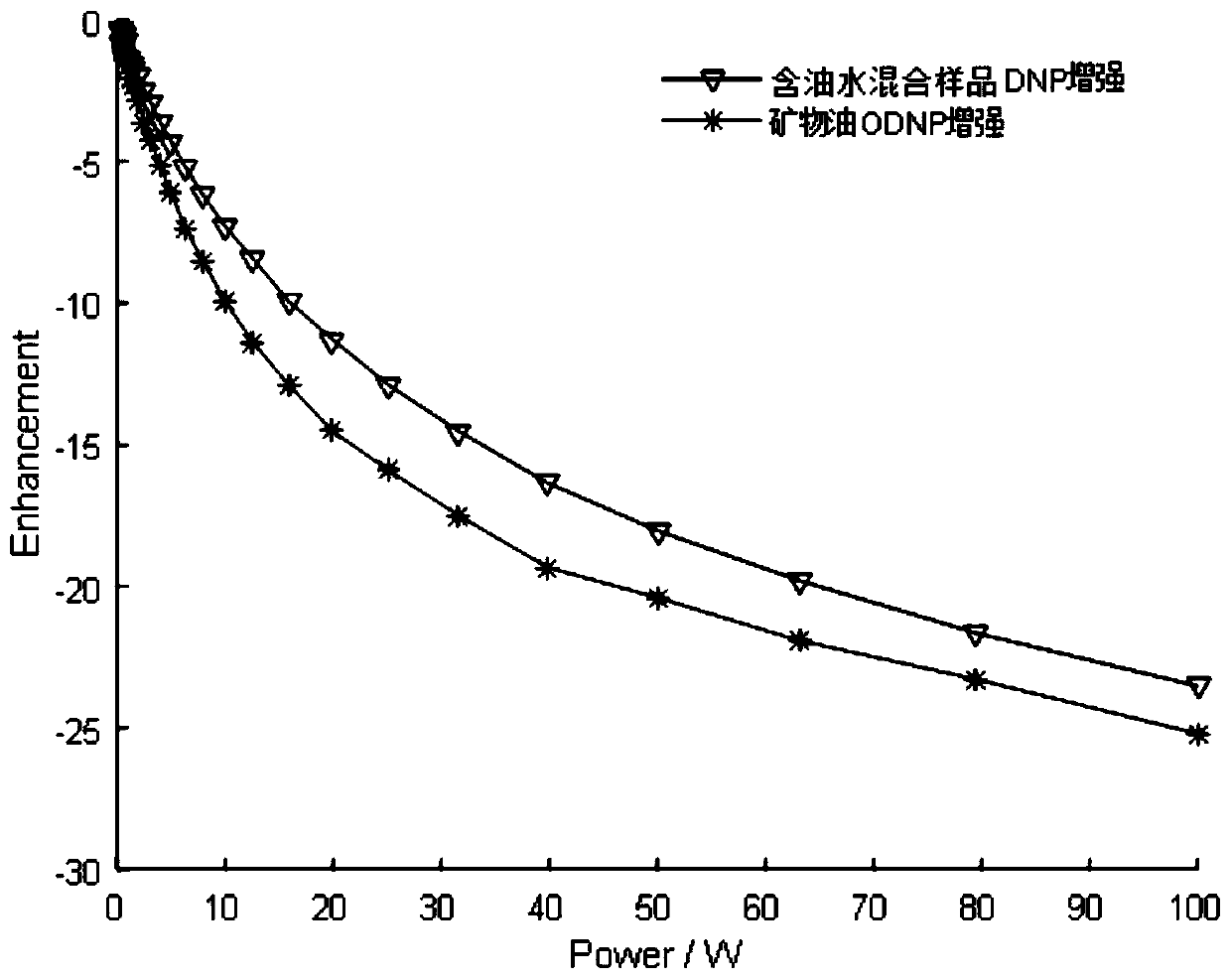
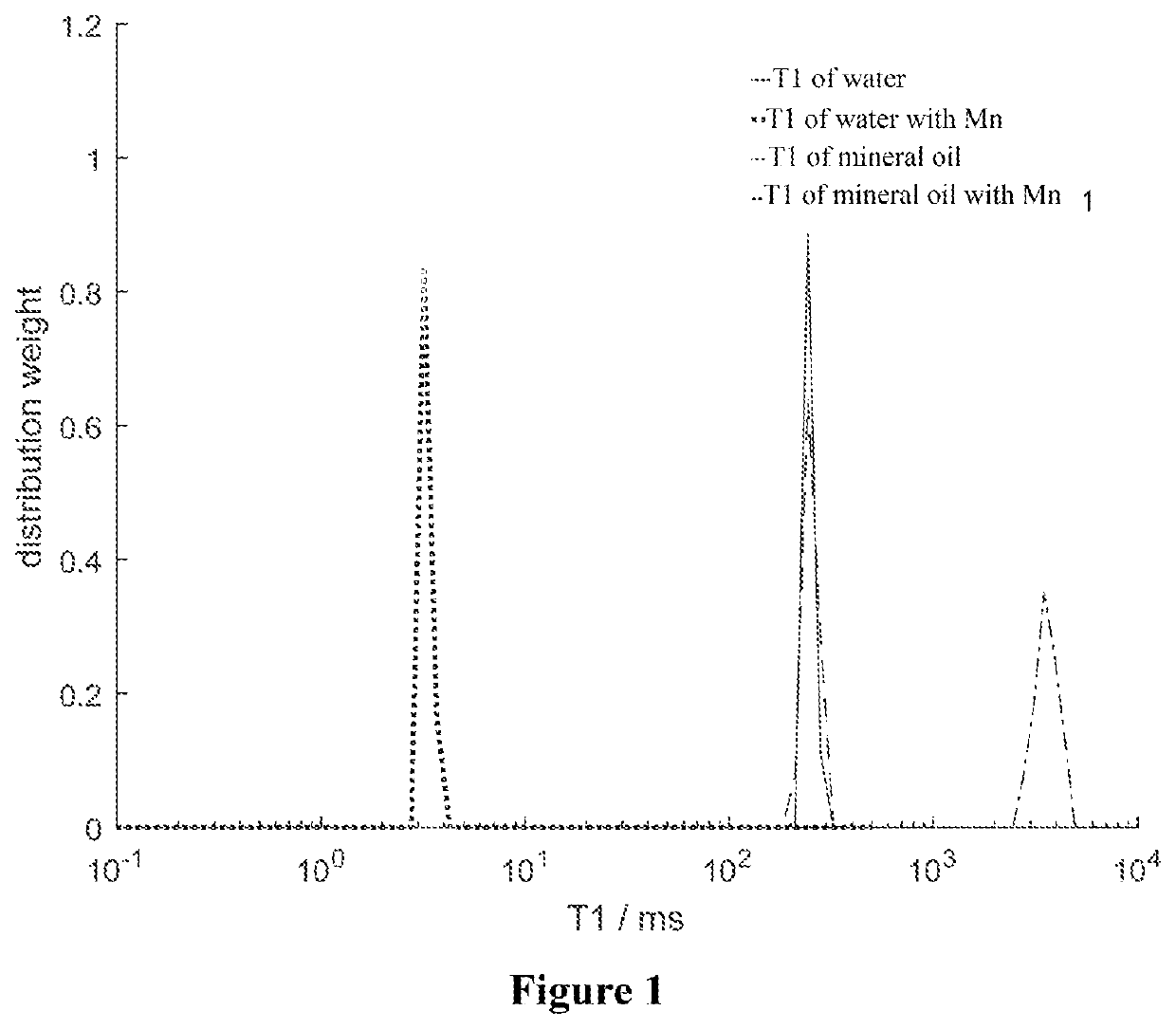
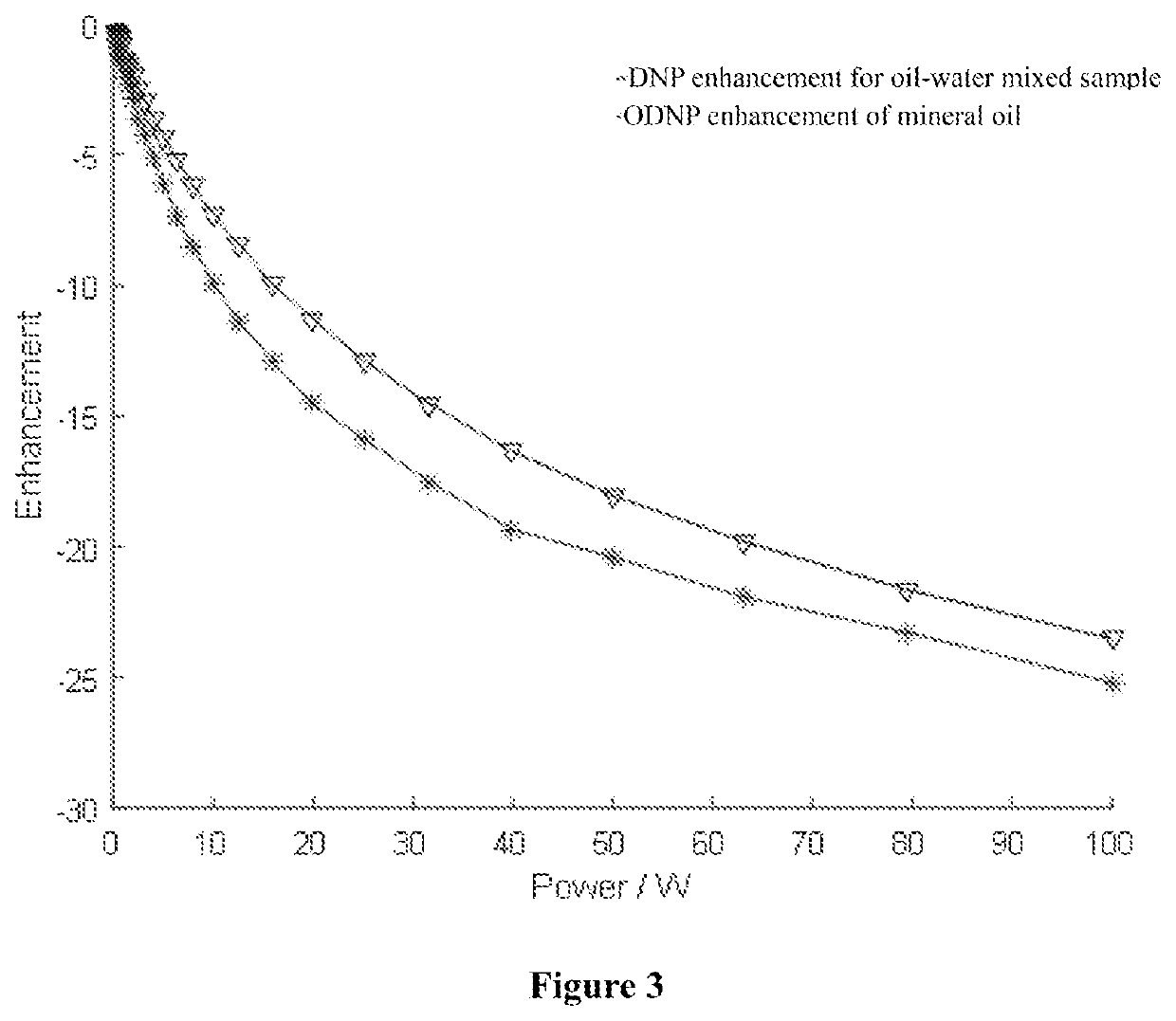
Method for separating oil-water two-phase NMR signal by utilizing dynamic nuclear polarization
InactiveCN110082382AEnhanced relaxationAchieve separationPreparing sample for investigationMeasurements using double resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
The invention discloses a method for separating an oil-water two-phase NMR signal by utilizing dynamic nuclear polarization, which specifically comprises the following steps: adding a free radical forenhancing an aqueous phase or an oil phase NMR signal into a to-be-detected sample containing oil and water, and then carrying out dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance analysis detection to obtain the aqueous phase or oil phase NMR signal. The method is simple and easy to operate, short in testing time and capable of efficiently separating oil-water two-phase NMR signals.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance method
ActiveUS9903925B2Measurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringWater useHydrogen atom
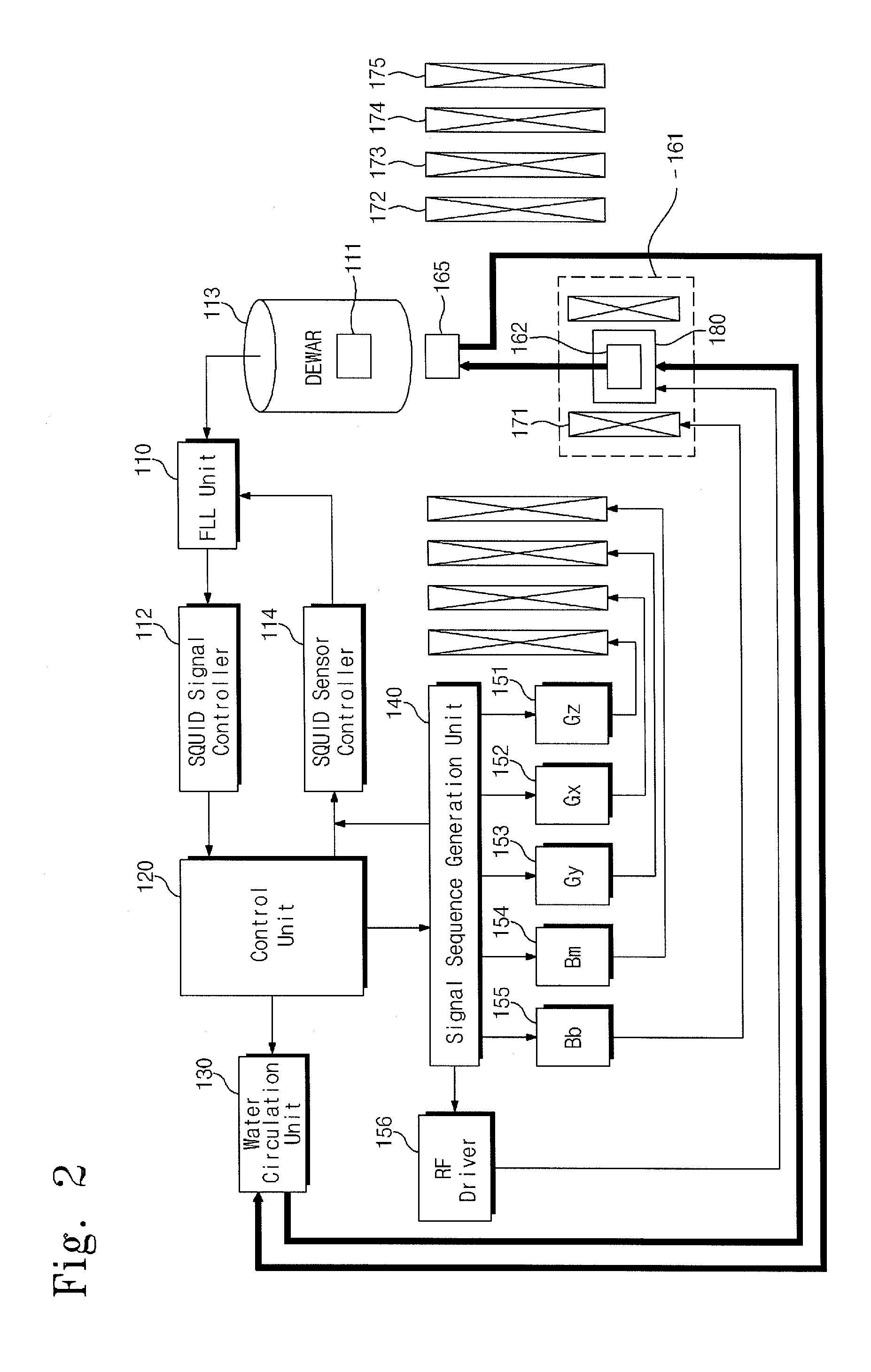
Provided are a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device and a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance method. The low-field nuclear magnetic resonance device includes a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) amplification unit to amplify the nuclear polarization of hydrogen atoms of water using a DNP-possible substance (DNP substance) to provide the amplified nuclear polarization to a measurement target, a sensor unit to measure a magnetic resonance signal of the measurement target using a SQUID sensor or an optically-pumped atomic magnetometer, and a measurement field coil to apply a measurement field to the measurement target. The DNP amplification unit is separated from the measurement target, the sensor unit, and the measurement field coil.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
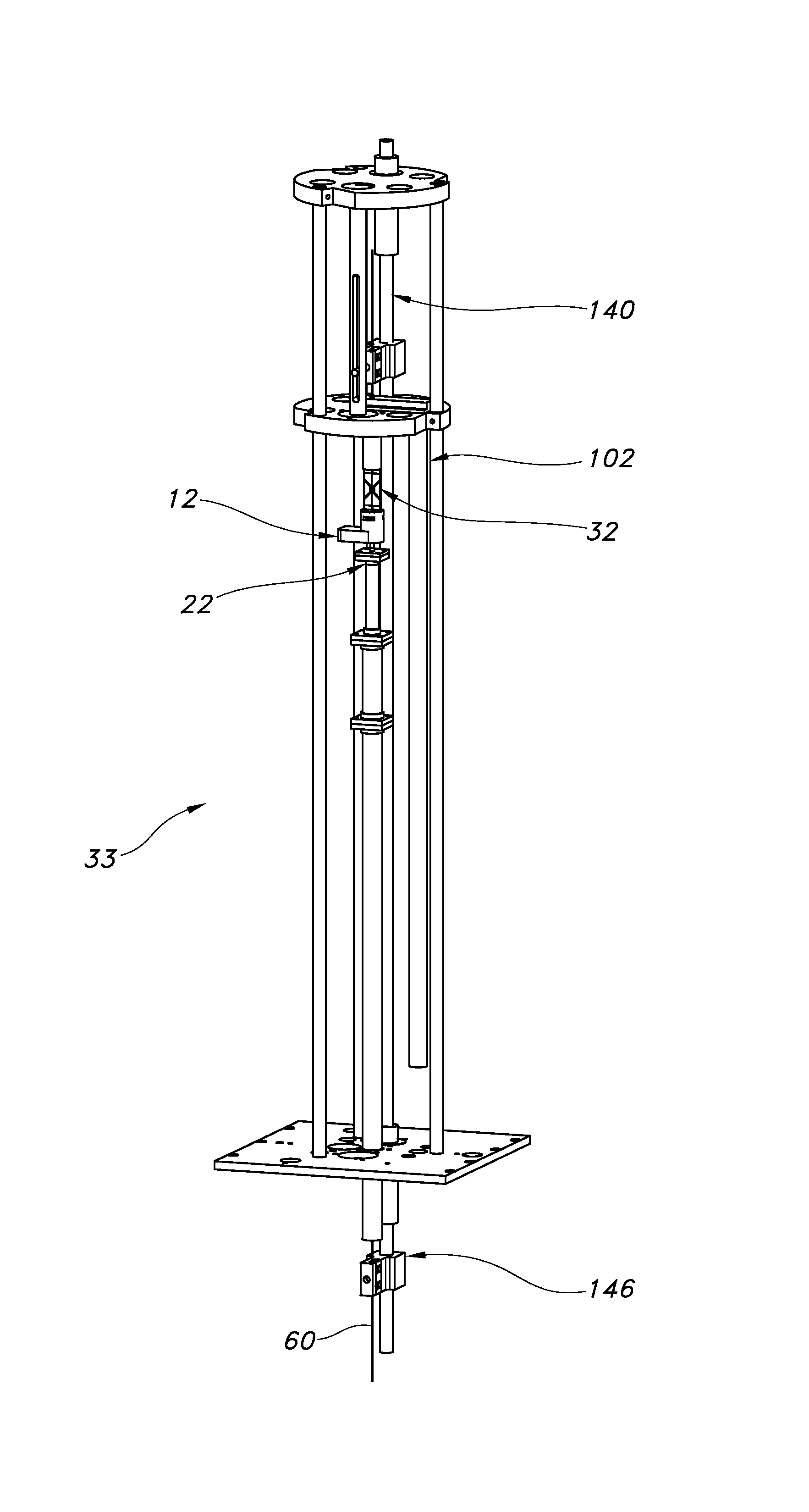
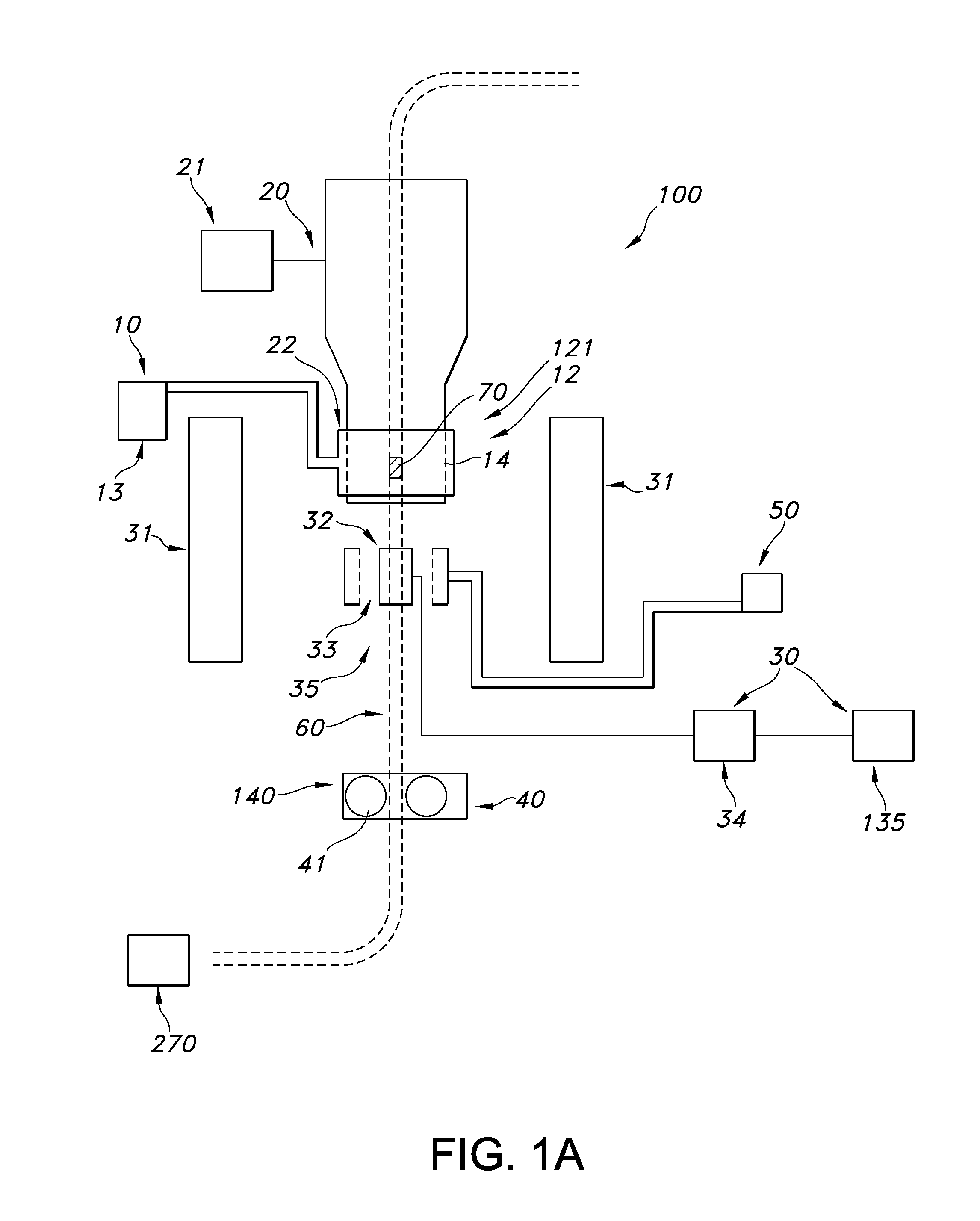
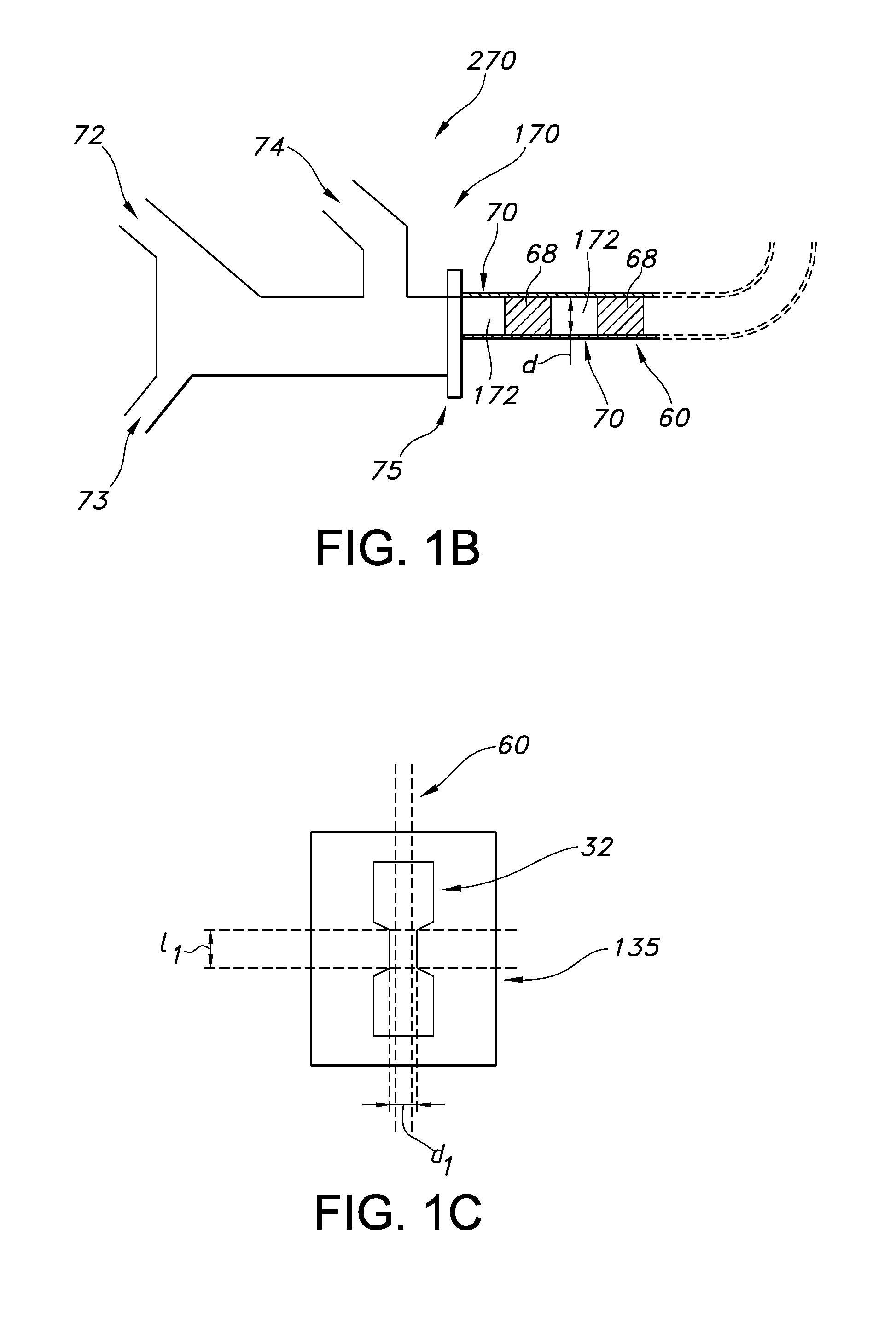
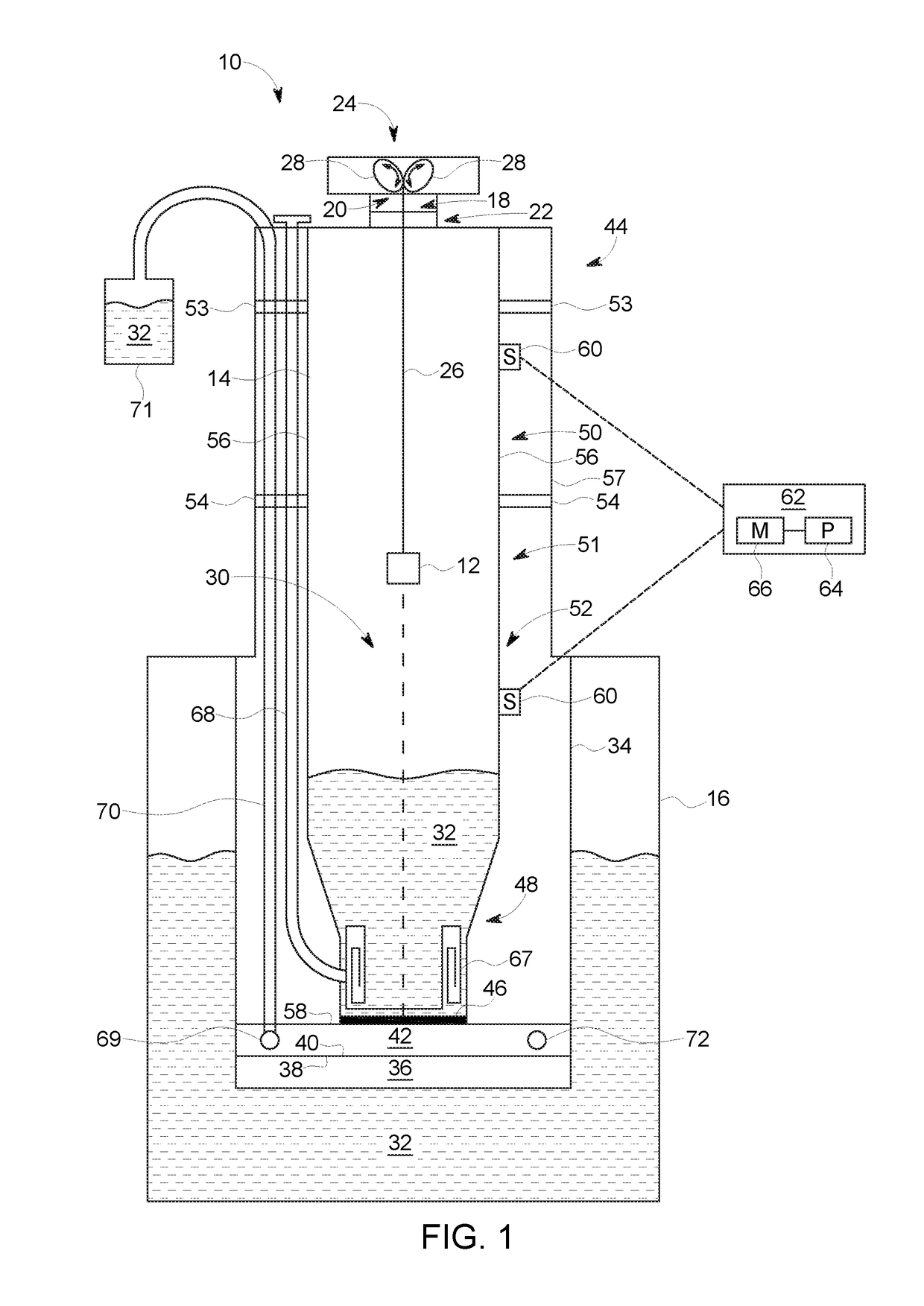
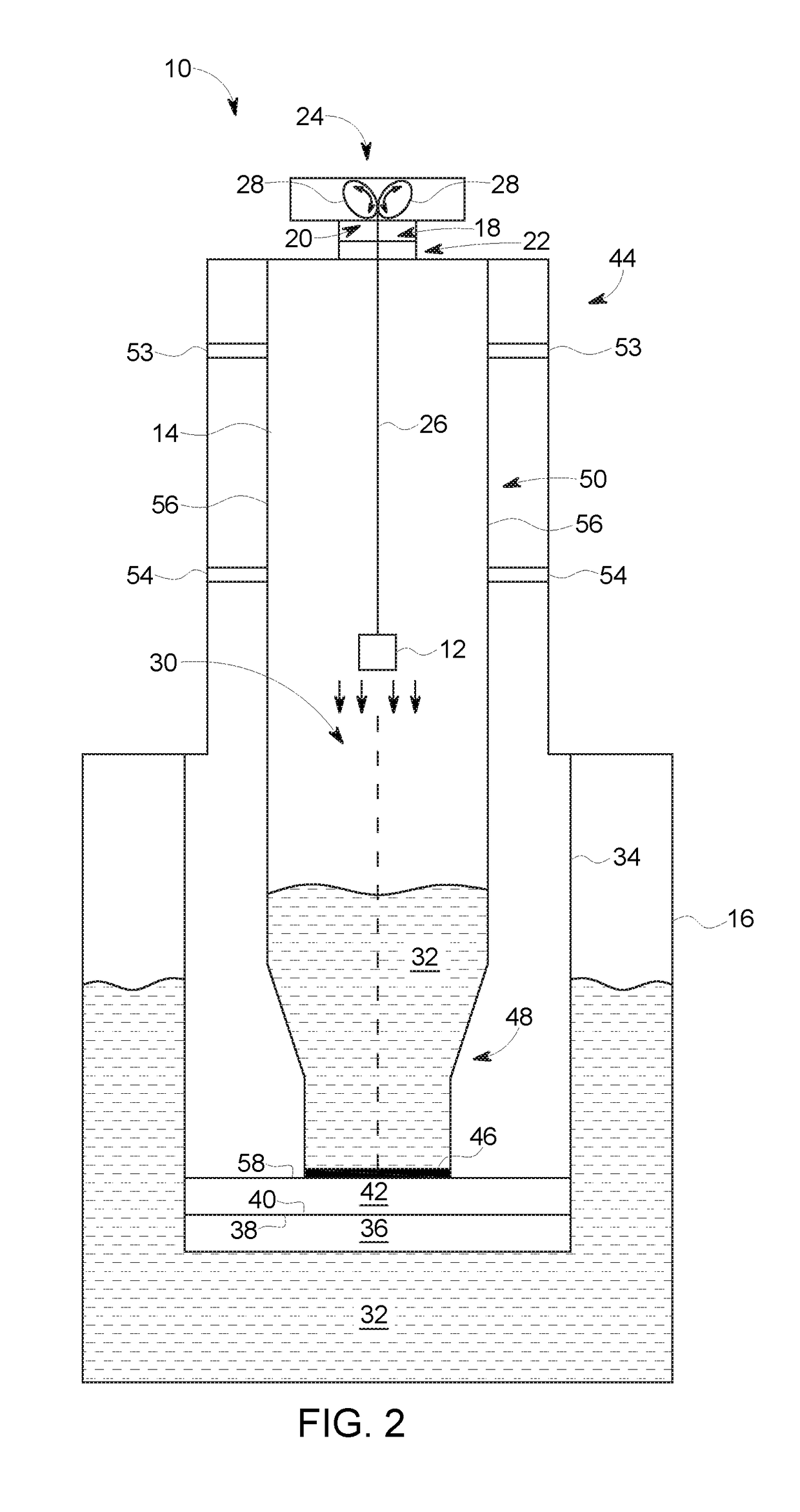
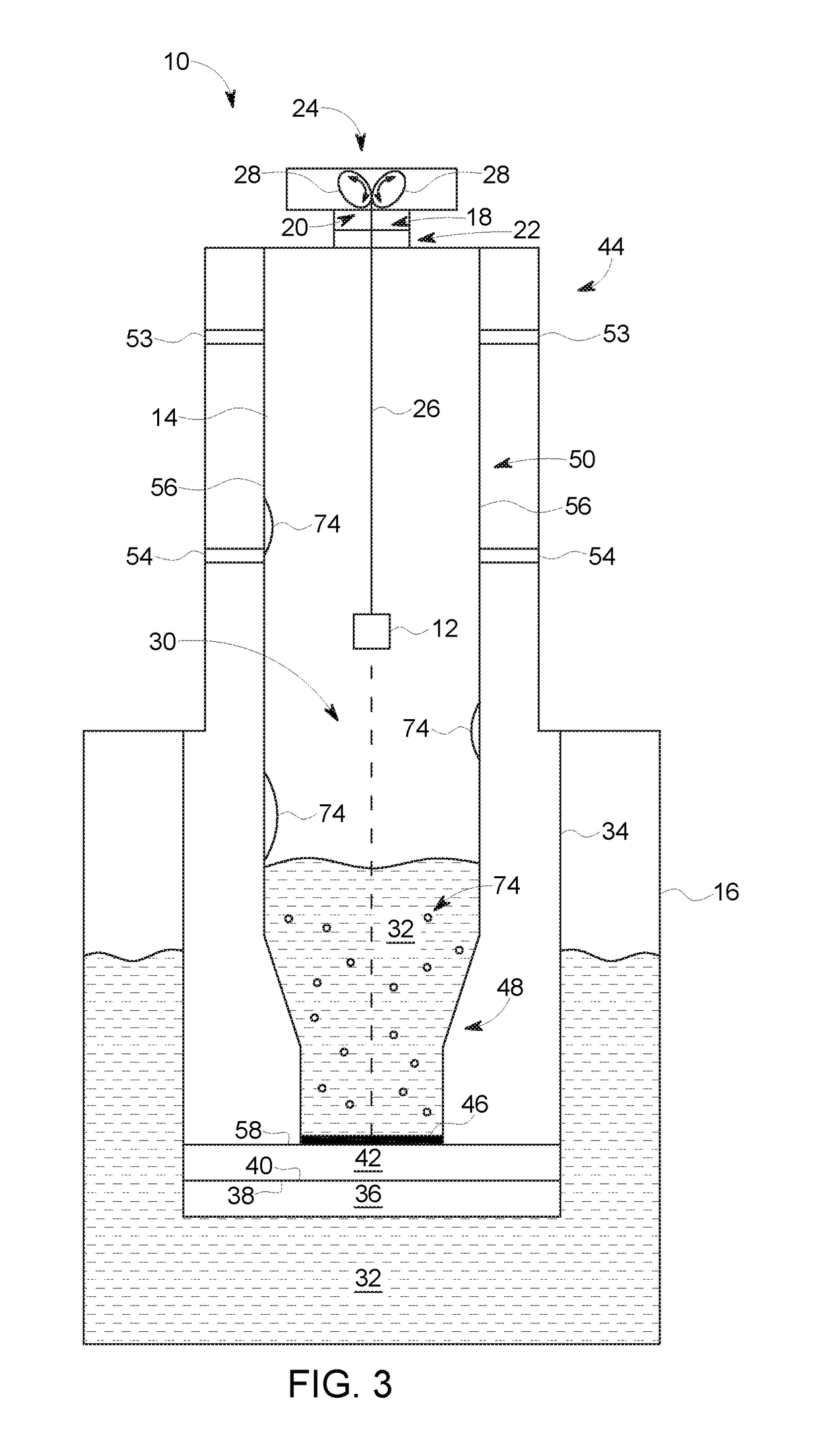
Dynamic nuclear polarization apparatus with sample transport system
InactiveUS20120256630A1Fast and reliableQuality improvementMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionTransport systemDynamic nuclear polarisation
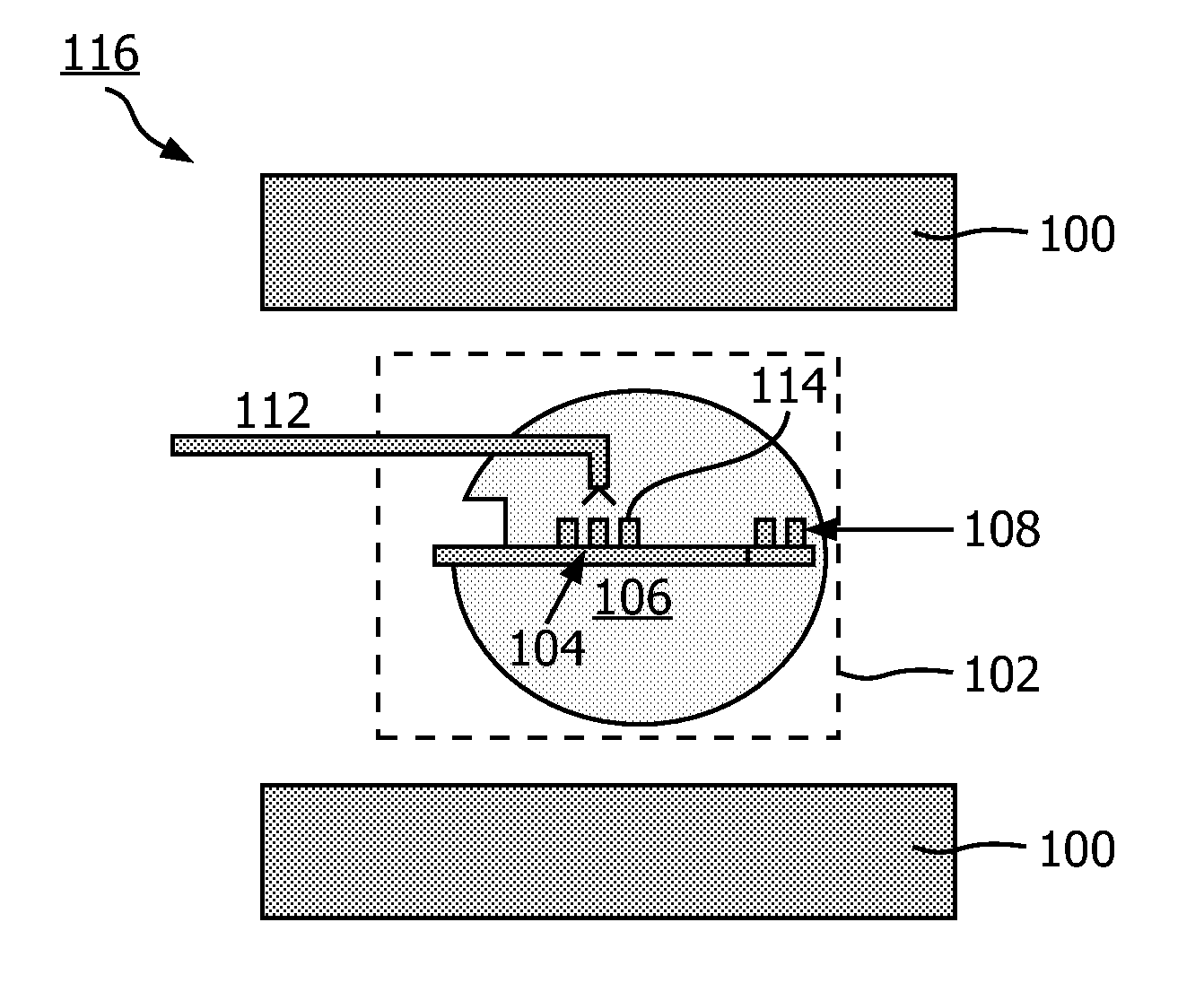
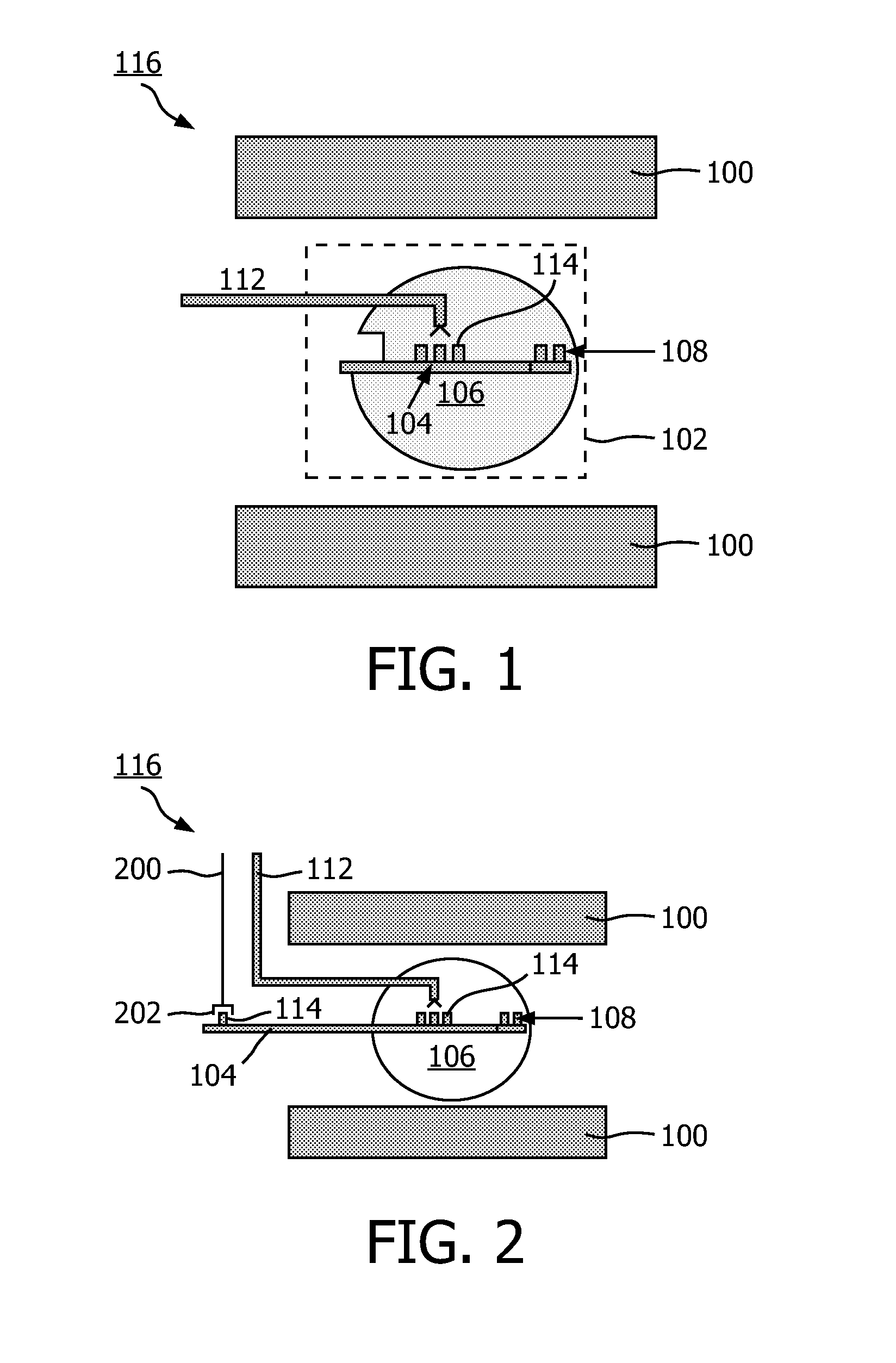
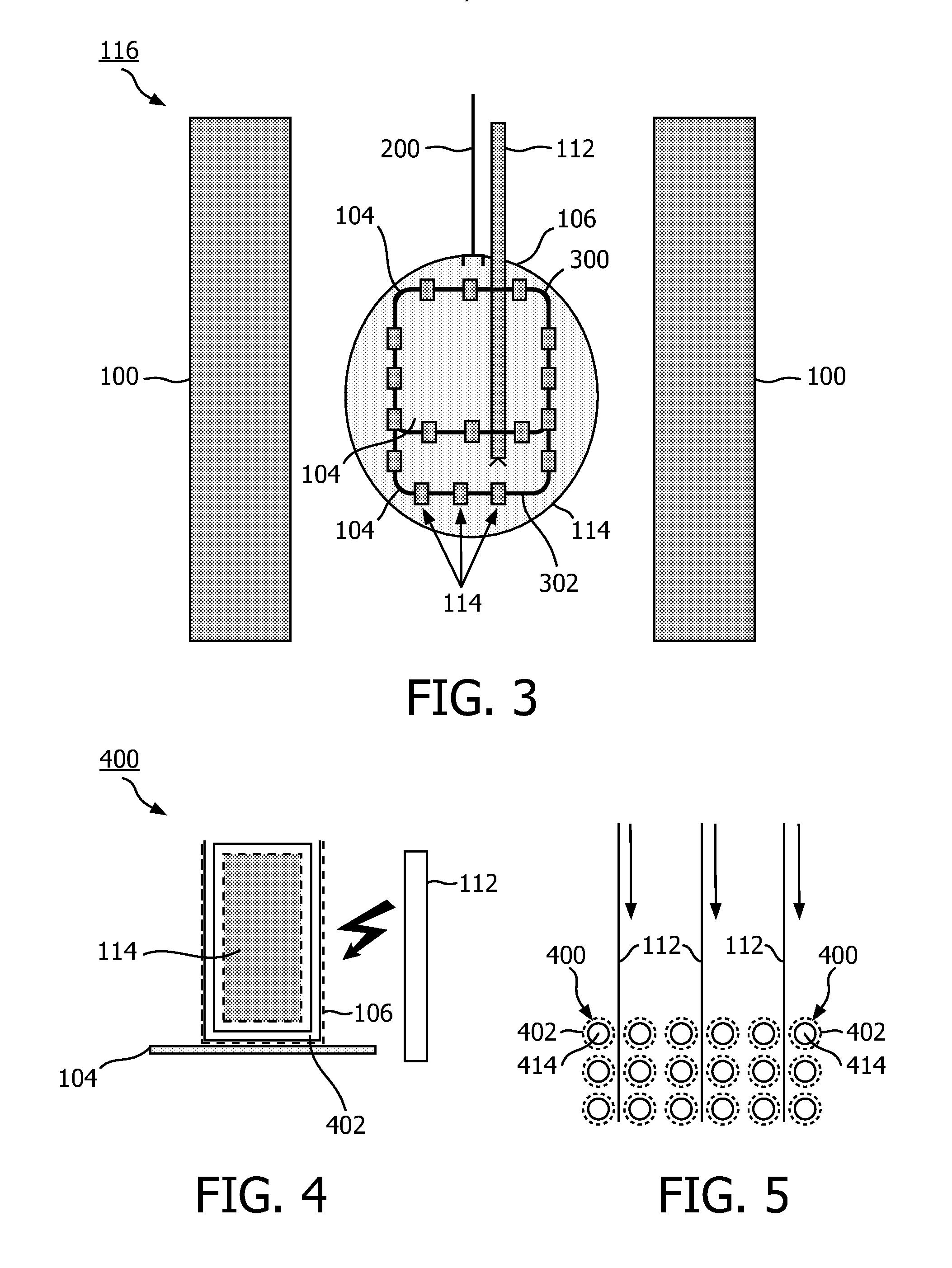
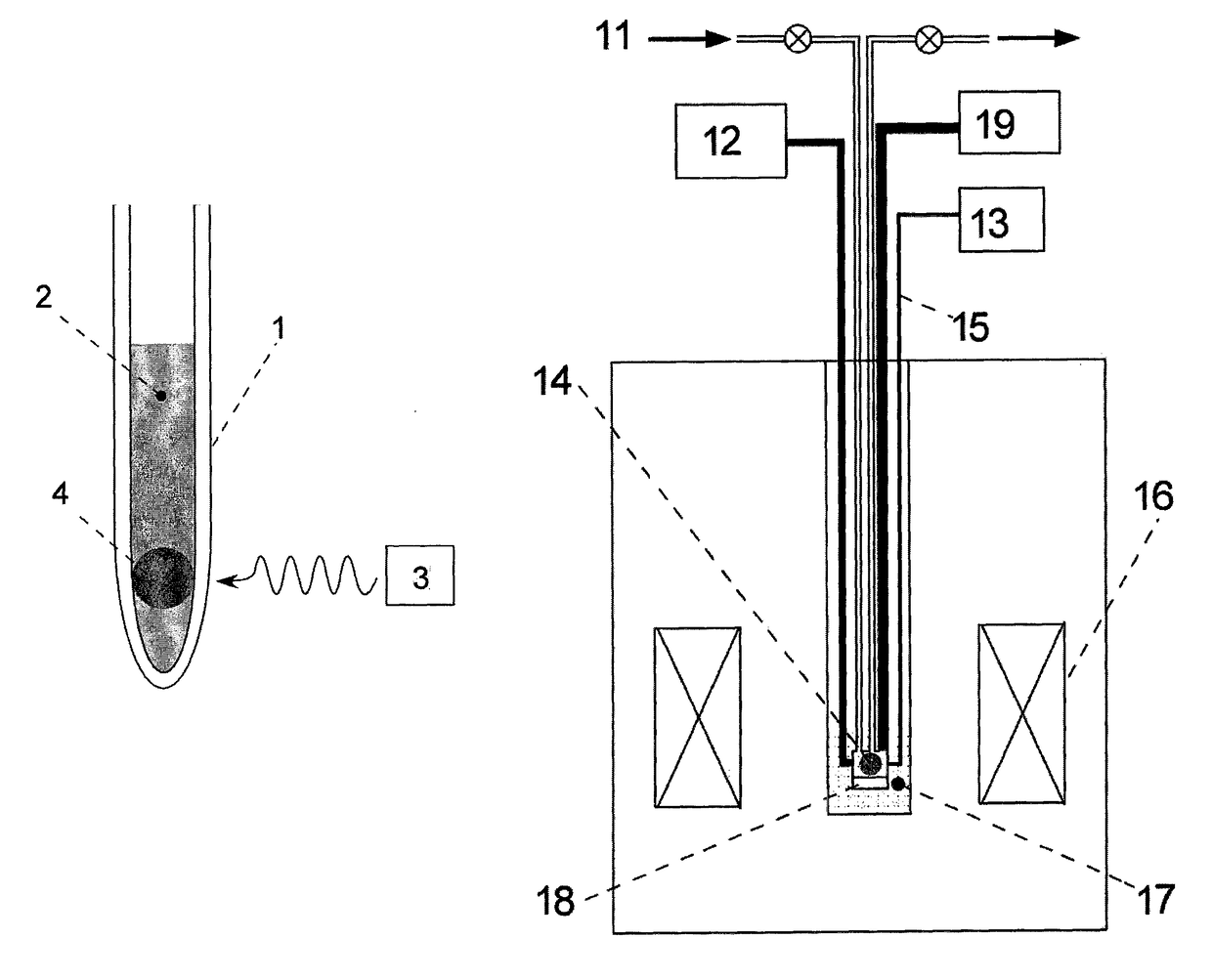
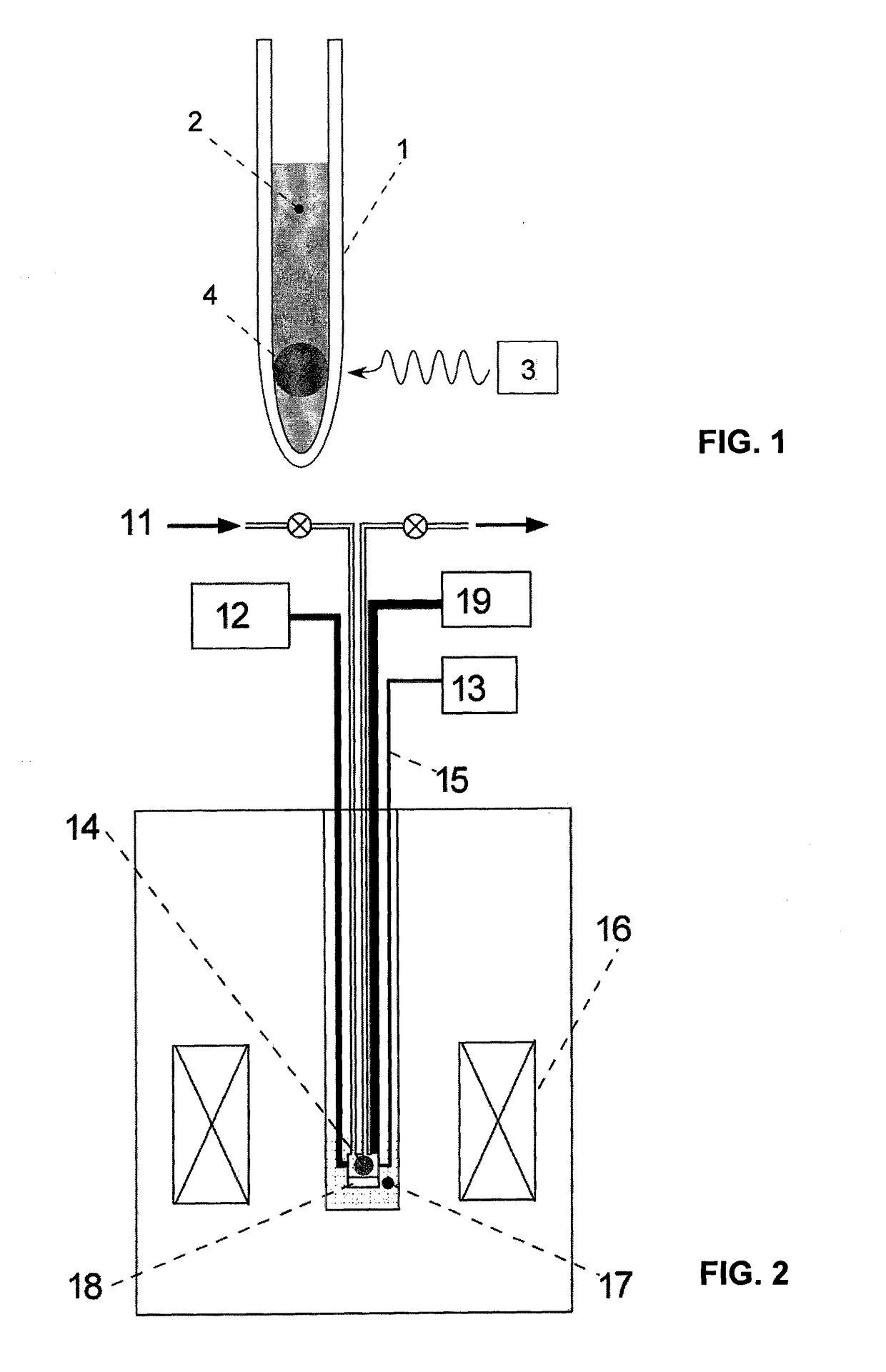
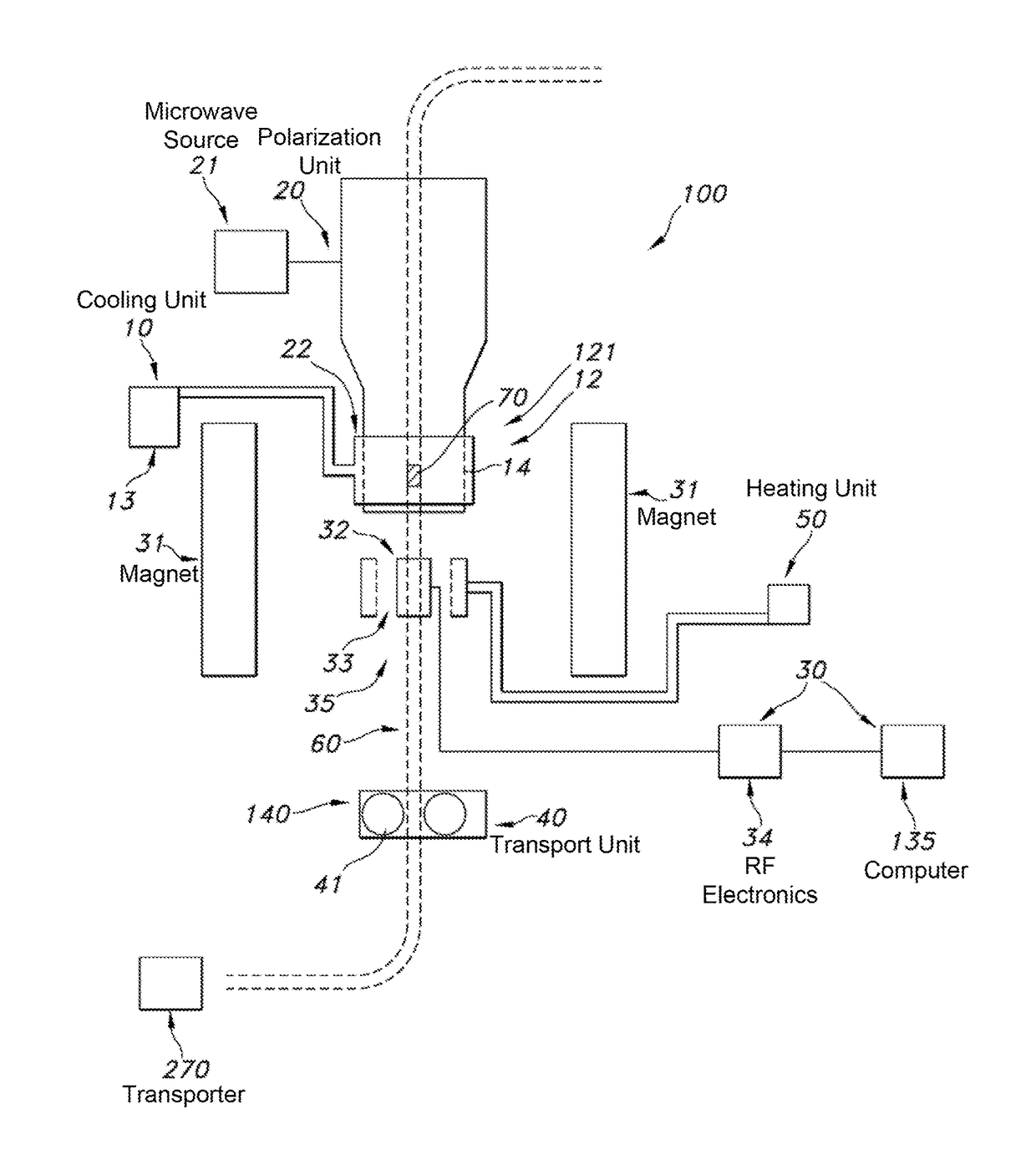
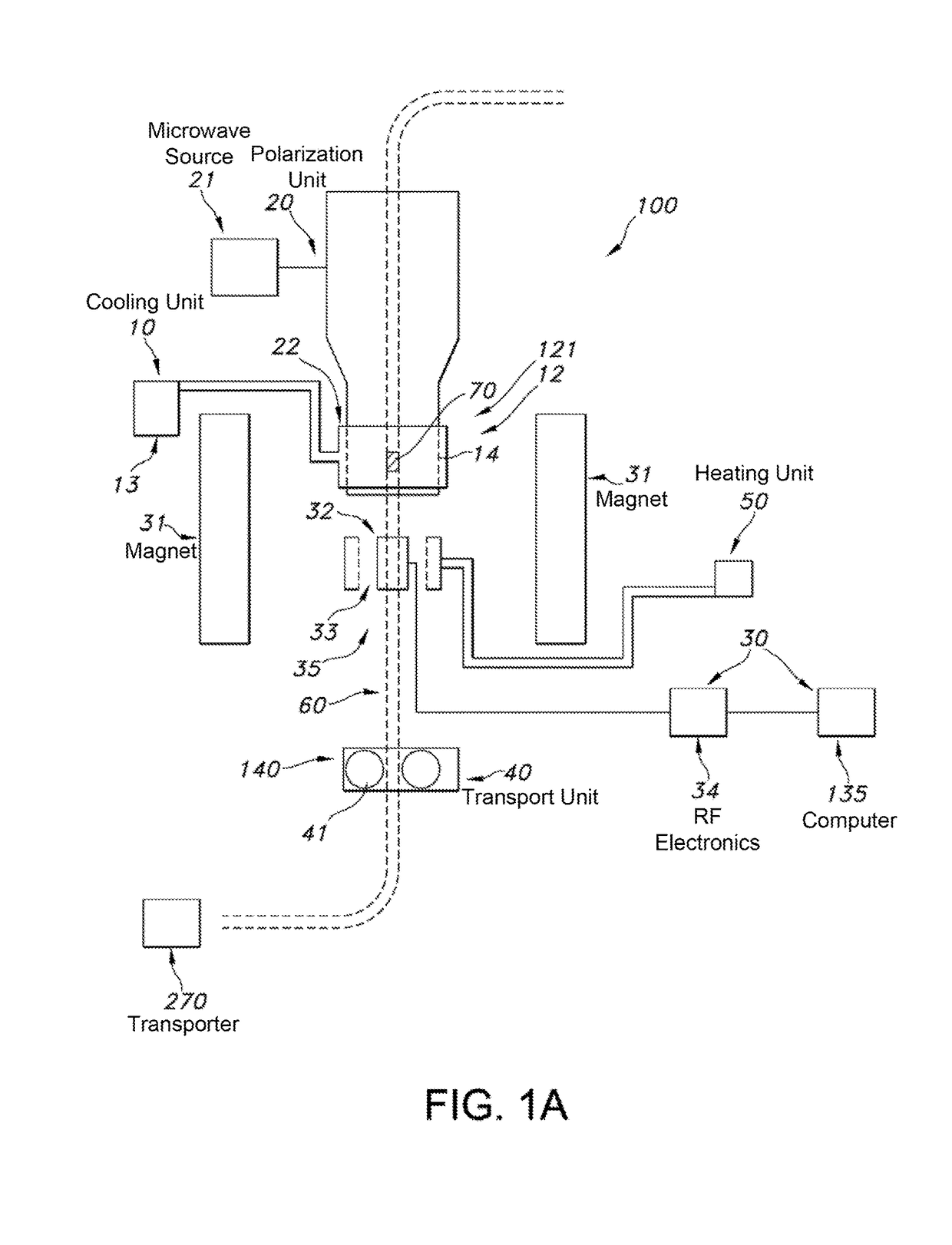
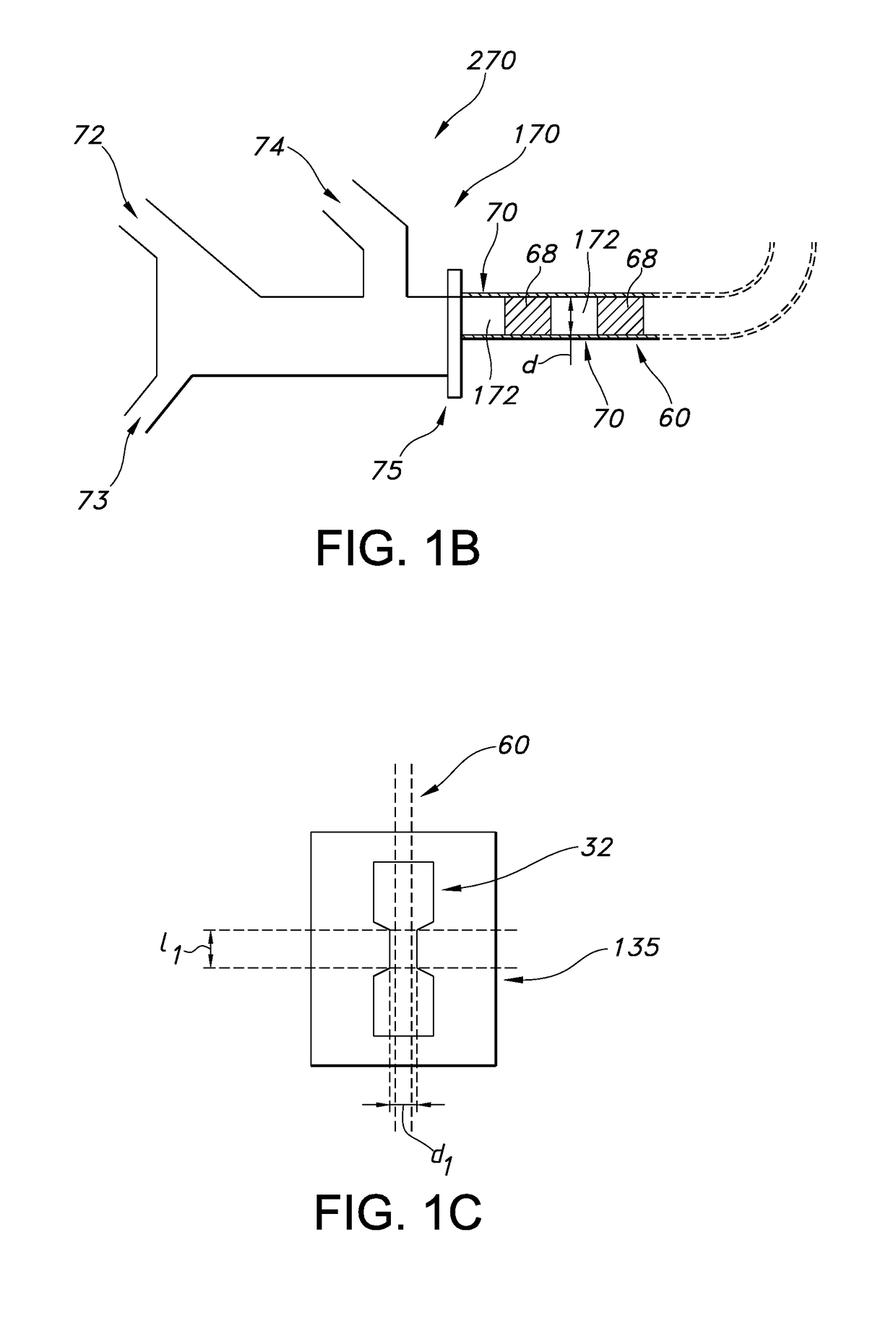
The invention relates to a dynamic nuclear polarization apparatus (116) for continuous provision of hyperpolarized samples (114) comprising dynamically nuclear polarized nuclear spins, the apparatus (116) comprising a polarization region (106) for polarization of said nuclear spins resulting in said hyperpolarized samples, wherein the apparatus (116) further comprises: a cryostat (102) for cooling the samples (114) in the polarization region (106), a magnet (100) for providing a magnetic field to the cooled samples in the polarization region (106), a radiation source (112) for concurrently to the magnetic field provision providing a nuclear polarizing radiation to the polarization region (106) for receiving the hyperpolarized samples, a sample transport system (104) for continuously receiving unpolarized samples (114), transporting the unpolarized samples to the polarization region (106) for nuclear spin polarization and providing the resulting hyperpolarized samples (114).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
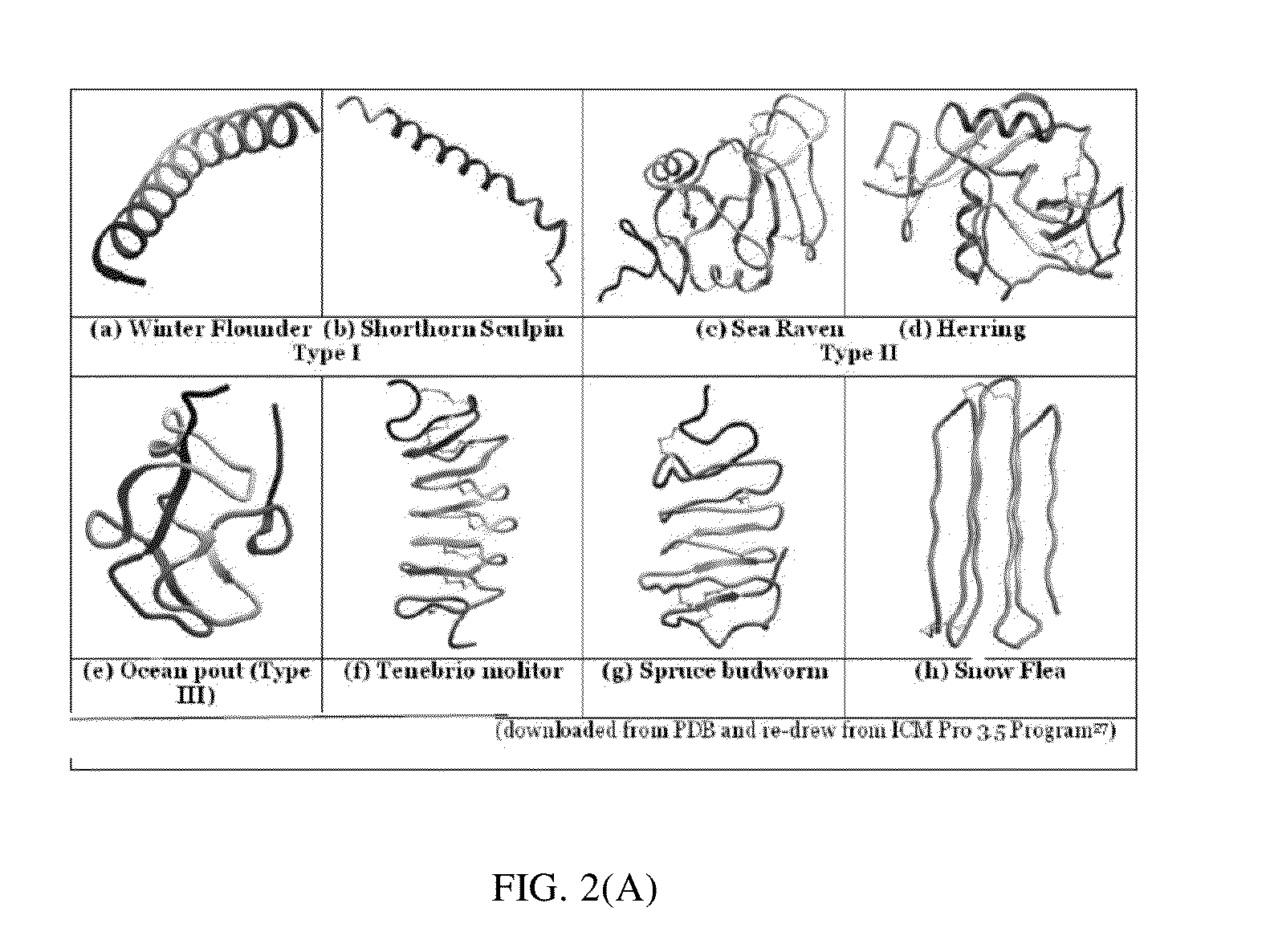
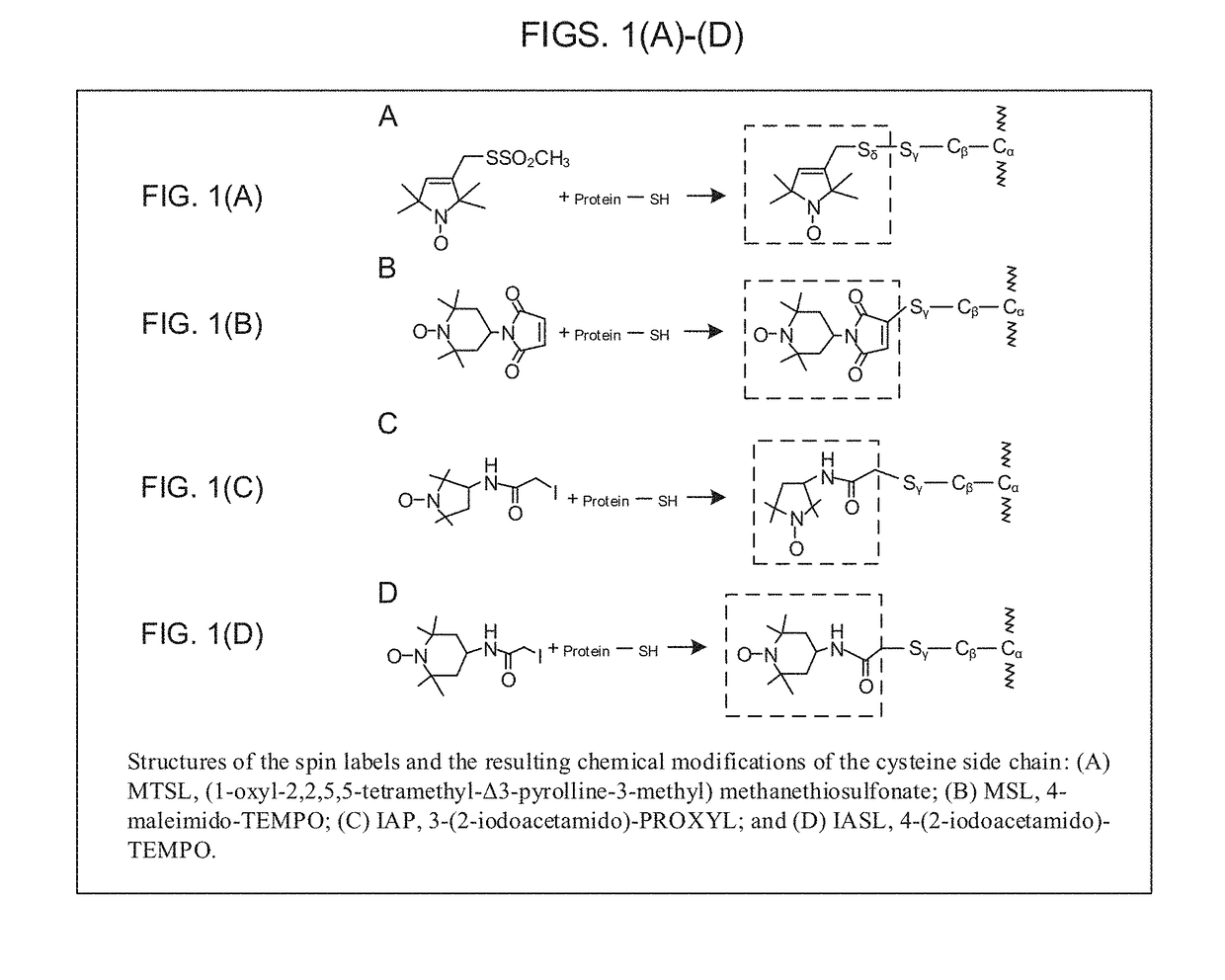
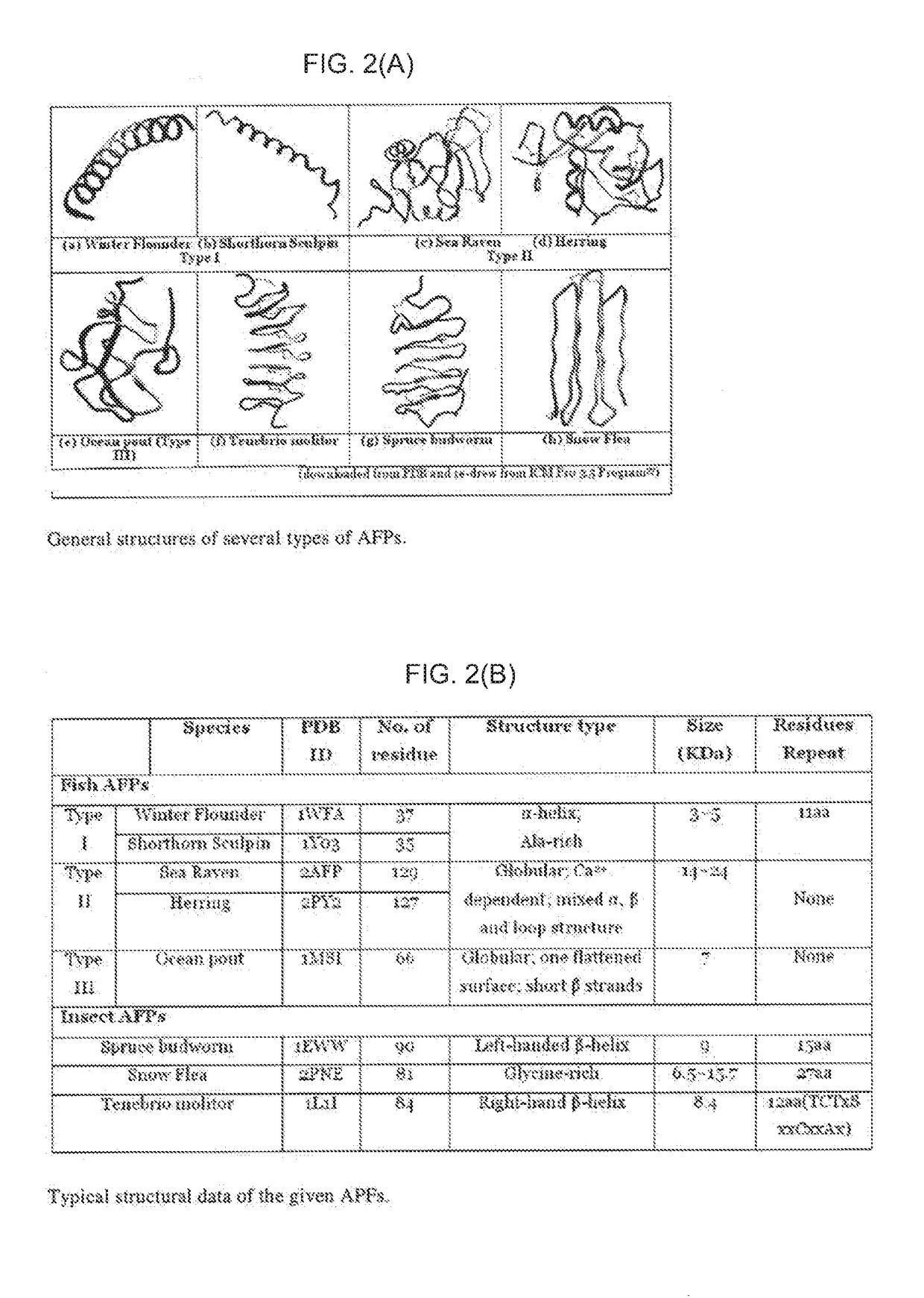
Electron spin labeled ice binding compounds used for carrying paramagnetic centers for dynamic nuclear polarization
ActiveUS20160207962A1Inhibit growthInhibition of recrystallizationOther chemical processesDepsipeptidesSolubilitySolvent
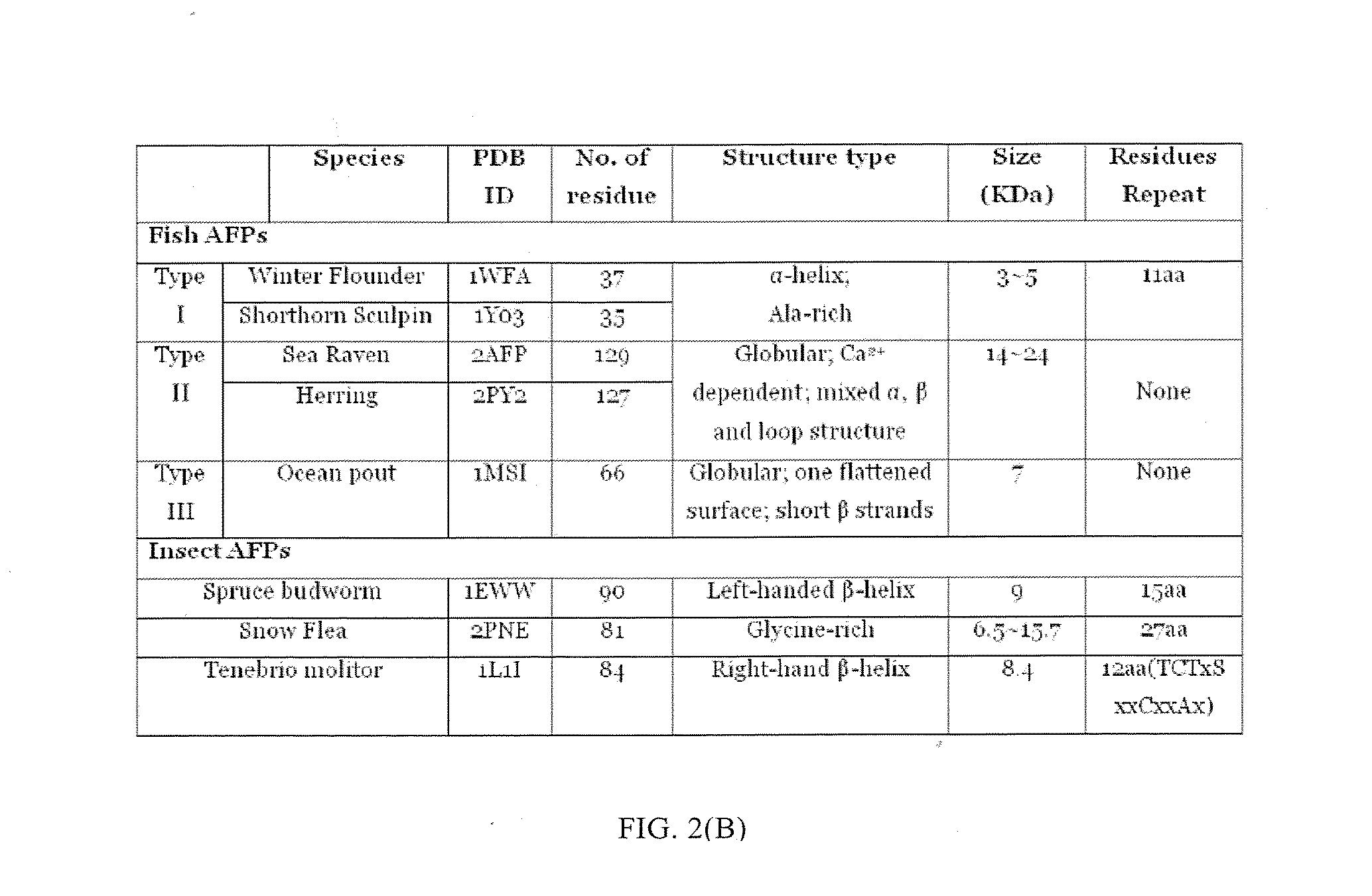
Spin labeled ice binding compounds (IBCs) including ice binding proteins (IBPs), also called antifreeze proteins (AFPs) and their analogs are exploited to carry the paramagnetic centers for dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP), for enhancing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal intensities. Use of spin labeled IBCs to perform DNP exploits the IBCs' ability to homogeneously distribute the paramagnetic centers in frozen water solution at low temperature, leading to high DNP efficiency. Other advantages of using spin labeled IBCs include: (1) ability to cryo-protect biological samples; (2) the relative positions and orientations of the spin labeling groups in an IBC may also be cryo-preserved; (3) positions and orientations of spin labeling groups to an IBC can be selected with great freedom and without technical barrier to making multiple spin labels in an IBC; and (4) water solubilities of spin labeled IBCs are potentially high, enabling use of a solvent that is primarily water for DNP at low temperatures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for the generation of radicals for dynamic nuclear polarization and uses thereof for NMR, MRS and MRI
ActiveUS10114088B2Highly polarized solid-state radical-free sampleIncreased polarizationMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUltravioletElectromagnetic radiation
A method for the preparation of a sample comprising highly polarized nuclear spins is proposed, comprising at least the following steps:a) provision of molecules with 1,2-dione structural units and / or molecules with 2,5-diene-1,4-dione structural units in the solid state;b) generation of radicals from these molecules by photo induced electron transfer by a first electromagnetic irradiation in the visible or ultraviolet frequency range in the solid state;c) dynamic nuclear polarization in the presence of a magnetic field in the solid state by applying a second electromagnetic irradiation with a frequency adapted to transfer spin polarization from the electrons to the nuclear spins leading to a highly polarized state thereof. Furthermore uses of correspondingly prepared samples for NMR, MRS and MRI experiments are proposed.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Preparation of solid amorphous substrates for dnp
InactiveUS20170252464A1Increased polarizationEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsVitrificationDynamic nuclear polarisation
A method for preparing a sample for dynamic nuclear polarization which comprises submitting a solid substrate to a milling process in the presence of a polarizing agent at a temperature lower than the glass-transition temperature (Tg) of said substrate. Preferably said substrate may be in crystalline form.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA +1
Rigid dinitroxide biradical compounds used as improved polarizing agents for dynamic nuclear polarization techniques
The invention concerns a dinitroxide biradical compound, in which the two nitroxide units are held by a rigid linkage, of general formula (I) in which—A is a carbon, an ammonium or a phosphonium, each of A1 to A6 is selected separately from the group comprising a single bond, O, N, N(O), S, S(O), SO2, C(O), a (C1-C4) alkyl chain, Z1 and Z2 are chosen from RI and R2 in combination, such that there is always, in the combination, at least one R2 group that needs to be substituted by an R3 group, RI is an H, a (C6-C18) aryl or a (C3-C18) heteroaryl, R2 a (C1-C17) alkyl chain, a (C1-C17) alkenyl chain, a (C1-C17) alkynyl chain, a (C4-C17) cycloalkyl, a (C4-C17) heterocycloalkyl, a (C6-C18) aryl, a (C3-C18) heteroaryl, R3 is a (C1-C17) alkyl chain, a (C1-C17) alkenyl chain, a (C1-C17) alkynyl chain, a (C4-C17) cycloalkyl, a (C4-C17) heterocycloalkyl, a (C6-C18) aryl, a (C3-C18) heteroaryl, an ether —OR, an ester —C(O)O—R (in which R is any hydrocarbon radical), an azide, and in which, when Z1 and Z2 are combined together with the same carbon atom of the nitroxide ring to which they are bonded, they form a spirocycloalkyl or a spiroheterocycloalkyl substituted by R3.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE +5
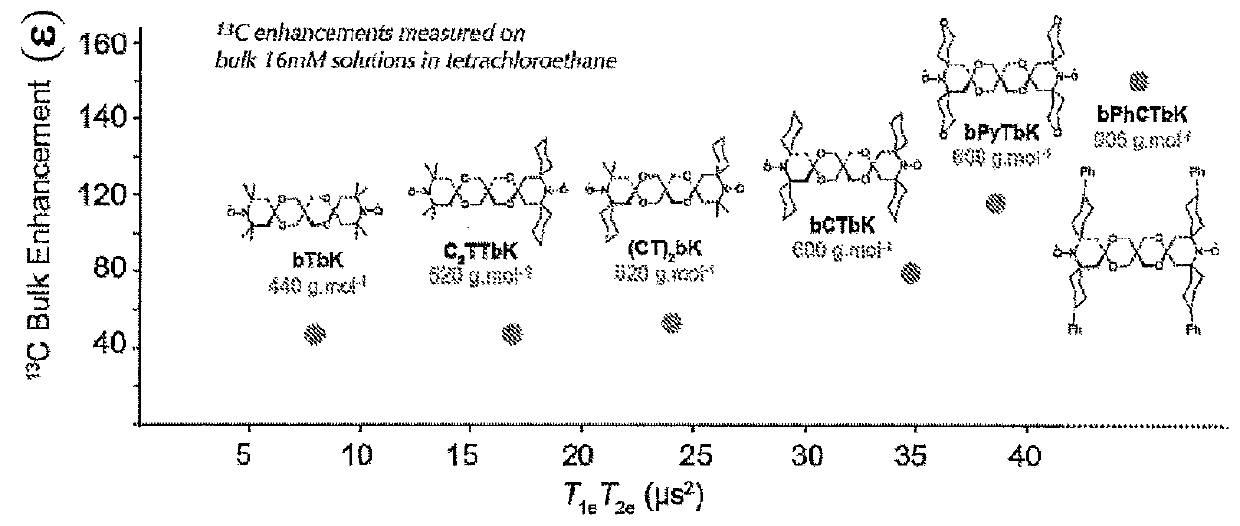
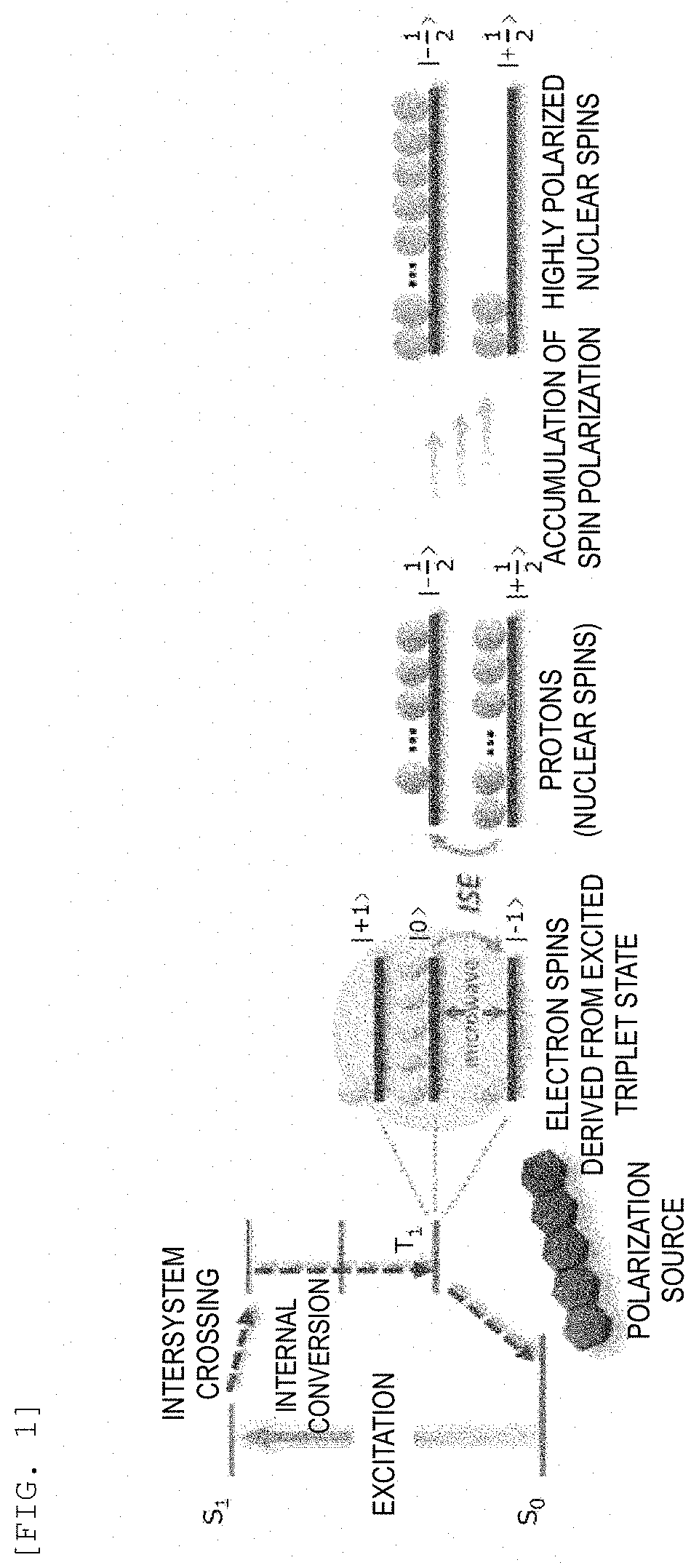
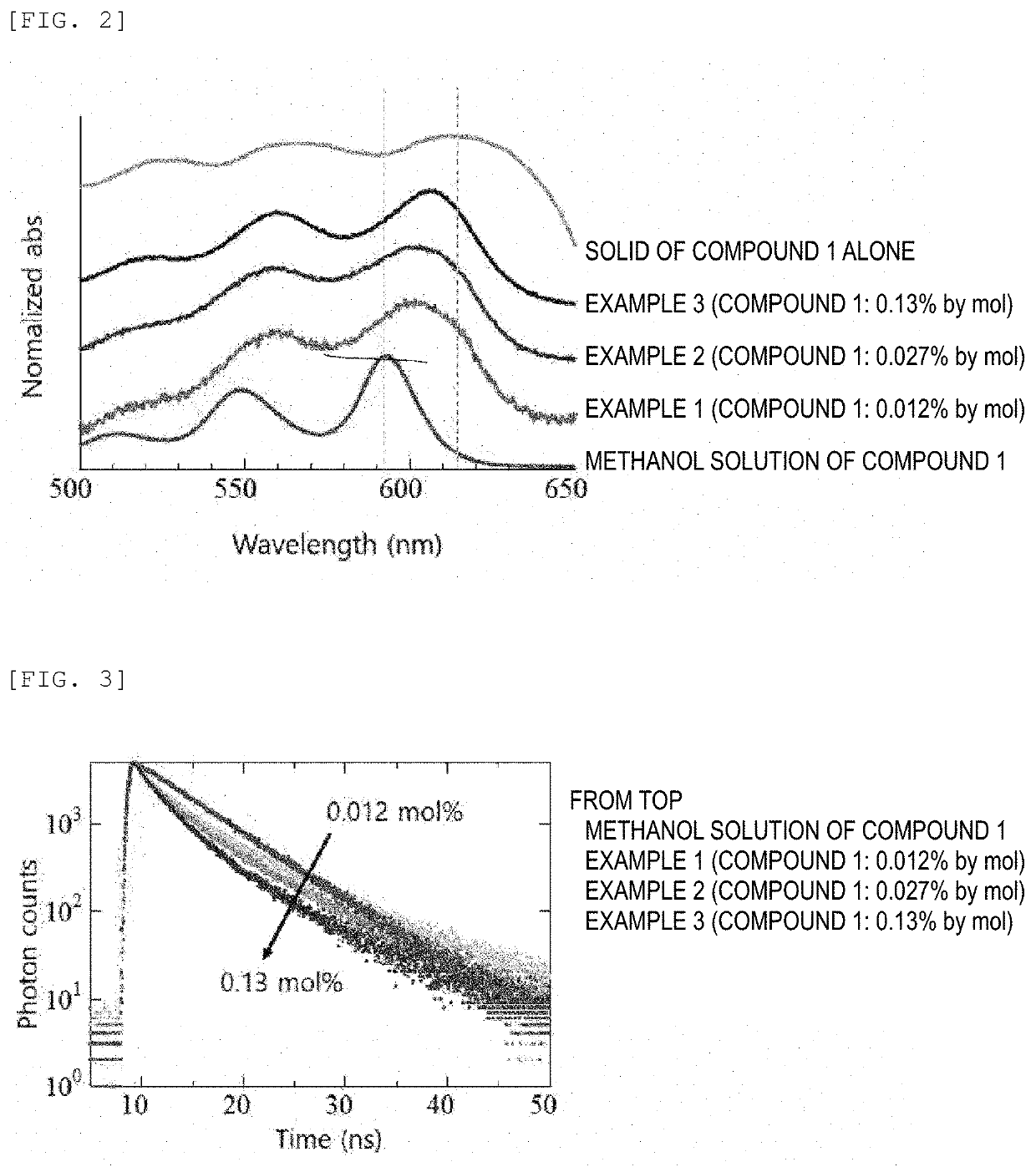
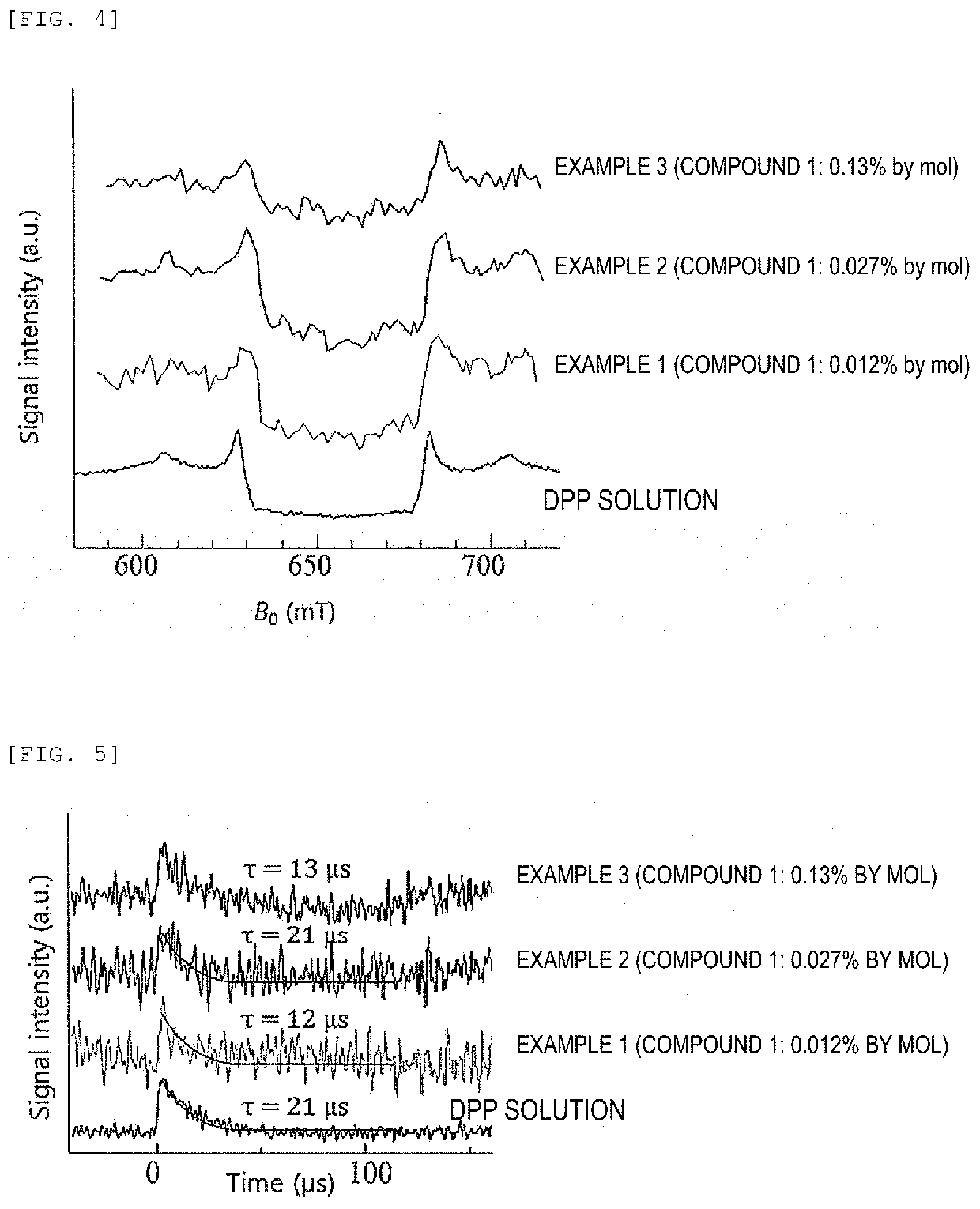
Composition, composition for dynamic nuclear polarization, polarization enhancing method, highly polarized substance, and nmr measurement method
InactiveUS20200289678A1Long spin-lattice relaxation timeEasy to introduceMeasurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A composition containing (1) a porous material and (2) a polarization source for dynamic nuclear polarization containing a molecule capable of being in an excited triplet state. According to the composition, a dynamic nuclear polarization system that has a long spin-lattice relaxation time and can readily introduce the polarization object thereto can be provided.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV +1
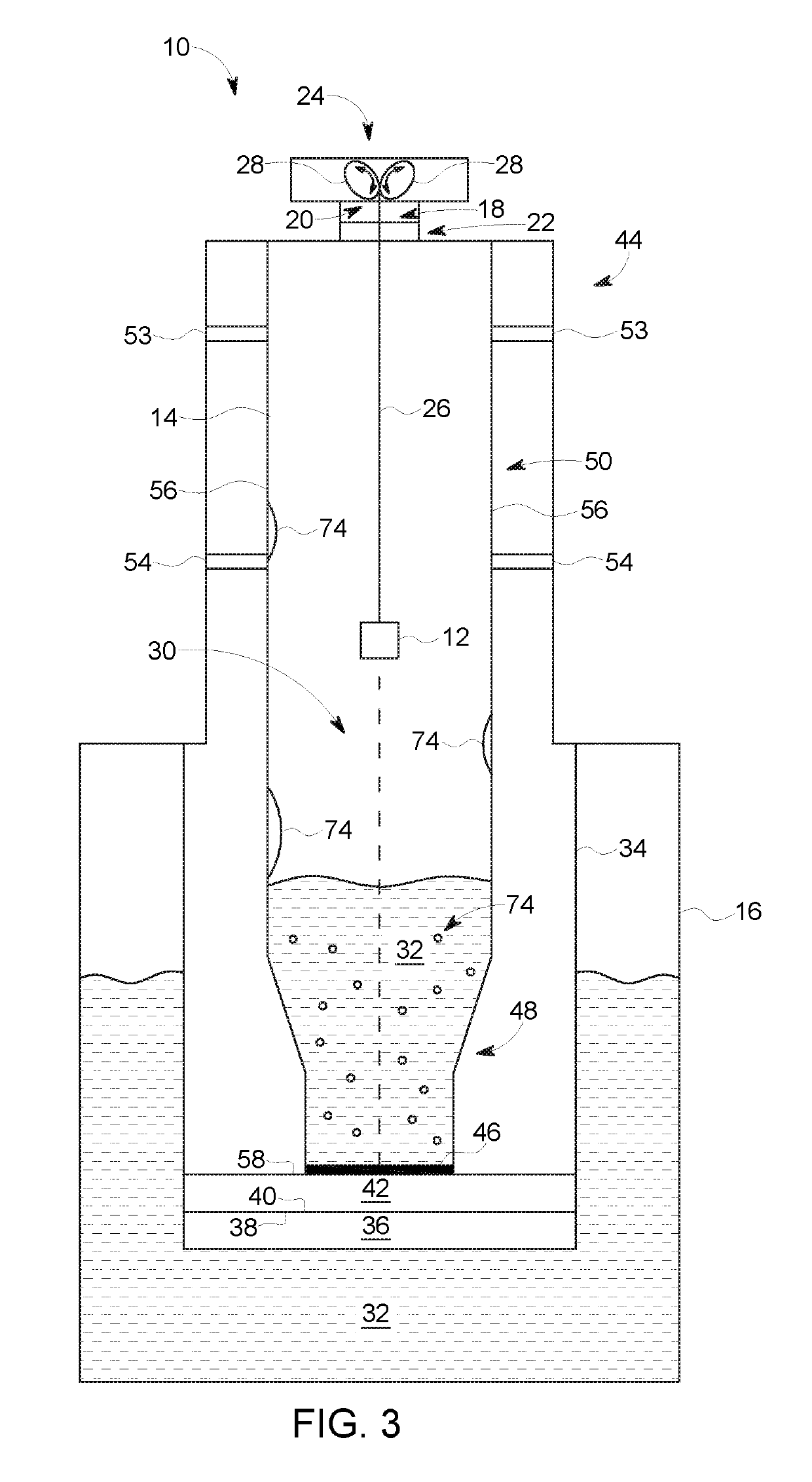
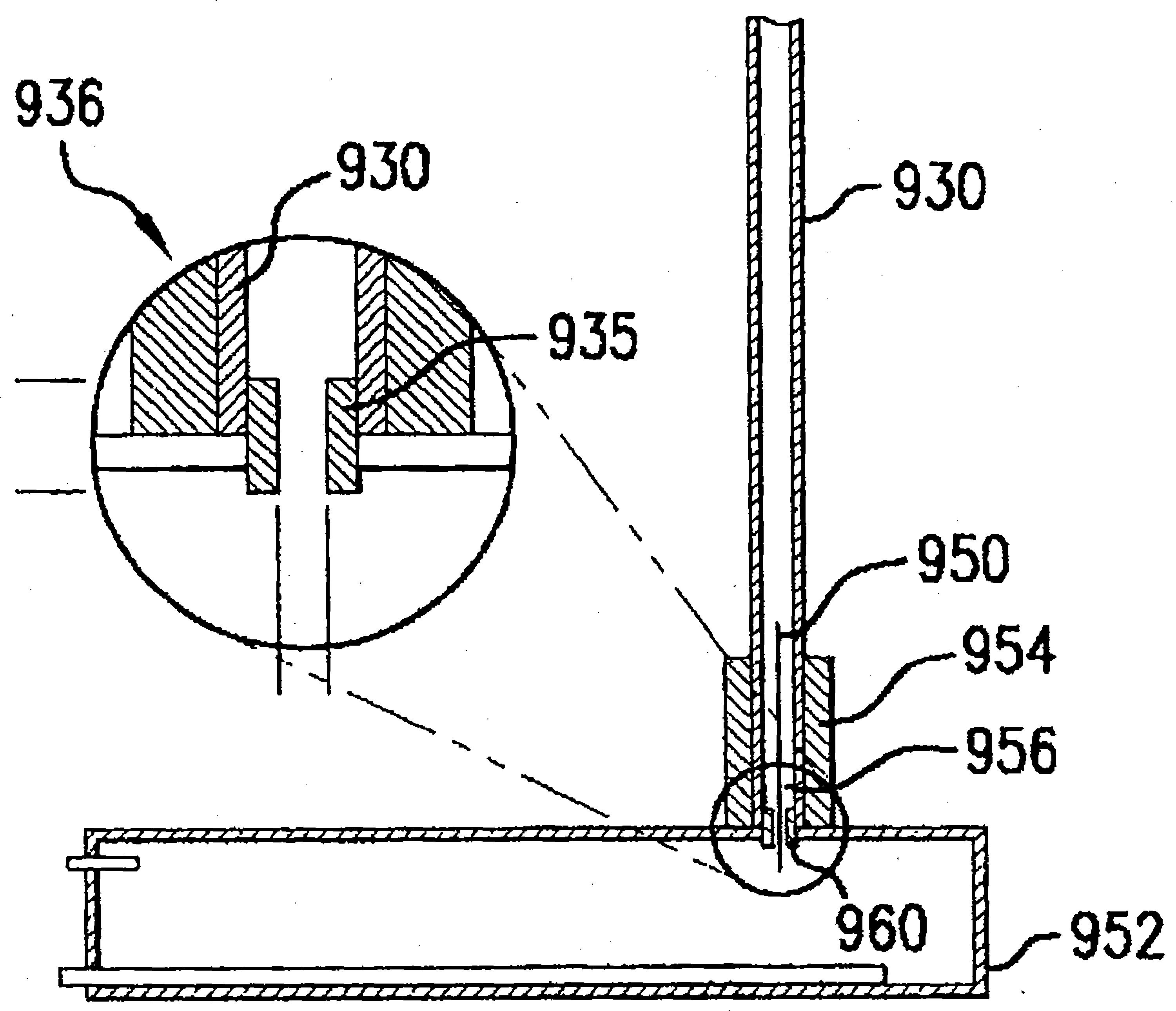
Fluid path insert for a cryogenic cooling system
ActiveUS20190025387A1Preparing sample for investigationRefrigeration devicesNuclear engineeringDynamic nuclear polarisation
A cooling system is provided. The cooling system is associated with a dynamic nuclear polarization system and configured to cool a sample to a temperature suitable for dynamic nuclear polarization to be carried out on the sample while the sample is in the cooling system. The cooling system includes a cryogenic chamber that includes a cryogenic fluid. The cooling system also includes a removable sample sleeve insertable within a portion of the cryogenic chamber. The removable sample sleeve is configured to define a sample path for the sample within the cryogenic chamber that is isolated from other parts of the cooling system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
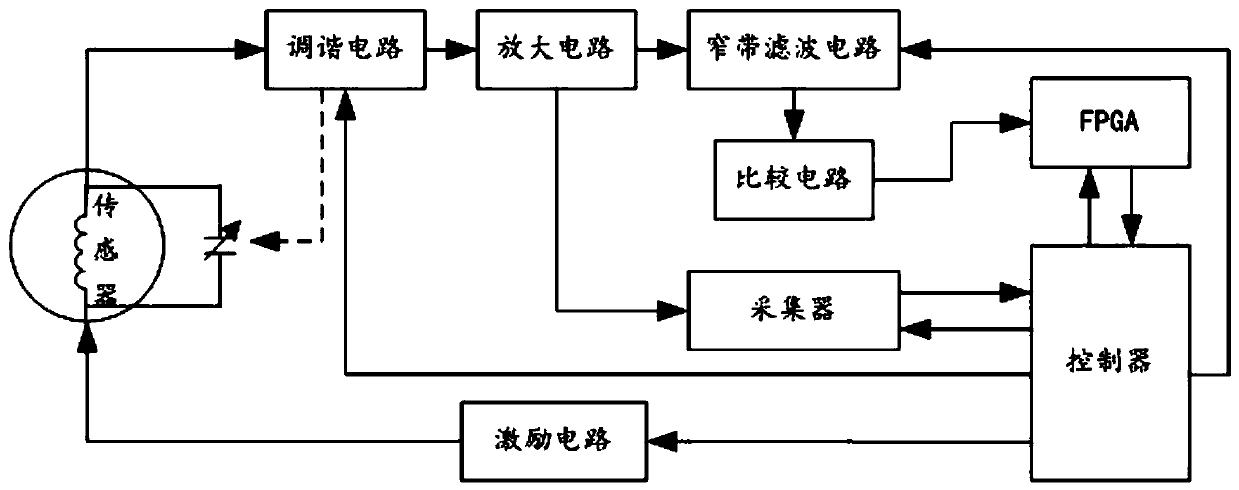
Noise suppression system and method suitable for proton magnetic precession signals
ActiveCN110632535ASuppress unknown noiseSuppress noiseMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsBandpass filteringFrequency measurements
The invention provides a noise suppression system and method suitable for proton magnetic precession signals. A dynamic nuclear polarization sensor receives excitation signals sent by an excitation circuit; proton magnetic precession signals are sensed; the signals are transmitted to a tuning circuit; the tuning circuit tunes the signals and transmits the tuned signals to an amplification circuit;the amplification circuit amplifies the signals; a narrowband filter performs band-pass filtering on the amplified signals to remove noises outside a central frequency band, and transmits the signalsto a comparison circuit; the comparison circuit shapes the signals processed by the narrow-band filter into square waves and transmits the signals to an FPGA; the FPGA performs later-stage signal processing; a collector is connected with a controller and performs data acquisition and processing; the controller is connected with the excitation circuit and controls the start and stop of the excitation signals; the controller is connected with the FPGA; the FPGA performs frequency measurement on the proton magnetic precession signals which have been shaped into the square waves and converts a measured frequency value into a magnetic field value; and the controller is connected with the narrow-band filter and adjusts the narrow-band center frequency of the narrow-band filter.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Fluid path insert for a cryogenic cooling system
ActiveUS10481222B2Preparing sample for investigationRefrigeration devicesNuclear engineeringDynamic nuclear polarisation
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electron Spin Labeled Ice Binding Compounds Used For Carrying Paramagnetic Centers For Dynamic Nuclear Polarization
ActiveUS20180044382A1Inhibit growthInhibition of recrystallizationDepsipeptidesIn-vivo testing preparationsSolubilityConfocal
Spin-labeled ice binding compounds (IBCs) including ice binding proteins (IBPs) or antifreeze proteins (AFPs) and their analogs may carry paramagnetic centers for dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP), for enhancing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal intensities. Use of spin-labeled IBCs to perform DNP exploits the IBCs' ability to homogeneously distribute the paramagnetic centers in frozen water solution at low temperature, leading to high DNP efficiency. Other advantages of using spin-labeled IBCs include cryo-protecting biological samples; cryo-preserving relative positions and orientations of the spin labeling groups; selecting positions and orientations of spin labeling groups with freedom and without technical barriers to making multiple spin labels in an IBC; and enabling use of a solvent that is primarily water for DNP at low temperatures in view of the potentially high water solubilities of spin-labeled IBCs.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF THE CALIFORNIA STATE UNIV
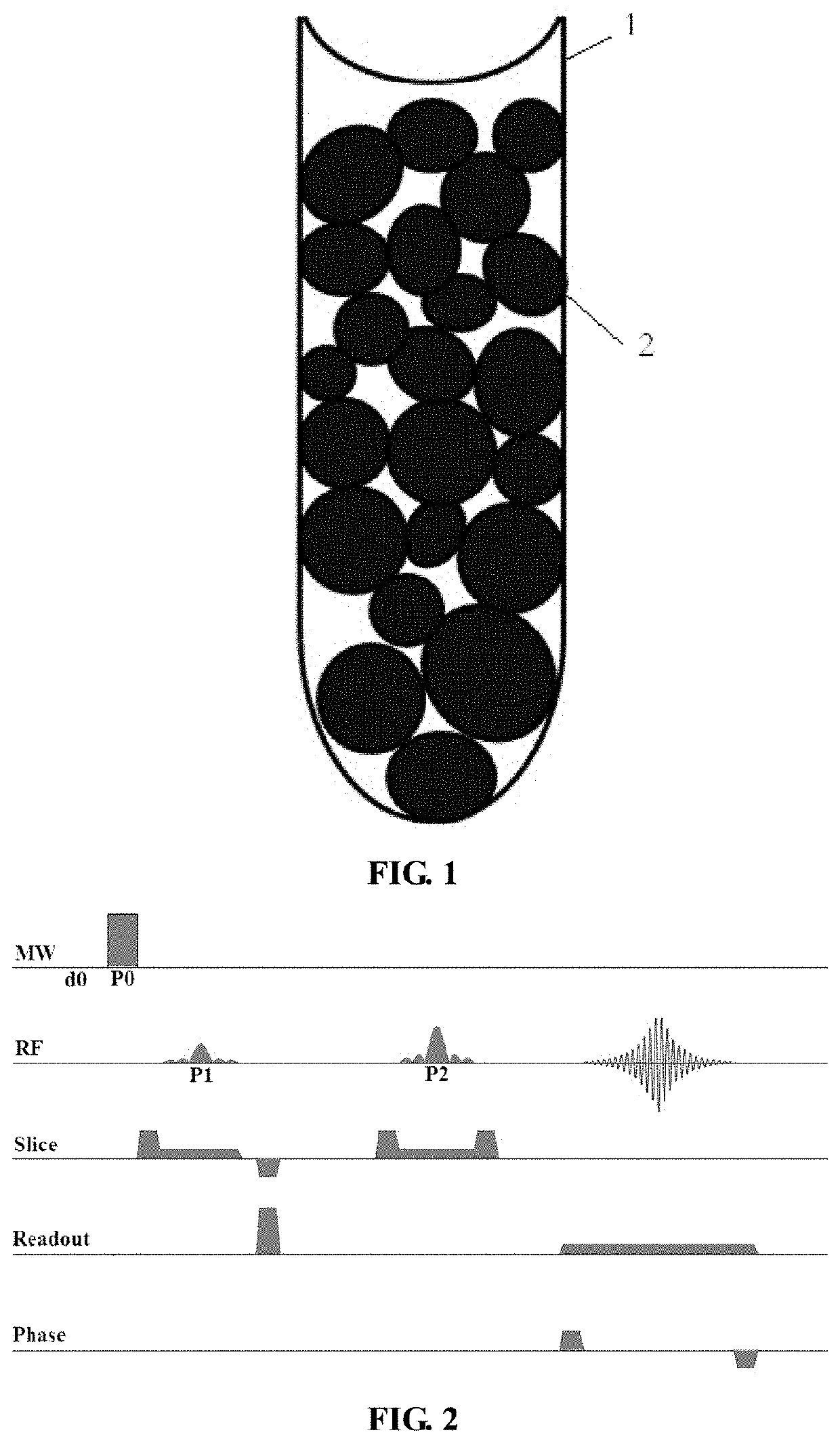
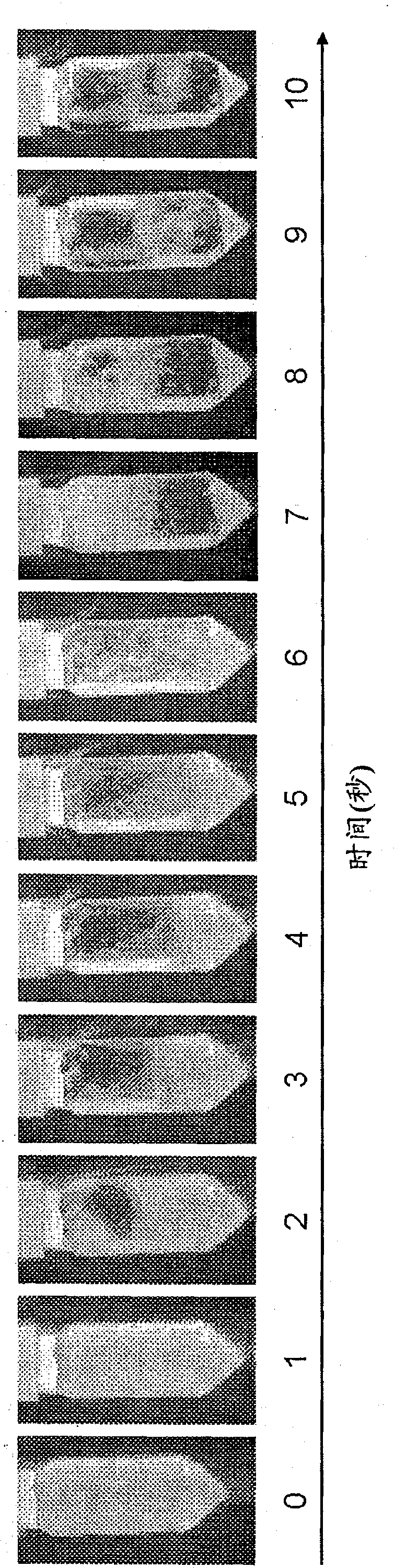
Method for measuring oil-water distribution using dynamic nuclear polarization for magnetic resonance imaging (dnp-mri)
ActiveUS20220057346A1Easy to operateShort measurement timeMeasurements using double resonanceWater resource assessmentNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A method for measuring oil-water distribution using DNP-MRI, comprising adding a free radical for DNP enhanced NMR signal of a water phase or an oil phase in a sample containing oil and water; performing an MRI experiment on the sample, and collecting an MRI image of the sample without DNP enhancement; applying microwave excitation for DNP-MRI experiment under the same MRI experiment condition as step 2, and collecting an MRI image of the sample after DNP enhancement; and comparing the MRI image after DNP enhancement with the MRI image without DNP enhancement. In the MRI image with DNP enhancement, an area with enhanced MRI signal intensity is a selectively enhanced fluid phase distribution area, and an area without obviously changed MRI signal intensity is a non-selectively enhanced fluid phase distribution area. The method is simple, convenient to operate, short in measurement time, and high in measurement efficiency.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
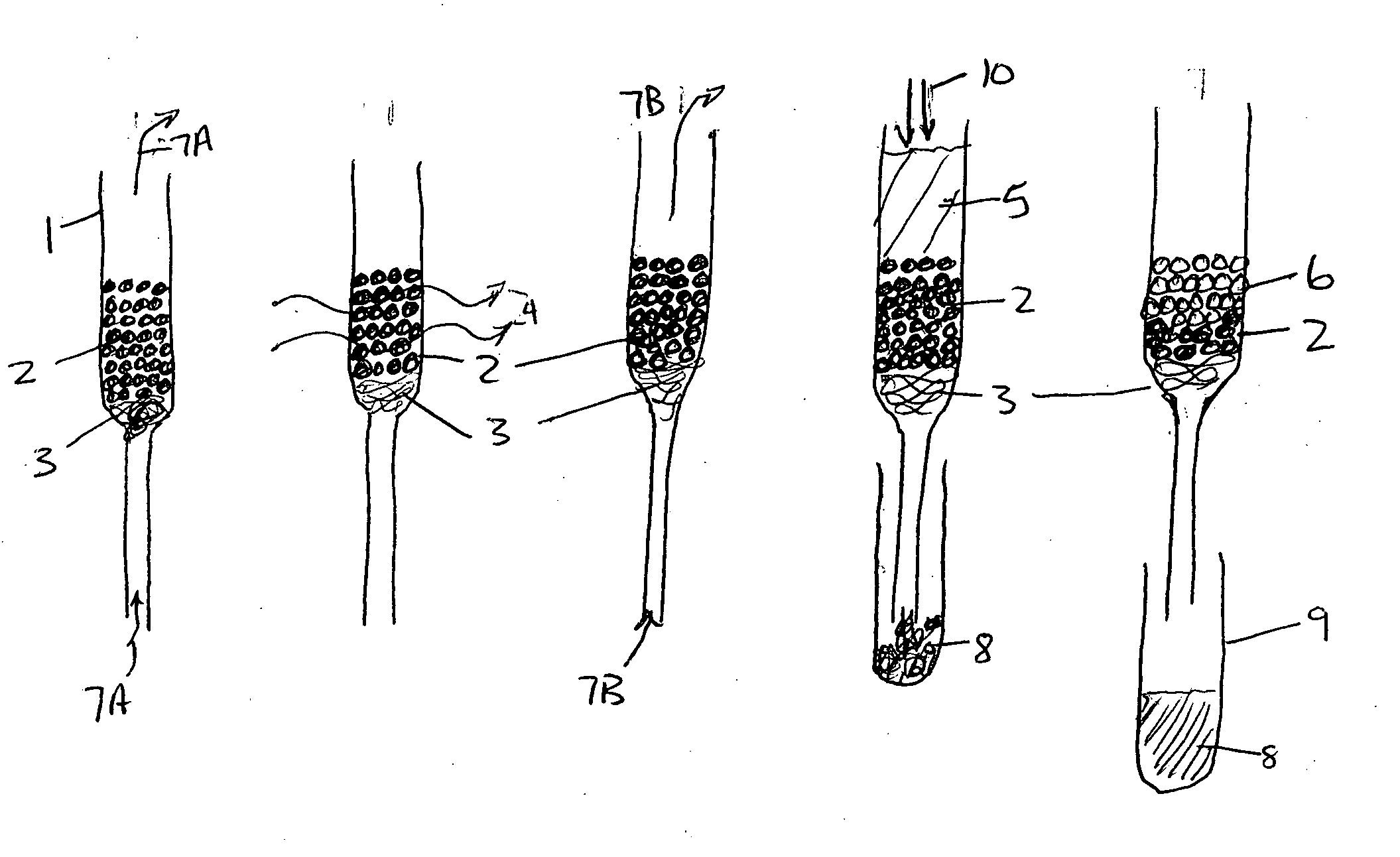
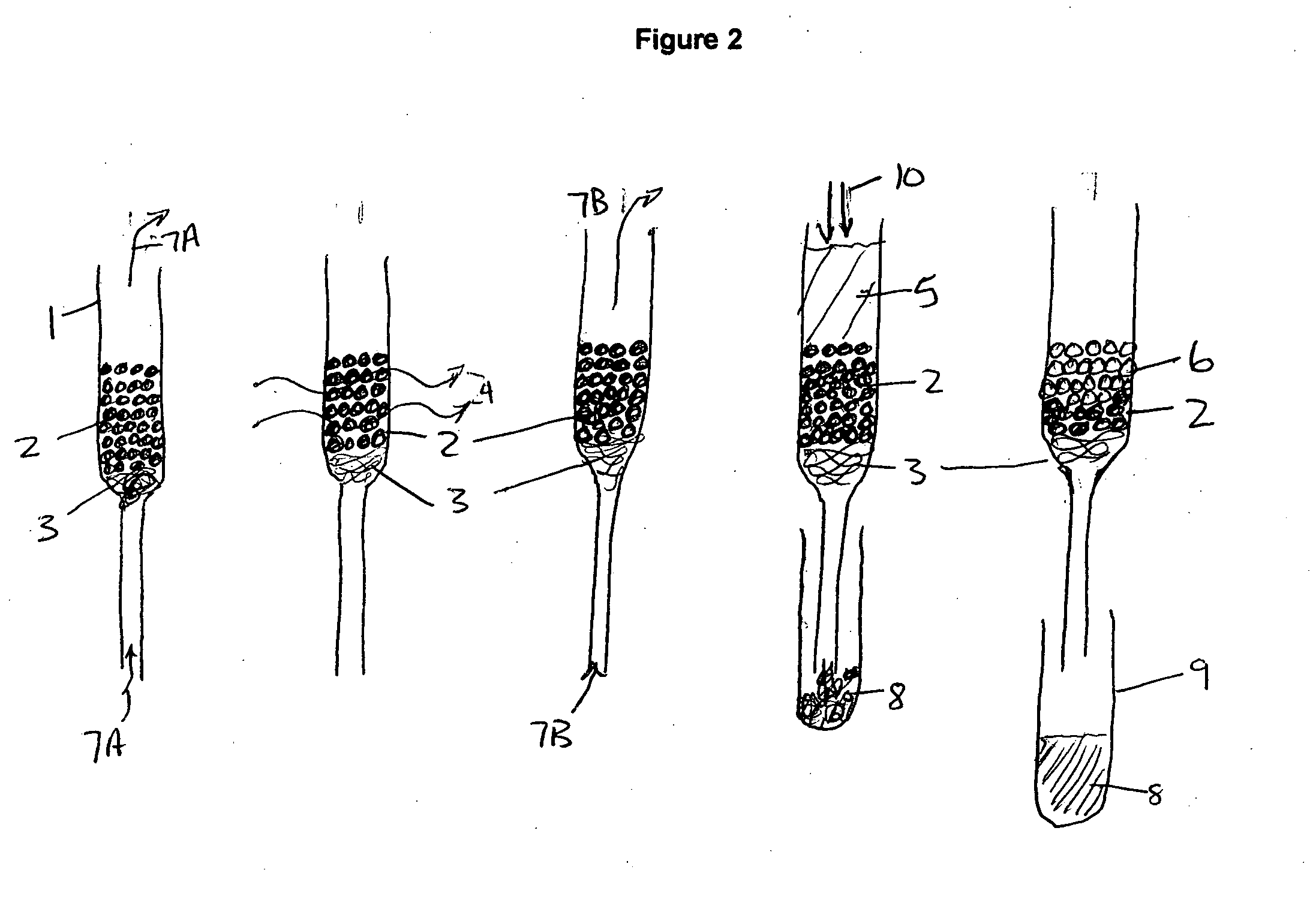
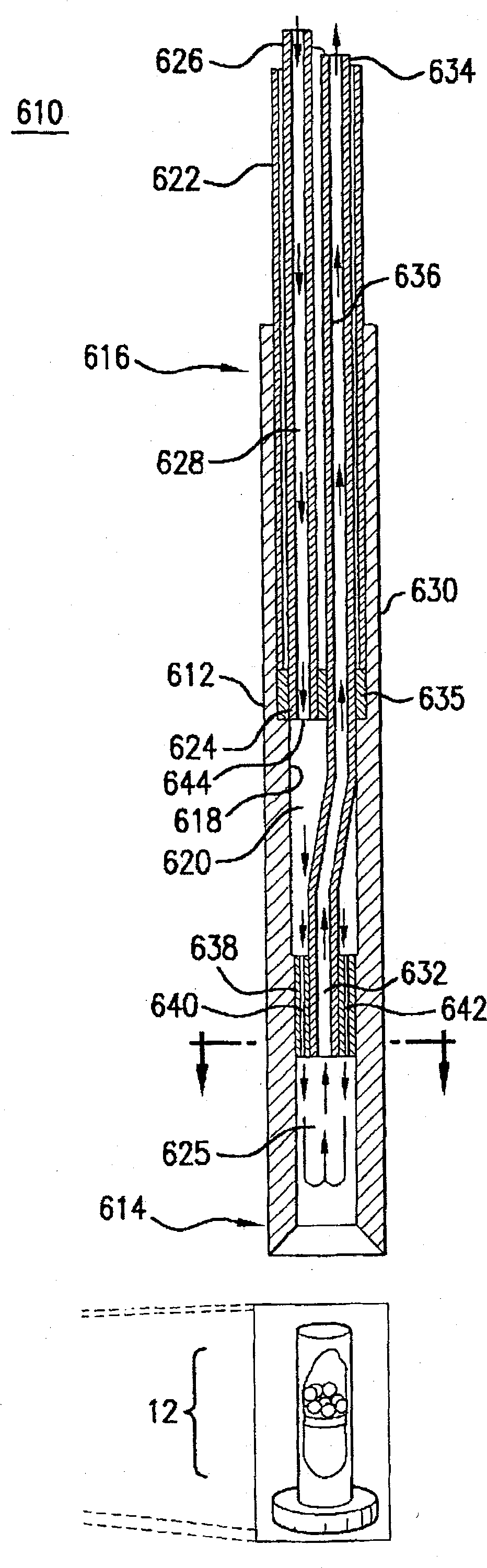
Apparatus for dissolving frozen polarized sample and applications
InactiveCN104076308APreparing sample for investigationMeasurements using double resonanceDynamic nuclear polarisationEngineering
DNP polarizer comprising a housing receiving a free end of a tubular fluid conduit positioned in fluid communication with a nozzle supported by said housing, said nozzle including an input port, a dispense port and a tapering inner surface or a stepped inner surface defining a nozzle flowpath extending in fluid communication between said input port and said dispense port.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
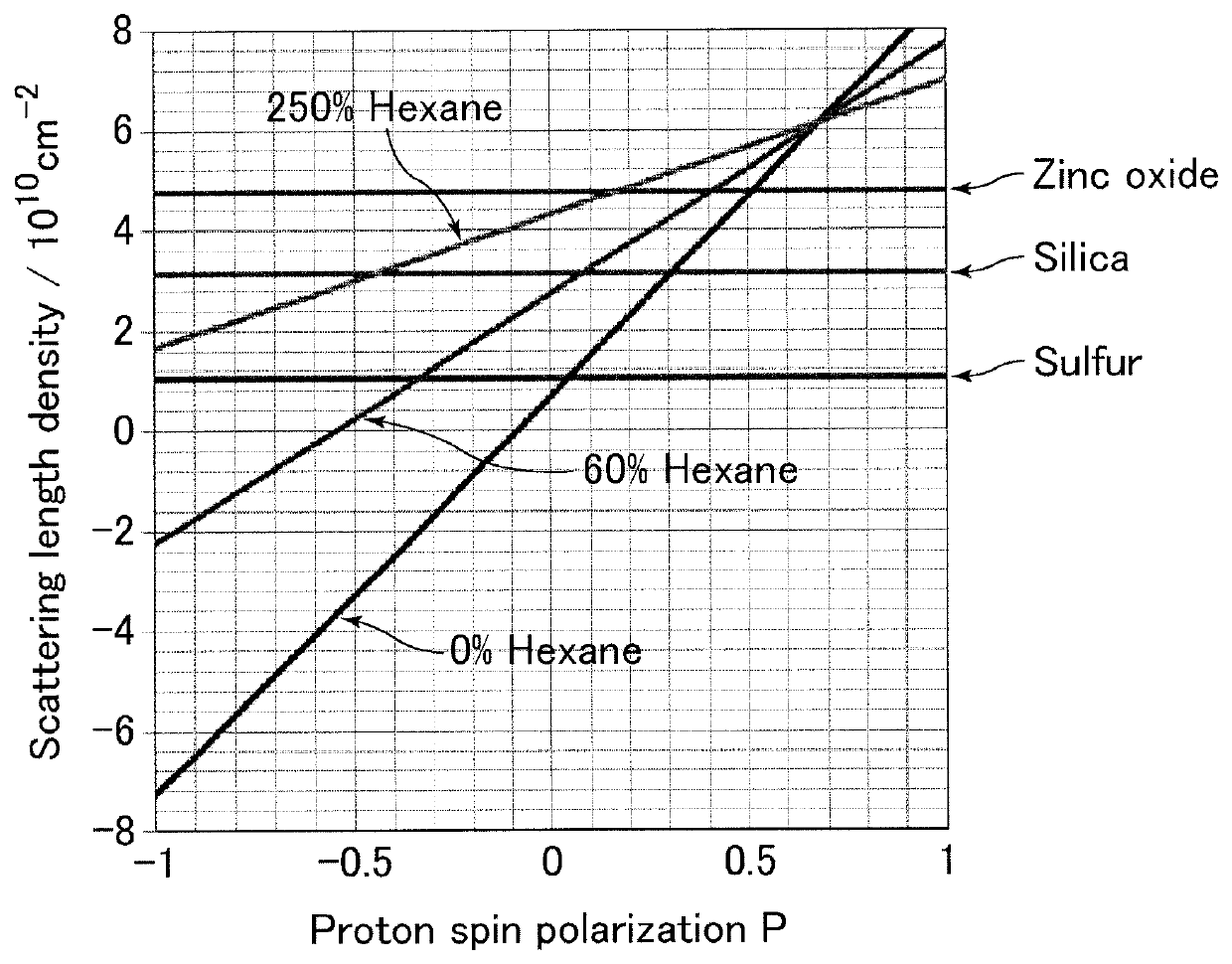
Polymer composite material for 1H dynamic nuclear polarization experiments and method for producing the same, and polymer composite material for 1H dynamic nuclear polarization contrast variation neutron scattering experiments
ActiveUS10712413B2High proton spin polarizationImprove experimental precisionPigmenting treatmentMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyPolymer scienceDynamic nuclear polarisation
Provided is a polymer composite material which has a high proton spin polarization even though it is a polymer composite material containing carbon black. The present invention relates to a polymer composite material for 1H dynamic nuclear polarization experiments, containing carbon black, having a thickness of 0.8 mm or less, and being doped with a paramagnetic radical compound.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Electron spin labeled ice binding compounds used for carrying paramagnetic centers for dynamic nuclear polarization
ActiveUS9738686B2Inhibit growthInhibition of recrystallizationDepsipeptidesIn-vivo testing preparationsSolubilitySolvent
Spin labeled ice binding compounds (IBCs) including ice binding proteins (IBPs), also called antifreeze proteins (AFPs) and their analogs are exploited to carry the paramagnetic centers for dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP), for enhancing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal intensities. Use of spin labeled IBCs to perform DNP exploits the IBCs' ability to homogeneously distribute the paramagnetic centers in frozen water solution at low temperature, leading to high DNP efficiency. Other advantages of using spin labeled IBCs include: (1) ability to cryo-protect biological samples; (2) the relative positions and orientations of the spin labeling groups in an IBC may also be cryo-preserved; (3) positions and orientations of spin labeling groups to an IBC can be selected with great freedom and without technical barrier to making multiple spin labels in an IBC; and (4) water solubilities of spin labeled IBCs are potentially high, enabling use of a solvent that is primarily water for DNP at low temperatures.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF THE CALIFORNIA STATE UNIV
Double-frequency DNP probe system for dynamic nuclear polarization system and assembling method thereof
ActiveCN110988011AAchieving double resonanceReduce volumeAssembly machinesAnalysis using double resonanceResonant cavityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a double-frequency DNP probe system for a dynamic nuclear polarization system and an assembling method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nuclear magnetic resonance. A first bottom plate and a second bottom plate are mainly disposed for cooperative use to the inner wall surface of an inner hole in a solenoid for radio frequency resonance to form a Terahertz resonant cavity, thus realizing dual resonance of a radio frequency band and a Terahertz frequency band, effectively reducing the volume of the DNP probe and having good applicability.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Method for separating oil-water two-phase nmr signals by using dynamic nuclear polarization
PendingUS20220057347A1Easy to operateShort test timePreparing sample for investigationMeasurements using double resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFluid phase
A method for separating oil-water two-phase NMR signals by using dynamic nuclear polarization comprising: using a combination of a non-selective free radical and a selective relaxation reagent to selectively enhance an NMR signal of an oil phase or a water phase, the relaxation reagent being capable of selectively suppressing dynamic polarization enhancement of the water phase or oil phase, thus achieving the polarization enhancement of a single fluid phase in the mixed fluid phases and realizing separation of the two-phase signals; or using a selective free radical to selectively enhance the NMR signal of the oil phase or the water phase, thus achieving the polarization enhancement of a single fluid phase in the mixed fluid phases and realizing separation of the oil-water two-phase NMR signals. The method is simple and easy to operate, has a short test time, and can efficiently separate NMR signals of oil and water phases.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
Rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS9945918B2Low costReduce complexityMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) NMR apparatus comprises (i) a cooling unit configured to cool a sample in a capillary, (b) a DNP polarization unit configured to polarize the sample in the capillary, (c) a stripline-based NMR detector comprising a stripline for NMR analysis of the sample in the capillary, (d) a transport unit configured to guide the capillary from the DNP polarization unit to the stripline of stripline-based NMR detector; and (e) a heating unit configured to heat the sample in the capillary before analysis of the sample by the stripline-based NMR detector. Fast (1D-3D) NMR measurements with high resolution may be obtained.
Owner:STICHTING KATHOLIEKE UNIV
Radical polarizing agents for dynamic nuclear polarization
InactiveUS8715621B2BiocideOrganic compound preparationDynamic nuclear polarisationStructural formula
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
A nonlocal resistive NMR measurement method
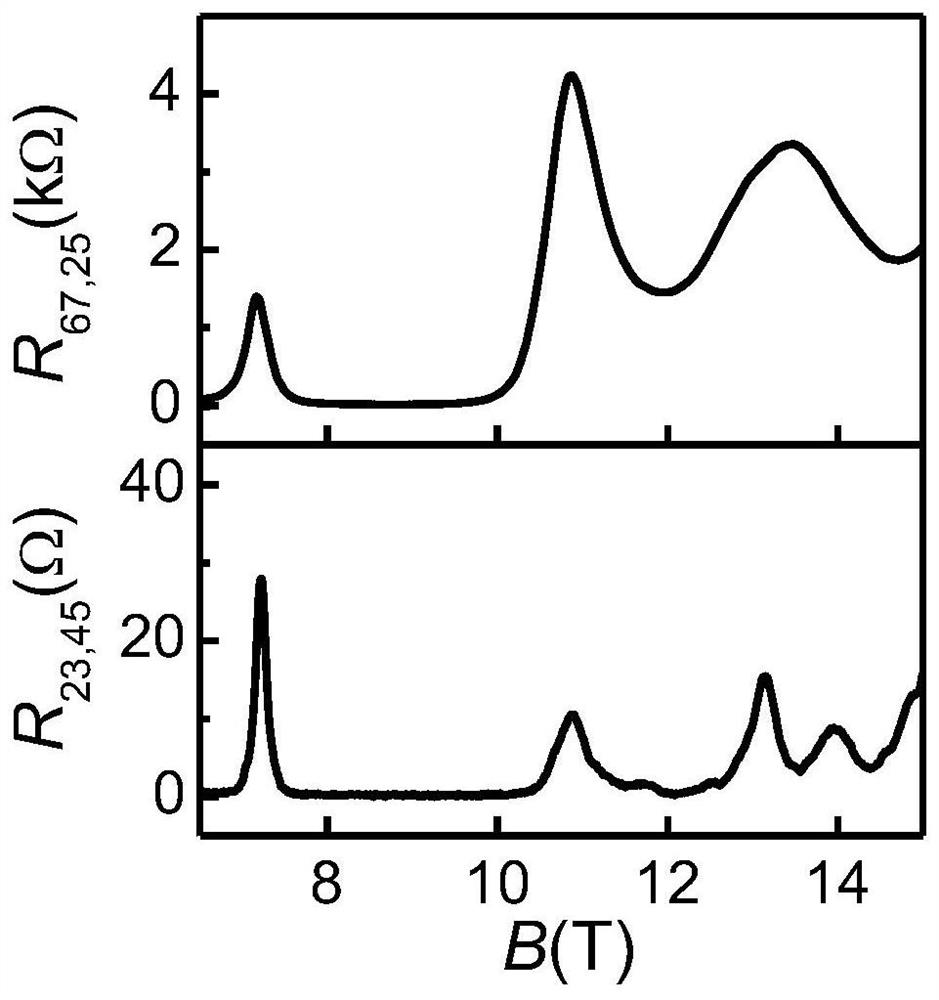
ActiveCN112113991BInduced current reductionReduce Hall BiasAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFerroicsMaterials science
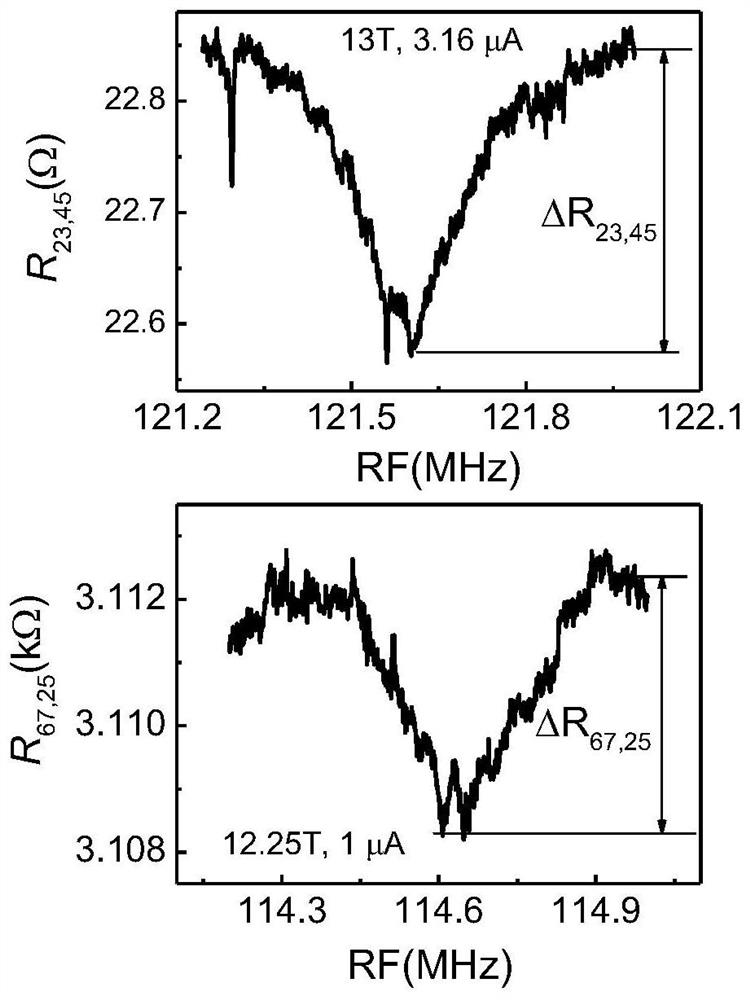
A non-local resistive NMR measurement method of the present invention belongs to the technical field of spintronics, and the main steps include: placing a two-dimensional electron gas Hall strip sample for non-local measurement on a sample rotating table In the cryostat, a quantum Hall ferromagnetic state with a magnetic domain structure is formed; non-local resistance measurement is performed on the quantum Hall ferromagnetic state, and the quantum Hall ferromagnetic state is obtained according to the relationship between the resistance peak and the inclination angle of the quantum Hall ferromagnetic state. According to the obtained NMR spectrum, the nuclear spin relaxation time T of the quantum Hall ferromagnetic state is measured. 1 and nuclear spin decoherence time T 2 Measurement. Through the introduction of the non-local measurement configuration, the present invention realizes the dynamic nuclear polarization under small current, thereby ensuring that the measured sub-state is always in an equilibrium state, and the non-local resistance of the measured sub-state is 2 orders of magnitude smaller than the normal measurement resistance , which improves the precision of resistive NMR measurement by an order of magnitude.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com