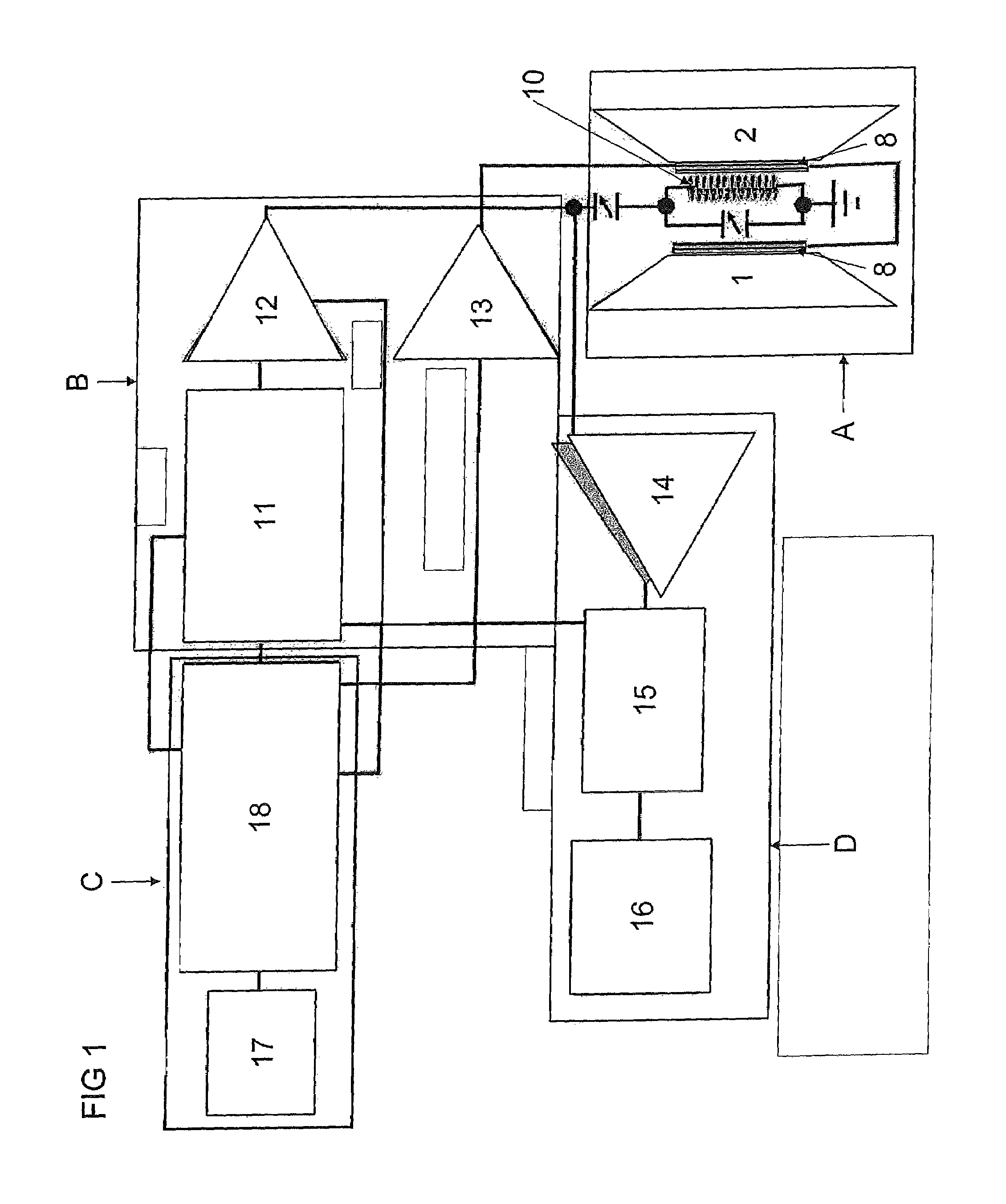
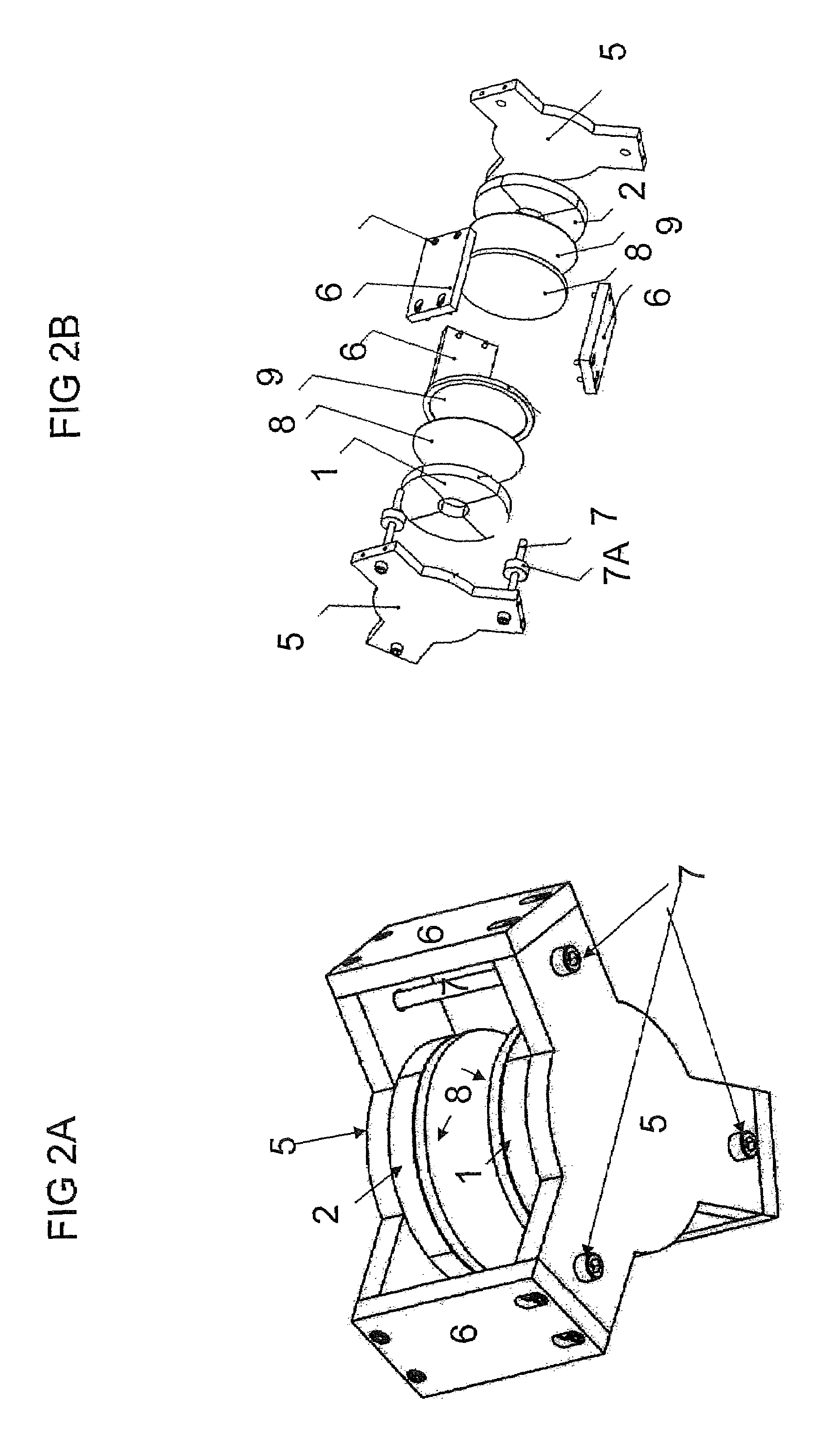
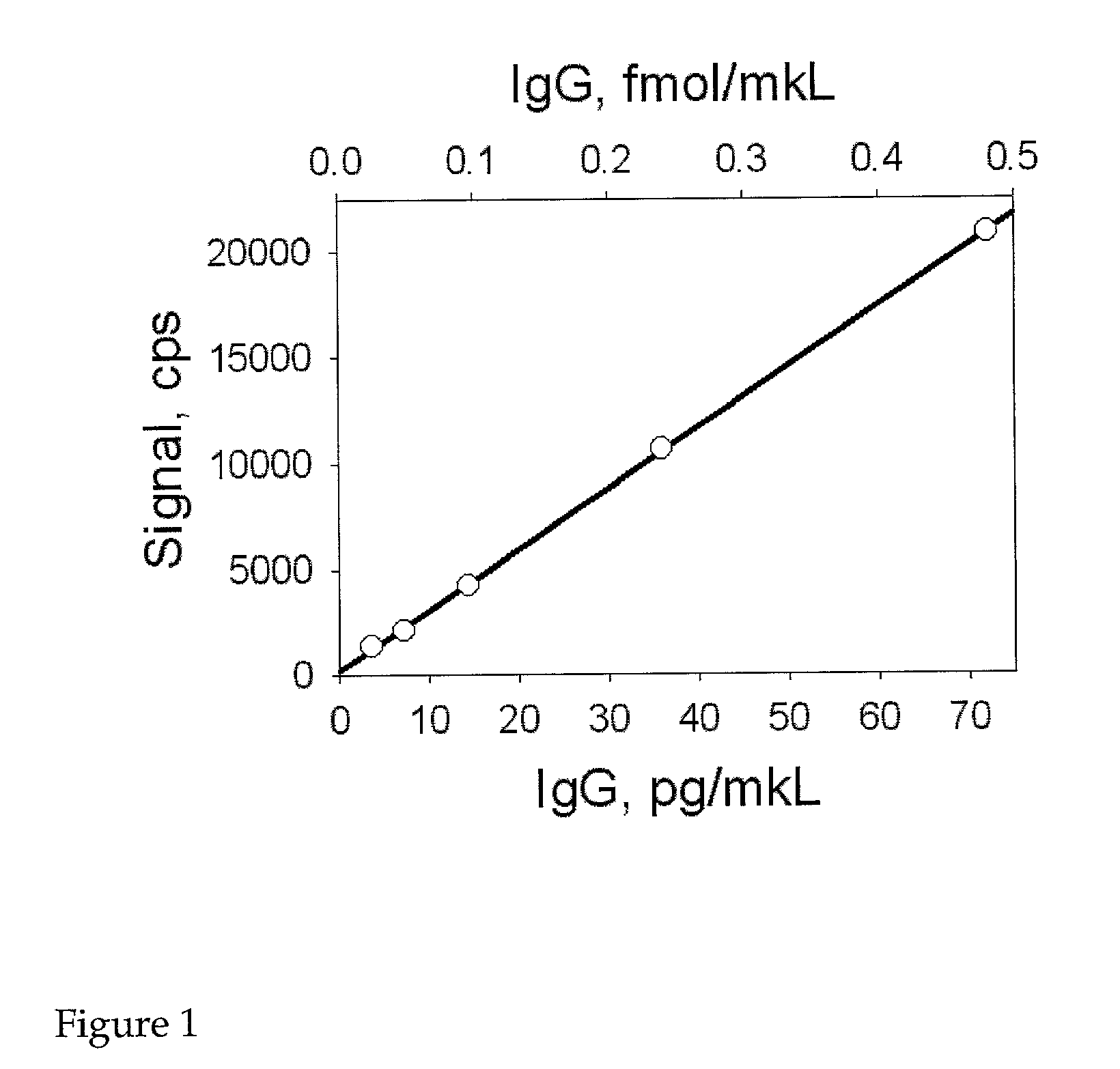
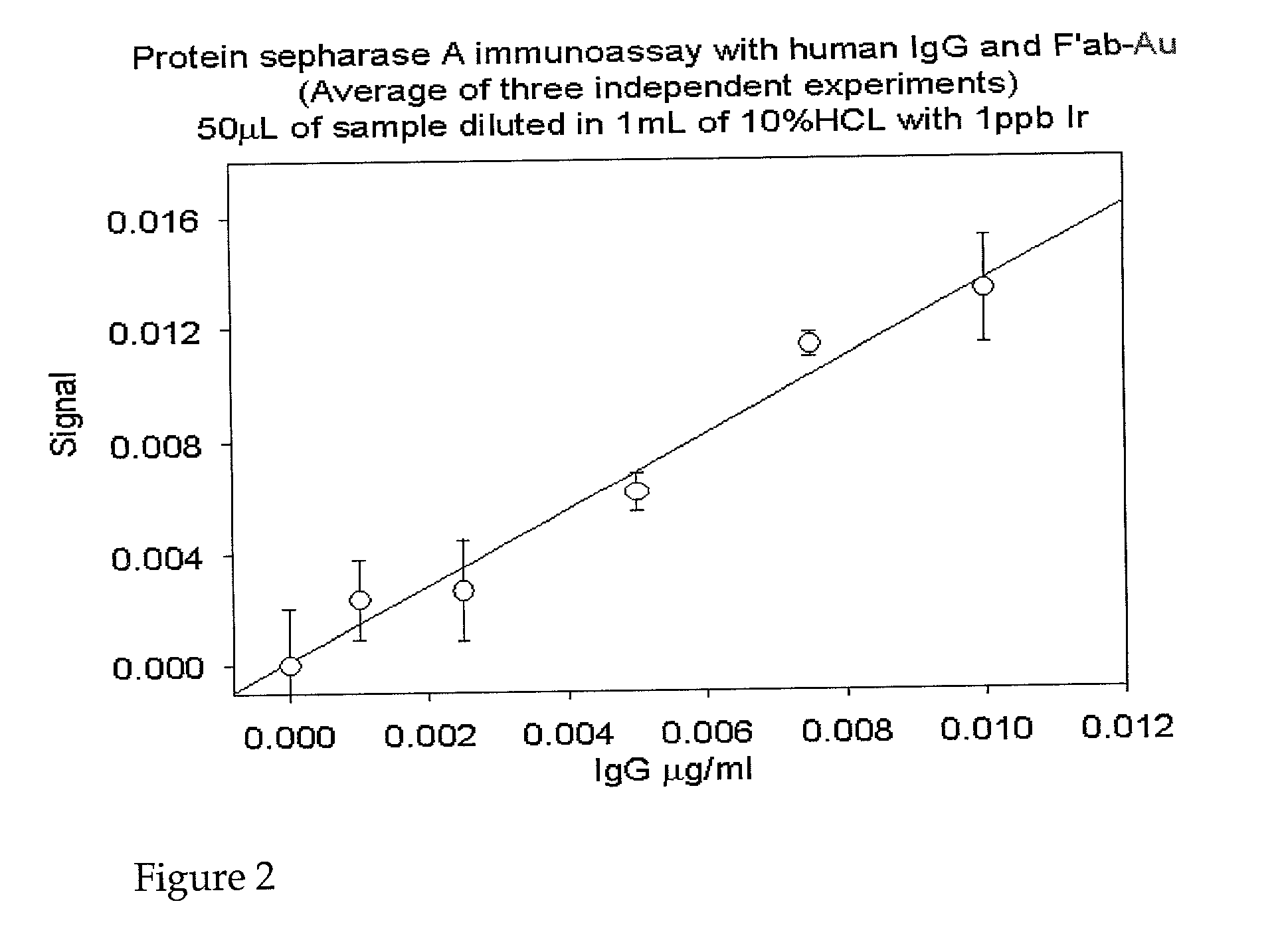
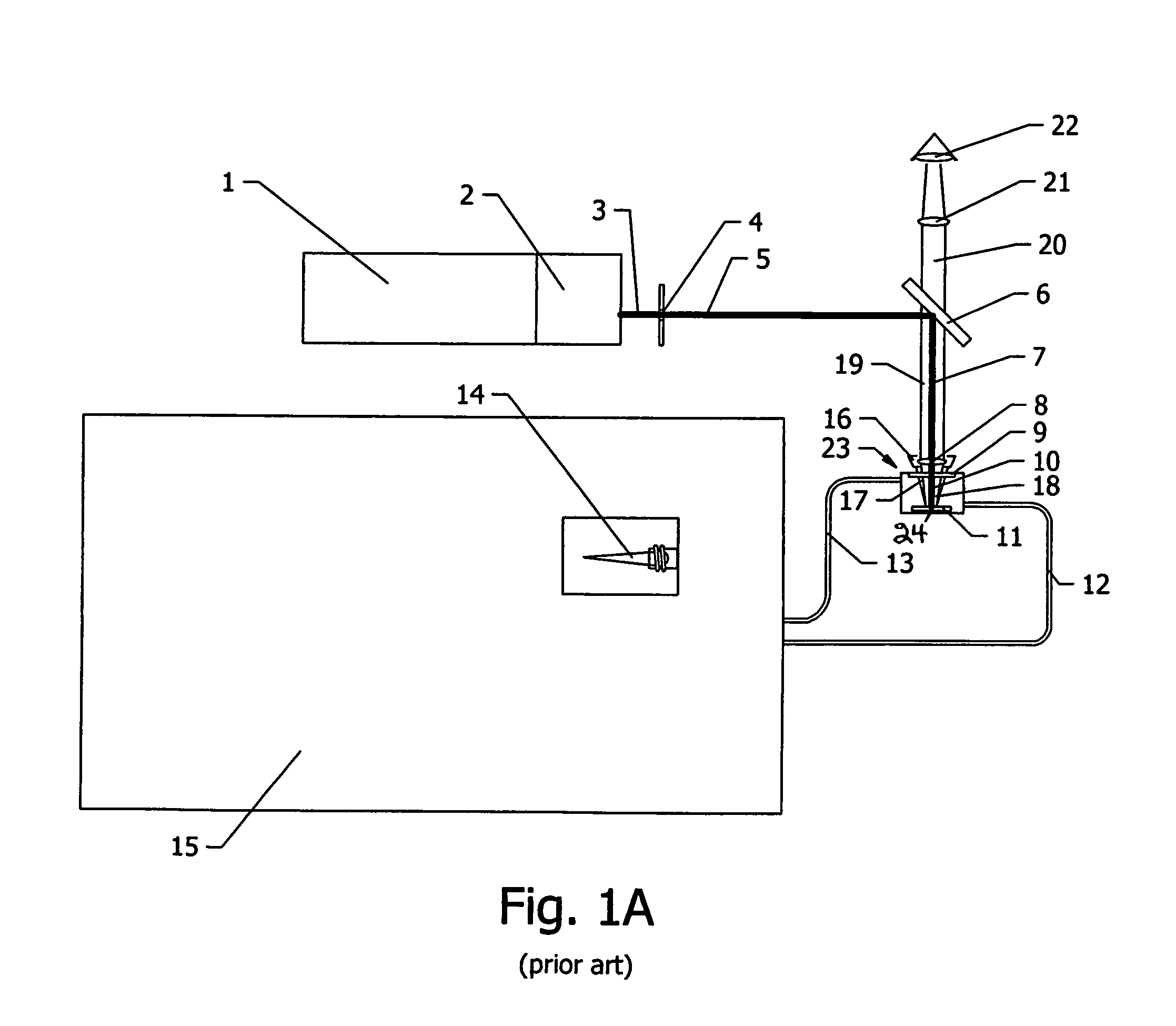
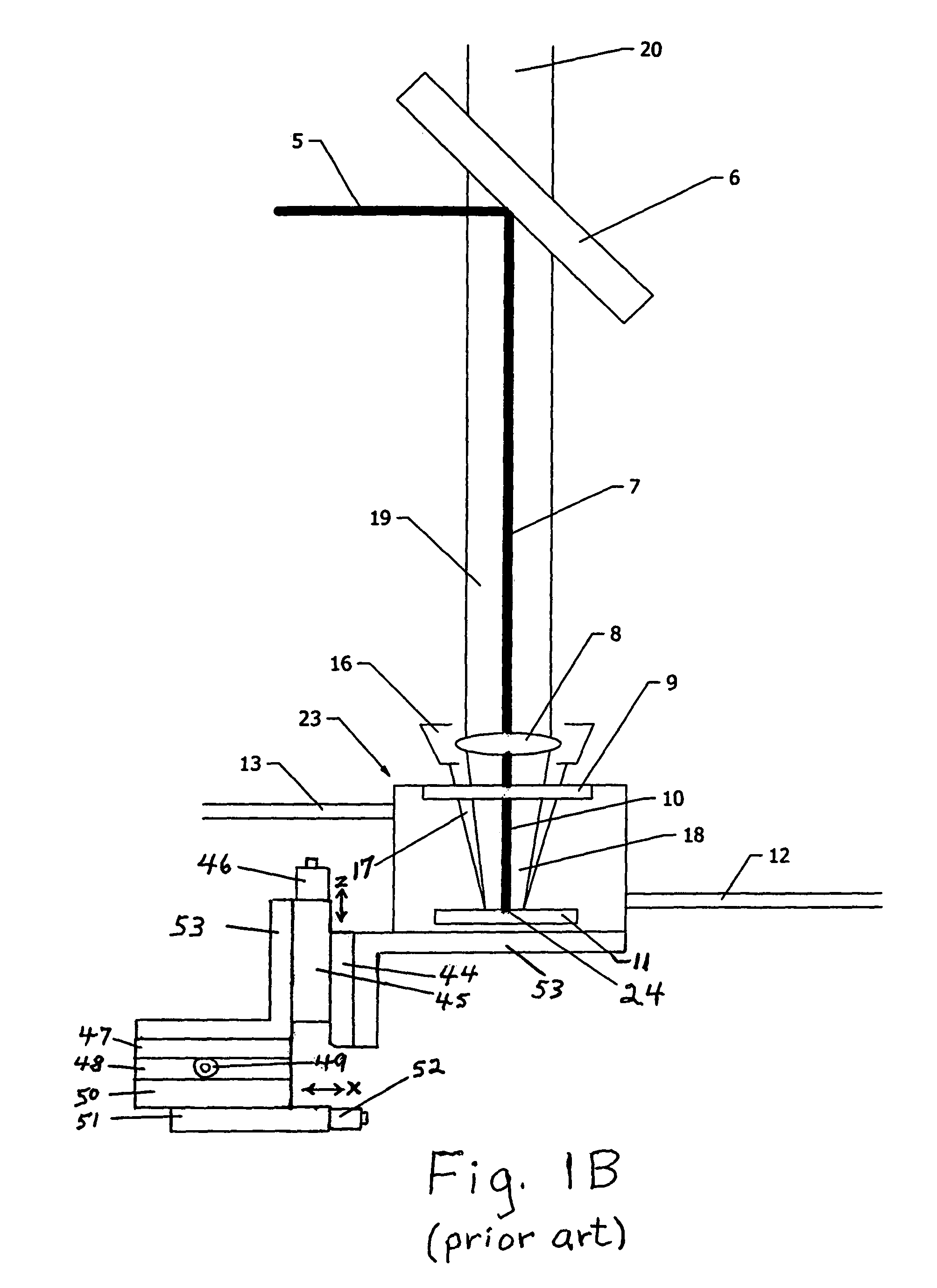
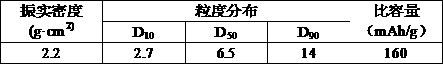
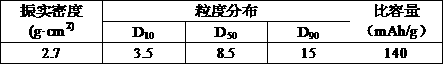
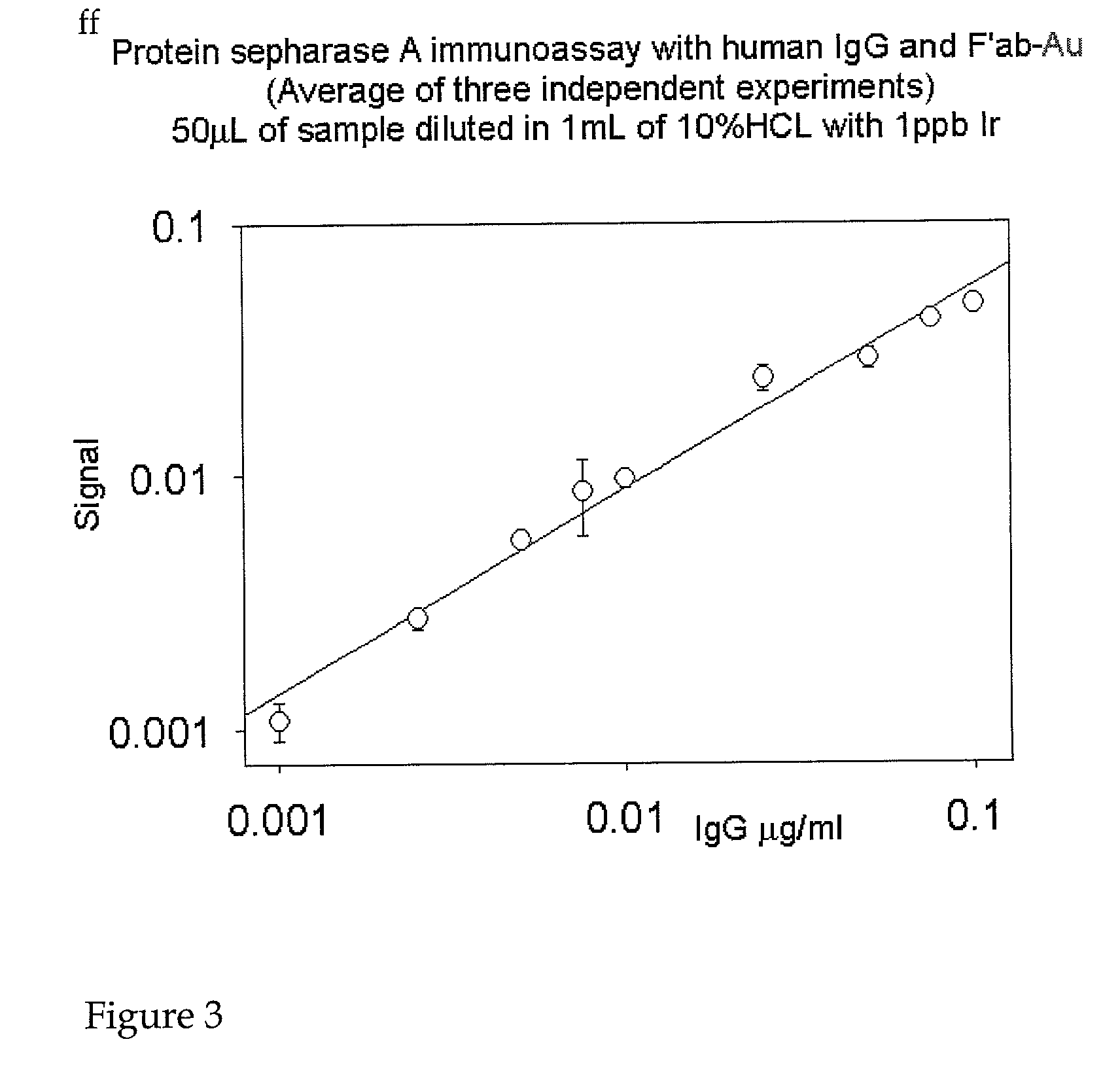Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
417 results about "Elemental analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elemental analysis is a process where a sample of some material (e.g., soil, waste or drinking water, bodily fluids, minerals, chemical compounds) is analyzed for its elemental and sometimes isotopic composition. Elemental analysis can be qualitative (determining what elements are present), and it can be quantitative (determining how much of each are present). Elemental analysis falls within the ambit of analytical chemistry, the set of instruments involved in deciphering the chemical nature of our world.
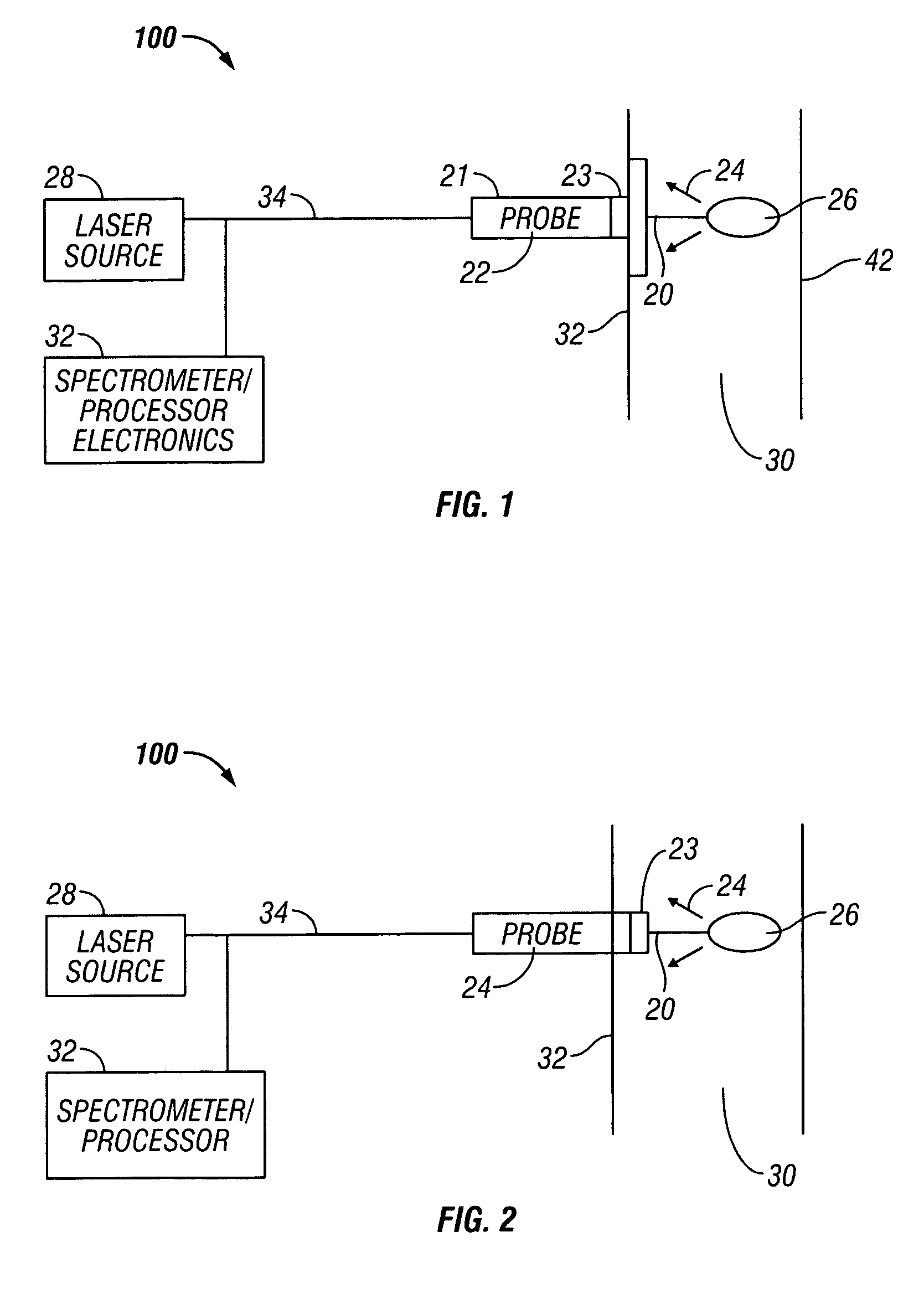
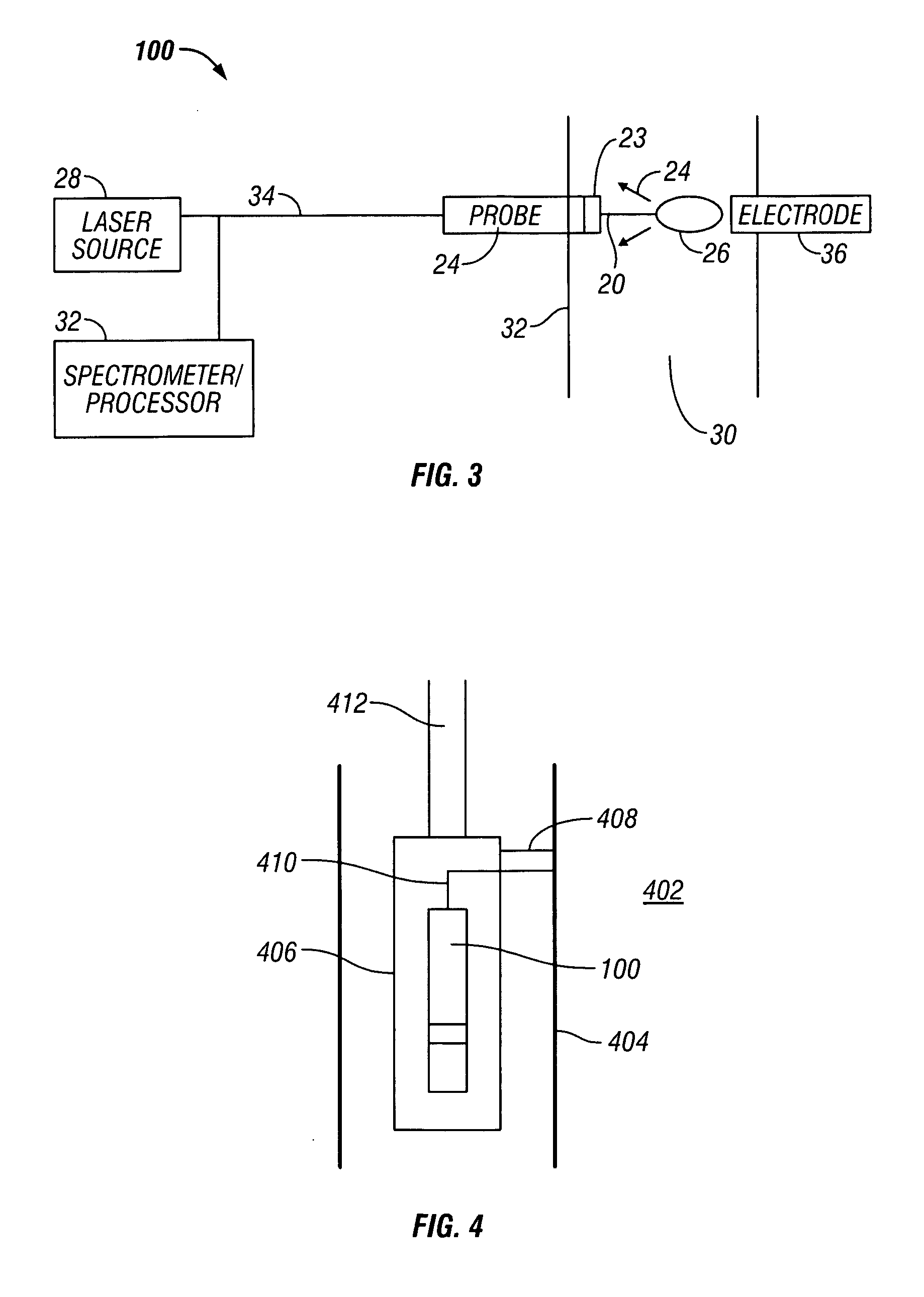
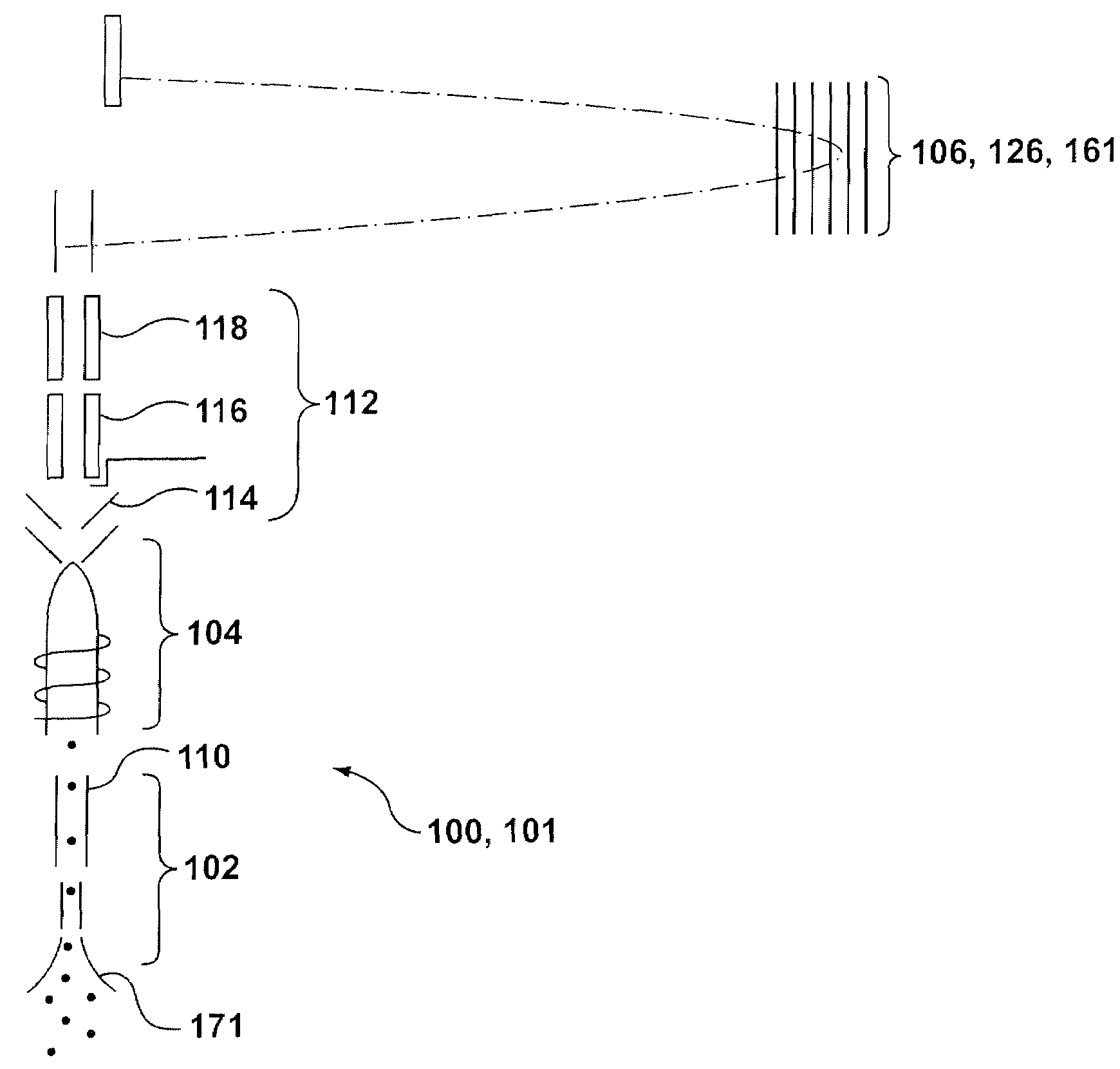
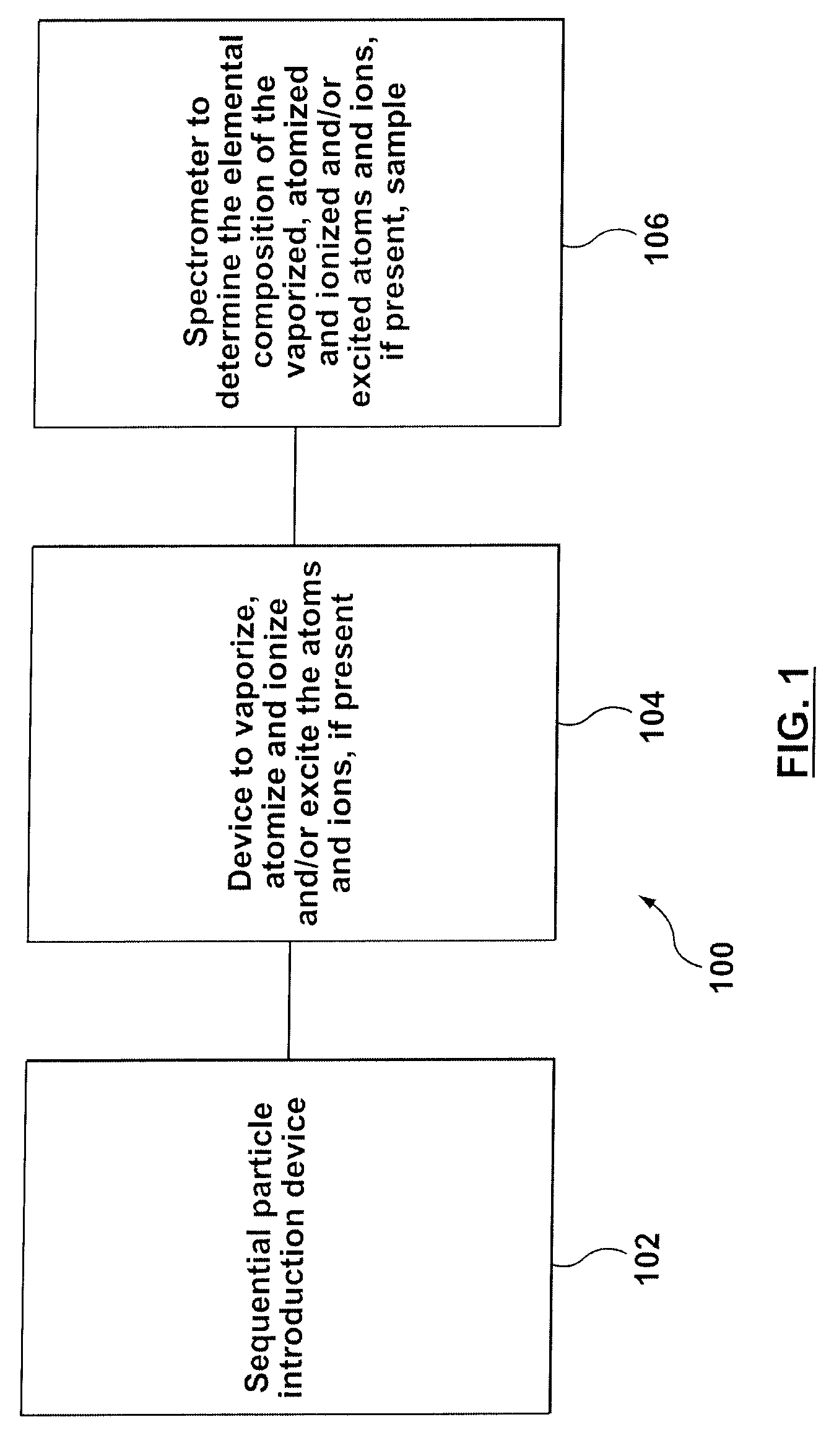
Method and apparatus for flow cytometry linked with elemental analysis
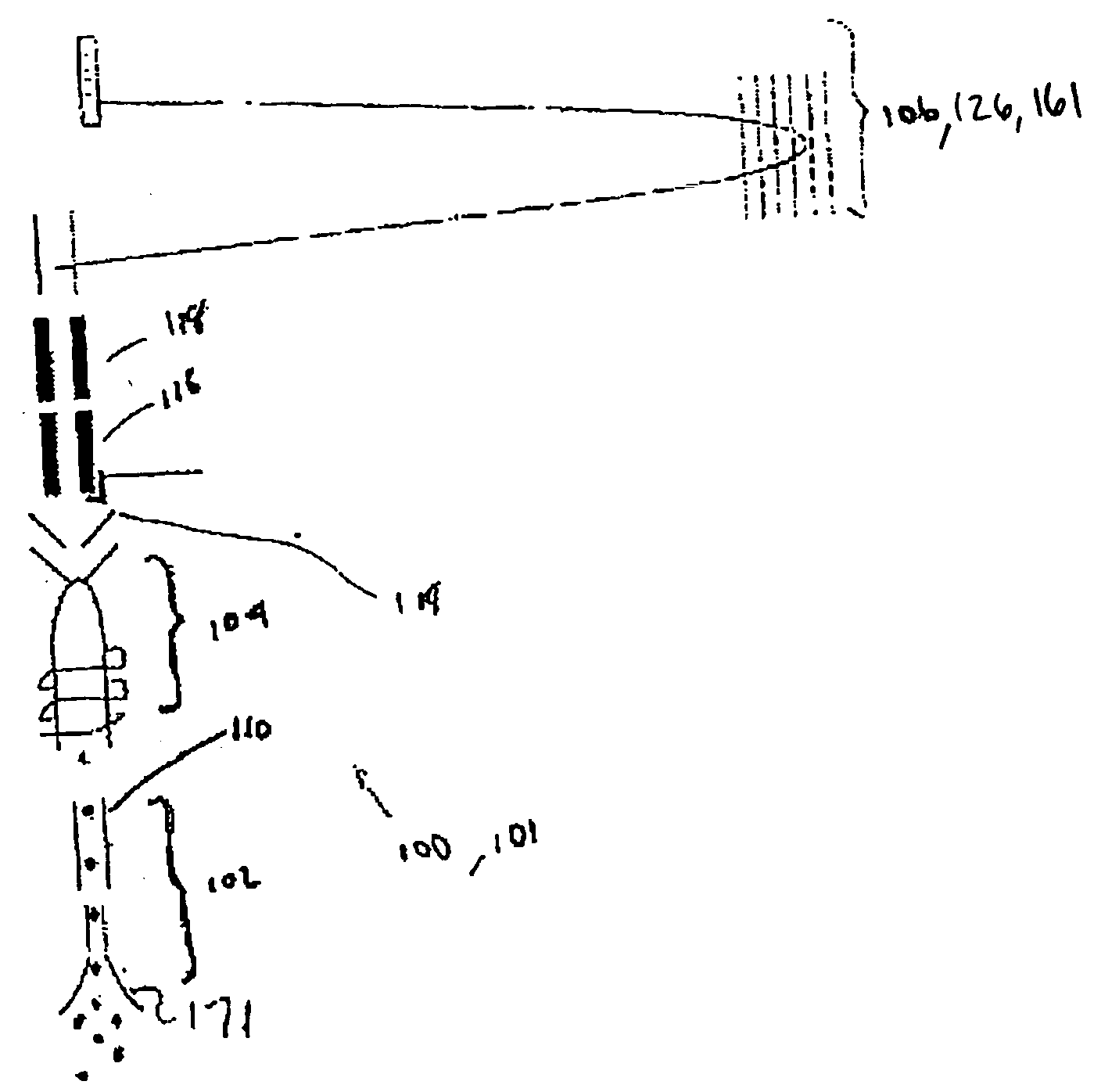
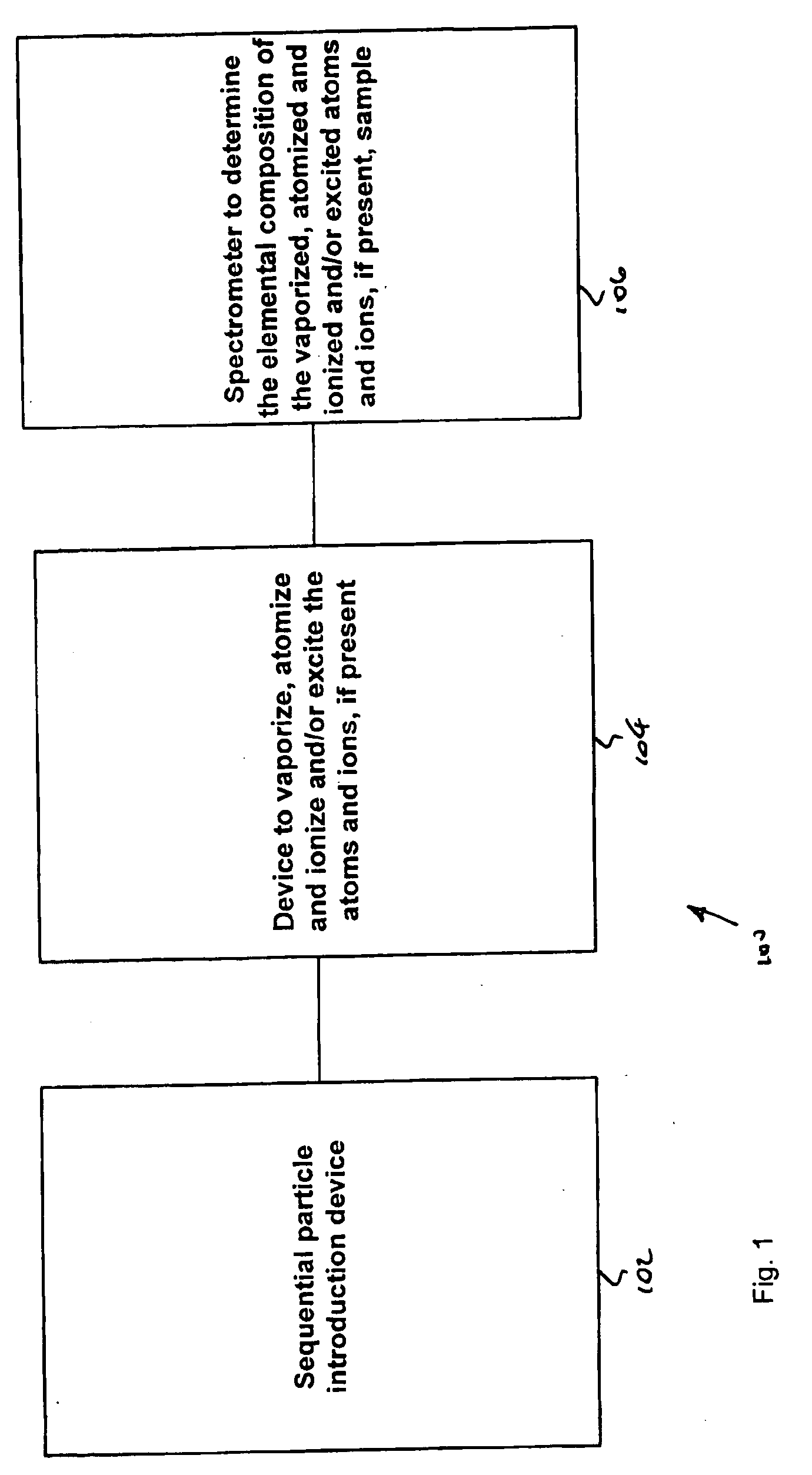
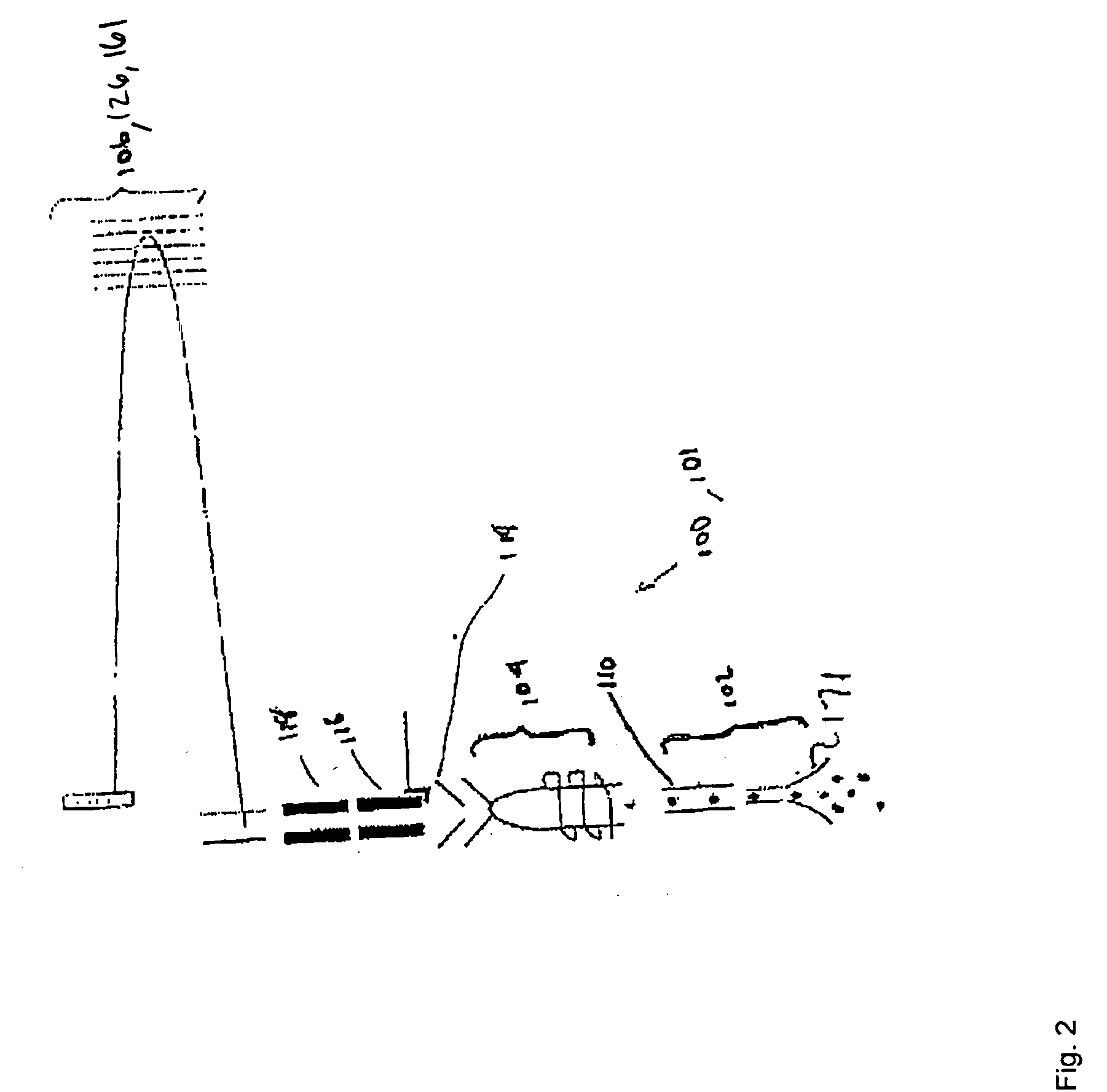
An apparatus (100) for sequentially analyzing particles such as single cells or single beads, by spectrometry. The apparatus, an elemental flow cytometer, includes means (102) for sequential particle introduction, means (104) to vaporize, atomize and excite or ionize the particles, or an elemental tag associated with an analyte on the particles, and means (106) to analyze the elemental composition of the vaporized, atomized and excited or ionized particles, or an elemental tag associated with the particles. Methods for sequentially analyzing particles such as singe cells or single beads by spectrometry are also described.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
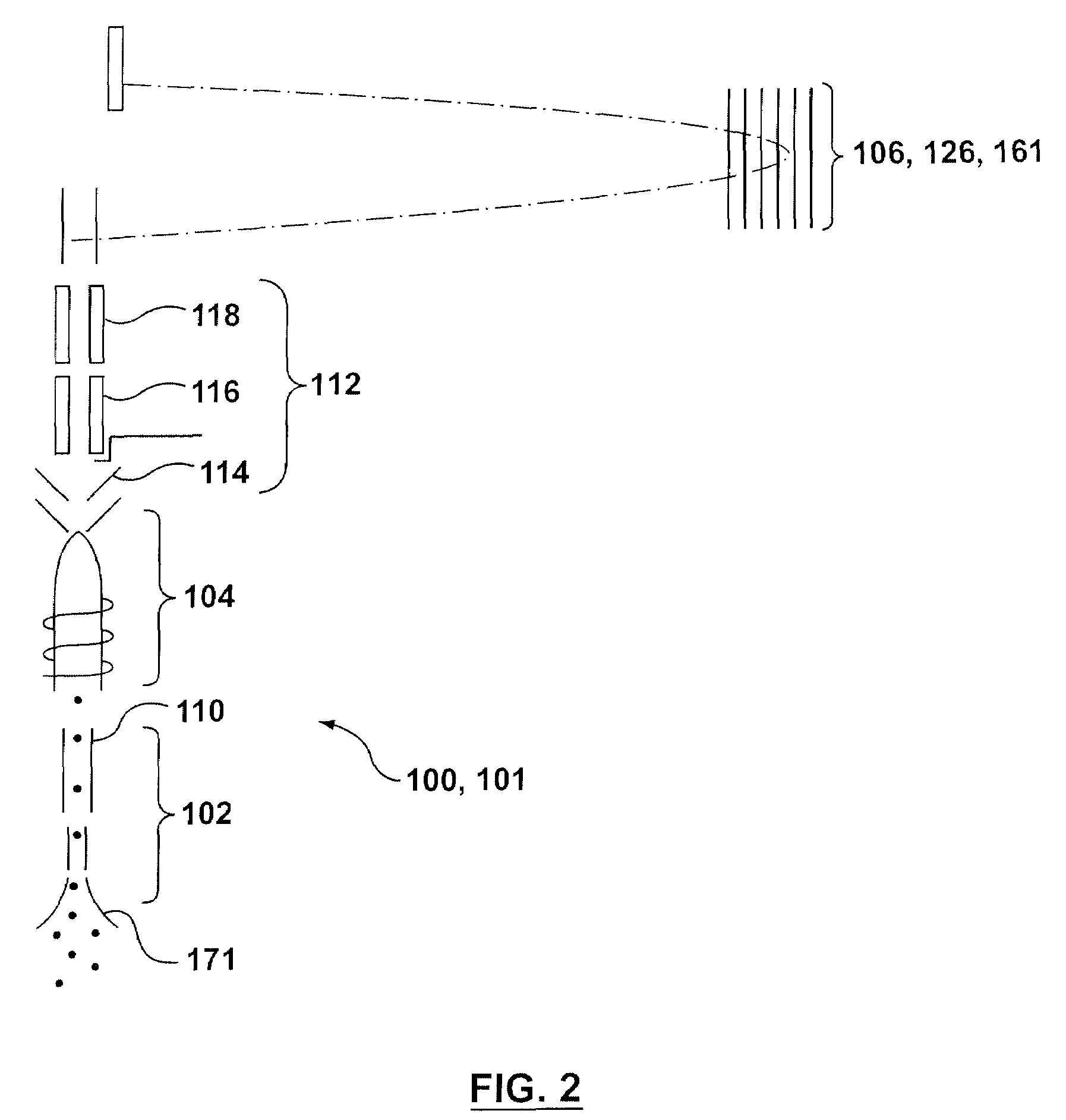
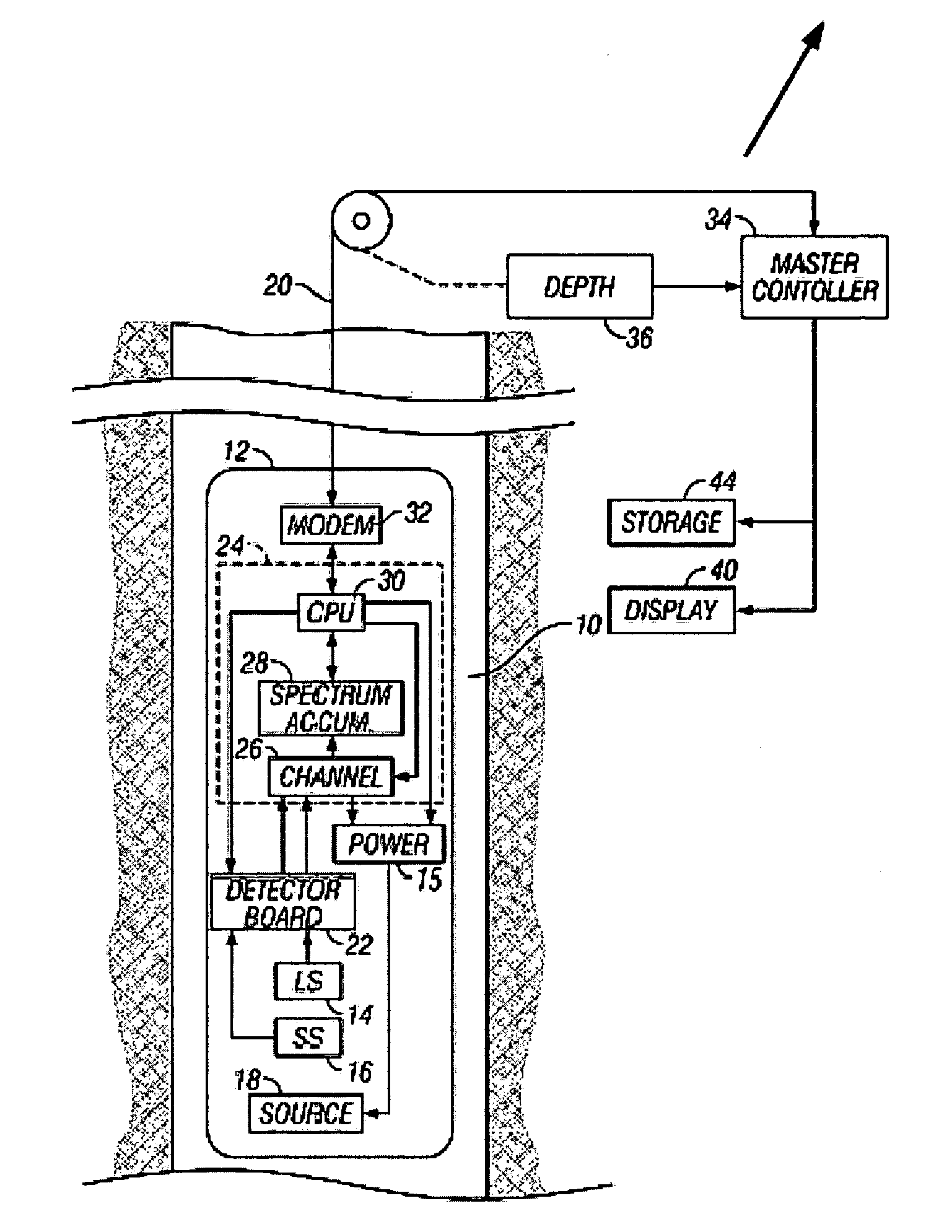
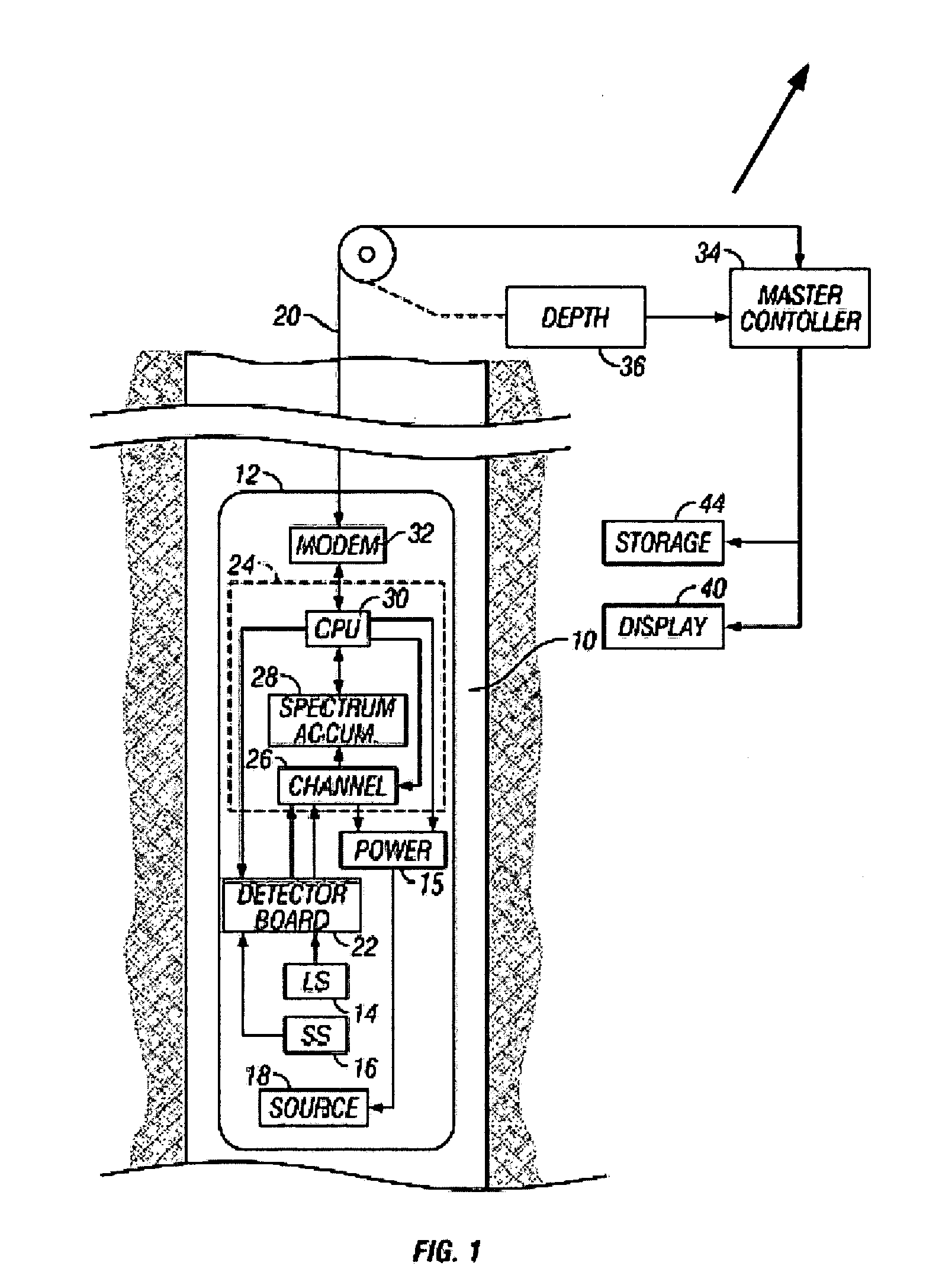
Method and apparatus for elemental analysis of a fluid downhole
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for performing elemental analysis of a formation fluid downhole. The present invention provides elemental analysis of a formation fluid downhole using breakdown spectroscopy. In one aspect of the invention, a method and apparatus are provided for performing laser induced breakdown on a formation fluid sample is provided. In another aspect of the invention a method and apparatus are provided for performing spark induced breakdown spectroscopy. Plasma is induced in a fluid under test downhole. Emissions from the plasma are analyzed to determine the elemental composition of the fluid under test. Emissions include but are not limited to light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions of the spectrum. A spectrometer is provided for elemental analysis of a fluid downhole. Elemental analysis yields information about the fluid and the formation from which the fluid originated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for flow cytometry linked with elemental analysis
An apparatus (100) for sequentially analyzing particles such as single cells or single beads, by spectrometry. The apparatus, an elemental flow cytometer, includes means (102) for sequential particle introduction, means (104) to vaporize, atomize and excite or ionize the particles, or an elemental tag associated with an analyte on the particles, and means (106) to analyze the elemental composition of the vaporized, atomized and excited or ionized particles, or an elemental tag associated with the particles. Methods for sequentially analyzing particles such as singe cells or single beads by spectrometry are also described.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Method and apparatus for determining aluminum concentration in earth formations
InactiveUS20060033023A1Earth material testingNuclear radiation detectionWell loggingElemental analysis
Elemental analysis of an earth formation (including Aluminum) is obtained using measurements from a gamma ray logging tool. The inelastic spectrum of Aluminum is determined from measurements made in a water tank. From the elemental analysis, an estimate of the mineralogy of the formation is made treating the problem as one of Linear Programming (maximizing an objective function subject to equality and / or inequality constraints.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Elemental gamma ray signature instrument
InactiveUS7205535B2Earth material testingNuclear radiation detectionElemental analysisLinear programming
Elemental analysis of an earth formation is obtained using measurements from a gamma ray logging tool. From the elemental analysis, an estimate of the mineralogy of the formation is made treating the problem as one of Linear Programming (maximizing an objective function subject to equality and / or inequality constraints).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
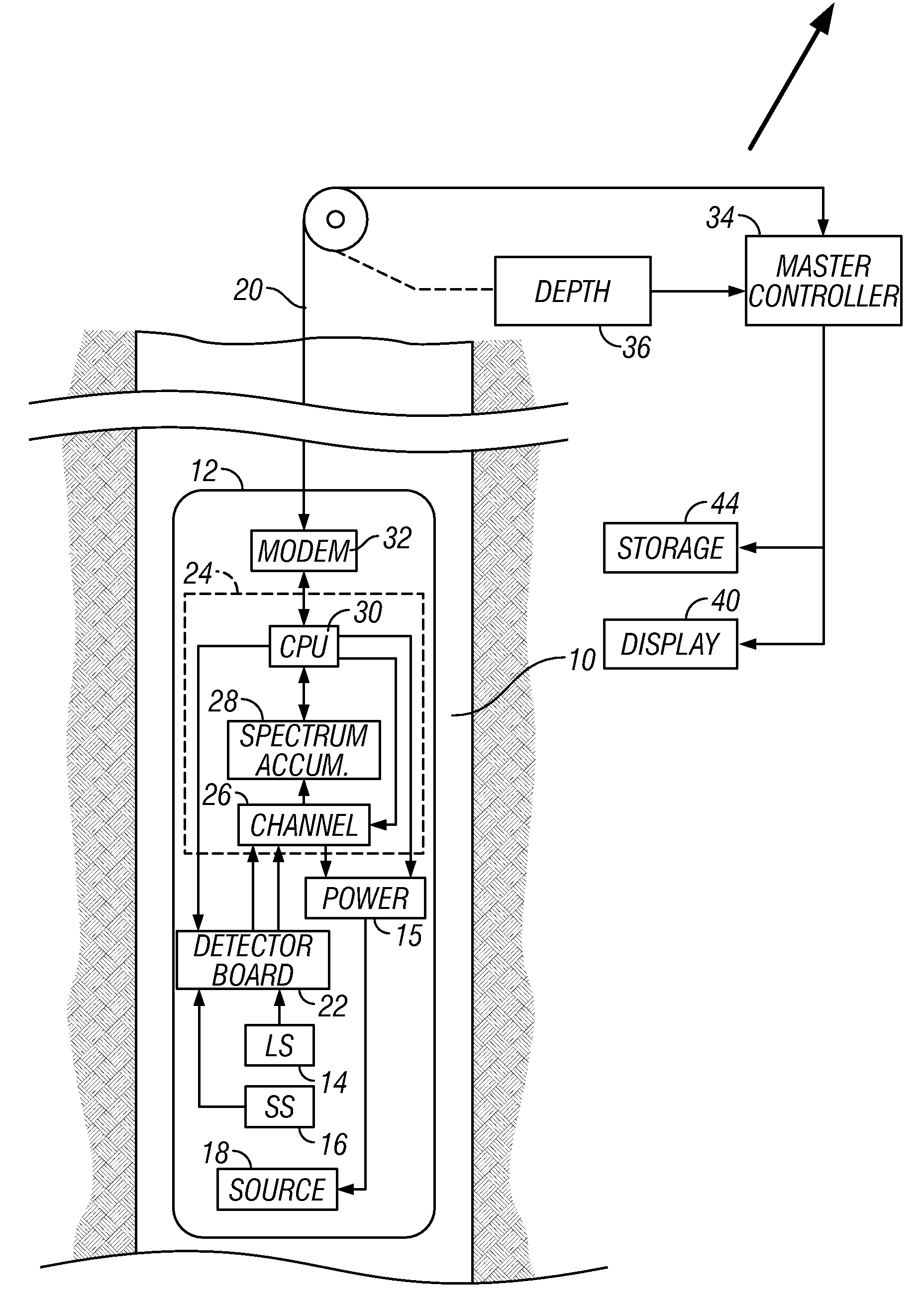
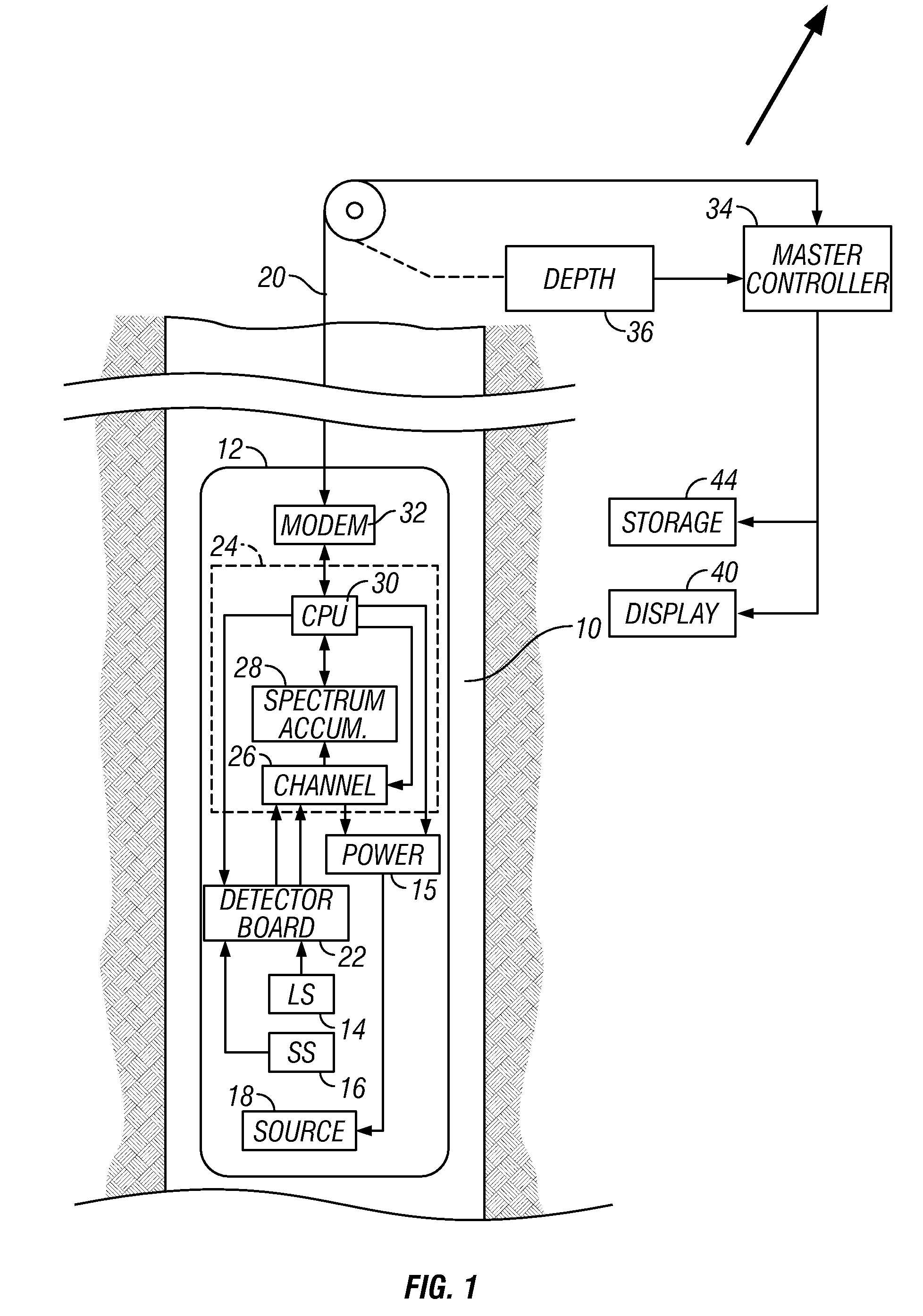
Compact and portable low-field pulsed NMR dispersion analyzer
ActiveUS7417426B2Small and portableLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientLiquid ratio
A compact and integrated portable device is provided for the analysis of dispersions by low-field pulsed NMR including: an NMR probe module, a means for generating radio frequency and magnetic field gradient pulses, a signal processor, and a master controller. Also provided are methods for using the device to measure one or more characteristics of phases or particles comprising a dispersion such as surface area, solid / liquid ratio, particle size, and elemental analysis.
Owner:XIGO NANOTOOLS
Elemental analysis of tagged biologically active materials
InactiveUS7135296B2Simple methodIn-vivo radioactive preparationsParticle separator tubesSpectroscopyElemental analysis
Improved methods for the detection and quantitation of labeled biological materials in a sample using elemental spectroscopic detection are described. Element-labeled biologically active materials, comprising antibodies, antigens, growth factors, hormones, receptors and other biologically active materials covalently attached to a stable elemental tag, can be used in specific binding assays and measured by elemental spectroscopic detection. Also described are methods for the determination of metals in samples of interest using specific antibodies to isolate the target metals and elemental spectroscopy for detection and quantitation.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Method for determining volume of organic matter in reservoir rock
ActiveUS20100057409A1Simple and robust techniqueApplied quickly and inexpensivelyEarth material testingComputation using non-denominational number representationVisual interpretationHydrocotyle bowlesioides
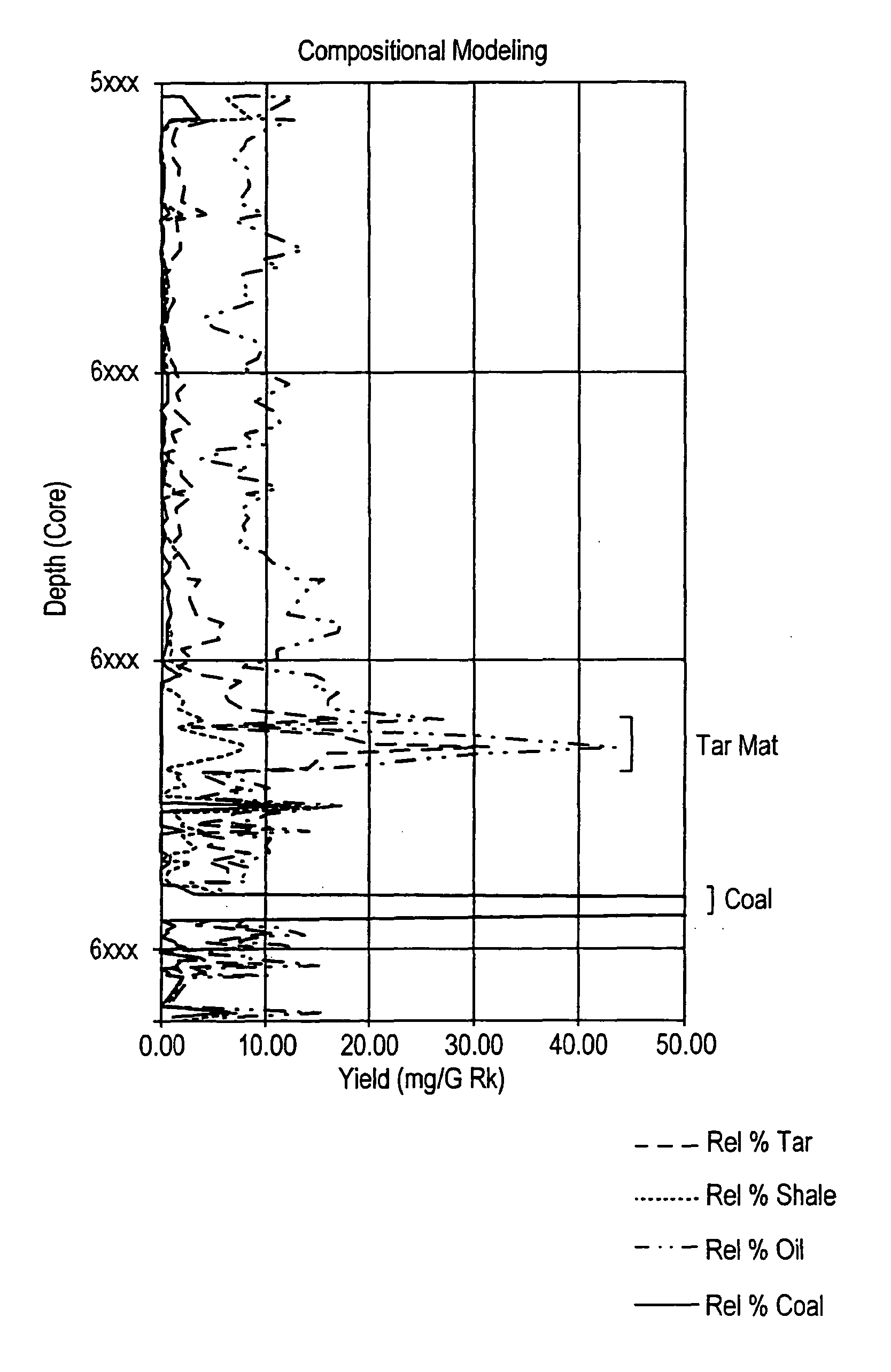
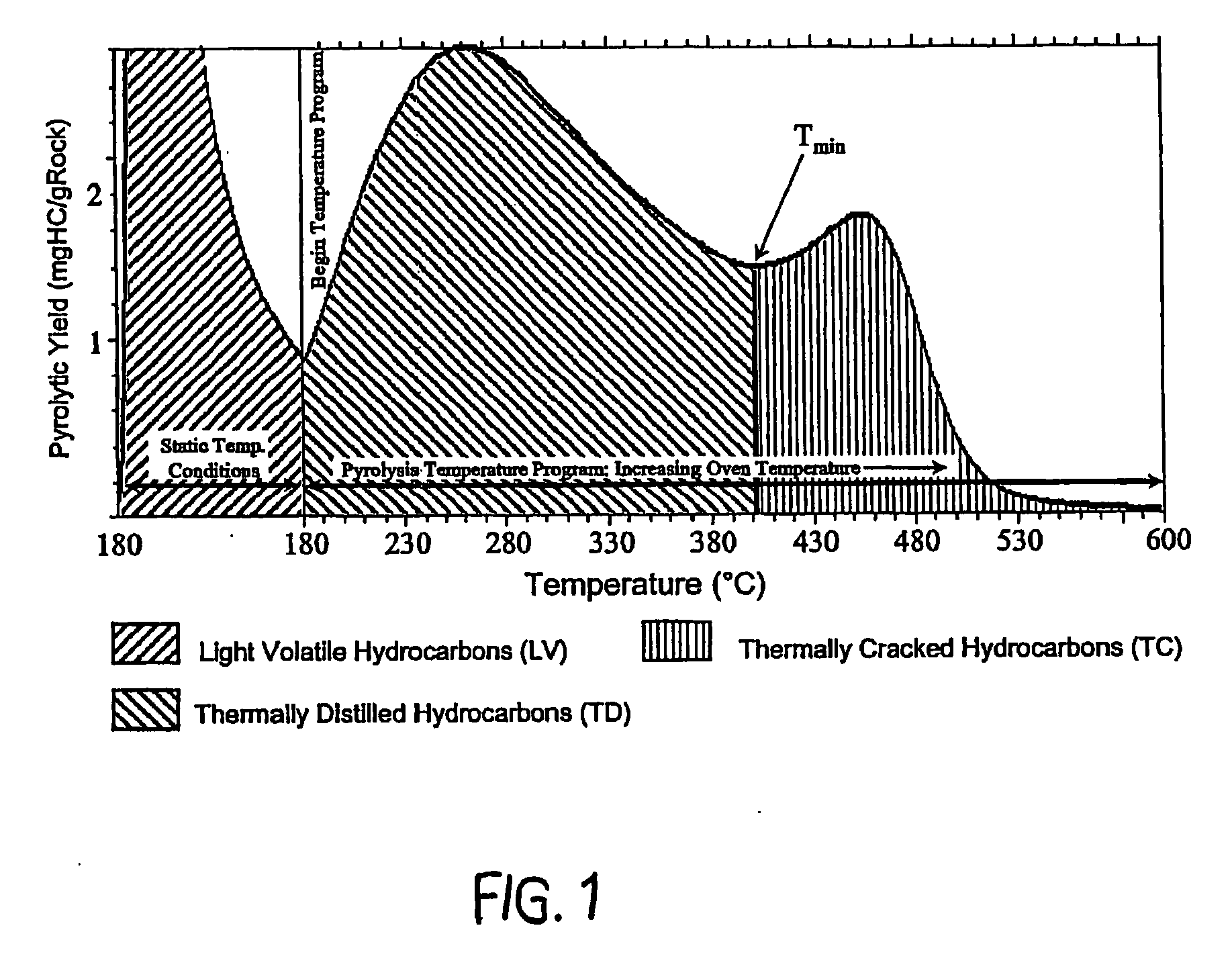
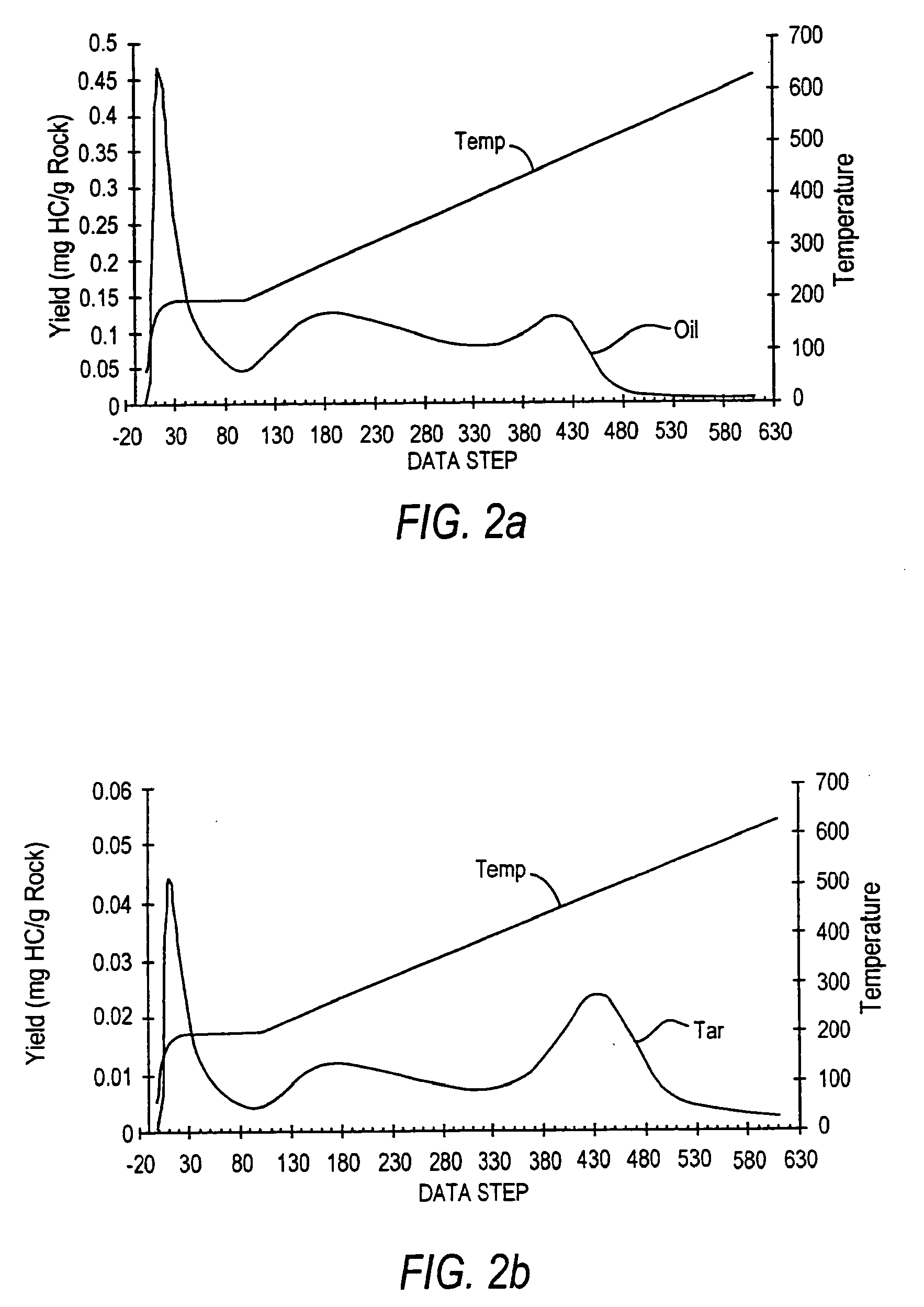
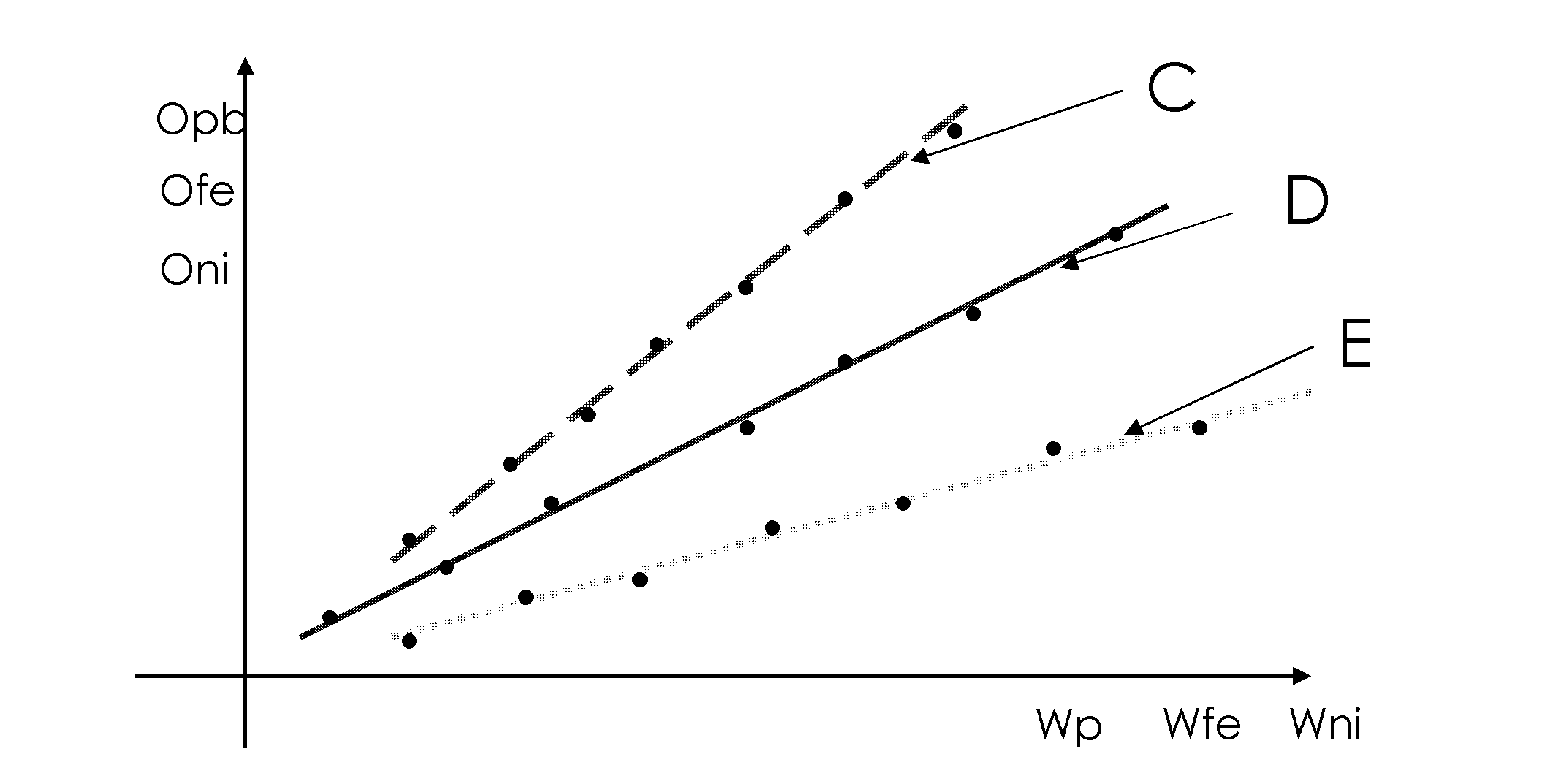
A method for calculating the volume of various predetermined organic end-members in samples of rock at various depths in oil reservoir rock is utilized to produce one or more graphic displays that are use to interpret the data to identify, e.g., tar mats, in order to improve the efficient production of hydrocarbons from the well. Data is collected from the samples by known pyrolysis and compositional modeling methods; additional data is obtained by elemental analysis to determine weight percentages of C, H, N, S and O in the selected end-members and characterization of physical properties of representative samples of the reservoir rock, e.g., from core samples; the data is then processed in accordance with the method to provide a series of data points used to produce the graphic displays for visual interpretation.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method for preparing nitrogen-doped porous carbon by taking cottonseed hull as raw material and application
InactiveCN108455597AWide range of resource sourcesLow costCarbon preparation/purificationCapacitancePorous carbon
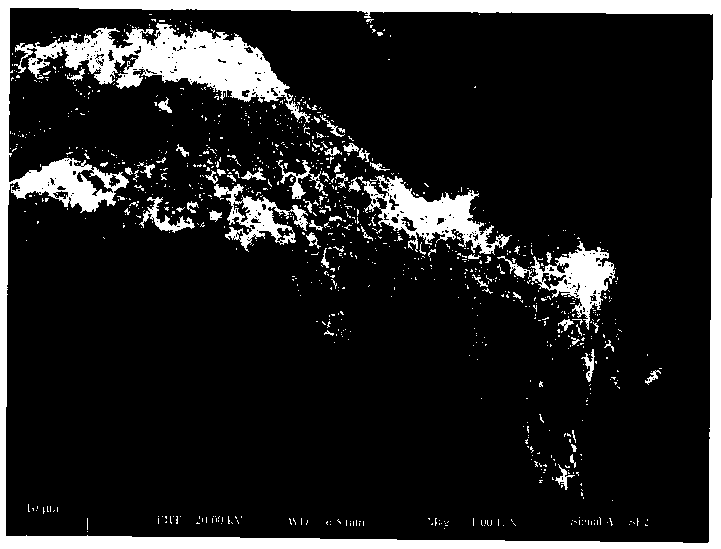
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen-doped porous carbon by taking cottonseed hull as a raw material and application. The method is characterized in that the nitrogen-doped porous carbon material is prepared by taking the cottonseed hull as a raw material and urea as a nitrogen source, stirring and uniformly mixing the substances with a sodium hydroxide solution, and then carrying out high-temperature carbonization and activation. An electron microscope photo shows that the prepared nitrogen-doped porous carbon material is of a three-dimensional inner cross-linking network structure. XPS and elemental analysis show that the nitrogen element is successively and uniformly doped in a carbon matrix; the XPS analysis shows that the nitrogen content is 1.84 to 7.35%; the elemental analysis shows that the nitrogen content is 2.07 to 6.52 % and the specific surface area is 1010 to 2500m<2> / g. The super-capacitor experiment shows that the prepared nitrogen-doped porous carbonmaterial has good electrochemical properties and the specific capacitance can reach 320 to 340F / g (current density is 0.5A / g). The method has the advantages of simplicity in preparation, wide range of renewable resources as raw materials, low price, low cost, easiness in large-scale industrialization application and capability of being applied to the field of energy storage.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application and preparation method of biomass-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon
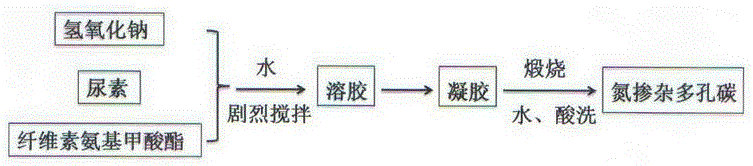
InactiveCN106629655ASimple processImprove stabilityHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationCelluloseCarbamate
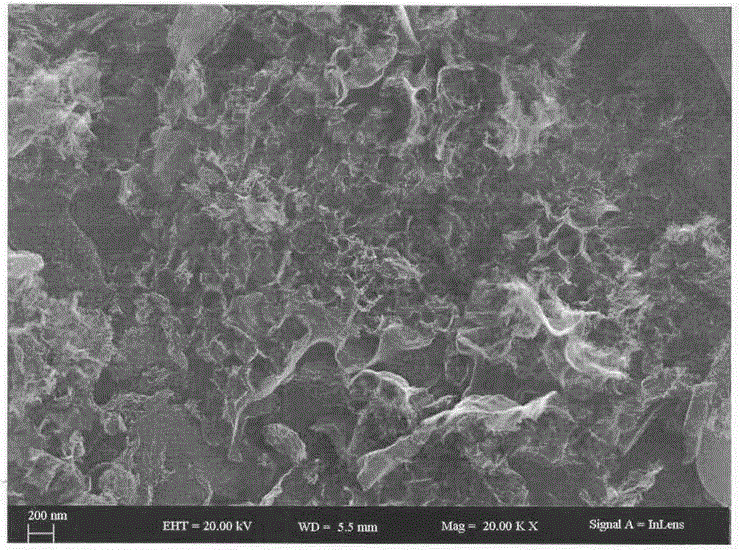
The invention discloses application and a preparation method of biomass-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon. The method includes: taking cheap cellulose carbamate as a raw material and urea as a nitrogen source, well mixing with sodium hydroxide solution, drying to form sol, and performing high-temperature calcination to obtain the porous-structure biomass-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon high in specific surface area and pore volume. According to electron microscopy images, the prepared material is in a three-dimensional inner-crosslinked porous structure; according to XPS and elemental analysis, nitrogen is successfully doped into a carbon substrate, the nitrogen content is 7.7-15.5%, and the specific surface area is 700-3700m<2> / g; according to supercapacitor experiments, the biomass-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon is great in electrochemical performance; according to pollutant adsorption experimental data, the material is high in adsorption rate and adsorption capacity in adsorption of dye pollutant methylene blue, and the adsorption capacity reaches 1520mg / g. The method is simple in preparation, the raw materials are renewable, and low cost is realized. In addition, sodium carbonate which is a by-product is obtained by washing of calcined samples, so that cost can be effectively reduced, and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Analytical laser ablation of solid samples for ICP, ICP-MS, and FAG-MS analysis
InactiveUS20090073586A1High sensitivityReduce decreaseMirrorsAnalysis by thermal excitationMolecular analysisPath length
The present invention facilitates improvements in laser ablation of solid samples to be analyzed by an external inductively coupled plasma (ICP) emission spectrometer, ICP / mass-spectrometer (ICP-MS), or flowing afterglow (FAG) mass spectrometer (FAG-MS) for elemental analysis (ICP and ICP-MS) or molecular analysis (FAG-MS). A novel invention mirror-with-hole beam combiner eliminates chromatic aberration in the invention sample view and allows rad-hardening the laser ablation invention for use in a radiation hot cell for analysis of high activity nuclear waste. Many other novel invention rad-hardening attributes facilitate a comprehensive rad-hardened laser ablation system (the world's first). In other embodiments, invention novelties include unusually large homogeneous focused laser spot diameters, unusually long laser objective lens focal length, wide range operationally variable laser path length with built-in re-alignment, operationally variable demagnification ratio and diameter of the focused laser spot, the use of significantly higher powered SMR lasers in a large spot diameter to facilitate high sensitivity bulk analysis of solid samples, a demountable and gravitationally self-sealing stack assembly laser ablation cell, and the world's first auto-samplers (mechanized sample changers) for analytical laser ablation.
Owner:FRY ROBERT C +3
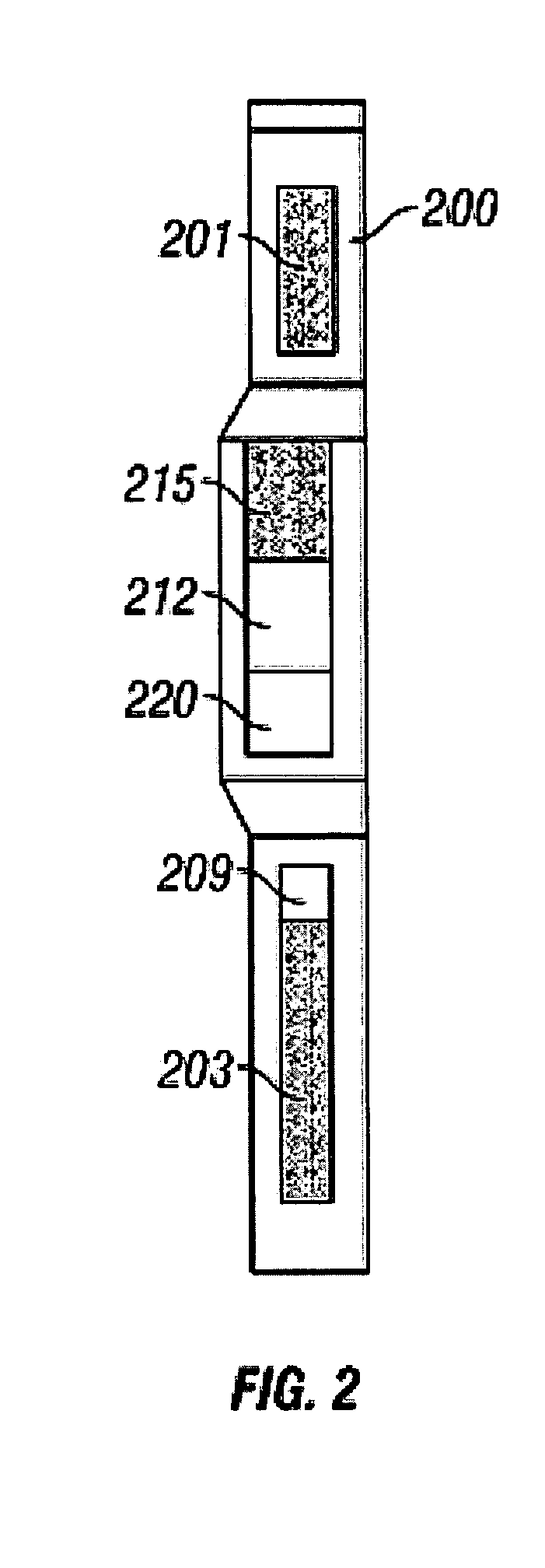
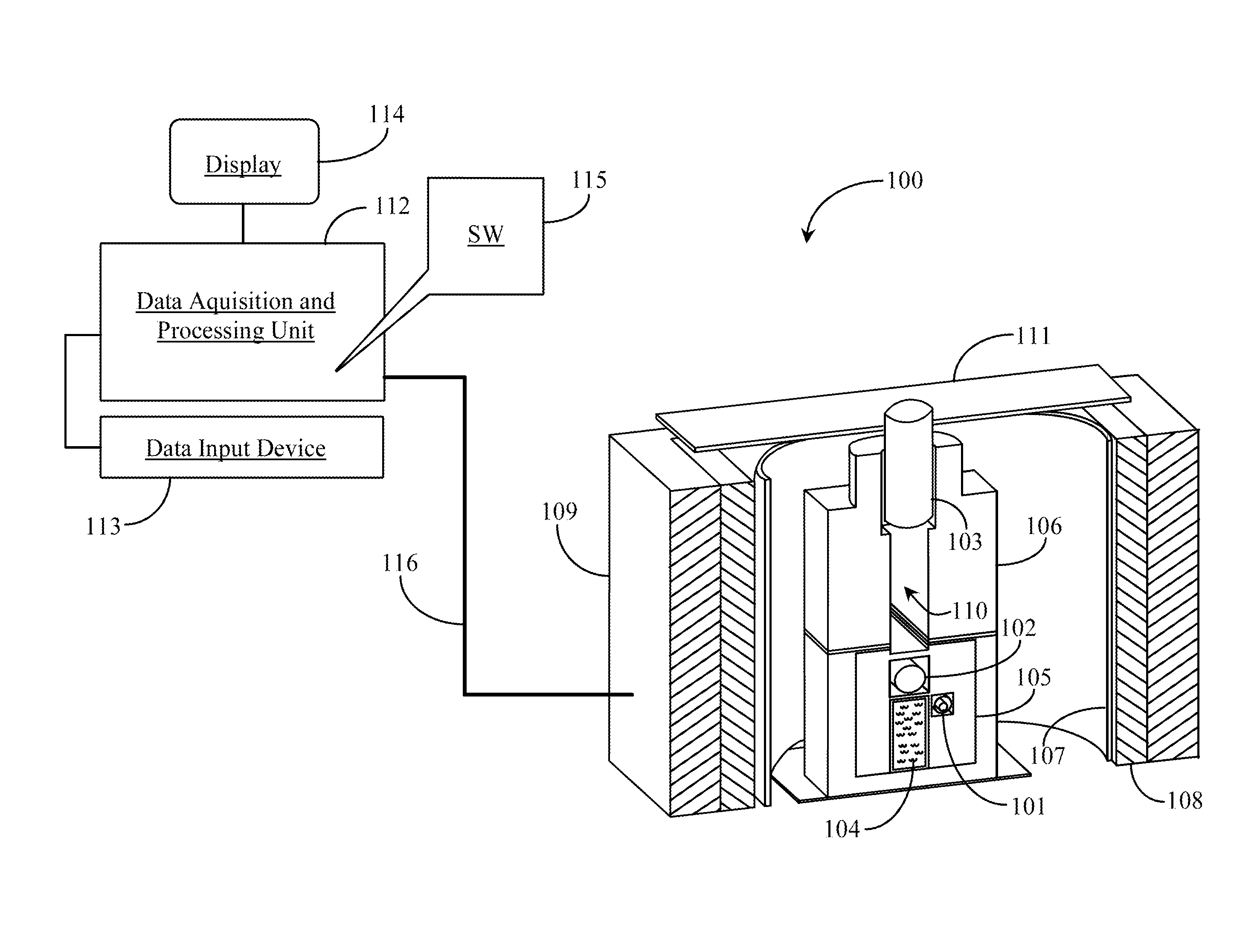
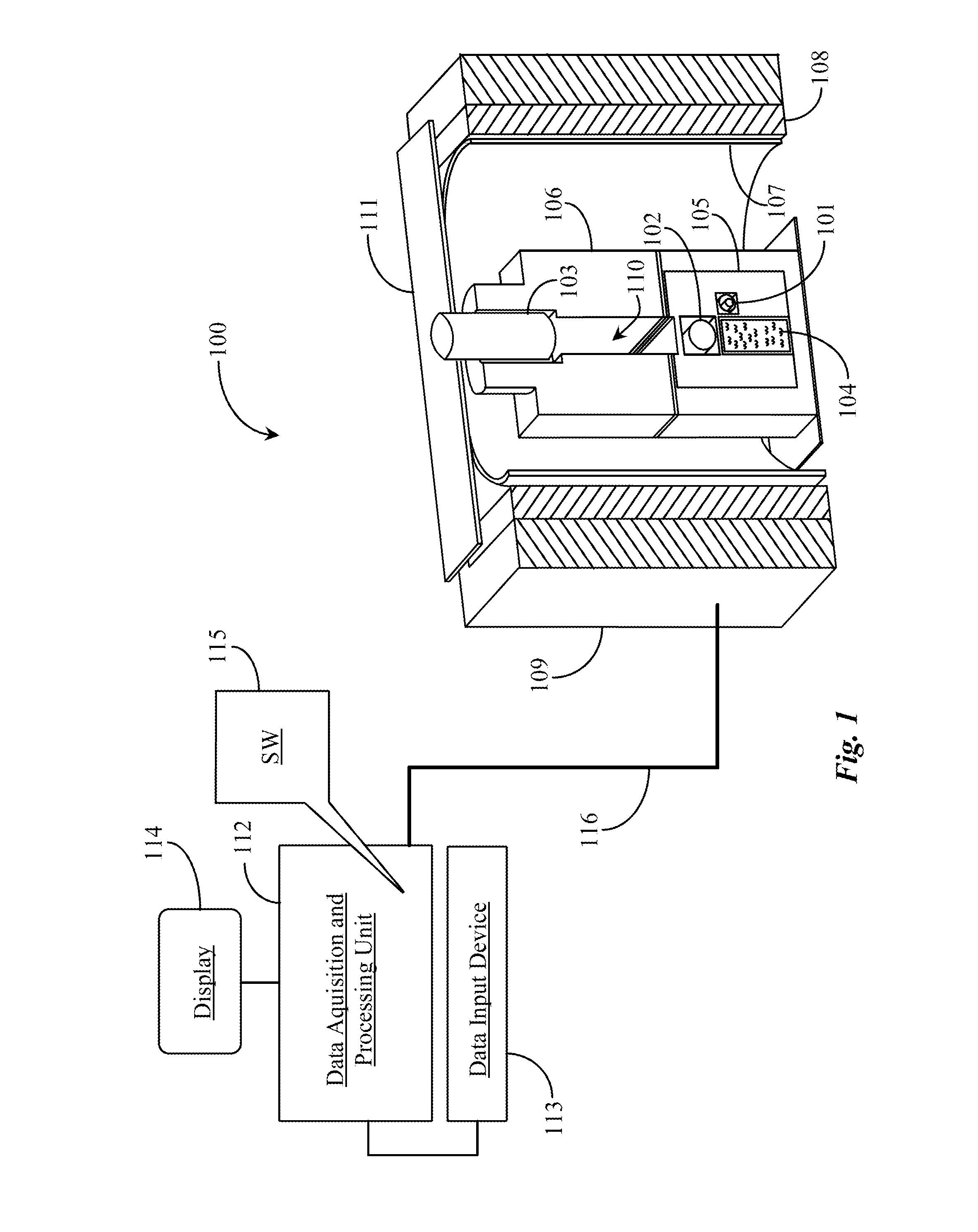
Portable System for Analyzing and Determining Elemental Composition of Rock Samples
InactiveUS20120046867A1No impediment to efficiencyLow costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElemental compositionNeutron emission
A portable system for elemental analysis includes one or more neutron emitters, a chamber for containing a test sample, at least one gamma ray detector electrically connected to a data acquisition system, and software or firmware executing on the data acquisition system from a non-transitory physical medium, the software or firmware providing a first function for producing one or more gamma ray spectrums, a second function for applying correction factors to the one or more gamma ray spectrums, and a third function for analyzing the corrected gamma ray spectrum or spectrums to determine a deconvolved elemental composition of the test sample.
Owner:HELIOCENTRIC TECH
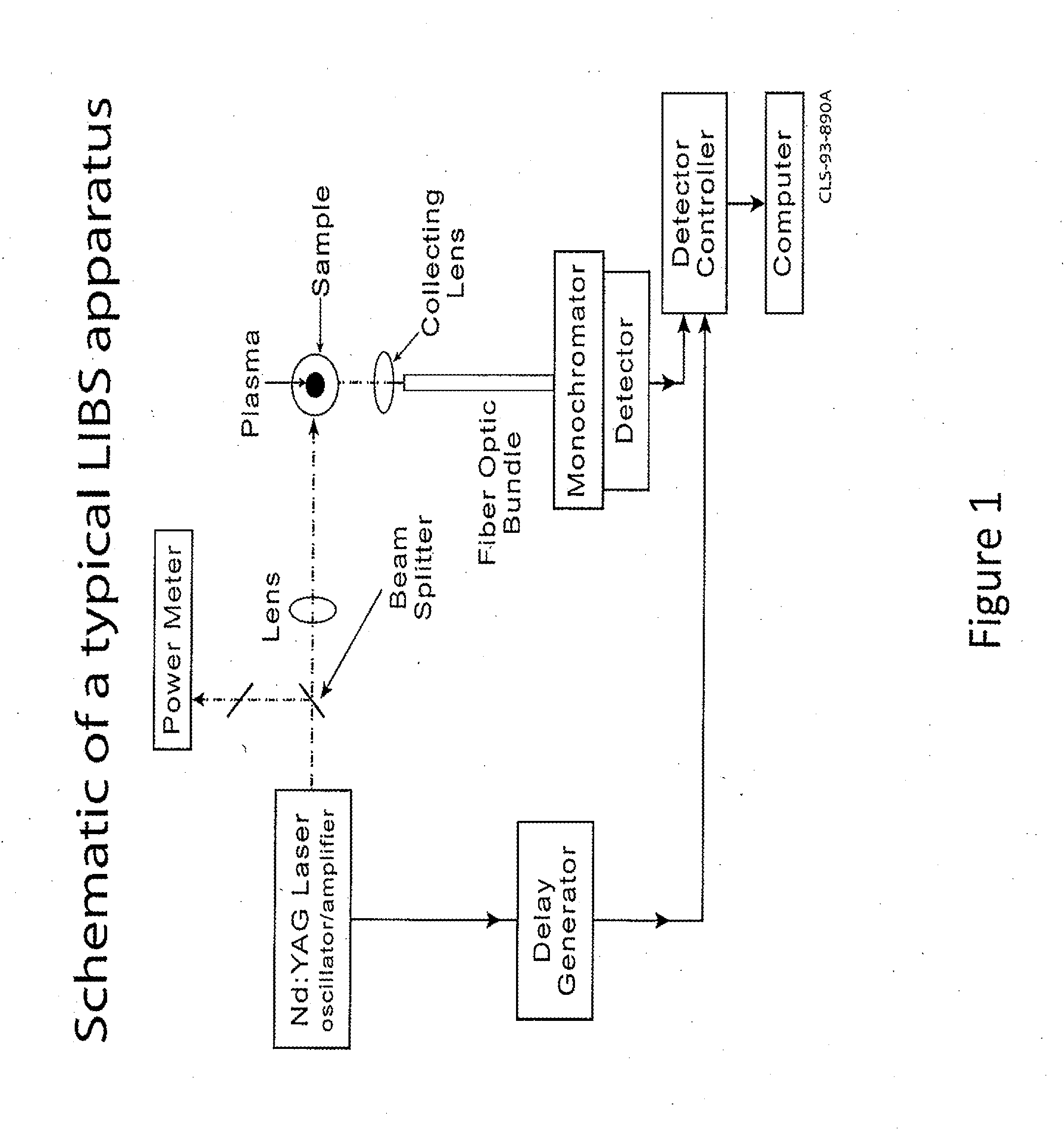
Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy instrumentation for real-time elemental analysis
InactiveUS20120033212A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElemental analysisLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
A backpack laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy LIBS system to provide rapid in-field elemental analysis of environmental samples important to the safeguarding of special nuclear materials.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Determining Organic Carbon Downhole From Nuclear Spectroscopy
Elemental analysis of an earth formation is obtained using measurements from a gamma ray logging tool. From the elemental analysis, an estimate of the Calcium, Magnesium and Carbon content of the formation is determined. The amount of organic carbon in the formation is estimated from the total Carbon content and the inorganic carbon associated with minerals in the formation. An indication of source rock may be obtained from the Th / U ratio. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b)
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
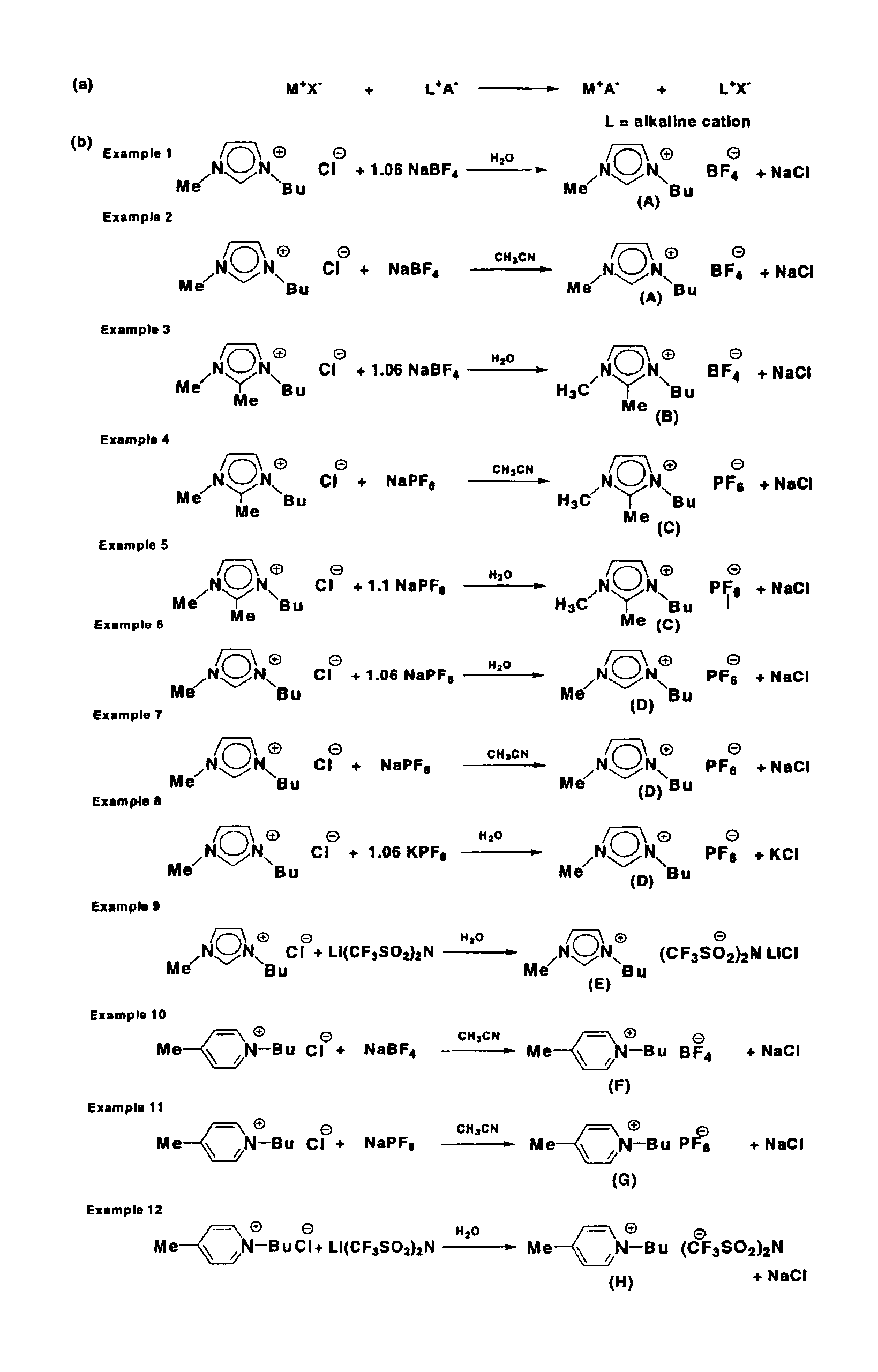
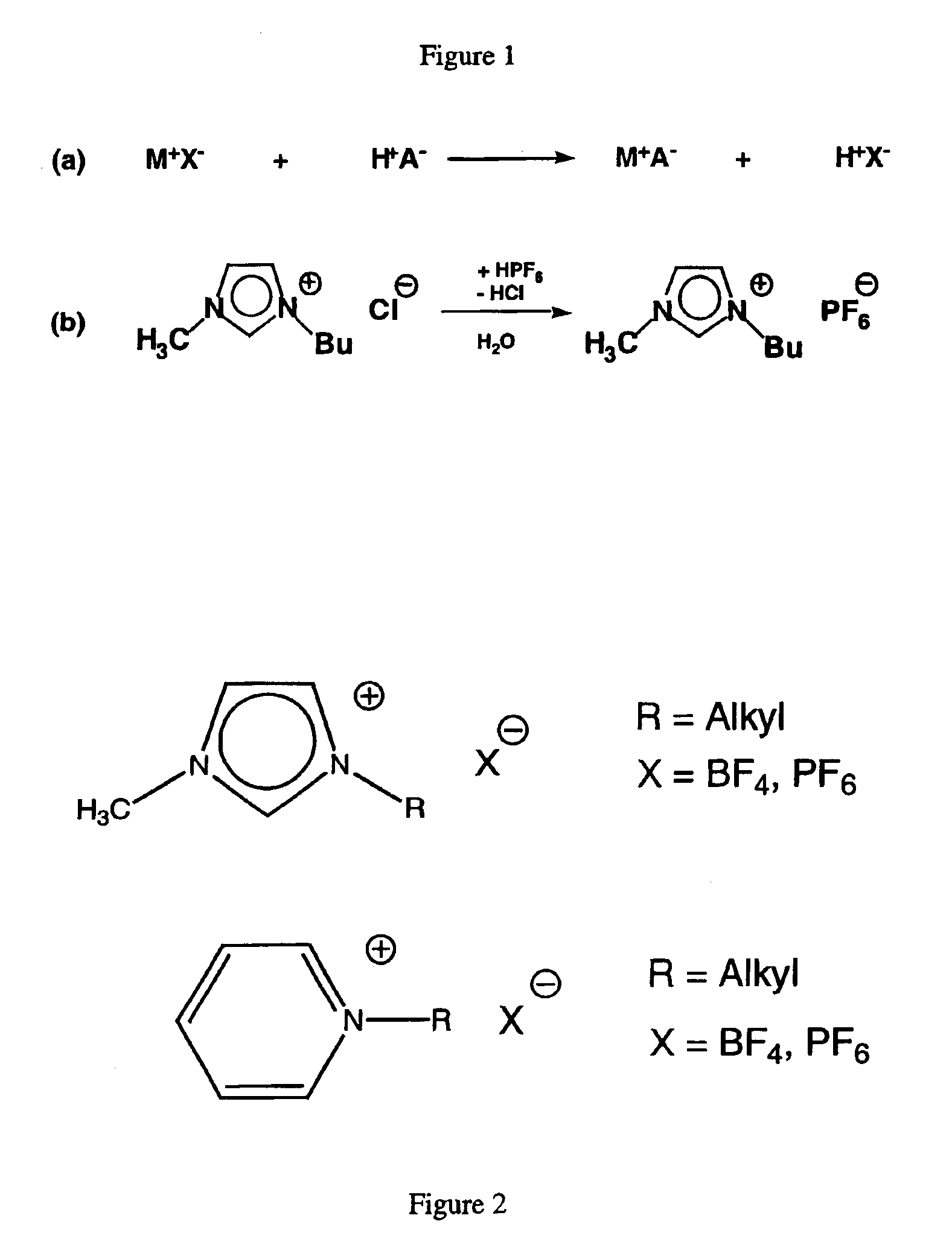
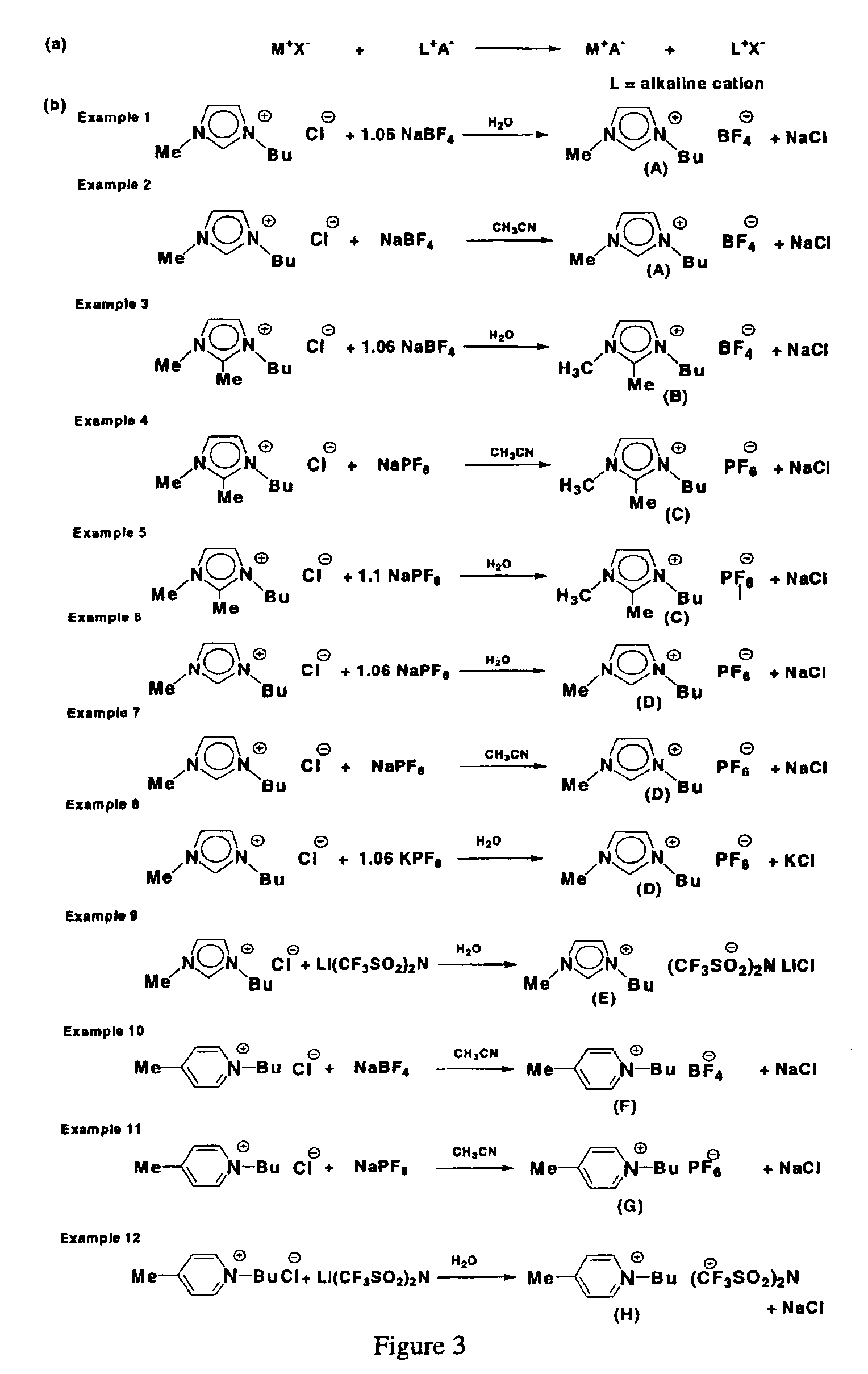
Method for preparing high-purity ionic liquids
A method for preparing a high-purity ionic liquid having a pH value of 7 and an elemental analysis deviation of less than 0.5 wt % between a calculated elemental analysis and a found elemental analysis for each of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, wherein the method comprises forming a monophasic or biphasic mixture of an ionic liquid and an inert liquid. When the monophasic mixture is formed, it is filtered to yield a filtrate from which the high-purity ionic liquid is recovered. When the biphasic mixtures is formed, it is separated into an aqueous phase and ionic liquid phase, whereby the ionic liquid phase is filtered to yield a filtrate from which the high-purity ionic liquid is recovered. Furthermore, the present purification procedure can be used for the clean-up of a contaminated ionic liquid by extracting it into a polar extractant to form an extract containing the ionic liquid. Water traces are removed from the extract. Then, the extract is filtered and the high-purity ionic liquid is recovered from the filtered extract.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
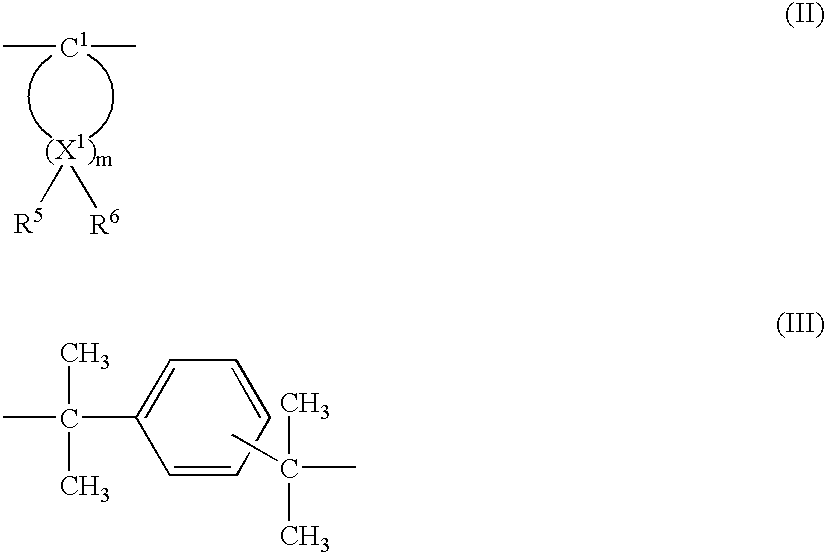
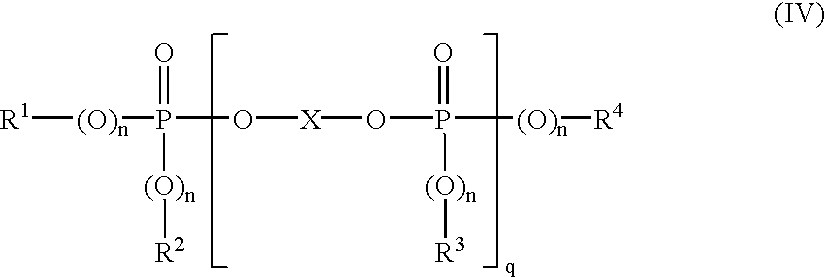
Mineral-reinforced impact-resistant modified polycarbonate blends
ActiveUS7001944B2High modulusImprove toughnessAlkaline-earth metal silicatesPhosphorus organic compoundsPolyesterExternal application
A mineral-filled, impact-resistant thermoplastic molding composition is disclosed. The composition contains at least one resin selected from the group consisting of polycarbonate and polyester carbonate B) impact resistance modifier, and C) wollastonite having carbon content greater than 0.1% relative to the weight of the wollastonite as determined by elemental analysis. Exhibiting high modulus of elasticity and a good toughness, in particular also at low temperatures, the composition is suitable for car body external applications.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
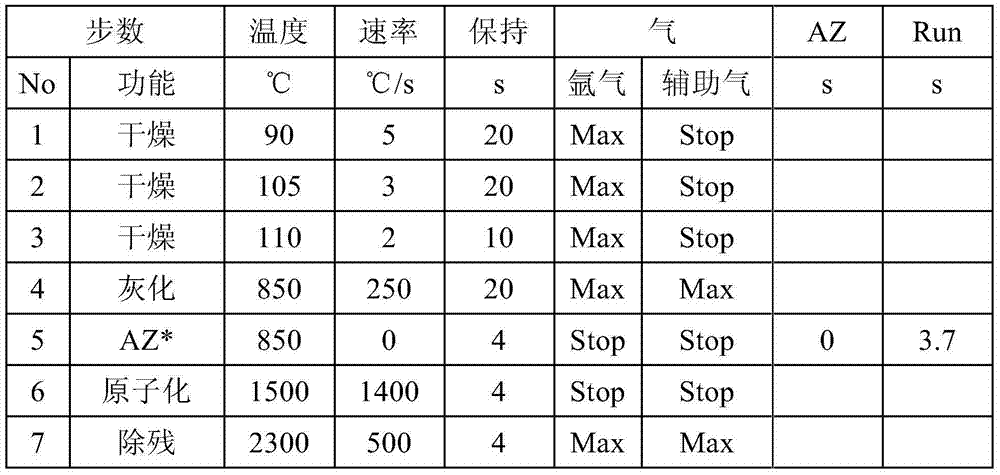
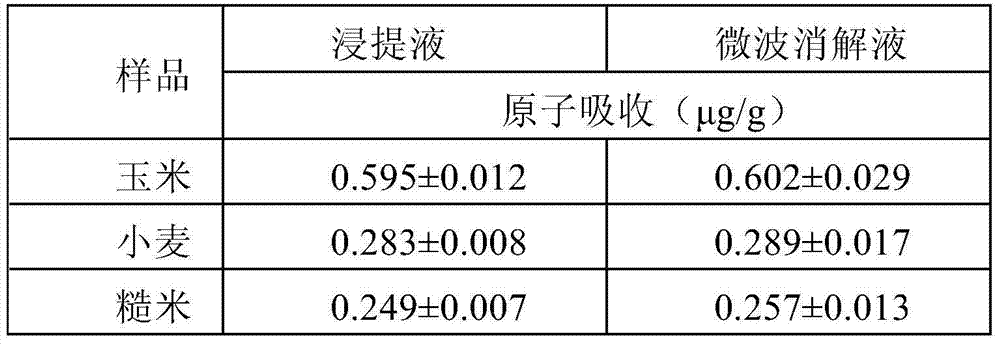
Method for rapidly and mildly extracting heavy metals from cereals
ActiveCN103575583AAvoid harmEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationElemental analysisInstrumentation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and mildly extracting heavy metals from cereals. The method comprises the following steps: crushing a cereal sample, uniformly mixing the cereal sample with dilute acid, and extracting heavy metal ions; after oscillating and whirling, standing or centrifuging, wherein cadmium, lead and other heavy metal elements in the cereal sample are basically transferred to supernatant, and the obtained supernatant is used for detection. The invention finds and reports the method for the first time; compared with the conventional extraction method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the time consumption is short, a lot of corrosive reagents are not required, a high temperature and a specific instrument are not required, the method can be completed at a room temperature, the operation is simple, and rapidness and practicality are achieved; by the method, the problems of complicated and cumbersome pretreatment, long time consumption, poor environmental protection property, difficult on-site detection and the like, which exist in analysis on harmful elements of food and products of the food for a long time, are solved; in combination with the refined deep processing technology of the cereals, the method also can be used for technologically removing the heavy metals from the cereals with excessive heavy metal pollutants.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
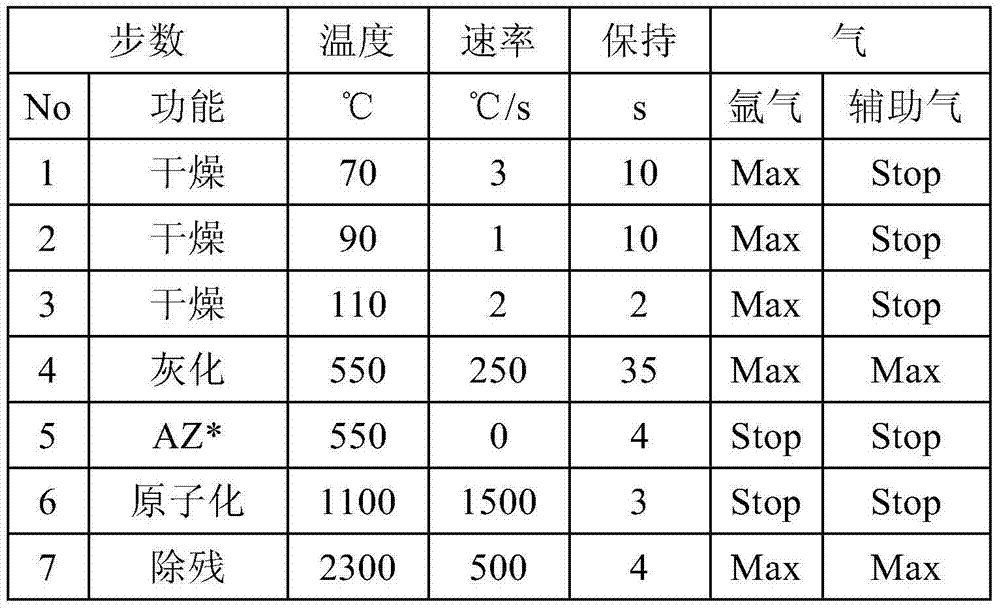
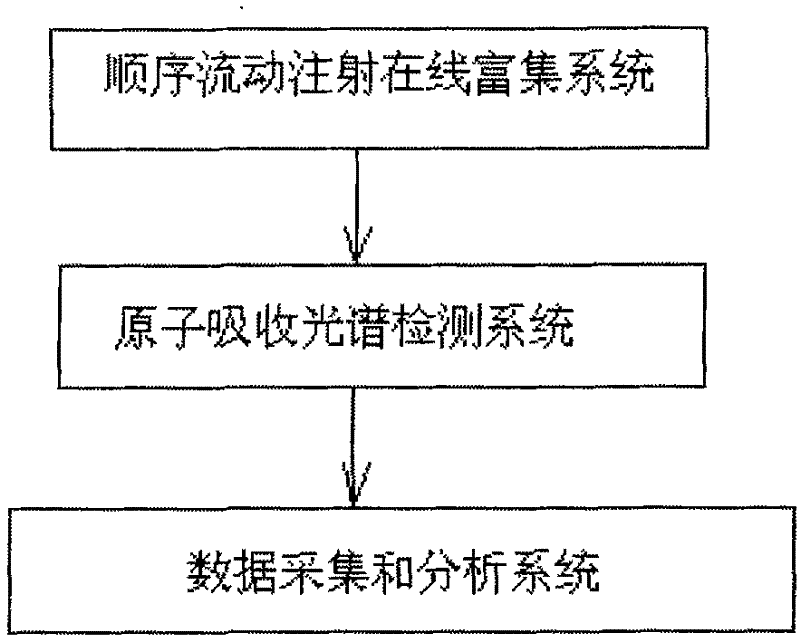
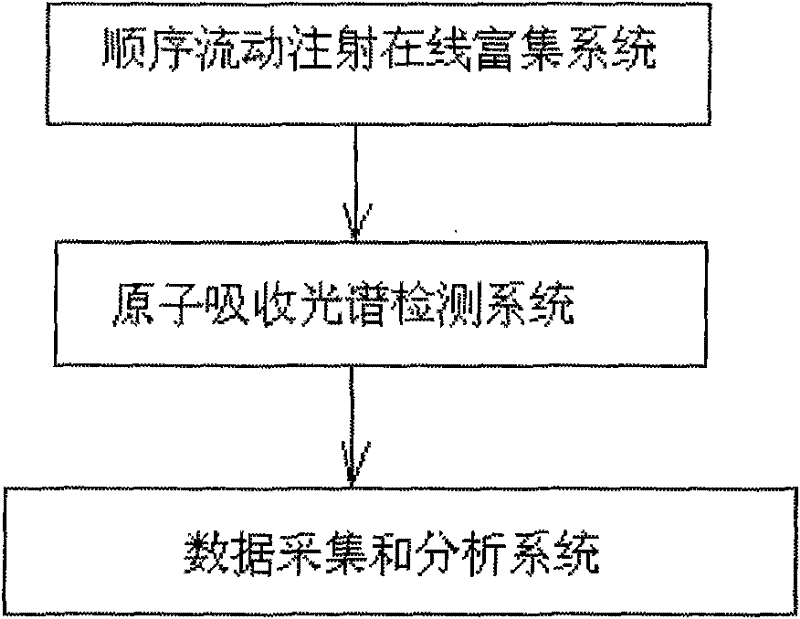
On-line enrichment atomic absorption spectroscopic analysis method and device for heavy metal elements
InactiveCN102262060ASolving Low Concentration Testing ProblemsSolve background distractionsPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsElemental analysisSalt water
The invention provides an online enrichment atomic absorption spectroscopic analysis method for heavy metal elements, which is characterized in that it includes the following steps: (a) online mixing of seawater samples and acidic solutions, and the acidic environment of the obtained mixed solution can realize the enrichment of heavy metals in seawater samples set; (b) the mixed solution flows through the enrichment soft column, and the heavy metals in the mixed solution are adsorbed in the adsorption material arranged in the enrichment soft column; (c) the enrichment is rinsed with eluent Soft column, wash out the mixed solution remaining in the enrichment soft column; (d) use the eluent to elute the heavy metals adsorbed in the enrichment soft column; (e) elute the elution obtained in step (d) The resulting solution was subjected to element detection and analysis. The invention also discloses the device of the method. The invention effectively solves the background interference problem of salt in seawater, solves the cumbersome manual pretreatment process and time-consuming problems at the same time, and realizes automatic and rapid analysis of trace heavy metal elements in seawater.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPECTRUM INSTR
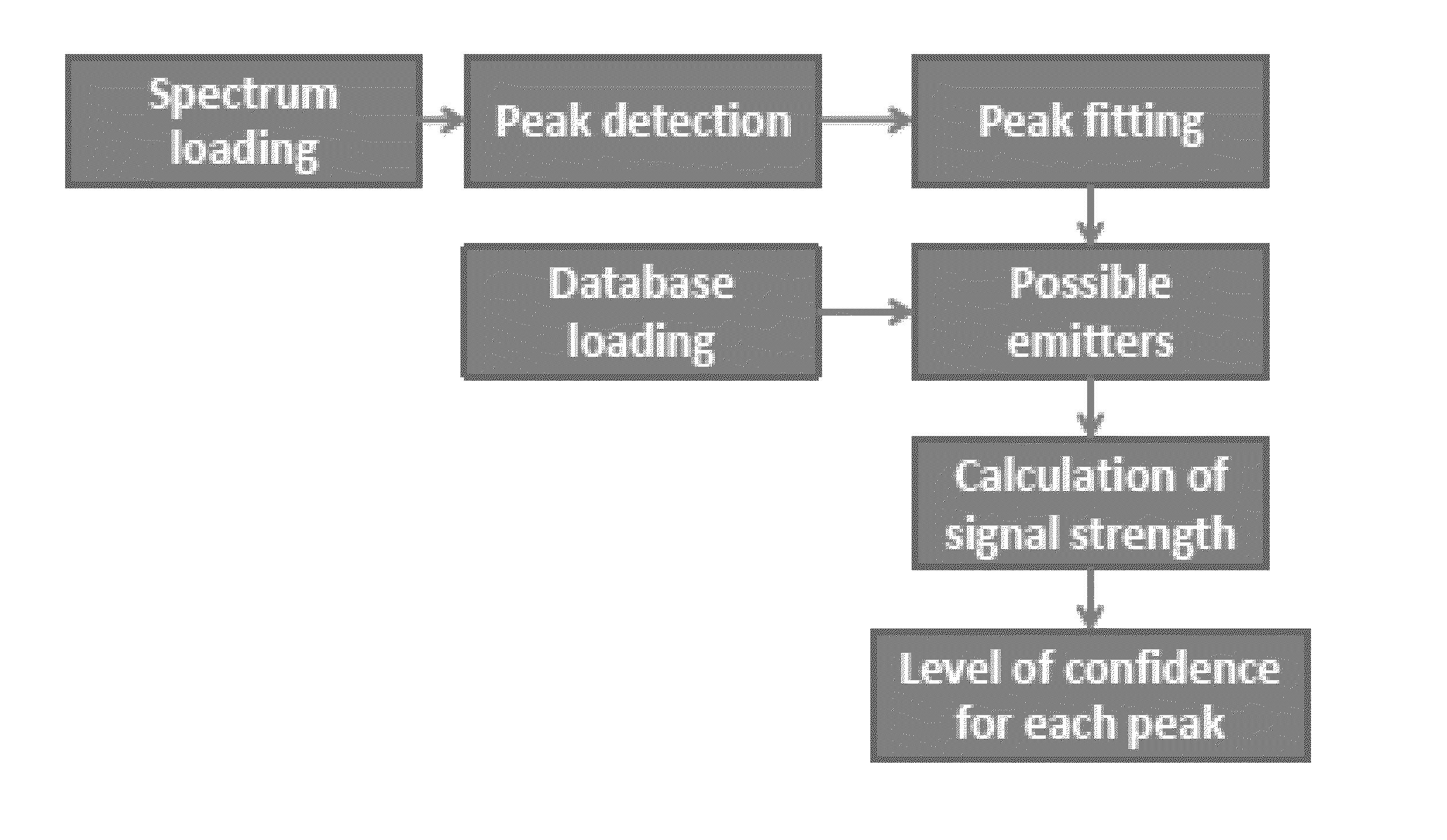
Quantitative elemental profiling in optical emission spectroscopy
ActiveUS20150153225A1Facilitate the spectrum beingAllocation is accurateSpectrum investigationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
The current invention considers the spectrum as a multimodal distribution over a list of structures containing the wavelength as the main entry and the other information mentioned above in the list as additional entries. Each line is then given a probability of contributing to the spectral line. In the case of multiple spectral lines, inference between spectral lines and their respective levels of confidence will provide a complete picture of the list of probable emitters with a probability factor for each line in order to provide a quantitative assignment of the spectral lines and profiling for a given spectrum.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
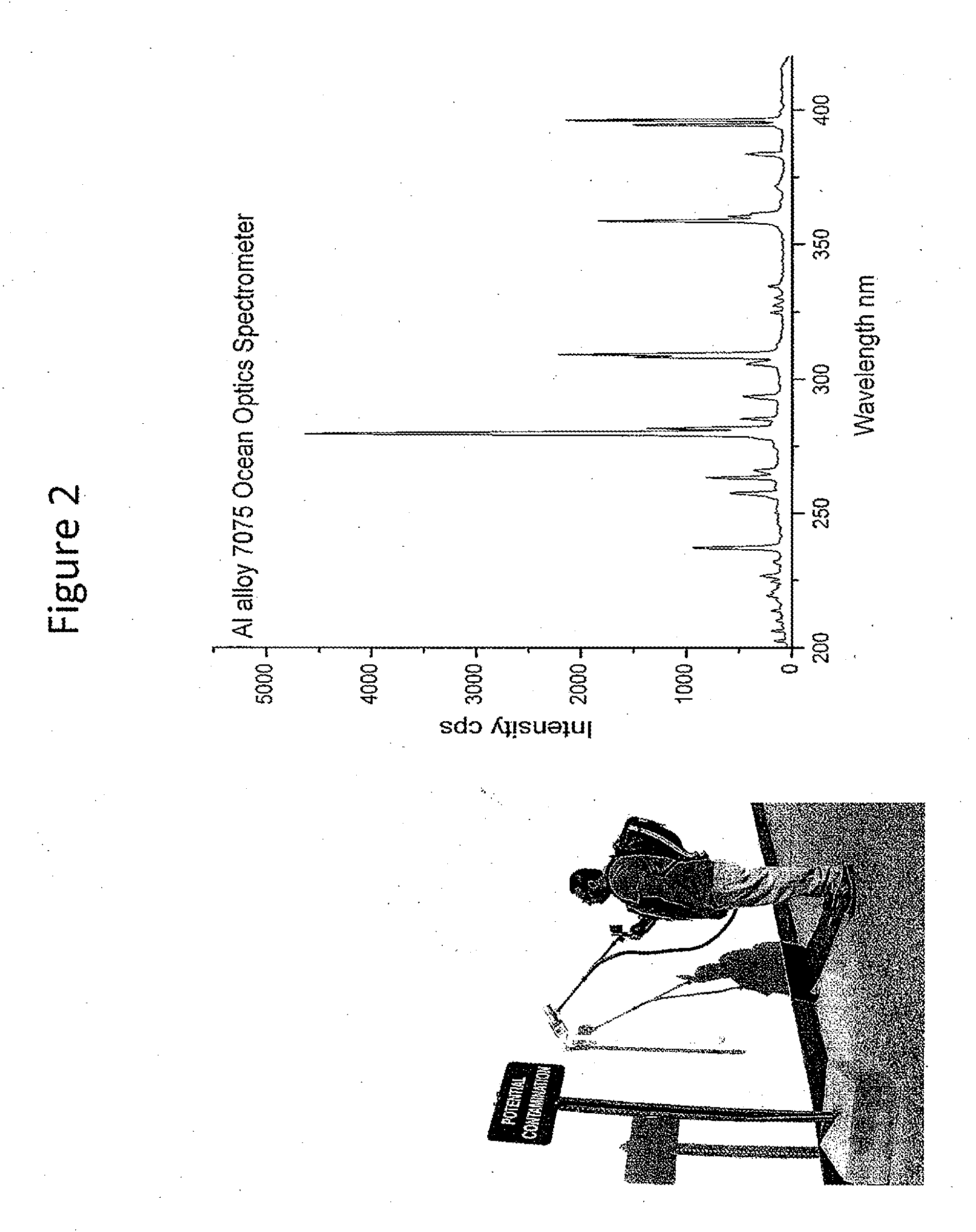
Ordinary brass full-elemental analysis apparatus based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and method thereof
InactiveCN102359953AFully automatedRealize real-time online sortingSpectrum investigationAnalysis by material excitationElemental analysisLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention relates to an ordinary brass full-elemental analysis apparatus based on a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and a method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The apparatus comprises a laser, a spectrometer, a delay generator, a focusing lens, a collecting lens, optical fiber, a sample and a computer. The laser and the spectrometer are respectivelyconnected to the delay generator. The spectrometer is connected with the computer. The optical fiber is connected with the spectrometer. The focusing lens is arranged between the laser and the sample. The collecting lens is connected with the spectrometer by the optical fiber. The analysis method comprises: establishing working curves of Cu, Pb, Fe and Ni, and verifying the working curves. The apparatus and the method are applicable for analyzing the Cu content, the Pb content, the Fe content and the Ni content in the ordinary brass.
Owner:AUTOMATION RES & DESIGN INST OF METALLURGICAL IND
Elemental Analysis Based on Complementary Techniques
InactiveUS20110079734A1Accurately determineX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTest sampleElemental analysis
Methods and apparatus for analyzing a test sample using complementary techniques, such as x-ray fluorescence (XRF) and optical emission spectroscopy (OES), are disclosed for registering two or more test instruments, in relation to the test sample, such that each of the instruments analyzes substantially the same region as is analyzed by the other instrument(s), and for communicating analytical results between or among the instruments, or between the instruments and another component, to enable one or more of the instruments, or the other component, to combine the results and, thereby, more completely and accurately determine the composition of the test sample. Such registration and communication enables, for example, separate XRF and OES instruments to collectively determine the composition of the test sample, including the absolute amounts of light and heavy elements in the test material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Mesophase pitch raw material as well as preparation method and application of mesophase pitch raw material in preparing high-performance carbon fiber
InactiveCN104087331ASimple preparation processImprove controllabilityWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansFibre chemical featuresCarbon fibersElemental analysis
The invention relates to a mesophase pitch raw material as well as a preparation method and an application of the mesophase pitch raw material in preparing a high-performance carbon fiber. By virtue of measurement based on an elemental analysis method for the mesophase pitch raw material, the molar ratio H / C of hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms in the molecular structure of the mesophase pitch raw material is 0.55-1.0; the molar ratio of the naphthenic carbon content to the total carbon content in the molecular structure measured by virtue of a nuclear magnetic resonance method is greater than 9%; the softening point temperature, measured by an insertion method, of the mesophase pitch raw material is 200-240 DEG C; the content, measured by a polarizing microscope method, of the mesophase is 100%. The preparation method comprises the following step: polymerizing naphthalene-based compounds such as methylnaphthalene used as raw materials in the presence of a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and boron trifluoride as a catalyst by virtue of controlling the polymerization conditions. Compared with the prior art, the mesophase pitch raw material has the advantages of good spinning stability and high pre-oxidation activity, and is conductive to the control and operation of the carbon fiber spinning and pre-oxidation processes, the operation process is simple and the mesophase pitch raw material is conducive to preparing a high-performance pitch-based carbon fiber.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
High Energy Crystal Generators And Their Applications
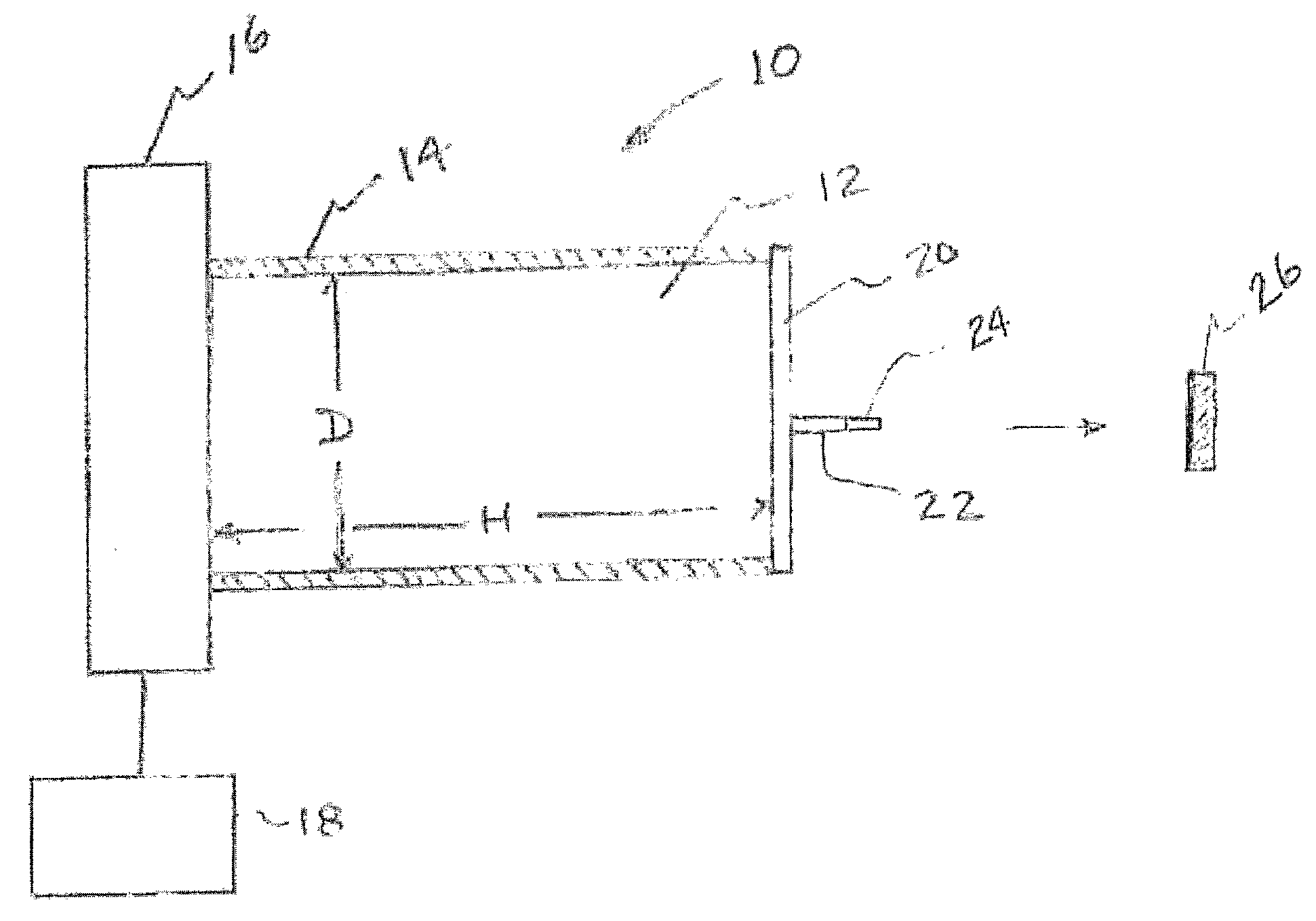
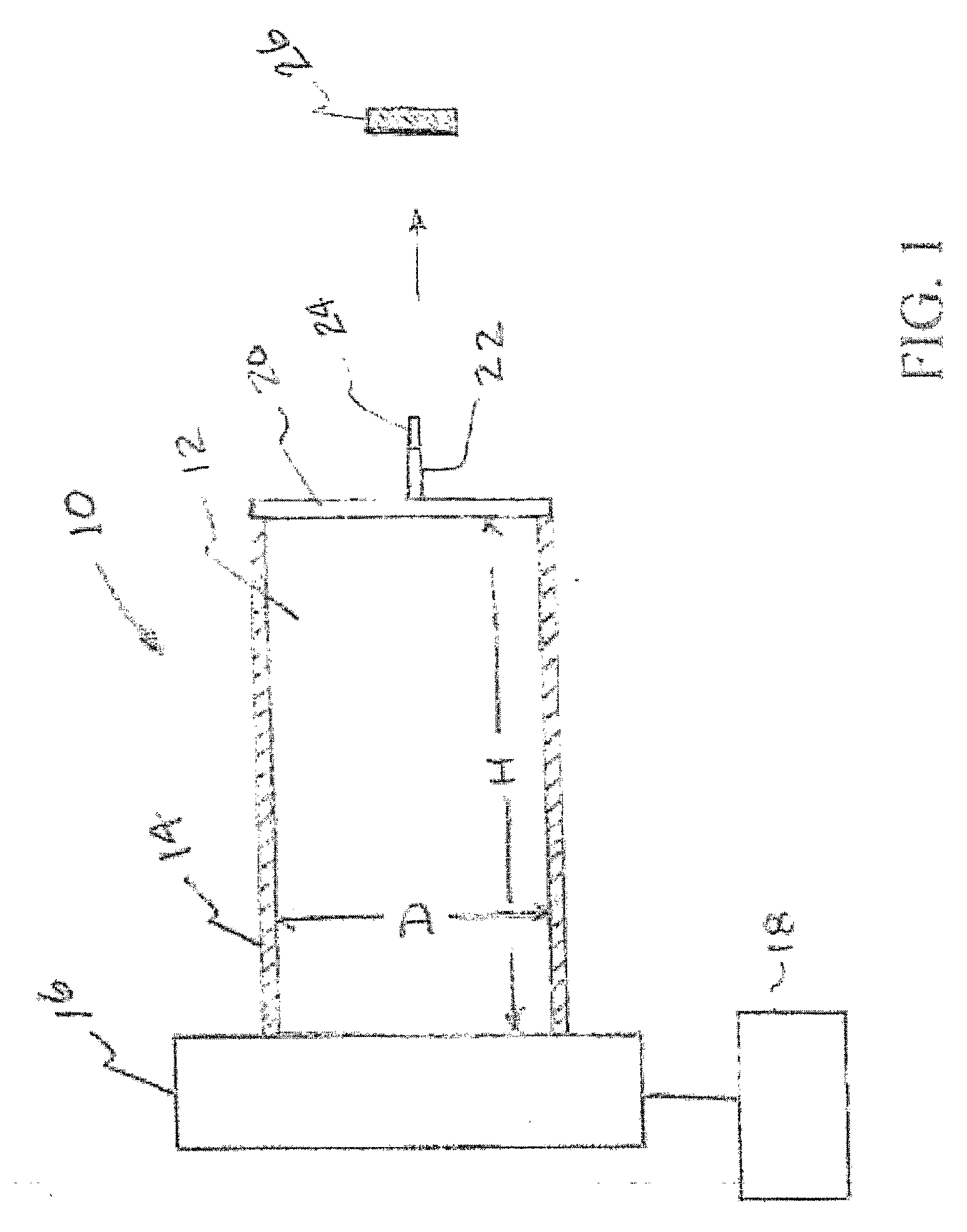
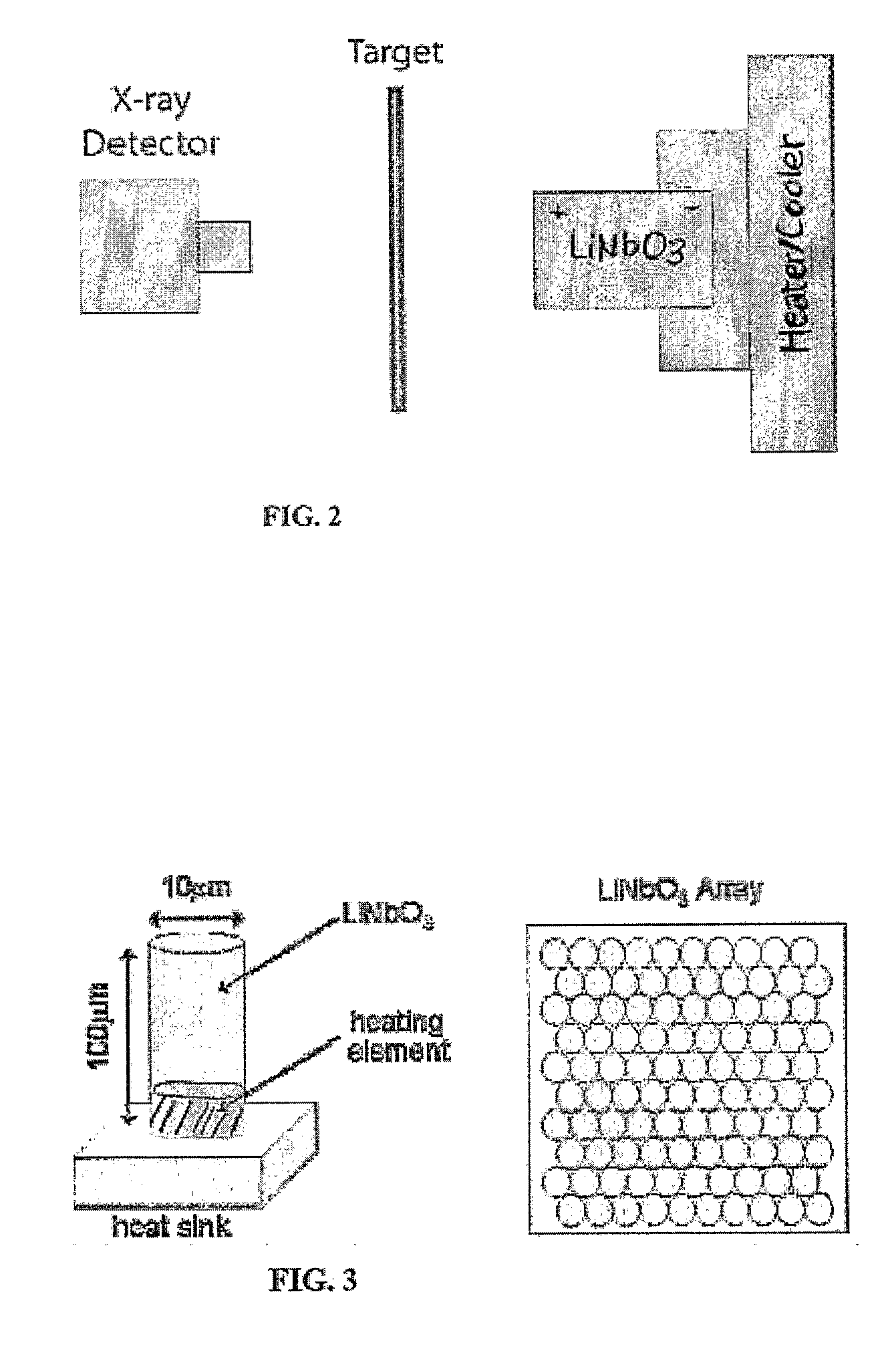
InactiveUS20080251735A1Improve efficiencyFiner and pixilatedNanoinformaticsElectrode and associated part arrangementsHigh energyX-ray
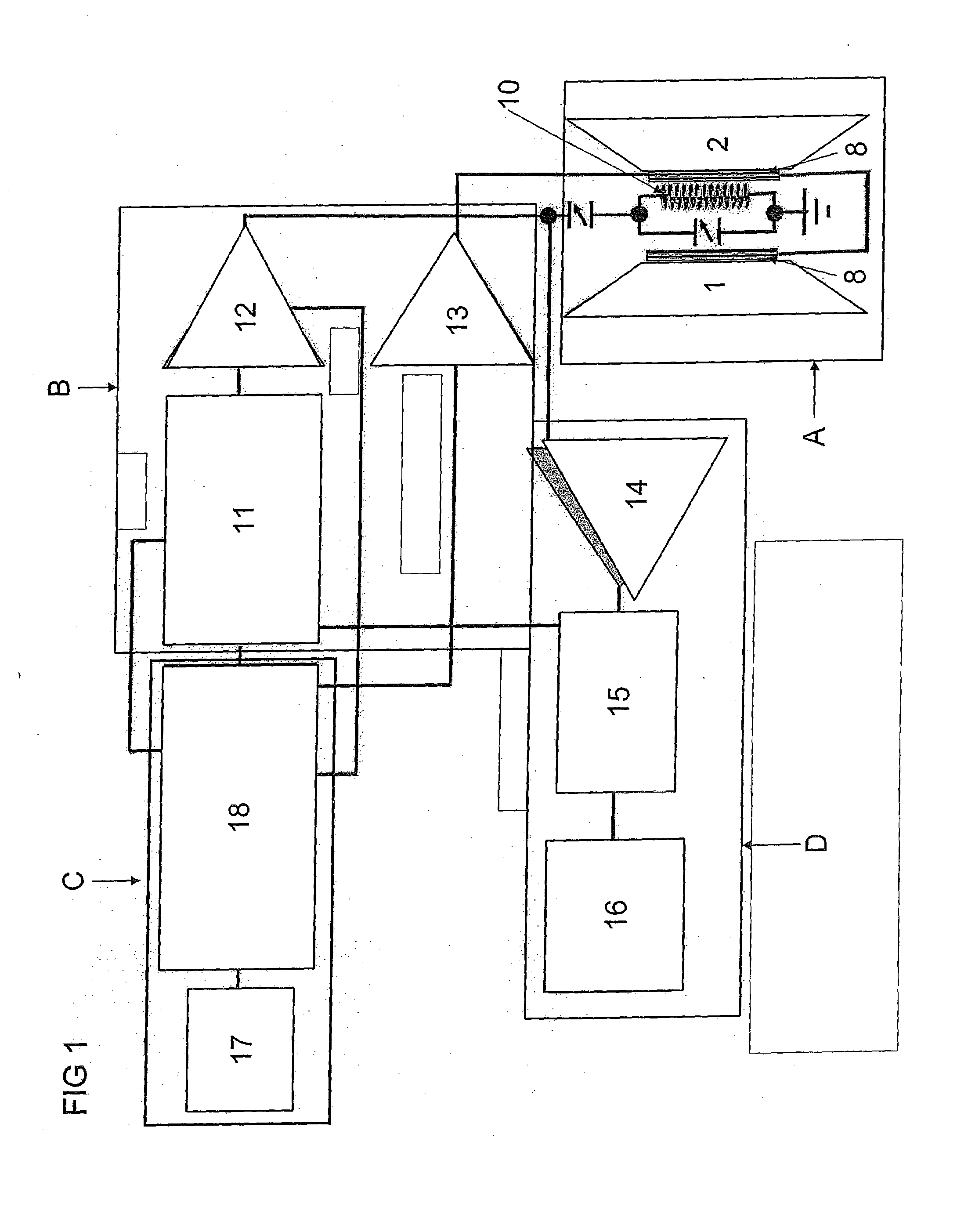
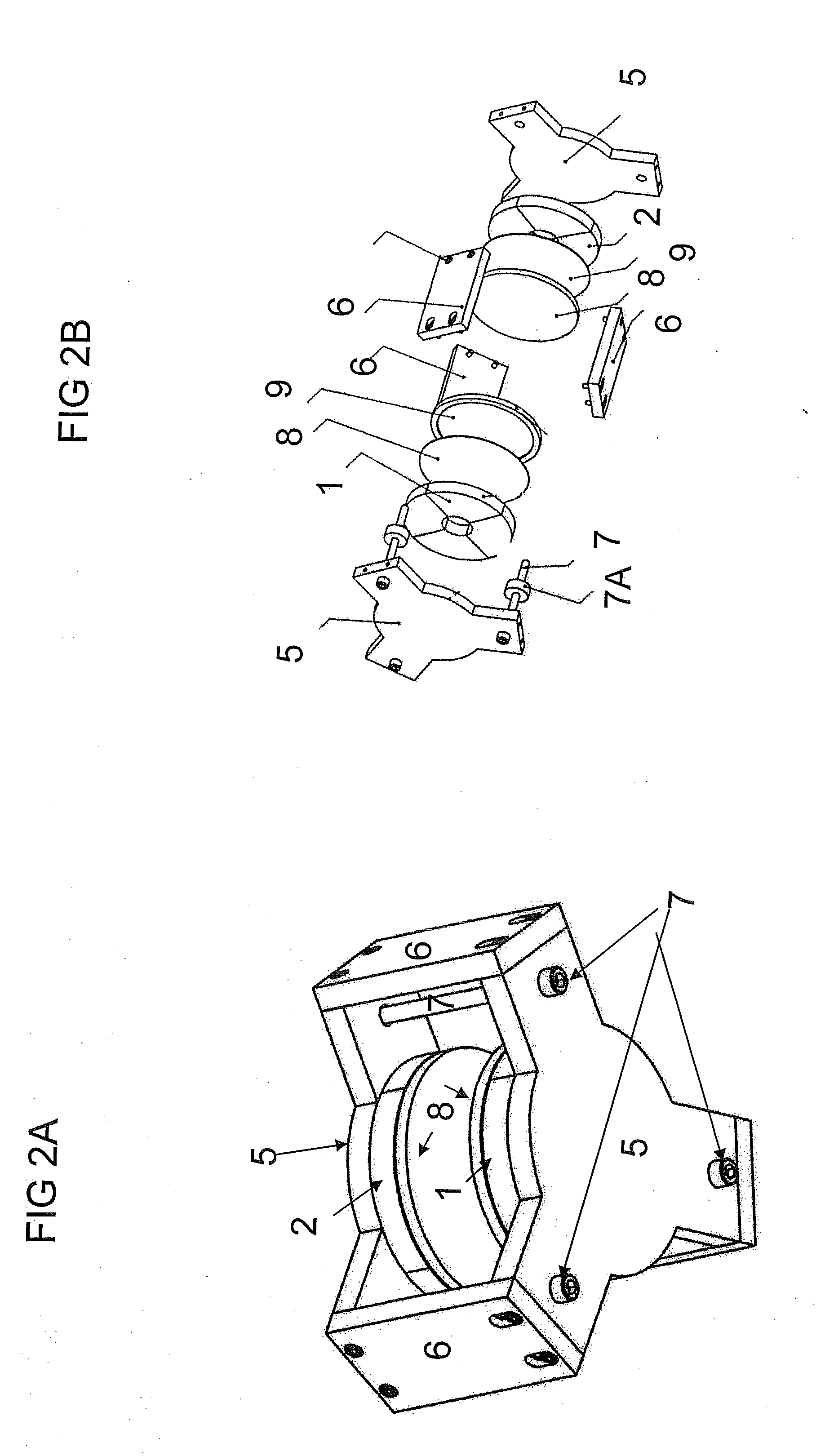
Ferroelectric, pyroelectric and piezoelectric crystals are used to generate spatially localized high energy (up to and exceeding 100 keV) electron and ion beams, which may be used in a wide variety of applications including pulsed neutron generation, therapeutic X-ray / electron devices, elemental analysis, local scanning chemical analysis, high energy scanning microscopy, point source compact transmission electron microscopy, compact ion beam sources, positron sources, micro-thrusters for ion engines, and improved fusion efficiency especially of the Farnsworth type. The high-energy emission can be created by simply heating the material or by application of external coercive electromagnetic and acoustic fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Analytical laser ablation of solid samples for ICP, ICP-MS, and FAG-MS analysis
InactiveUS8274735B2Eliminate chromatic aberrationMirrorsAnalysis by thermal excitationMolecular analysisPath length
The present invention facilitates improvements in laser ablation of solid samples to be analyzed by an external inductively coupled plasma (ICP) emission spectrometer, ICP / mass-spectrometer (ICP-MS), or flowing afterglow (FAG) mass spectrometer (FAG-MS) for elemental analysis (ICP and ICP-MS) or molecular analysis (FAG-MS). A novel invention mirror-with-hole beam combiner eliminates chromatic aberration in the invention sample view and allows rad-hardening the laser ablation invention for use in a radiation hot cell for analysis of high activity nuclear waste. Many other novel invention rad-hardening attributes facilitate a comprehensive rad-hardened laser ablation system (the world's first). In other embodiments, invention novelties include unusually large homogeneous focused laser spot diameters, unusually long laser objective lens focal length, wide range operationally variable laser path length with built-in re-alignment, operationally variable demagnification ratio and diameter of the focused laser spot, the use of significantly higher powered SMR lasers in a large spot diameter to facilitate high sensitivity bulk analysis of solid samples, a demountable and gravitationally self-sealing stack assembly laser ablation cell, and the world's first auto-samplers (mechanized sample changers) for analytical laser ablation.
Owner:FRY ROBERT C +3
Solid phase regeneration method of waste ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode material
InactiveCN107706477AEase vacanciesLarge repair regenerationWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingAir atmosphereElectrical battery
The invention discloses a solid phase regeneration method of a waste ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode material. The solid phase regeneration method comprises the following steps of (1) performing battery refined dismantling, taking out a positive electrode plate, and performing washing and drying on the positive electrode plate; (2) performing heat treatment on the positive electrodeplate at a temperature of 300-500 DEG C to realize screening and separating of a ternary positive electrode material and an aluminum foil or a conductive agent; (3) performing elemental analysis on the ternary positive electrode material and then matching with a lithium source, a cobalt source, a nickel source and a manganese source to adjust the element molar ratio; (4) performing mixing and ball milling on the added lithium source, cobalt source, nickel source and manganese source, and performing high-temperature sintering in an inert atmosphere or vacuum atmosphere to obtain a pre-sinteredsolid body; and (5) next, adding the conductive agent and doped metal ions, and performing secondary sintering in the air atmosphere to obtain the battery positive electrode material. The solid phaseregeneration method of the waste ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode material provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, economic and reasonable property, highcycle recovery rate and environment friendliness.
Owner:长沙佳纳锂业科技有限公司 +1
Lubricating oil compositions for automatic transmissions
InactiveUS20040167041A1Excellent characteristicsReduced strengthOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAutomatic transmissionPhosphorus calcium
A lubricating oil composition for automatic transmissions wherein the mass ratio of phosphorus:calcium:boron:sulfur determined by elemental analysis is 1:(0.1 to 2):(0.06 to 2):(0.2 to 20), the concentration of phosphorus is from 0.01 to 0.06 percent by mass, the concentration of the sulfur derived from a base oil is from 0 to 0.1 percent by mass, and the concentration of the sulfur derived from sulfur-based additives is from 0.01 to 0.15 percent by mass, based on the total amount of the composition. The lubricating oil composition can prevent the occurrence of scratch phenomenon even over a long period of time when used in a metal belt type continuously variable automatic transmission.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Method for measuring content of boron in cobalt-base alloy
ActiveCN101718688AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsElement analysisMaterial resources
The invention belongs to a technique for analyzing trace elements of an alloy, and relates to a method for measuring the content of boron in a cobalt-base alloy. By adopting an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and treating a sample of the cobalt-base alloy in particular a high-tungsten sample by using 20mL of hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, the method solves the puzzling problems that the past dissolved sample has large reagent dosage and high reagent blank and cannot be measured normally by an instrument; by performing interference experiments and spectrogram analyses, the method finds the optimal analytical line, overcomes the interferences caused by a plurality of elements such as major elements of cobalt, chromium, tungsten and the like in the cobalt-base alloy, and improves the measuring accuracy; the method has wide measuring ranges, the measuring lower limit is 0.002 percent, and the measuring upper limit is 0.20 percent and is 101 times of the measuring lower limit; and the method can perform measurement quickly, is simple and convenient to operate, and saves a large quantity of manpower and material resources.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Elemental analysis of tagged biologically active materials
InactiveUS7700295B2Simple methodIn-vivo radioactive preparationsOther chemical processesElement analysisSpectroscopy
Methods for the detection and measurement of tagged (labeled) biologically active materials in a sample are described. The tagged biologically active materials are detected using an atomic mass or optical spectrometer having a source of atoms or atomic ions. Element-labeled biologically active materials, comprising antibodies, antibody Fab′ fragments, antigens, aptamers, protein complexes, growth factors, hormones, receptors and other biologically active materials attached to a stable elemental tag, can be used in specific binding assays and measured by elemental spectroscopic detection. Also described are methods for the determination of metals in samples of interest using specific antibodies to isolate the target metals and elemental spectroscopy for detection and quantitation. Kits are provided comprising reagents to detect and measure labeled biologically active materials or labeled competition analytes.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Compact and portable low-field pulsed NMR dispersion analyzer
ActiveUS20070210798A1Small and portableLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientLiquid ratio
A compact and integrated portable device is provided for the analysis of dispersions by low-field pulsed NMR including: an NMR probe module, a means for generating radio frequency and magnetic field gradient pulses, a signal processor, and a master controller. Also provided are methods for using the device to measure one or more characteristics of phases or particles comprising a dispersion such as surface area, solid / liquid ratio, particle size, and elemental analysis.
Owner:XIGO NANOTOOLS
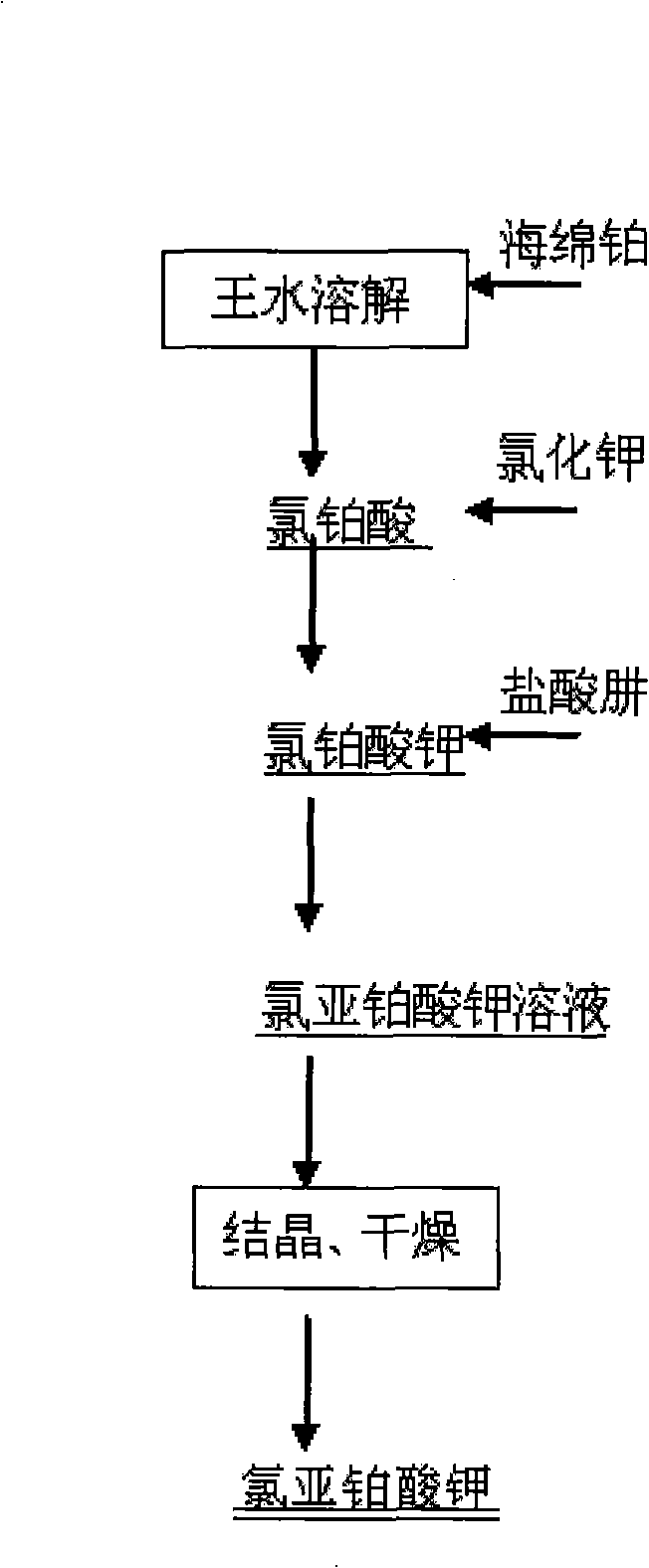
Preparation of potassium platinochloride
ActiveCN101279772AShort preparation processReduce manufacturing costRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsSodium/potassium compoundsPotassium tetrachloroplatinatePotassium
Disclosed is a method for the production of a potassium platinochloride, which relates to a process for preparing a pharmaceutical intermediate potassium platinochloride. The method of preparation is characterized in that the preparation process adopts a spongy platinum as a material to prepare a chloroplatinic acid solution which is reacted with a potassium chloride solution to prepare the potassium chloroplatinite, then a hydrazine hydrochloride is adopted as a reducing agent to reduce the potassium chloroplatinite for preparing the pharmaceutical intermediate potassium platinochloride. The product adopting the method of the invention has a platinum content of 46.9+-0.2 percent and a potassium content of 19.0+-0.2 percent through a total elemental analysis. The total content of metallic impurity is no more than 0.08 percent.
Owner:兰州金川科技园有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com