Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
573results about How to "Large grain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
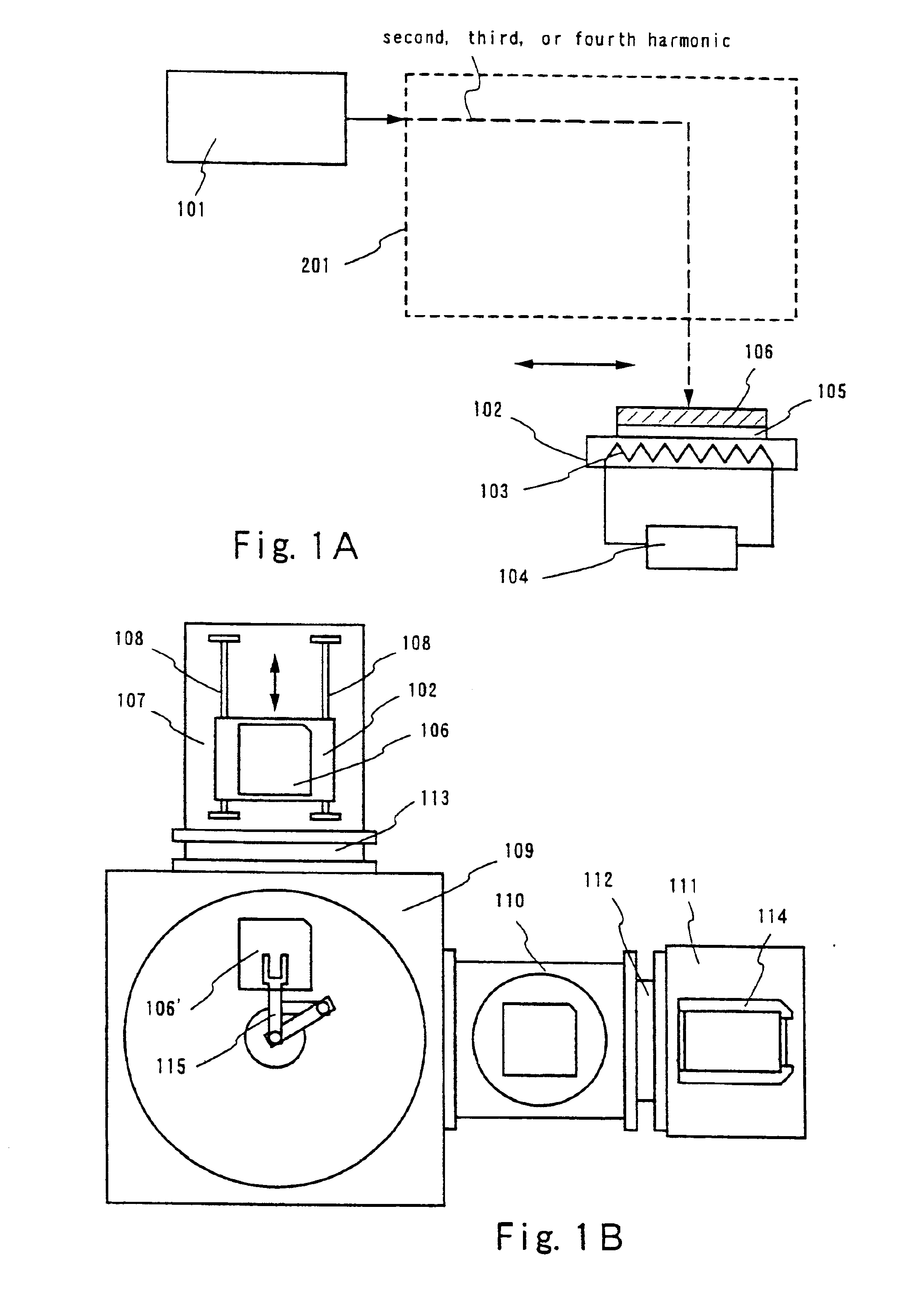
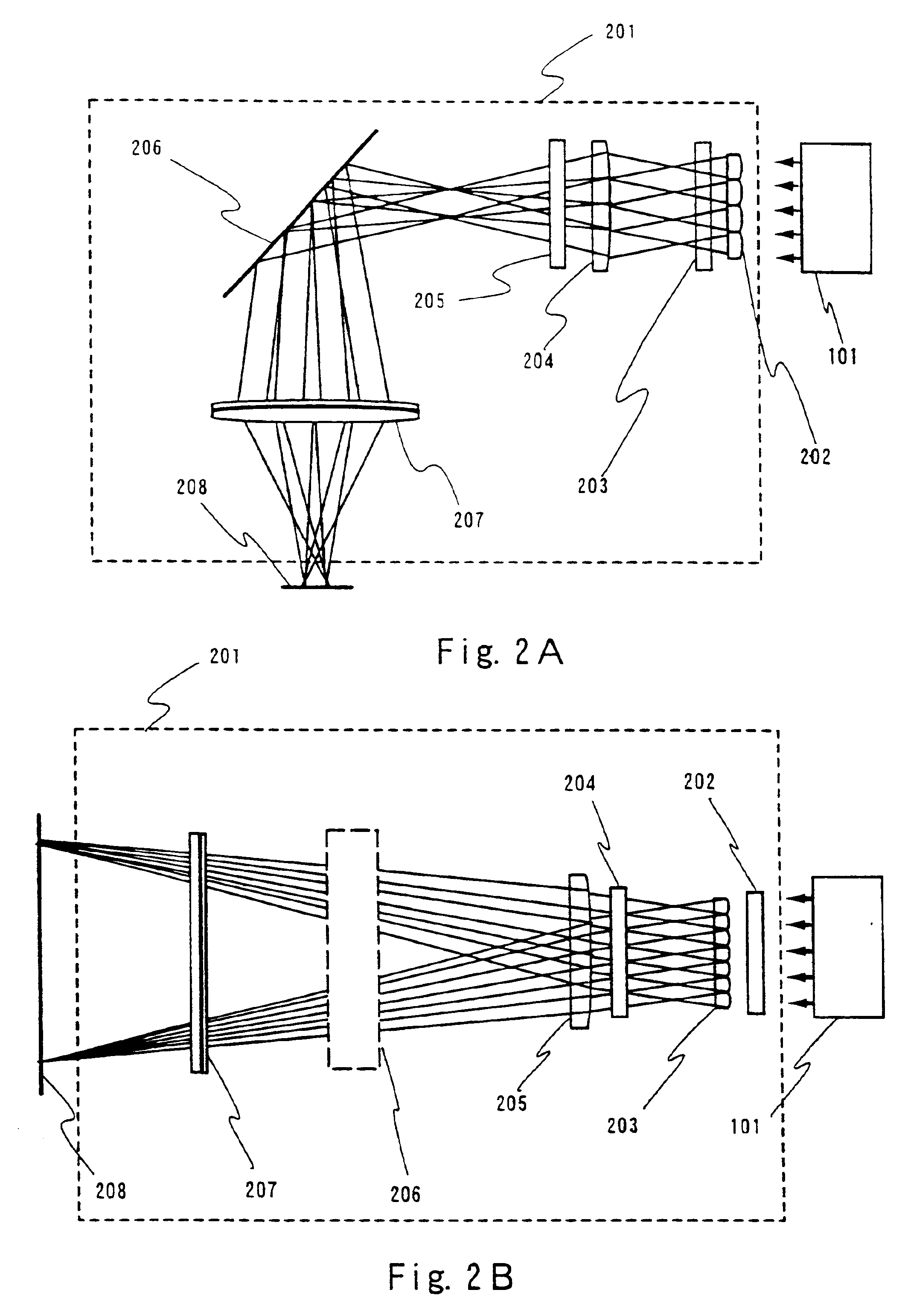
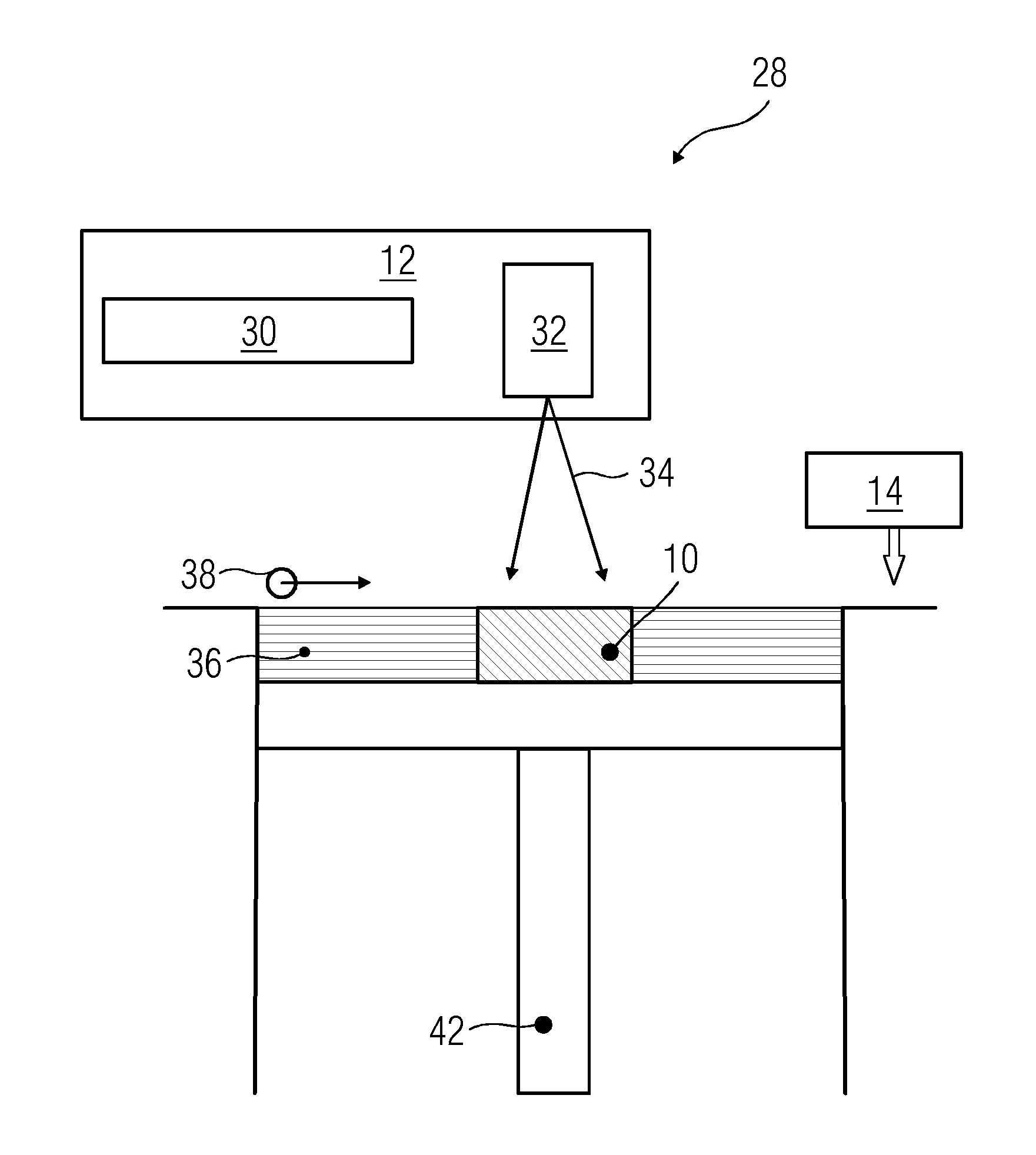
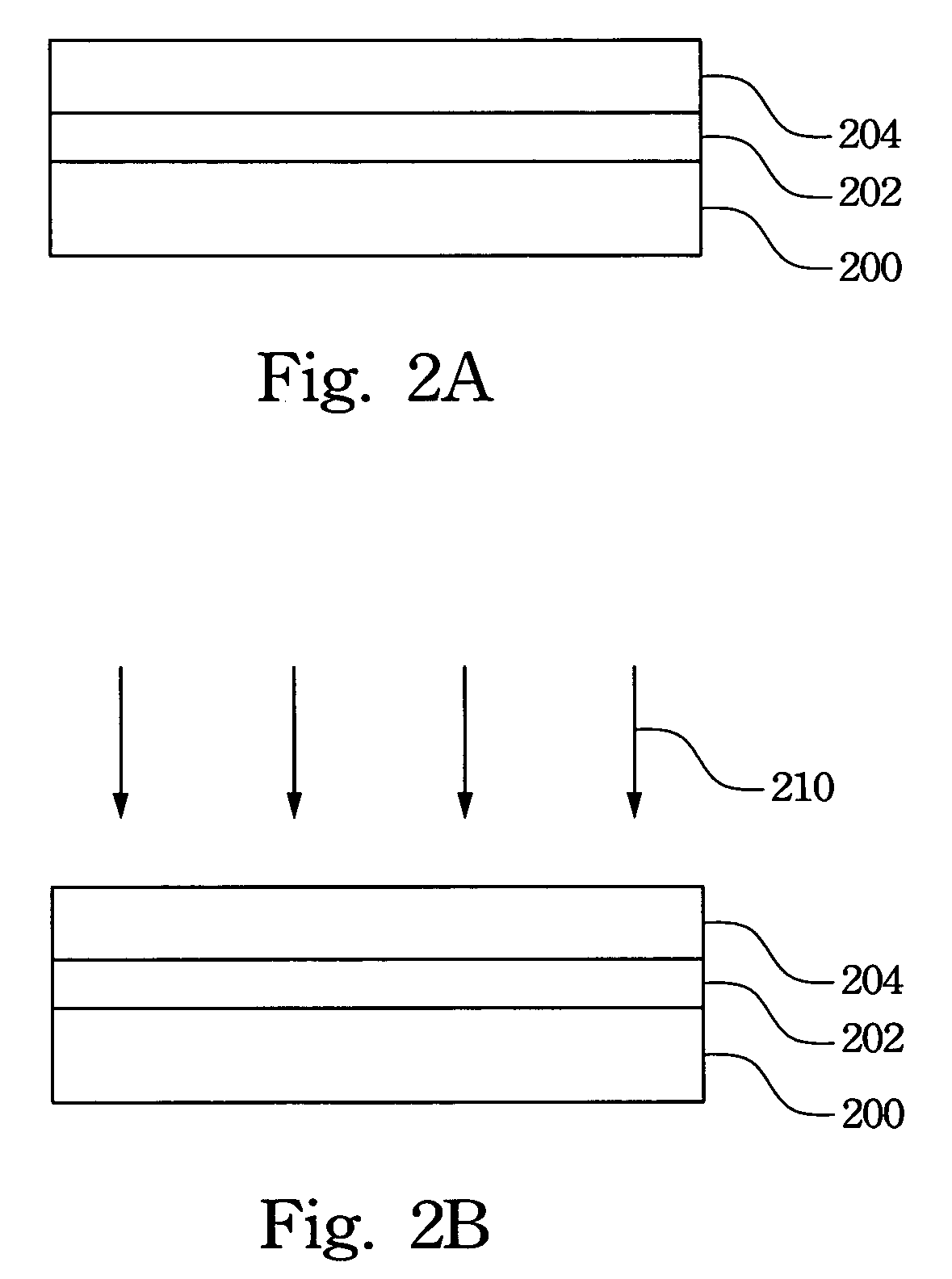
Laser apparatus, laser annealing method, and manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020048864A1Solution value is not highIncrease valueSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesLaser lightSolid-state laser
To provide a laser apparatus and a laser annealing method with which a crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size is obtained and which are low in their running cost. A solid state laser easy to maintenance and high in durability is used as a laser, and laser light emitted therefrom is linearized to increase the throughput and to reduce the production cost as a whole. Further, both the front side and the back side of an amorphous semiconductor film is irradiated with such laser light to obtain the crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Highly-oriented diamond film, method for manufacturing the same, and electronic device having highly-oriented diamond film
InactiveUS7311977B2Lower performance requirementsImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHydrogenDiamond crystal
A highly-oriented diamond film which has a flat surface but does not have non-oriented crystals in the surface can be provided by depositing a first diamond layer on a substrate by {111} sector growth of diamond crystals by a CVD method using a gaseous mixture of methane and hydrogen as material gas, and then depositing a second diamond layer on the first diamond layer by {100} sector growth of diamond crystals by a plasma CVD method using a gaseous mixture of methane, hydrogen, and oxygen as material gas under the conditions that the pressure of the material gas is 133 hPa or more; the material gas composition is determined such that ([C]−[O]) / [CH3+H2+O2] is −0.2×10−2 or more and [O] / [C] is 1.2 or less; and the substrate temperature is between 750° C. and 1000° C.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Laser apparatus, laser annealing method, and manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6974731B2Large grainLow running costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser lightSolid-state laser
To provide a laser apparatus and a laser annealing method with which a crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size is obtained and which are low in their running cost. A solid state laser easy to maintenance and high in durability is used as a laser, and laser light emitted therefrom is linearized to increase the throughput and to reduce the production cost as a whole. Further, both the front side and the back side of an amorphous semiconductor film is irradiated with such laser light to obtain the crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
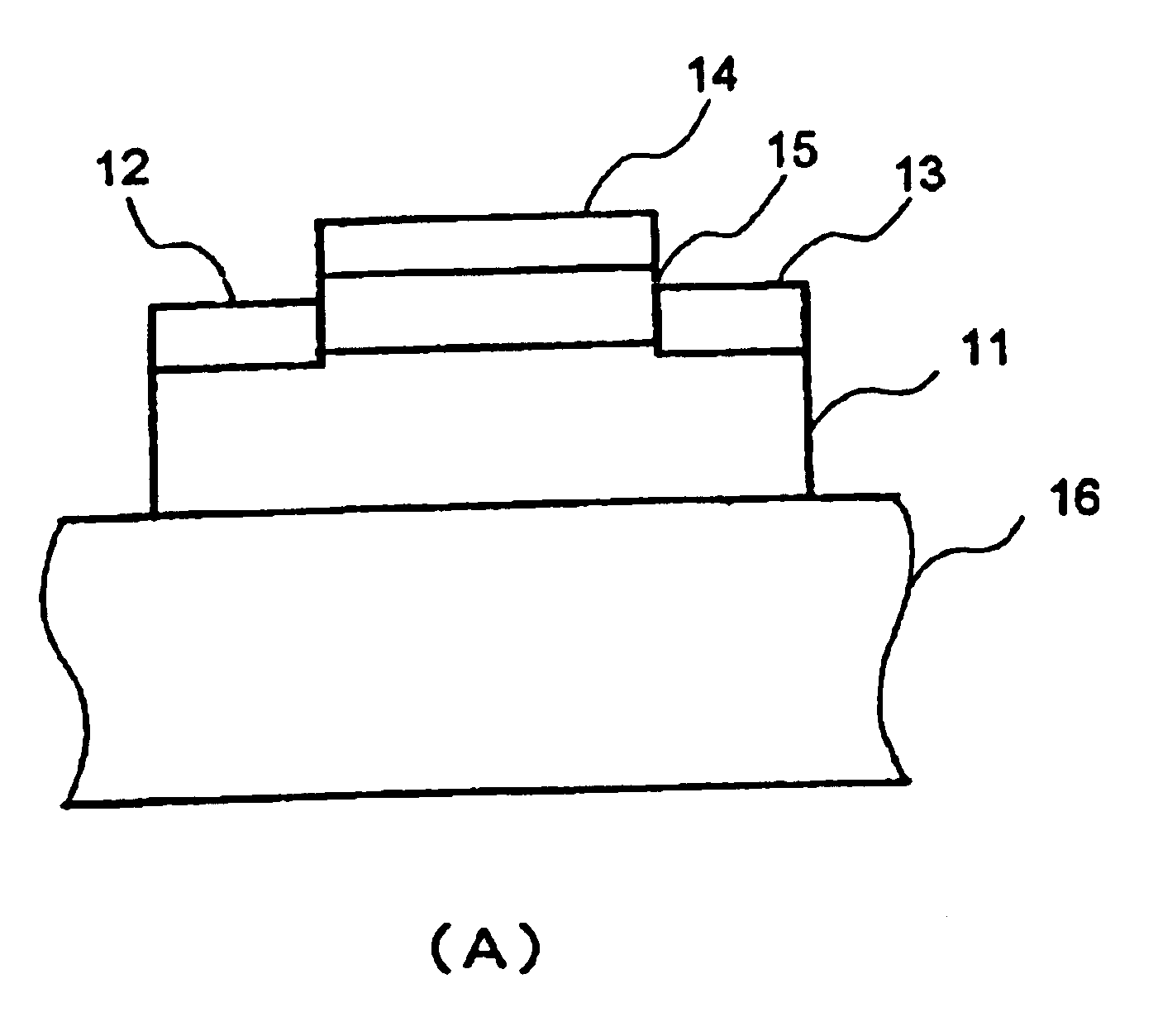
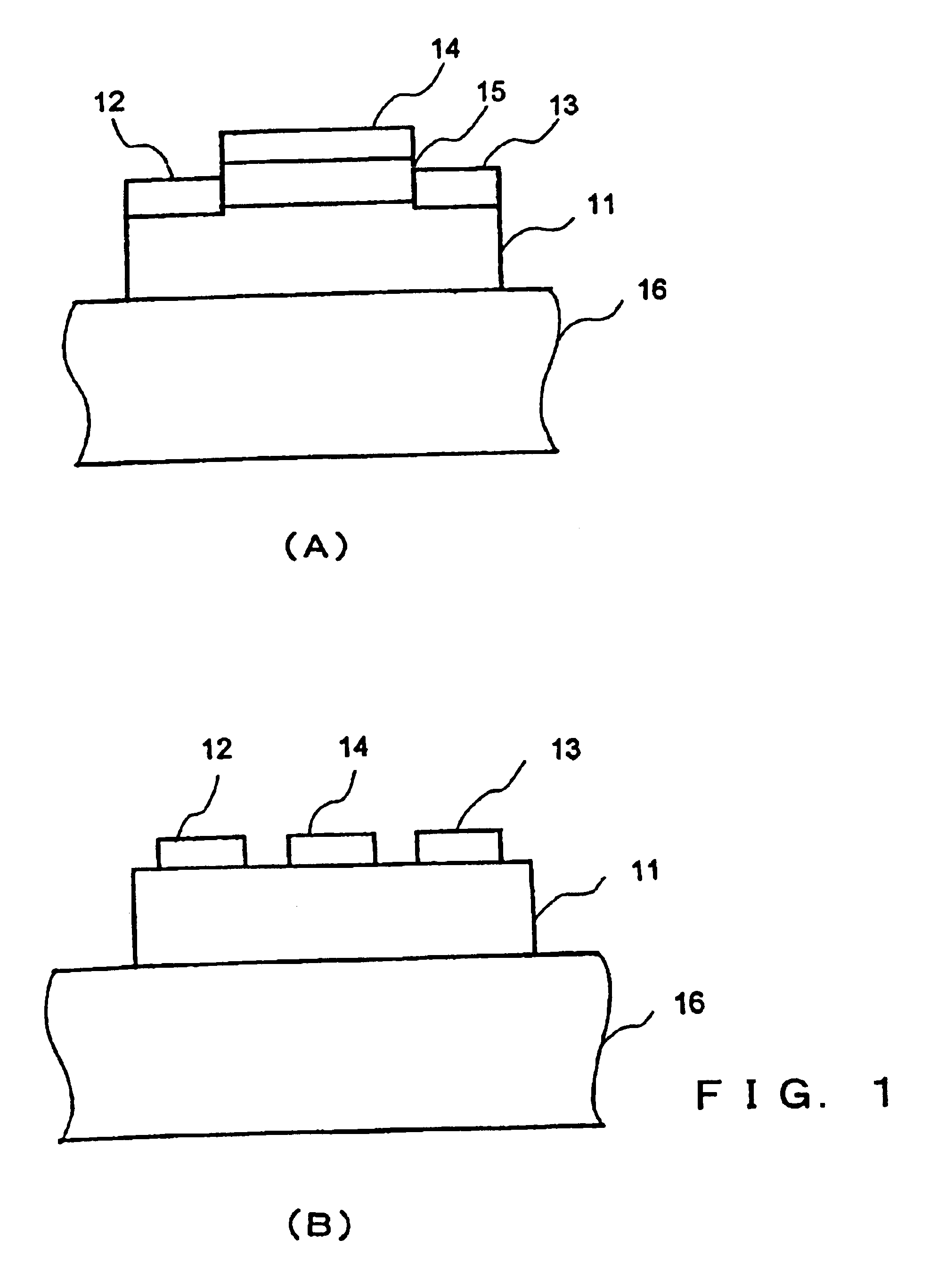
Semiconductor device
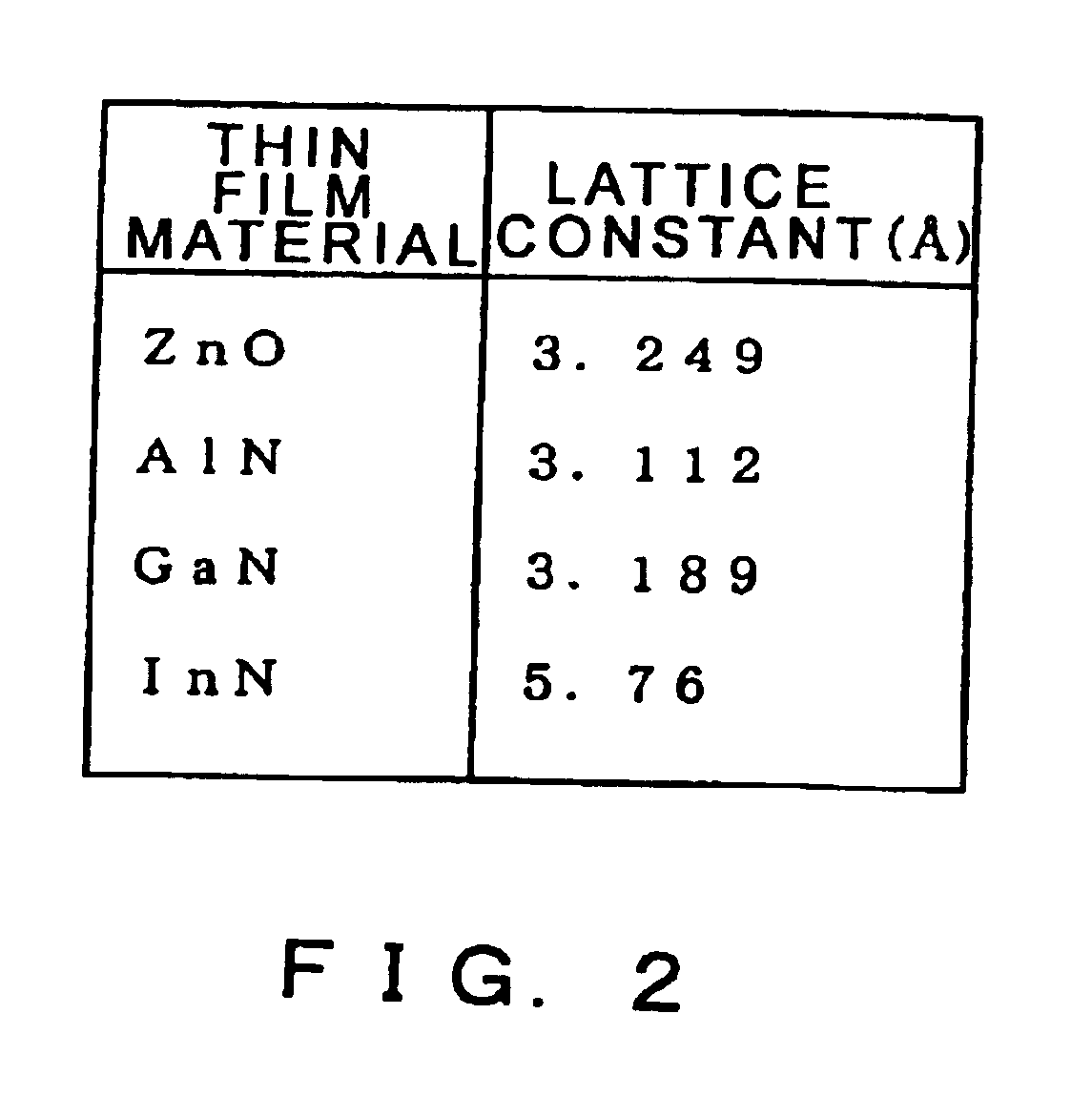
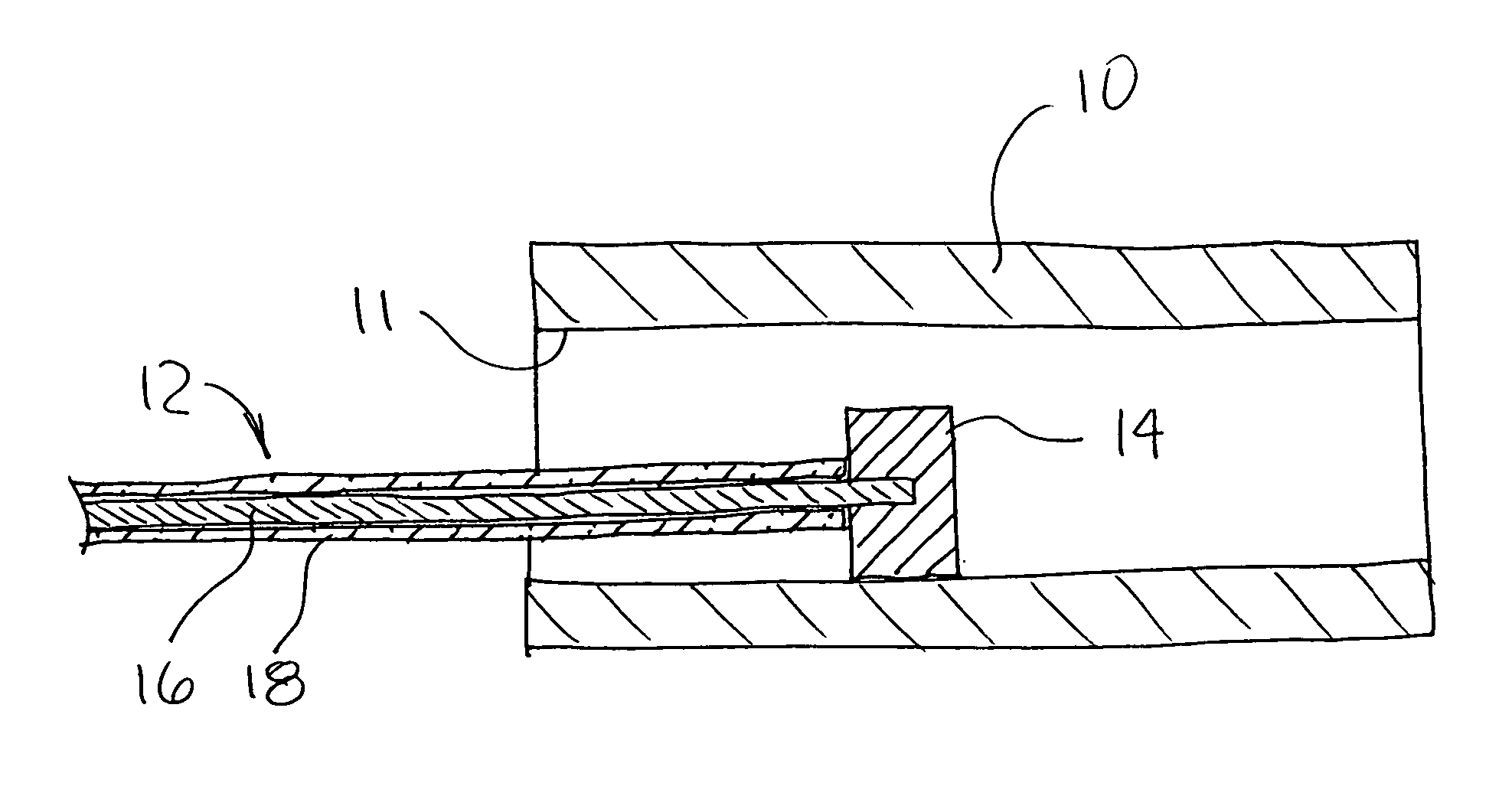
The present invention provides a high quality thin film comparable to a bulk single crystal and providres a semiconductor device with superior characteristics. A channel layer 11, for example, is formed of a semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO or the like. A source 12, a drain 13, a gate 14 and a gate insulating layer 15 are formed on the channel layer 111 to form an FET. For a substrate 16, a proper material is selected depending on a thin film material of the channel layer 11 in consideration of compatibility of both lattice constants. For example, if ZnO is used for the semiconductor of the channel layer as a base material, ScAlMgO4 or the like can be used for the substrate 16.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
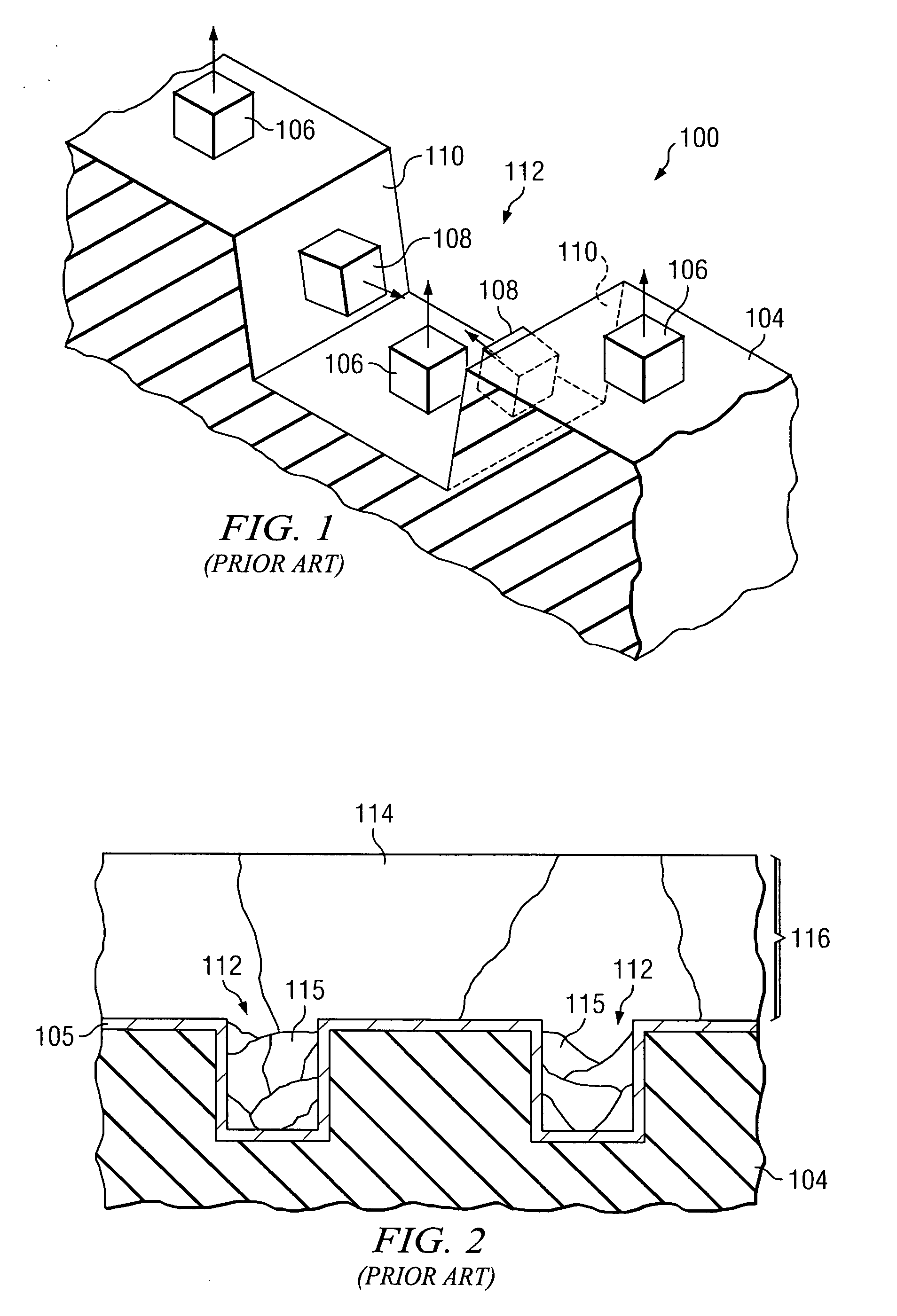
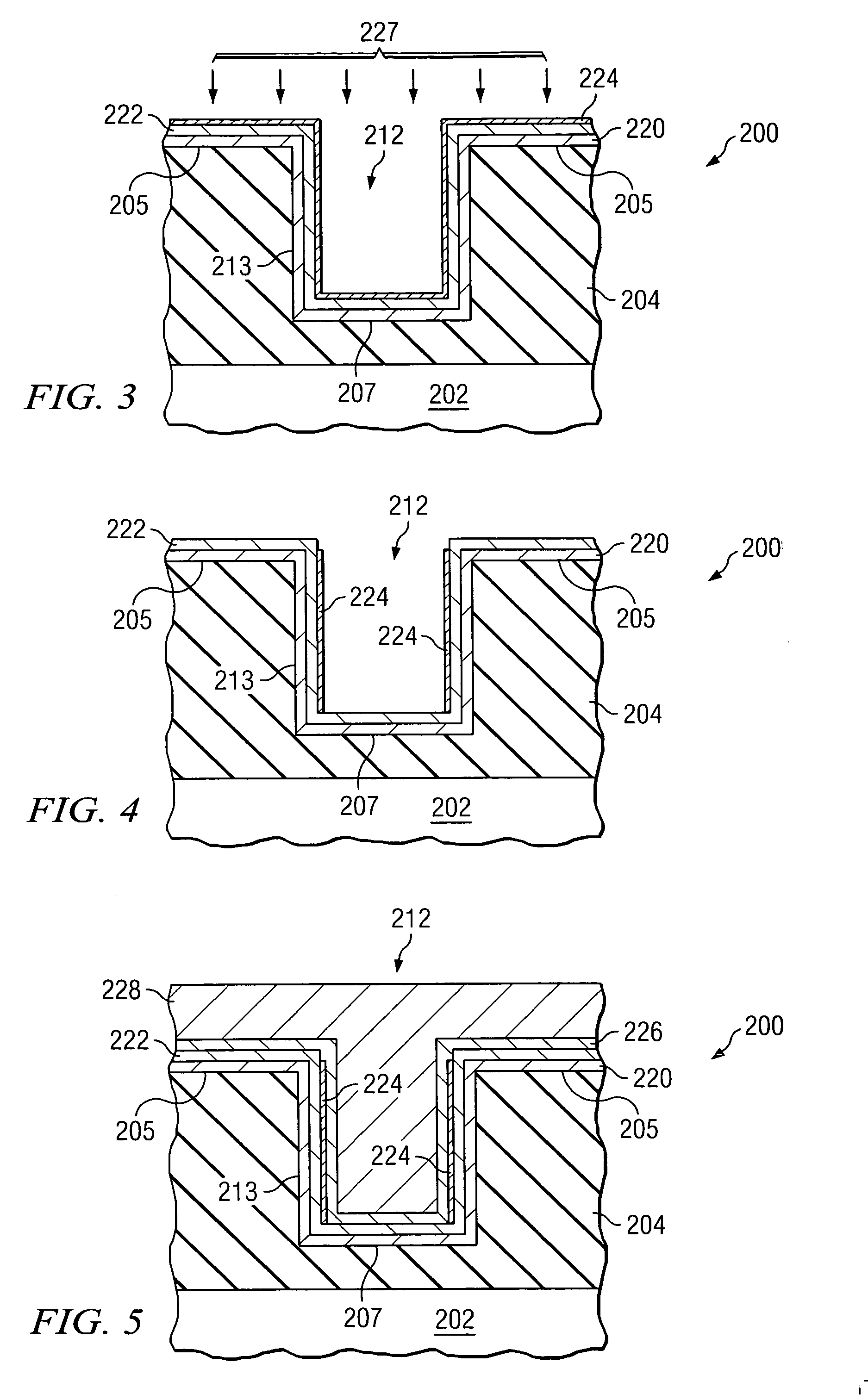
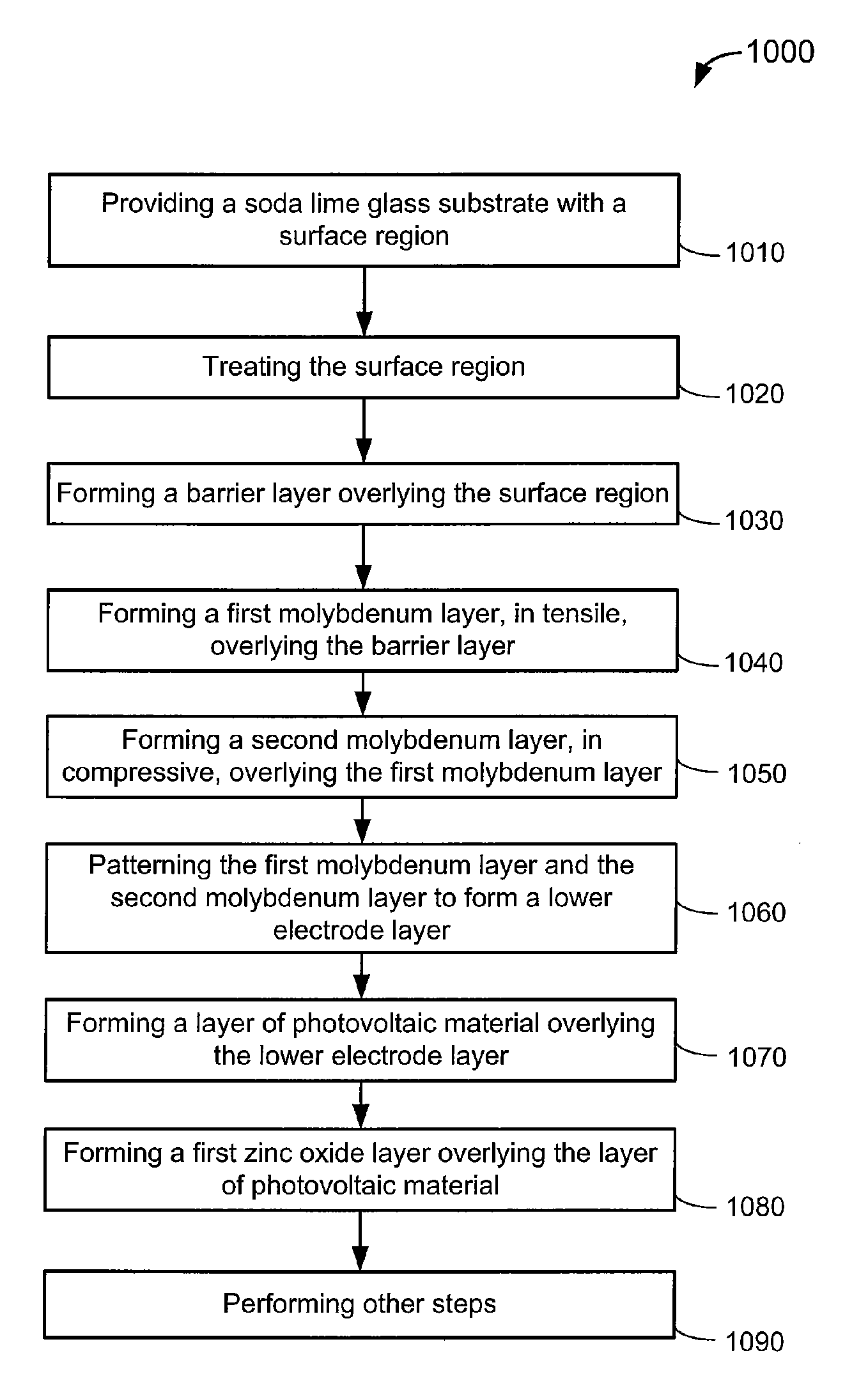
Thin film sodium species barrier method and structure for cigs based thin film photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20100258179A1Large grainImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationOptoelectronicsSpecies barrier
A method for fabricating a thin film solar cell includes providing a soda lime glass substrate comprising a surface region and a concentration of sodium oxide of greater than about 10 wt % and treating the surface region with one or more cleaning process, using a deionized water rinse, to remove surface contaminants having a particles size of greater than three microns. The method also includes forming a barrier layer overlying the surface region, forming a first molybdenum layer in tensile configuration overlying the barrier layer, and forming a second molybdenum layer in compressive configuration using a second process overlying the first molybdenum layer. Additionally, the method includes patterning the first molybdenum layer and the second molybdenum layer to form a lower electrode layer and forming a layer of photovoltaic material overlying the lower electrode layer. Moreover, the method includes forming a first zinc oxide layer overlying the layer of photovoltaic materials.
Owner:CM MFG
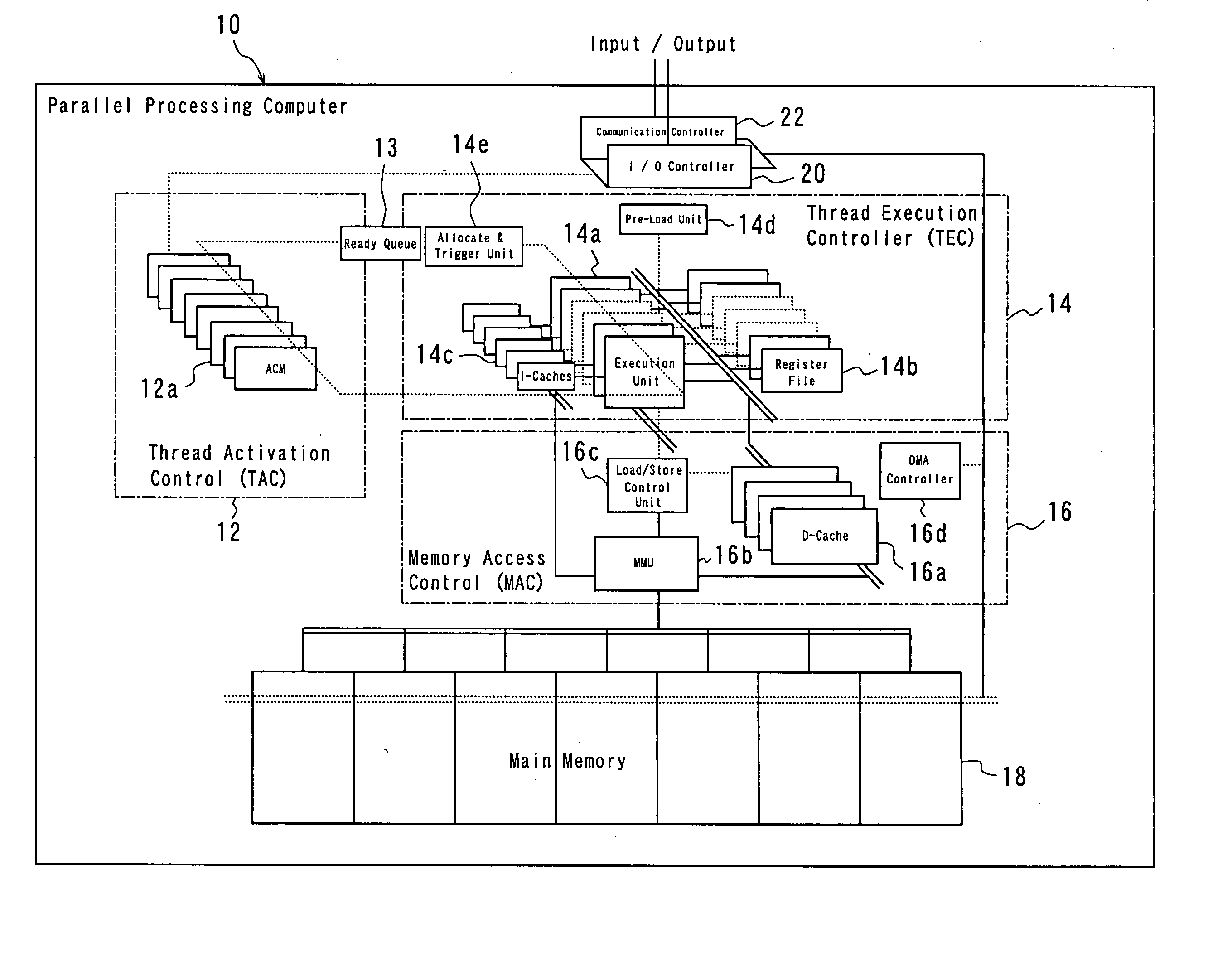
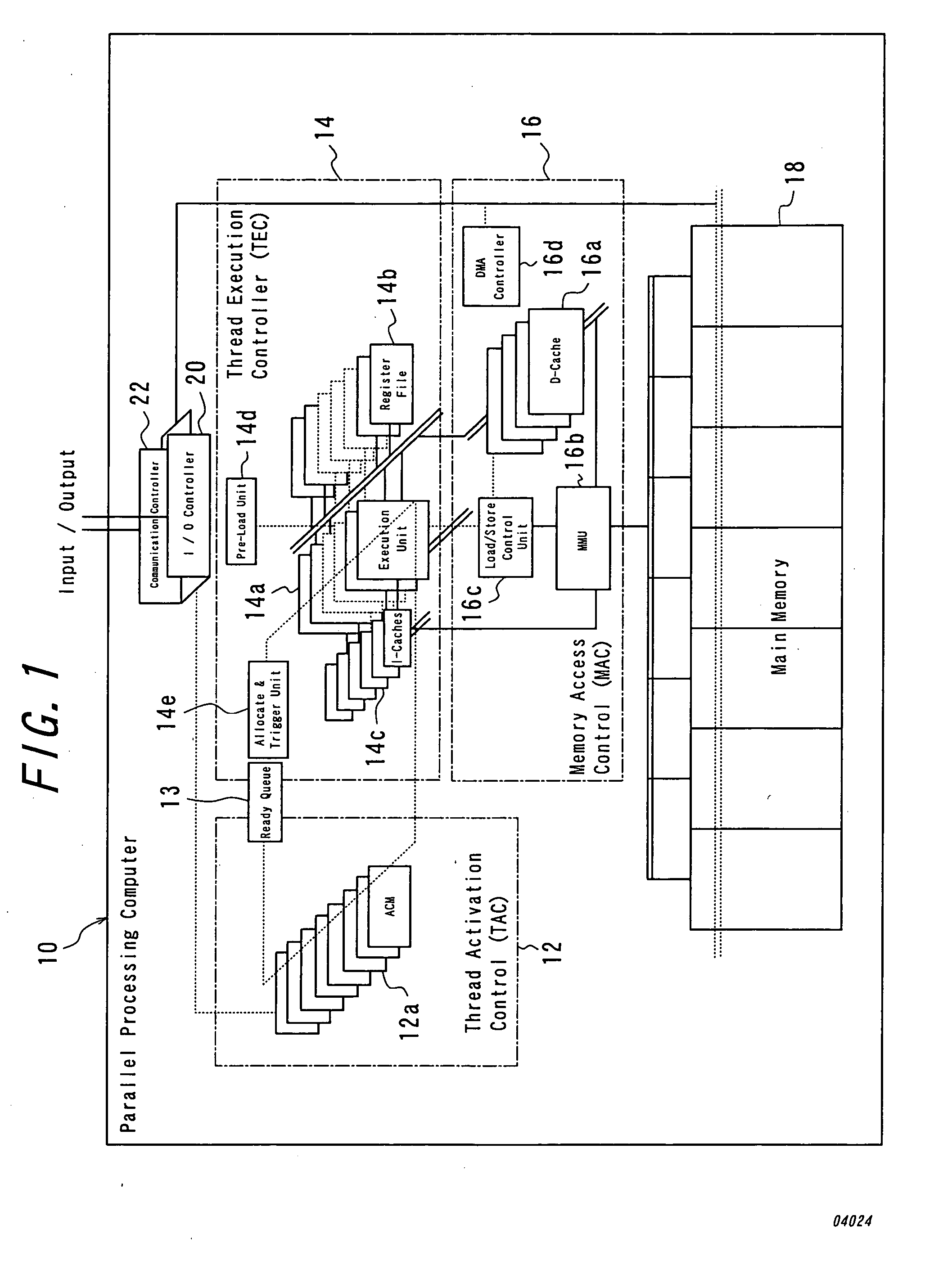
Parallel processing computer
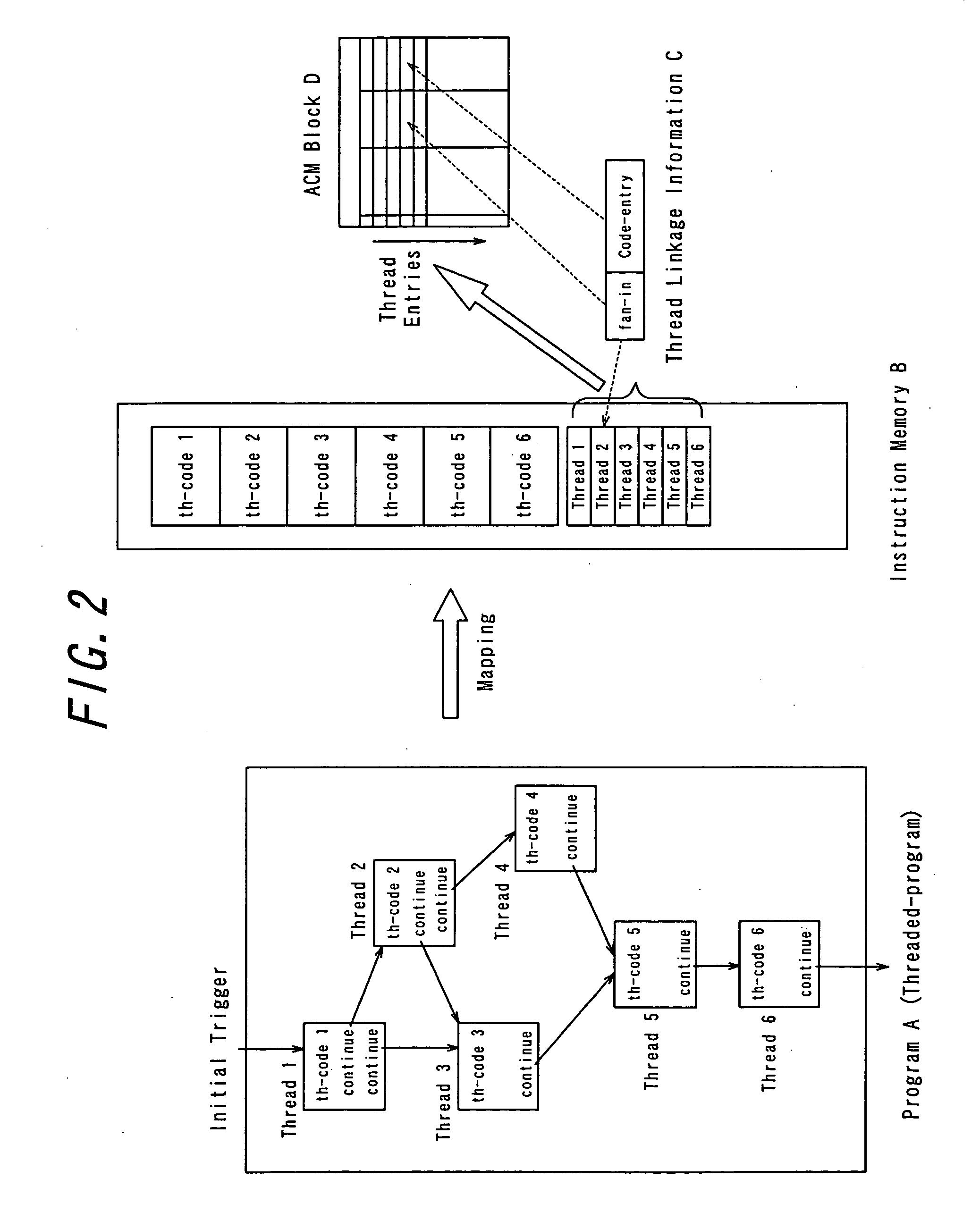
InactiveUS20050240930A1Efficient executionImprove throughputProgram initiation/switchingRegister arrangementsProgram fragmentFile allocation
There is provided a parallel processing computer for executing a plurality of threads concurrently and in parallel. The computer includes: a thread activation controller for determining whether or not each of threads, which are exclusively executable program fragments, is ready-to-run, to put the thread determined ready-to-run into a ready thread queue as ready-to-run thread; and a thread execution controller having a pre-load unit, an EU allocation and trigger unit, a plurality of thread execution units and a plurality of register files including a plurality of registers, and the pre-load unit, prior to when each ready-to-run thread in the ready thread queue is executed, allocates a free register file of the plurality of register files to the each ready-to-run thread, to load initial data for the each ready-to-run thread into the allocated register file, and the EU allocation and trigger unit, when there is a thread execution unit in idle state of the plurality of thread execution unit, retrieves ready-to-run thread from the top of the ready thread queue, and to allocate the retrieved ready-to-run thread to the thread execution unit in idle state, and to couple the register file loaded the initial data for the ready-to-run thread with the allocated thread execution unit in idle state, and to trigger the ready-to-run thread. The plurality of thread execution units execute the triggered threads concurrently in parallel.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Method of fabricating polysilicon film
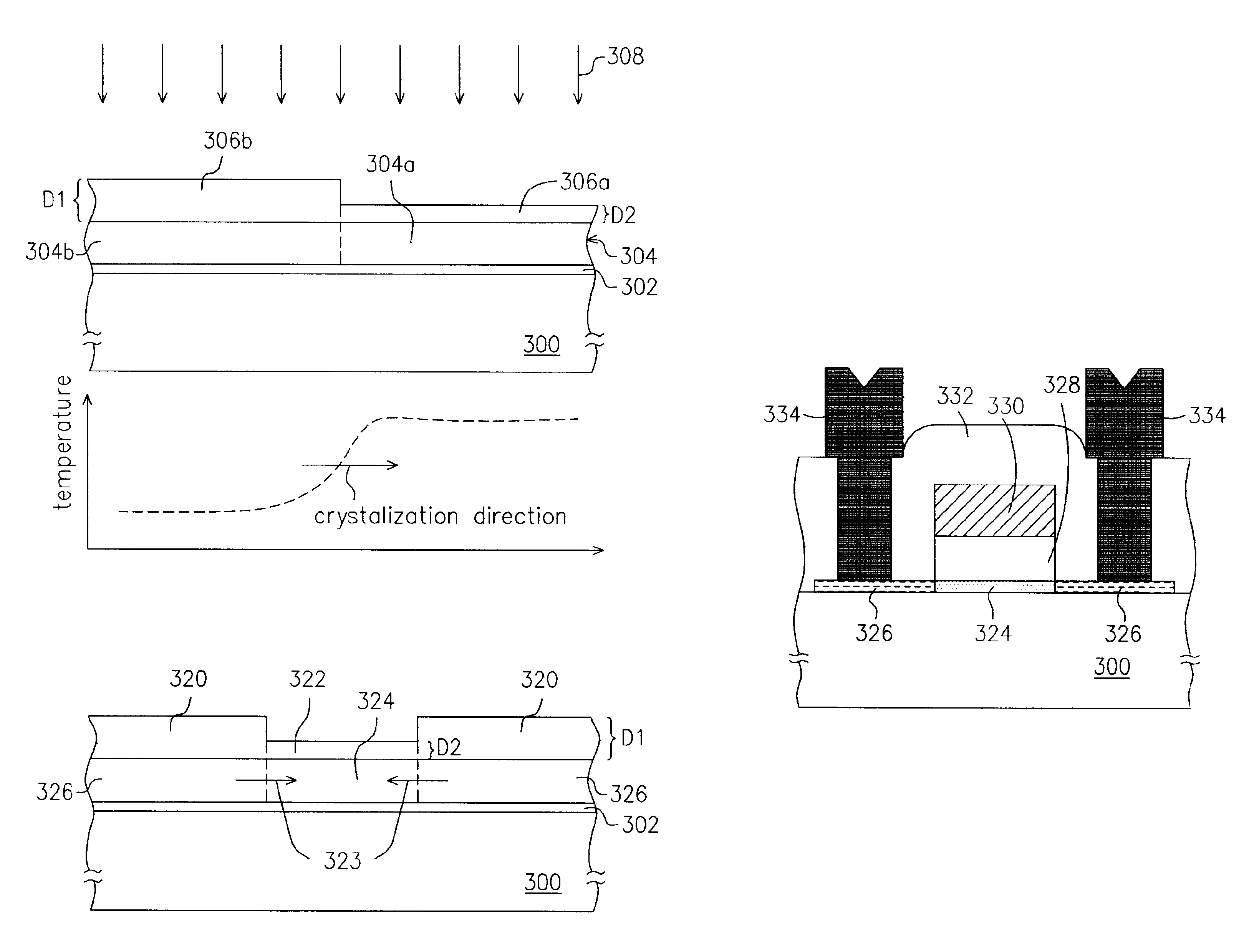
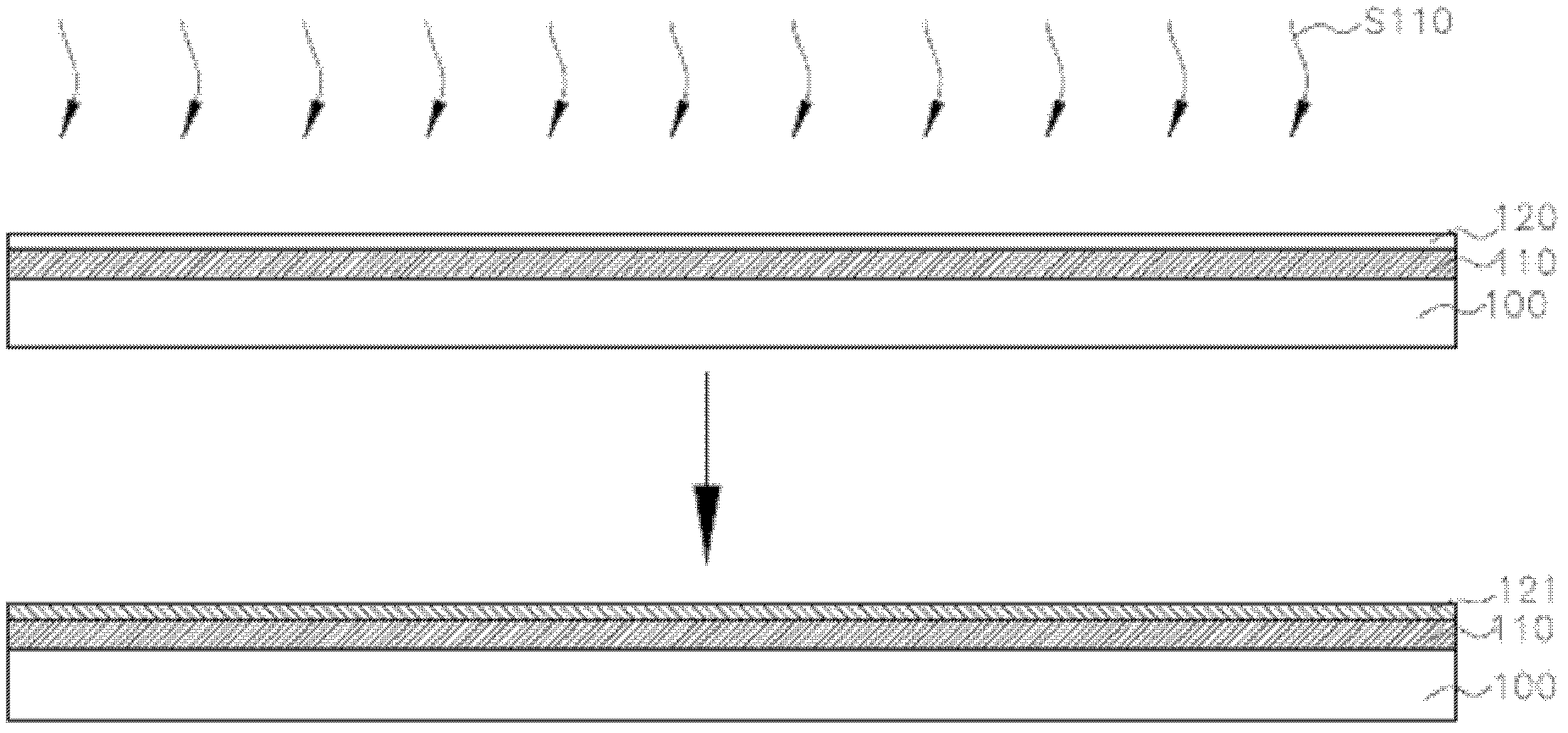
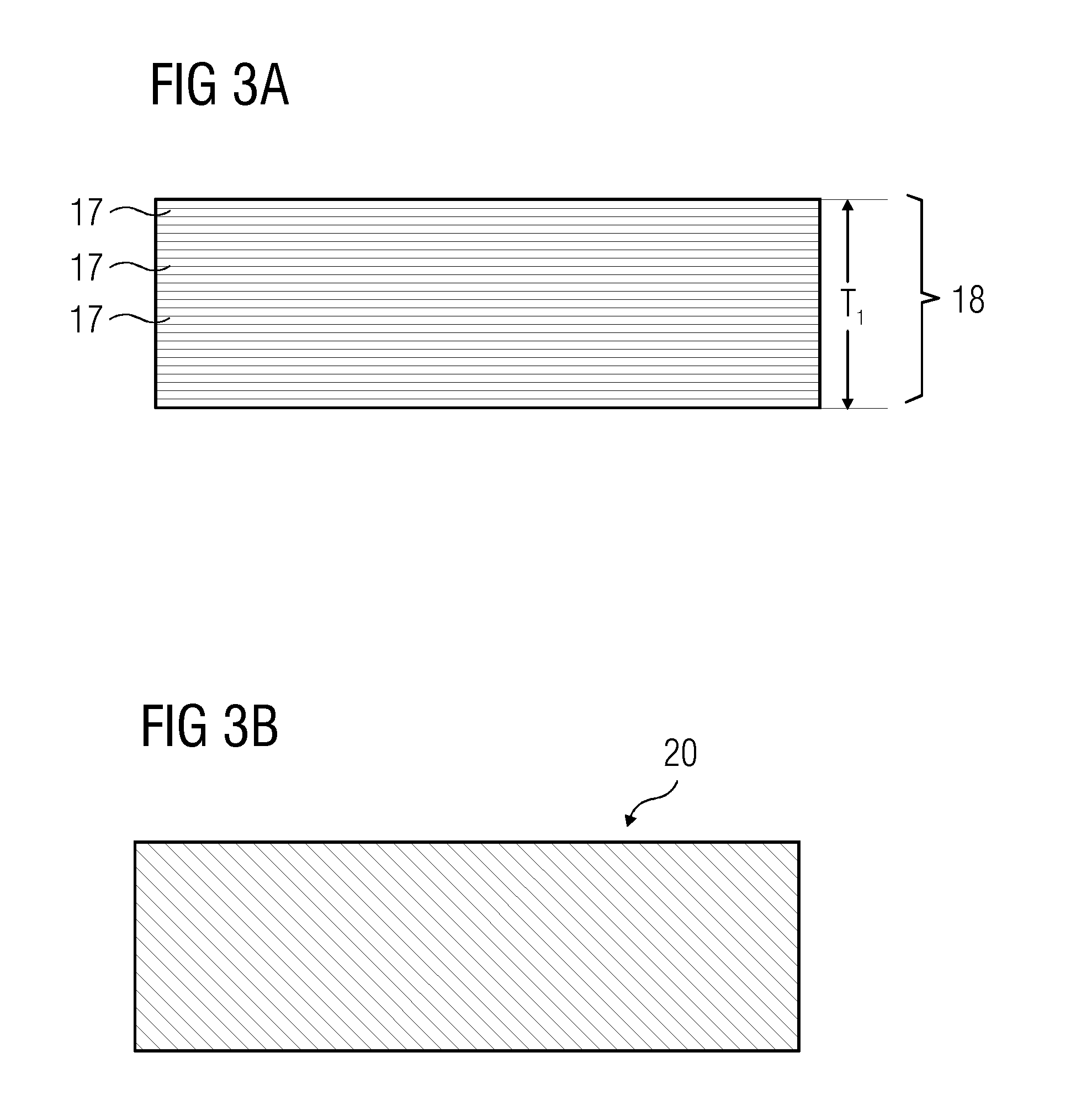
InactiveUS6916690B2Increasing lateral temperature gradientInduce lateral crystallizationTransistorSolid-state devicesAmorphous siliconLaser annealing
A method of fabricating polysilicon film is described. An amorphous silicon layer is formed on the substrate, an optical layer is formed on the amorphous silicon layer, wherein the optical has a first region having a first thickness and a second region having a second thickness, and the reflectivity of the first region for an excimer laser is higher than that of the second region. A laser annealing process is then preformed to transform the amorphous silicon layer into a polysilicon film.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Barrier layers for conductive features
InactiveUS20060202345A1Lower resistanceImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive materialsGrain growth
Barrier layers for conductive features and methods of formation thereof are disclosed. A first barrier material is deposited on top surfaces of an insulating material, and a second barrier material is deposited on sidewalls of the insulating material, wherein the second barrier material is different than the first barrier material. The first barrier material induces grain growth of a subsequently deposited conductive material at a first rate, and the second barrier material induces grain growth of the conductive material at a second rate, wherein the second rate is slower than the first rate.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Thin film sodium species barrier method and structure for cigs based thin film photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS8217261B2Large grainImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationBarrier methodWater rinsing
Owner:CM MFG
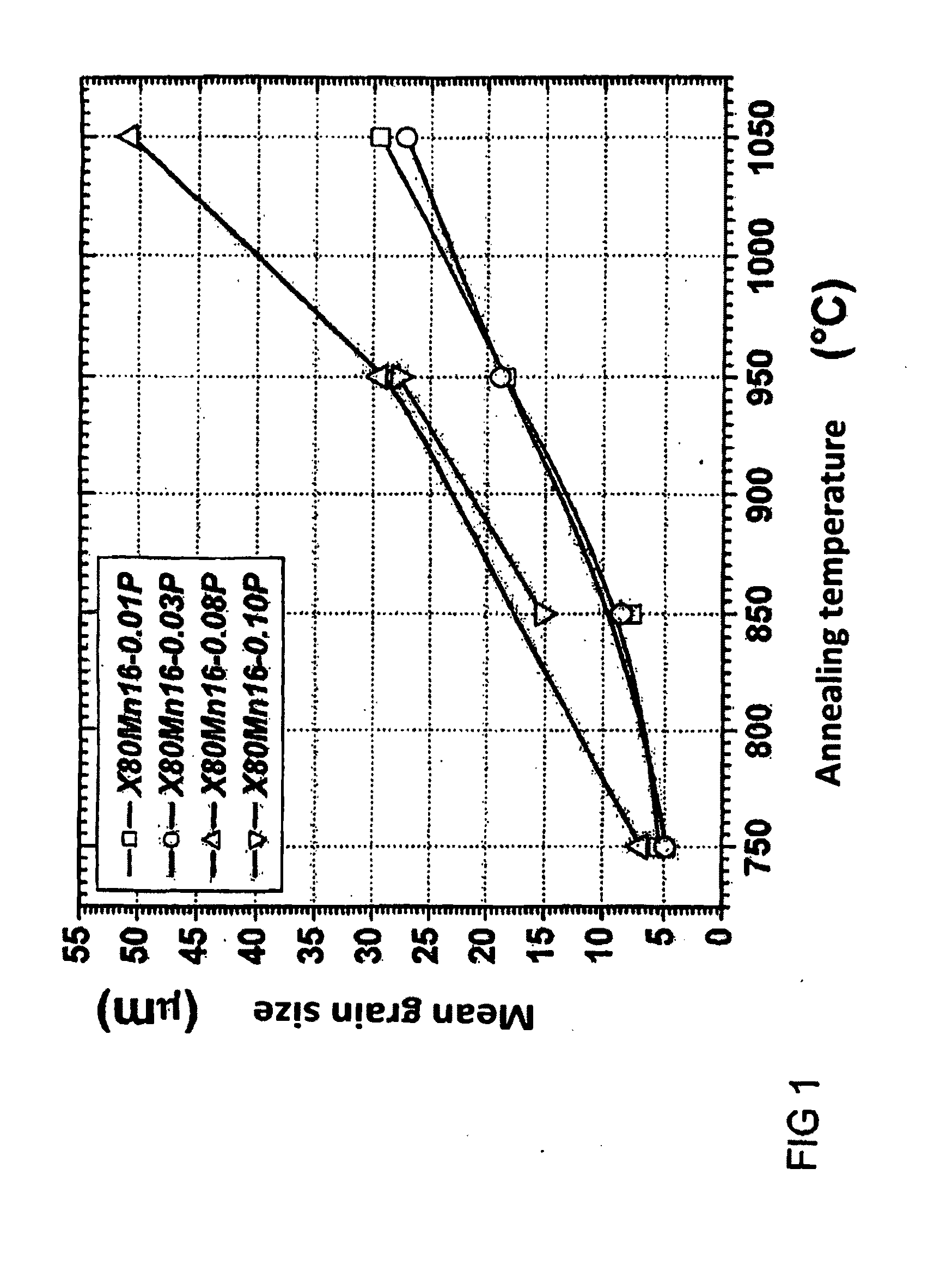
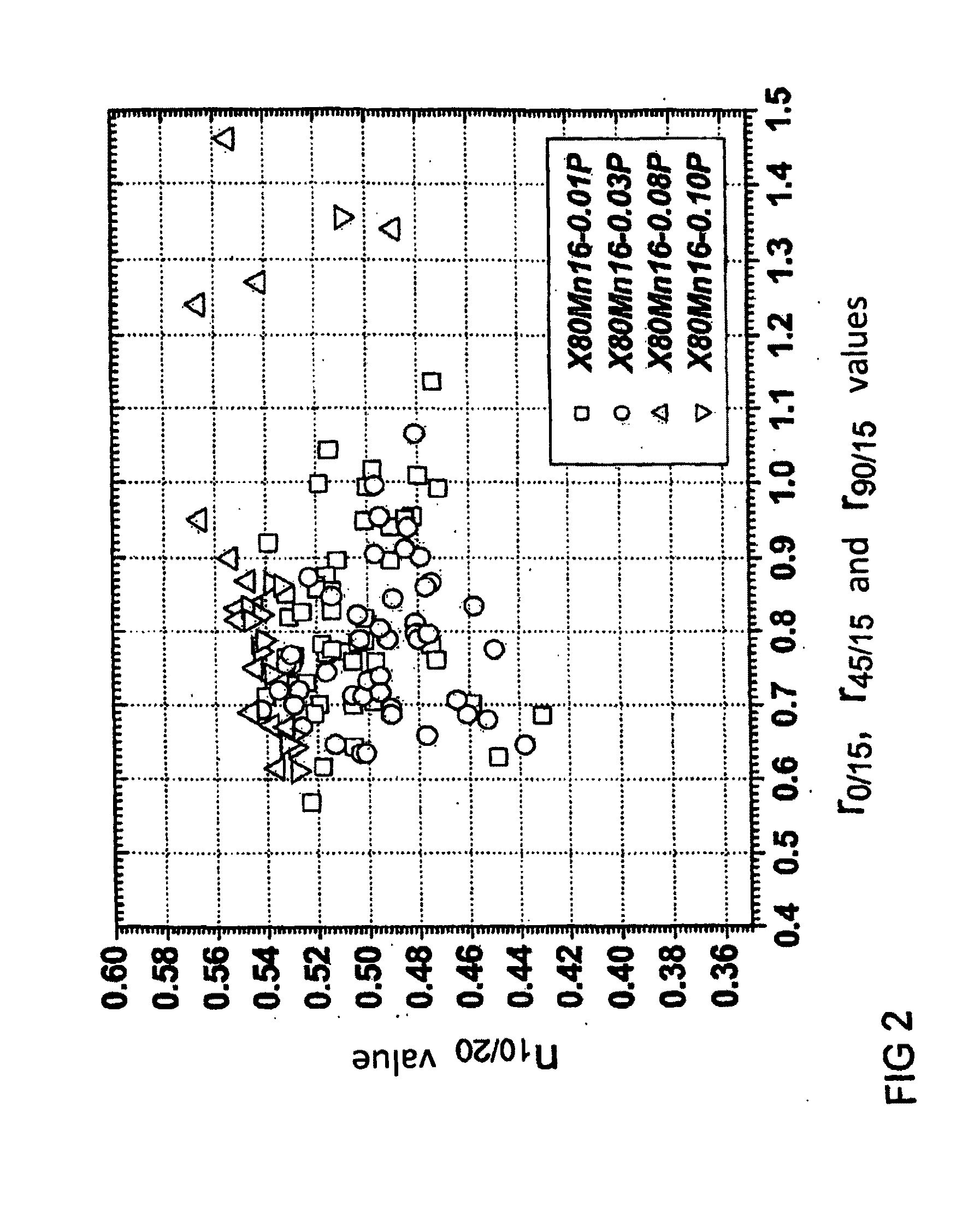
Manganese steel strip having an increased phosphorous content and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20110308673A1Improve solid solubilityImprove solubilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionManganese
A hot-rolled austenitic manganese steel strip having a chemical composition in percent by weight of 0.4%≦C≦1.2%, 12.0%≦Mn≦25.0%, P≧0.01% and Al≦0.05% has a product of elongation at break in % and tensile strength in MPa of above 65,000 MPa %, in particular above 70,000 MPa %. A cold-rolled austenitic manganese steel strip having the same chemical composition achieves a product of elongation at break in % and tensile strength in MPa of above 75,000 MPa %, in particular above 80,000 MPa %.
Owner:VOESTALPINE STAHL GMBH
Thin film transistor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS8119468B2High purityImprove featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesAmorphous siliconCrystalline particle
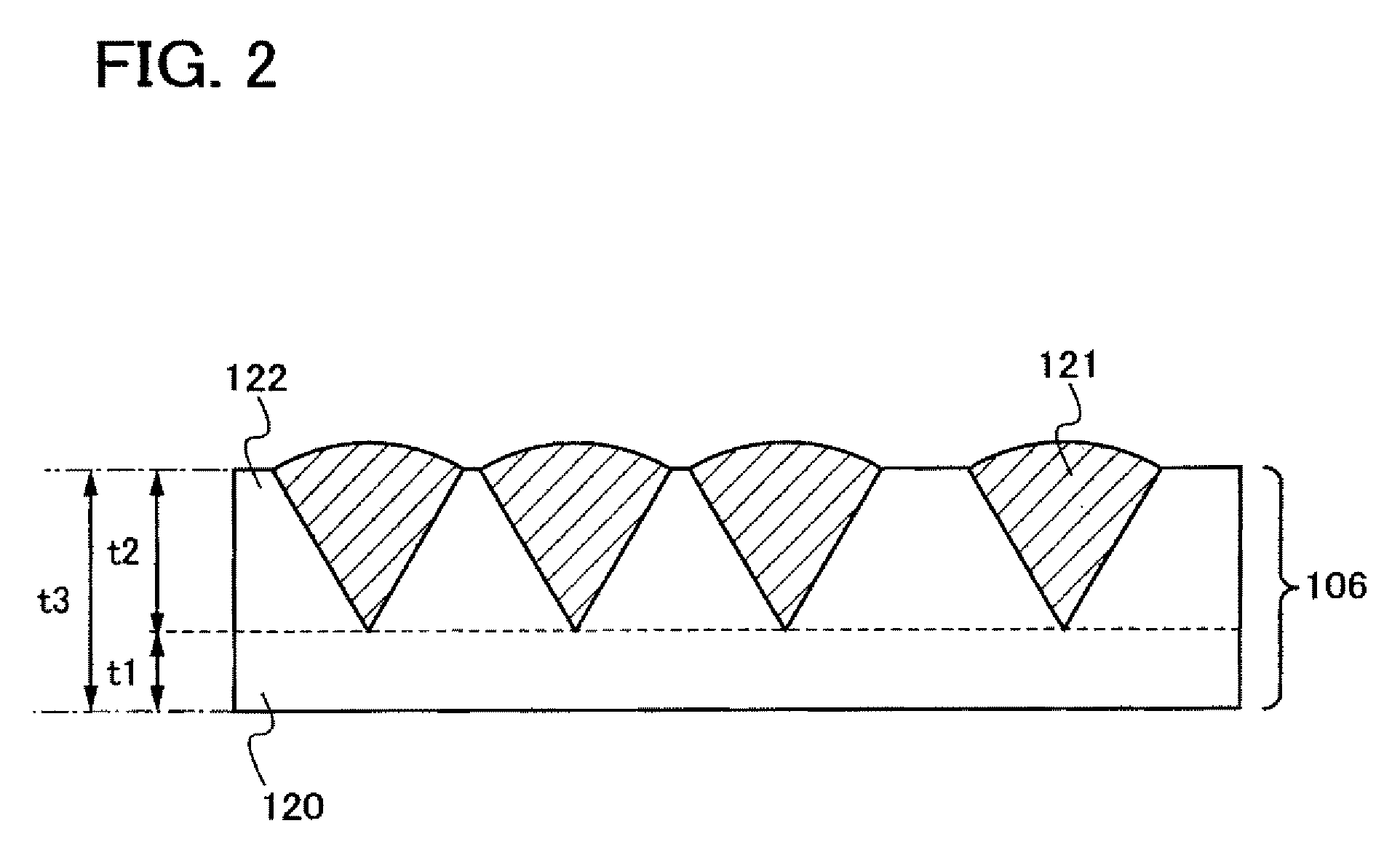
Disclosed is a thin film transistor which includes, over a substrate having an insulating surface, a gate insulating layer covering a gate electrode; a semiconductor layer which functions as a channel formation region; and a semiconductor layer including an impurity element imparting one conductivity type. The semiconductor layer exists in a state that a plurality of crystalline particles is dispersed in an amorphous silicon and that the crystalline particles have an inverted conical or inverted pyramidal shape. The crystalline particles grow approximately radially in a direction in which the semiconductor layer is deposited. Vertexes of the inverted conical or inverted pyramidal crystal particles are located apart from an interface between the gate insulating layer and the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor thin film decomposing method, decomposed semiconductor thin film, decomposed semiconductor thin film evaluation method, thin film transistor made of decomposed semiconductor thin film, and image display device having circuit constituted of thin film transistors
InactiveUS20050139830A1Reduce decreaseLong processing timeTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh energySemiconductor thin films
A surface roughness of a polycrystalline semiconductor film to be formed by a laser annealing method is reduced. A transmittance distribution filter is disposed at the optical system of a laser annealing apparatus. The transmittance distribution filter controls an irradiation light intensity distribution along a scanning direction of a substrate formed with an amorphous silicon semiconductor thin film to have a distribution having an energy part equal to or higher than a fine crystal threshold on a high energy light intensity side and an energy part for melting and combining only a surface layer. This transmittance distribution filter is applied to an excimer laser annealing method, a phase shift stripe method or an SLS method respectively using a general line beam to thereby reduce the height of protrusions on a polycrystalline surface.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Semiconductor thin film crystallization device and semiconductor thin film crystallization method
InactiveUS20060019474A1Flat surfaceFew defectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor thin films
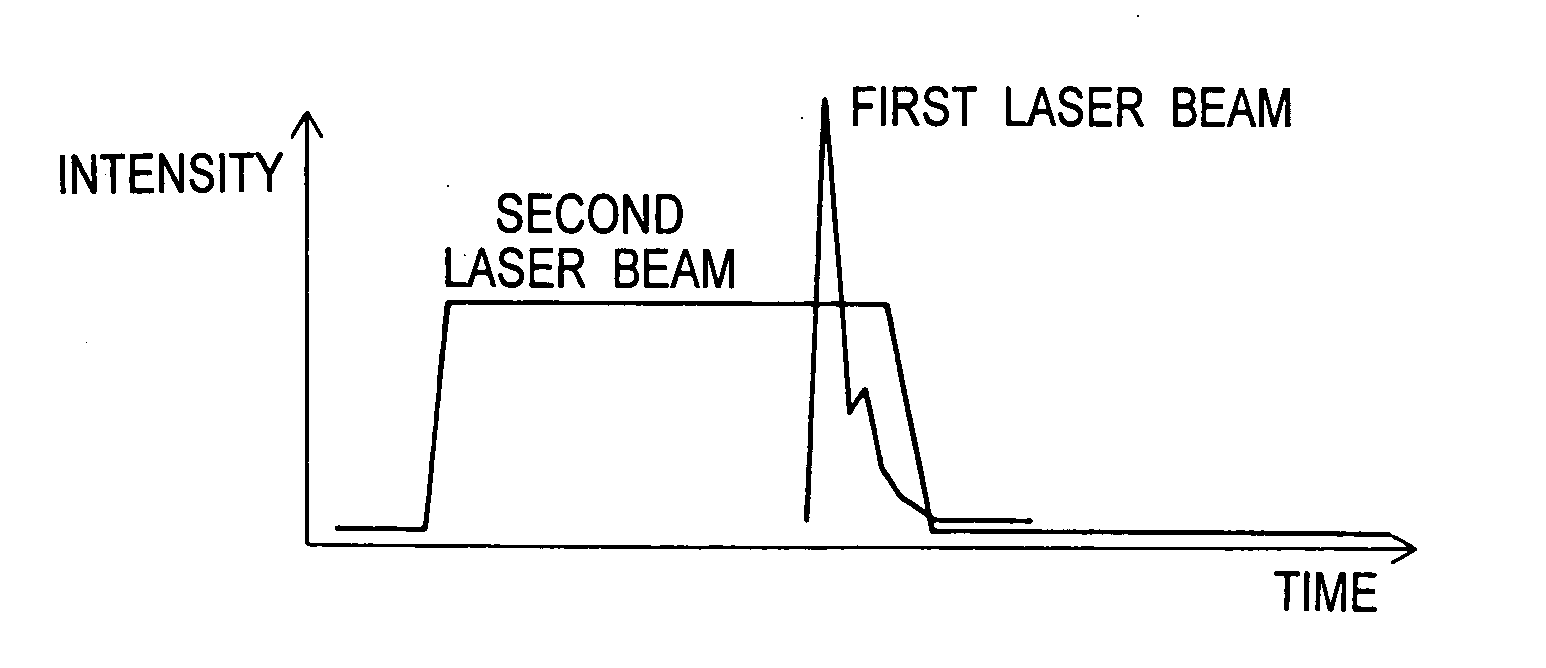
A first laser beam is emitted from a first laser oscillator in a pulsed manner at a high repetition frequency, and converged onto a substrate by a first intermediate optical system 2 so as to form a slit-like first beam spot. A second laser beam is emitted from a second laser beam oscillator in a pulsed manner to rise precedent to and fall subsequent to the first laser beam, and converged onto the substrate by a second intermediate optical system so as to form a second beam spot similar in configuration to the first beam spot and to contain the first beam spot. Crystallization of a semiconductor thin film on the substrate is carried out while the substrate or the first, second beam spots are moved. Thereby, the whole semiconductor thin film is formed into a crystal surface that has grown in one direction and free from ridges. Thus, the semiconductor thin film has an extremely flat surface, extremely few defects, large crystal grains and high throughput.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device having photosensor and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050199876A1Improve crystal propertyEasily detectTransistorStatic indicating devicesCrystal propertiesLaser annealing
When a photosensor was conventionally provided in a display device, separate modules manufactured in separate steps were installed in the same case. However, decreases in the number of parts and in cost could not be achieved, and a compact size and thinning of the display device was not proceeded. A photosensor is realized by a TFT provided on an insulating substrate. Photocurrent caused by incidence of external light onto a TFT when the TFT is turned-off is detected so that the TFT is used as a photosensor. By performing laser-annealing for a semiconductor layer of the photosensor, an average grain size of crystal particles of the semiconductor layer of the photosensor is made larger than those of a crystal particle of a display portion and a light emission element, thereby improving crystal properties. Thus, a generation efficiency of the photocurrent of the photosensor can be increased.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Micro-welded gun barrel coatings
InactiveUS20040140292A1High strengthImproved wear/erosion resistance and thermal managementArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusWear resistantRifling
A micro-welding process is used to apply erosion and wear resistant coatings to the internal diameter of gun barrels. The applied coatings are then treated by methods such as honing and / or rotary forging. The protective micro-welded coatings may comprise ceramic, cermet and / or refractory metal materials, and may be used with rifled or smooth gun barrels of various sizes.
Owner:KELLEY JOHN E +2
Method and apparatus for depositing and controlling the texture of a thin film
InactiveUS6837979B2Accelerate grain recoveryPromote growthCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialsElectroplating
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for plating a conductive material to a substrate and also modifying the physical properties of a conductive film while the substrate is being plated. The present invention further provides a method and apparatus that plates a conductive material on a workpiece surface in a “proximity” plating manner while a pad type material or other fixed feature is making contact with the workpiece surface in a “cold worked” manner. In this manner, energy stored in the cold worked regions of the plated layer is used to accelerate and enhance micro-structural recovery and growth. Thus, large grain size is obtained in the plated material at a lower annealing temperature and a shorter annealing time.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Crystallizing method, thin-film transistor manufacturing method, thin-film transistor, and display device
InactiveUS20090194769A1Reduce generationLarge grainTransistorLayered productsDisplay deviceLight beam
A crystallizing method of causing a phase shifter to phase-modulate a laser beam whose wavelength is 248 nm or 300 nm or more from an excimer laser unit into a laser beam with a light intensity profile having a plurality of inverted triangular peak patterns in cross section and of irradiating the pulse laser beam onto a substrate to be crystallized for crystallization. The substrate to be crystallized is such that one or more silicon oxide films which present absorption properties to the laser beam and differ in the relative proportions of Si and O are provided on a laser beam incident face.
Owner:SHARP KK
Laser apparatus, laser annealing method, and manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7179698B2Large grainLow running costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser lightSolid-state laser
To provide a laser apparatus and a laser annealing method with which a crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size is obtained and which are low in their running cost. A solid state laser easy to maintenance and high in durability is used as a laser, and laser light emitted therefrom is linearized to increase the throughput and to reduce the production cost as a whole. Further, both the front side and the back side of an amorphous semiconductor film is irradiated with such laser light to obtain the crystalline semiconductor film with a larger crystal grain size.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Manufacturing method of low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) thin film transistor (TFT)
ActiveCN102629558ALarge grainImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) thin film transistor (TFT). The method is characterized by: forming an amorphous silicon (a-Si) layer on a substrate; carrying out hydrogen relief treatment on the a-Si layer so that the a-Si layer becomes a microgranular; then, forming the a-Si layer which does not be performed with grain refining on the a-Si layer of the microgranular; and then carrying out the hydrogen relief treatment on the a-Si layer so that the a-Si layer becomes the microgranular; and continuously repeating so as to form the a-Si layer and carrying out the hydrogen relief treatment so as to form the a-Si layer with multilayer micromeritics; finally, carrying out excimer laser annealing (ELA) so that the a-Si layer with the multilayer micromeritics crystallizes into a poly-Si layer. After the poly-Si layer becomes the a-Si layer of the multilayer micromeritic through pretreatment, the ELA is performed so that the crystalline grain of the poly-Si layer becomes larger and a carrier mobility is high.
Owner:CENTURY DISPLAY (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Perovskite solar cell and preparation method thereof
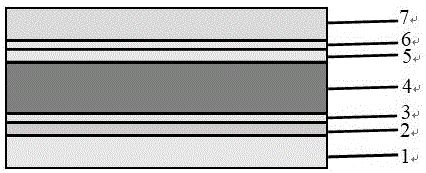
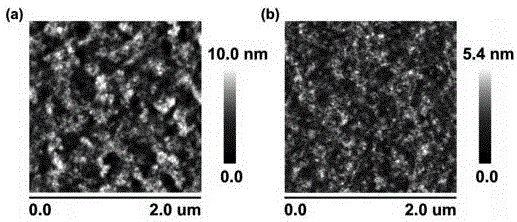
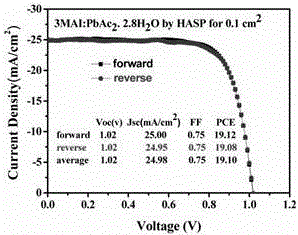
InactiveCN106684247AInhibitory complexImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHysteresisSpray coating
The invention discloses a perovskite solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The perovskite solar cell comprises a transparent conductive substrate, a hole transport layer, a decoration layer, a perovskite layer, an electron transport layer, a barrier layer and a metal electrode. The surfaces of PEDOT: PSS, NiOx and the hole transport layer are decorated by ionic liquid based on imidazole, atomic force microscope graphs before and after the decoration are compared, and the decorated surface appearance is more smooth, which is conducive to inhibiting the compounding of dark current. The perovskite layer is a new perovskite material 3MAI: PbAc2.xH2O (x is not smaller than 0 and is not greater than 3), and is prepared by quickly preheating a substrate and heating a perovskite precursor solution, namely instant heating assisted spray coating technology (HASP) at a low temperature (lower than 100 DEG C), which is conducive to increasing the grain size of perovskite and reducing the defects between perovskite grains so as to greatly improve the efficiency of the perovskite battery. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the final battery device is greater than 19%, the flexible device efficiency is 10.8%, no hysteresis effect is formed, and thus the preparation method has a broad application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
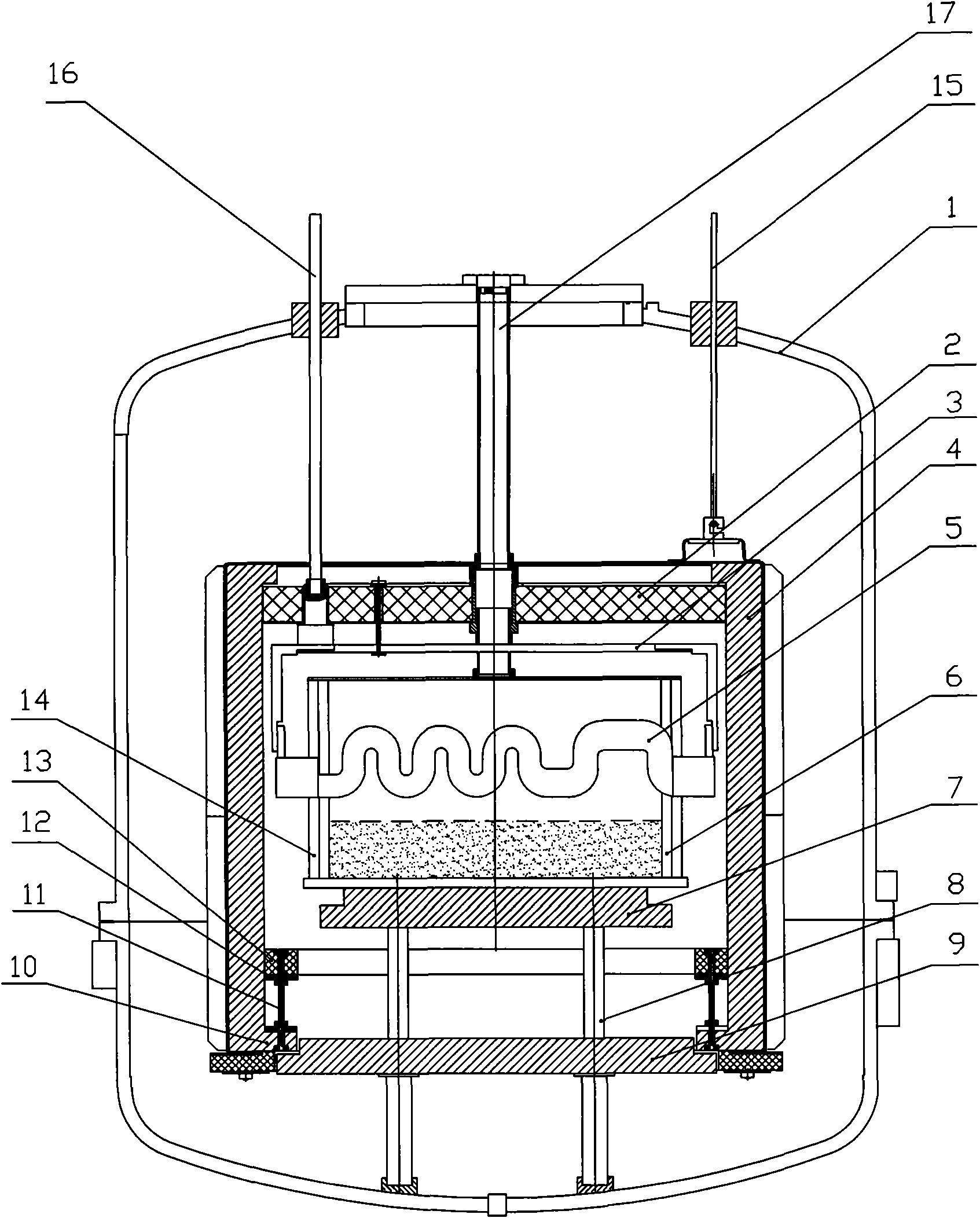
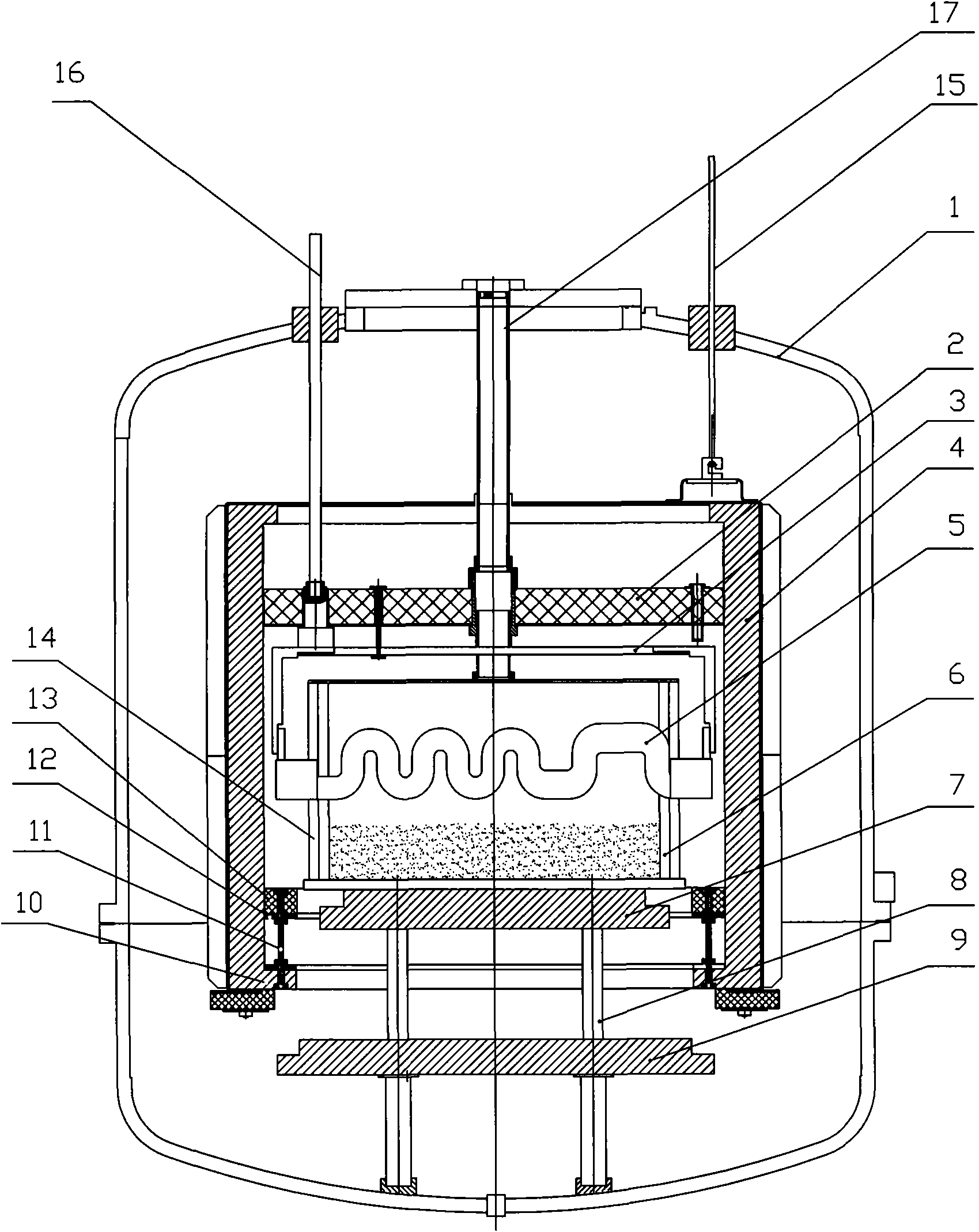
Ingot furnace thermal field structure based on multi-heater and operation method
ActiveCN102877117ASolve the problems of slow speed in the later stage and long crystal growth time at the cornersConvenient to achieve the purpose of not meltingPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsManufacturing technologyMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to the field of manufacturing technology of polycrystalline silicon ingot furnaces, aiming to provide an ingot furnace thermal field structure based on multi-heater and an operation method. The ingot furnace thermal field structure comprises a crucible arranged in a furnace chamber; a thermal field of the crucible comprises a top heater, a side heater, a heat exchanger table located on the bottom of the crucible and a bottom heater located on the bottom of the heat exchange table; an infrared temperature measuring instrument coordinates with the top heater and the side heater; the infrared temperature measuring instrument or a thermoelectric couple coordinates with the bottom heater. An operation process of the operation method comprises a heating stage, a melting stage, a crystal growing stage, an annealing stage and a cooling stage. The ingot furnace thermal field structure and the operation method can effectively monitor the temperature of various portions of the thermal field, regulate power output of various heaters, establish more reasonable temperature gradient, adapt to high-feeding capacity and large-size ingot trend, enable crystal nucleus to form more uniformly during early time of crystal growth, enlarge crystals, reduce crystal boundary, improve crystal direction, reduce energy consumption and finally improve quality of crystal ingots.
Owner:杭州慧翔电液技术开发有限公司 +1
Rice big grain gene and uses thereof
ActiveCN101161675ALarge grainIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesCell divisionAgricultural science
The present invention discloses a rice large-grain gene GW2 and the application thereof, the GW2 gene can be used to control the grain size of the crop, improve the yield or quality of the crop, regulate the cycle duration of cellular mitosis, and used as a molecular marker to identify the species of the crop to be a large-grain one or a small-grain one. The present invention also discloses a method to ameliorate the crop. The gene GW2 has a wide prospect on high-yield breeding of crops such as rice.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
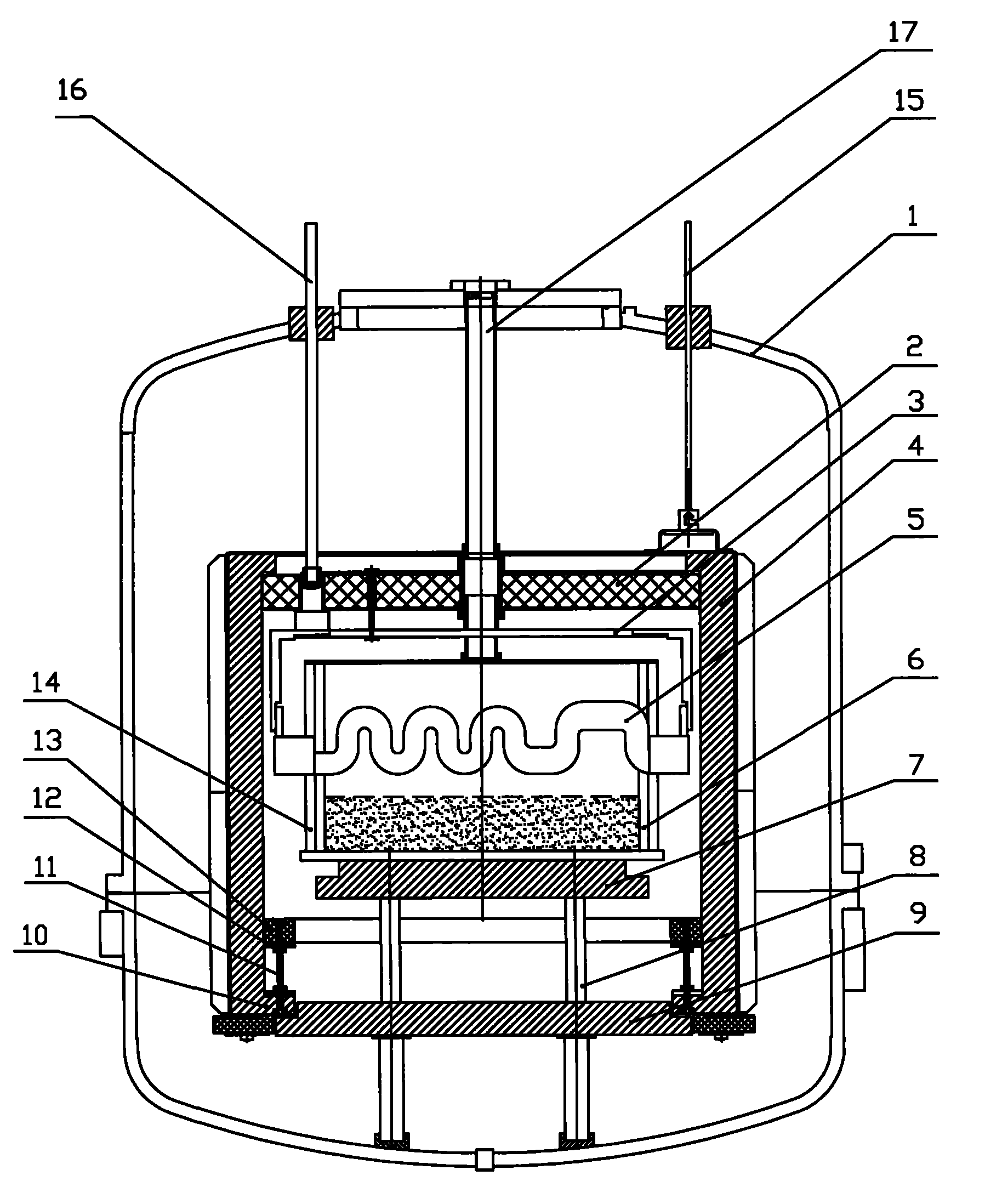
Follow-up heat insulation ring thermal field structure for vertical oriented growth of polysilicon
InactiveCN101775641ACrystal solidification process controlImprove temperature gradient distributionBy pulling from meltManufacturing technologyThermal insulation
The invention relates to the technical field of polysilicon ingot furnace designing and manufacturing, and aims to provide a follow-up heat insulation ring thermal field structure for the vertical oriented growth of polysilicon. The thermal field structure comprises a furnace chamber with a side surface enclosed heat insulation cage body, a crucible and a thermal field are arranged in the heat insulation cage body, and the upper end of the heat insulation cage body is connected with a lifting device; the upper part and the lower part of the heat insulation cage body are respectively provided with a top heat insulation board and a lower heat insulation body, wherein the top heat insulation board is fixedly suspended on an electrode, the lower heat insulation board and a heat exchange are fixed on a support column, the top heat insulation board and the upper end of the heat insulation cage body are movably connected, and the lower heat insulation board and the lower end of the heat insulation cage body are movably connected; and a circular follow-up heat insulation ring is fixed in the heat insulation cage body through a plurality of connecting devices. The follow-up heat insulation ring thermal field structure for the vertical oriented growth of polysilicon has reasonable design, can increase the grain size of polysilicon, reduce grain boundary and improve the verticality of the growing direction of polysilicon so as to improve the quality of polysilicon ingots, and simultaneously the follow-up heat insulation ring also plays the role of energy consumption reduction.
Owner:NINGBO JINGYUAN SOLAR ENERGY +1
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060024981A1Large grainSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beamsSemiconductor
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes irradiating a region to be crystallized of a non-monocrystalline semiconductor film with laser beam modulated by an optical modulator to have light intensity distribution having a minimum light intensity line or minimum light intensity spot to crystallize the region, and heating the crystallized region by irradiating light from a flash lamp onto the crystallized region.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
Bottom gate thin film transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070284580A1Large grainIncreasing field-effect mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBottom gateEngineering
A method of manufacturing a bottom gate thin film transistor (“TFT”) in which a polycrystalline channel region having a large grain size is formed relatively simply and easily. The method of manufacturing a bottom gate thin film transistor includes forming a bottom gate electrode on a substrate, forming a gate insulating layer on the substrate to cover the bottom gate electrode, forming an amorphous semiconductor layer, an N-type semiconductor layer and an electrode layer on the gate insulating layer sequentially, etching an electrode region and an N-type semiconductor layer region formed on the bottom gate electrode sequentially to expose an amorphous semiconductor layer region, melting the amorphous semiconductor layer region using a laser annealing method, and crystallizing the melted amorphous semiconductor layer region to form a laterally grown polycrystalline channel region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for improving mechanical properties of aramid fiber in supercritical fluid through stretching orientation
The invention relates to a method for improving mechanical properties of an aramid fiber in a supercritical fluid through stretching orientation. A supercritical carbon dioxide fluid is utilized for partially destroying interaction of a PPTA (poly-p-phenylene terephthamide) molecular chain in the aramid fiber under the action of certain tension, and the molecular chain is further oriented, so that the aramid fiber with good properties is obtained. The method for improving the mechanical properties of the aramid fiber in the supercritical fluid through stretching orientation mainly comprises the following steps: ensuring that the aramide fiber maintains certain tension in a closed container, introducing CO2 into the container at a certain temperature, so that the internal space of the closed container is in a supercritical CO2 state, carrying out swelling reaction for a period of time, and slowly releasing pressure, thus the highly stretching-oriented aramid fiber is obtained. The method for improving the mechanical properties of the aramid fiber in the supercritical fluid through stretching orientation guarantees that the aramid fiber is in a stretched state in a reaction process, so that orientation degree and crystallinity of a molecular chain are increased while stretching tension is changed, crystal particles are largened, and crystals are more and more complete.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
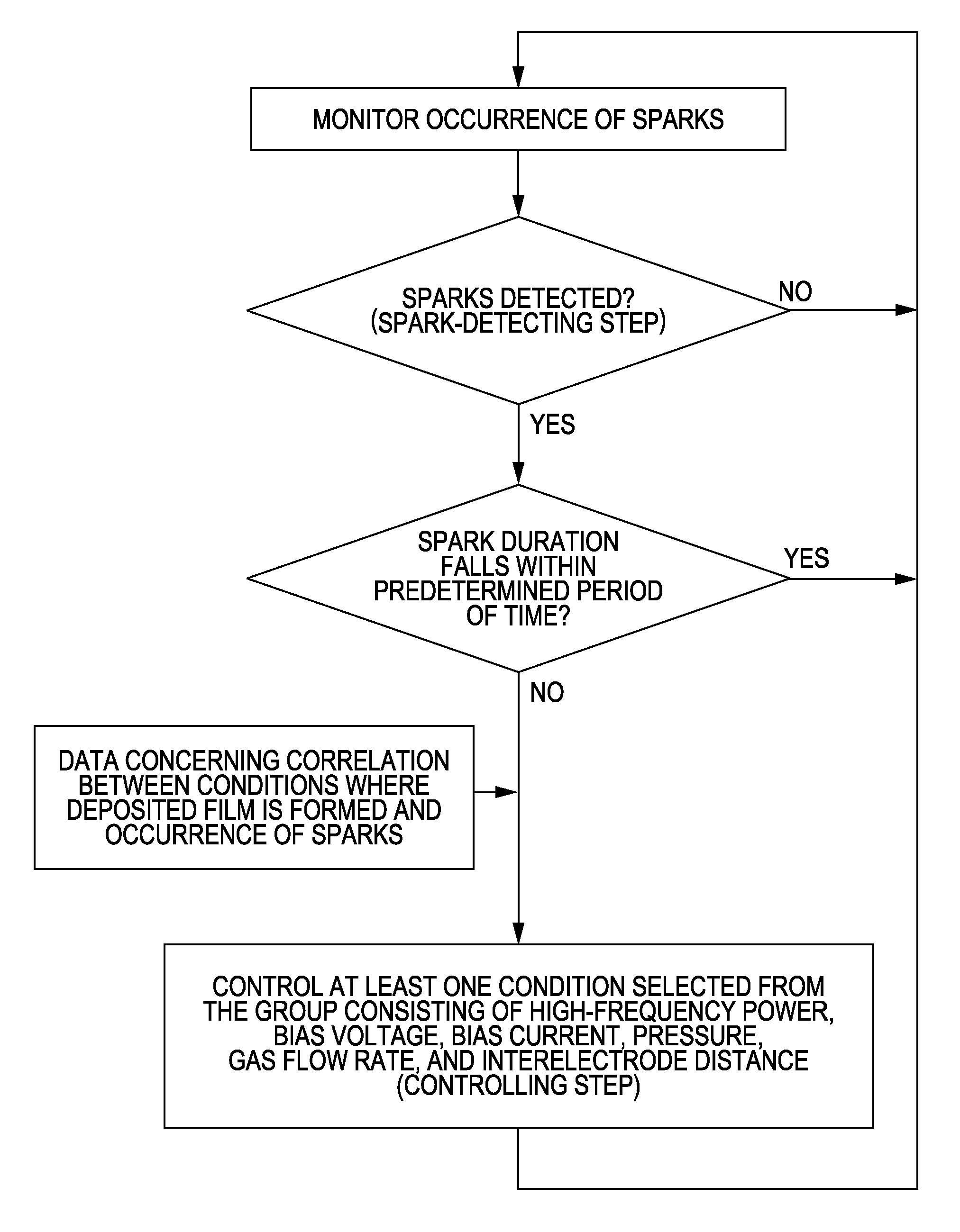
Method for forming semiconductor device and method for forming photovoltaic device
InactiveUS20080096291A1Sufficient crystal grain sizeSuppression of optical degradationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringVoltage
A method for forming a semiconductor device including a semiconductor layer, formed of a silicon-based deposited film containing crystals by plasma-enhanced CVD, includes the steps of applying a bias voltage between a high-frequency electrode and a substrate with the high-frequency electrode being negative when the semiconductor layer is formed; detecting sparks occurring on the high-frequency electrode or the substrate; and controlling at least one condition, selected from the group consisting of high-frequency power, bias voltage, bias current, pressure, gas flow rate, and interelectrode distance, based on the results of the detection so that the number of sparks with durations of 100 ms or more is 1 or less sparks per minute.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and an apparatus for controlling grain size of a component
InactiveUS20150266285A1Reduce grain sizeLarge grainAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAdditive layer manufacturingCrystallite
A method and an apparatus for controlling a grain size of a component generated using an additive manufacturing process. Construct a first fused layer of the component by fusing a plurality of layers of a fusible material, wherein the first fused layer has a thickness T1. Thereafter, introduce stress through the first fused layer of the component. The component is generated by repeating the aforementioned steps. Further, the component is heated to a temperature above a recrystallization start temperature (Rxst) to control the grain size of the component.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method of enhancing laser crystallization for polycrystalline silicon fabrication
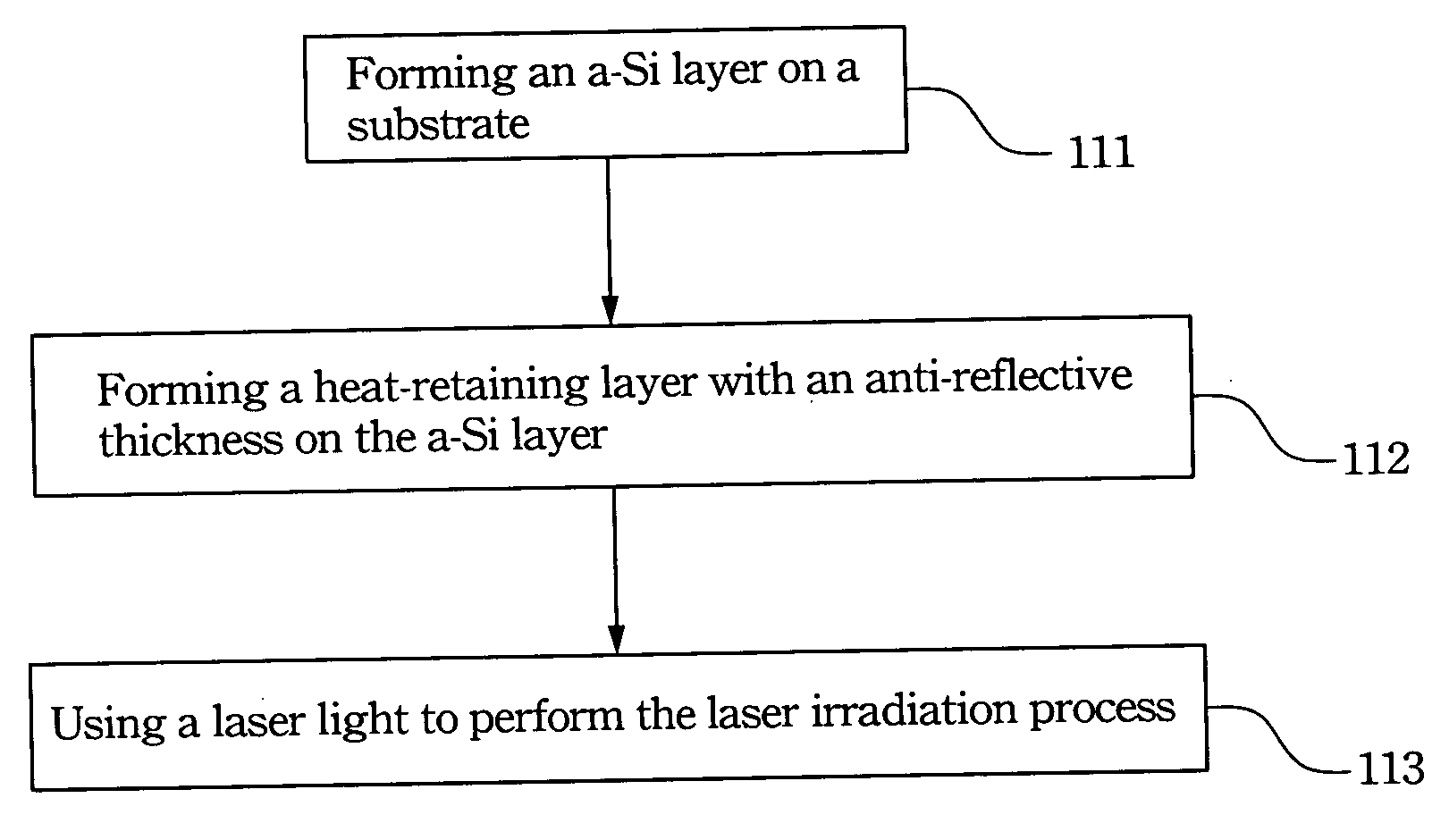
InactiveUS20060088986A1High crystallinityFine grainSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser crystallizationOptoelectronics
An amorphous silicon layer and at least a heat-retaining layer are formed on a substrate in turn. Wherein, the heat-retaining layer is controlled to have an anti-reflective thickness for reducing the threshold laser energy to effect the melting of the amorphous silicon layer. Then, a laser irradiation process is performed to transform the amorphous silicon layer into a polycrystalline silicon layer. During the laser irratiation process, a portion of the laser energy transmits the heat-retaining layer to effect the melting of the amorphous silicon layer, and another portion of the laser energy is absorbed by the heat-retaining layer.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
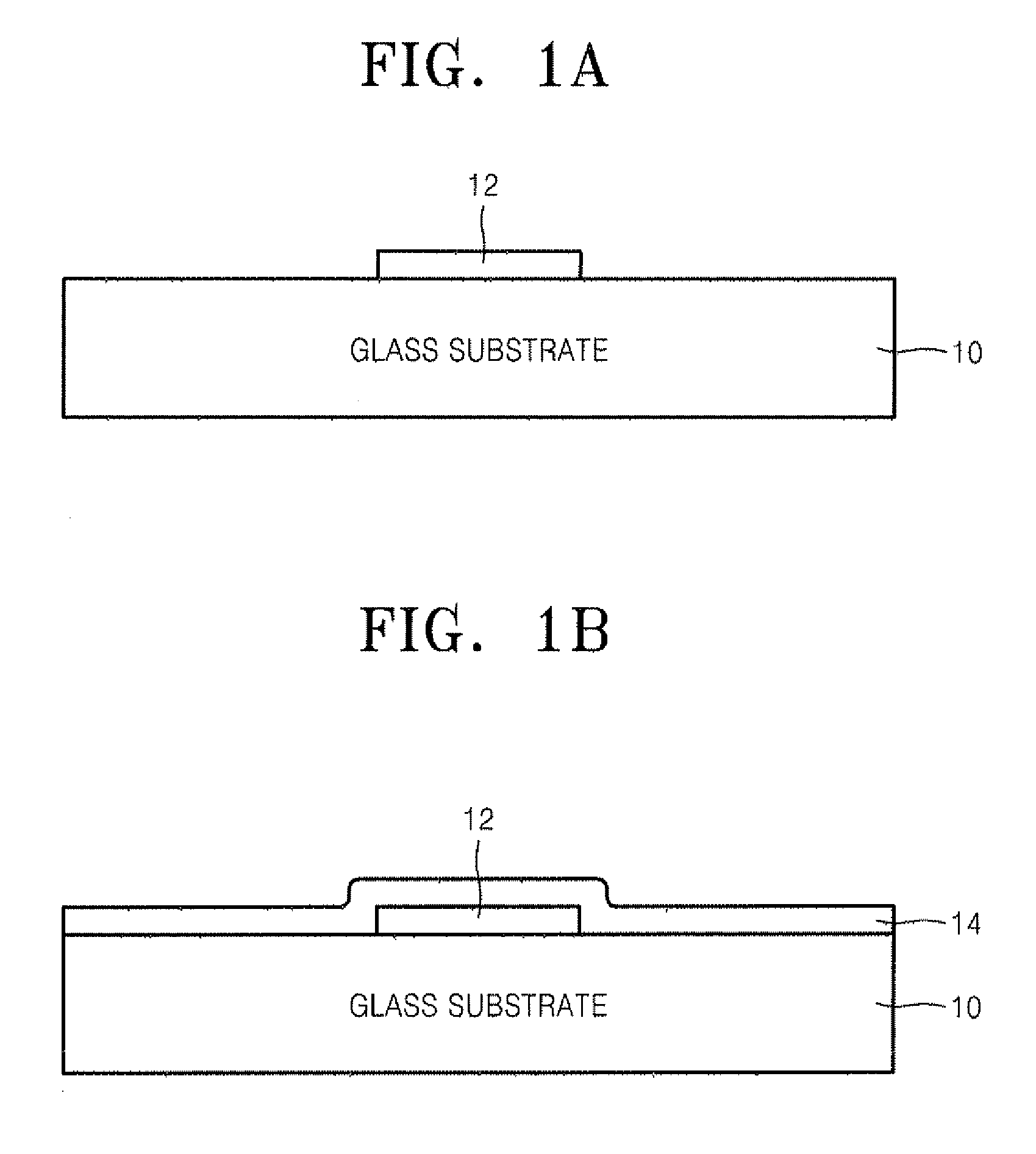
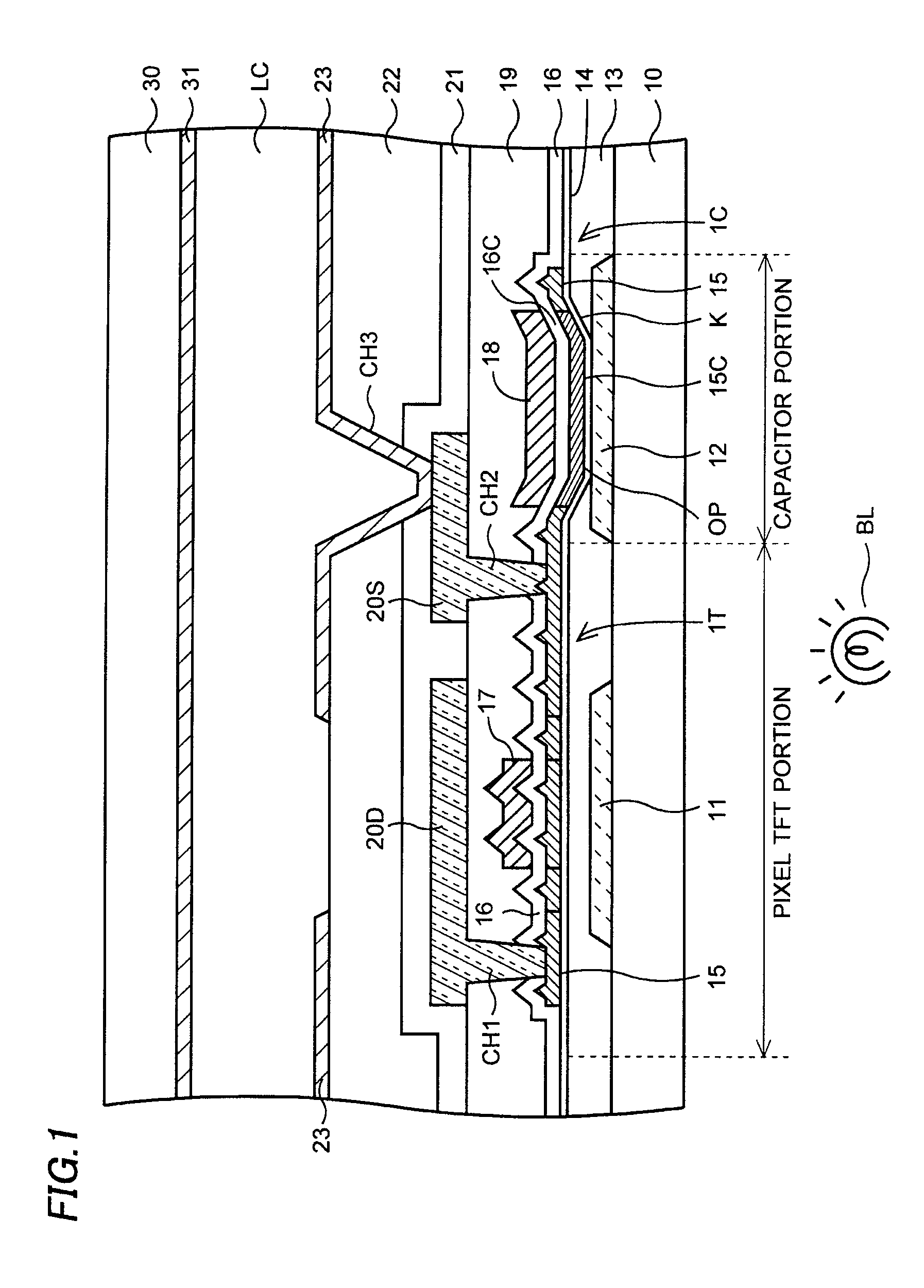
Display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8071985B2High surface flatnessDielectric strengthTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
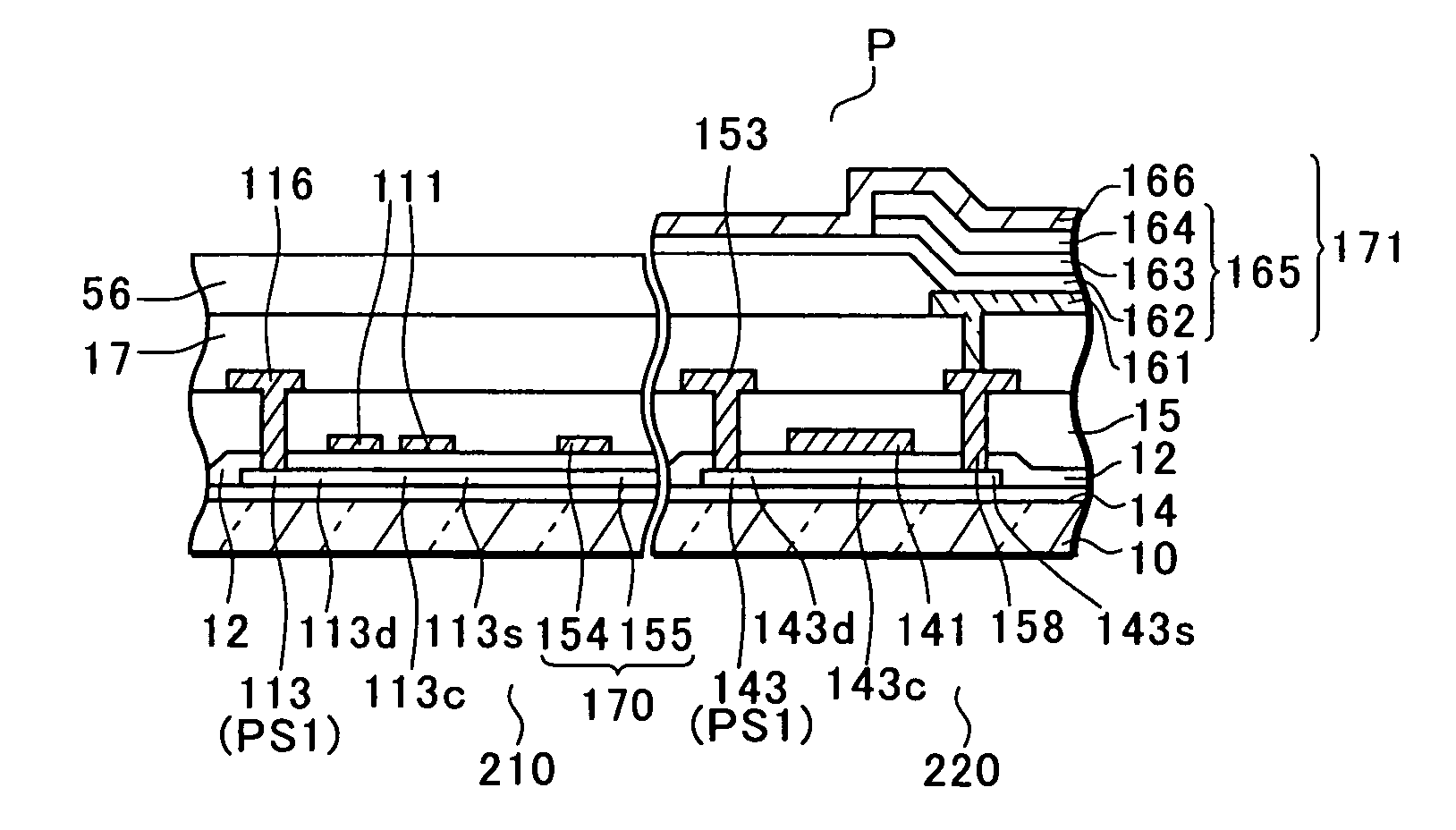
The invention provides a display device having a thin film transistor and a storage capacitor storing a display signal applied to a pixel electrode through this thin film transistor on a substrate, where dielectric strength between electrodes forming the storage capacitor is enhanced for increasing the yield. In the storage capacitor, a lower storage capacitor electrode, a thin lower storage capacitor film, a polysilicon layer, an upper storage capacitor film and an upper storage capacitor electrode are layered. The polysilicon layer is formed by crystallization by laser annealing. The polysilicon layer of the storage capacitor is microcrystalline and thus the flatness of its surface is enhanced. The pattern of the polysilicon layer (storage capacitor electrode) is formed larger than the bottom portion of an opening, and the edge of its peripheral portion is located on a buffer film on the slant portion of the opening or on the buffer film on the outside of the opening.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com