Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80results about How to "Lower gate voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
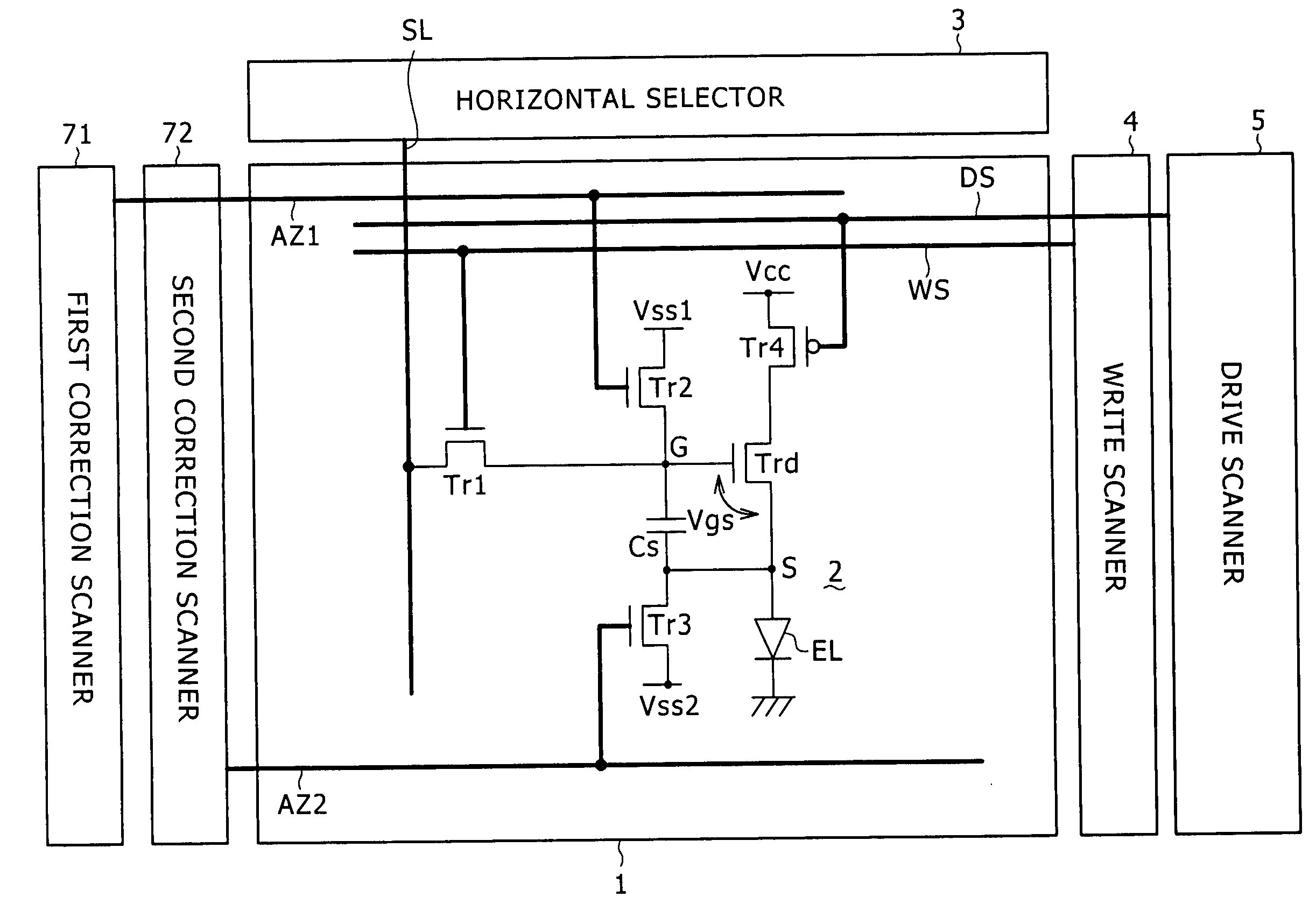
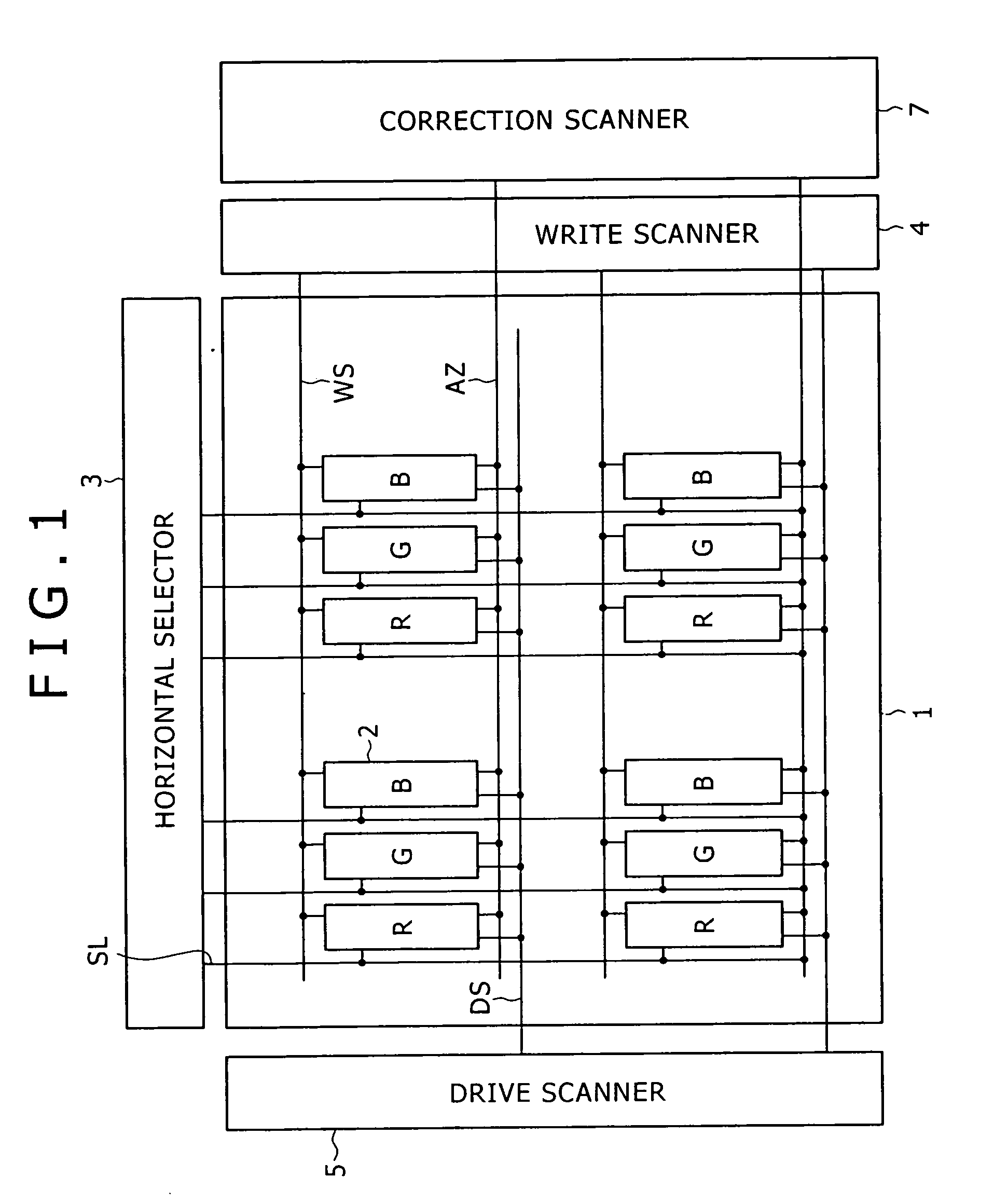
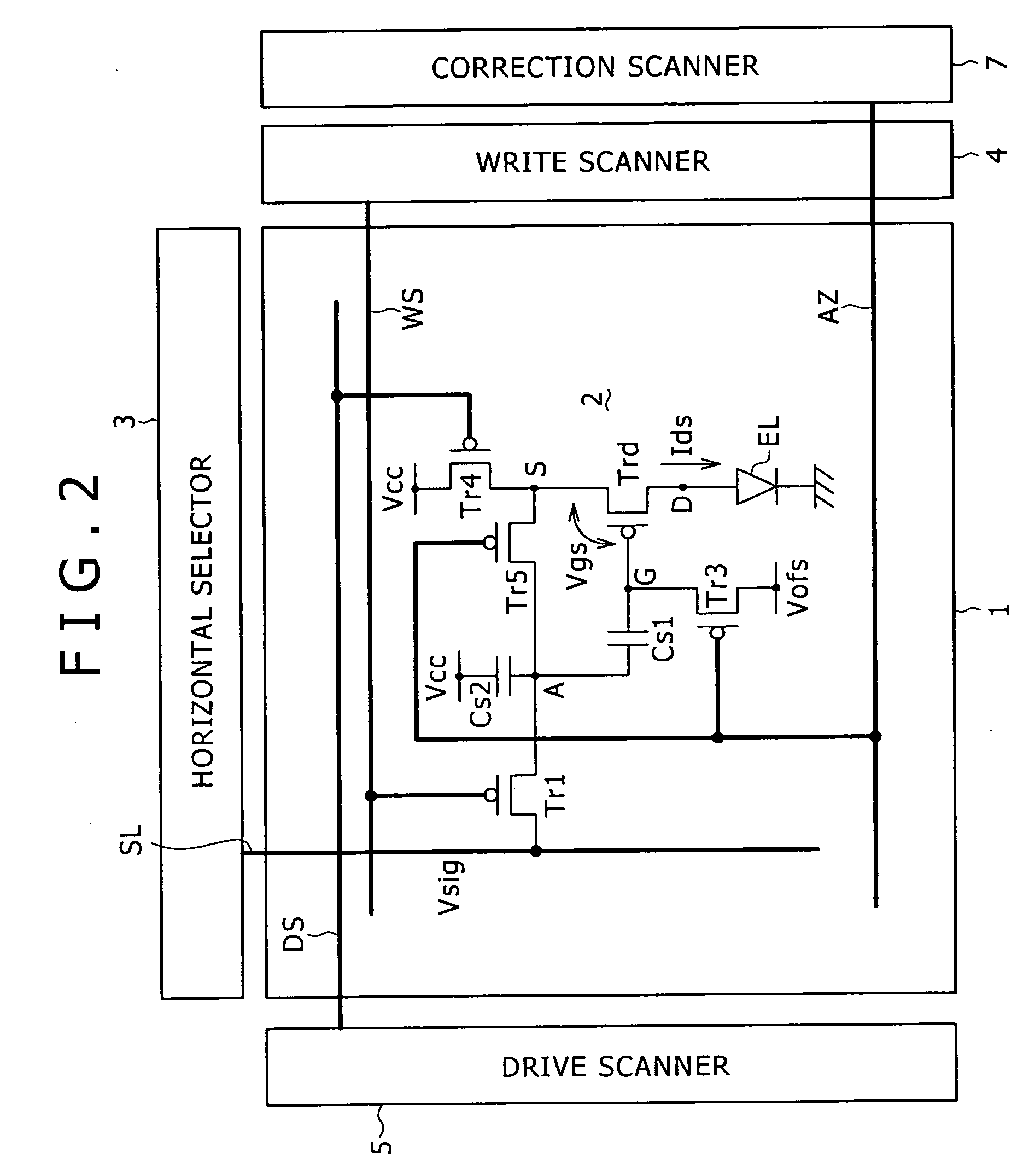
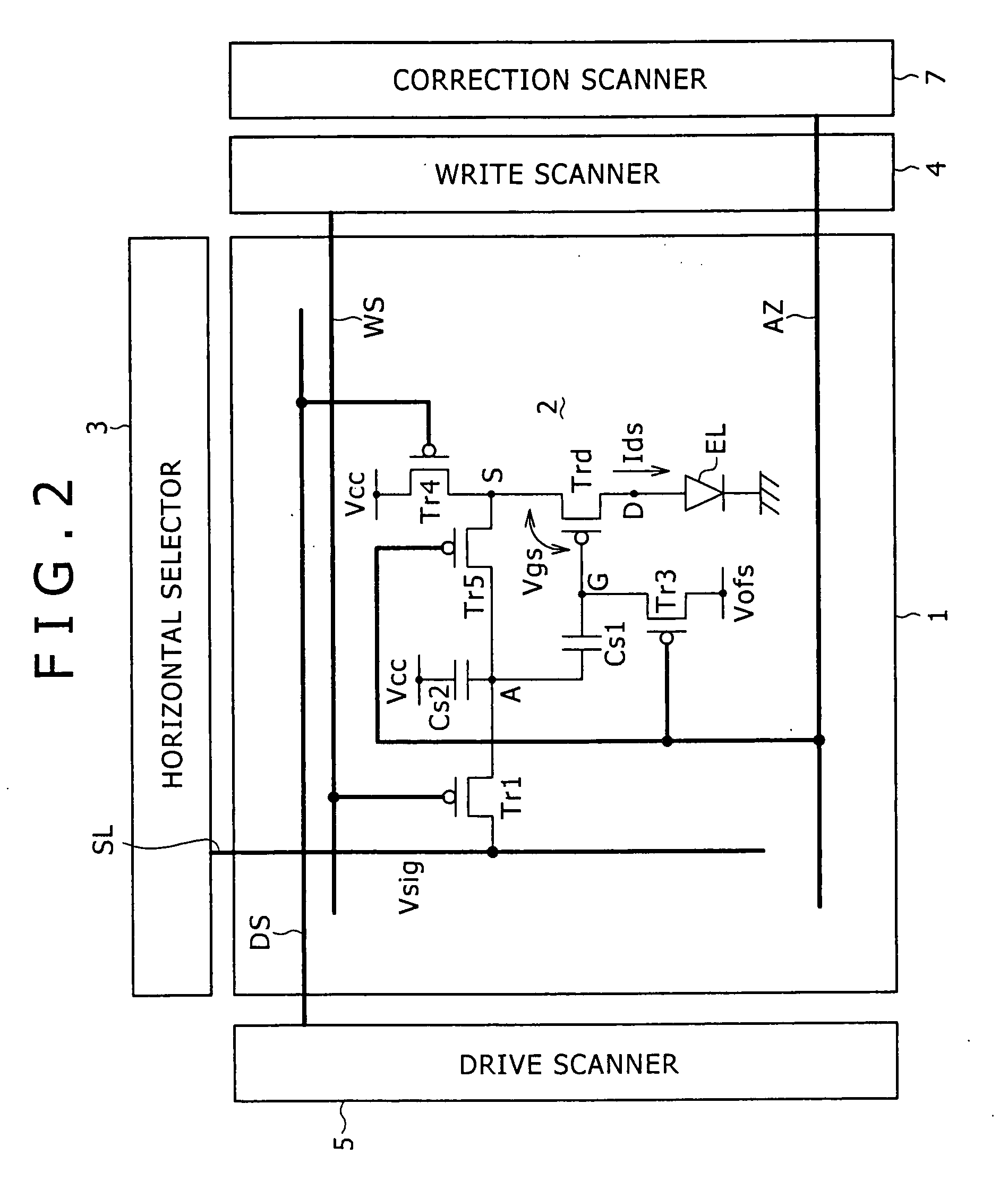
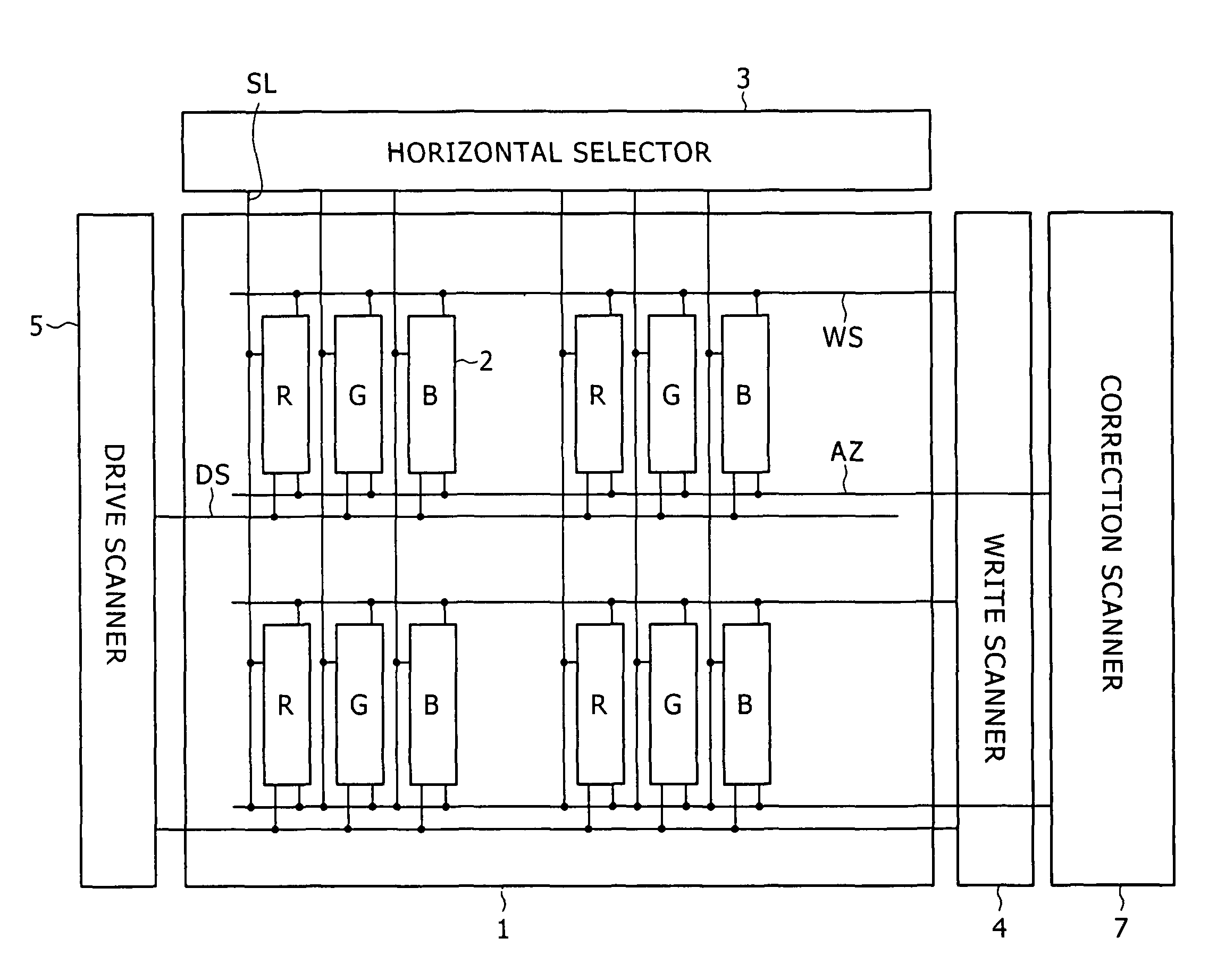
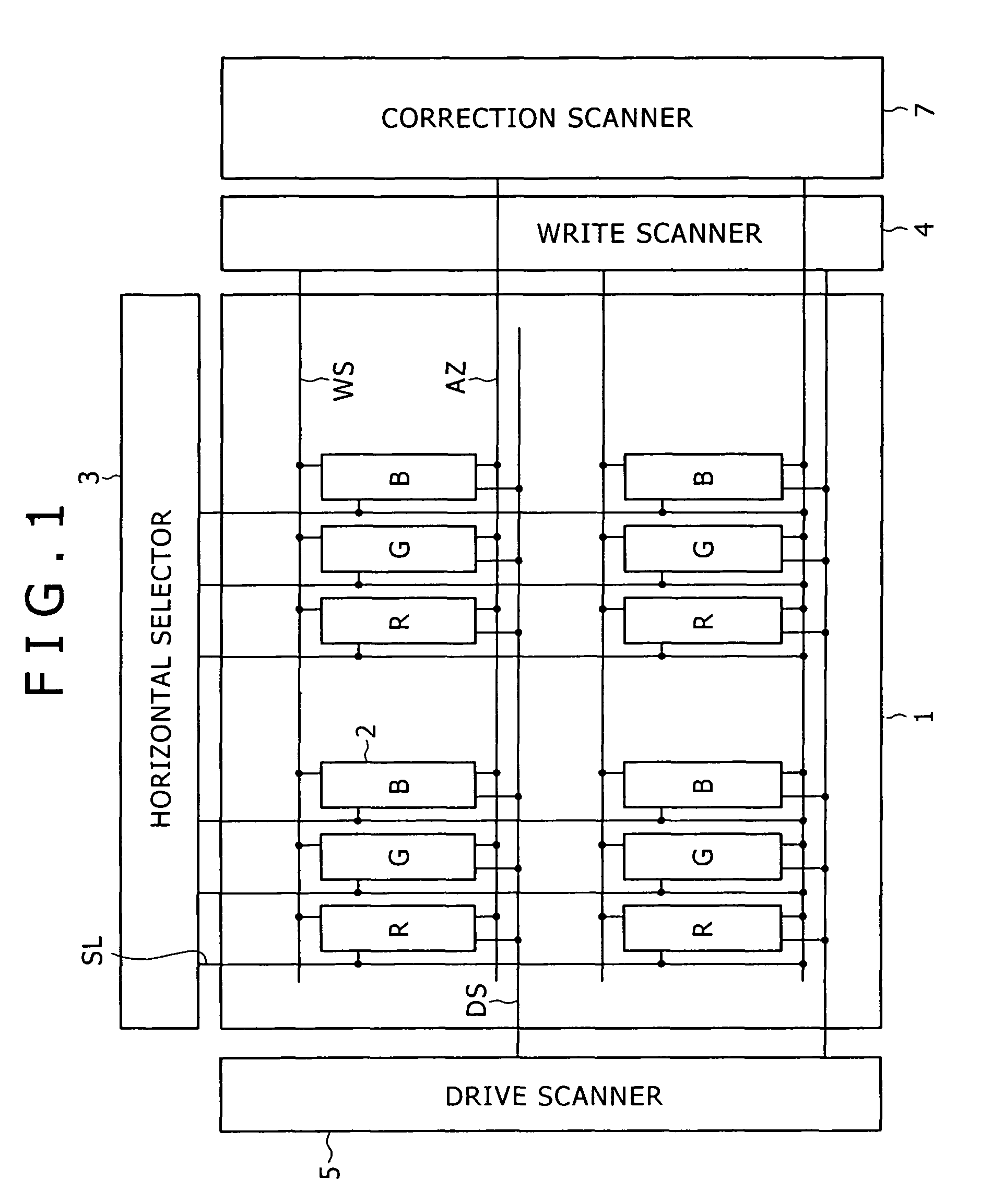
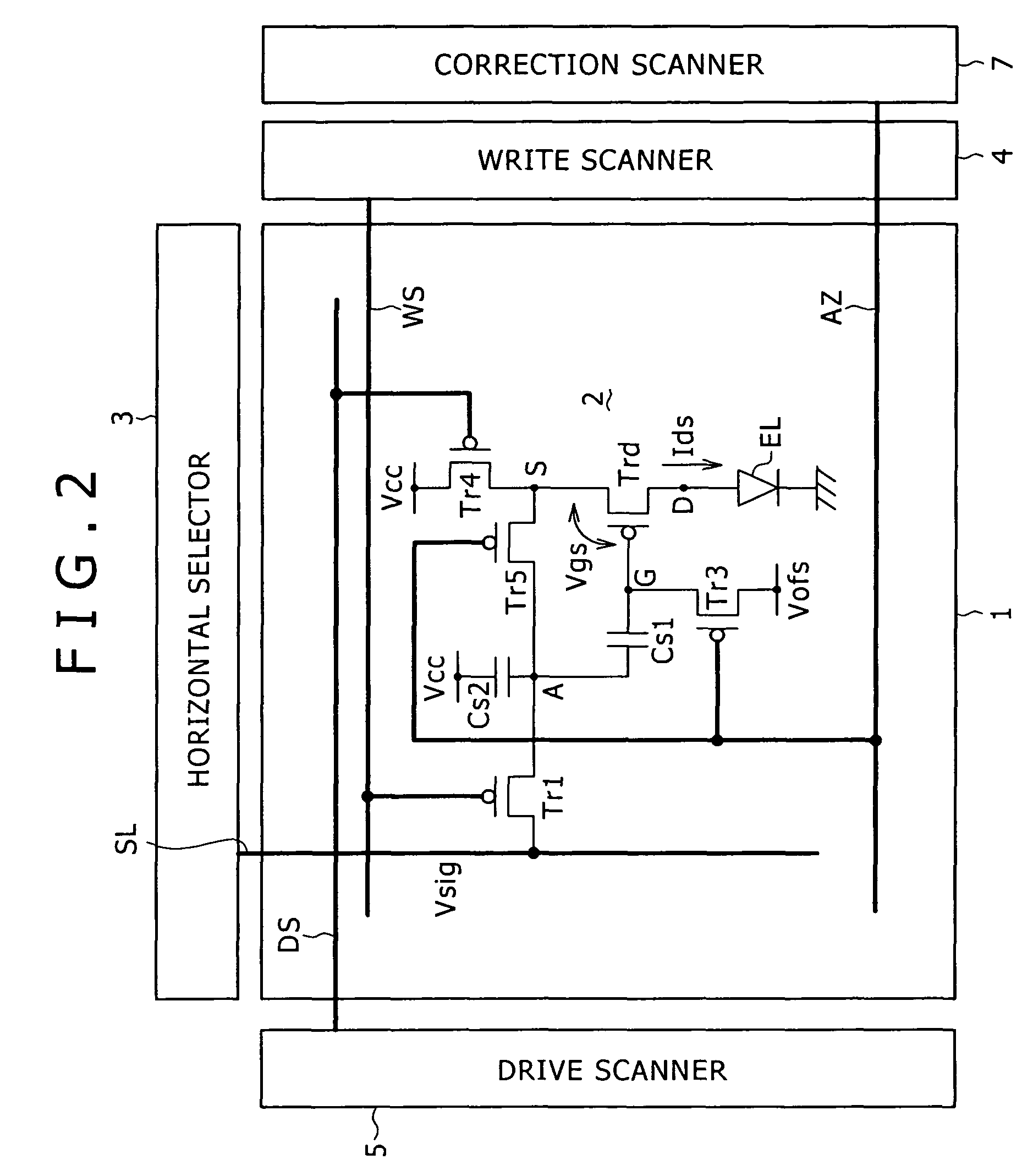
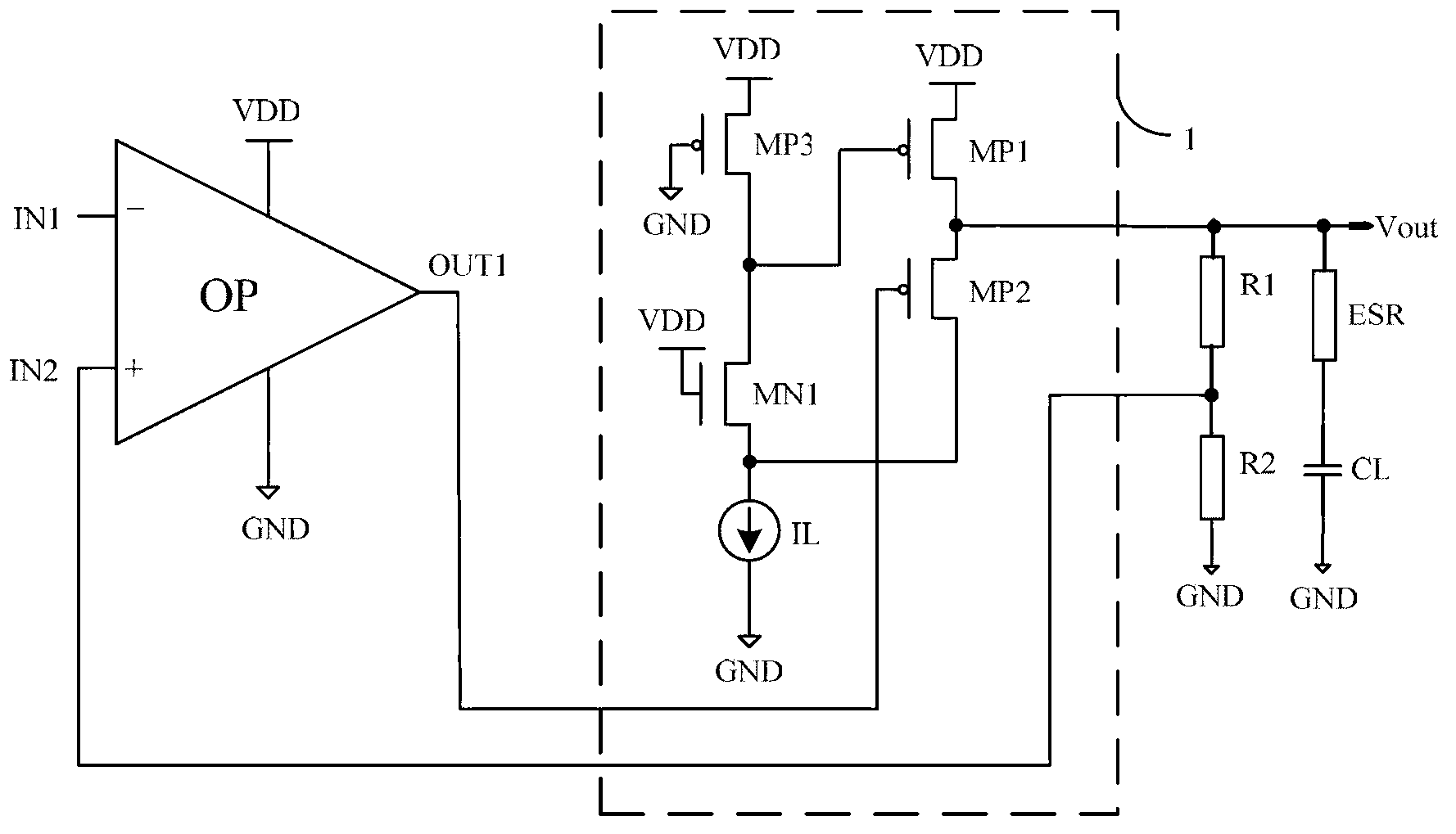
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060170628A1Eliminate dependenciesImprove mobilityElectroluminescent light sourcesHeater elementsCapacitanceScan line
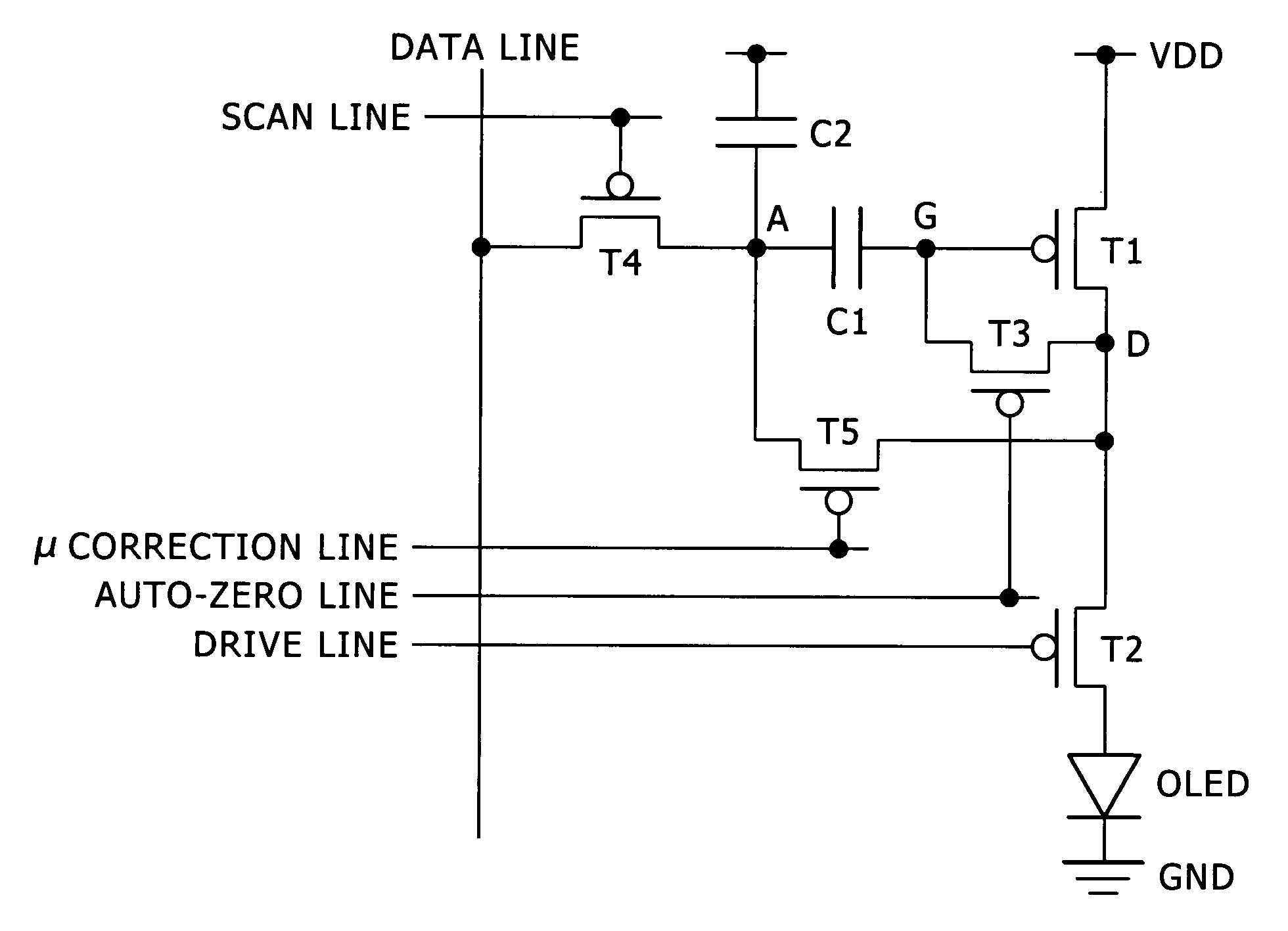
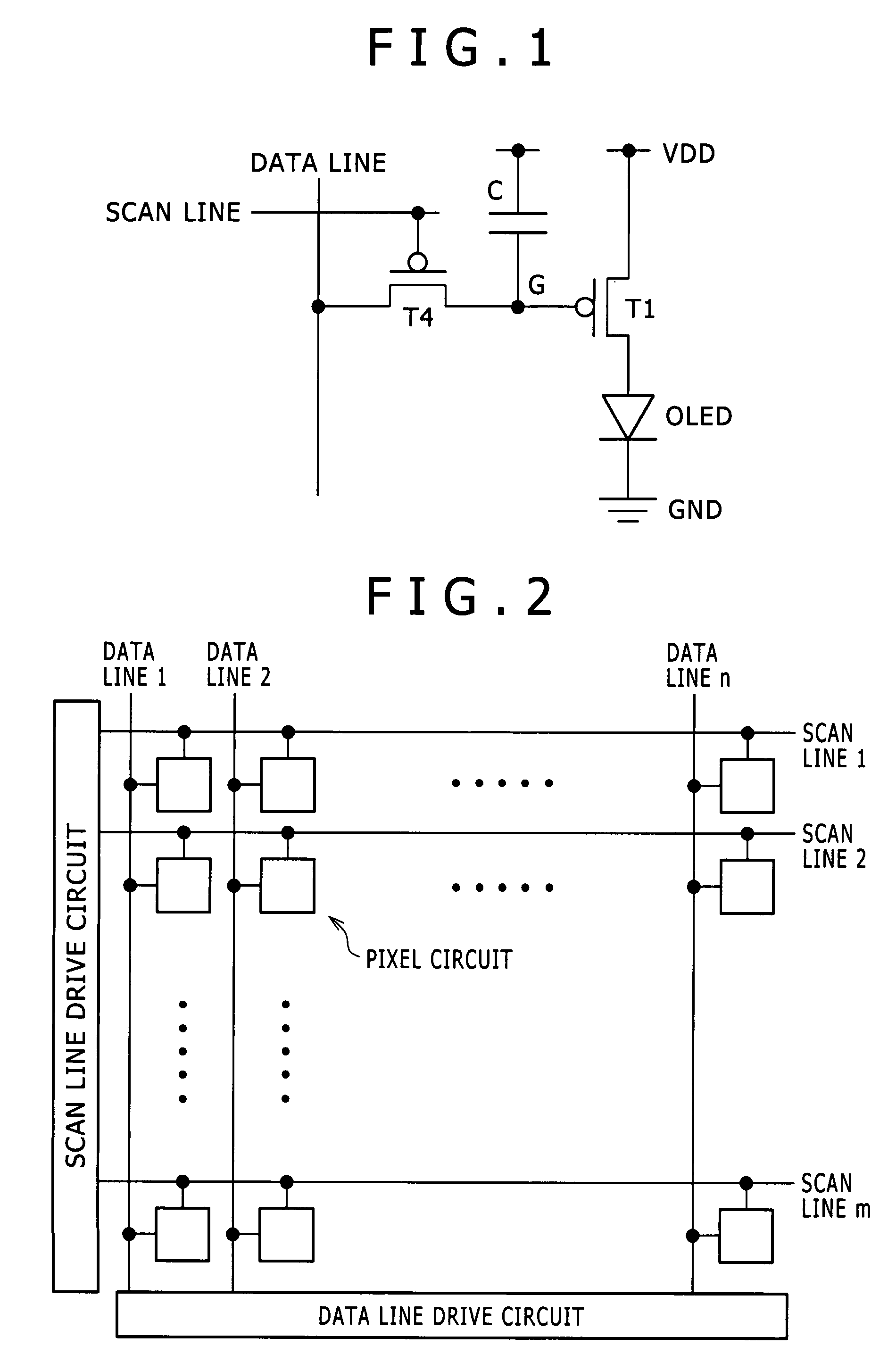
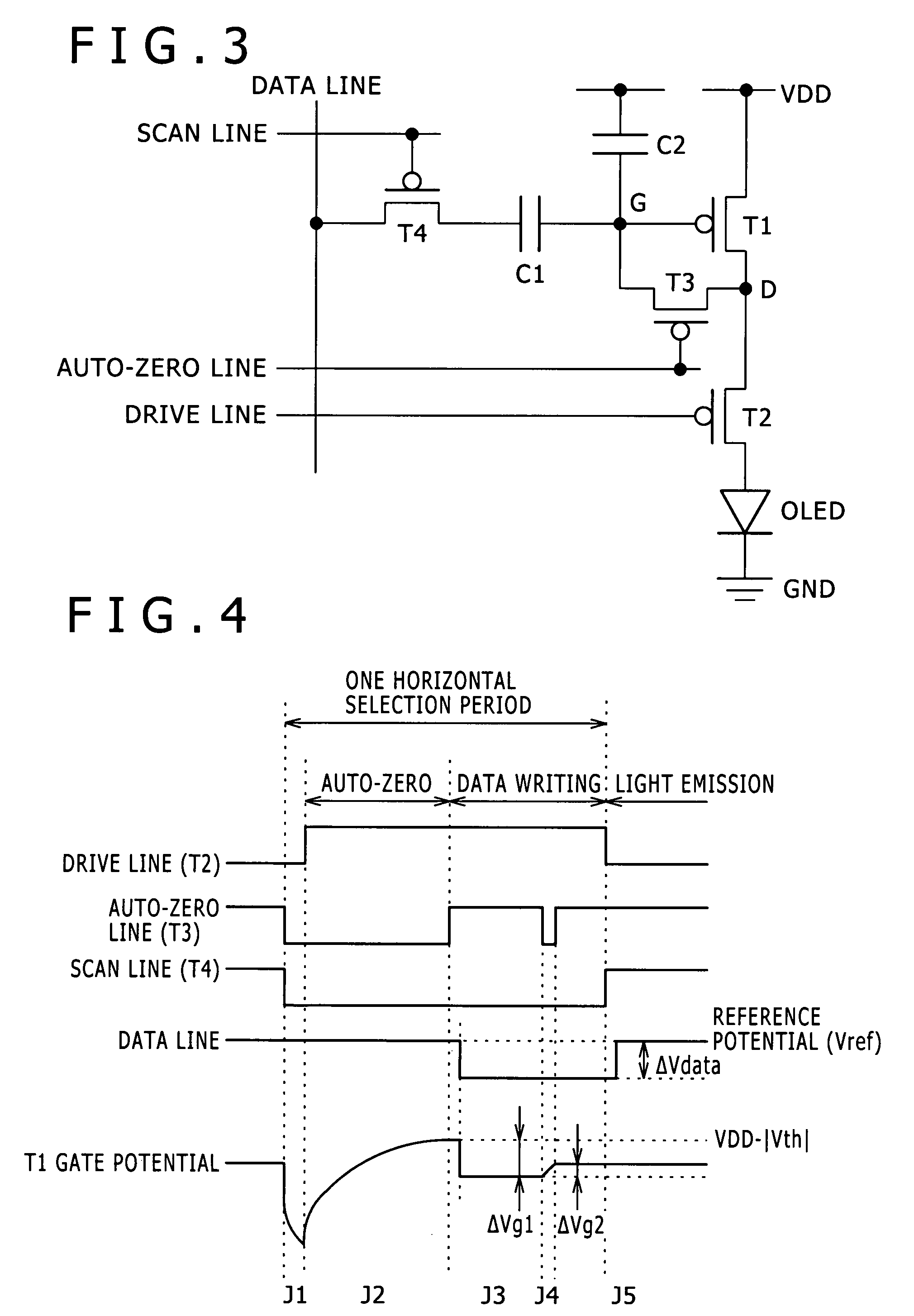
The invention provides a pixel circuit that can cancel the influence of the mobility of a drive transistor. A drive transistor supplies to a light-emitting element, an output current dependent upon an input voltage during a certain emission period. The light-emitting element emits light with a luminance dependent upon a video signal in response to the output current supplied from the drive transistor. The pixel circuit includes a correction unit that corrects the input voltage held by a capacitive part before the emission period or at the beginning of the emission period, in order to cancel the dependence of the output current on the carrier mobility. The correction unit operates during part of a sampling period in response to control signals supplied from scan lines. Specifically, the correction unit extracts the output current from the drive transistor while the video signal is sampled, and negatively feeds back the output current to the capacitive part to thereby correct the input voltage.
Owner:SONY CORP
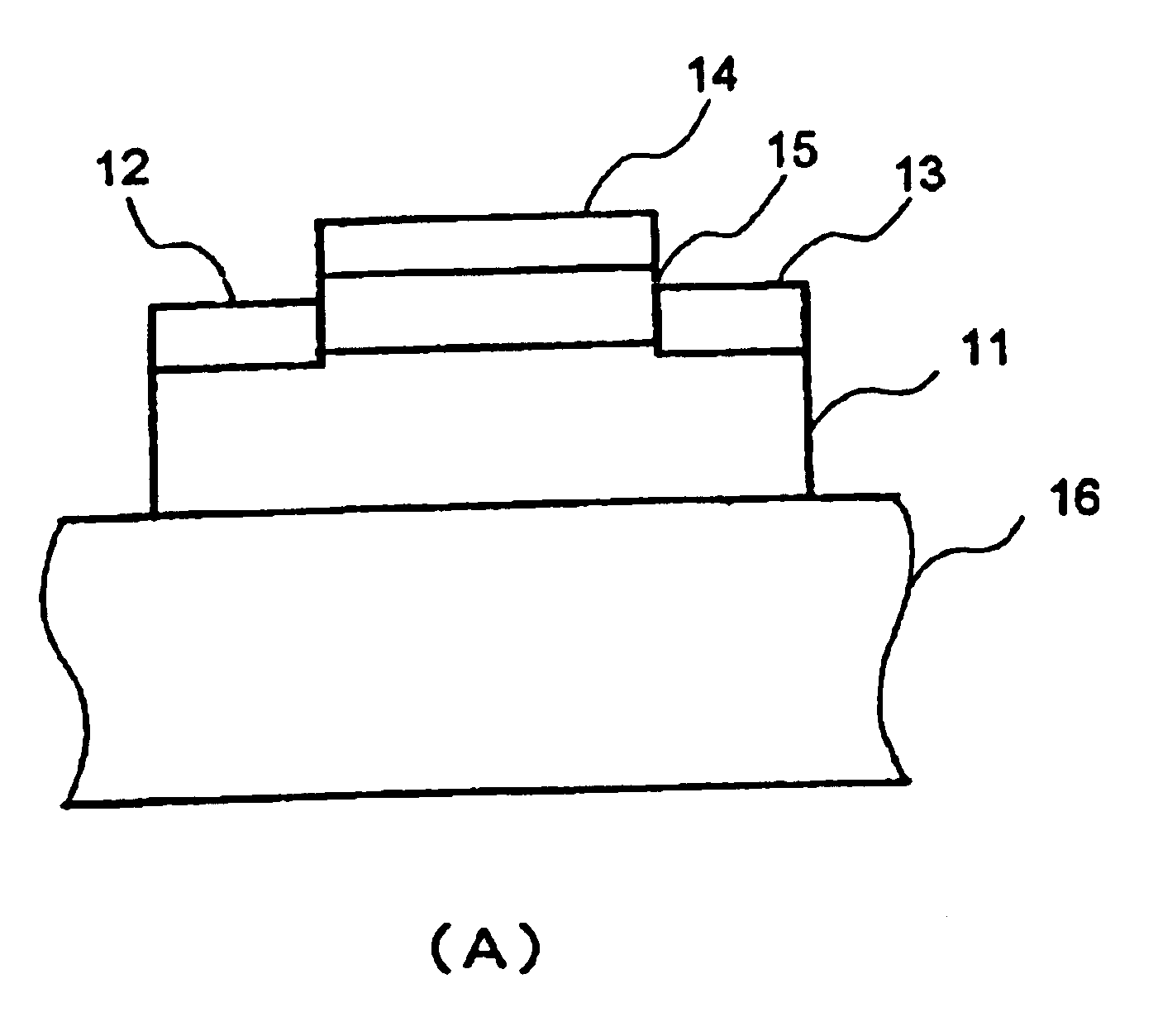
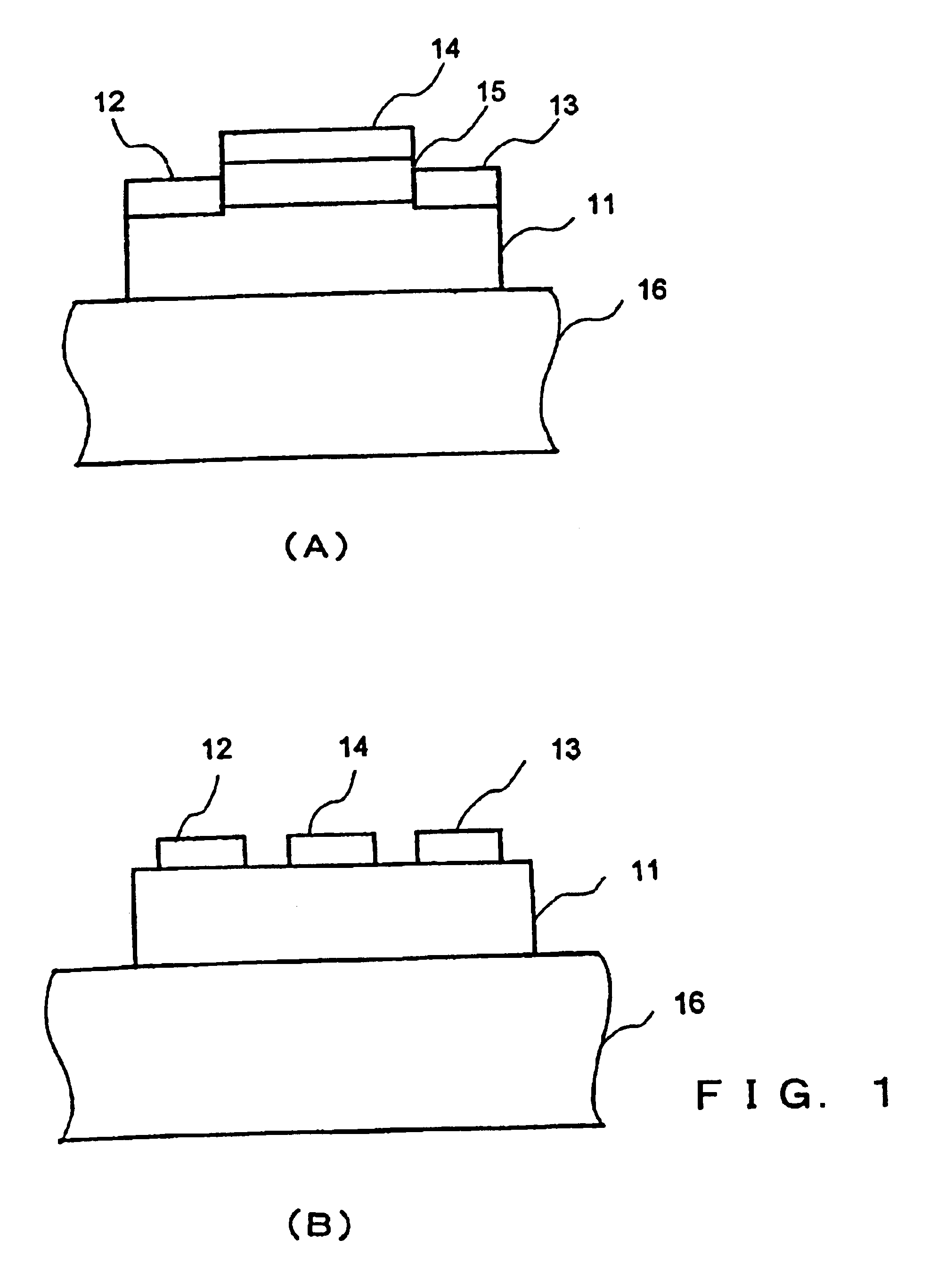
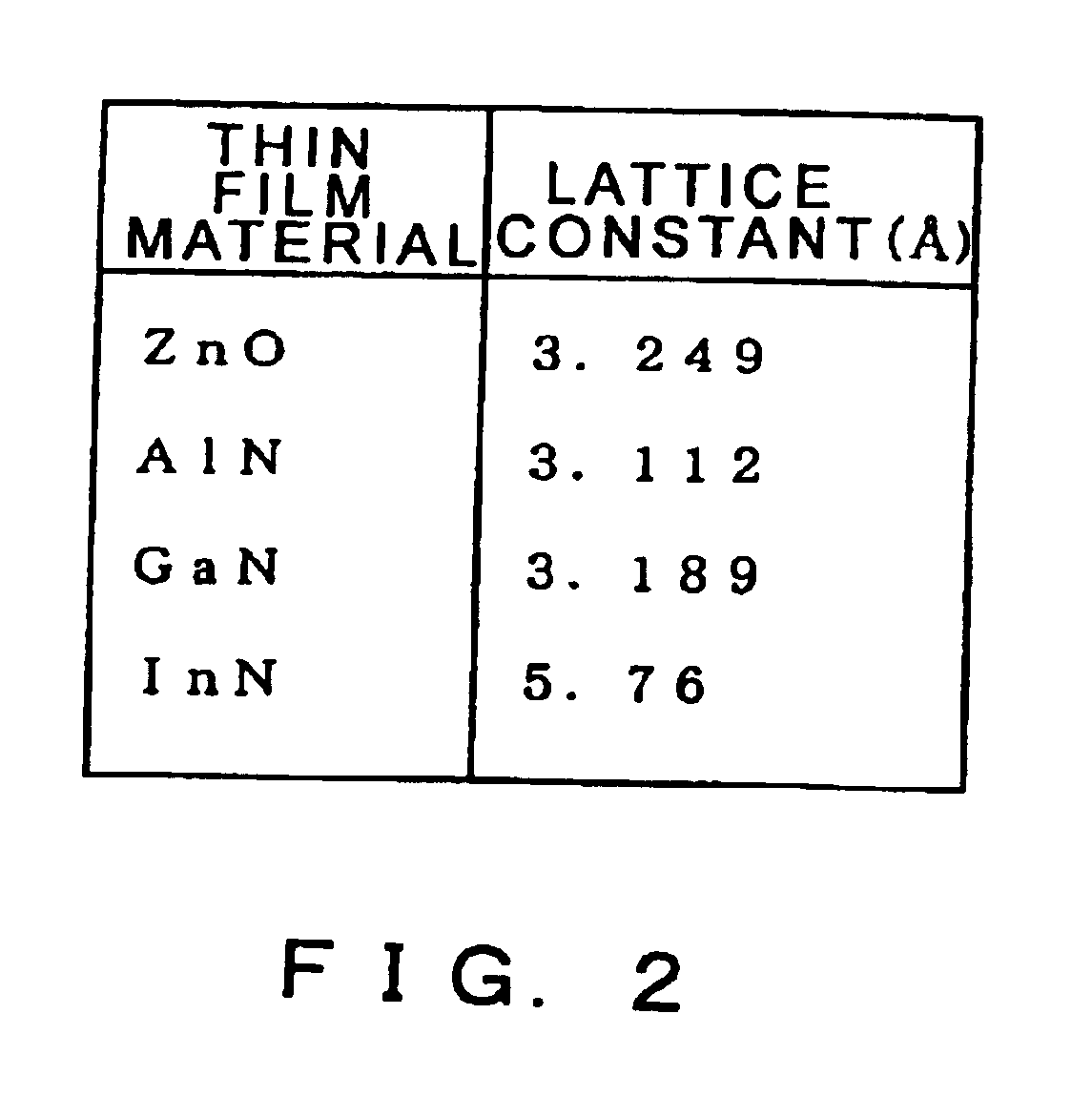
Semiconductor device
The present invention provides a high quality thin film comparable to a bulk single crystal and providres a semiconductor device with superior characteristics. A channel layer 11, for example, is formed of a semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO or the like. A source 12, a drain 13, a gate 14 and a gate insulating layer 15 are formed on the channel layer 111 to form an FET. For a substrate 16, a proper material is selected depending on a thin film material of the channel layer 11 in consideration of compatibility of both lattice constants. For example, if ZnO is used for the semiconductor of the channel layer as a base material, ScAlMgO4 or the like can be used for the substrate 16.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
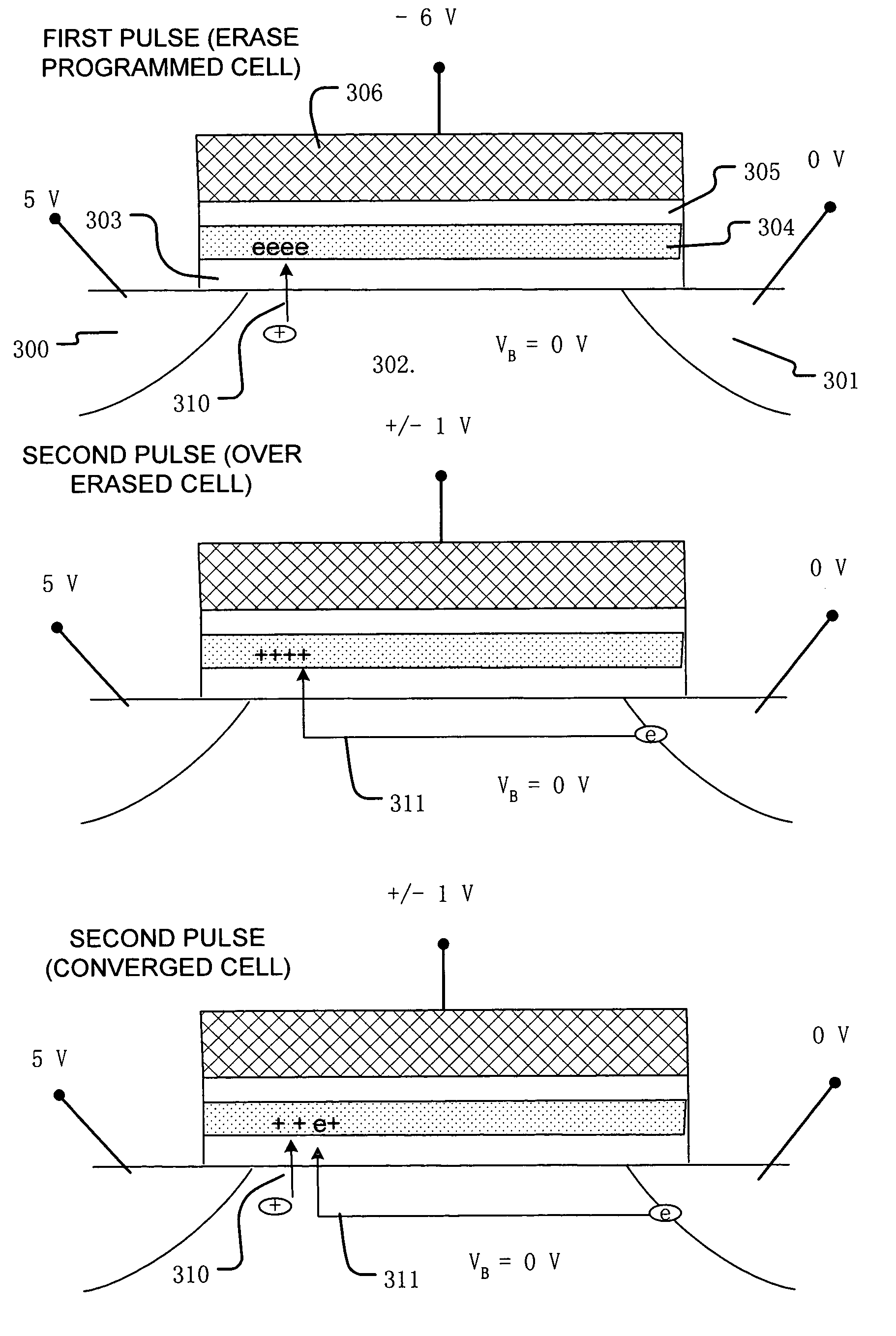
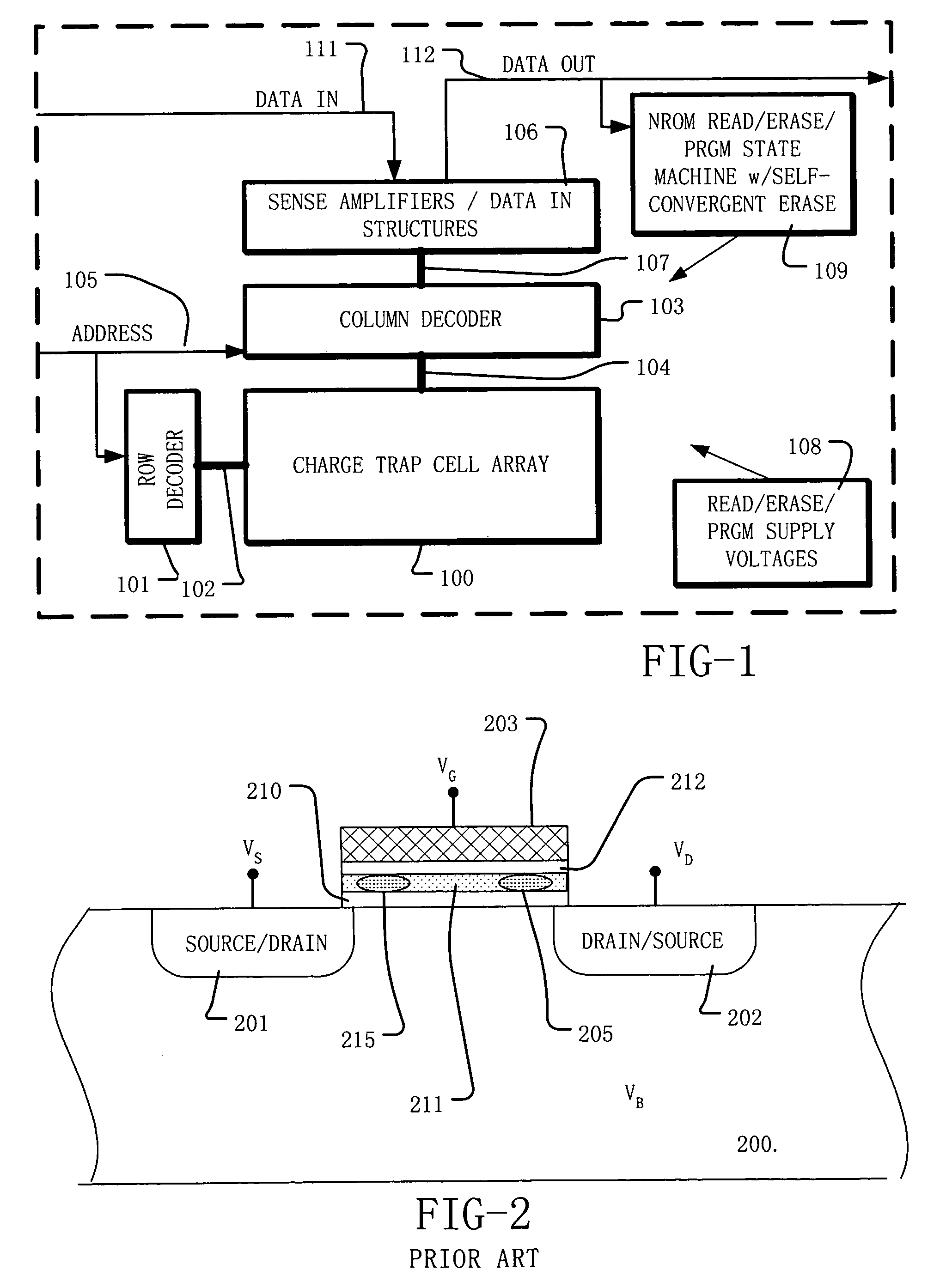
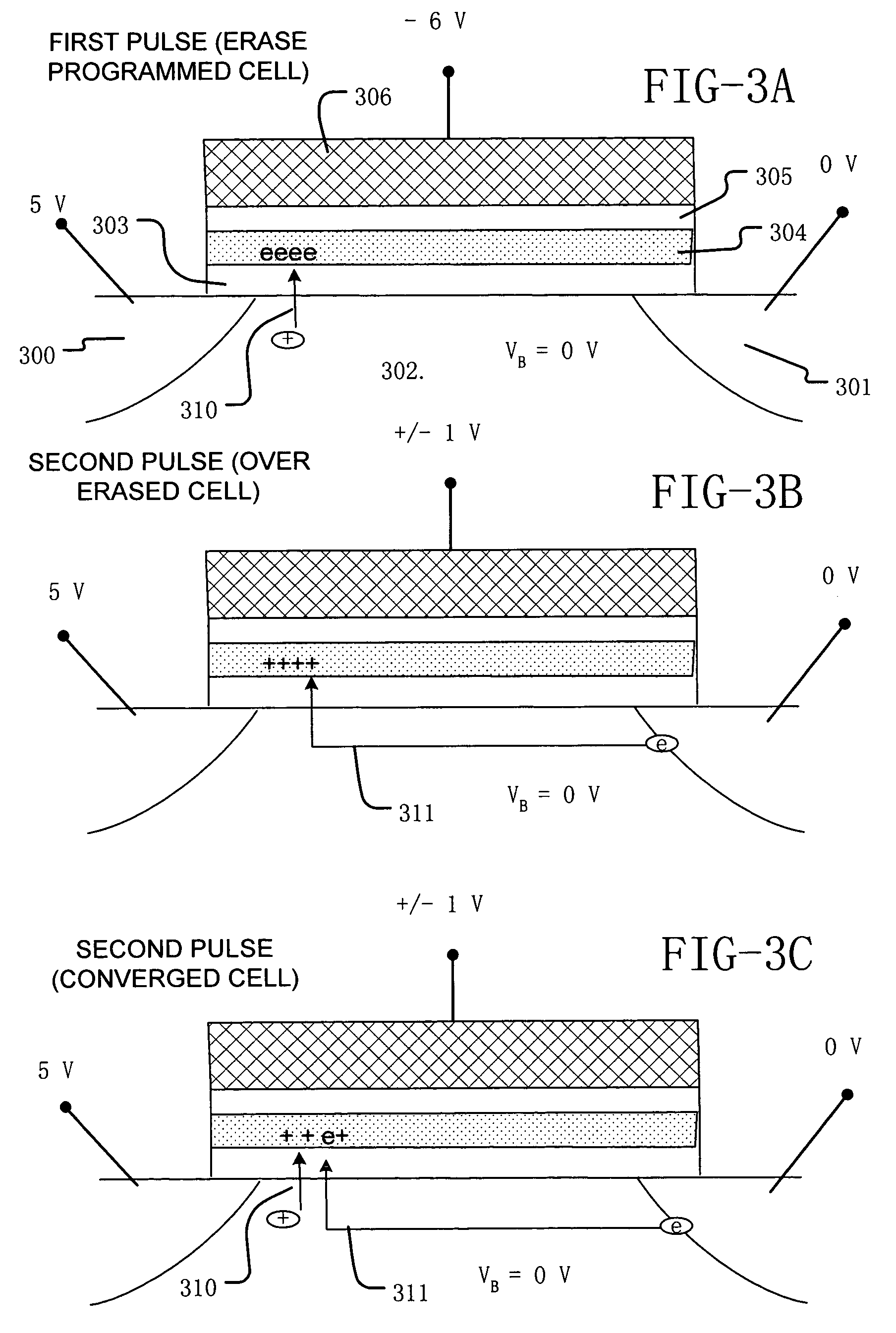
Method and system for self-convergent erase in charge trapping memory cells
A process and a memory architecture for operating a charge trapping memory cell is provided. The method for operating the memory cell includes establishing a high threshold state in the memory cell by injecting negative charge into the charge trapping structure to set a high state threshold. The method includes using a self-converging biasing procedure to establish a low threshold state for the memory cell by reducing the negative charge in the charge trapping structure to set the threshold voltage for the cell to a low threshold state. The negative charge is reduced in the memory cell by applying a bias procedure including at least one bias pulse. The bias pulse balances charge flow into and out of the charge trapping layer to achieve self-convergence on a desired threshold level. Thereby, an over-erase condition is avoided.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
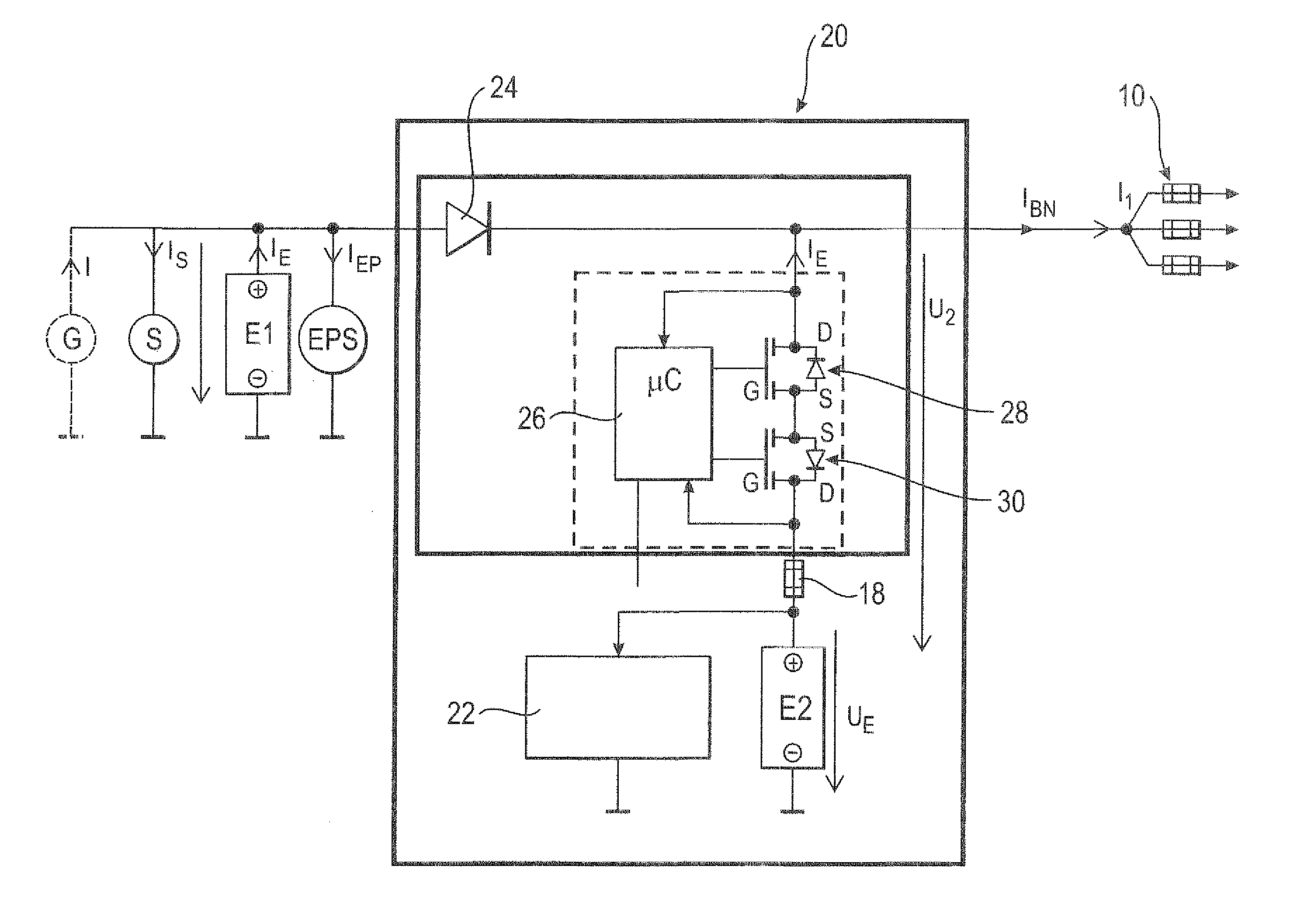
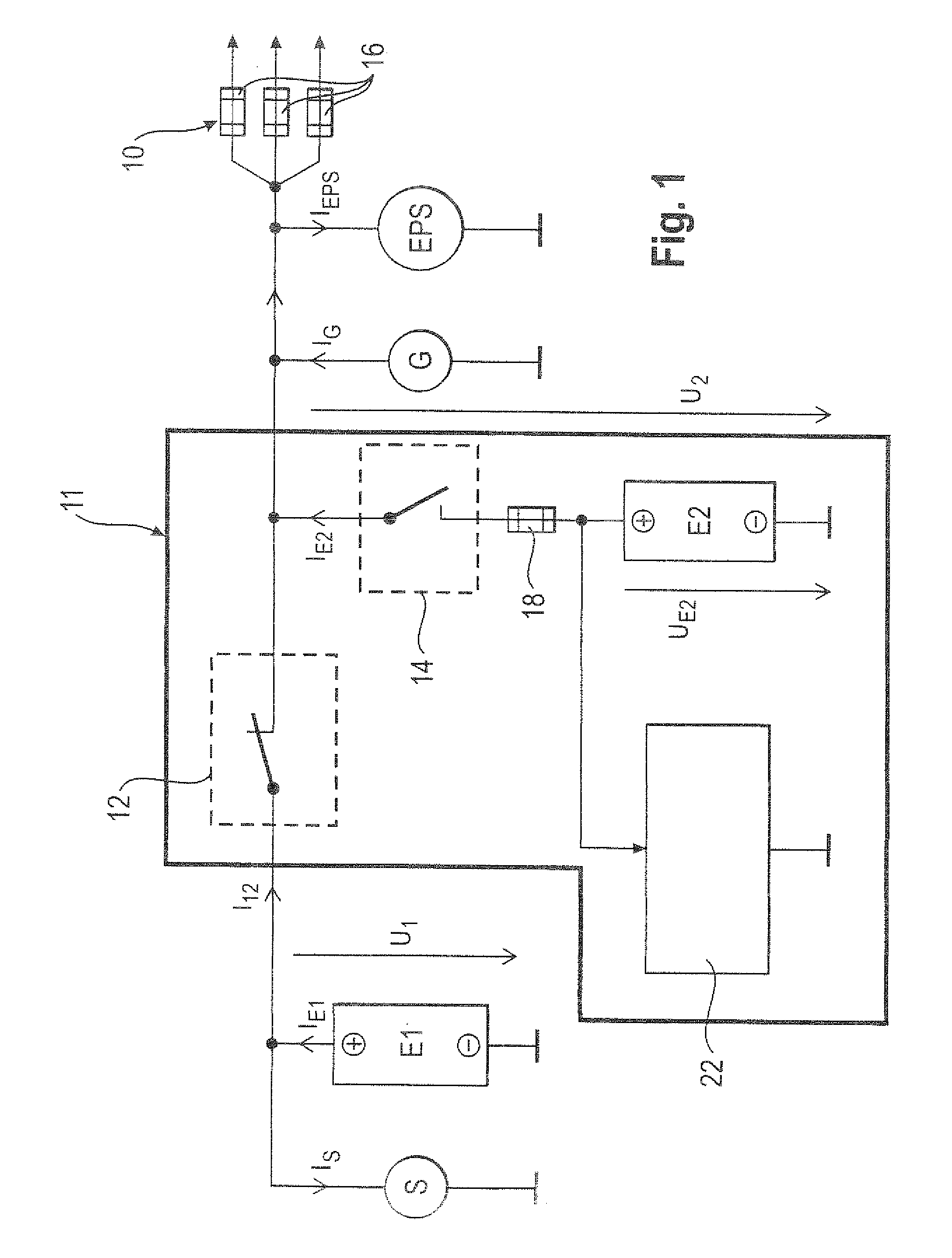
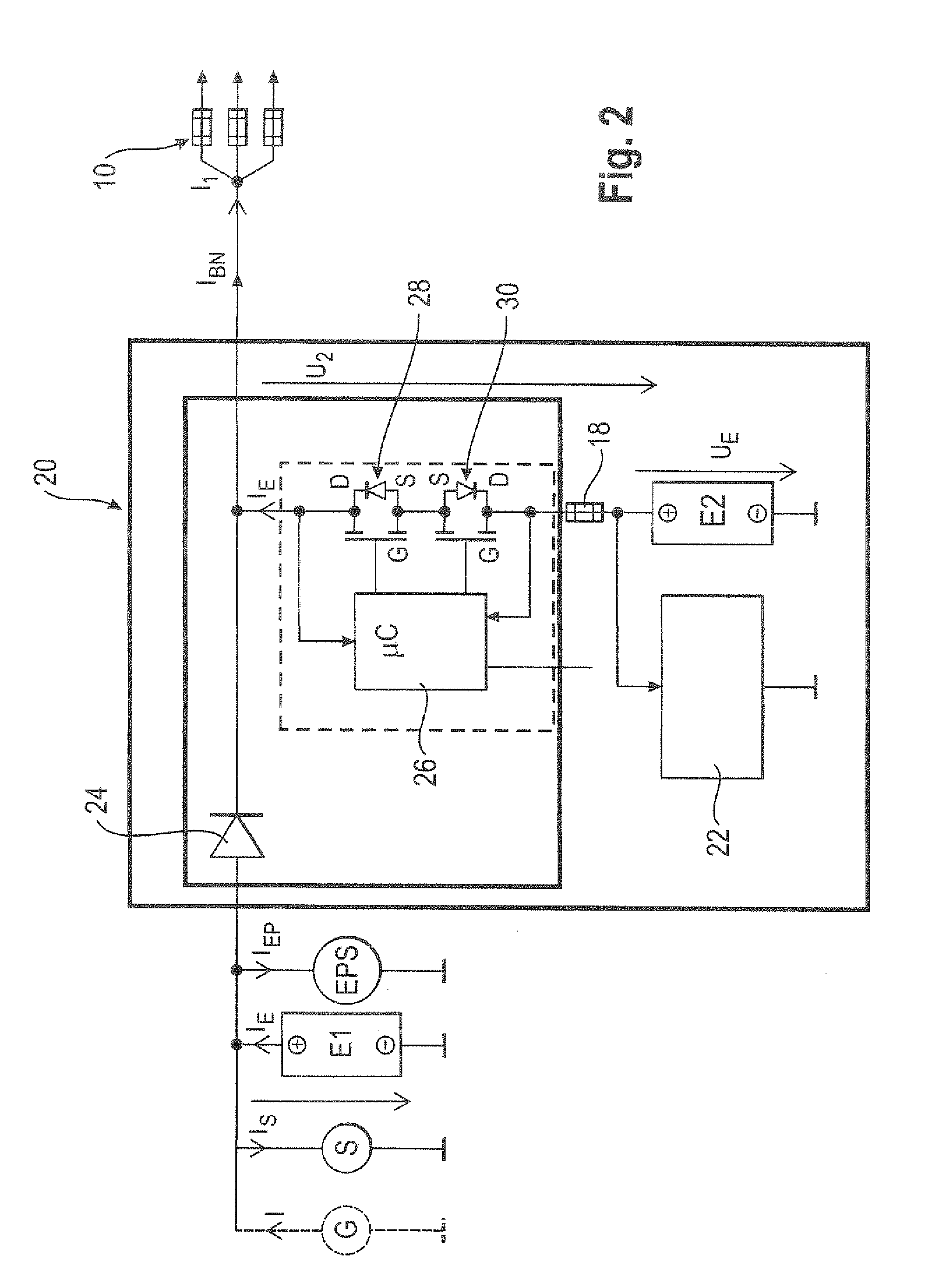
Circuit for voltage stabilization in an onboard power supply
ActiveUS20110012424A1Improve storage densityShort release timeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesMobile vehicleElectricity
The invention relates to a circuit (20, 50) for voltage stabilization in an onboard power supply (10), particularly for motor vehicles, which is electrically connected between the onboard power supply (10) to be stabilized and a first energy store (E1). The circuit (20, 50) comprises a diode element (24) which contains a plurality of semiconductor switches (34) connected in parallel, a pilot and control circuit (33) which determines the level of a current flowing through the diode element (24) and controls the semiconductor switches (34) of the diode element (24) on the basis of the determined current level, and a second energy store (E2) which is electrically connected to the diode element (24) and to the onboard power supply (10).
Owner:LISA DRAXLMAIER GMBH
Adaptive gate drive voltage circuit
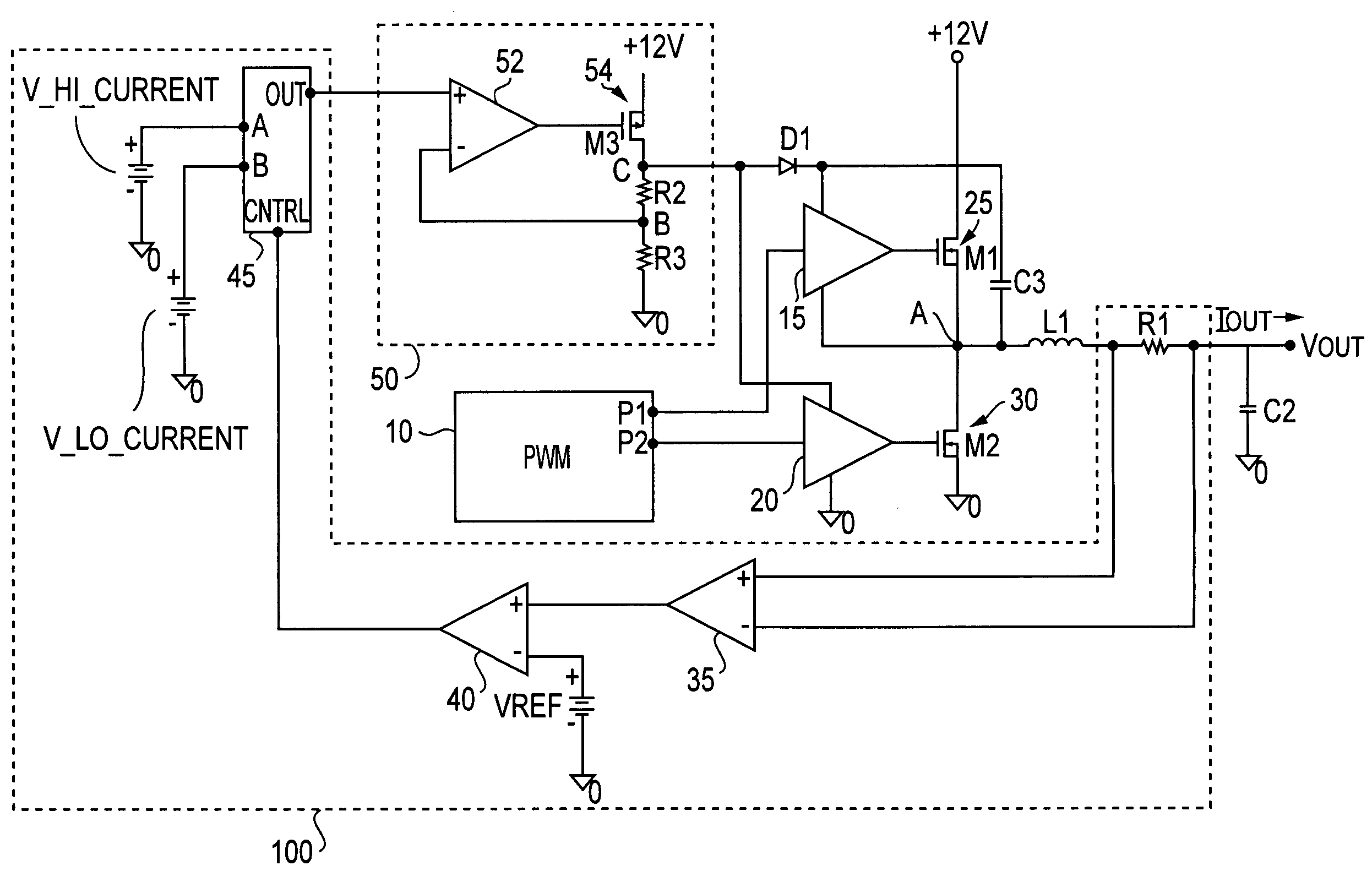
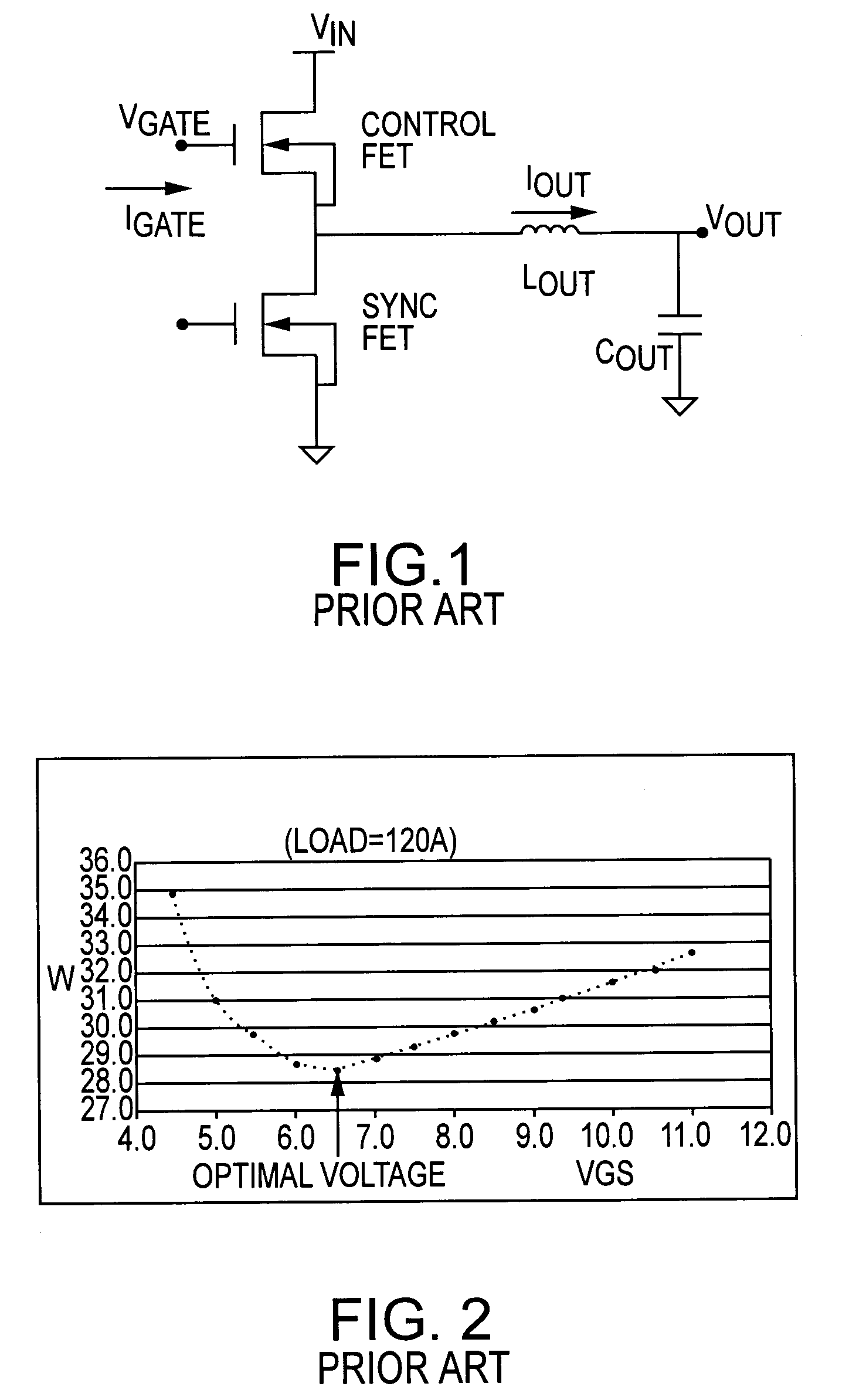
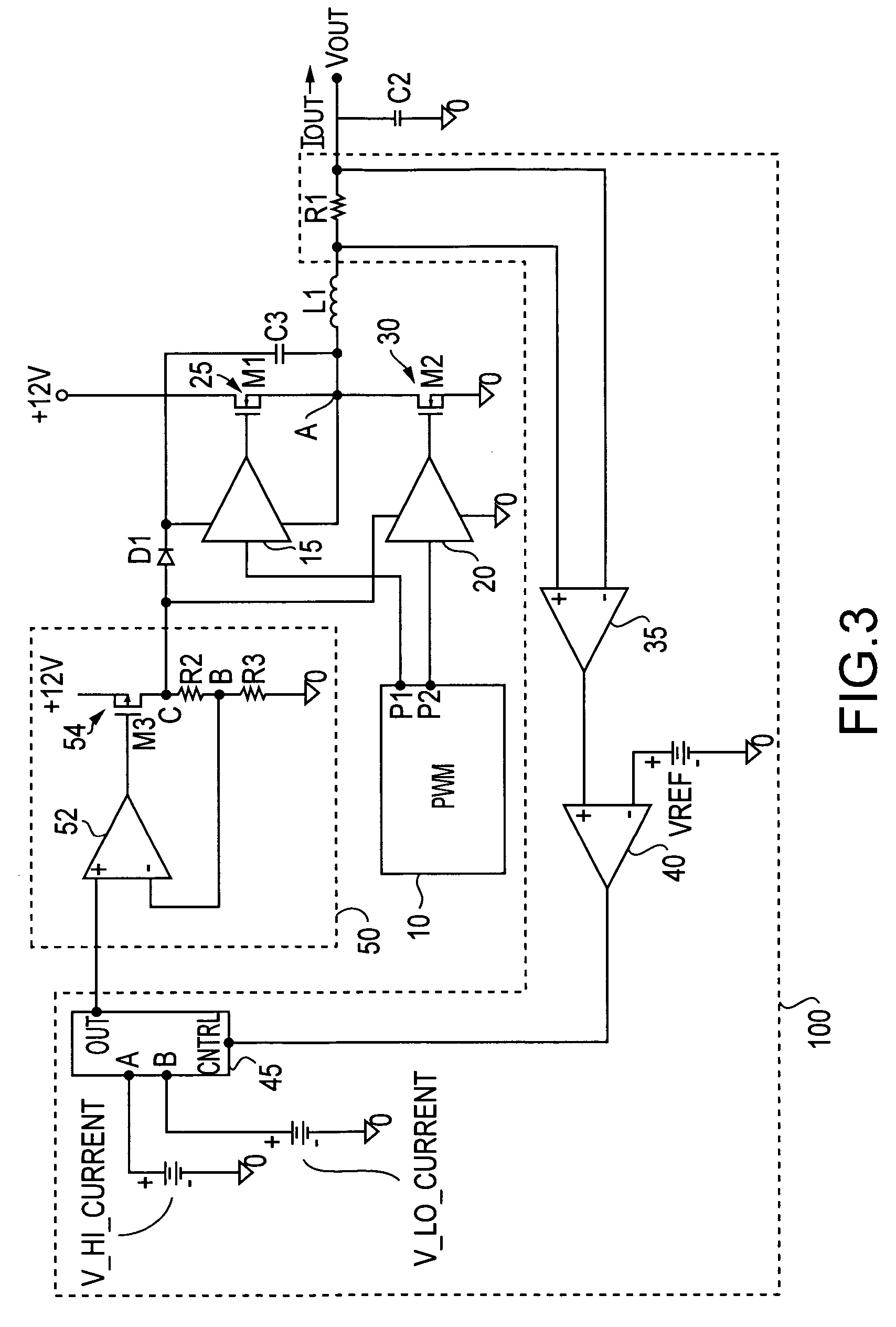
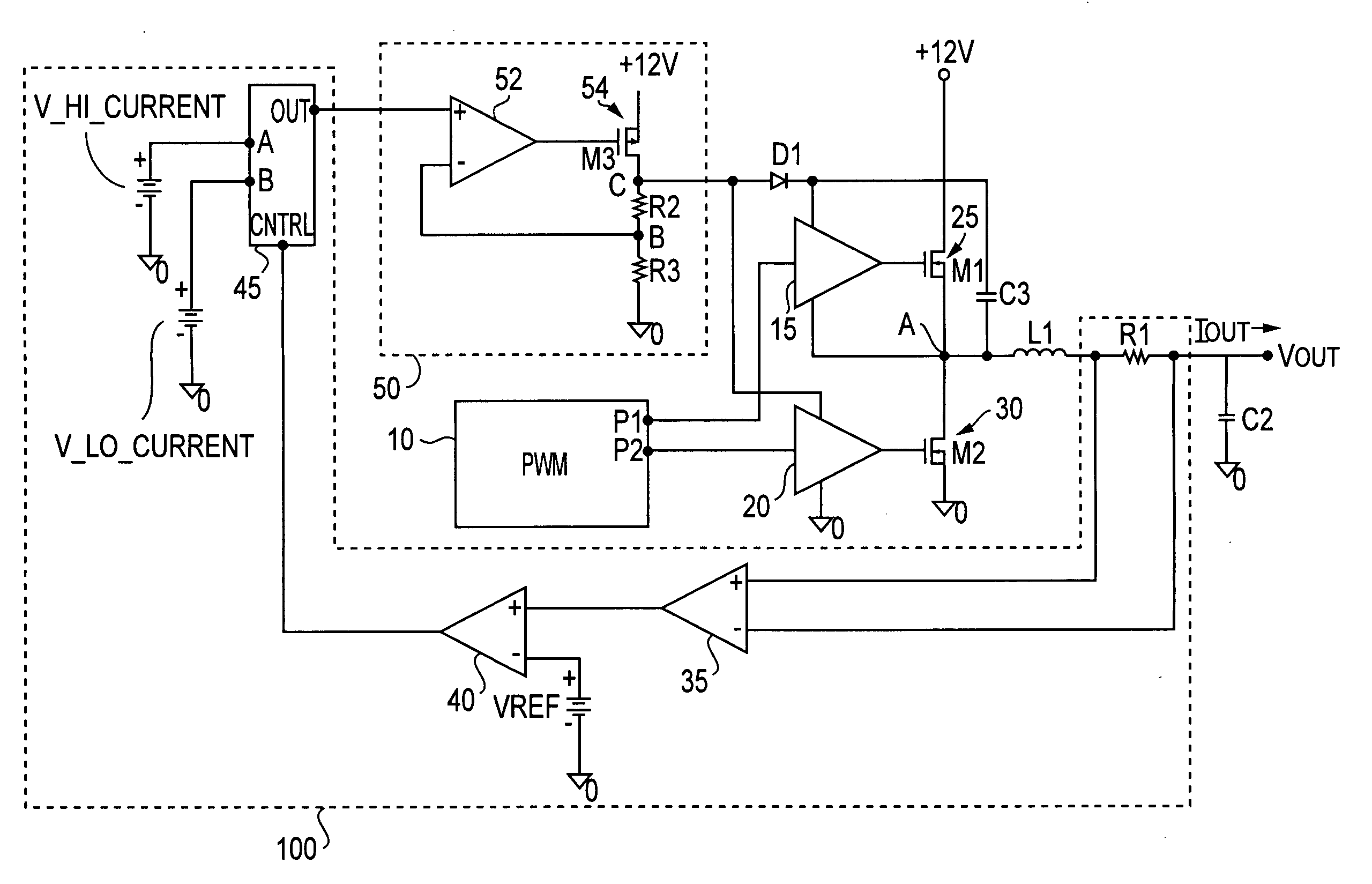
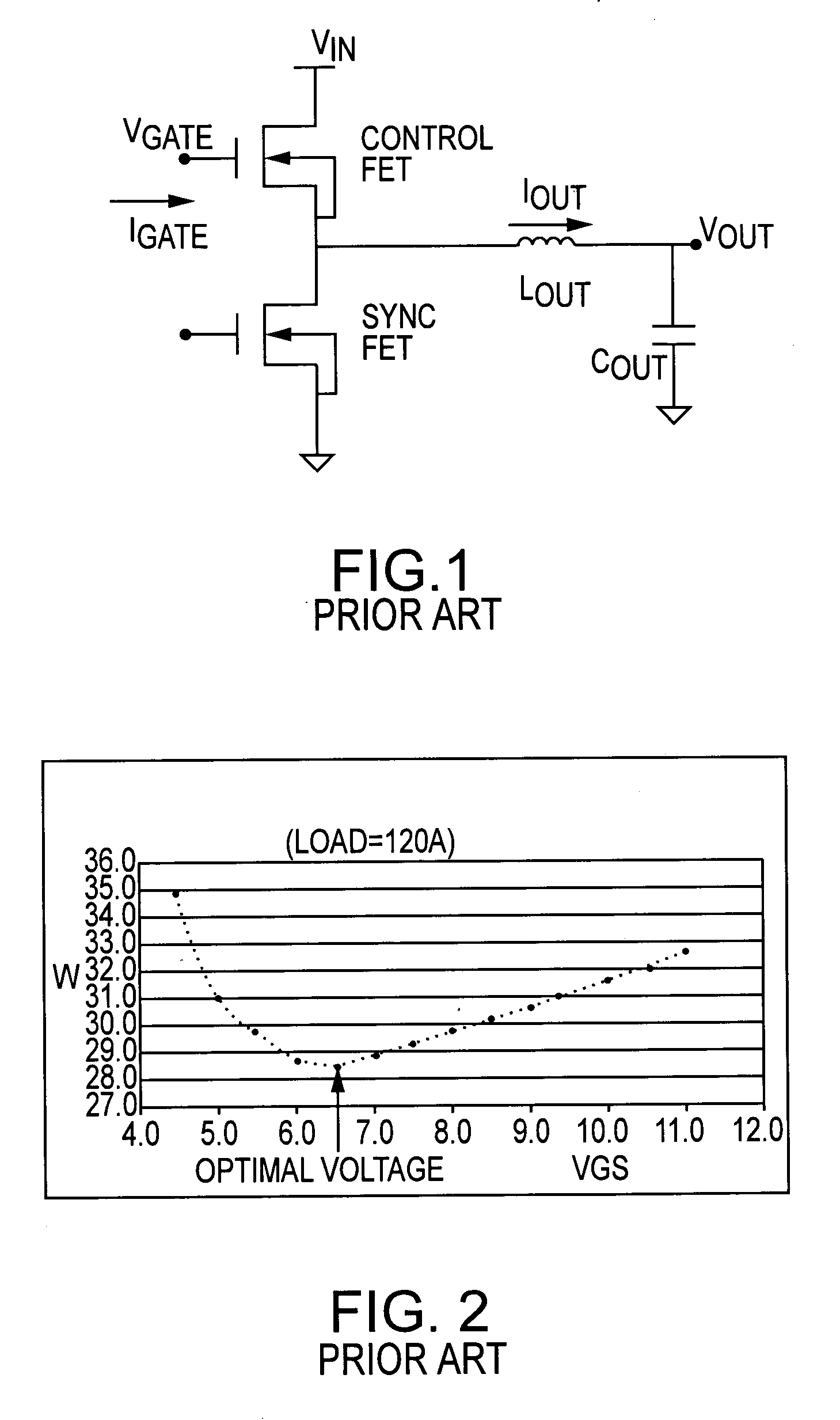
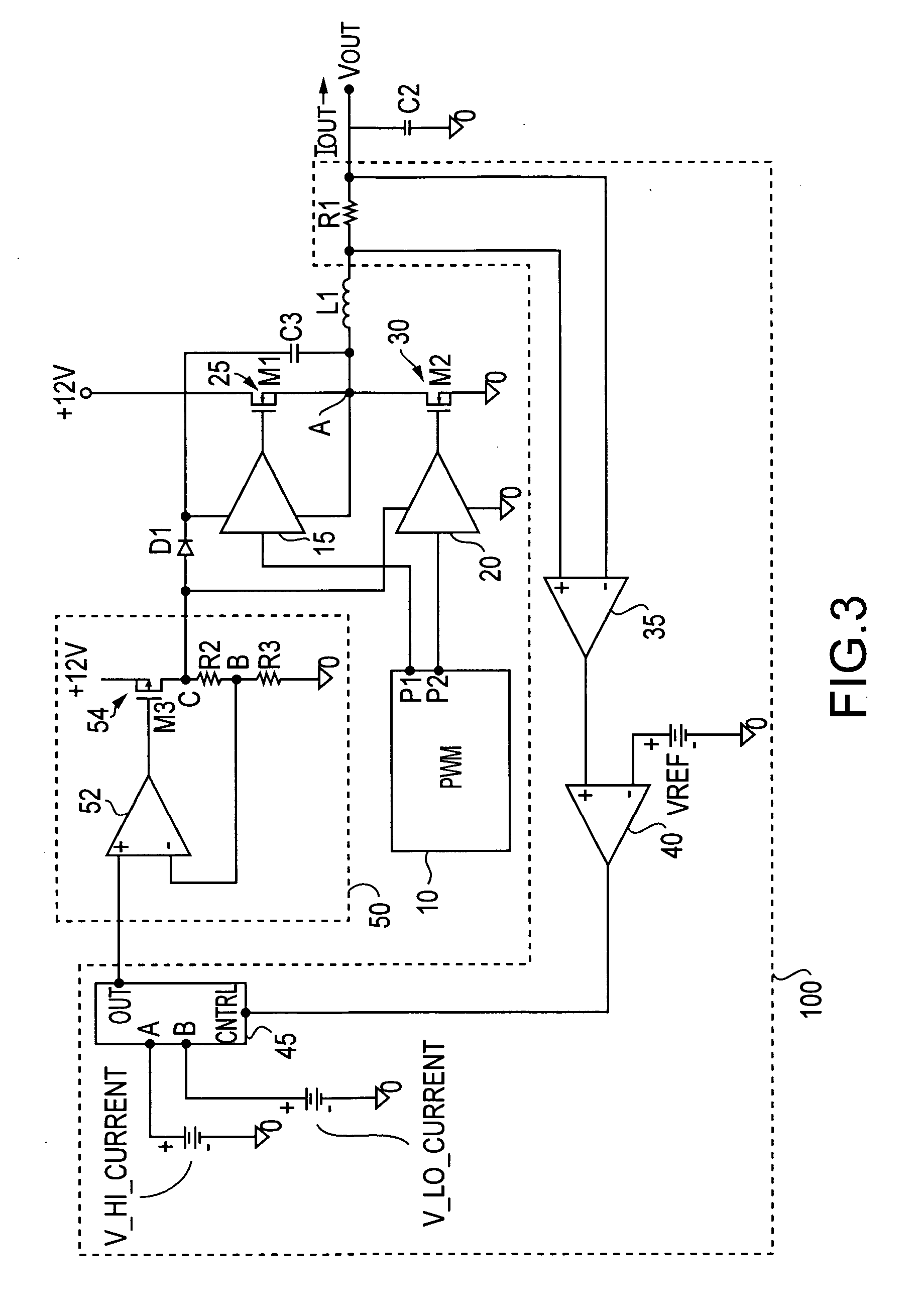
ActiveUS7265601B2Reduce lossesLower gate voltageTransistorAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesEngineeringSelf adaptive
A circuit and method for reducing losses in a DC / DC converter by optimizing gate drive voltage. The circuit and method detect a change in the output load, or more specifically the output current, and adjust the gate voltage accordingly; in other words, providing adaptive gate drive voltage. In response to a reduction of output current, the invention reduces the gate voltage so as to reduce both conduction and switching losses in the semiconductor switching devices in the output stage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Adaptive gate drive voltage circuit
ActiveUS20060038547A1Preventing unwanted noiseReduce power lossTransistorAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesEngineeringVoltage response
A circuit and method for reducing losses in a DC / DC converter by optimizing gate drive voltage. The circuit and method detect a change in the output load, or more specifically the output current, and adjust the gate voltage accordingly; in other words, providing adaptive gate drive voltage. In response to a reduction of output current, the invention reduces the gate voltage so as to reduce both conduction and switching losses in the semiconductor switching devices in the output stage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20070247399A1Improve mobilitySmall mobilityElectroluminescent light sourcesHeater elementsCapacitanceDisplay device
The invention provides a pixel circuit that can cancel the influence of the mobility of a drive transistor. A drive transistor supplies a light-emitting element with an output current dependent upon an input voltage. The light-emitting element emits light with a luminance dependent upon a video signal in response to the output current supplied from the drive transistor. The pixel circuit includes a correction unit that corrects the input voltage held by a capacitive part in order to cancel the dependence of the output current on the carrier mobility.
Owner:SONY CORP
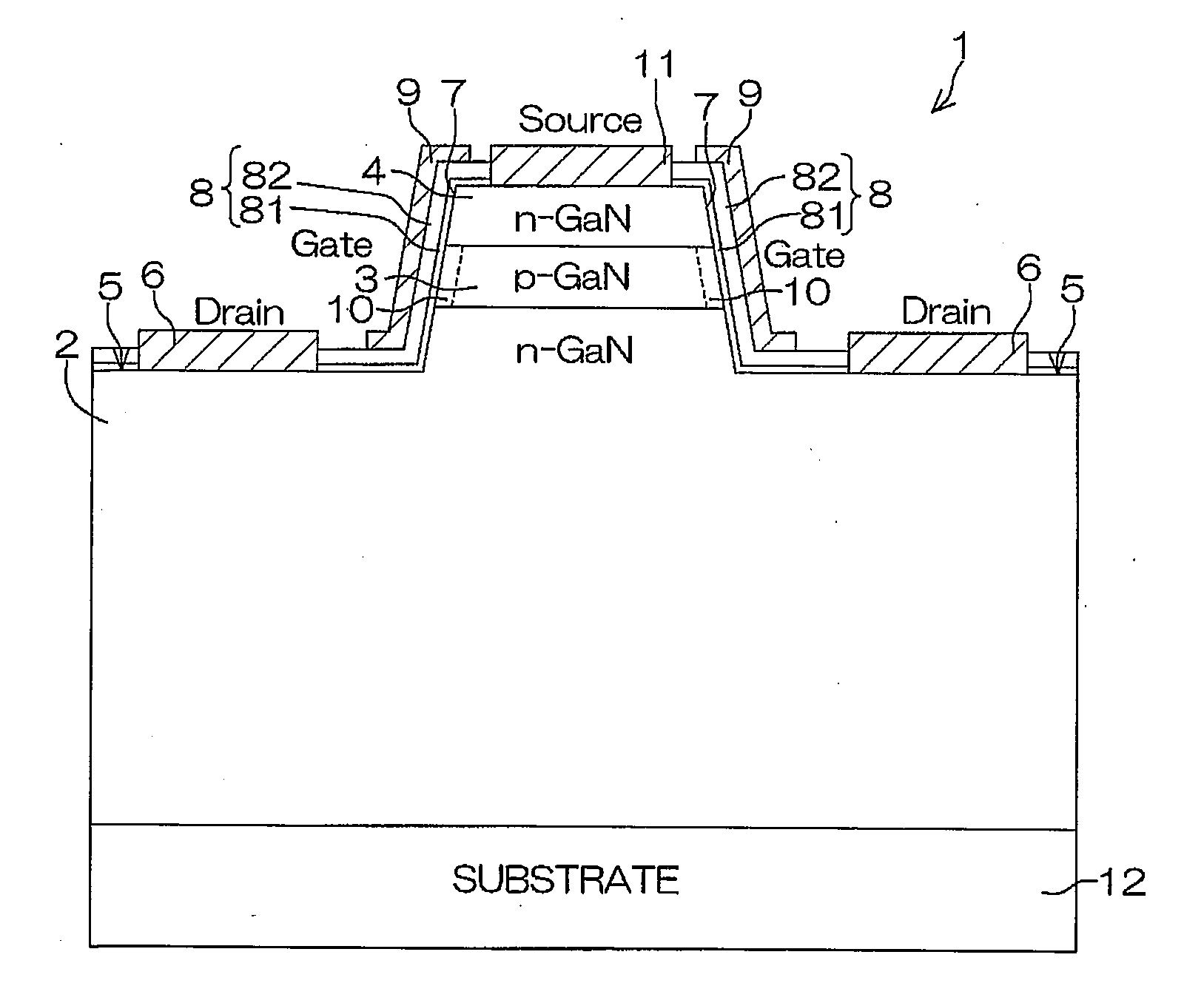
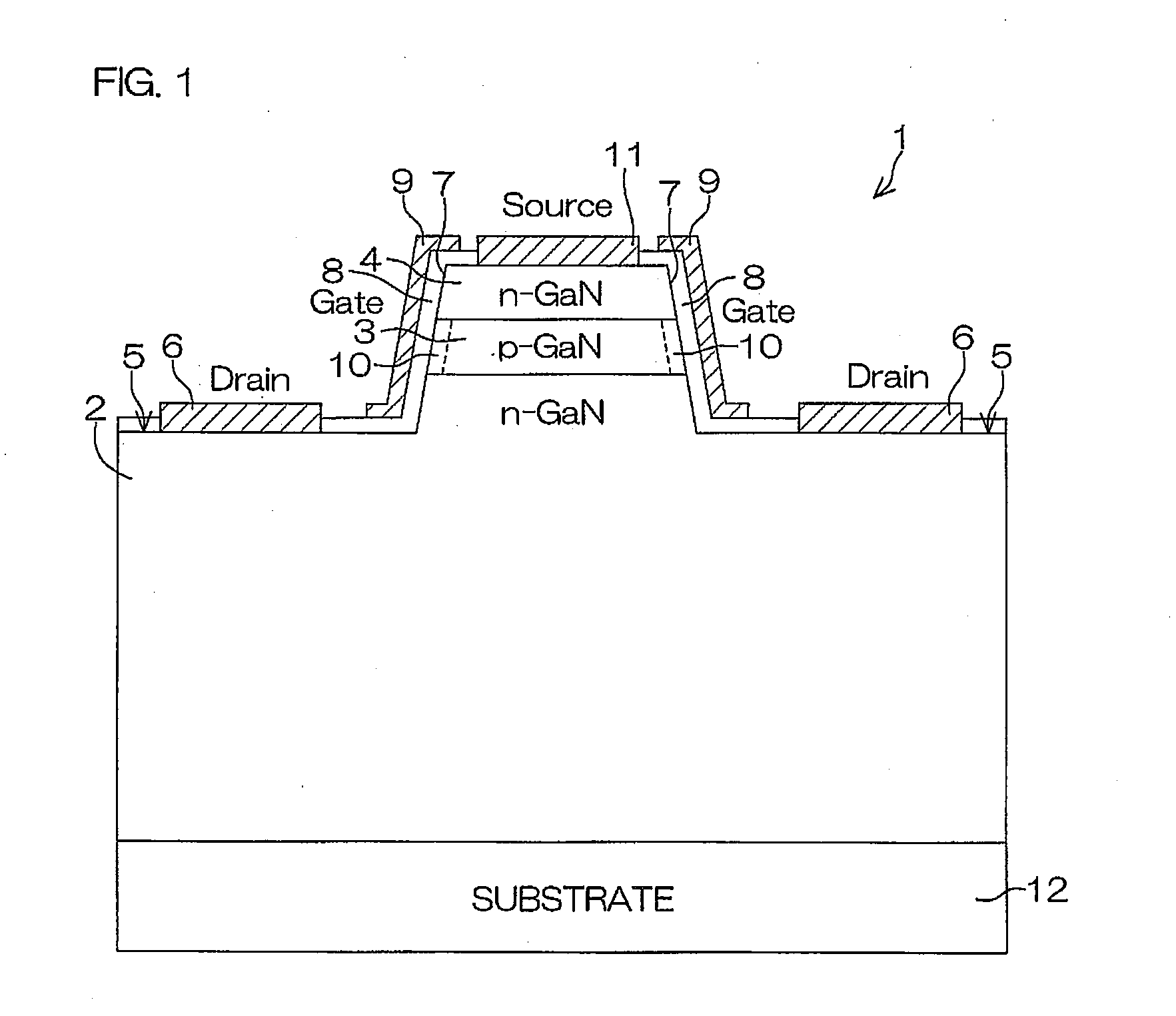
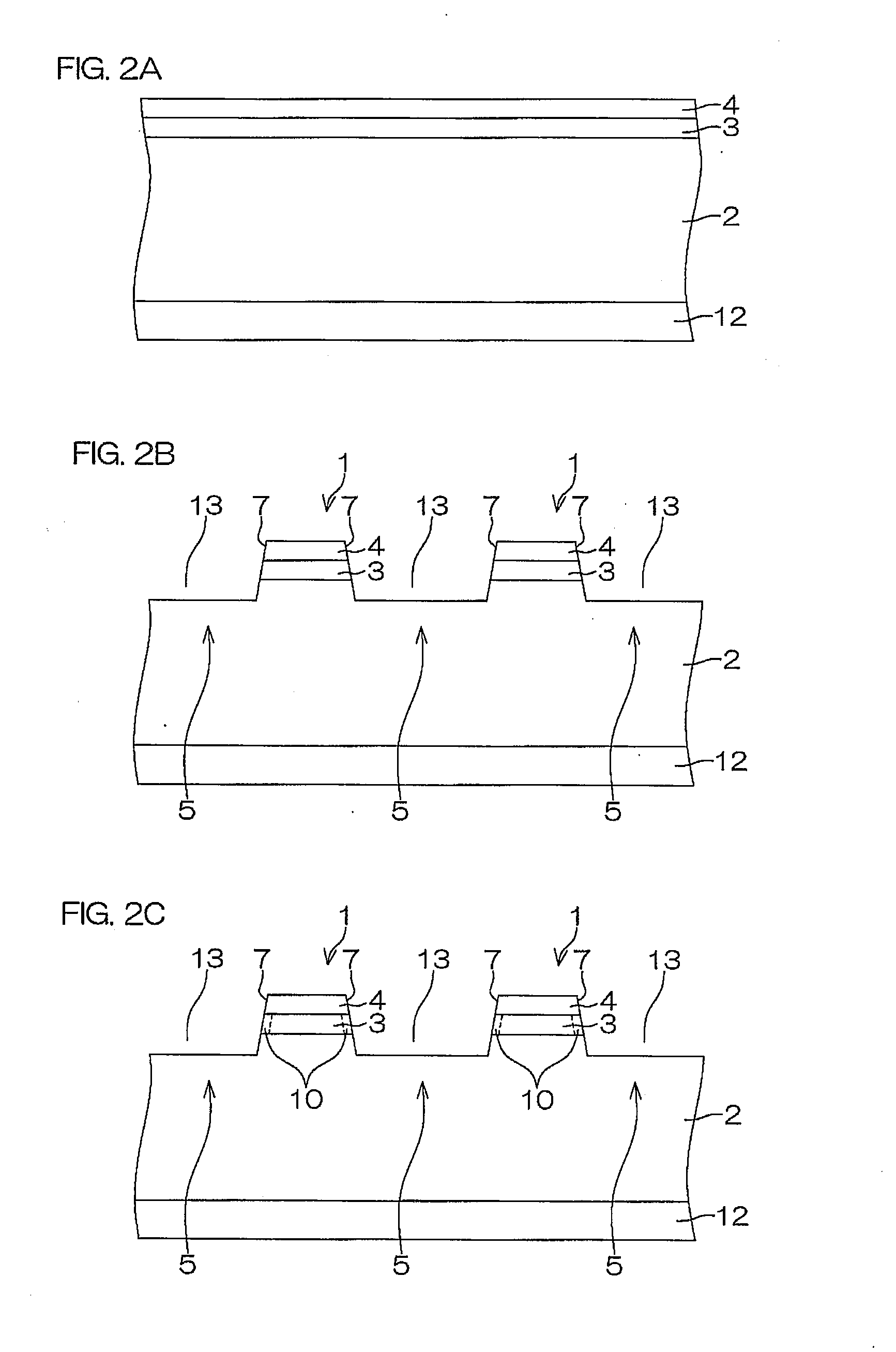
Nitride semiconductor device, nitride semiconductor package, and method for manufacturing nitride semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100078688A1Improve withstand voltage characteristicsLower gate voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageImpurity
A nitride semiconductor device of the present invention includes: a nitride semiconductor laminated structure including an n-type first layer, a second layer that is laminated on the first layer and contains a p-type impurity, and an n-type third layer laminated on the second layer, each layer of the nitride semiconductor laminated structure being made of a Group III nitride semiconductor, and having a wall surface extending from the first, second, to third layers; a fourth layer that is formed on the wall surface in the second layer and that has a different conductive characteristic from that of the second layer; a gate insulating film formed to contact the fourth layer; and a gate electrode formed as facing the fourth layer with the gate insulating film being sandwiched between the gate electrode and the fourth layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7948456B2Eliminate dependenciesImprove mobilityElectroluminescent light sourcesHeater elementsCapacitancePower flow
The invention provides a pixel circuit that can cancel the influence of the mobility of a drive transistor. A drive transistor supplies to a light-emitting element, an output current dependent upon an input voltage during a certain emission period. The light-emitting element emits light with a luminance dependent upon a video signal in response to the output current supplied from the drive transistor. The pixel circuit includes a correction unit that corrects the input voltage held by a capacitive part before the emission period or at the beginning of the emission period, in order to cancel the dependence of the output current on the carrier mobility. The correction unit operates during part of a sampling period in response to control signals supplied from scan lines. Specifically, the correction unit extracts the output current from the drive transistor while the video signal is sampled, and negatively feeds back the output current to the capacitive part to thereby correct the input voltage.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Semiconductor device
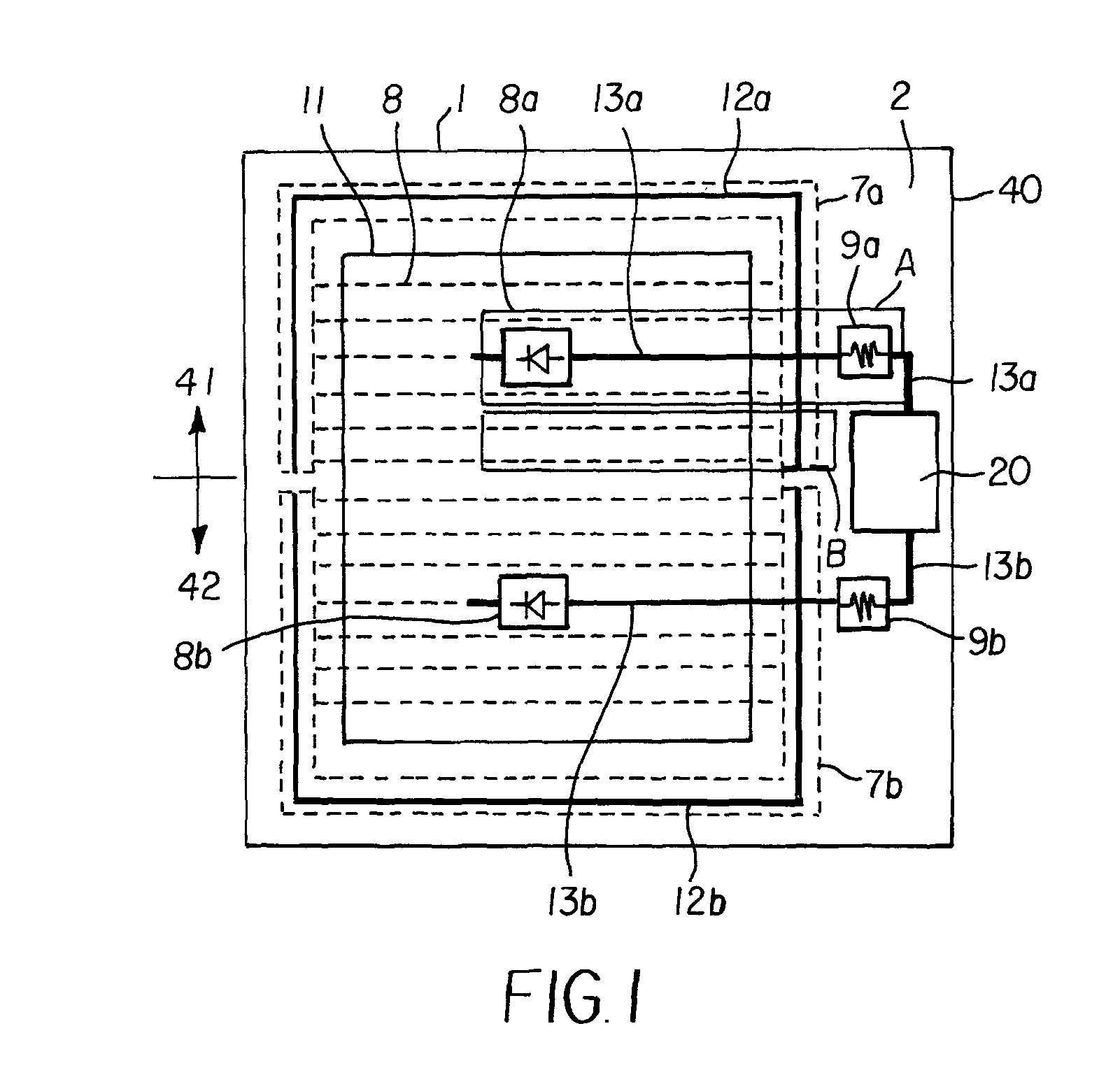
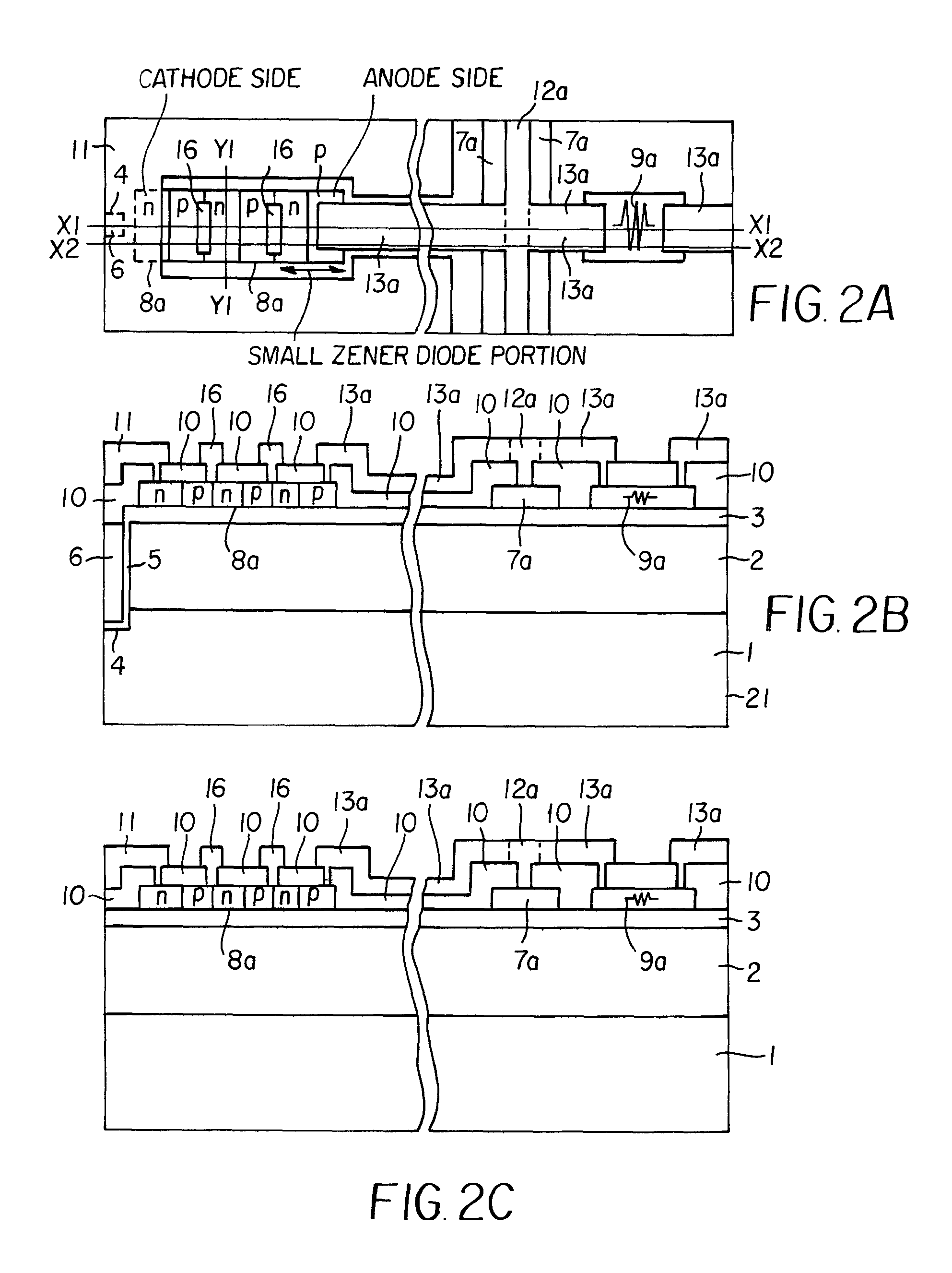
ActiveUS20100321092A1Improve reliabilityEfficient use of resourcesSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaicsDevice materialZener diode
An IGBT is disclosed which separated into two groups (first and second IGBT portioZenerns). First and second Zener diodes each composed of series-connected Zener diode parts are disposed so as to correspond to the groups respectively. Each of the first and second Zener diodes has an anode side connected to a corresponding one of first and second polysilicon gate wirings, and a cathode side connected to an emitter electrode. Temperature dependence of a forward voltage drop of each of first and second Zener diodes is used for reducing a gate voltage of a group rising in temperature to throttle a current flowing in the group and reduce the temperature of the group to thereby attain equalization of the temperature distribution in a surface of a chip. In this manner, it is possible to provide an MOS type semiconductor device in which equalization of the temperature distribution in a surface of a chip or among chips can be attained.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor Nanowire Transistor
ActiveUS20090321716A1Improve performanceReduce outputTransistorNanoinformaticsSemiconductor materialsNanowire
A nanowire wrap-gate transistor is realised in a semiconductor material with a band gap narrower than Si. The strain relaxation in the nanowires allows the transistor to be placed on a large variety of substrates and heterostructures to be incorporated in the device. Various types of heterostructures should be introduced in the transistor to reduce the output conductance via reduced impact ionization rate, increase the current on / off ratio, reduction of the sub-threshold slope, reduction of transistor contact resistance and improved thermal stability. The parasitic capacitances should be minimized by the use of semi-insulating substrates and the use of cross-bar geometry between the source and drain access regions. The transistor may find applications in digital high frequency and low power circuits as well as in analogue high frequency circuits.
Owner:QUNANO
Organic light emitting diode display
ActiveUS20160284784A1Minimizes parasitic capacitanceMinimize crosstalkStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesContact holeDisplay device
An organic light emitting diode display includes a substrate, a semiconductor disposed on the substrate that includes a channel for each of a plurality of transistors and doping regions formed at both sides of each channel; a gate insulating layer disposed on the semiconductor that includes an insulating layer opening through which the doping regions of two different transistors are exposed; a gate electrode disposed on the gate insulating layer that overlaps each channel; an interlayer insulating layer disposed on the gate electrode that includes a first and second contact holes through which the doping regions exposed within the insulating layer opening are each exposed; and data wirings disposed on the interlayer insulating layer that are each connected to the doping regions. The interlayer insulating layer includes an organic layer, and the first and second contact holes each include a first side wall positioned within the insulating layer opening.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, display panel and display device
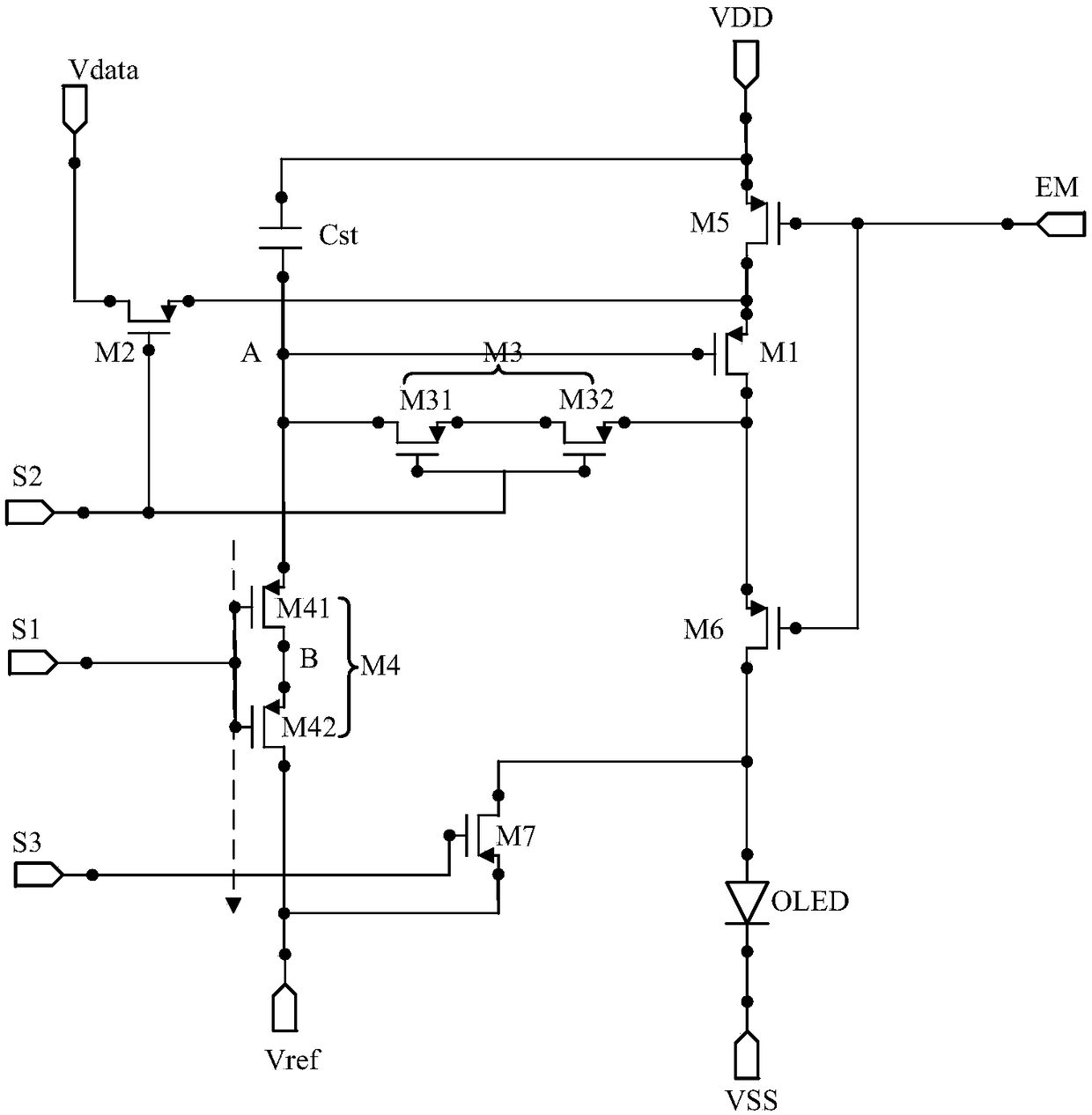
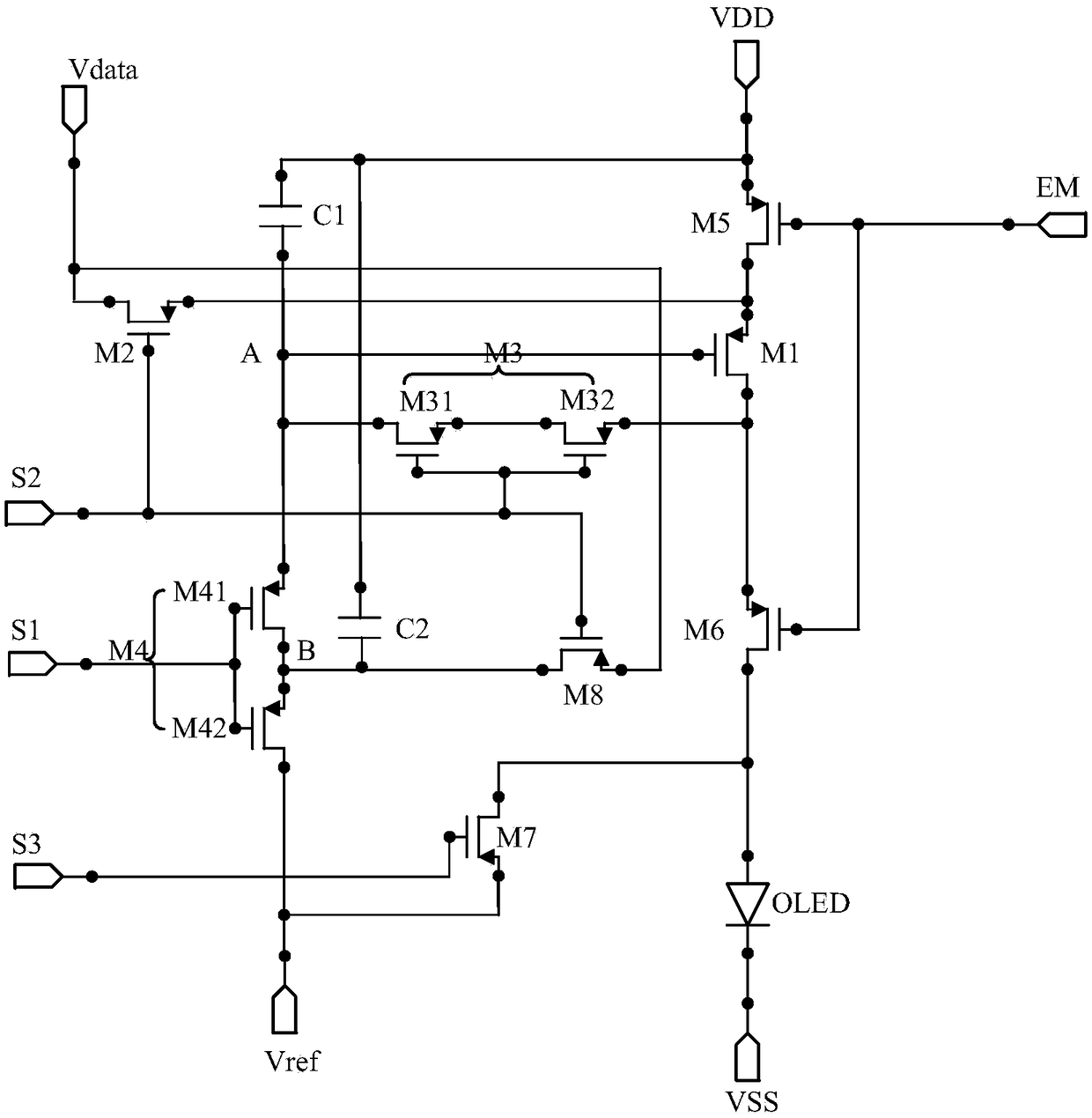
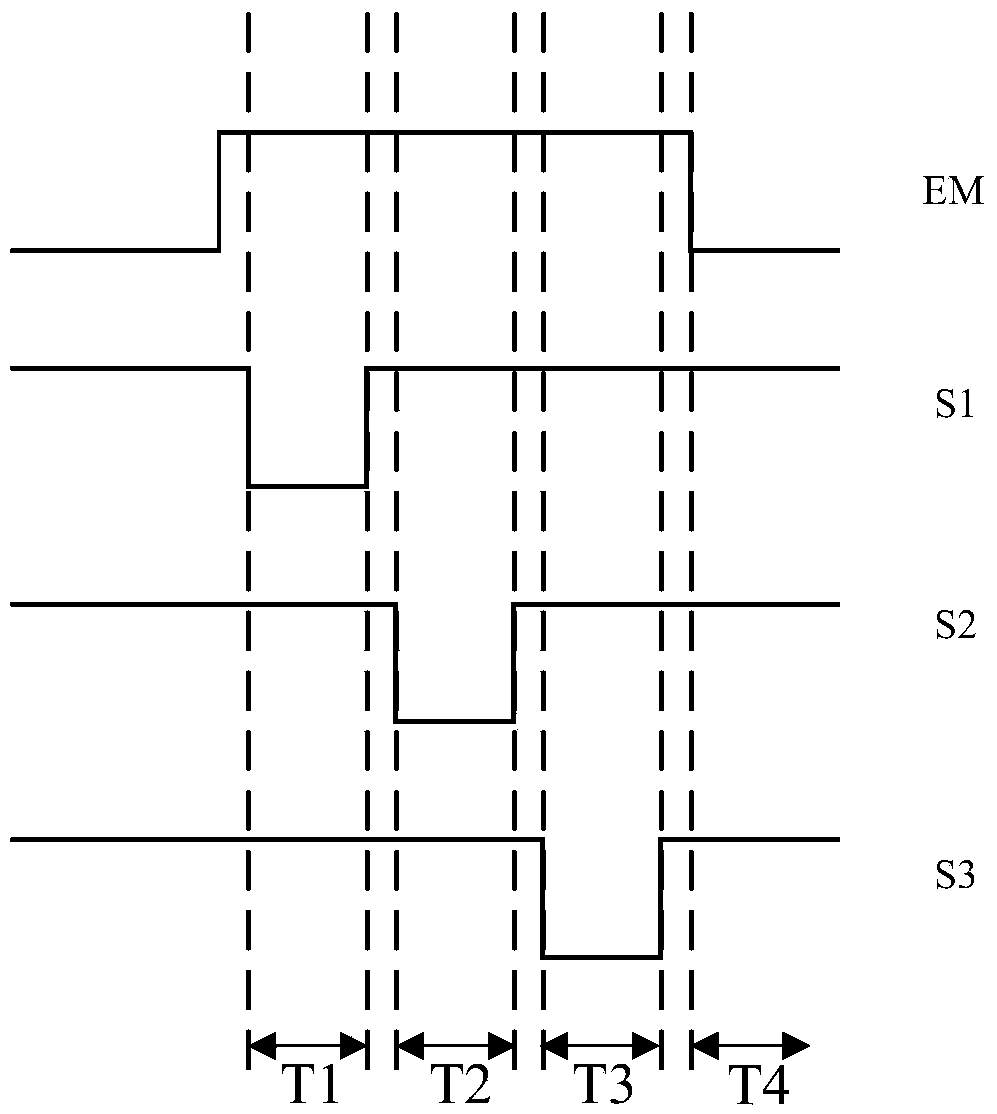
ActiveCN108847186ALower gate voltageImprove the display effectStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDriving current
The invention provides a pixel circuit and a driving method thereof, a display panel and a display device. The pixel circuit comprises eight transistors, two storage capacitors and an organic light emitting device (OLED), a threshold voltage of the first transistor is compensated through mutual cooperation of the transistors and the capacitors, a driving current for driving the OLED to emit lightis made to be independent of the threshold voltage of the first transistor, so influence of fluctuation of the threshold voltage of the first transistor on the OLED is avoided, a problem of uneven display brightness caused by this is solved, the display effect of the whole frame is improved, moreover, since the leakage current between the first storage capacitor and the second storage capacitor can be reduced by the eighth transistor, reduction of a gate voltage of the first transistor is avoided, a problem of scintillation caused by the leakage current is solved, and the display effect of thewhole display frame is further improved.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
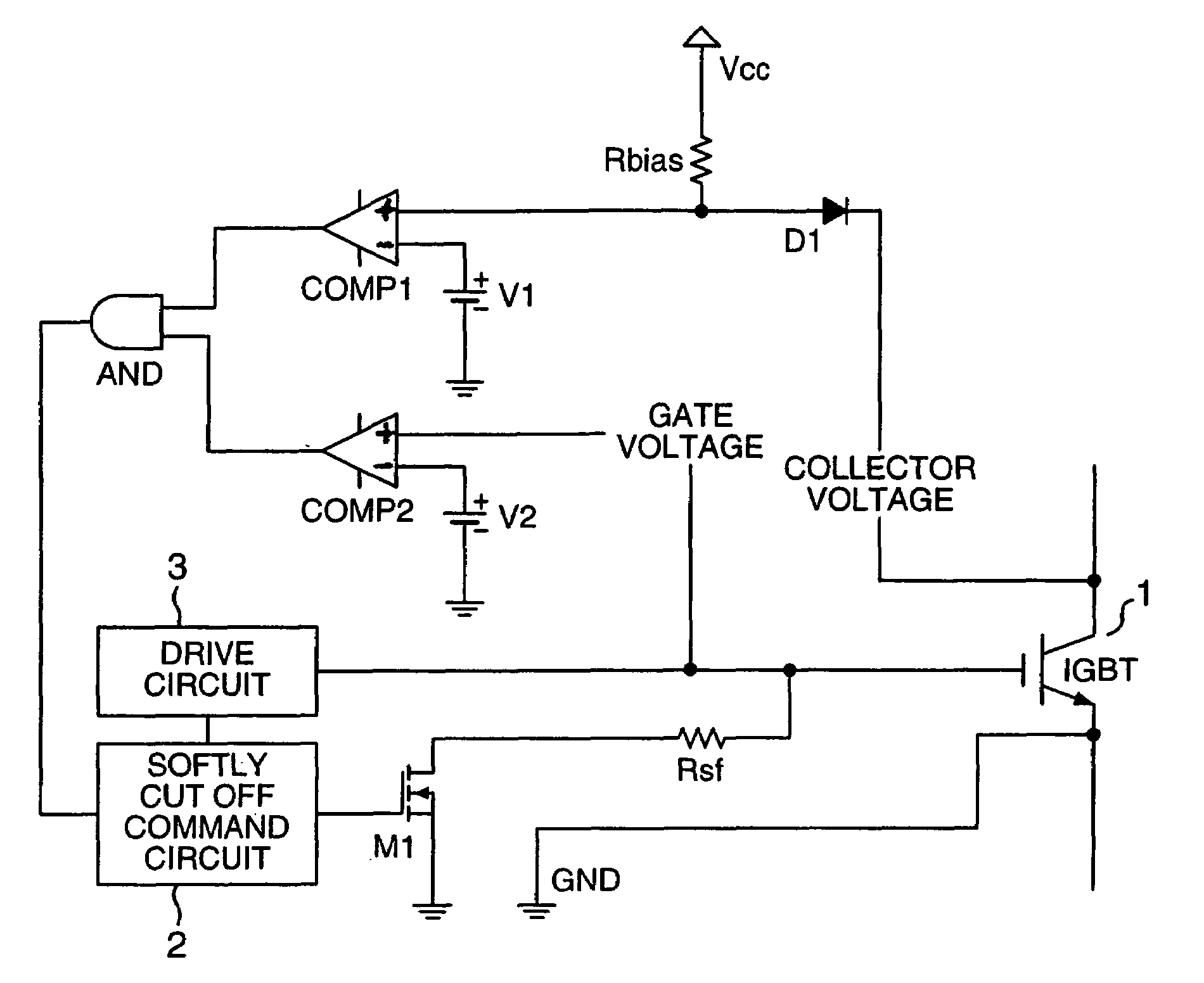
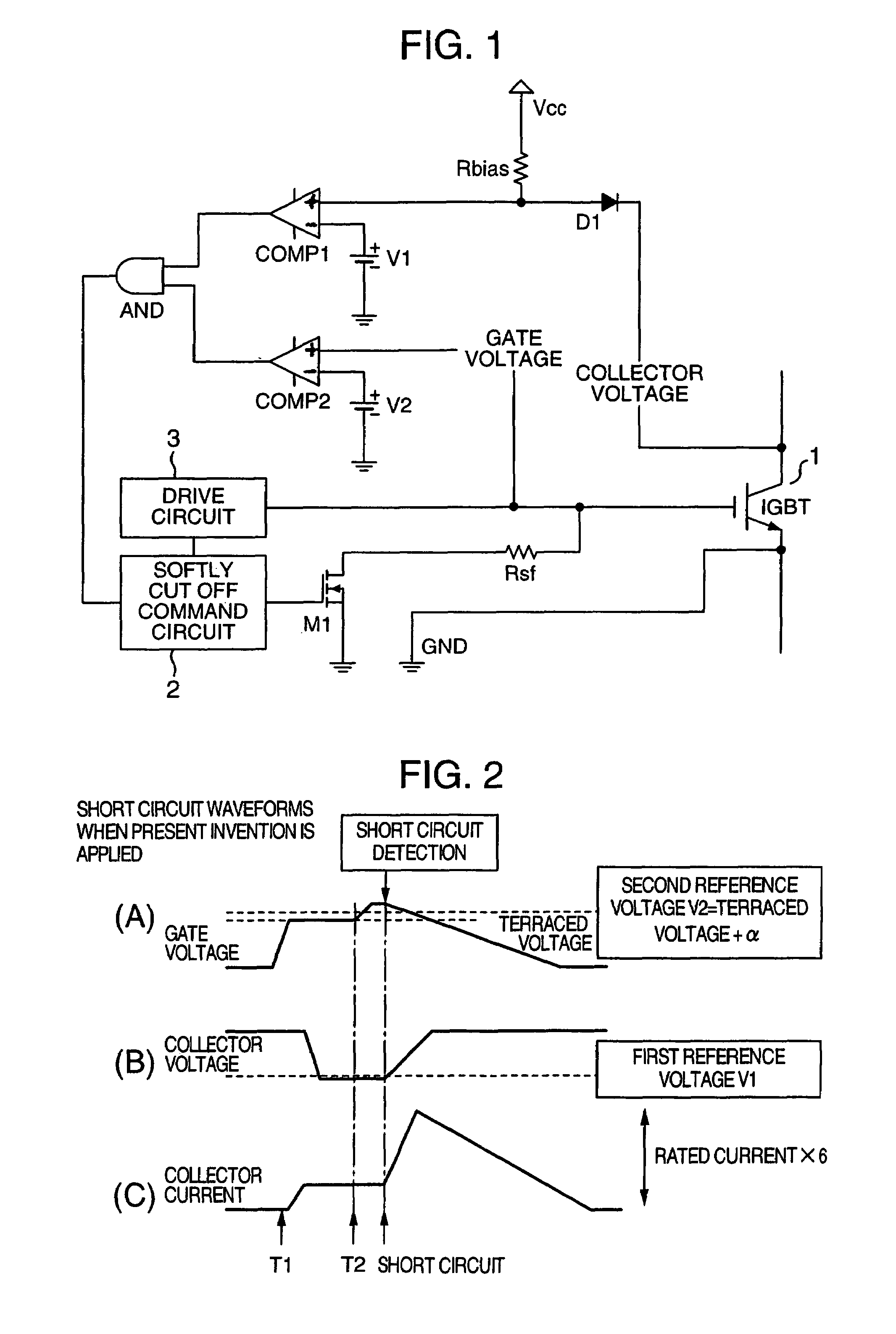
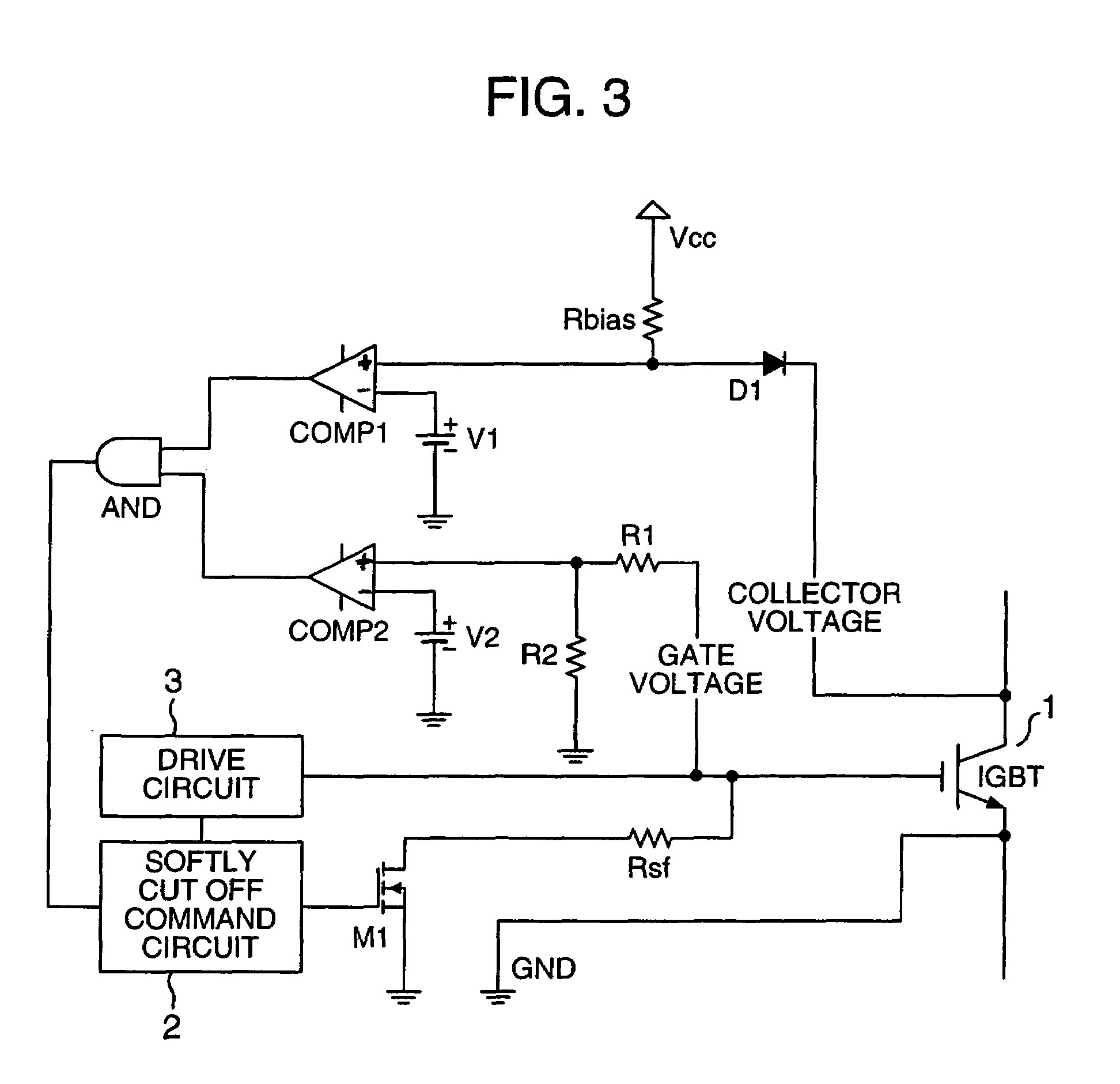
Protection circuit for power management semiconductor devices and power converter having the protection circuit
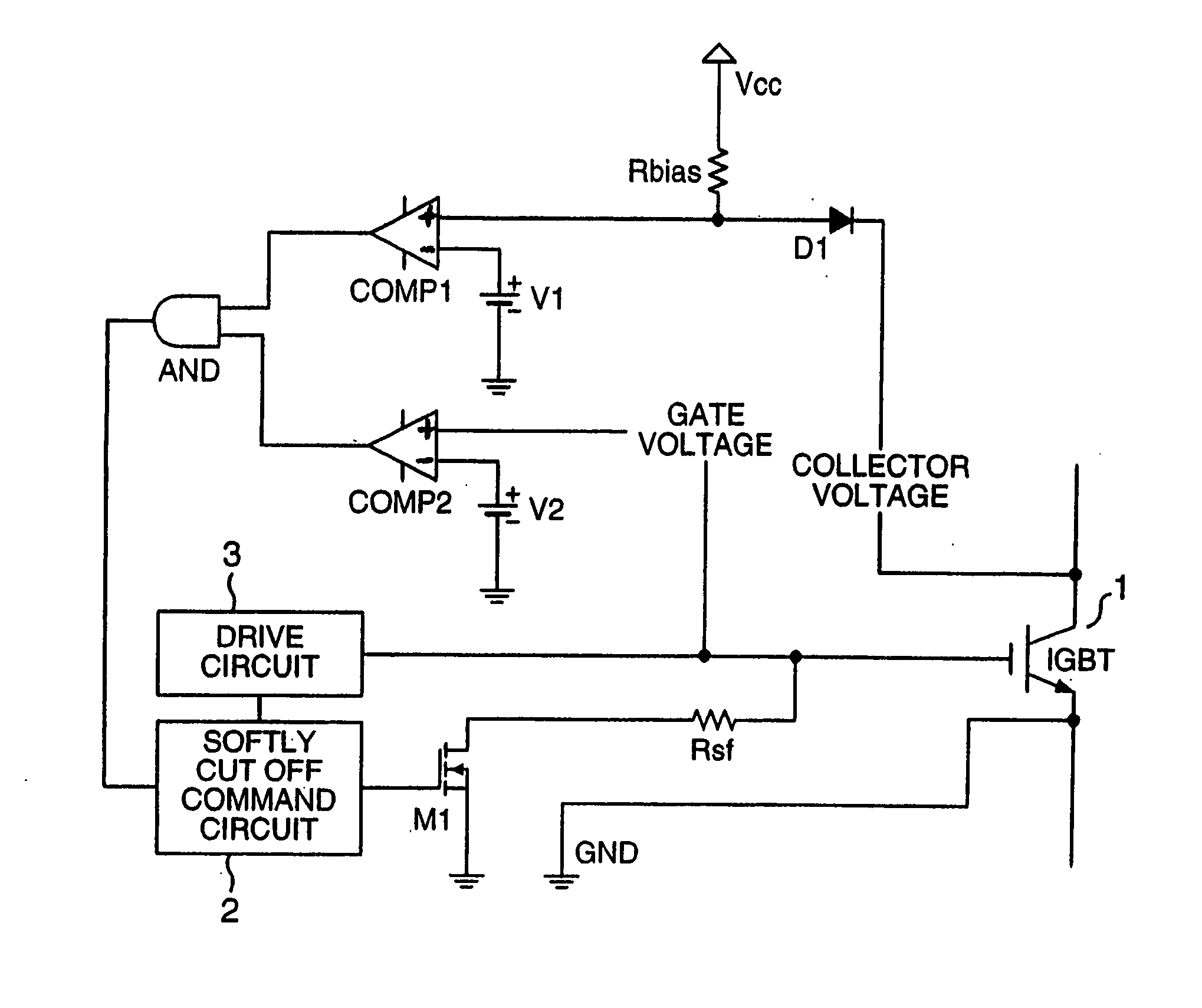
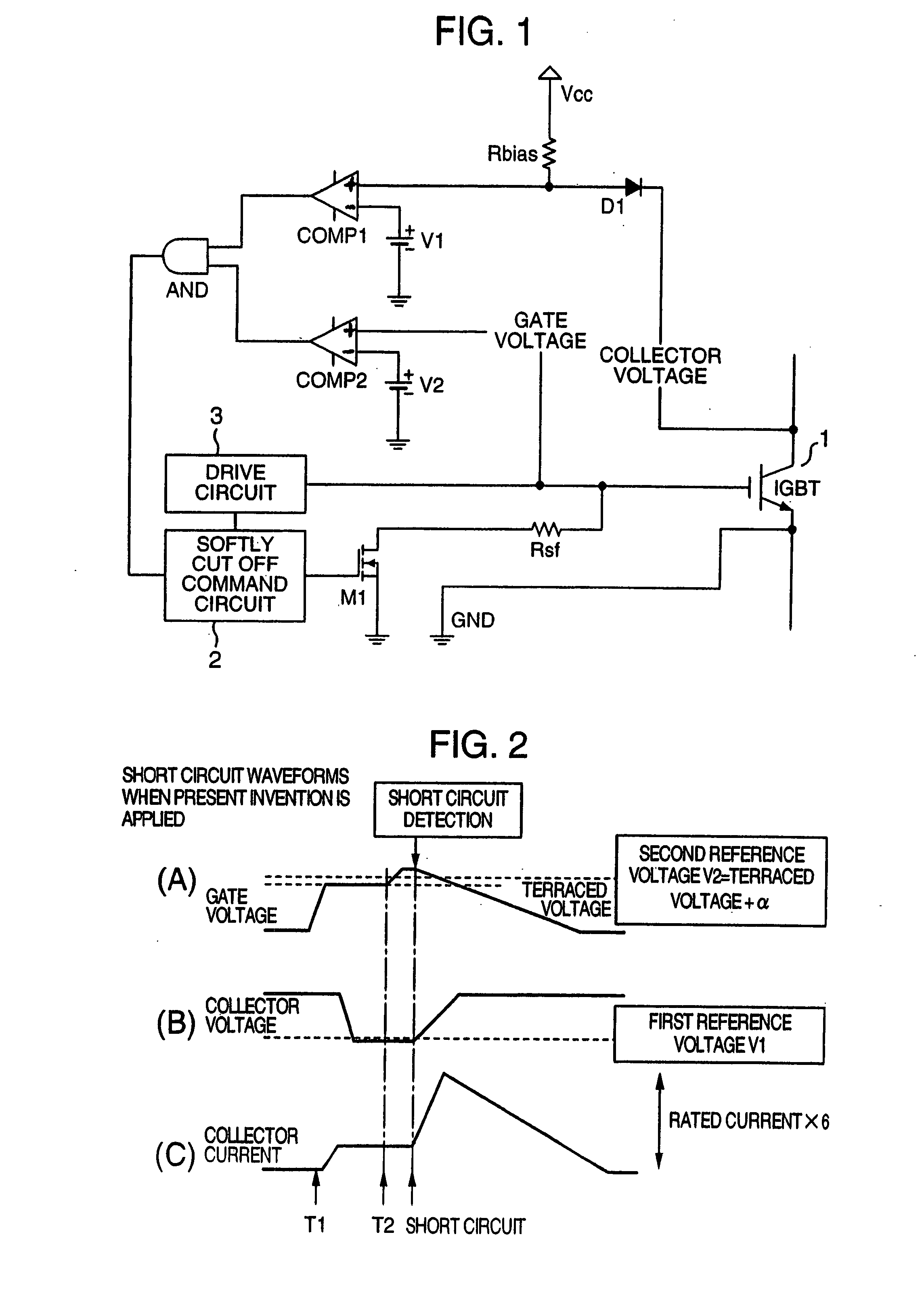
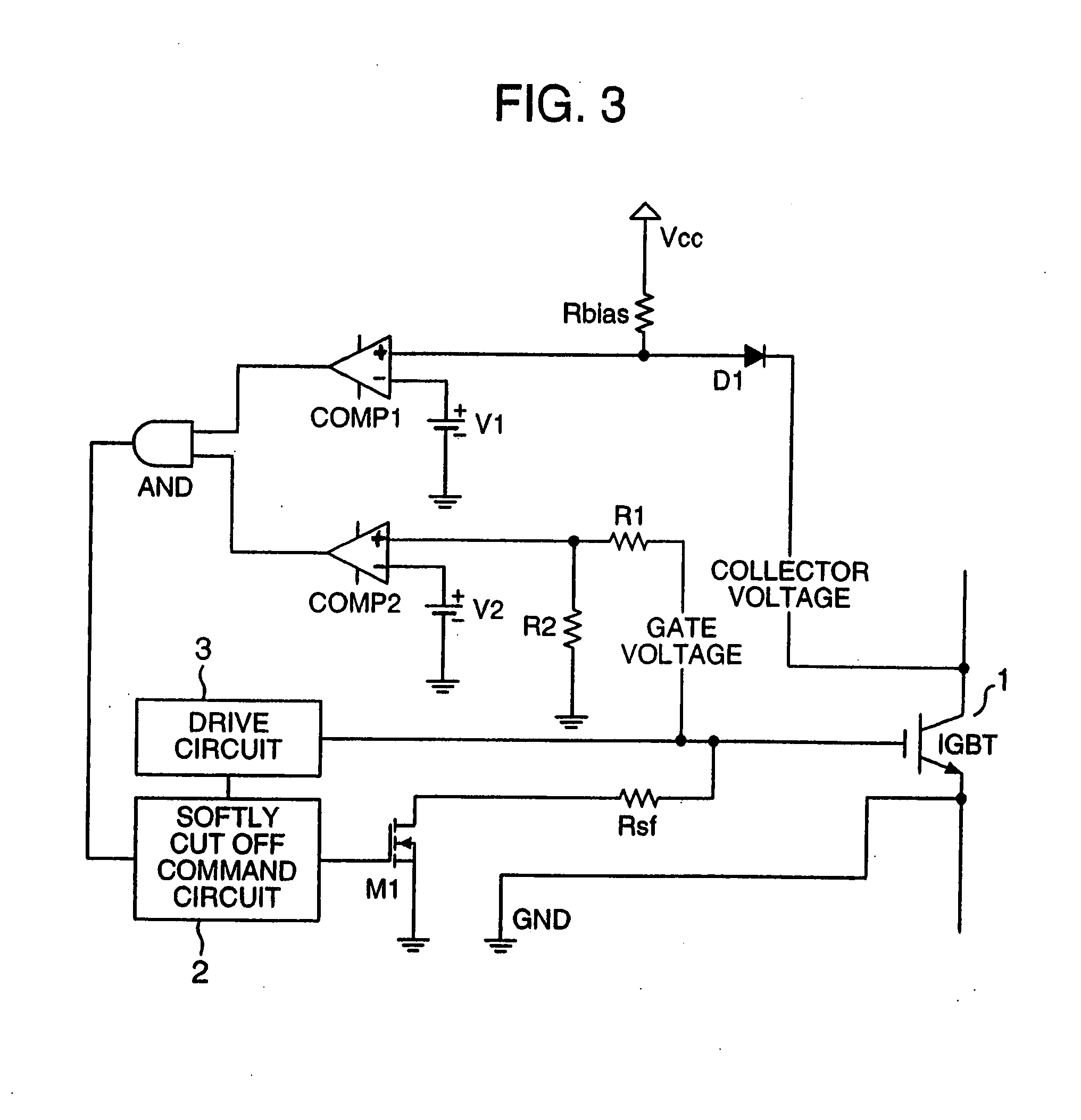
ActiveUS20080074819A1Lower gate voltageEarly detectionElectric devicesElectronic switchingOvervoltageDriver circuit
A collector voltage of a power management semiconductor device is detected by a first comparator, and when the detected collector voltage exceeds a first reference voltage, the first comparator outputs a first detection signal. Furthermore, a gate voltage of the power management semiconductor device is detected by a second comparator, and when the detected gate voltage exceeds a second reference voltage, the second comparator outputs a second detection signal. The second reference voltage is a minimum gate voltage for feeding a rated power to the power management semiconductor device or over, and less than a line power voltage of a drive circuit of the power management semiconductor device. When both the first detection signal and second detection signal are being outputted, the gate voltage is reduced by a gate voltage reduction means so as to protect the power management semiconductor device from overcurrent and overvoltage.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
Flash with finger-like floating gate
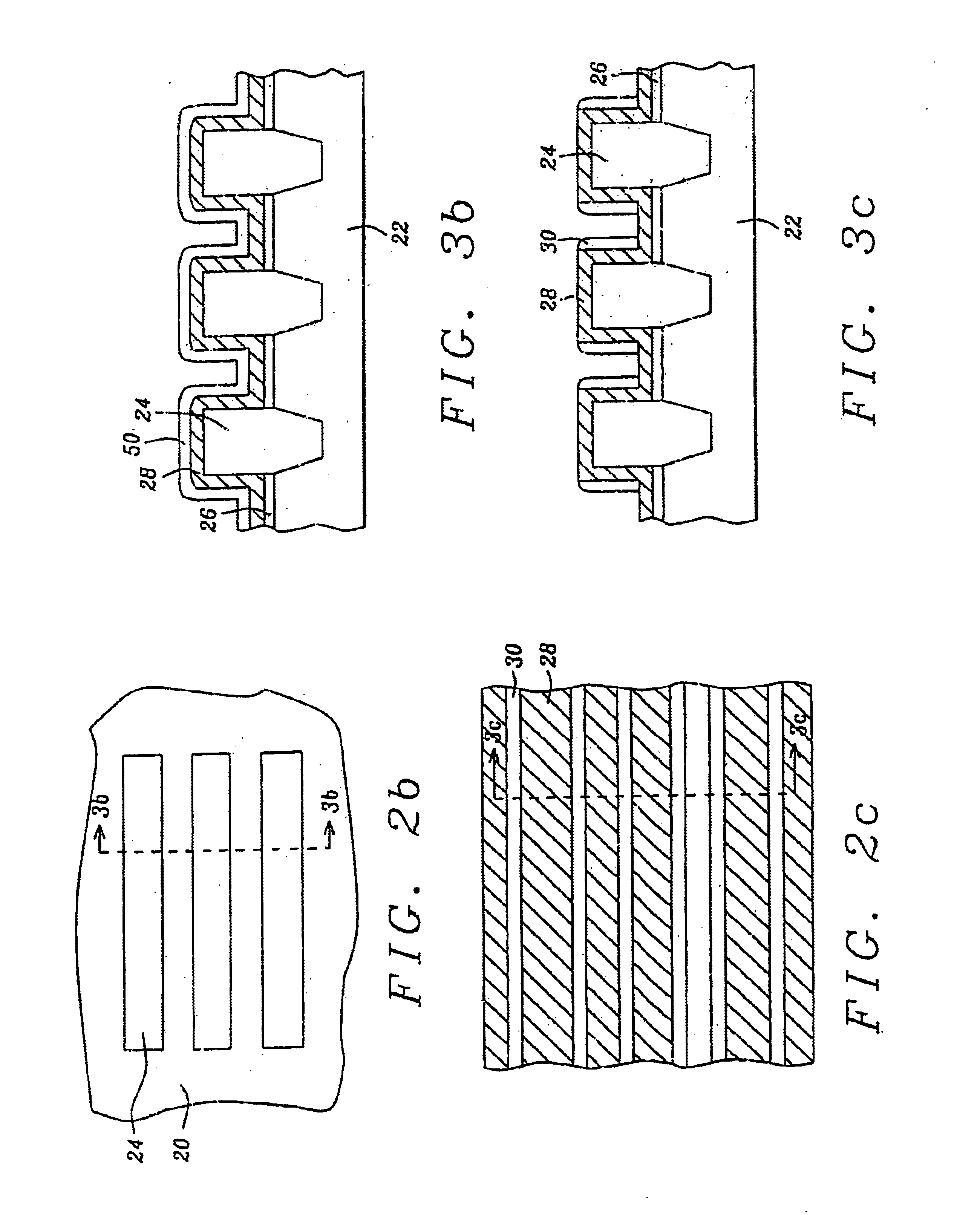
InactiveUS6876032B2Easy to controlImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDielectric layer
A finger-like floating gate structure in flash memory cells is disclosed. Raised isolation regions within a semiconductor region separate parallel active regions. A gate dielectric layer is disposed over the active regions. Finger-like floating gates are equally spaced along the active regions. The finger-like floating gates are comprised of a conductive base section that is disposed over the gate dielectric layer and three conductive finger sections that are in intimate electrical contact with the base section. An interlevel dielectric layer is patterned into equally spaced parallel stripes perpendicular to the active regions and each stripe is disposed over the corresponding composite floating gate for each active region. Word lines, which are composed of a third conductive layer, are parallel lines disposed over the interlevel dielectric layer and serve as control gates.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
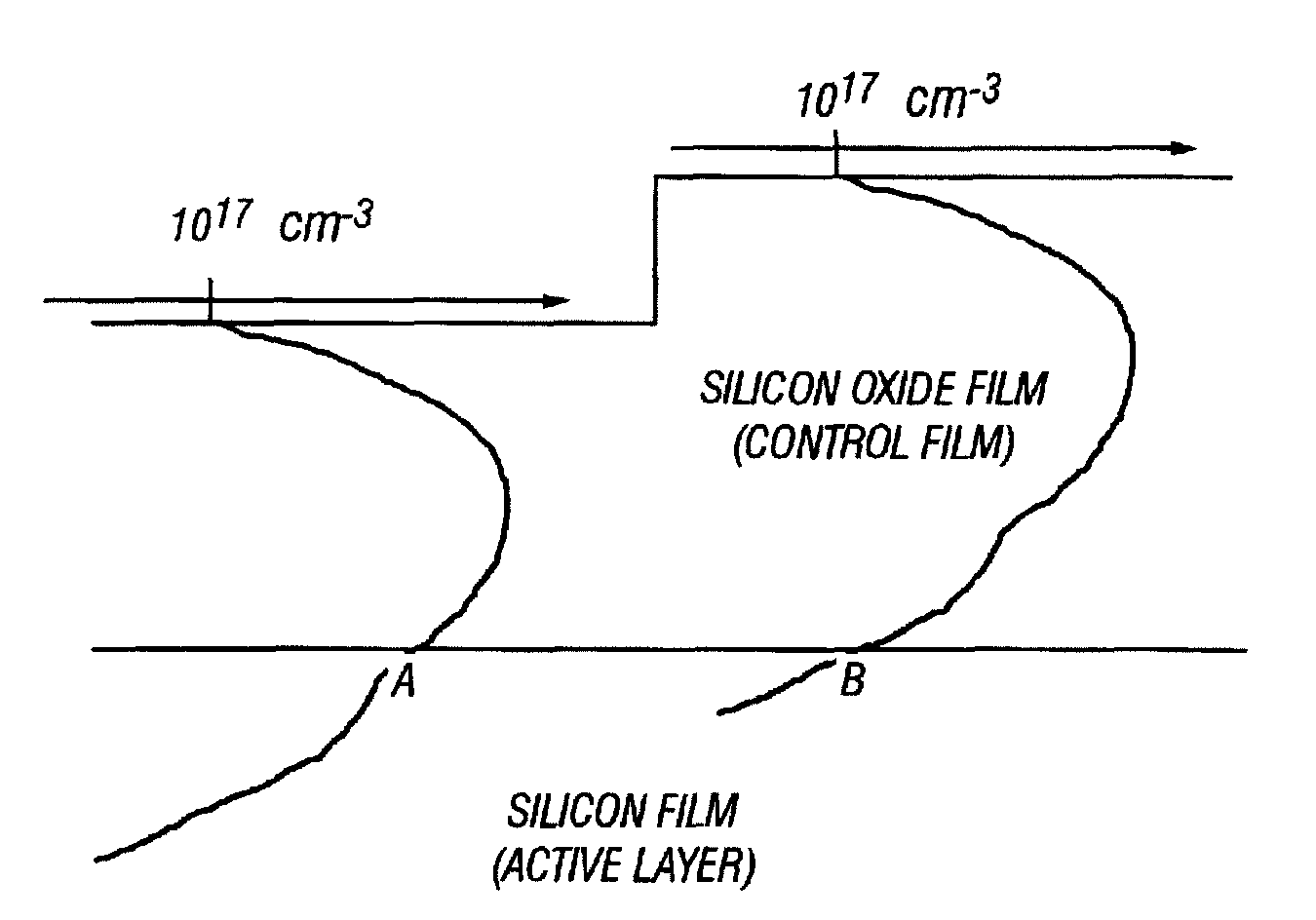
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080213954A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid delaySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
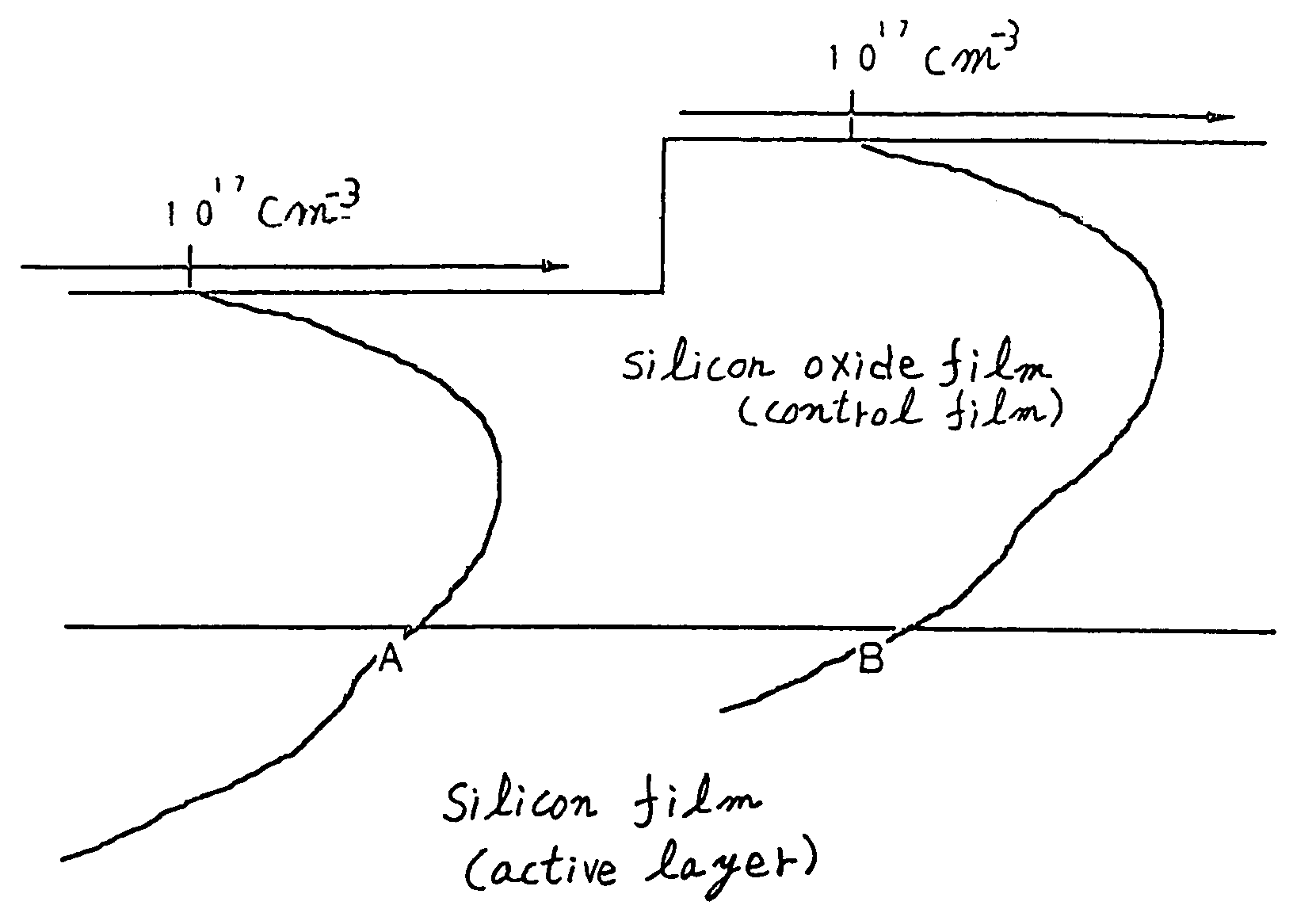
A TFT having a high threshold voltage is connected to the source electrode of each TFT that constitutes a CMOS circuit. In another aspect, pixel thin-film transistors are constructed such that a thin-film transistor more distant from a gate line drive circuit has a lower threshold voltage. In a further aspect, a control film that is removable in a later step is formed on the surface of the channel forming region of a TFT, and doping is performed from above the control film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7348227B1Eliminate differencesReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
A TFT having a high threshold voltage is connected to the source electrode of each TFT that constitutes a CMOS circuit. In another aspect, pixel thin-film transistors are constructed such that a thin-film transistor more distant from a gate line drive circuit has a lower threshold voltage. In a further aspect, a control film that is removable in a later step is formed on the surface of the channel forming region of a TFT, and doping is performed from above the control film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
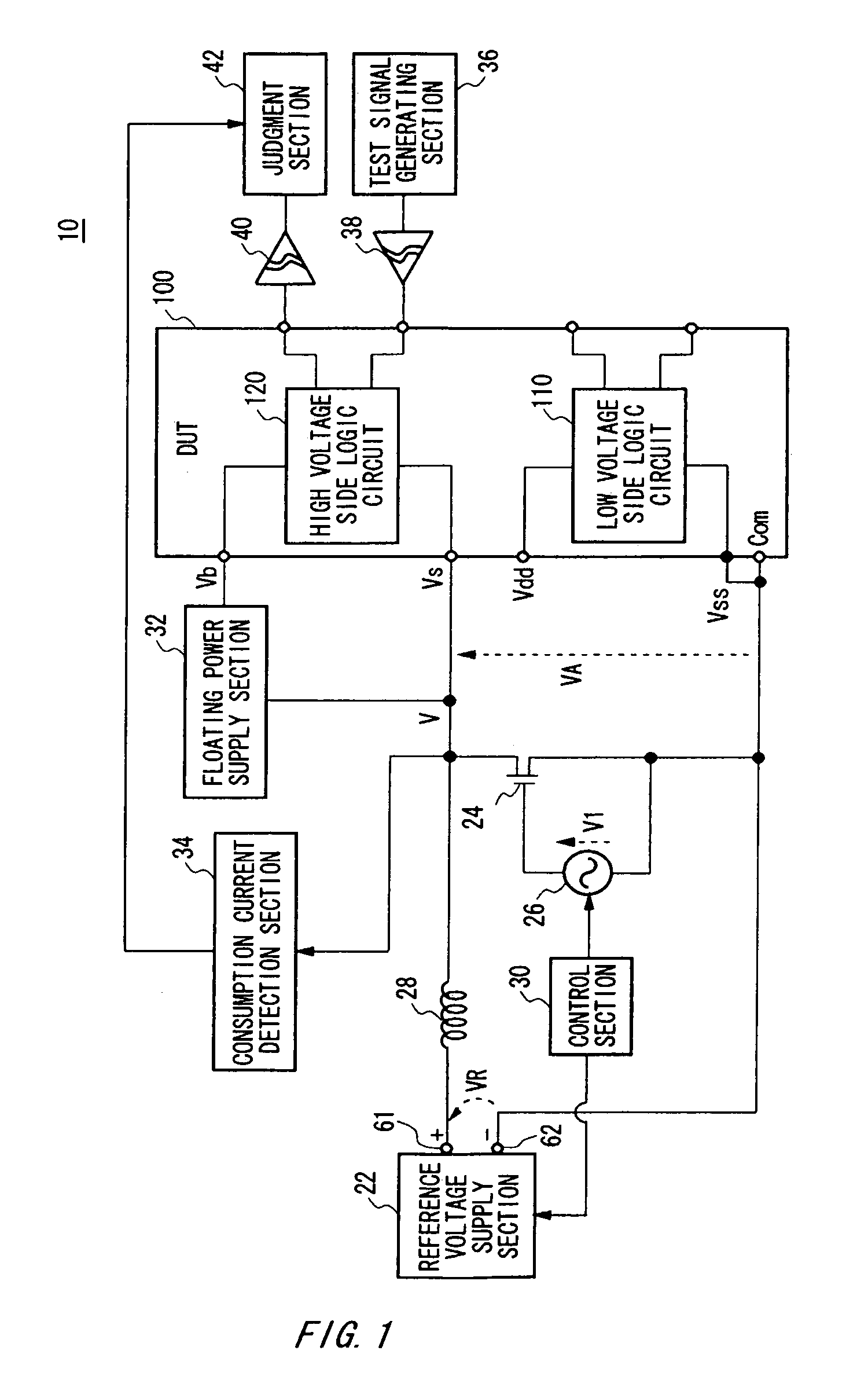
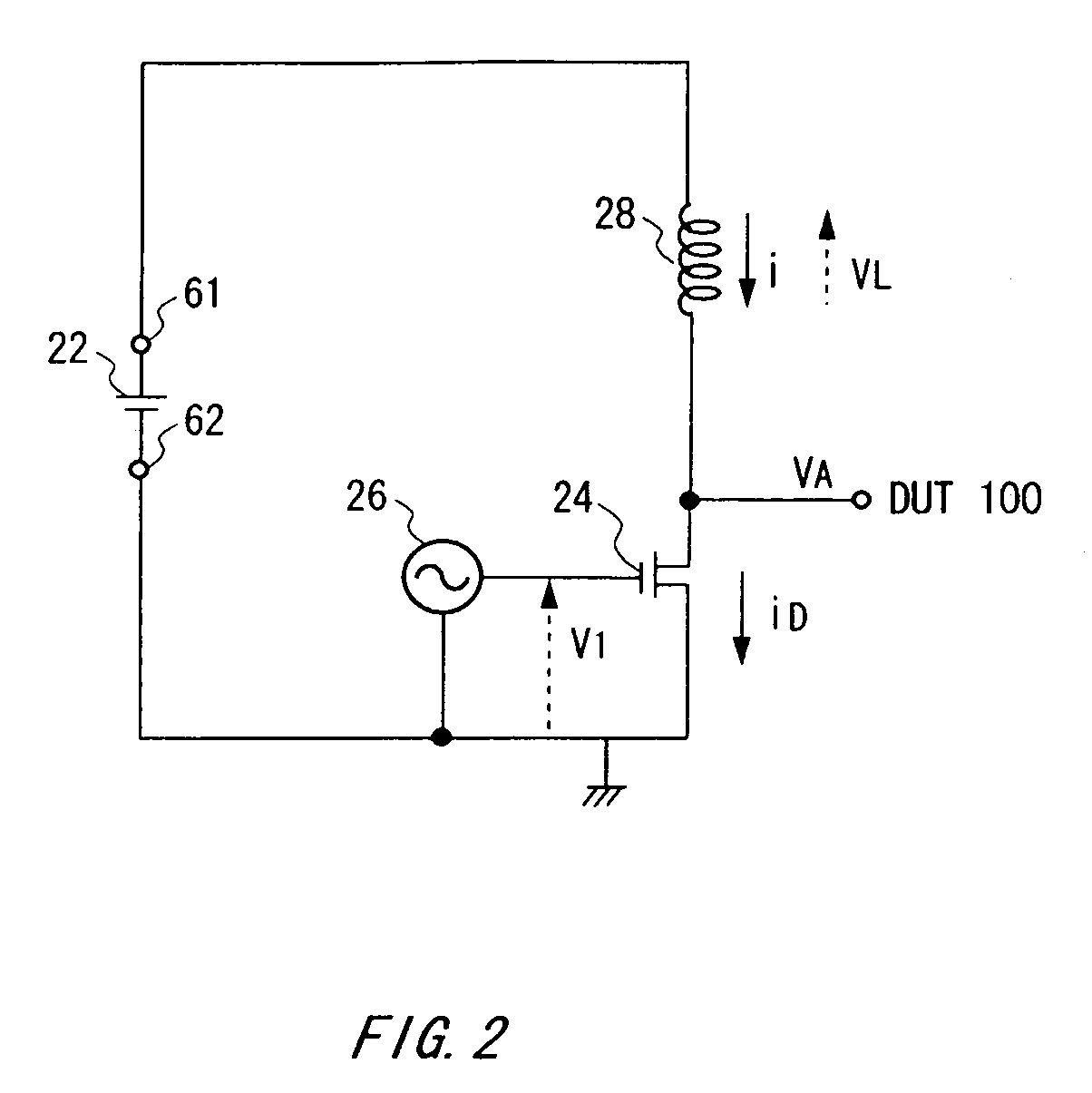
Test apparatus and test method
ActiveUS7298150B2Lower gate voltageHigh power supply voltageFault locationIndividual semiconductor device testingVoltage referenceTest fixture
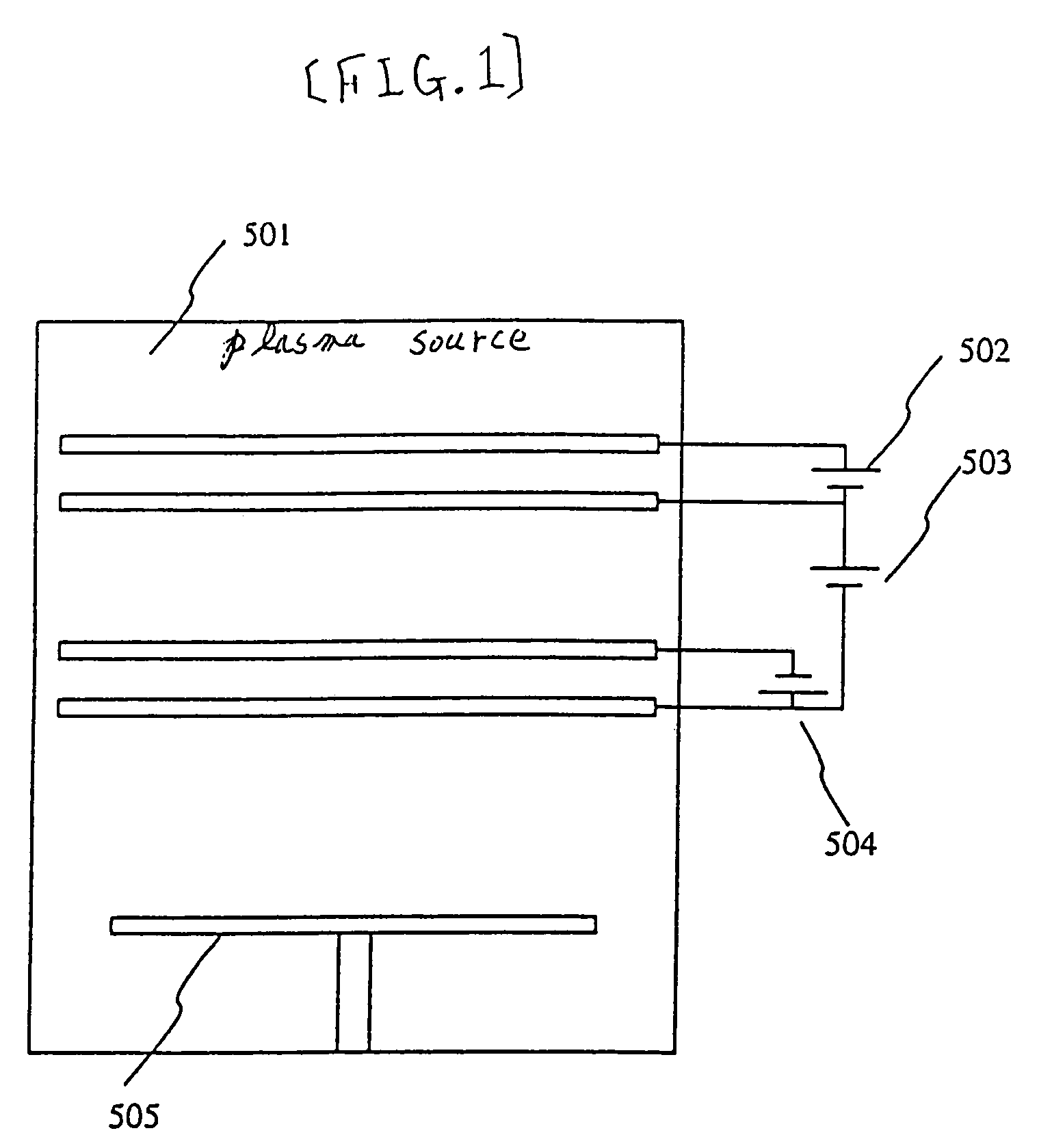
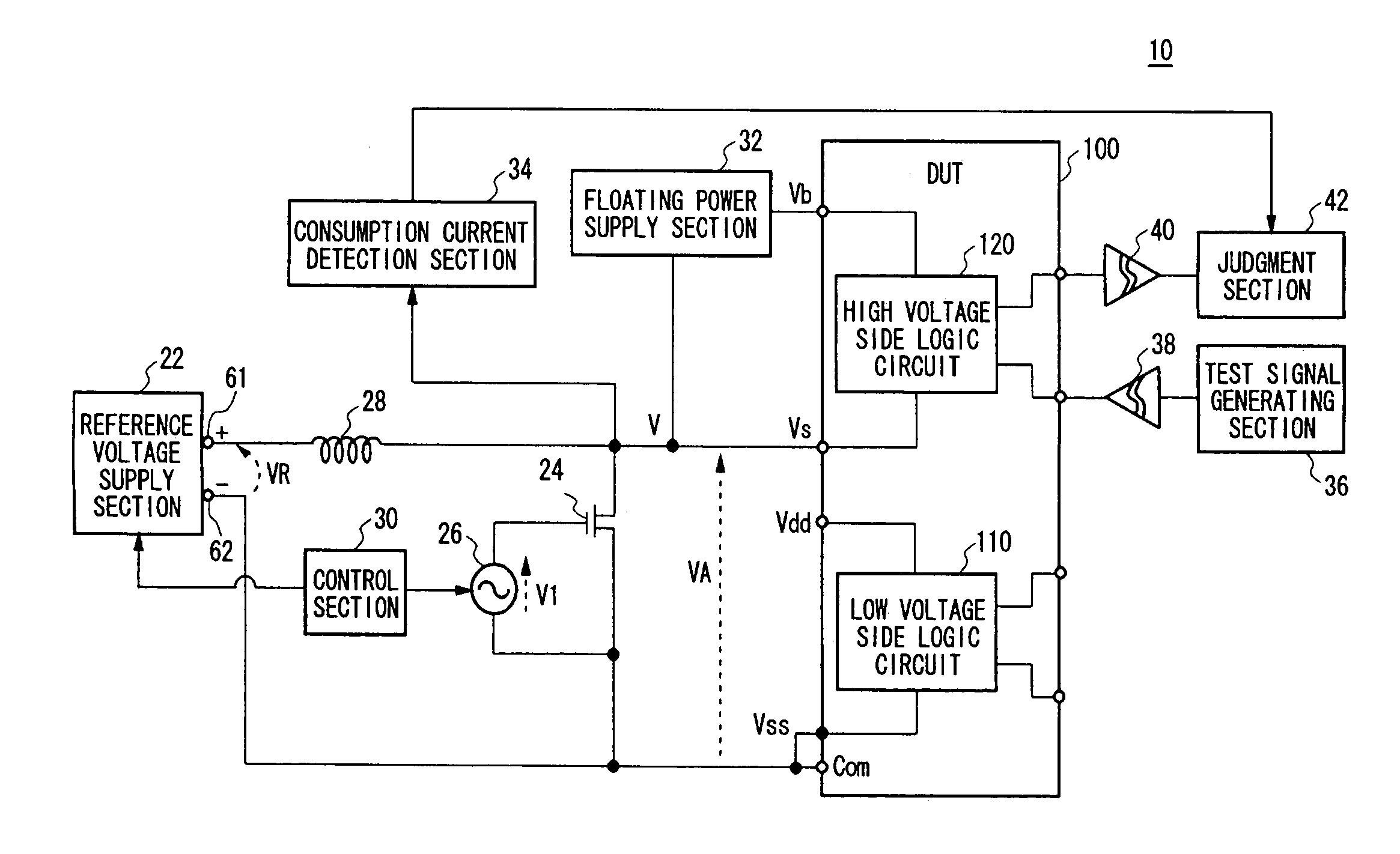
Change in power supply voltage supplied to a device under test is controlled. There is provided a test apparatus for testing a device under test, the test apparatus including: a reference voltage supply section for supplying a reference voltage; a field effect transistor provided between a positive side terminal and a negative side terminal of the reference voltage supply section, so that a drain terminal and a source terminal of the field effect transistor are in parallel connection with the device under test; an inductance that is connected between the positive side terminal and the negative side terminal of the reference voltage supply section, the inductance being in serial connection with the device under test between a positive-side power supply terminal and a negative-side power supply terminal of the device under test, and being in serial connection with the field effect transistor between the drain terminal and the source terminal of the field effect transistor; a control section for controlling a gate voltage of the field effect transistor, thereby changing a power supply voltage to be supplied to the device under test; and a judgment section for judging quality of the device under test, based on characteristic of the device under test in accordance with change in the power supply voltage.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Low drop-out linear voltage stabilizer and regulation circuit thereof
InactiveCN103076835AQuick responseStable output voltageElectric variable regulationOxide semiconductorN channel
The invention discloses a low drop-out linear voltage stabilizer and a regulation circuit thereof. The low drop-out linear voltage stabilizer comprises a first PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor, a second PMOS transistor, a third PMOS transistor, a first NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor and a first current source, wherein the grid electrode of the first PMOS transistor is connected with the drain electrode of the third PMOS transistor and the drain electrode of the first NMOS transistor; first voltage is input into the source electrode of the first PMOS transistor; the drain electrode is connected with the source electrode of the second PMOS transistor; the drain electrode of the first PMOS transistor is suitable to connect with the output end of the low drop-out linear voltage stabilizer; the grid electrode of the second PMOS transistor is suitable to connect with the output end of an error amplifier or buffer unit of the low drop-out linear voltage stabilizer; the drain electrode of the second PMOS transistor is connected with the source electrode of the first NMOS transistor and the first end of first current source; second voltage is input into the grid electrode of the third PMOS transistor, and the first voltage is input into the source electrode of the third PMOS transistor; the first voltage is input to the grid electrode of the first NMOS transistor; the second voltage is input into the second end of the first current source; and the voltage value of the first voltage is more than the voltage value of the second voltage.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Protection circuit for power management semiconductor devices and power converter having the protection circuit
ActiveUS7295412B2Early detectionFailure can be detectedElectric devicesElectronic switchingDriver circuitOvervoltage
A collector voltage of a power management semiconductor device is detected by a first comparator, and when the detected collector voltage exceeds a first reference voltage, the first comparator outputs a first detection signal. Furthermore, a gate voltage of the power management semiconductor device is detected by a second comparator, and when the detected gate voltage exceeds a second reference voltage, the second comparator outputs a second detection signal. The second reference voltage is a minimum gate voltage for feeding a rated power to the power management semiconductor device or over, and less than a line power voltage of a drive circuit of the power management semiconductor device. When both the first detection signal and second detection signal are being outputted, the gate voltage is reduced by a gate voltage reduction means so as to protect the power management semiconductor device from overcurrent and overvoltage.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
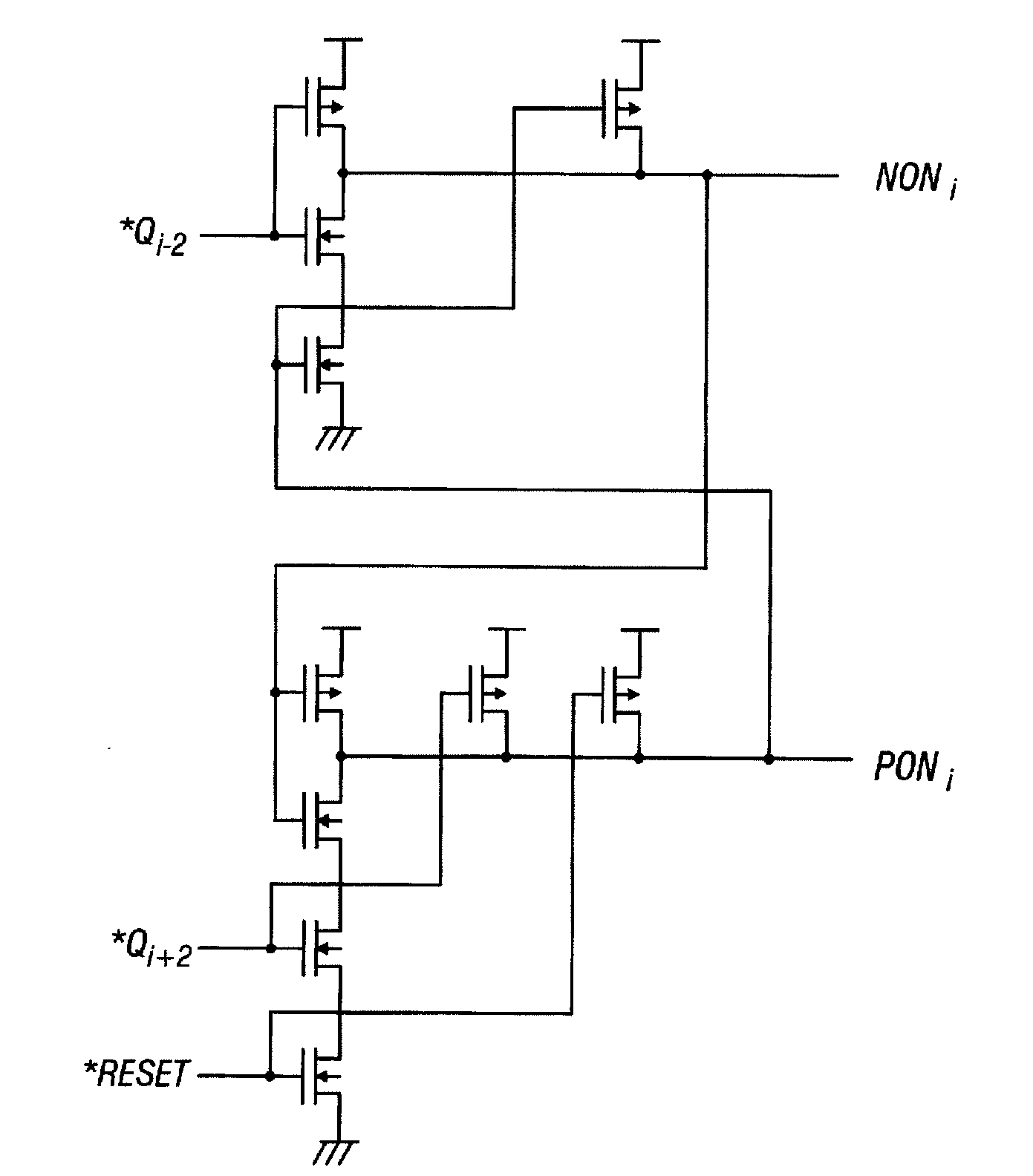
Pixel circuit
InactiveUS7825880B2Lower gate voltageInhibit currentElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesScan lineControl signal
A pixel circuit is disposed where a scan line arranged in a row direction to supply a control signal and a data line arranged in a column direction to supply a video signal intersect each other. The pixel circuit includes: a sampling transistor; a drive transistor; a capacitor connected between the current path end of the sampling transistor and the gate of the drive transistor; and a light-emitting device connected to the current path end of the drive transistor. The pixel circuit connects the mobility with negative feedback during a mobility connection period.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor memory and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050190605A1Reduce the ratioGate voltage to be applied to the control gate can be decreasedTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerP type silicon
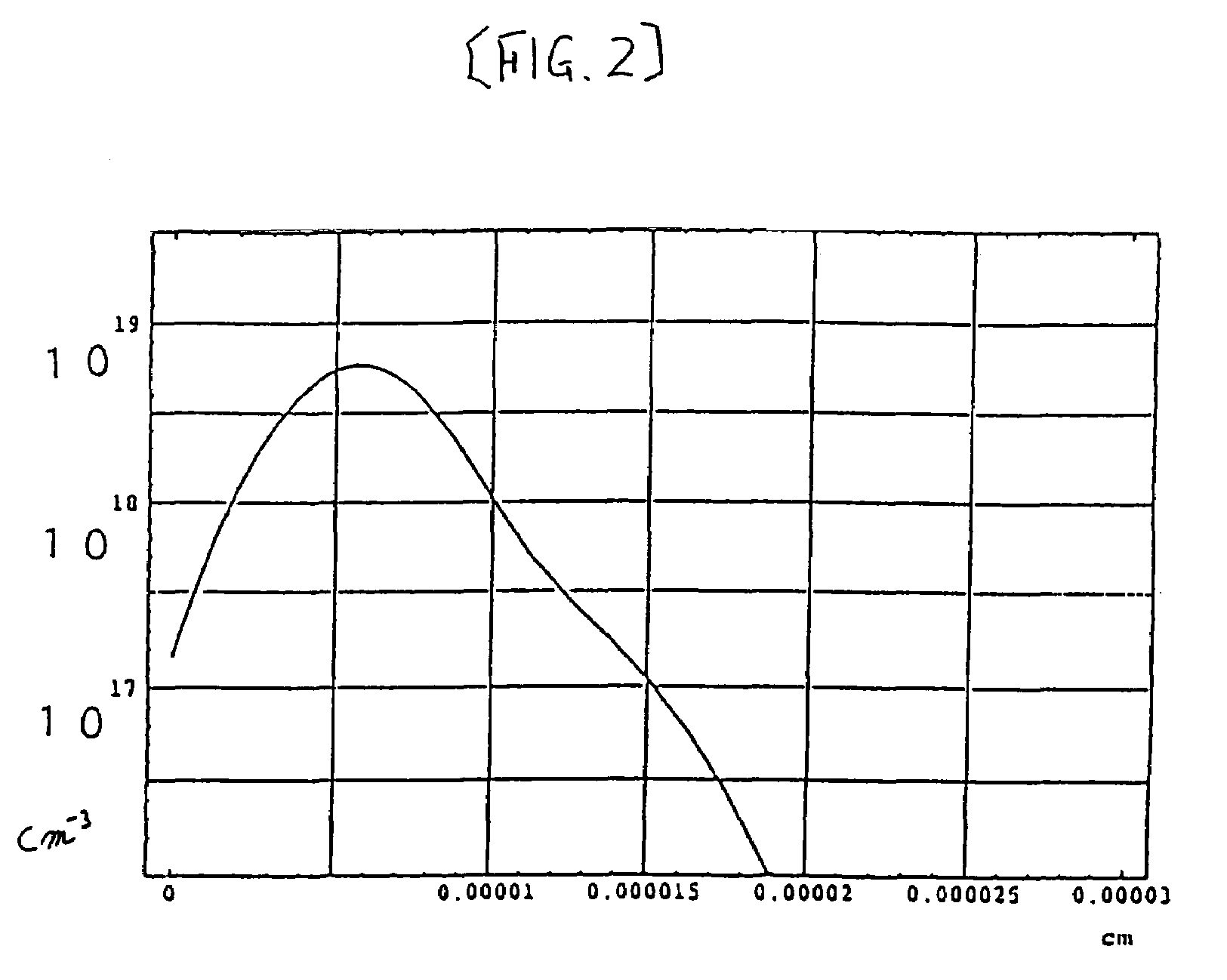
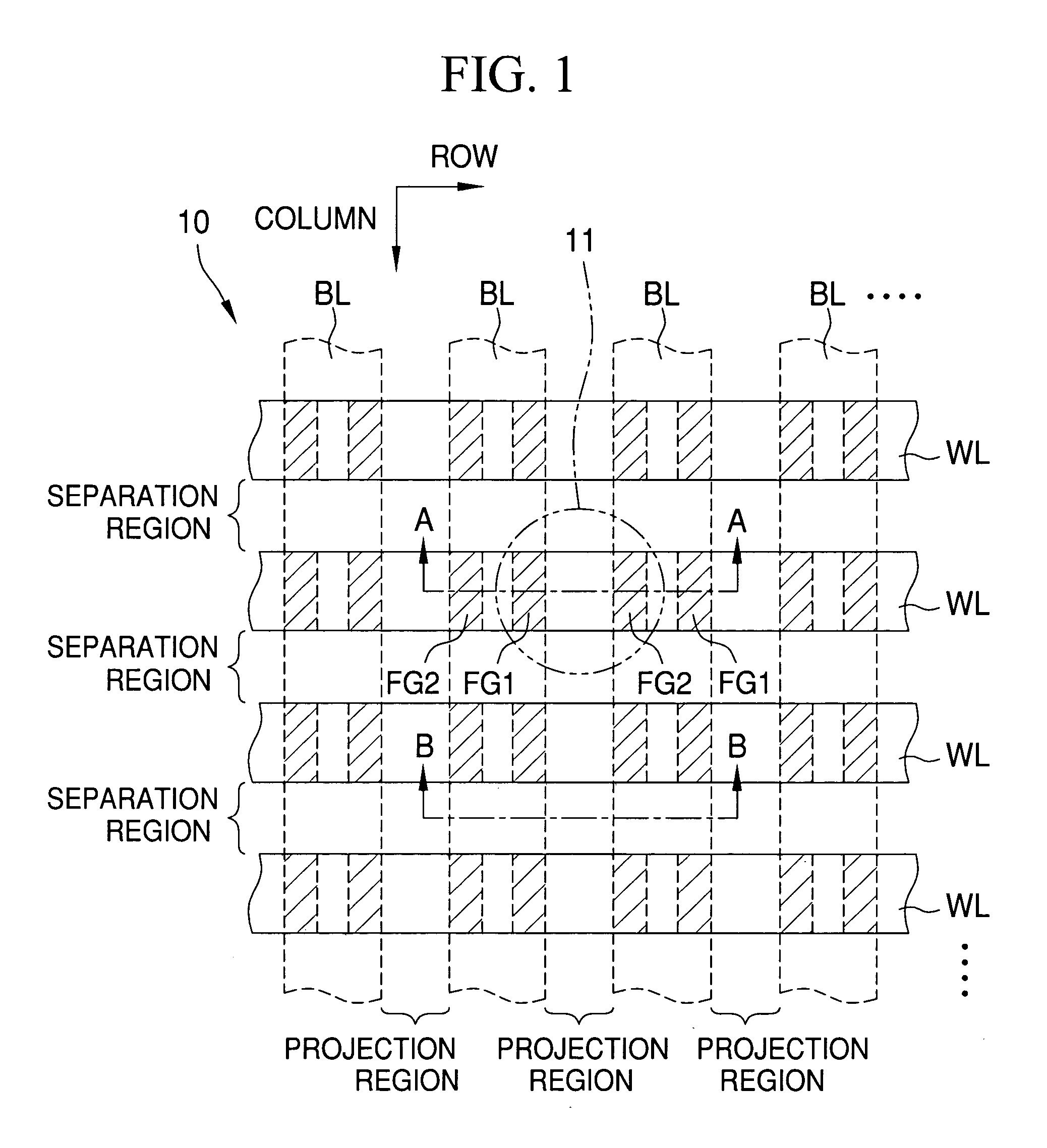
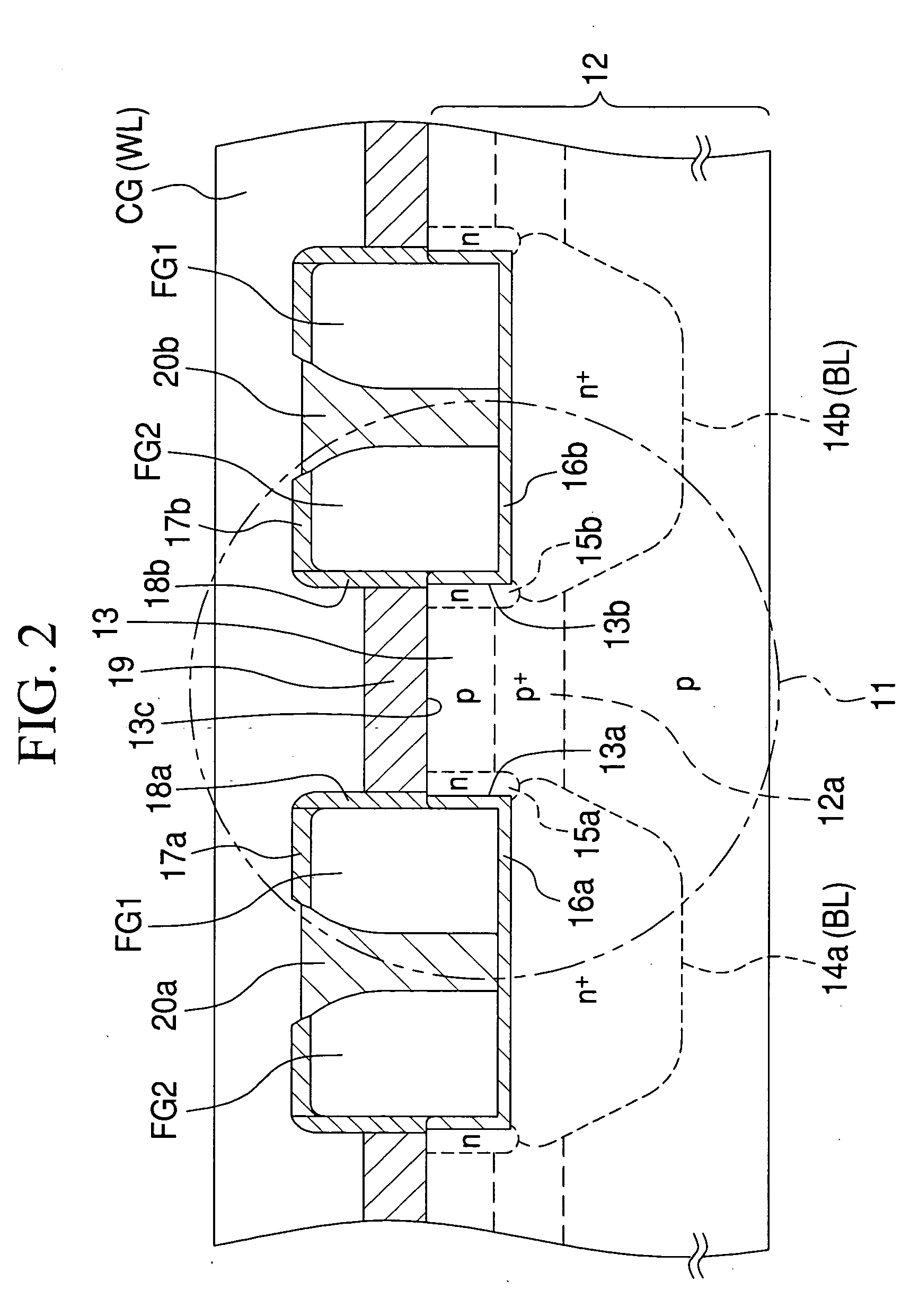
A semiconductor memory has plural cell transistors that are arranged in a matrix. The cell transistor comprises a silicon substrate, a control gate, a pair of electrically isolated floating gates. Plural projections are formed in the P type silicon substrate, and a pair of N type diffusion regions as the source and the drain is formed in both sides of the projection. The control gate faces the projection via a fourth insulation layer. The side surface of the floating gates faces the side surfaces of the projection via a first insulation layer, and faces the control gate via a third insulation layer. The floating gate faces the diffusion region via the first insulation layer.
Owner:INNOTECH CORP
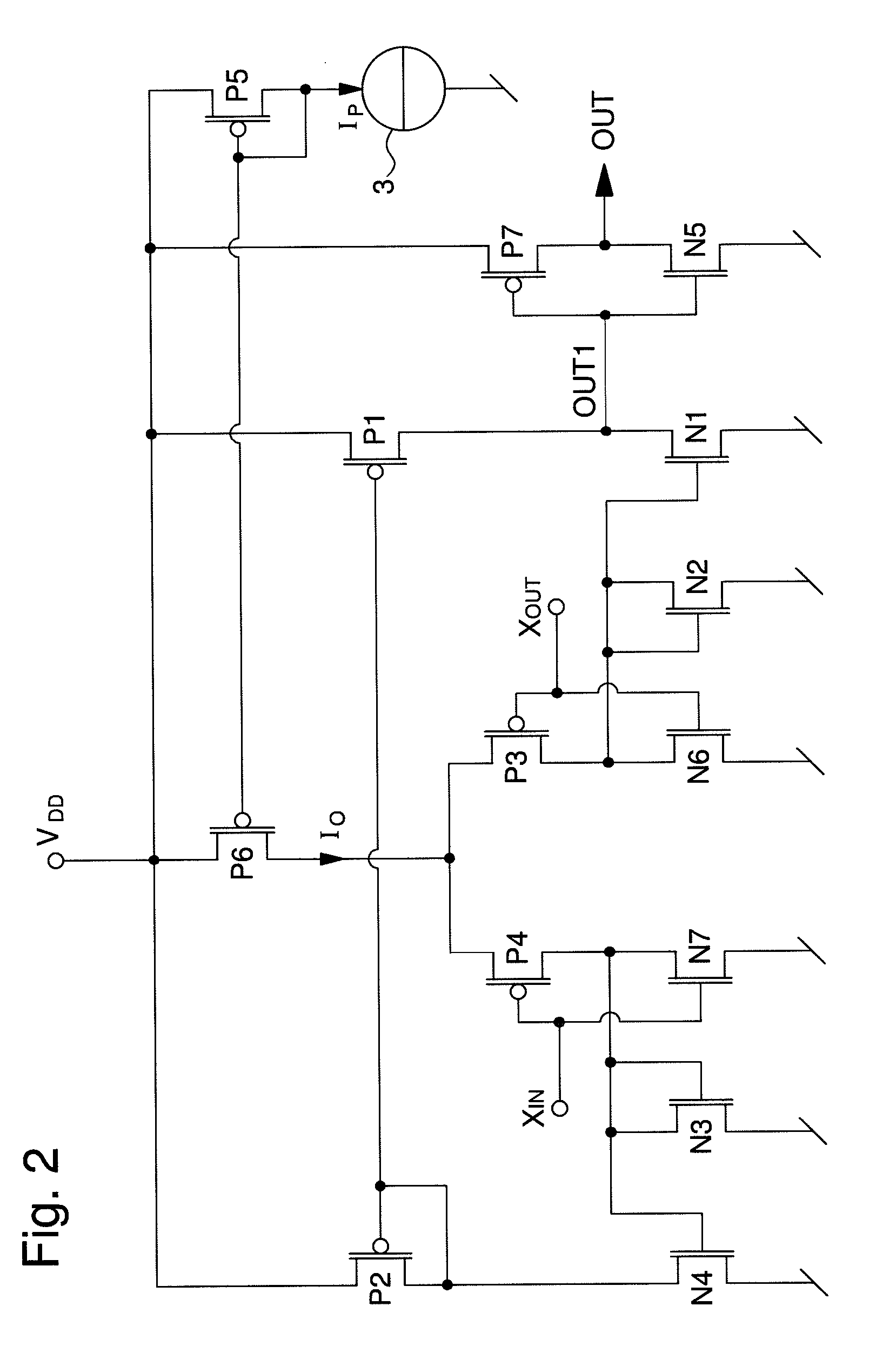
Low phase noise amplifier circuit
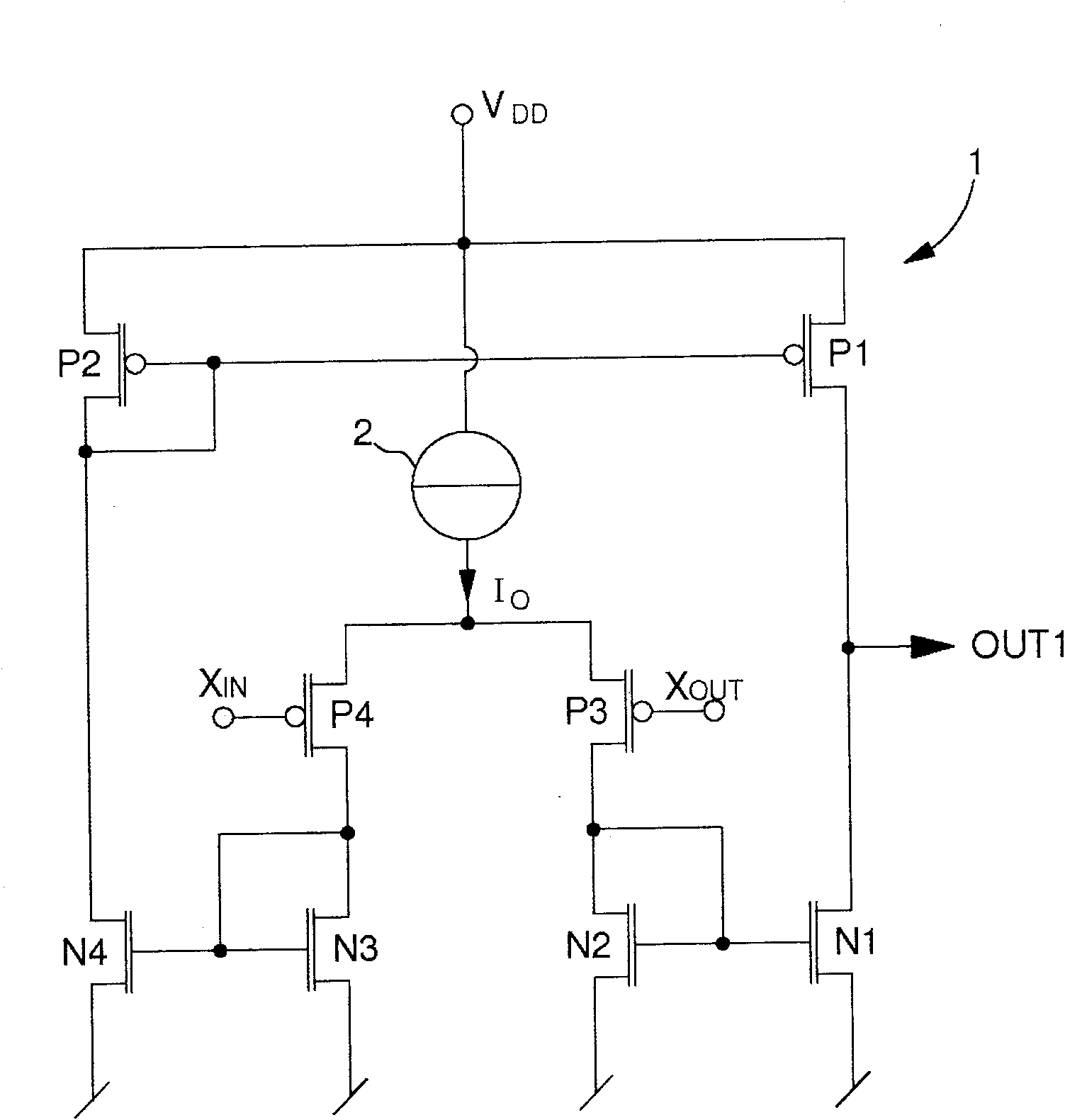
ActiveUS20100253433A1Simple processReduce noiseDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierPhase noise
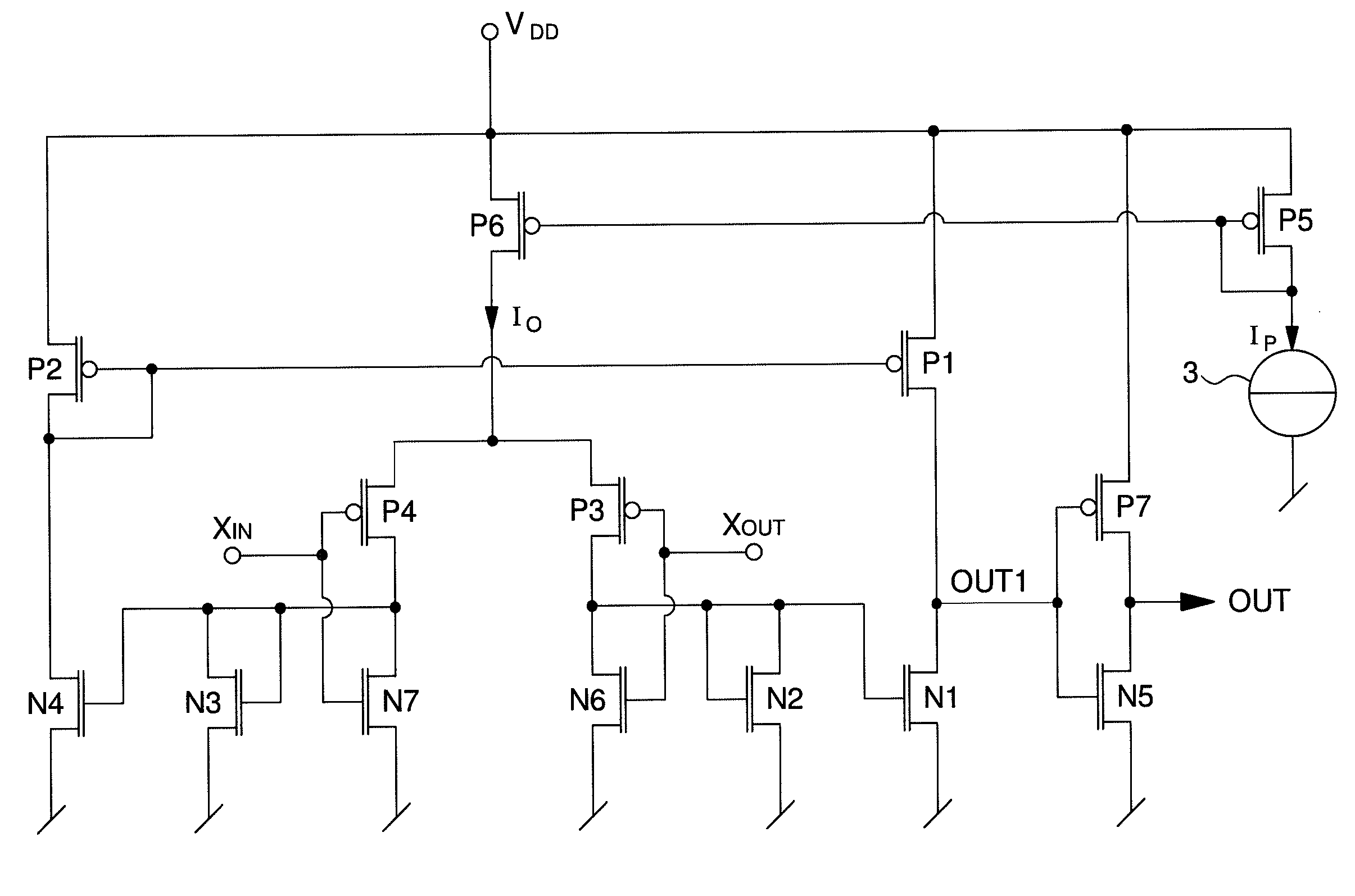
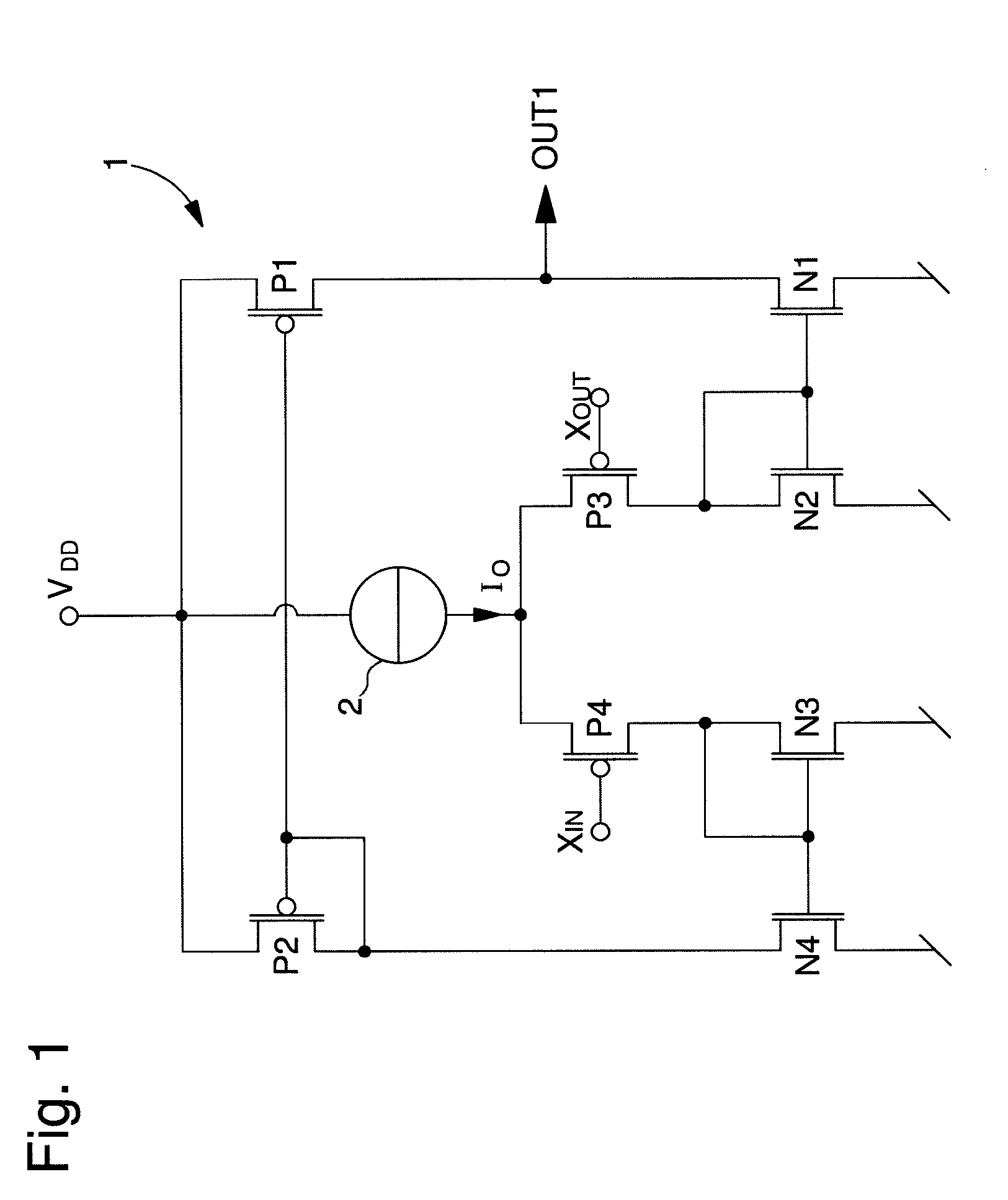
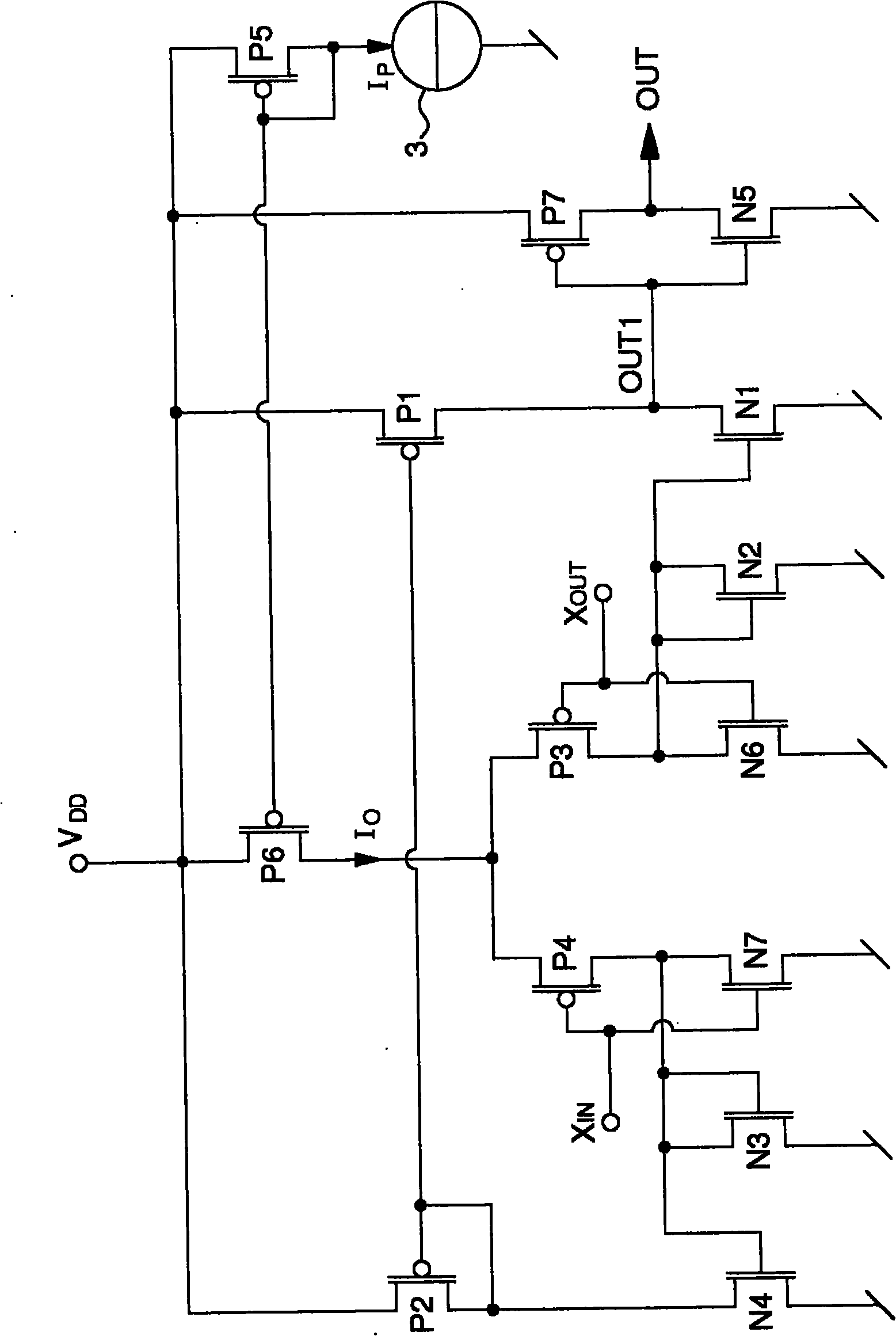
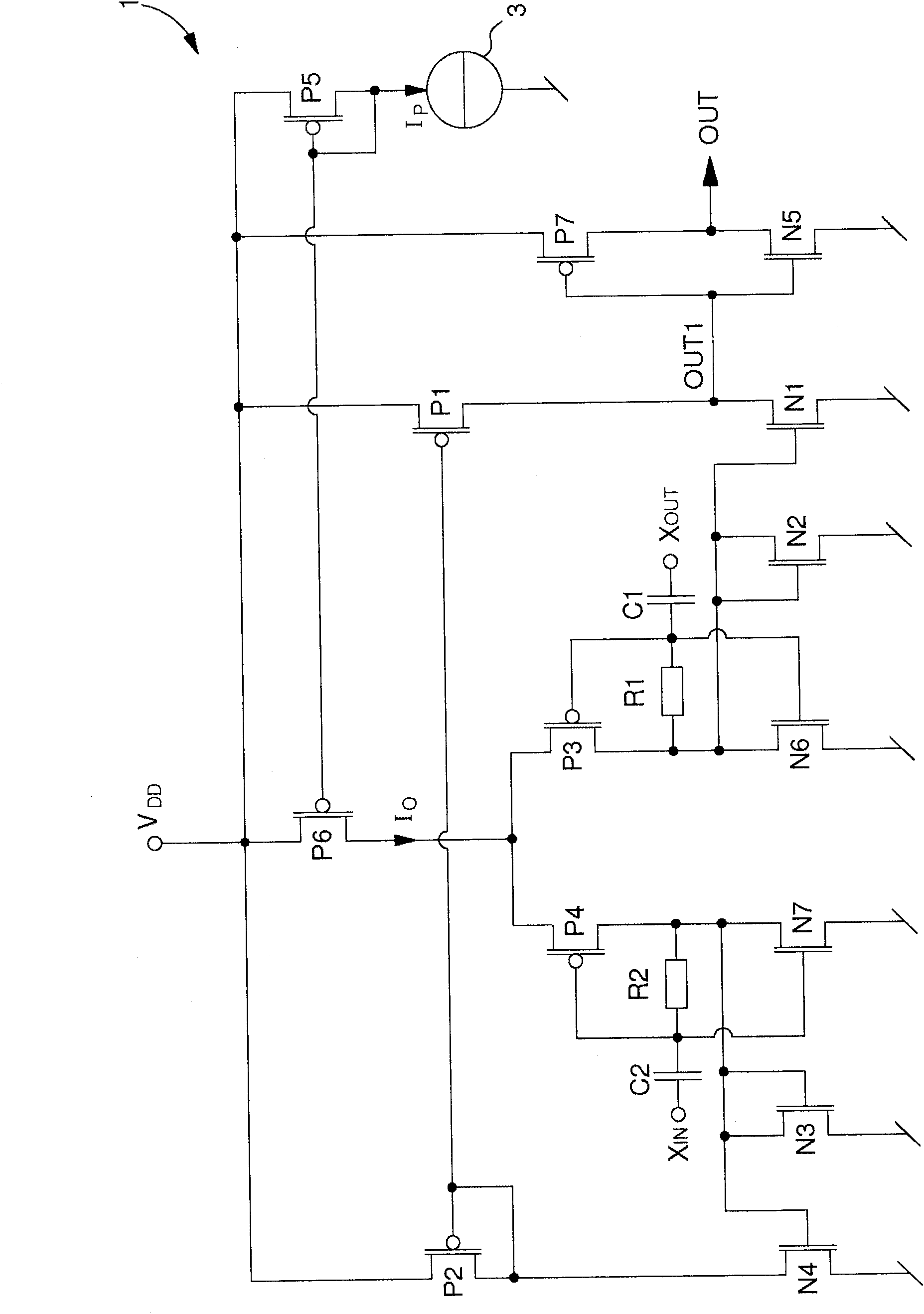
The amplifier circuit (1) includes a differential pair of PMOS transistors at input (P3, P4), whose source receives a current from a current source (3). The gate of the first transistor (P3) of the pair defines a non-inverting input (XOUT) and the gate of the second transistor (P4) of the pair defines an inverting input (XIN). A drain of the first transistor (P3) of the differential pair is connected to a diode connected NMOS transistor (N2) of a first current mirror (N1, N2), and a drain of the second transistor (P4) of the differential pair is connected to a diode connected NMOS transistor (N3) of a second current mirror (N3, N4). A diode connected PMOS transistor (P2) of a third current mirror is connected to the drain of a second NMOS transistor (N4) of the second current mirror, while a drain of a second PMOS transistor (P1) of the third current mirror is connected to the drain of a second NMOS transistor (N1) of the first current mirror to define a first output (OUT1), which is inverted by a reverser (N5, P7) to supply an inverted output signal (OUT) capable of varying rail to rail. A first complementary NMOS transistor (N6) is connected in the form of a reverser with the first PMOS transistor (P3) of the differential pair. A second complementary NMOS transistor (N7) is connected in the form of a reverser with the second MOS transistor (P4) of the differential pair.
Owner:THE SWATCH GRP RES & DEVELONMENT LTD
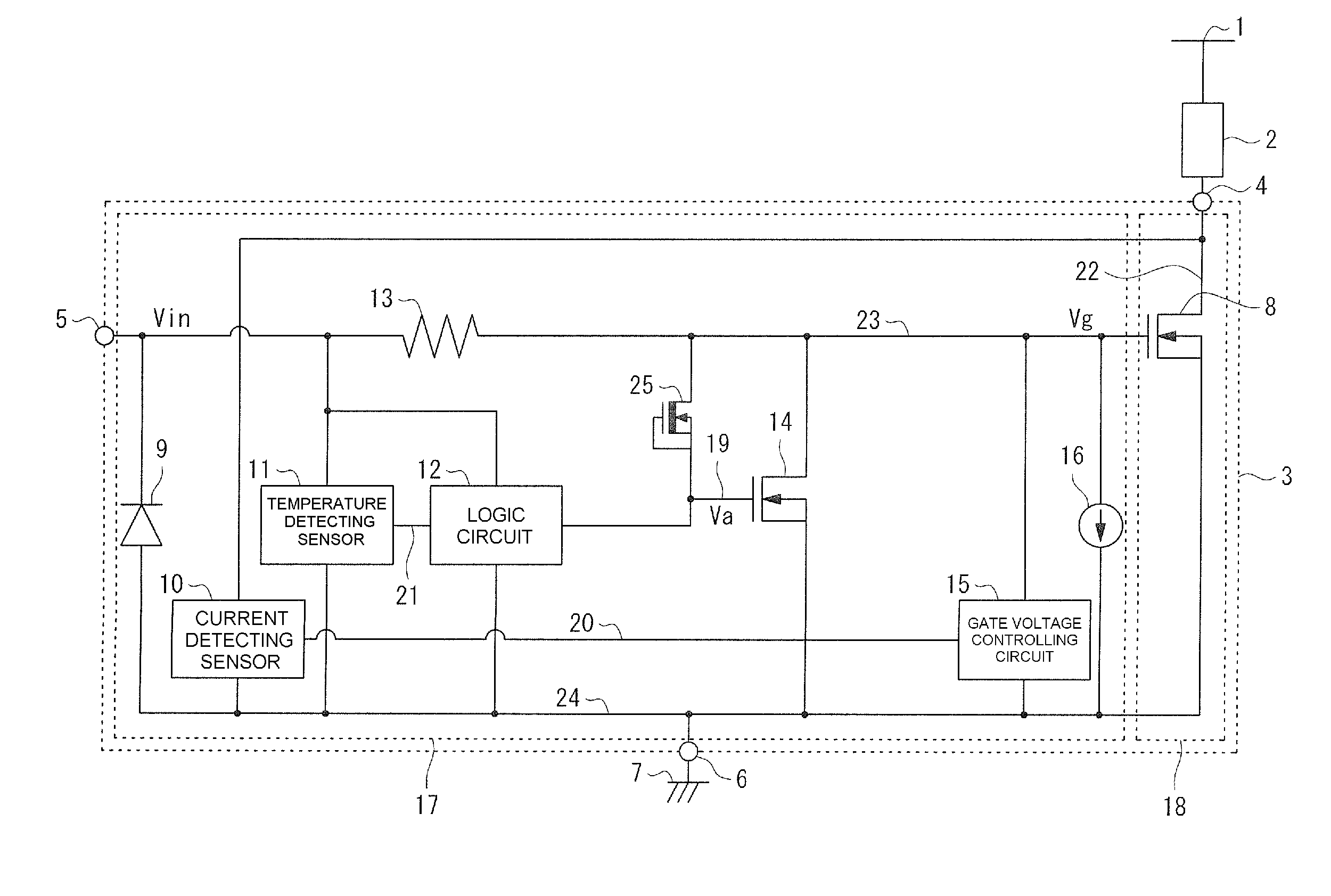
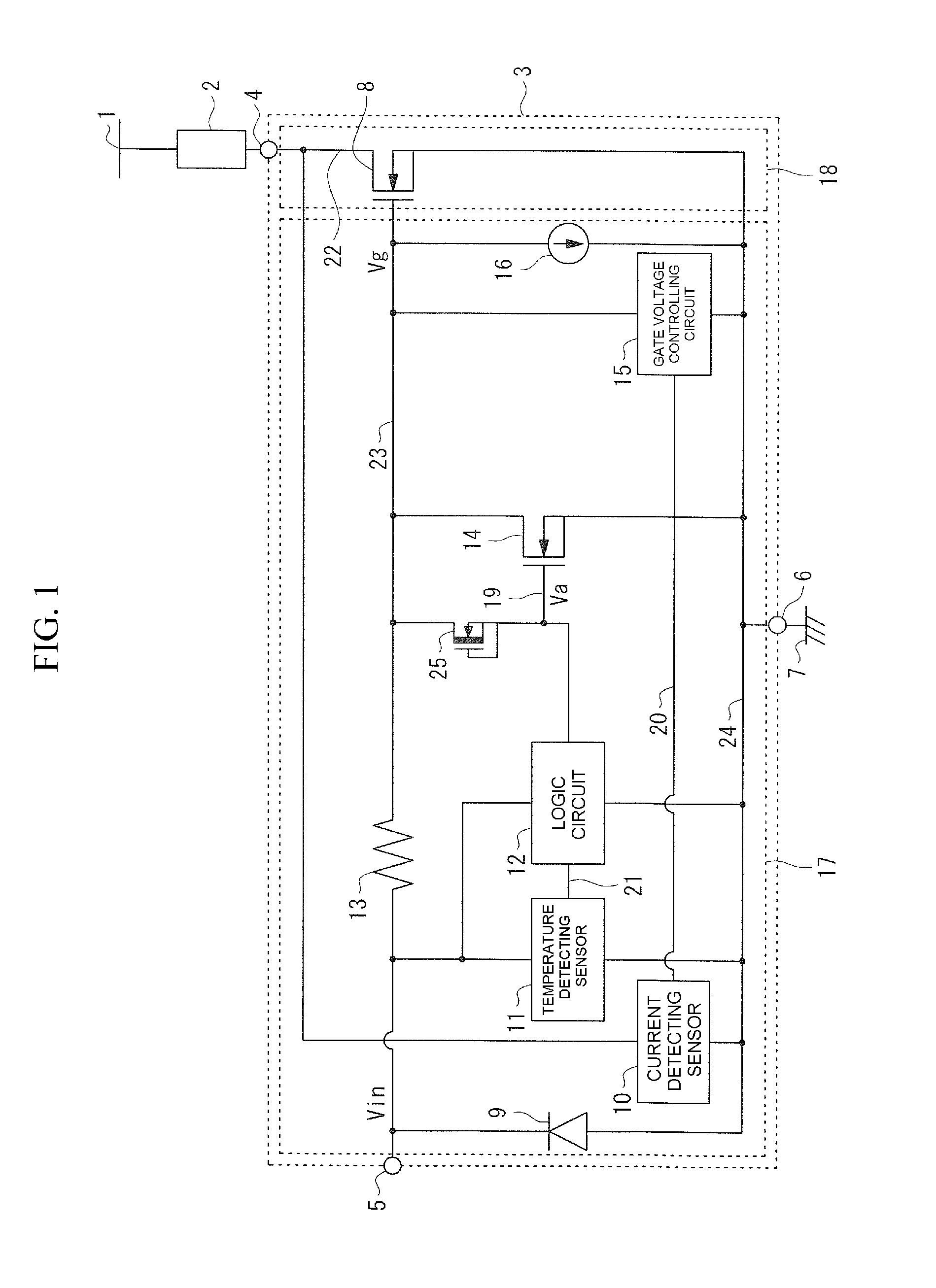
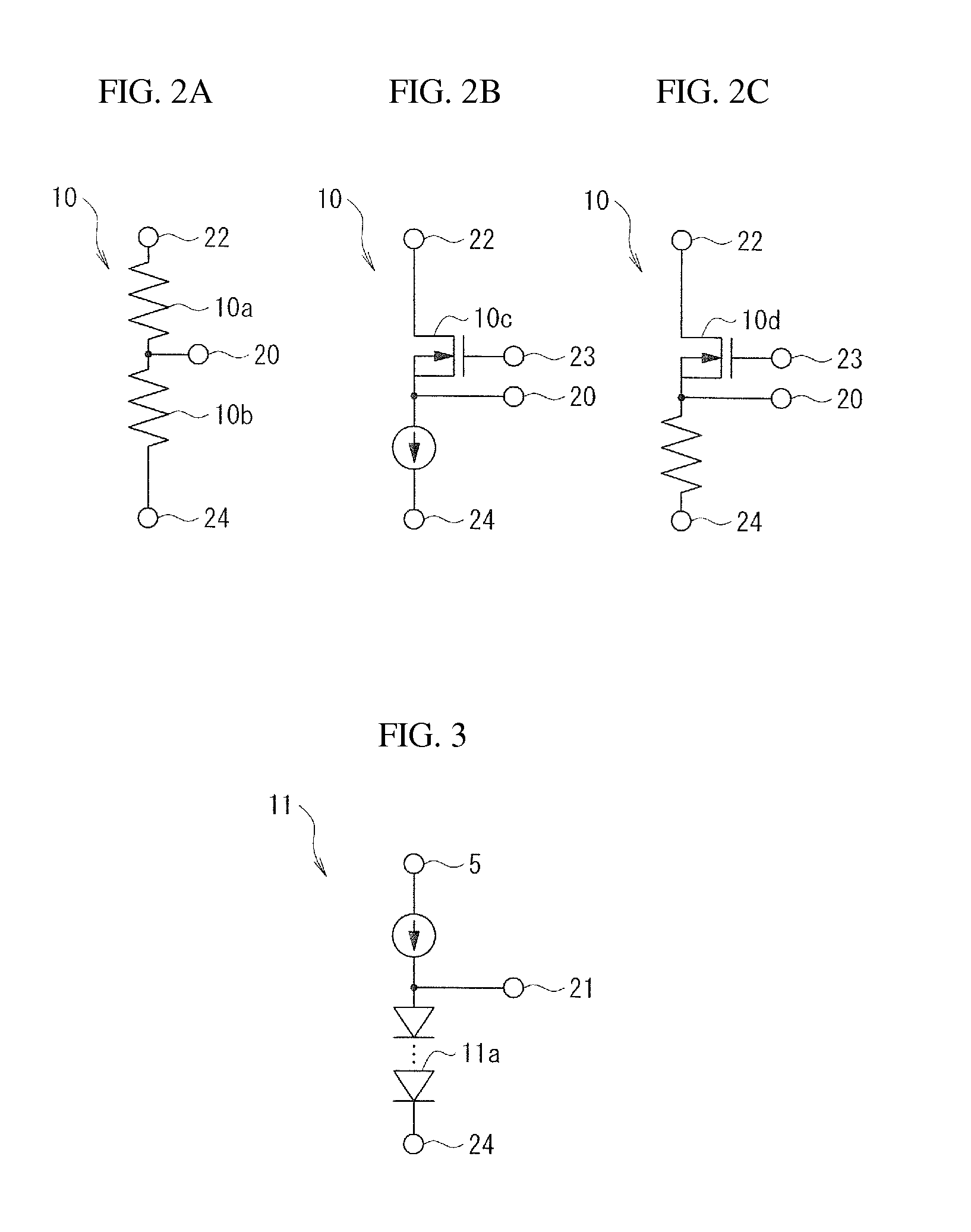
Driving circuit of insulated gate device
ActiveUS20120038392A1Prevention of faulty turning-onIncrease speedTransistorElectronic switchingParasitic capacitorPower flow
A driving circuit for driving an insulated gate semiconductor device based on a voltage of an externally-inputted gate signal, where the insulated gate semiconductor device has a source, a drain and a gate, and a parasitic capacitor exists between the drain and the gate. The driving circuit includes a gate voltage controlling semiconductor device disposed between, and connecting, the gate and the source of the insulated gate semiconductor device. The gate voltage controlling semiconductor device has a source and a gate, and is driven by a current charging the parasitic capacitor. The driving circuit also includes a pull-up device disposed between, and connecting, the source and the drain of the gate voltage controlling semiconductor device.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
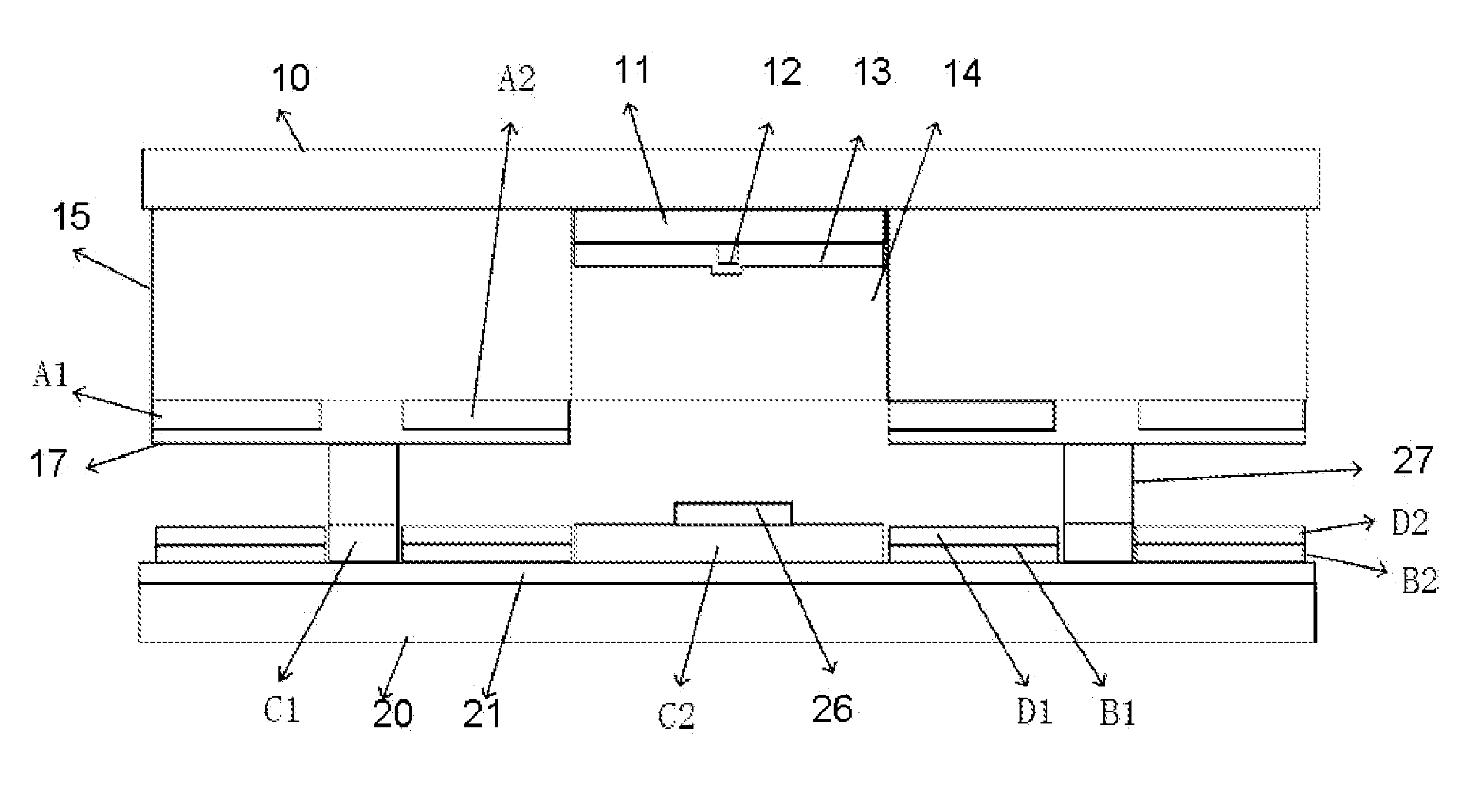
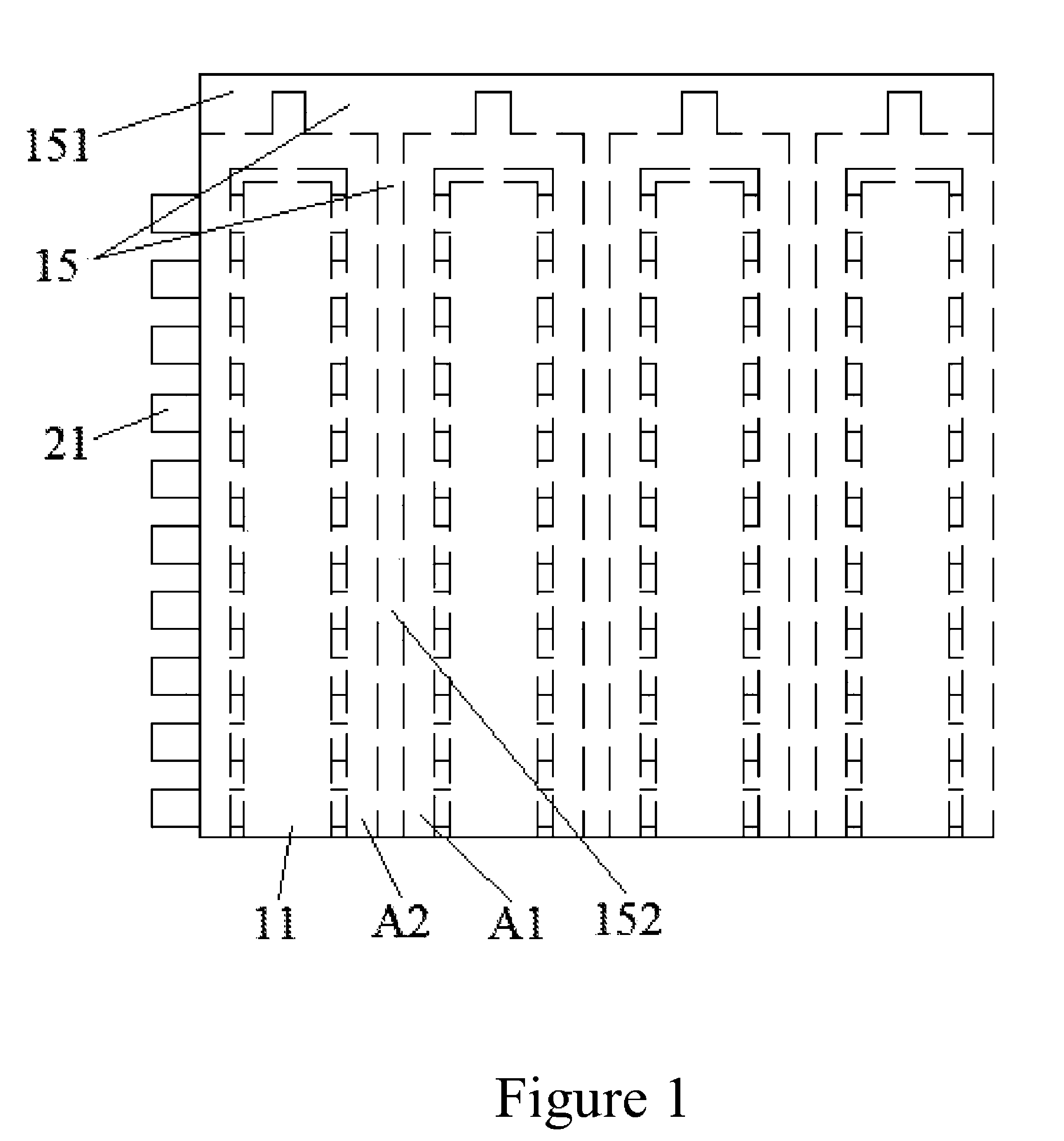
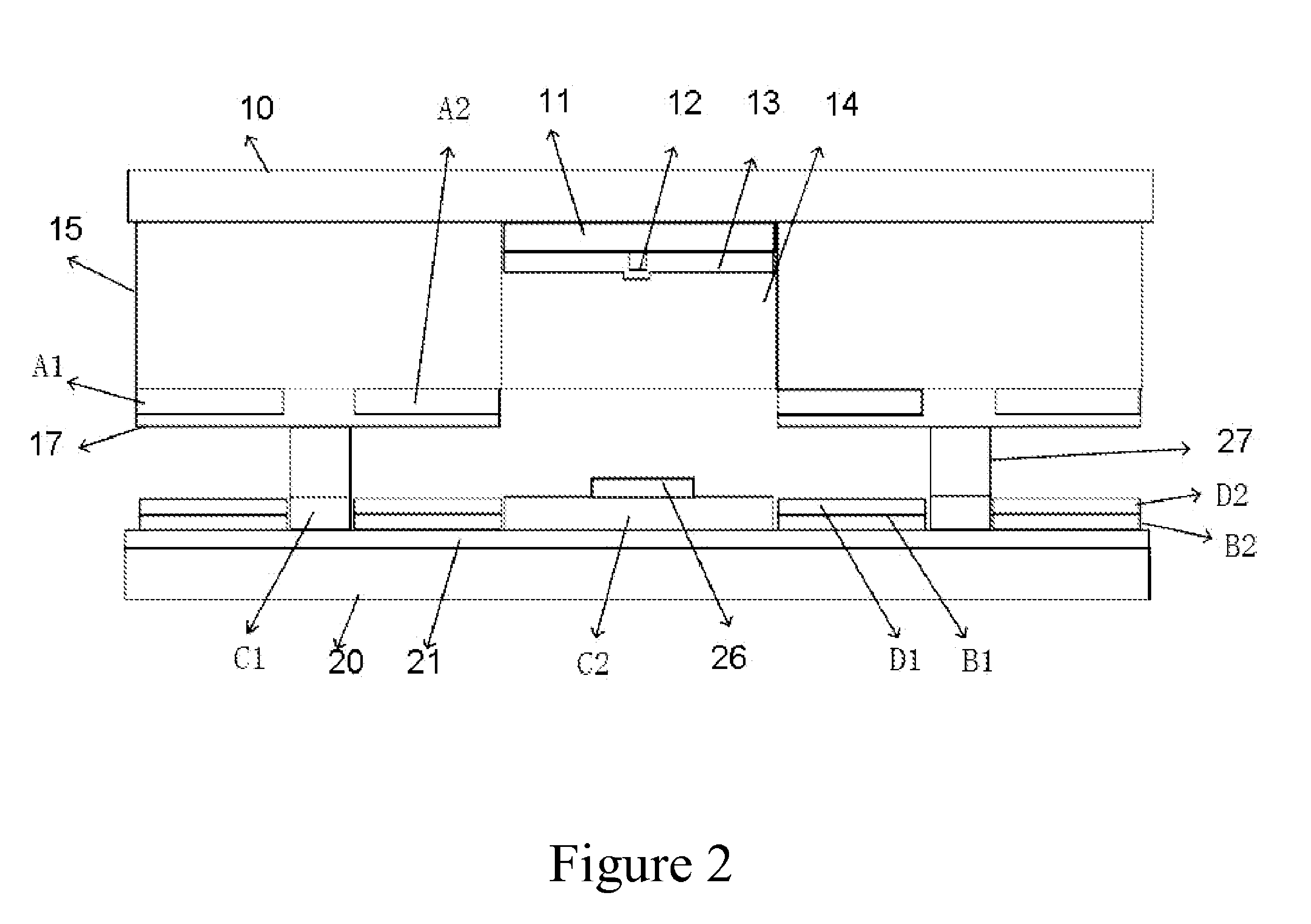
Symmetric quadrupole structured field emission display without spacer
ActiveUS20140111083A1Novel structureSimplify the manufacturing processDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesCurrent limitingPhosphor
The present invention relates to a symmetric quadrupole structured field emission display without spacer comprising the upper and under substrates with a dielectric layer in between, wherein comb-like dielectric layer with lateral connection belts and a number of longitudinal working belts and longitudinal anodes are arranged on the upper substrate, bus electrodes are arranged longitudinally along the center on each anode, on the top, longitudinal alternating phosphor layer and dielectric layer for isolation on anode, gate electrodes are arranged on both sides of each longitudinal work belts, with the bus electrode as symmetry center, forming interdigital gate electrodes, horizontal cathode electrodes and longitudinal auxiliary electrodes are on the under substrate, resistor layer for current limiting and dielectric layer for cathode protection are arranged alternating horizontally on each cathode electrode, each intersect of the auxiliary electrode and cathode is isolated by the dielectric layer for cathode
Owner:GUO TAILIANG +5
Amplifier circuit with reduced phase noise
ActiveCN101860332ALower gate voltageSignificant additional gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase noise
The amplifier circuit (1) includes a differential pair of PMOS transistors at input (P3, P4), whose source receives a current from a current source (3). The gate of the first transistor (P3) of the pair defines a non-inverting input (XOUT) and the gate of the second transistor (P4) of the pair defines an inverting input (XIN). A drain of the first transistor (P3) of the differential pair is connected to a diode connected NMOS transistor (N2) of a first current mirror (N1, N2), and a drain of the second transistor (P4) of the differential pair is connected to a diode connected NMOS transistor (N3) of a second current mirror (N3, N4). A diode connected PMOS transistor (P2) of a third current mirror is connected to the drain of a second NMOS transistor (N4) of the second current mirror, while a drain of a second PMOS transistor (P1) of the third current mirror is connected to the drain of a second NMOS transistor (N1) of the first current mirror to define a first output (OUT1), which is inverted by a reverser (N5, P7) to supply an inverted output signal (OUT) capable of varying rail to rail. A first complementary NMOS transistor (N6) is connected in the form of a reverser with the first PMOS transistor (P3) of the differential pair. A second complementary NMOS transistor (N7) is connected in the form of a reverser with the second MOS transistor (P4) of the differential pair.
Owner:THE SWATCH GRP RES & DEVELONMENT LTD
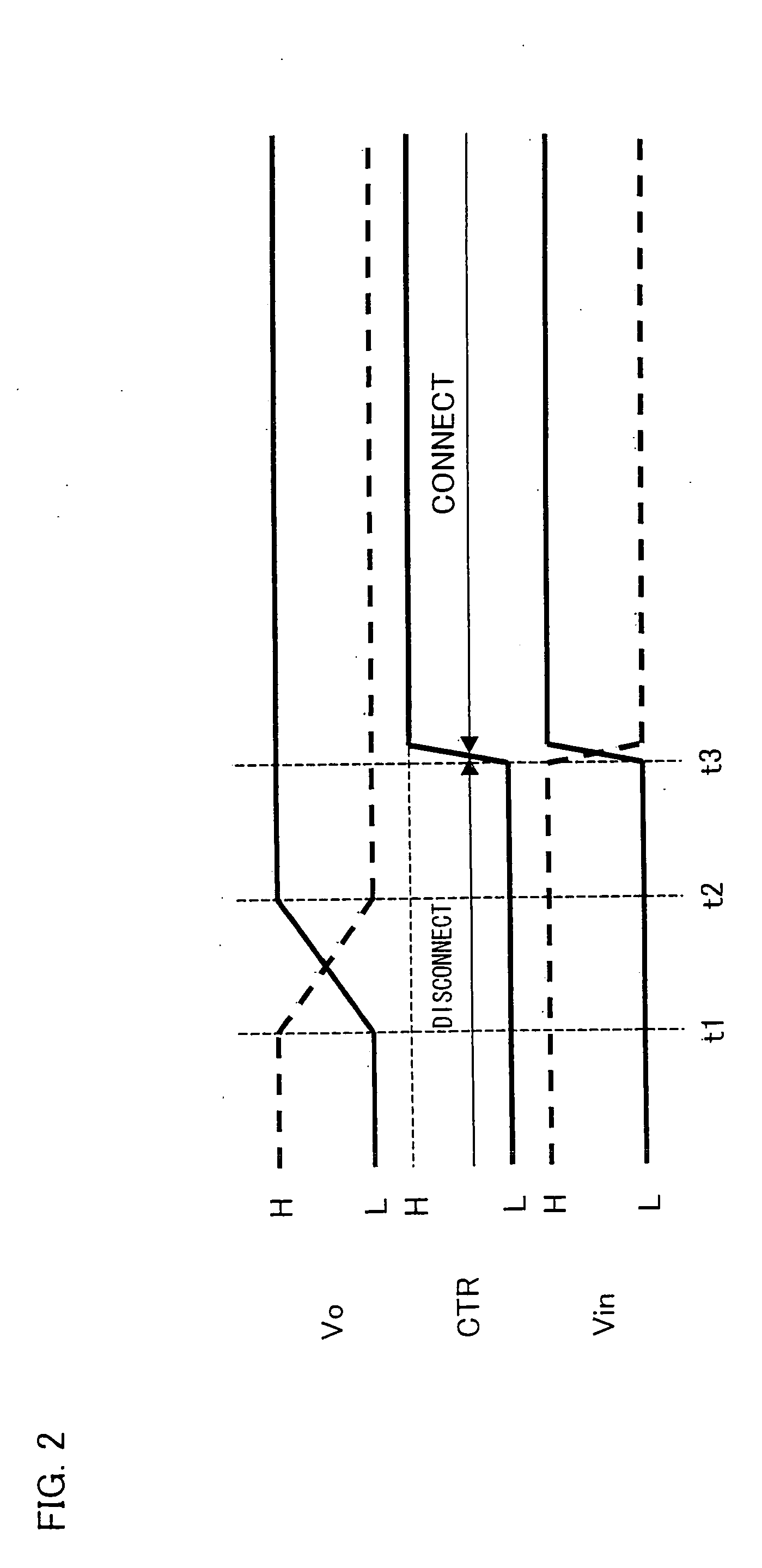
Display Device Driving Circuit, Data Signal Line Driving Circuit, and Display Device
InactiveUS20090167742A1Lower gate voltageHigh voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceData signal
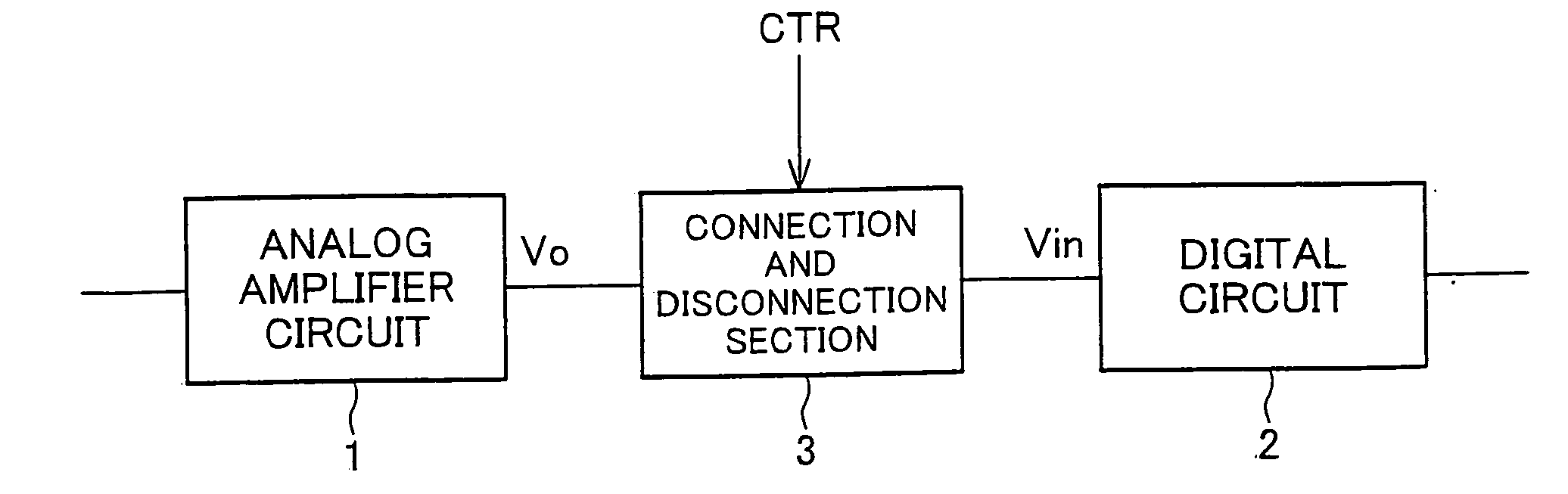
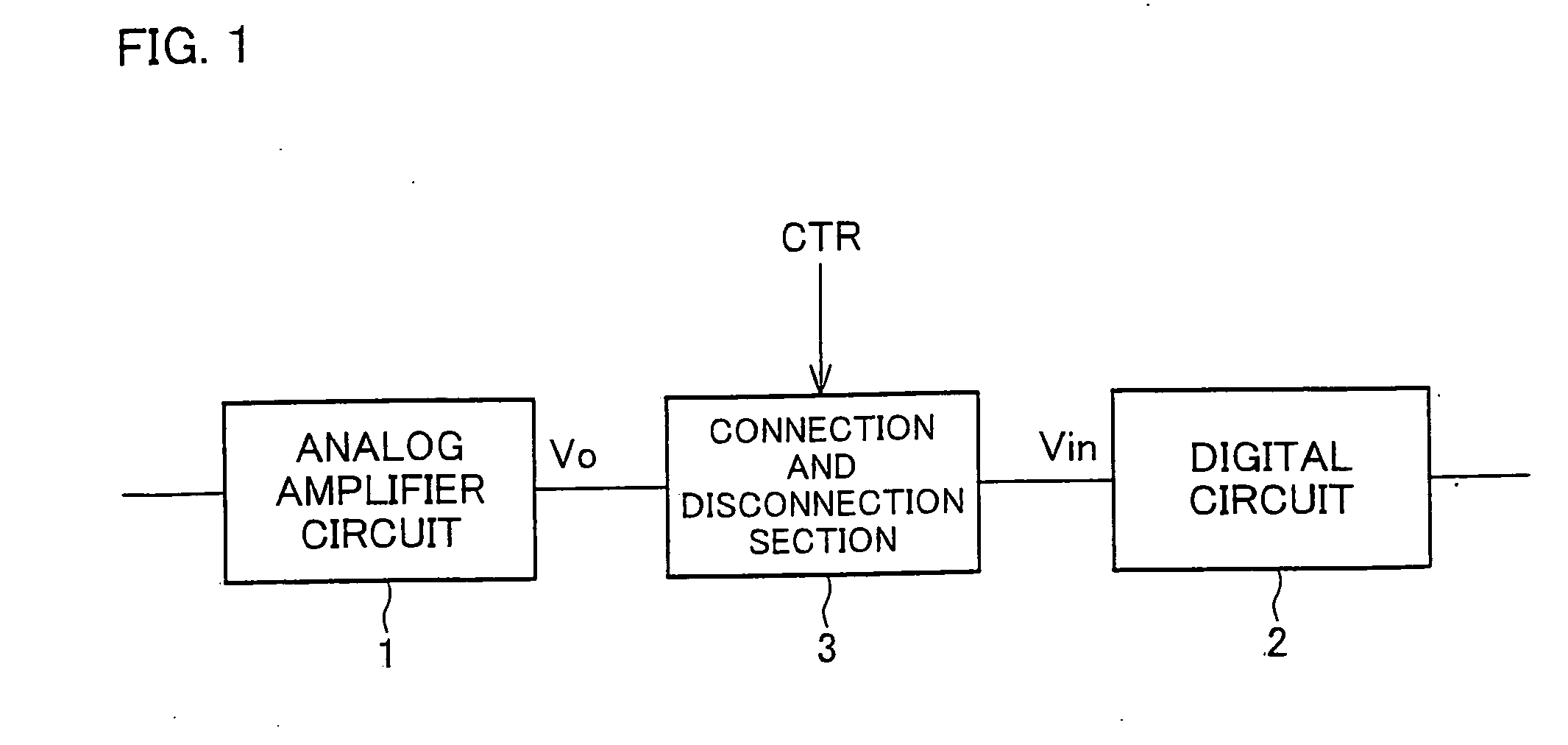
In one embodiment of the present invention, a driving circuit is disclosed of a display device, a connection and disconnection section is provided between an output of an analog amplifier circuit and an input of a digital circuit. The connection and disconnection section breaks an electrical connection between the output of the analog amplifier circuit and the input of the digital circuit until an output voltage of the analog amplifier circuit rises to a target DC level, and makes an electrical connection between the output of the analog amplifier circuit and the input of the digital circuit after the output voltage of the analog amplifier circuit has risen to the target DC level.
Owner:SHARP KK
Symmetric quadrupole structured field emission display without spacer
ActiveUS8803413B2Novel structureSimplify the manufacturing processControl electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensCurrent limitingPhosphor
Owner:GUO TAILIANG +5
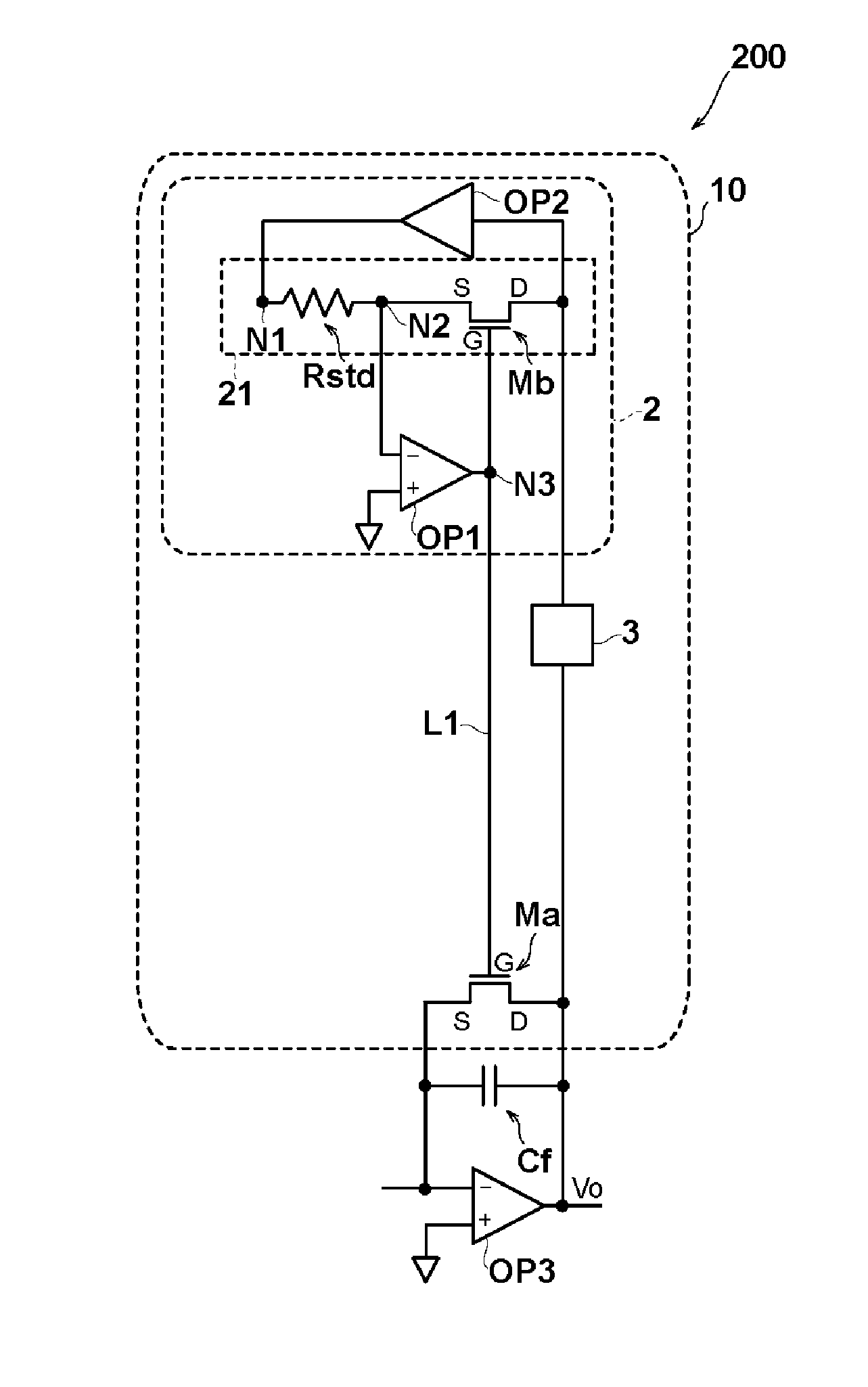
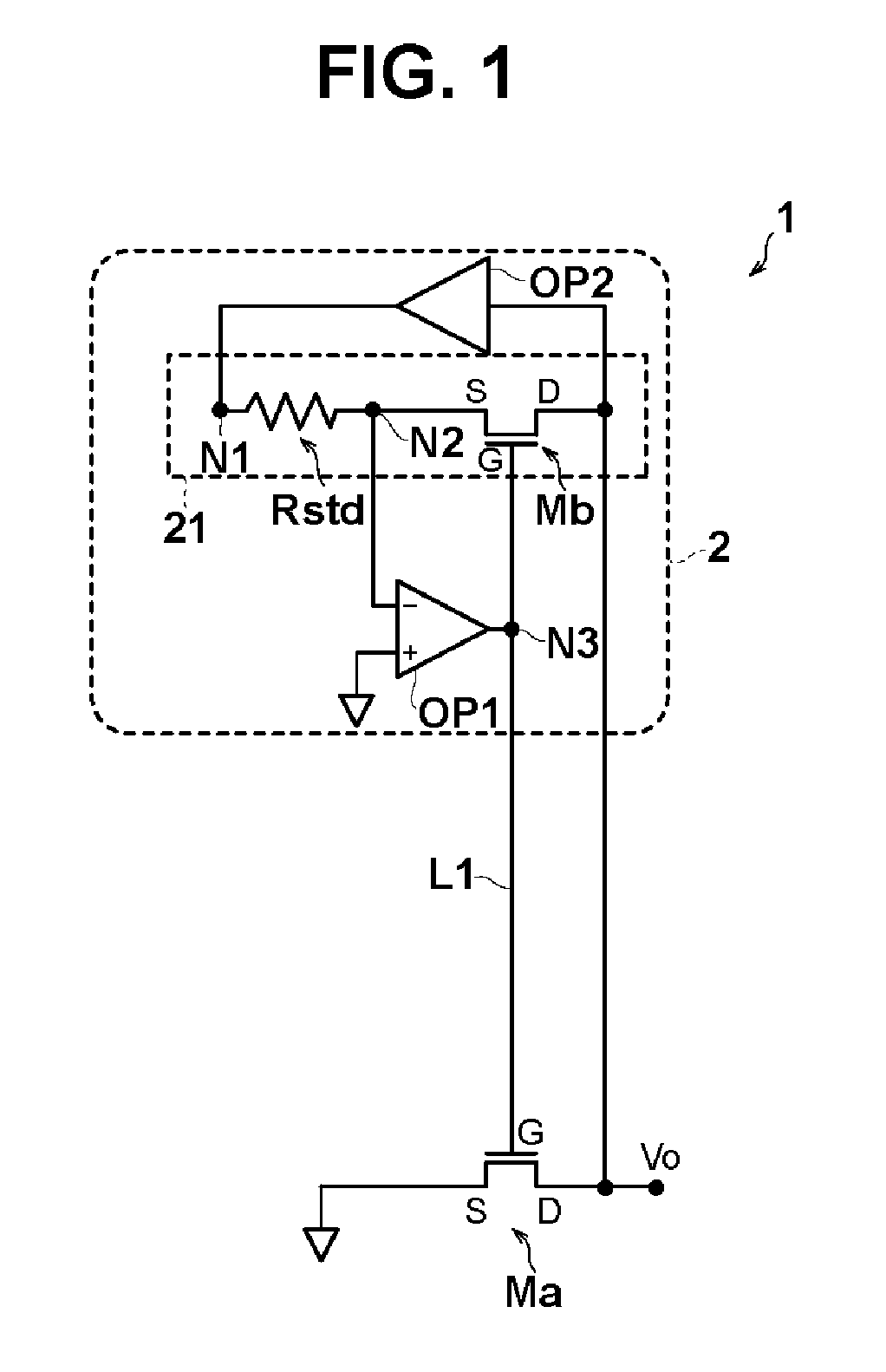
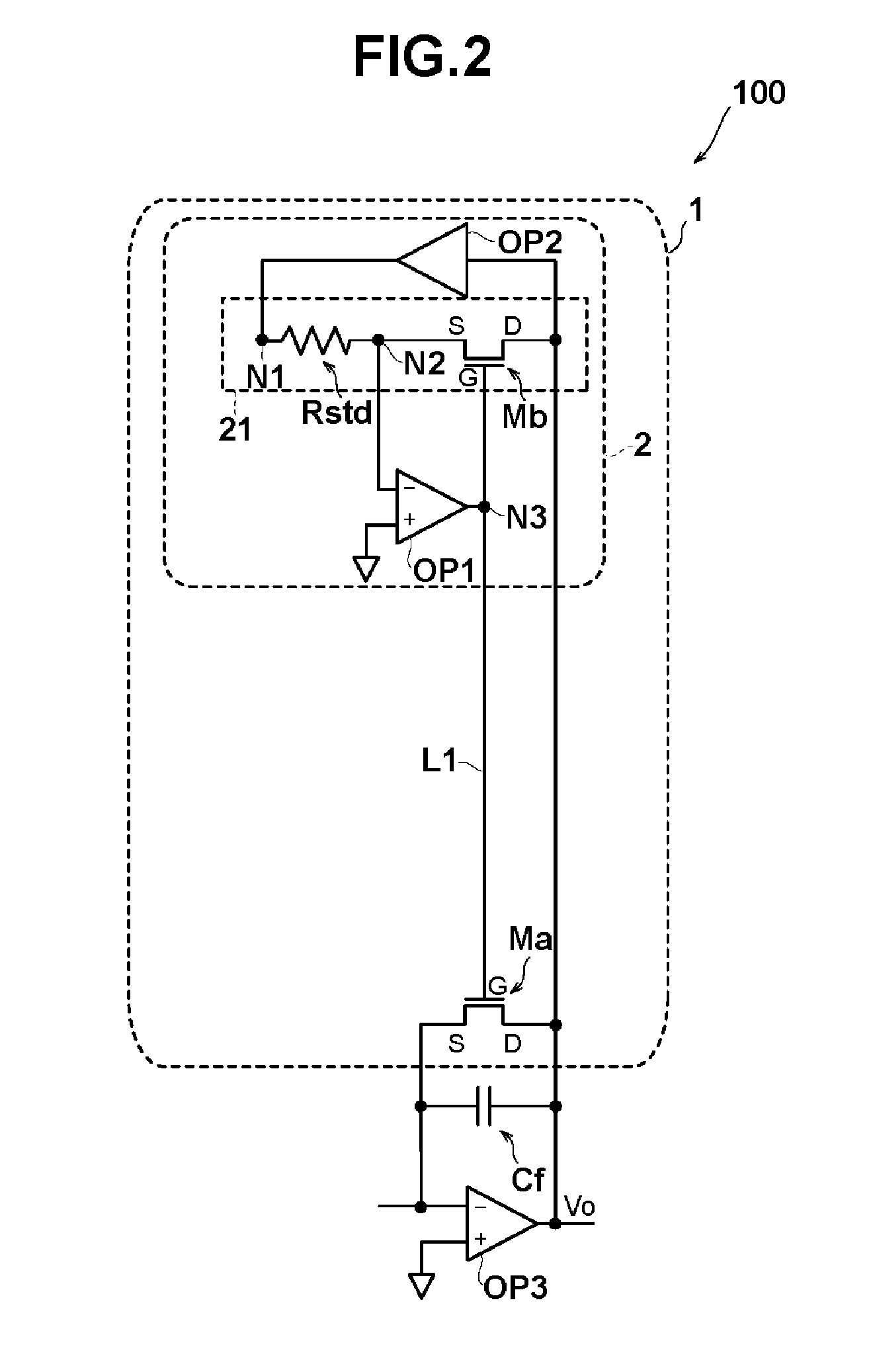
Psuedo resistor circuit and charge amplifier
ActiveUS20160020734A1Low temperature dependenceLower gate voltageNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCharge amplifiersAudio power amplifierDividing circuits
A pseudo resistor circuit and a charge amplifier include a first field effect transistor; a second field effect transistor having electrical characteristics matched with electrical characteristics of the first field effect transistor; and a voltage dividing circuit with terminal of a reference resistor electrically connected to a source terminal of the second field effect transistor. Further, a first operational amplifier with an output terminal is connected to a gate terminal of the first field effect transistor and a gate terminal of the second field effect transistor and in which midpoint voltage of the voltage dividing circuit is input into either an inverting or non-inverting input terminal and reference voltage is input into the other of the inverting and non-inverting input terminal. Furthermore, a second operational amplifier supplies voltage resulting from inversion and amplification of drain voltage of the first field effect transistor into the other terminal of the resistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7816195B2Reduce power consumptionAvoid delaySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor
A TFT having a high threshold voltage is connected to the source electrode of each TFT that constitutes a CMOS circuit. In another aspect, pixel thin-film transistors are constructed such that a thin-film transistor more distant from a gate line drive circuit has a lower threshold voltage. In a further aspect, a control film that is removable in a later step is formed on the surface of the channel forming region of a TFT, and doping is performed from above the control film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com