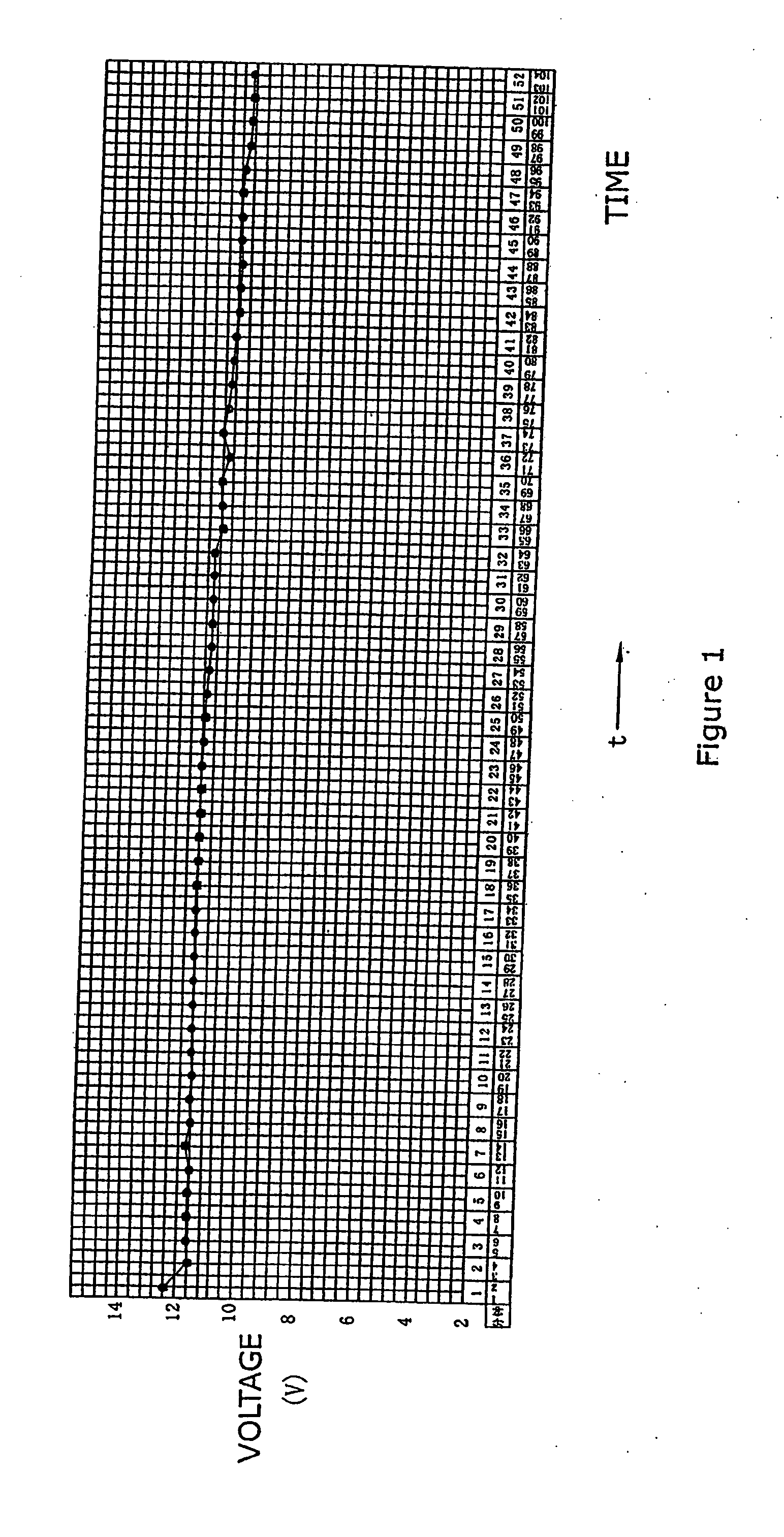
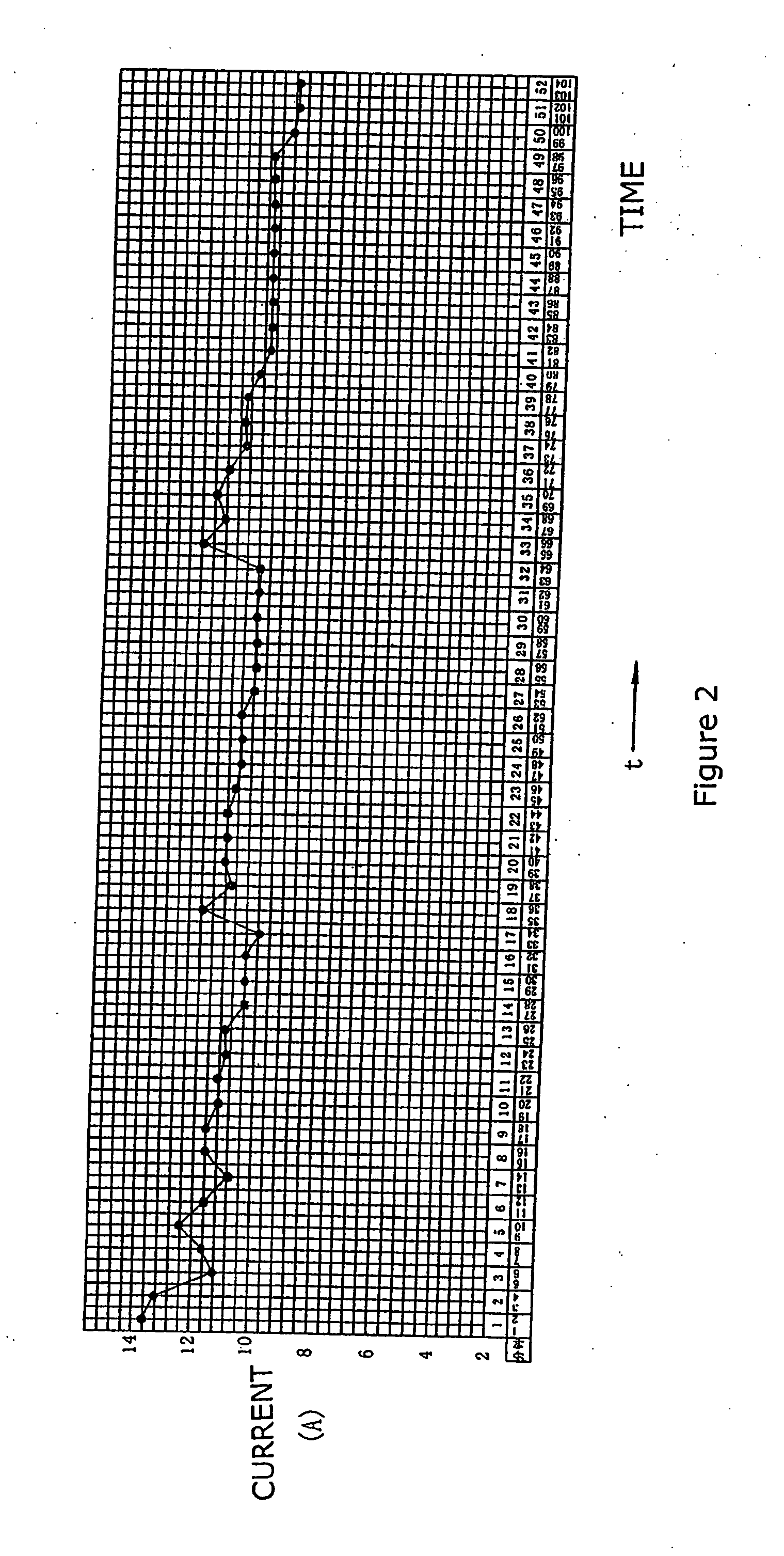
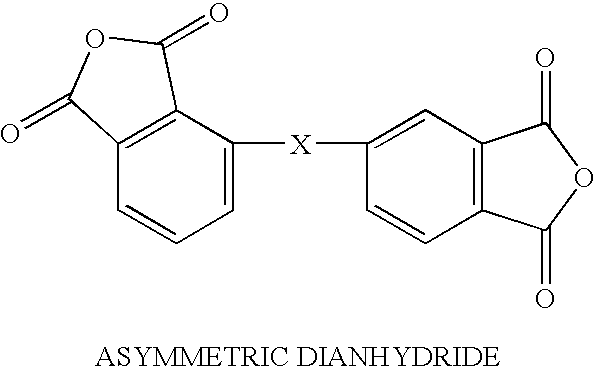
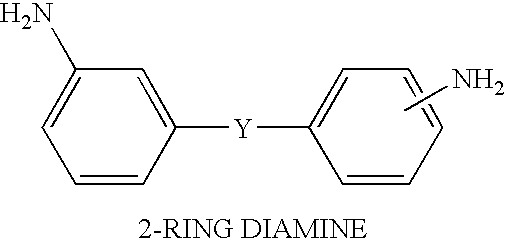
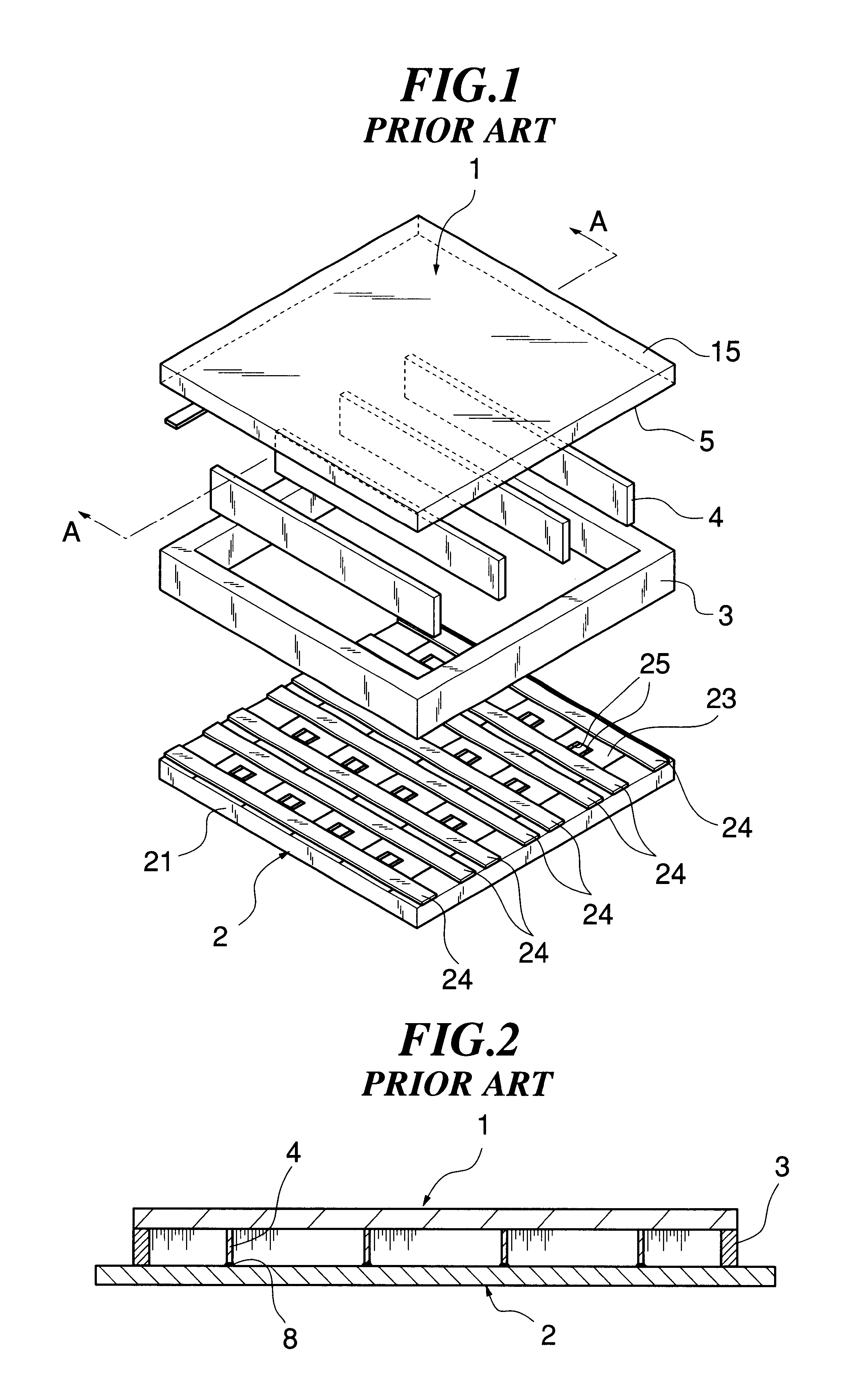
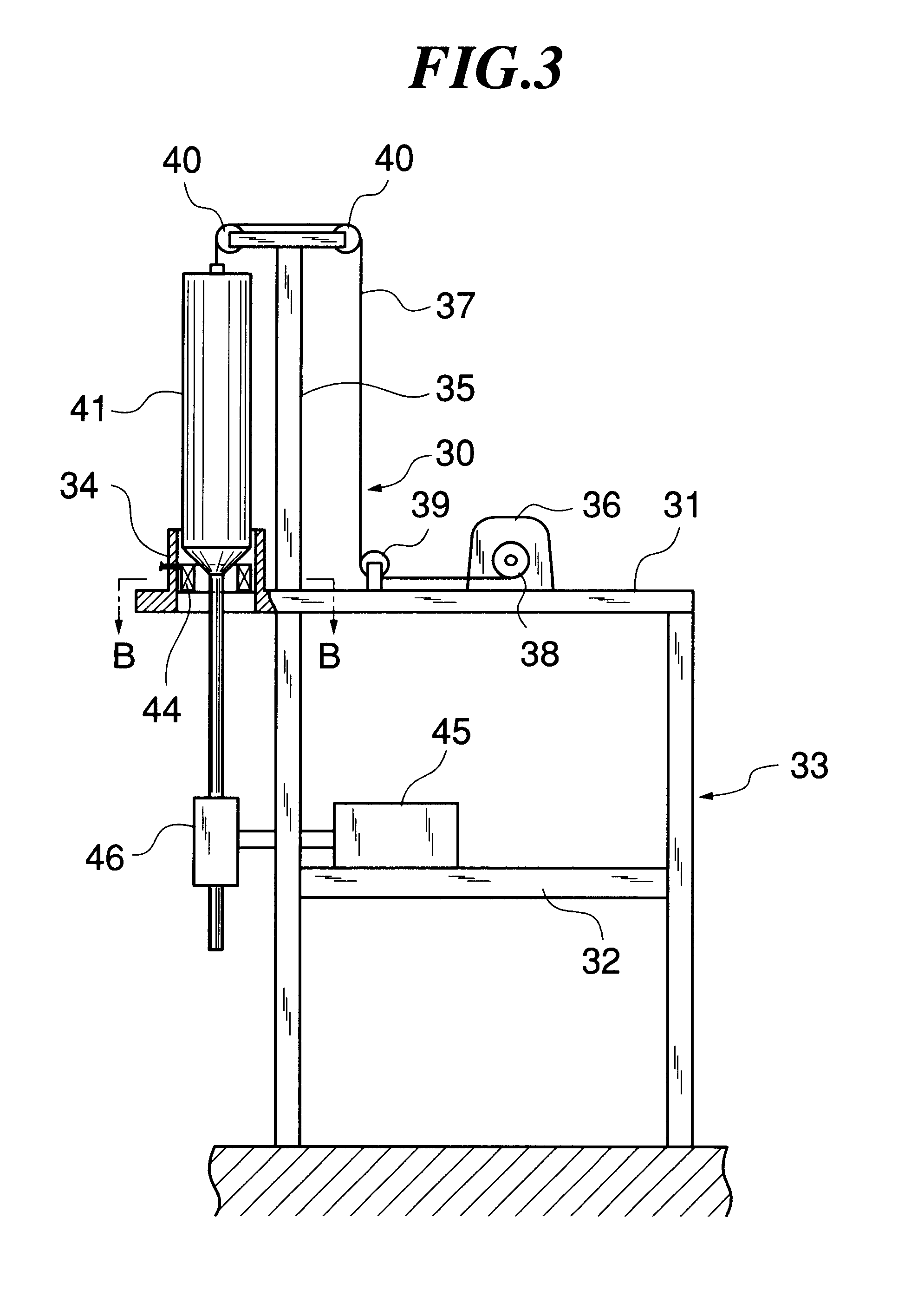
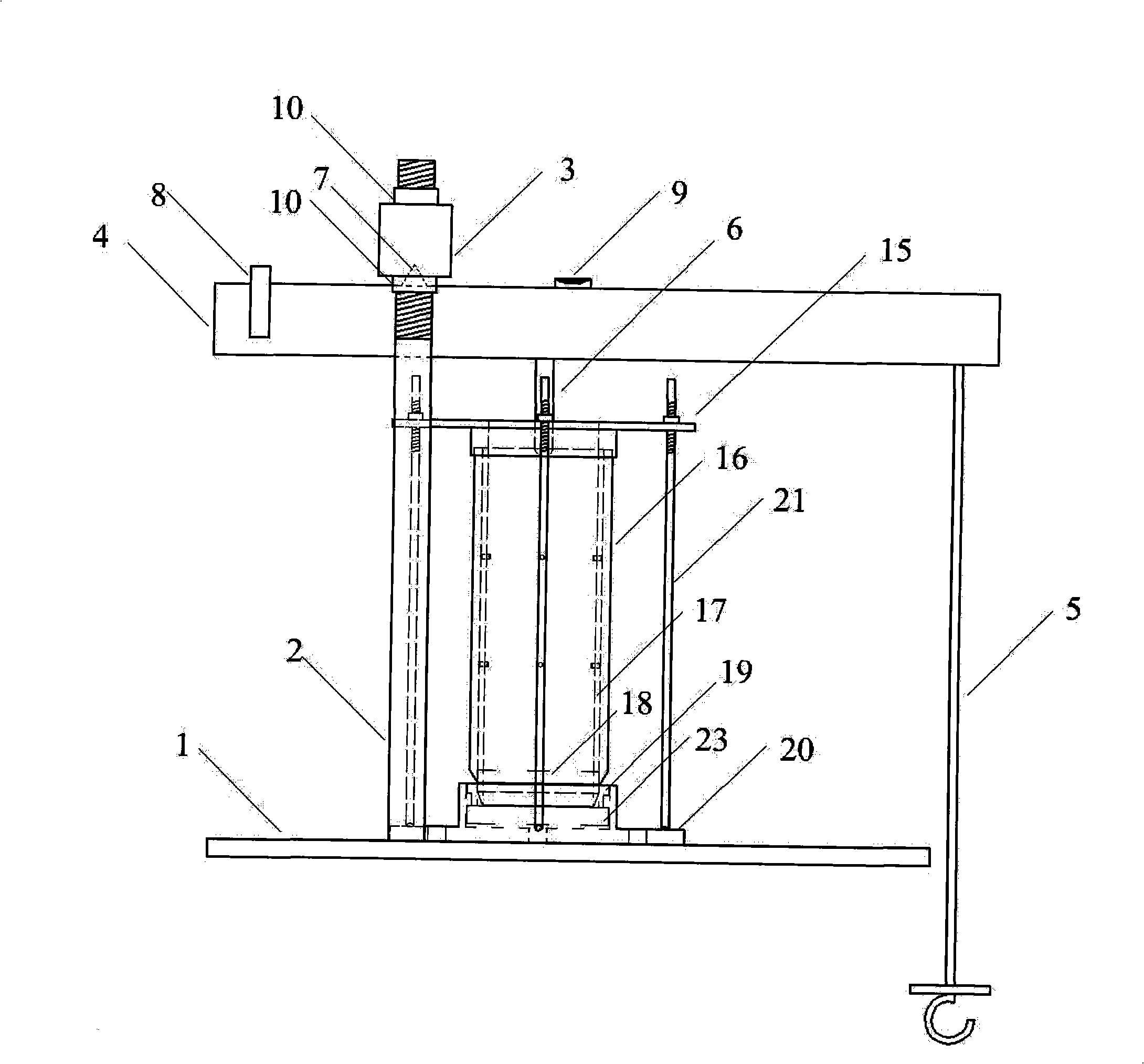
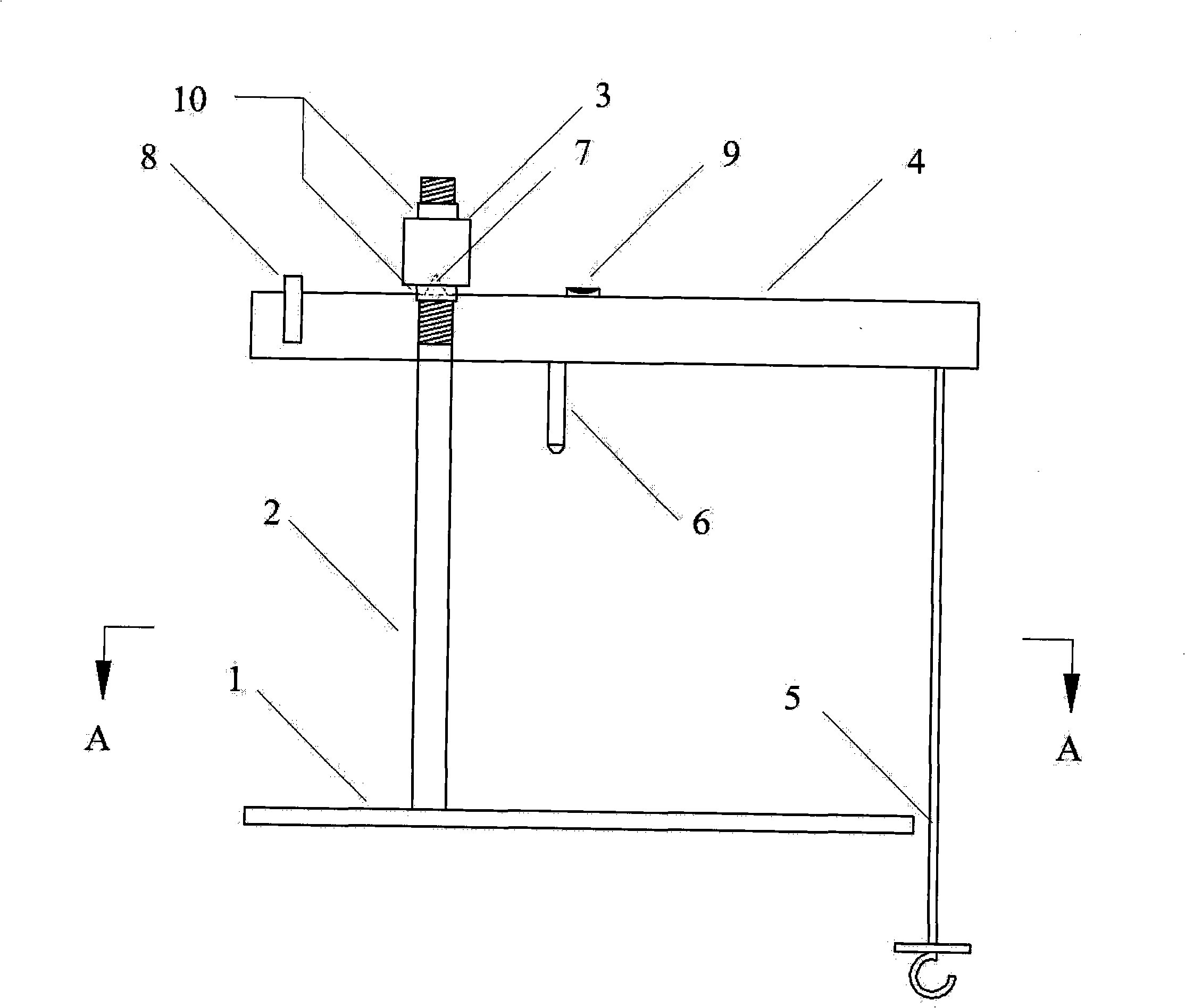
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
229 results about "Poise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The poise (symbol P; /pɔɪz, pwɑːz/) is the unit of dynamic viscosity (absolute viscosity) in the centimetre–gram–second system of units. It is named after Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille (see Hagen–Poiseuille equation). 1 P=0.1 kg·m⁻¹·s⁻¹=1 g·cm⁻¹·s⁻¹=1 dyne·s·cm⁻². The analogous unit in the International System of Units is the pascal-second (Pa⋅s): 1 Pa·s=1 N·s·m⁻²=1 kg·m⁻¹·s⁻¹=10 P. The poise is often used with the metric prefix centi- because the viscosity of water at 20 °C (NTP) is almost exactly 1 centipoise.
Fusion formable silica and sodium containing glasses
ActiveUS20110017297A1Point becomes highImprove battery efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSilicate glassThermal expansion
Sodium containing aluminosilicate and boroaluminosilicate glasses are described herein. The glasses can be used as substrates or superstrates for photovoltaic devices, for example, thin film photovoltaic devices such as CIGS photovoltaic devices. These glasses can be characterized as having strain points≧535° C., for example, ≧570° C., thermal expansion coefficients of from 8 to 9 ppm / ° C., as well as liquidus viscosities in excess of 50,000 poise. As such they are ideally suited for being formed into sheet by the fusion process.
Owner:CORSAM TECH
Method and system for forming shaped glass articles
ActiveUS20140234581A1Forming accuratelyLayered productsDigital data processing detailsPoiseGlass sheet
A method of forming a shaped glass article includes placing a glass sheet on a mold such that a first glass area of the glass sheet corresponds to a first mold surface area of the mold and a second glass area of the glass sheet corresponds to a second mold surface area of the mold. The first glass area and the second glass area are heated such that the viscosity of the second glass area is 8 poise or more lower than the viscosity of the first glass area. A force is applied to the glass sheet to conform the glass sheet to the mold surface. During the heating of the second glass area, the first mold surface area is locally cooled to induce a thermal gradient on the mold.
Owner:CORNING INC
Chalcogenide glass for low viscosity extrusion and injection molding
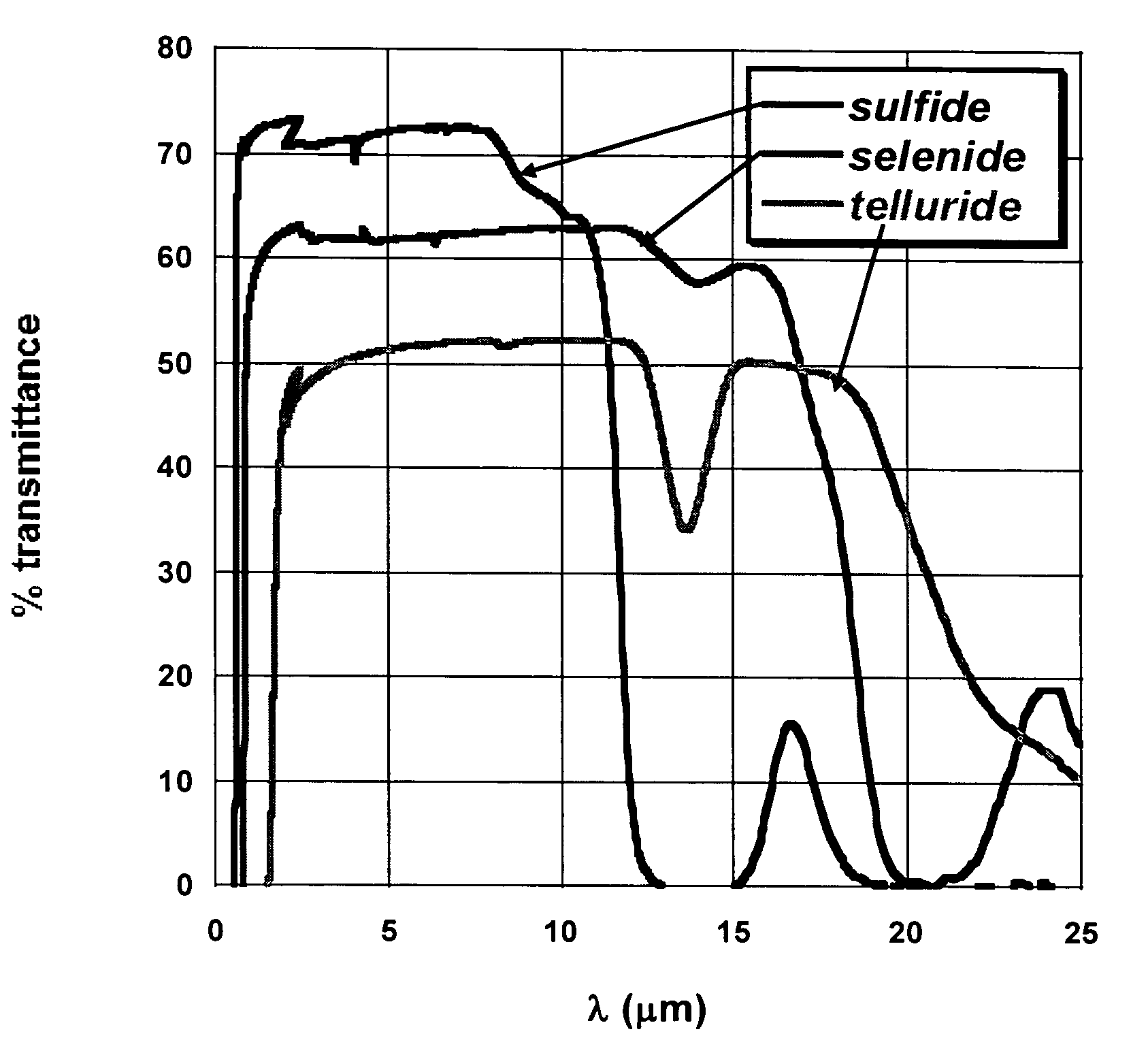
The invention is directed to chalcogenide glasses suitable for use in plastics forming processes. The glasses have the general formula YZ, where Y is Ge, As, Sb or a mixture of two or more of the same; Z is S, Se, Te, or a mixture of two or more of the same; and Y and Z are present in amounts (in atomic / element percent) in the range of Y=15–70% and Z=30–85%. The chalcogenide glasses of the invention have a 10,000 poise temperature of 400° C. and are resistant to crystallization when processed at high shear rates at their 10,000 poise temperature. The glasses can be used to make, among other items, molded telecommunication elements, lenses and infrared sensing devices.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for continuous casting of steel
A method of continuous casting of a steel employs a mold power having a viscosity of 0.5-1.5 poise at 1,300° C. and a solidification temperature of 1,190-1,270° C., in which the mass ratio of CaO to SiO2 is 1.2-1.9, and casting is carried out under the following conditions: casting speed is 2.5-10 m / minute; mold oscillation stroke is 4-15 mm; and specific cooling intensity in secondary cooling of a slab is 1.0-5.0 liter / kg-steel.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD
Aqueous coating compositions, methods for making same and uses thereof
InactiveUS6140386AImprove stabilityMinimum tendencyFilm/foil adhesivesOptical articlesOligomerEmulsion
An aqueous unpigmented coating and printing composition useful for gravure and flexographic printing on plastic and metal substrates is provided by preparing an aqueous emulsion of a hydrophobic UV curable oligomer and a photoinitiator and adding about 1 to 10% by weight of the composition of a water soluble or reducible polymeric thickener in an amount effective to provide a viscosity of about 10 to 50 poises and specified rheology properties whereby the composition is capable of yielding clear cured films as low as about 2 microns in thickness.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Chalcogenide glass for low viscosity extrusion and injection molding
ActiveUS20060233512A1Low cost manufacturingGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreSulfurChalcogenide glass
Owner:CORNING INC
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Disclosed are multicomponent fibers derived from a blend of a sulfopolyester with a water non-dispersible polymer wherein the as-spun denier is less than about 6 and wherein the water dispersible sulfopolyester exhibits a melt viscosity of less than 12,000 poise measured at 240° C. at a strain rate of 1 rad / sec, and wherein the sulfopolyester comprising less than about 25 mole % of residues of at least one sulfomonomer, based on the total moles of diacid or diol residues. The multicomponent fiber is capable of being drawn at a relatively high fiber speed, particularly at least about 2000 m / min, and may be used to produce microdenier fibers. Fibrous articles may be produced from the multicomponent fibers and microdenier fibers. Also disclosed is a process for multicomponent fibers, nonwoven fabrics, and microdenier webs.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Curable liquid resin composition
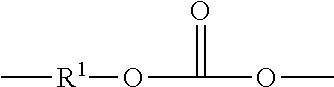
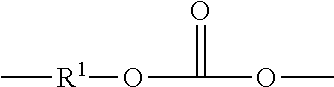
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 01871 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 3, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 3, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 2, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 46601 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 11, 1997A curable liquid resin composition containing 100 parts by weight of the following (meth)acrylic liquid resin (A) and 1 to 1,000 parts by weight of a (meth)acrylic monomer (B) having an unsaturated double bond in its molecule and having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 or less, the (meth)acrylic liquid resin (A) being a liquid resin which is obtained by polymerizing monomers containing an alkyl (meth)acrylate monomer (a-1-1) of the formula (1),CH2 C(R1)COO-R2(1)wherein R1 is a hydrogen atom or CH3 and R2 is an alkyl group, and / or an alkylene glycol (meth)acrylate monomer (a-1-2) of the formula (2),CH2=C(R1)COO(CnH2nO)mR3(2)wherein R1 is a hydrogen atom or CH3, R3 is an alkyl group or a phenyl group, n is an integer of 1 to 3, and m is an integer of 3 to 25, and other polymerizable vinyl monomer (a-2), an average of molecular weights of all the monomers being 100 to 1,500, the liquid resin having a number average molecular weight of 10,000 to 200,000 and a viscosity of 1 to 10,000 poise (measured at 50 DEG C.), or a modified product of the above liquid resin, the curable liquid resin composition can form a film as a film-forming material or as a resin for an adhesive without using a solvent and give a cured film.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
Method of producing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveUS6332338B1Avoid deformationIncrease speedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusProduction ratePoise
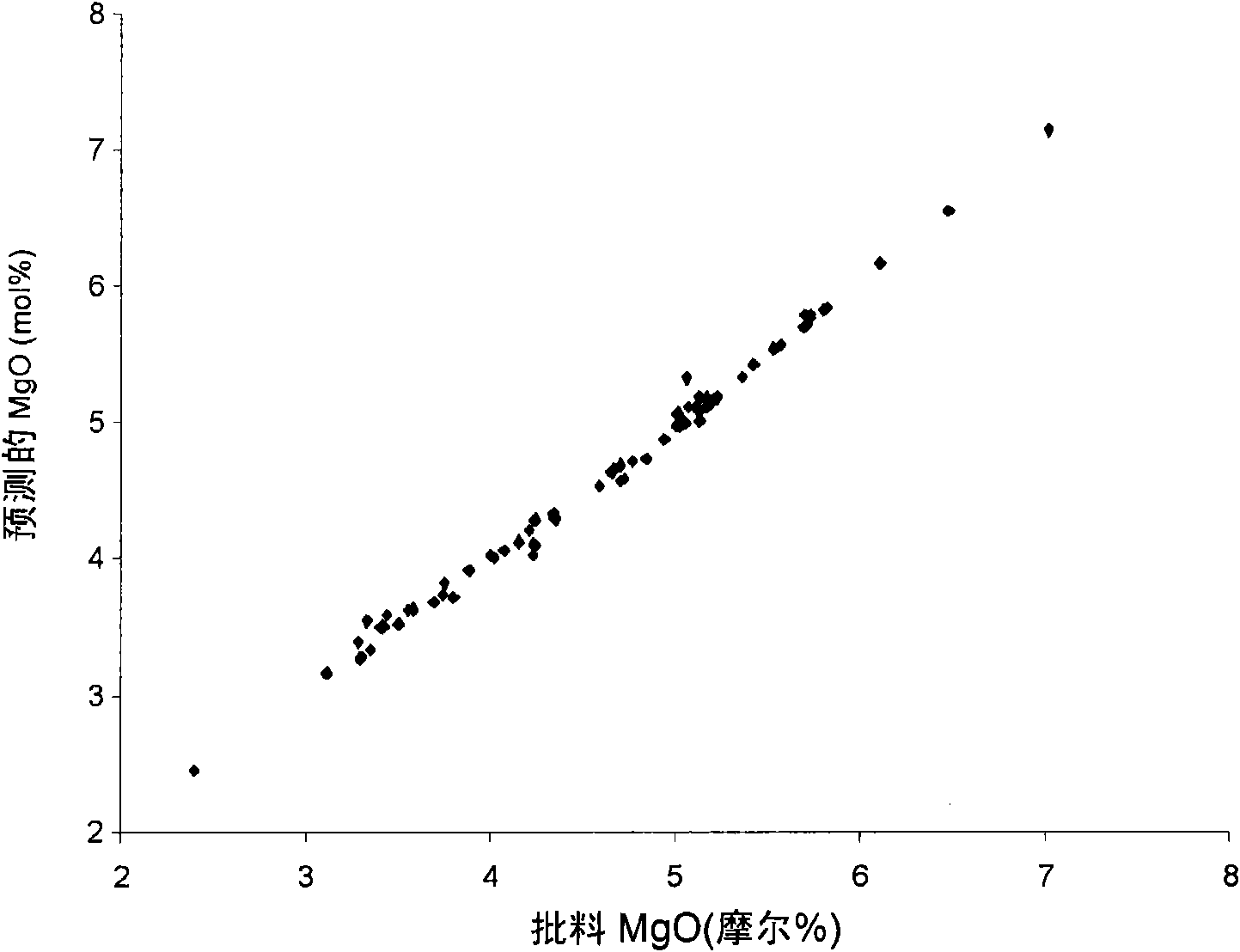
Disclosed is a process for producing a glass substrate for an information recording medium by press-shaping a molten glass which gives a glass containing 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and having properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and a viscosity of at least 10 poise in a shaping-allowable temperature range, or by preparing a preform formed of a glass which contains 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and has properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and shaping the preform in the form of a disc by a re-heat pressing method. According to the above process, there can be mass-produced, with high productivity, high-quality glass substrates to be used for information recording media such as a magnetic disc, an optical disc, a magneto-optic disc, and the like.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Glass for display substrate
ActiveUS20050209084A1Low densityReduce bloatVehicle body stabilisationGlass furnace apparatusThermal expansionPoise
A glass having a SiO2—Al2O3—B2O3—RO (RO is at least one of MgO, CaO, BaO, SrO and ZnO) based composition, a temperature corresponding to 102.5 poise being 1570° C. or higher and an alkali content of 0.01 to 0.2% and a ZrO2 content of 0.01 to 0.3%, as expressed in % by mass. And, a glass having a SiO2—Al2O3—B2O3—RO (RO is at least one of MgO, CaO, BaO, SrO and ZnO) based composition, a density of 2.5 g / cm3 or less, an average thermal expansion coefficient of 25 to 36×10−7 / ° C. in a temperature range of 30 to 380° C., a strain point of 640° C. or higher and an alkali content of 0.01 to 0.2% and a ZrO2 content of not less than 0.01% and less than 0.4%, as expressed in % by mass.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Liquid low-sodium silicate electrolyte used for a storage battery and manufactured by magnetization process, and the usage thereof
InactiveUS20080044726A1Improve liquidityHigh viscosityOther chemical processesMagnetic paintsMagnetizationBiological activation
A liquid low concentration sodium-containing silicate solution as electrolyte for lead-acid storage batteries and its applications, is prepared by mixing a silica gel containing 40˜60 wt % SiO2, the weight units of such a silica gel are 5˜15; add 15-25 weight units water and stir until the concentration of the mixture is 0.65˜0.85 0Be′ measured by a Baum densimeter, adjusting the pH value of this mixture to 1-4 using inorganic acid and magnetizing the mixture under 1000-6000 Gauss magnetic field for 5-10 minutes, stir the magnetized mixture until the viscosity of the mixture is less than 0.02 poise and finally obtain a liquid low concentration sodium-containing silicate solution. The electrolyte can be used as electrolyte or activation solution for common or special lead-acid storage batteries.
Owner:LIDU WANG
Solvent free low-melt viscosity imide oligomers and thermosetting polyimide composites
This invention relates to the composition and a solvent-free process for preparing novel imide oligomers and polymers specifically formulated with effective amounts of a dianhydride such as 2,3,3′,4-biphenyltetra carboxylic dianydride (a-BPDA), at least one aromatic diamine and an endcapped of 4-phenylethynylphthalic anhydride (PEPA) or nadic anhydride to produce imide oligomers that possess a low-melt viscosity of 1–60 poise at 260–280° C. When the imide oligomer melt is cured at about 371° C. in a press or autoclave under 100–500 psi, the melt resulted in a thermoset polyimide having a glass transition temperature (Tg) equal to and above 310° C. A novel feature of this process is that the monomers; namely the dianhydrides, diamines and the endcaps, are melt processable to form imide oligomers at temperatures ranging between 232–280° C. (450–535° F.) without any solvent. These low-melt imide oligomers can be easily processed by resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) or the resin infusion process with fiber preforms e.g. carbon, glass or quartz preforms to produce polyimide matrix composites with 288–343° C. (550–650° F.) high temperature performance capability.
Owner:NASA
Fusion formable sodium free glass
ActiveUS20100300536A1Improve battery efficiencyImprove film adhesionFinal product manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsSilicate glassThermal expansion
A compositional range of fusion-formable, high strain point sodium free, silicate, aluminosilicate and boroaluminosilicate glasses are described herein. The glasses can be used as substrates for photovoltaic devices, for example, thin film photovoltaic devices such as CIGS photovoltaic devices. These glasses can be characterized as having strain points≧540° C., thermal expansion coefficient of from 6.5 to 10.5 ppm / ° C., as well as liquidus viscosities in excess of 50,000 poise. As such they are ideally suited for being formed into sheet by the fusion process.
Owner:CORSAM TECH
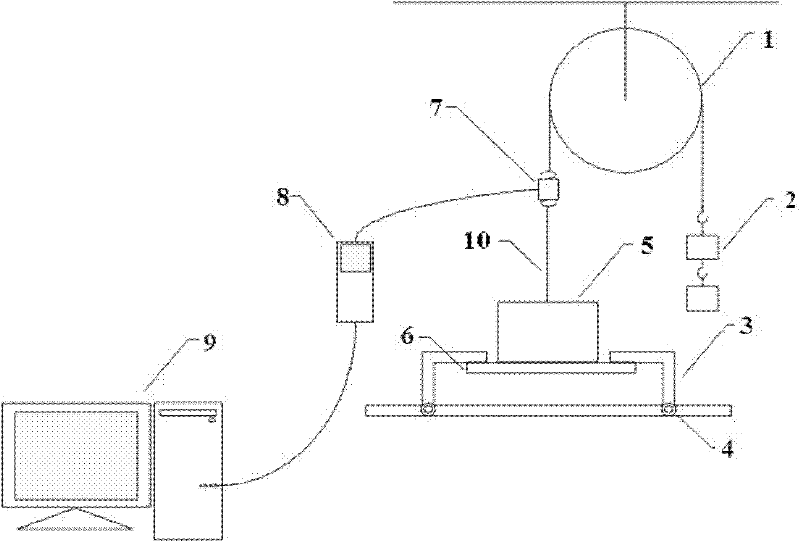
System and method for measuring ice coating adhesion strength on material surface
InactiveCN102288542ASimple structureEasy to operateUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisAdhesion forceEngineering
The invention discloses a system and a method for measuring the adhesion strength of ice coating on a material surface, belonging to the field of ice coating measurement. The system comprises a force applying poise, a tension gauge, an icing mold, a fixing device, a pulling rope, a fixed pulley and a computer, wherein the icing mold is connected with a sample to be measured through ice coating; the sample to be measured is fixed by the fixing device; one end of the pulling rope is connected with the icing mold through the tension gauge, and the other end of the pulling rope is connected with the force applying poise through the fixed pulley; and the data output end of the tension gauge is connected with the computer through a data transmission line. The system for measuring the adhesion strength of ice coating on the material surface disclosed by the invention has a simple structure, the method is easy to operate, and the system and the method are suitable for measuring and analyzing the adhesion force of ice coating on different material surfaces in units such as plants, laboratories and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Glasses for flat panel displays
Glasses are disclosed which are used to produce substrates in flat panel display devices. The glasses exhibit a density less than about 2.45 gm / cm3 and a liquidus viscosity greater than about 200,000 poises, the glass consisting essentially of the following composition, expressed in terms of mol percent on an oxide basis: 65-75 SiO2, 7-13 Al2O3, 5-15 B2O3, 0-3 MgO, 5-15 CaO, 0-5 SrO, and essentially free of BaO. The glasses also exhibit a strain point exceeding 650° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Disclosed are multicomponent fibers derived from a blend of a sulfopolyester with a water non-dispersible polymer wherein the as-spun denier is less than about 6 and wherein the water dispersible sulfopolyester exhibits a melt viscosity of less than 12,000 poise measured at 240° C. at a strain rate of 1 rad / sec, and wherein the sulfopolyester comprising less than about 25 mole % of residues of at least one sulfomonomer, based on the total moles of diacid or diol residues. The multicomponent fiber is capable of being drawn at a relatively high fiber speed, particularly at least about 2000 m / min, and may be used to produce microdenier fibers. Fibrous articles may be produced from the multicomponent fibers and microdenier fibers. Also disclosed is a process for multicomponent fibers, nonwoven fabrics, and microdenier webs.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Pressure-sensitive adhesive blends comprising ethylene/propylene-derived polymers and propylene-derived polymers and articles therefrom
InactiveUS6489400B2Reduce melt viscosityImprove throughputFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceHigh surface
The present invention relates to a blend of at least one amorphous ethylene / propylene-derived copolymer, at least one non-stereoregular propylene-derived polymer having a melt viscosity of greater than about 500 Poise, and an optional tackifier that provide pressure-sensitive adhesive compositions in which a good balance of adequate adhesion to both low and relatively high surface energy substrates can be achieved.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Curing agents curable compositions, compositions for optical materials, optical materials their production and liquid crystal displays and led's made by using the material
InactiveUS20040126504A1Liquid crystal compositionsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOptical transparencyLiquid-crystal display
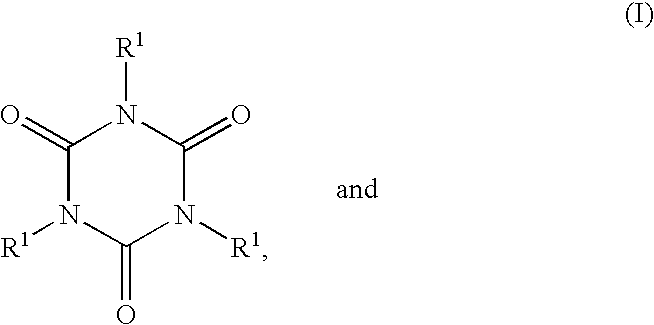
The invention aims at a curing agent, curable compositions or compositions for optical materials, capable of providing for cured artifacts having laudable heat resistance, optical transparency, and light resistance; optical materials and methods for their production; and liquid crystal displays and LED's made by using the materials. A curing agent, which comprises at least two SiH groups which is obtainable by subjecting an aliphatic organic compound (alpha1) having at least two carbon-carbon double bonds capable of reacting with a SiH group, said aliphatic organic compound containing 1 to 6 vinyl groups and having a molecular weight of less than 900 and a viscosity of less than 1,000 poises and an acyclic and / or cyclic polyorganosiloxane (beta1) having at least two SiH groups to hydrosilylation reaction, or a curing agent, which comprises at least two SiH groups which is obtainable by subjecting an organic compound (alpha2) represented by the formula (I) a cyclic polyorganosiloxane (beta2) having at least two SiH groups to hydrosilylation reaction.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Boroalumino silicate glasses
ActiveCN101591141AGlass forming apparatusIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationActive-matrix liquid-crystal displayAlkali free
The invention discloses alkali-free glasses having a liquidus viscosity of greater than or equal to about 90,000 poises, the glass comprising SiO 2 Al 2 O 3 , B 2 O 3 , MgO, CaO, and SrO such that, in mole percent on an oxide basis: 64 is less than or equal to SiO2 and SiO2 is less than or equal to 68.2; 11 is less than or equal to Al2O3 and Al2O3 is less than or equal to 13.5; 5 is less than or equal to B2O3 and B2O3 is less than or equal to 9; 2 is less than or equal to MgO and MgO is less than or equal to 9; 3 is less than or equal to CaO and CaO is less than or equal to 9; and 1 is less than or equal to SrO and SrO is less than or equal to 5. The glasses can be used to make a display glass substrate, such as thin film transistor (TFT) display glass substrates for use in active matrix liquid crystal display devices (AMLCDs) and other flat panel display devices.
Owner:CORNING INC
Compositions and articles of manufacture containing branched polycarbonate
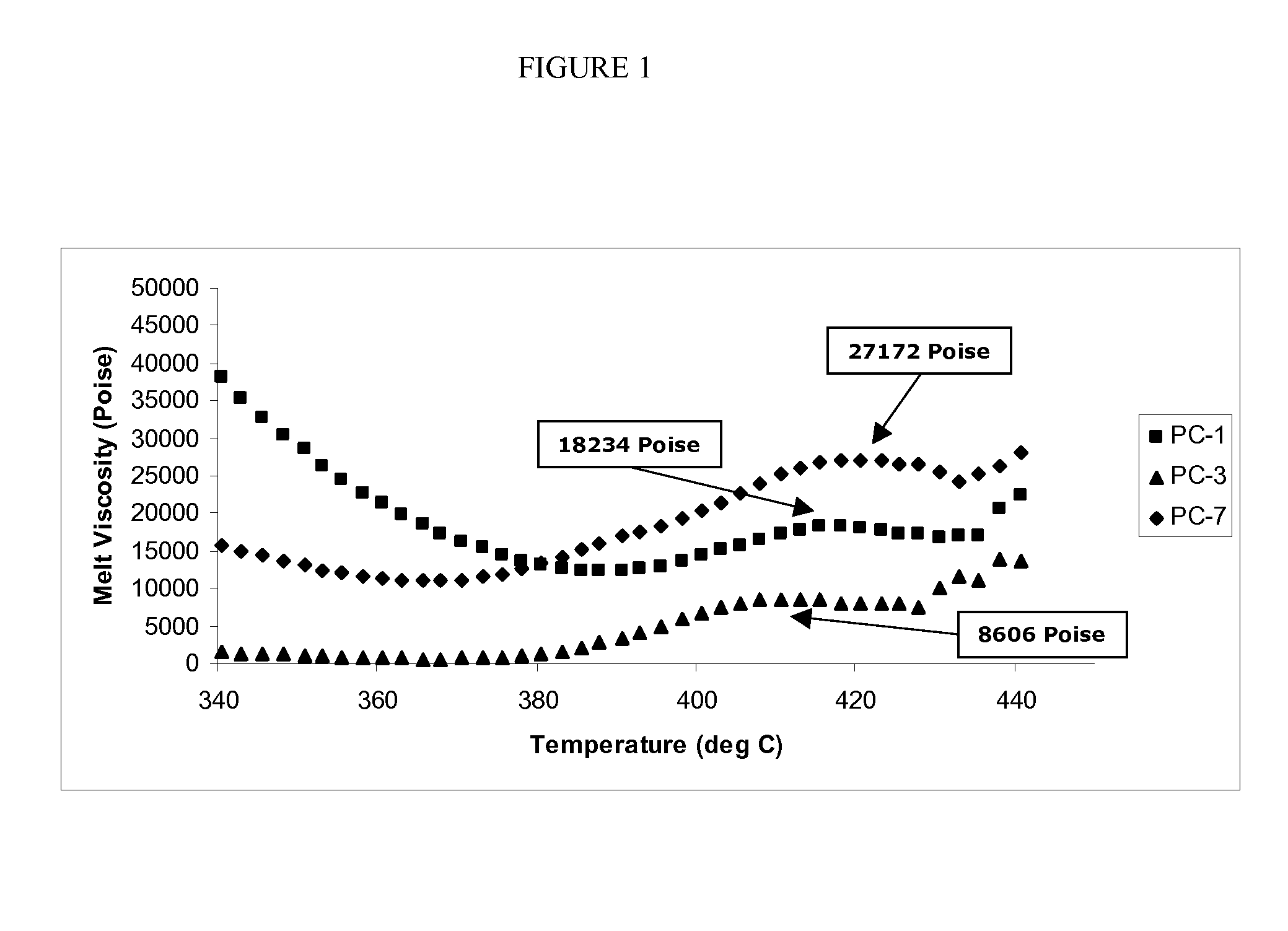
A polycarbonate containing composition comprising a peak melt viscosity of at least 8,000 poise when measured using a parallel plate melt rheology test at a heating rate of 10° C. / min at a temperature of between about 350° C. to about 450° C., and wherein a molded article of the composition has a UL 94 VO rating at a thickness of 1.0 mm, 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, or between 1.0 mm and 2.0 mm is disclosed.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
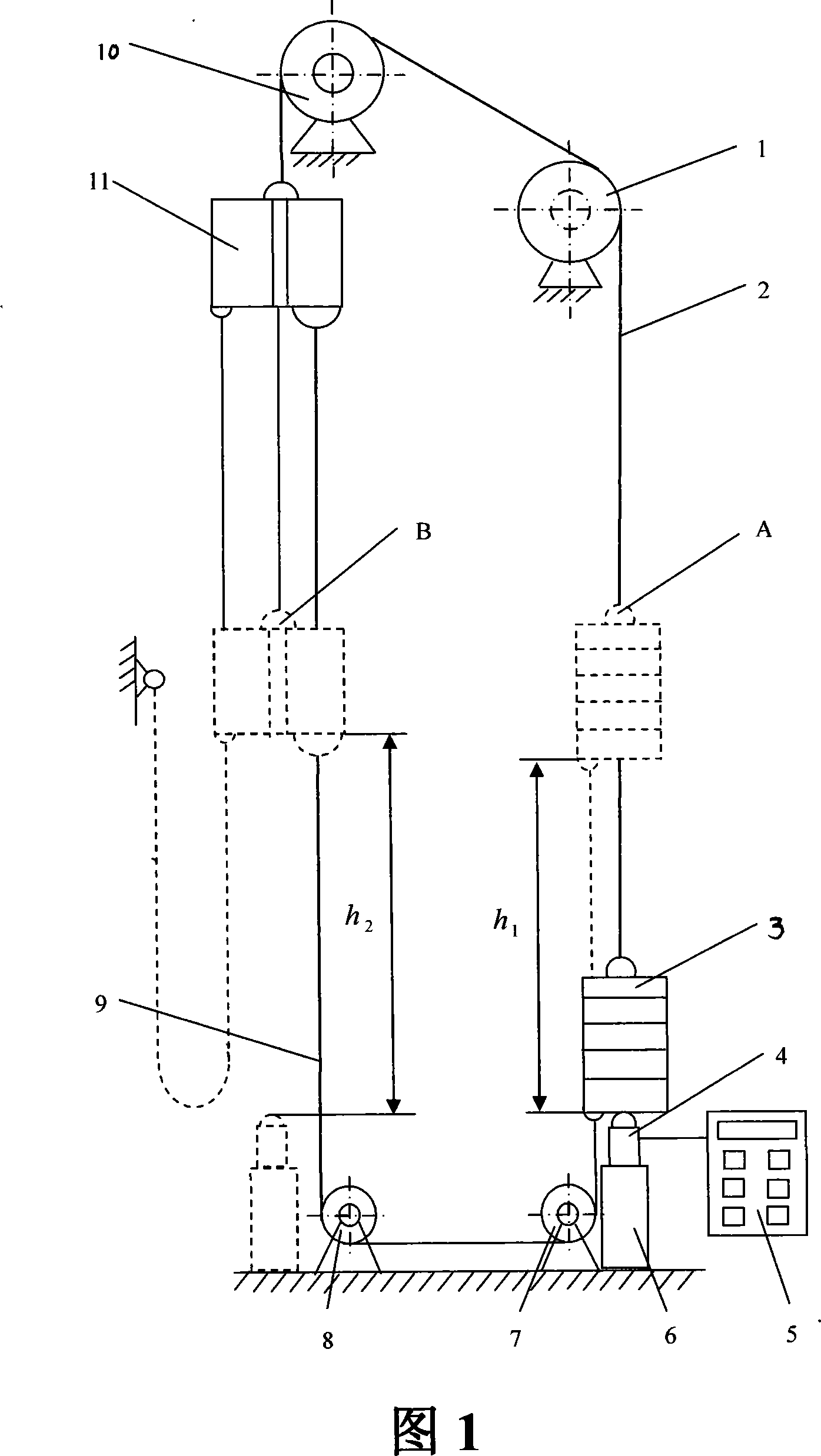
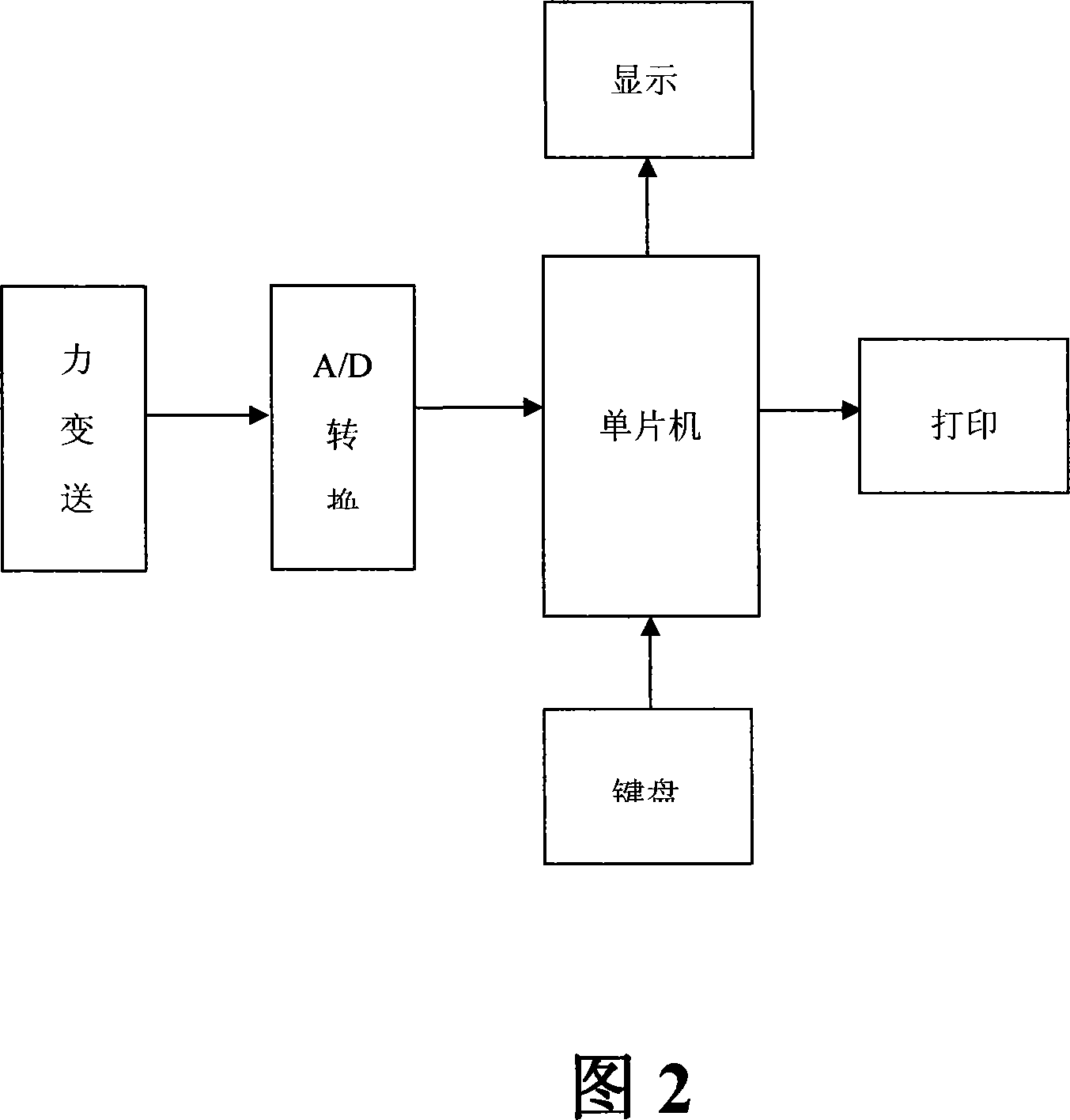
Method for measuring static state weight difference in two sides of elvator balancing coefficient
InactiveCN101082530AMeasure directlyAccurate measurementStatic/dynamic balance measurementElevatorsCarrying capacityFast measurement
The invention discloses a static two sides weight differential measurement method of lift coefficient of balance according to the lift balance coefficient formula (I)through measuring the weight differential Wg=(W-G) of the pair weight and the sedan wing and gives the lift rated load capacity Q then calculates the balance coefficient K. The method is that: at the condition of lift with no-load layouts the force transducer at the bottom of well corresponding with the pair weight and the pair weight falls down to the bottom of well and contacts with the force transducer then measures the weight differential Wg1 of the pair weight side and the sedan wing side; installs the poise with the carrying capacity QP in the sedan wing (QP is greater than the one-half of the lift rated carrying capacity) layouts the force transducer at the bottom of well corresponding with the sedan wing the sedan wing falls down to the bottom of well and contacts with the force transducer then measures the weight differential Wg2 of the sedan wing side and the pair weight side and calculates the balance coefficient K according to the formula(II)following the weight differentia Wg1, Wg2, the lift rated carrying capacity Q, and the bearing capacity QP. According to this method develop the lift balance coefficient test device which can measure the lift balance coefficient directly, accurately, and rapidly at the static case.
Owner:石成江 +1
Man-made vitreous fibres
Man-made vitreous fibers have a solubility of pH 4.5 of at least 20 nm per day and a melt viscosity of 10 to 70 poise at 1400° C. Novel fibers contain at least 18% Al2O3. Particular products include external wall insulation or cladding and pipe sections. A composition for making suitable fibres may be selected by determining solubility at pH 4.5 or in macrophage.
Owner:ROCKWOOL INT AS
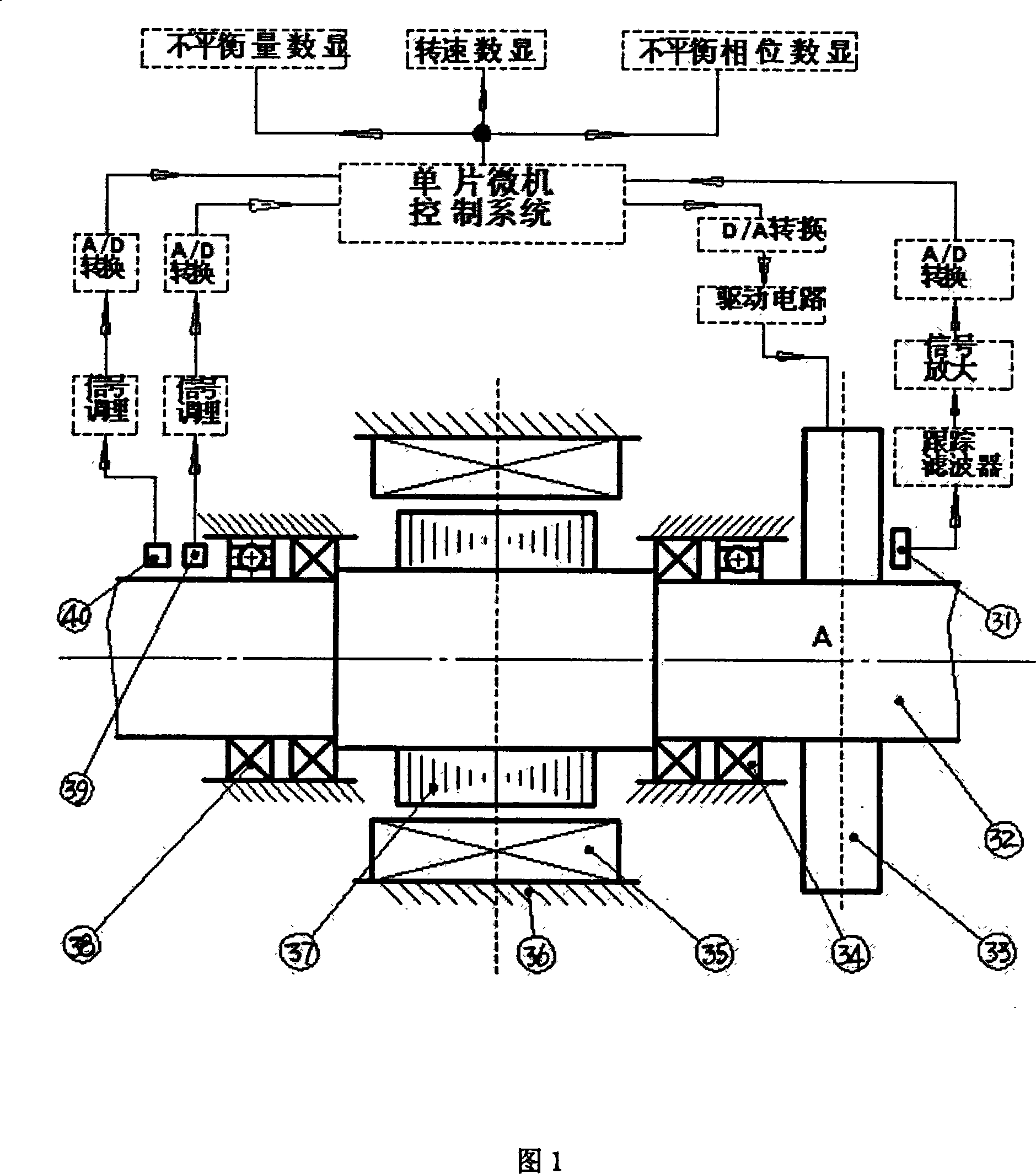
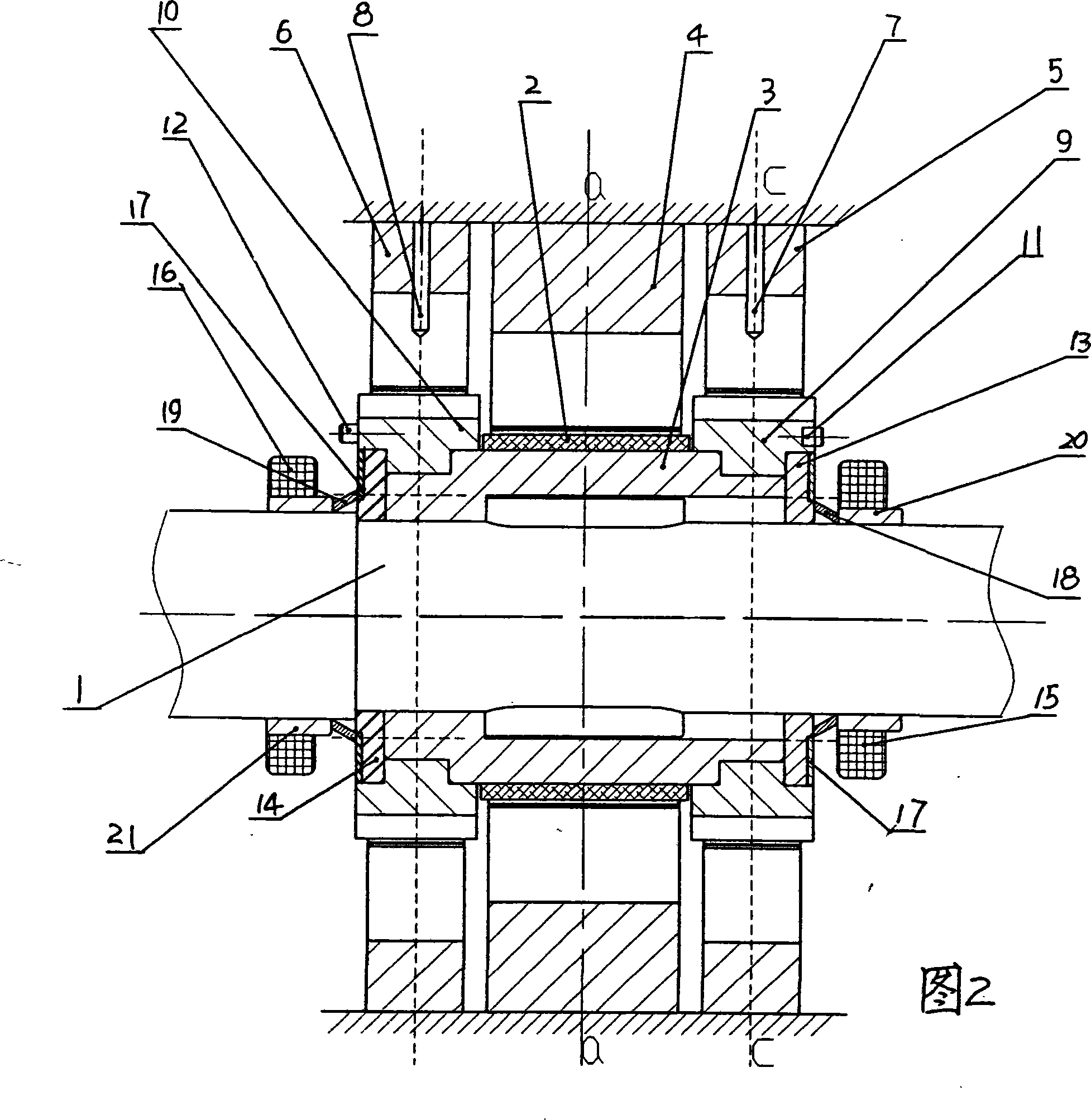
High speed chief axis on-line dynamic poise device
InactiveCN101158614AReal-time online dynamic balance compensation effectShort response timeStatic/dynamic balance measurementElastic componentDynamic balance
The invention relates to a high speed spindle balancing device, in particular to a high speed spindle inline dynamic balancing device. The invention solves the defects and deficiency of existing high speed spindle inline dynamic balancing device, particularly indirect inline dynamic balancing device and mixed model inline dynamic balancing device. The invention includes a slide disk seat with a ferromagnetic material layer arranged on the central circle surface, an indirect inline dynamic balancing mechanism of a stator, a stator and a transducer fixed to the stator, slide disks sleeved at both ends of the slide disk seat, and a balancing weight block fixed to the slide disk, a mixed model inline dynamic balancing mechanism of pressure plate fixedly sleeved on the main shaft and touches with the slide seat and slide disk end surface; an electromagnetic winding is arranged by one side of the pressure board, one end surface of the pressure board is coated with ferromagnetic material layer, a sleeve is fixedly arranged on the main shaft on one side of the pressure board, an elastic component sleeved on the main shaft is arranged between the sleeve and the pressure board. The balancing device is characterized by short response time and energy saving as inline dynamic balancing compensation effect for a high speed spindle.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Method of producing biosoluble inorganic fiber
InactiveUS20120247156A1Small diameterHigh viscosityInorganic material artificial filamentsGlass furnace apparatusFiber diameterPoise
A method of producing inorganic fibers includes heating and melting an inorganic raw material that includes 70 wt % or more of silica and 10 wt % to 30 wt % of magnesia and calcia in total in a container to obtain a melt having a melt viscosity of 15 poise or less, supplying the melt to a rotor that rotates at an acceleration of 70 km / s2 or more, drawing the melt due to a centrifugal force caused by rotation of the rotor to obtain fibers, blowing the fibers off by blowing air around the rotor, and collecting the fibers to obtain fibers having an average fiber diameter of 5 μm or less.
Owner:NICHIAS CORP
Alkali-free glass and manufacturing technique thereof
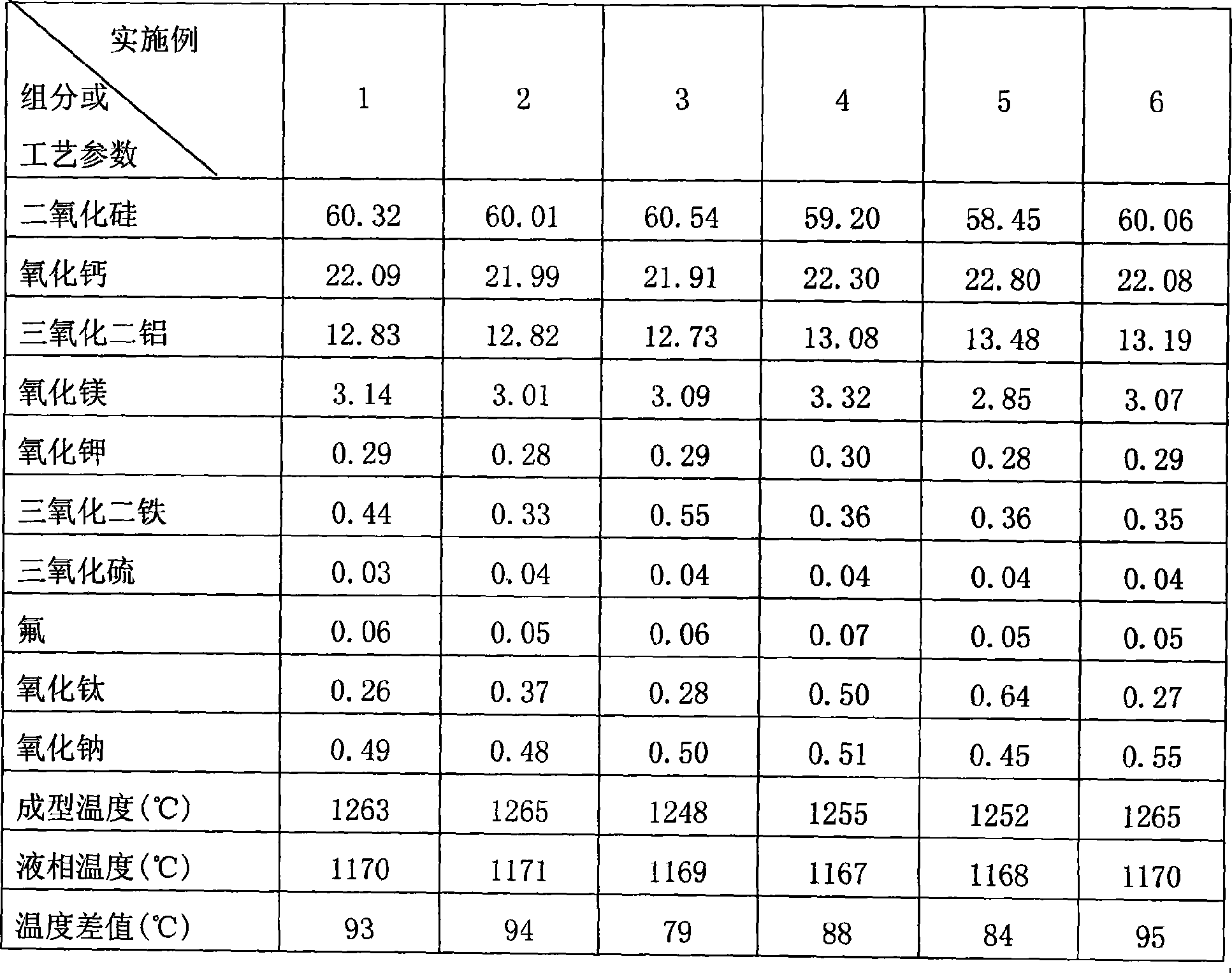
The invention relates to alkali-free glass for the production of continuous glass fiber product and production process thereof, pertaining to inorganic non-metallic material field. The main production raw materials of the alkali-free glass comprise quartz sand, limestone, pyrophyllite and dolomite; wherein, the production processes comprise proportioning, melting, fiber forming, fiber drawing and product processing; the temperature for fiber forming is 1160-1360 DEG C, the viscosity is 1000 poises and liquid phase temperature is at least 97 DEG C lower than that of the fiber forming; the weight proportions of compositions to the product are respectively that: silicon dioxide is 58-62 percent, calcium oxide 20-24 percent, aluminum oxide 12-14 percent, magnesium oxide 2-4 percent, fluorine 0-0.6 percent, potassium oxide and sodium oxide 0-2 percent in total, titanium oxide 0-2 percent, iron trioxide 0-0.6%, sulfur trioxide 0-0.6% and micro impurity 1%. By adjusting the variety and proportion thereof of glass raw materials, the invention removes fluoride materials such as fluorite and boride such as borocalcite from raw materials of glass, thereby controlling the origin of the waster gas pollutants.
Owner:JUSHI GRP CO
Surface mount device
InactiveUS20090321750A1Improve reliabilitySimple compositionFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsShear stressThermal fatigue
The disclosed subject matter is directed to a reliable surface mount device using a ceramic package, and includes LED devices that are simply composed and incorporate the use of the surface mount device. The surface mount device can include a ceramic package, a semiconductor optical chip mounted in the package, two soldering pads electrically connected to the chip electrodes and at least one dummy soldering pad located on either side of the soldering pads. Thermal fatigue located at or in the soldering connections connecting the chip electrodes to a mounting board can be reduced because the distance between the soldering pads can be reduced. The dummy soldering pad that is electrically insulated can allow the device to maintain a desirable location with poise during the reflow soldering process that occurs during manufacture, and can also reduce shear stress present at the soldering connections. Thus, the surface mount device and the LED device using the disclosed structure can maintain a high reliability even under harsh environmental conditions.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method of manufacturing glass spacers
InactiveUS6385998B1Cathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersImage/pattern display tubesMetallurgyPoise
A method of manufacturing glass spacers is provided which can enhance the degree of similarity in cross section between the mother glass and the drawn glass when manufacturing glass spacers by hot drawing the mother glass. A mother glass having a similar cross section to a desired cross section of the glass spacers is prepared. The mother glass is drawn while it is heated to a viscosity of 105 to 109 poise.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Compression tester without disturbed soil
InactiveCN101256126AEasy to operateNo disturbancePreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingEngineeringPoise
The invention discloses a compressionmeter of nondisturbed soil. A crossbeam is installed on the upper of the upright post of the bottom plating, a load bearing knife edge on the upper head face of the longitudinal girder and the groove on the bottom head face of the crossbeam are matched and fixed, the balancing counter poise is placed on the short longitudinal girder, the outer frame component comprising the load disk and the hook is equipped on the bottom of the long longitudinal girder; the bottom permeable stone, the spacing ring and the cutting ring are equipped in the hole of the foundation; the inner tube is composed of three petals and is inserted into the outer tube, the inner tube is matched with the excircle of the cutting knife, one ends of three fixed poles are respectively hinged joint with foundation, the other ends are equipped with top caps and press on the head face, when the soil body is pressed into the inner tube, the permeable stone is pressed on the soil body from the top cap, the top pressure cap is pressed on the permeable stone to form a pressure cabin component. The pressure cabin component is installed on the outer frame rack component bottom plating, the crossbeam and longitudinal girder location are adjusted, the pressure column is covered into the top pressure cap, the longitudinal girder is aimed at the top pressure cap center by pressure column, which form the nondisturbed soil compressionmeter. In order to provide nondisturbed soil sample for related research, the remoulded soil can be molded and pressed therein, and forms a sample without disturbance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for testing permeability stability of sand gravel material
InactiveCN102175585AHigh data reliabilityEasy to controlPermeability/surface area analysisSkyPressure system
The invention relates to a method for testing permeability stability of sand gravel material, belonging to the technical field of geotechnical engineering for testing the permeability stability of coarse grained soil in basic geotechnical test of the geotechnical engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting tightness of an instrument, washing the instrument, filling tested material, measuring a numeral value by the instrument, calculating and detecting bearing force of the tested material, and the like. The method can control a permeating water head and water inlet quantity; and the permeating water head is controlled by relative position relationship between two overflow devices. Permeated muddy water is guided into a mud sand settlement separating box from the bottom by a water guiding pipe; the muddy water is separated backwards under the action of gravity; the mud sand is completely separated with good effect; the load of a load pressuring system is controlled by the number of poises; settlement quantity of the sand gravel material is controlled by displacement measurement starry sky; mass change of the mud sand settlement separating box is recorded by a mass measuring system; the design of the test process can simultaneously record various test data, and the data reliability is high.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
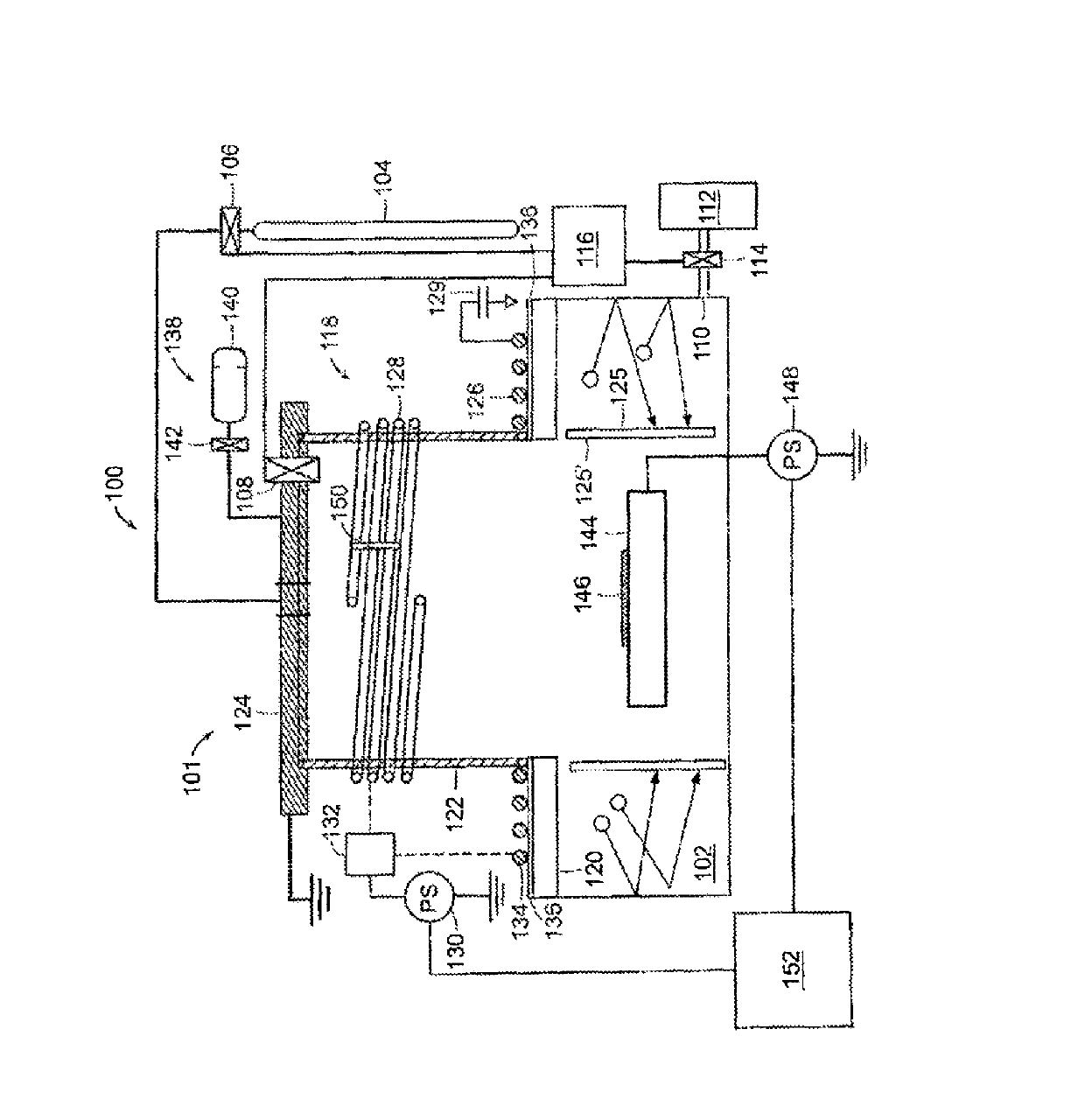
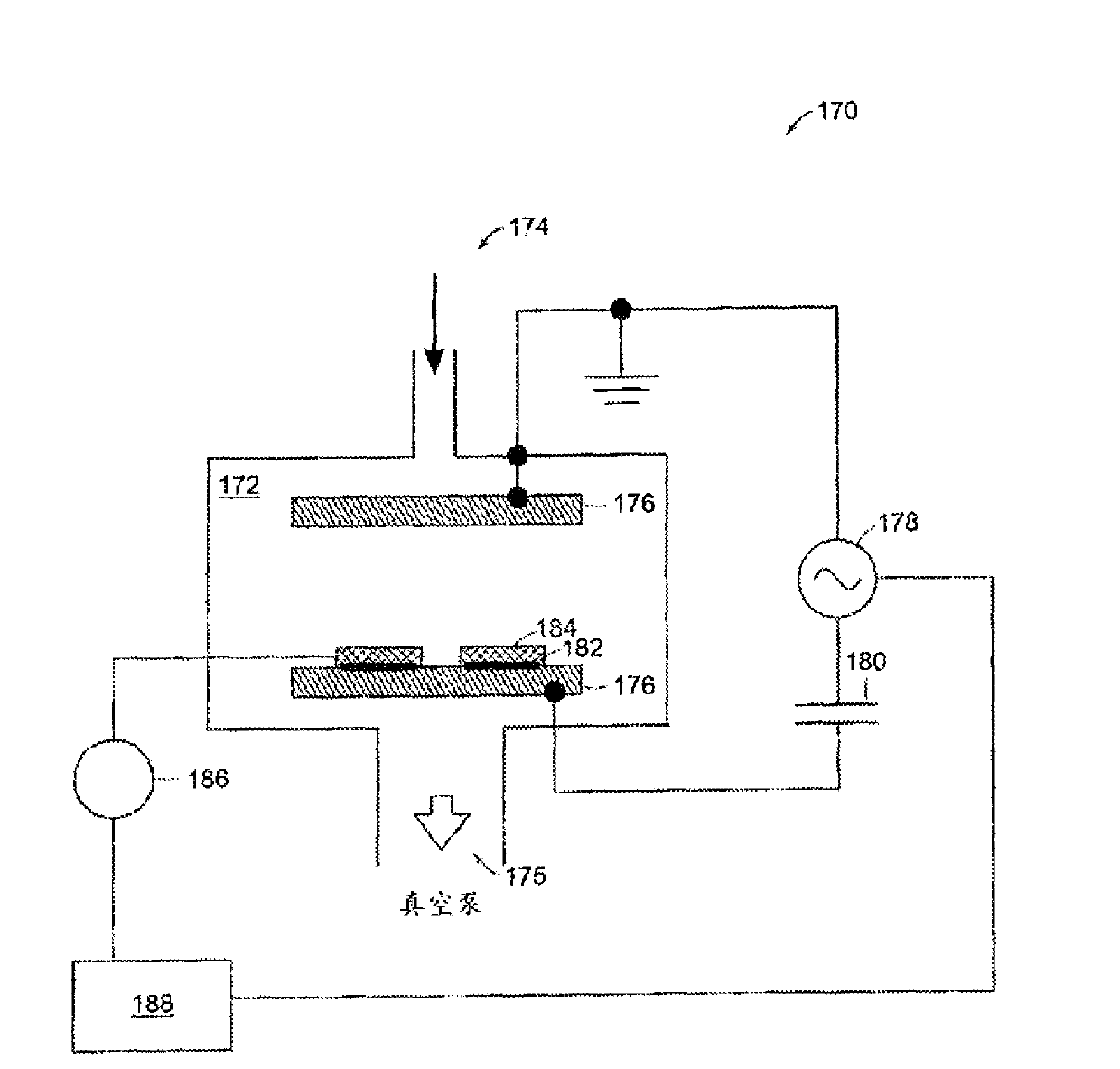
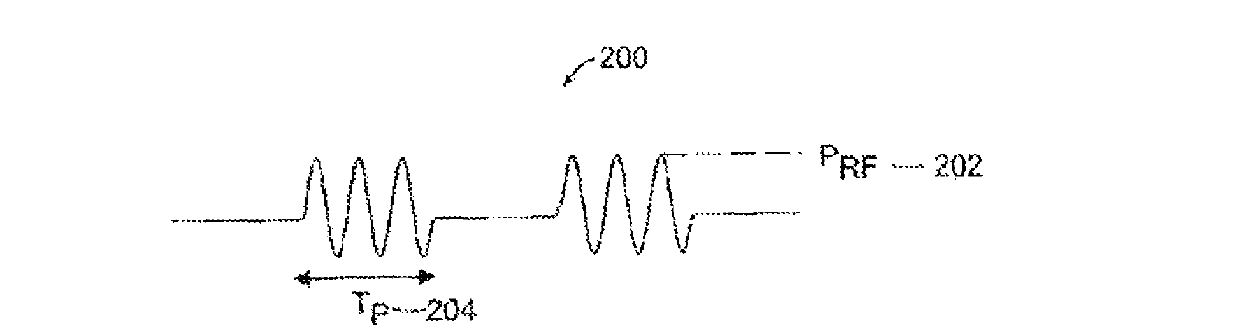
Techniques for plasma processing a substrate
Techniques for plasma processing a substrate are disclosed, In one particular exemplary embodiment, the tech Pique may be realized, with a method comprising introducing a feed gas proximate to a plasma source, whore the feed gas may comprise a first and second species, where the first and second species have different ionization energies; providing a multi-level RF power waveform to the plasma source, where the multi-level RF power waveform has at least a first power level during and a second power level during a second pulse duration where the second power level may be different from the first power level; ionizing the first species of the feed gas during the first pulse duration; ionizing the second species during the second pulse duration; and providing: a bias to the; substrate during the first poise duration.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com