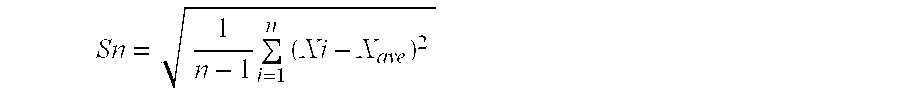Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2032 results about "Fiber diameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electret filter media
InactiveUS6119691AReduce filtration efficiencyImprove filtering effectSynthetic fibresBreathing filtersMicrometerFilter media
An electret filter media, and mask, that is made of a nonwoven web of thermoplastic microfibers. The thermoplastic microfibers are of substantially the same composition, are nonconductive, and have an effective fiber diameter less than about 15 micrometers. The nonwoven web also has sufficient unpolarized trapped charge to exhibit an initial filtration quality factor of at least 0.31 when measured under the DOP Penetration and Pressure Drop Test.
Owner:3M CO
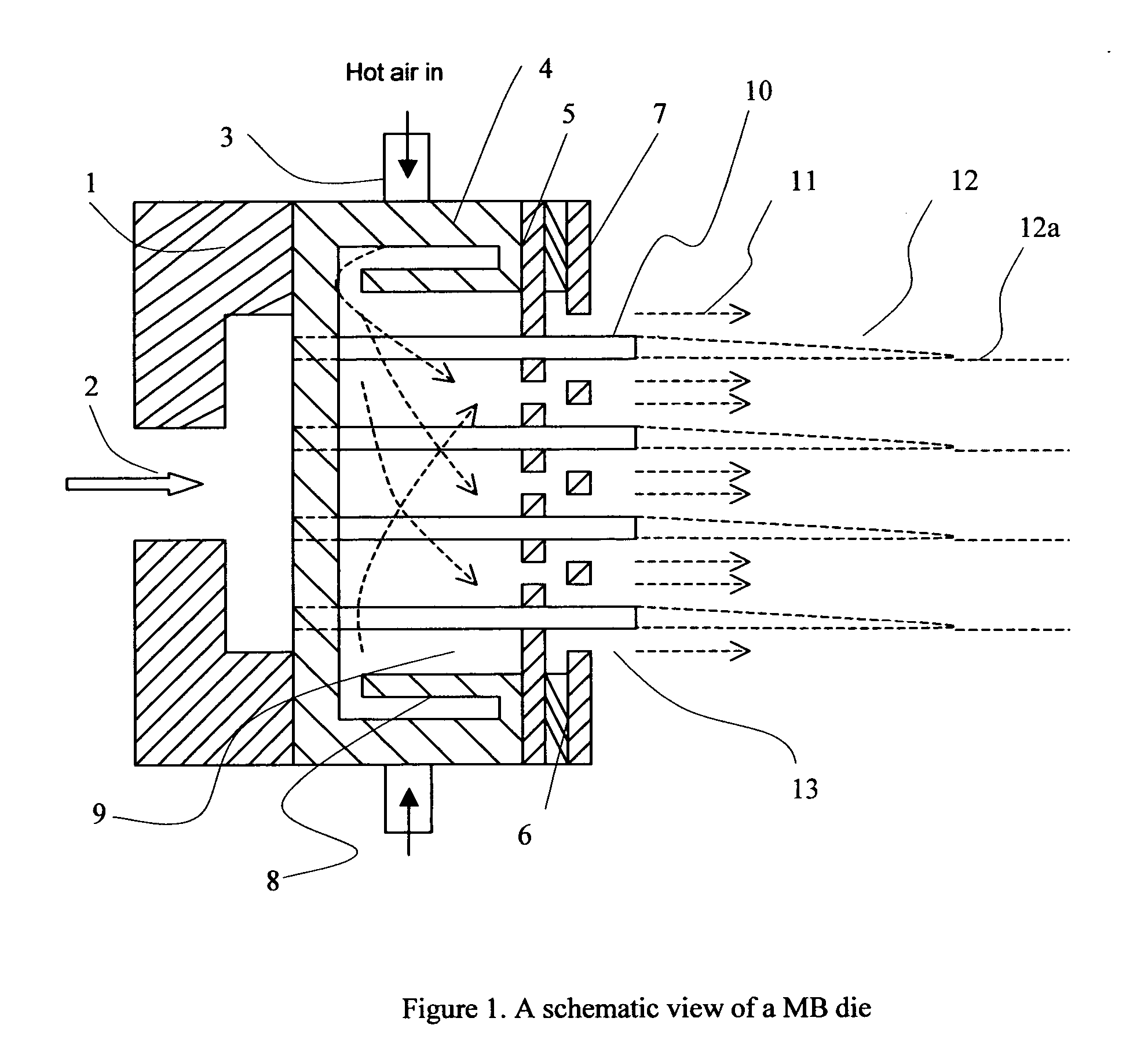
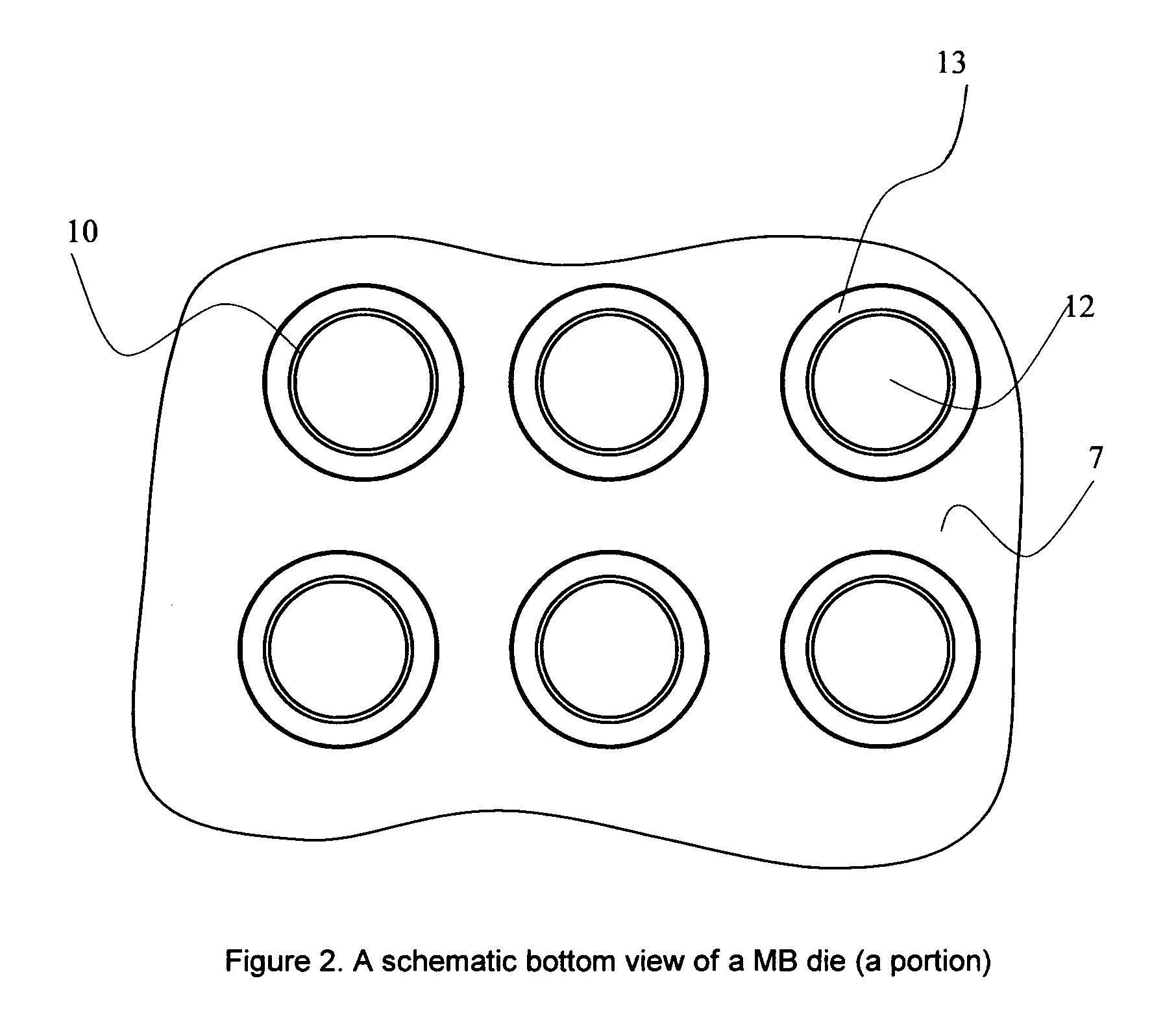
Process for forming micro-fiber cellulosic nonwoven webs from a cellulose solution by melt blown technology and the products made thereby
InactiveUS20050056956A1Artificial filament washing/dryingLoose filtering material filtersNon solventEngineering
This invention relates to a process of melt blowing a cellulose solution through a concentric melt blown die with multiple rows of spinning nozzles to form cellulosic microfiber webs with different web structures. The process comprises the steps of (a) extruding a cellulose solution (dope) through a melt blown spinneret with multiple rows of spinning nozzles; (b) drawing each individual extrudate filament to fine fiber diameter by its own air jet; (c) coagulating and entangling the fine fibers with a series of pressured hydro needling jets of recycling solution of the mixture of cellulose solvent and non-solvent in the spin-line; (d) collecting the stream of microfibers, air and needling jets on a moving collecting surface to form cellulosic fiber web; (e) hydro-entangling the said pre-bonded web downstream with at least one set of hydro needling jets of recycling solvent / non-solvent solution for forming well bonded nonwoven web; (f) regenerating the fine fibers in at least one bath for at least 5 seconds; (g) further regenerating and washing the fine fibers in another bath for at least 5 seconds; (h) pinching the well bonded melt blown cellulosic nonwoven with pressure rollers to remove major portions of the non-solvent; (i) drying the nonwoven web by heat, or vacuum or both, and (j) winding the nonwoven web into rolls.
Owner:BIAX FIBERFILM CORP
Fiber containing filter media
InactiveUS20040038014A1Efficient removalLow efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsUltrafiltrationPolymer scienceFilter media
Improved filtration media or filter bodies can be made from fine fiber and can be formed into a filtration structure having no internal defects. The filter media or filter body comprises a collection of spot in fiber with defined fiber diameter, layer thickness and media solidity. The fine fiber is formed into a media body and obtains substantial flux and filtration efficiency. The filtration media or body can comprise single or multiple layers of fine fiber combined into the improved filter body.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Vacuum insulating material and device using the same
Vacuum heat insulator comprising a laminated core made of a plurality of sheets of inorganic fibers having 10 μm or smaller in diameter and a certain composition including SiO2 as a main component, Al2O3, CaO, and MgO, a gas barrier enveloping member, and an absorbent. The vacuum heat insulator is characterized by having at least one groove formed therein after fabrication of the vacuum heat insulator. Further, the vacuum heat insulator is characterized by using inorganic fiber core of which a peak of distribution in fiber diameter lies between 1 μm or smaller and 0.1 μm or larger, and not containing binding material for binding the fiber material. Electronic apparatuses use the vacuum heat insulator. With use of the vacuum heat insulator, electronic and electric apparatuses superior in energy saving and not to present uncomfortable feeling to the user can be provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Nonwoven containing acoustical insulation laminate
The present invention relates to an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material. The high loft material of the present invention provides bulk to the first layer and may or may not have sound attenuating properties. Examples of the high loft material include, for example, fiberglass and high loft nonwoven webs. Also disclosed in a method of attenuating sound waves passing from a sound source area to a second area. The method includes positioning an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material, between the sound source area and the second area.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Melt-blown non-woven fabric, and nozzle piece for producing the same
InactiveUS6319865B1Efficient productionLayered productsMelt spinning methodsEngineeringFiber diameter
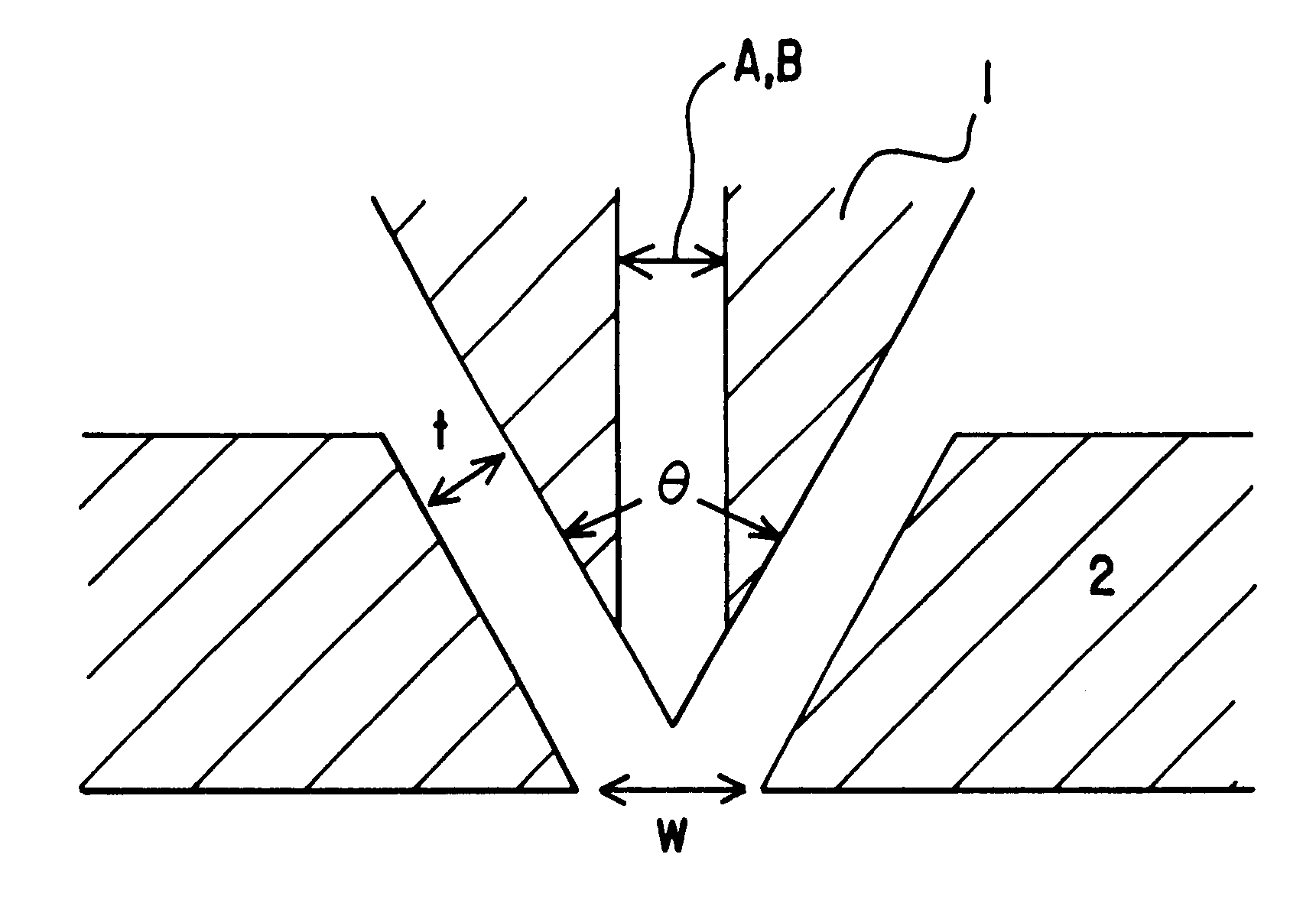
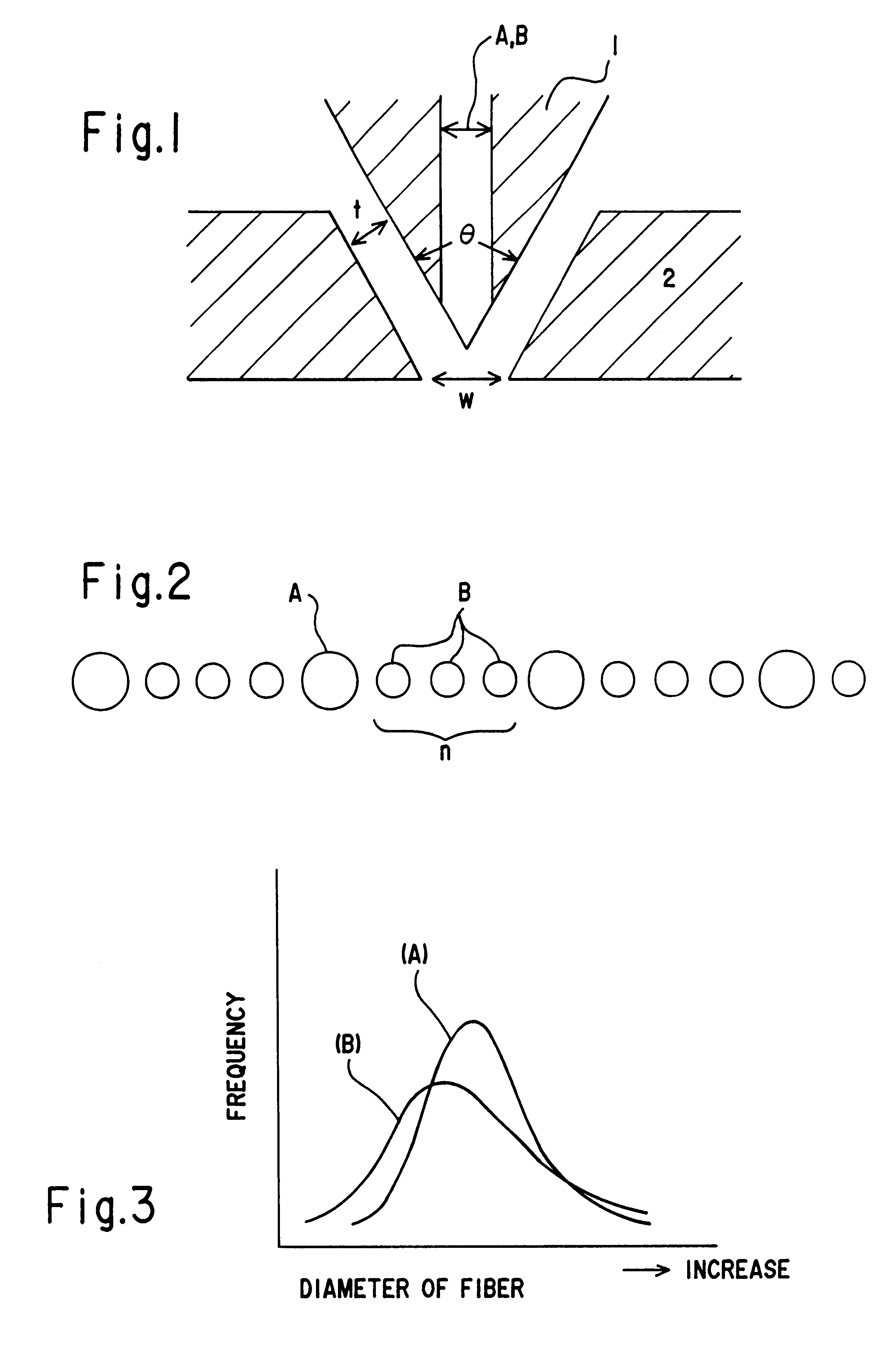
The nozzle piece of the present invention is provided with circular cross sectional nozzles having different sizes disposed in a row in front of the die, with n-numbered smaller nozzles B (hole diameter: Db) between adjacent larger nozzles A (hole diameter: Da). It gives melt-blown non-woven fabric of monolithic structure in one step, composed of fine fibers having a diameter in a range from 1 to 10 mum diameter Variance ratio F of 2.0 or more and wide fiber diameter distribution.
Owner:TONEN TAPYRUS
High efficiency synthetic filter medium
InactiveUS6123752AHigh strengthReduce basis weightOther chemical processesElectrostatic separationHEPAGram
A high efficiency filtration medium comprised of a nonwoven filter web of electret charged fibers of a nonconductive thermoplastic resin having a resistivity greater than 1014 ohm-cm, preferably polypropylene. The nonwoven filter web has a basis weight (BW) of less than 60 grams / m2, an effective fiber diameter (EFD) of less than 5 microns and a penetration (PEN) of less than 0.03%, wherein the ratio); BW / (EFD.PEN) is greater than 200. The invention filter medium can be easily used in applications requiring HEPA performance at relatively low pressure drops.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
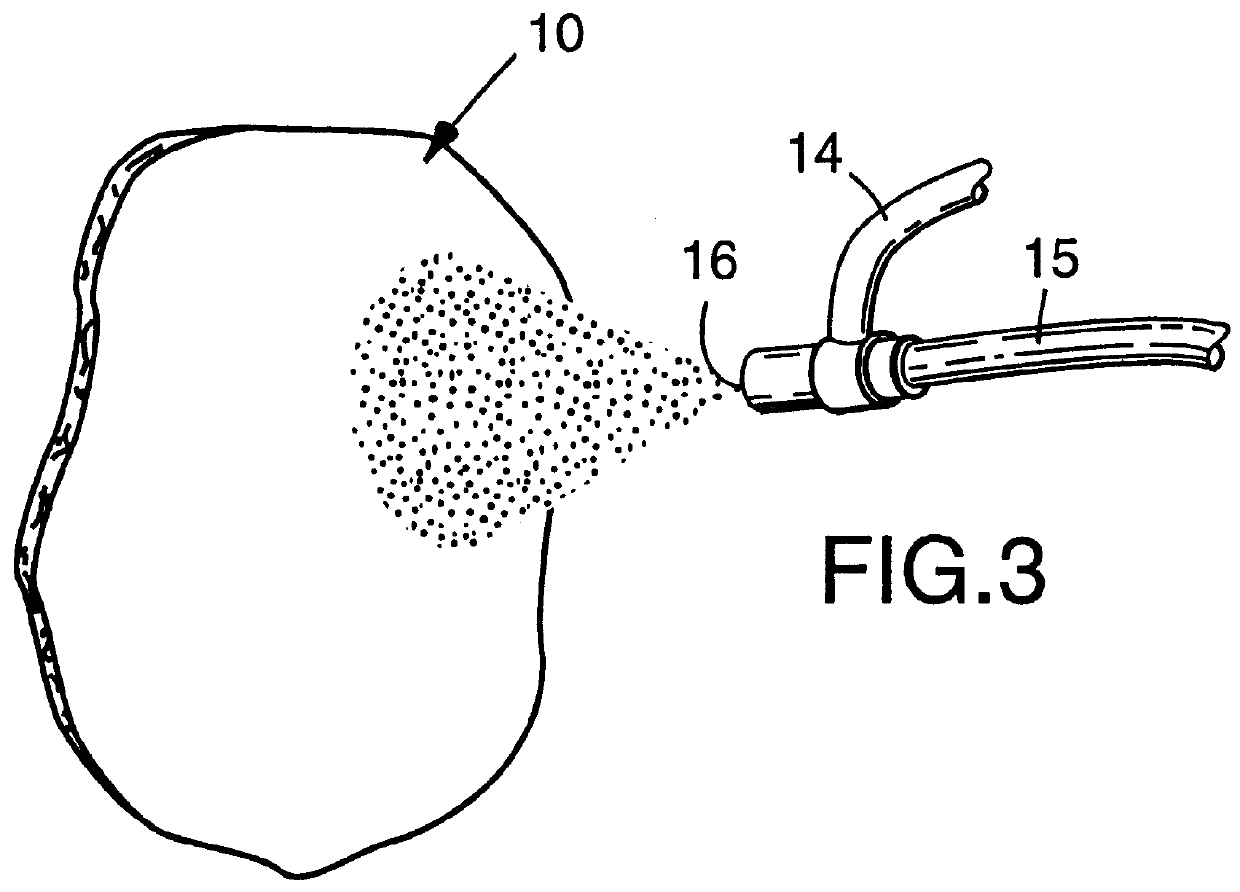
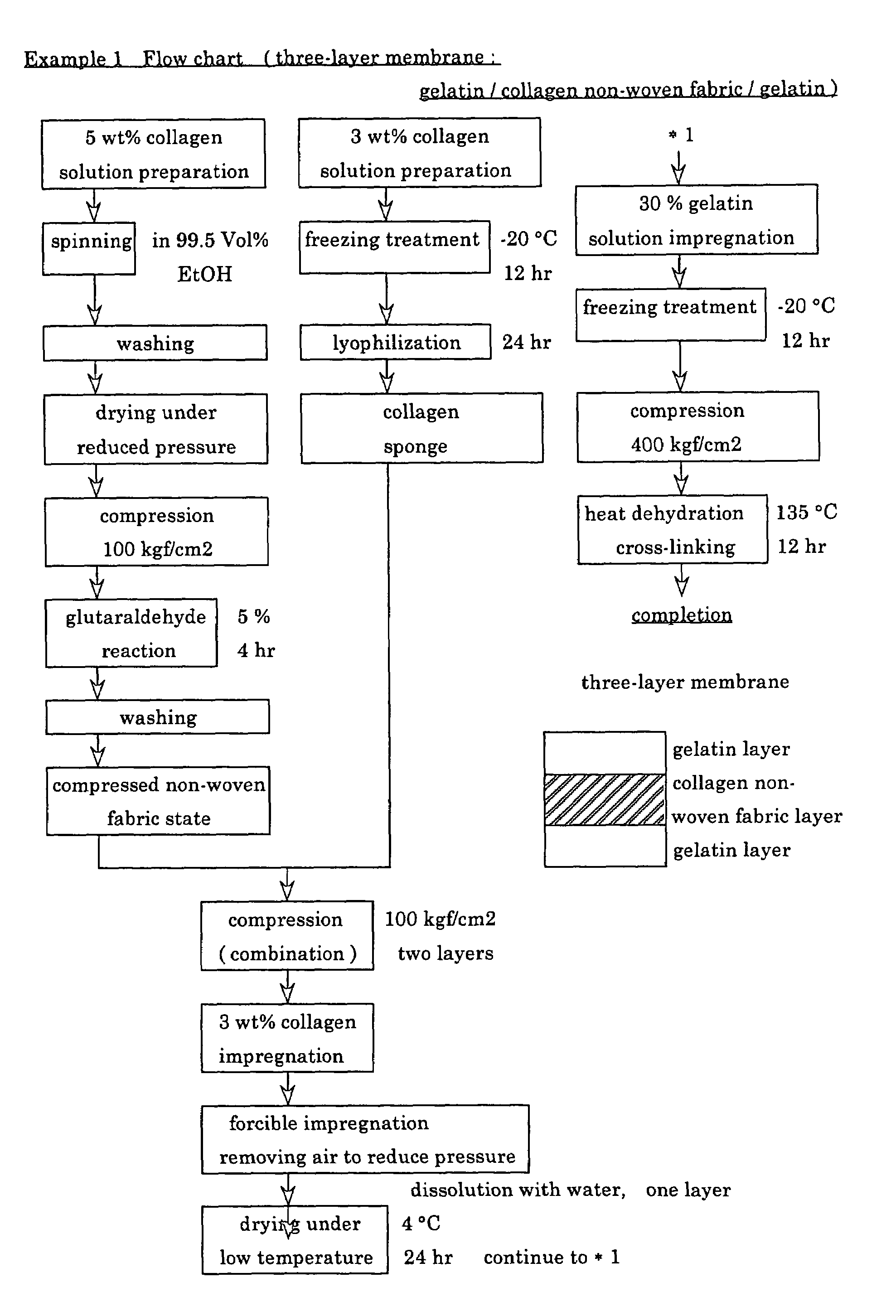
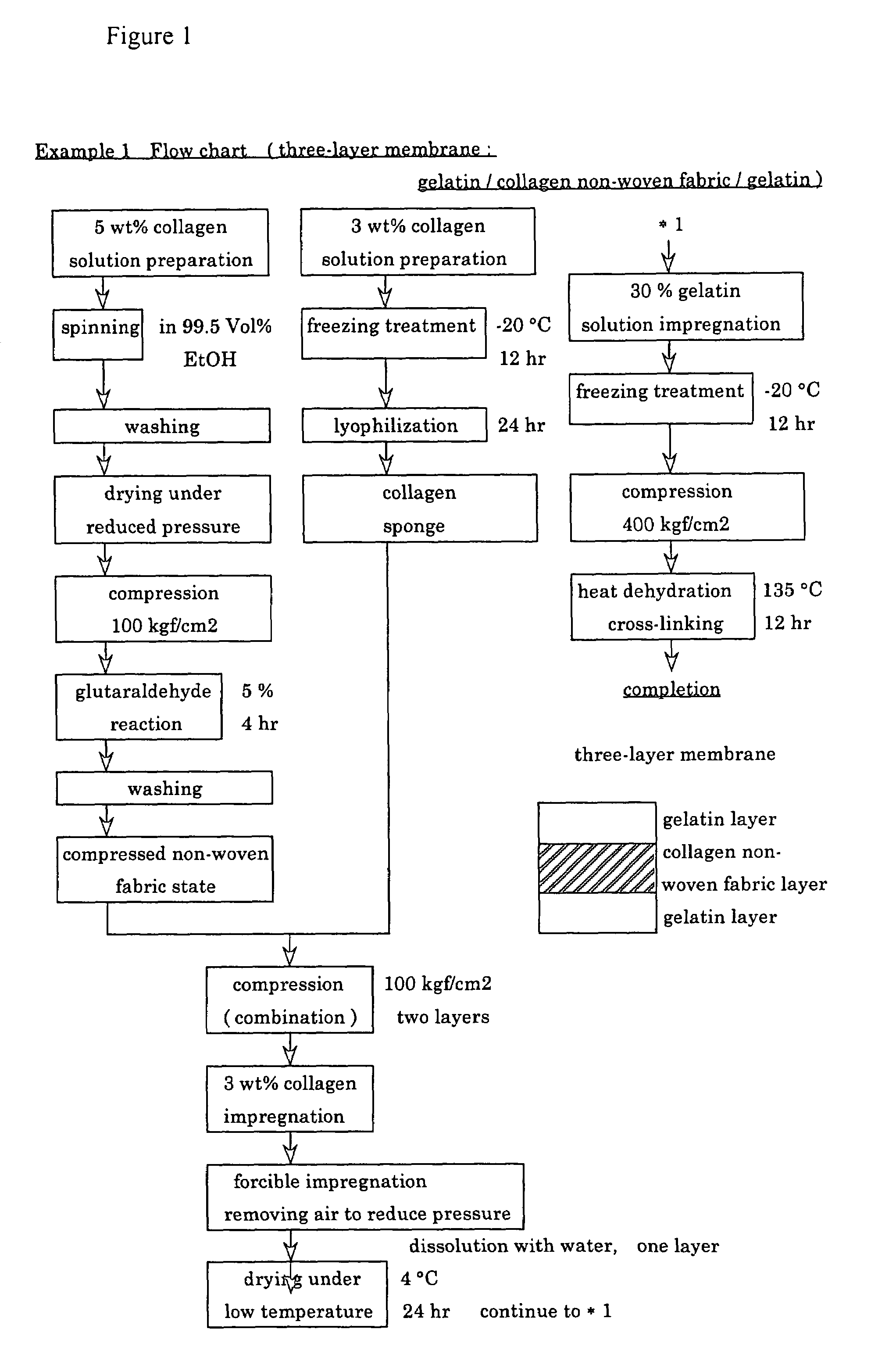
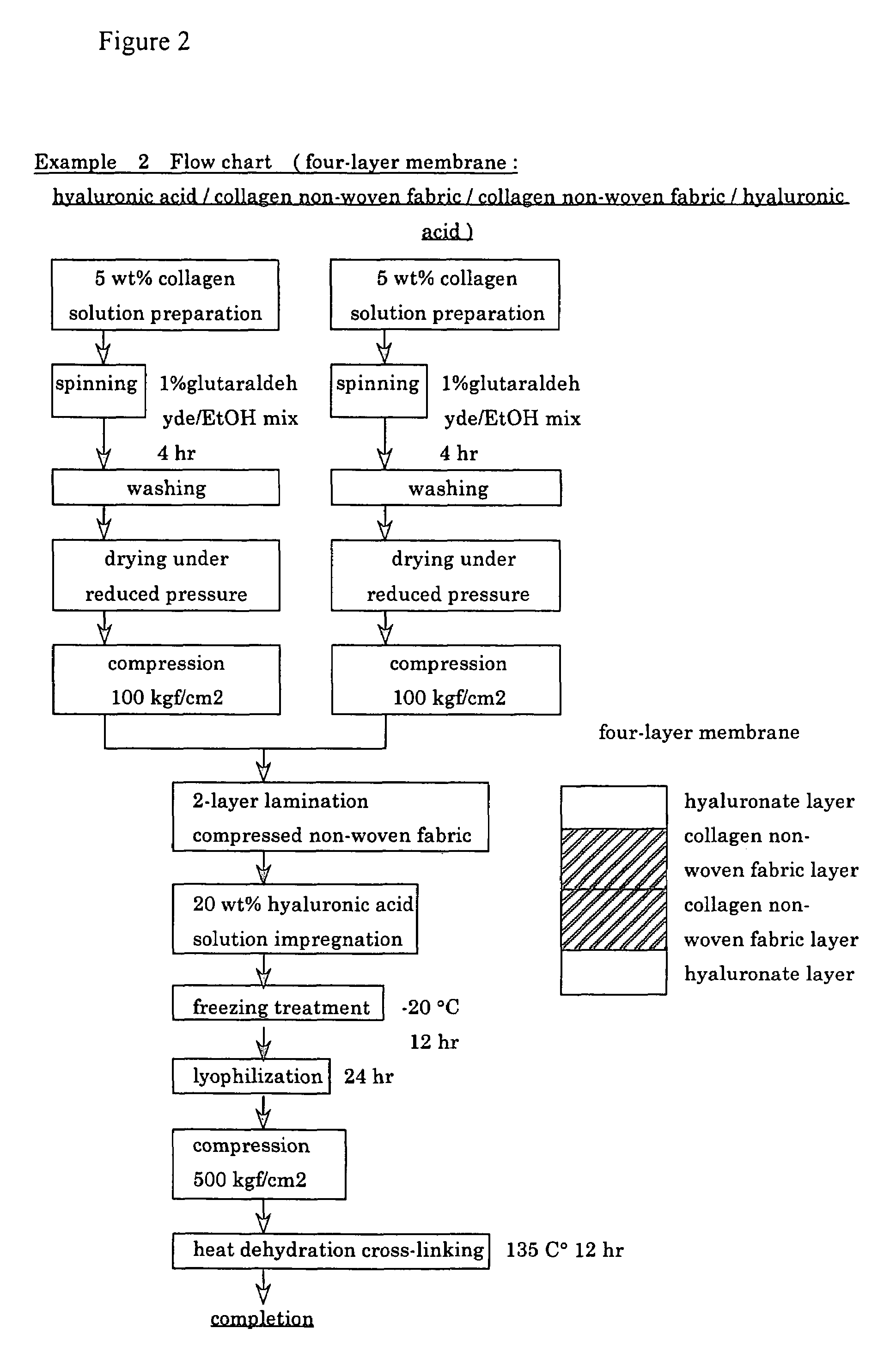
Suturable adhesion-preventing membrane
InactiveUS6977231B1High strengthGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkDecomposition
A suturable adhesion-preventing membrane has high suture strength, good biocompatibility, decomposition and absorption in a living body, sufficient adhesion-preventing effect, and desirable guided tissue regeneration. The membrane is composed of at least one non-woven fabric layer made of collagen fibers, or a laminated membranous substance consisting of at least one non-woven fabric layer made of collagen fibers and at least one sponge layer made of collagen, and a coating layer of gelatin or hyaluronic acid on the surface or surfaces of the above membrane. Preferably, the membrane comprises one to six compressed cross-linked collagen non-woven fabric layers wherein a layer has a fibers having a fiber diameter of 0.05 mm to 1.0 mm, a bulk density of 5.0×10−4 to 5 g / cm3 and a thickness of 0.1 mm to 50 mm, and a coating layer containing gelatin or hyaluronic acid and having a thickness of 0.05 mm to 20 mm, wherein the coating layer covers one or both sides or a part or whole of the surface of the membrane.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Coalescing filtration medium and process
A coalescing filtration medium is disclosed for removing liquid aerosols, oil and / or water from a gas stream. The medium contains a nanofiber web of at least one nanofiber layer of continuous, substantially polyolefin-free, polymeric nanofibers, each nanofiber layer having an average fiber diameter less than about 800 nm and having a basis weight of at least about 2.5 g / m2.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Coated nanofiber webs
ActiveUS20050008776A1Liquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPlasticizerNanoparticle
The present invention is directed to a method of forming nonwoven webs comprising coated fibers. The method of forming the nonwoven web generally comprises the steps of forming fibers from a melt fibrillation process, forming at least one fluid stream containing a coating substance, applying the coating substance onto the surface of the fiber, and depositing the coated fibers on a surface to form a web. Typically, the fibers are coated in flight. Preferably, the melt fibrillation process to form the fibers is a melt film fibrillation process. A melt film fibrillation process generally includes the steps of providing a polymeric melt, utilizing a central fluid stream to form an elongated hollow polymeric film tube, and using air to form multiple nanofibers from the hollow tube. The nonwoven web may comprise a layer having a significant number of nanofibers with diameters less than one micron. The layer may comprise two or more pluralities of fiber diameter distributions wherein at least one plurality has an average fiber diameter of less than about one micron. The coating substance can be selected from the group consisting of lotions, powders, surfactants, softeners, nanoparticles, creams, gels, conducting fluids, hydrophilic agents, hydrophobic agents, hygroscopic agents, emollients, plasticizers, absorbent gelling material, antimicrobial agents, and combinations thereof. A preferred coating substance is a surfactant. Another preferred coating substance is a hydrophilic or hydrophobic substance. The present invention is also directed to a nonwoven web comprising a layer having a significant number of nanofibers with diameters less than one micron and a coating substance is applied to a surface of said nanofibers
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Durable nanoweb scrim laminates
A filter media comprising a nanofiber layer and a substrate layer; the nanofiber layer comprising a polymer material and having a fiber diameter of about 0.01 to 1.0 micron, a basis weight of about 0.5 to 30 gsm, and a thickness of at least about 2 microns, the nanofiber layer further having a surface stability index of at least about 5 kN / m, the media further being pleated.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Vacuum heat insulating material and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20040253406A1Improve performanceLow thermal conductivityThermal insulationDomestic cooling apparatusSorbentDecreased pressure
Provided is a vacuum heat insulating material, using inorganic fibers as a core material, high in heat insulating performance (low in thermal conductivity), capable of maintaining the heat insulating performance for a long period, free of defects such as projections and depressions on a large scale on a surface thereof, short in manufacturing time and advantageous in terms of cost; and a manufacturing method therefor. A vacuum heat insulating material of the present invention is of a construction in which a core material 1 and a gas adsorbent 2 are housed in a bag 3 made from a gas barrier film and the interior thereof is reduced in internal pressure thereof and air-tightly sealed, wherein the core material 1 is a molded product obtained by coating a binder B on inorganic fibers having an average fiber diameter in the range of from 3 to 5 mum at a coating amount in the range of from 0.5 to 1.5 wt % relative to the fibers and heat pressing the inorganic fibers, or a laminate fabricated by stacking two or more sheets of the molded product.
Owner:ASAHI FIBER GLASS CO LTD
Vacuum thermal insulating material, process for producing the same and refrigerator including the same
A vacuum heat insulator according to the present invention includes a core molded to be plate-shaped with the use of a binding agent. The vacuum heat insulator assumes any one of the following configurations. A) The core is formed by curing a fiber aggregate by means of a binding agent. The fibers have an average fiber diameter of at least 0.1 μm but at most 10 μm, and voids defined by fibers have a void diameter of at most 40 μm. The core has a percentage of the voids of at least 80%. B) The binding agent is varied in concentration in a through-thickness direction of the core. C) A cured layer solidified by the binding agent is formed on at least one side surface of the core. D) The core contains fibers having a length of at most 100 μm. The fibers are oriented perpendicular to a direction of heat transmission. Such vacuum heat insulator is excellent in adiabatic property. Refrigerators, to which such a vacuum heat insulator is applied, are made small in size, or have a large inner volume, or contribute to energy saving.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Cellulose Nonwoven Fabric
ActiveUS20070207692A1Raw materials are simpleSimple structureFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPaper/cardboardPorosityCellulose fiber
Disclosed is a cellulose nonwoven fabric containing cellulose fibers having a maximum fiber diameter of not more than 1500 nm and a crystallinity determined by solid state NMR techniques of not less than 60%. The porosity of the cellulose nonwoven fabric is not less than 40% and not more than 99%.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Fiber-reinforced composite material and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20090054552A1Moisture absorptivity and transparencySolid-state devicesThin material handlingAlcoholFiber-reinforced composite
Disclosed is a highly transparent fiber-reinforced composite material including an assembly of cellulose fibers of 4 to 200 nm average fiber diameter impregnated with a matrix material so as to not only remedy the moisture absorbency attributed to cellulose fibers but also further improve transparency. There is provided a fiber-reinforced composite material including an assembly of cellulose fibers impregnated with a matrix material. In the fiber-reinforced composite material, hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers are chemically modified through a reaction with one or more chemical modifiers selected from the group consisting of an acid, an alcohol, a halogenating reagent, an acid anhydride, and an isocyanate so that the ratio of a functional group introduced by the chemical modification is 5 to 40 percent by mole based on the hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers before the chemical modification. The chemical modification of hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers can reduce the hydrophilicity of cellulose fibers to thereby reduce the moisture absorbency of fiber-reinforced composite material. Further, the affinity between cellulose fibers and matrix material can be enhanced to thereby further improve transparency.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +2
Wet type nonwoven fabric and filter
ActiveUS20100133173A1Suitable for collectionLayered productsSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperPolymer scienceSingle fiber
The present invention is a wet type nonwoven fabric that includes two or more kinds of fibers, wherein the wet type nonwoven fabric includes a short fiber A that is constituted of a fiber-forming thermoplastic polymer and has a fiber diameter D of from 100 to 1000 nm and the ratio of a fiber length L to the fiber diameter D, L / D, in the range of from 100 to 2500 in from 4 to 50% by weight relative to the total weight of the nonwoven fabric, and a binder fiber B that has a single fiber fineness of 0.1 dtex or less in from 10 to 50% by weight relative to the total weight of the nonwoven fabric.
Owner:TEIJIN FRONTIER CO LTD
High Capacity Filter Medium
InactiveUS20070220852A1Low activation temperatureCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationPolymer scienceCost effectiveness
Various high performance, high efficiency, long service interval air filter media that are cost effective and easy to manufacture are provided. The filter media of the present invention can have at least two layers comprising blends of binder and non-binder fibers that are thermally bonded to one another and set to caliper in a high velocity forced draft oven. The layers can also be subsequently resin saturated, dried, and optionally cured. The resulting media can be characterized as having a gradient in properties such as fiber composition, fiber diameter, solidity, basis weight, and saturant content.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH VOSE
Fiber composite
InactiveUS20100272980A1High transparencyLow water absorptionMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentRecord information storageThermal expansionCellulose fiber
To provide a cellulose fiber composite having high transparency, low water absorption and low coefficient of linear thermal expansion.A fiber composite which comprises fibers having an average fiber diameter of at most 30 nm and a matrix material and which has a haze of at most 5 according to JIS K-7136 when the fiber composite has a thickness of 100 μm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Absorbent Article With Barrier Component
InactiveUS20100028638A1Super breathableEasy to fold, ply or wrinklePersonal careSynthetic resin layered productsFiber diameterMaterials science
An absorbent article may comprise a barrier component, the barrier component may comprise a nonwoven barrier sheet, the nonwoven barrier sheet may comprise a spunbond nonwoven web comprising spunbond fibers, and the nonwoven barrier sheet may further comprise a meltblown nonwoven web comprising meltblown fibers. The spunbond fibers may have a number average fiber diameter of from about 6 to about 18 microns. The meltblown fibers may have a number average fiber diameter from about 1 to about 5 microns. And, the total weight percentage (by basis weight of the nonwoven barrier sheet) of the meltblown web may be from about 5% to about 30%.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Antimicrobial, dustproof fabric and mask
InactiveUS20110232653A1Type of reductionReduce infectionLayered productsDiagnosticsNanofiberFiber diameter
An antimicrobial, dustproof fabric includes a textile material layer which is composed of microfibers with an average fiber diameter of from 1 to 100 μm and contains an inorganic porous substance, and a nanofiber nonwoven fabric layer which is laminated on the textile material layer and has an average fiber diameter of at least 1 nm but less than 1,000 nm. Hygienic products such as masks obtained using the fabric efficiently block microbes such as viruses, and inactivate or destroy the captured microbes.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
Nonwoven fabric composed of ultra-fine continuous fibers, and production process and application thereof
InactiveUS20050079781A1Increase flexibilityIncrease softnessSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingPolymer sciencePolyvinyl alcohol
A nonwoven fabric composed of ultra-fine continuous fibers having a mean fineness of not more than 0.5 dtex is prepared. The nonwoven fabric comprises a water-soluble thermoplastic resin in a proportion of not more than 5% by weight relative to the nonwoven fabric, has an absorbing height of not less than 30 mm as determined at 20° C. after 10 minutes based on Byreck method when the nonwoven fabric immersion-treated for 60 minutes in a water of 80° C. is used, and satisfies the following formula: (B) / (A)≧0.25, wherein the symbol (B) represents a tensile strength [N / 5 cm] in the longitudinal direction and the lateral direction of the nonwoven fabric and the symbol (A) represents a fabric weight [g / m] of the nonwoven fabric. In the nonwoven fabric, not less than 30% of the surface may be coated with the water-soluble thermoplastic resin. The water-soluble thermoplastic resin may be a water-soluble thermoplastic polyvinyl alcohol, e.g., a modified polyvinyl alcohol containing an ethylene unit in a proportion of 3 to 20 mol %. The present invention provides a nonwoven fabric composed of ultra-fine continuous fibers, having a high flexibility or softness, and having a high mechanical strength even when the fiber diameter is small, and having an excellent water absorbency, as well as a production process and an application thereof.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Methods for producing di-block polymers
The current major way of making nanofibers is electrospinning. However, the minimum fiber diameter is limited to be about 300–500 nm, which is not compliant with the physical definition of nano structures (in the region of 1 to 100 nm). Futher, the productivity is relatively low. This invention provides a method for manufacturing a nano-sized di-block polymer including at least a hard-segment polymer and a soft-segment polymer. First, a sample containing the hard-segment polymer, the soft-segment polymer, and a catalyst is dissolved in a first solvent. Then the dissolved sample is cast on substrate, and then the first solvent to is removed form a dried sample. Finally, the nano-sized di-block polymer is formed by crew-cutting.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Coated nanofiber webs
The present invention is directed to a method of forming nonwoven webs comprising coated fibers. The method of forming the nonwoven web generally comprises the steps of forming fibers from a melt fibrillation process, forming at least one fluid stream containing a coating substance, applying the coating substance onto the surface of the fiber, and depositing the coated fibers on a surface to form a web. Typically, the fibers are coated in flight. Preferably, the melt fibrillation process to form the fibers is a melt film fibrillation process. A melt film fibrillation process generally includes the steps of providing a polymeric melt, utilizing a central fluid stream to form an elongated hollow polymeric film tube, and using air to form multiple nanofibers from the hollow tube. The nonwoven web may comprise a layer having a significant number of nanofibers with diameters less than one micron. The layer may comprise two or more pluralities of fiber diameter distributions wherein at least one plurality has an average fiber diameter of less than about one micron.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Negative Electrode Material for Lithium Battery, and Lithium Battery
InactiveUS20070275302A1Lower electrode resistanceHigh electrode strengthNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsCarboxymethyl celluloseCarbon fibers
The present invention relates to a negative electrode material for a lithium battery characterized by comprising a carbonaceous negative electrode active substance having a specific surface area of 1 m2 / g or more, a binder formed of styrene-butadiene rubber and a carbon fiber having a fiber diameter of 1 to 1,000 nm; and to a lithium battery using the negative electrode material, which has excellent characteristics, i.e., low electrode resistance, high electrode strength, excellent electrolytic solution permeability, high energy density, and good high-speed charging / discharging performance. The negative electrode material contains carbon fiber in the amount of 0.05 to 20 mass % and the binder formed of styrene-butadiene rubber in 0.1 to 6.0 mass %, and may further contain a thickner such as carboxymethyl cellulose in the amount of 0.3 to 3 mass %.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK +1
Fiber containing filter media
InactiveUS20050163955A1Improve lifetimeImprove propertiesPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUltrafiltrationPolymer scienceFilter media
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Filter media suitable for hydraulic applications
ActiveUS20100252510A1Water/sewage treatmentMembrane filtersGlass fiberElectrical resistance and conductance
Filter media, including those suitable for hydraulic applications, and related components, systems, and methods associated therewith are provided. The filter media described herein may include two or more layers, at least one of the layers having a relatively high percentage of microglass fibers. Additionally, the filter media may be designed such that the ratio of average fiber diameters between two layers is relatively small, which can lead to a relatively low resistance ratio between the layers. The filter media has desirable properties including high dirt holding capacity with low basis weight and a low resistance to fluid flow. The media may be incorporated into a variety of filter element products including hydraulic filters.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH VOSE
Preparation method of silicon-carbide-fibrofelt-enhanced silica aerogel composite material
The invention relates to a preparation method of a silicon-carbide-fibrofelt-enhanced silica aerogel composite material, and relates to an aerogel composite material. According to the invention, a carbon-rich silicon carbide micro-nano ceramic fibrofelt with small fiber diameter, high porosity, communicating pores, fast impregnation speed, and good compatibility with a substrate is prepared with a static electro-spinning technology combined with a precursor conversion method; a silica sol is prepared with an acid-alkali two-step method; with an infiltration technology, the electro-spun silicon carbide ceramic fibrofelt or precast is soaked into the sol; and through processes such as gel process, aging, curing, solvent exchange, supercritical drying, and the like, the silicon-carbide-fibrofelt-enhanced silica aerogel composite material is obtained. The prepared composite material has the characteristics of low density, large specific surface area, super-hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and the like. The strength and toughness of the material are also greatly improved. The carbon-rich silicon carbide fiber has an infrared shielding effect, such that composite material thermal insulation effect and ultra-high-temperature stability can be improved.
Owner:ZHONGKE RUNZI (CHONGQING) ENERGY SAVING TECH CO LTD
Stretch nonwoven fabric and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20060141883A1Feel goodNarrow distributionWoven fabricsNon-woven fabricsPolymer scienceThermoplastic polyurethane
A spunbonded elastic nonwoven fabric according to the invention comprises fibers formed from a polymer comprising a thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer, wherein the thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer has a solidifying point of 65° C. or above as measured by a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and contains 3.00×106 or less polar-solvent-insoluble particles per g as counted on a particle size distribution analyzer, which is based on an electrical sensing zone method, equipped with an aperture tube having an orifice of 100 μm in diameter, and wherein the fibers have diameters such that the standard deviation of fiber diameters (Sn) divided by the average fiber diameter (Xave) (Sn / Xave) gives a value of 0.15 or less.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Medical adhesive tape or sheet
InactiveUS20080095979A1Reduce void ratioImprove textureLayered productsAdhesive articlesAdhesive beltFiber diameter
The present invention provides a medical adhesive tape or sheet having a superior texture, which can be easily cut with hands to form a good cross-section. The medical adhesive tape or sheet of the present invention is characterized in that it comprises a support, which is a multi-layer laminate of non-woven fabrics having different fiber diameters and treated with a sealer, and an adhesive layer laminated on one surface of the support, wherein at least the support is perforated, the perforation forms plural pores sequenced at least in one direction, the ratio (b / a) of interval a of the perforated part and interval b of the non-perforated part in one direction is 1-1.5, and the ratio (c / d) of the tensile strength c in the longitudinal direction and the tensile strength d in the width direction is 0.8-1.7. Consequently, a medical adhesive tape or sheet having a superior texture, which can be easily cut with hands to form a good cross-section without using a cutting tool such as scissors and the like is provided.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Scaffold
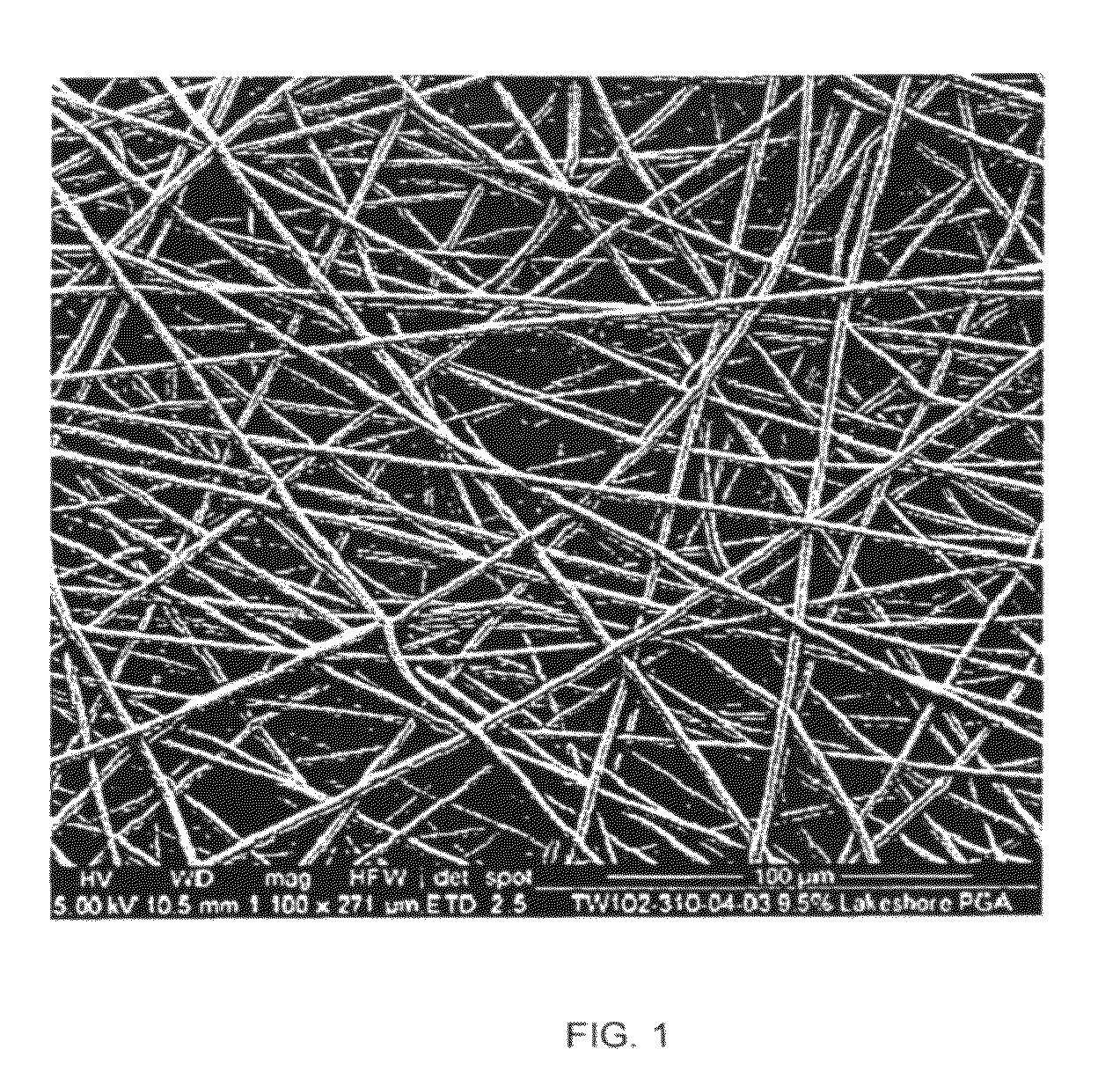
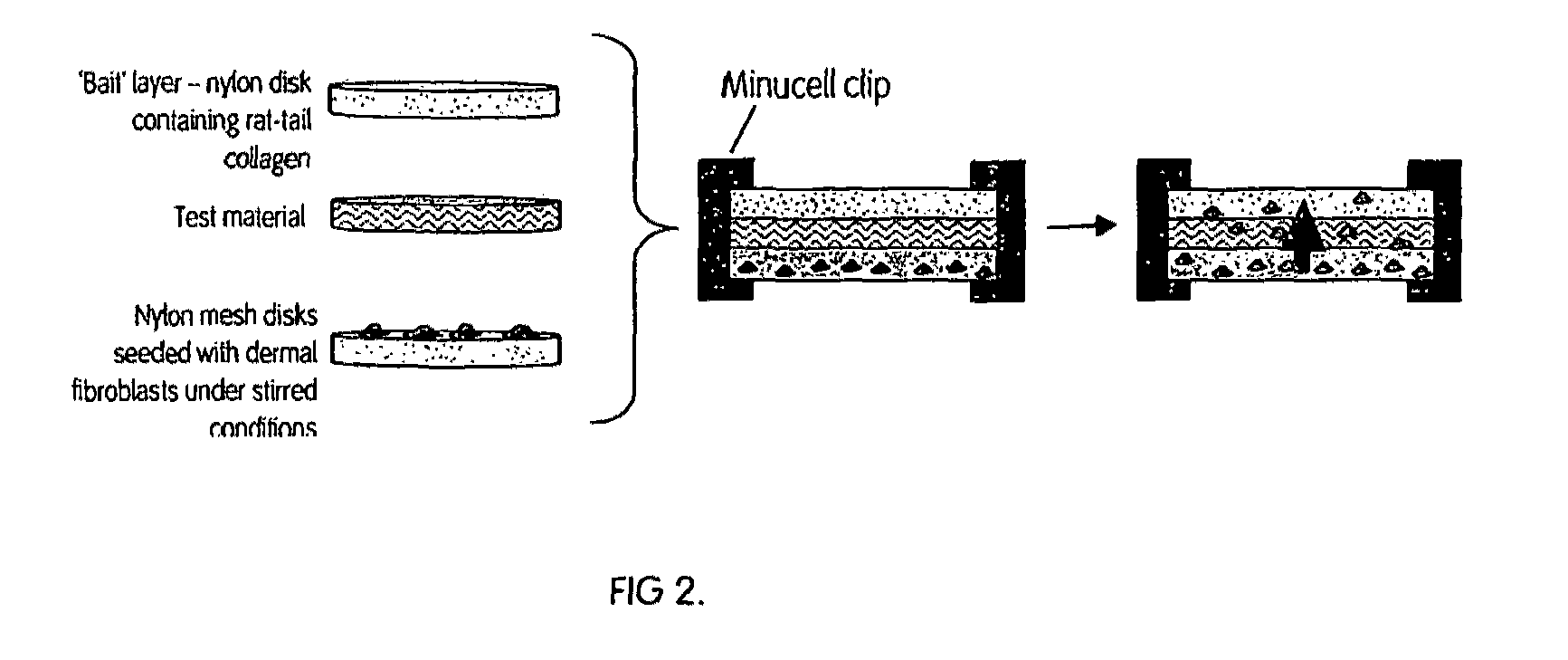
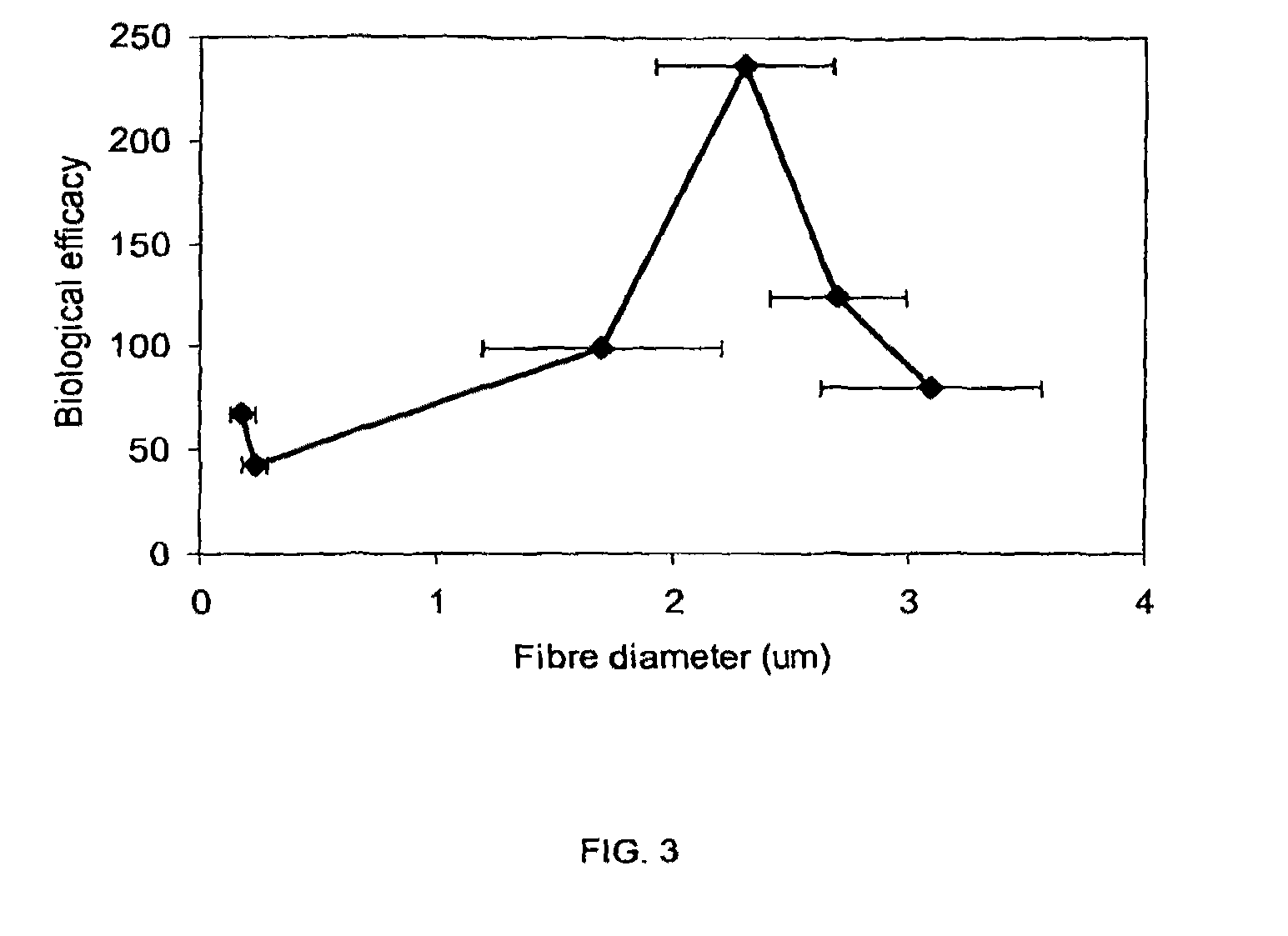
ActiveUS8338402B2Time requiredPromote migrationBiocideElectric discharge heatingSource materialFiber diameter
The present invention relates to scaffolds which can be used as medical devices for guided tissue regeneration and repair, in particular the invention is directed to a scaffold comprising fibers having a mean fiber diameter of between from about 1.2 to 4.0 microns, wherein the fibers comprise a glycolide. The invention further relates to the use of the scaffolds for the selective capture of cell populations for a cell source material.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com