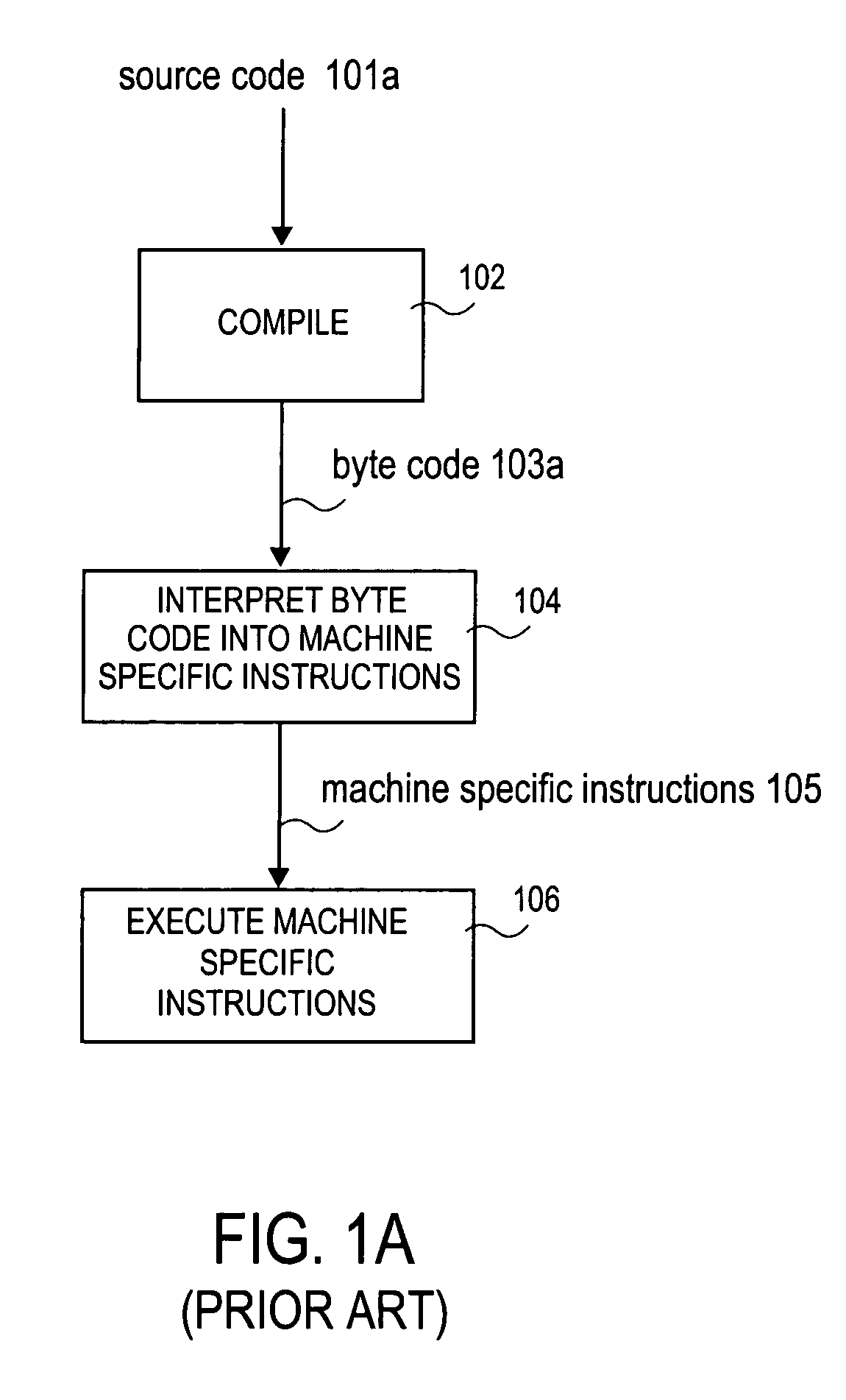
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
431 results about "Byte code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
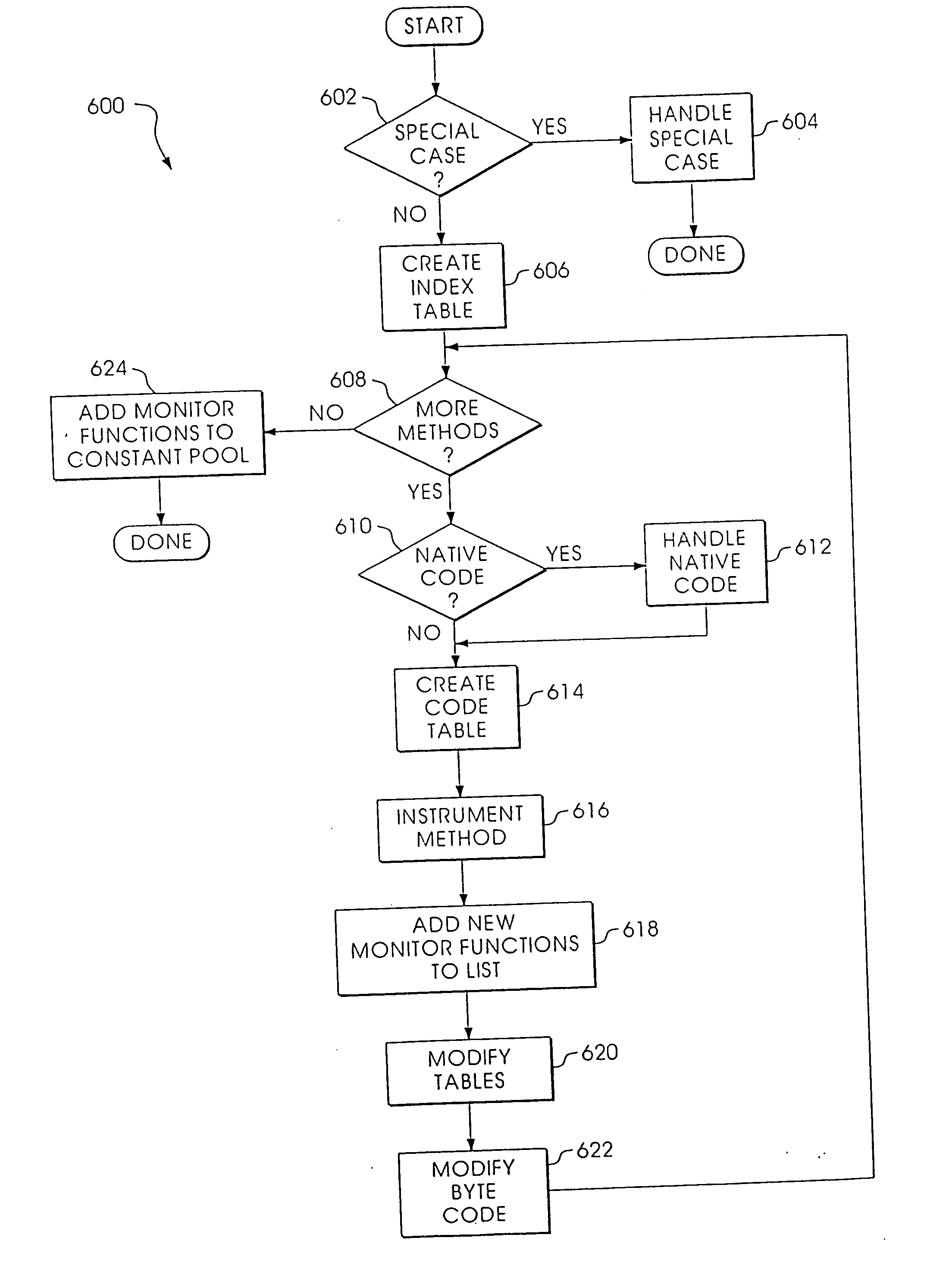
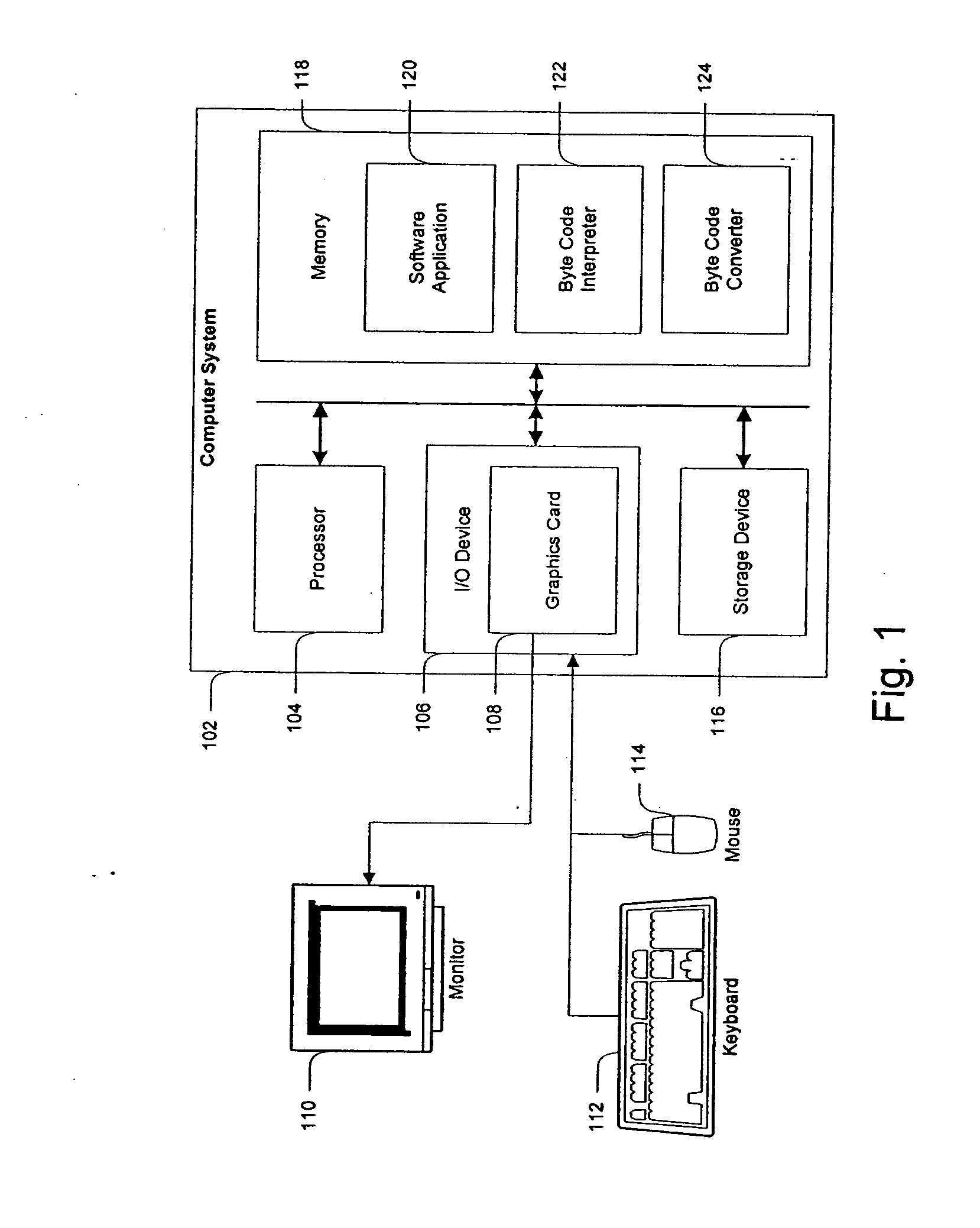
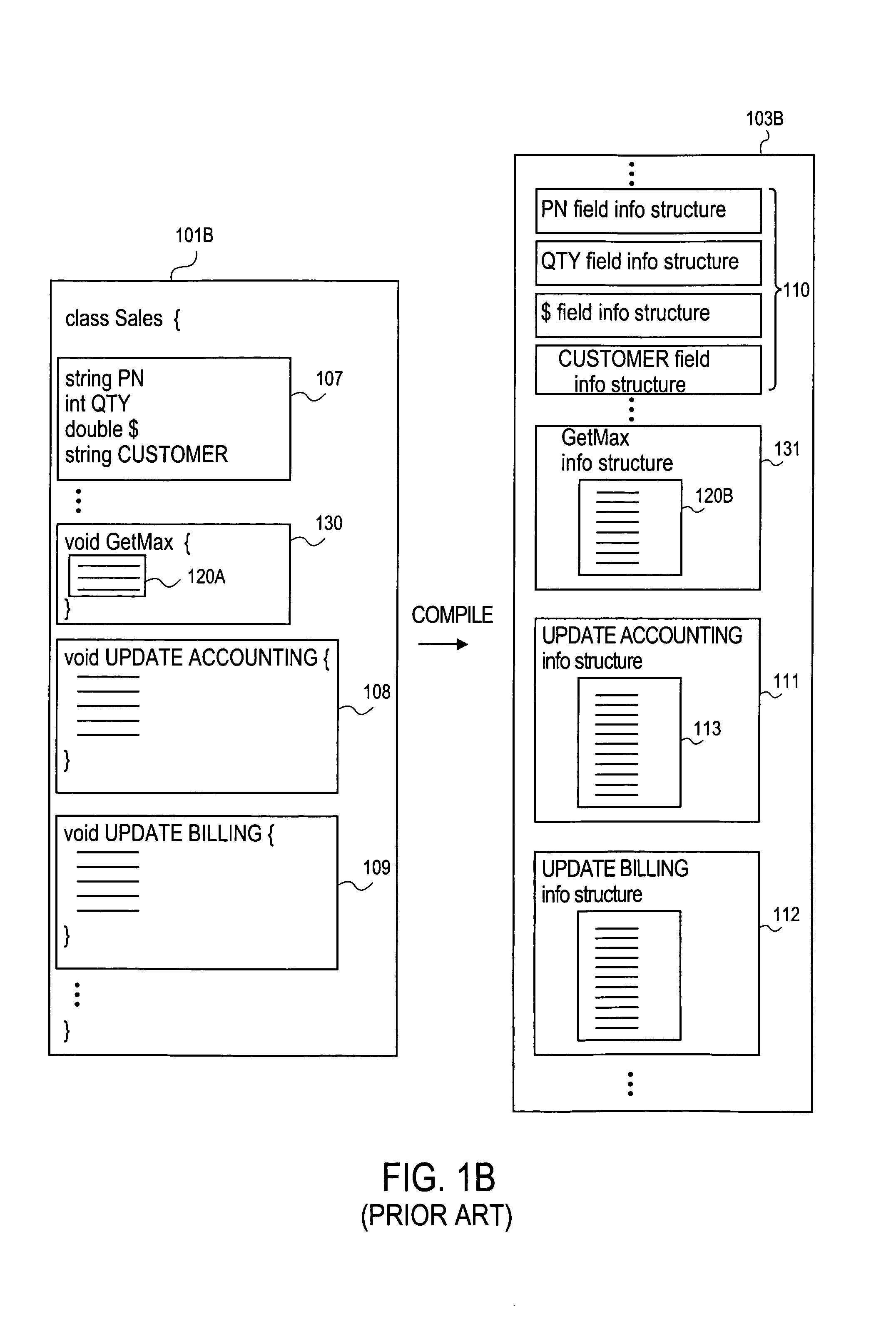
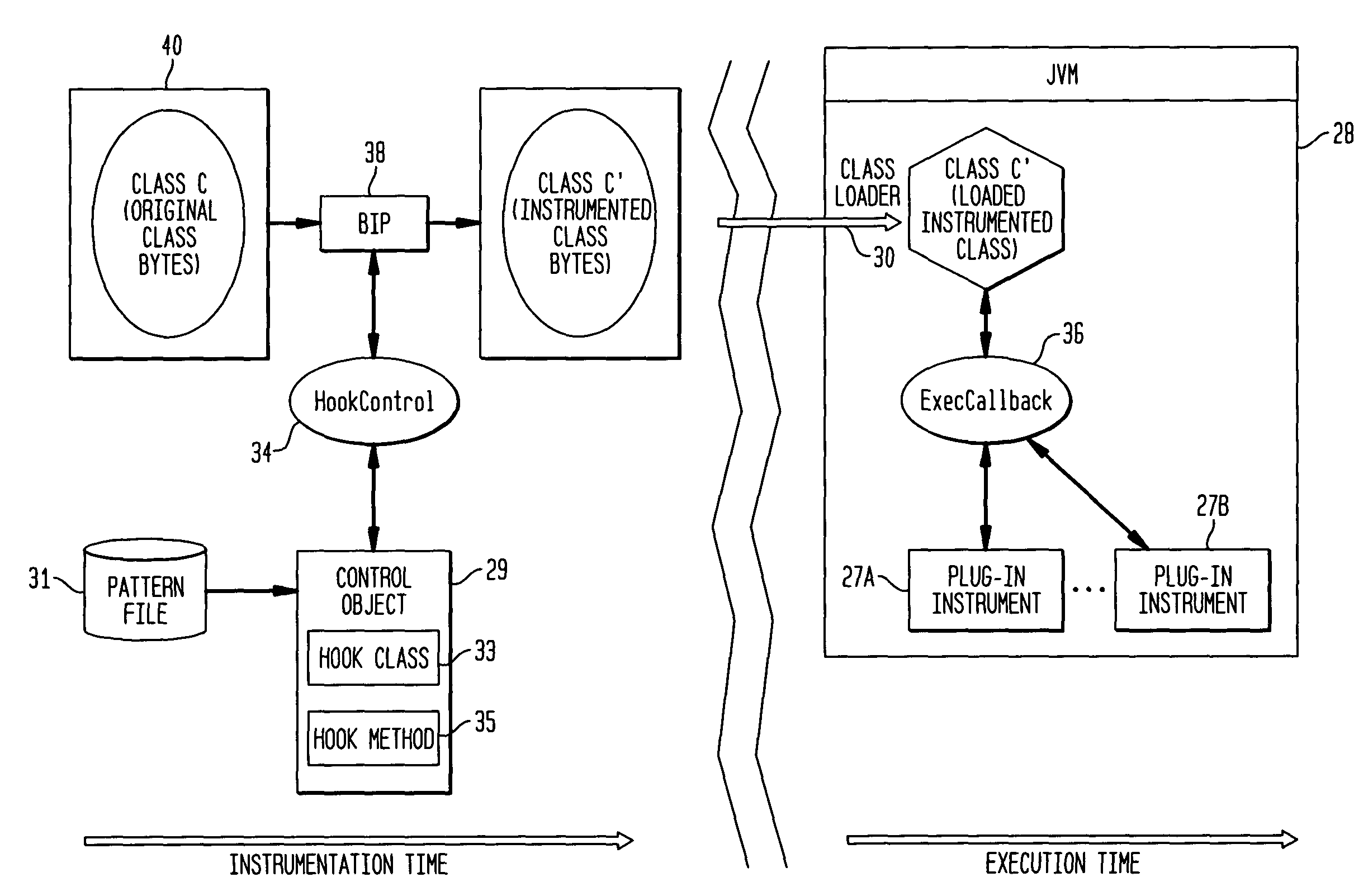
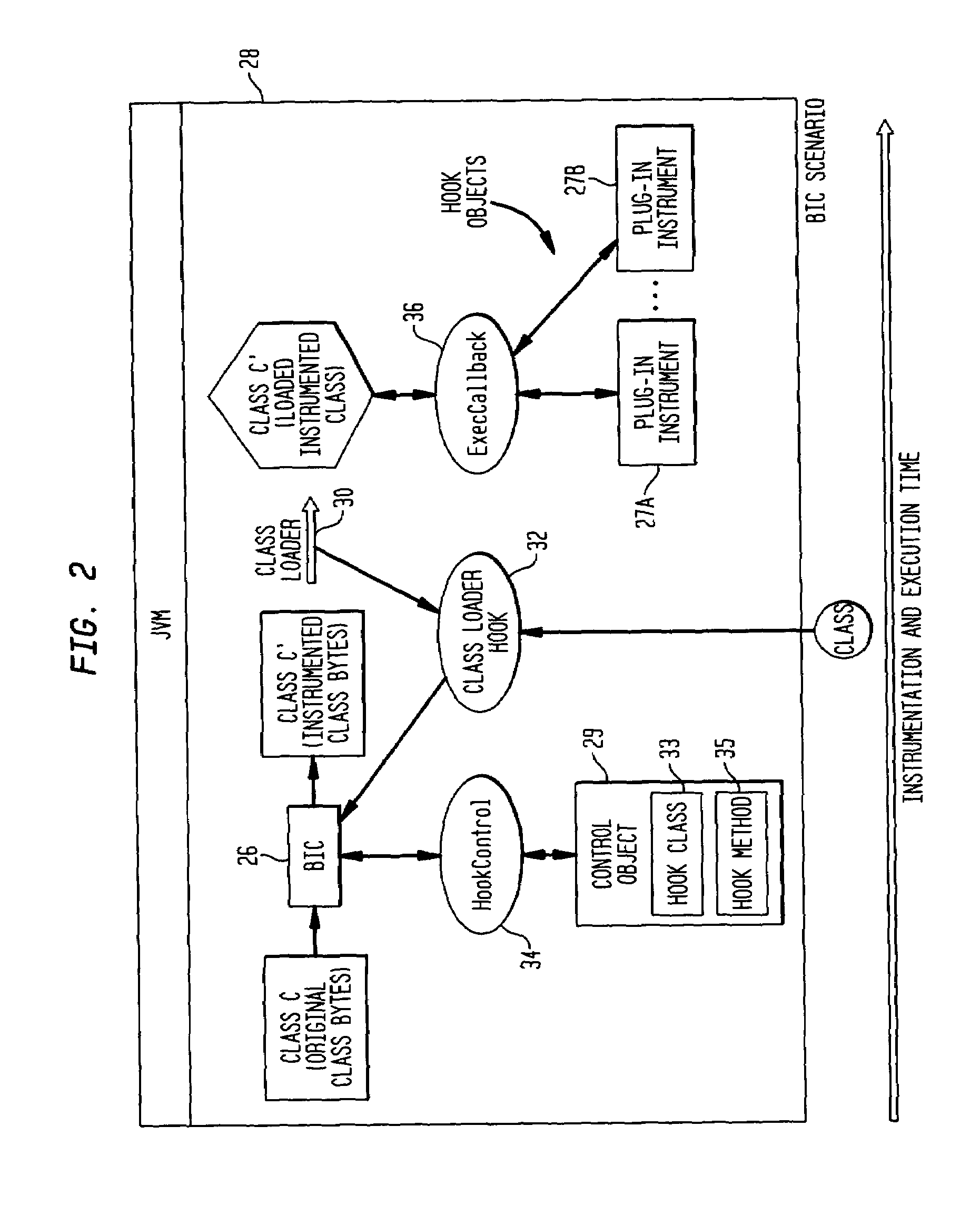
Byte code instrumentation
InactiveUS6314558B1Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsMessage flowTime function
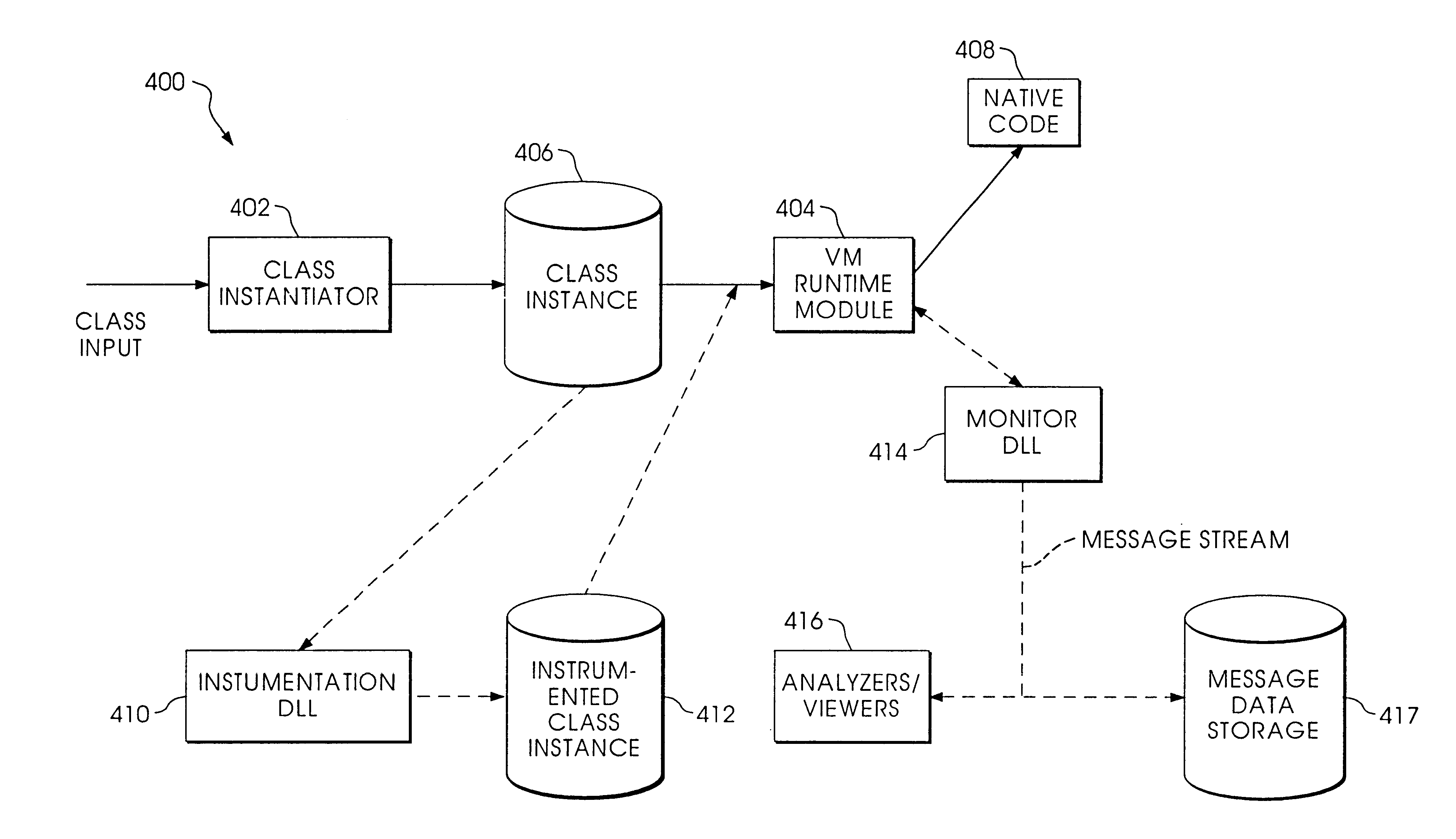
Instrumenting a computer program to provide instrumented byte code includes examining the byte code, selecting portions of the byte code for instrumentation, and instrumenting the portions to provide instrumented byte code. Selecting the portions may include choosing portions of the byte code corresponding to method entry, method exit, a throw, a method call, or a new line number. Instrumenting a portion of the byte code corresponding to a method call may include instrumenting a local line number of source code corresponding to the byte code being instrumented. Instrumenting the portions may include adding calls to instrumentation runtime functions that pass parameters indicative of the portions being instrumented. At least one of the parameters that is passed may include a line number of the source code corresponding to the portion being instrumented or a object pointer for the method corresponding to the portion being instrumented. Data from instrumentation may be passed via a message stream that is viewed as the data is being generated and / or stored.
Owner:BORLAND
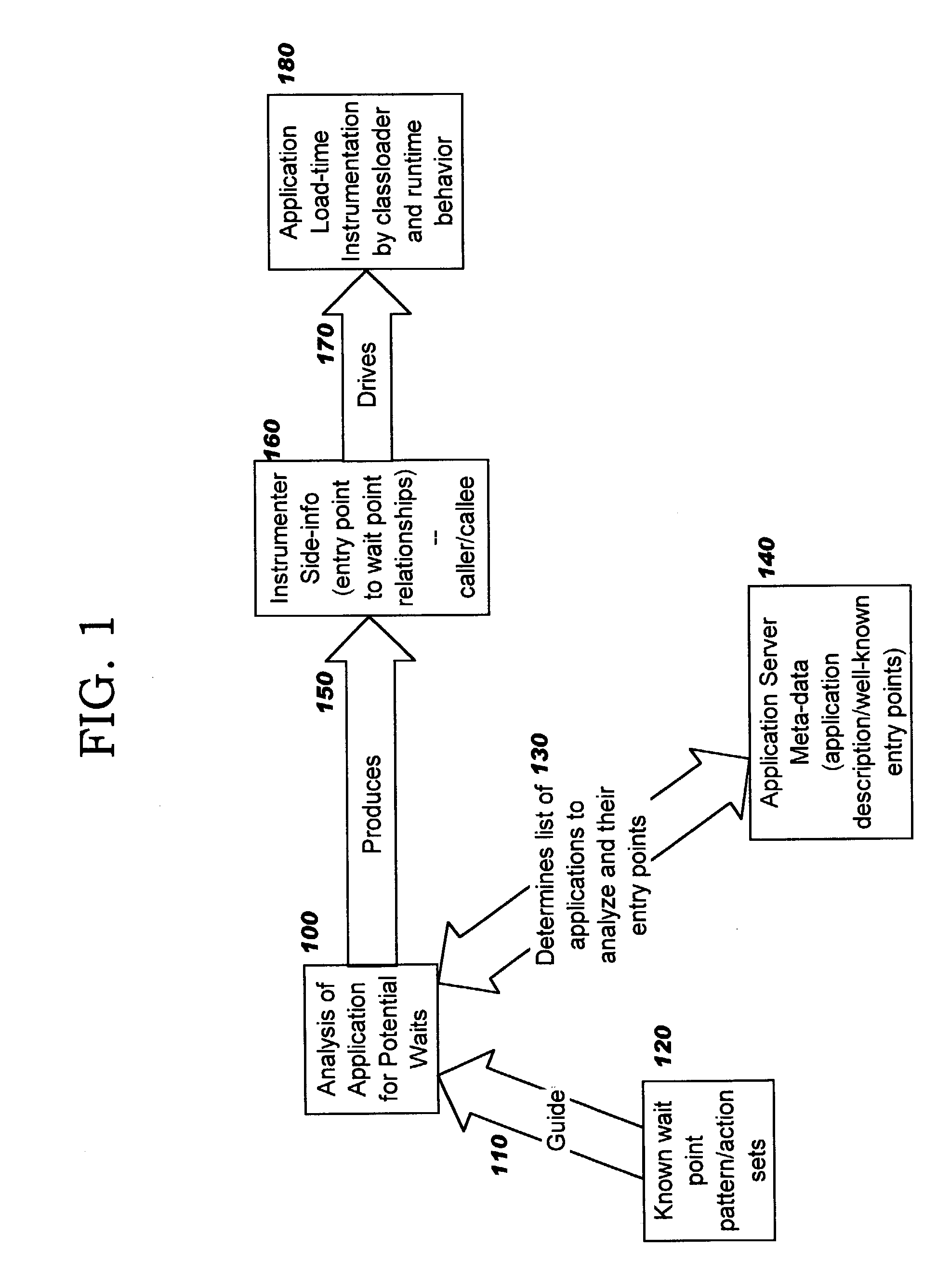
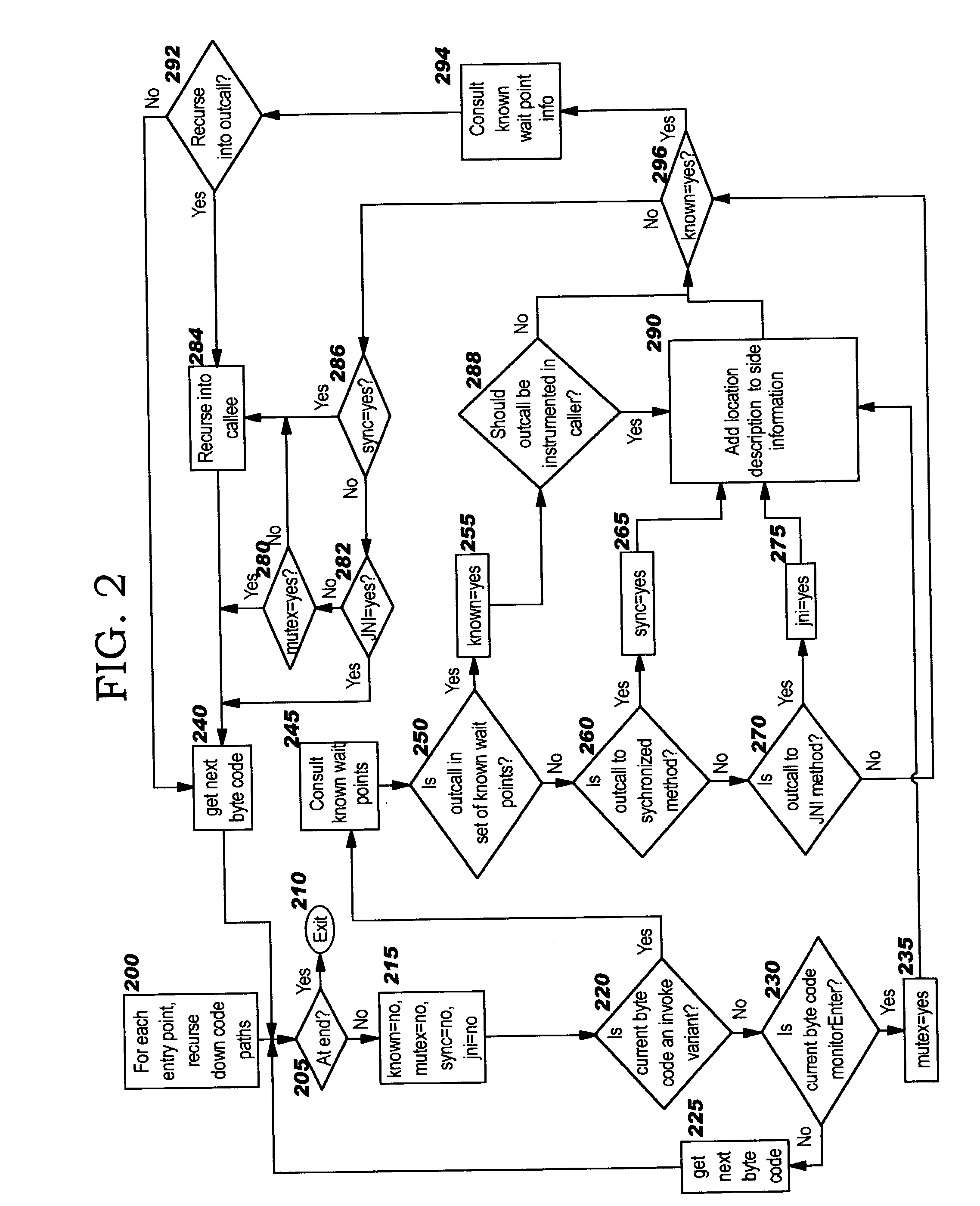
Run-time wait tracing using byte code insertion
InactiveUS20040158819A1Minimal disruptionError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsLoad timeParallel computing
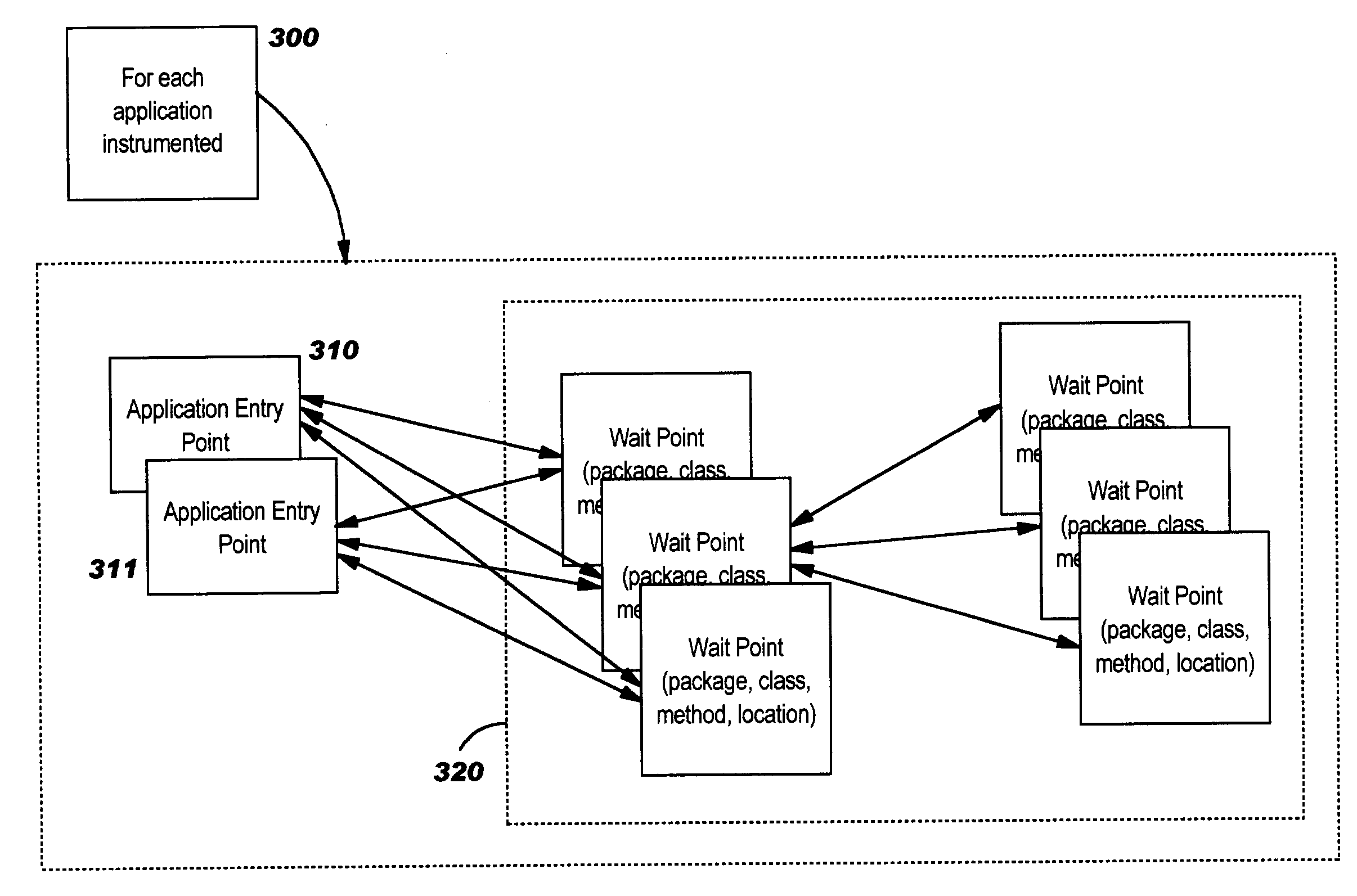
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business whereby programmatically-generated byte code insertion is used to perform run-time tracing of code that potentially encounters a wait during execution. The byte code insertion is performed at load time, and inserts byte codes before and after a located (potential) wait point. The inserted byte code functions to gather execution statistics, such as a time stamp before invoking a located wait point and a time stamp after invoking the located wait point. Preferred embodiments allow this tracing to be selectively activated / deactivated.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
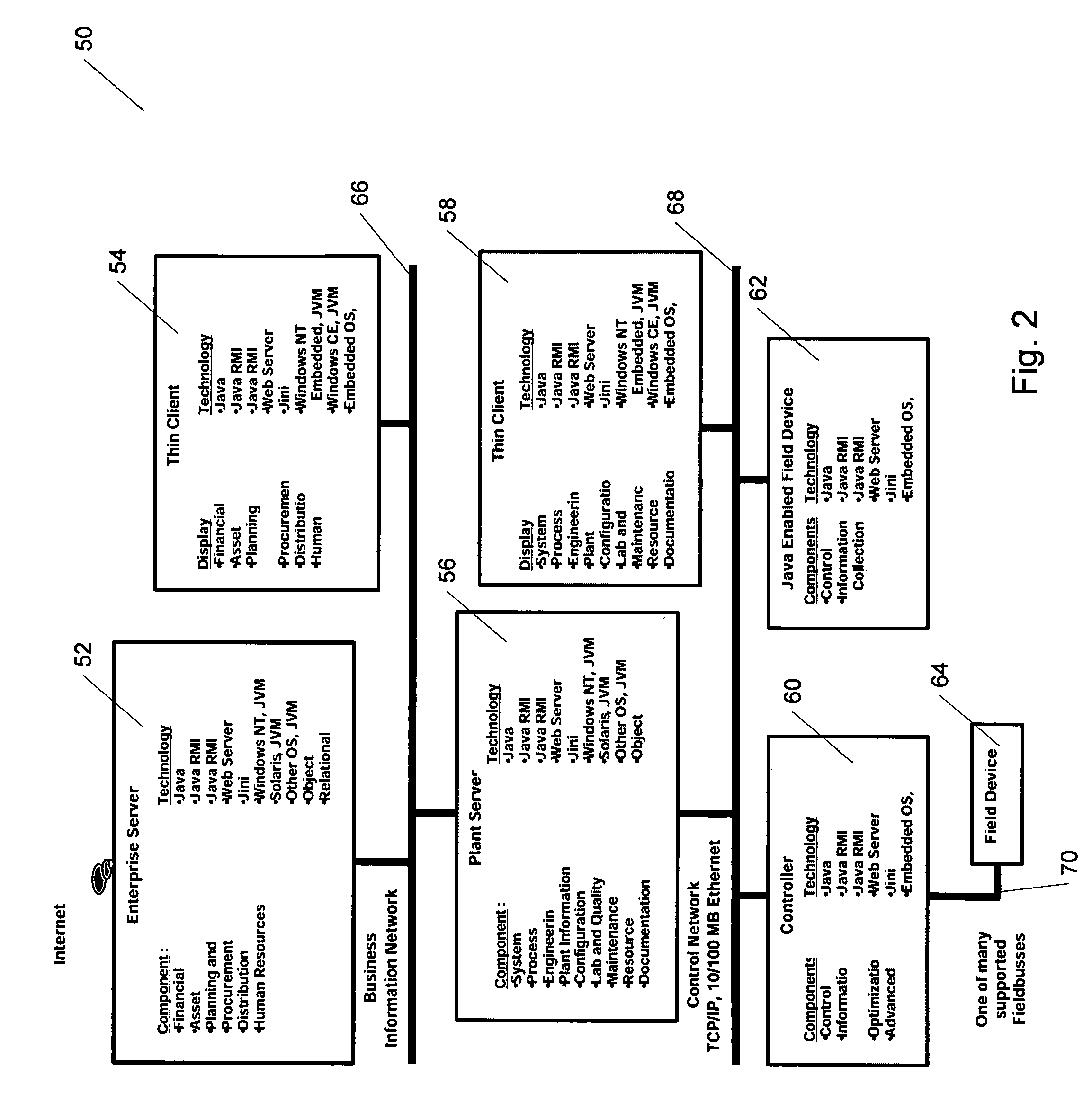
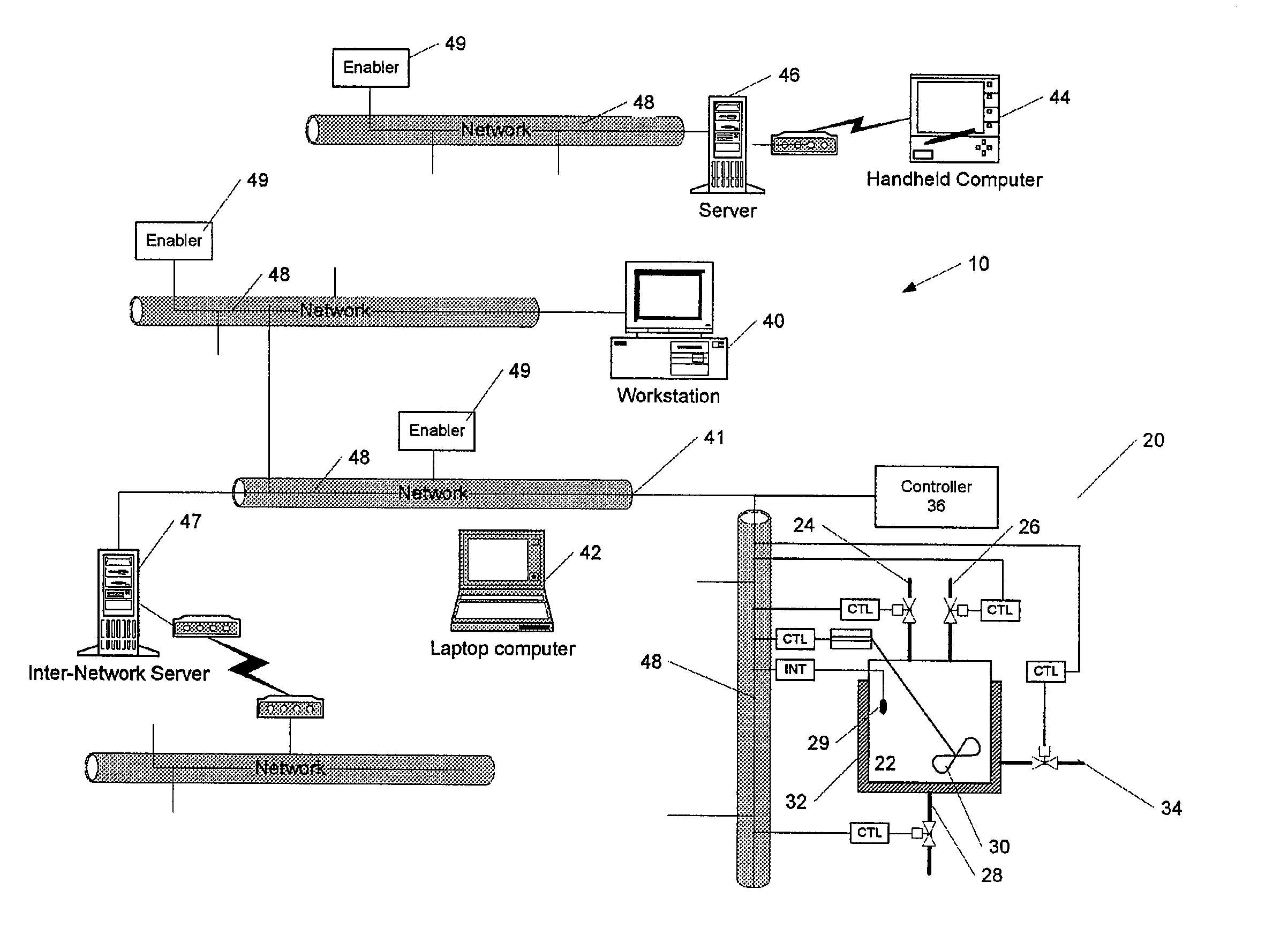
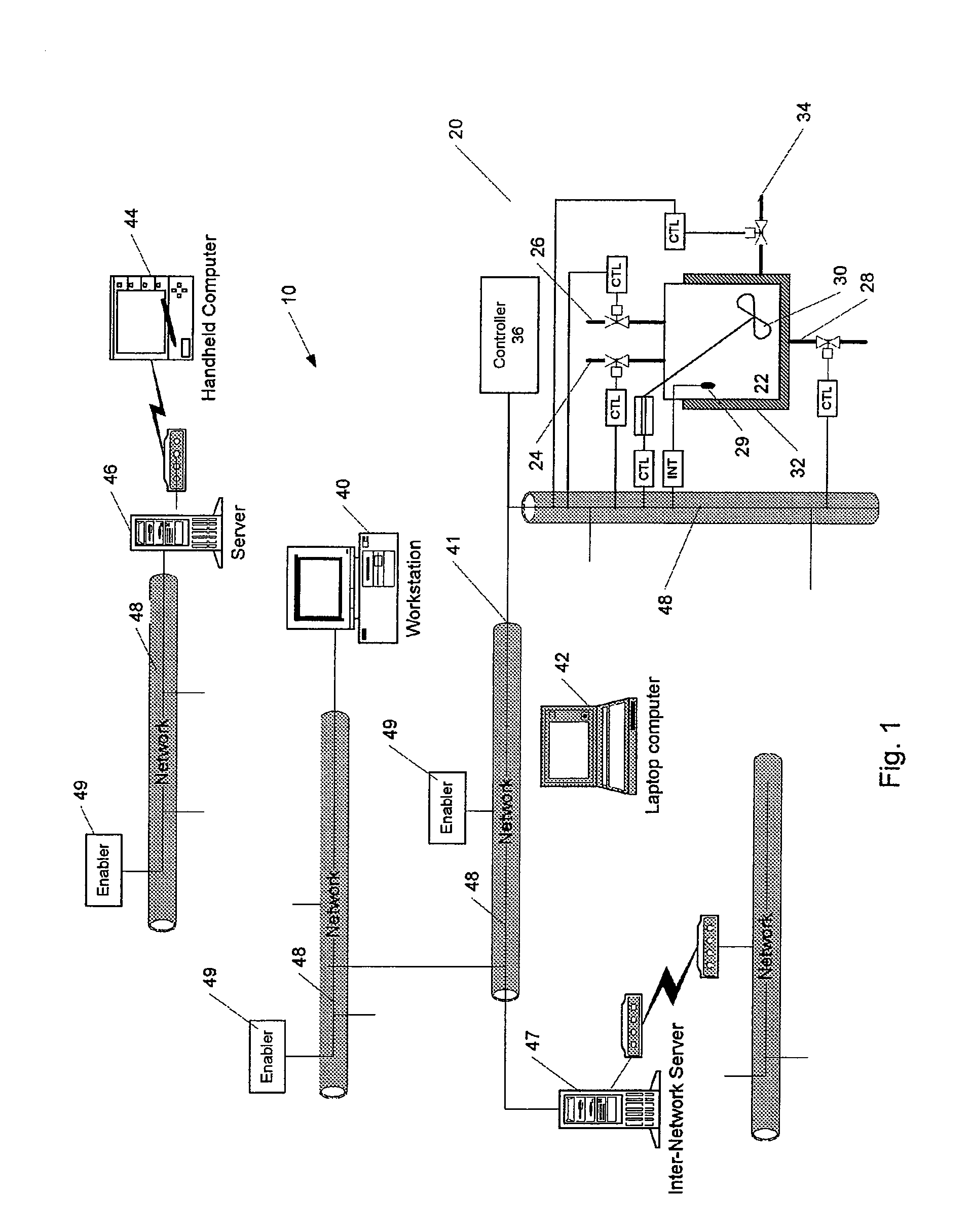
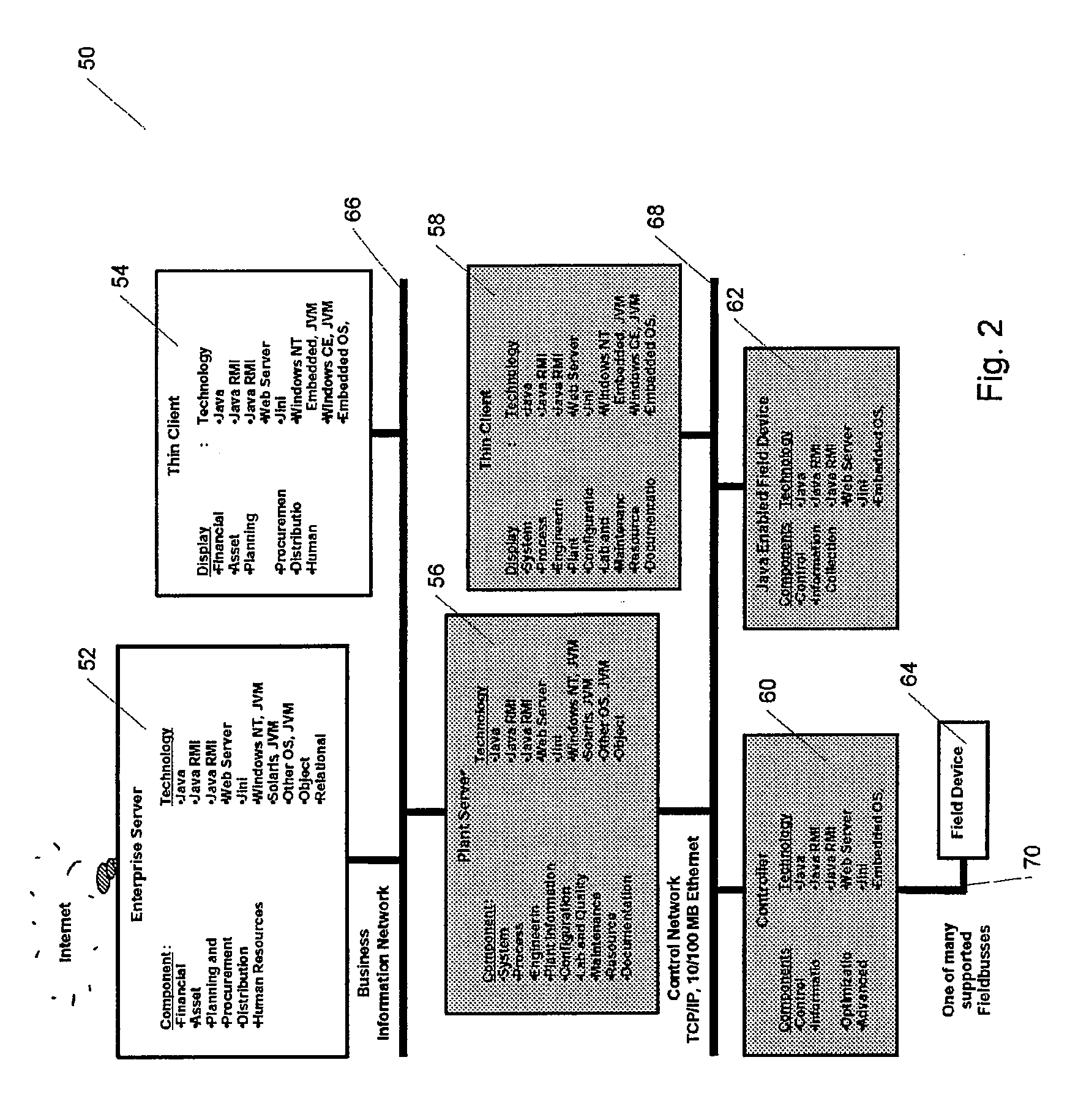
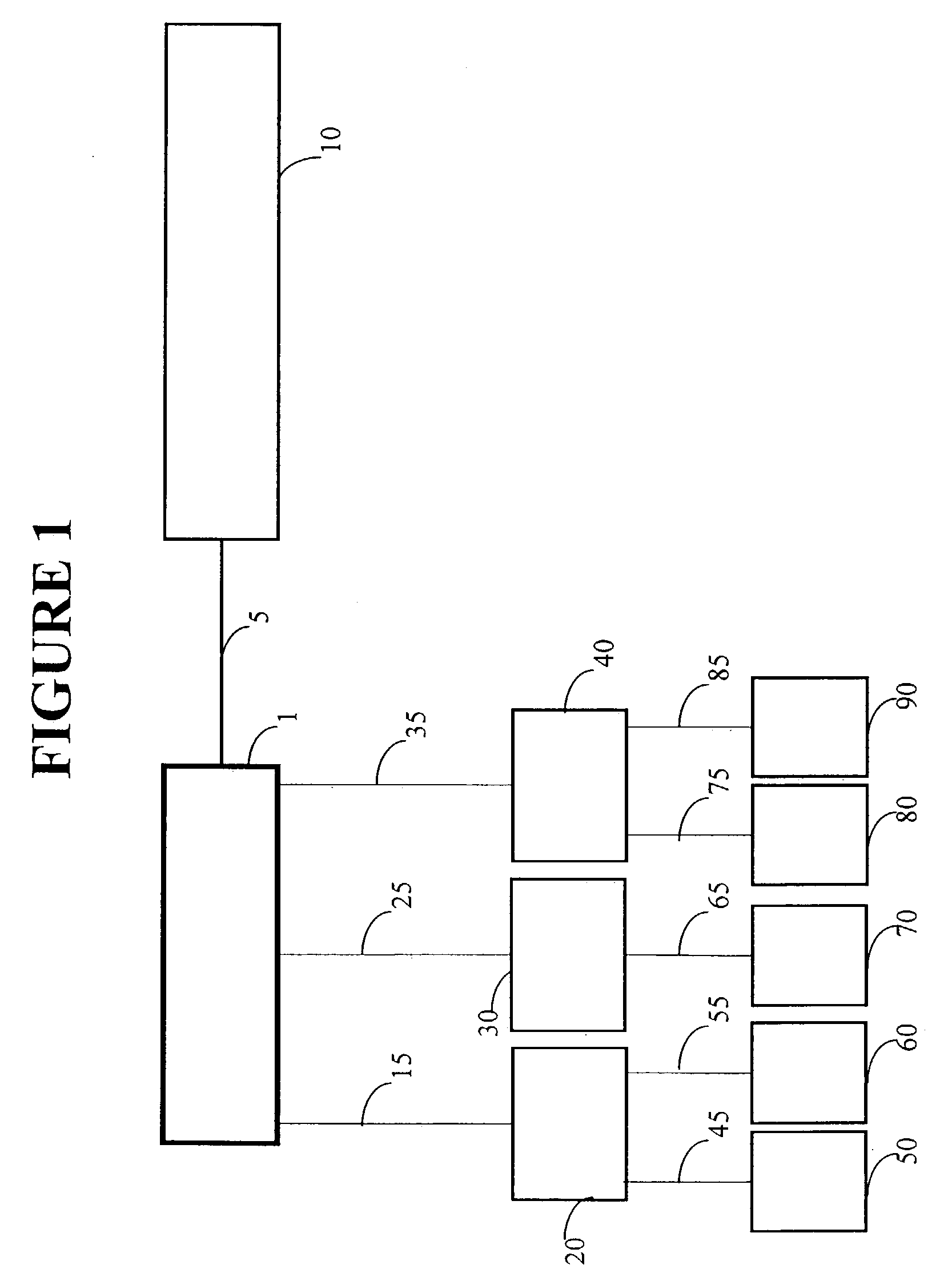
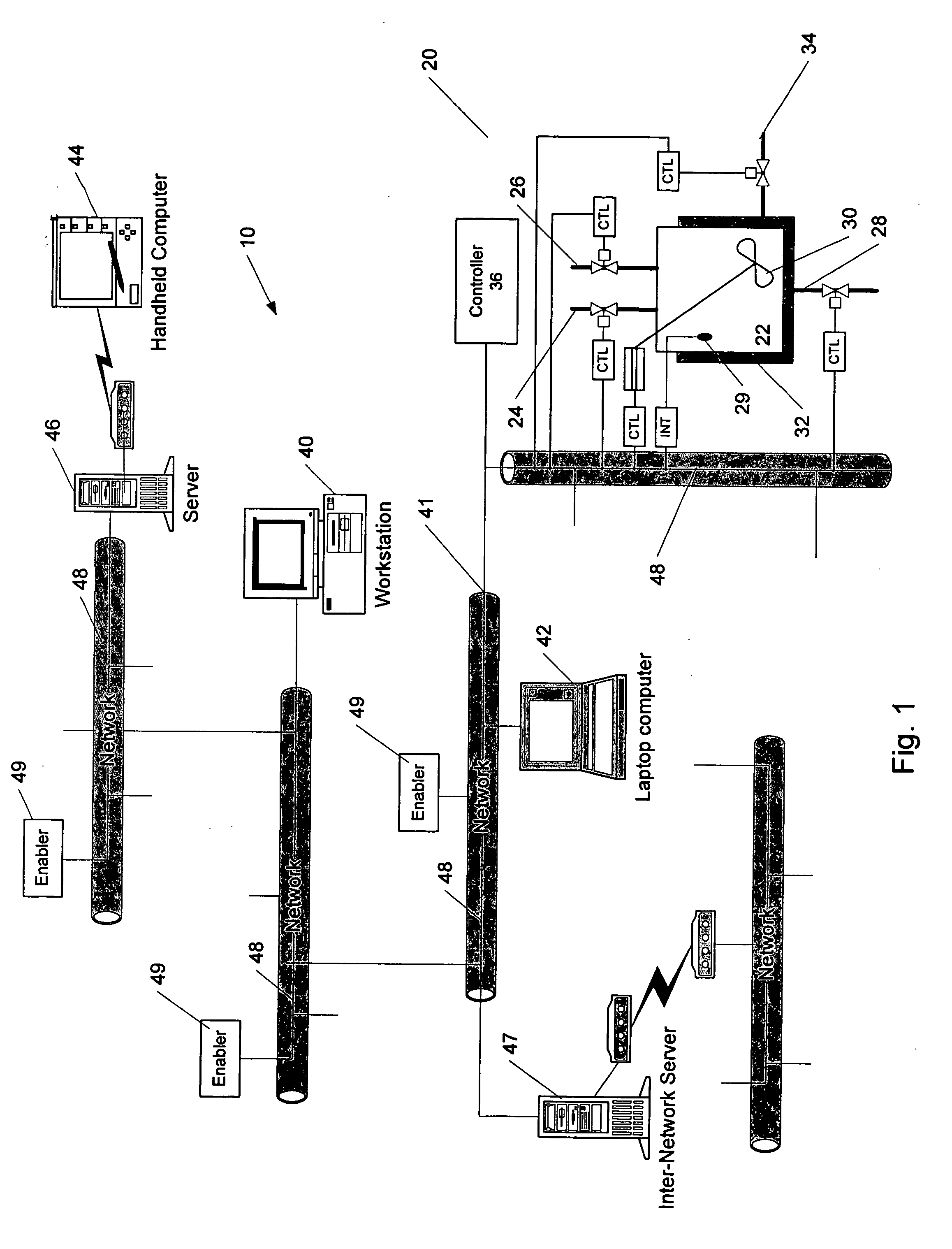
Methods and apparatus for control using control devices that provide a virtual machine environment and that communicate via an IP network
The invention provides improved methods and apparatus for control using field and control devices that provide a virtual machine environment and that communicate via an IP network. By way of non-limiting example, such field device can be an “intelligent” transmitter or actuator that includes a low power processor, along with a random access memory, a read-only memory, FlashRAM, and a sensor interface. The processor can execute a real-time operating system, as well as a Java virtual machine (JVM). Java byte code executes in the JVM to configure the field device to perform typical process control functions, e.g., for proportional integral derivative (PID) control and signal conditioning. Control networks can include a plurality of such field and control devices interconnected by an IP network, such as an Ethernet.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
Byte code instrumentation
InactiveUS20040133882A1Reliability increasing modificationsSoftware testing/debuggingMessage flowParallel computing
Instrumenting a computer program to provide instrumented byte code includes examining the byte code, selecting portions of the byte code for instrumentation, and instrumenting the portions to provide instrumented byte code. Selecting the portions may include choosing portions of the byte code corresponding to method entry, method exit, a throw, a method call, or a new line number. Instrumenting a portion of the byte code corresponding to a method call may include instrumenting a local line number of source code corresponding to the byte code being instrumented. Instrumenting the portions may include adding calls to instrumentation runtime functions that pass parameters indicative of the portions being instrumented. At least one of the parameters that is passed may include a line number of the source code corresponding to the portion being instrumented or a thispointer for the method corresponding to the portion being instrumented. Data from instrumentation may be passed via a message stream that is viewed as the data is being generated and / or stored.
Owner:BORLAND
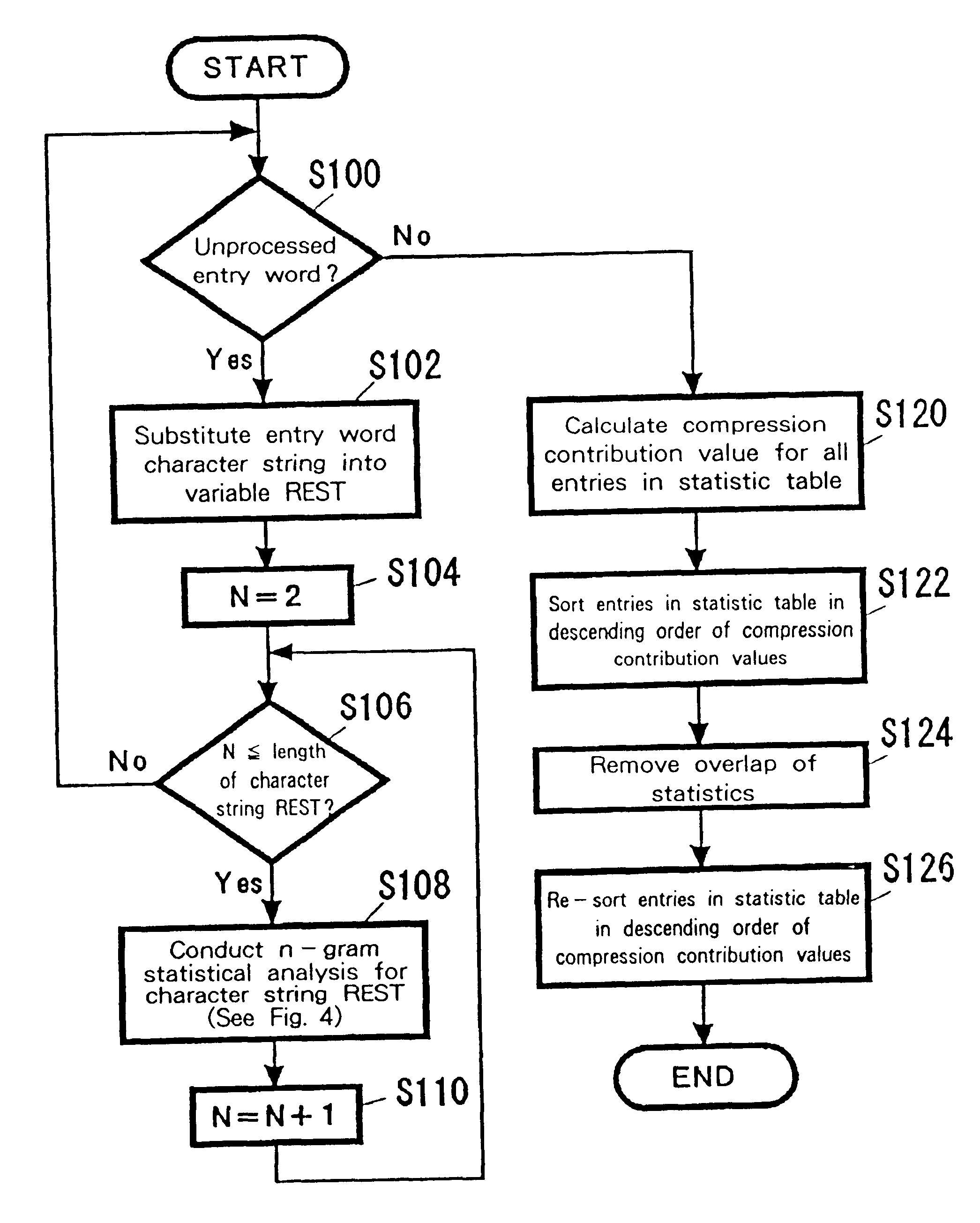
Compression method, method for compressing entry word index data for a dictionary, and machine translation system
A n-gram statistical analysis is employed to acquire frequently appearing character strings of n characters or more, and individual character strings having n characters or more are replaced by character translation codes of 1 byte each. The correlation between the original character strings having n characters and the character translation codes is registered in a character translation code table. Assume that a character string of three characters, i.e., a character string of three bytes, "sta," is registered as 1-byte code "e5" and that a character string of four characters, i.e., a character string of four bytes, "tion," is registered as 1-byte code "f1." Then, the word "station," which consists of a character string of seven characters, i.e., seven bytes, is represented by the 2-byte code "e5 f1," so that this contributes to a compression of five bytes.
Owner:IBM CORP
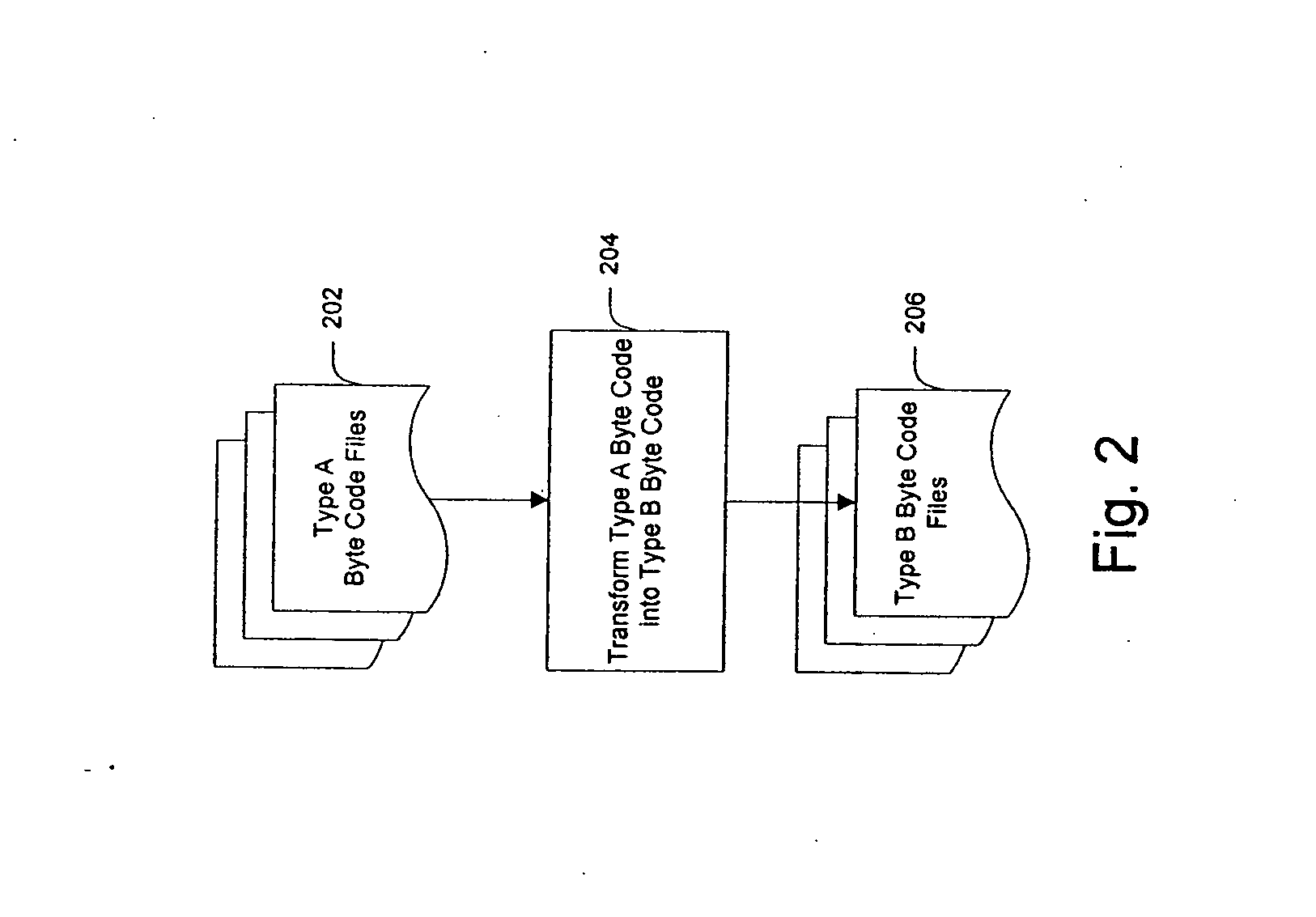
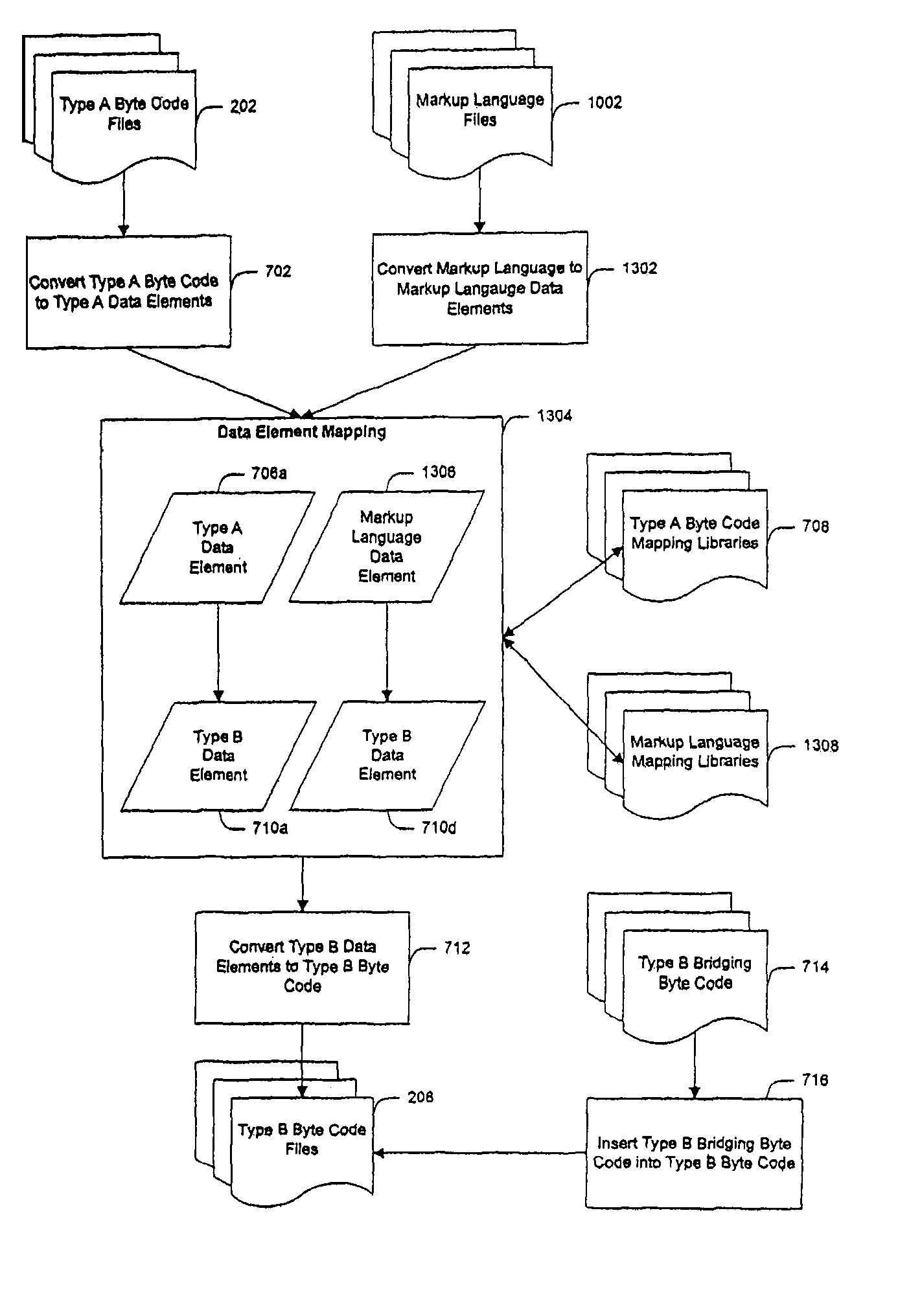
System and method for creating target byte code
InactiveUS20060253508A1Facilitate efficient lookup and mappingBinary to binaryProgram controlData elementByte
A system and method for converting byte code of a first type into byte code of a second type. Byte code of a first type and markup language code are received as inputs. The first byte code is converted into constituent byte code data elements that can comprise any logical unit or grouping of at least a portion of a software application. The markup language code is converted into constituent markup language data elements that can comprise individual markup language tags and references to data or functionality in the first byte code. The first byte code data elements and markup language data elements are mapped to data elements of a second byte code type. The second byte code data elements are assembled into a resulting second byte code.
Owner:APPCELERATOR
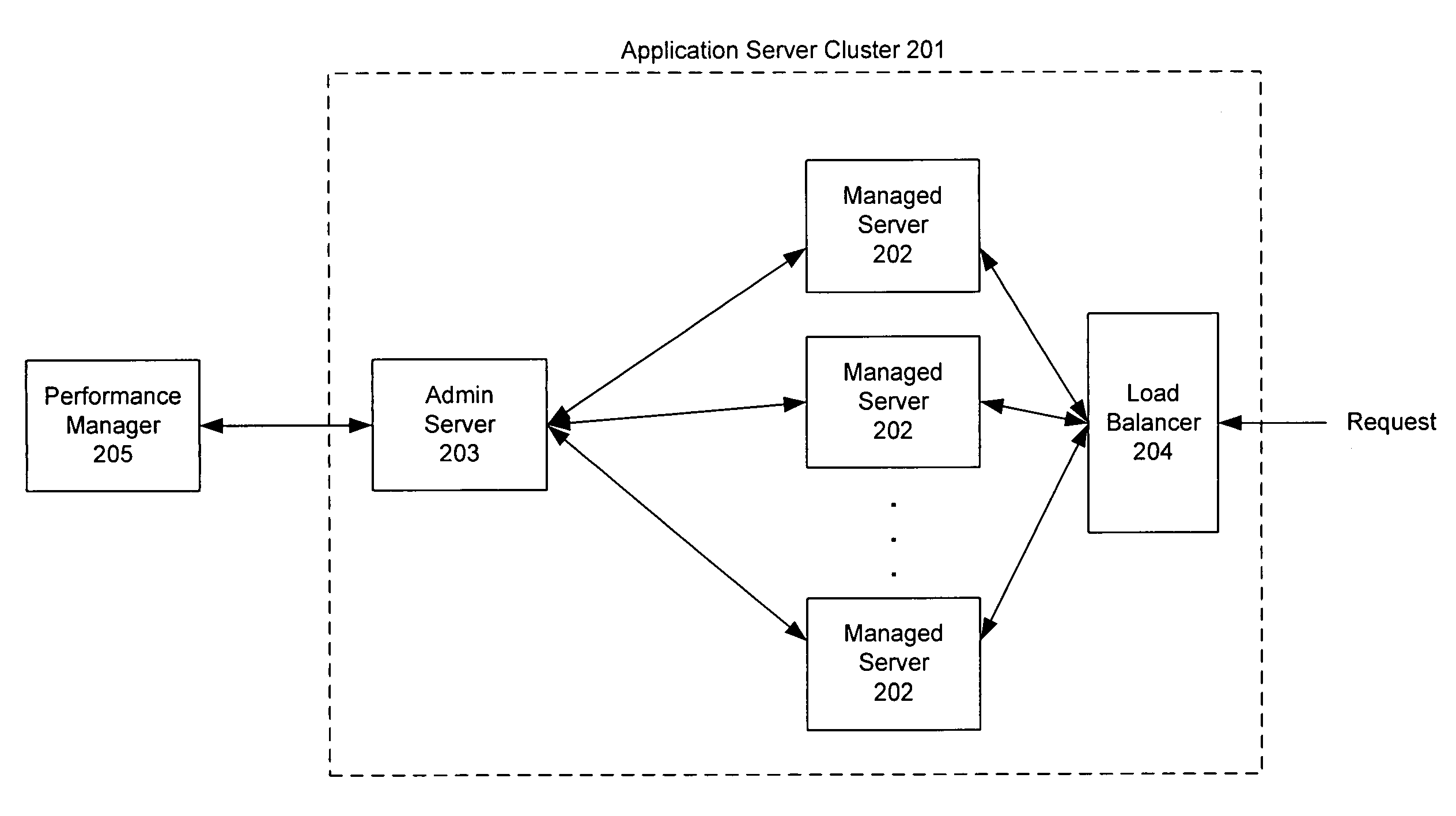
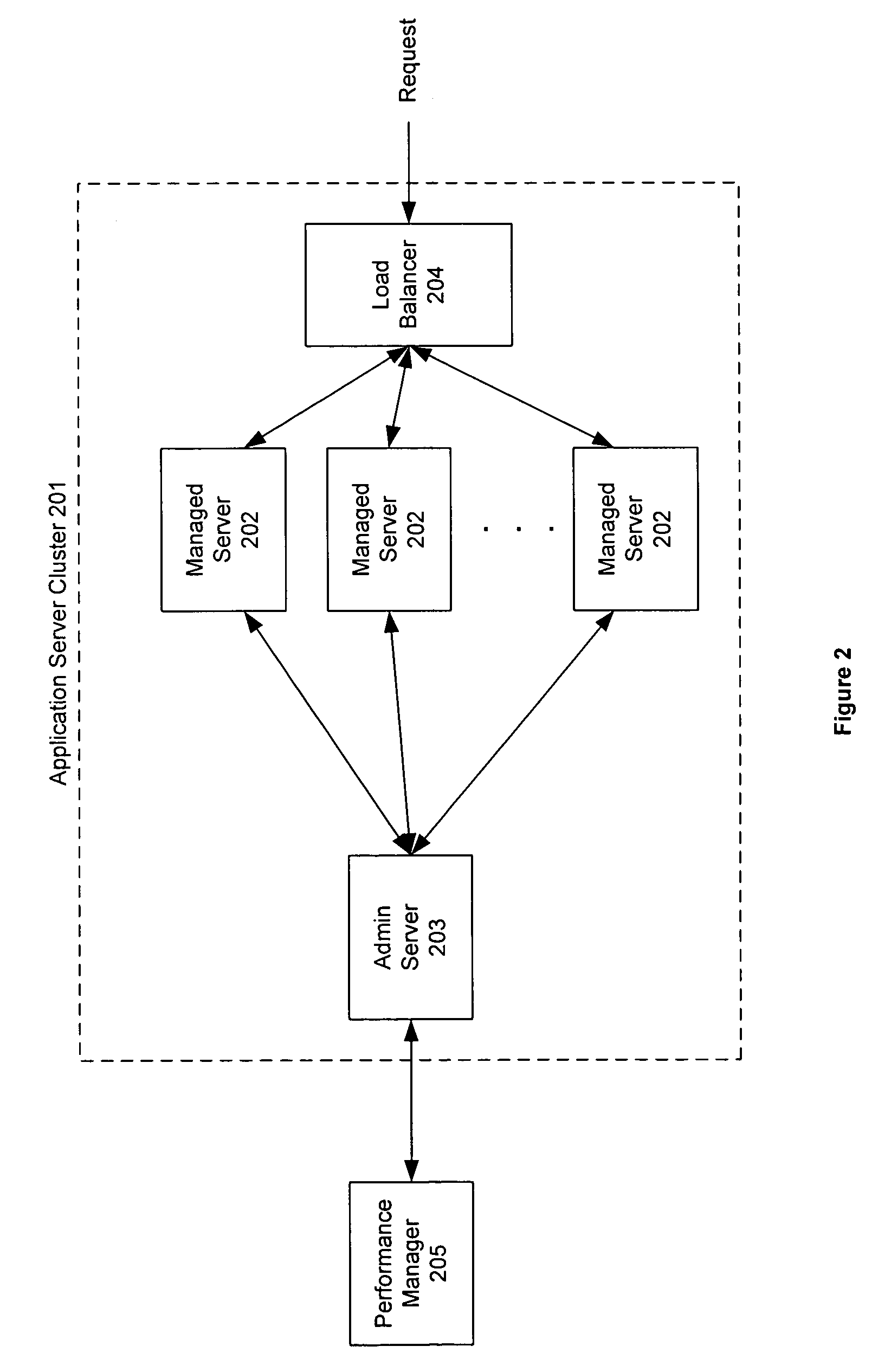
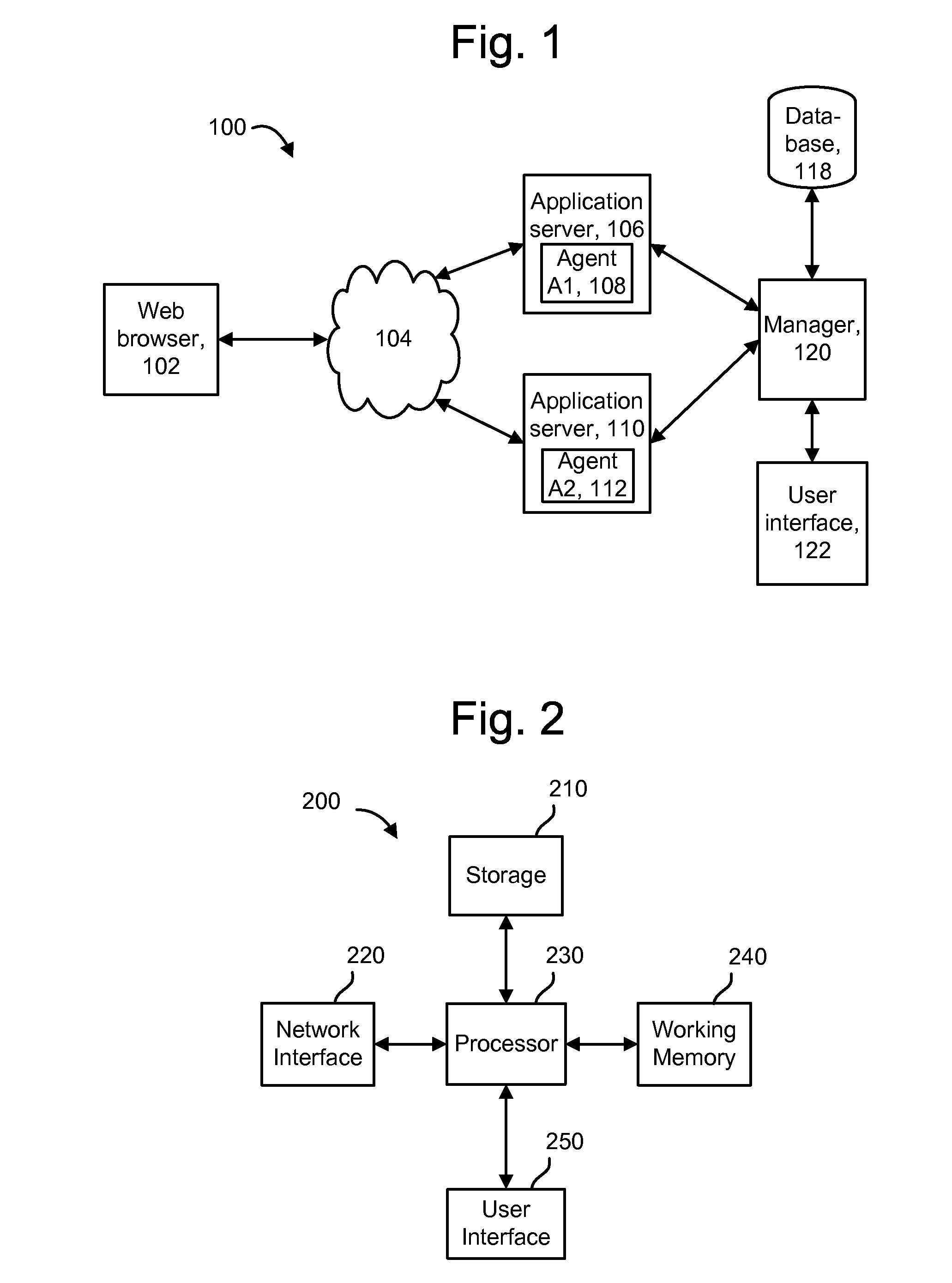
Monitoring and performance management of component-based applications
ActiveUS7627671B1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsManagement toolApplication software
Invention manages underlying application objects that support implemented business functions. A performance manager accesses and interprets application metadata and execution environment metadata, using a hierarchical entity to model complex relationships between application abstractions, components and resources. The performance manager encodes common behavioral and architecture information in models resulting from analysis of component architecture standards, vendor application servers, development tools and administration tools. The performance manager conducts inter-component dependency and control flow analysis, for example by generating control flow graphs from application metadata and performing byte code analysis without access to application source code. The performance manager collects metrics from standardized and vendor-specific sources, instruments interpreters (such as the Java Virtual Machine), and collects and utilizes resource metrics, code performance metrics, configuration parameters, and transaction, failure and lifecycle events.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
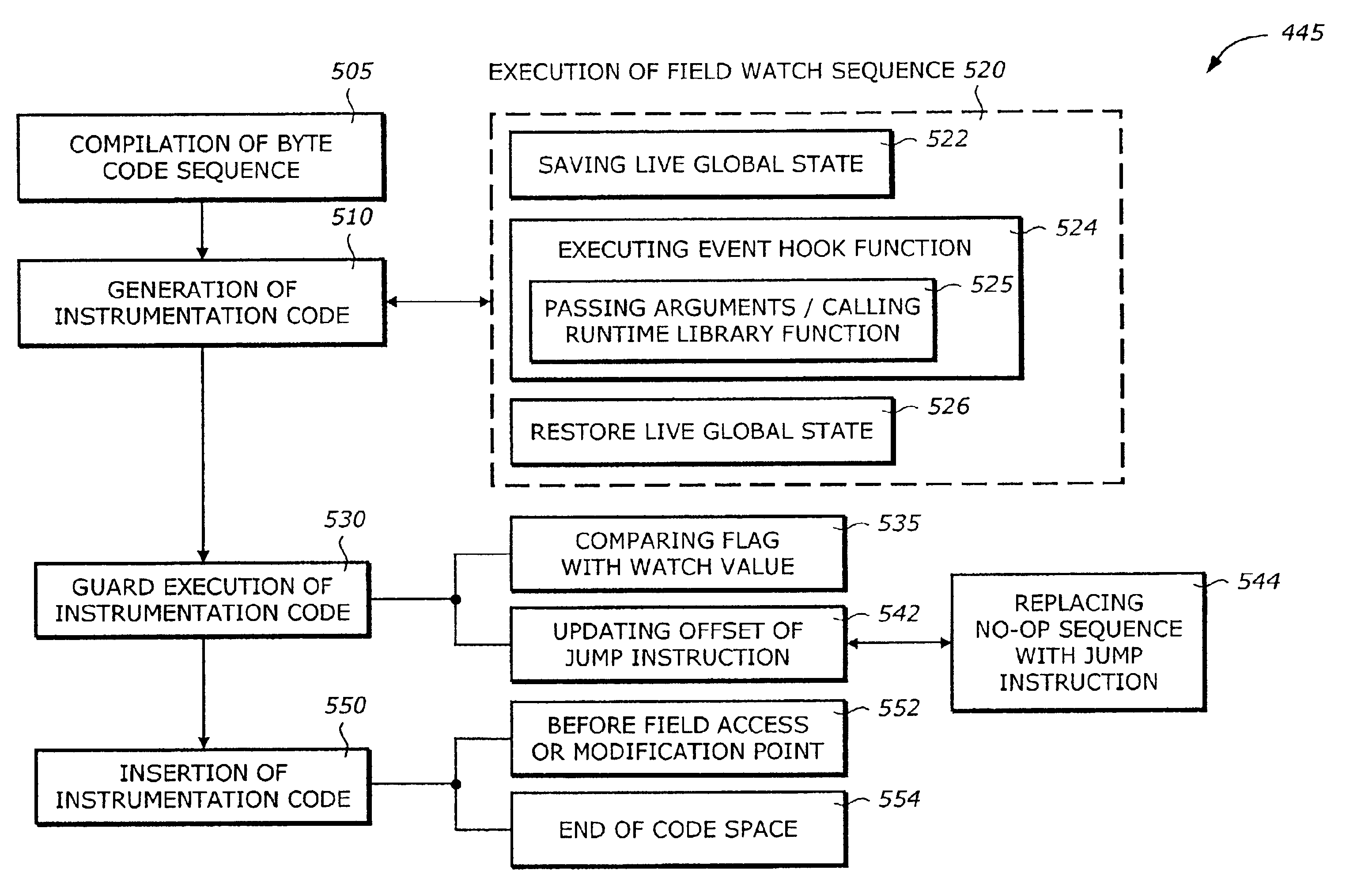
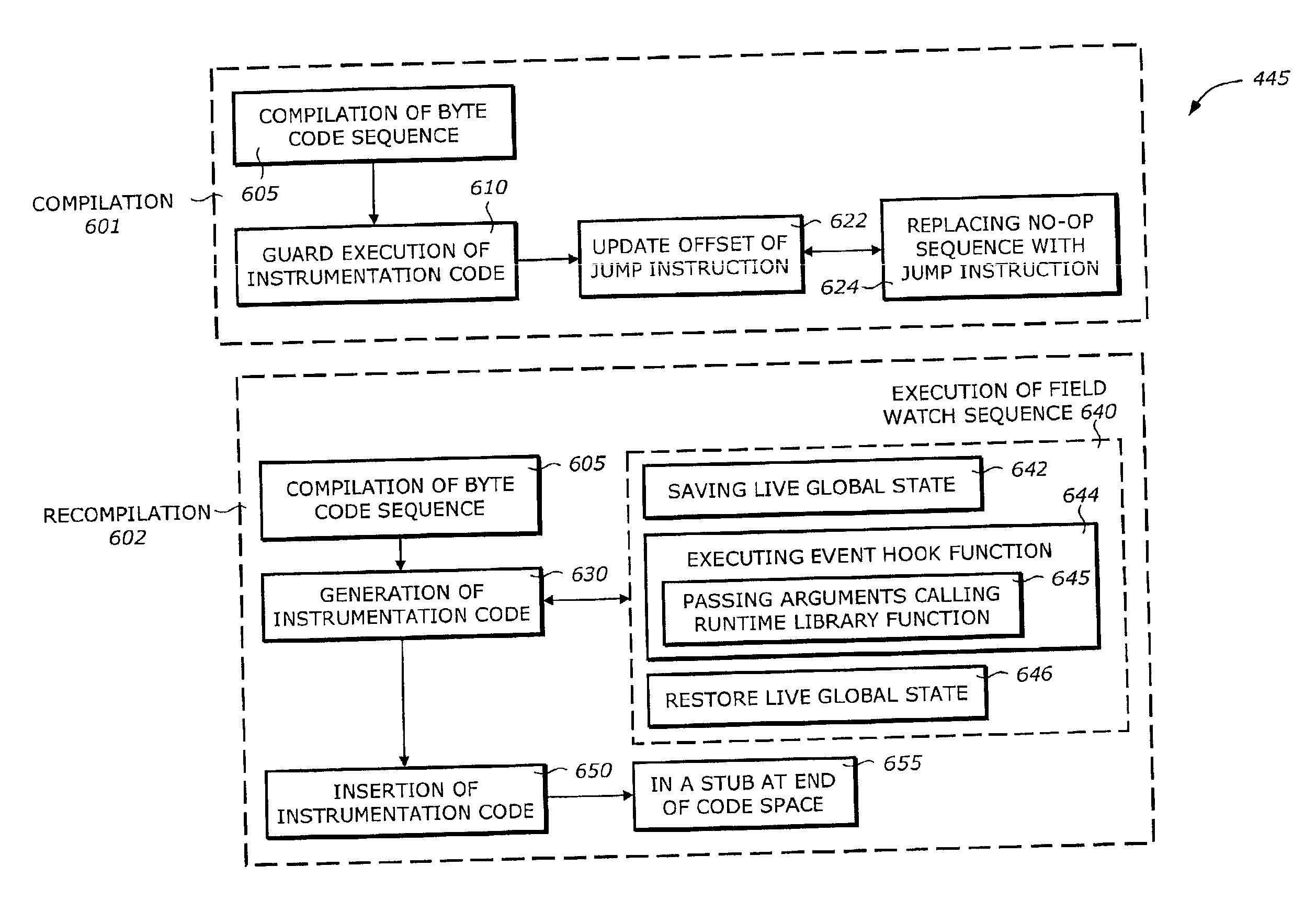
Static compilation of instrumentation code for debugging support
The present invention is a method and system to support debug. A function is compiled. The function includes a byte code sequence having a field byte code that accesses or modifies a field. The compiled function provides a native code and occupies a code space. An instrumentation code corresponding to a field match of a field is generated. The instrumentation code is inserted to the native code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
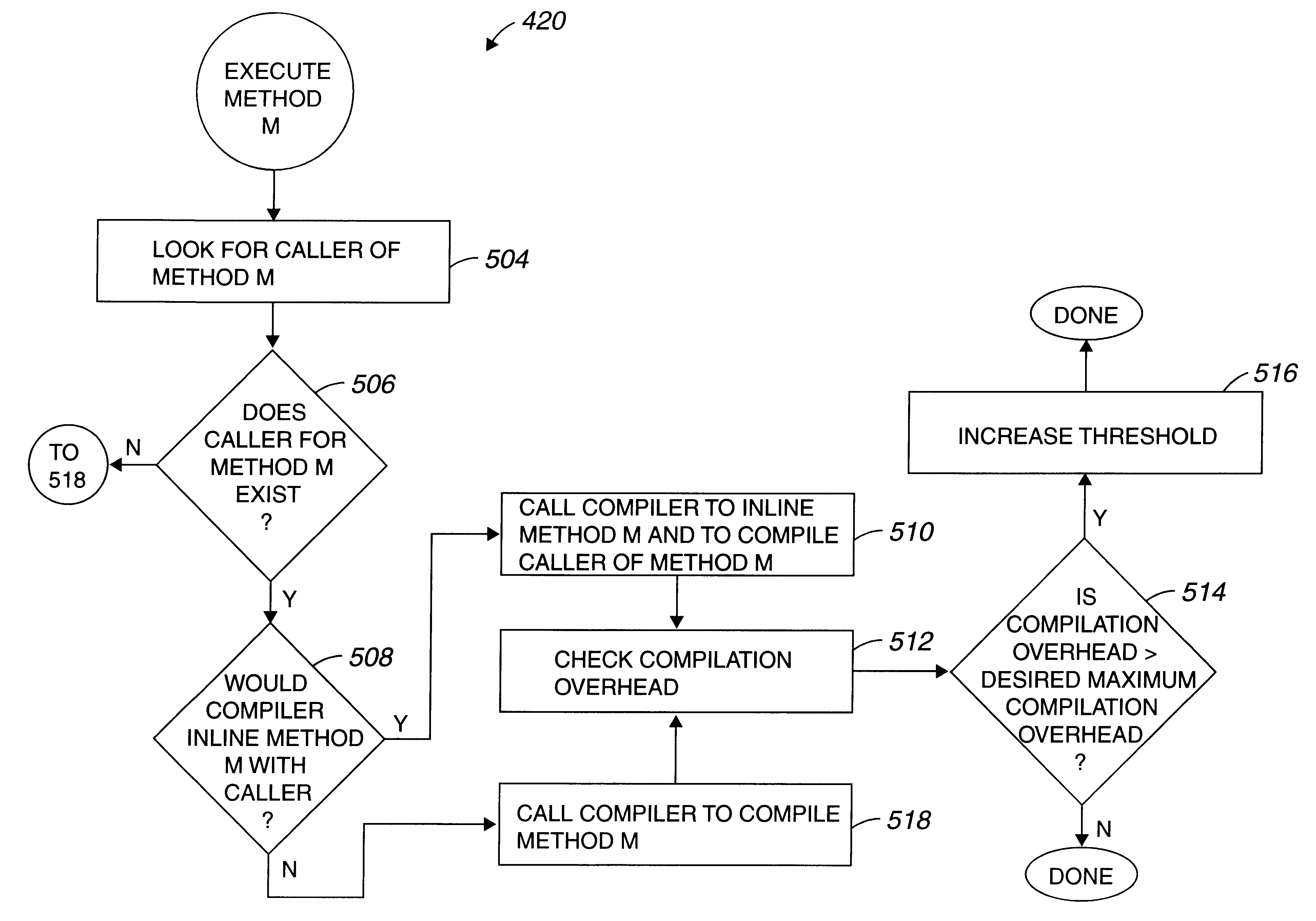
Method and apparatus for dynamically optimizing byte-coded programs
Methods and apparatus for dynamically determining whether portions of code should be interpreted or compiled in order to optimize a software application during run-time are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, computer-implemented method for run-time processing of a computer program which includes byte-codes arranged as a plurality of methods includes invoking a first method selected from the plurality of methods. Invoking the first selected method involves interpreting the first selected method. An invocation tracker which is arranged to track the number of invocations of the first selected method is updated, and a determination is made regarding when the invocation tracker indicates that the number of invocations of the first selected method exceeds a threshold value. The first selected method is compiled when it is determined that the invocation tracker indicates that the number of invocations of the first selected method exceeds a threshold value. This threshold value is periodically adjusted to keep the compilation and the interpretation overheads within acceptable ranges.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method, computer program product, and system for non-blocking dynamic update of statically typed class-based object-oriented software
ActiveUS20110283256A1Efficient forwardingSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware updateInit
Under the present invention, a method, computer program product, and system for non-blocking dynamic update of statically-typed class-based object-oriented software executing as byte-code on a virtual machine within an actively running computer system is provided. A set of objects instantiated from an existing module or multiple modules (identifiable collections of application resources and class definitions in the form of byte-code representations) is ready for execution on a virtual machine in an actively running computer system. New versions of one or more modules corresponding to those already loaded into the actively running virtual machine are dynamically loaded into the virtual machine for the purpose of updating the running software. The class definitions within the loaded modules are prepared for dynamic update by inserting byte-code that enables; transparent state transfer and shared object identity between objects of a former version and the new version of a class. On the event of a software update, the objects instantiated from a former version of an updated class become un-initialized surrogate objects with the potential to redirect to their future corresponding objects. Corresponding objects are created lazily on first access of the declaring class members. Besides lazy redirection of the behavior of objects and classes, non-blocking dynamic update is achieved by lazy migration of the state of former objects and classes while locking on a temporary field access lock. Thus, the algorithm for controlling field access and state migration is completely lock-free both before and after state migration; hence the performance degradation is minimal. Finally, any unreferenced objects are removed from memory.
Owner:ZEROTURNAROUND
System and method for detecting malicious executable code
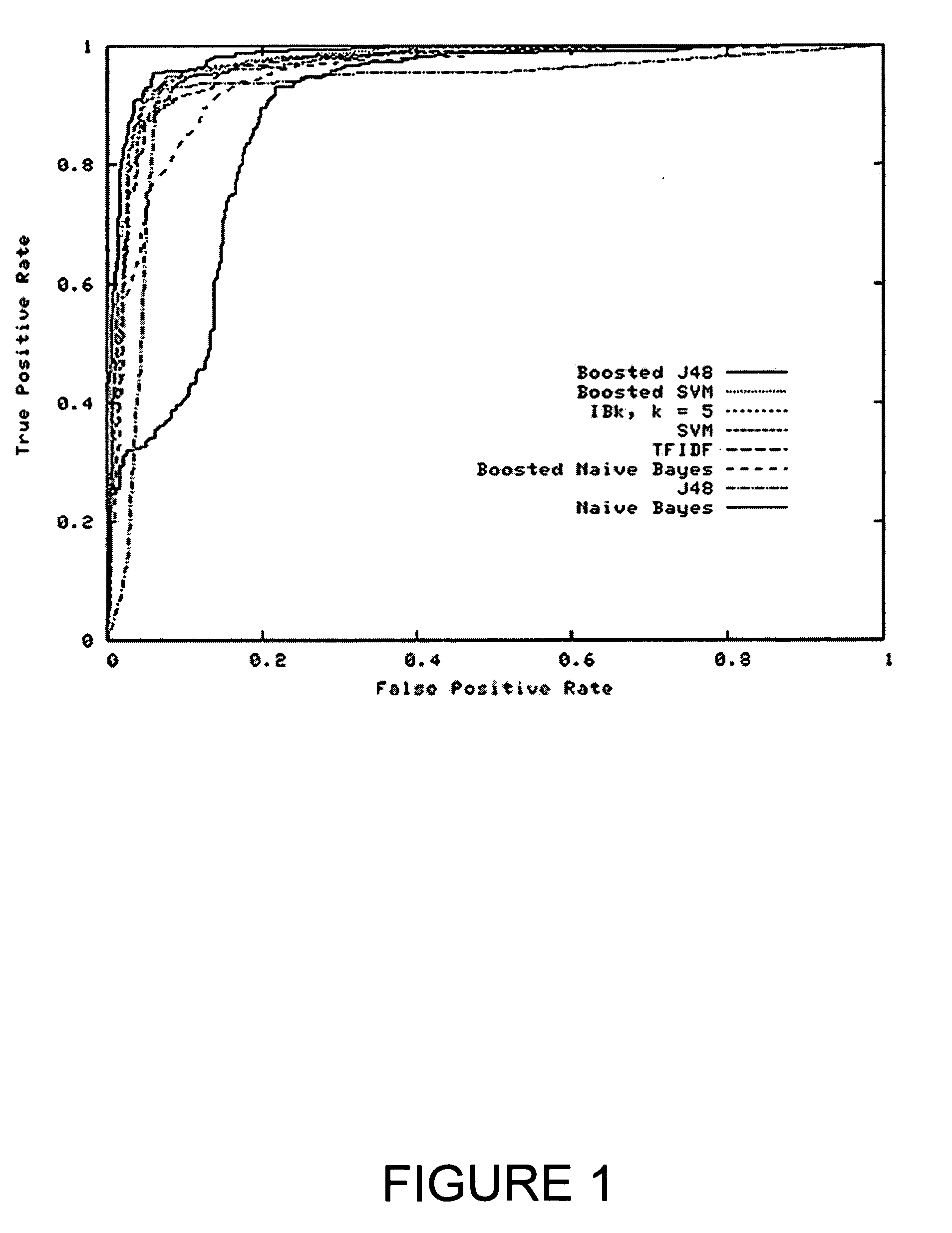
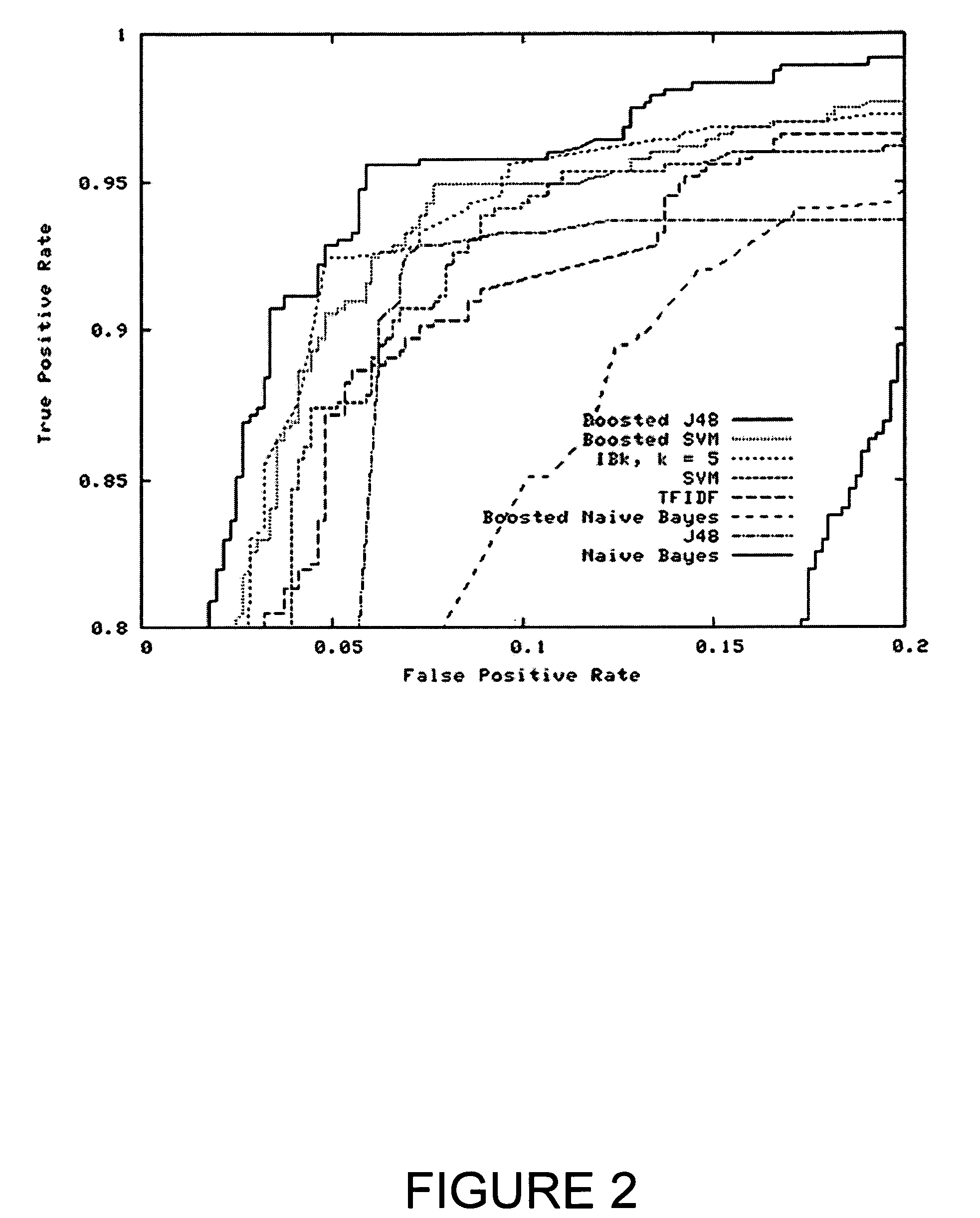
ActiveUS20060037080A1Boosted SVMsFacilitate decision-makingMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionSupport vector machineInductive method
A system and method for detecting malicious executable software code. Benign and malicious executables are gathered; and each are encoded as a training example using n-grams of byte codes as features. After selecting the most relevant n-grams for prediction, a plurality of inductive methods, including naive Bayes, decision trees, support vector machines, and boosting, are evaluated.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
System, method and software for creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of complex data objects and their data relationships
InactiveUS20030046266A1Digital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesApplication softwareByte
The invention provides systems, methods and software for creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of complex data objects and associated data stores. In one aspect, the invention also relates to an application programming object capable of creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of data objects or data object graphs without the necessity of inserting any byte codes or modification of the object graph. Virtually any java object or object praph can be transparently persisted. Further, copies of a data graph or of a portion of the data graph can be automatically reconciled and changes persisted without any persistence coding in the object model.creating.
Owner:MULLINS WARD +1
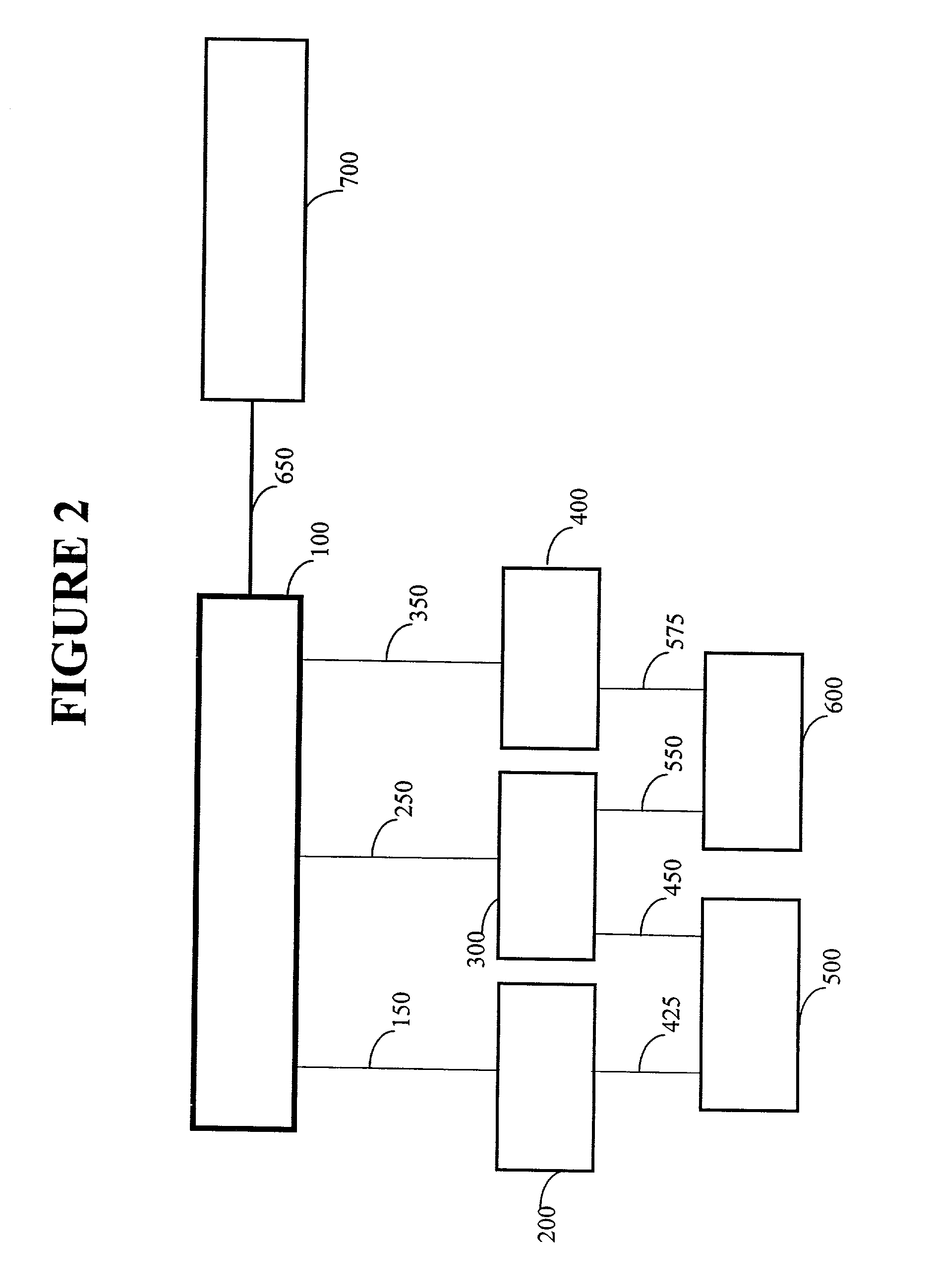
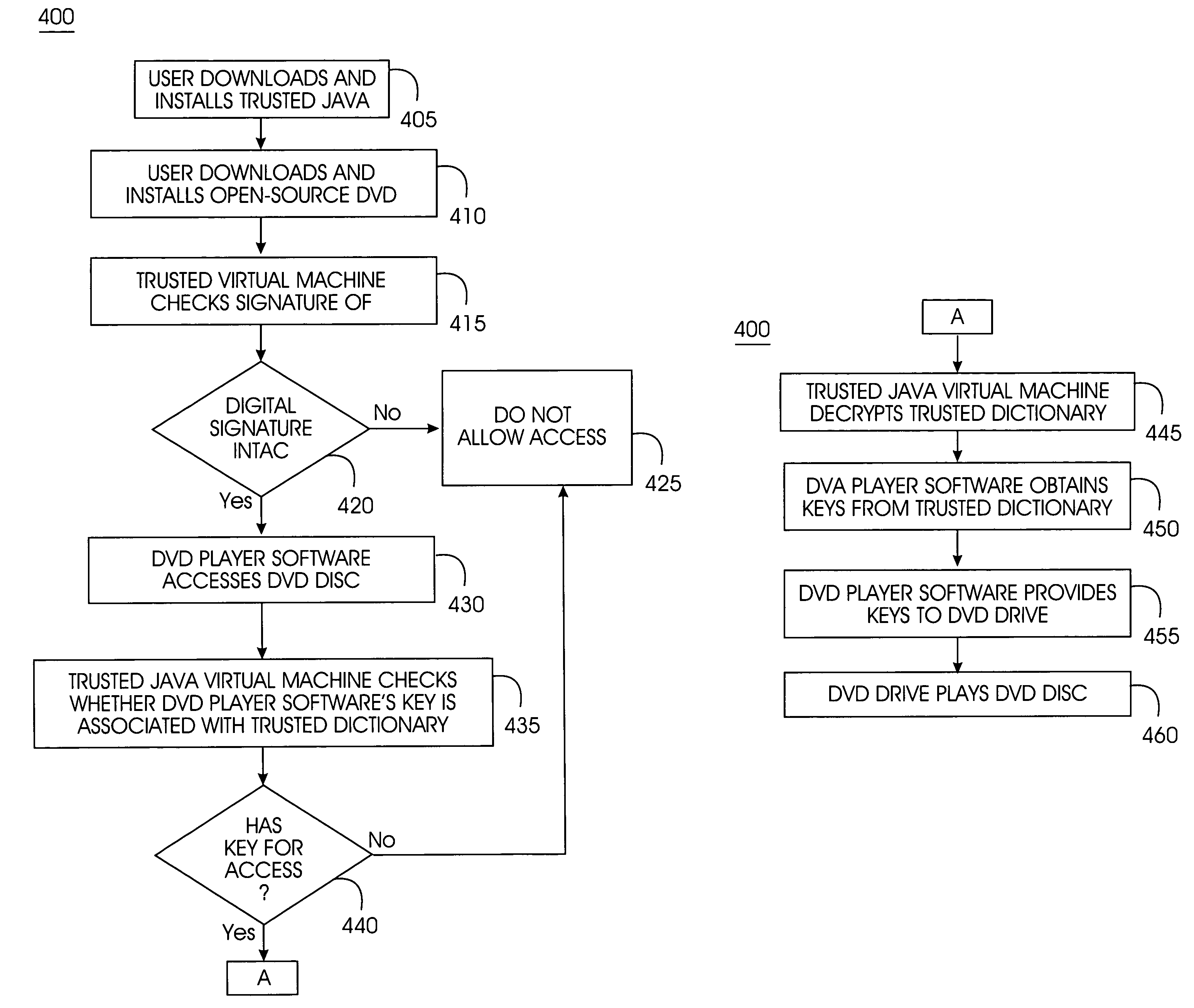
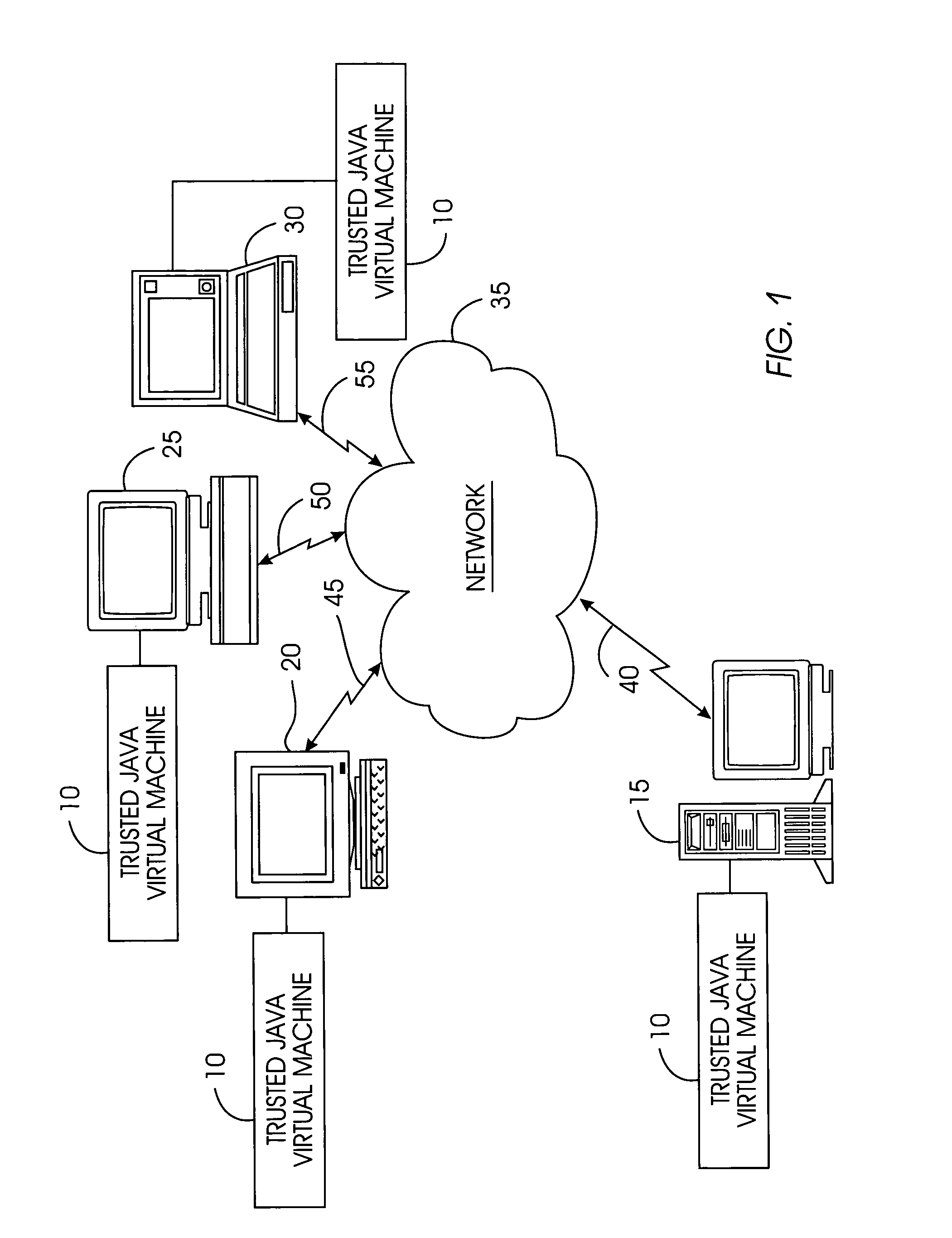
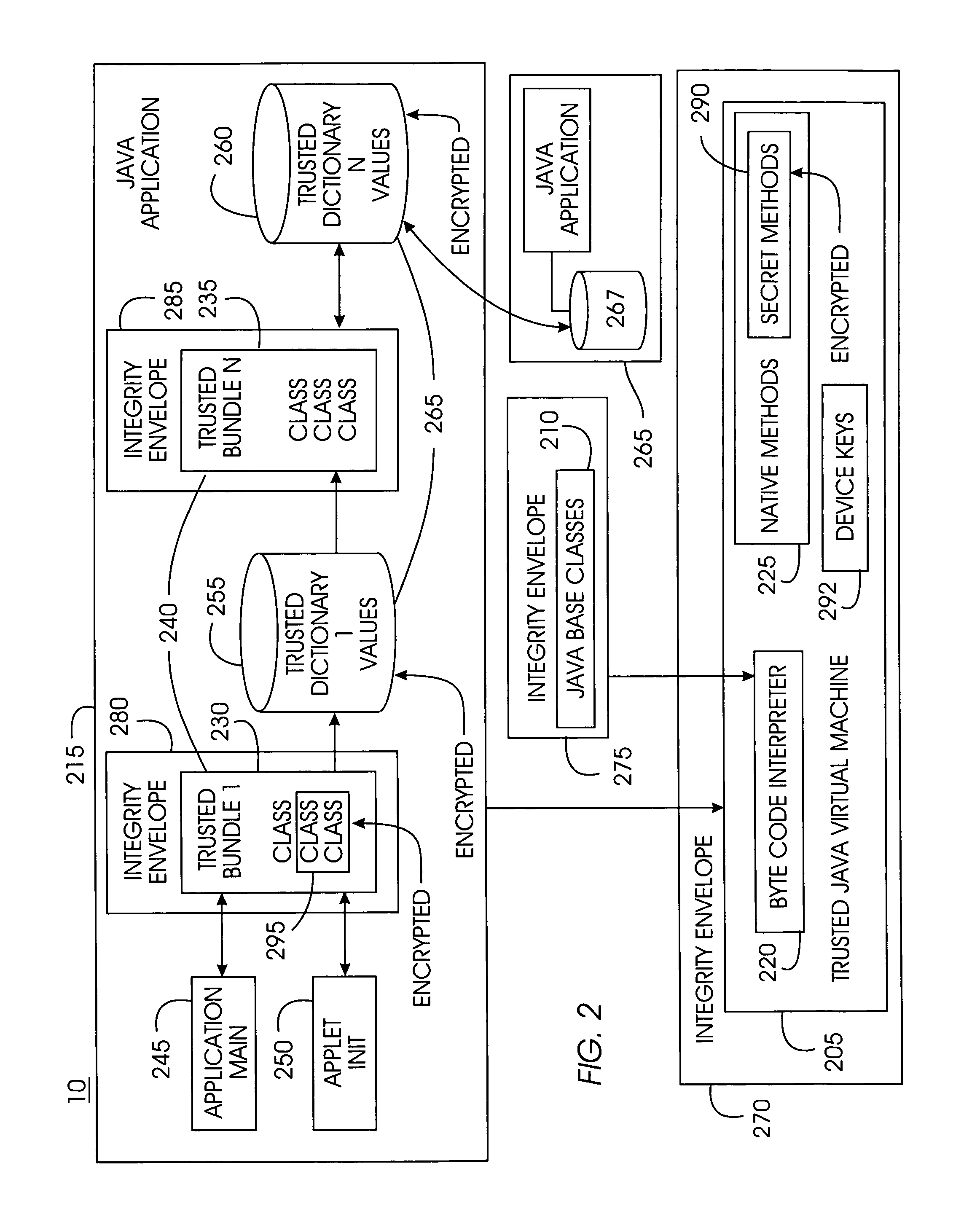
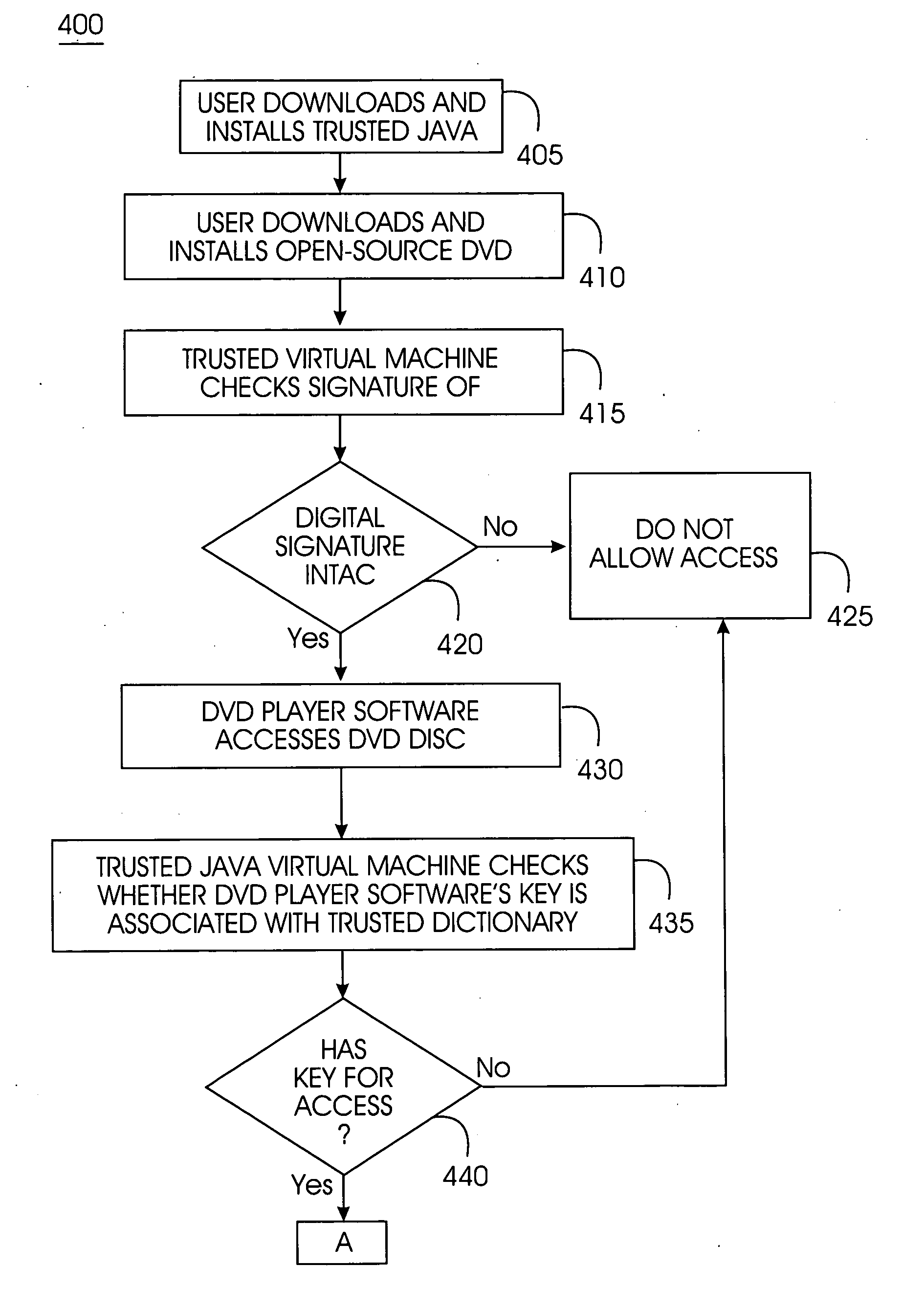
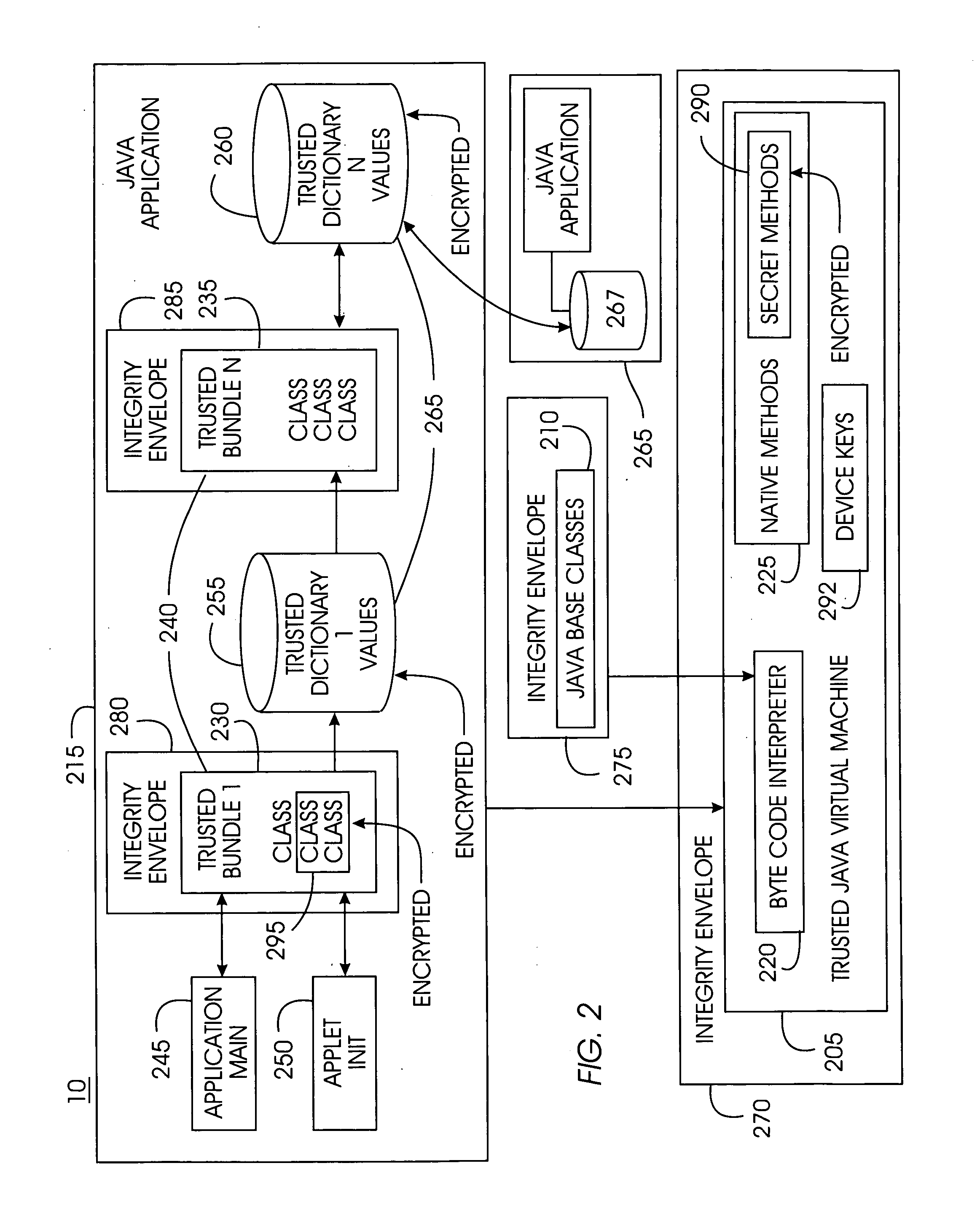
Tamper-resistant trusted java virtual machine and method of using the same
InactiveUS7516331B2Slow processEnsure integrityProgram control using stored programsUser identity/authority verificationOpen sourceProgram security
A trusted Java virtual machine provides a method for supporting tamper-resistant applications, ensuring the integrity of an application and its secrets such as keys. The trusted Java virtual machine verifies the integrity of the Java application, prevents debugging of the Java application, and allows the Java application to securely store and retrieve secrets. The trusted Java virtual machine environment comprises a TrustedDictionary, a TrustedBundle, an optional encryption method for encrypting and decrypting byte codes, and an underlying trusted Java virtual machine. The encrypted TrustedDictionary protects data while the TrustedBundle protects programming code, allowing applications to store secret data and secure counters. The application designer can restrict TrustedBundle access to only those interfaces that the application designer explicitly exports. The open source code may optionally be encrypted. Secrets required by the open source programming code of the application are encrypted in TrustedDictionary.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System, method and computer program product for providing a fare analytic engine
An exemplary embodiment of a system, method and / or computer program product for creating a fare analytic database, may include: receiving, by at least one processor, fare(s) and fare related data; and creating a graph database of the fare(s) and fare related data; where the creating may include: creating one or more node(s) of the graph database representing at least one component of the fare and fare related data; creating one or more relationship(s) between a plurality of the nodes; and applying at least one property to the node(s) and the relationship(s). A fare analytic engine may further incorporate the database, and the engine may process queries traversing the database for fare and fare related data; and functional programming methods may be used to generate Boolean byte code routines from fare restrictions, according to exemplary embodiments disclosed.
Owner:AIRLINE TARIFF PUBLISHING COMPANY
Tamper-resistant trusted java virtual machine and method of using the same
InactiveUS20050114683A1Easy to processSatisfies needProgram control using stored programsUser identity/authority verificationOpen sourceProgram security
A trusted Java virtual machine provides a method for supporting tamper-resistant applications, ensuring the integrity of an application and its secrets such as keys. The trusted Java virtual machine verifies the integrity of the Java application, prevents debugging of the Java application, and allows the Java application to securely store and retrieve secrets. The trusted Java virtual machine environment comprises a TrustedDictionary, a TrustedBundle, an optional encryption method for encrypting and decrypting byte codes, and an underlying trusted Java virtual machine. The encrypted TrustedDictionary protects data while the TrustedBundle protects programming code, allowing applications to store secret data and secure counters. The application designer can restrict TrustedBundle access to only those interfaces that the application designer explicitly exports. The open source code may optionally be encrypted. Secrets required by the open source programming code of the application are encrypted in TrustedDictionary.
Owner:IBM CORP
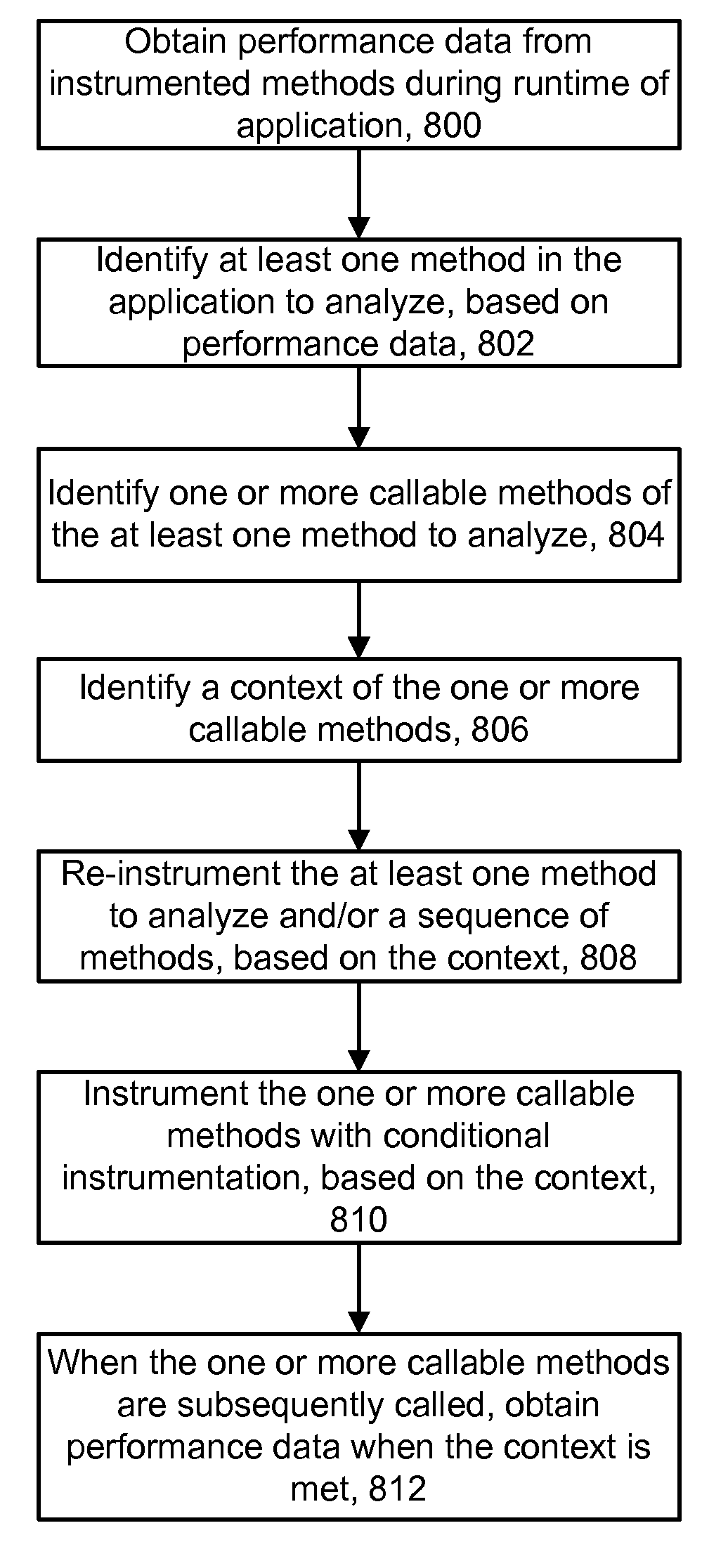
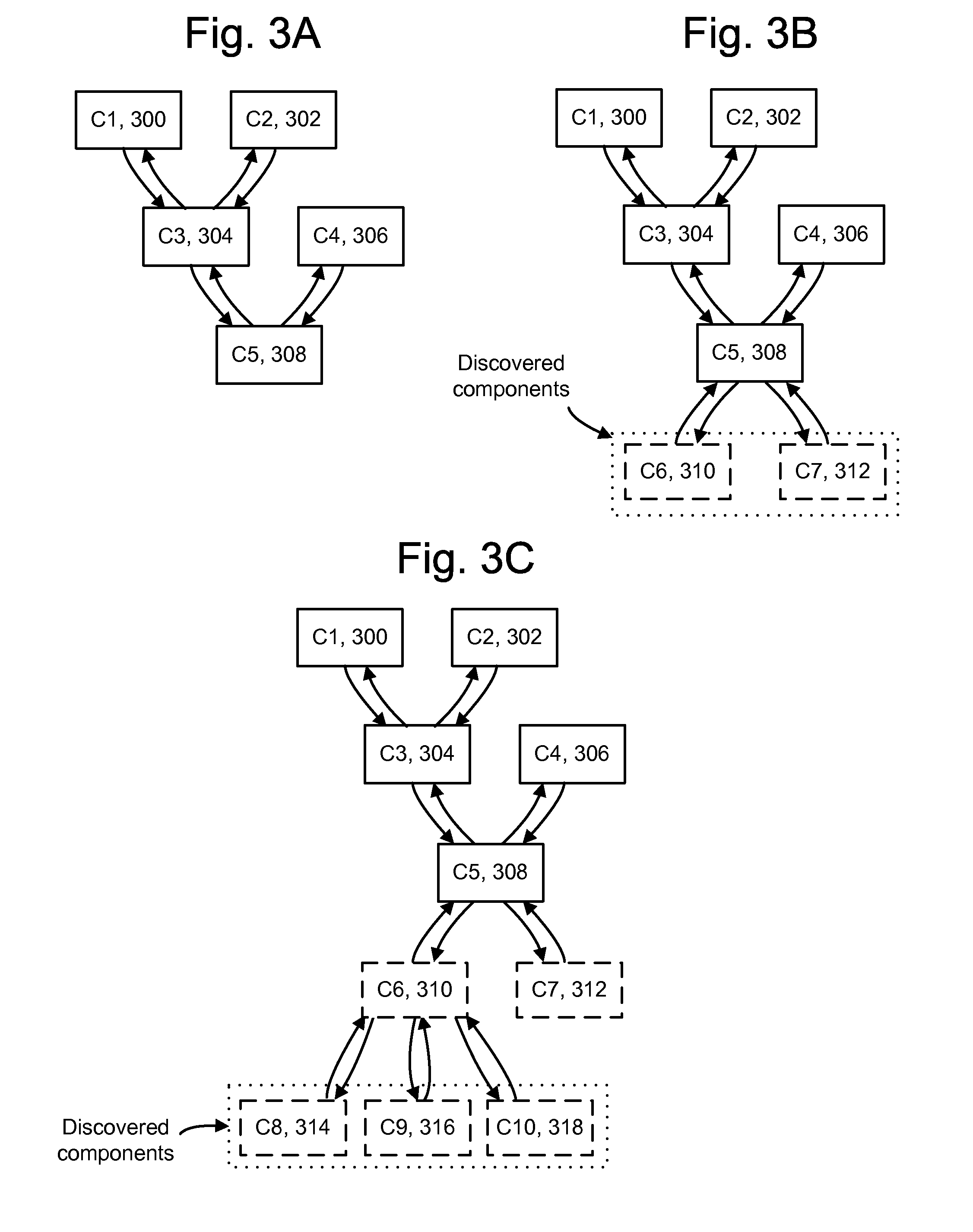
Conditional dynamic instrumentation of software in a specified transaction context
ActiveUS20110283263A1Error detection/correctionSoftware maintainance/managementDynamic instrumentationTransaction data
Techniques for analyzing software in which un-instrumented components can be discovered and conditionally instrumented during a runtime of the software. Initially, software such as an application can be configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. As the application runs, performance data gathered from the instrumentation may indicate that the performance of some methods is below expectations. To analyze this, any methods which are callable from a method at issue are discovered, such as by inspecting the byte code of loaded classes in a JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM). To limit and focus the diagnosis, the instrumentation which is added to the discovered components can be conditional, so that the instrumentation is executed only in a specified context. The context can involve, e.g., a specified sequence of components in which a discovered component is called, and / or transaction data in which a discovered component is called.
Owner:CA TECH INC
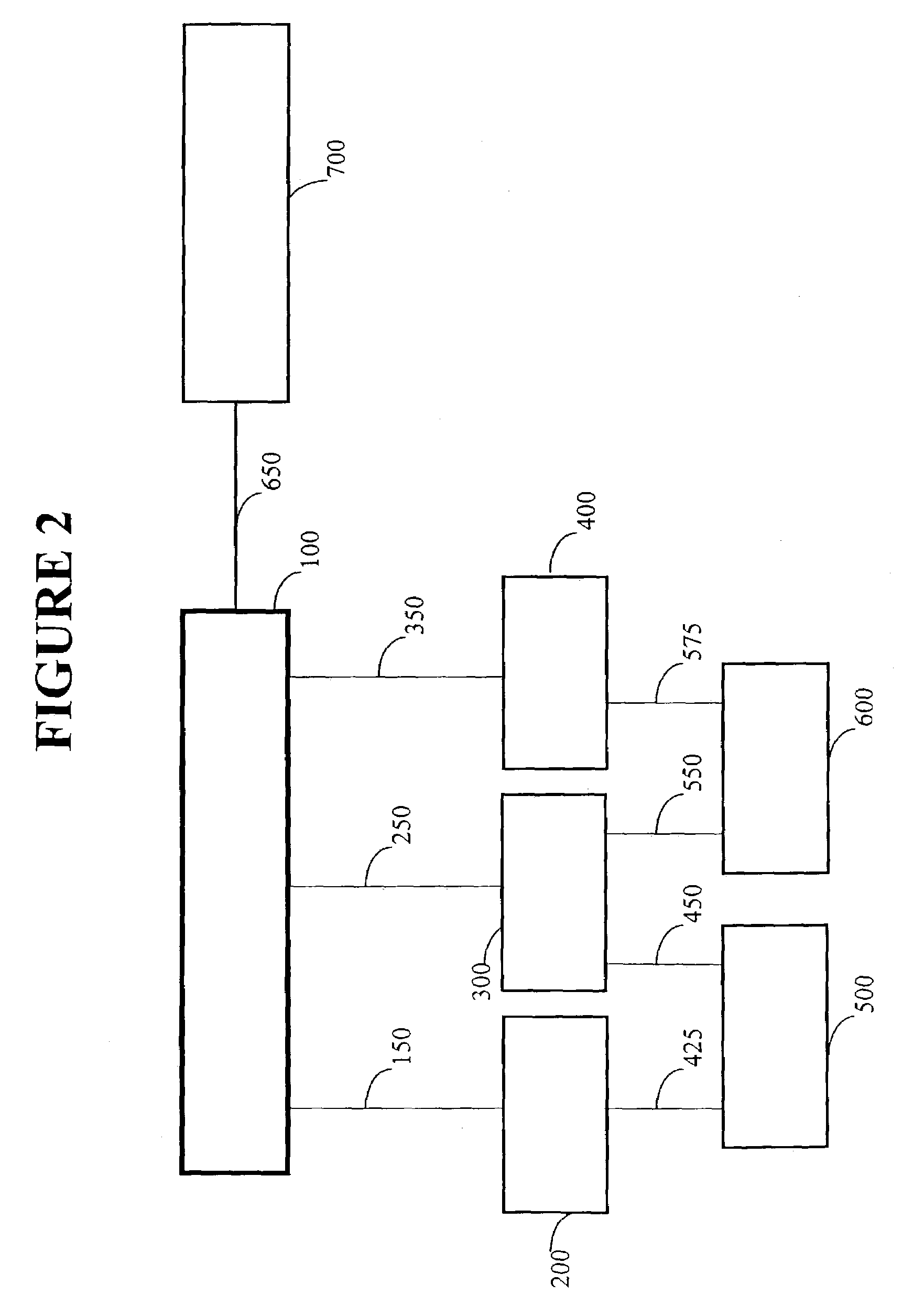
Methods and apparatus for control using control devices that provide a virtual machine environment and that communicate via an IP network
InactiveUS20080040477A1Reduce complexityReduce confusionMultiple digital computer combinationsResourcesOperational systemActuator
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
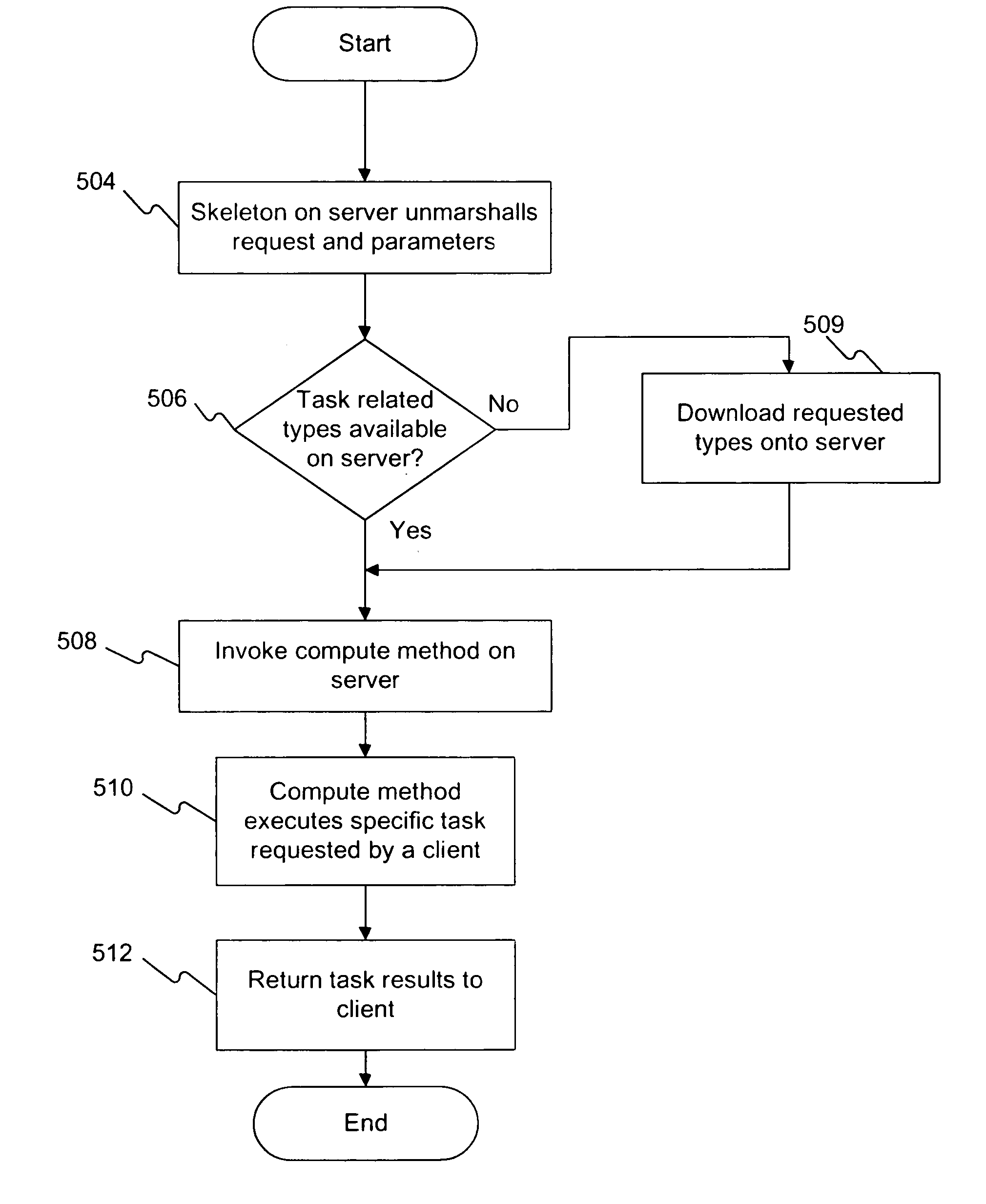
Method and apparatus for dynamic distributed computing over a network
A homogeneous execution environment operates within a heterogeneous client-server network. A client selects a server and transmits a procedure call with parameters. In response, a server dynamically and securely downloads code to a compute server; invokes a generic compute method; executes the code on the compute server; and returns the results to the calling client method, preserving the result on the compute server if requested. This technique is efficient in that it does not require multiple copies of code to be downloaded or compiled since server byte-codes can be executed on each of the different systems, therefore downloading or compiling multiple copies of code can be avoided. The code can be compiled once and downloaded as needed to the various servers as byte-codes and then executed.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Byte code modification for testing, debugging and/or monitoring of virtual machine based software
ActiveUS7367025B1Flexible and scalable architectureError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsEntry pointParallel computing
A method is disclosed that comprises modifying a method's byte code instructions for purposes of testing, debugging and / or monitoring. Additional byte code instructions are inserted into the method's byte code instructions at an entry point of the method and at an exit point of the method. The first additional byte code instruction causes a first output function to be executed for the method as a consequence of the entry point being reached during runtime. The second additional byte code instruction causes a second output function to be executed for the method as a consequence of the exit point being reached during runtime. The Application of the method to Distributed Statistical Record (DSR) keeping is also disclosed.
Owner:SAP AG
Protecting software from unauthorized use by converting source code modules to byte codes
ActiveUS7124445B2Difficult to operateDifficult to determineDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionObfuscationApplication software
Owner:PACE ANTI PIRACY
Targeted runtime compilation
ActiveUS7788657B2Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsJust-in-time compilationApplication software
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
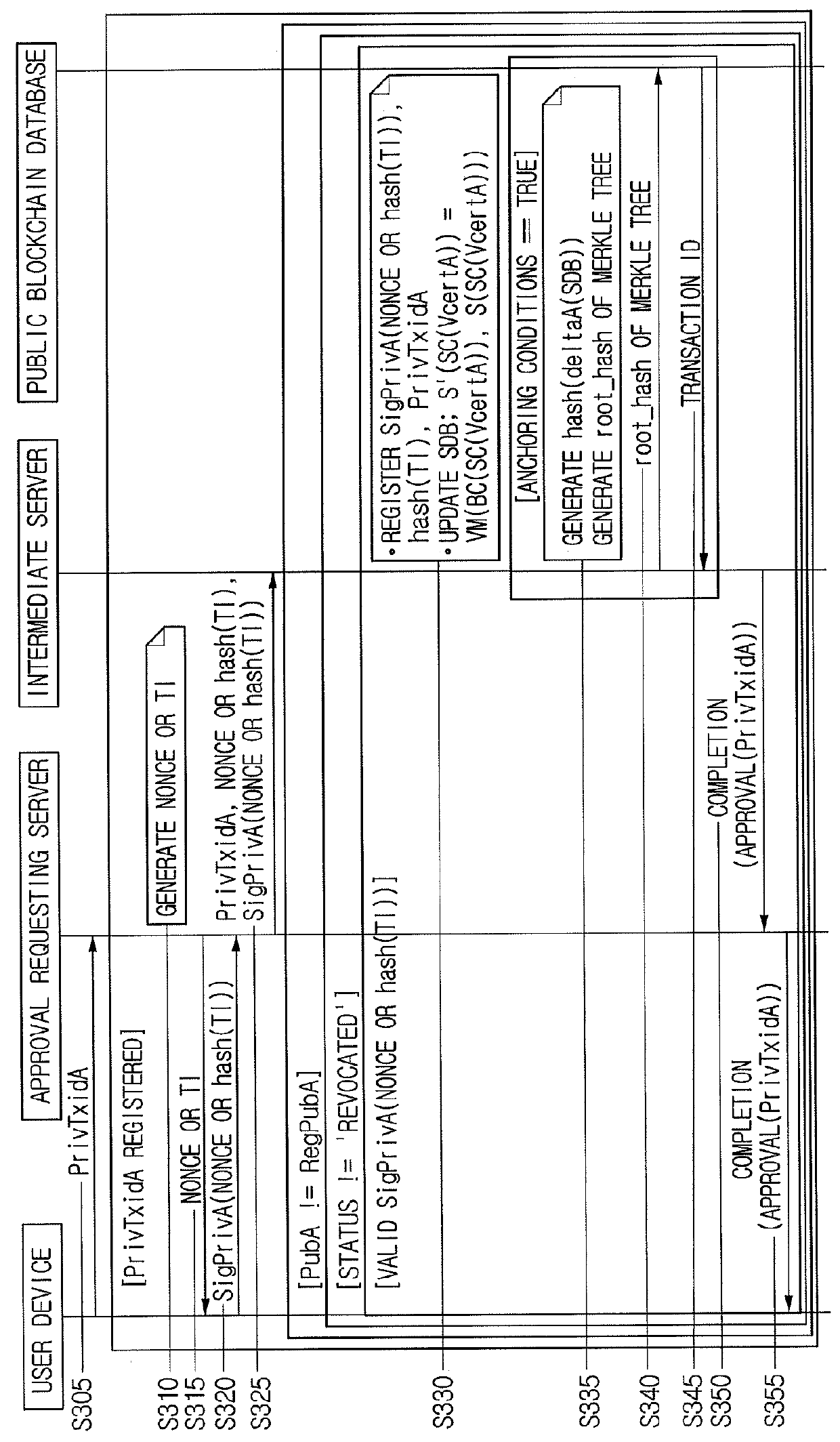
Method for providing certificate service based on smart contract and server using the same
ActiveUS20180109516A1Reduce transaction costsPrevent forgeryPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationUser deviceSmart contract
A method for providing a certificate registration service based on a smart contract, wherein the smart contract is source code compilable into executable byte code, is configured to perform procedures if particular conditions are satisfied, and wherein integrity is verified by a consensus, is provided. The method includes steps of: (a) acquiring a public key PubA of a user device, an IdhashA which is hashed personal information, and a VcertA which includes validity conditions, acquiring the smart contract corresponding to the validity conditions and byte code; (b) registering the PubA, the IdhashA and the byte code with a private blockchain database, and acquiring PrivTxidA locating certificate information in the private blockchain database; (c) registering the PrivTxidA and a state of the smart contract with an SDB; and (d) acquiring and registering a hash value calculated using the PubA, the IdhashA and the byte code, and its neighboring hash value.
Owner:COINPLUG LNC
Displayable presentation page and SQL searchable relational data source implementation of a system, method and software for creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of complex data objects and their data relationships
The invention provides systems, methods and software for creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of complex data objects and associated data stores. In one aspect, the invention also relates to an application programming object capable of creating or maintaining distributed transparent persistence of data objects or data object graphs without the necessity of inserting any byte codes or modification of the object graph. Virtually any java object or object praph can be transparently persisted. Further, copies of a data graph or of a portion of the data graph can be automatically reconciled and changes persisted without any persistence coding in the object model.
Owner:THOUGHT
Methods and apparatus for control using control devices that provide a virtual machine environment and that communicate via an IP network
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Synthesizing application response measurement (ARM) instrumentation
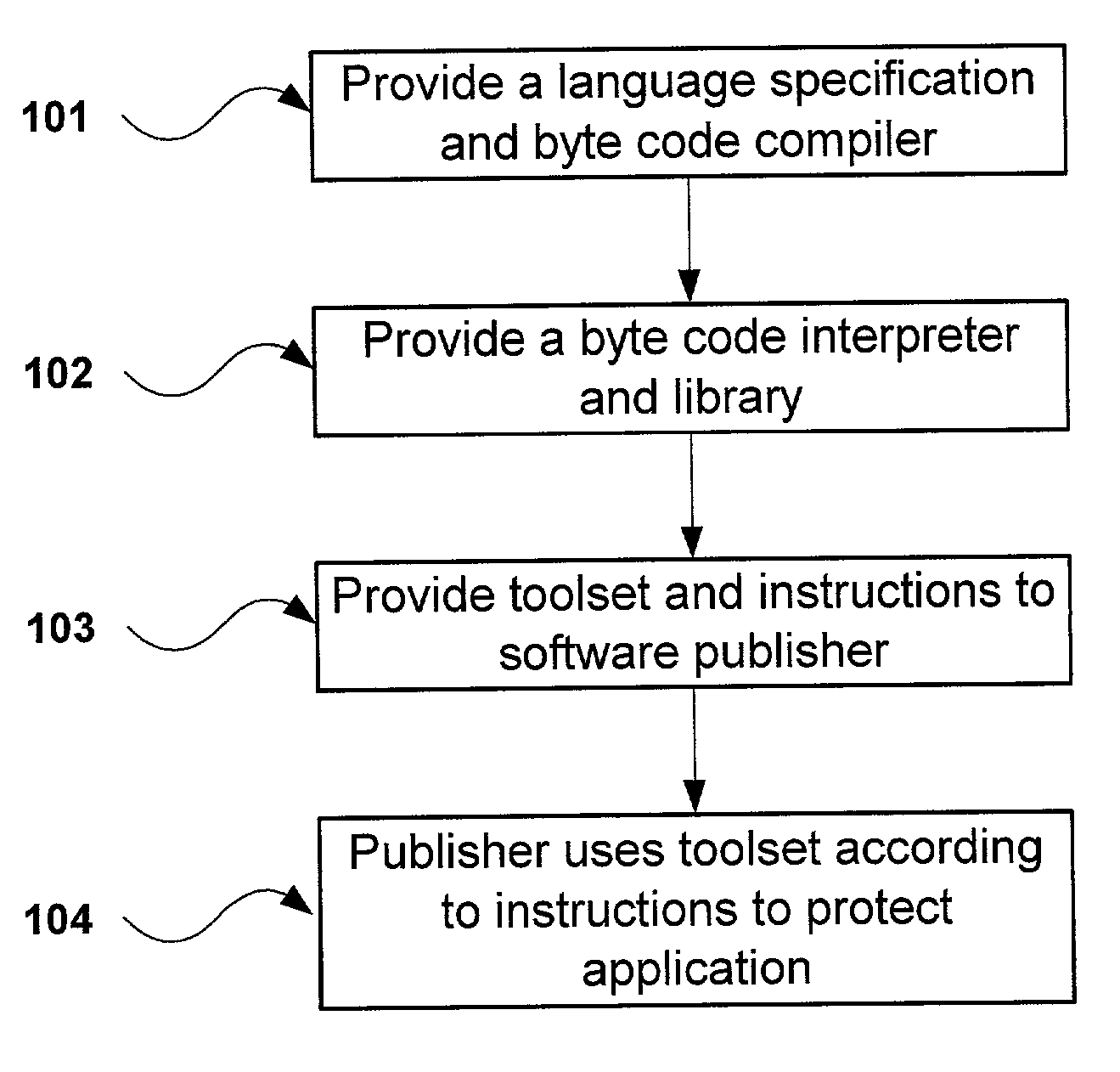
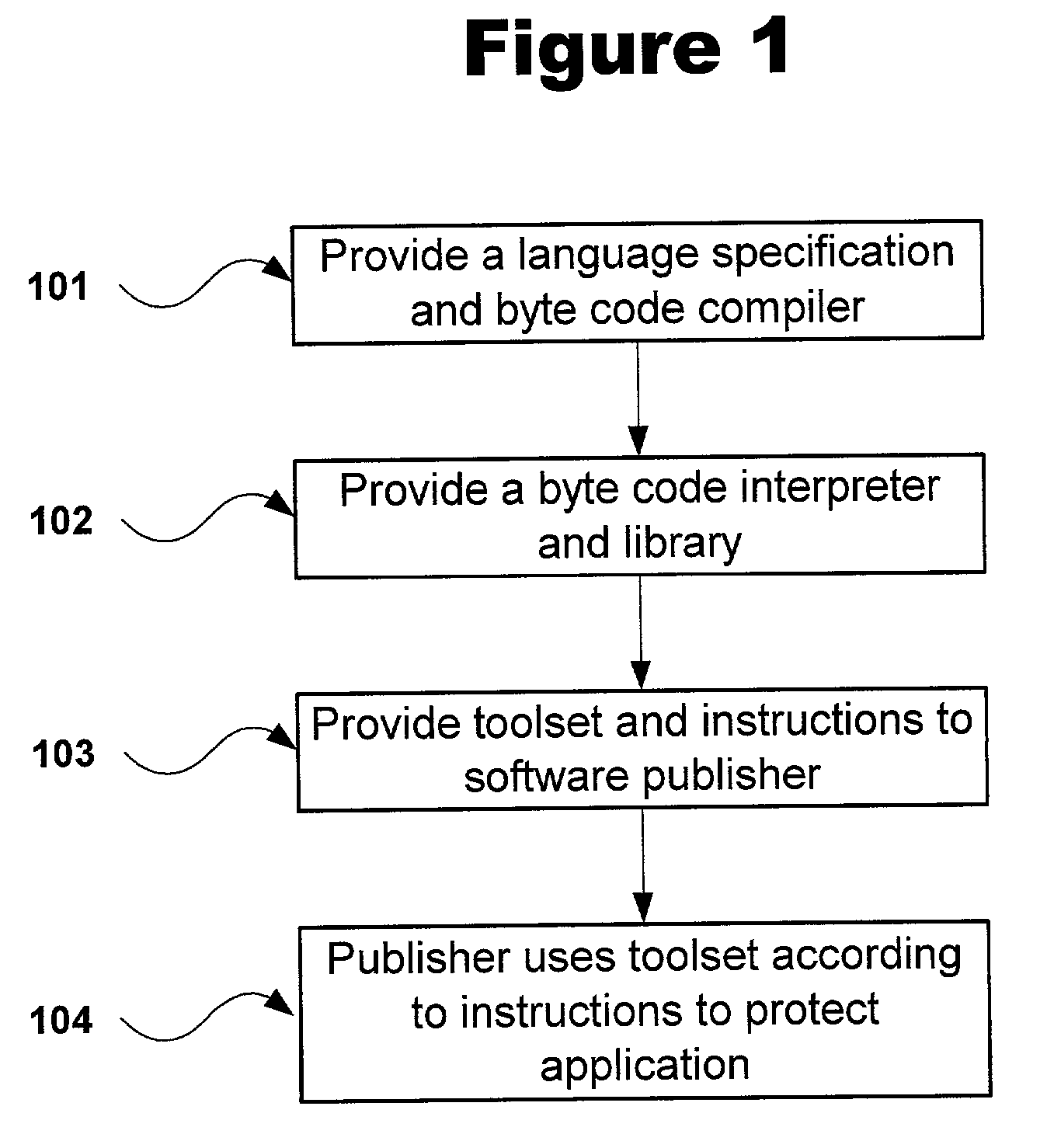
InactiveUS7496903B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsApplication Response MeasurementStart time
A system for monitoring response time of a method or function associated with a Java software component is disclosed. The system comprises an instrumentation engine for inserting instrumentation code in a byte code representation of said method or function, said instrumentation code effecting generation of a start time marker and a stop time marker upon start and completion, respectively, of the method or function. The system can further comprise an interface module that is invoked by the instrumentation code upon start and completion of said method or function, and an application response measurement (ARM) agent that is in communication with the interface module. The interface module, upon invocation by said instrumentation code, calls the ARM agent to cause generation of the start and stop time markers by the ARM agent.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
System for and method of improving discrete event simulation using virtual machines
ActiveUS20060036426A1Efficient checkpointingLoad balancingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsByteSource code
The system and method of the present invention can allow the imbedding of simulation primitives within a conventional programming language in order to use the full capabilities of the conventional programming language and its compiler without modification in the programming of efficient, scalable simulators. The simulation primitives are designed to be preserved through the compilation process, thus allowing a rewriter to modify the compiler's byte code output without accessing the source code. Also, since the rewriter output is a set of class files and a kernel can be written in the conventional programming language, and the system and method of the present invention can execute within a conventional virtual machine associated with the conventional programming language.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Debugging support using dynamic re-compilation
The present invention is a method and system to support debug. A function is re-compiled when a field watch for a field is activated. The function includes a byte code sequence having a field byte code that accesses or modifies the field. The re-compiled function provides a native code and occupies a code space. An instrumentation code corresponding to the field watch of the field is generated. The instrumentation code is inserted to the native code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for creating target byte code
InactiveUS7844958B2Facilitate efficient lookup and mappingBinary to binaryProgram controlData elementApplication software
A system and method for converting byte code of a first type into byte code of a second type. Byte code of a first type and markup language code are received as inputs. The first byte code is converted into constituent byte code data elements that can comprise any logical unit or grouping of at least a portion of a software application. The markup language code is converted into constituent markup language data elements that can comprise individual markup language tags and references to data or functionality in the first byte code. The first byte code data elements and markup language data elements are mapped to data elements of a second byte code type. The second byte code data elements are assembled into a resulting second byte code.
Owner:APPCELERATOR
JAVA DSP acceleration by byte-code optimization
ActiveUS7146613B2Significant performanceSignificant energySoftware engineeringComputer security arrangementsParallel computingDirect execution
A digital system and method of operation is which the digital system has a processor with a virtual machine environment for interpretively executing instructions. First, a sequence of instructions is received (404) for execution by the virtual machine. The sequence of instructions is examined (408–414) to determine if a certain type of iterative sequence is present. If the certain type of iterative sequence is present, the iterative sequence is replaced (412) with a proprietary code sequence. After the modifications are complete, the modified sequence is executed in a manner that a portion of the sequence of instructions is executed in an interpretive manner (418); and the proprietary code sequences are executed directly by acceleration circuitry (420).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for creating target byte code
InactiveUS7707547B2Efficient mappingSmaller and faster byte code of a second typeBinary to binaryDigital data processing detailsData elementByte
Owner:APPCELERATOR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com