Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197 results about "Relative cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relative costs are expenses that change depending on where the company does business, such as the costs of transporting goods. Although controllable cost and relative costs may seem like different concepts, a cost can be both controllable and relative.
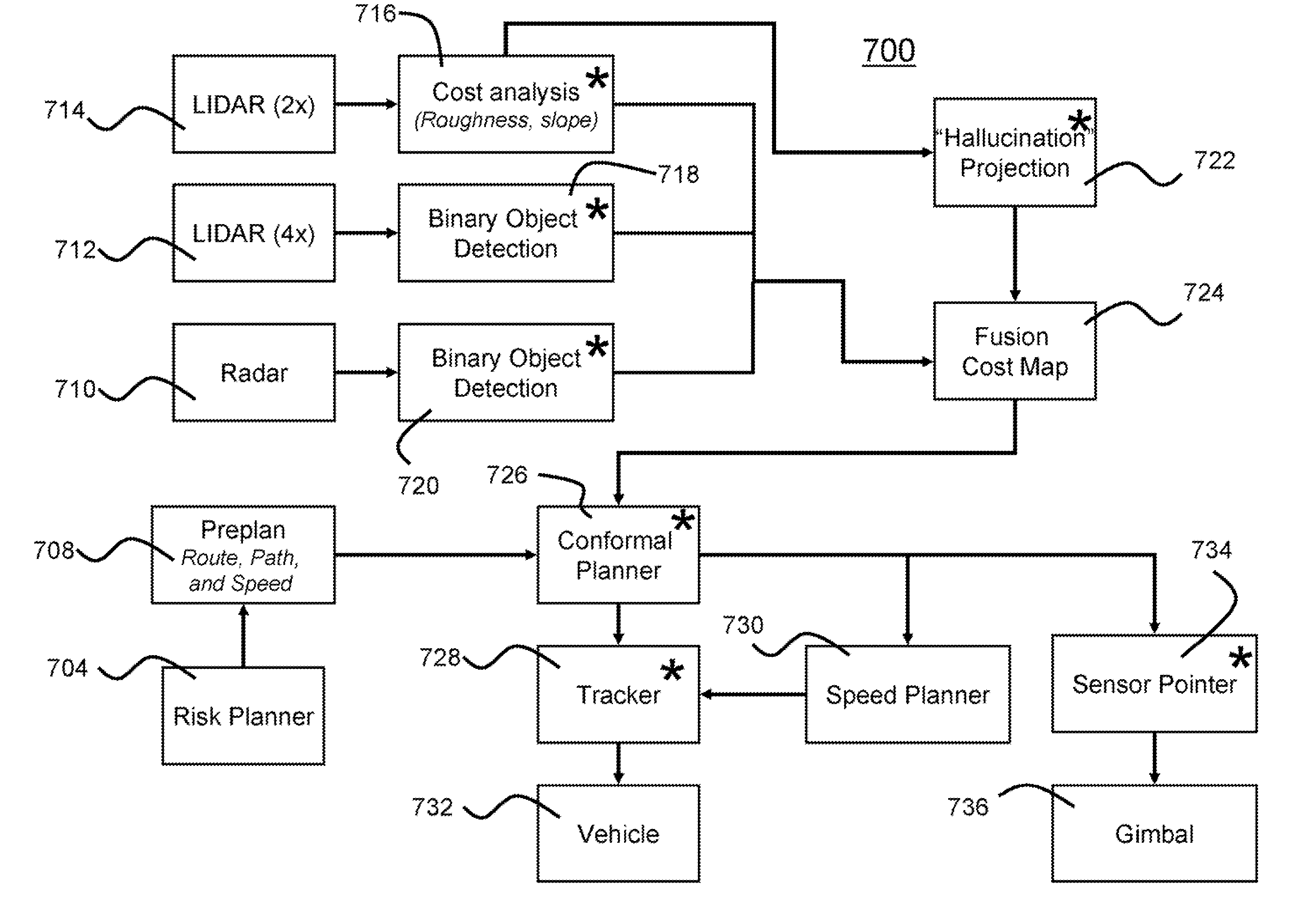
Software architecture for high-speed traversal of prescribed routes
InactiveUS20080059015A1Reduce computing loadImprove abilitiesPlatooningVehicle position/course/altitude controlTerrainLocal environment
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for high-speed navigation. The present invention preferably encompasses systems, methods, and apparatuses that provide for autonomous high-speed navigation of terrain by an un-manned robot. By preferably employing a pre-planned route, path, and speed; extensive sensor-based information collection about the local environment; and information about vehicle pose, the robots of the present invention evaluate the relative cost of various potential paths and thus arrive at a path to traverse the environment. The information collection about the local environment allows the robot to evaluate terrain and to identify any obstacles that may be encountered. The robots of the present invention thus employ map-based data fusion in which sensor information is incorporated into a cost map, which is preferably a rectilinear grid aligned with the world coordinate system and is centered on the vehicle. The cost map is a specific map type that represents the traversability of a particular environmental area using a numeric value. The planned path and route provide information that further allows the robot to orient sensors to preferentially scan the areas of the environment where the robot will likely travel, thereby reducing the computational load placed onto the system. The computational ability of the system is further improved by using map-based syntax between various data processing modules of the present invention. By using a common set of carefully defined data types as syntax for communication, it is possible to identify new features for either path or map processing quickly and efficiently.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
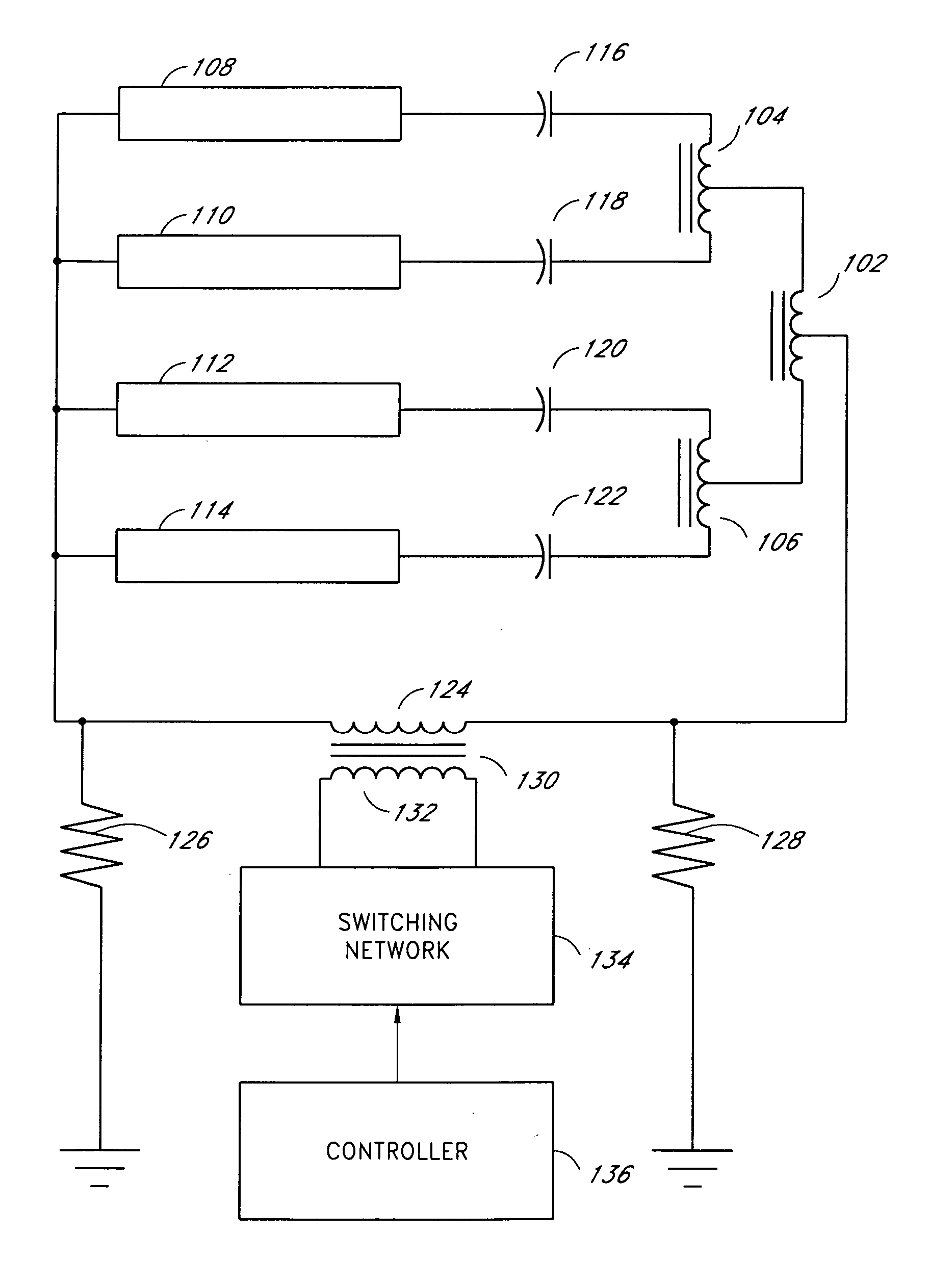
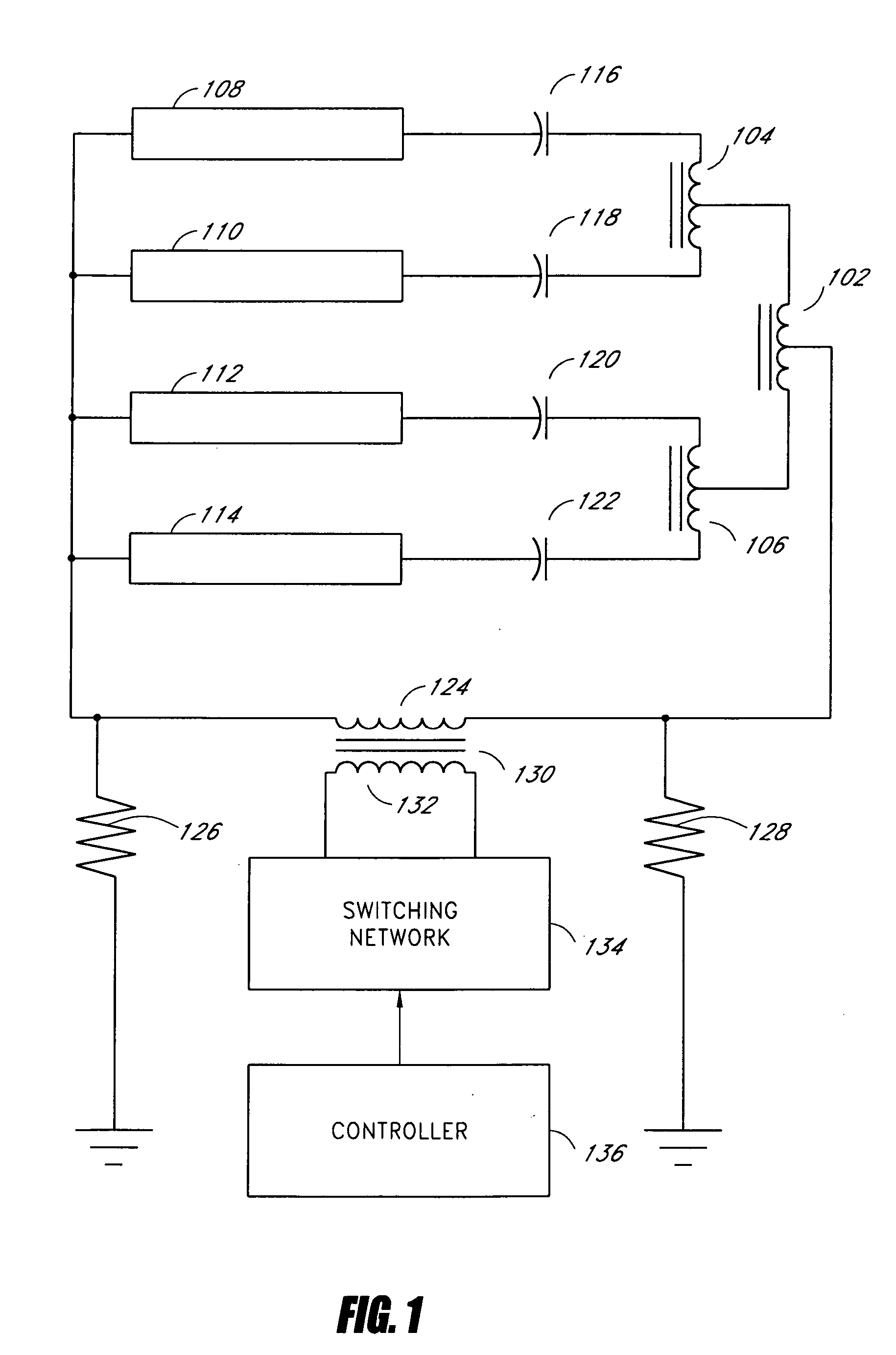
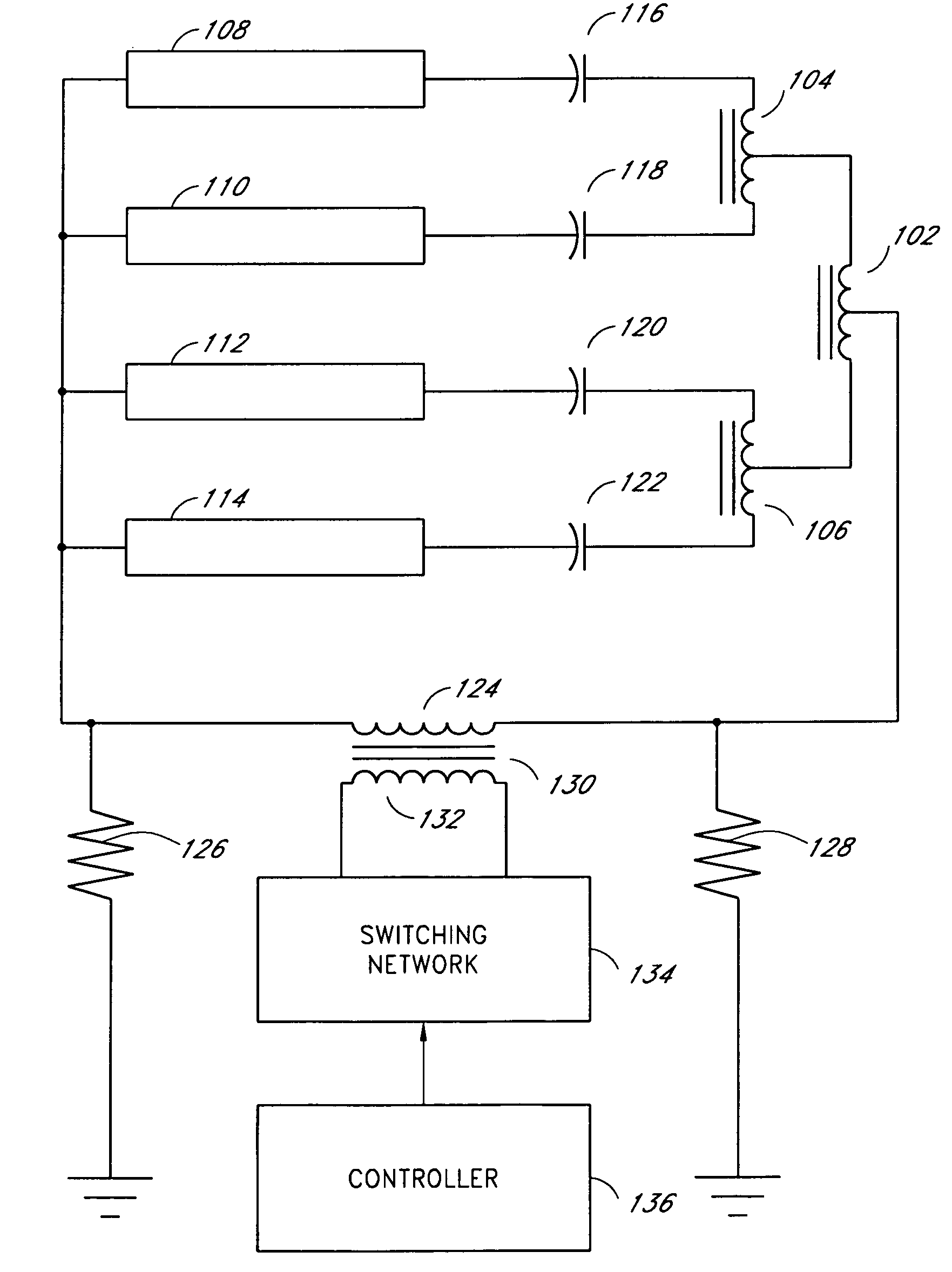
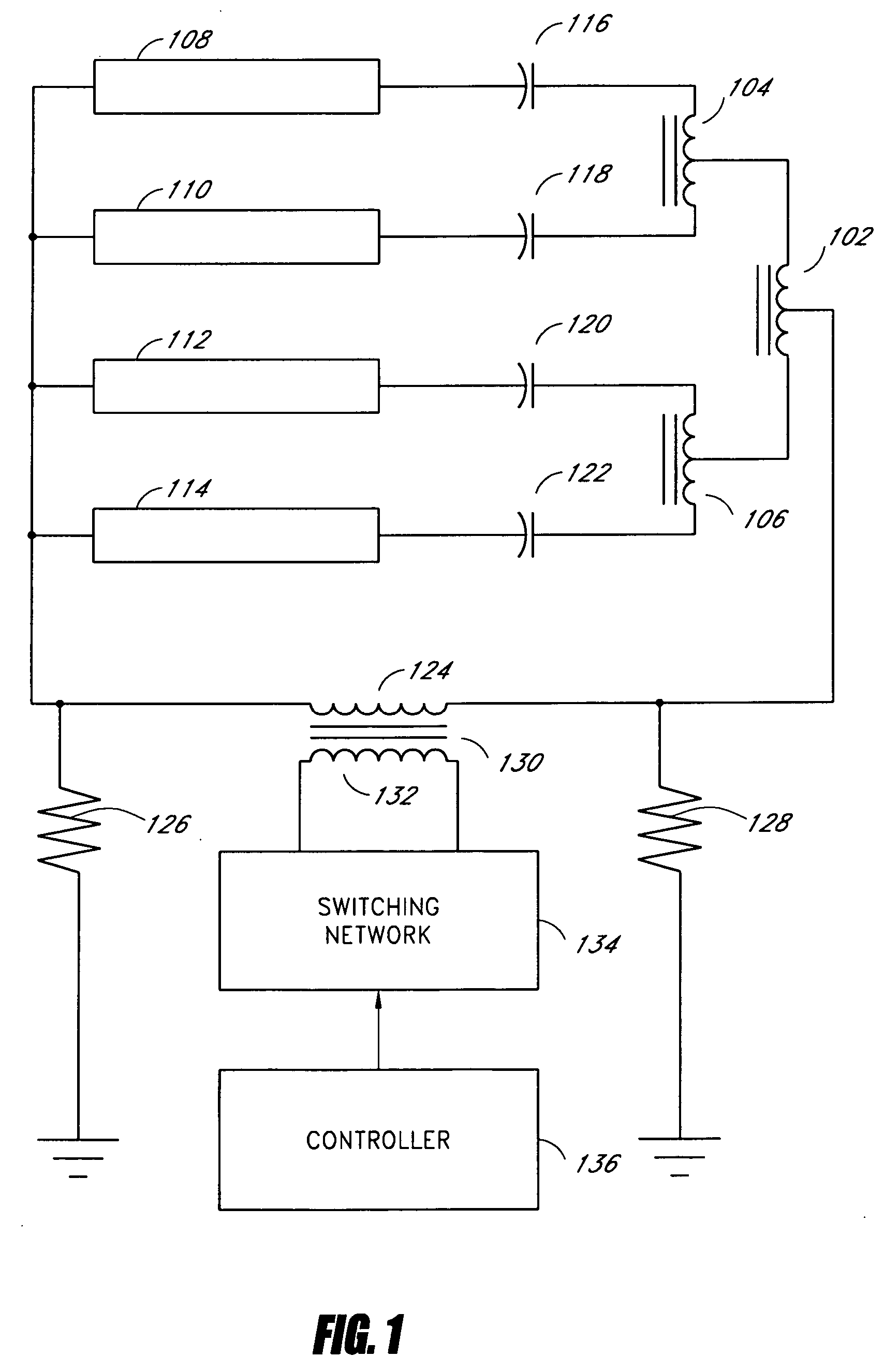
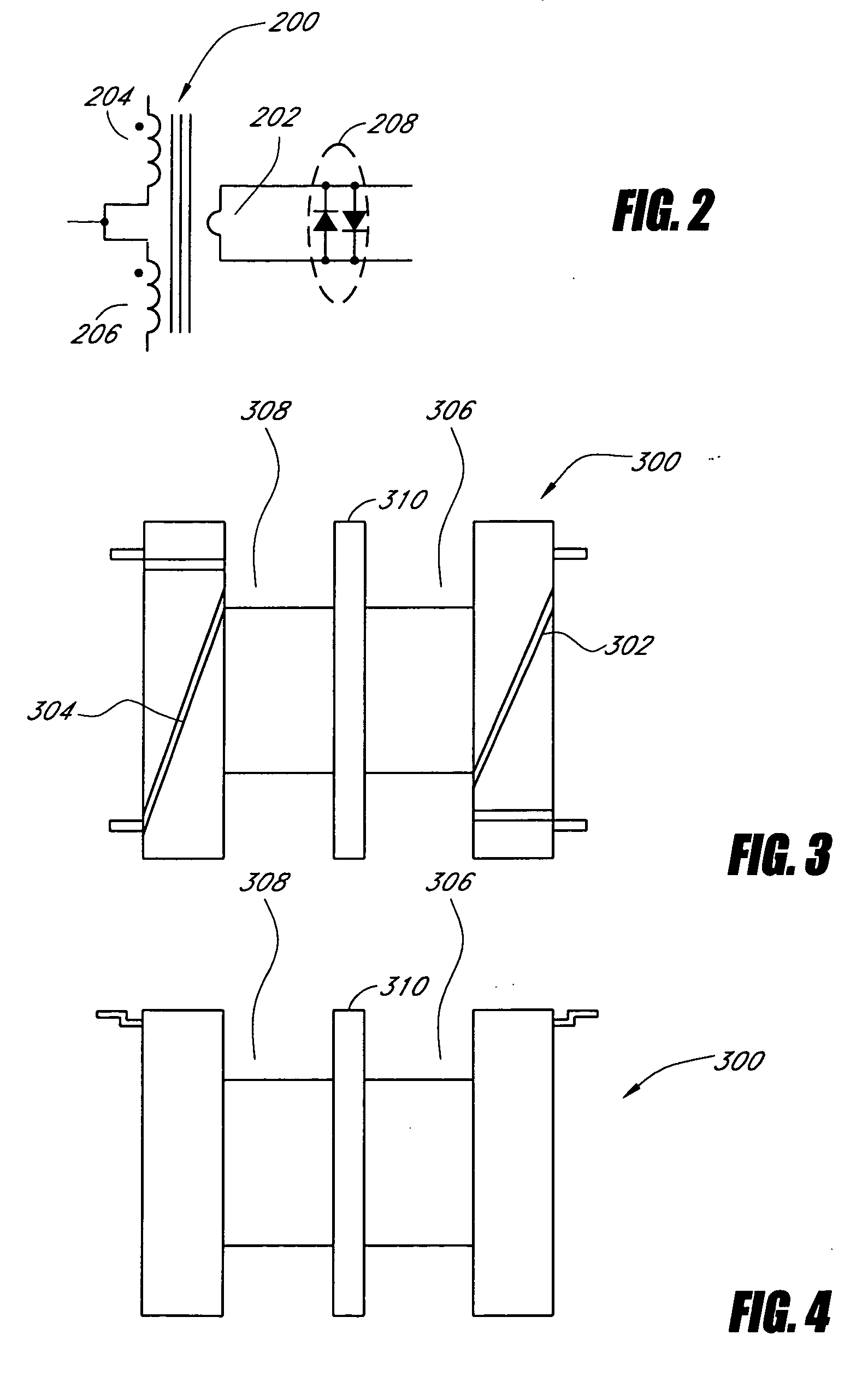
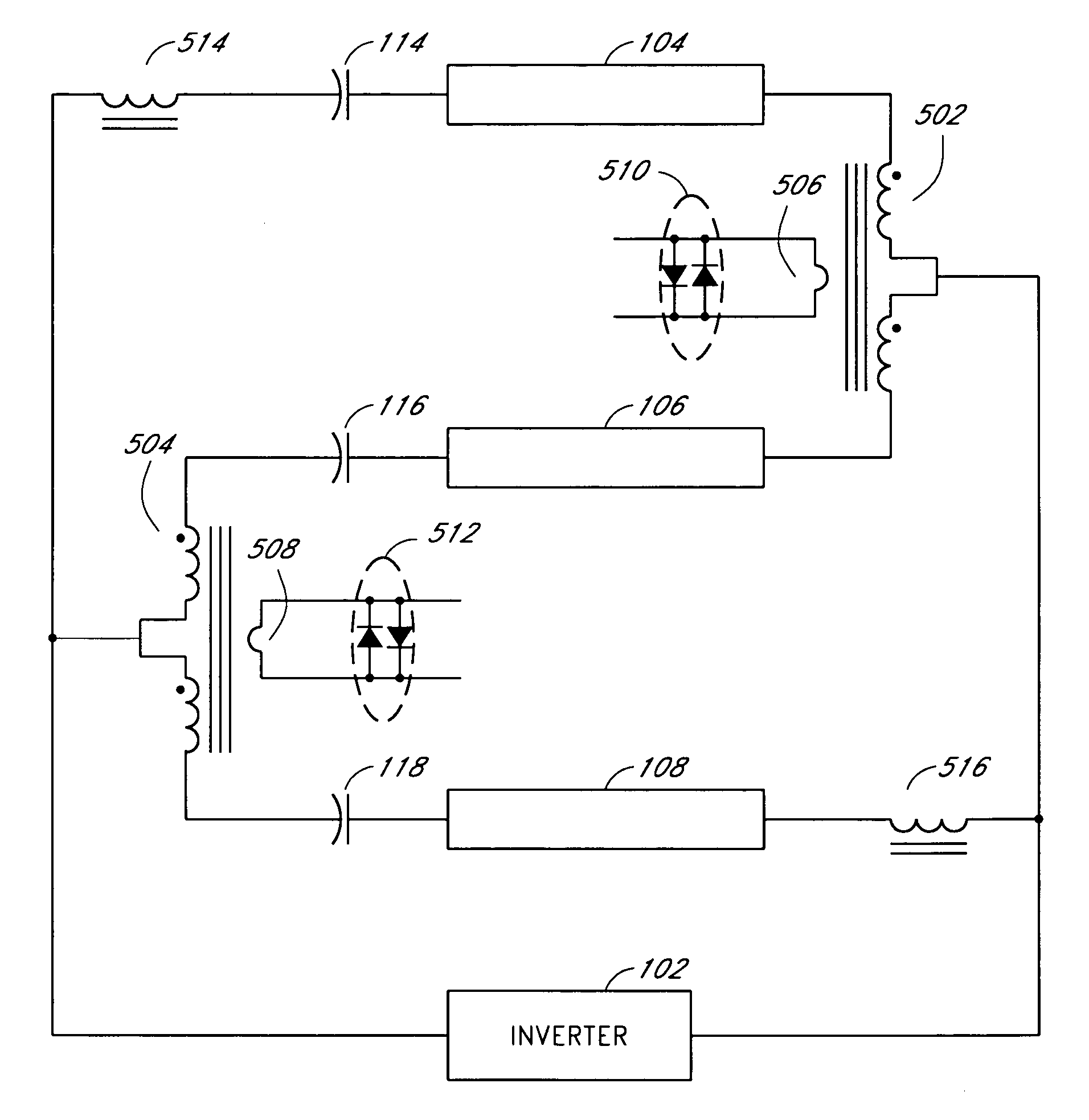
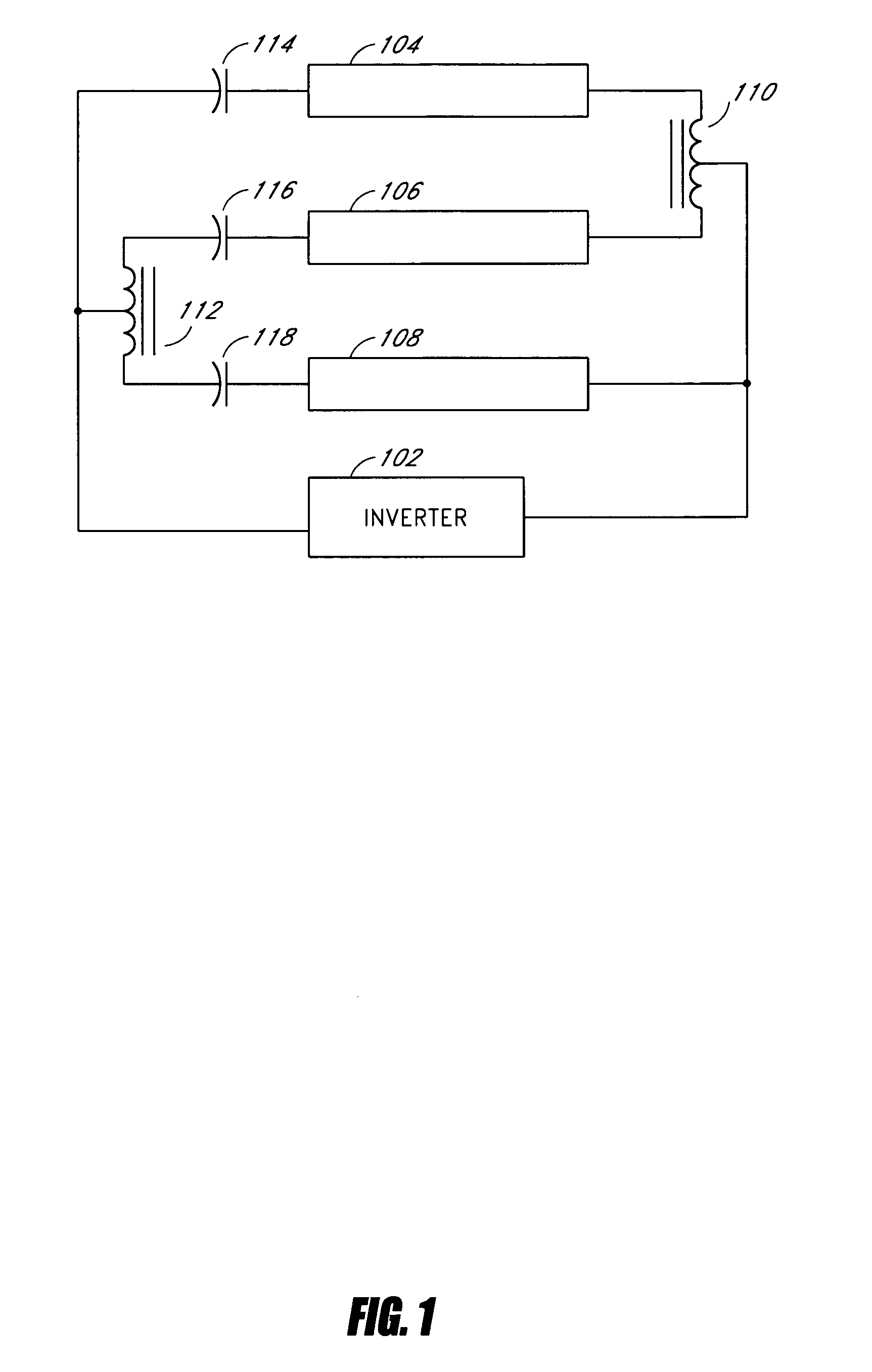
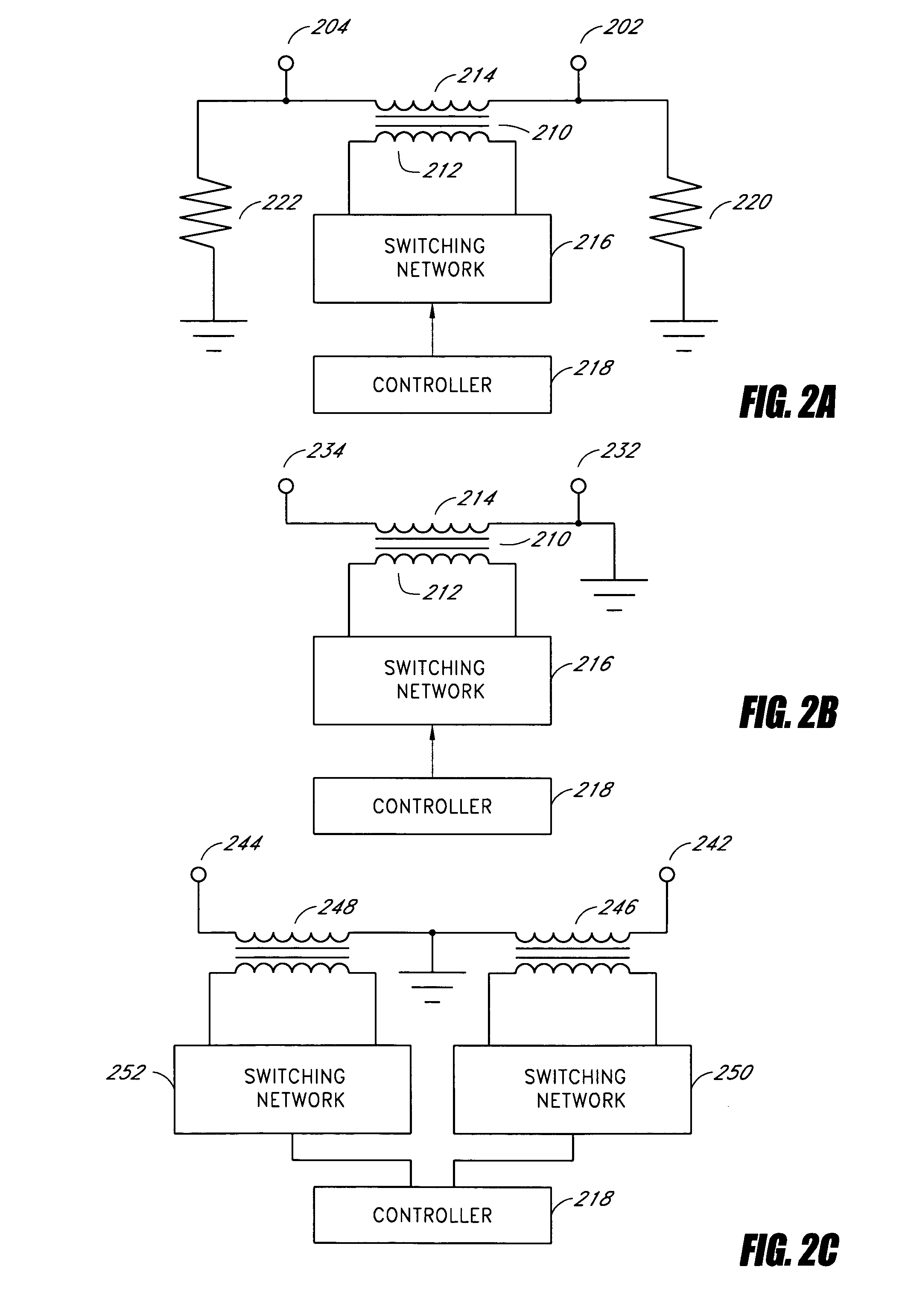
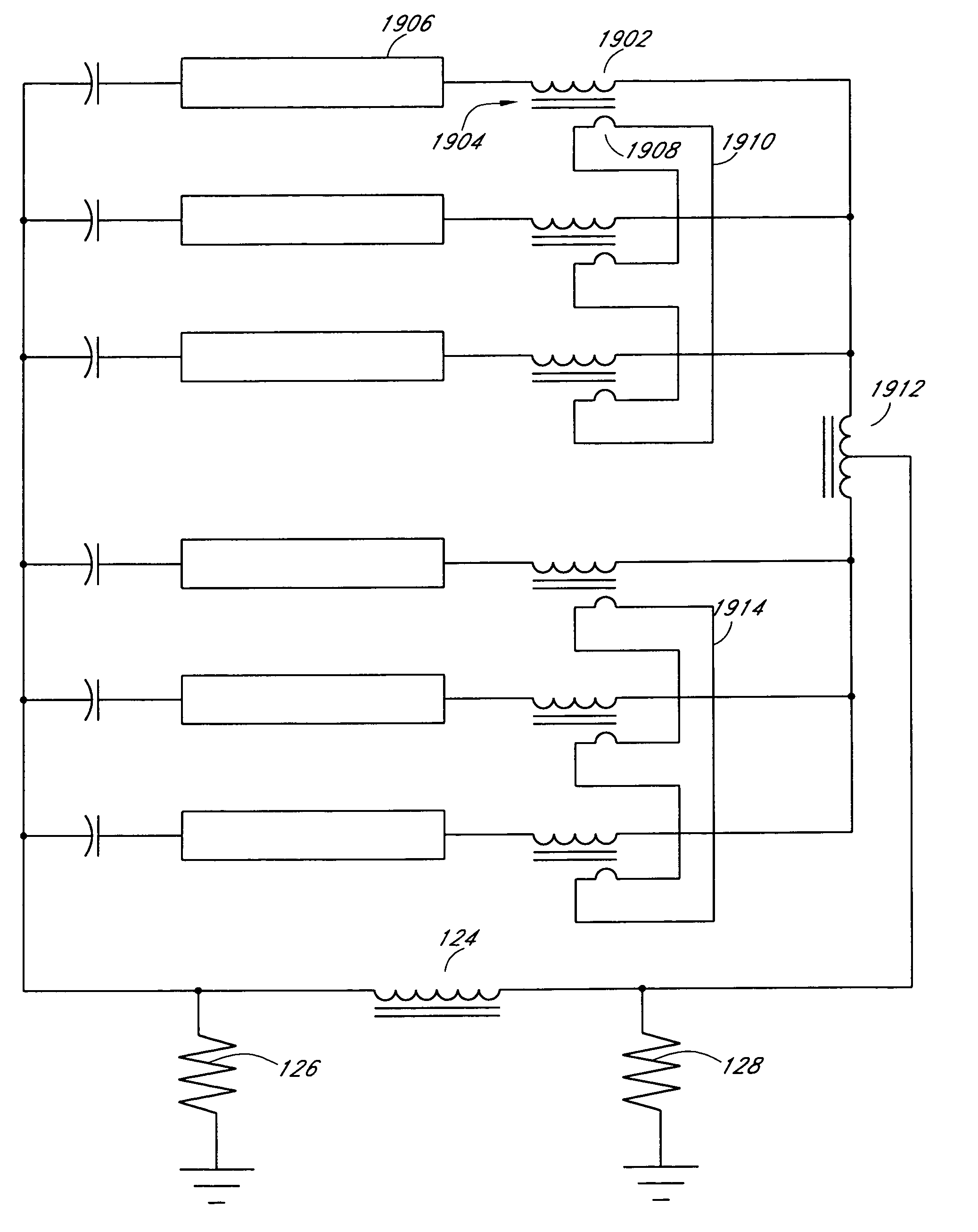
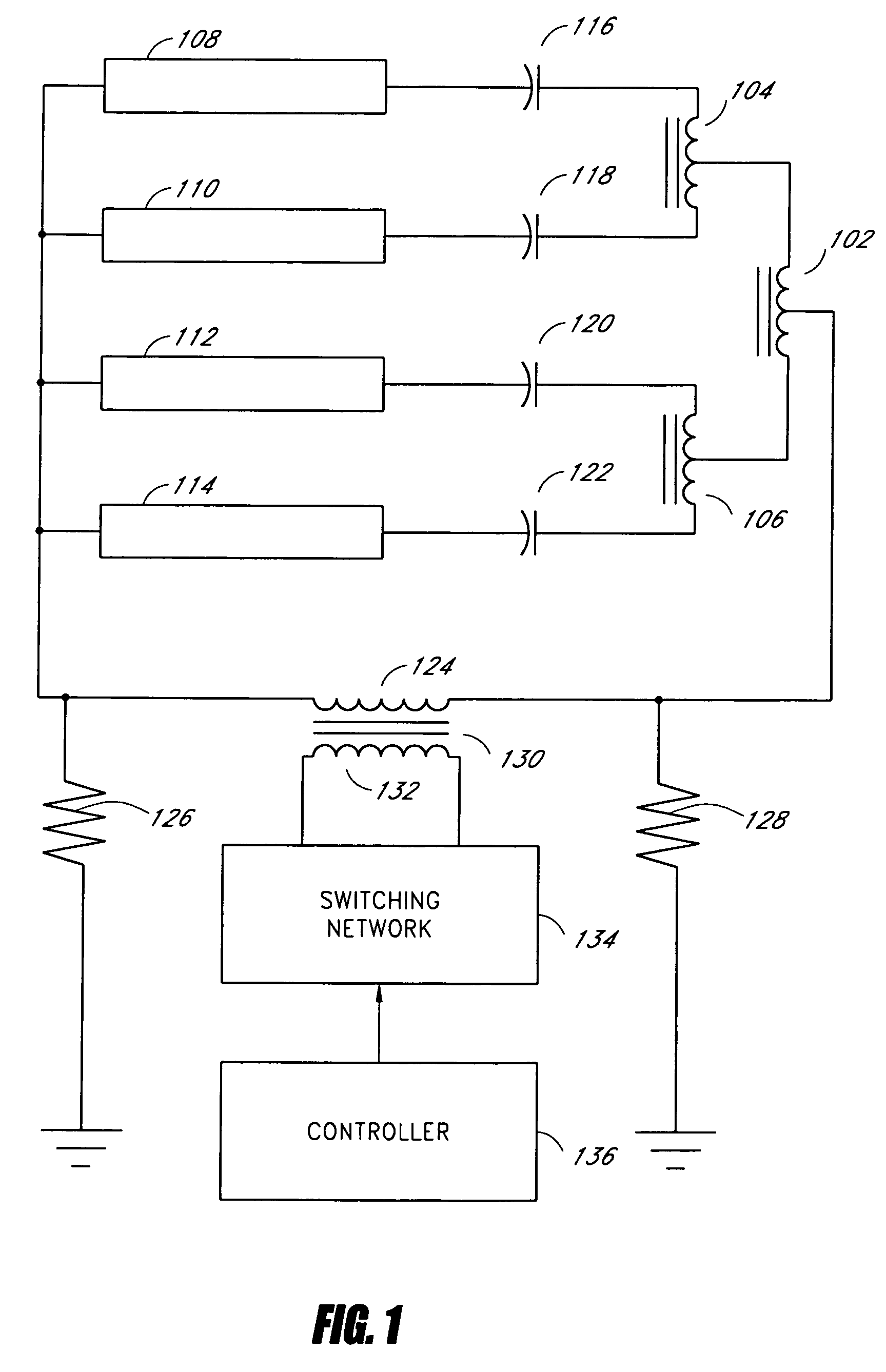
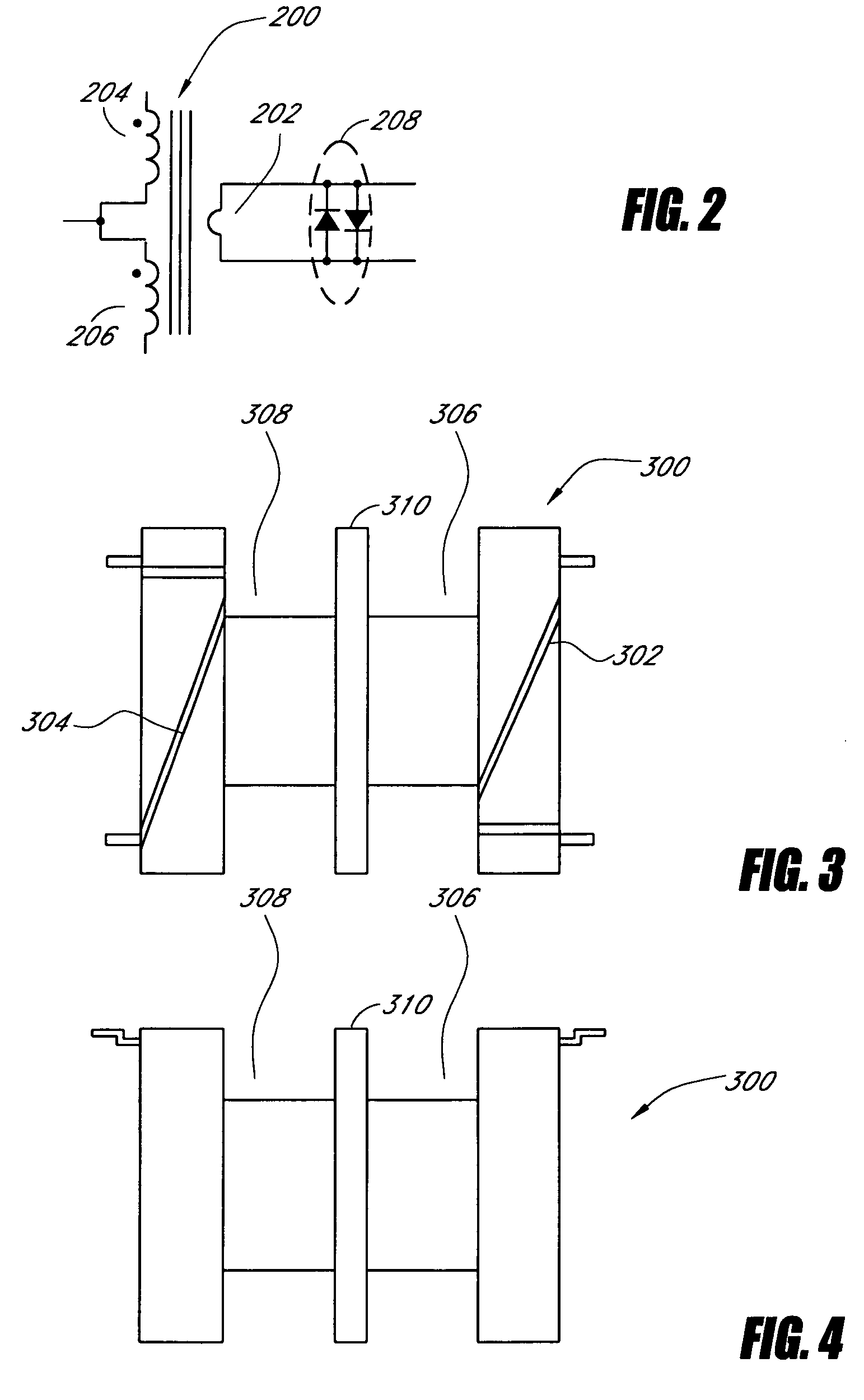
Systems and methods for fault protection in a balancing transformer
InactiveUS20050093484A1None provide any indicationImprove balanceElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
An apparatus and methods for balancing current in multiple negative impedance gas discharge lamp loads. Embodiments advantageously include balancing transformer configurations that are relatively cost-effective, reliable, efficient, and good performing. Embodiments include configurations that are applicable to any number of gas discharge tubes, such as cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The balancing transformer configuration techniques permit a relatively small number of power inverters, such as one power inverter, to power multiple lamps in parallel. One embodiment of a balancing transformer includes a safety winding which can be used to protect the balancing transformer in the event of a lamp failure and can be used to provide an indication of a failed lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Systems and methods for a transformer configuration with a tree topology for current balancing in gas discharge lamps
InactiveUS20050093482A1None provide any indicationImprove balanceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric light circuit arrangementPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
An apparatus and methods for balancing current in multiple negative impedance gas discharge lamp loads. Embodiments advantageously include balancing transformer configurations that are relatively cost-effective, reliable, efficient, and good performing. Embodiments include configurations that are applicable to any number of gas discharge tubes, such as cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The balancing transformer configuration techniques permit a relatively small number of power inverters, such as one power inverter, to power multiple lamps in parallel. One embodiment of a balancing transformer includes a safety winding which can be used to protect the balancing transformer in the event of a lamp failure and can be used to provide an indication of a failed lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
Backup path convergence in the APS environment
ActiveUS20070263532A1Eliminate timeLow costError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableBackup path
A SONET network terminated by routers includes working paths and backup paths. The routers pre-establishes in their link state data bases the links in both for both the working and backup paths. However, the links involved in the backup paths are given higher costs, then the links working paths, that the routers select only the links in the working path. If there is a failure in a link in a working path, an APS arrangement provides rapid switchover of the optical links so as to substitute one or more links in the corresponding backup path. This is accomplished by changing the relative costs of the working and backup links involved, so that the routers select the backup links for their routing tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
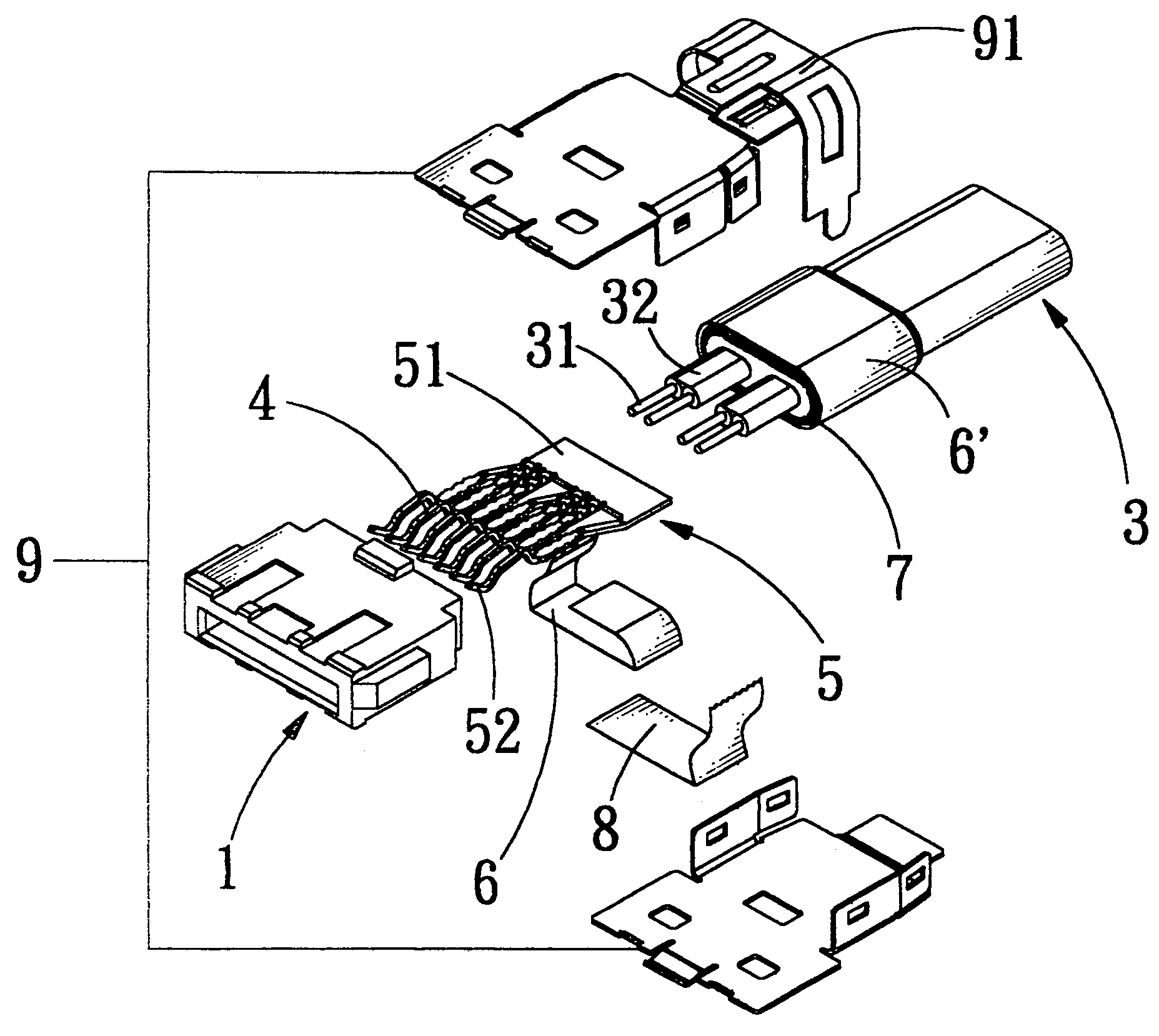
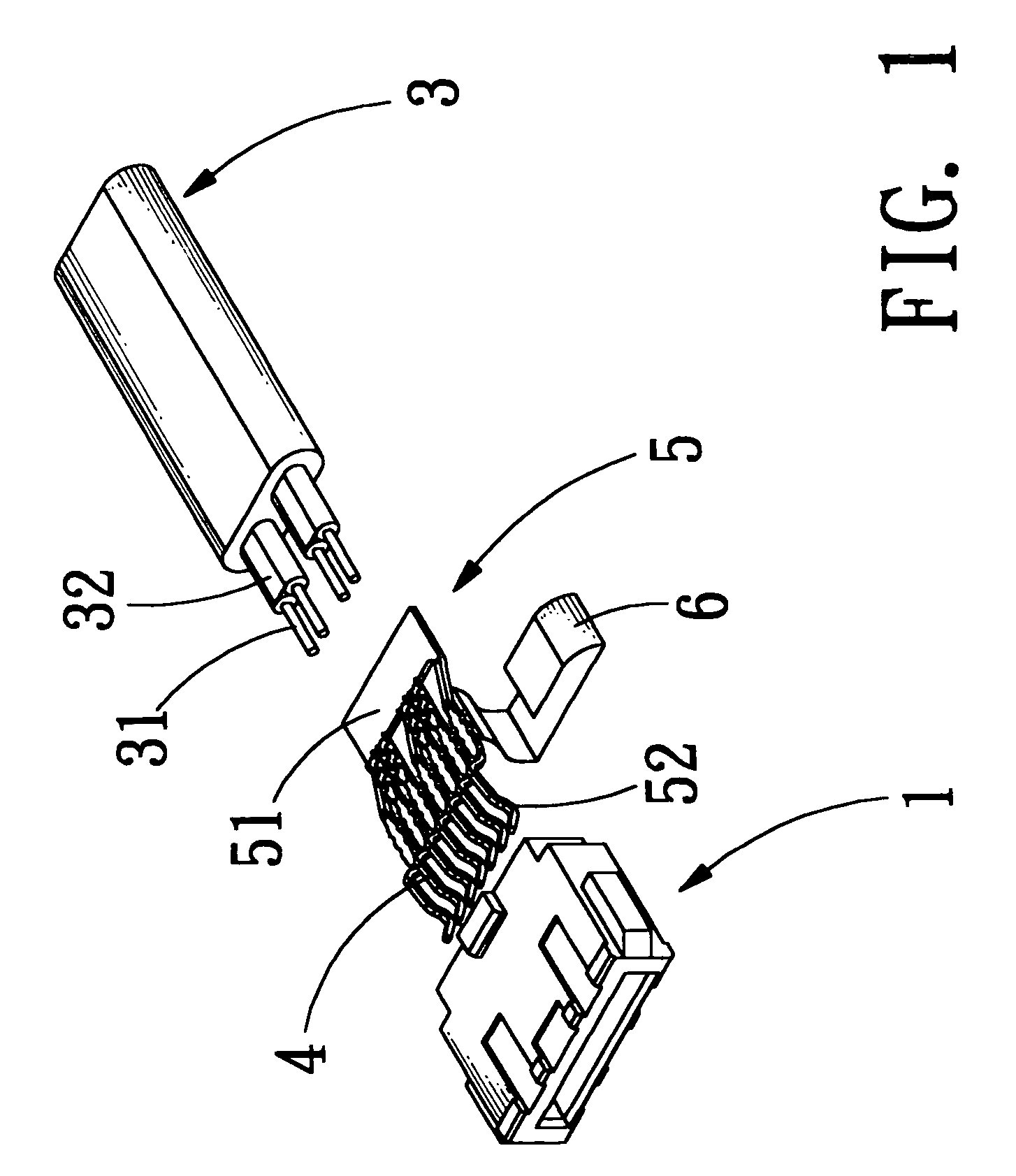
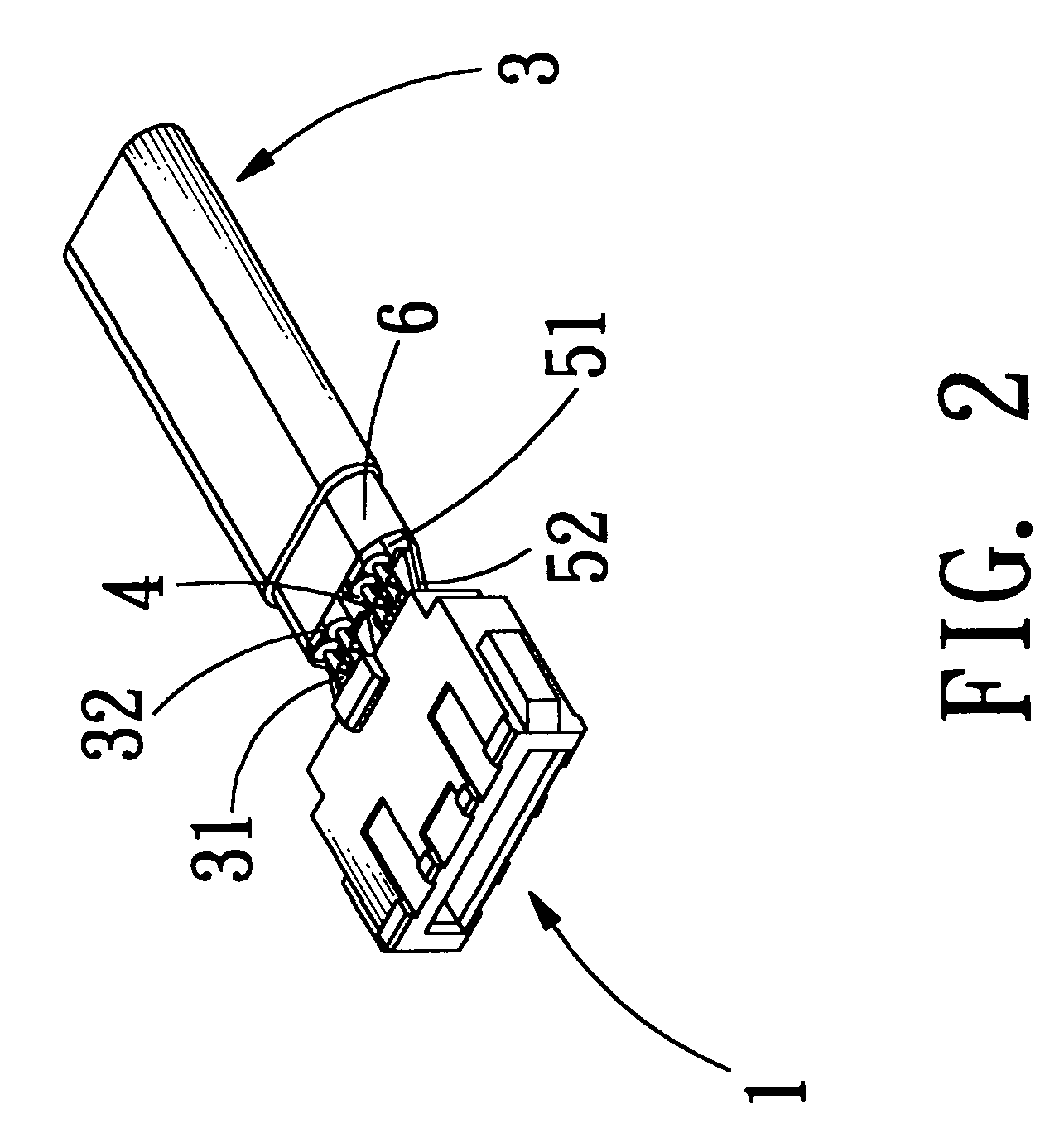
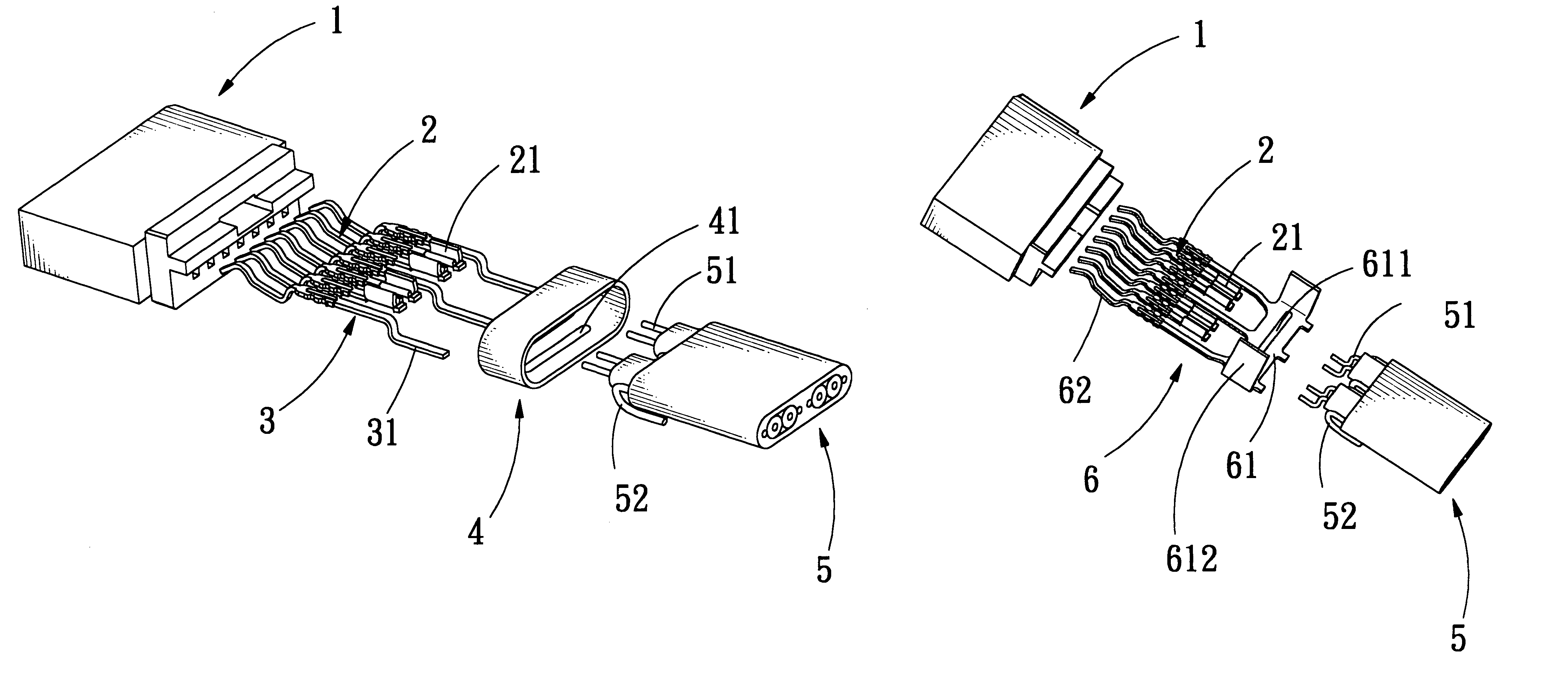
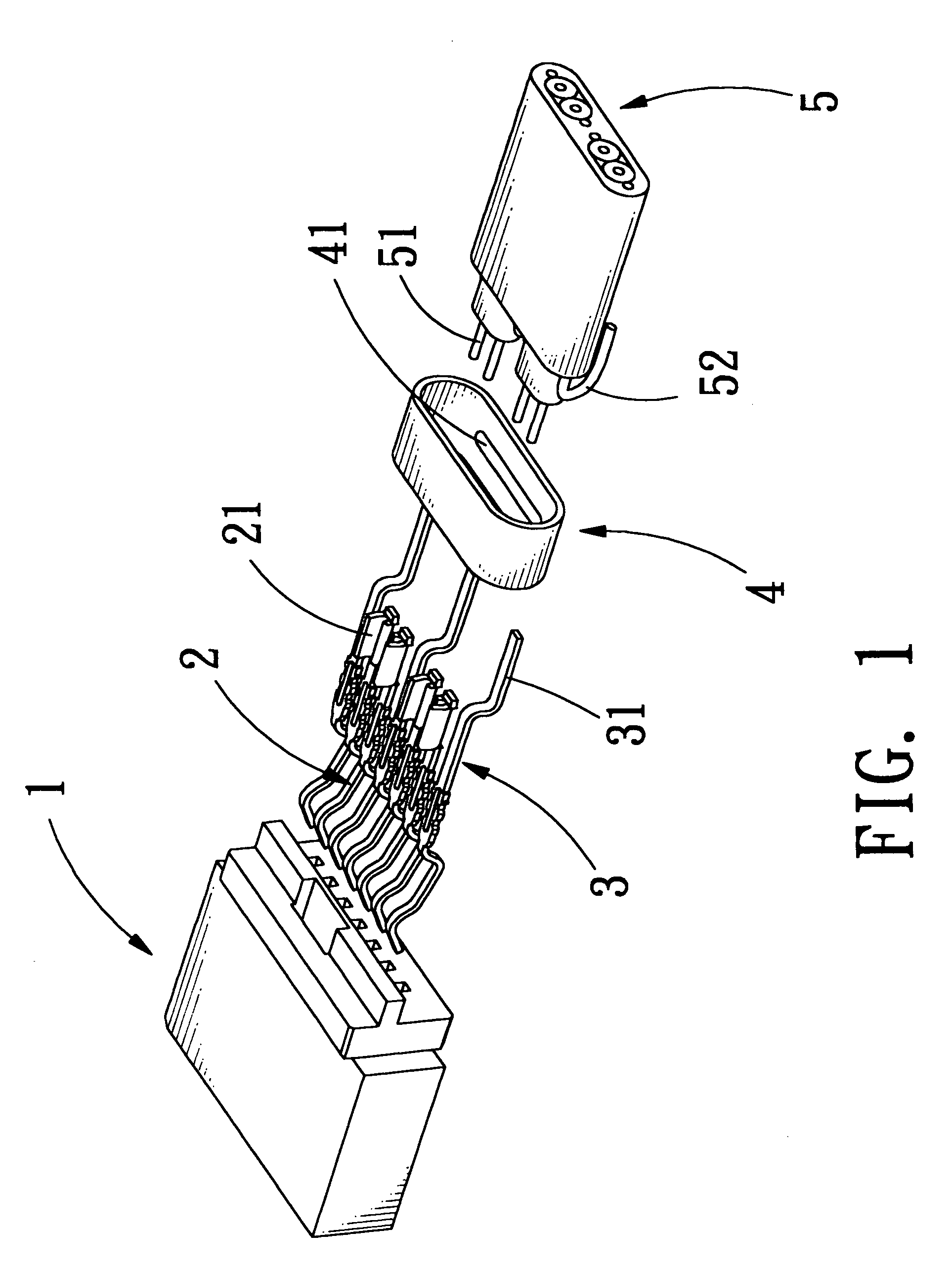
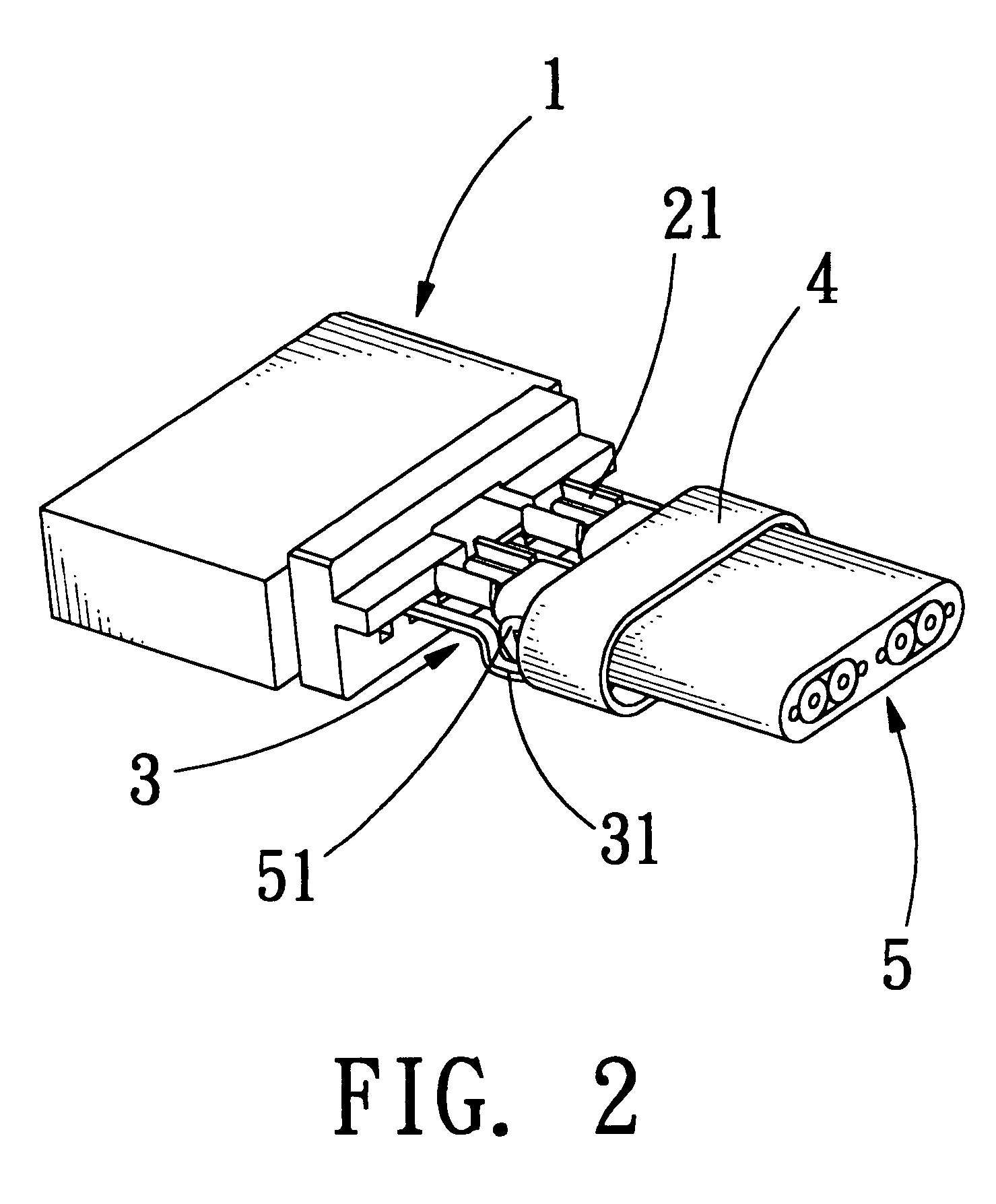
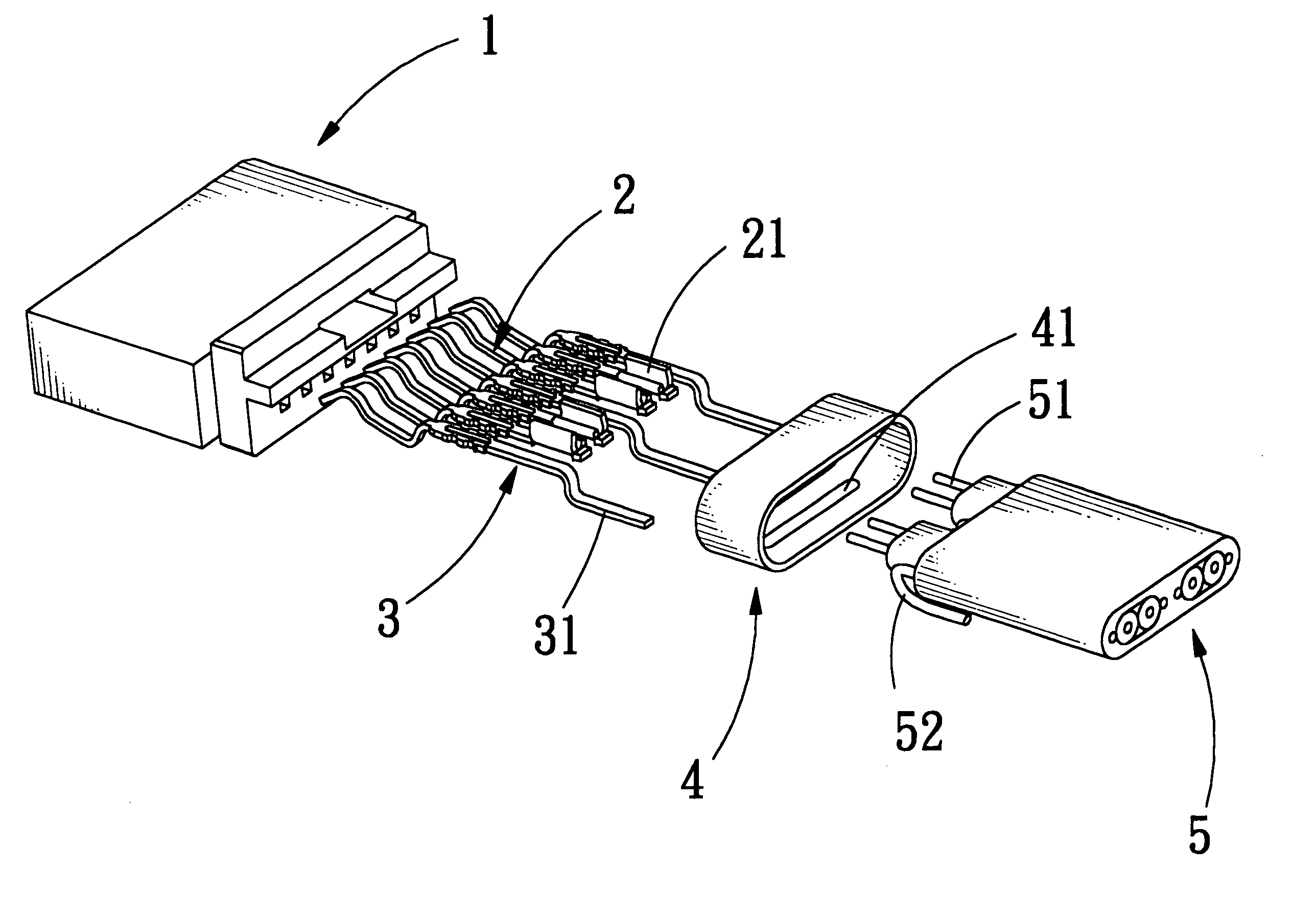
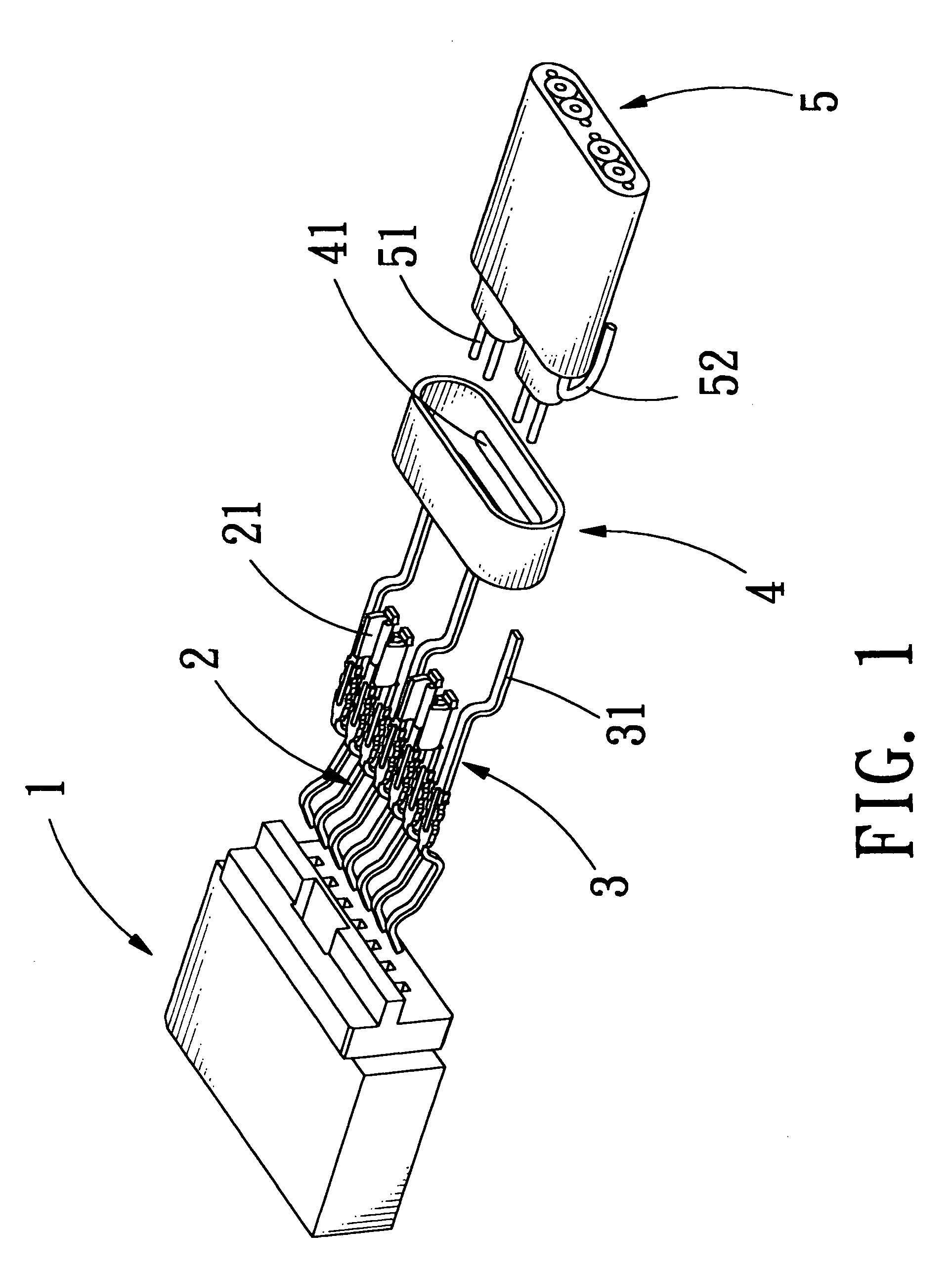
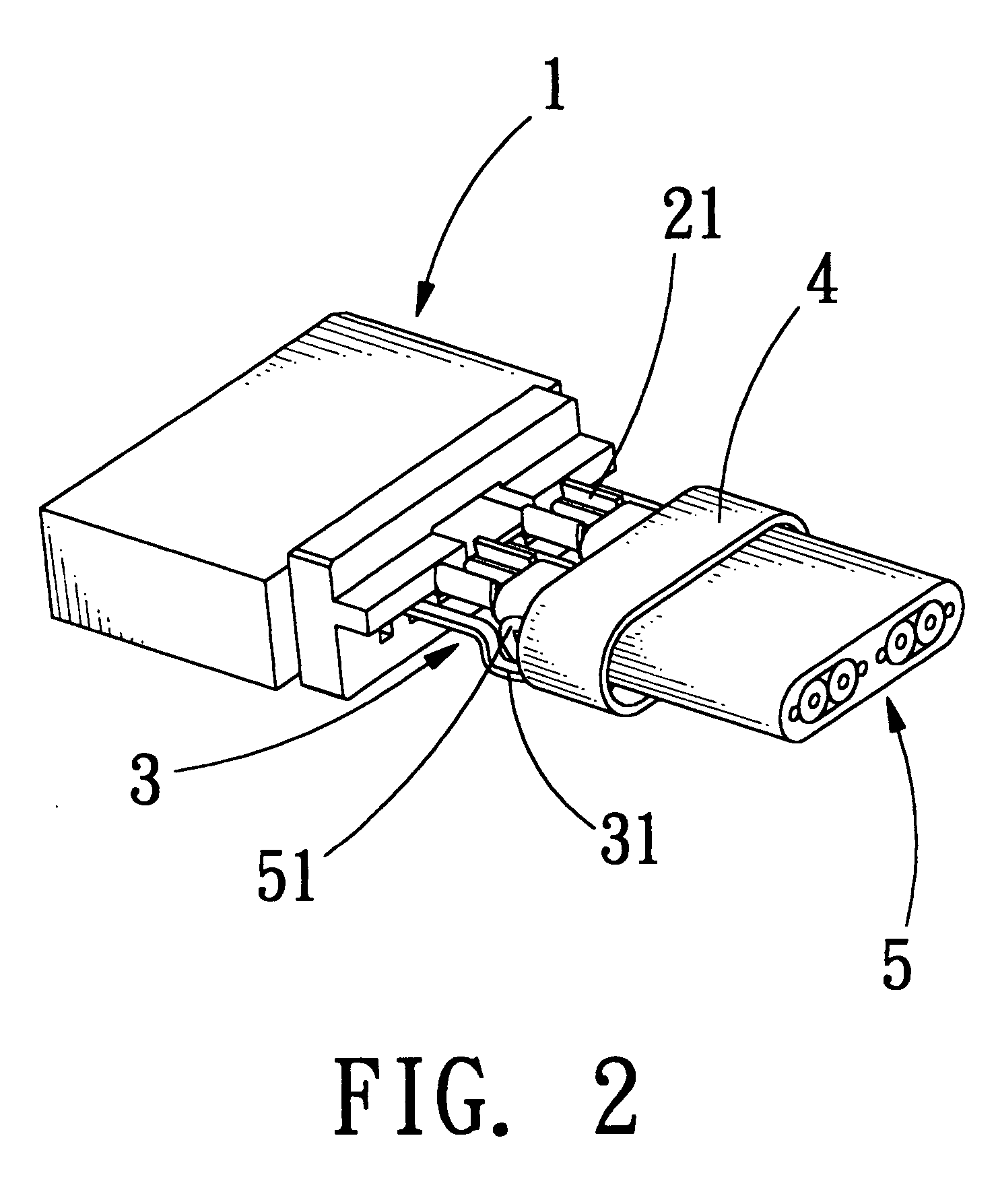
Electrical connector with grounding effect
InactiveUS7214097B1Reduce weldingImprove electrical characteristicsElectrically conductive connectionsTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityBody contact
The present invention relates to an electrical connector with grounding effect, which mainly has grounding part inserted inside the insulating body contacted with the jacket layer enclosed over the signal transmitting units with fixing and contacting effect for generating electrical characteristics, such that the cable assembly of the electrical connector has grounding effect without any grounding line positioned inside cable assembly; wherein, the grounding part has contacting part for providing the jacket layer to contact with, besides it further comprise predetermined grounding terminals extended directly from the grounding part for inserting into the insulating body; such that the cable assembly of the electrical connector of the present invention has grounding effect without any grounding line positioned inside the cable assembly; furthermore, it also can lessen the soldering process and prevent the mistaken probability of the soldering process generated such that the entire assembly process and the relative cost can be reduced.
Owner:ING SHANG LUN
Zigzag topology for balancing current among paralleled gas discharge lamps
InactiveUS7061183B1Minimized unevenness in brightnessImprove balanceElectric lighting sourcesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
An apparatus and methods for balancing current in multiple negative impedance gas discharge lamp loads. Embodiments advantageously include balancing transformer configurations that are relatively cost-effective, reliable, and efficient. Embodiments include configurations that are applicable to an unrestrained number of gas discharge tubes, such as cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The balancing transformer configuration techniques permit a relatively small number of power inverters, such as one power inverter, to power multiple paralleled lamps or paralleled groups of lamps with balancing transformers coupling the lamps or groups of lamps in a zigzag topology. One embodiment of a balancing transformer includes a safety winding which can be used to protect the balancing transformer in the event of a lamp failure and can be used to provide an indication of a failed lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Grounding structure of an electrical connector
InactiveUS7052292B2Best electrical characteristicEasy to connect partsCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialElectricityEngineering
The present invention relates to a grounding structure of an electrical connector suitable for high frequency transmitting. The high frequency connector mainly has a connecting part being combined with a plurality of grounding lines to improve the electrical characteristics of the high frequency connector when it transmits a signal. Wherein, the connecting part further comprises a wing portion and a protrusion portion; thereby the connecting part can engage the grounding terminals with the grounding line of the cable to form electrical contact. Furthermore, one end of the connecting part is extended directly and comprises predetermined grounding terminals, such that the grounding line can be directly connected to connecting part; such as, the electrical connector can have better electrical characteristics and the grounding line can directly be coupled to the grounding terminals without the soldering process by using aforesaid structure meanwhile, the entire assembly process and the relative cost can be lessened.
Owner:ING SHANG LUN
Systems and methods for a transformer configuration for driving multiple gas discharge tubes in parallel
InactiveUS7141933B2None provide any indicationImprove balanceElectric light circuit arrangementSolid cathode detailsGas-discharge lampPower inverter
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
Systems and methods for a transformer configuration for driving multiple gas discharge tubes in parallel
InactiveUS20050093483A1None provide any indicationImprove balanceElectric light circuit arrangementSolid cathode detailsPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
An apparatus and methods for balancing current in multiple negative impedance gas discharge lamp loads. Embodiments advantageously include balancing transformer configurations that are relatively cost-effective, reliable, efficient, and good performing. Embodiments include configurations that are applicable to any number of gas discharge tubes, such as cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The balancing transformer configuration techniques permit a relatively small number of power inverters, such as one power inverter, to power multiple lamps in parallel. One embodiment of a balancing transformer includes a safety winding which can be used to protect the balancing transformer in the event of a lamp failure and can be used to provide an indication of a failed lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI
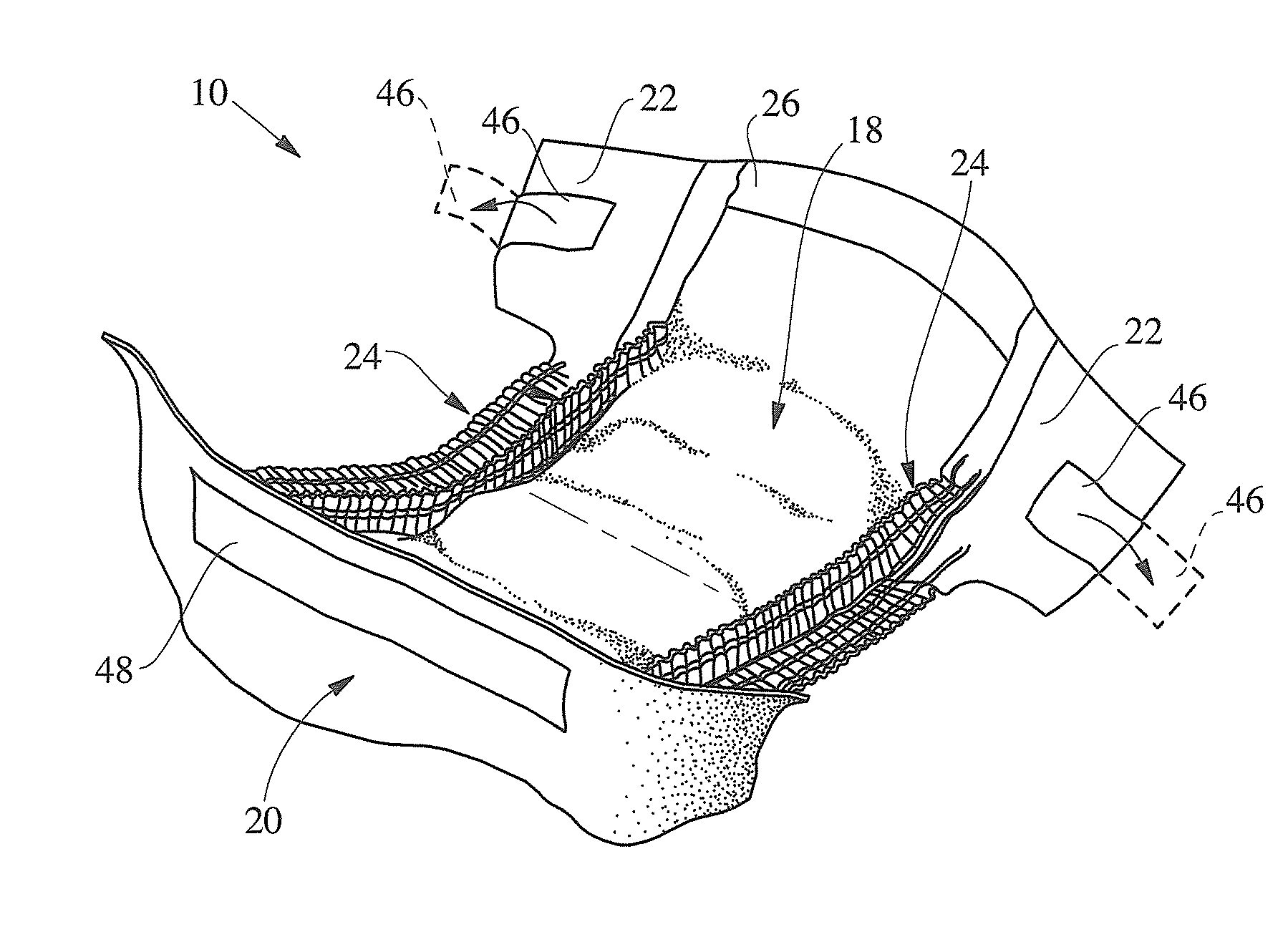
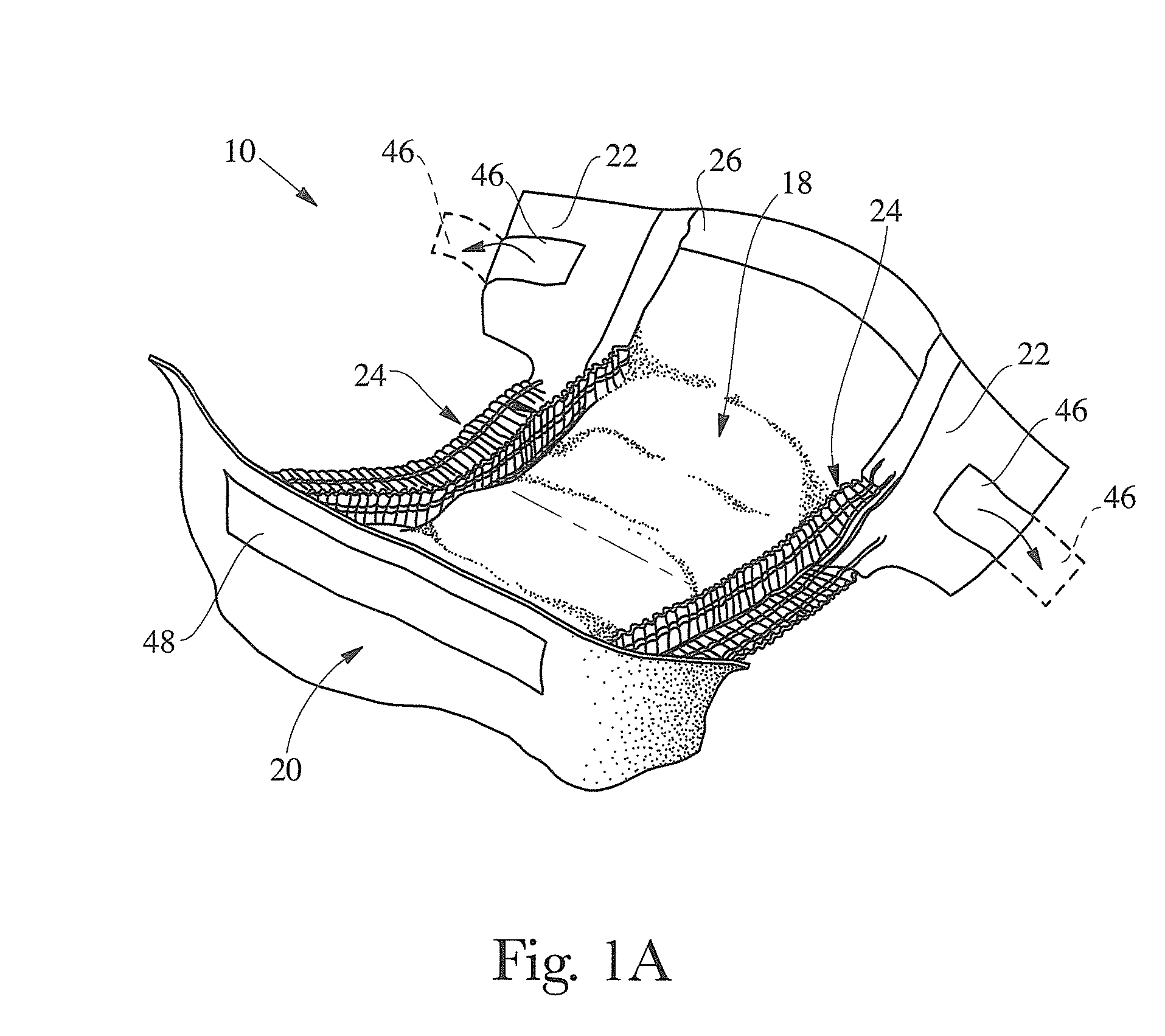
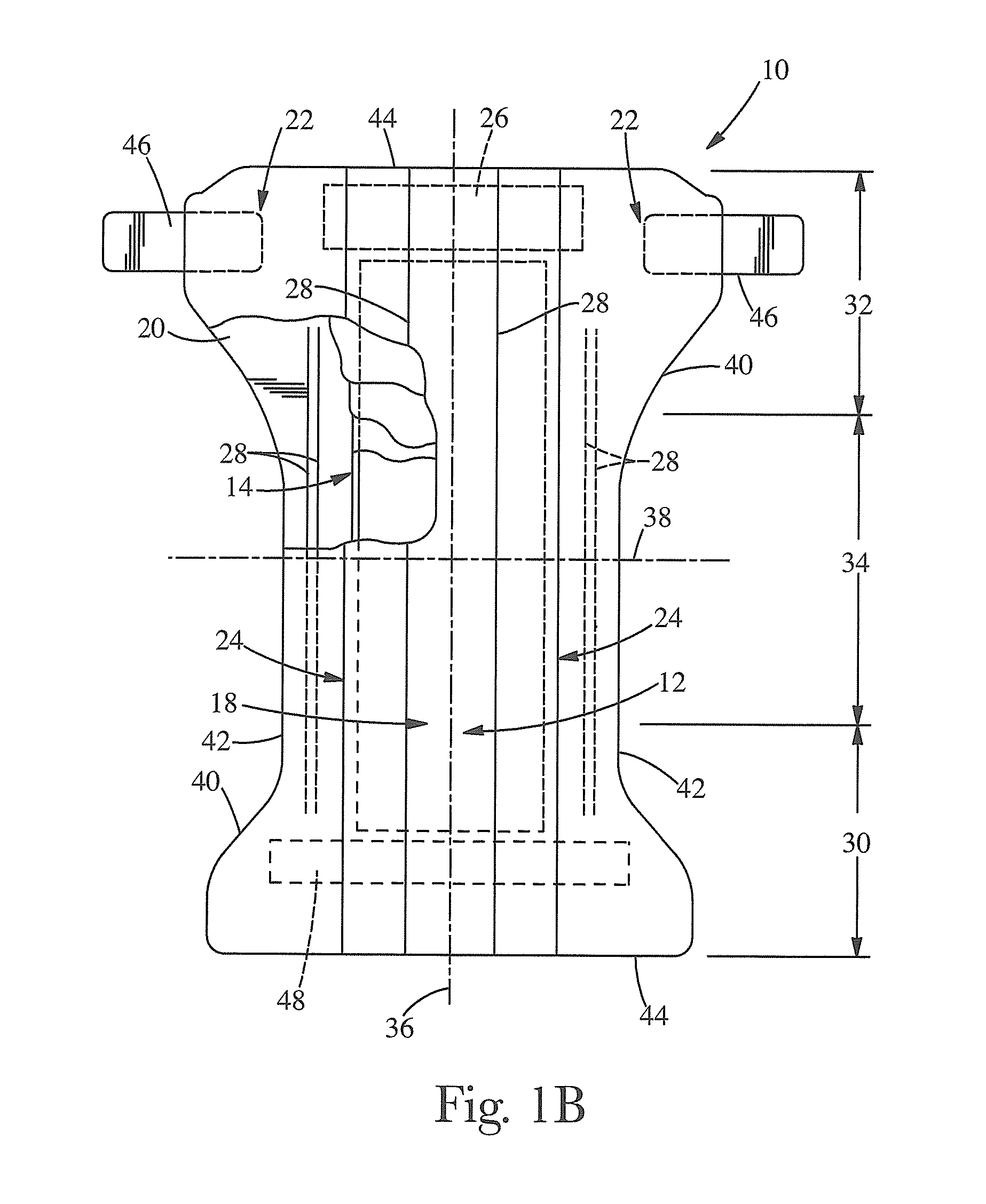
Absorbent Article and Components Thereof Having Improved Softness Signals, and Methods for Manufacturing
An absorbent article having improved softness signals is disclosed. The article may include a topsheet or a backsheet including a nonwoven web. The web may have a basis weight of 30 gsm or less, may be formed of spunlaid fibers including polyolefin and up to 5 percent by weight TiO2, and may be impressed with a pattern of bond impressions to a bond area percentage of at least 10 percent forming a pattern of bonded regions and raised regions. The web may have opacity of 42 or greater; have an average height difference between bonded regions and raised regions of at least 280 μm; be hydroengorged; and / or have a cross-direction tensile strength of 350 gf / cm. A nonwoven web manufactured to have a suitable combination of such features exhibits an enhanced appearance of softness, soft tactile feel and satisfactory mechanical attributes, while being relatively cost effective.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
Absorbent Article and Components Thereof Having Improved Softness Signals, and Methods for Manufacturing
An absorbent article having improved softness signals is disclosed. The article may include a topsheet or a backsheet including a nonwoven web. The web may have a basis weight of 30 gsm or less, may be formed of spunlaid fibers including polyolefin and up to 5 percent by weight TiO2, and may be impressed with a pattern of bond impressions to a bond area percentage of at least 10 percent forming a pattern of bonded regions and raised regions. The web may have opacity of 42 or greater; have an average height difference between bonded regions and raised regions of at least 280 μm; be hydroengorged; and / or have a cross-direction tensile strength of 350 gf / cm. A nonwoven web manufactured to have a suitable combination of such features exhibits an enhanced appearance of softness, soft tactile feel and satisfactory mechanical attributes, while being relatively cost effective.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
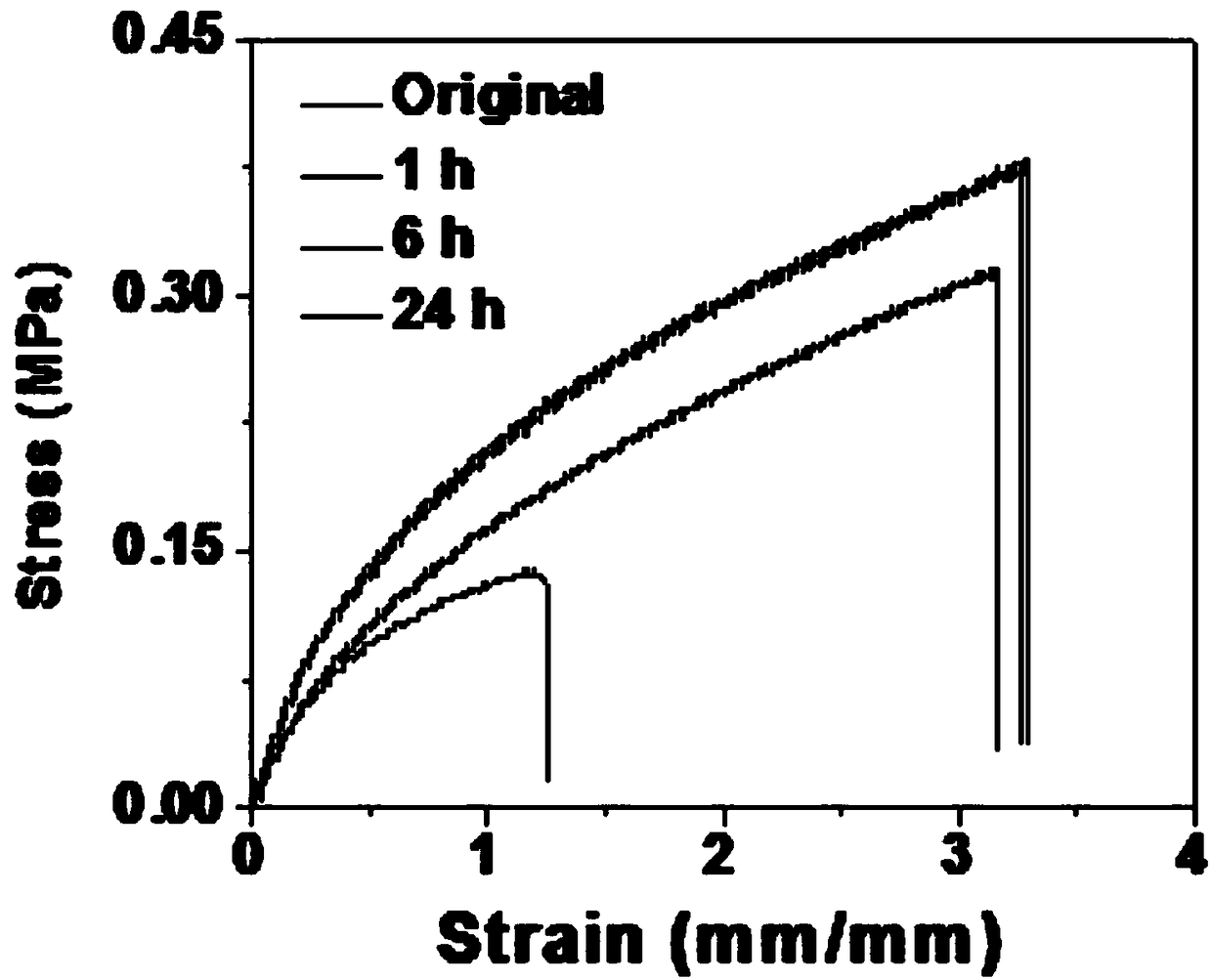
Self-repairing reprocessable polyurea material as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN108559045AGood mechanical propertiesHave transparencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnti-corrosive paintsMechanical propertyPolyurea
The invention relates to the field of new materials, in particular to a self-repairing reprocessable polyurea material as well as a preparation method and application. The self-repairing reprocessablepolyurea material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3 to 13 parts of a cross-linking agent, 79 parts of amino-terminated polyetheramine, 8 to 18 parts of diisocyanate, and 1 to 5 parts of a catalyst. The polyurea material is obtained by reacting an amino group with isocyanate, and is a novel heat-responsive dynamic bond under the action of high temperature or the catalyst,so that the material can be self-repaired at 80 DEG C, and the interaction of hydrogen bonds between urea bonds can improve the mechanical strength of the material; and the polyurea material is excellent in mechanical properties, endowed with certain transparency, good in reworking properties, high in self-repairing efficiency, relatively low in repair temperature, simple in preparation technology, and low in relative cost.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
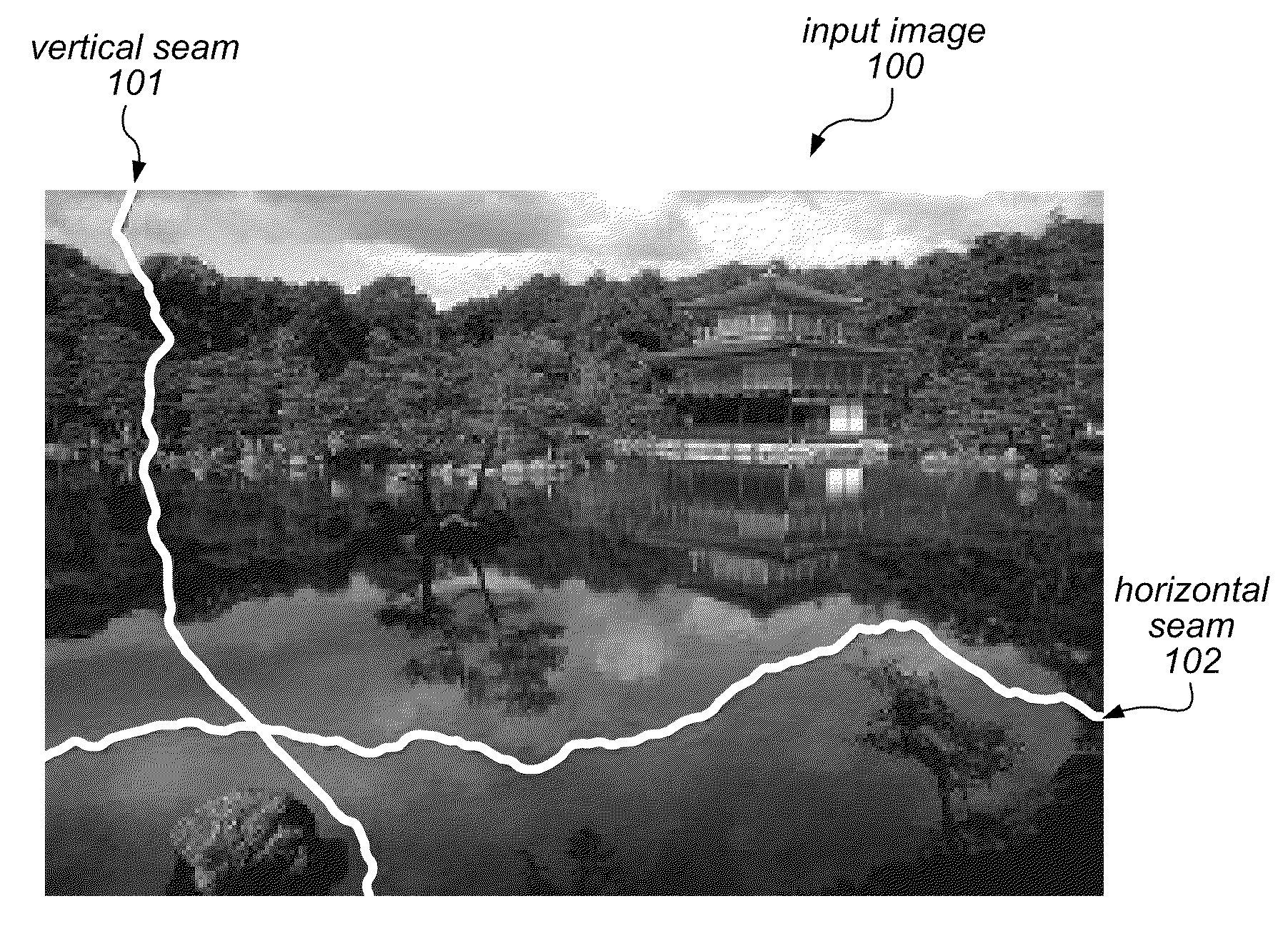
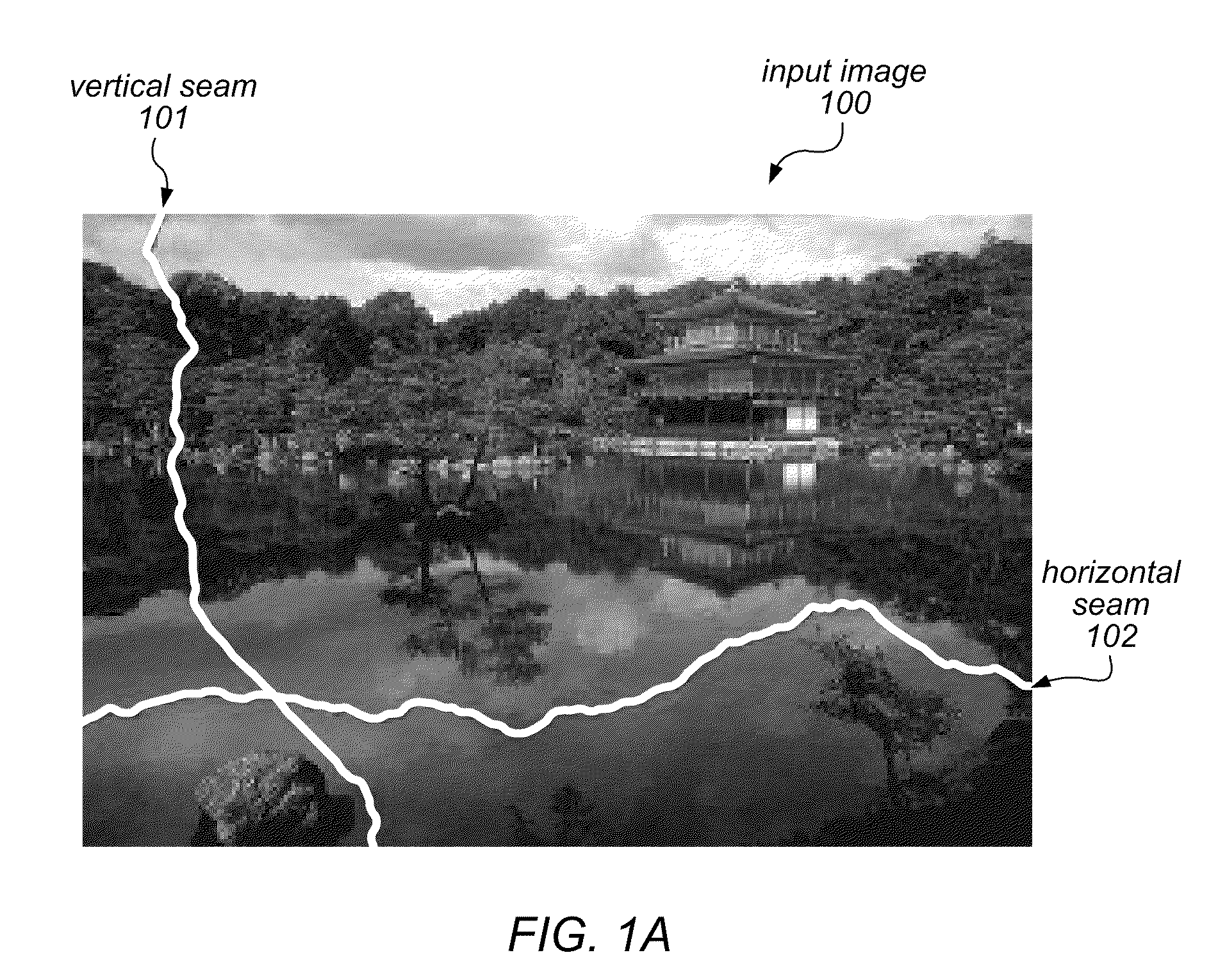
System and Method for Content Aware Hybrid Cropping and Seam Carving of Images
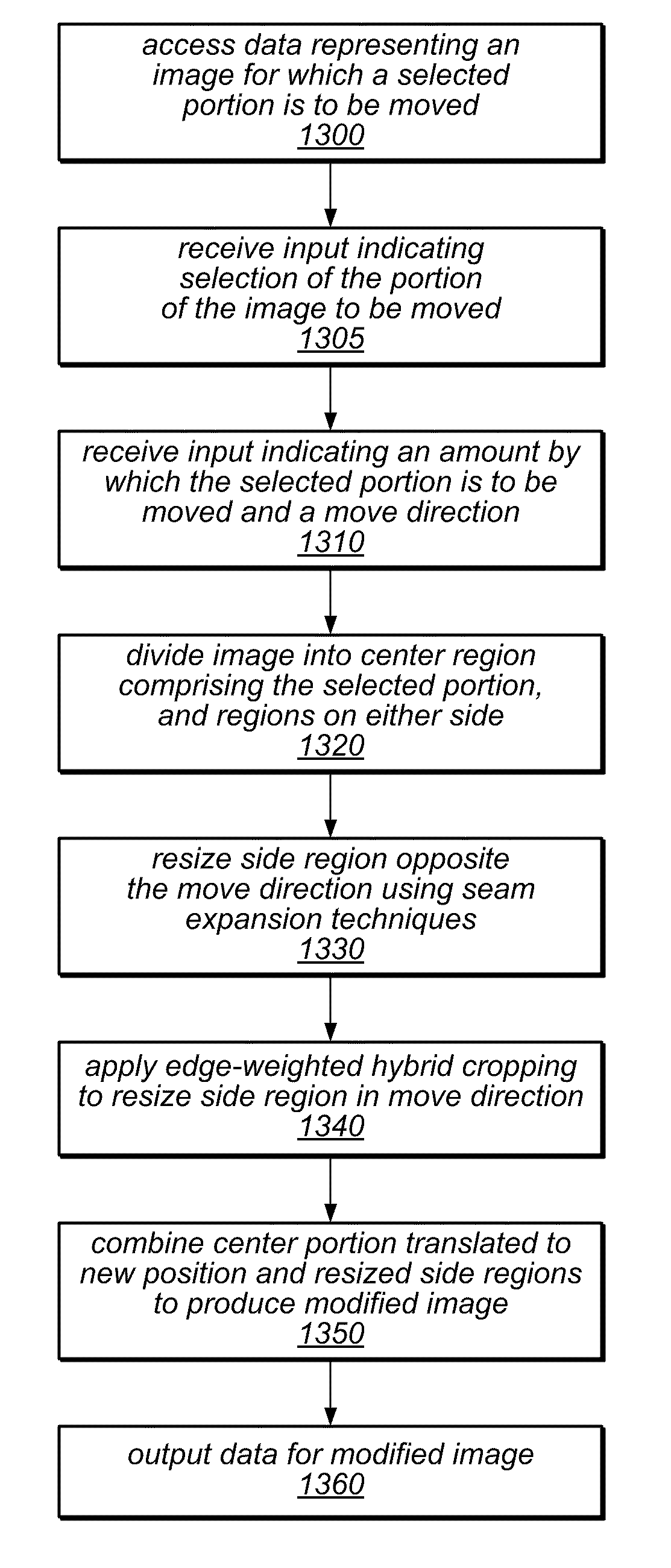
ActiveUS20130127915A1Low costSmall sizeTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationSeam carvingLower priority
A system and method for performing content aware cropping / expansion may be applied to resize an image or to resize a selected object therein. An image object may be selected using an approximate bounding box of the object. The system may receive input indicating a lowest priority edge or corner of the image or object to be resized (e.g., using a drag operation). Respective energy values for some pixels of the image and / or of the object to be resized may be weighted based on their distance from the lowest priority edge / corner and / or on a cropping or expansion graph, and relative costs may be determined for seams of the image dependent on the energy values. Low cost seams may be removed or replicated in different portions of the image and / or the object to modify the image. The selected object may be resized using interpolated scaling and patched over the modified image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Predictive and preemptive planning and scheduling for different job priorities system and method
InactiveUS6895292B2Multiprogramming arrangementsTechnology managementComputer control systemSystem controller
For an automated manufacturing system having a number of modules with numerous alternative capabilities, a computer-controlled system provides for configuration-specific reprioritization of jobs. The computer-controlled system includes at least one system controller for planning and scheduling utilization of selected module capabilities in the production of jobs having not less than one work unit. Module capabilities include the relative costs of the module capabilities.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
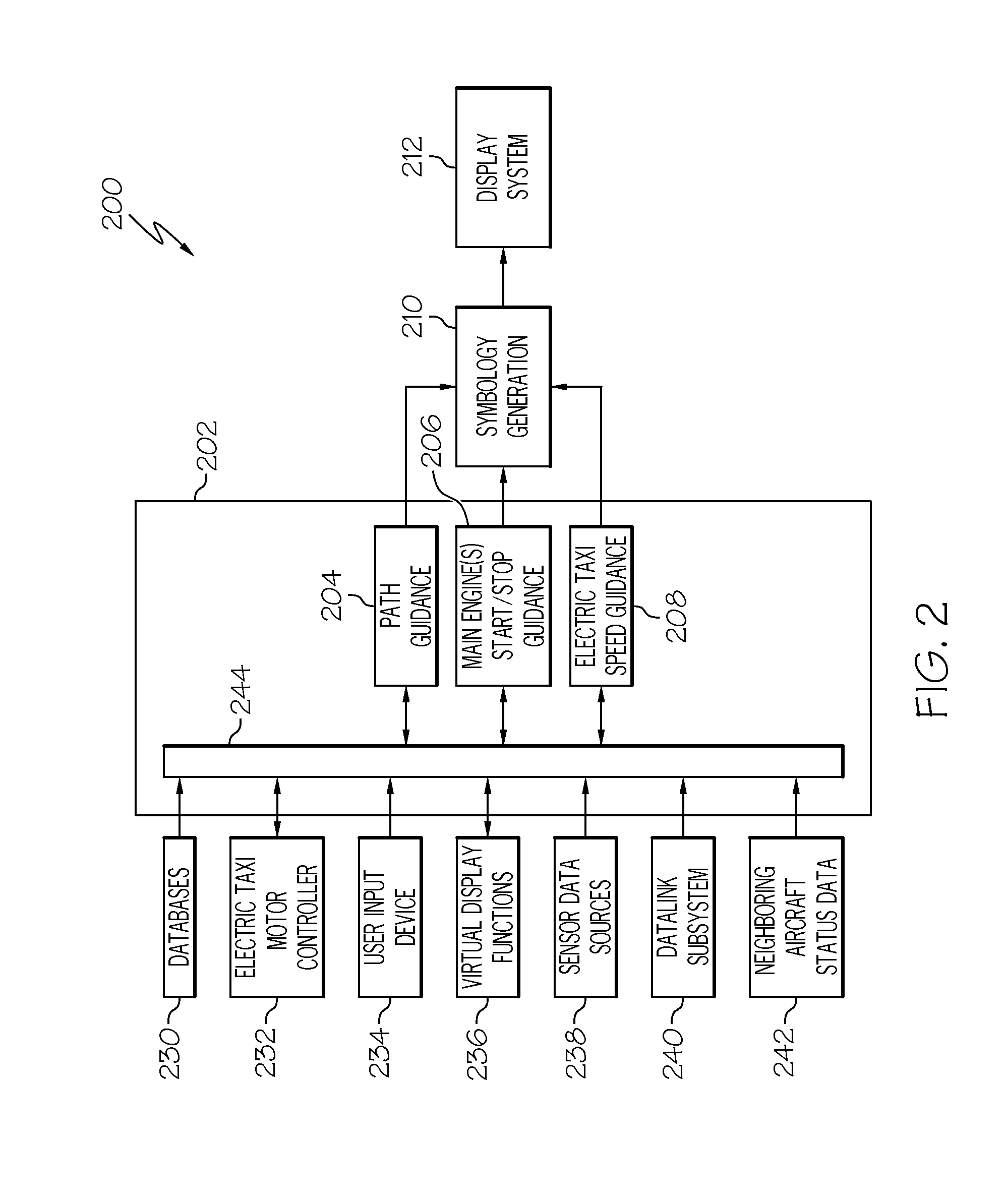
System and method for generating and displaying an electric taxi index
ActiveUS20130131888A1Cost effectiveDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsFlight vehicleAirplane
A taxi method for an aircraft having a primary thrust engine taxi system and an electric taxi system is provided. The method involves obtaining aircraft and airport status data and generating therefrom taxi drive information indicative of the relative cost of taxiing the aircraft along a predetermined route using the electric taxi system versus the aircraft engine taxi system. The taxi drive index information is presented to a user.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Absorbent Article and Components Thereof Having Improved Softness Signals, and Methods for Manufacturing
An absorbent article having improved softness signals is disclosed. The article may include a topsheet or a backsheet including a nonwoven web. The web may have a basis weight of 30 gsm or less, may be formed of spunlaid fibers including polyolefin and up to 5 percent by weight TiO2, and may be impressed with a pattern of bond impressions to a bond area percentage of at least 10 percent forming a pattern of bonded regions and raised regions. The web may have opacity of 42 or greater; have an average height difference between bonded regions and raised regions of at least 280 μm; be hydroengorged; and / or have a cross-direction tensile strength of 350 gf / cm. A nonwoven web manufactured to have a suitable combination of such features exhibits an enhanced appearance of softness, soft tactile feel and satisfactory mechanical attributes, while being relatively cost effective.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
Method and system for motion compensation
ActiveUS20070014477A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionMotion vector
Described herein is a method and system for motion compensation. This system and method use confidence for motion vector selection. Relative cost and an estimate of noise power may be used to characterize residual values and influence confidence determination.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Computerized data-aware agent systems for retrieving data to serve a dialog between human user and computerized system
ActiveUS20140229405A1Low costMedium costFinanceNatural language data processingData retrievalComputerized system
A system and method for data gathering system, comprising a data-aware knowledge base storing knowledge on relative costs of obtaining various data items; and a data retrieval decision-making processor operative, when an individual data element is sought to be retrieved, to determine whether or not to retrieve the data element by comparing at least one parameter representing need for the data element, also termed herein a utility value, with at least one parameter, retrieved from the data-aware knowledge base, which represents relative cost of obtaining the data element.
Owner:PERSONETICS TECH
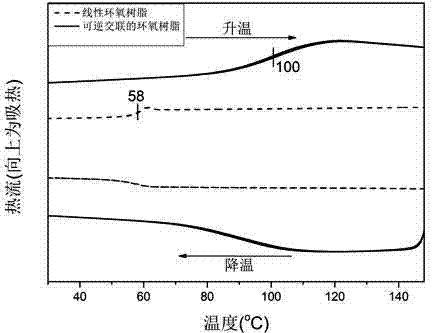
Reversible covalent cross-linked epoxy resin and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a reversible covalent cross-linked epoxy resin. The reaction between diene monoamine and an epoxy resin monomer is adopted for obtaining a linear epoxy resin with a diene on a side chain, the linear epoxy resin and a dienophile cross-linking agent form a Diels-Alder reversible reaction cross-linked point on the side chain, the reversible covalent cross-linked bond of the cross-linked epoxy resin breaks at a temperature of 100 to 150 DEG C, and can be restored again when the temperature is lowered to below 90 DEG C, so that the crosslink reversibility can be achieved. The reversible covalent cross-linked epoxy resin and the preparation method, provided by the invention, have the advantages that: (1), the reversible covalent cross-linked point is introduced to the side chain of the linear epoxy resin, so that the thermostability, solvent corrosion resistance and mechanical property of the material are improved, and by changing the cross-linking density, the material performance can be adjusted within a larger range; (2), both structures of the diene and the dienophile in the cross-linked epoxy resin have reversible reaction properties, so that recycling and reprocessing under certain conditions can be conducted; (3), the preparation method is simple and convenient, and is easy to implement, the relative cost is low, and raw material sources are wide.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method and apparatus for flooding link state packets to achieve faster convergence
ActiveUS20060072461A1Efficient floodingLow costError preventionTransmission systemsLink state packetDistributed computing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Grounding structure of an electrical connector
InactiveUS20050176300A1Improve electrical characteristicsEasy to connect partsCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialElectricityEngineering
The present invention relates to a grounding structure of an electrical connector suitable for high frequency transmitting. The high frequency connector mainly has a connecting part being combined with a plurality of grounding lines to improve the electrical characteristics of the high frequency connector when it transmits a signal. Wherein, the connecting part further comprises a wing portion and a protrusion portion; thereby the connecting part can engage the grounding terminals with the grounding line of the cable to form electrical contact. Furthermore, one end of the connecting part is extended directly and comprises predetermined grounding terminals, such that the grounding line can be directly connected to connecting part; such as, the electrical connector can have better electrical characteristics and the grounding line can directly be coupled to the grounding terminals without the soldering process by using aforesaid structure, meanwhile, the entire assembly process and the relative cost can be lessened.
Owner:ING SHANG LUN
Absorbent article and components thereof having improved softness signals, and methods for manufacturing
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO +1
Overheating air-burn preventing device of gas stove and preventing method
InactiveCN101881469AAvoid burnsMeet the needs of safe useDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusMicrocontrollerSolenoid valve
The invention discloses an overheating air-burn preventing device of a gas stove and a preventing method. The overheating air-burn preventing device comprises a temperature sensor, a temperature sensor control circuit, a singlechip microprocessor, a main solenoid valve and a main solenoid valve control circuit, wherein the temperature sensor is used for detecting the temperature of the bottom of a cooker; the main solenoid valve and the main solenoid valve control circuit are arranged on a main gas pipe; in addition to the traditional low-temperature flameout defensive function, the device adds intelligent high temperature protection, has sensitive sense to the cooker temperature, prevents the air burn by overheating detection and overheating curve judgment so as to achieve the effect of preventing the air burn of majority of cookers, thereby effectively preventing fire accidents caused by abnormal high temperature of the air burn of the cooker, and protecting family property and personal safety all the way. The invention has high precision, simple and stable system and relative low cost and can meet the requirement of people on using the gas stove.
Owner:SAKURA BATH & KITCHEN PRODS CHINA
System and Method for Determining an Objective Measure of Human Beauty
InactiveUS20090257654A1Data processing applicationsPackaging toiletriesObjective measurementComputer science
An objective measure of human beauty is determined by a beauty quantification system. The beauty quantification system comprises a beauty quantification processor, a beauty measure datastore, a beauty score datastore, a user computing device, and a network. The beauty measure datastore comprises quantifiable measures of beauty of a body region. The beauty quantification processor comprises instructions for receiving user data indicative of physical attributes of a selected body region of the user, obtaining measures of beauty from the beauty measures datastore associated with the selected body region, evaluating the user data against the beauty measures of the selected body region, determining a user score indicative of the beauty of the selected body region of the user, storing the user score in the beauty score datastore, and comparing the user score to a score stored in the beauty score datastore. The beauty quantification processor may also suggest enhancements to one or more body regions to improve the user score. The suggested enhancements may be presented as an ordered listed organized by a relative cost benefit measure.
Owner:YOUDOCS
Fault management system for a communications network
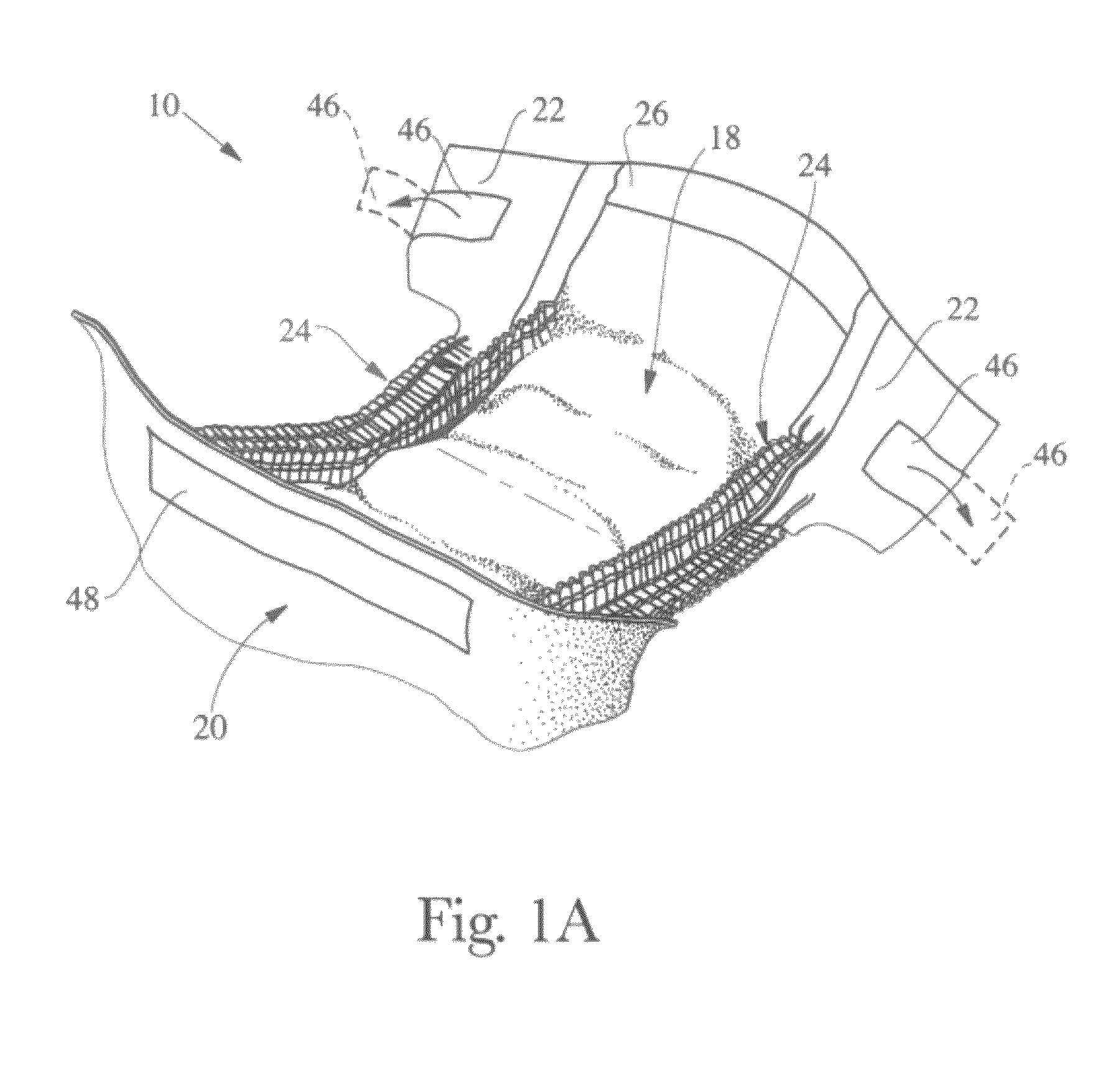
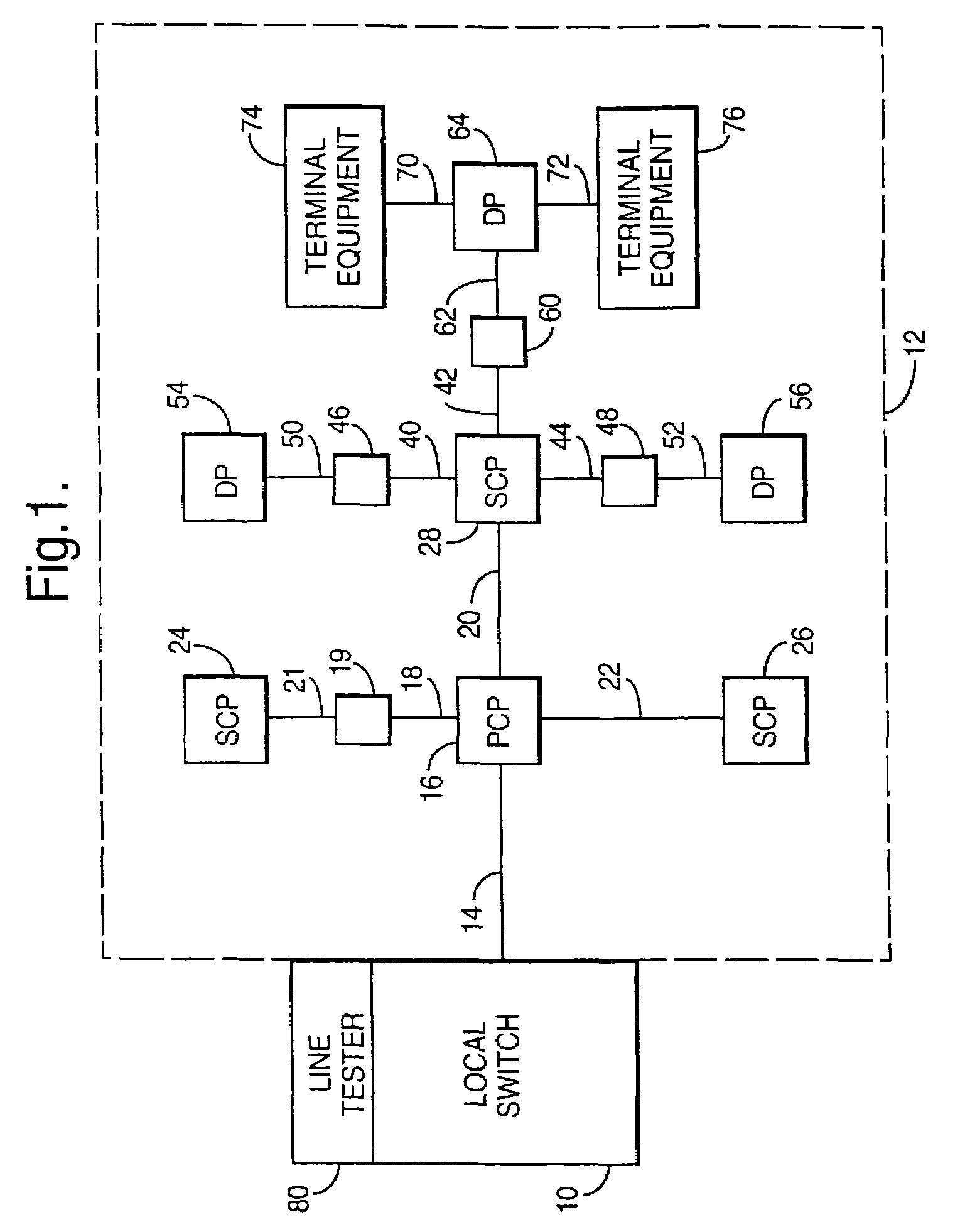
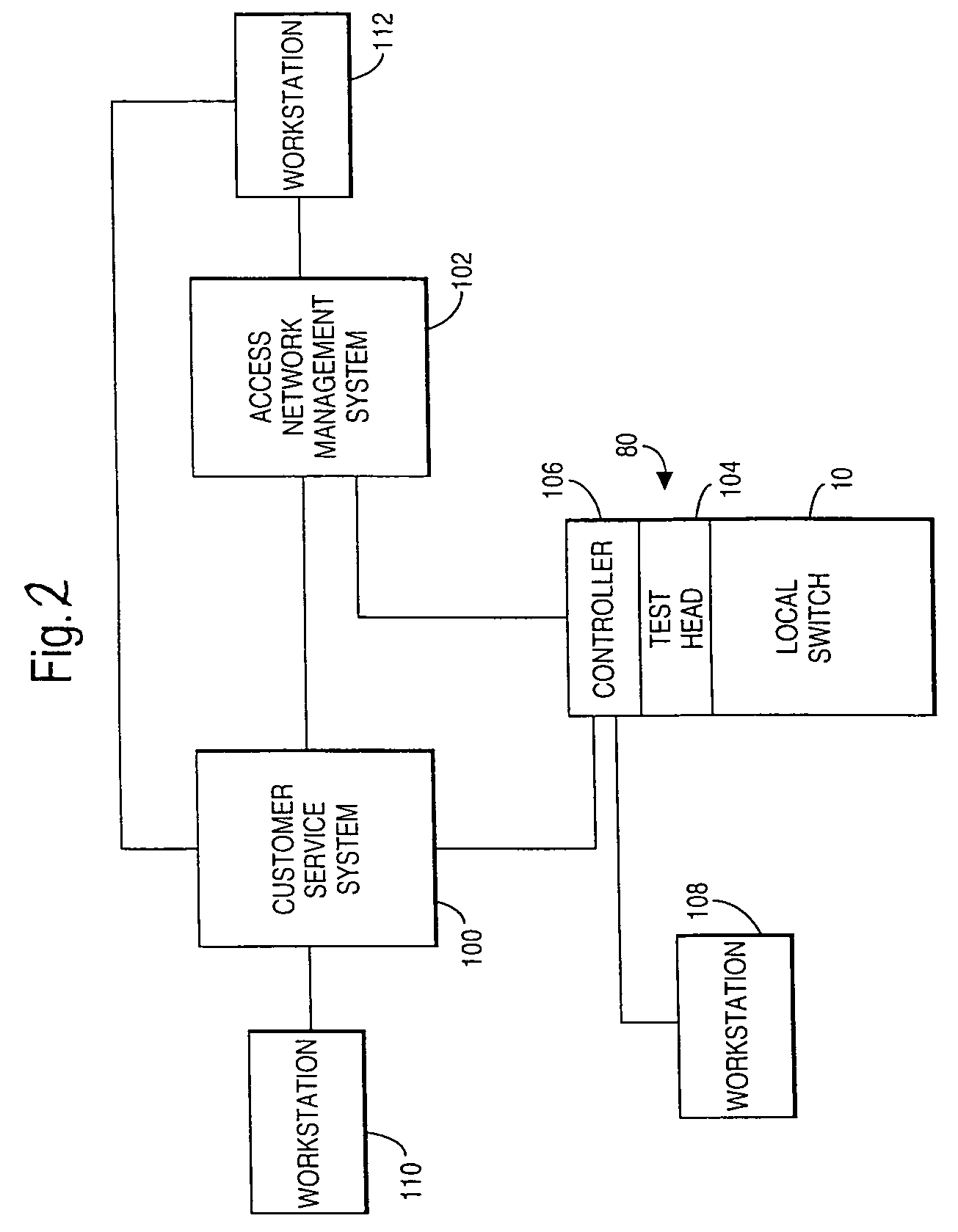
ActiveUS7251754B2Error detection/correctionSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsAccess networkCopper wire
A fault management system is directed to the access network part of a communications network where terminating lines in the form of pairs of copper wires extend from a local switch through a series of nodes to terminal equipment provided for user of the network. Each night, a test head performs a series of tests on each of the terminating lines. The results of the tests are transmitted to an access network management system where they are analyzed with respect to a set of parameters to identify characteristics that would indicate that a fault is likely to occur on the associated circuit within a predetermined period e.g. 1 year. Further analysis can then be carried out to establish the probability of the fault actually occurring and / or whether the potential fault analyzed is going to occur in either the underground or the over-ground part of the network. Further analysis determines relative costs of repair for circuits or network elements in which faults or potential faults have been identified.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
System and method for content aware hybrid cropping and seam carving of images
ActiveUS8963960B2Low costSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSeam carvingLower priority
A system and method for performing content aware cropping / expansion may be applied to resize an image or to resize a selected object therein. An image object may be selected using an approximate bounding box of the object. The system may receive input indicating a lowest priority edge or corner of the image or object to be resized (e.g., using a drag operation). Respective energy values for some pixels of the image and / or of the object to be resized may be weighted based on their distance from the lowest priority edge / corner and / or on a cropping or expansion graph, and relative costs may be determined for seams of the image dependent on the energy values. Low cost seams may be removed or replicated in different portions of the image and / or the object to modify the image. The selected object may be resized using interpolated scaling and patched over the modified image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
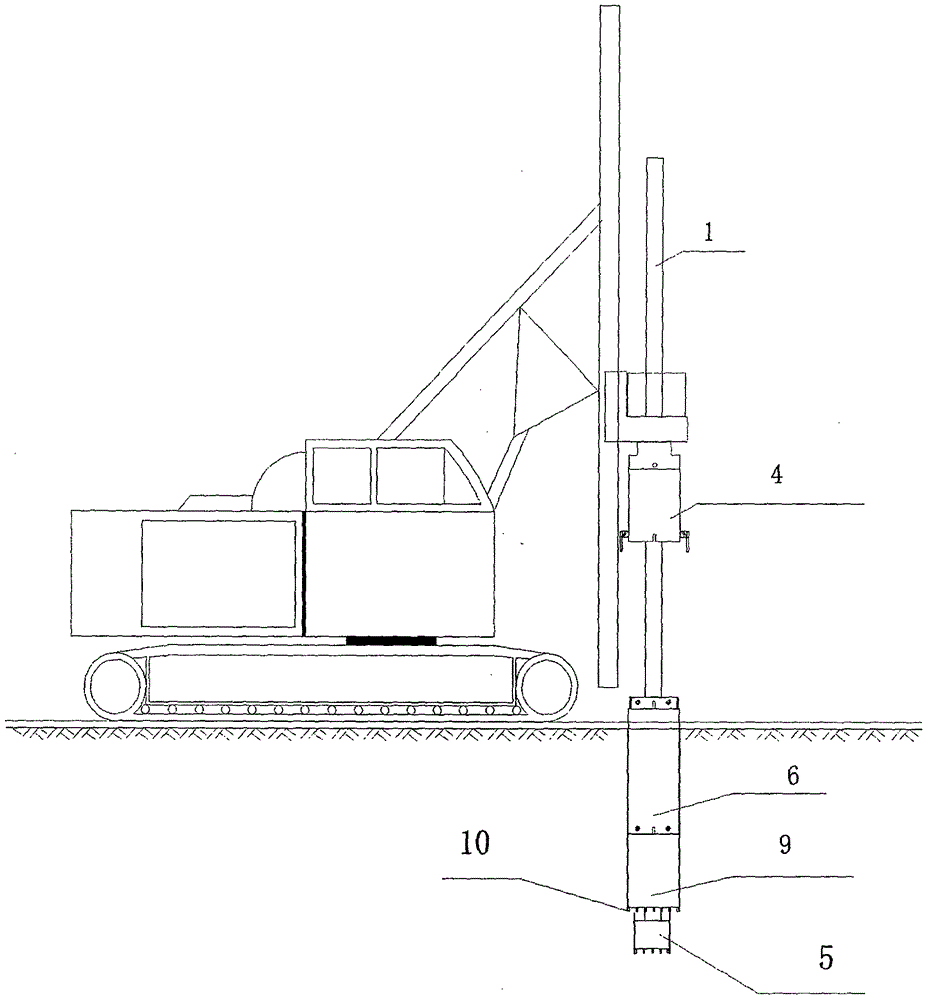
Bridge pile foundation rotary excavating drilling rig cutting type whole guard barrel follow-up pile forming construction method and system
ActiveCN105735251AAvoid the phenomenon of collapse, quicksand and sand gushingNo pollution in the processRotary drillingRotary-drilling machinesAlloyAssembly structure
The invention relates to the technical field of rotary excavating drilling rig whole guard barrel follow-up, in particular to a bridge pile foundation rotary excavating drilling rig cutting type whole guard barrel follow-up pile forming construction method and system. According to the method, a rotary excavating drilling technology and a cutting type whole steel guard barrel assembly structure are combined; soil is sunk by rotary excavating, drilling and cutting; and a guard barrel is designed to be of a double-layer structure; the technical problems that when a drilling rig conducts drilling conduction on a nonresistant strata, hole collapse is serious, and the construction efficiency is low are effectively solved by the structural designs of a guard barrel embedded interface, a built-in pin shaft, a bottom joint mounting alloy cutter and the like and the mode that the guard barrel is quickly connected through a connecting guiding device and a spiral guiding device. The cutting type steel guard barrel can be used in a recycling ode, is low in relative cost and safe and efficient in construction, saves energy, and is environmentally friendly; site operation and construction are simple and convenient; the construction process can be mastered by an operator easily; and the pile foundation hole forming quality and the pile foundation pouring quality can be well guaranteed.
Owner:赵立财
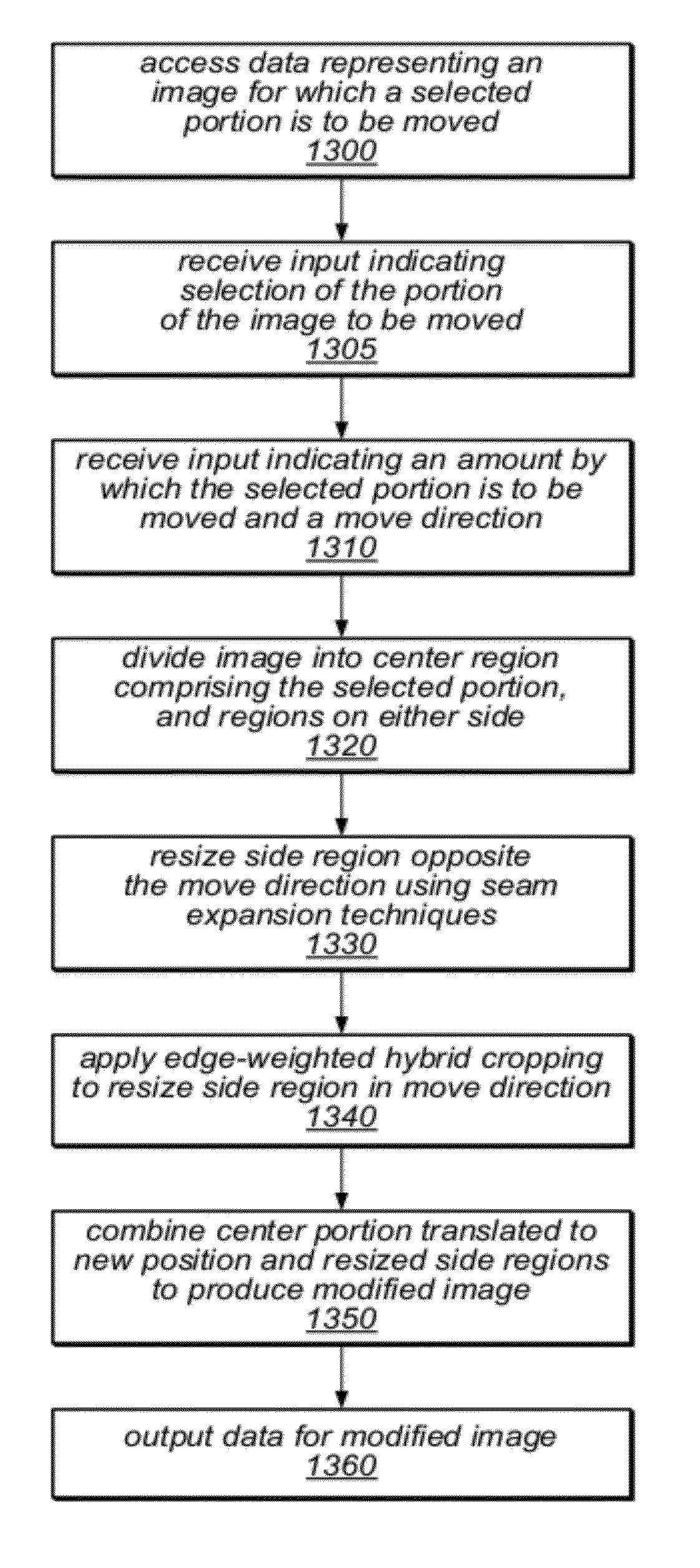
System and method for content aware in place translations in images
ActiveUS8358876B1Low costImprove performanceGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionLower priorityImage area
A system and method for performing content aware cropping or expansion may be applied to translate an object within an image. The object may be selected by defining an approximate bounding box of the object. The method may receive input indicating a lowest priority edge or corner of the object to be translated (e.g., using a drag operation). Respective energy values for pixels in regions of the image adjacent to a region comprising the selected object may be weighted based on their distance from the region and / or lowest priority edge / corner, on a cropping or expansion graph, and / or on the translation dimension and direction. Relative costs may be determined for seams of these regions dependent on the energy values. Low cost seams may be removed from one region and replicated in another region, and the region comprising the translated object may be combined with these resized regions in a modified image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
System and method for risk adjusted cost index measurements for health care providers
An improved method of evaluating and comparing the cost-effectiveness of healthcare providers across a wide spectrum of specialties and health conditions of their patients. The method includes the steps of determining criteria for determining a provider's relative cost-effectiveness at providing healthcare at a reasonable cost, and then applying those criteria to assign or exclude a provider from a preferred network of healthcare providers that have an established history of providing the same care at a lower cost than other providers.
Owner:HEALTH CARE SERVICE A MUTUAL LEGAL RESERVE
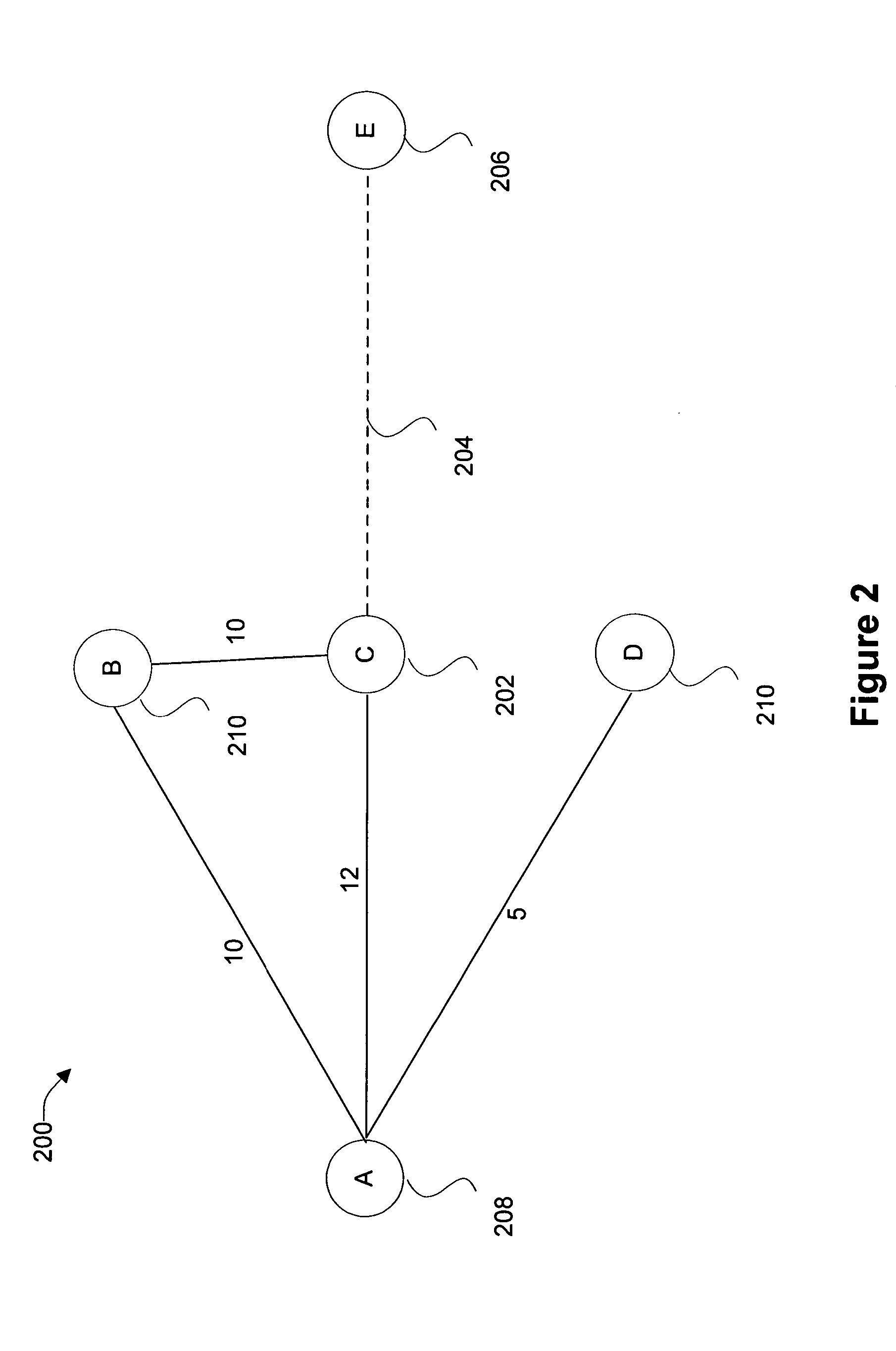
Minimum cost routing based on relative costs of node resources
InactiveUS7161910B2Minimal costMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionRouting decisionRelative cost
In a communications network, each network node includes a first module that handles a group of channels between its input and output ports as a route decision unit and a second module that handles a channel between its input and output ports as a route decision unit. A module state database stores module cost data of the first and second modules and a link state database stores link cost data of the links. Using the module and link state databases a route of minimum cost is determined and a connection is established between an incoming link and one of the input ports of the first and second modules and a connection is established between one of the output ports of the first and second modules and an outgoing link. The contents of the module and state databases are broadcast to the network.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com