Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
310 results about "Maximum gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
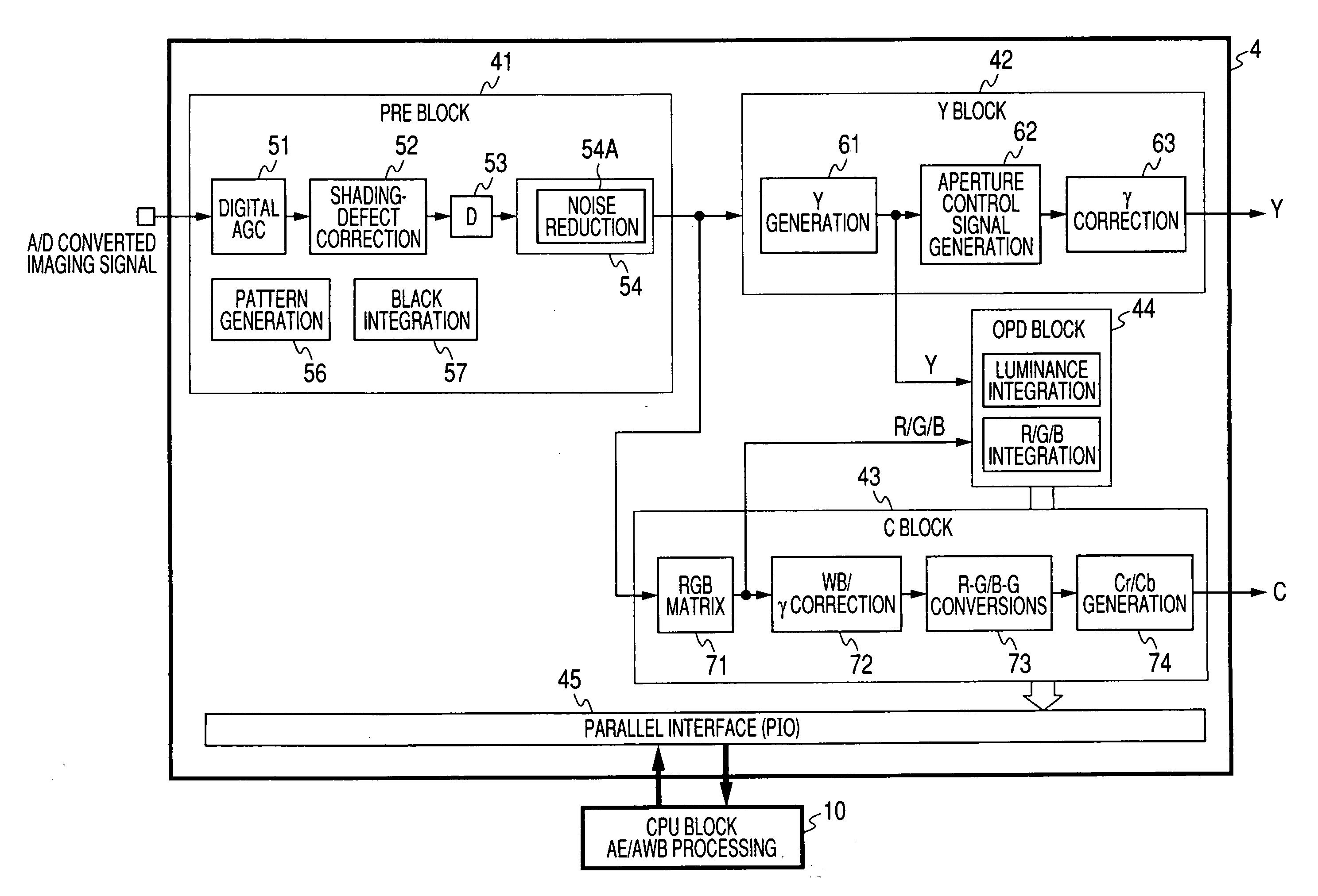
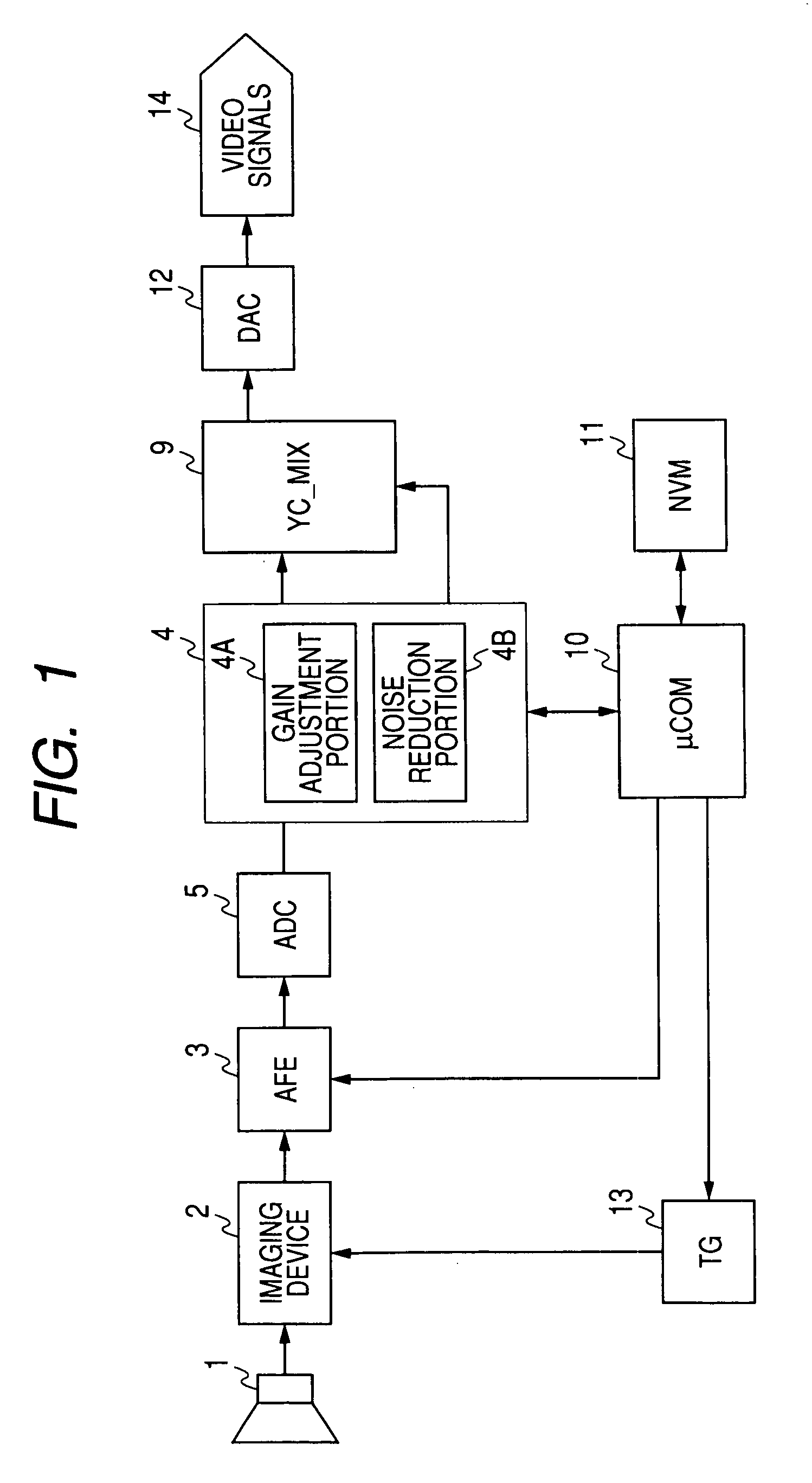
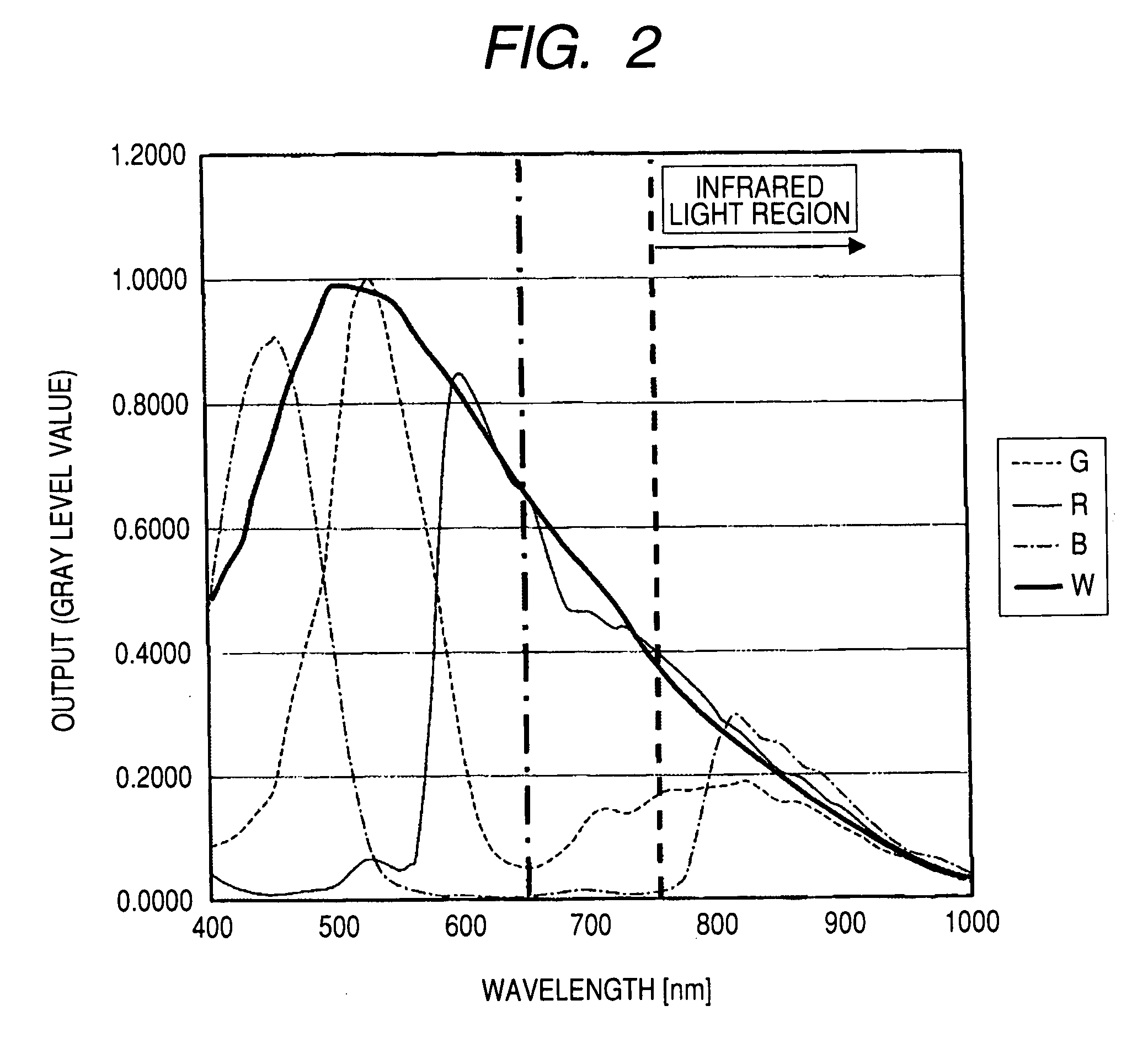
Video input processor, imaging signal-processing circuit, and method of reducing noises in imaging signals
InactiveUS20080284880A1Noise-reducing capability is preventedReduce gainTelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceRelative magnitudeSignal processing circuits
A video input processor is disclosed. The processor includes: an imaging signal-generating portion configured to image a subject and producing first imaging signals containing visible light components and a second imaging signal containing near-infrared light components; a gain adjustment portion configured to adjustably set a maximum gain value according to a relative magnitude between the visible light components and the near-infrared light components and adjust a gain for the first imaging signals at the set maximum gain value; and a noise reduction portion configured to reduce noises in the first imaging signals after the gain has been adjusted.
Owner:SONY CORP
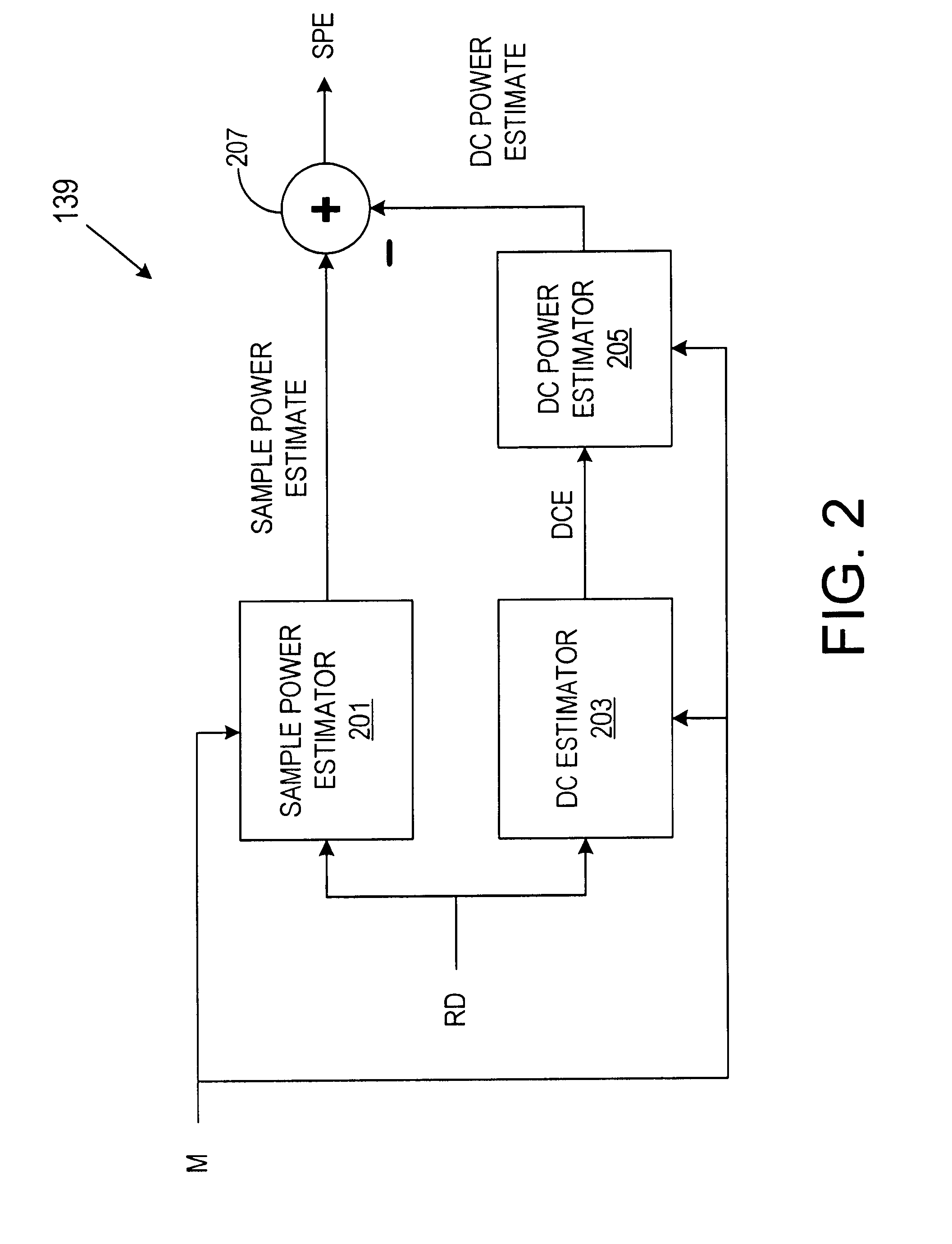
Automatic gain control system and method for a ZIF architecture
A system and method for controlling amplification of a signal received by a ZIF radio having a power level within a full power range relative to a minimum noise floor. The ZIF radio includes a ZIF receiver front end, an overload detector, an ADC, a saturation detector, a DC and power estimator, and control logic. The control logic utilized full visibility of the ADC to limit gain of the baseband amplifier to a maximum gain setting sufficient to view the minimum noise floor and to view a received signal having a power level within any of several segments of the power spectrum. The segmentation of the power spectrum is based on an overload condition of the ZIF receiver front end and a saturation condition of the ADC. The control logic further employs limited gain stepping of the baseband amplifier to avoid exceeding a DC budget of the ADC.
Owner:M RED INC
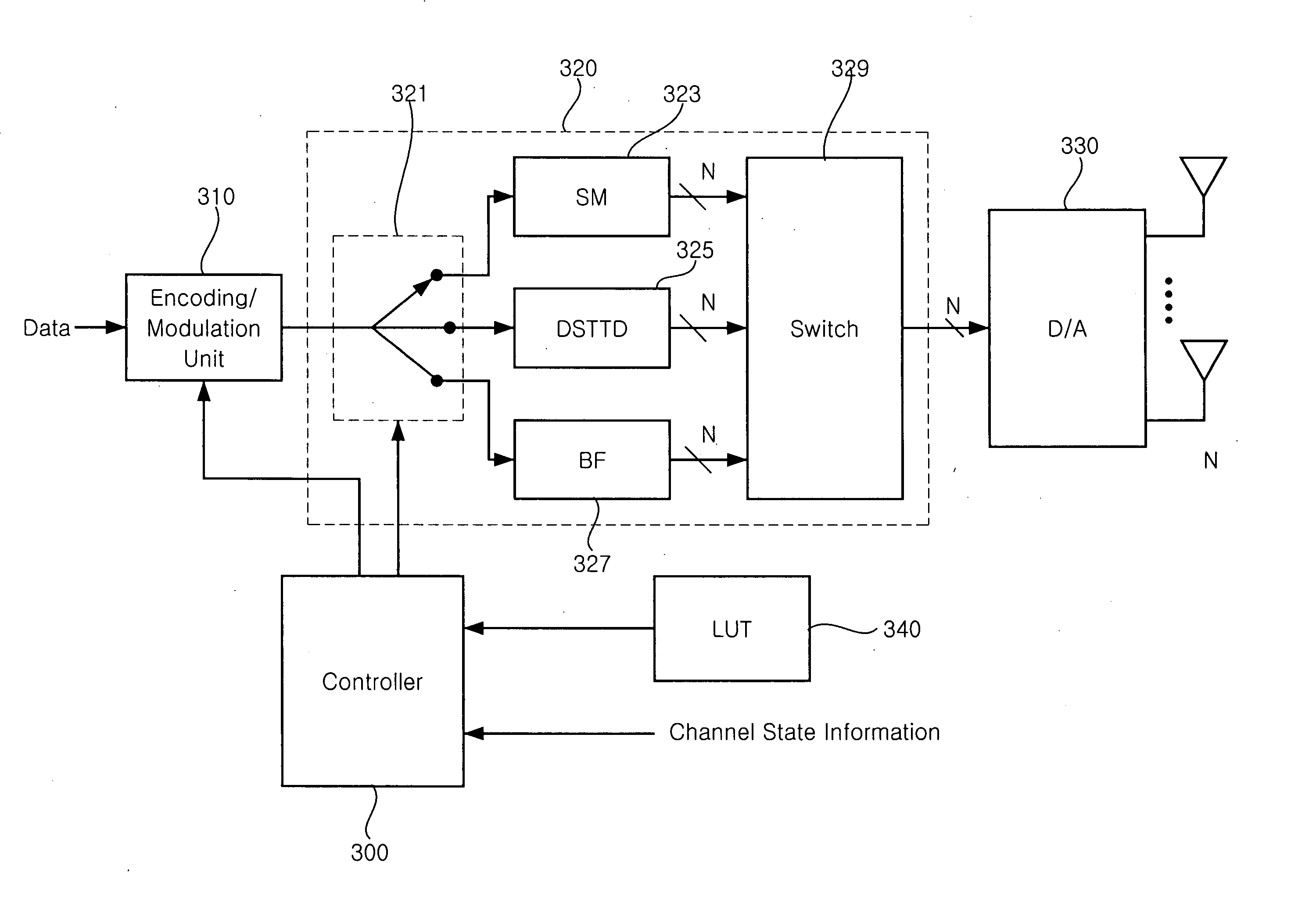
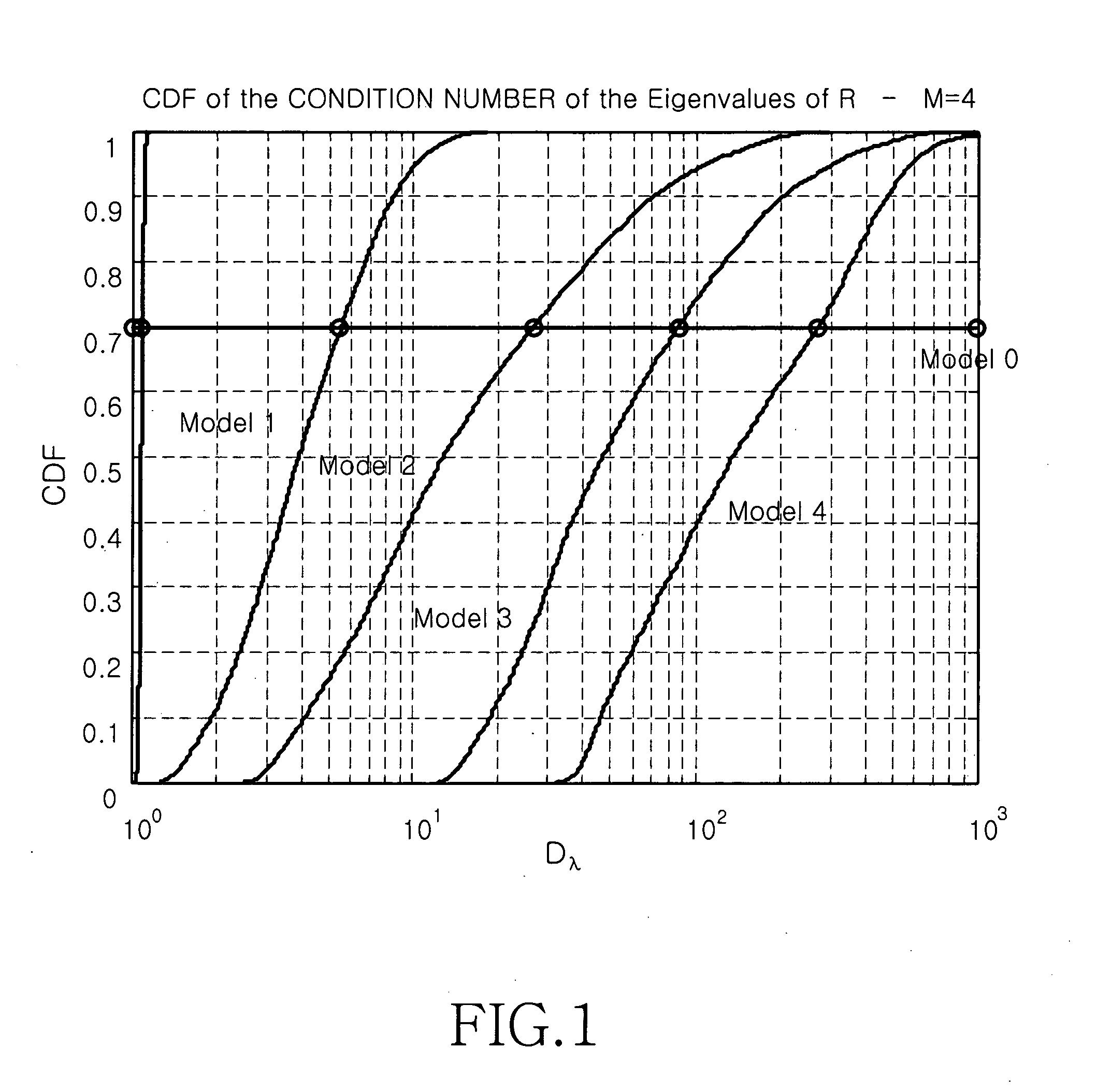
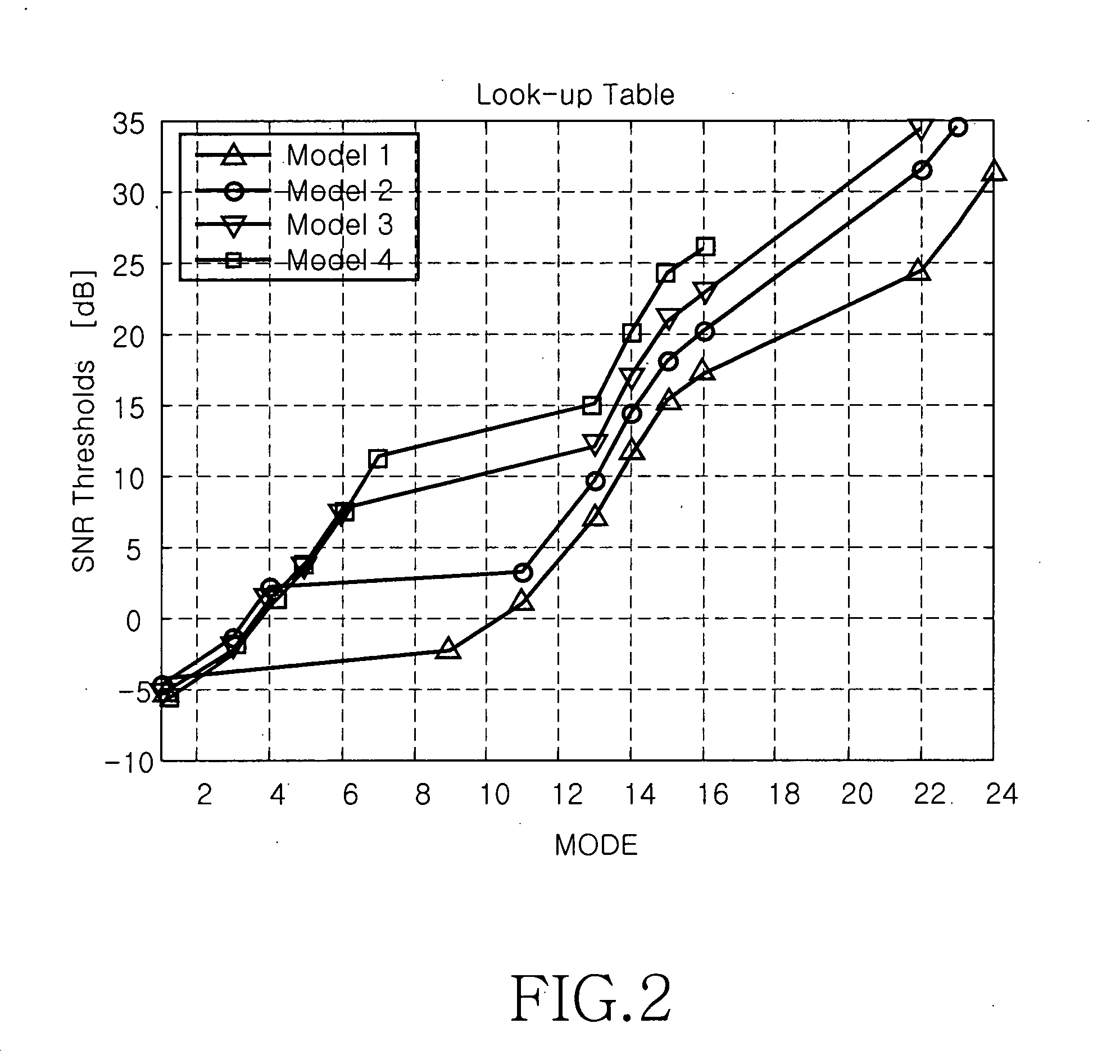
MIMO communication system using an adaptive transmission mode switching technique
ActiveUS20060083195A1Improve spectral efficiencyMultiplex communicationRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumMimo transmission
A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless communication system. A transmitter that includes a plurality of transmit antennas selects one of a spatial multiplexing scheme and a spatial diversity scheme, processes a signal in the selected transmission scheme, and transmits the signal through the plurality of transmit antennas. A receiver that includes a plurality of receive antennas processes a signal in a reception scheme mapped to a transmission scheme of the transmitter. The transmission schemes include a transmission scheme for maximizing diversity gain and a transmission scheme for maximizing spectral efficiency. The MIMO communication system using an adaptive transmission mode switching technique performs switching between MIMO transmission modes using spatial selectivity of a channel, thereby obtaining maximum gain in a signal to noise ratio (SNR) and spectral efficiency according to channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
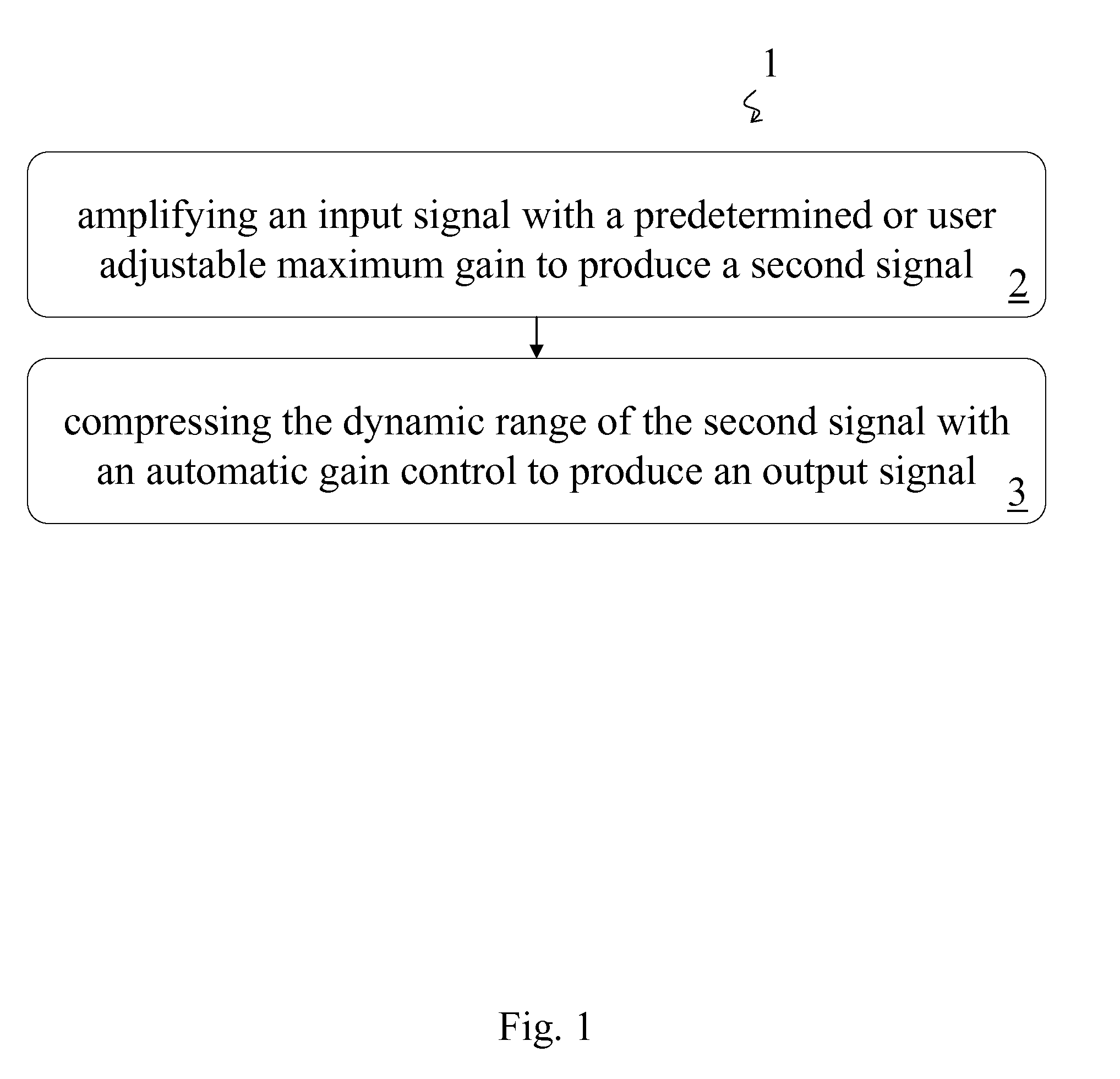
Amplifier and Method of Amplification
InactiveUS20080069385A1Cancel noiseVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersFrequency response correctionAudio power amplifierEngineering
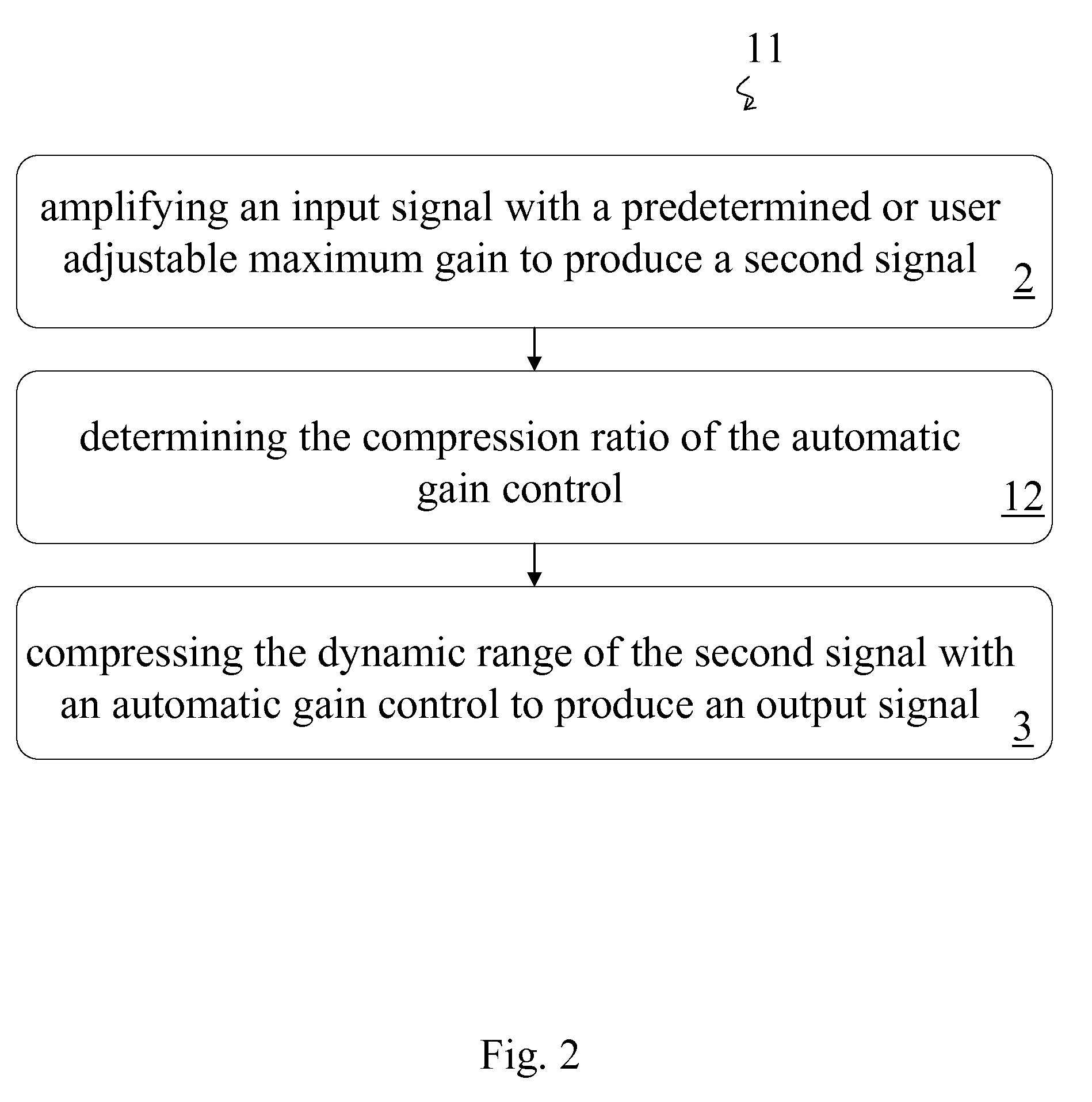
A method of amplification includes amplifying an input signal with a predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain to produce a second signal and compressing the dynamic range of the second signal with an automatic gain control to produce an output signal. The compression ratio of the automatic gain control is greater than one for output signals below a predetermined threshold output signal level and is essentially one for output signals above the predetermined threshold output signal level. The compression ratio may be predetermined or the method may include determining the compression ratio of the automatic gain control. The compression ratio may be determined according to the amplitude of the output signal or according to an input-output curve. The input-output curve my be predetermined and may be selected according to the auditory needs of a listener. Preferably the input-output curve is determined according to the predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain.
Owner:REVITRONIX
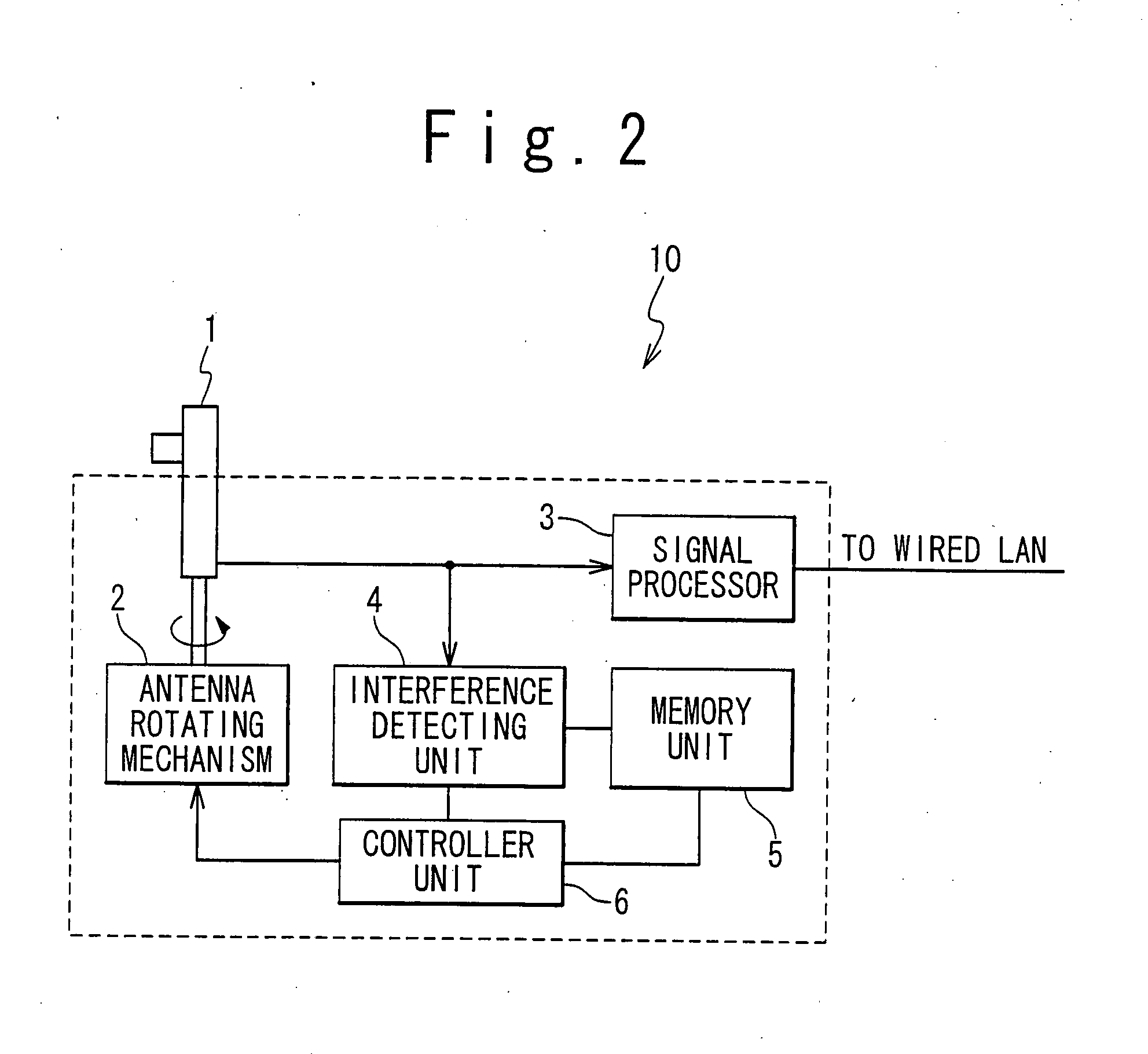
Wireless LAN technologies for reducing interference between or among wireless LAN access points
InactiveUS20040106436A1Reduce distractionsIncrease contact areaSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTelecommunicationsDirectional antenna
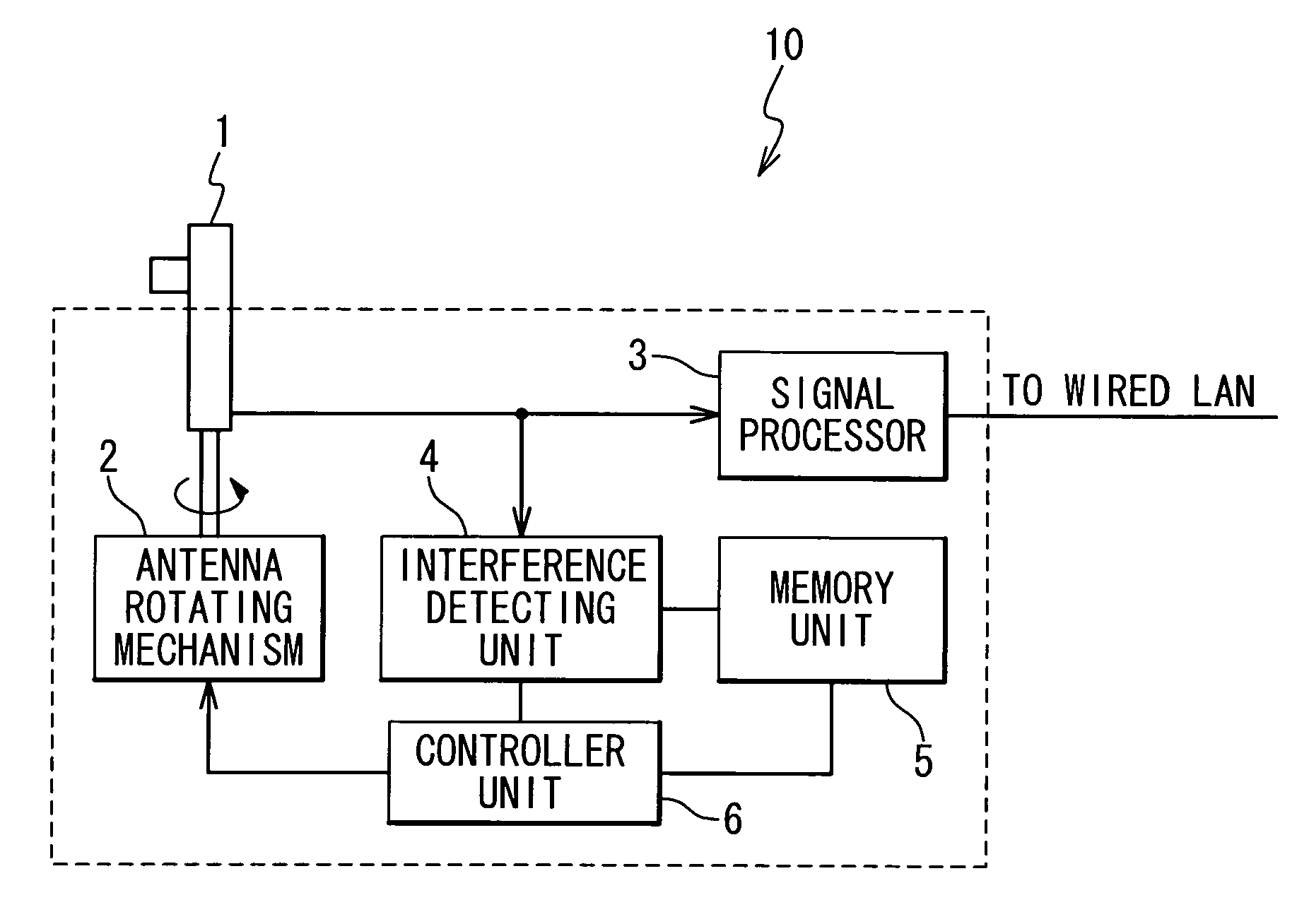
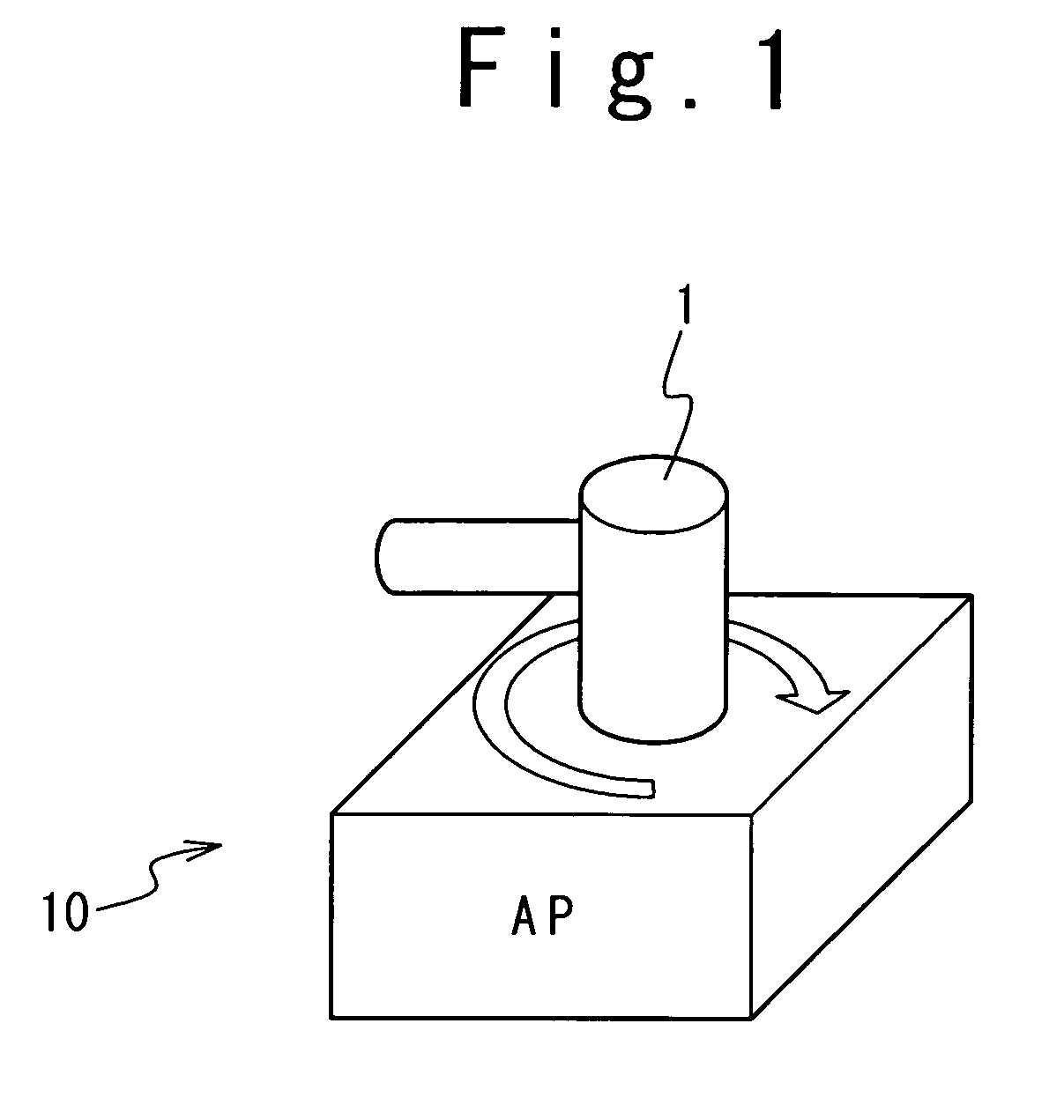
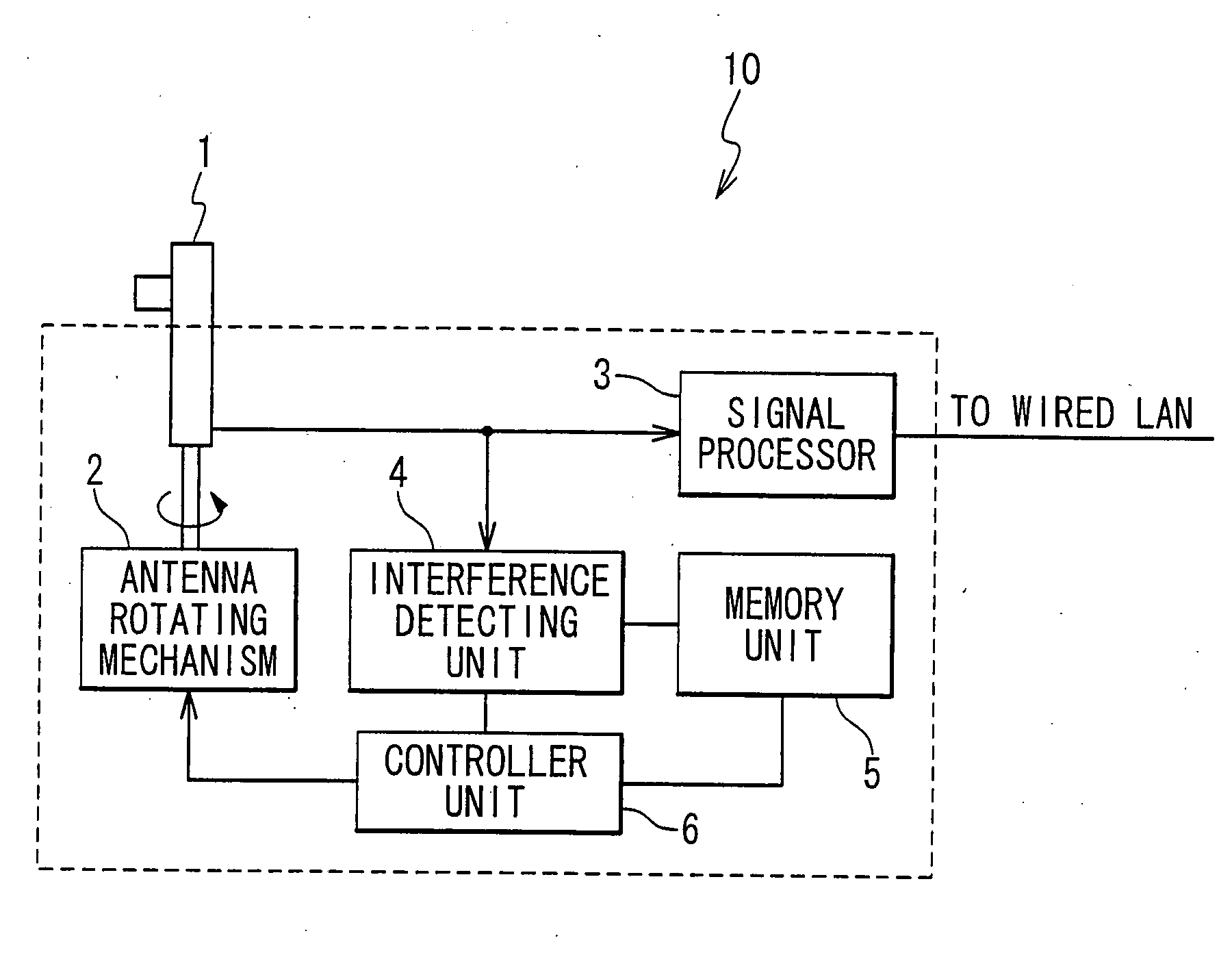
A wireless LAN technology for reducing interference between (or among) wireless LAN access points is provided. A wireless LAN access point is provided with a directional antenna, an interference detector detecting interference effected by another wireless LAN access point on the directional antenna, and a direction adjusting mechanism adjusting a maximum gain direction of the directional antenna in response to the detected interference.
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
RF tag module, RF tagged article and RF tag reading apparatus utilizing same
InactiveUS20050077353A1Efficient readingSimple structureMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsCoaxial cableEngineering
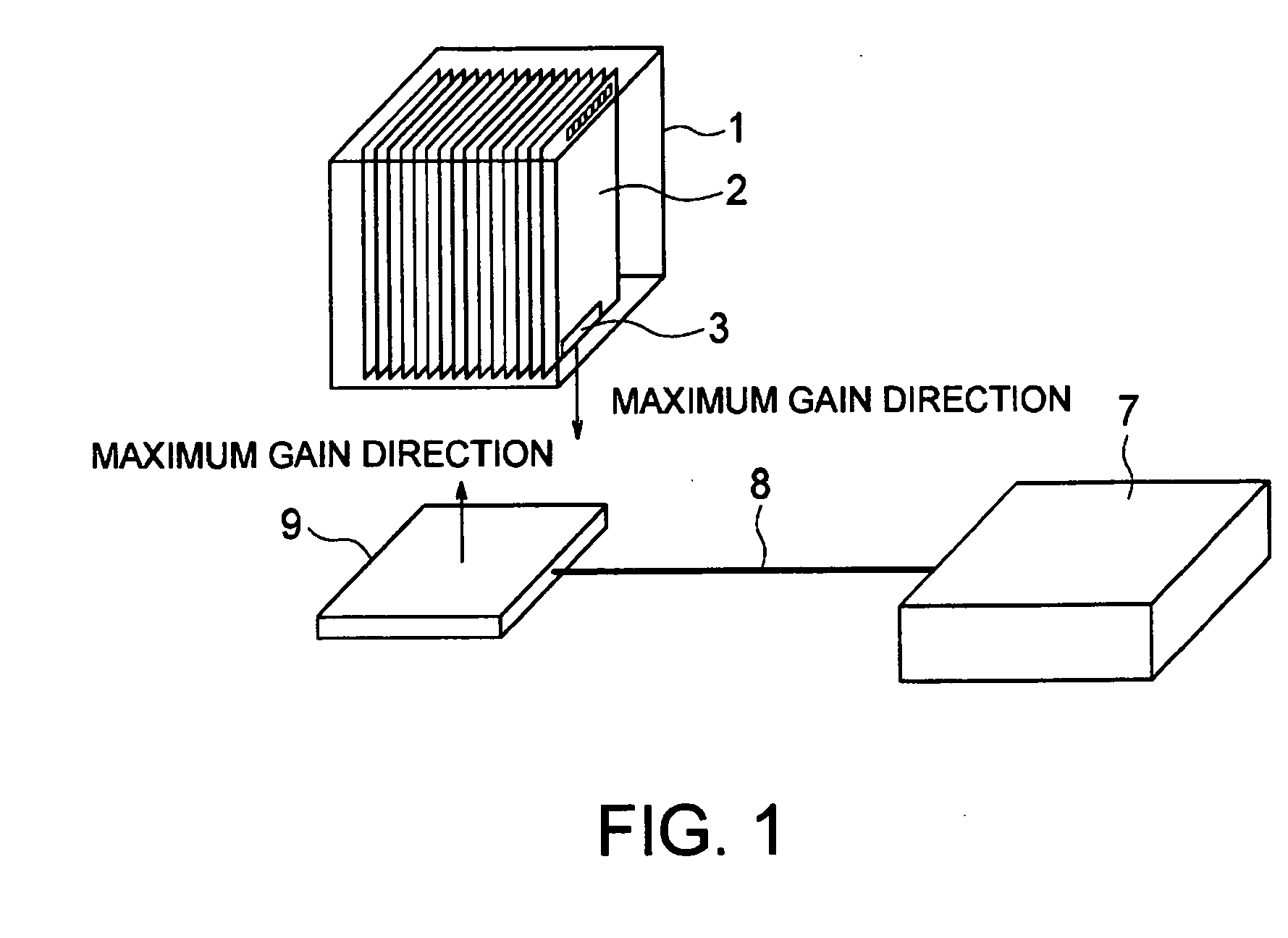
An RF tag reading apparatus reads information from RF tags affixed to postal envelopes by a single operation. An article container contains a large number of postal envelopes provided with RF tags. A reader antenna, which is connected to an interrogator via a coaxial cable, is disposed under the article container. Maximum gain directions of the RF tags of the respective postal envelopes are uniformly directed to the reader antenna. The respective postal envelopes contained in the article container are arranged face to face with each other in a direction orthogonal to the maximum directions of the RF tags. Since a maximum gain direction of the reader antenna is oriented toward a base end surface of the article container, the maximum gain directions of the RF tags are opposed to the maximum gain direction of the reader antenna.
Owner:TOSHIBA TEC KK
Broadband sensor location selection using convex optimization in very large scale arrays
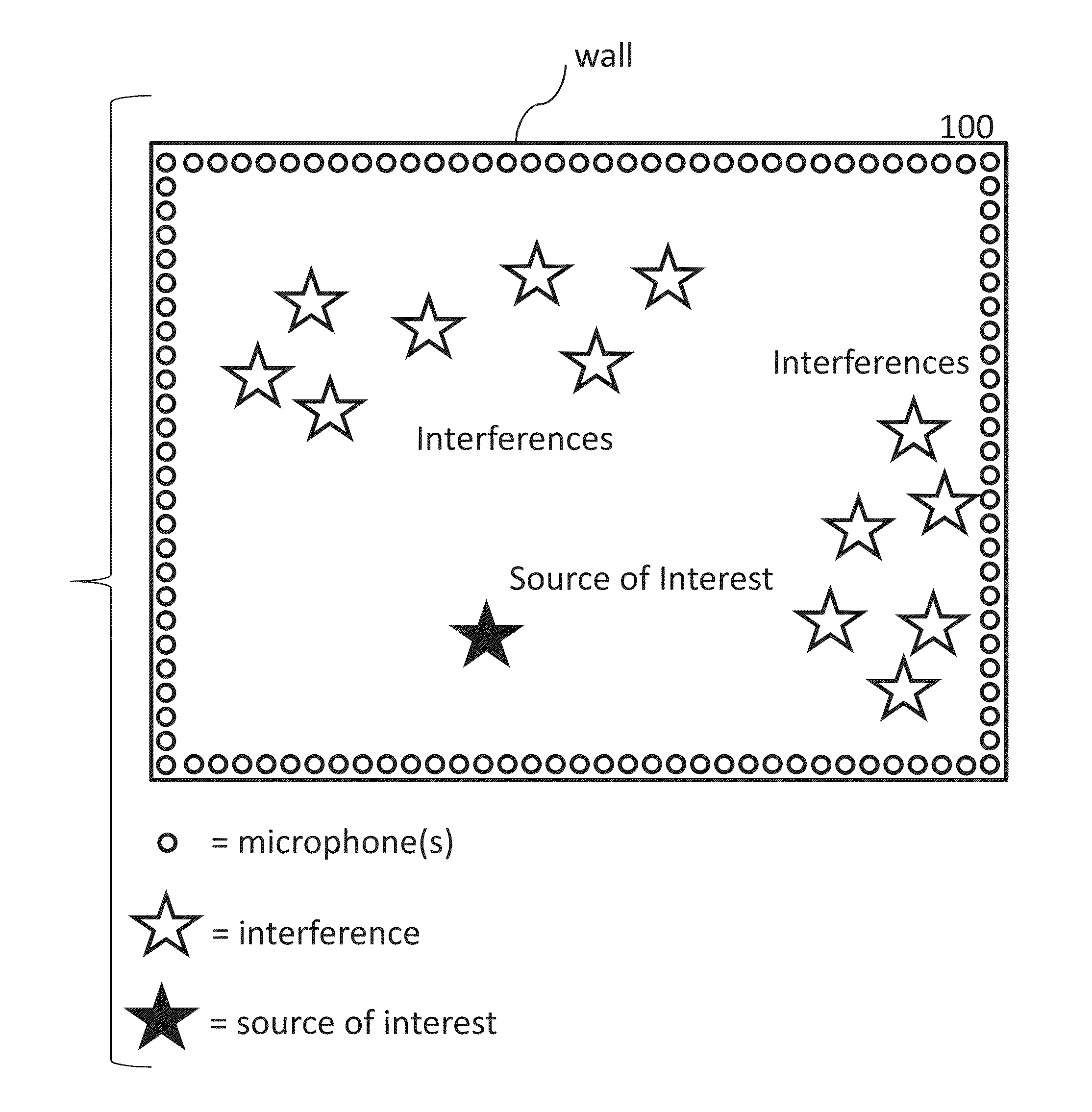
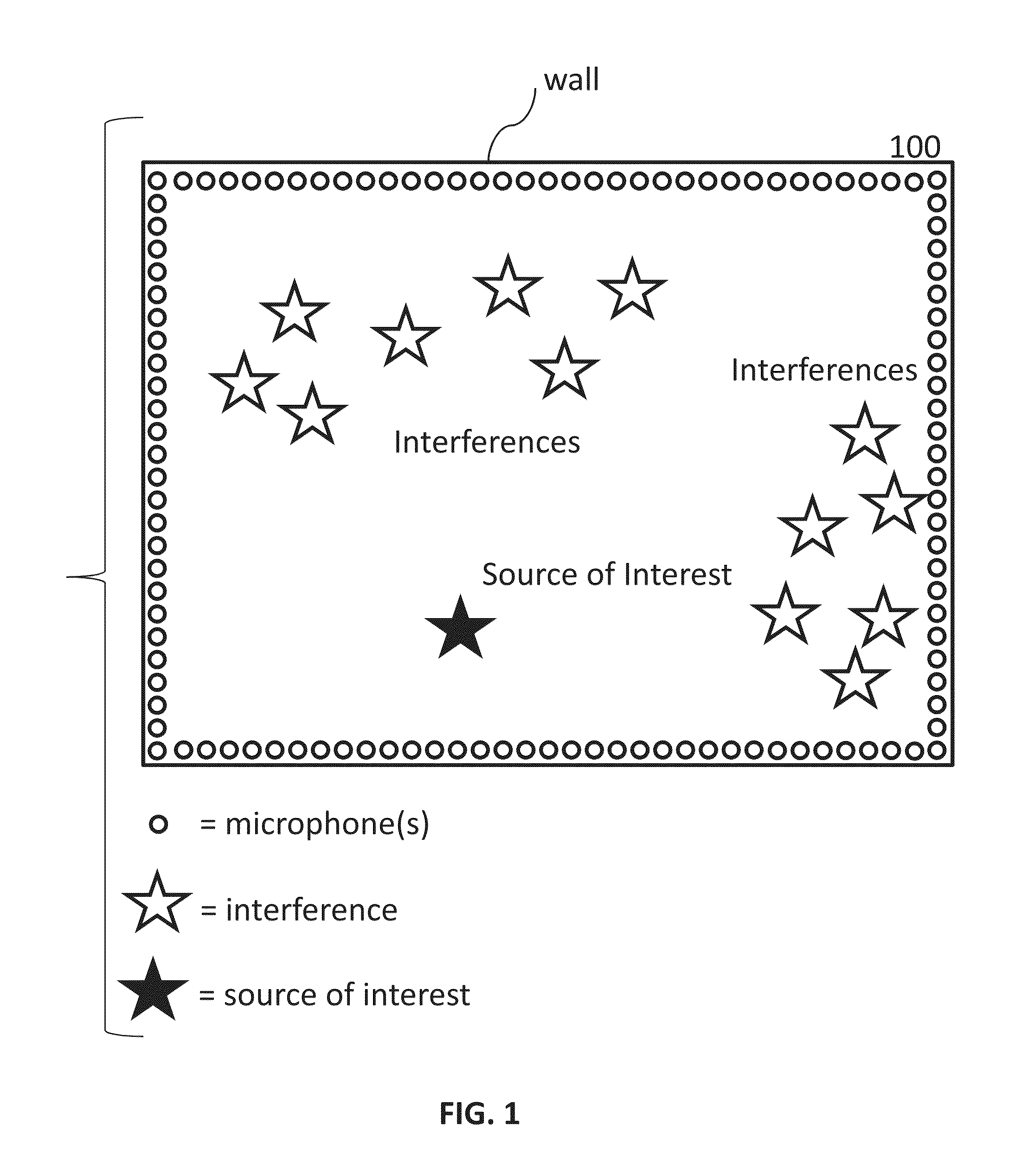
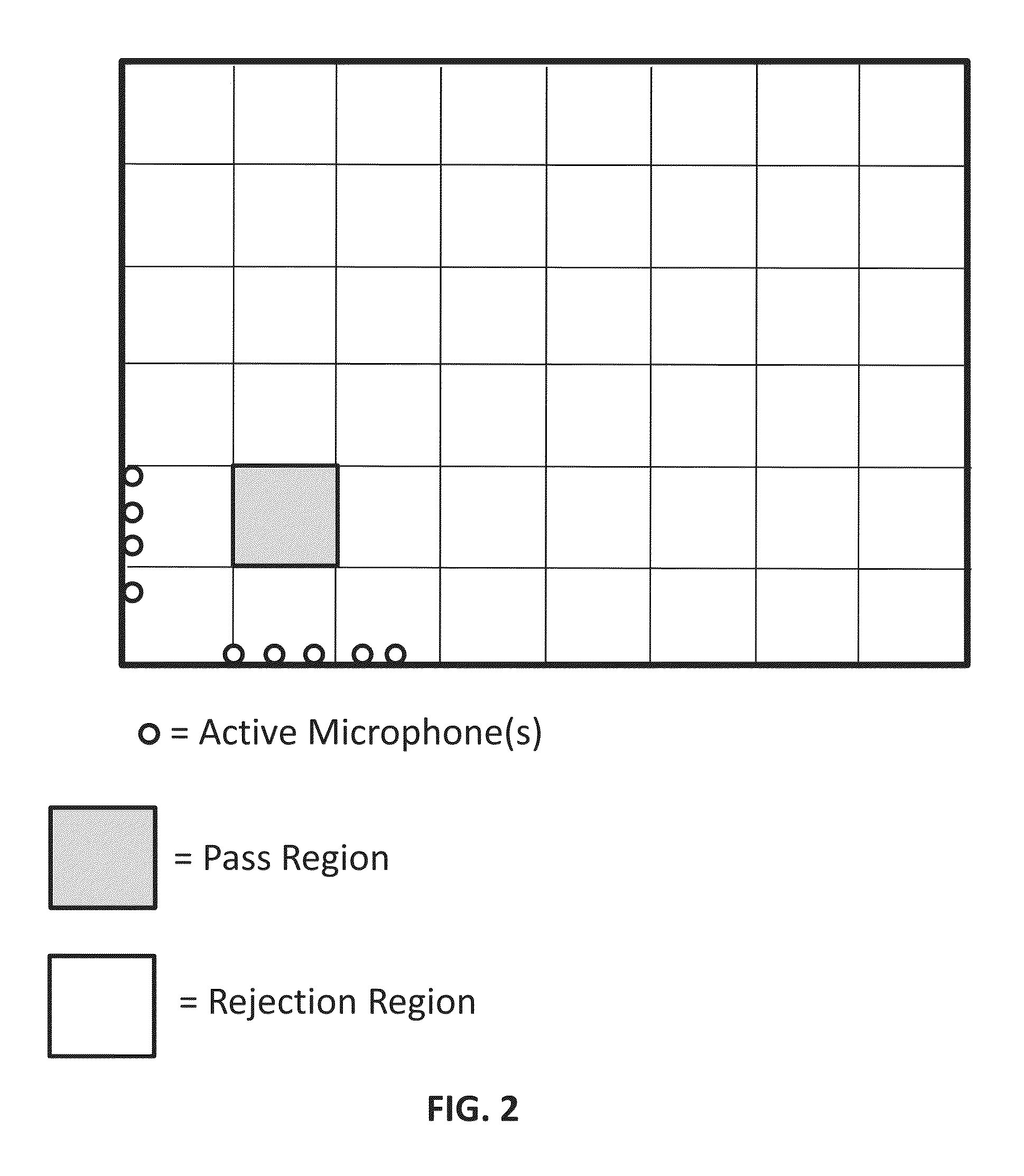
Systems and methods are provided to determine a subset of D microphones in a set of N microphones on a perimeter of a space to monitor a target location. The space is divided into L interference locations. An equation is solved to determine microphone weights for the N microphones by minimizing the maximum gain for signals related to the target location and interference locations, further optimized over an l1 penalty by applying a Lagrange multiplier to an l1 norm of the microphone weights in a manner that determines a set of D non-zero microphones weights and a set of (N−D) microphone weights that are zero or close to zero. Microphone weights are determined for at least 2 different frequencies.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
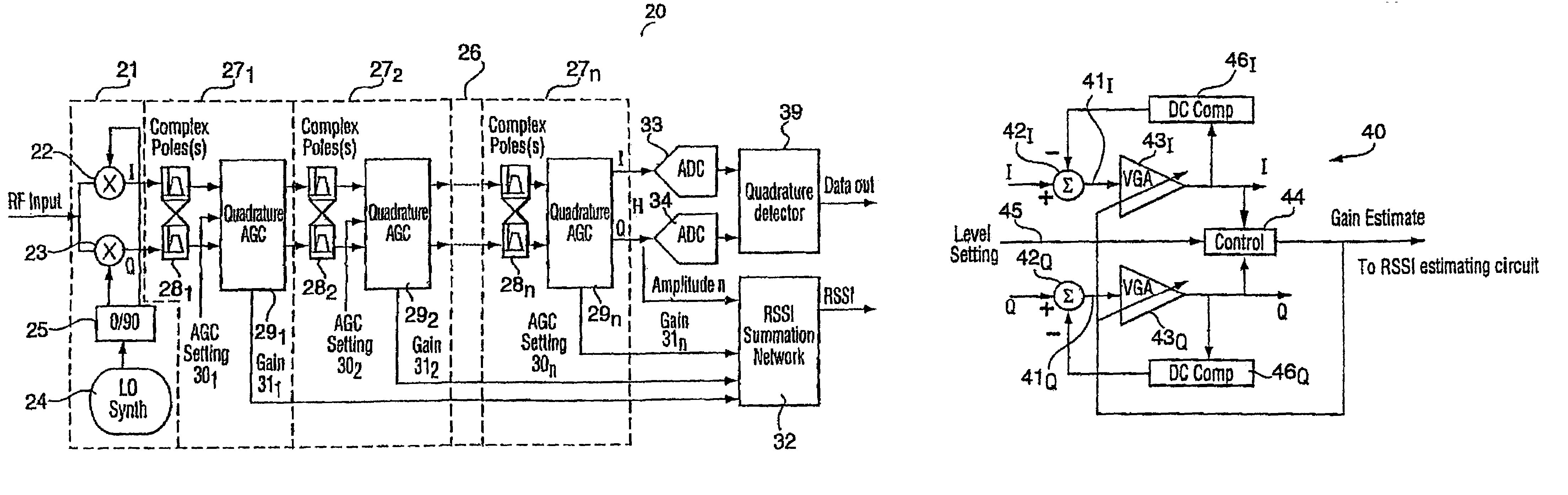
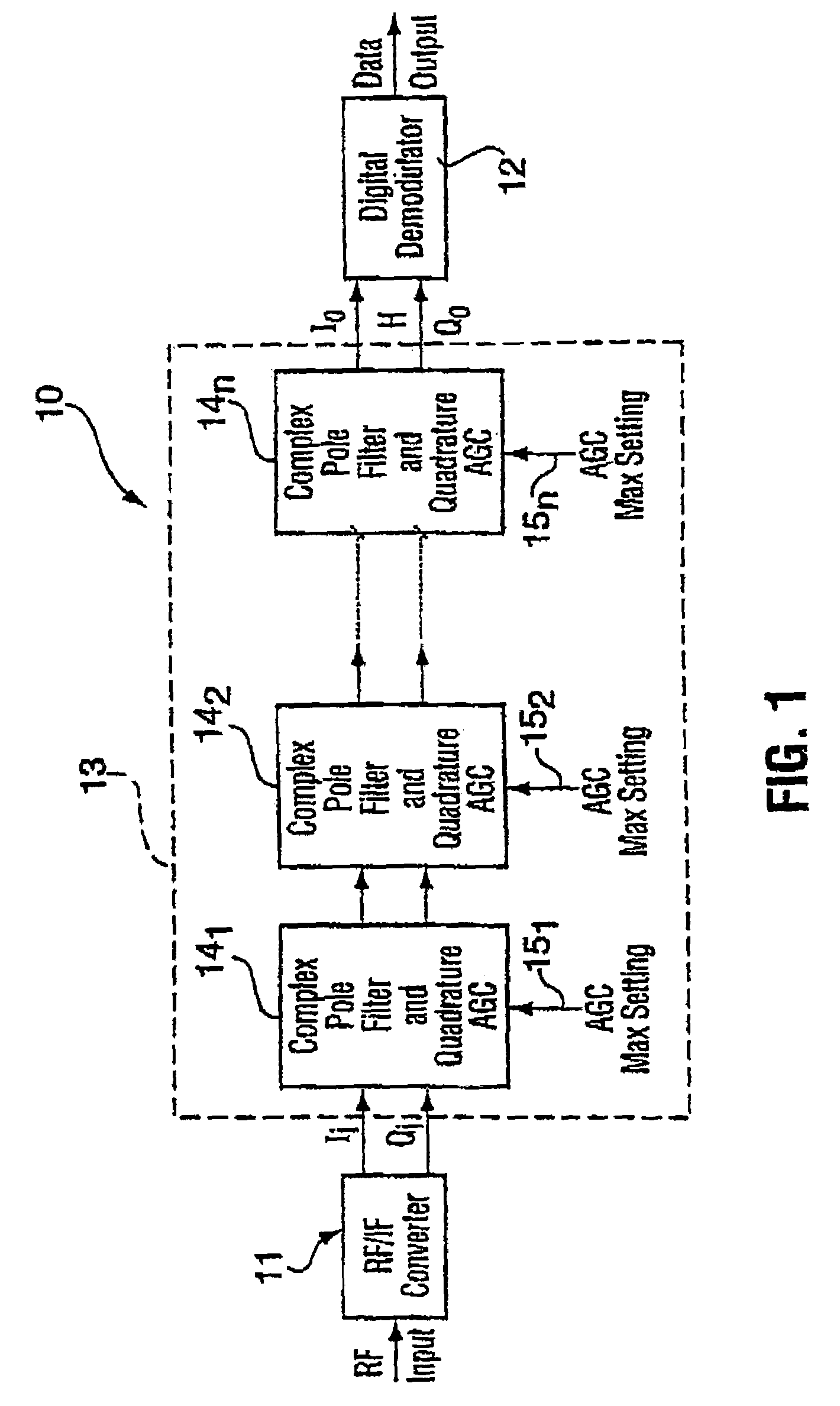
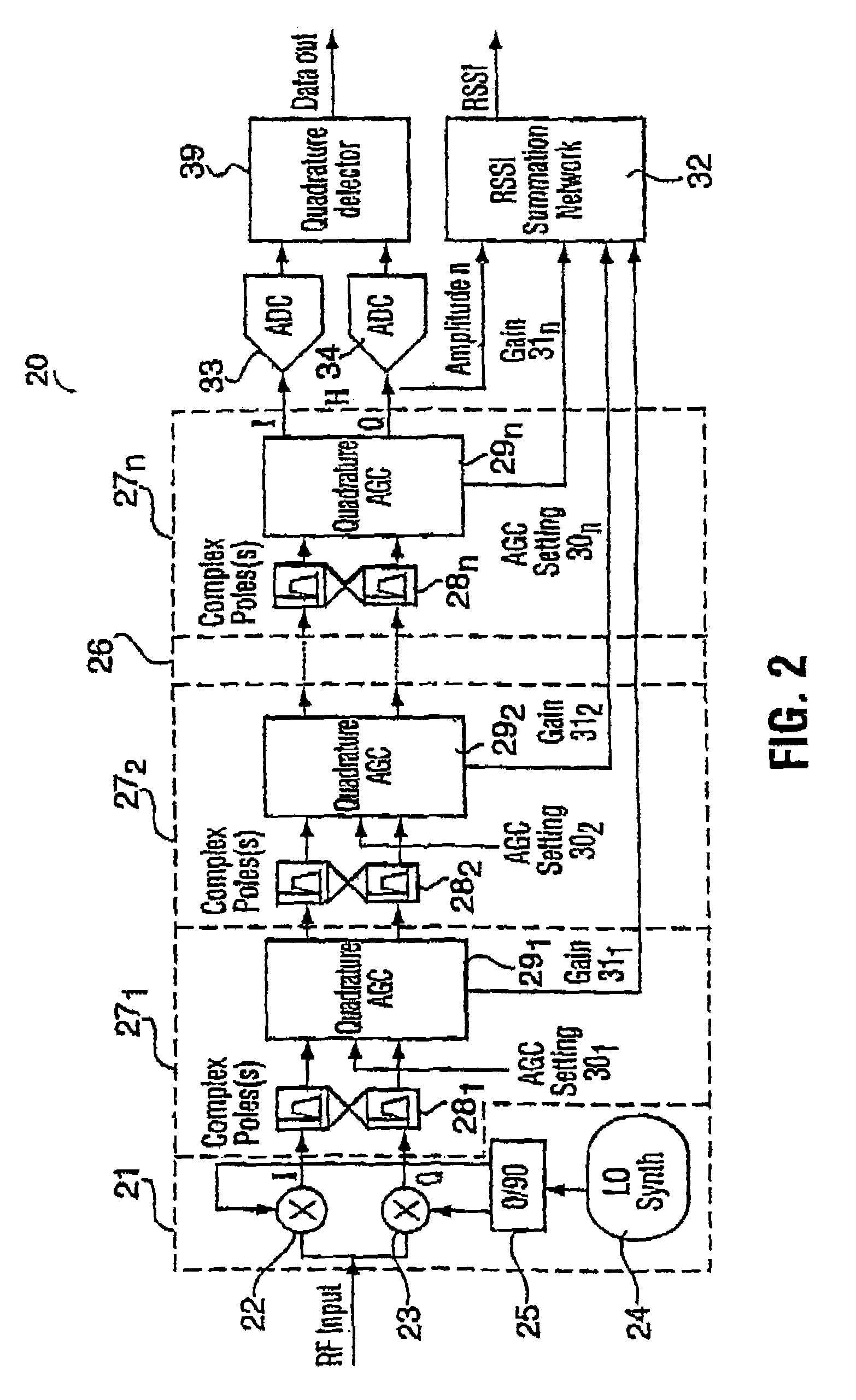
Complex filtering/AGC radio receiver architecture for low-IF or zero-IF
InactiveUS6977976B1Reduce power consumptionLow powerGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio receiverIntermediate frequency
A low power IF strip architecture suitable for Zero-IF (ZIF) or low-IF (LIF) radio receivers for filtering and amplifying a received signal. The apparatus includes a plurality of sequentially connected complex filter / amplifier stages. Each stage includes a complex filter having one or more poles and an automatic gain controlled amplifier (AGC). Each AGC may be feedback or feedforward with fixed minimum and maximum gains. Each stage further includes a control circuit that produces a gain control signal for controlling the amplifier gain within the fixed minimum and maximum gains as a function of a projected amplitude level. The received signal passes through multiple stages of filtering and controlled amplification to attenuate the interfering signal and amplify the desired signal. This is done at a restricted level in each stage such that the circuits in the stages operate at efficient power saving levels. The individual gain control signals from each stage are summed in a received signal strength indicator to provide the overall gain of the apparatus. The overall gain when taken with the amplitude of the apparatus output signal determines the original strength of the desired received signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
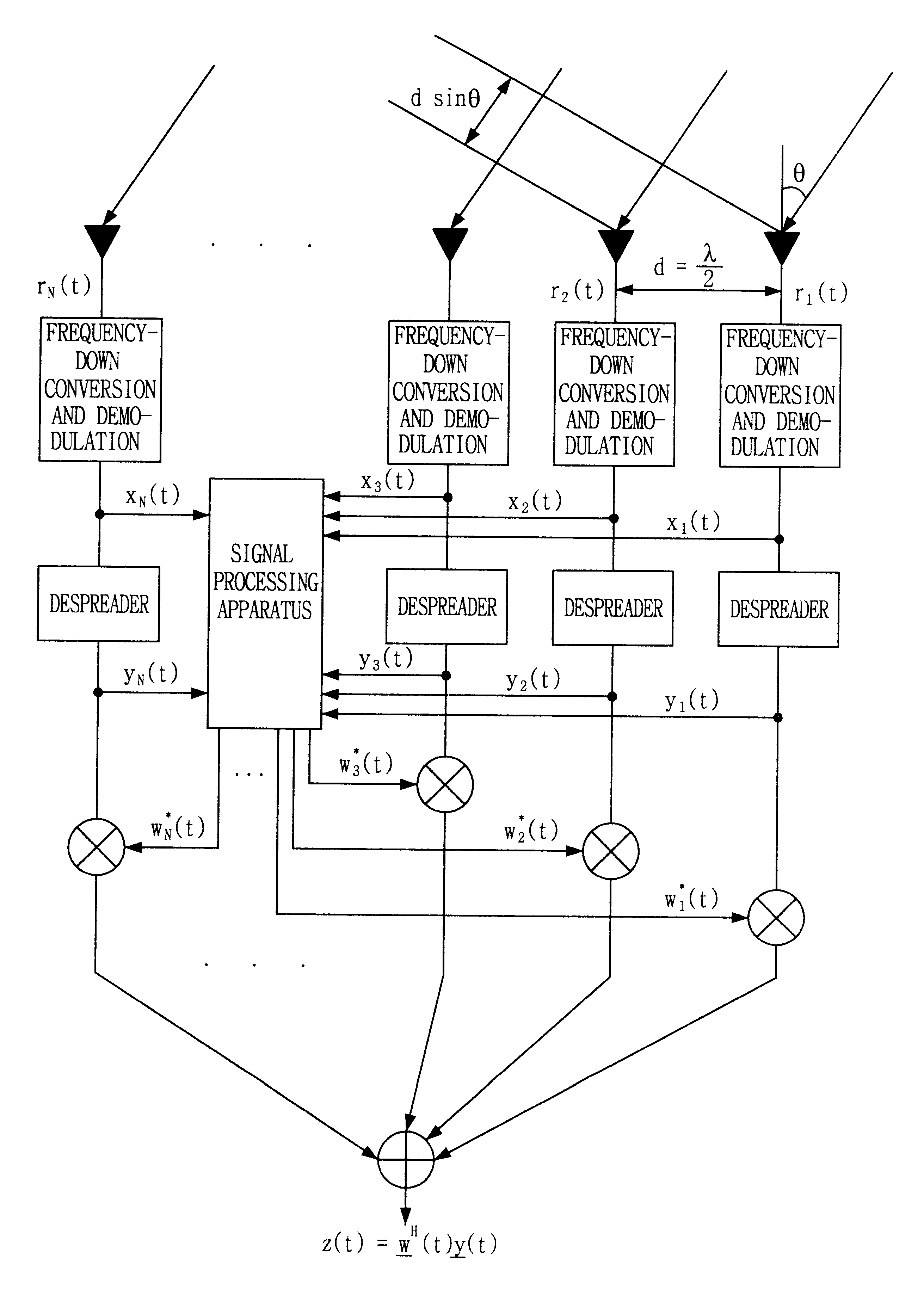
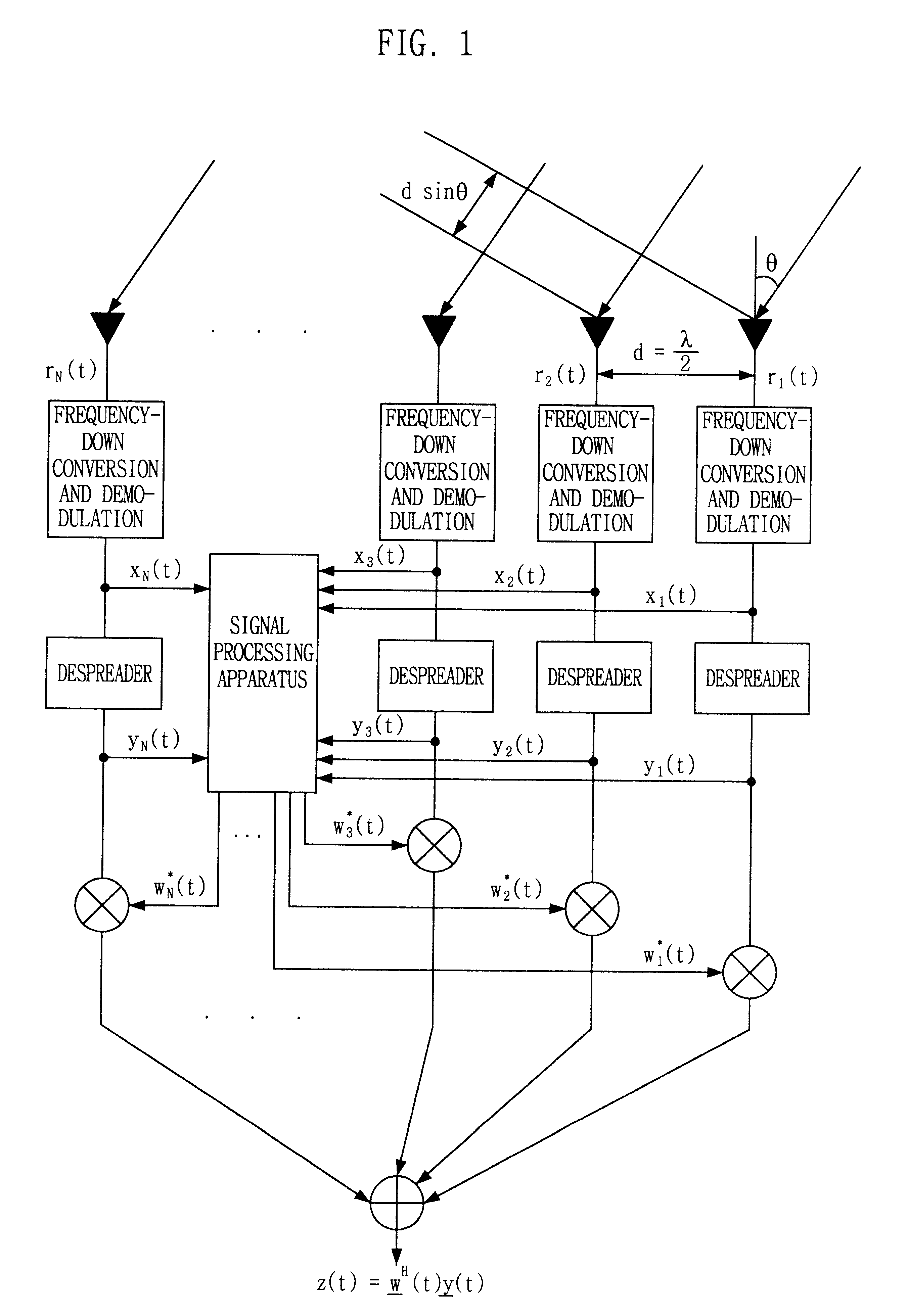
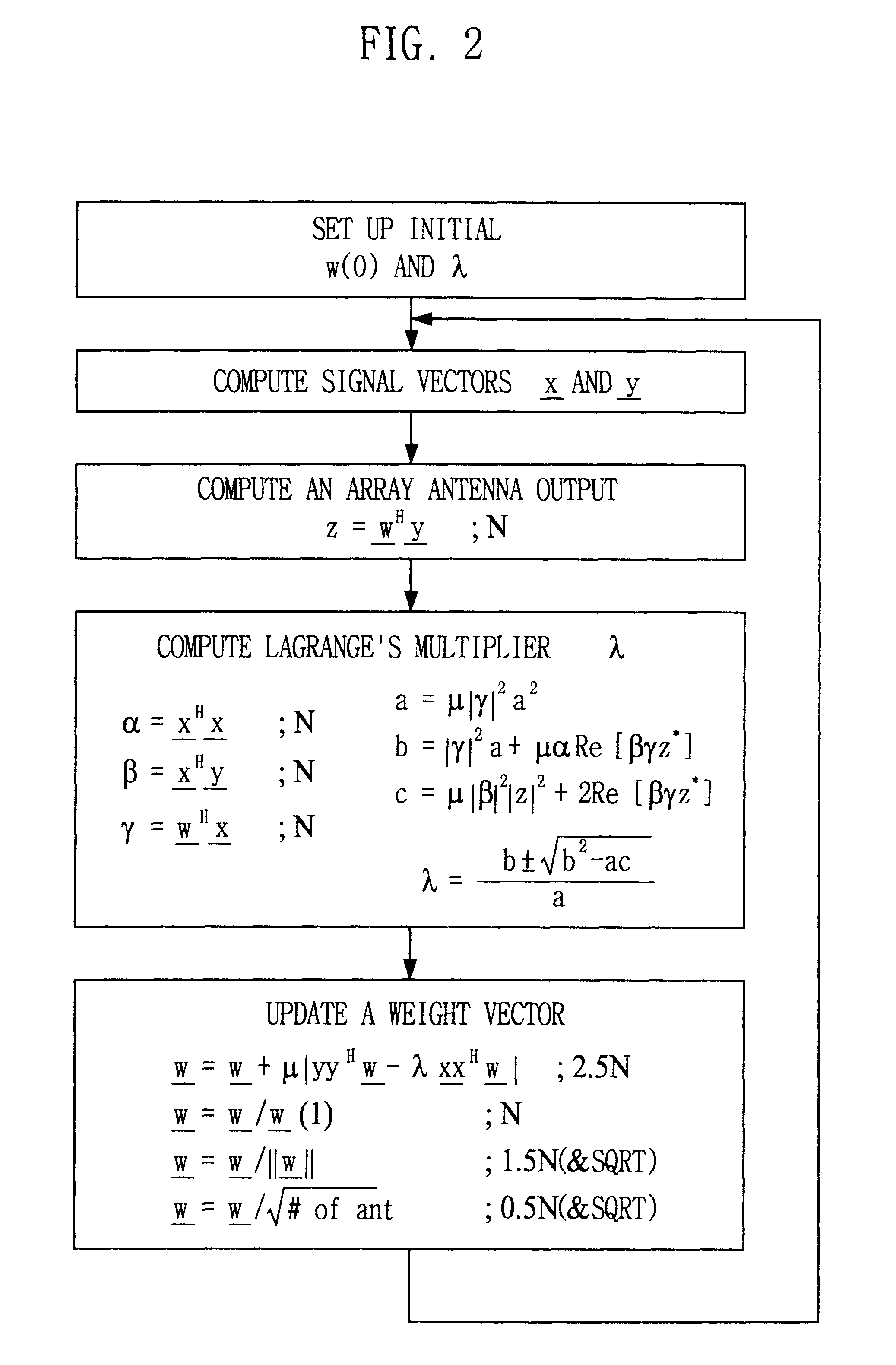
Signal processing method and apparatus for computing an optimal weight vector of an adaptive antenna array system
InactiveUS6462709B1Simple and accurate wayMaximizes the signal to interference plus noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOff the shelfTarget signal
This invention relates to a signal processing method and apparatus for an adaptive array antenna. The objective is to suggest an adaptive procedure of computing the suboptimal weight vector for an array antenna system that provides a beampattern having its maximum gain along the direction of the mobile target signal source in a blind signal environment, where the transmitted data are not known (or not to be estimated) at the receiver. It is the ultimate goal of this invention to suggest a practical way of enhancing both the communication quality and communication capacity through the optimal weight vector of the array system that maximizes SINR(Signal to Interference+Noise Ratio). In order to achieve this goal, the method of Lagrange multiplier is modified in such a way that the suboptimal weight vector is produced with the computational load of about O(8N), which has been found to be small enough for the real-time processing of signals in most land mobile communications with the digital signal processor (DSP) off the shelf, where N denotes the number of antenna elements of the array.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
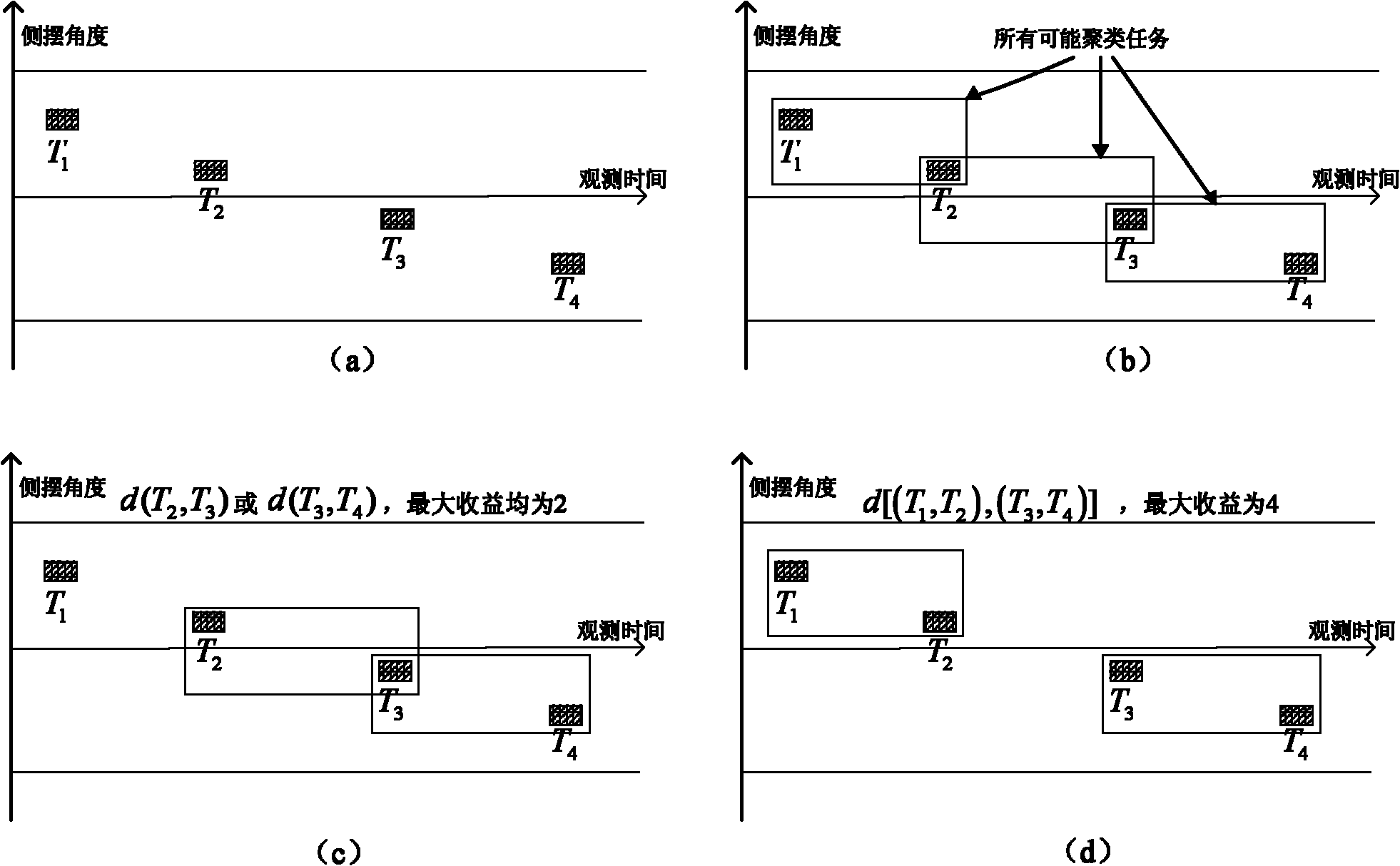
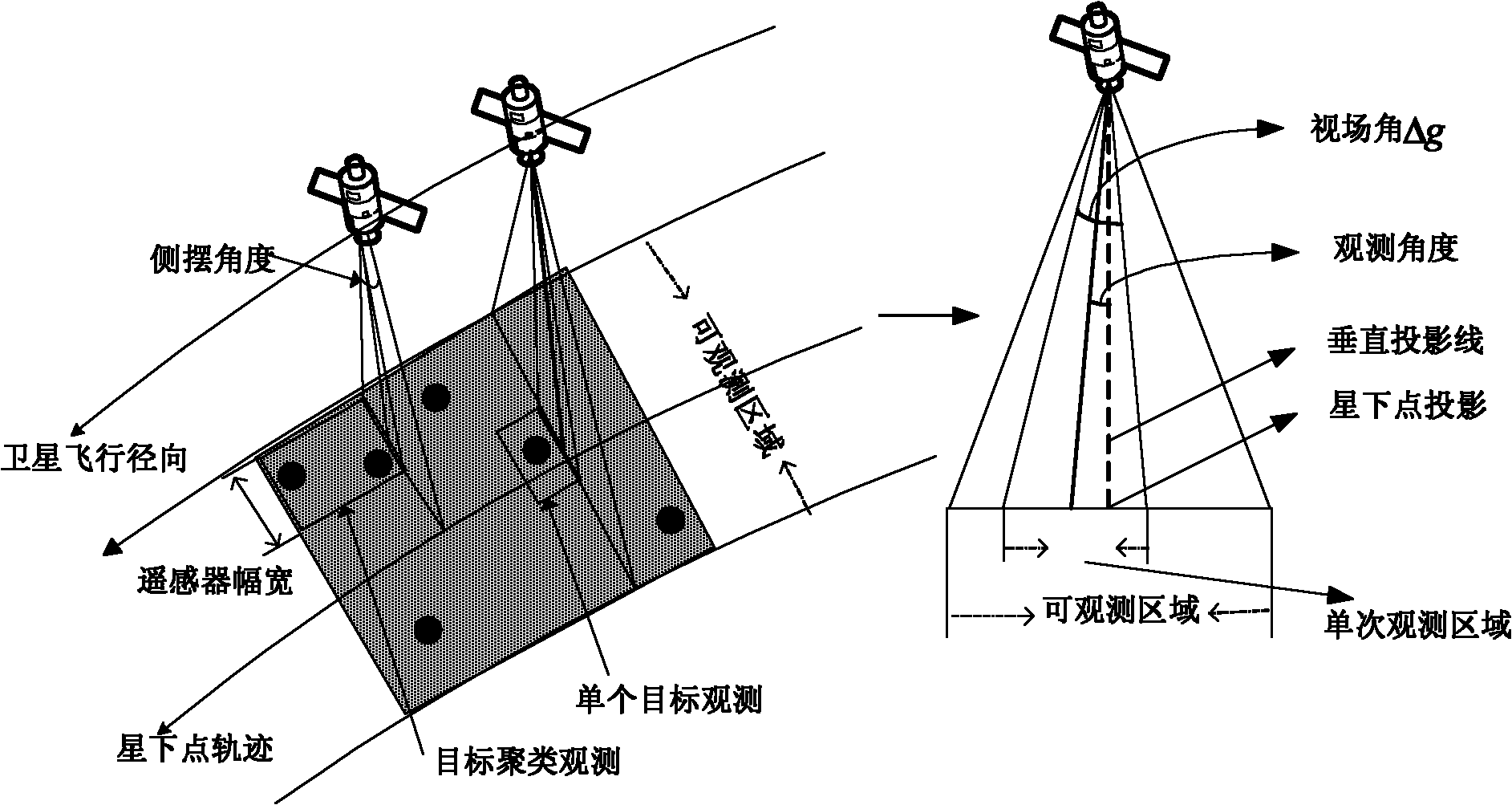
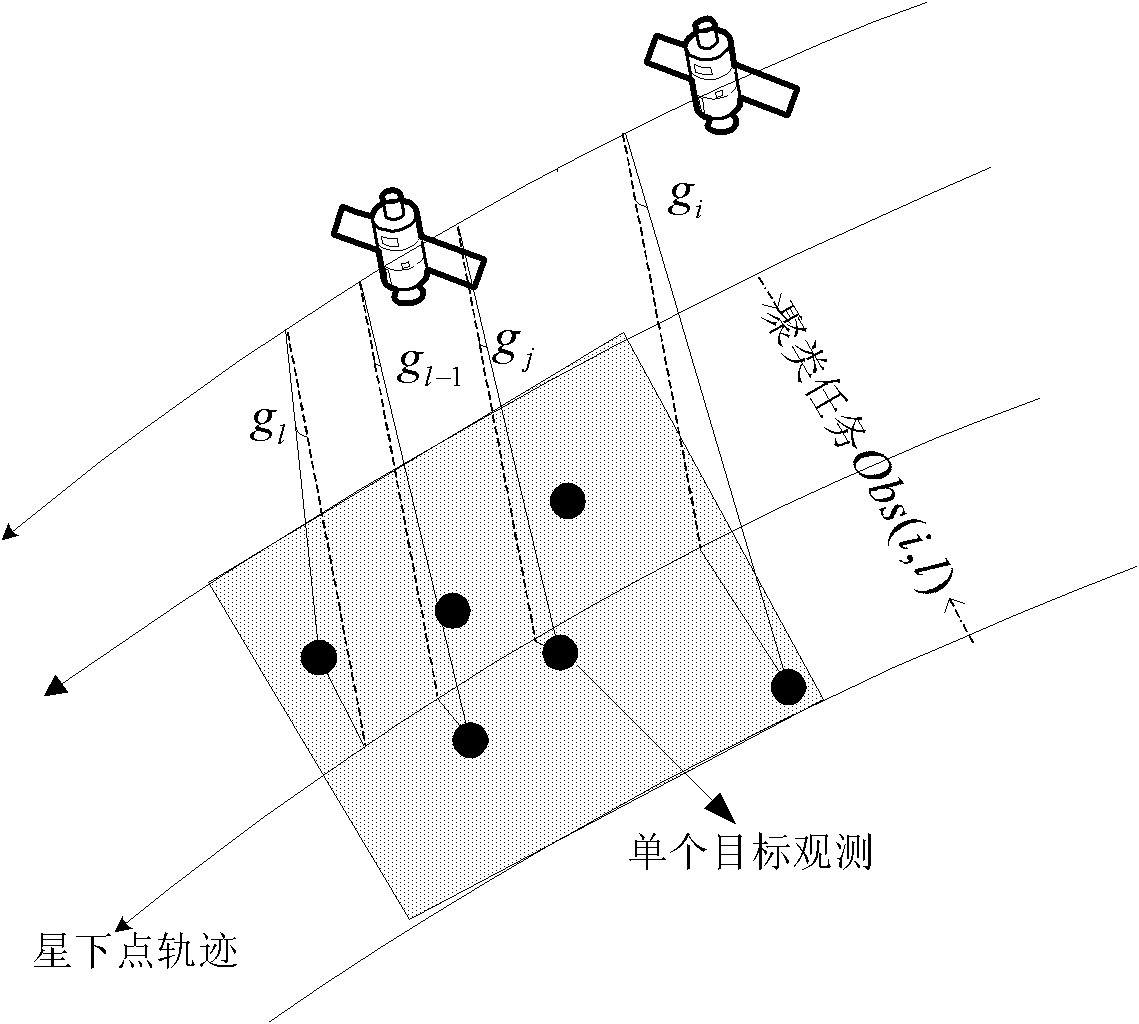
Target clustering method of imaging satellite observation scheduling
InactiveCN101894367AIncrease incomeMeet the needs of observation tasksImage analysisSatellite observationMethod of images
The invention discloses a target clustering method of imaging satellite observation scheduling. In the method, an optimal target clustering scheme is obtained by obtaining target clustering conditions and qualities of satellite observation, a maximum gain value of the target clustering scheme of a satellite in the orbit circle and an optimal target clustering scheme and finishing a target clustering step, and a set of targets covered by various observation activities of the satellite is further obtained. The target clustering method of the imaging satellite observation scheduling can satisfy using rules and performance characteristics of various operations of the satellite with small computation cost, ensure that the satellite can finish more observation tasks within the given time and improve the using efficiency and the benefits of satellite resources, and has small imaging distortion.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Tunable antenna system
InactiveUS6677914B2Easy to assembleEasy to dismantleResonant antenna detailsIndividually energised antenna arraysElectronic control systemControl system
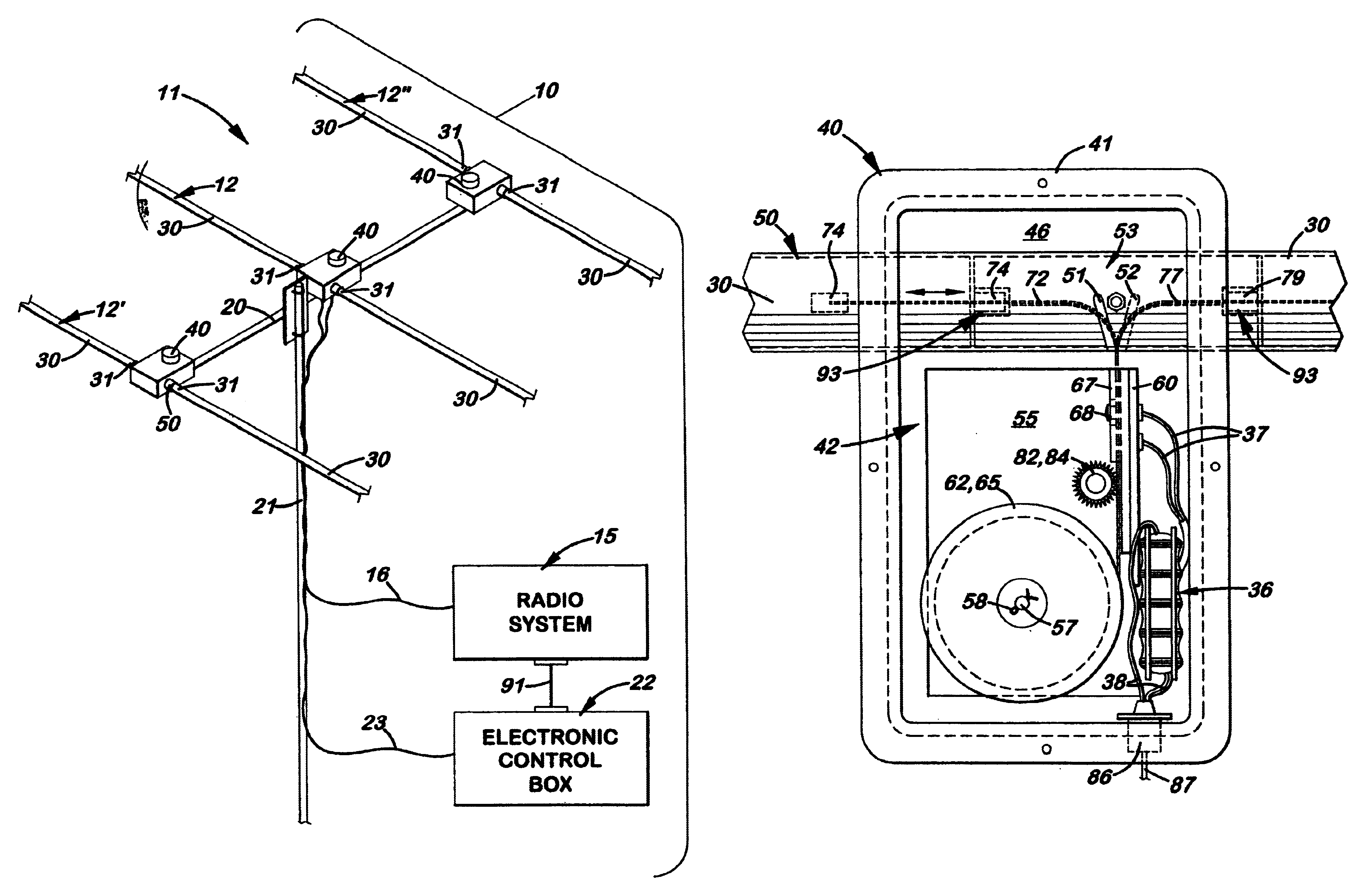
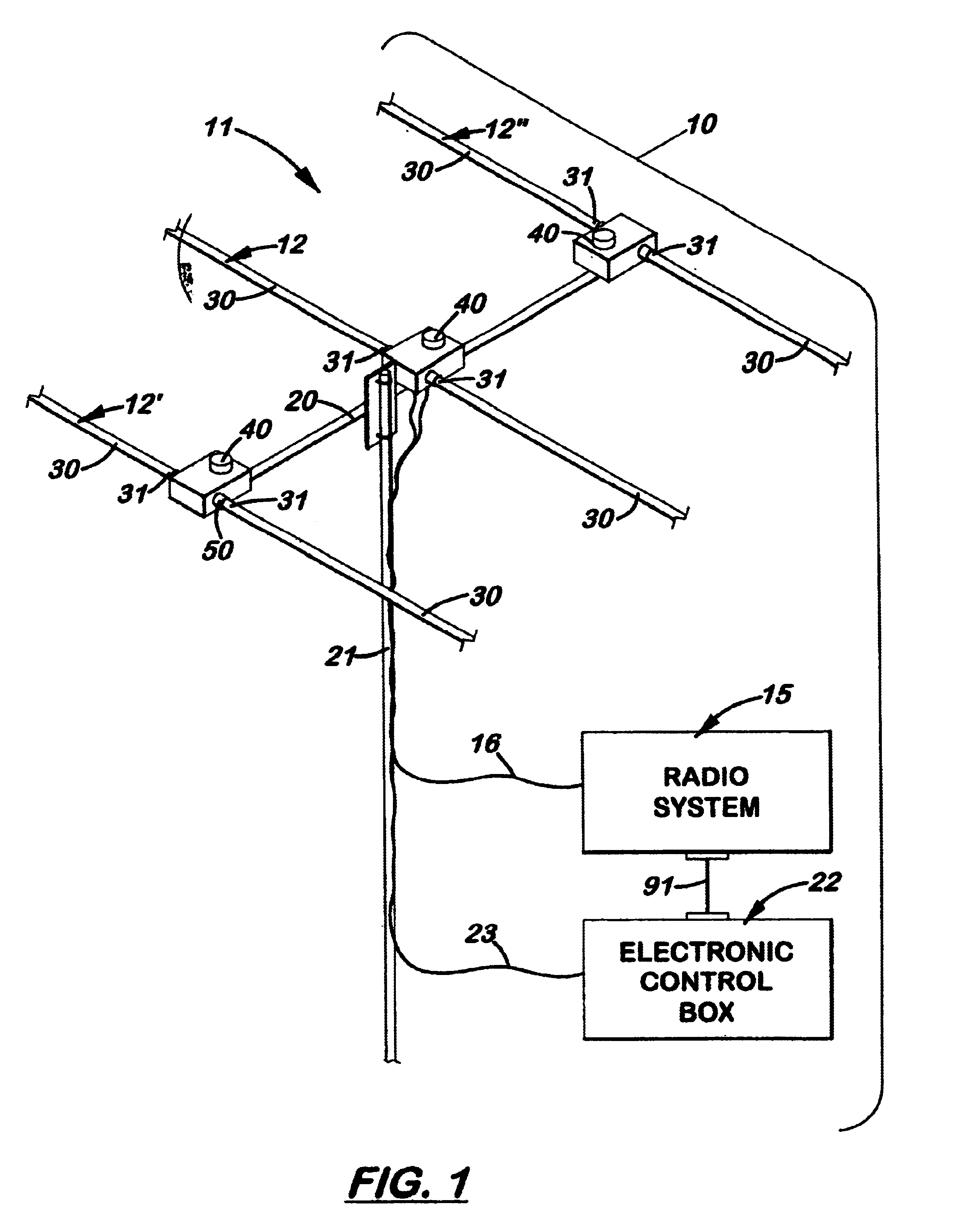
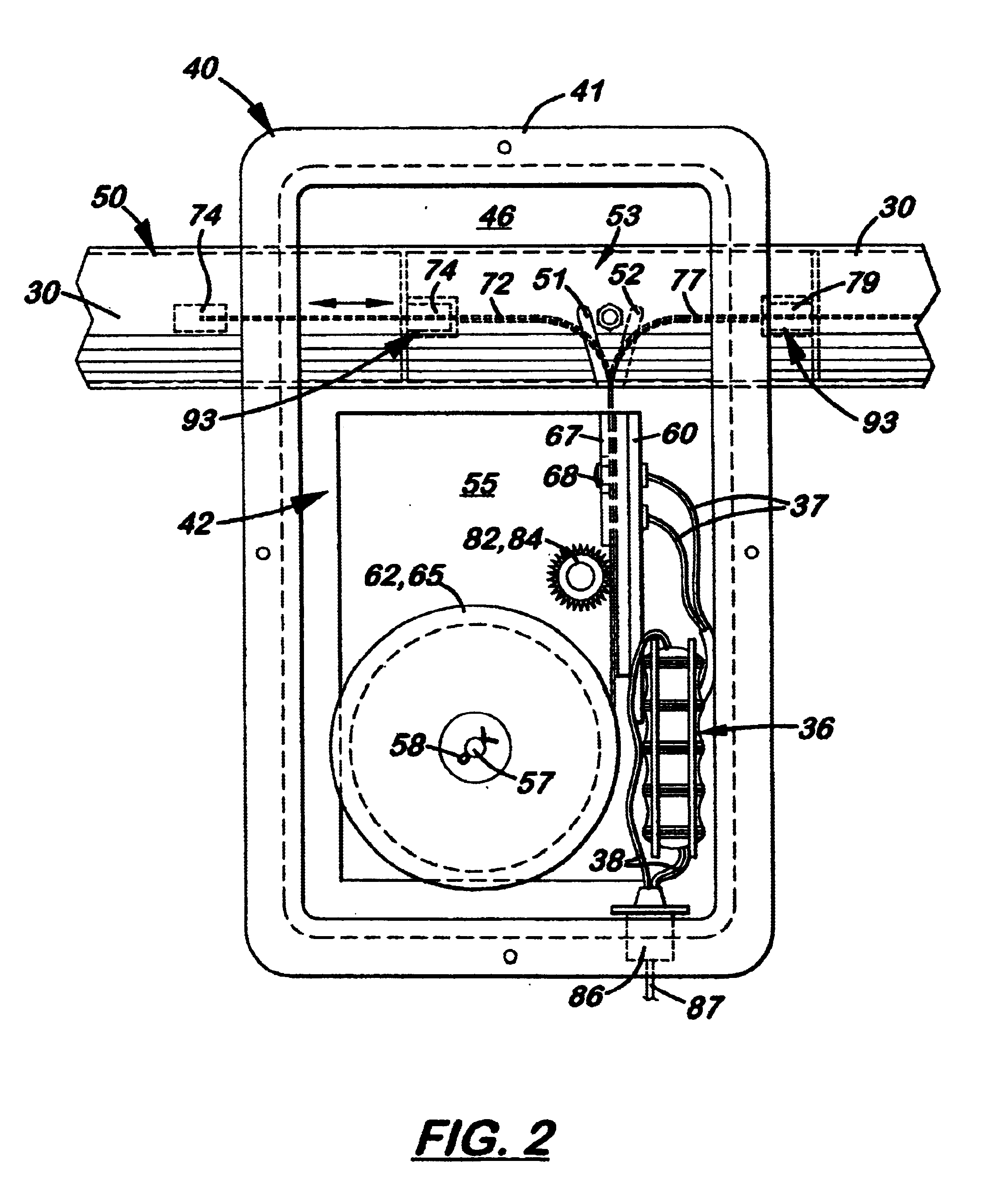
An antenna system with at least one tunable dipole element with a length adjustable conductive member disposed therein that enables the antenna to be used over a wide range of frequencies. The element is made of two longitudinally aligned, hollow support arms made of non-conductive material. Disposed longitudinally inside each element is a length adjustable conductive member electrically connected at one end. In the preferred embodiment, each conductive member is stored on a spool that is selectively rotated to precisely extend the conductive member into the support arm. The support arms, which may be fixed or adjustable in length, are affixed at one end to a rigid housing. During use, the conductive members are adjusted in length to tune the element to a desired frequency. The antenna is especially advantageous when configured as a Yagi-style antenna that can be optimally tuned at a specific frequency for maximum gain, maximum front-to-back ratio, and to provide a desired feed point impedance at the driven element. The antenna can also function as a bi-directional antenna by adjusting the reflector element to function as a director. An electronic control system allows the length of the conductive members to be manually or automatically adjusted to a desired frequency.
Owner:STEPPIR COMM SYST INC
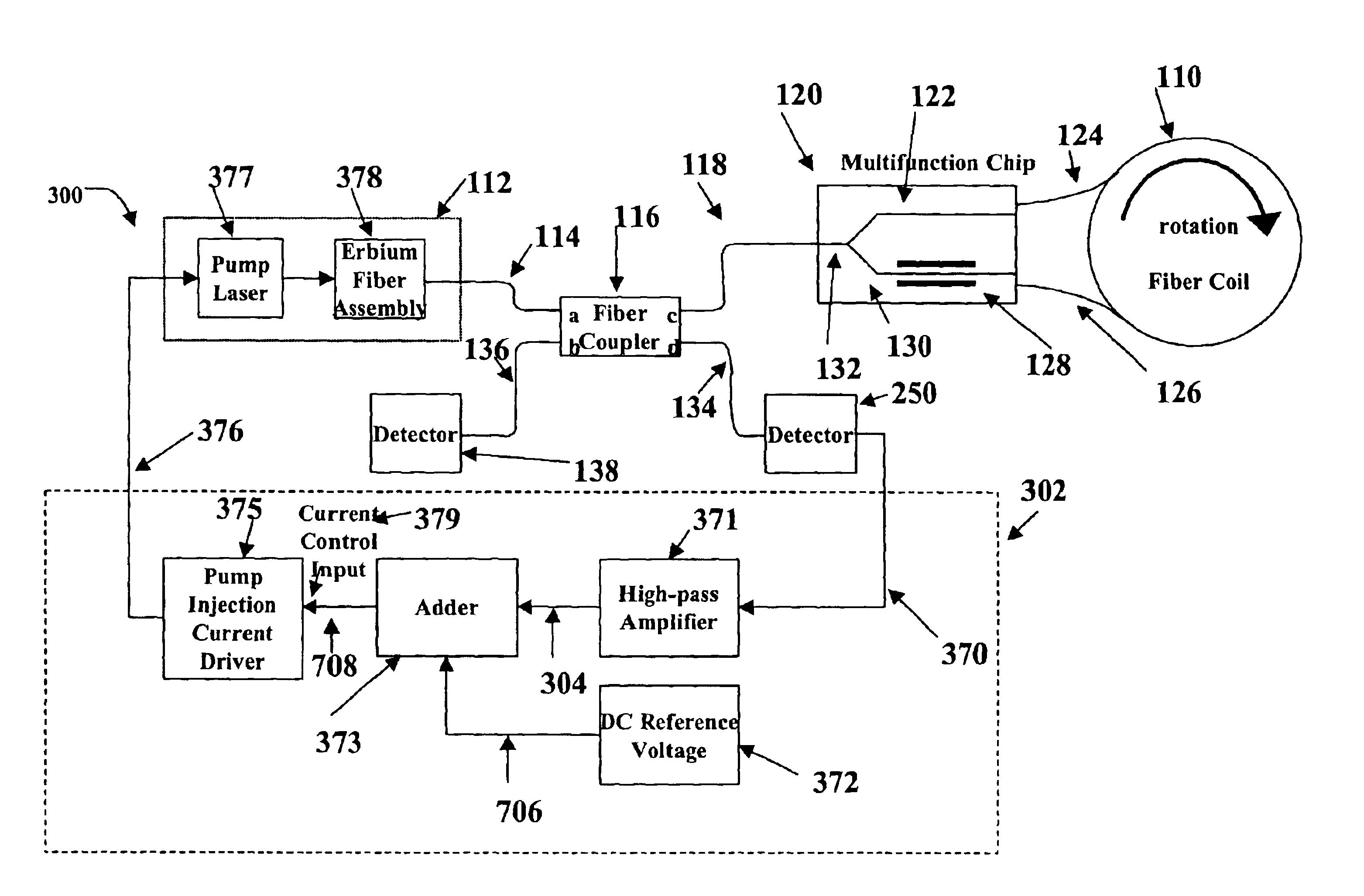
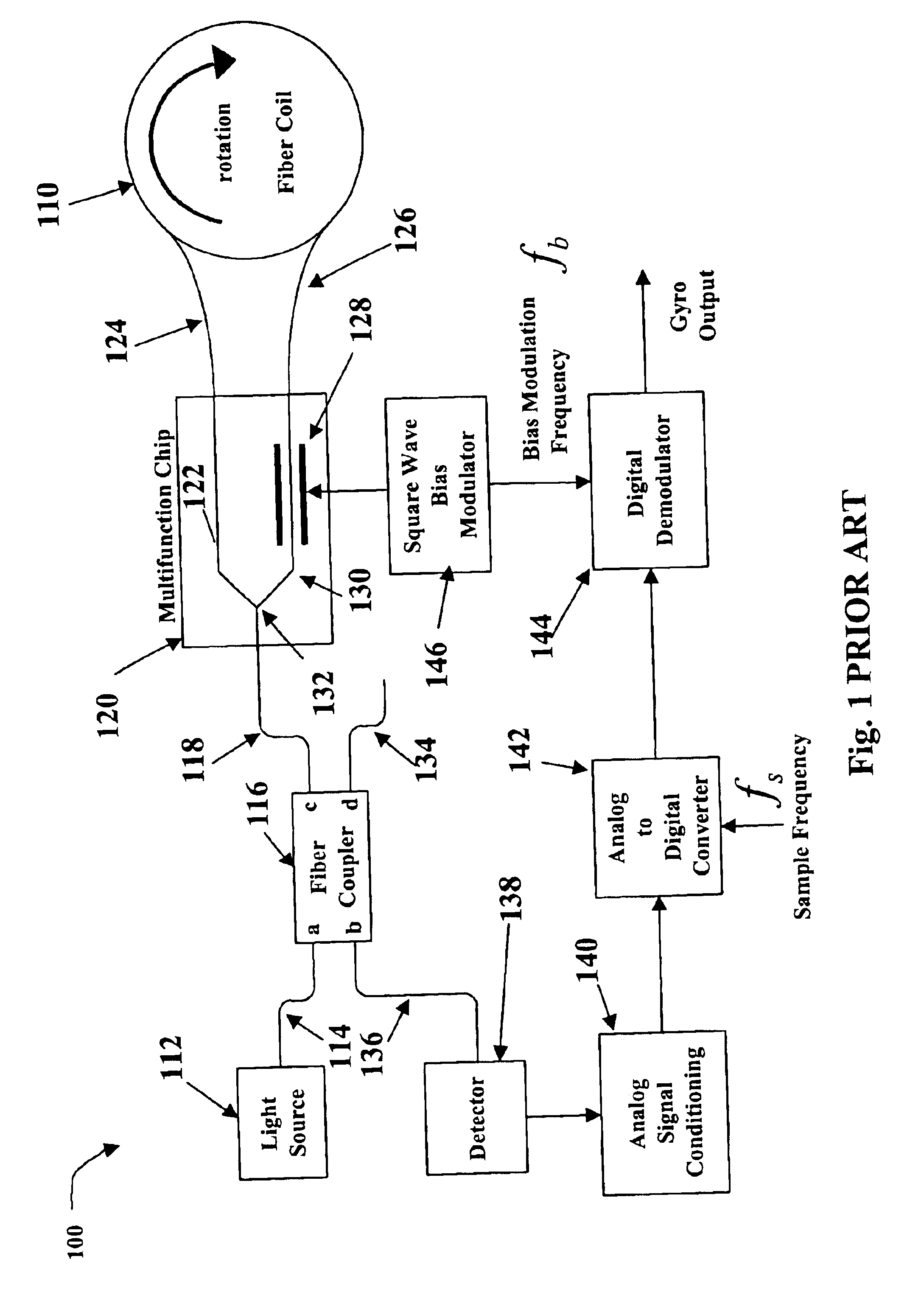
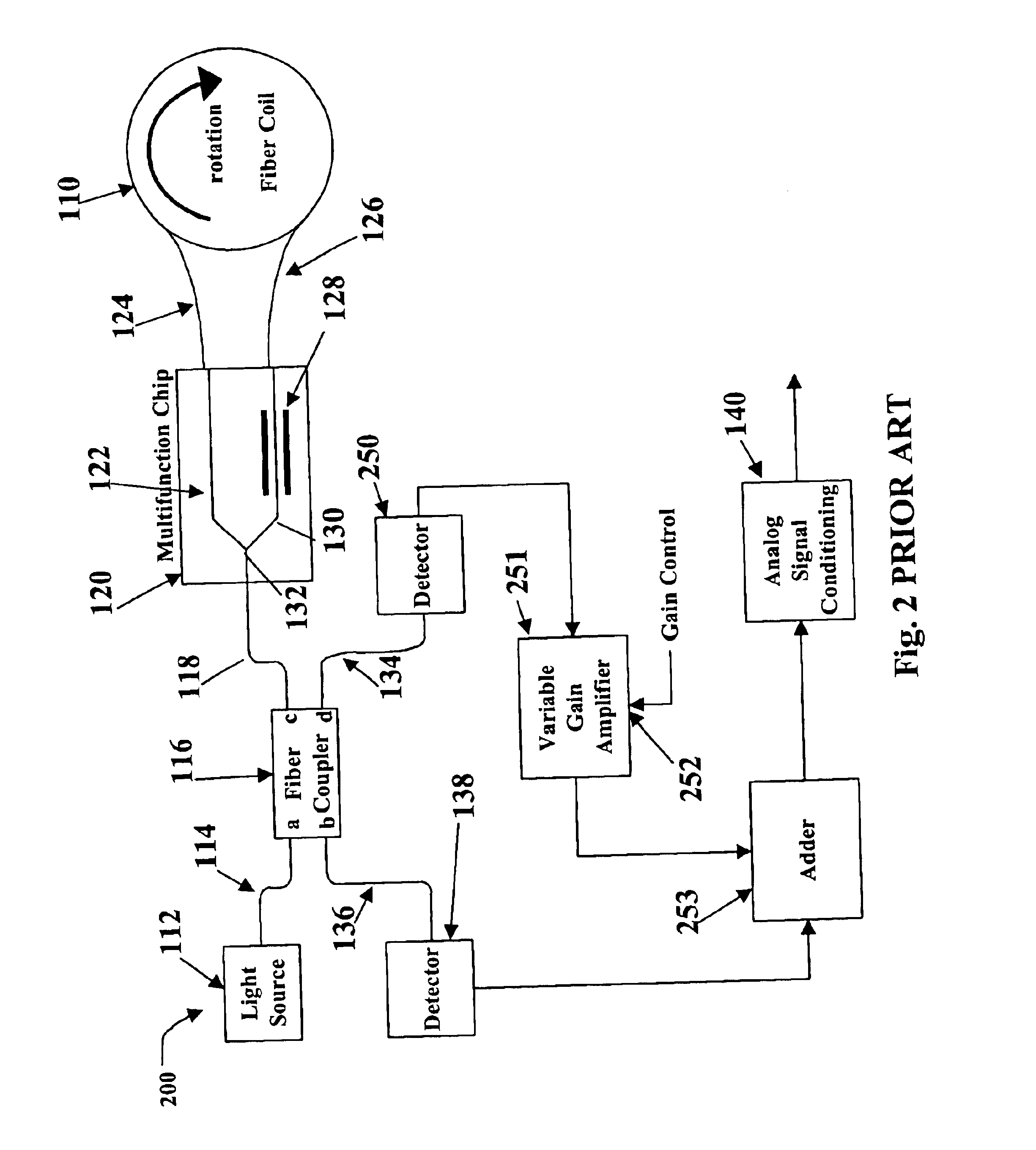
Relative intensity noise controller with maximum gain at frequencies at or above the bias modulation frequency or with second order feedback for fiber light sources
InactiveUS6765678B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberNegative feedback
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
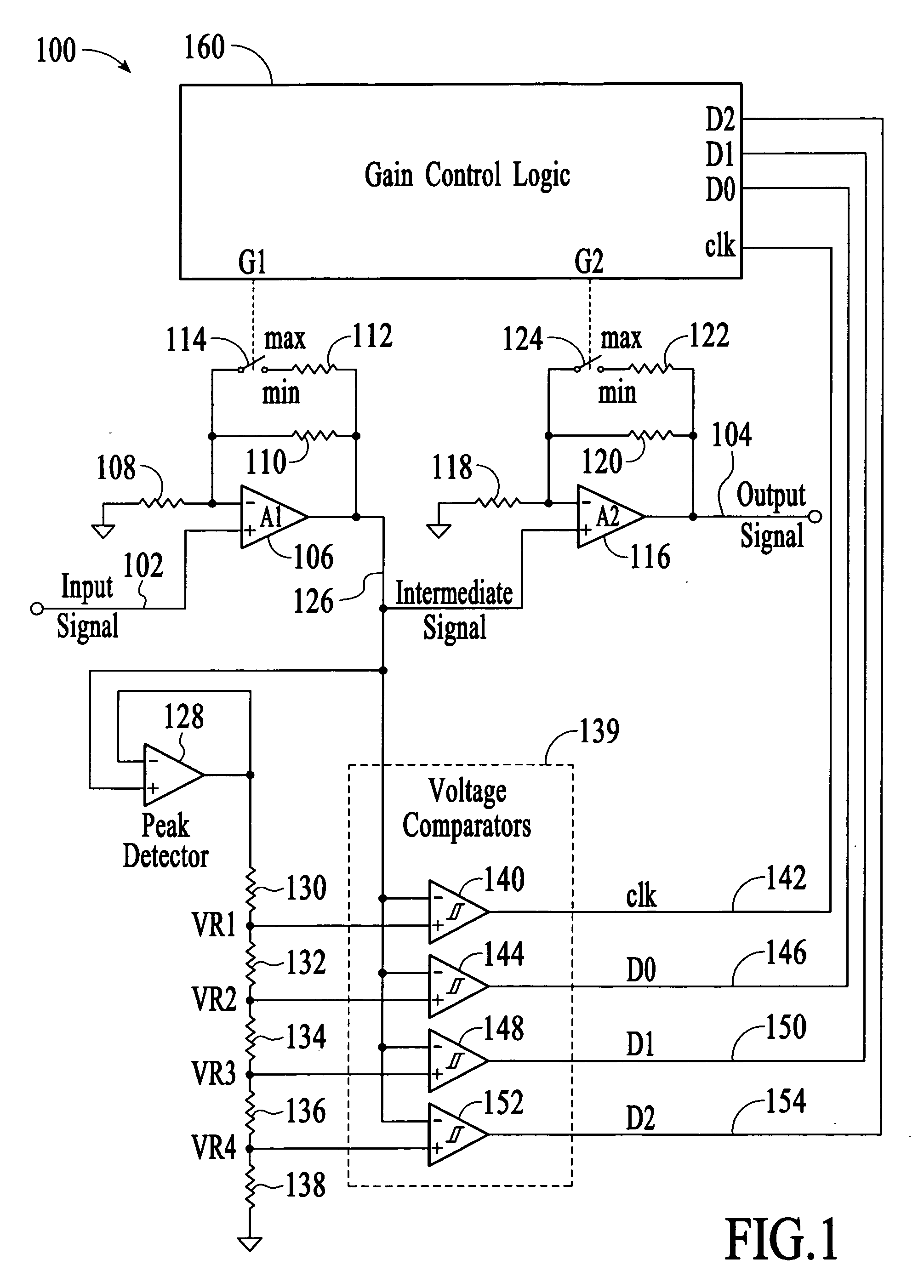
Fast-settling digital automatic gain control
InactiveUS20070139118A1Analog signal digital controlDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A fast-settling digital automatic gain control circuit comprises first and second gain-controllable amplifiers in series. Each amplifier can be digitally switched between minimum and maximum gains by control logic that receives inputs from a multi-level voltage comparator. A peak detector connected to the output of the first gain-controlled amplifier is used to set the overall operating ranges for several threshold detectors. Four reference voltages are generated from the peak detector. The highest reference voltage is used to clock and reset the gain control logic with a hysteresis comparator to the instantaneous input signal from the first gain-controlled amplifier. The three other lower reference voltages are used to provide three-bits of digital input data to the gain control logic. Two digital controls are output, a min / max gain bit for the first gain-controlled amplifier, and a similar min / max gain bit for the second gain-controlled amplifier.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP
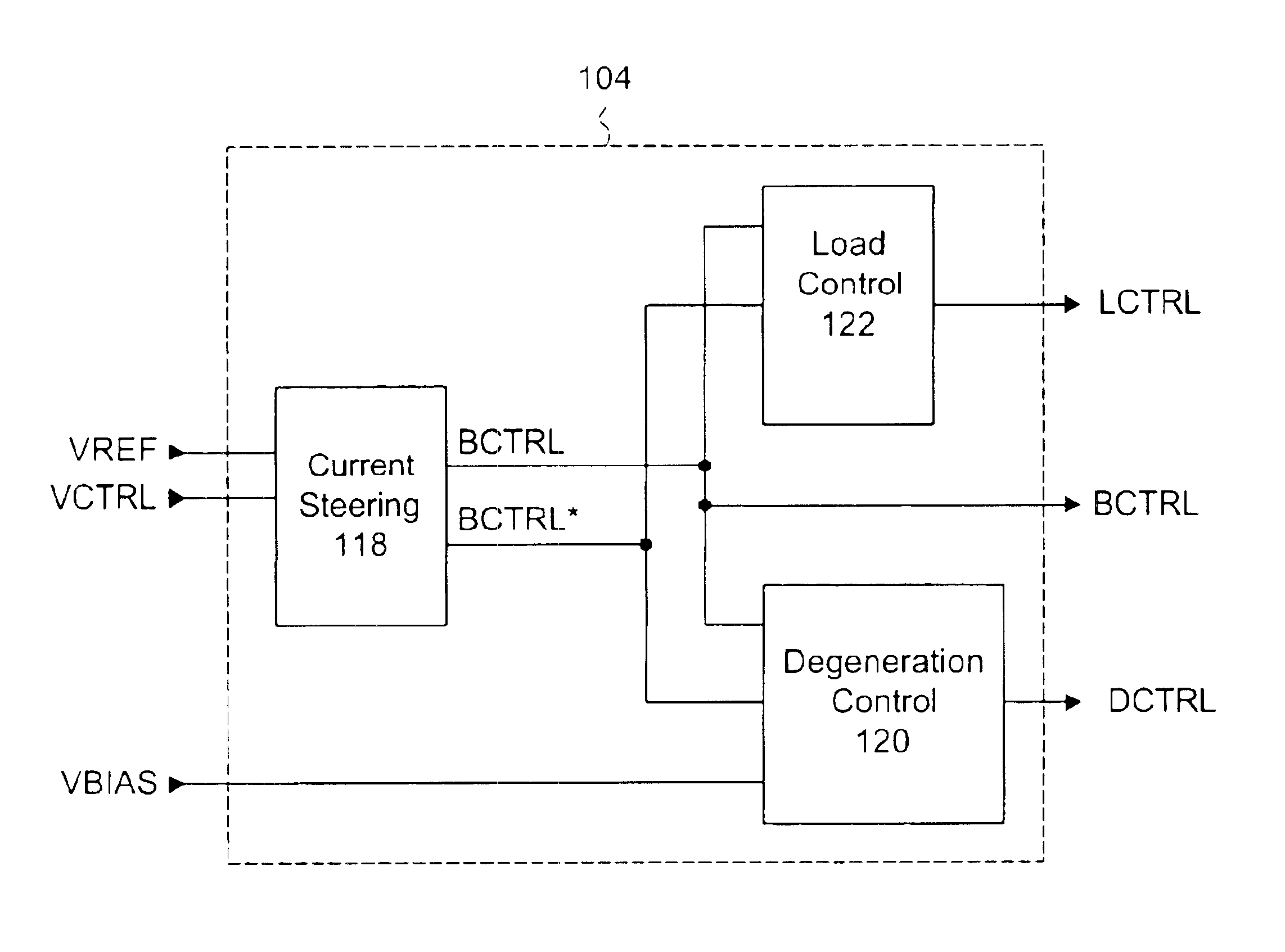
System and method of amplifier gain control by variable bias and degeneration
A gain control circuit that permits a variable gain amplifier circuit to operate with high input linearity and low power consumption is disclosed. The variable gain amplifier includes a standard differential bipolar transistor input circuit and a pair of degeneration transistors connected to a current source transistor. The gain control circuit provides a variable degeneration control voltage to vary the effective resistance of the degeneration transistors and a variable bias voltage to vary the current of the current source transistor. The input linearity of the variable gain amplifier is controlled independently of gain by adjusting the effective resistance and the current in an inverse relationship such that at maximum gain the current is at a maximum while the degeneration resistance is at a minimum, and at minimum gain the current is at a minimum while the degeneration resistance is at a maximum. Therefore the variable gain amplifier can be controlled to operate with high input linearity and low power at lower ranges of gain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
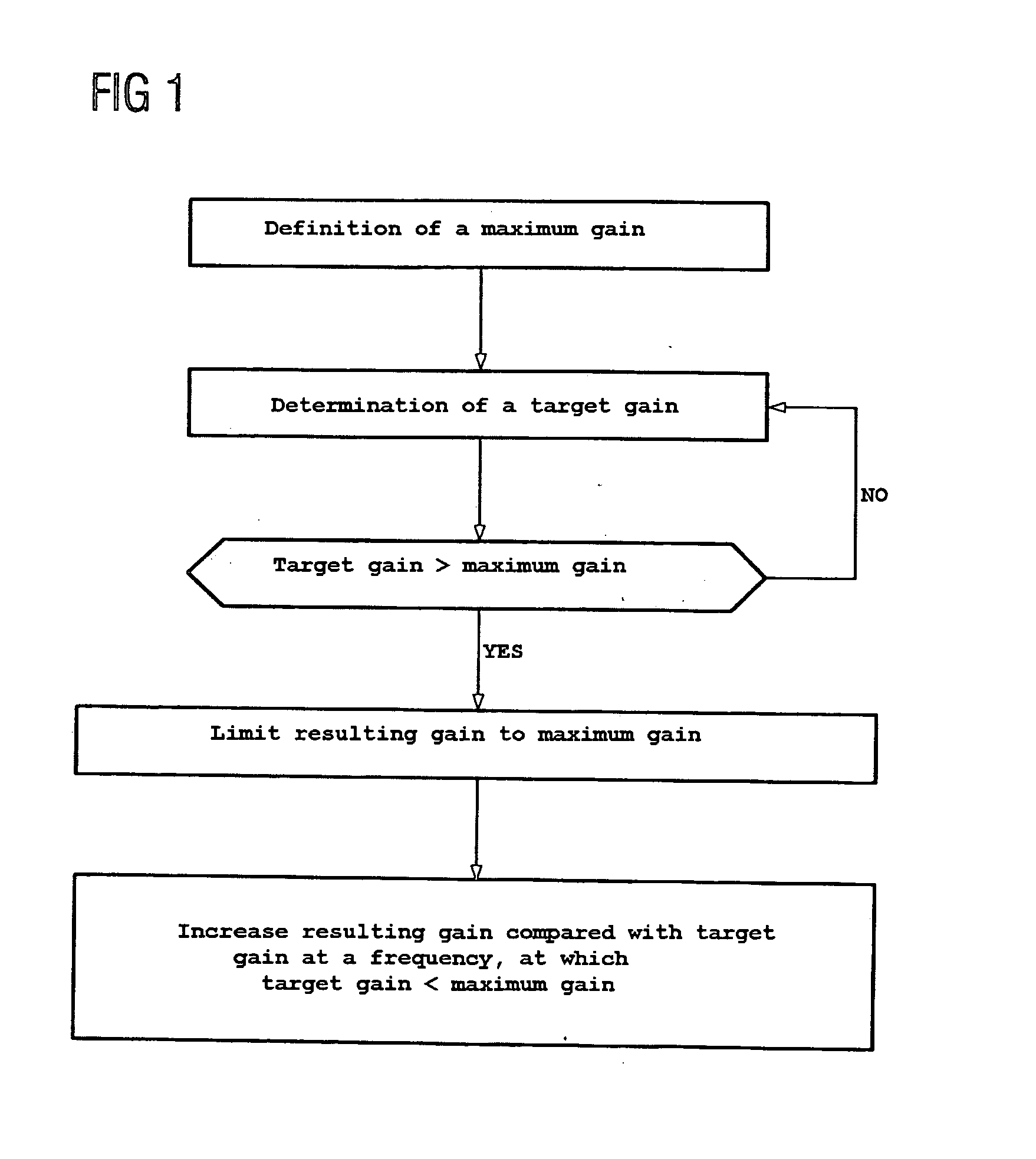
Automatic gain adjustment for a hearing aid device
InactiveUS20060245610A1Improve speech clarityHearing aids signal processingDeaf aid adaptationEngineeringHearing aid
The object of the claimed hearing aid device is to improve the speech intelligibility of a speech signal transmitted by the hearing aid device. To this end provision is made to define a maximum gain of the input signal and to determine a target gain at least at a first and second frequency of an input signal. A resulting gain is set in the hearing aid device, which does not exceed the maximum gain. A reduction of the resulting gain compared with the target gain at the first frequency is compensated for according to the invention by an automatic increase in the set resulting gain compared with the target gain at the second frequency, with compensation preferably being achieved by improving the speech intelligibility of a speech signal transmitted with the aid of the hearing aid device.
Owner:SIEMENS AUDIOLOGISCHE TECHN
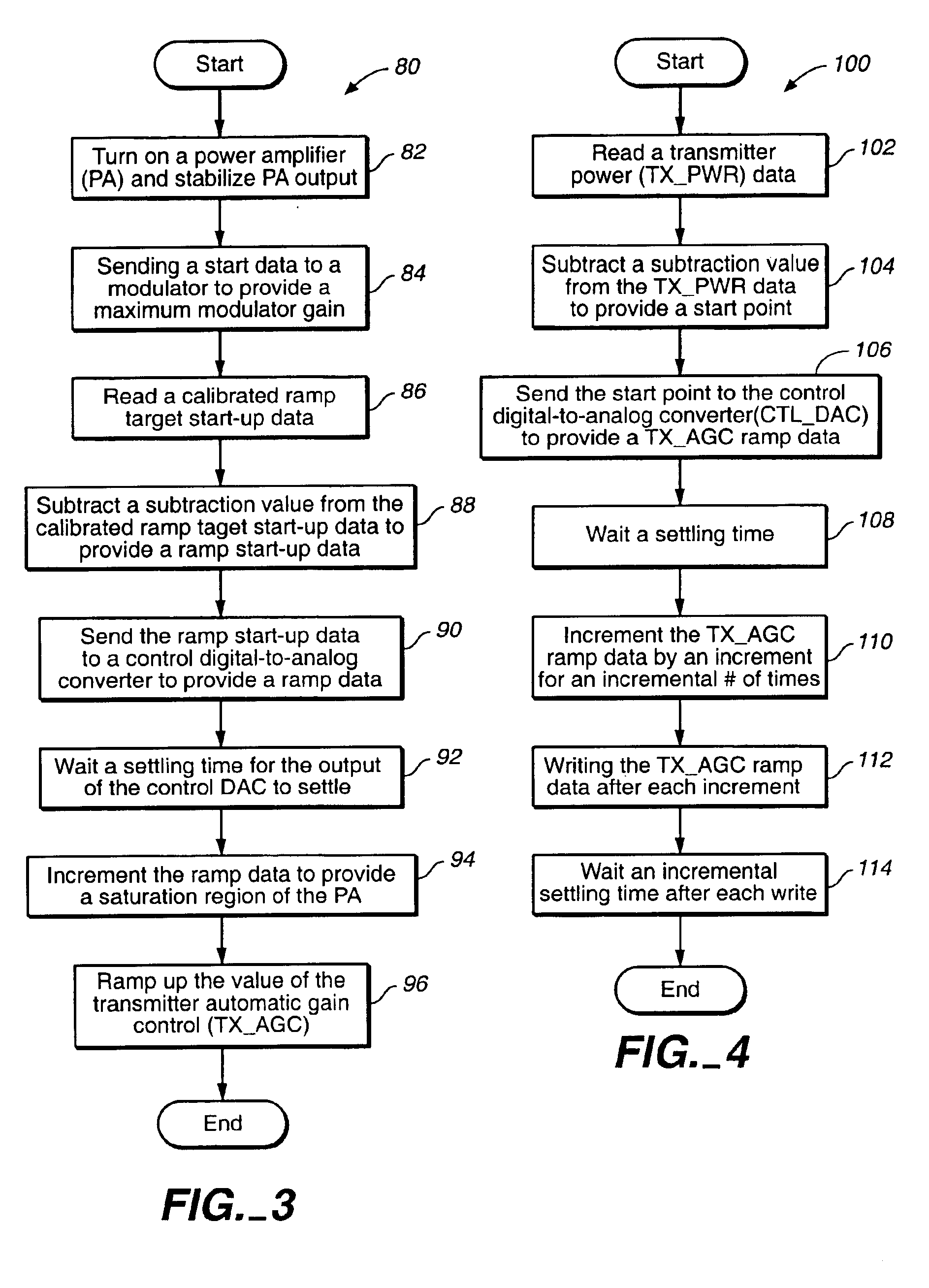
Apparatus and method for power ramp up of wireless modem transmitter
InactiveUS6876697B2Increase intensityEasy to controlResonant long antennasSecret communicationDigital dataModem device
A transmitter of a wireless modem may be ramped up with quicker ramp up times and better splatter control by using software controllable ramp up techniques. A digital data signal source sends data to digital-to-analog converters used to generate a ramp with the desired duration and shape for maximum gain with minimum splatter. A transmitter digital-to-analog converter is sent constant I / Q data to bias the input of the I / Q modulator to maximum gain when combined with a direct current voltage. A controller digital-to-analog converter is sent incremented ramp data to shape the ramp and provide maximum gain at the output of the I / Q modulator.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS
System and method for controlling a power generation system based on a detected islanding event
ActiveUS20150249416A1Dc network circuit arrangementsGenerator control circuitsIslandingControl signal
In one aspect, a method for controlling the operation of a power generation system configured to supply power to an electrical grid may generally include detecting an occurrence of an islanding event associated with the power generation system and adjusting a regulator gain applied within a regulator of the power generation system to an islanding gain value in response to the detection of the islanding event, wherein the islanding gain value exceeds a maximum gain value defined for the regulator in the event of an occurrence of any ride-through transient event. In addition, the method may include controlling a power converter of the power generation system based on a control signal generated by the regulator as the power generation system is being isolated from the electrical grid and shutting down the power generation system upon isolation of the power generation system from the electrical grid.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
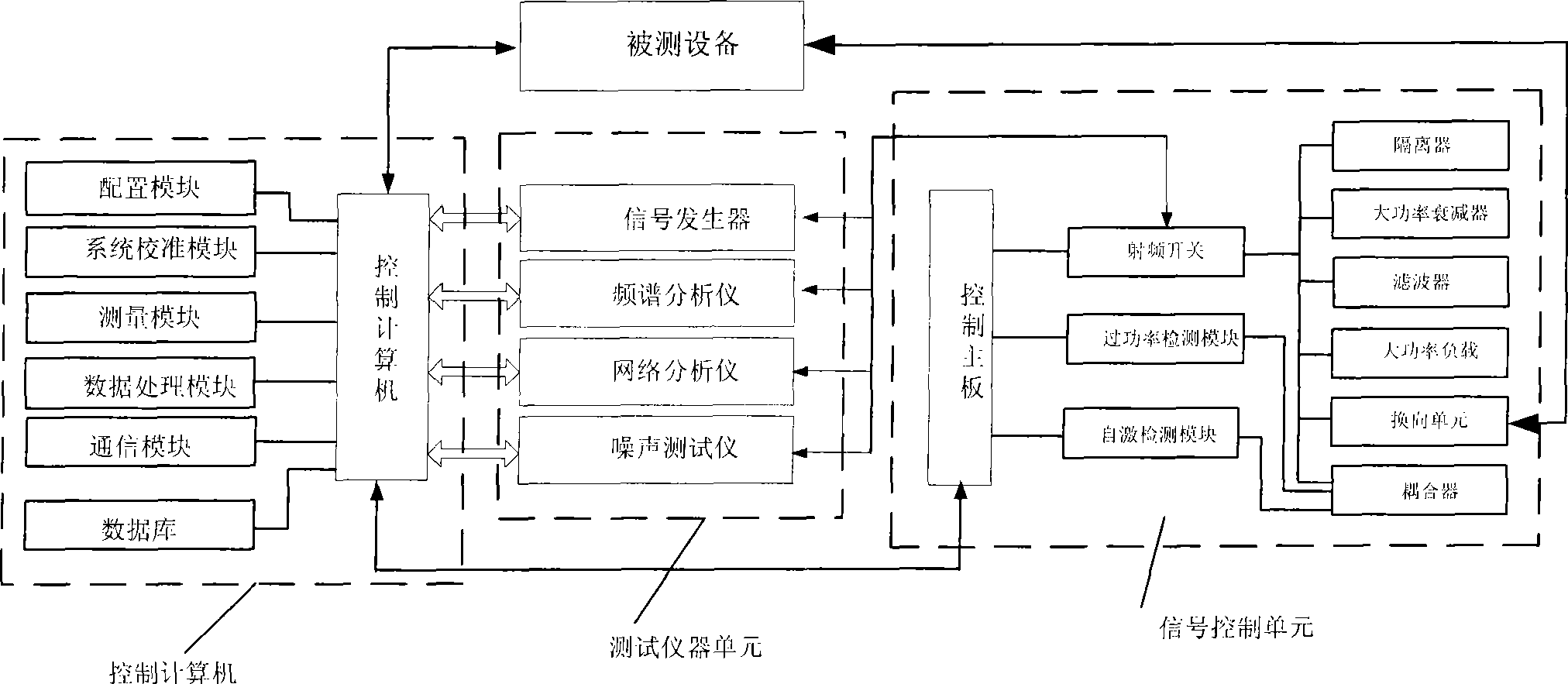
Detection system for repeater product radio frequency performance, and detection method thereof
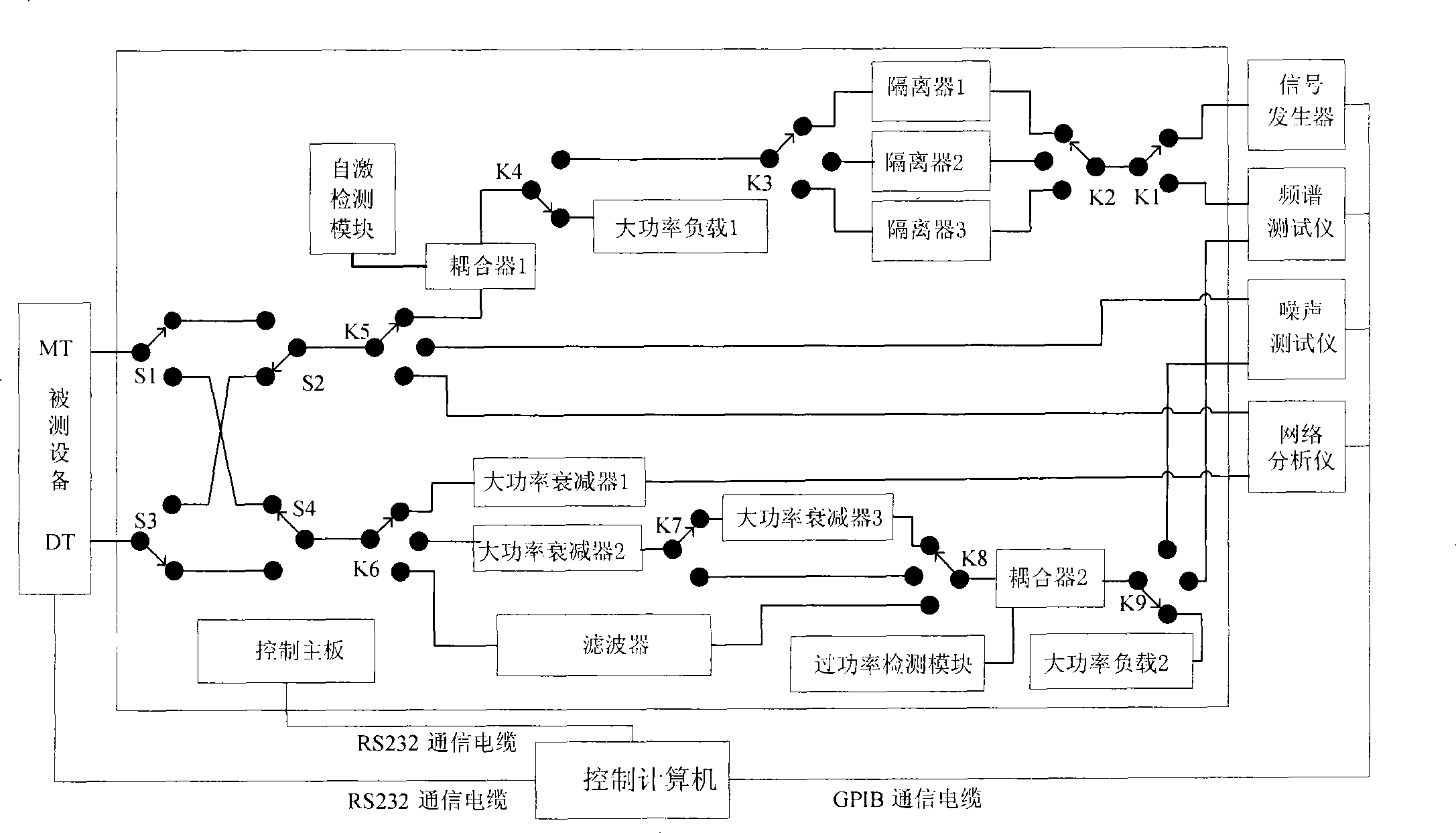
InactiveCN101453276AQuick testTest accurateTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTest performanceEngineering
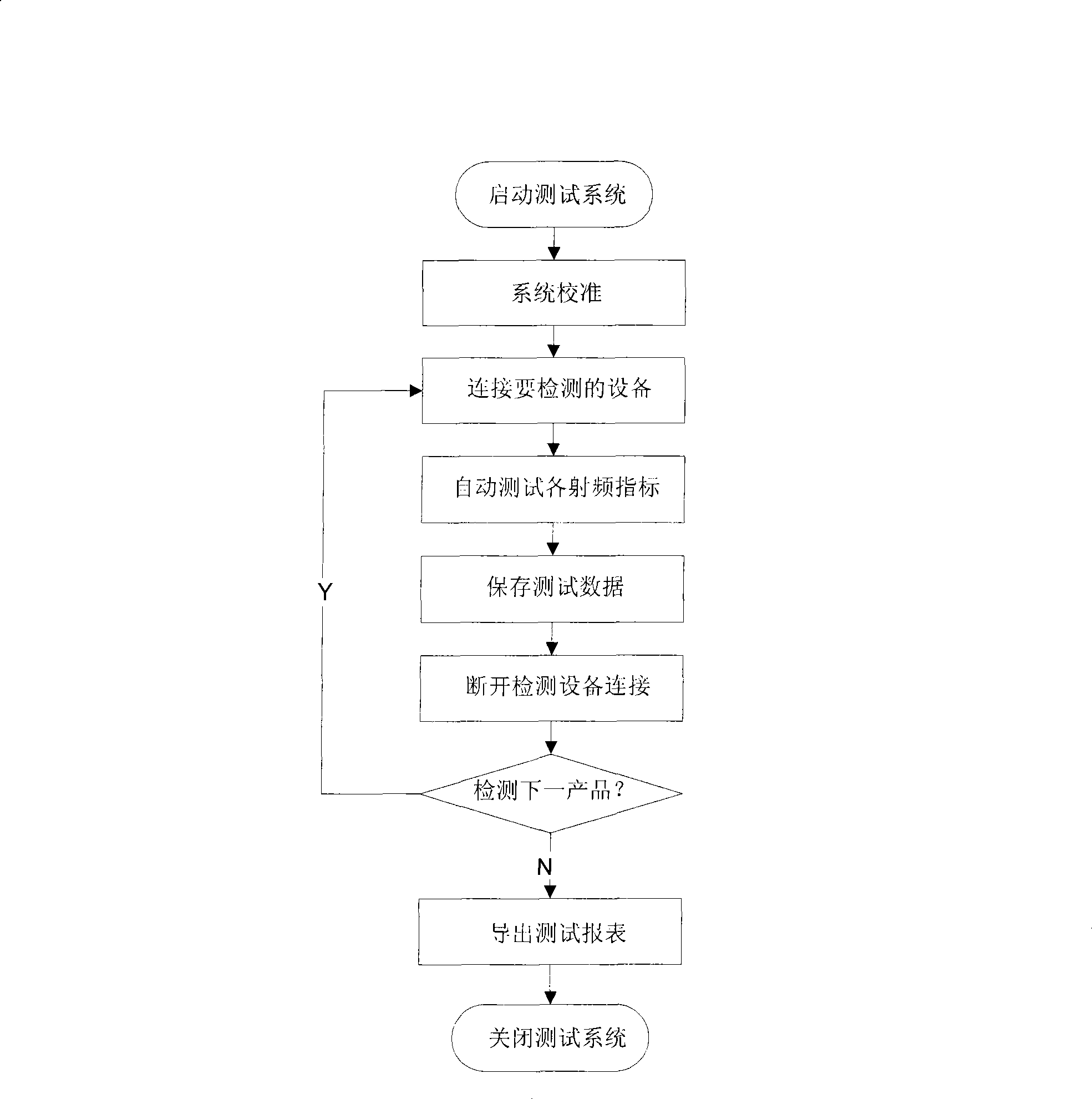
The invention discloses a detection system for radio frequency performance of a repeater product, which comprises a control computer, a testing instrument unit, a signal control unit and tested equipment. The control computer is respectively connected with the testing instrument unit, the signal control unit and the tested equipment through communication cables, and is also connected with a printer through a data wire. A method for realizing the detection system comprises the steps of starting the detection system, calibrating the system, connecting the tested equipment, automatically testingvarious radio frequency indexes, saving test data, disconnecting the tested equipment, performing system inquiry, exporting a test report form, closing the detection system and so on. The detection system can automatically, accurately and quickly test performance indexes of the repeater product such as maximum gain, output power, in-band fluctuation, noise factor, transmission time delay and so on, and form a report form with a unified form to be convenient for the maintenance and management of engineering personnel.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST (GUANGZHOU) LTD
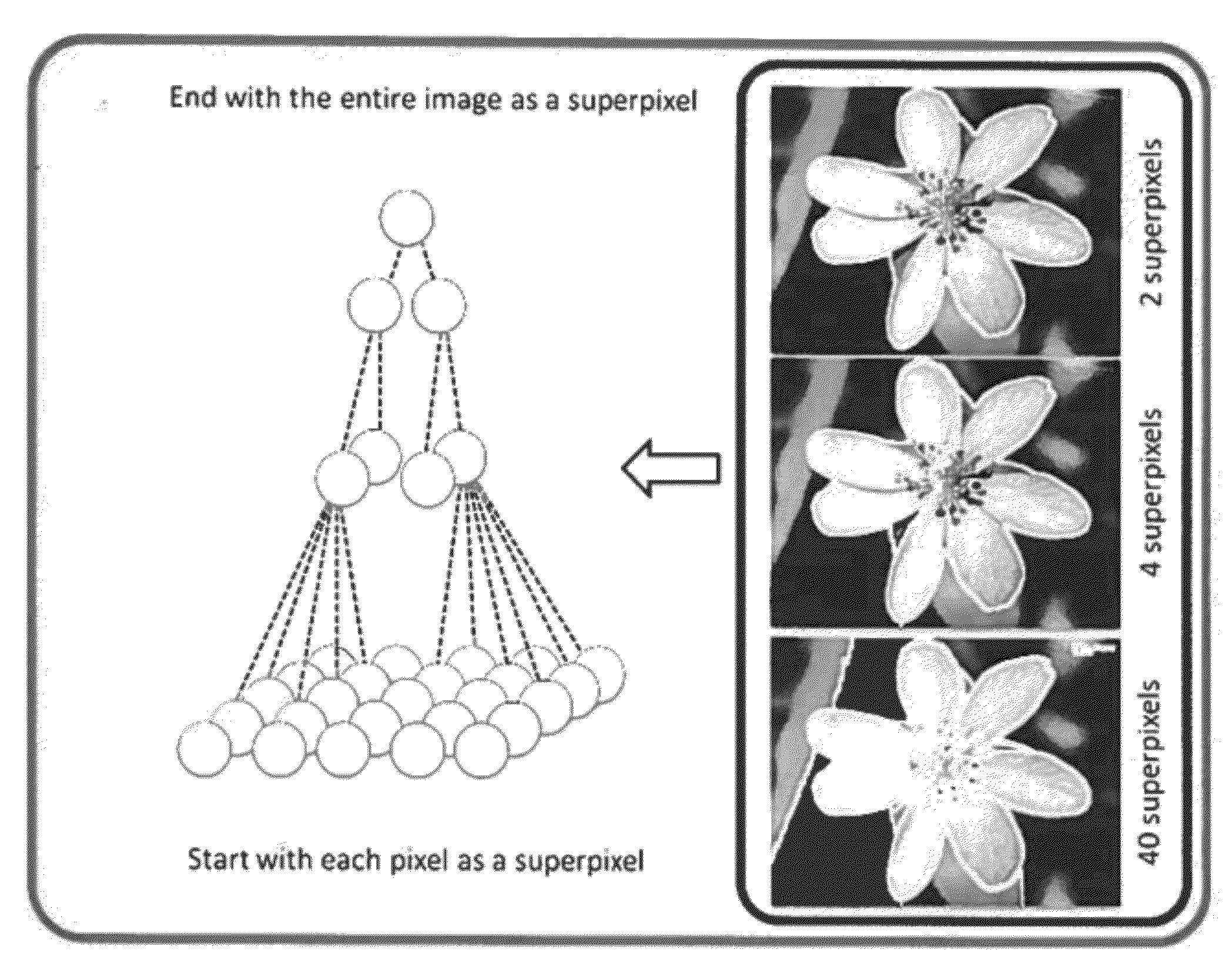
Method for Segmenting Images Using Superpixels and Entropy Rate Clustering
An image is segmented into superpixels by constructing a graph with vertices connected by edges, wherein each vertex corresponds to a pixel in the image, and each edge is associated with a weight indicating a similarity of the corresponding pixels, A subset of edges in the graph are selected to segment the graph into subgraphs, wherein the selecting maximizes an objective function based on an entropy rate and a balancing term. The edges with maximum gains are added to the graph until a number of subgraphs is equal to some threshold.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Technique for accurate estimate of large antenna inertial two dimensional orientation using relative GPS spatial phase
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Video input processor, imaging signal-processing circuit, and method for reducing noises in imaging signals
InactiveCN101309360ATelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceRelative magnitudeNoise reduction
A video input processor is disclosed. The processor includes: an imaging signal-generating portion configured to image a subject and producing first imaging signals containing visible light components and a second imaging signal containing near-infrared light components; a gain adjustment portion configured to adjustably set a maximum gain value according to a relative magnitude between the visible light components and the near-infrared light components and adjust a gain for the first imaging signals at the set maximum gain value; and a noise reduction portion configured to reduce noises in the first imaging signals after the gain has been adjusted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Band pass filter
InactiveUS7081788B2Easily variableOscillations generatorsTransmissionBandpass filteringCenter frequency
A band pass filter includes a first band pass filter constructed of a biquad circuit and having a first center frequency, and a second bandpass filter constructed of a biquad circuit and having a second center frequency different from the first center frequency, and the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter are series connected, in which the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter have center frequency adjusting variable resistors varied at the same time, and a fixed resistor is connected in parallel to the center frequency adjusting variable resistor of one of the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter. As a result, the center frequency and / or the maximum gain can be made variable while the band width is fixed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Wireless LAN technologies for reducing interference between or among wireless LAN access points
InactiveUS20070191068A1Reduce distractionsIncrease contact areaSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTelecommunicationsDirectional antenna
A wireless LAN technology for reducing interference between (or among) wireless LAN access points is provided. A wireless LAN access point is provided with a directional antenna, an interference detector detecting interference effected by another wireless LAN access point on the directional antenna, and a direction adjusting mechanism adjusting a maximum gain direction of the directional antenna in response to the detected interference.
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
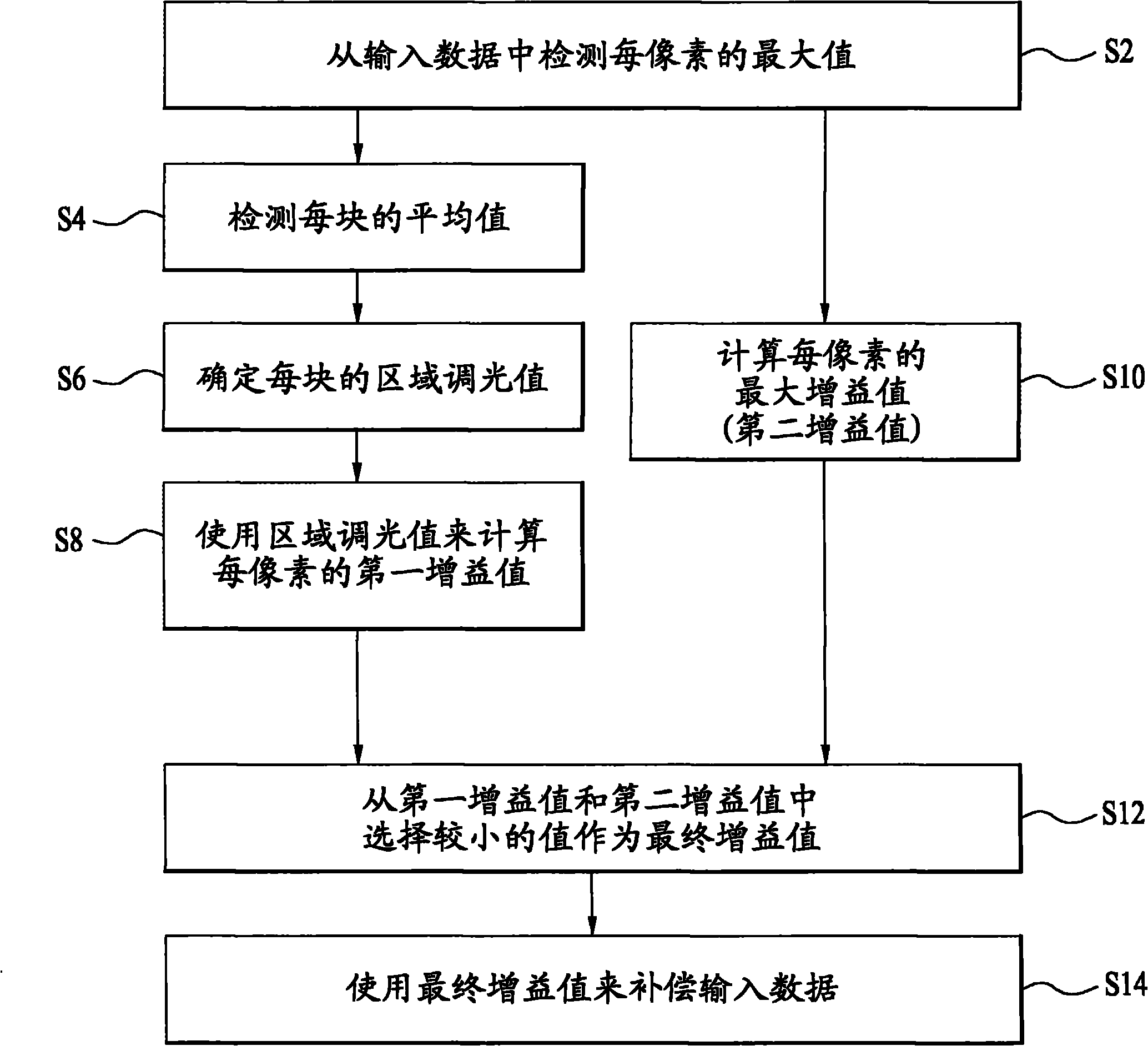
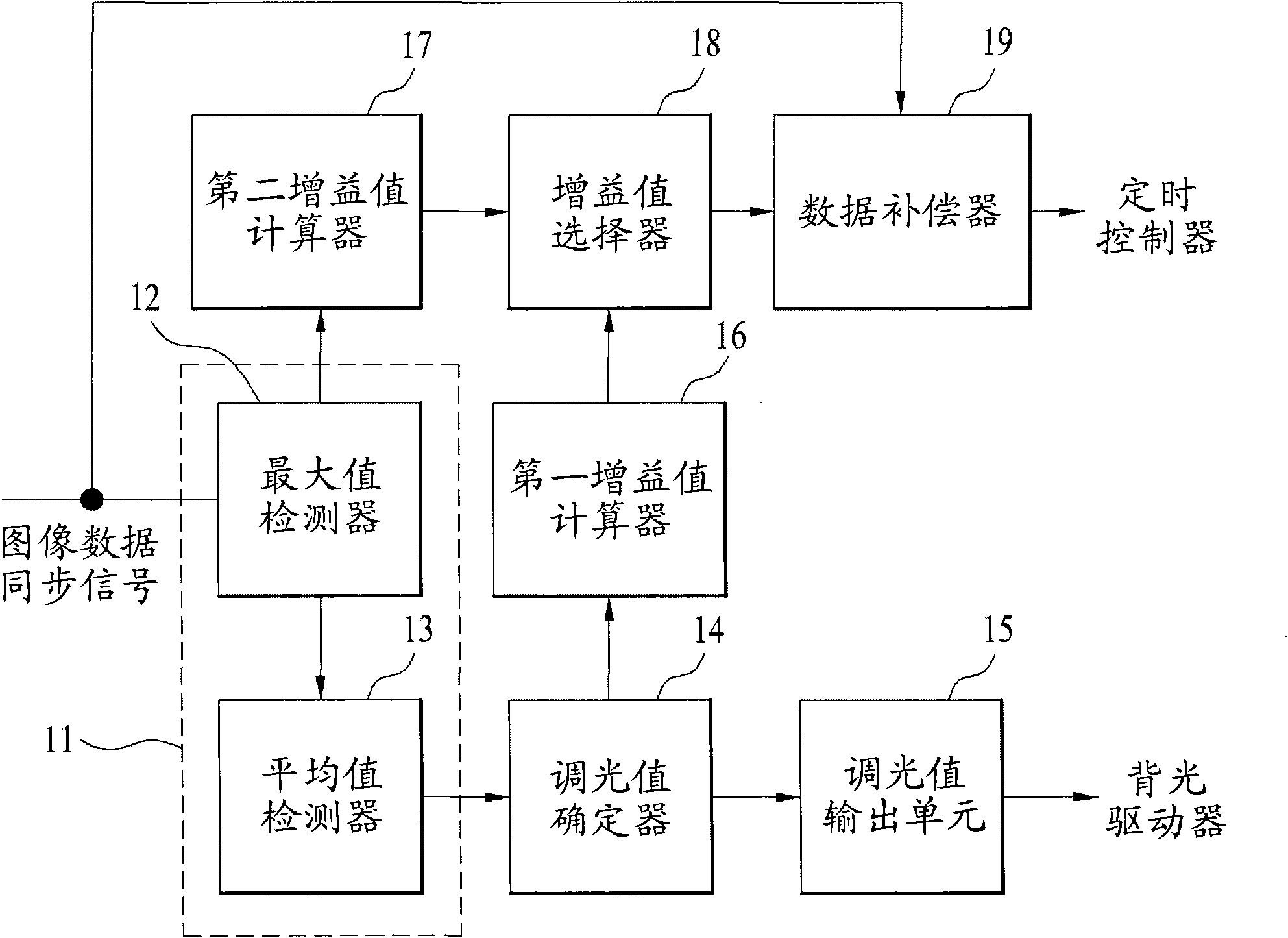
Local dimming driving method and device of liquid crystal display device
InactiveCN102097068AAvoid color changesStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayColor changes
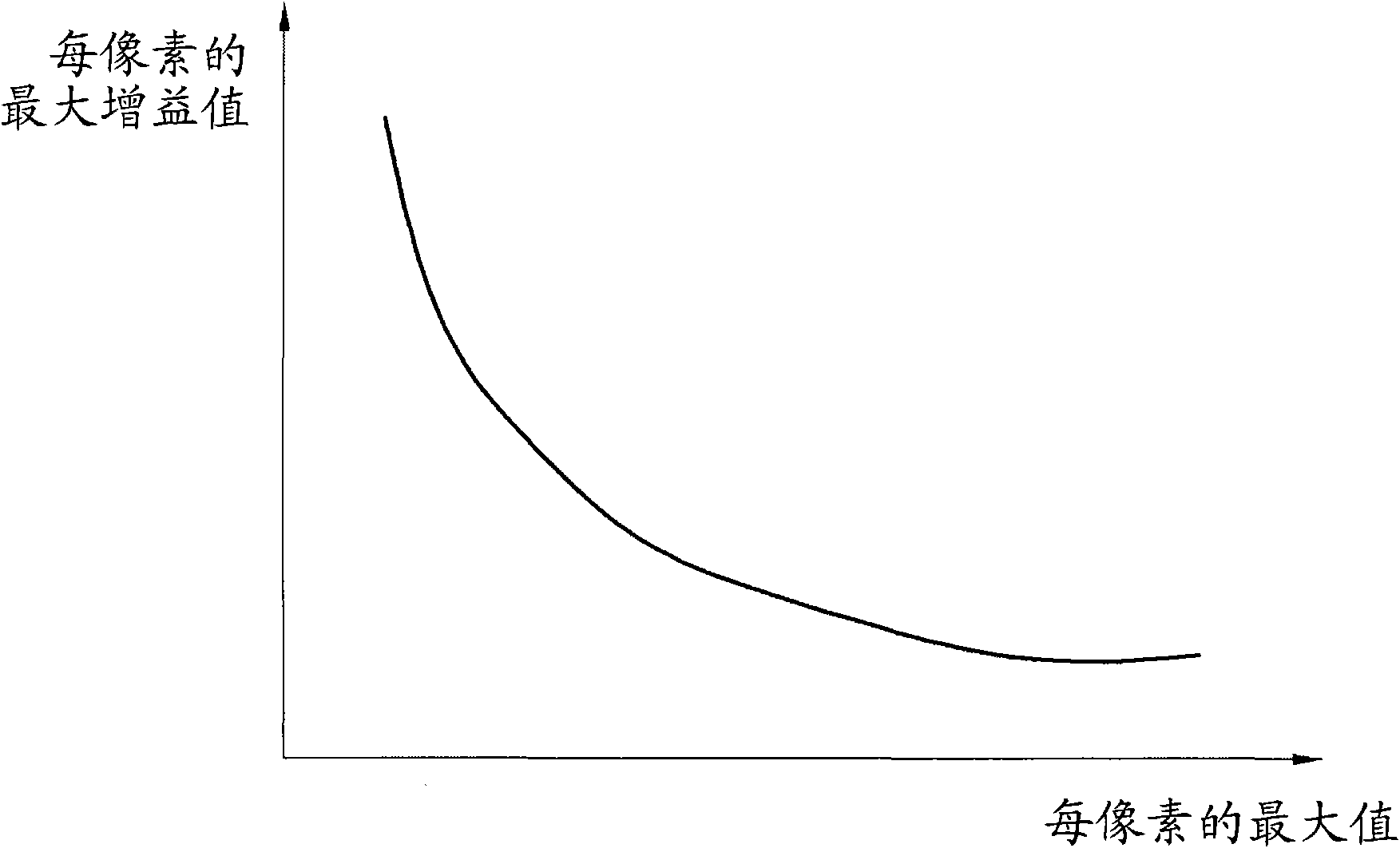
The invention relates to a locak dimming driving method and device of liquid crystal display device. Disclosed herein is the local dimming driving method and device of the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) device, which is capable of preventing color change due to gray scale saturation when data is compensated while enabling local dimming. The local dimming driving method of the LCD device includes detecting maximum values per pixel from input image data, analyzing the maximum values per pixel on a block-by-block basis, and determining local dimming values per block according to the analysis result, calculating a first gain value using the local dimming values per block, calculating a maximum gain value per pixel using the maximum value per pixel as a second gain value, selecting a smaller value of the first and second gain values as a final gain value, compensating the input image data using the final gain value, and controlling luminance of a backlight unit on the block-by-block basis using the local dimming value per block.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
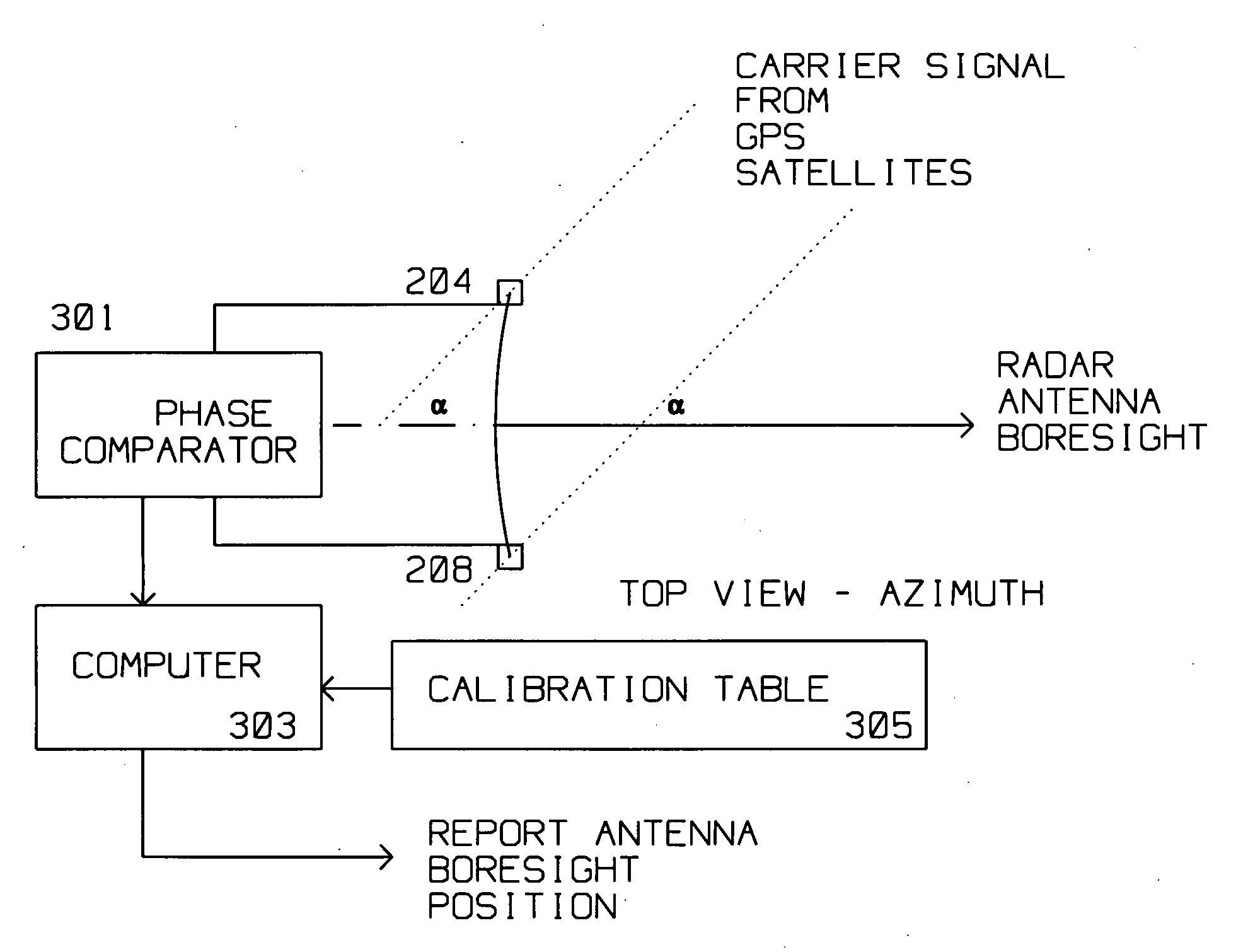
Technique for accurate estimate of large antenna inertial two dimensional orientation using relative GPS spatial phase
A radar antenna has a reflector and maximum gain along its boresight. The reflector has a periphery, typically circular, rectangular or elliptical. A plurality of Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite signal receiving antennas are rigidly, mechanically attached to the reflector near its periphery. The plurality of GPS satellite signal receiving antennas are connected pairwise to a phase comparator for comparing a plurality of first phase differences induced by a first GPS satellite signal received concurrently between the plurality of GPS satellite signal receiving antennas. A Phase comparator measures the phase difference of the signal received at GPS satellite signal receiving antennas pairwise thus performing a differential phase measurement. This differential phase measurement is supplied to a computer for identifying an ambiguous boresight position using the phase differences measured by the phase comparator. The position of the GPS satellites is known with respect to the geo-location of the antenna. Thus, the boresight angle is derived from the phase difference of the carrier signal from the GPS satellite being received and the mechanical alignment information between the GPS satellite receiving antennas and radar antenna boresight stored during calibration / manufacture of the radar antenna. The ambiguity in the computed boresight position is resolved by making differential phase readings using the same GPS antennas from a second GPS satellite signal supplied by a second satellite.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Array antenna pattern time domain measurement method
InactiveCN102854401AShorten test timeFacilitate precise synthesisAntenna radiation diagramsDigital signal processingTime domain
An array antenna pattern time domain measurement method belongs to the technical field of antennas, and comprises the following steps: measuring the patterns of array antenna units firstly, irradiating the array units from different angles (theta and Phi) by uniform plane waves, measuring the transient state responses of the array units under the irradiation of the plane waves by a digital oscilloscope, normalizing the transient state responses to obtain patterns of the array units under the conditions of uniform amplitude and cophase excitation, and synthesizing the array pattern through adopting a digital signal processing technology and a superposition principle of the patterns of the array antenna unit finally. The array antenna pattern time domain measurement method has the advantages that (1) the array pattern is beneficial for the precise synthesis under the array circumstance; (2) the patterns of the array units under the random given excitation can be measured; and (3) the array scanning grain pattern can be synthesized so as to be more beneficial for obtaining the maximum gain distribution area and the scanning blind point distribution area. The array antenna pattern time domain measurement method has the characteristics of simplicity in operation and high testing efficiency, and reduces the site requirement and the testing cost at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
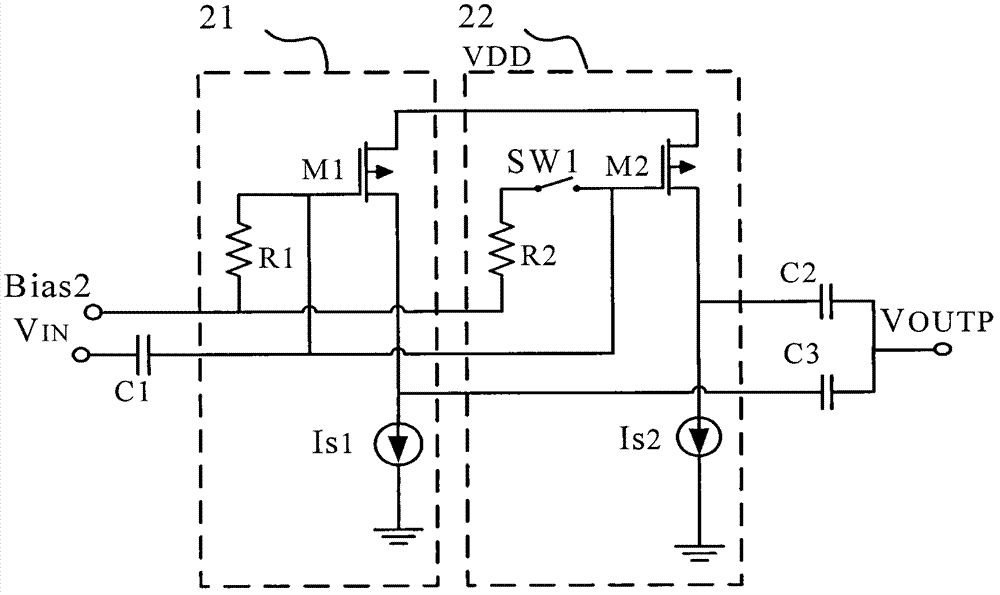
Single ended differential gain amplifier with configurable radio frequency broadband gain
ActiveCN102790595AAchieve amplified outputStrong interference signal suppressionGain controlDifferential amplifiersControl signalMultiple modes
The invention discloses a single ended differential gain amplifier with a configurable radio frequency broadband gain. The gain amplifier comprises a single ended differential circuit with a configurable gain, a broadband amplifying circuit with the configurable gain and a buffer driving circuit with the configurable gain which are sequentially connected in series. Gain control ends of the circuits are connected with a gain control signal from an outer digital base band processing module to form a gain value of the single ended differential gain amplifier with the configurable radio frequency broadband gain in combination, according to the control of each circuit at a set fixed step pitch, fine adjustment on the gain is implemented, thus a range of the broadband signal output by the differential conforms to a range value of a set signal, and strong disturbance is effectively restrained. Since the strong detection and processing capability of a digital processing module chip of the outer base band is good for a gain control mode, the gain control is enabled not to be affected from temperature, process, noise and the like, and more precise and flexible control can be realized. The control range of the gain is a summation of the maximum gain control ranges of the three circuits with the configurable gains, so that the gain amplifier is suitable for application of the high dynamic input with strong disturbance or weak signal, and is suitable for a radio frequency chip with multiple frequencies and multiple modes of a single ended broadband radio frequency signal input.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
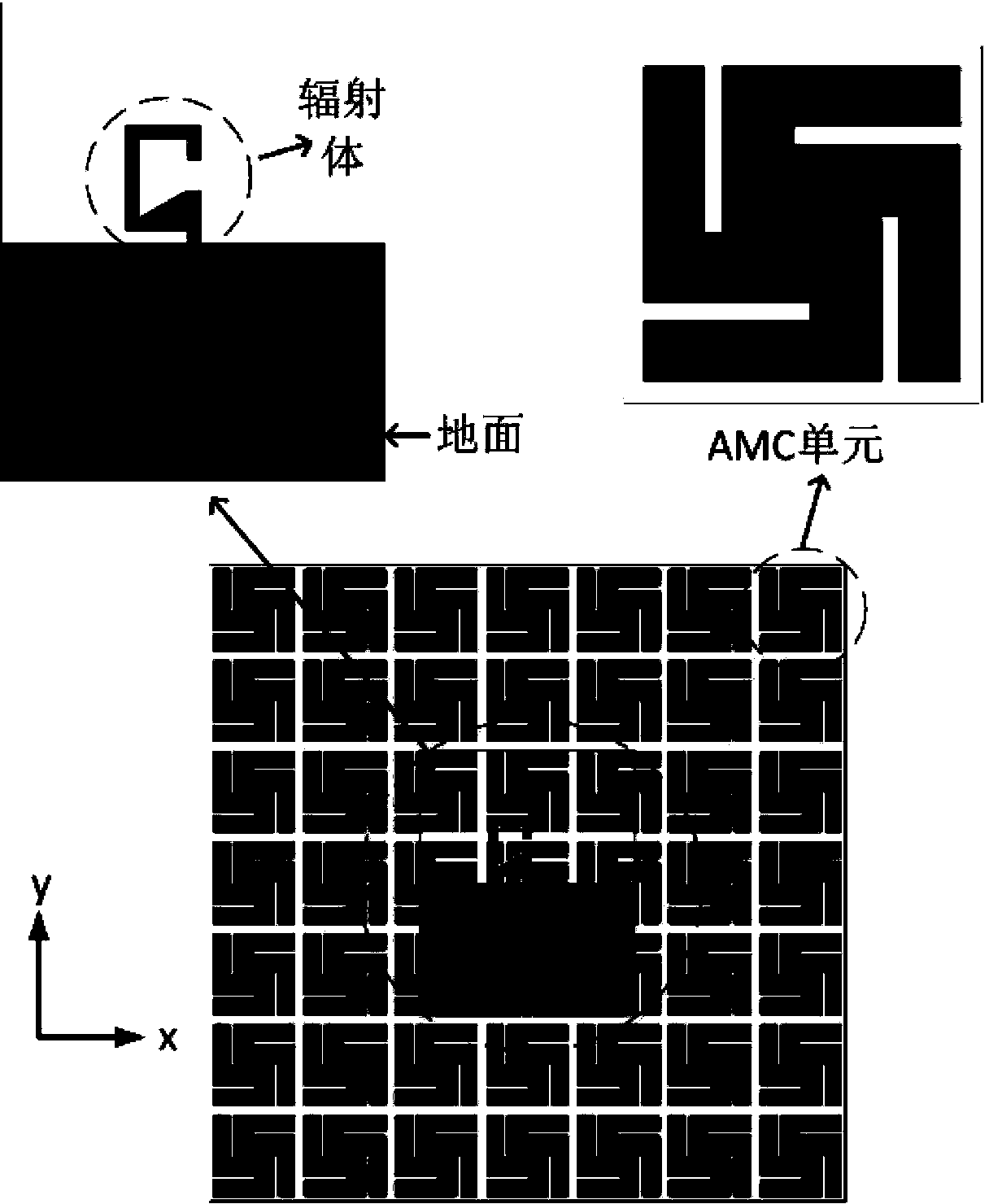
High-gain G-shaped dual-frequency monopole antenna with loaded dual-frequency AMC reflection plate
InactiveCN103367881ASimple structureCompact structureSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDual frequencyHigh-gain antenna
The invention relates to a high-gain G-shaped dual-frequency monopole antenna with a loaded dual-frequency AMC reflection plate, and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetism propagation and receiving. According to the micro-strip-line-feed G-shaped dual-frequency monopole antenna with the loaded dual-frequency AMC reflection plate, the dual-frequency AMC reflection plate is loaded under the G-shaped dual-frequency antenna. The antenna is characterized in that under the condition that the section of the antenna is kept low, the maximum gain of a 2.4-GHz frequency band and a 5.2-GHz frequency band in a WLAN system reaches 7.2dBi, and backward radiation of the 2.4-GHz frequency band and the 5.2-GHz frequency band in the WLAN system reduces by 14.1dB and 13.7dB respectively. The designed high-gain dual-frequency antenna with the loaded AMC reflection plate can be used for a 2.4-GHz system (2.4GHz-2.48GHz) and a 5.2-GHz system (5.15 GHz-5.35GHz) in the WLAN system, and provides guidance for a high-gain antenna working in a dual-frequency WLAN system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Communication power control method, communication equipment and communication system based on RSSI
InactiveCN103188778AExtended service lifeEmission reductionPower managementHigh level techniquesWireless transceiverCommunications system
In current applications, when a short distance wireless transceiver chip transmits and receives data, transmitting power and receiving power are fixed, usually in order to achieve the purpose of signal communication, the data are transmitted and received by utilization of maximum power / maximum gain, in actual applications, under most conditions, the data are not needed to be transmitted and received by utilization of the maximum power / maximum gain, and extremely large waste of power consumption is caused. The invention provides a method dynamically controlling the transmitting power and the receiving power of the transceiver chip, communication equipment and a communication system based on an RSSI, the transmitting power and the receiving power are further lowered according to the actual applications, the power consumption is reduced, and the service life of a battery is prolonged.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
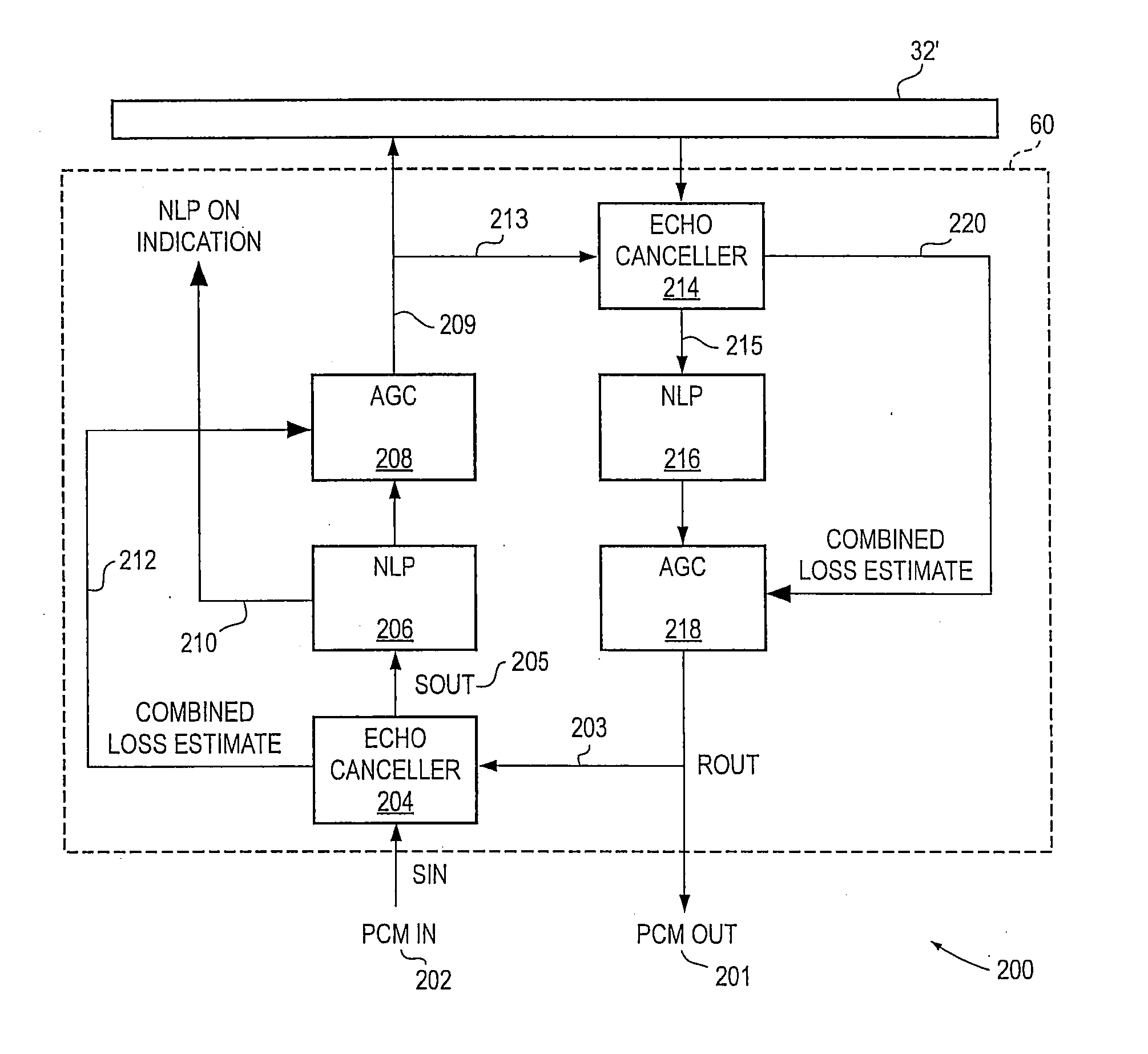
Adaptive gain control based on echo canceller performance information
InactiveUS20070127711A1Ensure stabilityIncrease volumeTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsBroadband local area networksLoss rateSelf adaptive
A system and method for provide a stable gain from an adaptive gain control device in a signal path. An echo canceller is also located in the signal path, and is used to provide performance information regarding losses in the signal. This performance information is fed to the automatic gain control device via a connection. The automatic gain control device thereafter uses the performance information to determine a maximum gain that might be provided based upon losses cause by echo conditions. The gain however is limited in order to provide for a stable system. The performance information includes a loss rate that includes a combination of the echo return loss and the echo return loss enhancement.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com