Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2058results about "Signal generator with single pick-up device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system to increase X-Y resolution in a depth (Z) camera using red, blue, green (RGB) sensing
ActiveUS20060221250A1Quick fixHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersTime correlationImage resolution
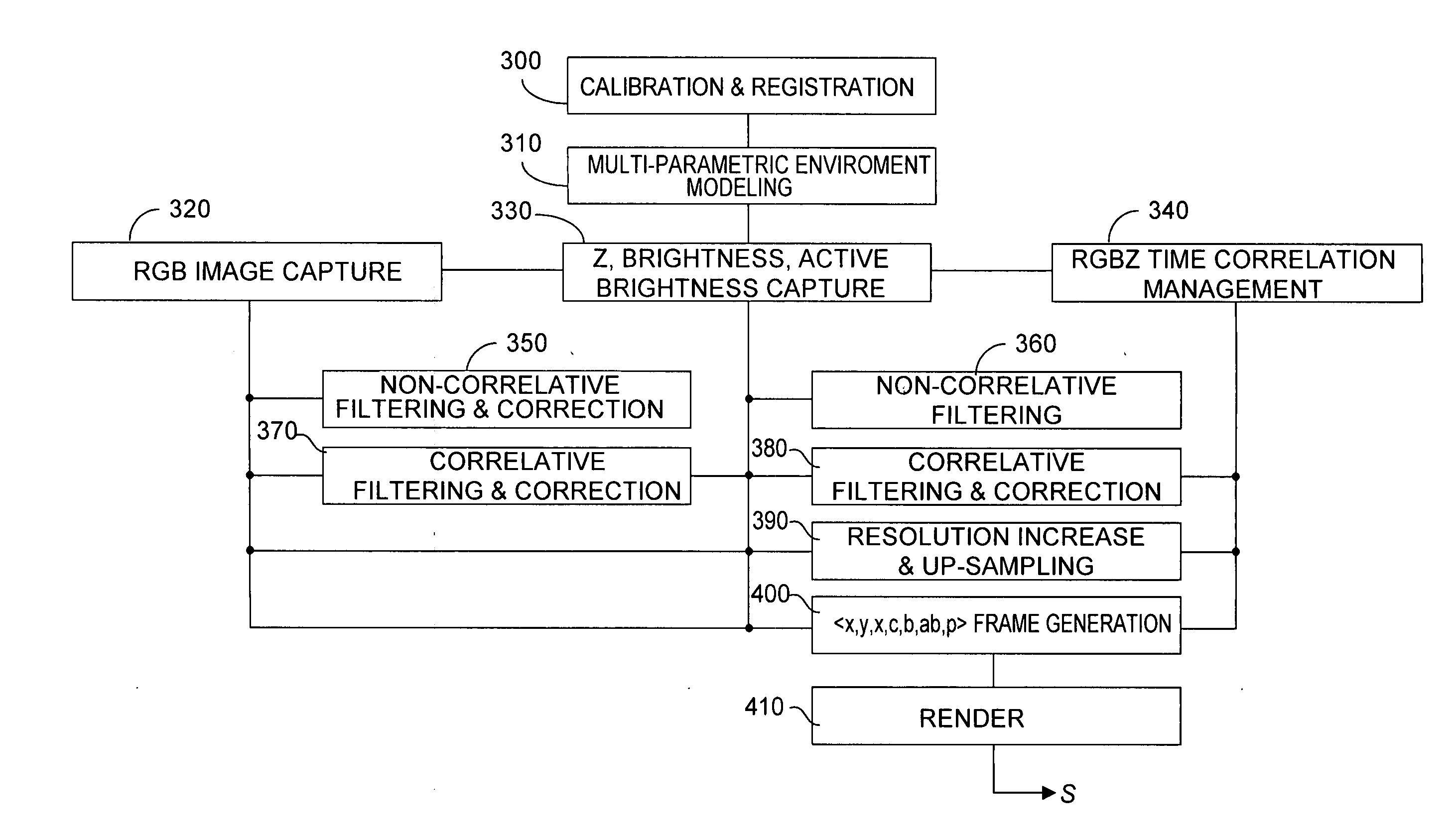
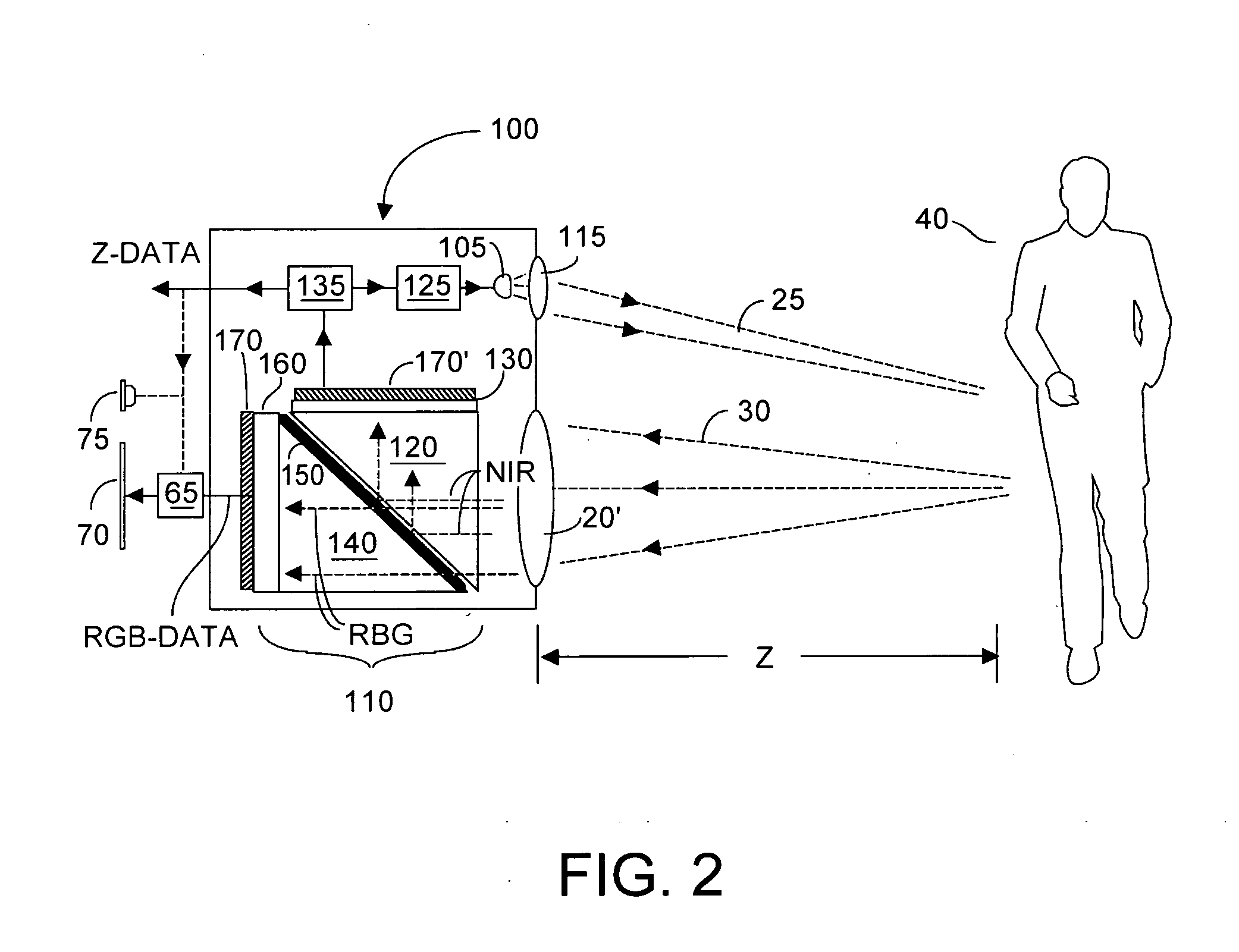
An imaging system substantially simultaneously acquires z-depth and brightness data from first sensors, and acquires higher resolution RGB data from second sensors, and fuses data from the first and second sensors to model an RGBZ image whose resolution can be as high as resolution of the second sensors. Time correlation of captured data from first and second sensors is associated with captured image data, which permits arbitrary mapping between the two data sources, ranging from 1:many to many:1. Preferably pixels from each set of sensors that image the same target point are mapped. Many z-depth sensor settings may be used to create a static environmental model. Non-correlative and correlative filtering is carried out, and up-sampling to increase z-resolution occurs, from which a three-dimensional model is constructed using registration and calibration data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
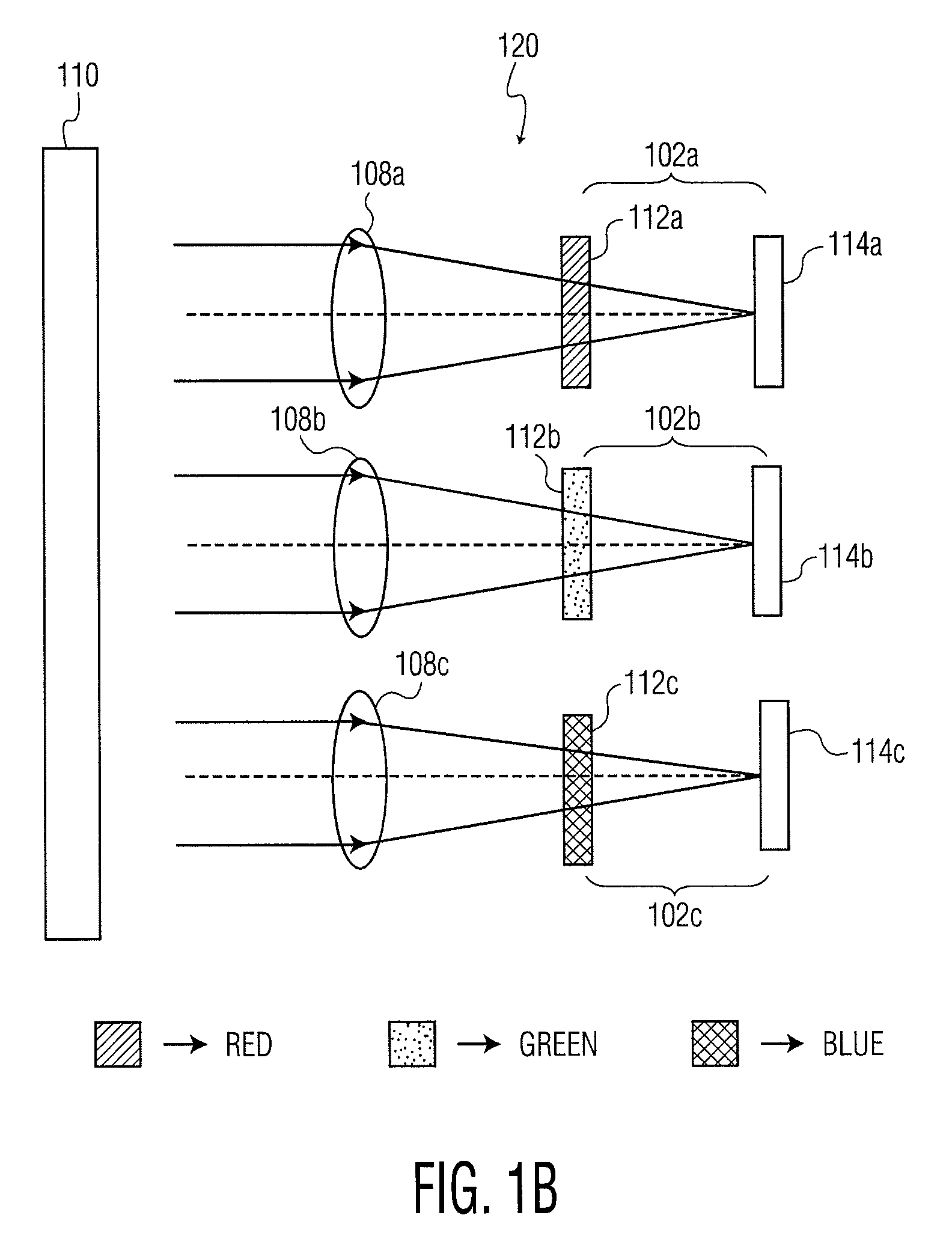
Thin color camera
ActiveUS20050225654A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageImage resolution
A color camera includes at least three sub-cameras, each sub-camera having an imaging lens, a color filter, and an array of detectors, The color camera combines images from the three sub-cameras to form a composite multi-color image, wherein the three sub-cameras include a total number of detectors N and a total number of different color sets X, wherein a first number of signals of a first color set is less than N / X and a second number of signals of a second color set is greater than N / X, signals of the second color set being output from at least two of the three sub-cameras, wherein resolution of a composite image of the second color set is greater than resolution of an individual sub-camera and a resolution of the composite image. Corresponding images of the same color set may be shifted, either sequentially or simultaneously, relative to one another.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
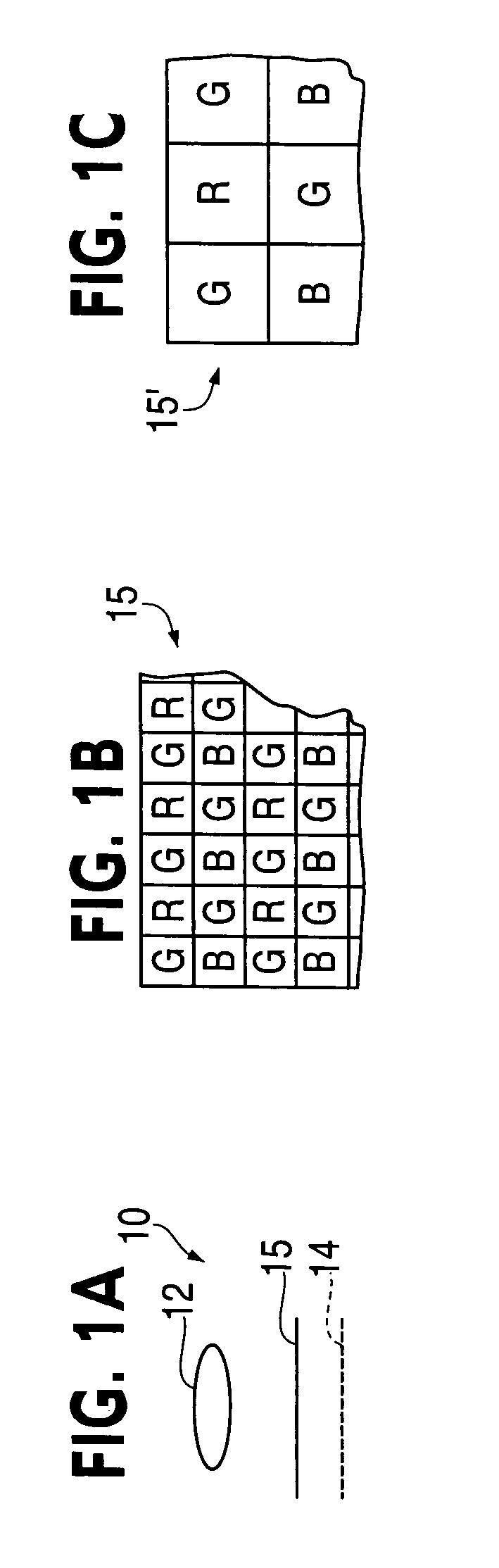
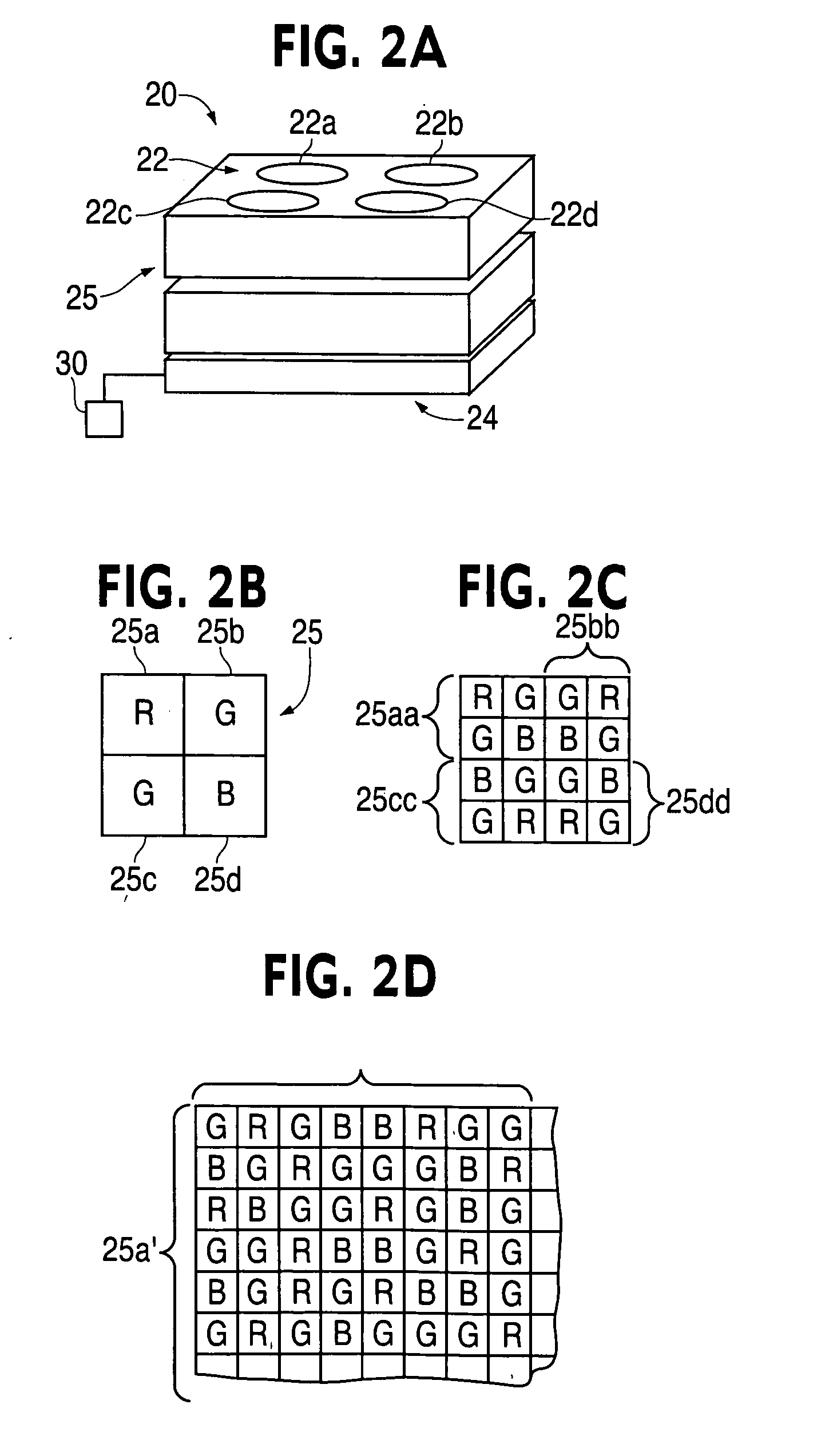
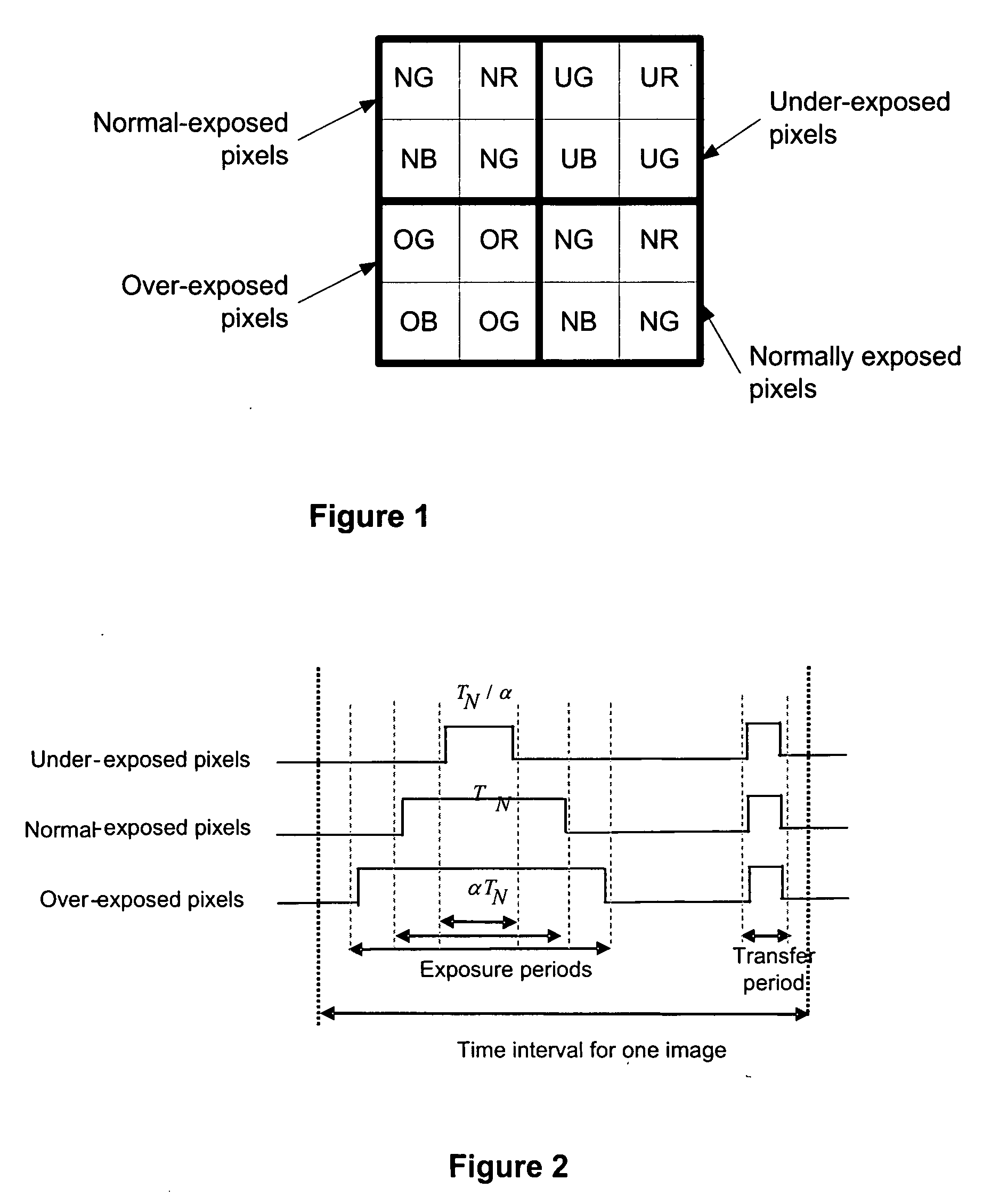
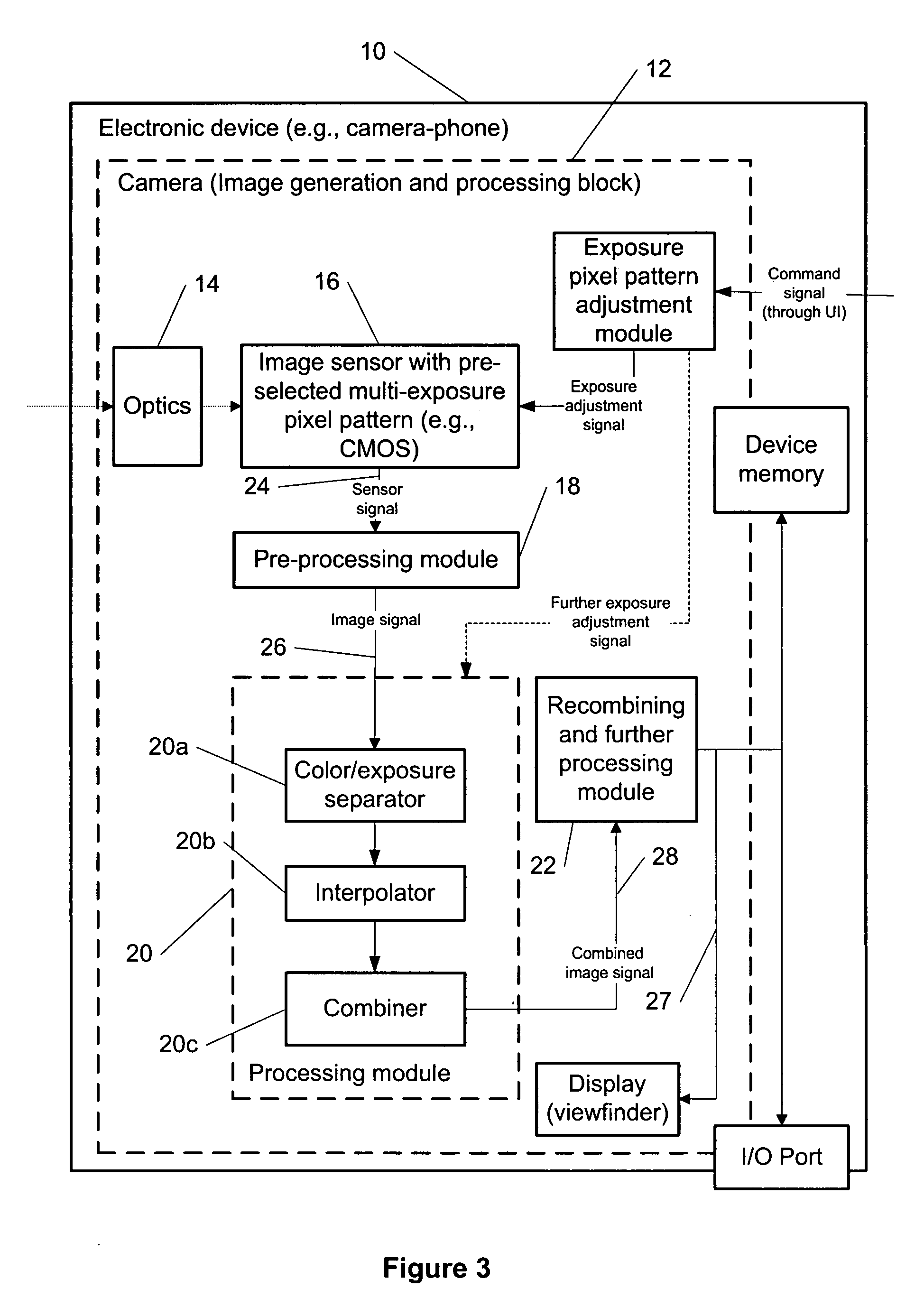
Multi-exposure pattern for enhancing dynamic range of images
ActiveUS20090091645A1Extended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsViewfinderComputer science
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for enhancing a dynamic range of an image with a multi-exposure pixel pattern taken by an image sensor of a camera for one or more color channels, wherein a plurality of groups of pixels of the image sensor have different exposure times (e.g., pre-selected or adjusted by a user through a user interface using a viewfinder feedback, or adjusted by a user through a user interface after taking and storing RAW image, etc.). Processing of the captured image for constructing an enhanced image of the image for each of the one or more color channels can be performed using weighted combination of exposure times of pixels having different pre-selected exposure times according to a predetermined criterion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Image input device
InactiveUS20060072029A1Quality improvementHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionComplementary colors
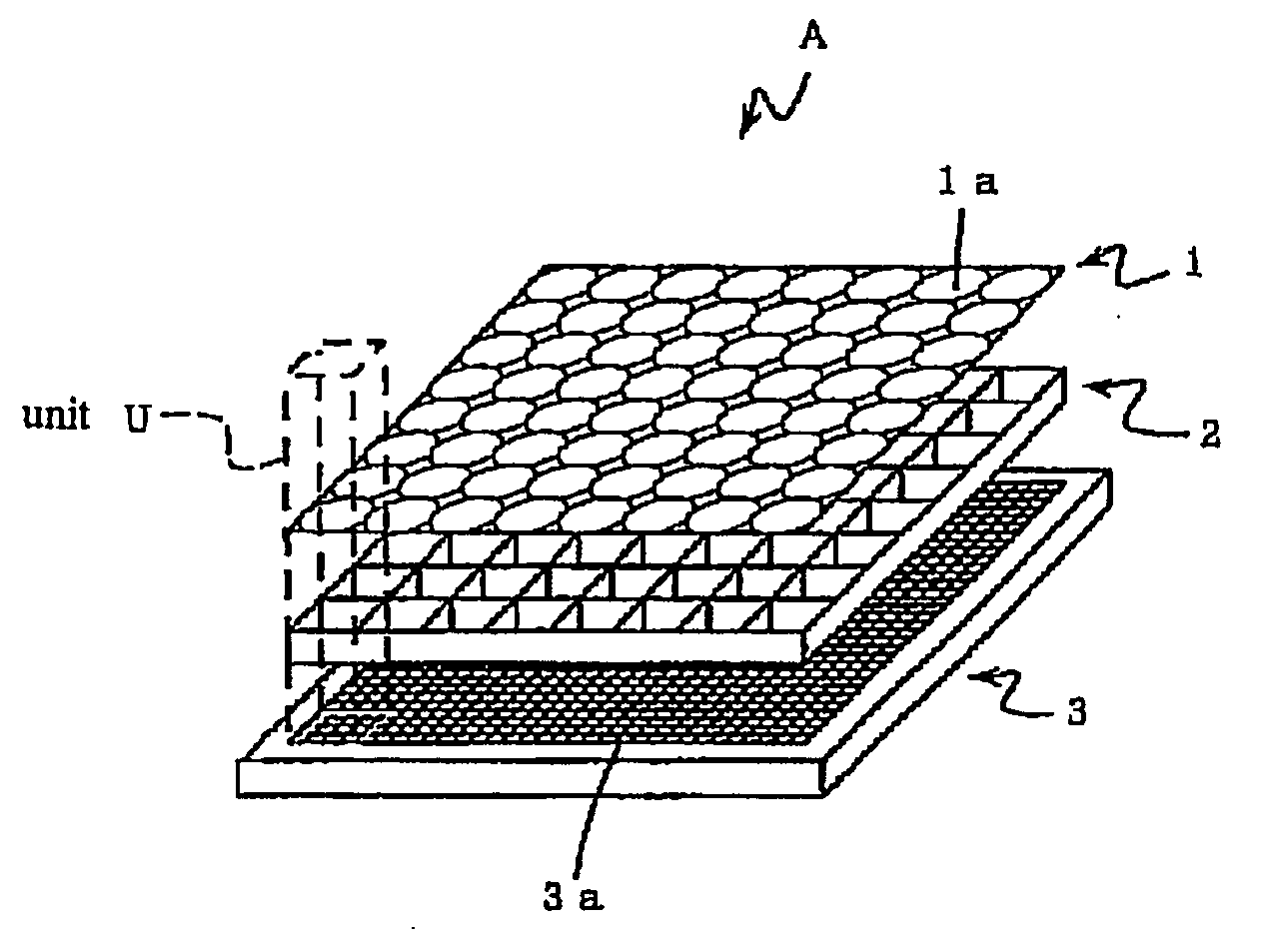
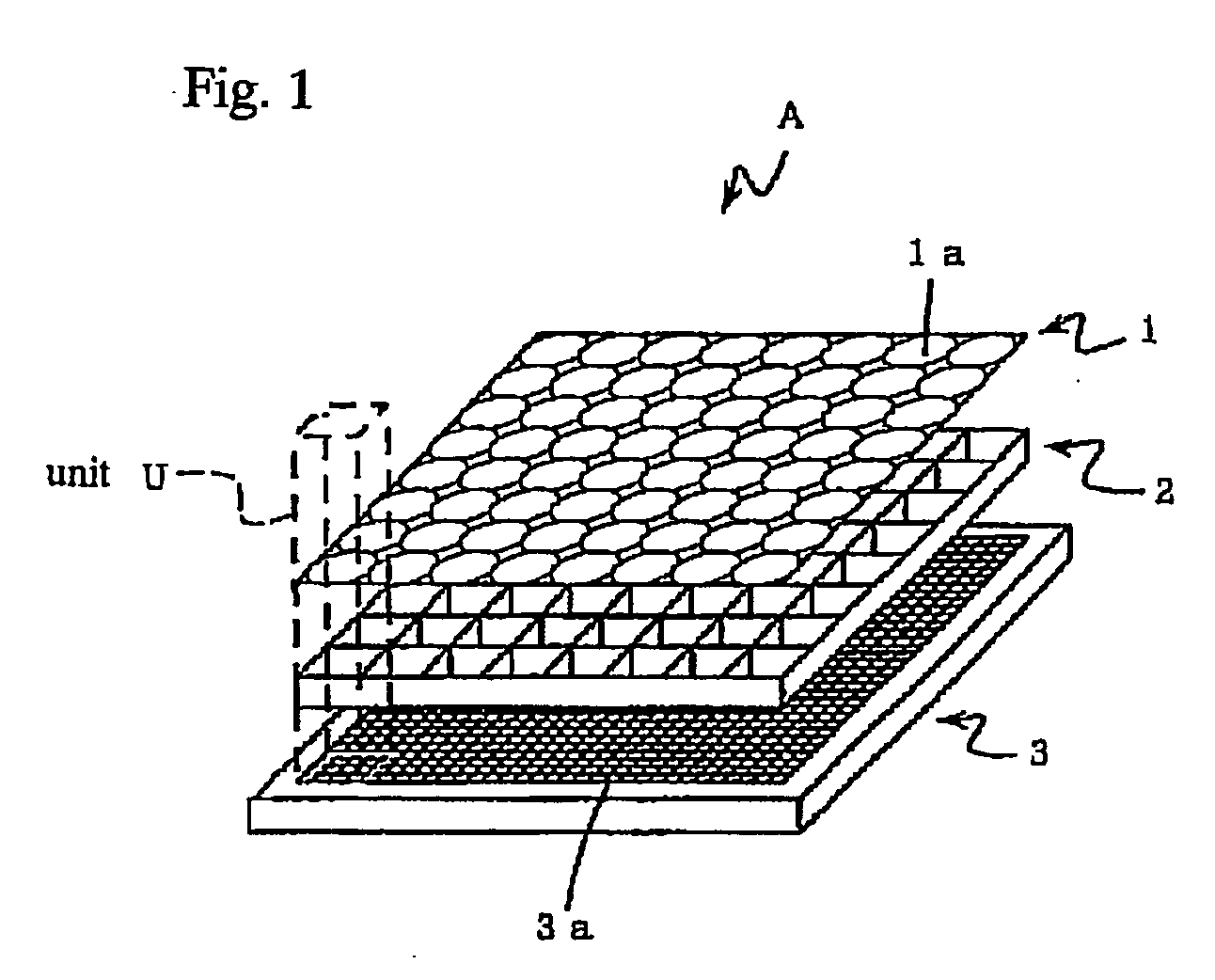
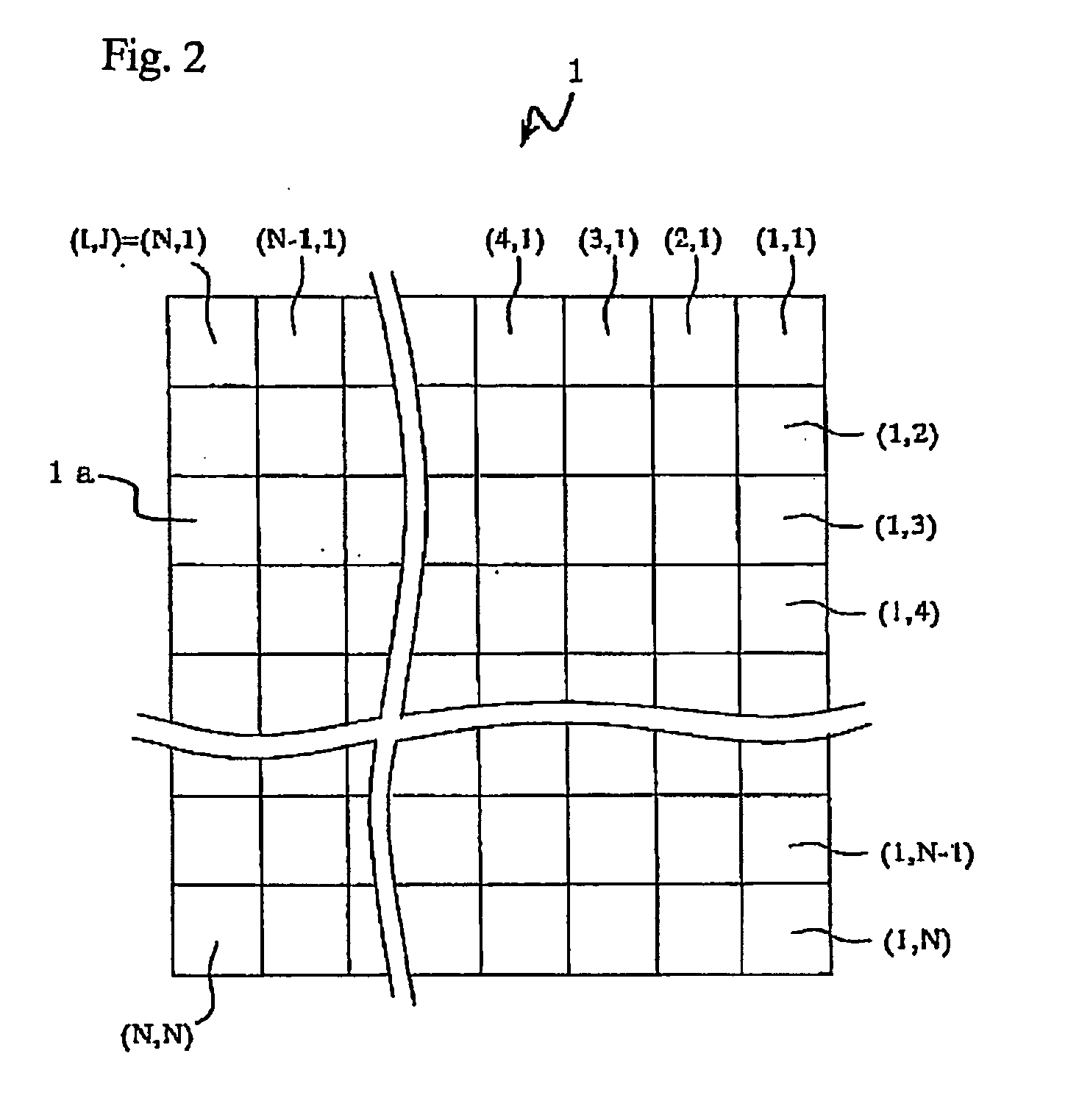
An image input apparatus which reconfigures a single reconfigured image from a plurality of low-resolution, object reduced images formed in a specified region on the light detecting element by the micro-lens array, wherein a high-resolution, single reconfigured image can be obtained even if the distance between the subject and the micro-lens array is long (infinitely long, for example), and further a reconfigured image can be realized in colors. The image input apparatus is characterized in that the relative distance between a micro-lens (1a) and light detecting cells (3a) in a specified region, where object reduced images corresponding to the micro-lens (1a) are formed, is different in each micro-lenses (1a). In addition, the light detecting cells (3a) are divided into a plurality of regions, and color filters (primary color filter, or complementary color filter, for example) are disposed in each of the divided regions.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Electronic endoscope
InactiveUS6476851B1Correct distortionAvoid shadowsTelevision system detailsEndoscopesOptical axisLight beam
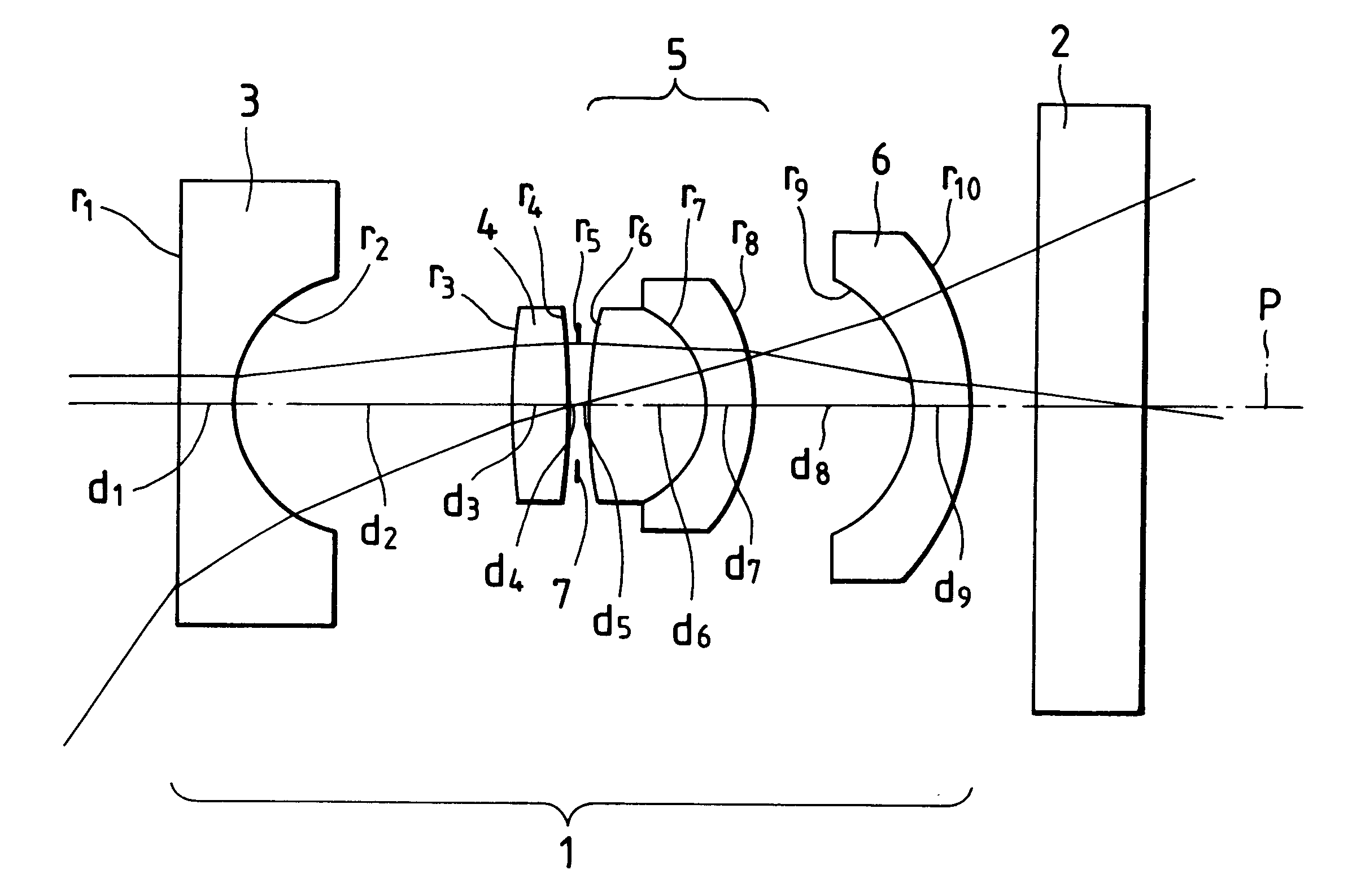
An electronic endoscope includes an objective lens system in which chief rays directed toward the maximum image height are inclined outwardly with respect to the optical axis and a solid-state image sensor which has a light-receiving surface on which many pixels are arrayed and which provides a light beam inclined outwardly with respect to the optical axis and incident on the light-receiving surface with a higher power, in separating from the center of the light-receiving surface, than a light beam incident perpendicularly on the light-receiving surface. In doing so, distortion is favorably corrected and shading can be prevented.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Signal processing apparatus for solid-state imaging device, signal processing method, and imaging system
InactiveUS20070146511A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTransducerComputer science
A signal processing apparatus corrects color mixture between pixel cells in a solid-state imaging device in which the pixel cells including photoelectric transducers are two-dimensionally arranged in an array and in which color filters having primary color components for generating luminance components and other color components are arranged over the pixel cells. The signal processing apparatus includes correction processing means for performing the correction to the signal from a target pixel by using the signals from multiple neighboring pixels adjacent to the target pixel in the solid-state imaging device and correction parameters independently set for the signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solid-state image sensor
InactiveUS7990447B2High color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionColor correction
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for improving low-light performance for small pixel image sensors
ActiveUS20080278591A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer visionPixel image
Method and apparatuses processing pixel values from a captured image include receiving an array of digital pixel values corresponding to a captured image, and computing a rolling sum of the array of pixel values. Computing a rolling sum includes selecting successive groupings of the pixel values, each grouping comprising N×M pixel values, summing pixel values in each of the successive groupings, and forming an output image using the summed pixel values.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
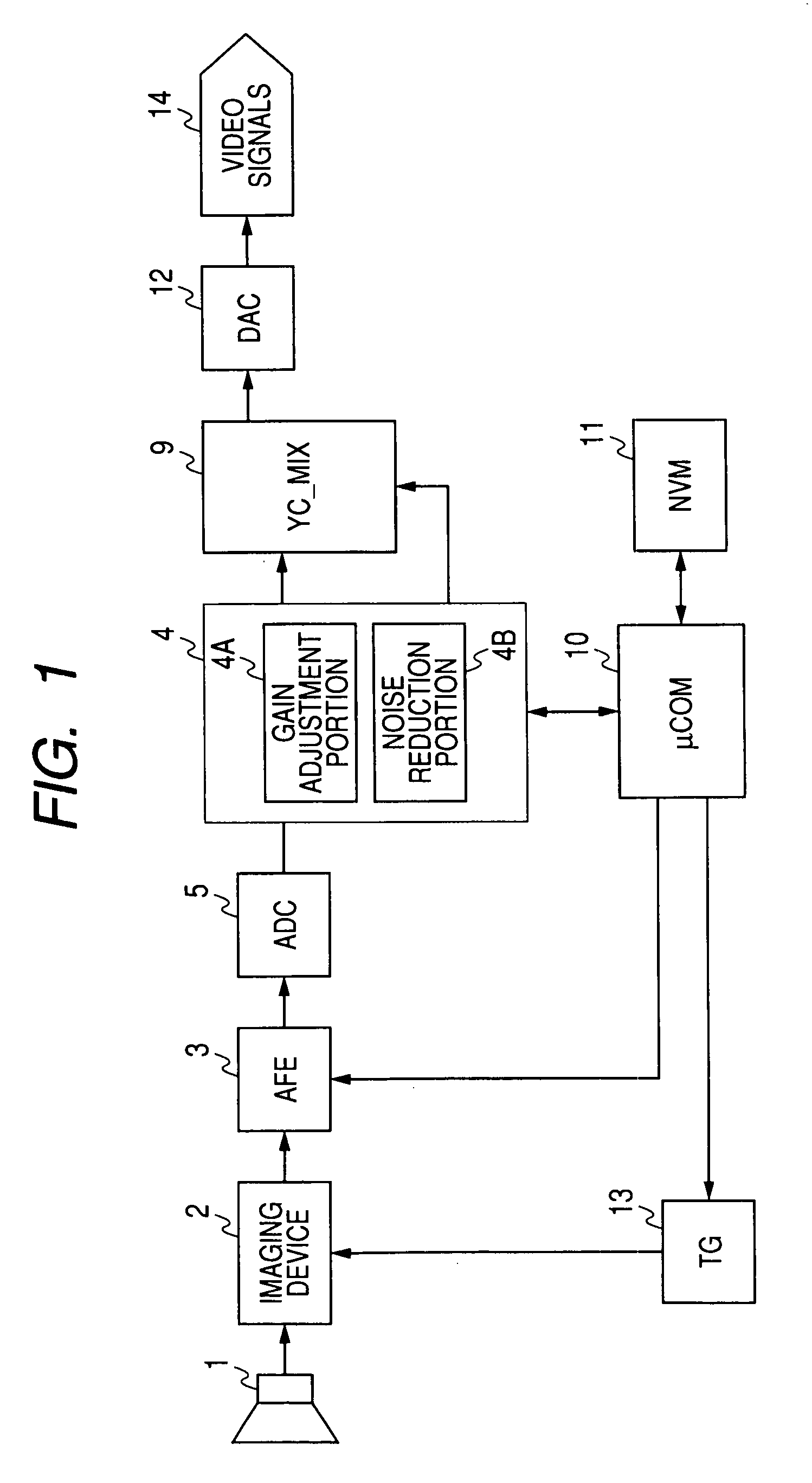
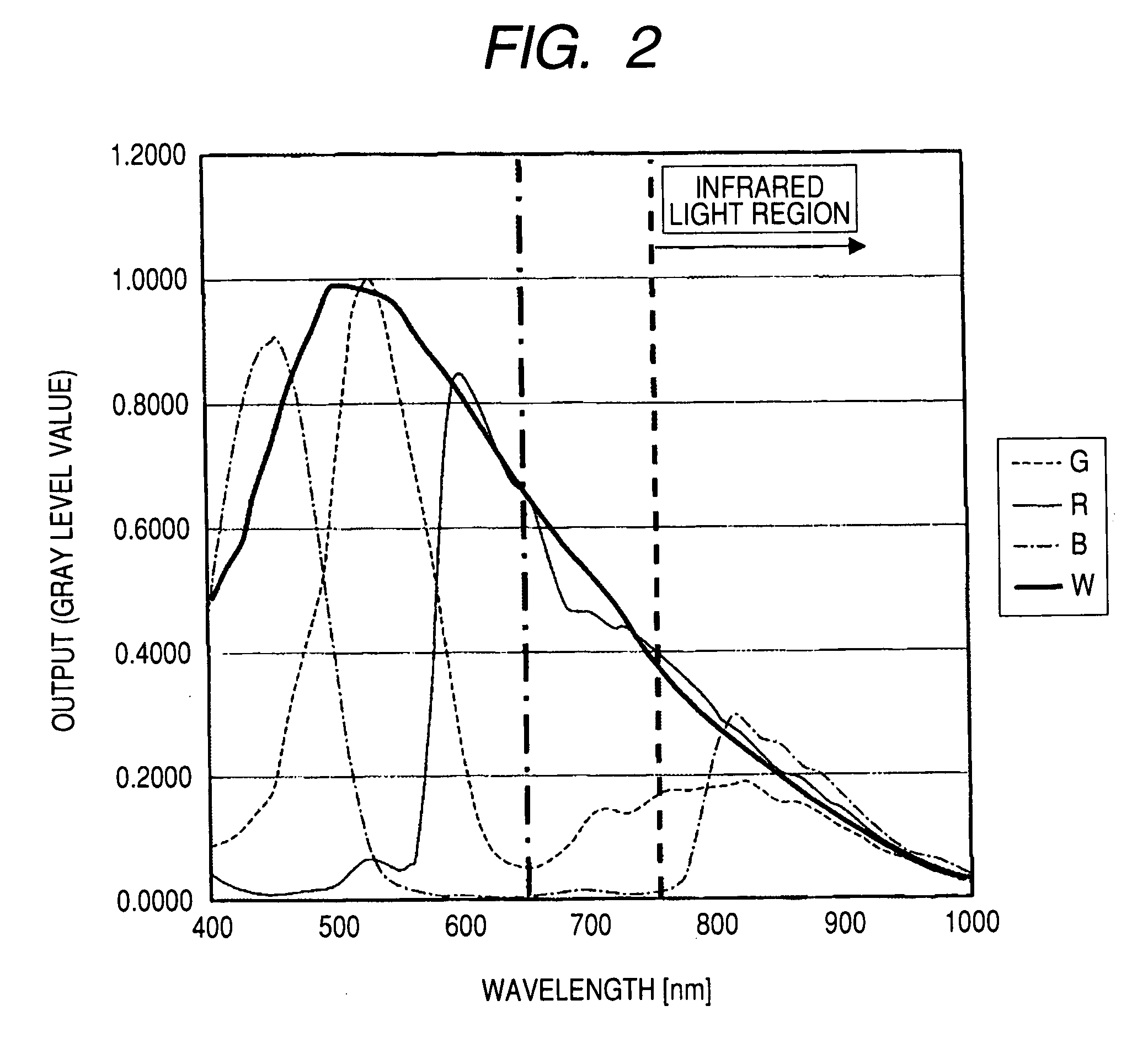
Video input processor, imaging signal-processing circuit, and method of reducing noises in imaging signals
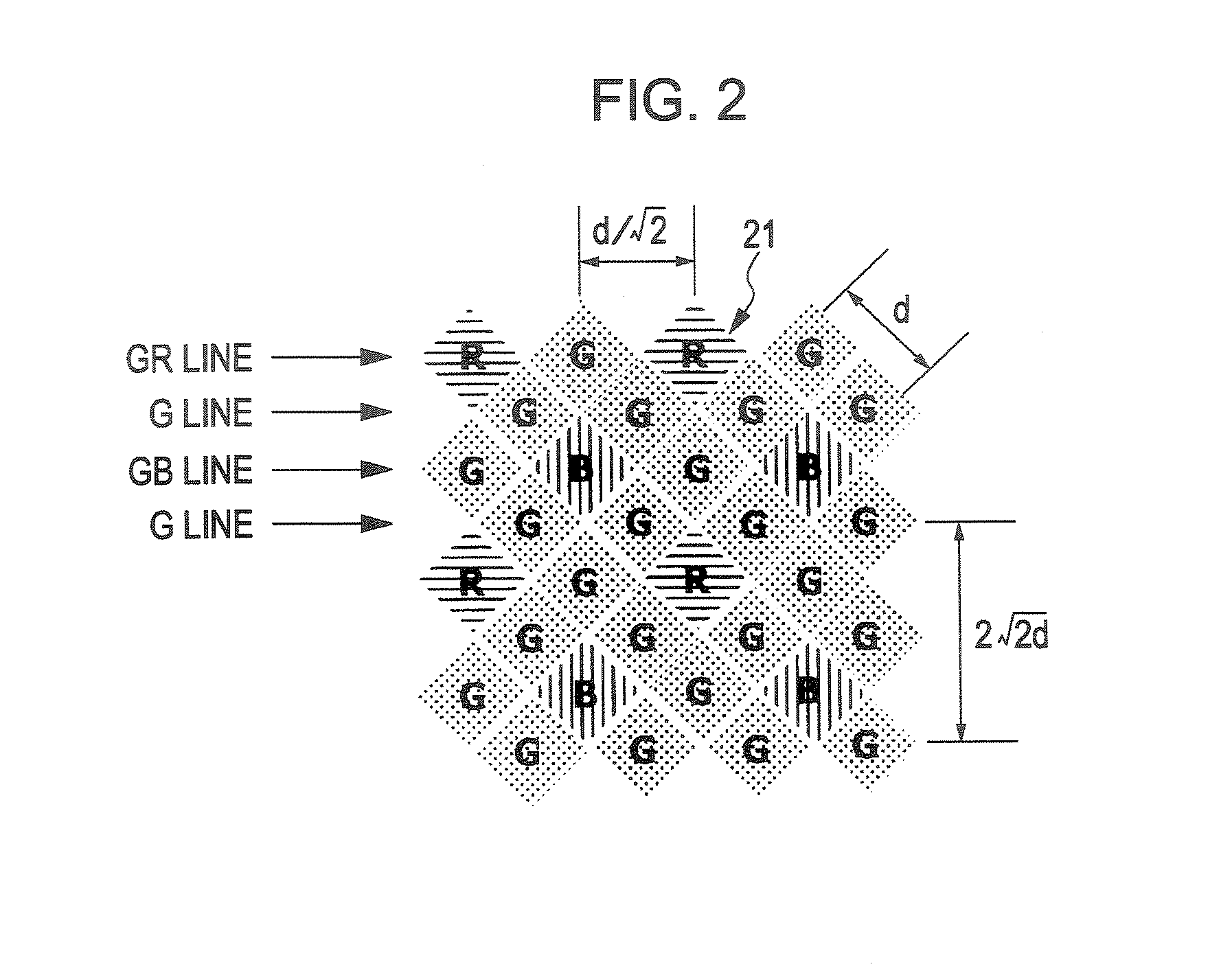
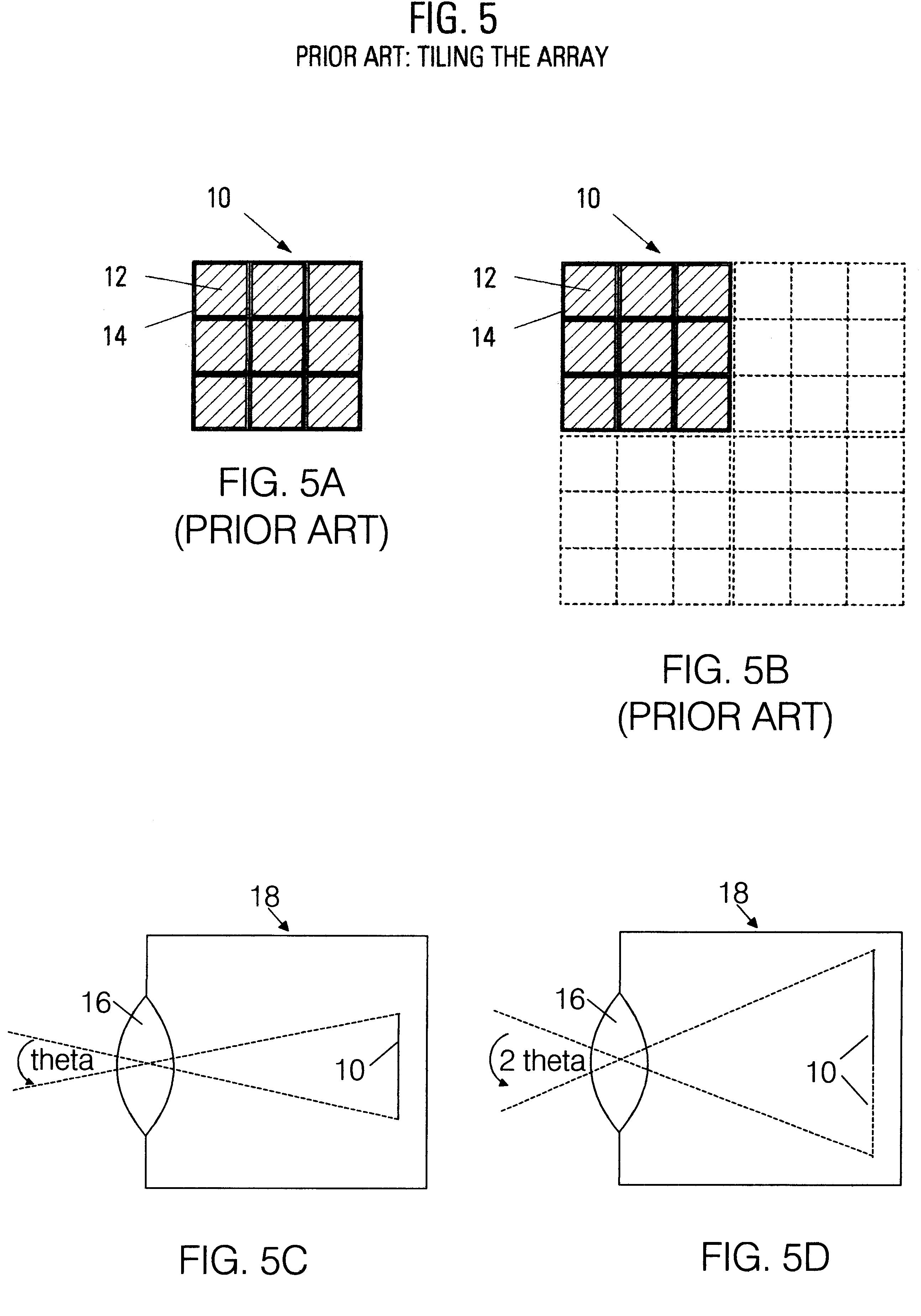
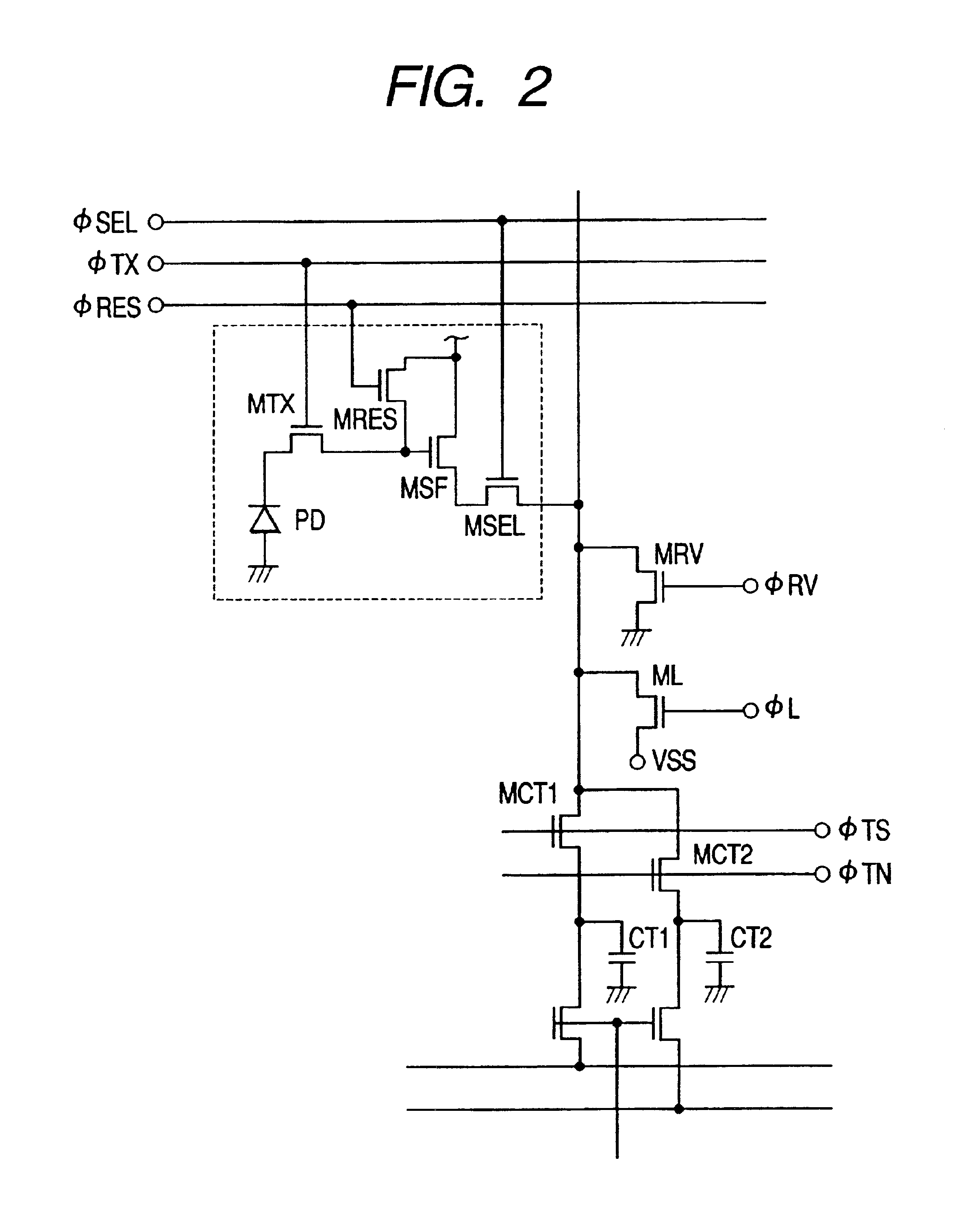
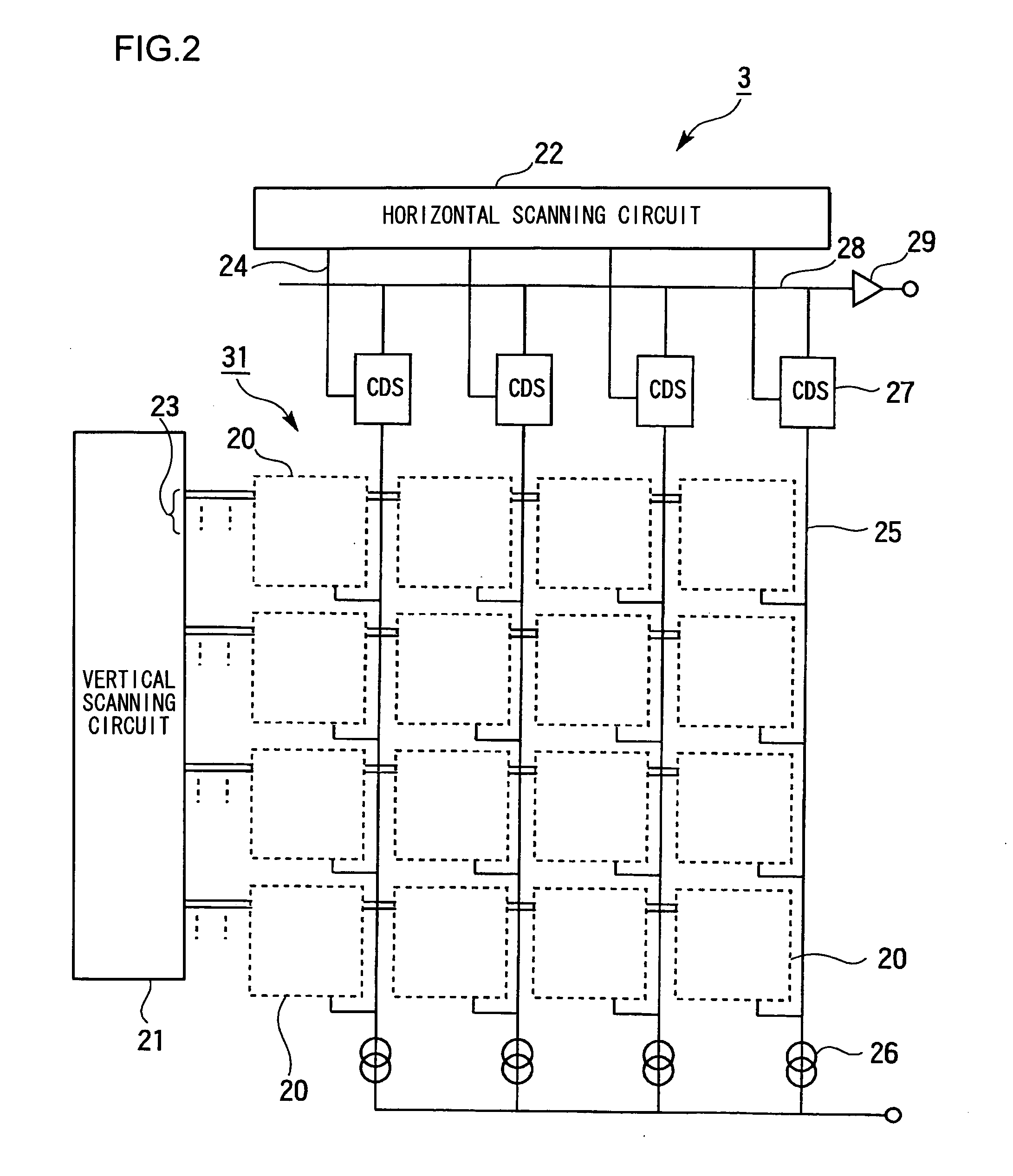
InactiveUS20080284880A1Noise-reducing capability is preventedReduce gainTelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceRelative magnitudeSignal processing circuits
A video input processor is disclosed. The processor includes: an imaging signal-generating portion configured to image a subject and producing first imaging signals containing visible light components and a second imaging signal containing near-infrared light components; a gain adjustment portion configured to adjustably set a maximum gain value according to a relative magnitude between the visible light components and the near-infrared light components and adjust a gain for the first imaging signals at the set maximum gain value; and a noise reduction portion configured to reduce noises in the first imaging signals after the gain has been adjusted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-array sensor with integrated sub-array for parallax detection and photometer functionality
Methods and systems of imaging to correct parallax. Color information is received from multi-array sensors. Luminance information is received from a sub-array sensor arranged with the multi-array sensors. Color information received from at least one of the multi-array sensors is correlated with the luminance information received from the sub-array sensor. Color information is shifted among the multi-array sensors, based on the correlation, to correct the parallax.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
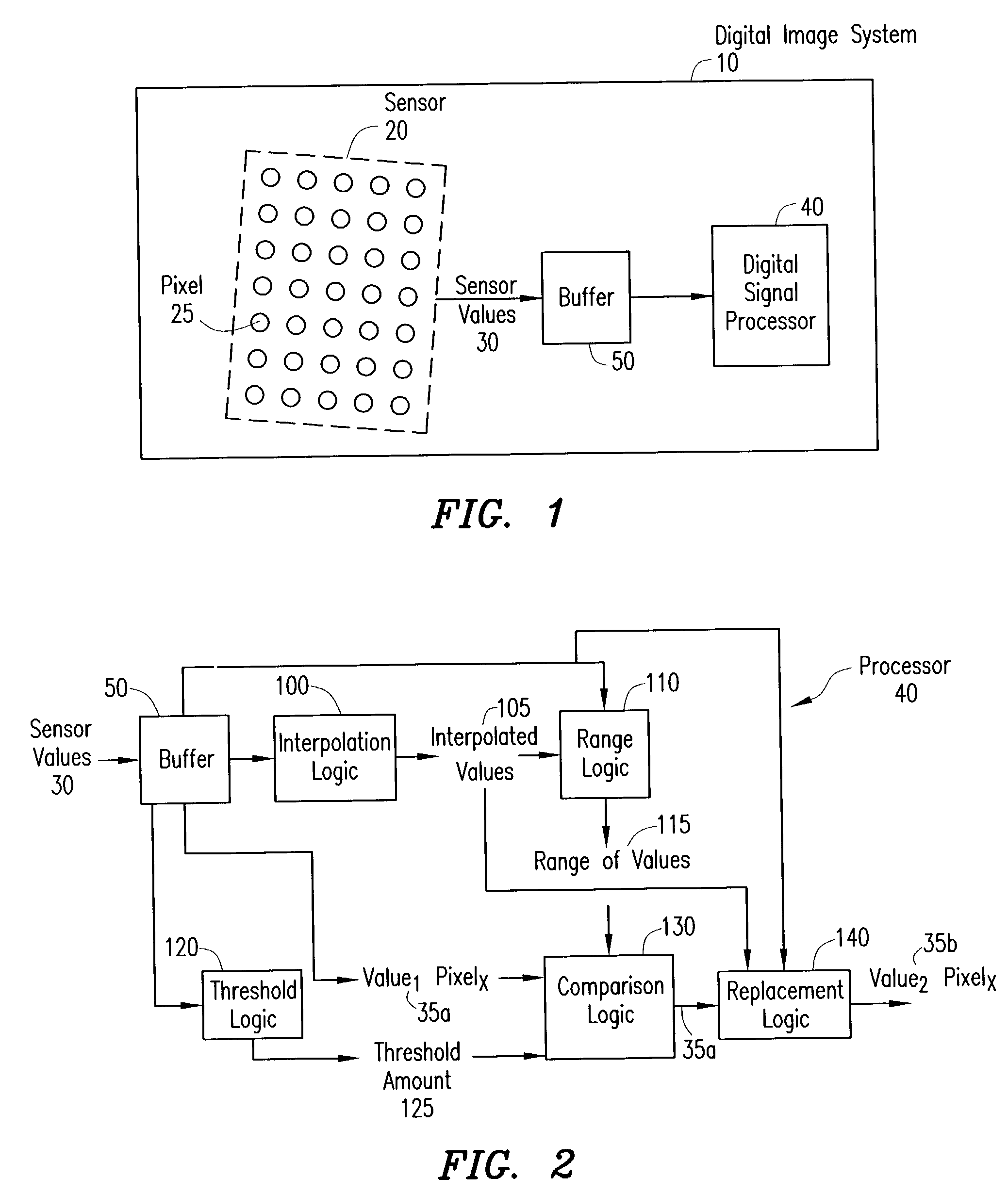
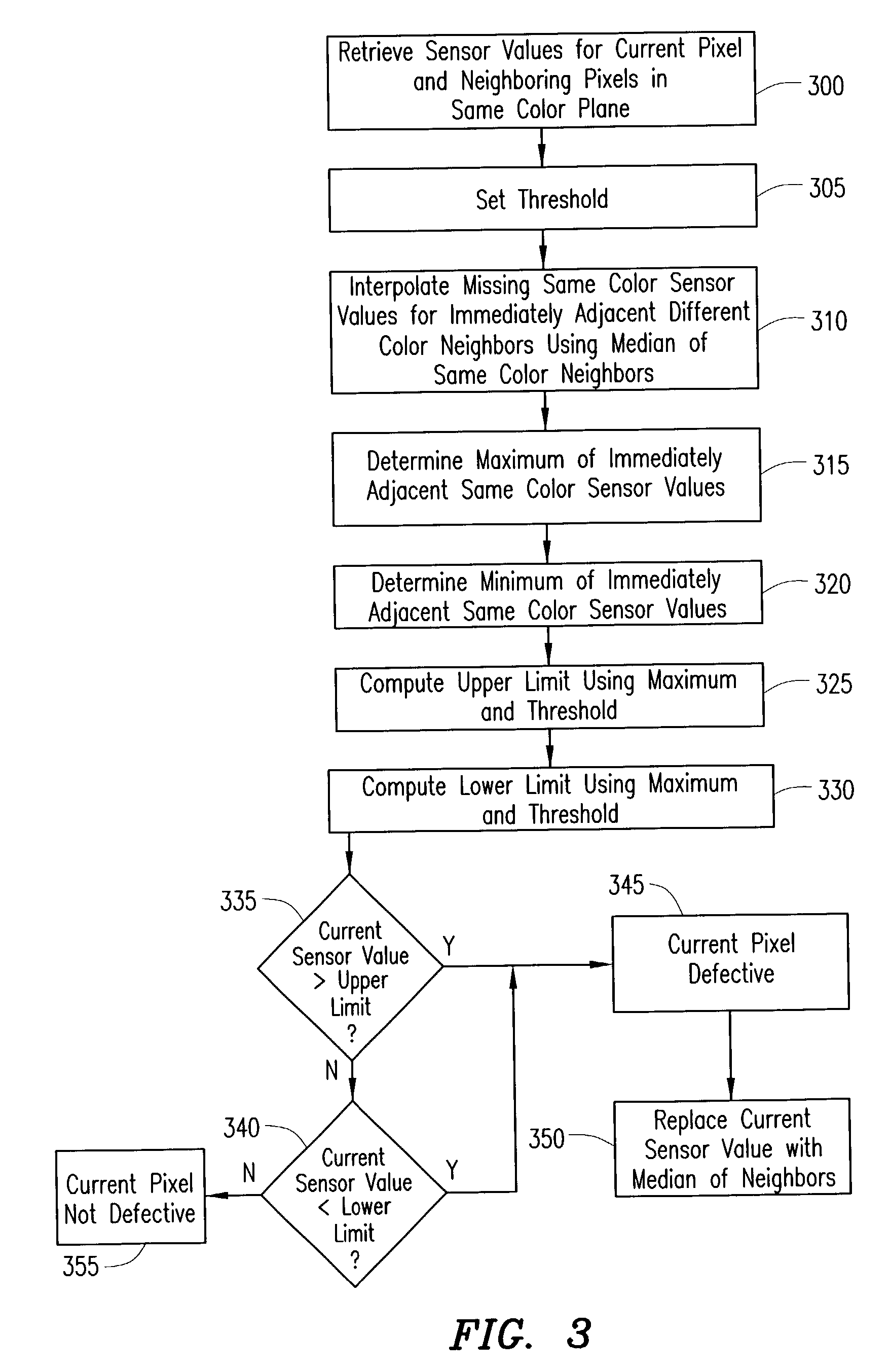
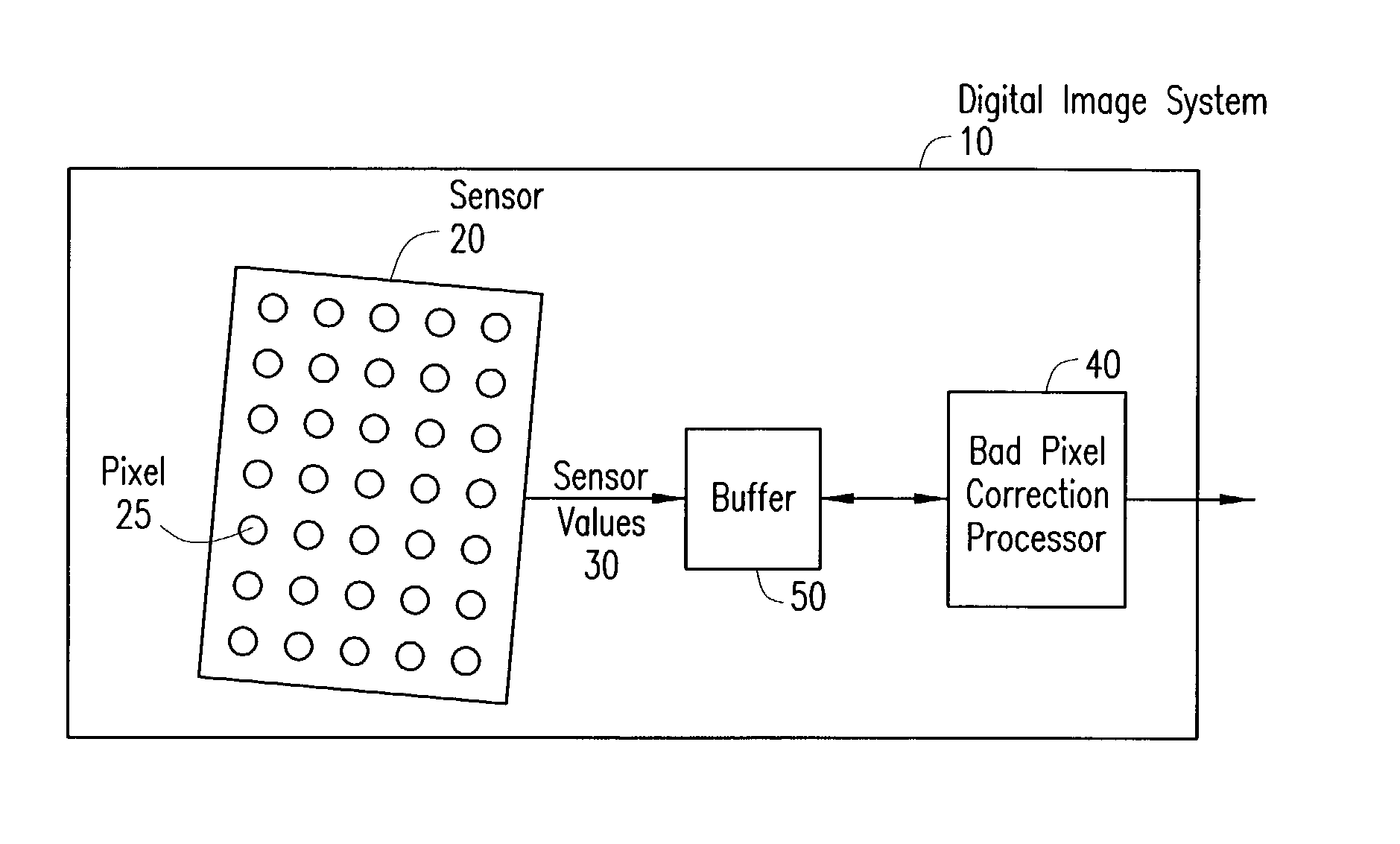
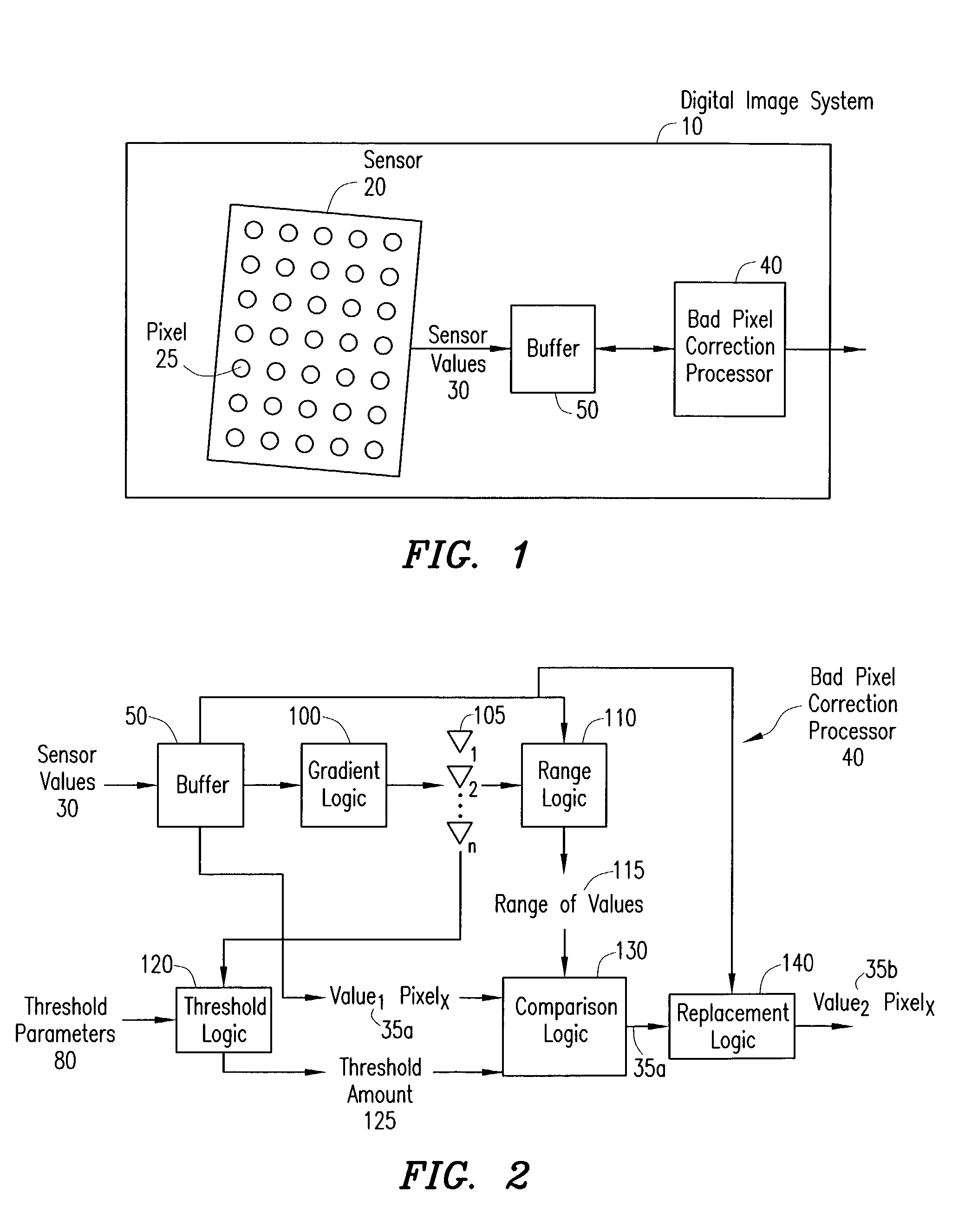
Digital image system and method for combining demosaicing and bad pixel correction
A digital image system and method for combining bad pixel correction and demosaicing in a single process is provided by interpolating sensor values for pixels immediately spatially adjacent to the current pixel being examined to detect defective pixels, and using the interpolated values for demosaicing. If the sensor value of the current pixel being examined is outside of a range of sensor values determined from the interpolated values by more than a configurable threshold amount, the current pixel is considered defective, and replaced using an estimated value from the neighboring pixels. The interpolated values calculated for use in detecting bad pixels can further be used as the interpolated values for demosaicing purposes
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Photoelectric conversion element and solid-state image pickup device
InactiveUS20080035965A1Effective reduction in dark currentTotal current dropTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A photoelectric conversion element comprises a photoelectric conversion section that includes: a pair of electrodes; and a photoelectric conversion layer disposed between the pair of electrodes, wherein the photoelectric conversion section further comprises between one of the pair of electrodes and the photoelectric conversion layer a first charge-blocking layer that restrains injection of charges from the one of the electrodes into the photoelectric conversion layer when a voltage is applied to the pair of electrodes, and the first charge-blocking layer comprises a plurality of layers.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
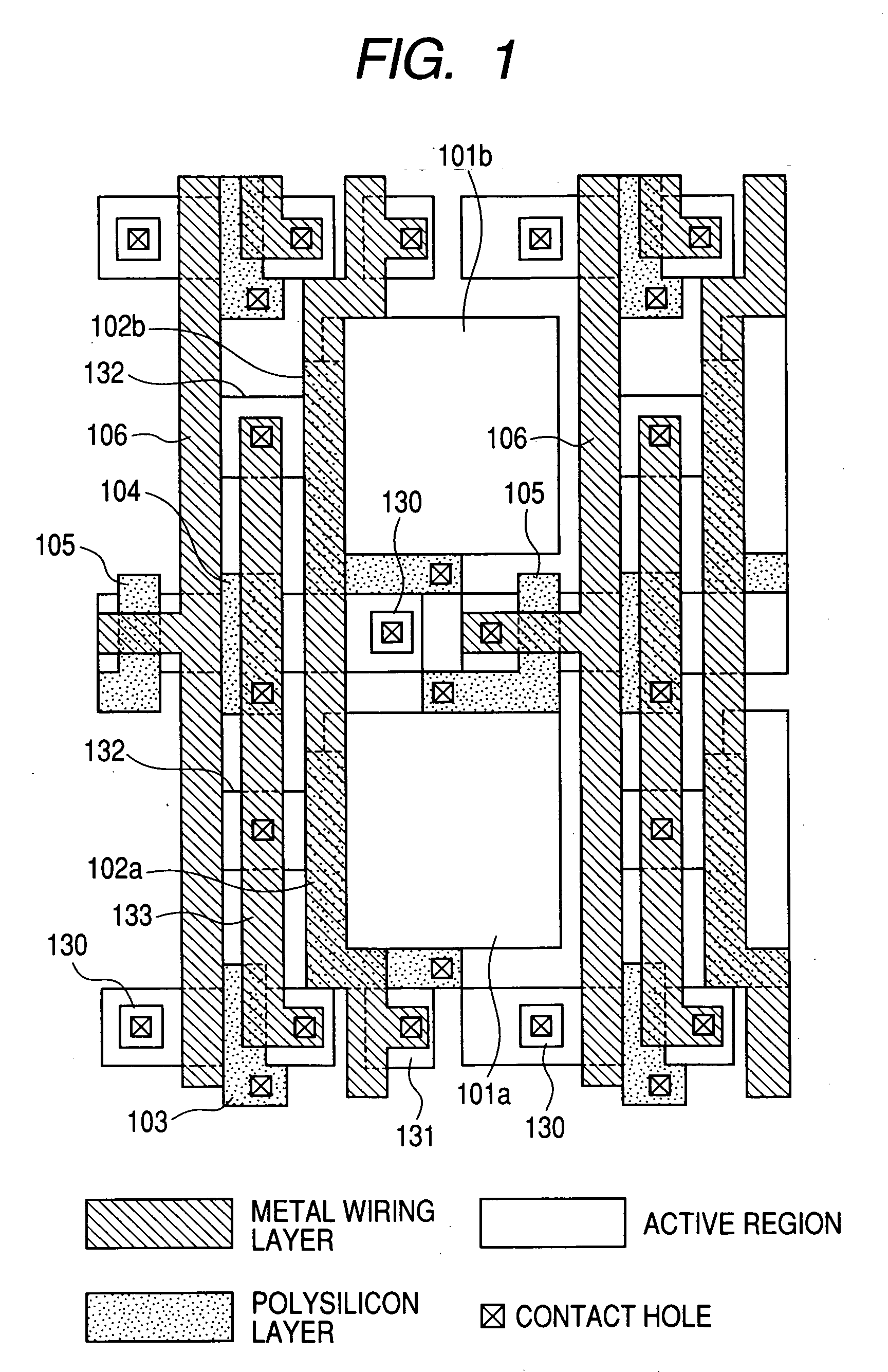
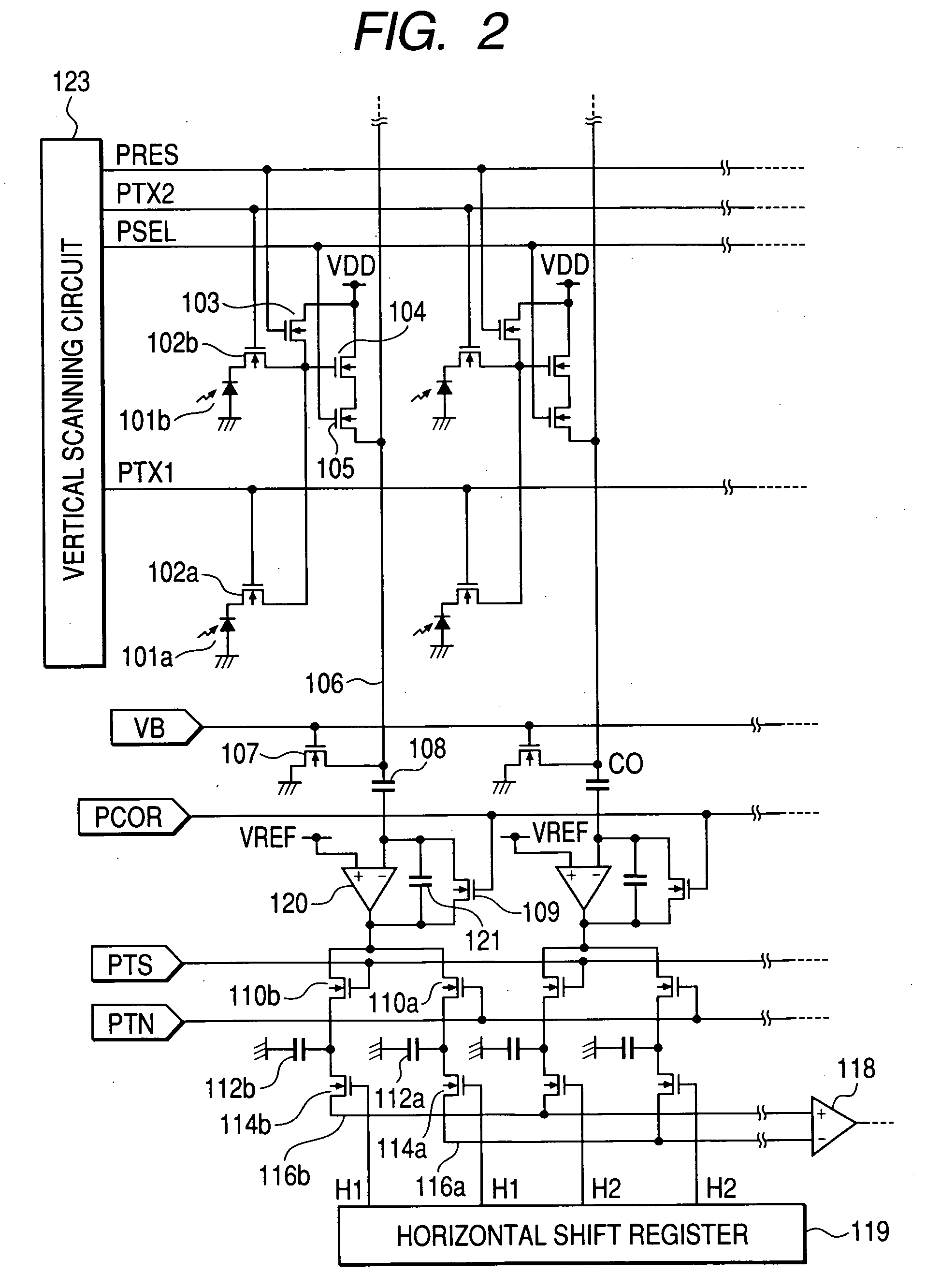
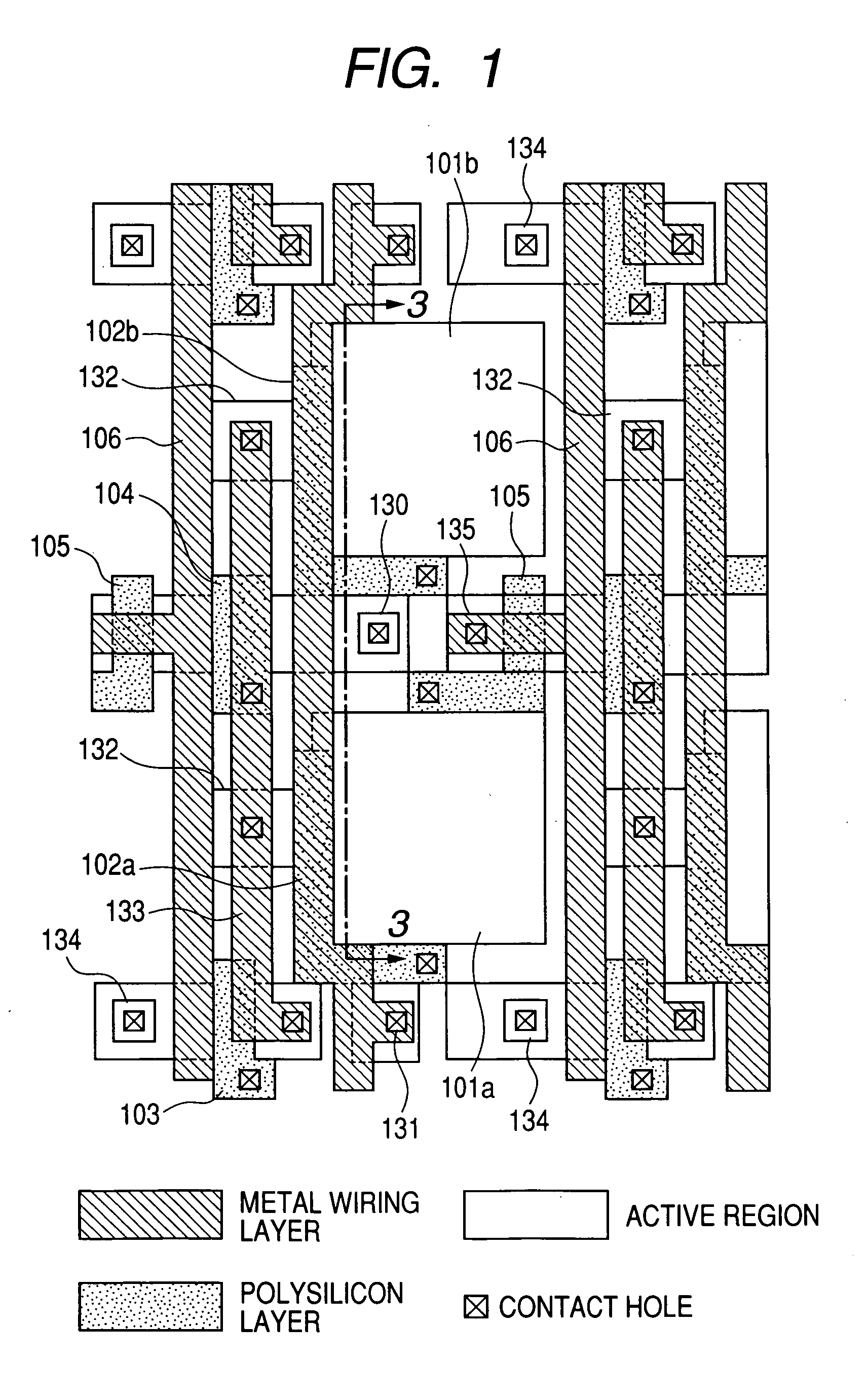
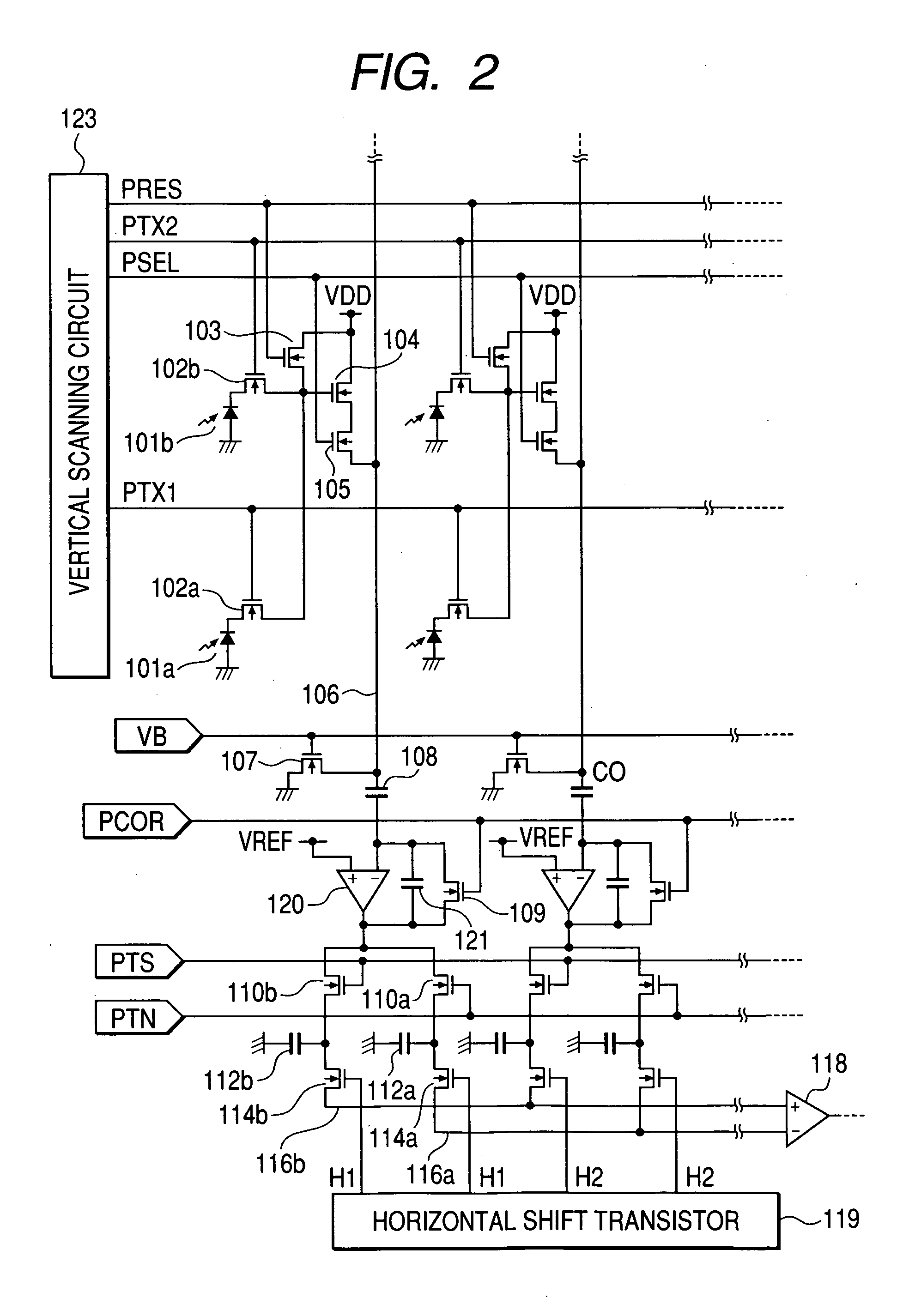
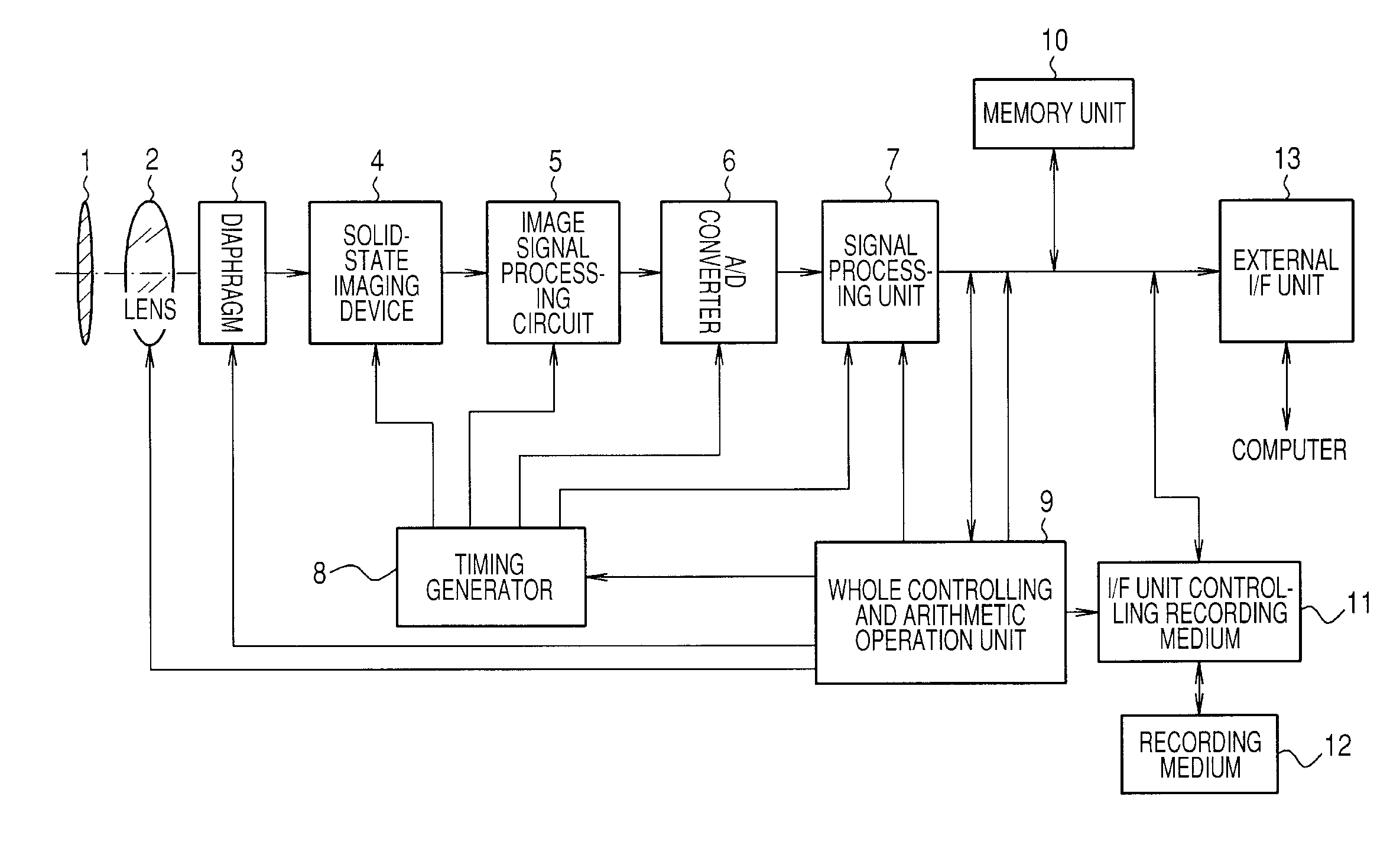
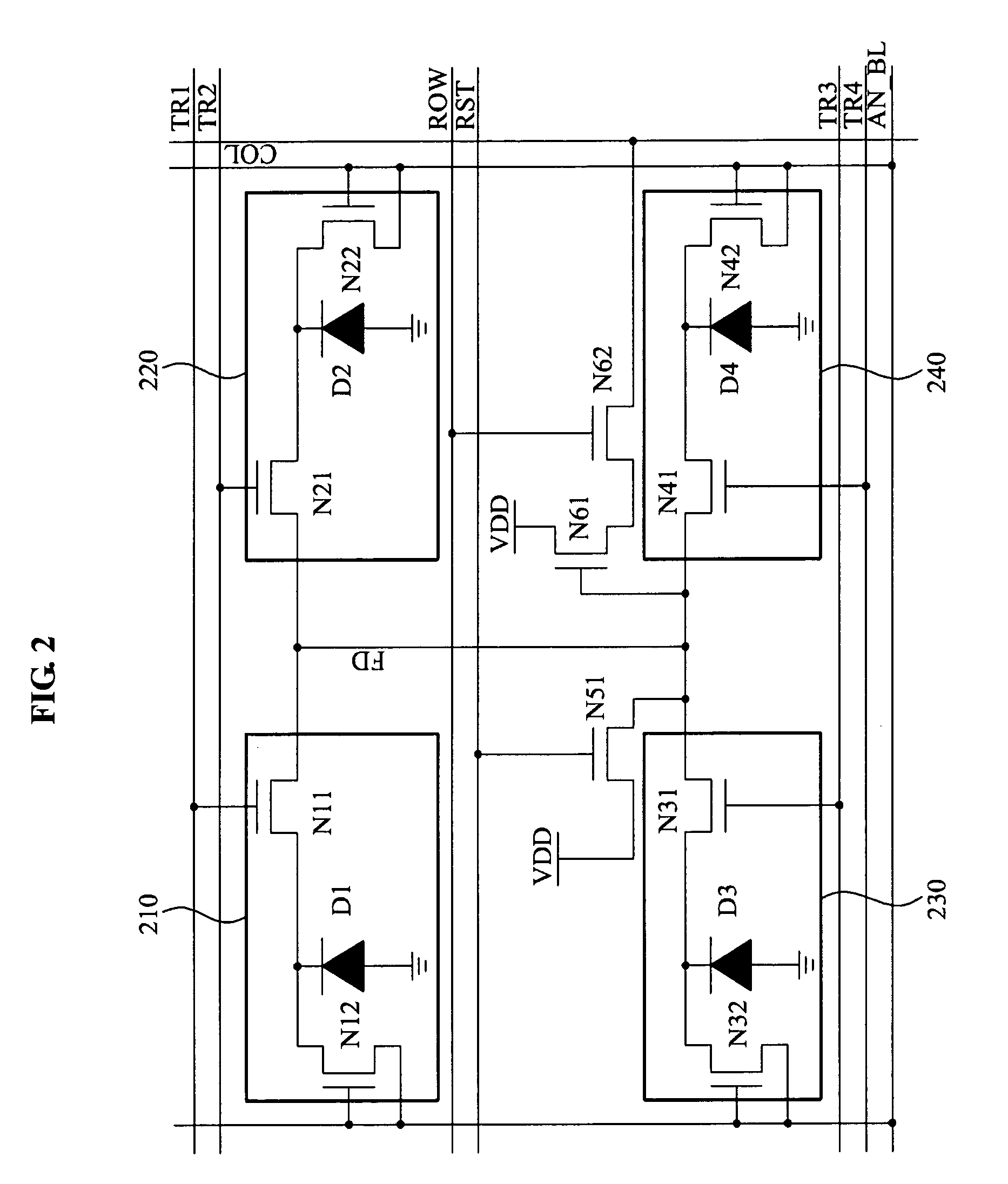
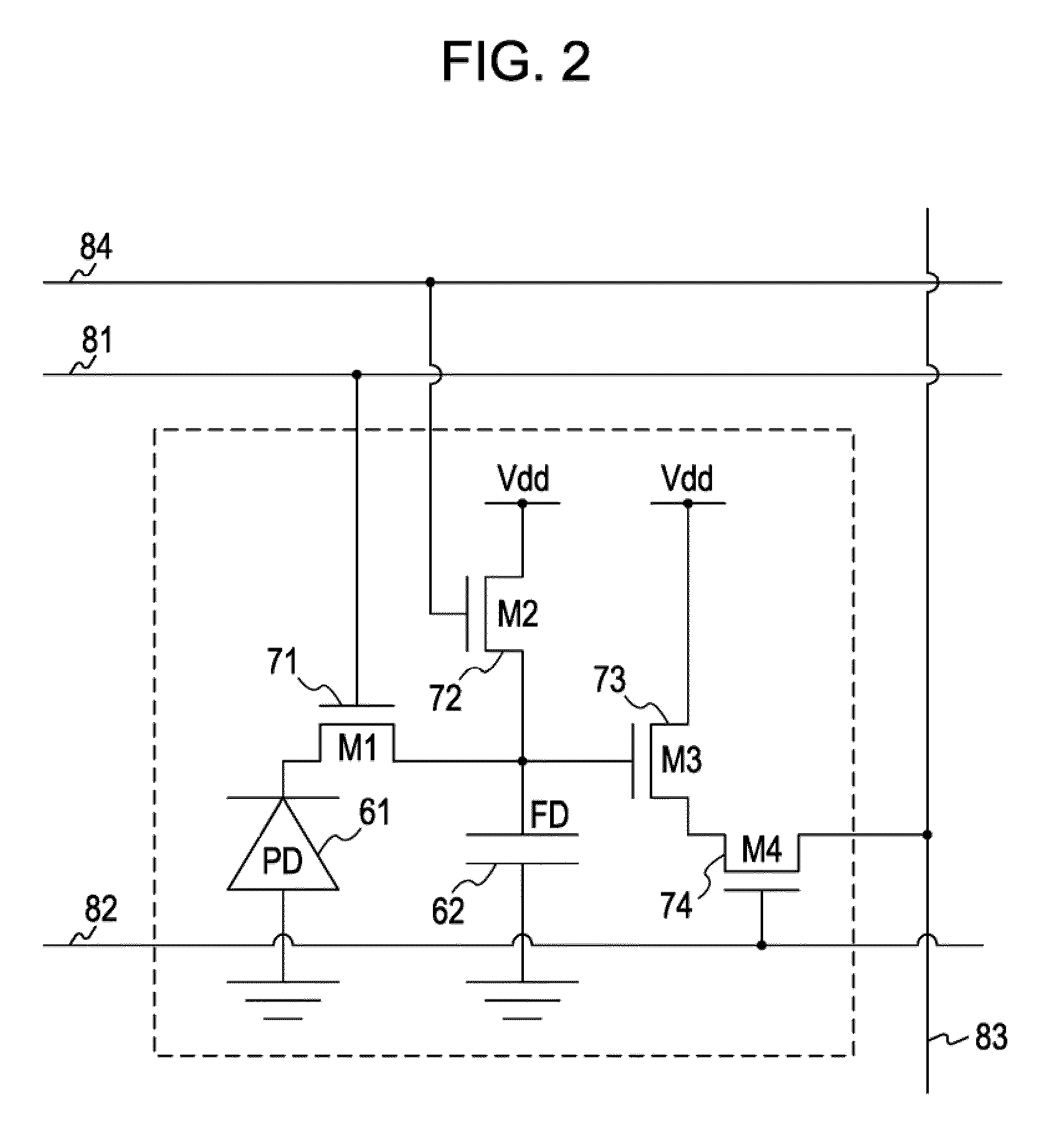
Imaging device and imaging system
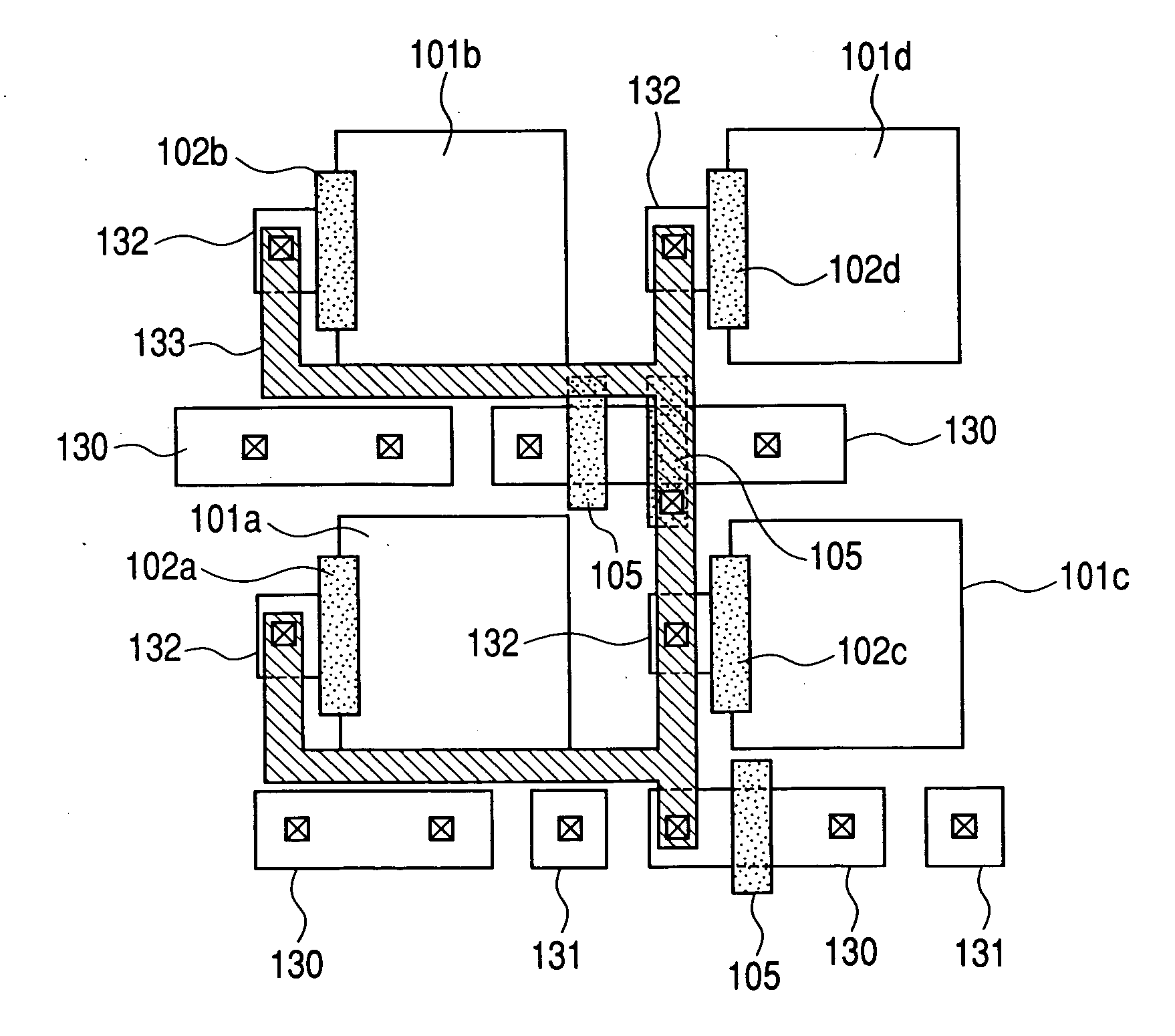
An object of the present invention is to prevent a sensitivity difference between pixels. There are disposed plural unit cells each including plural photodiodes 101A and 101B, plural transfer MOSFETs 102A and 102B arranged corresponding to the plural photodiodes, respectively, and a common MOSFET 104 which amplifies and outputs signals read from the plural photodiodes. Each pair within the unit cell, composed of the photodiode and the transfer MOSFET provided corresponding to the photodiode, has translational symmetry with respect to one another. Within the unit cell, there are included a reset MOSFET and selecting MOSFET.
Owner:CANON KK
Multiple component readout of image sensor
ActiveUS20090021612A1Wide applicationEasy to useTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayQuantum
A method for obtaining image data from an image sensor array including the steps of: providing an image sensor array having a first component subset of panchromatic pixels for integrating charge and a second component subset of color pixels for integrating charge; reading pixel charge to produce pixel signals from the first component subset of the panchromatic pixels while exposing the second component subset of color pixels and digitizing and storing the first component subset signals; and reading pixel charge to produce pixel signals from the second component subset of color pixels that were exposed for at least a portion of time during the reading of pixel signals from the first component subset of the panchromatic pixels and digitizing and storing the second component subset signals.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Image input apparatus
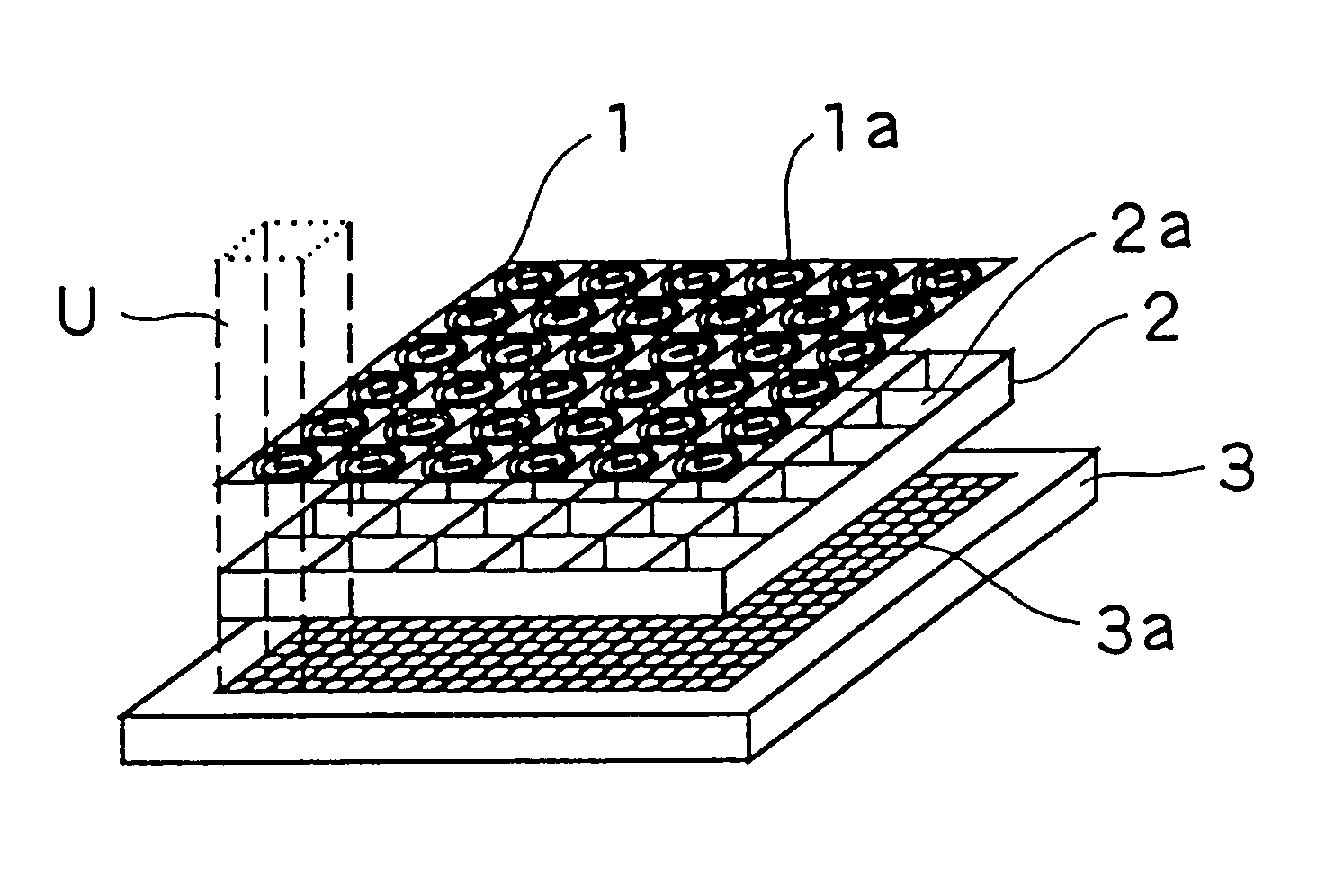
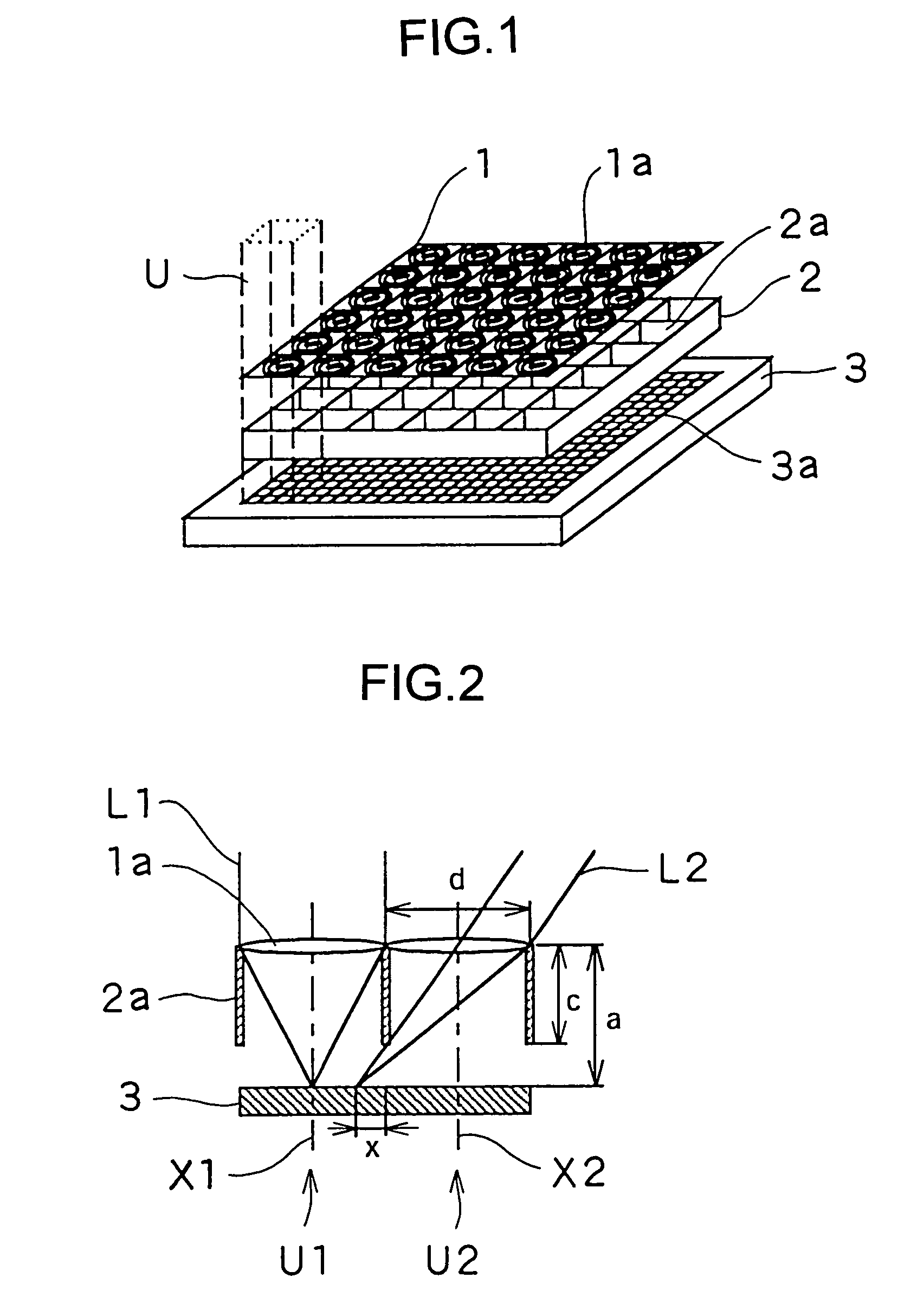
InactiveUS7009652B1Easy constructionHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesLight beamImage formation
An image input apparatus has a photoelectric converter element having a flat photosensitive surface and an image formation unit array having a plurality of image formation units arranged in an array. This image formation units individually receive light beams substantially from an identical area and focus the received light beams on different regions of the photosensitive surface of the photoelectric converter element to form images thereon.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD +1
Image Pickup Apparatus, Image Processing Method, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20080012969A1High-quality image dataTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingExposure control
An image pickup apparatus includes an image pickup device that has high-sensitivity pixel devices receiving a relatively large amount of light and low-sensitivity pixel devices receiving a relatively small amount of light, an exposure control unit independently controlling exposure periods of the high-sensitivity pixel devices and the low-sensitivity pixel devices, and an image generation unit performing image generation on the basis of an output signal of the image pickup device. The image generation unit compares a high-sensitivity pixel evaluation image generated using data output from the high-sensitivity pixel devices with a low-sensitivity pixel evaluation image generated using data output from the low-sensitivity pixel devices by obtaining a difference or ratio between pixel values of corresponding pixels in the two evaluation images, and performs different types of image processing for a region composed of pixels each having a small difference and a region composed of pixels each having a large difference.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
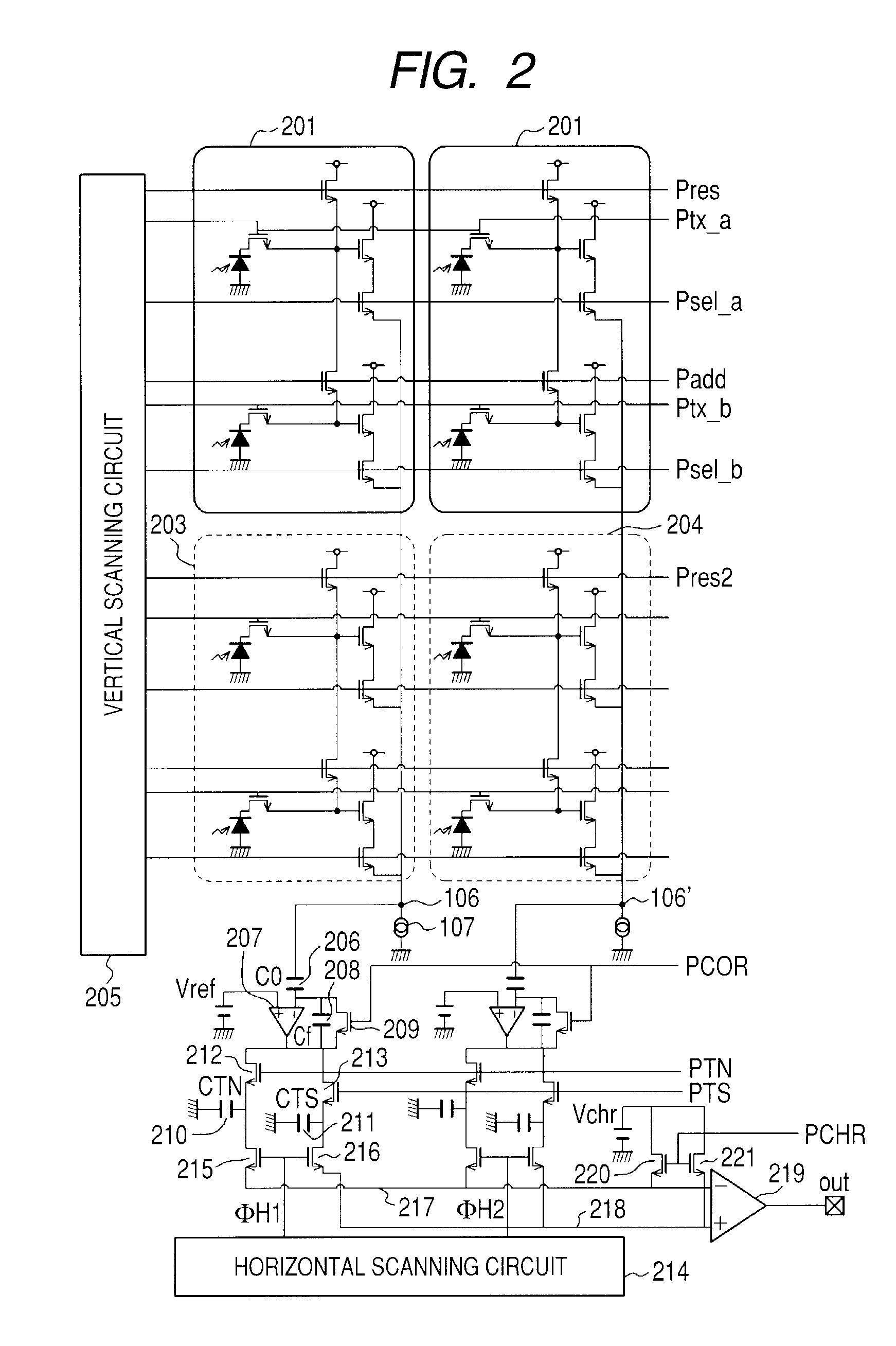
Image pickup device and image pickup system
ActiveUS20060044439A1Prevent floweringTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMOSFETEngineering
Unit cells each having a plurality of photodiodes 101a and 101b, a plurality of transfer MOSFETs 102a and 102b provided in correspondence to the plurality of photodiodes, respectively and a common amplifying MOSFET 104 for amplifying and outputting signals read out from the plurality of diodes are arranged two-dimensionally, and, plural photodiodes are disposed around the photodiode 101b and trapping regions 130, 134, 135 and 132 are for trapping excessive carriers from the photodiode 101b are provided between the photodiode 101b and the plural photodiodes, respectively.
Owner:CANON KK
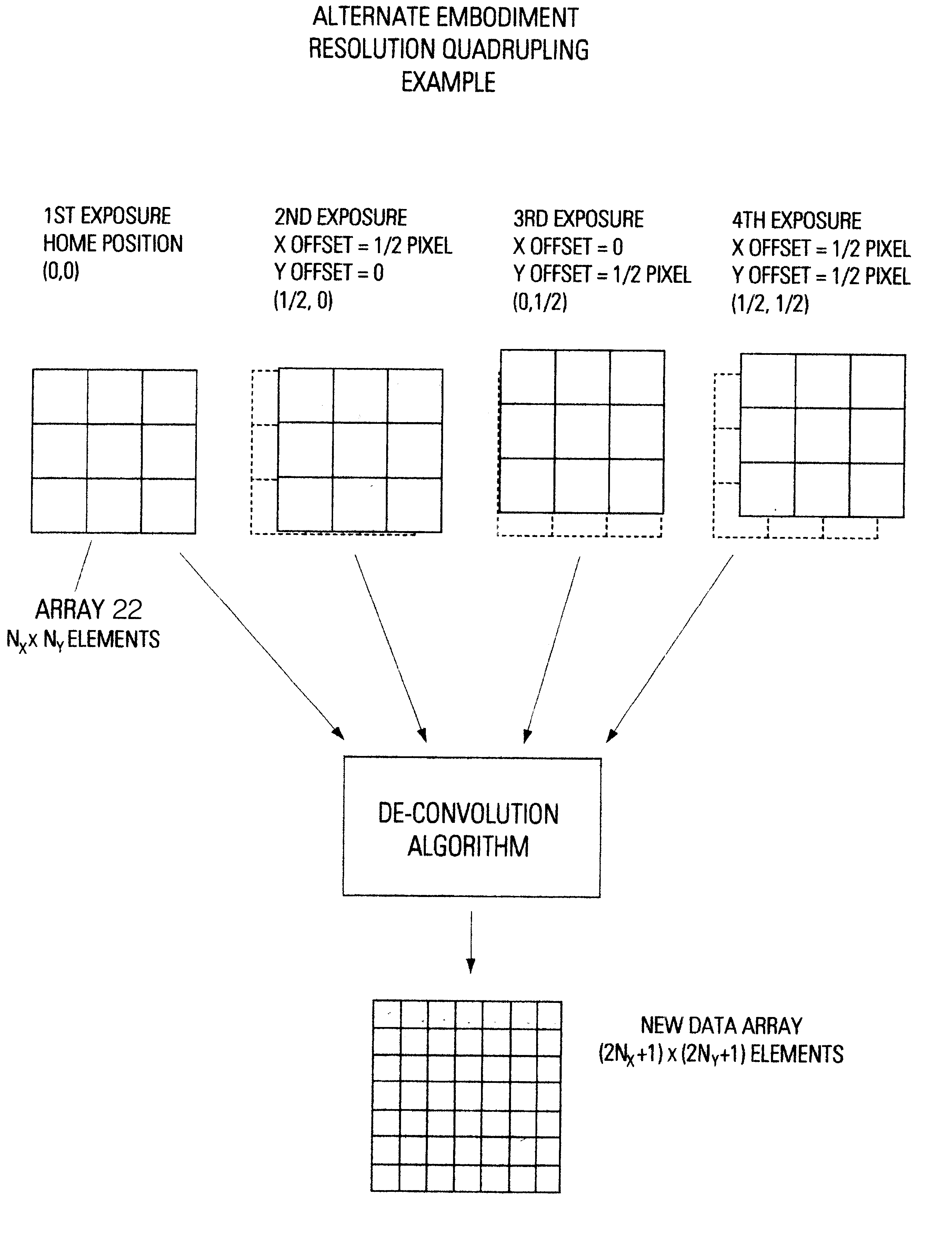
Resolution-enhancement method for digital imaging
InactiveUS6570613B1High resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingImage resolution
A method for resolution enhancement of a still-image made by a digital imaging device. The method allows the use of high-aperture-ratio sensing arrays that produce resolution-enhancement, independent of the angle of view. Resolution-enhancement is achieved using a multiple-exposure technique of a sub-pixel overtap in conjunction with a whole-pixel shift. The method suppresses color-aliasing in a multiple-exposure native-resolution mode and enables the use of a single camera for single-exposure and multiple-exposure modes.
Owner:HOWELL
Electronic image sensor
InactiveUS20060164533A1Avoid complicationsAccurate exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFrame rate
An electronic imaging sensor. The sensor includes an array of photo-sensing pixel elements for producing image frames. Each pixel element defines a photo-sensing region and includes a charge collecting element for collecting electrical charges produced in the photo-sensing region, and a charge storage element for the storage of the collected charges. The sensor also includes charge sensing elements for sensing the collected charges, and charge-to-signal conversion elements. The sensor also includes timing elements for controlling the pixel circuits to produce image frames at a predetermined normal frame rate based on a master clock signal (such as 12 MHz or 10 MHz). This predetermined normal frame rate which may be a video rate (such as about 30 frames per second or 25 frames per second) establishes a normal maximum per frame exposure time. The sensor includes circuits (based on prior art techniques) for adjusting the per frame exposure time (normally based on ambient light levels) and novel frame rate adjusting features for reducing the frame rate below the predetermined normal frame rate, without changing the master clock signal, to permit per frame exposure times above the normal maximum exposure time. This permits good exposures even in very low light levels. (There is an obvious compromise of lowering of the frame rate in conditions of very low light levels, but in most cases this is preferable to inadequate exposure.) These adjustments can be automatic or manual.
Owner:E PHOCOS
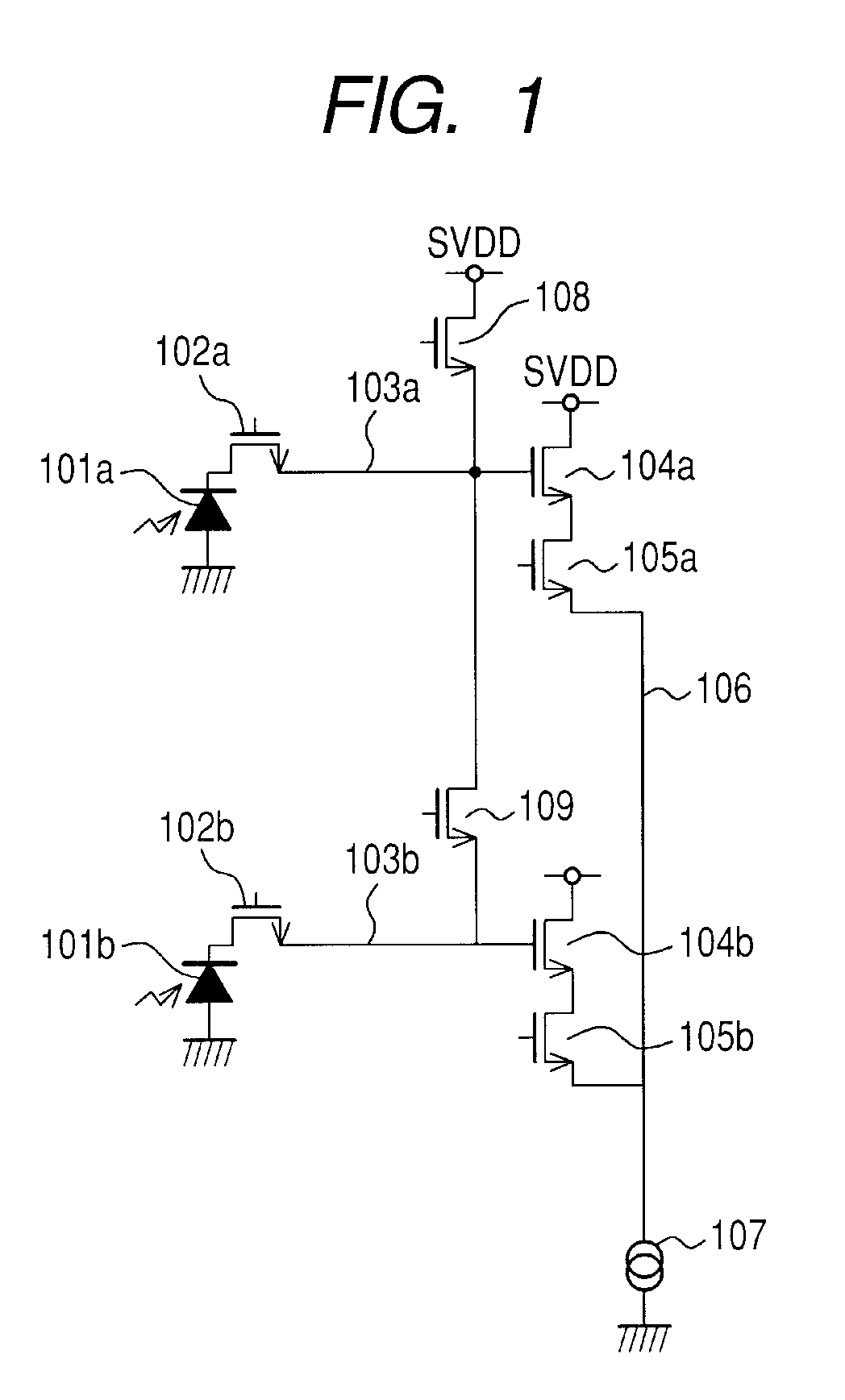
Solid-state imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100182465A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A solid-state imaging apparatus wherein an FD capacitor value is variable without increasing the number of elements. There is provided a solid-state imaging apparatus including a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction, for generating an electric charge by photoelectric conversion; a plurality of transfer transistors each connected to each of the photoelectric conversion elements, for transferring the electric charge generated by the plurality of photoelectric conversion elements; a plurality of floating diffusion regions for holding the electric charge transferred by the transfer transistors; a plurality of amplifiers each connected to each of the floating diffusion regions, for amplifying a signal based on the electric charge in the plurality of floating diffusion regions; and a connecting unit for connecting and disconnecting between the plurality of floating diffusion regions.
Owner:CANON KK
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS6956605B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
To provide an image pickup apparatus capable of adding signals from a plurality of photoelectric conversion portions, an image pickup apparatus including a plurality of unit cells arranged in an array, each unit cell including a plurality of photoelectric conversion portions and a common circuit for inputting signals from the plurality of photoelectric conversion portions and outputting the signals from the unit cell, a first addition circuit for adding the signals from the plurality of photoelectric conversion portions in the unit cell, and a second addition circuit for adding the signals from the plurality of photoelectric conversion portions outside the unit cell is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS20100020209A1Reduce image sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight detectorVisible spectrum
Disclosed are an imaging method and apparatus. The apparatus may include an image sensor that may include a plurality of pixels, wherein at least one pixel of the plurality of pixels includes a light-detector element and a filter that band-passes a select visible light component to the light-detector element and band-passes a select non-visible light component to the light-detector element. A color value and depth value may be obtained using the same pixel through the image sensor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for demosaicing images with highly correlated color channels
ActiveUS20120206582A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationSpatial correlationImage resolution
In one embodiment of the invention, an apparatus is disclosed including an image sensor, a color filter array, and an image processor. The image sensor has an active area with a matrix of camera pixels. The color filter array is in optical alignment over the matrix of the camera pixels. The color filter array assigns alternating single colors to each camera pixel. The image processor receives the camera pixels and includes a correlation detector to detect spatial correlation of color information between pairs of colors in the pixel data captured by the camera pixels. The correlation detector further controls demosaicing of the camera pixels into full color pixels with improved resolution. The apparatus may further include demosaicing logic to demosaic the camera pixels into the full color pixels with improved resolution in response to the spatial correlation of the color information between pairs of colors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20090128658A1Accurate brightnessPrevent color balanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsParallaxImaging processing
An image pickup apparatus includes an image-pickup lens having an aperture diaphragm, an image-pickup element that has a color filter which is periodically allocated colors in units of a predetermined unit array and that generates picked-up image data including pixel data of colors using received light, the color filter being adjacent to a light receiving surface, a microlens array unit that is arranged on an image forming surface of the image-pickup lens and whose microlenses are each allocated a plurality of pixels of the image-pickup element, and an image processing unit that performs image processing on the picked-up image data generated by the image-pickup element. The image processing unit includes a parallax component image generation unit that generates a plurality of parallax component images and an interpolation processing unit that performs color interpolation processing for each of the parallax component images.
Owner:SONY CORP
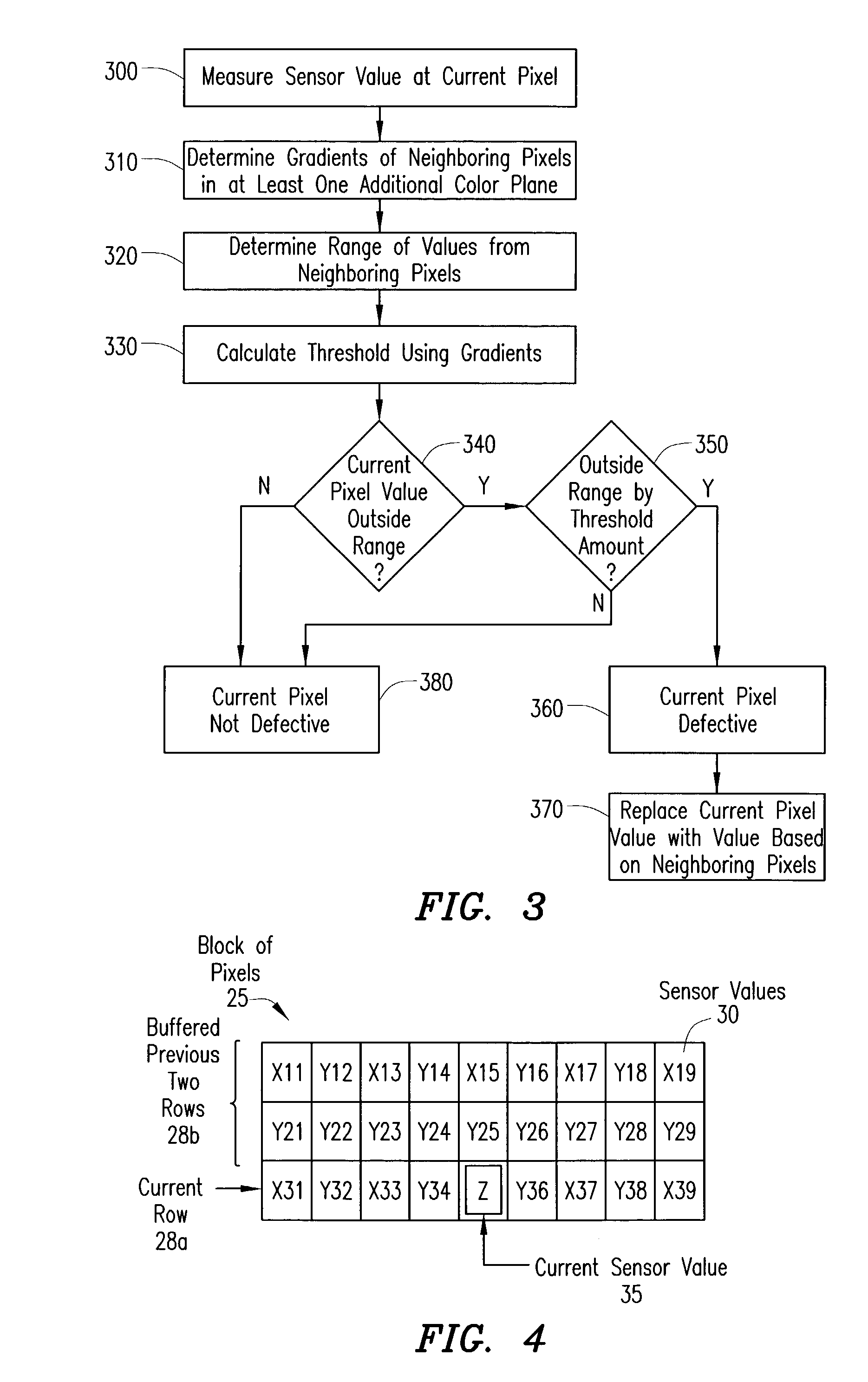
Method for detecting and correcting defective pixels in a digital image sensor
ActiveUS20040051798A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionColor image
A bad pixel correction (BPC) algorithm that can be implemented on the image sensor chip is provided for detecting and correcting defective pixels in a digital color image sensor. Gradients of neighboring pixels in at least one other color plane than the color plane of a current pixel and a range of sensor values from neighboring pixels in the same color plane as the current pixel are determined. If the sensor value of the current pixel is outside of the range by a threshold amount that is calculated using one or more of the gradients, the current pixel is determined to be a defective pixel, and replaced using the sensor values of the neighboring pixels in the same color plane.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Image pickup apparatus having plural pixels arranged two-dimensionally, and selective addition of different pixel color signals to control spatial color arrangement
InactiveUS6992714B1Preferable image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor filter arrayComputer science
An image pickup apparatus comprises a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix form, first color filters arranged in an oblique direction for the pixels, second and third color filters arranged so that a same color is arranged in a horizontal direction, a circuit for adding together signals of two or more pixels each having the first color filter, which are adjacent to each other in an oblique direction, and a circuit for adding together the signals of two or more pixels each having the second color filter, which are arranged in a horizontal direction, and for adding together the signals of two or more pixels each having the third color filter, which are arranged in the horizontal direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Electro-optic displays, and processes for their production
ActiveUS8902153B2Reduce edge effectsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceComputer science
A color display has continuous areas of a single color covering a plurality of sub-pixel electrodes. Each sub-pixel of a given color has sub-pixels of the same given color disposed along at least two of its adjacent edges. Each area of a single color may cover a 2×2 array of sub-pixel electrodes. The colors used may be red / green / blue / white (RGBW), red / green / blue / yellow (RGBY), or orange / lime / purple / white.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
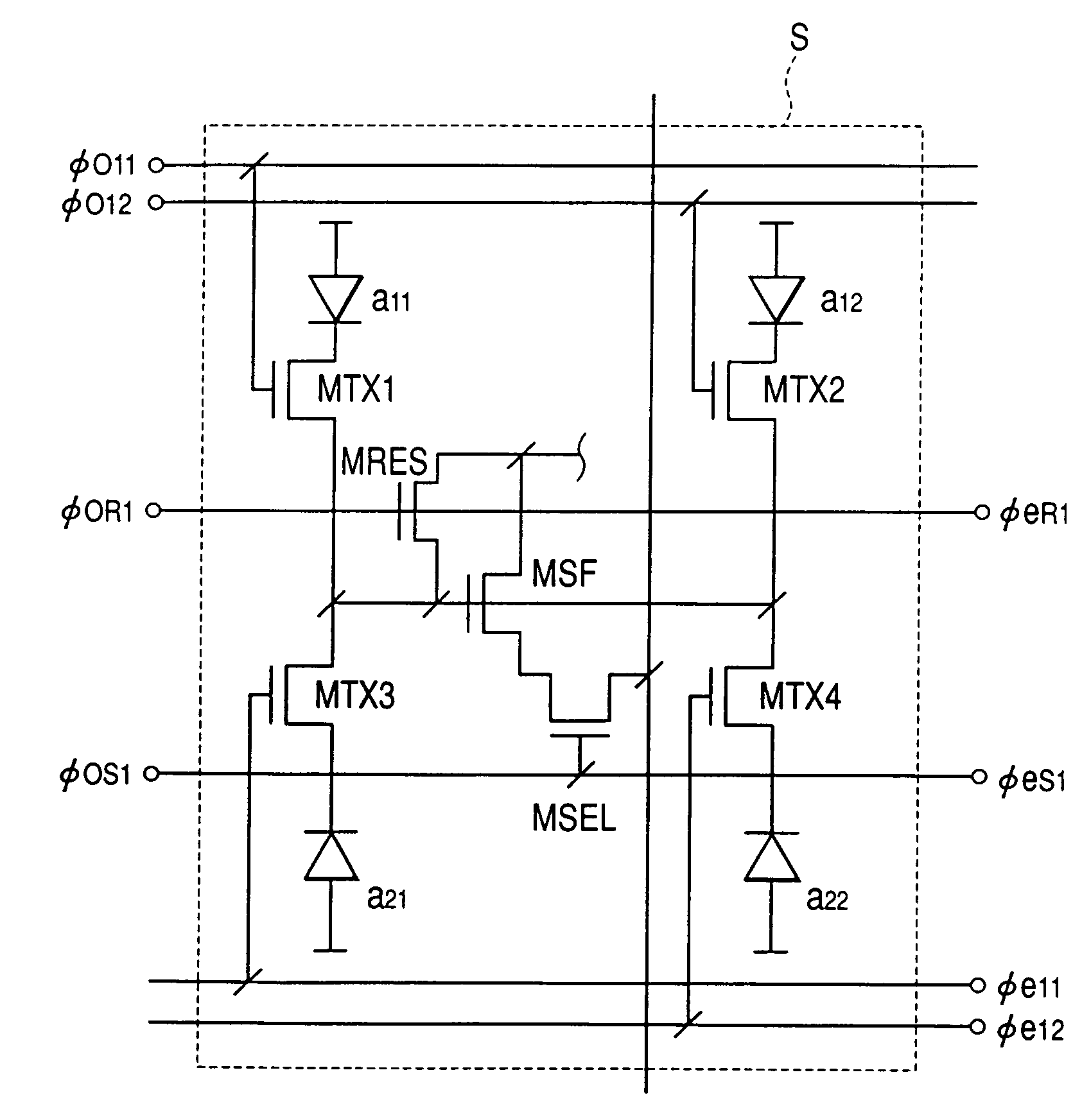
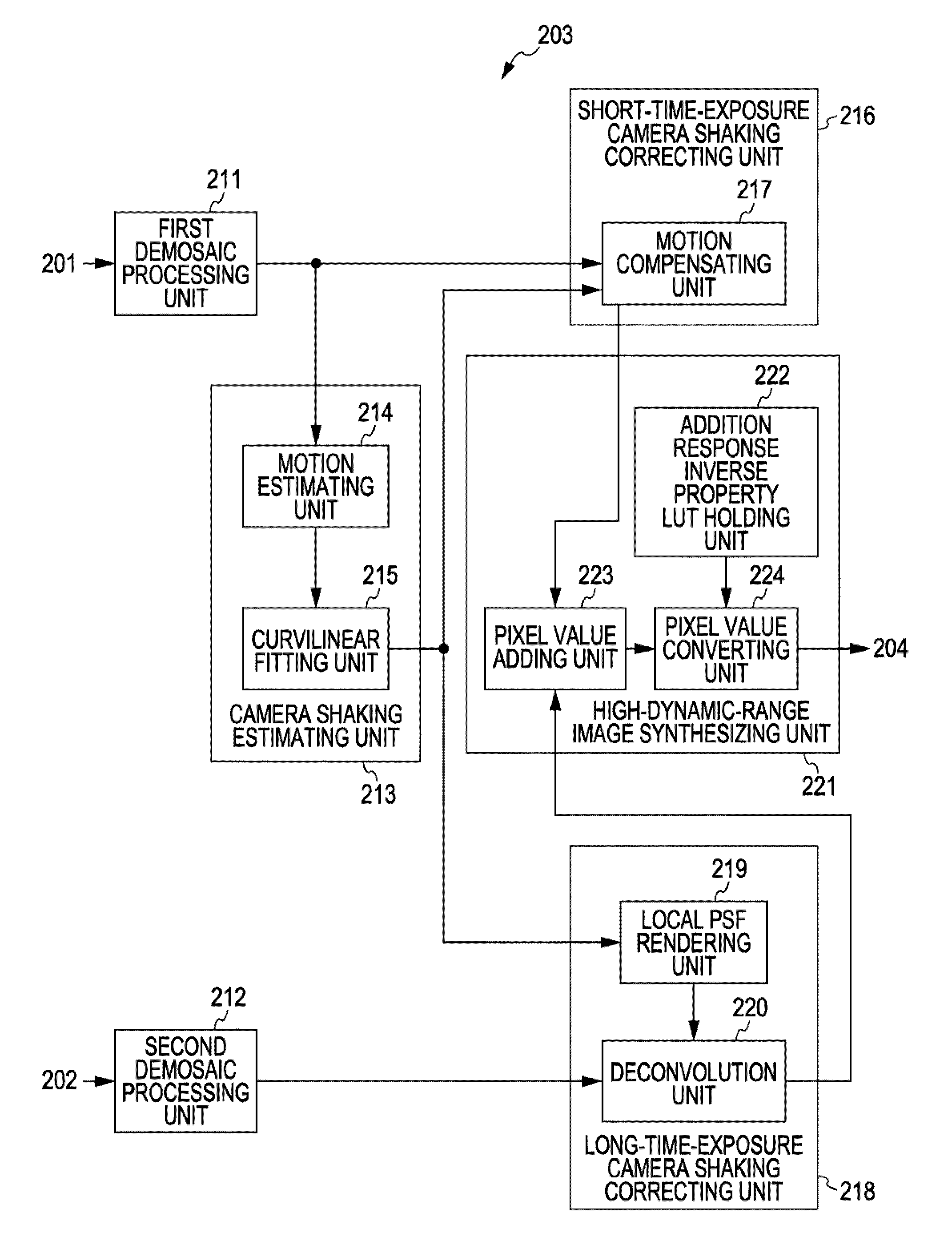
Image Processing Apparatus, Imaging Apparatus, Solid-State Imaging Device, Image Processing Method and Program
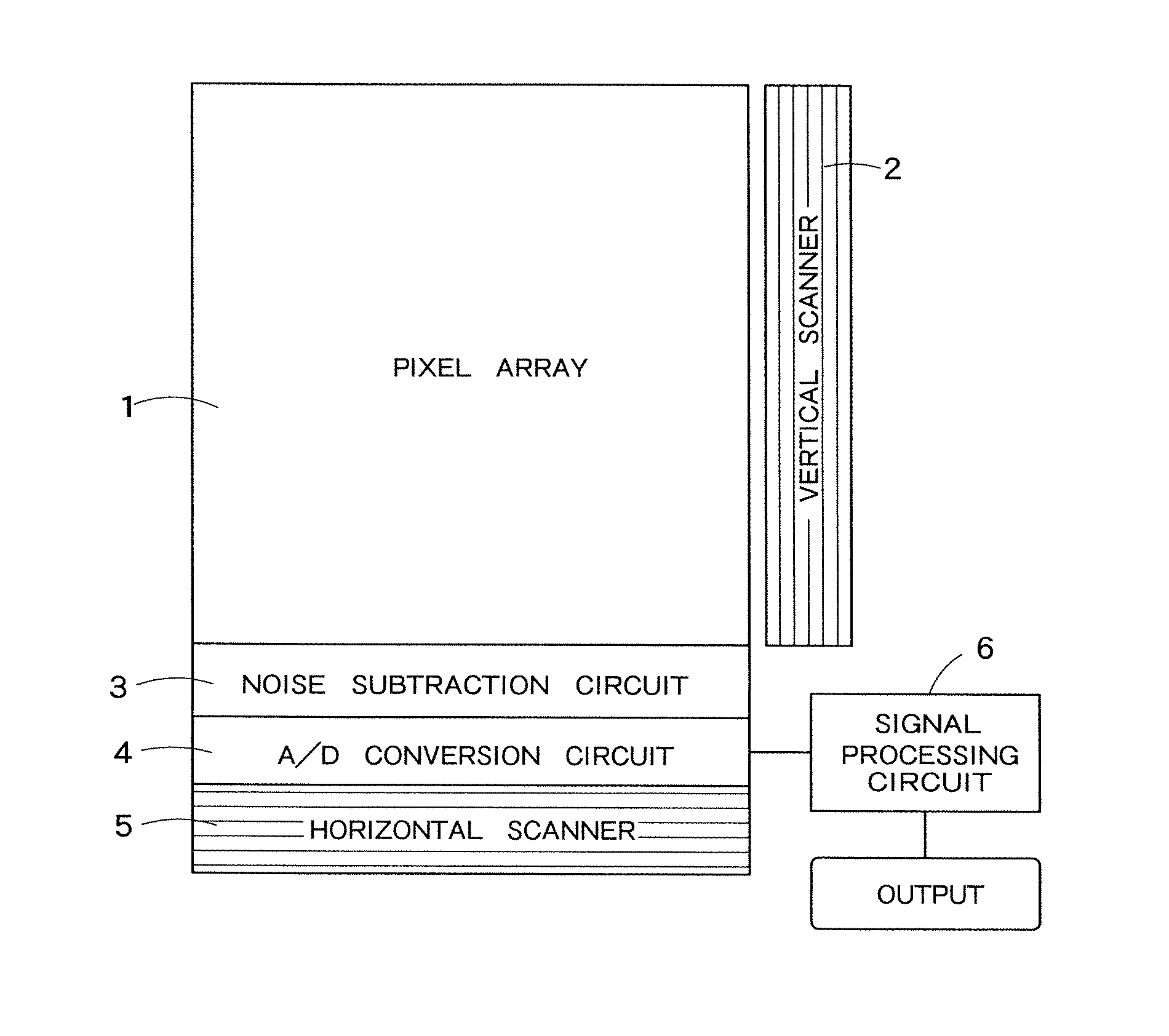
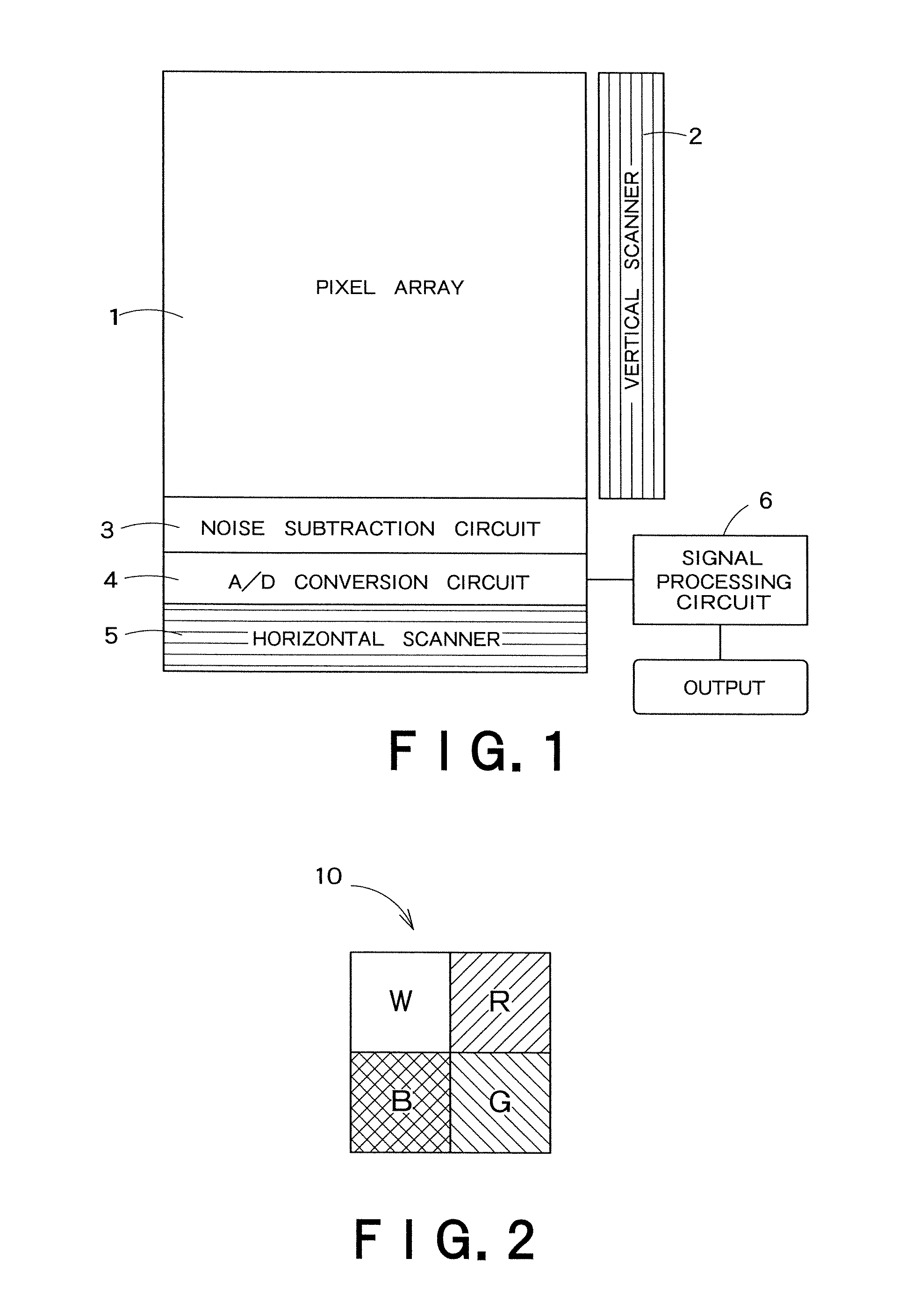
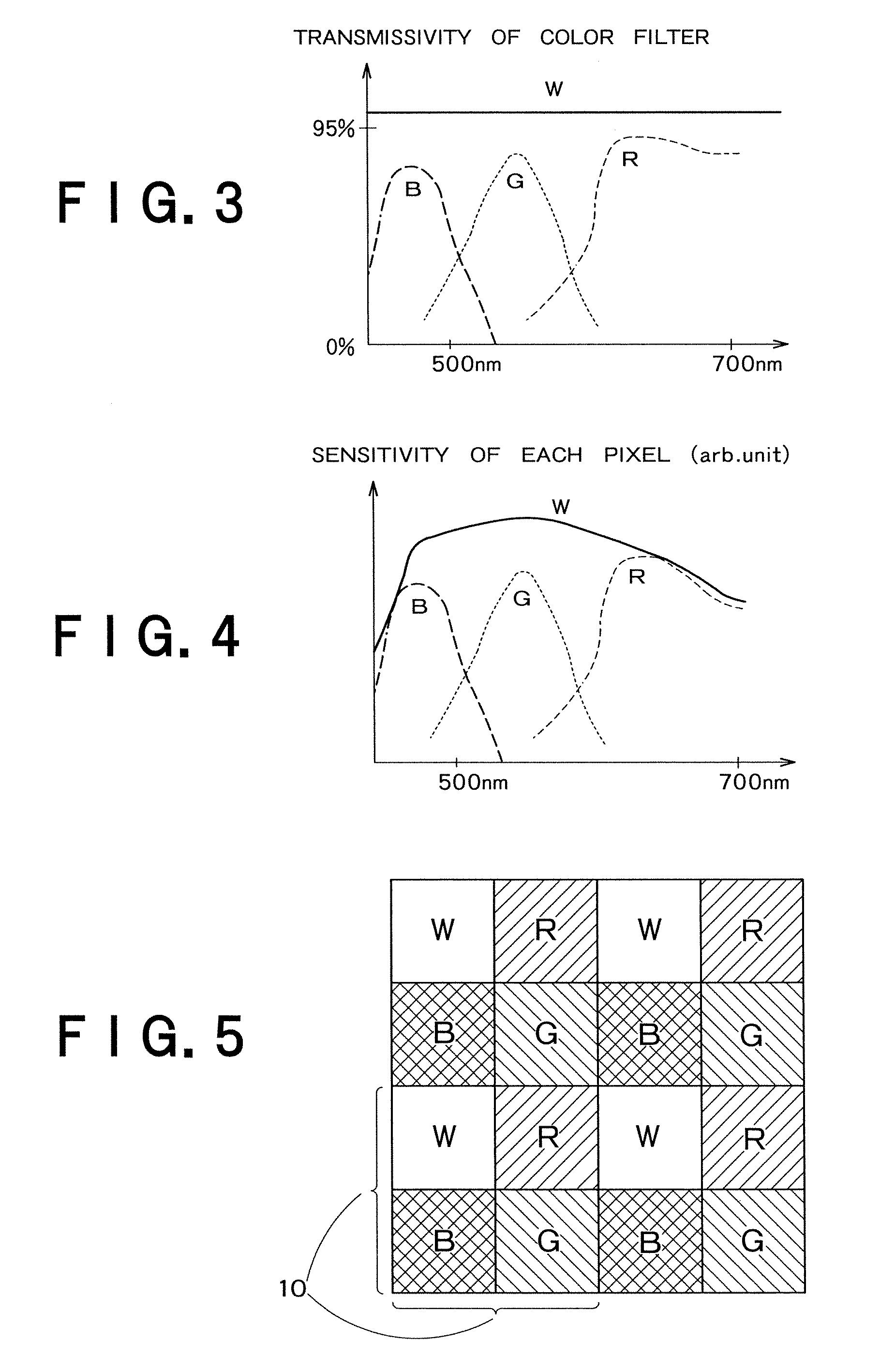
InactiveUS20100053346A1Television system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceImaging processingTime segment
An image processing apparatus includes: a shaking estimating unit configured to estimate the shaking information of an image generated within a predetermined period of time; a short-time-exposure shaking correcting unit configured to correct the shaking of a plurality of short-time-exposure images generated due to intermittent exposure within the predetermined period of time based on the estimated shaking information; a long-time-exposure shaking correcting unit configured to correct the shaking of a long-time-exposure image generated due to consecutive exposure within the predetermined period of time based on the estimated shaking information; and an image synthesizing unit configured to synthesize the corrected short-time-exposure images and the corrected long-time-exposure image.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
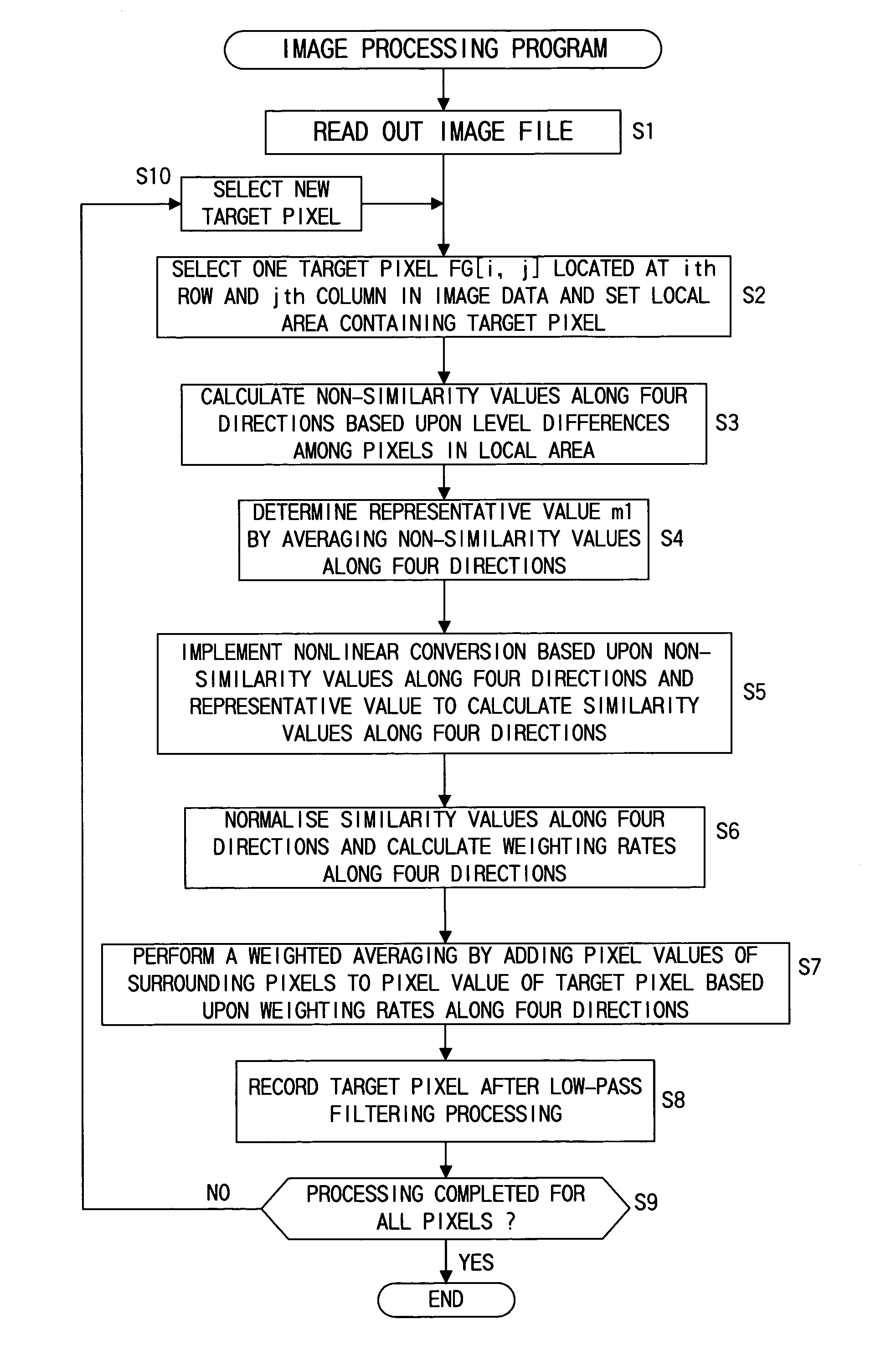
Image processing method for direction dependent low pass filtering
InactiveUS7016549B1Without losing fine structure of imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingJaggies
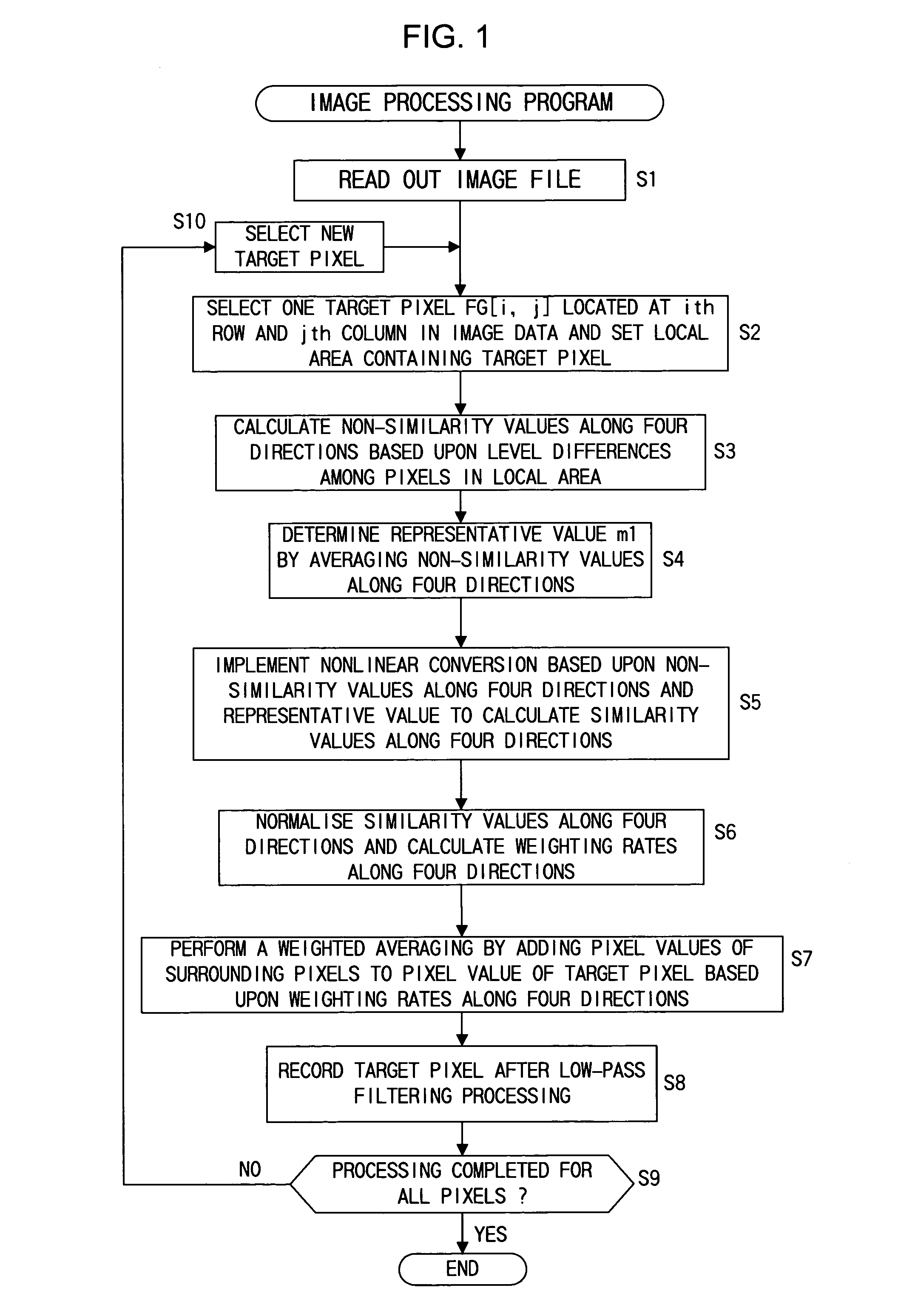
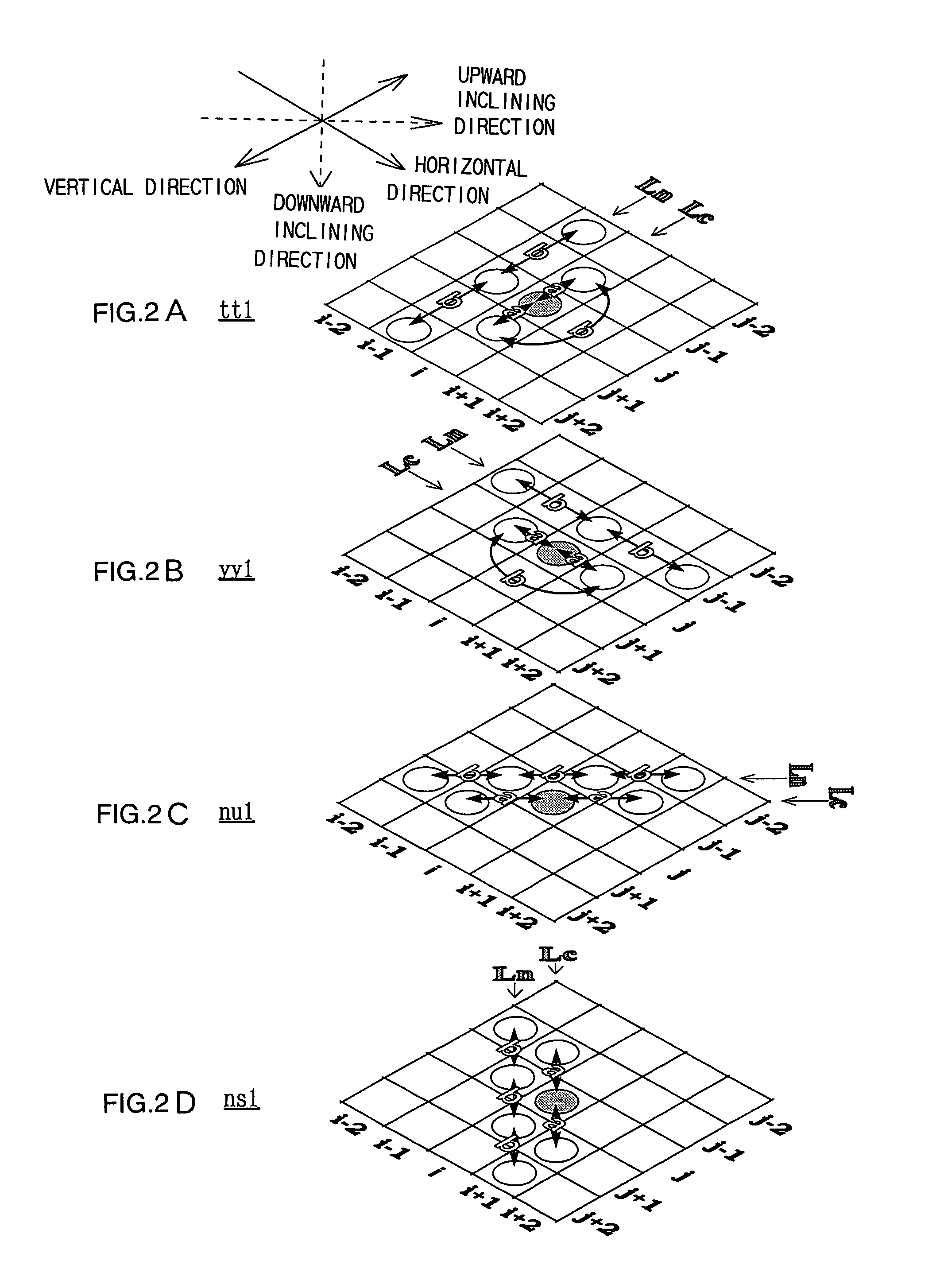
First similarity values along at least four directions are ascertained within a local area containing a target pixel and weighted averaging is performed by adding the pixel values of pixels around the target pixel value to the pixel value of the target pixel, adding weight along a direction having a small first similarity value (along a direction manifesting a high degree of similarity). By incorporating the pixel value level differences among a plurality of pixels on adjacent lines extending adjacent to the target pixel into the first similarity values, it becomes possible to effectively remove jaggies that are difficult to eliminate in the prior art. Furthermore, by making a judgment on degrees of similarity by incorporating color information such as characteristics differences among different color pixels, a more accurate judgment can be made with regard to the image structure to enable very accurate direction-dependent low-pass filtering.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Solid-state image sensor and imaging apparatus equipped with solid-state image sensor
ActiveUS20100091161A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionImaging equipment
A solid-state image sensor executing photoelectric conversion for a subject image includes: a plurality of pixels disposed in a two-dimensional pattern and each equipped with a photoelectric conversion unit that generates and stores an electrical charge, wherein: the plurality of pixels are each one of a first pixel and a second pixel; the plurality of pixels are divided into a plurality of pixel blocks; the pixel blocks each include m×n pixels with m pixels and n pixels among the plurality of pixels set respectively along a columnar direction and along a row direction; at least one of the pixels in each pixel block is the first pixel; color filters assuming a single color are disposed at first pixels belonging to a common pixel block; and at least one pixel in at least one pixel block among the plurality of pixel blocks is the second pixel.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com