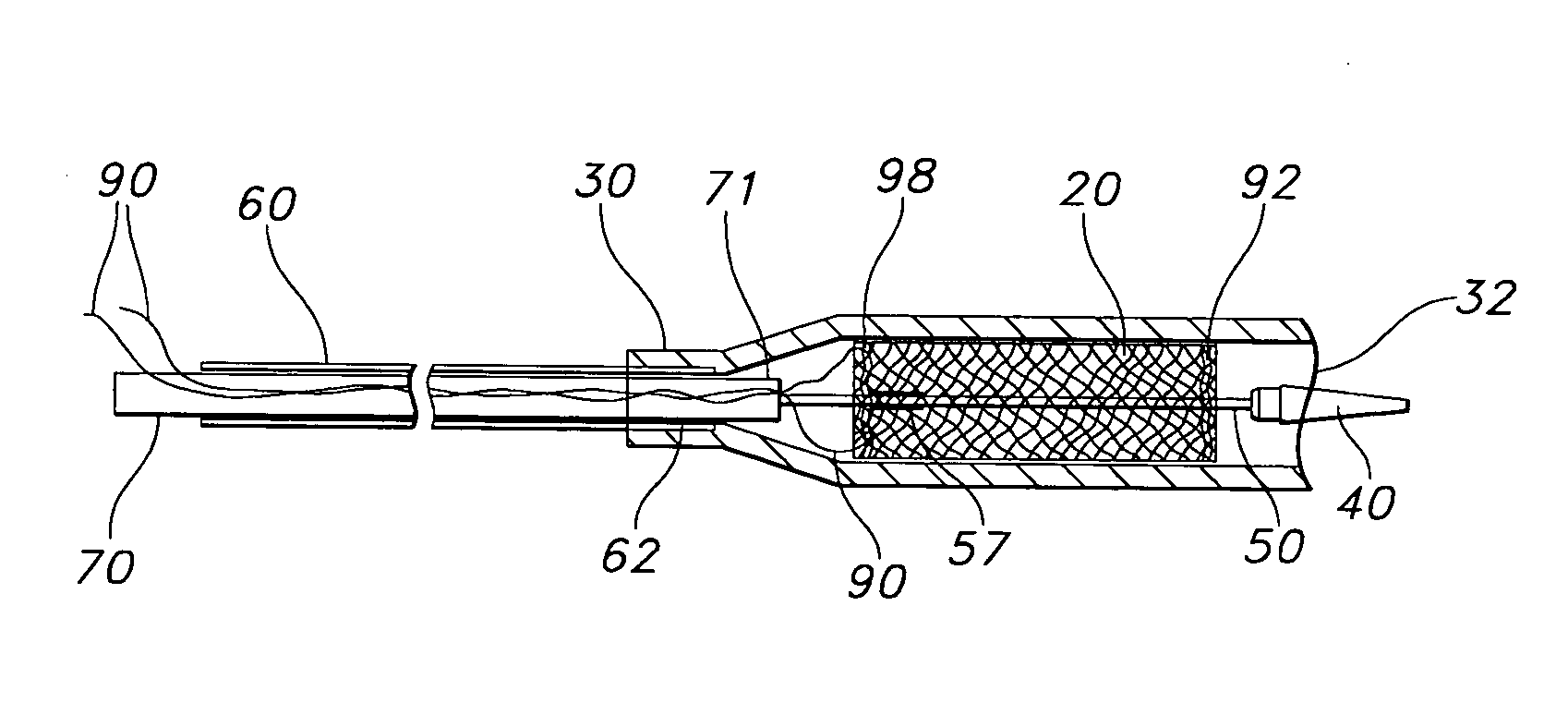
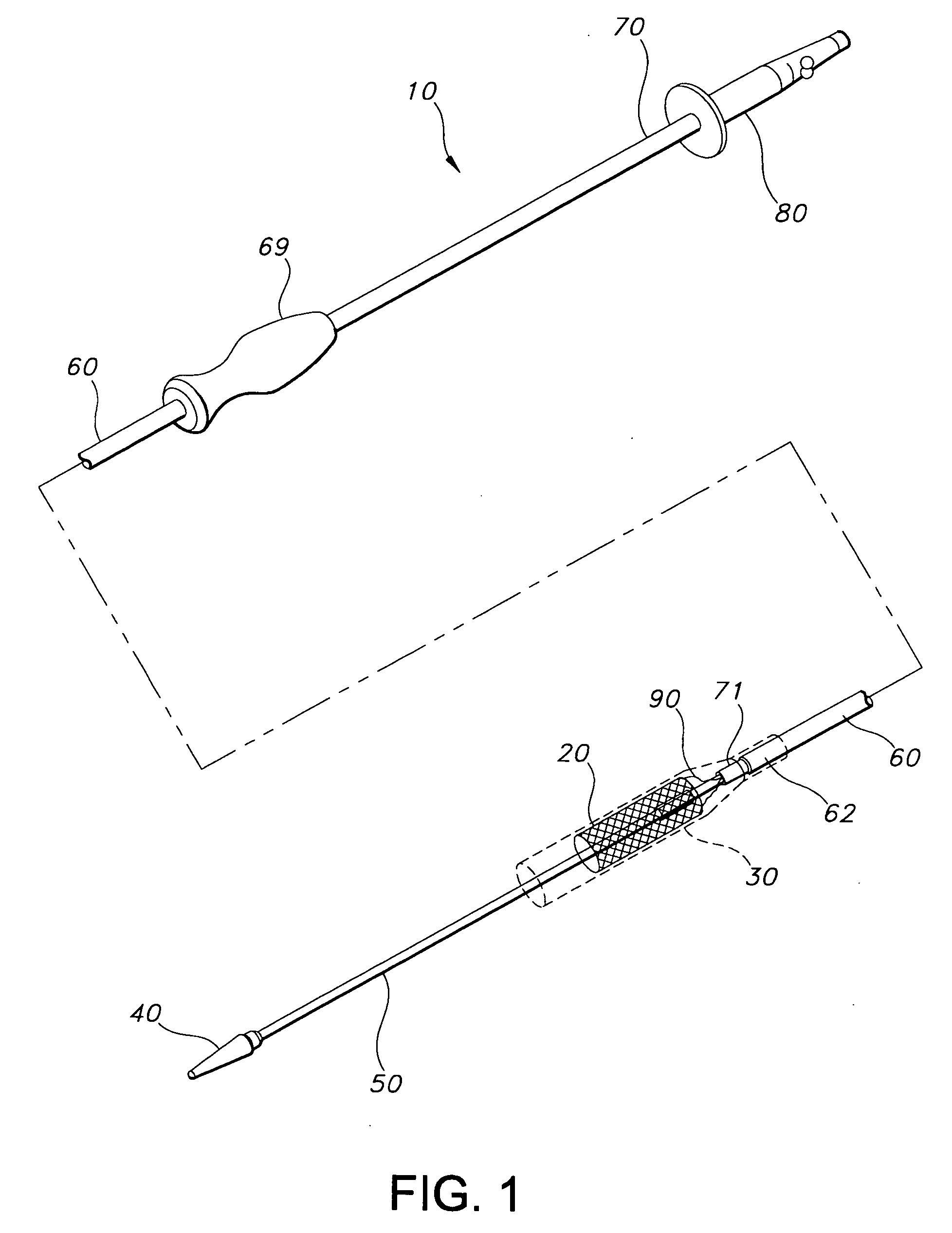
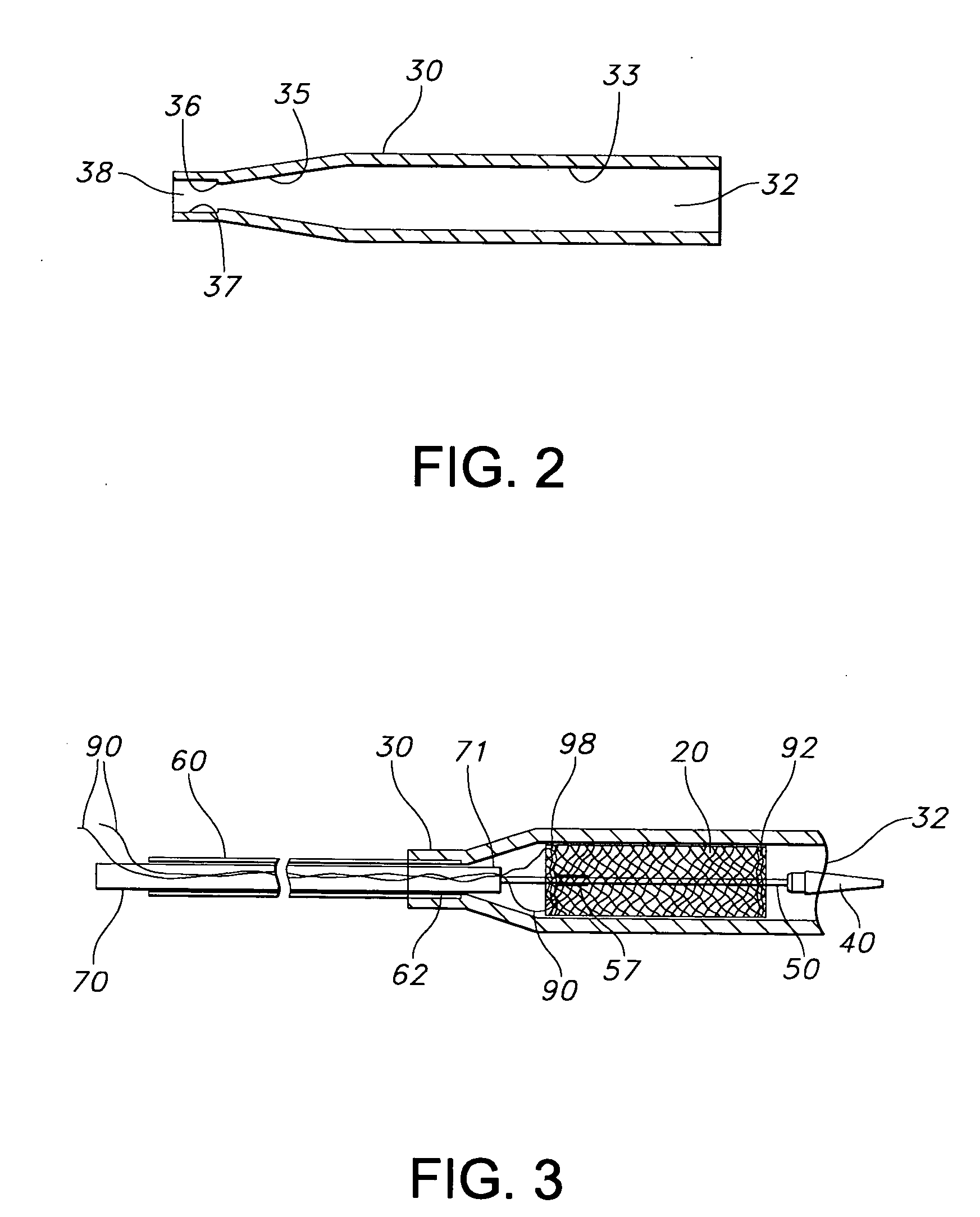
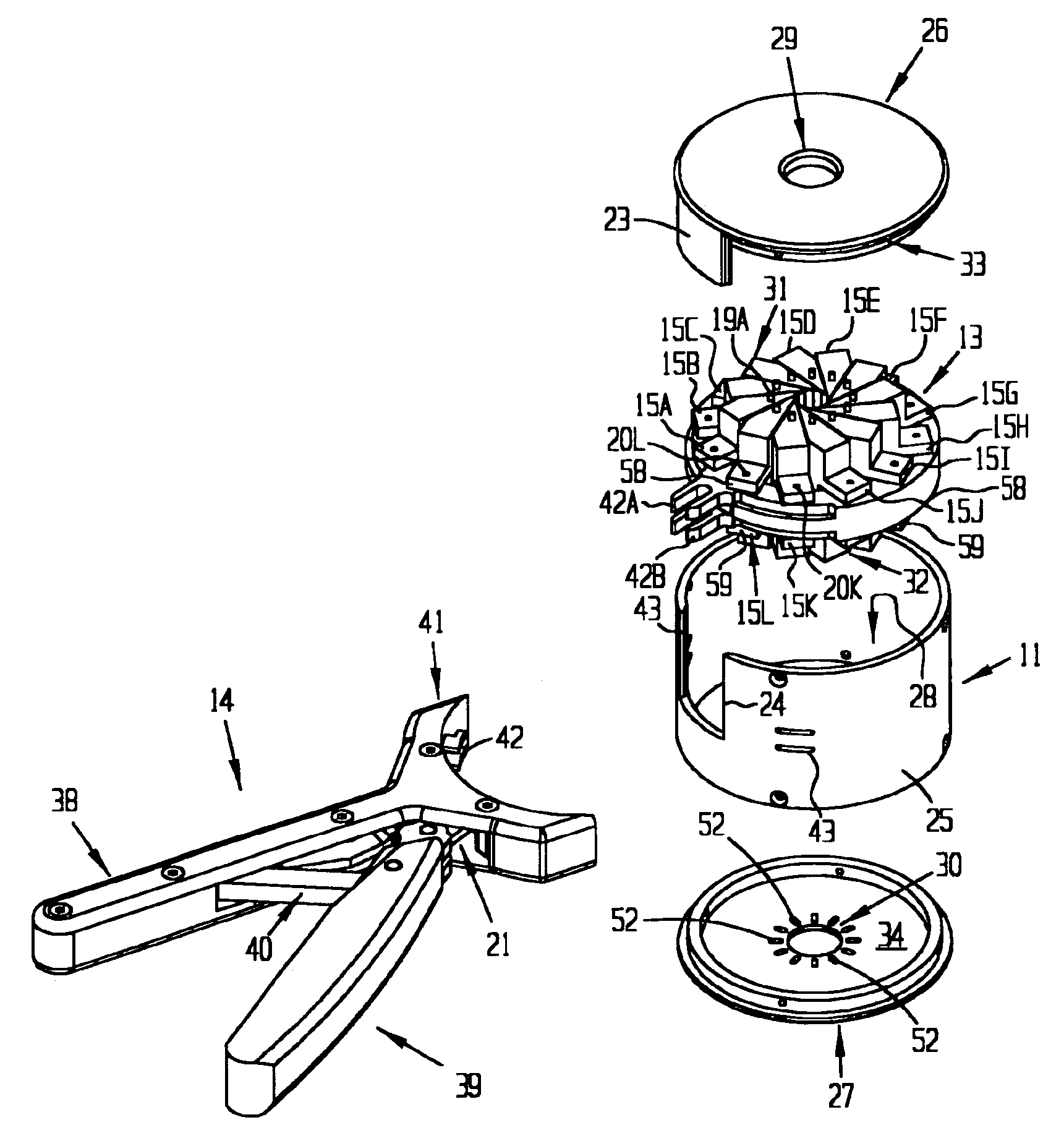
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
569 results about "Radial compression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
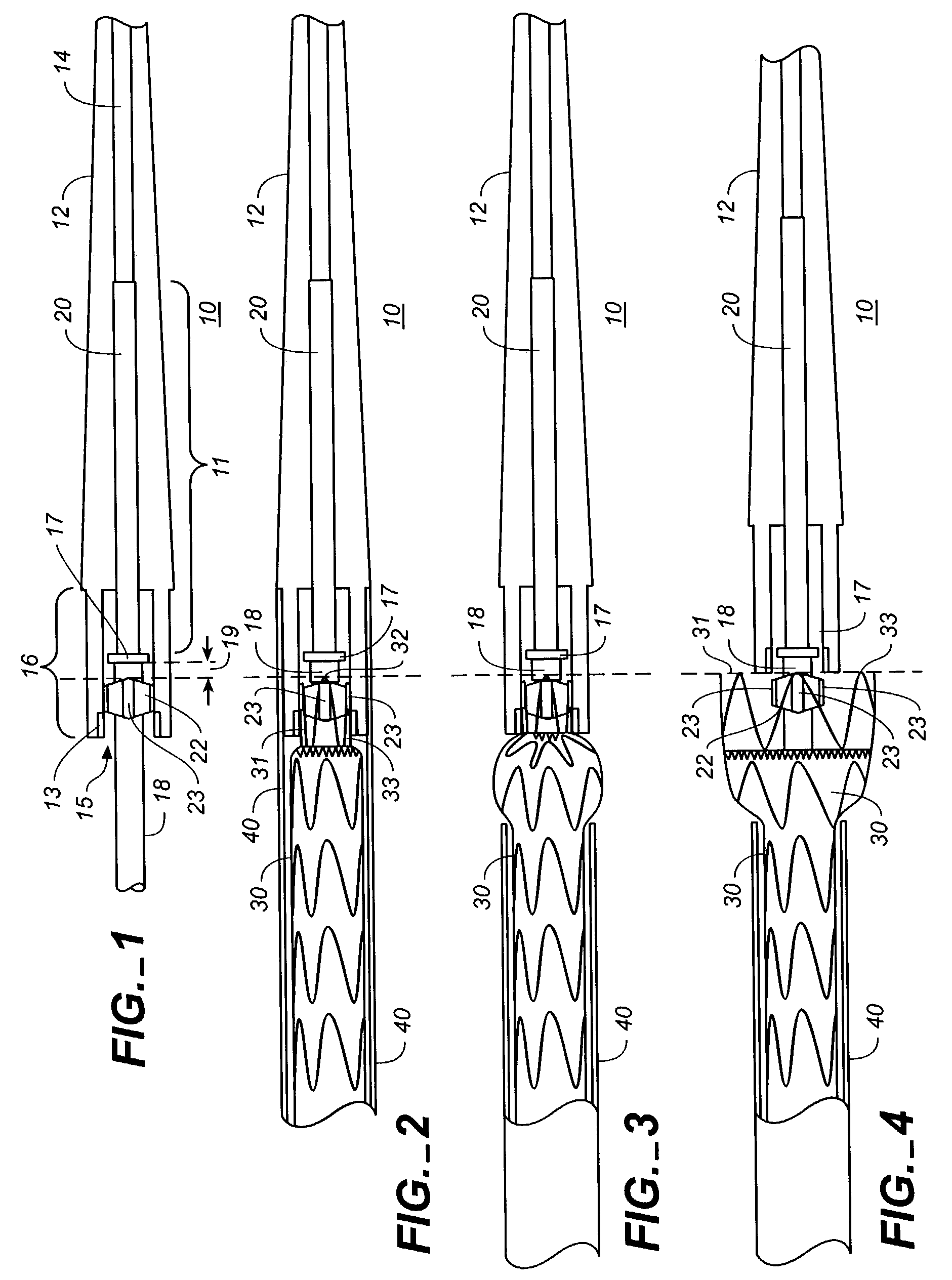
Heart valve
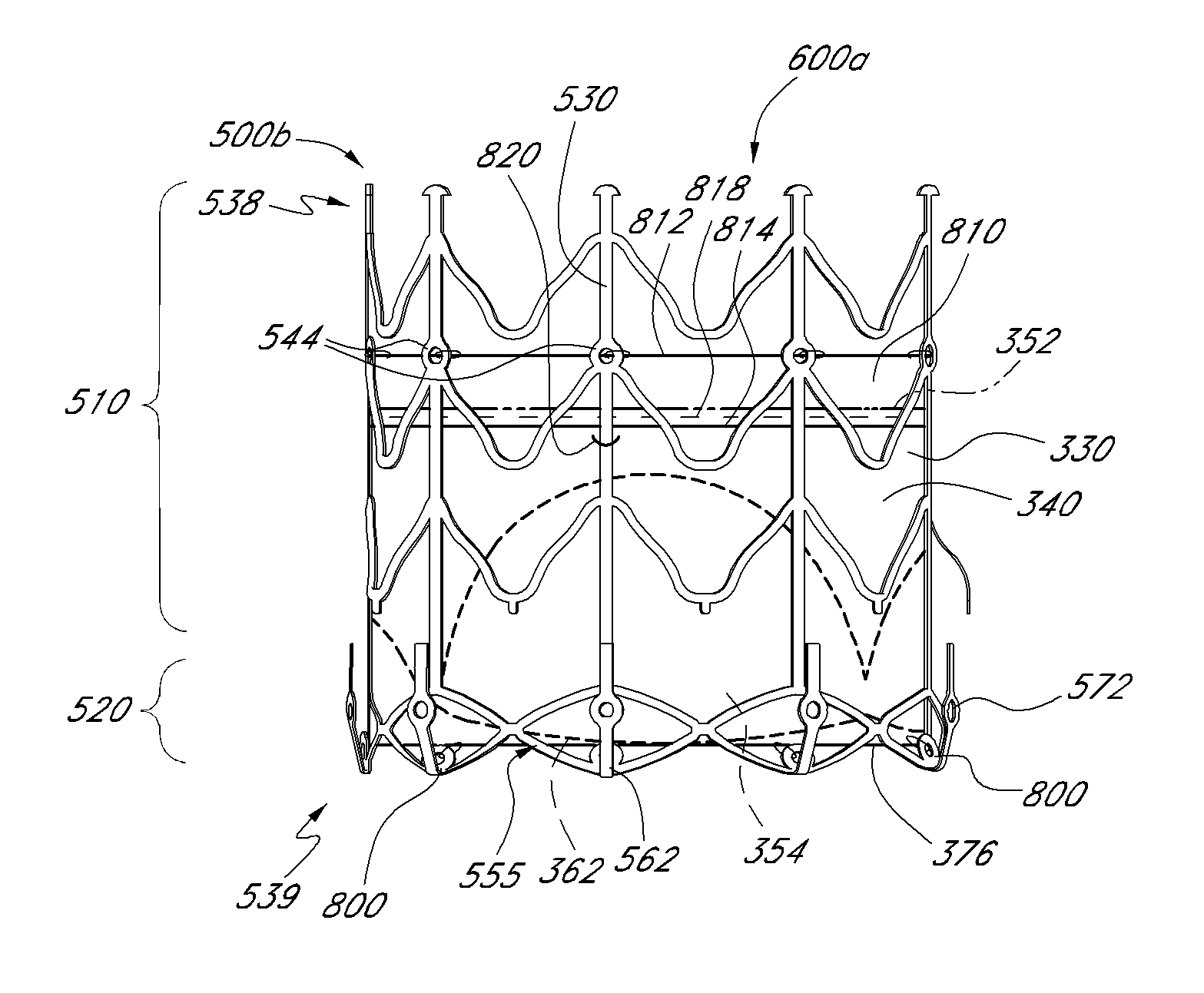
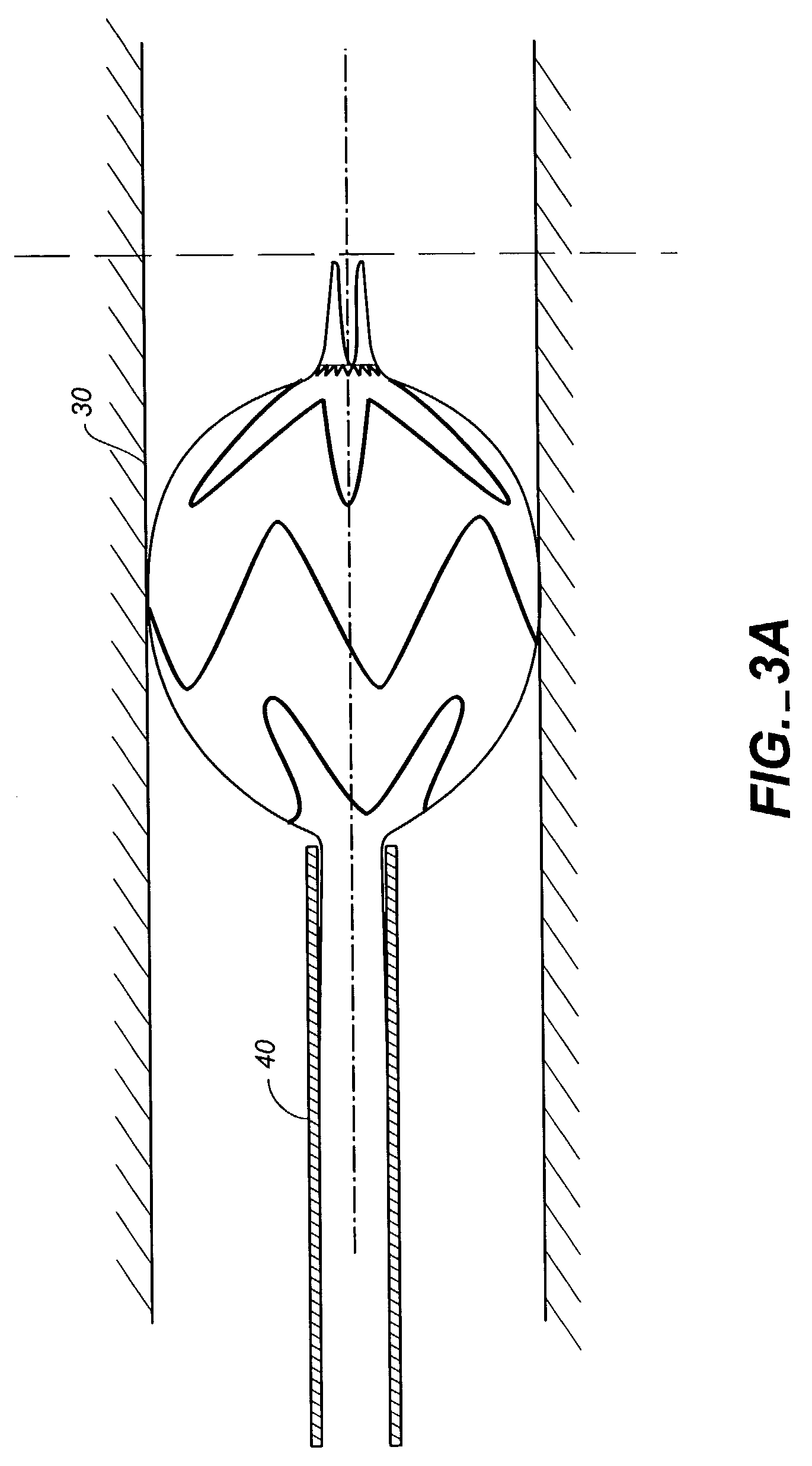
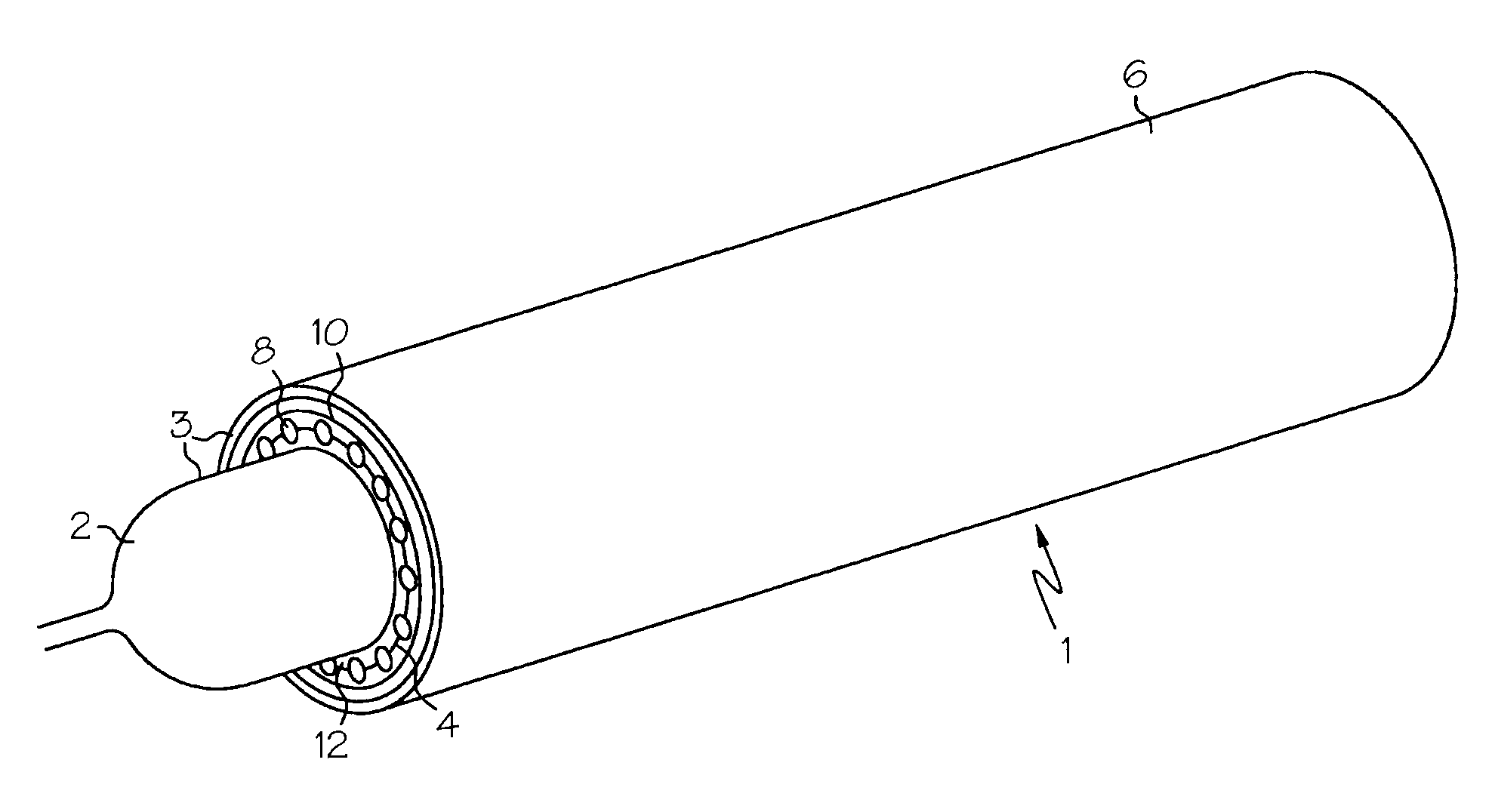
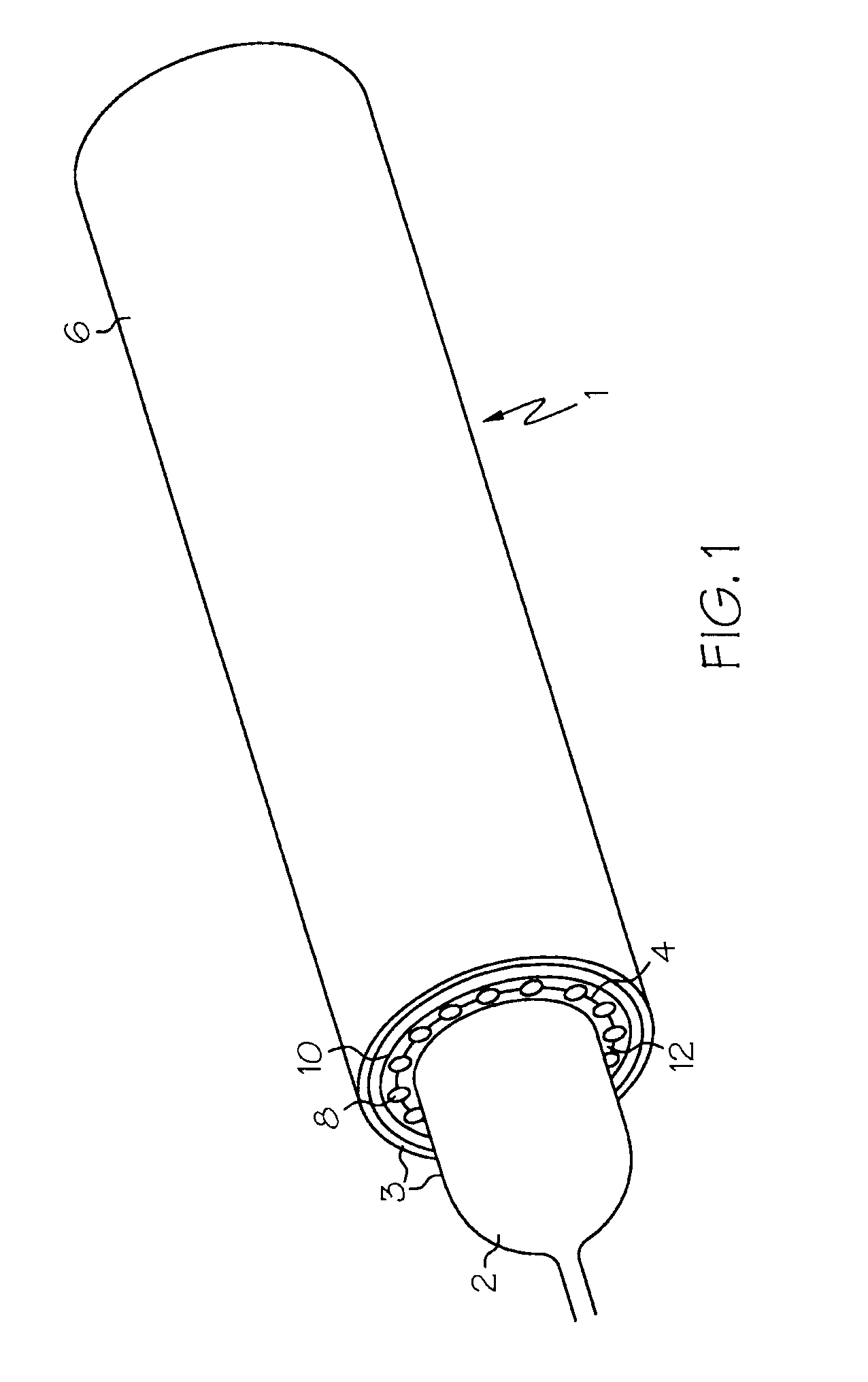
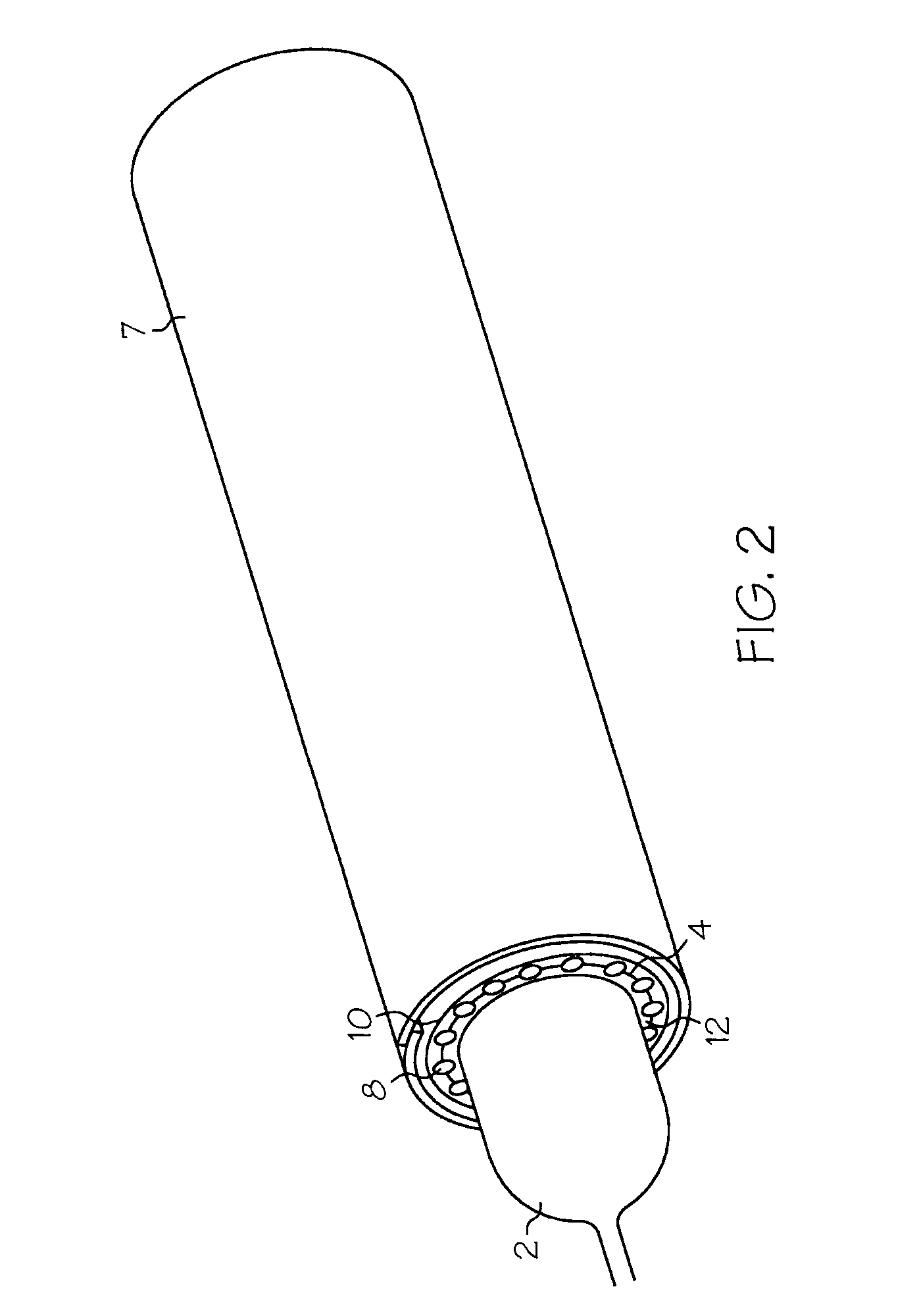
A replacement heart valve can comprise a valve body and an elongate frame. The valve body can define a plurality of leaflets adapted to move between an open state and a coapted state. The elongate frame can be configured to move between a radially compacted state and a radially expanded state, the frame comprising a plurality of struts. Stitches attach the valve body to the plurality of struts. At least one of the stitches can be a loose stitch configured to freely slide over the corresponding strut when the frame is moved between the radially compacted and radially expanded states.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Expandable impeller pump
ActiveUS7393181B2Easy to compressReduced form requirementsPropellersEngine manufactureImpellerEngineering
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
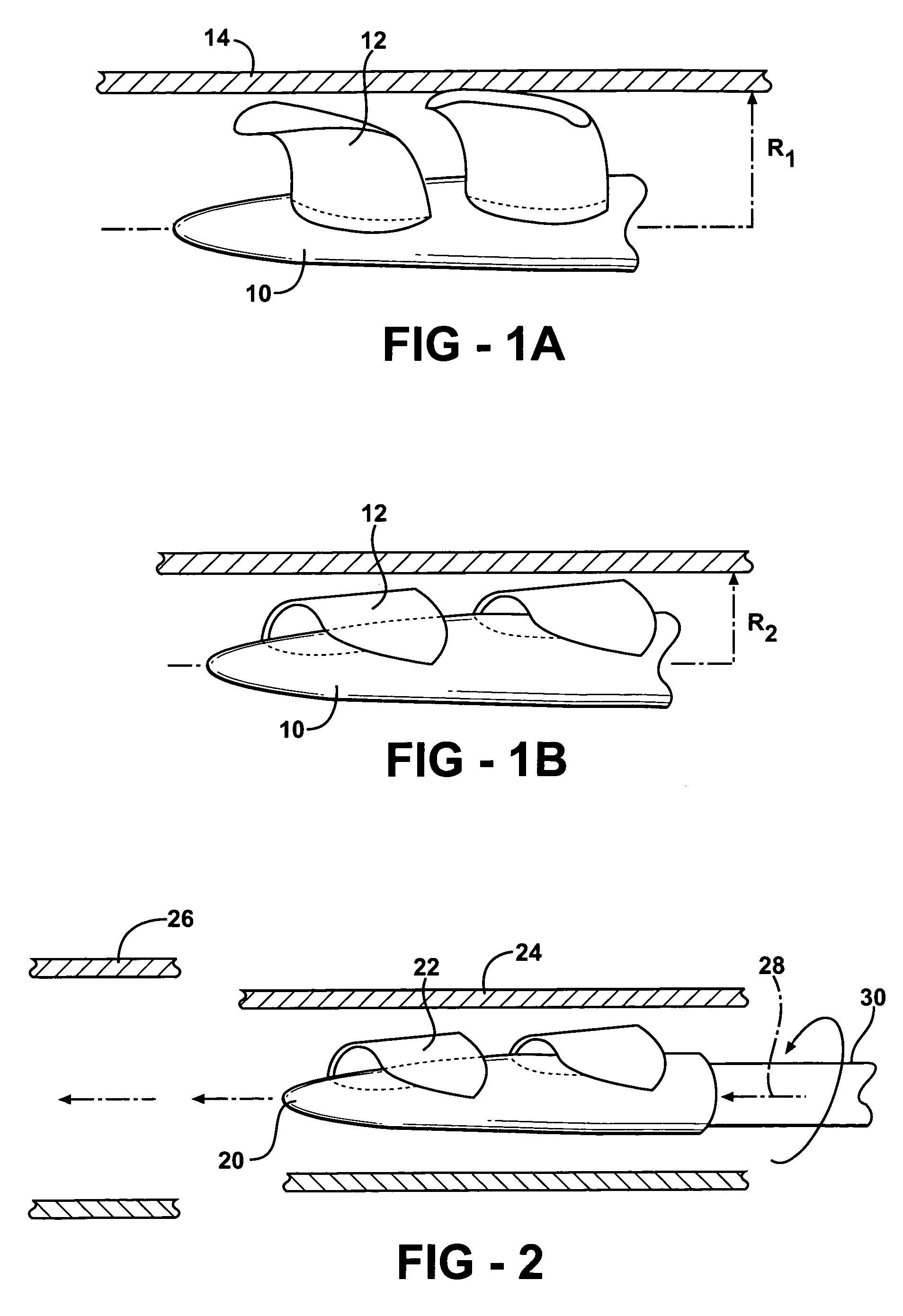
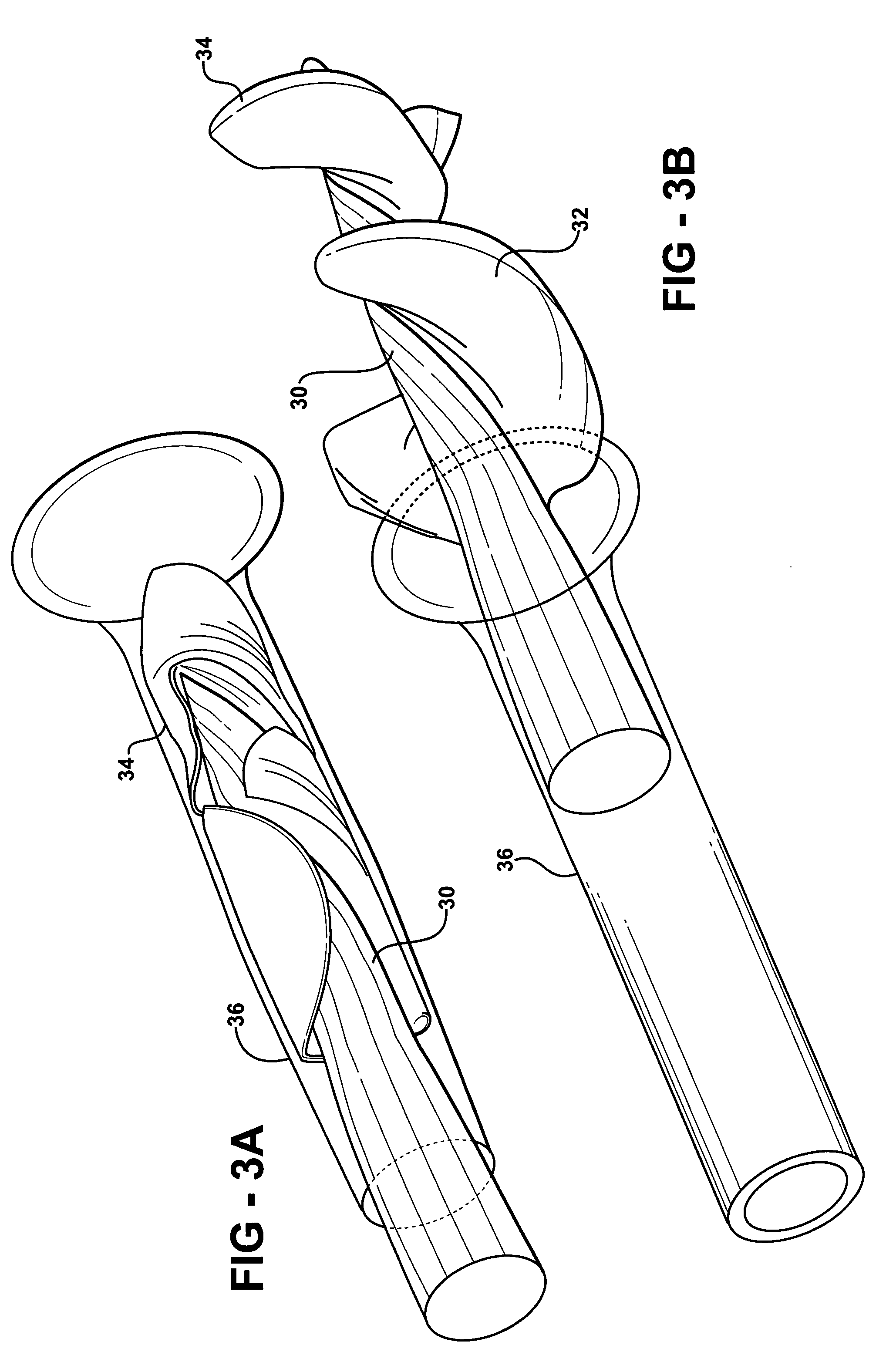
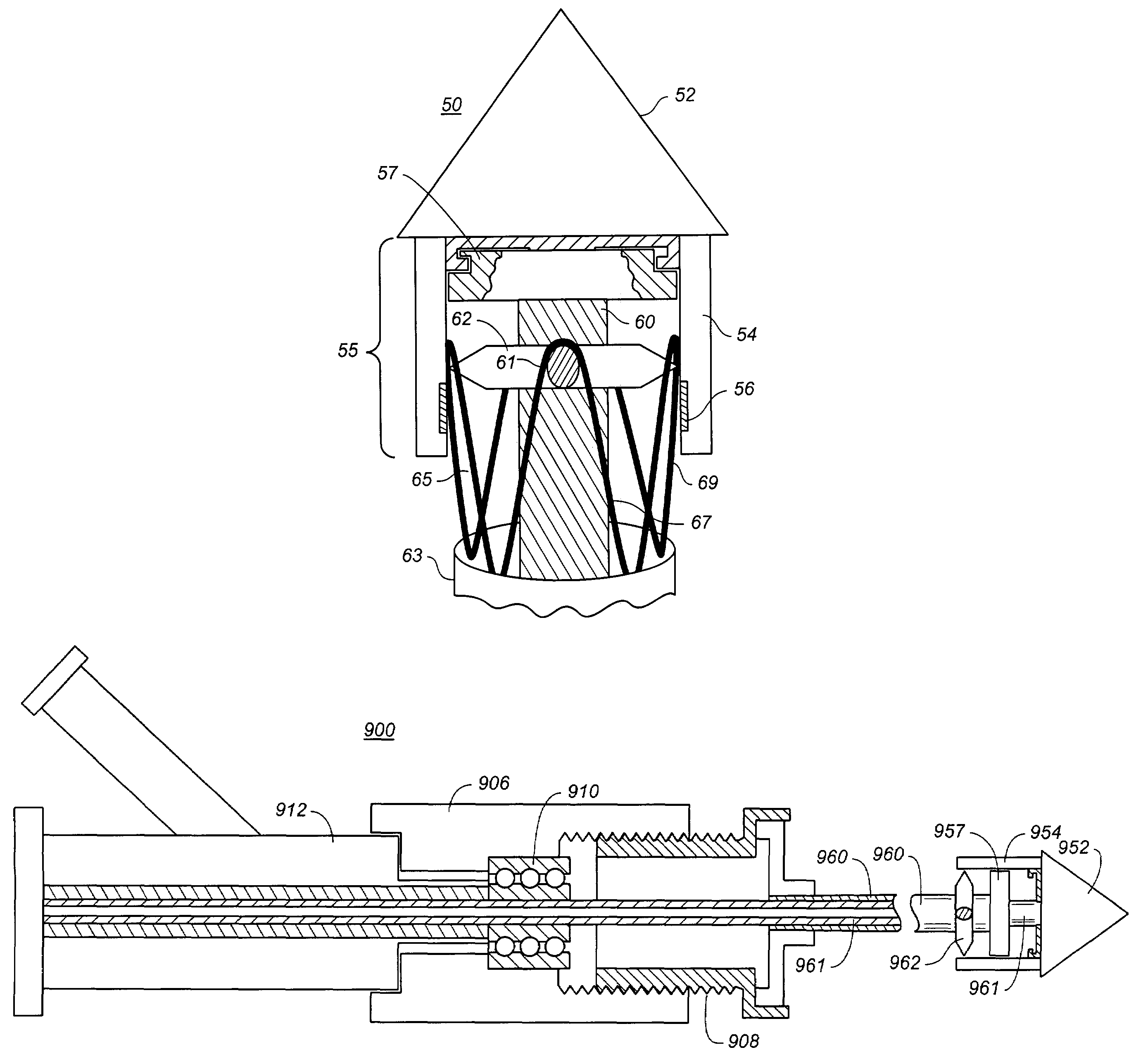
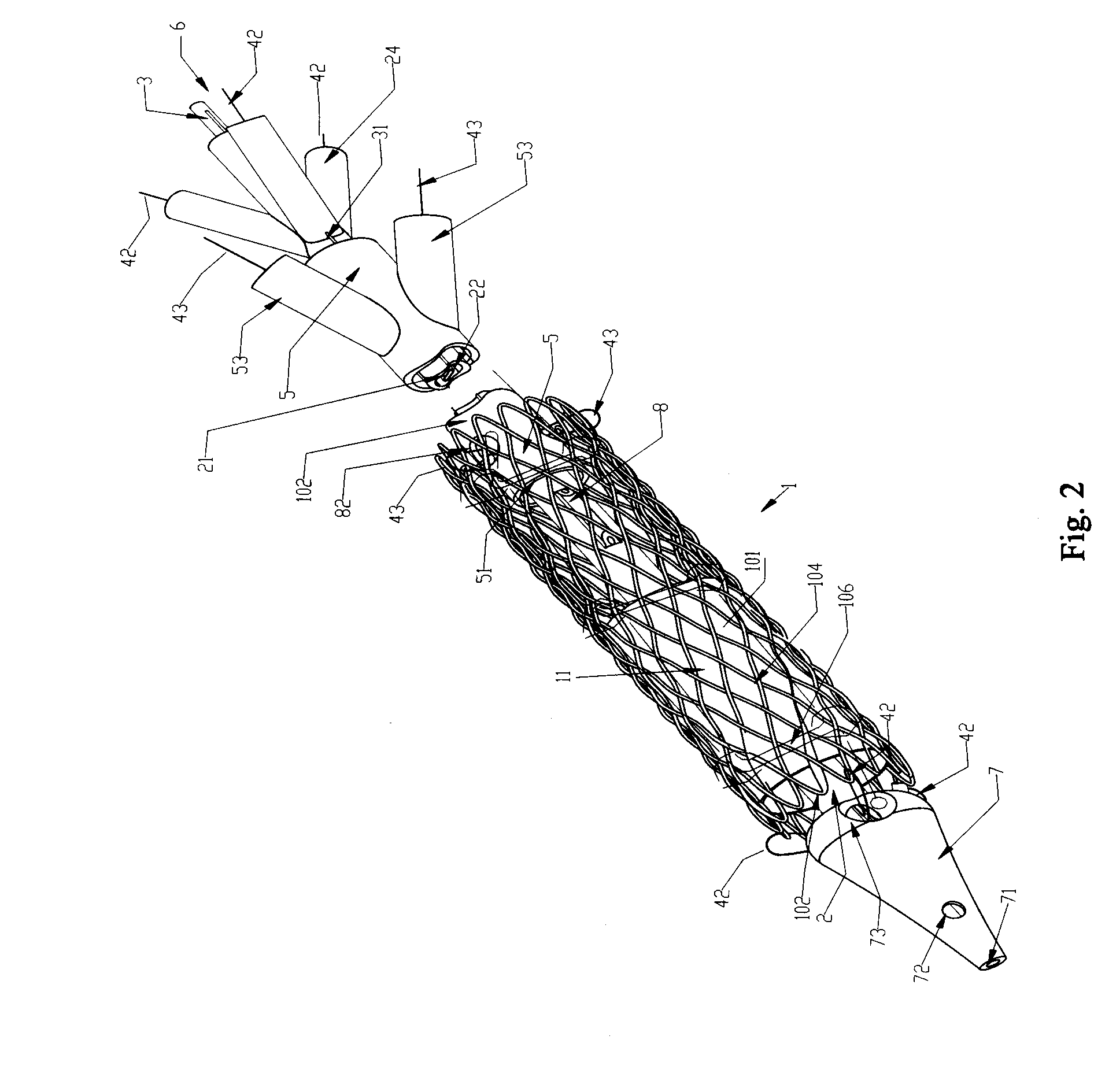
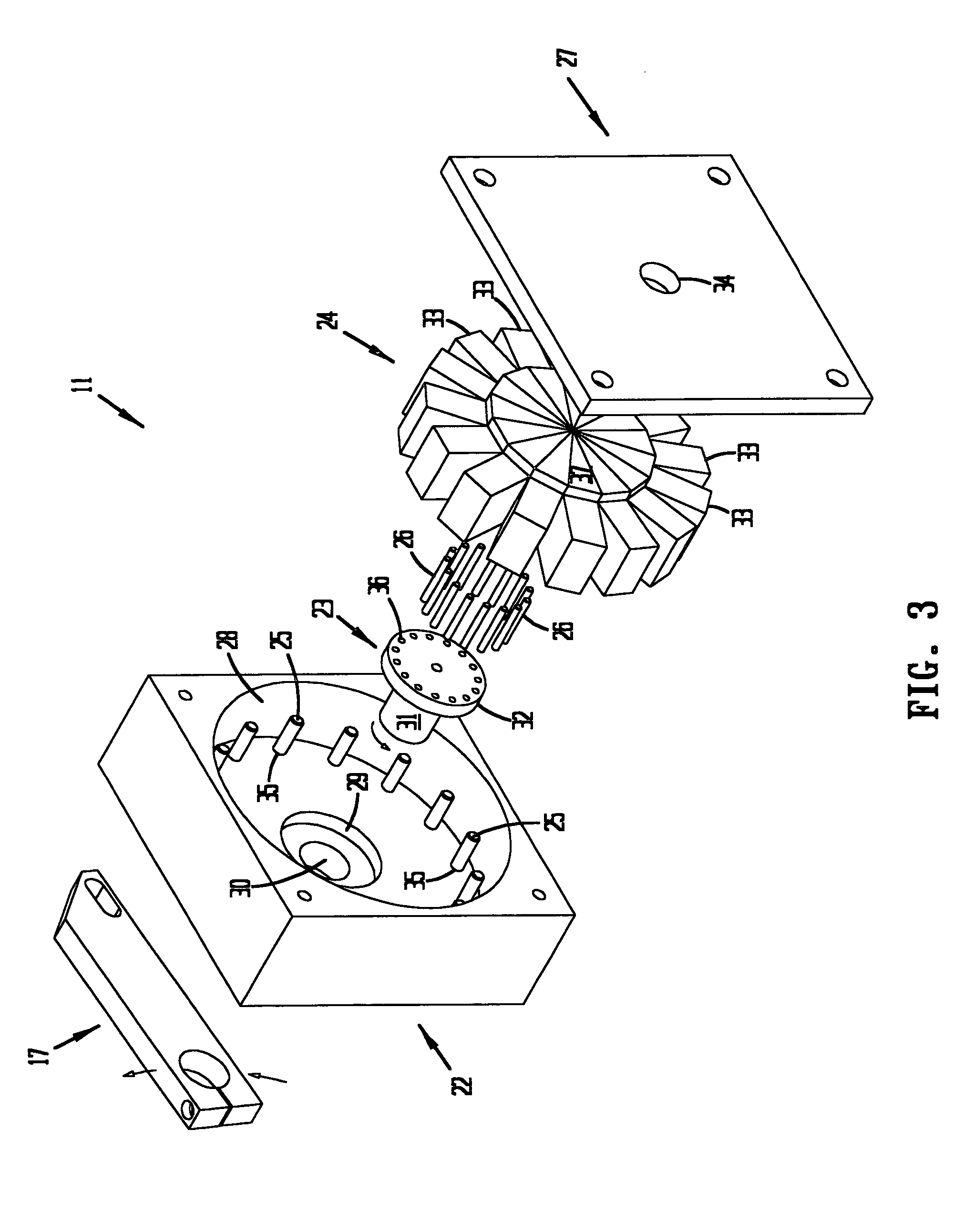
Controlled deployment delivery system
A controlled stent-graft deployment delivery system (10 50 or 900) includes a stent-graft (30 or 63), a retractable primary sheath (40) containing the stent-graft in a first constrained diameter configuration, an outer tube (18) within the retractable primary sheath and within the stent-graft, and an inner tube (20) within the outer tube, where the inner tube and the outer tube both axially move relative to the retractable primary sheath and to each other. The system further includes a cap (15) coupled to a distal end of the inner tube and configured to retain at least a portion of a proximal area of the stent-graft in a radially compressed configuration. A distal assembly (100) provides controlled relative axial movement between the outer tube and the inner tube enabling the release of the proximal end (65, 67, 68, and 69) of the stent-graft from the cap and from the radially compressed configuration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Replacement heart valves, delivery devices and methods
A replacement heart valve and method of treating valve insufficiency includes an expandable frame configured to engage a native valve annulus. A valve body is coupled to the frame. The valve body can include a leaflet portion and possibly a skirt portion. A portion of the frame has a foreshortening portion configured to longitudinally expand when urged to a radially compacted state and longitudinally contract when urged to a radially expanded state. In one embodiment the valve skirt is attached to the frame so that it can adapt to changes in the length of the frame. A delivery device in some embodiments can use one or more coverings, such as sheaths, to controllably release the replacement heart valve at a native heart valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
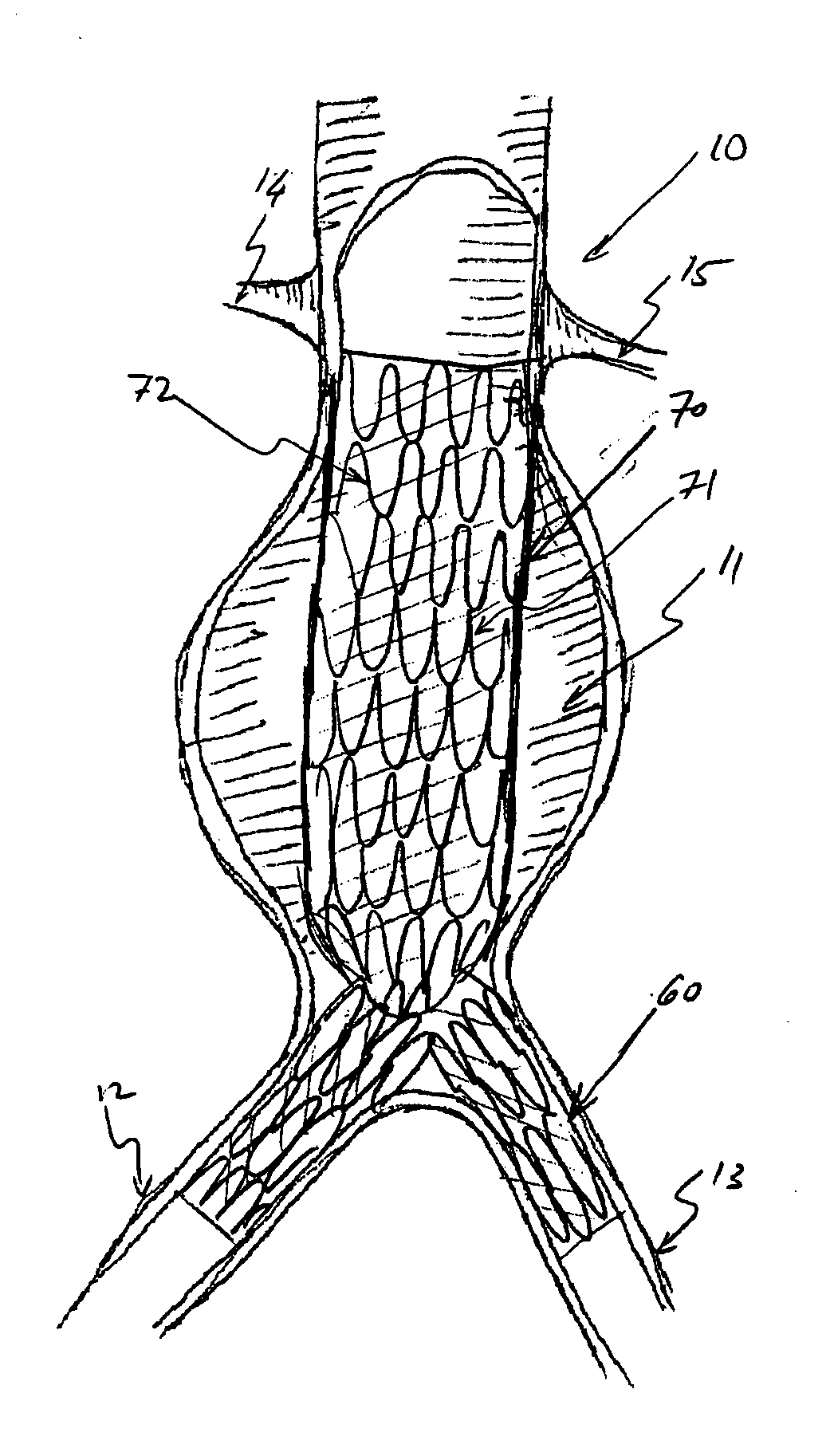
Multi-section filamentary endoluminal stent
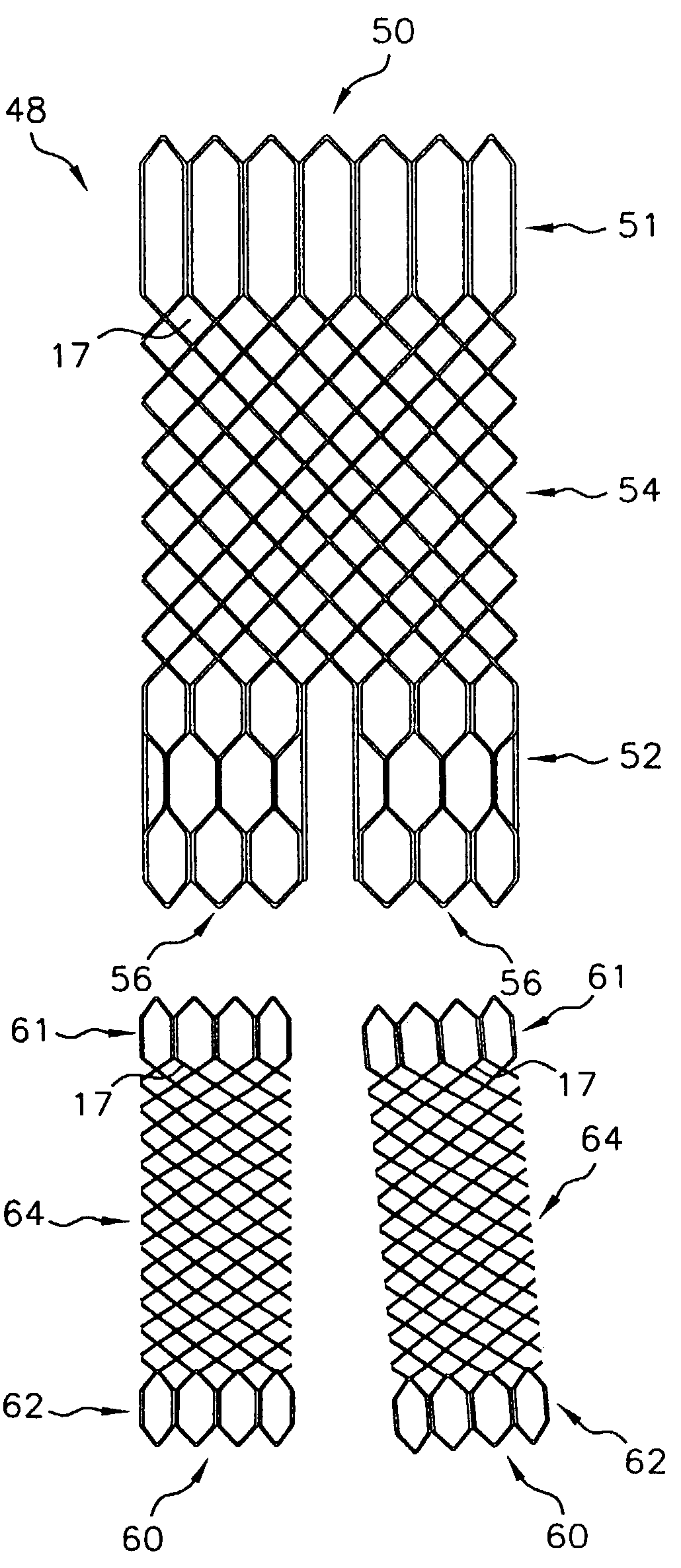
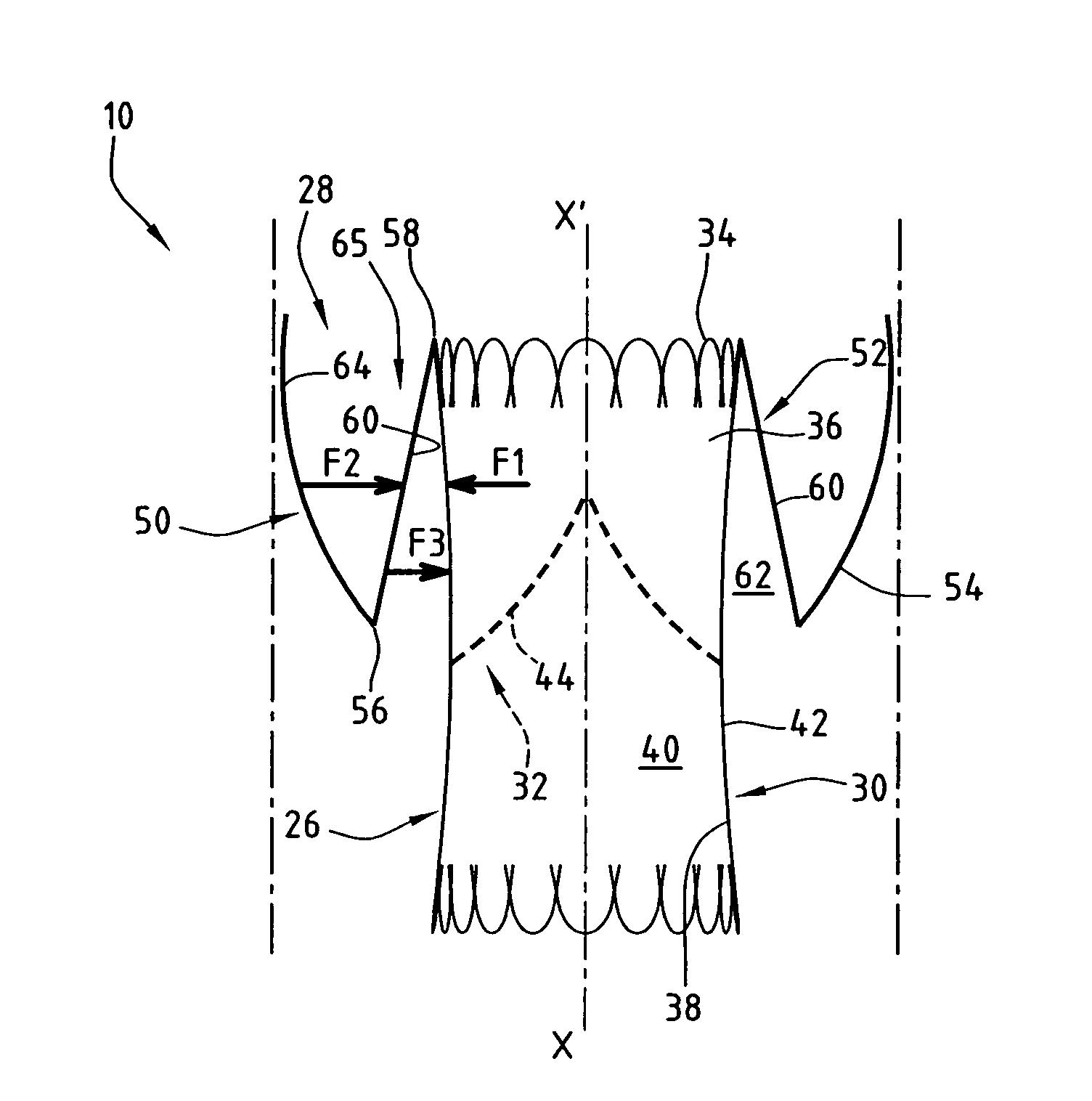
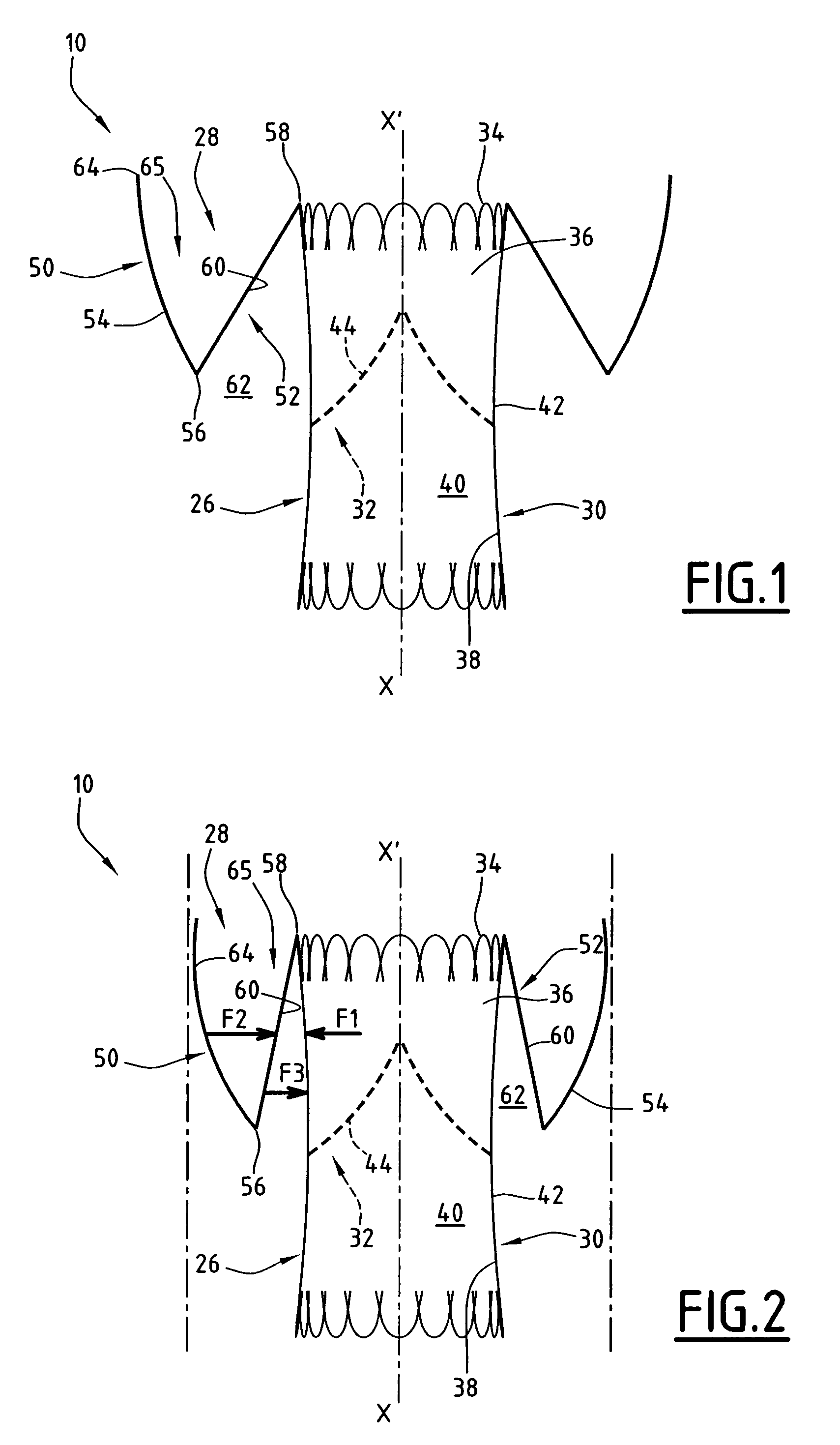
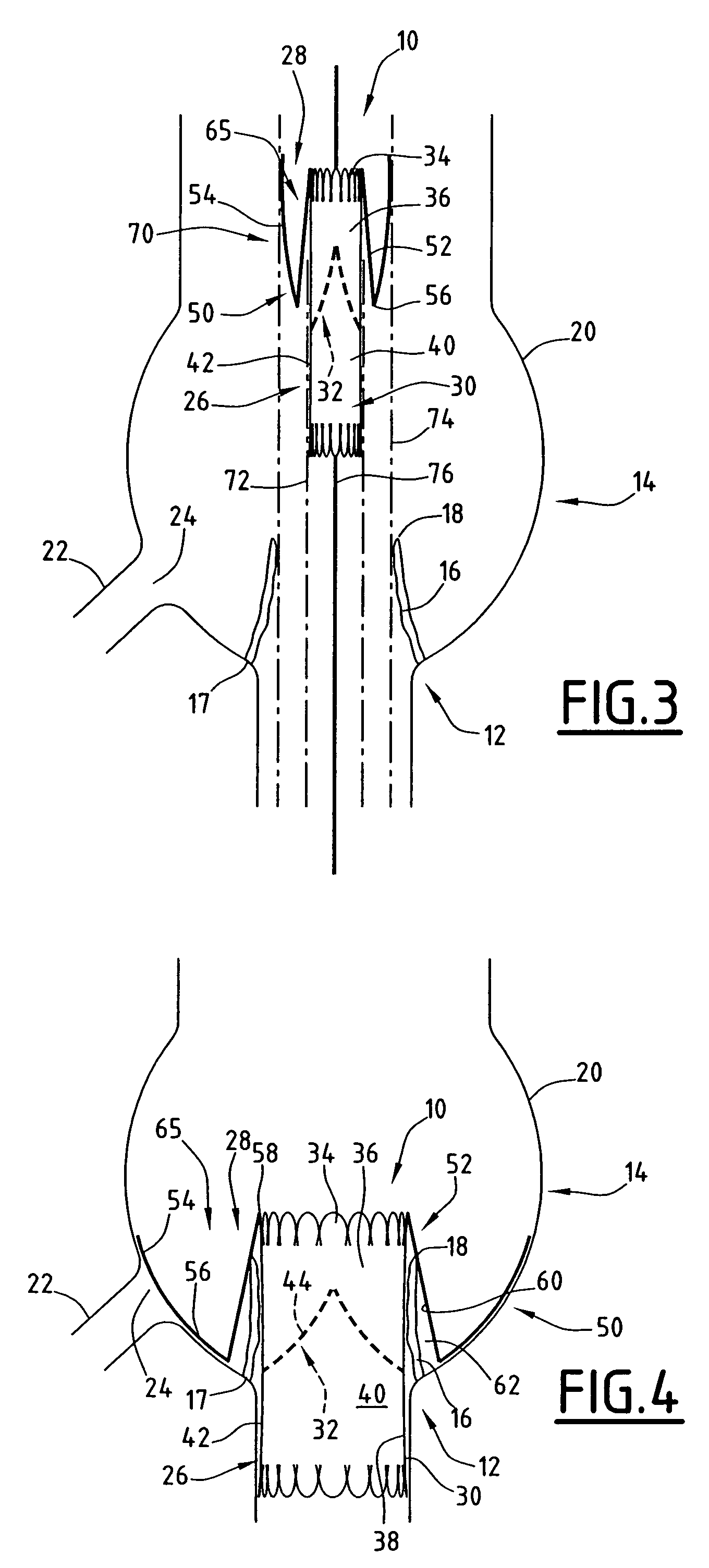
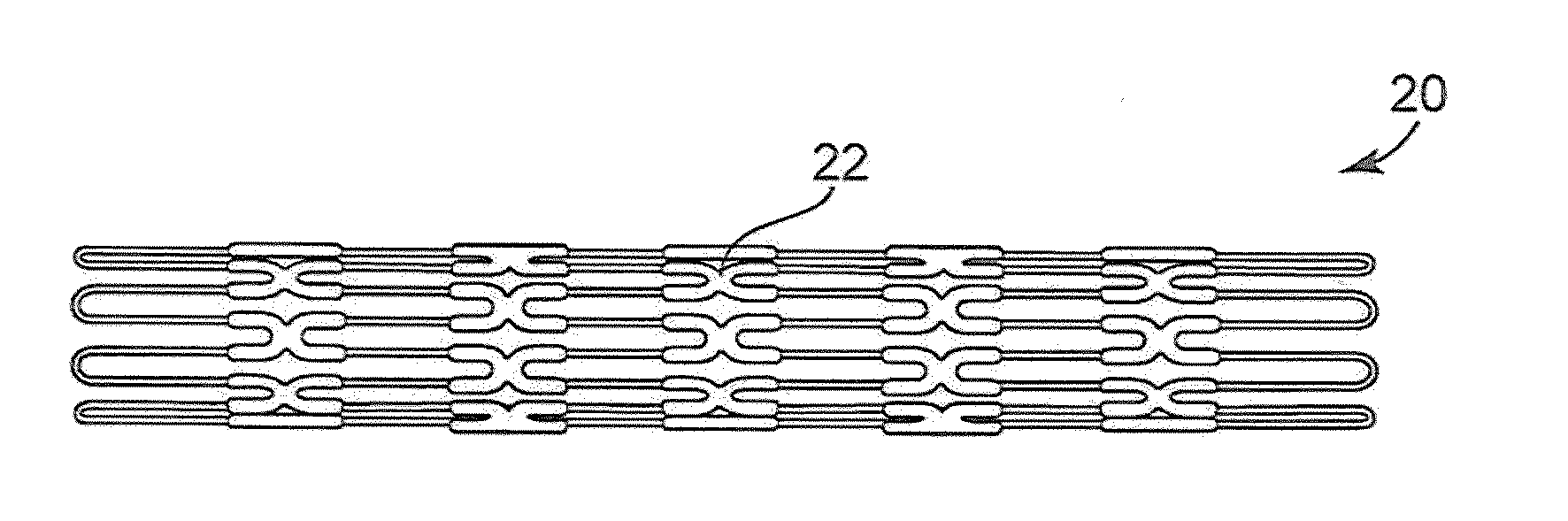
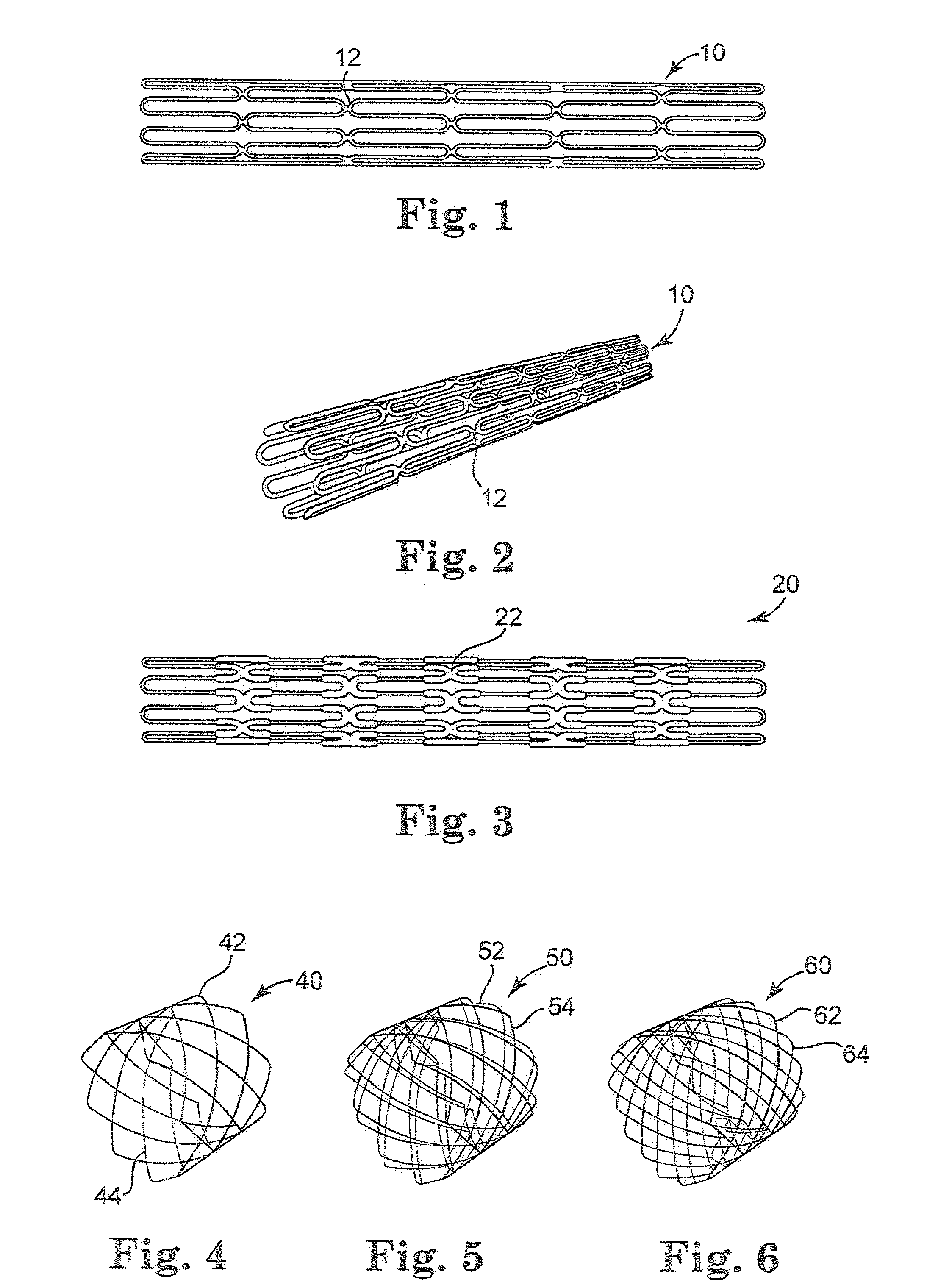
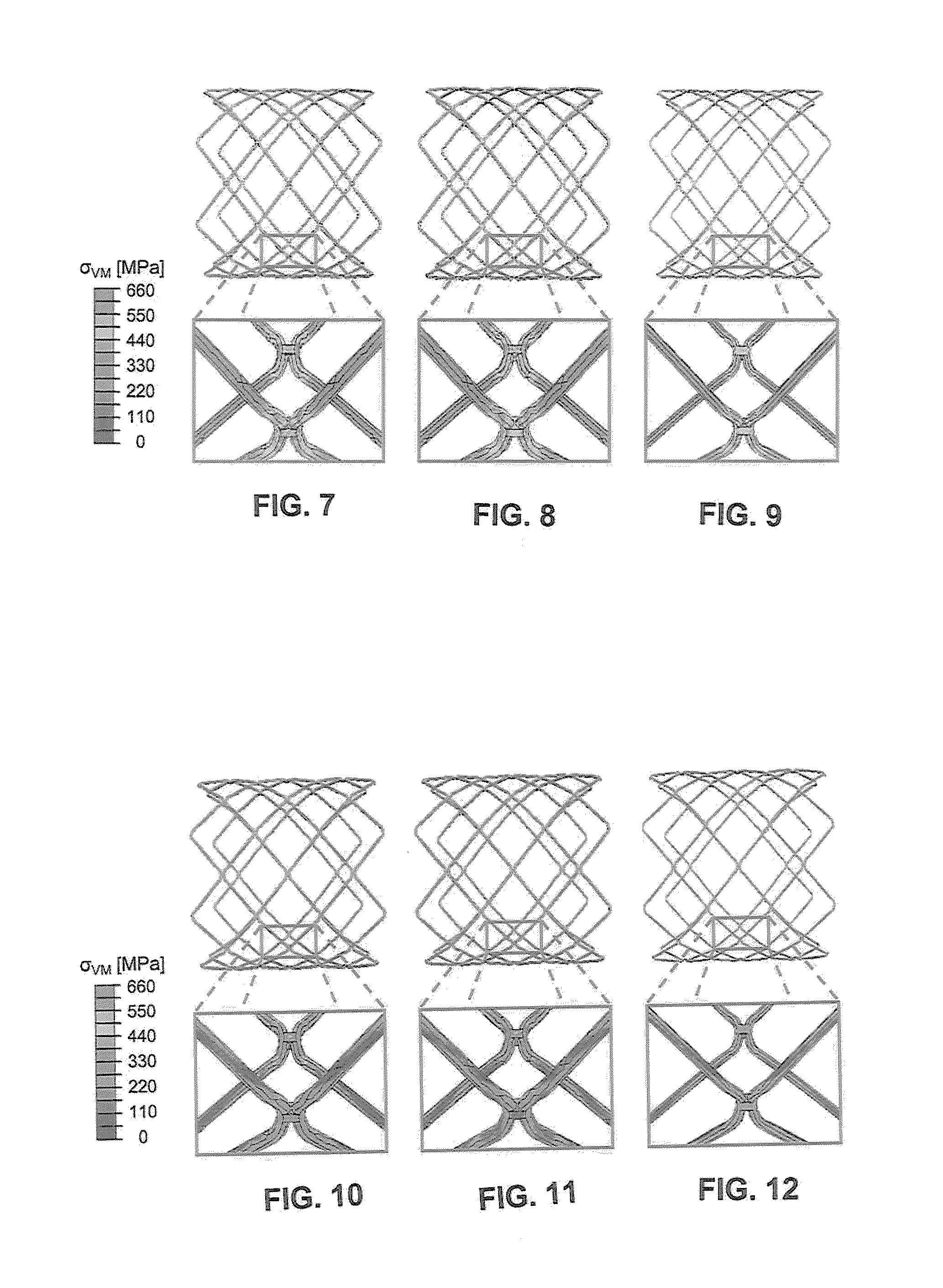
A multi-section filamentary stent comprises a braided section, which is a cylindrical mesh of a first set of filaments, connected to at least one wound section comprising a second set of one or more filaments having a repeating configuration with a bent portion. The two sections are preferably connected by at least one continuous filament extending into both sections. The two sections may be connected by a weld, a suture, a common graft, an overlapping portion of the two sections, or one or more filaments of one section looping through portions of the other section. The stent may comprise a first section, having a braided first stent architecture with a first flexibility and a first radial force, and a second section, having a non-braided second stent architecture with a second flexibility less than the first flexibility and a second radial force greater than the first radial force, in which at least one continuous filament is integral to both the first and second sections. The stent may have a radially compressed configuration and a radially expanded configuration, in which the first section has a first shortening ratio, and the second section has a second shortening ratio less than the first shortening ratio. Such multi-section stents may comprise modular components of a modular stent, such as a bifurcated modular stent, adapted for joining together in situ. The multi-section stent may comprise a first section having a first percentage of open area and a second section having a second percentage of open area. The stent may also comprise a first section having a first stent architecture with an end effect wherein the radial strength at the end is less than elsewhere in the stent, and a second section having a second stent architecture to counteract the end effect. Methods for treating body lumen by implanting the stents as described herein are also disclosed, as is a method for counteracting a stent architecture end effect.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Expandable impeller pump
An impeller according to an example of the present invention comprises a hub, and at least one blade supported by the hub. The impeller has a deployed configuration in which the blade extends away from the hub, and a stored configuration in which the impeller is radially compressed, for example by folding the blade towards the hub. The impeller may comprise a plurality of blades, arranged in blade rows, to facilitate radial compression of the blades. The outer edge of a blade may have a winglet, and the base of the blade may have an associated indentation to facilitate folding of the blade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +2
Axial Pullwire Tension Mechanism for Self-Expanding Stent
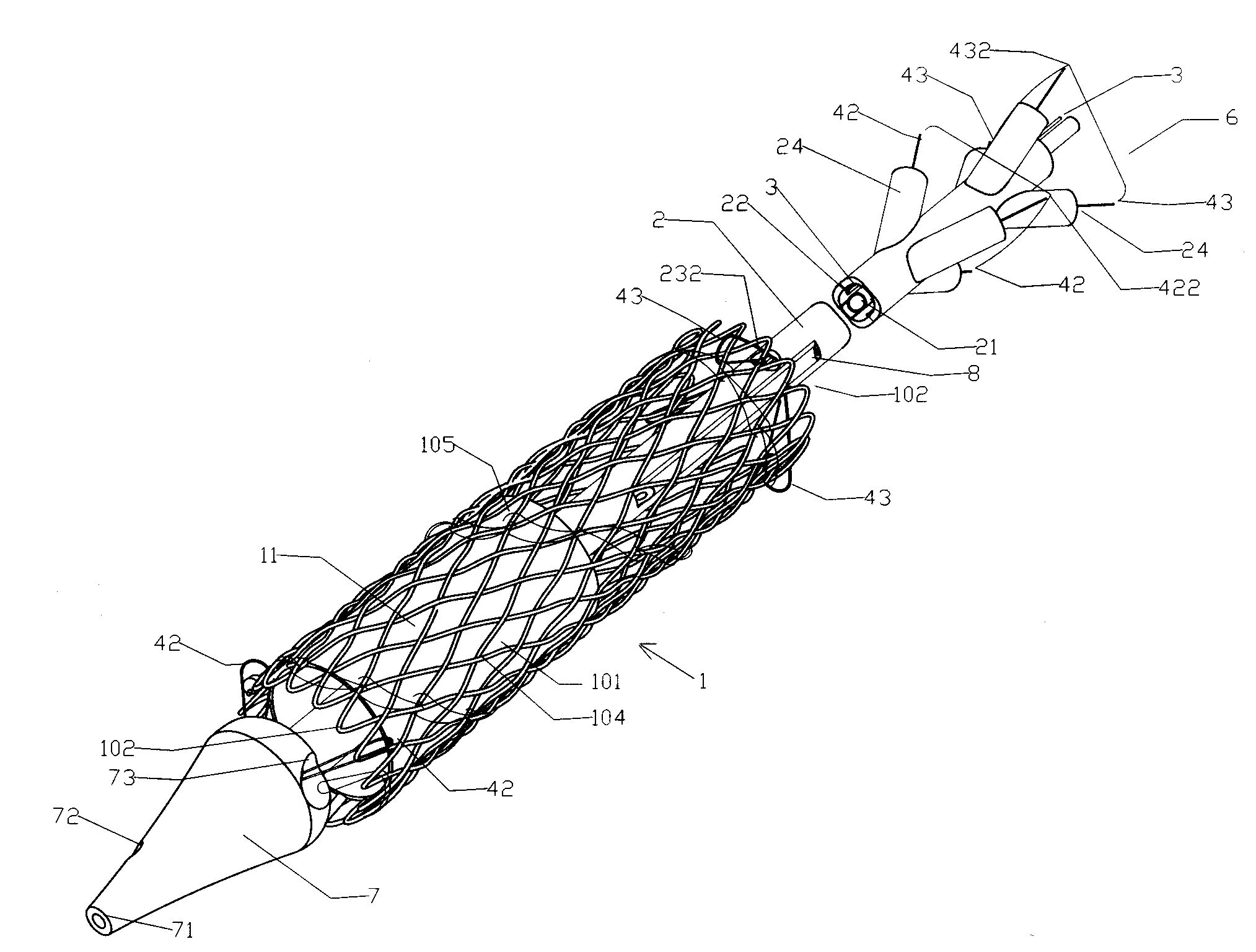
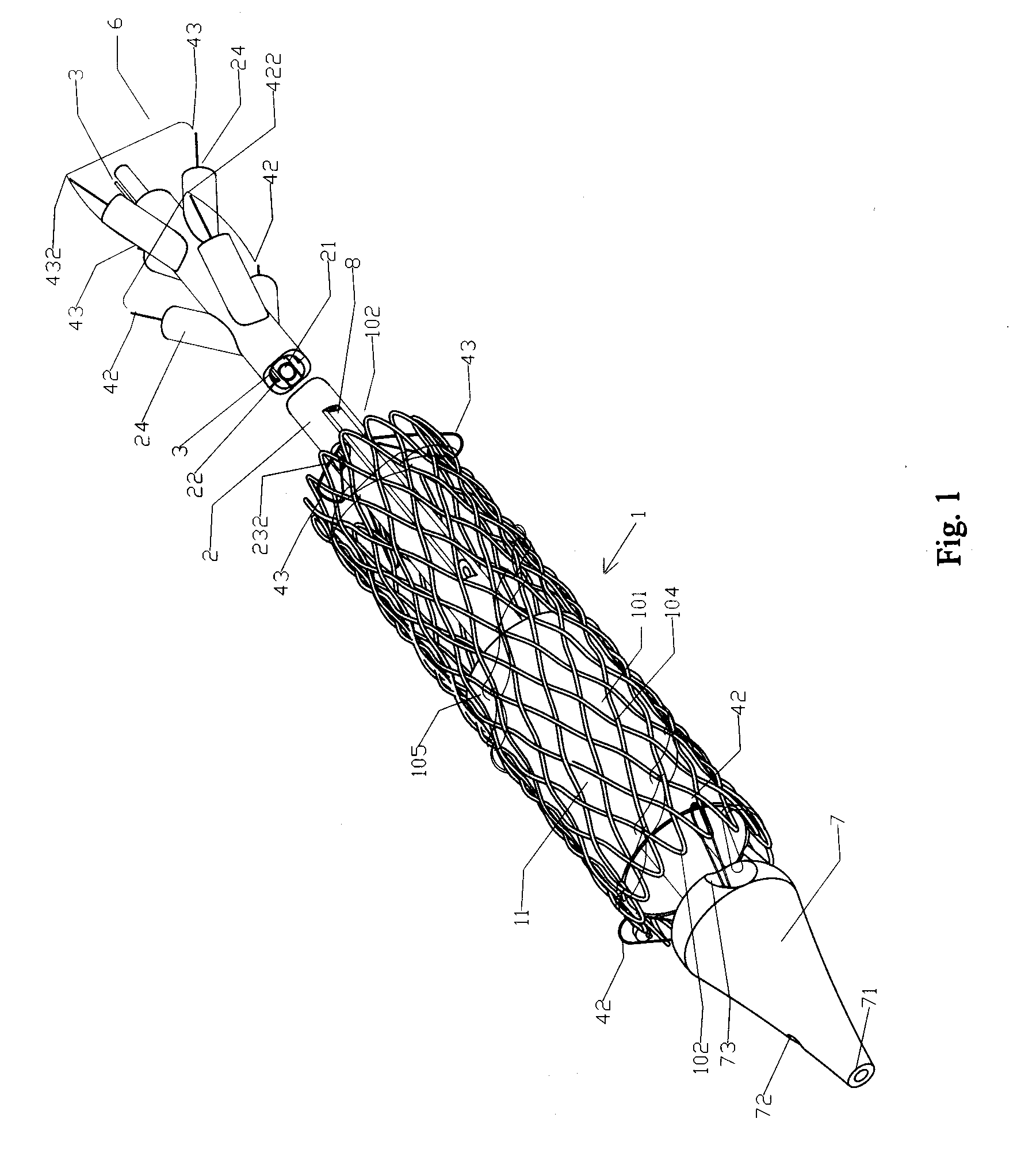
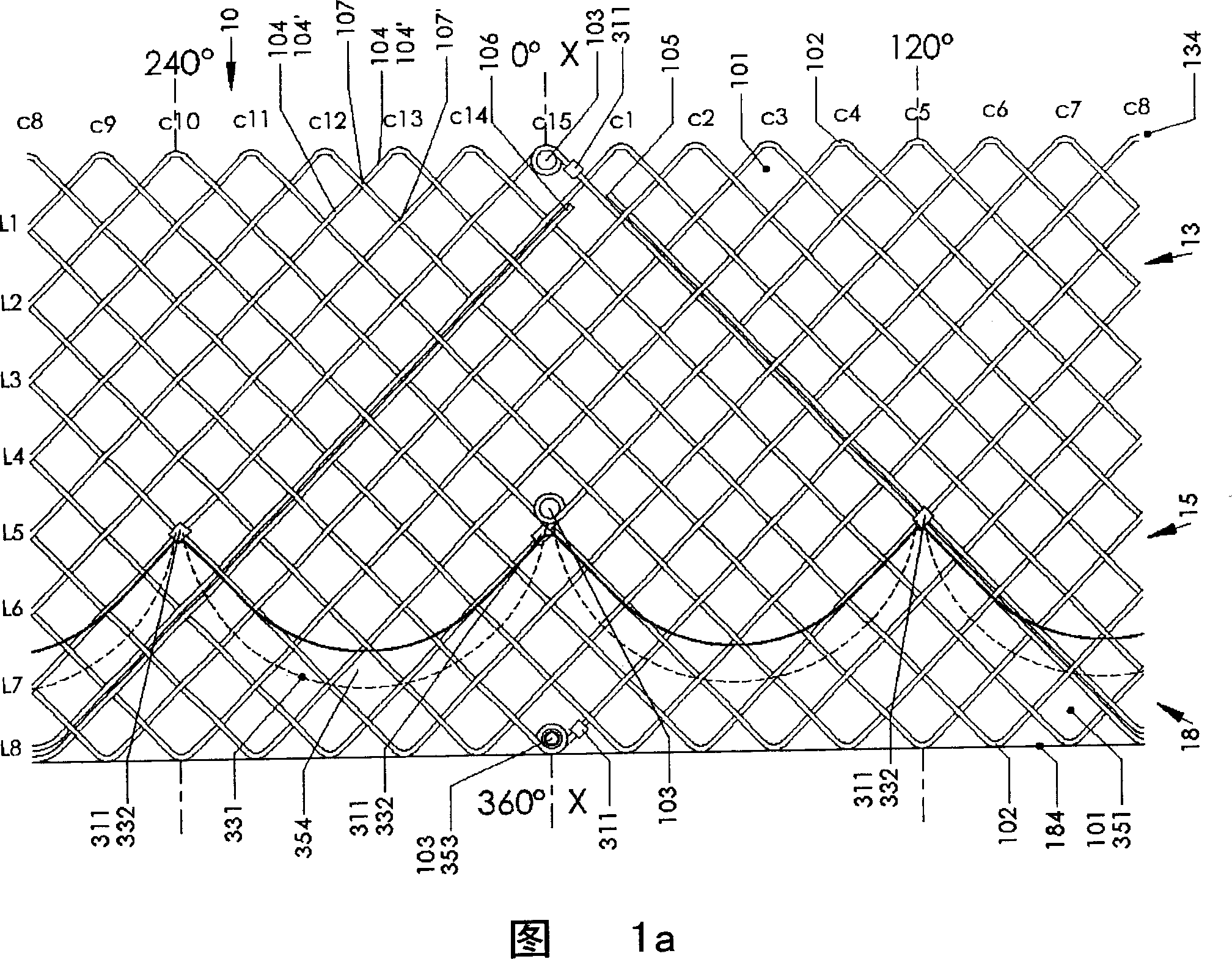
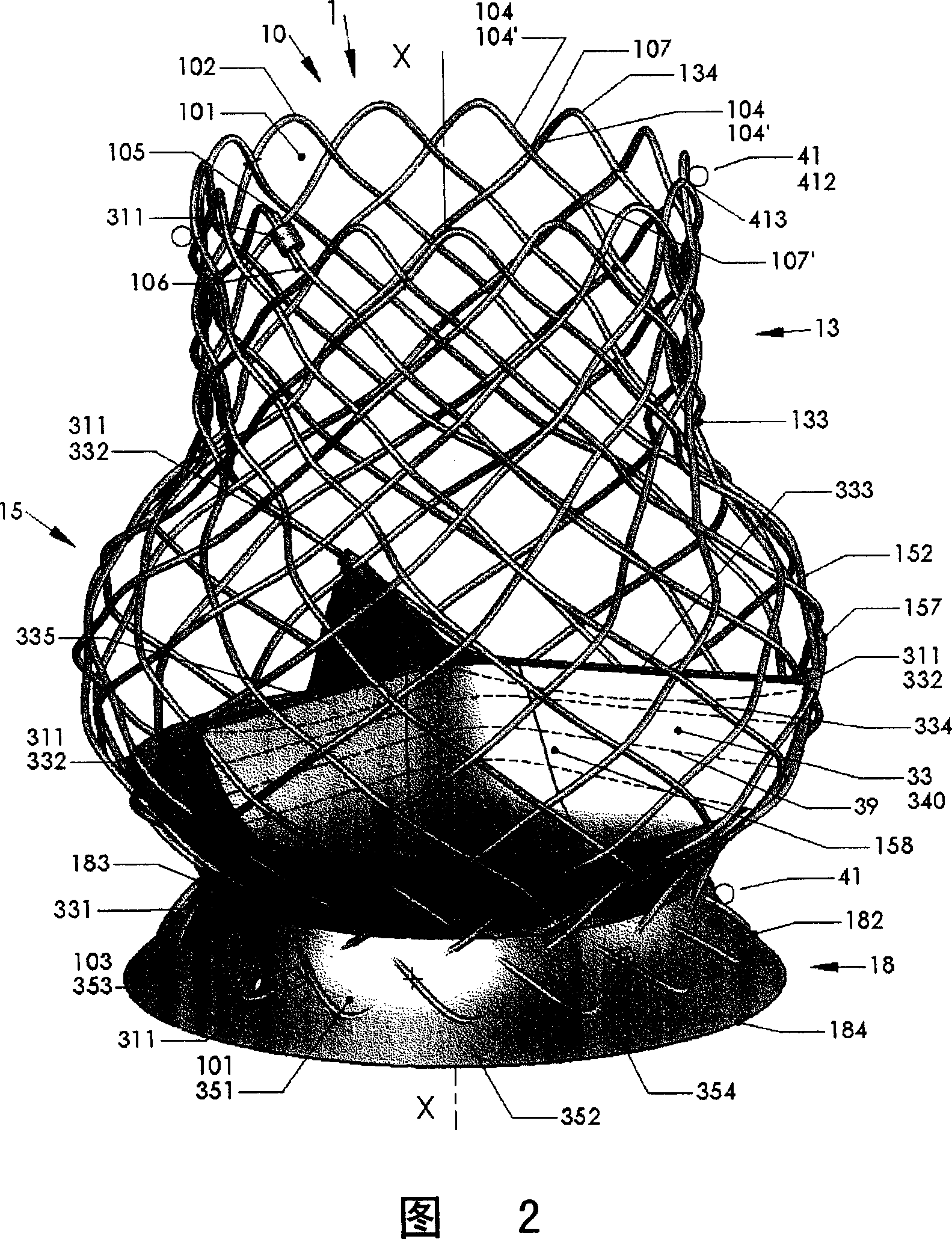
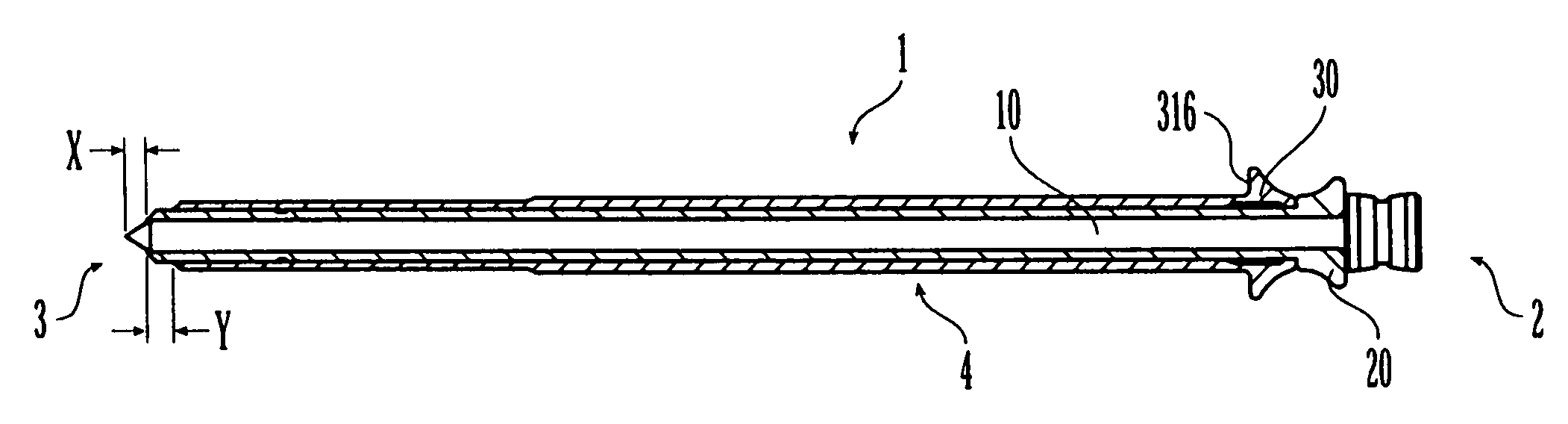
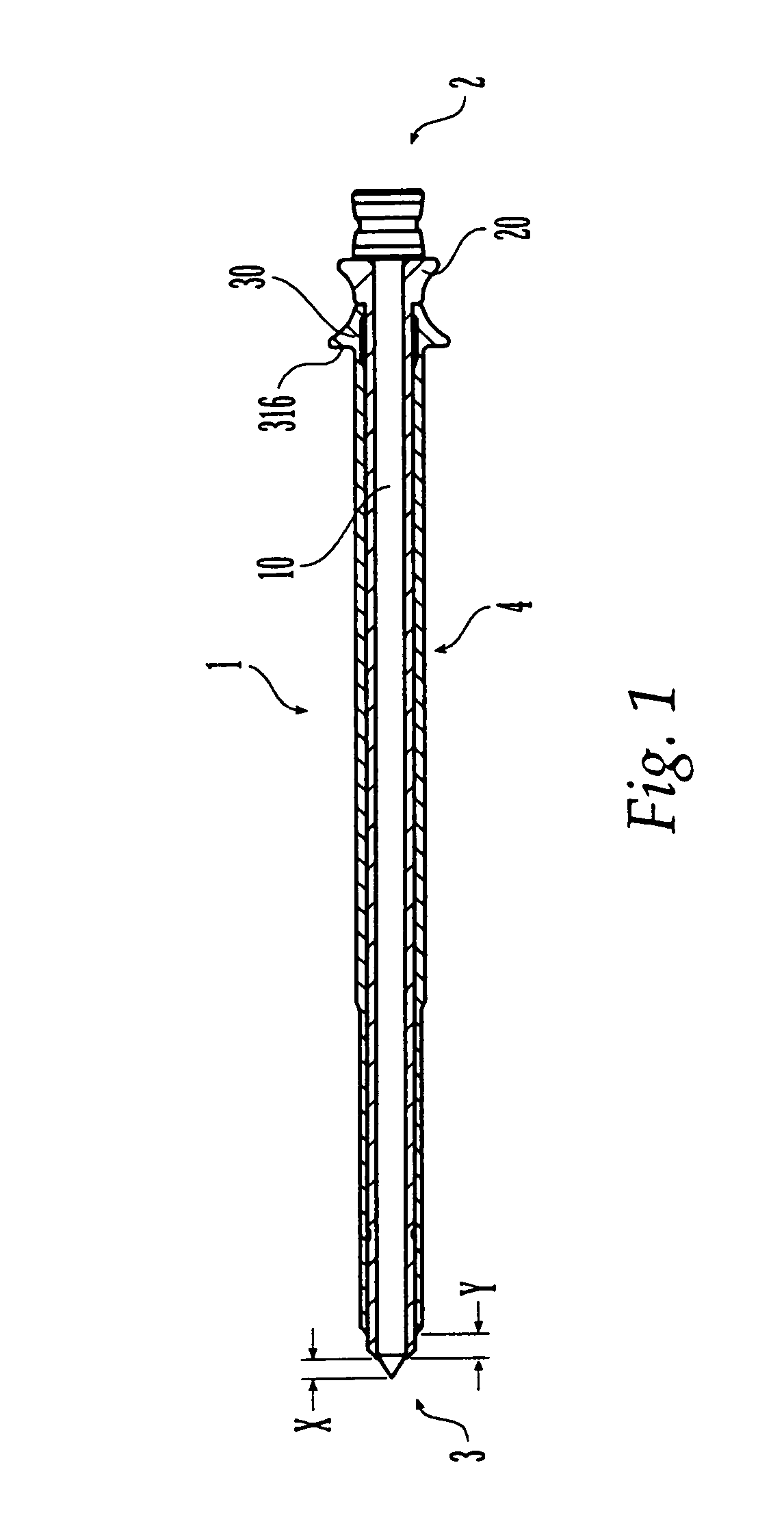
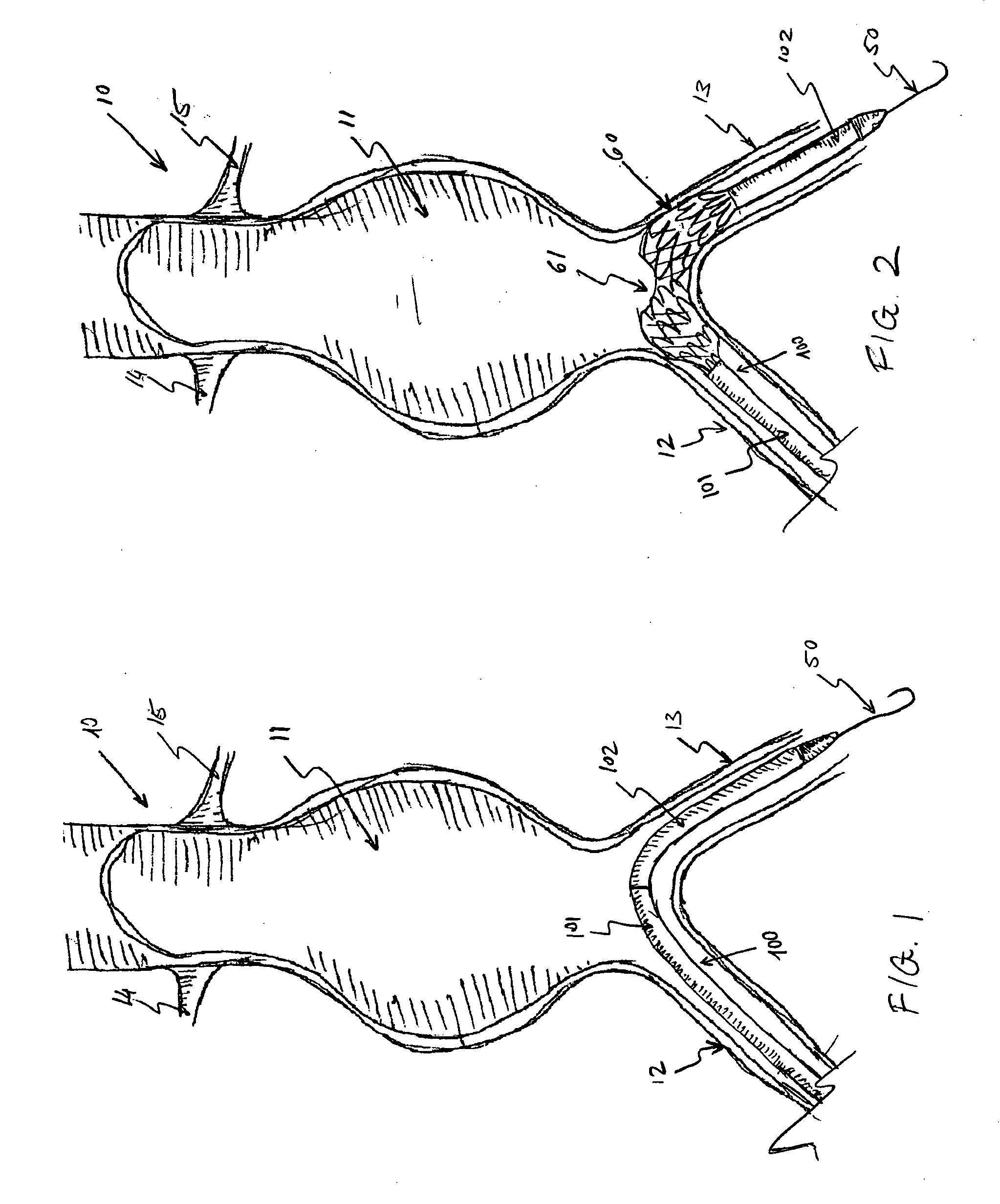
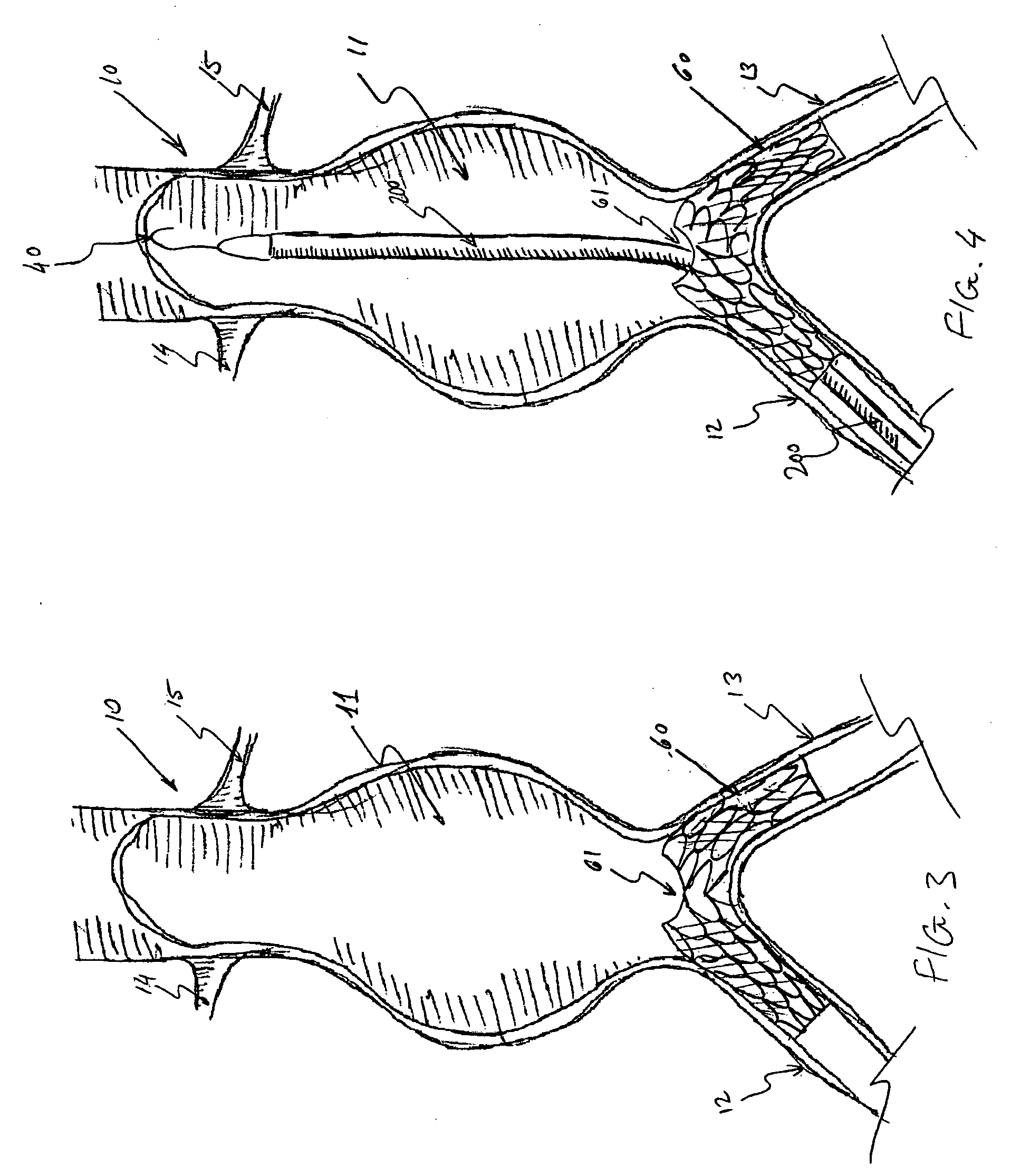
An axial pull wire tension mechanism for a self expanding stent includes a delivery system composed of an inner tube (2), a middle tube (5) and a lock wire (3), open wire knees (102) and / or close wire eyelets (103) at the both ends of the stent, and pull wires (4) for tensioning the stent. The pull wires (4) include at least one distal pull wire (42) and at least one proximal pull wire (43). A pull wire ring (421, 431) is provided at the distal end of each of the pull wires. Each pull wire passes through an opening of the inner tubing head (7) or the inner tube (2) or the middle tube (S) after the pull wire ring at its distal end is threaded through and locked temporarily by the lock wire, and travels between the open wire knees (102) or the close wire eyelets (103) at one end of the stent to constitute a temporary stent connection, thus forming the pull wire tension mechanism that can axially tension the stent. The present invention can locate the self-expanding stent in terms of its axial and rotational positions with great precision when in collaboration with the delivery system and the radially compression mechanism during the process of delivering the self-expanding stent into the patient's body, and is capable of either further adjustment should the position prove to be less ideal, or recycling should the stent prove to be incongruous after the expansion of the stent.
Owner:WENG NING
Implant which is intended to be placed in a blood vessel
This implant comprises an endoprosthesis having an axis which can be spontaneously deployed in a radial manner between a compressed configuration and a dilated configuration. The implant comprises at least one radial runner which comprises a separation surface which extends radially with respect to an outer surface of the endoprosthesis and a member which can be deployed away from the axis. The runner is arranged so as to delimit a confinement housing which extends between the separation surface and the outer surface and a radial spacer which is defined by the separation surface and the deployable member. When the implant is retained in a state of radial compression, the maximum radial width of the housing is less than the maximum radial width of the spacer which is not equal to zero.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
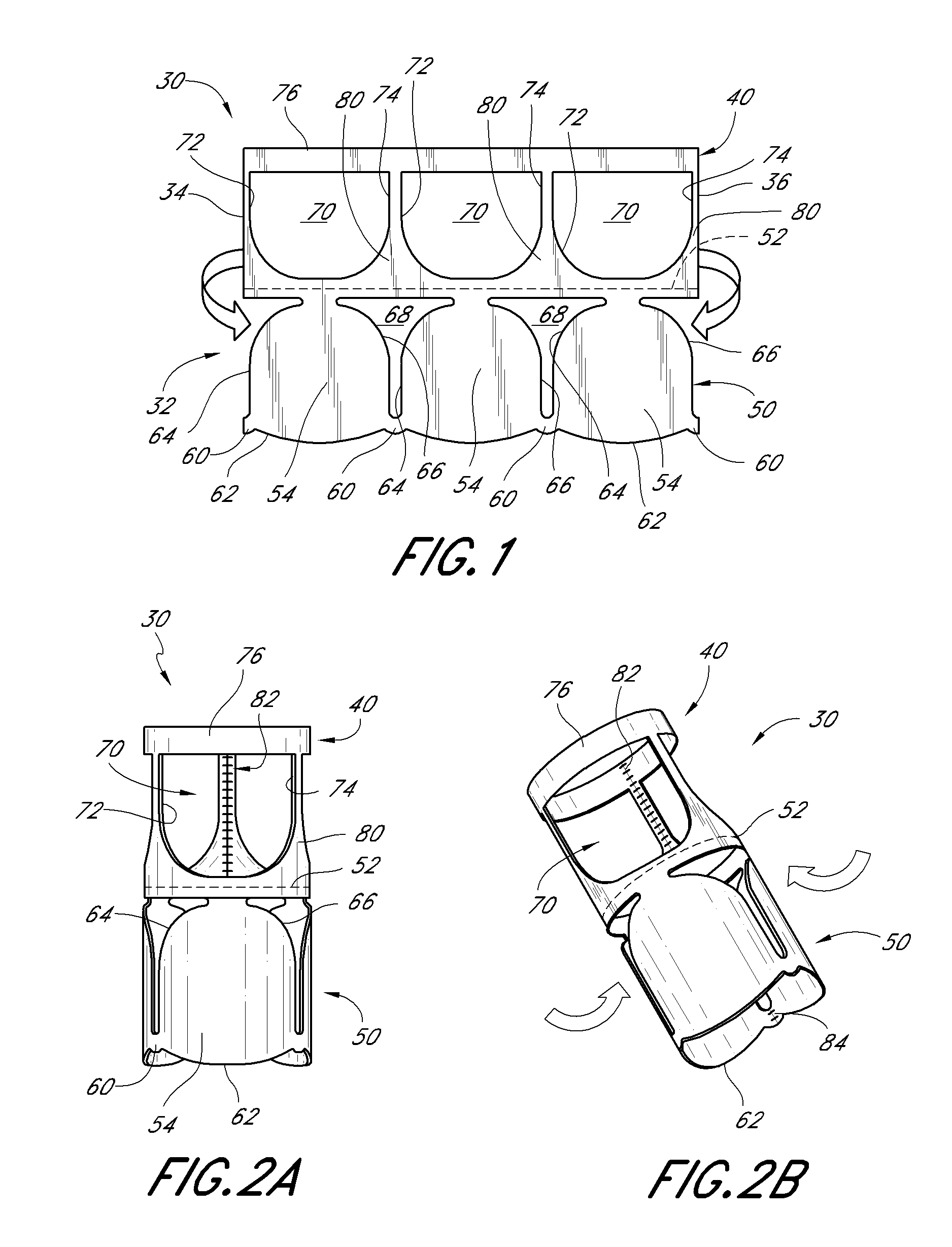
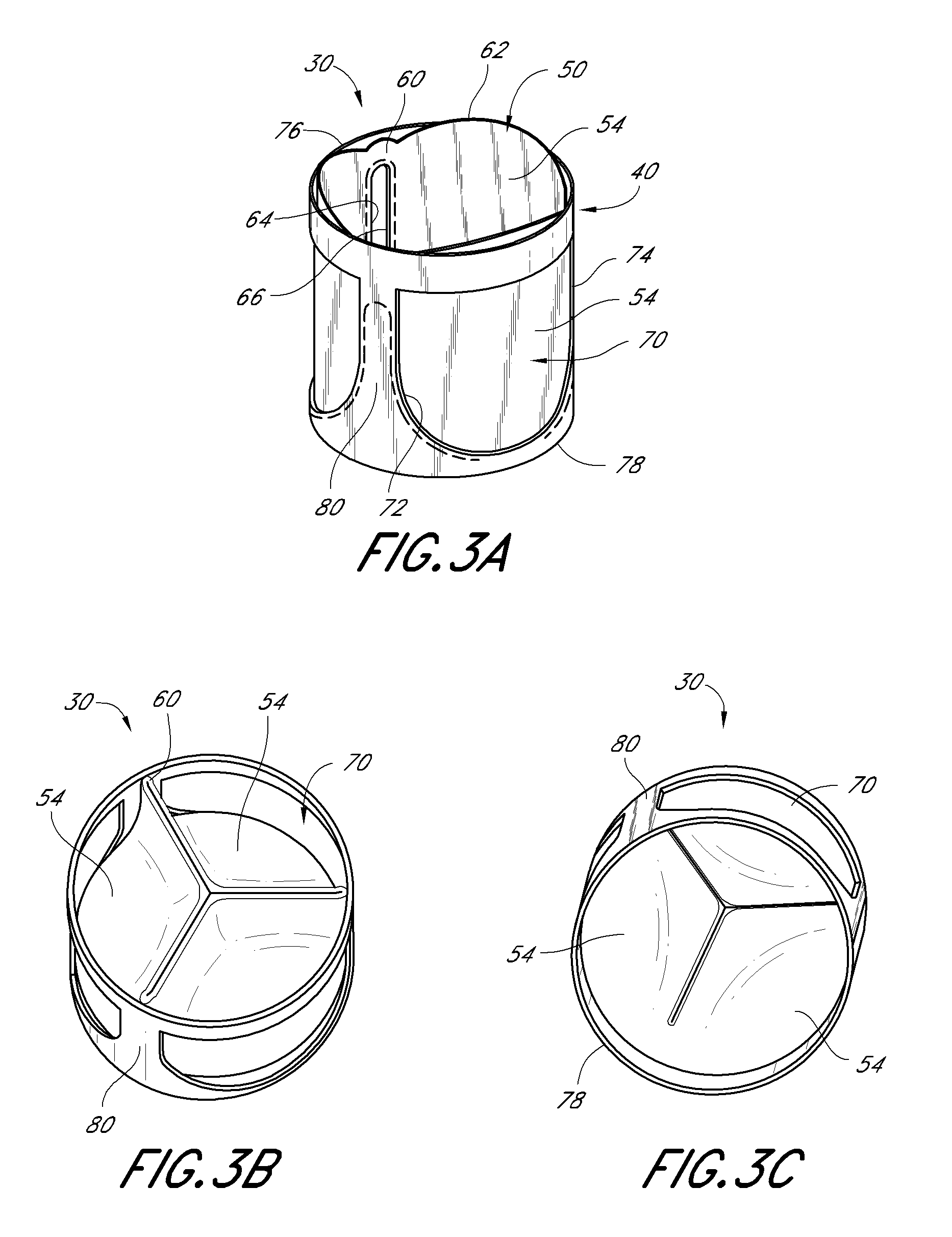
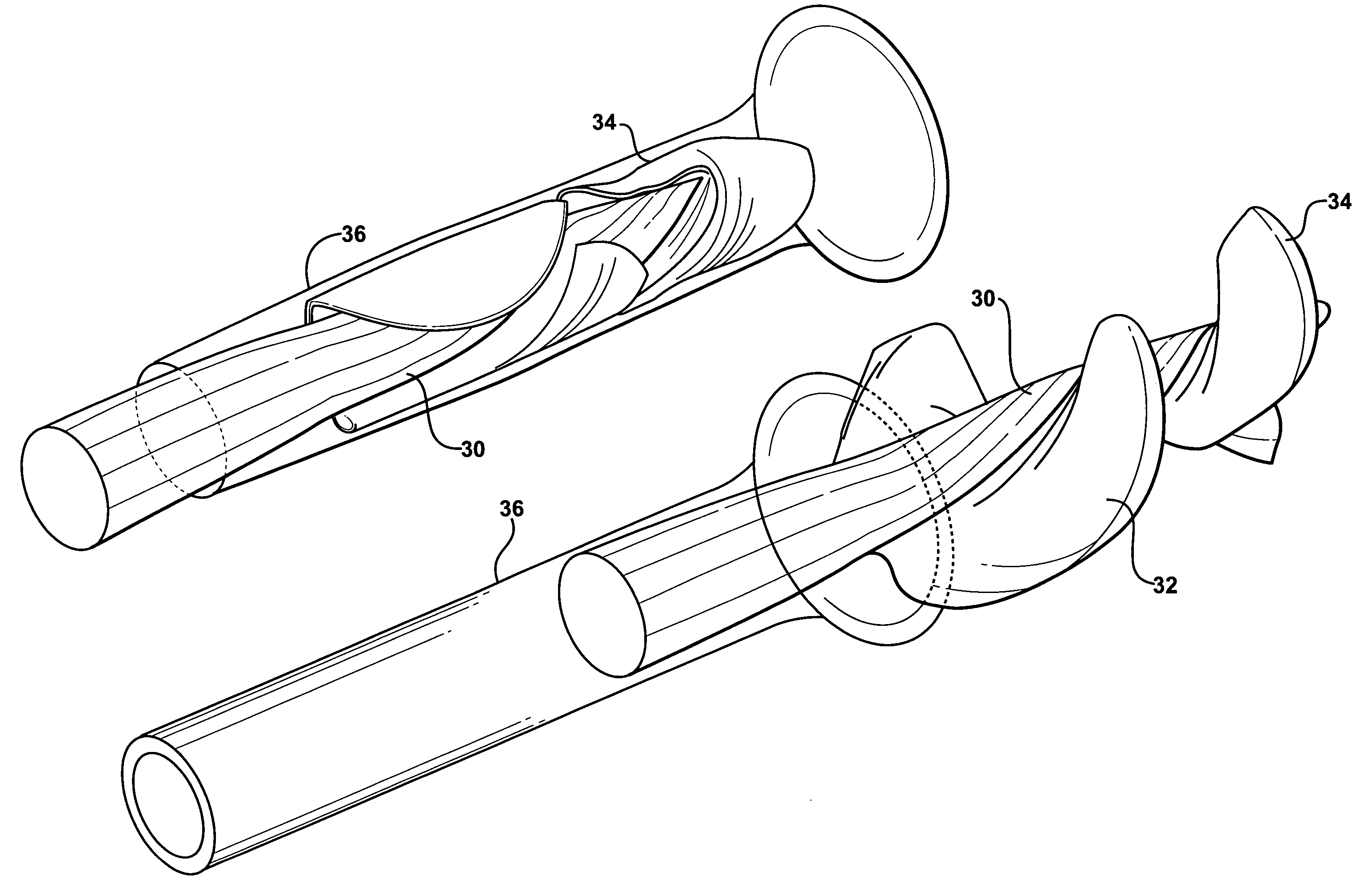
Injection port
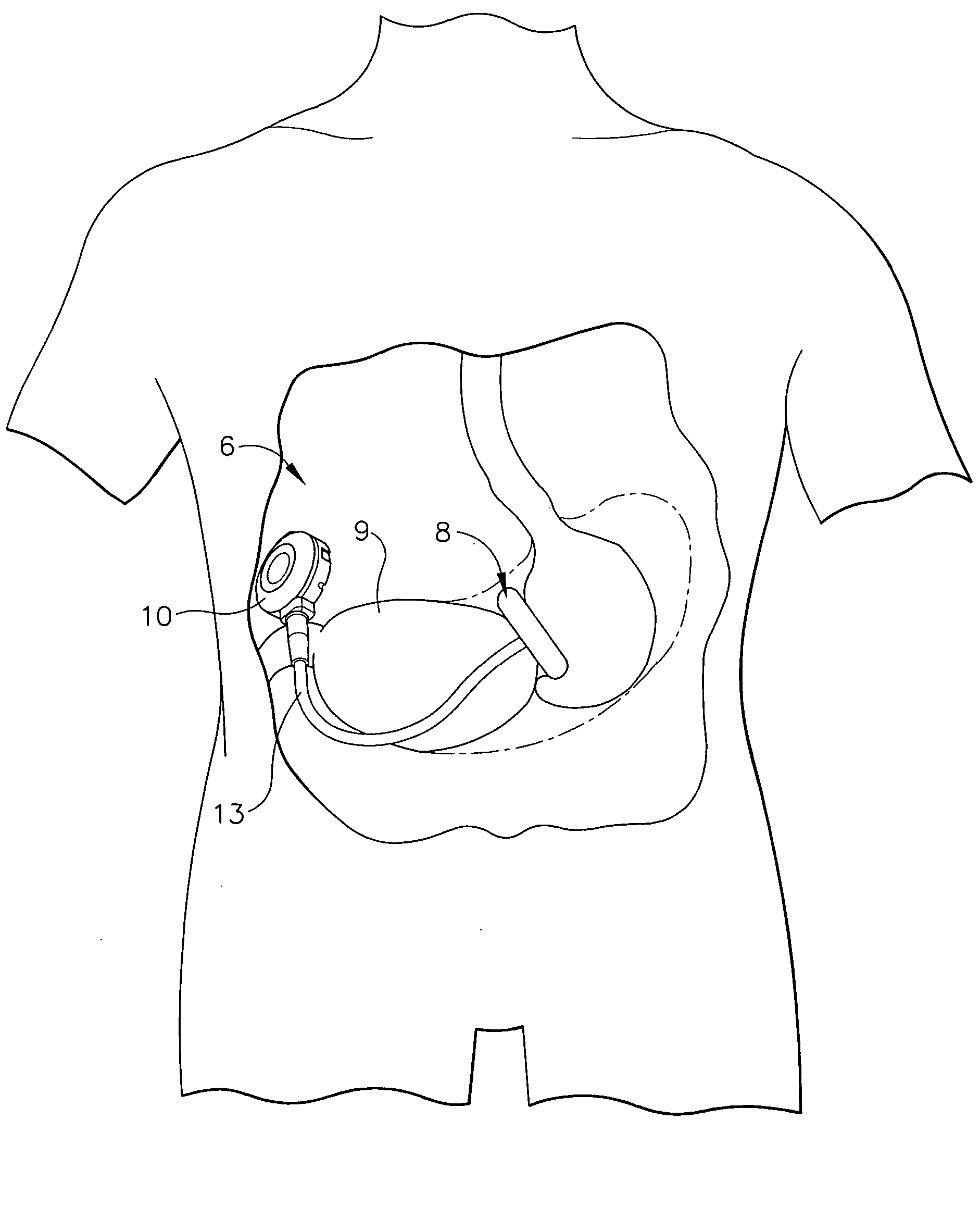
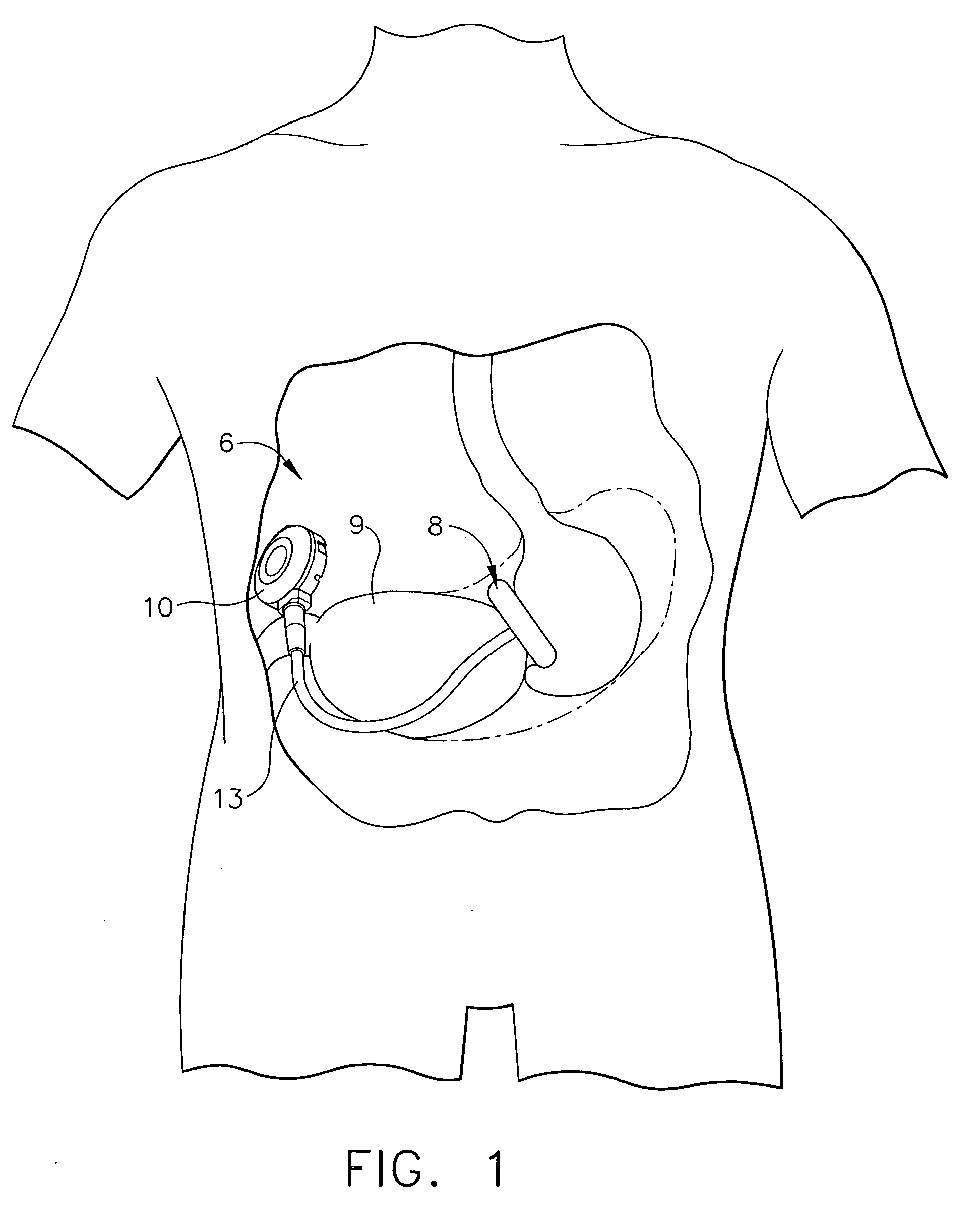
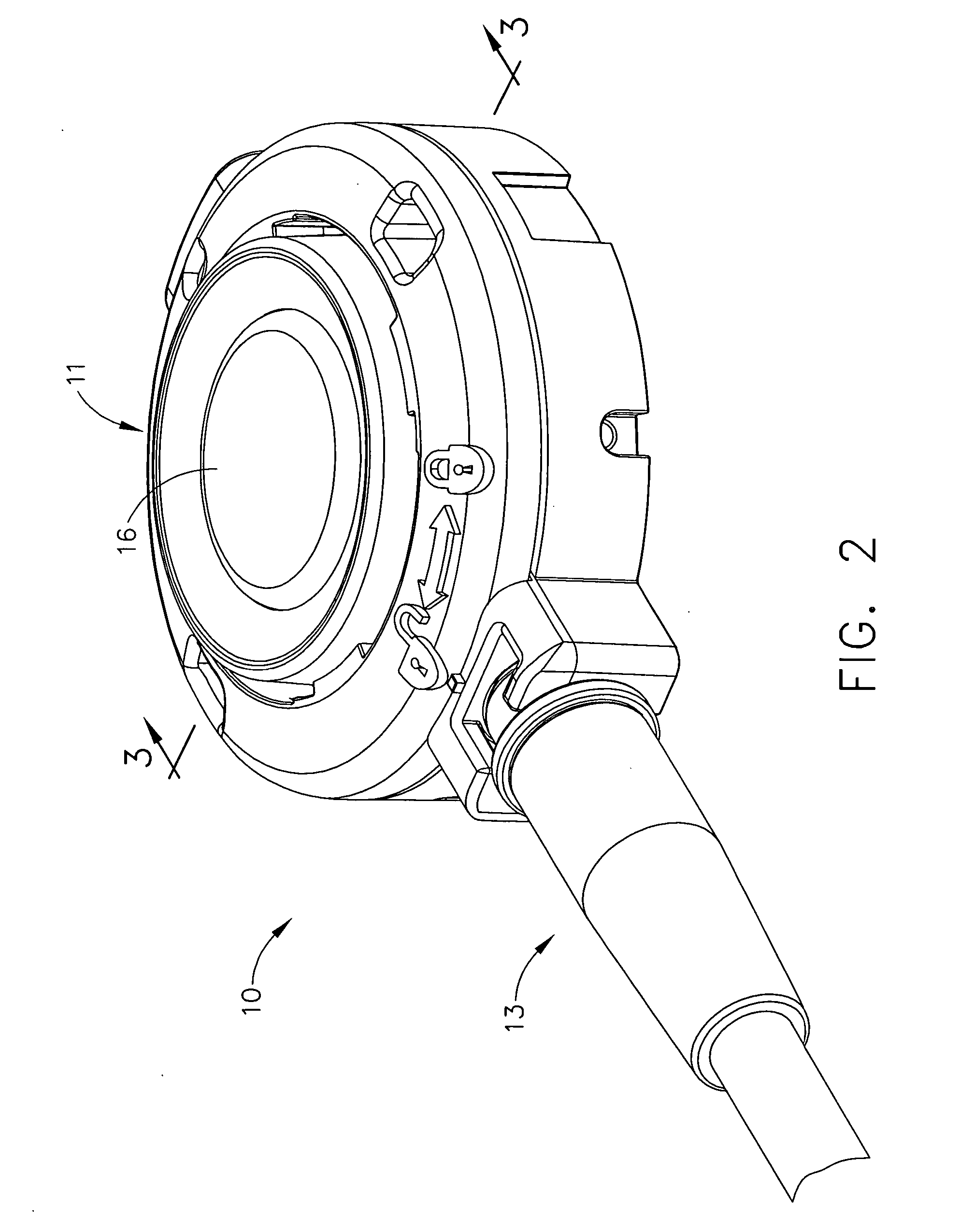
A port, which may be used with a gastric banding assembly, having a septum therein that is subjected to multi-directional compression forces to aid in sealing imperfections caused by multiple needle sticks. Multi-directional compression forces, including axial compression and radial compression, may be created by providing a tapered septum. Such multi-directional compression forces may also be created by providing a tapered lead-in for inserting a septum into a port body.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Self-sealing male connector device with collapsible body
ActiveUS7651481B2Good flexibilityLess wall thicknessInfusion syringesInfusion devicesRigid wallRadial compression
A self-sealing male connector device for connection with a female Luer connector. The device has an elongated male body configured with lengthwise relatively rigid and flexible wall segments cooperating to allow the body to be radially compressed from an expanded configuration to a contracted configuration. A closure cap formed with a resealable aperture is disposed on the distal end of the male body so as to be responsive to the compression of the male body. The relatively flexible wall segments may be installed within notches in the male body or be formed integral with the relatively rigid wall segments.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Spinal implant and method of use
A spinal implant having a smaller transverse cross-sectional dimension in the radially compressed configuration than in a first expanded configuration and a more linear configuration in the second delivery configuration than in the first curved configuration. The implant assumes the radially compressed configuration and second delivery configuration during delivery to the disc space and assumes the first curved configuration and first expanded configuration upon placement within the disc space. The implant further moves towards the radially compressed configuration once implanted in response to a load placed on the implant by the vertebral bodies.
Owner:REX MEDICAL LP
Embolectomy device
InactiveUS20110152920A1Good removal effectEasy to adjustDilatorsSurgical pincettesMedicineRadial compression
It is one object of the present invention to provide a device for extracting a clot from a blood vessel in a non fragmented manner, comprising: 1. an endless wire coupled to a spring-like helical member having a plurality of loops; said loops are positioned at an angle A relatively to the main longitudinal axis of said blood vessel; and, are adapted to radially encircle at least a portion of the outer circumference of said clot; and, 2. a tubular mesh-like net for both enveloping said helical member and enclosing said clot therein; wherein at least a portion of said clot is contemporaneously confined within said loops and said mesh-like net, such that radial compression forces and longitudinal shearing forces are exerted on said clot and the tendency of said clot to fragment is mitigated.
Owner:RAPID MEDICAL
Cylindrical roller stent crimper apparatus with radiation shield
A stent loading apparatus for loading a deformable stent onto a deployment device. The stent loading apparatus includes an elastic member defining a passage therein formed for longitudinal receipt of the deformable stent in an uncrimped condition. A first member includes a first compression region; and a second member includes a second compression region positioned substantially adjacent the first compression region at a first position. At this first position, the elastic member and the deformable stent in the uncrimped condition may be received between the opposed first and second compression regions. The first compression region and the second compression region are further configured to provide rolling support and compression of the elastic member during relative movement between the first position and a second position for rolling radial compression of the deformable stent onto the deployment device.
Owner:ISOSTENT
Artificial heart valve with scaffold
The invention relates to an artificial heart support valve, wherein it comprises tubular mesh support, valve blade, sealing film, impermeable x-ray mark, and flexible coiple ring; the middle part of mesh support is round or cylinder, or arranged with radial protrusion, or arranged with outer annular structure, or arranged with outer free tone, or arranged with radial protrusion and outer free tone. The invention can radial compress to transmit into accurate position via medium device, to be expanded, while the expanded valve will meet the shape of valve, without leakage. The invention can avoid being pushed when the blood refluxes and it is closed.
Owner:BEIJING BALANCE MEDICAL
Snap-lock for drill sleeve
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Accommodating intraocular lens device
ActiveUS20160030161A1Constant volumeImprove optical qualityIntraocular lensIntraocular lensEngineering
An accommodating intraocular lens (IOL) can be implanted either alone or as part of a two-part lens assembly. The IOL comprises an optic, a flexible membrane and a peripheral edge coupling the optic and the flexible membrane. The peripheral edge comprises an external circumferential surface having a height and a force transmitting area defined along a portion of the height of the external circumferential surface. A closed volume spaces apart the optic and the flexible membrane. The optic is axially displaced and the flexible membrane changes in curvature about a central axis when a radial compressive force is applied to the force transmitting area. A volume defined by the closed volume remains fixed when the optic is axially displaced and the flexible membrane changes in curvature and / or when the radial compressive force is applied to the force transmitting area.
Owner:LENSGEN INC
Apparatus and method for loading and delivering a stent
InactiveUS20070270937A1Restrict movementAvoid damageStentsOesophagiRadial compressionCatheter device
An assembly for delivering a self-expanding stent into a body lumen comprising a catheter adapted to deliver the self-expanding stent, the catheter having a stent delivery passage adapted to contain the stent in an at least partially radially compressed state, and a stent transfer member communicating with a distal end of the catheter, the stent transfer member having a cylindrical passage sized to circumferentially surround at least a portion of the stent in an at least partially radially expanded state, the stent transfer member further including a tapered passage disposed between the cylindrical passage and the delivery passage to radially compress the stent as the stent moves from the cylindrical passage into the tapered passage.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Hand held stent crimping apparatus and method
A hand actuatable apparatus and method for crimping a stent or processing other articles by segmental radial compression. The apparatus includes a stationary base housing; a rotatable drive hub which is moveable in relation to the base housing; a crimping head communicatively coupled to the base housing and to the drive hub; and an actuator handle connected to the base housing and to the drive hub. The crimping head includes a plurality of segments oriented about a center aperture which receives a stent or article to be compressed. The segments each have a proximal end and an angled distal end with at least one angled side face terminating in an edge of a predetermined length and defining the center aperture. Actuation of the handle rotates the drive hub, which causes the segments to move and pivot, resulting in closure of the center aperture and compression of the stent or other article.
Owner:MACHINE SOLUTIONS
Collet Based Locking Mechanism
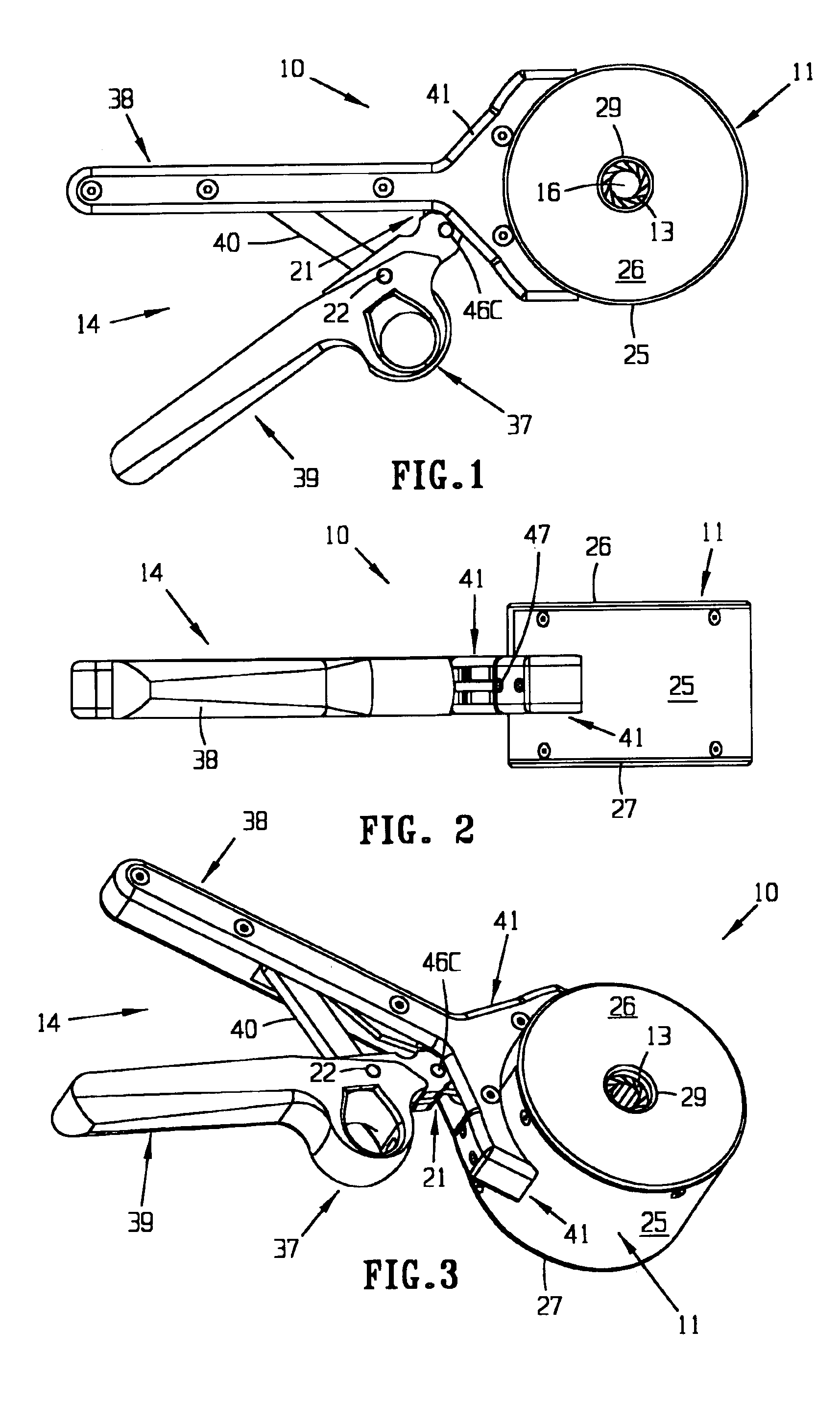
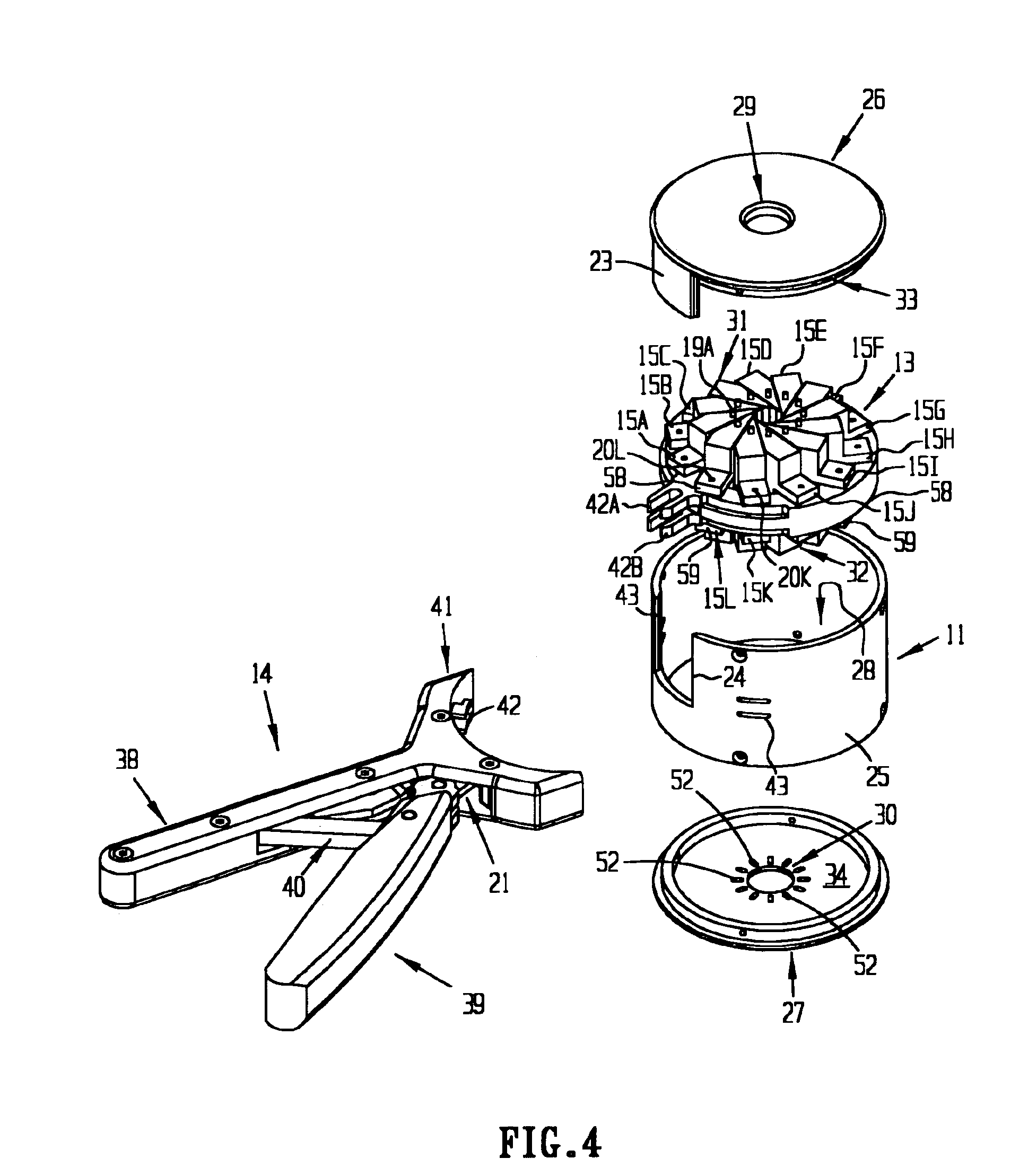
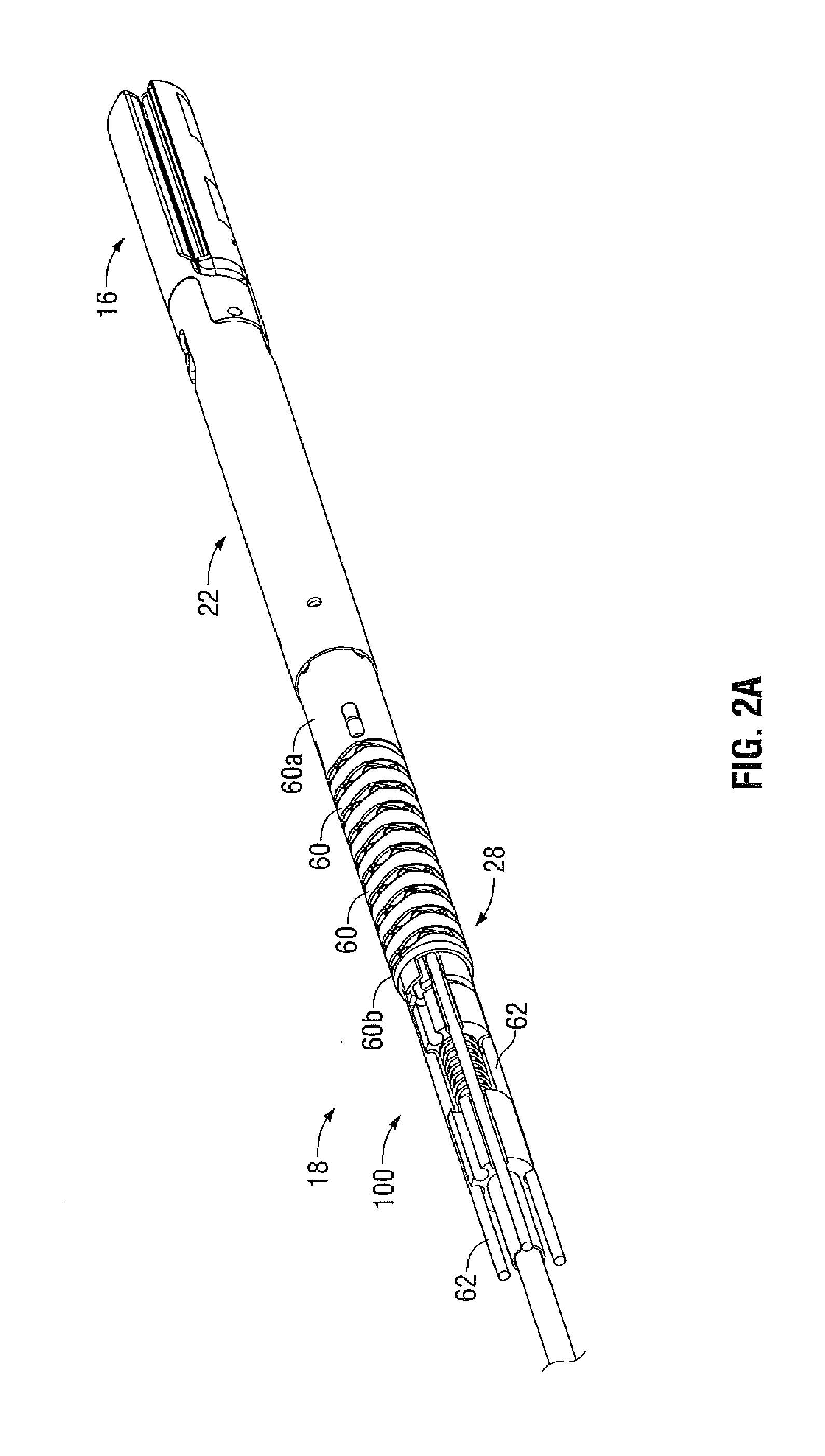
ActiveUS20120059408A1Facilitate radial compressionSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsDistal portionLocking mechanism
A surgical instrument includes a housing supporting first and second actuators, an elongated shaft extending distally from the housing, and an end effector supported by a distal portion of the elongated shaft. A tensile member extending through the elongated shaft is coupled to the first actuator and the end effector such that first actuator may be manipulated to induce motion of the end effector. A locking mechanism associated with the tensile member selectively impedes motion of the end effector. The locking mechanism includes a collet disposed about the tensile member and a collet clamp for receiving the collet. Receipt of the collet into the collet clamp induces radial compression of the collet to impede the motion of the tensile member therethrough. An actuation member extending through the elongated shaft induces insertion and withdrawal of the collet from the collet clamp.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Fracture fixation systems
ActiveUS20120029102A1Firmly connectedImprove permeabilityImpression capsSurgical adhesivesResorbable polymersPolymer resin
Systems for bone fracture repair are disclosed. One system includes a biocompatible putty that may be packed about a bone fracture to provide full loadbearing capabilities within days. The disclosed putties create an osteoconductive scaffold for bone regeneration and degrade over time to harmless 5 resorbable byproducts. Fixation devices for contacting an endosteal wall of an intramedullary (IM) canal of a fractured bone are also disclosed. One such fixation device includes a woven elongated structure fabricated from resorbable polymer filaments. The woven elongated structure has resilient properties that allow the woven 10 structure to be radially compressed and delivered to the IM canal using an insertion tube. When the insertion tube is removed, the woven structure expands towards its relaxed cross-sectional width to engage the endosteal wall. The woven elongated structure is impregnated with a resorbable polymer resin that cures in situ, or in the IM canal.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Multi-layered stents and methods of implanting
InactiveUS20100179641A1Promote and limit tissue ingrowthMinimize and avoid occurrenceStentsVenous valvesRadial compressionDelivery system
A method of percutaneously delivering a multi-layered stent assembly to a desired implantation location of a patient including the steps of radially compressing a multi-layered stent assembly to a compressed size for implantation in a patient, the multi-layered stent assembly including a first stent, a second stent coaxially positioned within at least a portion of a length of the first stent, and a valve, wherein the first stent comprises at least one different material property than the second stent. The method further includes delivering the multi-layered stent assembly to the desired implantation location of the patient using a delivery system and substantially simultaneously expanding the first stent and the second stent of the multi-layered stent assembly at the desired implantation location to a radially expanded size that is larger than the compressed size.
Owner:RYAN TIMOTHY R +3
Self-sealing male connector device with collapsible body
ActiveUS20060149213A1Good flexibilityLess wall thicknessInfusion syringesInfusion devicesEngineeringRigid wall
A self-sealing male connector device for connection with a female Luer connector. The device has an elongated male body configured with lengthwise relatively rigid and flexible wall segments cooperating to allow the body to be radially compressed from an expanded configuration to a contracted configuration. A closure cap formed with a resealable aperture is disposed on the distal end of the male body so as to be responsive to the compression of the male body. The relatively flexible wall segments may be installed within notches in the male body or be formed integral with the relatively rigid wall segments.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Force distributing system for delivering a self-expanding stent
The invention provides a system that distributes along the length of a stent those forces exerted on the stent during release of the stent from a sheath. The system includes a catheter inner member, a stent, and a sheath. Multiple longitudinally spaced protrusions extend from the outer surface of a distal portion of the inner member. Complementary longitudinally spaced apertures are formed in the wall of the stent. The stent is mounted on the inner member with the inner member protrusions received within the stent apertures. The sheath encloses the stent and is movable with respect to the stent. The system is assembled by aligning the protrusions and apertures and radially compressing the stent about the inner member. The resulting interlocked protrusions and apertures allow the stent to be withdrawn from a radial compression device into the sheath by pulling on the inner member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
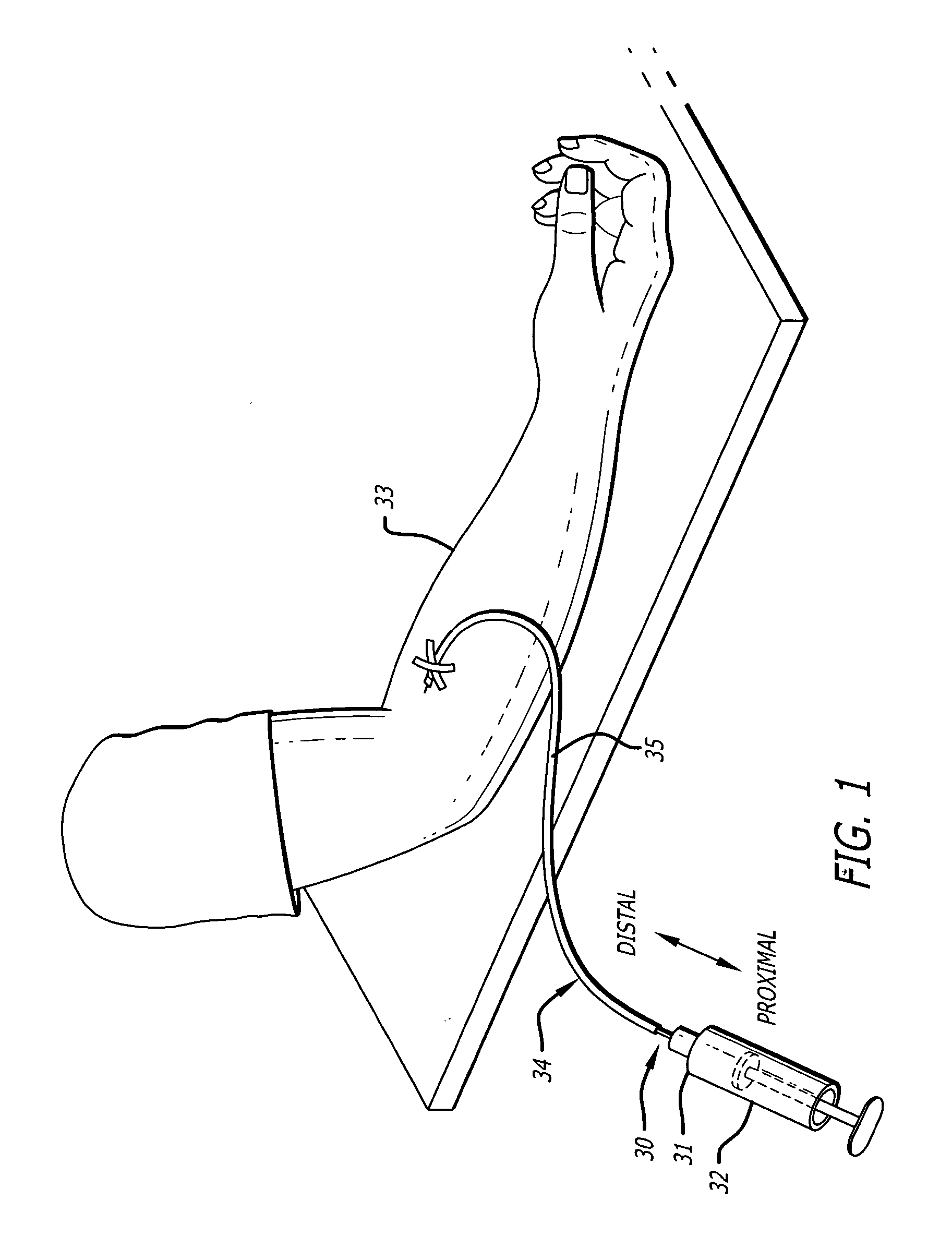
Radial compression hemostasis band with doppler confirming vascular patency
A hemostatic compression system facilitates patent hemostasis of an arterial access site on the arm of a wearer. The system includes a radial compression band and a Doppler probe. The radial compression band includes an elongated arm band sized to receive the arm. The compression band also includes a pressure surface coupled to the arm band and facing radially inward for compressive engagement with the access site. The Doppler probe is coupled to the arm band adjacent the pressure surface and is configured to sense blood flow through the artery. Hemostatic compression applied by the radial compression band is variable in response to the sensed blood flow so as to ensure patency of the artery during hemostasis of the site.
Owner:MEDICAL INGENUITIES
Medical device retaining sheath and medical device delivery system employing same
An endoluminal prosthetic delivery system provides a delivery sheath possessing a yield strength capable of allowing implantation of the prosthesis with increased efficiency. An endoluminal prosthesis is inserted in a body in a radially compressed condition, and expanded at an implantation site, whereby a delivery sheath or the prosthesis itself possesses a yield strength sufficient to allow radial expansion of the prosthesis. A method of implanting an endoluminal prosthesis is also herein provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Multi-component expandable supportive bifurcated endoluminal grafts and methods for using same
ActiveUS20100063575A1Reduce laborReduce complicated multi-step medical procedureStentsBlood vesselsRadial compressionLesion
A multiple-component expandable endoluminal system for treating a lesion at a bifurcation including a self expandable tubular root member having a side-looking engagement aperture, a self expandable tubular trunk member comprising a substantially blood impervious polymeric liner secured therealong; both having a radially compressed state adapted for percutaneous intraluminal delivery and a radially expanded state adapted for endoluminal support.
Owner:ENDOSPAN
Stent crimping method
An apparatus for crimping a stent by segmental radial compression, comprising a stationary base member; a rotatable drive hub which is moveable in relation to the stationary base member; and a crimping head aligned with respect to the stationary base member and to the rotatable drive hub. The crimping head includes at least ten segments. The segments each have a proximal end and an angled distal end with at least one angled side face terminating in an edge of a predetermined length, each segment having a centerline between the proximal and distal ends, each segment having a proximal point and a distal point, the distal point being disposed on the centerline and the proximal point being disposed off the centerline, and the proximal point being pivotally coupled by pins to the stationary base member and the distal point being pivotally coupled by pins to the rotatable hub member. The segments are arranged so that the segment distal ends are disposed adjacent to and a predetermined distance away from a central point and defining a central aperture with a cylindrical dimension. Also, the segment centerlines extend therefrom toward the segment distal ends and are oriented away from the central point. The segment distal ends move closer to the central point upon rotation of the rotatable hub member in a predetermined direction, whereby the stent is disposed around a base substrate, aligned in the central aperture and crimped round the base substrate upon rotation of the rotatable hub. A method of crimping a stent is also disclosed.
Owner:MACHINE SOLUTIONS
Clutch device for locks
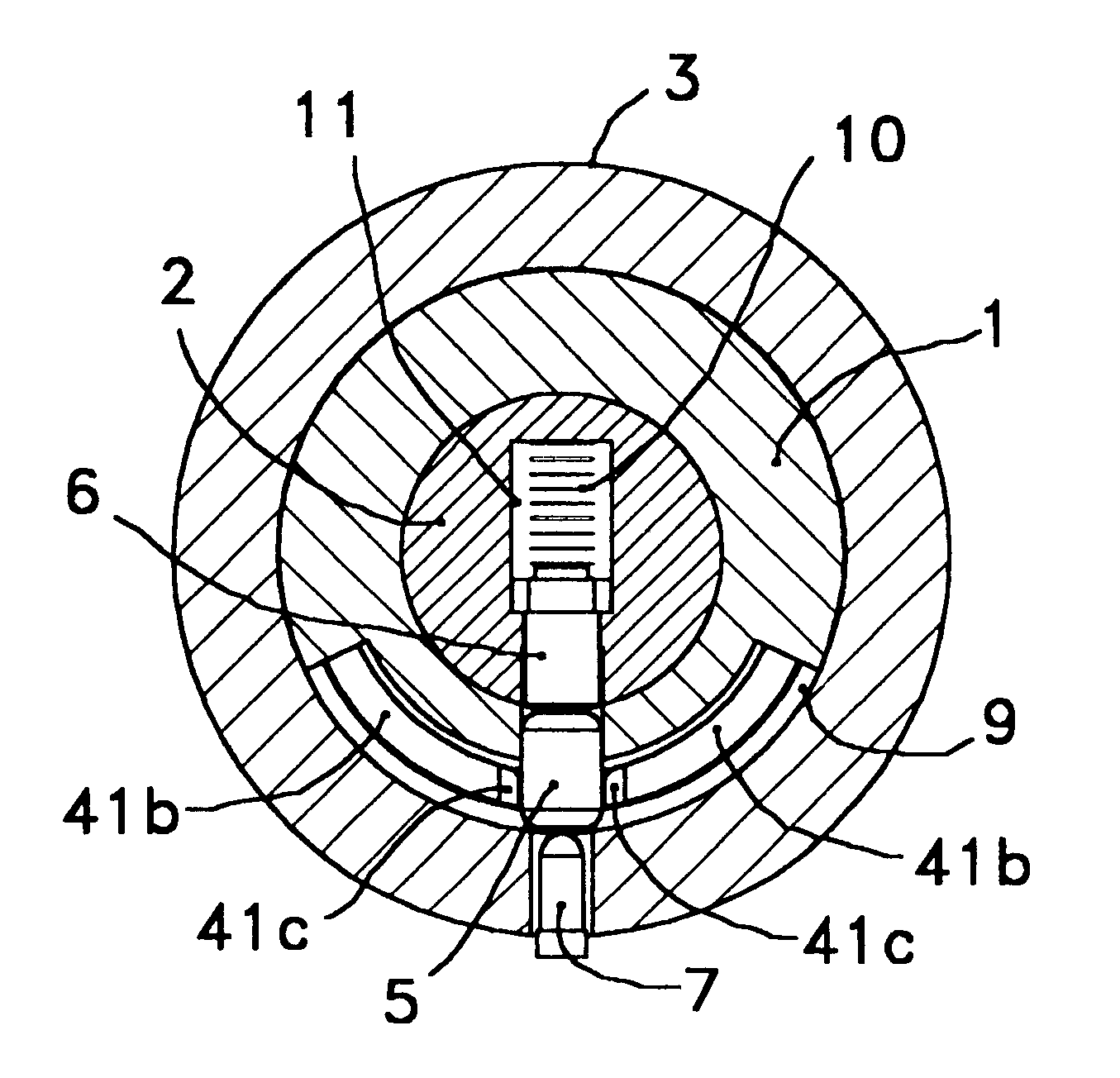
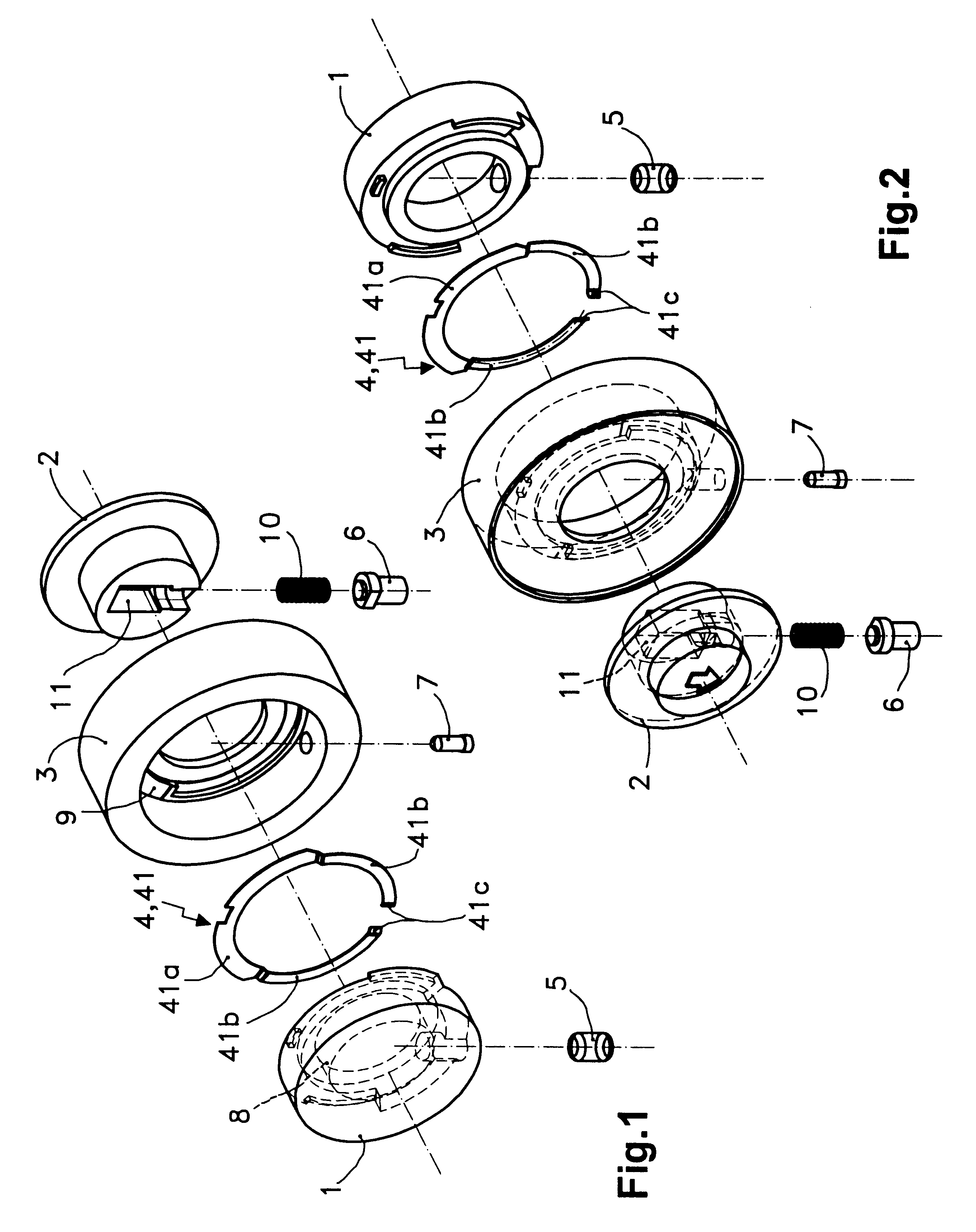
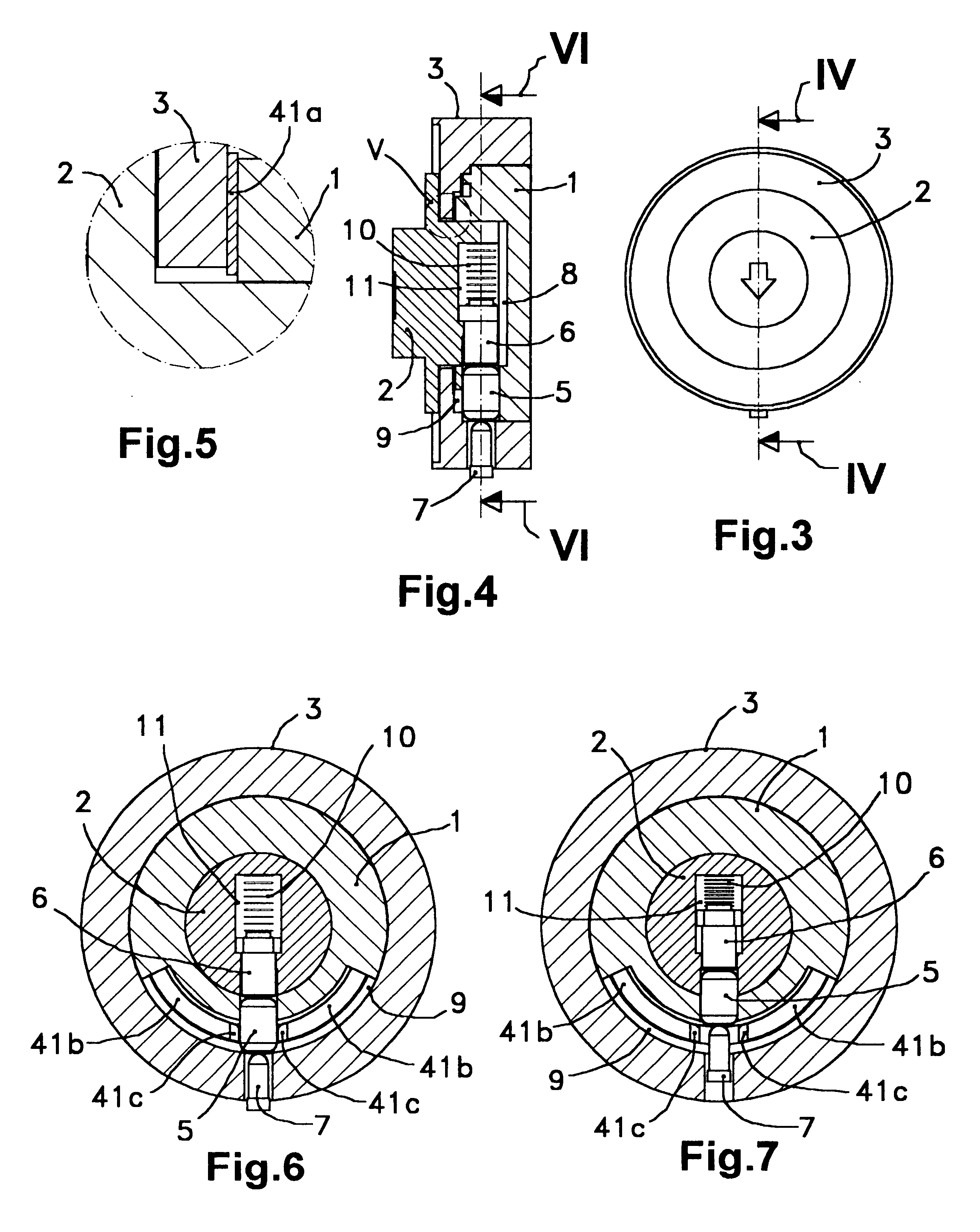
Clutch device for locks which consists of an interior axis, an exterior axis, a frame or static body, an elastic element, a radial trigger, a radial trigger lock and a radial actuator; wherein: the interior axis, exterior axis and static body comprise a coaxial assembly in which the exterior axis penetrates an axial cavity of the interior axis while both axes are assembled within the static body, the elastic element is in a fixed relative position with respect to the static body and in an annular housing defined between this static body and the interior axis, the radial trigger is lodged in a movable position within the interior axis and has a length equal to the difference between the exterior diameter of the exterior axis and the interior diameter of the static body, the radial trigger lock is installed within the exterior axis with its tip in the exterior diameter of this exterior axis and with its tail end placed against one end of a radial compression spring.
Owner:TALLERES DE ESCORIAZA SA
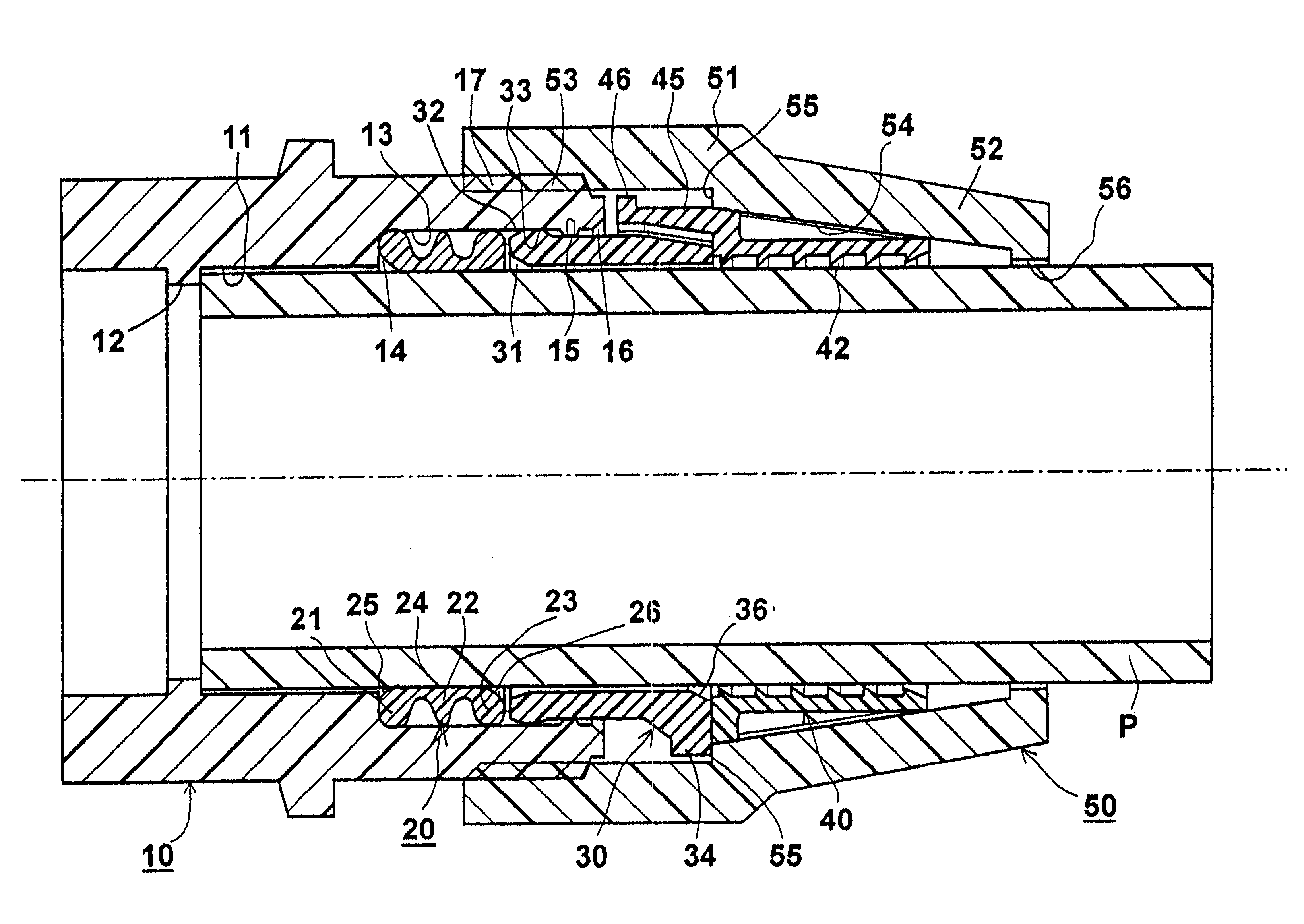
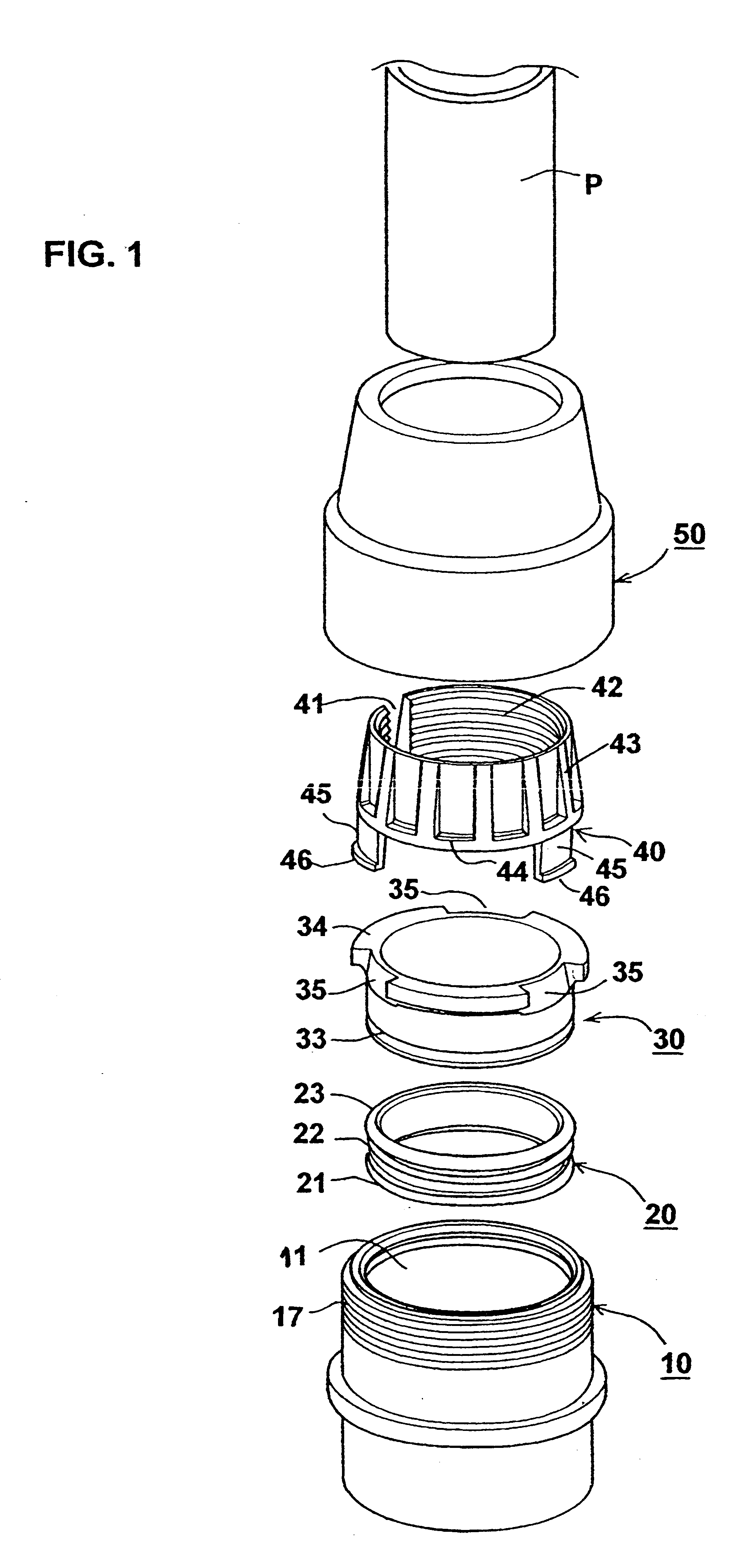
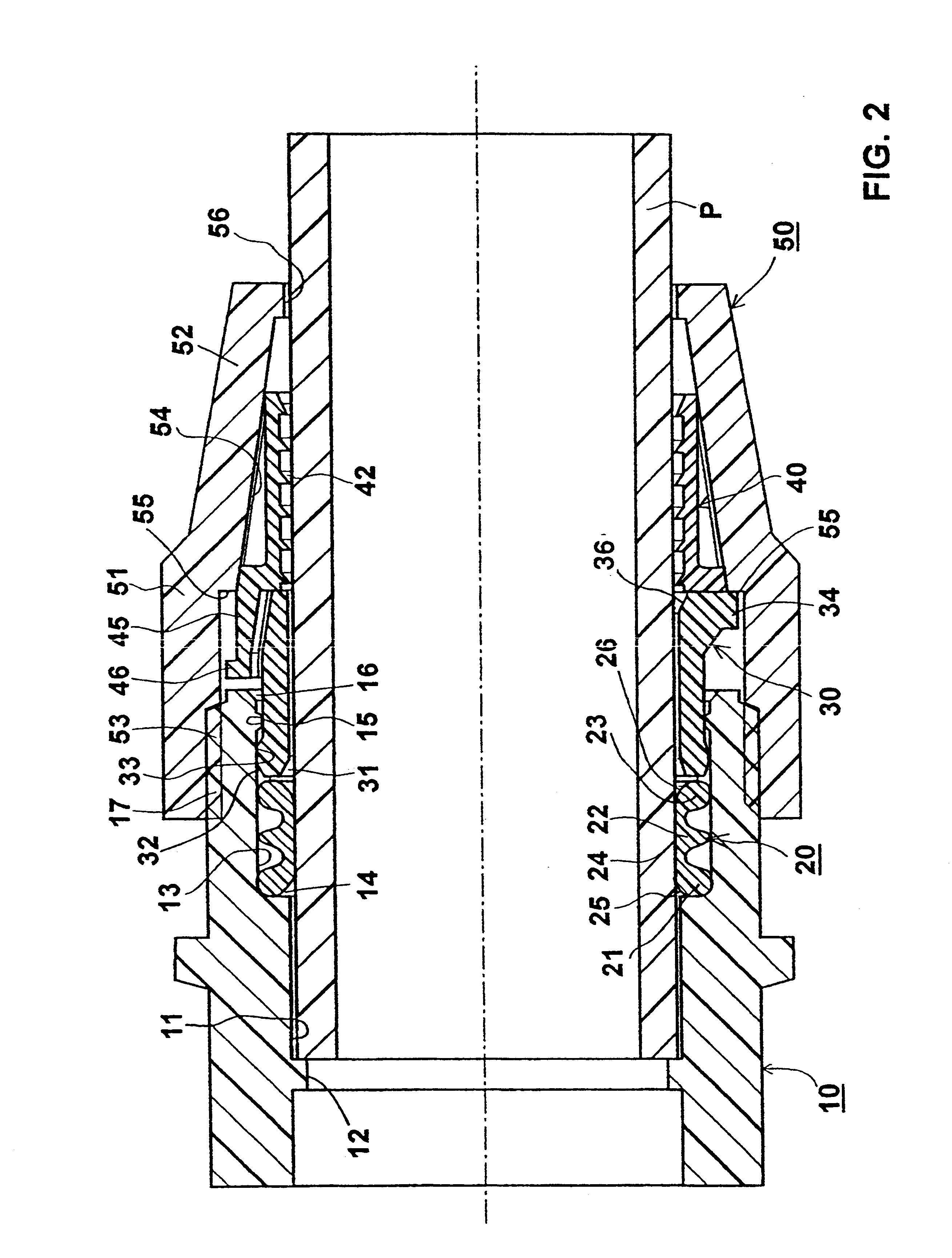
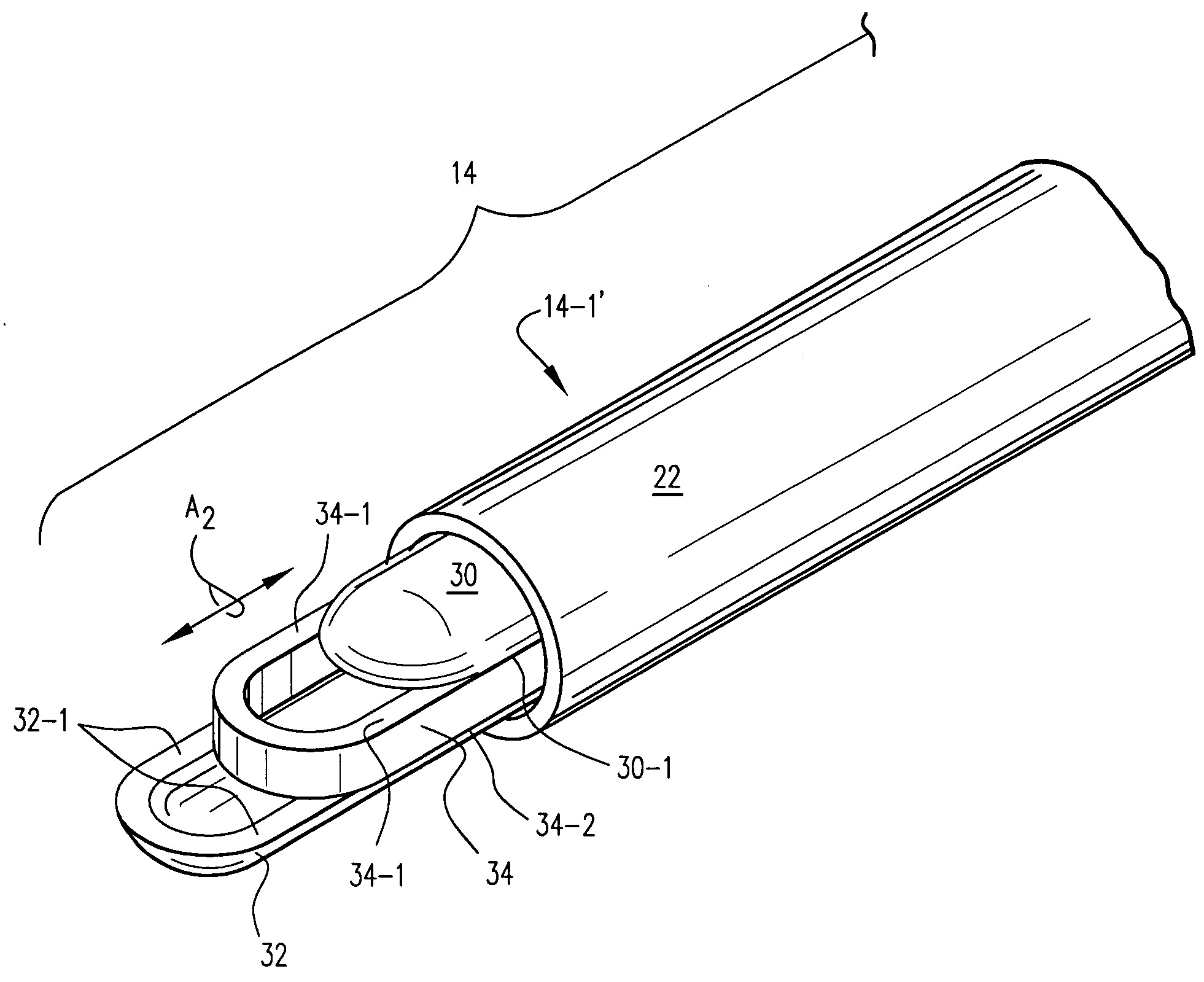
Pipe coupling
A pipe coupling includes a body member (10) formed with a bore (11) for receiving one end of a pipe (P) to be coupled; a sealing ring (20) and a compression sleeve (30) receivable within the bore (11); a radially-deformable gripping ring (40) having one end abuttable against the compression sleeve (30), a securing nut (50) threaded on the body member (10) and engageable with the gripping ring (40) to move the gripping ring (40) axially and to effect a sealing action via the compression sleeve (30) and the sealing ring (20), and also to compress the gripping ring (40) radially to effect a gripping action of the pipe (P) received in the bore (11); and an axially-extending limit element (45) between the gripping ring (40) and the body member (10) effective to cause the nut (50), when tightened; (a) in an initial stage, to move the gripping ring (40) and the compression sleeve (30) until the limit element engages (45) prevents further axial movement of the gripping ring (40); and (b) in a final stage, to radially deform the gripping ring (40) to produce the gripping action, and then to compress the sealing ring (20) against the internal annular shoulder (14) of the body member to produce the sealing action.
Owner:PLASSON LTD
Surgical instruments which are especially useful for ophthalmic surgical procedures, and methods of making the same
Surgical instrument include a longitudinally sectioned needle member establishing respective needle segments, and an outer sleeve member which exerts a circumferentially radial compression onto the needle segments yet allows for relative longitudinal movements between at least one and another of the needle segments. The needle member may be longitudinally bifurcated so as to establish said one and another needle segments. Alternatively, the needle member may be longitudinally trifurcated so as to establish a pair of stationary outer needle segments, and an intermediate needle segment sandwiched between but longitudinally moveable relative to said outer needle segments. Thus, collectively the needle segments define respective opposed longitudinal bearing edges which contact one another and thereby allow for one of the needle segments to be moveable longitudinally relative to another of the needle segments. As such, the lumen within the sectioned needle member may be maximized while the overall dimension of the instrument is minimized.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com