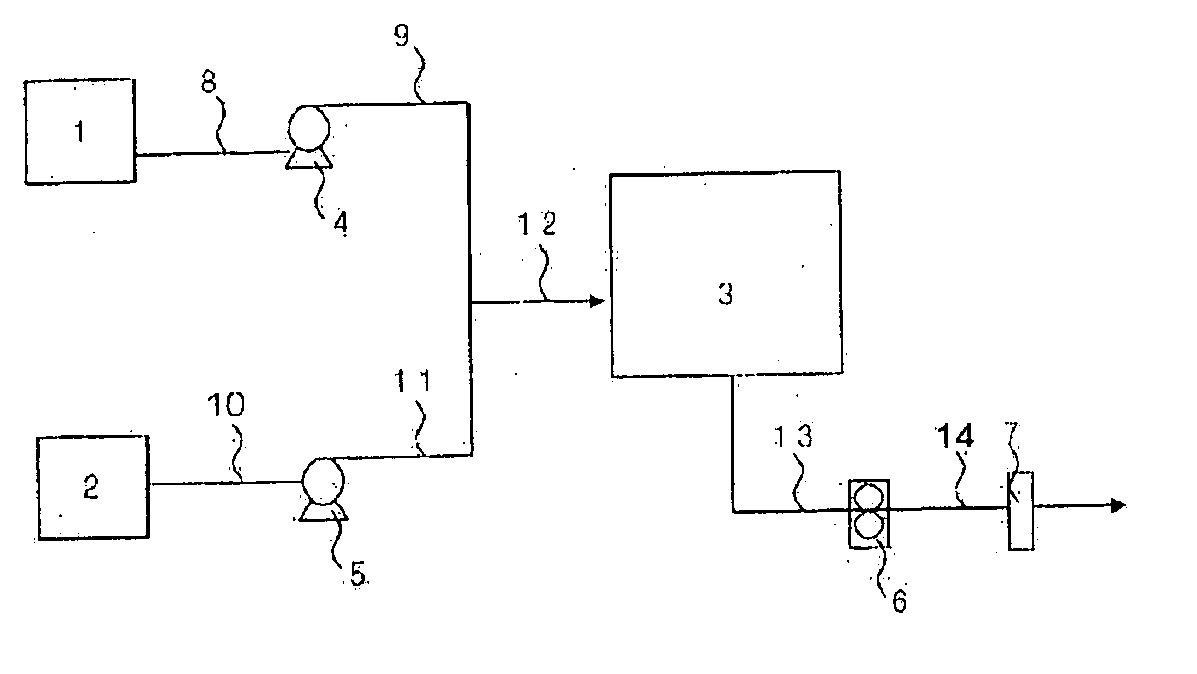
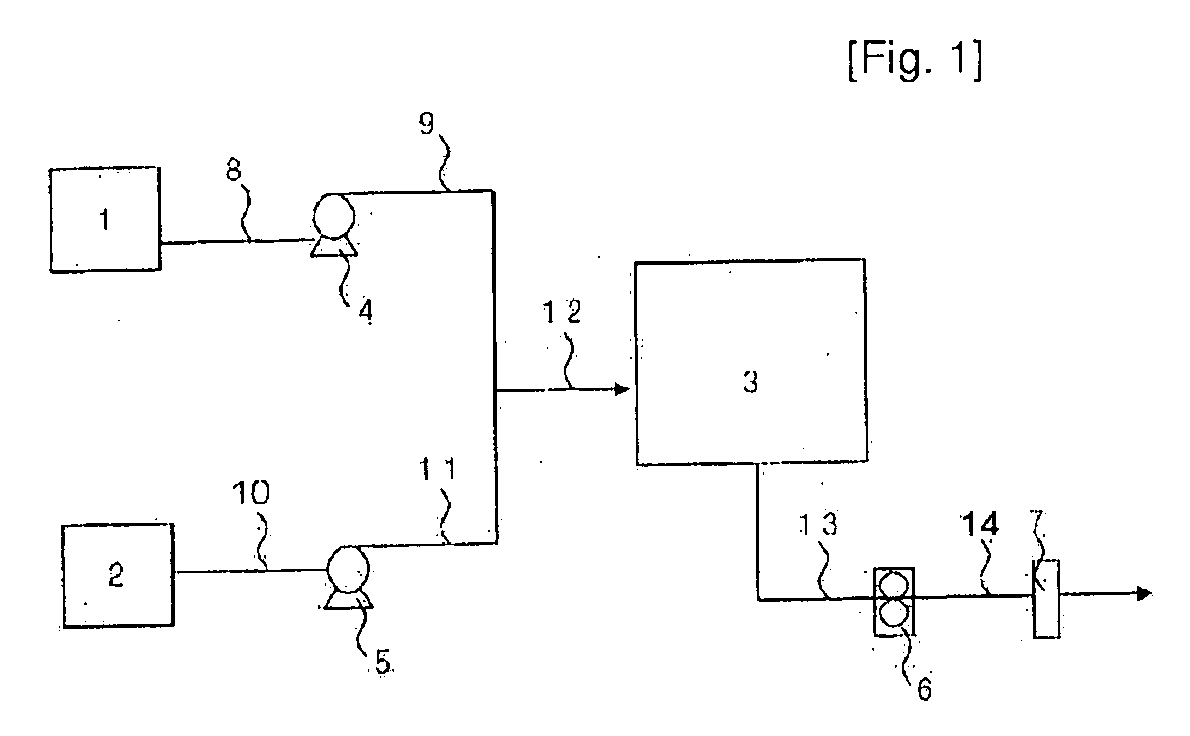
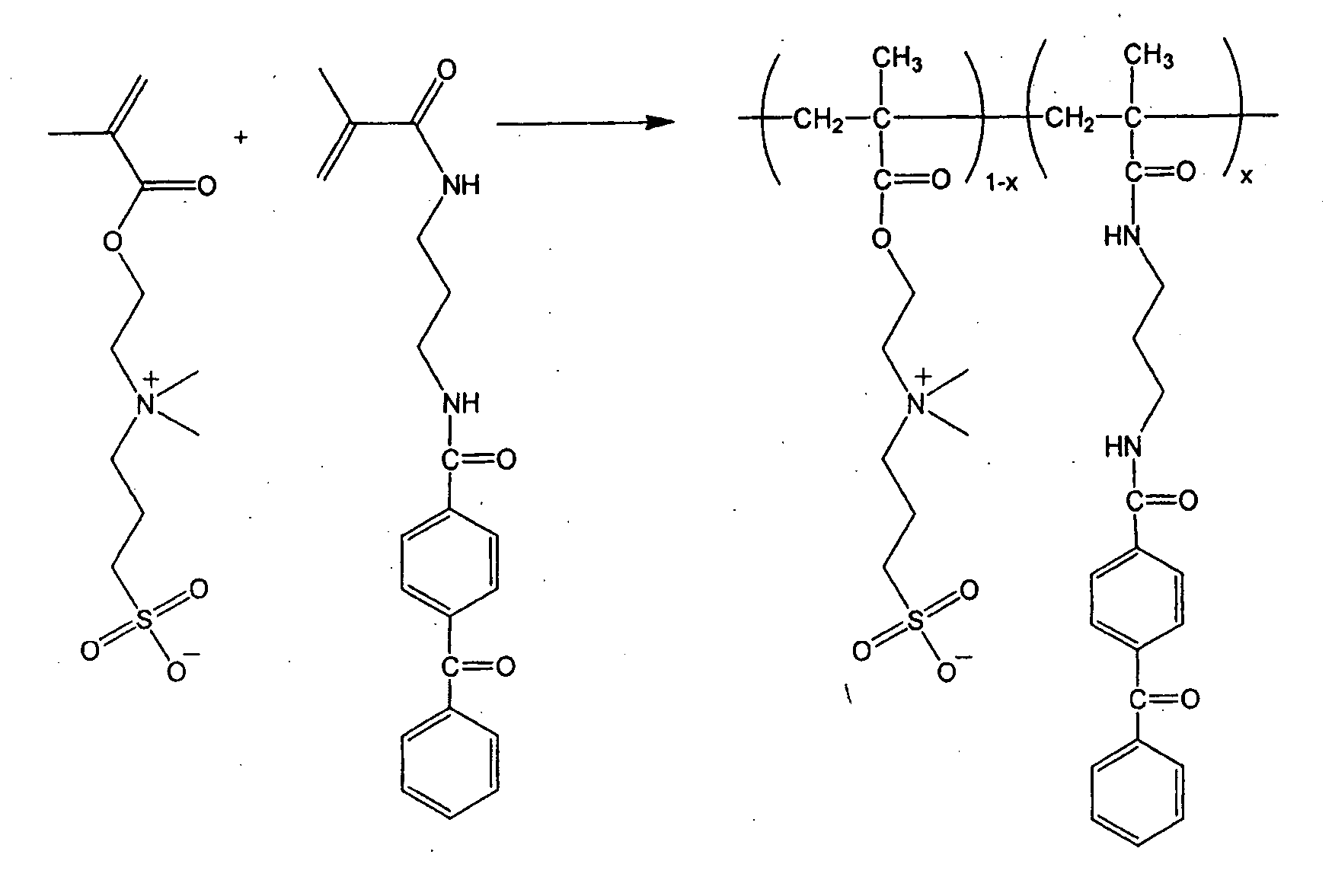
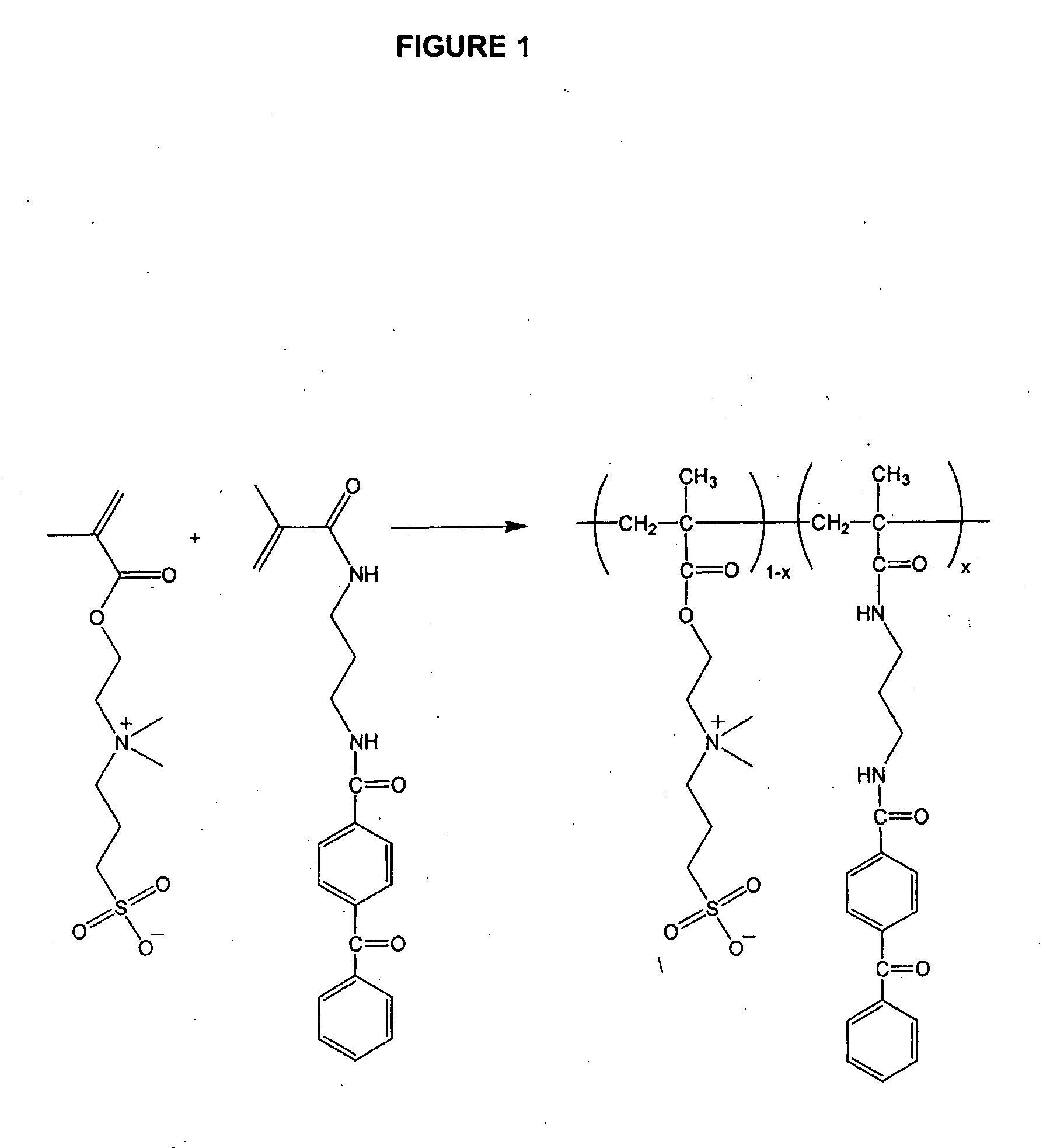
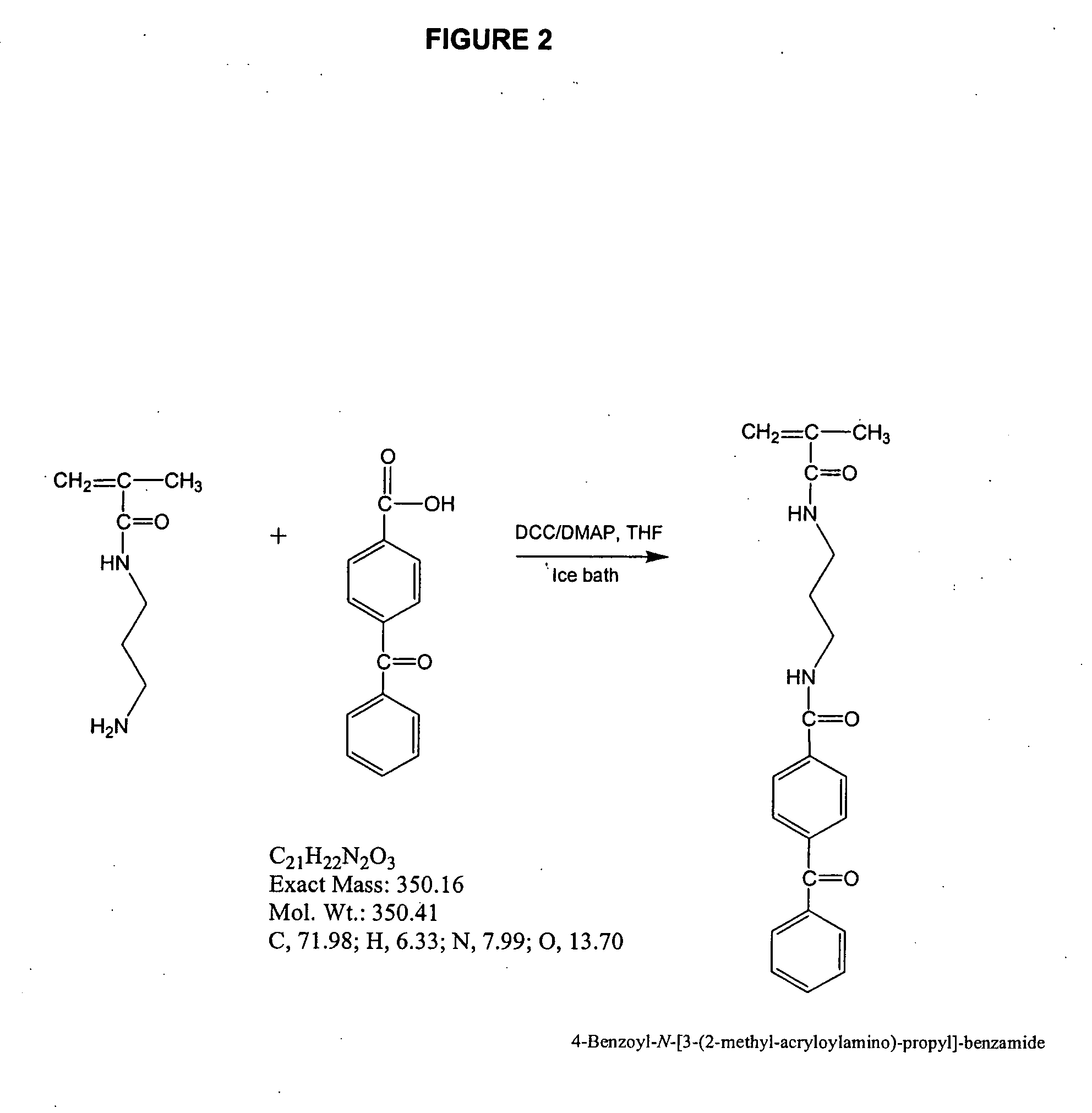
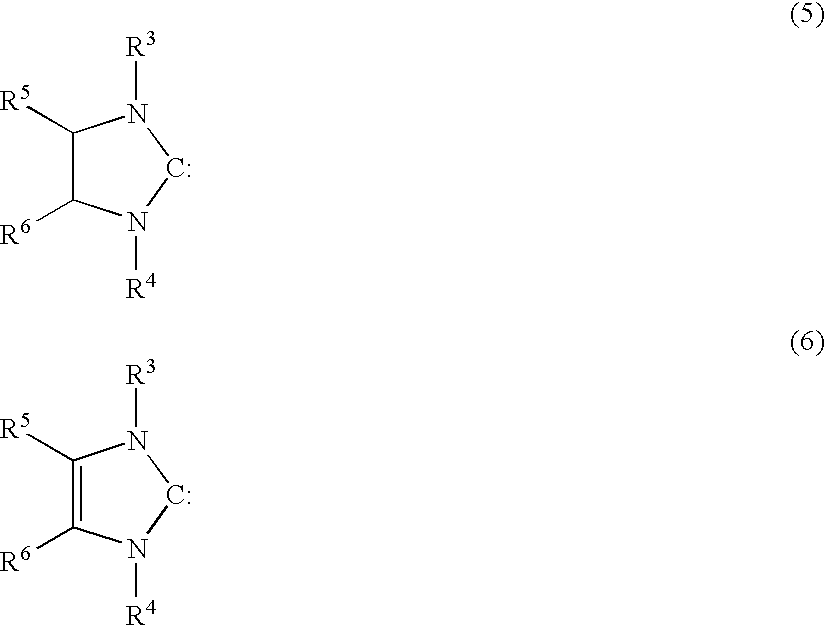
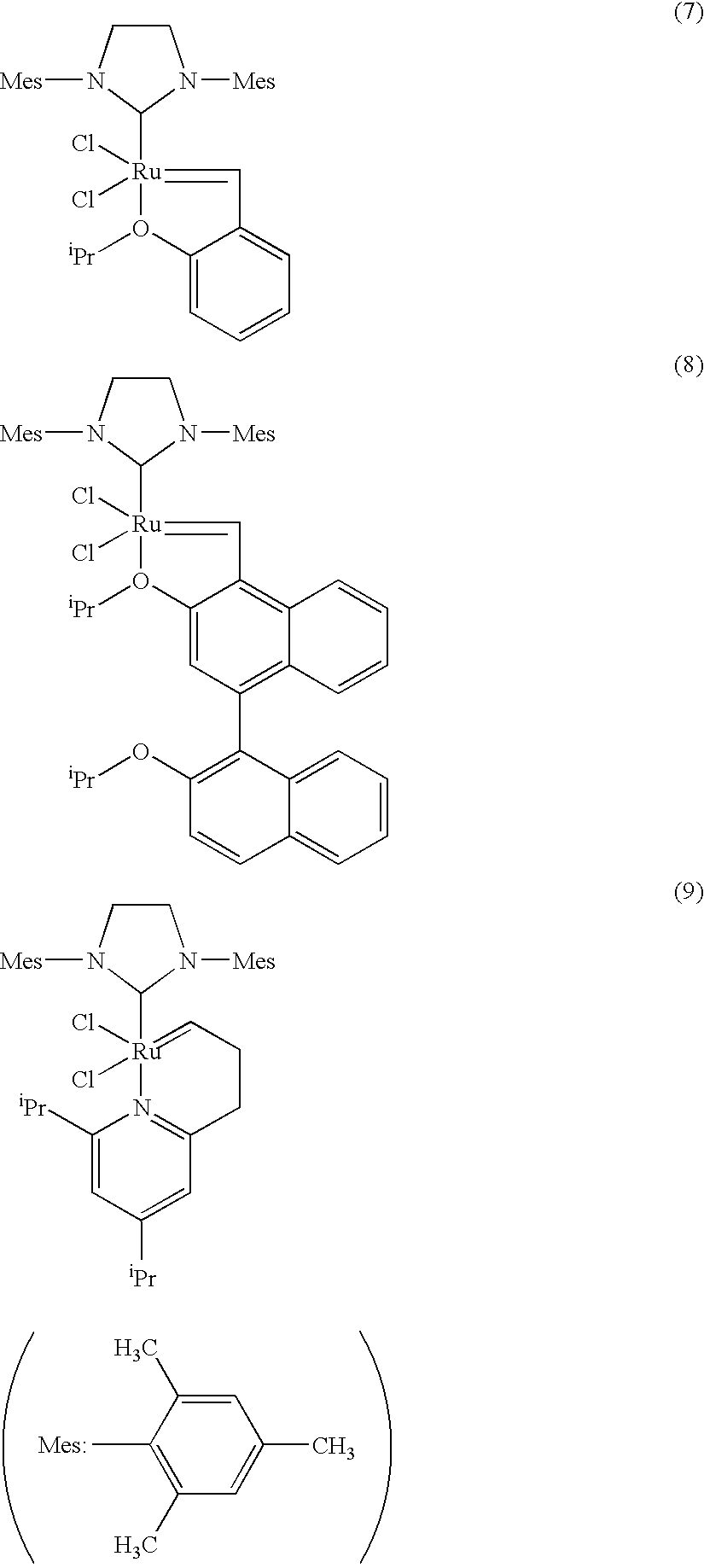
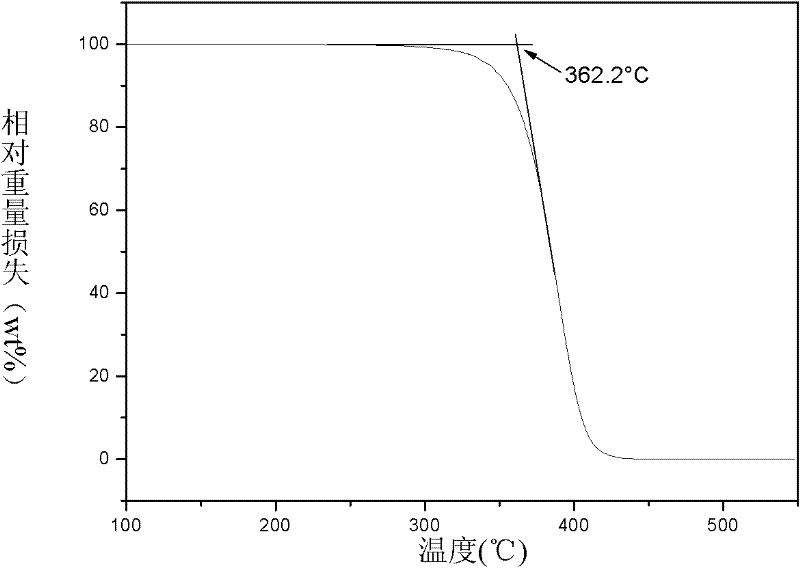
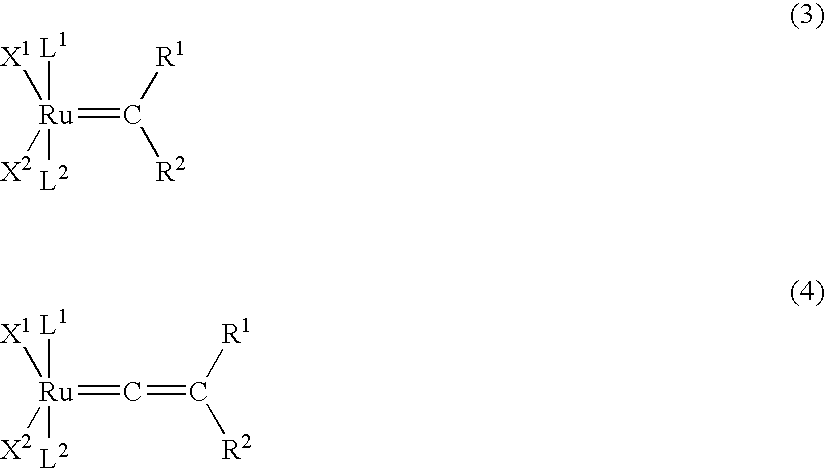Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
976 results about "Bulk polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bulk polymerization or mass polymerization is carried out by adding a soluble radical initiator to pure monomer in liquid state. The initiator should dissolve in the monomer. The reaction is initiated by heating or exposing to radiation. As the reaction proceeds the mixture becomes more viscous. The reaction is exothermic and a wide range of molecular masses are produced.
Bulk polymerization process for producing polydienes
ActiveUS7094849B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHalogenBulk polymerization
A method of producing cis-1,4-polydienes, the method comprising the step of contacting conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst system in the presence of less than 20% by weight of organic solvent based on the total weight of monomer, organic solvent, and resulting polymer, where the lanthanide-based catalyst system is the combination of or reaction product of (a) a lanthanide compound, (b) an organoaluminum hydride, (c) a trihydrocarbylaluminum, and (d) a halogen-containing compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method for Preparing Adhesive Acrylic Ester Polymer Syrup
InactiveUS20070299226A1Improve performanceThe polymerization process is stableEster polymer adhesivesContinuous reactorProduction rate
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an acrylic ester polymer syrup by bulk polymerization, and more particularly, to a method for preparing an acrylic ester polymer syrup, which comprises the steps of: supplying a monomer solution and an initiator solution to a monomer solution reservoir and an initiator solution reservoir, respectively; supplying the monomer solution and the initiator solution to a complete-mixing type continuous reactor, while maintaining the dissolved oxygen in the monomer solution reservoir and the initiator solution reservoir at 0.0001 to 3 ppm, separately or after mixing prior to the supply; and performing bulk polymerization continuously while maintaining the solution mixture supplied to the continuous reactor at 70 to 150 ° C. and 1 to 10 atm, with a mean residence time of 30 to 240 minutes. In accordance with the present invention, an acrylic ester polymer syrup can be obtained with a degree of polymerization of 20 to 70% at a low polymerization temperature, even with a small amount of initiator. Productivity can be improved by reducing reaction time with the use of an initiator having a short half-life and polymerization can be performed very stably and continuously without gelation.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Zwitterionic polymers
InactiveUS20060183863A1Improve utilizationImprove versatilitySolid sorbent liquid separationCross-linkLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
Zwitterionic polymers bearing positive and negative charges are readily prepared from easily accessible precursors. The polymers show enhanced binding affinities for analytes under high salt conditions, compared to similar polymers bearing a charge of a single polarity. The polymers can also include an energy absorbing moiety for use in matrix assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry. The polymer can also include a photo-curable group, which can be used to form cross-links within the bulk polymer or between the polymer and a surface functionalized with a polymerizable moiety. The polymers are incorporated into devices of use for the analysis, capture, separation, or purification of an analyte. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention provides a substrate coated with a polymer of the invention, the substrate being adapted for use as a probe for a mass spectrometer.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Bulk polymerization process
A method for the continuous production of polydienes, the method comprising the steps of (a) charging a mixture of one or more monomer, catalyst system, and less than 50% weight percent organic solvent based on the total weight of the monomer, catalyst and solvent, into first vessel, (b) polymerizing the monomer to a conversion of up to 20% by weight of the monomer to form a mixture of reactive polymer and monomer, (c) removing the mixture of reactive polymer and monomer from the vessel, and (d) terminating the reactive polymer prior to a total monomer conversion of 25% by weight.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
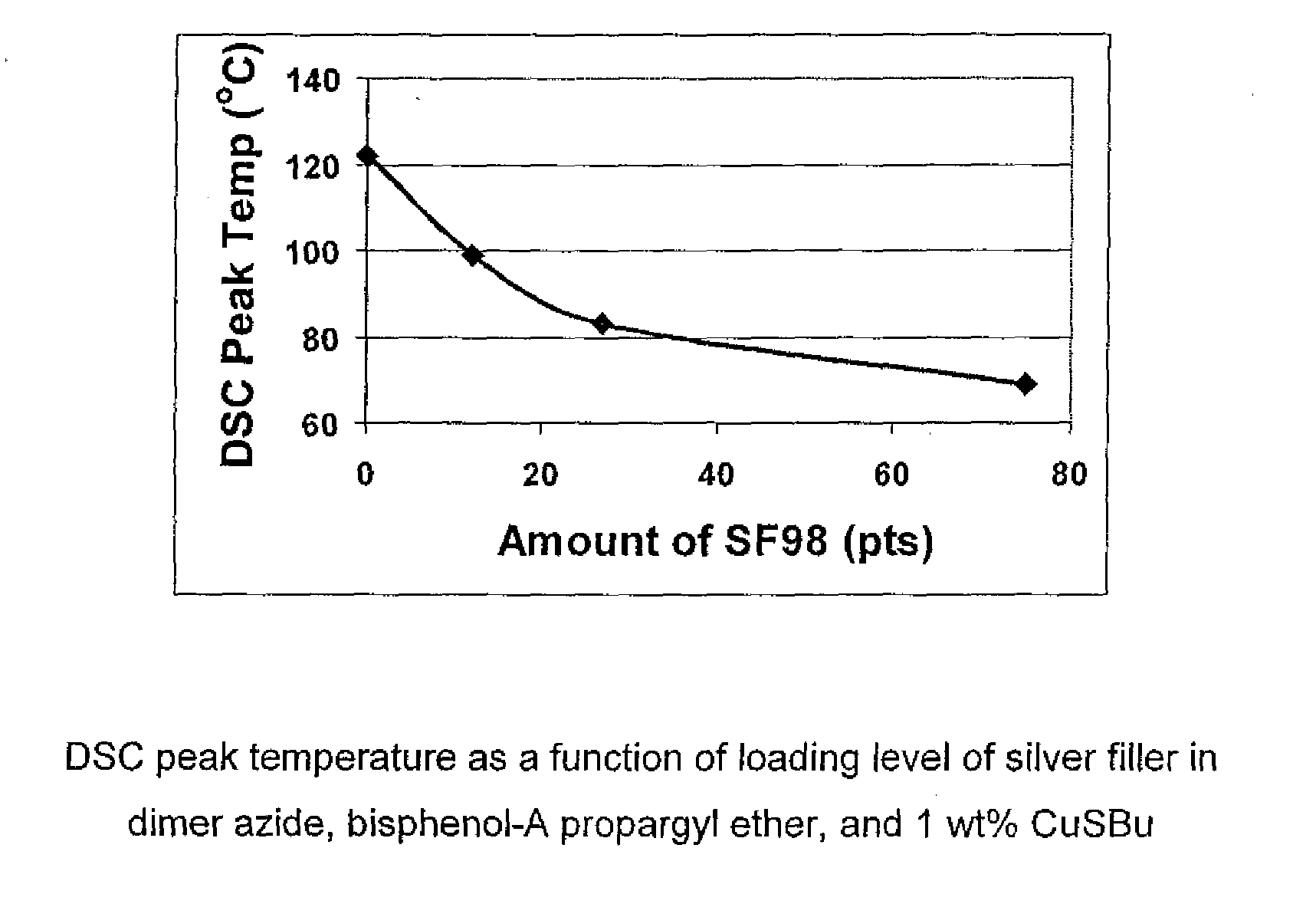
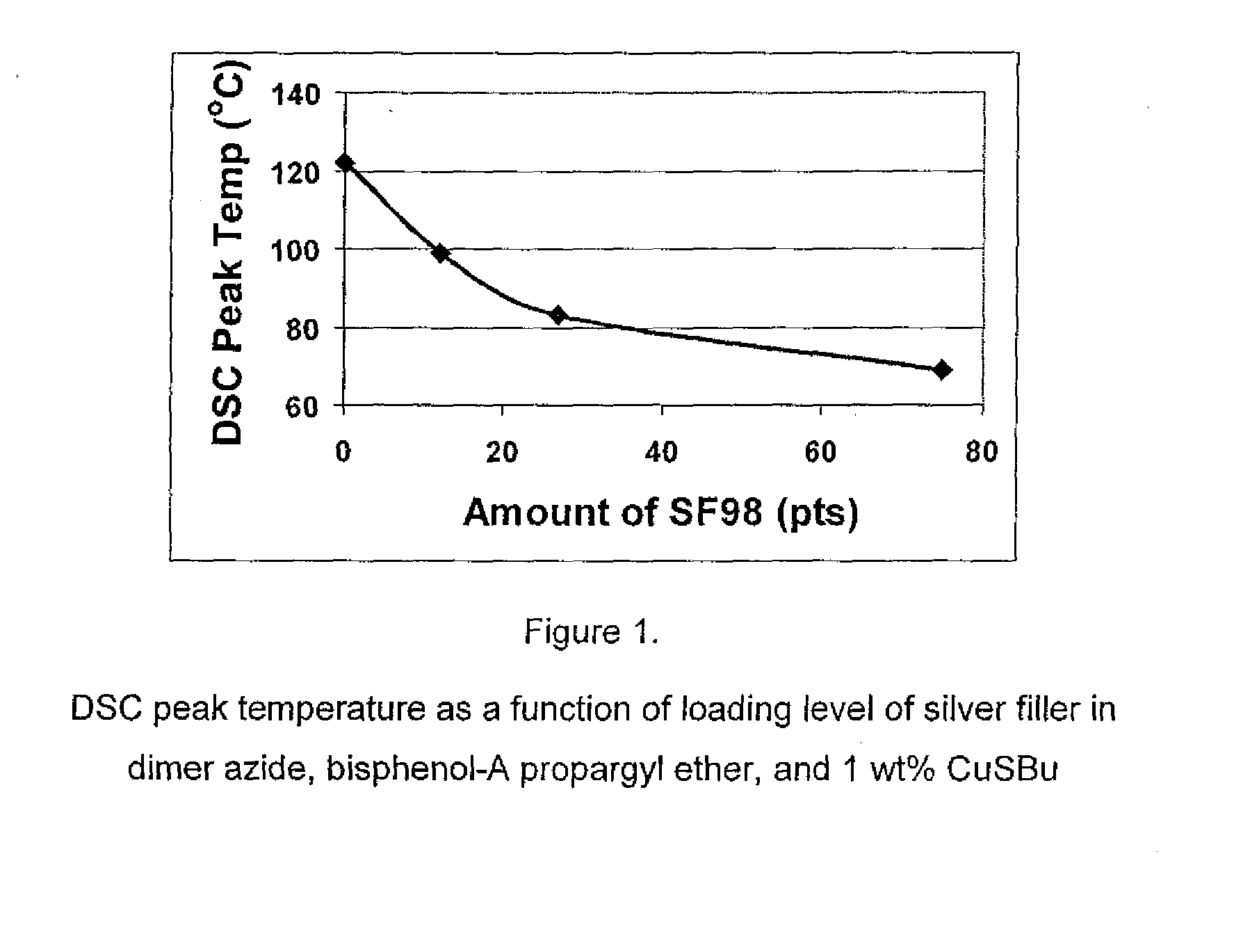
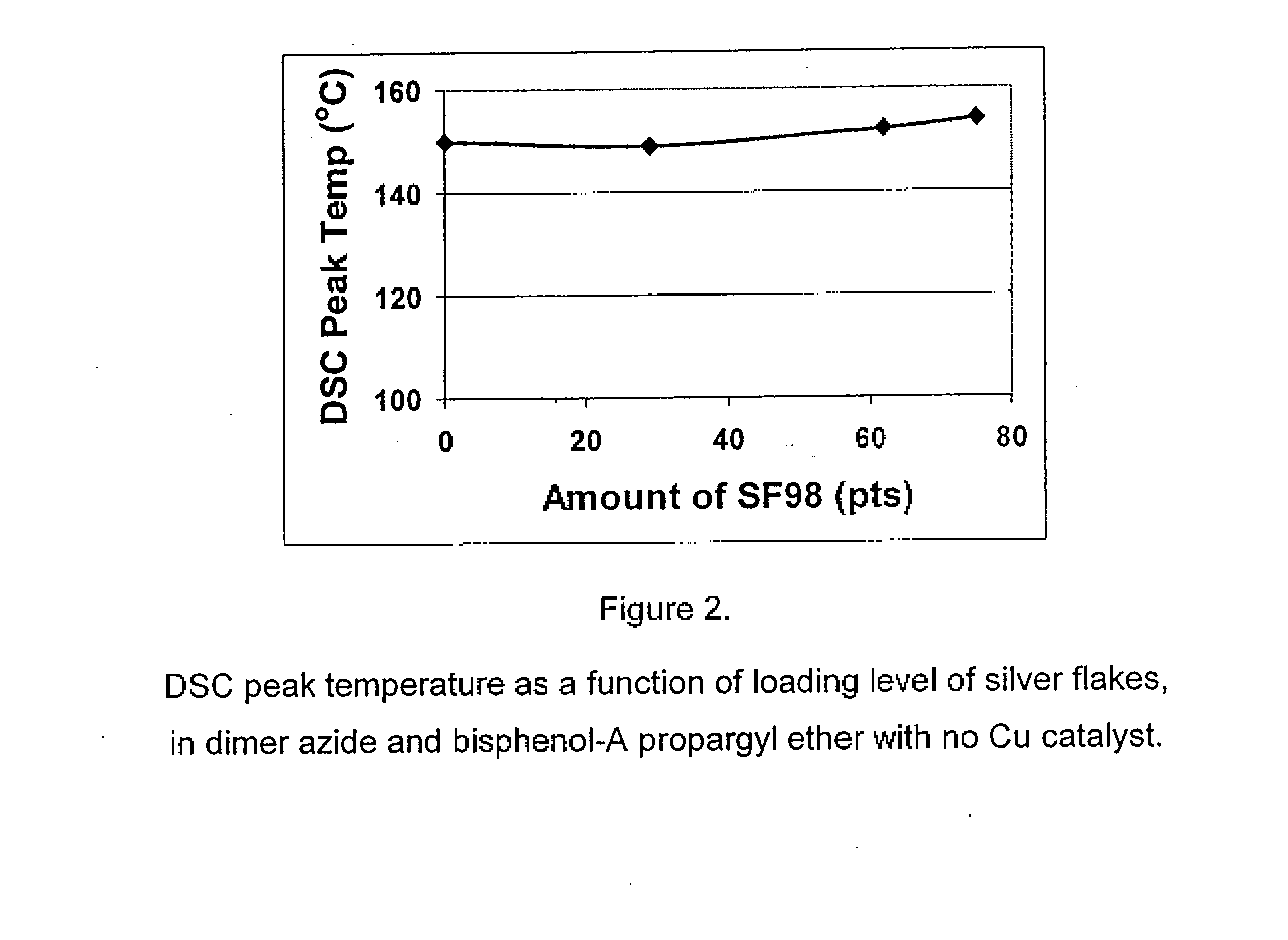
1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of azides to alkynes
InactiveUS20100121022A1Decreased DSC peak temperatureIncrease loadAdhesivesOligomer1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Expandable particles for producing polymethacrylimide foamed material and application thereof
The invention discloses expandable particles for producing a polymethacrylimide foamed material and application thereof. The expandable particles are prepared by the following steps of: putting acrylic acid or methacrylic acid, acrylonitrile or methacrylonitrile, an initiator, a molecular weight regulator, a foaming agent, a foam stabilizer, a cross-linking agent and an additive into a mold; performing a primary bulk polymerization reaction at the temperature of between 30 and 50 DEG C for 10 to 72 hours; performing a further bulk polymerization reaction at the temperature of between 50 and 100 DEG C for 1 to 30 hours to obtain a copolymer plate; smashing and screening the copolymer plate to obtain the expandable particles for producing the polymethacrylimide foamed material. Pre-foamed particles can be prepared by pre-foaming the expandable particles at the temperature of between 150 and 230 DEG C for 0.1 to 2 hours, and polymethacrylimide foam particles can be prepared by foaming the pre-foamed particles at the temperature of between 190 and 260 DEG C and curing the foamed particles at the temperature of between 150 and 230 DEG C. The expandable particles expand the use range of the polymethacrylimide foamed material.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for directly synthesizing pure solid high-performance polycarboxylate water-reducer in one step
The invention relates to a method for directly synthesizing a pure solid high-performance polycarboxylate water-reducer in one step, belonging to the field of water-reducers. According to the method, the pure solid high-performance polycarboxylate water-reducer is prepared by taking an acrylic compound and unsaturated polyoxyethylene ether as polymerization reaction monomers, adding a molecular weight regulator and carrying out free-radical polymerization reaction under the action of an initiator and under a solvent-free environment. The method disclosed by the invention is strong in controllability, high in polymerization degree, low in cost, environment-friendly and pollution-free, achieves the purpose of preparing the absolutely anhydrous pure solid polycarboxylate water-reducer by bulk polymerization, not only has the fluidity and holding property of cement paste, cement adaptability and concrete application performance which are similar to those of a polycarboxylate water-reducer prepared from a common solution by polymerization and can be prepared into any concentration of solution according to actual demands as the pure solid high-performance polycarboxylate water-reducer prepared by direct polymerization is an anhydrous pure solid, but also is free of postprocessing working procedures, such as heat drying or solvent separation and is more convenient to transport, saved in transport cost and favorable in market competitiveness and application prospect.
Owner:HUIZHOU JIANKE IND
Method for preparing durable hydrophilic polyether modified amino polysiloxane soft agent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a perdurable hydrophilic polyether modified amino-polysiloxane softener. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: octamethylcy-clotetrasiloxane and amino silane coupling agents with different structures are used as raw materials; with a bulk polymerization method, under the analysis of an alkali catalyst, firstly, an amino organic polysiloxane softener with high ammonia value is generated through ring-opening polymerization; and secondly, on the basis of the amino organic polysiloxane softener, amidogen is subjected to etherifying modification, thereby synthesizing the hydrophilic polyether modified amino-polysiloxane softener with good hand feeling and hydrophilic property. The prepared softener keeps the hydrophilic property and simultaneously improves the softness of hydrophilic silicon oil so that the hand feeling of textile can reach the hand feeling of the prior linearity amino silicon oil after the textile is treated by the softener and the treated textile can keep the hydrophilic property permanently.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Novel selective water shutoff agent for oil well water shutoff
The invention relates to a novel selective water shutoff agent for oil well water shutoff, belonging to the technical field of tertiary oil recovery. The water shutoff agent is a composite system of gel particles with the mass concentration of 0.5-5% and a cross-linking agent with the mass concentration of 1-2%, which is prepared by using oilfield injection water; and the water shutoff agent is applicable to water plugging of an oil well at a temperature of 60-120 DEG C. The gel particles are formed by an acrylamide monomer or compounding the acrylamide monomer with a temperature resistant and salt-resistant auxiliary monomer and a cross-linking monomer through copolymerization; the cross-linking monomer is an ester monomer which has a double-bond structure and is easy to resolved when being heated, the expanding and resolving time of the cross-linking monomer at different temperatures can be controlled through adjusting the concentration of the cross-linking monomer, and bulk polymerization or inverse emulsion polymerization is adopted as a polymerization method. In the invention, basically no gel is formed on an oil layer, and high-strength gel can be formed on a water layer, thus defects in the prior art are overcome, the error shutoff phenomenon easily caused by the traditional polymer bulk gel in the oil layer is reduced to the greatest extent, and the capacity of an oil well suffering from water shutoff is ensured.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Continuous bulk polymerization and esterification process and compositions
InactiveUS20050059782A1High viscosityWater-repelling agents additionTransportation and packagingPolymeric surfacePolymer science
A continuous bulk polymerization and esterification process includes continuously charging into a reaction zone at least one ethylenically unsaturated acid-functional monomer and at least one linear or branched chain alkanol having greater than 11 carbon atoms. The process includes maintaining a flow rate through the reaction zone sufficient to provide an average residence time of less than 60 minutes and maintaining a temperature in the reaction zone sufficient to produce a polymeric product incorporating at least some of the alkanol as an ester of the polymerized ethylenically unsaturated acid-functional monomer. The polymeric product is used in various processes to produce water-based compositions including emulsions and dispersions such as oil emulsions, wax dispersions, pigment dispersions, surfactants and coatings which contain the polymeric product. A polymeric surfactant includes at least one ethylenically unsaturated acid-functional monomer which has been radically incorporated into the polymeric surfactant and at least one ester of the incorporated ethylenically unsaturated acid-functional monomer which has a linear or branched chain alkyl group with greater than 11 carbon atoms. The molar critical micelle concentration of the polymeric surfactant is less than 1.0×10−2 moles / liter. Aqueous 2 percent solutions of certain polymeric surfactants have a surface tension of less than 45 mN / m at 30° C. and exhibit a decrease in surface tension of at least 5 mN / m as the temperature warms from 30° C. to 50° C.
Owner:BASF CORP
Process for preparing reabsorbable polyesters by mass polymerization
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Polymetallic catalysts and method of preparing same
InactiveUS6054406AHigh elongationImprove propertiesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSolubilityElectron donor
Disclosed is a polymetallic supported catalyst component comprising an activated anhydrous MgCl2 solid support which has been treated with at least one treatment of at least two halogen-containing transition metal compounds, wherein one is a halogen-containing titanium metal compound and one is a halogen-containing non-titanium transition metal compound, optionally, in the presence of an electron donor and the processes for producing the component. A catalyst for the polymerization of at least one alpha-olefin of the formula CH2=CHR, where R is H or a C1-12 branched or straight chain alkyl or substituted or unsubstituted cycloalkyl, by reacting this supported catalyst component with an organometallic cocatalyst, optionally in the presence of an electron donor, and the polymerization of at least one alpha-olefin with the catalyst are also disclosed. The resulting polymers, particularly propylene polymers, have a controllable atactic content, which is expressed herein in terms of its xylene solubility at room temperature (XSRT), wherein the ratio of the I.V. of the XSRT fraction to the I.V. of the bulk polymer is greater than or equal to 0.50.
Owner:MONTELL NORTH AMERICA
Method for producing urethane elastomer and application
ActiveCN101148494AGood spinning stabilityIncrease elasticityMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentPolyesterPolyurethane elastomer
The process of producing polyurethane elastomer with the material including one component A of polyether glycol and / or polyester polyol, one component B of organic diisocyanate and one component C of small molecular diol as the chain expanding agent, includes the following steps: melting the components while adding organic tin catalyst in 0.001-0.05 wt% to the component A, metering precisely with one metering system, and mixing and bulk polymerizing in a double screw extruder with precise temperature control system at 180-260 deg.c for 3-15 min to obtain the polyurethane elastomer. The polyurethane elastomer is applied in melt spinning to produce elastic polyurethane fiber. The production process is simple, easy in control and low in cost, and elastic polyurethane fiber produced with the polyurethane elastomer has high quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI YITAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Aligned nanostructured polymers
Novel, simple methods are presented directed to the synthesis of aligned nanofibers of polyaniline and substituted derivatives on a substrate. The production of these fibers is achieved via various methods by controlling the concentration of aniline monomer or substituted aniline derivatives or an oxidant in the reaction medium and maintaining said concentration at a level much lower than conventional polyaniline synthesis methods. Methods are disclosed relating to the use of a permeable membrane to control the release of a monomer and / or oxidant as well as a bulk polymerization method.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Aqueous photo-curing polyurethane resin and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101372530AAdjust dispersionAdjust water solubilityPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolymer scienceAdhesive
The invention relates to a method for preparing waterborne light-cured urethane resin. The waterborne light-cured urethane resin consists of polyatomic alcohol components, diisocyanate, hydroxyl (methyl) acrylic ester, a neutralizer, a catalyst, a solvent, a polymerization inhibitor and water. The target resin is prepared by one-step solution polymerization or bulk polymerization, and the preparation method is simple and easily operated. The densities of the light-curable group and hydrophilic group of the resin prepared are adjustable, and the resin has the advantages of unique hydrophilicity, superior light curing performance and high hardness of film forming matters, and has wide application prospect in the fields of coating, adhesives, ink, etc.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS FUNCTION MATERIAL RES INST
Preparation method of slow-release solid polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a slow-release solid polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent, which comprises the following steps: pretreating carboxylic acid small monomer containing unsaturated double bond by using amine organic small molecule; and after heating to melt the pretreated unsaturated acrylic small monomer and unsaturated polyethenoxy ether big monomer, dropwisely adding unsaturated ester small monomer to perform mass polymerization reaction under the action of an initiator and a chain-transfer agent in a water-free organic-solvent-free environment. The slow-release solid polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent prepared by the mass polymerization process in the water-free solvent-free environment has the advantages of simple and controllable technique, transportation cost saving, environment friendliness, no pollution and the like, achieves the goal of slow release and keeping the slump for 3-4 hours without loss in concrete, and has wide market application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU CHINA RAILWAY ARIT NEW MATEIRALS CO LTD
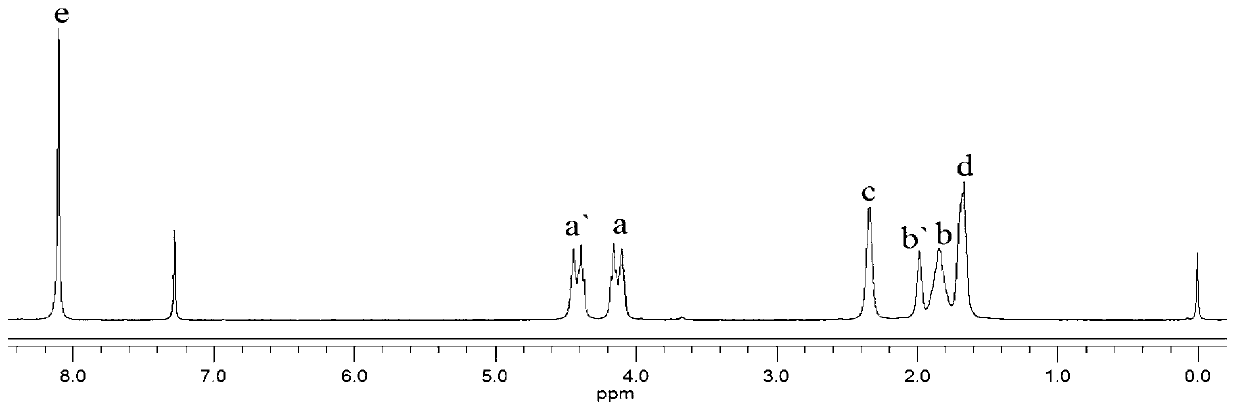
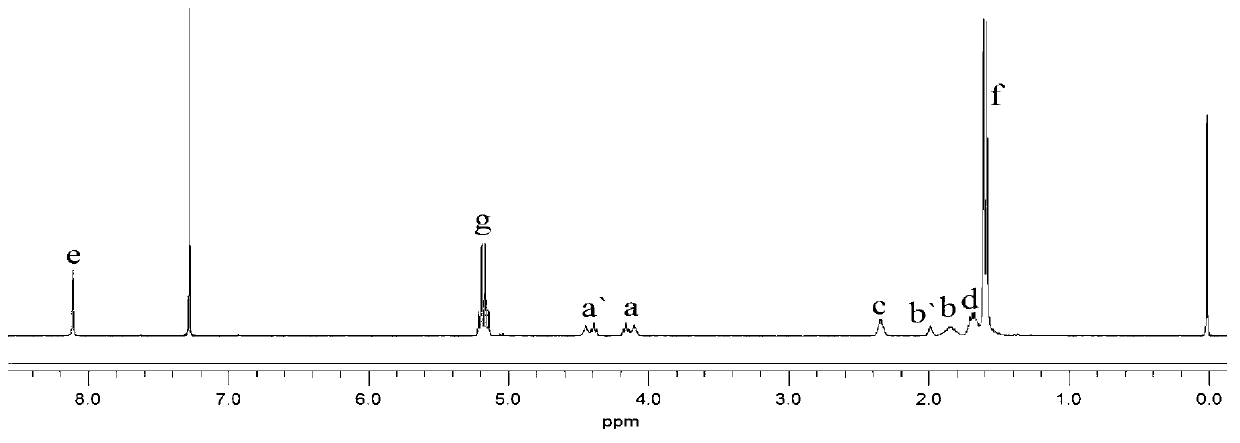
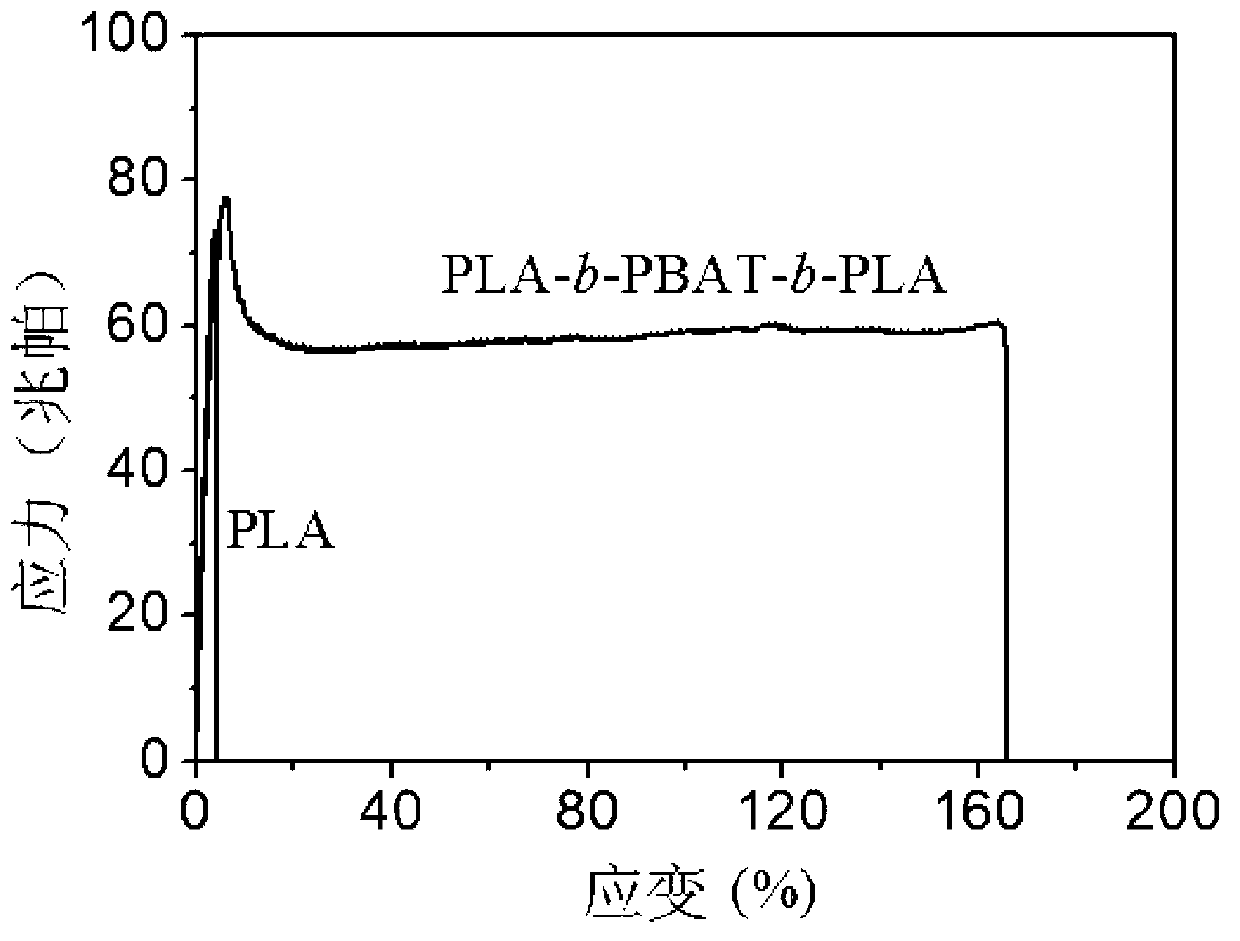
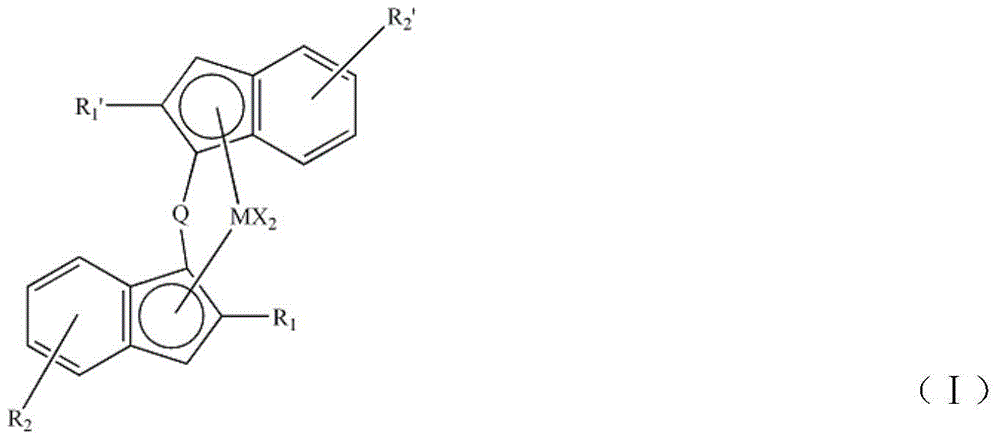
Polylactic acid block polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polylactic acid block polymer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing poly(adipic acid-terephthalic acid)butanediol copolyester, lactide and a first catalyst, and heating to a molten state to react, thereby obtaining the polylactic acid block polymer disclosed as Formula (I). Compared with the polymer obtained by the PLA-PBAT chain extension reaction initiated by diisocyanate in the prior art, the invention uses the molten-state poly(adipic acid-terephthalic acid)butanediol copolyester as the reactant to directly initiate the ring-opening polymerization of lactide, and the polymerization method is mass polymerization without adding the chain extender diisocyanate or any organic solvent, thereby avoiding jeopardizing the human body and environment; the raw materials can be mixed and heated to react to obtain the polylactic acid block polymer, so that the preparation method is simpler and lowers the preparation cost; and the polylactic acid block polymer provided by the invention has definite structure and narrow molecular weight distribution.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microencapsulated and macroencapsulated drag reducing agents
InactiveUS6841593B2Easy to manufacturePipeline systemsGlass/slag layered productsHigh concentrationBulk polymerization
High concentration drag reducing agents may be prepared by microencapsulating and / or macroencapsulating polymer drag reducing agent. The encapsulation may be performed prior to, during, or after the polymerization of monomer into effective drag reducing polymer. If encapsulation is done before or during polymerization, a catalyst may be present, but little or no solvent is required. The result is very small scale bulk polymerization within the capsule. The inert capsule or shell may be removed before, during or after introduction of the encapsulated drag reducer into a flowing liquid. No injection probes or other special equipment is expected to be required to introduce the drag reducing slurry into the liquid stream, nor is grinding (cryogenic or otherwise) of the polymer necessary to form a suitable drag reducing agent.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Preparation method for high performance water reducer made from high water reducing solid polycarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a preparation method for high performance water reducer made from high water reducing solid polycarboxylic acid. The prepartion method specifically comprises the following steps: performing heat fusion on two unsaturated polyoxyethylene ether composite macromonomers with different molecular weights; then dropwise adding a mixed liquid of an unsaturated carboxylic micromonomer, an unsaturated amide micromonomer and a chain transfer agent under the reaction of an initiator; and preparing the water reducer through a free radical polymerization reaction, and after the reaction, using a neutralizing agent to adjust a pH value to 5-6 and then cooling and grinding the water reducer in a solid particulate shape. The preparation method provided by the present invention has advantages of being simple in process, high in conversion rate and environmental-friendly and free of pollution, and has the characteristics of high water reduction and low adulterate amount in concrete and dry-mixed mortar, and the transportation cost in long distance transportation is greatly lowered.
Owner:JIANGSU CHINA RAILWAY ARIT NEW MATEIRALS CO LTD
Aqueous polyurethane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102532463AMacromolecular chain lengthGood film flexibilityFibre treatmentPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPropanoic acidOrganic solvent
The present invention provides a preparation method for aqueous polyurethane. The method comprises the following steps: mixing aliphatic diisocyanate, an aliphatic polyol, dimethylol propionic acid and a catalyst, and carrying out a reaction to obtain a prepolymer; adding a neutralizing agent to the prepolymer, and carrying out a stirring reaction to obtain an intermediate product; adding water and a chain extender to the intermediate product, stirring and dispersing to obtain the aqueous polyurethane, wherein the chain extender is polyoxyethylene polyamine or polyoxypropylene polyamine. The invention further provides the aqueous polyurethane prepared by the method. According to the present invention, the bulk polymerization method is adopted, the use of the organic solvent is not required, and no environmental pollution is generated; the polyoxyethylene polyamine or the polyoxypropylene polyamine is adopted as the chain extender, and is used for emulsion chain extending, such that the obtained polyurethane emulsion has good film-forming flexibility, the mechanical property of the obtained polyurethane can not be reduced, the large R value is not required, and the final produced polyurethane film is soft.
Owner:SICHUAN DOWELL SCI & TECH INC
Bulk polymerization process for producing polydienes
ActiveUS20100004413A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer scienceBulk polymerization
A process for preparing a polydiene, the process comprising the step of polymerizing conjugated diene monomer with a lanthanide-based catalyst system including the combination or reaction product of: (a) a lanthanide compound selected from the group consisting of lanthanide organophosphates, lanthanide organophosphonates, and lanthanide organophosphinates, (b) an alkylating agent, and (c) a chlorine-containing compound, where said step of polymerizing takes place within a polymerization mixture that includes less than 20% by weight of solvent based on the total weight of the polymerization mixture.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method of manufacturing thermoplastic resin, crosslinked resin, and crosslinked resin composite material
InactiveUS20060211834A1Efficient productionAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceBulk polymerization
The invention relates to a process for the production of post-crosslinkable thermoplastic resins by bulk-polymerizing a polymerizable composition (A) comprising (I) a monomer fluid containing a cyclic olefin (α) having two or more metathetical ring-opening reaction sites in the molecule in an amount 10 wt % or above based on the total amount of the monomers or a monomer fluid containing a norbornene monomer and a crosslinking agent, (II) a metathetical polymerization catalyst, and (III) a chain transfer agent; thermoplastic resins obtained by this process; and a process for producing crosslinked resins or crosslinked resin composite materials which comprises laminating such a thermoplastic resin with a substrate at need and then crosslinking the thermoplastic resin. According to the invention, thermoplastic resins which are free from odor due to residual monomers and excellent in storage stability can be efficiently obtained by a simple process of bulk-polymerizing the composition (A). The process is not only easy and simple but also applicable to continuous production, thus being industrially advantageous. The crosslinked resins and crosslinked resin composite materials obtained according to the invention are excellent in electrical insulation properties, mechanical strengths, heat resistance, dielectric characteristics and so on, thus being useful as electrical materials or the like.
Owner:ZEON CORP
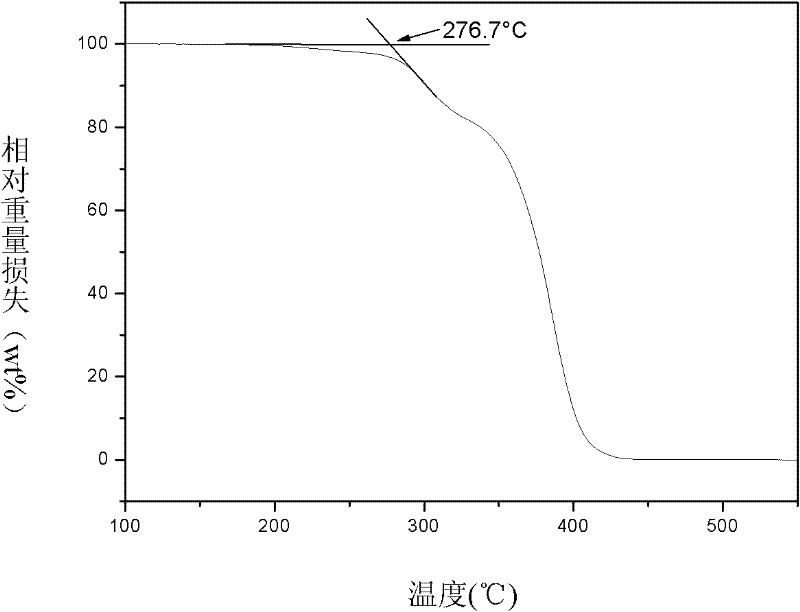
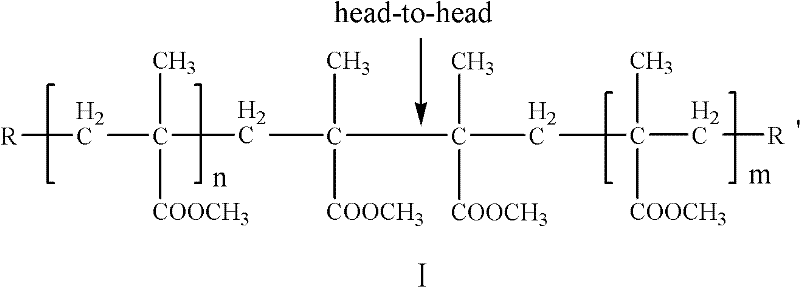
Preparation method for polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) resin with high thermal stability
ActiveCN102336864AHigh thermal degradation resistanceImprove thermal stabilityCross-linkPolymer science
The invention provides a preparation method for a methyl methacrylate polymer with high thermal stability, and continuous bulk polymerization or solution polymerization is adopted in the invention. According to the invention, no free radical scavengers or cross-linking agents need to be added in the preparation method; instead, unstable structures like a head-to-head structure and a terminal unsaturated double bond in the molecular structure of the methyl methacrylate polymer is gradually eliminated by controlling polymerization temperature, devolatilization temperature, polymerization time and devolatilization time in the continuous polymerization process of methyl methacrylate, thereby achieving the goal of improving thermal stability of PMMA. Preparing a PMMA resin with the method not only enables the PMMA resin to have excellent thermal degradation resistance, but also enables other inherent excellent properties of the PMMA resin to be guaranteed. The methyl methacrylate polymer prepared by the method in the invention has high thermal degradation resistance, with a starting thermal degradation temperature being higher than 360 DEG C. With utilization of the method, light transmittance of the PMMA resin is guaranteed to be 93%, and molecular weight distribution of the PMMA resin is guaranteed to be less than 1.8, while thermal stability of the PMMA resin is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing viscosity-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer
The invention provides a method for preparing viscosity-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer. The viscosity-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer is prepared through a bulk polymerization reaction, and the method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether and polyoxyethylene ether, controlling the temperature at 40-60 DEG C, stirring the mixture evenly, and then adding an initiator and a mixture of unsaturated carboxylic acids, hydroxyalkyl unsaturated carboxylate and a chain transfer agent; and (2) performing aging for 1-1.5 hours after the step (1) is completed, and reducing the temperature to obtain the viscosity-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Since the bulk polymerization reaction is carried out at a low temperature, the method has strong operability, mild conditions and low energy consumption; the viscosity-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer prepared by using the method is at a liquid state at room temperature, has effective concentration of 100% and stable storage performance, and is suitable for long-distance transportation and use; meanwhile, the viscosity of a concrete mixture can be reduced effectively through the superplasticizer so that stirring, transportation and pumping of concrete can be facilitated, and the superplasticizer is suitable for the promotion and application of high-rise engineeringand high-performance concrete.
Owner:JIAHUA CHEM MAOMING
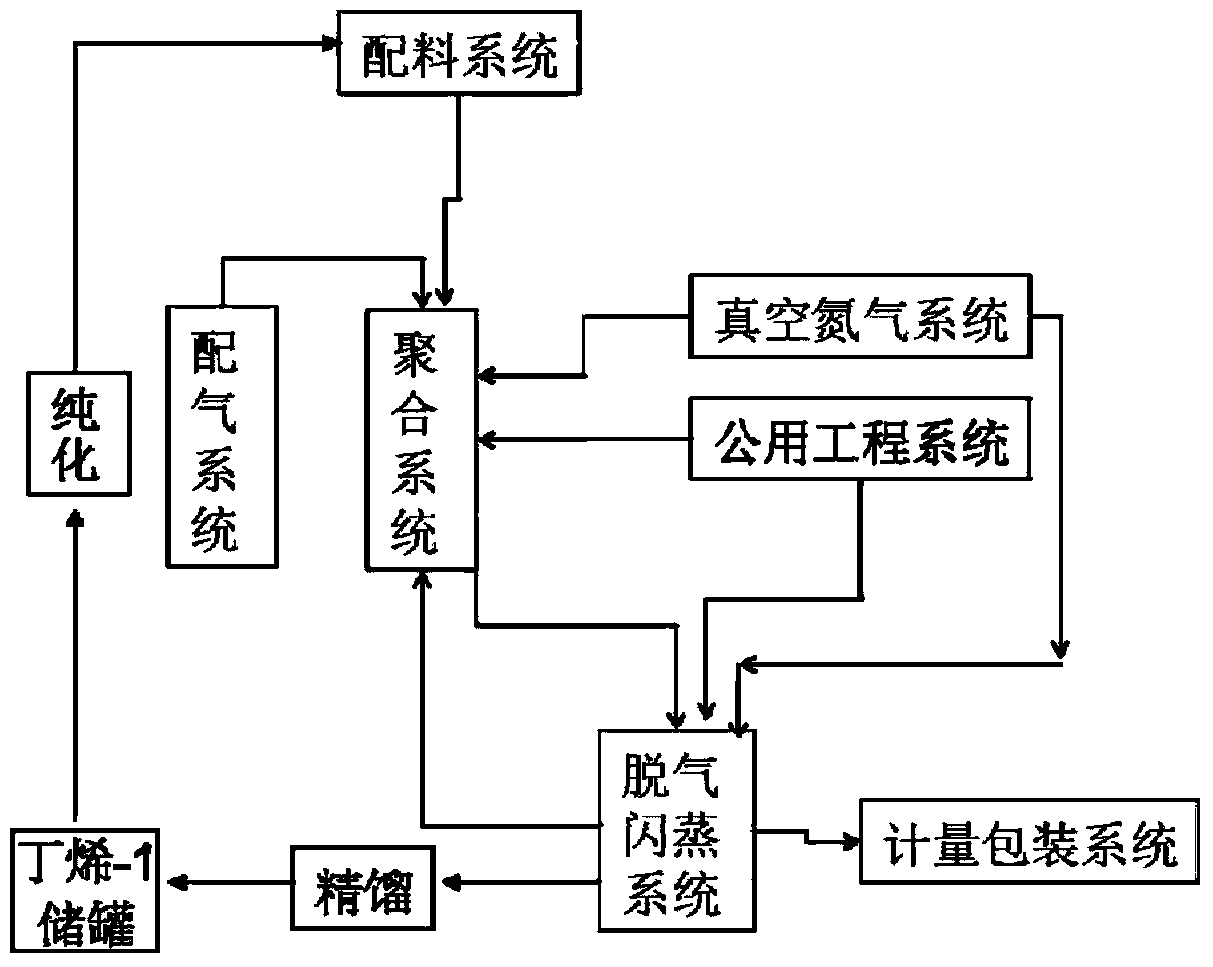
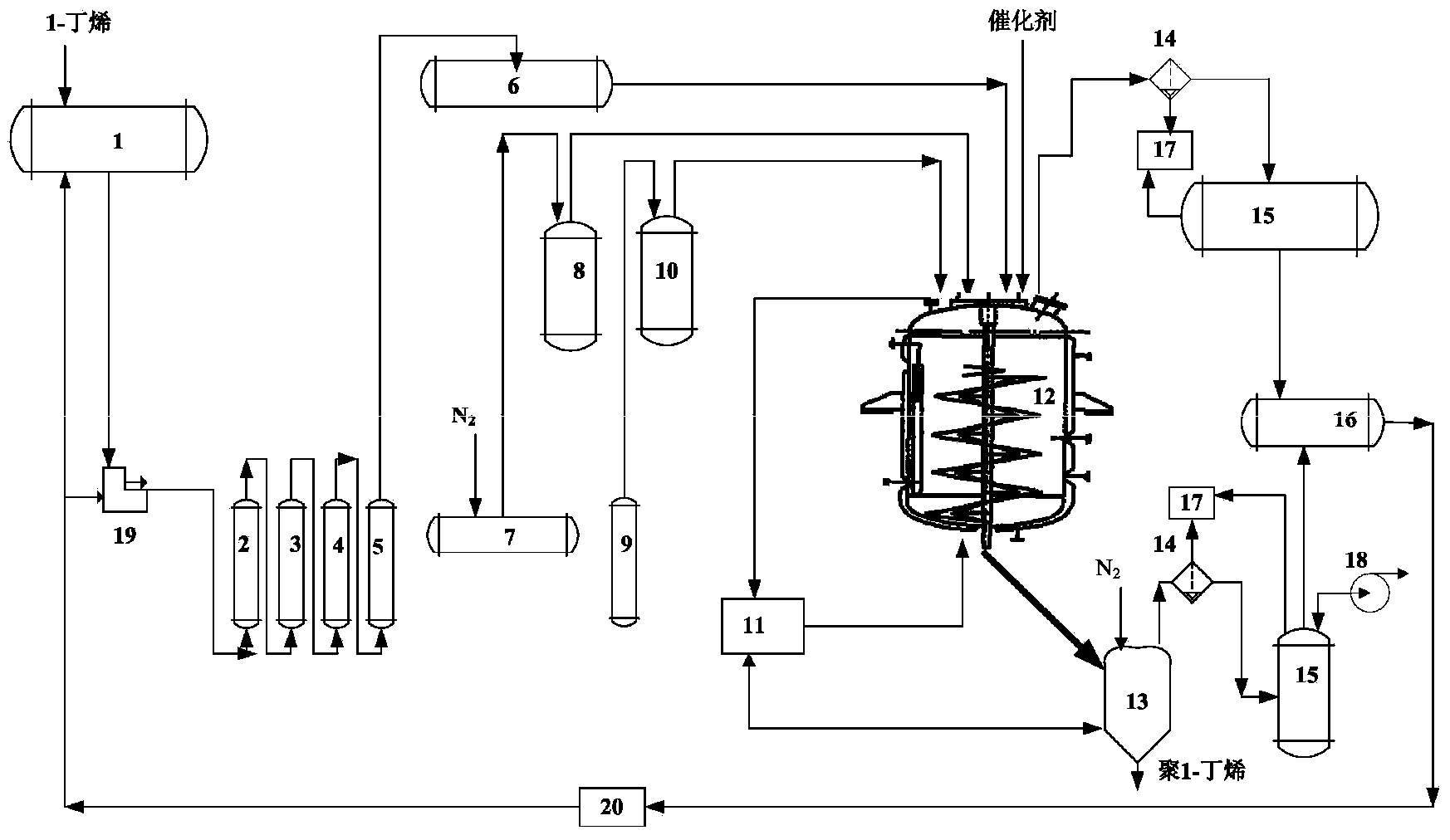
Industrial production method of high isotactic polybutylene and device for implementing method
The invention discloses an industrial production method of high isotactic polybutylene and a device for implementing the method. The production method comprises the process flows of carrying out bulk polymerization on a liquid-phase butylene-1 monomer in a polymerization kettle at the temperature of 10 DEG C below zero to 70 DEG C above zero to synthesize isotactic polybutylene, and recovering part of unreacted butylene-1 into a butylene gasometer through primary pressure reduction after polymerizing for a certain period of time; then, transferring high isotactic polybutylene from the polymerization kettle to a flash distillation kettle, carrying out reduced-pressure flash distillation, and further recovering the unreacted butylene-1 monomer into the butylene gasometer; sequentially introducing nitrogen gas and air into the flash distillation kettle to replace, discharging a granular high isotactic polybutylene product through an emptying valve at the bottom of the kettle, and packaging. The device comprises a proportioning system, a polymerization system, a gas distribution system, a vacuum nitrogen system, a degassing and flash distillation system and a utility system. Through the industrial production method and the device, the industrial synthesis of the high isotactic polybutylene can be realized, and no organic solvents, waste gases, waste water and waste residues are discharged; in addition, the industrial production method belongs to a green and clean production process.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENT HONGYE CHEM +1
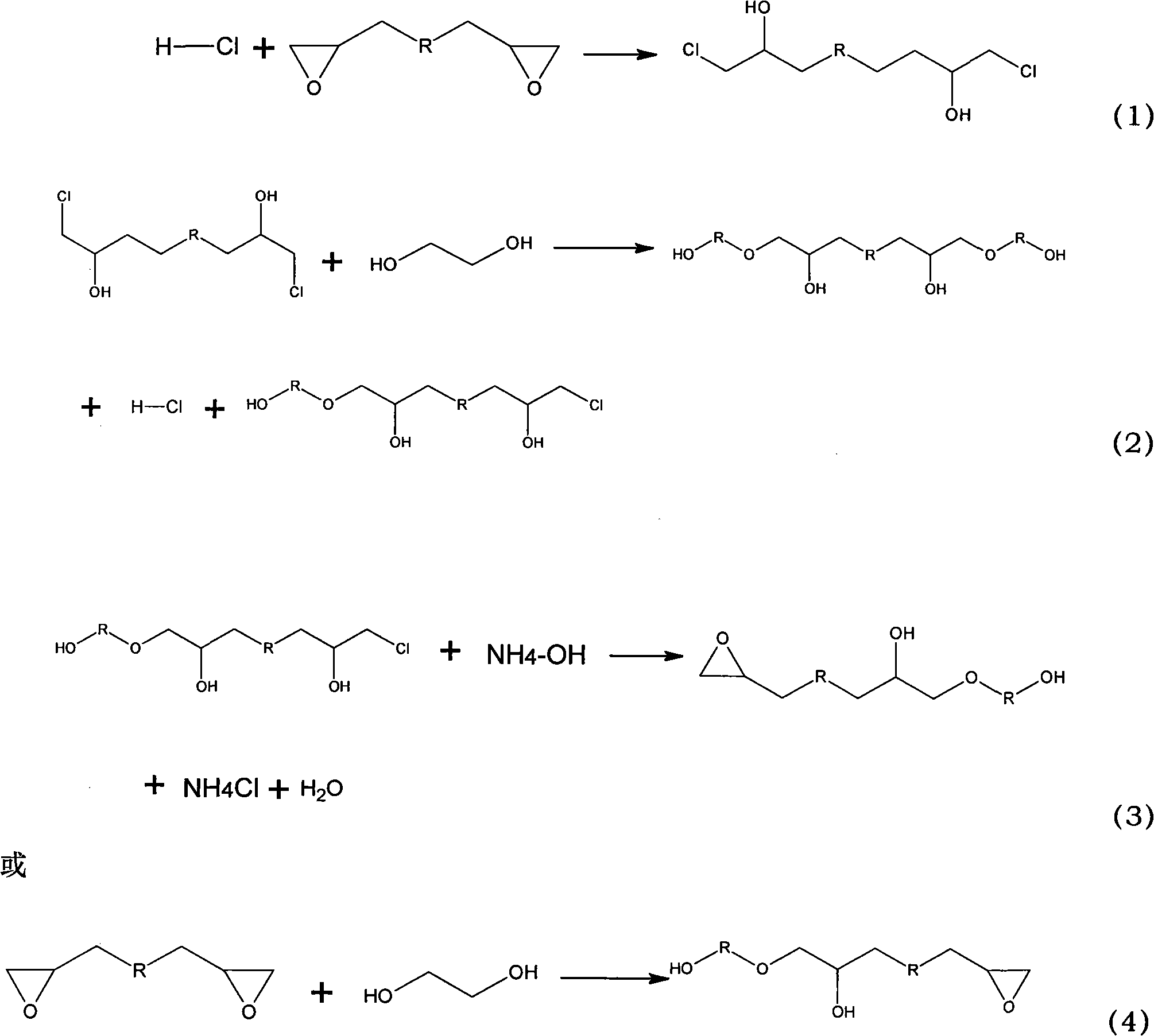
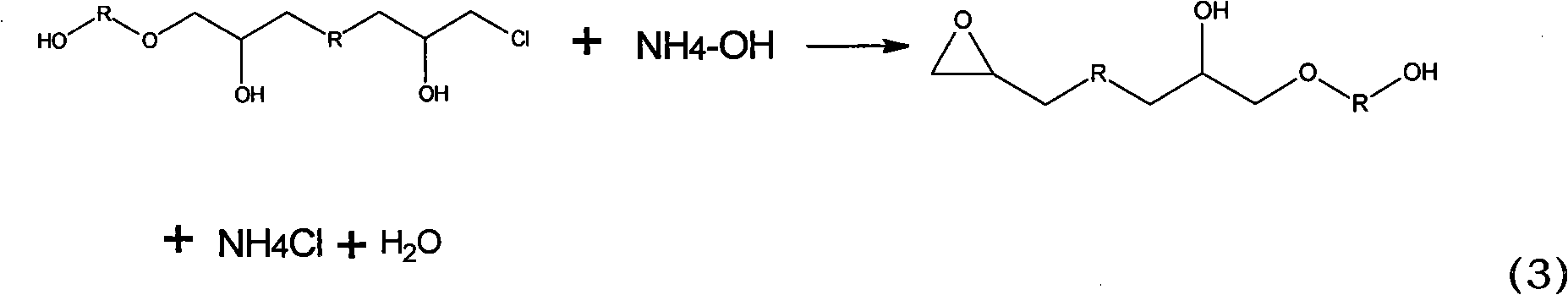
Polyalcohol modified epoxy resin carbon fiber emulsion sizing agent component and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyalcohol modified epoxy resin carbon fiber emulsion sizing agent component and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of ring-opening the preparing modified epoxy. The modified epoxy resin has hydropathy, can be dissolved in water, and can be prepared into a modified epoxy emulsion under certain conditions. The modified epoxy emulsion is the polyalcohol modified epoxy resin carbon fiber emulsion sizing agent component. A foreign emulsifying agent is added in the preparation process, and the modified epoxy emulsion belongs to a self-emulsifying system without breaking the emulsion and demixing and has controllable and proper viscosity, good standing stability, excellent pH value stability and high-temperature stability. The foreign emulsifying agent does not remain on the fiber after the sizing; and compared with the carbon fiber without being sized, the carbon fiber coated with the sizing agent component has less broken filament amount and good bundling performance, and can ensure that the interface performance is improved because of a structure that one end of the modified epoxy resin is a polyether bond and the other end is an epoxy group.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Surface functionalized nano-particle and method for preparing its polymer nanometre composite material
InactiveCN101343536AUnique optical propertiesImprove mechanical propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescencePhenanthroline
The invention relates to nanometer particle surface functionalization and the preparation method of the transparent polymer nanometer composite material, which belongs to the chemical material field. The functionalization for the surface of the nanometer particles can be performed by using an organic small molecule with a nitrogen-containing function (eg. 8-hydroxy quinoline and phenanthroline derivative) though a method of ligand exchanging or direct situ decorating. The functional nanometer particles can be coated directly during the synthetic process or synthetized through ligand exchanging later, and the nanometer particles have a good fluorescence property. The functionalized nanometer particles and the polymer are compounded for preparing the transparent polymer nanometer composite material through a solution co-blending method and a situ bulk polymerization method. The method for functionalizing nanometer particle integrate the functions of organic functional molecules and the functions of nanometer particles into one, and a novel approach for constructing novel functional nanometer particles is provided. The prepared functional nanometer particles / polymer composites material have important application value in the fields, such as photoelectric apparatus, display devices and solar batteries, and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of polypropylene wax
The invention relates to a preparation method of polypropylene wax. The method is characterized in that a liquid phase bulk polymerization technology is used, a supported metallocene catalyst is used, hydrogen is adopted as a molecular weight regulator, and a granular polypropylene wax product is directly obtained through catalyzing liquid propylene polymerization. The propylene polymerization reaction activity is not lower than 1000 times / h. The method has the characteristics of simple operation and high polymerization reaction activity, and the molecular weight of the polypropylene wax product obtained in the invention is adjustable and has narrow distribution.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing high-toughness thermoplastic fluorine-containing polyurethane elastomer
ActiveCN101717485AKeep the elastomer perfectly linearLower surface energyPolyurethane elastomerThermoplastic
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-toughness thermoplastic fluorine-containing polyurethane elastomer, which is characterized in that a bulk polymerization two-step method is adopted to synthesize the fluorine-containing polyurethane elastomer, the isocyanate index is 0.98, and the hard segment content is between 20 and 40 weight percent. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing 6 to 40 parts of non-fluorine macromolecular polylol and / or 30 to 80 parts of fluorine-containing polyether diol in a reactor, performing vacuum dehydration on the mixture for 2h at thetemperature of 120 DEG C, cooling the mixture to be between 70 and 100 DEG C, adding 16 to 33 parts of polyisocyanate into the mixture, stirring the mixture to react for 3h, heating the mixture to bebetween 120 and 140 DEG C, adding 0.1 to 15 parts of low molecular (fluorine-containing) diol chain extender into the mixture, uniformly stirring the mixture, then dumping the mixture into a preheated container, and performing vacuum baking for 20 hours at the temperature of between 120 and 140 DEG C to obtain the high-toughness thermoplastic fluorine-containing polyurethane elastomer.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Styrene polymer resin and composition thereof
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a styrene-based polymer having the steps of continuously feeding raw materials into one end of two or more polymerization vessels connected in series; polymerizing a styrenic monomer in the coexistence of a (meth)acrylate ester monomer by using an organic radical generating agent as an initiator by a mass or solution polymerization method of continuous process; and continuously taking out a product from another end of the polymerization vessels, wherein polymerization conditions are controlled in ranges specified by the following items (a) and (b): (a) a composition of monomers to be fed is 60 to 97% by weight of a styrenic monomer(s) and 3 to 40% by weight of a (meth)acrylate ester monomer(s); and (b) a concentration of the (meth)acrylate ester monomer(s) at any part of the polymerization vessels exceeds 1% by weight based on total monomers at any time during the polymerization.
Owner:PS JAPAN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com