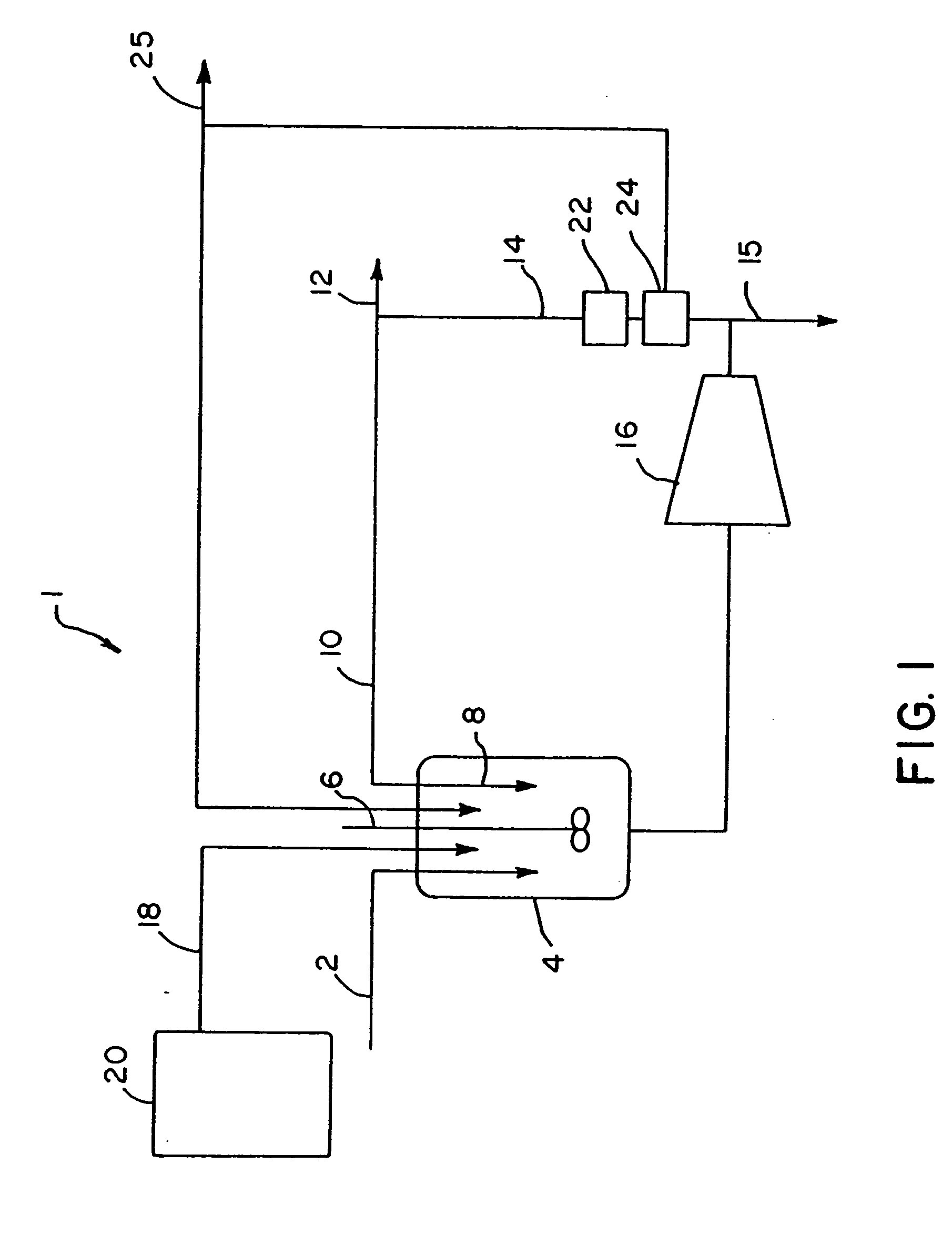
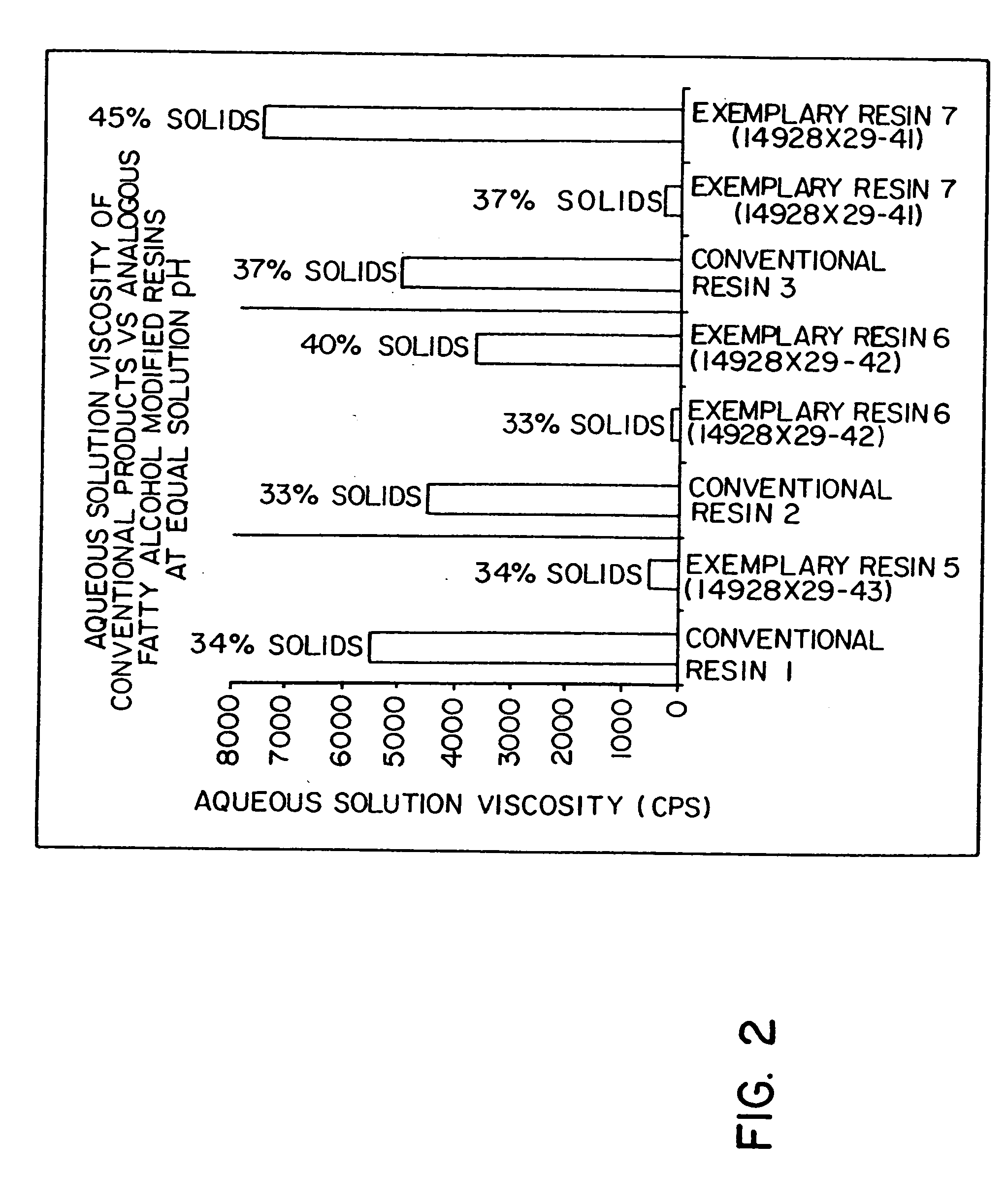
Continuous bulk polymerization and esterification process and compositions
a polymerization and esterification process technology, applied in the field of bulk polymerization and esterification process, can solve the problems of easy ignition, high cost, and high cost of organic solvents, and achieve the effect of improving the viscosity profile of aqueous pigment dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Preparation of Exemplary and Conventional Resins
Exemplary resins created by the invention described above are described below in the various examples. The materials and products described in the examples are characterized by a number of standard techniques. The molecular weight of each polymer was determined via gel permeation chromatography (“GPC”) techniques using tetrahydrofuran (“THF”) as eluent and poly(styrene) standards. The poly(styrene) standards employed are presently available from Polymer Laboratories Limited (Church Stretton, Great Britain) and are further characterized as having number average molecular weights of 2,250,000; 1,030,000; 570,000; 156,000; 66,000; 28,500; 9,200; 3,250; and 1,250. Acid numbers were determined by titration with a standardized base and are defined as the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide needed to neutralize one gram of polymer. Viscosity was measured using a Brookfield viscometer available from Brookfield Engineering Laboratorie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com