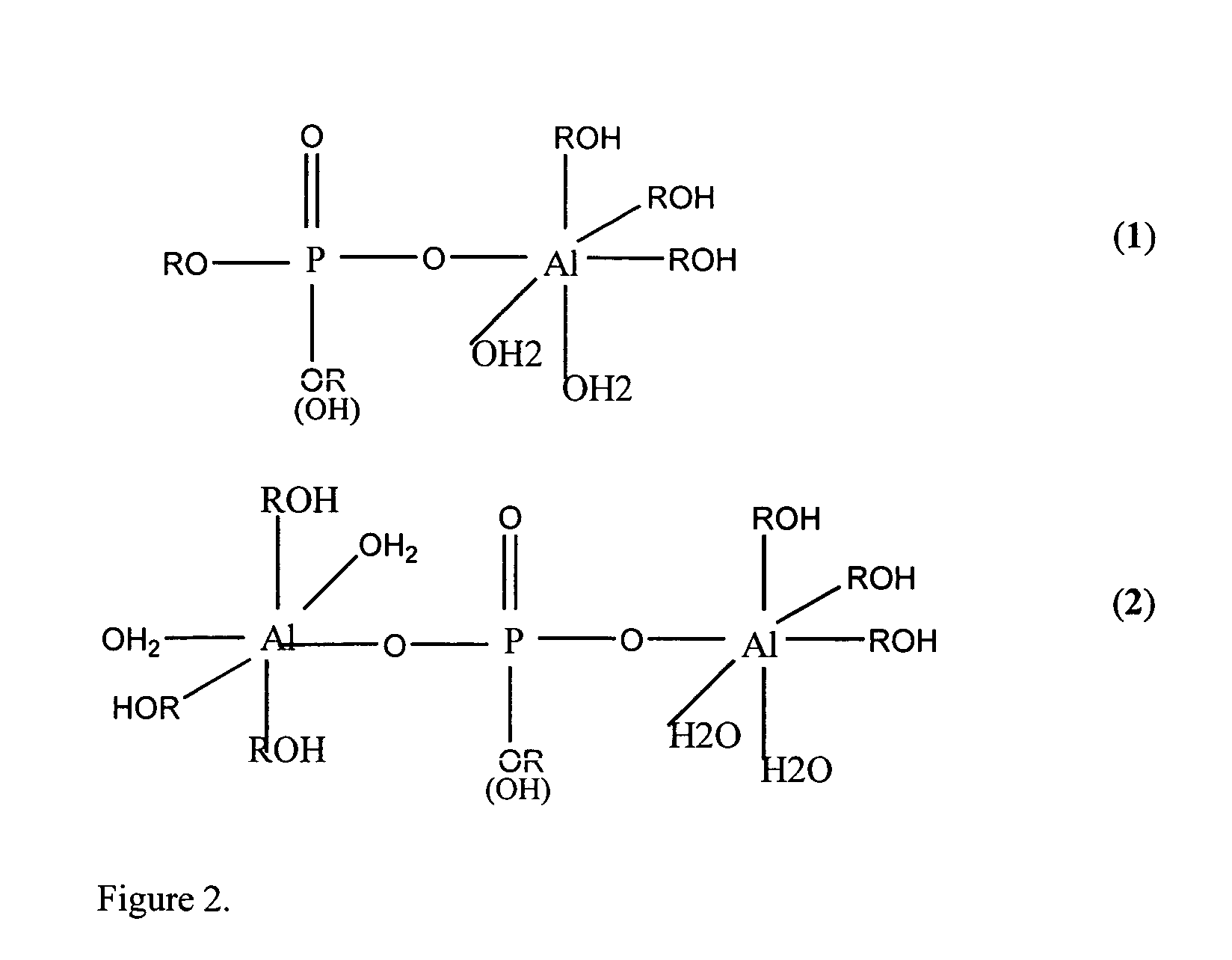
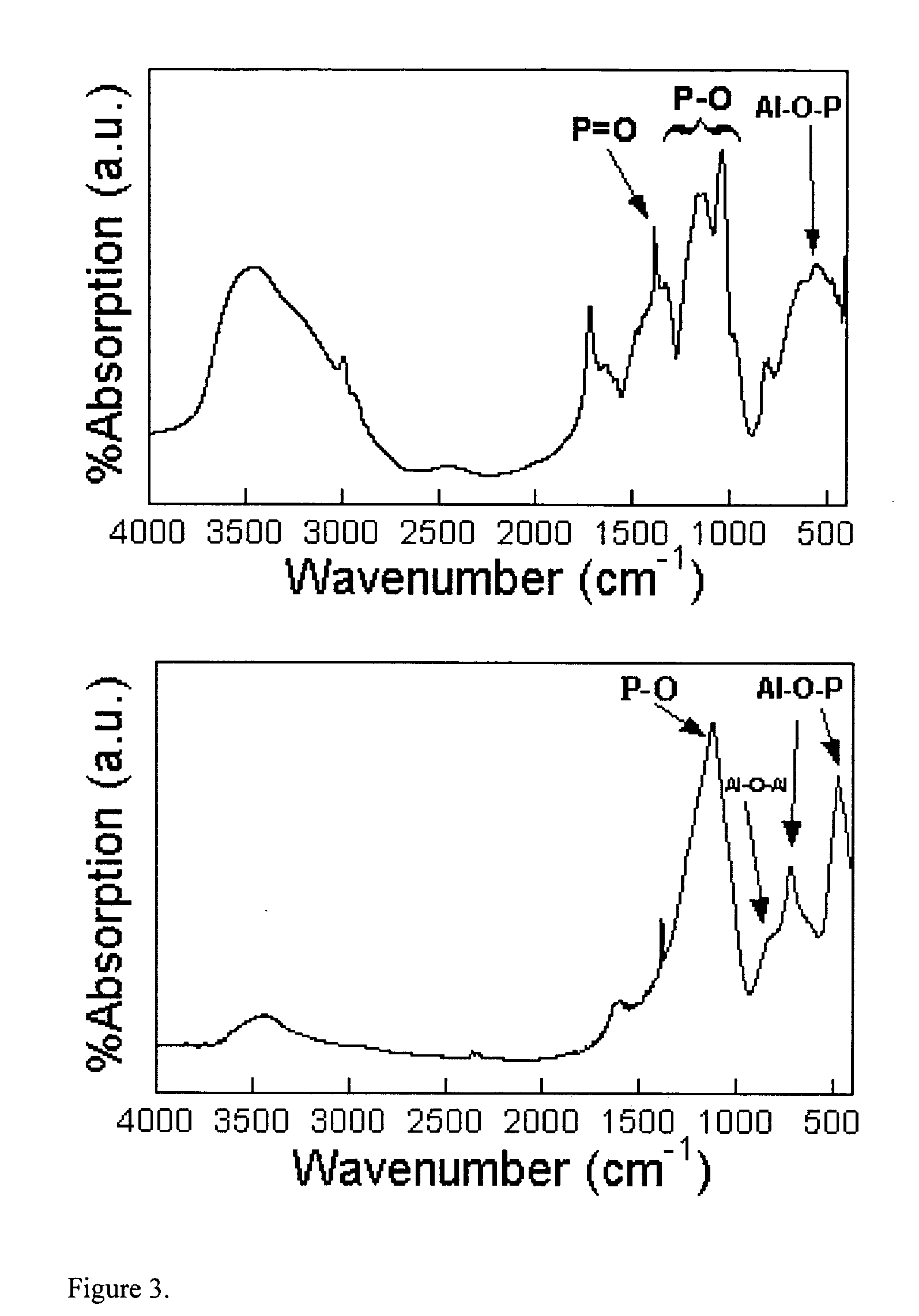
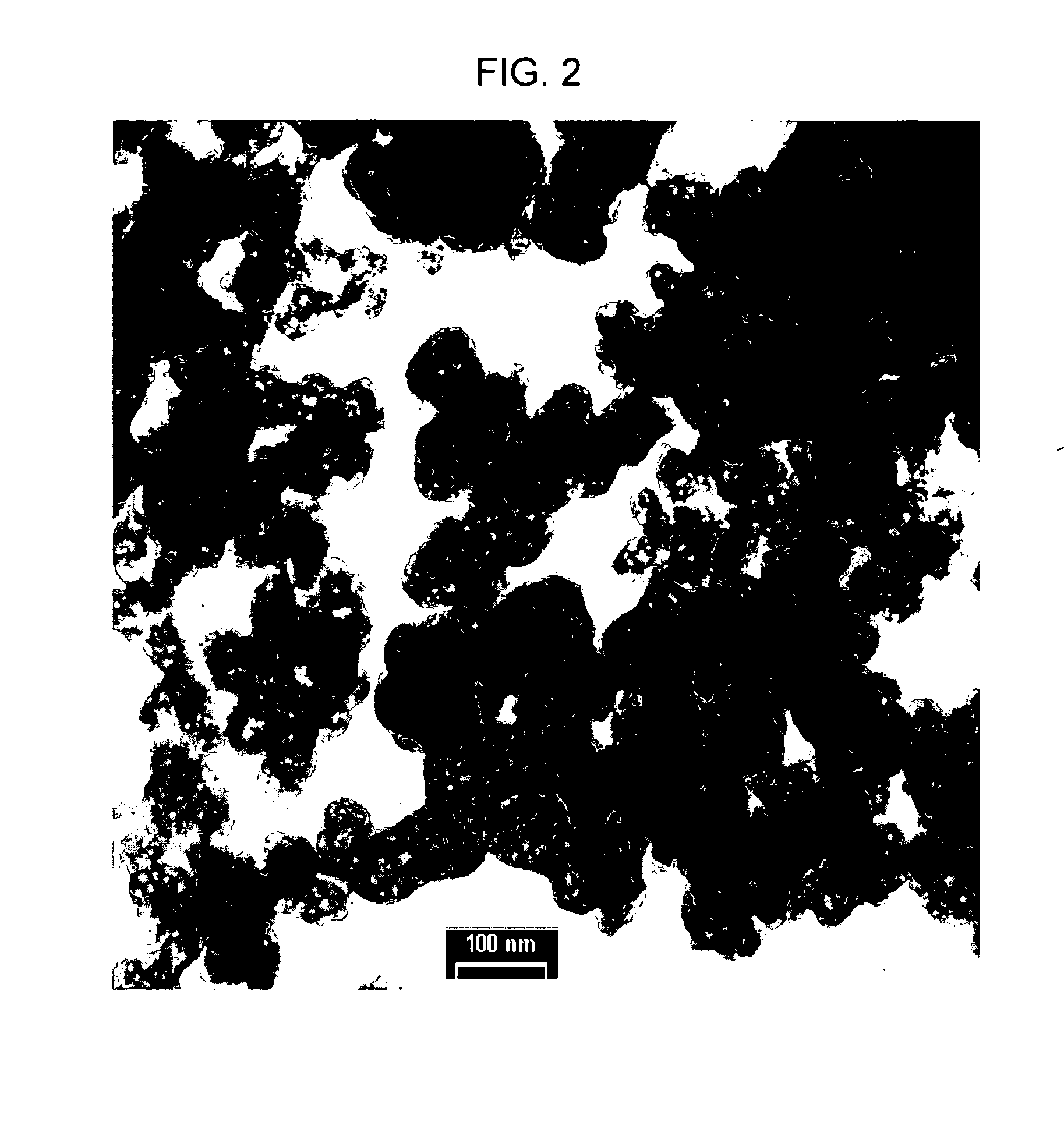
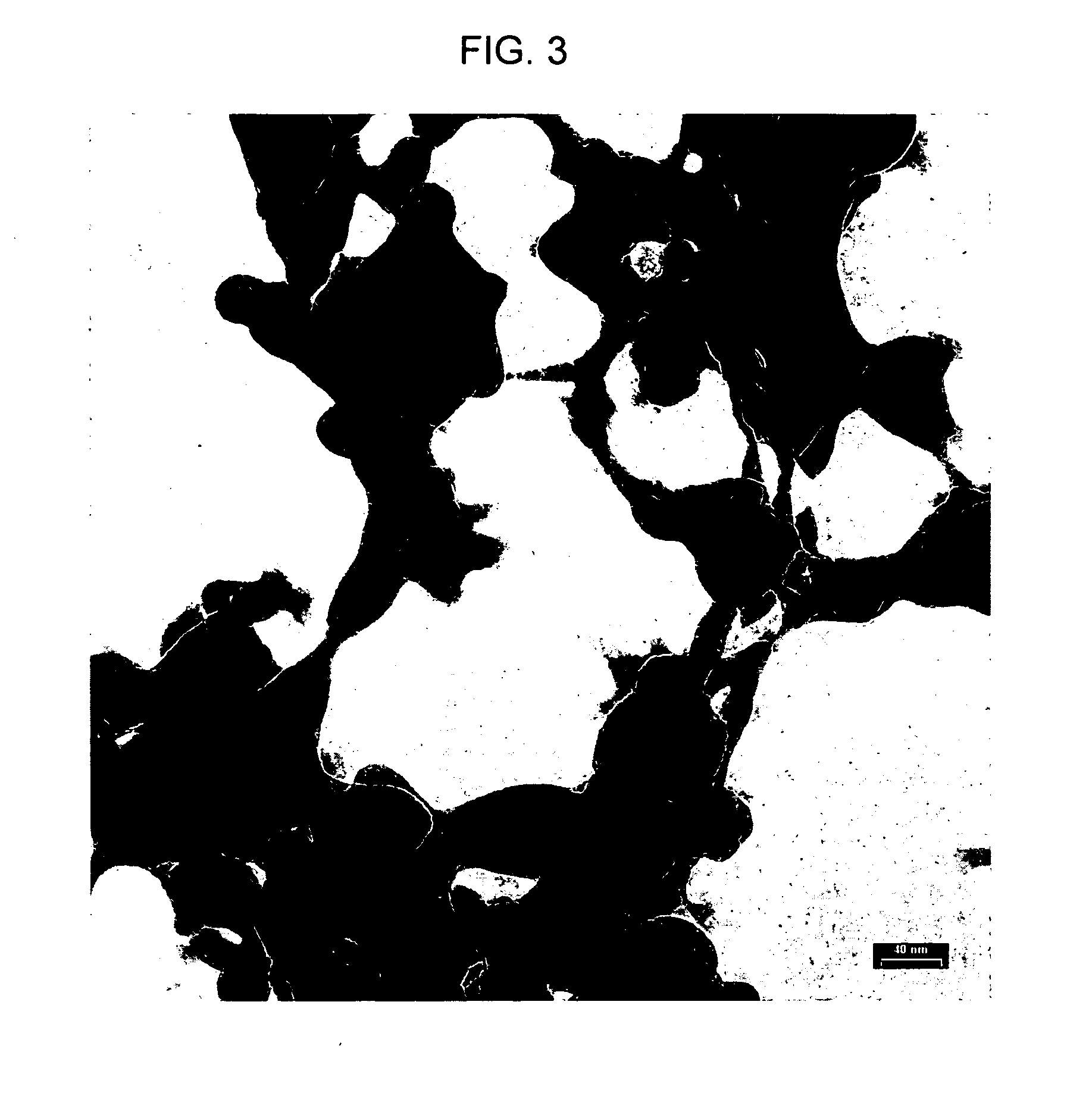
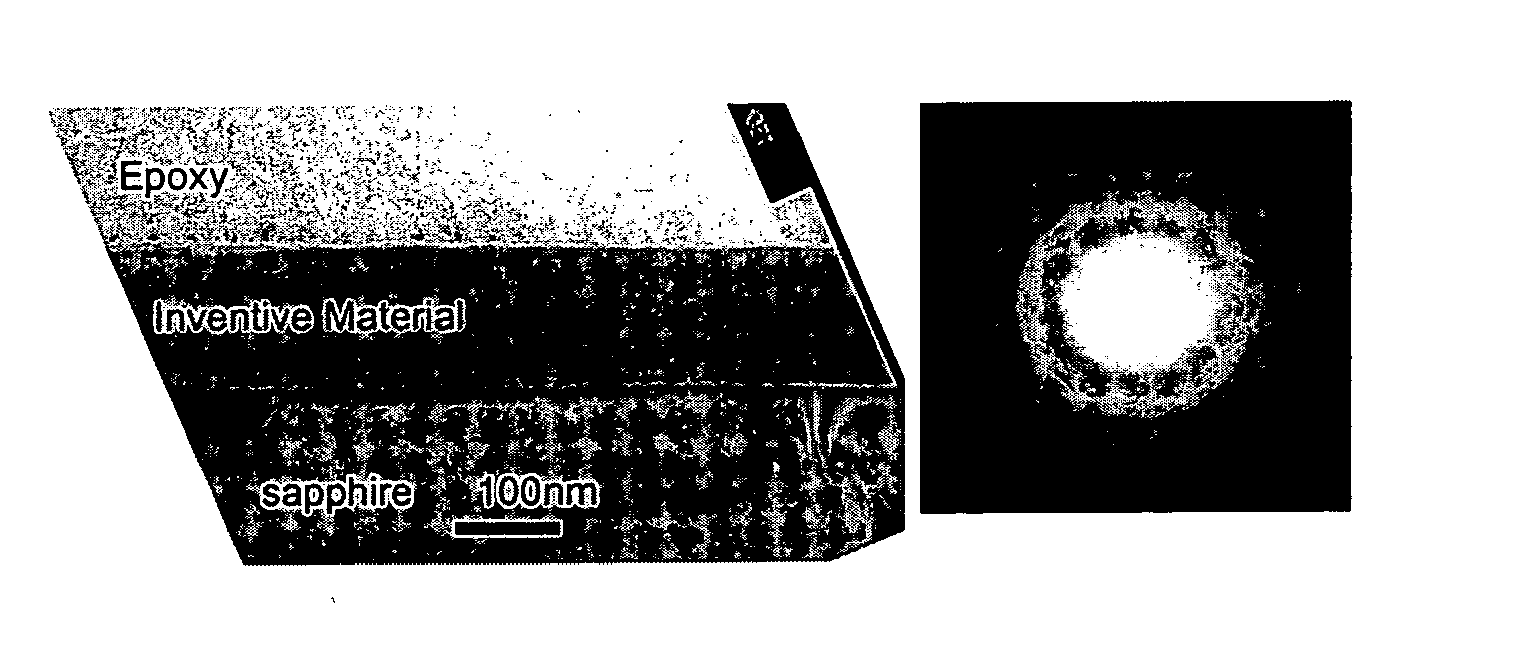
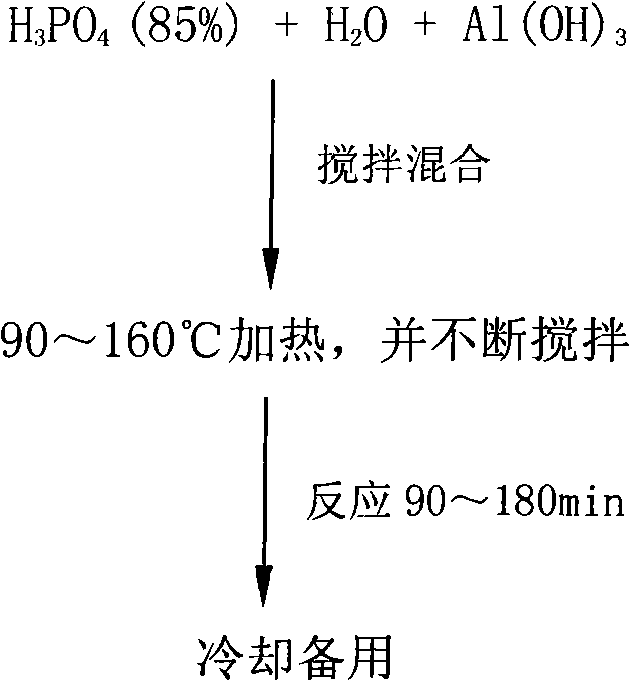
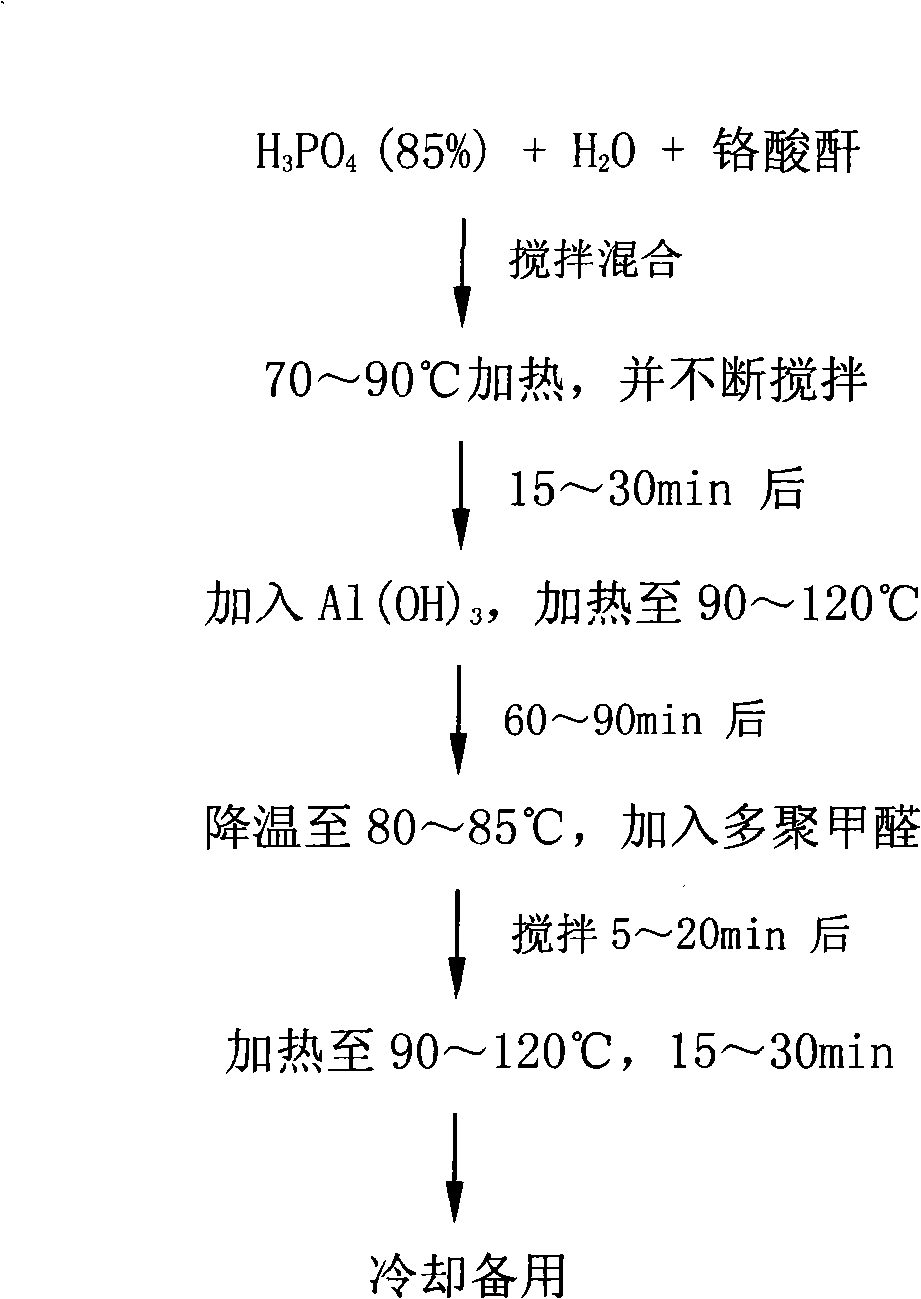
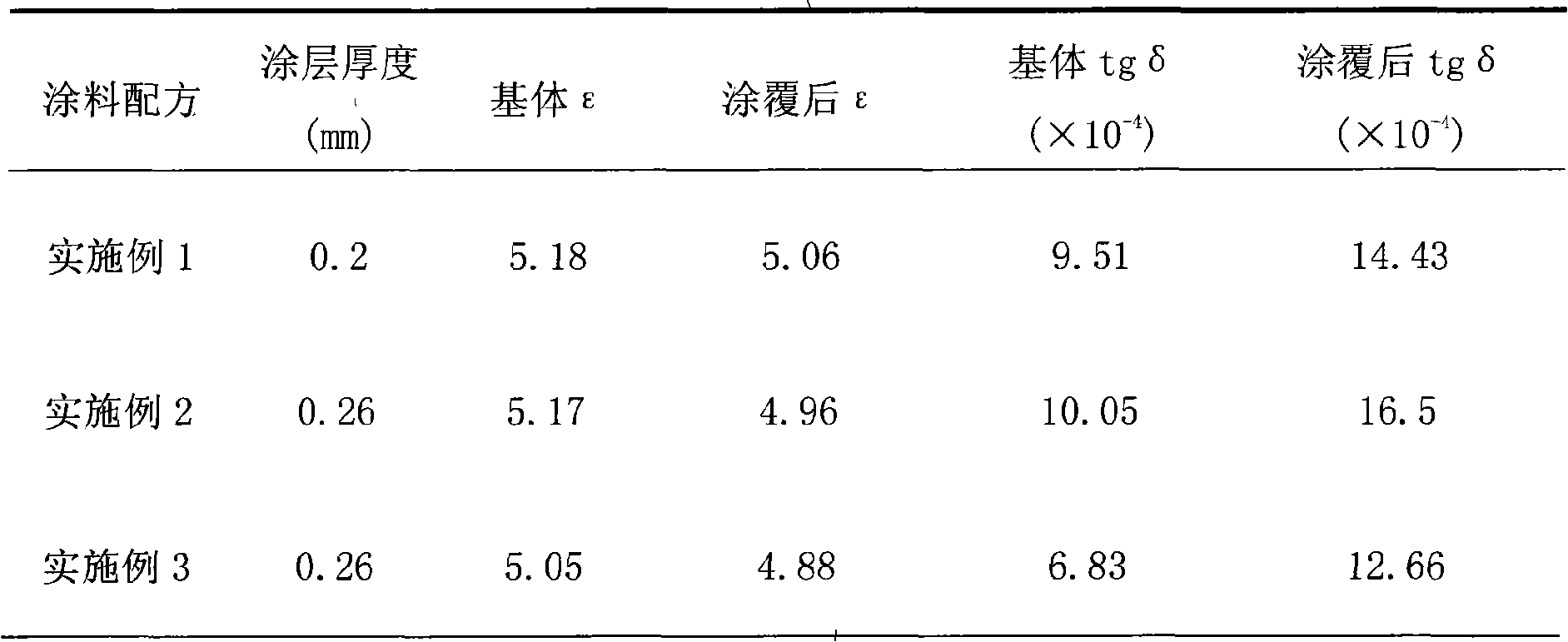
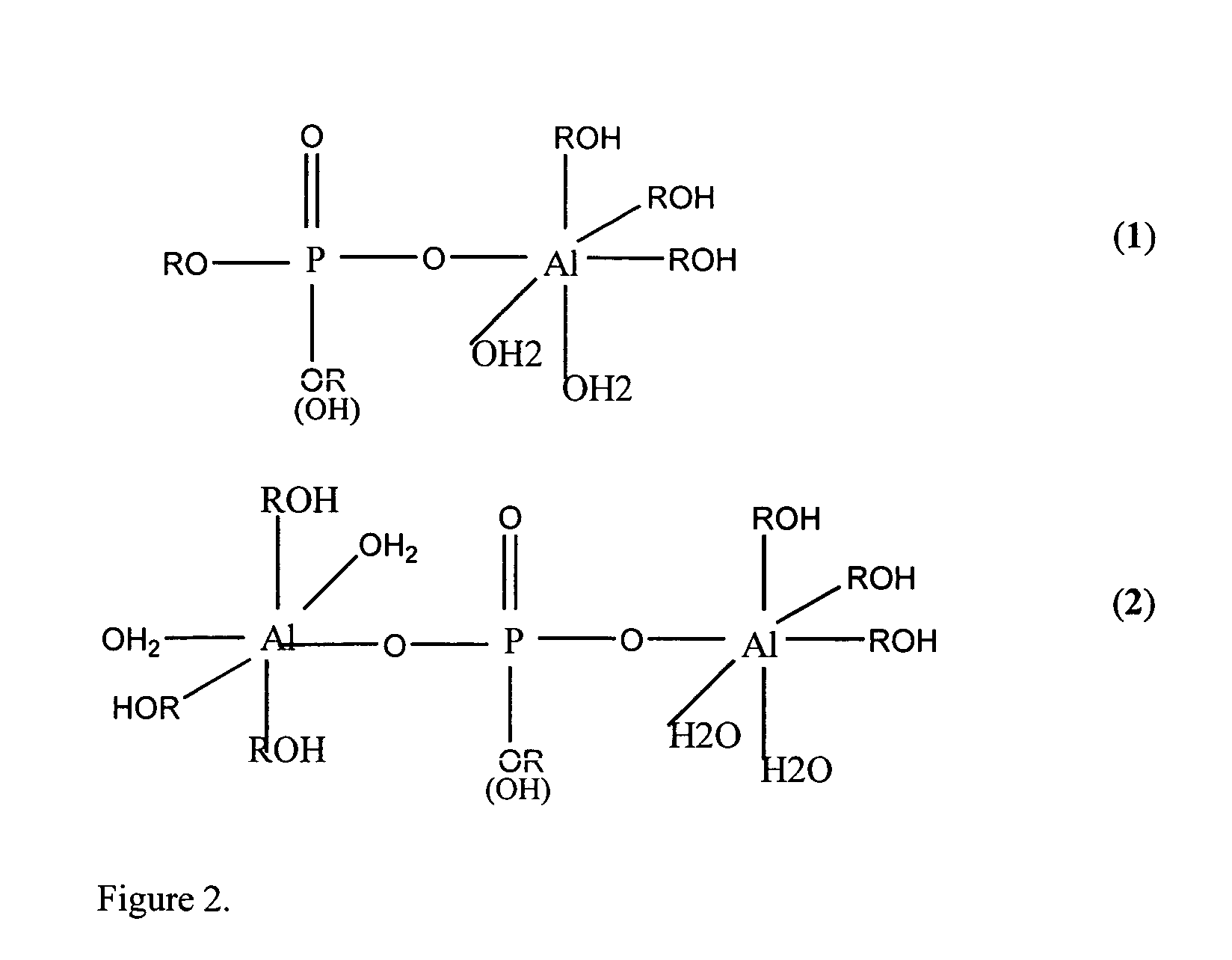
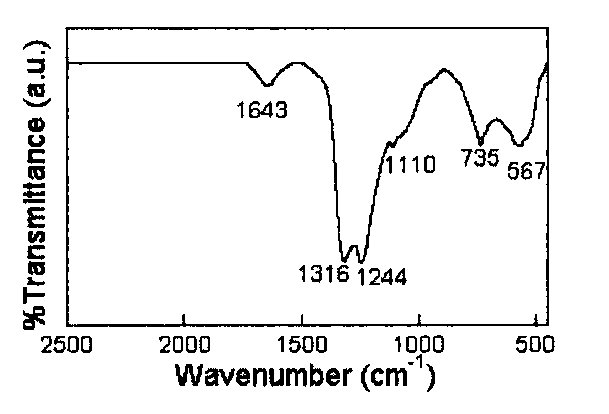
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1805 results about "ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aluminium phosphate (AlPO4) is a chemical compound. The anhydrous form is found in nature as the mineral berlinite. Many synthetic forms of anhydrous aluminium phosphate are known.
Aluminum phosphate compounds, compositions, materials and related metal coatings
ActiveUS20040138058A1Improve heat transfer efficiencyIncrease temperaturePhysical/chemical process catalystsMetallic material coating processesMetal coatingMetallurgy
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Water industrial antirust paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101045843AHigh hardnessStrong adhesionAnti-corrosive paintsEmulsion paintsEpoxyALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
This invention relates to a aquosity industry anti-rust paint and its preparation method. According to weight it includes 8 to 11% aquosity acroleic acid modified epoxy, 33 to 40% acroleic acid latices, 0.1 to 0.3% defoamer, 0.05 to 0.15% wetting agent, 0.3 to 0.5% dispersant, 0.3 to 0.5% rust-resistant agent, 7.5 to 9% iron oxide red, 6 to 8% French chalk, 5 to 10% modified zinc phosphate, 2.5 to 10% trimerization aluminum phosphate, 3 to 3.5% precipitated baryte , 0.5 to 1% zinc oxide, 3 to 5% mica ferric oxide, alcohol ester twelve 1 to 2%, triethanolamine 1 to 2%, thickening agent 0.3 to 0.6%, preservative 0.05 to 0.1%, 5 to 20% de-ionized water, through pretreatment, color paste preparation and blending and adjusting to gain product.
Owner:邹磊
Process of making a water dispersible titanium dioxide pigment useful in paper laminates
The present invention relates to a process for making a titanium dioxide pigment having consisting of titanium dioxide and single layer of inorganic surface treatment consisting of aluminum phosphate wherein the pigment is characterized by and isoelectric point which is greater than pH 6 and a negative zeta potential of at a pH of 7.5 or more.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate particles for use as pigments in paints and method of making same
InactiveUS20060045831A1PhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesAluminium sulfateOrganic acid
An aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment product is made by a process comprising contacting phosphoric acid with aluminum sulfate and an alkaline solution to produce an aluminum phosphate based product; and optionally calcining the aluminum phosphate based product at an elevated temperature, wherein the process is substantially free of an organic acid. The aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment is amorphous. The amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate characterized by a bulk density of less than 2.30 grams per cubic centimeter and a phosphorus to aluminum mole ratio of greater than 0.8. The composition is useful in paints and as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS +1
Phosphate film-coated powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101045828AUniform particlesParticle size distribution andNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesDepolymerizationDouble decker
This invention relates to a method of preparing envelope powder. The shattering, depolymerization and coating processed at same time, and solid phase acid-base reaction participate the method. This envelope powder possess double-decker or three-layer structure, inner core is composed by oxide or hydrate or inorganic oxysalt, crust composed by inorganic oxysalt, envelope by aluminum phosphate or boron phosphate. This low cost powder be able to used as fortifier, power stuff, colorant and so on, applied to plastic, rubber, ceramics, dope, binder and paper, set foundation for popularization of ultramicro and nanometer powder.
Owner:张义纲 +1
Aluminum phosphate compounds, coatings, related composites and applications
ActiveUS20060057407A1Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperconductor devicesPorous substratePhosphoric acid
Composites comprising an aluminum phosphate-based coating component and methods for sealing porous substrate surfaces.
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Aluminum phosphate compounds, compositions, materials and related composites
InactiveUS20050106384A1Control spreadImprove adhesionFilm/foil adhesivesPretreated surfacesNon oxide ceramicsMetallurgy
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Method for synthesizing silicon aluminum orthophosphate molecular sieve using white bole
InactiveCN101176851AGood hydrothermal stabilityHigh reactivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesALUMINUM PHOSPHATEWhite Bole
The invention relates to a method of molecular sieve catalyst synthesis using the kaolin for the synthesis of silicon aluminum phosphate molecular sieve, belonging to the technical field of the preparation of the catalyst materials. The invention is characterized in utilizing the low-cost kaolin as materials. Through (1) roasting the kaolin in the high temperature to gain the crystal aluminum sources and silicon sources; (2) mixing the kaolin with the phosphorus sources and the template agent with the deionized water, processing hydro-thermal crystallization, and roasting and activating the products after washing and drying, the catalyst of the silicon aluminum phosphate molecular sieve can be gained. The structure of the silicon aluminum phosphate molecular sieve is CHA or the intergrowth of CHA and AEI. The invention has the advantages of smaller or lamellar structure molecular sieve gains of the prepared catalyst, which can be used for the process of making olefin from the oxygenic compounds like the limited diffuse alcohol ether to gain the good activity of reaction and the product selectivity, and further the directly application of the catalyst carried by the kaolin micro sphere into fluidized bed reactor.
Owner:CHINA NAT CHEM ENG GRP CORP LTD +1
Aluminum phosphate coatings
InactiveUS7311944B2Improve hydrophobicityImprove functionalityFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsComposite filmBiofouling
Aluminophosphate compounds and compositions as can be used for substrate or composite films and coating to provide or enhance, without limitation, planarization, anti-biofouling and / or anti-microbial properties.
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Methods for making environmental barrier coatings and ceramic components having cmas mitigation capability
ActiveUS20100159150A1Liquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingRare-earth elementALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
Methods of making components having calcium magnesium aluminosilicate (CMAS) mitigation capability involving providing a component; applying an environmental barrier coating to the component, the environmental barrier coating having a separate CMAS mitigation layer including a CMAS mitigation composition selected from rare earth elements, rare earth oxides, zirconia, hafnia partially or fully stabilized with alkaline earth or rare earth elements, zirconia partially or fully stabilized with alkaline earth or rare earth elements, magnesium oxide, cordierite, aluminum phosphate, magnesium silicate, and combinations thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation of aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate particles
InactiveUS20080038556A1High mixingHigh shear stress performanceMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSodium aluminatePolyphosphate
A process for the preparation of amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment by reacting aluminum phosphate and sodium aluminate is provided. The amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate is characterized by a skeletal density of less than 2.50 grams per cubic centimeter and a phosphorus to aluminum mole ratio of greater than 0.8. In one embodiment, the composition is useful in paints as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS +1
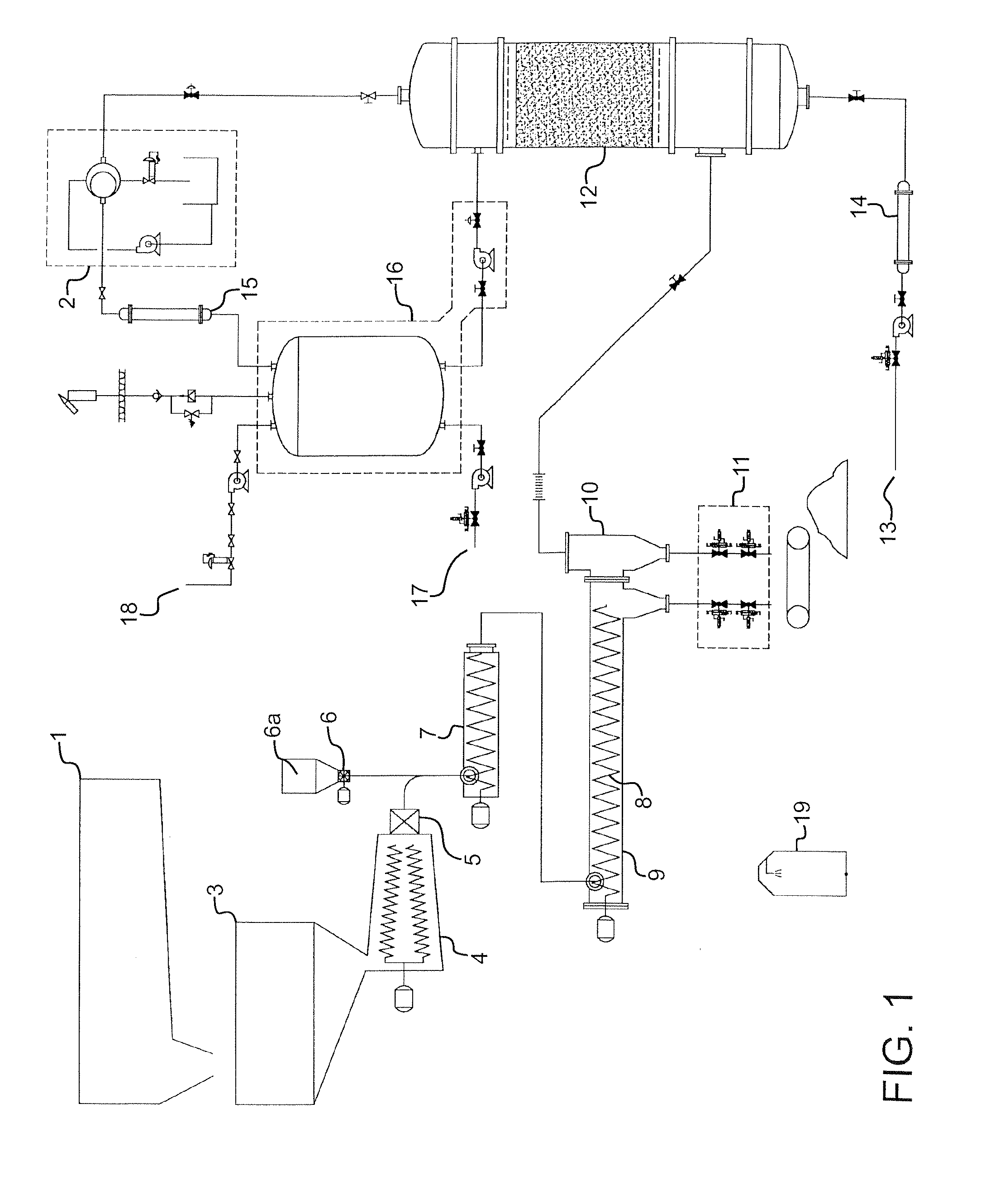
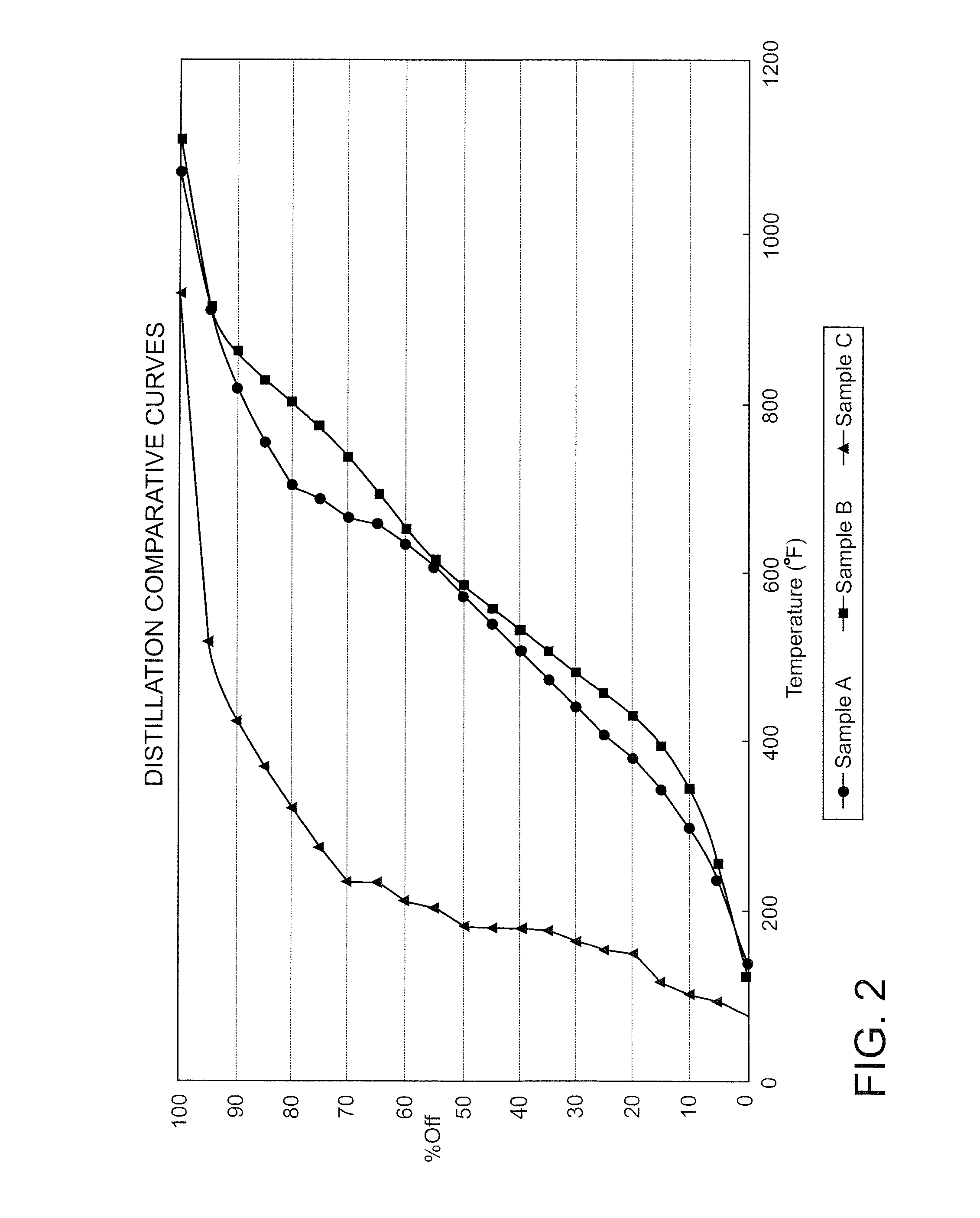
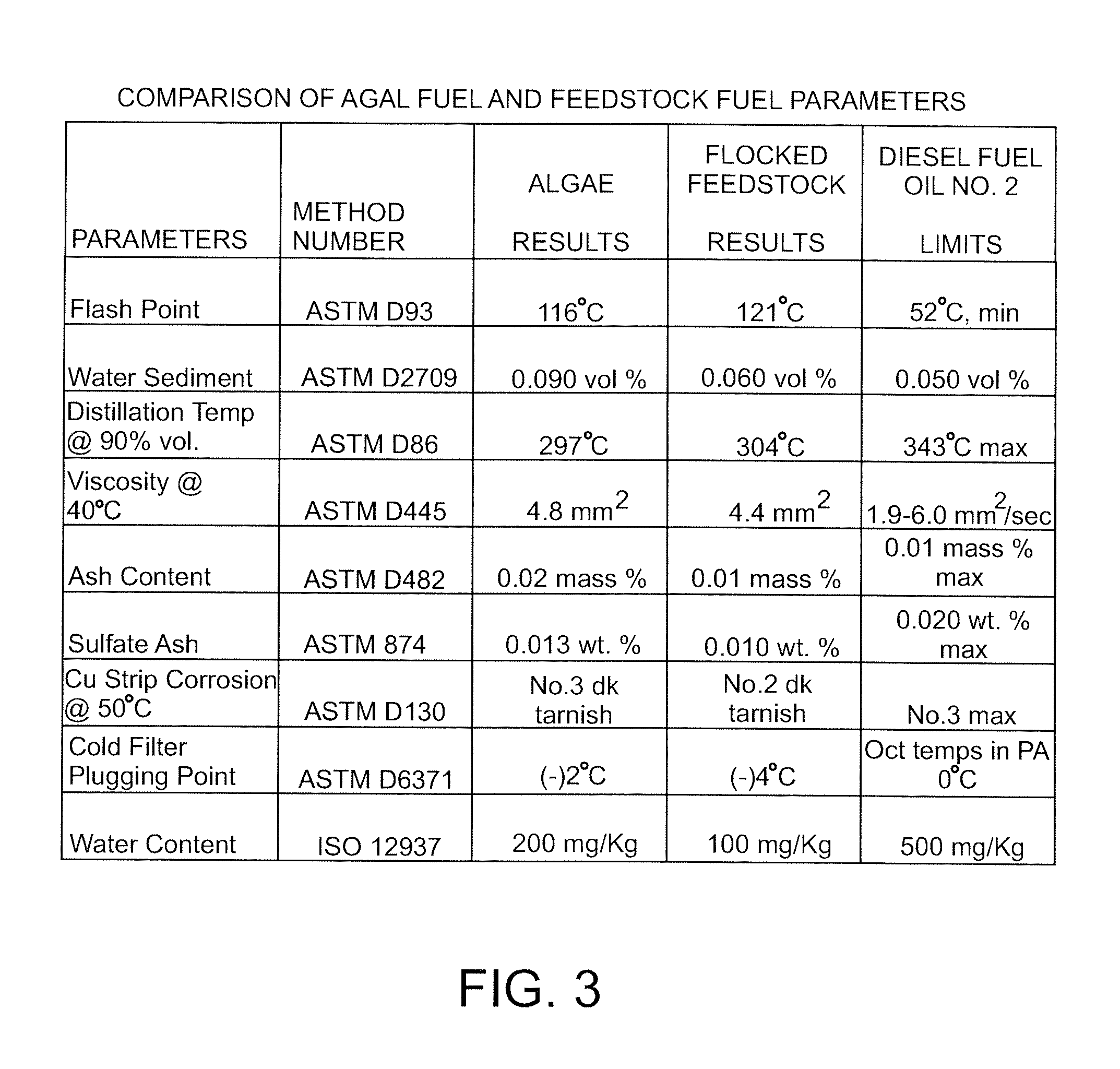
Vacuum Pyrolytic Gasification And Liquefaction To Produce Liquid And Gaseous Fuels From Biomass
InactiveUS20110011721A1Facilitate heavy fuel distillation operationBiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationRare-earth elementVacuum pressure
A biofuel production method, catalyst and system. The method may include combining a feedstock comprising a carbonaceous material with a consumable catalyst to produce a feedstock / catalyst mixture, and subjecting the feedstock / catalyst mixture to a vacuum pyrolytic gasification and liquefaction process to produce one or more biofuels. The catalyst includes effective amounts of various catalyst constituents, which may include some or all of kaolin, zeolite, amorphous silica, alumina aluminum phosphate and rare earth elements. The system may include apparatus for heating the feedstock / catalyst mixture under selected temperature and vacuum pressure conditions to produce a gaseous effluent comprising one or more hydrocarbon fractions, and additional distillation and condensation apparatus to produce one or more liquid and gaseous fuels.
Owner:CHAMPAGNE GARY E
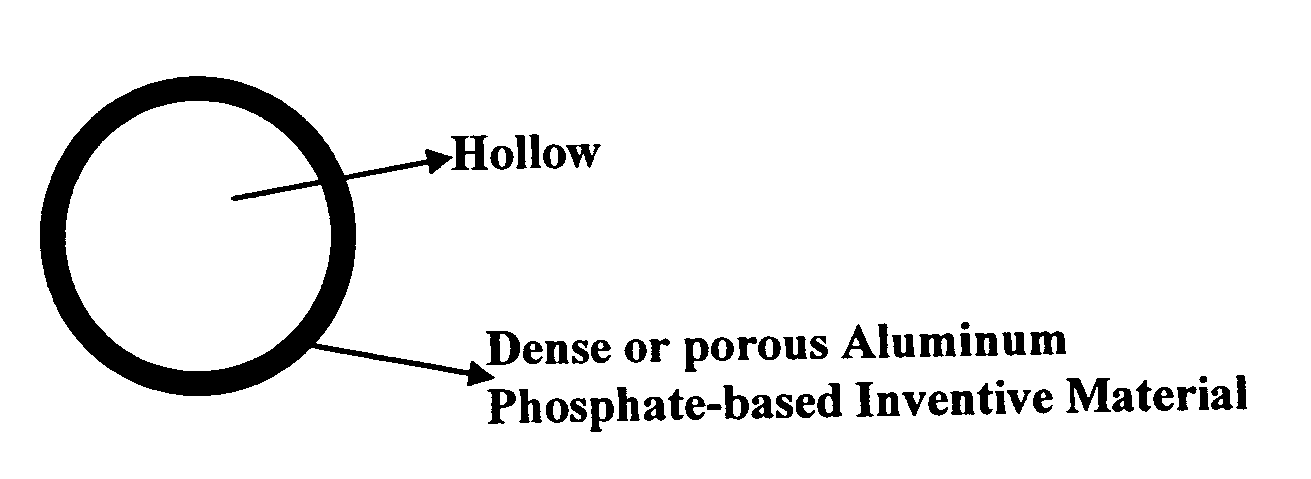
Aluminum phosphate based microspheres
ActiveUS20080035021A1Low densityImprove thermalPigmenting treatmentEnvelopes/bags making machineryMicrosphereALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Cmas mitigation compositions, environmental barrier coatings comprising the same, and ceramic components comprising the same
Calcium magnesium aluminosilicate (CMAS) mitigation compositions selected from rare earth elements, rare earth oxides, zirconia, hafnia partially or fully stabilized with alkaline earth or rare earth elements, zirconia partially or fully stabilized with alkaline earth or rare earth elements, magnesium oxide, cordierite, aluminum phosphate, magnesium silicate, and combinations thereof when the CMAS mitigation composition is included as a separate CMAS mitigation layer in an environmental barrier coating for a high temperature substrate component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
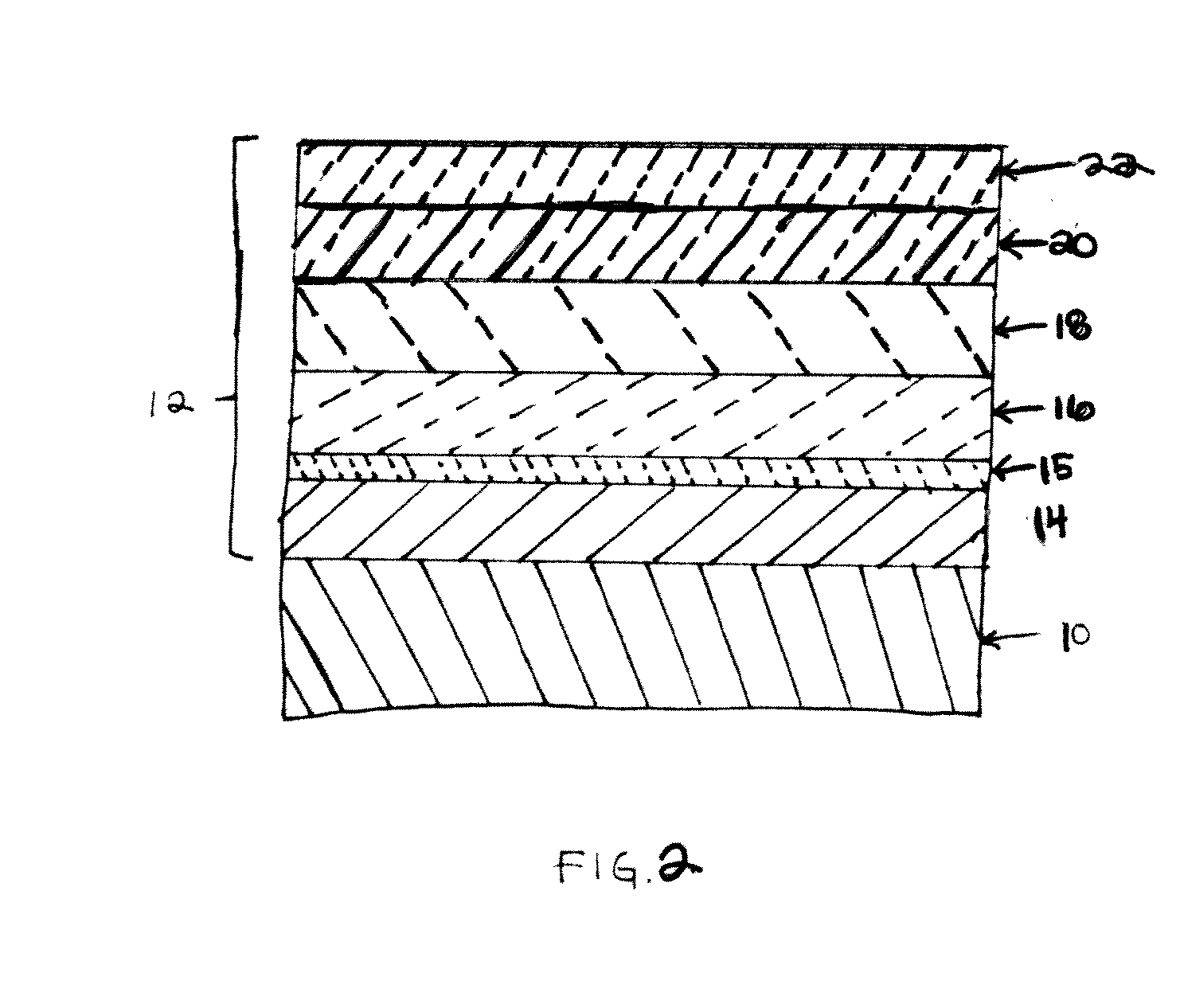
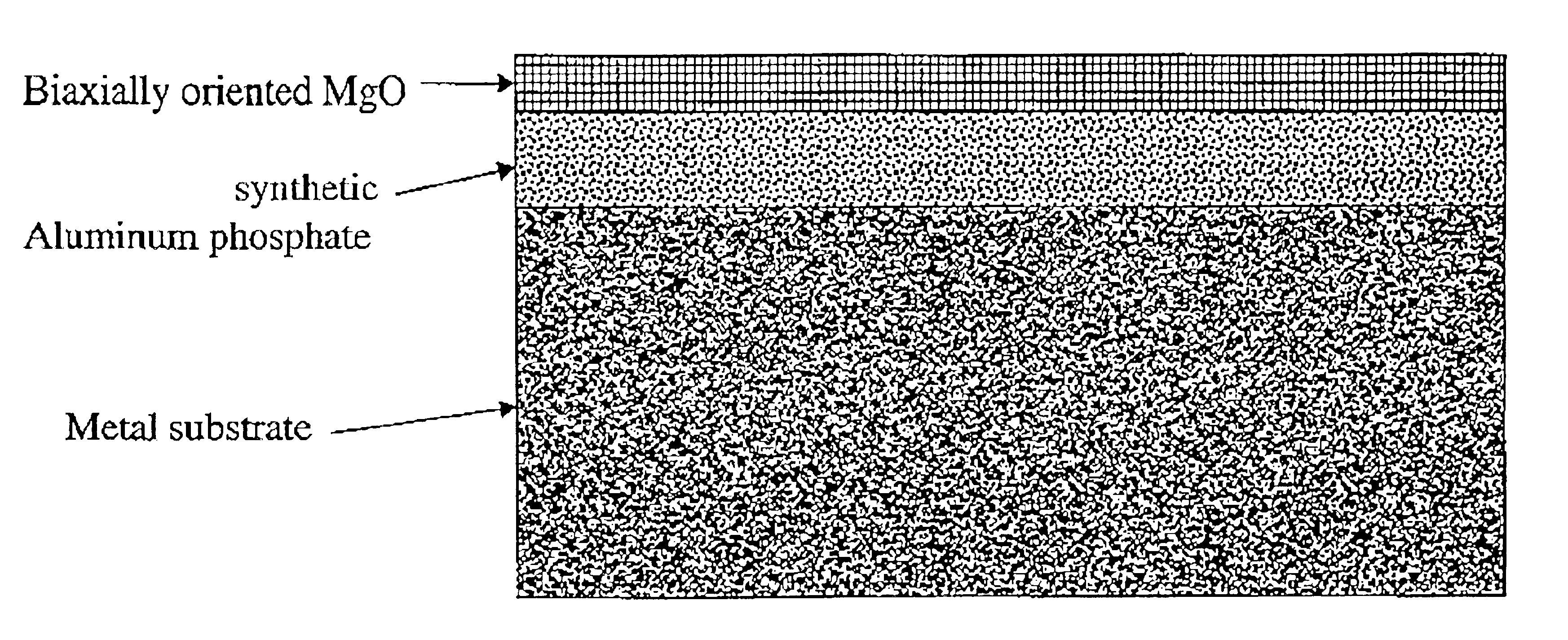
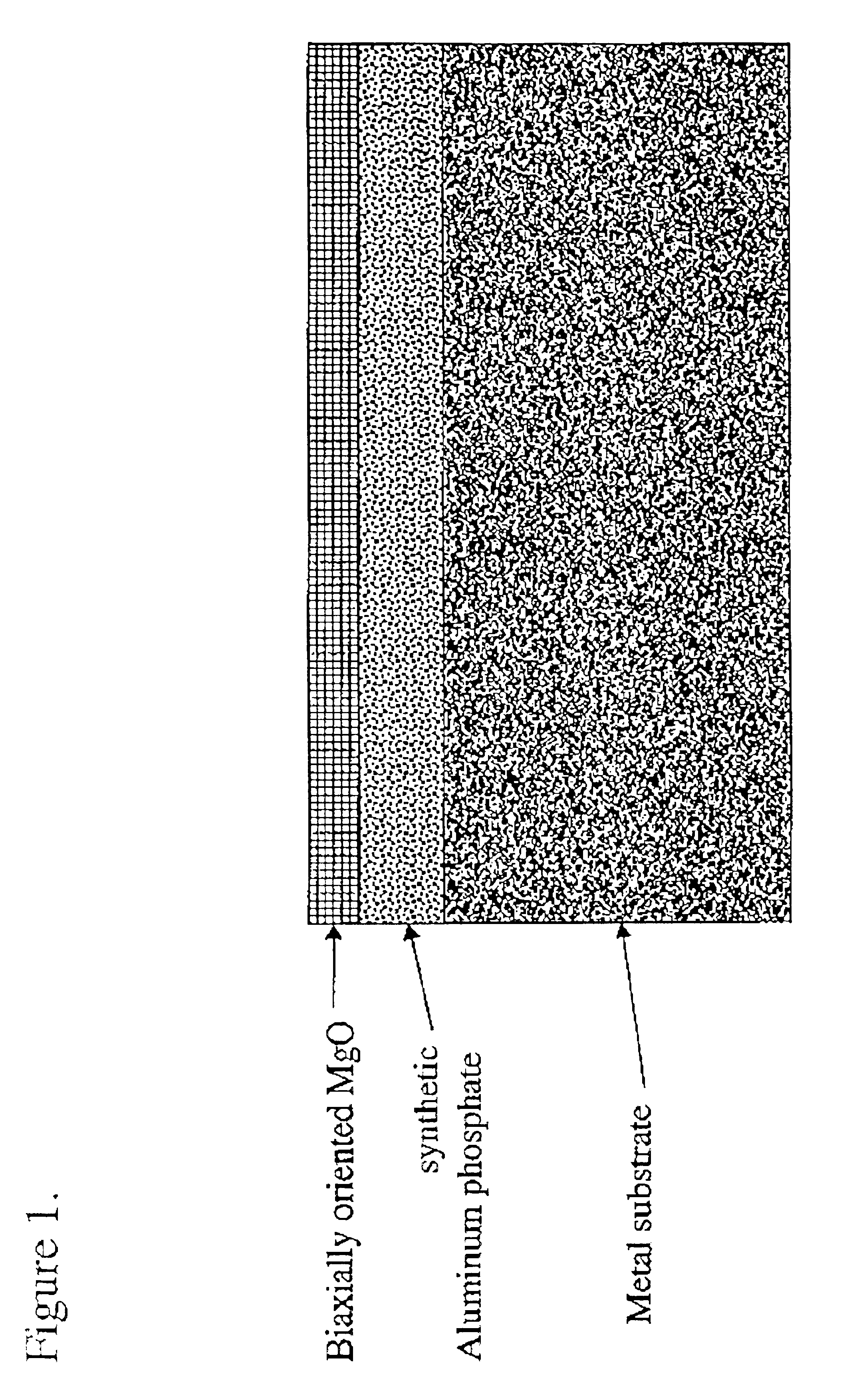
Biaxially textured composite substrates
InactiveUS6884527B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingPhosphateComposite substrate
An article including a substrate, a layer of a metal phosphate material such as an aluminum phosphate material upon the surface of the substrate, and a layer of an oriented cubic oxide material having a rock-salt-like structure upon the metal phosphate material layer is provided together with additional layers such as a HTS top-layer of YBCO directly upon a layer of a buffer material such as a SrTixRu1−xO3 layer.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Environment-friendly solvent-free humidified and rusted anticorrosive paint
InactiveCN101747825AEasy pretreatmentConvenient anti-corrosion solutionAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsOrganic filmSolvent free
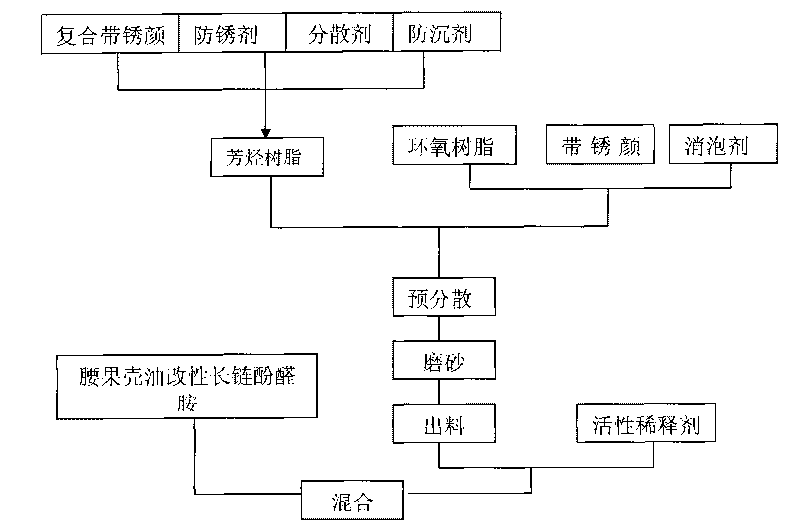
The invention relates to a paint material with formed organic film, in particular to an epoxy solvent-free anticorrosive paint applied to low surface treatment steel structure. The anticorrosive paint is prepared by efficiently compounding rusted coating pigments such as zinc molybdate, zinc phosphate, aluminium trippolyhosphate, iron oxide red and the like, using cashew nut oil modified long-chain amine phenolic aldehyde as, alicyclic glycidyl ether as active diluent, thus overcoming the problems that surface treatment technique in coating construction costs high and heavy anticorrosive paint with high solvent content pollutes the environment, having easy preparation and construction, low cost, fast solidification at high temperature, good mechanical and anticorrosive performance, solvent-free and environment-friendly properties, and being applicable to heavy anticorrosive projects of steel structures such as ship, train, bridge and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aluminum phosphate, polyphosphate and metaphosphate particles and their use as pigments in paints and method of making same
An aluminum phosphate composition comprising aluminum phosphate, aluminum polyphosphate, aluminum metaphosphate, or a mixture thereof. The composisition may be characterized by, when in powder form, having particles wherein some of the particles have at least one or more voids per particle. In addition, the composition is characterized by exhibiting two endothermic peaks in Differential Scanning Calorimetry between about 90 degrees to about 250 degrees Celsius. The composition is also characterized by, when in powder form, having a dispersibility of at least 0.025 grams per 1.0 gram of water. The composition is made by a process comprising contacting phosphoric acid with aluminum sulfate and an alkaline solution to produce an aluminum phosphate based product; and optionally calcining the aluminum phosphate, polyphosphate or metaphosphate based product at an elevated temperature. The composition is useful in paints and as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS +1
Preparation method of special foamed ceramic filter for magnesium alloy
InactiveCN1410393ALow priceGood chemical stabilityProcess efficiency improvementFiltration separationAluminum sulphateFoam polyurethanes
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOHUA MOLD
Preparation method for high-light fastness titanium dioxide pigment
ActiveCN102585559AImprove controllabilityGood reproducibilityInorganic pigment treatmentInorganic compound additionAluminium hydroxidePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-light fastness titanium dioxide pigment. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing aqueous suspension of a titanium dioxide initial product; depositing a layer of dense silicon dioxide cladding layer on a titanium dioxide pigment; depositing an aluminum phosphate compound on the silicon dioxide-coated titanium dioxide pigment; depositing aluminum hydroxide by using a parallel-flow method; after the aluminum hydroxide is coated, stirring and aging; and filtering, washing, drying, and performing fluid energy milling and organic treatment to obtain the high-light fastness titanium dioxide pigment. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high controllability, reproducibility, high operability and the like, facilitates industrial production and has a good application prospect. The titanium dioxide pigment prepared by the method has the advantages of high light fastness, high light resistance, high non-transparency, high color-change resistance and the like, and can be used in decoration paper, laminated paper and coating and plastic products which have high requirements on the light resistance.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
High-temperature antioxidizing paint for lowering oxidation burning of steel in heating furnace
InactiveCN101462859AReduce high temperature oxidation burning lossReduce oxidation burning loss per unit areaLithium metasilicateHigh pressure water
The invention relates to a high temperature anti-oxidation coating capable of reducing the oxidation burning loss of stainless steel in a heating furnace. The high temperature anti-oxidation coating is characterized in that the coating comprises solid materials consisting of 46 to 92 percent of basic filler and 8 to 54 percent of composite binder, and water which is 0.5 to 20 folds of the weight of the solid materials. The basic filler comprises several chemical components selected from silicon dioxide, alumina, magnesia, calcium oxide and boric oxide. The composite binder consists of several components selected from sodium silicate, lithium metasilicate and aluminum phosphate. The coating can be painted at the normal temperature or sprayed onto the surface of a stainless steel billet from the room temperature to 1,000 DEG C. The coating can form a protective coat at the high temperature, thereby greatly reducing the high temperature oxidation burning loss of stainless steel at 1,400 DEG C, and reducing the unit area oxidation burning loss by more than 90 percent. After stainless steel is drawn out of the furnace, the iron oxide scale can be fully stripped off under the actions of temperature reduction or high pressure water; the amount of the produced iron oxide scale is also obviously reduced; and the stainless steel surface quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Titanium dioxide pigment, process for producing the same, and resin composition containing the same
InactiveUS6576052B1Good light fastnessMinimized change in colorPigmenting treatmentALUMINUM PHOSPHATEWear resistance
The titanium dioxide pigment of the present invention comprises titanium dioxide particles, the coating layer containing the aluminum phosphate compound and the coating layer containing the hydrolyzate of the organosilane compound, on the surface of the particles, in which a difference in water content between 100° C. and 300° C., determined by the Karl Fischer method, is not greater than 1500 ppm, and is thus excellent in light fastness, hydrophobicity and dispersibility. In particular, the titanium dioxide pigment of the invention is extremely advantageous as a colorant for plastics, which requires light fastness (resistance to discoloration) lacing resistance and dispersibility, to a high degree.
Owner:ISHIHARA SANGYO KAISHA LTD
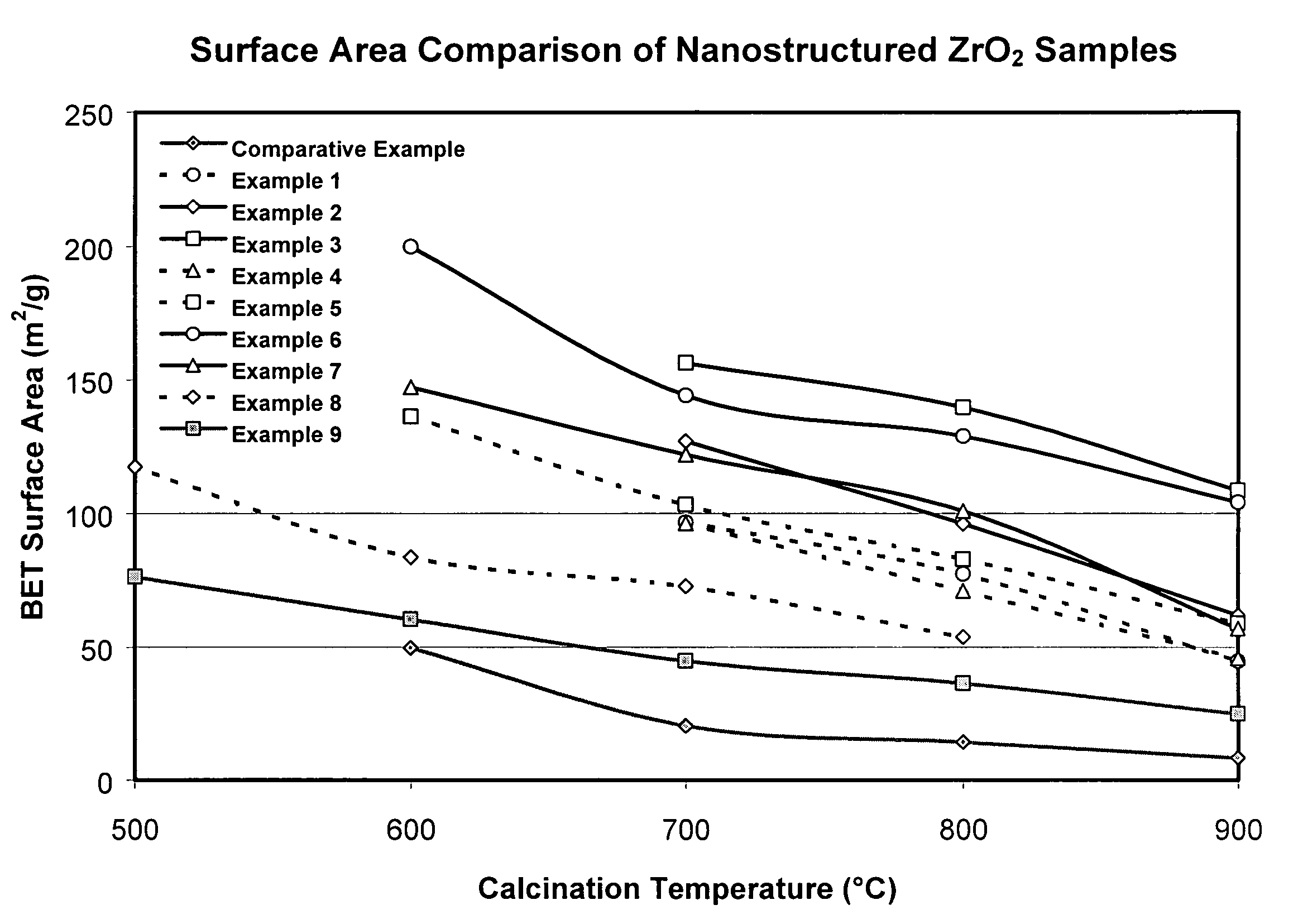
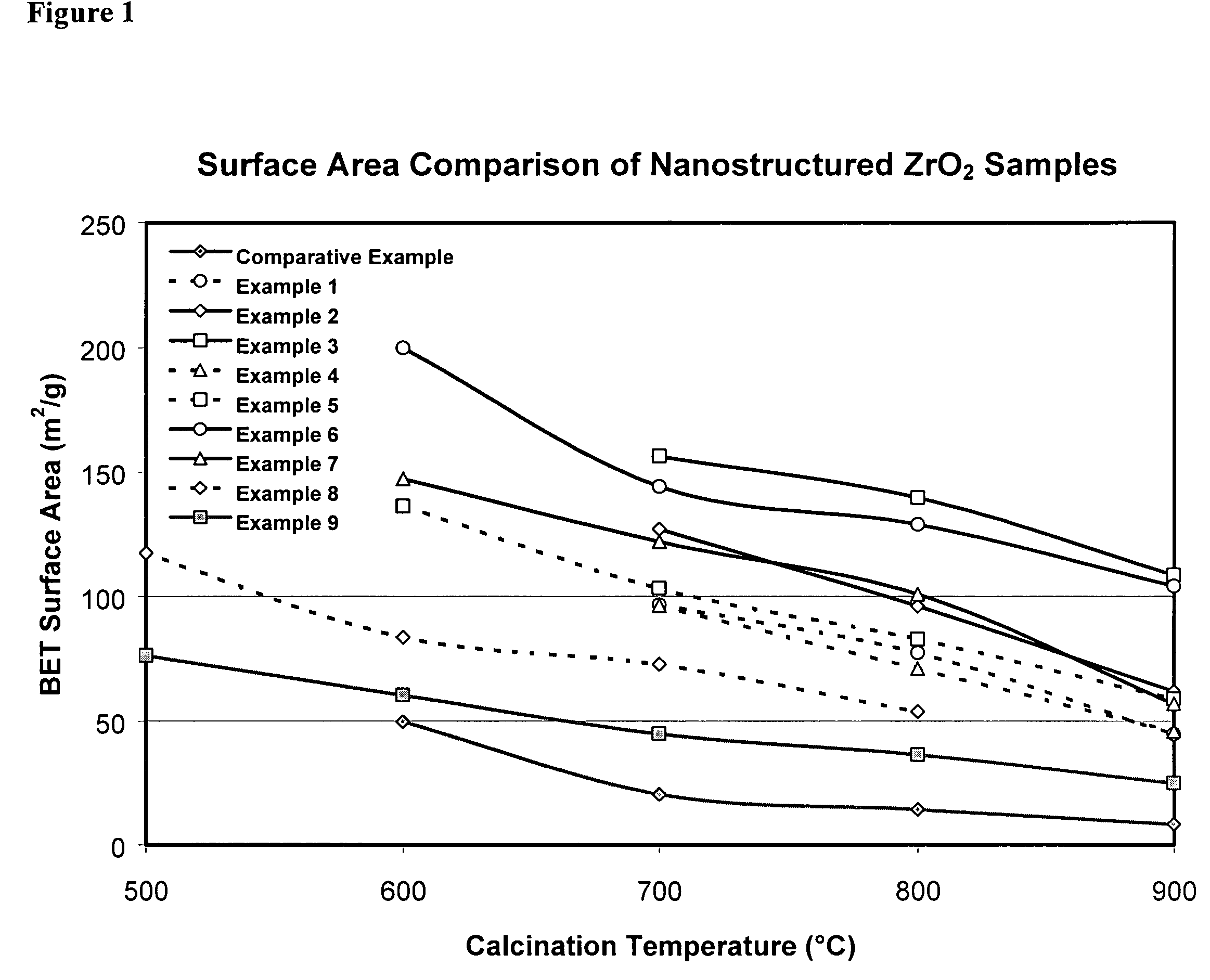
Nano-structured particles with high thermal stability
ActiveUS7125536B2Large specific surface areaImprove thermal stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
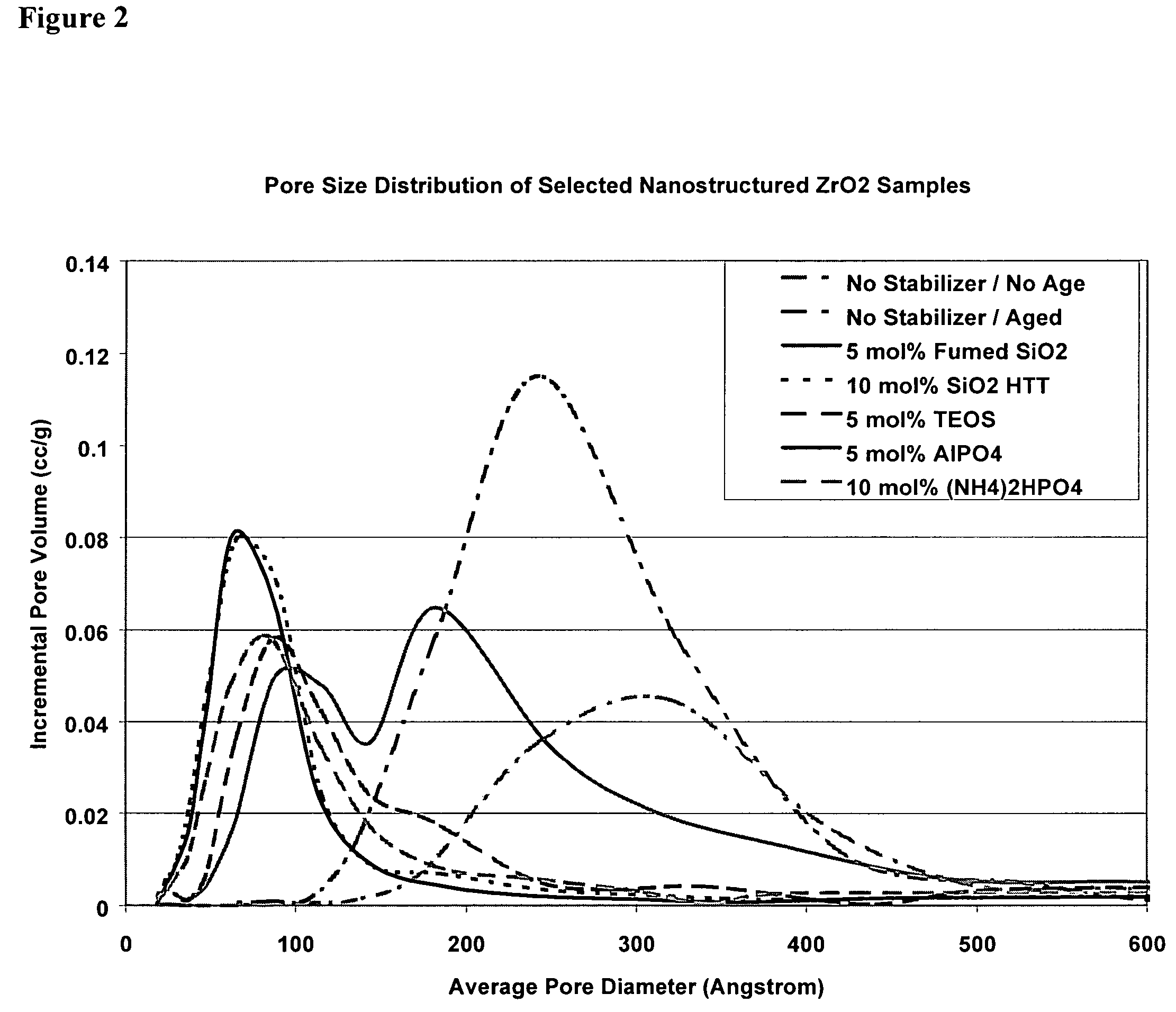
This invention relates to a composition comprising nano-structured metal oxide particles (particularly, zirconia) and at least one stabilizing agent, a method to produce the composition, and a method to produce the thermally stable nano-structured particles. The method to produce the nano-structured particles comprises first preparing a base solution and a nanoparticle precursor solution, then combining these solutions at a final pH 7 or greater to precipitate a colloidal hydrous oxide. The colloidal hydrous oxide is then treated with at least one silicate, phosphate, or aluminum phosphate stabilizing agent and dried. These nano-structured particle products have high thermal stability and are particularly advantageous in applications as catalysts or catalyst supports that operate at high temperatures.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Atomic layer deposition of metal phosphates and lithium silicates
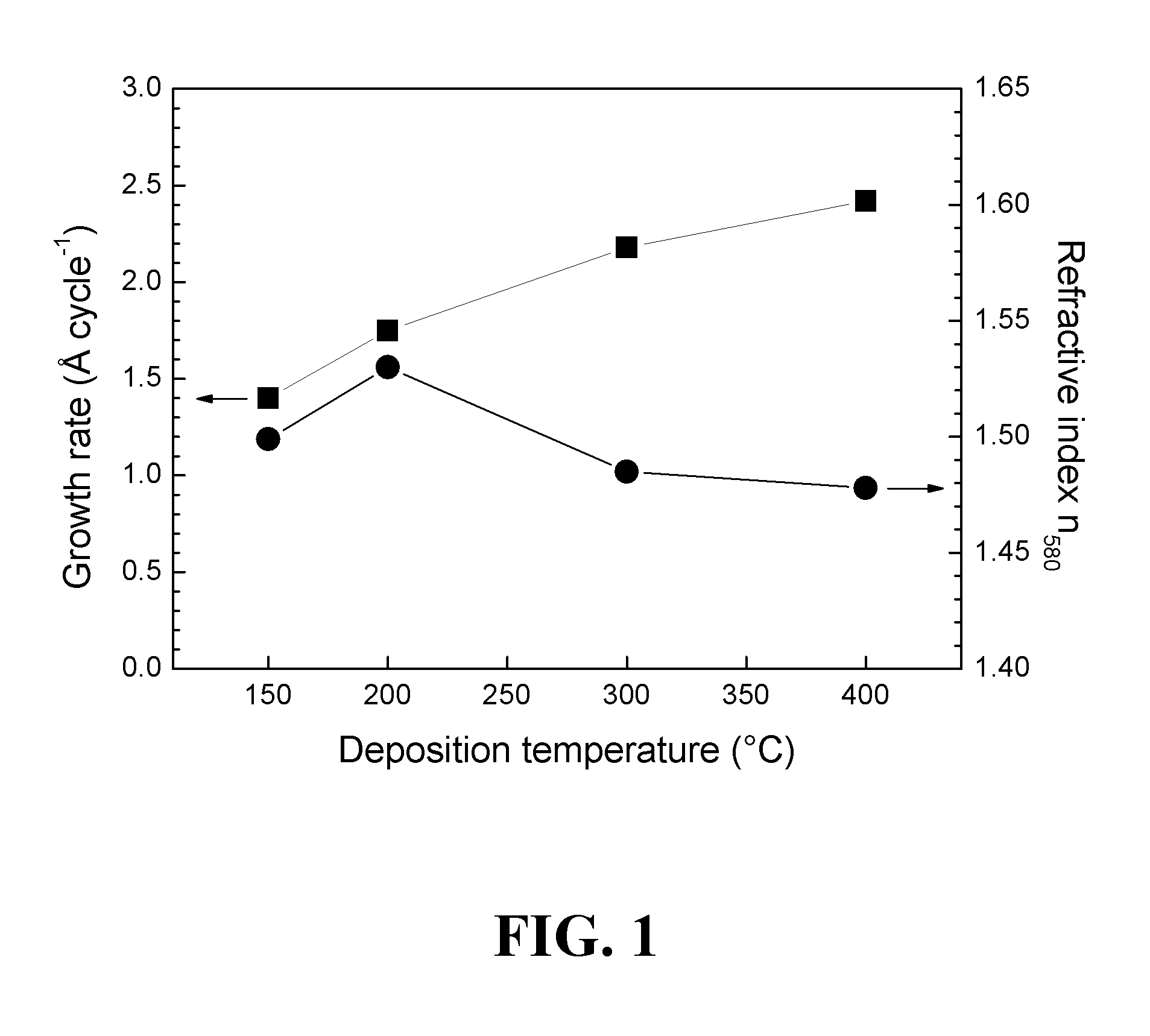
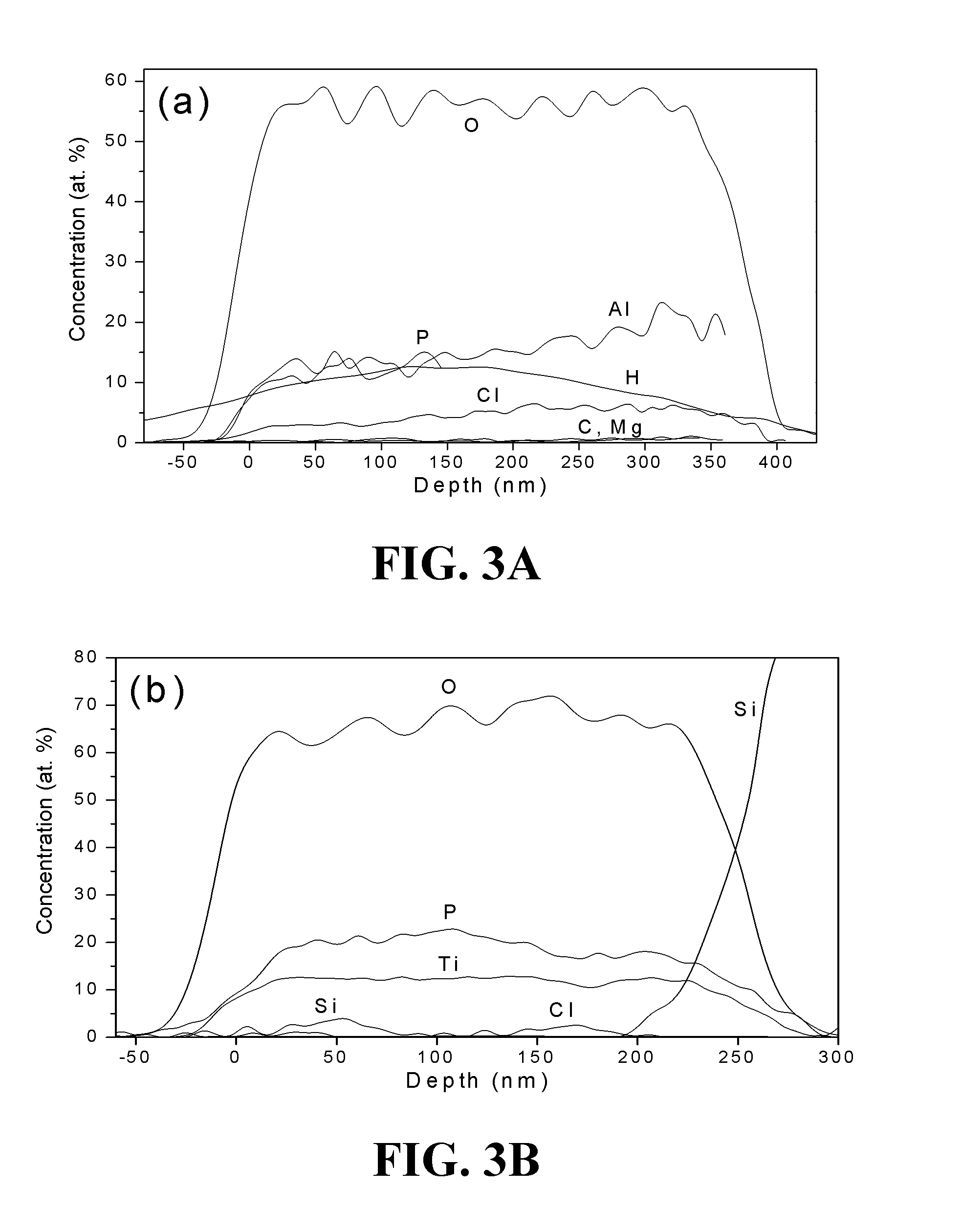
ActiveUS20120276305A1Increase amount of lithiumSpecial surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium phosphateALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
The present application relates to atomic layer deposition (ALD) processes for producing metal phosphates such as titanium phosphate, aluminum phosphate and lithium phosphate, as well as to ALD processes for depositing lithium silicates.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Thermosetting Powder Coating Composition
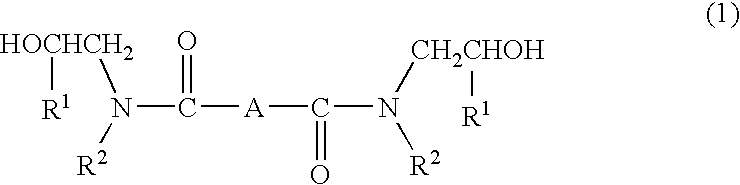
InactiveUS20080085965A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove moisture resistancePolyester coatingsStrontium carbonatePreservative
The present invention provides a thermosetting powder coating composition that is capable of forming a coating film having excellent moisture resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, etc. More specifically, the present invention provides a thermosetting powder coating composition comprising a carboxy-containing resin (A), a β-hydroxyalkylamide curing agent (B), and an anticorrosive (C) that comprises a strontium carbonate-modified aluminum phosphate.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Preparation method of high-volume-fraction diamond/aluminum composite material with heat conduction function
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of composite materials, and relates to a preparation method of a high-volume-fraction diamond / aluminum composite material with heat conduction function. The diamond / aluminum alloy interface binding performance is improved by metallizing the diamond grain salt bath coated surface, using gel injection molding prefabricated body technique by adding high-temperature aluminum phosphate adhesive, improving the constituent of aluminum alloy and other means. The composite material is prepared by a non-pressure impregnation technique which has the advantages of low cost and is simple to operate and implement. The diamond / aluminum composite material has uniform and compact microstructure, and has favorable diamond / aluminum alloy interface binding performance; and the density is 3.17g / cm<3>, the heat conductivity is up to 518W / m.K, the thermal expansion coefficient is only 4.61*10<-6> / K, the bending strength is 306Mpa, and the Young's modulus is 280GPa. The invention completely satisfies the requirements of superhigh heat conductivity, low density and low thermal expansion coefficient for the high-density electronic packaging material.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Phosphate-silicon dioxide low-dielectric high temperature-resistant coating and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a low-dielectric high-temperature-resistant phosphate-silicon dioxide coating, with the mass percentage content between the components and the raw material as follows: 50-80% of percentage content of inorganic compound binder, 15-50% of high-temperature filler, 0.5-1.5 wt% of curing agent, 2-5 wt% of thickener, and 0.3-1.5wt% of surfactant; the inorganic compound binder is the mixture of aluminum phosphate or aluminium-chromium phosphate and silicon collosol; the high-temperature resistant filler is the mixture of fused quartz powder and refined quartz powder or alpha-Al2O3 power; the curing agent is MgO; the thickener is fumed silica; the surfactant is non-ionic surfactant. The phosphate binder is firstly prepared, followed by phosphate / silicon collosol compound binder; then the non-ionic surfactant and the high-temperature resistant filler are added to the compound binder, followed by the thickener and the curing agent, then the mixture is evenly mixed. The invention can be used for the surface protection of porous inorganic materials or non-porous inorganic materials and is typically used as wave-transparent material for aerospace crafts.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Aluminum phosphate compounds, compositions, materials and related metal coatings
ActiveUS7678465B2Control spreadImprove adhesionPhysical/chemical process catalystsMetallic material coating processesMetal coatingALUMINUM PHOSPHATE
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Aluminum phosphate compounds, coatings, related composites and applications
ActiveUS8021758B2Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperconductor devicesPorous substrateMetallurgy
Owner:APPL THIN FILMS INC
Water-based ceramic anticorrosive coating containing aluminum phosphate as well as preparation and curing methods thereof
The invention discloses a water-based ceramic anticorrosive coating containing aluminum phosphate as well as preparation and curing methods thereof. The water-based ceramic anticorrosive coating containing aluminum phosphate is prepared by adopting aluminium dihydrogen phosphate as a bonding agent, magnesium oxide and zinc oxide as a curing agent, aluminum powder as filler, magnesium chromate as a passivating agent and tetraethyl orthosilicate as an auxiliary agent. The coating is used for preparing a metal ceramic coating layer on a metallic matrix, and the coating layer can tolerate 1000h of neutral salt fog test and keep stable. The coating layer has good high-temperature oxidation resistance in a high-temperature (600 DEG C) oxidation environment. The coating layer can well protect metals in a normal-temperature salt-containing environment and a high-temperature oxidation environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for rapid synthesis of aluminum orthophosphate salt polyalcohol
InactiveCN101172596AProduction Method AdvantagesShort synthesis timePhosphorus compoundsMicrowave ovenPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for rapidly synthesizing aluminum phosphate salt polymeric compound. The method is characterized in that the mixture of phosphoric acid and aluminum hydroxide reacts and the mixture is synthesized under microwave condition. The method comprises the following steps: the phosphoric acid and the aluminum hydroxide are added with water to be mixed and stirred uniformly according to mol ratio; the mixture after being stirred uniformly is put into a microwave oven, and the defrosting and heating mode is selected to radiate the mixture; 750 W is selected to heat the mixture; white aluminum tripolyphosphate powder is gotten through hydrating, drying and grinding. The aluminum tripolyphosphate powder product is put into the microwave oven again to be radiated with 900 W power, and aluminum metaphosphate powder is gotten. The method integrates the reaction and polymerization of the prior art, reduces the composition time, saves the energy and the equipment, and improves the production efficiency. Because of the penetrating action of the microwave, the composition is not limited by the material quantity, and the synthetic ratio of the aluminum tripolyphosphate and the aluminum metaphosphate is improved. Related equipment can be adopted during the industrial production to realize continuous scale production.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com