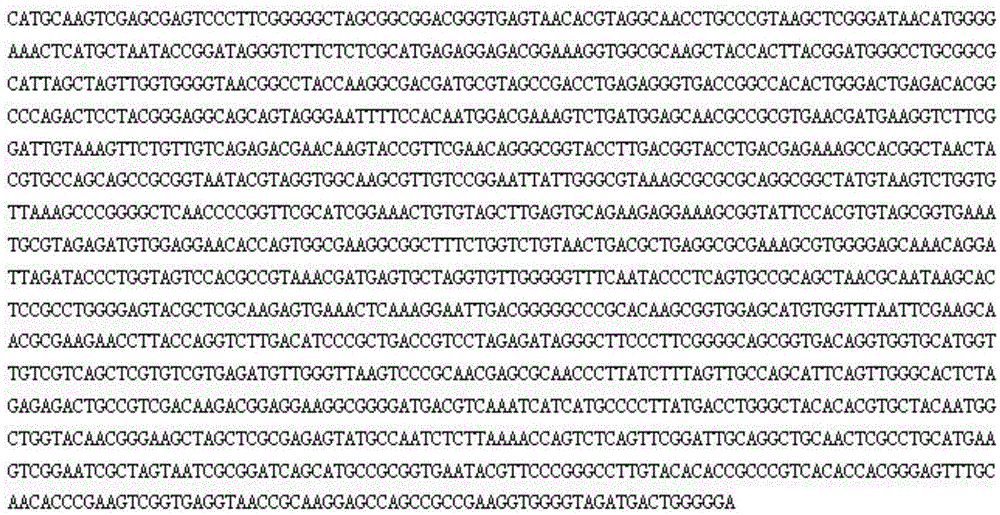Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Exocellulase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
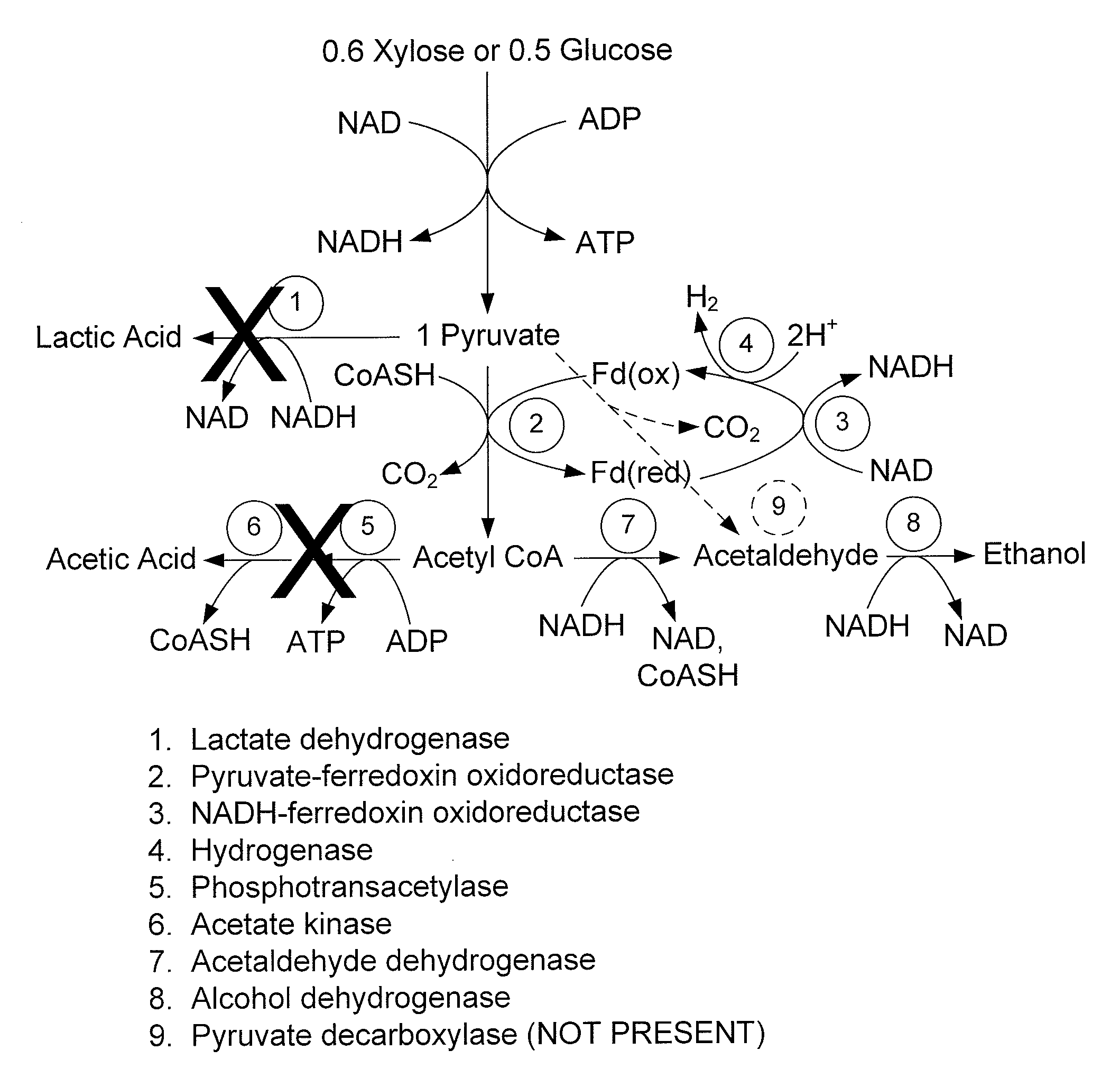
Thermophilic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
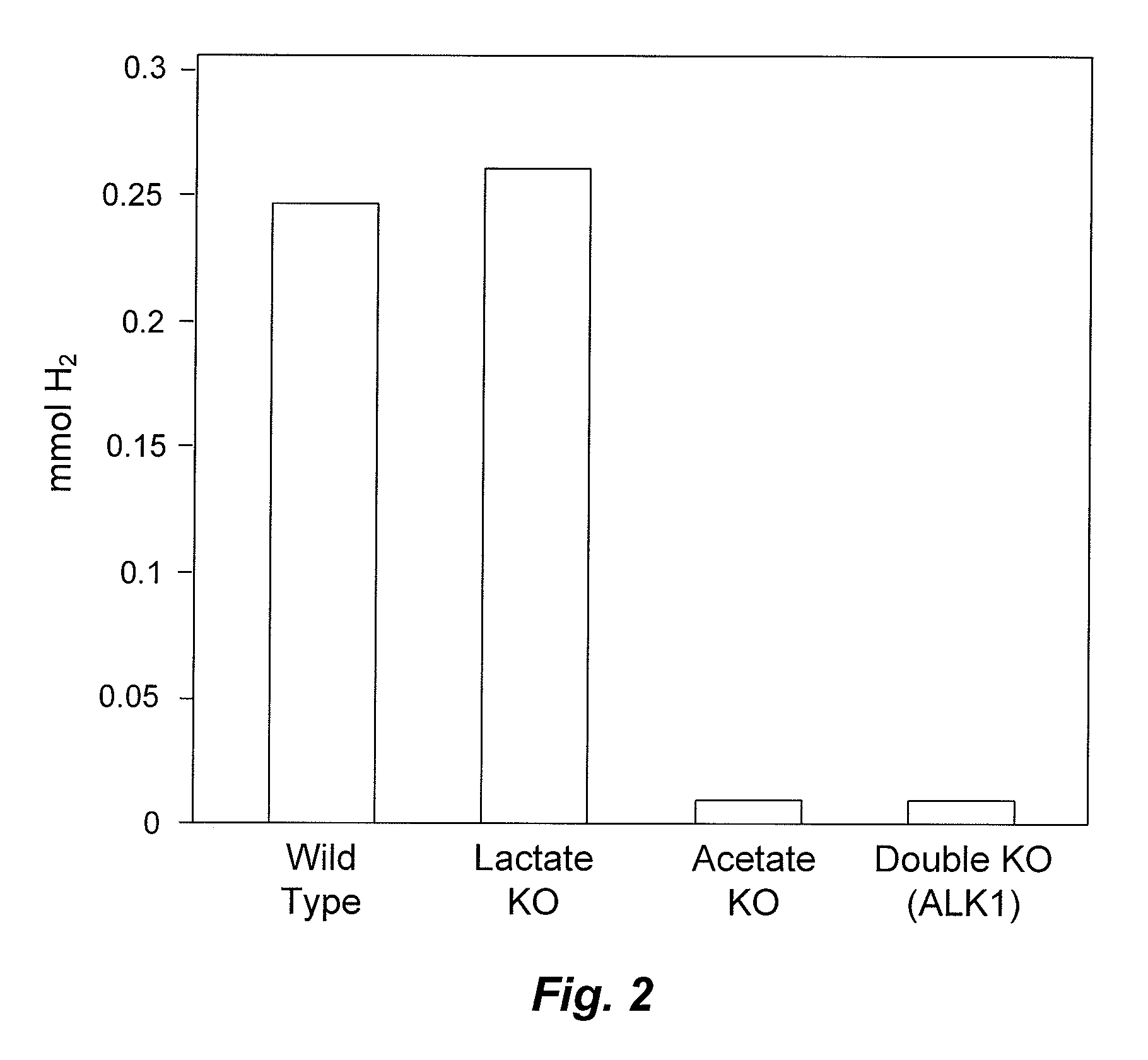
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. The organisms may be utilized for example in thermophilic SSF and SSCF reactions performed at temperatures that are optimal for cellulase activity to produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Thermostable cellulase and methods of use
A Clostridium thermocellum thermostable cellulase enzyme with both endocellulase activity and exocellulase activity that is able to degrade cellulose in the absence of scaffolding and other cellulosomic proteins is provided. The use of the enzyme to degrade cellulosic materials to soluble sugars is also provided.
Owner:BRUMM PHIL
Straw-decomposing inoculant
InactiveCN103725631ASpeed up the ripening processHigh activityFungiBacteriaPotassiumOrganic content
The invention discloses a straw-decomposing inoculant which comprises the following active components: bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, trichoderma viride, phanerochaete chrysosporimn and geobacillus stearothermophilus. In the straw-decomposing inoculant, the total content of effective viable bacteria is (1-2)* 10<8> / ml. With adoption of the straw-decomposing inoculant, the fertilizer prepared from straws can be rapidly degraded, and the normal compost fermentation is performed in advance for at least 15 days. When the straw organic fertilizer prepared from the straw-decomposing inoculant is used as the base fertilizer, alkali-hydrolyzale nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus, potassium and organic contents in the soil are higher than that in the soil in which straws are directly utilized and no fertilizer is applied, and the urease activity and cellulase activity in the soil are obviously higher than that in the soil in which straws are directly utilized and no fertilizer is applied.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Process for Sugar Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass Using Alkali Pretreatment
InactiveUS20100143974A1Prevents inhibition of usedReduce material costsBiofuelsFermentationFiberLignocellulosic biomass
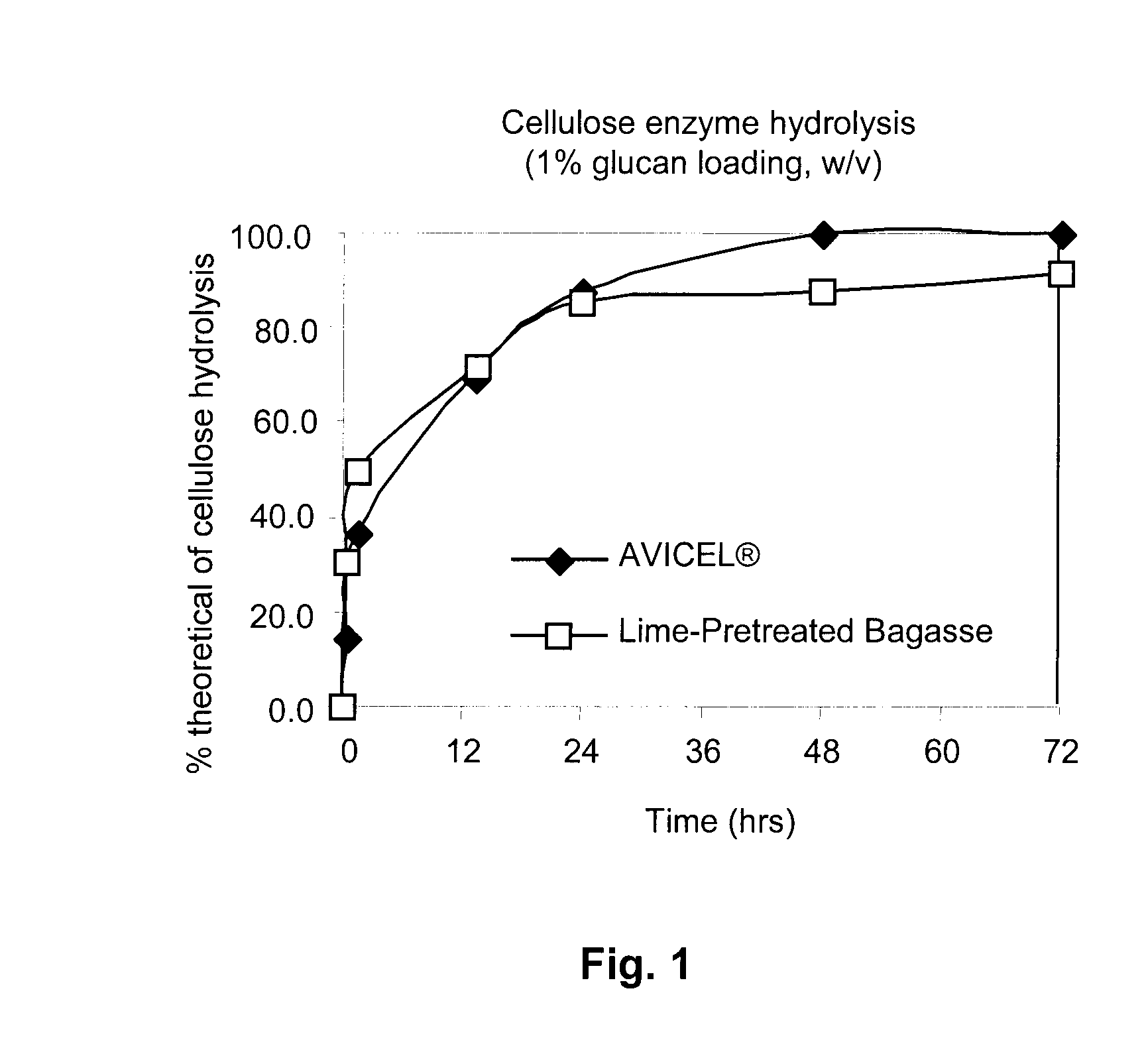
We have discovered a new method to treat biomass with alkali, for example lime. The lime and lignin was sufficiently removed from the treated biomass b> squeezing with a high pressure device to remove alkali and other potential inhibitors of the cellulase enzymes added for sacchaπfication. The resulting fibrous material was rapidly solubilzed by cellulases, even at solid loads ranging from 10 to 30% (w / w) without inhibitory effects on the cellulase activity. The lime pretreatment removed lignin effectively and left the cellulose and hemicellulose almost intact. The method yielded a biomass with structure capable of being enzyme solubilzed and fermented readily at a solids loading of 10-30% for a production of ethanol.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Preparation method of straw decomposition agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a straw decomposition agent. The straw decomposition agent is prepared by using bacillus subtilis, aspergillus oryzae, lactobacillus plantarum, trichoderma reesei and saccharomyces cerevisiae as preparation strains, carrying out activation and primary and secondary culture on the strains respectively to obtain various strain solutions with bacterial count of 106-108 / ml and mixing the strain solutions according to a certain proportion. The straw decomposition agent has the beneficial effects that the straw decomposition agent can be used for quickly degrading straws to prepare fertilizers and ensures that the straw decomposition time is at least 15 days ahead of the normal composting fermentation time; organic straw fertilizers prepared by the preparation method are used as base fertilizers, so that the contents of available nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus, potassium and organic matters in soil are higher than those of available nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus, potassium and organic matters in the soil in which straws are directly used and fertilizers are not applied; the urease activity and cellulase activity of the soil are obviously improved compared with those of the soil in which straws are directly used and fertilizers are not applied.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Cellulase activity control by a terminator
InactiveUS6077818APreventing tensile strength lossOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsCelluloseCellulose breakdown
The present invention relates to detergent compositions comprising a cellulase termination composition and cellulase in order to prevent potential tensile strength loss related to the hydrolytic activity of cellulase on cellulose substrates while maintaining the desired benefits from the use of cellulase.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for breeding high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout
ActiveCN103865949AReduce loadPromote productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BAmylase
The invention discloses a method for breeding a high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The method for breeding the high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout comprises the step of knocking out an amylase gene of the cellulase producing strain. A high-producing strain of cellulase is aspergillus niger without the amylase gene. An amylase gene knockout plasmid is obtained by connecting the front half part of the recombinant segment amylase gene-hygromycin B-an expression unit of a resistant gene- the rear half part of the amylase gene to a pCAMBIA1300 plasmid. Then, the plasmid is converted into agrobacterium, and the amylase gene is knocked out by agrobacterium-mediated conversion of the aspergillus niger. By using the gene knockout technology, the amylase gene of the aspergillus niger is knocked out. After the amylase gene is knocked out, the cell load is reduced, thereby facilitating production of a lot of cellulase. The cellulase activity of the high-producing strain of cellulase obtained can reach 21U / g.
Owner:中农华威生物制药(湖北)有限公司
Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain capable of highly producing cellulase and application thereof
ActiveCN106978360AIncrease productionIncrease secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyExtracellular proteins
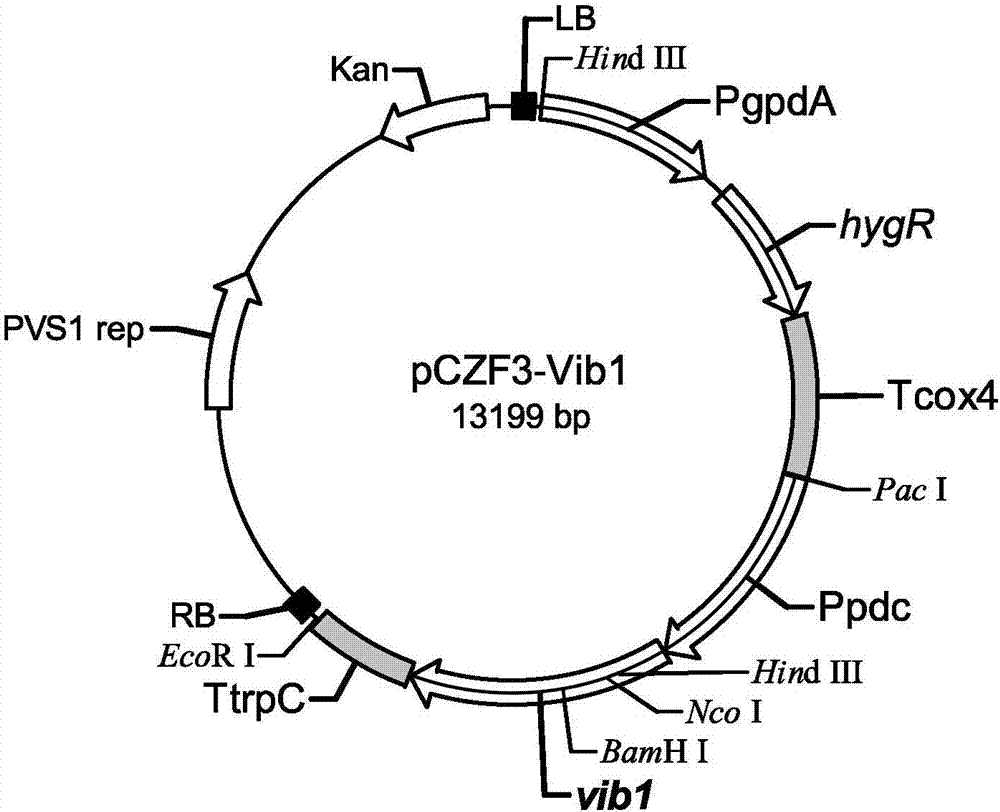
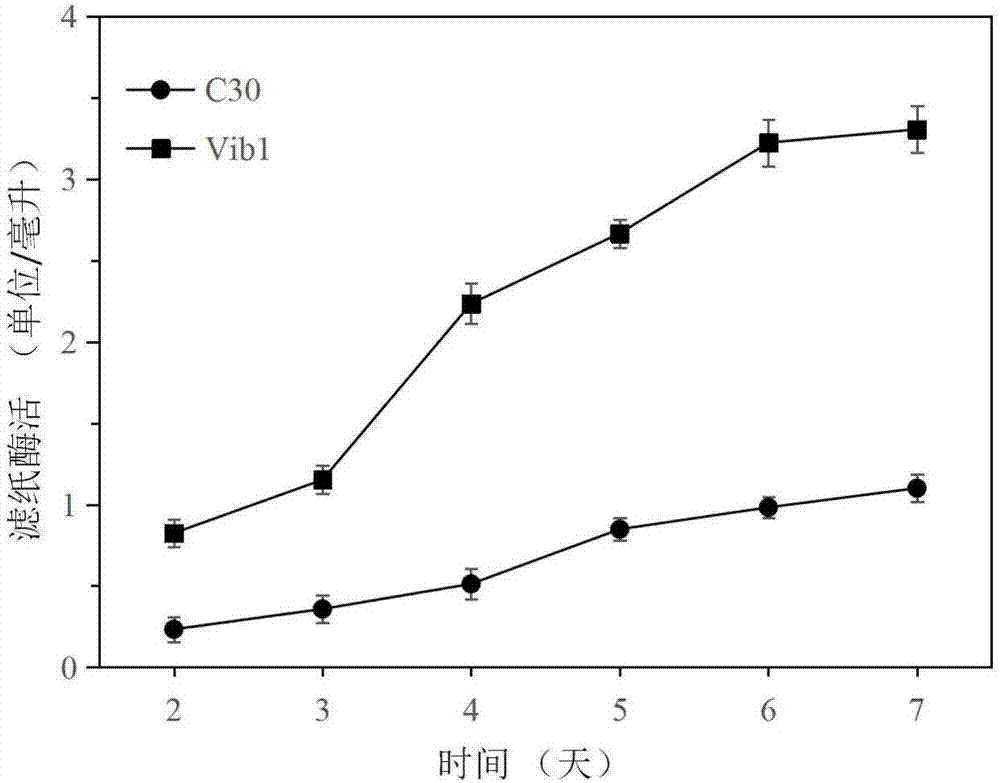
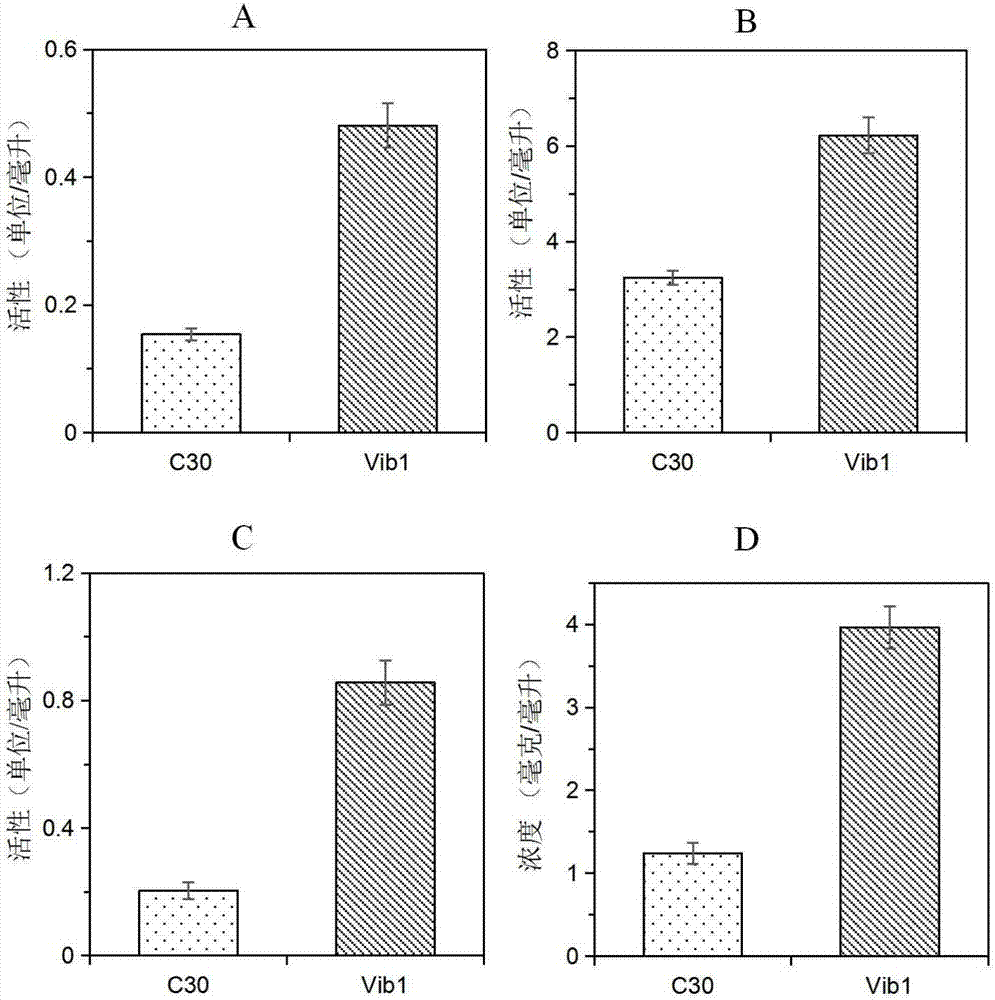
The invention discloses a trichoderma reesei recombinant strain capable of highly producing cellulase and application thereof. Vlbltr which grows an incompatible repression protein gene is transformed into trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, so as to obtain the trichoderma reesei Vib1 (CCMCC No.13578). Compared with the strain Vib1 and the trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, the trichoderma reesei recombinant strain has the advantages that the excretion of extracellular protein and the production of cellulase are obviously improved; compared with the trichoderma reesei Rut-C30, the activity of cellulase in the Vib1 in cellulose and bran culture mediums is increased by about 200%, and reaches 3.3U / ml; the enzyme activities of cellobiohydrolase, endo-cellulase and beta-glucosidase are respectively improved; the excretion amount of the extracellular protein in the Vib1 strain is equal to 2.19 times of the excretion amount of trichoderma reesei Rut-30; proved by the results of hydrolysis reaction of pretreated corn straw, compared with the Rut-30 strain, the output of glucose in the Vib1 strain cellulase hydrolyte is increased by 20%.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Genes, plasmid, bacterial strain and application of xylanase
The invention provides genes, an expression vector, a production bacterial strain and application of xylanase with high temperature resistance, strong base resistance, high efficiency and stability in pulp bleaching. The genes of the xylanase provided in the invention realize high expression in Pichia pastoris by utilizing a codon optimizing and multi-copy technique; the expressed xylanase has no cellulase activity, high temperature resistance and high base resistance; and the xylanase can be applied to wheat straw pulp bleaching; when applied to an elemental chlorine free (ECF) bleaching procedure, the xylanase saves chlorine dioxide by 10%; when applied to a hydrogen peroxide (OP) bleaching procedure, the xylanase saves hydrogen peroxide by 10%.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of bioorganic fertilizer
InactiveCN104692844ASpeed up the ripening processHigh activityClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersDecompositionPotassium
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Enzyme method of extracting oils and proteins from vegetable matter in an aqueous medium
ActiveUS20120196332A1Volume of water is minimizedReduce sewagePeptide preparation methodsFermentationVegetable matterEmulsion
Method for extracting oils, proteins and fermentable sugars from vegetable material in an aqueous medium, includes:a) adding water to the vegetable material;b) adding an enzyme mixture containing at least one cellulase, at least one hemicellulase, and at least one pectinase, the ratio between the pectinase activity and the cellulase activity being at least 0.14, and the ratio between the pectinase activity and the hemicellulase activity being at least 7.10−3, the pectinase activity being less than 120 μmol / min / mL;c) incubating the vegetable material and the enzyme mixture with stirring to release oils, proteins and fermentable sugars in the reaction medium;d) separating the reaction medium to obtain free oil, an aqueous phase containing proteins and fermentable sugars, and a solid phase;e) optionally separating and recycling an emulsion of free oil or aqueous phase, to the medium;f) separating the proteins and fermentable sugars from the aqueous phase.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LORRAINE
Complex inoculant and application thereof in degrading cellulose in poultry and livestock manure
The invention relates to a complex inoculant and an application thereof in degrading cellulose in poultry and livestock manure. The complex inoculant consists of a bacterium strain which is cultivated in a beef extract-peptone medium and a fungus strain which is cultivated in a PDA culture medium at the volume ratio of a culture solution of 1:1. According to the complex inoculant provided by the invention, optimum enzyme-production temperatures of the various strains correspond to temperatures in different stages of composting fermentation, and changing curves of the two parts (the optimum enzyme-production temperatures of the various trains and the temperatures in different stages of the composting fermentation) fit and are matched; the various strains grow in a coordinated mode and continuously produce enzyme, so that a relatively stable cellulase producing environment is formed, and stable enzyme activity is guaranteed; the enzyme can be continuously produced in different fermentation temperature stages of a composting process, so that decomposition of the cellulose in the poultry and livestock manure is promoted; and since a reaction substrate is continuously utilized by the various strains, a level and a peak of cellulase activity of composting fermentation of the poultry and livestock manure cellulase can be also improved in advance and the fermentation time of a compost can be shortened, so that adaptability and a decomposing effect of the compost are enhanced.
Owner:徐州中知知识产权服务有限公司
Agricultural straw degrading fungus penicillium oxalicum NJGZ-2 and fungal agent thereof
The invention relates to a normal-temperature fungus NJGZ-2 capable of degrading agricultural waste straw, belonging to the agricultural waste resource utilization technology. The class of the strain NJGZ-2 is named penicillium oxalicum, and the culture is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number CGMCC No.7527. Tests indicate that after the rice straw is inoculated with a spore suspension (1% 10<7> spores / mL), the weight loss ratio of the rice straw is 59.7% after 7 days of 170r / min liquid fermentation culture at 30 DEG C. In the fermentation crude enzyme extraction liquid, the activities of incision enzyme, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, beta-xylosidase and total cellulose are 113.3U / gds, 11.6U / gds, 1,439.7U / gds, 2.0U / gds and 13.8U / gds respectively. The crude enzyme liquid can hydrolyze low-concentration alkali-treated corncob to generate high-concentration reducing sugar (962.2mg of reducing sugar / gram of substrate). According to the invention, the agricultural waste straw is degraded by the microbial fermentation technology and is converted into organic fertilizer, therefore, the waste can be turned into wealth to protect the environment, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Marine streptomyces viridochromogenes strain for producing alkali-tolerant and salt-tolerant xylanase and application of marine streptomyces viridochromogenes strain
InactiveCN102586134AGreat application potentialGood colorBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFiber
A marine streptomyces viridochromogenes strain for producing alkali-tolerant and salt-tolerant xylanase and application of the marine streptomyces viridochromogenes strain belong to the field of biotechnology. The strain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the collection number is 5565. The strain can normally grow under the extreme alkaline environment of pH11, shows a good oligotrophy-tolerant characteristic, can degrade a variety of hemicellulose-containing biomasses including corn straws, rice straws, Jerusalem artichoke straws, kelp fibers andthe like, and has a broad application prospect in utilizing cheap biomass resources to produce bio-based chemicals. The strain can produce xylanase under optimum conditions, and the enzymatic activity of the xylanase can be as high as 68.9U / ml. The produced xylanase has the following properties: the optimum pH value is 6.0, the optimum temperature is 70 DEG C, the optimum substrate is beech xylan, and the produced xylanase does not have cellulase activity, has high pH stability and thermal stability, and can tolerate high-concentration NaCl. As an enzyme preparation coming from the ocean, thexylanase can be widely used in papermaking, food, feed, wine making, energy and other industries.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Trichoderma koningii, and compound microbial agent composition and application thereof
ActiveCN103275875AIncrease enzyme activitySolve pollutionFungiFood processingBiotechnologyMycoprotein
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and specifically relates to trichoderma koningii, and a compound microbial agent composition and an application thereof. The invention discloses trichoderma koningii HK43-5 (CGMCC No7422), a compound microbial agent composition composed of a glycosylated bacterial preparation and a forage yeast preparation which are packaged separately, wherein the glycosylated bacterial preparation comprises the trichoderma koningii HK43-5 (CGMCC No7422). Cellulose produced by the trichoderma koningii HK43-5 (CGMCC No7422) has high activity, can be used as an efficient glycosylated bacterial preparation in production of industrial and agricultural residual protein forage. The compound microbial agent composition can efficiently utilize industrial and agricultural residues, particularly potato residues, to produce single cell protein. Crude protein content in fermented mycoprotein is 50.49% which is far superior to that reported in a conventional technology. The industrial and agricultural residues are changed to wealth; and the produced bacterial protein can be applied in the forage to partly substitute soybean meal or fish meal. At the same time, the environment pollution problems resulted from the industrial and agricultural residues are solved.
Owner:马伟超 +1
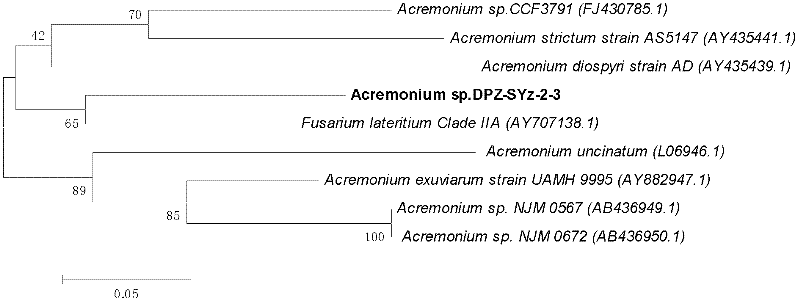
New fungus Acremonium sp. DPZ-SYz-2-3 for high efficiency cellulose degradation and application thereof
InactiveCN102363748AHas cellulase activityHigh cellulolytic activityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a new fungus Acremonium sp. DPZ-SYz-2-3 for the high efficiency cellulose degradation and an application thereof. Acremonium sp. DPZ-SYz-2-3 is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) on 05 / 16 / 2011 and has a preservation number of CGMCC No: 4810, wherein the address of the CGMCC is No.3 of No.1 Beichen Road West, Chaoyang District, Beijing, Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences. The fungus of the invention, which has a cellulase production activity, can be used for producing cellulase, so the fungus has important values to the production and the utilization of cellulase; and the fungus can be further used for making a biological organic matter degradation bacterial fertilizer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Decomposition agent for branch composting treatment and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112481176AEfficient lignin degradation functionPromote degradationBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a decomposition agent for branch composting treatment. The microbial agent is a solid biological microbial agent which is obtained by inoculating a composite bacterial liquidcontaining active ingredients of bacillus velezensis, bacillus arabinodoxae, bacillus megaterium, bacillus kaempferiae and bacillus megatherium on a solid fermentation substrate and fermenting, wherein the effective viable count of the microbial agent is not less than 1.0 * 10 < 10 > cfu / g. The cellulase activity, the laccase activity, the manganese peroxidase activity and the lignin peroxidase activity in the solid biological agent are not lower than 100.0 U / g, 1.0 U / g, 1.0 U / g and 1.5 U / g respectively, and when the solid biological agent is used for composting treatment, the degradation efficiency of lignin and cellulose can be improved, and the composting rate and quality can be improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCE SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for measuring activity of ruminant tumor gastric juice cellulase
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal husbandry, and is a method of detecting the activity of cellulose in tumor gastric juice of ruminant. Testing subjects can be three fistula cows, and tumor gastric juice can be sampled 2h after the early feeding to be used for conducting the external detection of the activity of cellulose. Cellulose mainly contains: (1) microcrystalline cellulose, (2) carboxymethyl cellulose and (3) salicin.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase
InactiveCN106367409ALow costReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationTrichoderma reesei
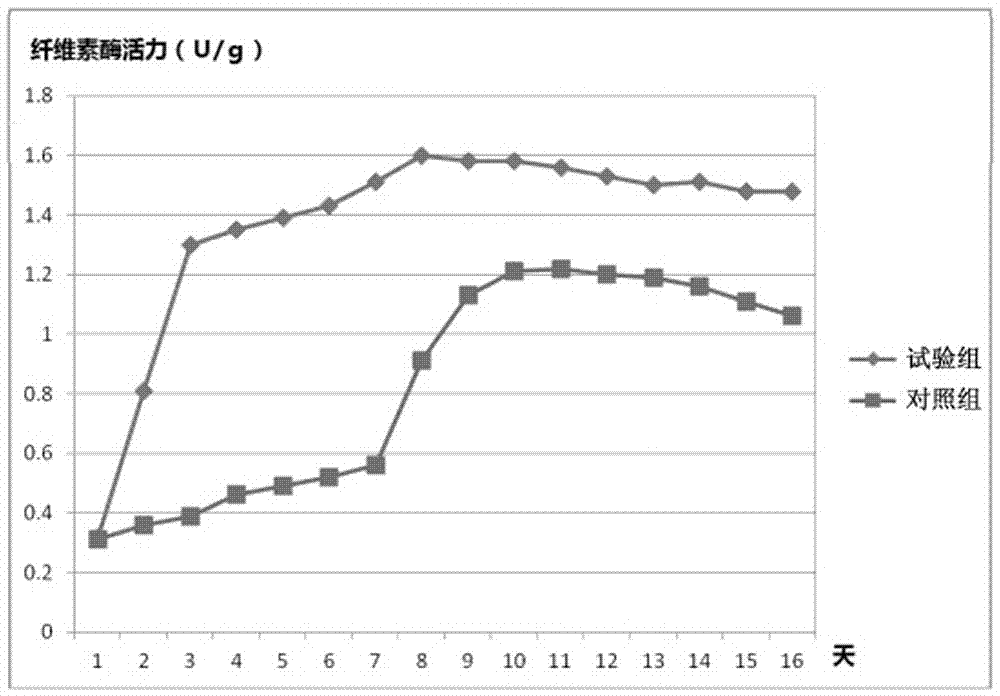
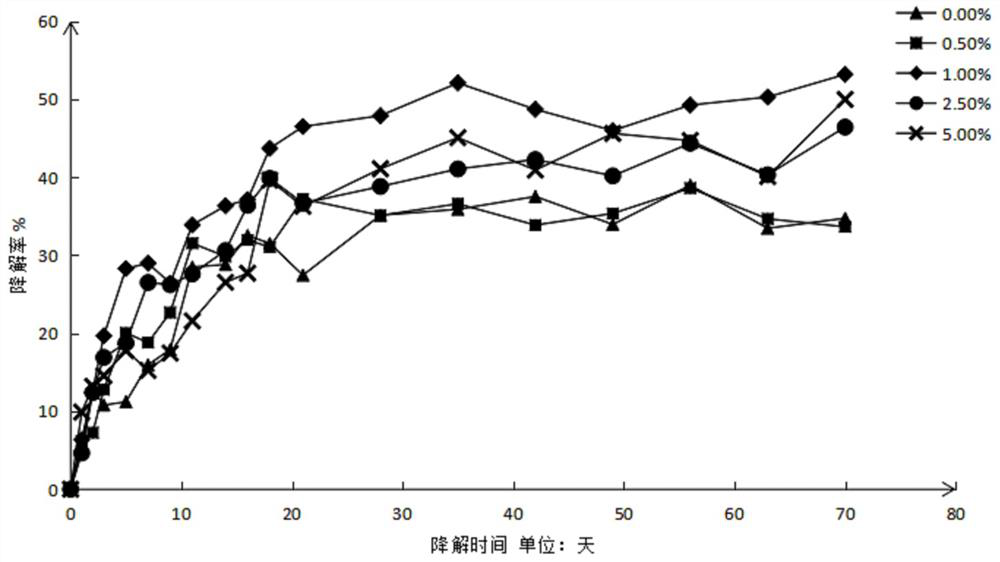
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase. The operating method for simultaneous high-yield production of the [beta]-glucosidase and the cellulase is implemented by the following steps: expressing polypeptide, which has a cellobiase activity, in trichoderma reesei so as to obtain a recombinant trichoderma reesei strain, and conducting fed-batch fermentation by taking a soluble inducer of a glycose transglycosylation product as a carbon source. According to the method provided by the invention, cultivation is conducted in a fermentation tank by virtue of a fed-batch fermentation technology for 156h, so that the activity of the [beta]-glucosidase in a recombinant strain fermentation broth exceeds 300CBU / mL, which is more than 60 times above that of an original strain, and meanwhile, the activity of the cellulase exceeds 50FPU / mL. With the application of the method provided by the invention, shortcoming in the prior art that the [beta]-glucosidase of a trichoderma reesei cellulase system is too low in enzymatic activity is overcome, the compounding cost of the cellulase is reduced and the enzymolysis efficiency of lignocellulose is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
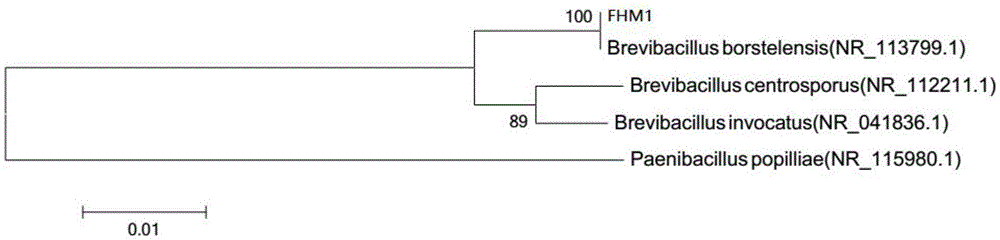
High-temperature-resistant garden waste decomposition bacterium FHM1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105647832AExtension of timeSpeed up the ripening processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant cellulose decomposition bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis, collected under CGMCC No. 12138. This bacterium can produce massive enzymes at a high temperature of 40-70 DEG C, has high cellulose activity, features high temperature resistance and efficient cellulose degradation, can be used as a microbial agent for application in high-temperature composting systems and is applicable to garden waste composting.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Natural plant feed additive capable of fattening meat-sheep
InactiveCN101507467AGain weight fastImprove utilization efficiencyFood processingAnimal feeding stuffGizzardPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a natural plant feedstuff additive for fattening mutton sheep, which relates to a mutton sheep feedstuff additive. The mutton sheep feedstuff additive solves the problems that the prior antibiotic feedstuff additive makes pathogenic microorganisms invading into the bodies of the mutton sheep develop drug resistance after long-term feeding and generates drug residues and toxic side effects on mutton products and the surrounding environment so that the weight increasing rate of the mutton sheep is low. The natural plant feedstuff additive for fattening the mutton sheep consists of gizzard skin, charred triplet, elecampane, dried orange peel, radish seed, betel nut and radix codonopsitis. The natural plant feedstuff additive can improve the daily gain of the mutton sheep, improve the utilization efficiency of protein, the energy and fiber of daily rations and improve the function of the cellulose activity in rumen juice of the mutton sheep, does not influence livers of the mutton sheep, and is a safe and efficient feedstuff.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Bio-organic fertilizer fermented liquid microbial agent and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105543136AFormulation ScienceHeating up fastFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisMicrobial agent
The invention provides a bio-organic fertilizer fermented liquid microbial agent. The microbial agent is prepared from bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactobacilli and aspergillus niger. The bio-organic fertilizer fermented liquid microbial agent has the advantages of being scientific in formula, short in fermentation time, high in enzyme activity, large in viable count, good in deodorization effect and the like, temperature in the fermentation initial stage rises fast, high temperature duration time is long, and protease and cellulase are high in activity and stable. The invention further provides a preparing method of the bio-organic fertilizer fermented liquid microbial agent.
Owner:鹤壁市人元生物技术发展有限公司
Endoglucanases
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified thermostable enzyme derived from the archael bacterium AEPII 1a. In one aspect, the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 60.9 kilodaltons and has a cellulase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells, and can be used to aid in the digestion of cellulose. The invention also provides polypeptides having endoglucanase activity having homology to SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Talaromyces transformants
InactiveUS8802415B2Few undesirable side activityLow production costMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementInducerGene
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
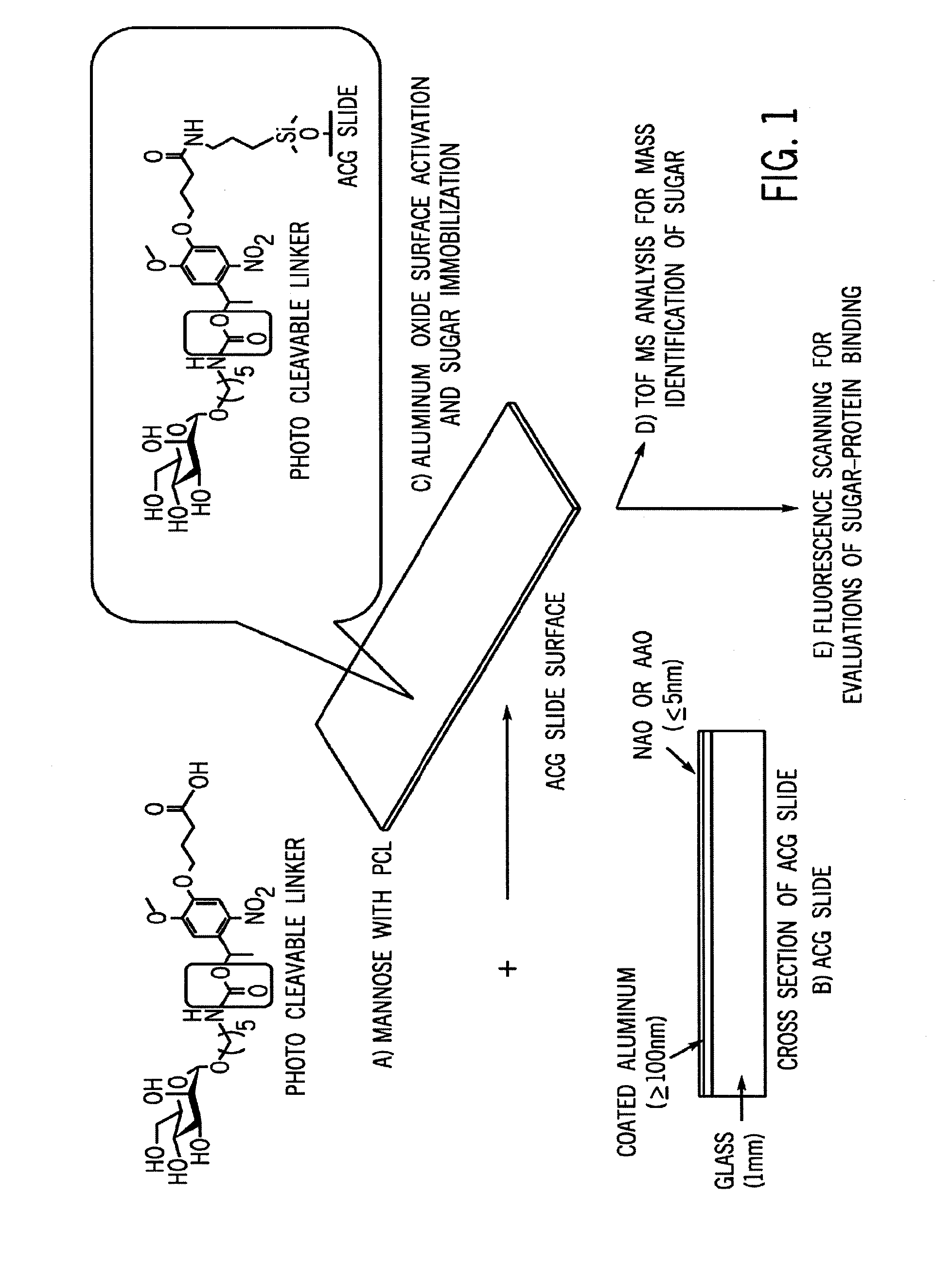
Glycan arrays on ptfe-like aluminum coated glass slides and related methods
ActiveUS20170038378A1Raise the ratioLow rateTime-of-flight spectrometersSaccharide librariesFluorescenceMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Aluminum coated glass slides provide a novel glycan array platform. Specifically, aluminum coated glass slides increase sensitivity of fluorescent based assay methods. Additionally, aluminum coated glass slides allows for mass spectroscopic analysis of carbohydrates and provide a platform for examining activity of cellulases. The unique properties of ACG slides include: 1) the metal oxide layer on the surface can be activated for grafting organic compounds such as modified oligosaccharides; 2) the surface remains electrically conductive, and the grafted oligosaccharides can be simultaneously characterized by mass spectrometry and carbohydrate-binding assay; and 3) the slides are more sensitive than transparent glass slides in binding analysis.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
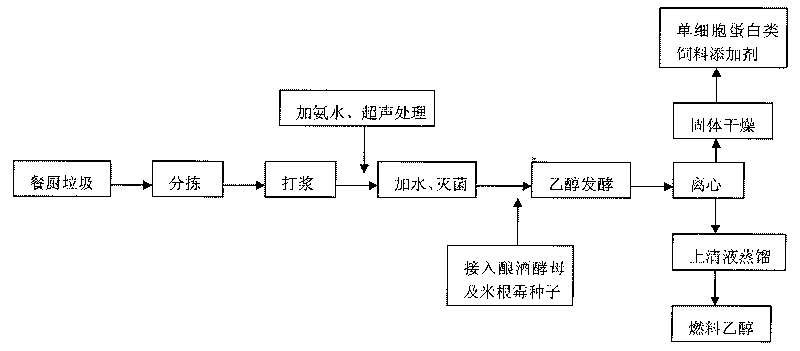
Method of co-fermenting kitchen waste with mixed bacteria for producing fuel ethanol
InactiveCN101760498AImprove utilizationSimple componentsBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesCelluloseRhizopus oryzae
The invention relates to a new method of co-fermenting kitchen waste raw materials with mixed bacteria for producing fuel ethanol, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, separating and screening a rhizopus oryzae strain which simultaneously has amylase activity and cellulase activity; and 2, taking the kitchen waste as a raw material only, and mixing the rhizopus oryzae and saccharomyces cerevisiae in a certain proportion for co-fermenting to produce the fuel ethanol. The method of the invention avoids the problems that in the process of fermenting the kitchen waste for producing the fuel ethanol, the raw material can not hydrolyze because of enzymic inactivation, glucose is lacked in the fermentation liquor, and ethanol fermentation can not be completely carried out. No catalyst and nutrient need to be added in the fermentation process, the availability of large molecule organic substances of starch, cellulose and the like in the waste is high, thus the invention reduces the production cost of ethanol by the kitchen waste, has the advantages of energy saving, simple required equipment and low investment cost, and is a new way with good practical value for recycling the kitchen waste.
Owner:TAIZHOU VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Enzyme method of extracting oils and proteins from vegetable matter in an aqueous medium
ActiveUS8679794B2Volume of water is minimizedReduce sewagePeptide preparation methodsFermentationProteinExocellulase activity
Method for extracting oils, proteins and fermentable sugars from vegetable material in an aqueous medium, includes:a) adding water to the vegetable material;b) adding an enzyme mixture containing at least one cellulase, at least one hemicellulase, and at least one pectinase, the ratio between the pectinase activity and the cellulase activity being at least 0.14, and the ratio between the pectinase activity and the hemicellulase activity being at least 7.10−3, the pectinase activity being less than 120 μmol / min / mL;c) incubating the vegetable material and the enzyme mixture with stirring to release oils, proteins and fermentable sugars in the reaction medium;d) separating the reaction medium to obtain free oil, an aqueous phase containing proteins and fermentable sugars, and a solid phase;e) optionally separating and recycling an emulsion of free oil or aqueous phase, to the medium;f) separating the proteins and fermentable sugars from the aqueous phase.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LORRAINE
Method for preparing high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase
ActiveCN103865902AStrong alkali resistanceHigh specific vitalityMicroorganism based processesPulp bleachingSubmerged fermentationPapermaking
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase, belonging to the technical field of preparation of enzyme preparations. Bacillus thermophilus 701 capable of producing high-temperature alkaline xylanase is taken as a starting strain, and high-temperature-resistant alkaline xylanase, which has strong high-temperature resistance and alkali resistance, wide acting conditions, no cellulase activity and is suitable for the fields such as papermaking, food and feed, is prepared by optimizing the culture medium composition and fermentation process in a way of liquid submerged fermentation. The specific activity of the enzyme is 350-420IU / ml; the optimal reaction temperature is 65 DEG C, the application temperature range is 40-75 DEG C; the optimal reaction pH value is 10.0 and the pH range applicable to reaction is 5.0 to 11.0.
Owner:南宁雄晋生物科技有限公司
Soil conditioner for tobacco field acidic soil, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110184066AImprove use valueRaise the pHAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesDecompositionPotassium
The invention discloses a soil conditioner for tobacco field acidic soil, wherein the soil conditioner comprises, by weight, 40-80 parts of shells, 20-60 parts of potassium feldspar, 10-50 parts of limestone, and 15-40 parts of dolomite. According to the present invention, the soil conditioner can neutralize the active acid and the exchangeable acid in the soil, obviously increase the pH value ofthe soil, increase the soil plough layer exchangeable Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> concentrations, improve the soil microbial environment, increase the numbers of soil bacteria, actinomycetes and aerobic cellulose decomposition bacteria, improve the activities of urease, acid phosphatase, catalase and cellulase, passivate the heavy metals in the soil, reduce the heavy metals in tobacco, reduce the occurrenceof tobacco root diseases, improve the aroma quality, the aroma amount and the concentration of tobacco leaves, and reduce the irritation, the miscellaneous gas and the like of tobacco leaves.
Owner:青岛农特生物科技有限责任公司 +1
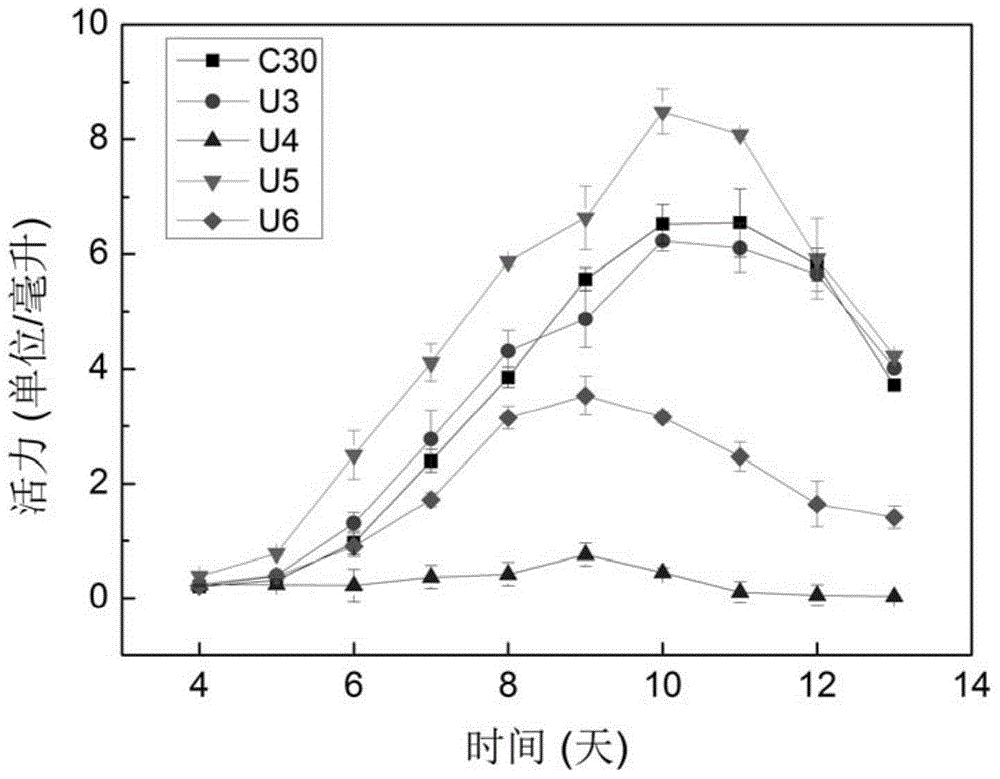
Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain containing artificial zinc finger transcription factor and application of Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain
InactiveCN104862237AIncrease β-glucosidase activityIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesWild typeMicroorganism resource
The invention discloses a Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain containing artificial zinc finger transcription factor and application of the Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain, and belongs to the field of microbial biotechnology. The Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain is stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 16, 2015, and the accession number is CGMCC No. 10649. The Trichoderma reesei recombinant strain is named Trichoderma reesei U5, which is a high-yield cellulose strain obtained by transferring an artificial zinc finger protein transcription factor into the starting strain of Trichoderma reesei C30, and then being subjected to cellulase activity screening. Under the condition of bran inducing, the cellulase activity of the high-yield cellulose strain is increased by about 35% as compared with that of a wild type Trichoderma reesei C30, reaching 8.4 enzyme-activity units per milliliter; beta-glucosidase of the Trichoderma reesei U5 is increased by 3.5 times as compared with that of the wild type Trichoderma reesei C30, reaching 8.8 enzyme-activity units per milliliter. The increase in cellulase secretion activity of the Trichoderma reesei U5 shows the potential application value of the Trichoderma reesei U5 in the field of renewable energy, and new microbial resources are provided for the efficient degradation of biomass.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


















![Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6856e52f-3a38-4e19-8ded-6659381e363d/HDA0001092747240000011.png)
![Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6856e52f-3a38-4e19-8ded-6659381e363d/HDA0001092747240000021.png)
![Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase Method for simultaneous high-yield production of cellulase and [beta]-glucosidase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/6856e52f-3a38-4e19-8ded-6659381e363d/HDA0001092747240000022.png)