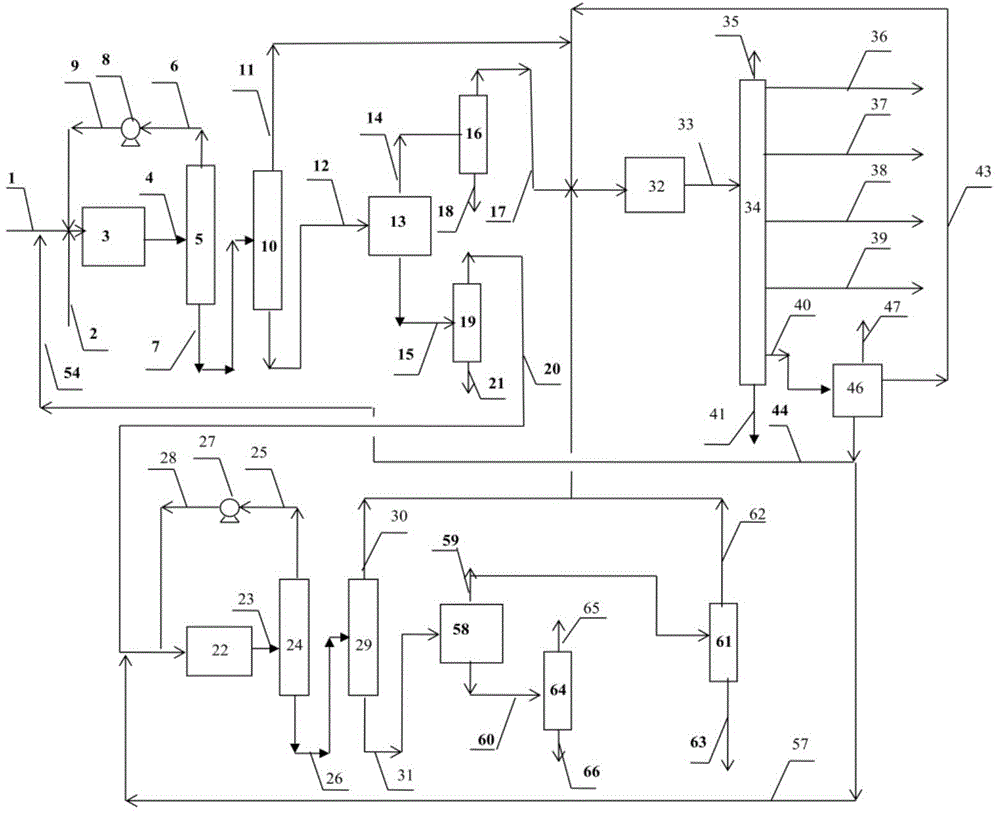
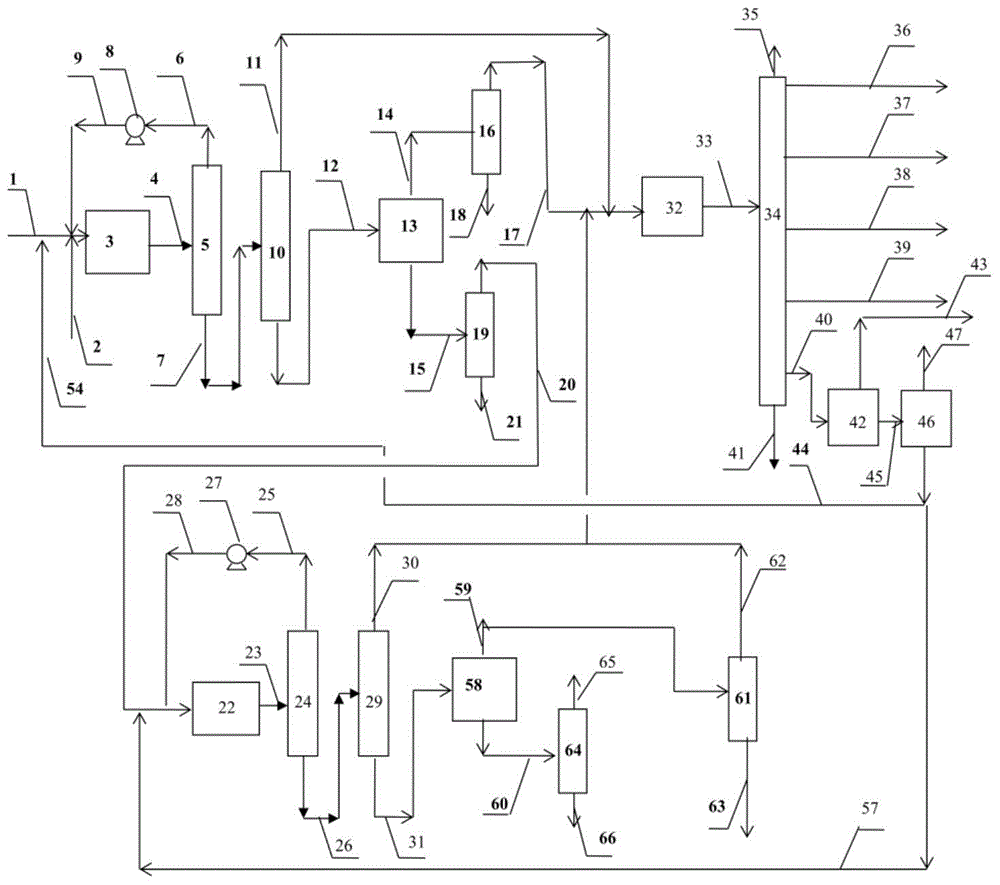
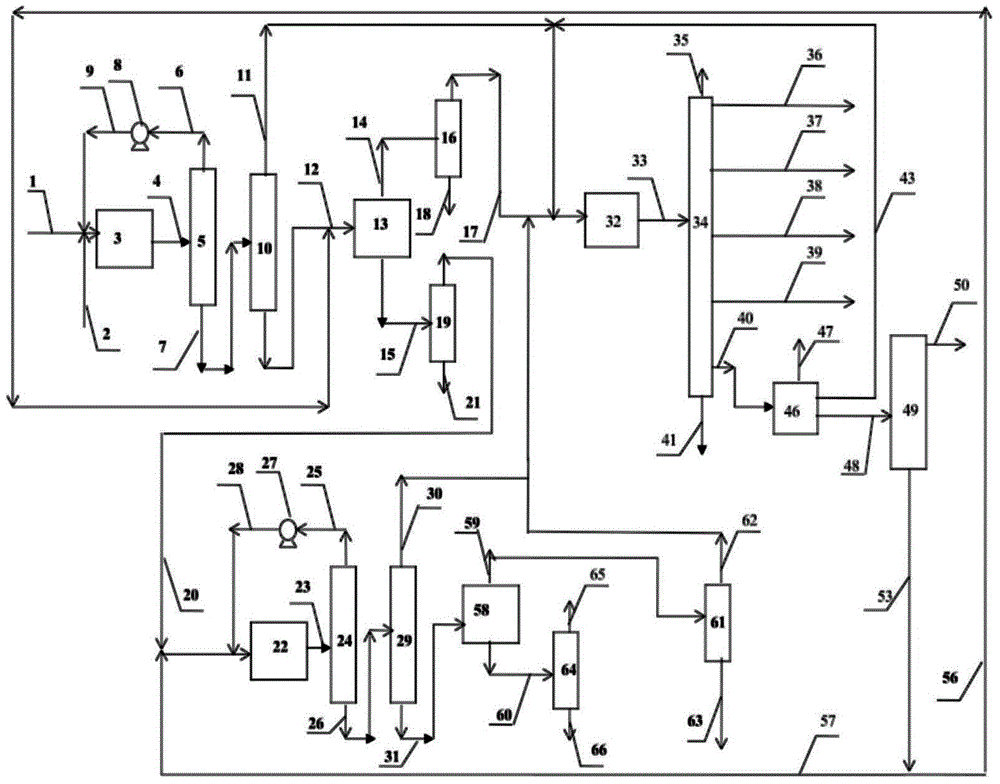
Method for producing olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons with naphtha as raw material
A technology for naphtha and aromatic hydrocarbons, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, petroleum industry, hydrocarbon cracking to produce hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problem of decreased yields of propylene and butadiene, high benzene content in reformed gasoline, and ineffective naphthenic hydrocarbons. use, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0071] In this example, naphtha is hydrorefined.
[0072] In a 20 ml fixed bed continuous flow reactor, 20 ml of hydrofinishing catalyst A containing 0.03% by mass of CoO, 2.0% by mass of NiO, and 19.0% by mass of WO 3 , 0.7% by mass of F and 78.27% by mass of Al 2 o 3 .
[0073] The naphtha with the composition and properties listed in Table 1 was heated at 290°C, the hydrogen partial pressure was 1.6MPa, the hydrogen / hydrocarbon volume ratio was 200:1, and the feed volume space velocity was 8.0h -1 Under certain conditions, it is passed into the reactor filled with catalyst A for pre-hydrogenation and refining. The reaction product enters the water cooler and is separated into two phases of gas and liquid, which are measured separately and analyzed for composition. Table 2.
[0074] It can be seen from the results in Table 2 that after prehydrofining, the contents of olefins, sulfur, nitrogen, arsenic, and lead in naphtha all meet the feed requirements for catalytic refo...
example 2
[0080] According to the method of the present invention, liquid-liquid extraction is used to separate naphtha.
[0081] Carry out liquid-liquid extraction with sulfolane as a solvent, the naphtha listed in Table 2 is contacted with sulfolane in the extraction tower at a flow rate of 100 kg / hour, the solvent / raw material mass ratio is 5, and the pressure at the top of the extraction tower is 1.2MPa , the reflux ratio is 0.25, and the top temperature of the liquid-liquid extraction tower is 140°C. A rich solvent containing aromatics and naphthenes is obtained from the bottom of the extraction tower, and a raffinate containing alkanes and naphthenes is obtained from the top of the tower. The rich solvent is separated from sulfolane by distillation to obtain an extracted oil containing aromatics and naphthenes. The raffinate is washed with water to remove residual traces of solvent to obtain raffinate oil containing alkanes and cycloalkanes. See Table 3 for the production flow r...
example 3
[0083] Carry out liquid-liquid extraction with pentaethylene glycol as solvent, the naphtha listed in table 2 is contacted with pentaethylene glycol in the extraction tower with the flow rate of 100 kg / hour, solvent / raw material mass ratio is 7, extracts tower top The pressure is 0.8MPa, the reflux ratio is 0.2, and the temperature at the top of the liquid-liquid extraction tower is 150°C. A rich solvent containing aromatics and naphthenes is obtained from the bottom of the extraction tower, and a raffinate containing alkanes and naphthenes is obtained from the top of the tower. After the rich solvent is separated from the extraction solvent by distillation, the extracted oil containing aromatics and cycloalkanes is obtained, and the raffinate is washed with water to remove the residual trace solvent to obtain the raffinate oil. See Table 3 for the production flow rate, group composition and distribution ratio of various hydrocarbons in the extracted oil and raffinated oil.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com