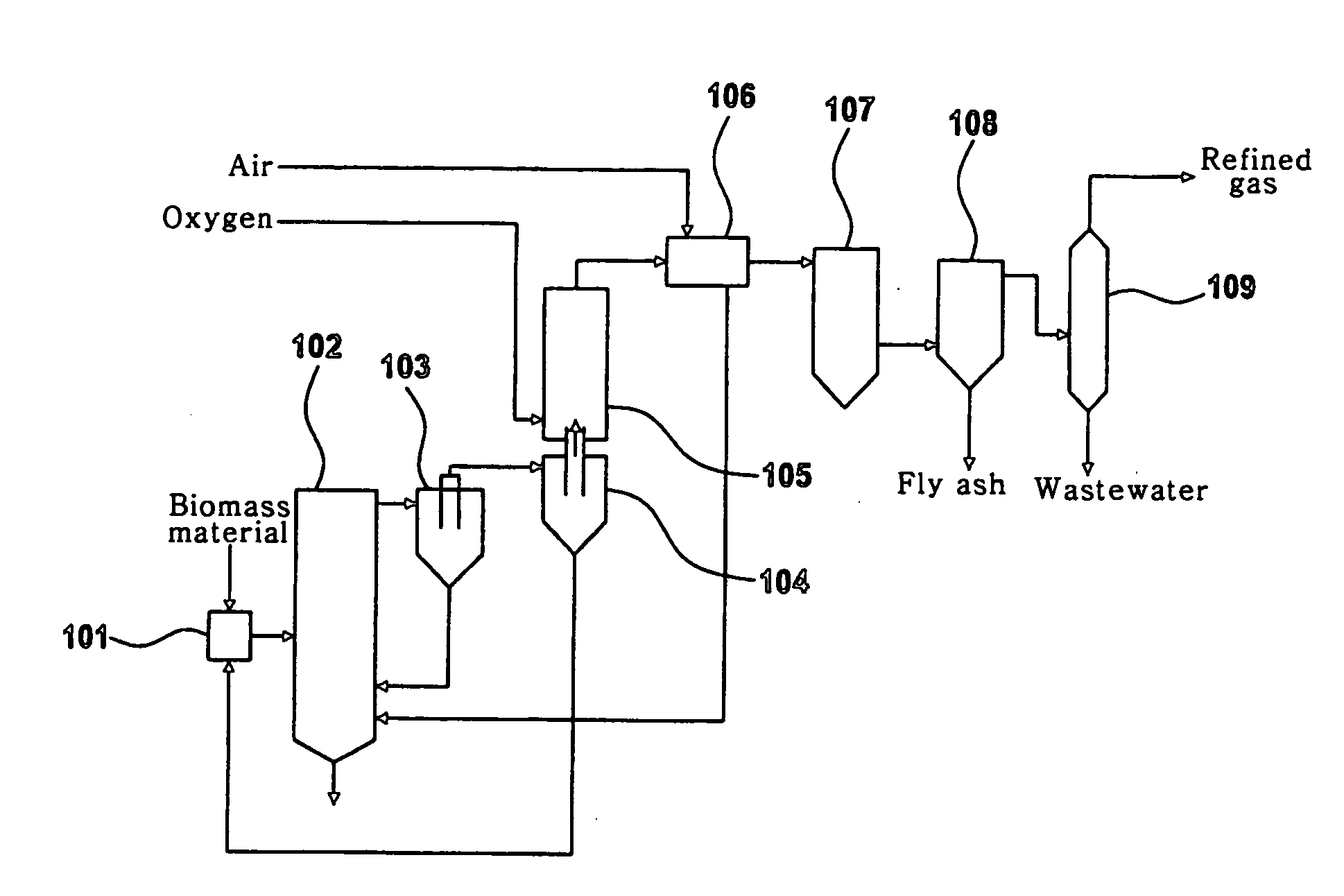
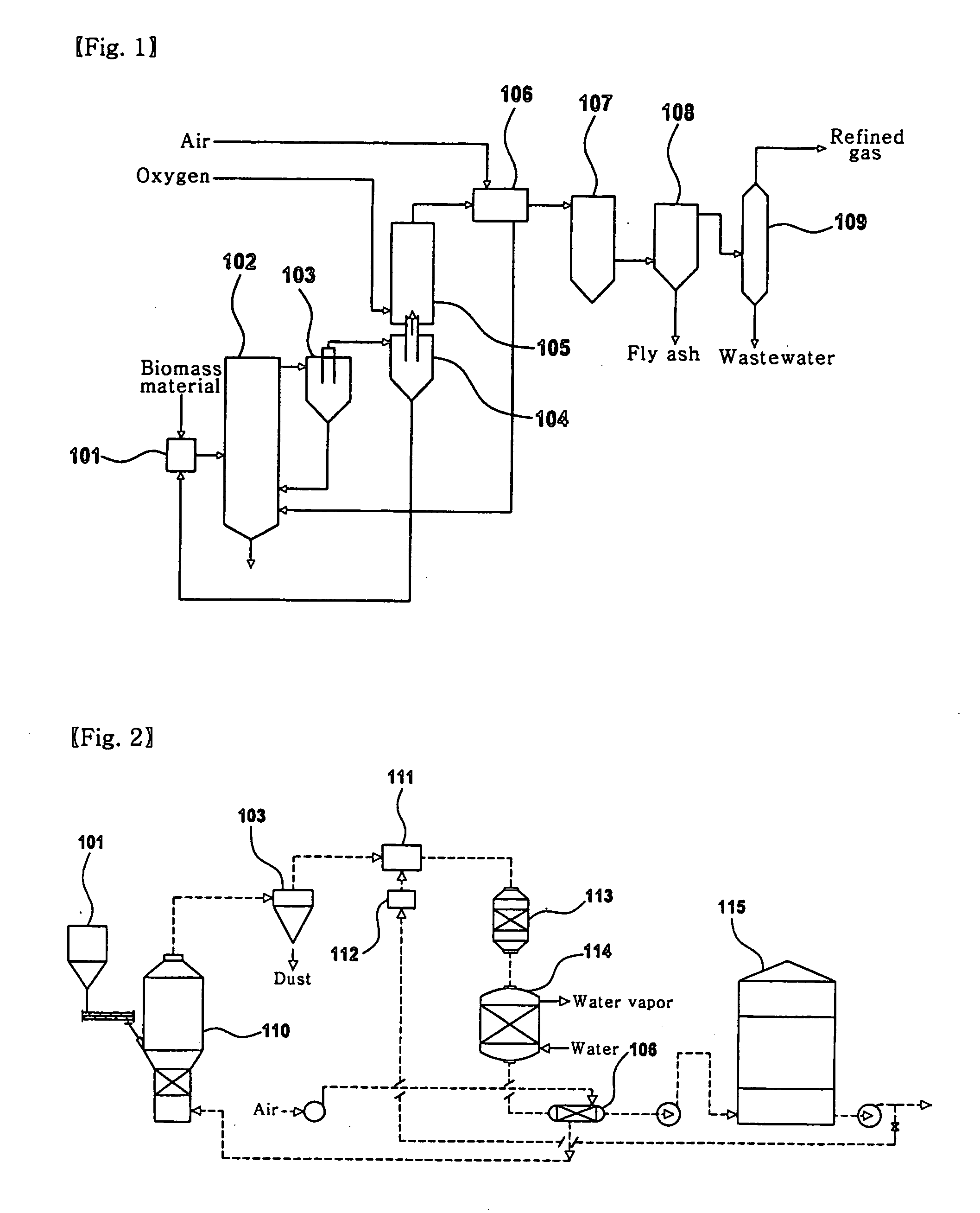
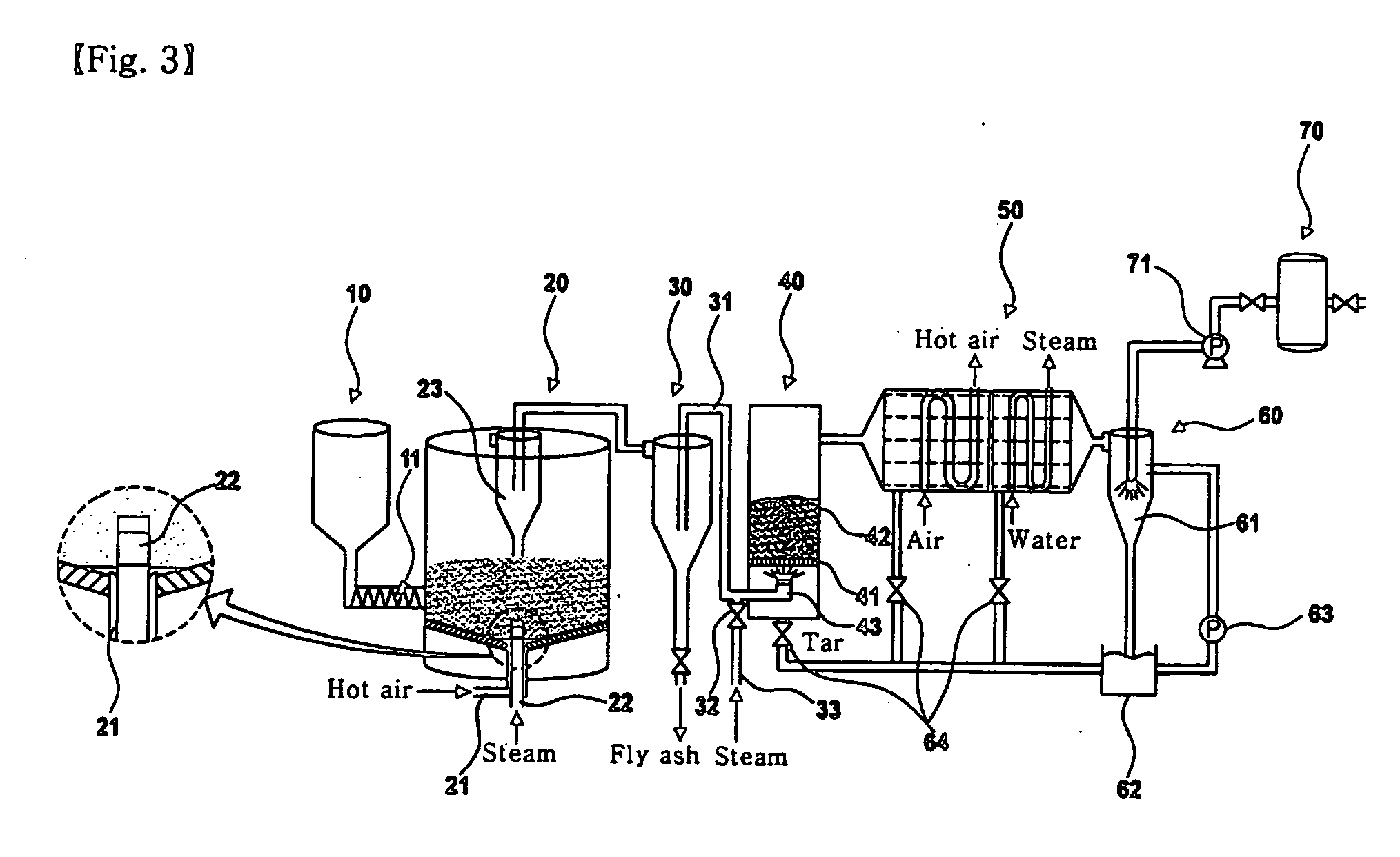
Apparatus of catalytic gasification for refined biomass fuel at low temperature and the method thereof
a technology of biomass fuel and catalytic gasification, which is applied in the direction of combustible gas purification/modification, physical/chemical process catalysts, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve the problems of reducing requiring a lot of energy, and requiring a large amount of energy, etc., to achieve the reduction of the oxygen consumption required to maintain the operation temperature, the effect of compact apparatus and low cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Improvement Of Gas Generation Efficiency BY Catalytic Gasification
[0069] For gasification of SOCA (Sludge-Oil-Coal Agglomerates) in the presence of a catalyst mixture comprising Fe2O3 and CaO, the catalyst mixture and SOCA were uniformly mixed at a weight ratio of 3.4:1 under operation conditions similar to gasification in the absence of a catalyst, thus obtaining a gas product. The state of the product is shown in FIG. 4. The gasification in the presence of the catalyst mixture was initiated at 230° C., which was considerably lower than 560° C. required for gasification in the absence of a catalyst. In addition, compared to gasification in the absence of a catalyst, CO conversion was lower, and more hydrocarbons were generated. In particular, almost all hydrocarbons generated were confirmed to be methane gas. In the gasification in the absence of a catalyst, hydrocarbons were generated at 850° C. or more, and CO was generated at 1050° C. or more. However, when using a catalyst mix...
example 2
Less Generation Of Tar and Fuel-N Pollutant By Two-Stage Catalytic Gasification
[0070] As shown in FIG. 5, when a CaO catalyst, which is an oxide of an alkali earth metal, was used in the first stage gasification and an NiO catalyst was used in the second stage catalytic reformation, CO was similarly generated but a slightly larger amount of hydrocarbon was generated, compared to gasification using only CaO as the first stage catalyst Thereby, the reaction was completed in a shorter time. However, as is apparent from Table 1 below, in the case where calcium oxide was used as a first stage catalyst and NiO or MnO2 was used as a second stage catalyst, the generation of tar, NH3 and HCN was remarkably lower than when using only a first stage catalyst. It was considered that tar was reformed and fuel-N was converted into N2. In addition, the MnO2 catalyst was inferior in tar reformation to the NiO catalyst, by which fuel-N was converted not into ammonia but into HCN. Thus, the NiO catal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com