Microfluidic device and method for preparing microgel by using microfluidic device
A microfluidic device and microgel technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems affecting cell activity, product performance differences, and restrictions on wide application, and achieve strong stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
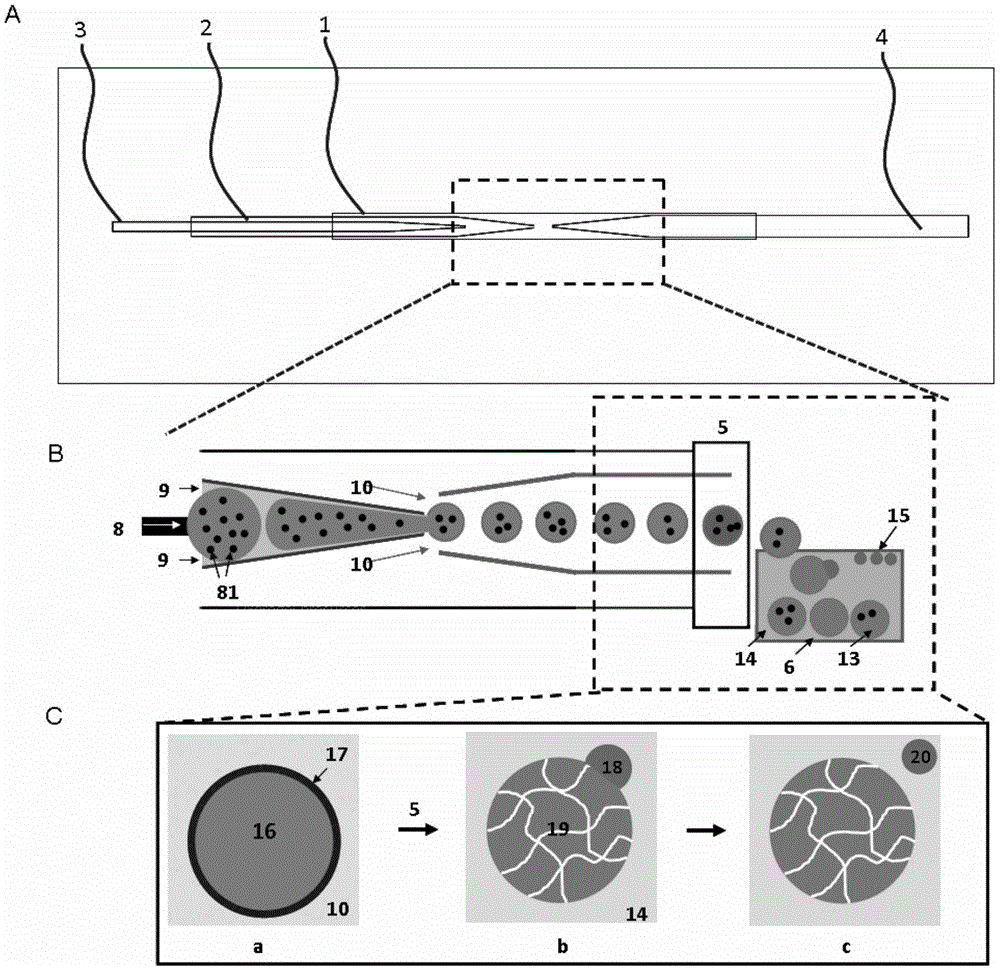
[0074] The method of preparing monodisperse cell-carrying microgels using the ultra-thin shell-layer core-shell structure double emulsion as a template of the present invention will be further illustrated below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
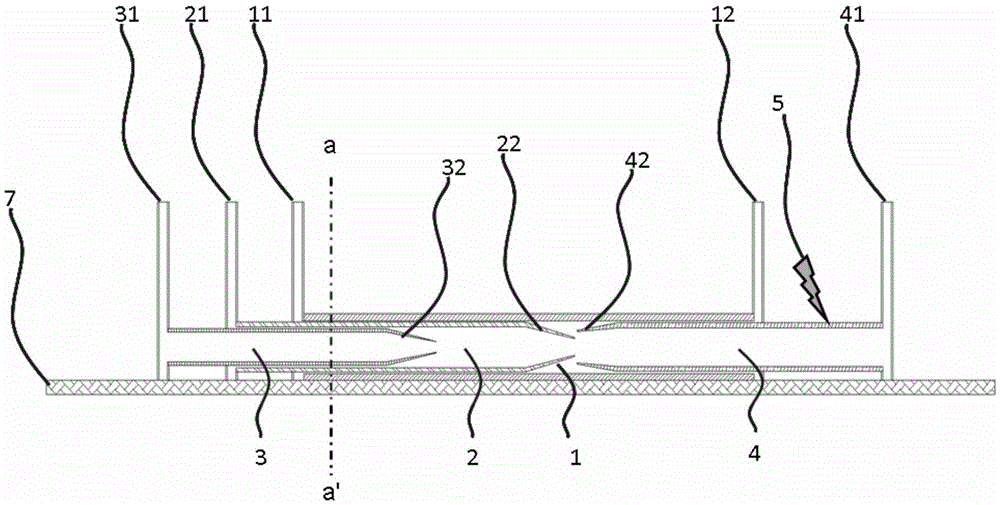
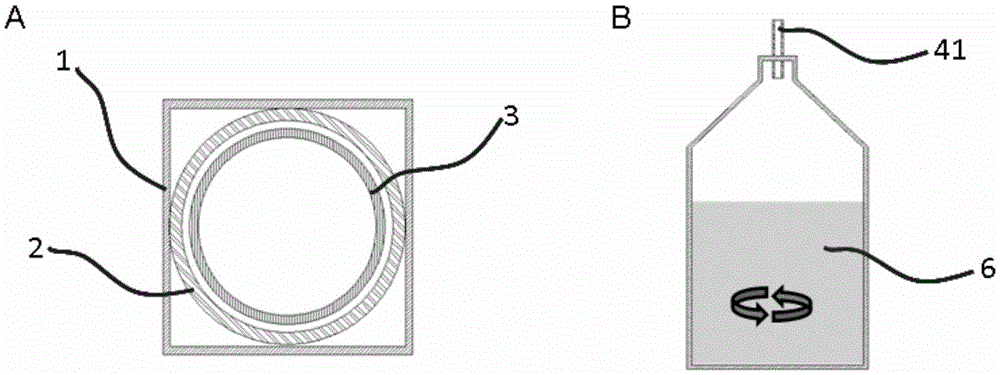
[0075] Such as figure 1 Said, a microfluidic device comprising a first microchannel, a second microchannel, a third microchannel, an output channel, an ultraviolet light source and a collection container, the first microchannel, the second microchannel and the third microchannel The channels respectively have a sample sending end and an insertion end, and the insertion end of the second microchannel is inserted into the first microchannel without sealing from the sample sending end of the first microchannel to the insertion end; the insertion end of the third microchannel The second microchannel is unsealedly inserted into the second microchannel from the sample sending end to the insertion end to form a sleeve; one end of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Using the microfluidic device described in Example 1, the method for preparing microgels includes the following steps:
[0084] (1) Configure internal phase, intermediate phase and external phase solutions:
[0085] The configuration of the internal phase solution: combine polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) and light curing agent (1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-phenyl]-2-hydroxy-2 under normal temperature and pressure -Methyl-1-propan-1-one) is dissolved in deionized water, the final concentration of PEGDA in the solution is 10w / v%, and the concentration of the light curing agent is 1w / v%.
[0086] Preparation of the mesophase solution: the mesophase is a mixed solution of oil and surfactant, and the Span80 surfactant solution is added to the mineral oil to make the concentration in the mineral oil 0.5v / v%.
[0087] Configuration of the external phase solution: Dissolve polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) in deionized water with a final mass concentration of 5%.
[0088] (2) Preparation of wate...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Using the microfluidic device described in Example 1, the method for preparing a microgel with living cells includes the following steps:
[0094] (1) Configure internal phase, intermediate phase and external phase solutions:
[0095] The configuration of the internal phase solution: methacrylate grafted gelatin and light curing agent (1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-phenyl]-2-hydroxy-2-methyl at room temperature and pressure -1-propan-1-one), dissolved in the cell culture medium to obtain the hydrogel prepolymer solution. The cell culture medium is Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM, Sigma-Aldrich), plus 10% v / v fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco). Disperse the live cells cultured and expanded in vitro in the cell culture medium, and add the above-mentioned hydrogel prepolymer solution so that the cell concentration in the final solution is 1×10 6 Cells / ml, the concentration of methacrylate grafted gelatin is 10w / v%, and the concentration of light curing agent is 1w / v%.
[0096] Pre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com