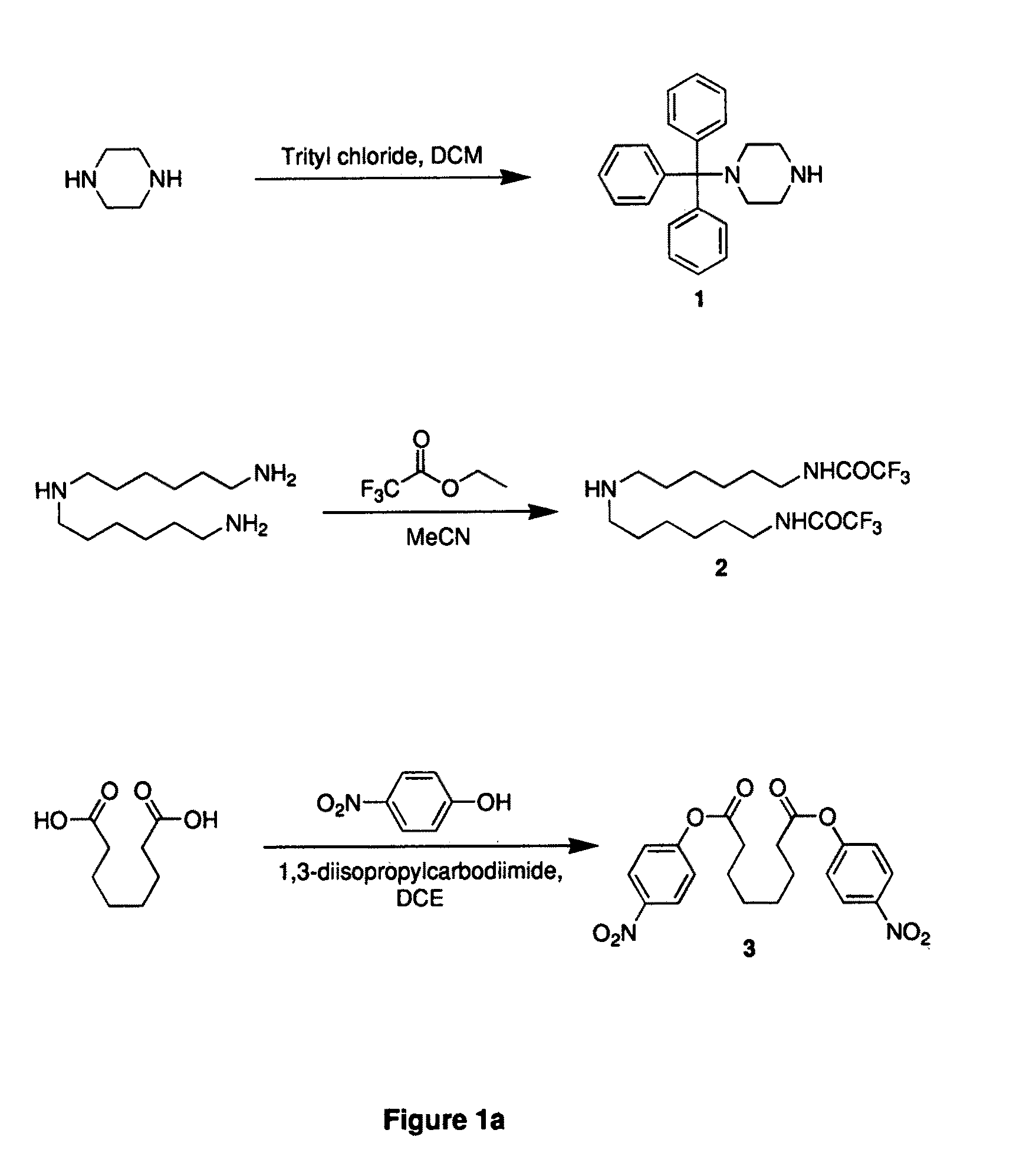
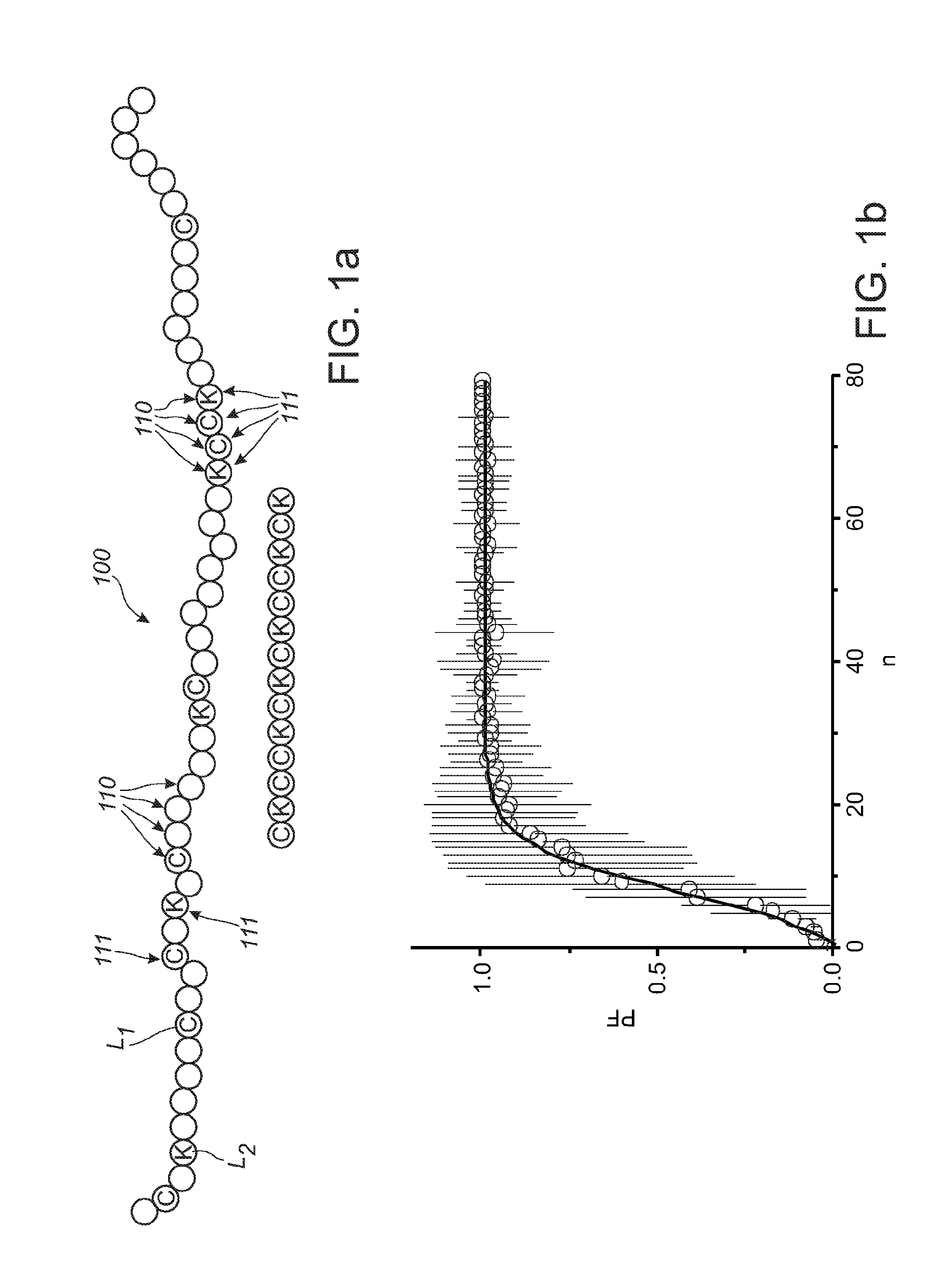
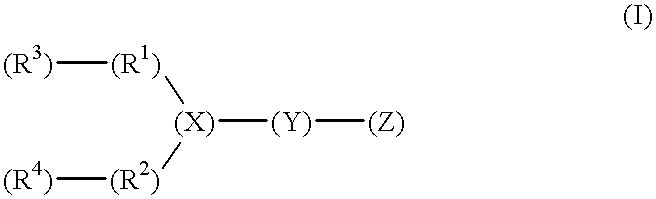Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Molecular Transport" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
According to cell biology, molecular transport involves the movement of molecules into and out of cells across a cell membrane. Two different types of molecular transport exist: active transport and passive transport. Active transport is transporting molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.
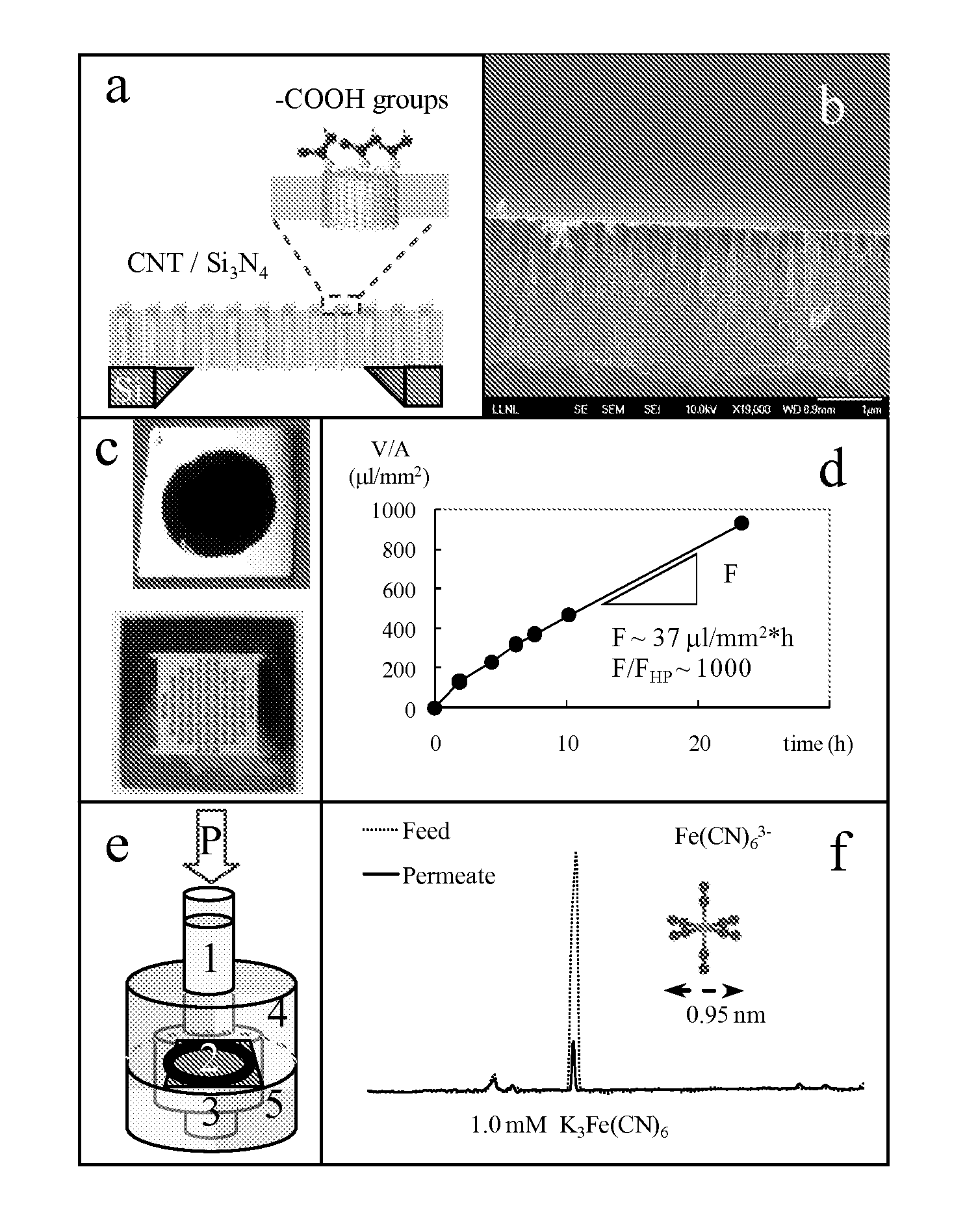
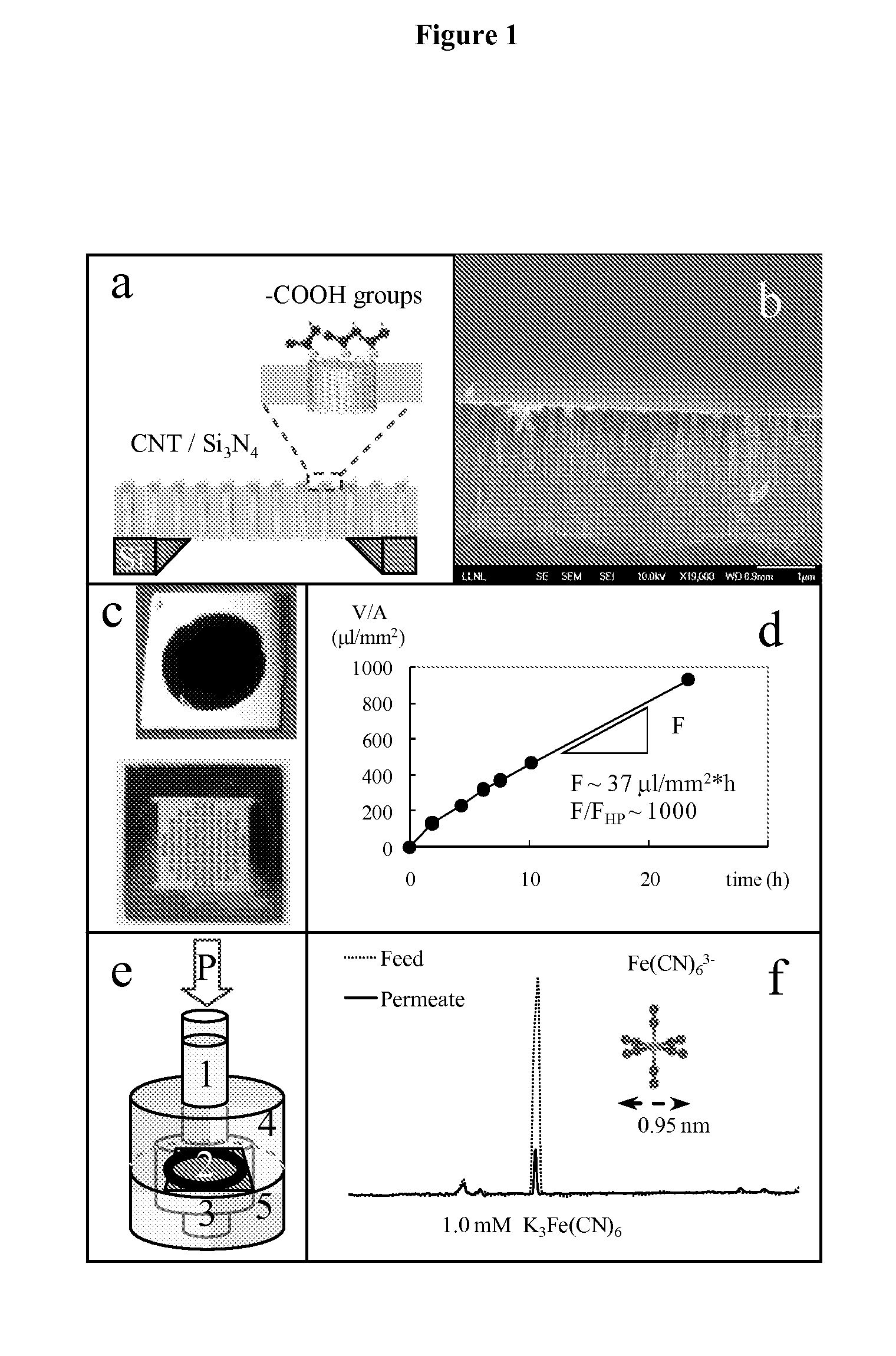
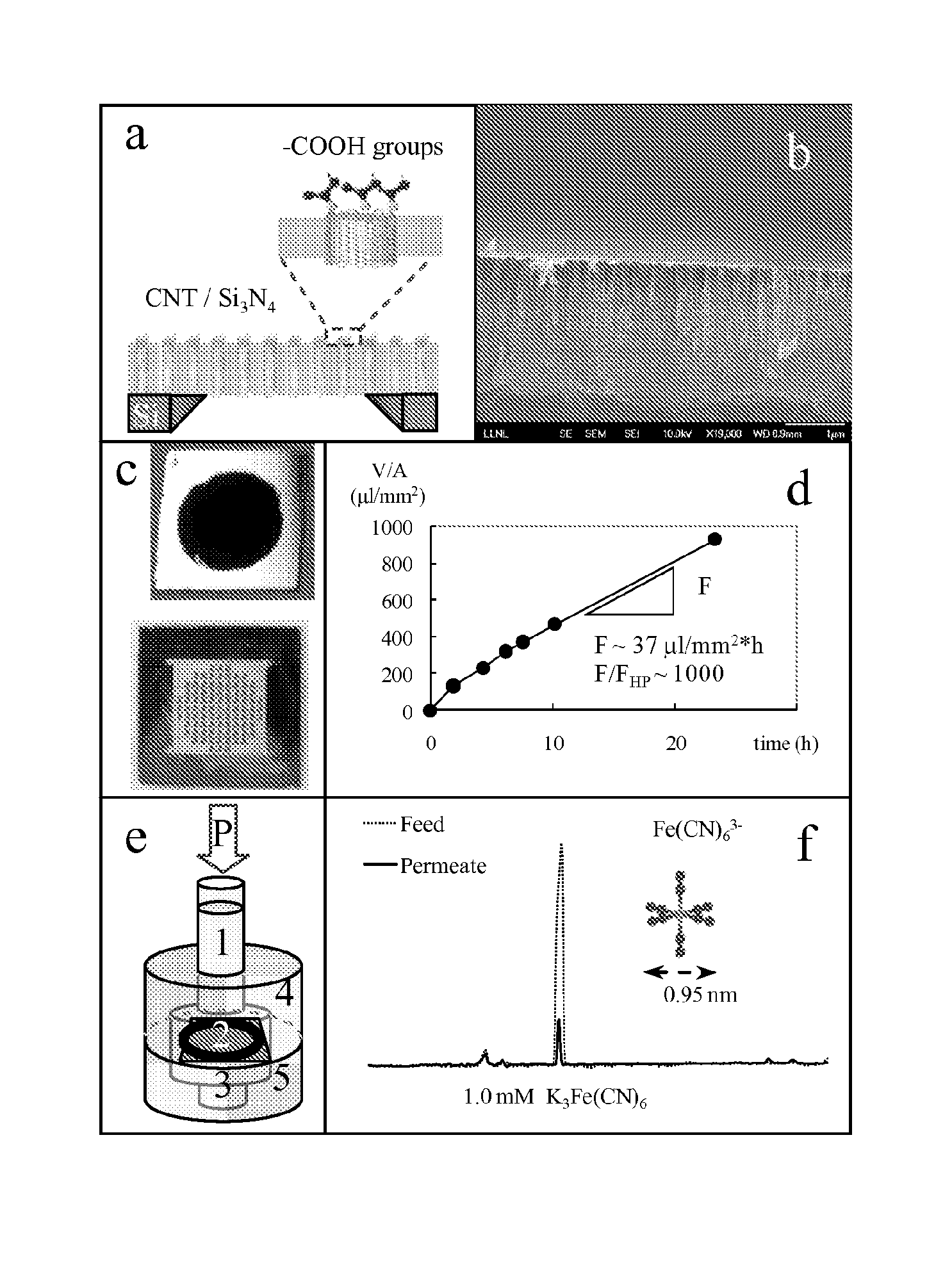
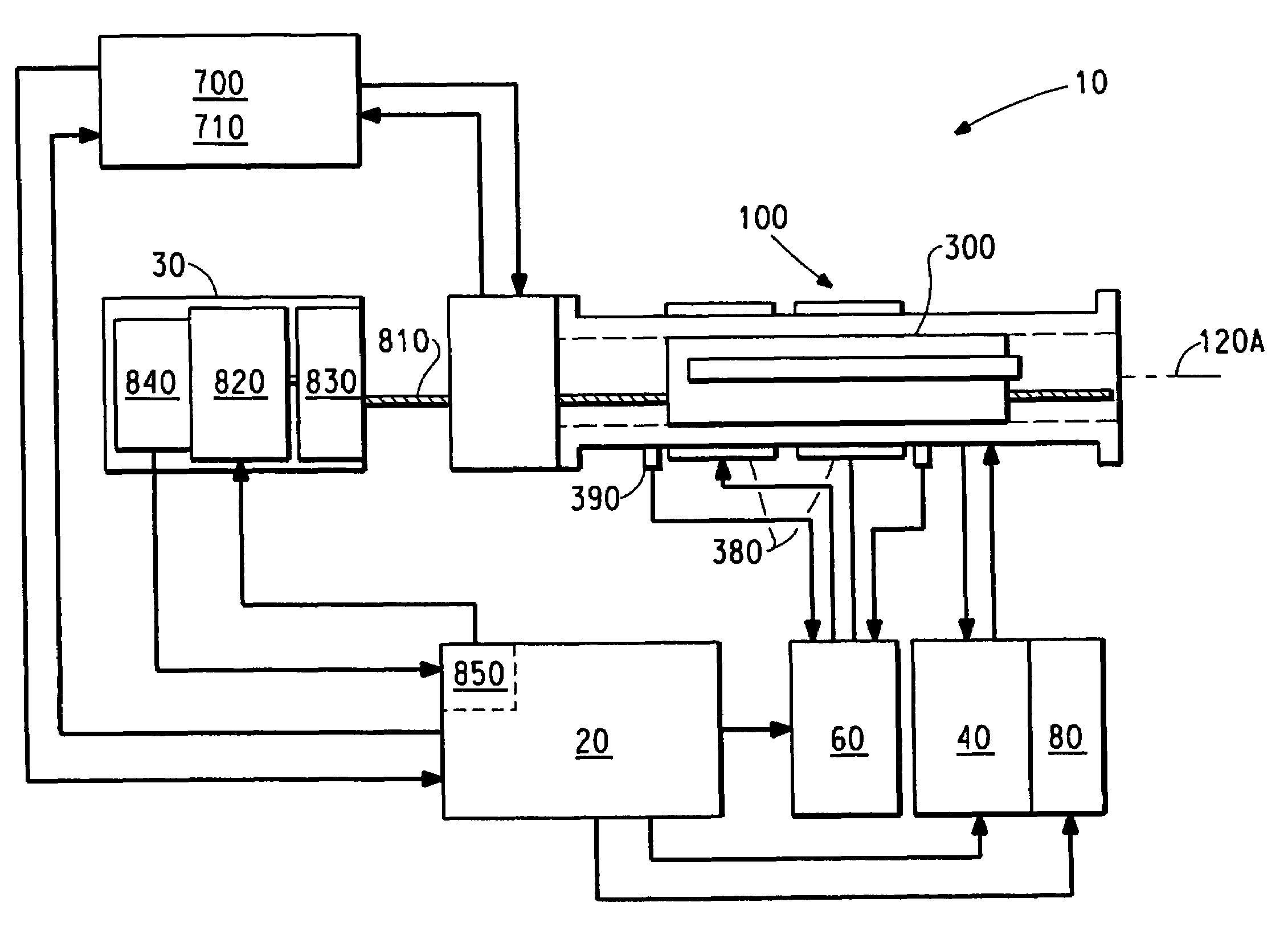
Membranes With Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Pores For Selective Transport
ActiveUS20110220574A1Easy to transportMaterial nanotechnologyGeneral water supply conservationDesalinationNanoporous membrane
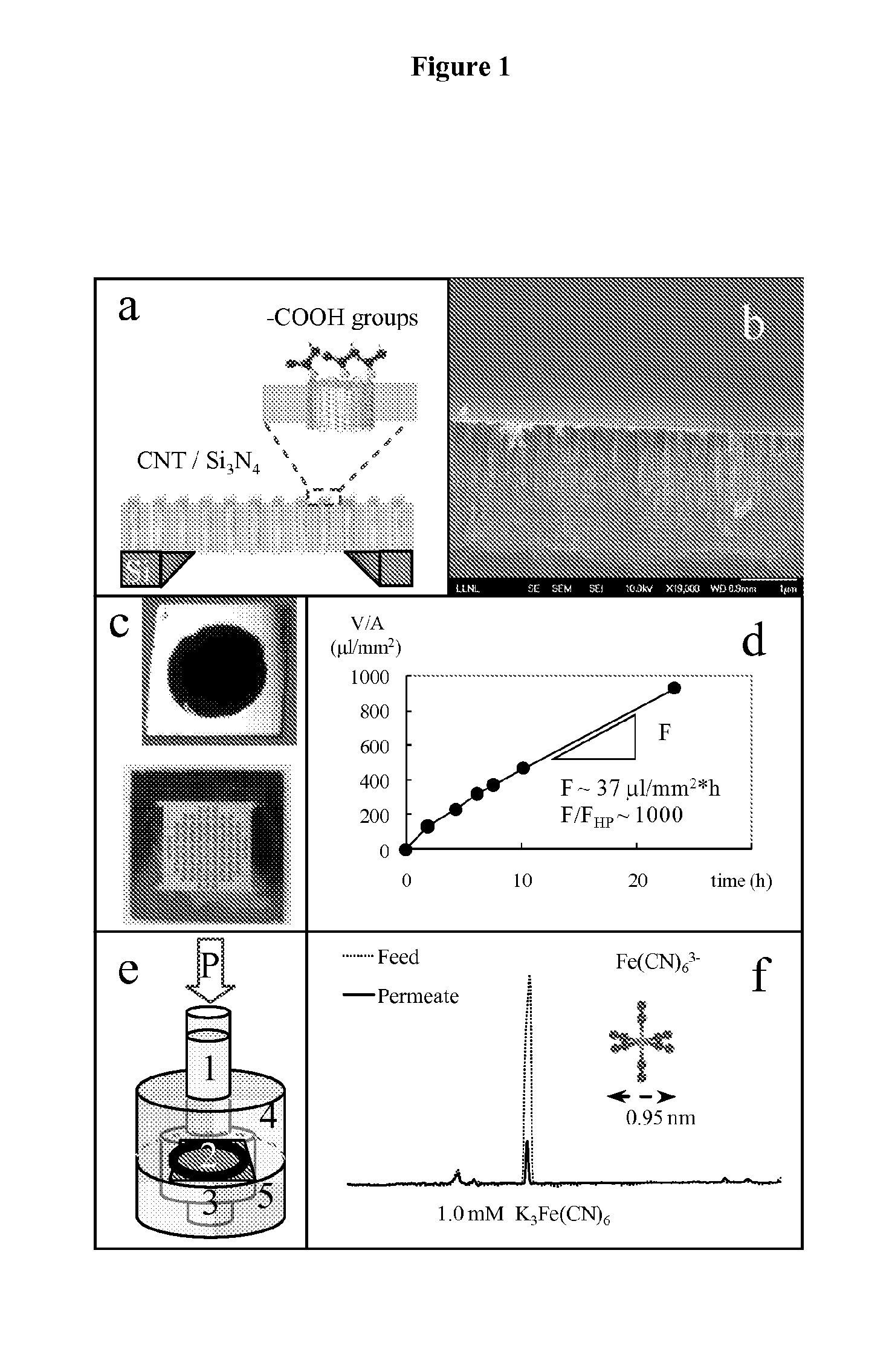
Provided herein composition and methods for nanoporous membranes comprising single walled, double walled, or multi-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in a matrix material. Average pore size of the carbon nanotube can be 6 nm or less. These membranes are a robust platform for the study of confined molecular transport, with applications in liquid and gas separations and chemical sensing including desalination, dialysis, and fabric formation.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Membranes with functionalized carbon nanotube pores for selective transport
InactiveUS20110253630A1Easy to transportMaterial nanotechnologyGeneral water supply conservationDesalinationNanoporous membrane
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Molecular transporter compositions comprising dendrimeric oligoguanidine with a triazine core that facilitate delivery into cells in vivo
InactiveUS7935816B2Improve bioavailabilityImprove securitySugar derivativesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn vivoMolecular Transport
Preparations of novel molecular transporter compositions and their use for transporting bioactive substances into cells in living animals are disclosed. To afford in vivo delivery, the composition is covalently linked to the bioactive substance and the resultant composite structure is introduced into the subject. The transporter composition includes multiple guanidine moieties on a dendrimeric scaffold having a triazine core.
Owner:GENE TOOLS
Nanoengineered membranes for controlled transport
InactiveUS7641863B2Small scaleEasy to mergeMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesFiberCarbon fibers
A nanoengineered membrane for controlling material transport (e.g., molecular transport) is disclosed. The membrane includes a substrate, a cover defining a material transport channel between the substrate and the cover, and a plurality of fibers positioned in the channel and connected to and extending away from a surface of the substrate. The fibers are aligned perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, and have a width of 100 nanometers or less. The diffusion limits for material transport are controlled by the separation of the fibers. In one embodiment, chemical derivatization of carbon fibers may be undertaken to further affect the diffusion limits or affect selective permeability or facilitated transport. For example, a coating can be applied to at least a portion of the fibers. In another embodiment, individually addressable carbon nanofibers can be integrated with the membrane to provide an electrical driving force for material transport.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Stimuli responsive mesoporous materials for control of molecular transport
InactiveUS20050013988A1Increase in inter-pore spacingModulating transportSilicaLayered productsStimuli responsiveChemical physics
The present subject matter relates generally to design, synthesis, and characterization of materials with well-defined porous networks of molecular dimensions in which the size and surface energy of the pores can be externally and reversibly controlled to dynamically modulate the adsorption and transport of molecular species.
Owner:FU QIANG +8
Sodium alginate-flaky ZIF-8 hybrid composite membrane, and preparation and application thereof
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Nanospearing for molecular transportation into cells
InactiveUS20070231908A1Facilitate easyFacilitate reliable attachmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechVaccinationDelivery vehicle
A nanostructured molecular delivery vehicle comprising magnetic materials and configured to receive passenger biomolecules. The application of a an appropriate magnetic field having a gradient orients and drives the vehicle into a biological target, which may comprise cells, cell masses, tissue slices, tissues, etc. Under the control of the magnetic field, these vehicles can penetrate cell membranes. Then, the biomolecules carried by the vehicle can be released into the cells to perform their functions. Using this “nanospearing” technique, unprecendented high transfection efficiency has been achieved in several difficult-to-transfect cells. These include, but are not limited to, Bal 17 cells, ex vivo B cells, primary cultured cortical neurons, etc. This method advances the state of the art, providing an improved technique for the introduction of exogenous molecules to cells, with the clinical applications including, but not being limited to, drug delivery, gene therapy, vaccination, etc.
Owner:NANOLAB
Molecular transporter compositions comprising dendrimeric oligoguanidine with a triazine core that facilitate delivery into cells in vivo
InactiveUS20090171075A1Inhibition of translationImprove bioavailabilitySugar derivativesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTriazeneIn vivo
Preparations of novel molecular transporter compositions and their use for transporting bioactive substances into cells in living animals are disclosed. To afford in vivo delivery, the composition is covalently linked to the bioactive substance and the resultant composite structure is introduced into the subject. The transporter composition includes multiple guanidine moieties on a dendrimeric scaffold having a triazine core.
Owner:GENE TOOLS
Compositions and methods for transepithelial molecular transport
The invention relates to fragments of Clostridium botulinum HC that can be linked with an entity (e.g., an antigen, a particle, or a radionuclide) and used to deliver the entity across a non-keratinized epithelial membrane of an animal. The fragments are useful, for example, for making vaccines, antidotes, and anti-toxins and in situations in which rapid uptake of an agent by an animal is desired.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Single molecule protein sequencing
InactiveUS20150185199A1Minimal ambiguityError minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein insertionProtein Sequence Determination
The invention provides a device for determining the type of protein in a liquid, the device comprising (a) an immobilized ATP dependent protease based molecular transporter machine configured to guide a protein that is functionalized with labels through a detection area of a detector, (b) said detector, configured to detect a signal as function of the labels of the labelled amino acids, (c) a processor unit, configured to identify from the detector signal a sequence of amino acids of the functionalized protein, wherein the processor unit is further configured to compare the identified sequence of amino acids with the occurrence of such sequence in a database of proteins and to identify the type of protein.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Modular antigen transporter molecules (MAT molecules) for modulating immune reactions, associated constructs, methods and uses
ActiveCN1738901AEffective specific immune responseEffective immune responseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntipyreticAntigenAntigen processing
By adding the novel developed modular antigen transporter molecules (MAT molecules) and other instruments related thereto, the immune system of an individual can be effectively modulated in a targeted manner. The MAT molecules contain a translocation module which transports the MAT molecule inside the cell, an active intracellular targeting molecule resulting in intracellular transport of the MAT molecule to the organelles of the cell which are responsible for antigen processing and an antigen module which determines the specificity of the immune response modulated by the MAT molecule. Optionally, other modules such as tag modules or spacer modules can be contained in the MAT molecule. The invention comprises the inventive MAT molecules, antibodies which are produced using said MAT molecules and therapeutic agents and diagnostic reagents which are produced with MAT molecules. The invention also comprises applications containing said MAT molecules, antibodies, therapeutic agents and diagnostic reagents.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Modular transport systems for molecular substances and production and use thereof
InactiveUS20050266020A1Excludes or minimizes disadvantages concerning gene therapeutic treatmentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVirusesTransport systemMolecular Transport
The invention relates to transport systems for molecular substances, comprising a mosaic of recombinant partial units (individual components). The invention further relates to production of the molecular transport system and use thereof.
Owner:ACGT PREGENOMICS
Inositol-based molecular transporters and processes for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20060280796A1Efficient transportPowder deliveryOrganic chemistryNuclear membraneBiochemistry
Inositol derivatives in accordance with the present invention are effective in significantly enhancing the transportation of various therapeutic molecules across a biological membrane, which may include the plasma membrane, nuclear membrane or blood-brain barrier.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Method for designing and controlling microstructure of explosive based on supramolecular assembly and disassembly
ActiveCN102898258AVerify changesEasy to operateNitrated acyclic/alicyclic/heterocyclic amine explosive compositionsDetonationCombustion
The invention discloses a method for designing and controlling the microstructure of an explosive based on supramolecular assembly and disassembly. The method comprises the following steps of: forming an energetic supramolecular cocrystal system through supramolecular self-assembly with energetic materials as host molecules and guest molecules; disassembling the guest molecules in the supramolecular cocrystal system under the action of an external force to obtain an energetic material with a special microstructure; and completing the design and control of the explosive microstructure. The method provided by the invention can design the microstructure of the energetic material from a molecular level, thereby realizing the controllable molecular transport and operation of the energetic material supramolecular system. The control of the inter-molecule action force from a micro level has influence on the change of a larger microstructure. The detonation performance and combustion performance of the obtained energetic material with the special microstructure are improved.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Modular antigen transporter molecules (MAT molecules) for modulating immune reactions, associated constructs, methods and uses
By adding the novel developed modular antigen transporter molecules (MAT molecules) and other instruments related thereto, the immune system of an individual can be effectively modulated in a targetedmanner. The MAT molecules contain a translocation module which transports the MAT molecule inside the cell, an active intracellular targeting molecule resulting in intracellular transport of the MATmolecule to the organelles of the cell which are responsible for antigen processing and an antigen module which determines the specificity of the immune response modulated by the MAT molecule. Optionally, other modules such as tag modules or spacer modules can be contained in the MAT molecule. The invention comprises the inventive MAT molecules, antibodies which are produced using said MAT molecules and therapeutic agents and diagnostic reagents which are produced with MAT molecules. The invention also comprises applications containing said MAT molecules, antibodies, therapeutic agents and diagnostic reagents.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Cationic amphipile compositions for interacelluar delivery of therapeutic molecules
InactiveUS20020013282A1High level of expressionImprove expression of transgeneAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemistrySteroid Compound
Novel cationic amphiphiles are provided that facilitate transport of biologically active (therapeutic) molecules into cells. By this invention, such cationic amphiphile is used in a state in which it is capable of accepting additional protons, i.e., it is not fully protonated. For purposes of this invention, cationic amphiphiles may be considered to encompass four general categories: (A) T-shaped / steroid-based amphiphiles; (B) T-shaped / non steroid-based amphiphiles; (C) non T-shaped / steroid based amphiphiles and (D) non T-shaped / non steroid-based amphiphiles.
Owner:MARSHALL JOHN +7
Fiber-optic biosensor and biosensing methods
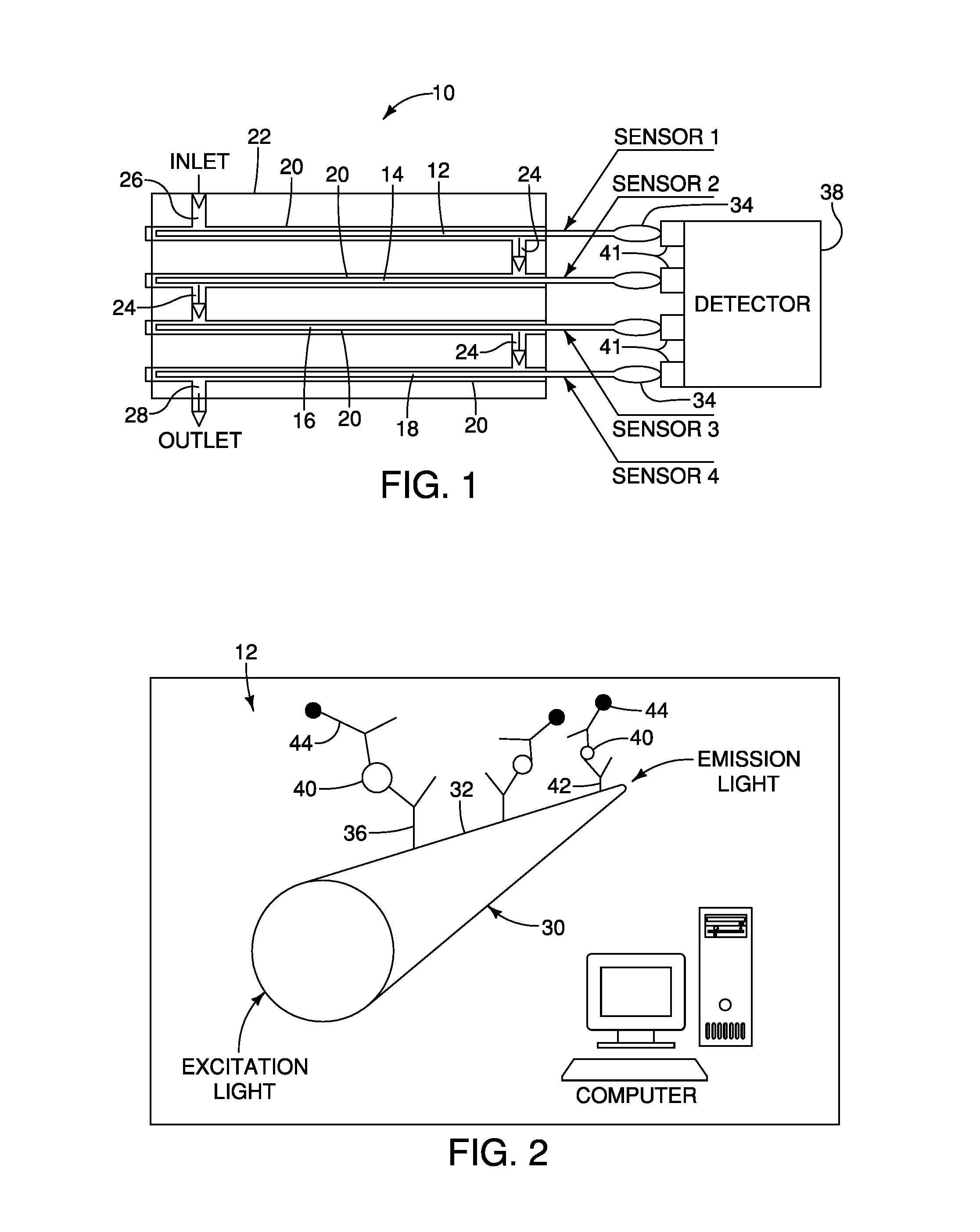
InactiveUS20140030150A1Good senseShorten detection timeComponent separationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMolecular TransportMicrofluidic channel
A biosensor device that includes a module defining at least one microfluidic channel, an optical waveguide exposed along at least a portion of its length to fluid flow within the microfluidic channel, where a surface of the optical waveguide being prepared to bind a target biomarker, and an excitation source to couple an excitation wavelength of light into the optical waveguide. The device also includes a sensor for detecting emission light from the optical waveguide at an emission wavelength characteristic of binding of the target biomarker. Particular devices include multiple waveguides in multiple microfluidic channels. Particular devices include microfluidic channels with serpentine bump structures that aid molecular transport.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Molecular Transporters Based on Sugar and Its Analogues and Processes For the Preparation Thereof
ActiveUS20080249296A1Improve breathabilityEfficient transportBiocideSugar derivativesNuclear membraneSugar
The inventive molecular transporter compound shows significantly high permeability through a biological membrane such as a plasma membrane, nuclear membrane and blood-brain barrier, and accordingly, can be effectively used in delivering various biologically active molecules.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Application of cationic polyvinylamine linear macromolecules as transgenic vector
ActiveCN109136271AGood biocompatibilityHigh gene transfection efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesMolecular TransportTransfection
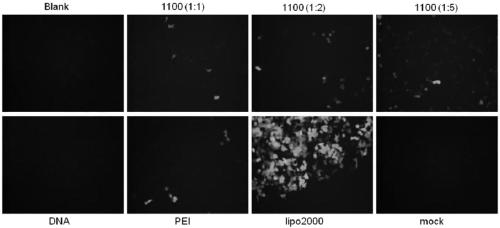
The invention provides a cationic polyvinylamine linear macromolecular transgenic vector, commercially named XELOREXTM RS 1100. The invention provides application of the linear macromolecular transgenic vector as a nucleic acid molecular transport vector. The vector herein provides efficient transfection during cell transfection. The material cost is low; cell toxicity during transfection is low;genetic molecules can be transported to cells effectively and safely. The linear macromolecular transgenic vector has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity and low price.
Owner:西安九清医疗科技有限公司
Nanochannel compositions and methods
ActiveUS20160355882A1Carbon compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular TransportChemistry
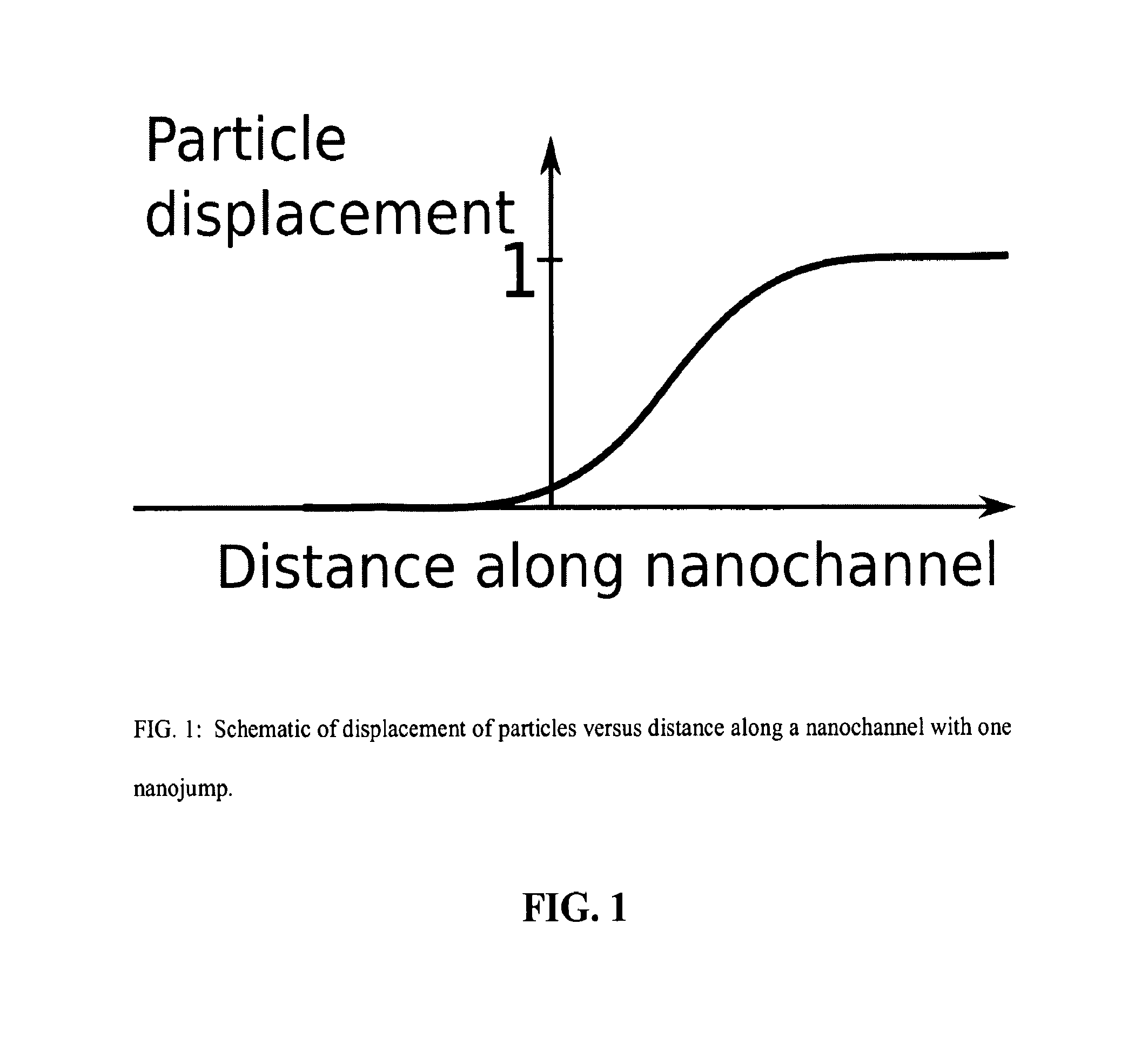
Disclosed herein is a composition comprising a nanochannel and a contained substance, wherein the nanochannel comprises a single-file nanochannel and the contained substance comprises a plurality of substance particles arranged in a single-file chain within the nanochannel. Methods and systems for molecular transport of a substance through a nanochannel are also provided that rely upon the use of nanojumps, where nanojumps mediate the transport through the nanochannel.
Owner:LICHTER SETH HARVEY +1
Sodium alginate-flaky zif-8 hybrid composite membrane and its preparation and application
The invention relates to a sodium alginate-flaky ZIF-8 hybrid composite membrane, and belongs to the field of membrane separation. At first, Zn(NO3)2 and 2-methylimidazole are used as raw materials, and flaky ZIF-8 is prepared in a water phase form through control of synthesis conditions; then, the prepared platy ZIF-8 is dispersed in a sodium alginate water solution to prepare a casting solution, after standing and defoaming, the casting solution spirally coats the surface of a porous polymer ultrafiltration membrane, after drying, the porous polymer ultrafiltration membrane is crosslinked with a calcium chloride solution, and after drying again, the sodium alginate- flaky ZIF-8 hybrid composite membrane is obtained. The hybrid composite membrane can be used for dehydration through pervaporation of an ethanol / water system. Through utilization of the second-dimensional structure and the porous structure of the flaky ZIF-8, the screening effect of the hybrid composite membrane on molecular transport is enhanced, so that the separation performance of the hybrid composite membrane is improved. The preparation process is simple, raw materials are easy to obtain, the structure is controllable, the large-scale preparation and amplification are convenient, and the sodium alginate-flaky ZIF-8 hybrid composite membrane has a good application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing chemical reactions in a plurality of samples
InactiveUS7373259B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionChemical reactionGas phase
A method and apparatus for simultaneously performing chemical reactions and determining molecular transport dynamics on a plurality of samples such as thin film samples. The apparatus of the present invention is capable of containing multiple samples in individual sample holding positions in a sample holder within a housing and maintaining those holding positions in chemical isolation from each other. Under control of a computerized controller, the apparatus positions the sample holder so that each sample holding position may be positioned adjacent to one or more ports connected to a distribution manifold. The apparatus exposes each sample to one or more fluids in liquid or gas phase, thereby carrying out a chemical reaction and / or determining molecular transport dynamics under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. The sample holding positions may be positioned in an analytical measurement station within the housing so that the resulting chemical compound or mixture may be characterized.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Conjugates and processes for their preparation and their use for transporting molecules across biological membranes
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Naphthalimide modified dendrimer transgenic carrier and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108753830AEasy to operateHigh yieldOther foreign material introduction processesDendrimerCytotoxicity
The invention provides a naphthalimide modified dendrimer transgenic carrier which comprises a dendritic polymer skeleton and a naphthalimide containing functional group, wherein the naphthalimide containing functional group is covalently attached to surfaces of dendritic polymers. The invention further provides a preparation method of the dendrimer transgenic carrier and an application of the dendrimer transgenic carrier serving as a nucleic acid molecular transport carrier. A brand new modification method and the functional group are adopted to modify the dendritic polymers, and simple and efficient reaction and high yield are achieved; efficient transfection effect is achieve din the process of cell transfection, simple material production and low cost are achieved, the transfection process has low cytotoxicity, and genetic molecules can be effectively and safety transported into cells; the dendrimer transgenic carrier has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low price and easiness in synthesis.
Owner:西安九清医疗科技有限公司
Compositions and processes for synthesizing cubic mesoporous silicas having "noodle-like" morphology
InactiveUS20150251164A1SilicaCatalyst activation/preparationTetramethylammonium hydroxideMesoporous silica
Cubic mesoporous silicas having substantially cylindrical morphology may be prepared using a combination of a first structure-directing template, such as tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide; water; a second structure-directing template, such as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide; a morphology-directing template, such as a poloxamer having a weight average molecular weight ranging from 5,000 to 20,000 Daltons; and a silica source; in the substantial absence of an alcohol solvent. The resulting materials may exhibit a three-dimensional channel structure, a length from 3 to 10 micrometers and a width from 300 nanometers to 10 micrometers, resulting in an aspect ratio from 1 to 300. Further characterization may include a surface area from 1300 to 1500 square meters per gram, an average pore diameter from 20 to 26 angstroms, and an average pore volume ranging from 0.7 to 1.1 cubic centimeters per gram. These materials are useful for molecular transport and release applications in a variety of uses, including, for example, membrane separations, metal incorporation, electronic devices, drug delivery, and adsorption.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Molecular transporters based on sugar and its analogues and processes for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS7846975B2Improve breathabilityEfficient transportBiocideSugar derivativesNuclear membraneBiological membrane
The inventive molecular transporter compound shows significantly high permeability through a biological membrane such as a plasma membrane, nuclear membrane and blood-brain barrier, and accordingly, can be effectively used in delivering various biologically active molecules.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
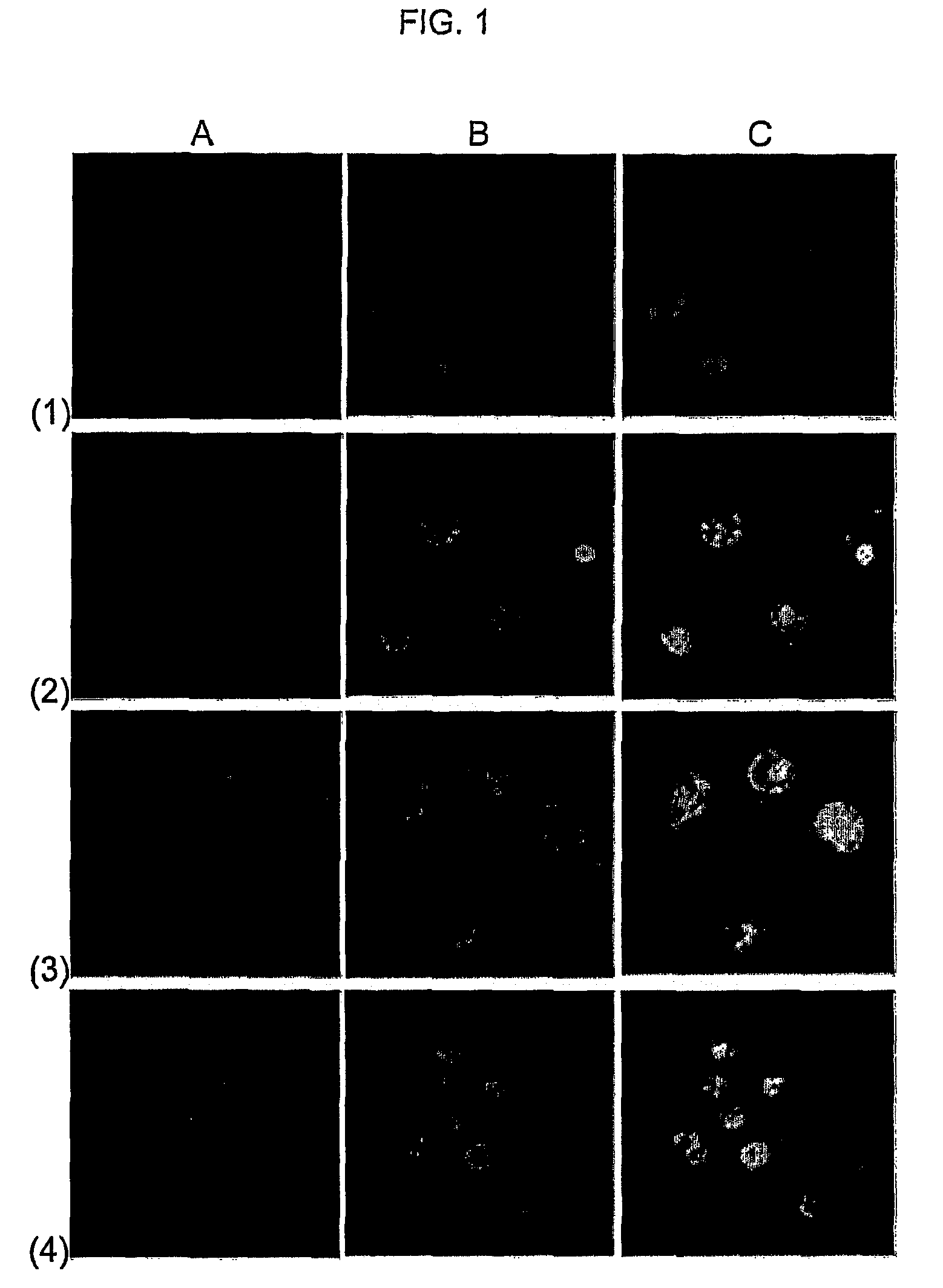
Transferrin receptor-binding molecules, conjugates thereof and their uses
PendingUS20220090050A1Prolonged plasma half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to Variable Domain of Camelid Heavy Chain-only (VHH) molecules which bind TfR and the uses thereof e.g., to transport molecules of pharmaceutical or diagnostic interest into cells and in organs, in pathological conditions including cancer.
Owner:VECT HORUS +2
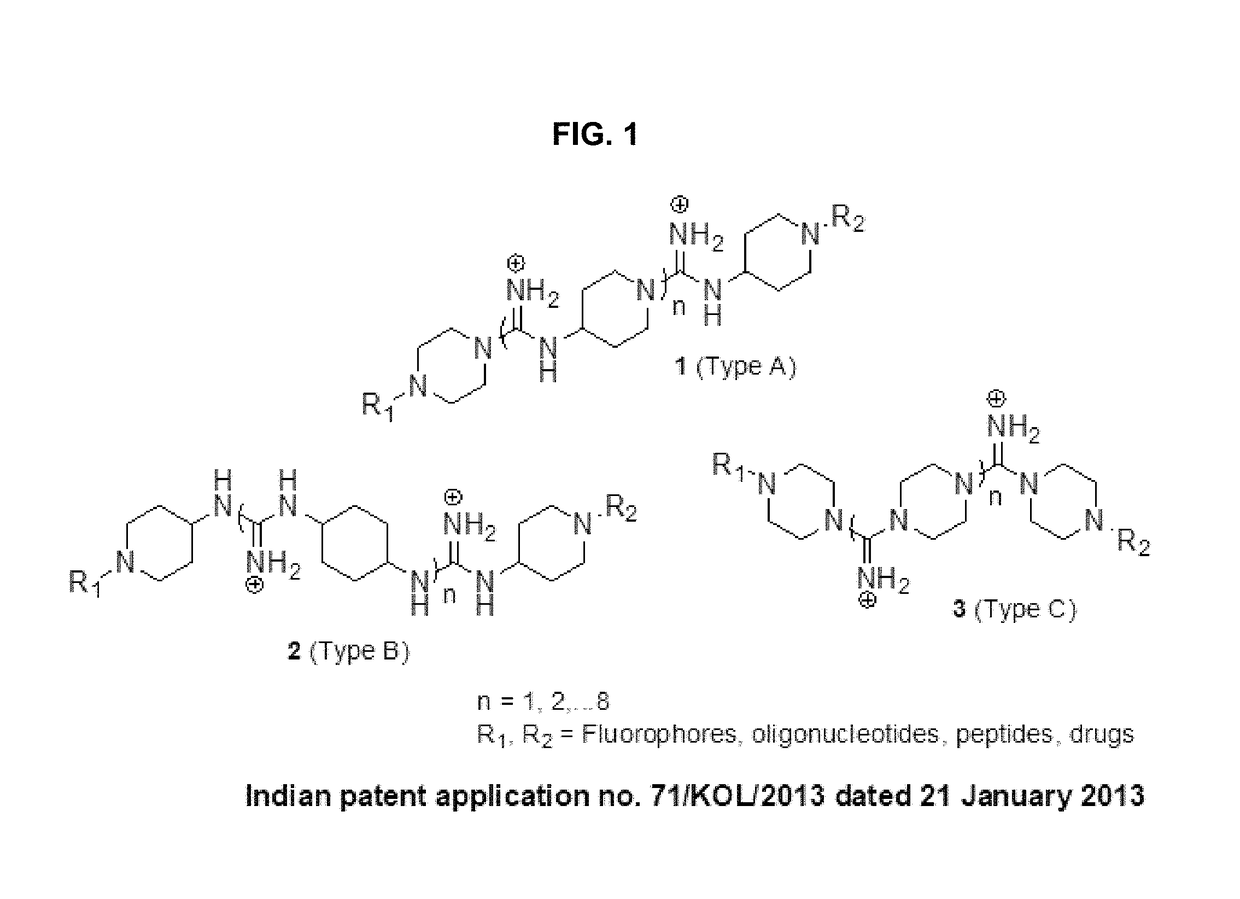
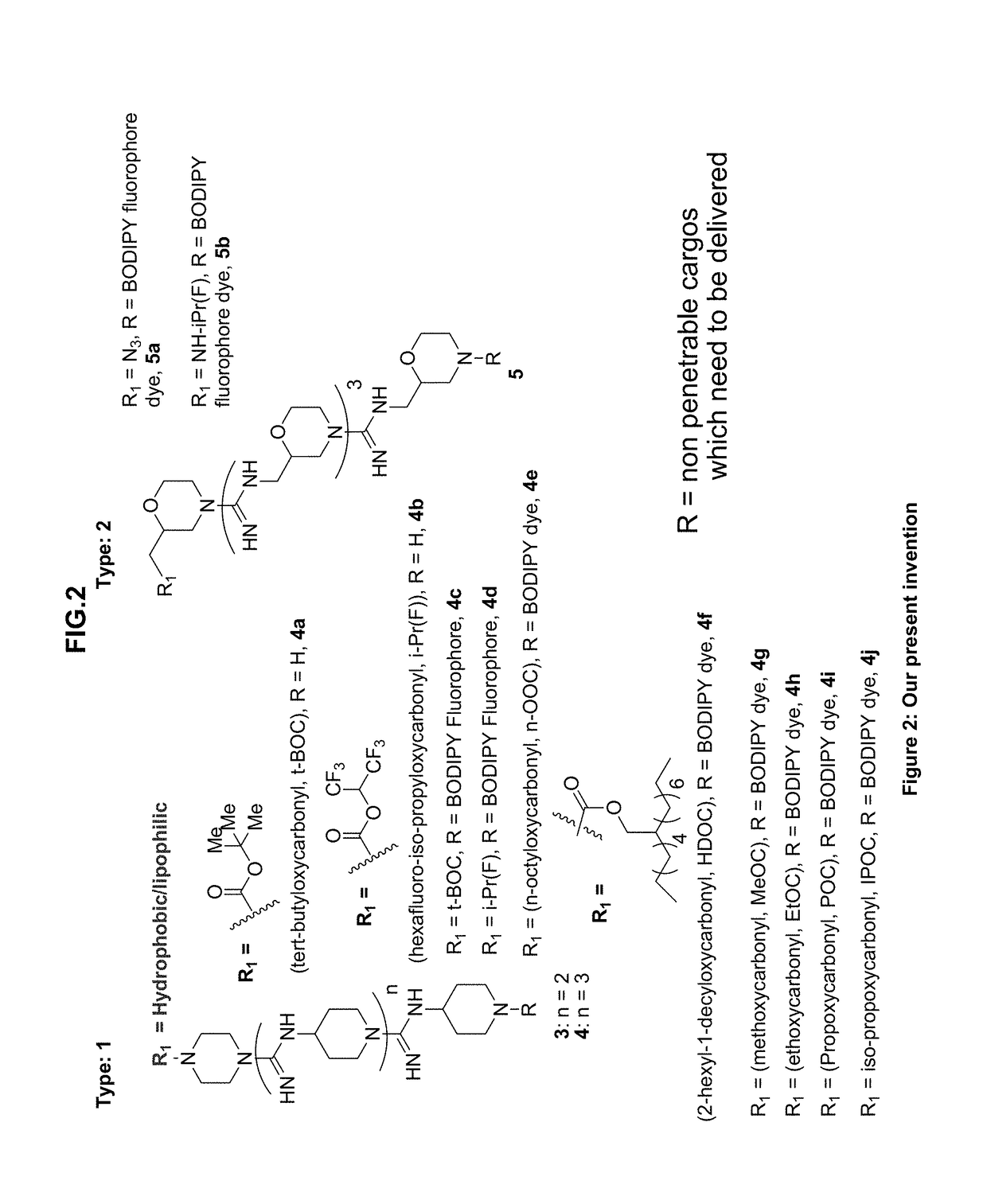
Oligo-guanidines based cellular transporter comprising heterocyclic rings with hydrophobic and/or lipophilic groups at n-terminal for effective delivery of nonpenetrable cargos in-vitro and in-vivo
ActiveUS20190002408A1Improve permeabilityEnhanced cellular uptakeOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMorpholineHeteroatom
An oligo-guanidine as cell penetrating agents / carriers includes a heterocyclic ring including 4-aminopiperidine, piperazine, morpholine having at least one N-terminal based heterocyclic ring or at least one O-heteroatom based heterocyclic ring tailored with hydrophobic and / or lipophilic group. The oligo-guanidine is adapted as an effective molecular transporter to transport and / or delivery therapeutics, therapeutic candidates, probes, or other molecules of interest across biological barriers including oligonucleotides. Advantageously, the oligo-guanidine is capable of being internalized into cells (in-vitro and in-vivo) with enhanced cellular uptake in nanomolar concentration.
Owner:INDIAN ASSOC FOR THE CULTIVATION OF SCI
Oligo-guanidines based cellular transporter comprising heterocyclic rings with hydrophobic and/or lipophilic groups at N-terminal for effective delivery of nonpenetrable cargos in-vitro and in-vivo
ActiveUS10919857B2Improve permeabilityEnhanced cellular uptakeOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMorpholineHeteroatom
An oligo-guanidine as cell penetrating agents / carriers includes a heterocyclic ring including 4-aminopiperidine, piperazine, morpholine having at least one N-terminal based heterocyclic ring or at least one O-heteroatom based heterocyclic ring tailored with hydrophobic and / or lipophilic group. The oligo-guanidine is adapted as an effective molecular transporter to transport and / or delivery therapeutics, therapeutic candidates, probes, or other molecules of interest across biological barriers including oligonucleotides. Advantageously, the oligo-guanidine is capable of being internalized into cells (in-vitro and in-vivo) with enhanced cellular uptake in nanomolar concentration.
Owner:INDIAN ASSOC FOR THE CULTIVATION OF SCI
Optimizing pumping of variable viscosities via microtextured miniaturized tesla pump
ActiveUS20210363997A1Reduce distanceIncrease shear stressSpecific fluid pumpsPump componentsComputer printingEngineering
An integrated flow source is a limiting factor in numerous microfluidic applications. In addition to precise gradients and controlling molecular transports, a built-in source of stable and accurate flow can enable novel shear stress modulations for long-term cell culturing studies. The Tesla turbine, when used as a pump on the microfluidic regime, produces stable and accurate fluid gradients by utilizing laminar flow between its rotating discs Utilizing a stereolithography based 3D printer, a tesla pump (Ø10 cm) and associated housing capable of driving a microfluidic gradient is provided having a printed rotor surface topology of the pump in order to enhance pumping of biological fluids like blood at elevated viscosities. The surface topology is tuned via 3D pixilation, and this modulation completely recovered the pressure loss between pumping water at 1 cP versus glycerol solution at 3 cP. As a result, increased fluid viscosities, and even Non-Newtonian viscosities, can be used.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com