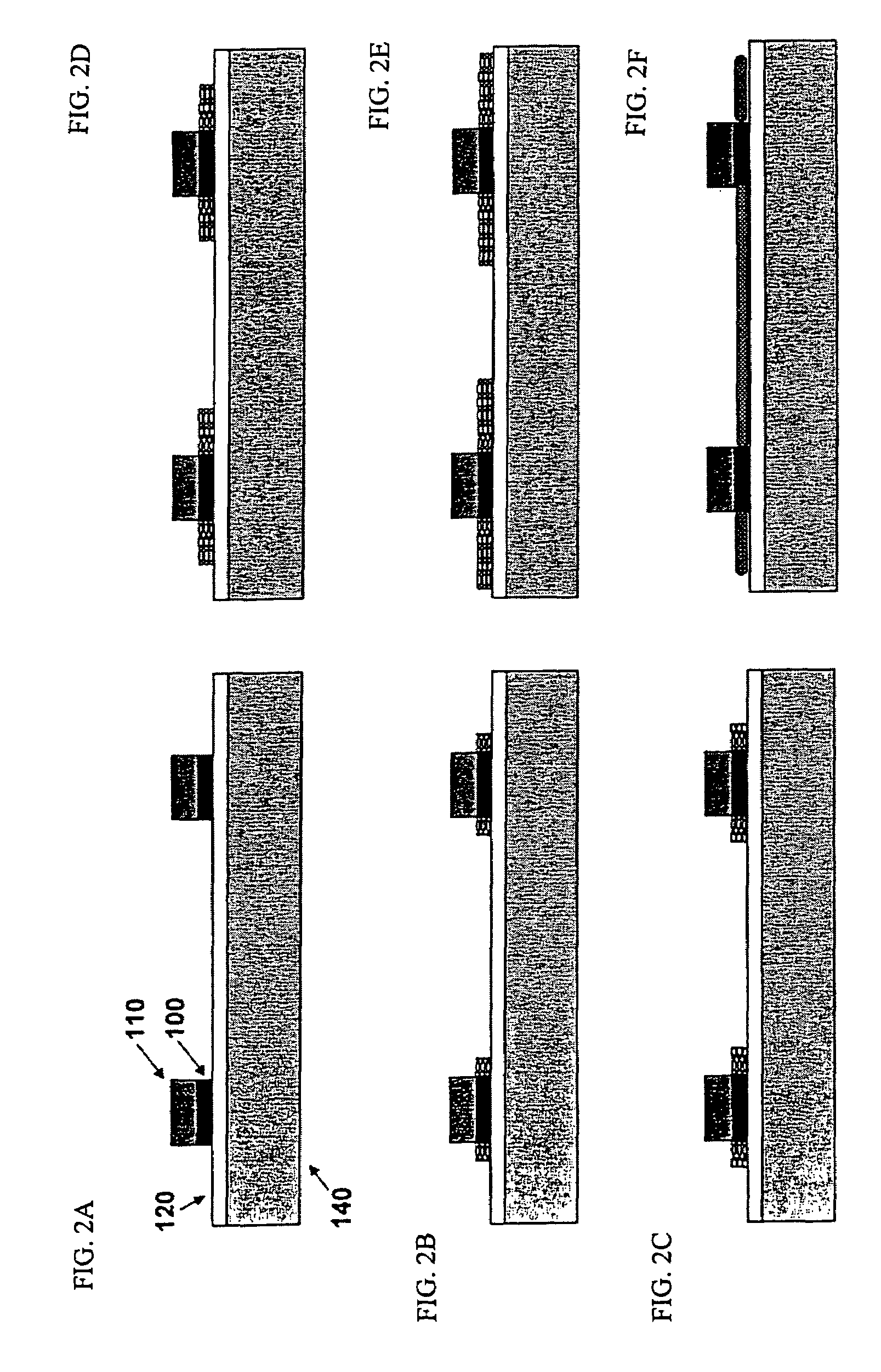
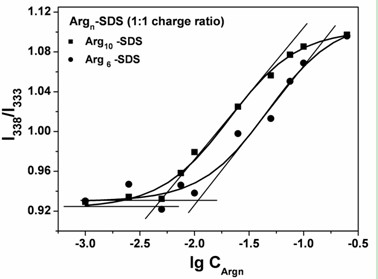
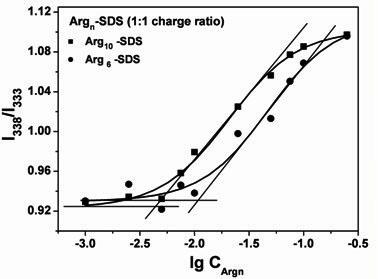
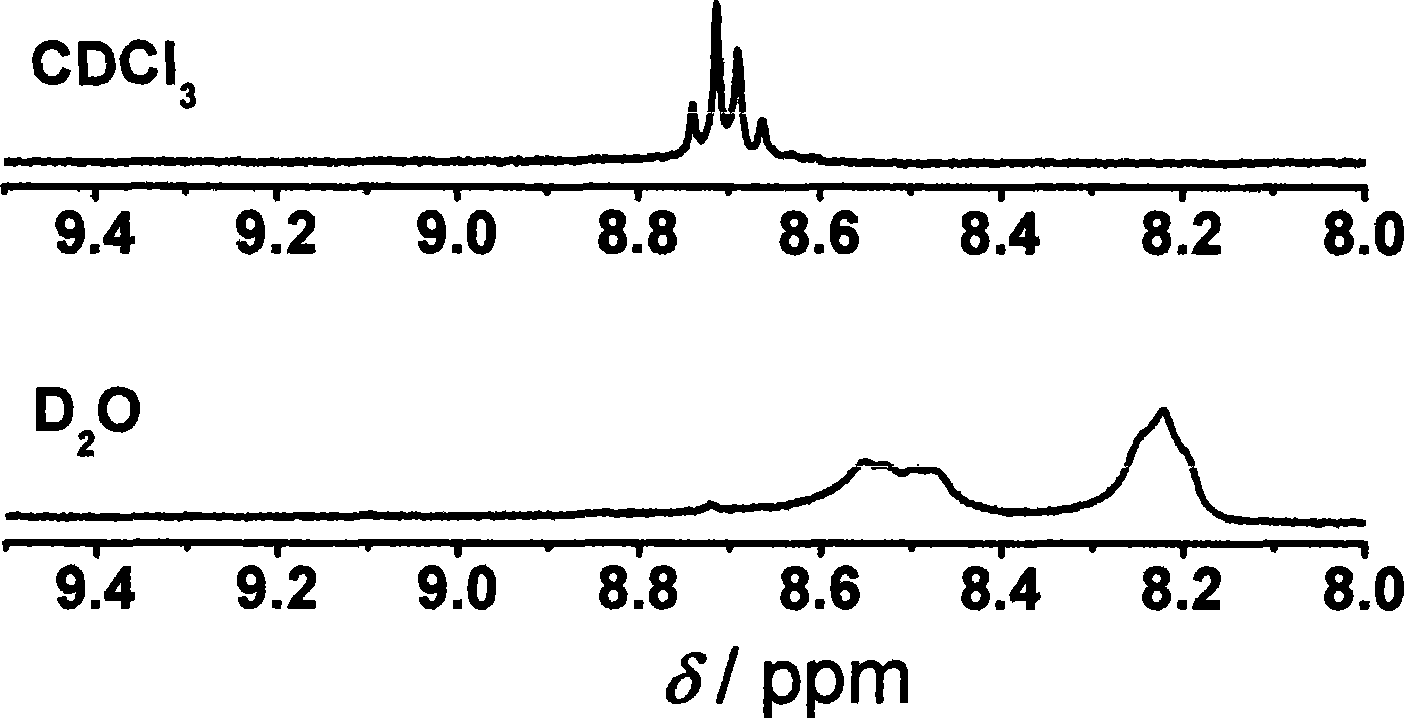
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
253 results about "Supramolecular assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A supramolecular assembly or "supermolecule" is a well defined complex of molecules held together by noncovalent bonds. While a supramolecular assembly can be simply composed of two molecules (e.g., a DNA double helix or an inclusion compound), it is more often used to denote larger complexes of molecules that form sphere-, rod-, or sheet-like species. Micelles, liposomes and biological membranes are examples of supramolecular assemblies. The dimensions of supramolecular assemblies can range from nanometers to micrometers. Thus they allow access to nanoscale objects using a bottom-up approach in far fewer steps than a single molecule of similar dimensions.
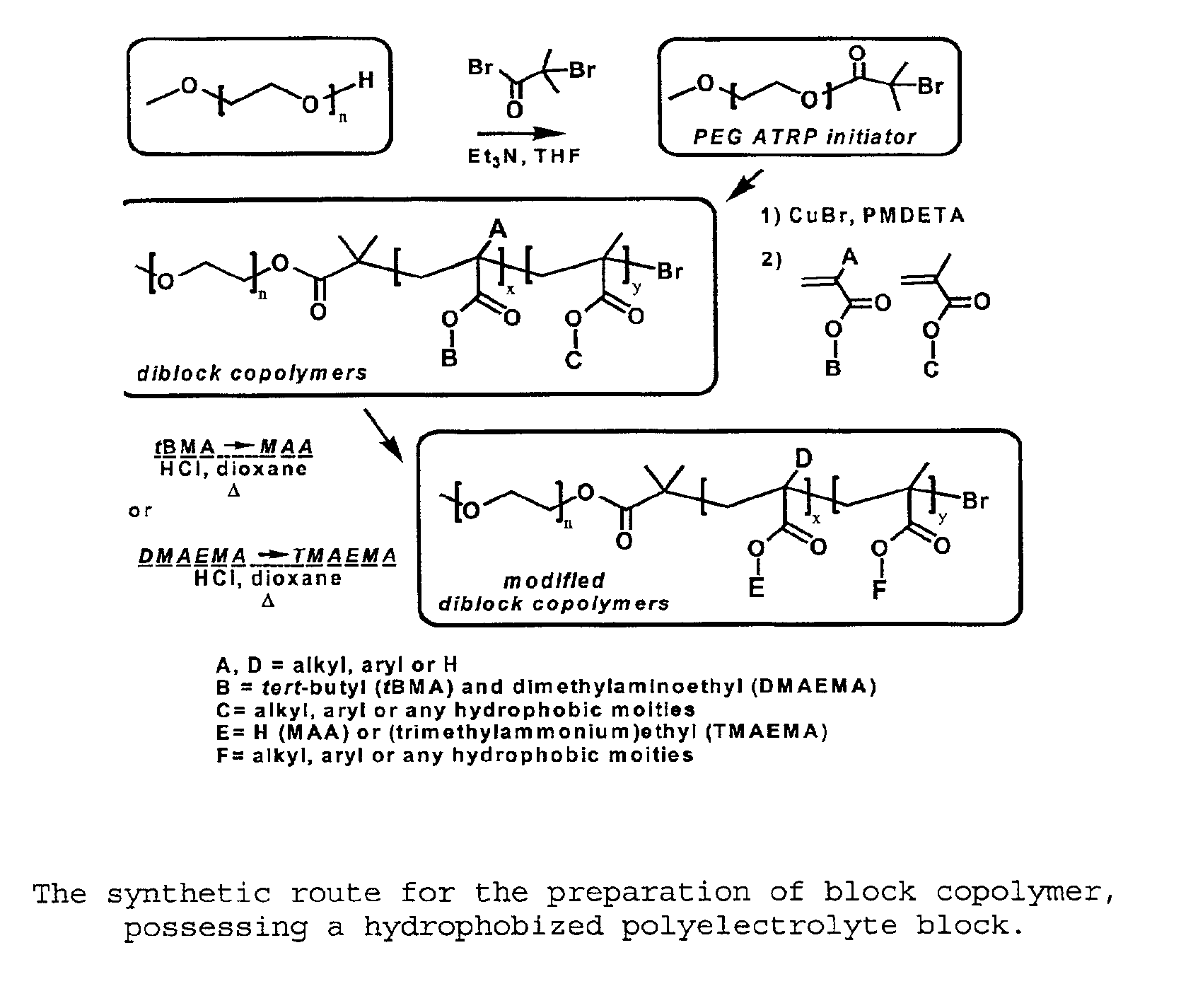
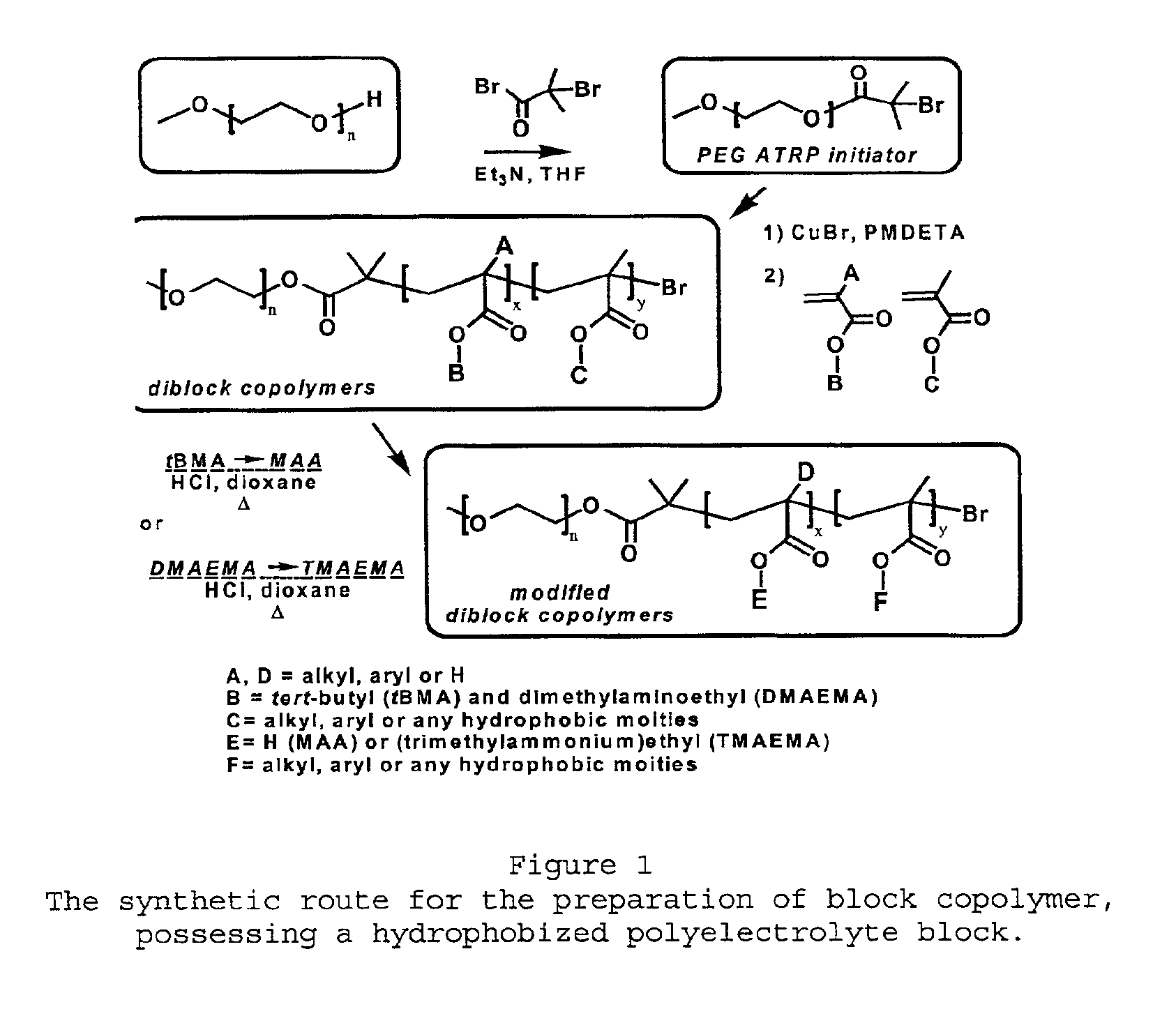
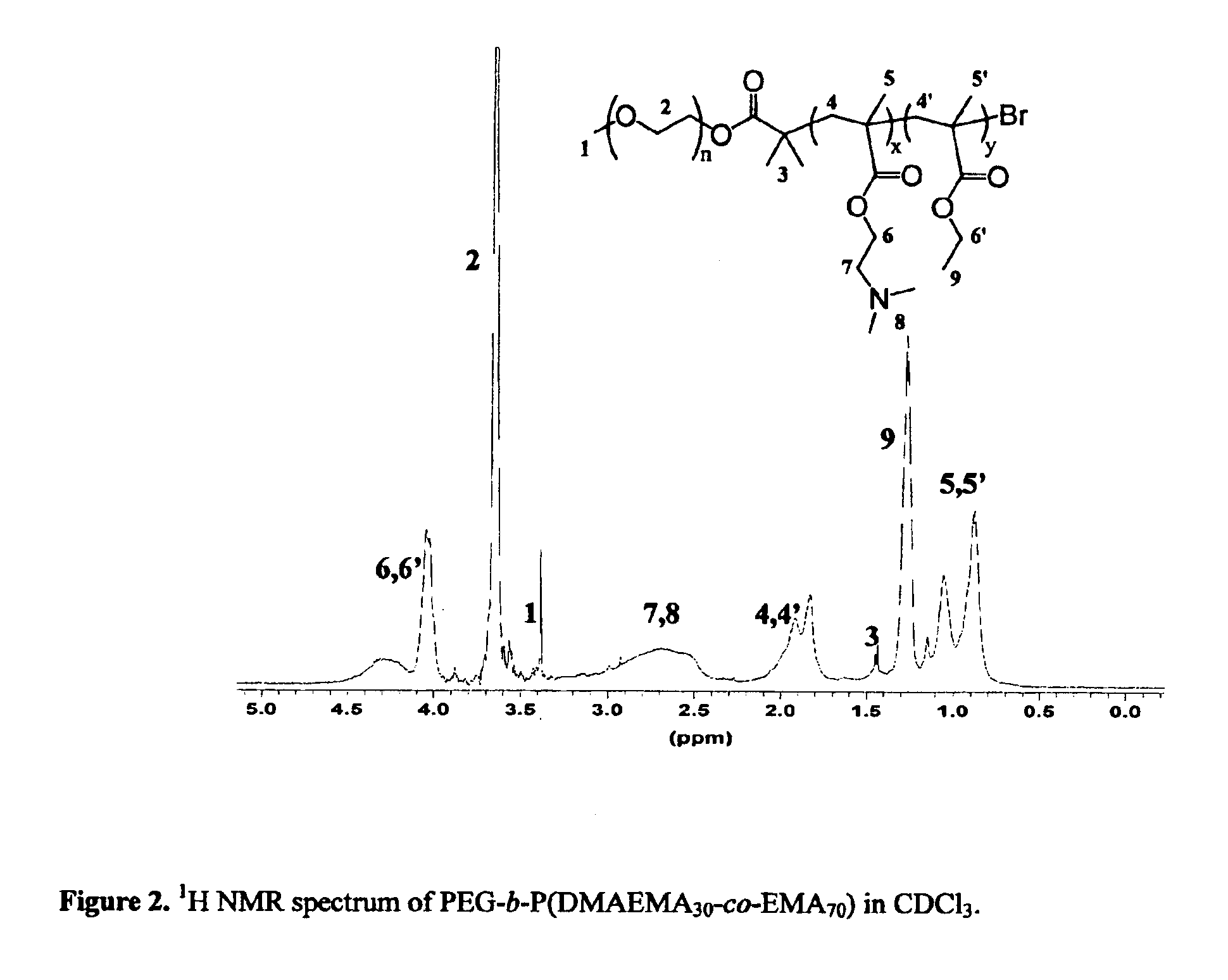
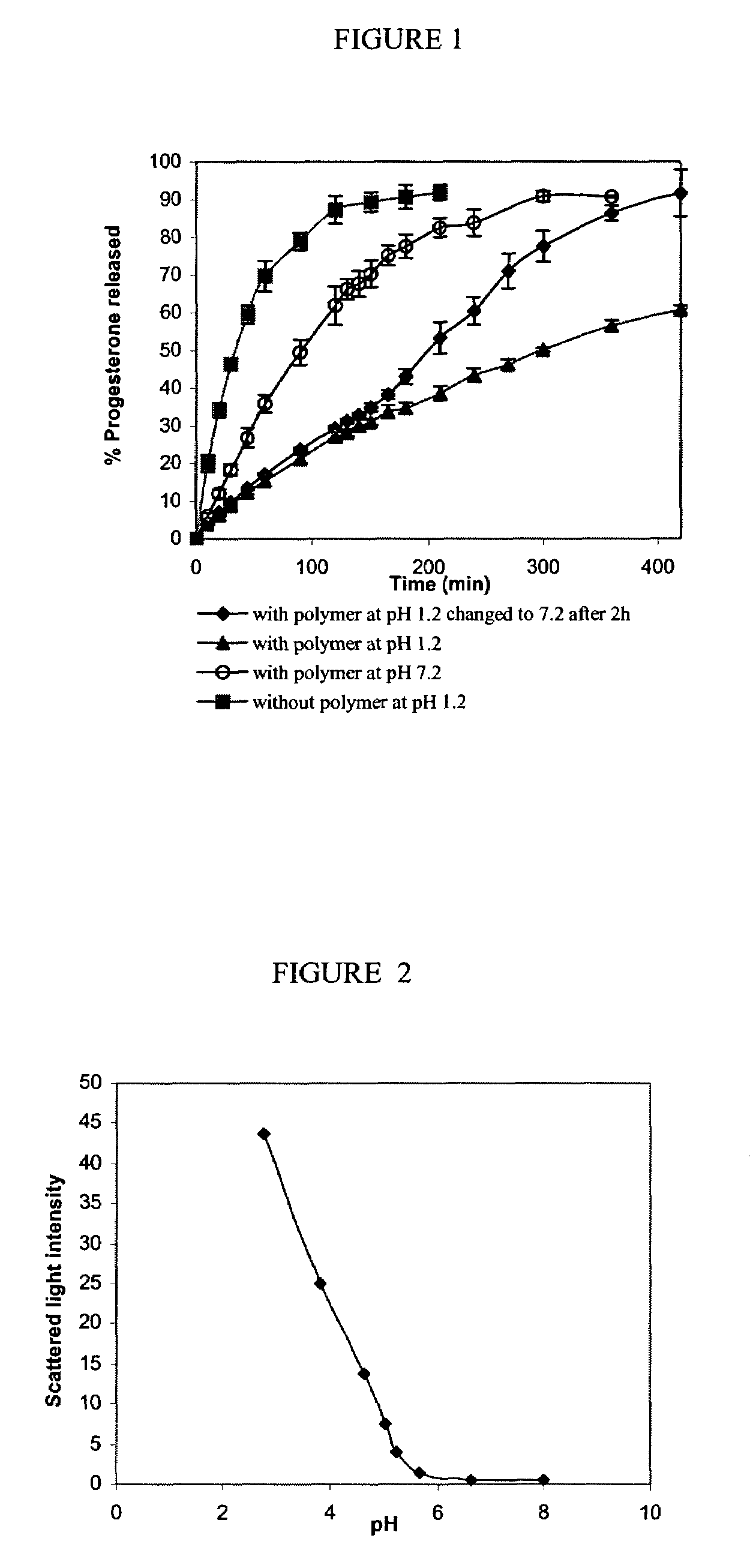
Water-soluble stabilized self-assembled polyelectrolytes
InactiveUS6939564B2Increase attractivenessImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryPolyelectrolyteHydrophilic polymers
Owner:LABOPHARM BARBADOS LTD 36646
Compositions For the Treatment of Diabetes
A supramolecular insulin assembly and supramolecular exendin-4 assembly, which is useful as a protein therapeutic agent for the treatment of metabolic disorders particularly diabetes. The supramolecular assemblies disclosed in the present invention consists of insoluble and aggregated oligomers the protein. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the supramolecular assembly.
Owner:EXTENDED DELIVERY PHARMA
Water-soluble stabilized self-assembled polyelectrolytes
InactiveUS20030059398A1Pharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryPolyelectrolyteHydrophilic polymers
The present invention is directed toward water-soluble supramolecular self-assemblies and a process for their preparation via micellization of polyelectrolytes through the use of hydrophobic monomeric units. In this invention the polyelectrolyte segment ultimately forms the core of the supramolecular assembly whereas the shell consists of uncharged hydrophilic polymers or oligomers. It has been determined that the inclusion of the hydrophobic co-monomers to the polyelectrolyte segment forming the micelle core leads to a structure of enhanced stability.
Owner:LABOPHARM BARBADOS LTD 36646
pH-sensitive block copolymers for pharmaceutical compositions
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition of a biologically active agent and a block copolymer composed of a poly(ethylene oxide) forming hydrophilic segment and a poly(butyl (alkyl)acrylate-co-(alkyl)acrylic acid) that is capable of forming supramolecular assemblies or micelles under favourable conditions. The supramolecular assemblies or micelles formed from said polymers associate or dissociate reversibly upon changes in the environmental pH. The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention contain hydrophobic drugs, cations or polycationic compounds, which can be delivered to the body by oral route or other routes of administration.
Owner:PALADIN LABS INC
Method for providing resistance to biofouling in a porous support
The invention is a process useful for providing a treated support comprising a porous nanoweb coating wherein the treated support is characterized by a biofilm cell count of less than 50% that of an untreated porous support control. The process is useful for modifying porous materials, such as filter media and barrier fabrics to provide resistance to biofouling. The porous nanoweb coating is comprised of fibrous structures derived from gelation and drying of supramolecular assemblies of non-covalently bonded organogelators. Typical organogelators useful in the invention include those that assemble via hydrogen bonding and π-stacking.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
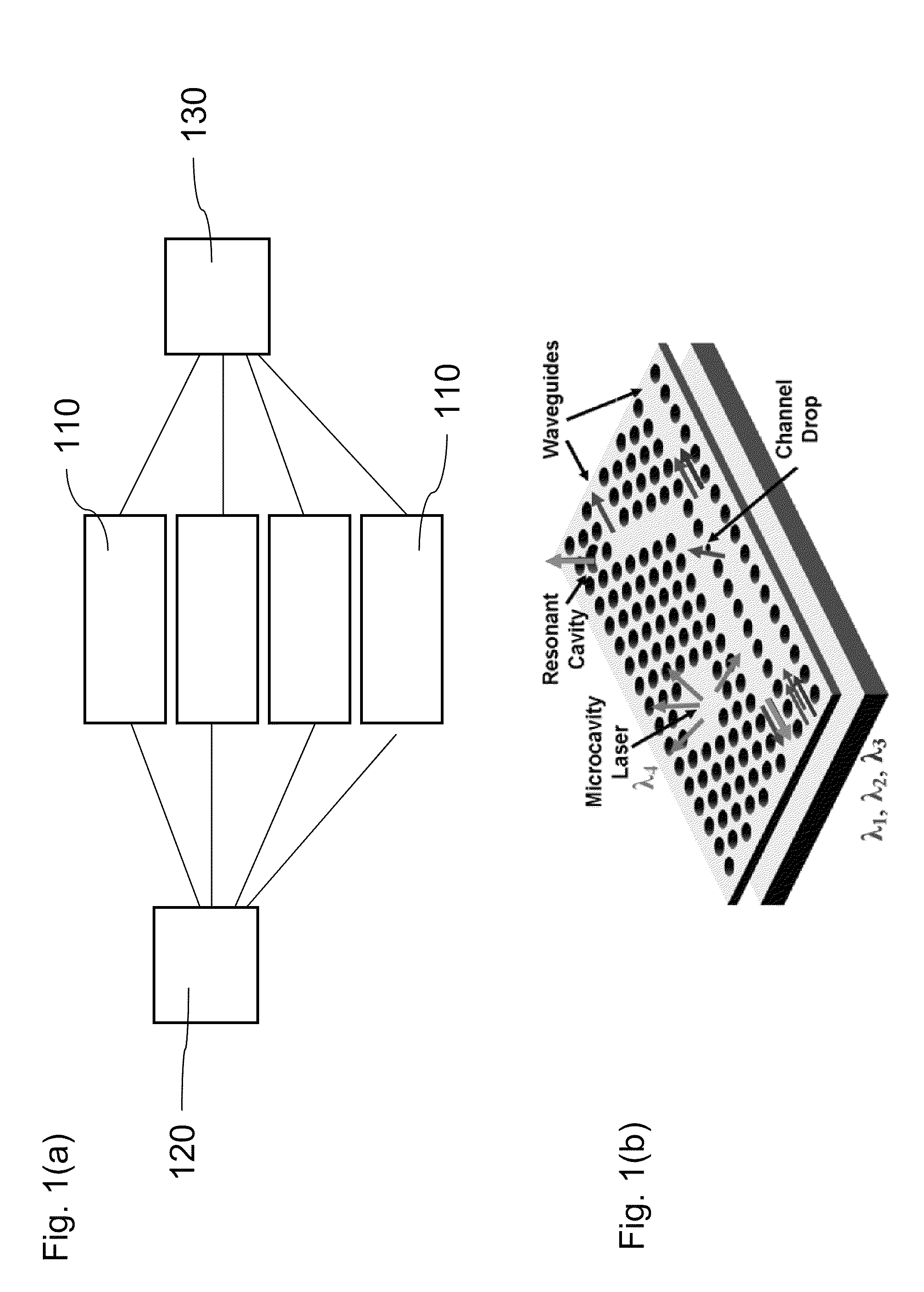
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with high-q or slow light
InactiveUS20090136181A1Remarkable effectEnhanced interactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireFluorescence
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Graphene/hyaluronic acid assembly taking cyclodextrin as medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103920160AImprove stabilityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCancer cellBiocompatibility Testing
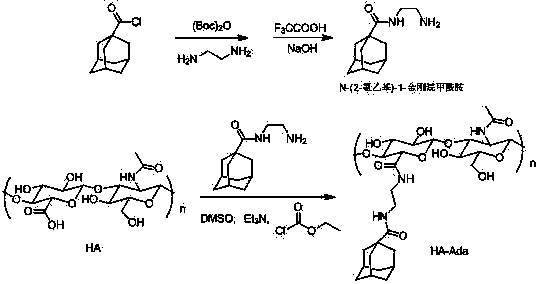
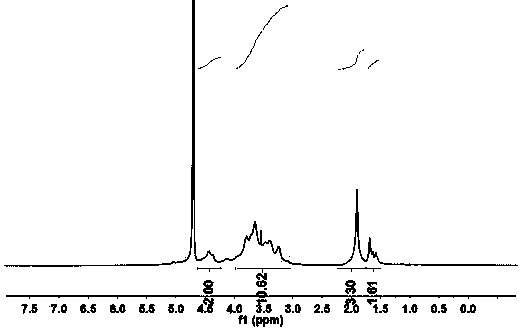
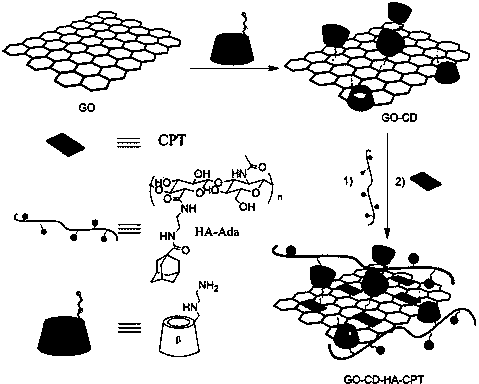
The invention discloses a graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly taking cyclodextrin as a medium. The graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly is a nano supermolecule assembly synthesized based on beta-cyclodextrin-modified graphene and adamantine-modified hyaluronic acid, wherein graphene is modified by beta-cyclodextrin; by virtue of strong host-guest interaction between beta-cyclodextrin and adamantine, graphene and hyaluronic acid are combined together to form the supermolecule assembly. The graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly has the advantages that the supermolecule assembly greatly improves stability and biocompatibility of the cyclodextrin-modified graphene under physiological conditions; by utilizing targeted recognition action of hyaluronic acid on tumor cells, the supermolecule assembly can selectively kill the cancer cells, and has anti-cancer activity higher than that of pure drug camptothecin; the targeted drug transmission system is simple in preparation process, easy to implement and low in material cost, and has potential application prospect in clinic treatment of cancers.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
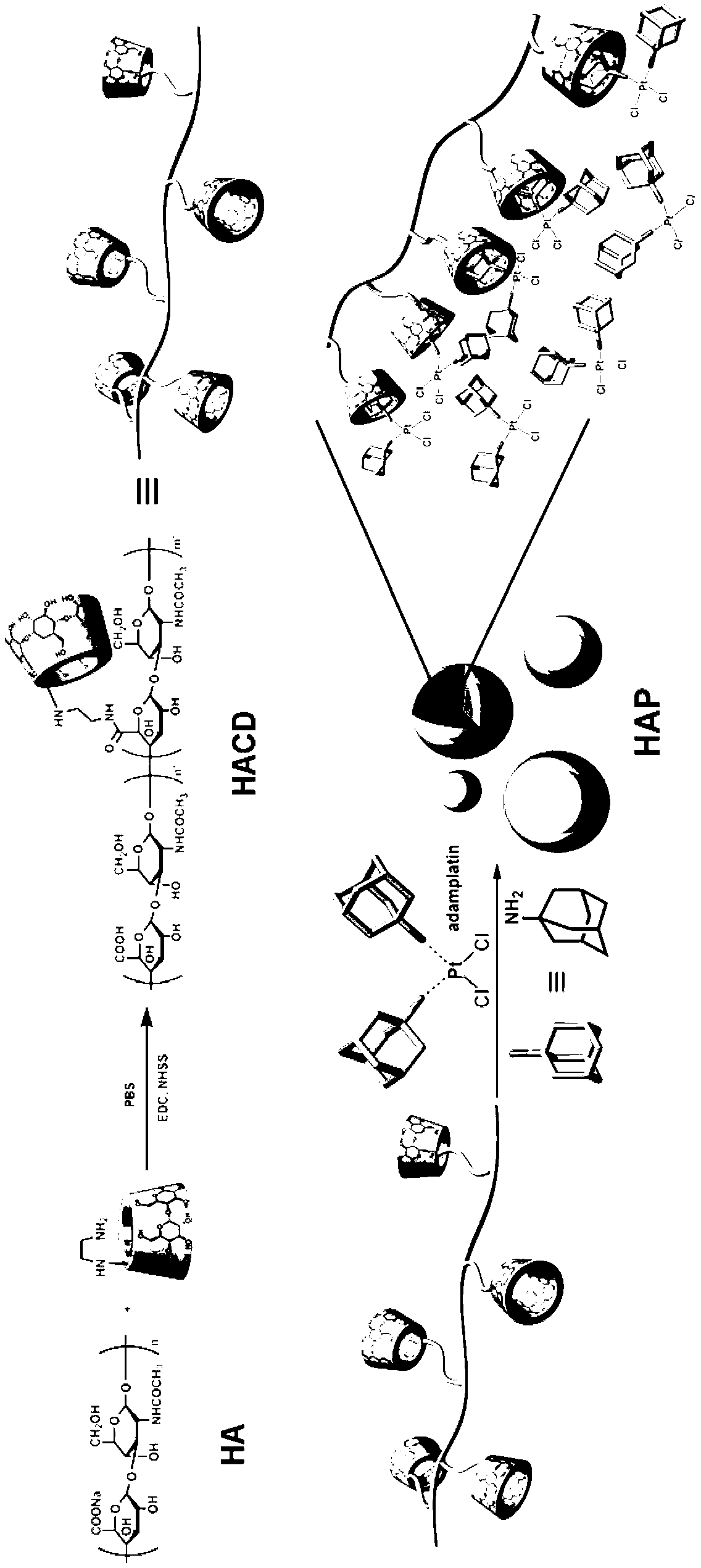
Supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin and preparation of supramolecule assembly
InactiveCN102698286AAchieve selective killingSmall toxicityHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin. The supramolecule assembly is a binary supramolecule assembly which is synthesized on the basis of cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and adamplatin. A preparation method of the supramolecule assembly is characterized in that the cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and the adamplatin are respectively synthesized, and through the strong non-covalent interaction of cyclodextrin and adamantine and the amphiphilic action of molecules, a supermolecule nano particle which takes the hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as a shell and the adamplatin as a core is formed. The supramolecule assembly disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the supramolecule assembly of the targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin has a simple synthetic route, is low in preparation cost and high in productivity, and is suitable for amplification synthesis and practical production application; and through endocytosis in which a malignant cell surface hyaluronic acid receptor serves as a medium, the supramolecule assembly (HAP) is brought in cancer cells in a target manner, so that the protection of normal cells and the targeting selective killing of cancer cells are realized, the anti-cancer activity is obviously improved, and toxic and side effects are obviously reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for constructing monatomic catalyst based on lignin/metal supramolecular assembly
ActiveCN108246330ALow priceIncrease space distanceCatalyst activation/preparationPh regulationAcid washing
The invention relates to a method for constructing a monatomic catalyst based on lignin / metal supramolecular assembly and belongs to the technical fields of preparation method of a catalytic materialand application of lignin. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) mixing a lignin and metal ionic solution with a certain concentration uniformly and adjusting the pH to form lignin / metalsupramolecular assembly precipitate; 2) centrifuging and drying to obtain a catalyst precursor; and 3) mixing the precursor and a nitrogen source and performing program high-temperature sintering under the protection of inert gas to obtain the monatomic catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the method has distinct characteristics of low raw material cost (the lignin serves as a ligand and a carrier), simple process (pH regulation and control of the precursor and stripping without acid washing), metal dispersing uniformity (coordinated complexation and increment of defect site regulation andcontrol) and the like, and large-scale production of the monatomic catalyst is easily realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
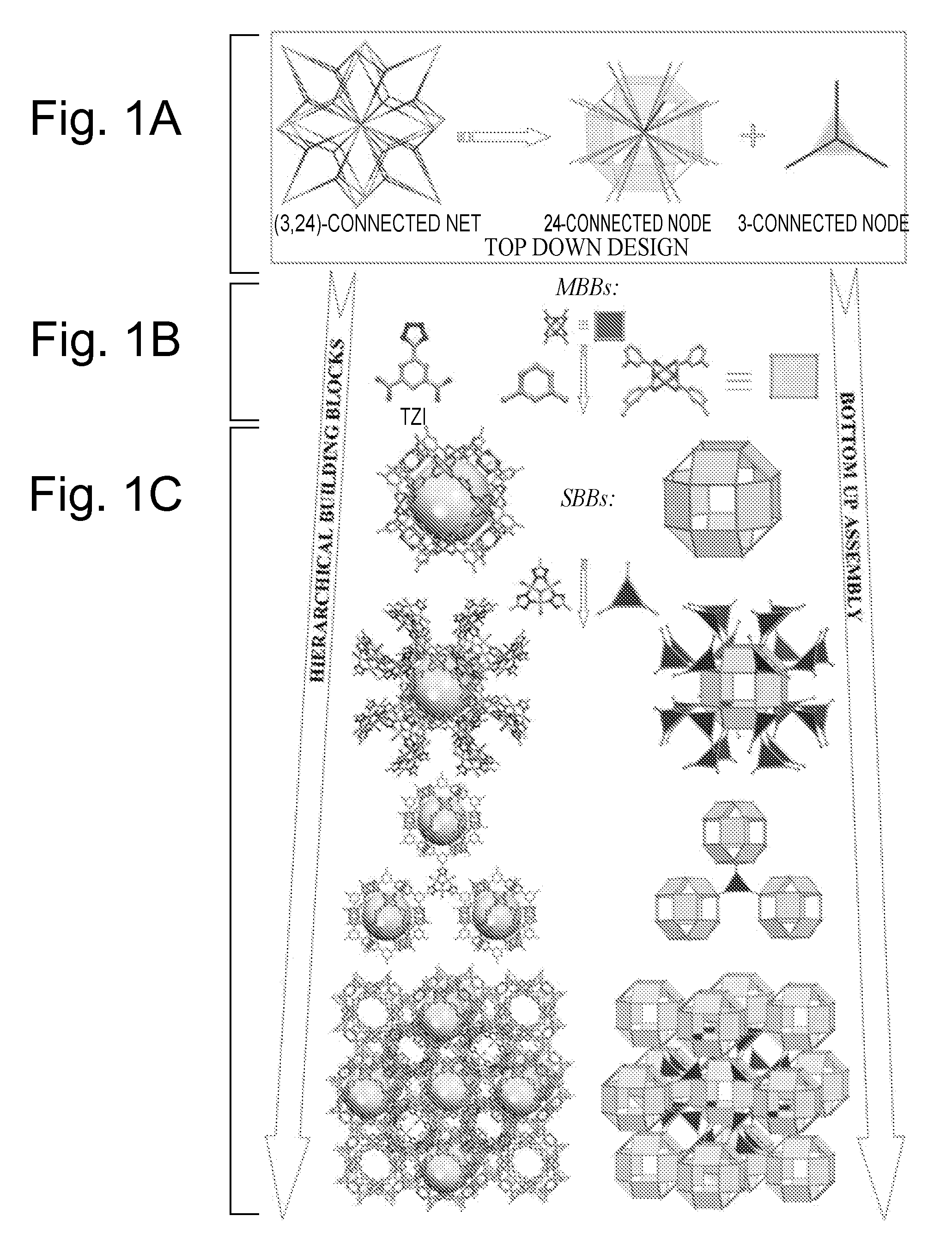
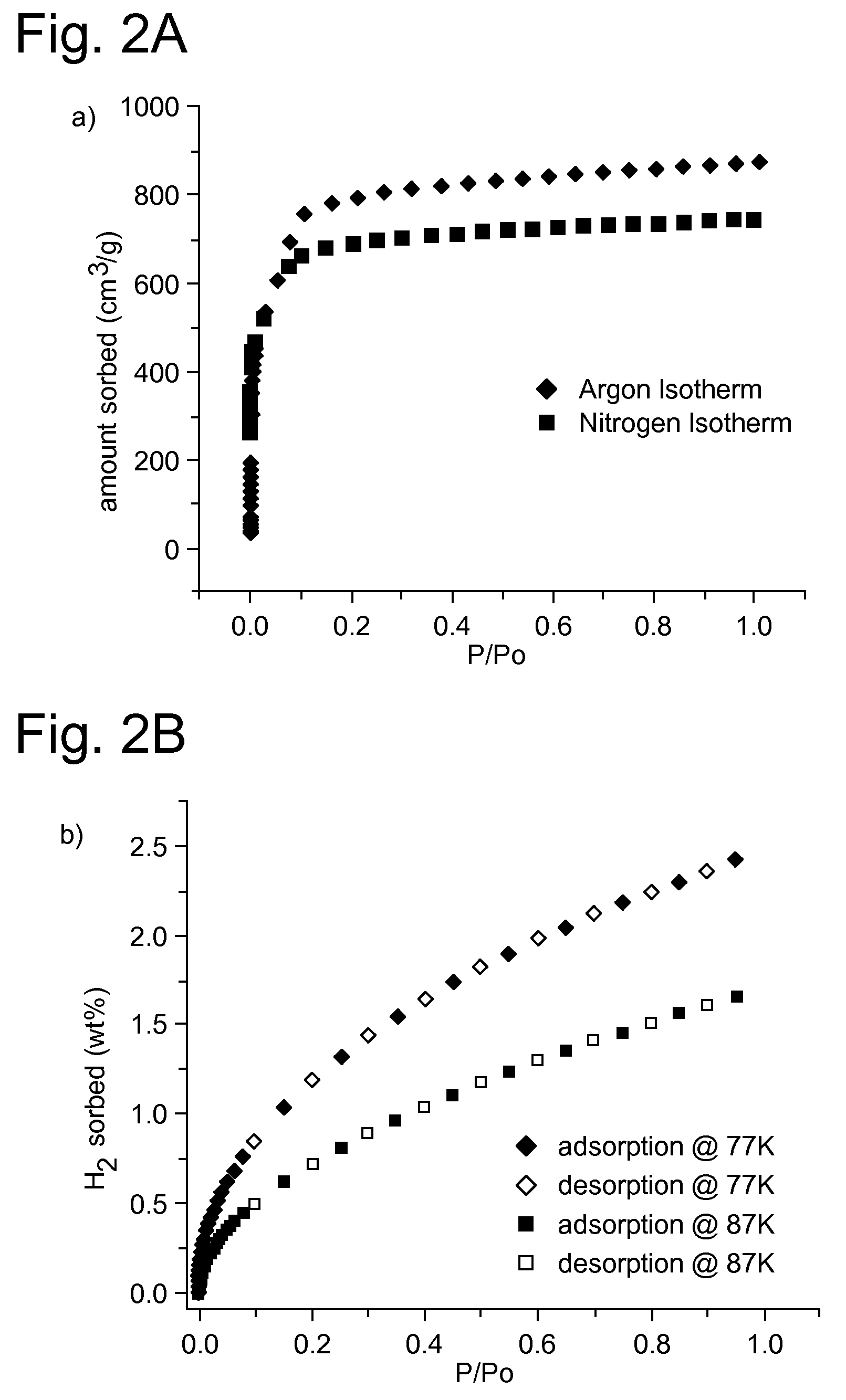
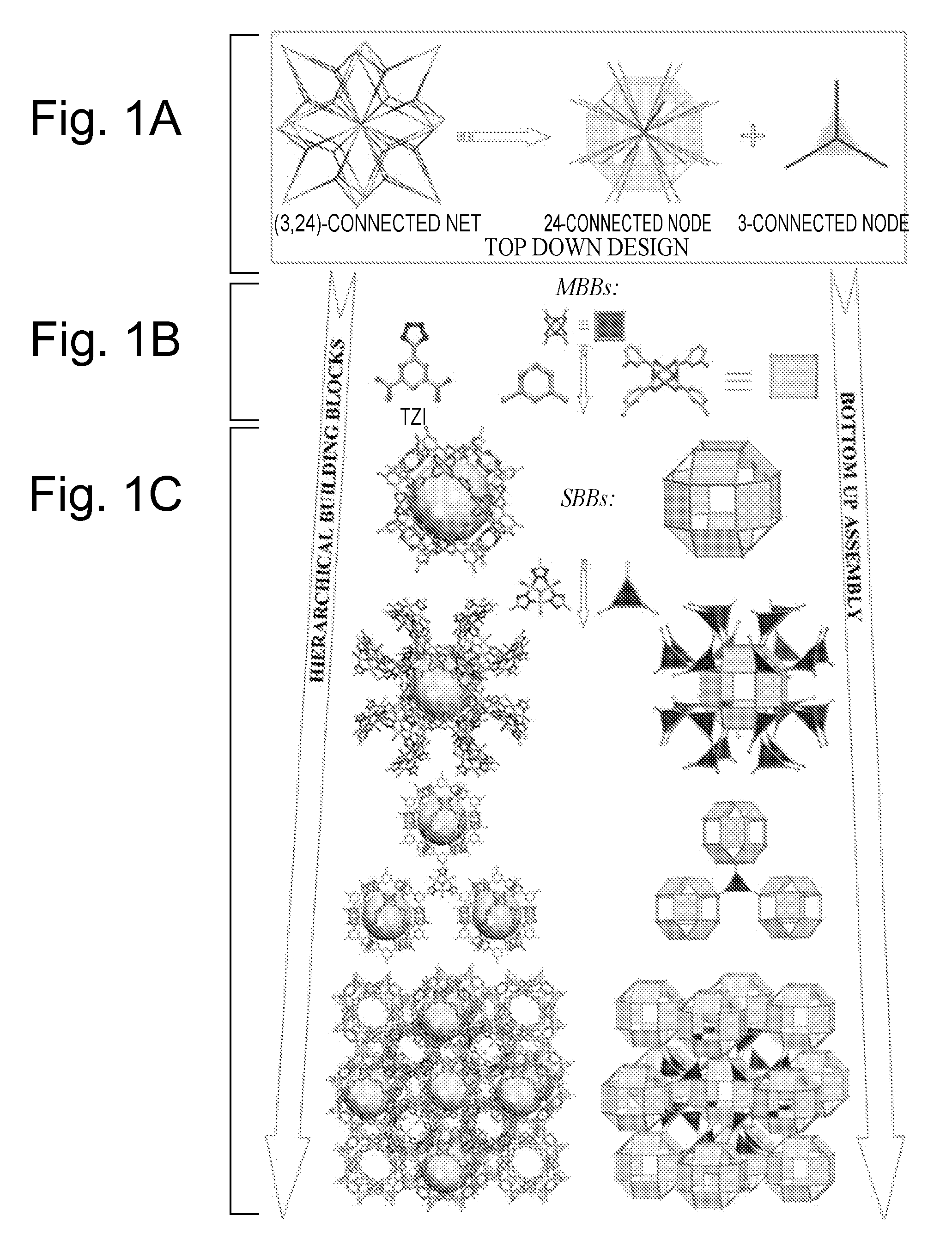
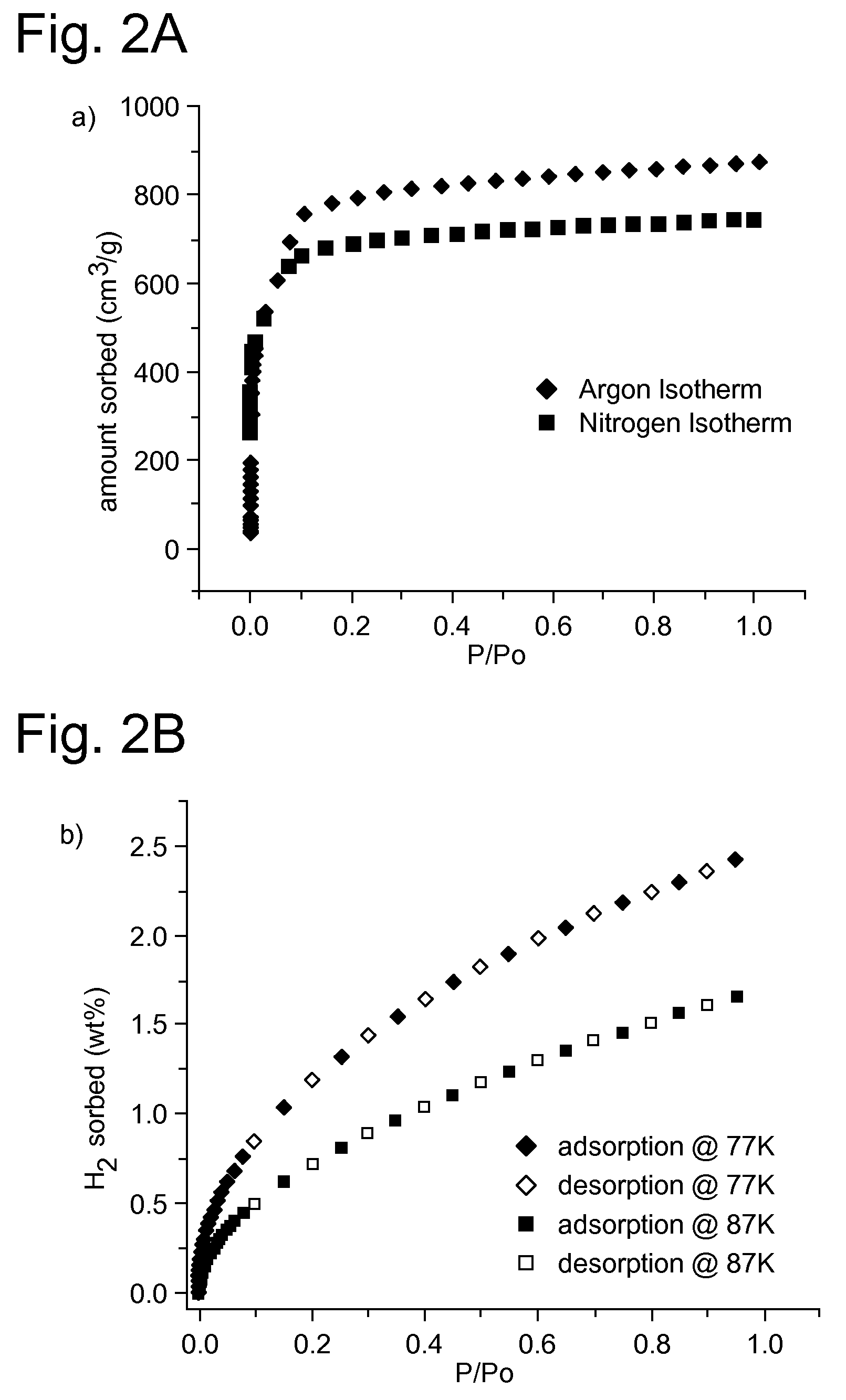
Supramolecular Assemblies and Building Blocks
ActiveUS20090143596A1Large specific surface areaLarge hole volumeGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSupramolecular assemblyStructural unit
The present invention generally relates to supramolecular assemblies and their modes of synthesis. The supramolecular assemblies include a 1:8 ratio of a supermolecular polyhedral building block and a triangular molecular building block, the supermolecular polyhedral building block having points of extension corresponding to the vertices of a rhombicuboctahedron for linking the supermolecular polyhedral building block to the triangular building block.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
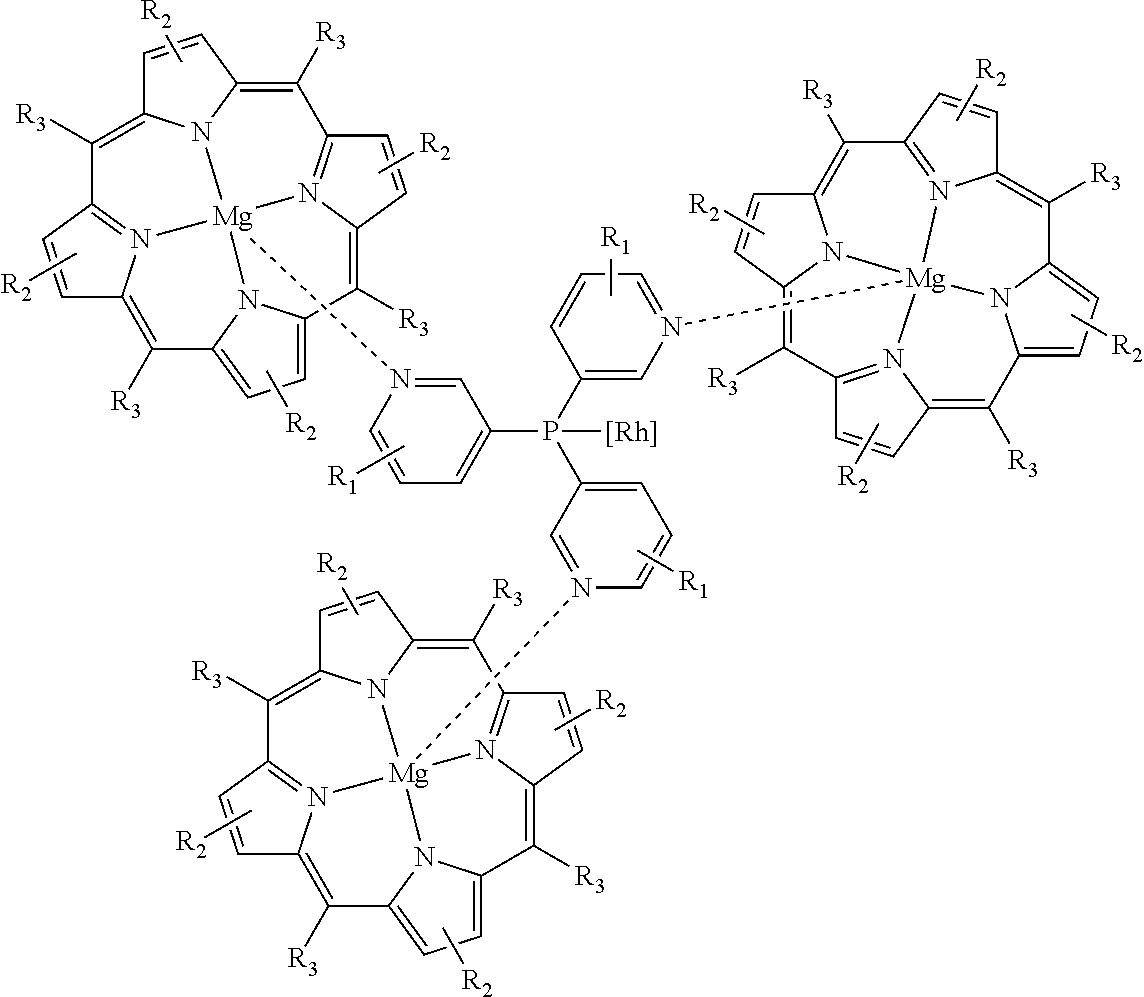
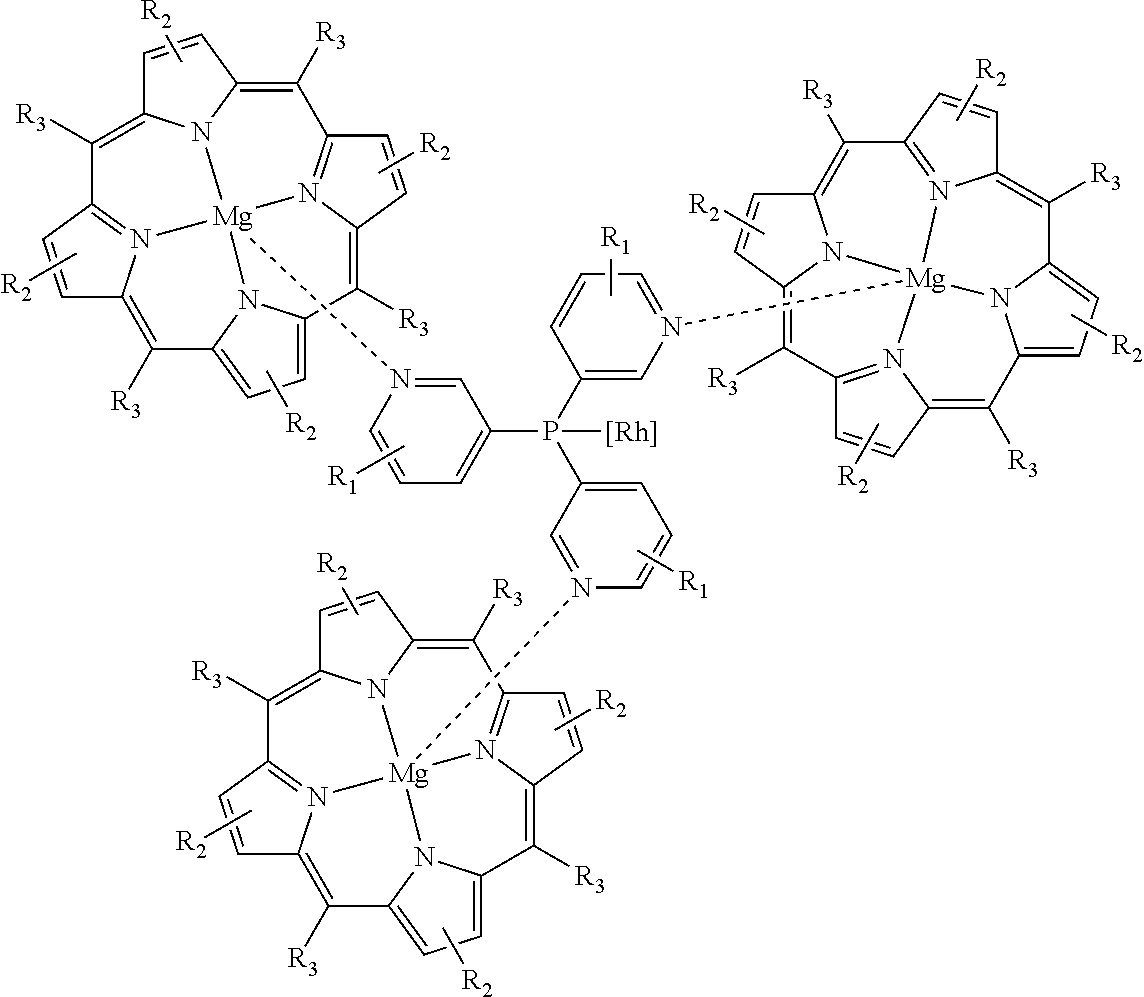
Catalysts and process for producing aldehydes
ActiveUS8710275B2Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts1-OctenePorphyrin
Modification of a unique supramolecular assembly of a pyridylphosphine ligand and a metal centered porphyrin complex is shown to give unprecedented selectivities to branched aldehydes via rhodium catalyzed hydroformylation of propylene and 1-octene. Use of magnesium in the porphyrin center provides the highest reported concentrations of iso-butyraldehyde and 2-methyl-octanal.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with High-Q or slow light
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Acetal-substituted glucosamide, preparation method and method for preparing supramolecular gel
InactiveCN104478847AThixotropicHigh response rateOrganic chemistryFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesDyeing wastewaterSupramolecular assembly
The invention discloses acetal-substituted glucosamide, a preparation method and a method for preparing a supramolecular gel. The acetal-substituted glucosamide is as shown in formula I (as shown in Specification), wherein n is selected from 1-10, 12, 14, 16 or 18. The supramolecular gel formed from the acetal-substituted glucosamide disclosed by the invention in a solution is thixotropic, high in recovery rate and controllable. The gel factors are capable of achieving oil and water separation, dye wastewater purification and the like. The supramolecular gel can be used for preparing coatings, ink and lubricants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Supramolecular hydrogel microsphere prepared by taking liquid drop as template and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104262643AAvoid pollution problems such as monomer residuesHigh monodispersity indexMacromolecular non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHigh concentrationCyclodextrin
The invention belongs to the fields of supramolecular polymer polymer chemistry and drop formation control, and particularly relates to supramolecular hydrogel microsphere modified with cyclodextrin water-solubility polymer and adamantine water-solubility polymer and formed by assembling subjective and objective bodies in a liquid drop, and a preparation method and application thereof. The first purpose of the invention is to provide novel supramolecular hydrogel microsphere formed by assembling subjective and objective bodies and a preparation method thereof method, the second purpose of the invention is to adopt liquid drop as a template to realize supramolecular assembly and achieve uniform particle size and controllable dimension of the supramolecular hydrogel microsphere, and the third purpose of the invention is to provide application of the type of supramolecular hydrogel microsphere in adriacin doxorubicin and taxol water-solubility antitumor drug sustained release, so as to achieve the purpose that a drug can keep a high concentration level for a long time.
Owner:NANJING WISDOM BIOTECH
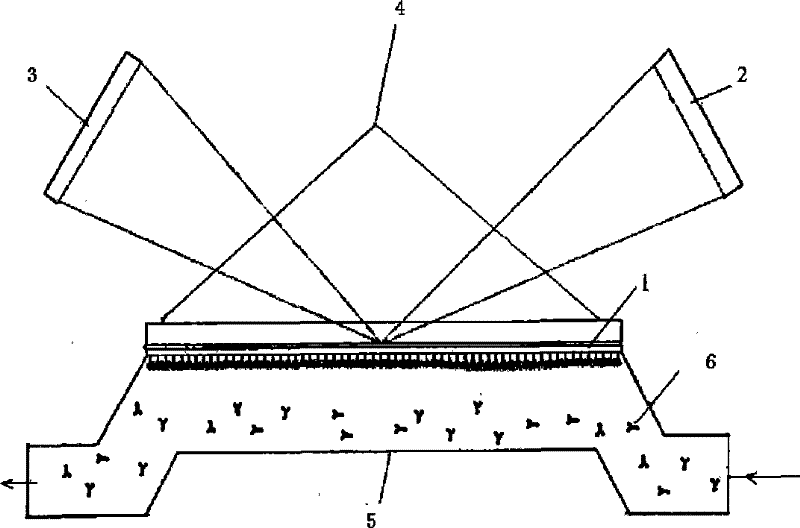
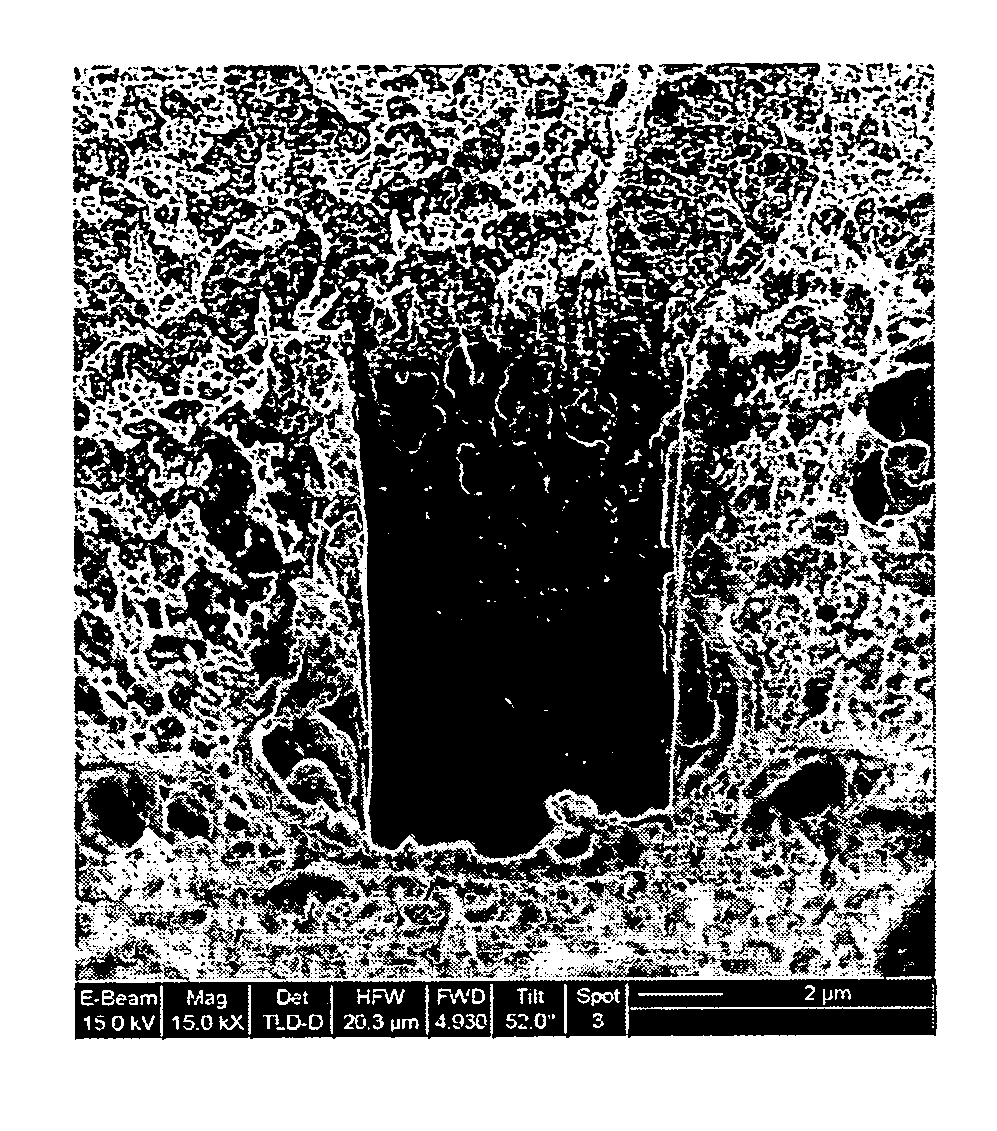
Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene
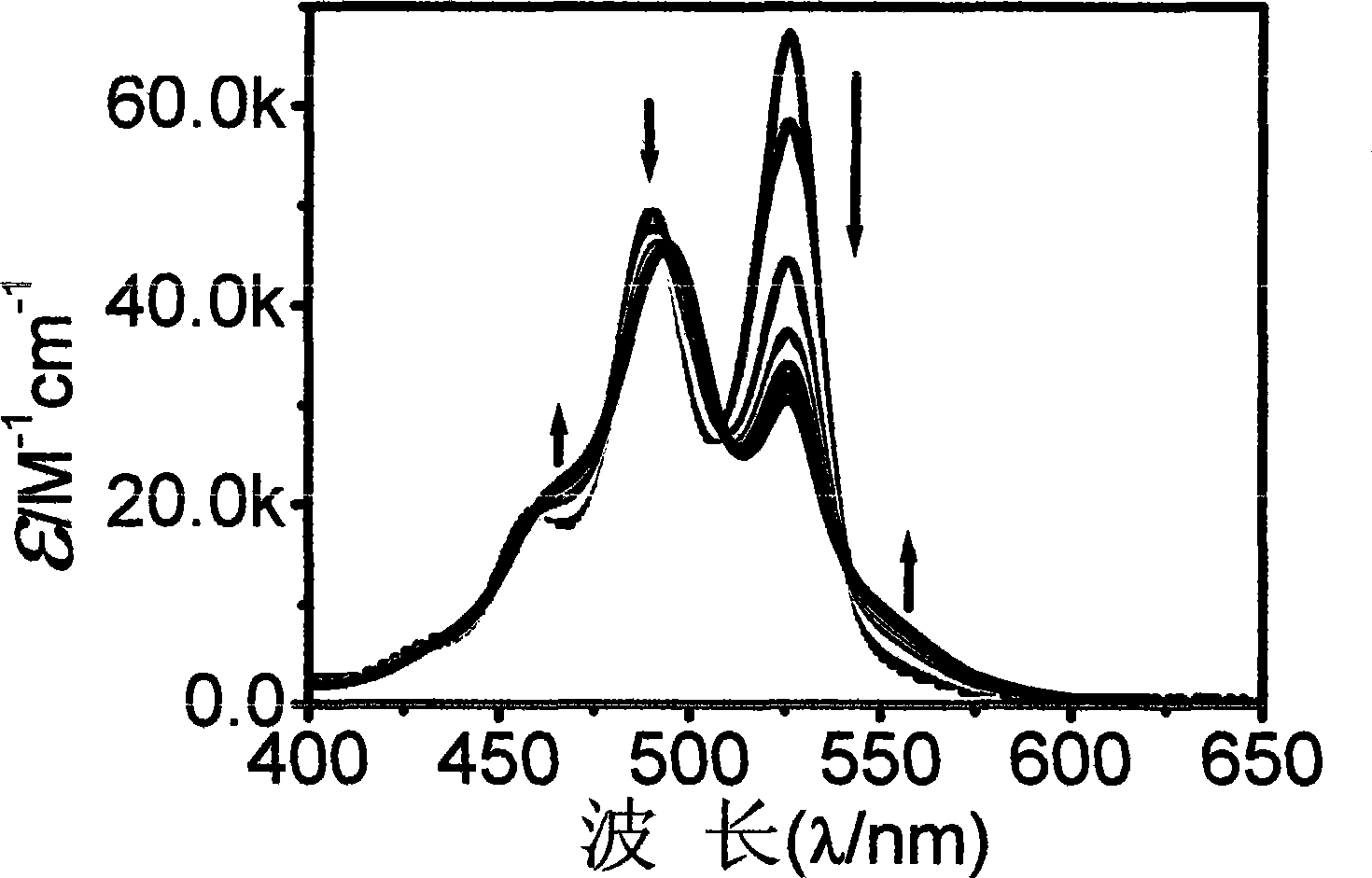
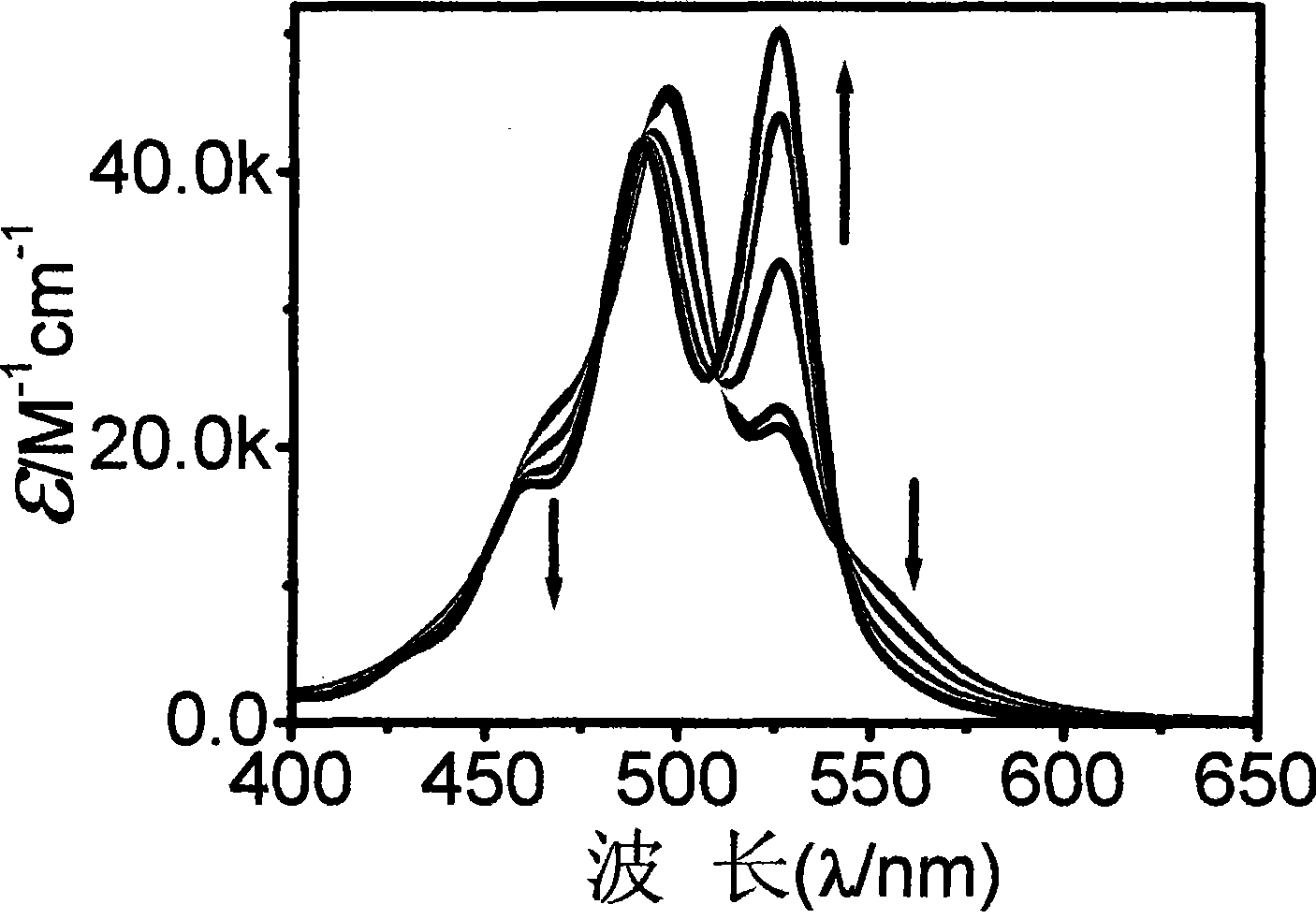
InactiveCN102258471AEasy to prepareMulti-stimuli responsiveOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellMedicine
The invention relates to preparation of sulfonated calix [4] arene-based nano supramolecular vesicles. According to the construction unit, sulfonated calix [4] arene is used as a subject (C4AS), asymmetrical purpurine is used as an object (MVC12), and a supramolecular assembly is constructed by including and coordinating interaction of the subject and the object. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving the C4AS and the MVC12 into water, and uniformly mixing the C4AS and the MVC12. The invention has the advantages that: the preparation method is simple and convenient; the consumption of raw materials of the subject and the object is low, and the subject and the object have high medicament load rate; the supramolecular vesicles have good response to the stimulus of external temperature, oxidation and reduction, addition of cyclodextrin and the like in short time; the supramolecular vesicles can load hydrophilic anti-cancer adriamycin; compared with pure adriamycin, the killing effect of the loaded adriamycin on cancer cells is not changed, and the toxic effect of the loaded adriamycin on normal cells is obviously reduced; and the supramolecular vesicles have broad application prospect in the fields of load, transport and targeted release of anti-cancer medicaments.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
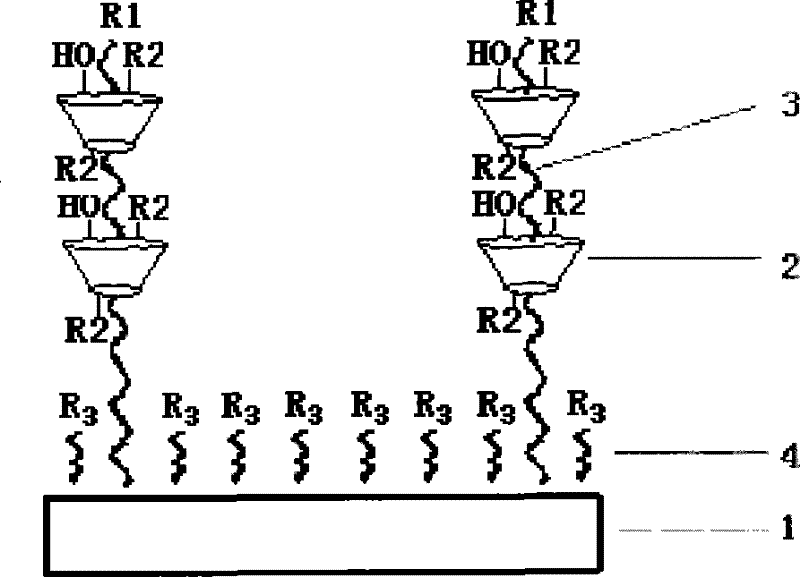
Supramolecular self-assembly biological chip, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102539777ARich varietyReduce non-specific adsorptionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by material excitationPolyrotaxaneThree-dimensional space
The invention provides a supramolecular self-assembly biological chip. The supramolecular self-assembly biological chip comprises a substrate (1), first chain molecules (3) which are fixed on the surface of the substrate, and second chain molecules (4) which are fixed on the surface of the substrate, wherein the first chain molecules and the second chain molecules are fixed on the substrate at intervals; part of one end, which is far away from the substrate, of each first chain molecule is included by cyclodextrin (2); the cyclodextrin comprises a functional group which can be directly or indirectly bound with protein molecules; and each second chain molecule is not longer than each first chain molecule. Poly(pseudo)rotaxane which is formed by coating the cyclodextrin and the first chain molecules and the second chain molecules which are arranged uniformly at the intervals are arranged on a self-assembly layer on the surface of the biological chip, a three-dimensional space has a dense, controllable and changeable structure, and compared with a two-dimensional surface, the three-dimensional space can fix more detection molecules such as the protein molecules. Moreover, the invention also provides a preparation method and application of the biological chip.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Formation of carbon and semiconductor nanomaterials using molecular assemblies
ActiveUS7544546B2Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthMetal oxide nanoparticlesGas phase
The invention is directed to a method of forming carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials. The method comprises providing a substrate and attaching a molecular precursor to the substrate. The molecular precursor includes a surface binding group for attachment to the substrate and a binding group for attachment of metal-containing species. The metal-containing species is selected from a metal cation, metal compound, or metal or metal-oxide nanoparticle to form a metallized molecular precursor. The metallized molecular precursor is then subjected to a heat treatment to provide a catalytic site from which the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials form. The heating of the metallized molecular precursor is conducted under conditions suitable for chemical vapor deposition of the carbon nanomaterials or semiconductor nanomaterials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method for detecting trypsin using unmarked fluorescence
InactiveCN102680442AEasy to makeLow costAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesActive agent
A method for detecting trypsin using unmarked fluorescence belongs to the technical field of interdisciplinary subjects of material, biology, and analytical chemistry, and particularly relates to the method for detecting the trypsin based on disassembly of supramolecular assemblies under enzymatic hydrolysis. The method is characterized by including: firstly, determining critical micellar concentration of a surfactant; secondly, forming the supramolecular assemblies with the surfactant and polyelectrolyte with opposite charges through hydrophobic and electrostatic interaction, and embedding hydrophobic dyes serving as fluorescent probes into the inner cavities of the supramolecular assemblies; thirdly, adding enzyme which can lead to hydrolysis in the polyelectrolyte so as to lead the disassembly of the supramolecular assemblies and release the embedded hydrophobic dyes, and detecting enzyme activity by lowering fluorescence intensity. The method is simple to prepare, low in cost, real-time in detection, and wide in application prospect in fields such as diagnosis and detection of biomolecules, and biosensors.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
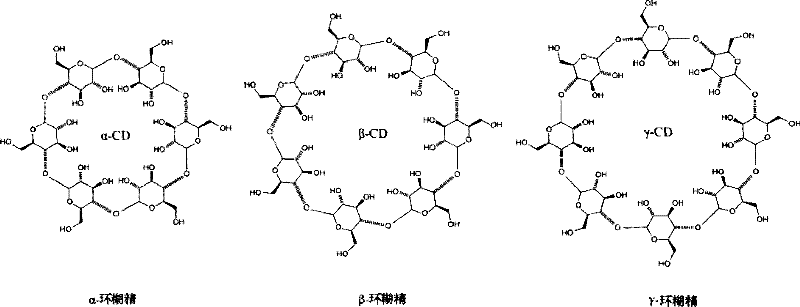
Perylene-cyclodextrin nano supermolecule assembly, as well as preparation and application thereof
The invention pertains to the technical field of nanometer supramolecular materials, and relates to a nanometer supramolecular assembly of a perylene diimide derivate modified by full methylated Beta-cyclodextrin loaded by polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the molecular assembly is C138H226N2O72, and the structure thereof is shown as in an attached drawing. The perylene diimide derivate modified by the red fully methylated Beta-cyclodextrin is dissolved to obtain the nanometer supramolecular assembly. The method adopts the strong fluorescence of solid perylene as a detecting singnal, takes an empty chamber of the fully methylated Beta-cyclodextrin as a receptor of an air molecule, thereby solving two difficulties of strong fluorescence in a solid state in the construction of a fluorescence sensor and the introduction of a suitable air molecular receptor. The nanometer supramolecular assembly of the perylene diimide derivate modified by full methylated Beta-cyclodextrin loaded by PVDF member realizes quick detection of the fluorescence sensing function of the air molecules of nitromethane, nitroethane and nitrobenzene in 10s.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
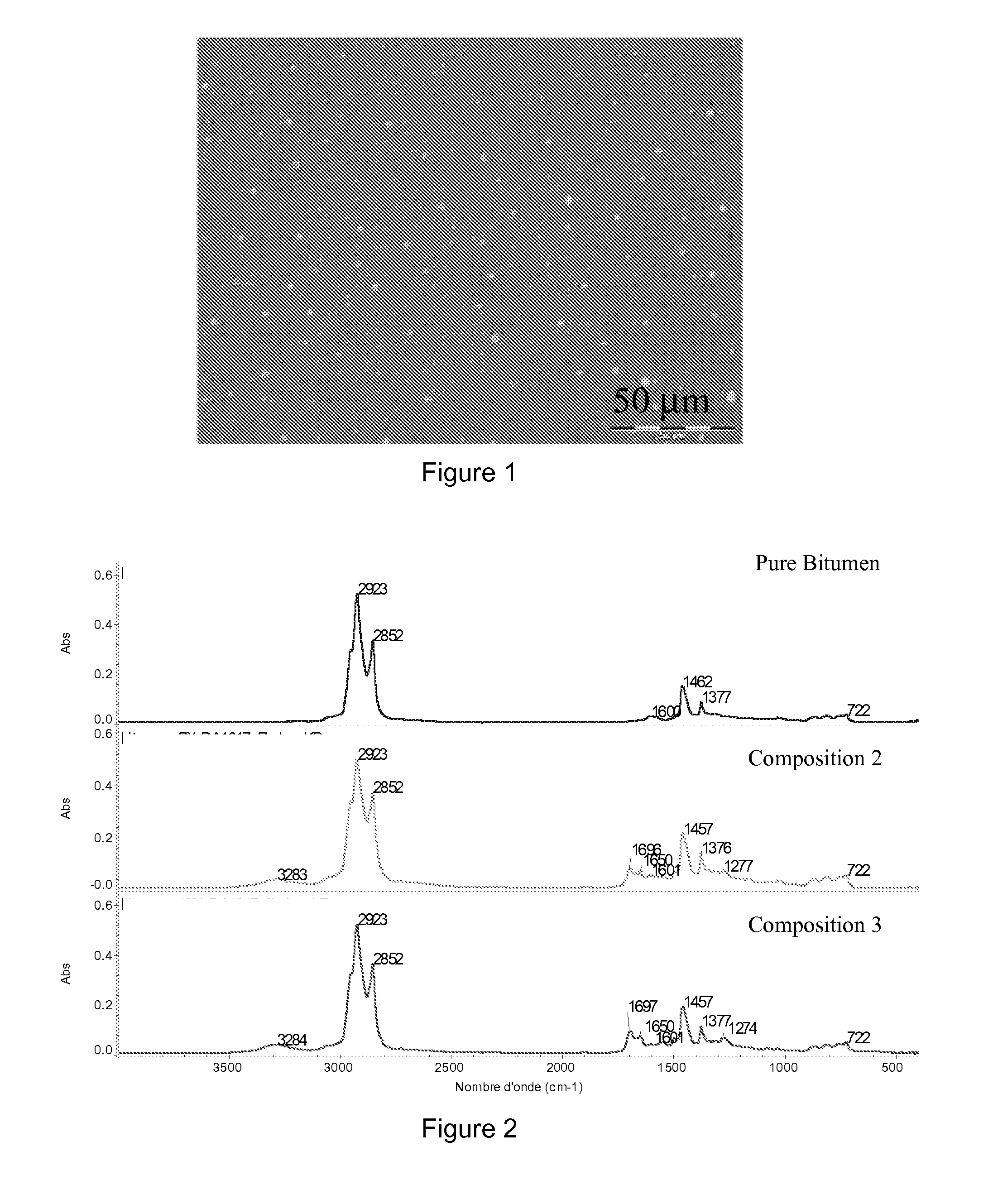
Bituminous compositions
InactiveUS20110009533A1Easy to recycleImprove liquidityIn situ pavingsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansSupramolecular assemblyAsphalt
This invention relates to the modification of bitumen by polymeric materials used particularly for the preparation of asphalt mixtures with enhanced mechanical properties, wherein the polymeric materials are selected from additives capable of forming a supramolecular assembly. The modified bitumen may be used for the fabrication of asphalts mixtures with mineral aggregates used in construction or maintenance of sidewalks, roads, highways, parking lots or airport runaways and service roads and any other rolling surfaces.
Owner:CECA SA
Supramolecular assemblies and building blocks
InactiveUS8034952B2Large specific surface areaLarge hole volumeGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSupramolecular assemblyRhombicuboctahedron
The present invention generally relates to supramolecular assemblies and their modes of synthesis. The supramolecular assemblies include a 1:8 ratio of a supermolecular polyhedral building block and a triangular molecular building block, the supermolecular polyhedral building block having points of extension corresponding to the vertices of a rhombicuboctahedron for linking the supermolecular polyhedral building block to the triangular building block.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
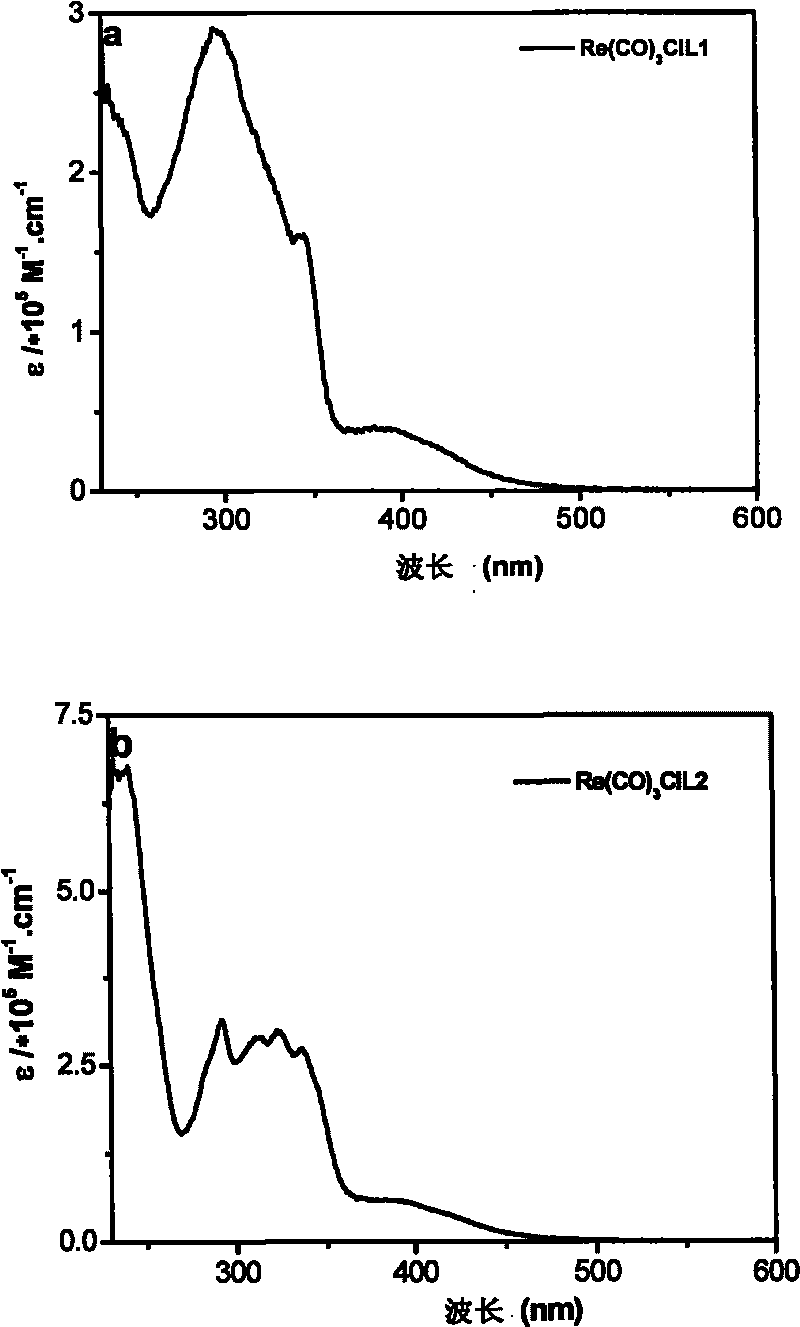
Tricarbonal rhenium (I) complexes containing carrier-transporting groups (oxadiazole or carbazole), preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101698672AEasy to synthesizeEasy to purifySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRheniumPhotoluminescence
The invention provides substituted tricarbonal chloride [2-(2-pyridyl) benzimidazole] co-rhenium complexes or substituted tricarbonal chloride (2,2'-dipyridyl amine) co-rhenium, which are tricarbonal chloride [1-(4-5'-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole phenyl)-2-(2-pyridyl) benzimidazole] co-rhenium (I), tricarbonal chloride [1-(4-N-carbazolyl phenyl)-2-(2-pyridyl) benzimidazole] co-rhenium (I), tricarbonal chloride [N-(4-5'-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole phenyl)-2,2'-dipyridyl amine] rhenium co (I) and tricarbonal chloride [N-(4-N-carbazolyl phenyl)-2,2'-dipyridyl amine] co-rhenium (I). The complexes have a structural formula as follows. The tricarbonal rhenium (I) complexes having the advantages of simple synthesis, help to purification, high yield and stable properties in air can be applied to molecular catalysis, solar energy conversion, colorimetric analysis, molecular recognition, supramolecular assembly, optical information storage, photoluminescence probes in organisms, and other fields. The invention discloses a preparation method for the complexes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
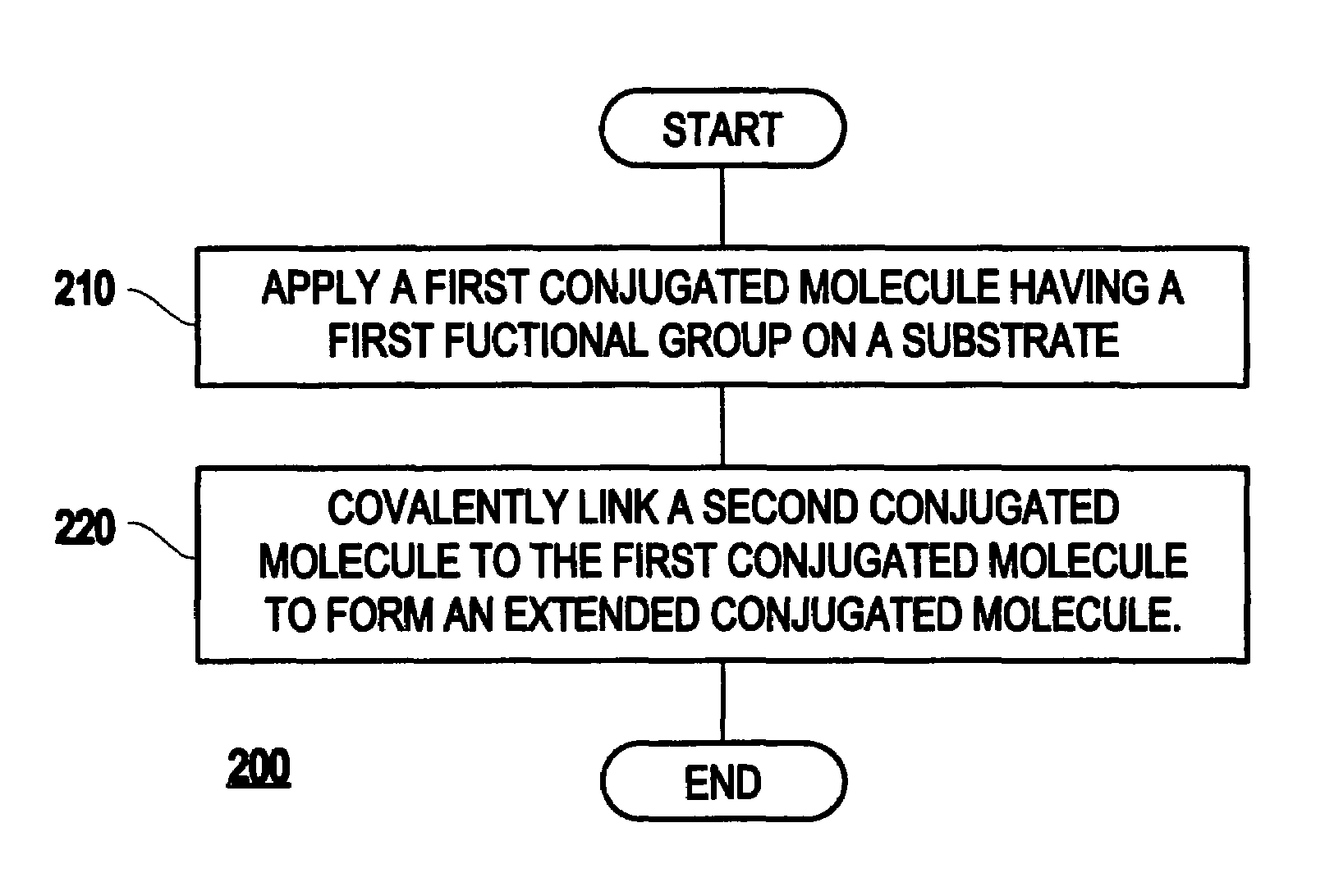
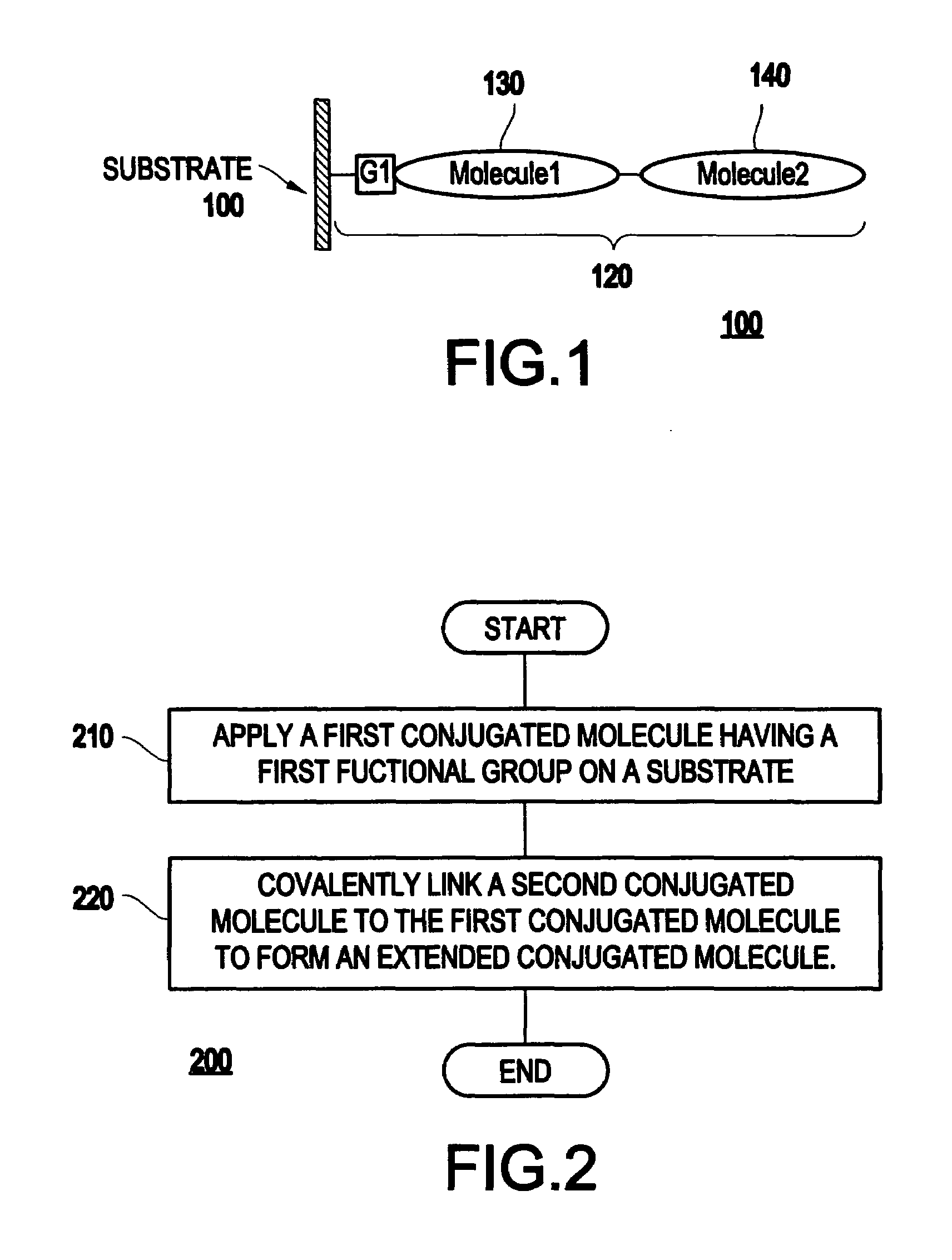
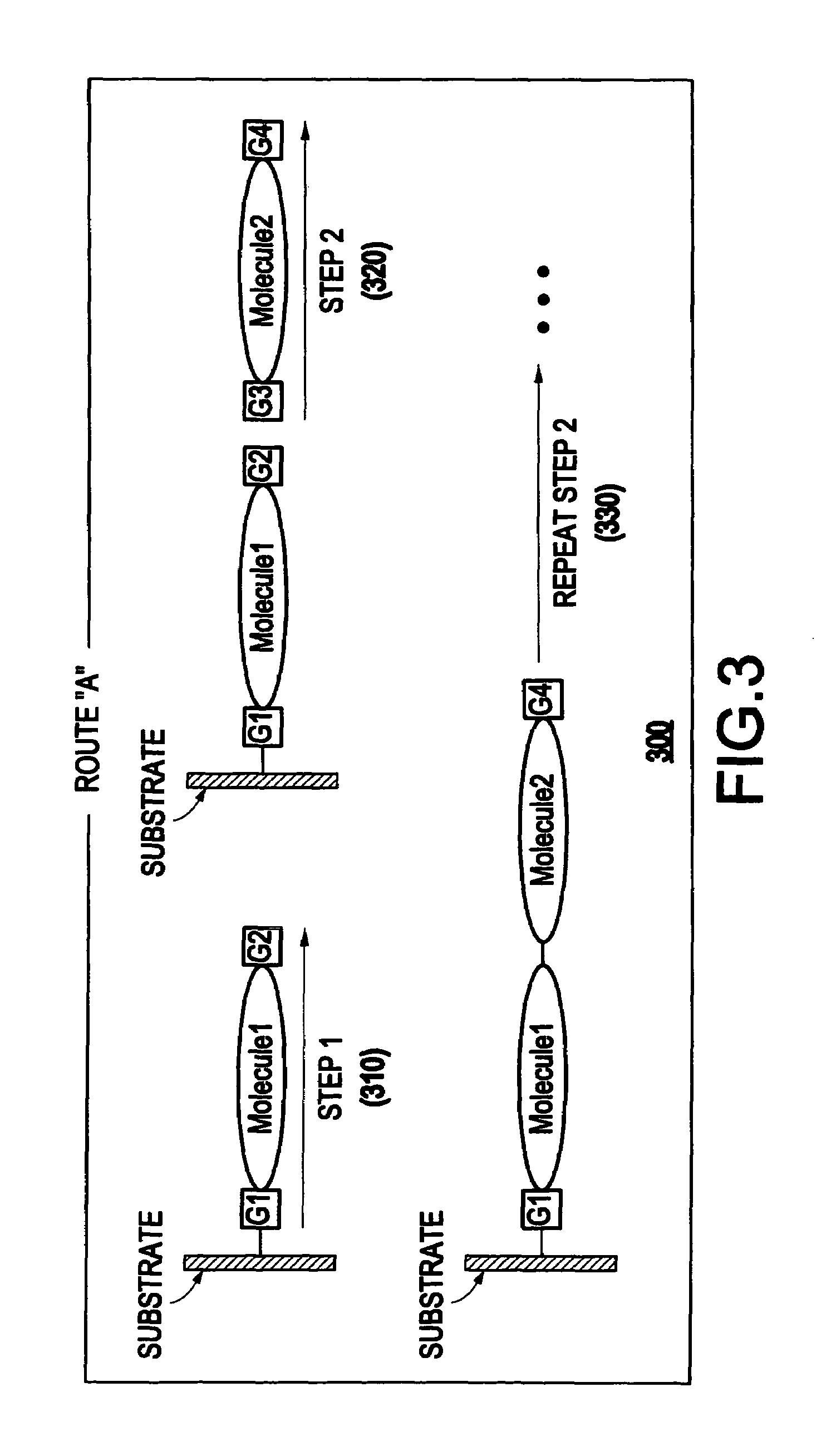
Method of preparing a conjugated molecular assembly
InactiveUS7166327B2Improve propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsOrganic groupSupramolecular assembly
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Preparation method of supermolecular nanometer aggregate with triple responses of temperature, UV (ultraviolet) and reducing agent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a supermolecular nanometer aggregate with triple responses of temperature, UV (ultraviolet) and reducing agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of using a beta-cyclodextrin-modified thermo-sensitive copolymer (beta-CD-P(MEO2MA-co-OEGMA)) as a host molecule, and using an azobenzene-terminated amphiphilic blocking copolymer (Azo-PCL-SS-PEG) as a guest molecule, and building a supermolecular assembly with a mutual electrostatic action of the host molecule and the guest molecule; using a sulfonation and bromination product of the beta-cyclodextrin to initiate ATRP (atom transfer radical polymerization) reaction, so as to obtain the host molecule; using chain-extended 4-hydroxyazobenzene to open a loop of caprolactone, and performing a two-step esterification reaction, so as to obtain the guest molecule; respectively dissolving the host molecule and the guest molecule into water, and uniformly mixing, so as to obtain a supermolecular self-assembly micellar solution. The preparation method has the advantages that by applying outside irritation to the system, the shape and size of the micelle can be reversibly and controllably transformed; the application prospect in the fields of medicine loading and controllable release, biological intelligent switches, nanometer intelligent reactors and the like is wide.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
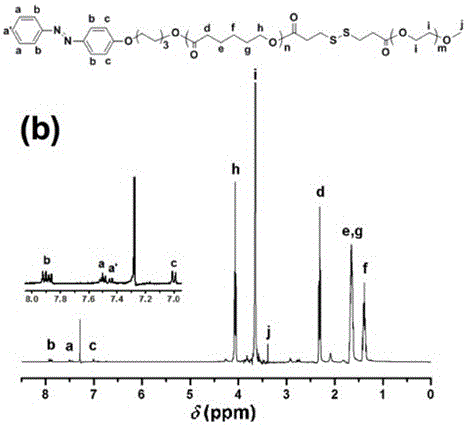
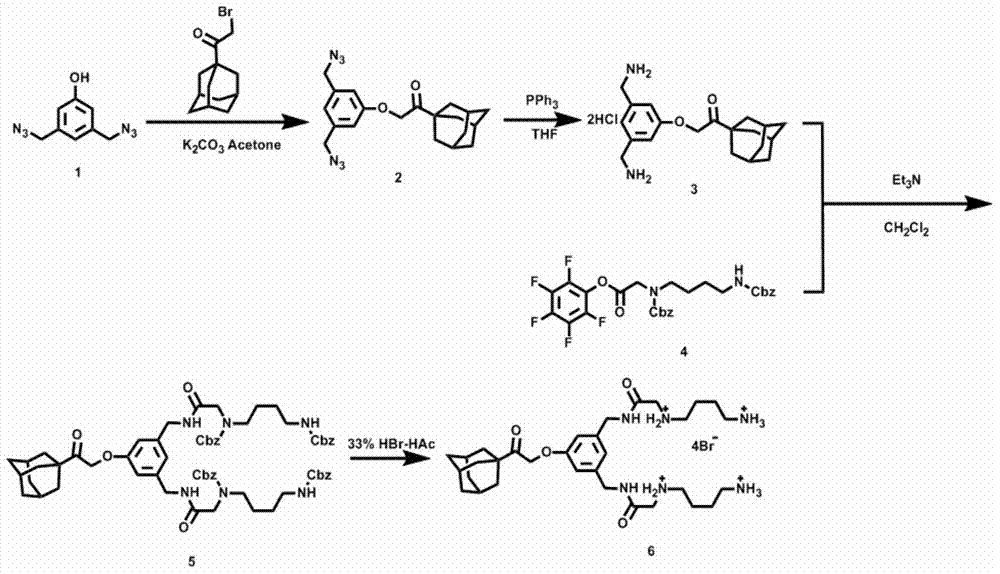
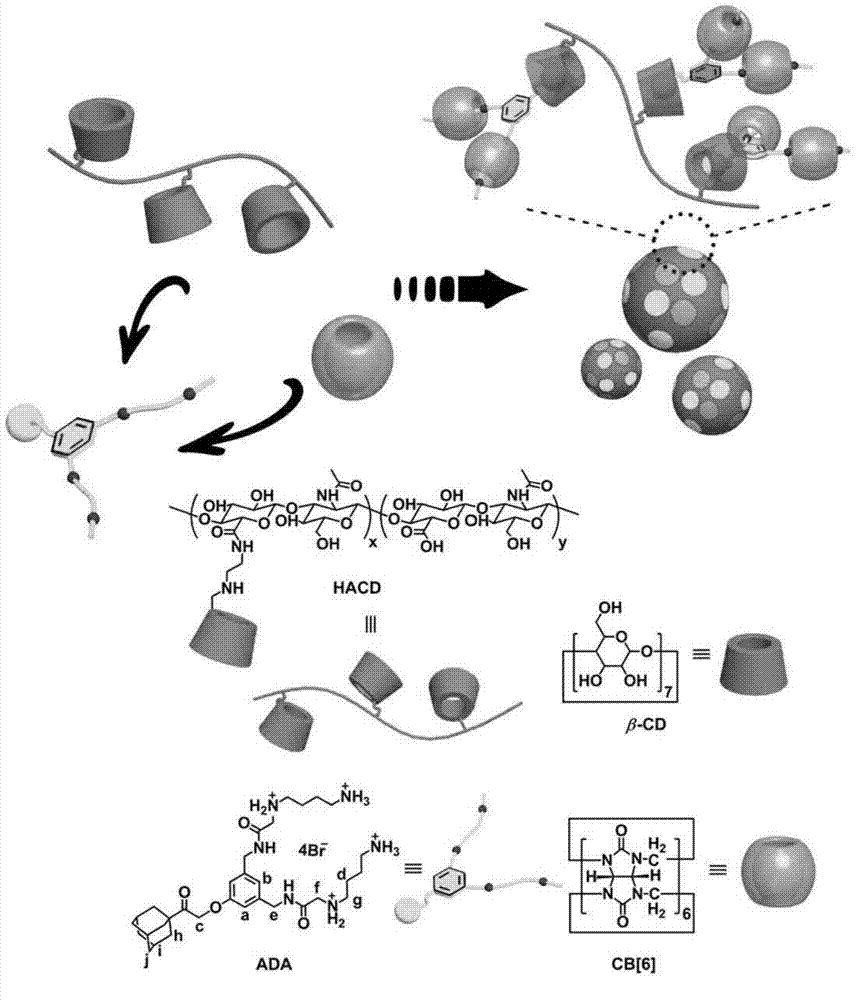
Supermolecular assembly for small interfering RNA targeting delivery and preparation method
InactiveCN104840975AAvoid decomposition and inactivationImprove gene transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention relates to a supermolecular assembly for small interfering RNA targeting delivery. The supermolecular assembly is a four-element supermolecular assembly synthesized on the basis of beta-cyclodextrin modified hyaluronic acid, an adamantine polyamine compound, cucurbituril [6] and small interfering RNA. The four-element supermolecular assembly is based on the strong non-covalent interaction between beta-cyclodextrin and adamantine and between adamantine polyamine chain and cucurbituril [6], and the electrostatic interaction between the adamantine polyamine chain and small interfering RNA, and forms supermolecular nanoparticles with hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as the shell. The supermolecular assembly provided by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis and construction route, low production cost and high yield, and is suitable for amplified synthesis and actual production application. Through the endocytosis of a malignant tumor cell surface overexpressed hyaluronic acid receptor as a medium, the four-element supermolecular assembly can be brought into cancer cells targetedly, thus realizing effective silencing to exogenous gene expression and significantly reducing the toxic and side effect at the same time.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Regenerative Nanosensor Devices
ActiveUS20140191186A1Improved probe immobilizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnalyteDesorption
The present invention provides a regenerative nanosensor device for the detection of one or more analytes of interest. In certain embodiments, the device comprises a nanostructure having a reversible functionalized coating comprising a supramolecular assembly. Controllable and selective disruption of the assembly promotes desorption of at least part of the reversible functionalized coating thereby allowing for reuse of the regenerative device.
Owner:YALE UNIV
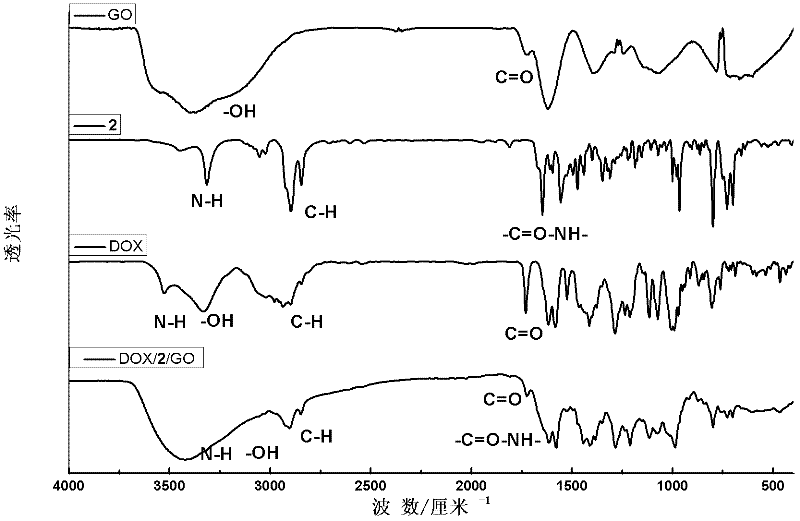
An assembly for targeted delivery of doxorubicin anticancer drug and its preparation method
InactiveCN102258788AAchieve selective killingLow costOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsChemical compoundCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a targeted transmission assembly of an adriamycin anticancer medicine. The targeted transmission assembly is a ternary supermolecular assembly synthesized by using graphene oxide, folic acid modified cyclodextrin compound and adamantine modified porphyrin compound. The preparation method comprises: synthesizing folic acid modified beta-cyclodextrin and adamantine modified porphyrin respectively, absorbing the folic acid modified beta-cyclodextrin onto the graphene oxide under pi-pi action by using porphyrin as a medium, introducing folic acid onto the surface of graphene by using the strong noncovalent action of the adamantine and beta-cyclodextrin, and preparing the assembly by using the surface of the graphene oxide as the carrier of the pi-system adriamycin anticancer medicine. The invention has the advantages that: the synthesis route of the targeted medicine transmission assembly is simple, the yield of the targeted medicine transmission assembly is high, and the targeted medicine transmission assembly is suitable for amplified synthesis and use in actual production; and the assembly 1 / 2 / DOX / GO is brought into a targeted cancer cell under endocytosis with a folic acid receptor in a malignant cell as a medium, so that the protection of normal cells and the targeted selective killing of cancer cells are realized.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for separating mixer of 2,4-dichlorophenol and 2,5-dichlorophenol
ActiveCN101412664AHigh purityHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSpatial structureDichlorophenol
The invention provides a method for separating a mixture of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and 2, 5-dichlorophenol. Based on the fundamental principle of supramolecular assembly, the method uses topology match between subjective molecules and objective molecules, and separates 2, 4 / 2, 5-mixed dichlorophenol by identifying molecules. Because of different molecular spatial structures of the 2, 4-dichlorophenol and the 2, 5-dichlorophenol and certain difference on polarities, specific different identifying capability among the subjective molecules exists, while difficulty or ease of intermolecular actions among the subjective molecules and other heterocyclic compound is different, therefore, the aim of separation can be achieved through identifying the molecules. The product obtained from the 2, 4 / 2, 5-mixed dichlorophenol by the method has high purity, and can be directly used after being separated, but does not need to be recrystallized to improve purity; and the method has high yield, is simple and practical, and is easy to industrialize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescent nanoparticle solution, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a fluorescent nanoparticle solution. A building unit of the fluorescent nanoparticle uses sulfonato calix[4]arene derivative as the host and tetraphenylethylene quaternary ammonium salt as the guest. A supramolecular assembly is built through interactions of inclusion and complexation of the host-guest among the building units. The sulfonato calix[4]arene derivative is a single-bridged sulfonato calix[4]arene containing a sulfonato calix[4]arene unit or double-bridged sulfonato calix[4]arene containing two sulfonato calix[4]arene units. A preparation method provided by the invention is as follows: tetraphenylethylene quaternary ammonium salt is firstly prepared, and then tetraphenylethylene quaternary ammonium salt and sulfonato calix[4]arene derivative are dissolved into water and mixed uniformly to obtain the final product. The fluorescent nanoparticle solution provided by the invention has the advantages that: (1) the nanoparticle has the specific gathered fluorescence emission characteristic of tetraphenylethylene and the tetraphenylethylene derivatives; and (2) with the fluorescent nanoparticle, a high sensitive sensing to 2,4,6-trinitrophenol can be realized, which means that the fluorescent nanoparticle has a broad application prospects in the sensing technology field of explosive nitro compounds.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
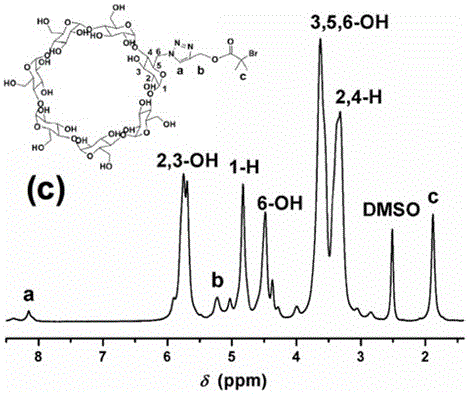
Application and application method of cucurbit(10)uril-based supramolecular self-assembly
ActiveCN106902553AEffective Broad Spectrum CaptureEffective Broad Spectrum PrecipitationSedimentation separationSupramolecular assemblyPrecipitation
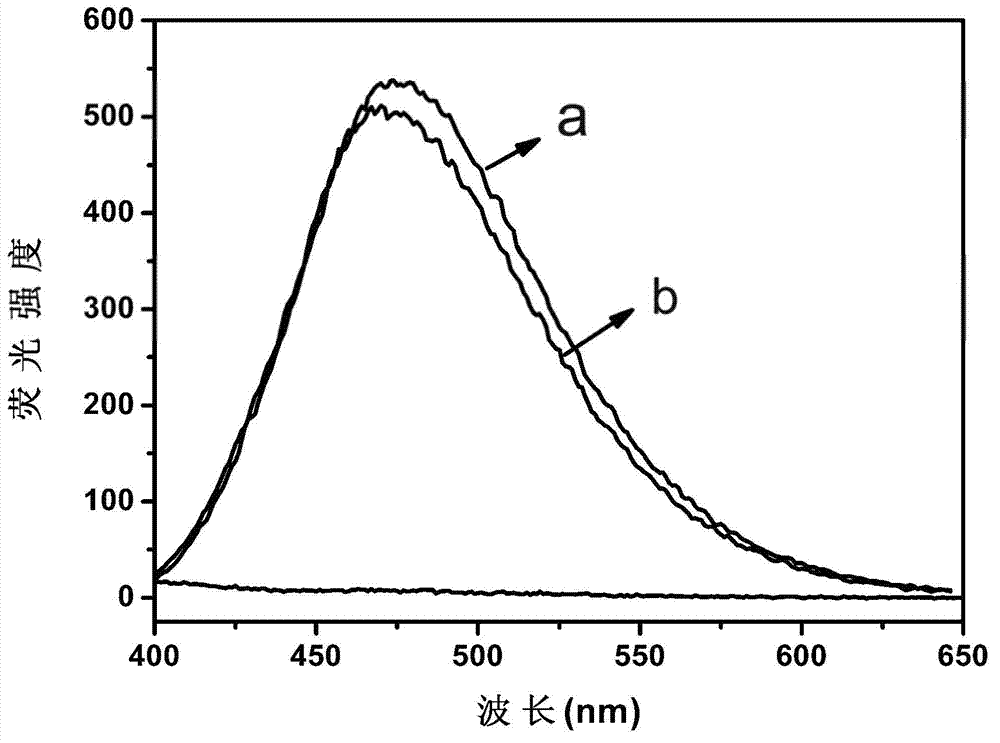
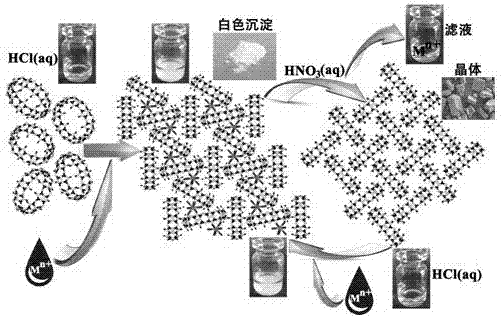
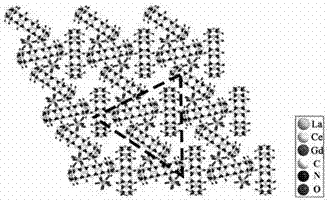
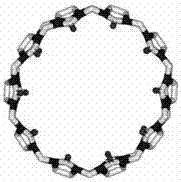
The invention discloses application and an application method of a cucurbit(10)uril-based supramolecular self-assembly. The cucurbit(10)uril-based supramolecular self-assembly captures, precipitates and releases metal ions. Effective wide-spectrum trap and precipitation of metal ions can be achieved, and specific metal ions can be captured in a specific system. After capturing, crystals can be dissolved in a nitric acid system to obtain cucurbit(10)uril with no metal ions.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com























![Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/778ed604-4a0f-4530-b4b8-48a482934b48/HDA0000056889960000011.PNG)
![Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/778ed604-4a0f-4530-b4b8-48a482934b48/HDA0000056889960000012.PNG)
![Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene Preparation and application of a nano-supramolecular vesicle based on sulfonated calix[4]arene](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/778ed604-4a0f-4530-b4b8-48a482934b48/HDA0000056889960000021.PNG)