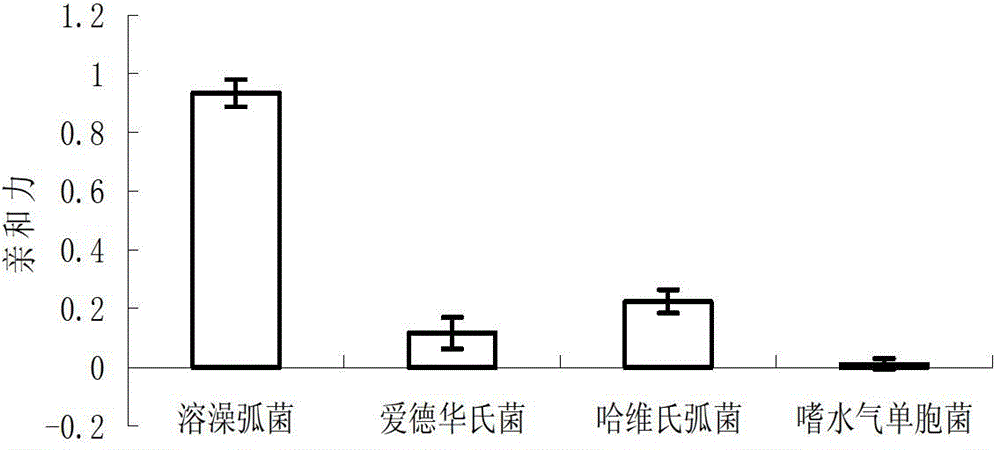
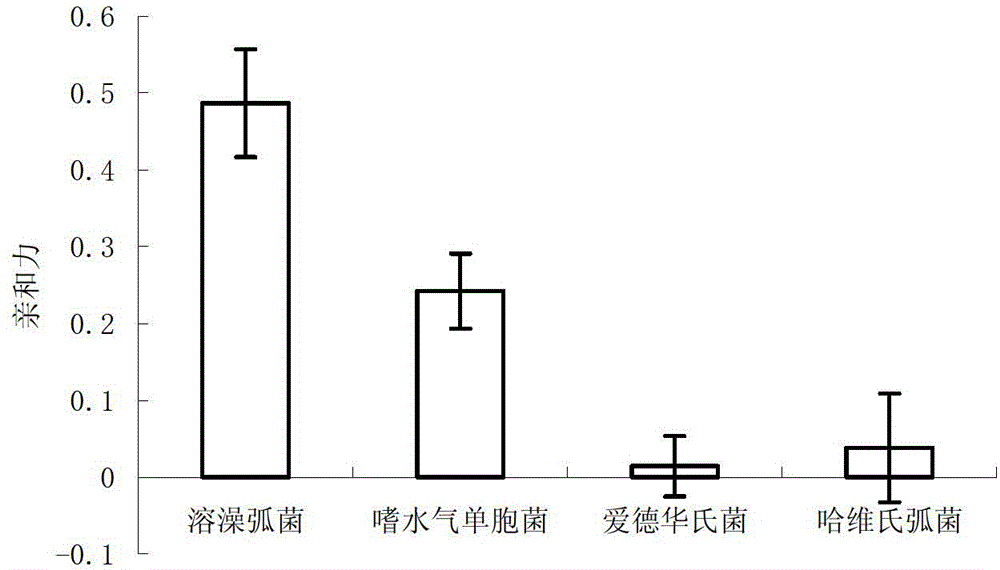
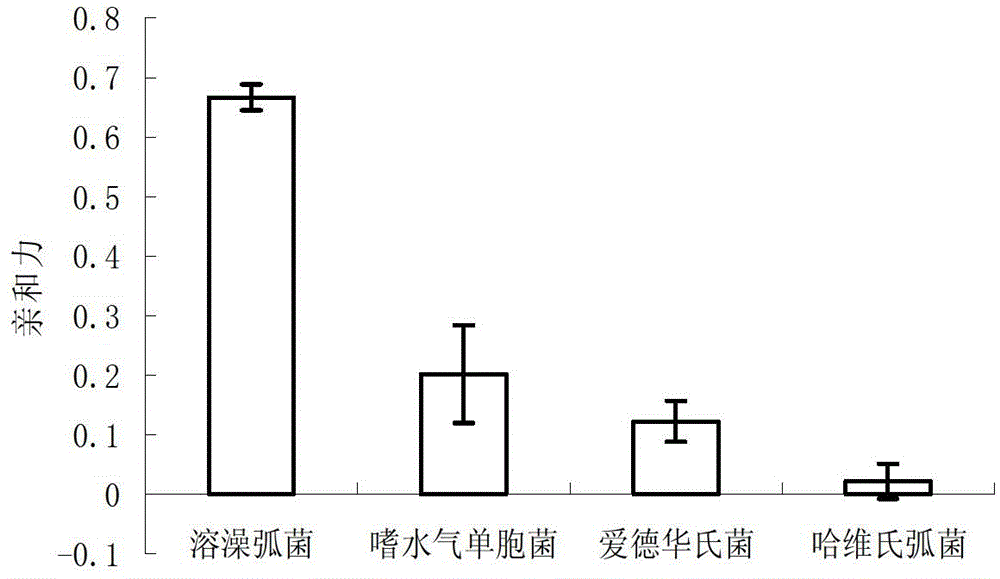
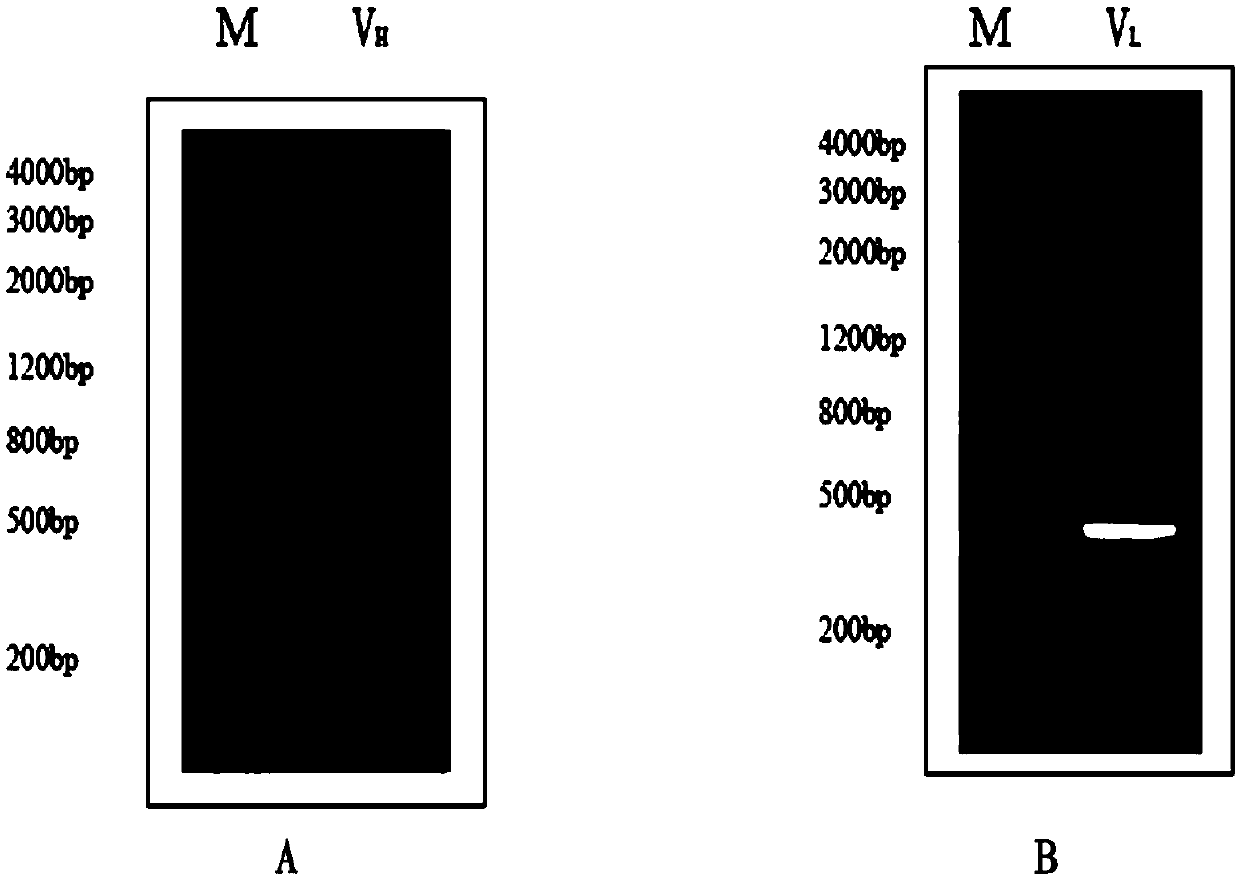
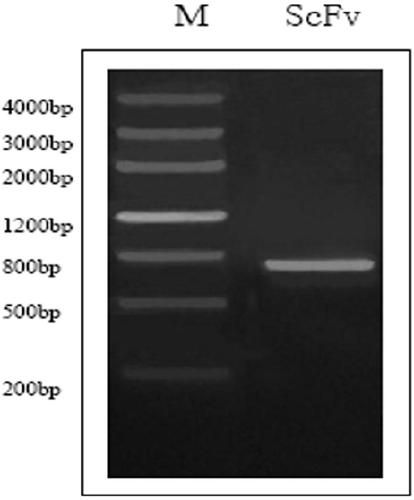
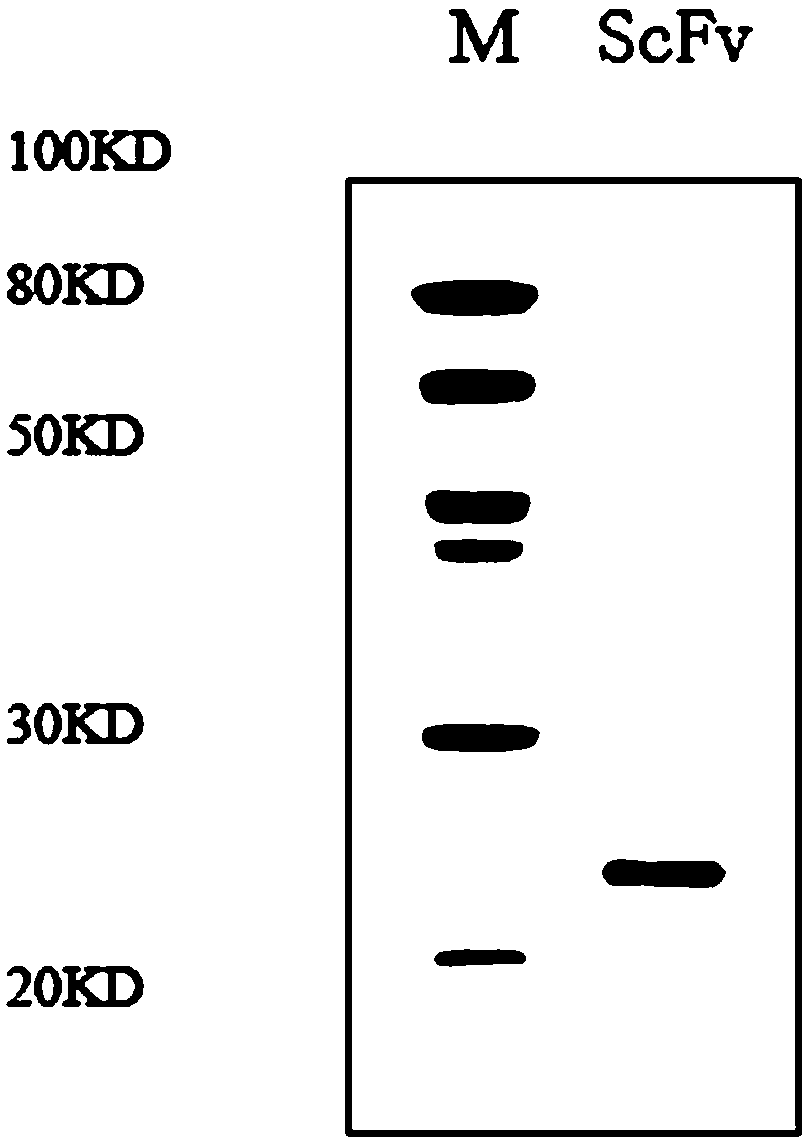
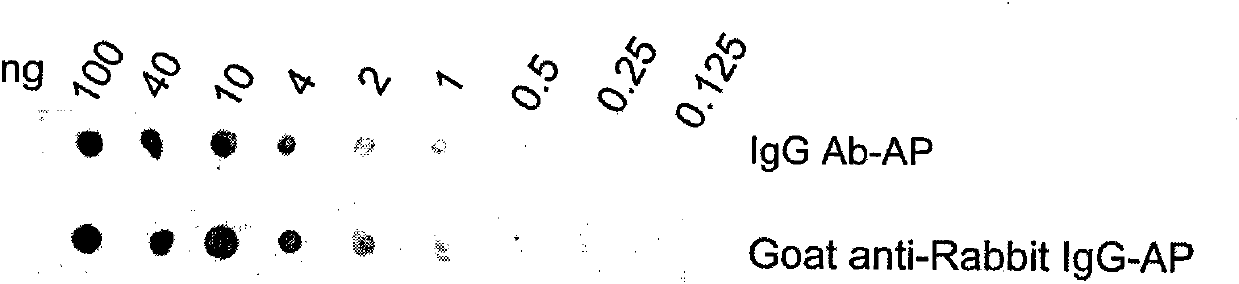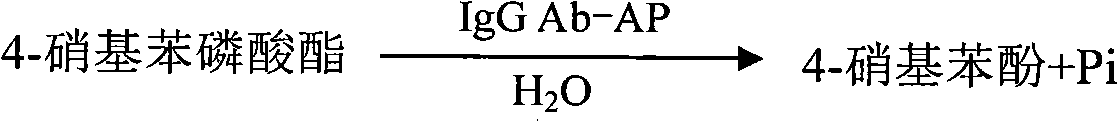Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Affinity constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Affinity constant. (1) A mathematical constant that describes the bonding affinity between two molecules at equilibrium. (2) The reverse of dissociation constant. It is the measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate.
Six oligonucleotide sequences and application thereof
InactiveCN103060326AImprove stabilityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationOligonucleotideAntibody
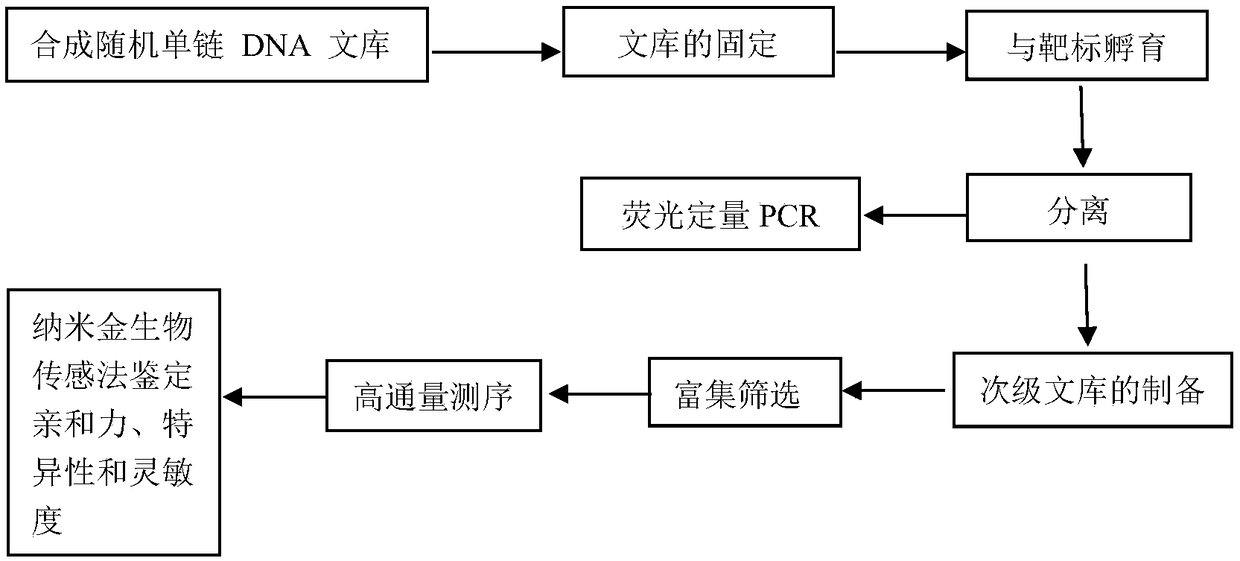
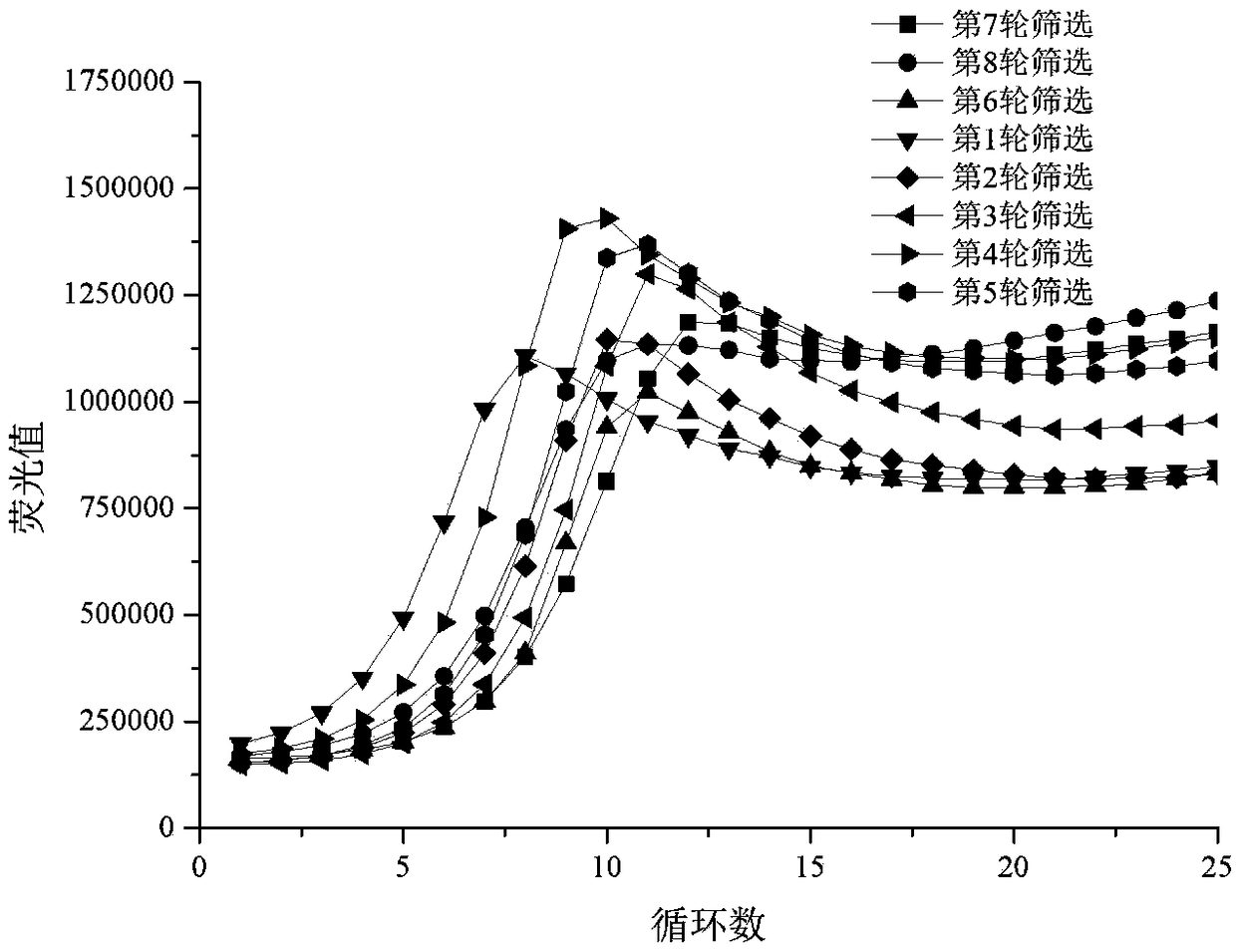
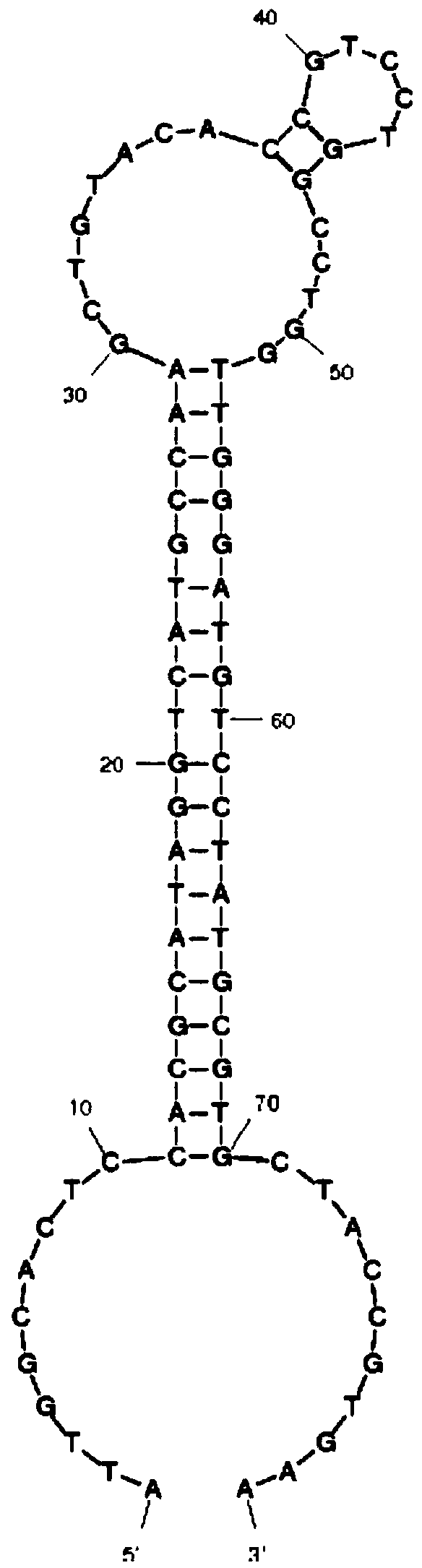
The invention relates to six oligonucleotide sequences and an application thereof, relating to the recognition detection of vibrio alginolyticus. The invention provides six oligonucleotide sequences capable of inactivating the recognition detection of vibrio alginolyticus, a preparation method and an application thereof. The oligonucleotide sequence has the characteristics of being quick in detection, simple in operation, superior to that of antibody and the like in stability, and the preparation method is easy and relatively short in preparation period. The six oligonucleotide sequences comprise oligonucleotide sequences of SEQ ID No.1-6, and the recognition detection of vibrio alginolyticus can be inactivated by adopting one of the oligonucleotide sequences. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an ssDNA oligonucleotide library used for filtering; carrying out SELEX filtering after the oligonucleotide library is mixed with inactivated vibrio alginolyticus till the affinity is not raised obviously; then cloning and sequencing; and selecting a highly copied ssDNA thereof to carry out verification of affinity specificity and determination of affinity constants so as to obtain corresponding an aptamer. The six oligonucleotide sequences can be used for recognition detection of inactivated vibrio alginolyticus.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Anti-human cardiac troponin I specific monoclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101942416AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesSocial benefitsMortality rate
The invention relates to an anti-human cardiac troponin I hybridoma cell line, with the preservation number of CGMCCNO. 3951, and a monoclonal antibody secreted from the anti-human cardiac troponin I hybridoma cell line CGMCC3951. The class and subclass of immunoglobulin of the monoclonal antibody are respectively IgG and IgG3 and the monoclonal body is specifically combined with human cardiac troponin I; the potency is 1:16000 and the affinity constant is 1.08x10 to 9mol / L. By applying the monoclonal antibody of the invention to clinical diagnosis, the study on complete localization of diagnosis kit for cardiac troponin I is tremendously promoted, correctness of clinical diagnosis and prognosis for cardiovascular diseases is enhanced while suffering of patients and death rate are both reduced, thus prominent economical and social benefits are obtained.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Single-chain antibody of human source anti-alexin C3d molecules and application thereof
ActiveCN109575132AReduce severityImprove survival rateGenetically modified cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody of human source anti-alexin C3d molecules. A light chain and a heavy chain of the antibody have a unique CDR region; excellent antigen binding activityis realized; the affinity constant reaches 1.22*10<-7> mol / L. Biological distribution experiments prove that the anti-C3d single-chain antibody provided by the invention can be highly gathered in thearthritis positions after entering a mouse model with rheumatoid arthritis; the arthritis serious degree of the three ScFv treatment groups is obviously lower than that of a PBS group; the healing degree has the obvious dose dependency relationship; the result shows that the excellent anti-adhesion / anti-inflammatory targeted inhibition effects are achieved. In the treatment process on MRL / lpr mice with lupus erythematosus, the anti-C3d single-chain antibody provided by the invention can obviously improve the survival rate of the mice; the symptoms of proteinuria, glomerular score, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis and crescent / necrosis and the like in the treatment group are obviously relieved. The result shows that the anti C3d single-chain antibody provided by the invention has excellent application prospects in the preparation of medicine for treating autoimmune diseases.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
Canine parvovirus hybridoma, monoclonal antibody and application
ActiveCN104928258AHigh bonding strengthReactiveImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism based processesCanine parvovirus infectionTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a hybridoma prepared from canine parvovirus antigens. An anti-canine-parvovirus monoclonal antibody secreted from the hybridoma has quite high relative affinity constant and good neutralizing activity, and a vaccine composition prepared from the monoclonal antibody can effectively prevent and treat canine parvovirus infections. A canine parvovirus detection kit prepared with two kinds of monoclonal antibodies has the advantages of quickness, convenience, accuracy, good sensitivity, specificity and repeatability and has higher sensitivity than colloidal gold-labeled commercial test strips.
Owner:LUOYANG PULIKE WANTAI BIOTECH
Bioanalytical assay
InactiveUS20040076948A1Small sizeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual molecule manipulationEnergy transferExcited state
The present invention relates to a nanoparticle comprising a specific binding reactant, said nanoparticle being useful for determining an analyte to which analyte or complex comprising said analyte said binding reactant is specific. Characteristic for the nanoparticle is that the diameter of said nanoparticle is less than 200 nm, said nanoparticle is coated with multiple said specific binding reactants to the extent that the affinity constant of said nanoparticle towards said analyte essentially exceeds that of free said binding reactant towards said analyte and / or the association rate constant between said nanoparticle and said analyte essentially exceeds the association rate constant between free said binding reactant and said analyte; and said nanoparticle comprises a detectable feature. The invention also relates to biochemical assays using said nanoparticle. The assay further relates to a proximity based homogenous assay comprising a first group labeled with an energy donating compound (donor) and a second group labeled with an energy accepting compound (acceptor), wherein the donor is luminescent and has a long excited state lifetime and the acceptor is luminescent having a short or long excited state lifetime or the acceptor is non-luminescent, and the increase or decrease, respectively, in the energy transfer from the donor to the acceptor resulting from shortening or lengthening, respectively, of the distance between said groups, is measured. Characteristic for the assay is that the donor is a nanoparticle.
Owner:INNOTRAC DIAGNOSTISC
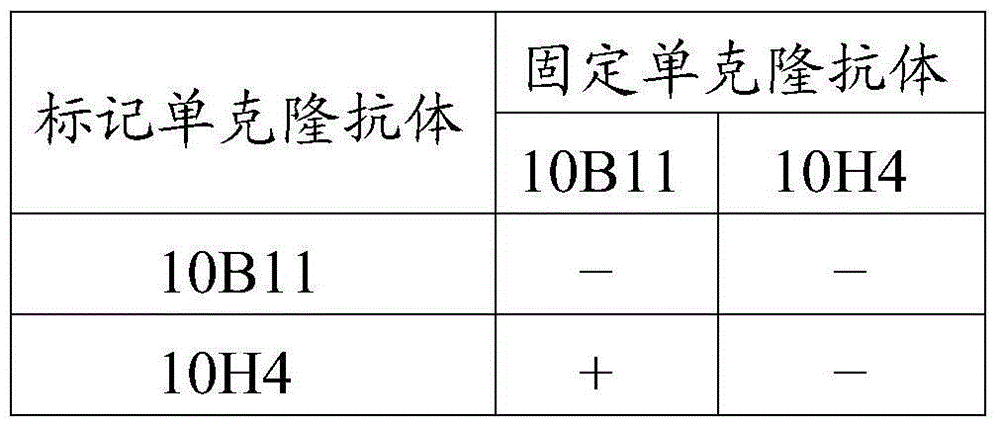
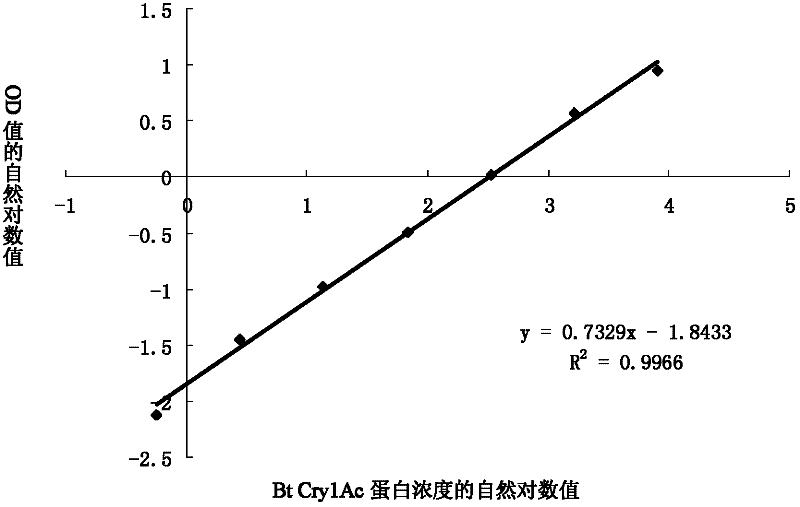
Method for detecting insecticidal crystal proteins Bt Cry1Ab/Ac and special enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit thereof
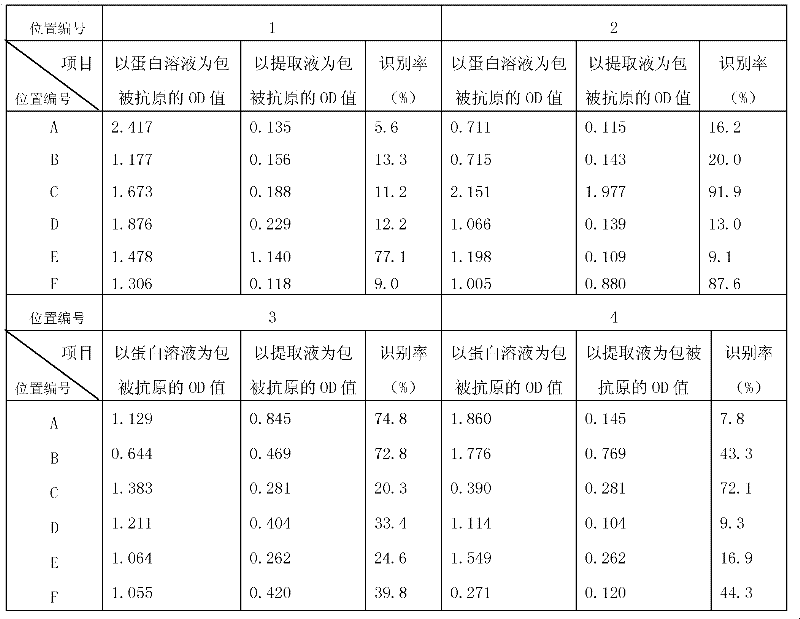
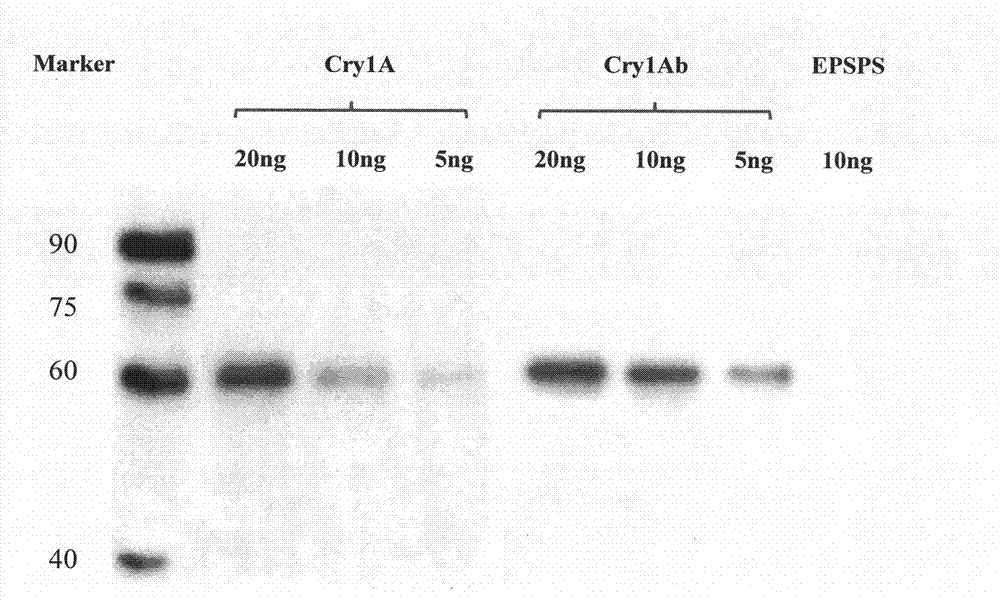
The invention discloses a method for detecting insecticidal crystal proteins Bt Cry1Ab / Ac and a special enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit thereof. An anti-Bt Cry1Ab / Ac monoclonal antibody used by the method and the kit is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain Bt2F9, and the application number of the hybridoma cell strain in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) is CGMCC No.5162. The monoclonal antibody is obtained by simultaneously using a Bt Cry1Ac protein solution and an extracting solution of Bt Cry1Ac transgenic cotton plant leaves as a coating antigen and screening hybridoma cells through an indirect non-competitive ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) method, the monoclonal antibody has high affinity for Bt Cry1Ab / Ac protein expressed in plants, and the affinity constant is 1.03*10<9>M<-1>. The double-antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit prepared by the monoclonal antibody is used for qualitatively or quantitatively detecting proteins Bt Cry1Ab / Ac in transgenic plants such as cotton and corn, the linear detection range is 0.78-50ng / mL, and the kit has the advantages of fastness and sensitiveness.
Owner:FUJIAN ANXIN RUIJIE BIOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method of hybrid tumor of monoclonal antibody inhibiting common bacillus thuringiensis CryI, and application of monoclonal antibody thereof
ActiveCN102816235AWide range of usesStrong characteristicImmunoglobulins against bacteriaTissue cultureAntigenBacillus thuringiensis
The invention relates to a broad-spectrum monoclonal antibody aiming at a bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) CryI protein common in gene transformation, and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims at providing a novel monoclonal antibody which can be used for detecting whether Bt protein exists in natural transgenic plants (paddy rice, cotton, corn, and the like). A special antigen for the monoclonal antibody is prepared through the coupling of a polypeptide designed according to an amino acid sequence of the common Bt CryI protein and carrier protein. A subtype of the monoclonal antibody is IgG2a, and an affinity constant reaches 3.84*10<9>. The monoclonal antibody can identify a plurality of proteins in a CryI family, and can be used in detections of various Bt CryI proteins. The invention also provides a hybrid tumor cell line 70647s-9 which secret the monoclonal antibody. The collection number of the cell line is CGMCC No.4856. The cell line can stably secret the monoclonal antibody with high titer.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEIN INNOVATION
Nucleic acid aptamer for specifically identifying di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate and screening method and application of nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN110257383AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerNucleotide
The invention provides a nucleic acid aptamer for specifically identifying di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate. The nucleic acid aptamer is one of the following nucleotide sequences: a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also provides a screening method of the nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer can rapidly and conveniently detect di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate, has high specificity, and has no cross reaction with a di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate analogue; the affinity is high, and the affinity constant is 2.26 + / - 0.06 nM; the sensitivity is high: the linear detection range is 7.629 pg / mL<-2> mu g / mL, and the lowest detection limit (LOD) of the di (2-ethyl) hexyl phthalate is 0.103 pg / mL.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
Mold toxin penicillic acid monoclone antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101429250ANo cross reaction rateHigh sensitivityTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsElisa kitCulture expansion
The invention provides a mycotoxin penicillic acid monoclonal antibody and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of coupling penicillic acid to carrier protein respectively so as to obtain complete antigen, immunizing a mouse with the complete antigen, adopting a hybridoma technique and obtaining the monoclonal antibody by cell fusion, screening, cloning, culture expansion and an animal in vivo induction ascites method. The obtained antibody has the titer of 1:2.05x10<5>, is of an IgG1 type, has no cross reaction rate with aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, T-2 toxin and Fumonisins, has the affinity constant of 1.54x10<8> L / mol, and can be used for developing ELISA kits for detecting the penicillic acid.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
IgG antibody affinity peptide-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein
InactiveCN101948545ABiologically activeHigh activityHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisAntibody affinity
The invention discloses an IgG antibody affinity peptide-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein which is a fusion protein formed by an IgG antibody affinity peptide and alkaline phosphatase, can be used for immunoassay as a substitute enzyme-labelled antibody. The fusion protein has the binding activity with an IgG antibody and the AP (Alkaline Phosphatase) catalytic activity once generated, the label ratio of the binding activity and the AP catalytic activity is 1:1, the enzyme specific activity of the fusion protein is 386 plus / minus 82U / mg, and an affinity constant Ka with a rabbit IgG antibody is congruent to 6.7*107L.mol-1. A preparation method of the IgG antibody affinity peptide-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein comprises the following steps of: firstly, connecting an IgG antibody affinity peptide gene with an alkaline phosphatase gene to construct a recombinant vector; secondly, carrying out electrotransformation on Pichia pastoris; thirdly, screening a high copy expression strain with G418 resistant pressure; fourthly, culturing the strain, and carrying out induced expression; and fifthly, extracting the purified IgG antibody affinity peptide-alkaline phosphatase fusion protein.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Bioanalytical assay
Owner:PETTERSSON KIM
Tetanus toxoid monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN105039262AImproving immunogenicityMeet the integration needsAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesTetanus toxoidsImmunologic function
The invention relates to a tetanus toxoid monoclonal antibody and application thereof, and belongs to the field of immunology. Mouse spleen cells and mouse myeloma cells are fused with one another after mice are subjected to tetanus toxoid immunization, tetanus-toxoid-resistant specific monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strains can be generated by means of screening, and a preservation number of the hybridoma cell strains is CGMCC No.10590. The tetanus toxoid monoclonal antibody and the application have the advantages that the potency of the monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strains can reach 10<7>, an affinity constant of the monoclonal antibody is 1.24*10<9>M<-1>, and the tetanus toxoid monoclonal antibody can be used for preparing tetanus toxoid antigen detection reagent kits, also can be applied to detecting tetanus vaccine production procedures by the aid of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and detecting the content of toxoid in finished vaccine and has a broad application prospect and high market value.
Owner:SINOVAC RES & DEV
Enzyme linked immunoassay kit for detecting abamectin and preparation method and detection method of enzyme linked immunoassay kit
InactiveCN104280557AImprove stabilityStrong specificityBiological testingAbamectinEnzyme linked immunoassay
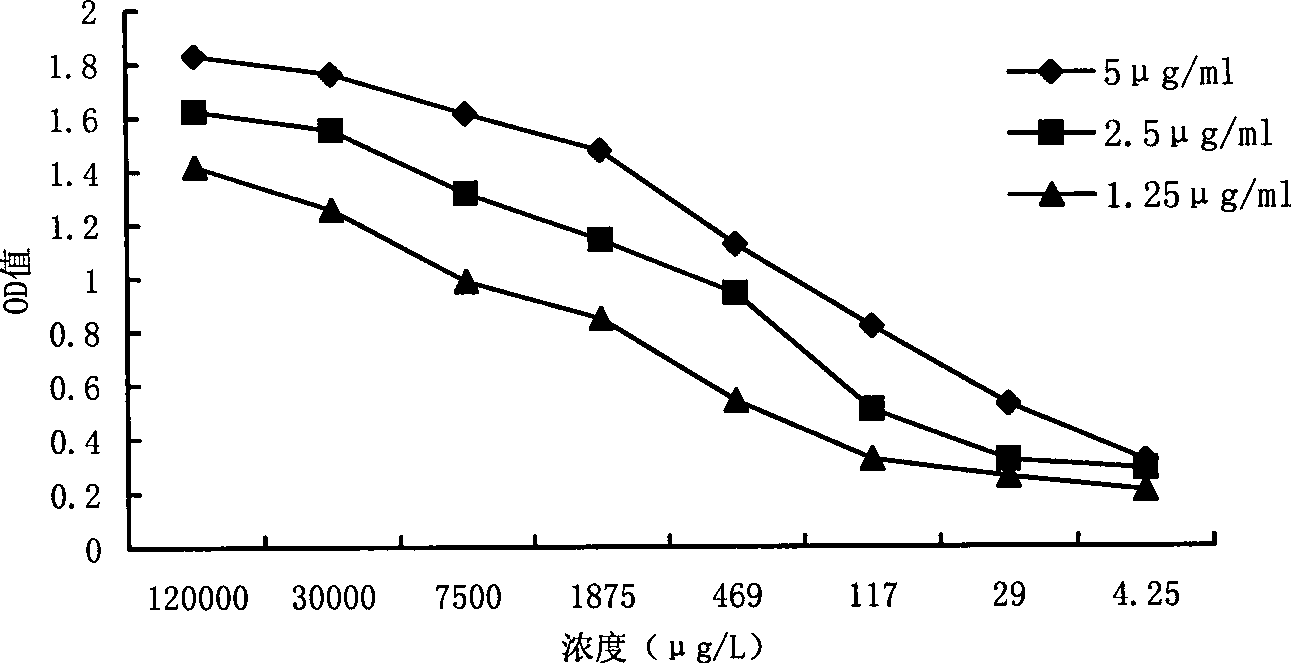
The invention relates to the technical field of abamectin detection, and in particular relates to an enzyme linked immunoassay kit for detecting abamectin and a preparation method and a detection method of the enzyme linked immunoassay kit. The enzyme linked immunoassay kit comprises an immunogen, a coating antigen, a monoclonal antibody, an enzyme-labeled second antibody and TMB substrate developing liquid, wherein the immunogen is obtained by coupling abamectin and BSA according to a combination ratio of 24 to 1; the coating antigen is obtained by coupling abamectin and BSA according to a combination ratio of 21 to 1; the immunoglobulin subclass of the monoclonal antibody is IgG1, the molecular weight is 165.7KDa, the quantity of chromosomes is 89-94, and the affinity constant is 1.80*10<10>M<-1>; the TMB substrate developing liquid consists of liquid A and liquid B. The enzyme linked immunoassay kit has the advantages of high stability, excellent specificity, long expiration date, simple preparation technology, relatively high sensitivity, relatively high accurate abamectin detection and simplicity in use.
Owner:贵州勤邦食品安全科学技术有限公司 +1
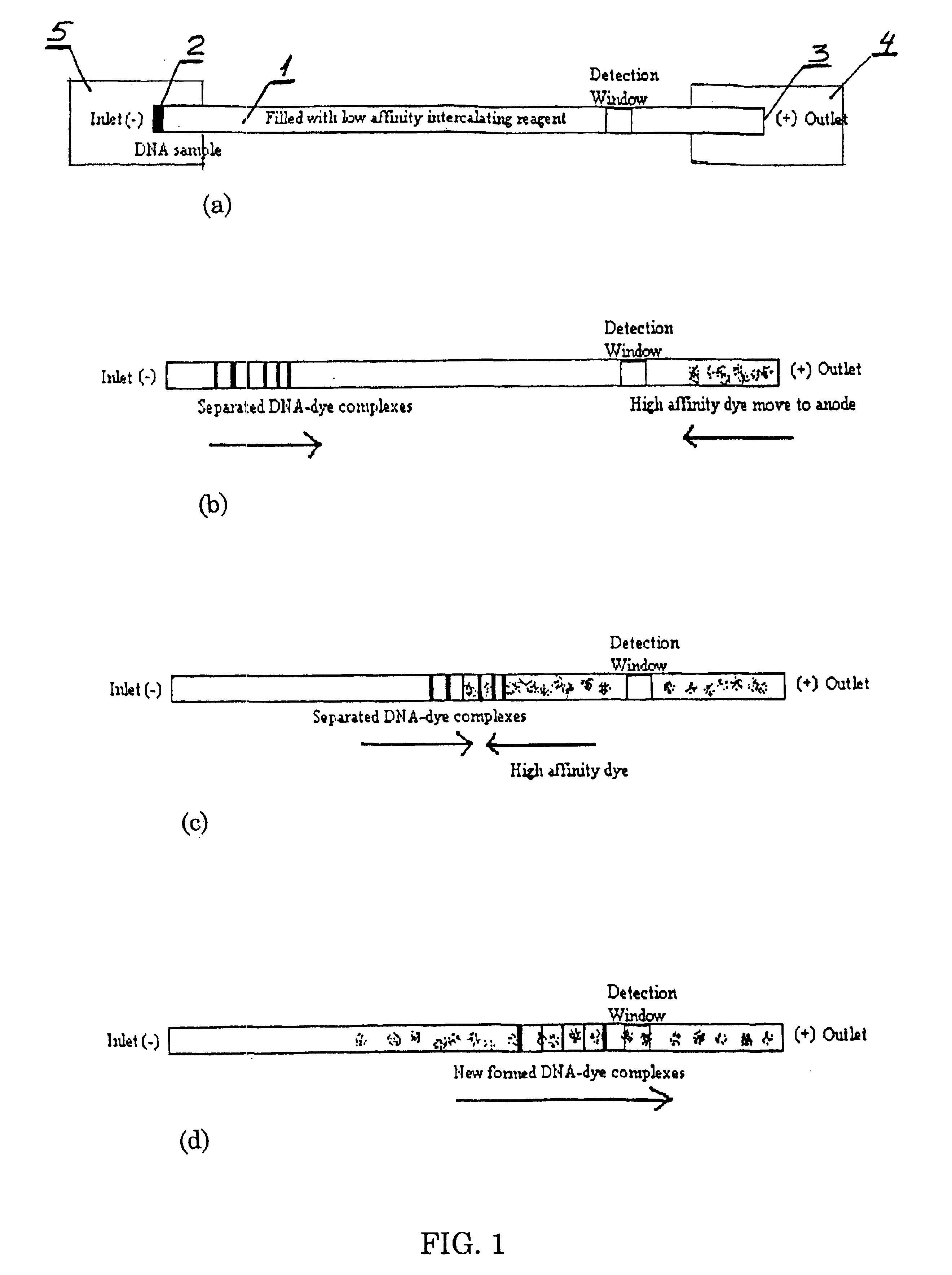
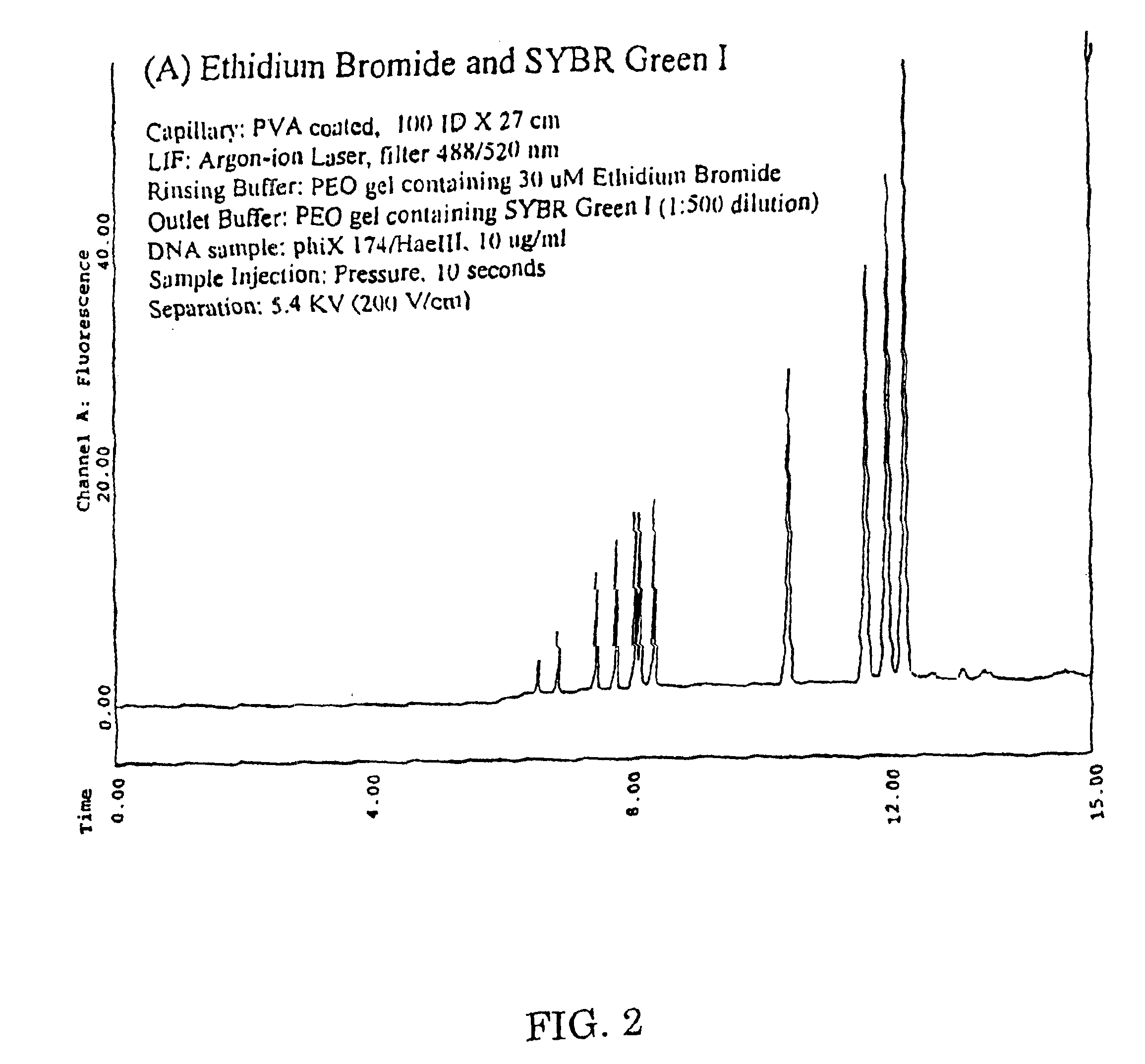
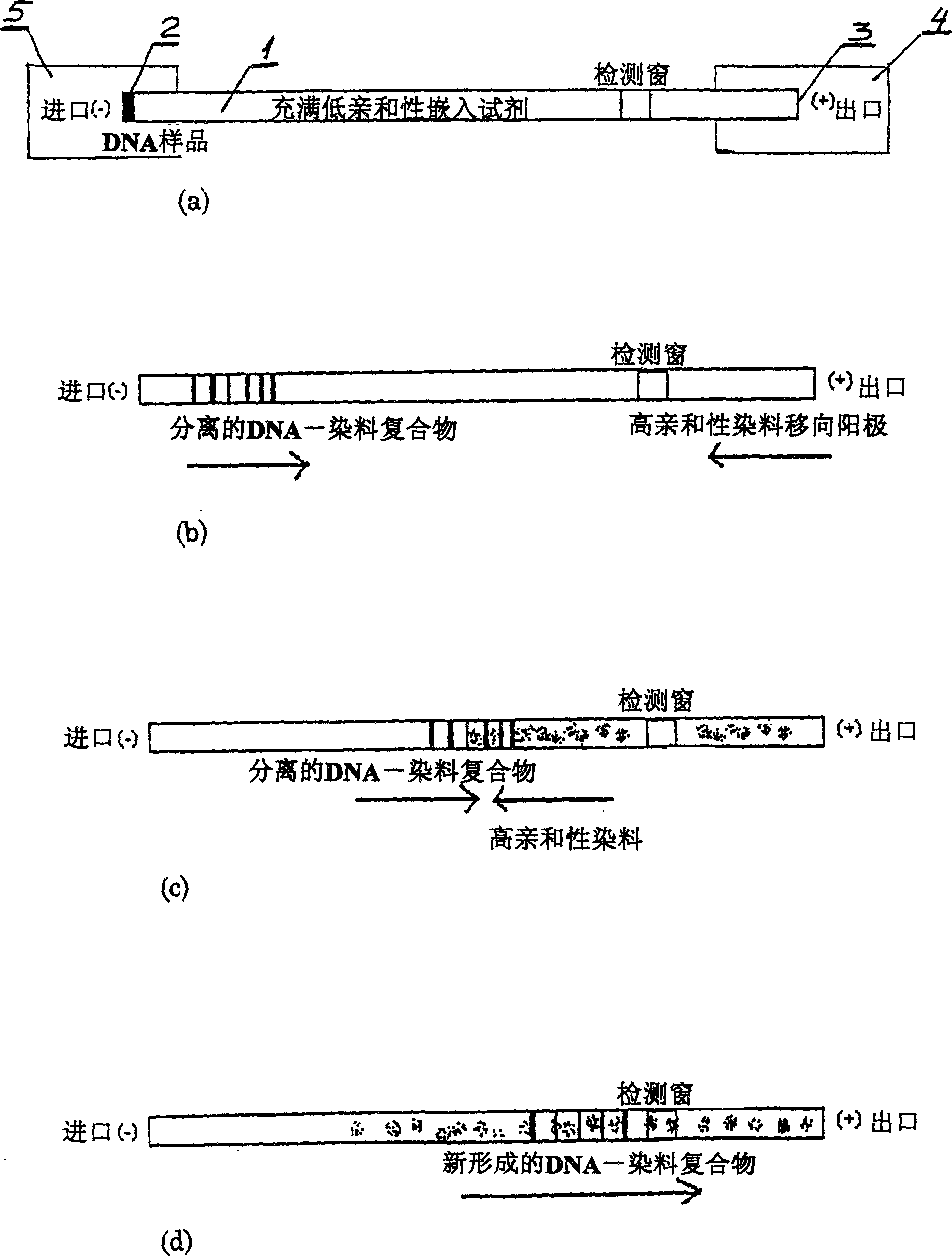
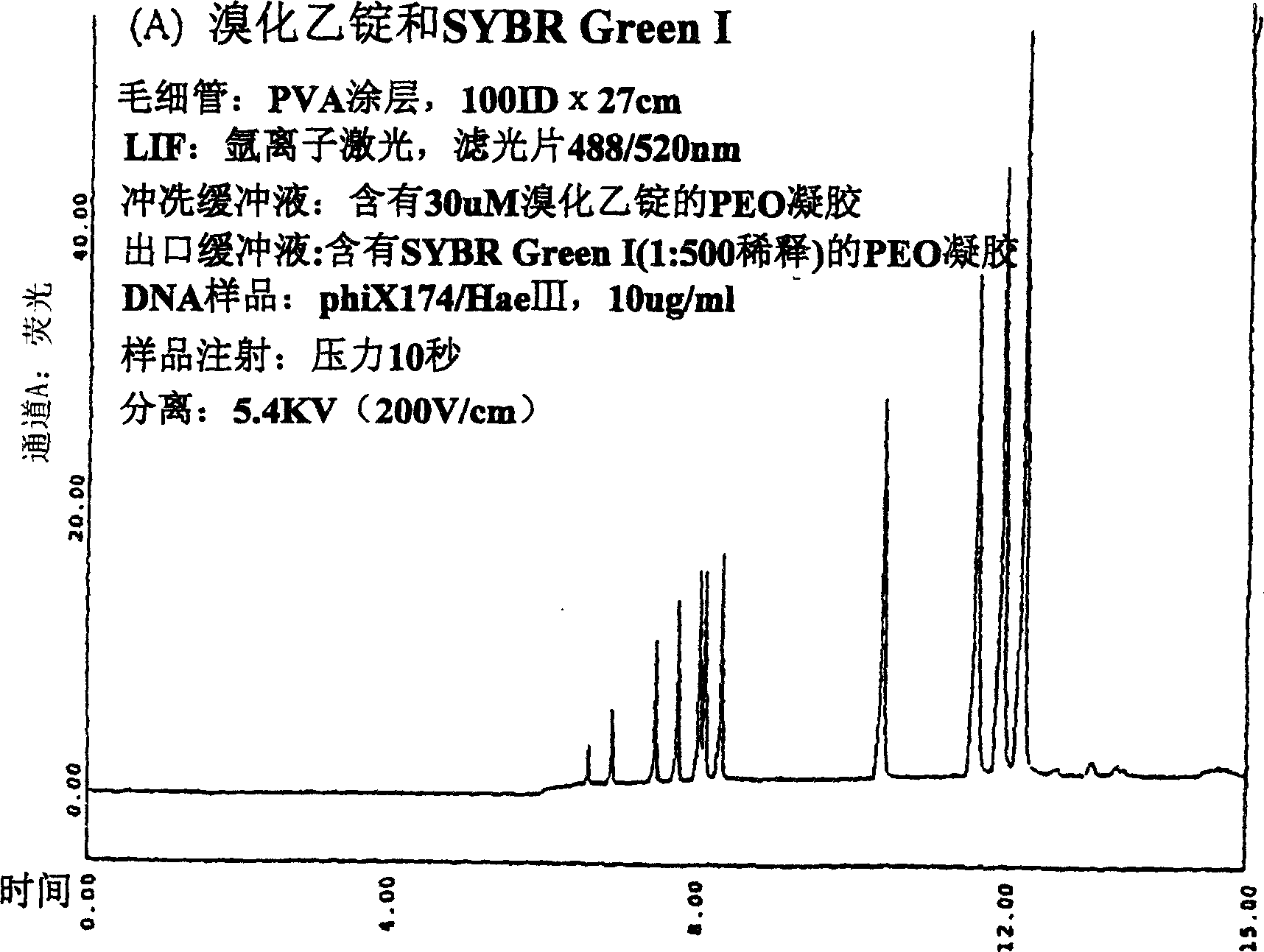
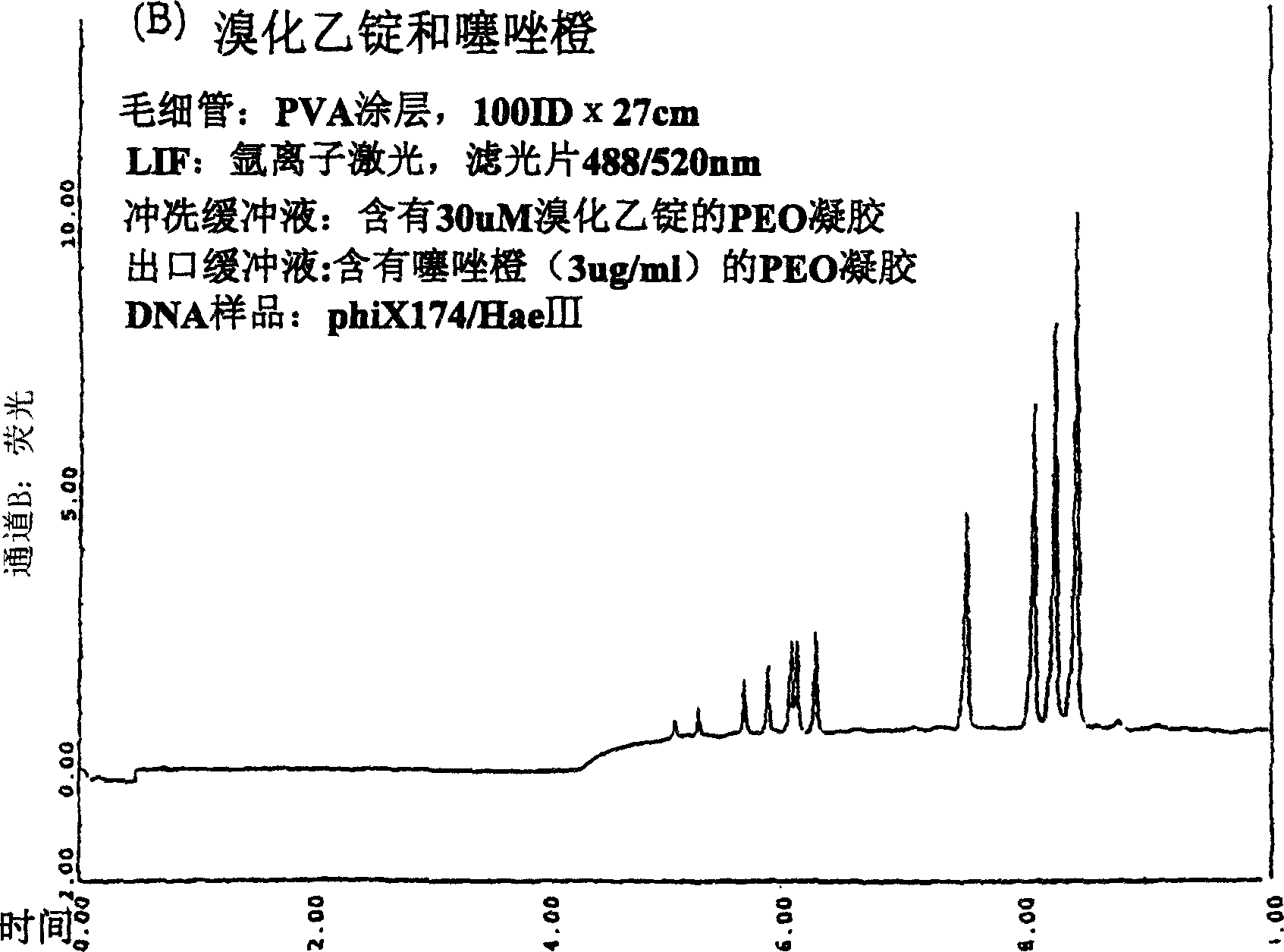
Nucleic acid separation and detection by electrophoresis with a counter-migrating high-affinity intercalating dye
InactiveUS6887668B2Easy to separateImprove reliabilityElectrolysis componentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElectrophoresisImage resolution
The invention provides novel electrophoretic methods for high-resolution separation and high-sensitivity detection of nucleic acids. The methods involve the use of a high-resolution buffer and a counter-migrating high-affinity intercalating dye in an electrophoresis system to achieve superior separation and detection of nucleic acids. A kit for separation and detection of nucleic acids in a sample by electrophoresis is also provided. The kit comprises a gel buffer containing a high-resolution intercalating dye with a resolution of at least 2.0 between the 271-bp and 282-bp φX 171 HAIII nucleic acid fragments nucleic acid fragments; and a high-affinity intercalating dye having a positive charge and DNA affinity constant of at least 106M−1.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Nucleic acid aptamer for detecting clenbuterol hydrochloride and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN108977448AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerNucleotide
The invention provides a nucleic acid aptamer for detecting clenbuterol hydrochloride. The nucleic acid aptamer is selected from one of following nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleicacid aptamers with same lengths are cut from both ends of the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the cutting length is 1 to 11bp; the nucleic acid aptamers with same cutting lengths of 1 to 11bp at the two ends respectively have the corresponding nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.12 to SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a screening method and application of the nucleic acidaptamer. The nucleic acid aptamer has the advantages that the specificity is strong, and the nucleic acid aptamer does not generate crossing reaction with clenbuterol hydrochloride analogues; the affinity is high, and the affinity constant is (42.17+ / -8.97) nM; the sensitivity is high; the minimum detection limit of clenbuterol hydrochloride is 1.2ng / mL.
Owner:HUBEI NORMAL UNIV
Anti-PD-1-anti-VEGFA bispecific antibodies, pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof
PendingCN112830972AReduced activityEliminate binding activityHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsMolecular ImmunologyIntravenous gammaglobulin
The invention belongs to the field of tumor treatment and molecular immunology, and relates to an anti-VEGFA-anti-PD-1 bispecific antibody and an application thereof. Specifically, the anti-VEGFA-anti-PD-1 bispecific antibody comprises a PD-1-targeting first protein functional region and a VEGFA-targeting second protein functional region, according to an EU numbering system, a heavy chain constant region of immune globulin contained in the bispecific antibody mutates at two sites of 234 and 235, and after mutation, the affinity constant of the bispecific antibody is reduced compared to the affinity constant of Fc [gamma] RI, Fc [gamma] RIIa, Fc [gamma] RIIIa and / or C1q before mutation. The bispecific antibody disclosed by the invention can be specifically combined with VEGFA and PD-1, specifically relieve immunosuppression of VEGFA and PD-1 on an organism and inhibit angiogenesis caused by tumors at the same time, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:AKESO BIOPHARMA
Nucleic acid separation and detection by electrophoresis with a counter-migrating high-affinity intercalating dye
InactiveCN1646557AHigh resolutionHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresesOrganic chemistry
The invention provides novel electrophoretic methods for high-resolution separation and high-sensitivity detection of nucleic acids. The methods involve the use of a high-resolution buffer and a counter-migrating high-affinity intercalating dye in an electrophoresis system to achieve superior separation and detection of nucleic acids. A kit for separation and detection of nucleic acids in a sample by electrophoresis is also provided. The kit comprises a gel buffer containing a high-resolution intercalating dye with a resolution of at least 2.0 between the 271-bp and 282-bp phiX 171 HAIII nucleic acid fragments nucleic acid fragments; and a high-affinity intercalating dye having a positive charge and DNA affinity constant of at least 10<6>M<-1>.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Nanometer antibody resisting to rabies virus G protein and application of nanometer antibody
ActiveCN109369803AInhibit bindingImprove specific recognition abilityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsCranial nervesViral infection
The invention discloses a nanometer antibody resisting to a rabies virus G protein. The nanometer antibody has three unique complementary determining regions CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3. The invention furtherprovides an application of the nanometer antibody to the preparation of a drug for preventing and / or treating rabies. The nanometer antibody provided by the invention has highly specific identification and binding capacities for the rabies virus G protein, has the highest affinity constant up to 1.36E-10, and can be specifically bound with the G protein to competitively inhibit the binding of theG protein and a newly born SD rat cranial nerve cell receptor so as to be proved to be capable of taking an effective immune protection effect in prevention and / or treatment of rabies virus infectionand to be shown to have a good application prospect in the preparation of the drug for preventing and / or treating rabies.
Owner:深圳市国创纳米抗体技术有限公司
C-reactive protein chemiluminiscence immunoassay kit and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112051403AImprove linear rangeHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDisease diagnosisMagnetic beadAntibody m
The invention discloses a C-reactive protein chemiluminiscence immunoassay kit and a preparation method and application thereof. The C-reactive protein chemiluminiscence immunoassay kit comprises an Mreagent, an R reagent, a luminescent substrate solution and a calibrator, the M reagent is a magnetic bead reagent coated with an antibody M, the R reagent is an enzyme labeling reagent connected with an antibody R, and both the antibody M and the antibody R can be specifically combined with C-reactive protein; the ratio of the affinity constants of the antibody M and the antibody R is 1 * 10<-7>to 1 * 10<-2> or 1 * 10<2> to 1 * 10<7>. By changing the affinity of the antibody M coated by the magnetic beads and the antibody R labeled by the enzyme, the affinity constants of the antibody M andthe antibody R are remarkably different, so that the linear range and sensitivity of the C-reactive protein chemiluminescence immunoassay kit are improved, and the problems of low sensitivity and high sensitivity of the traditional immunoturbidimetry, and the chemiluminescence immunoassay is narrow in linear range, so that accurate detection of the C-reactive protein is achieved in clinical use.
Owner:WUHAN LIFE ORIGIN BIOTECH LTD
Optimization of gene expression analysis using immobilized capture probes
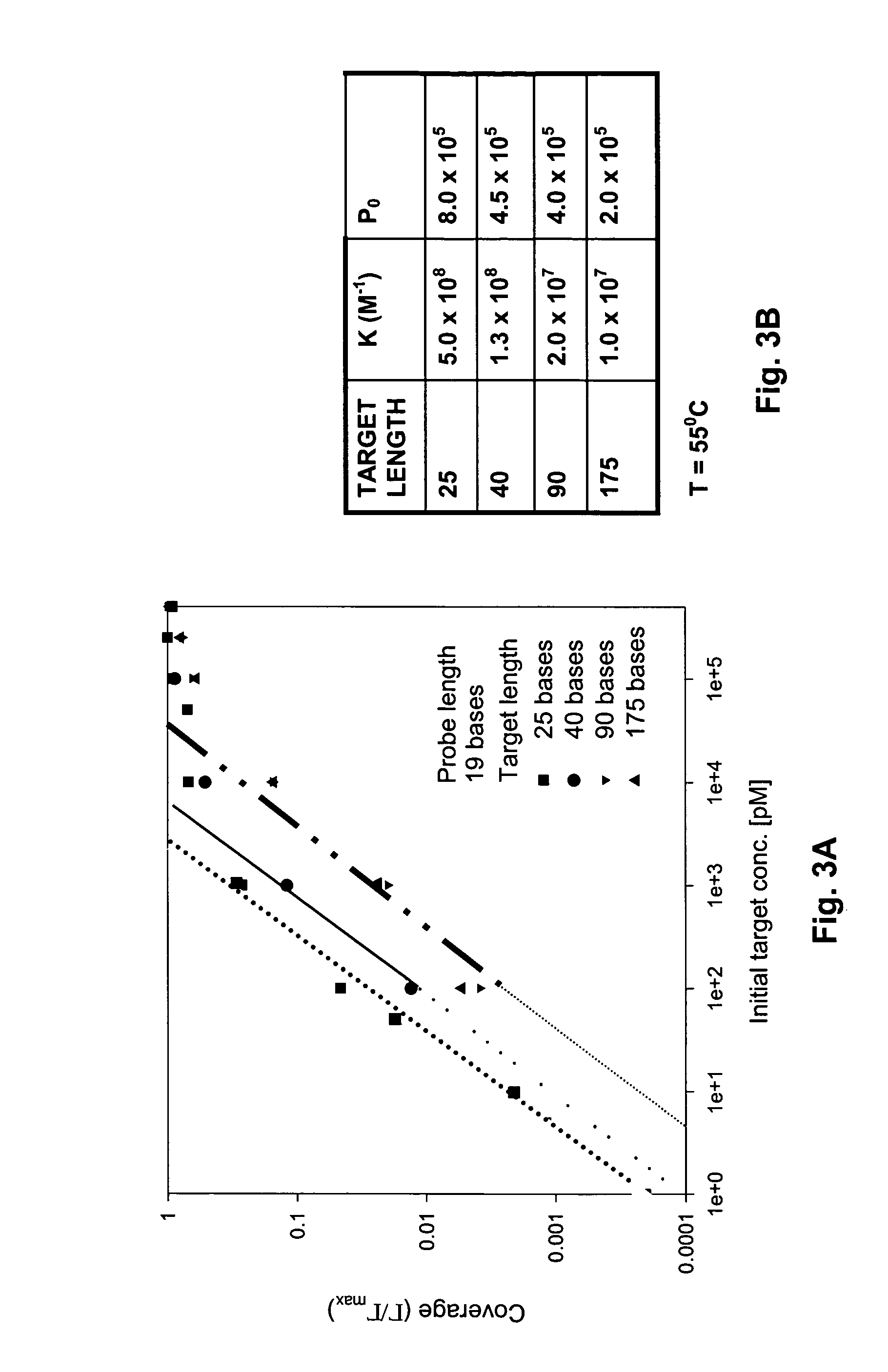
ActiveUS7563569B2Minimize target reannealing in solutionStrong specificityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDynamic range compressionQuantitative determination
Disclosed are methods of multiplexed analysis of oligonucleotides in a sample, including: methods of probe and target “engineering”, as well as methods of assay signal analysis relating to the modulation of the probe-target affinity constant, K by a variety of factors including the elastic properties of target strands and layers of immobilized (“grafted”) probes; and assay methodologies relating to: the tuning of assay signal intensities including dynamic range compression and on-chip signal amplification; the combination of hybridization-mediated and elongation-mediated detection for the quantitative determination of abundance of messages displaying a high degree of sequence similarity, including, for example, the simultaneous determination of the relative expression levels, and identification of the specific class of, untranslated AU-rich subsequences located near the 3′ terminus of mRNA; and a new method of subtractive differential gene expression analysis which requires only a single color label.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Biomolecule affinity constant determination method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) origami
InactiveCN102955047AAccurate measurementReduce dosageScanning probe microscopyCrystallographyDNA origami
The invention discloses a biomolecule affinity constant determination method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) origami. The biomolecule comprises a reactant I and a reactant II which are integrated together and dissociated. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) connecting the reactant I to the tail of a staple chain of the DNA origami, and then, executing self-assembly together with a scaffold chain to form the DNA origami; (2) adding the reactant II, after reaching equilibrium in reaction, collecting data by executing scanning imaging with an atomic force microscope, calculating the concentration [AbAg] of a compound of the reactant I and the reactant II, the concentration[Ag] of the free reactant I and the concentration [Ab] of the free reactant II; and (3) substituting the formula K=[AbAg] / [Ag][Ab] with the obtained data to calculate the affinity constant of the reactant I and the reactant II. The method can be used for accurately calculating the affinity constant of the biomolecule at the molecular level, thereby having the advantages of high efficiency, excellent repeatability and less usage of samples.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Monoclonal antibody resisting skeletal muscle troponin I and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN109705216AStrong controllabilityGood repeatabilityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesElisa kitImmunologic function
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody resisting skeletal muscle troponin I and an application of the monoclonal antibody, and belongs to the technical fields of immunology and food safety analysis. The monoclonal antibody resisting skeletal muscle troponin I is secreted by hybridoma strains of which the preservation number is CCTCC NO:C2018217. The antibody titer is 1 to 106, the subtypeis IgG1, and the affinity constant Ka=8.1 *10<8>L / mol. The monoclonal antibody can be used for preparing an enzyme-linked immunoreagent kit and a colloidal gold test chromatography test strip of the skeletal muscle troponin I in raw fresh meat and products thereof, so as to realize the purpose of quickly and acutely detecting the beef-derived components in animal derived foods.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Amantadine monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof
InactiveCN105112376AHigh detection sensitivityHigh affinityMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureBALB/cPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses an amantadine monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of immunological detection in food safety. After amantadine complete antigens and equivalent Freund's immunologic adjuvants TM are mixed evenly, BALB / c mice are immunized through back multipoint injection. Splenocytes of the immune mice are fused with myeloma cells of the mice according to a PEG (polyethylene glycol) method, and the hybridoma cell strain named as 1E5 is obtained through indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay), indirect competition ELISA screening and three-time subcloning. The hybridoma cell strain is collected in China general microbiological culture collection center, and the collection number is CGMCC No.10865. Monoclonal antibodies secreted by the cell strain 1E5 have high affinity and detection sensitiveness on amantadine, the affinity constant is 8.04*109L / mol, the IC50 value of detection sensitiveness is 1ng / mL, and the monoclonal antibodies can be used for amantadine content detection in food safety.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Immunoassay kit and special antibody for detecting fumonisins
InactiveCN101955542AProduction economyEasy to produceFungiBacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesHeavy chain
The invention discloses an immunoassay kit and a special antibody for detecting fumonisins. A single-chain antibody is prepared by sequentially connecting a heavy chain variable region, short peptide connecting the heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, and the light chain variable region, wherein the amino acid sequence of the heavy chain variable region is represented by 1st to 118th amino acid residues of a sequence 1 from an N end; and the amino acid sequence of the light chain variable region is represented by 134th to 246th amino acid residues of the sequence 1 from the N end. The affinity constant of the antibody is 1.73*10<9>L / mol, and the half abatement (IC50) is 0.15 ng / mL. In the invention, antibody sources with high valence and high specificity are provided for establishing a method for detecting fumonisins residues in food. The kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, high accuracy, high precision, high specificity for fumonisins B1 and low cost. Therefore, the antibody, the kit and the detection method play an important role in detecting the fumonisins B1.
Owner:北京维德维康生物技术有限公司
Anti-goat skeletal muscle troponin I monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN109810191AStrong controllabilityGood repeatabilityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureElisa kitImmunologic function
The invention relates to an anti-goat skeletal muscle troponin I monoclonal antibody and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of immunology and the technical field of food safety analysis. The monoclonal antibody is generated through secretion of a hybridoma cell line with the preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: C2018218; the titer of theantibody is 1 to 2.56*10<5>, a subtype is IgM, and an affinity constant Ka is equal to 7.6*10<8>L / mol. The monoclonal antibody provided by the invention can be used for preparing an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit and a colloidal gold chromatography test strip, which are used for detecting goat skeletal muscle troponin I in fresh mutton and products thereof, so that the aim of rapidly and sensitively detecting mutton derived components in animal derived foods is realized.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Monoclonal antibody against human alpha1 acid glycoprotein and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101921336AGuaranteed singularityConvenience guaranteedImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureLow affinityExperimental methods
The invention aims to prepare a specific monoclonal antibody aiming at alpha1 acid glycoprotein (AGP, Serum alpha1-acid glycoprotein) and establish a corresponding experimental method. Particularly, the monoclonal antibody can selectively identify glycosylation modified natural AGP, but has low affinity with prokaryotically expressed non-glycosylation modified AGP. The subtype of the monoclonal antibody is IgG1, and the affinity constant is 9*108. The invention provides a hybridoma cell line BPI-AGP for secreting the monoclonal antibody, wherein the collection number of the hybridoma cell line is CGMCC 2868, and the hybridoma cell line can stably secrete high-valence monoclonal antibody against AGP natural protein. The BPI-AGP can be used for inspecting the AGP in the blood. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a method for preparing monoclonal antibody hybridoma aiming at the glycosylation modified protein.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEIN INNOVATION
Nano antibody for resisting toxoplasma gondii SAG1 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108503707AEfficient detectionGood water solubilityImmunoglobulinsFermentationSolubilityAntigen
The invention discloses a nano antibody for resisting toxoplasma gondii SAG1 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. A VHH chain amino acid sequence of the nano antibody is as shown by SEQ ID NO. 4. The nano antibody comprises two VHH chains. The nano antibody for resisting the toxoplasma gondii SAG1 is obtained by immunizing a camel by virtue of toxoplasma gondii SAG1 antigen, obtainingan anti-SAG1 nano antibody library, and selecting a nano antibody with good performance from the nano antibody library. The nano antibody has high solubility and conformation stability and high antigen affinity and excellent tissue penetration capability, and has high affinity with SAG1 antigen, the affinity constant KD value is 1.66nM, the toxoplasma gondii can be efficiently detected, and the nano antibody can be used for preparing toxoplasma gondii detection kit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Physarum polycephalum 14-3-3 protein monoclonal antibodies and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103627676AGood for commercial useHigh efficiency of secreting antibodiesMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureExtremely goodPhysarum polycephalum
The invention discloses three physarum polycephalum 14-3-3 protein (P14-3-3) monoclonal antibodies, and the three monoclonal antibodies are mAb alpha+, mAb beta+ and mAb gamma+; the microbial preservation number of hybridomas cell strains McAb alpha+, McAb beta+ and McAb gamma+ which respectively express and secrete the above three monoclonal antibodies is CCTCC NO: C2012131, C2012132 and C2012133, and the preservation position is China Center for Type Culture Collection; and the purpose is to provide an effective means for researching the structure and the function of 14-3-3 protein and the P14-3-3 expression variation with cell cycle and life cycle. The prepared antibodies all have the titer higher than 100 K and the affinity constant higher than 2.12*10<8>, are applicable to research the structure and the function of low-grade eukaryote 14-3-3 protein and the 14-3-3 protein expression variation rule with cell cycle and life cycle, and have extremely good commercial use.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV +1
Oligonucleotide sequence as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104388422ASynthetic preparation is simpleQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCloning sequencingOligonucleotide
The invention provides an oligonucleotide sequence as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the identification and detection of inactivated Vibrio harveyi. The oligonucleotide sequence has the characteristics of quickness in detection, high simplicity in operation, higher stability than the stability of antibodies, simple preparation method, short preparation period, and so on. The oligonucleotide sequence is SEQ ID No. 1 which can be used to identify and detect the inactivated Vibrio harveyi. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an ssDNA oligonucleotide library for screening; mixing the ssDNA oligonucleotide library with the inactivated Vibrio harveyi and screening the mixture by using the SELEX technology until the affinity no longer increases obviously; carrying out clone sequencing and selecting high copy ssDNA to undergo affinity and specificity verification and affinity constant determination, thereby obtaining the corresponding aptamer; The oligonucleotide sequence can be used to identify and detect the inactivated Vibrio harveyi in various samples.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Anti-beta-conglycinin monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN103333862ALow detection limitWide detection rangeOther chemical processesImmunoglobulins against plantsProtein.monoclonalSoybean product
The invention discloses an anti-beta-conglycinin monoclonal antibody and an application of the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain 2C4CGMCC No.7109; experiments prove that the affinity constant of the beta-conglycinin monoclonal antibody reaches 6.2*10<11>L / mol, the beta-conglycinin monoclonal antibody is applied to detecting beta-conglycinin by means of a competitive ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) for antibody detection, and the detection limit is 0.1ng / ml-8.1ng / mol. The beta-conglycinin monoclonal antibody, a detection method using the monoclonal antibody and a kit with the monoclonal antibody provided by the invention have the advantages of low detection limit, wide detection range, high efficiency, and accuracy, and can be widely applied to the qualitative and quantitative detection of the beta-conglycinin in soybean and a soybean product.
Owner:北京龙科方舟生物工程技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com