Canine parvovirus hybridoma, monoclonal antibody and application
A hybridoma, monoclonal antibody technology, applied in the field of monoclonal antibodies, can solve problems such as low sensitivity and achieve good neutralizing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Example 1 Preparation, purification, identification and testing of anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody
[0073] 1.1 Preparation and purification of monoclonal antibody against canine parvovirus
[0074] The canine parvovirus CVCC AV298 strain was prepared according to the operating method of Harlow E et al. (Harlow E, Lane D. Antibodies: a laboratory manual [M]. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1998, 139-312) The 10B11 strain and the hybridoma cell 10H4 strain were further prepared and purified for anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody 10B11 and anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody 10H4 respectively.
[0075] Among them, the preservation number of the hybridoma cell 10B11 strain is CCTCC No: C201578, which was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation address was Wuhan, Wuhan University, China, and the preservation time was May 20, 2015. It secretes anti-canine parvovirus Monoclonal antibody 10B11; h...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Example 2 Pairing of Monoclonal Antibodies
[0110] 2.1 Selection of monoclonal antibody pairing mode
[0111] When screening monoclonal antibody pairing combinations, the following factors are mainly considered: first, the activity of the monoclonal antibody; second, whether there is a non-specific reaction between the monoclonal antibody and other viruses except canine parvovirus; third, the background color development.
[0112] 2.2 Detection of Monoclonal Antibody Activity
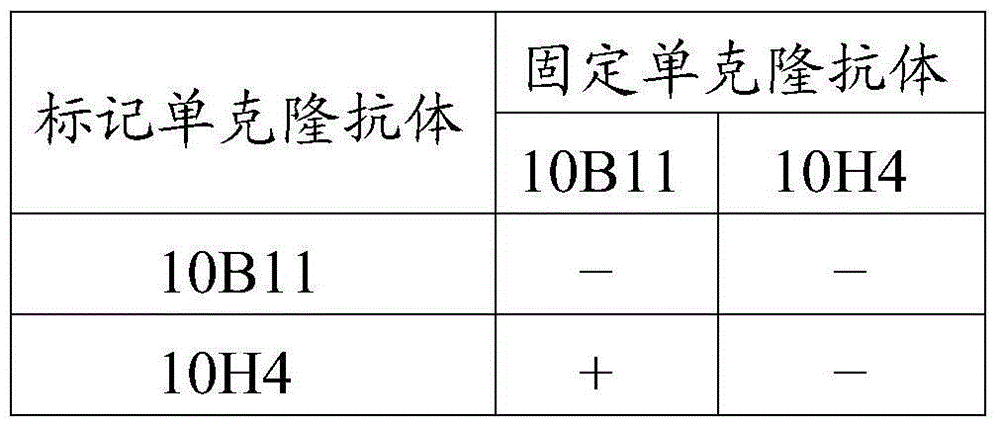
[0113] The canine parvovirus CVCC AV298 strain was selected, diluted to 0.01HA, and tested for different matching modes. The results are shown in Table 4:
[0114] Table 4 Monoclonal Antibody Matching Detection
[0115]
[0116] Note: + means positive reaction, - means negative reaction.
[0117] The results showed that except for the solid-phase monoclonal antibody 10B11 and the enzyme-labeled monoclonal antibody 10H4, the detection of the 0.01HA canine parvovirus CVCC AV298 strain virus ...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Example 3 Preparation of Canine Parvovirus ELISA Kit
[0120] 3.1 Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeling of monoclonal antibodies
[0121] According to the monoclonal antibody 10H4 prepared in Example 1, according to Tijssen P et al. (Tijssen P, Kurstak E. Highly efficient and simple methods for the preparation of peroxidase and active peroxidase antibody conjugates for enzyme immunoassays [J]. : 451-457) were labeled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibodies.
[0122] 3.2 Immobilization of monoclonal antibodies
[0123] The monoclonal antibody 2 prepared in Example 1 was immobilized on the nitrocellulose membrane with a BioDot XYZ3050 three-dimensional spraying platform.
[0124] 3.3 Composition of the detection kit
[0125] The detection kit includes detection test strips, sample processing solution, sample processing tube, and sample preservation solution.
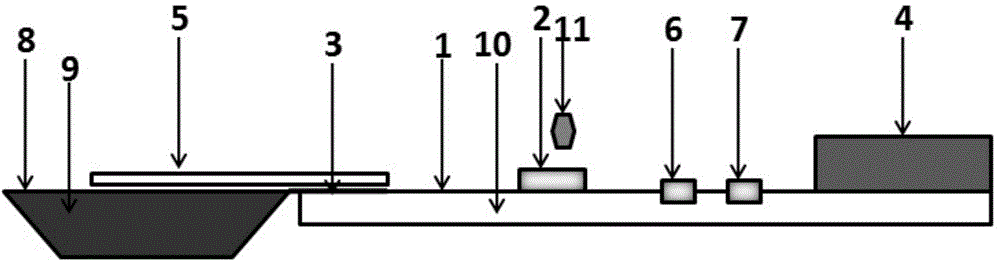
[0126] (1) Detection test strips (the side schematic diagram is sh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com