Stents for angioplasty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
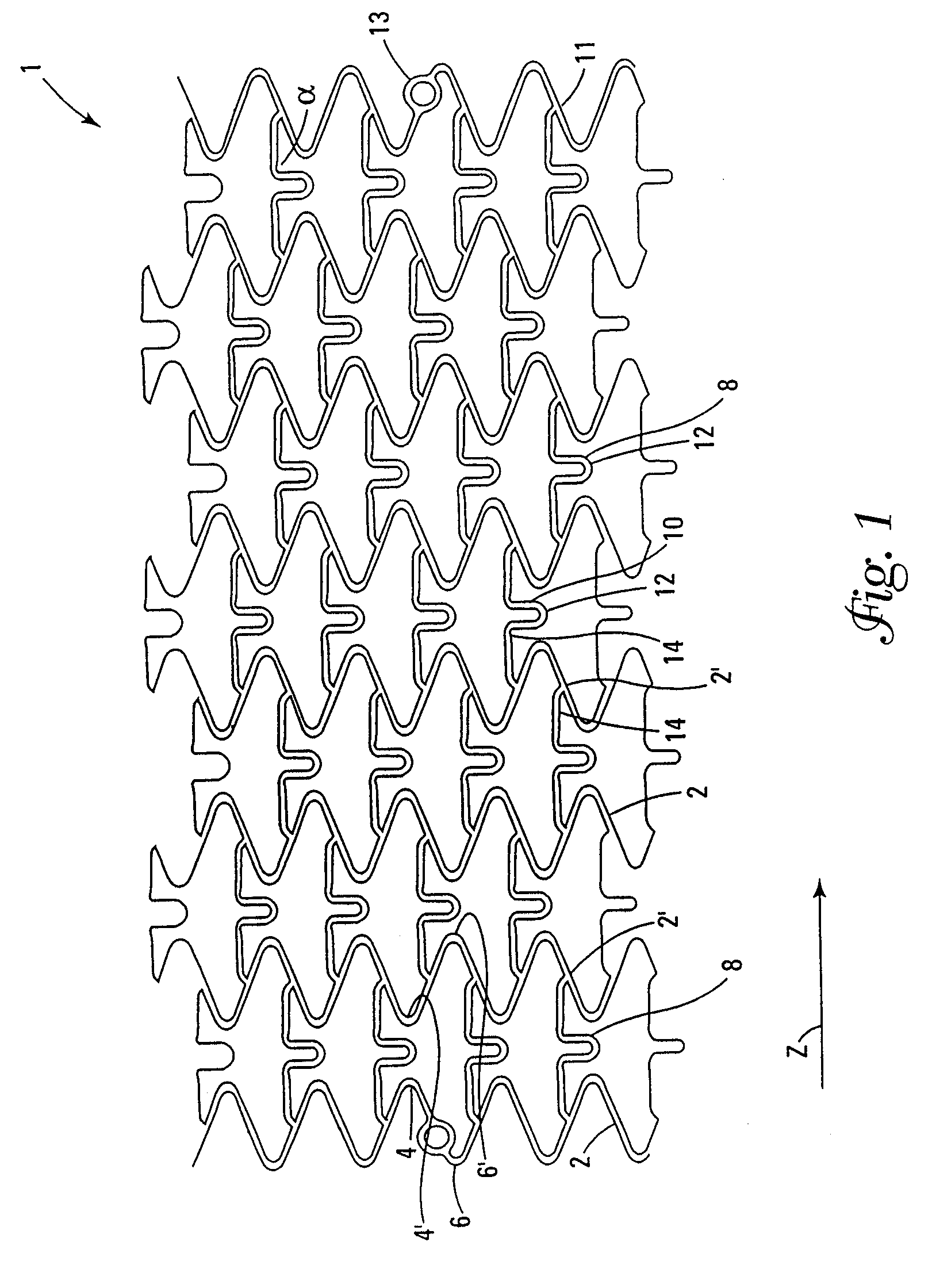
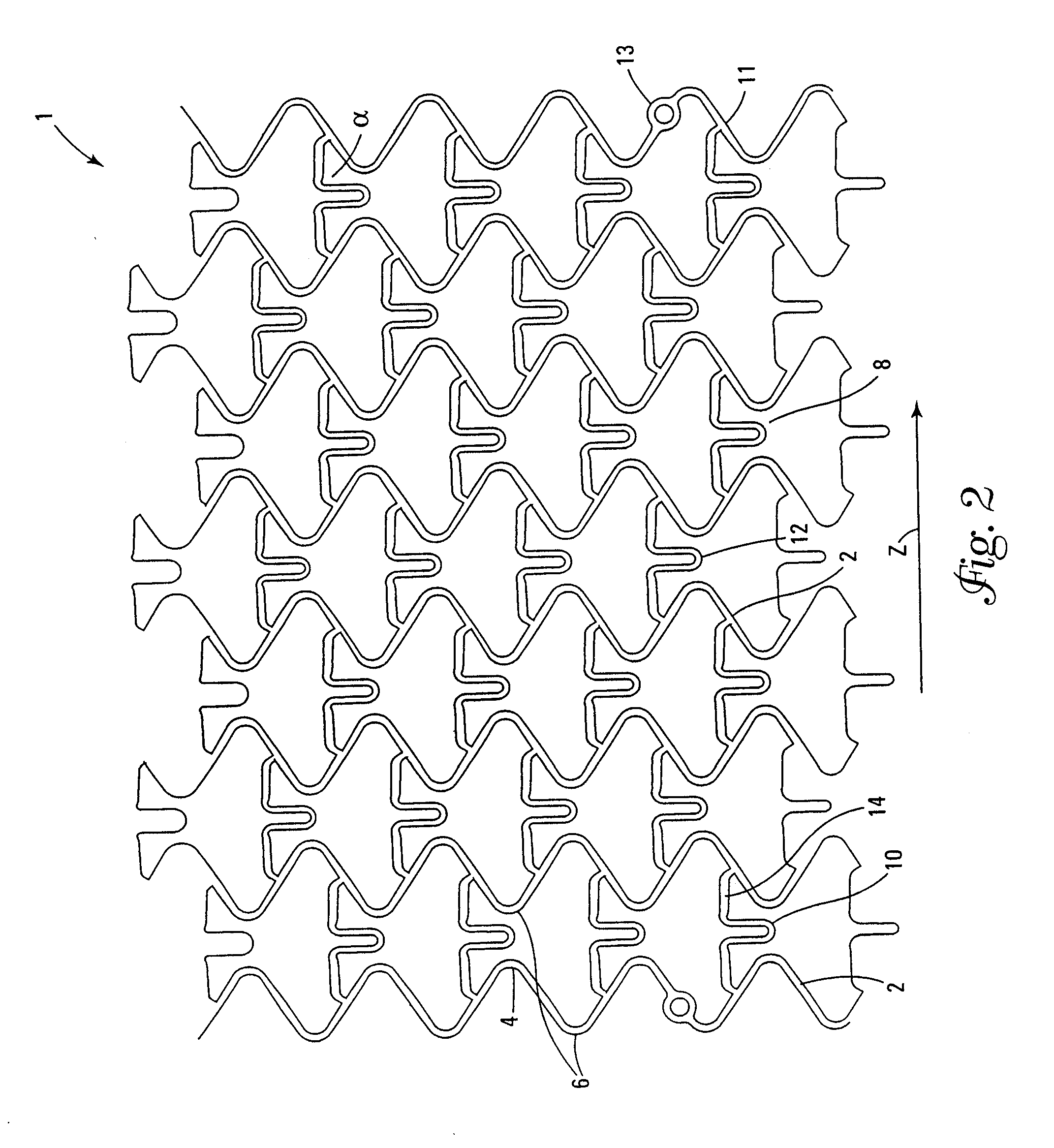
[0032]A stent is inserted into a lumen, such as a blood vessel, at a site where stenosis, i.e., narrowing or stricture, is to be corrected. The stent is a tubular envelope, tubular body, or cylinder having apertured walls, such as, for example, a mesh-like structure. The stent typically has dimensions between several millimeters and several tens of millimeters in length, and a wall thickness of the order of, for example, several hundredths of millimeters. The stent is normally positioned in situ by catheterisation through the vasculature followed by radial expansion from an introduction diameter of, for example, about 1.0 to 1.5 mm, to an expanded diameter of, for example, about 3 to 4 mm. In this expanded condition, the stent exerts a supporting force on the lumen, thereby avoiding or at least slowing restenosis of the vessel. In general, the external diameter of the stent in the radially-contracted condition is chosen to enable the introduction of the stent into a lumen, while the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com