Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126 results about "Vapor bubble" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
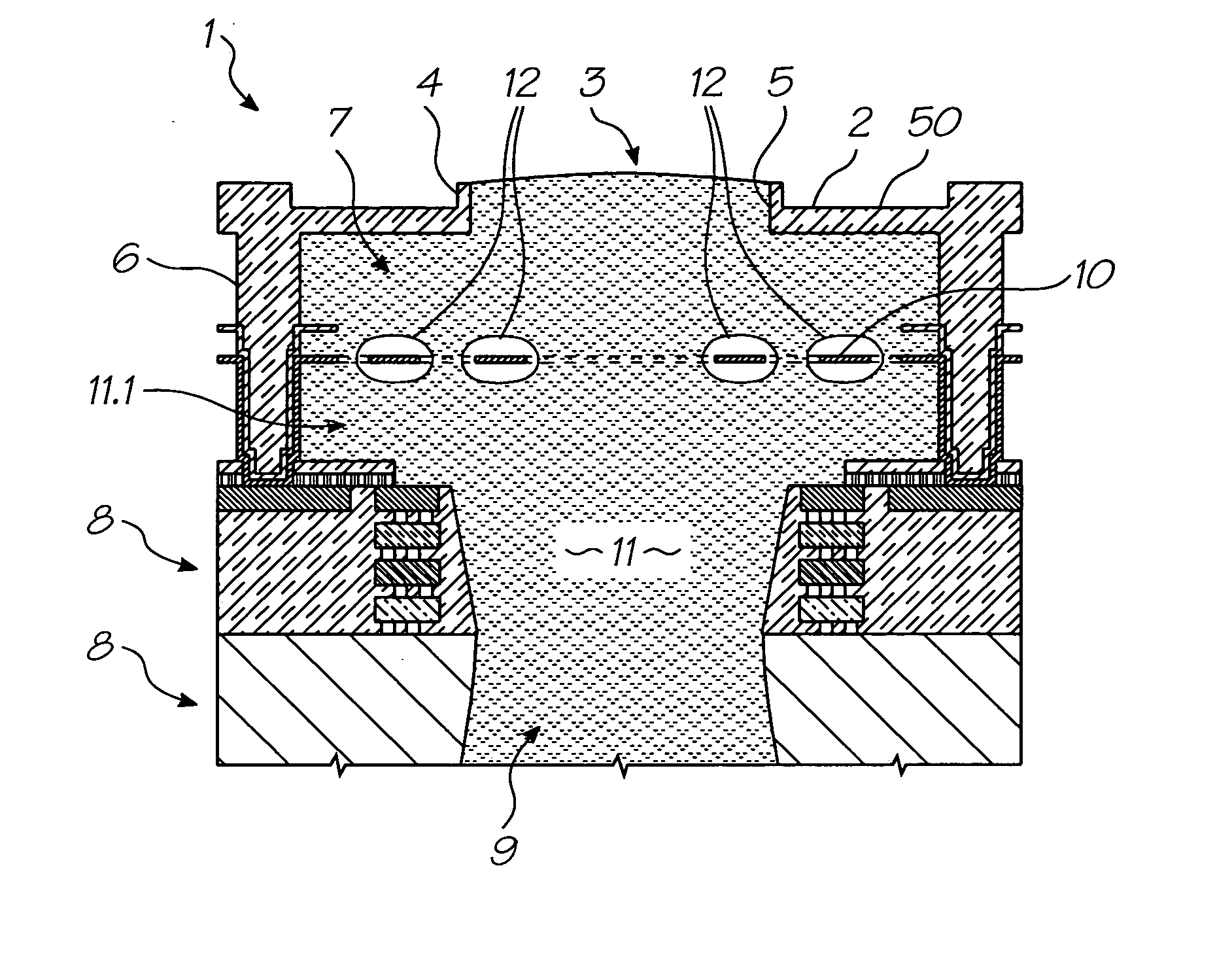
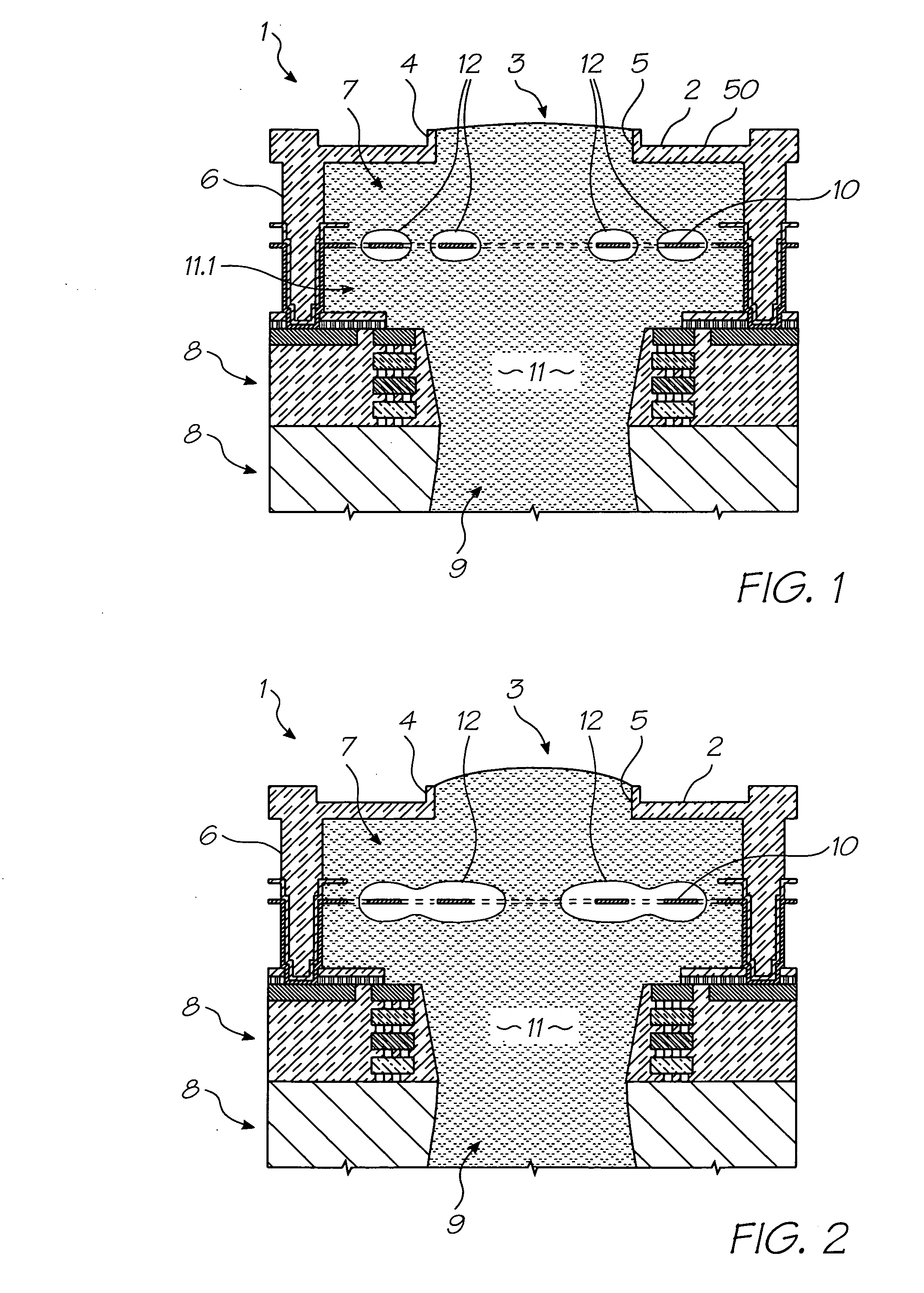
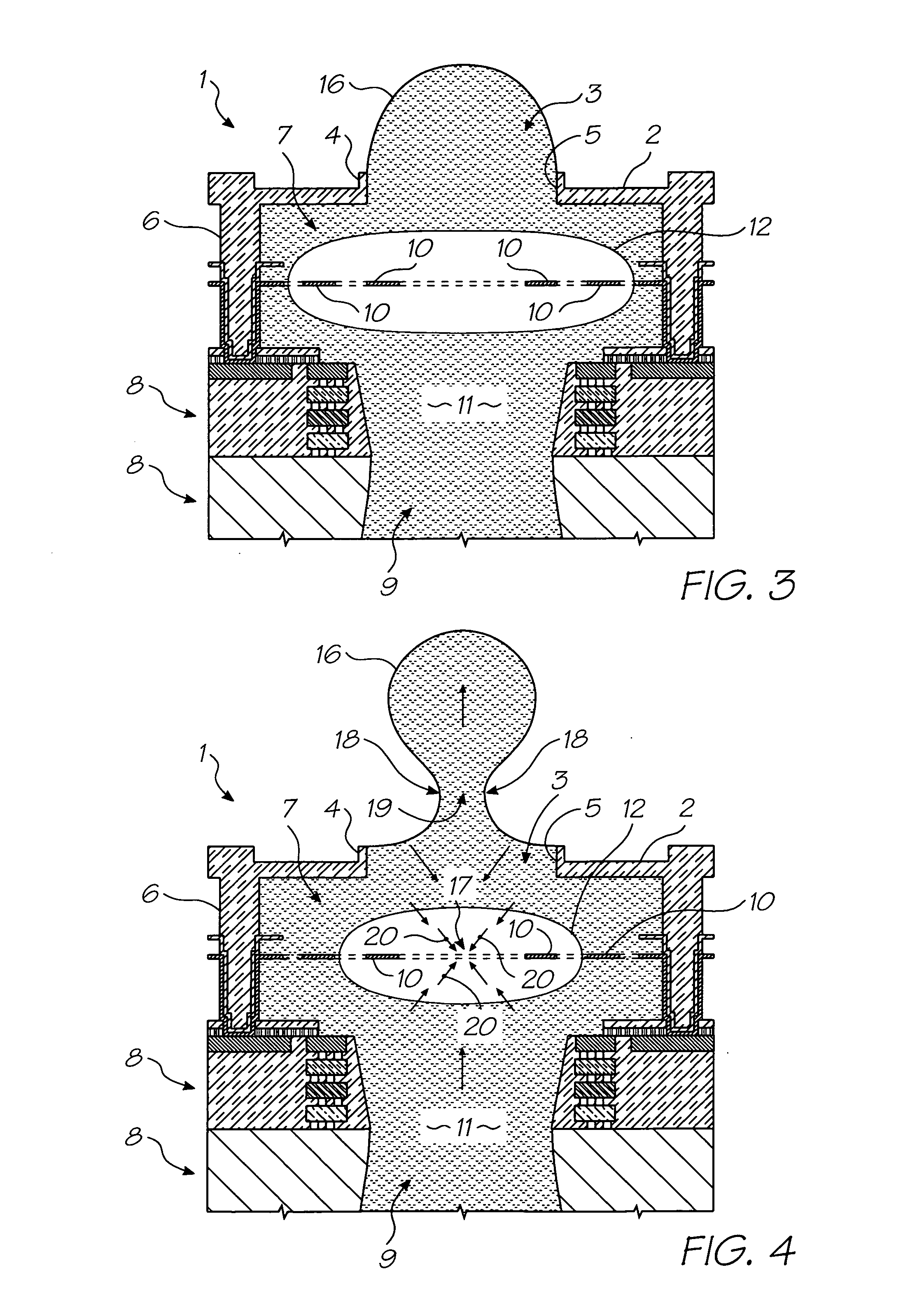
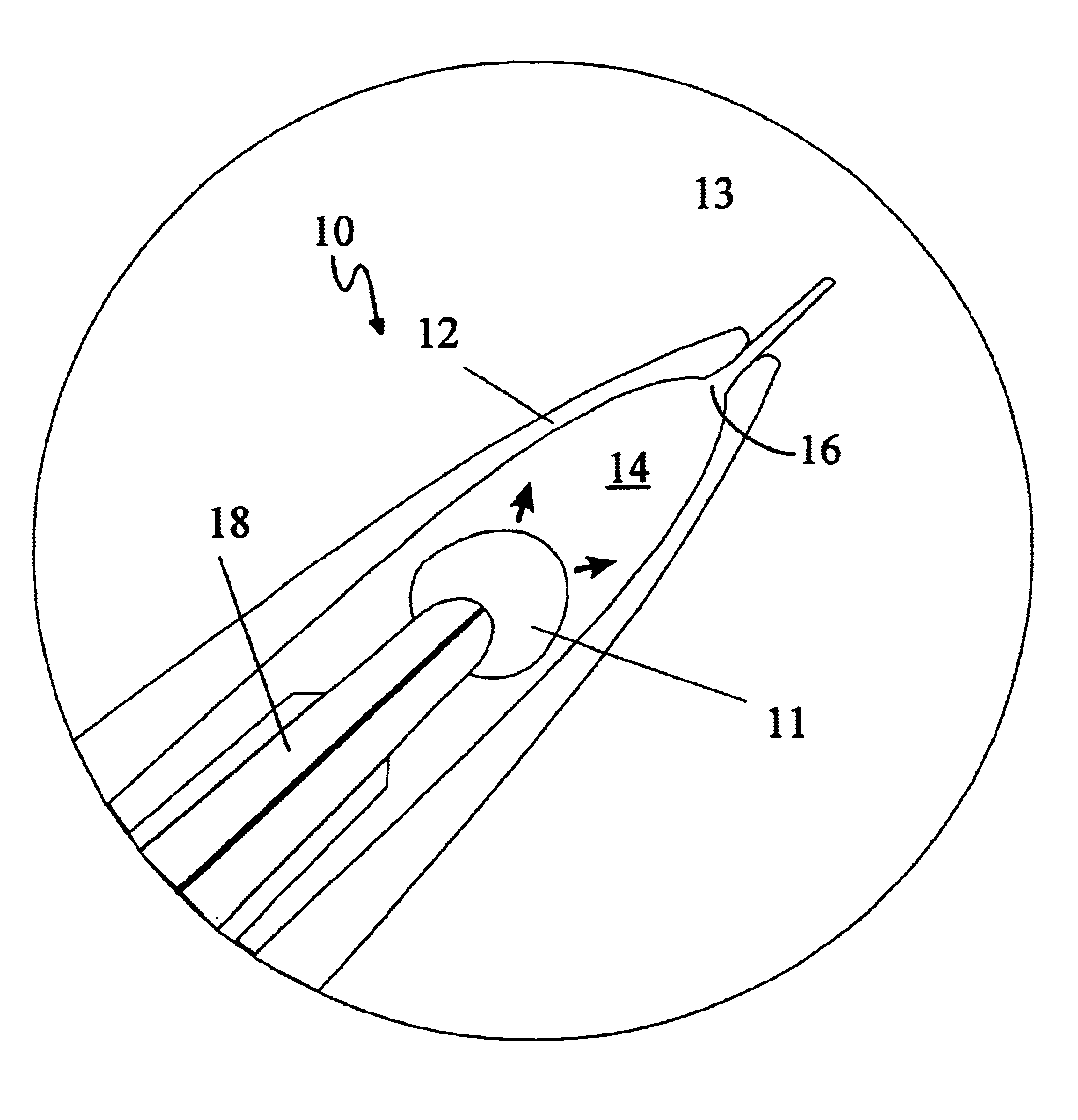
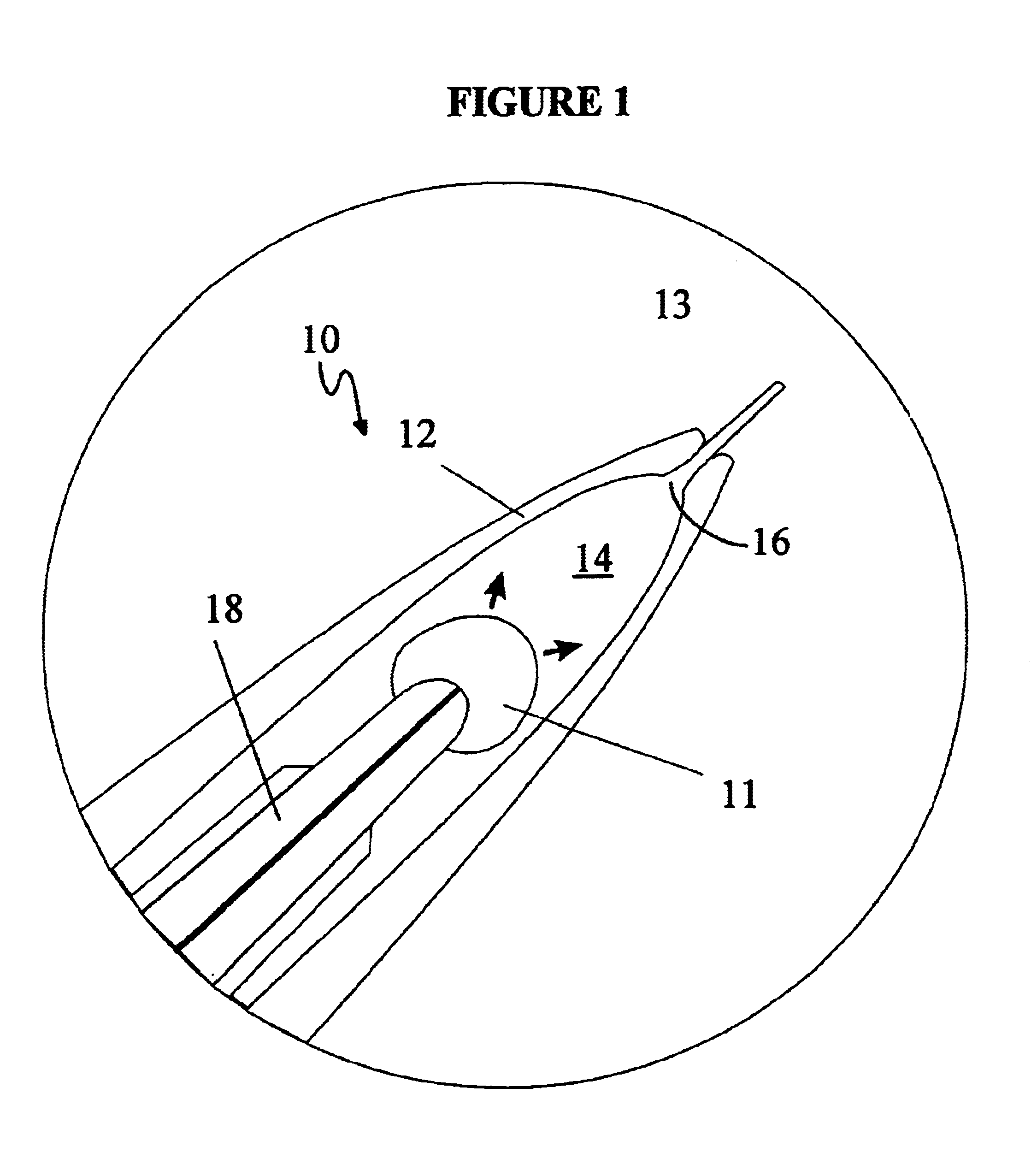
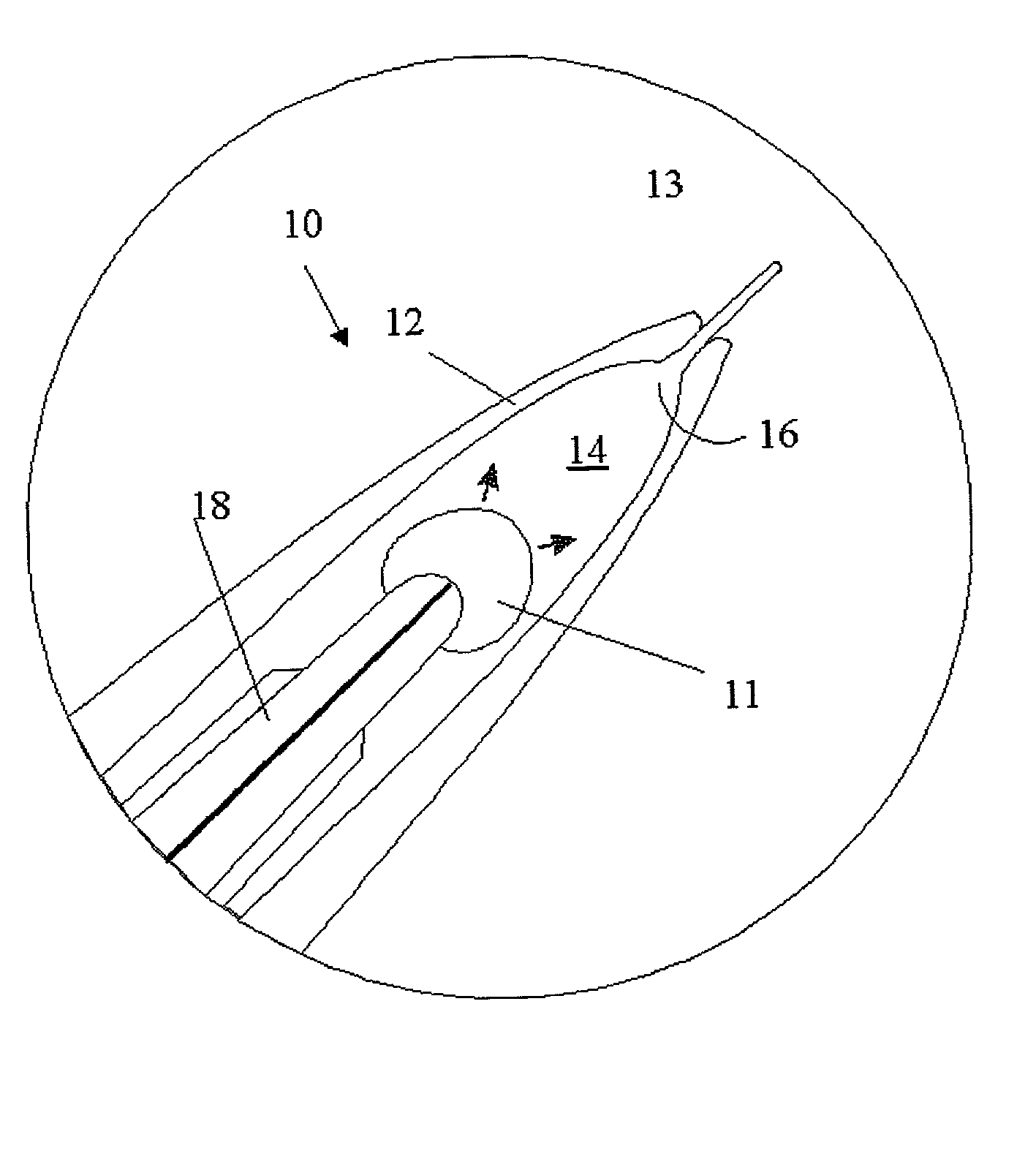
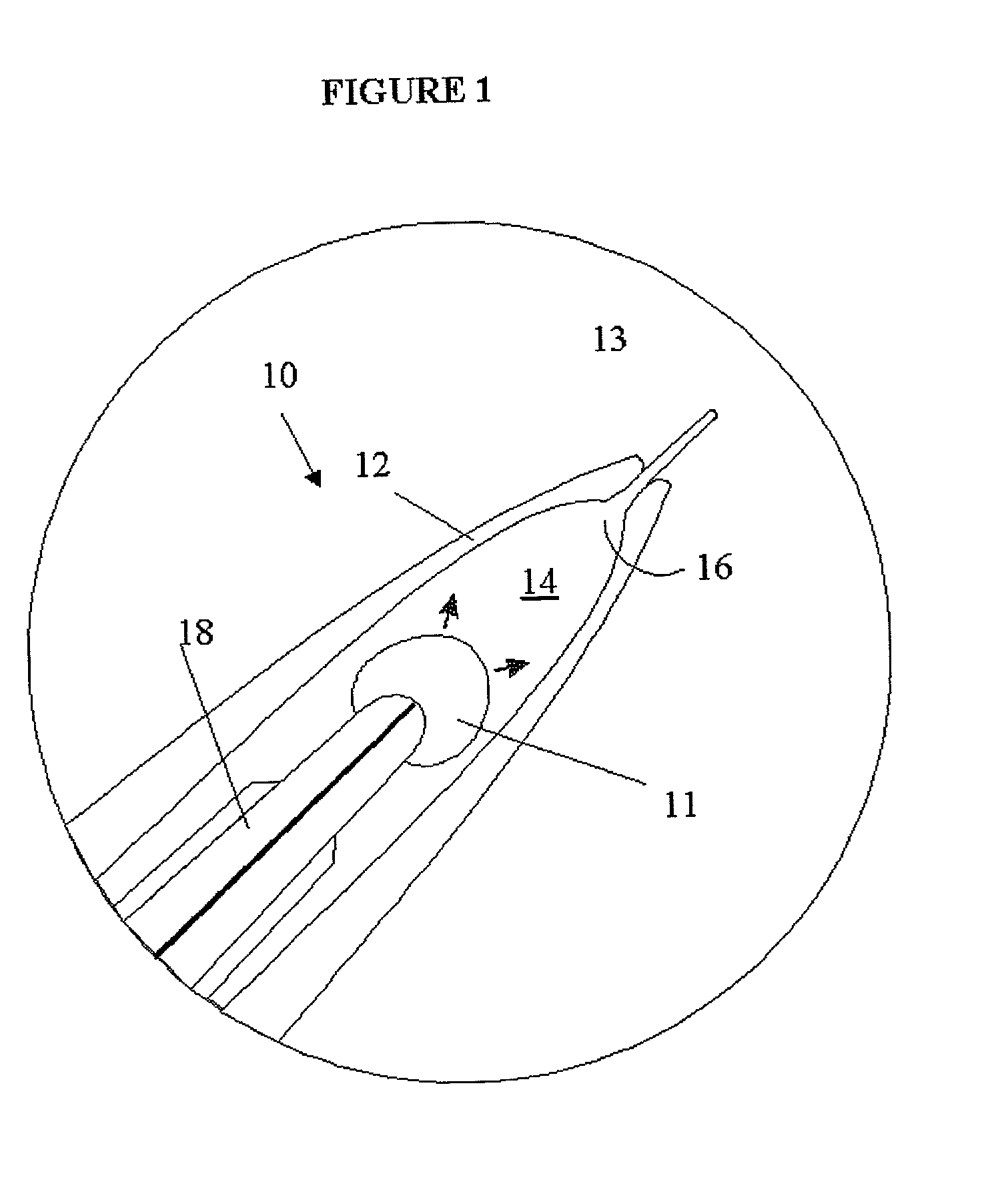
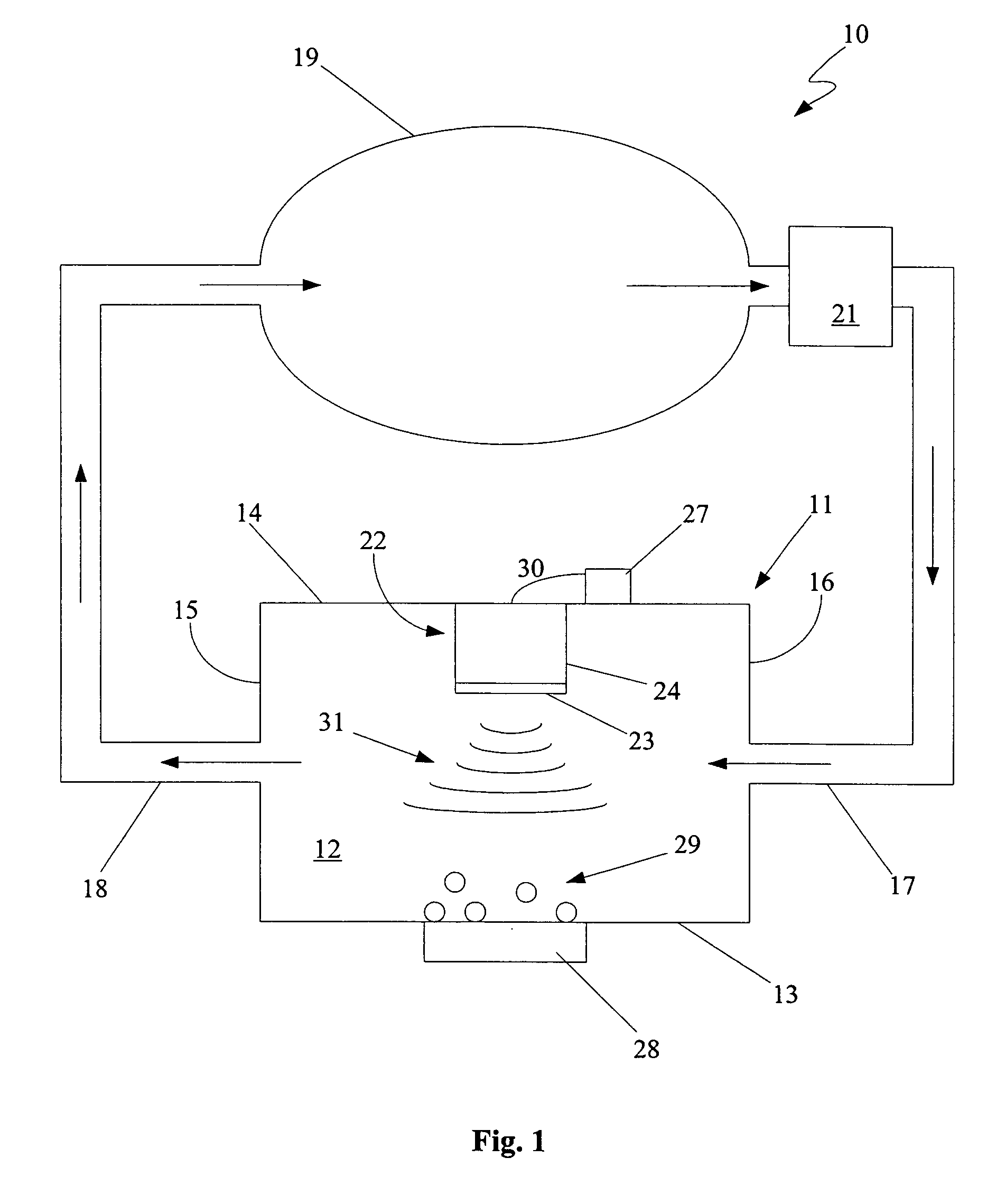
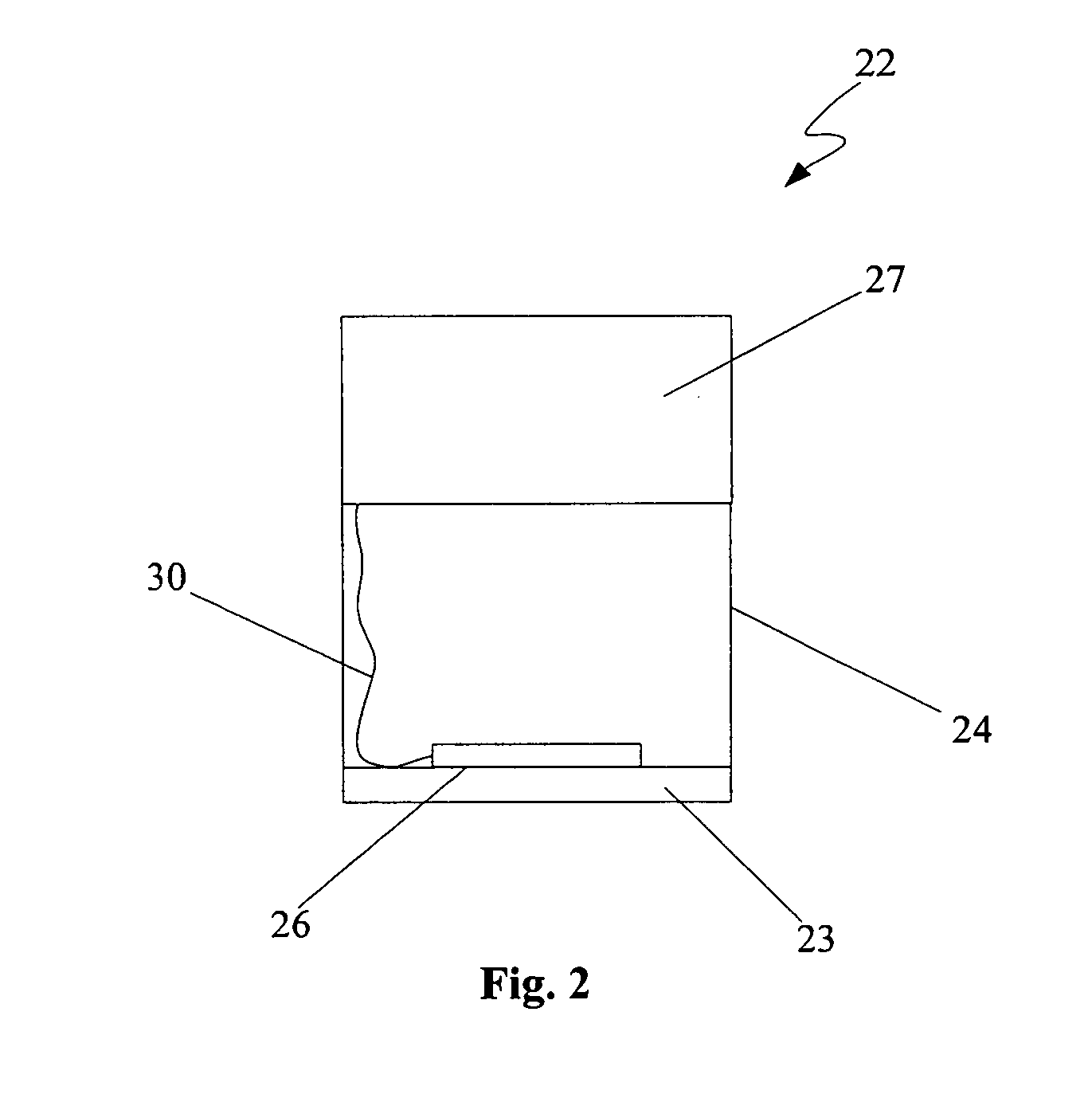
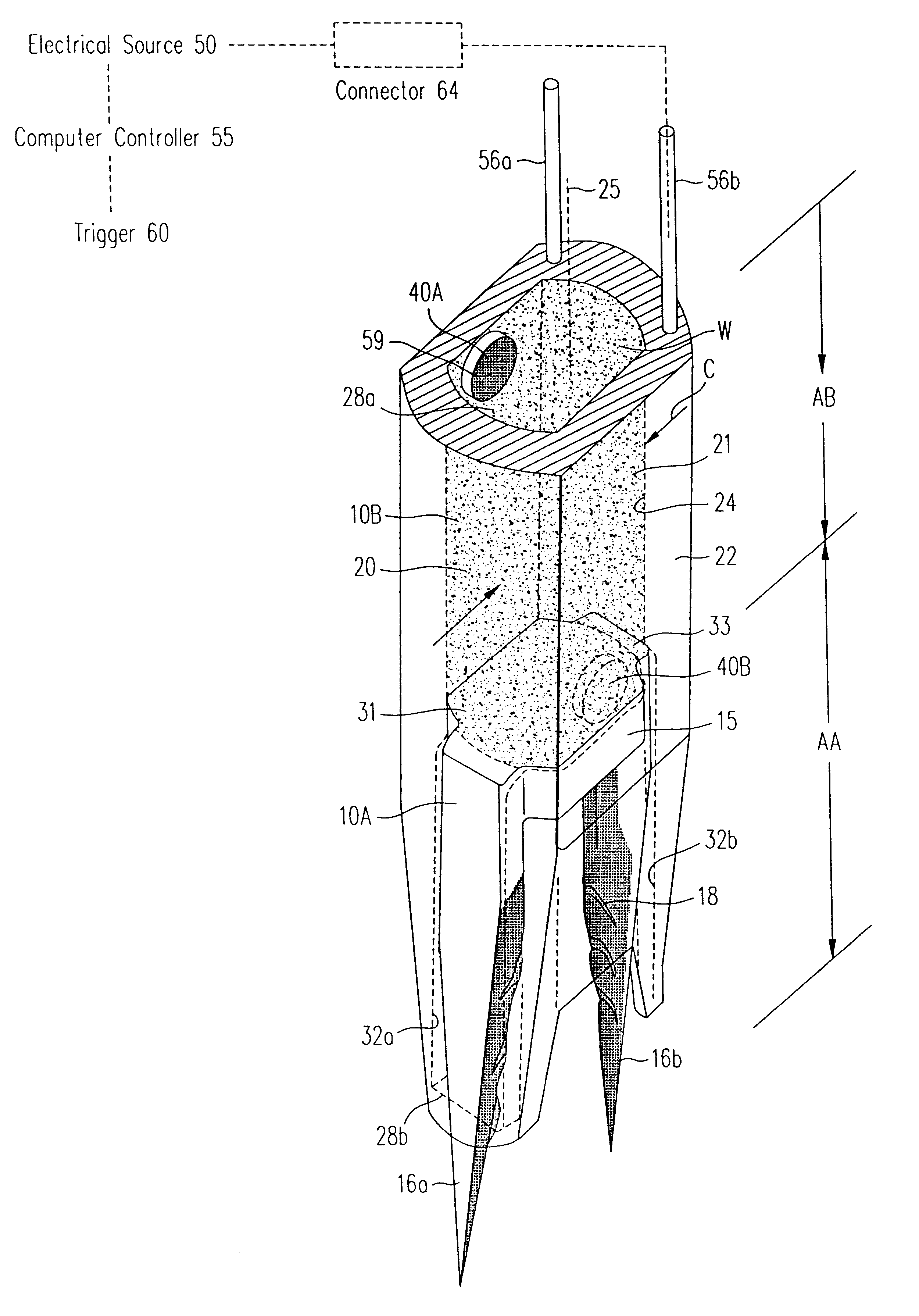
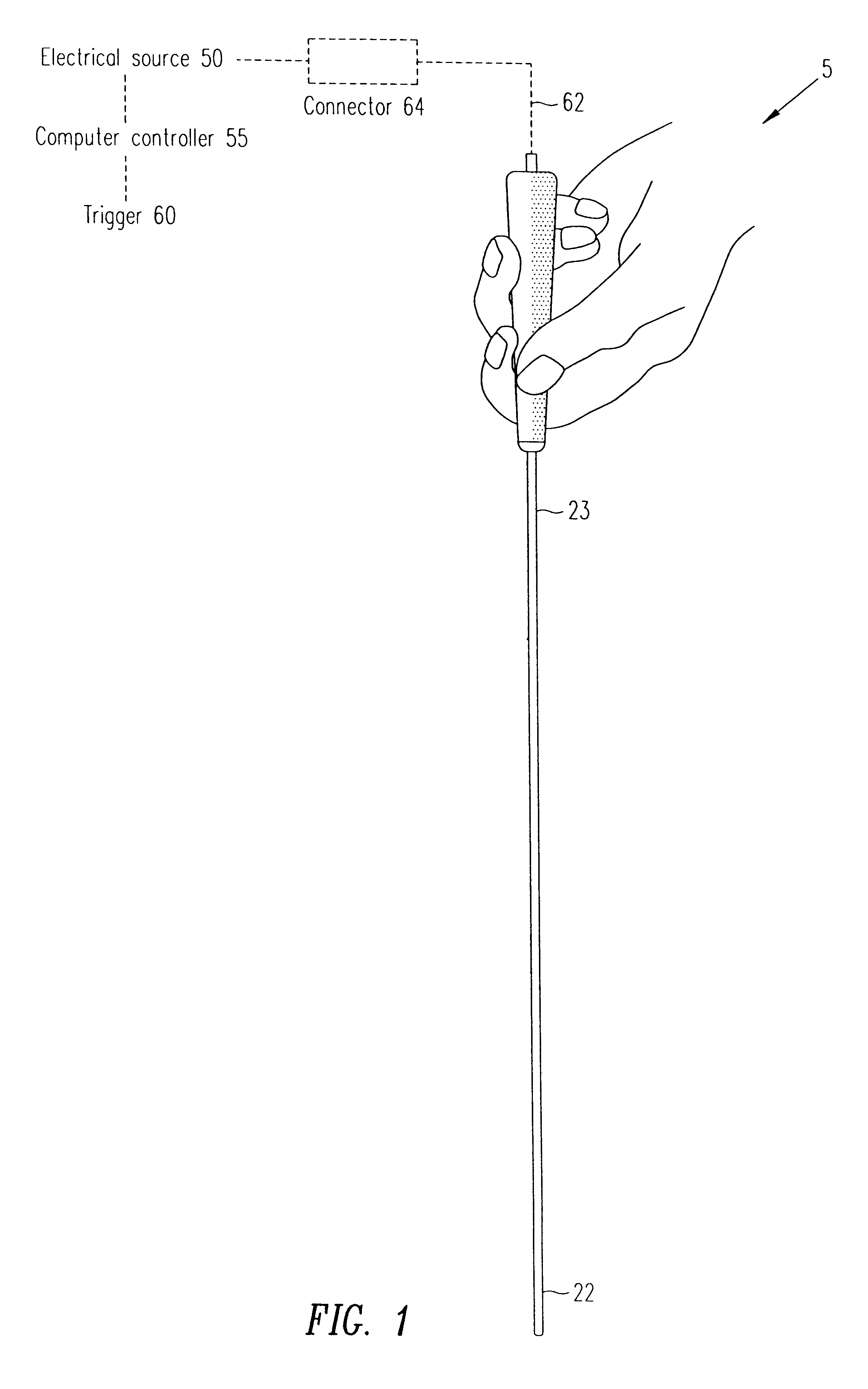
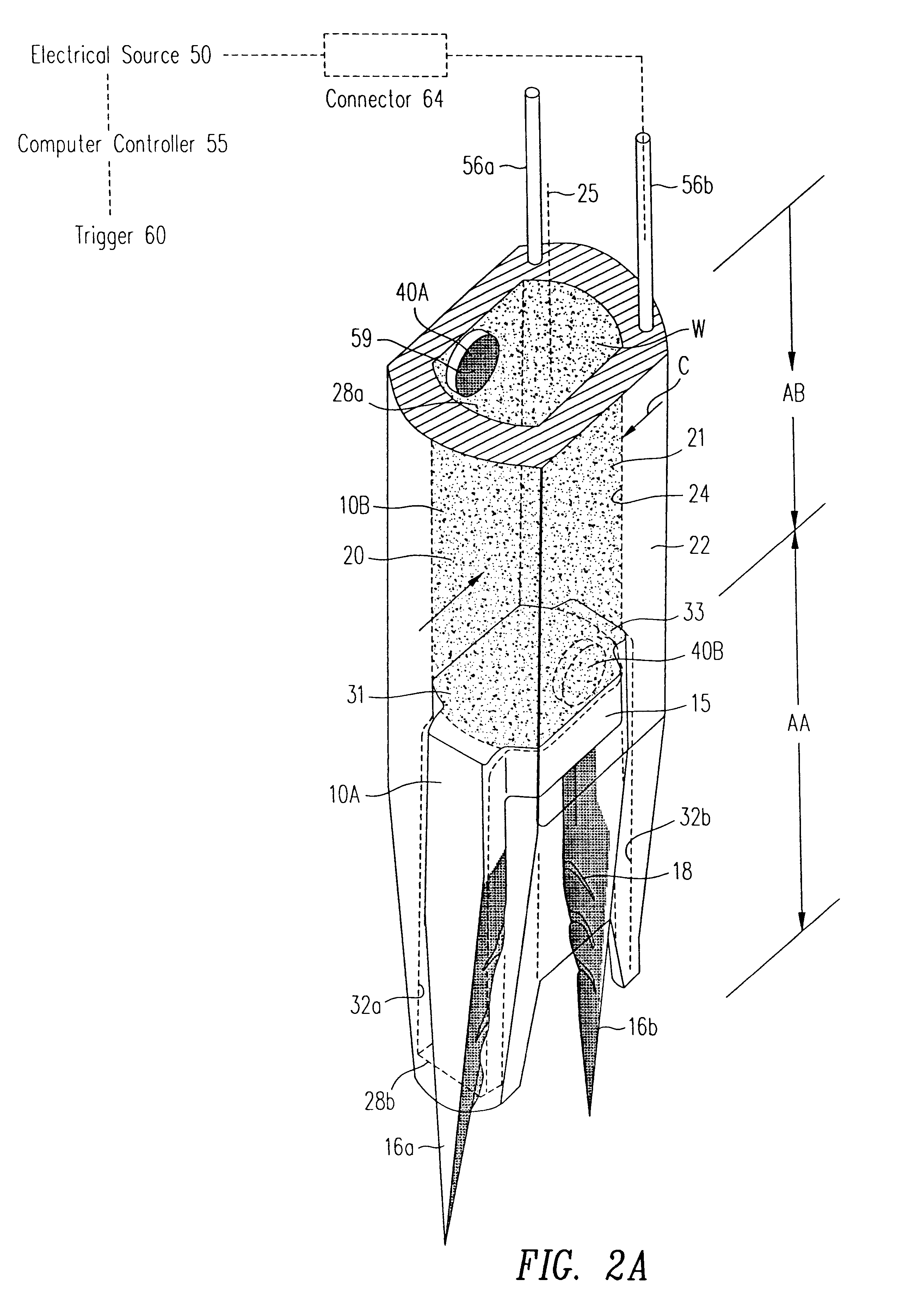
Electrosurgical system
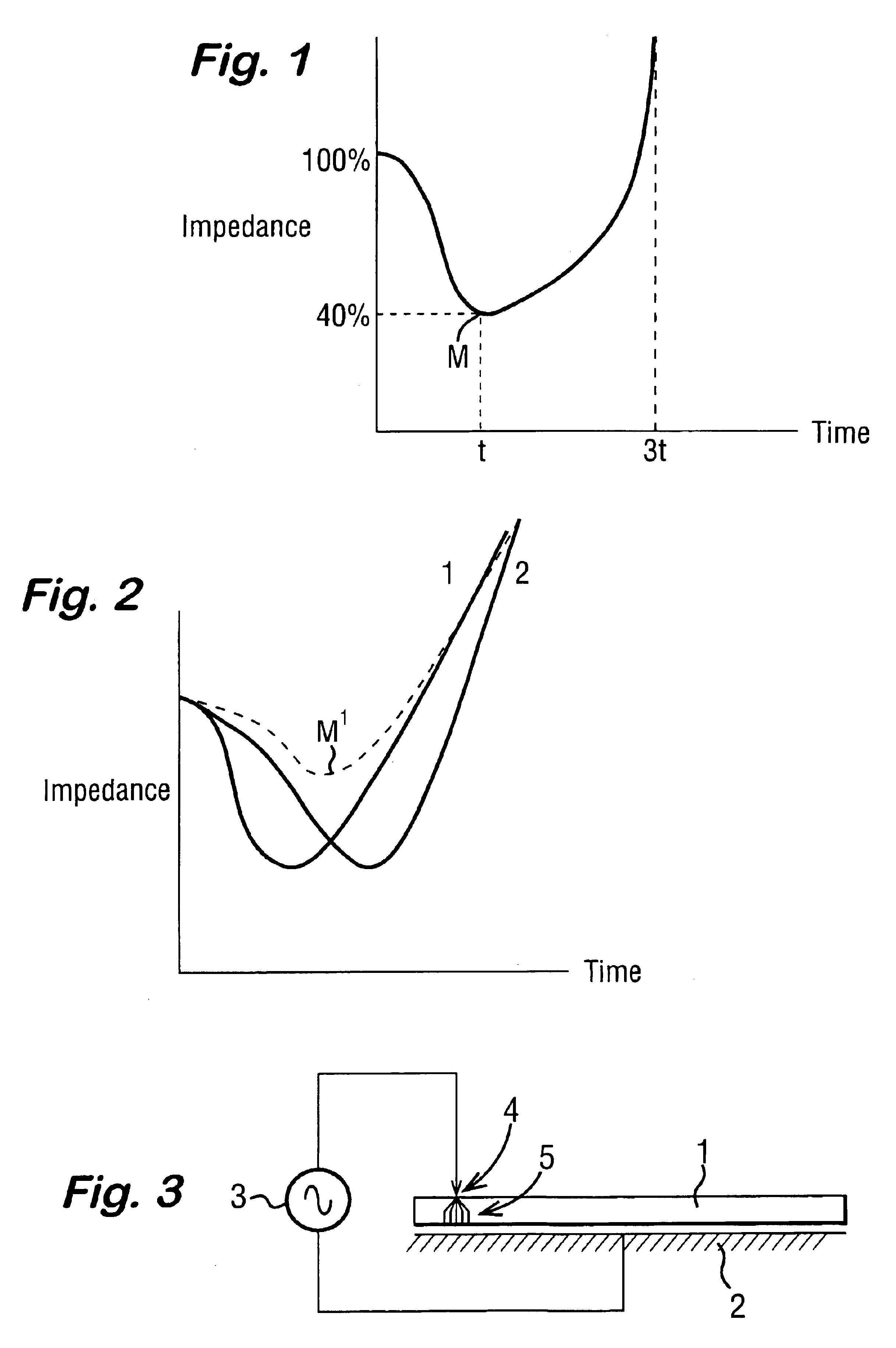
InactiveUS6843789B2Reduce riskRepeatable end-pointSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsVapor bubbleBipolar electrosurgery
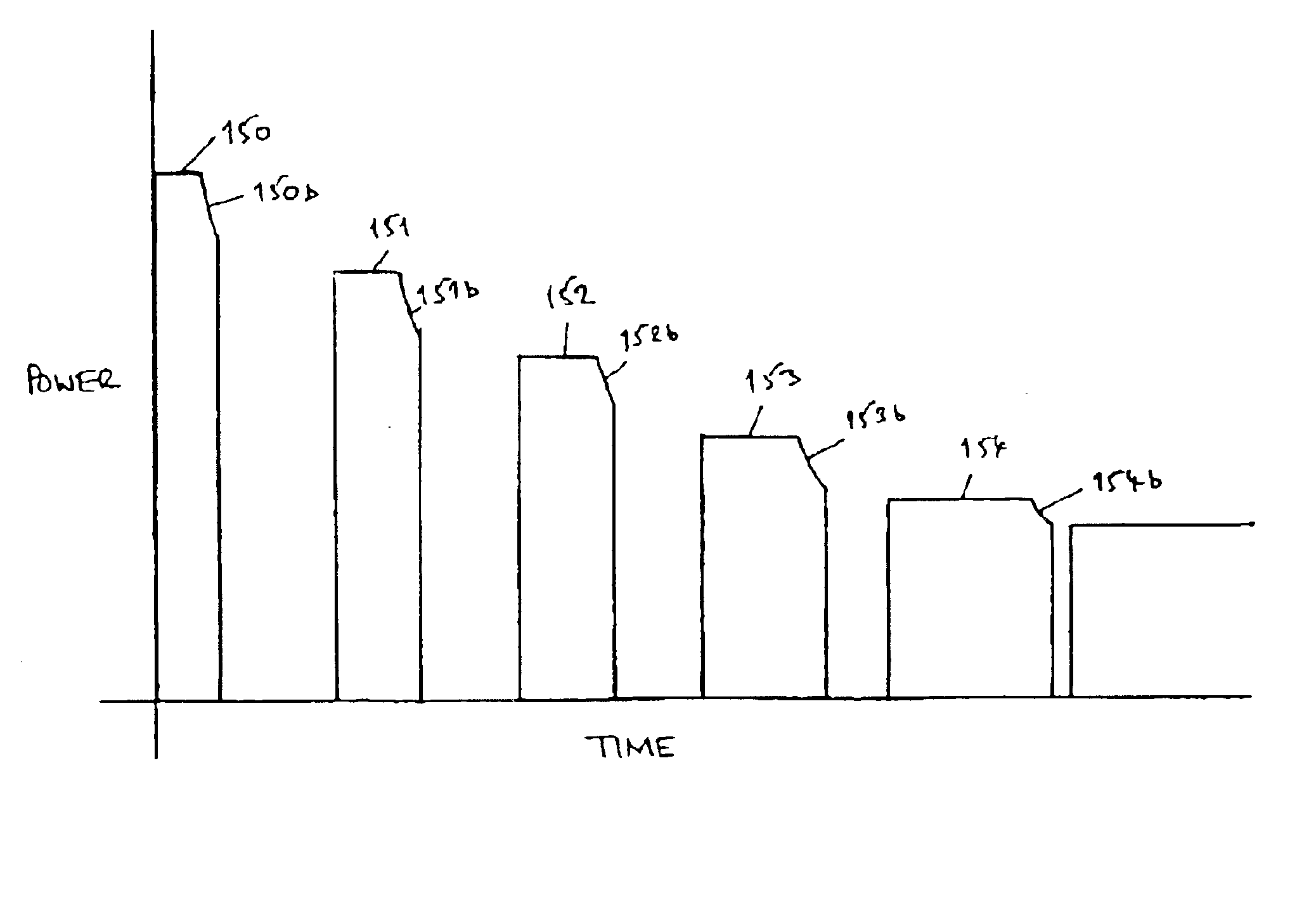
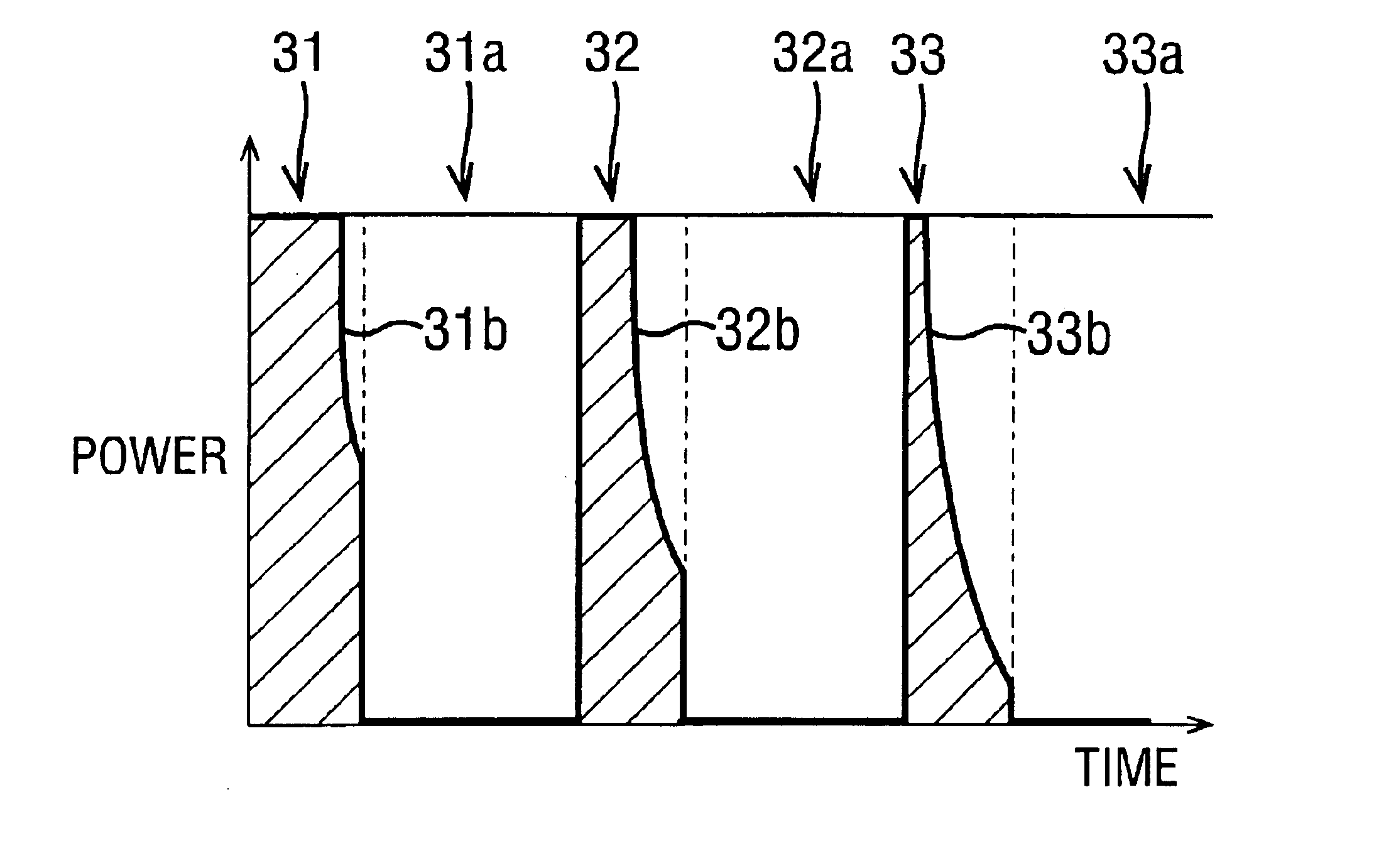
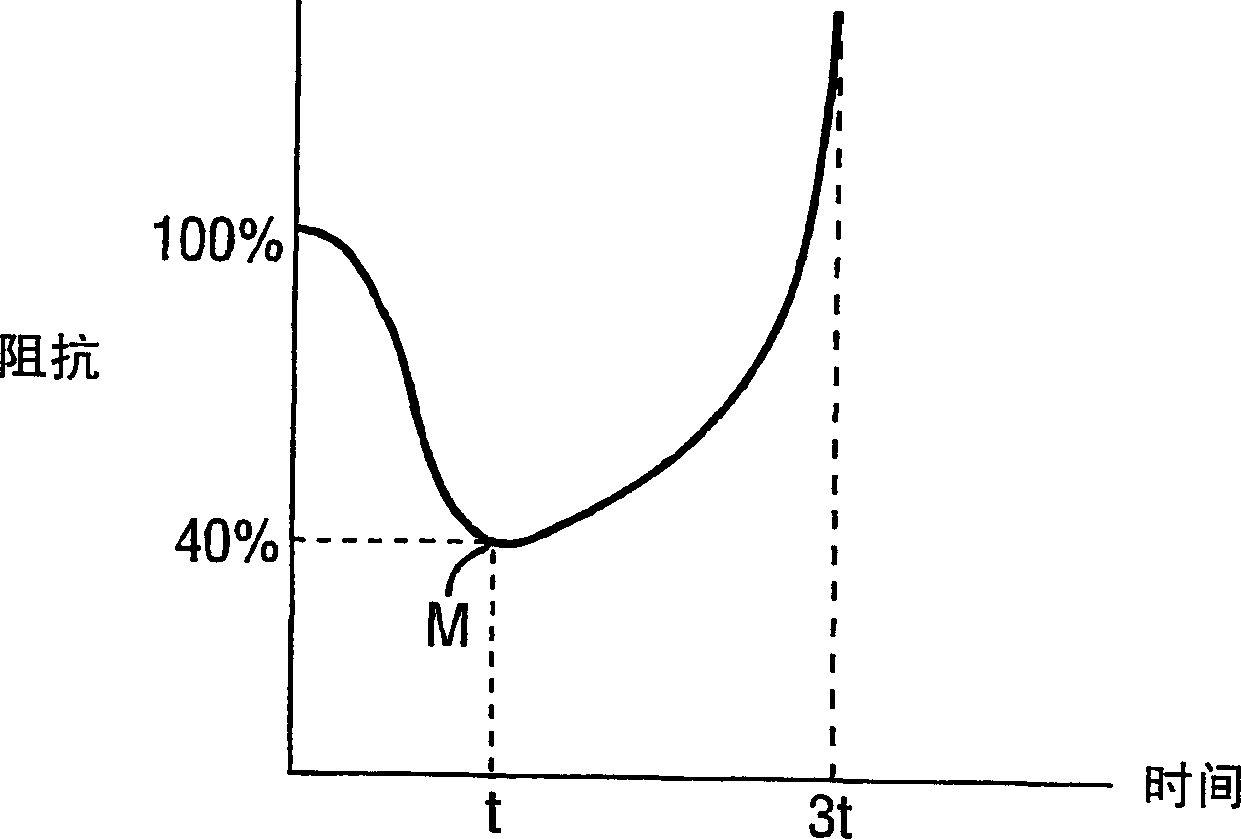
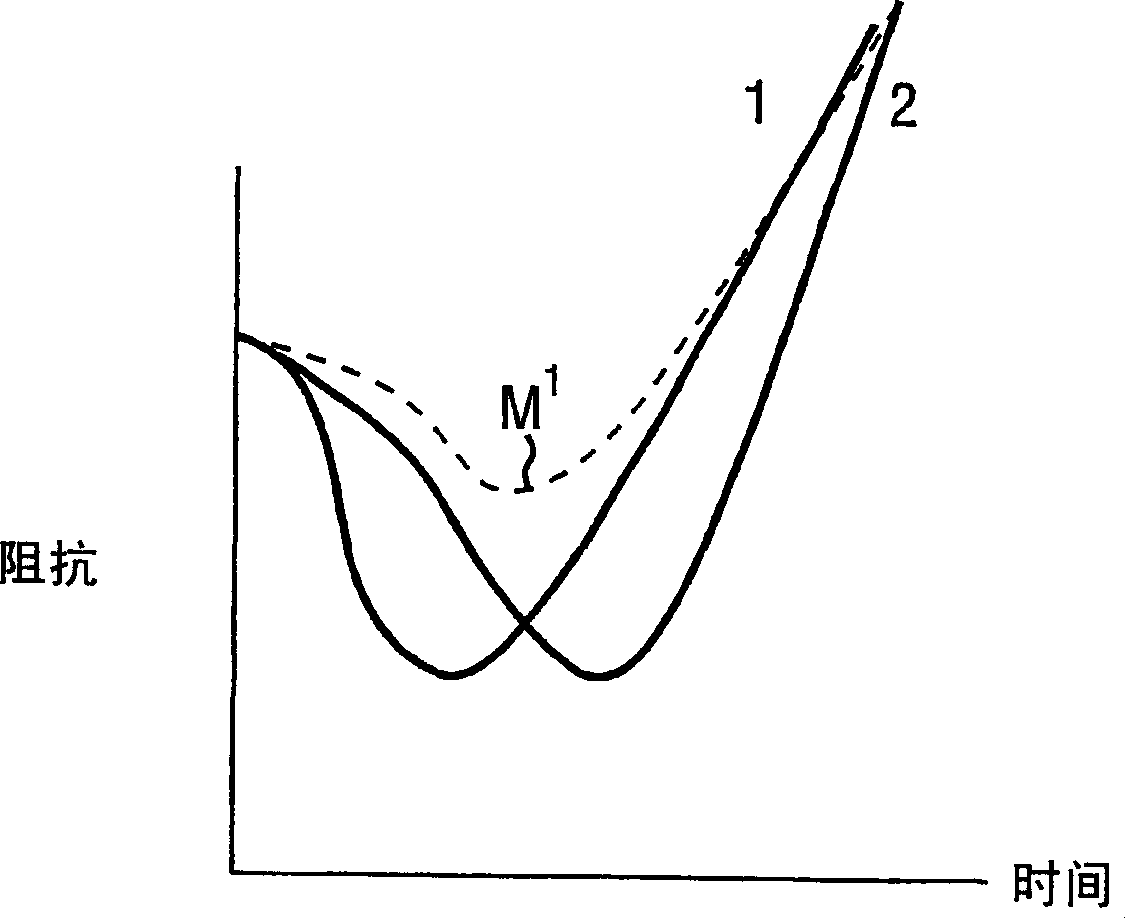
An electrosurgical system has an electrosurgical generator and a bipolar electrosurgical instrument, the generator being arranged to perform a treatment cycle in which radio frequency energy is delivered to the instrument as an amplitude-modulated radio frequency power signal in the form of a succession of pulses characterized by successive pulses of progressively increasing pulse width and progressively decreasing pulse amplitude. There are periods of at least 100 milliseconds between successive pulses, and the treatment cycle begins with a predetermined pulse mark-to-space ratio. Energy delivery between pulses is substantially zero. Each burst is of sufficiently high power to form vapor bubbles within tissue being treated and the time between successive pulses is sufficiently long to permit condensation of the vapor.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Electrosurgical system
InactiveUS6893435B2Sufficient powerImproving impedanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringRadio frequency
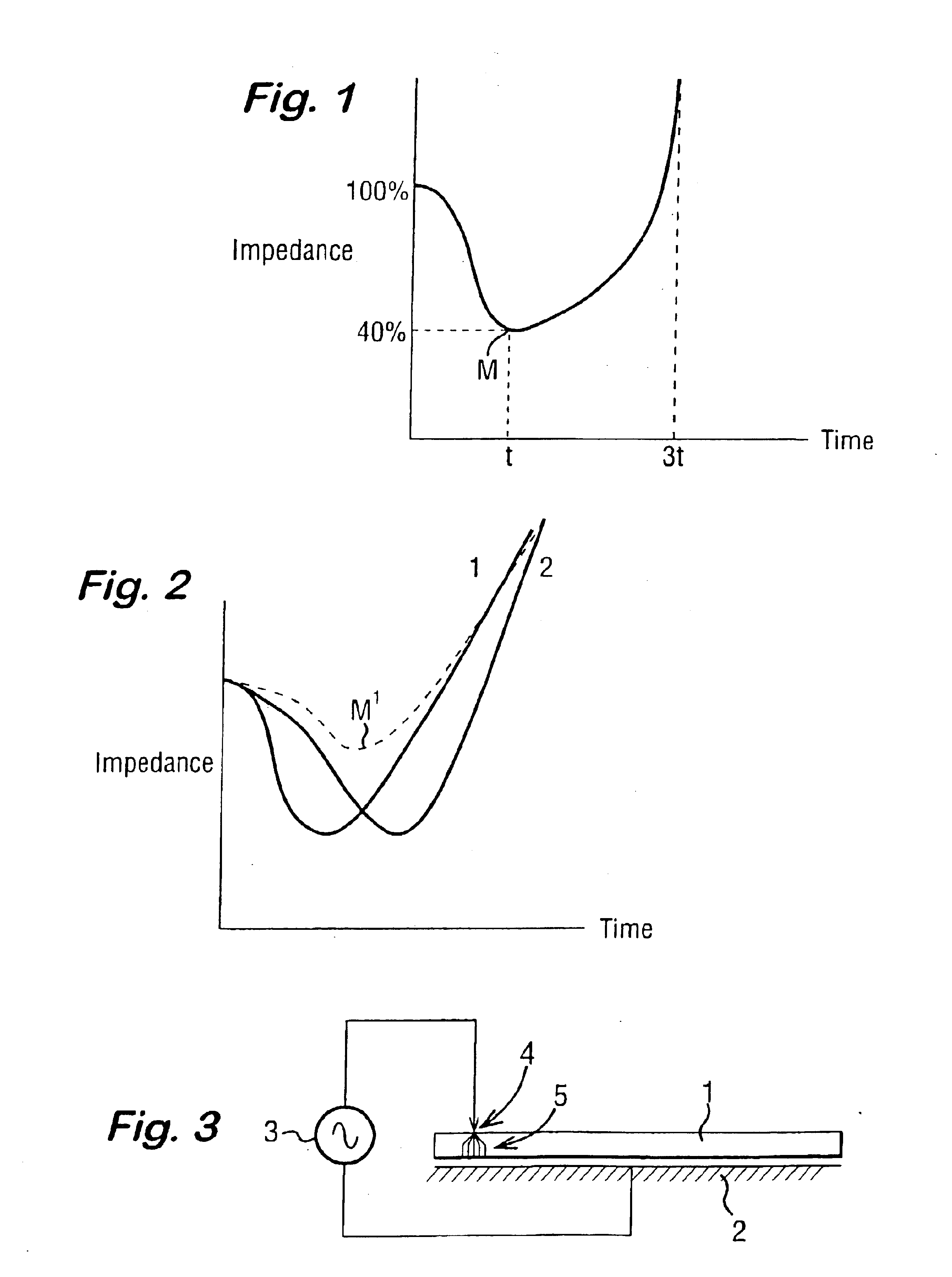
An electrosurgical system has an electrosurgical generator and a bipolar electrosurgical instrument, the generator being arranged to perform a treatment cycle in which radio frequency energy is delivered to the instrument as an amplitude-modulated radio frequency power signal in the form of a succession of pulses characterized by periods of a least 100 milliseconds between successive pulses and by a predetermined pulse mark-to-space ratio. Energy delivery between pulses is substantially zero and the mark-to-space ratio is typically 1:4 or less. Each burst is of sufficiently high power to form vapor bubbles within tissue being treated and the time between successive pulses is sufficiently long to permit condensation of the vapor. The treatment cycles may each include an initial period and a subsequent period, the pulse duty cycle being increased or energy being delivered continuously in the subsequent period in order that tissue coagulation can be achieved quickly despite increasing tissue impedance.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
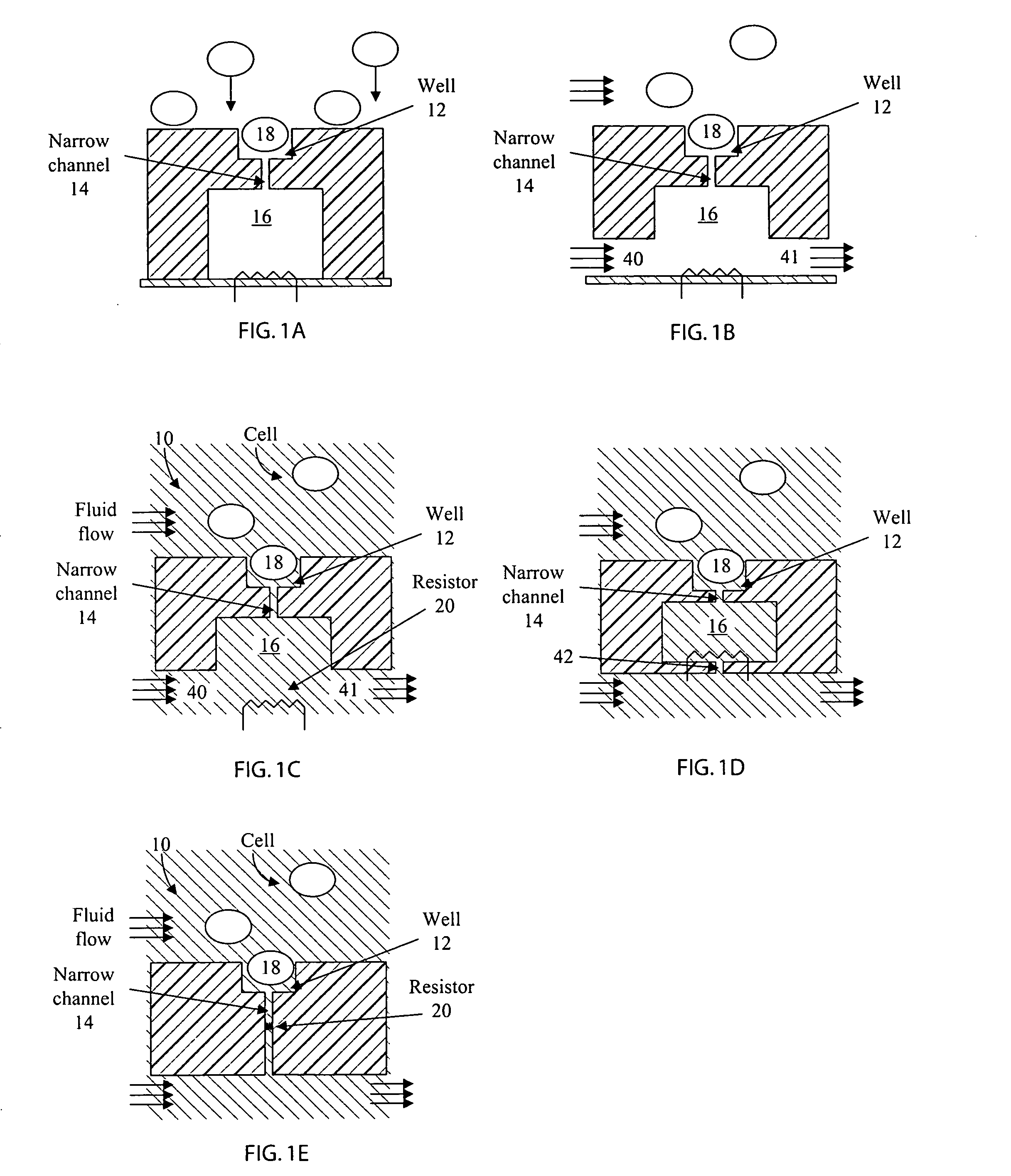
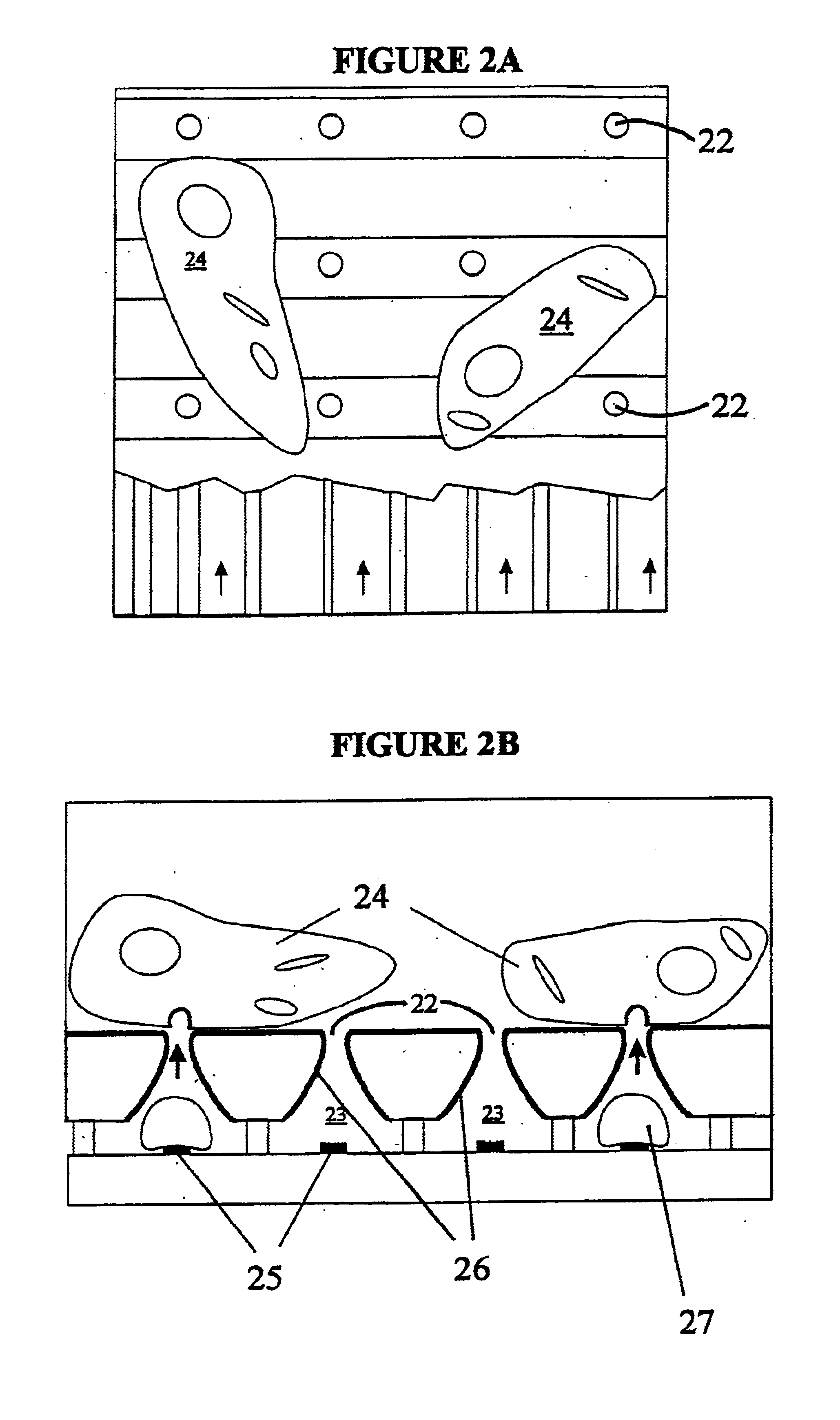
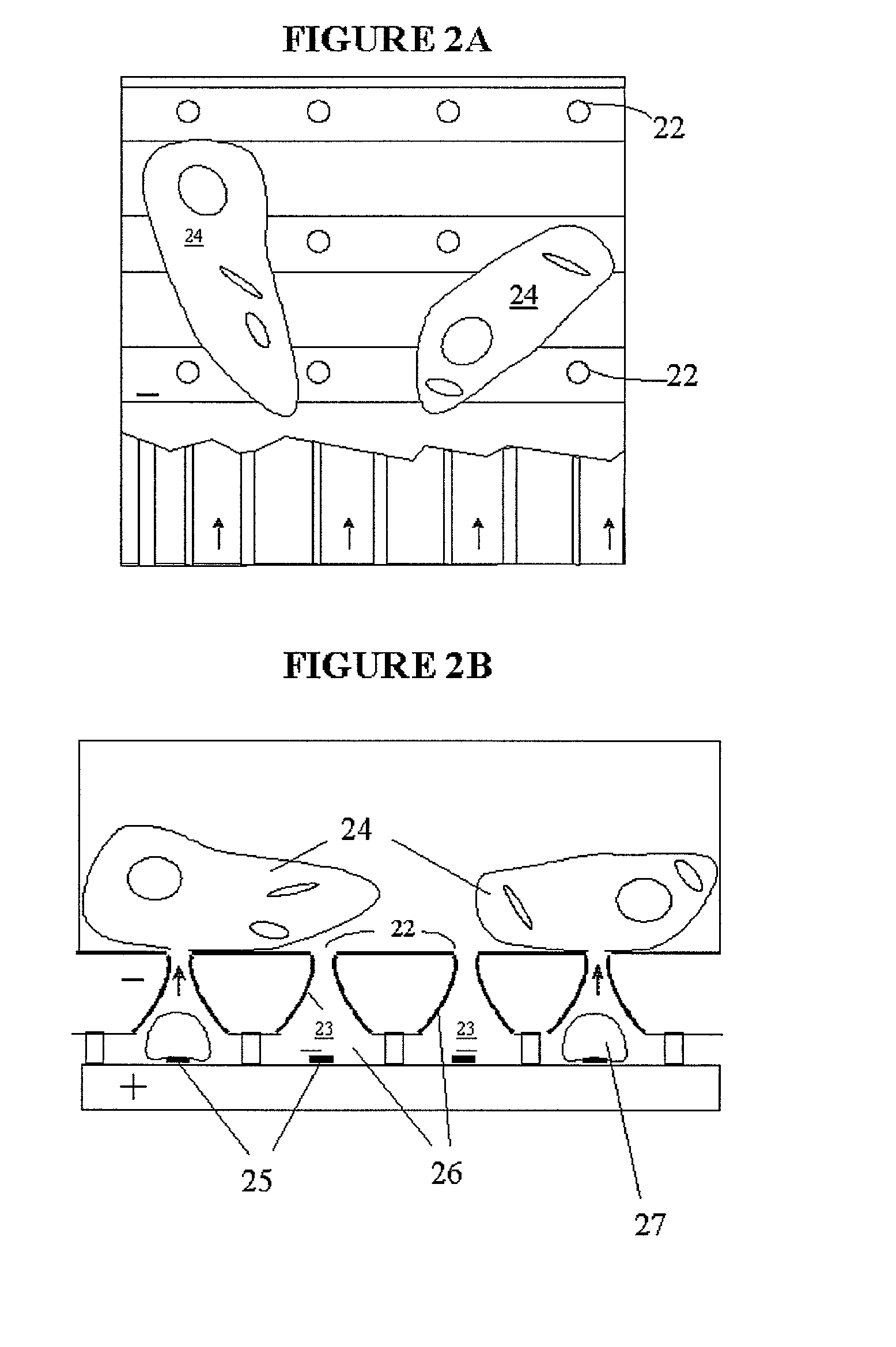
Hydrodynamic capture and release mechanisms for particle manipulation
InactiveUS20060128006A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceMicrobubbles
A cell analysis and sorting apparatus is capable of monitoring over time the behavior of each cell in a large population of cells. The cell analysis and sorting apparatus contains individually addressable cell locations. Each location is capable of capturing and holding a specified number of cells, and selectively releasing that specified number of cells from that particular location. In one aspect of the invention, the cells are captured and held in wells, and released using vapor bubbles as a means of cell actuation. Disclosed are: a cell manipulation apparatus design; various resistive heater configurations for nucleating microbubbles; various well designs, each in communication with a nucleation chamber or channel, for capturing a specified number of cells; and methods of fabrication and cell population manipulation.
Owner:GERHARDT ANTIMONY L +6
Photoacoustic removal of occlusions from blood vessels
Partial or total occlusions of fluid passages within the human body are removed by positioning an array of optical fibers in the passage and directing treatment radiation pulses along the fibers, one at a time, to generate a shock wave and hydrodynamic flows that strike and emulsify the occlusions. A preferred application is the removal of blood clots (thrombi and emboli) from small cerebral vessels to reverse the effects of an ischemic stroke. The operating parameters and techniques are chosen to minimize the amount of heating of the fragile cerebral vessel walls occurring during this photoacoustic treatment. One such technique is the optical monitoring of the existence of hydrodynamic flow generating vapor bubbles when they are expected to occur and stopping the heat generating pulses propagated along an optical fiber that is not generating such bubbles.
Owner:SELVA MEDICAL +2
Vapor driven aerosol generator and method of use thereof
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Vapor driven aerosol generator and method of use thereof
An aerosol generator includes a fluid supply which supplies fluid to a fluid passage, a main heater which heats the fluid into a gaseous state and a preheater which delivers a volume of fluid to the main heater. The preheater can be located in or adjacent a metering chamber which receives a predetermined volume of fluid, the preheater heating a portion of the fluid so as to form a vapor bubble which ejects the remaining fluid from the chamber. An outlet of the aerosol generator is arranged to receive the volatilized fluid formed by the main heater and direct the volatilized fluid out of the fluid passage. The aerosol generator can be used to generate aerosols containing medicated materials.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
MEMS bubble generator
ActiveUS20060250453A1High material strengthHigh densityInking apparatusOther printing apparatusVapor bubbleSuperalloy
A MEMS vapor bubble generator with a chamber for holding liquid and a heater positioned in the chamber for heating the liquid above its bubble nucleation point to form a vapour bubble; wherein, the heater is formed from a superalloy.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
Intravascular Diagnostic or Therapeutic Apparatus Using High-Intensity Pulsed Light
InactiveUS20080221560A1Method is invasiveMinimally invasiveEndoscopesLaproscopesVapor bubbleRemove blood
An intravascular diagnostic or therapeutic apparatus capable of removing blood in an intravascular lumen to be observed using a minimally invasive method is provided. The apparatus includes high-intensity pulsed light generating means and high-intensity pulsed light transmitting means for transmitting high-intensity pulsed light, capable of irradiating the interior of a blood vessel with high-intensity pulsed light, producing water-vapor bubbles and temporarily removing the blood in the blood vessel.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
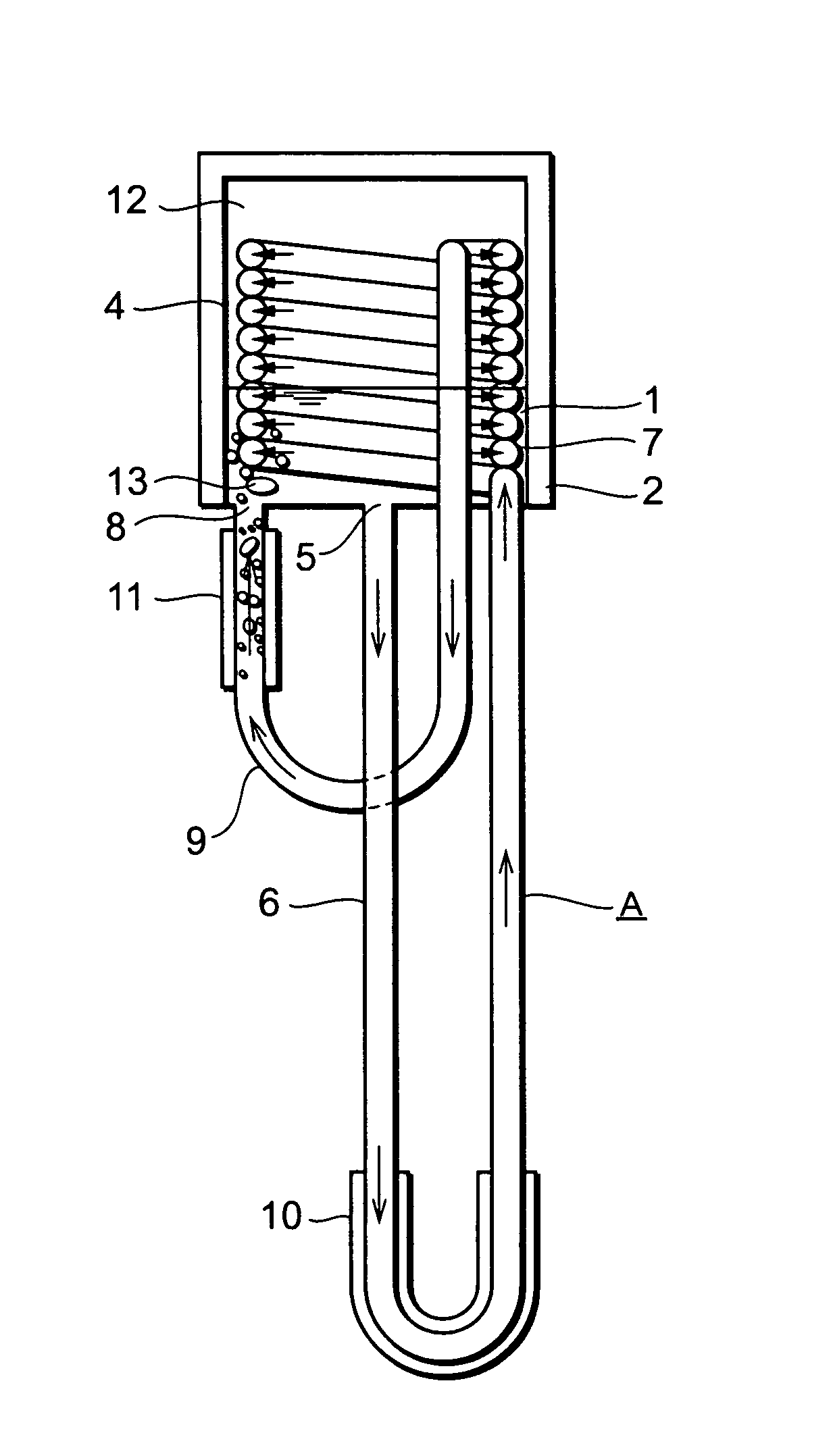
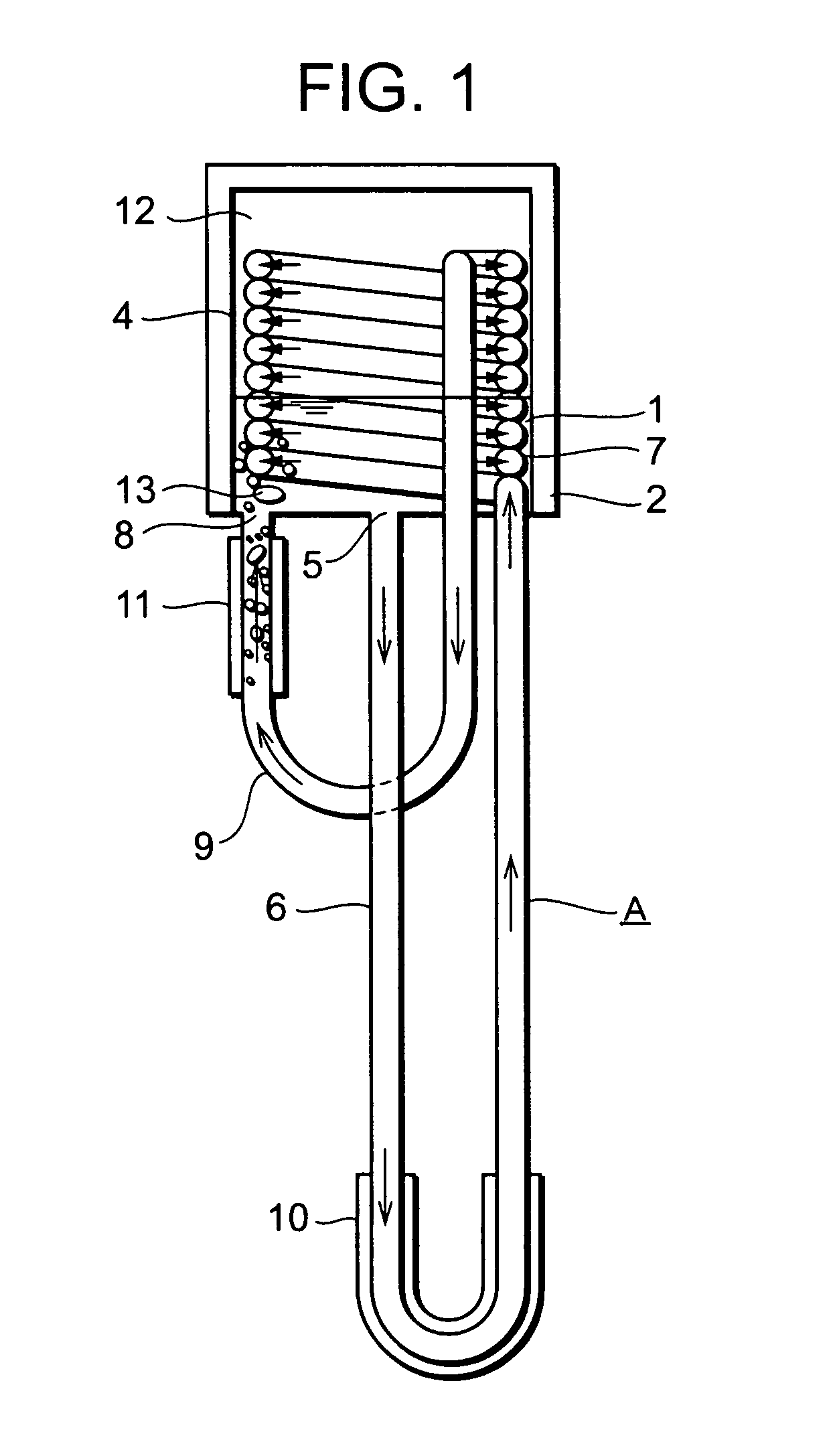
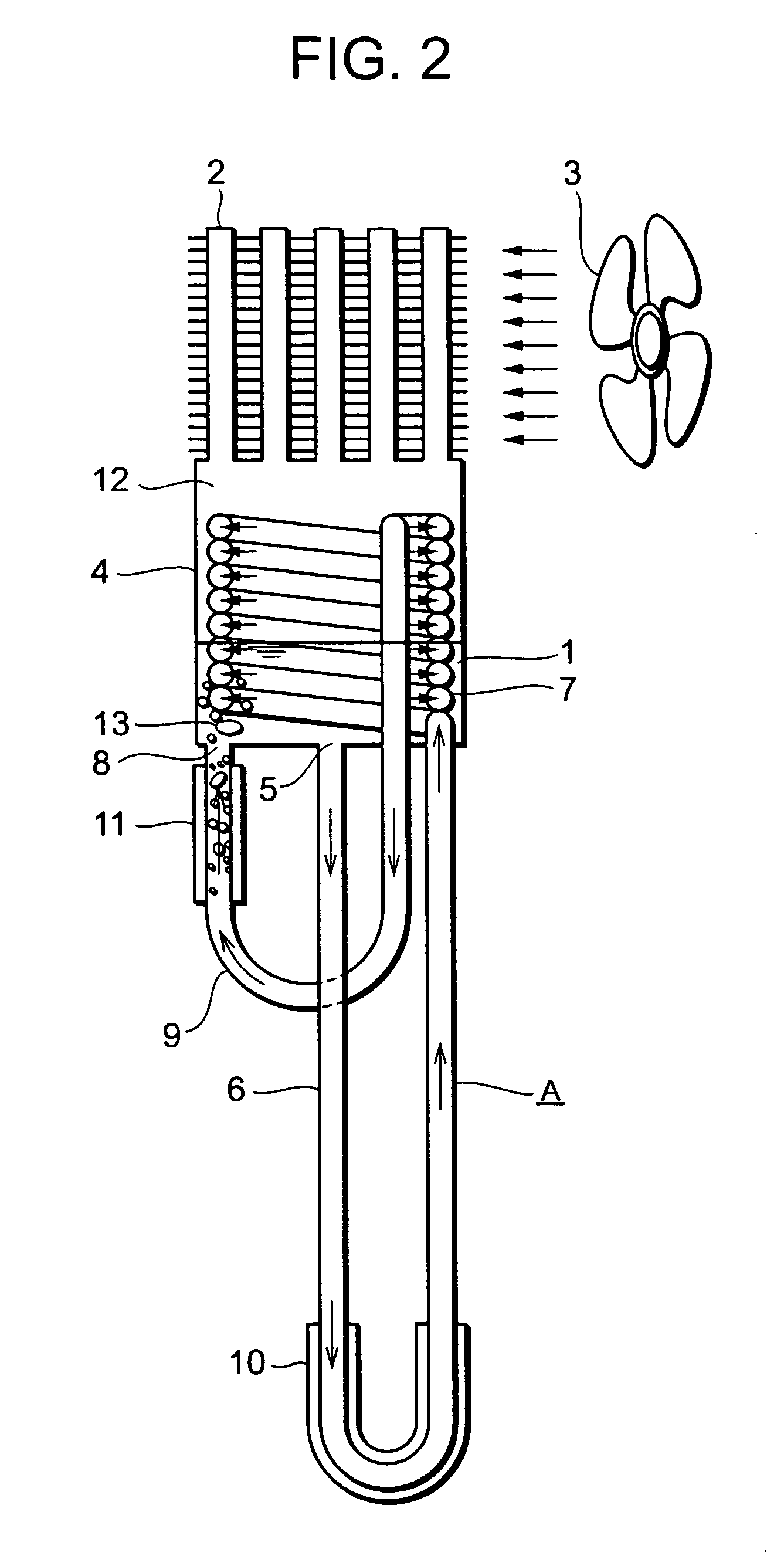
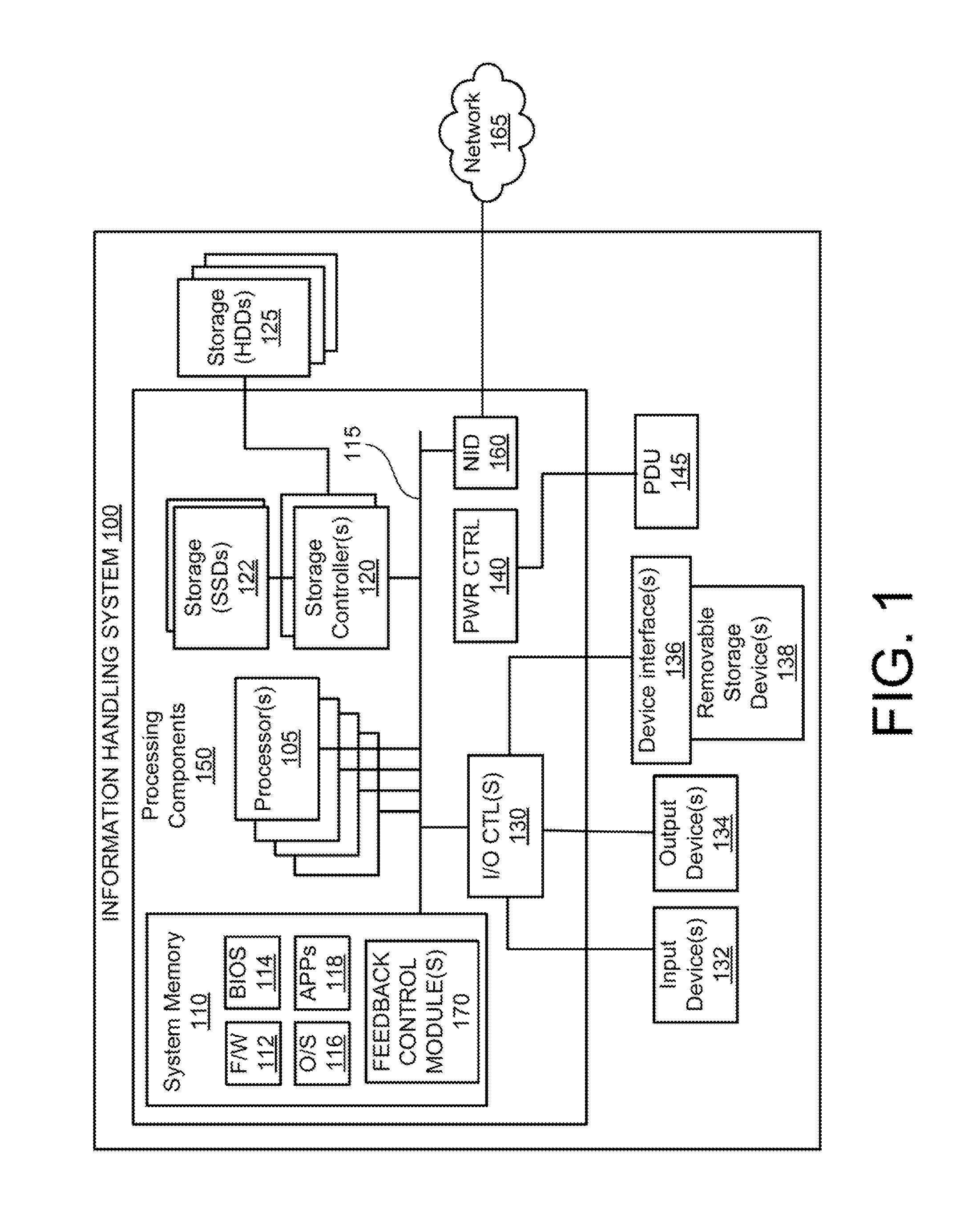
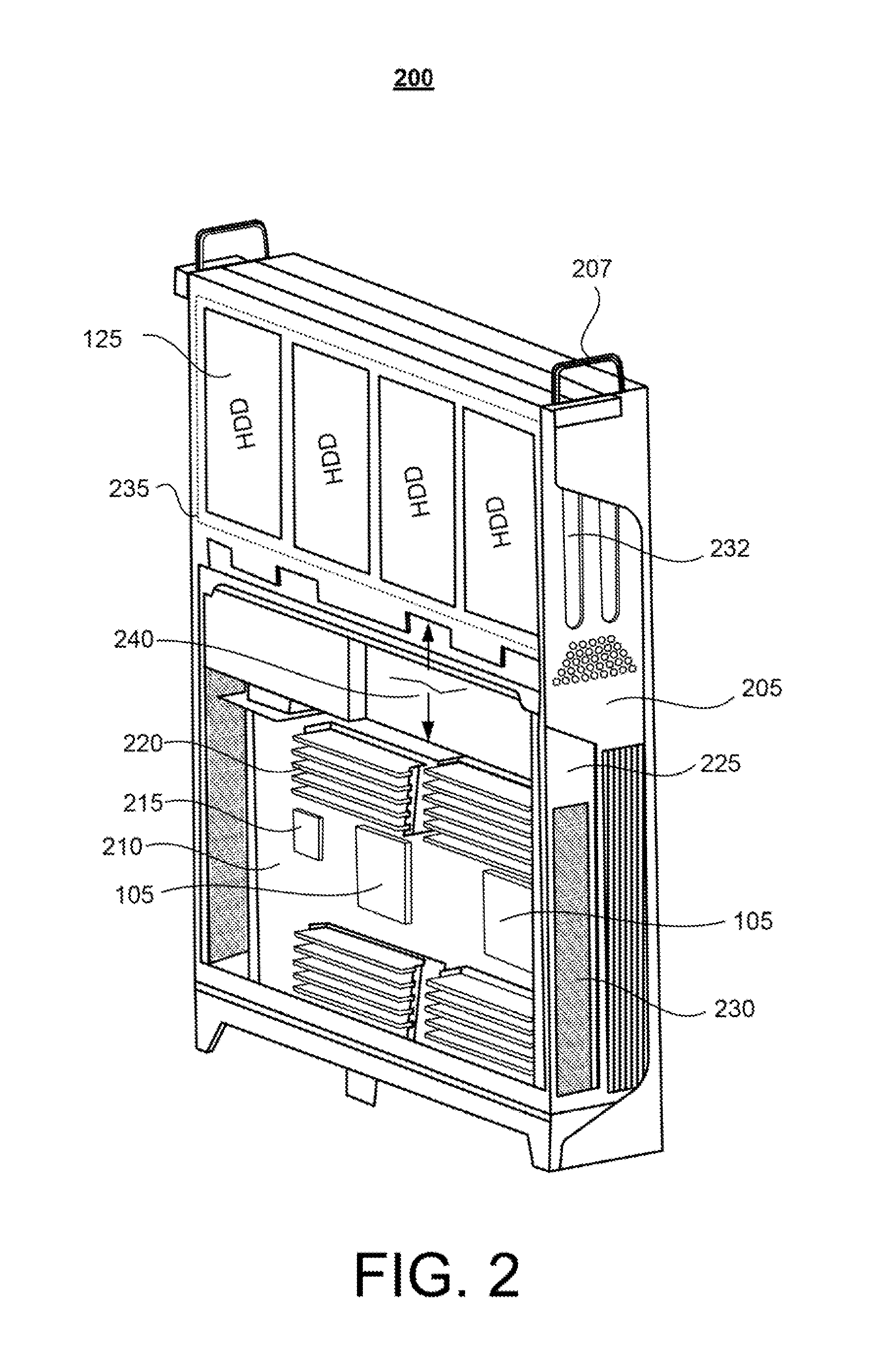
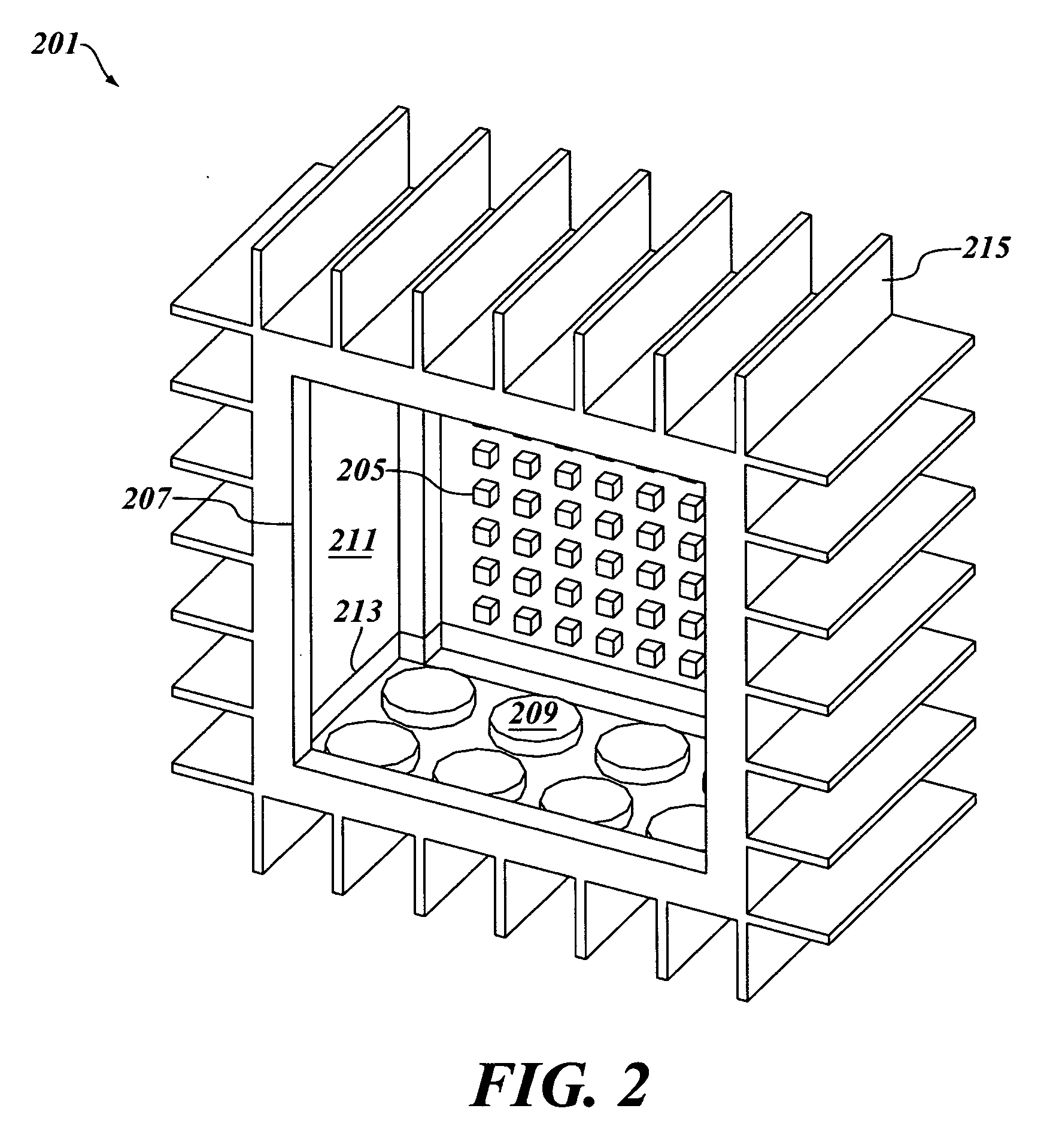
Vertically-Oriented Immersion Server with Vapor Bubble Deflector
ActiveUS20140218861A1Maximize heat absorptionDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsVapor bubbleComputer science
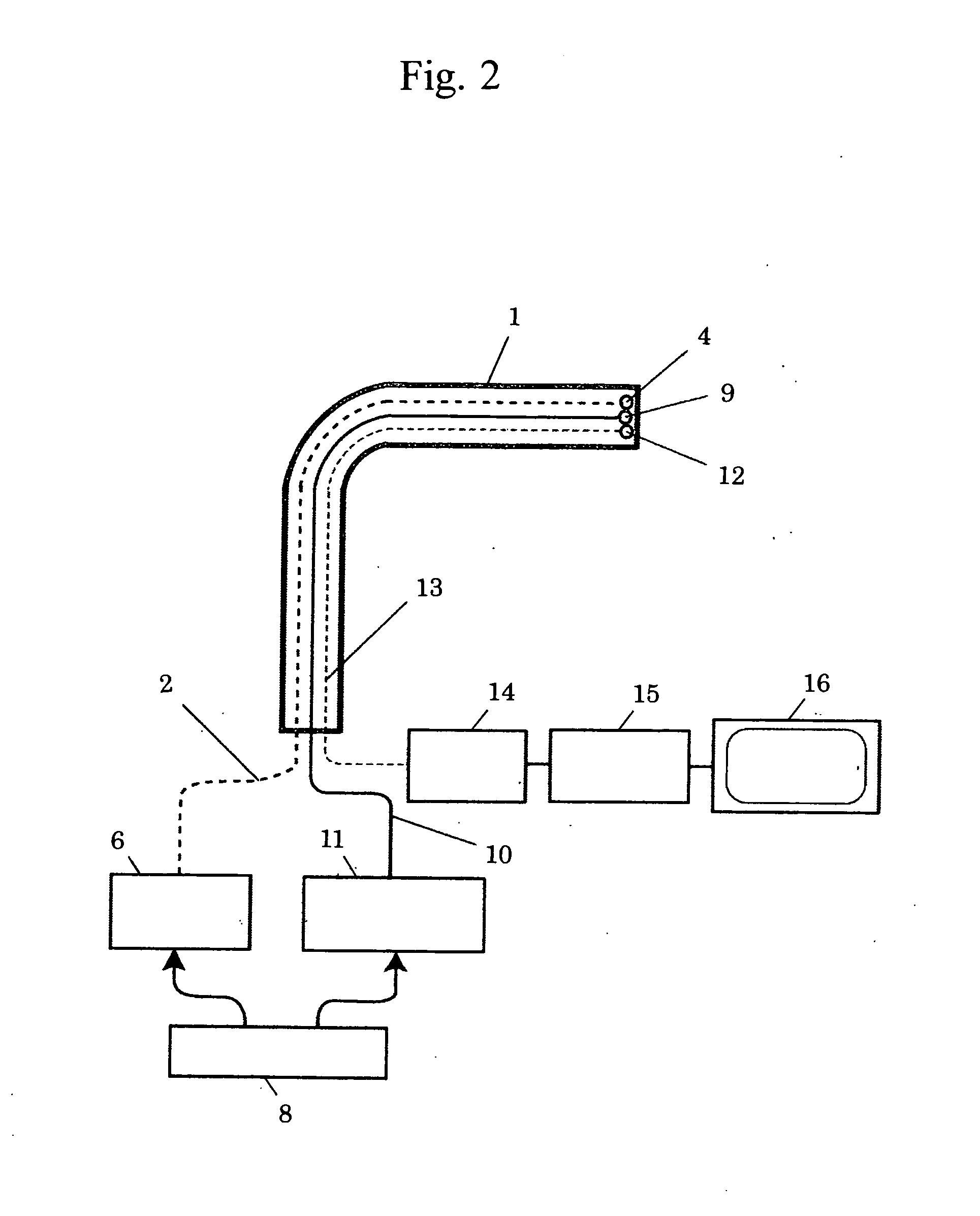
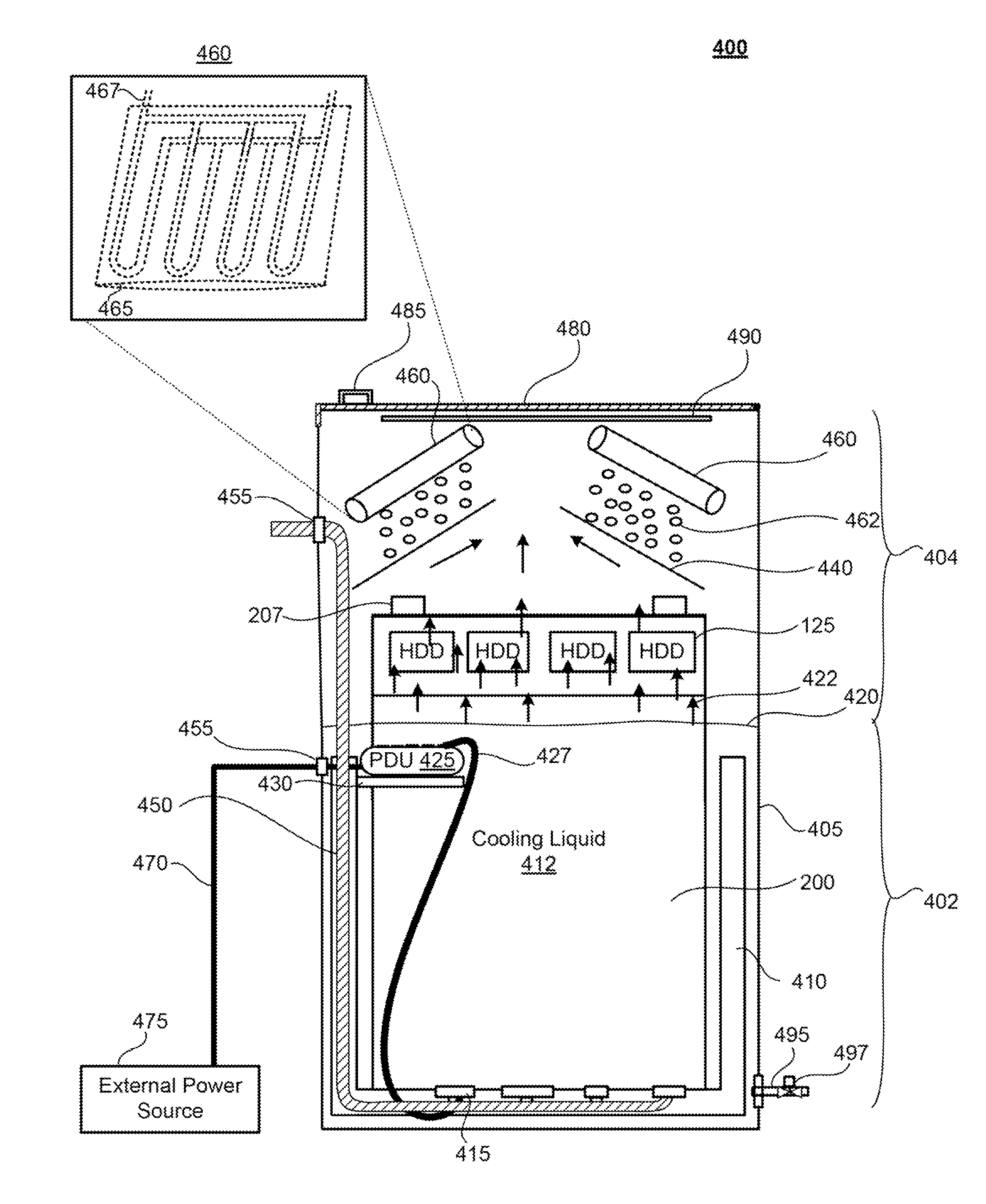
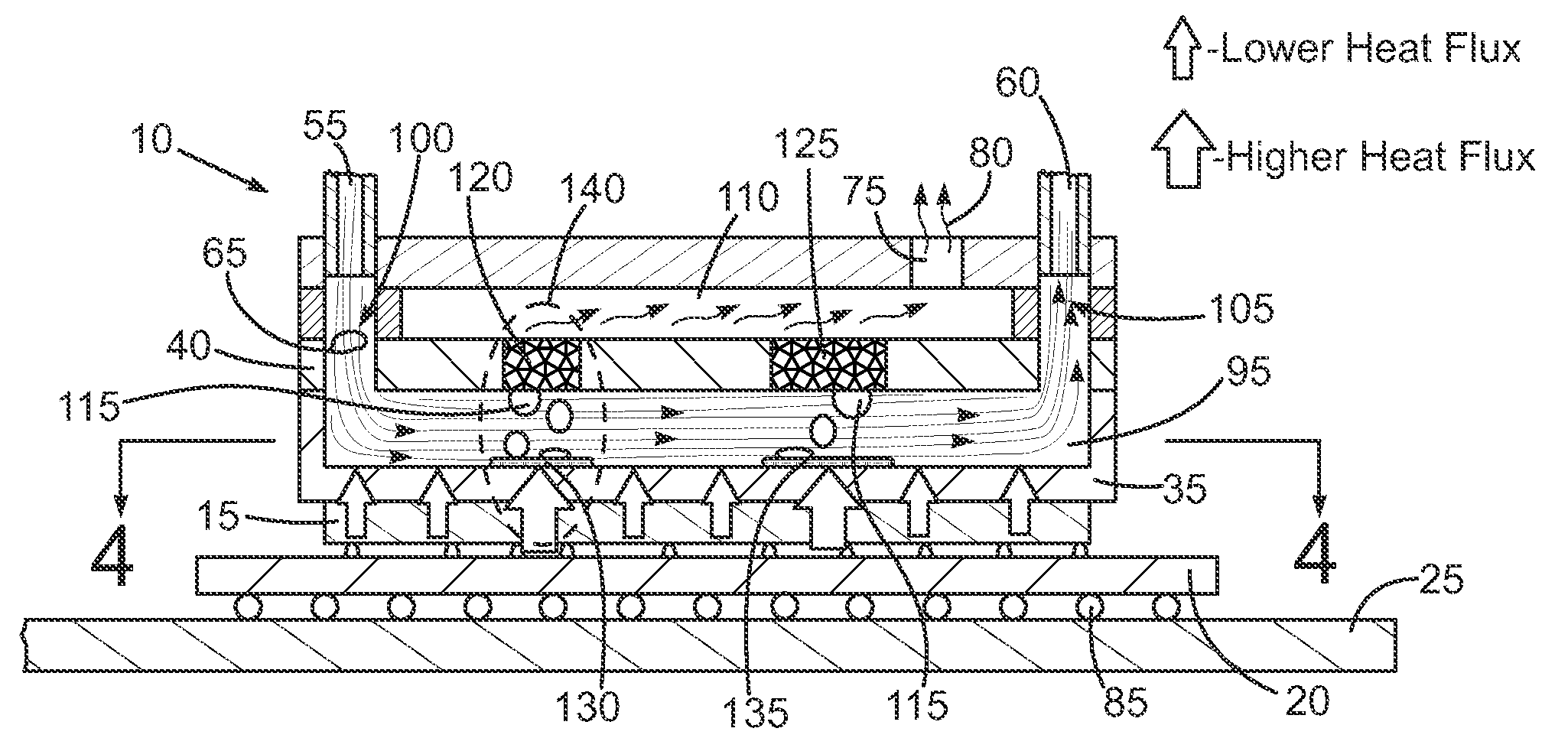
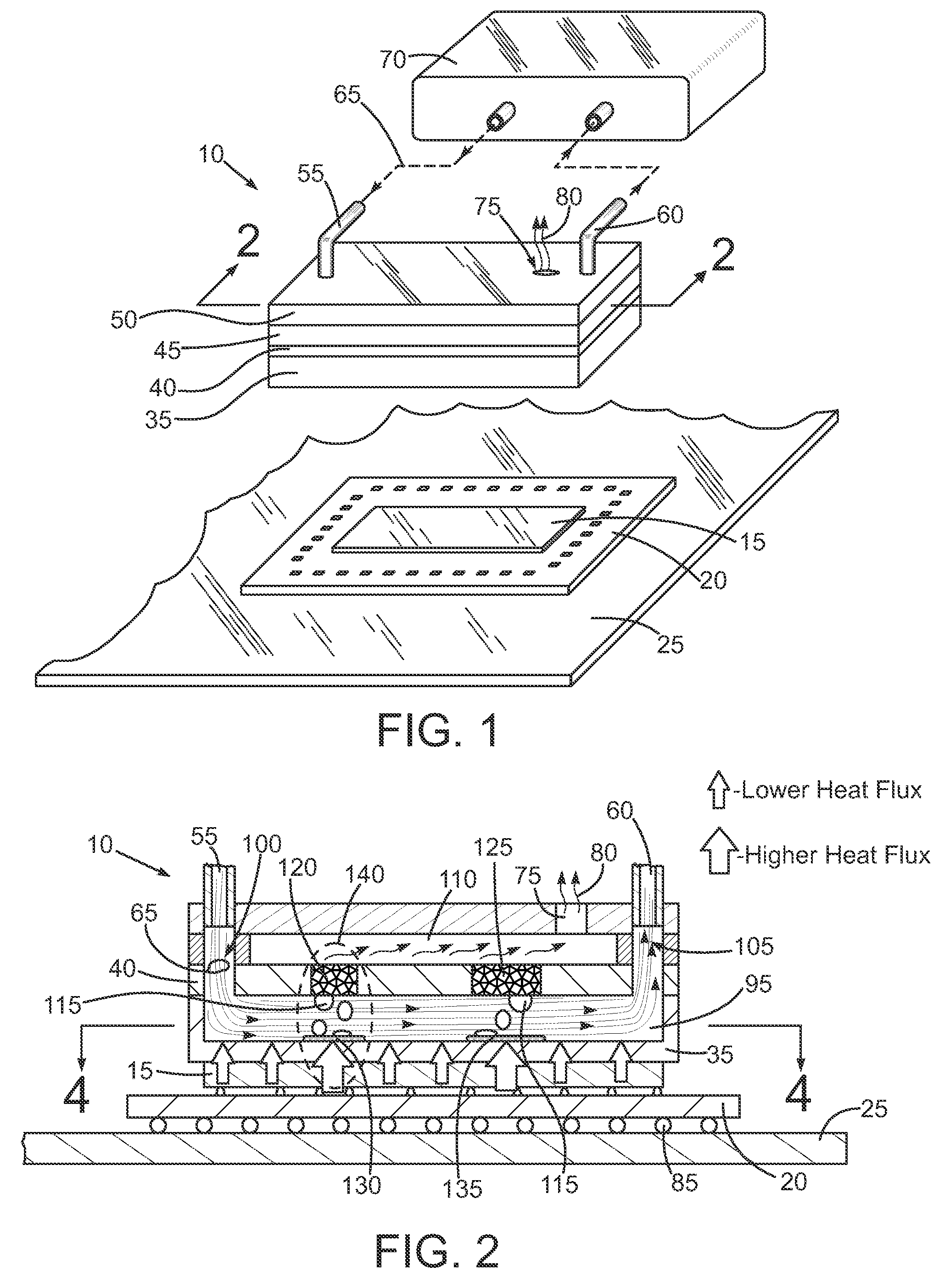
An immersion server includes: a first surface that is exposed when the server is submerged within a cooling liquid; and at least one vapor bubble deflector physically abutting the first surface and extending away from the first surface at an angle. The deflector divides the first surface into an upper segment and a lower segment when the server is upright. When the server is submerged, the cooling liquid surrounding the lower segment absorbs sufficient heat to evaporate and generate vapor bubbles rising to the liquid surface. The vapor bubble deflector deflects the rising vapor bubbles away from the surface of the upper segment. This enables superior liquid contact with heat dissipating components at the upper segment and better cooling of those components. The deflector can be a device-level deflector separating two or more components or a component-level deflector separating a lower segment from an upper segment of a single component.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Microfluidic devices and methods for producing pulsed microfluidic jets in a liquid environment
Microfluidic devices and methods for their use in producing pulsed microfluidic jets in a fluid environment are provided. The subject microfluidic devices are characterized by the presence of a microfluid chamber at their distal ends. The microfluid chamber is bounded by an opening at one end, a vapor producing means opposite the opening, and side walls between the opening and the vapor producing means. The microfluid chambers are further characterized in that the only way fluid can exit the microfluid chambers is through the opening. In using the subject devices to produce a fluid jet in a fluid environment, the chamber is first contacted with the fluid environment. The vapor producing means is then actuated in a manner sufficient to produce a vapor bubble in the chamber which, in turn, produces a microfluidic jet in the fluid environment. The subject devices and methods find use in a variety of different applications, e.g., cutting tissue, introducing fluid into a cell, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microfluidic devices and methods for producing pulsed microfluidic jets in a liquid environment
InactiveUS20020045911A1Reduced collateral damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsVapor bubbleEngineering
Microfluidic devices and methods for their use in producing pulsed microfluidic jets in a fluid environment are provided. The subject microfluidic devices are characterized by the presence of a microfluid chamber at their distal ends. The microfluid chamber is bounded by an opening at one end, a vapor producing means opposite the opening, and side walls between the opening and the vapor producing means. The microfluid chambers are further characterized in that the only way fluid can exit the microfluid chambers is through the opening. In using the subject devices to produce a fluid jet in a fluid environment, the chamber is first contacted with the fluid environment. The vapor producing means is then actuated in a manner sufficient to produce a vapor bubble in the chamber which, in turn, produces a microfluidic jet in the fluid environment. The subject devices and methods find use in a variety of different applications, e.g., cutting tissue, introducing fluid into a cell, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microscale fluid delivery system
InactiveUS20120060868A1Raise transfer toGood removal effectHollow article cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVapor bubbleEngineering
A microscale fluid delivery system has a method of addition and removal of fluids to the internals of solids is in an enclosed system. The system includes a processing chamber comprising the steps of submerging the object within the chamber in a fluid, isolating the chamber, reducing the pressure to form vapor bubbles on the object's internal surfaces, increasing the pressure to introduce fluid to the object's internal surfaces, and repeating the decrease and increase in pressure until the object is fully processed.
Owner:GRAY DONALD
Thermal management system for LED array
ActiveUS20080219007A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsVapor bubbleLed array
Owner:NUVENTIX
Suture bandage
InactiveUS20050284801A1Easily cut to sizeAvoid difficult choicesThreshersWound clampsVapor bubbleBandage
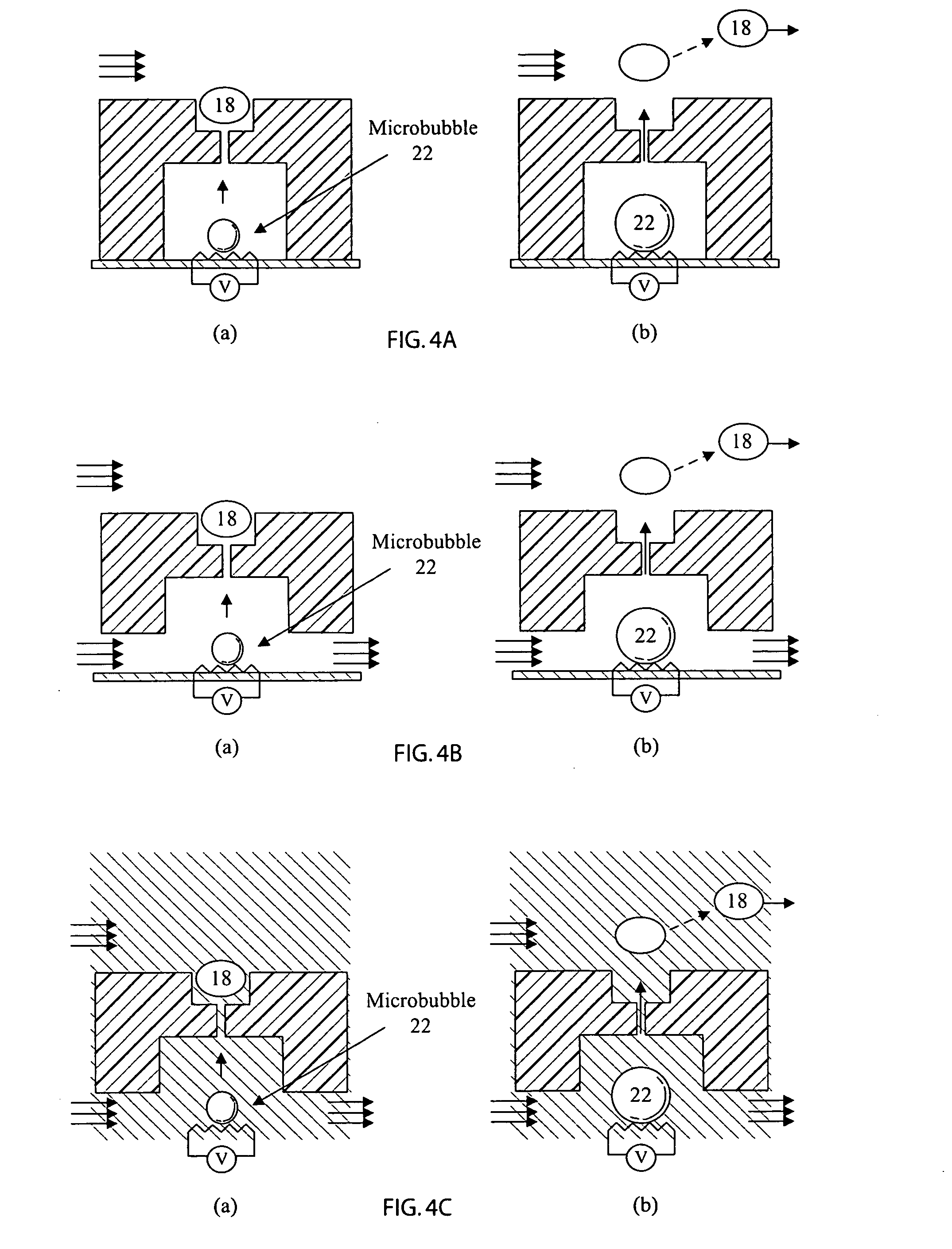
A method and apparatus are presented for a microscopic valve. The valve is electronically activated. Sensors for detecting objects in the flow may be external or formed in the channels of the valve. Many valves can be formed in parallel and in sequence on a single substrate. Multiple channels may feed each junction. Closure of the valve is accomplished by the formation of a vapor bubble or bubbles. Virtual walls may be formed by a sequence of bubbles. Logic and driver circuitry for producing bubbles may be external or included in the substrate. Such an array is ideally suited for sorting cells. Other materials in a suspension may also be sorted by a variety of criteria. A multi lumen output can produce a continuous distribution of cells or particles thus sorted.
Owner:TACKLIND CHRISTOPHER A
High rangeability control valve
InactiveUS20030226600A1Reduce gapReduces and eliminates cavitation erosion damageValve members for absorbing fluid energySlide valveVapor bubbleEngineering
A guided control valve comprising a vapor recovery area that encourages collapse of vapor bubbles. In a cage-guided valve, a seal comprising inner and outer members reduces flow through a radial clearance between a plug and a cage. The vapor recovery area is positioned below the seal and above a seat interacting with the plug. The vapor recovery area encourages collapse of vapor bubbles to reduce damage to the valve trim.
Owner:DRESSER LLC
Variable heat exchanger
InactiveUS20100314093A1Temperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterior spaceVapor bubble
Various apparatus and methods for thermally managing a heat generating device. In one aspect, a method of thermally managing a heat generating device is provided that includes placing a heat exchanger in thermal communication with the heat generating device. The heat exchanger has an interior space. A membrane is in the interior space between a first chamber and a second chamber. The membrane has a gas impermeable portion and at least one gas permeable portion to enable vapor bubbles in the second chamber to pass through the membrane at the at least one gas permeable portion and into the first chamber. A liquid is moved through the second chamber.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
High rangeability control valve
InactiveUS6807985B2Reduces and eliminates cavitation erosion damageExpand the adjustment rangeValve members for absorbing fluid energyMultiple way valvesVapor bubbleControl valves
A guided control valve comprising a vapor recovery area that encourages collapse of vapor bubbles. In a cage-guided valve, a seal comprising inner and outer members reduces flow through a radial clearance between a plug and a cage. The vapor recovery area is positioned below the seal and above a seat interacting with the plug. The vapor recovery area encourages collapse of vapor bubbles to reduce damage to the valve trim.
Owner:DRESSER LLC
Pump-free water-cooling system
InactiveUS7380584B2Large capacityReduce thermal resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVapor bubbleEngineering
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Vertically-oriented immersion server with vapor bubble deflector
ActiveUS9195282B2Maximize heat absorptionDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsVapor bubbleComputer science
An immersion server includes: a first surface that is exposed when the server is submerged within a cooling liquid; and at least one vapor bubble deflector physically abutting the first surface and extending away from the first surface at an angle. The deflector divides the first surface into an upper segment and a lower segment when the server is upright. When the server is submerged, the cooling liquid surrounding the lower segment absorbs sufficient heat to evaporate and generate vapor bubbles rising to the liquid surface. The vapor bubble deflector deflects the rising vapor bubbles away from the surface of the upper segment. This enables superior liquid contact with heat dissipating components at the upper segment and better cooling of those components. The deflector can be a device-level deflector separating two or more components or a component-level deflector separating a lower segment from an upper segment of a single component.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Thermal management system for LED array
ActiveUS20080151541A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsVapor bubbleLed array
Owner:NUVENTIX
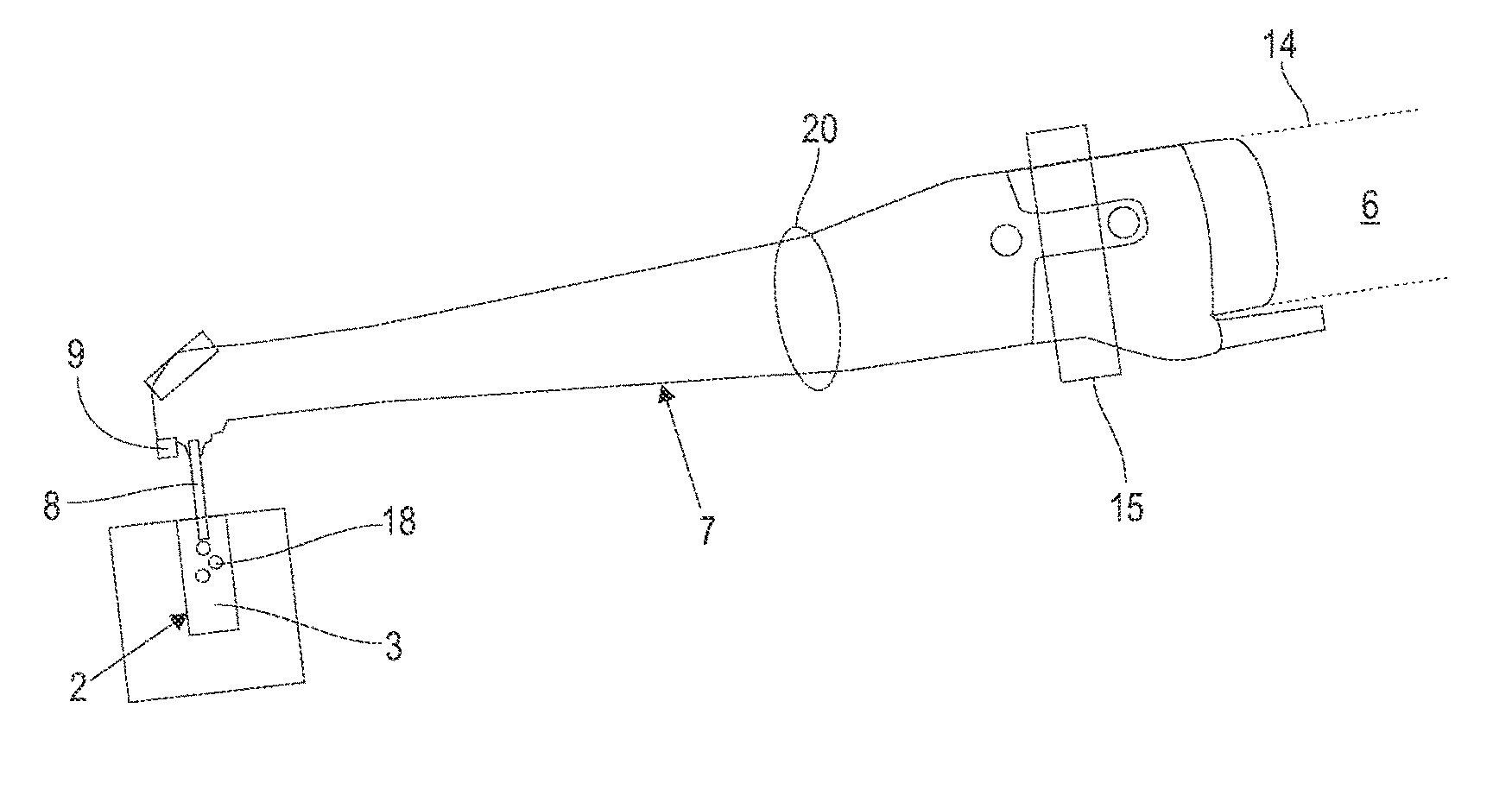
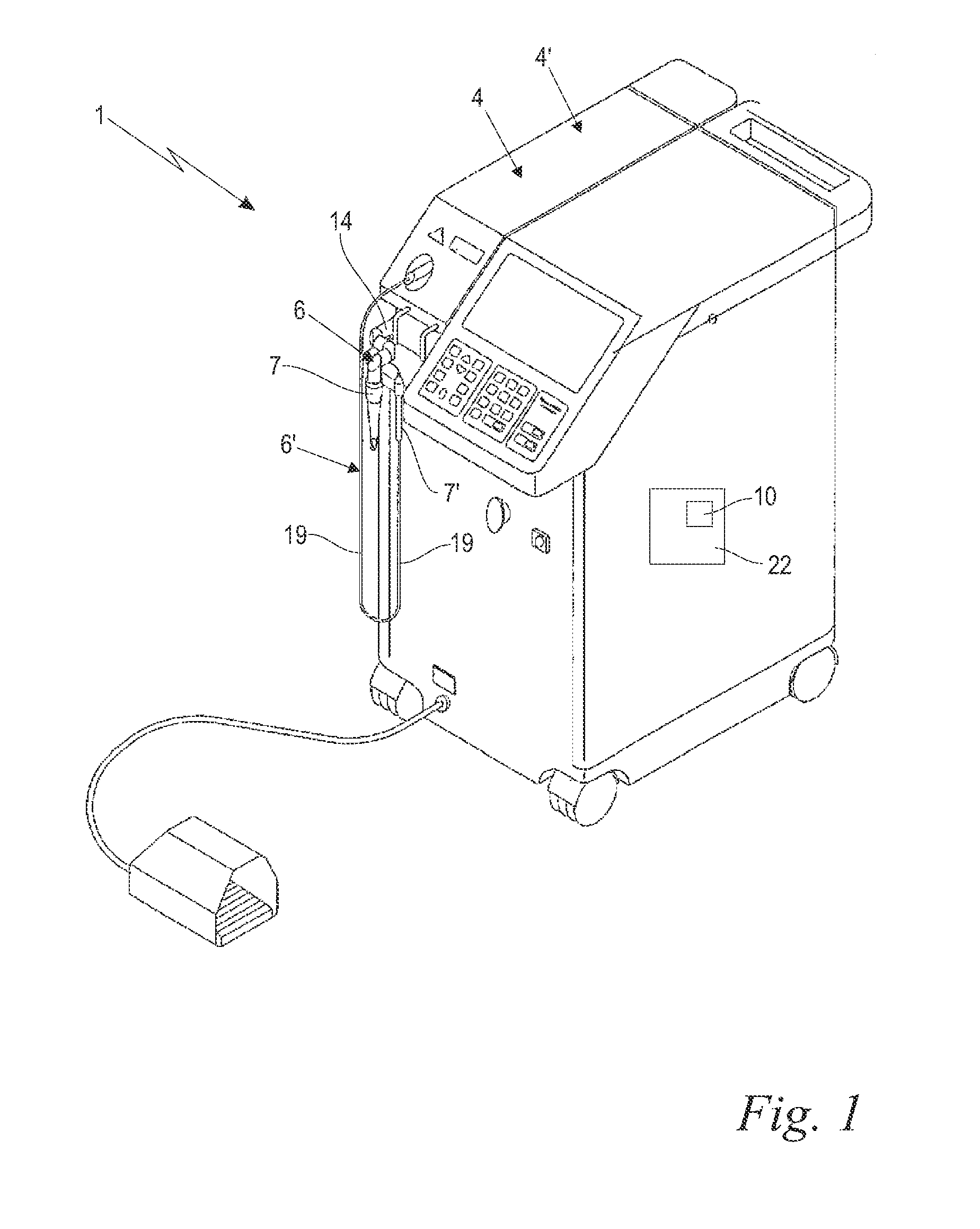
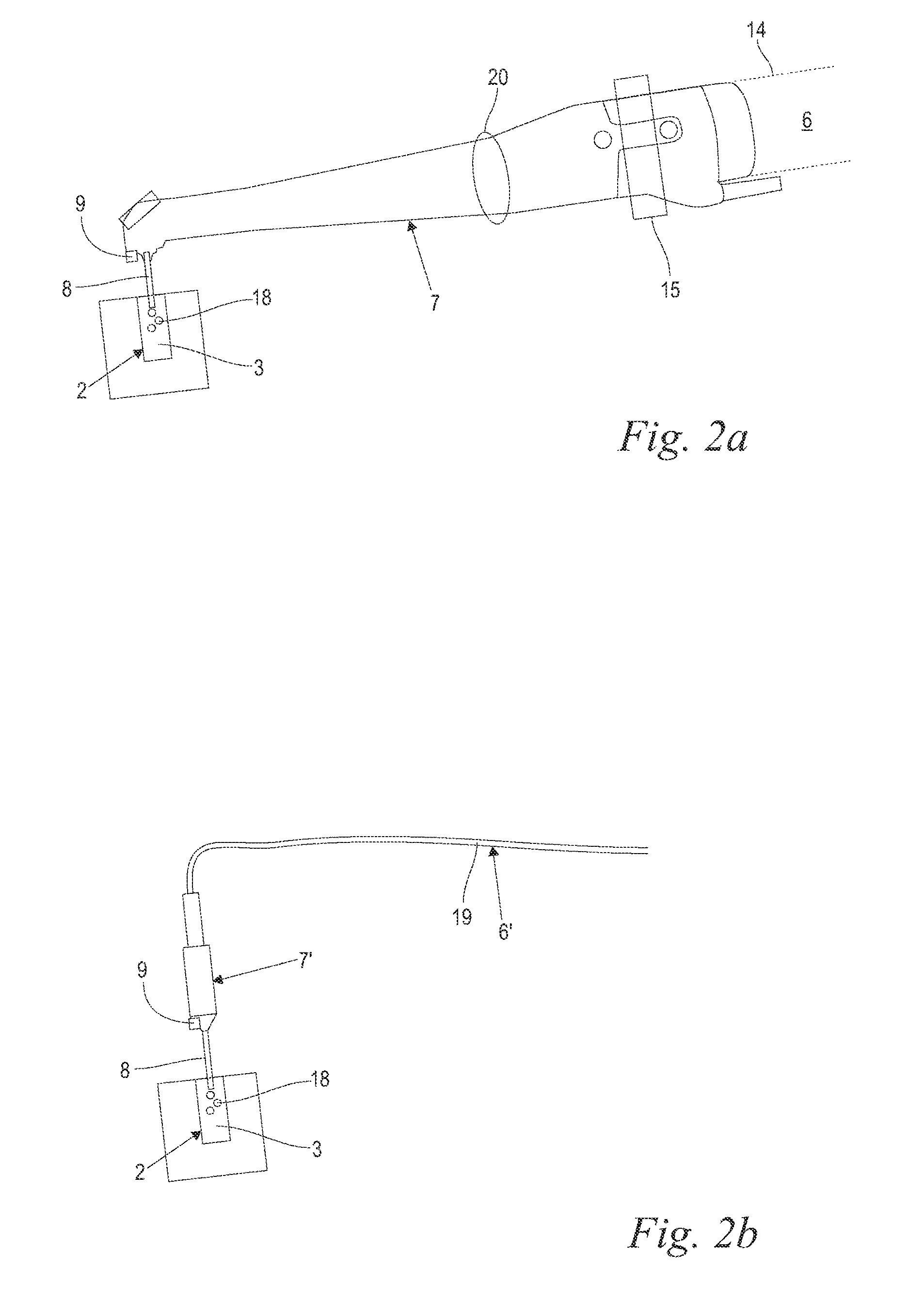
Laser system and method for operating the laser system
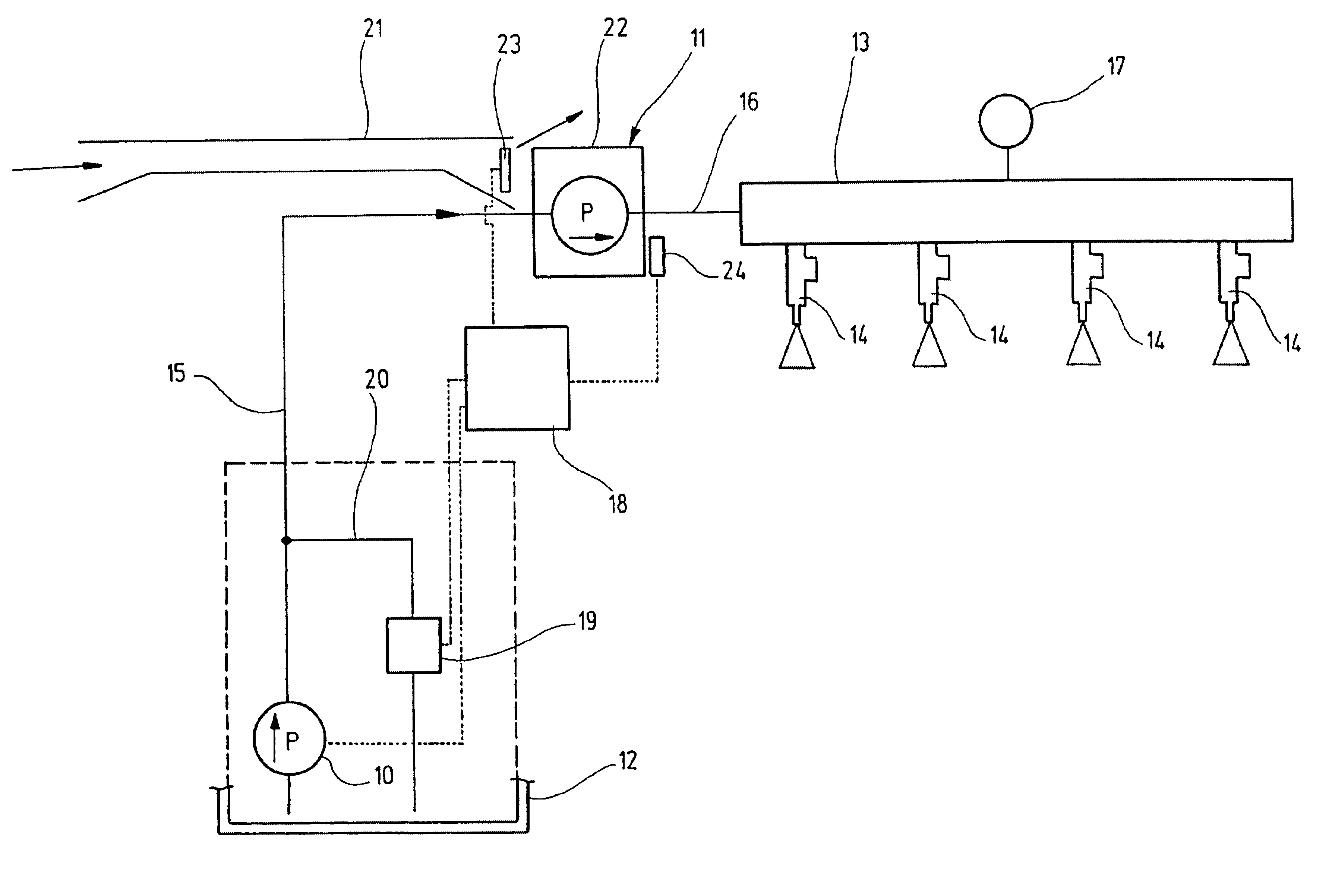
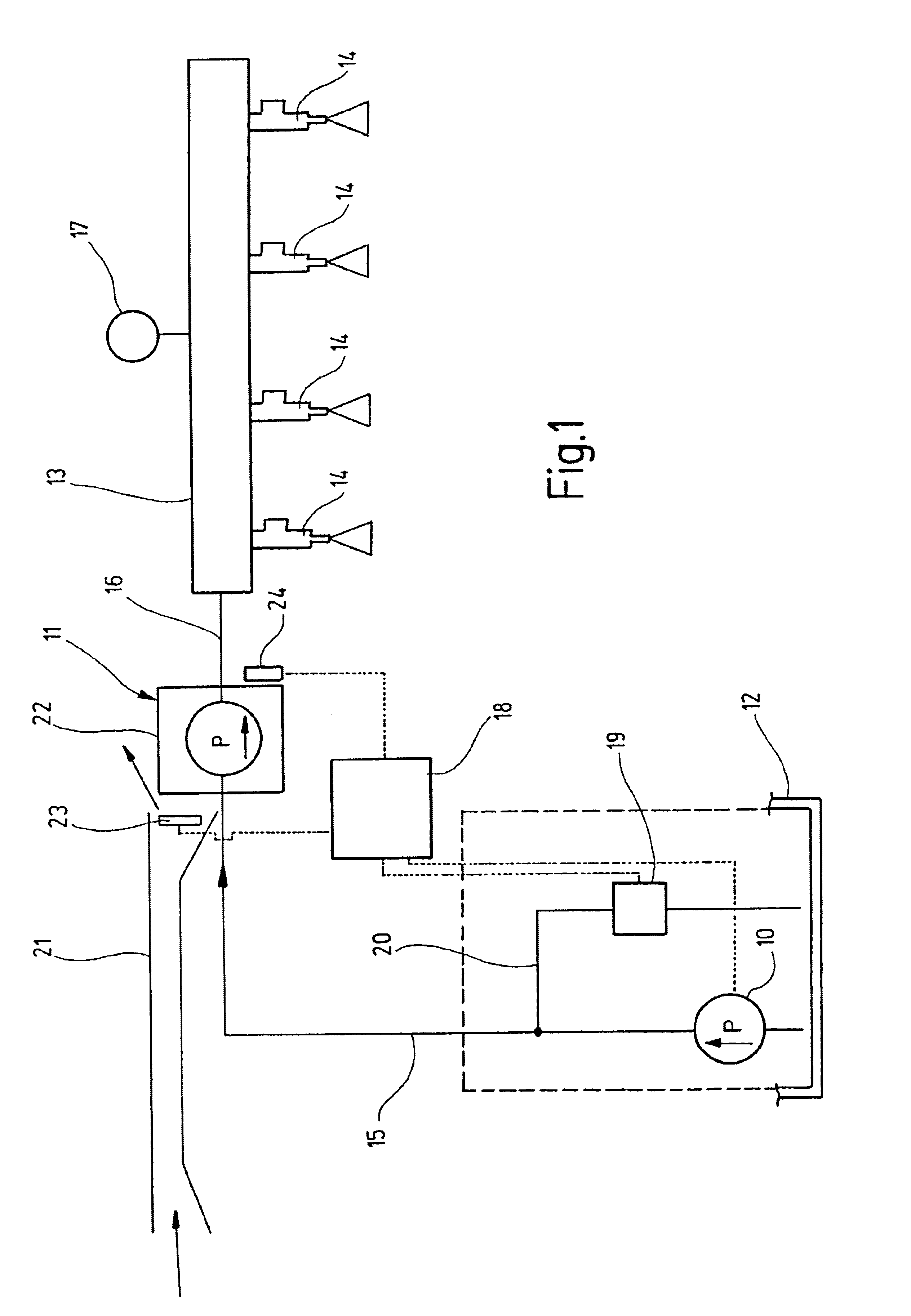
ActiveUS9572632B2Improve scienceExtended durationGum massageSurgical instrument detailsVapor bubbleLength wave
A dental irrigation system is provided with a laser source for generating a laser beam and an optical delivery system for the laser beam. The laser beam wavelength ranges from 0.4 μm to 11.0 μm. The laser system operates in pulsed operation with pulse sets of 2 to 20 individual pulses of temporally limited pulse length. The pulse sets follow one another with temporal separation. The individual pulses follow one another with pulse repetition rate. The laser system generates at least one vapor bubble within the liquid irradiated with the laser beam. A single pulse causes the vapor bubble to oscillate between a maximal and a minimal volume with a bubble oscillation frequency. The pulse repetition rate within one pulse set is adjusted relative to the bubble oscillation frequency such that synchronization between delivery of the pulses and bubble oscillation is achieved.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
Printhead heaters with short pulse time
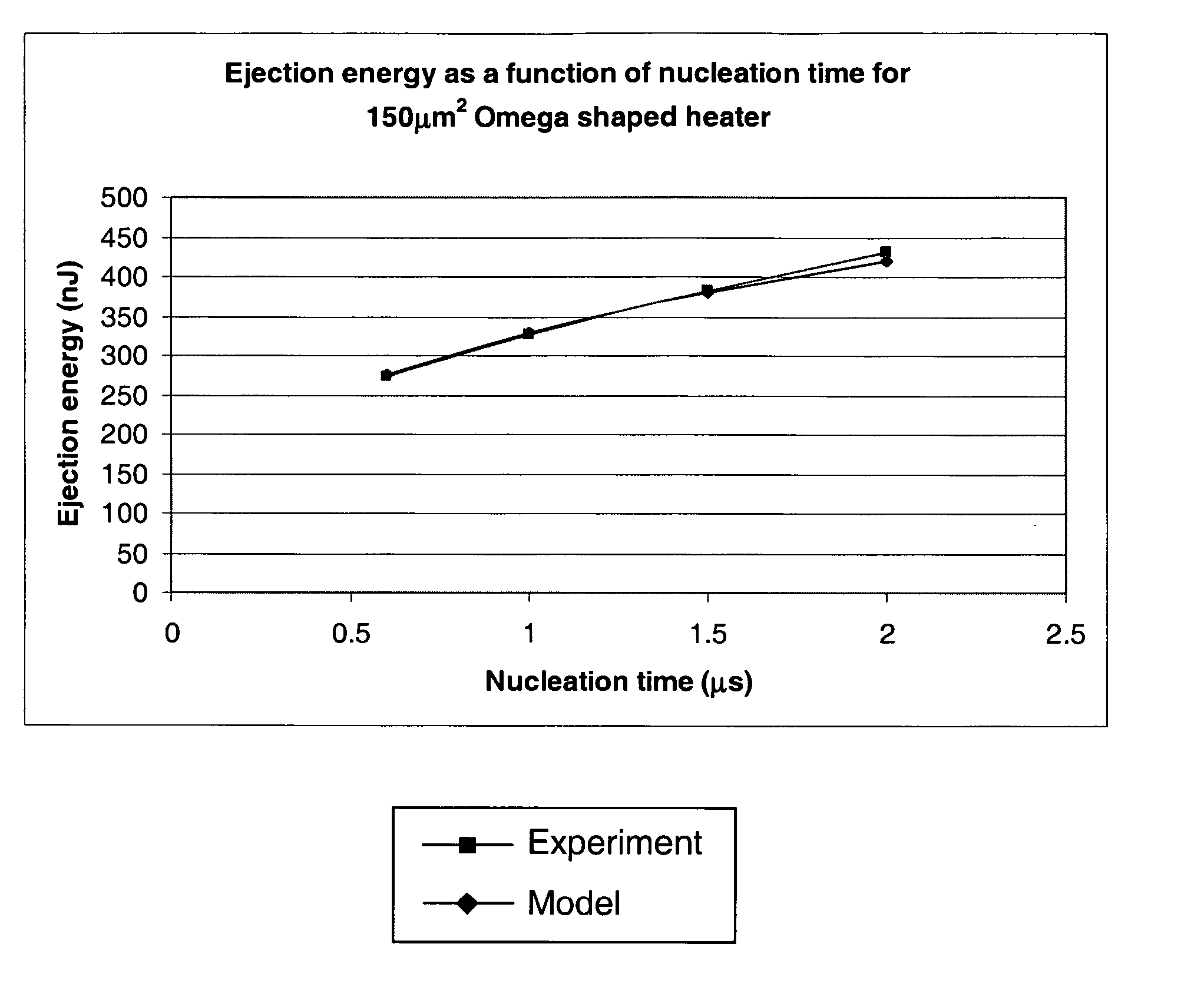
A thermal inkjet printhead with heater elements disposed in respective bubble forming chambers whereby each heater element is configured for receiving an energizing pulse to form a gas bubble in an ejectable liquid that causes the ejection of a drop of the ejectable liquid from the nozzle. The energizing pulse has duration less than 1.5 micro-seconds (μs) and the nozzles are “self cooling”, in the sense that in the sense that the only heat removal required by the chip is the heat removed by ejected droplets. The printhead is designed for operation with reduced pulse duration, so the amount of heat that diffuses into the liquid and the substrate prior to nucleation of the vapor bubble is reduced. This facilitates self cooling operation.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
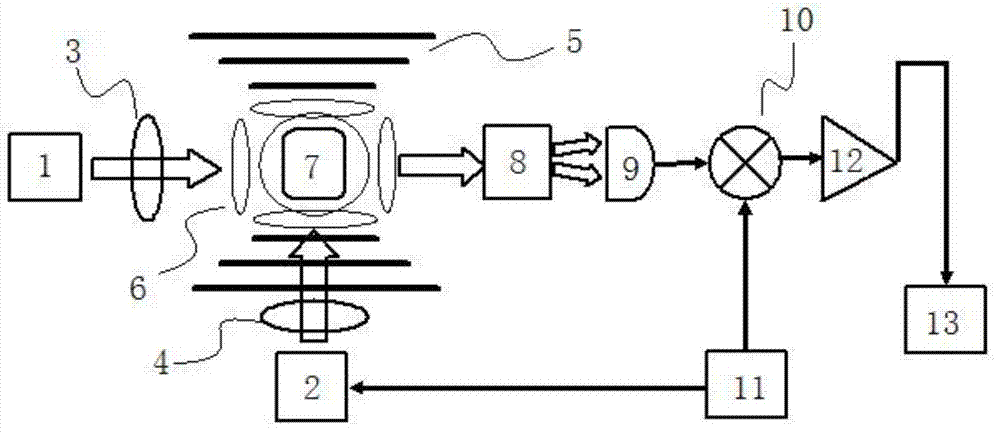
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device and measurement method based on laser atomic magnetometer
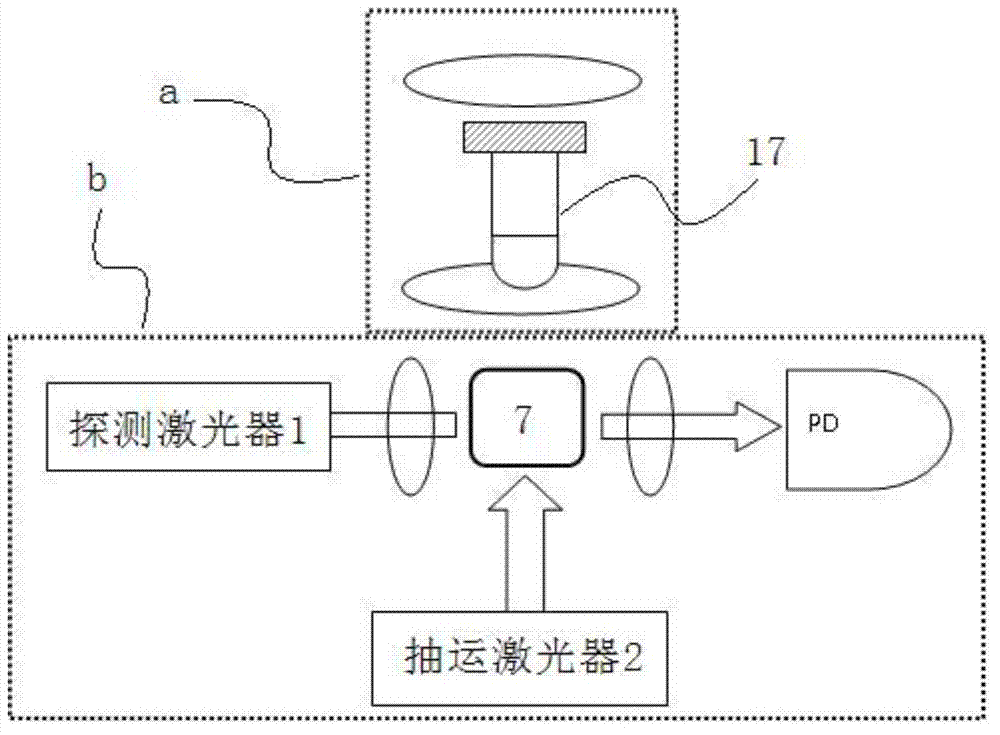
ActiveCN102830381AHigh detection sensitivityLow running costMeasurements using NMRHelmholtz coilProton NMR
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device based on a laser atomic magnetometer, and the NMR device comprises a cesium atom vapor bubble, a magnetic shielding bushing which is sleeved on the cesium atom vapor bubble, three groups of Helmholtz coils which are arranged inside the magnetic shielding bushing, a polarization device which is used for polarizing cesium atoms inside the cesium atom vapor bubble, a laser transmitting device which is used for transmitting detection laser to the cesium atom vapor bubble, a detection device which is used for detecting an NMR signal of the detection laser penetrating the cesium atom vapor bubble and a pneumatic sample feeding device which is used for pre-polarizing a sample to be detected and can place the pre-polarized sample on the cesium atom vapor bubble. The invention also discloses a measurement method of an NMR based on the laser atomic magnetometer. The device and the method are high in detection sensitivity, free from needing low-temperature refrigeration, low in running cost and lower in working temperature.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
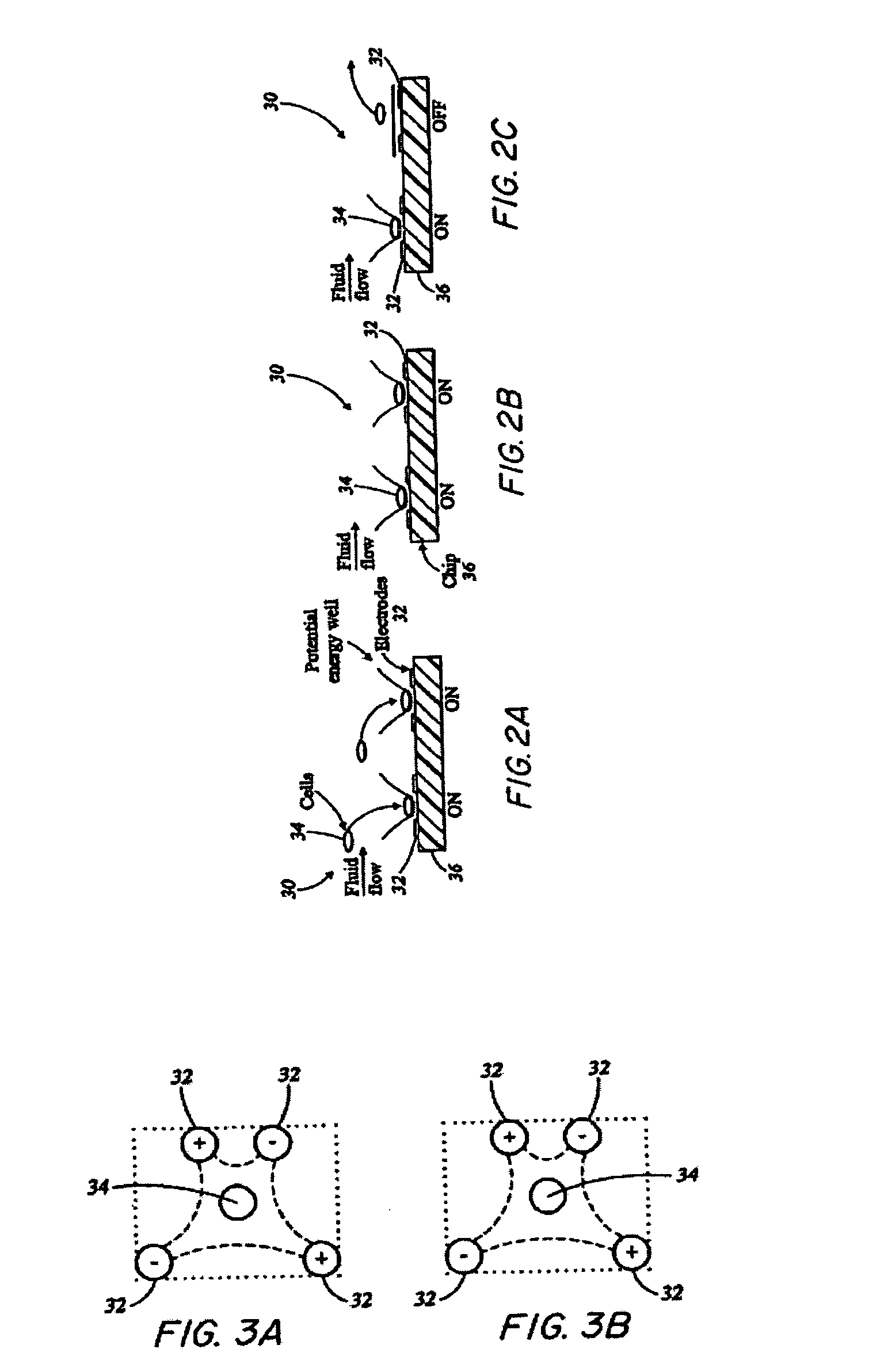
Method and apparatus for avalanche-mediated transfer of agents into cells
ActiveUS7923251B2Other foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentVapor bubbleElectrical battery
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for transferring an agent into a cell. The method includes the steps of providing an agent outside of a cell and generating a vapor bubble and a plasma discharge between an avalanche electrode and a conductive fluid surrounding the cell. The vapor bubble and plasma discharge generate a mechanical stress wave and an electric field, respectively. The combination of this mechanical stress wave and electric field results in permeabilization of the cell, which in turn results in transfer of the agent into the cell.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
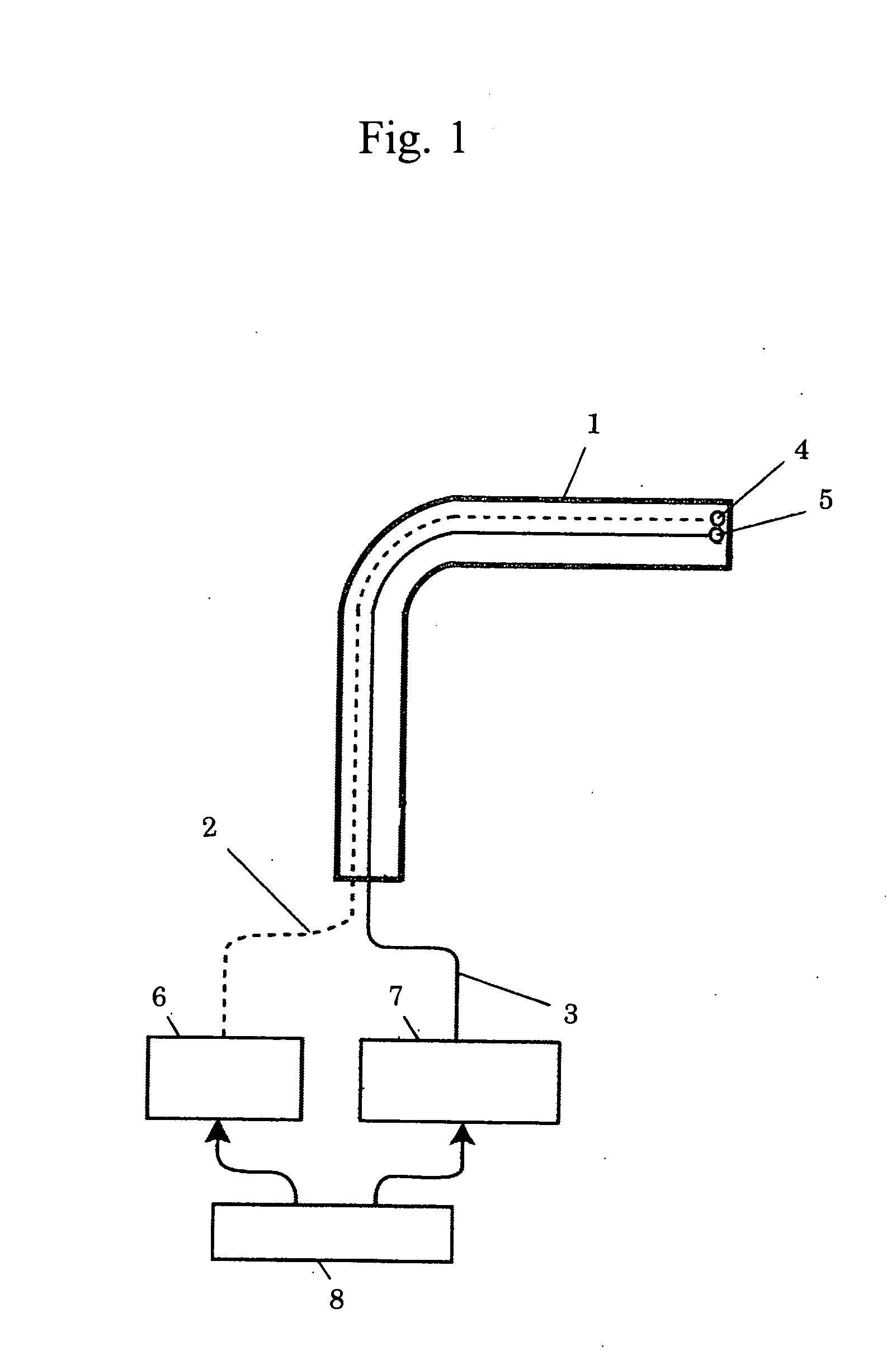
Inkjet printhead with low voltage ink vaporizing heaters
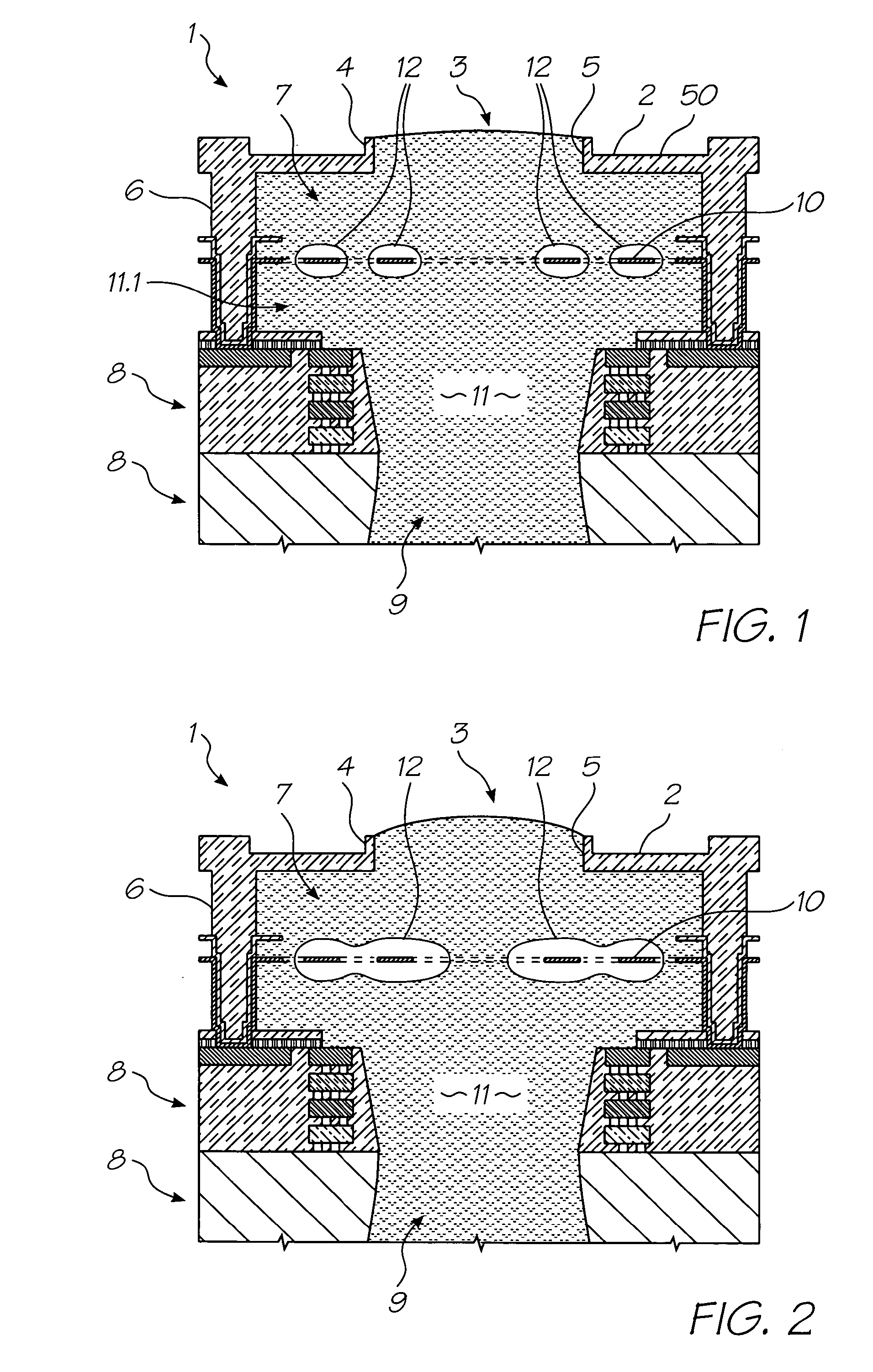
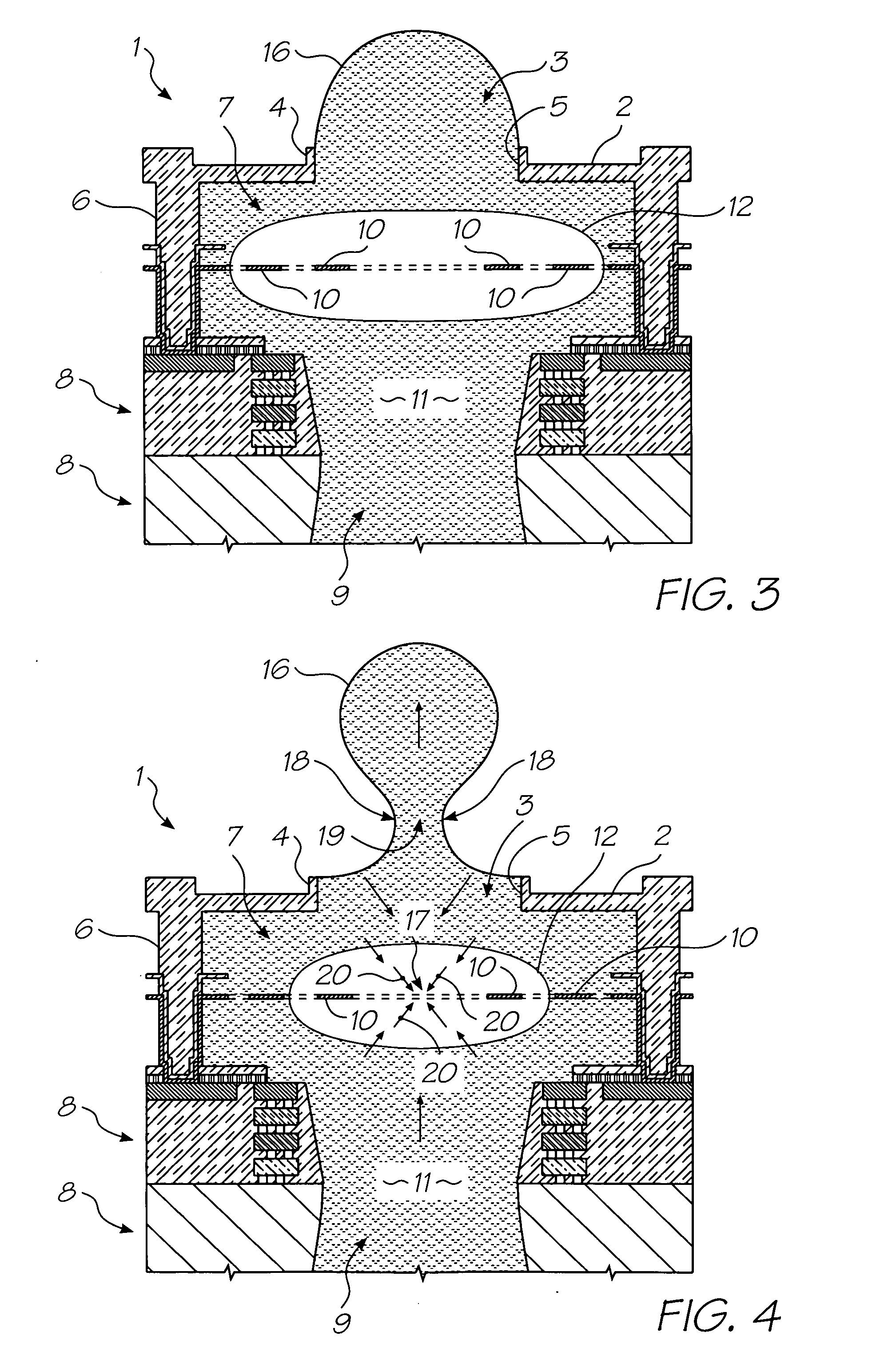
InactiveUS7581822B2Improve efficiencySimple power supplyInking apparatusOther printing apparatusVapor bubbleLow voltage
There is disclosed an ink jet printhead which comprises a plurality of nozzles and one or more heater elements 10 corresponding to each nozzle. Each heater element 10 is configured to heat a bubble forming liquid 11 in the printhead to a temperature above its boiling point to form a gas bubble 12 therein. The generation of the bubble 12 causes the ejection of a drop of an ejectable liquid (such as ink) through an ejection aperture 5 in each nozzle, to effect printing. In each nozzle, the heater element 10 requires an electrical pulse with a voltage less than 8 volts and a duration less than 1.5 microseconds, to form the vapor bubble that causes the ejection of the drop. With the realization that drive pulse voltages above, say, 12 volts are not a fixed parameter of printhead design, the benefits of low voltage printhead operation can be incorporated into a design that yields efficiencies that negate the circumstances that created the initial demand for high voltage operation.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD +1
Apparatus and method for enhanced heat transfer
InactiveUS20060060331A1Consume energyExceeding performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVapor bubbleEnhanced heat transfer
One embodiment of the system is implemented as a device for two-phase heat transfer. This device comprises a chamber containing a fluid, where a heated wall makes up a portion of the chamber. The device also comprises an actuator that emits pressure vibrations. The pressure vibrations dislodge vapor bubbles that form at the heated wall due to the heat in the wall.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FLUIDICS +1
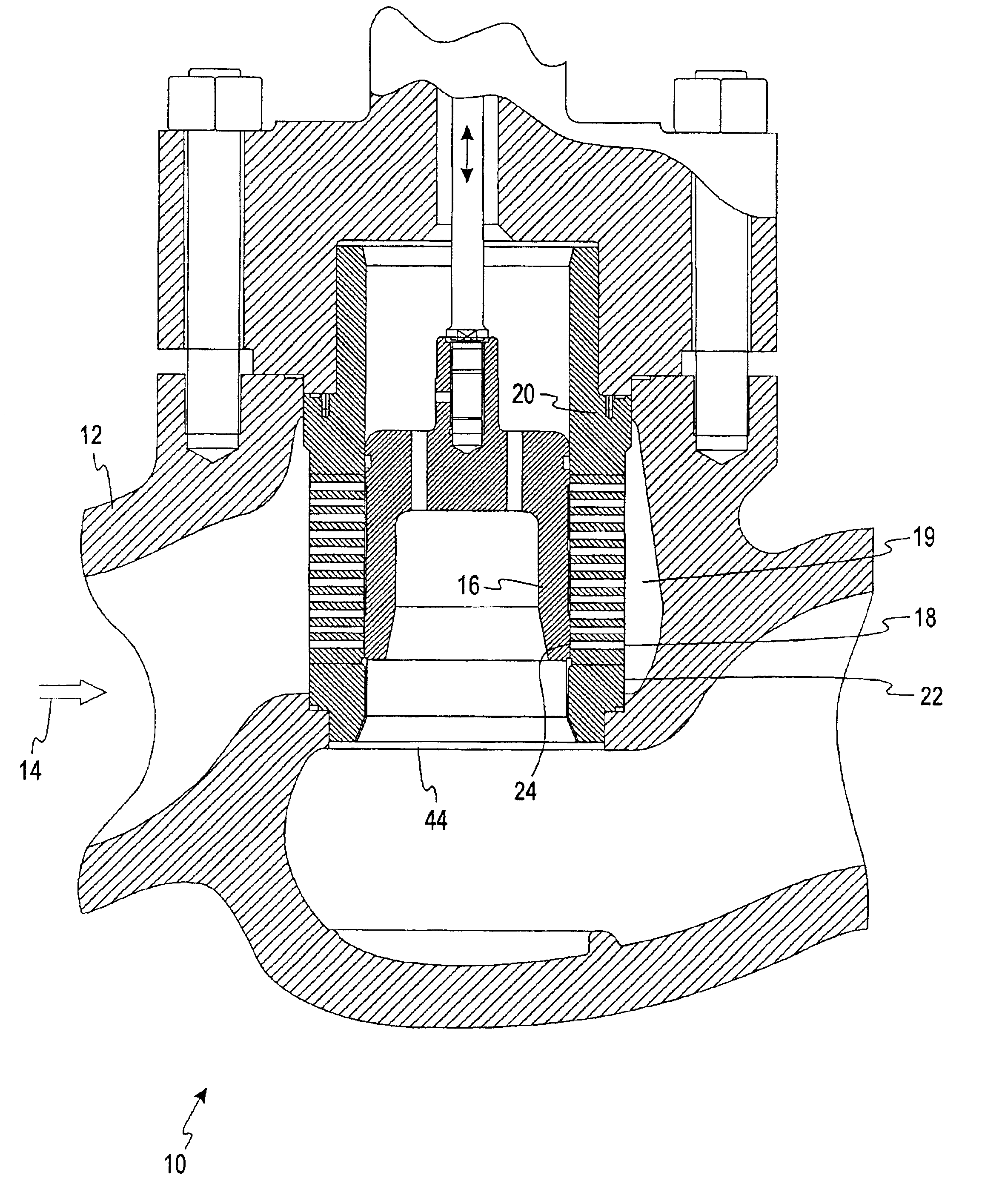
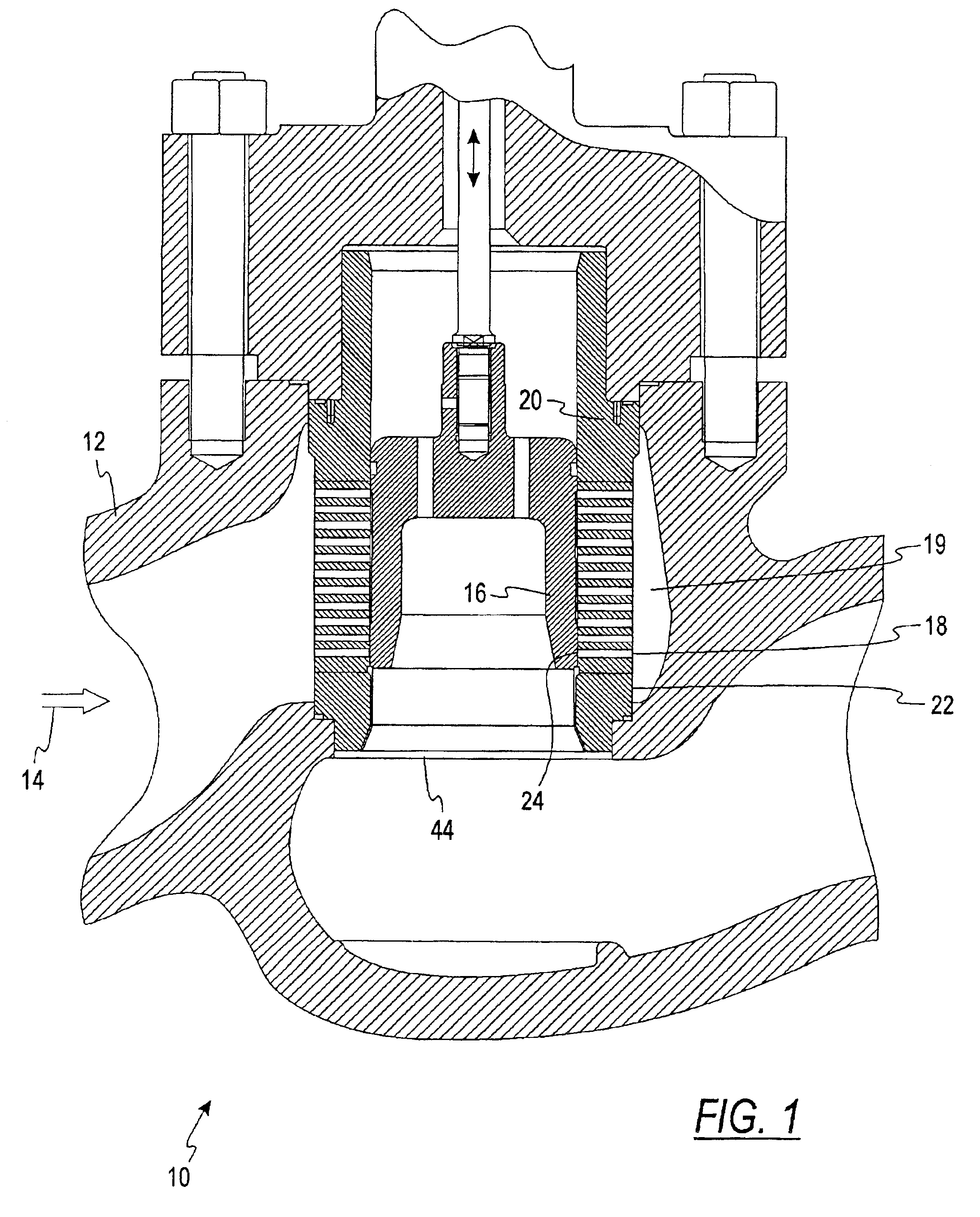
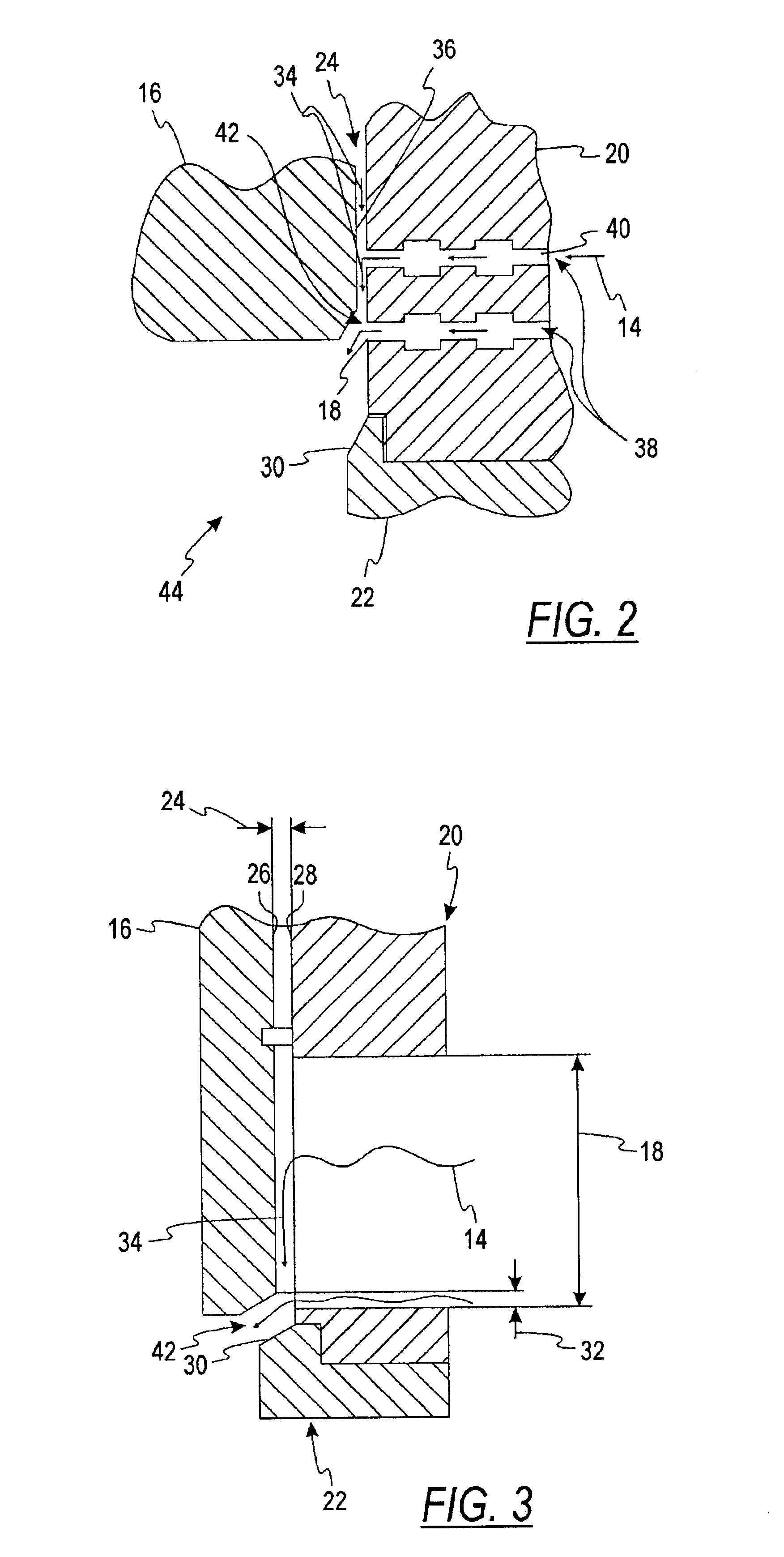
Fuel supply system for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6840219B2Adequate heat dissipationImprove cooling effectLiquid coolingElectrical controlNuclear engineeringHigh pressure
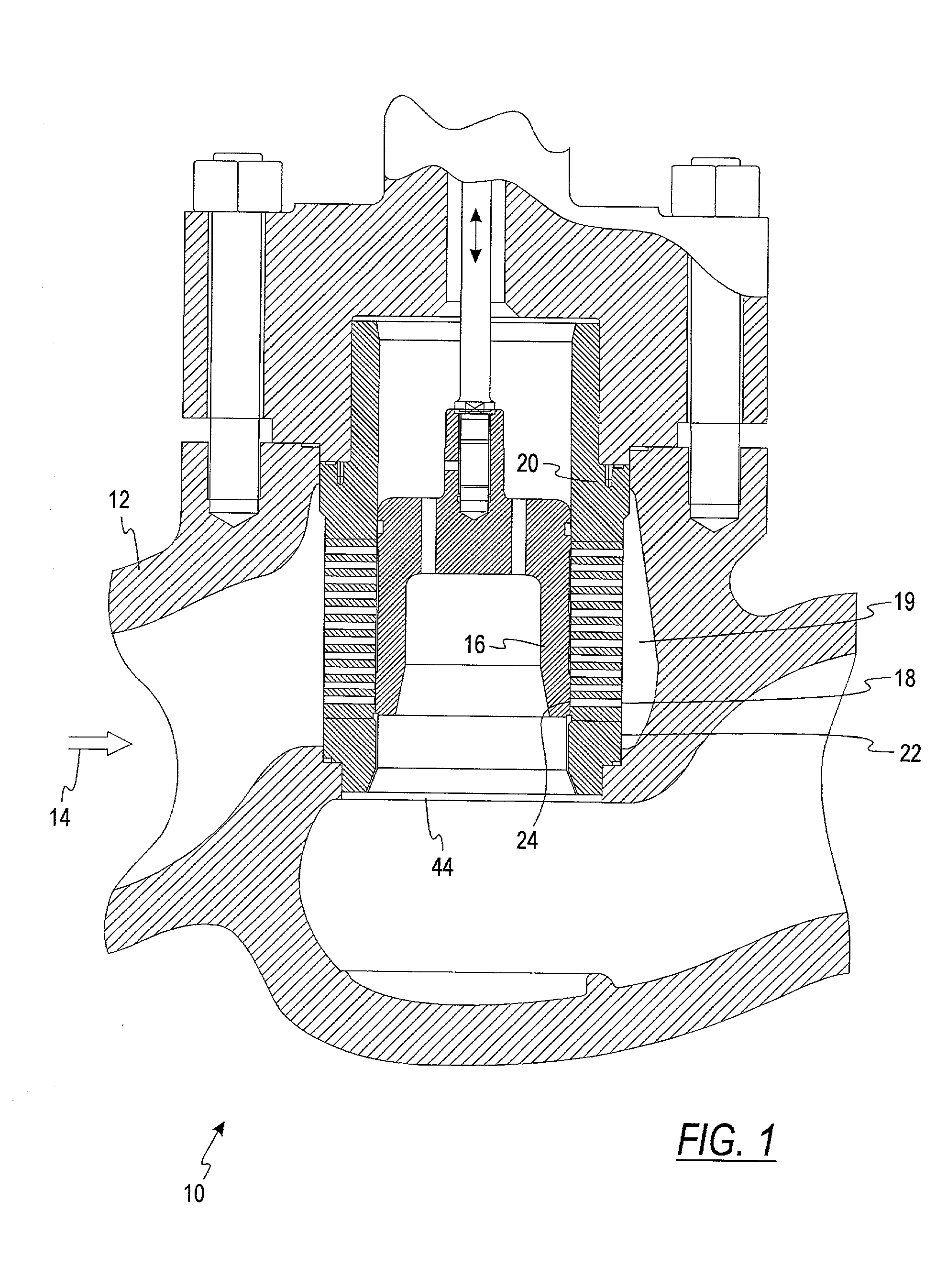
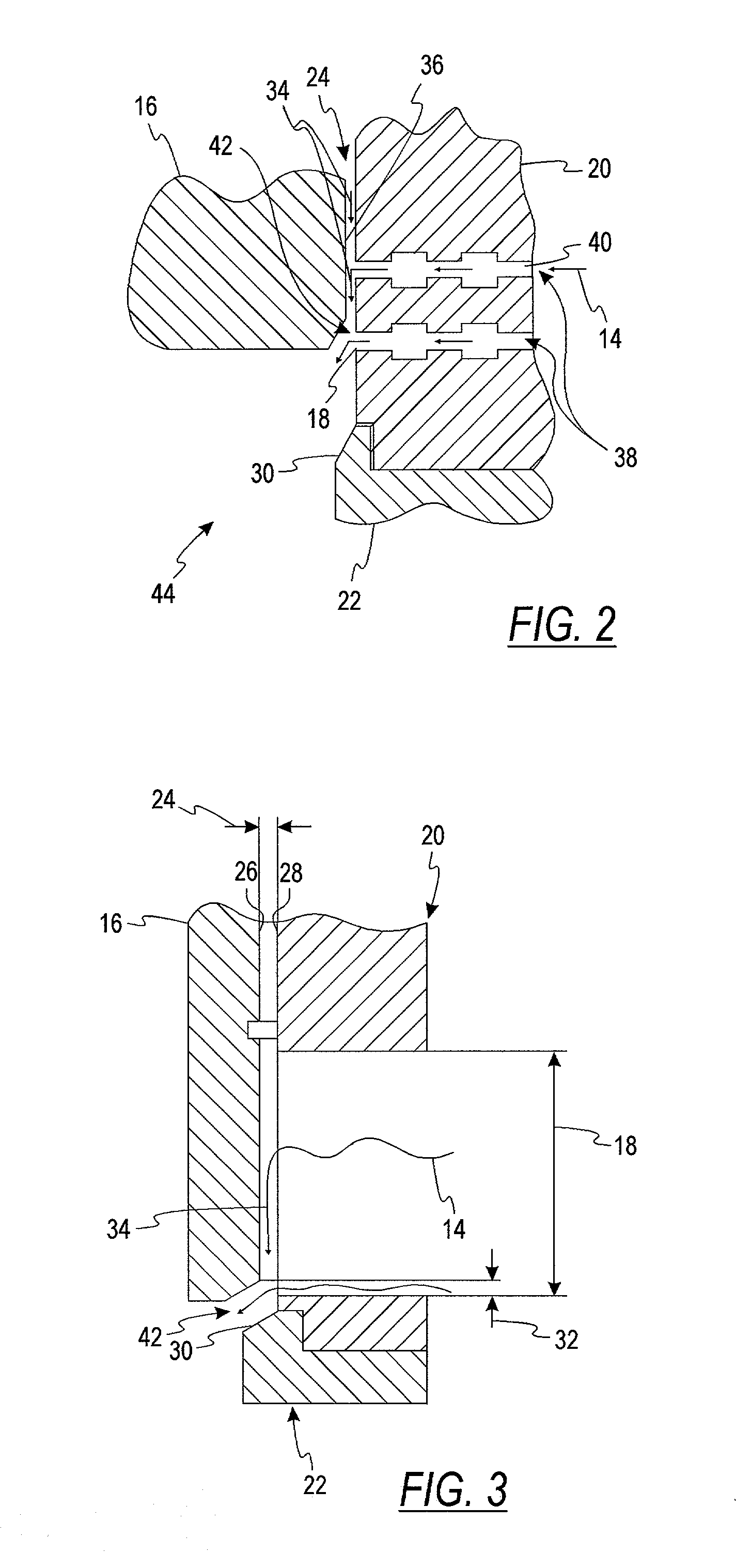
A fuel delivery system for an internal combustion engine, having a fuel feed pump, which delivers fuel which is at pilot pressure to a high-pressure fuel pump that communicates on the high-pressure side with at least one injection valve, in order to deliver fuel at high pressure to the injection valve or valves. To prevent vapor bubble development in the high-pressure fuel pump, which impairs its pumping capacity and pressure generation, a coolant medium flow can be delivered to the high-pressure fuel pump via at least one coolant conduit, in order to keep the temperature (THDP) of the high-pressure fuel pump below a critical operating temperature (Tk1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Ocular gene therapy using avalanche-mediated transfection
The present invention provides a method of treating an ocular disease in a subject. In a first step, a nucleic acid is introduced into cells or a tissue. The nucleic acid is introduced by electron avalanche transfection. With this technique, a high electric field induces a vapor bubble and plasma discharge between an electrode and the surrounding medium. The formation of a vapor bubble generates mechanical stress. Plasma discharge through the ionized vapor in the bubble enables connectivity between the electrode and the surrounding medium, so that mechanical stress and electric field are applied simultaneously, which results in permeabilization of the cells or tissue. This permeabilization in turn allows the nucleic acid to enter the cell or tissue. Cells or tissue containing the nucleic acid are then transplanted into an ocular region of the subject.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Electrical discharge surgical fastener for meniscal repairs
InactiveUS6277130B1Control rateEasy to controlSuture equipmentsStaplesHigh pressureSurgical department
A surgical fastener system that utilizes a very intense electrical discharge in a captured fluid volume to cause fluid vaporization thereby to drive a fastener body distally from an open-ended channel in an introducer member. More in particular, the fastener system comprises proximal and distal fastener components that are carried in a channel in an introducer. The proximal fastener component is a fluid sealed in a volume proximal to the head of a fastener body. The distal component of the fastener system is the fastener body itself, which typically defines a head portion and extending leg portion. The system further provides a high voltage electrical source coupled to 1.sup.st and 2.sup.nd electrode terminations that are in substantial contact with the captured fluid volume. Upon actuation of a switch mechanism, an electrical discharge is induced between the 1.sup.st and 2.sup.nd electrodes which causes an intense thermal effect within the captured fluid which generates a vapor bubble therein. The explosive expansion pressures caused by such bubble formation thereby imparts driving forces against the fastener body to drive the fastener outwardly into or through the targeted structure. The driving force applied to the fastener head can be selected by controlling the power level of the electrical discharge.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
Electrosurgical system
InactiveCN1473024APriority and more even distributionReduce lateral marginSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsVapor bubbleBipolar electrosurgery
An electrosurgical system has an electrosurgical generator and a bipolar electrosurgical instrument, the generator being arranged to perform a treatment cycle in which radio frequency energy is delivered to the instrument as an amplitude-modulated radio frequency power signal in the form of a succession of pulses characterized by periods of a least 100 milliseconds between successive pulses and by a predetermined pulse mark-to-space ratio. Energy delivery between pulses is substantially zero and the mark-to-space ratio is typically 1:4 or less. Each burst is of sufficiently high power to form vapor bubbles within tissue being treated and the time between successive pulses is sufficiently long to permit condensation of the vapor. The treatment cycles may each include an initial period and a subsequent period, the pulse duty cycle being increased or energy being delivered continuously in the subsequent period in order that tissue coagulation can be achieved quickly despite increasing tissue impedance.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com