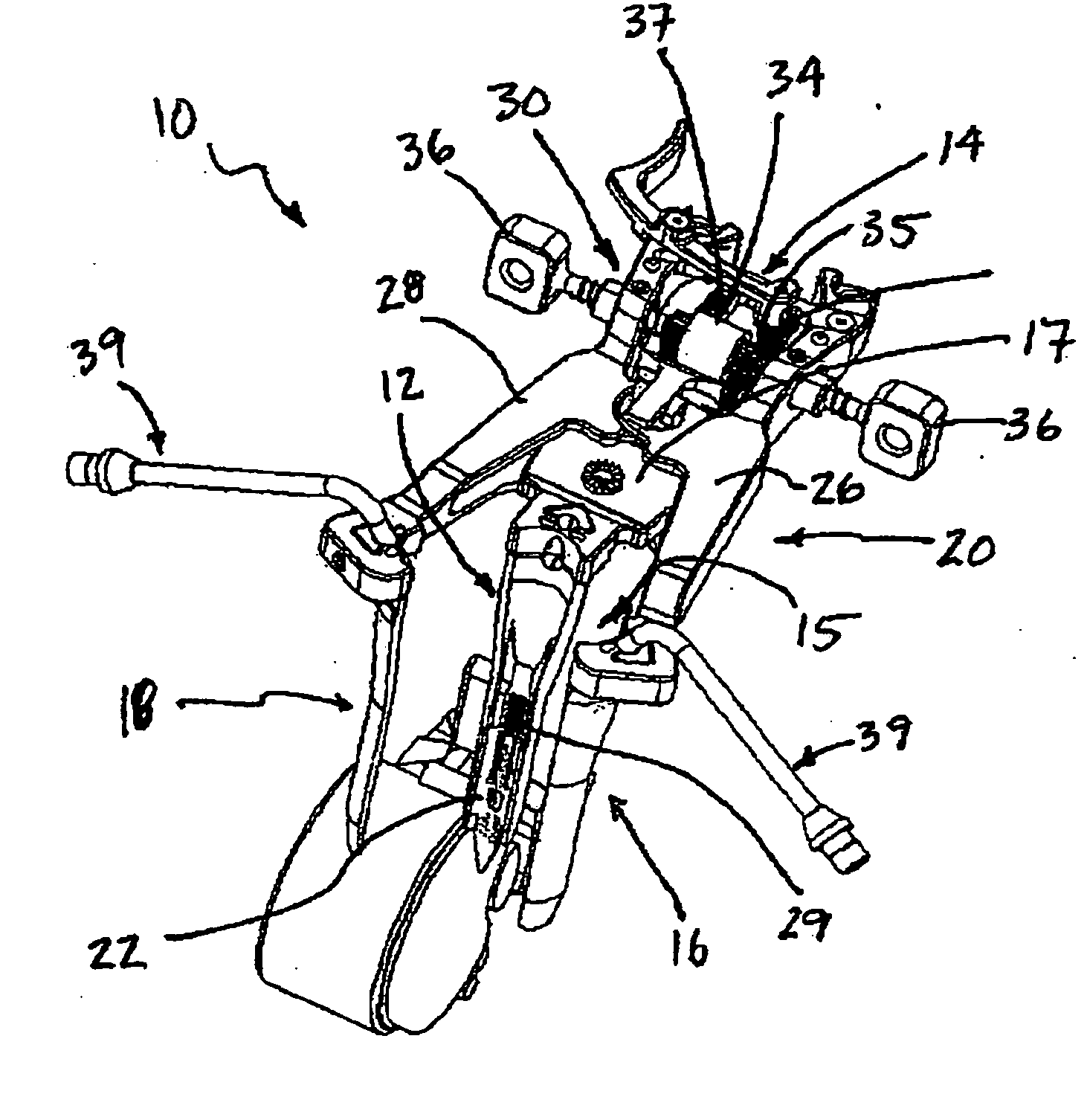
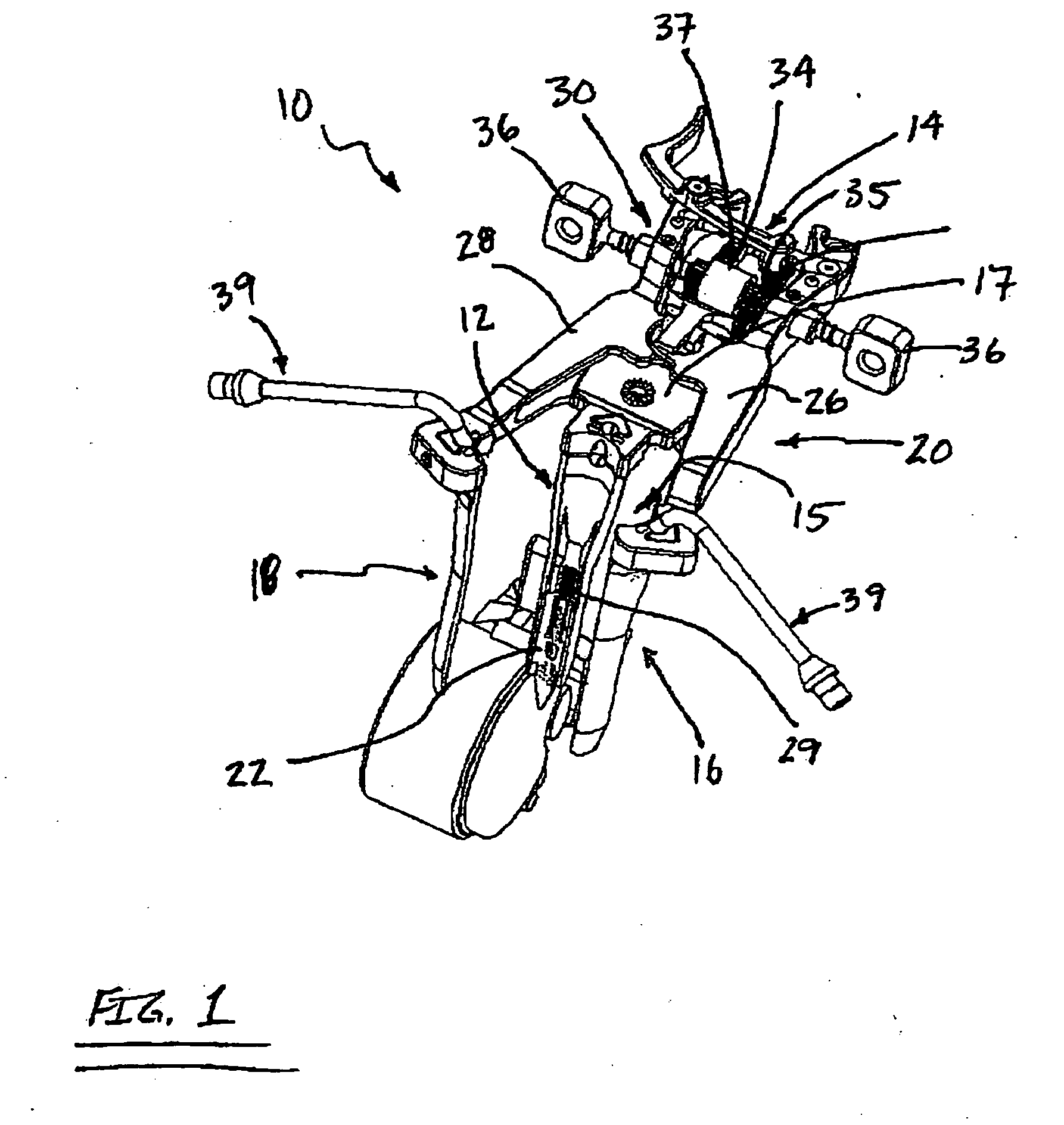
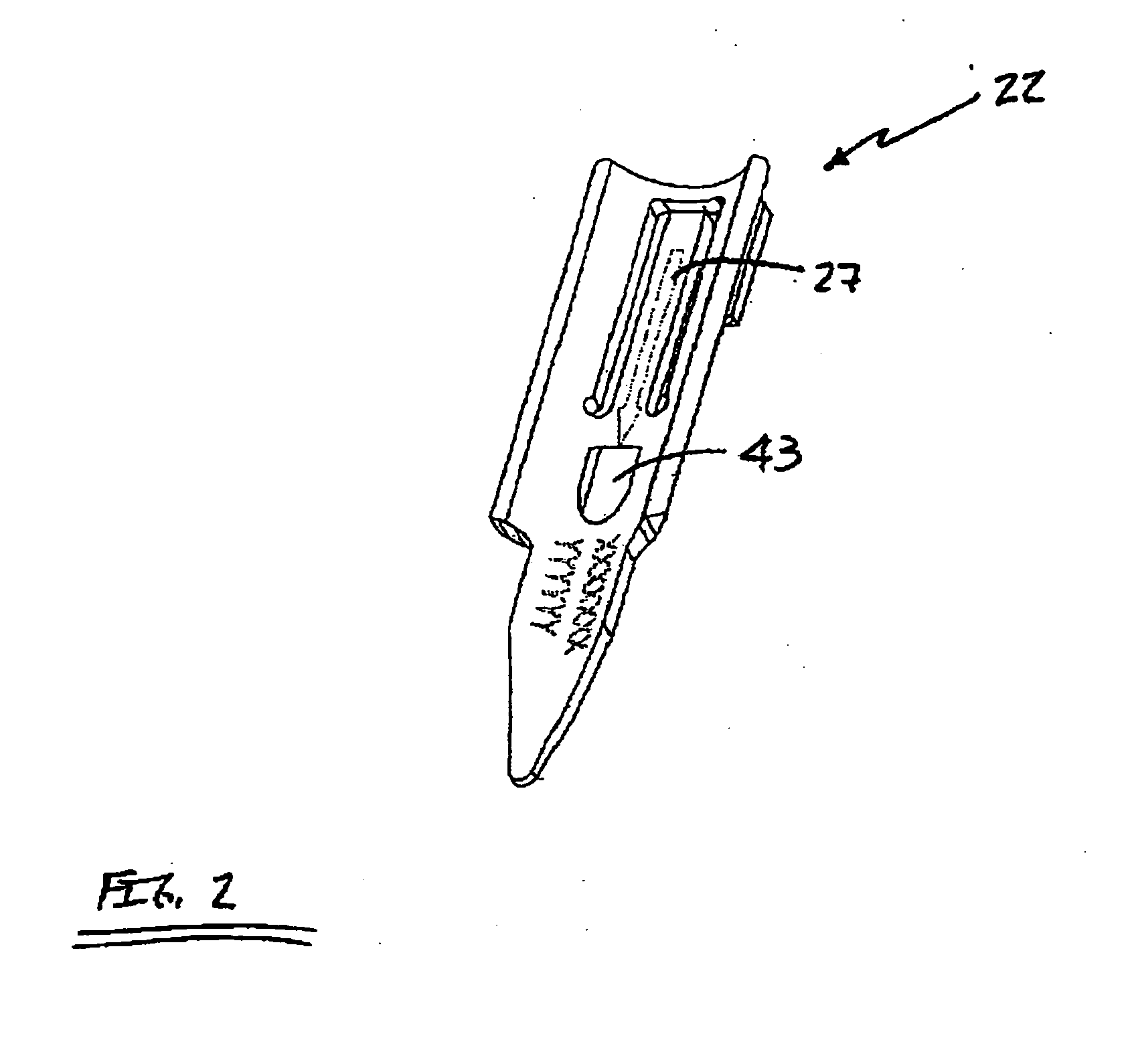
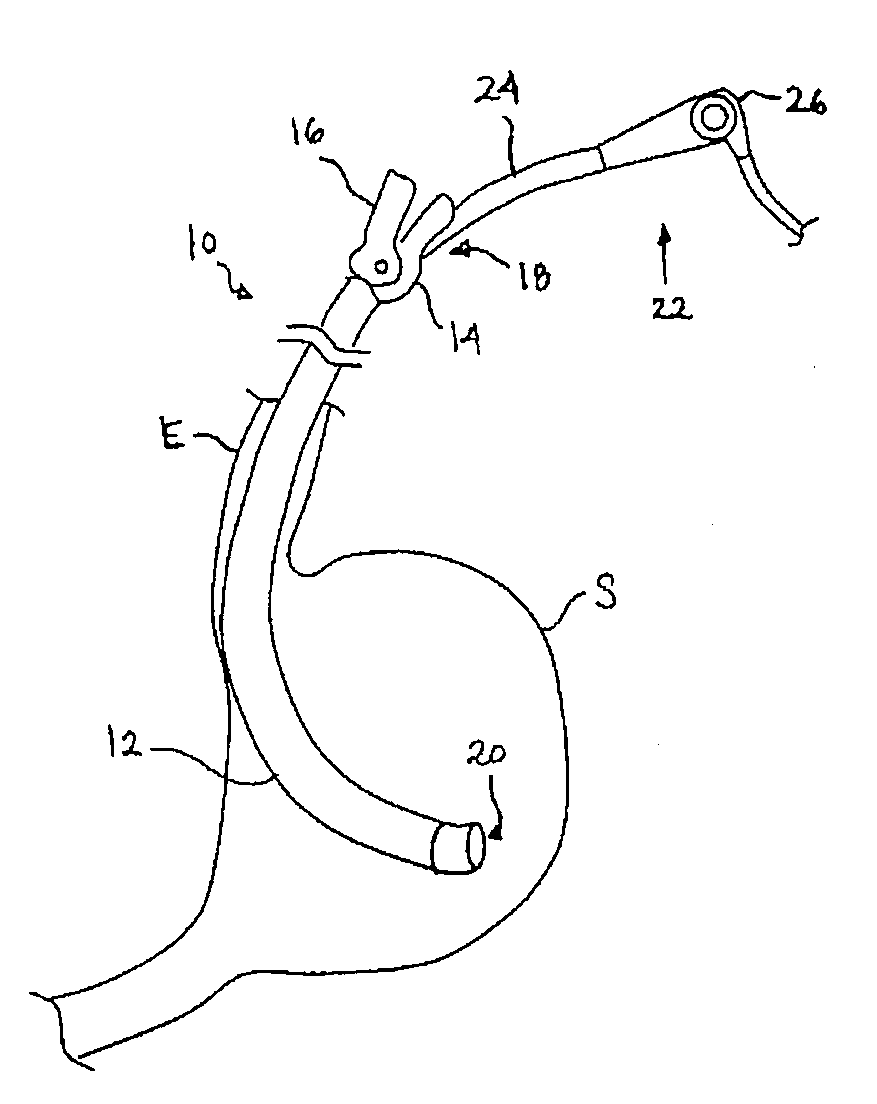
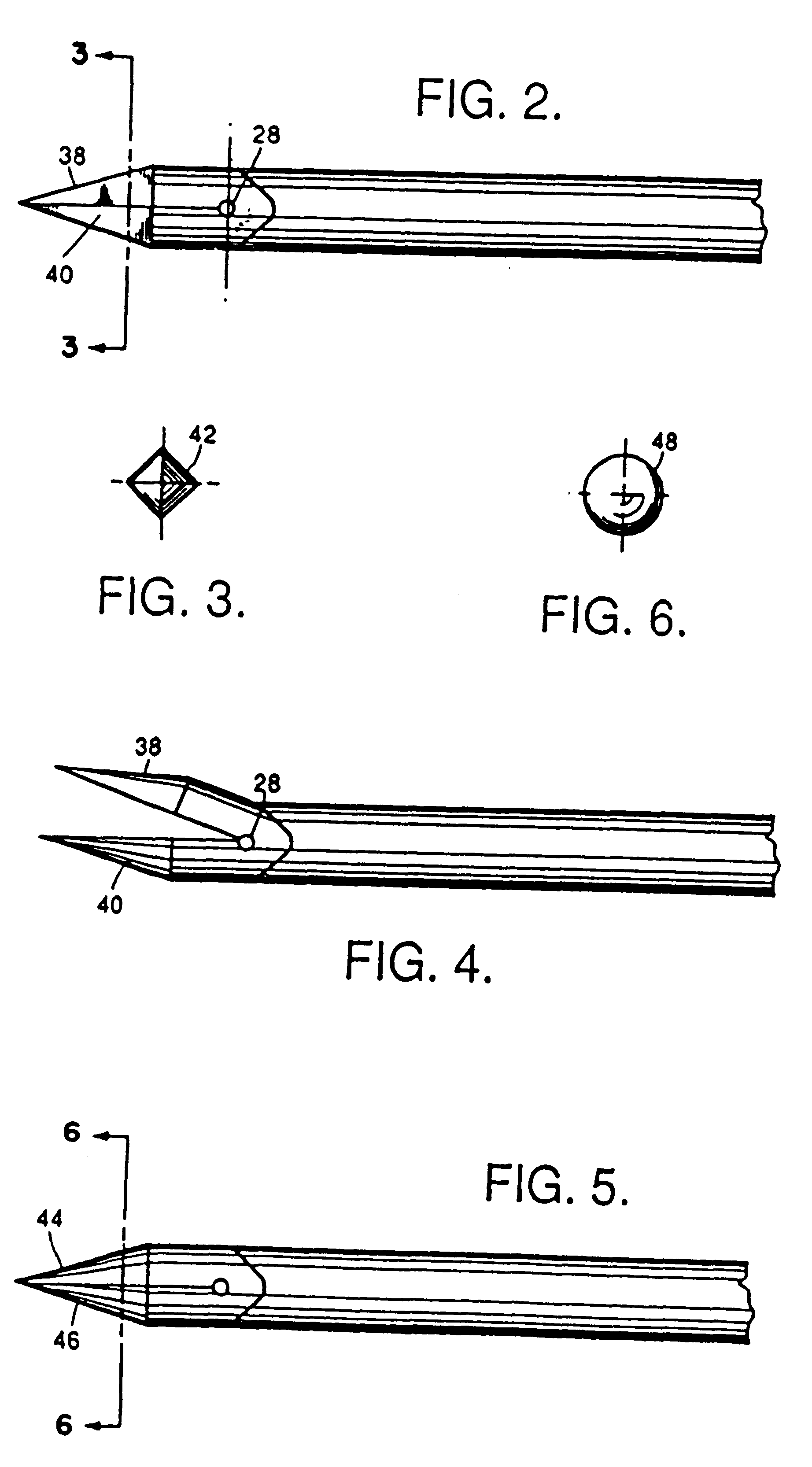
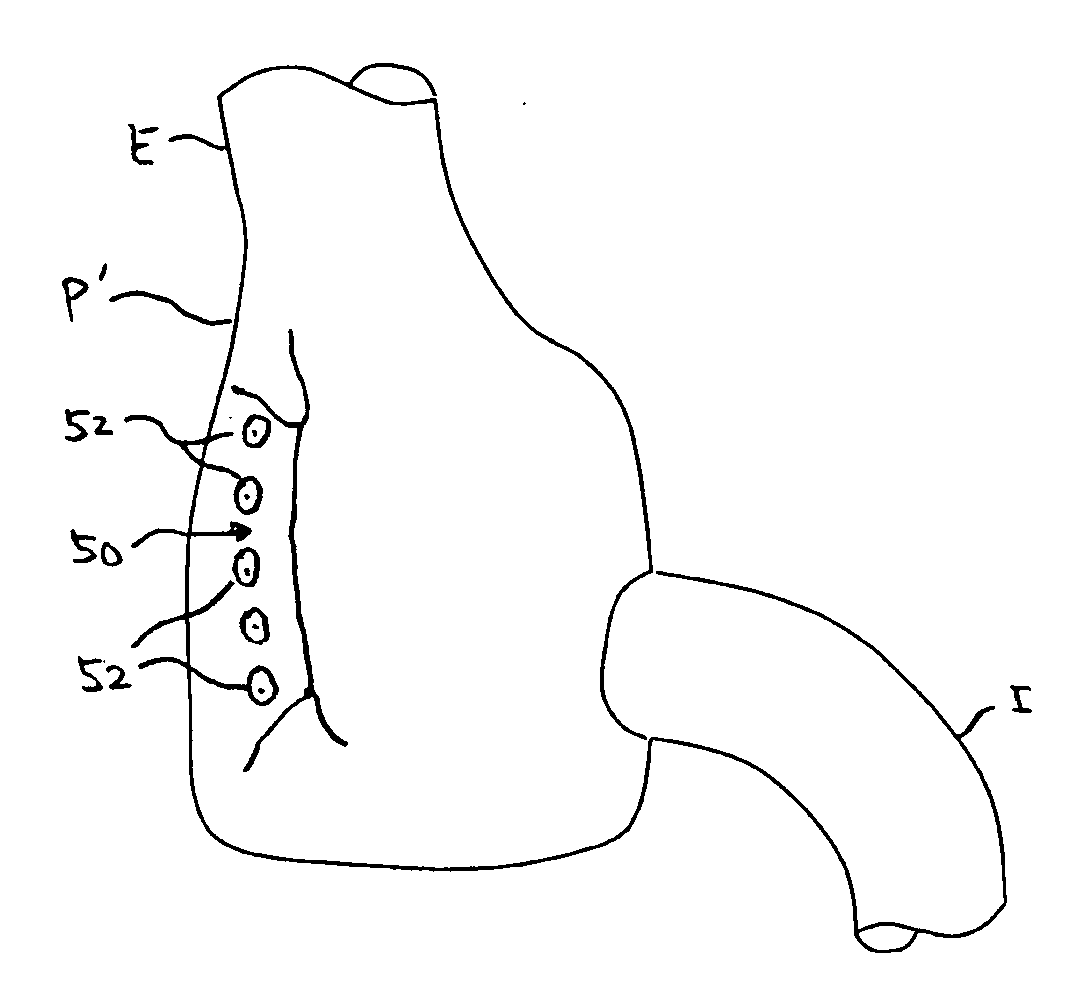
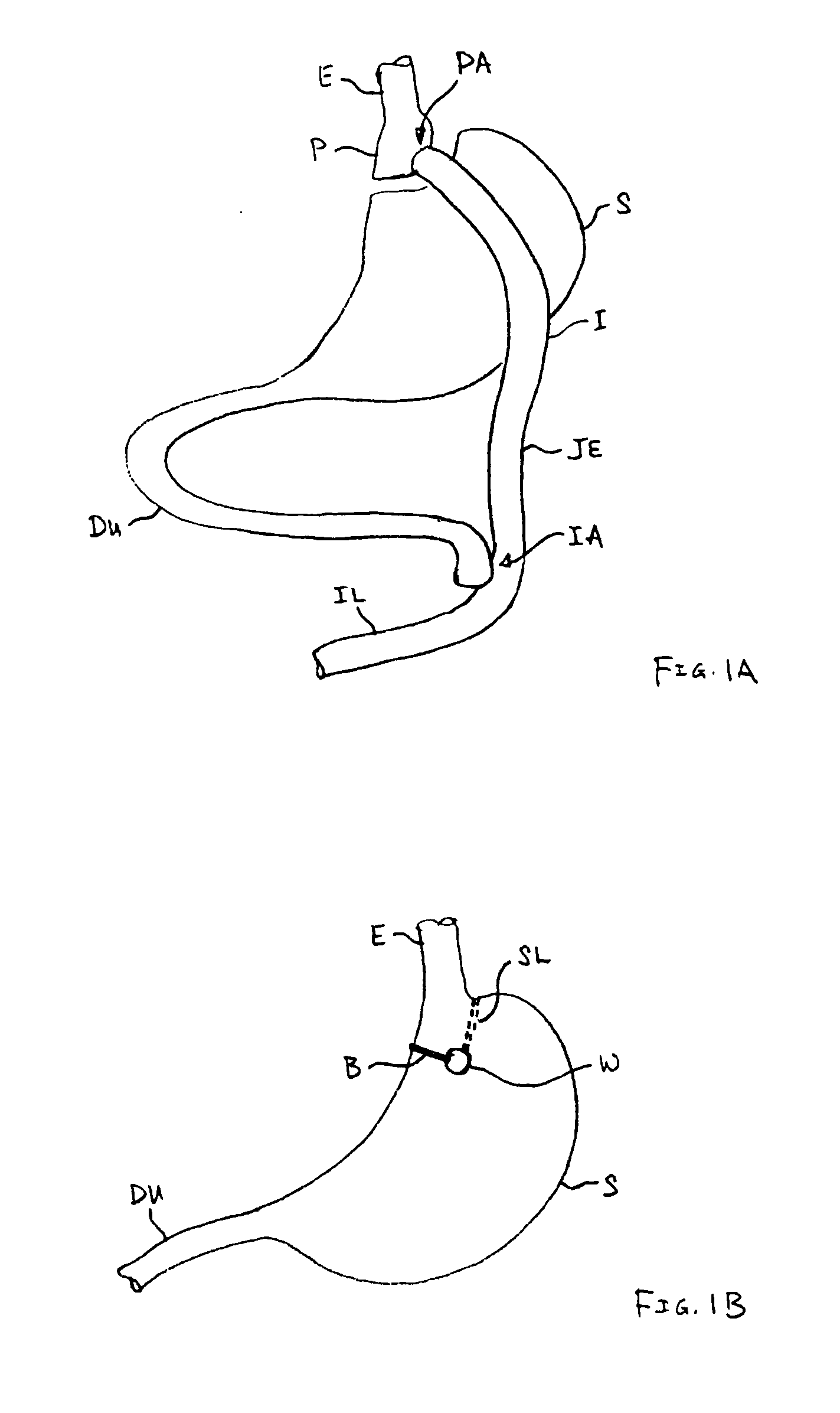
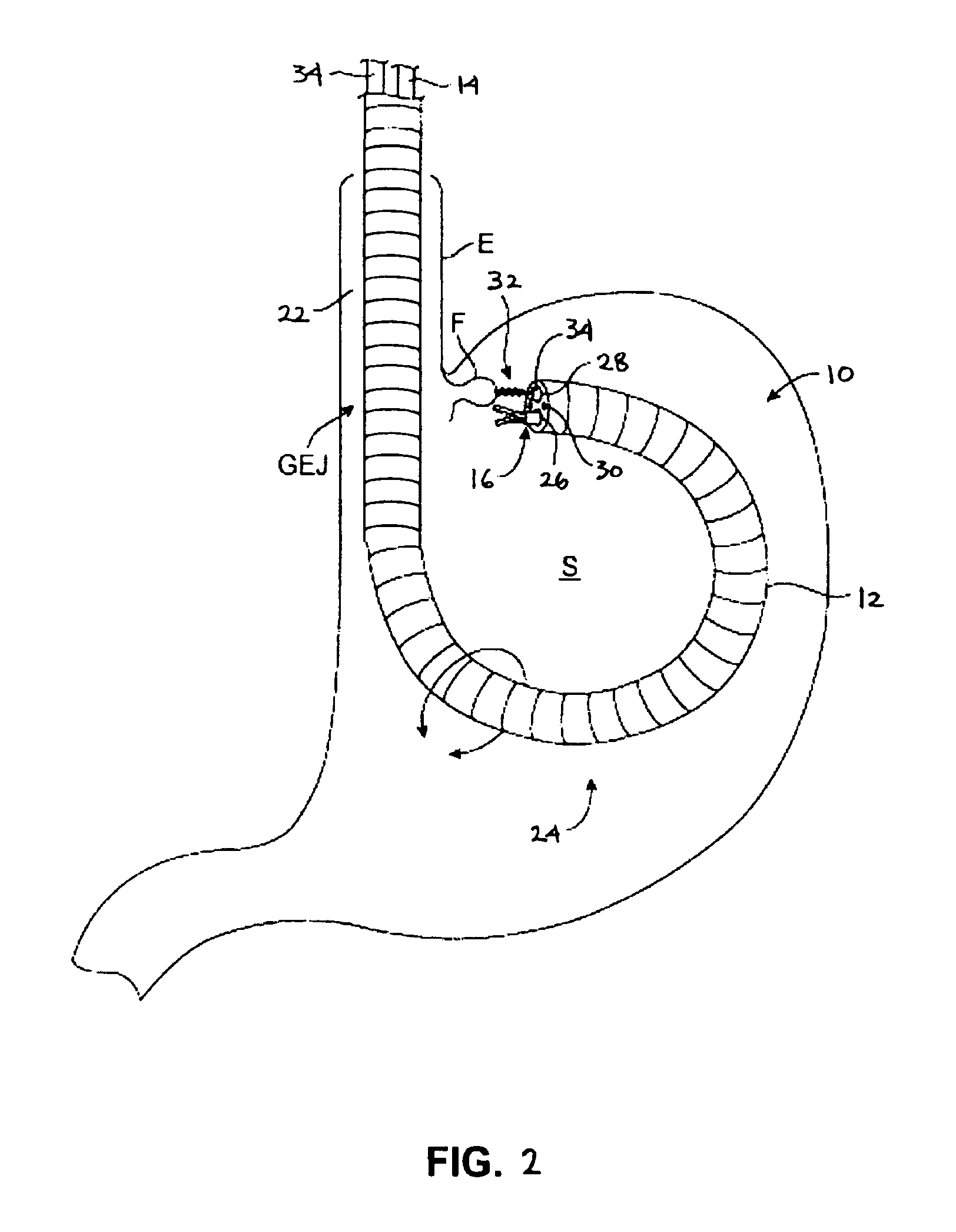
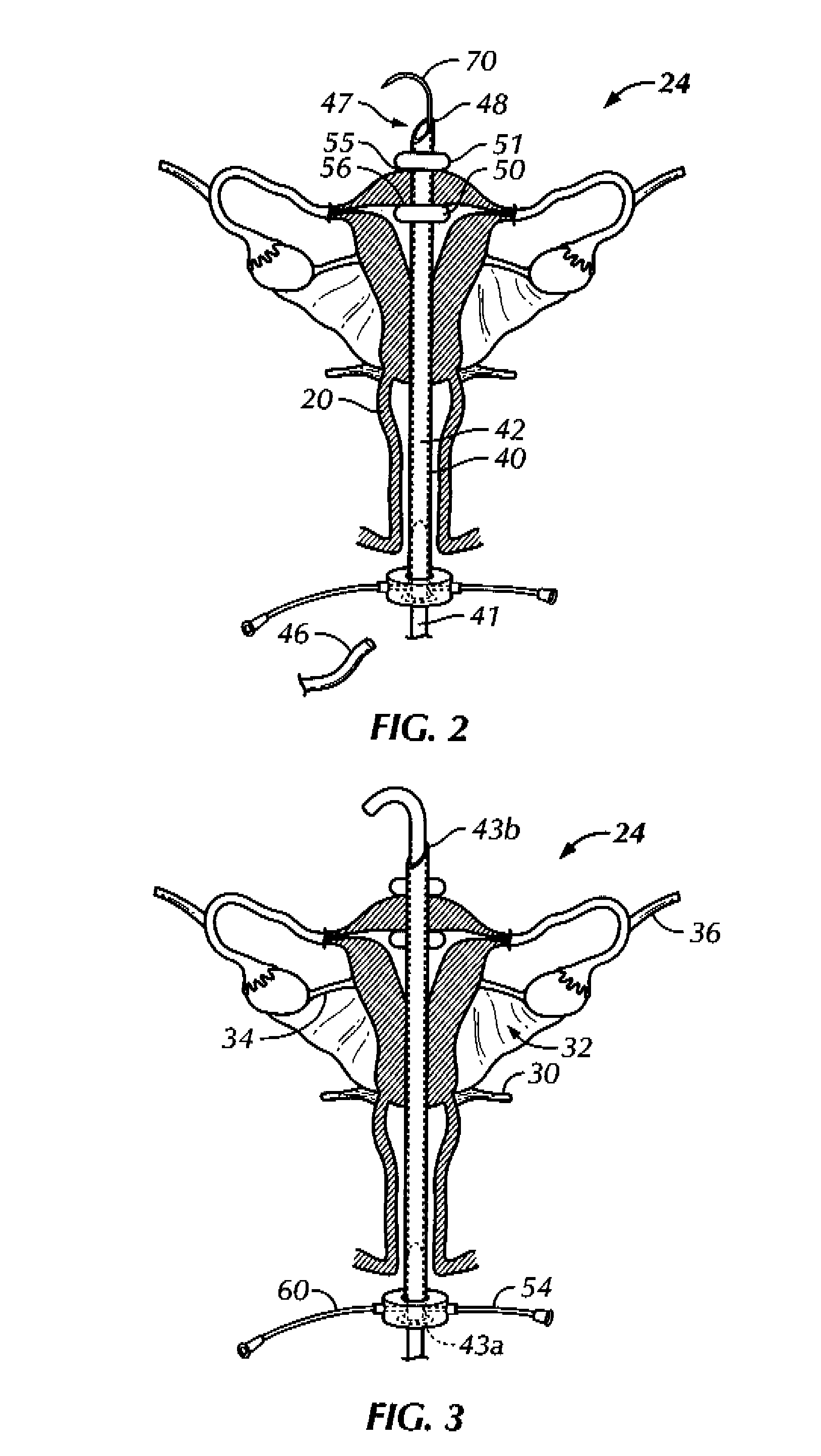
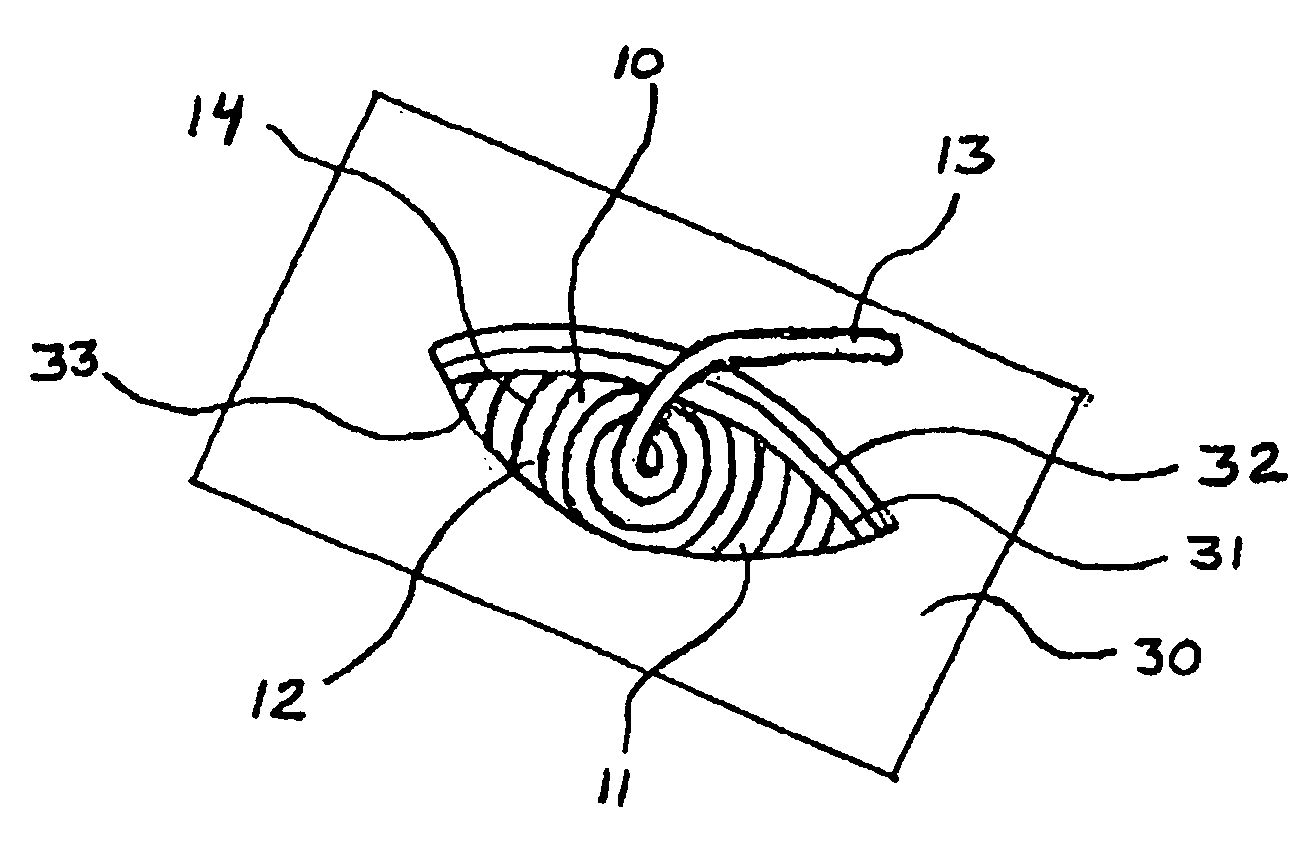
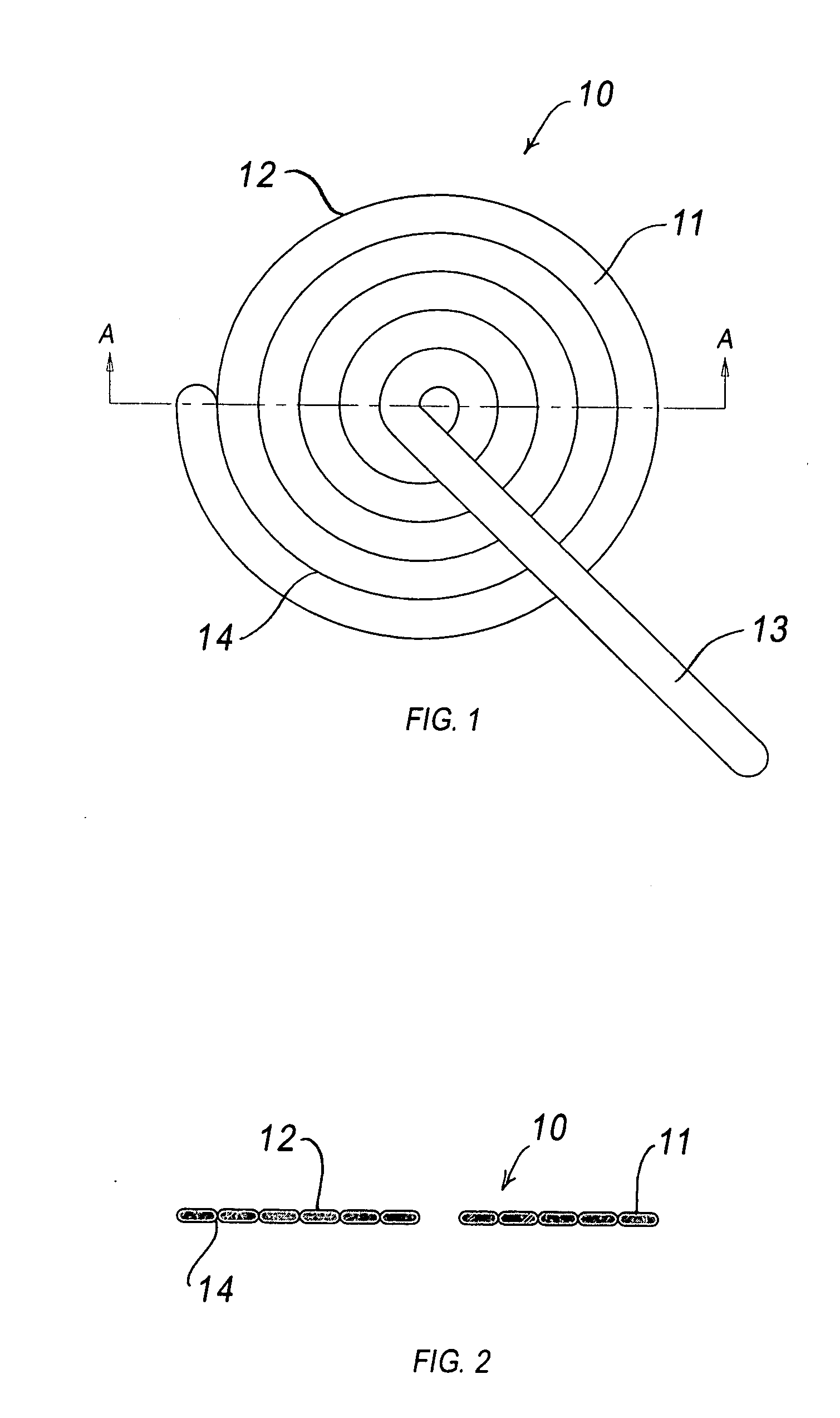
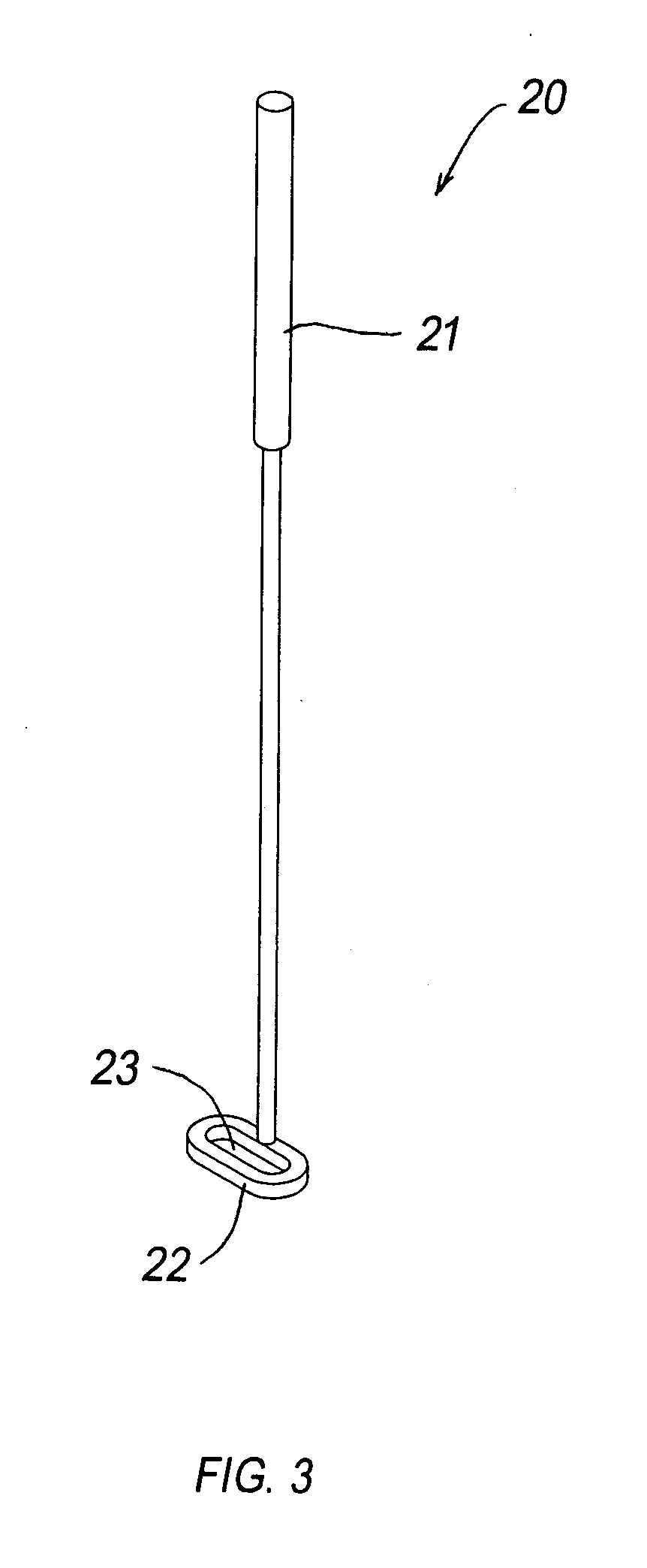
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
268 results about "Peritoneum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
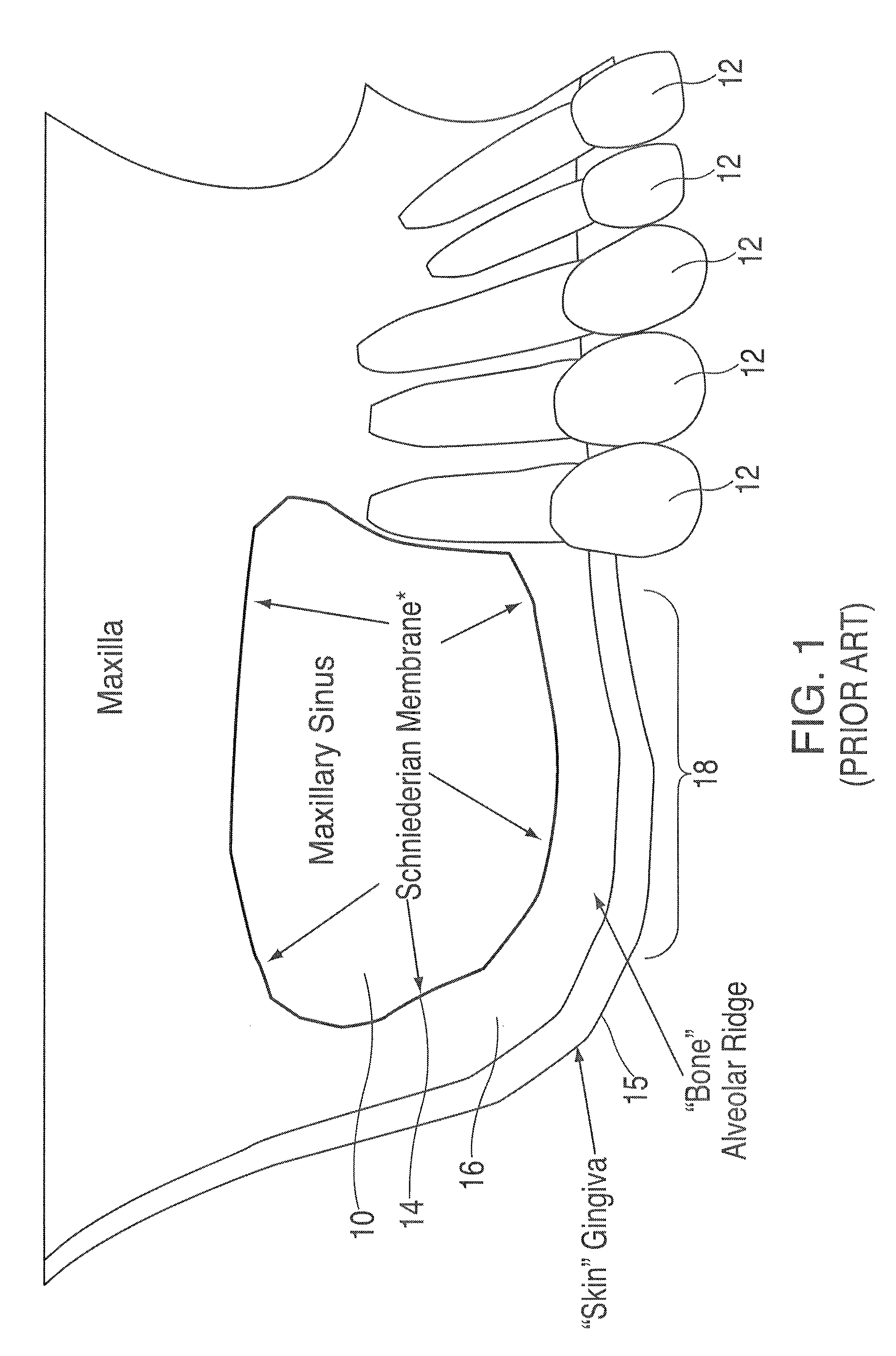
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
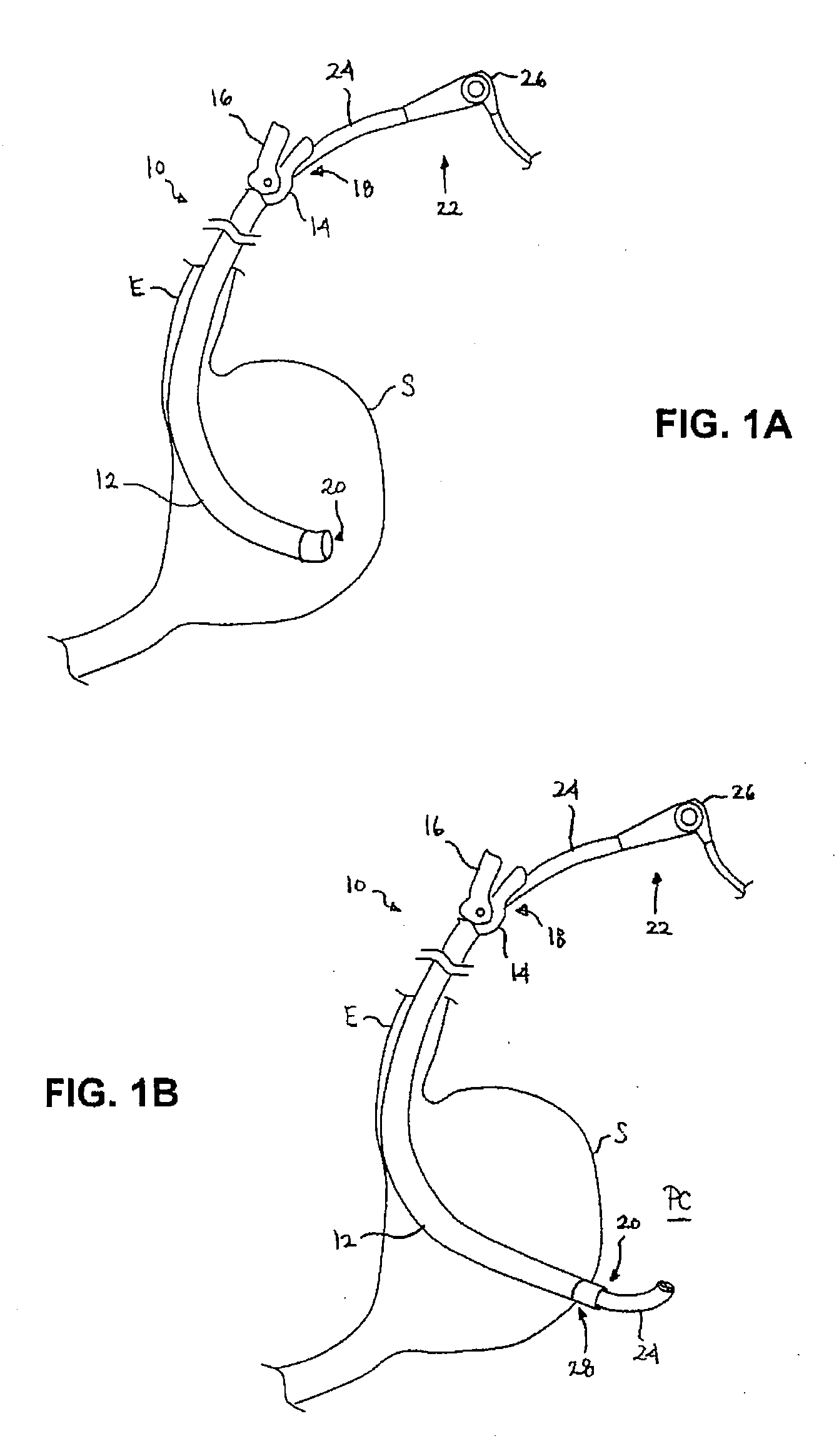
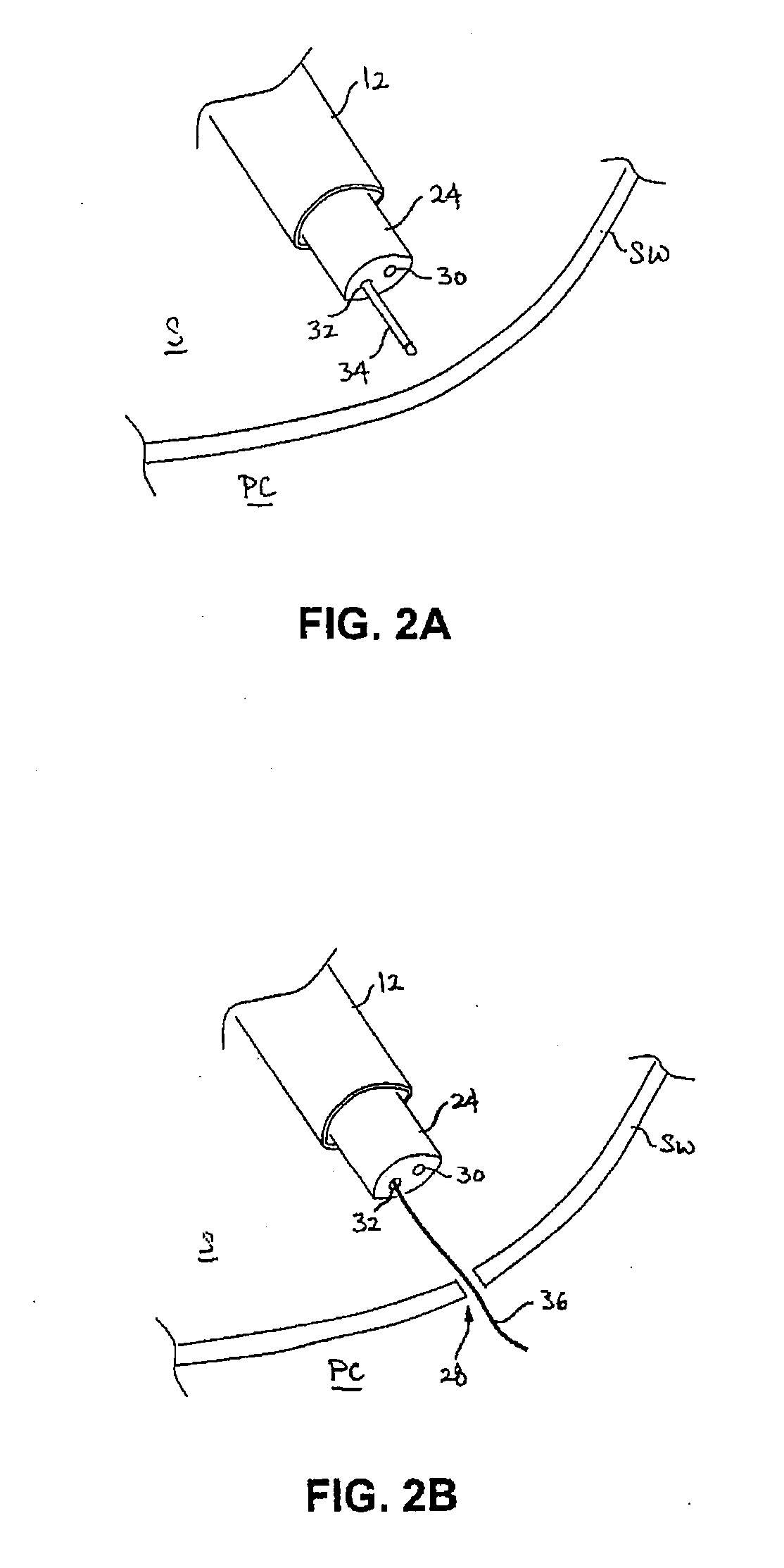
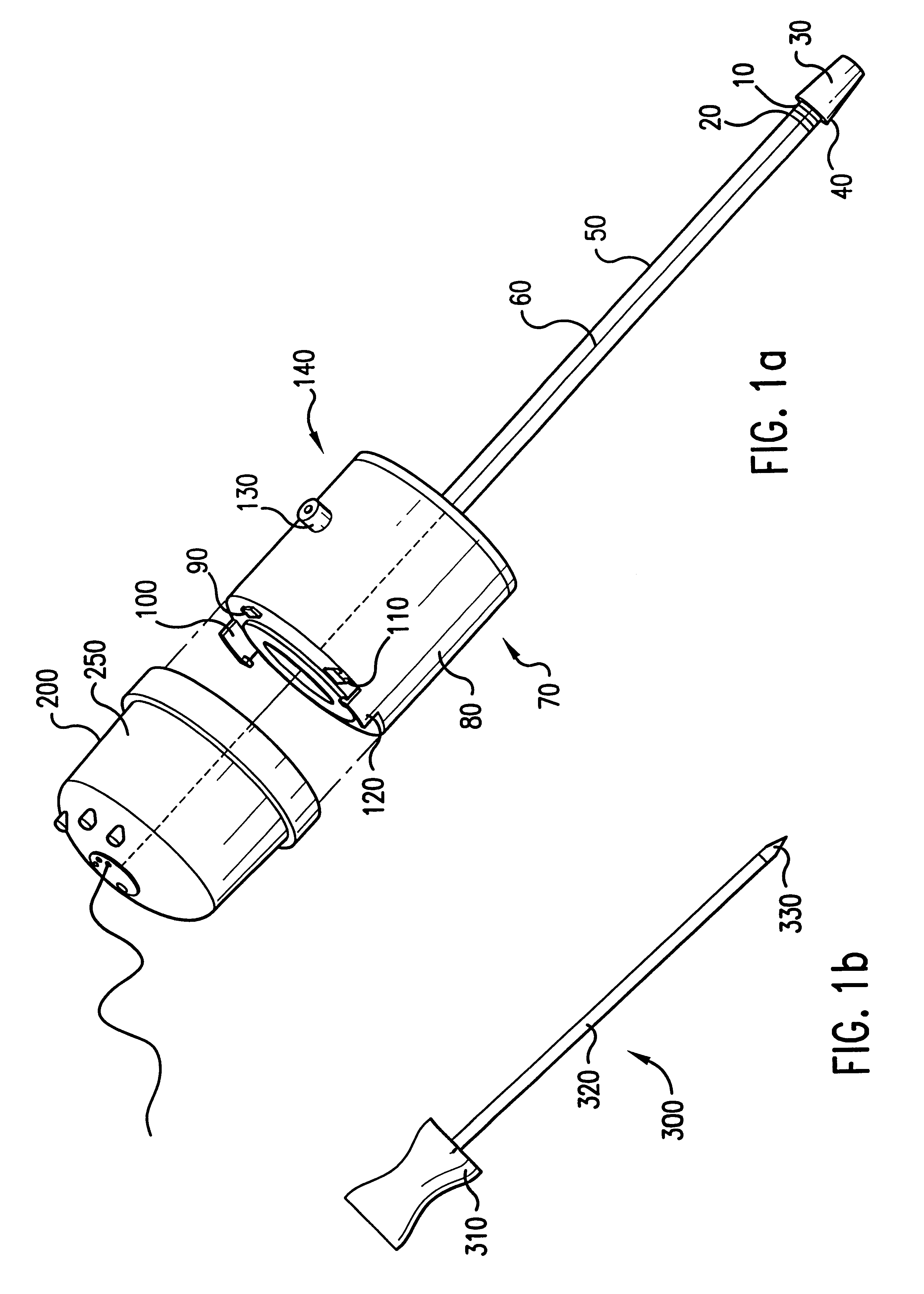
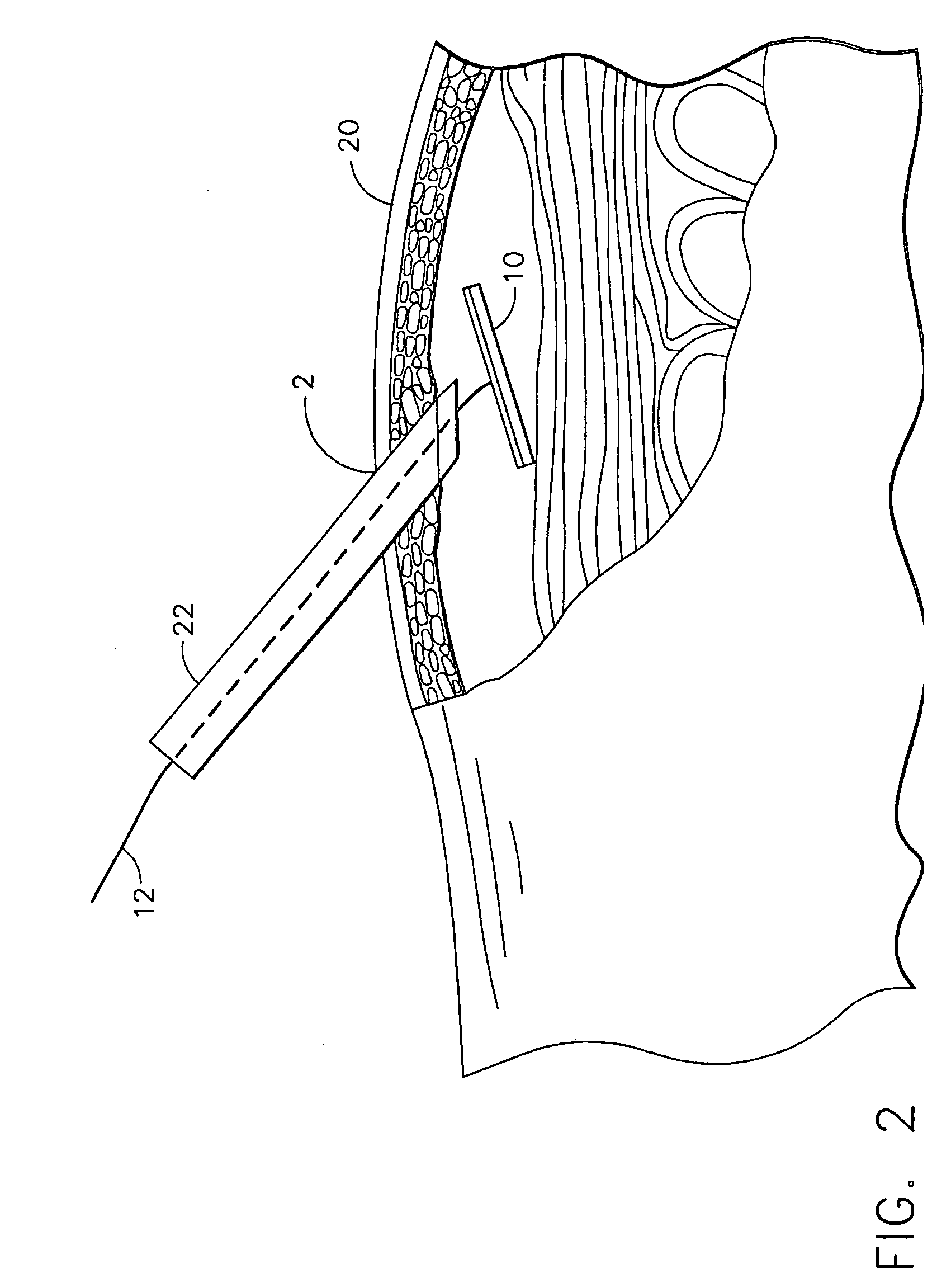
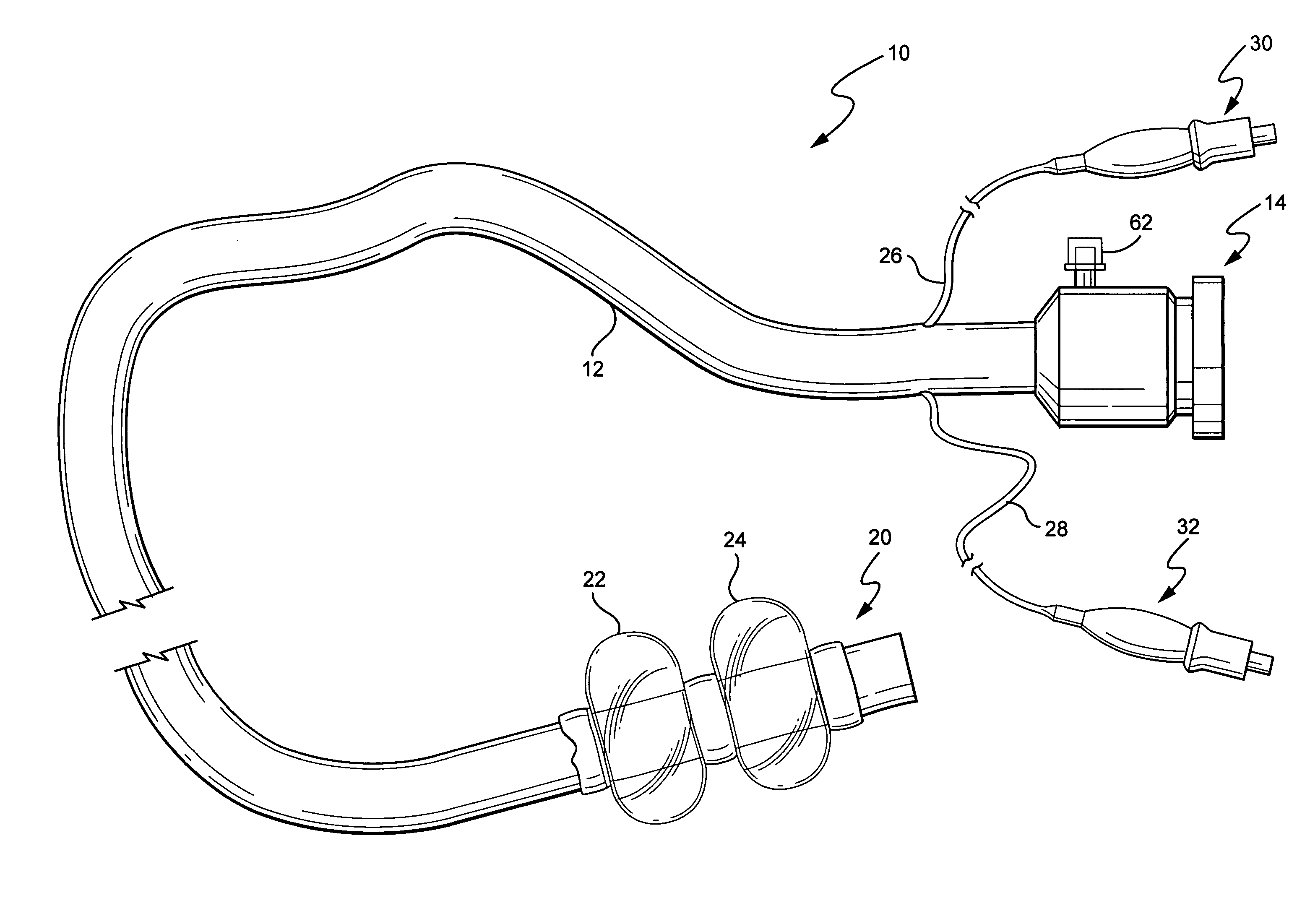
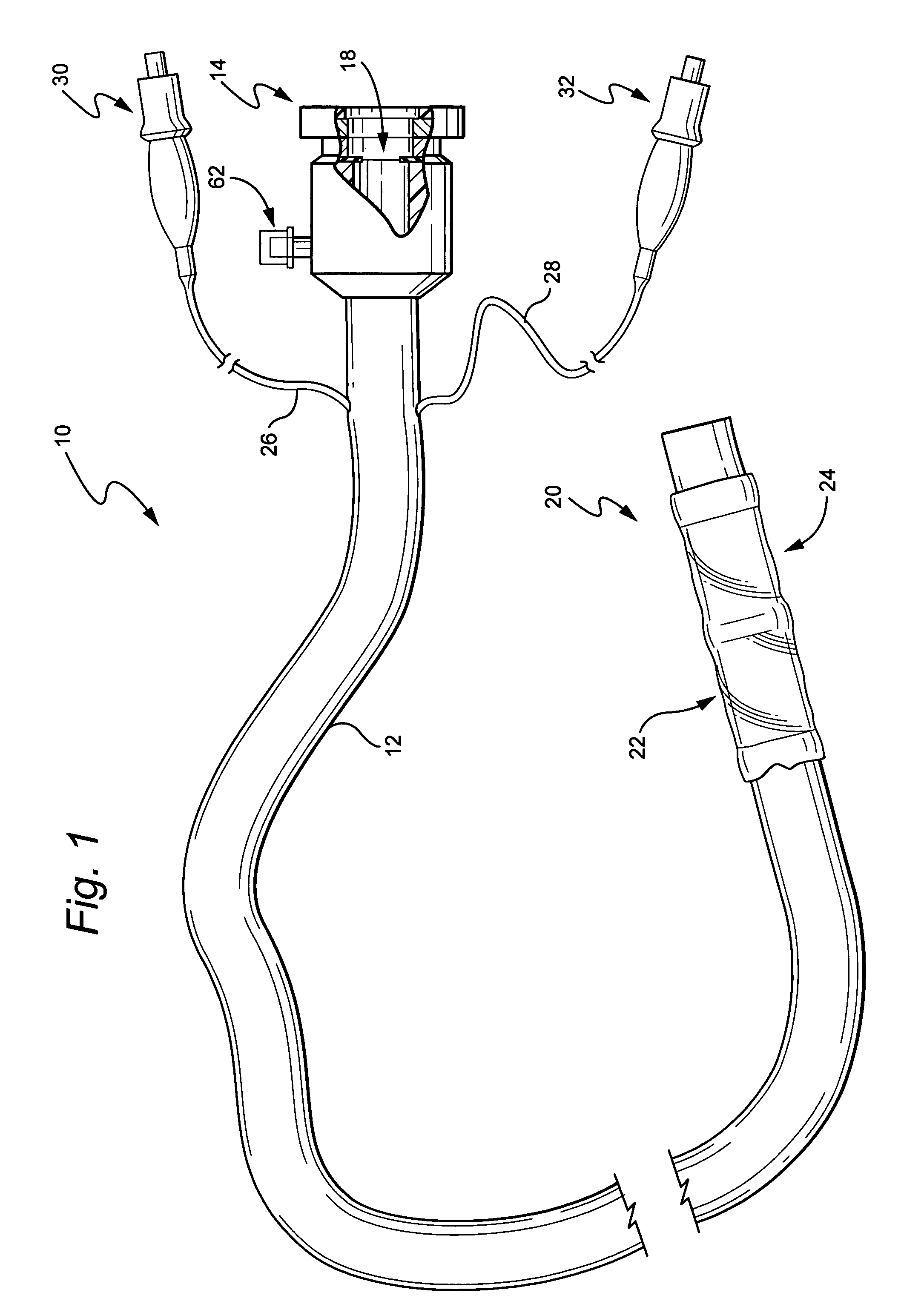
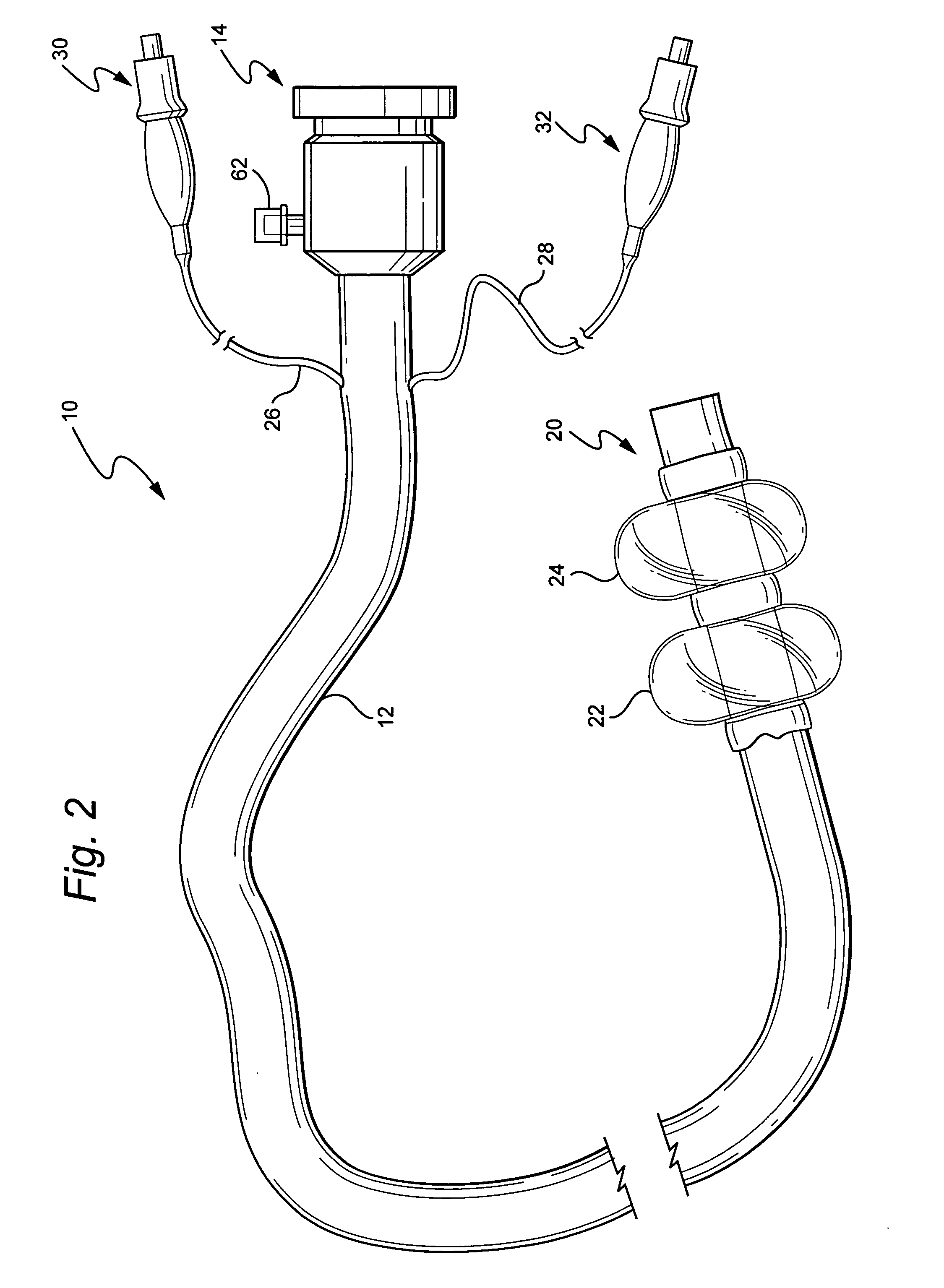
Surgical access system and related methods
ActiveUS20050149035A1Increase the number ofStructural damageSurgeryJoint implantsDistractionNerve structure
A surgical access system including a tissue distraction assembly and a tissue retraction assembly, both of which may be equipped with one or more electrodes for use in detecting the existence of (and optionally the distance and / or direction to) neural structures before, during, and after the establishment of an operative corridor to a surgical target site. Some embodiments of the surgical access system may be particularly suited for establishing an operative corridor to a surgical target site in the spine. Such an operative corridor may be established through the retroperitoneal space and the psoas muscle during a direct lateral, retroperitoneal approach to the spine.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Instrument assisted abdominal access
InactiveUS20070123840A1Precise positioningIncrease the diameterSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesStomach wallsAbdominal wall
Instrument assisted abdominal access methods and apparatus are described herein. A shape-lockable elongate body can be advanced endoluminally in a flexible state into the stomach, where an opening is created through the stomach wall. The opening can be created endoluminally or by incising instruments placed through the abdominal wall. The elongate body can be transitioned to a rigid state prior to, during, or after advancement into the patient and is passed through the opening into the peritoneal cavity. To assist in the passage of the elongate body, a helical tissue engager can be advanced into the peritoneal cavity and temporarily anchored into a tissue wall. By pulling the helical tissue engager proximally and pushing the elongate body over a flexible length of the engager, the elongate body can be brought into the peritoneal cavity
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Methods and devices for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity
A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity is described. More specifically, a technique for accessing the peritoneal cavity via the wall of the digestive tract is provided so that examination of and / or a surgical procedure in the peritoneal cavity can be conducted via the wall of the digestive tract with the use of a flexible endoscope. As presently proposed, the technique is particularly adapted to transgastric peritoneoscopy. However, access in addition or in the alternative through the intestinal wall is contemplated and described as well. Transgastric and / or transintestinal peritoneoscopy will have an excellent cosmetic result as there are no incisions in the abdominal wall and no potential for visible post-surgical scars or hernias.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Systems and methods for reducing post-surgical complications
InactiveUS6645198B1Easy to holdLimit depth of insertionDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical incisionAbdominal wall
The present invention provides systems and methods for applying RF energy to injured tissue, particularly the peritoneum, in order to prevent harmful post-surgical adhesions. One aspect of the invention is RF energy delivery systems employing trocars, which are designed for use in laparotomies and laparoscopies. Another aspect of the invention is an RF delivery system comprising a surgical sheet with one or more electrodes for delivering the RF energy to the injured tissue resulting from conventional surgical incisions into the abdominal wall. Additionally, another aspect of the invention provides methods for controlling the treatment dosage of RF heat to the injured tissue using parameters such as treatment time, change in tissue temperature, and change in tissue impedance.
Owner:NTERO SURGICAL
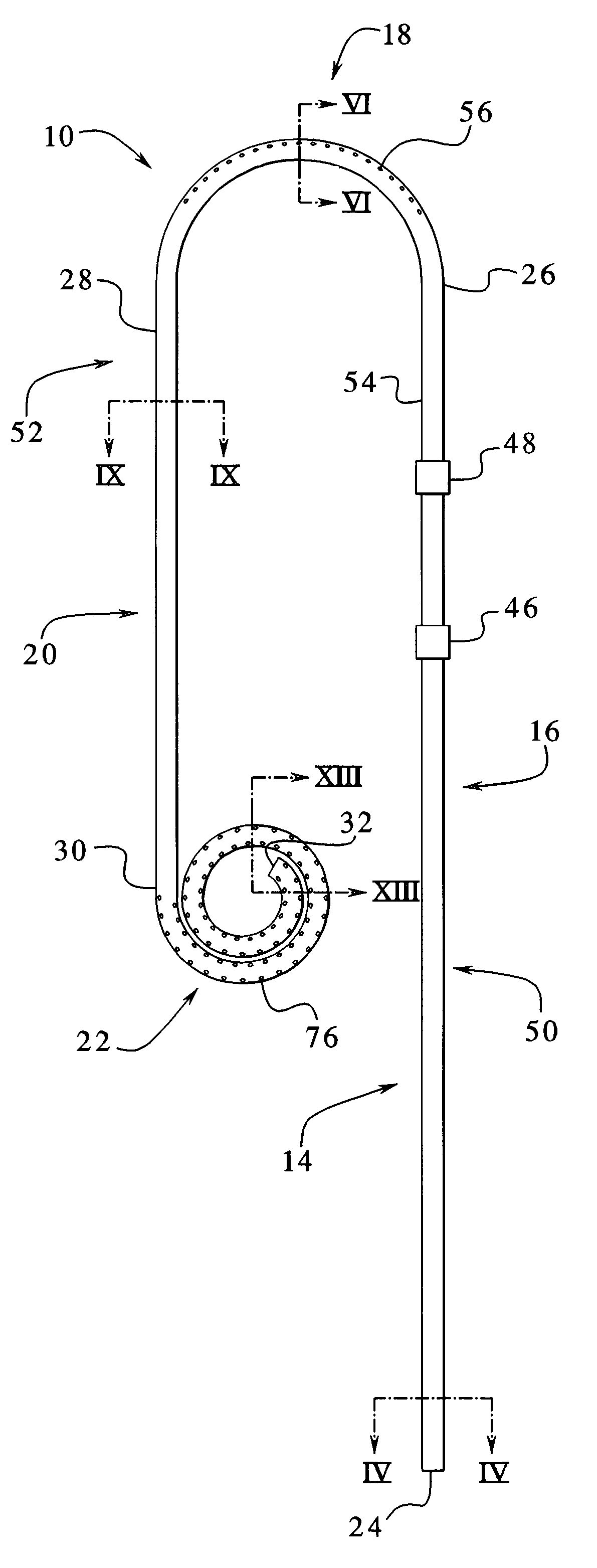
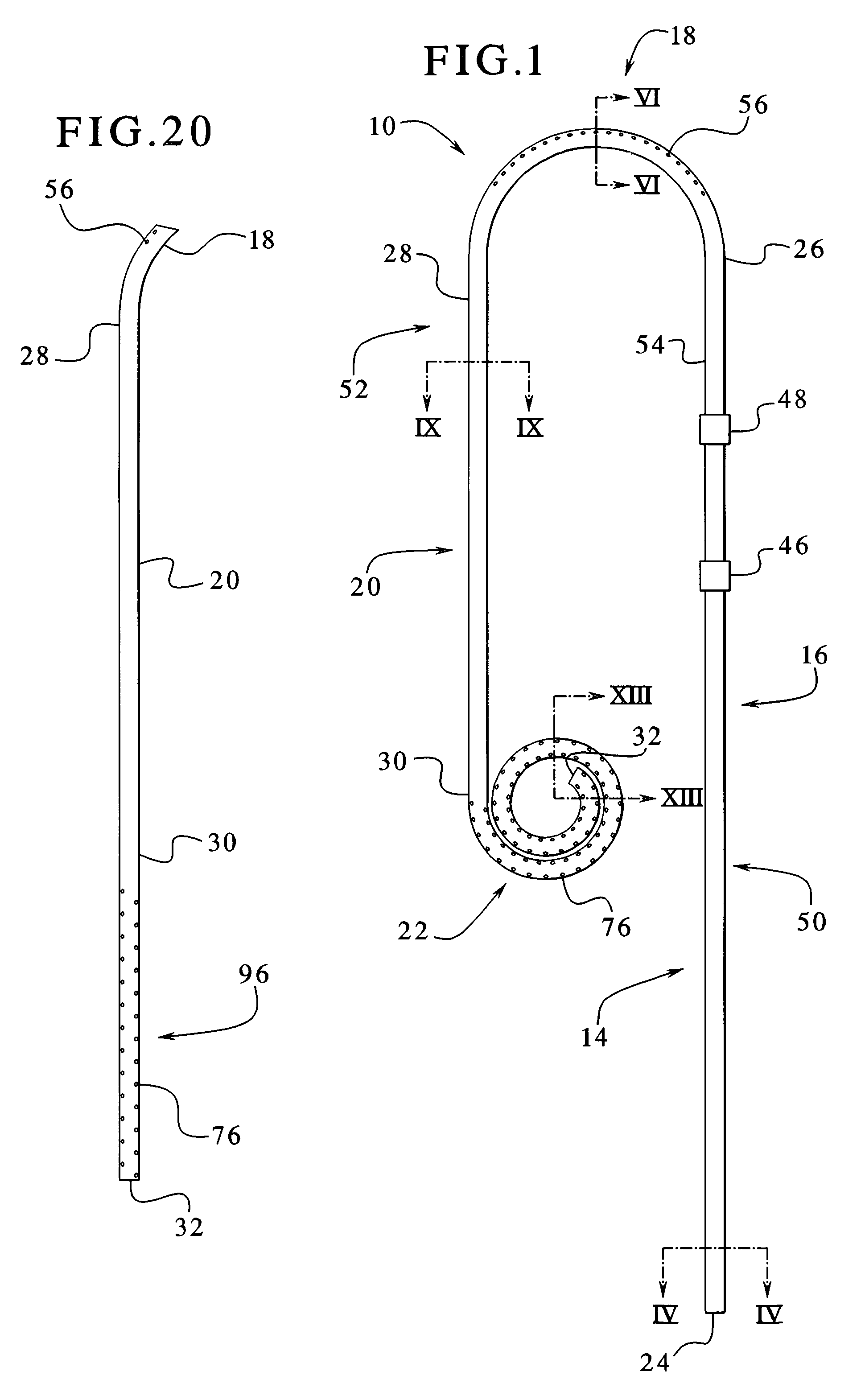
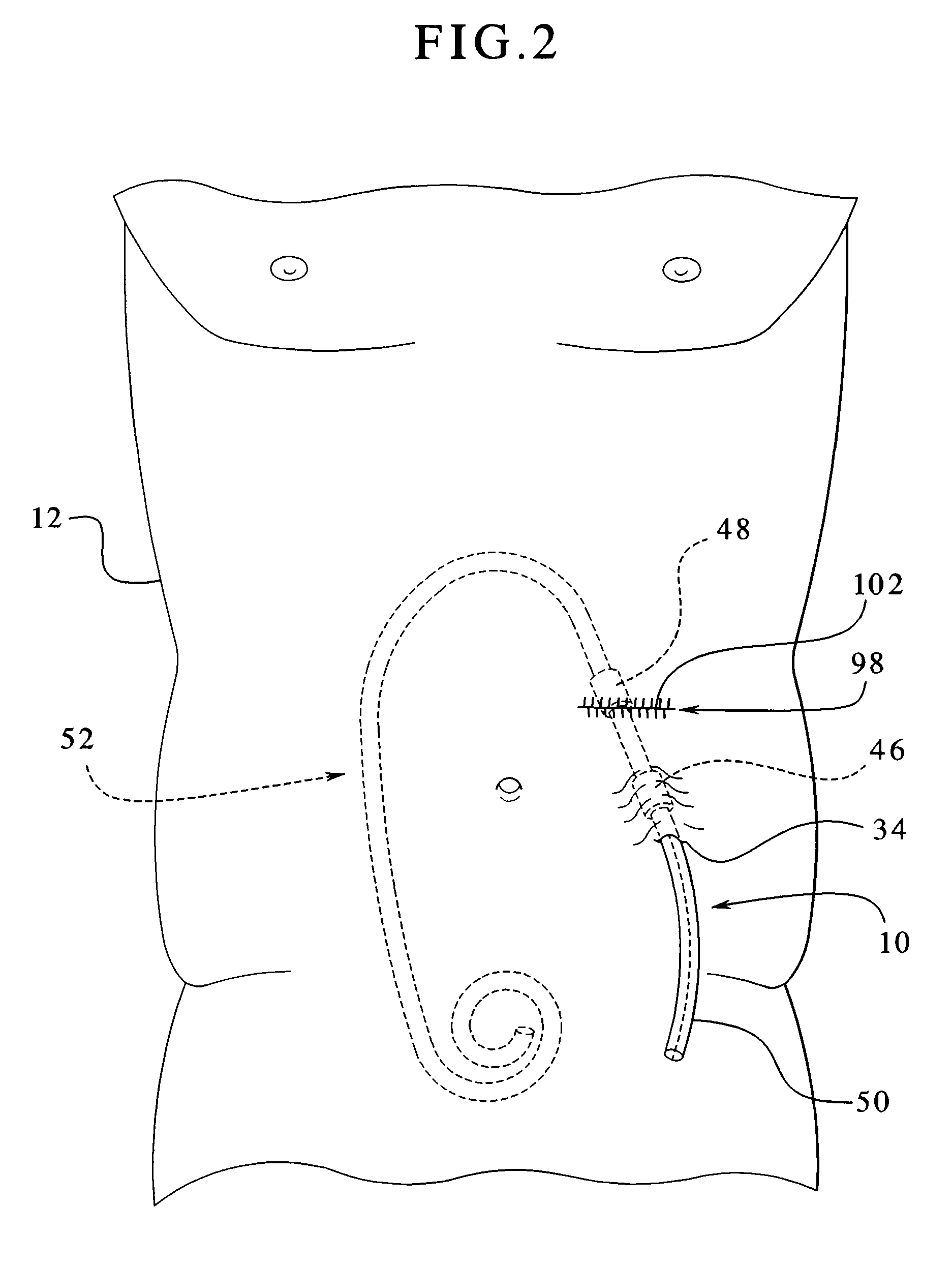
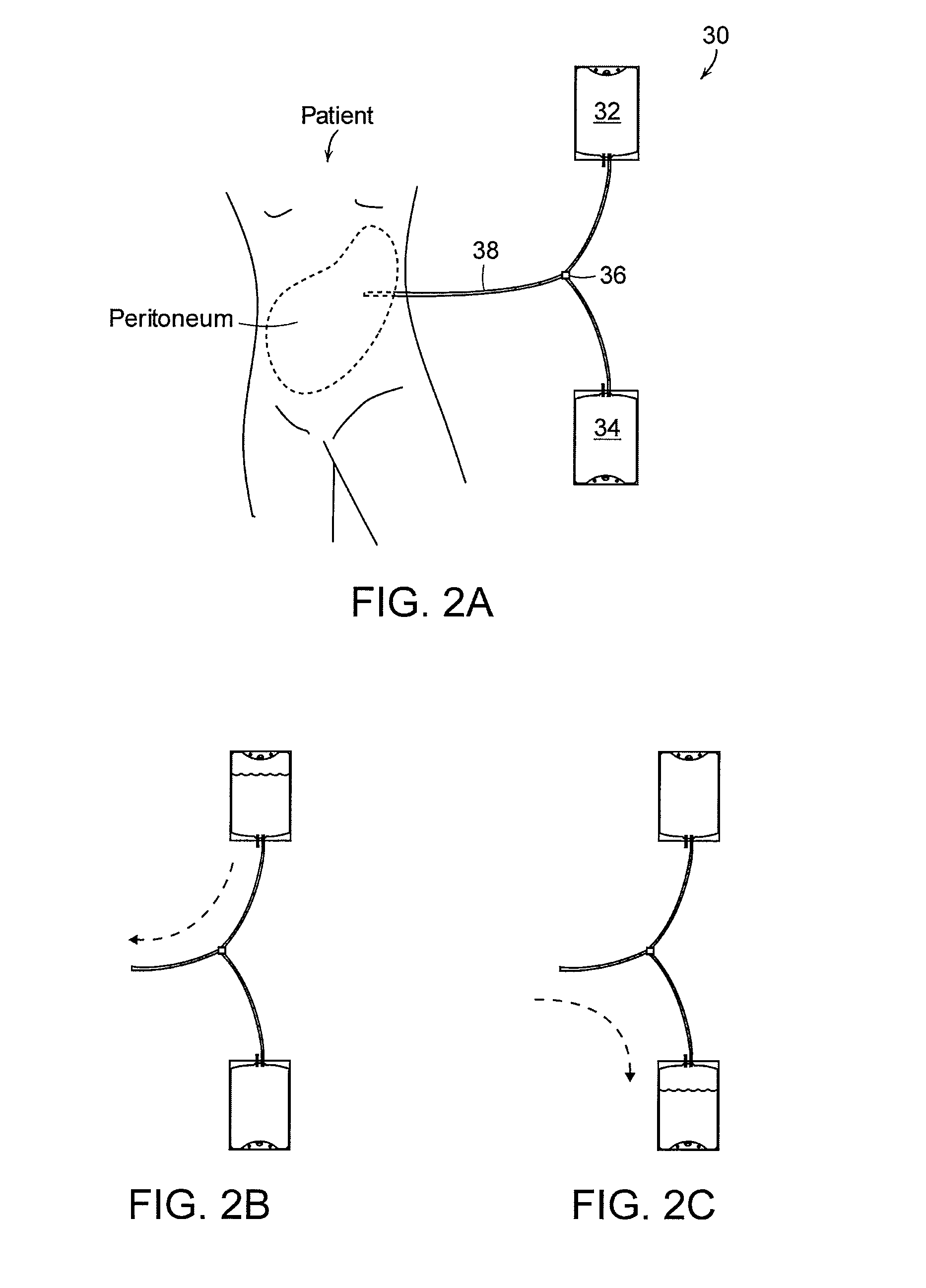
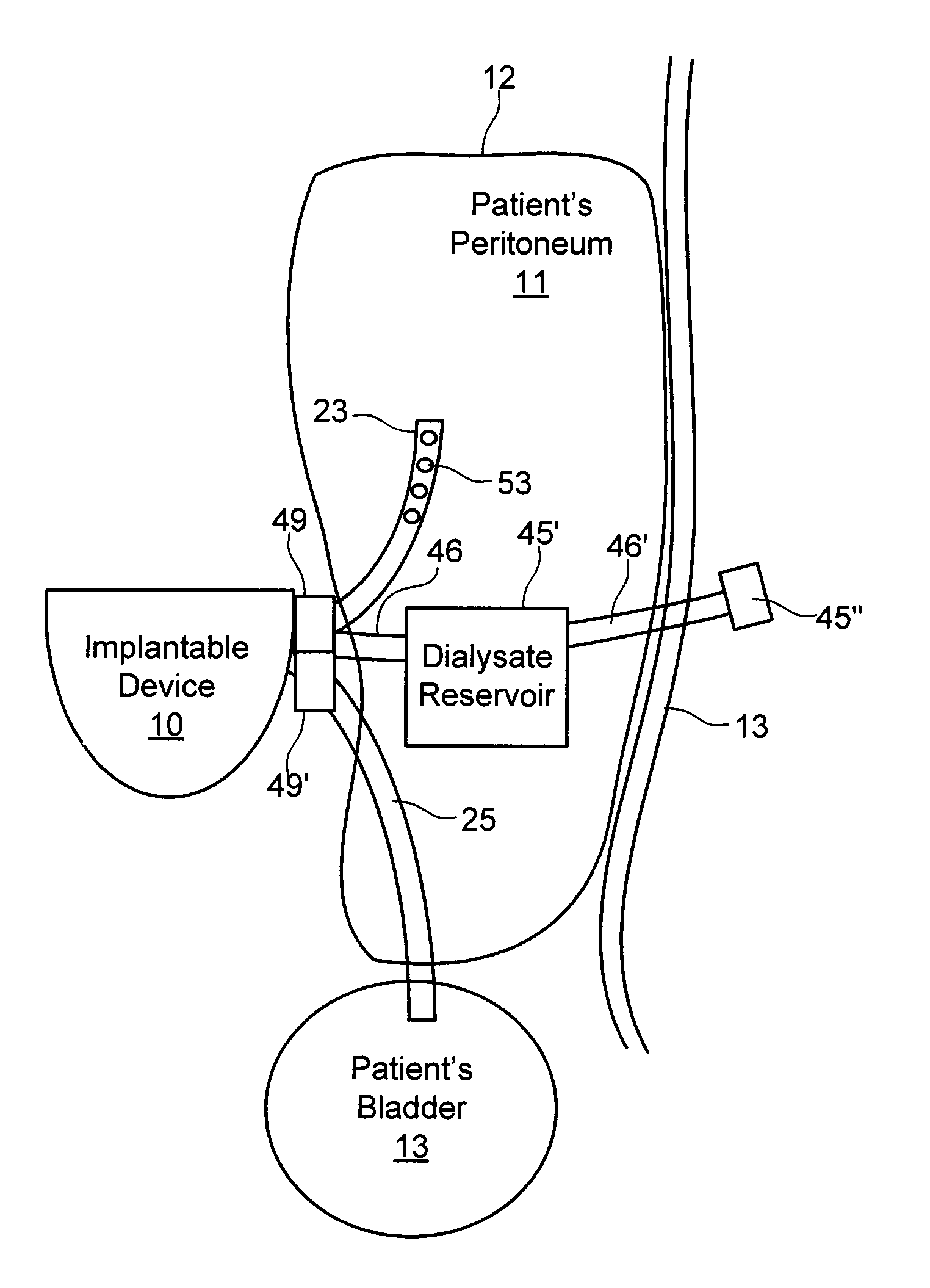
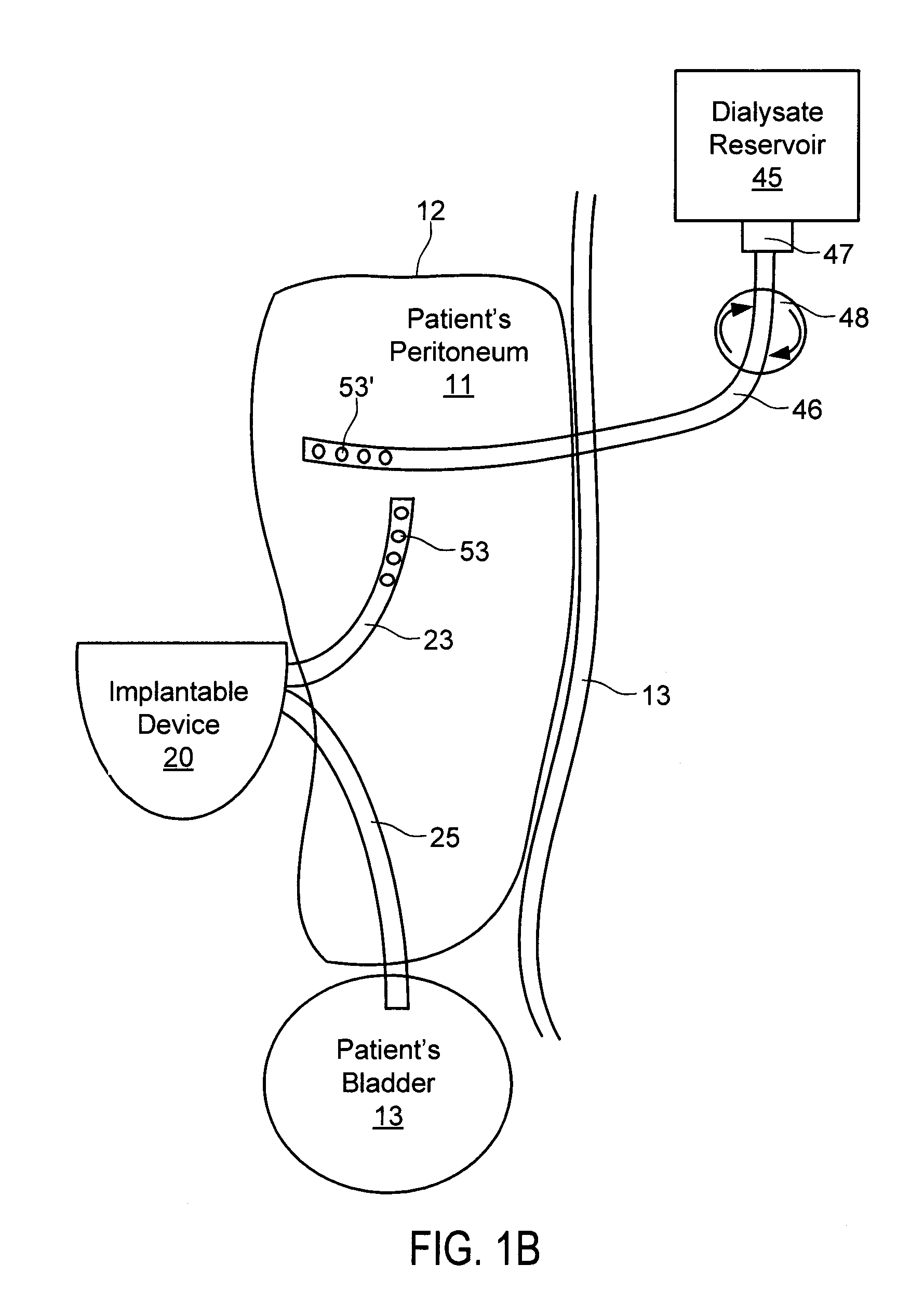
Dialysis implant and methods of use
ActiveUS20060058731A1Prevent excessive bladder pressureLow and high pressureMedical devicesCatheterPeritoneal dialysisRenal Failures
A device and methods for treating renal failure are disclosed. One embodiment of the device is an implantable peritoneal dialysis device. When in use, the device can have a semi-permeable reservoir implanted in the peritoneal cavity. The reservoir can receive blood waste and drain through one or more conduits, via a pump, to the biological bladder. Solids and / or a solution benefiting dialysis can be pumped to the reservoir and / or implanted in the peritoneal cavity.
Owner:SEQUANA MEDICAL NV
Systems and methods for reducing post-surgical complications
InactiveUS6520185B1Reduce morbidityMinimizes and eliminates formationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSurgical incisionAbdominal wall
The present invention provides systems and methods for applying RF energy to injured tissue, particularly the peritoneum, in order to prevent harmful post-surgical adhesions. One aspect of the invention is RF energy delivery systems employing trocars, which are designed for use in laparotomies and laparoscopies. Another aspect of the invention is an RF delivery system comprising a surgical sheet with one or more electrodes for delivering the RF energy to the injured tissue resulting from conventional surgical incisions into the abdominal wall. Additionally, another aspect of the invention provides methods for controlling the treatment dosage of RF heat to the injured tissue using parameters such as treatment time, change in tissue temperature, and change in tissue impedance.
Owner:NTERO SURGICAL
Method and device for minimally invasive implantation of biomaterial
A minimally invasive method of placing a delivery device substantially adjacent to vascular tissue and a device for use with such a method are disclosed. The delivery device may be a flexible biological construct with a flexible tethering means. The delivery device may be percutaneously inserted near vascular tissue such as, for example, peritoneal tissue. When the delivery device has been inserted, the tether may be used to pull the delivery device toward the vascular tissue and secure the device thereto. Contact between the front surface of the delivery device and the vascular tissue may be maintained by making and keeping the tether substantially taut. The delivery device may serve accomplish sustained delivery of active agents.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Methods and devices for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity
A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity is described. More specifically, a technique for accessing the peritoneal cavity via the wall of the digestive tract is provided so that examination of and / or a surgical procedure in the peritoneal cavity can be conducted via the wall of the digestive tract with the use of a flexible endoscope. As presently proposed, the technique is particularly adapted to transgastric peritoneoscopy. However, access in addition or in the alternative through the intestinal wall is contemplated and described as well. Transgastric and / or transintestinal peritoneoscopy will have an excellent cosmetic result as there are no incisions in the abdominal wall and no potential for visible post-surgical scars or hernias.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Peritoneal dialysis catheters
InactiveUS6976973B1Well mixedMinimize shuntingMedical devicesCatheterPeritoneal dialysis catheterCatheters dialysis
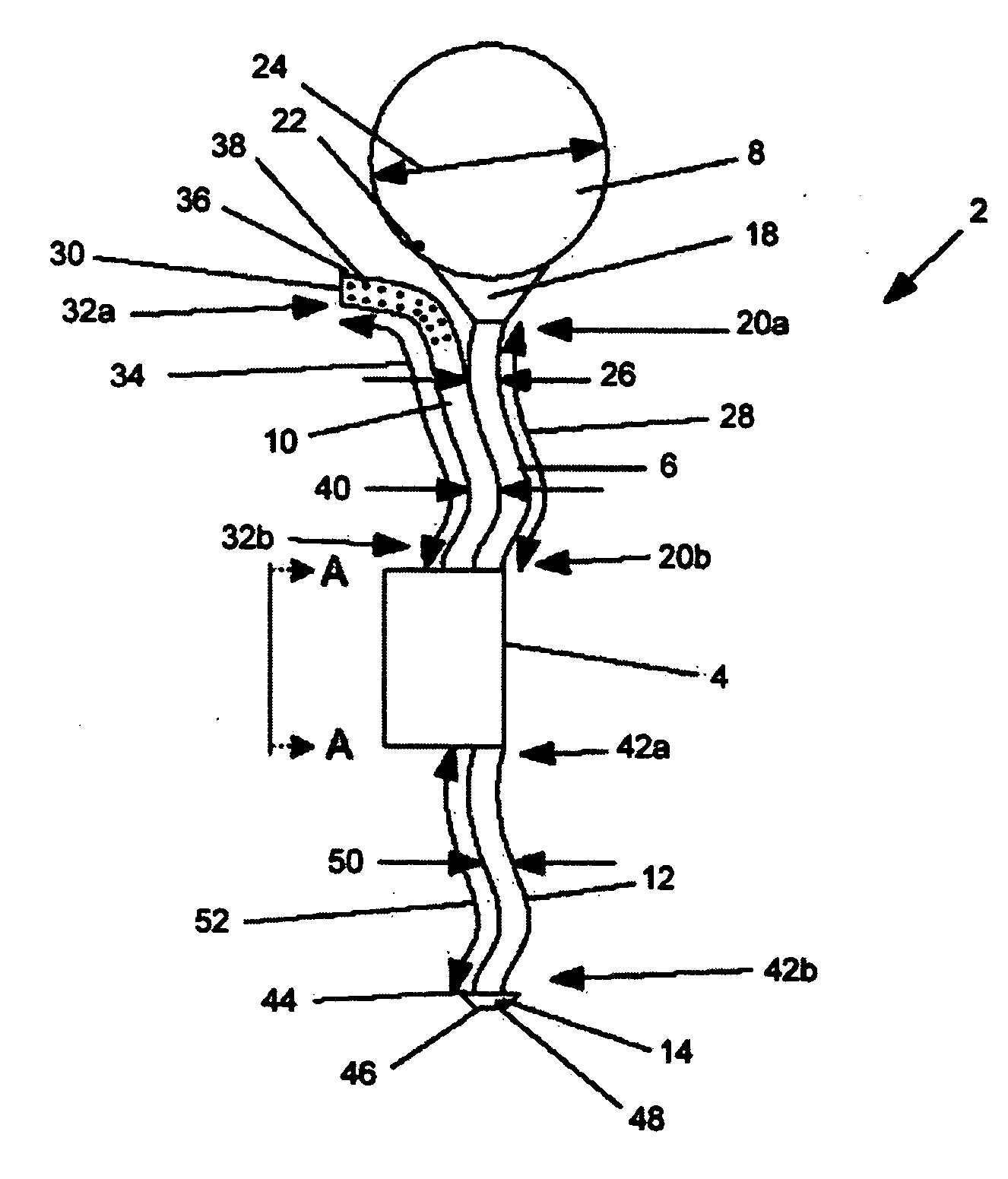
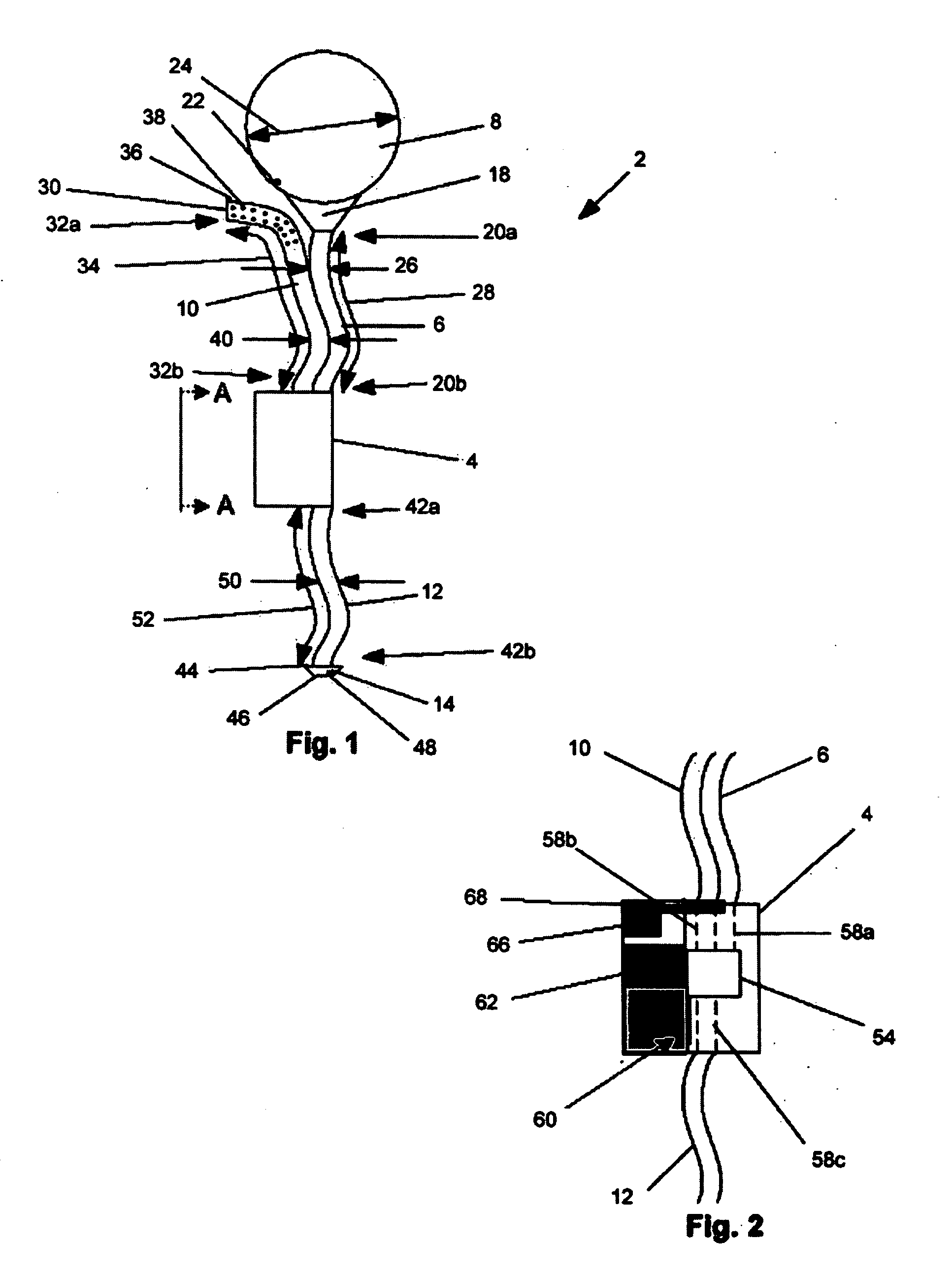
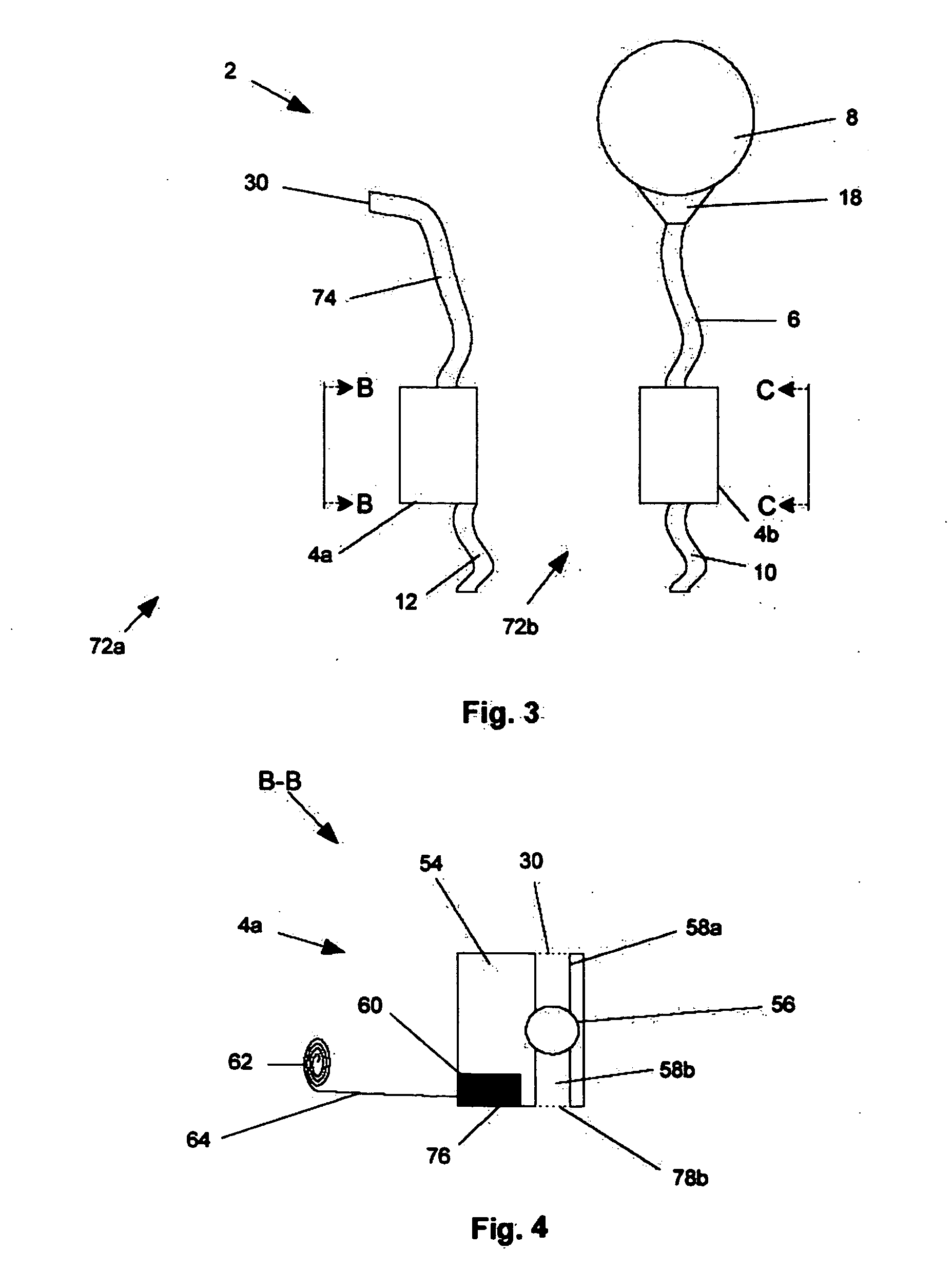
A catheter suitable for use in performing peritoneal dialysis. The catheter is a dual lumen catheter which allows for continuous flow peritoneal dialysis. Dialysate flows through the catheter into the patient via one lumen and simultaneously flows through the catheter out of the patient via the second lumen. The dual lumen dialysis catheter has a flexible tube which has an implantable portion extending from an external patient portion. Both of the lumens have openings in the external patient portion for connecting to a supply and drain of dialysate, respectively. The implantable portion has a preformed curved segment which has an outlet for the first lumen to flow dialysate into the patient's peritoneal cavity. The implantable portion has an opening for the second lumen at the distal end to flow dialysate out of the peritoneal cavity and removal from the patient. The catheter facilitates mixing of fresh and spent dialysate inside the peritoneal cavity by inflowing fresh dialysate into the cavity at a location substantially separated from the cavity outflow location, and by directing the inflow of dialysate into the cavity opposite the cavity outflow location.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
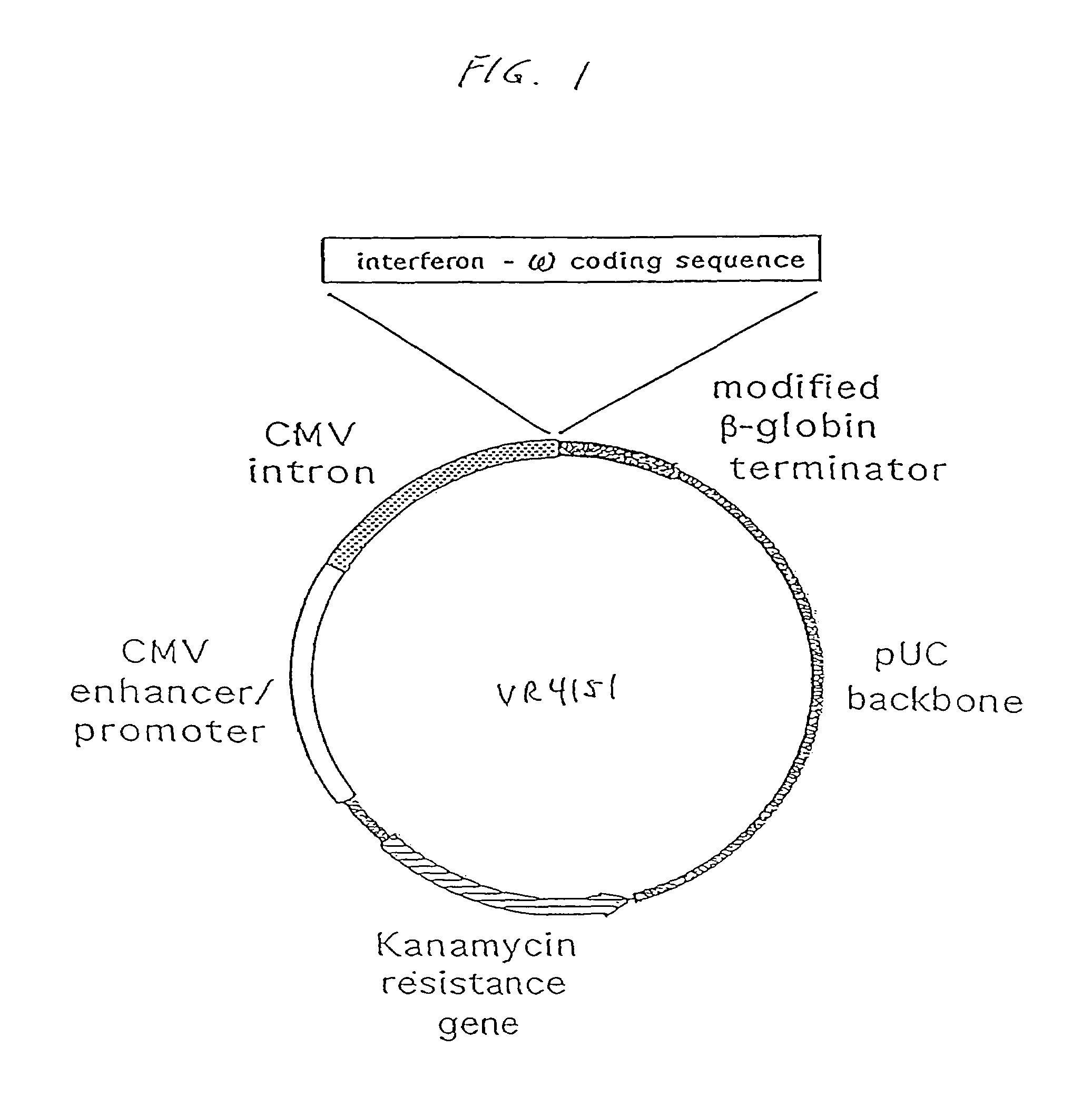
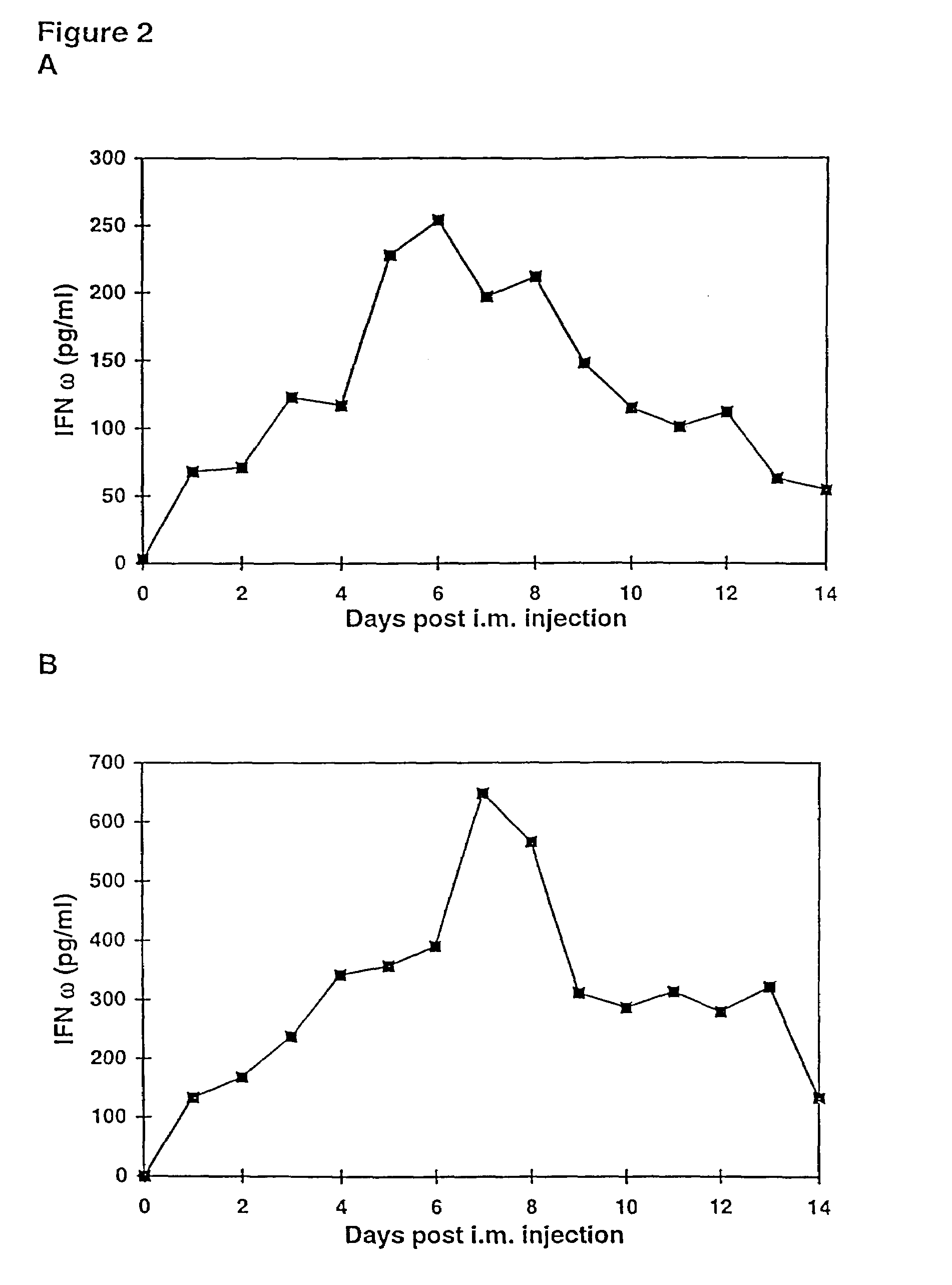
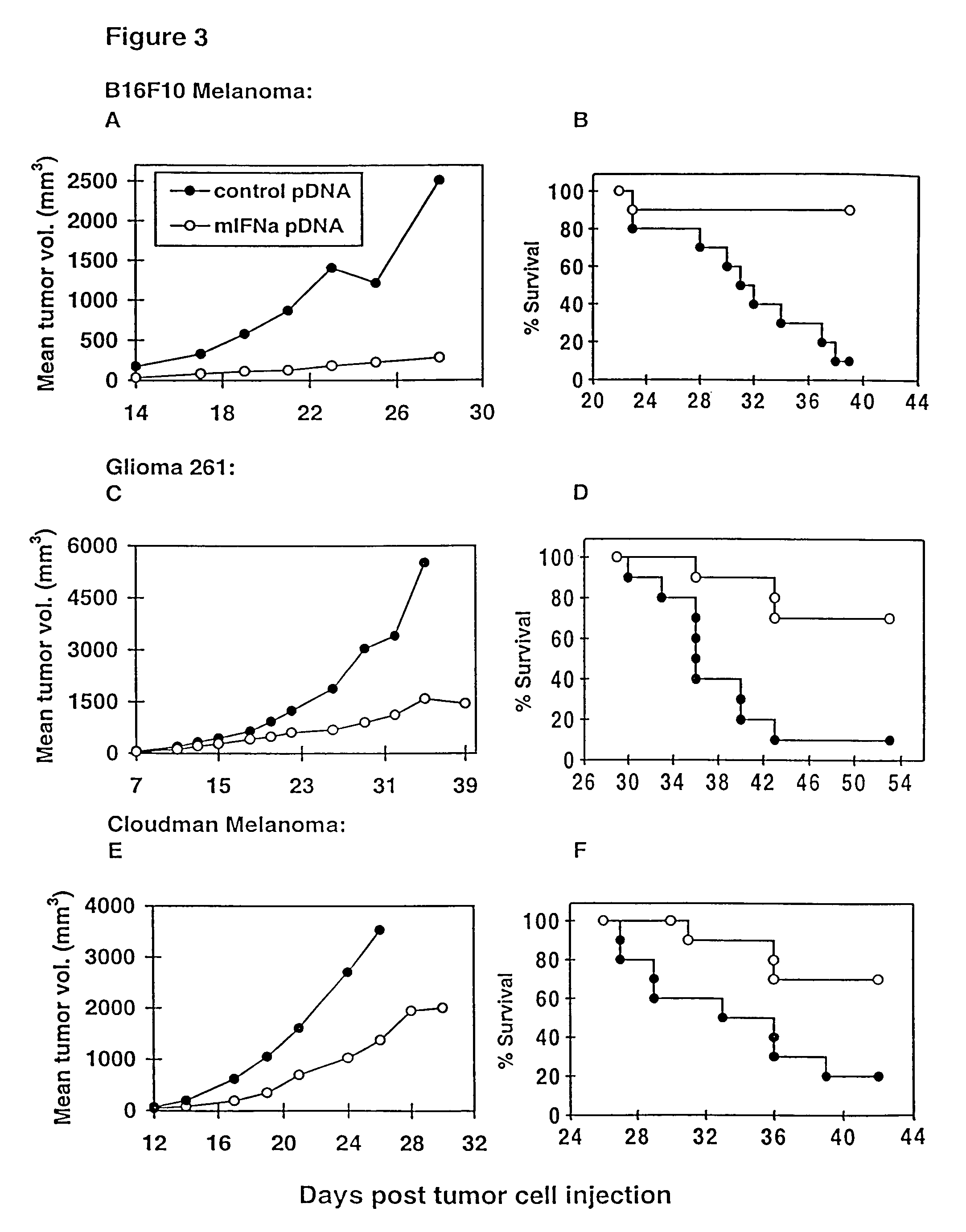
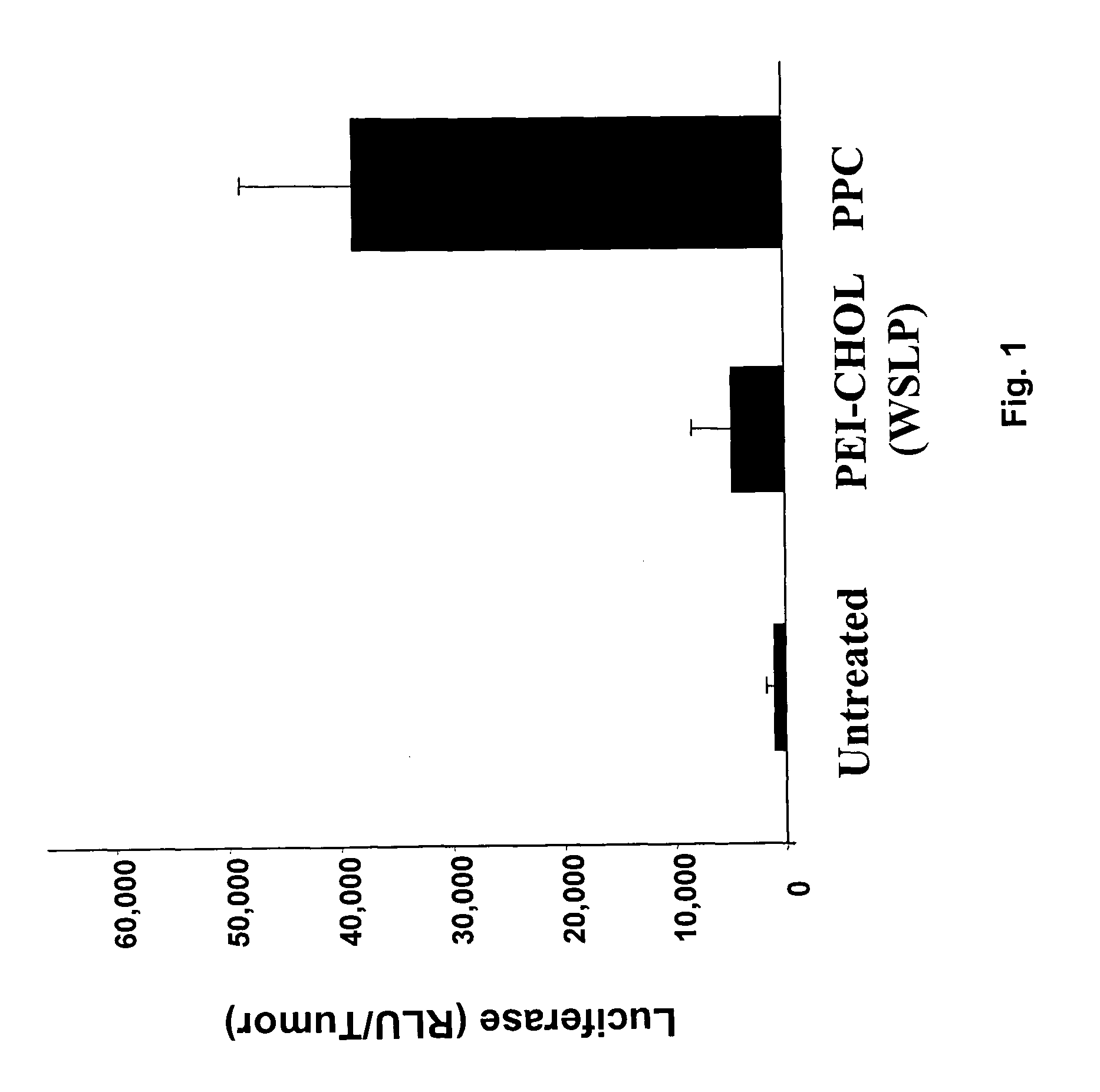
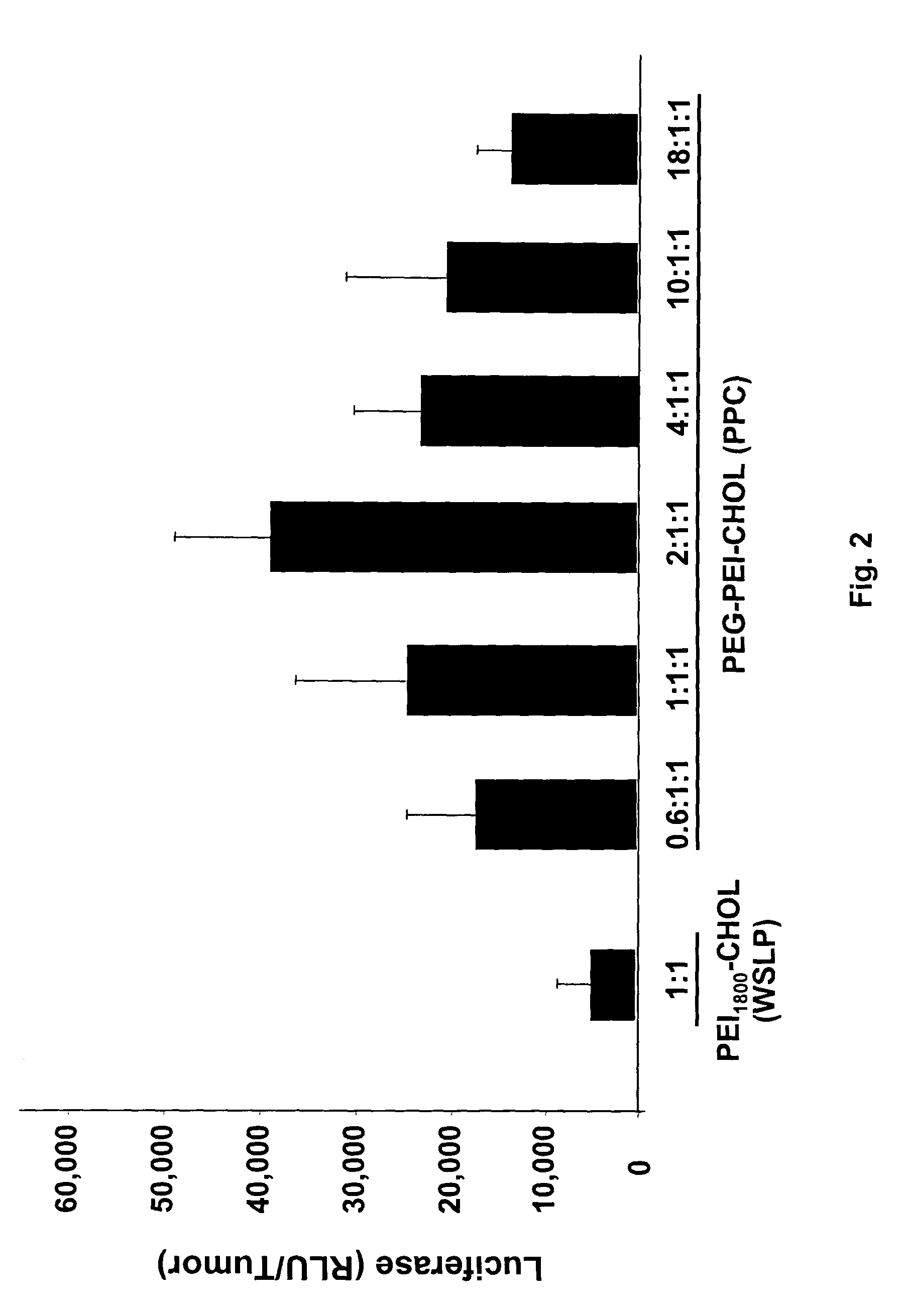
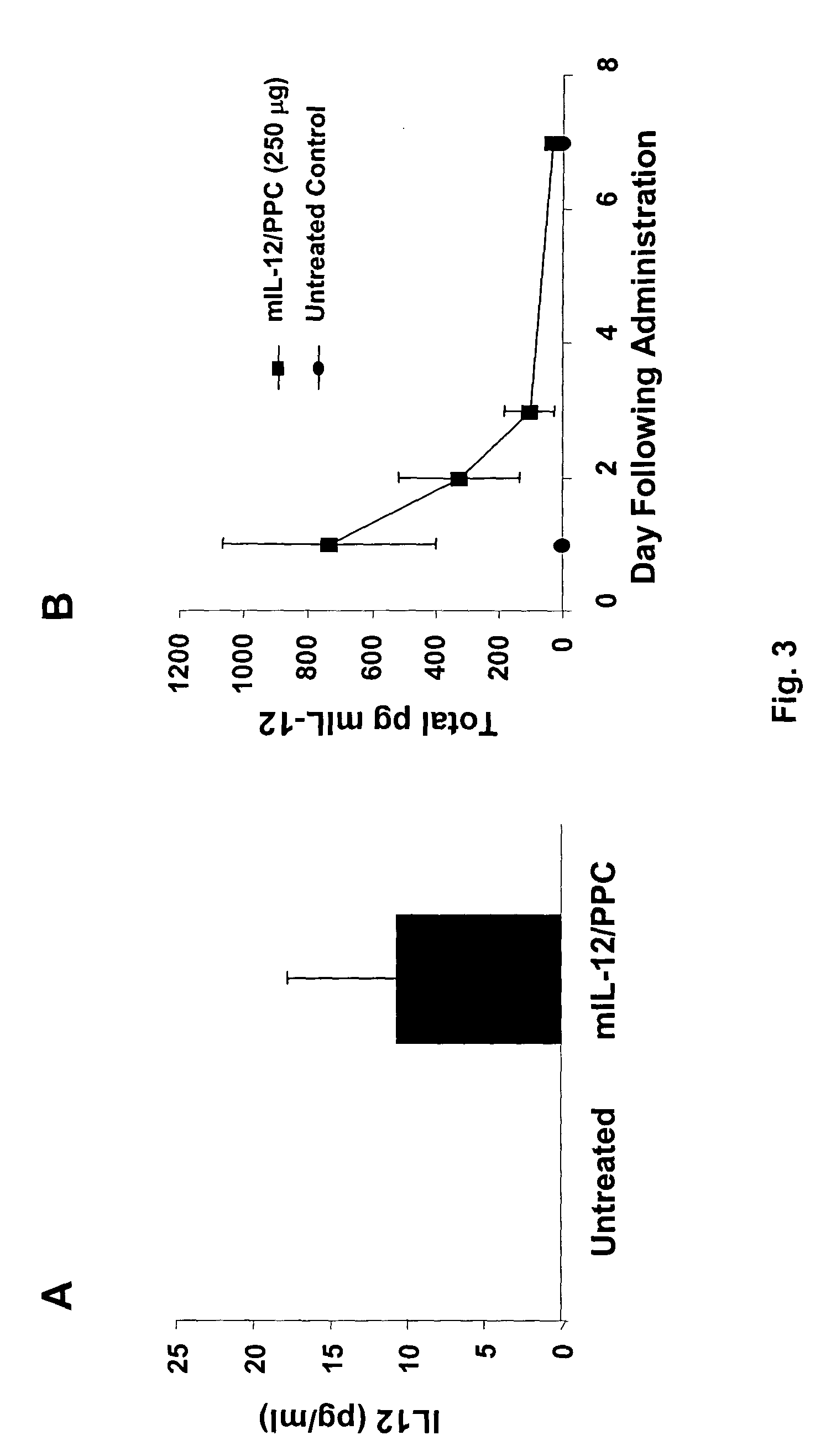
Methods for treating cancer using cytokine-expressing polynucleotides
InactiveUS7268120B1Improved in vivo polypeptide expressionMinimizing adverse side effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMammalSodium phosphates
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising a non-infectious, non-integrating polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an interferon ω and one or more cationic compounds. The present invention also provides methods of treating cancer in a mammal, comprising administering into a muscle of the mammal a non-infectious, non-integrating DNA polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding a cytokine. In addition, the present invention also relates to the methodology for selective transfection of malignant cells with polynucleotides expressing therapeutic or prophylactic molecules in intra-cavity tumor bearing mammals. More specifically, the present invention provides a methodology for the suppression of an intra-cavity dissemination of malignant cells, such as intraperitoneal dissemination. Furthermore, the invention relates to compositions and methods to deliver polynucleotides encoding polypeptides to vertebrate cells in vivo, where the composition comprises an aqueous solution of sodium phosphate.
Owner:VICAL INC
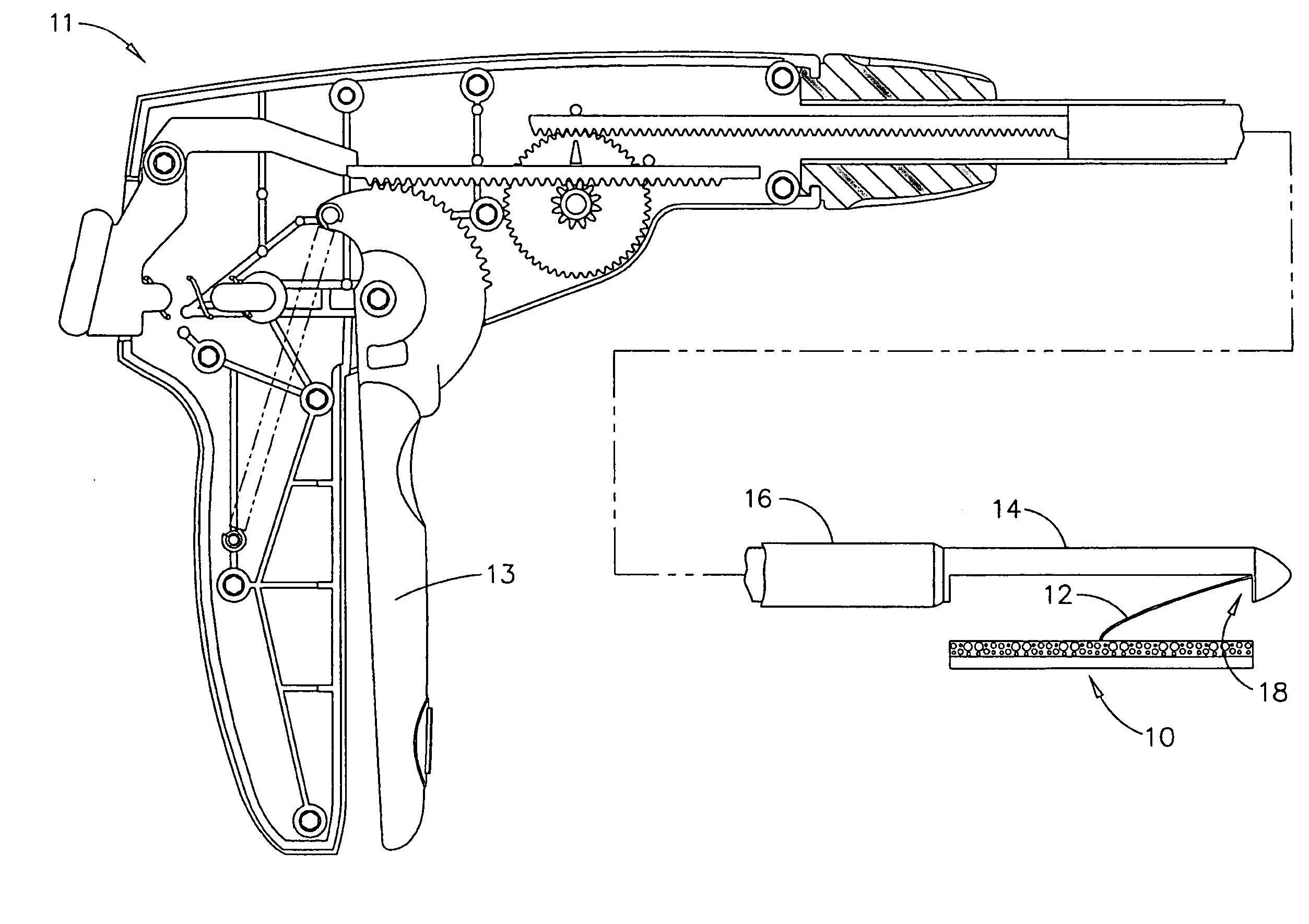
Insertable suture passing grasping probe and methodology for using same
InactiveUS6183485B1Quick controlEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgical departmentOperative incision
A surgical instrument, guide, and method capable of being used for closure of peritoneum fascia, occlusion of bleeding vessels such as inferior epigastric, and for all uses related to accurately passing suture material through a guide into tissue. A tip of a surgical instrument in a standard suture- / needle-driving position with a sharp tip that opens and closes with the surgeon grasping suture material with the sharp tip is provided. Insertion of the tip / suture through tissue until the tip is seen through the peritoneum by direct vision begins the wound-closing procedure. The suture is released by opening and withdrawing the tip from the guide. The suture is recovered by using the guide to redirect the tip and puncturing the tissue opposite the first point of insertion. The tip grasps the suture and pulls the suture through the guide. The suture is pulled outside the wound, providing for rapid closure of the surgical incision. The guide is insertable within the wound to be closed and guides the surgical instrument at a predetermined angle from the longitudinal axis of the guide for optimum wound closure. Alternative embodiments of the guide include providing a slot through which non-linear surgical instruments may pass through an open or enclosed passageway.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
Methods and apparatus for revision of obesity procedures
ActiveUS20070175488A1Lower the volumeReduce the overall diameterSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsStomaPeritoneal cavity
Methods and apparatus for the endoluminal revision of previously performed obesity procedures which have failed are described. One or more endoluminal instruments may be advanced per-orally into the previously formed failed pouch where a number of different procedures can be performed. One or more tissue folds can be formed and secured to reduce the size of the pouch, or the stoma connecting the pouch to the intestinal tract can be reduced in size using endoluminally deployed tissue anchors. These procedures can be performed entirely from within the pouch lumen or upon the exterior surface of the pouch via transgastric entry of the instruments into the peritoneal cavity of a patient. Alternatively, the interior tissue within the pouch can be injured or sclerosed to shrink the pouch lumen. In another alterative, a length of the Roux limb can be shortened endoluminally to create a malabsorptive region.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Combination of immuno gene therapy and chemotherapy for treatment of cancer and hyperproliferative diseases
ActiveUS7964571B2Inhibiting growth and metastasisImprove survivalHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryWhole body
Owner:CLSN LAB
Method and apparatus for anchoring implants
InactiveUS20060069400A1Reduce risk of migrationReduce intrusionStentsHeart valvesLaparoscopyTherapeutic Devices
Methods, devices and systems facilitate retention of a variety of therapeutic devices. Devices generally include an anchoring element, which has been designed to promote fibrotic ingrowth, and an anchored device, which has been designed to firmly engage the complementary region of the anchoring element. The anchoring element may be placed in a minimally invasive procedure temporally separated from the deployment of the anchored device. Once enough time has passed to ensure appropriate fixation of the anchoring element by tissue and cellular ingrowth at the site of placement, the anchored device may then be deployed during which it firmly engages the complementary region of the anchoring element. In this manner, a firm attachment to the implantation site may be made with a minimum of required hardware. Some embodiments are delivered through a delivery tube or catheter and while some embodiments may require laparoscopy or open surgery for one or more of the placement procedures. Some embodiments anchor devices within the cardiovascular tree while others may anchor devices within the gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleural, pulmonary, urogynecologic, nasopharyngeal or dermatologic regions of the body.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Transmuscular left ventricular cardiac stimulation leads and related systems and methods
InactiveUS20100069983A1Increase contractilityTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac stimulation system and method delivers a left ventricle stimulator from a right ventricle lead system in the right ventricle chamber, into a right side of an interventricular septum at a first location, and transmuscularly from the first location to a second location along the left side of the septum. The left ventricle stimulator is affixed at the second location for transmuscular stimulation of the left ventricle conduction system. A biventricular stimulation system further includes a right ventricle stimulator also delivered by the right ventricle lead system to the first location along the right side of the septum for right ventricular stimulation. An energy source is coupled to the transmuscular stimulation system, i.e., a pacemaker, and / or defibrillator, or to enhance contractility, and may be coupled directly or via “leadless” system(s). Various highly beneficial particular arrangements of stimulators and leads are further described.
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body
InactiveUS20050165276A1Avoid excessive forceAccurately advancedEndoscopesLaproscopesThoracic structureAutomatic control
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body are disclosed herein. Using an endoscopic device having an automatically controllable proximal portion and a selectively steerable distal portion, the device generally may be advanced into the body through an opening. The distal portion is selectively steered to assume a selected curve along a desired path within the body which avoids contact with tissue while the proximal portion is automatically controlled to assume the selected curve of the distal portion. The endoscopic device can then be used for accessing various regions of the body which are typically difficult to access and treat through conventional surgical techniques because the device is unconstrained by “straight-line” requirements. Various applications can include accessing regions of the brain, thoracic cavity, including regions within the heart, peritoneal cavity, etc., which are difficult to reach using conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
Method and apparatus for performing maxillary sinus elevation
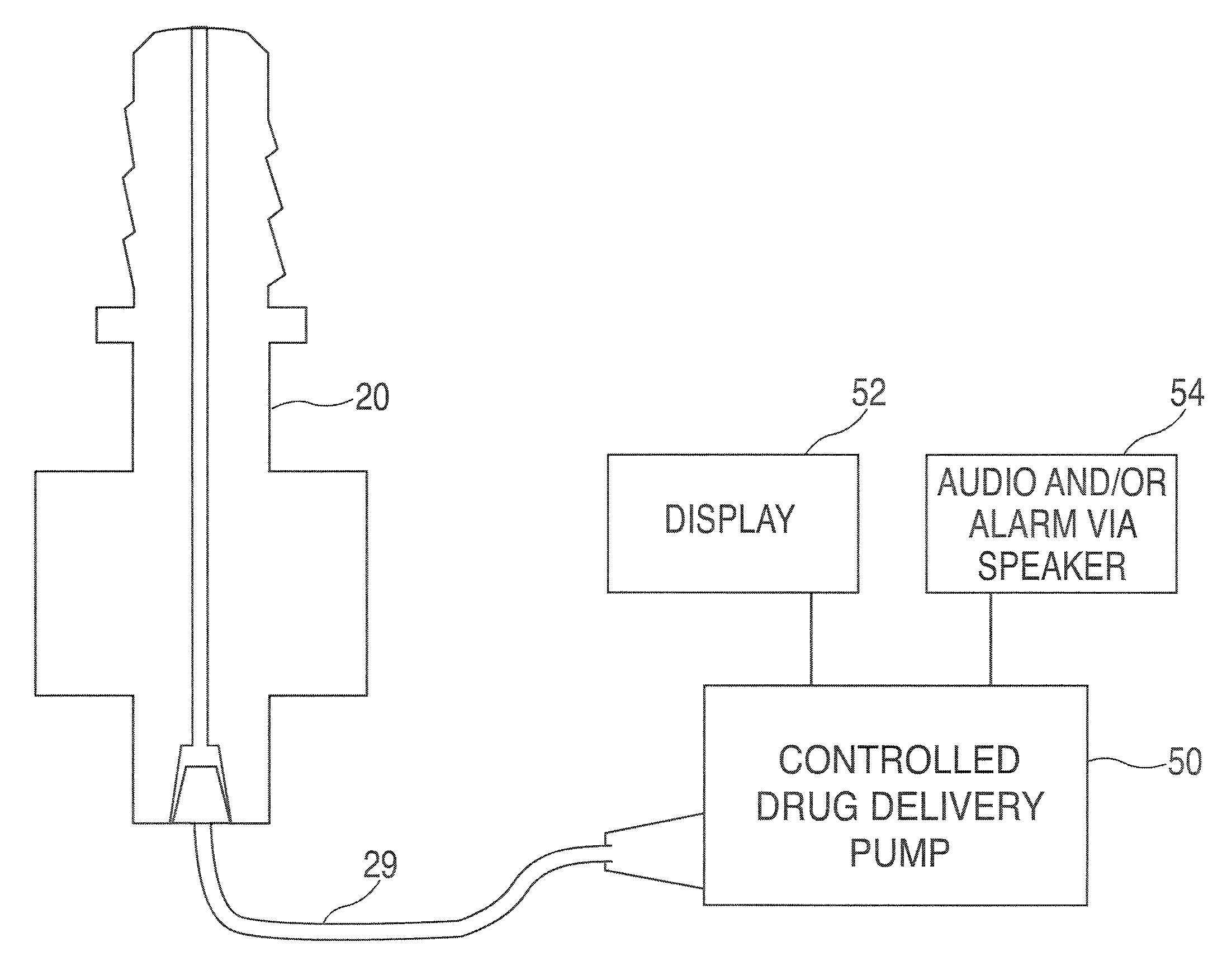
InactiveUS7510397B2Miss massEffective placementDental implantsFastening prosthesisPeritoneumBiomedical engineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for providing implants in the upper jaws of a person. A sleeve is inserted through the alveolar ridge to the maxillary sinus. The sleeve is used to raise the subantral membrane and form a cavity. A filler, such as a bone growth stimulant is injected through the sleeve into the cavity. In the process, the sleeve also can cut and / or condense the bone around itself so that the bone can hold an implant. Optionally, the bone growth stimulant is also introduced into the bone surrounding the sleeve. During the injection, the pressure within the sleeve or the cavity is monitored to detect and prevent the rupture of the subantral membrane.
Owner:HOCHMAN MARK N
Methods and compositions for treating mammalian nerve tissue injuries
ActiveUS20050069520A1Promote recoveryLoss in its effectivenessNervous disorderSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsIntraperitoneal routeIn vivo
To achieve, an in vivo repair of injured mammalian nerve tissue, an effective amount of a biomembrane fusion agent is administered to the injured nerve tissue. The application of the biomembrane fusion agent may be performed by directly contacting the agent with the nerve tissue at the site of the injury. Alternatively, the biomembrane fusion agent is delivered to the site of the injury through the blood supply after administration of the biomembrane fusion agent to the patient. The administration is preferably by parenteral administration including including intravascular, intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intraperitoneal injection of an effective quantity of the biomembrane fusion agent so that an effective amount is delivered to the site of the nerve tissue injury.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
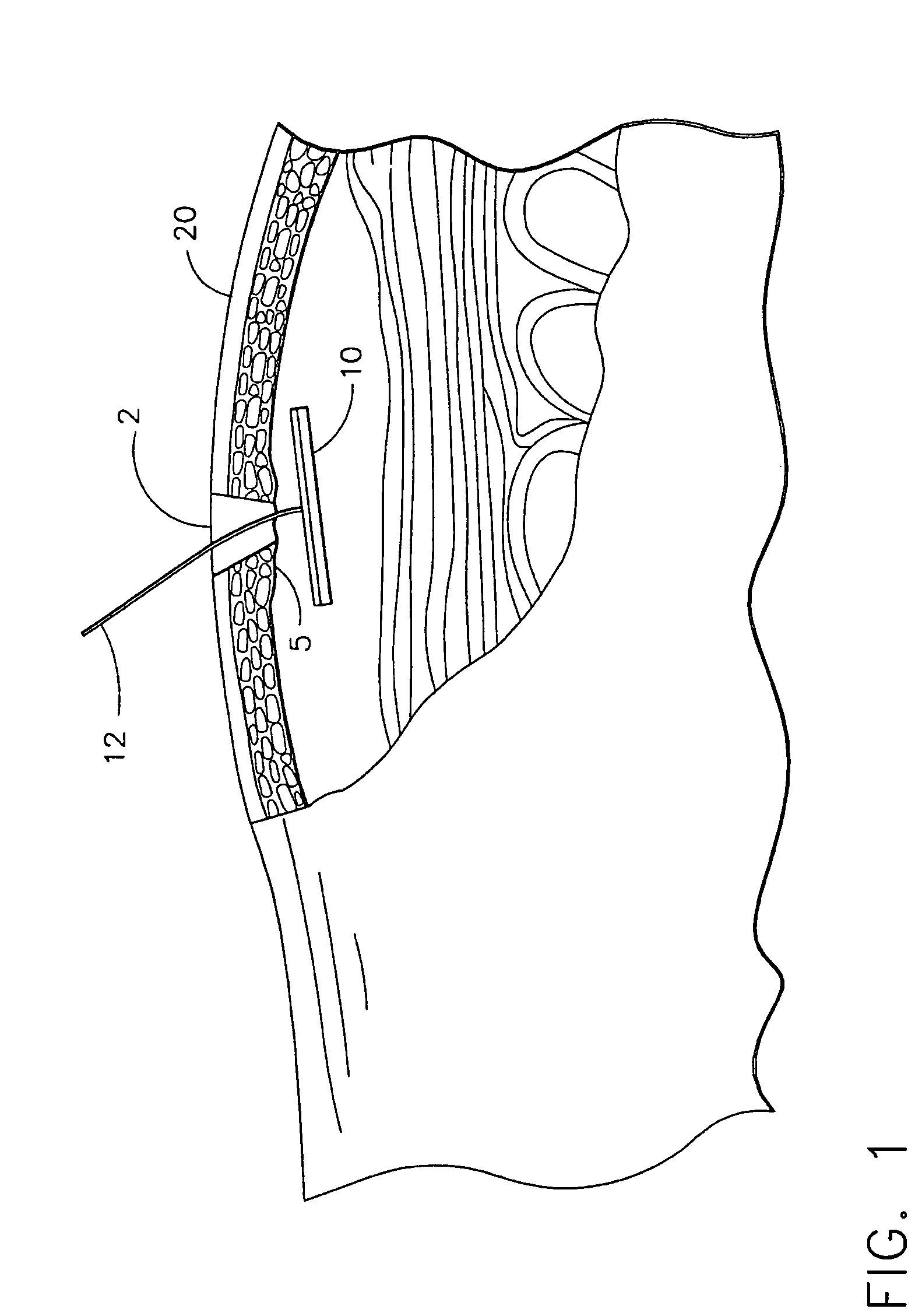
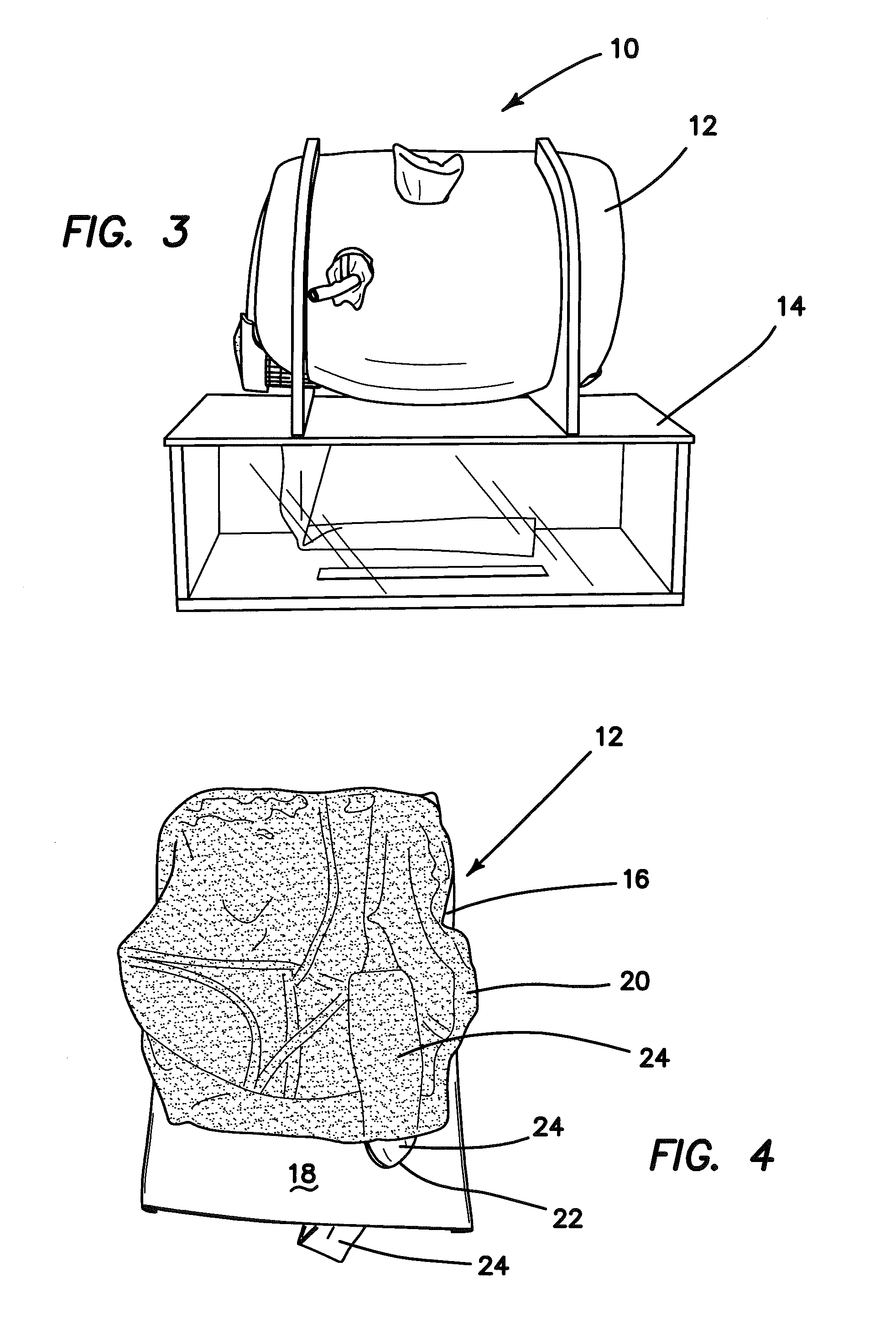
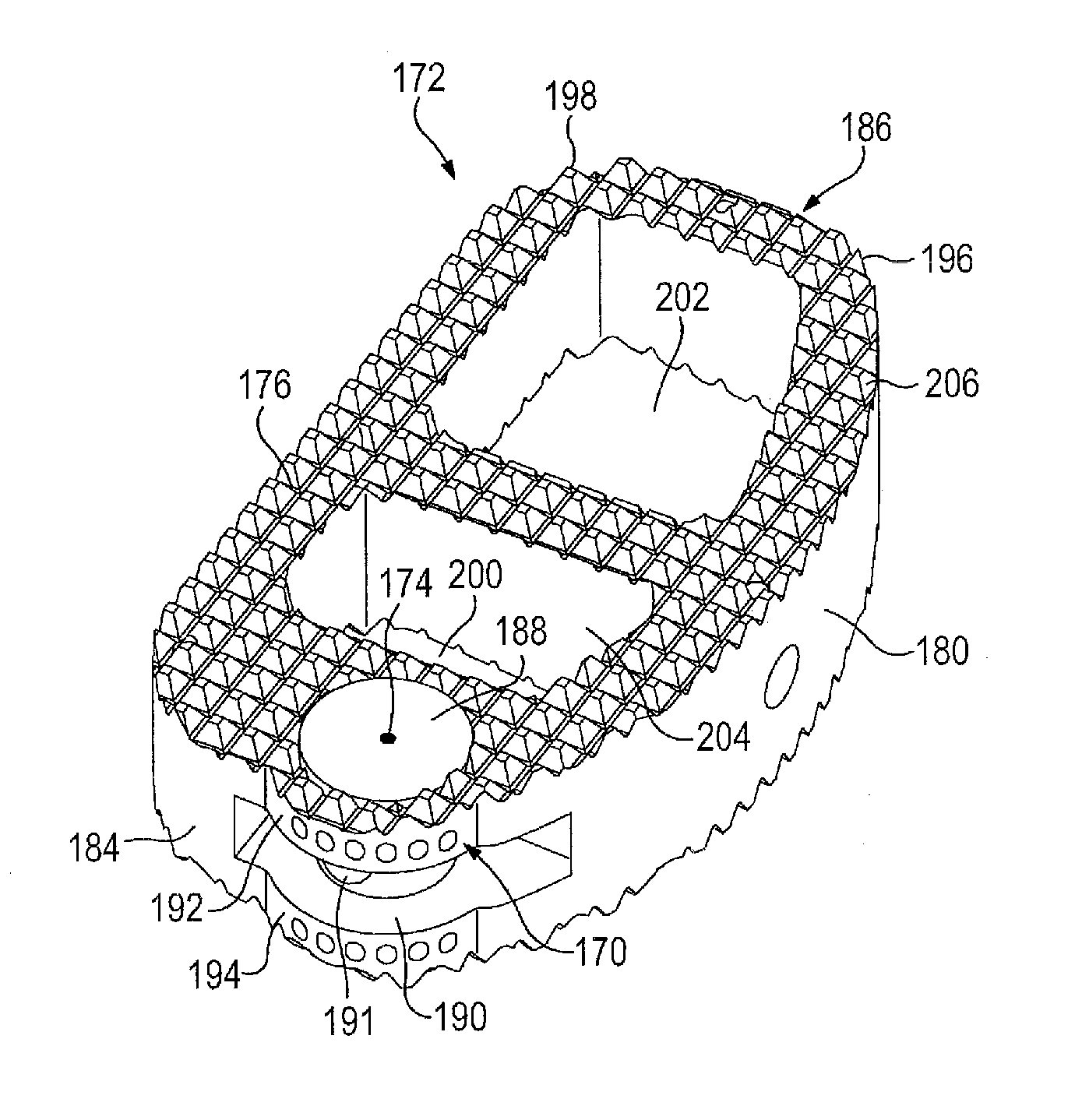
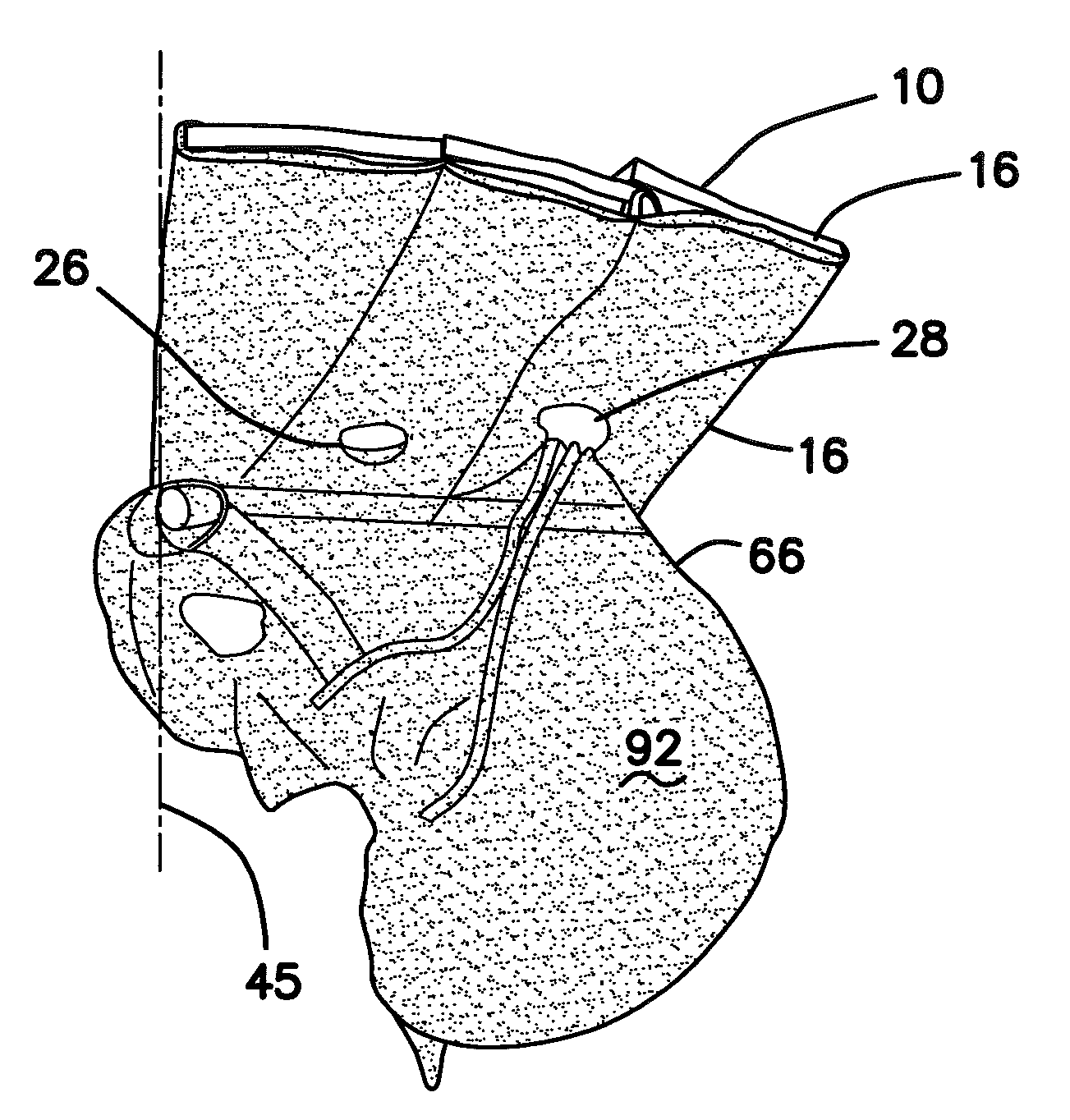
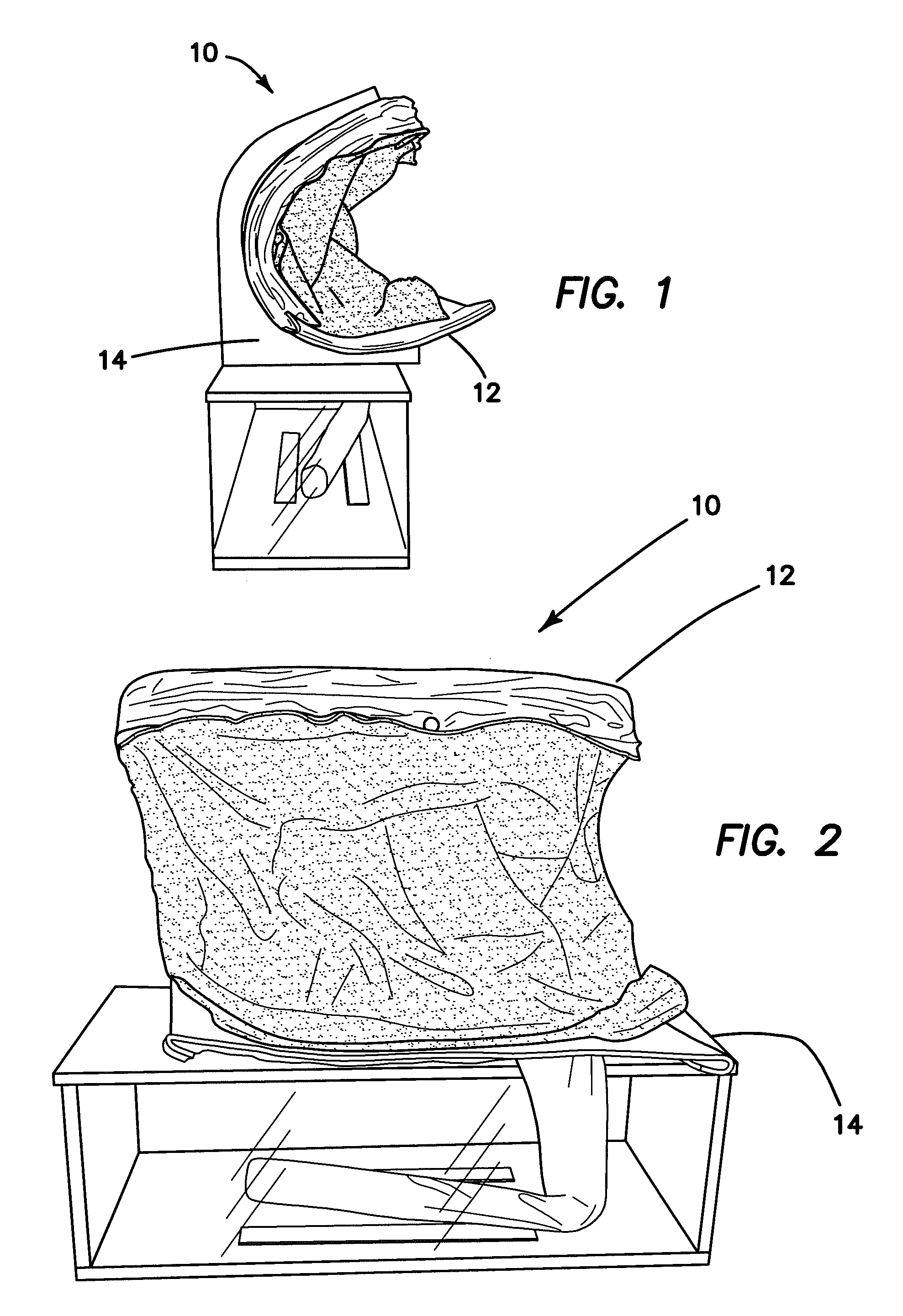
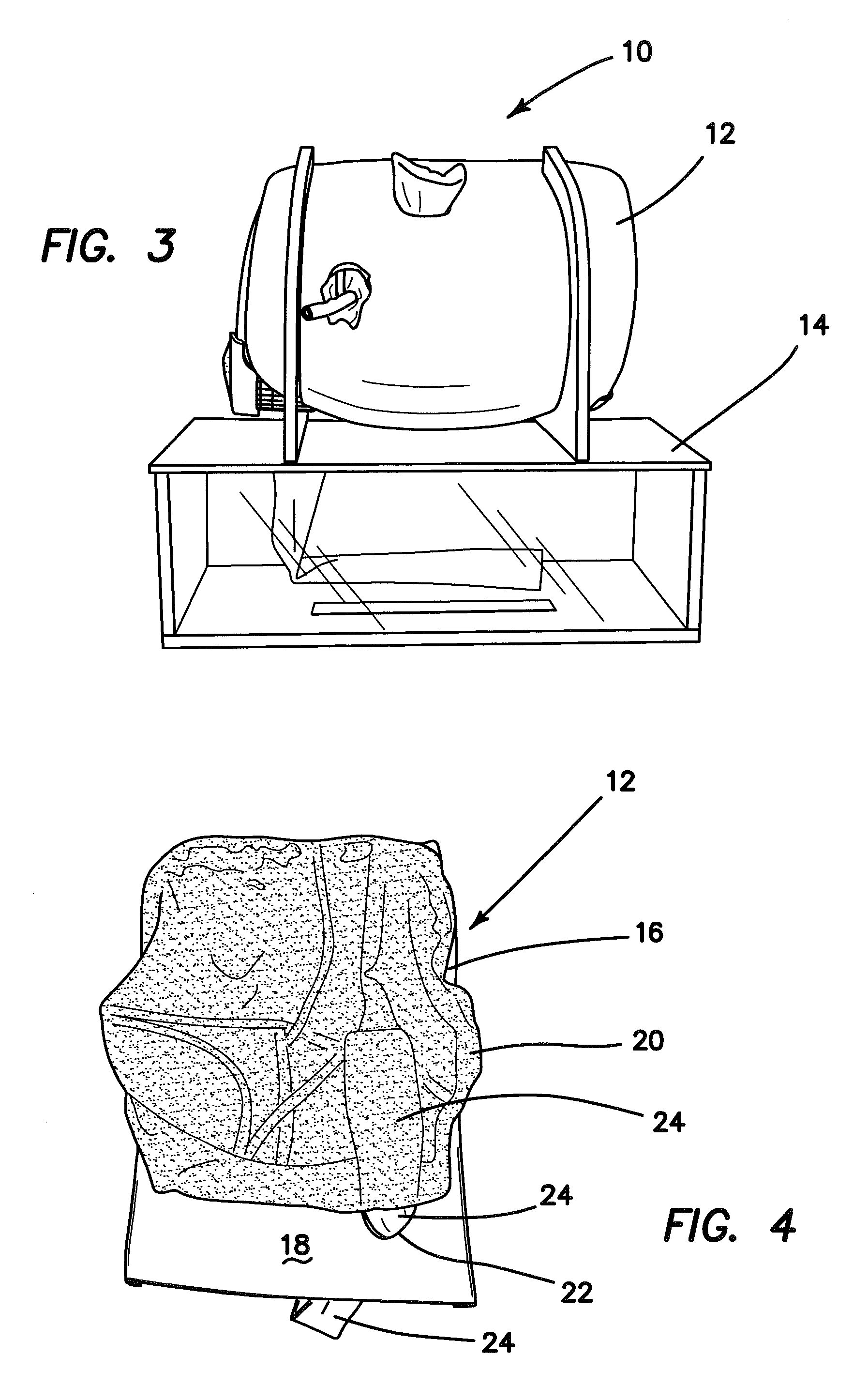
Hernia model
ActiveUS20140342334A1Safely repairRealistic resiliencyEducational modelsAnatomical structuresTransabdominal preperitoneal
A model for practicing transabdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) and total extraperitoneal (TEP) approaches for laparoscopic hernia repairs is provided. The model simulates an insufflated space between the abdominal muscles and peritoneum. A spring layer may be incorporated to provide a realistic resiliency to the model while in the simulated insufflated configuration. At least one hole is provided in the model from which synthetic tissue protrudes to simulate a hernia. The model is used to selectively simulate direct, indirect and femoral inguinal hernias as well as incisional hernias by removably placing the protruding simulated tissue into any one of several openings. The model contains all important anatomical structures and sits on a base frame or is connected to a rigid simulated pelvis. When located inside a laparoscopic trainer with an angled top cover, the model provides an ideal simulation for teaching and practicing laparoscopic hernia repair.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
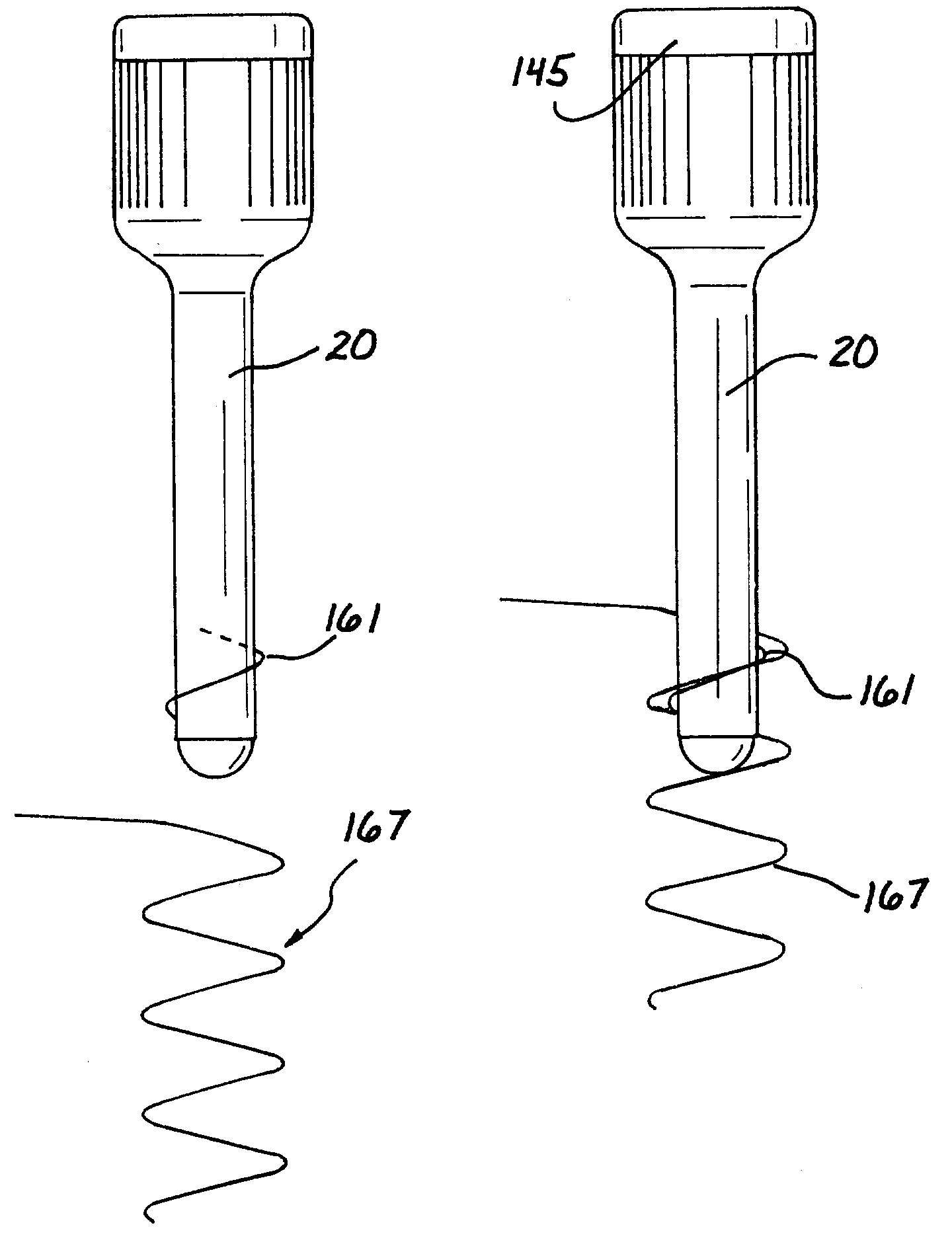
Surgical access apparatus and method
InactiveUS7070586B2Improve visualizationAvoid attenuationCannulasInfusion syringesEngineeringAbdominal wall
A trocar system for providing access across a body wall includes a trocar and an anchor provided in the form of a first helix. The anchor is adapted for placement in an operative position wherein the anchor extends at least partially through the body wall. A second helix formed on the trocar is size and configured to engage the first helix of the anchor so that rotation of the trocar relative to the anchor moves the second helix along the first helix. In this manner, the trocar is drawn into the anchor as it moves into the body wall. A proximal force applied to the anchor resists tenting of the abdominal wall. The anchor also holds the layers of the body wall together thereby resisting peritoneal separation.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Apparatus and methods for early stage peritonitis detection and for in vivo testing of bodily fluid
InactiveUS20080183126A1Easy to cleanIncreased turbulenceDiagnostics using lightMedical devicesFiberIn vivo
The invention provides, inter alia, automated medical methods and apparatus that test PD effluent in a flow path (e.g., with an APD system or CAPD setup) to detect, for example, the onset of peritonitis, based on optical characteristics of the effluent resolved at cellular scales of distance. For example, according to one aspect of the invention, an APD machine includes, in an effluent flow path, apparatus for early stage peritonitis detection comprising an illumination source and a detector. The source is arranged to illuminate peritoneal effluent in a chamber that forms part of the flow path, and the detector is arranged to detect illuminant scattered by the effluent. The detector detects that reflected or scattered illuminant at a cellular scale of resolution, e.g., on a scale such that separate cellular-sized biological (or other) components in the effluent can be distinguished from one another based on scattering events detected by the detector. Other aspects of the invention provide automated medical testing methods and apparatus that detect the onset of peritonitis and other bodily conditions by testing fluids in the body in vivo, e.g., the patient's peritoneum. Such apparatus and methods utilize a first fiber optic bundle to carry illuminant from a source of the type described above into a bodily organ or cavity, and a second fiber optic bundle to carry illuminant scattered by fluid in that organ or cavity to a detector as described above.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Spinal implant for use during retroperitoneal lateral insertion procedures
InactiveUS20120010717A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral space
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:SPANN SCOTT
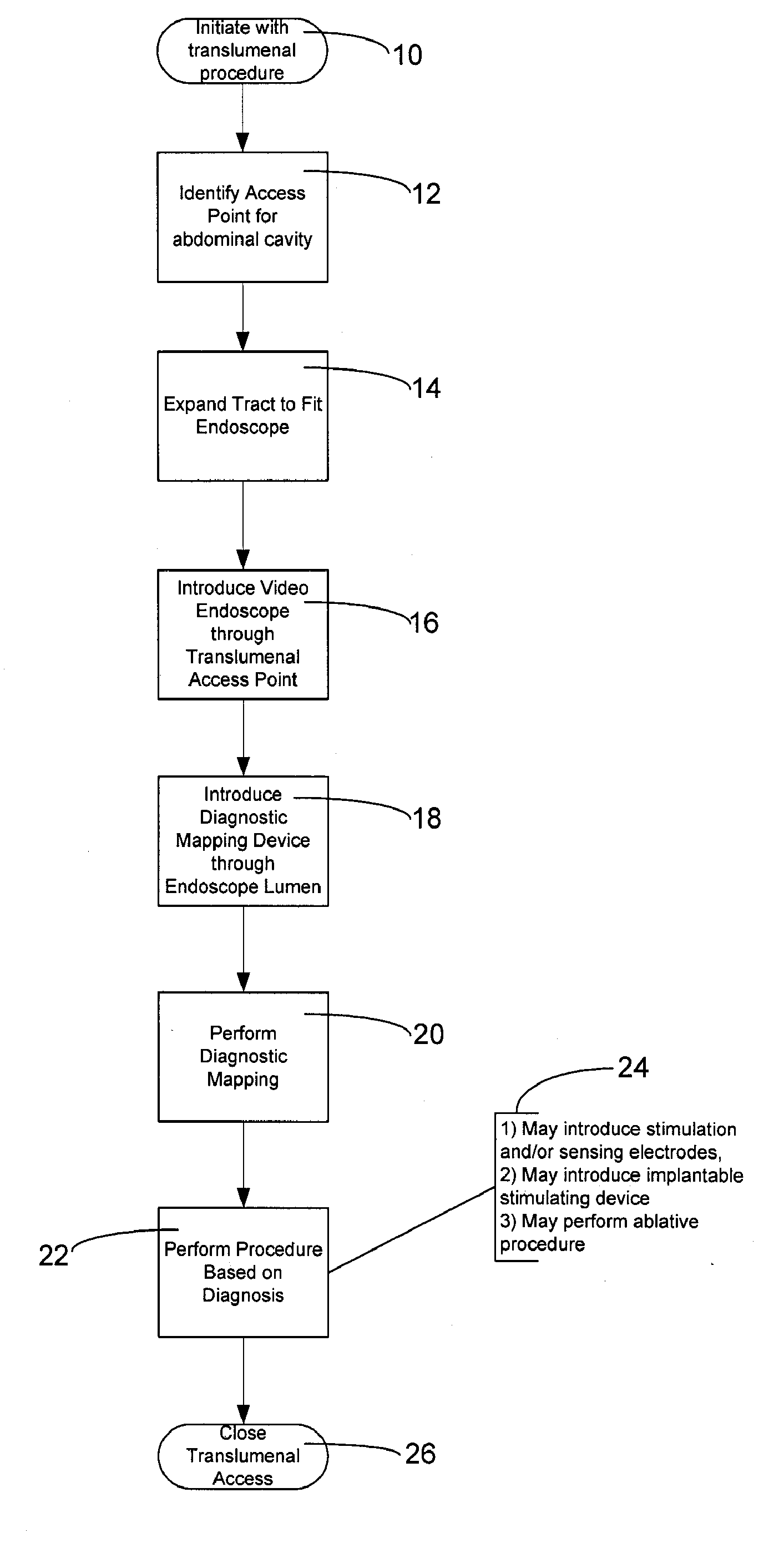
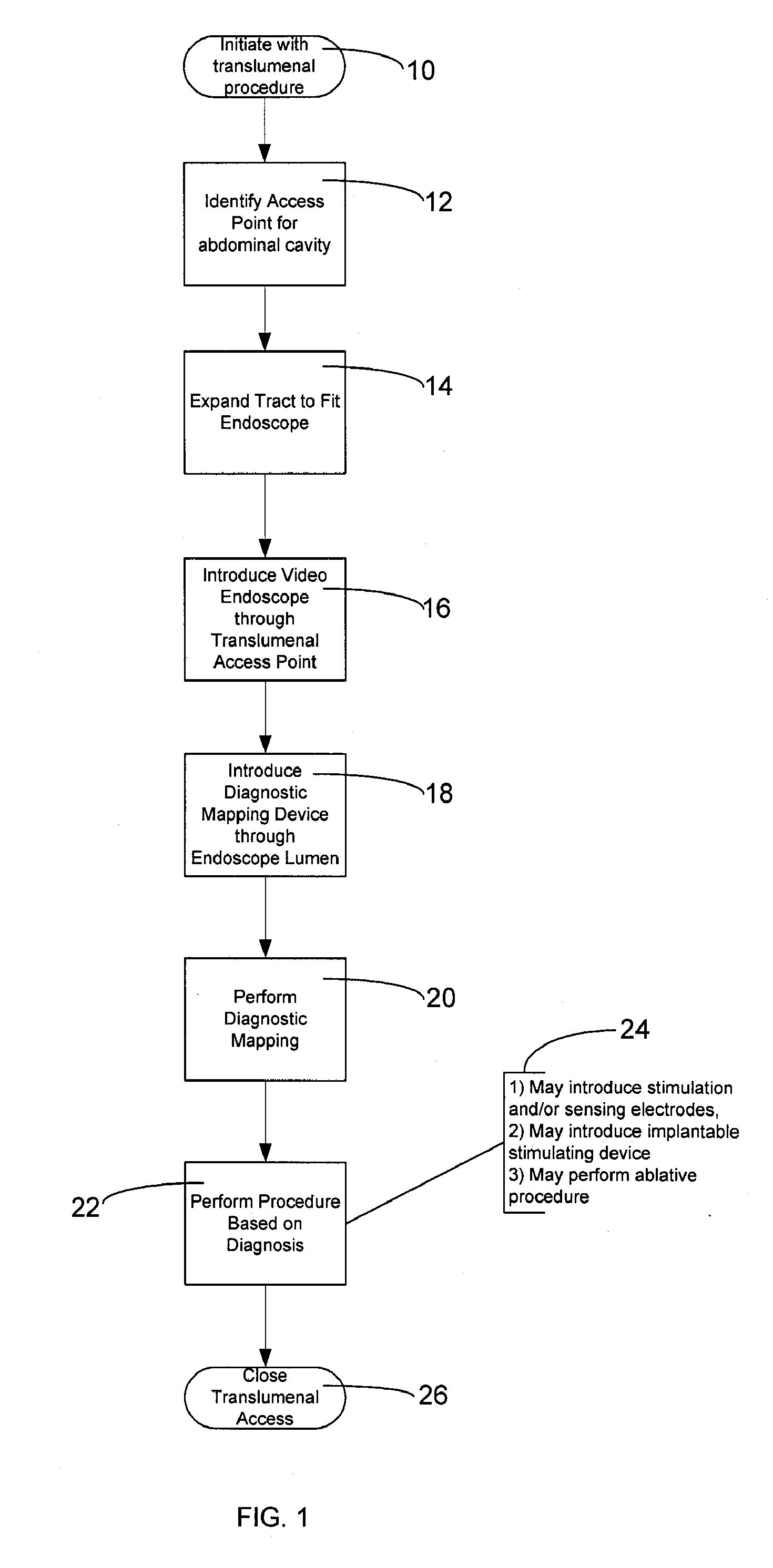
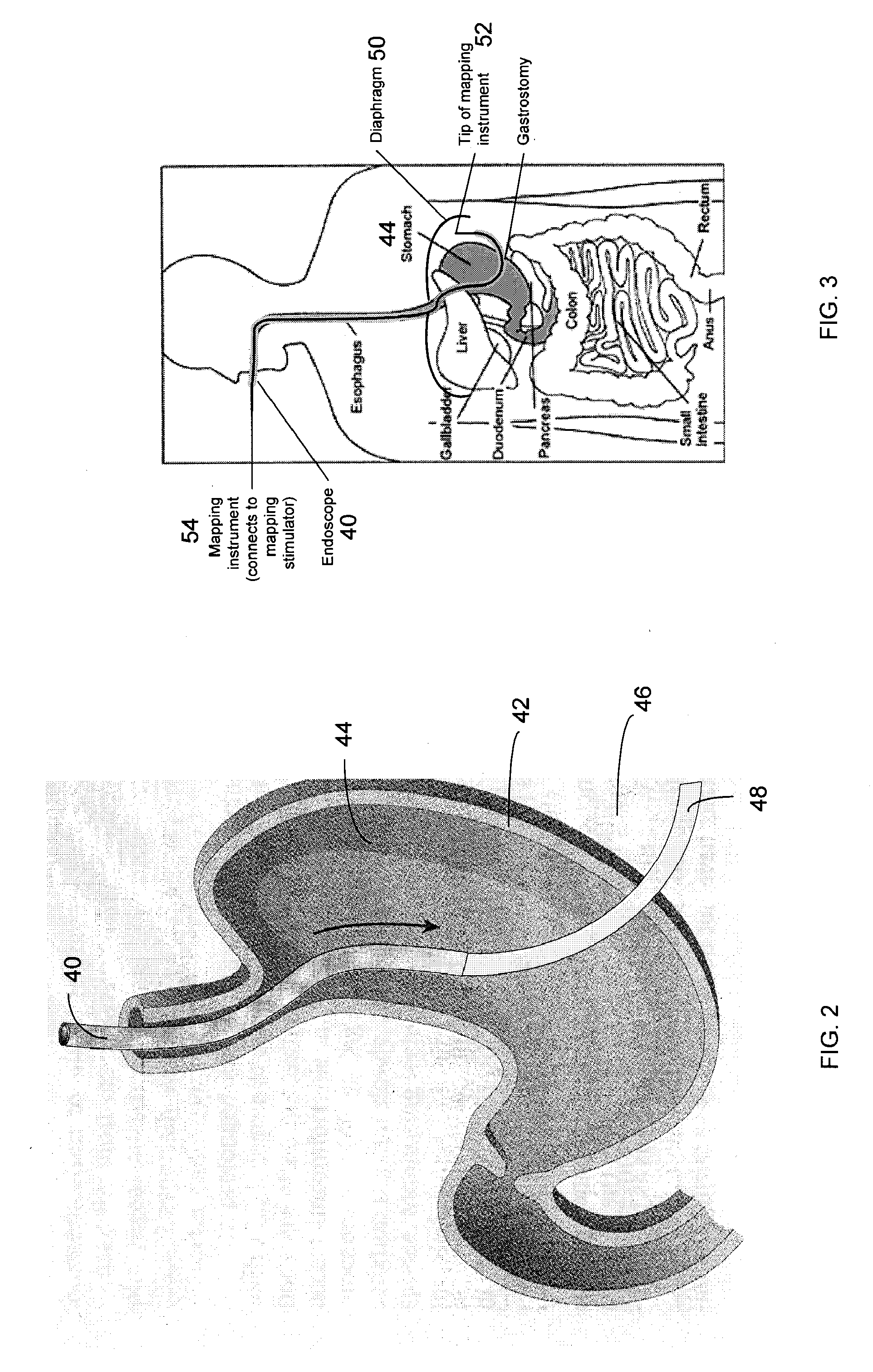
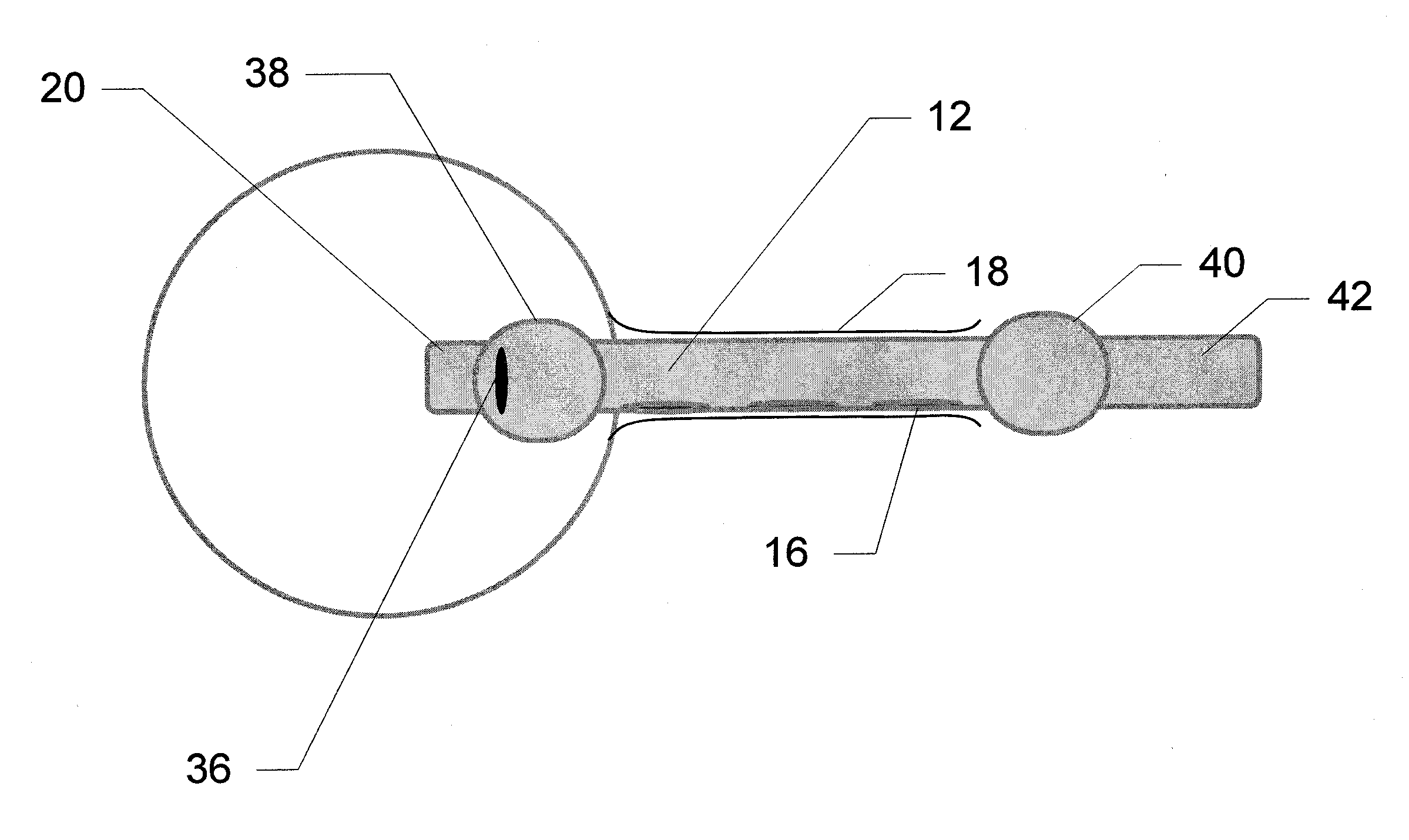
Method And Apparatus For Transgastric Neurostimulation
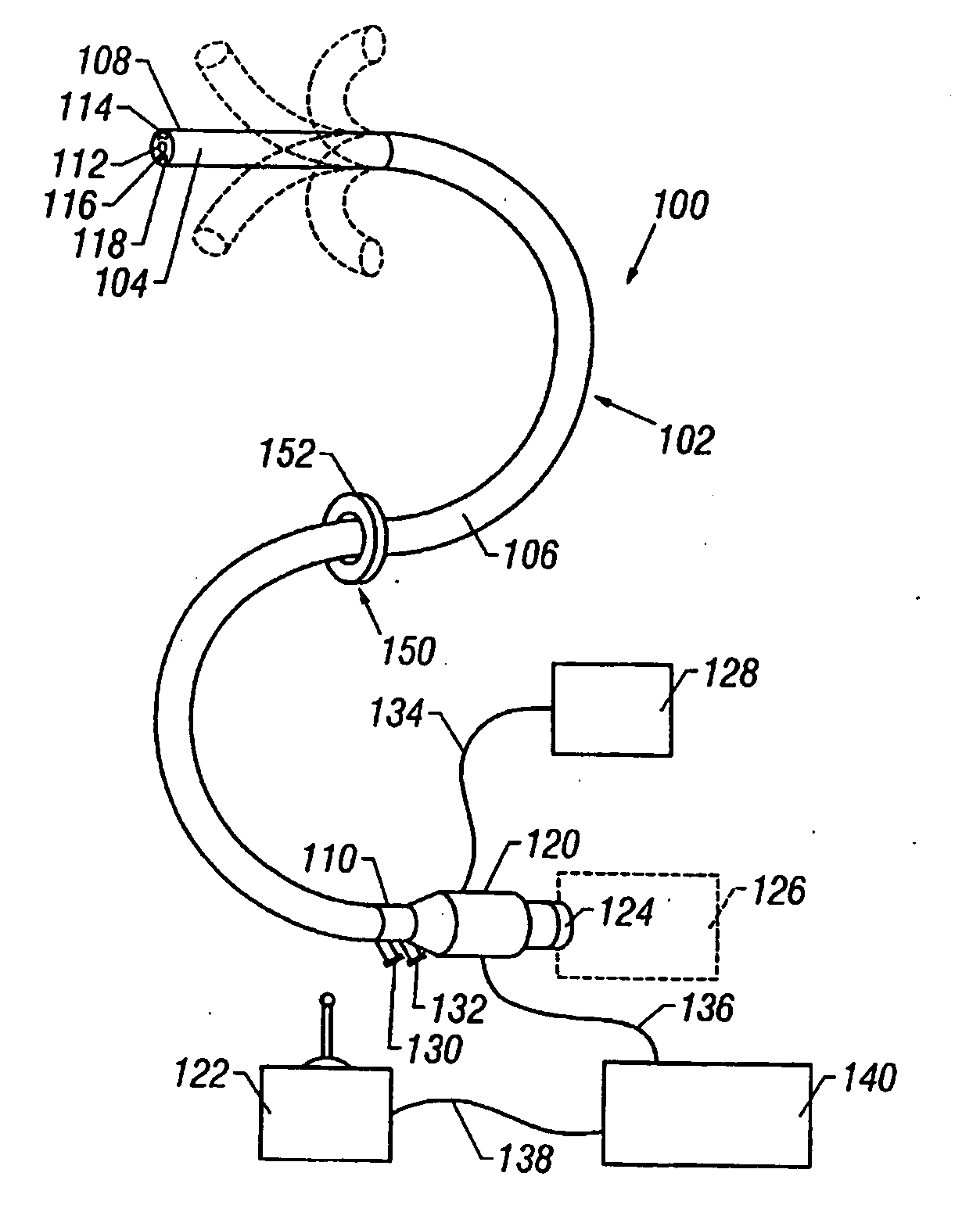
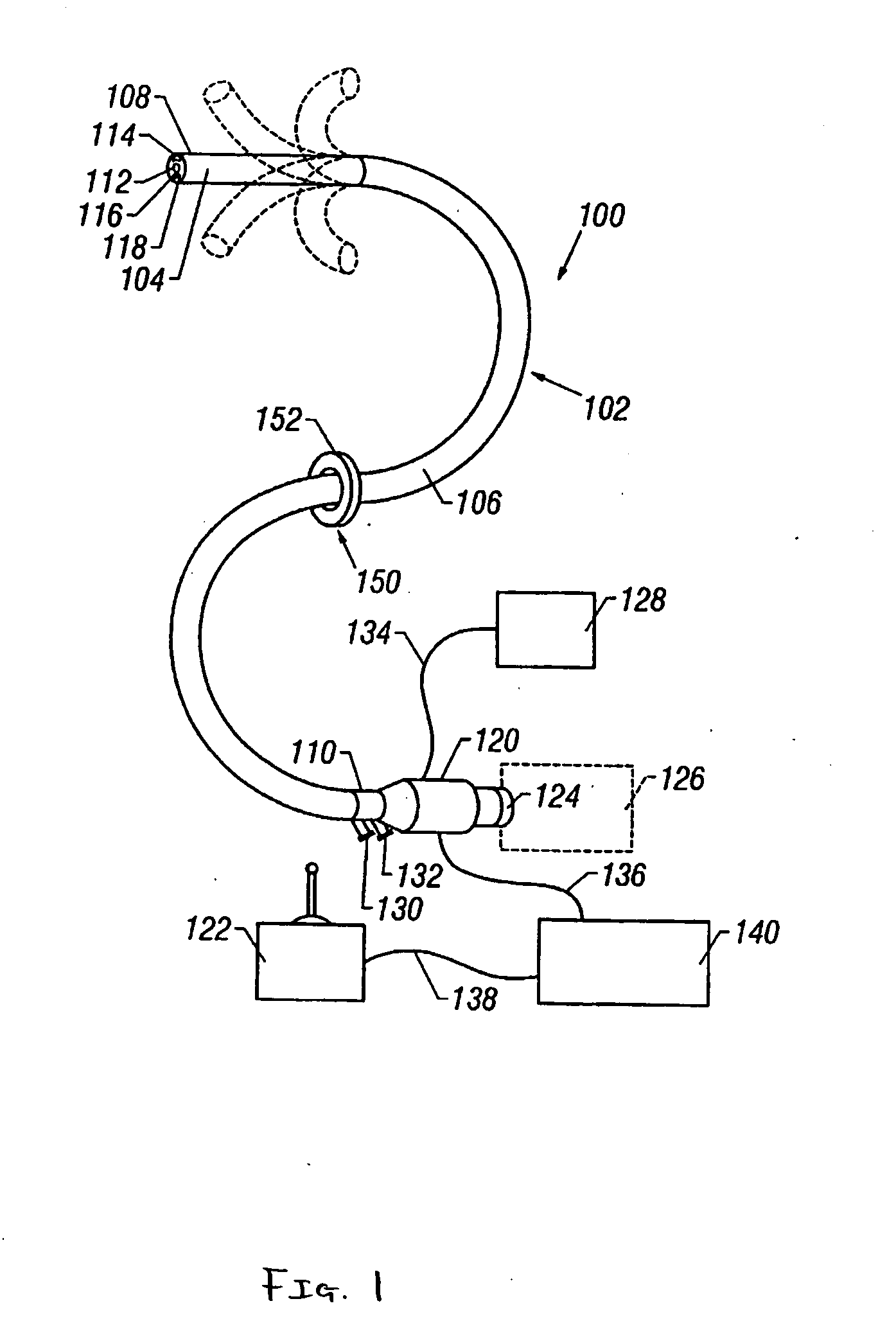
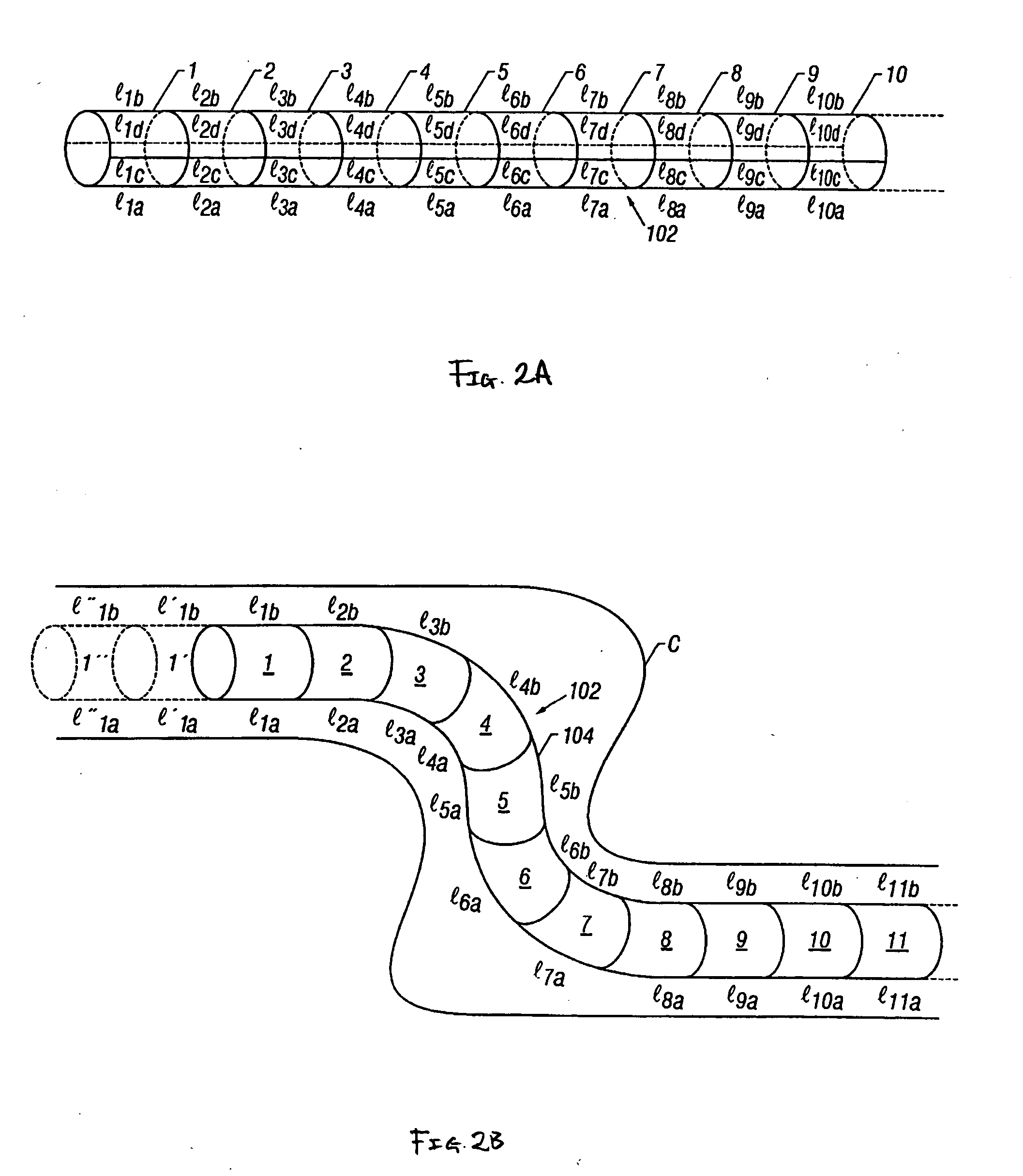
A method of placing an electrode in a peritoneal cavity including the following steps: inserting an endoscope through a patient's mouth into the patient's stomach; passing the endoscope through an opening in the stomach into the peritoneal cavity; and using the endoscope to place the electrode in contact with tissue within the peritoneal cavity other than stomach tissue. Another aspect of the invention provides a method of electrically mapping tissue accessed from a peritoneal cavity including the following steps: inserting an endoscope through a patient's mouth into the patient's stomach; passing the endoscope through an opening in the stomach into the peritoneal cavity; passing an electrode through the endoscope; placing the electrode in contact with tissue within the peritoneal cavity other than stomach tissue; and applying a mapping stimulation signal to the electrode from a mapping stimulator.
Owner:SYNAPSE BIOMEDICAL INC
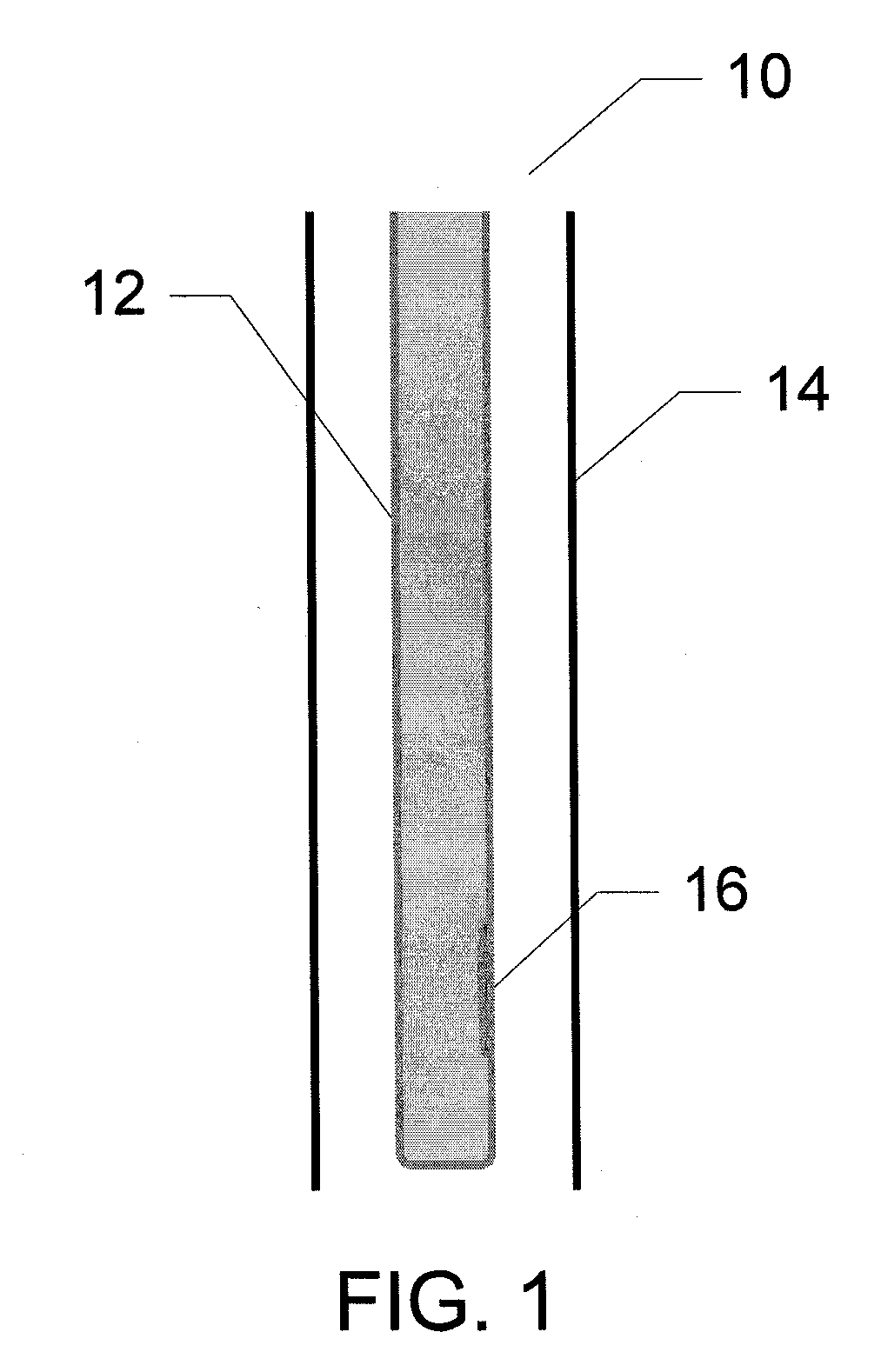
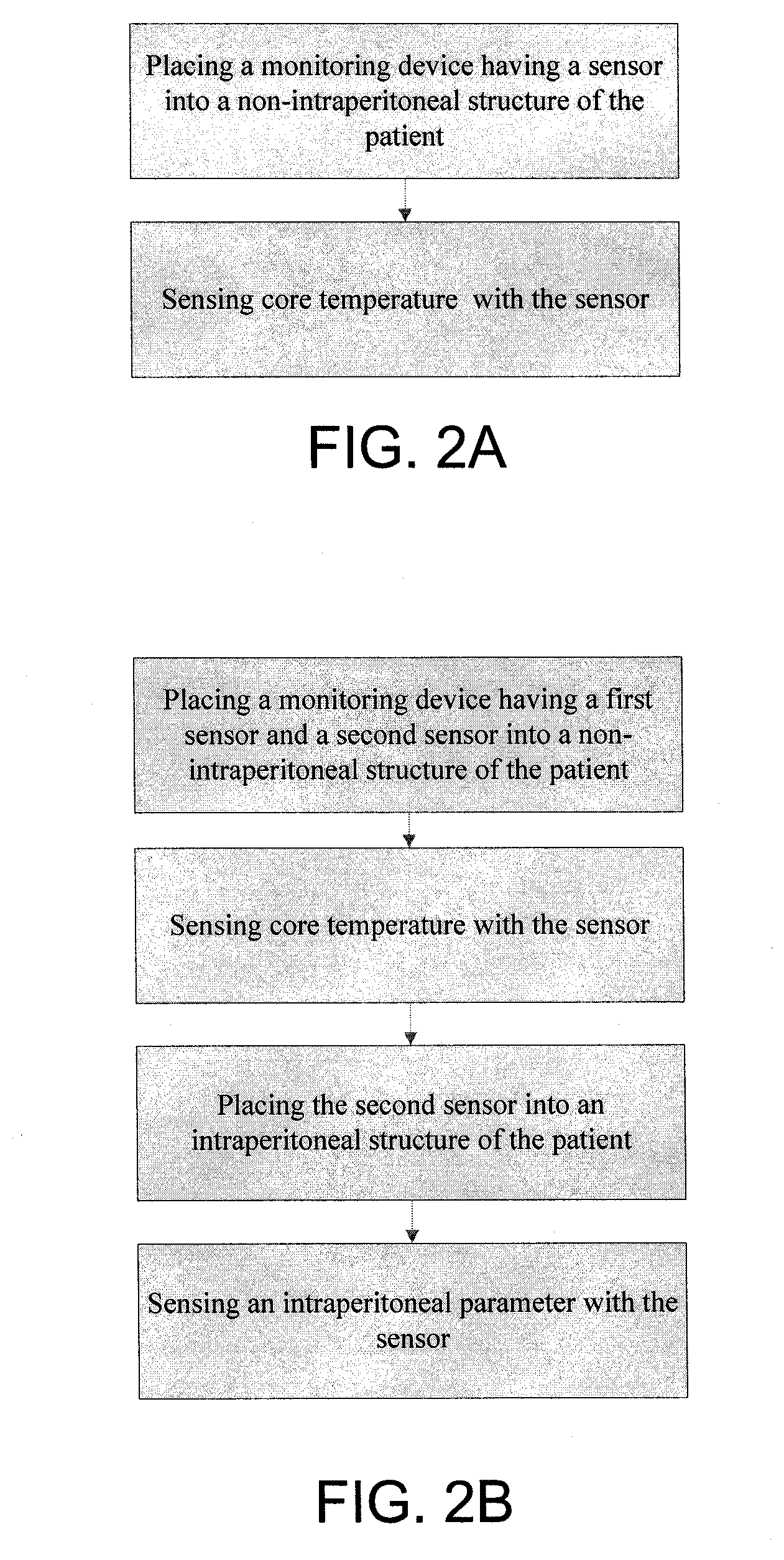
Devices and Methods for Monitoring Core Temperature and an Intraperitoneal Parameter
Methods and apparatus for monitoring core temperature of a patient receiving intraperitoneal hypothermia or hyperthermia are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is placing a monitoring device having a sensor into a non-intraperitoneal cavity of a patient. The non-intraperitoneal cavity can be a urethra, a rectum, an anal sphincter, a stomach, an esophagus, the peripheral vasculature, or a vagina, for example. Another feature is sensing core temperature of the patient with the sensor.
Owner:VELOMEDIX
Methods and apparatus for natural orifice vaginal hysterectomy
InactiveUS8025670B2Great flexingAssist with structureSuture equipmentsMale contraceptivesPeritoneal spaceEndometrium
A transuterine cannula through which an endoscope can be advanced into the peritoneal space to provide visualization of tissue cutting in the peritoneal space pursuant to a vaginal hysterectomy.
Owner:MINOS MEDICAL
Viscera retainers, surgical drains and methods for using same
InactiveUS20060241689A1Easy to disassembleEasy to separateSuture equipmentsWound drainsResidual bodySurgical drains
Viscera retainer which facilitates wound closure, for example, in the abdominal region, includes a body portion containing a tear seam. The body portion is inserted into the wound prior to closure to act as a physical barrier between the peritoneum and the viscera. A free extension of the body, or an attachment to the body, remains accessible outside the wound while a membranous layer of the abdominal wall is closed. When that closure is almost complete, the body portion is withdrawn from the abdomen by extracting it as a continuous ribbon through an opening. As the ribbon is withdrawn, the body tears along the tear seam generating free ribbon and shrinking the size of the residual body, until the entire body is removed from the abdominal cavity. The closure is then completed. A surgical drain has a planar body portion formed from a wound or wrapped tubular form having perforations in the body portion.
Owner:LEIBOFF ARNOLD R +1
Systems and methods for treating chronic liver failure based on peritoneal dialysis
ActiveUS20130211322A1Reduce the burden onOvercomes drawbackMedical devicesCatheterArtificial liverTransceiver
An artificial liver system for treating liver failure includes a reservoir to provide albumin-containing dialysis fluid to the patient's peritoneum, an implantable device including a pump to pump the fluid from the peritoneum to the bladder via respective catheters, control circuitry, battery and transceiver; a charging and communication system configured to periodically charge the battery and communicate with the implantable device to retrieve data reflective of the patient's health; and monitoring and control software, suitable for use with conventional personal computers, for configuring and controlling operation of the implantable device and charging and communication system. The monitoring and control software allows a treating physician to remotely adjust the volume, time, and frequency with which fluid is pumped from the peritoneal cavity to the bladder based on the data reflective of the patient's health.
Owner:SEQUANA MEDICAL NV
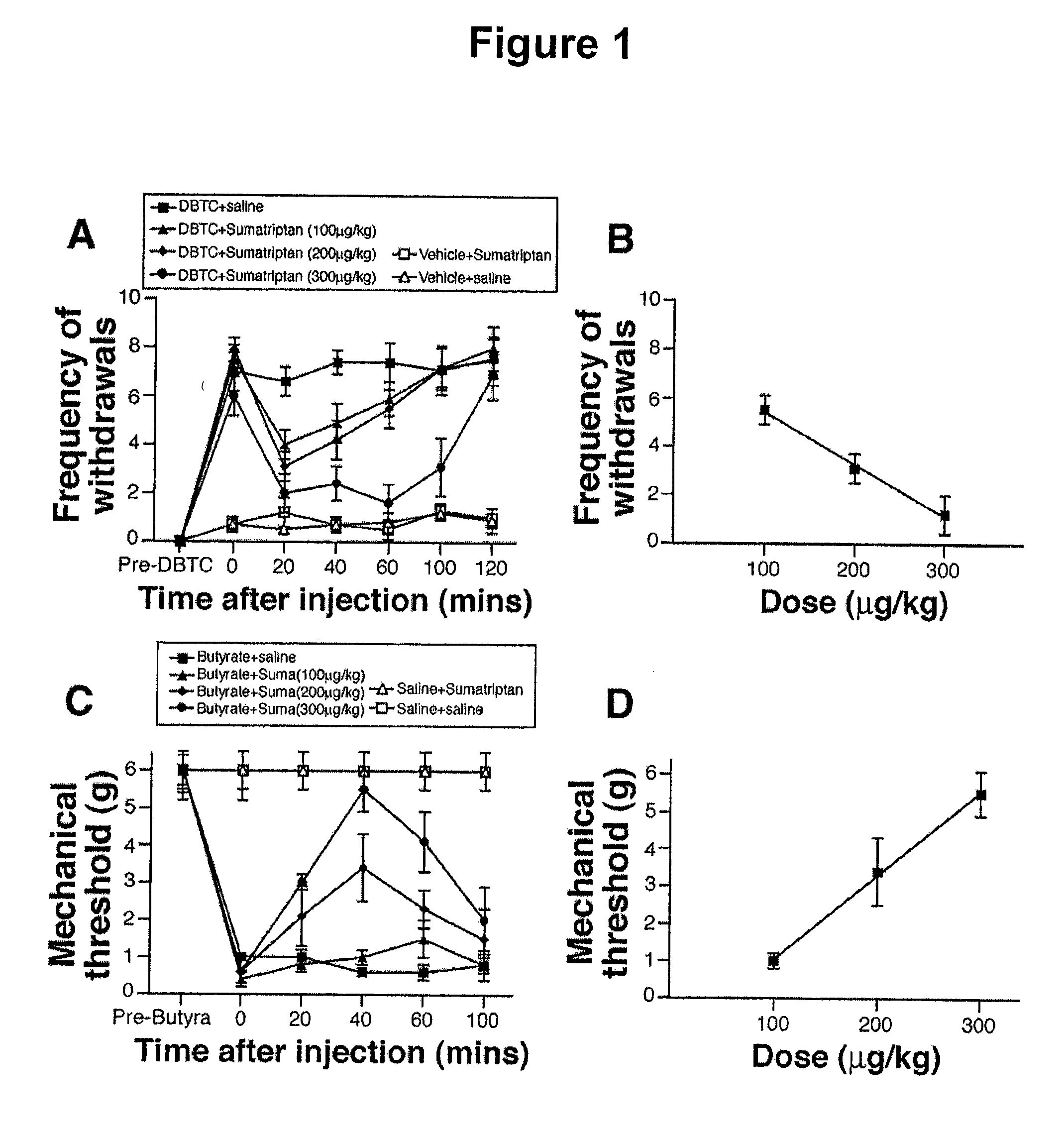
Methods for treating visceral pain
InactiveUS20090163451A1Minimal effectBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsDiseaseIntestinal structure
The invention features methods of treating visceral pain in humans by administering an effective amount of a 5HT1B or 5HT1D receptor agonist, (e.g., a triptan). These methods can be used, for example, to treat a human suffering from visceral pain secondary to an underlying disease of a visceral organ, such as pancreatitis. Visceral pain treatable by the methods of the invention may also be secondary to a disease of the liver, kidney, ovary, uterus, bladder, bowel, stomach, esophagus, duodenum, intestine, colon, spleen, pancreas, appendix, heart, or peritoneum.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Continuous blood glucose monitor
A device may be implanted subcutaneously with an attached catheter inserted within, e.g., the peritoneal cavity of a subject. The catheter and / or device may also be inserted into another space, e.g., subcutaneous, vascular, peritoneal, cerebrospinal, pleural spaces, etc. The peritoneal fluid which normally collects and / or flows through the peritoneal cavity may be detected by the catheter and analyzed via the device to detect the concentration of glucose within the fluid.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Hernia model
ActiveUS9449532B2Safely repairRealistic resiliencyEducational modelsAnatomical structuresTransabdominal preperitoneal
A model for practicing transabdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) and total extraperitoneal (TEP) approaches for laparoscopic hernia repairs is provided. The model simulates an insufflated space between the abdominal muscles and peritoneum. A spring layer may be incorporated to provide a realistic resiliency to the model while in the simulated insufflated configuration. At least one hole is provided in the model from which synthetic tissue protrudes to simulate a hernia. The model is used to selectively simulate direct, indirect and femoral inguinal hernias as well as incisional hernias by removably placing the protruding simulated tissue into any one of several openings. The model contains all important anatomical structures and sits on a base frame or is connected to a rigid simulated pelvis. When located inside a laparoscopic trainer with an angled top cover, the model provides an ideal simulation for teaching and practicing laparoscopic hernia repair.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com