Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "In vivo bildgebung" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
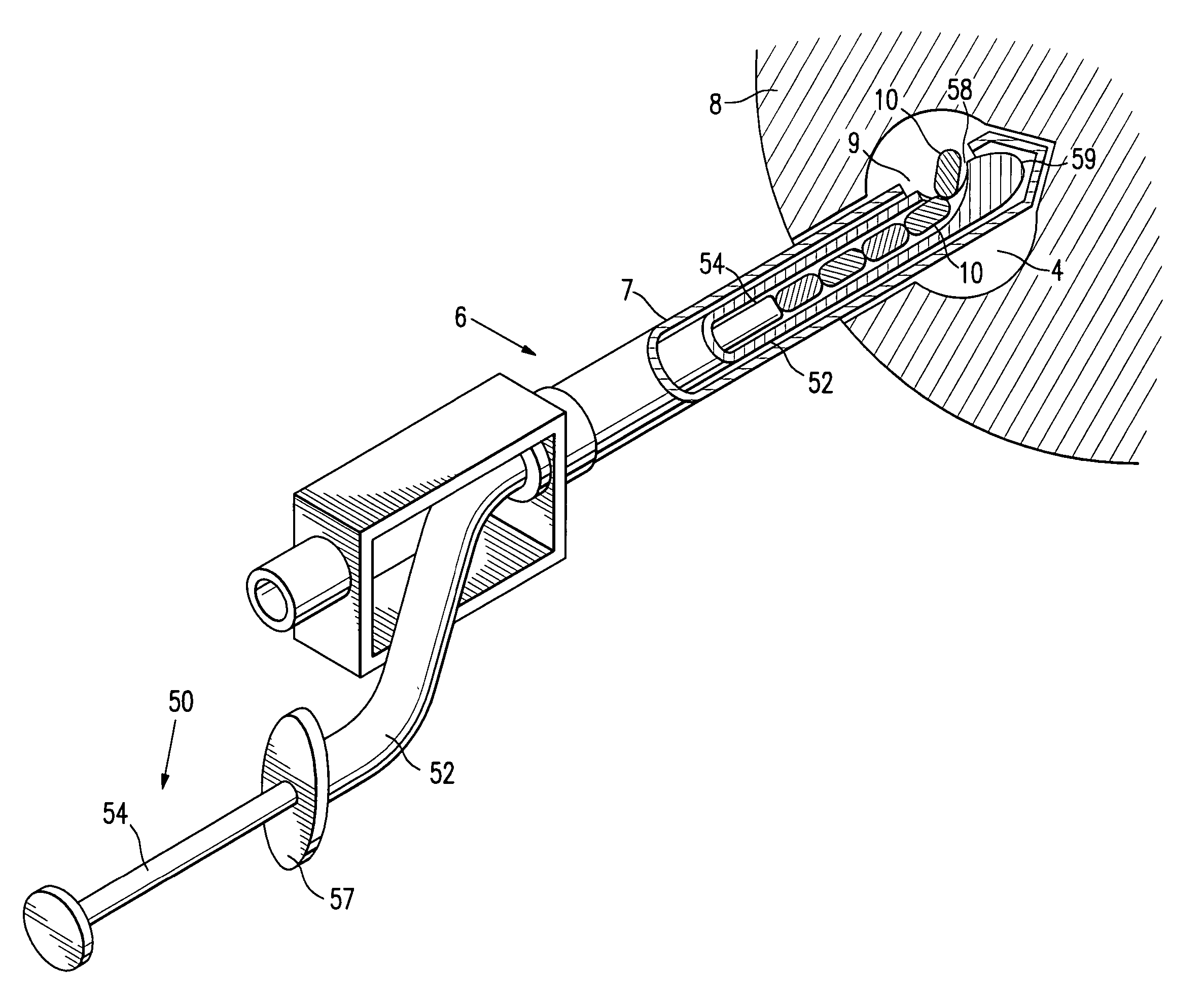
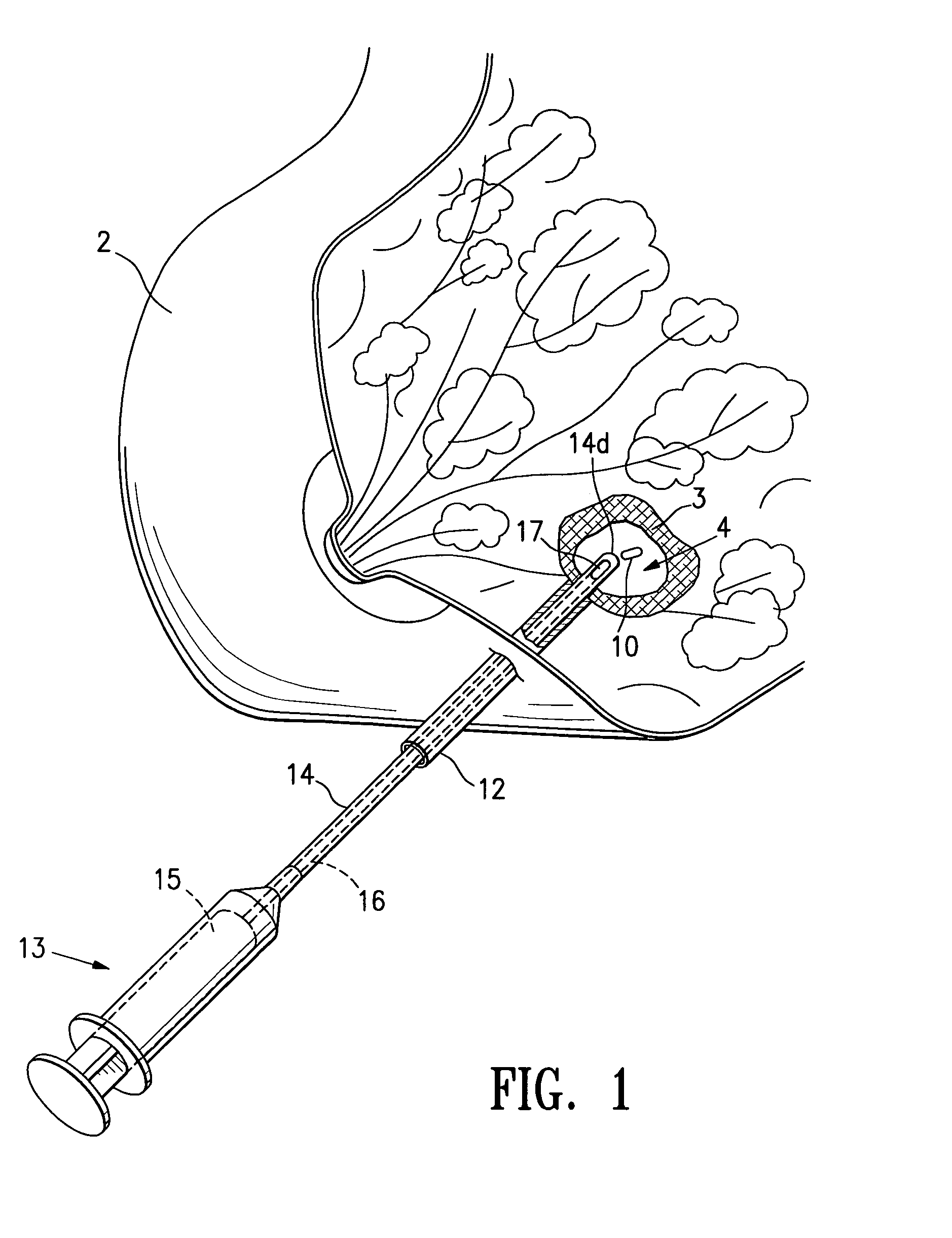
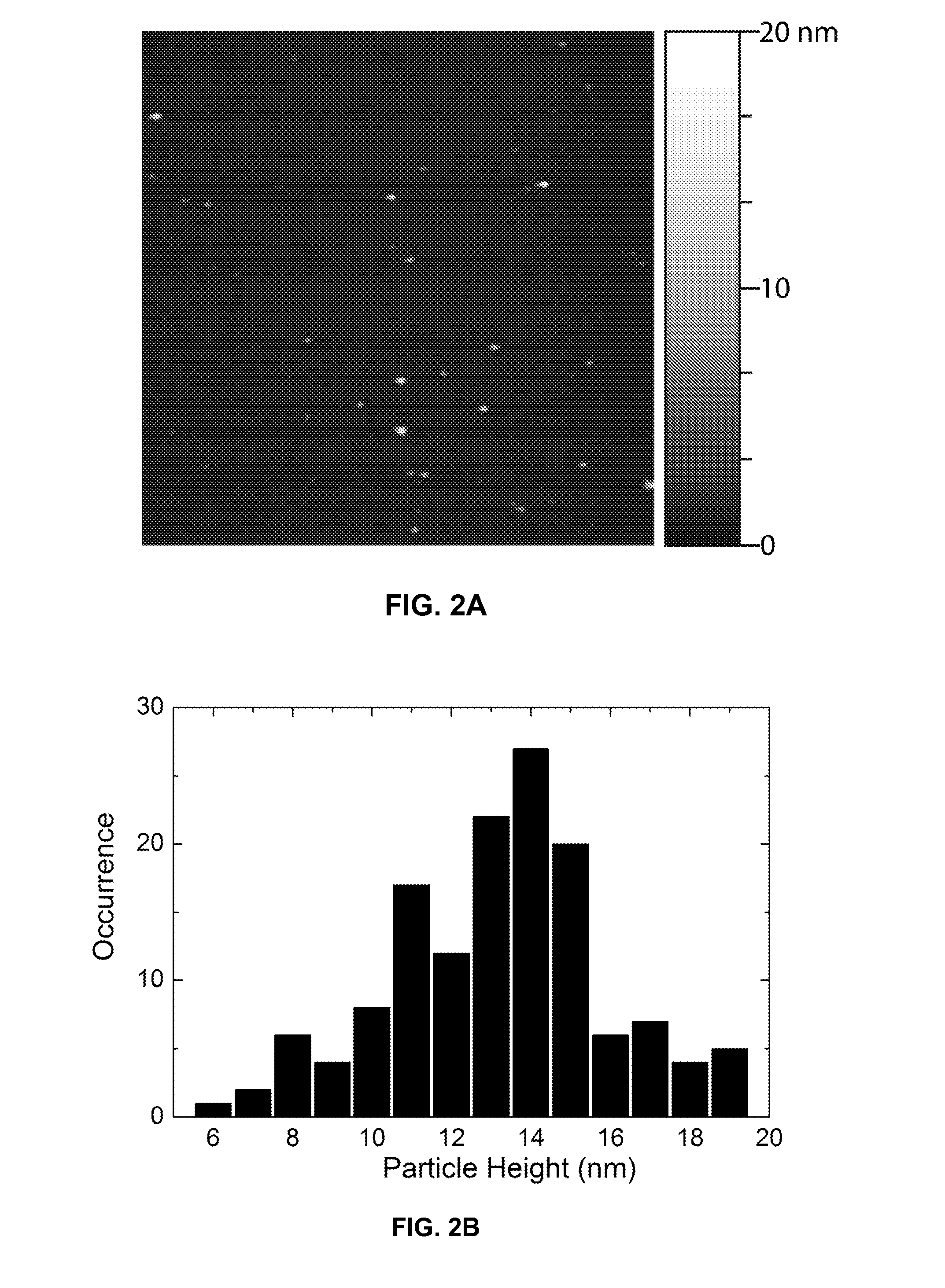
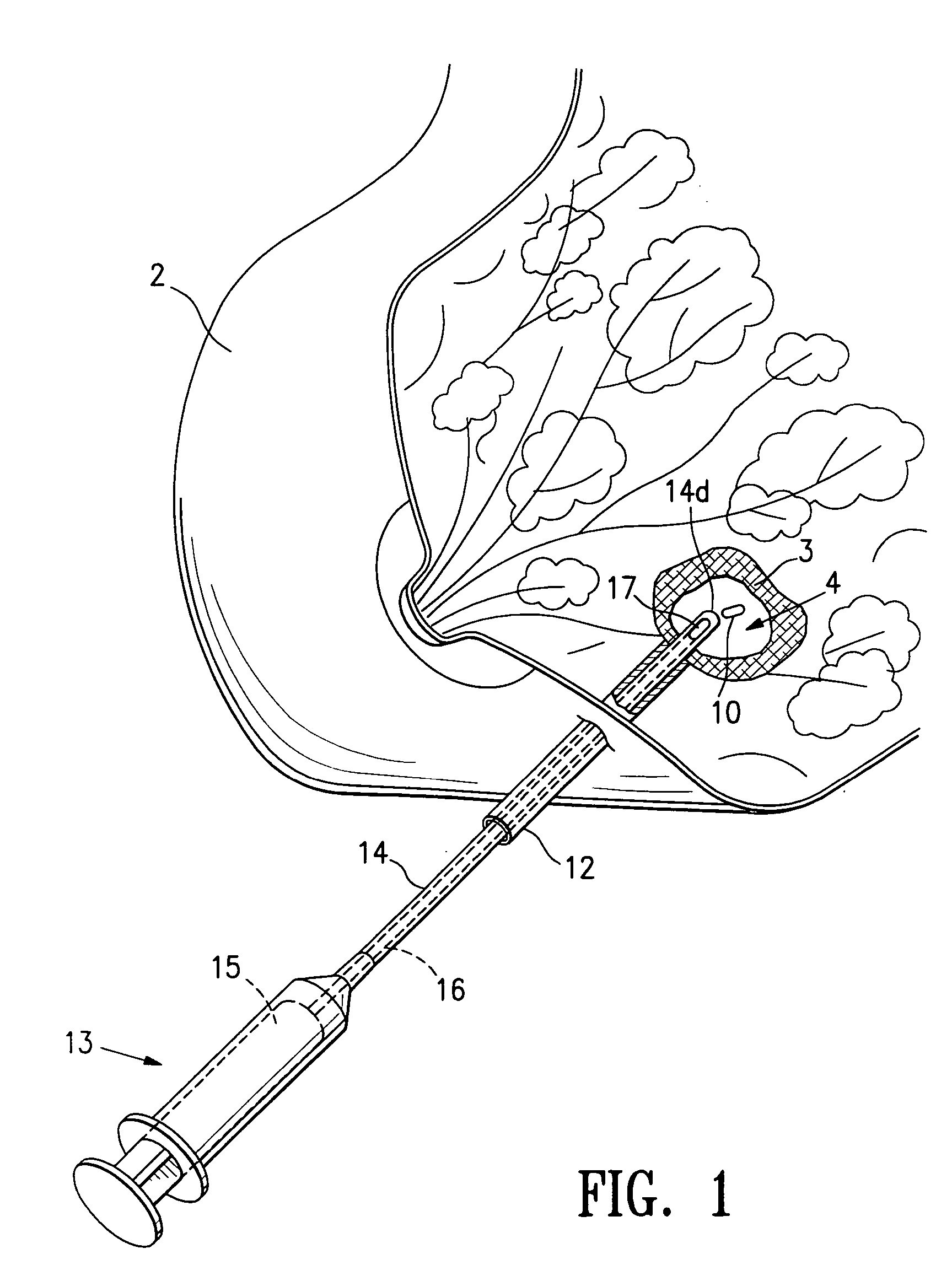
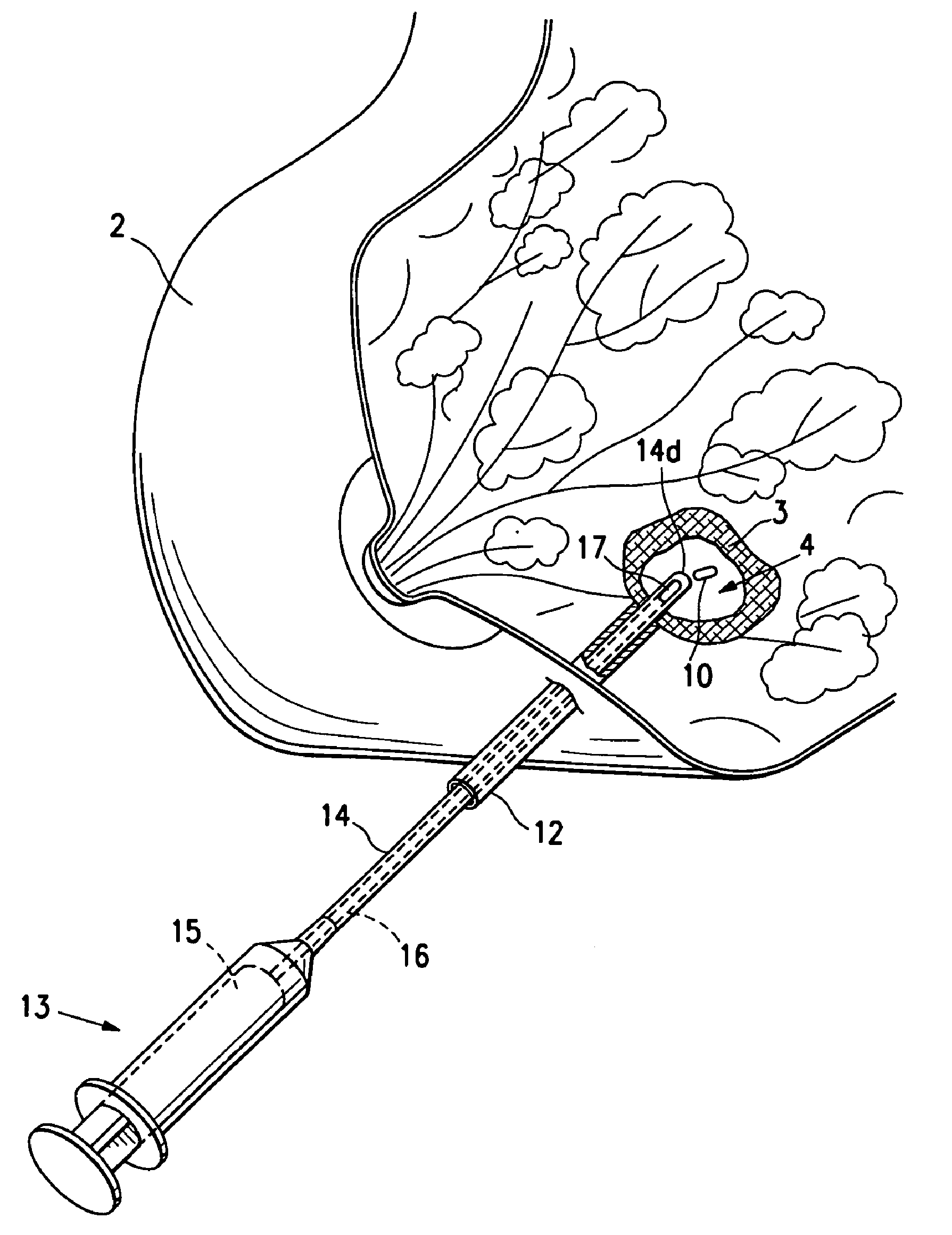
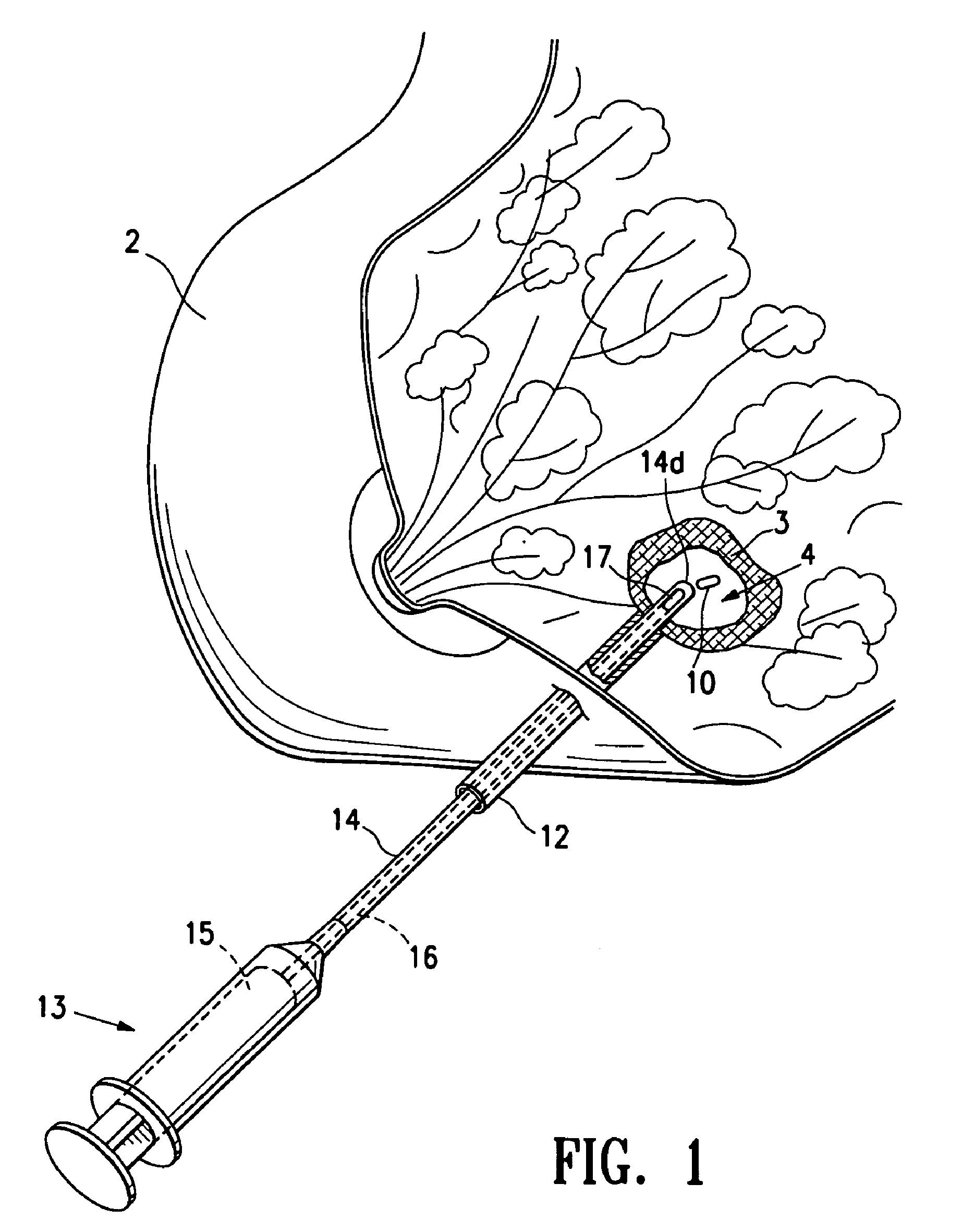
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS6993375B2Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
Owner:SENORX
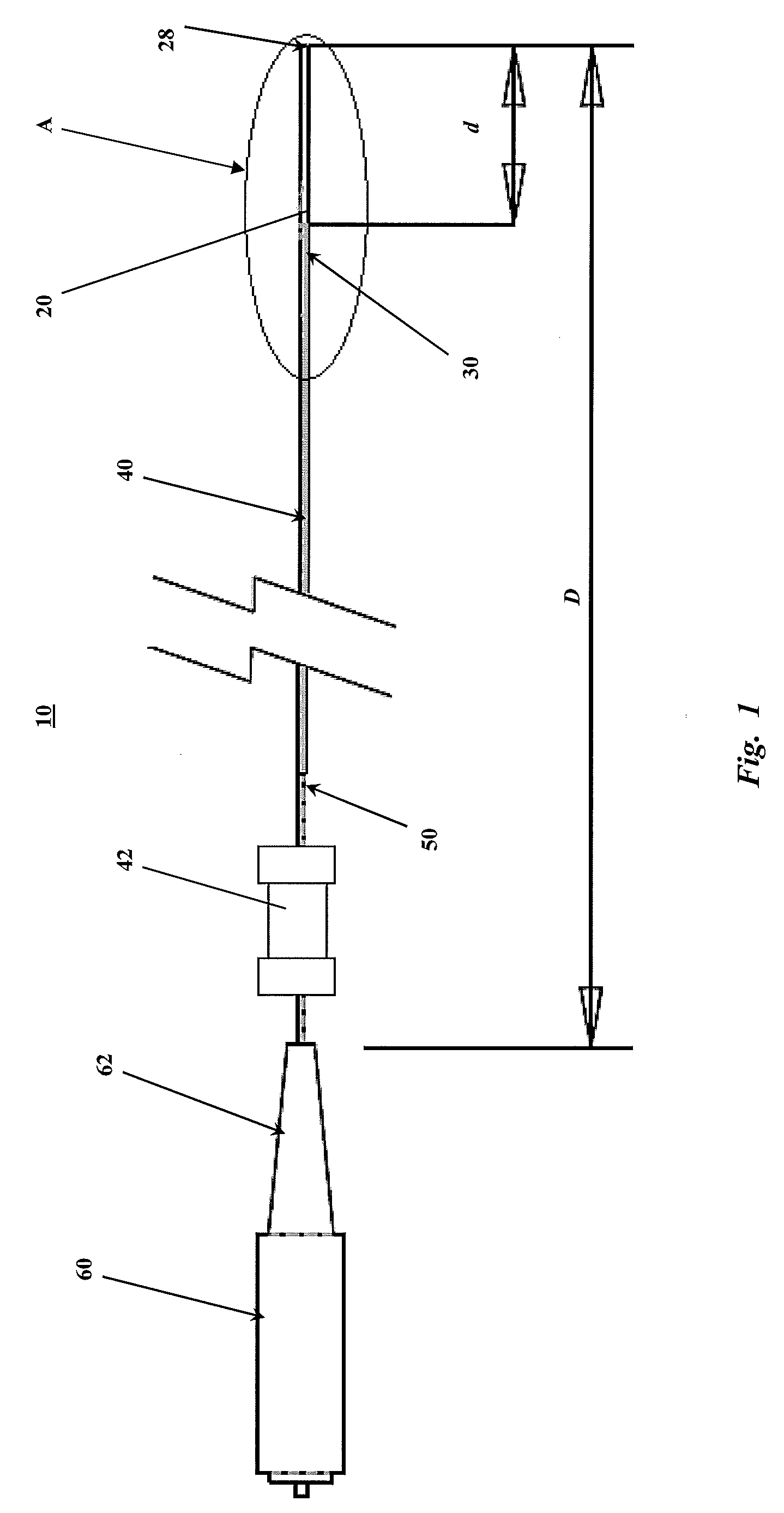
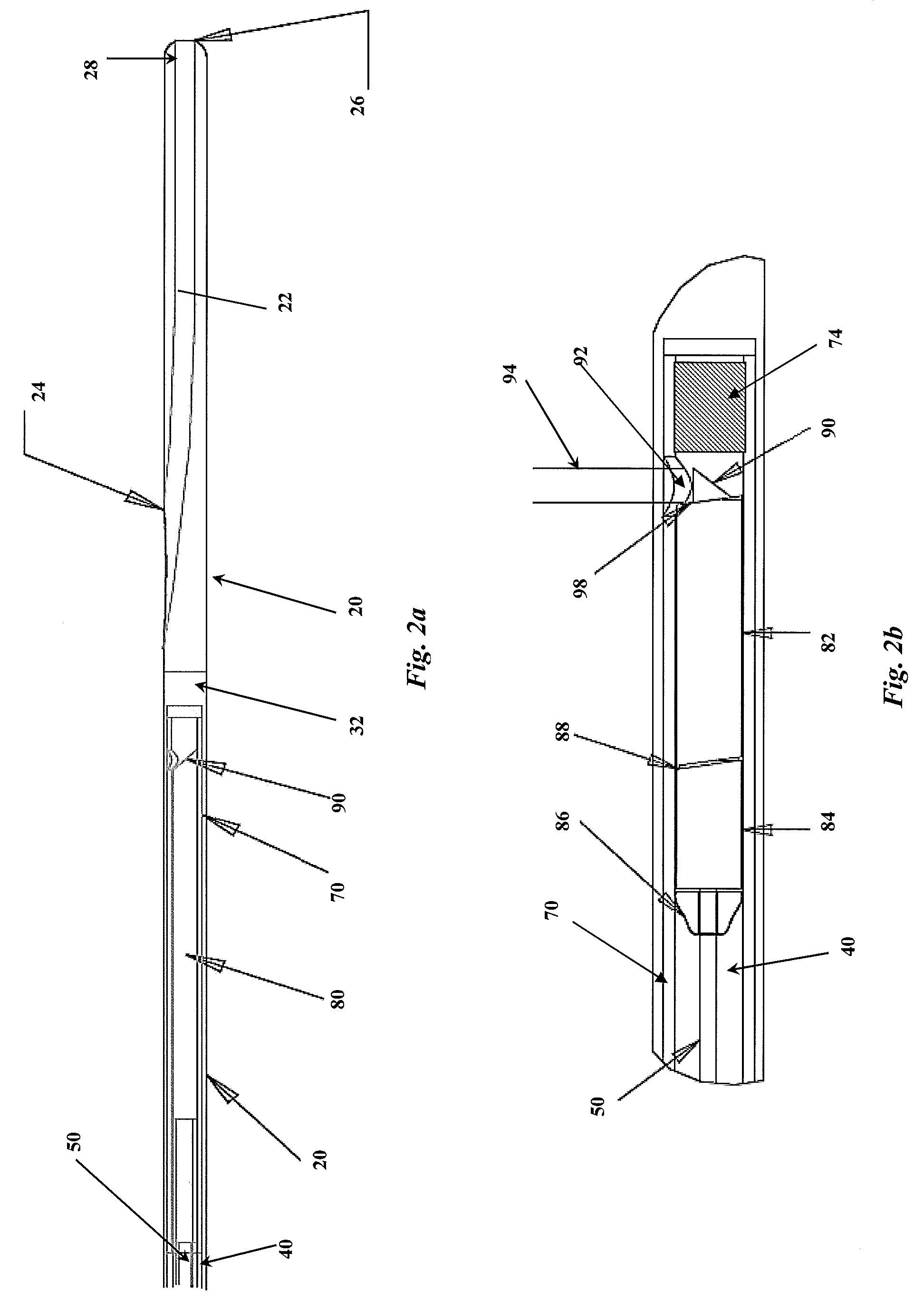
Catheter for in vivo imaging
A catheter for in vivo imaging comprising a monolithic outer sheath terminating in a monolithic atraumatic tip having a guidewire lumen. The catheter for in vivo imaging comprising a rotary drive shaft that passes through a central lumen of the monolithic outer sheath to impart rotary motion.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
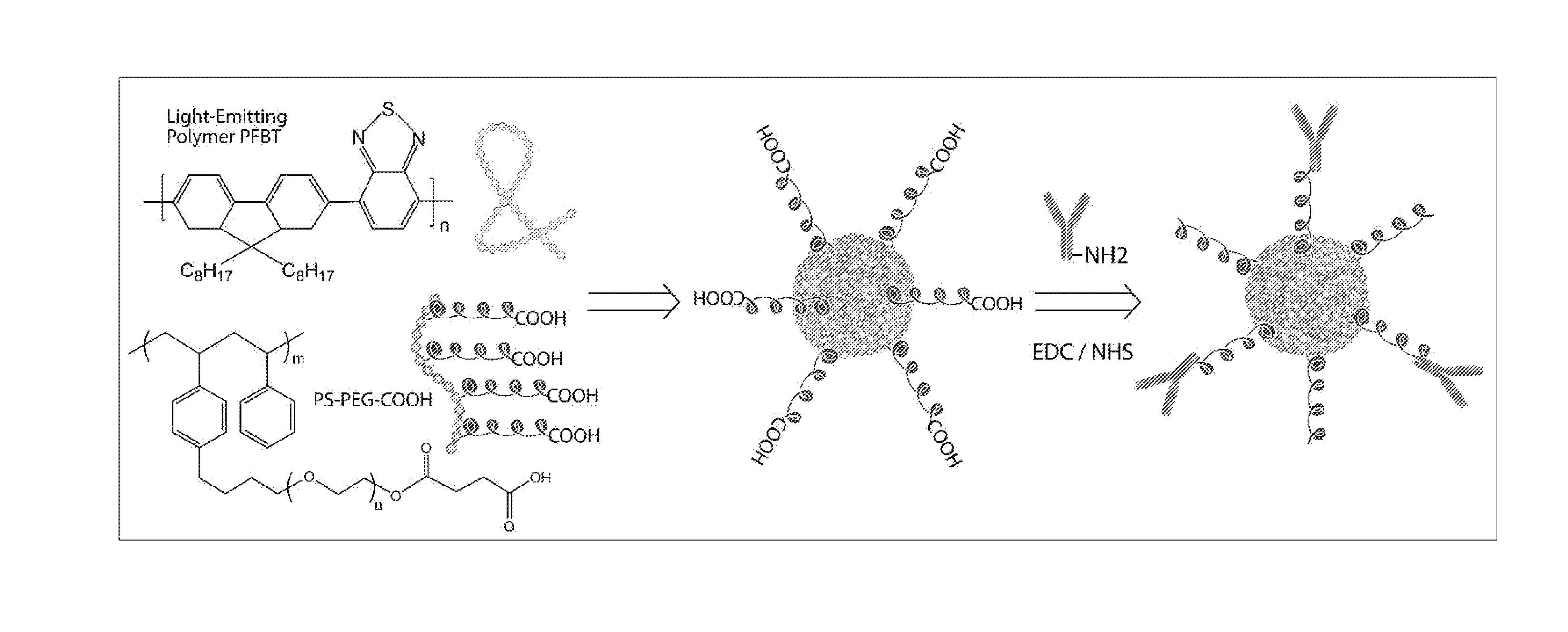
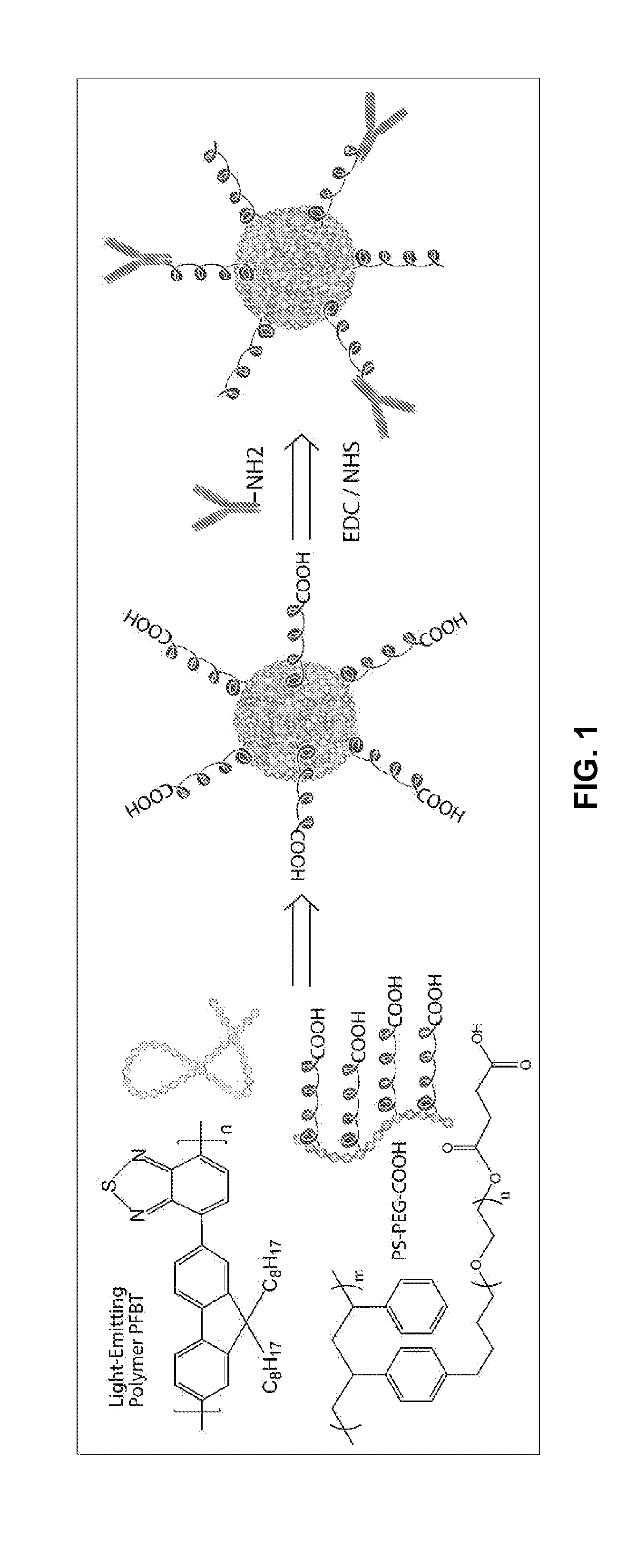
Functionalized chromophoric polymer dots and bioconjugates thereof
ActiveUS20120282632A1Reduces non-specific adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiological testingCombinatorial chemistryIn vivo
The present invention provides, among other aspects, functionalized chromophoric polymer dots comprising a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic cap, and bioconjugates thereof. Also provided are improved methods for preparing functionalized chromophoric polymer dots. Methods for in vivo imaging and molecular labeling are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20050063908A1Small volumeImprove reflectivityLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
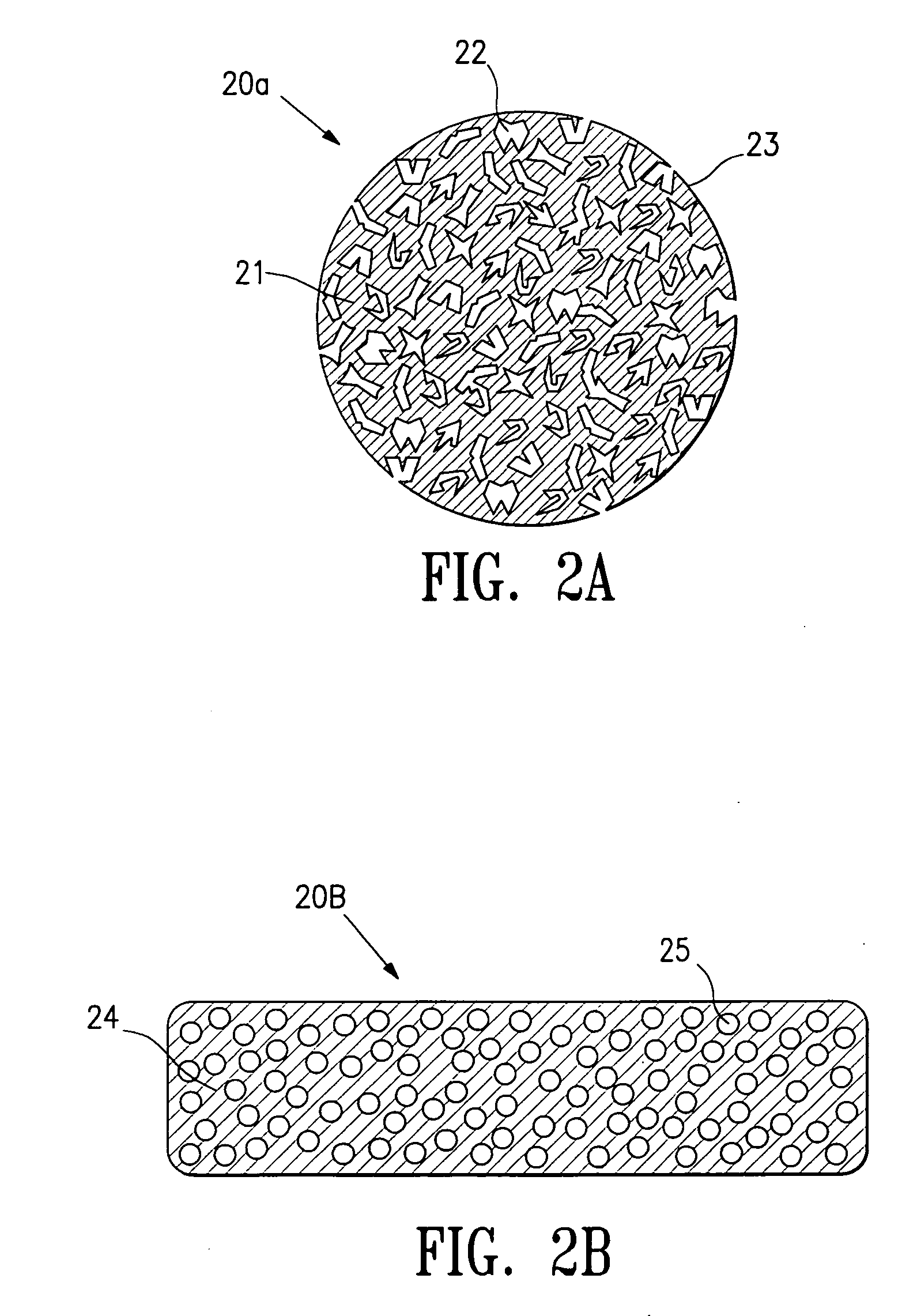
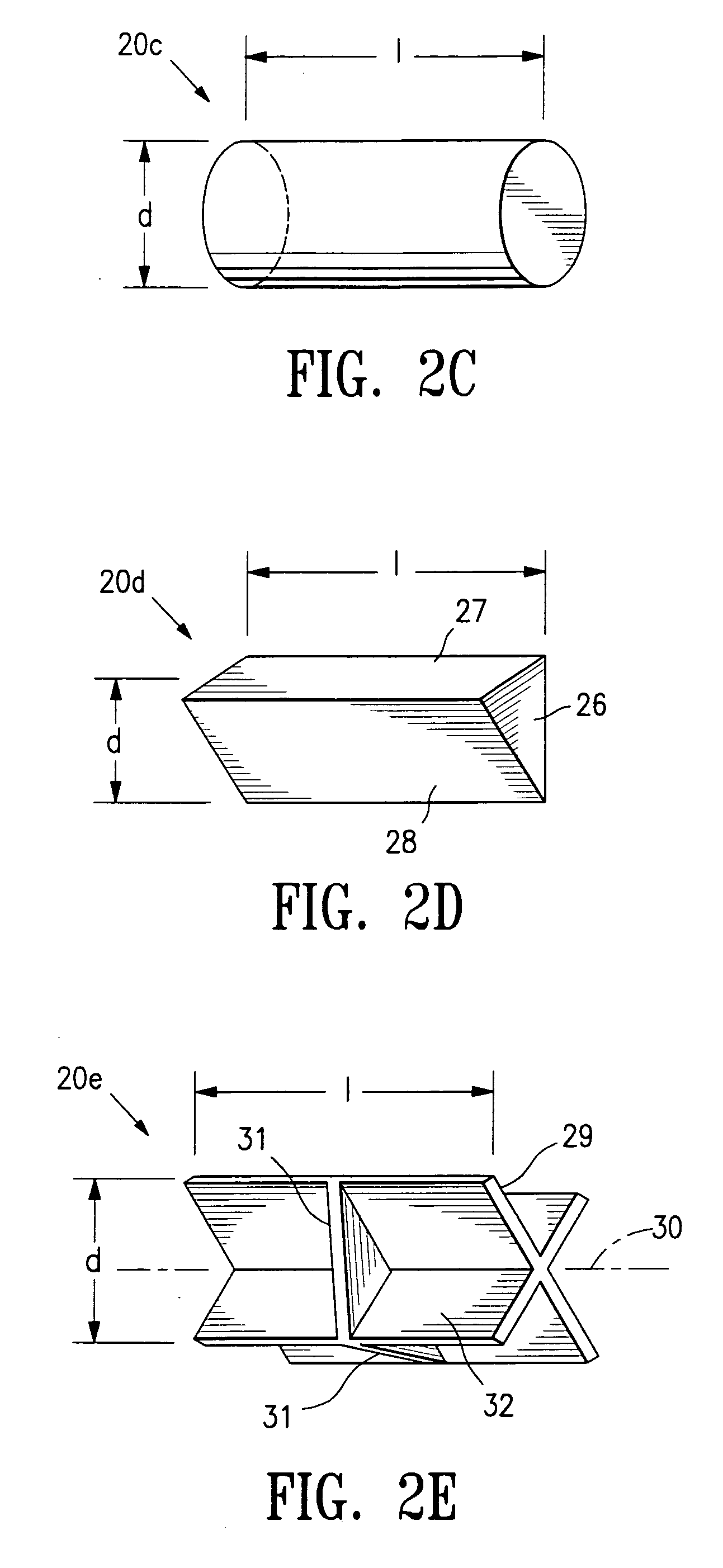
The invention is directed biopsy site markers and methods of marking a biopsy site, so that the location of the biopsy cavity is readily visible by conventional imaging methods, particularly by ultrasonic imaging. The biopsy site markers of the invention have high ultrasound reflectivity, presenting a substantial acoustic signature from a small marker, so as to avoid obscuring diagnostic tissue features in subsequent imaging studies, and can be readily distinguished from biological features. The several disclosed embodiments of the biopsy site marker of the invention have a high contrast of acoustic impedance as placed in a tissue site, so as to efficiently reflect and scatter ultrasonic energy, and preferably include gas-filled internal pores. The markers may have a non-uniform surface contour to enhance the acoustic signature. The markers have a characteristic form which is recognizably artificial during medical imaging. The biopsy site marker may be accurately fixed to the biopsy site so as to resist migration from the biopsy cavity when a placement instrument is withdrawn, and when the marked tissue is subsequently moved or manipulated.
Owner:SENORX
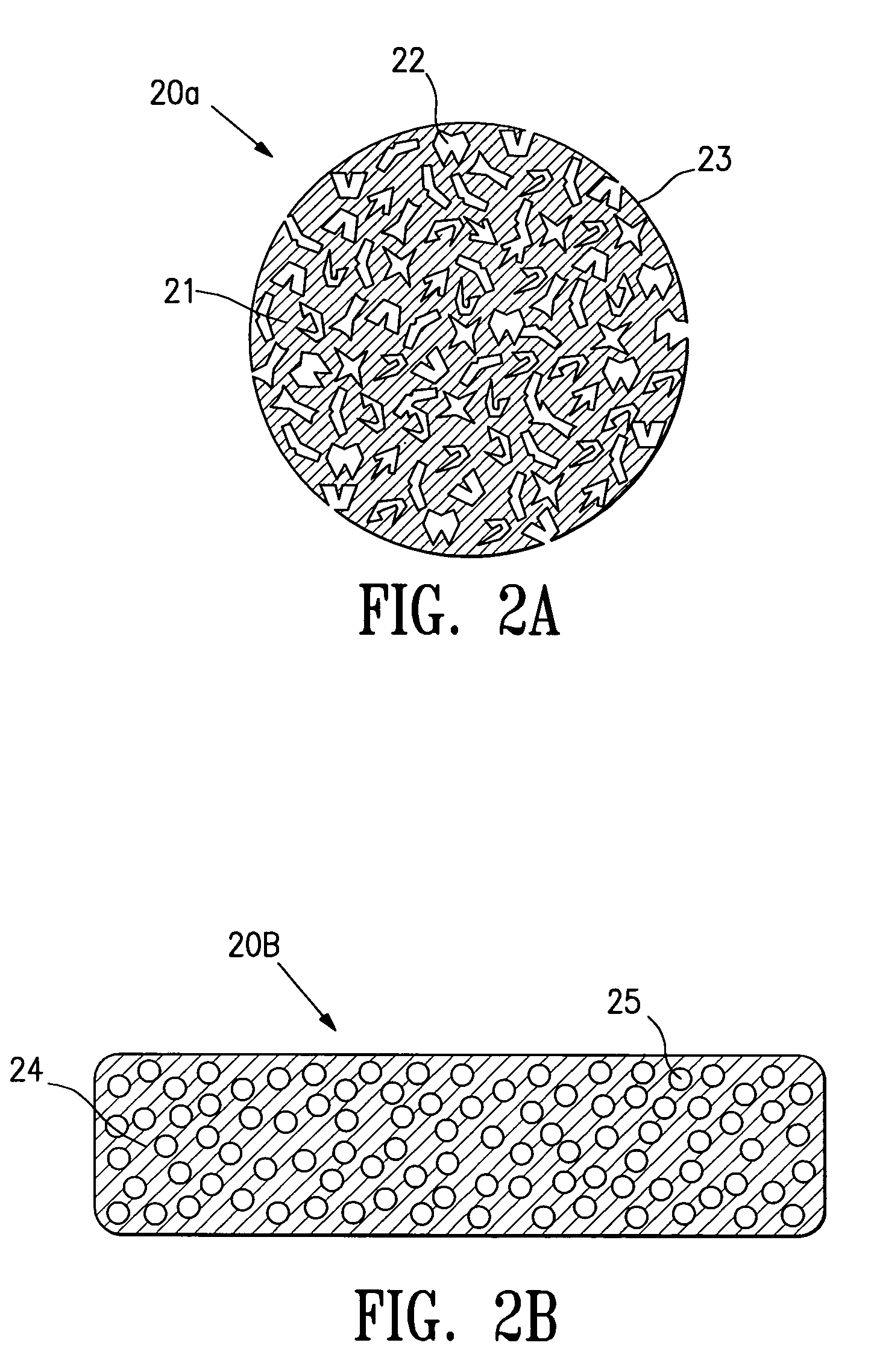
Biocompatible Fluorescent Silicon Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080102036A1Efficiently labeledUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoNanometre
The invention features biocompatible fluorescent nanoparticle and their use in in vivo imaging methods.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20100298698A1Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryContrast levelAcoustic signature
The invention is directed biopsy site markers and methods of marking a biopsy site, so that the location of the biopsy cavity is readily visible by conventional imaging methods, particularly by ultrasonic imaging. The biopsy site markers of the invention have high ultrasound reflectivity, presenting a substantial acoustic signature from a small marker, so as to avoid obscuring diagnostic tissue features in subsequent imaging studies, and can be readily distinguished from biological features. The several disclosed embodiments of the biopsy site marker of the invention have a high contrast of acoustic impedance as placed in a tissue site, so as to efficiently reflect and scatter ultrasonic energy, and preferably include gas-filled internal pores. The markers may have a non-uniform surface contour to enhance the acoustic signature. The markers have a characteristic form which is recognizably artificial during medical imaging. The biopsy site marker may be accurately fixed to the biopsy site so as to resist migration from the biopsy cavity when a placement instrument is withdrawn, and when the marked tissue is subsequently moved or manipulated.
Owner:SENORX
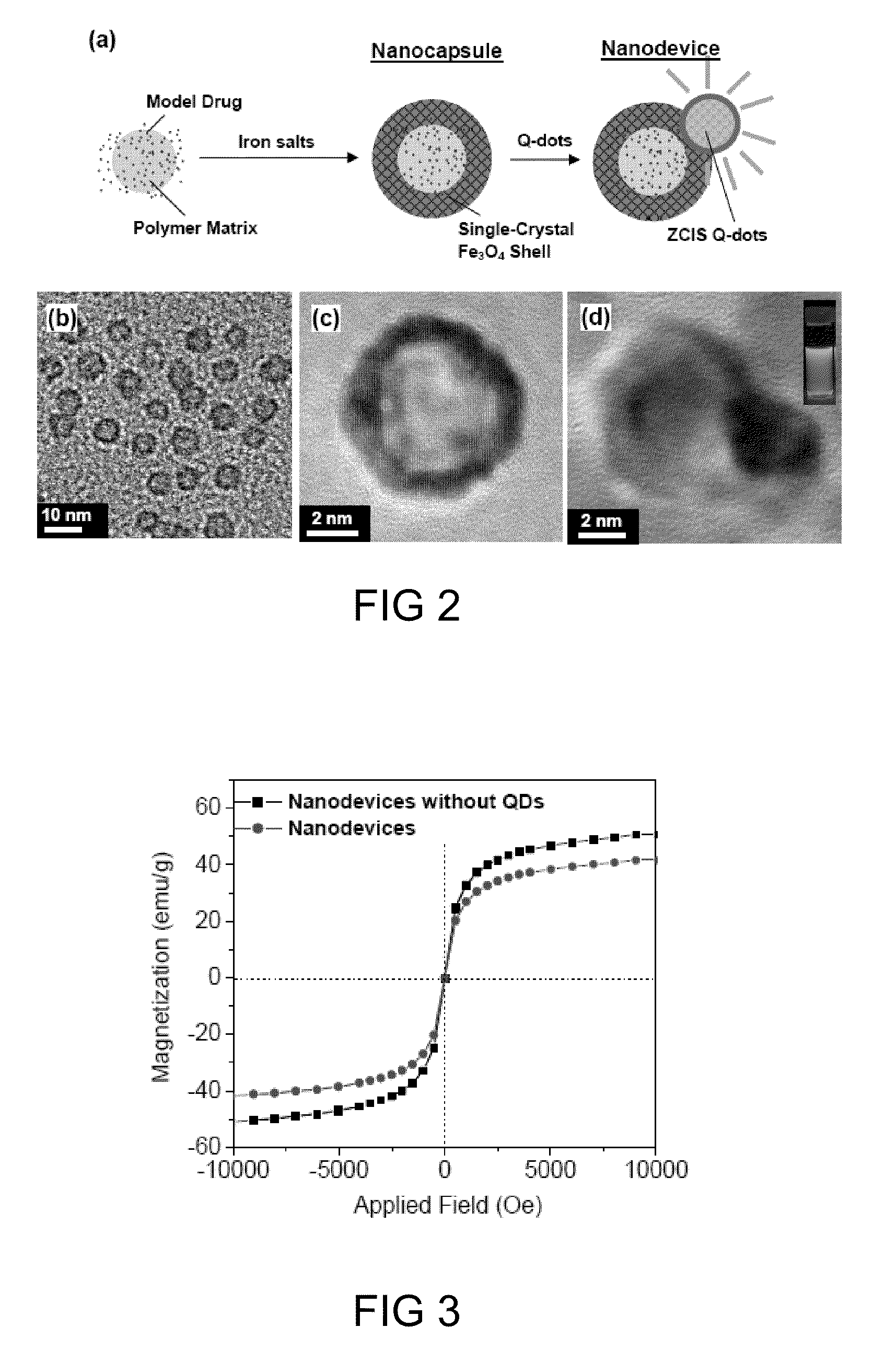
Drug Delivery Nanodevice, its Preparation Method and Uses Thereof
Nanodevice and method for in vivo monitoring and release of drugs are provided. The disclosed nanodevice is characterized in having a drug-loaded nanosphere that is capable of releasing the encapsulated drugs upon magnetically stimulation. The nanodevice may also be used as a contrast agent for in vivo imaging and monitoring the concentration and distribution of the released drugs and / or active compounds injected separately into a target site of a subject.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Nir materials and nanomaterials for theranostic applications
InactiveUS20130039858A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryMetal oxide nanoparticlesFluorescence
Novel fluorescent dye comprising metal oxide nanoparticles are prepared where the nanoparticles are as small as 3 nm or up to 7000 nm in diameter and where the dye is bound within the metal oxide matrix. In some embodiments the invention, novel dyes are covalently attached to the matrix and in other embodiments of the invention a dye is coordinate or ionic bound within the metal oxide matrix. A method for preparing the novel covalently bondable modified fluorescent dyes is presented. A method to prepare silica comprising nanoparticles that are 3 to 8 nm in diameter is presented. In some embodiments, the fluorescent dye comprising metal oxide nanoparticles are further decorated with functionality for use as multimodal in vitro or in vivo imaging agents. In other embodiments of the invention, the fluorescent dye comprising metal oxide nanoparticles provide therapeutic activity and incorporated therapeutic temperature monitoring.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Functionalized chromophoric polymer dots and bioconjugates thereof
ActiveUS10191060B2Reduces non-specific adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiological testingCombinatorial chemistryIn vivo
The present invention provides, among other aspects, functionalized chromophoric polymer dots comprising a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic cap, and bioconjugates thereof. Also provided are improved methods for preparing functionalized chromophoric polymer dots. Methods for in vivo imaging and molecular labeling are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Second harmonic imaging nanoprobes and techniques for use thereof
ActiveUS20120141981A1Enhances electric fieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell signalingPhoton
Second harmonic nanoprobes for imaging biological samples and a method of using such probes to monitor the dynamics of biological process using a field resonance enhanced second harmonic (FRESH) technique are provided. The second harmonic generating (SHG) nanoprobes are comprised of various kinds of nanocrystals that do not possess an inversion symmetry and therefore are capable of generating second harmonic signals that can then be detected by conventional two-photon microscopy for in vivo imaging of biological processes and structures such as cell signaling, neuroimaging, protein conformation probing, DNA conformation probing, gene transcription, virus infection and replication in cells, protein dynamics, tumor imaging and cancer therapy evaluation and diagnosis as well as quantification in optical imaging.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
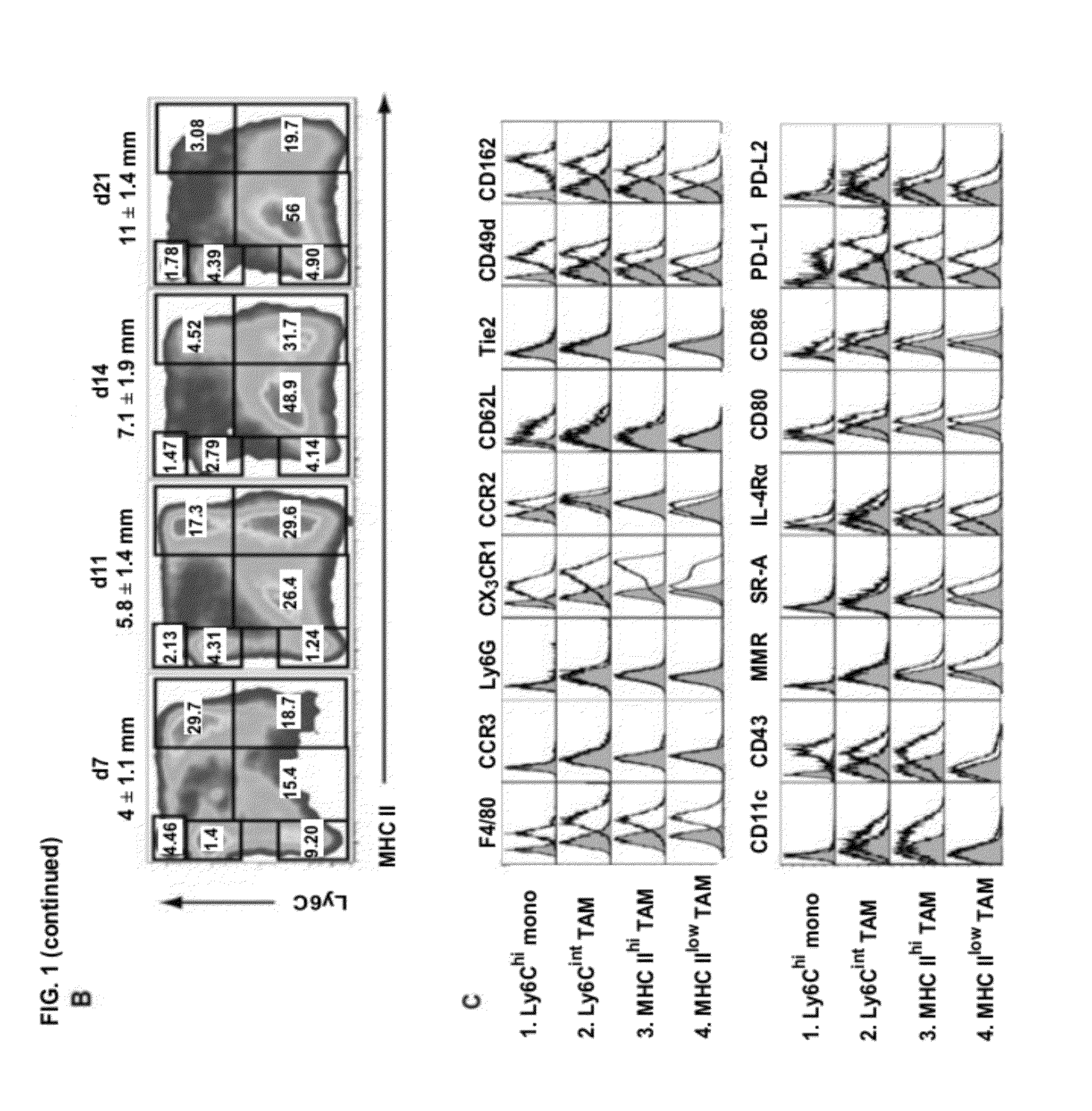
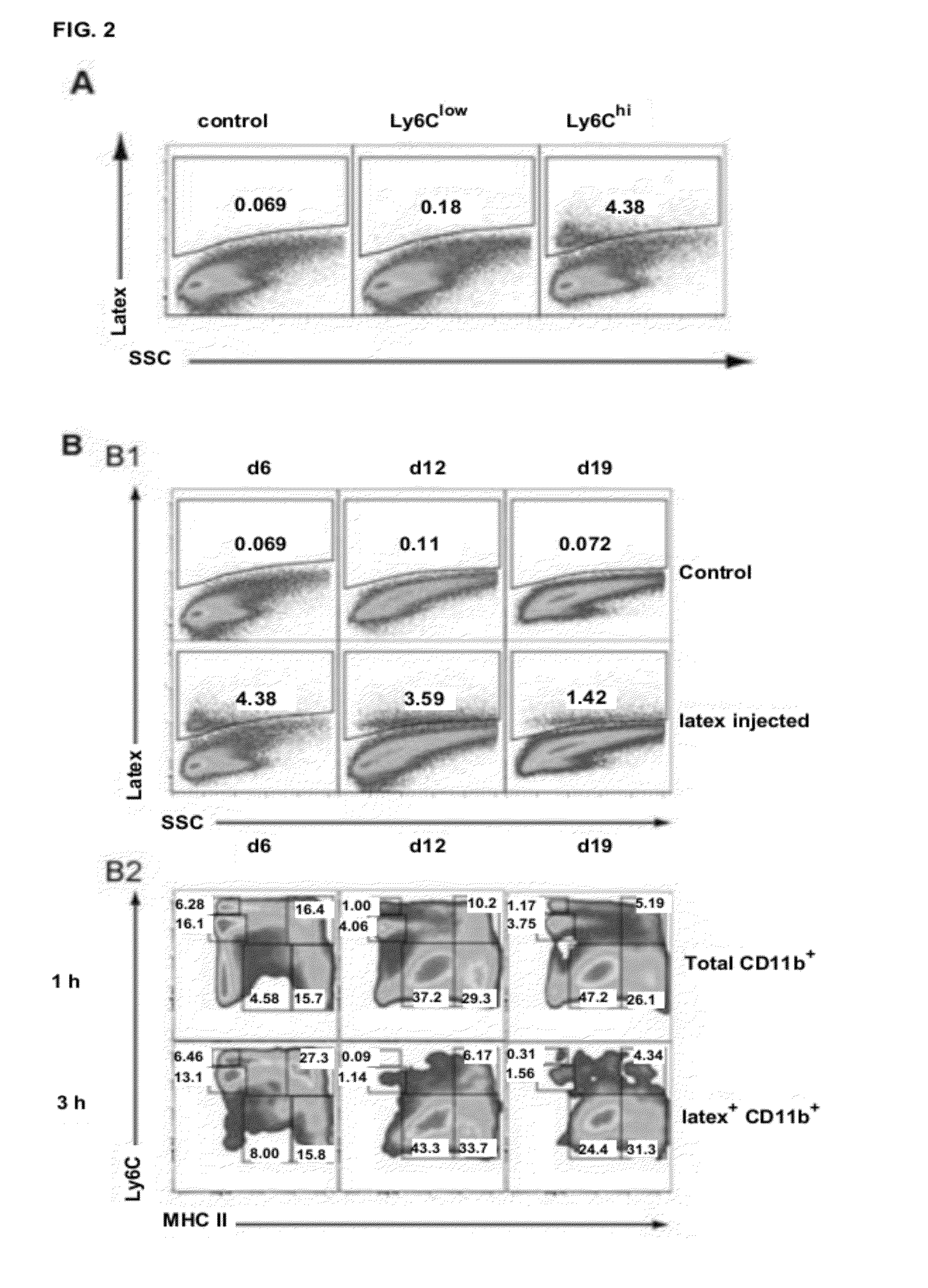
Targeting and in vivo imaging of tumor-associated macrophages
ActiveUS20120301394A1Efficient targetingReduce signalingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesTumor-associated macrophageIn vivo
The invention relates to activities and characteristics of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). In particular, immunoglobulin single variable domains are provided against markers of TAMs, and methods using the same for in vivo imaging of tumor cells, as well as cancer diagnostics and therapeutics.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Novel imaging agents
InactiveUS20060275215A1Useful imageAntibacterial agentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTherapy monitoringCaspase 3
The present invention relates to diagnostic imaging agents for in vivo imaging. The imaging agents comprise a synthetic caspase-3 inhibitor labelled with an imaging moiety suitable for diagnostic imaging in vivo. The invention also provides pharmaceutical and radiopharmaceutical compositions comprising the imaging agents, together with kits for the preparation of the radiopharmaceuticals. Also described are chelator conjugates of the caspase-3 inhibitor, which are suitable for the preparation of imaging agents comprising a radioactive or paramagnetic metal ion. The imaging agents are useful for the diagnostic imaging and or therapy monitoring in vivo of various disease states where caspase-3 is involved.
Owner:HISCOCK DUNCAN +2
Substituted silaxanthenium red to near-infrared fluorochromes for in vitro and in vivo imaging and detection
ActiveUS20140314677A1Reduce molecular weightSignificant cell permeabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideChemical ligationFluorescence
The invention provides a family of fluorescent compounds. The compounds are substituted silaxanthenium compounds that can be chemically linked to one or more biomolecules, such as a protein, nucleic acid, and therapeutic small molecule. The compounds can be used for imaging in a variety of medical, biological and diagnostic applications. The dyes are particularly useful for in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo imaging applications.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Methods and composition related to in vivo imaging of gene expression
InactiveCN101171337AVectorsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMethod of imagesIn vivo
Disclosed are nucleic acid sequences encoding a recombinant seven transmembrane G-protein associated receptor (GPCR) amino acid sequence operatively coupled to a tissue-selective promoter sequence. Also disclosed are methods of imaging or treating cells in a subject that involve introducing a nucleic acid encoding a reporter detectable in vivo using non-invasive methods operatively coupled to a tissue-selective promoter or amplified tissue specific promoter to the subject, and subjecting the subject to a non-invasive imaging technique or a therapeutic that selectively interacts with the reporter or gene of interest. For example, the subject may be a subject with cancer, and the therapeutic may be an anti-cancer agent. In particular, the hTERT promoter or amplified hTERT promoter drives expression of a reporter such hSSTR2 and / or hSSTR2 derivative) and these may be linked to a gene of interest. Imaging may be performed by a variety of methods including nuclear medicine.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
In vivo label-free histology by photoacoustic microscopy of cell nuclei
InactiveUS20140356897A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotoacoustic microscopyUltraviolet lights
The present disclosure is directed to methods of non-invasively imaging cell nuclei. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to methods of imaging cell nuclei in vivo using ultraviolet photoacoustic microscopy (UV-PAM), in which ultraviolet light is used to excite unlabeled DNA and RNA in cell nuclei to produce photoacoustic waves.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Optical probes for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20070297988A1Improve stabilityHigh dye concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryNanoparticleIn vivo
Disclosed is an image probing conjugate. The conjugate comprises a nanoparticle and a targeting agent. The nanoparticle comprises a dye which is encapsulated by a functionalized polymer, and the targeting agent is bound to the functional group of the polymer. The nanoparticle provides the conjugate with improved stability and an increased concentration of the dye. Therefore, the conjugate of the invention can be used for probing a small target which otherwise cannot be detected. Bonding the targeting agent to the nanoparticle allows precise image probing from the location where the targeting agent is placed.
Owner:WU BIN
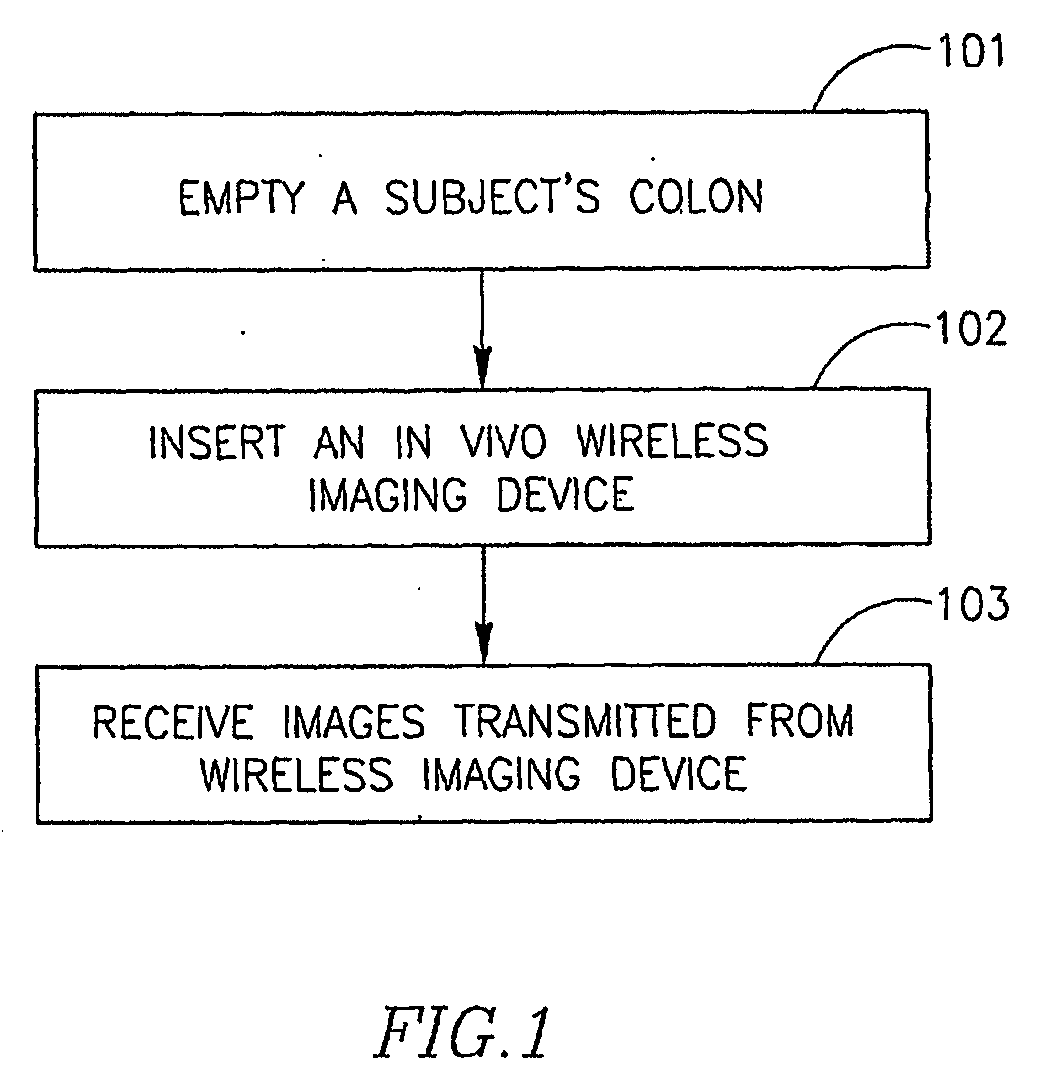
Device, System and Method for In-Vivo Examination
InactiveUS20090105537A1Effective timePatient compliance is goodBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsStimulantRadiology
A device, a system and a method for in-vivo examination. A method for in-vivo examination includes substantially emptying a subject's colon from content, and inserting an autonomous in-vivo imaging device into the subject's gastrointestinal tract. An in-vivo examination kit includes an autonomous in-vivo imaging device, a wireless receiver, an antenna set, a laxative, and optionally a stimulant and an instructions leaflet.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
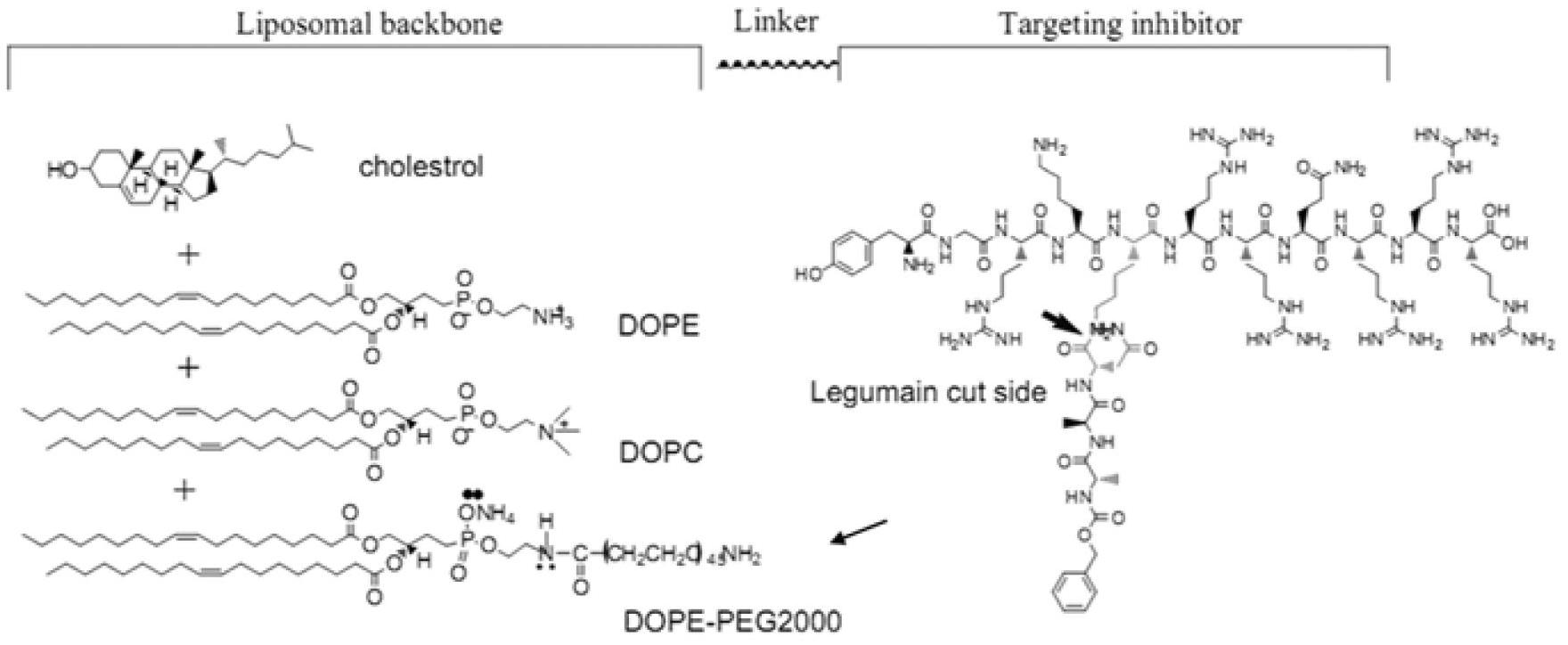
Nano particle carrier having tumor and tumor-associated macrophage targeting multiple functions and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102688495AAchieve targetedEfficient and sensitive positioningPowder deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsEnzyme digestionTumor therapy
The invention relates to a nano particle carrier having tumor and tumor-associated macrophage targeting multiple functions, which can be used for tumor therapy and in vivo imaging and positioning. The carrier is a liposome nano particle mediated by a tumor focus induction-activated cell-penetrating peptide, can be specifically enriched on the tumor focus through a circulating system after being subjected to intravenous injection, and simultaneously has the functions of molecule imaging and carrying multiple biomacromolecules and medicines. Concretely, by using a TAT cell-penetrating peptide of closed active center amino acid of a Legumain specificity-identified enzyme digestion substrate to connect PEG-modified liposome nano particles, after the circulating system reaches the tumor focus position, Legumain expressed by tumor and tumor-associated macrophage can separate the enzyme digestion substrate from the TAT active center, thereby realizing the enrichment on the tumor focus. The nano particle can pack various biomacromolecules or medicines, and has the functions of killing tumor, in vivo tumor tracing and performing early prevention on tumor.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Fluorescent-CT bimodal imaging probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104721841AReduce the risk of adverse reactionsLow equipment requirementsX-ray constrast preparationsFreeze-dryingIodixanol
The invention relates to a fluorescent-CT bimodal imaging probe and a preparation method thereof, specifically relates to a fluorescent-CT bimodal iodine doped carbon quantum dot prepared by a one-step hydrothermal carbonization method and application of the fluorescent-CT bimodal iodine doped carbon quantum dot in biomedical images, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. The specific scheme is as follows: dissolving iodixanol and glycine in an aqueous solution according to a certain mass ratio to serve as precursors, putting the solution in a hydrothermal reaction kettle with polytetrafluoroethylene lining, heating up to 120-200 DEG C to react for 4 hours, dialyzing and freeze drying nigger-brown reaction liquid to remove residues and water to obtain black powdery nanoparticles, namely iodine doped carbon quantum dots. The iodine doped carbon quantum dot prepared by the method has such excellent properties as stable fluorescence, efficient X-ray attenuation capacity and good biocompatibility, and is successfully applied to live cell fluorescent imaging in vitro and CT imaging in vivo. The method has the advantages of simple operation, environmental protection and easy mass production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for detecting dysplasia
The present invention provides a method of imaging useful in the determination of sites of dysplasia in patients suffering from Barrett's oesophagus. The method comprises the use of an optical imaging agent comprising a vector which targets the extracellular domain of EGFR, the vector also being selective for EGFR over Her2. The vector is labelled with an optical reporter suitable for in vivo imaging using light in the green to near-infrared wavelength 500-1200 nm. Also provided are novel optical imaging agents suitable for use in the method.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Small cell lung carcinoma biomarker panel
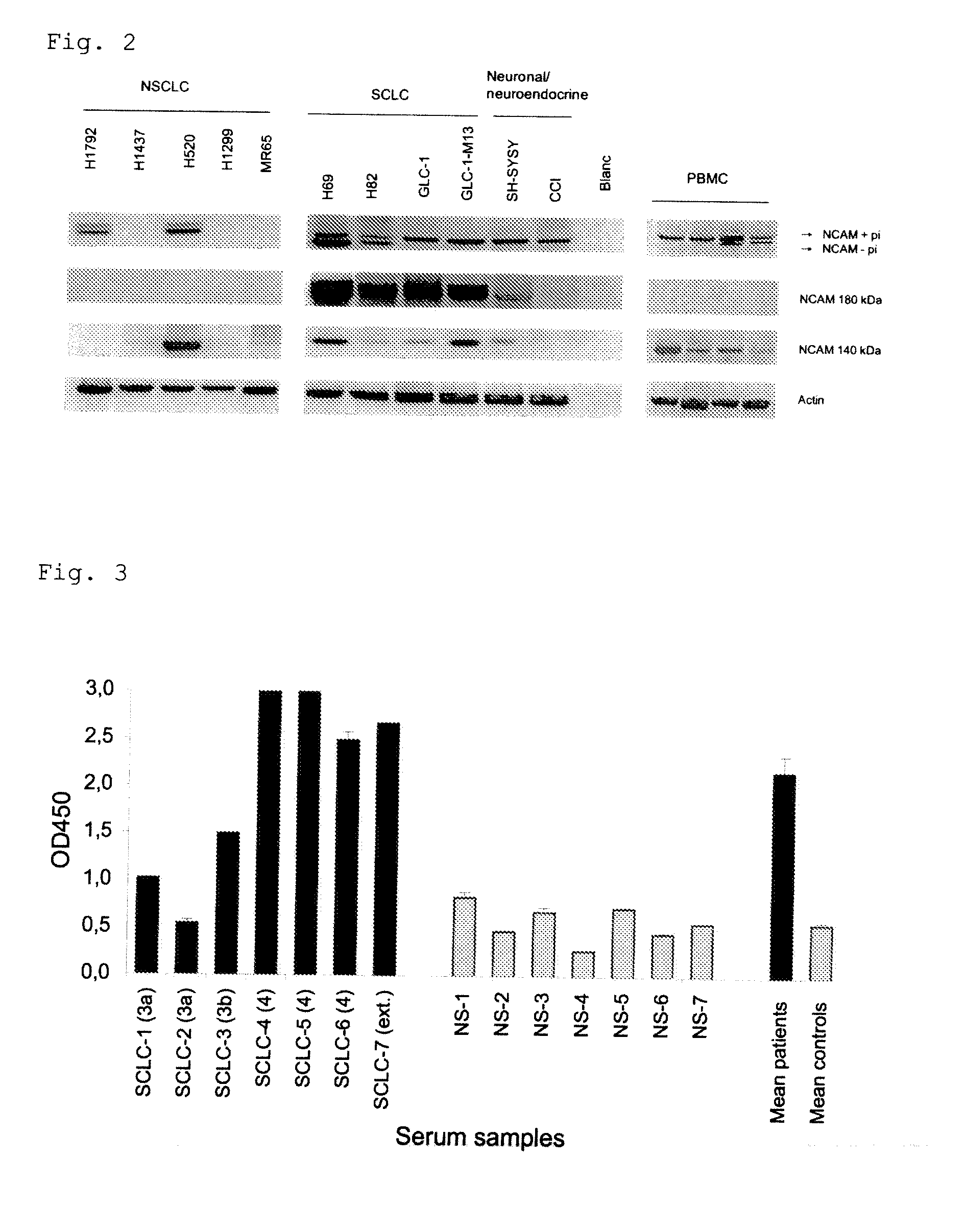
InactiveUS20110053156A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker panelCompanion animal
The invention relates generally to the field of cancer detection, diagnosis, subtyping, staging, prognosis, treatment and prevention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection, and / or diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging of lung cancer in a patient. Based on a particular panel of biomarkers, the present invention provides methods to detect, diagnose at an early stage and / or differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and within NSCLC to differentiate between squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), adenocarcinomas (AC), within SCC to discriminate G2 and G3 stage and within lung cancer to differentiate for lung cancers with or without neuroendocrine origin. It further provides the use of said panel of biomarkers in monitoring disease progression in a patient, including both in vitro and in vivo imaging techniques. The in vitro imaging techniques typically include an immunoassay detecting protein or antibody of the biomarkers on a sample taken from said patient, e.g. serum or tissue sample. The in vivo imaging techniques typically include chest radiographs (X-rays), Computed Tomography (CT) imaging, spiral CT, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), PET-CT and scintigraphy for molecular imaging and diagnosis and to monitor disease progression and treatment response in patients. It is accordingly a further aspect to provide a kit to perform the aforementioned diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging assay and the imaging techniques, comprising reagents to determine the gene expression or protein level of the aforementioned panel of biomarkers for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:MUBIO PRODS BV
Hydrophilic nanoparticles surface-modified with monosaccharide phosphate or monosaccharide phosphate derivatives, its colloidal solution and use thereof
ActiveUS20140161734A1Easy to produceGood water dispersibilityBiocidePowder deliveryMRI contrast agentHyperthermia Treatment
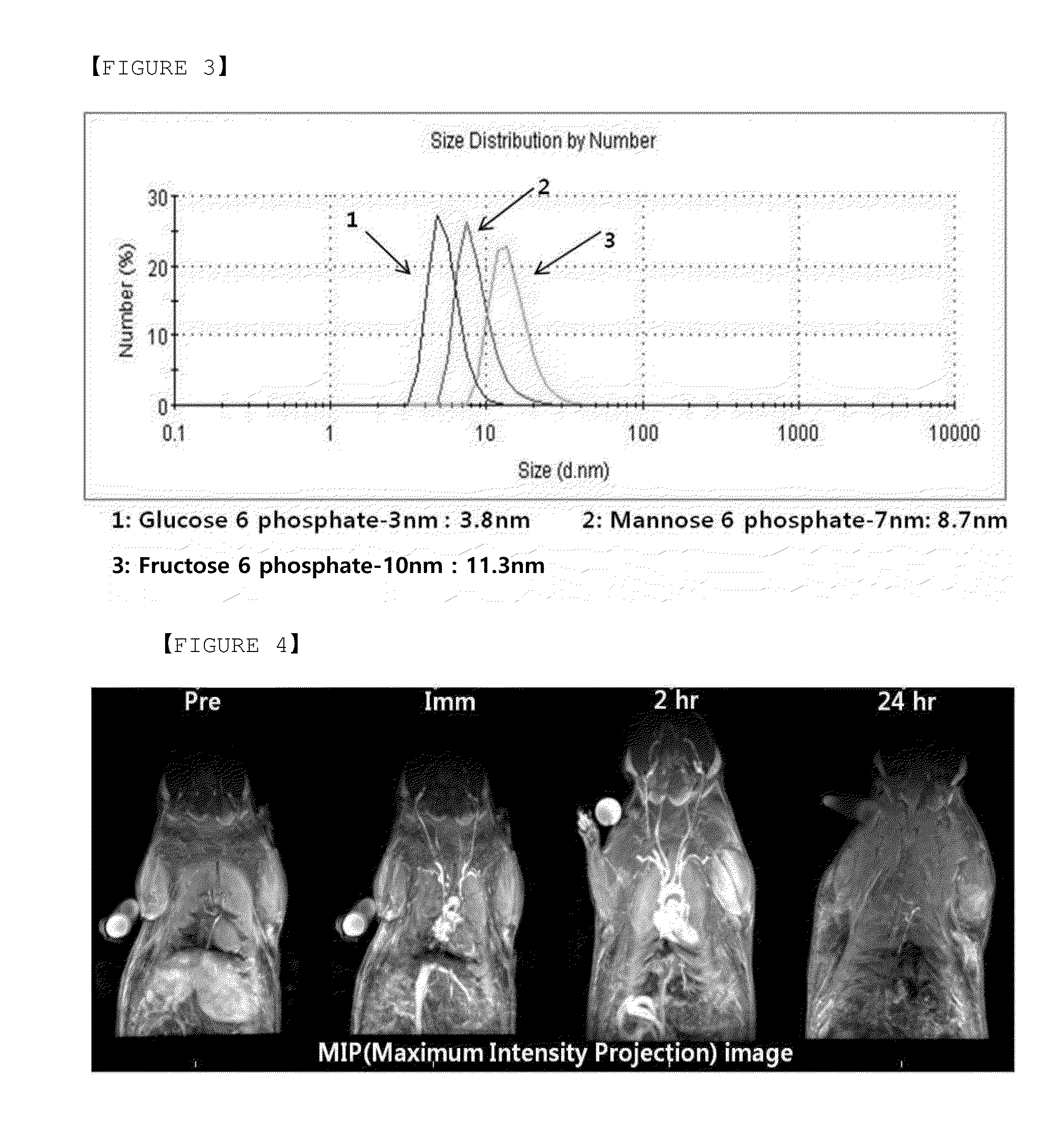
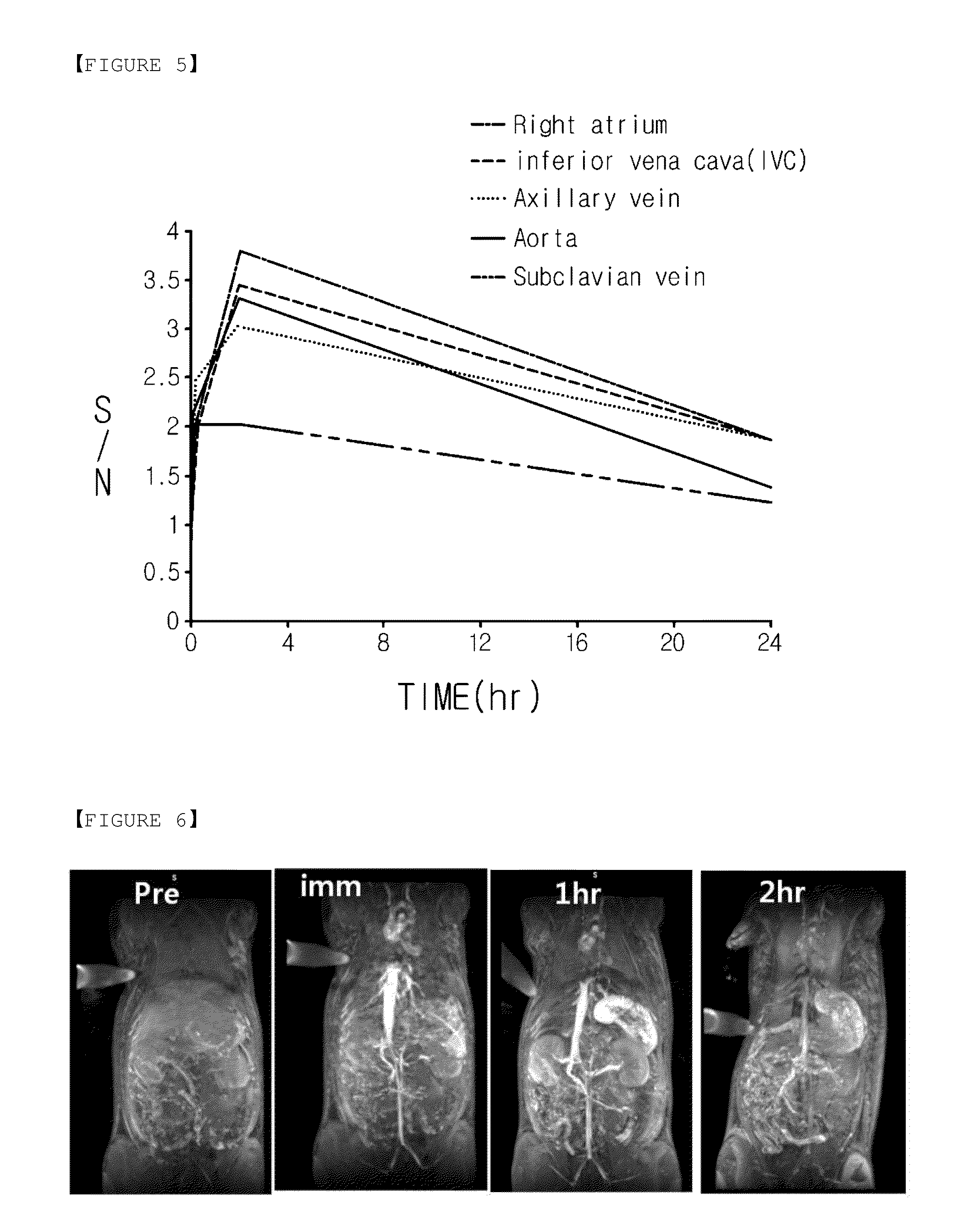
Disclosed are a composition including hydrophilic nanoparticles that have a monosaccharide-phosphate or a derivative thereof adhered to the surface thereof, a colloidal solution of the composition dispersed in water, and a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent including the colloidal solution. According to the present invention, nanoparticles having biocompatibility and excellent water-dispersibility can be prepared by modifying the surface of inorganic nanoparticles. The prepared nanoparticles may be effectively used in a variety of applications including, for example, in vivo imaging applications such as an MRI contrast agent, nano-electronic convergence technologies such as a quantum dot light emitting device, biomedical applications such as hyperthermia, or the like. Moreover, compared to existing nanoparticles dispersed by a dispersion stabilizer known in the art, excellent dispersion stability and a relatively small hydrodynamic diameter may be attained.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
Substituted silaxanthenium red to near-infrared fluorochromes for in vitro and in vivo imaging and detection
ActiveCN105073761AEvaluate effectivenessSilicon organic compoundsPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesIn vivo bildgebungEx vivo
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Methods for cell labeling and medical imaging
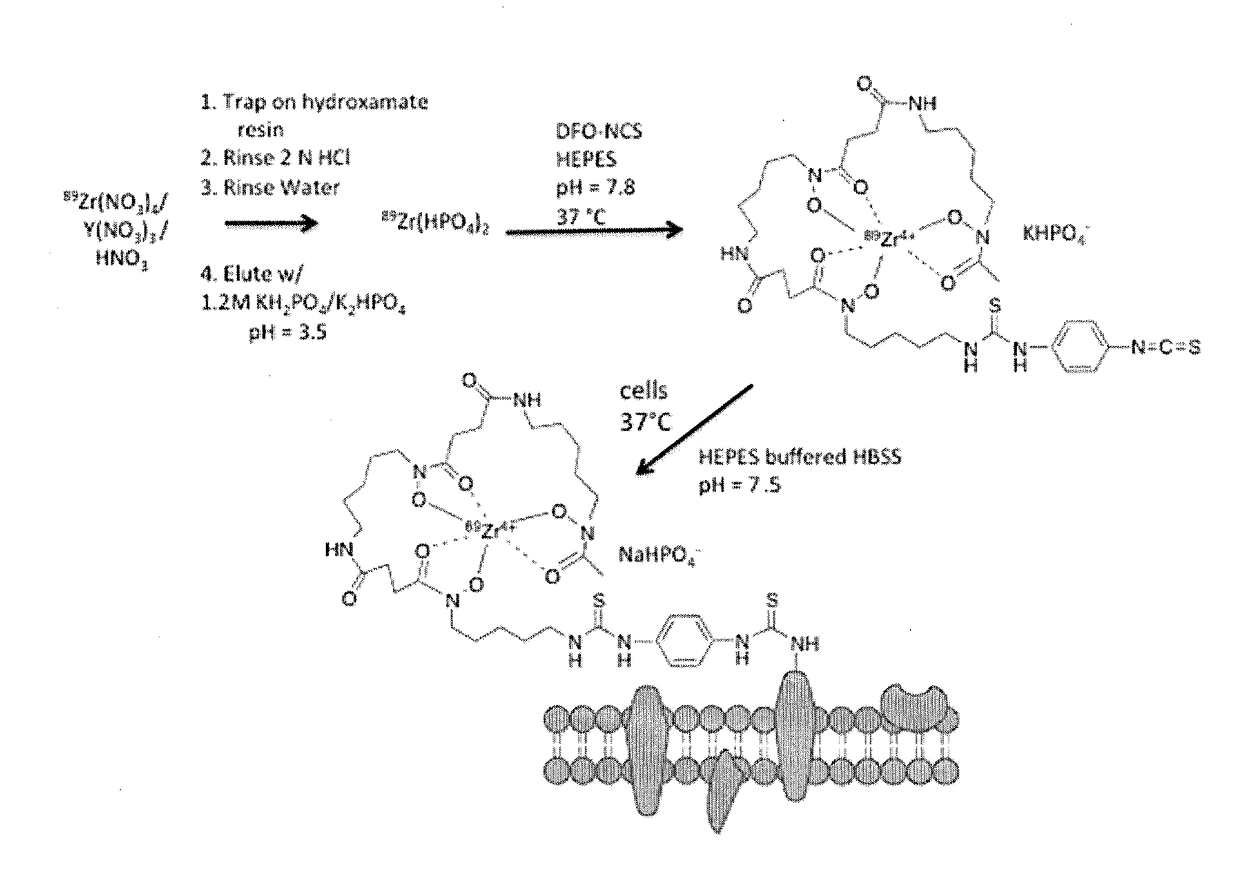
ActiveUS20180043041A1Radioactive preparation carriersRadioactive preparation formsMedical imagingBiological materials
Methods of ex vivo labeling of a biological material for in vivo imaging, methods of labeling a biological material in vivo, methods for preparing a labeling agent, and methods for in vivo imaging of a subject using a biological material labeled with a labeling agent are disclosed. In one non-limiting example, the biological material is selected from cells and the labeling agent is a 89Zr-Desferrioxamine-NCS labeling agent.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
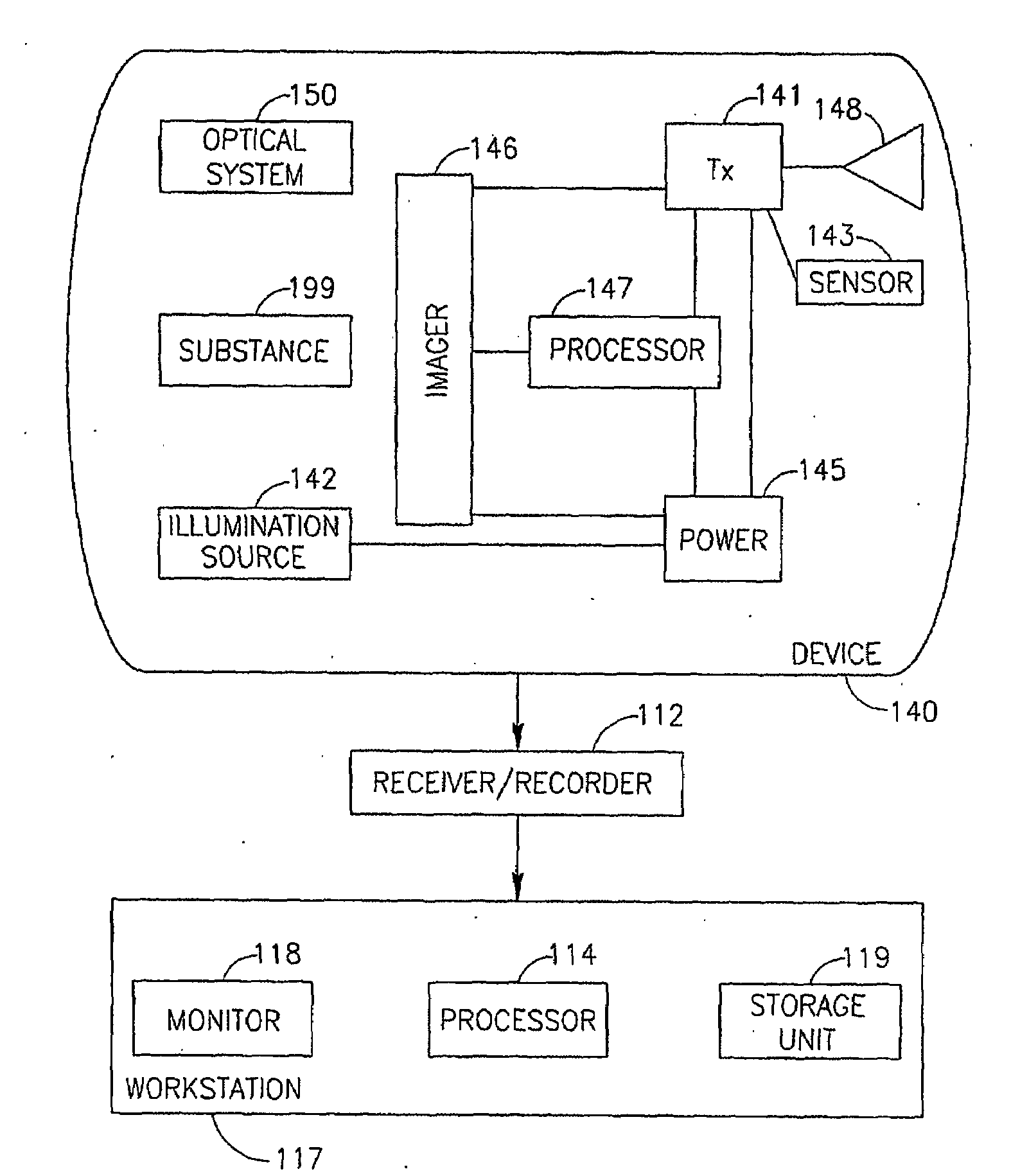
In vivo imaging device, display device, imaging and displaying system and intra-subject indwelling system using the same
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
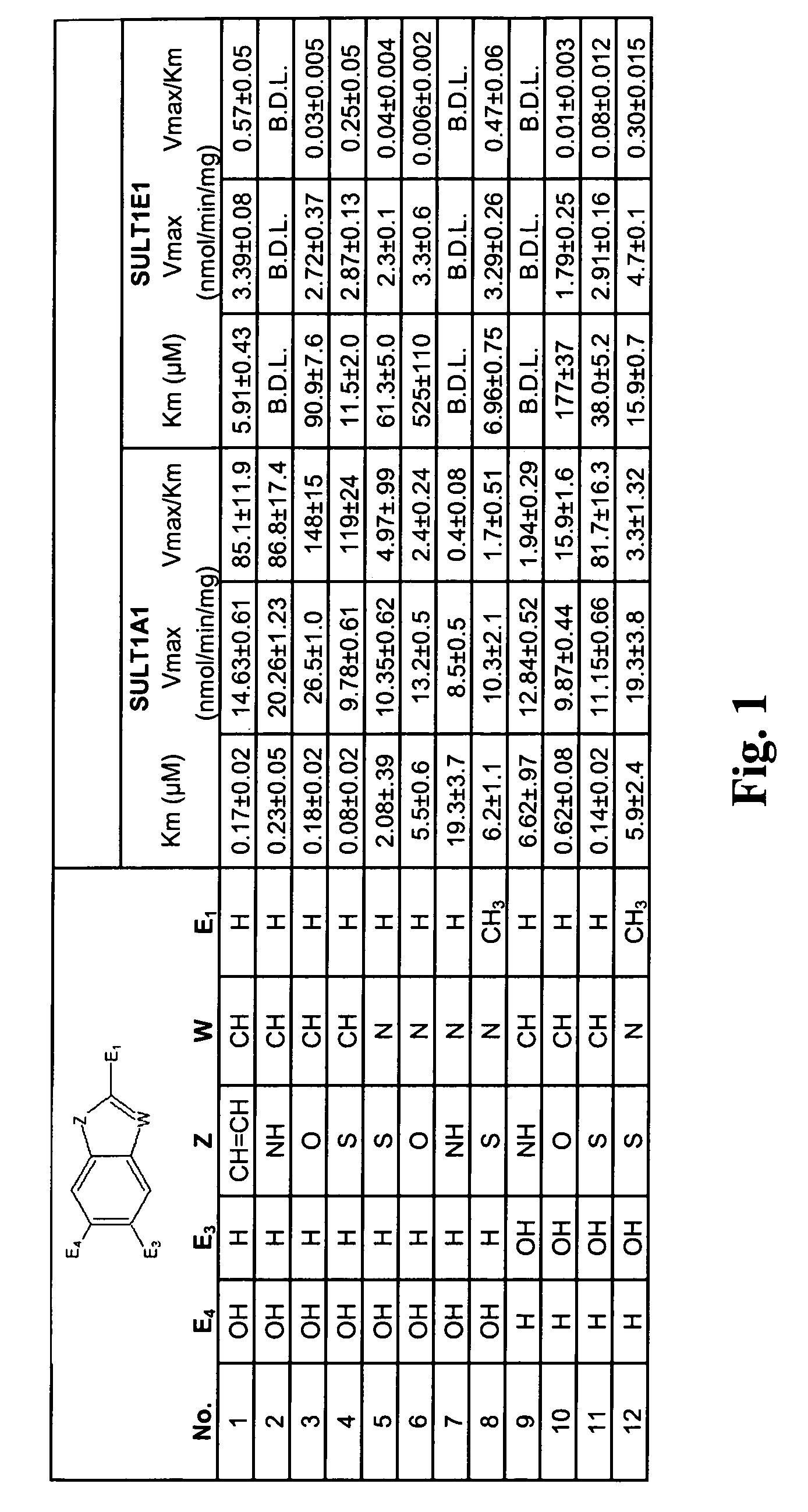
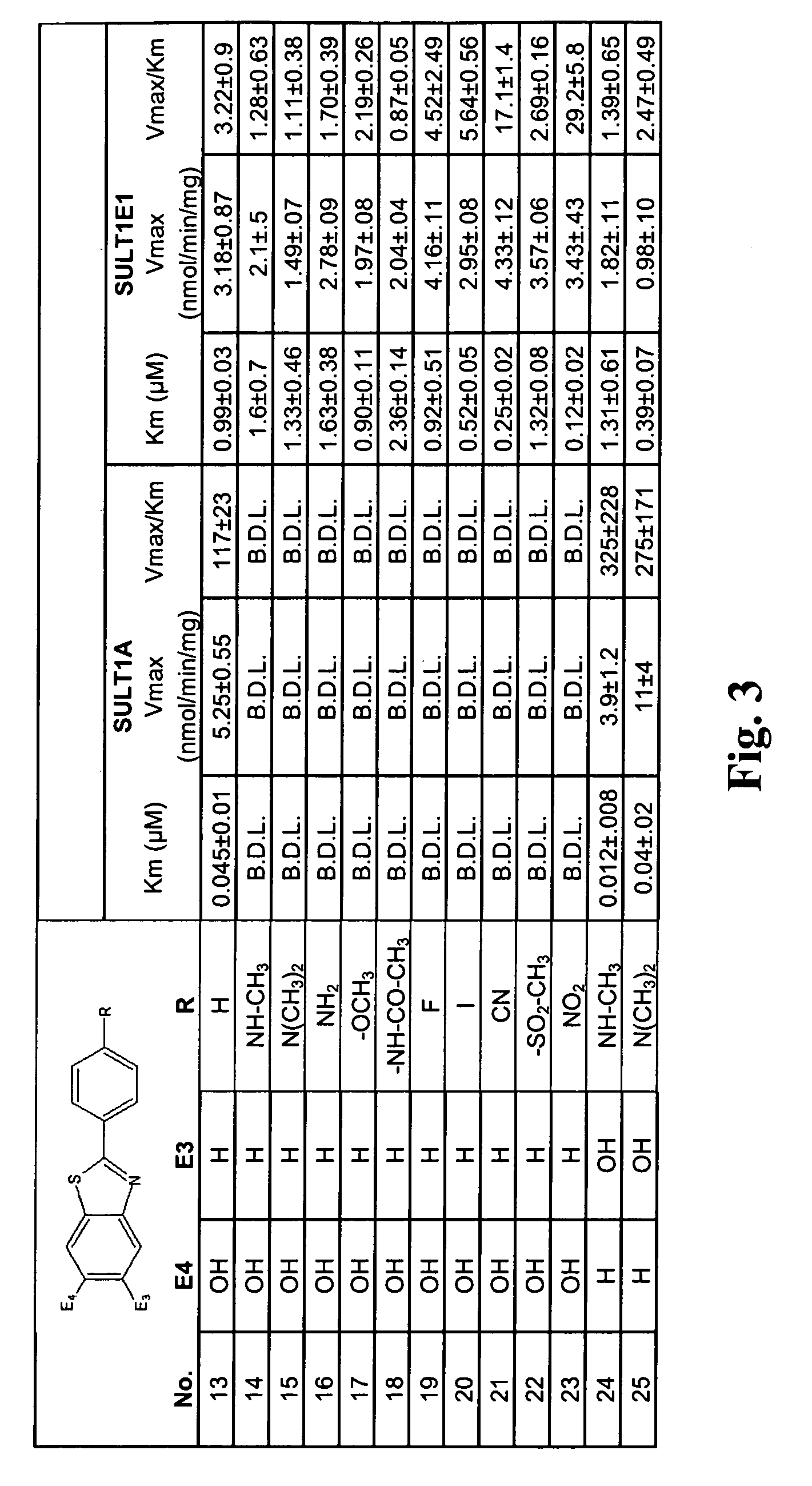
In vivo imaging of sulfotransferases
Radiolabeled tracers for sulfotransferases (SULTs), their synthesis, and their use are provided. Included are substituted phenols, naphthols, coumarins, and flavones radiolabeled with 18F, 123I, 124I, 125I, or 11C. Also provided are in vivo techniques for using these and other tracers as analytical and diagnostic tools to study sulfotransferase distribution and activity, in health and disease, and to evaluate therapeutic interventions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
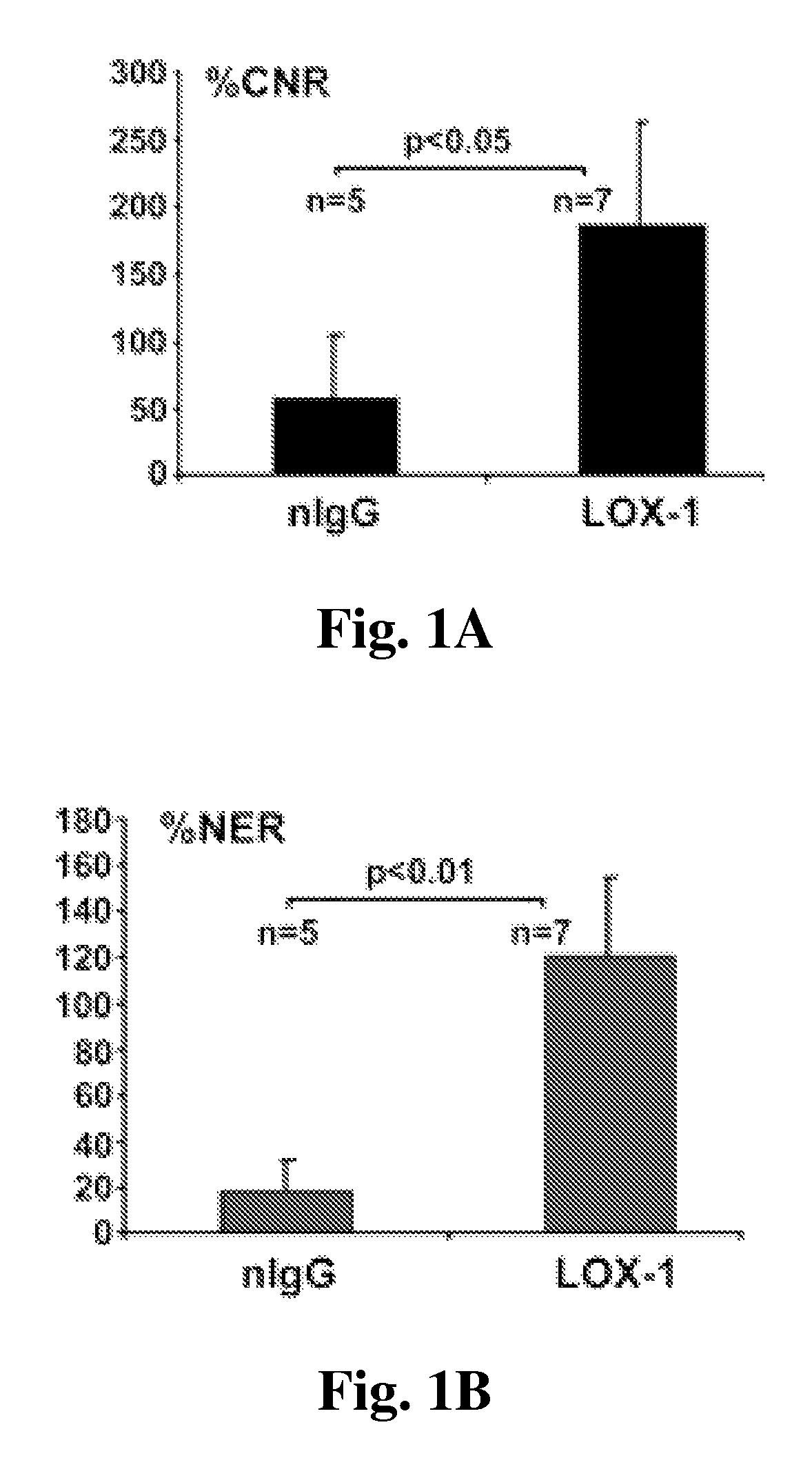
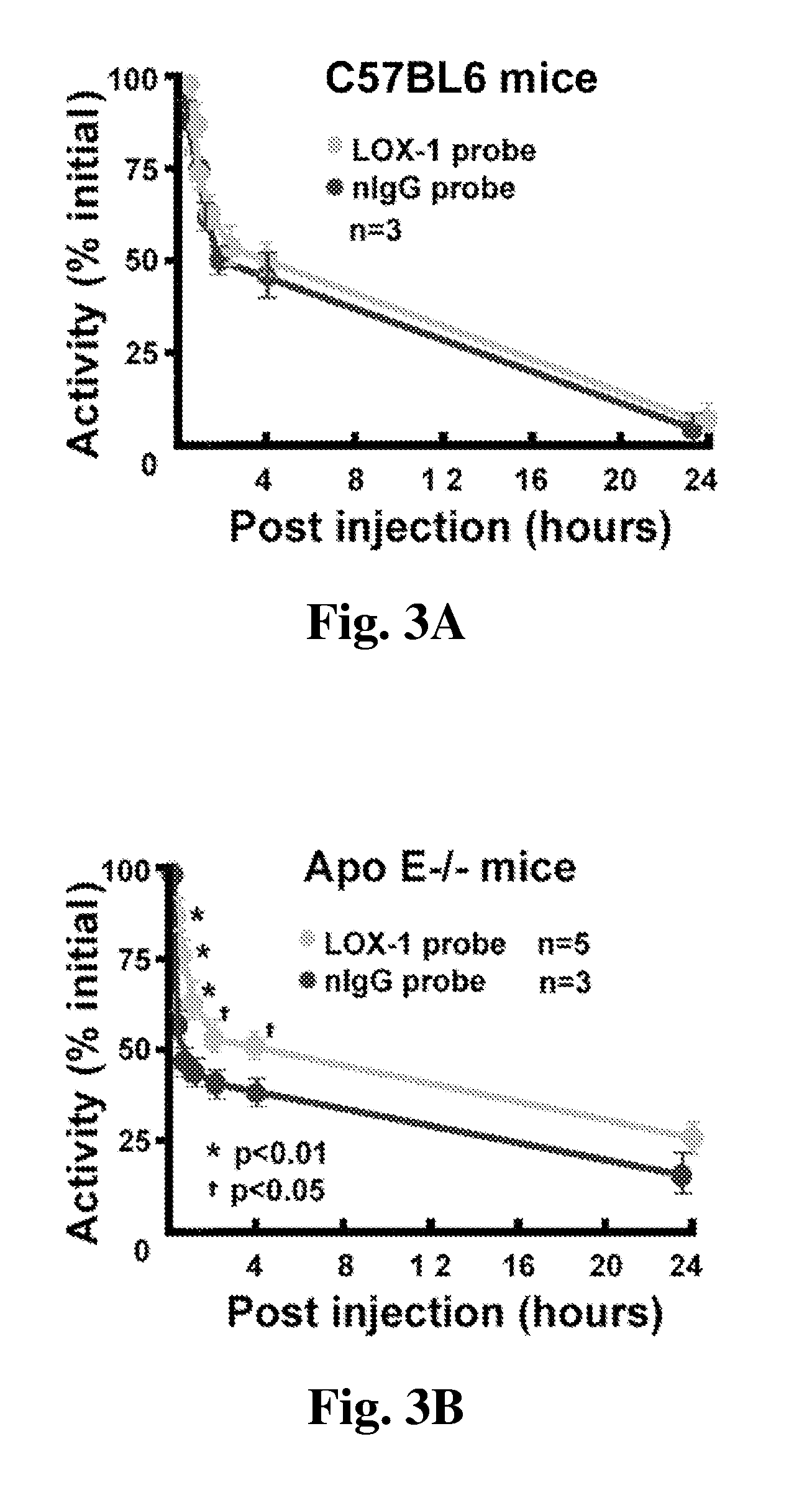
Multimodal imaging of atherosclerotic plaque targeted to LOX-1
The present invention provides multiple modalities for detecting LOX-1. More particularly, an imaging composition is provided that allows for the in vivo imaging of atherosclerotic plaque.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method for carrying out bio-orthogonal polysaccharide labeling from microbiome level, and applications thereof
InactiveCN107760755AFacilitate the identification of bacterial speciesFacilitate biological function researchMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFloraMicrobiome
The present invention provides a method for carrying out bio-orthogonal polysaccharide labeling from a microbiome level. The method comprises: placing microbial flora in a culture medium added with afirst probe, and culturing to obtain a microbial flora labeled with the first probe, wherein the first probe is one or a variety of unnatural saccharides; and carrying out a bio-orthogonal reaction onthe microbial flora labeled with the first probe and a second probe to obtain a microbial flora labeled with the second probe, wherein the second probe is a chemical marker capable of being subjectedto a bio-orthogonal reaction with the first probe. According to the present invention, with the method, a variety of bacteria capable of being metabolized and labeled with unnatural saccharides can be rapidly screened in the high-throughput manner, the specific types of the unnatural saccharides for metabolizing and labeling different bacteria can be determined, the possibility can be provided for the in vivo imaging of the specific microbiome, and the powerful tool is provided for the exploring of the biological functions of the macromolecules containing the polysaccharide structure in the bacteria difficultly cultured separately.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
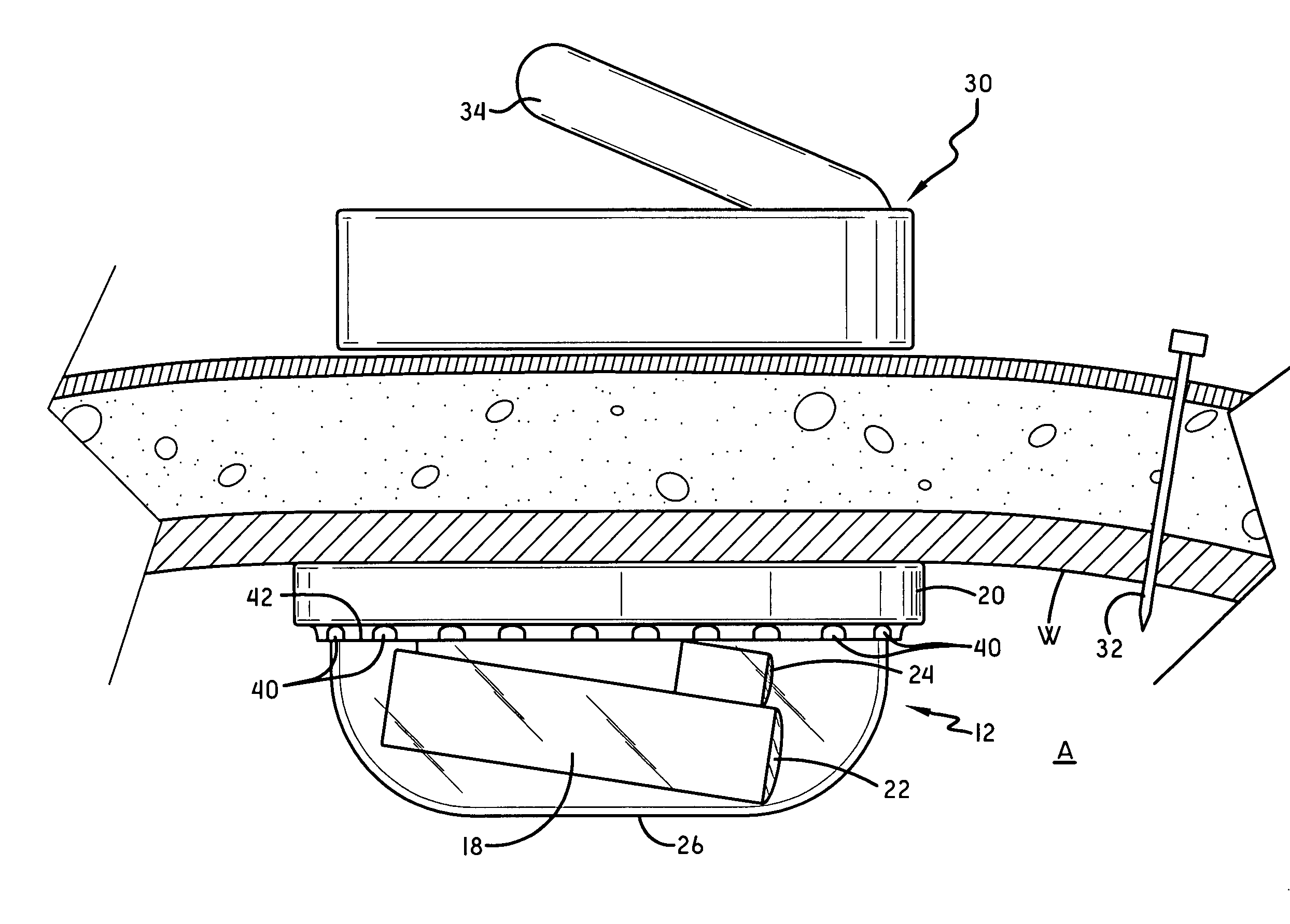
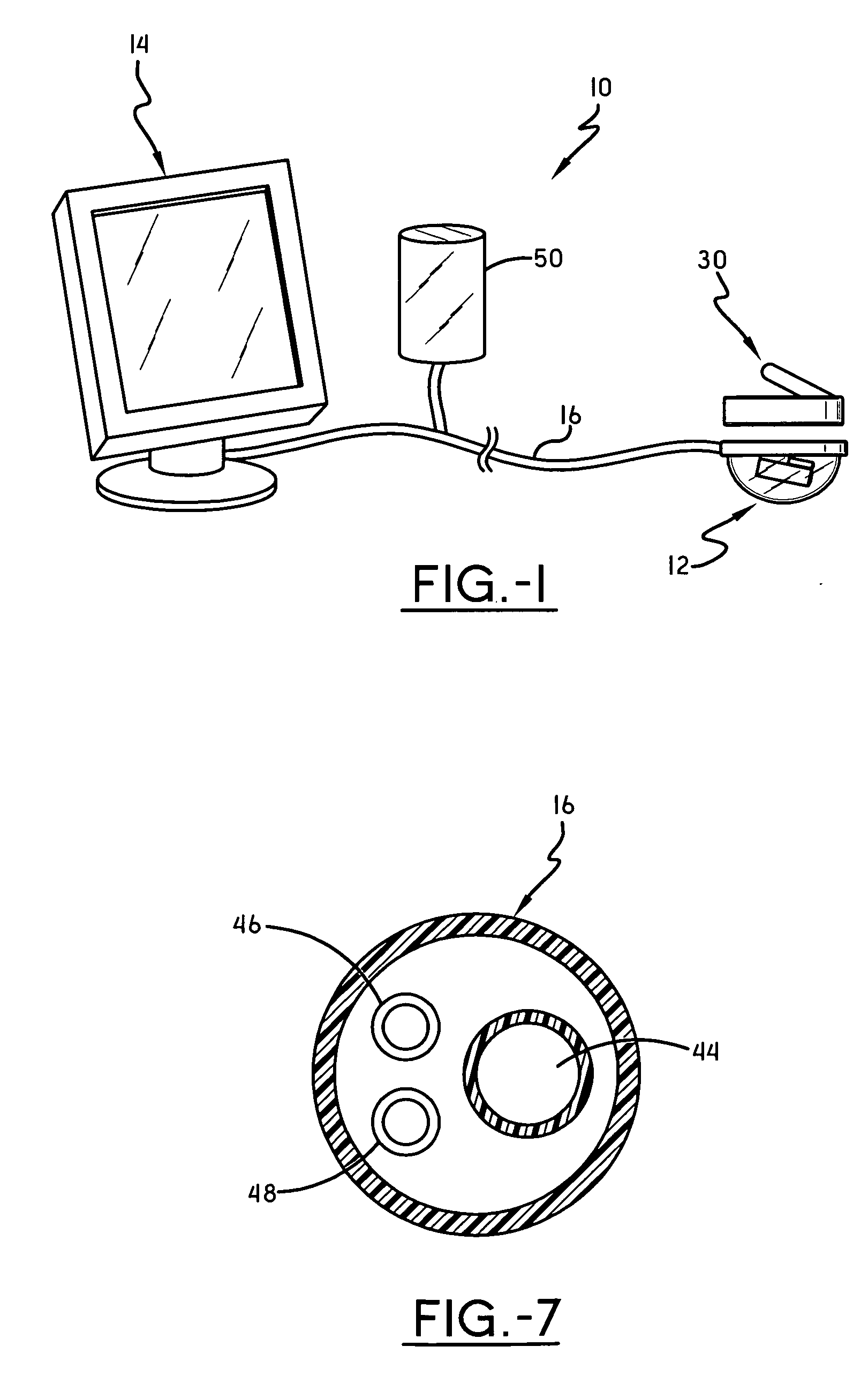
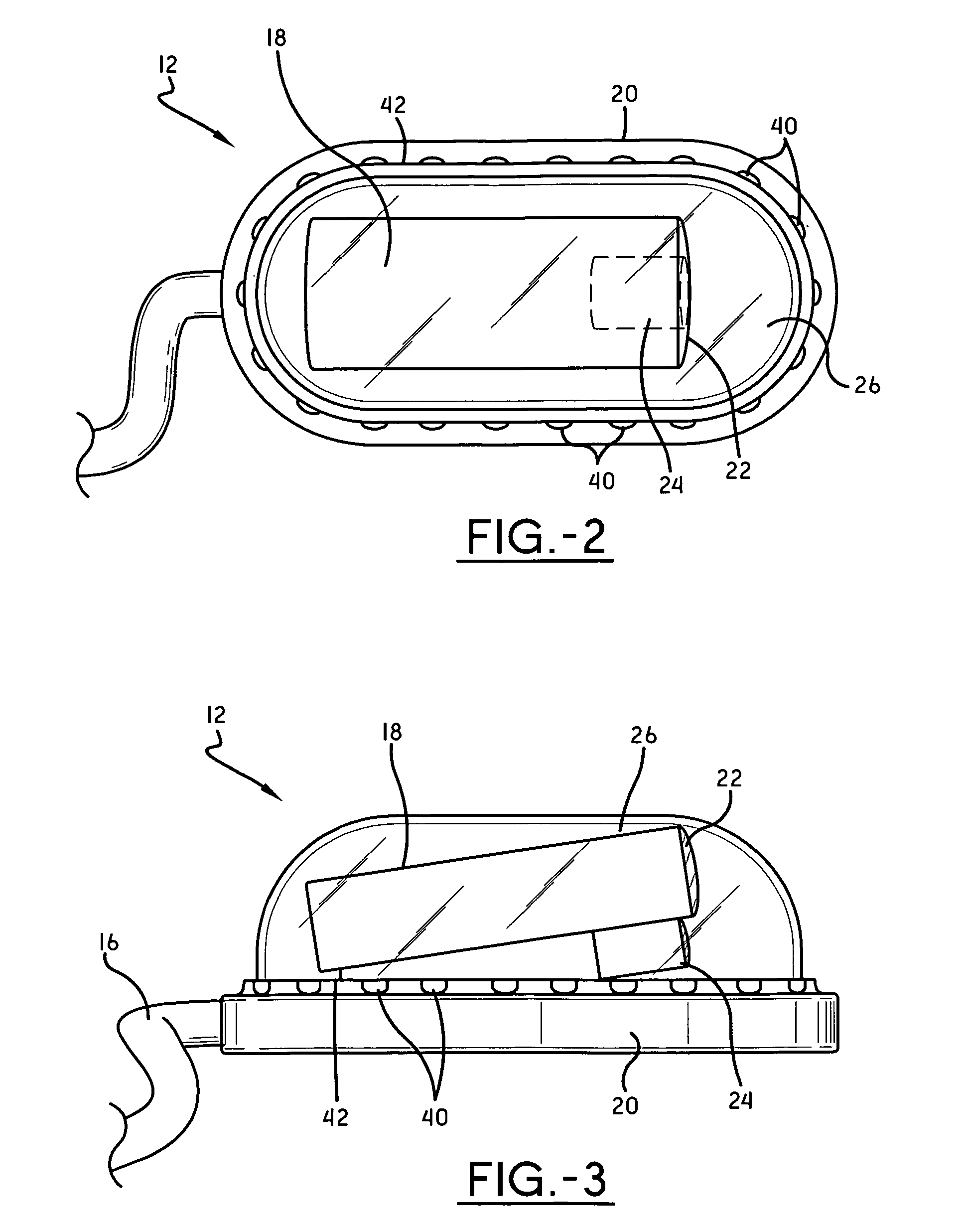
In vivo imaging system
An in vivo imaging system for viewing the interior of an organism includes a camera mounted to a sled body that is placed in the interior of the organism. The camera includes a lens, and a dome covers the lens. An image display device is provided to display images received from the camera. A cable communicates images to the image display device according to a viewing angle of the lens. A magnetic source body placed on the exterior of the organism magnetically attracts the sled body to hold the sled body in place in the interior of the organism.
Owner:MYERS STEPHEN R
Methods and compositions to reduce scattering of light during therapeutic and diagnostic imaging procedures
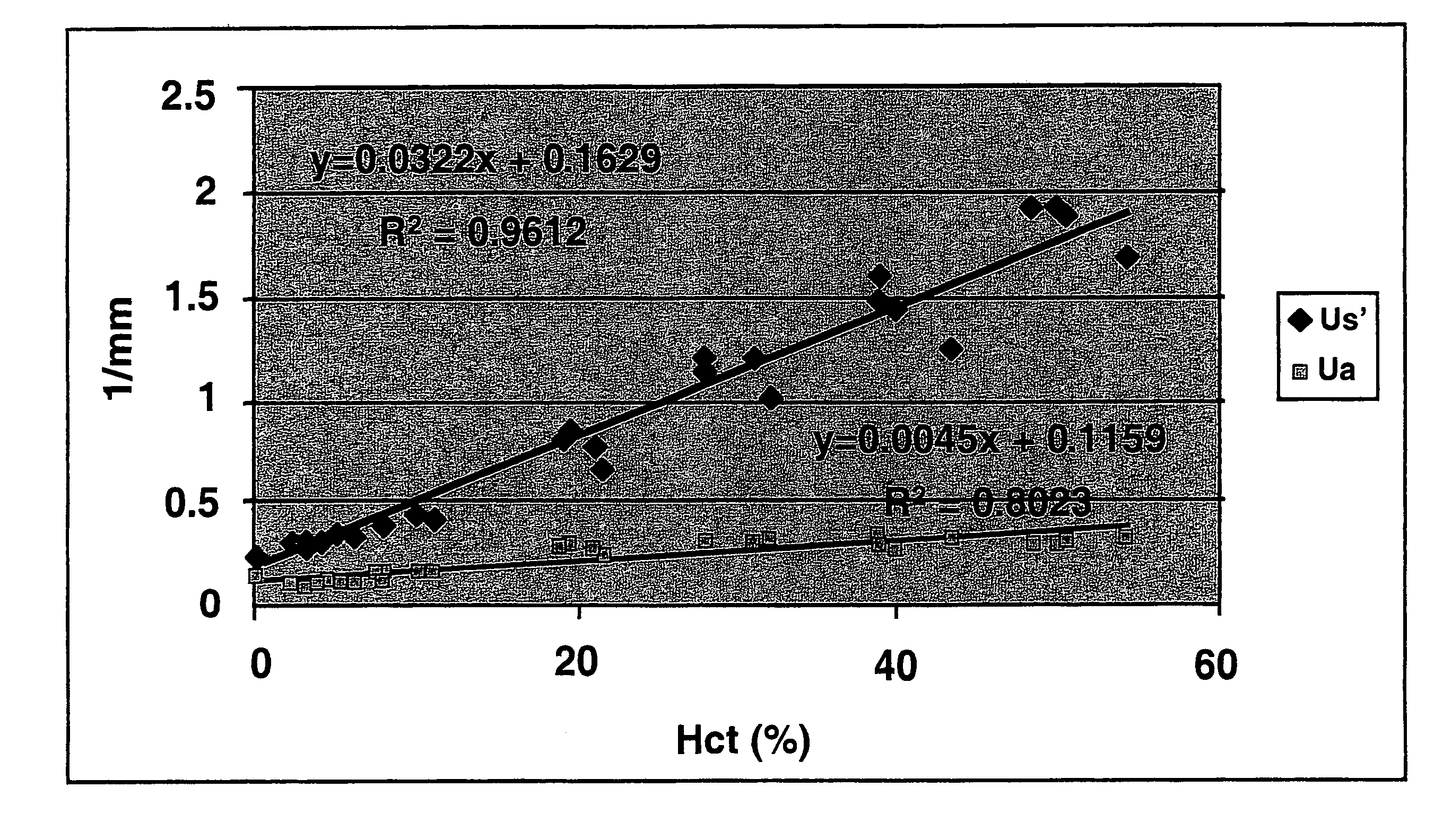
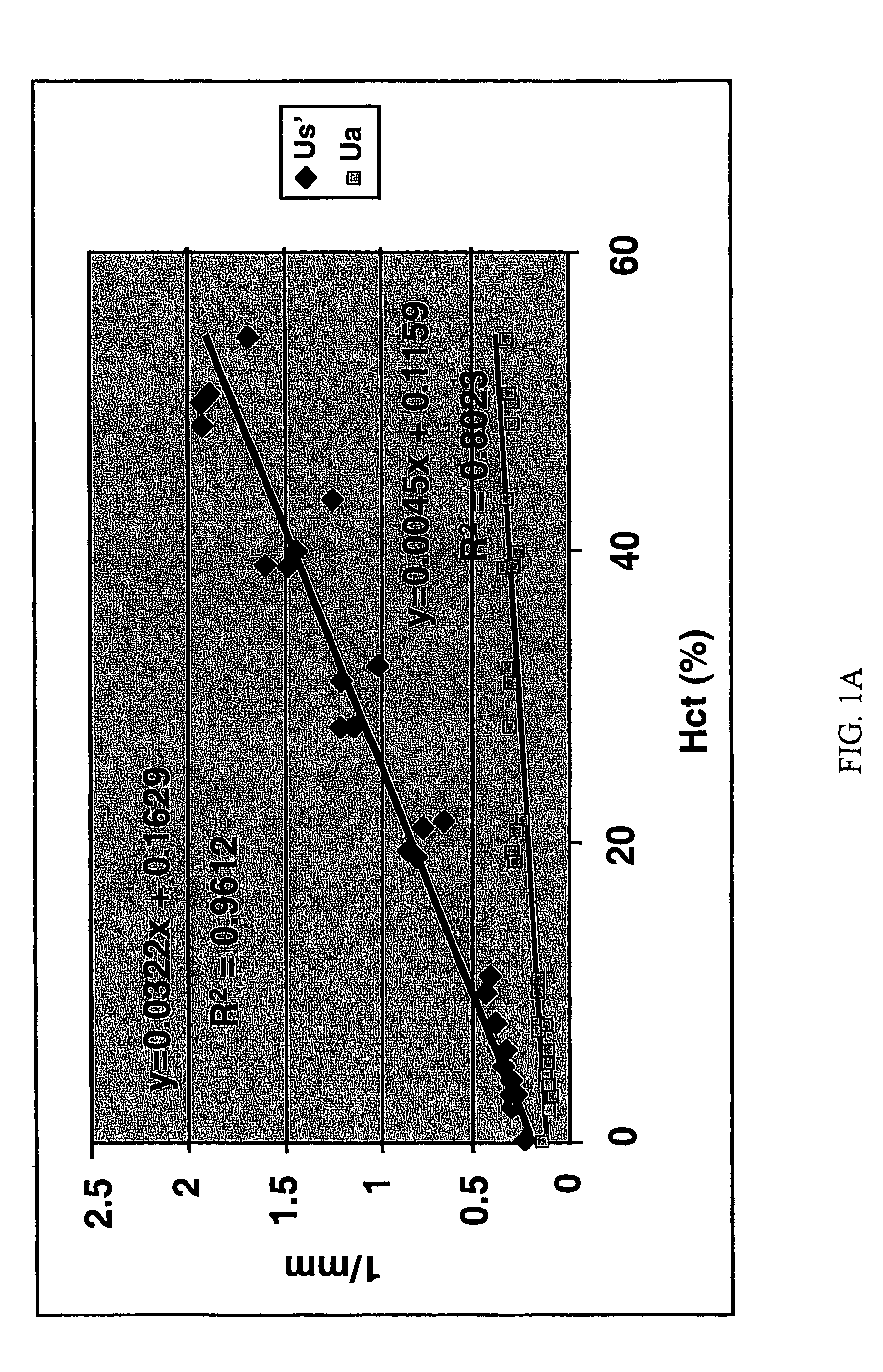
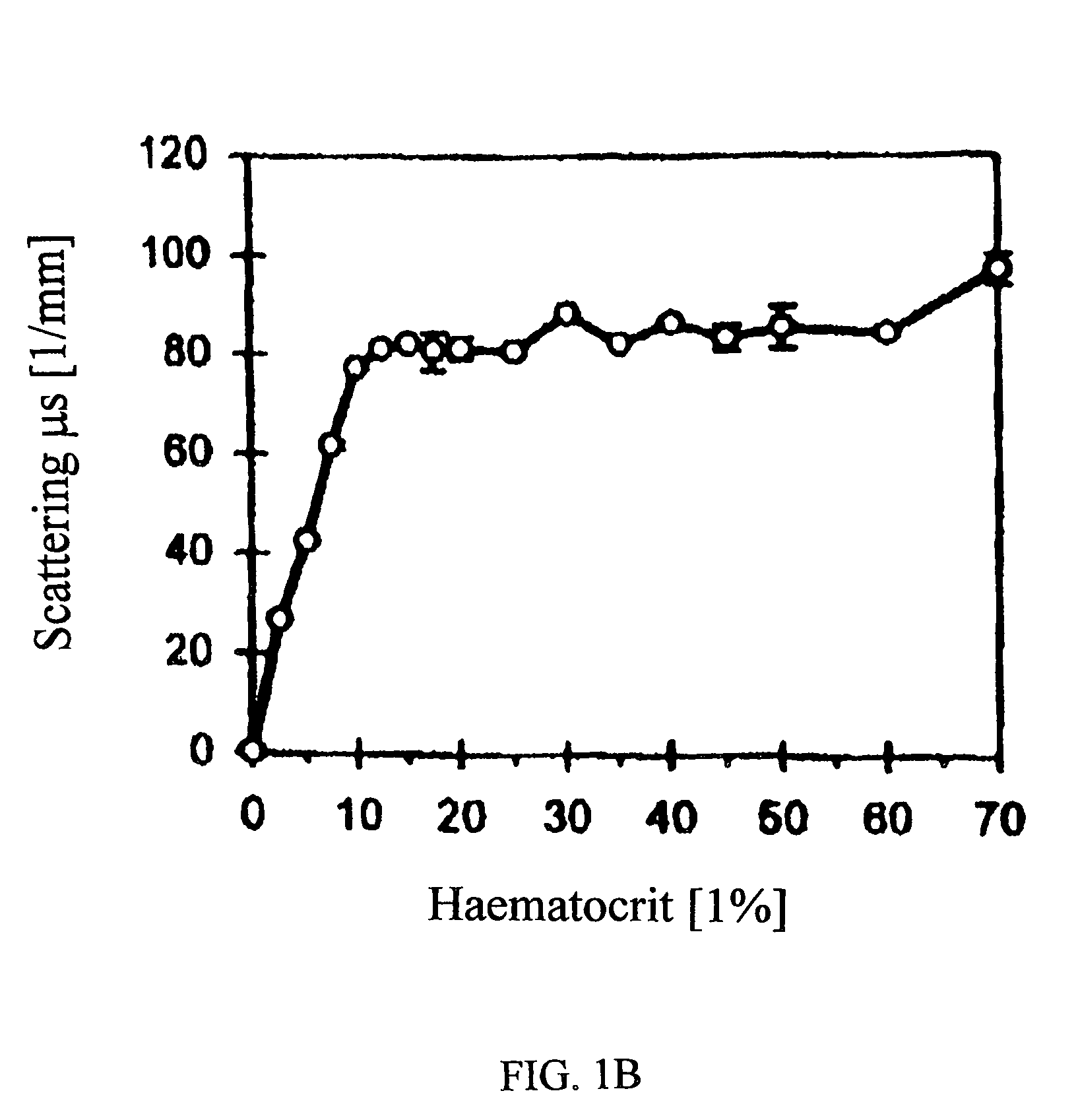
InactiveUS7747315B2Rapid and high resolution imagingReduce signal attenuationDiagnostics using tomographySensorsVascularizesHematological test
Disclosed are improved methods and compositions for use in light-based in vivo imaging and treatment. The techniques described involve the use of low-scattering, oxygen-carrying blood substitutes in imaging and treatment methods, including OCT imaging. The invention has particular advantages in imaging within the cardiovascular system and highly vascularized or oxygen-dependent tissues.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com