Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Point of load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Point load is that load which acts over a small distance. Because of concentration over small distance this load can may be considered as acting on a point. Point load is denoted by P and symbol of point load is arrow heading downward (↓).
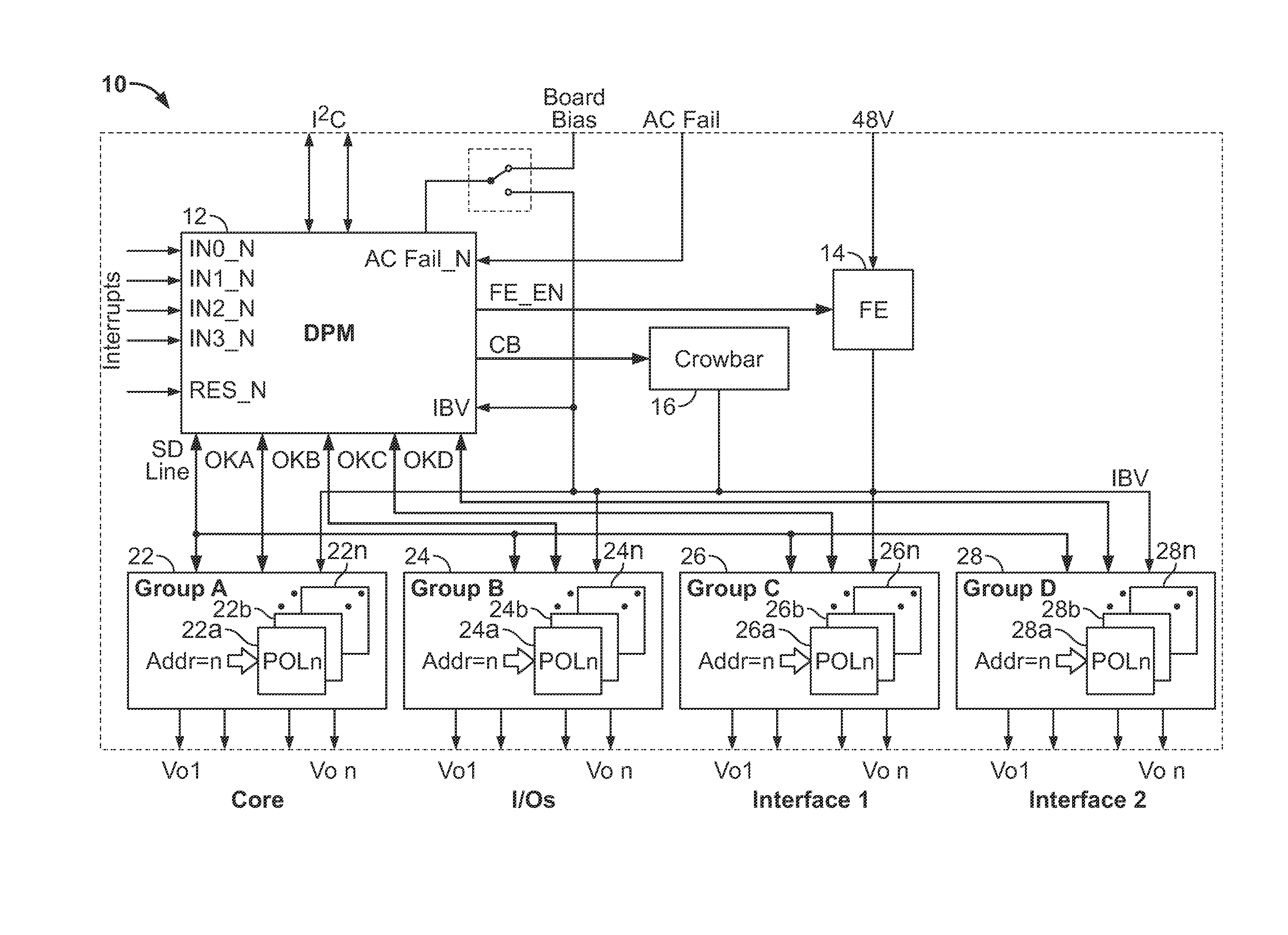
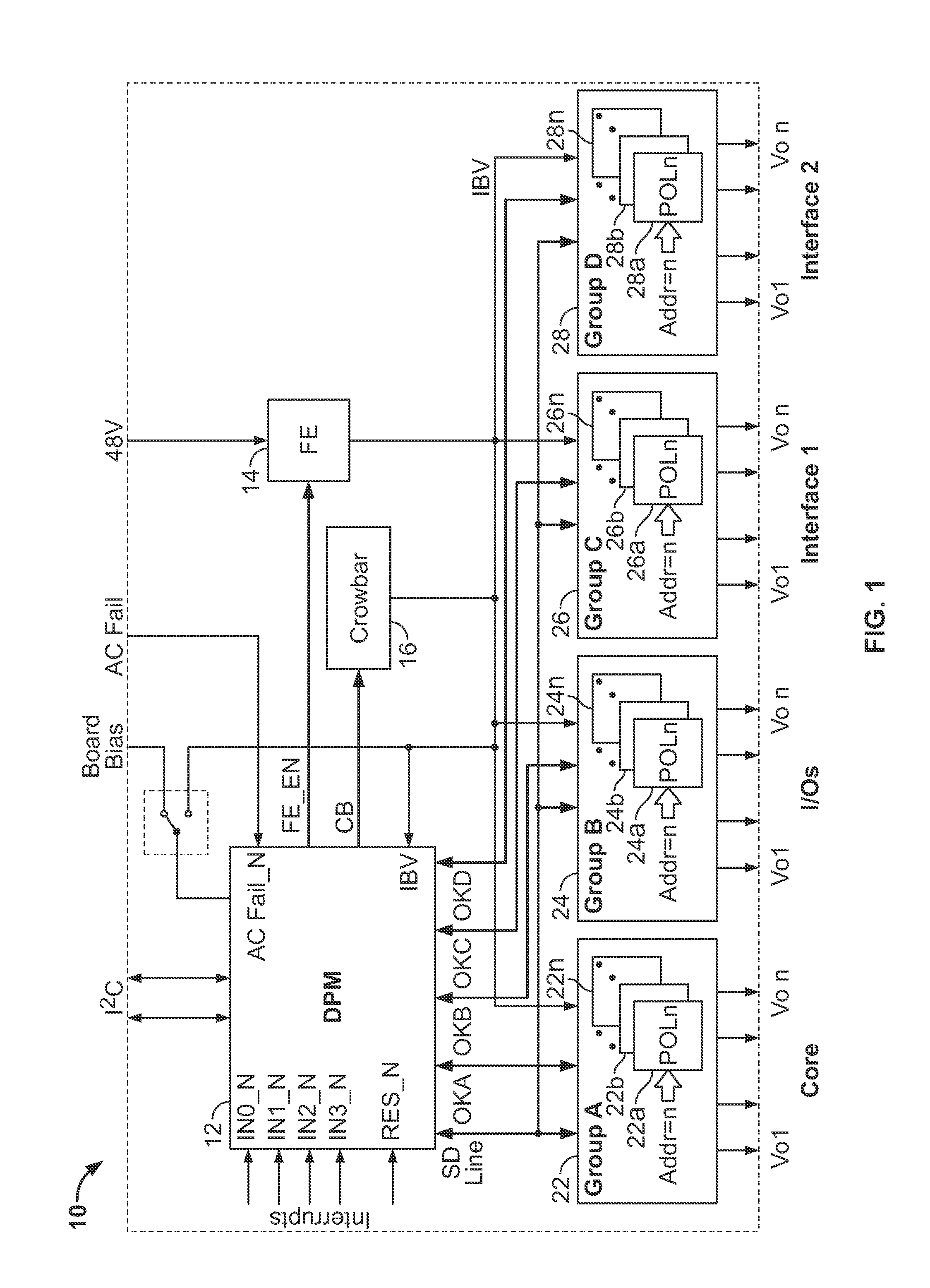
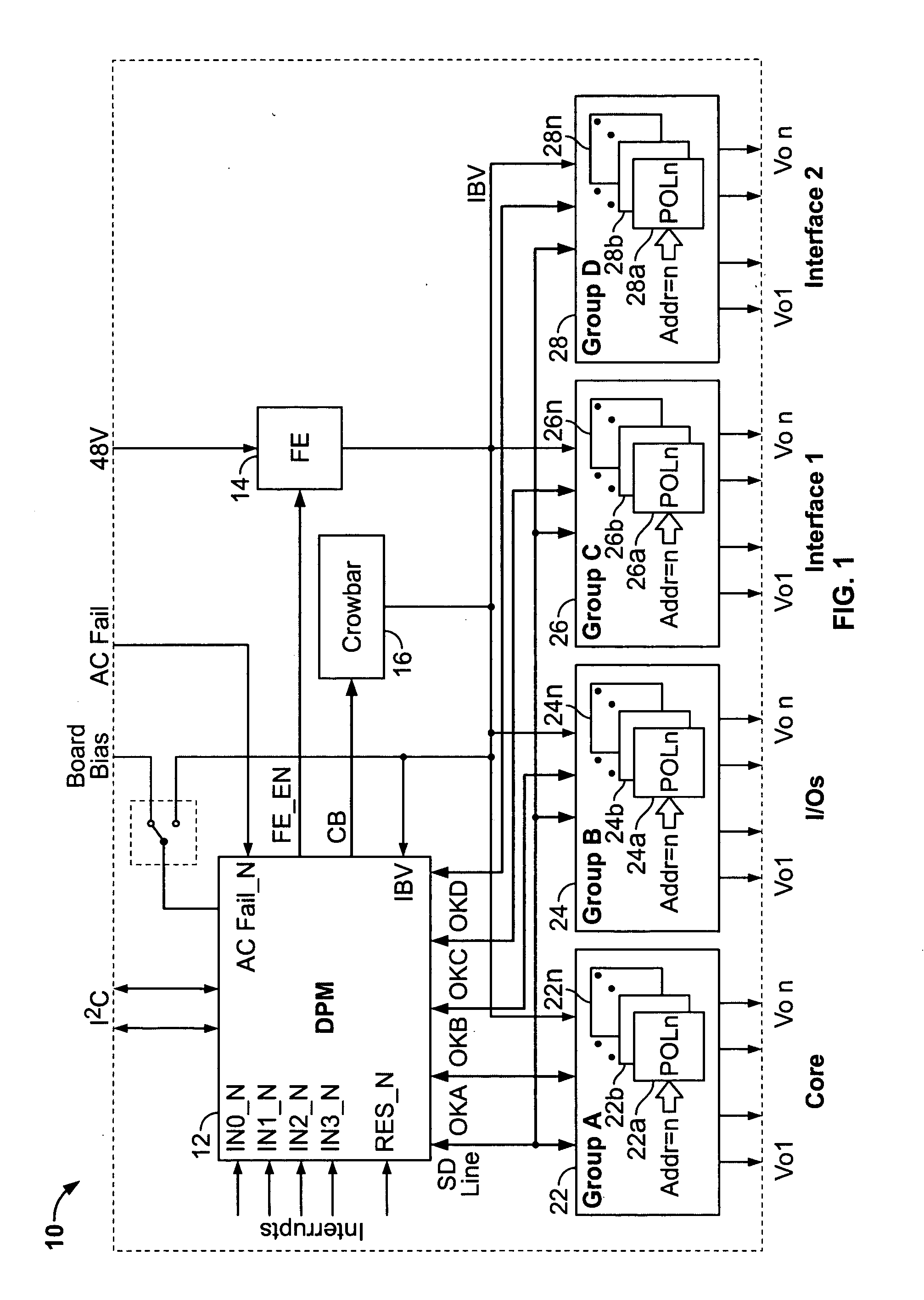
Point of load regulator having a pinstrapped configuration and which performs intelligent bus monitoring
ActiveUS20060149396A1Low costVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringPoint of loadVoltage converter
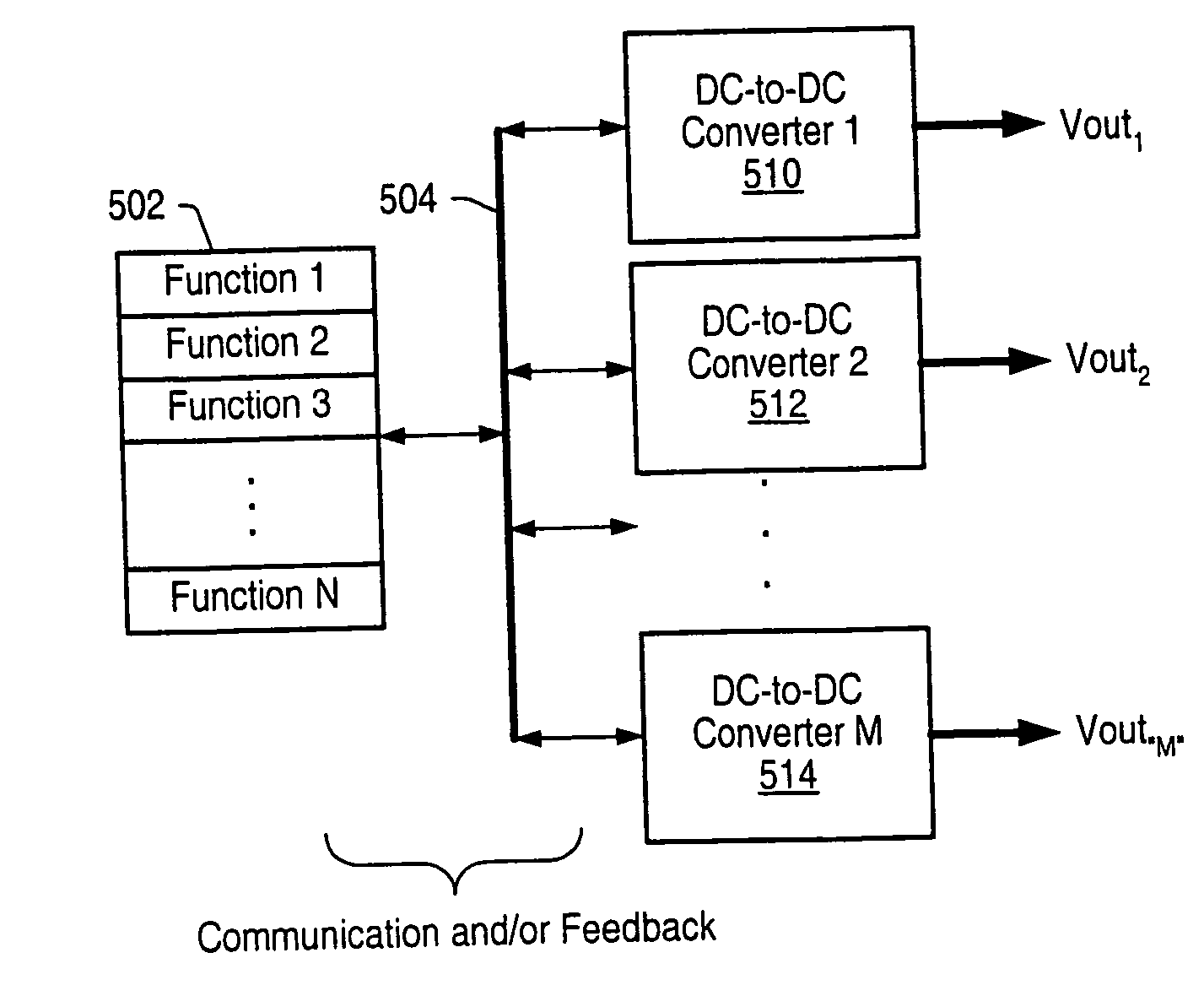
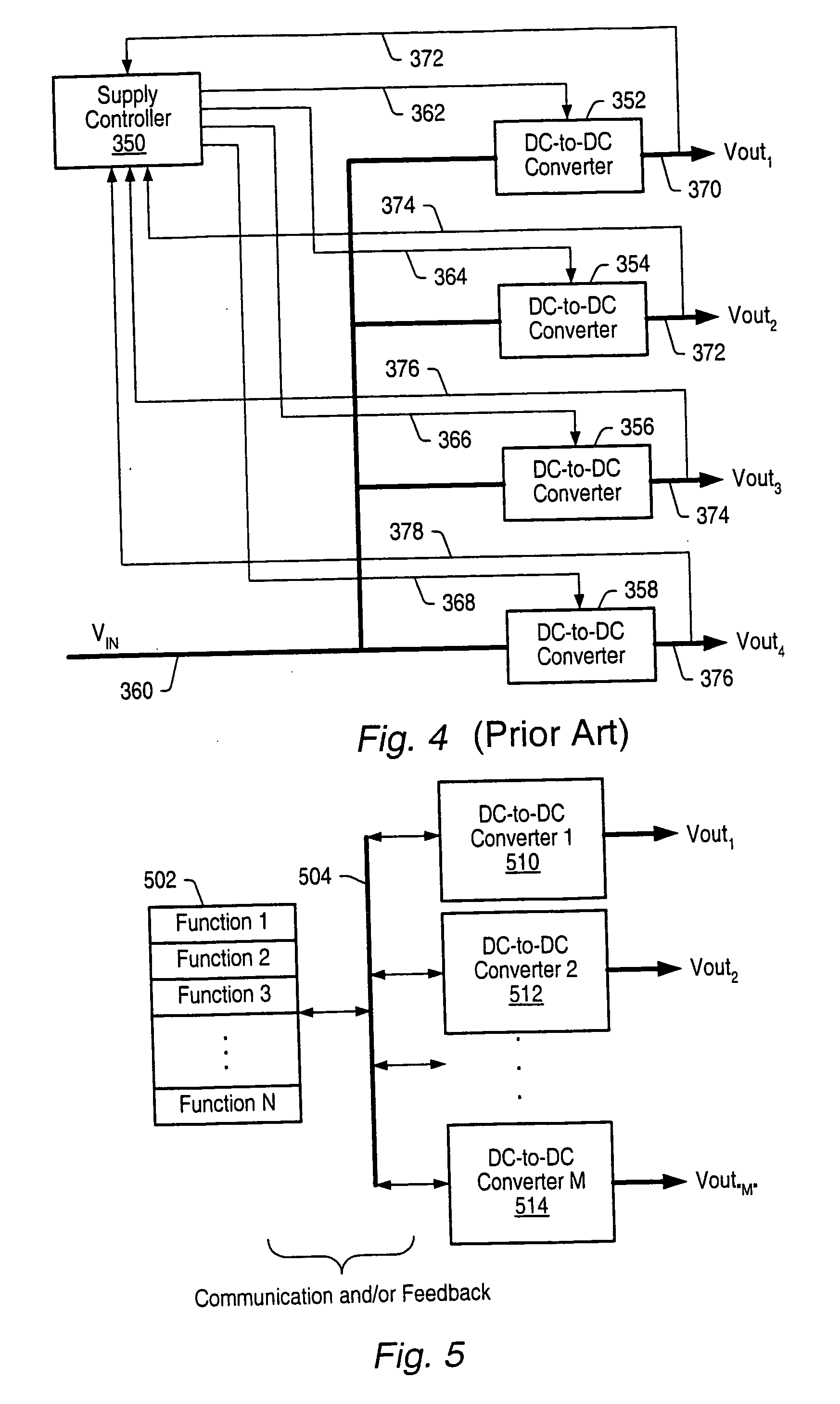
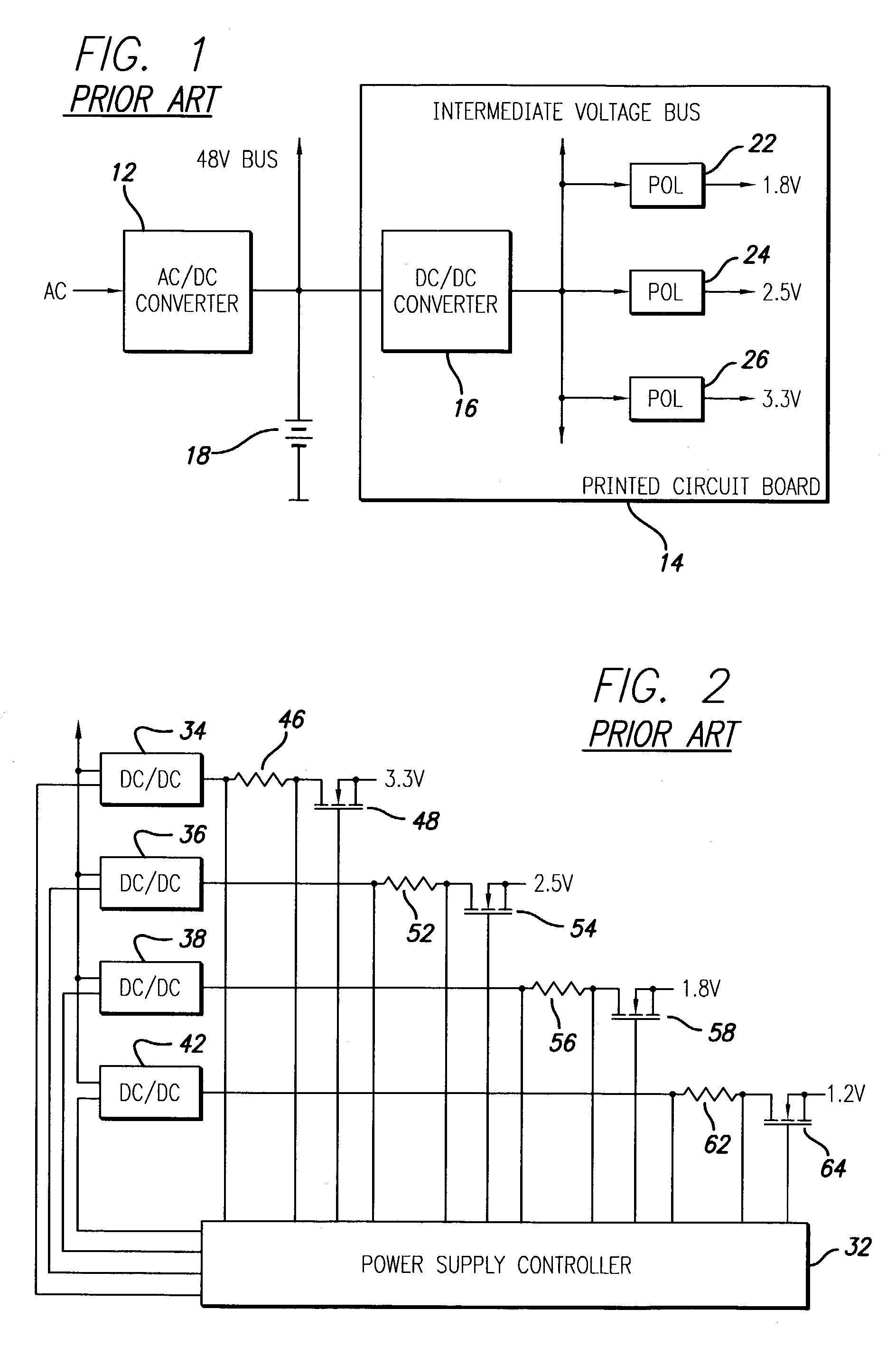
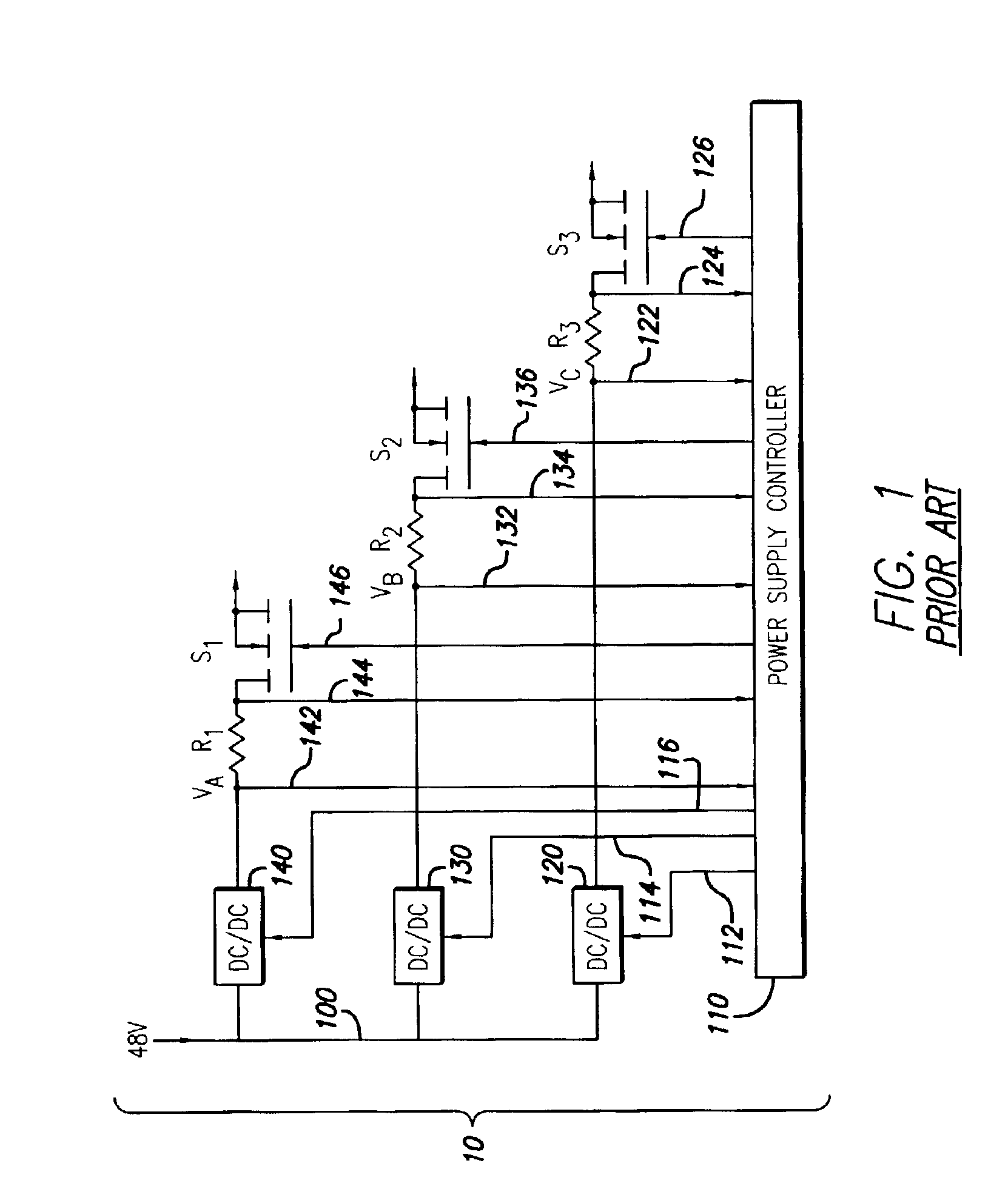
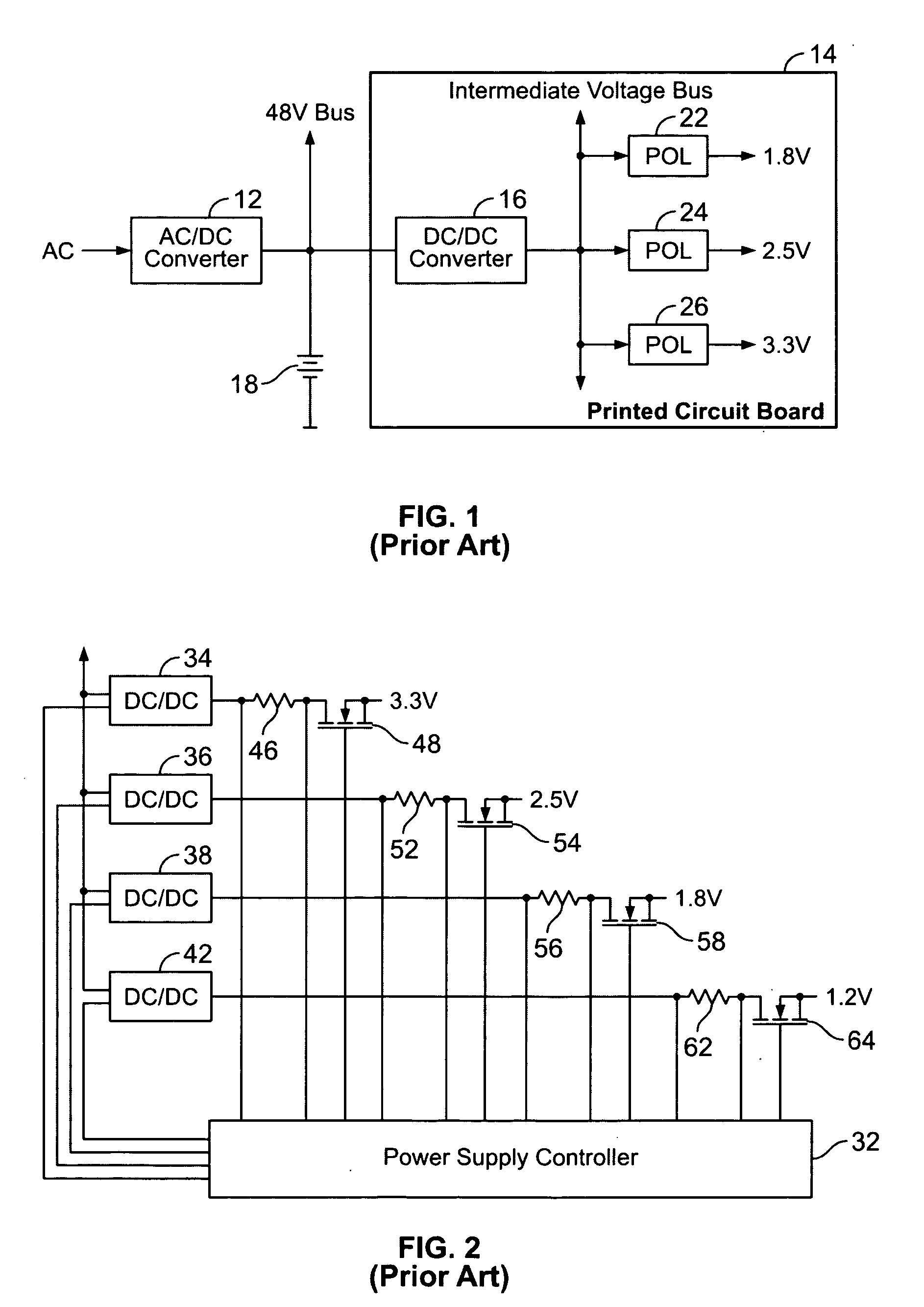
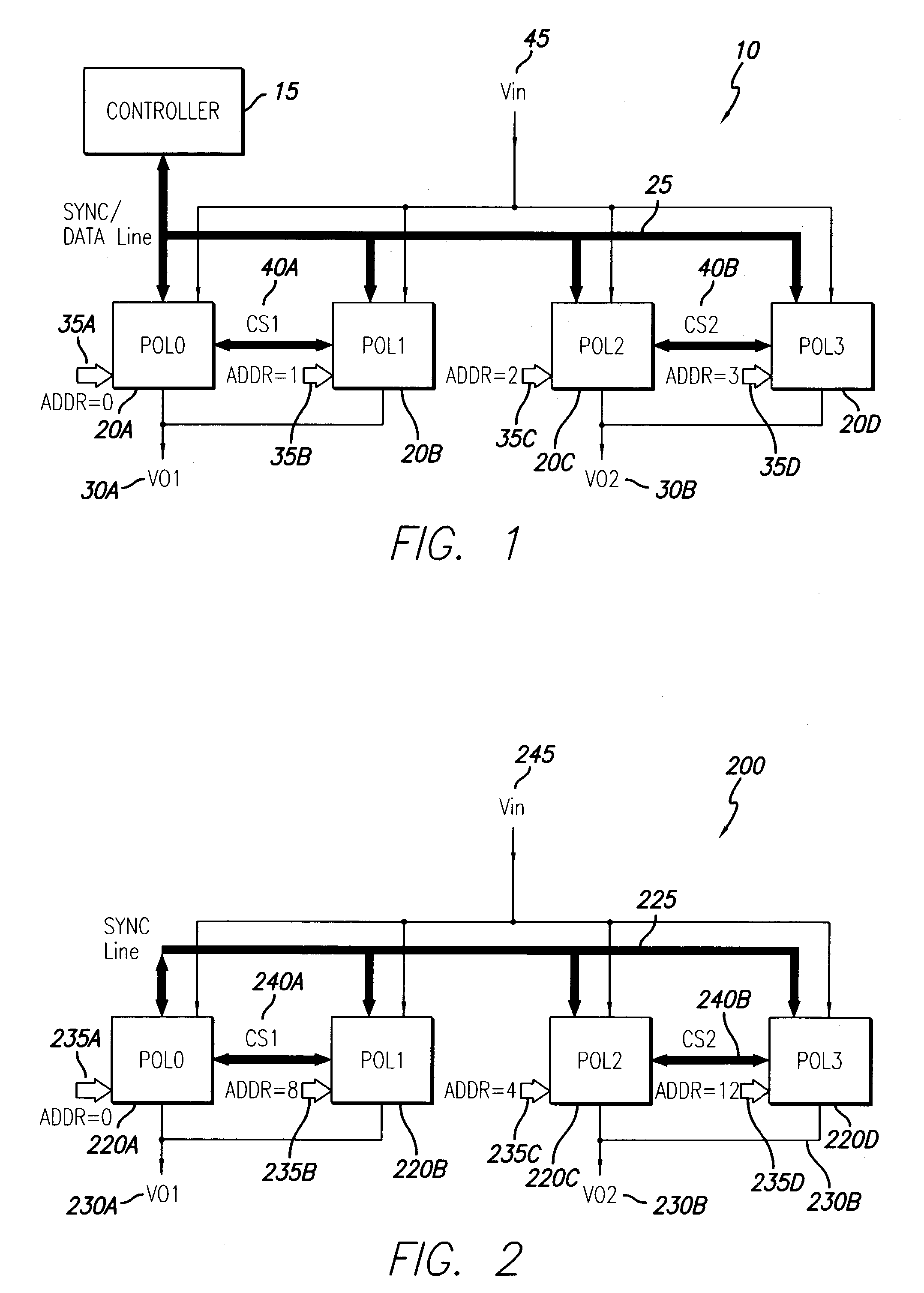
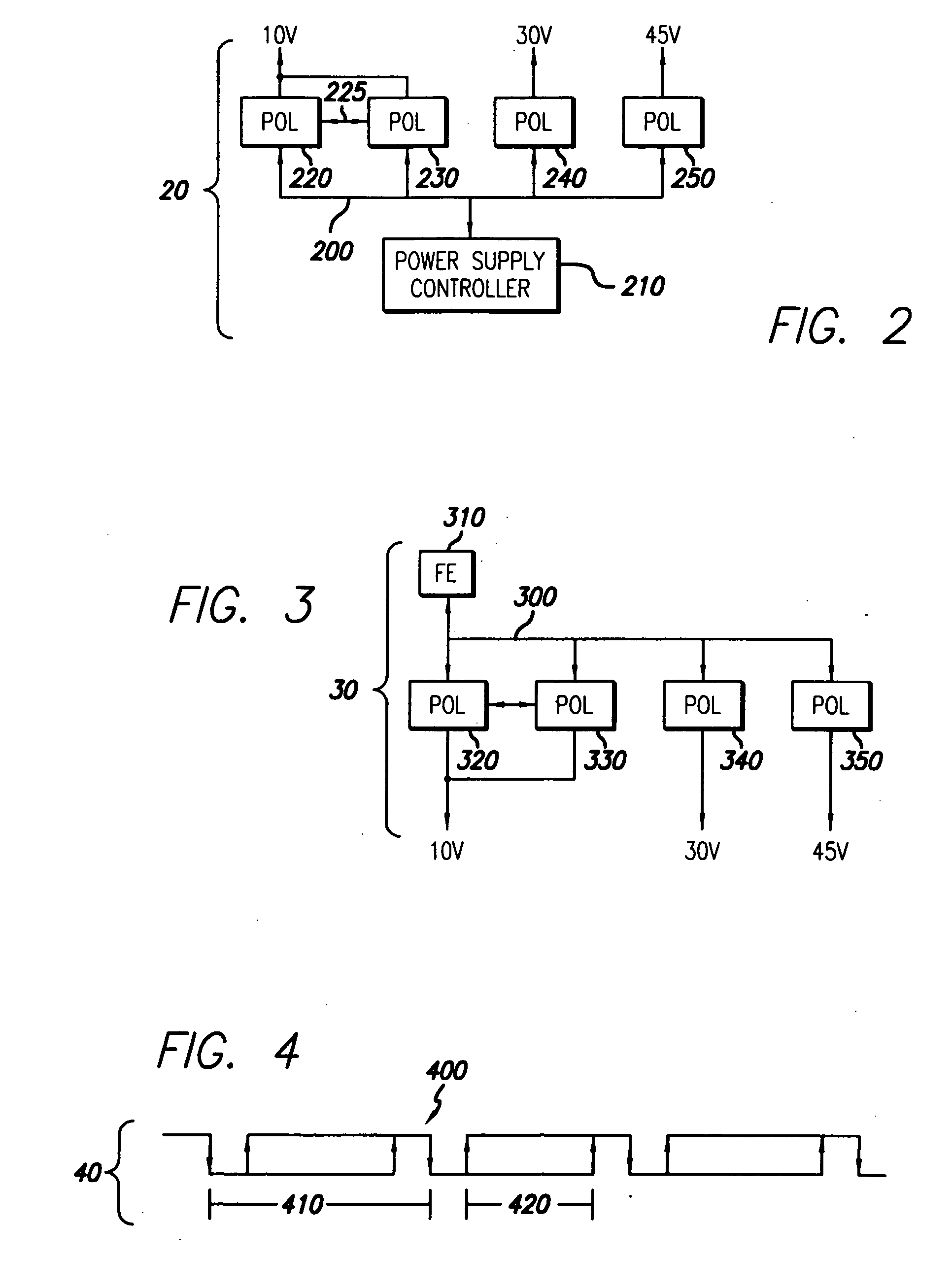
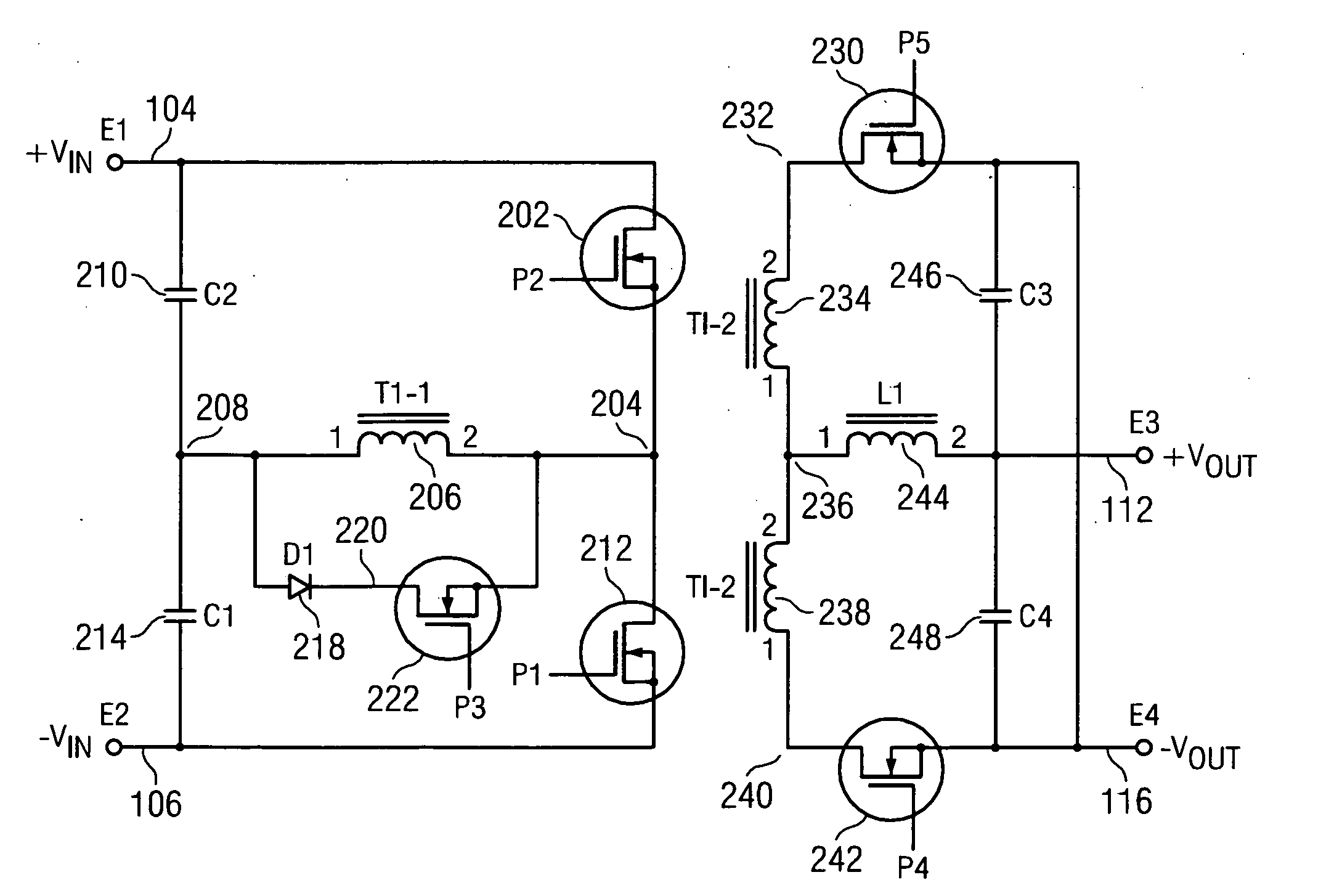
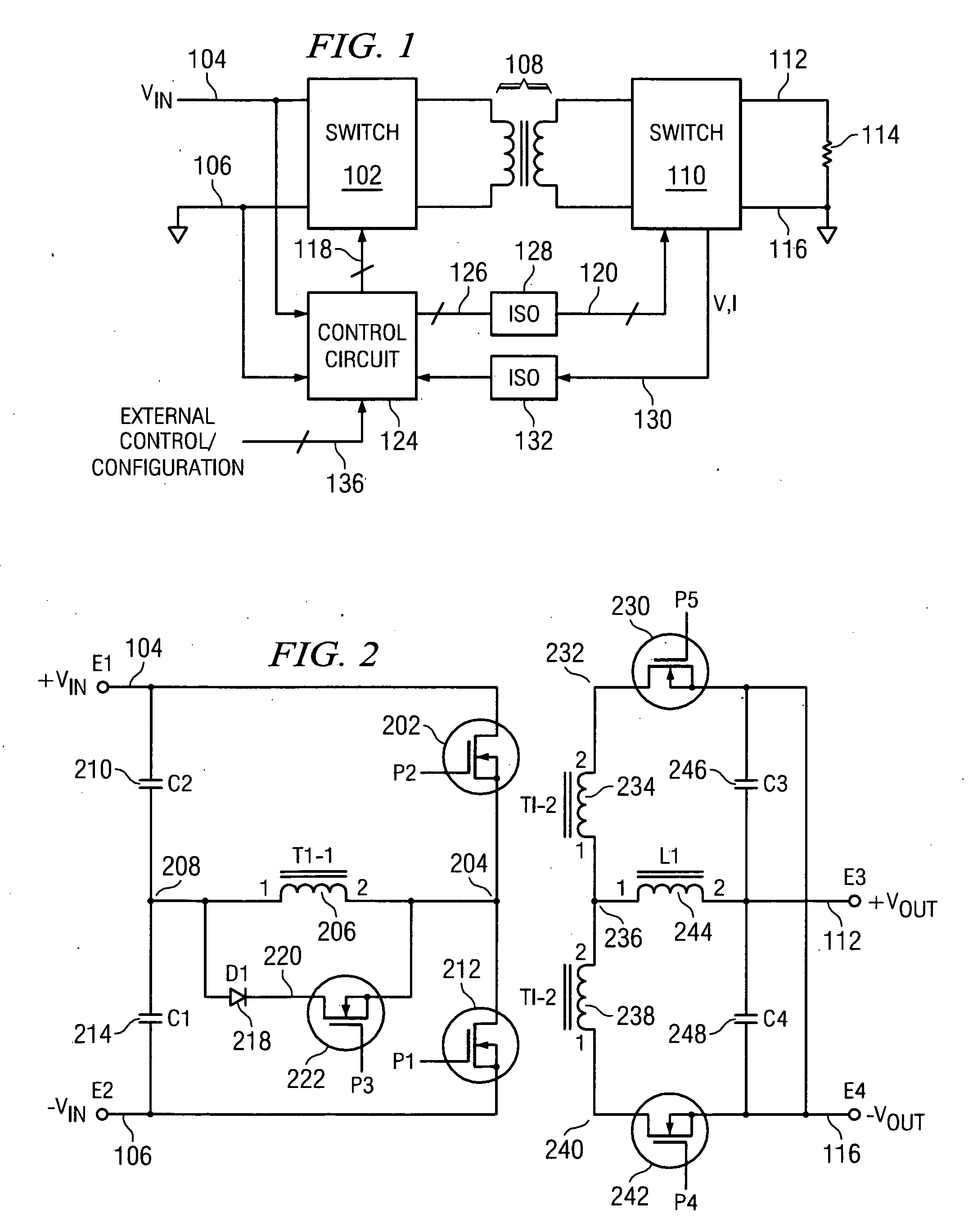
A new system-level approach to managing the delivery of DC voltage and current. Several system level functions may be enabled without requiring separate ICs to perform those functions. Supervisory functions for a voltage converter may be performed by a central control module or chip that may be coupled to point-of-load voltage converters comprised in digital power management devices (DPMD) through a serial digital bus. The DPMDs may also use the high-speed serial digital bus to provide real-time feedback information to the central control module or chip. Single DPMDs may be combined together in a current sharing configuration in a “plug-and-play” fashion, where the control logic in each DPMD is capable of automatically establishing control loops required a multi-phase supply. Feedback necessary for establishing control may be transmitted across the digital bus coupling the devices. The supervisory functions may be included in each DPMD, which may communicate with each other over a serial digital bus, where the DPMDs singly or together may operate to perform control of their respective POLs, enabling configurations that do not require a central control module.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
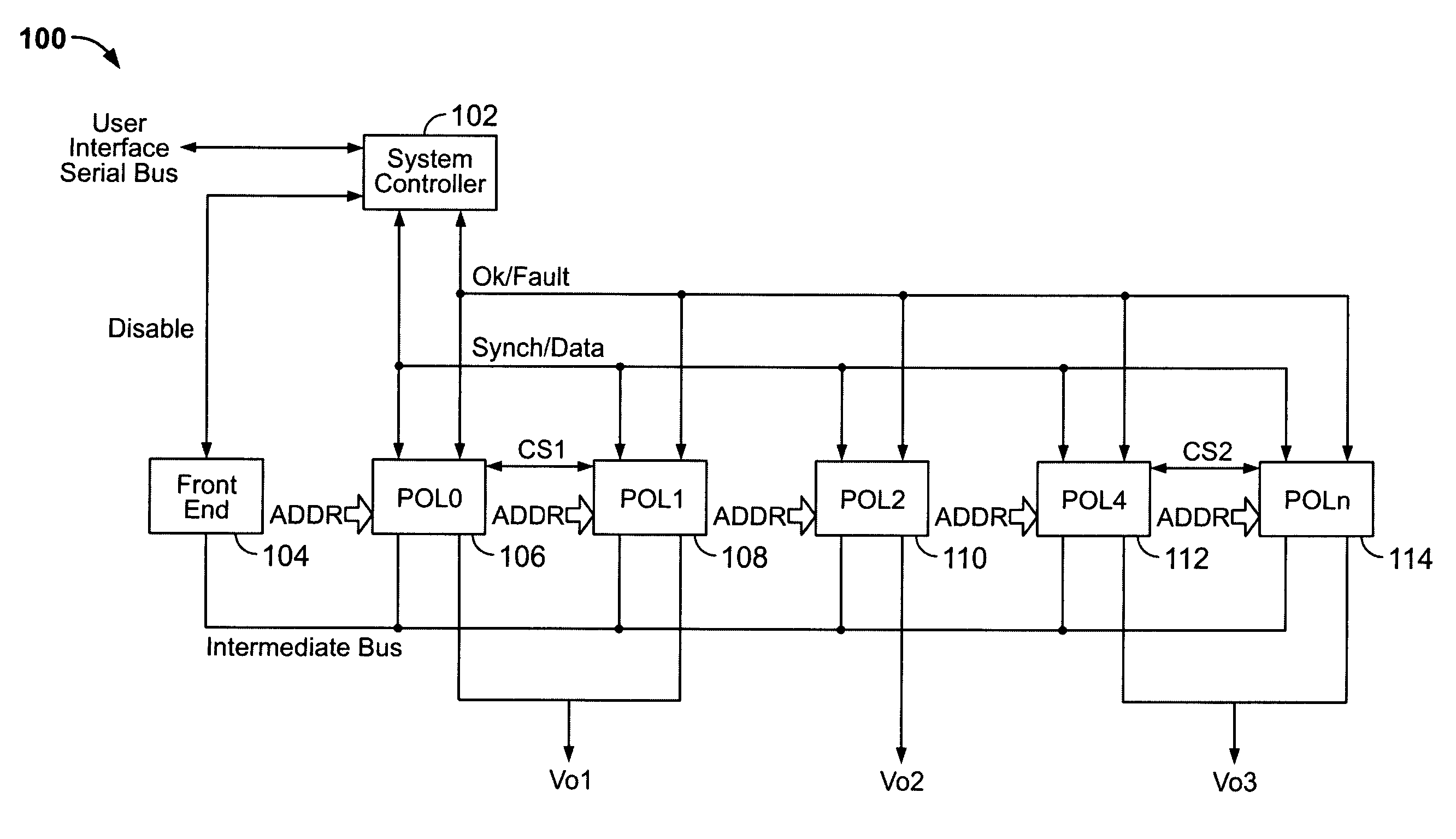
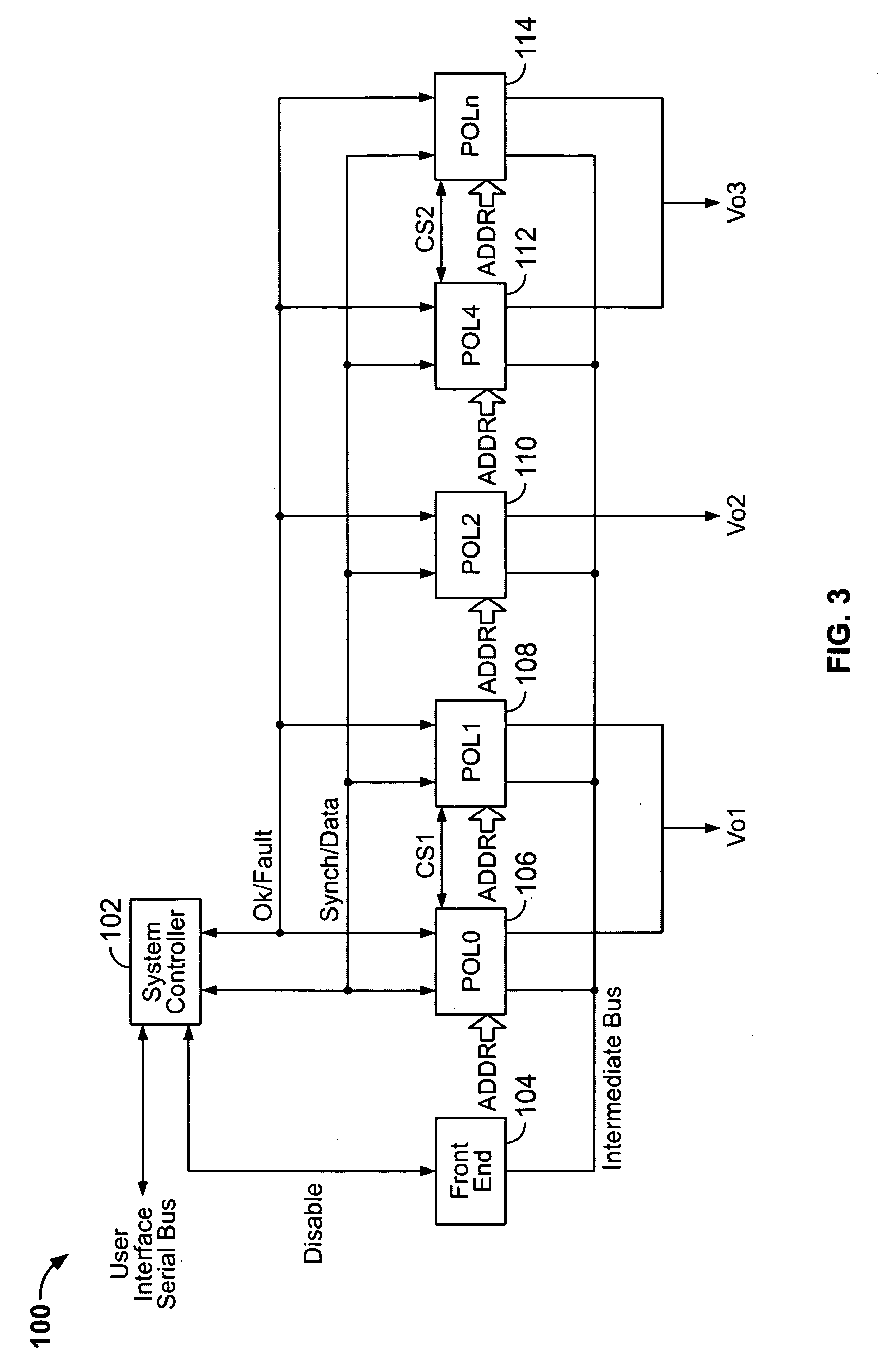
Method and system for controlling and monitoring an array of point-of-load regulators
ActiveUS7000125B2Complete understandingVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringDigital dataPoint of load
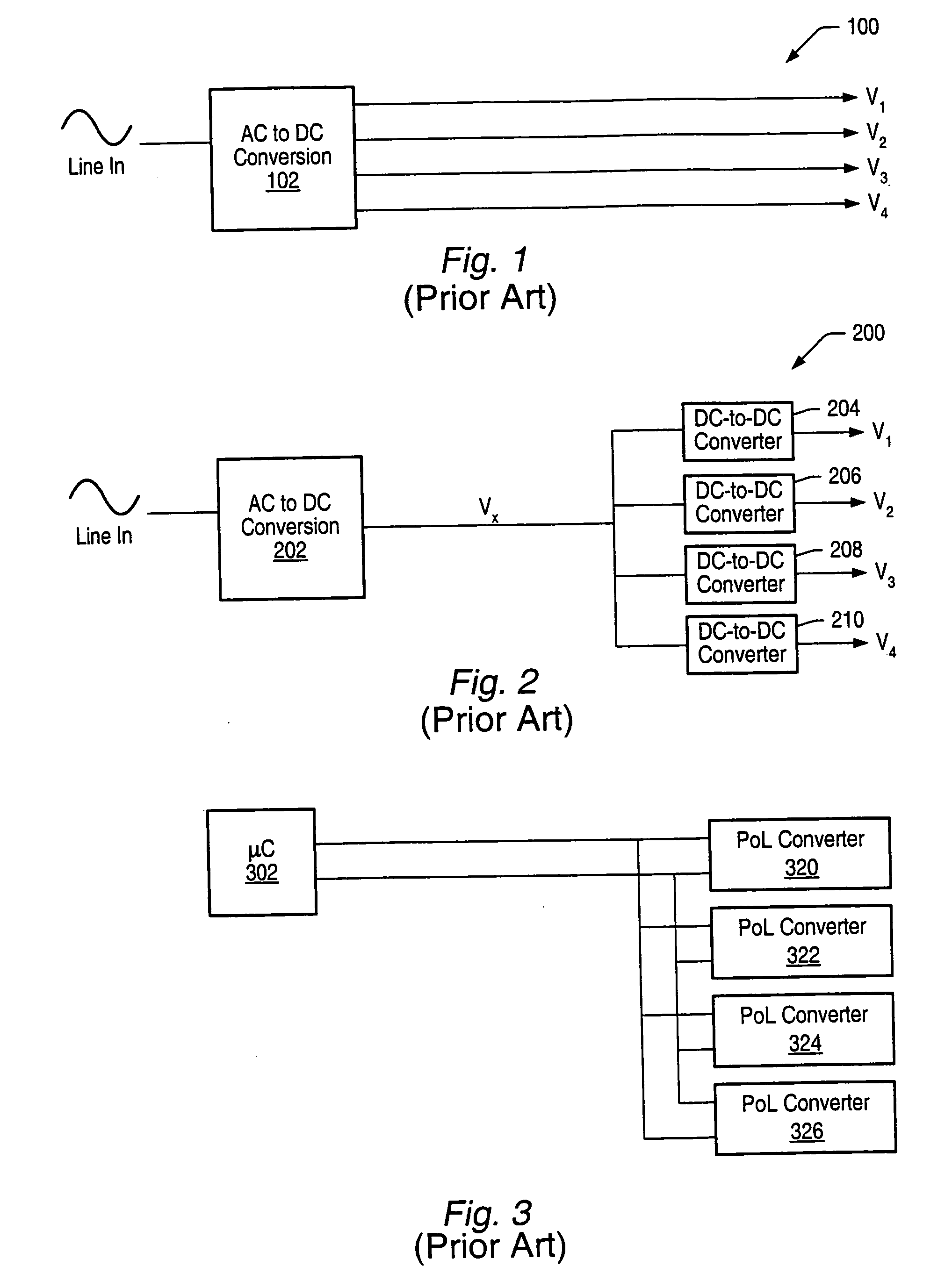
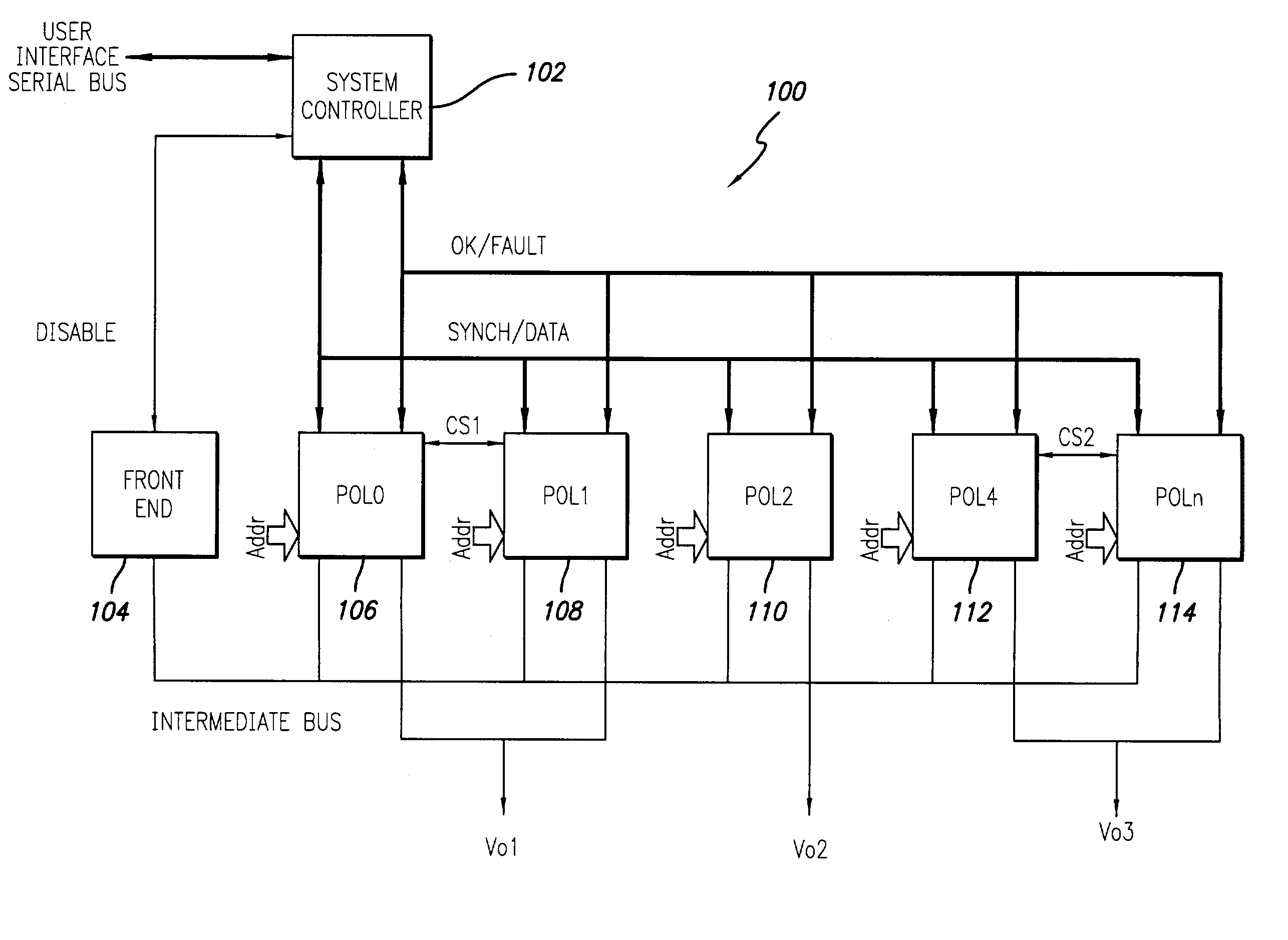
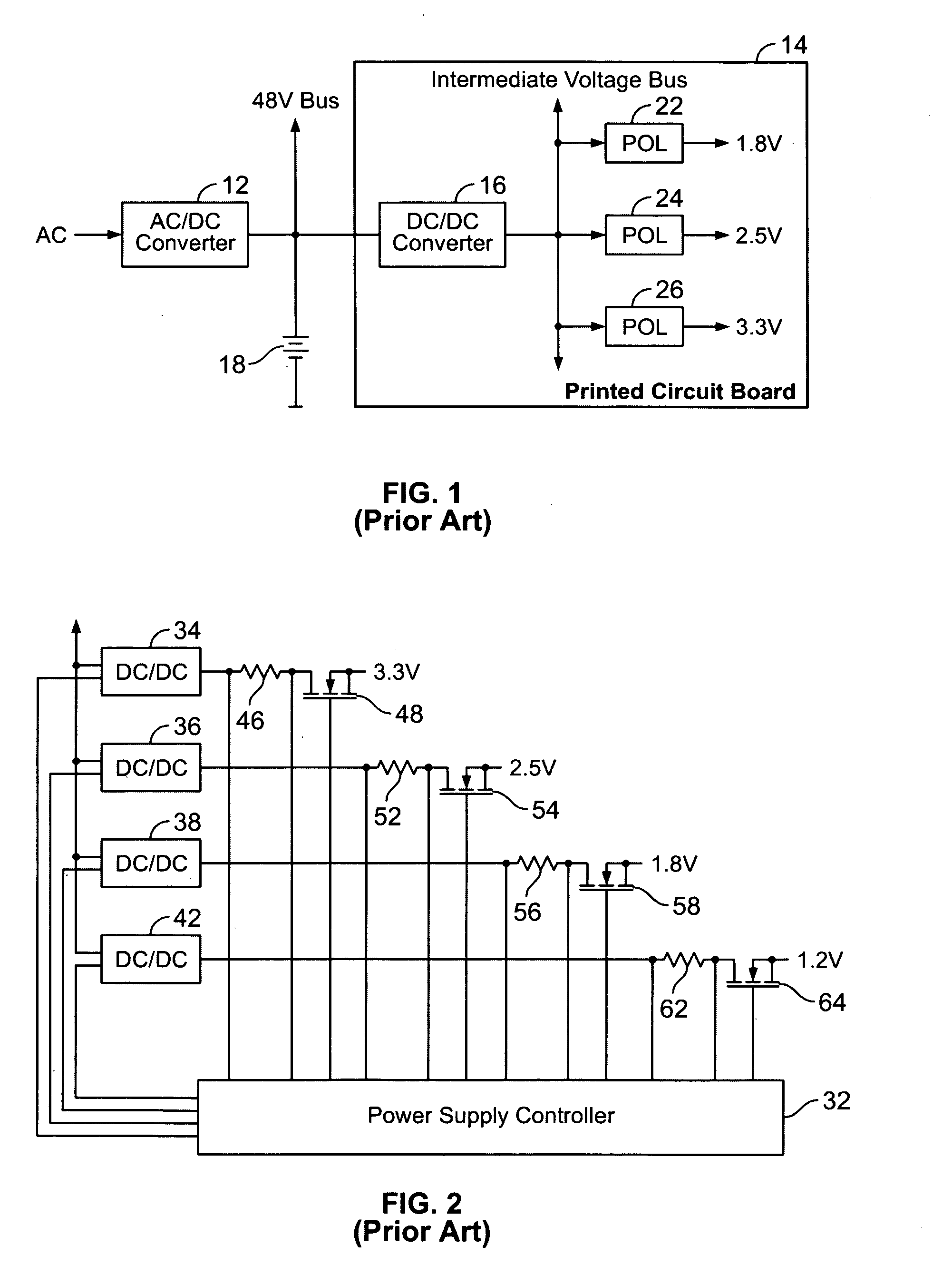
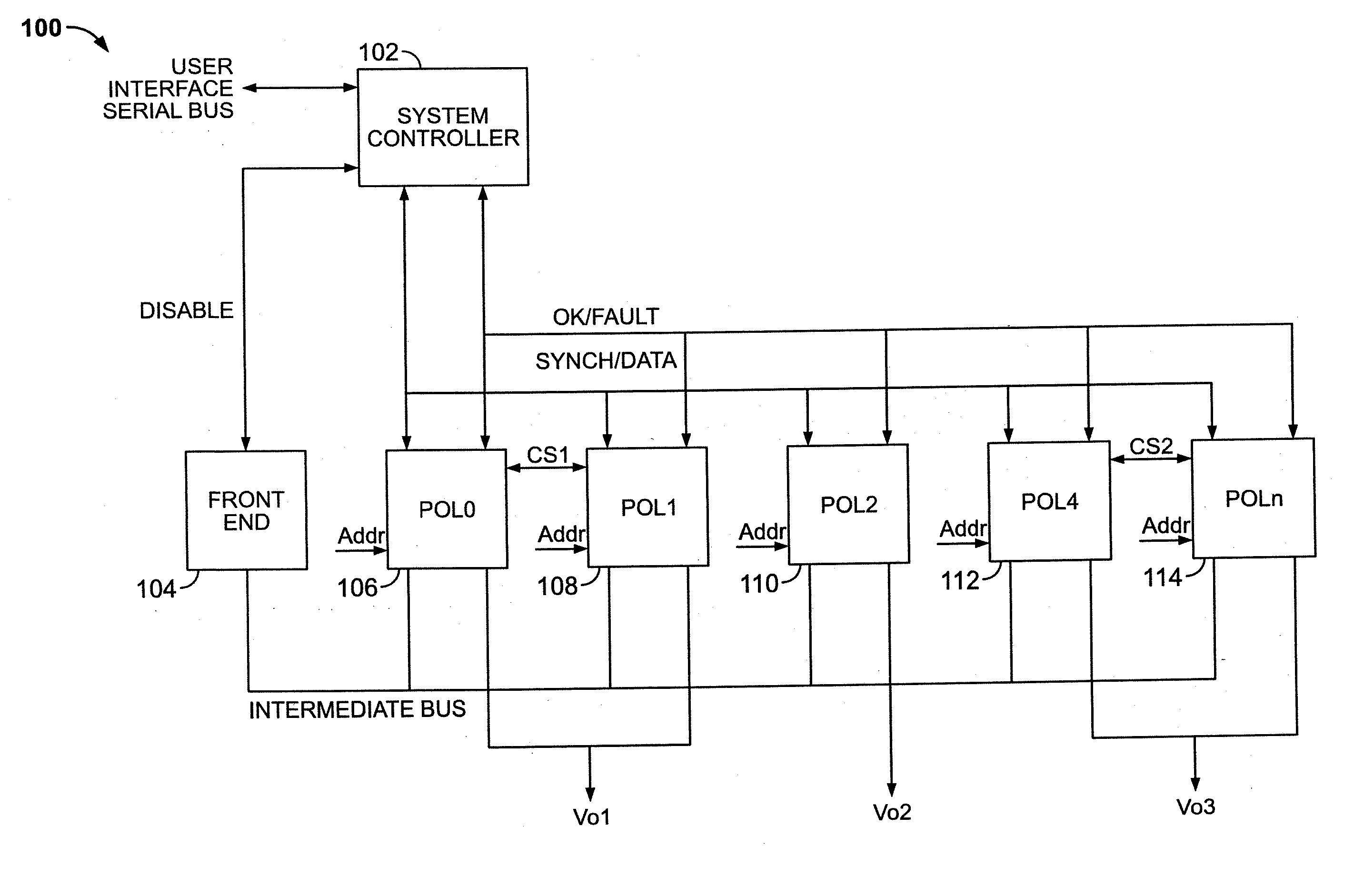
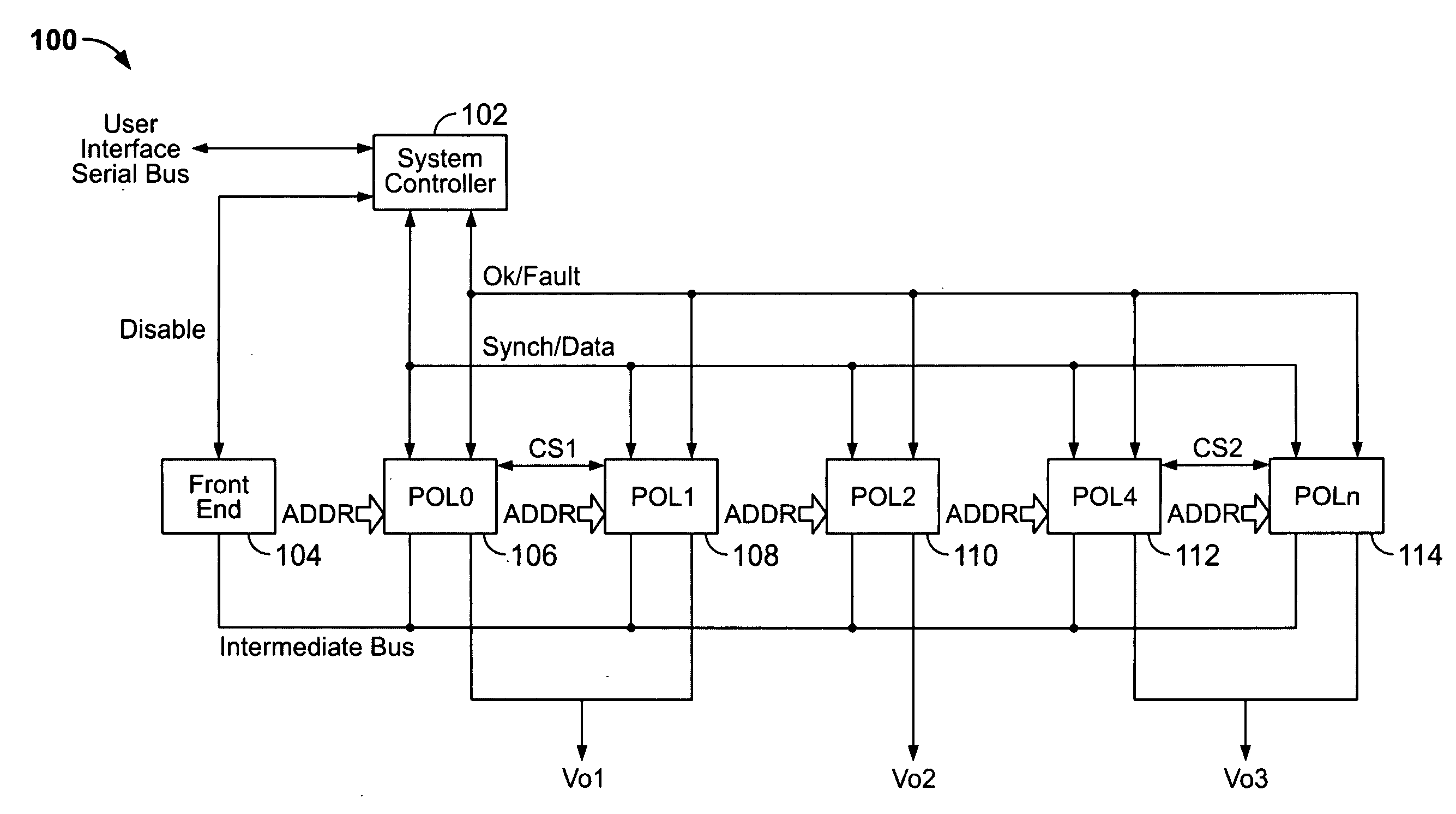
A power control system comprises a plurality of POL regulators, at least one serial data bus operatively connecting the plurality of POL regulators, and a system controller connected to the serial data bus and adapted to send and receive digital data to and from the plurality of POL regulators. The serial data bus further comprises a first data bus carrying programming and control information between the system controller and the plurality of POL regulators. The serial data bus may also include a second data bus carrying fault management information between the system controller and the plurality of POL regulators. The power control may also include a front-end regulator providing an intermediate voltage to the plurality of POL regulators on an intermediate voltage bus.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
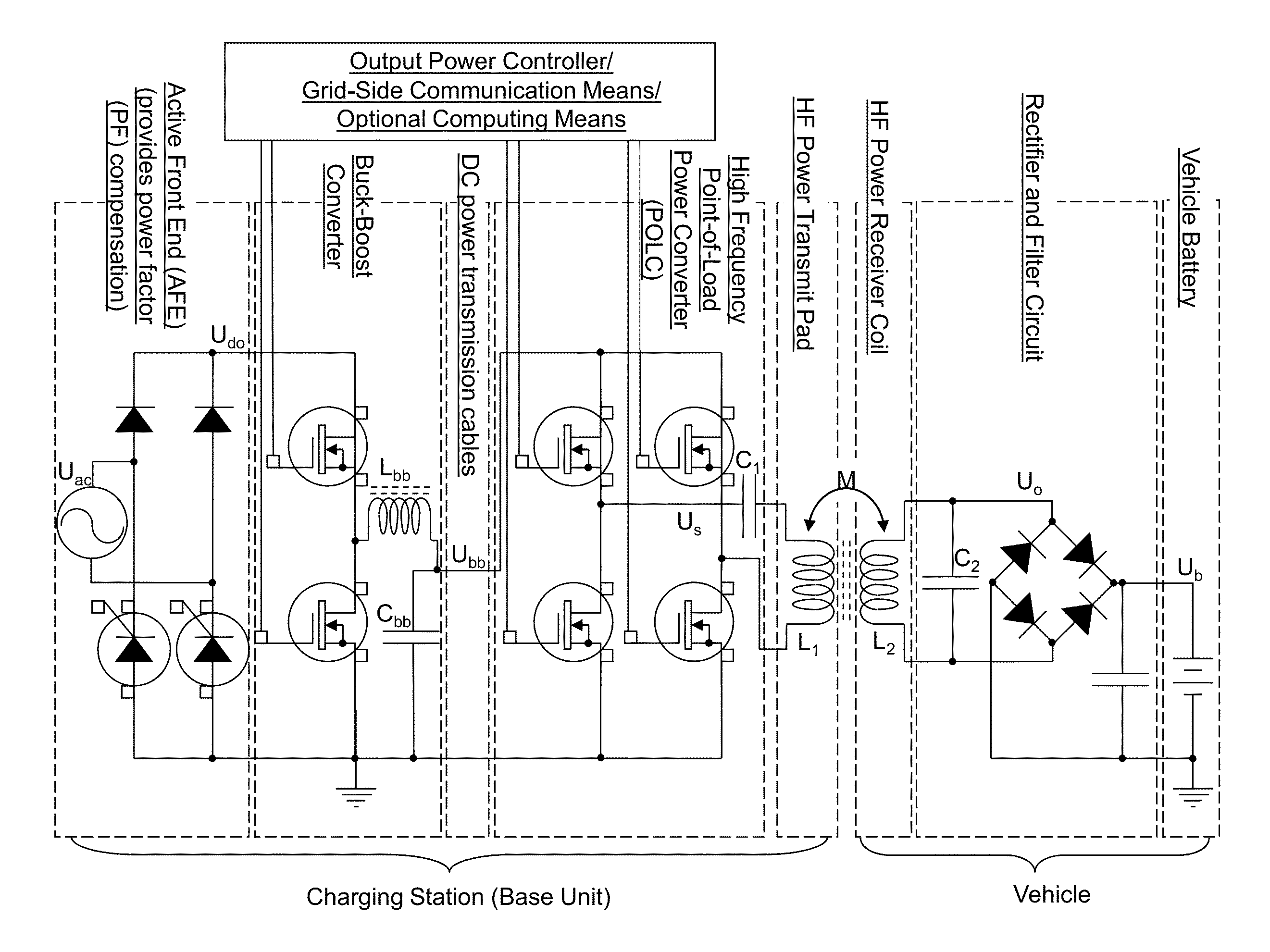
Wireless power charging using point of load controlled high frequency power converters
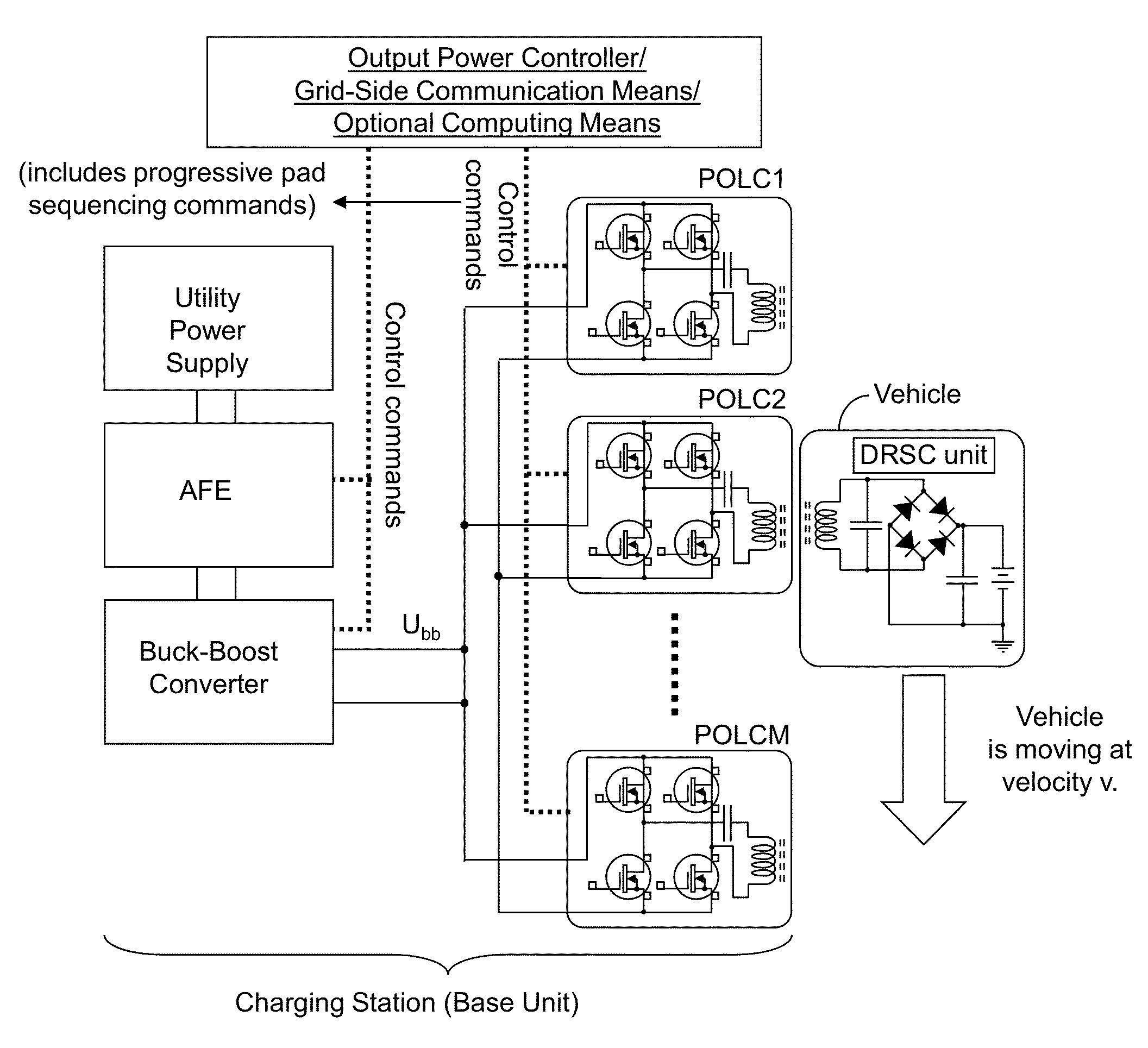
An apparatus for wirelessly charging a battery of an electric vehicle is provided with a point of load control. The apparatus includes a base unit for generating a direct current (DC) voltage. The base unit is regulated by a power level controller. One or more point of load converters can be connected to the base unit by a conductor, with each point of load converter comprising a control signal generator that transmits a signal to the power level controller. The output power level of the DC voltage provided by the base unit is controlled by power level controller such that the power level is sufficient to power all active load converters when commanded to do so by any of the active controllers, without generating excessive power that may be otherwise wasted.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
System and method for controlling output-timing parameters of power converters
A system and method is provided for utilizing output-timing data to control at least one output timing parameter of a point-of-load (“POL”) regulator. Specifically, a power supply controller (“controller”) is adapted to transmit output-timing data to at least one POL regulator. In one embodiment of the present invention, each POL regulator includes an output builder, a control unit and a storage device. The control unit is adapted to store the output-timing data in the storage device. The control unit and the output builder are then adapted to produce an output having at least one output timing parameter in accordance with the output-timing data. Examples of output-timing data include sequencing data, turn-on data, turn-off data, termination data, slew-rate data, etc. For example, a POL regulator may be adapted to utilize output-timing data, or a portion thereof (e.g., slew-rate data), to generate an output having a particular slew rate. Similarly, a POL regulator may be adapted to utilize output-timing data, or a portion thereof (e.g., sequencing data, turn-on data, etc.), to determine (or calculate) a period of time to wait (e.g., delay period) before the output is generated. In other words, output-timing data can be used to produce a series of outputs in a particular order, or sequence.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
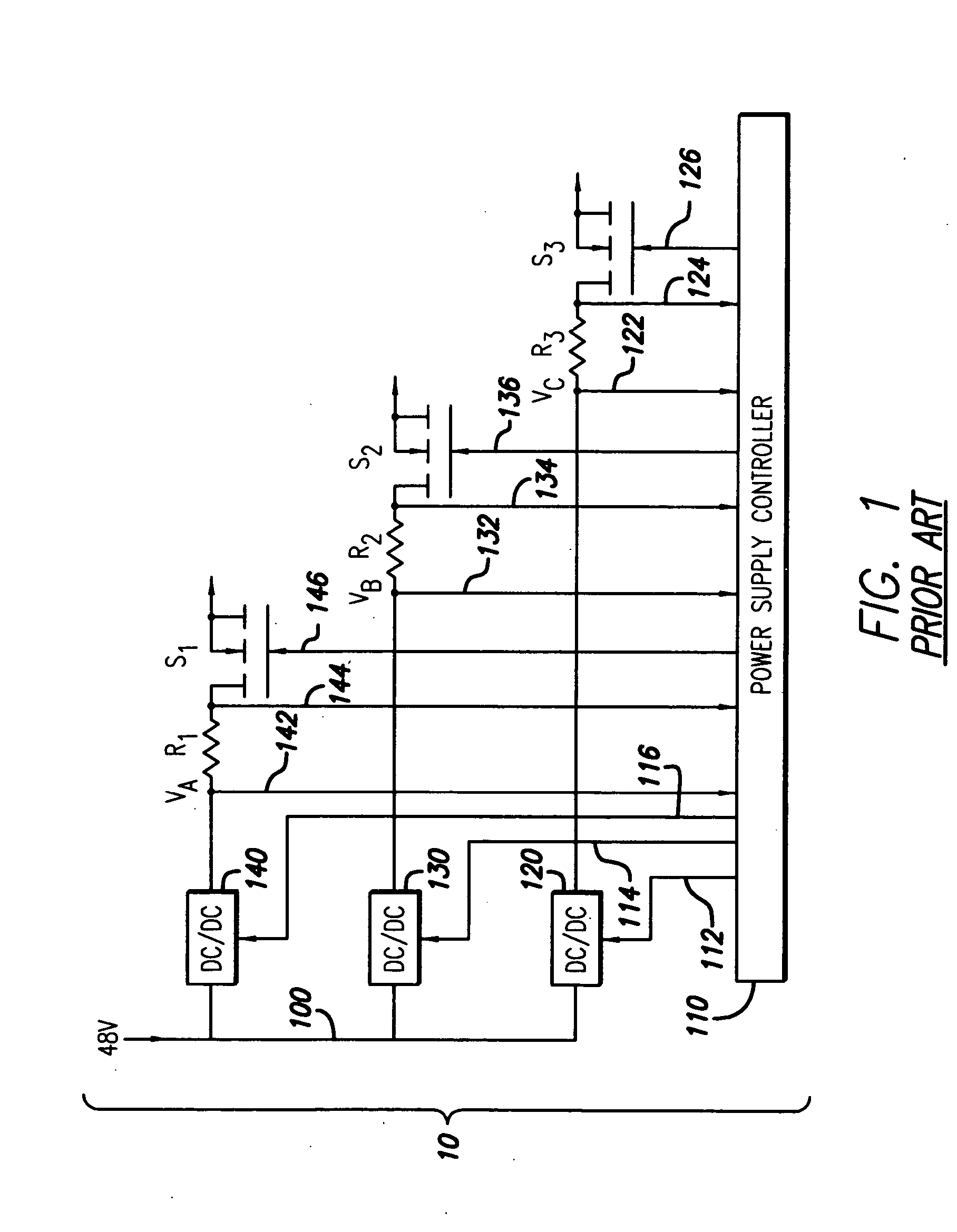
System and method for controlling a point-of-load regulator
ActiveUS6949916B2Three-or-more-wire dc circuitsDc source parallel operationPoint of loadPower controller
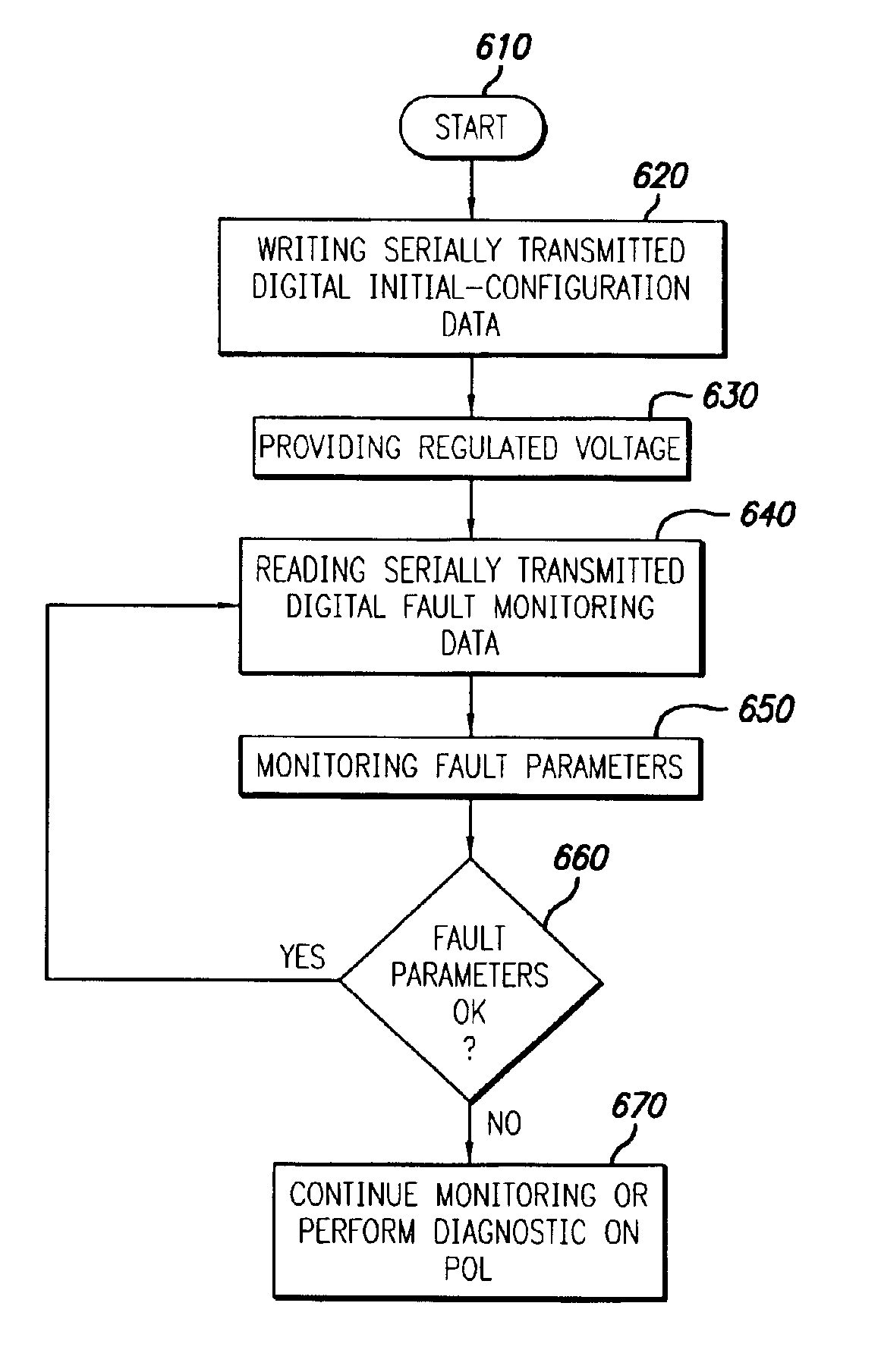
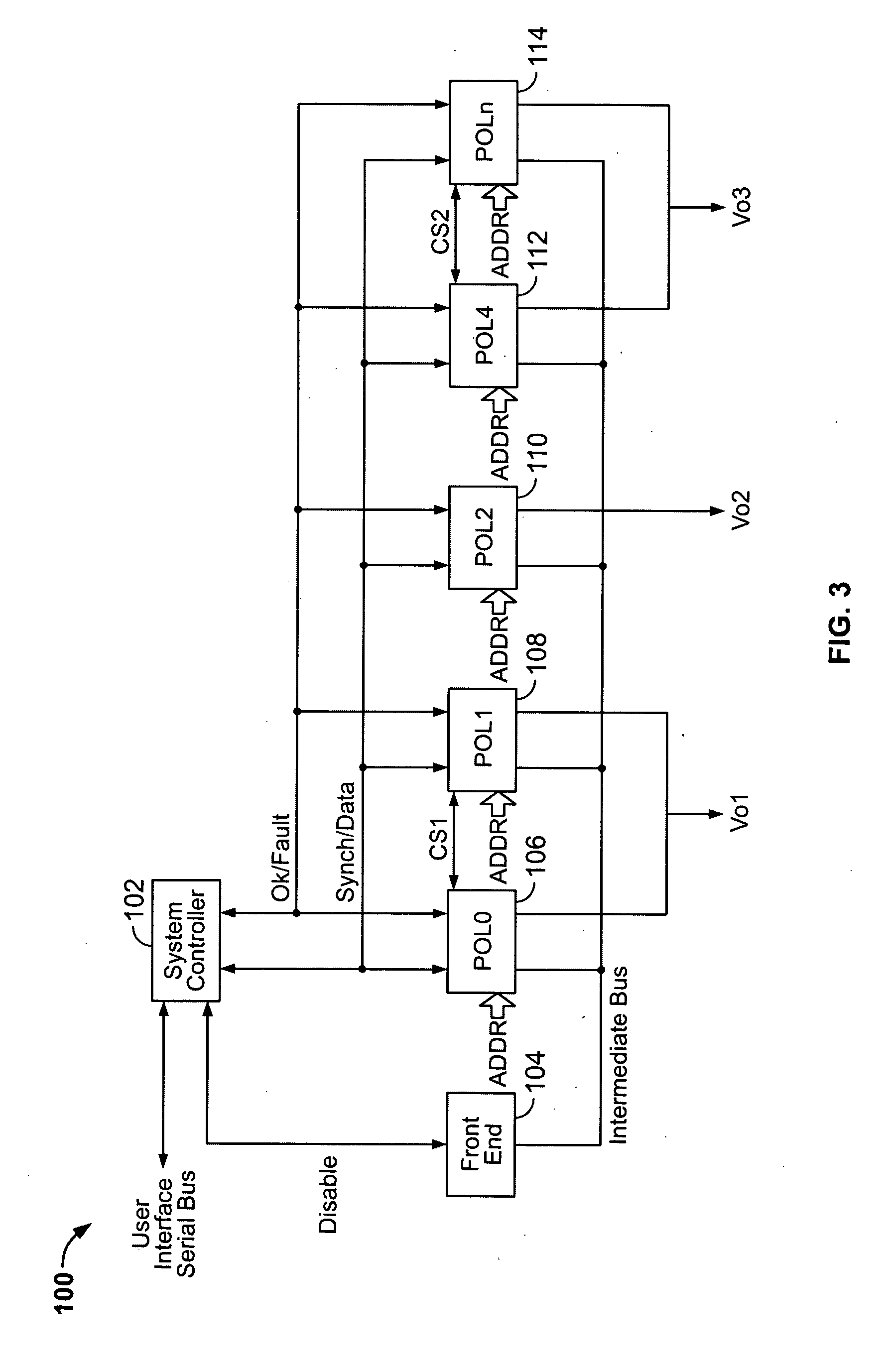
A system and method is provided for using a serial bus to communicate (either passively or actively) with a point-of-load (“POL”) regulator. Specifically, a power supply controller (“controller”) communicates with at least one POL regulators by writing and / or reading data (either synchronously or asynchronous) over a unidirectional or bi-directional serial bus. In one embodiment of the present invention, the controller is adapted to write initial-configuration data (e.g., output voltage set-point, current limit set-point, etc.) to at least one POL regulator via the serial bus. At least a portion of the initial-configuration data is then used by the POL regulator to produce a particular output. In another embodiment of the invention, each POL regulator includes at least one register for maintaining POL information, such as unique identification information, fault protection information, output voltage set-point data, current limit set-point data, etc. The controller is then adapted to monitor and retrieve this information (i.e., fault-monitoring data) via the serial bus while the POL regulators are operating.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
Method and system for controlling and monitoring an array of point-of-load regulators
InactiveUS20050289373A1Less complexityReduce the amount requiredTemperatue controlVolume/mass flow measurementPoint of loadDigital data
A power control system comprises a plurality of POL regulators, at least one serial data bus operatively connecting the plurality of POL regulators, and a system controller connected to the serial data bus and adapted to send and receive digital data to and from the plurality of POL regulators. The serial data bus further comprises a first data bus carrying programming and control information between the system controller and the plurality of POL regulators. The serial data bus may also include a second data bus carrying fault management information between the system controller and the plurality of POL regulators. The power control may also include a front-end regulator providing an intermediate voltage to the plurality of POL regulators on an intermediate voltage bus.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
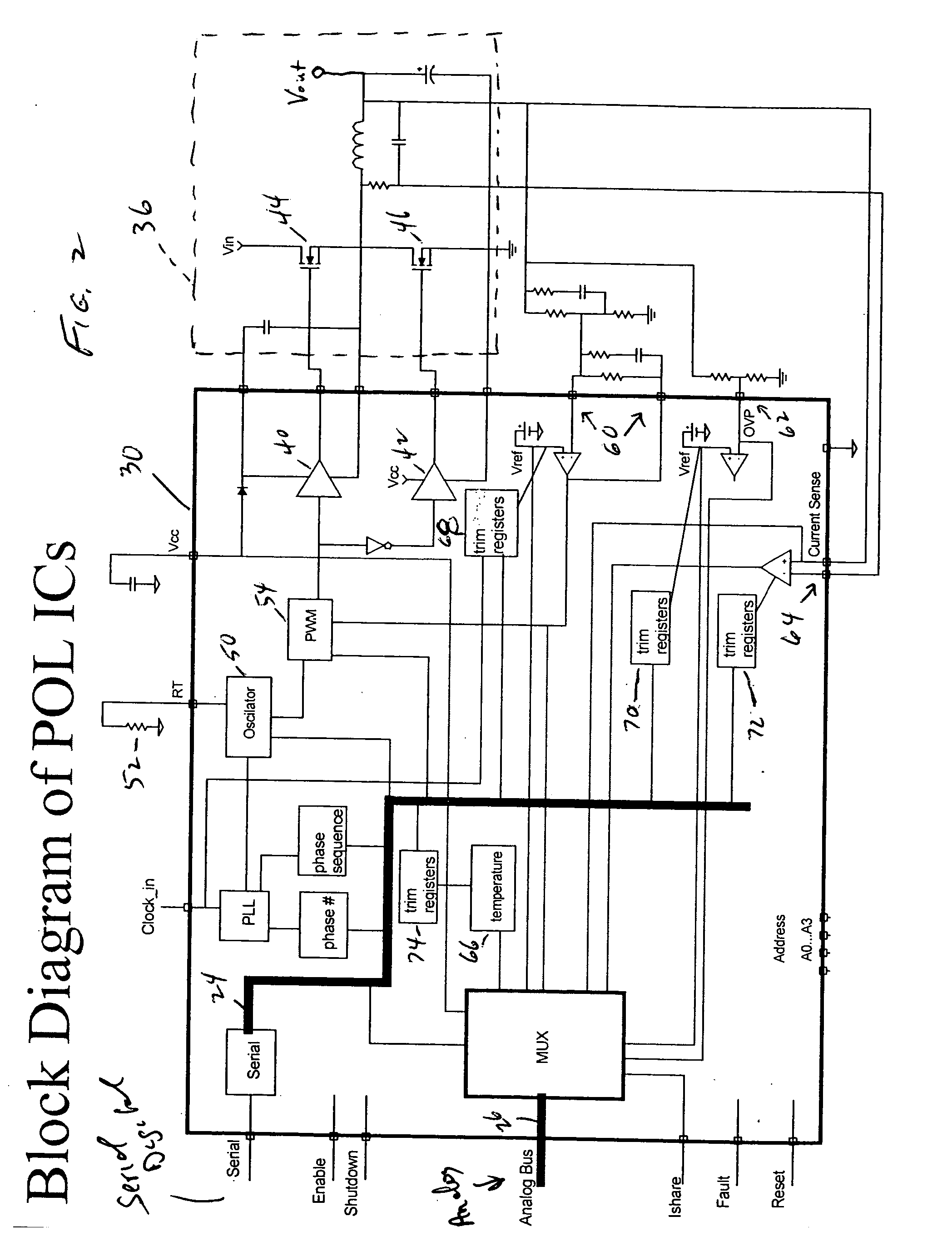
Pol system architecture with analog bus
ActiveUS20060212138A1Increase heightImprove accuracyProgramme controlDc network circuit arrangementsPoint of loadAudio power amplifier
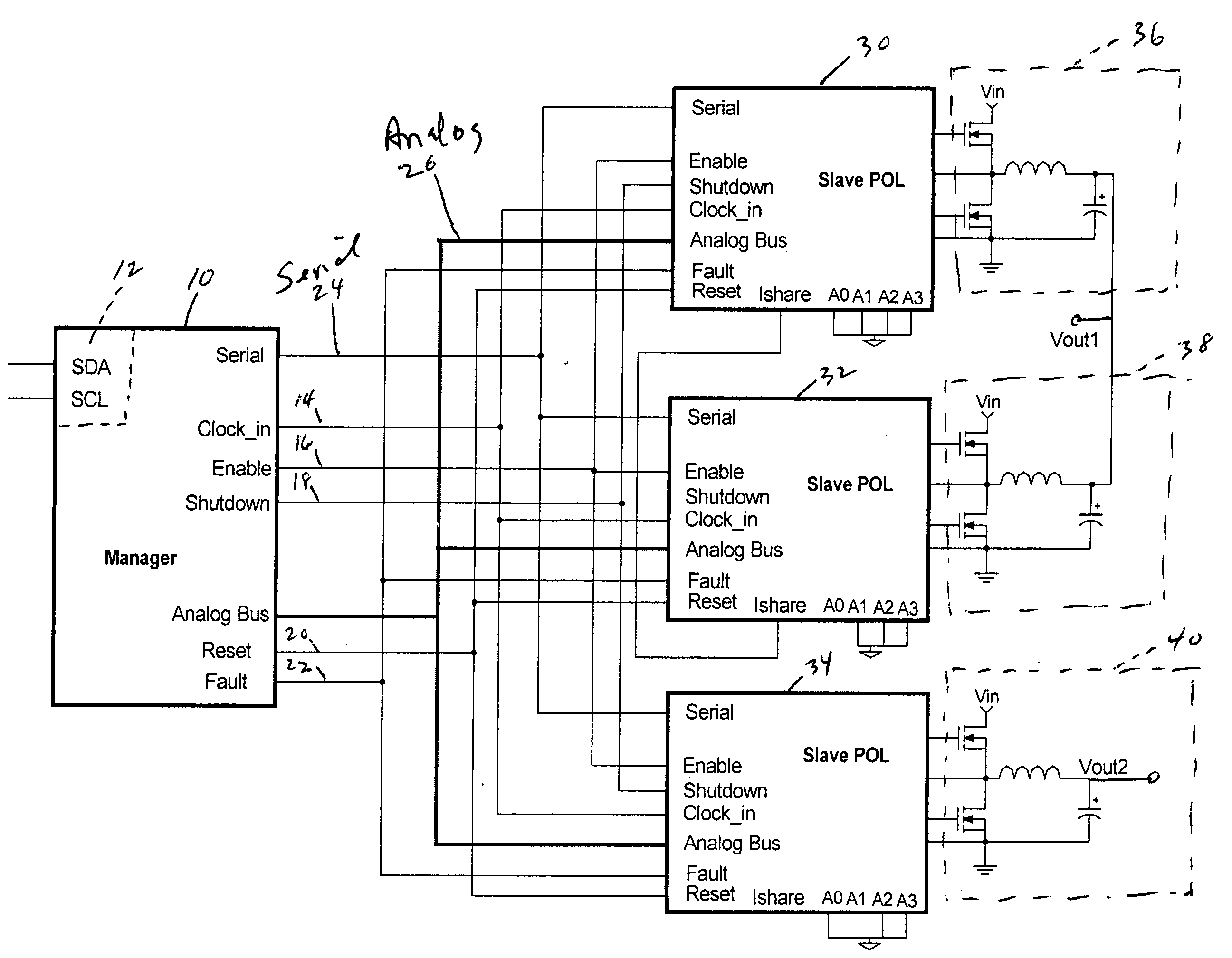
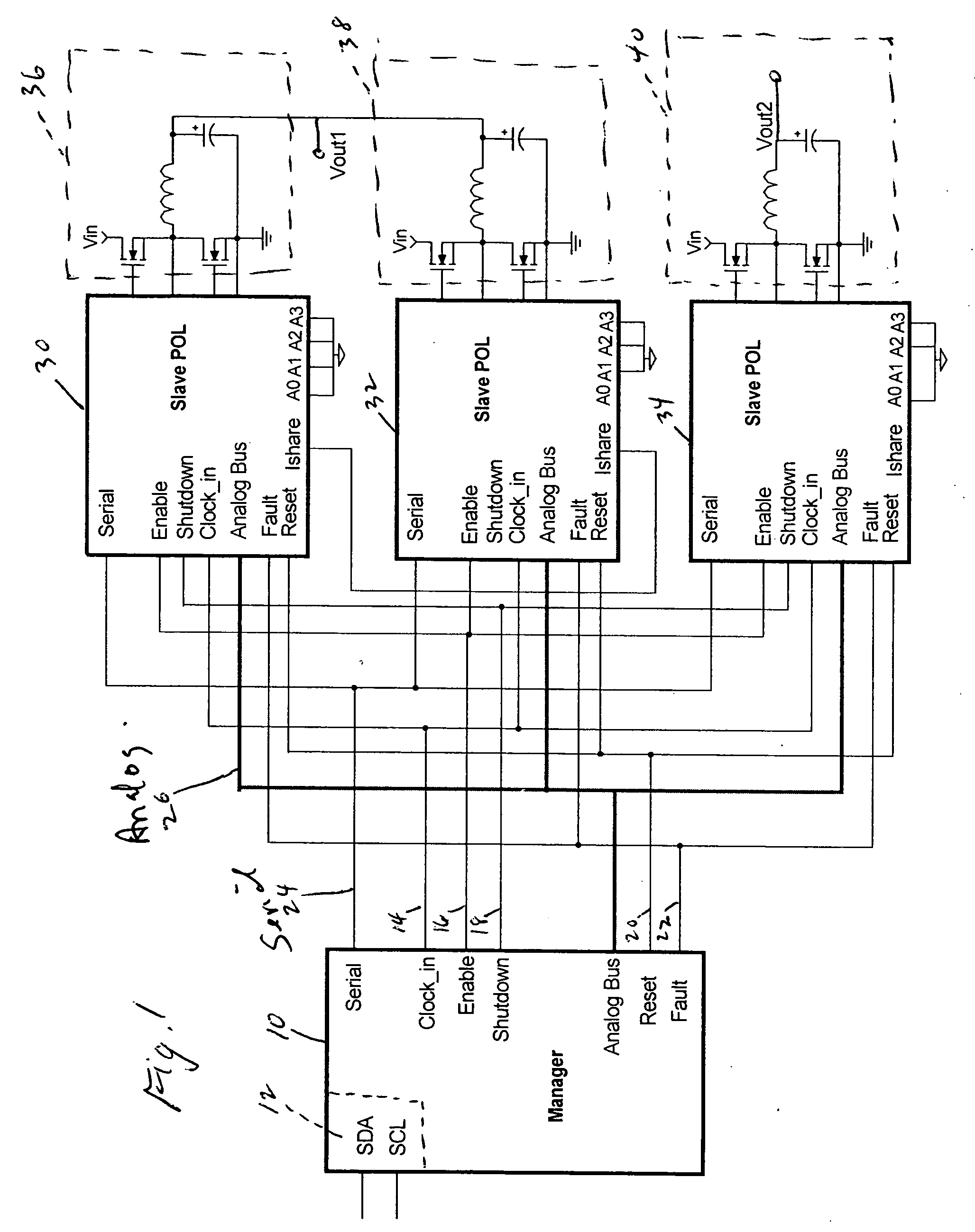
A power control system and method including a plurality of point-of-load regulators (POL) providing corresponding regulated output voltages; a manager for communicating control signals and operational parameters with said point-of load regulators; a digital bus to carry control signals therebetween; and an analog bus to carry operational parameters therebetween. Analog sensing circuits and a mutliplexer on the POL communicate operational parameters to and from the manager via the analog bus and are controlled via the digital bus. The operational parameters include output voltage, output current, over voltage, temperature, amplifier or comparator offset, and amplifier gain. The analog sensing circuits are calibrated by trim registers on the POL under digital control by the manager.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Wireless power charging using point of load controlled high frequency power converters
ActiveUS20130214591A1Circuit monitoring/indicationElectromagnetic wave systemPoint of loadHigh frequency power
An apparatus for wirelessly charging a battery of an electric vehicle is provided with a point of load control. The apparatus includes a base unit for generating a direct current (DC) voltage. The base unit is regulated by a power level controller. One or more point of load converters can be connected to the base unit by a conductor, with each point of load converter comprising a control signal generator that transmits a signal to the power level controller. The output power level of the DC voltage provided by the base unit is controlled by power level controller such that the power level is sufficient to power all active load converters when commanded to do so by any of the active controllers, without generating excessive power that may be otherwise wasted.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Three-dimensional package structure
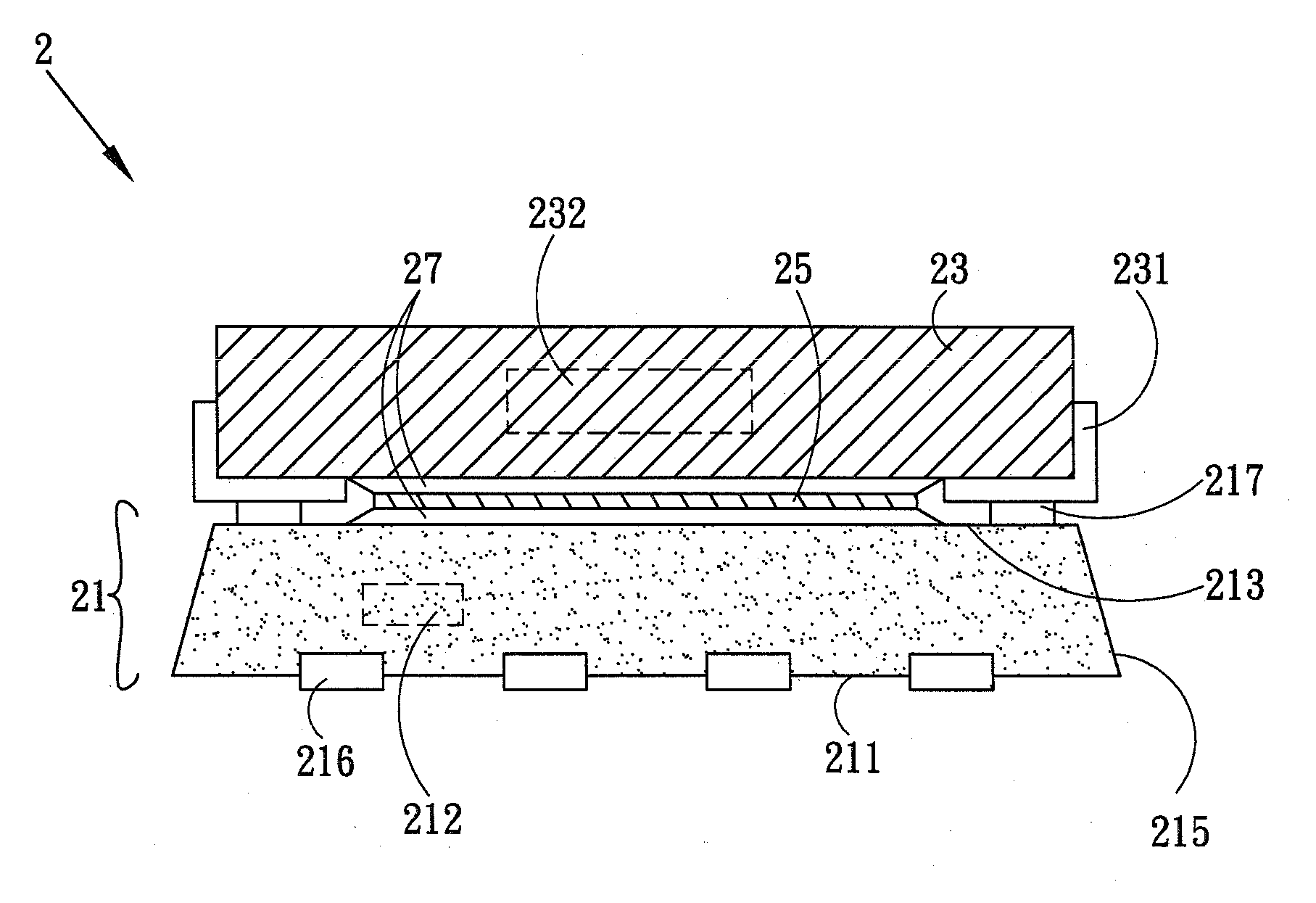
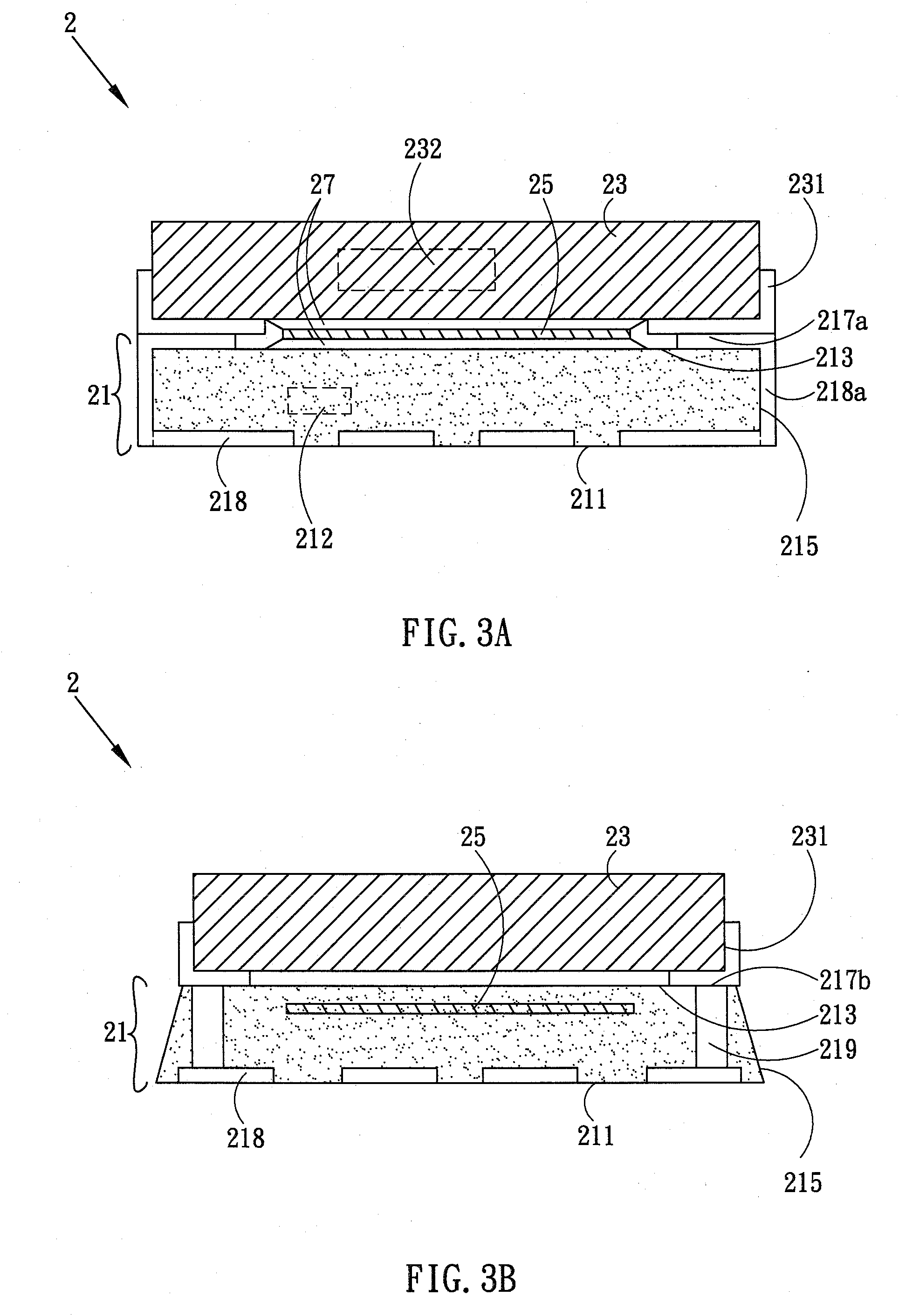
ActiveUS20080303125A1Inhibit and reduce EMISmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPoint of loadElectromagnetic interference
A three-dimensional package structure includes an energy storage element, a semiconductor package body and a shielding layer. The semiconductor package body has a plurality of second conductive elements and at least one control device inside. The energy storage element is disposed on the semiconductor package body. The energy storage element including a magnetic body is electrically connected to the second conductive elements. The semiconductor package body or the energy storage element has a plurality of first conductive elements to be electrically connected to an outside device. The shielding layer is disposed between the control component and at least part of the magnetic body to inhibit or reduce EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference) from the energy storage element and to get a tiny package structure. The three-dimensional package structure is applicable to a POL (Point of Load) converter.
Owner:CYNTEC
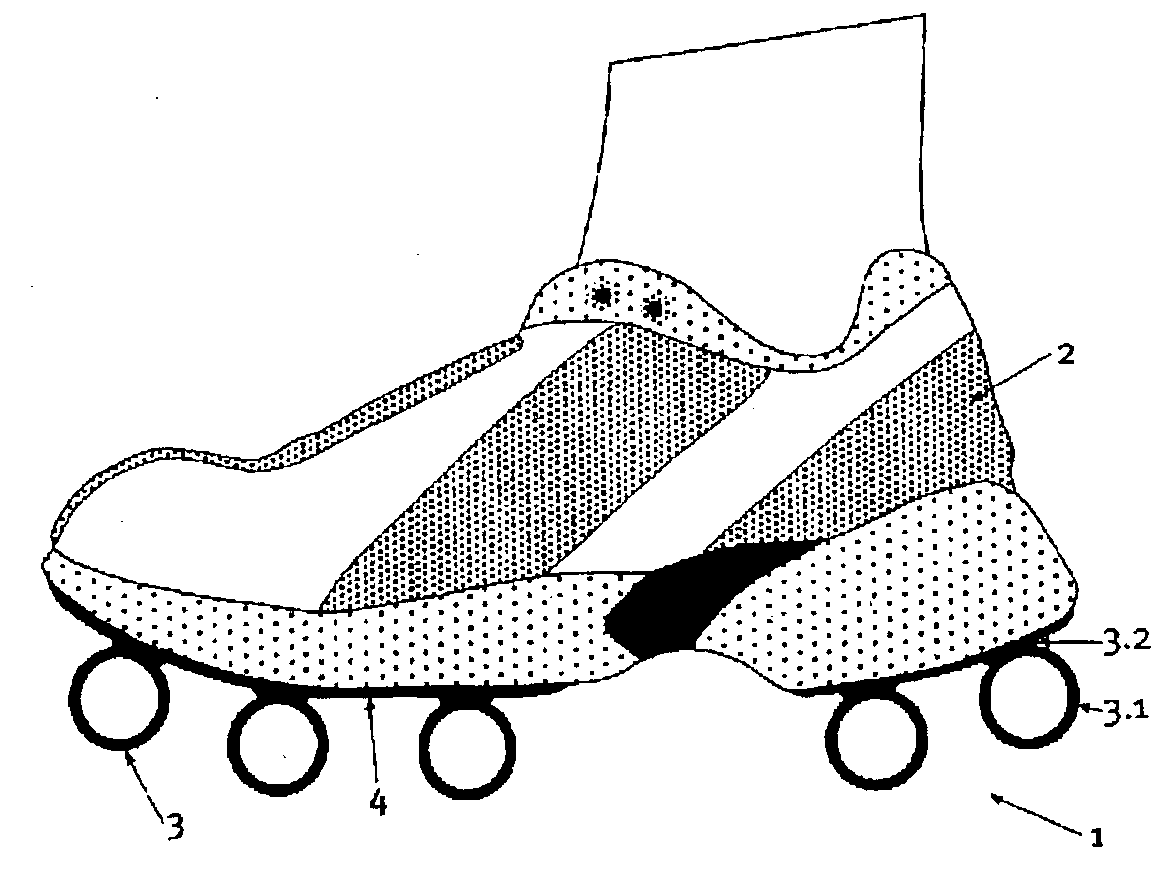
Outsole
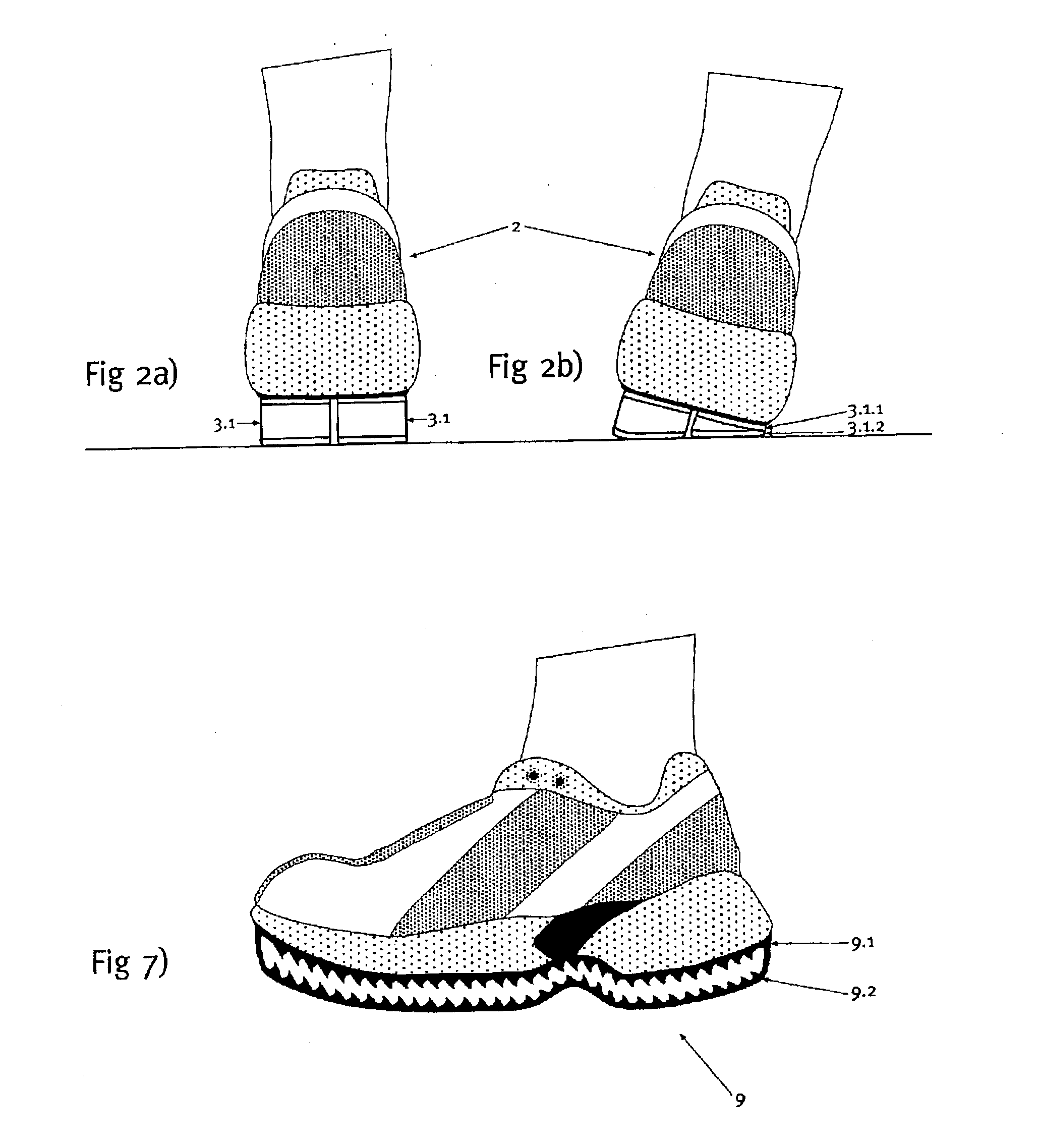
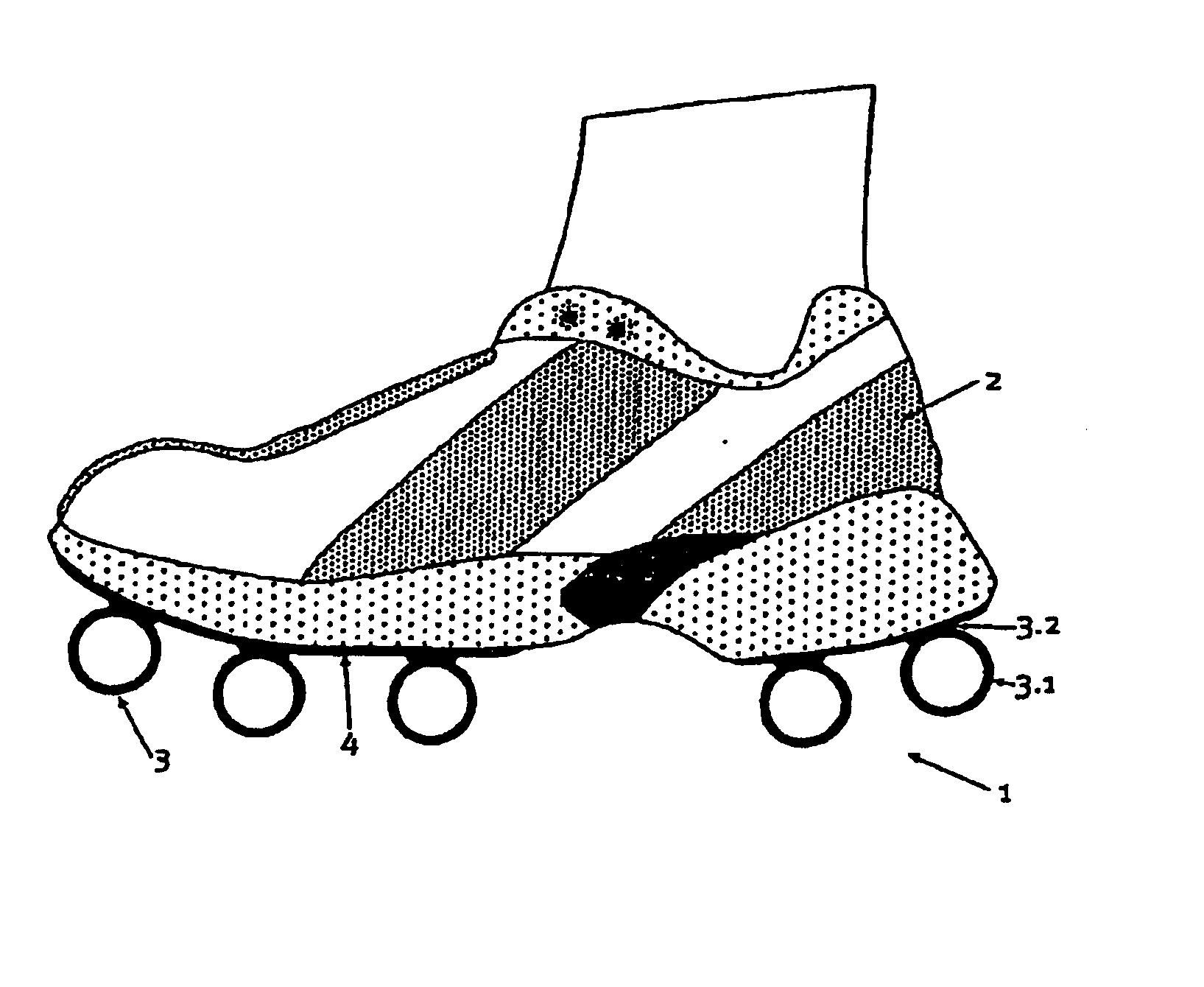
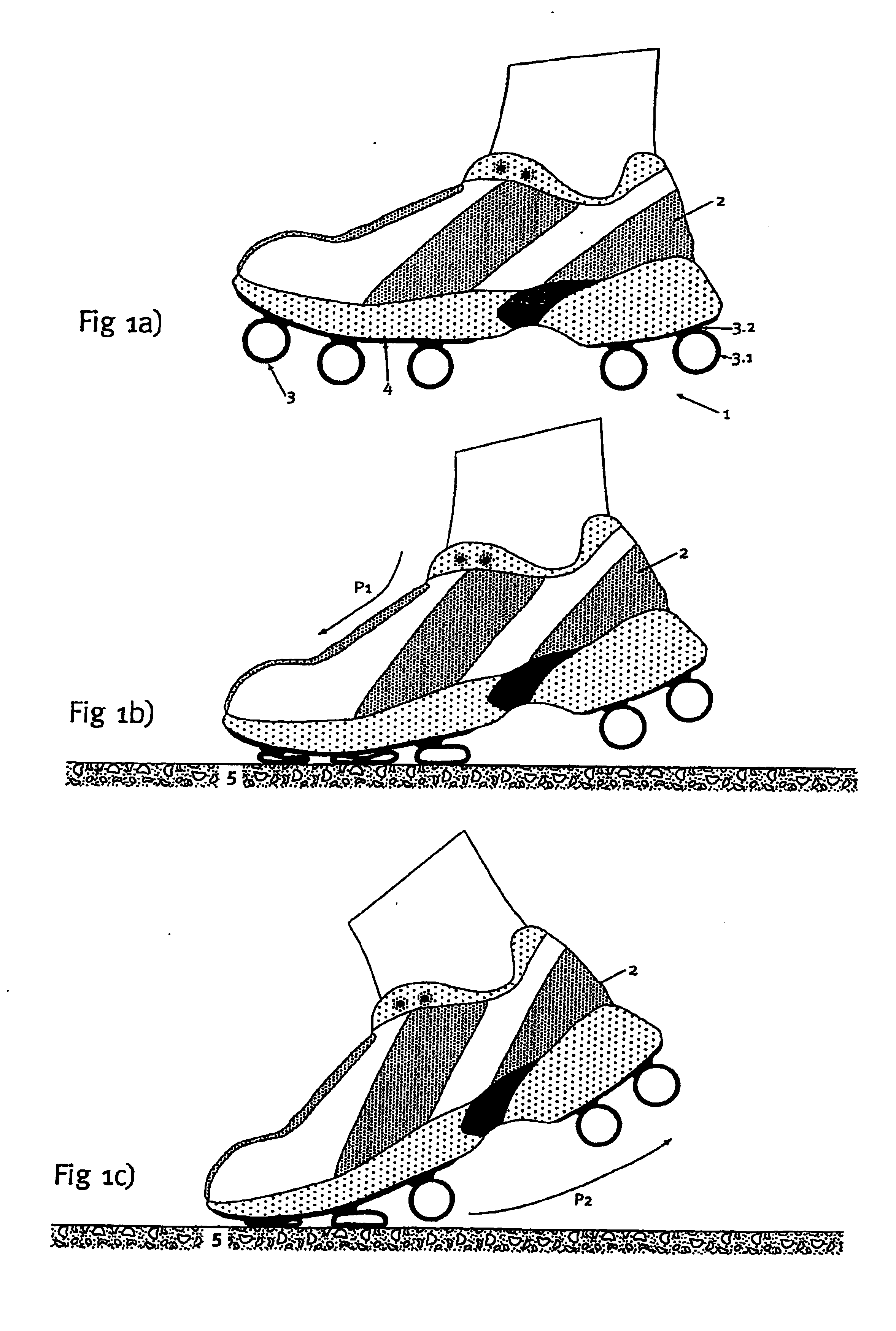
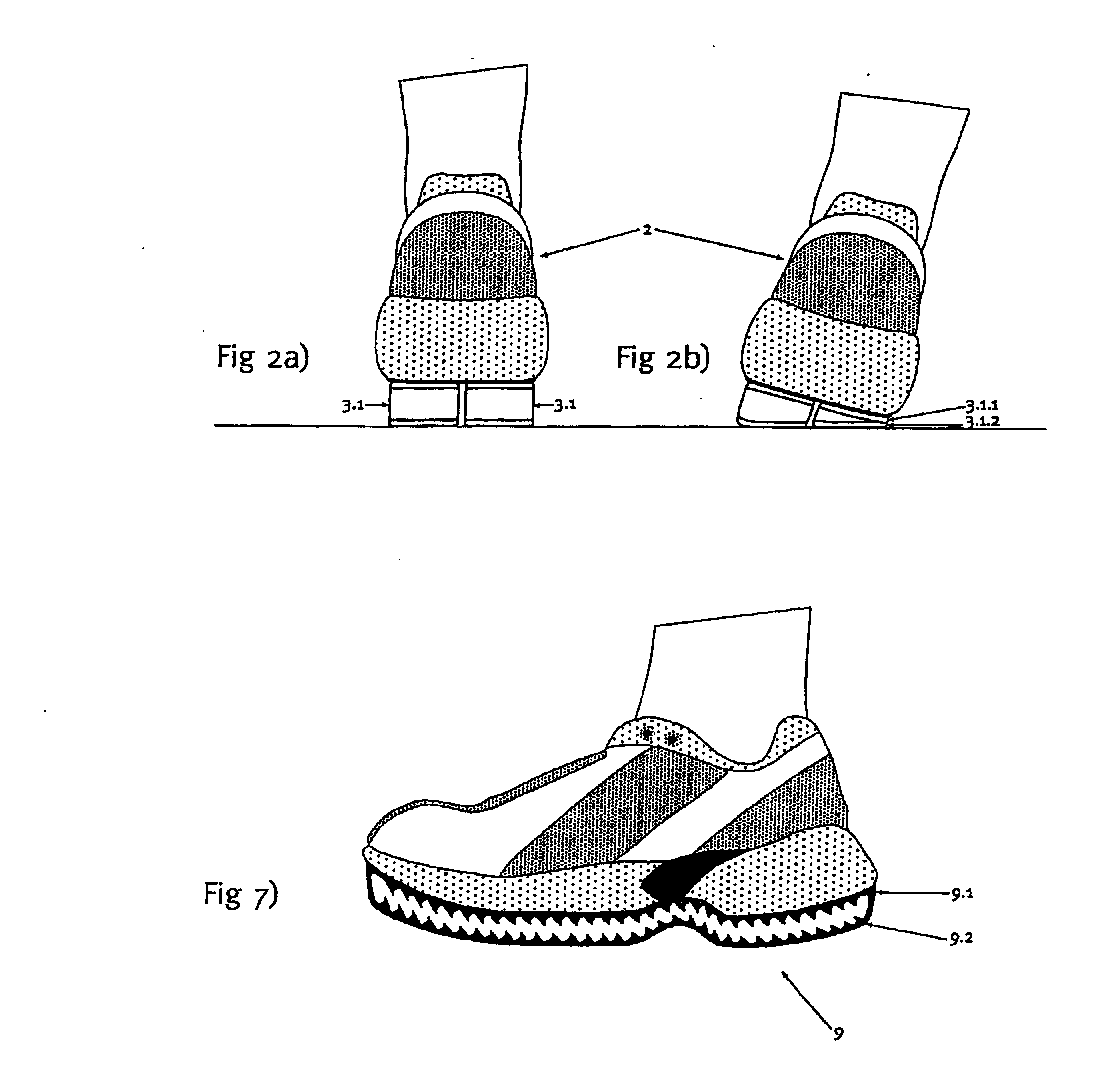
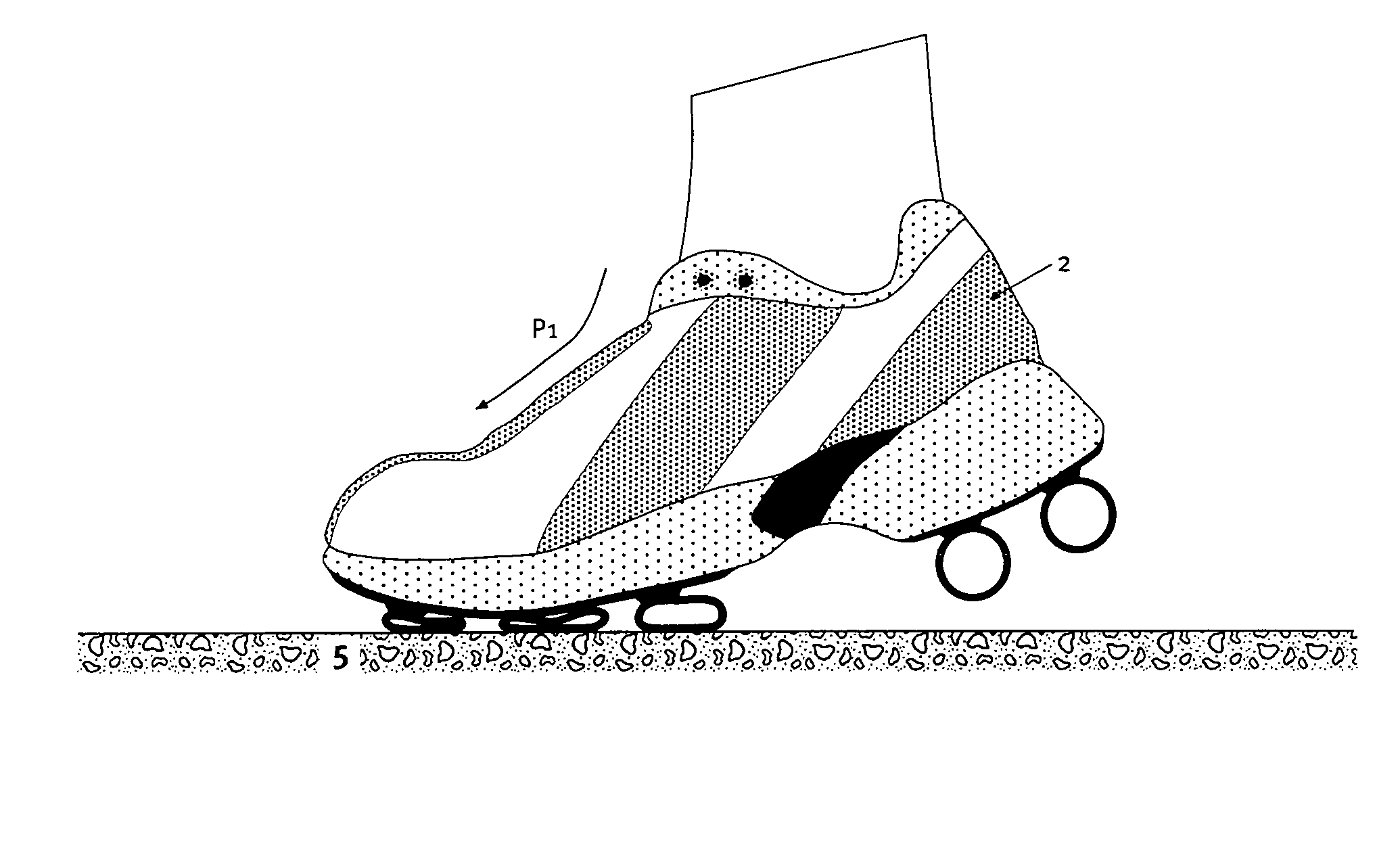
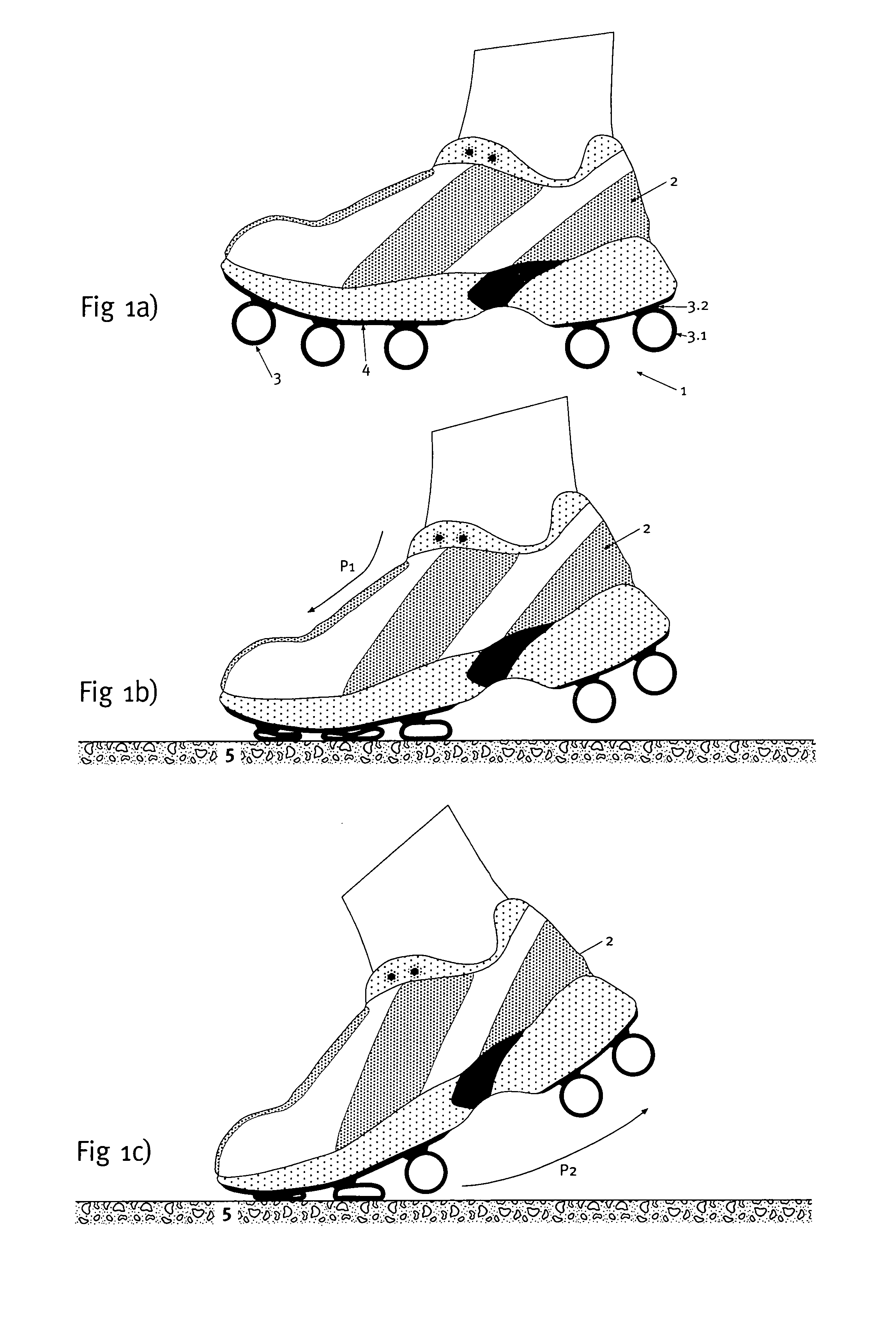
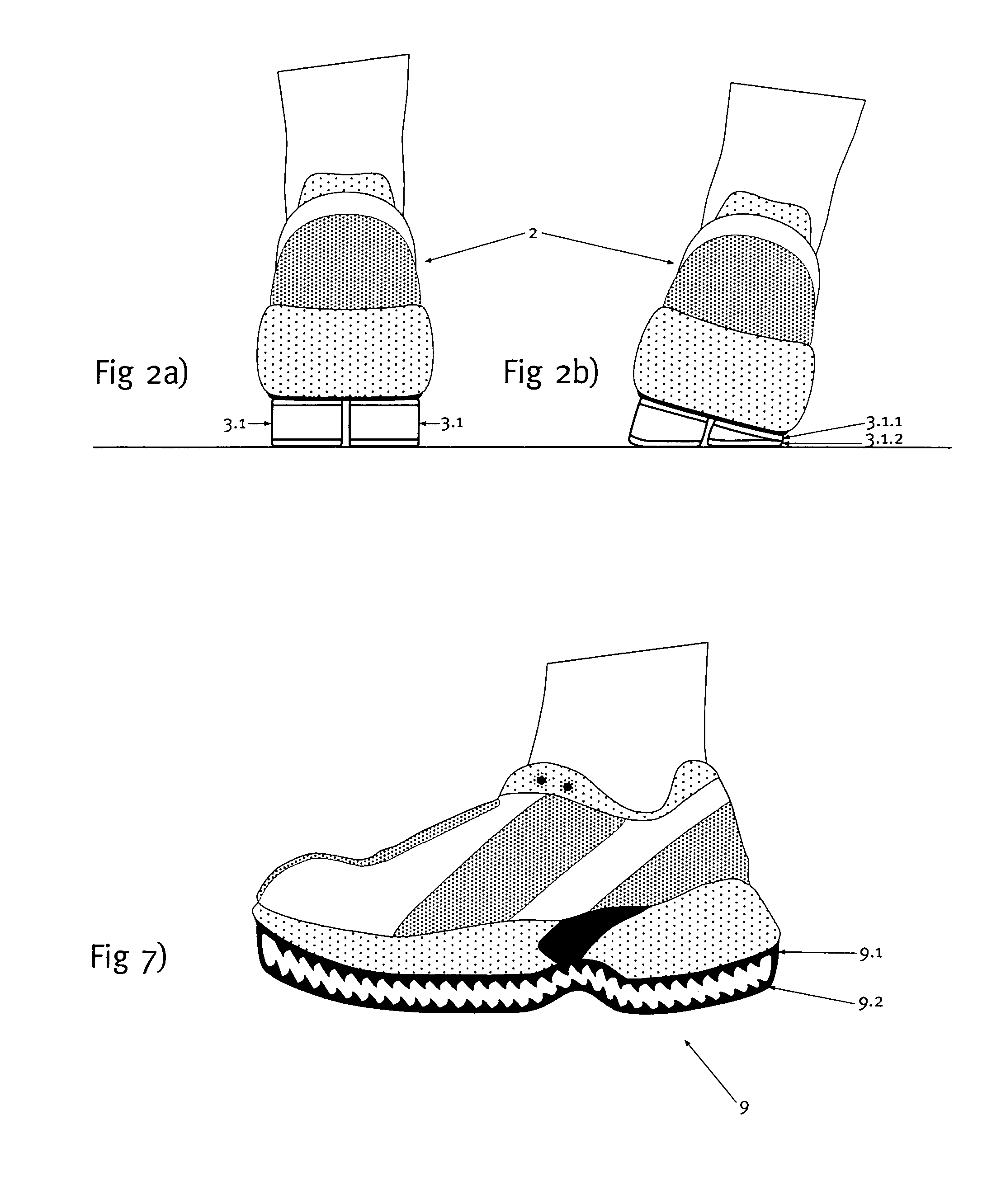
An outsole (1, 3), in particular, for athletic shoes (2) can be realized with a significant elastic deformability in the tangential direction so as to also achieve a superior shock-absorption when the foot contacts the ground obliquely and with a slight propulsive force. According to the invention, the sole (1) essentially is only rigid to a tangential deformation beyond at least one critical point of deformation in the region that is deformed to this critical point. This results in a correspondingly increased stability for the runner in the respective point of contact or load application. The runner is also able to push off from the point of load application without any loss in distance. A floating effect on the sole is prevented.
Owner:ON CLOUDS GMBH
Method and system for controlling an array of point-of-load regulators and auxiliary devices
InactiveUS7266709B2Complete understandingEnergy efficient ICTClimate change adaptationDigital dataPoint of load
A power control system comprises at least one POL regulator, at least one auxiliary device, a serial data bus operatively connecting the POL regulator and the auxiliary device, and a system controller adapted to exchange digital data with the POL regulator and auxiliary device via the serial data bus. The auxiliary device may include a power regulation device, a switching device, a motor control device, a temperature control device, and / or a peripheral device. At least one auxiliary device controller may be operatively coupled between the auxiliary device and the serial data bus. The auxiliary device controller may be integrated with the system controller, or may be external to the system controller. The auxiliary device controller may further comprise at least one register adapted to store the programming data, with the programming data including at least one of turn-on delay, turn-off delay, polarity of input / output signals, fault configuration, and group membership. The auxiliary device controller may be further adapted to receive monitoring data from the auxiliary device, with the auxiliary device controller communicating the monitoring data to the system controller via the serial data bus.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
Outsole
An outsole (1, 3), in particular, for athletic shoes (2) can be realized with a significant elastic deformability in the tangential direction so as to also achieve a superior shock-absorption when the foot contacts the ground obliquely and with a slight propulsive force. According to the invention, the sole (1) essentially is only rigid to a tangential deformation beyond at least one critical point of deformation in the region that is deformed to this critical point. This results in a correspondingly increased stability for the runner in the respective point of contact or load application. The runner is also able to push off from the point of load application without any loss in distance. A floating effect on the sole is prevented. The sole can be affixed, as a whole or in a plurality of parts, also detachably to an intermediate sole (4) of the shoe (2).
Owner:GLIDEN LOCK
Method And System For Optimizing Filter Compensation Coefficients For A Digital Power Control System
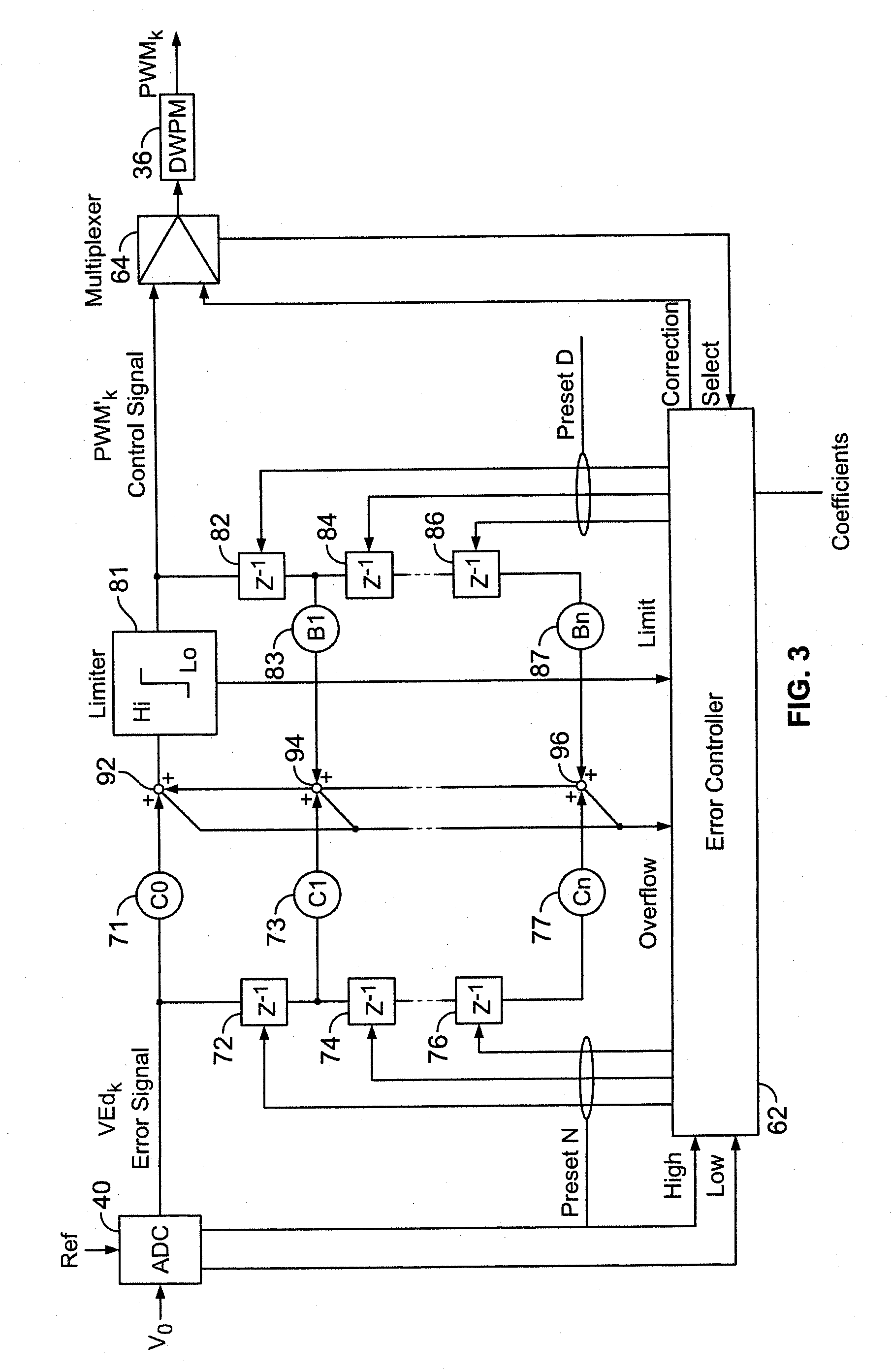
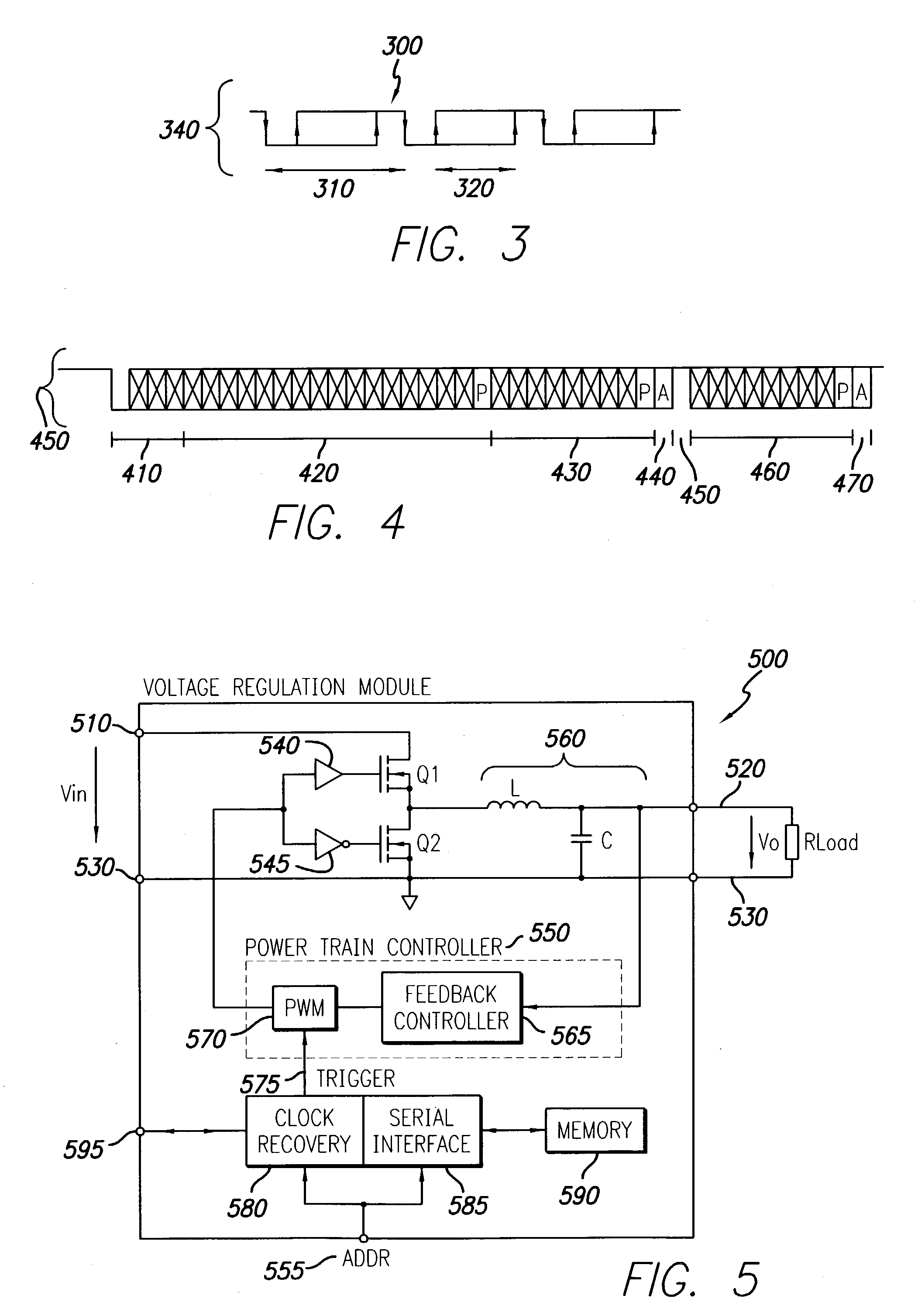
A method and system is provided for optimizing the digital filter compensation coefficients of a digitally controlled switched mode power supply within a distributed power system. A power control system comprises at least one point-of-load (POL) regulator having a power conversion circuit adapted to convey power to a load and a digital controller coupled to the power conversion circuit though a feedback loop. The digital controller is adapted to provide a pulse width modulated control signal to the power switch responsive to a feedback measurement of an output of the power conversion circuit. The digital controller further comprises a digital filter having a transfer function defined by plural filter coefficients. The digital controller periodically stores a successive one of a plurality of samples of the feedback measurement. A serial data bus operatively connects the POL regulator to a system controller. The system controller retrieves each successive stored sample from the digital controller via the serial data bus. After retrieving a pre-determined number of the samples, the system controller calculates optimized filter coefficients for the digital filter and communicates the optimized filter coefficients to the digital controller. The digital controller thereafter uses the optimized filter coefficients in the digital filter.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
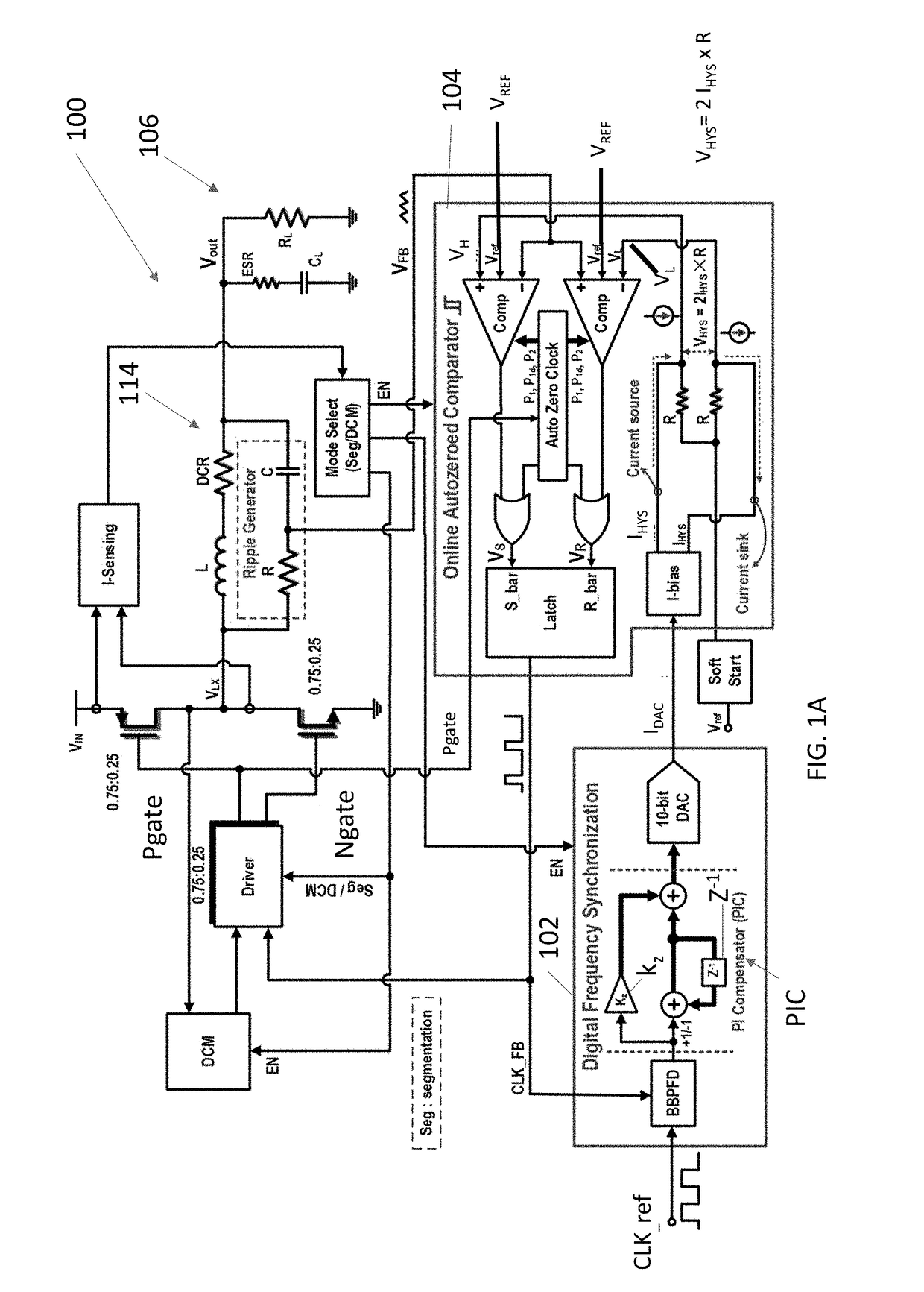
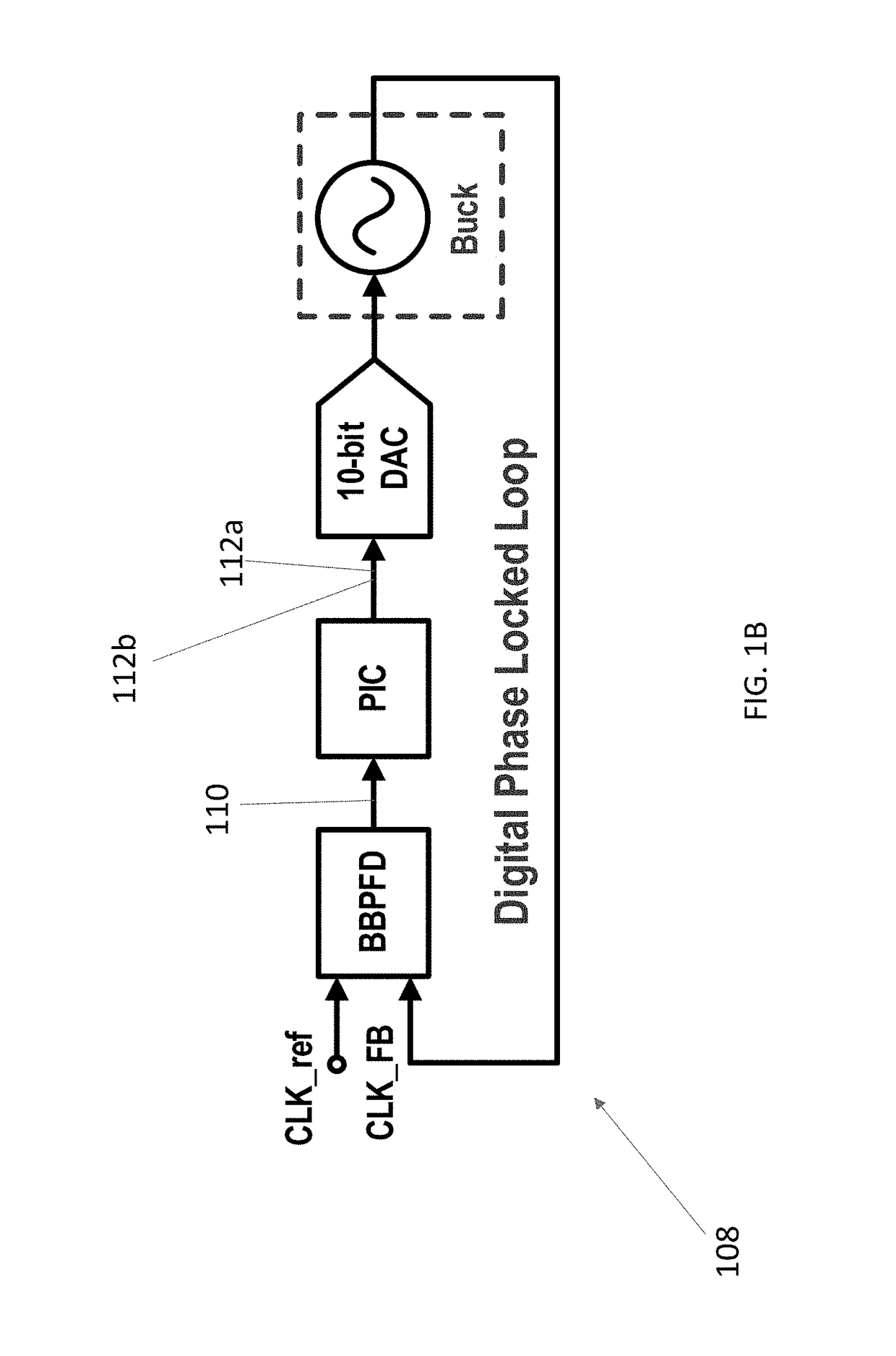
Digital multiphase hysteretic point-of-load dc/dc converter
ActiveUS20180048232A1Improve transient responseOptimal recovery timePulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionPoint of loadConstant frequency
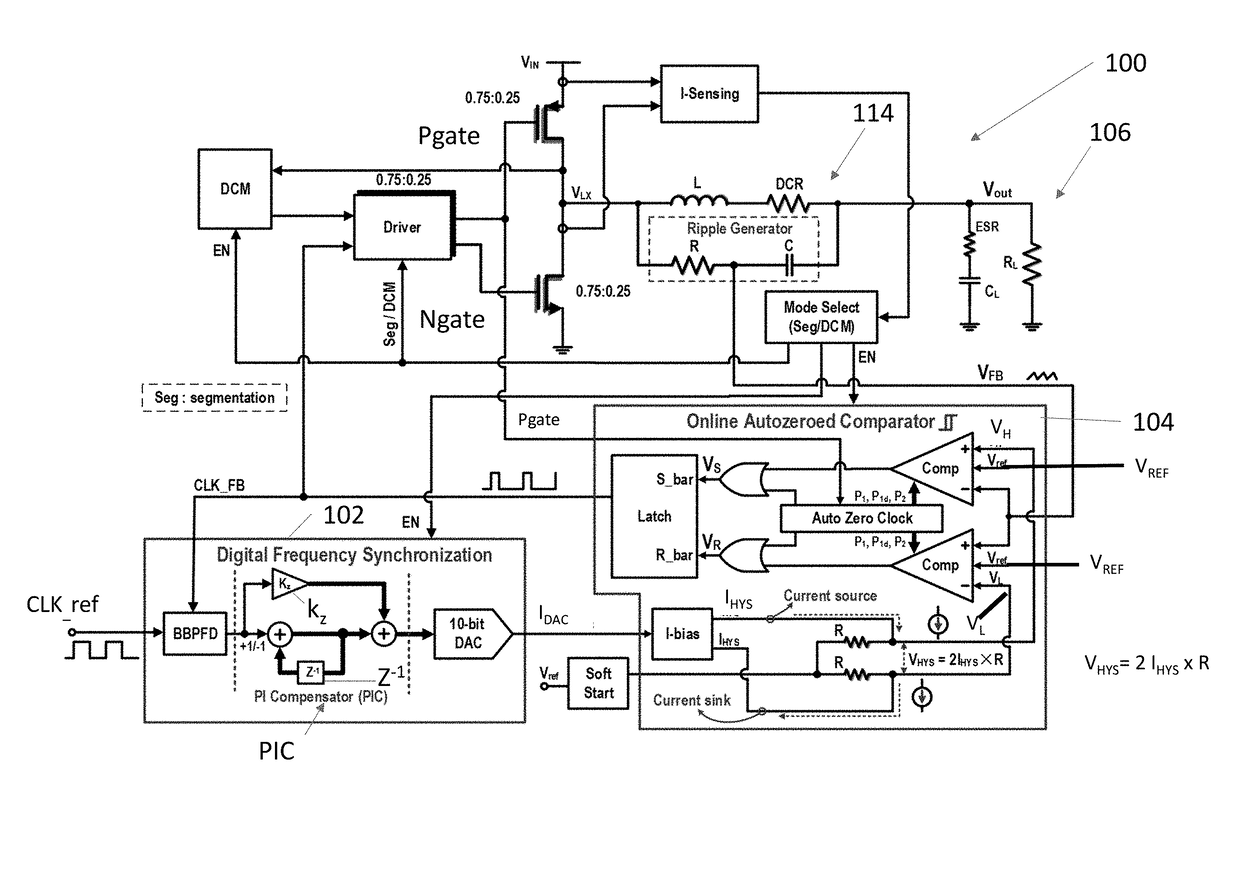
An autozeroed comparator controls a frequency fsw of the input voltage inputted to a DC / DC converter. A digital frequency synchronization circuit is connected to the autozeroed comparator so as to form a phase locked loop, wherein the DES circuit controls the hysteretic window of the autozeroed comparator so as to lock fsw to a clock reference frequency. A plurality of slave phase circuits may be connected to the master phase circuit including the DFS circuit and the autozeroed comparator. Duty cycle calibration circuits adjust a duty cycle signal applied to each of the slave phase circuits, in response to average current measured in the slave phase circuits, so that each slave phase circuit is synchronized with the master phase circuit. A 6 A 90.5% peak efficiency 4-phase hysteretic quasi-current-mode buck converter is provided with constant frequency and maximum ±1.5% current mismatch between the slave phases and the master phase.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
System for controlling and monitoring an array of point-of-load regulators by a host
InactiveUS7456617B2Less complexityReduce the amount requiredTemperatue controlVolume/mass flow measurementPoint of loadDigital data
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
System and method for interleaving point-of-load regulators
ActiveUS7373527B2Reduce system noiseImprove Noise PerformanceDigital data processing detailsThree-or-more-wire dc circuitsPoint of loadSwitching cycle
A system and method for providing interleaving point-of-load (POL) regulators such that each regulator's switching cycle is phase displaced with respect to those of other POL regulators in the array is disclosed. As a result, the aggregate input and / or output reflected ripple and noise of the input, output, or both is reduced. Each regulator in the array is associated with an unique address. A serial data-line writes the phase spacing programmed to each addressable POL regulator in the array. The present invention permits phase displacement of POL regulators without limitation to the input and output voltages of each of the regulators in the array. The array of POL regulators may also operate in a phase displaced mode with only a single control line. The need for separate controllers and multiple control lines is thereby eliminated.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
Method and system for controlling an array of point-of-load regulators and auxiliary devices
InactiveUS20060174145A1Complete understandingEnergy efficient ICTClimate change adaptationDigital dataPoint of load
A power control system comprises at least one POL regulator, at least one auxiliary device, a serial data bus operatively connecting the POL regulator and the auxiliary device, and a system controller adapted to exchange digital data with the POL regulator and auxiliary device via the serial data bus. The auxiliary device may include a power regulation device, a switching device, a motor control device, a temperature control device, and / or a peripheral device. At least one auxiliary device controller may be operatively coupled between the auxiliary device and the serial data bus. The auxiliary device controller may be integrated with the system controller, or may be external to the system controller. The auxiliary device controller may further comprise at least one register adapted to store the programming data, with the programming data including at least one of turn-on delay, turn-off delay, polarity of input / output signals, fault configuration, and group membership. The auxiliary device controller may be further adapted to receive monitoring data from the auxiliary device, with the auxiliary device controller communicating the monitoring data to the system controller via the serial data bus.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
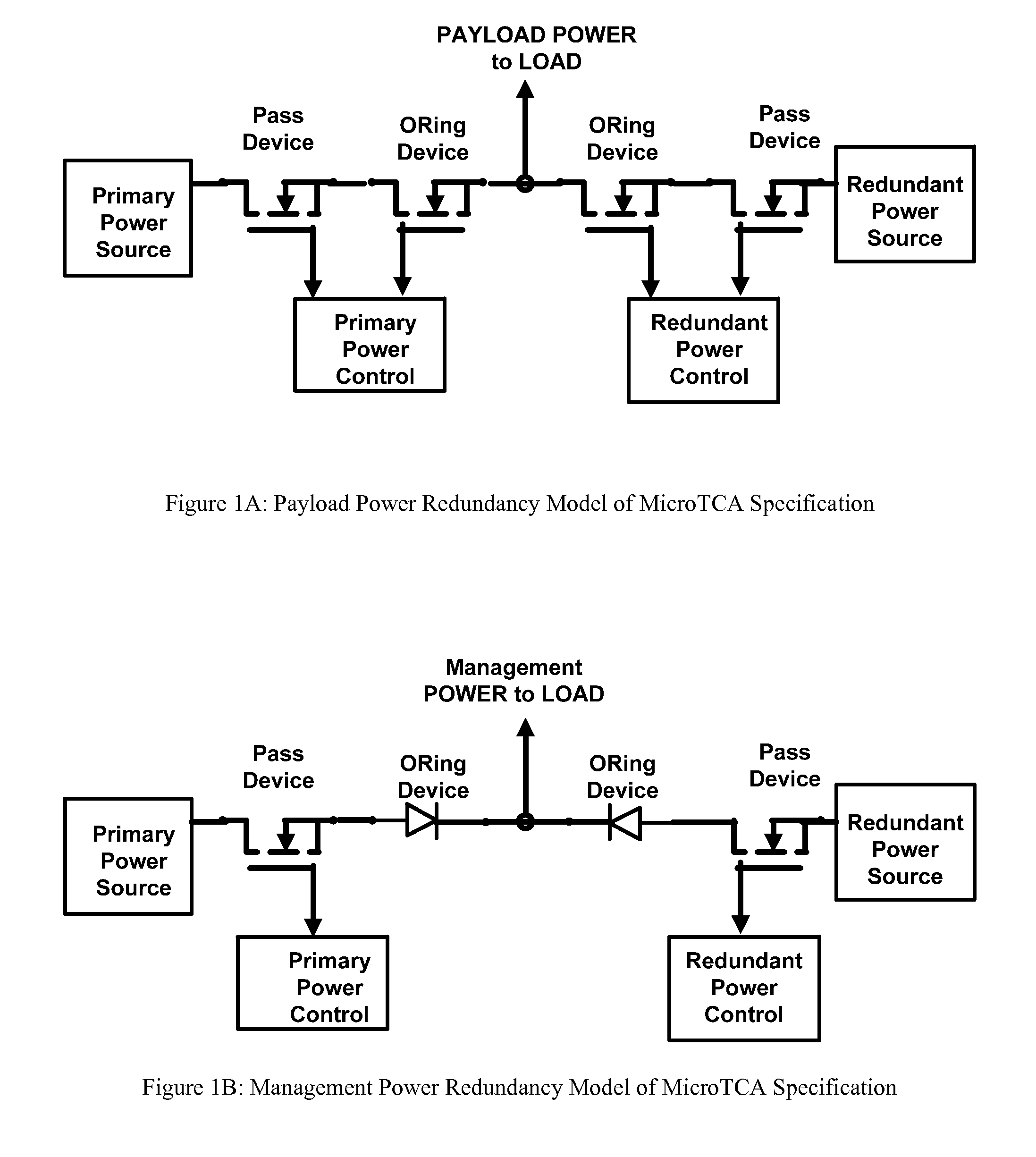
Redundant power supply architecture with voltage level range based load switching
InactiveUS20080164759A1Permit useReduce the number of partsBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPoint of loadPotential difference
A voltage level range based redundant power supply architecture is described wherein at least two power supplies are connected to an external load and maintained in an energized state. However, only one of the power supplies sources all the current requirements of the load while the other power supply remains in standby mode. This is achieved by manually or programmatically adjusting the voltage output of a first power supply and a second power supply connected in parallel to the external load such that the first power supply always outputs a higher potential difference at the point of load than the second power supply, thereby implementing a voltage level range of outputs of the power supplies so as to guarantee that all the current requirement of the load is sourced from the first power supply. The second power supply remains energized and upon failure of the first power supply instantaneously takes over the function of the failed power supply and powers the load.
Owner:SLT LOGIC
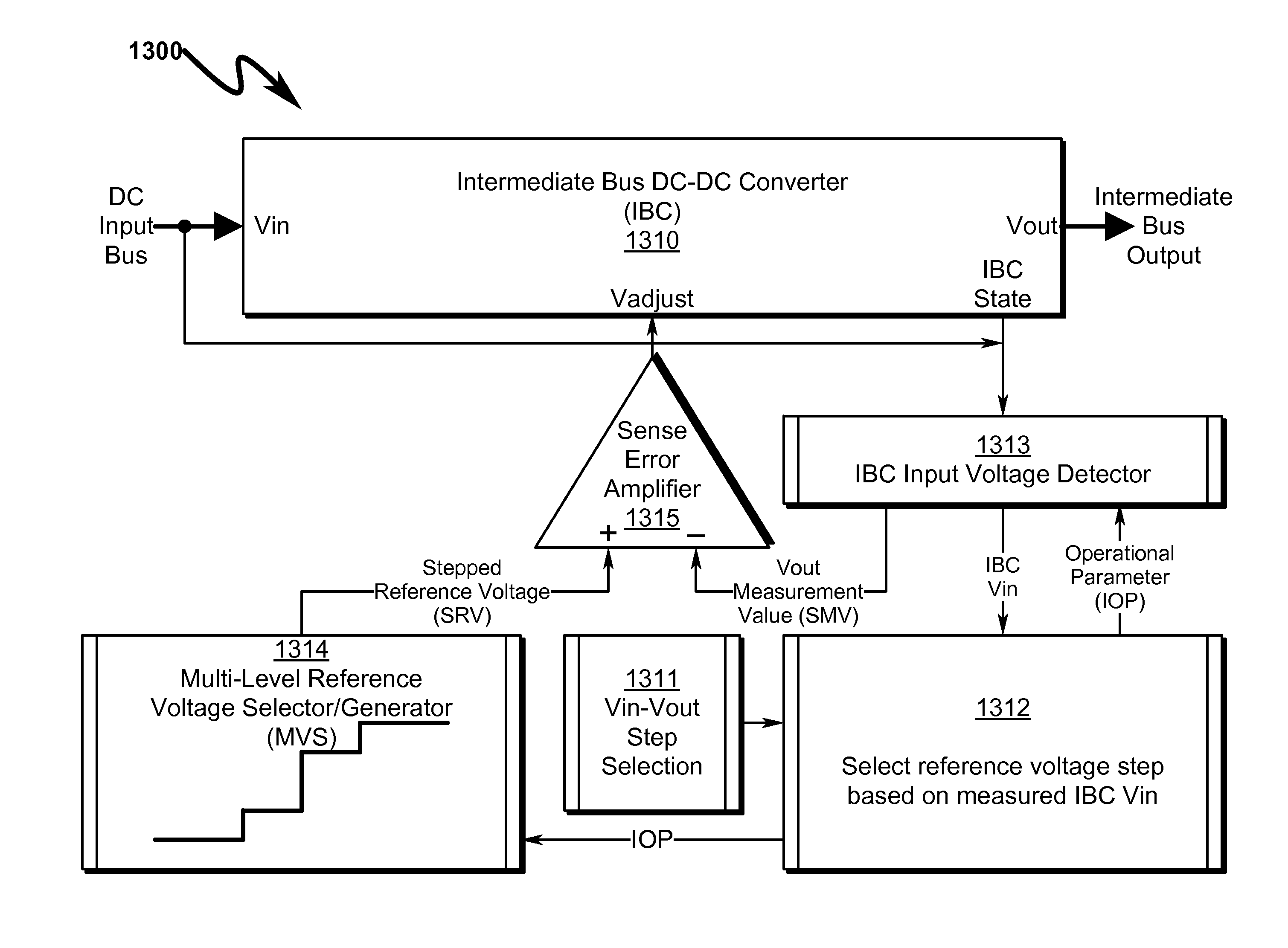
Multi-level voltage regulator system and method
ActiveUS20130335043A1Lower potentialGuaranteed uptimeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionHysteresisPoint of load
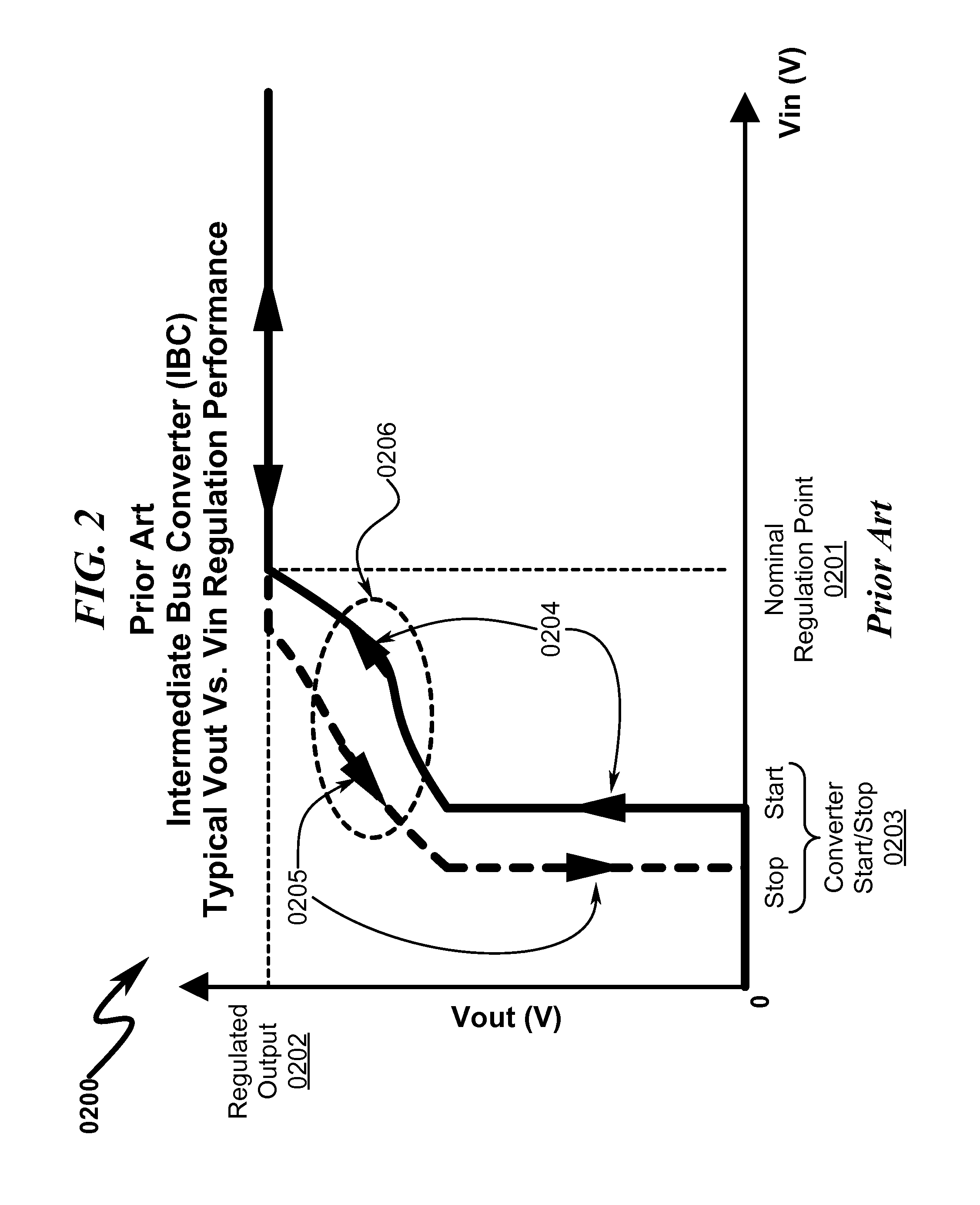
A multi-level voltage regulator system / method providing discrete regulation of a DC-DC intermediate bus converter (IBC) output voltage (Vout) is disclosed. The disclosed system / method allows IBC Vout to be regulated in discrete steps during periods where IBC input voltage (Vin) falls below nominal operating values. Rather than shutting down or degrading IBC Vout in an unpredictable non-linear fashion based on IBC input / loading, IBC Vout is regulated in fixed discrete steps, allowing IBC-connected point-of-load (POL) converters to obtain stable power input that is well-defined over IBC Vin. IBC operating parameters may define multi-dimensional operational state spaces of IBC Vout regulation that ensure optimum power flow to attached POLs while maintaining operational stability within the IBC regulator. Instabilities in IBC / POL performance across variations in IBC Vin, load transients, POL loading, and environmental variables may be prevented using Vin voltage step hysteresis.
Owner:TDK LAMBDA CORP
Outsole
An outsole (1, 3), in particular, for athletic shoes (2) can be realized with a significant elastic deformability in the tangential direction so as to also achieve a superior shock-absorption when the foot contacts the ground obliquely and with a slight propulsive force. According to the invention, the sole (1) essentially is only rigid to a tangential deformation beyond at least one critical point of deformation in the region that is deformed to this critical point. This results in a correspondingly increased stability for the runner in the respective point of contact or load application. The runner is also able to push off from the point of load application without any loss in distance. A floating effect on the sole is prevented.
Owner:ON CLOUDS GMBH
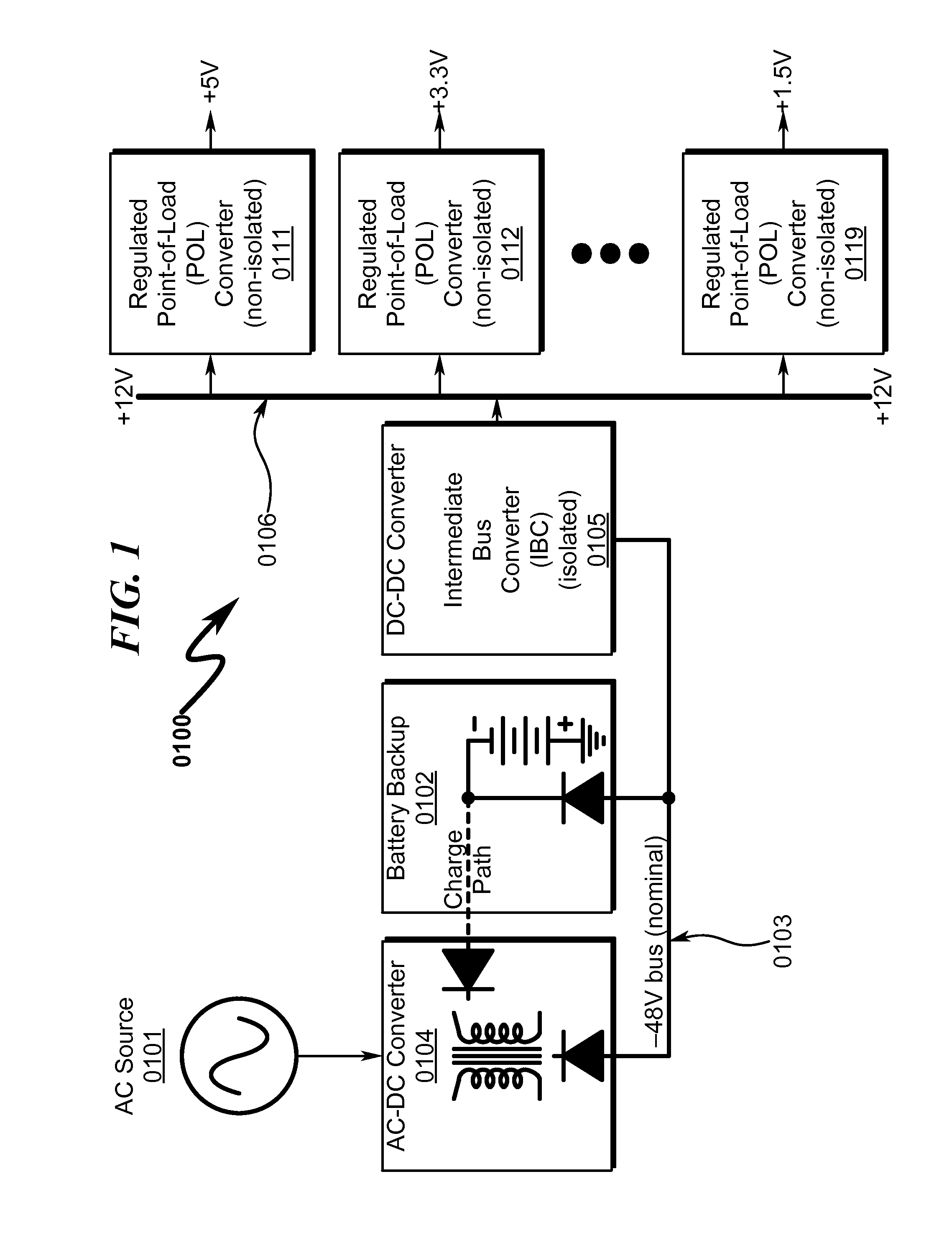
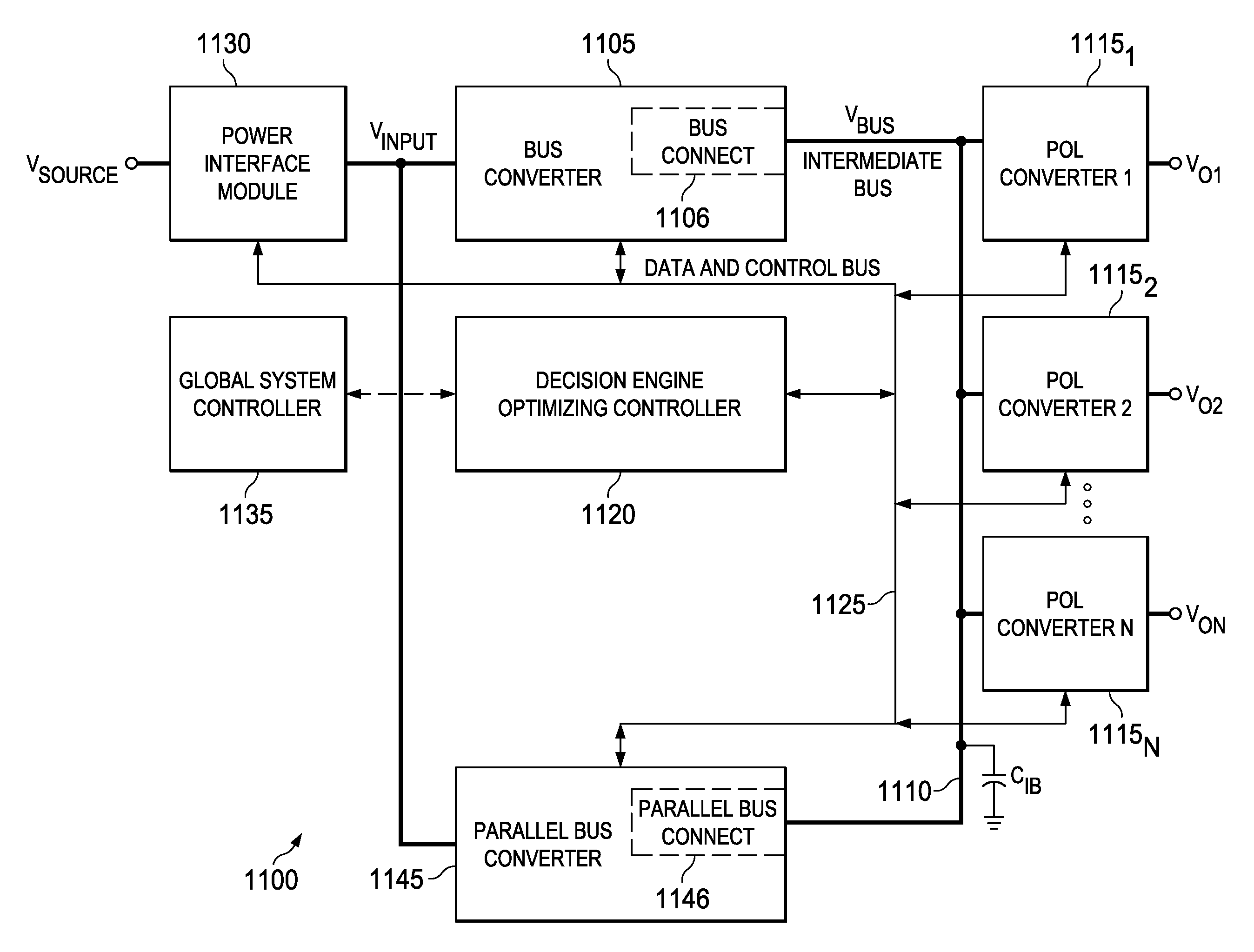
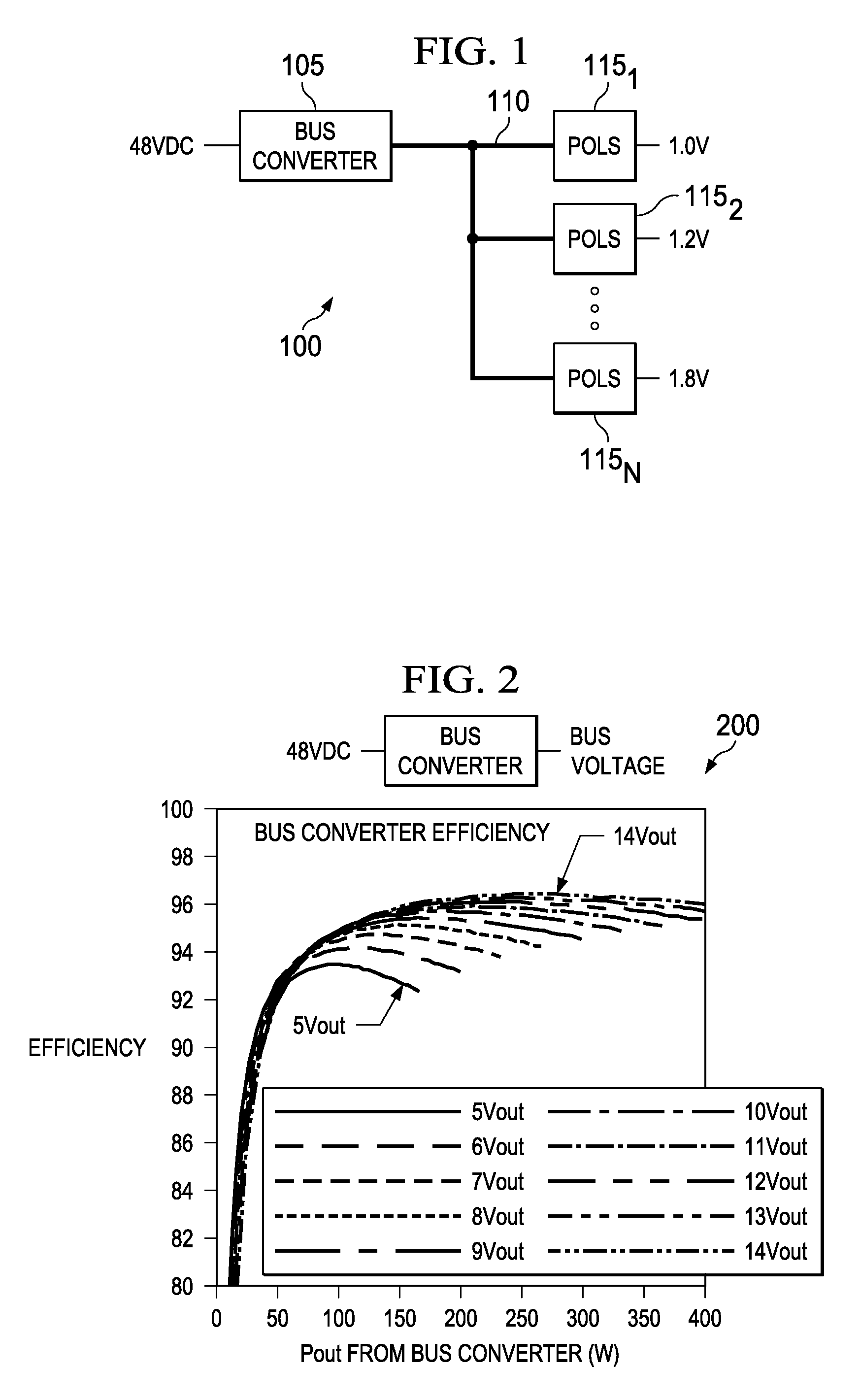
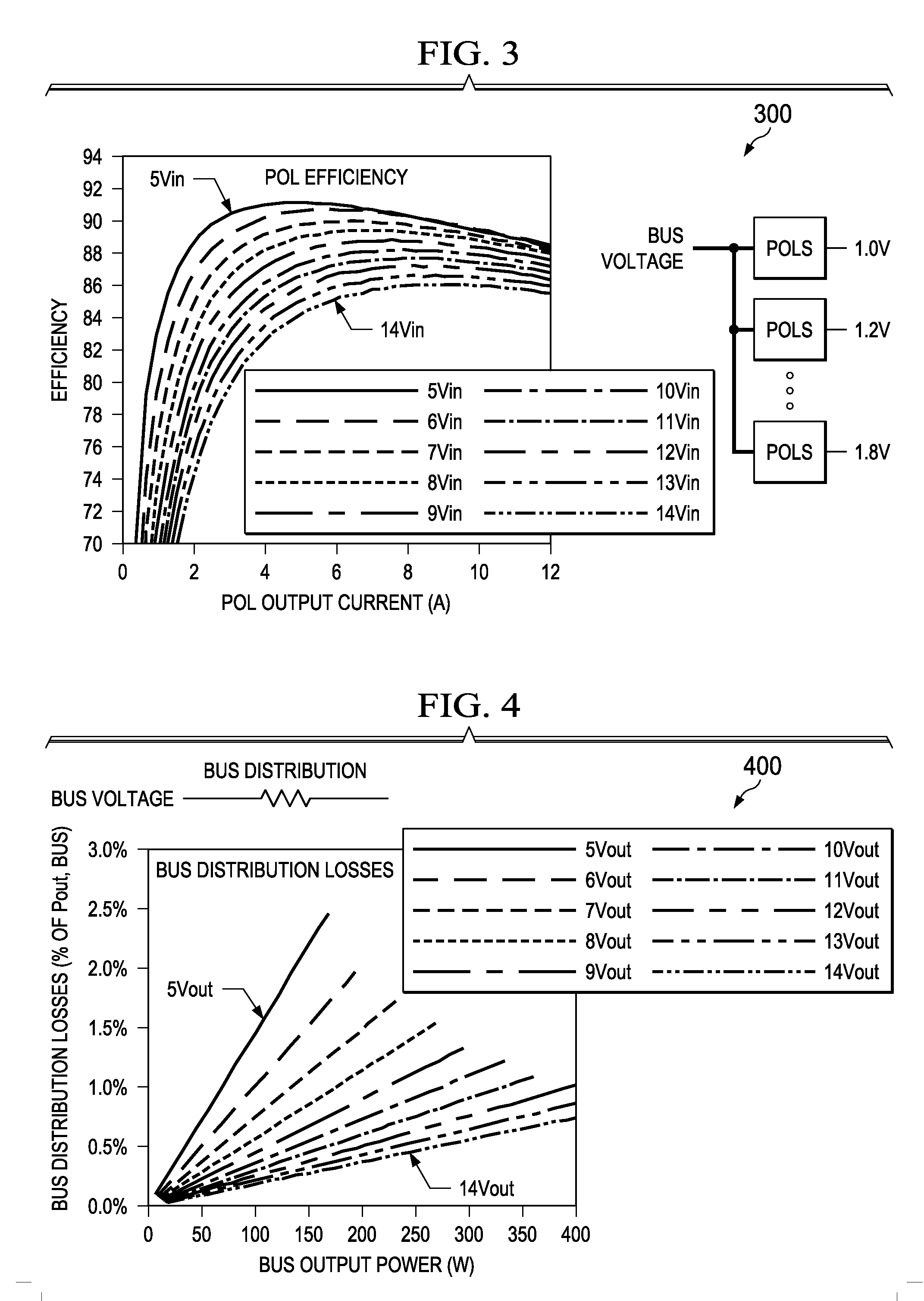
Controlled intermediate bus architecture optimization
InactiveUS20120297104A1Improve system performanceEnergy efficient ICTDc source parallel operationPoint of loadElectric power system
An intermediate bus architecture power system includes a bus converter that converts an input voltage into a bus voltage on an intermediate bus and a point-of-load converter that supplies an output voltage from the bus voltage on the intermediate bus. Additionally, the intermediate bus architecture power system includes a decision engine optimizing controller that controls a system variable to improve an overall system performance based on a monitored system variable or a system constraint. In another aspect, a method of operating an intermediate bus architecture power system includes converting an input voltage into a bus voltage on an intermediate bus and converting the bus voltage on the intermediate bus into an output voltage. The method also includes controlling a system variable to improve overall system performance based on a monitored system variable or a system constraint.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
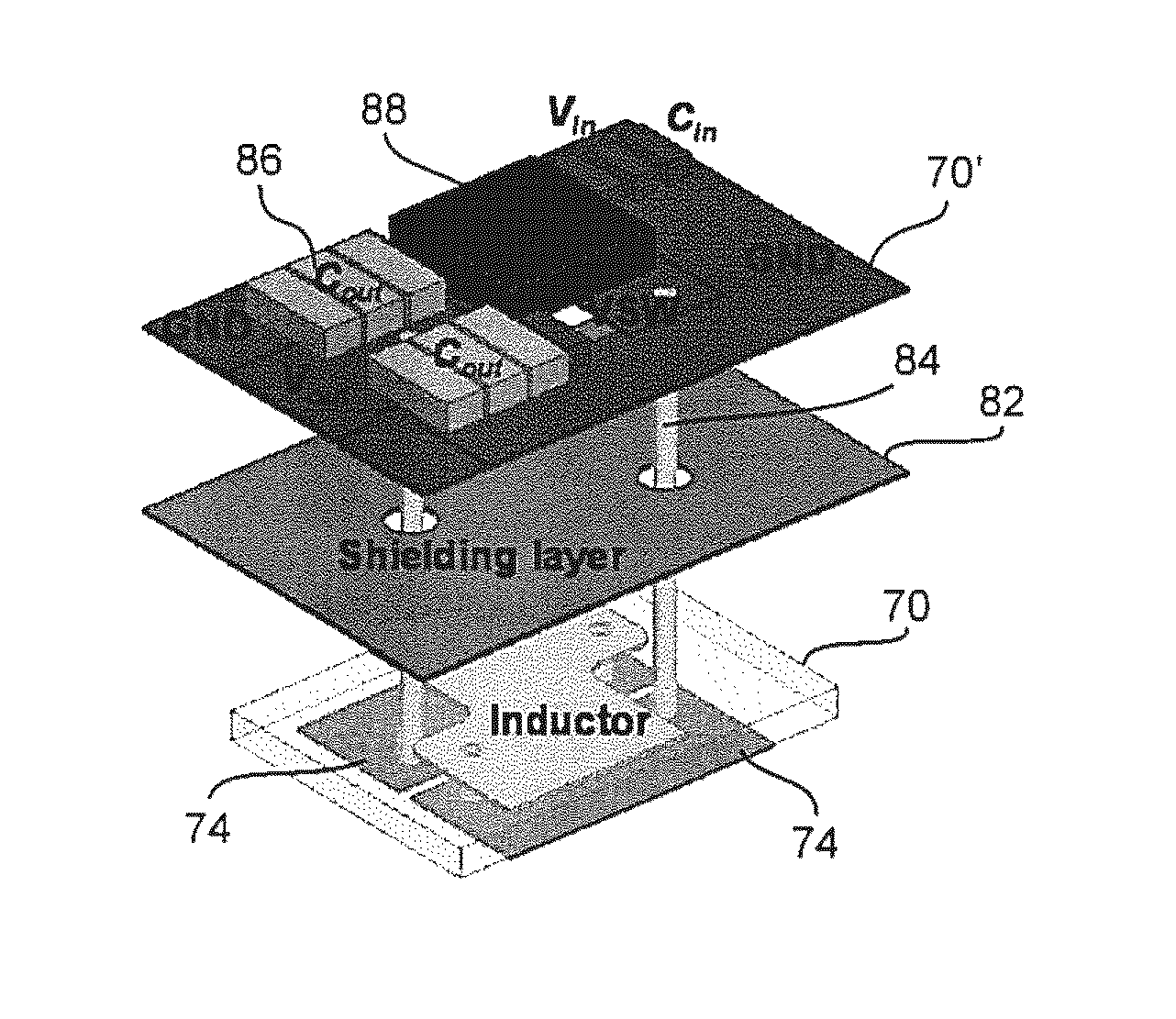
High Frequency Integrated Point-of-Load Power Converter with Embedded Inductor Substrate
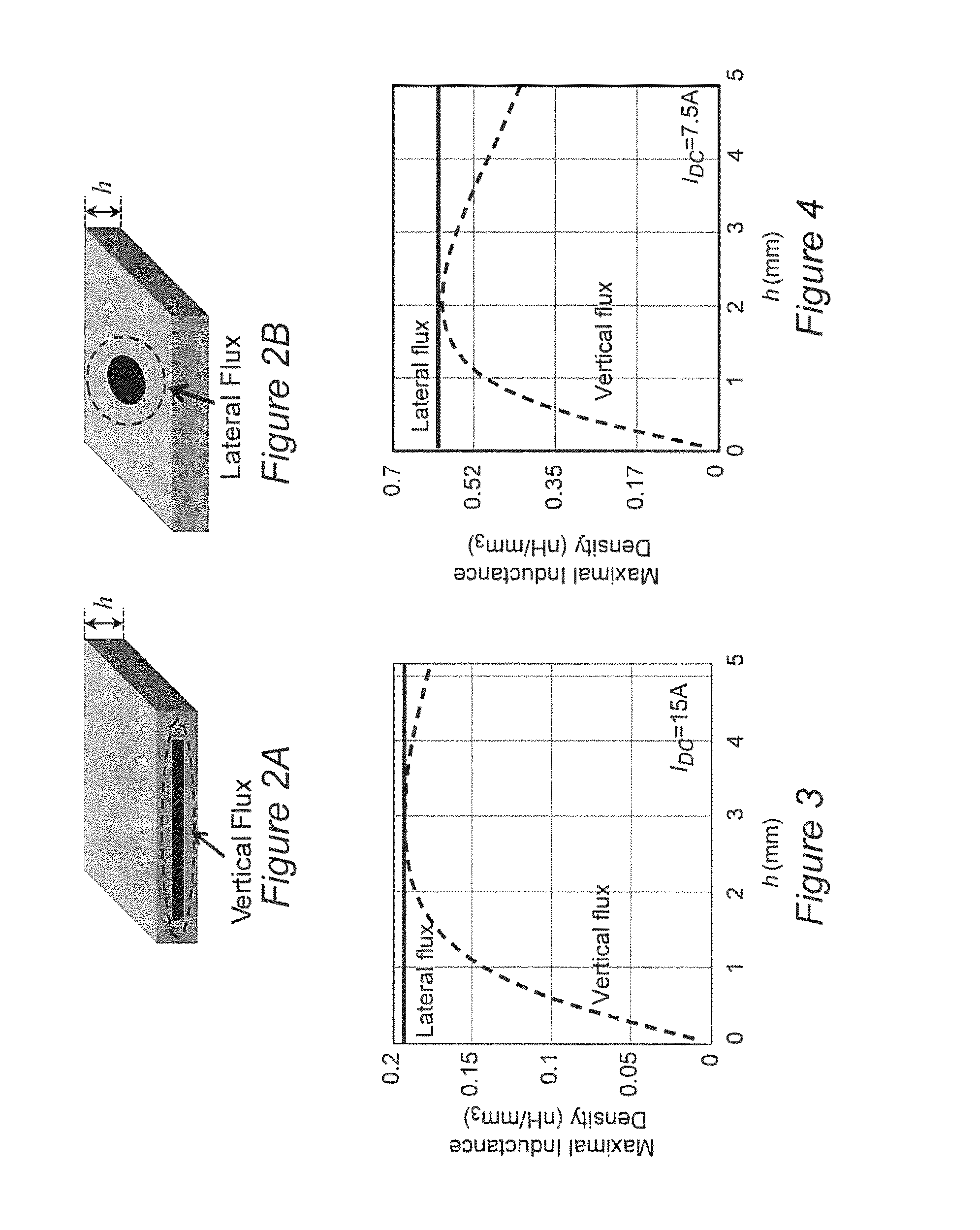
ActiveUS20150062989A1The implementation process is simpleLow profileCross-talk/noise/interference reductionCircuit arrangements on support structuresPoint of loadInductor windings
A low profile power converter structure is provide wherein volume is reduced and power density is increased to approach 1 KW / in3 by at least one of forming an inductor as a body of magnetic material embedded in a substrate formed by a plurality of printed circuit board (PCB) lamina and forming inductor windings of PCB cladding and vias which may be of any desired number of turns and may include inversely coupled windings and which provide a lateral flux path, forming the body of magnetic material from high aspect ratio flakes of magnetic material which are aligned with the inductor magnetic field in an insulating organic binder and hot-pressed and providing a four-layer architecture comprising two layers of PCB lamina including the embedded body of magnetic material, a shield layer and an additional layer of PCB lamina, including cladding for supporting and connecting a switching circuit, a capacitor and the inductor.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
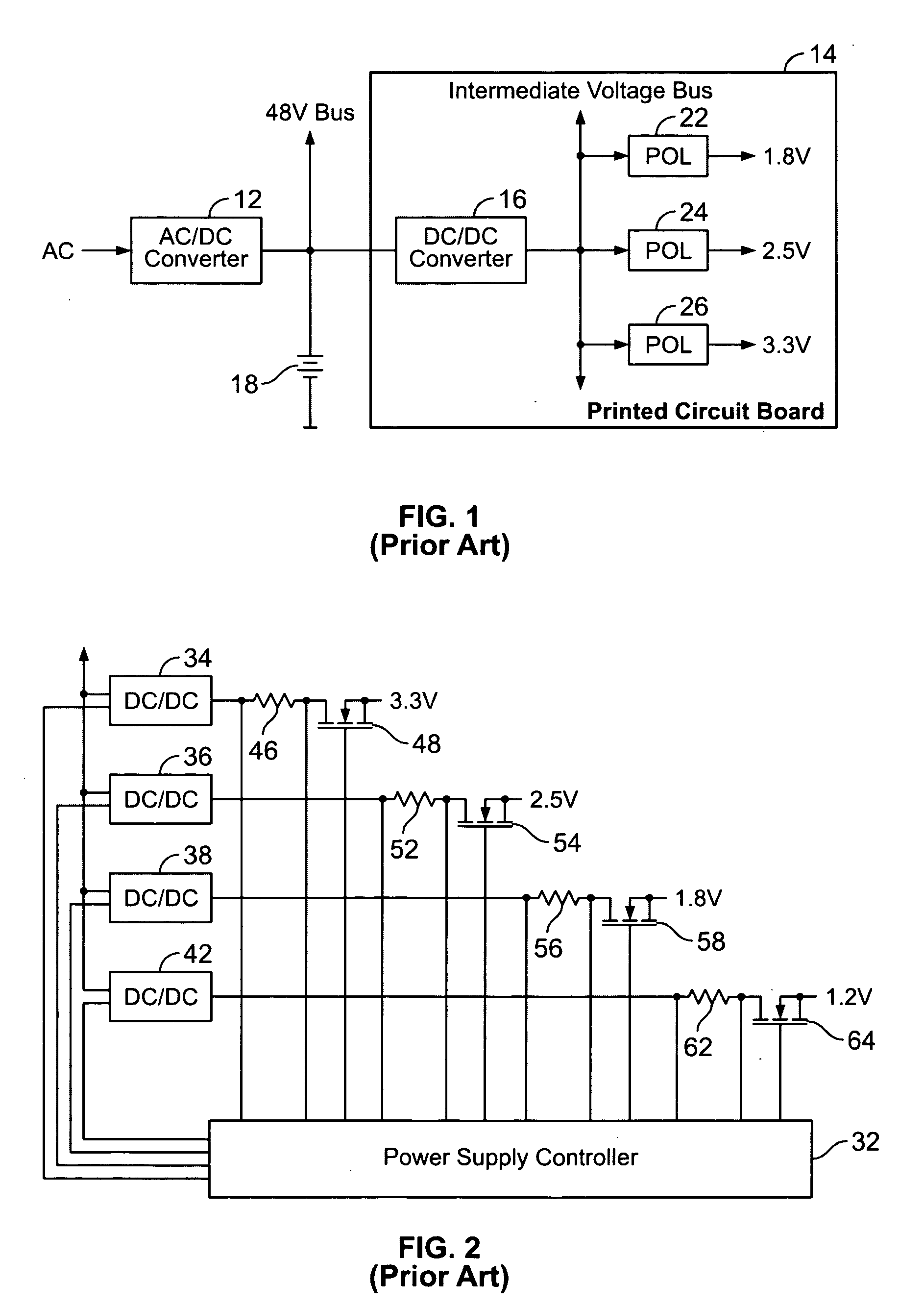
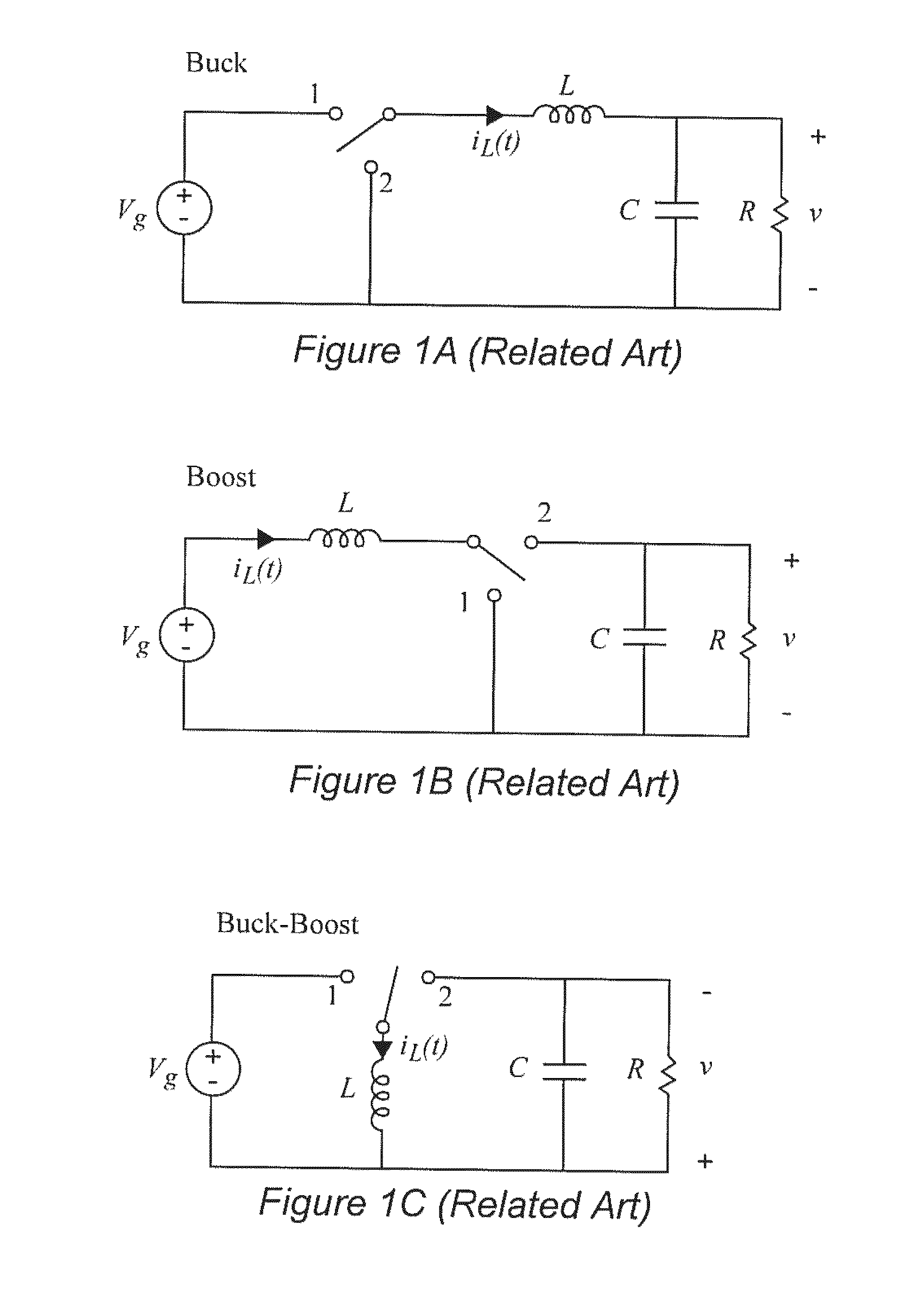
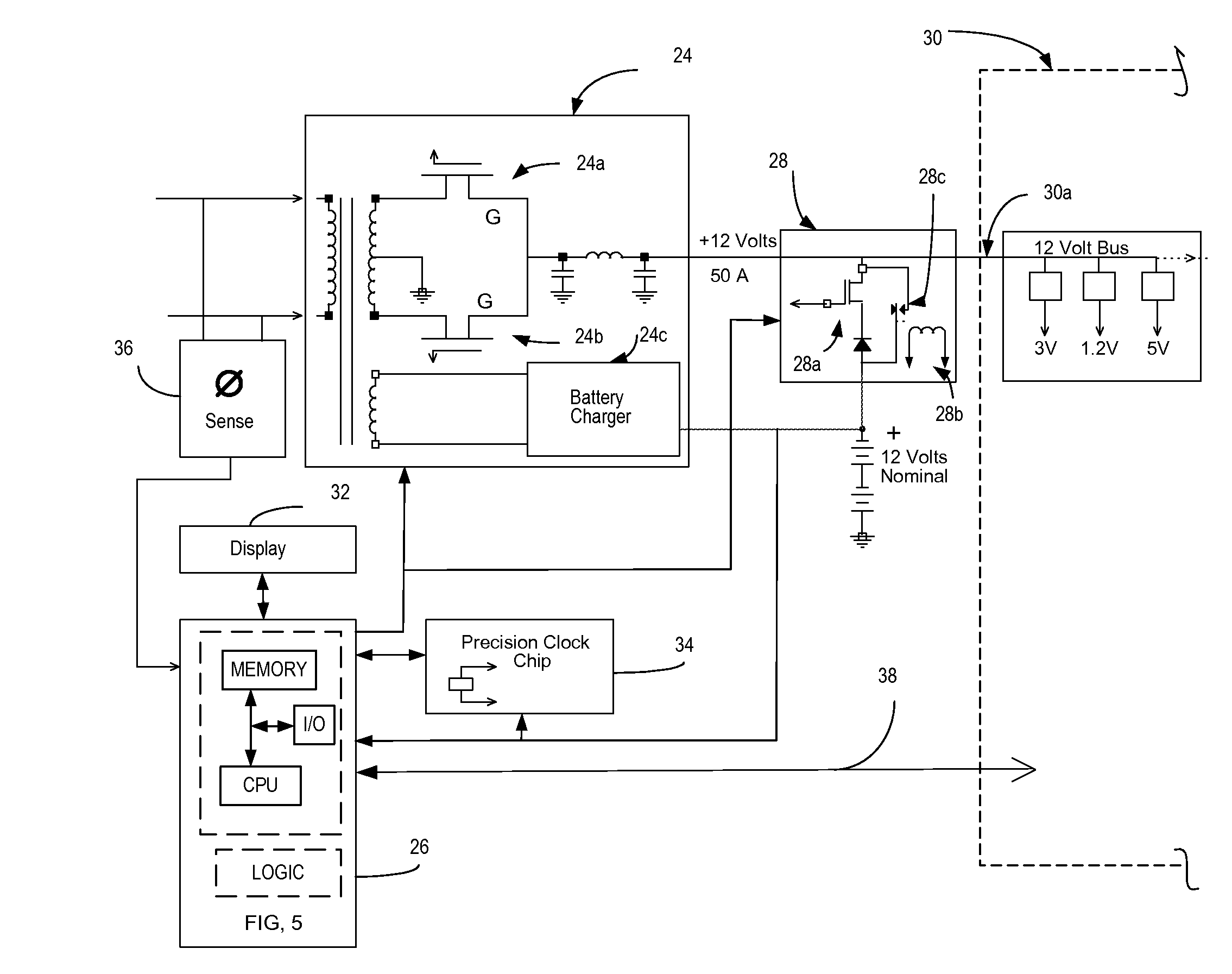
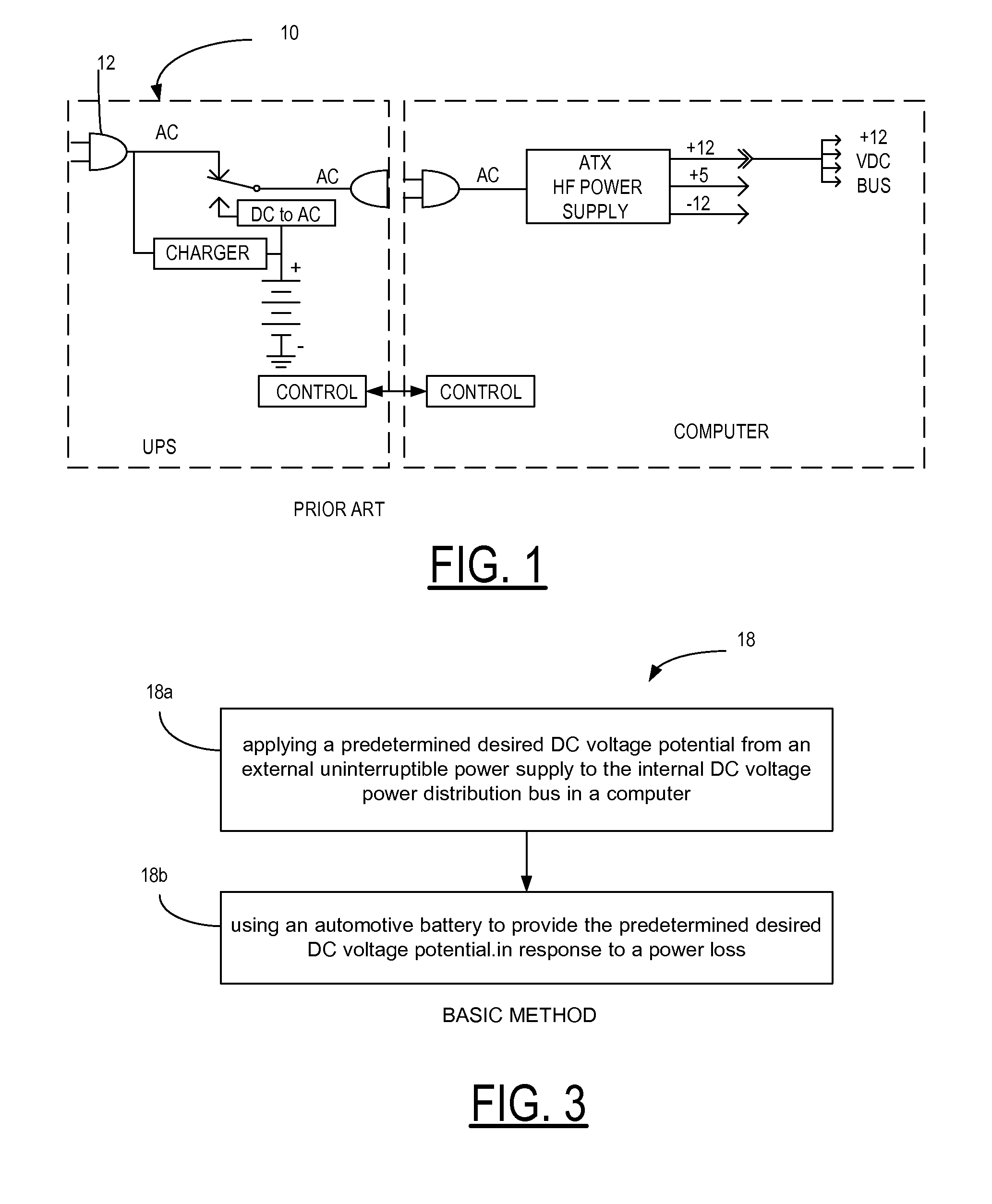
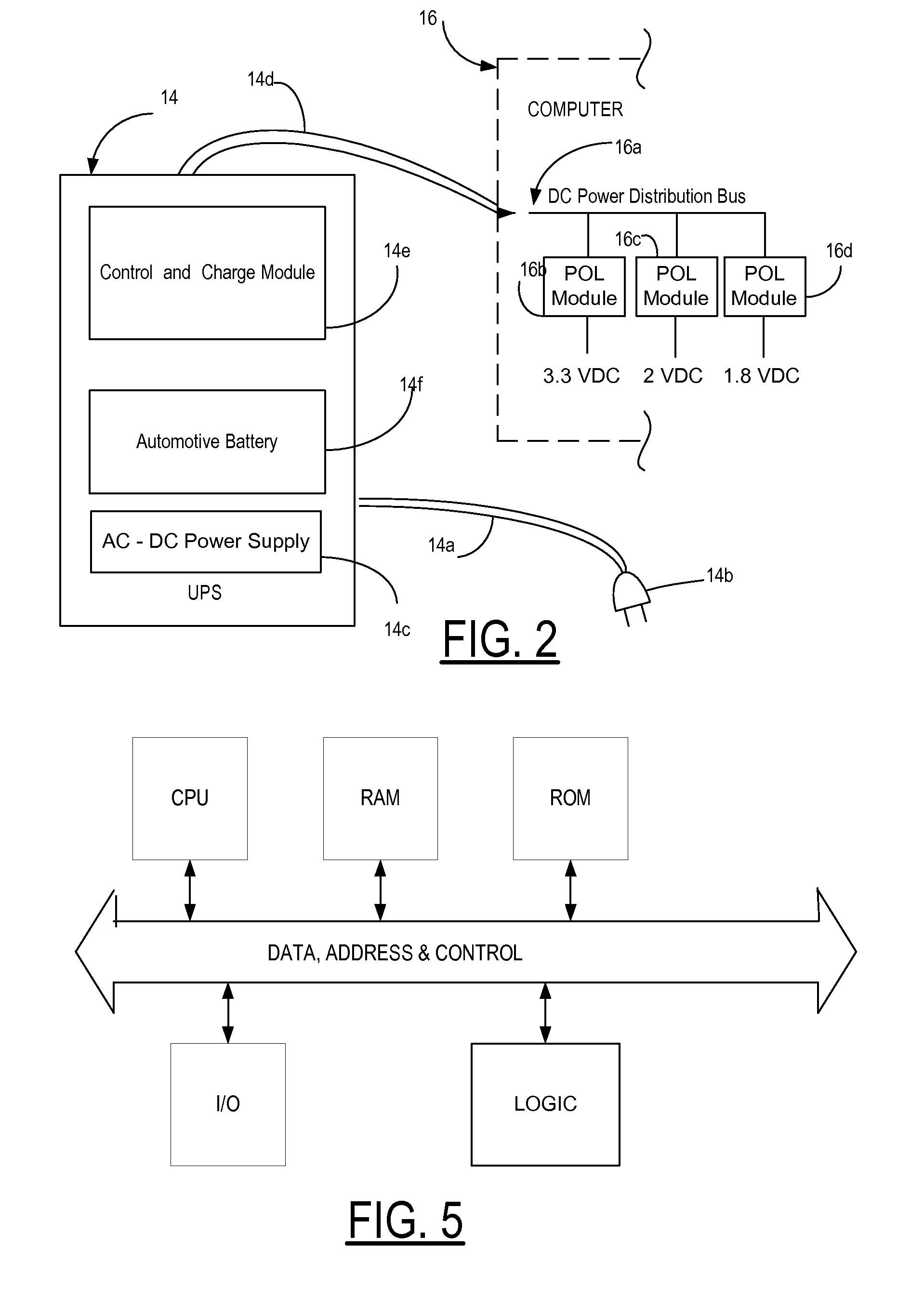
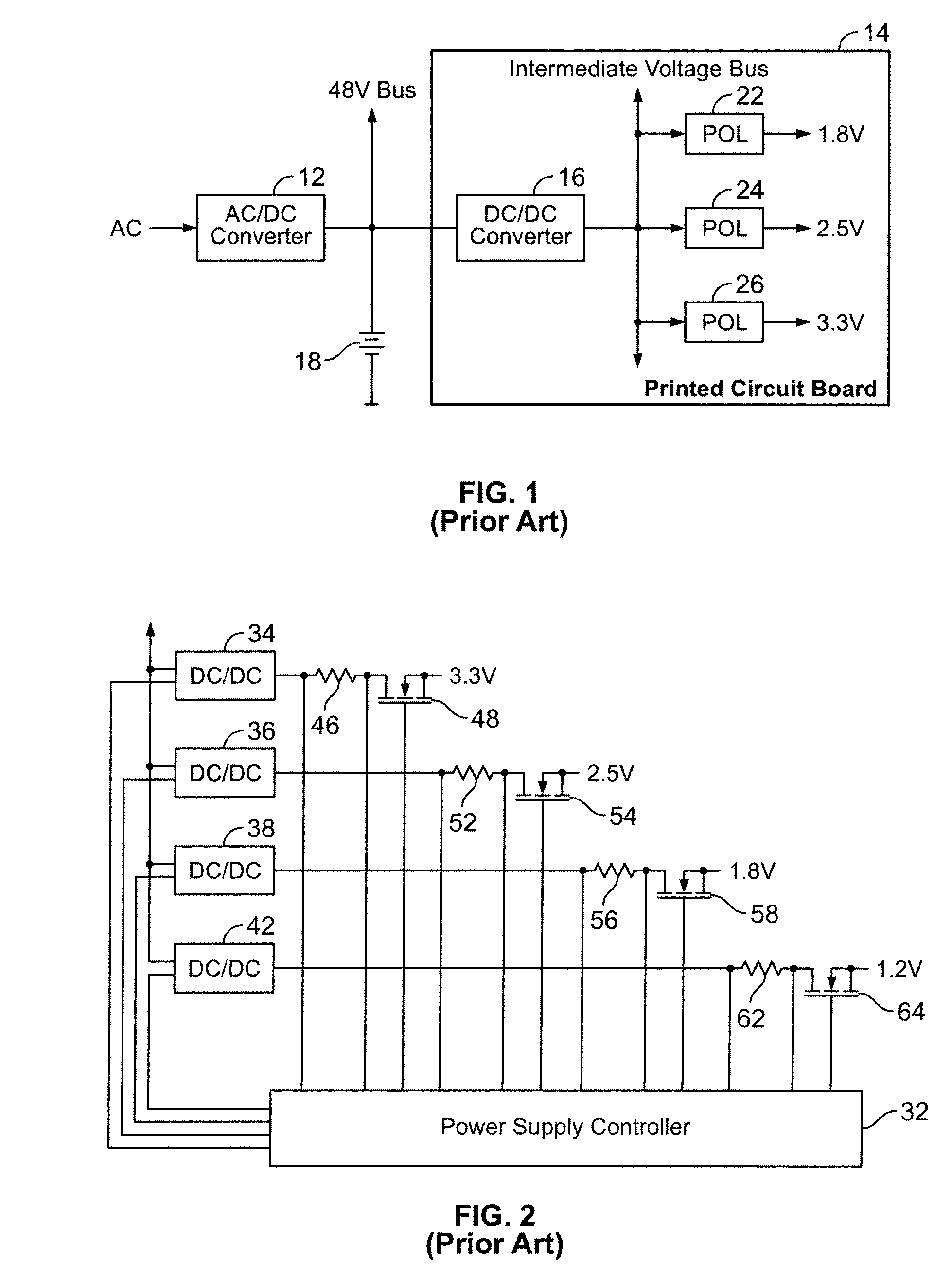
Uninterruptible power supply
An external uninterruptible power supply (“UPS”), and a related method, are presented in which a predetermined desired DC voltage potential is applied directly to the internal DC voltage power distribution bus in a computer. The UPS is configured to use an automotive battery to provide the predetermined desired DC voltage potential in the event of the loss of the AC voltage input signal. In a preferred embodiment, the UPS includes an inverterless AC-DC power supply, such as a bridge rectifier circuit, for supplying a predetermined desired direct current voltage potential at its output. That output potential in turn is carried by a suitably arranged cord or power cable connected to the internal direct current voltage distribution bus in the computer. The distribution bus may be connected to one or more points-of-load, also known as “point-of-power” voltage conversion modules, each of which provide a regulated voltage to power the various high density chip loads, components and circuitry in the computer. The input voltage to a point-of-load power chip can vary over a wide range allowing unregulated voltages ranging from 11 to 14 volts which may be used to supply the point-of-load power chips with no operating problems since the chips are inherently an on-card switching regulator operating at a high frequency.
Owner:GRADY JOHN K
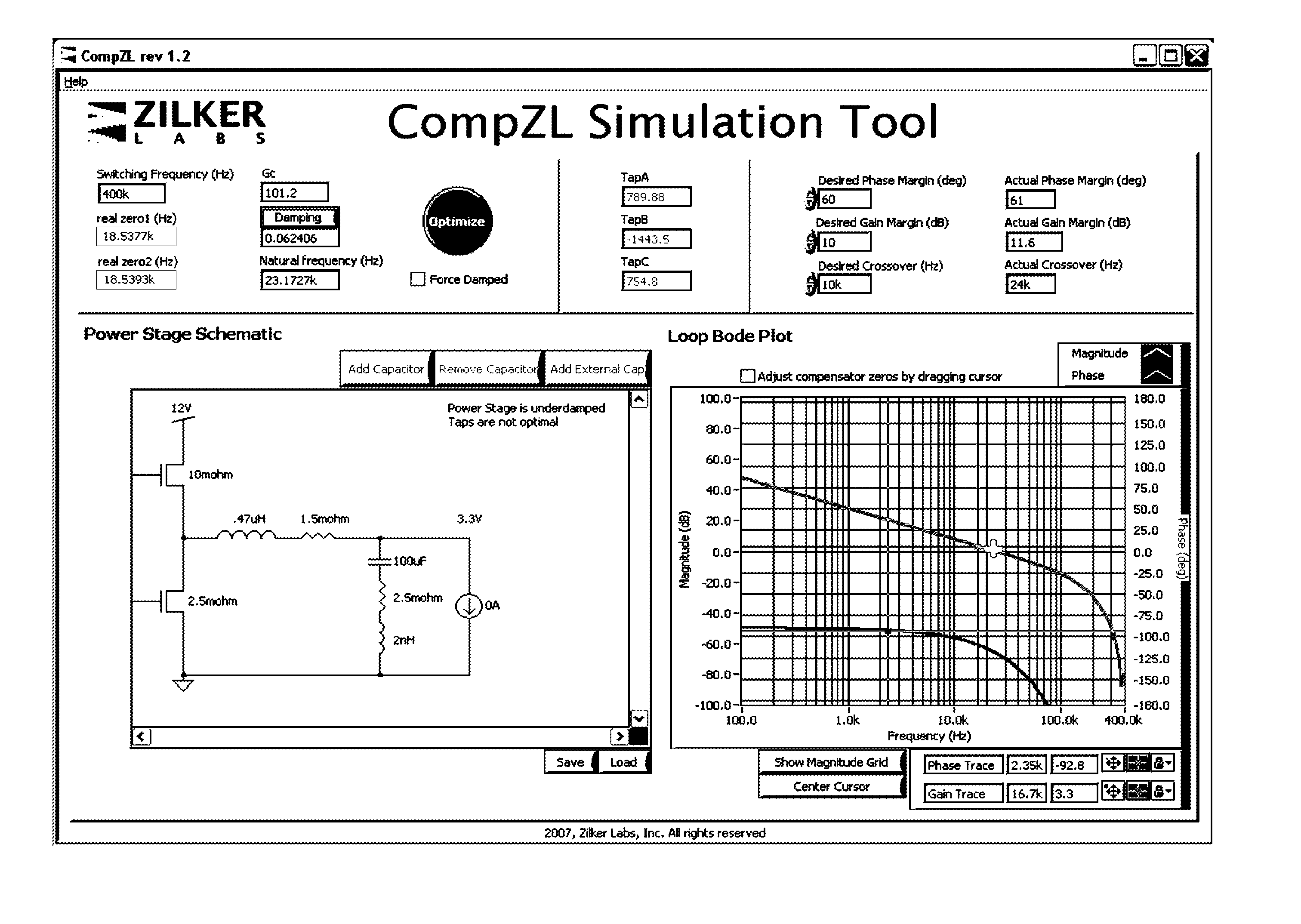
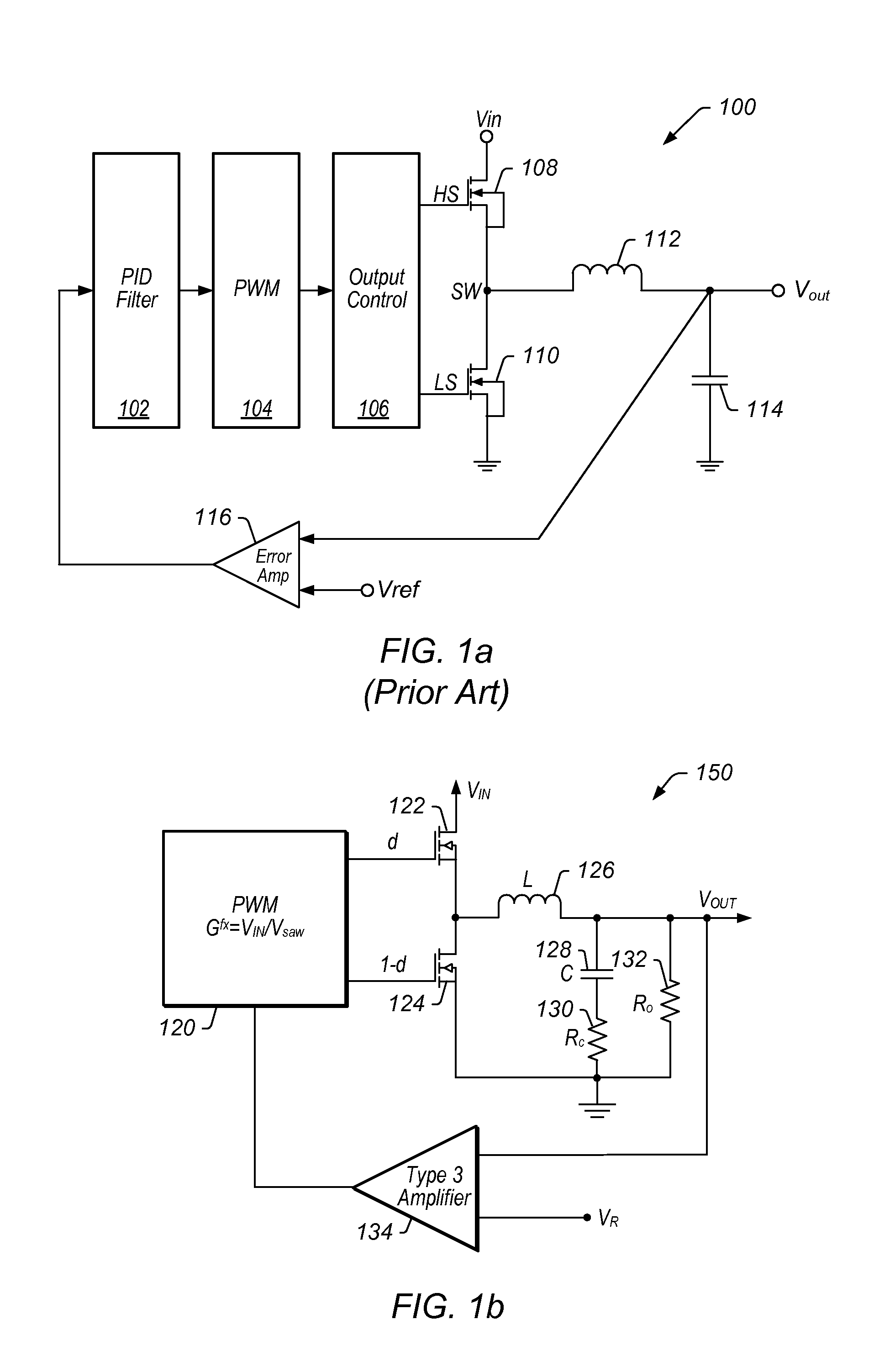
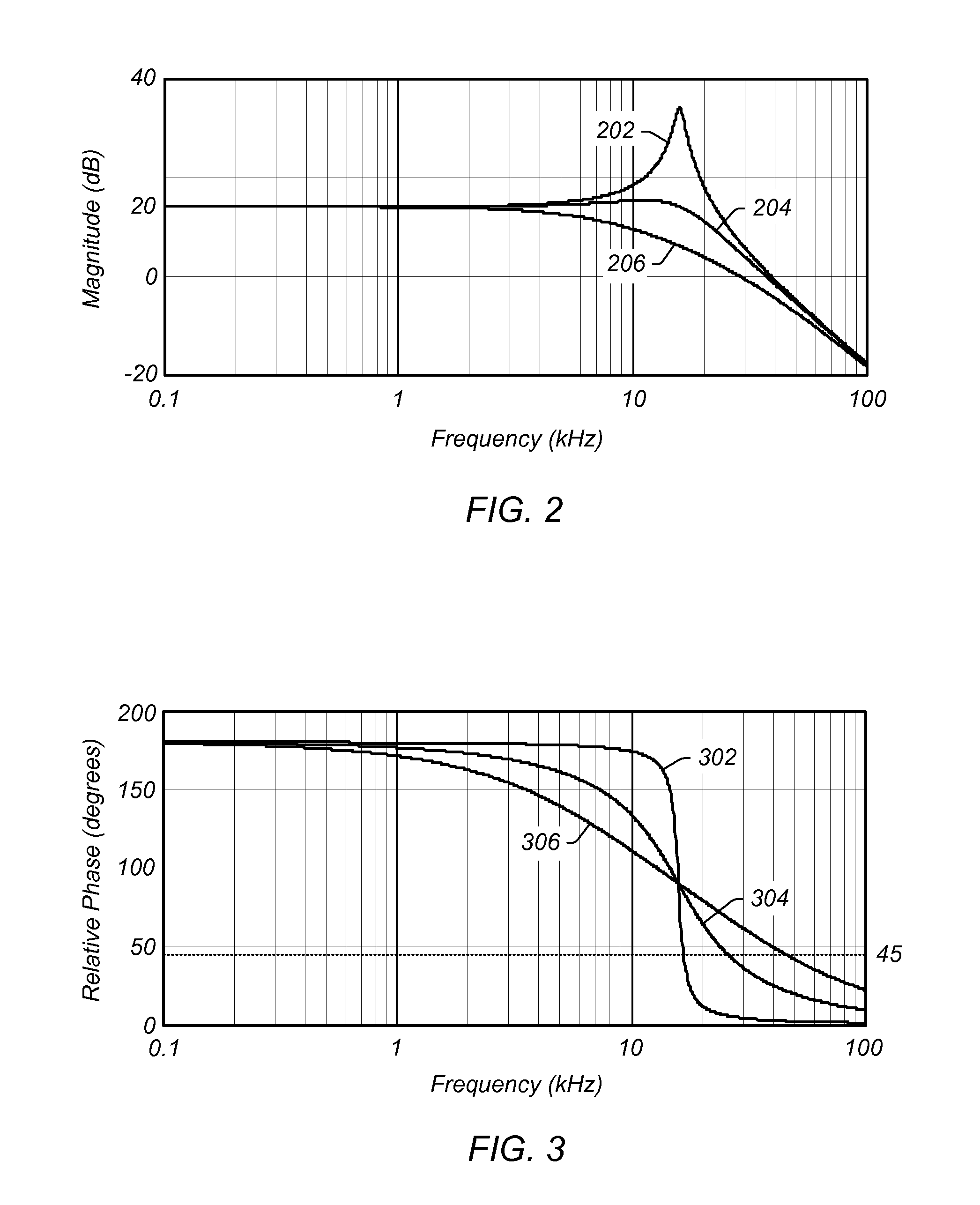
Adaptive compensation in digital power controllers
Complex filters may be used to achieve compensation of a plant, corresponding for example to a power regulator or point-of-load (POL) regulator. Digital filter coefficients may be mapped to analogous poles and zeros, or they may be mapped to values of the quality factor (Q) of the output, frequency, and gain. The plant may be observed and characterized using a network analyzer to generate the Bode plot (or Nyquist plot) for the plant. The digital filter coefficients may be mapped to features that may be identified on the Bode plot (or Nyquist plot) to easily correlate characteristics of the digital filter or digital compensator to the plant characteristics. The mapped features may be adjusted, for example by a user, either manually or by executing one or more optimization algorithms, to achieve the desired results relative to the Bode plot (or Nyquist plot). The mapped features may then be reverse mapped to the digital filter or digital compensator coefficients to fine tune and implement the digital filter or digital compensator.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
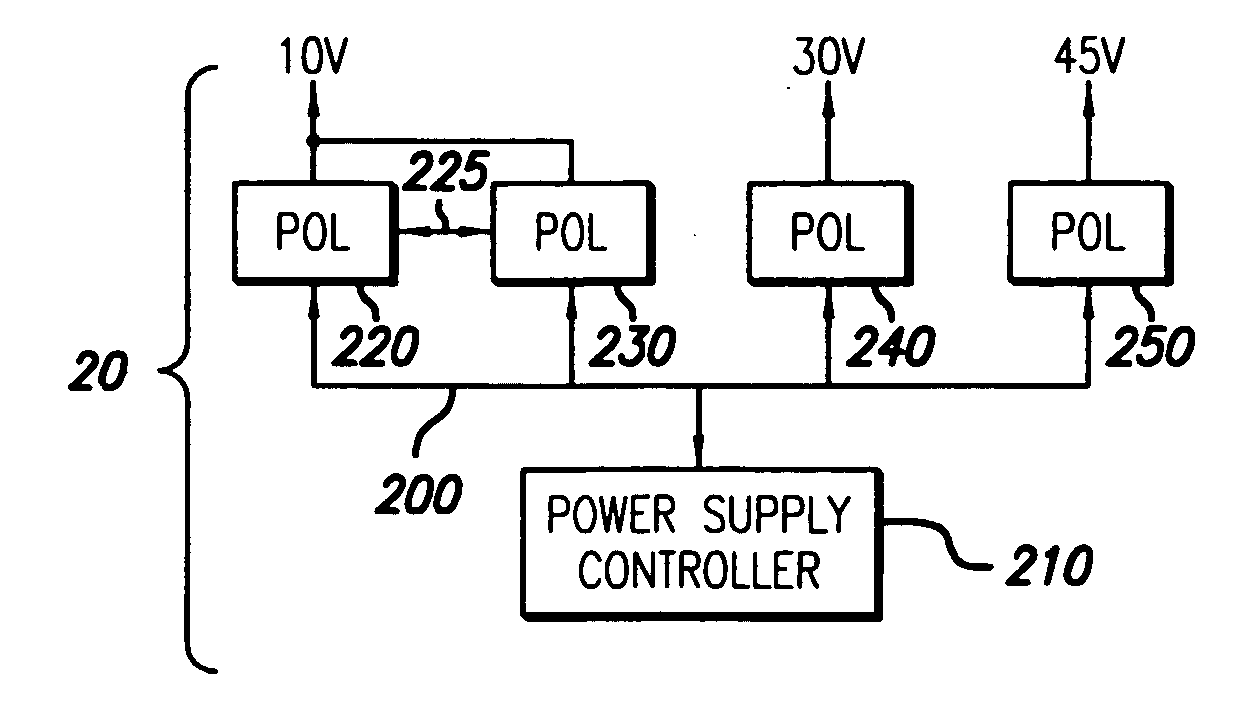
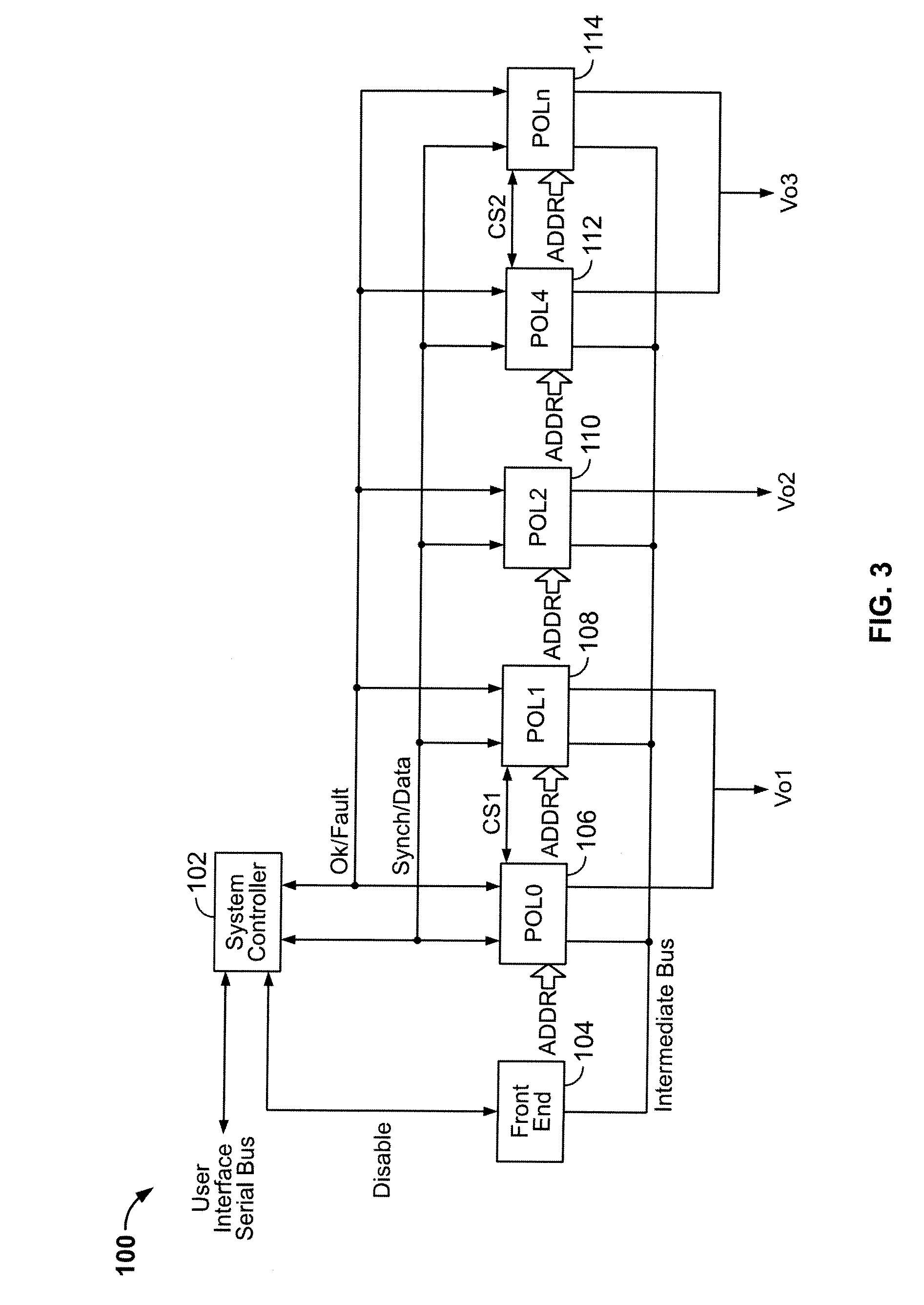
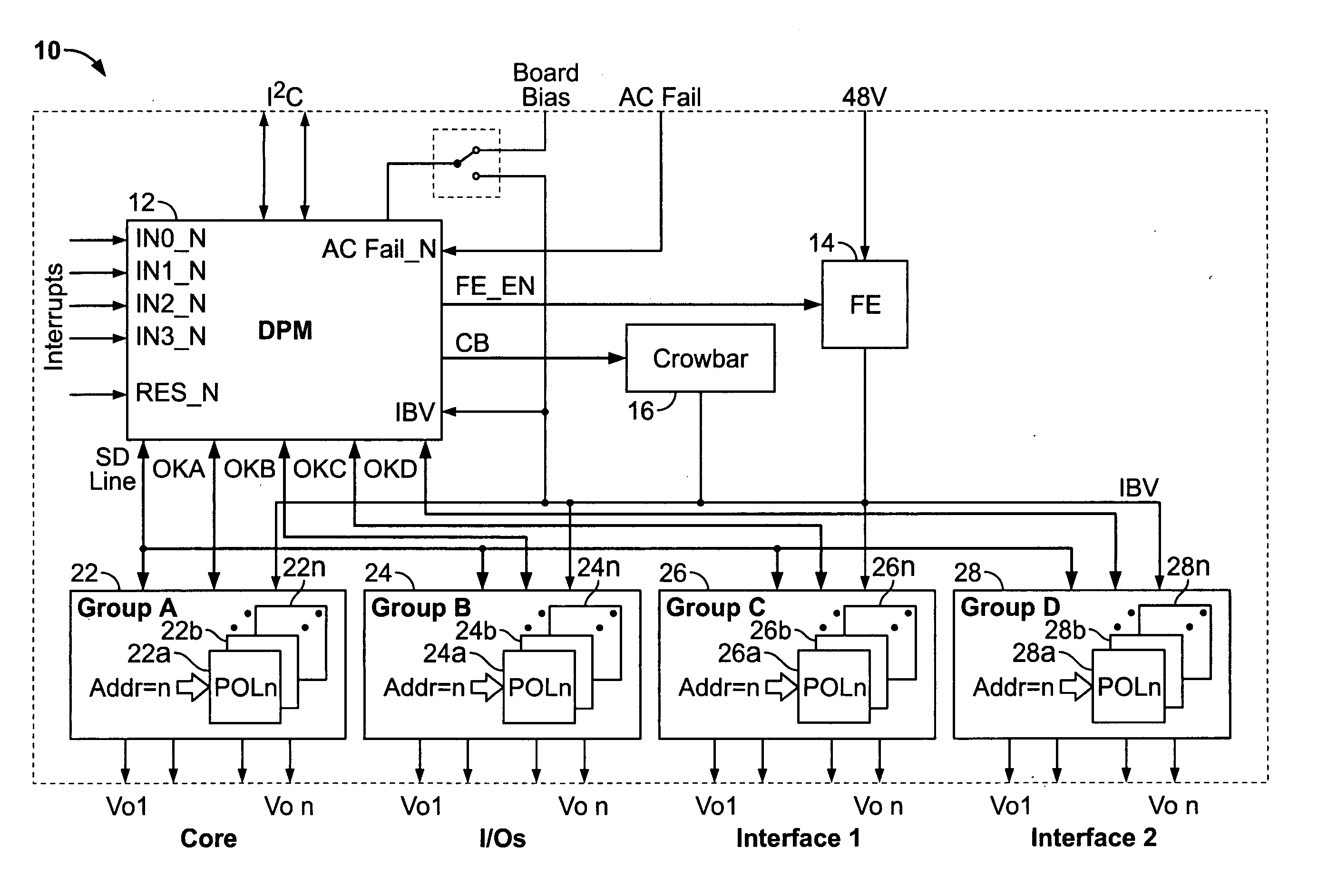
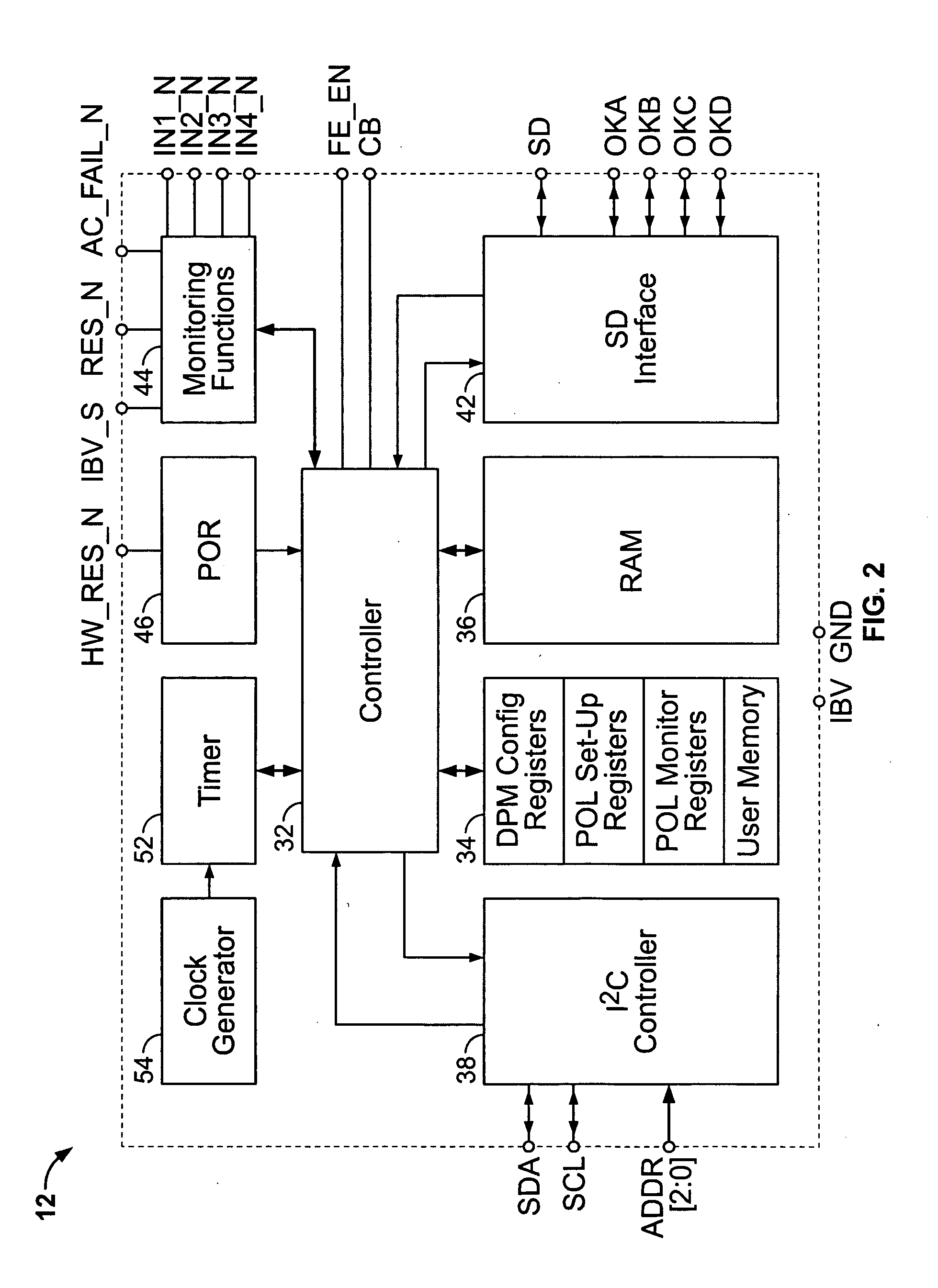
Digital Power Manager For Controlling And Monitoring An Array Of Point-Of-Load Regulators
InactiveUS20080074373A1Digital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPoint of loadPower control system
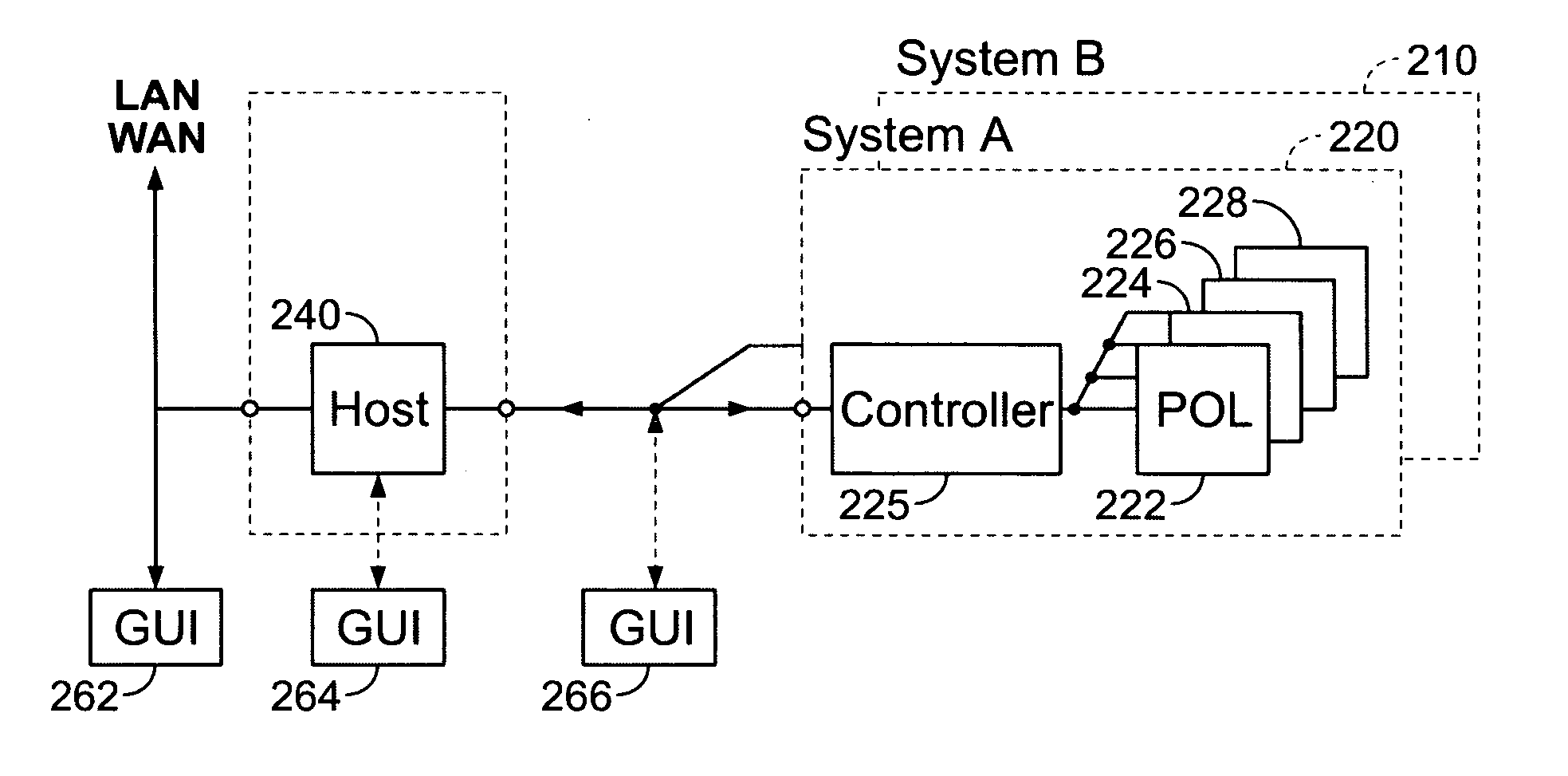
A power control system comprises a plurality of point-of-load (POL) regulators each adapted to convey regulated power to a load, a serial data bus operatively connecting the plurality of POL regulators, and a digital power manager connected to the data bus. The digital power manager includes a controller adapted to execute stored instructions to program operational parameters of the plurality of POL regulators via the serial data bus and receive monitoring data from the plurality of POL regulators via the serial data bus. The digital power manager further comprises a user interface, such as an I2C interface, adapted to receive programming data therefrom and send monitoring data thereto. The digital power manager further comprises a non-volatile memory containing a plurality of registers, including a digital power manager configuration register containing data values defining a configuration of the power control system, a POL set-up register containing data values reflecting programming state of one of the POL regulators, a POL monitor register containing data values reflecting status of operating conditions within one of the POL regulators, and a user-definable space. The digital power manager is adapted to program voltage margining of each of the POL regulators.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
System and method for controlling a point-of-load regulator
ActiveUS20050200344A1Three-or-more-wire dc circuitsDc source parallel operationPoint of loadCurrent limiting
A system and method is provided for using a serial bus to communicate (either passively or actively) with a point-of-load (“POL”) regulator. Specifically, a power supply controller (“controller”) communicates with at least one POL regulators by writing and / or reading data (either synchronously or asynchronous) over a unidirectional or bi-directional serial bus. In one embodiment of the present invention, the controller is adapted to write initial-configuration data (e.g., output voltage set-point, current limit set-point, etc.) to at least one POL regulator via the serial bus. At least a portion of the initial-configuration data is then used by the POL regulator to produce a particular output. In another embodiment of the invention, each POL regulator includes at least one register for maintaining POL information, such as unique identification information, fault protection information, output voltage set-point data, current limit set-point data, etc. The controller is then adapted to monitor and retrieve this information (i.e., fault-monitoring data) via the serial bus while the POL regulators are operating.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
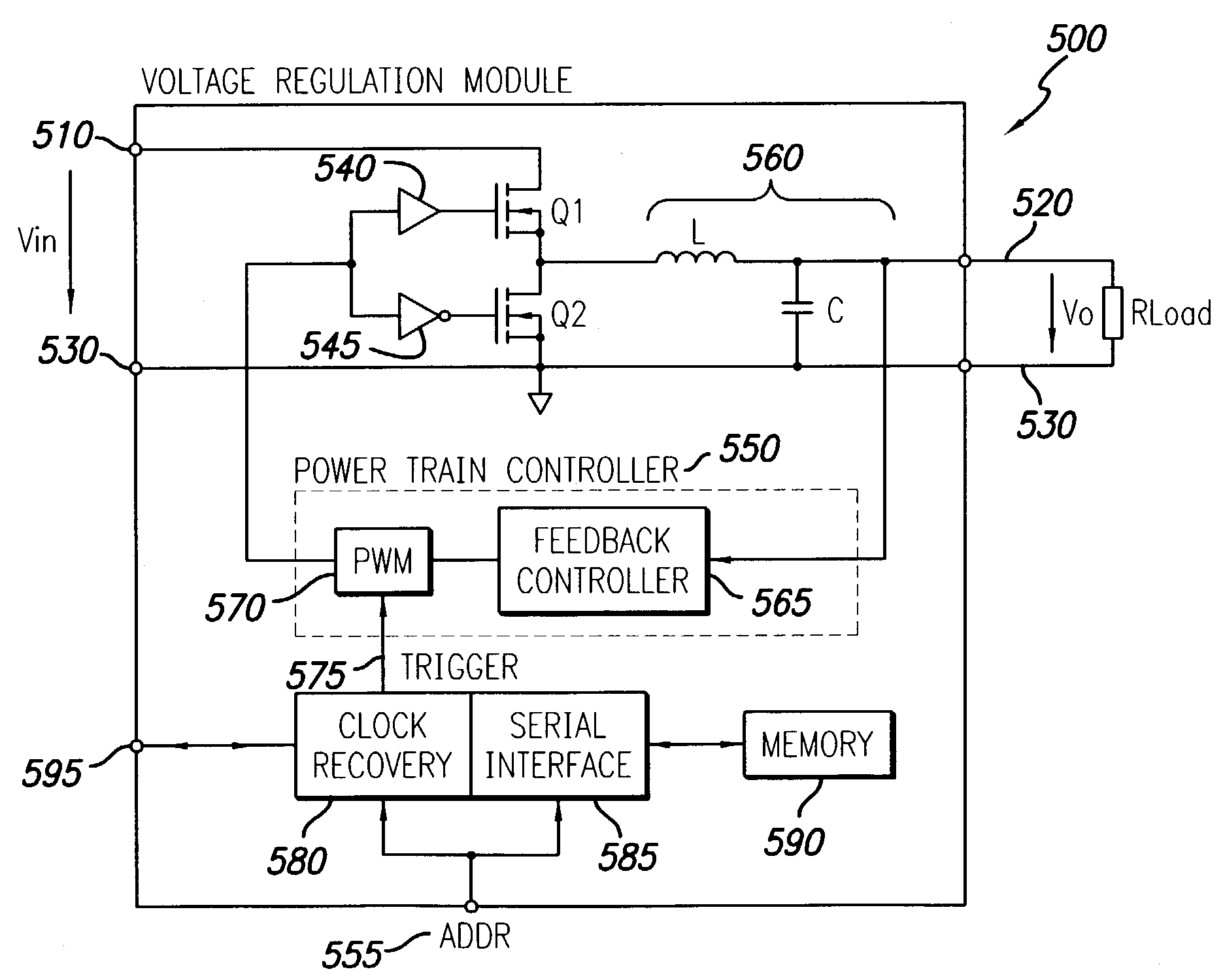
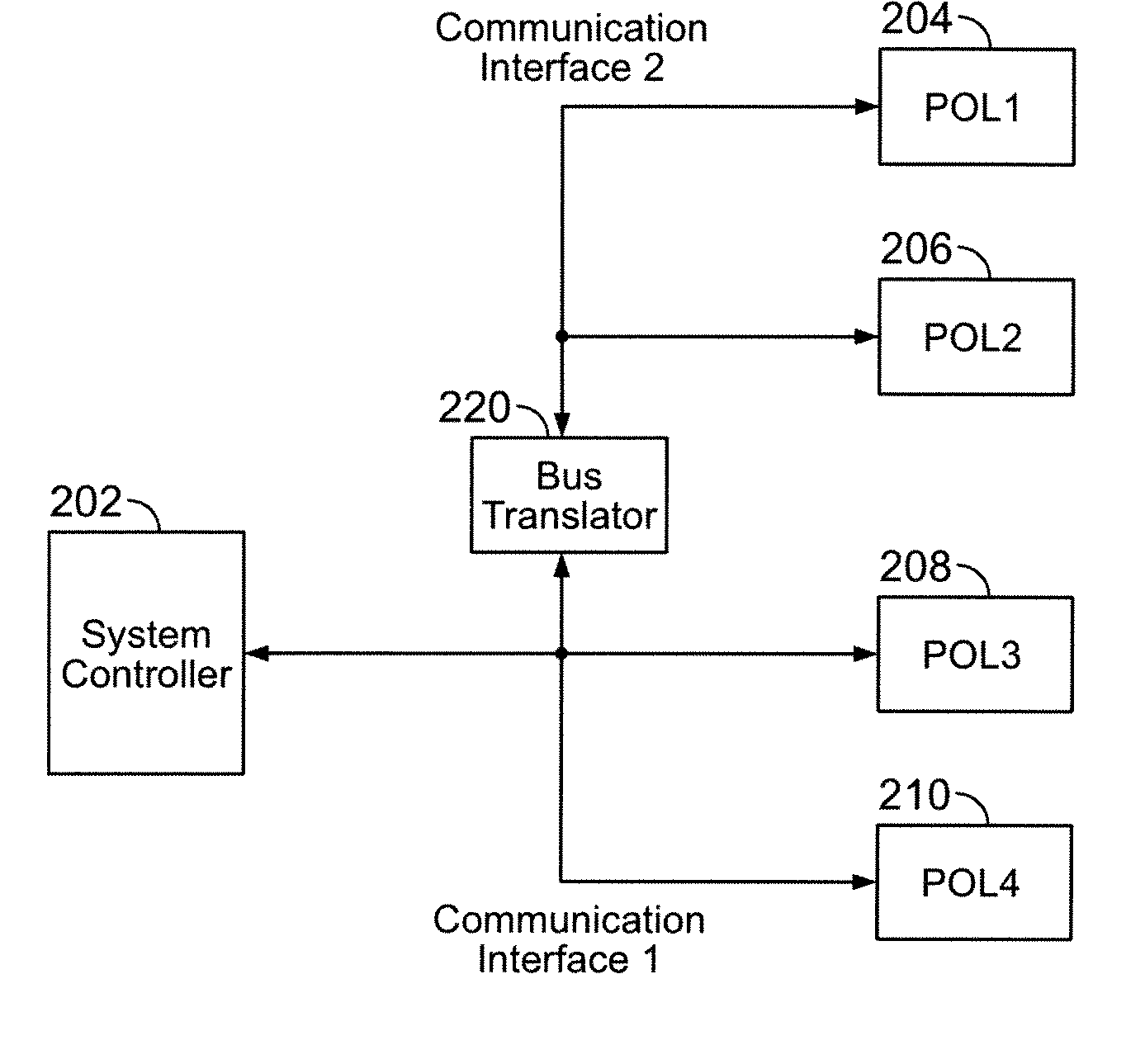
Method and system for controlling a mixed array of point-of-load regulators through a bus translator
A power control system comprises at least one point-of-load (POL) regulator adapted to provide an output voltage to a corresponding load and a system controller operatively connected to the at least one POL regulator via a data bus and adapted to send a first data message in a first format to the at least one POL regulator via the data bus. A bus translator is interposed along the data bus between the at least one POL regulator and the system controller. The bus translator converts the first data message from the first format to a second format that is compatible with the at least one POL regulator. The bus translator is adapted for bi-directional operation to convert a second data message communicated from the at least one POL regulator in the second format to the first format compatible with the system controller. The first and second data formats may comprise either a digital data format or an analog data format. The bus translator may further include a phase-locked loop circuit adapted to synchronize operation of the bus translator to a detected data rate of the data bus.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
MCU/driver point of load digital controller with optimized voltage
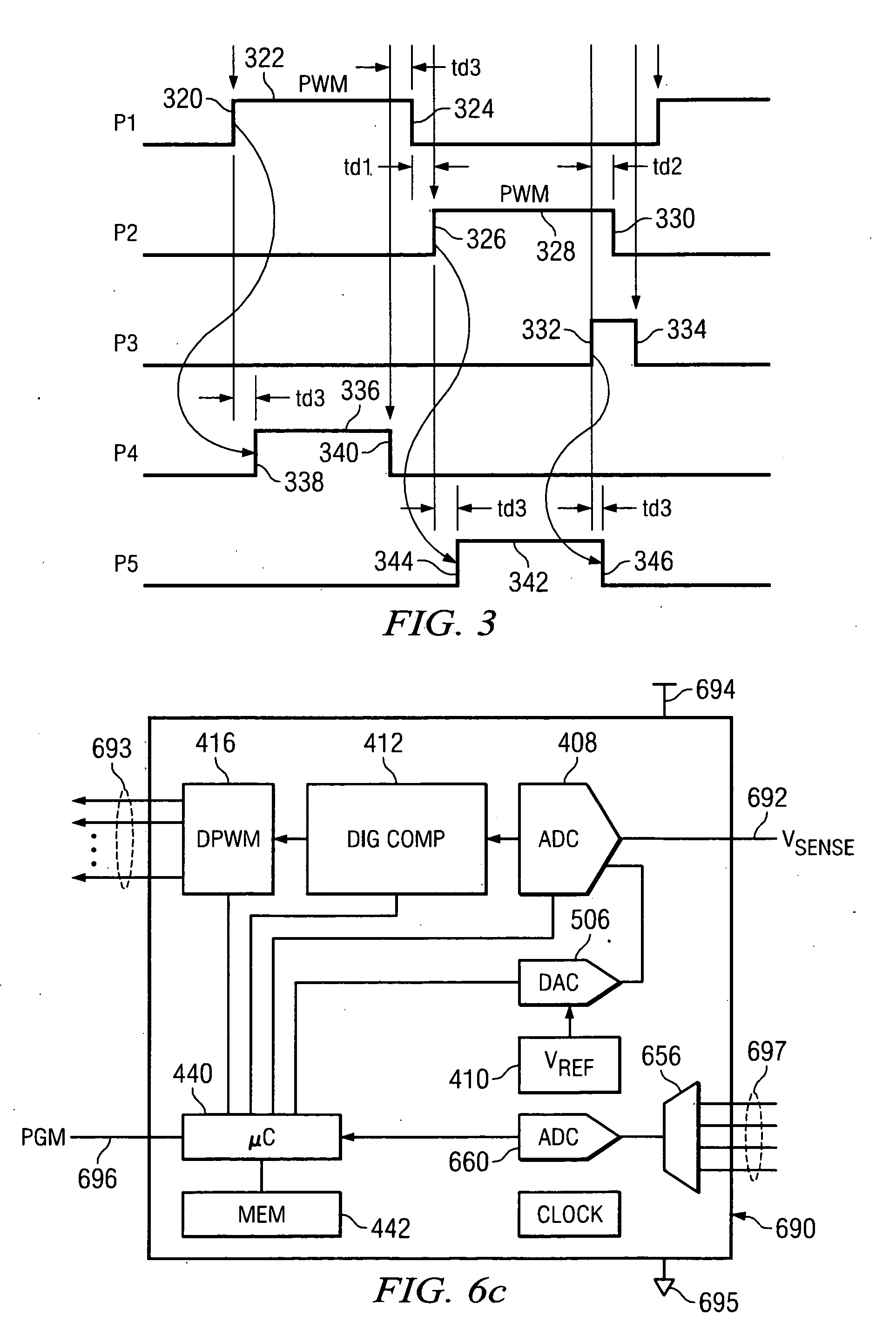
ActiveUS20070139973A1Improve power efficiencyMaximize power efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPoint of loadControl signal
A system for optimizing the power efficiency of a switching power converter operating at a switching frequency includes a digital controller for receiving an analog signal representing an output DC voltage of the switching power converter for comparison to a desired output voltage level and generating switching control signals to control the operation of the power supply to regulate the output DC voltage to said desired output voltage level. At least two of the switching control signals have a dead time between a first edge of a first control signal and a second edge of a second control signal. The dead time is programmable to control a power efficiency of the switching power converter. The switching control signals additionally switch the power supply between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode responsive to a mode control signal. The operation of the digital controller is parameterized by a set of operating parameters. A driver circuit is connected to an output of the digital controller to drive the switching control signals and further includes an input for a regulated voltage. The voltage regulator selects the regulated voltage to the driver circuit responsive to a voltage control signal. A micro controller determines the parameters used by said digital controller, establishes the programmable dead time between the control signals to substantially maximize power efficiency of the switching power converter, generates a voltage control signal to substantially maximize the power efficiency of the switching power converter and generates the mode control signal responsive to a current signal from the switching power converter. The micro controller operates independently of the operation of the digital controller.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Digital power manager for controlling and monitoring an array of point-of-load regulators
InactiveUS20060015616A1Digital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPoint of loadPower control system
A power control system comprises a plurality of point-of-load (POL) regulators each adapted to convey regulated power to a load, a serial data bus operatively connecting the plurality of POL regulators, and a digital power manager connected to the data bus. The digital power manager includes a controller adapted to execute stored instructions to program operational parameters of the plurality of POL regulators via the serial data bus and receive monitoring data from the plurality of POL regulators via the serial data bus. The digital power manager further comprises a user interface, such as an I2C interface, adapted to receive programming data therefrom and send monitoring data thereto. The digital power manager further comprises a non-volatile memory containing a plurality of registers, including a digital power manager configuration register containing data values defining a configuration of the power control system, a POL set-up register containing data values reflecting programming state of one of the POL regulators, a POL monitor register containing data values reflecting status of operating conditions within one of the POL regulators, and a user-definable space. The digital power manager is adapted to program voltage margining of each of the POL regulators.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
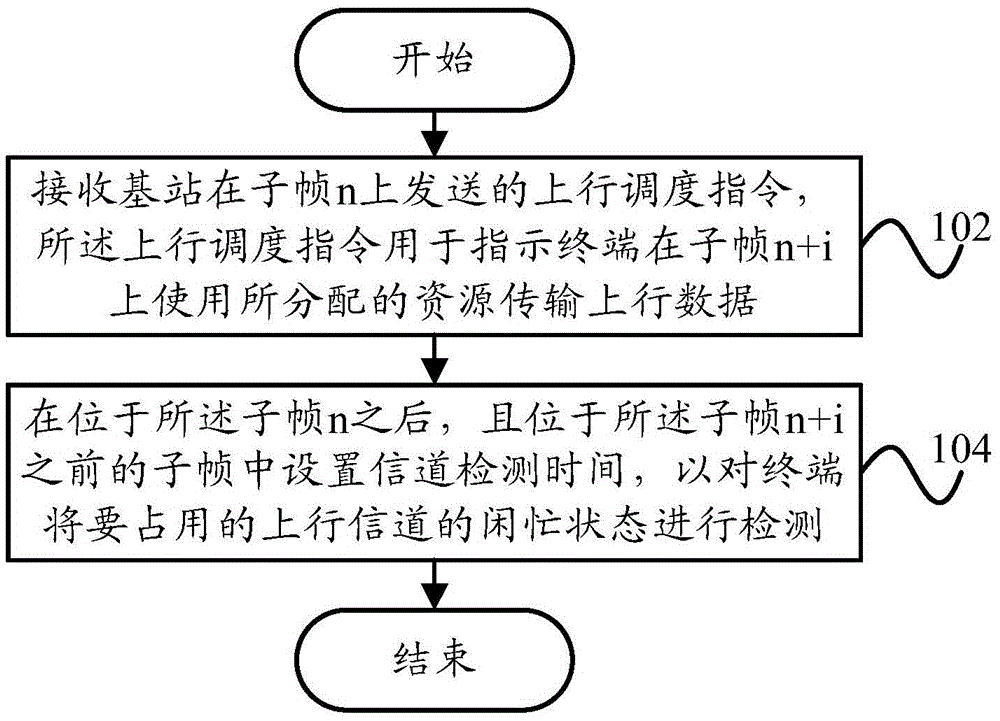
Channel detection method and device, terminal and base station
InactiveCN105657847AImprove preemptionReduce power consumptionNetwork planningPoint of loadUplink transmission
The invention provides a channel detection method and device for use during working of an LTE (Long Term Evolution) system on an unauthorized frequency band, a terminal and a base station. The channel detection method for use during working of the LTE system on the unauthorized frequency band comprises the following steps: receiving an uplink scheduling instruction sent by the base station on a sub-frame n, wherein the uplink scheduling instruction is used for instructing the terminal to transmit uplink data by using allocated resources on a sub-frame n+i; and setting channel detection time in sub-frames positioned after the sub-frame n and before the sub-frame n+i in order to detect an idle / busy state of an uplink channel to be occupied by the terminal. Through adoption of the technical scheme of the invention, a starting point of load-based CCA (Clear Channel Assessment) detection time can be determined during scheduling-based uplink transmission of the terminal, so that the problem of relatively high power consumption caused by blind CCA detection of the terminal can be solved, and meanwhile the channel preemption probability of the terminal can be increased.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com