Outsole
a technology of outsoles and rubber soles, applied in the field of outsoles, can solve the problems of affecting the stability of runners, floating effect, and insufficient yield, and achieve the effect of softness, resilience, and simple design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] One embodiment of the invention is initially described below with reference to FIG. 1. Although this embodiment does not necessarily represent the most preferred embodiment of the invention, it suffices for explaining the essential characteristics of the invention.
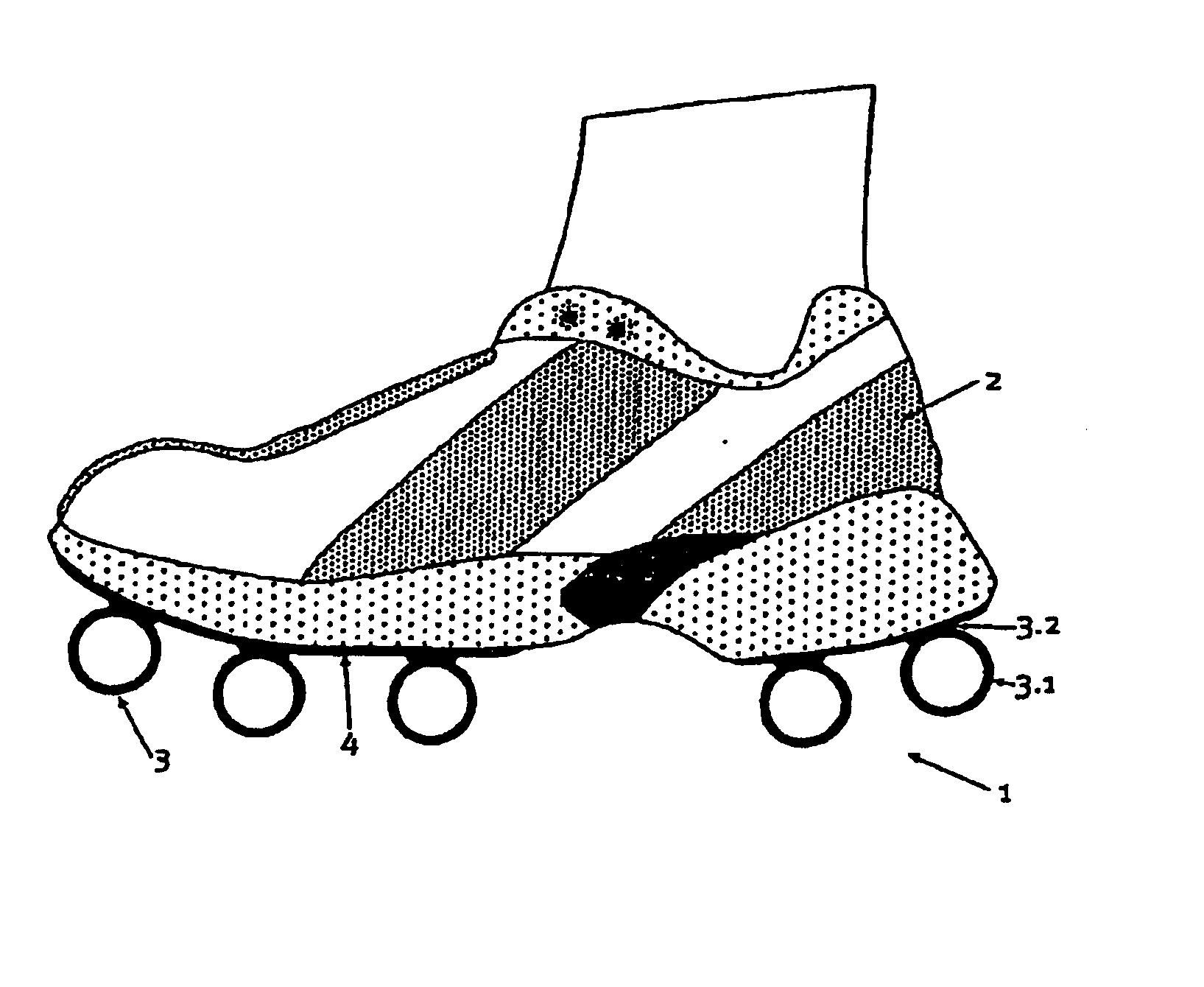
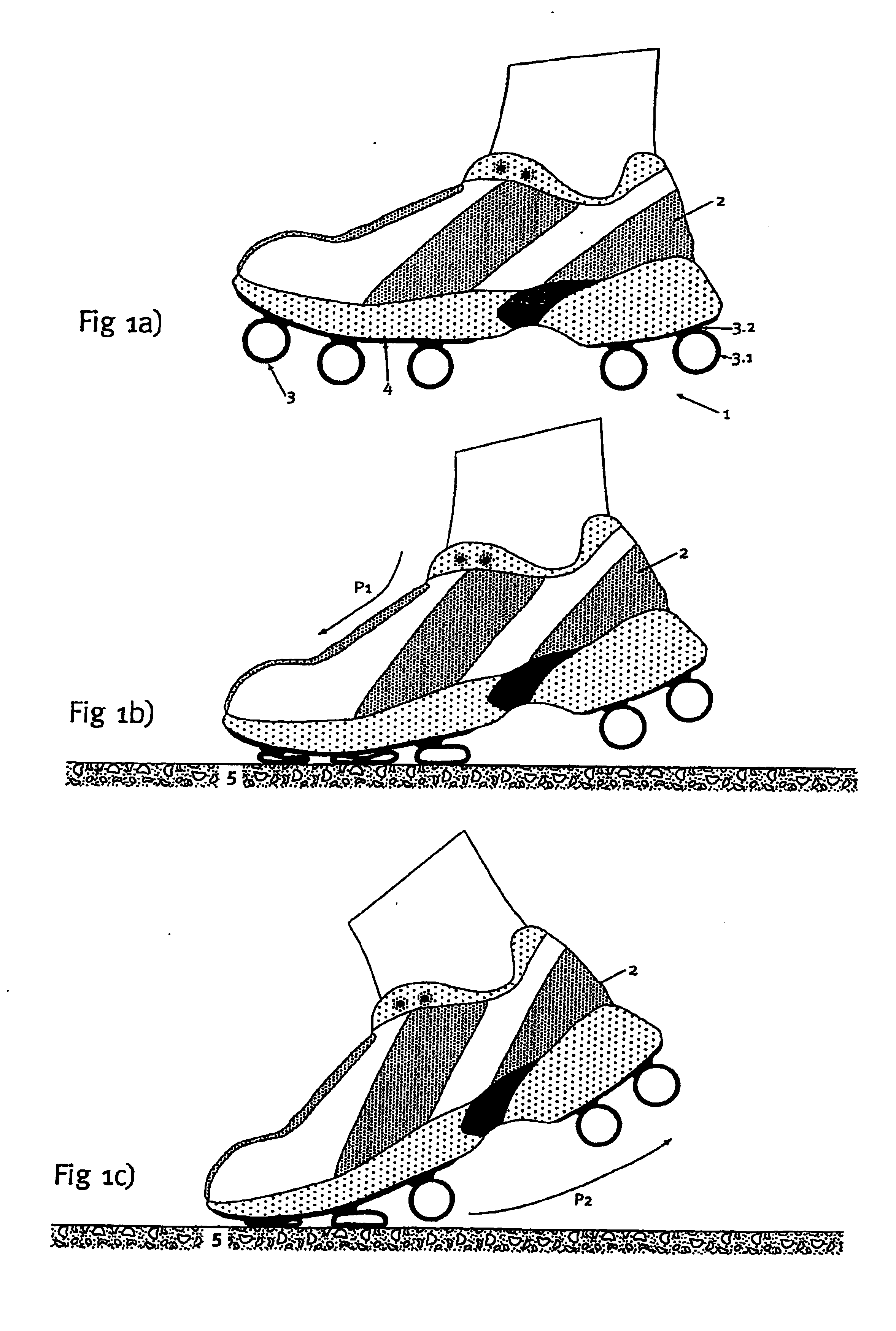
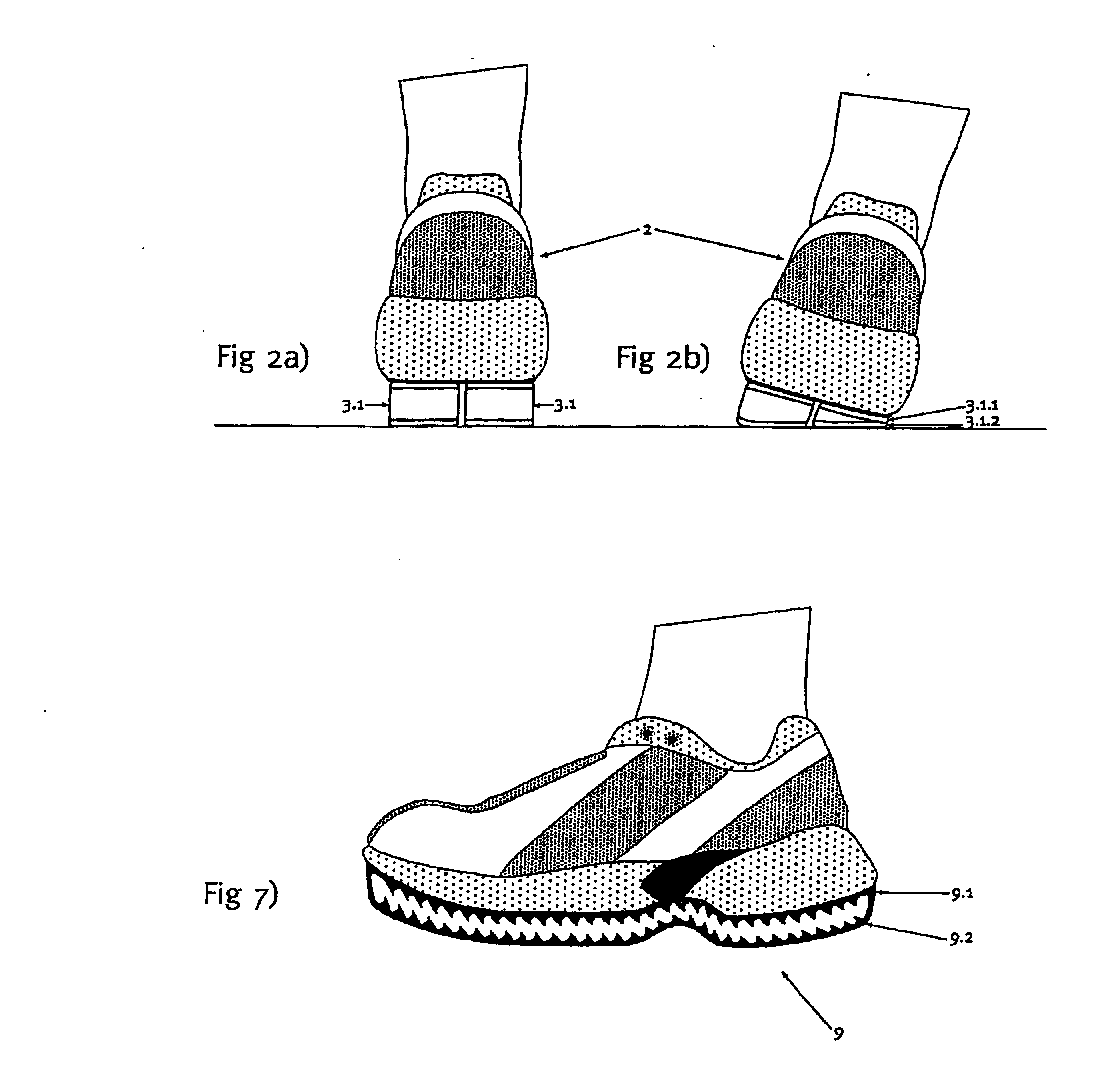
[0026]FIG. 1 shows a running shoe 2 that is equipped with an outsole 1 according to the invention. The outsole 1 is formed by a plurality of profile-like hollow elements 3 that contain tubular parts 3.1 and are fixed to the underside of an intermediate sole 4 of the running shoe 1 with webs 3.2 that are integrally formed thereon, e.g., by means of bonding. The hollow elements 3 are, for example, manufactured from a rubber material that is able to at least partially deform in an elastic fashion under the loads that occur while running. The material preferably has a high static friction with respect to other materials, but also with respect to itself. Several hollow elements 3 are arranged behind one another in the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com