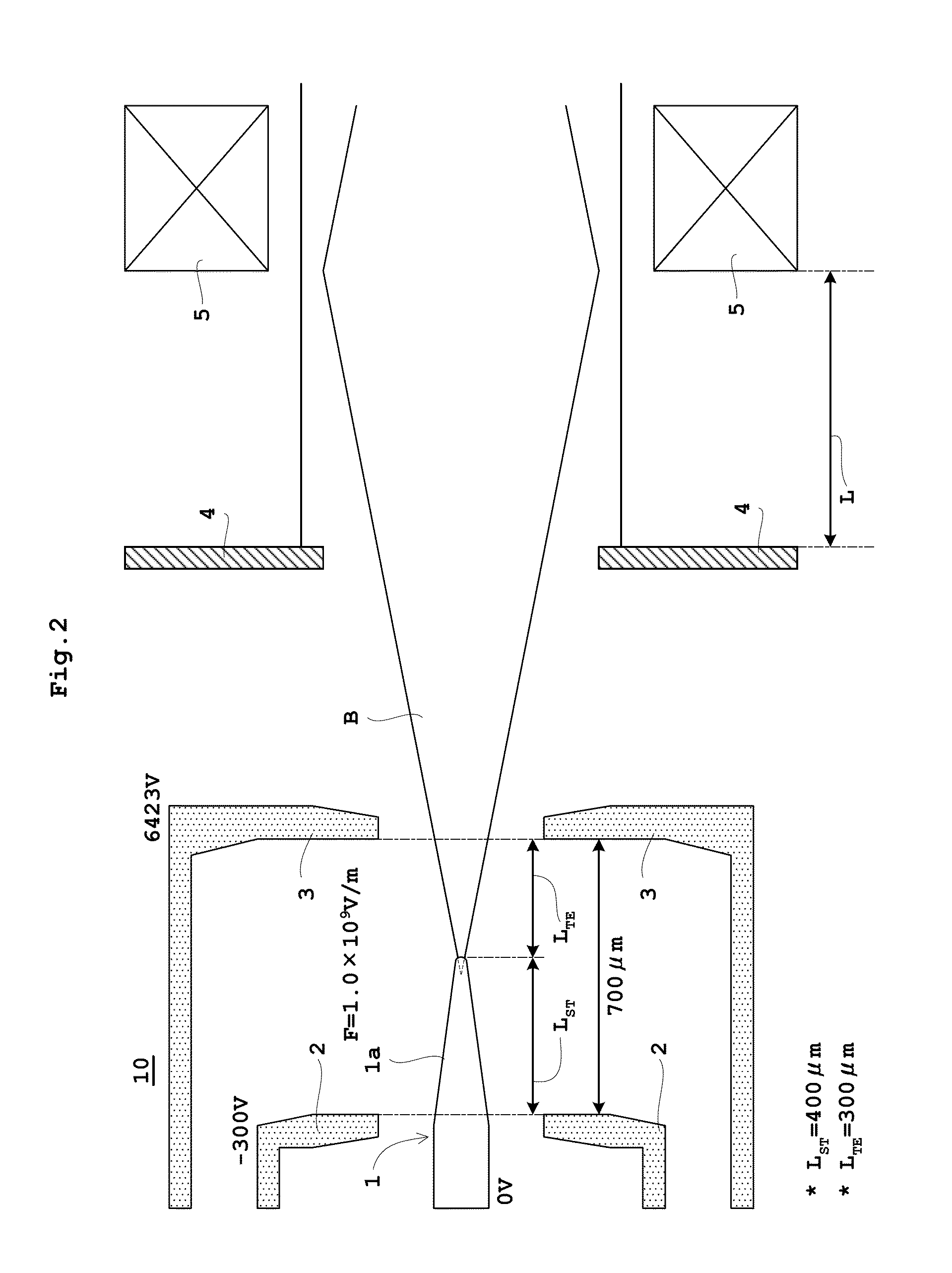
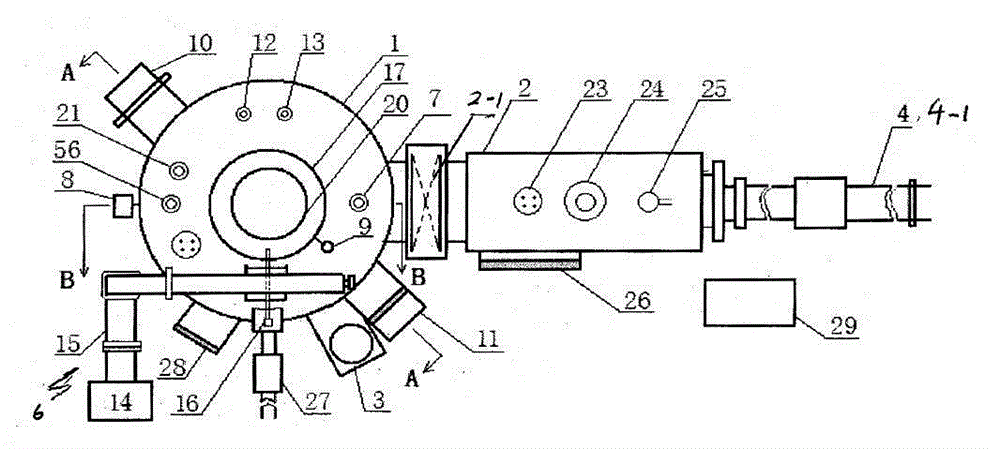
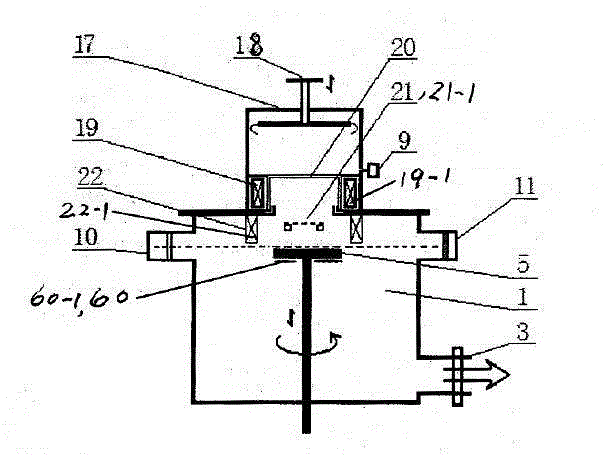
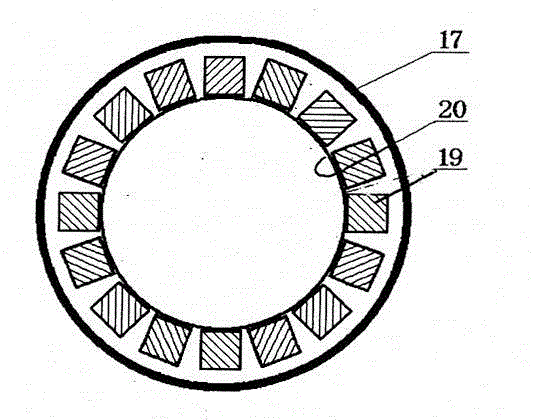
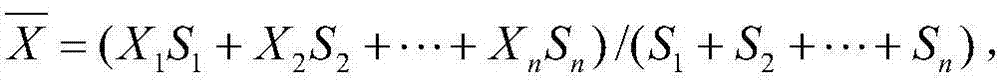Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Electron probe microanalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
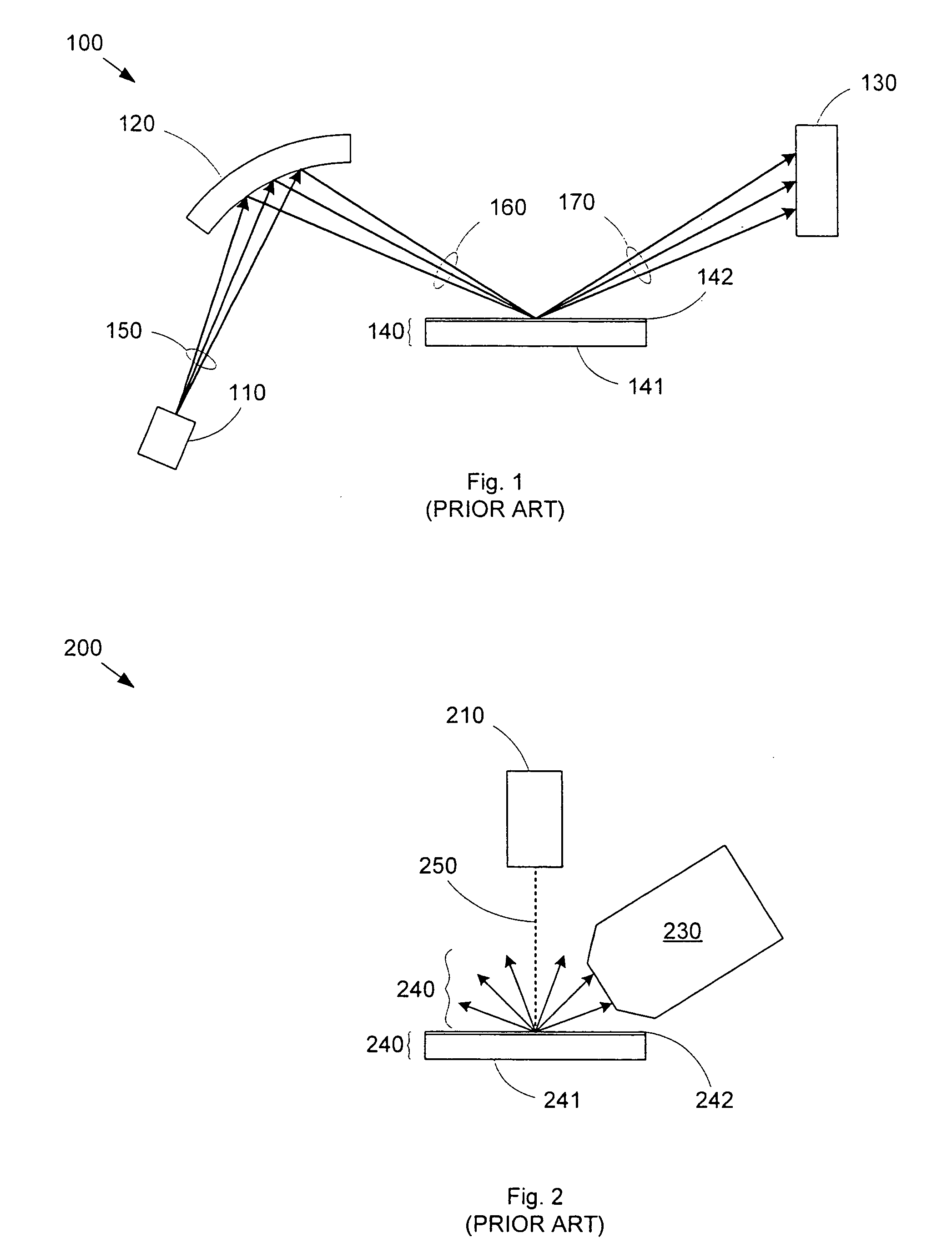
An electron microprobe (EMP), also known as an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) or electron micro probe analyzer (EMPA), is an analytical tool used to non-destructively determine the chemical composition of small volumes of solid materials.
Resin composition for temperature control indication
ActiveCN102516789ARepeatable and reversible instructionsFlexible color designTemperature controlElectron probe microanalysis
The invention relates to a resin composition for temperature control indication. The resin composition comprises the following ingredients, by weight: 10-90 parts of thermoplastic resin, 10-90 parts of thermoplastic elastomer, 0-5.0 parts of compatilizer, 0.1-5.0 parts of sheet pigment and 0.1-2.0 parts if processing auxiliary agent. Compared with a prior art, the thermoplastic resin composition prepared by the invention can be used for temperature control and alarm indication; compared with traditional temperature display methods of electron microprobe, infrared radiation and mercury thermometer, the preparation method has advantages of simpleness, effectiveness, sensitive reaction and low cost, can be widely applied to temperature control alarm of large and small machinery equipment and apparatuses and has huge market prospect in fields of machinery and material processing, chemical engineering, electronic apparatus and monitor on various experiment processes, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI KUMHO SUNNY PLASTICS
Long working distance incoherent interference microscope
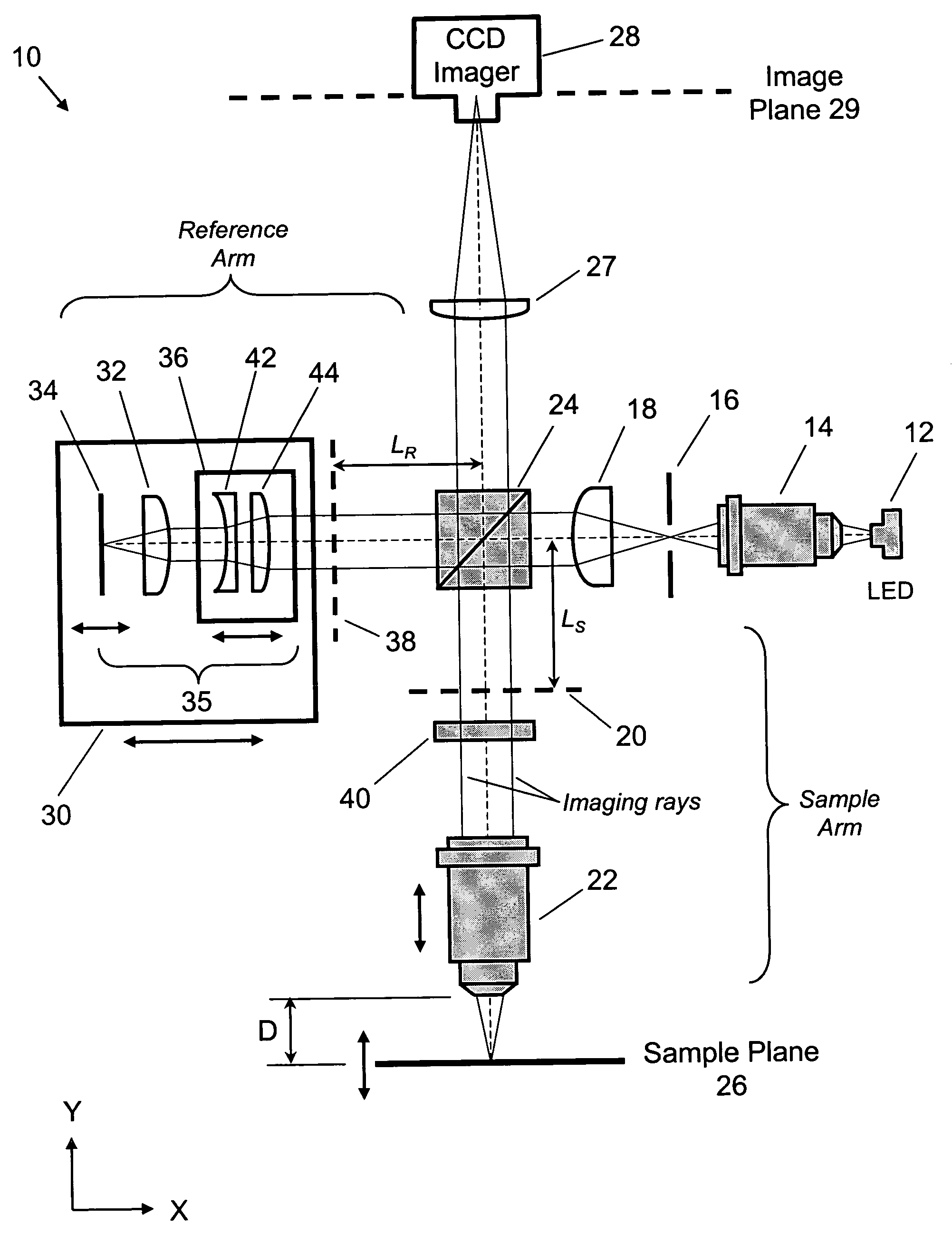
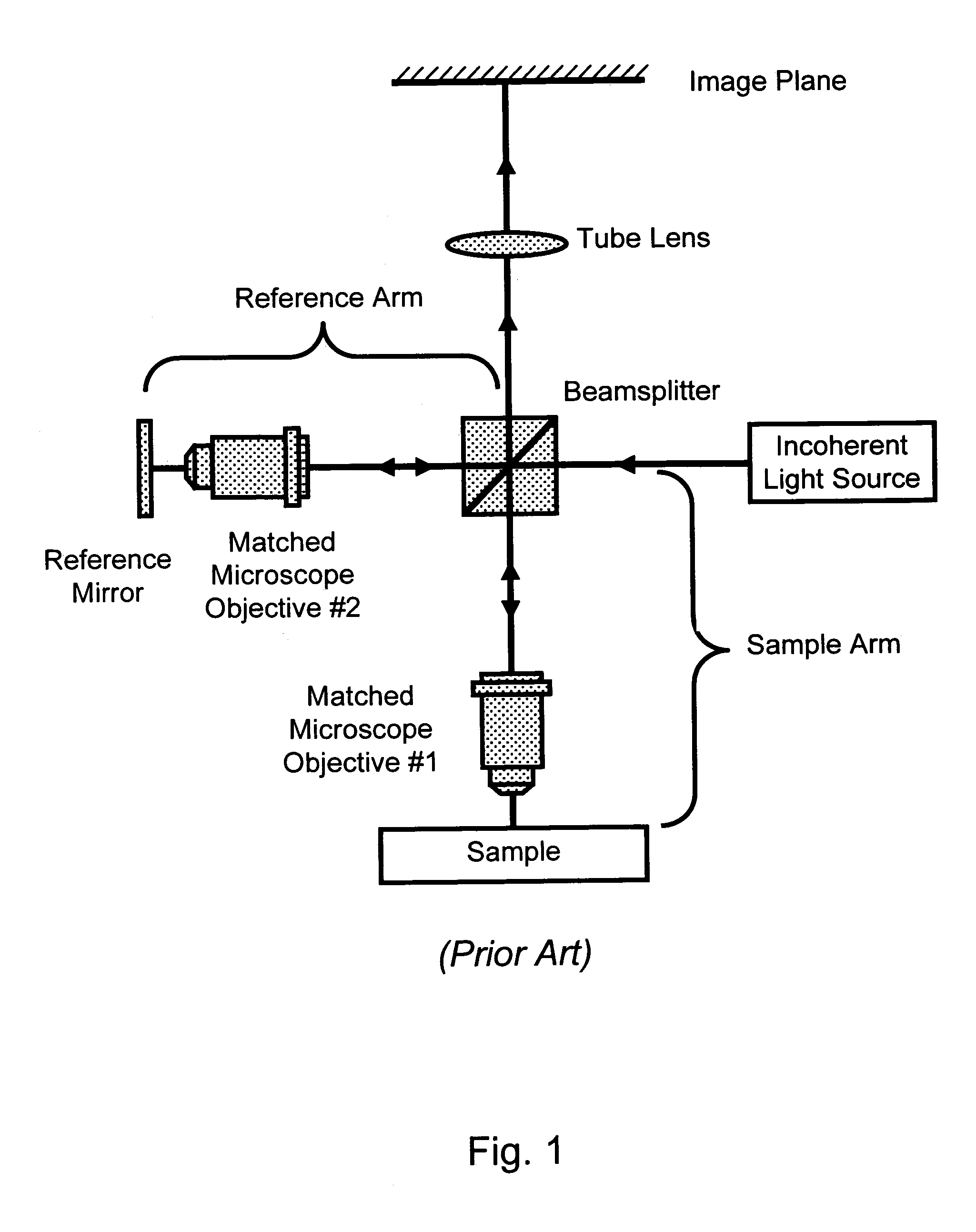
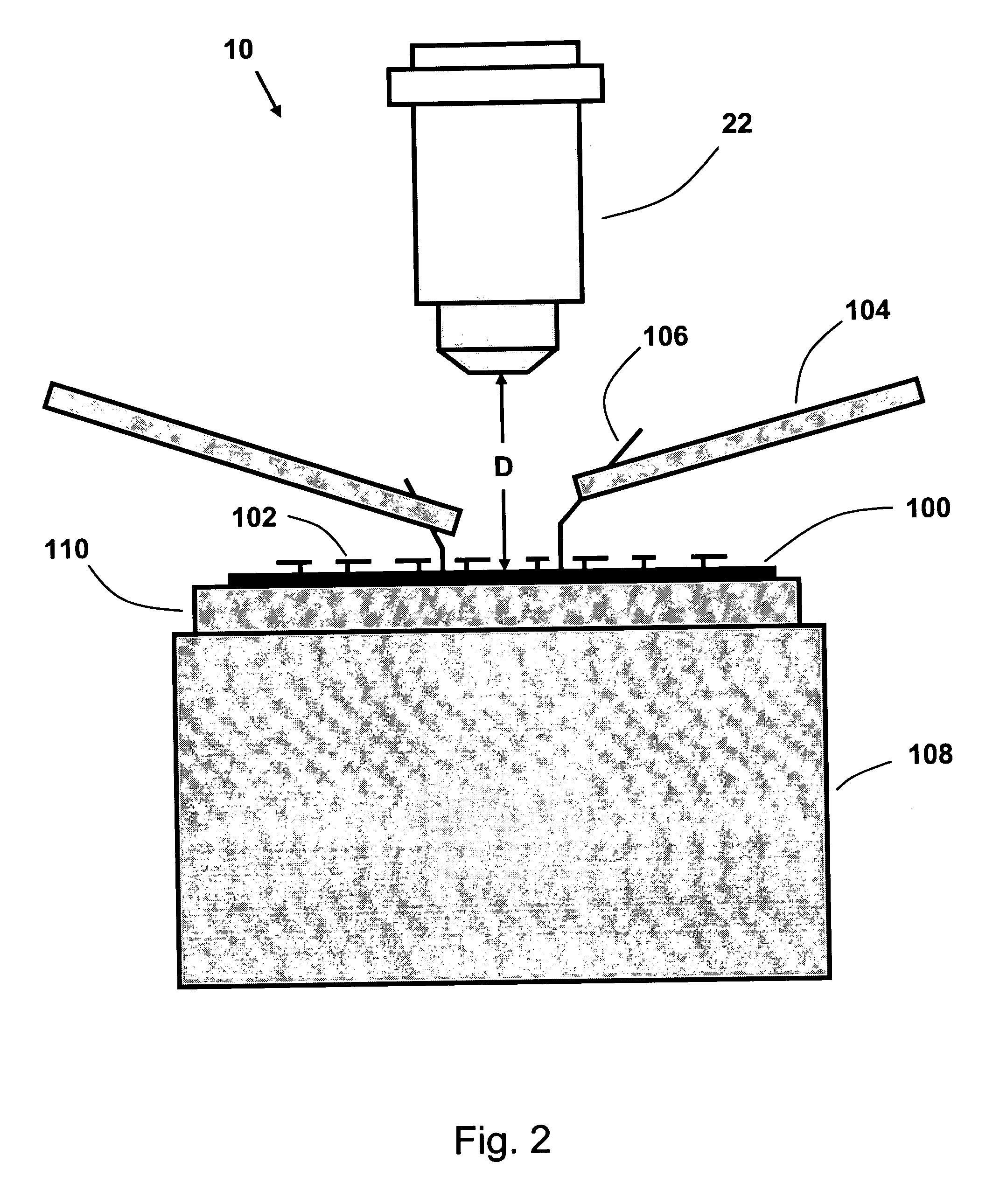
ActiveUS7034271B1Low costShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesElectron probe microanalysisProbe card
A full-field imaging, long working distance, incoherent interference microscope suitable for three-dimensional imaging and metrology of MEMS devices and test structures on a standard microelectronics probe station. A long working distance greater than 10 mm allows standard probes or probe cards to be used. This enables nanometer-scale 3-dimensional height profiles of MEMS test structures to be acquired across an entire wafer while being actively probed, and, optionally, through a transparent window. An optically identical pair of sample and reference arm objectives is not required, which reduces the overall system cost, and also the cost and time required to change sample magnifications. Using a LED source, high magnification (e.g., 50×) can be obtained having excellent image quality, straight fringes, and high fringe contrast.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Multi-technique thin film analysis tool
InactiveUS7039158B1Low costImprove throughputX-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansElectron probe microanalysisComposition analysis
A thin film analysis system includes multi-technique analysis capability. Grazing incidence x-ray reflectometry (GXR) can be combined with x-ray fluorescence (XRF) using wavelength-dispersive x-ray spectrometry (WDX) detectors to obtain accurate thickness measurements with GXR and high-resolution composition measurements with XRF using WDX detectors. A single x-ray beam can simultaneously provide the reflected x-rays for GXR and excite the thin film to generate characteristic x-rays for XRF. XRF can be combined with electron microprobe analysis (EMP), enabling XRF for thicker films while allowing the use of the faster EMP for thinner films. The same x-ray detector(s) can be used for both XRF and EMP to minimize component count. EMP can be combined with GXR to obtain rapid composition analysis and accurate thickness measurements, with the two techniques performed simultaneously to maximize throughput.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Dip-formed synthetic polyisoprene latex articles with improved intraparticle and interparticle crosslinks
ActiveUS8087412B2Uniform curingMale contraceptivesSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkVulcanization
A synthetic polyisoprene latex emulsion has pre-vulcanization composition and post vulcanization composition. The pre-vulcanization composition comprises soluble sulfur with high S8 ring structure that is catalytically broken by a zinc dithiocarbamate. Surfactants present in the pre-vulcanization composition wets synthetic polyisoprene particles and permeates small sized sulfur and accelerator molecules into the interior of these particles thereby pre-vulcanizing the particles. The degree of pre-vulcanization is verified by isopropanol index test. The latex emulsion has post-vulcanization composition with accelerators that crosslink inter-particle region during post vulcanization cure cycle. The dipped synthetic polyisoprene article is substantially uniformly cured both in the inter-particle and intra-particle regions and reliably exhibits high cross link density, uniform distribution of double bonds in TEM and zinc segregation at the boundaries or original particles by electron microprobe analysis. The films exhibit high tensile strength, tensile modulus, tear strength, burst pressure and burst volume.
Owner:LIFESTYLES HEALTHCARE PTE LTD
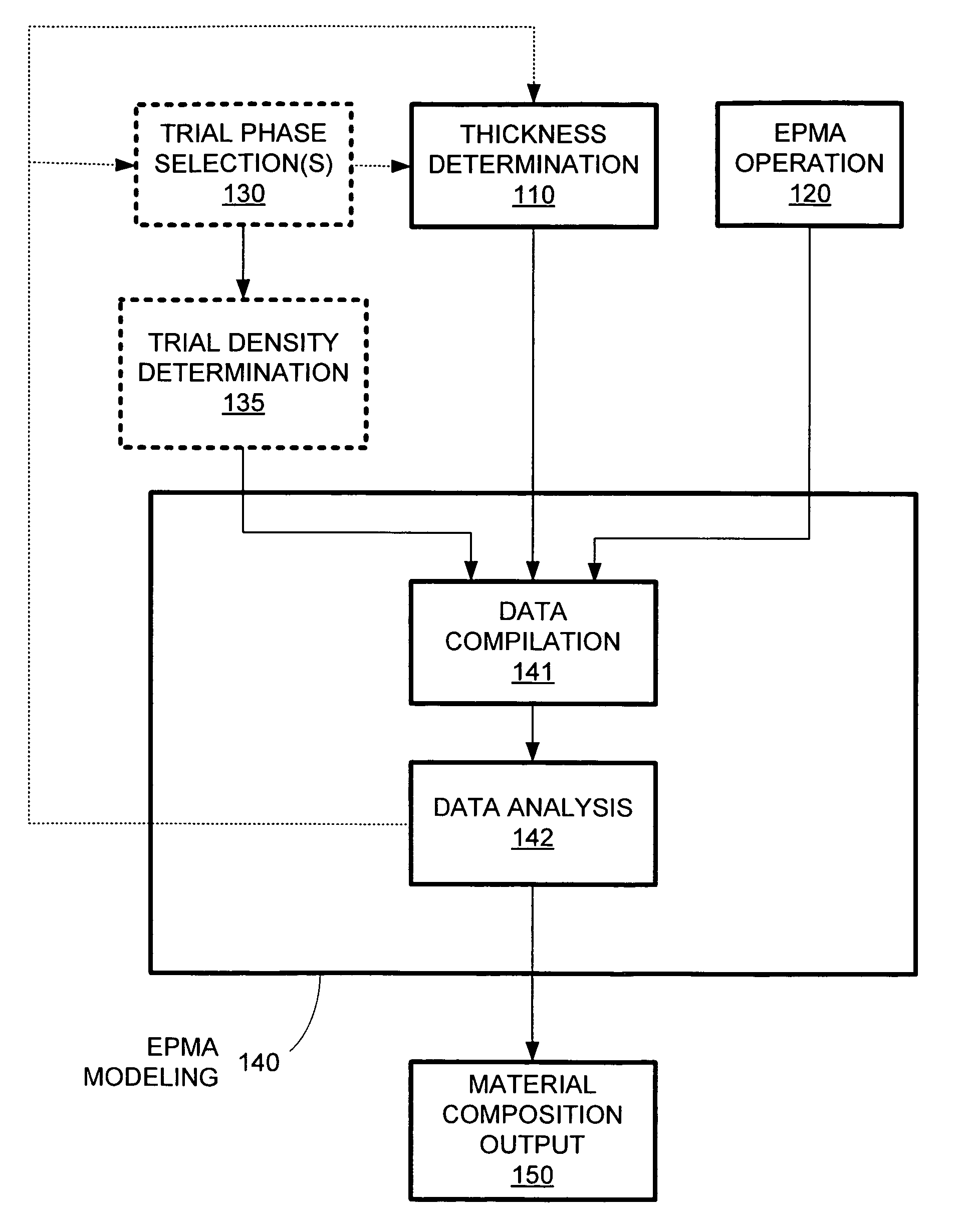
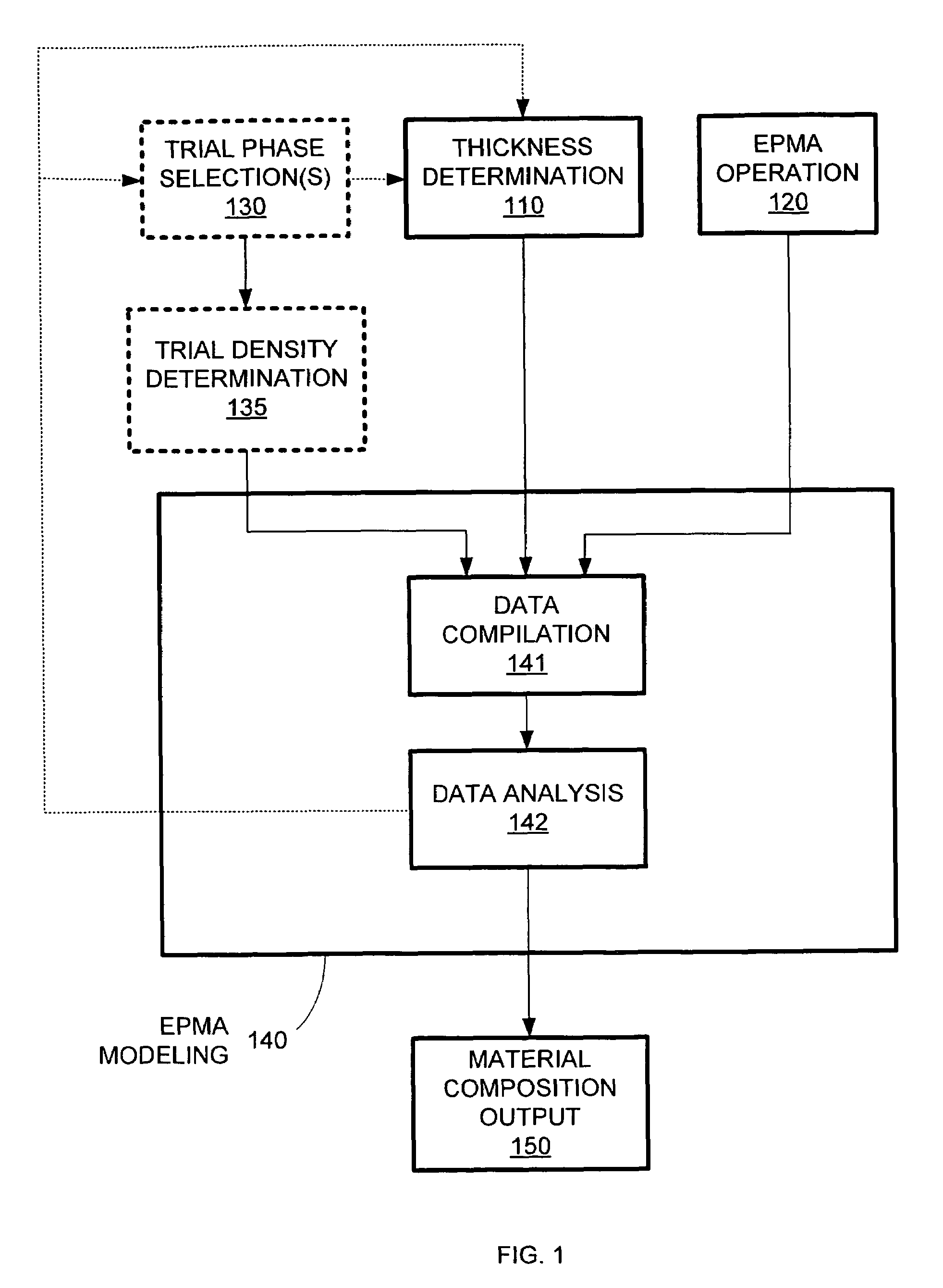
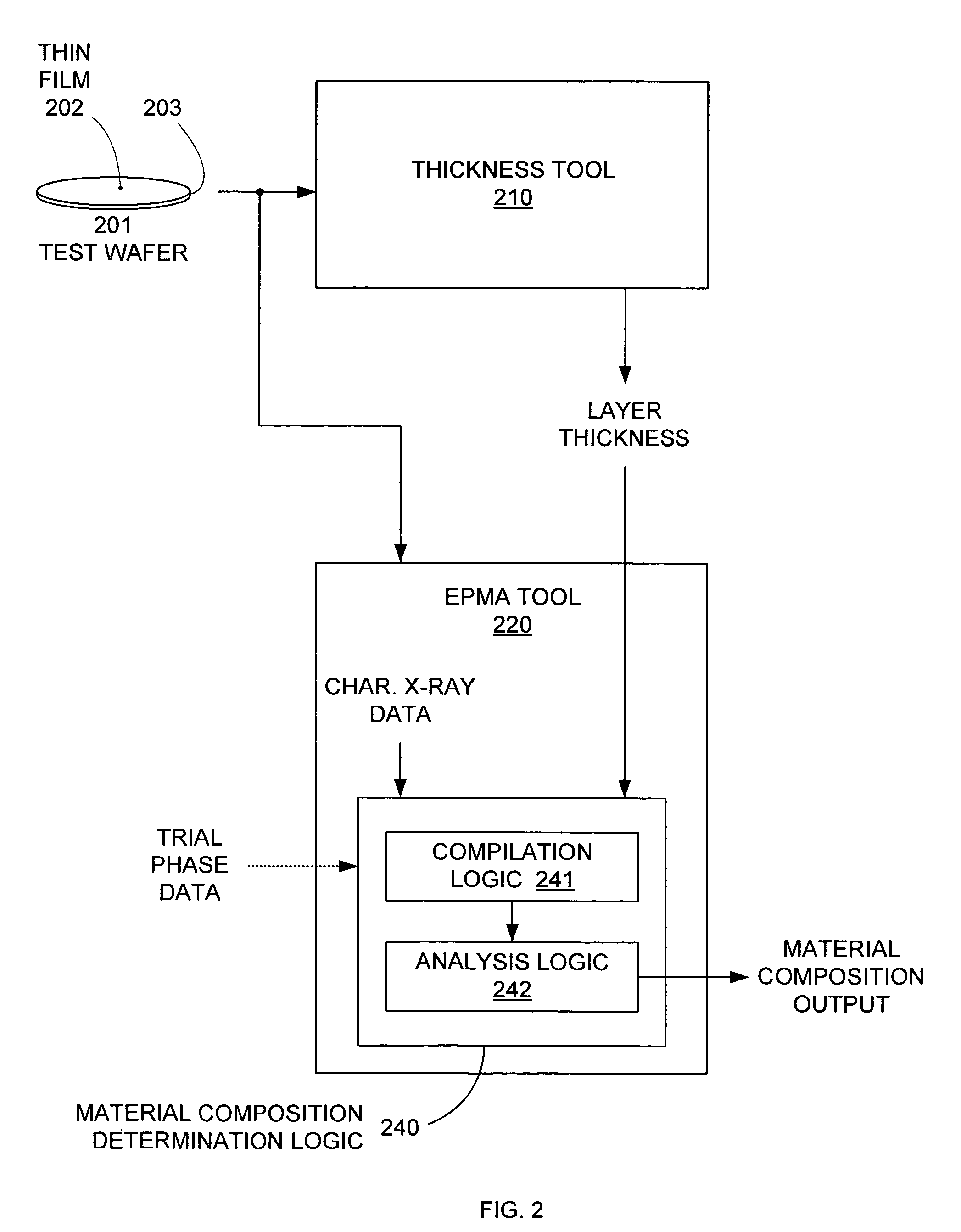
Material composition analysis system and method
InactiveUS7358494B1Accurately determine phaseEfficiently and accurately determineX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElemental compositionMetrology
The material composition of a thin film formed on a substrate or covered by a cap layer that shares one or more elements with the thin film can be determined by combining characteristic material data, such as characteristic x-ray data, from a material composition analysis tool, such as an electron probe-based x-ray metrology (EPMA) operation, with thickness data and (optionally) possible material phases for the thin film. The thickness data and / or the material phase options can be used to determine, for example, the penetration depth of a probe e-beam of the EPMA tool. Based on the penetration depth and the thin film thickness, the characteristic x-ray data from the EPMA operation can be analyzed to determine the composition (e.g., phase or elemental composition) of the thin film. An EPMA tool can include ellipsometry capabilities for all-in-one thickness and composition determination.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
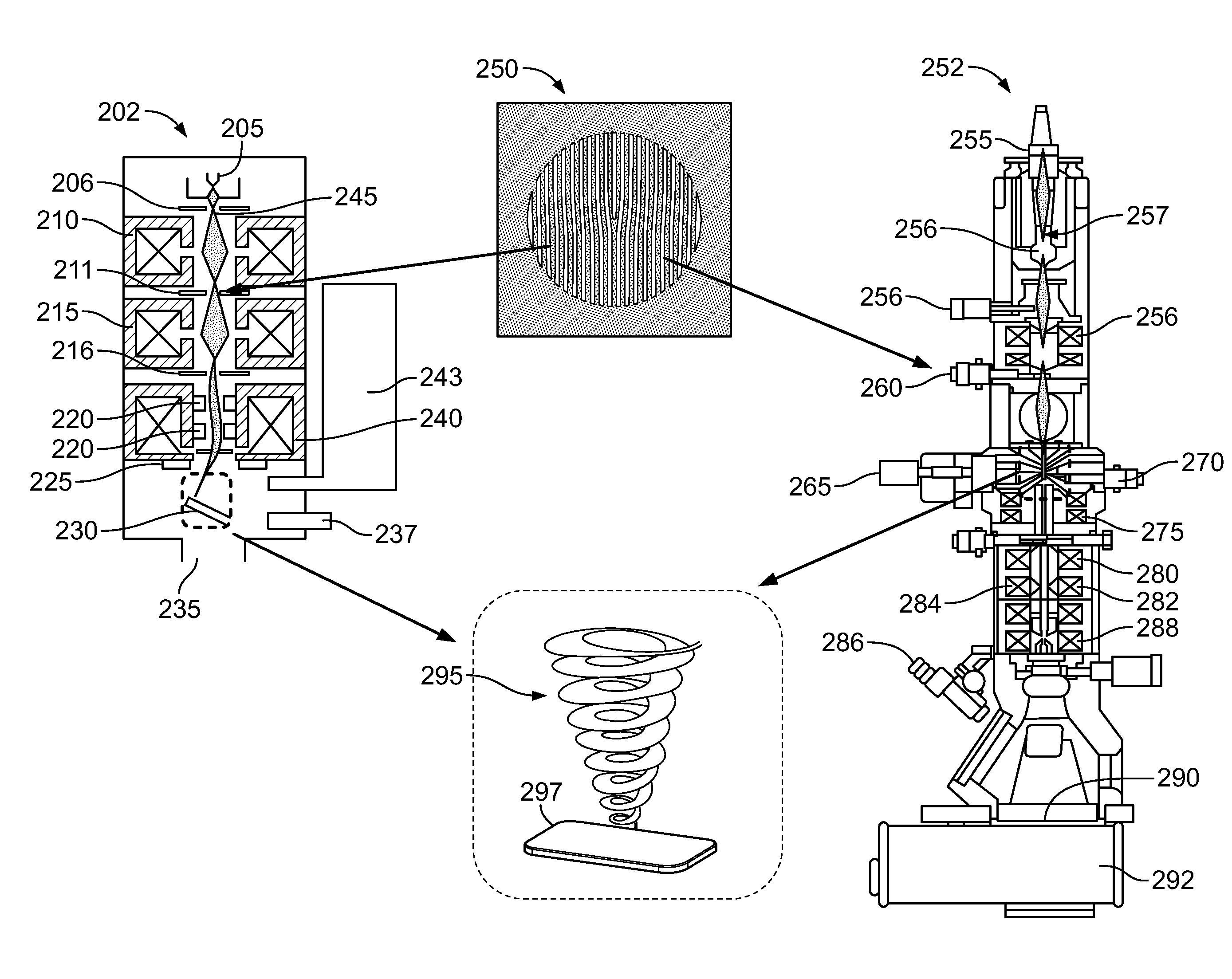
System and method for producing and using multiple electron beams with quantized orbital angular momentum in an electron microscope
InactiveUS20120153144A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesGratingElectron probe microanalysis
A system and method for using electron beams with engineered phase dislocations as scanned probes in electron probe beam instruments such as scanning transmission electron microscopes. These types of electron beams have unique properties and can provide better information about a specimen than conventional electron beams. Phase dislocations may be created based on a pattern disposed on a nanoscale hologram, which may be placed in the electron optical column of the electron probe beam instrument. When an electron beam from the instrument is directed onto the hologram, phase dislocations may be imprinted onto the electron beam when electrons are diffracted from these holograms. For example, electron probe beams with spiral phase dislocations may occur. These spiral phase dislocations are formed using a hologram with a fork-patterned grating. Spiral phase dislocations may be used to provide magnetic contrast images of a specimen.
Owner:MCMORRAN BENJAMIN
Dual detector optics for simultaneous collection of secondary and backscattered electrons
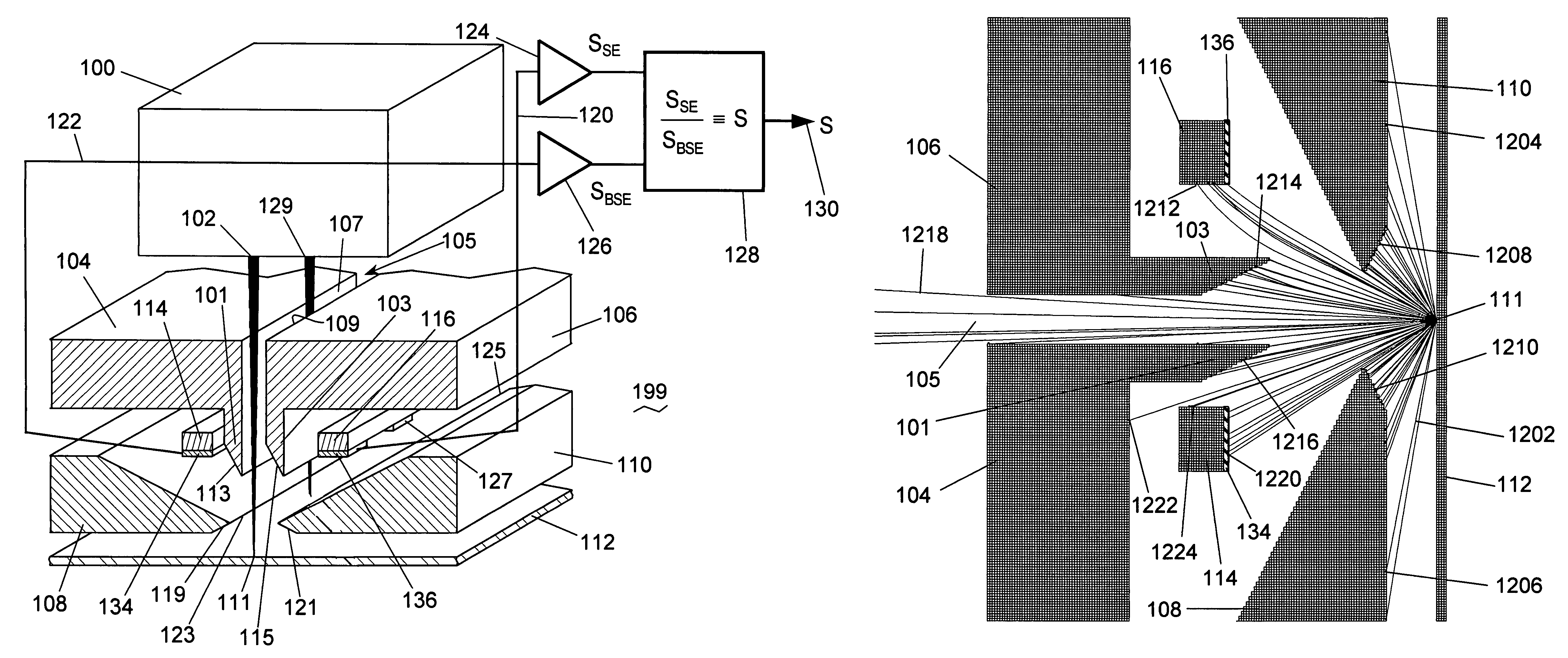
ActiveUS7227142B2Reduce complexityLow costThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElemental compositionElectron probe microanalysis
A detector optics system for an electron probe system is disclosed. Aspects of the detector optics system include: the ability to simultaneously detect two electron populations, secondary electrons (SEs) and backscattered electrons (BSEs), wherein both populations are emitted from a substrate due to the impact of the electron probe. The design of the detector optics utilizes a field-free tunnel and substrate electric-field control electrodes to enable separation of the SEs and BSEs into two detectors, allowing simultaneous acquisition of topographic and elemental composition data, with minimal impact on the electron probe. The secondary electron signal is a monotonically-varying function of the voltage on the substrate surface. The ratio of the SE signal to the BSE signal gives a testing signal which is independent of the primary beam current and serves as an absolute voltage probe of surface voltages without the need for an external reference voltage.
Owner:MULTIBEAM CORP
Electron beam control method, electron beam generating apparatus, apparatus using the same, and emitter
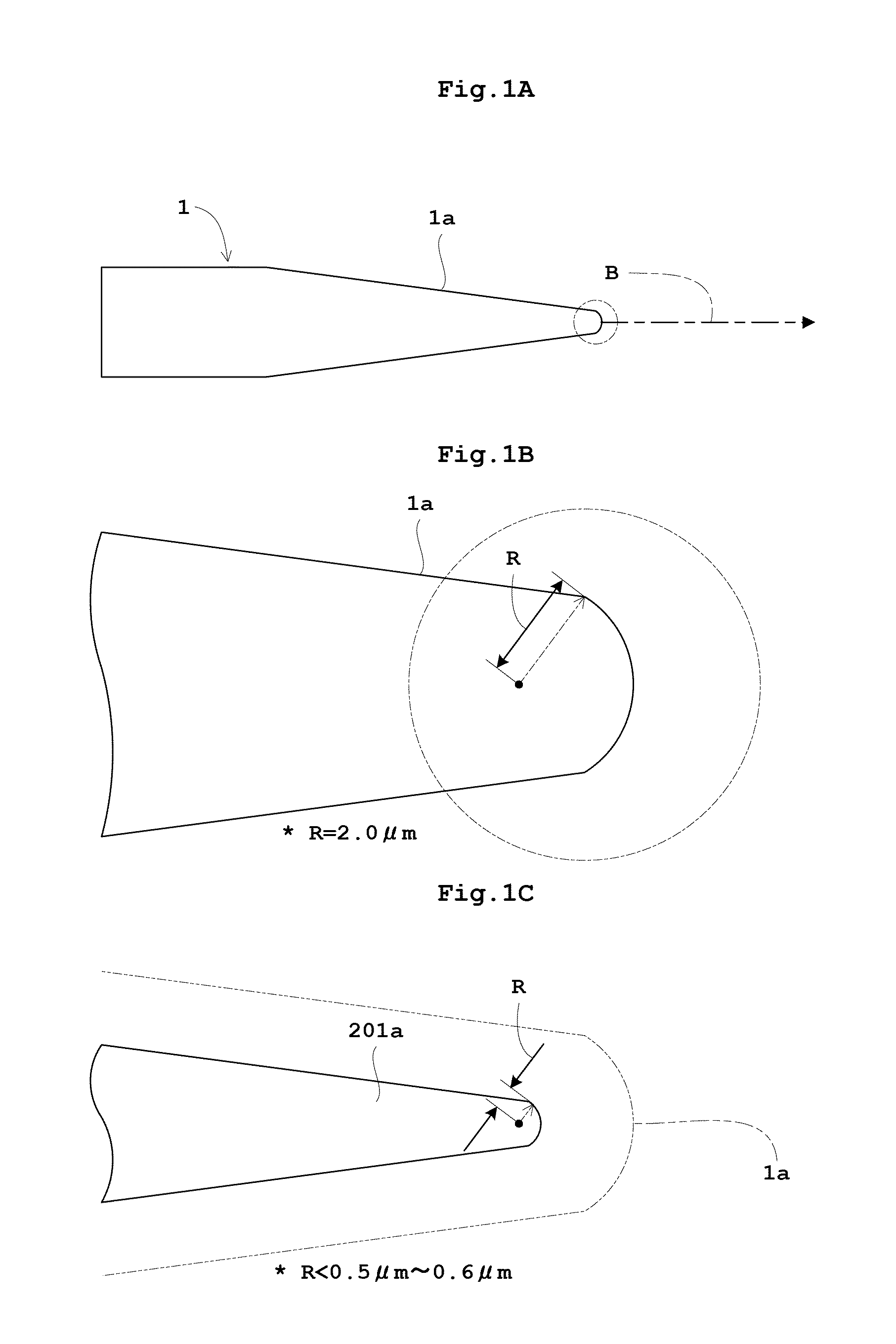
ActiveUS20100127170A1Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisElectron-beam lithography
Provided is a Schottky emitter having the conical end with a radius of curvature of 2.0 μm on the emission side of an electron beam. Since a radius of curvature is 1 μm or more, a focal length of an electron gun can be longer than in a conventional practice wherein a radius of curvature is in the range of from 0.5 μm to not more than 0.6 μm. The focal length was found to be roughly proportional to the radius of the curvature. Since the angular current intensity (the beam current per unit solid angle) is proportional to square of the electron gun focal length, the former can be improved by an order of magnitude within a practicable increase in the emitter radius. A higher angular current intensity means a larger beam current available from the electron gun and the invention enables the Schottky emitters to be used in applications which require relatively high beam current of microampere regime such as microfocus X-ray tube, electron probe micro-analyzer, and electron beam lithography system.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
Facility for manufacturing vertical GaN-based LED chips by metal substrates
ActiveCN102751399AHigh densityImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingElectron probe microanalysisGas phase
The invention discloses a facility for manufacturing vertical GaN-based LED chips by metal substrates. The facility comprises a computer information acquisition controller, a reaction room, a metal substrate feeding room, a gaseous-phase metal organism supply device, a nitrogen and / or hydrogen and / or ammonia supply device, an ECR (electron cyclotron resonance) plasma resource supply device, a vacuum degree meter and an imaging display formed relatively by a reflection high-energy electron diffractometer and a fluorescent screen, and is mainly characterized by further comprising a magnetic field coil support cylinder, a photoelectric alarm, a Faraday cylinder, an electronic probe and a direct-current bias voltage. The facility is reasonable in structure, high in film-coating quality and working efficiency, low in chip manufacture cost and the like.
Owner:GAOYOU INST CO LTD DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Dip-Formed Synthetic Polyisoprene Latex Articles with Improved Intraparticle and Interparticle Crosslinks
ActiveUS20090272384A1Uniform curingMale contraceptivesSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkVulcanization
A synthetic polyisoprene latex emulsion has pre-vulcanization composition and post vulcanization composition. The pre-vulcanization composition comprises soluble sulfur with high S8 ring structure that is catalytically broken by a zinc dithiocarbamate. Surfactants present in the pre-vulcanization composition wets synthetic polyisoprene particles and permeates small sized sulfur and accelerator molecules into the interior of these particles thereby pre-vulcanizing the particles. The degree of pre-vulcanization is verified by isopropanol index test. The latex emulsion has post-vulcanization composition with accelerators that crosslink inter-particle region during post vulcanization cure cycle. The dipped synthetic polyisoprene article is substantially uniformly cured both in the inter-particle and intra-particle regions and reliably exhibits high cross link density, uniform distribution of double bonds in TEM and zinc segregation at the boundaries or original particles by electron microprobe analysis. The films exhibit high tensile strength, tensile modulus, tear strength, burst pressure and burst volume.
Owner:LIFESTYLES HEALTHCARE PTE LTD
Scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS20040173747A1Easy to useMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron probe microanalysisScanning tunneling microscope
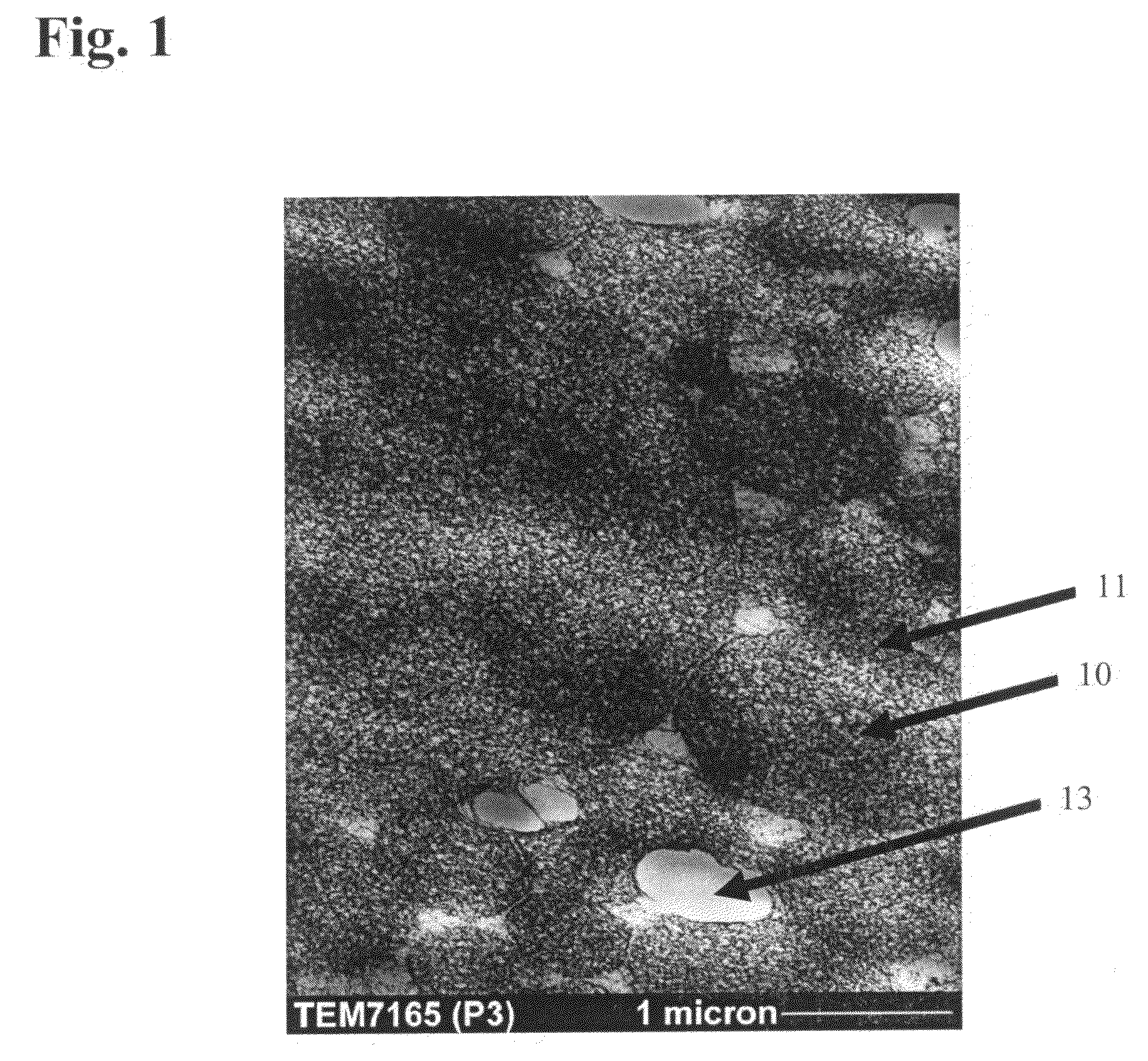
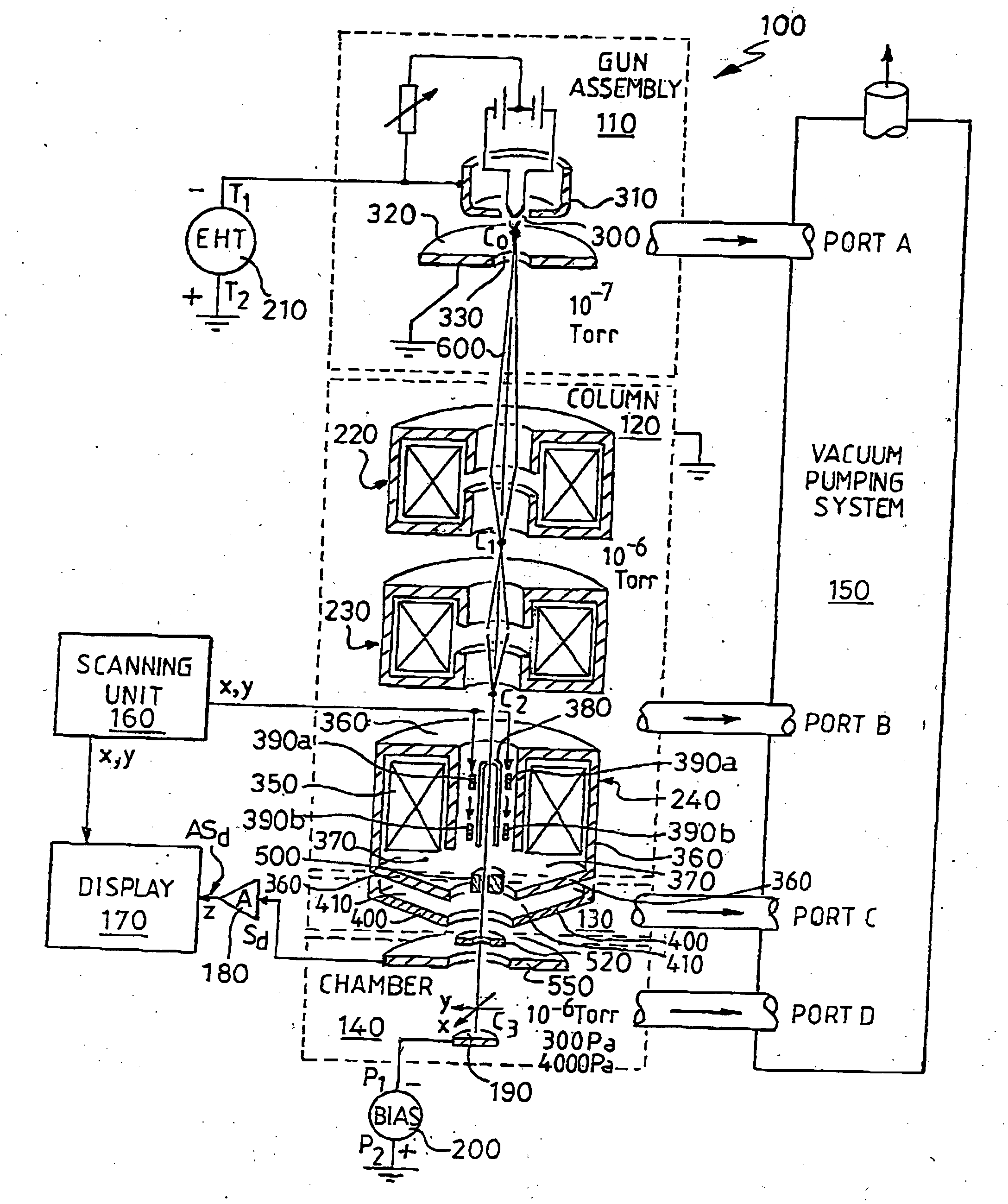
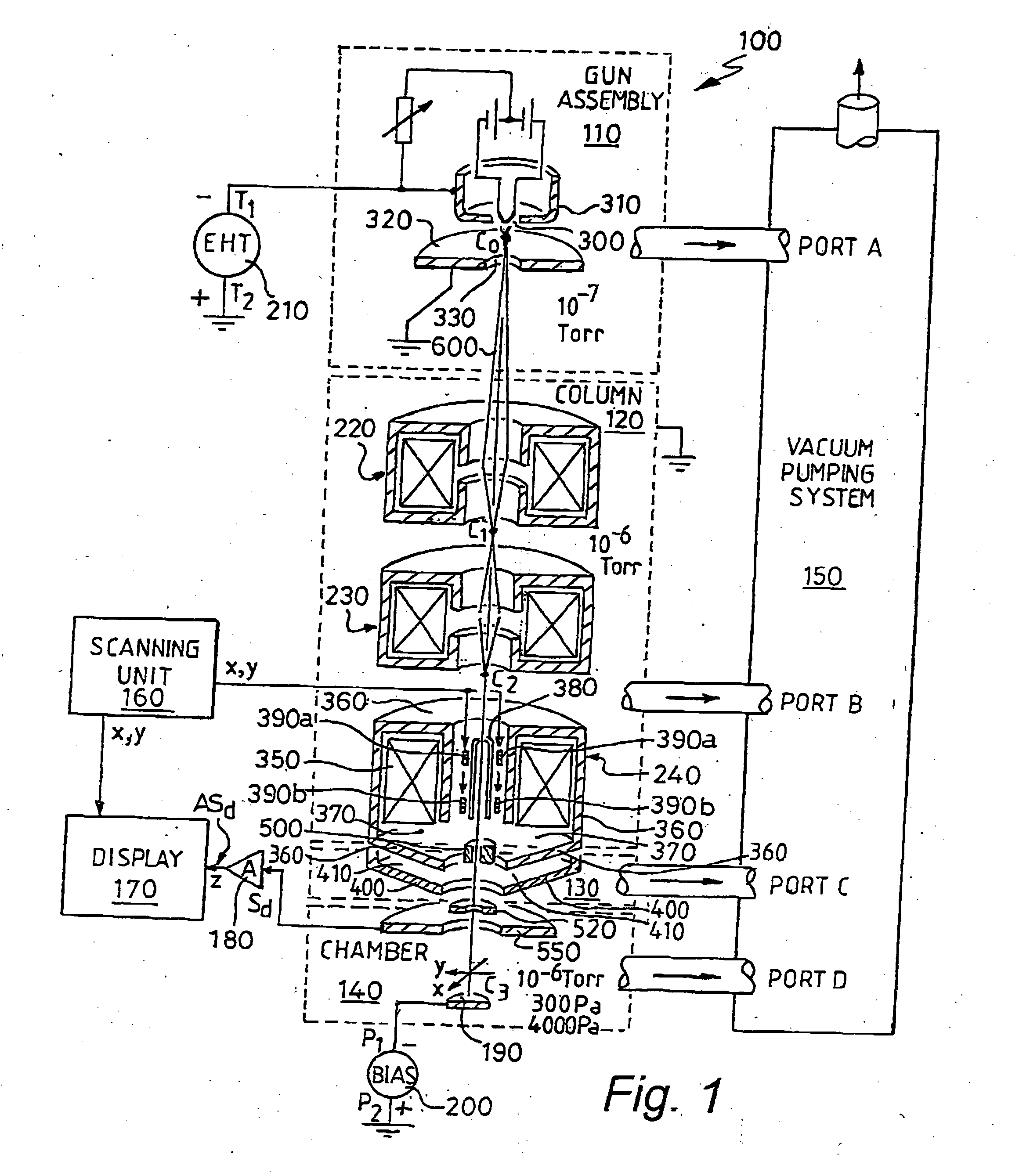
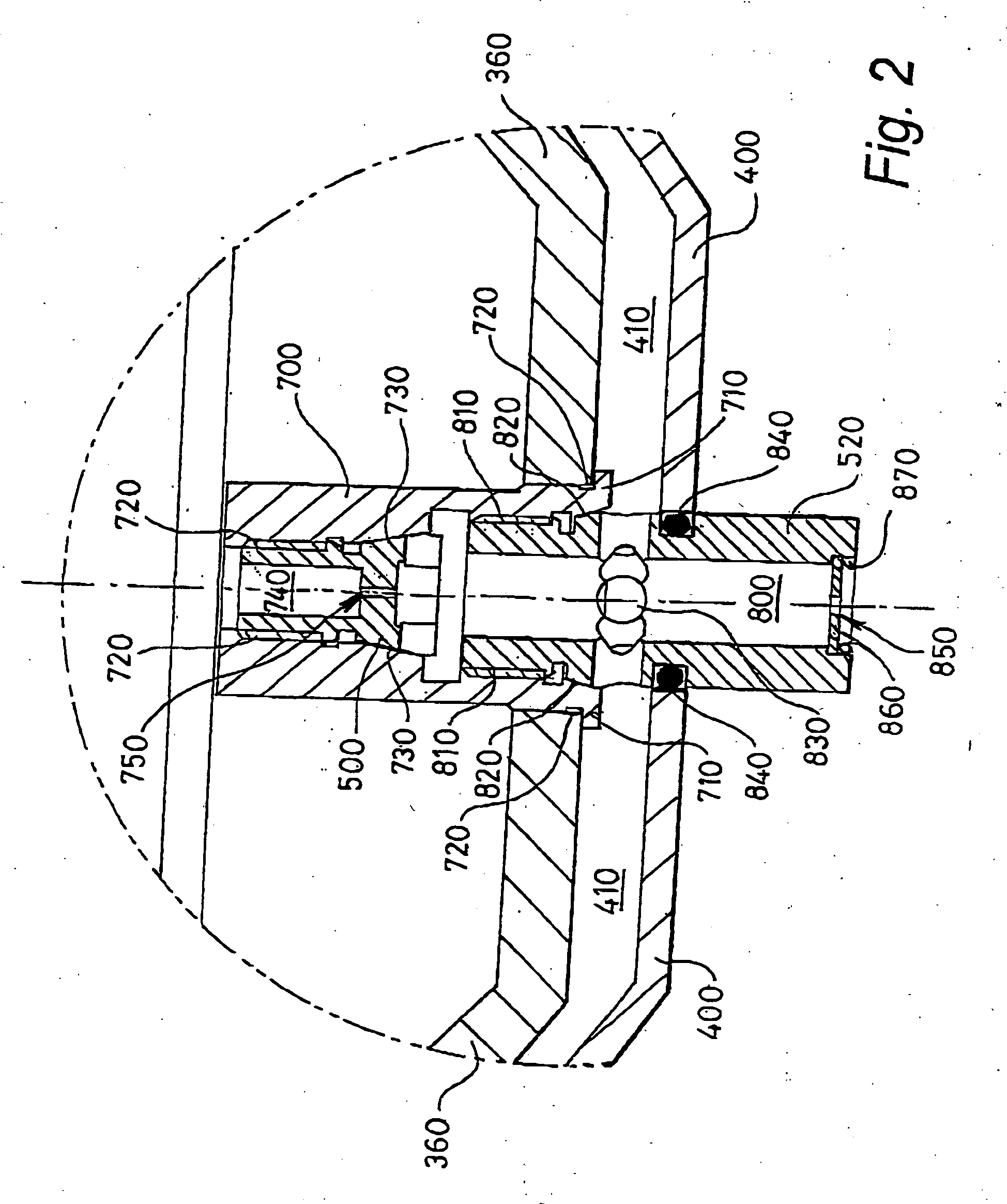
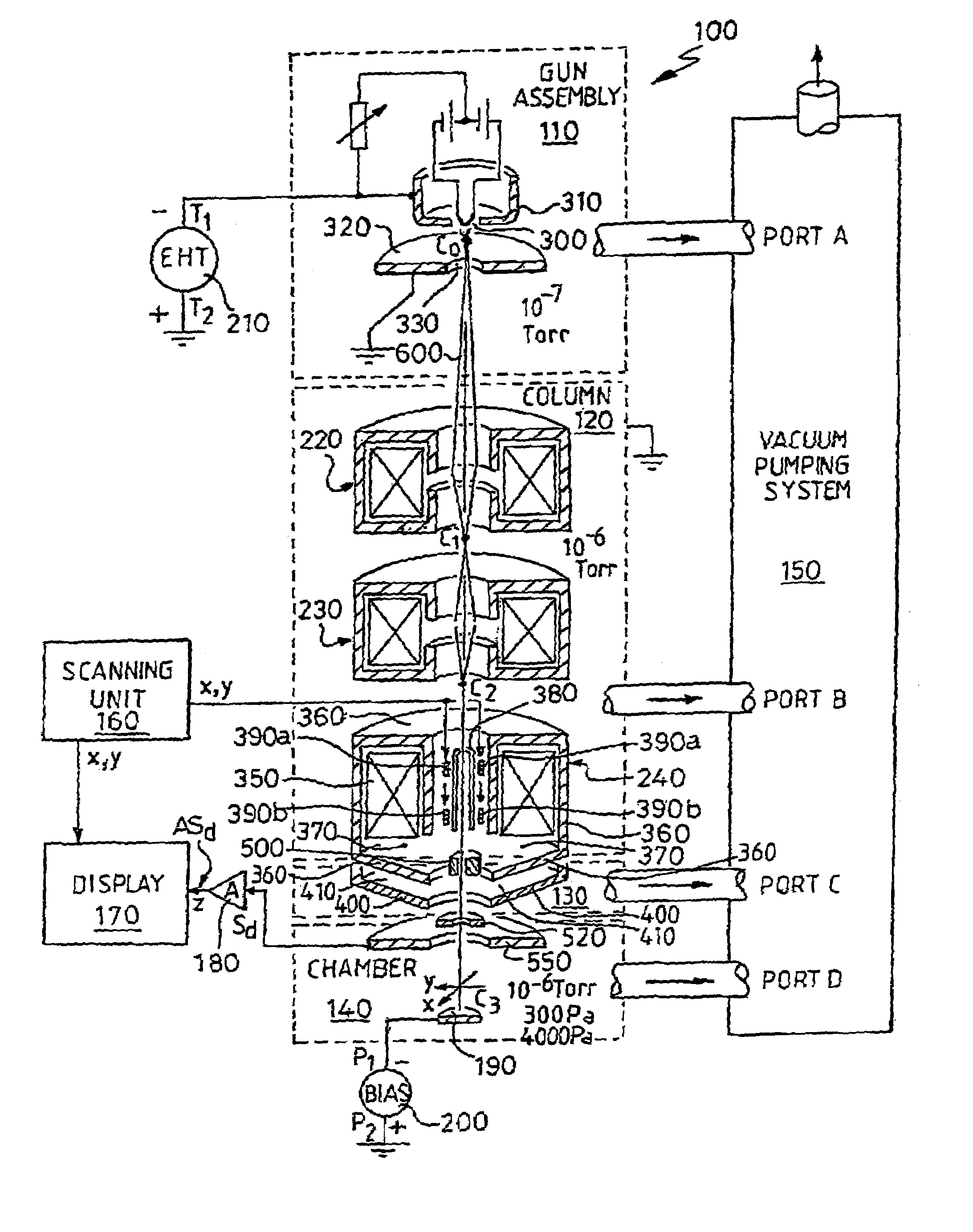
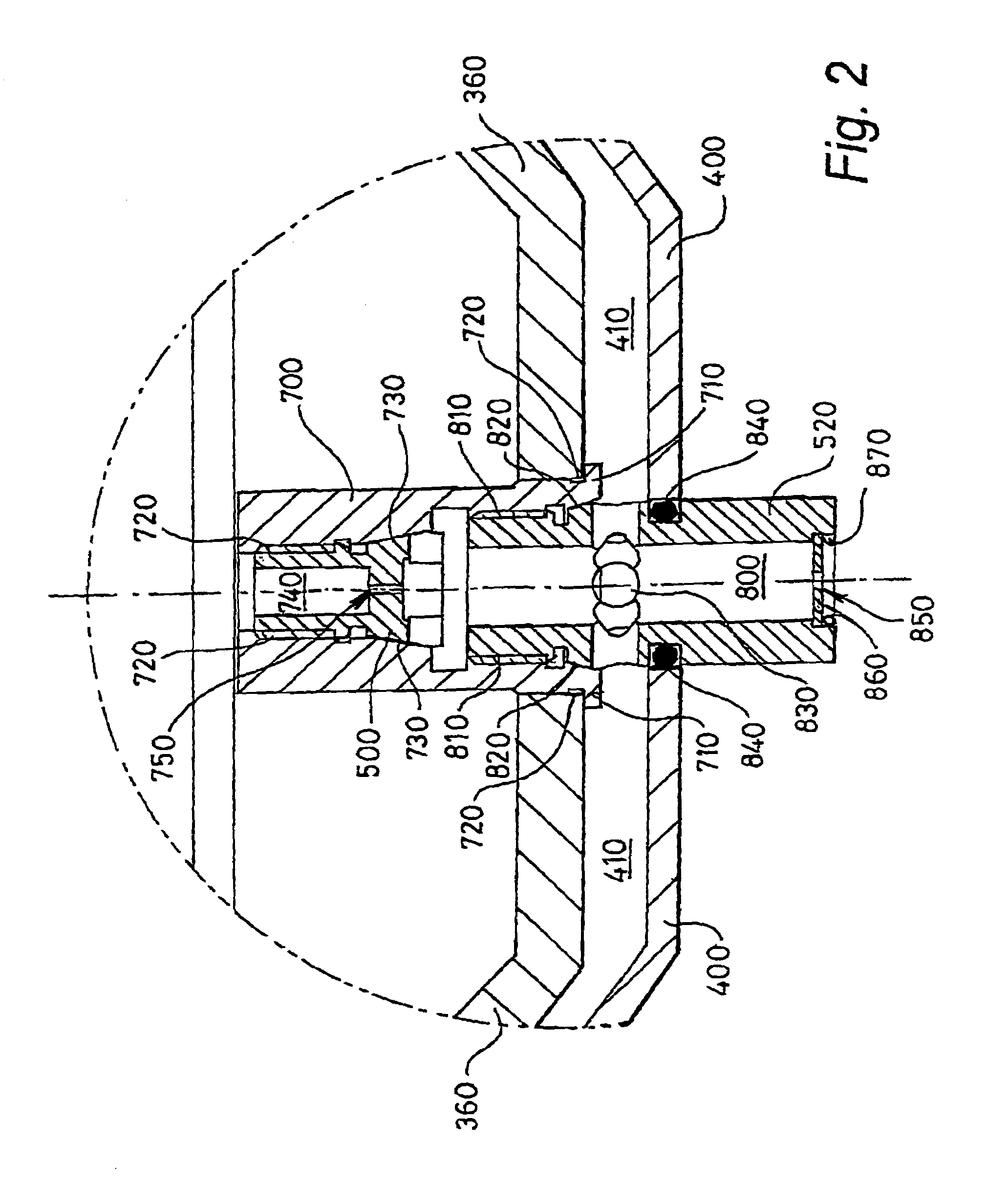
There is provided a reconfigurable scanning electron microscope (RSEM) (100) comprising: (a) a gun assembly (110) and an associated electron optical column (120) for generating an electron beam (600), for demagnifying the electron beam (600) to generate an electron probe (C3) and for scanning the probe (C3) across a sample (190); (b) an electron detector (550) for detecting emissions from the sample (190) in response to scanned electron probe irradiation thereof and for generating a corresponding detected signal (Sd) indicative of the magnitude of the emissions; and (c) a display (170) for receiving the detected signal (Sd) and scanning signals (x, y) indicative of the position of the probe (C3) relative to the sample (190) for generating the image of the sample (190). The RSEM (100) is distinguished in that it further includes aperture bearing members (500, 520), each member (500, 520) including an associated electon-beam transmissive aperture, for at least partially gaseously isolating the gun assembly (110) and the electron optical column (110) from the sample (190), thereby enabling the RSEM (100) to be reconfigurable as a high-vacuum scanning electron microscope and also as an environmental scanning electron microscope, the RSEM (100) being reconfigurable to include no aperture members, one aperture member (500, 750) and a plurality of aperture members (500, 750; 520 850, 860).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT LTD
Surface-coated cermet cutting tool with hard coating layer having excellent chipping resistance
ActiveUS7273665B2Improve impact performanceImprove wear resistancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
There is provided a surface-coated cermet cutting tool with a hard-coating layer having excellent chipping resistance. The surface-coated cermet cutting tool is formed by coating, on a surface of a tool substrate made of WC-based cemented carbide or TiCN-based cermet, a hard-coating layer including the following upper and lower layers (a) and (b): (a) as the lower layer, a Ti compound layer having at least one or two of a TiC layer, a TiN layer, a TiCN layer, a TiCO layer and a TiCNO layer, all of which are deposited by chemical vapor deposition, the titanium compound layer having a total average thickness of 3 to 20 μm, and (b) as the upper layer, a heat-transformed α-type Al oxide layer formed by carrying out a heat-transforming treatment in a state that titanium oxide particulates satisfying the composition formula: TiOY, (where value Y is 1.2 to 1.9 in an atomic ratio to Ti when measured by Auger Electron Spectroscopy) and chemically deposited as a transformation starting material are dispersedly distributed on a surface of an Al oxide layer having a κ-type or θ-type crystal structure deposited by chemical vapor deposition and satisfying the composition formula: (Al1-XZrX)2O3 (where value X is 0.003 to 0.05 in an atomic ratio when measured by an electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA)) to thereby transform the crystal structure of the Al oxide layer having the κ-type or θ-type crystal structure into an α-type crystal structure, the heat-transformed α-type Al oxide layer having an average thickness of 1 to 15 μm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Method of testing uraninite formation age
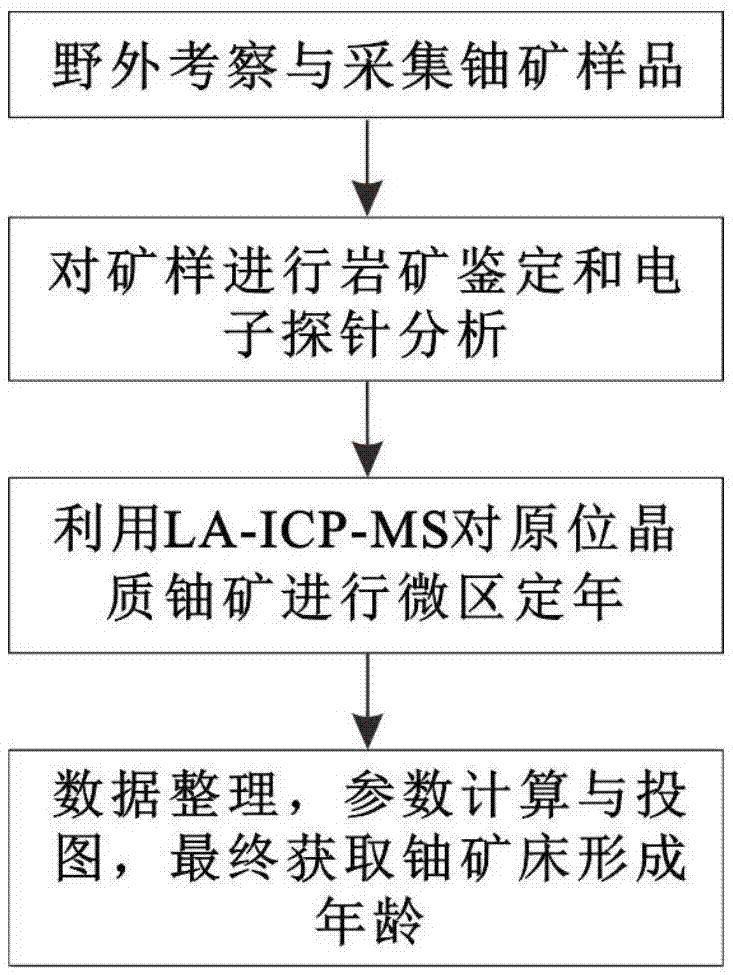
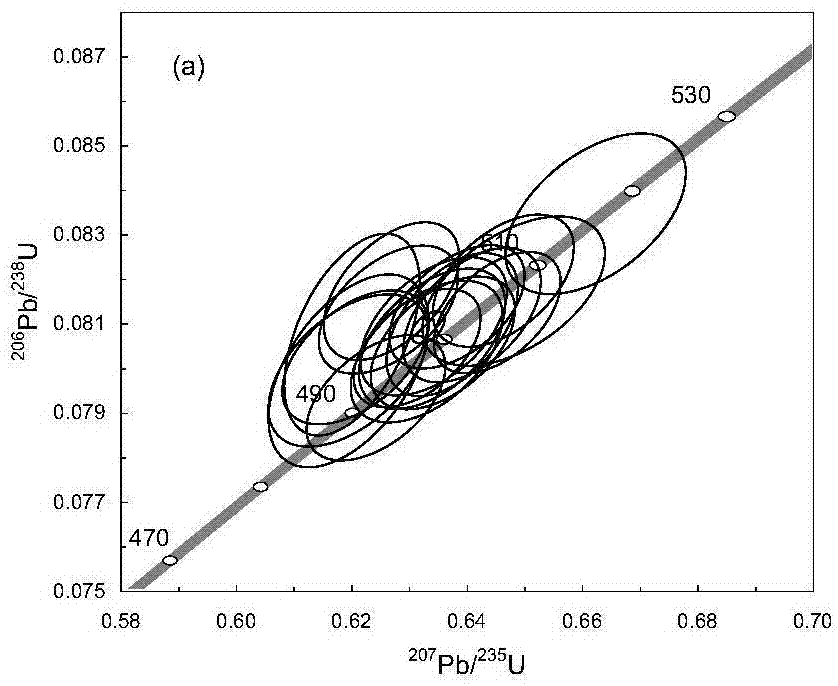
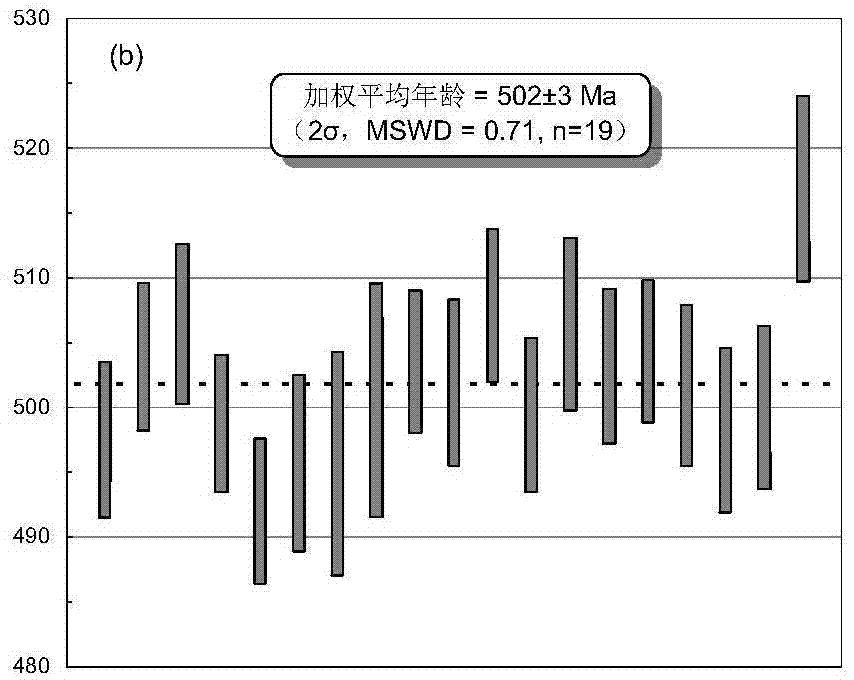
InactiveCN106932837AAnalytical testing requirements are clearEasy to operateGeological measurementsUraniniteElectron probe microanalysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of uranium ore, and specifically relates to a method for testing the formation age of crystalline uranium ore; The age of uranium deposits and the role of metallogenic evolution analysis, decomposing the key elements and main ore-controlling factors of each metallogenic period from complex geological phenomena, providing ideas for uranium deposit exploration, and guiding specific ore-prospecting work to test crystal quality The method for the formation age of uranium ore; including the following steps: Step 1, field investigation and collection of uranium ore samples; Step 2, rock ore identification and electronic probe analysis on the ore samples; Step 3, using LA-ICP-MS Micro-zone dating of crystalline uranium ore; step 4, data collation, parameter calculation and mapping, and finally the formation age of uranium ore is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Method for quantitatively examining center segregations of wire rod
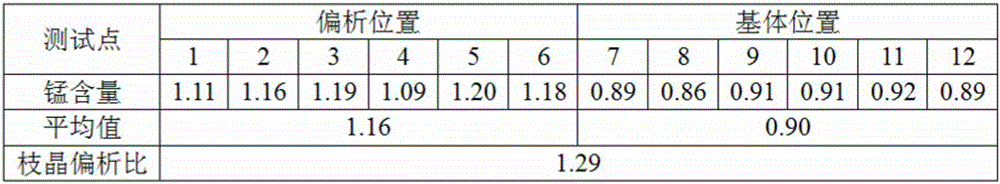
InactiveCN102954976AGuaranteed StrengthPrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisX-ray
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively examining the center segregation of a wire rod. The method comprises the following steps: taking two wire rod samples, rubbing down the cross section of one of the wire rod samples, splitting the other sample at the 2 / 3 position along the vertical direction of the wire rod sample, rubbing down the profile of the lager sample, putting the two rubbed surfaces next to each other in a same plane, inlaying through using a conductive resin, grinding the samples, polishing the plane when the width of the vertical profile of the wire rod sample is equal to the diameter of the other wire rod sample, and corroding the samples through using an alcohol solution of nitric acid; marking through drawing a line at the severest segregation position, and polishing the samples; and putting the samples in an electronic probe analyzer, finding the made mark through using a secondary electron image, carrying out C and Mn element X-ray intensity line analysis measurement of the full width of the samples through utilizing element characteristic X-ray spectrum analysis under an acceleration voltage of 10-20kV, an electron beam current of above 100nA and a beam spot dimension of 20-50mum, recording through using curves, testing the X-ray intensities of a standard sample of the analytic elements under same test conditions, converting the X-ray intensities in the curves into concentration contents, obtaining maximum concentrations and average concentrations from the curves, and obtaining the center segregation rates through calculating according to a formula of the center segregation rate=(the maximum value / the average value)*100%.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
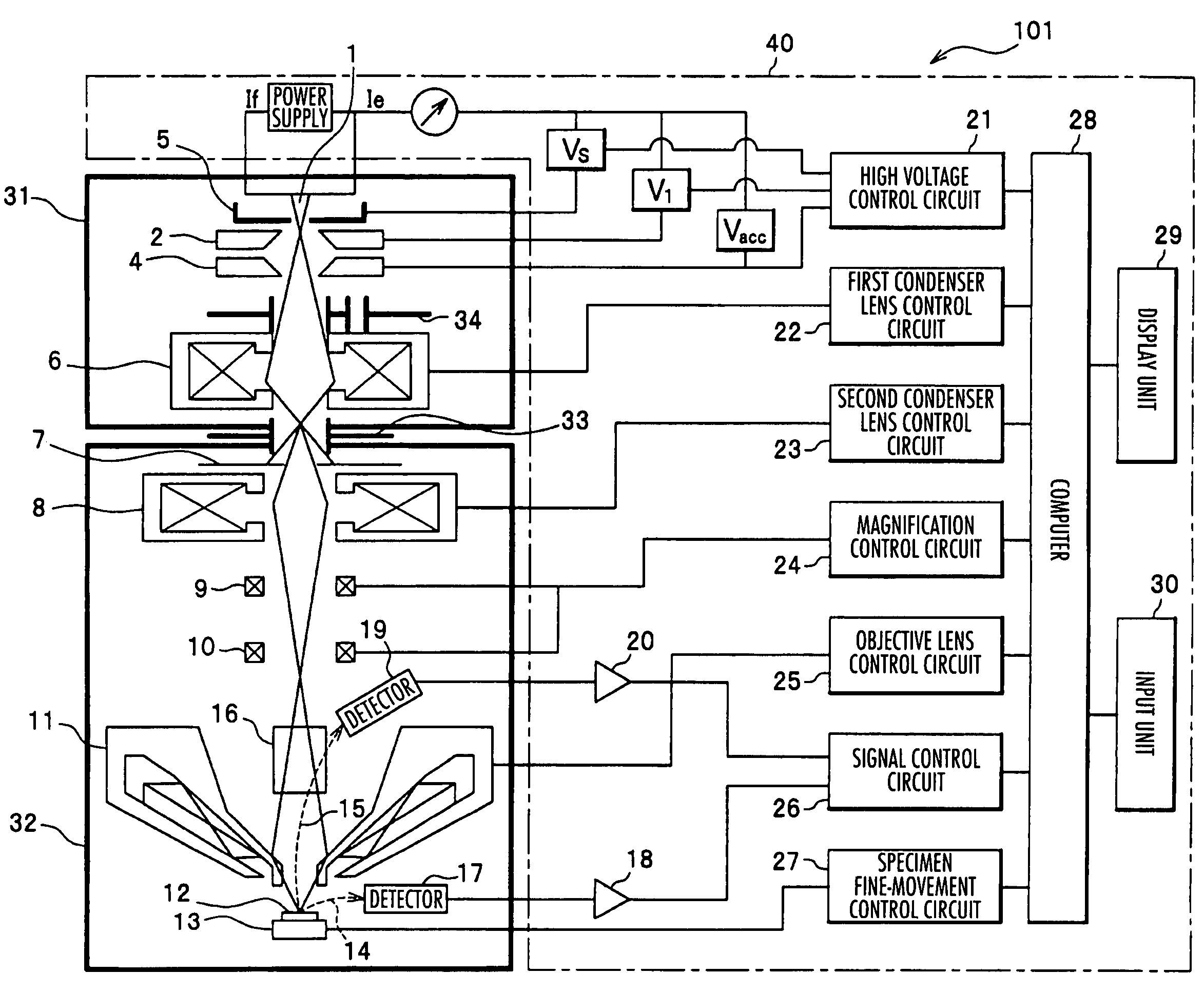
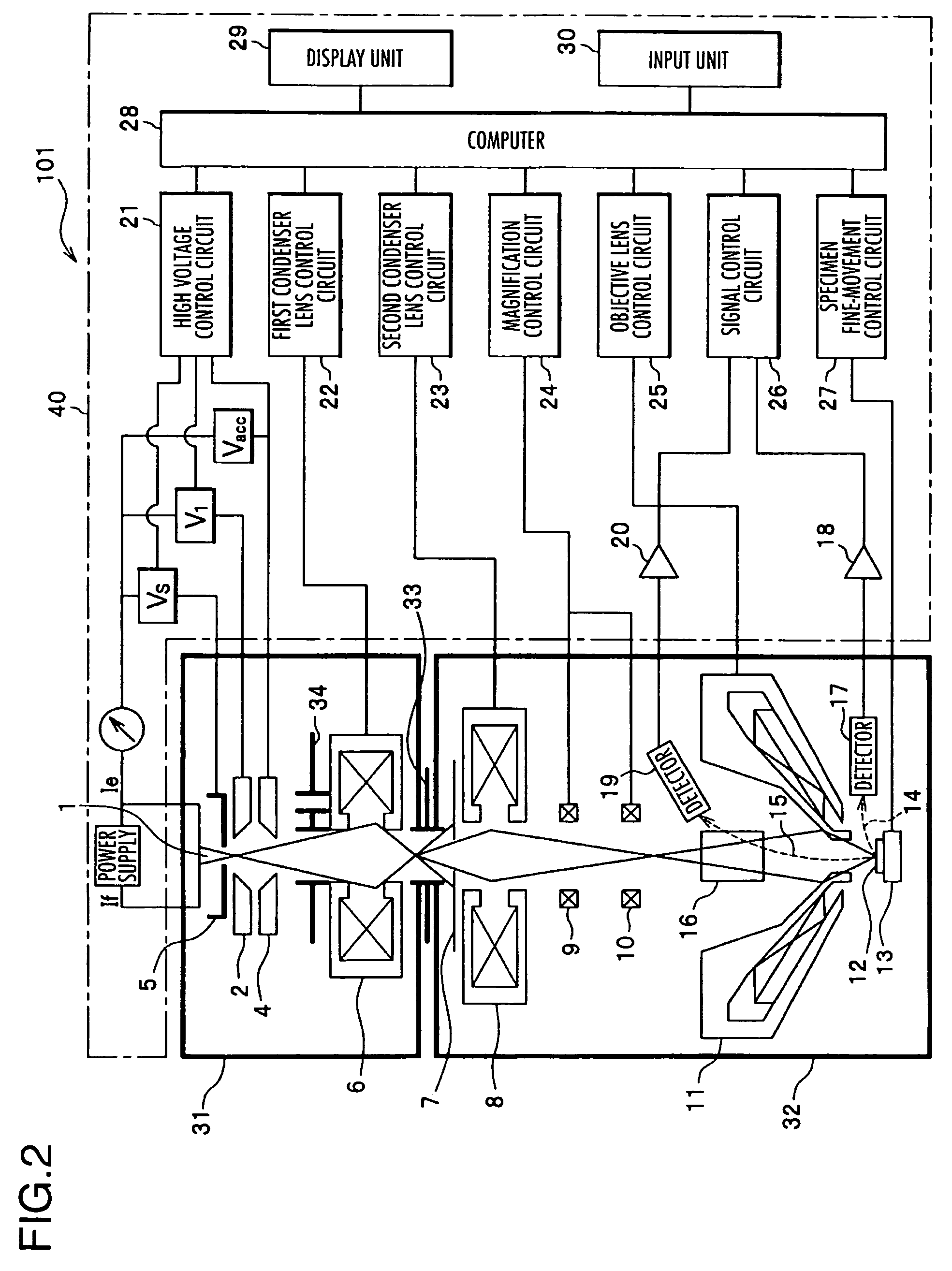
Electron beam device and its control method
InactiveUS7550724B2Pollution suppressionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron probe microanalysisVacuum level
An electron beam device includes an electron gun section having an internal space kept at an ultrahigh vacuum level for generating a primary electron beam, a mirror section having an internal space kept at a vacuum level lower than that of the electron gun section for scanning a specimen with an electron probe of the primary electron beam generated in the electron gun section and focused on the specimen, a differential exhaust diaphragm for providing communication in internal space between the electron gun section and the mirror section and passing the primary electron beam, and a control section for controlling respective constituent elements in the electron beam device. A diaphragm mechanism having a plurality of different diaphragm aperture diameters is provided between a second anode and a first condenser lens.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Measuring method of equilibrium phase of multi-component Ti-Al-X intermetallic compound
InactiveCN104535571AReduce workloadMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationDiffusionElectron probe microanalysis
The invention relates to a measuring method of the equilibrium phase of a multi-component Ti-Al-X intermetallic compound. The measuring method comprises the steps of firstly carrying out diffusion-couple reference alloy composition design;preparinga diffusion-couple reference alloy casting ingot byadopting a vacuum-induction electric arc melting technology; cutting the melted diffusion-couple reference alloy casting ingot into a test sample; grinding the test sample till the surface is smooth and flat, and then carrying out vacuum prewelding; then carrying out long-time balance diffusion treatment on the pre-welded sample, and forming a diffusion layer between two reference alloys; then preparing a middle diffusion layer into a metallographic sample, andobserving; testing the contents of Al and Ti of the two ends of a phase interface of the sample by adopting an electronic probe technology, drawing concentration distribution curve of the Al and the Ti from an alpha-phase area to a gamma-phase area and obtaining equilibrium compositions of the two phases. Compared with the prior art, the measuring method has important theoretical guidance and practice significance on research ofthe equilibrium phase of multi-component Ti-Al-X intermetallic compound.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
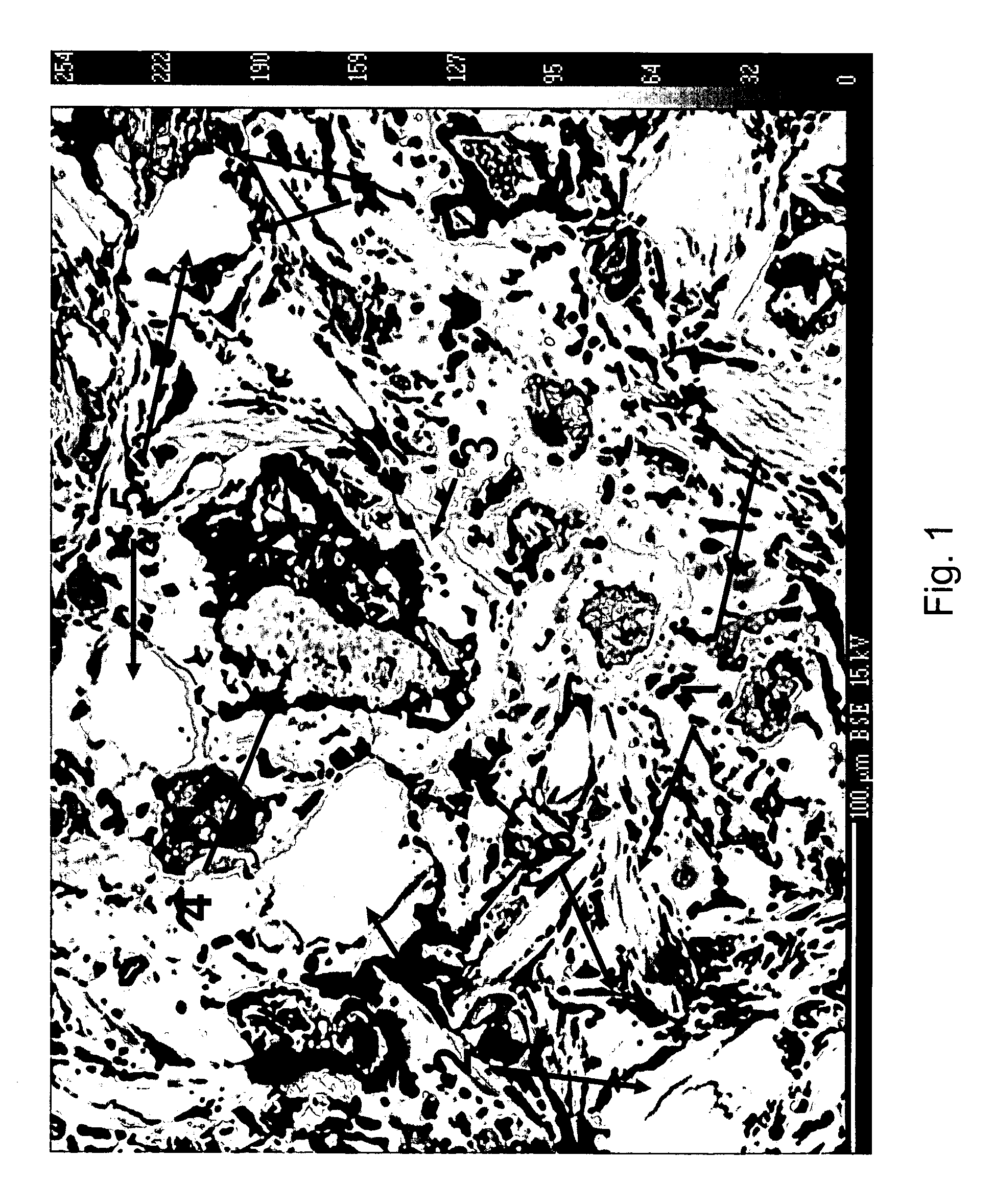
Total-rock component testing method based on in-situ electronic probe analysis
InactiveCN104122283AEasy to makeQuick analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisX-ray
The invention discloses a total-rock component testing method based on in-situ electronic probe analysis. The total-rock component testing method comprises the steps of jet-plating a manufactured rock X-ray plate or a thin X-ray plate with a carbon conductive film, putting a jet-plated sample into an electronic probe sample chamber for analysis, shooting a back scattering electronic image under the condition of a magnification factor of 450-550, performing precision quantitative analysis on different minerals in the image through an electronic probe wavelength dispersive spectrometer, and counting the area percentages of the different minerals in the shot back scattering image by adopting a grid method; calculating a result which is the content of a total-rock element of the rock sample by performing a weighing average operation on an element content average value of different analysis points of the same mineral and the area percentages of the minerals. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of no destroy to the sample, in-situ microbeam analysis, high analysis precision, easiness in sample preparation, zero pollution and the like, and has an extremely good application prospect in the analysis of aerolite, gem-jade and precious rare rock samples.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Tapered monocapillary-optics for point source applications
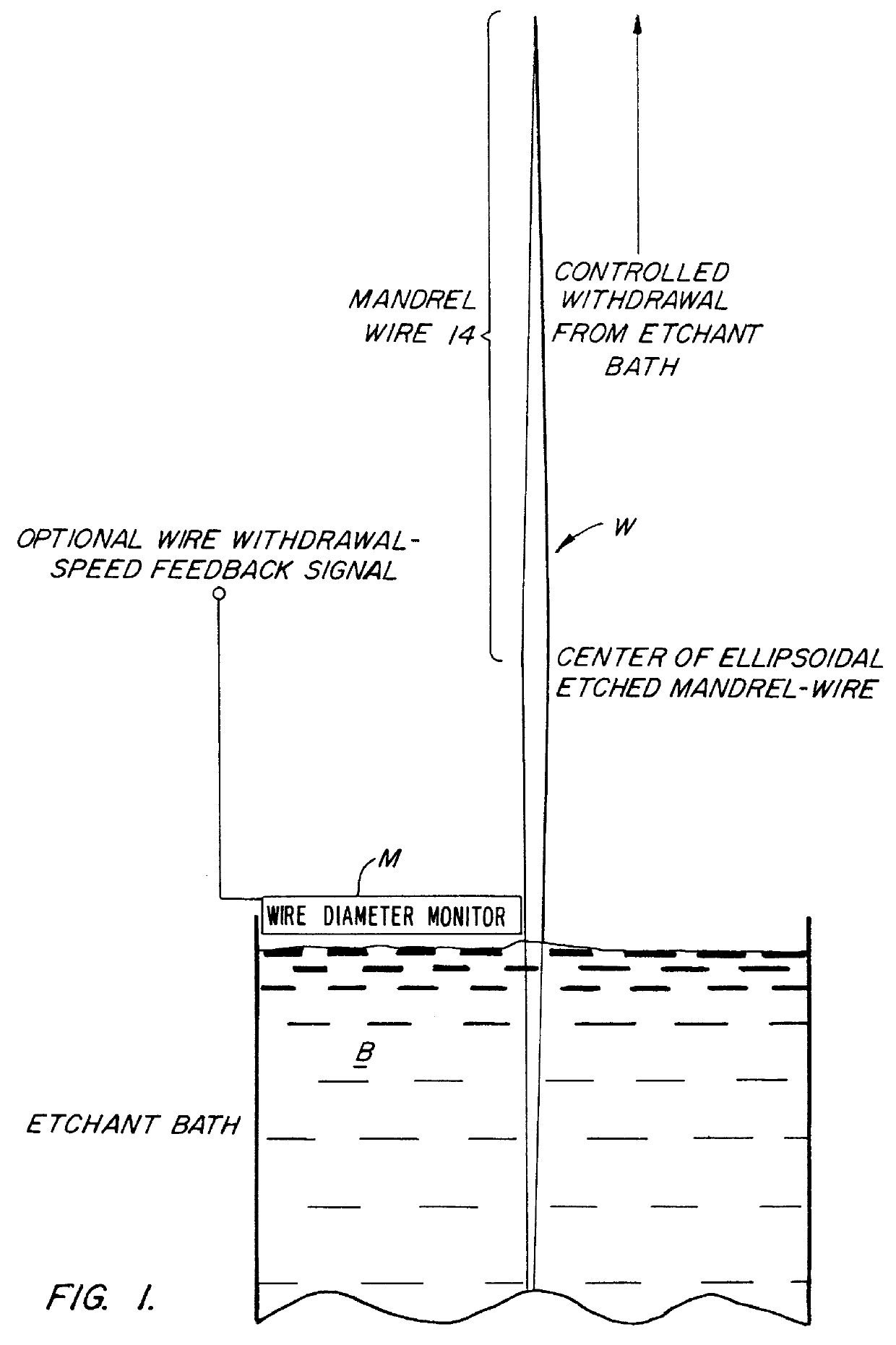
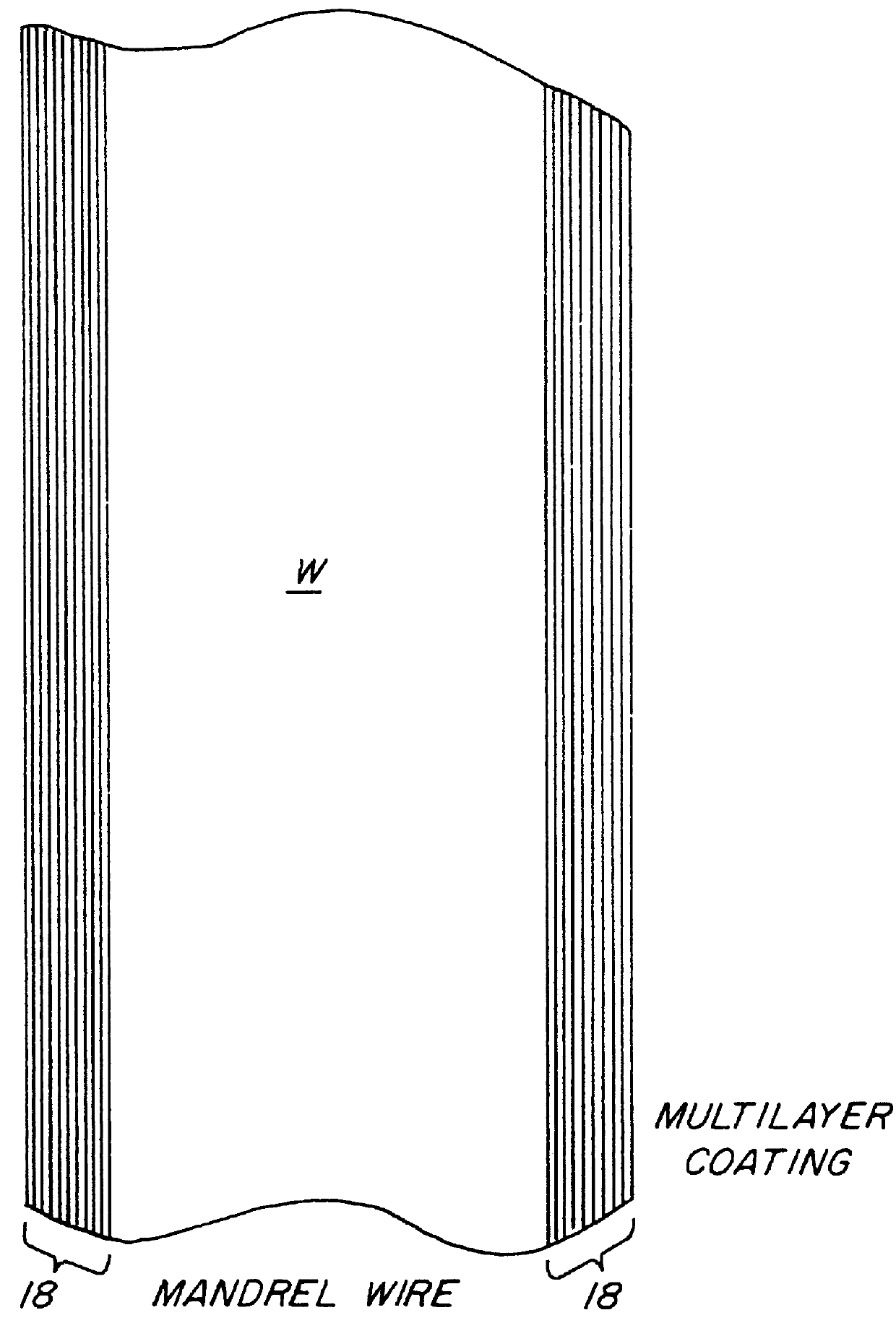
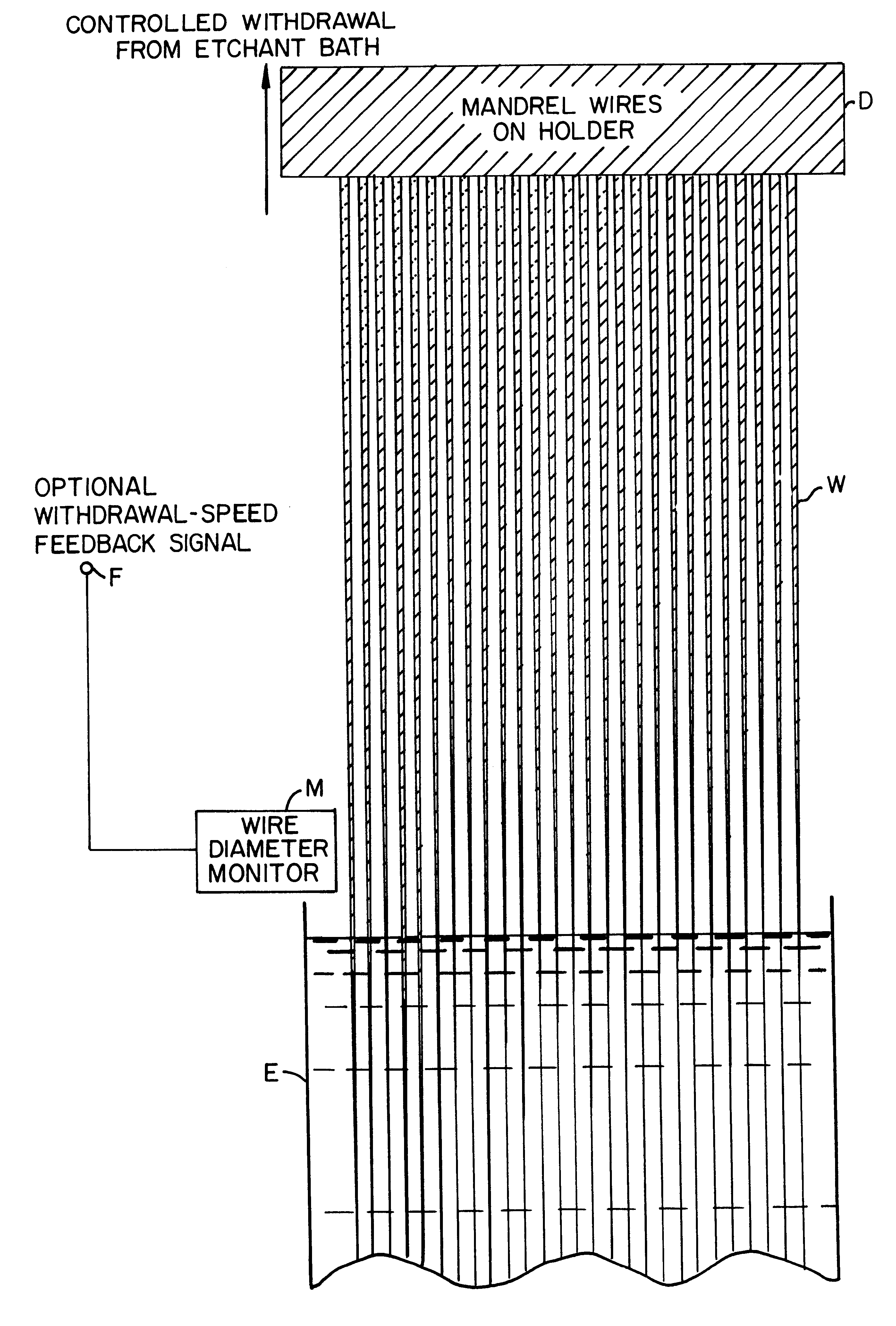
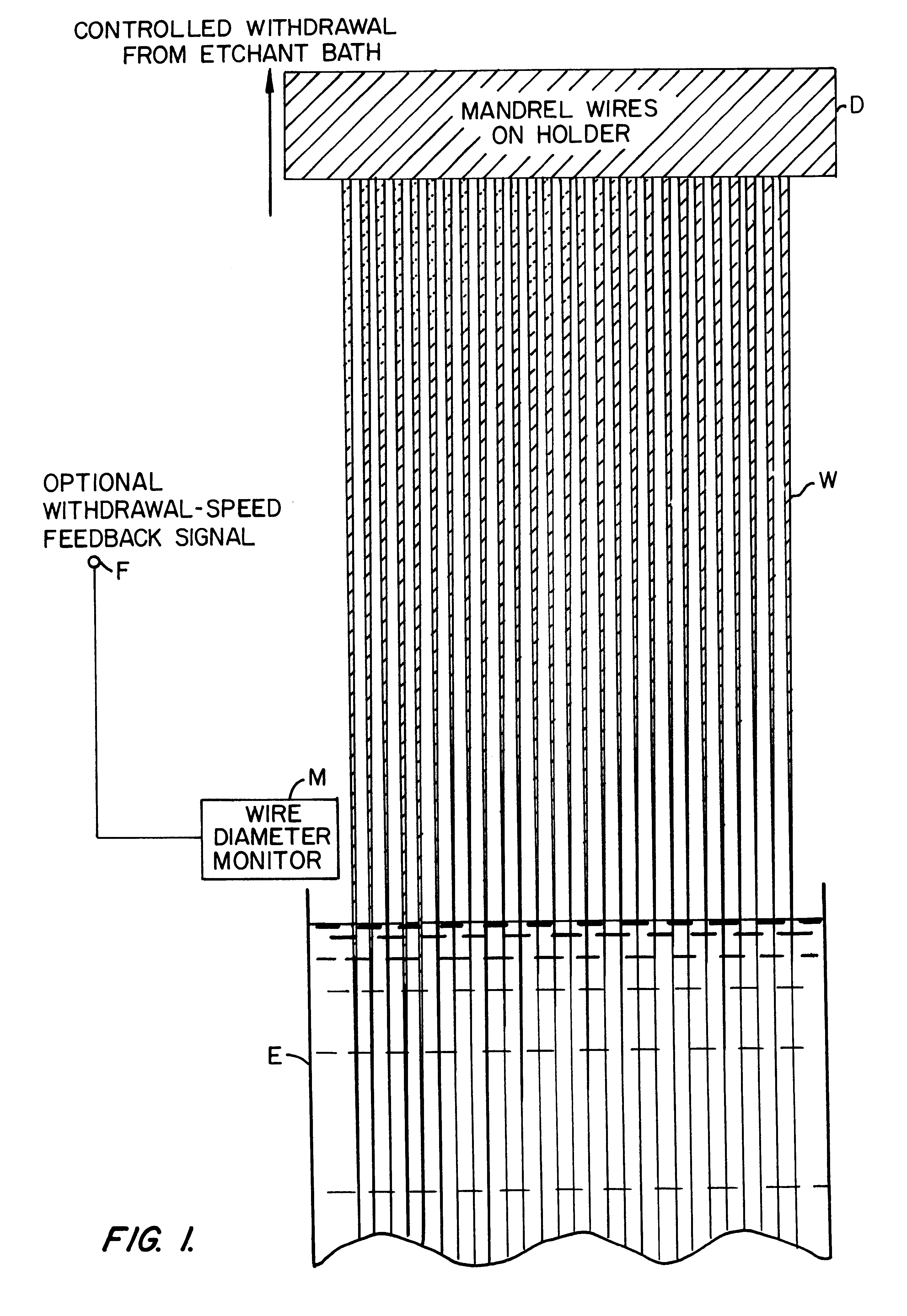
InactiveUS6126844APaper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsElectron probe microanalysisElectron
A glass or metal wire is precisely etched to form the paraboloidal or ellipsoidal shape of the final desired capillary optic. This shape is created by carefully controlling the withdrawal speed of the wire from an etchant bath. In the case of a complete ellipsoidal capillary, the etching operation is performed twice in opposite directions on adjacent wire segments. The etched wire undergoes a subsequent operation to create an extremely smooth surface. This surface is coated with a layer of material which is selected to maximize the reflectivity of the radiation. This reflective surface may be a single layer for wideband reflectivity, or a multilayer coating for optimizing the reflectivity in a narrower wavelength interval. The coated wire is built up with a reinforcing layer, typically by a plating operation. The initial wire is removed by either an etching procedure or mechanical force. Prior to removing the wire, the capillary is typically bonded to a support substrate. One option for attaching the wire to the substrate produces a monolithic structure by essentially burying it under a layer of plating which covers both the wire and the substrate. The capillary optic is used for efficiently collecting and redirecting the divergent radiation from a source which could be the anode of an x-ray tube, a plasma source, the fluorescent radiation from an electron microprobe, or some other source of radiation.
Owner:HIRSCH GREGORY
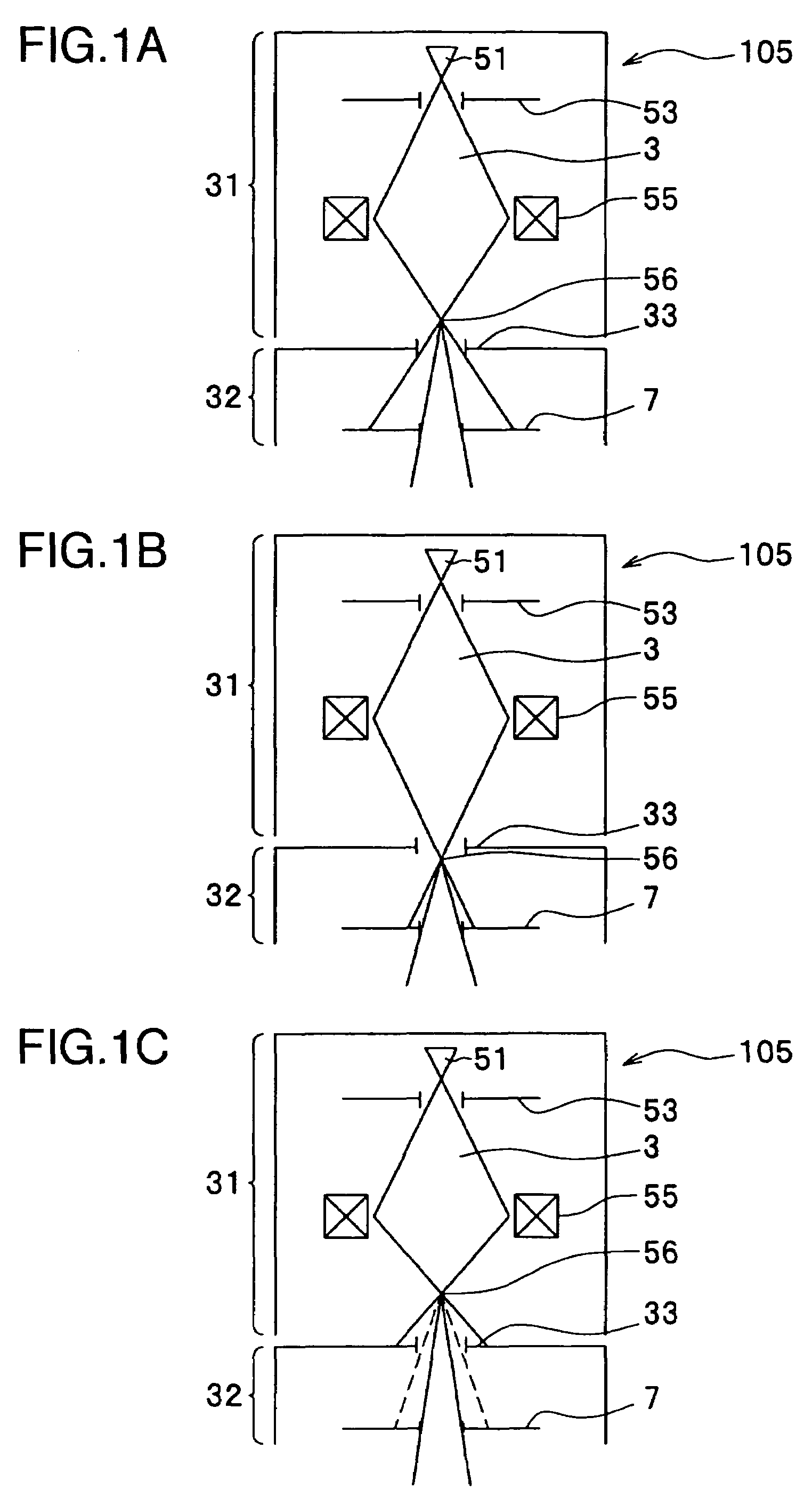
Method and device for time-resolved pump-probe electron microscopy
InactiveUS20170271123A1Efficiently omittedAccurate resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron probe microanalysisElectron Microscopy Facility
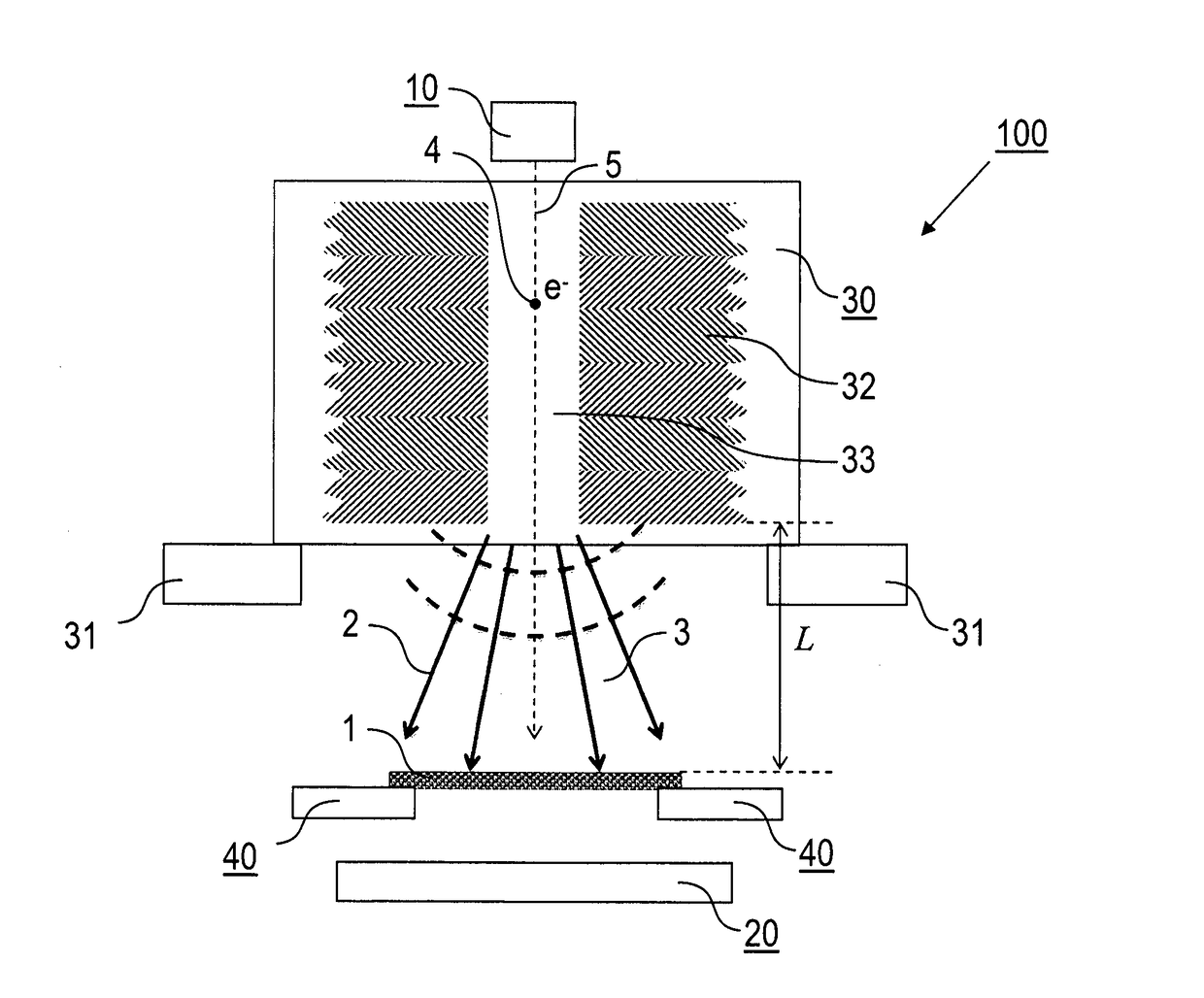
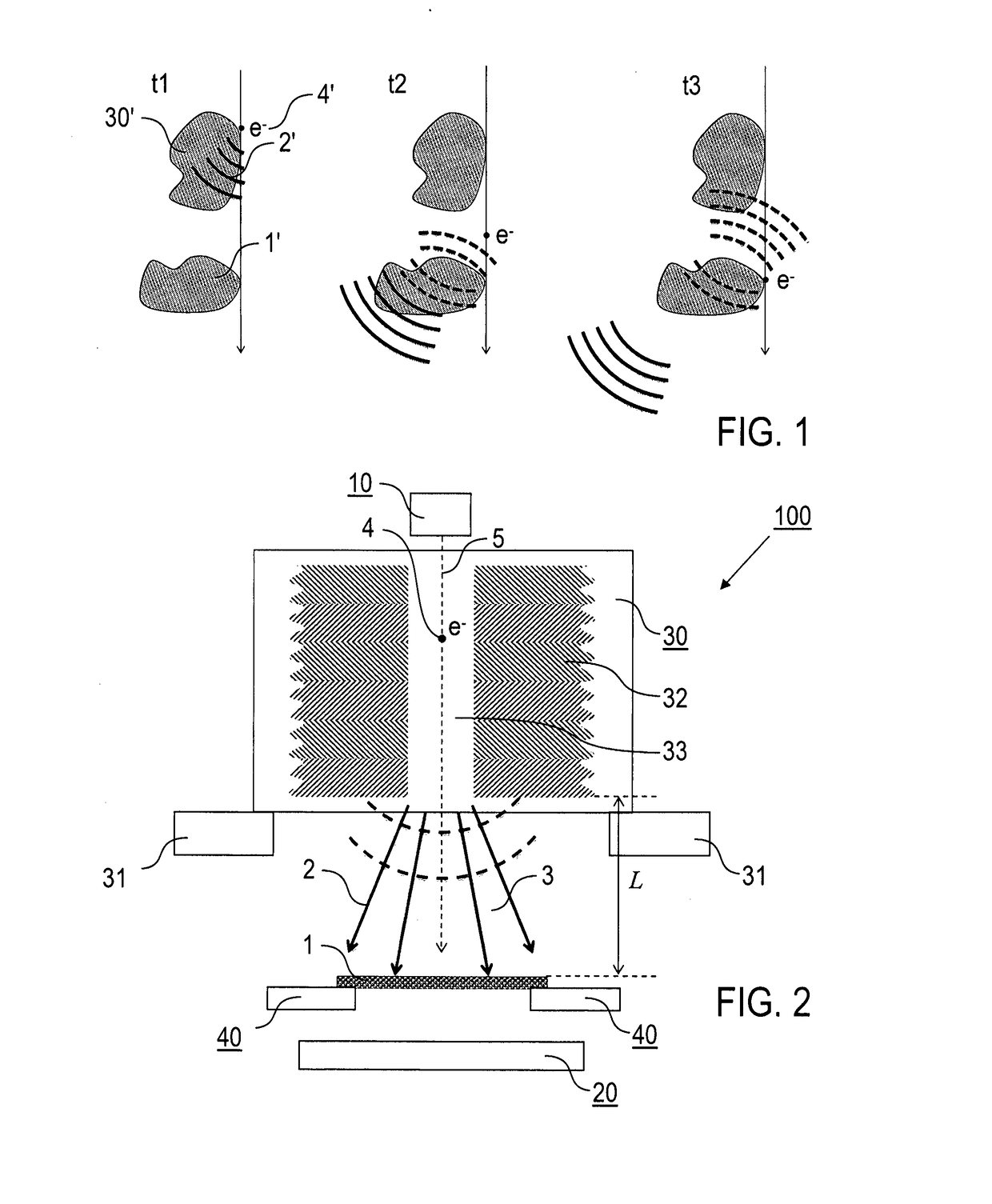
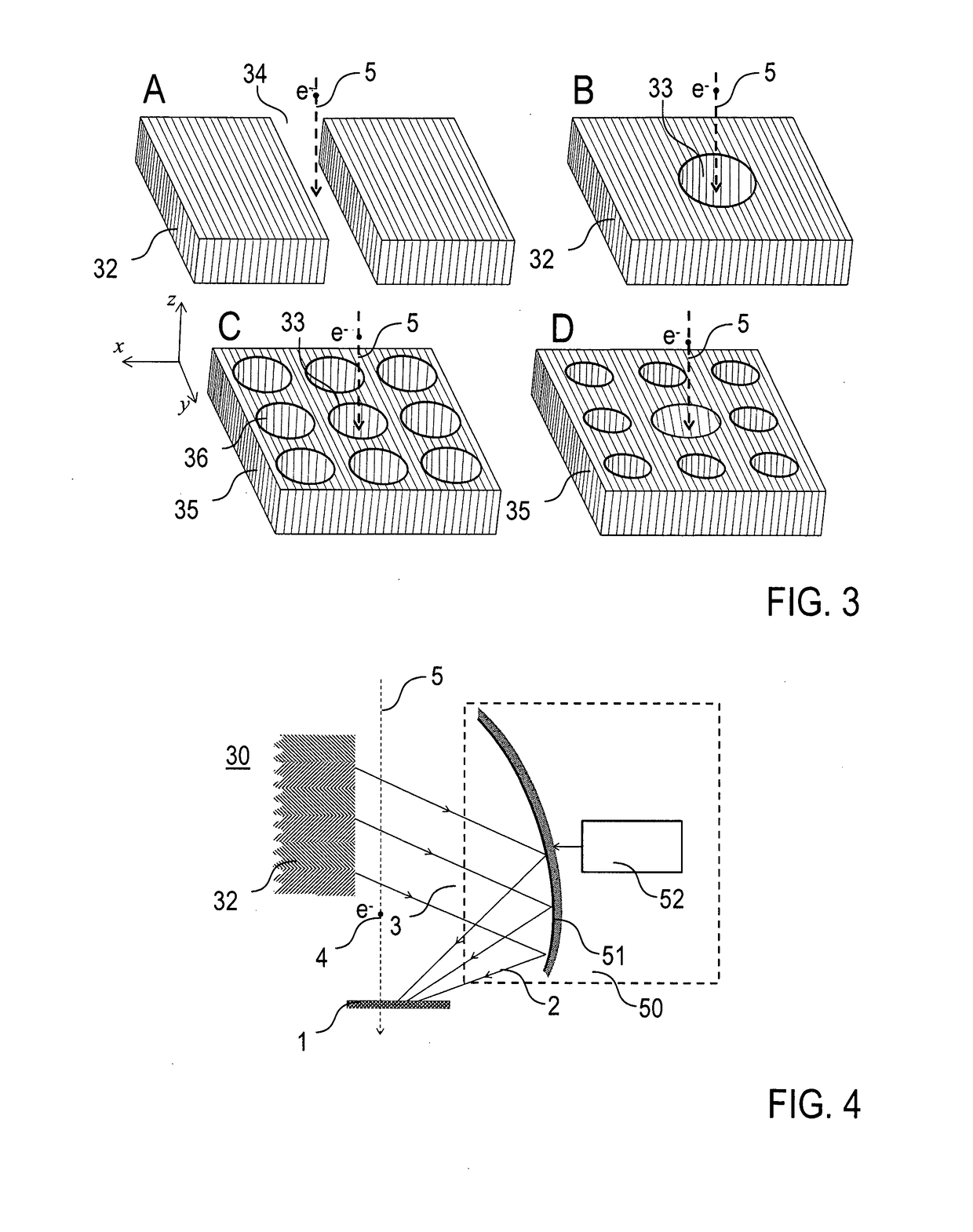
A method of time-resolved pump-probe electron microscopy, comprises the steps of irradiating a sample (1) with a photonic pump pulse (2) being directed on a pump pulse path (3) from a photonic source to the sample (1), irradiating the sample (1) with an electron probe pulse (4) being directed on an electron pulse path (5) from an electron pulse source (10) to the sample (1), wherein the photonic pump pulse (2) and the electron probe pulse (4) arrive at the sample (1) with a predetermined temporal relationship relative to each other, and detecting a sample response to the electron probe pulse (4) irradiation with a detector device (20), wherein the photonic source comprises a photonic lattice structure (30) being arranged adjacent to the electron pulse path (5), and the photonic pump pulse (2) is created by an interaction of the electron probe pulse (4) with the photonic lattice structure (30). Furthermore, an electron microscopy apparatus, configured for time-resolved pump-probe electron microscopy, and a sample supply device (200) for an electron microscopy apparatus (100) are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Quantitative analysis method for continuous casting billet dendritic segregation
InactiveCN106596615APrecise positioningImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationElectron probe microanalysisElement analysis
Belonging to the technical field of metal material detection, the invention relates to a quantitative analysis method for continuous casting billet dendritic segregation. The method includes: sample preparation: controlling the sample diameter less than or equal to 30mm; electron probe surface analysis: setting an acceleration voltage of 15-30kV, and a beam current of 100-500nA, etc.; selection of segregation and substrate position; electron probe quantitative analysis: applying a "Quantitative" module for quantitative element analysis using ZAF correction method; and result analysis and data processing: representing the dendritic segregation degree of an element with dendrite segregation ratio, etc. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of strong pertinence and high result analysis accuracy.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
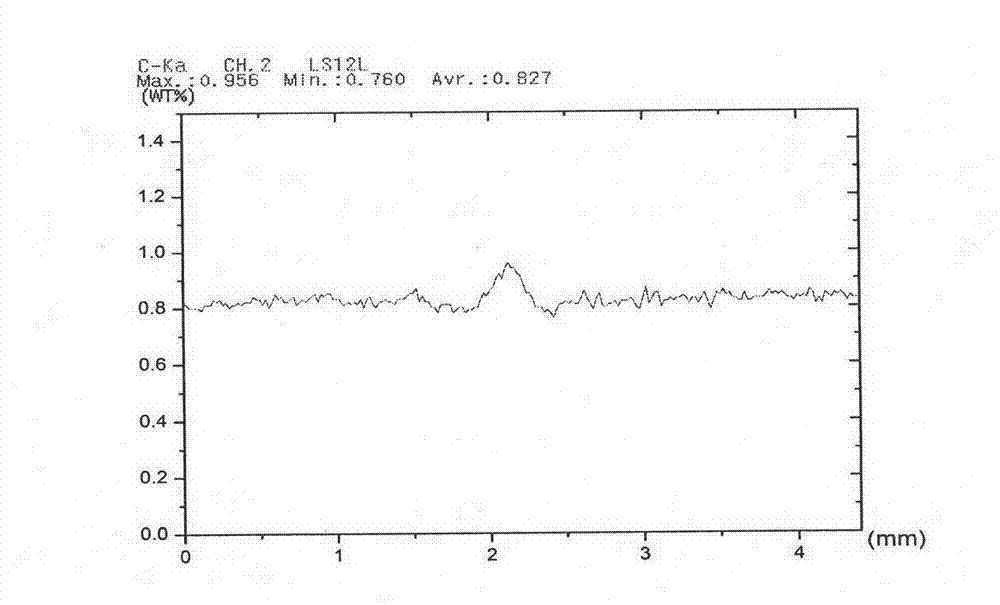
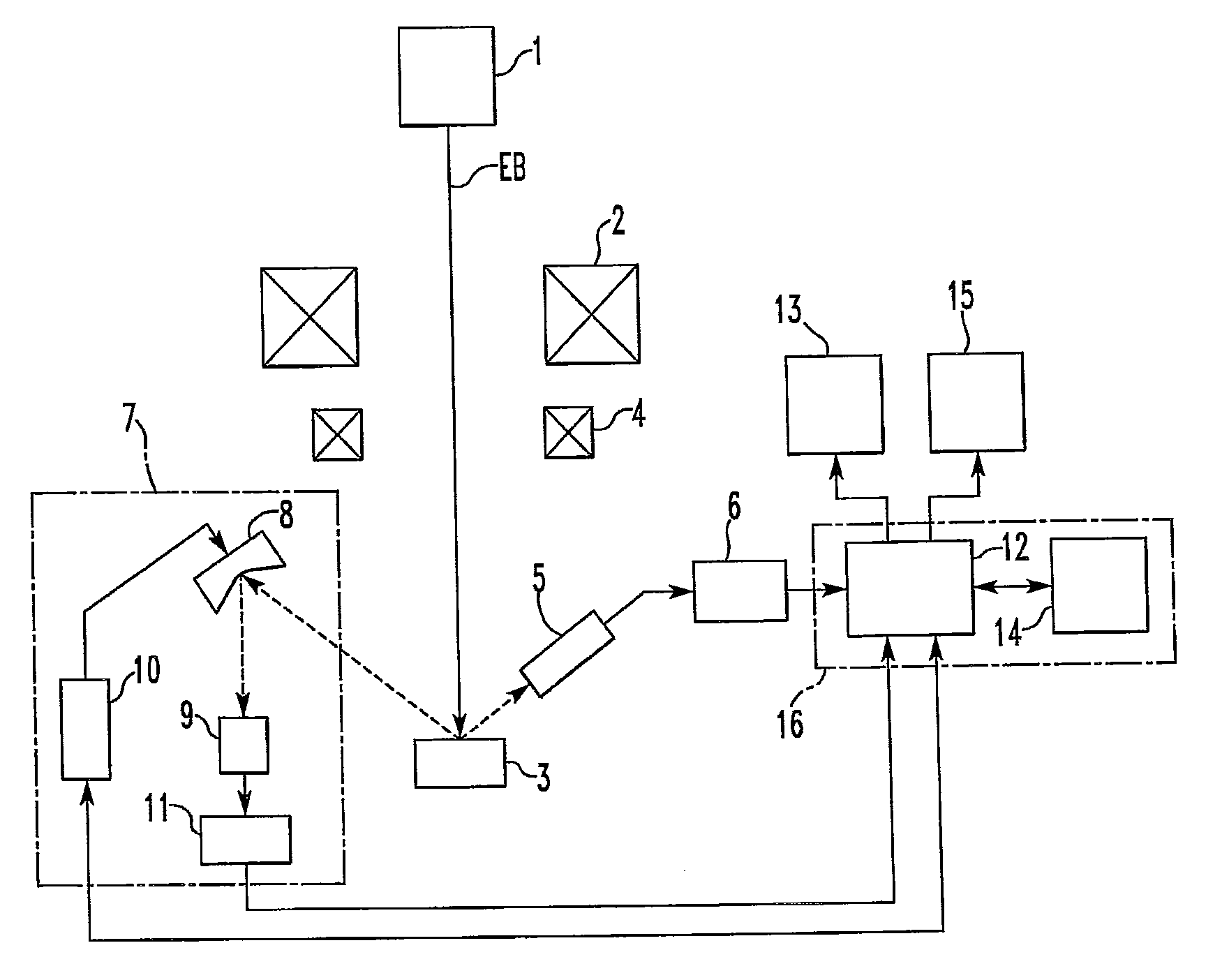
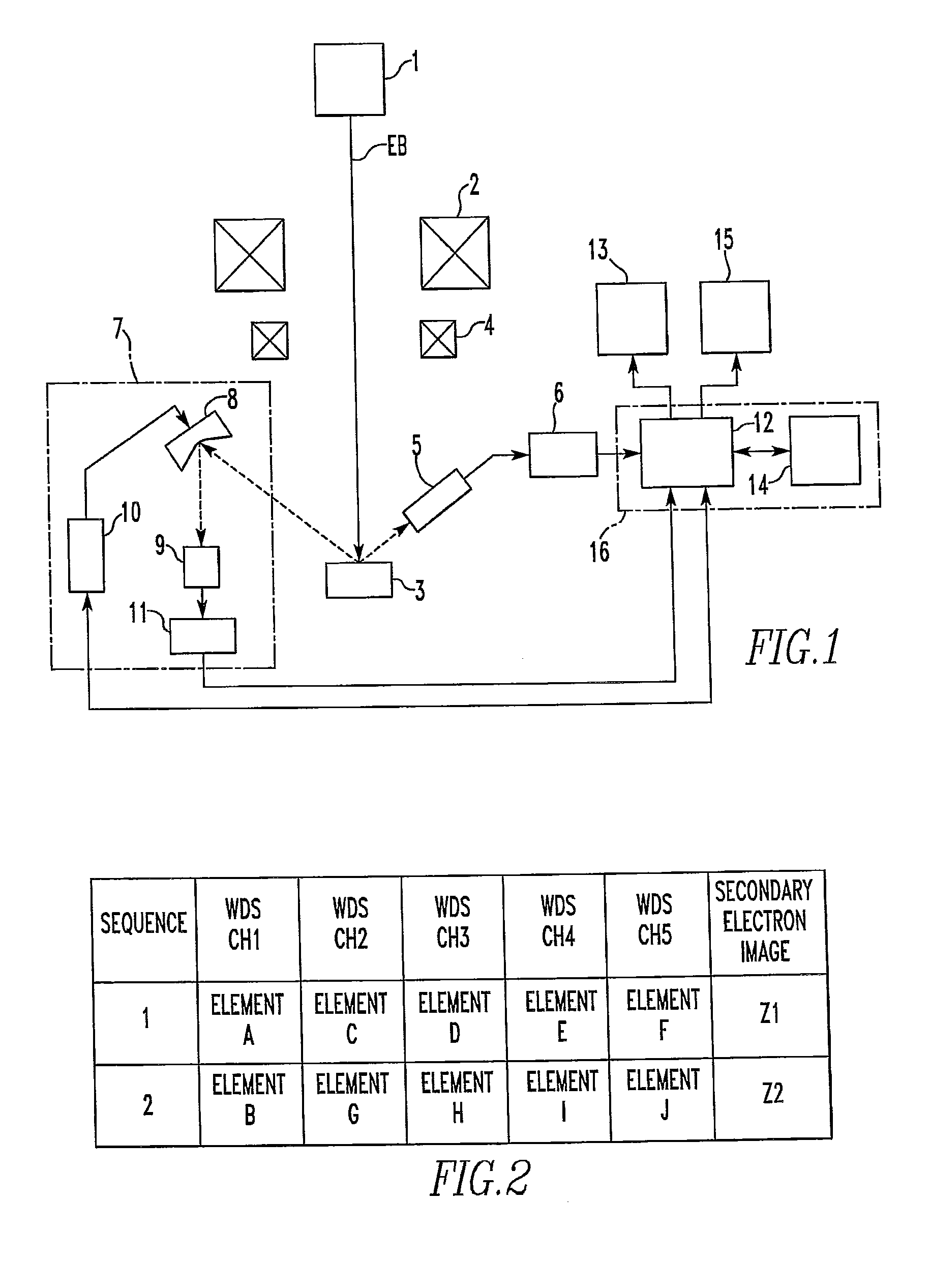
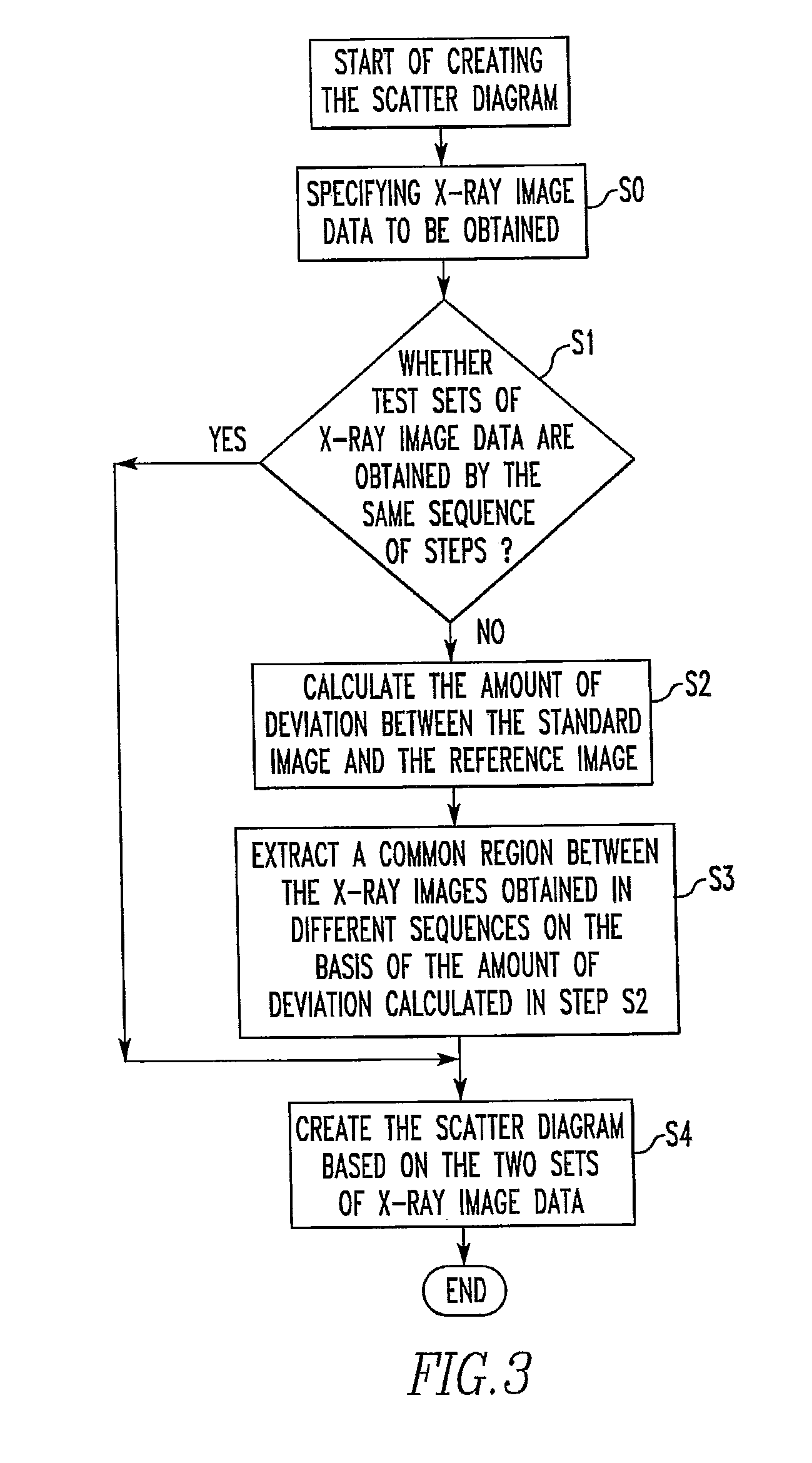
Electron Probe Microanalyzer and Data Processing Method Implemented Therein
ActiveUS20120181425A1Image obtainedLaser detailsPhotoelectric discharge tubesSoft x rayElectron probe microanalysis
In an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) and a method of use thereof, even if plural sets of X-ray image data are obtained at different timings from regions between which a positional deviation occurs, processing for obtaining the correlation is performed precisely. The sets of X-ray image data are obtained from the same region of a sample using the EPMA at different timings and stored in memory along with sets of electron image data based on detection of secondary or backscattered electrons arising from the region. The sets of electron image data obtained at the different timings are compared, and the amount of positional deviation is calculated. An operation for extracting a region common to the regions respectively producing the sets of X-ray image data obtained at the different timings is performed on these sets of X-ray image data based on the calculated amount of positional deviation.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Preparation for inferface composite semi-conductor nano thinfilm optical catalyst
InactiveCN1404919AUniform film surfaceEnhanced light absorptionCatalyst activation/preparationElectron probe microanalysisComposite film
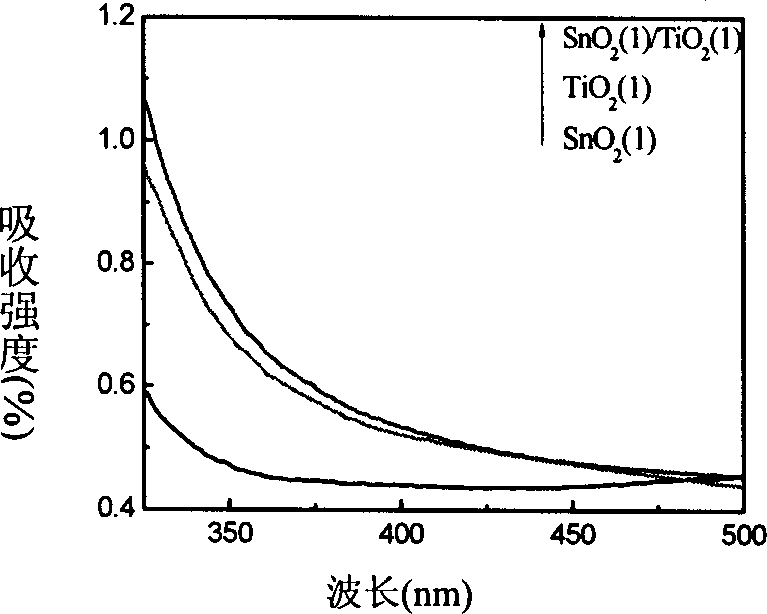
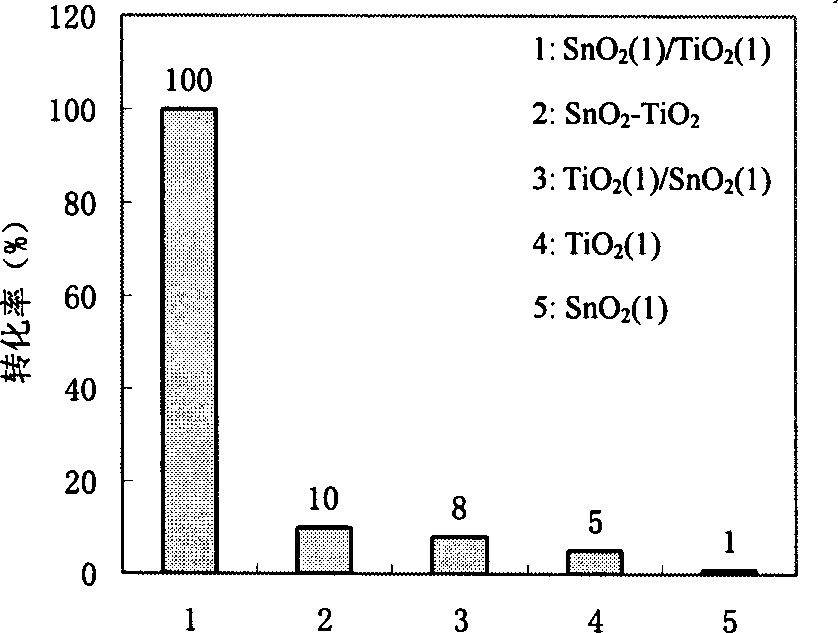
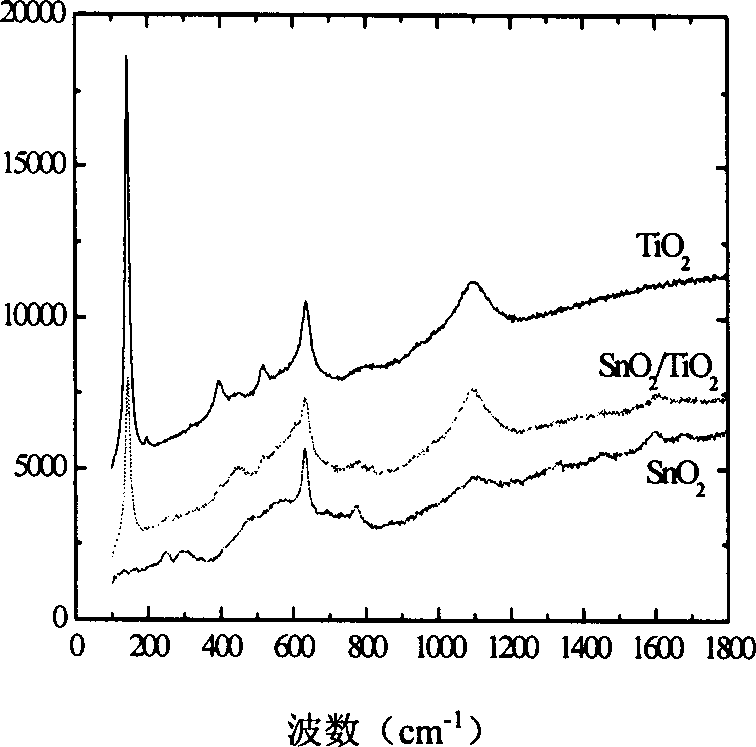
The preparation method of interface composite semiconductor nano film photocatalyst retales to a method for preparing SnO2 / TiO2 interface composite film photocatalyst by using sol-gel method. Said method is characterized by that on the SnO2 film surface formed into crystal phase a TiO2 film is coated to form SnO2 / TiO2 interface composite nano film photocatalyst. Said invention utilizes the scanning electronic microscope, Raman spectrum, UV-visible spectrum and Auger electron microprobe techniques to research its surface form and structure, and utilizes the static photocatalysis estimation device to estimate its activity, and its interface is projected, and its catalytic activity is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Bundled monocapillary optics
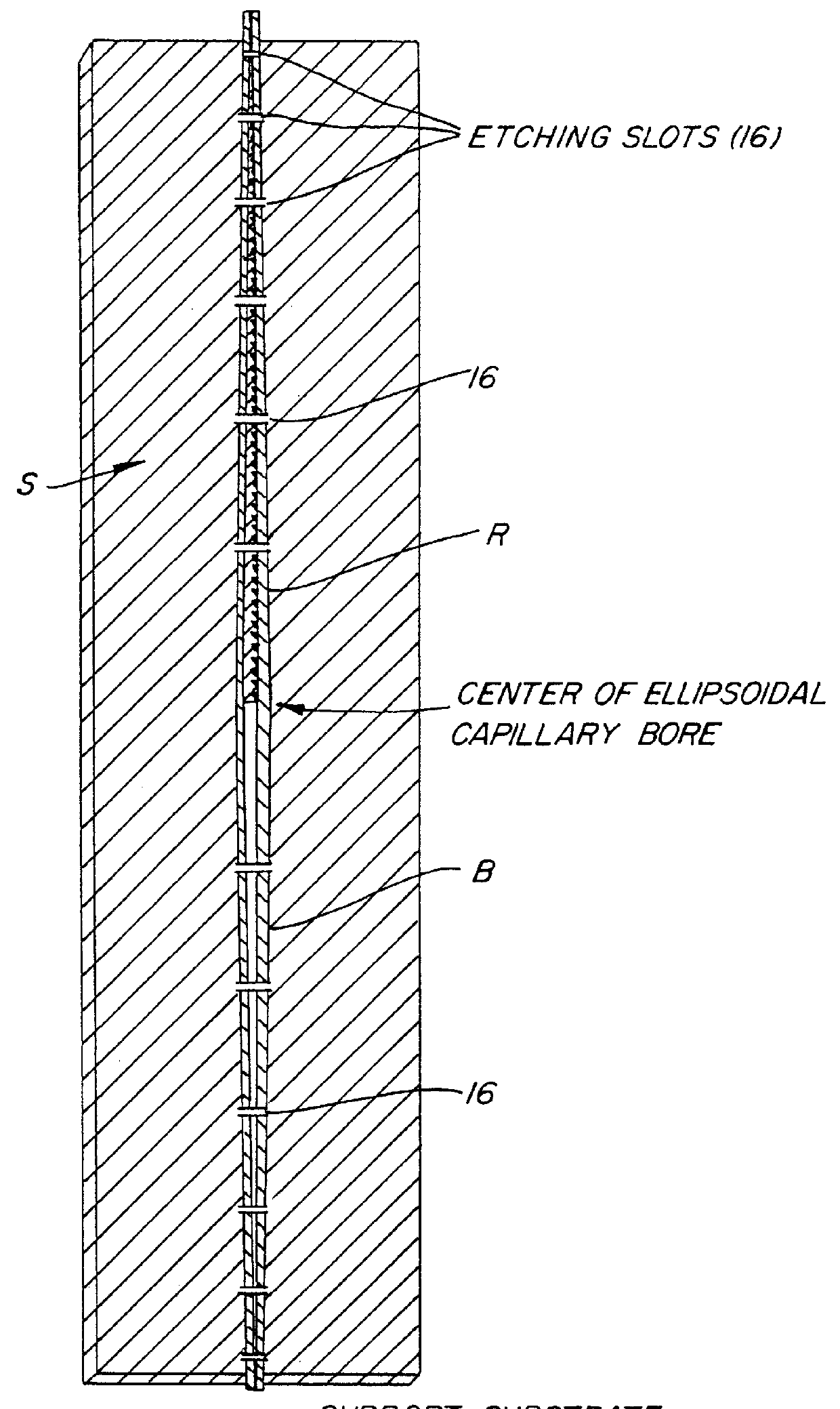
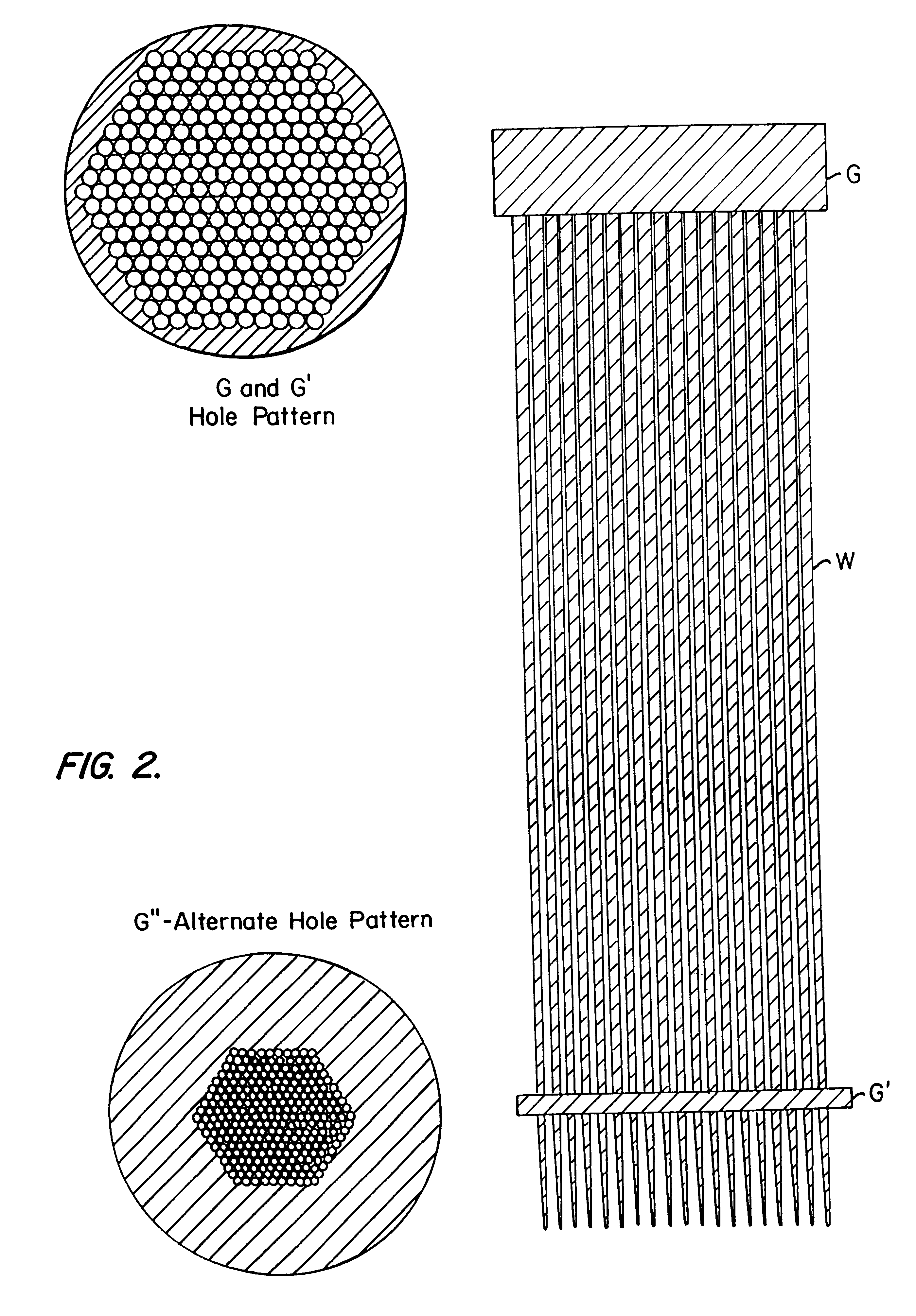
InactiveUS6415086B1Coupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideElectron probe microanalysisEtching
A plurality of glass or metal wires are precisely etched to form the desired shape of the individual channels of the final polycapillary optic. This shape is created by carefully controlling the withdrawal speed of a group of wires from an etchant bath. The etched wires undergo a subsequent operation to create an extremely smooth surface. This surface is coated with a layer of material which is selected to maximize the reflectivity of the radiation being used. This reflective surface may be a single layer of material, or a multilayer coating for optimizing the reflectivity in a narrower wavelength interval. The collection of individual wires is assembled into a close-packed multi-wire bundle, and the wires are bonded together in a manner which preserves the close-pack configuration, irrespective of the local wire diameter. The initial wires are then removed by either a chemical etching procedure or mechanical force. In the case of chemical etching, the bundle is generally segmented by cutting a series of etching slots. Prior to removing the wire, the capillary array is typically bonded to a support substrate. The result of the process is a bundle of precisely oriented radiation-reflecting hollow channels. The capillary optic is used for efficiently collecting and redirecting the radiation from a source of radiation which could be the anode of an x-ray tube, a plasma source, the fluorescent radiation from an electron microprobe, a synchrotron radiation source, a reactor or spallation source of neutrons, or some other source.
Owner:HIRSCH GREGORY
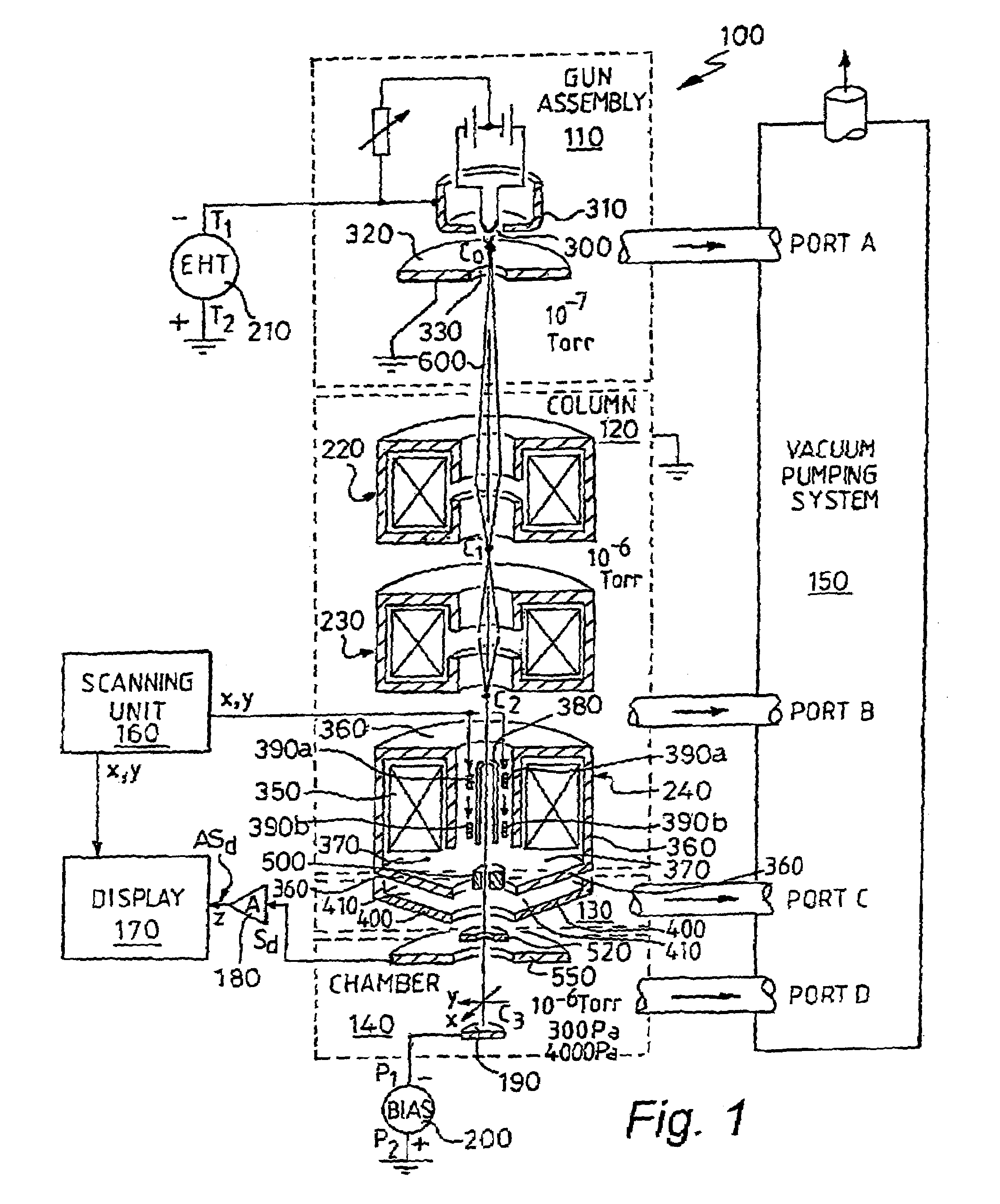
Scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS7186976B2Easy to useMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron probe microanalysisScanning tunneling microscope
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT LTD
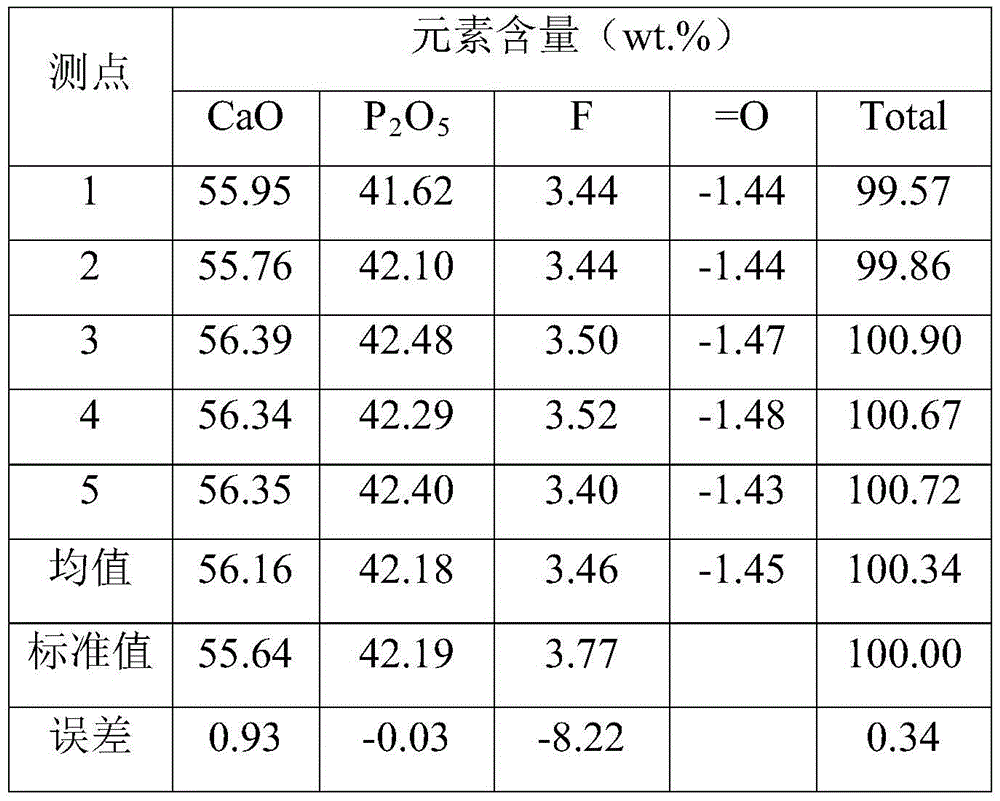
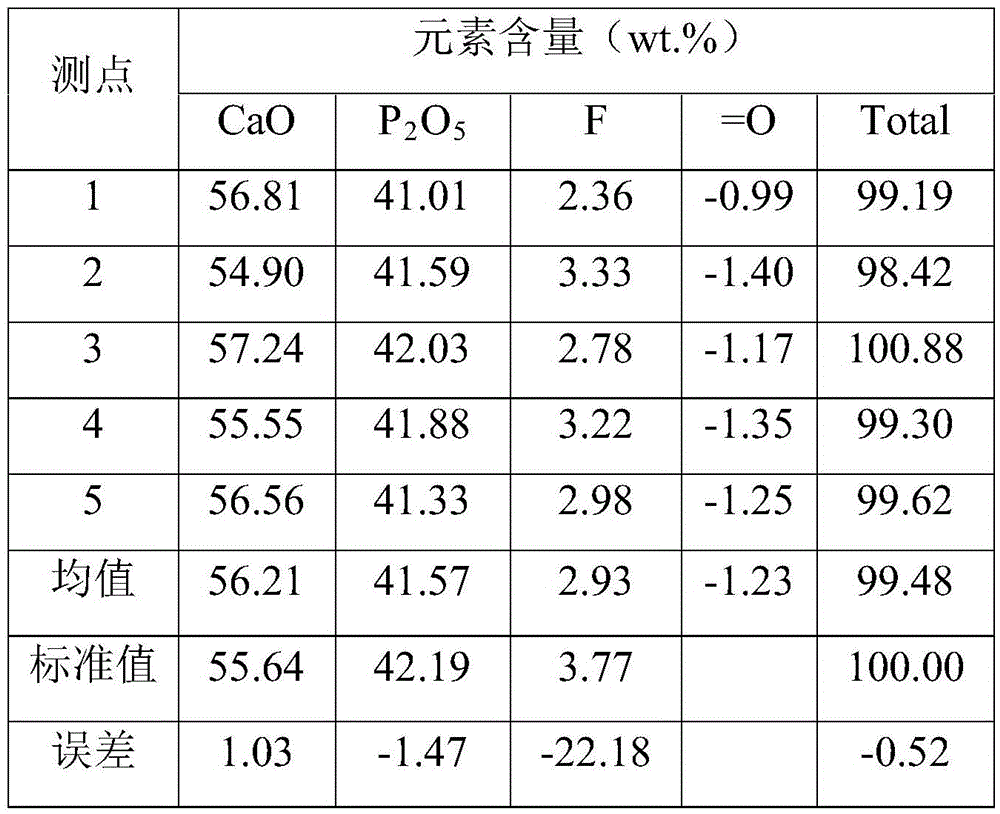
Electronic probe quantitative analysis method for testing content of F in natural ore
InactiveCN106841263ABest Analytical Test ConditionsAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisInterference factor
The invention belongs to the technical field of F-element micro-cell in-situ testing, and in particular discloses an electronic probe quantitative analysis method for testing content of F in natural ore. The electronic probe quantitative analysis method comprises the following steps: grinding a natural ore sample into a sample to be tested, and coating the sample to be tested and a standard sample with carbon; checking and confirming F-containing ore to be tested according to an X-ray energy spectrum; sequentially measuring counting strength of the standard sample and counting strength of the F-containing ore to be tested under same quantitative analysis conditions; comparing and analyzing the counting strength of the standard sample and the counting strength of the F-containing ore to be tested, and modifying comparison and analysis results, thereby obtaining the content of the element F. By adopting the electronic probe quantitative analysis method, interference factors in the testing process are eliminated to the maximum extent, optimal electronic probe analysis testing conditions are confirmed, and the purpose of accurately testing the content of the element F in the natural ore in a microcosmic scale is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Synthesized hybrid rock composition, method, and article formed by the method
ActiveUS7704907B2Zero open porosityLess porousSolid waste managementTransportation and packagingPorosityElectron probe microanalysis
The invention relates to synthetic hybrid rock compositions, articles of manufacture and related processes employing mineral waste starting materials such as mine tailings, mine development rock, ash, slag, quarry fines, and slimes, to produce valuable articles of manufacture and products, which are characterized by superior physical and structural characteristics, including low porosity, low absorption, increased strength and durability, and retained plasticity. The resulting materials are compositionally and chemically distinct from conventional synthetic rock materials as demonstrated by scanning electron microprobe analysis, and are useful in a wide variety of applications, particularly with respect to commercial and residential construction.
Owner:CERAMEXT LLC
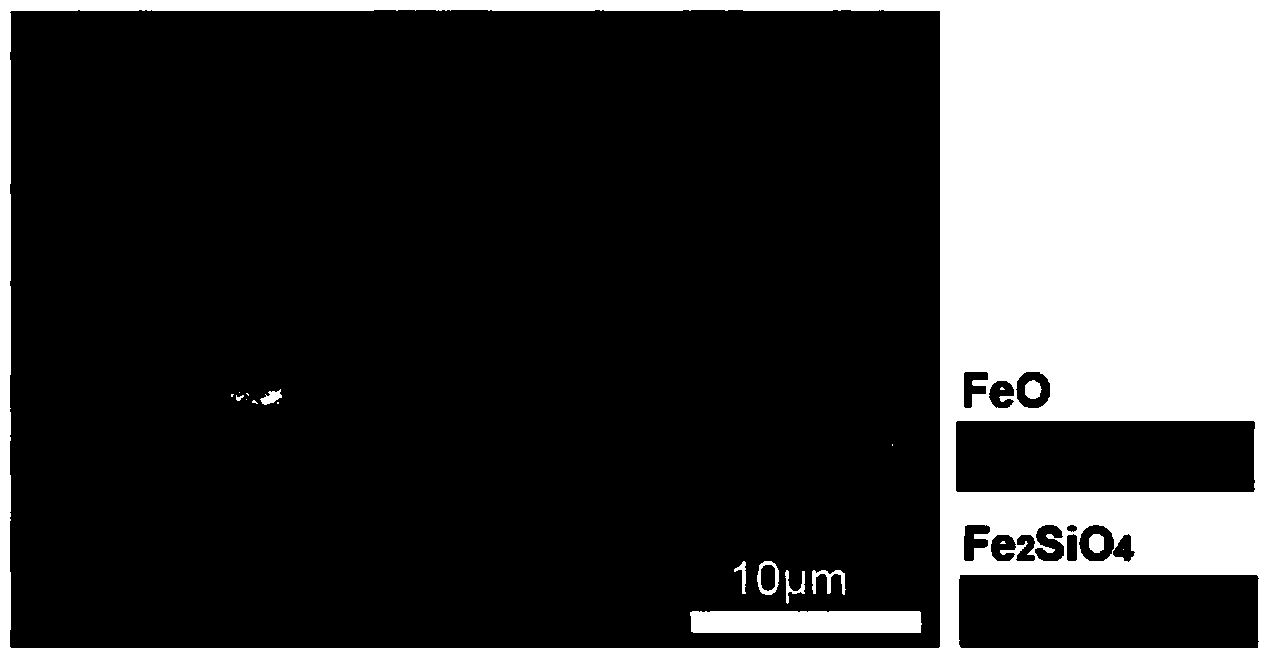
Characterization method for distinguishing multi-phase sinter in hot-rolled silicon steel
InactiveCN103969277ASolve hard-to-identify puzzlesThe analysis result is accurateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisElectron
The invention relates to a characterization method for distinguishing multi-phase sinter in hot-rolled silicon steel, and belongs to the technical field of status analysis of steel and iron materials. The method adopts an electron probe and an EBSD (electron backscatter diffraction) device arranged on a scanning electronic microscope for micro-structural characterization on four phases of Fe2O3, Fe3O4, FeO and Fe2SiO4 on the surface of the polished hot-rolled silicon steel. The method comprises the following steps: according to the diversities of L Beta / L Alpha peak intensity ratios of the Fe elements in different valence states, through the adoption of the status analysis of the electron probe to resolve three typical oxides of Fe, and the use of the middle-phase resolution function of the EBSD technology to distinguish Fe2SiO4, the in-depth research on the microstructures of the sinter containing different phases is carried out in order to eventually realize the comprehensive characterization of the multi-phase sinter.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
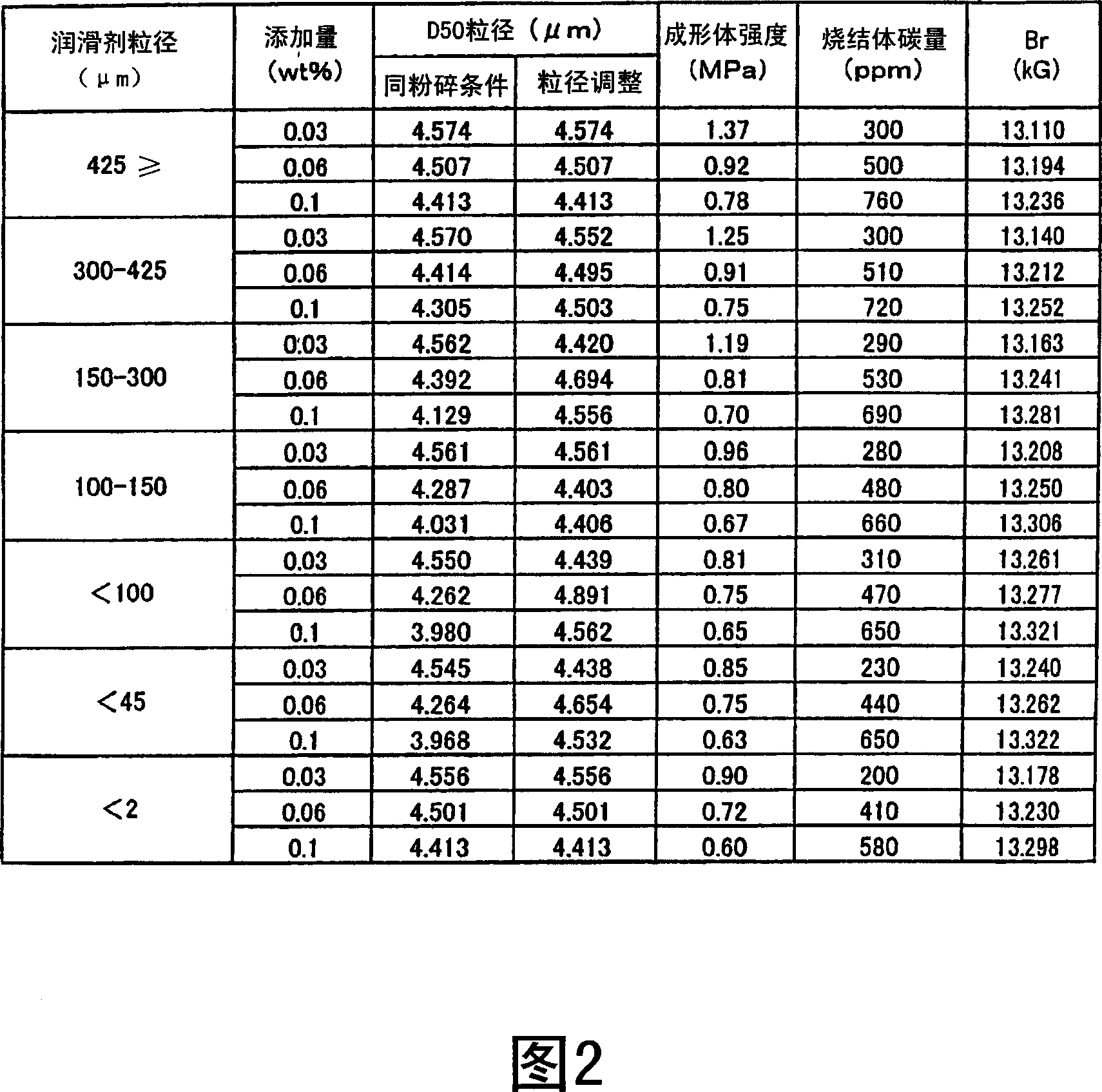
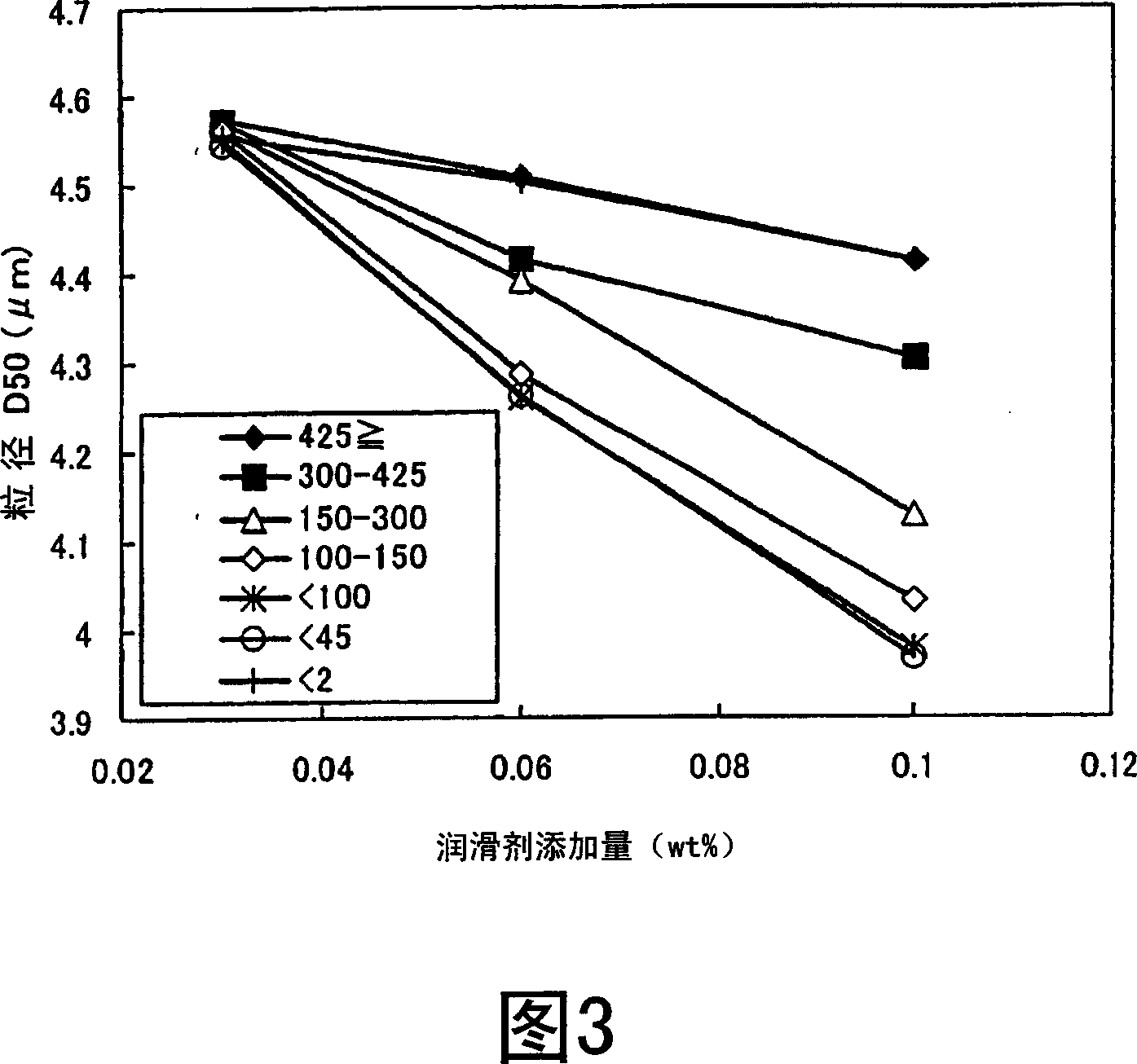
Rare earth sintered magnet, raw material alloy powder for rare earth sintered magnet, and process for producing rare earth sintered magnet
ActiveCN1947208AHigh magnetic flux densityEasy to useTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusElectron probe microanalysisX-ray
A rare earth sintered magnet that realizes a high remanent flux density without detriment to coercive force and mechanical strength. There is provided a rare earth sintered magnet comprised of a sintered body whose carbon content determined by mass spectrometry is in the range of 500 to 1500 ppm, and wherein the cv-value of carbon content at a rupture plane thereof is = 200. This rare earth sintered magnet can be produced through the step of performing, in a magnetic field, pressure molding of a raw material alloy powder whose carbon content determined by mass spectrometry is = 1200 ppm and wherein providing that with respect to the characteristic X-rays of carbon determined by EPMA (Electron Probe Micro Analyzer), Cmax refers to the maximum value of X-ray intensity while Cmin refers to the minimum value of X-ray intensity, the ratio of Cmax / Cmin is = 15 to thereby obtain a molding, and the step of sintering the molding.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
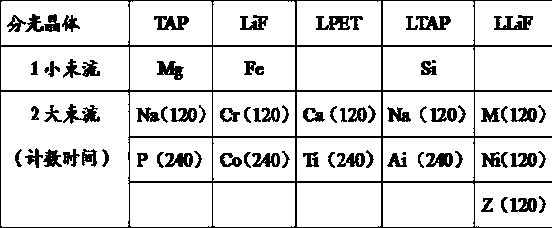
Method for high-precision analysis on trace elements of olivine
InactiveCN107796841AHigh resolutionSatisfy the high rate of variabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron probe microanalysisTrace element
The invention relates to a method for high-precision analysis on trace elements of olivine. The elements of olivine are analyzed by using an electronic probe. The method is characterized in that highacceleration voltage is supplied to the electronic probe; when main elements of the olivine are analyzed, small-beam current is supplied to the electronic probe; when trace elements of the olivine areanalyzed, large-beam current is supplied to the electronic probe; the electronic probe is equipped with five spectrometers. Under an abnormal experiment condition that high-acceleration voltage, small-beam current and large-beam current are combined, the detection limit of specific elements is optimized to a grade of 10ppm to several ppm, and requirements of high resolution and high precision analysis on trace elements on olivine are completely met.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150349329A1Improve the immunityDissatisfactory in output characteristicsFinal product manufactureConductive materialLithium iron phosphateConductive materials
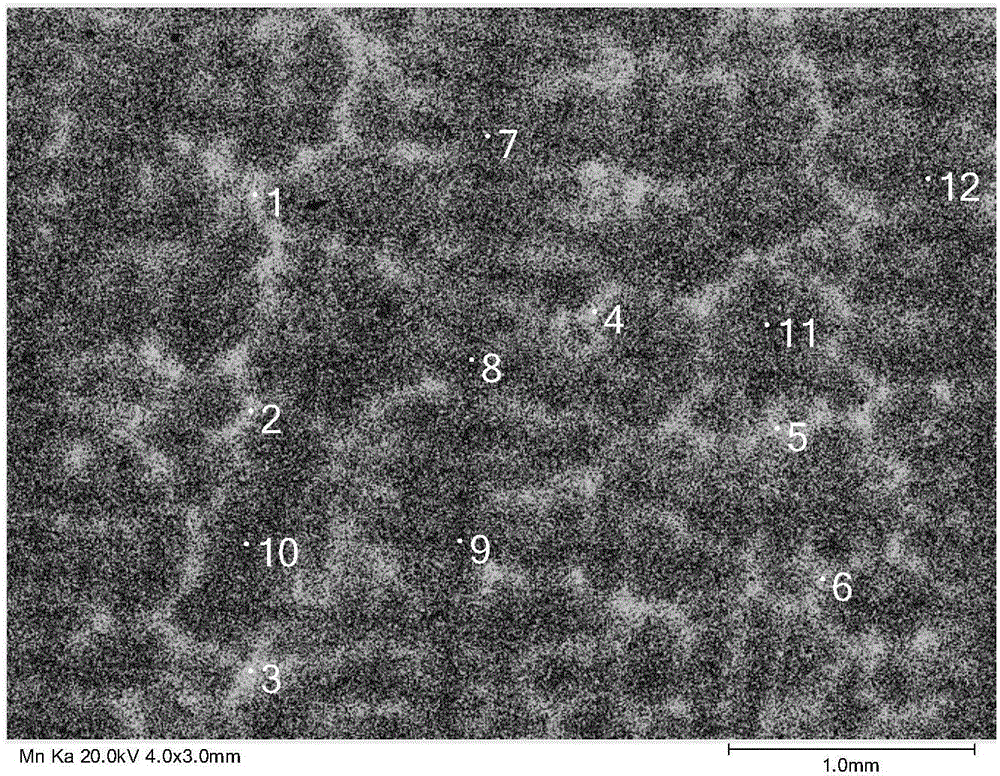
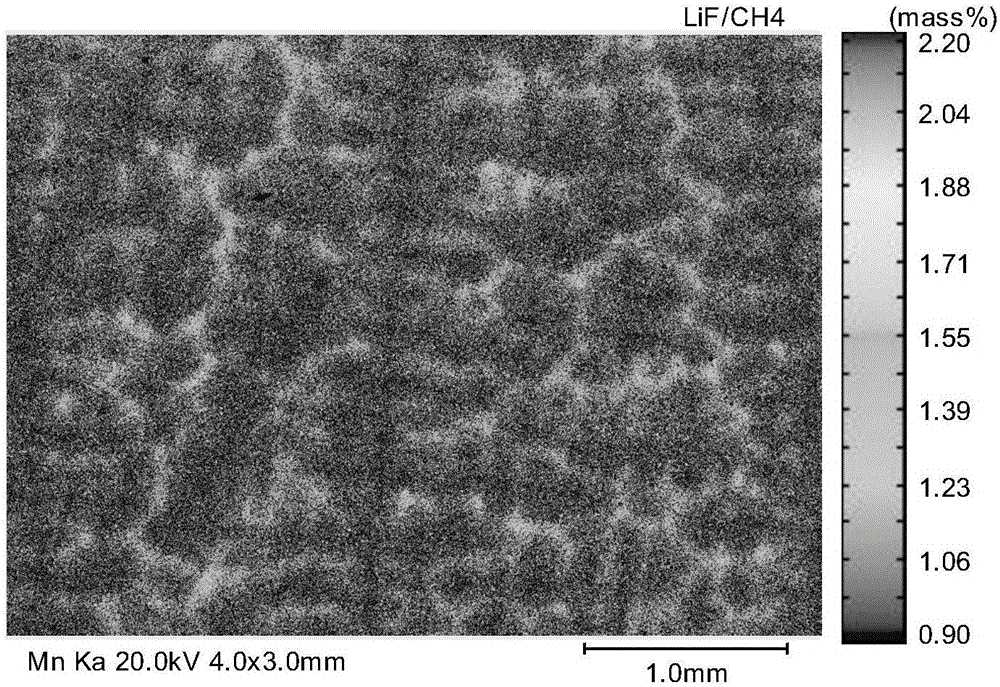
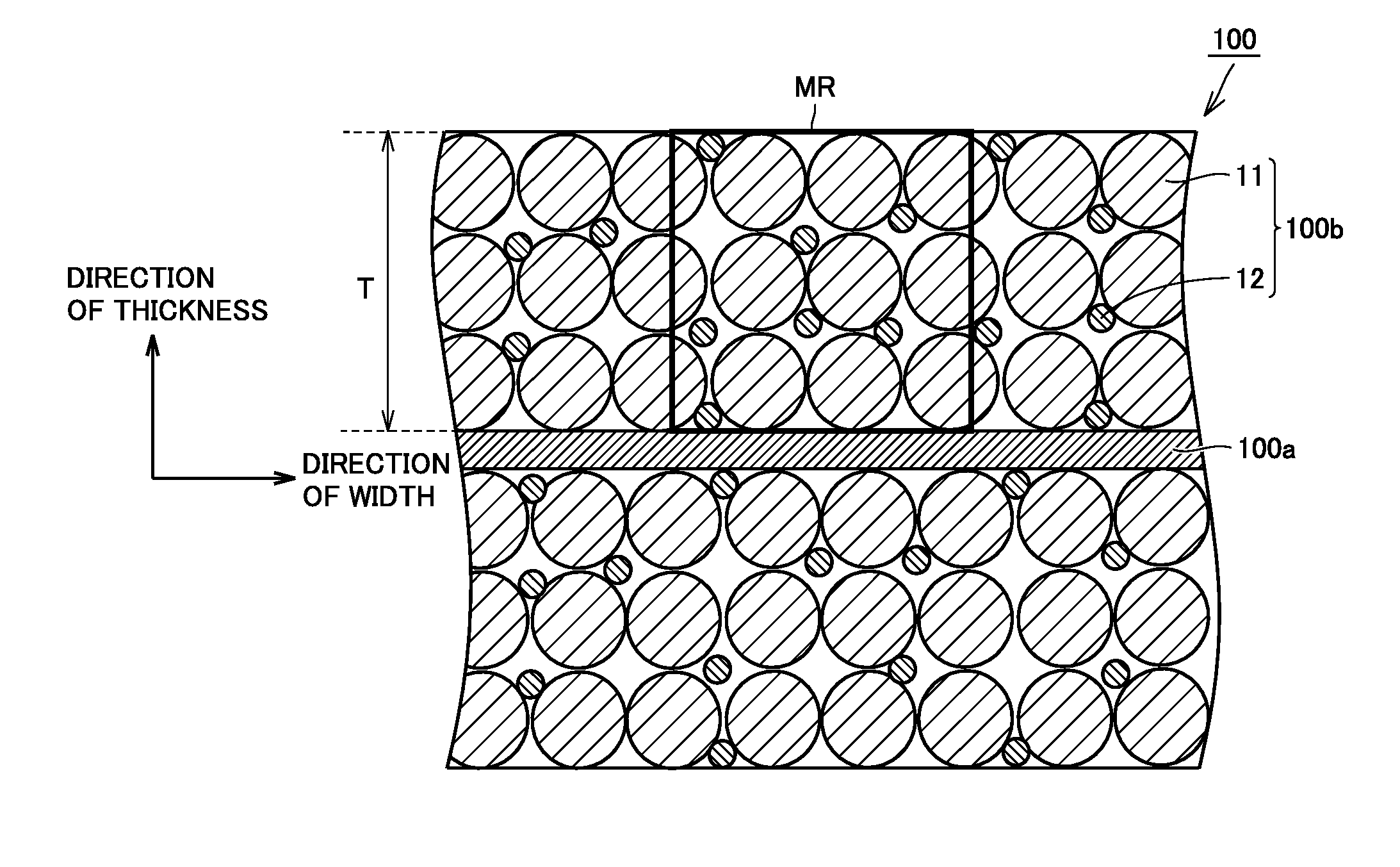
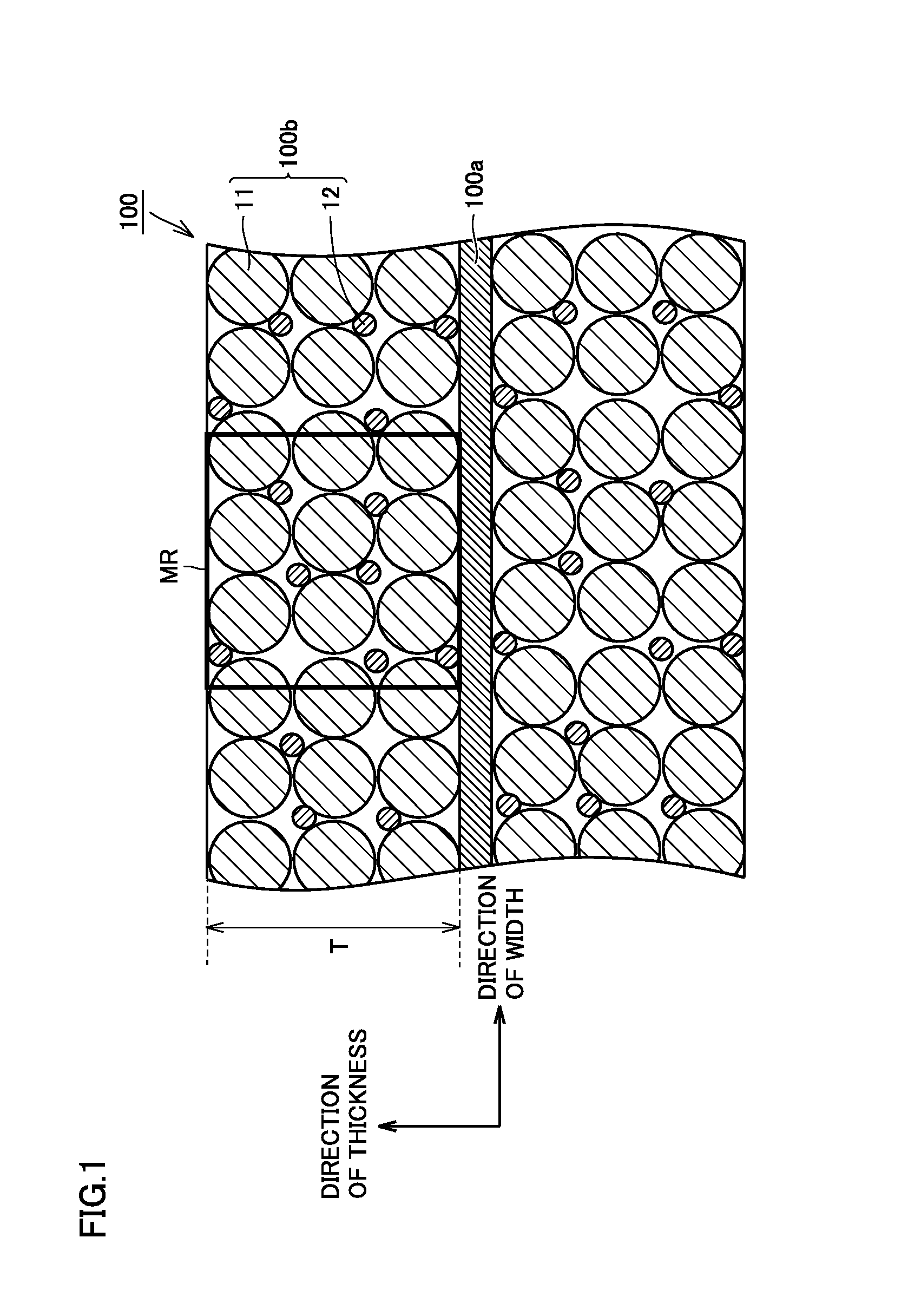
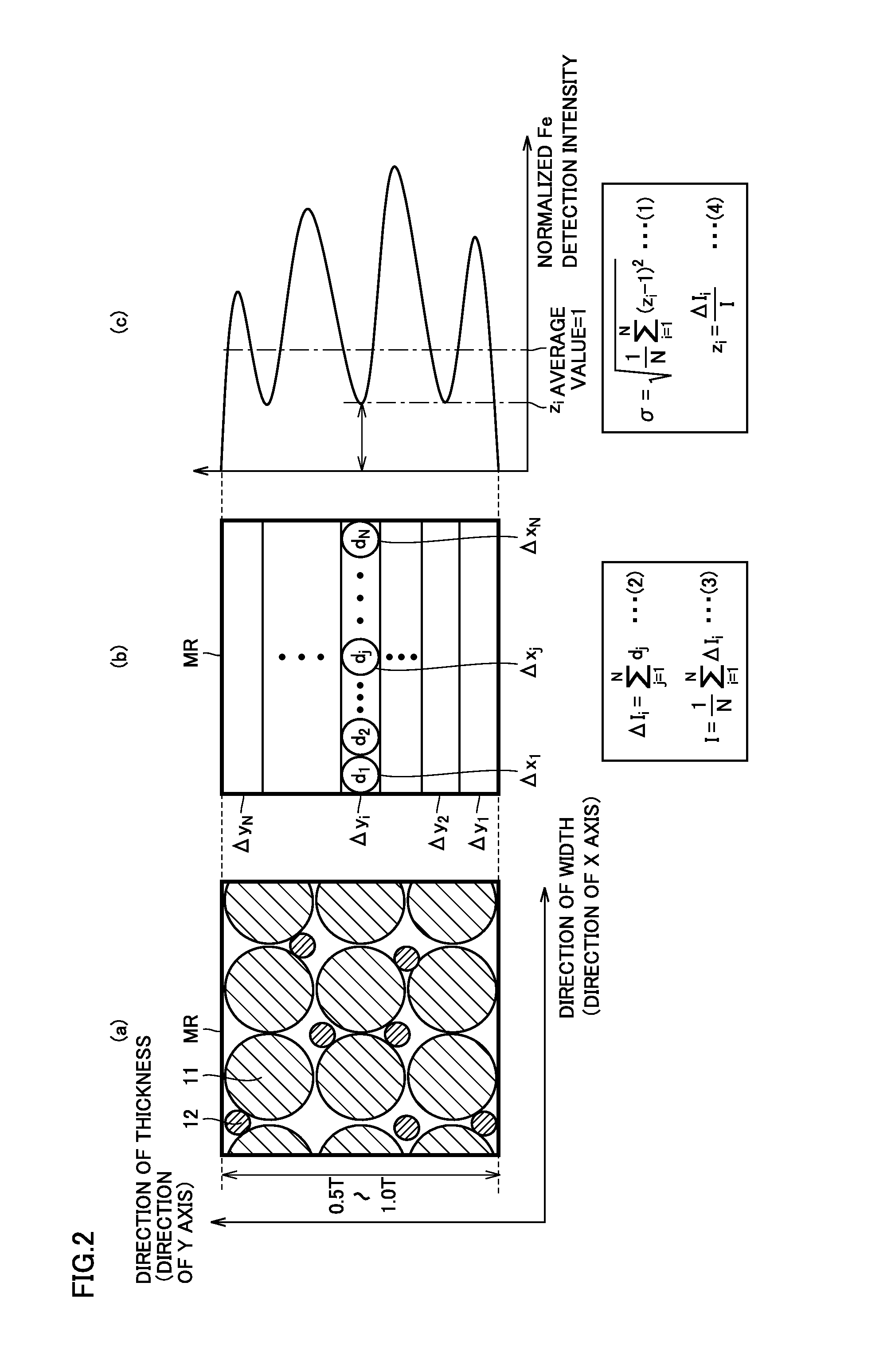
A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery includes a positive electrode composite material layer containing first positive electrode active material particles containing a lithium nickel composite oxide, second positive electrode active material particles containing lithium iron phosphate, and a conductive material. A ratio of the second positive electrode active material particles in a total mass of the first positive electrode active material particles and the second positive electrode active material particles is not lower than 5 mass % and not higher than 20 mass %. A standard deviation σ representing distribution of an iron element satisfies a condition of 0.28≦σ≦0.52 when distribution of the iron element is determined by conducting area analysis with an electron probe microanalyzer in a cross-section of the positive electrode composite material layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com