Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86results about How to "Reduce electrical impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
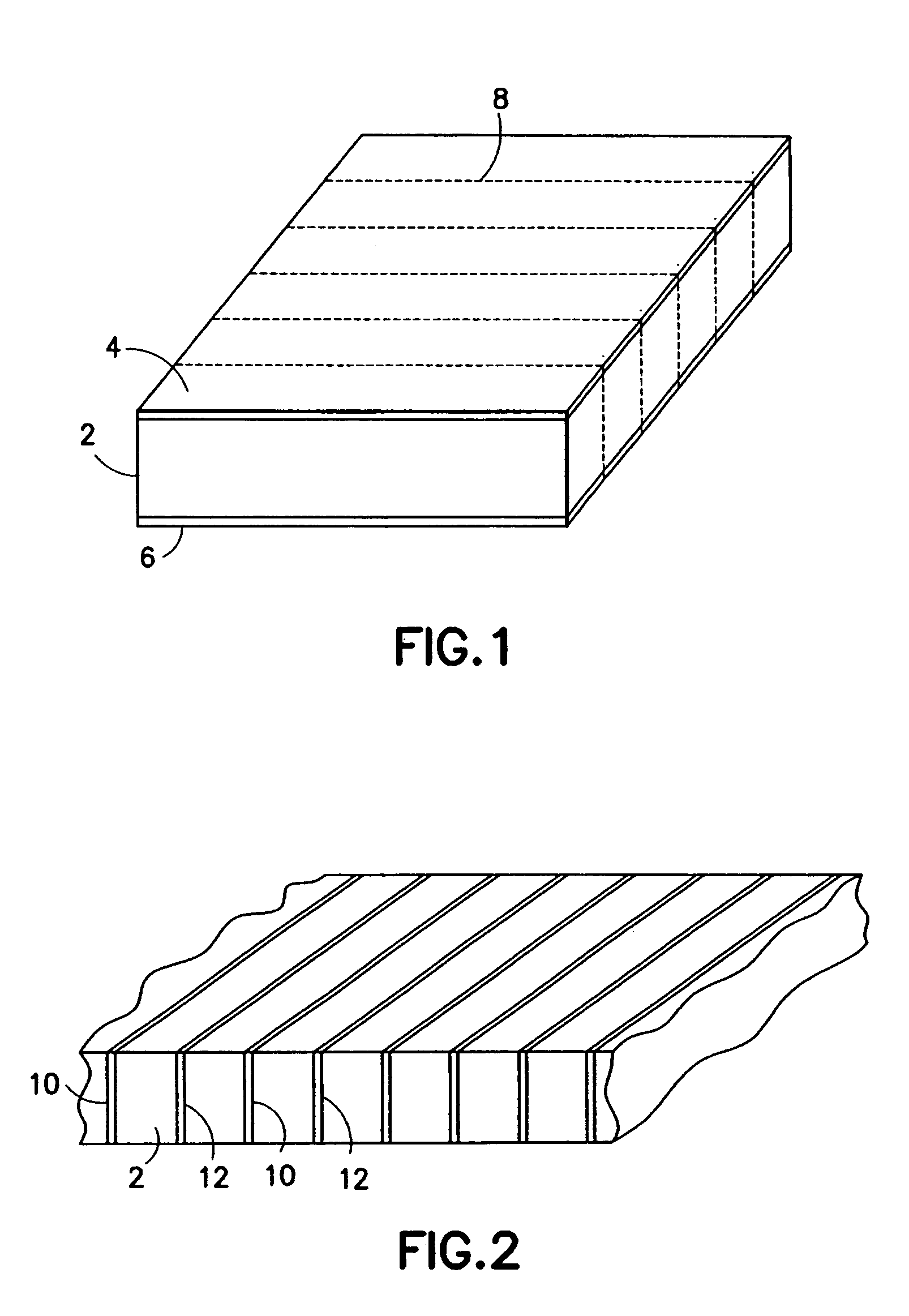
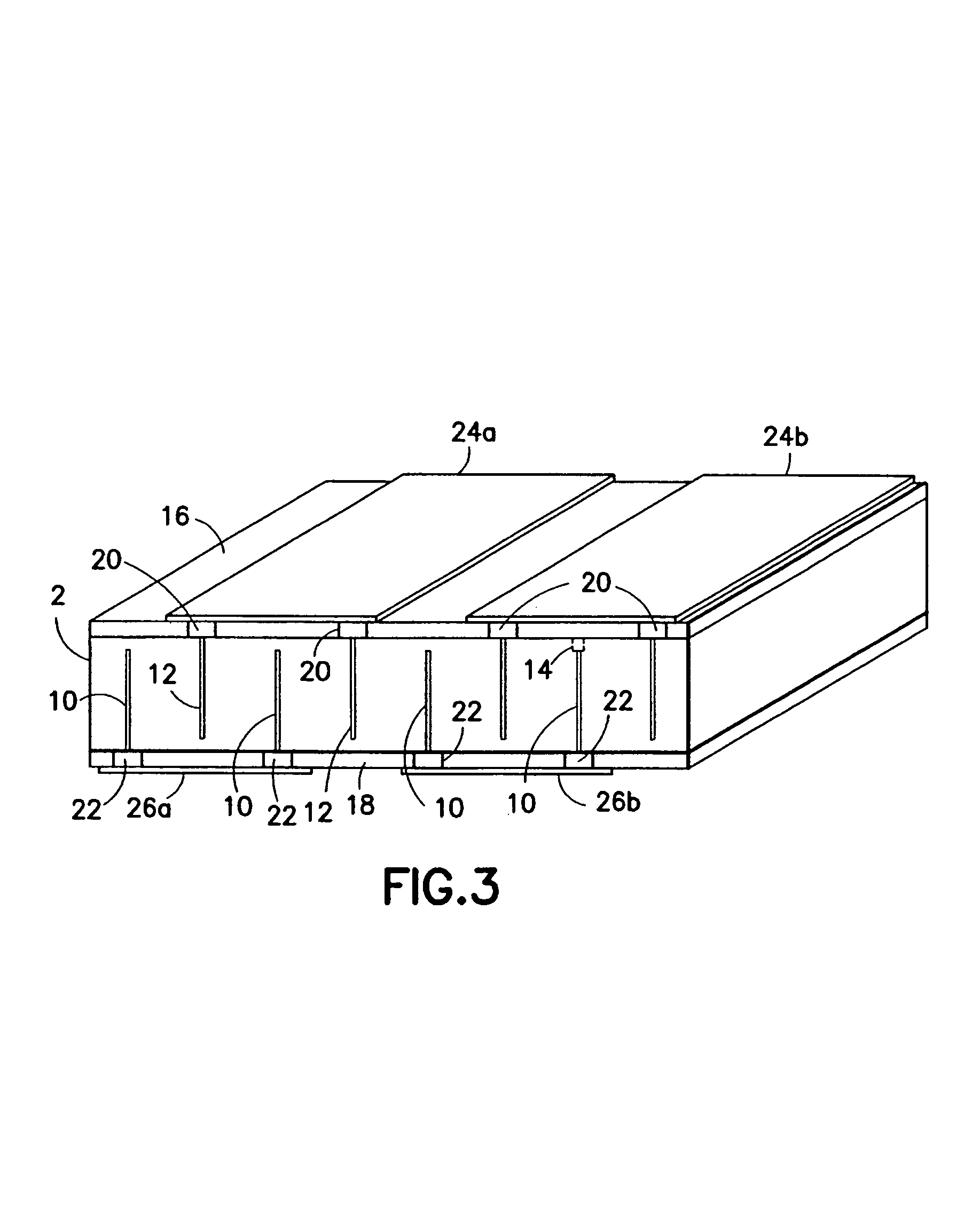
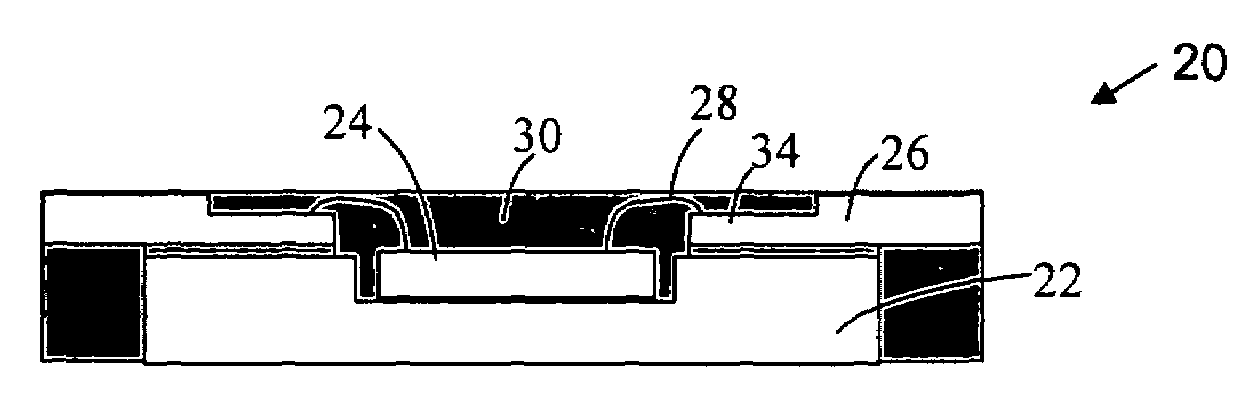
Preparation for transmission and reception of electrical signals
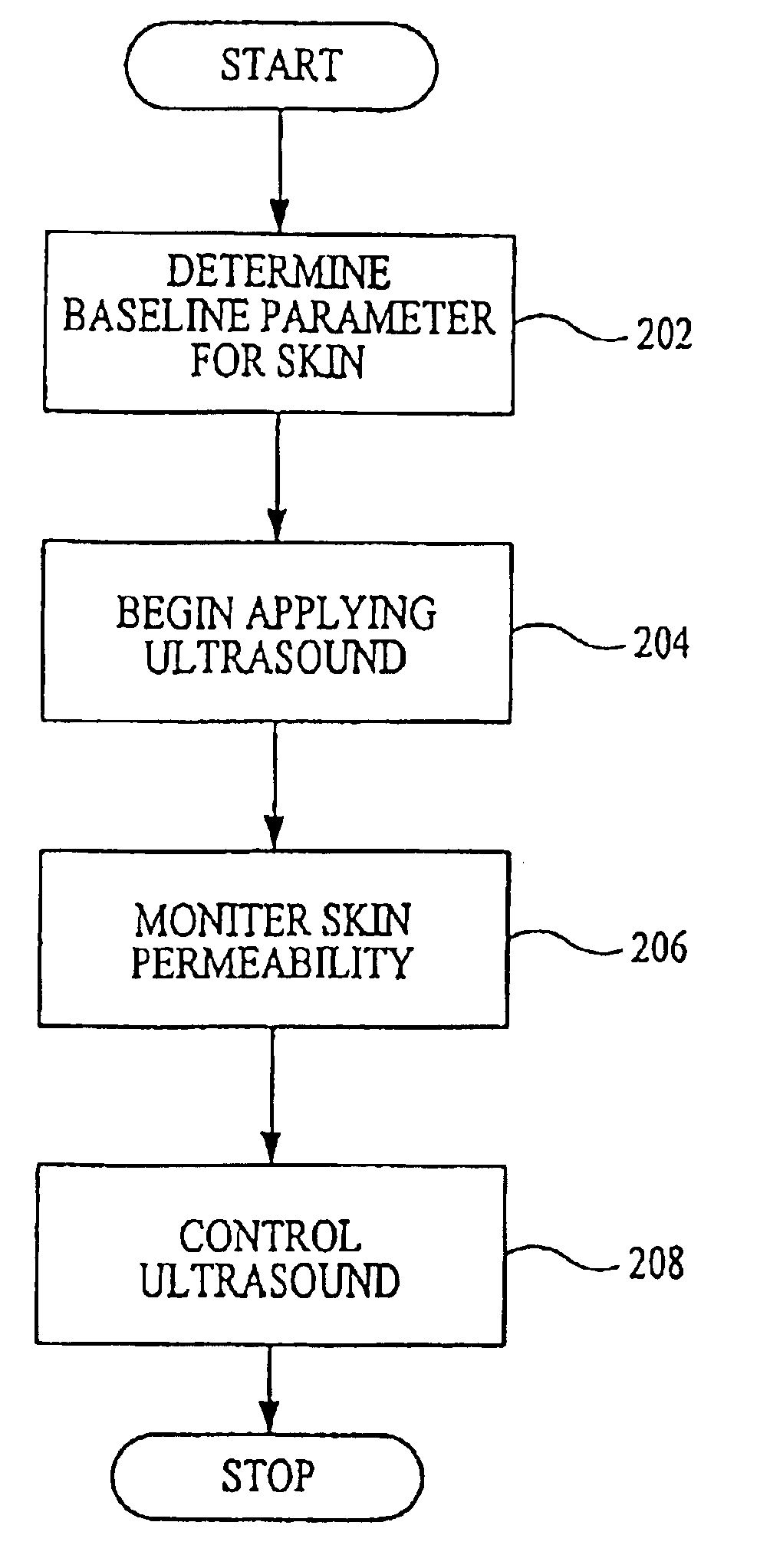
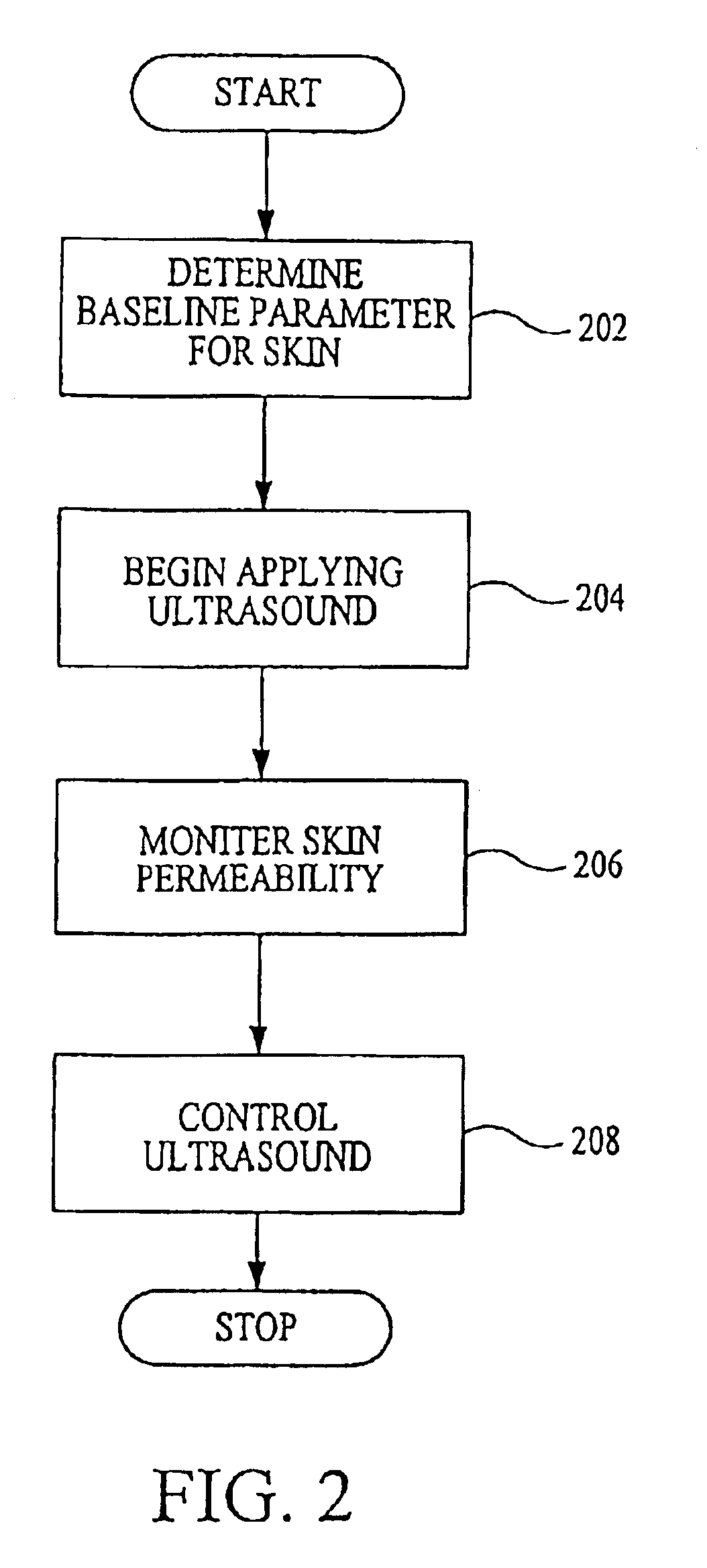
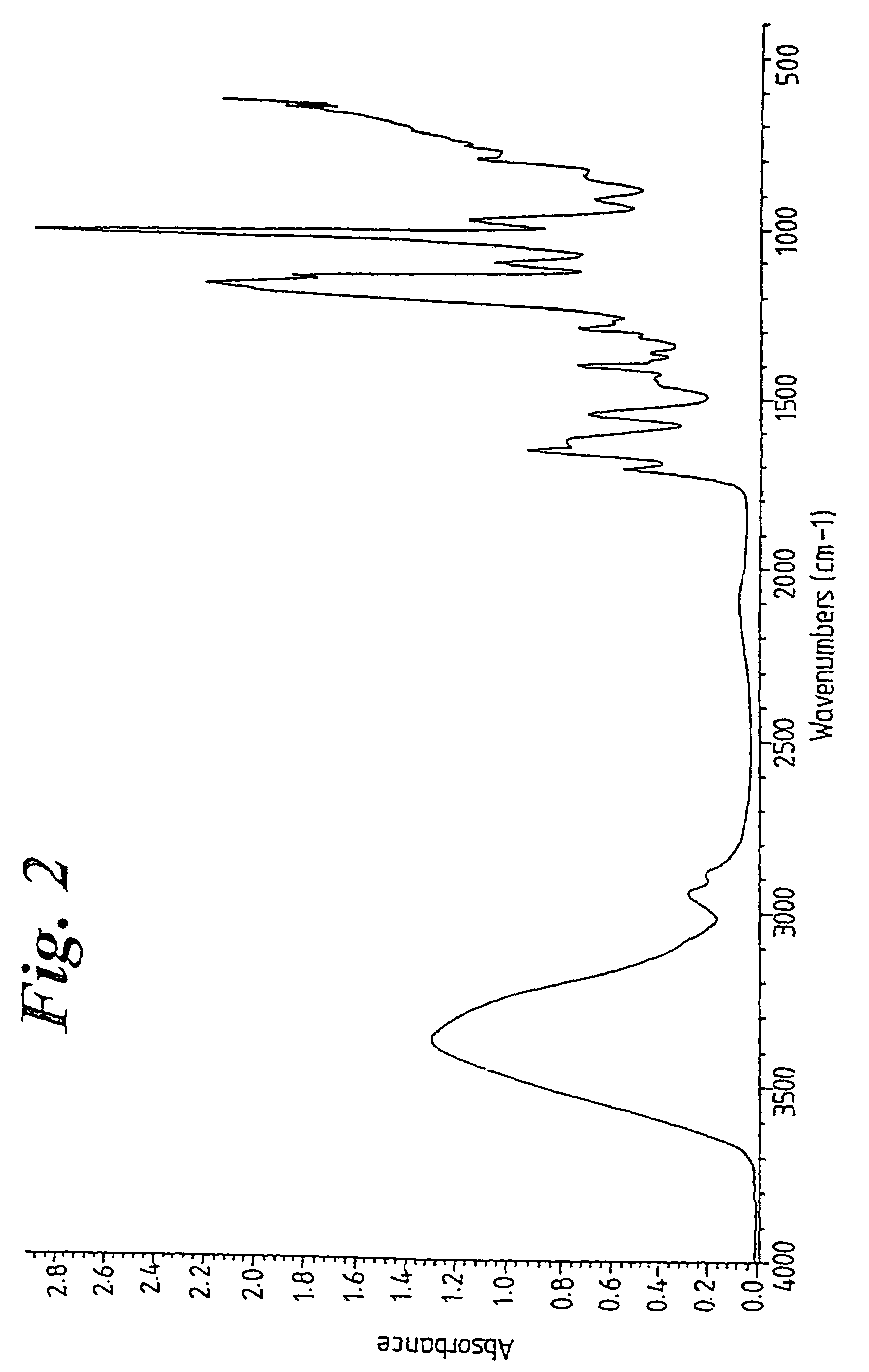
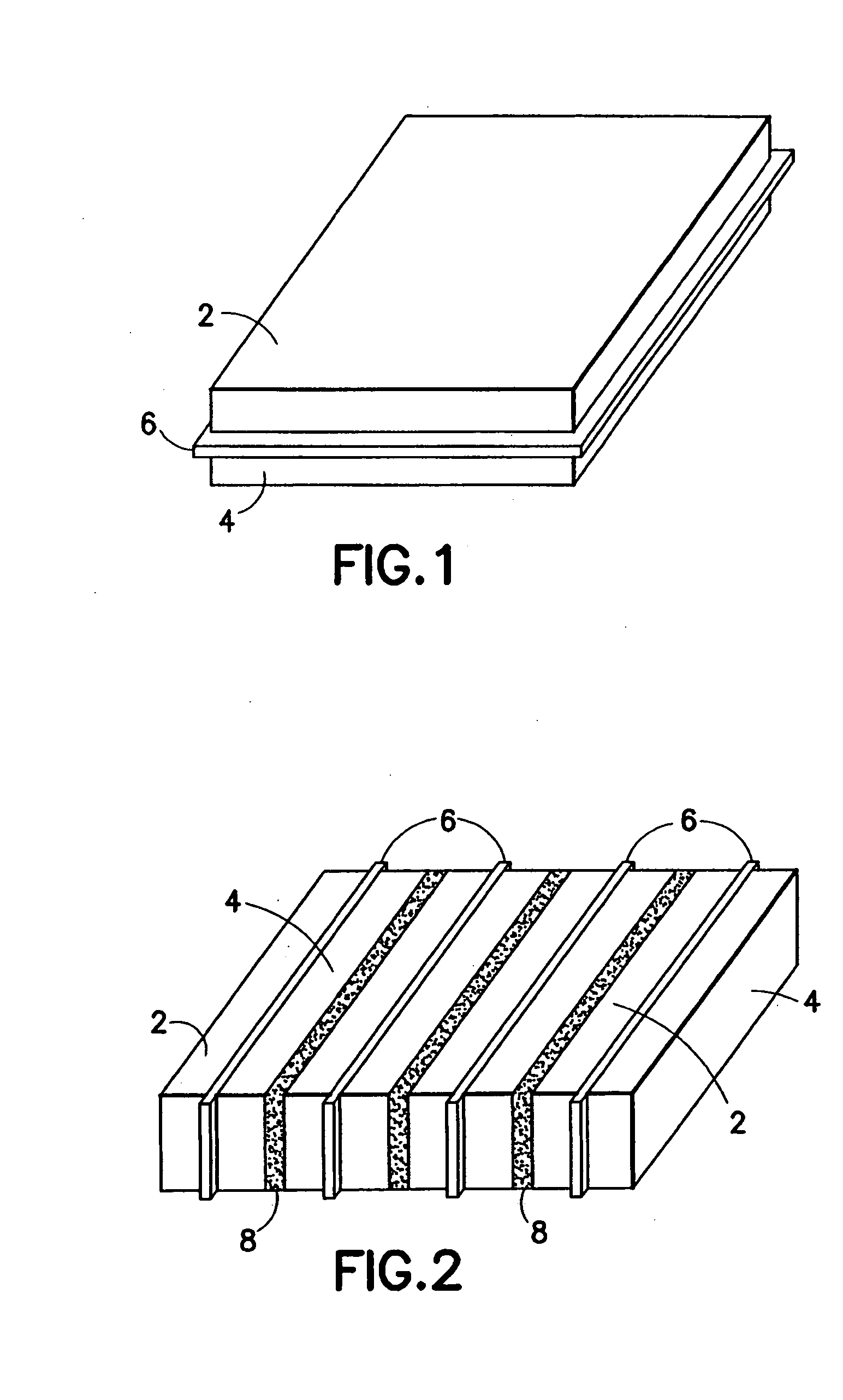
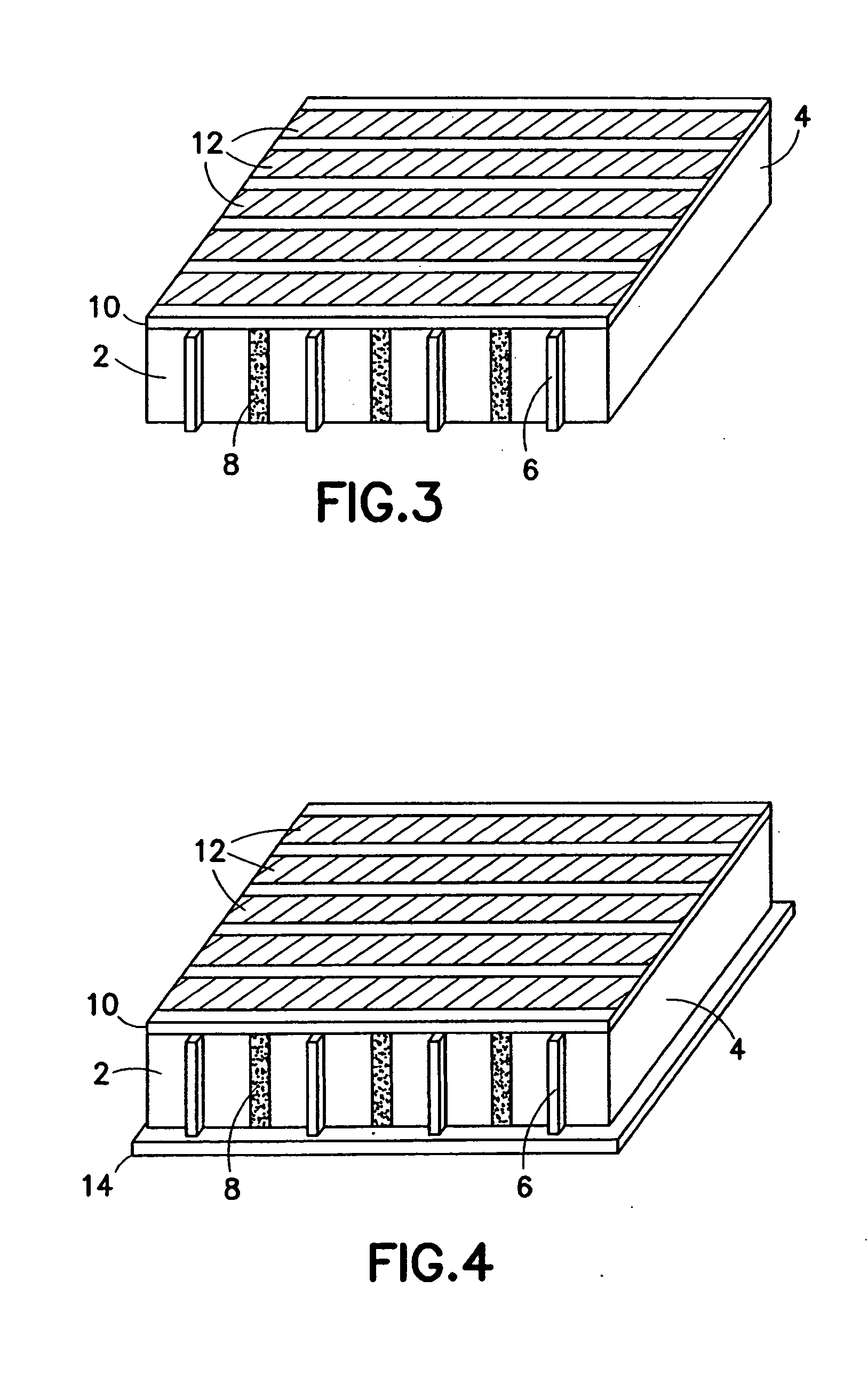
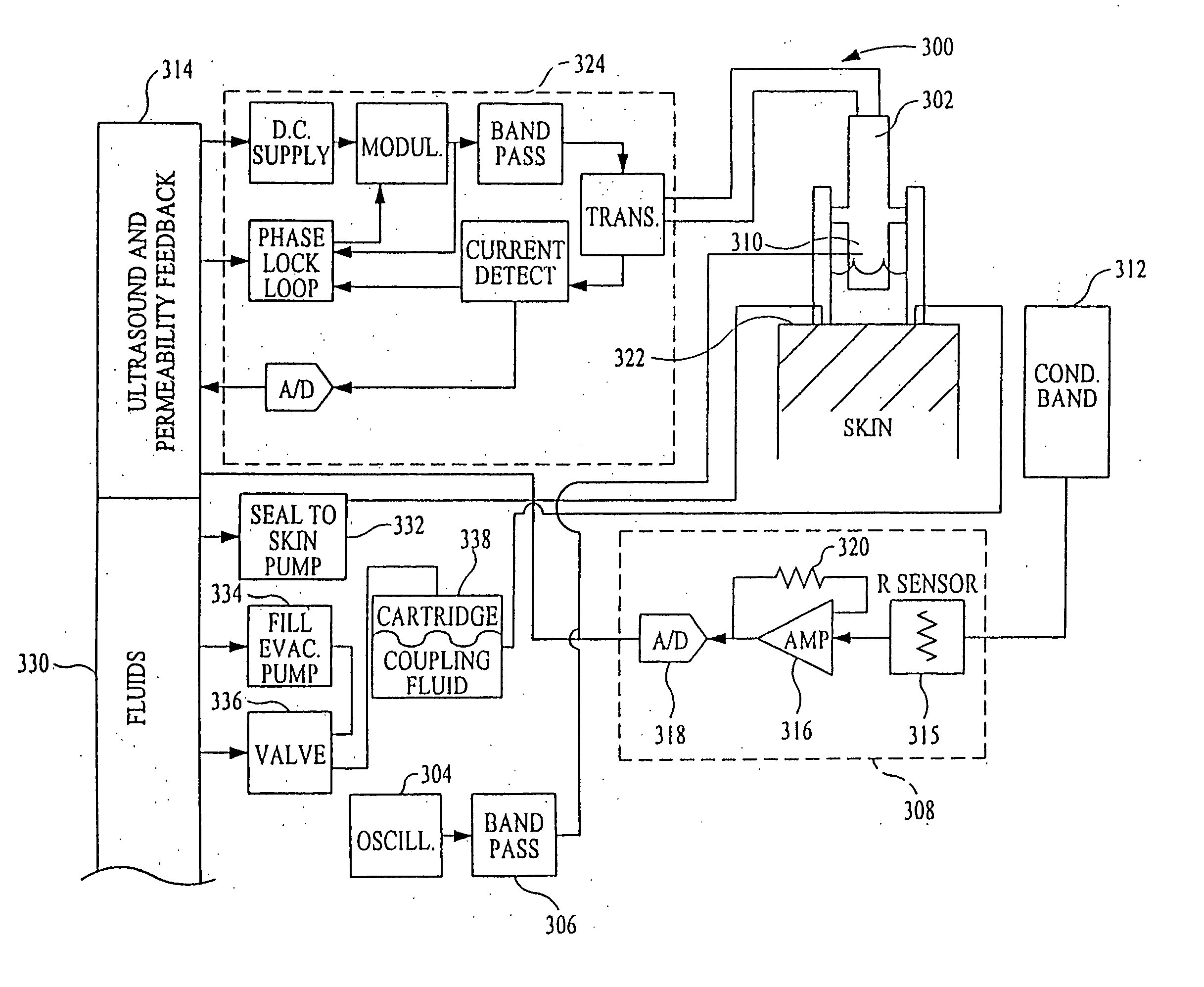
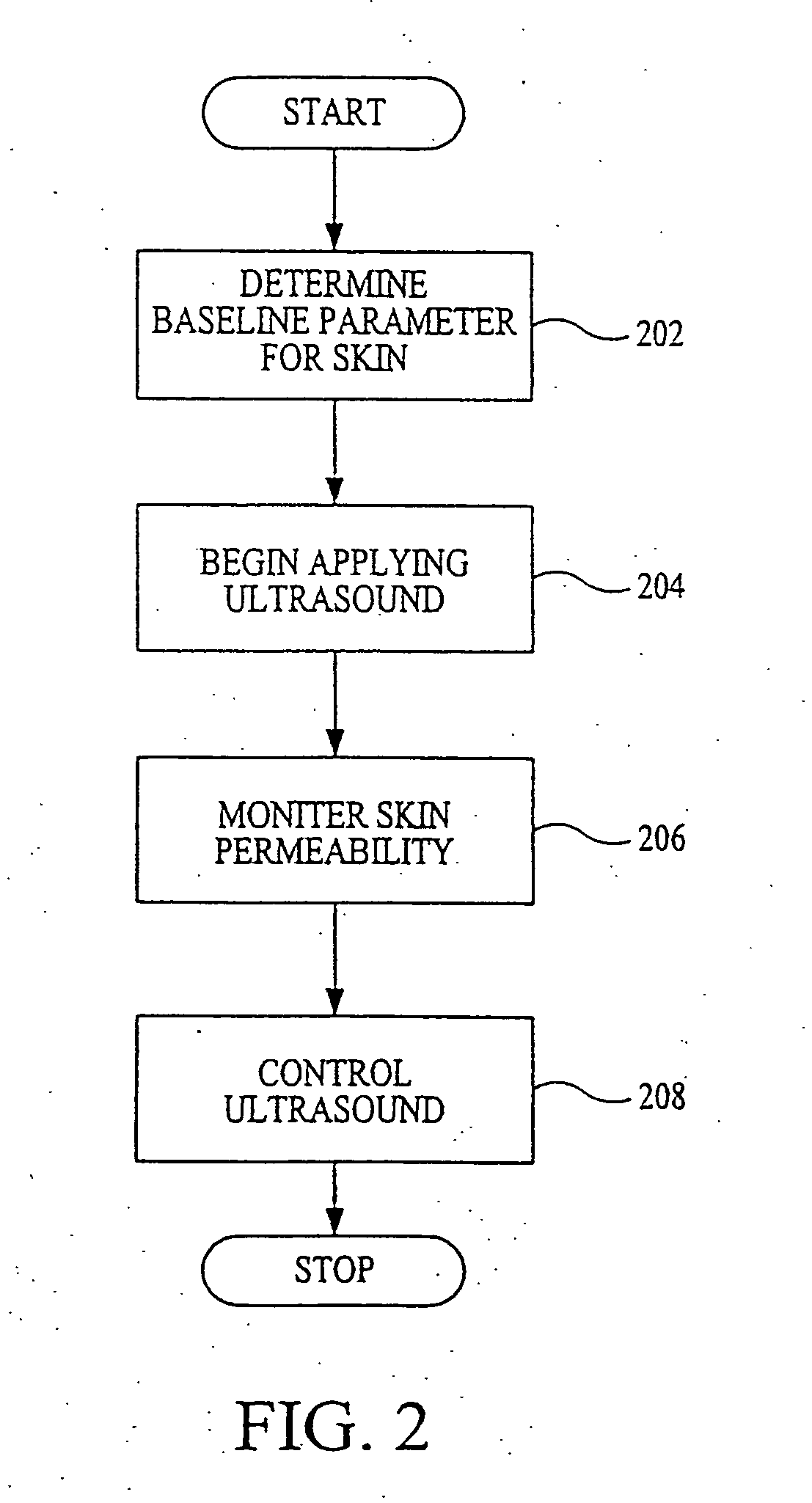
InactiveUS6887239B2Overcome or reduce one orThe process is convenient and fastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricitySkin integrity
The invention provides a convenient and non-invasive means to prepare cells, tissues, and organs for electrical transmission and reception. In an embodiment of the invention, a control method comprises the use of at least one skin electrode, as a reference electrode, and an electrical sensor to measure periodically or continuously the skin's electrical conductance at the site of preparation. The dynamic change in the conductance through the skin is measured while the ultrasound is applied. Signal processing is performed on the measurement and the level of skin impedance change is controlled by performing a mathematical analysis and using the results of such analysis to control the application of ultrasonic energy. A desired level of skin impedance can be set at a predetermined value or based on a chosen level of skin integrity, subject's sensation of discomfort, or duration of the ultrasound application.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
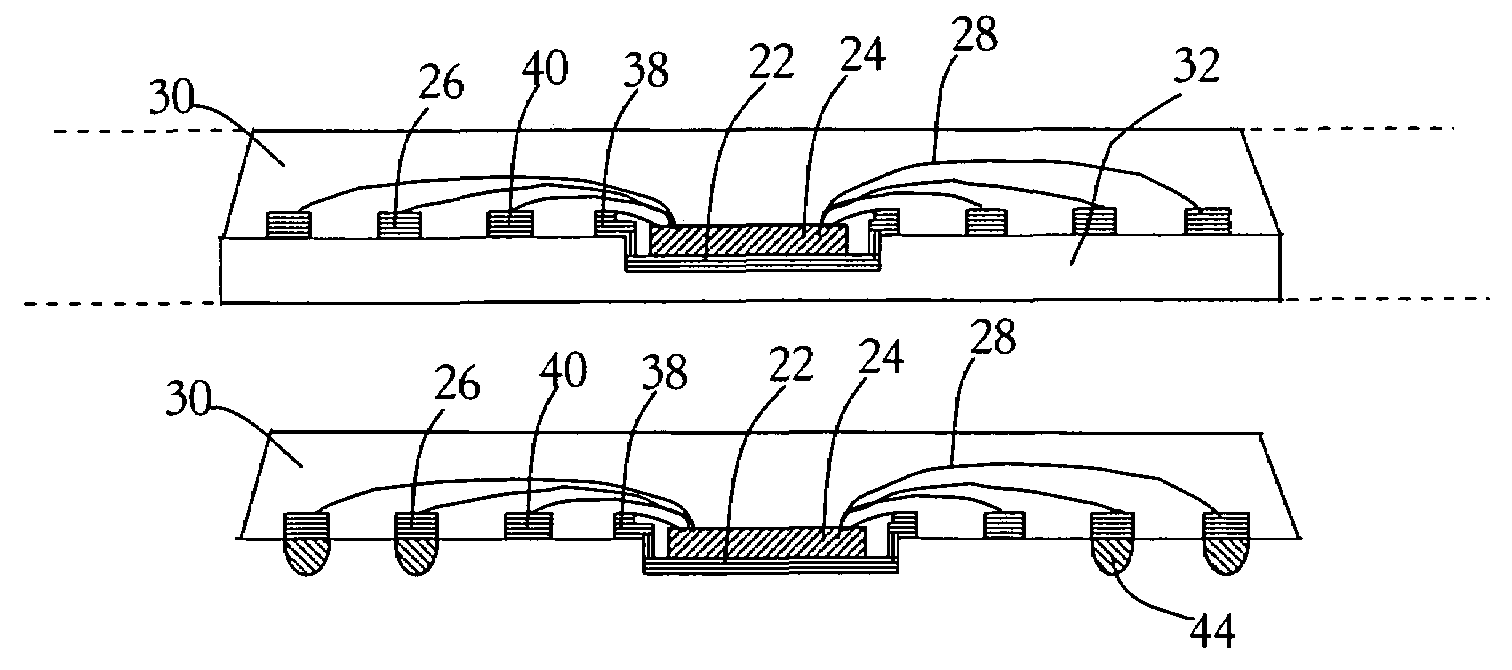
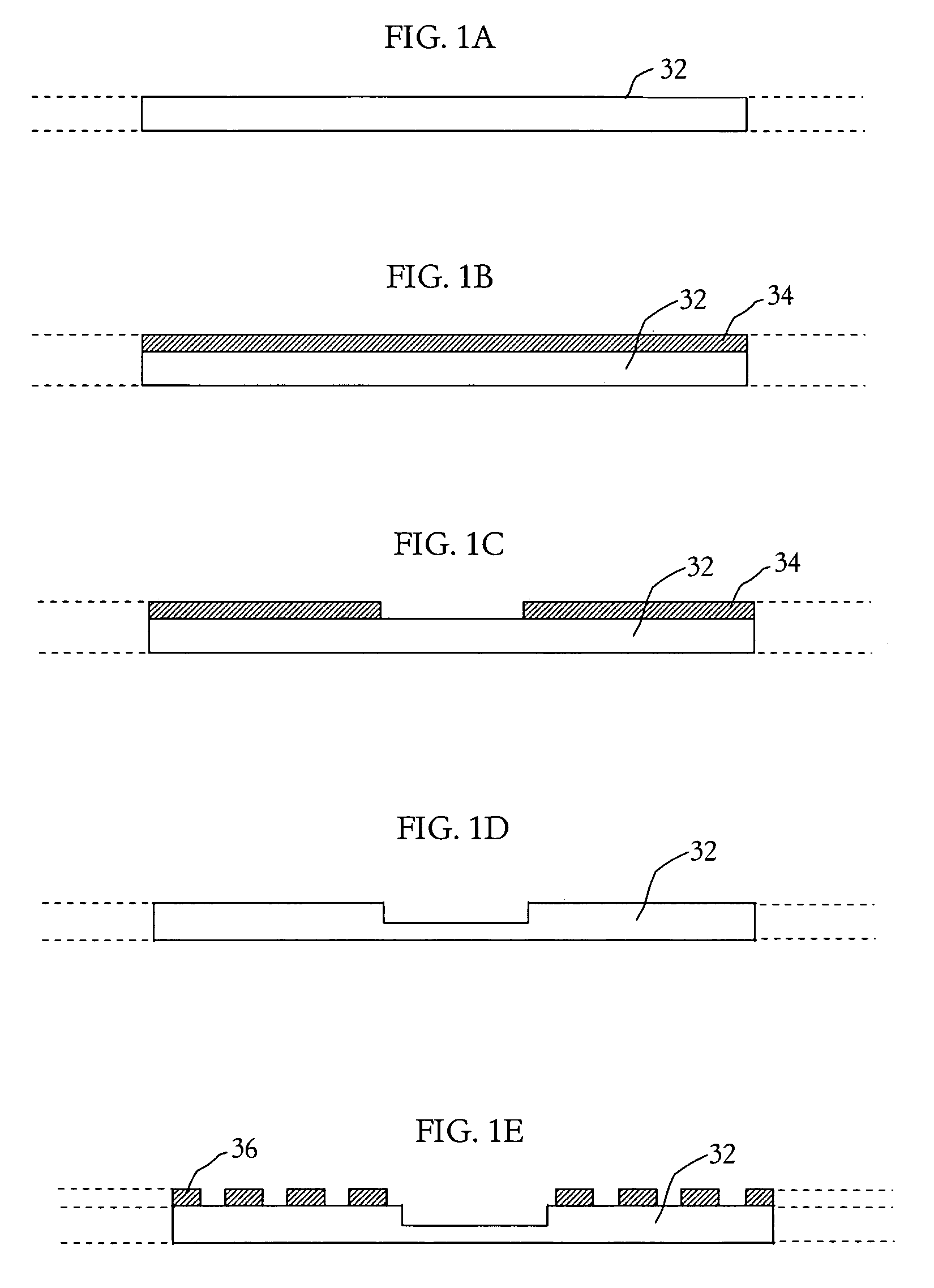
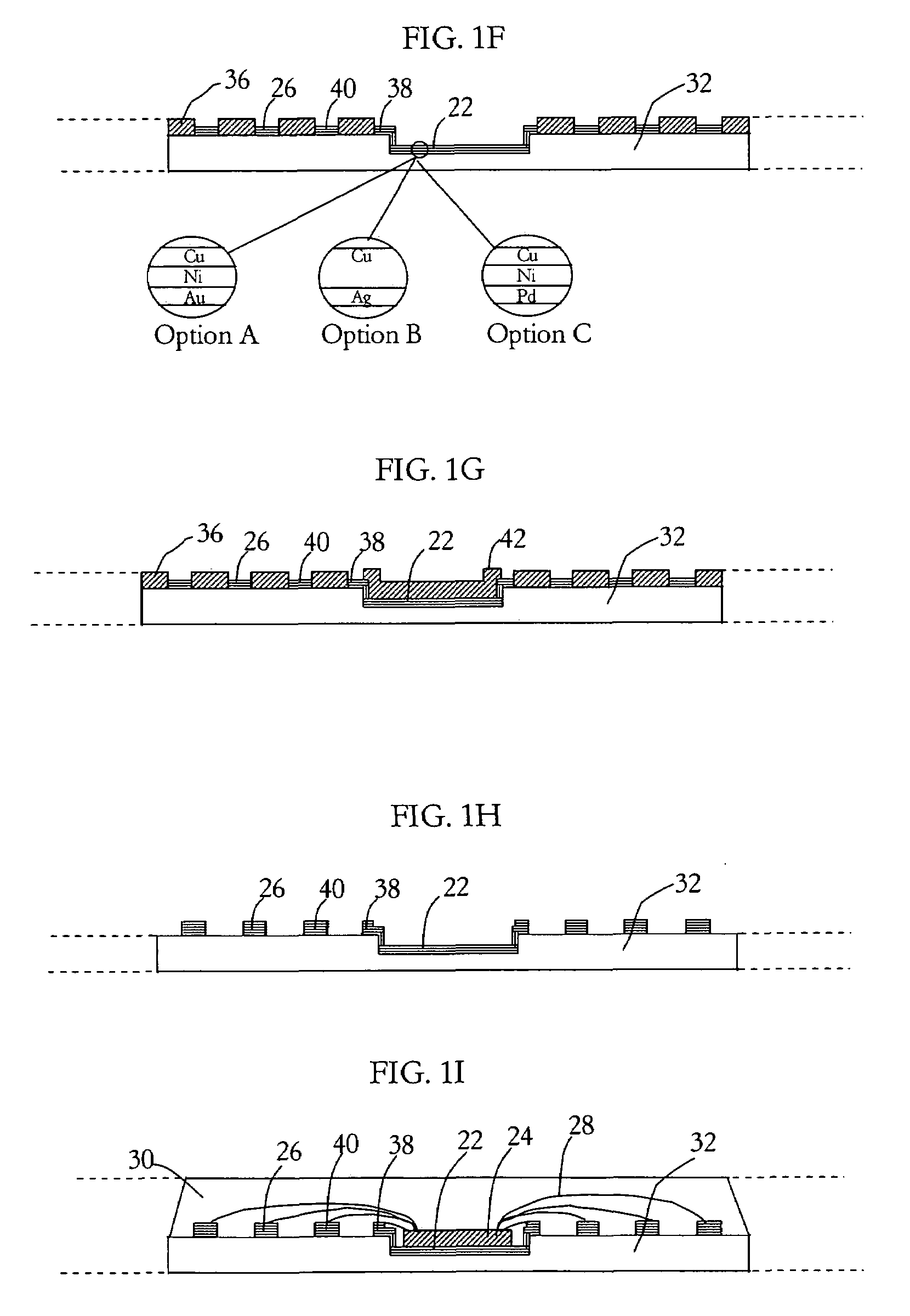
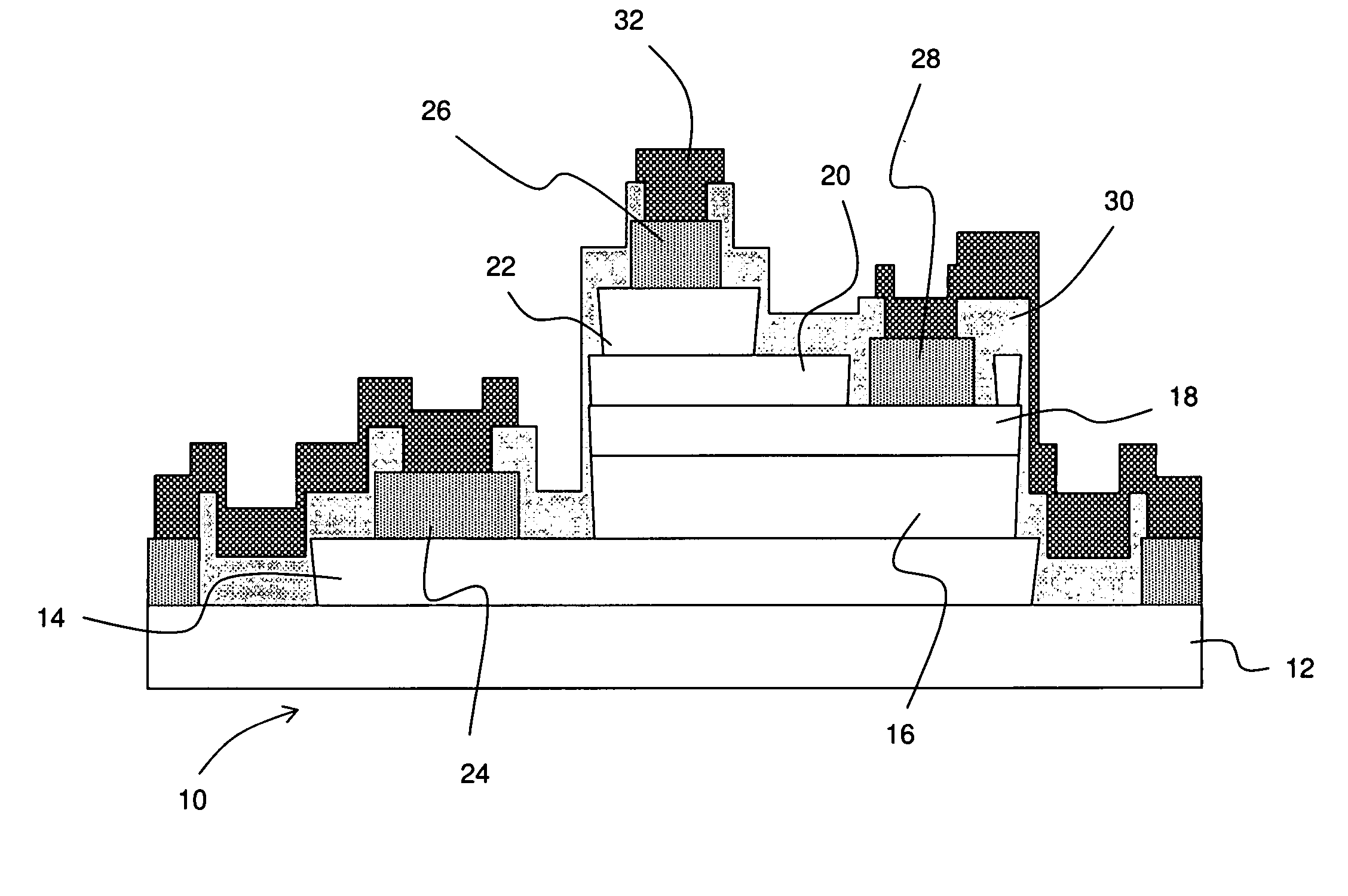
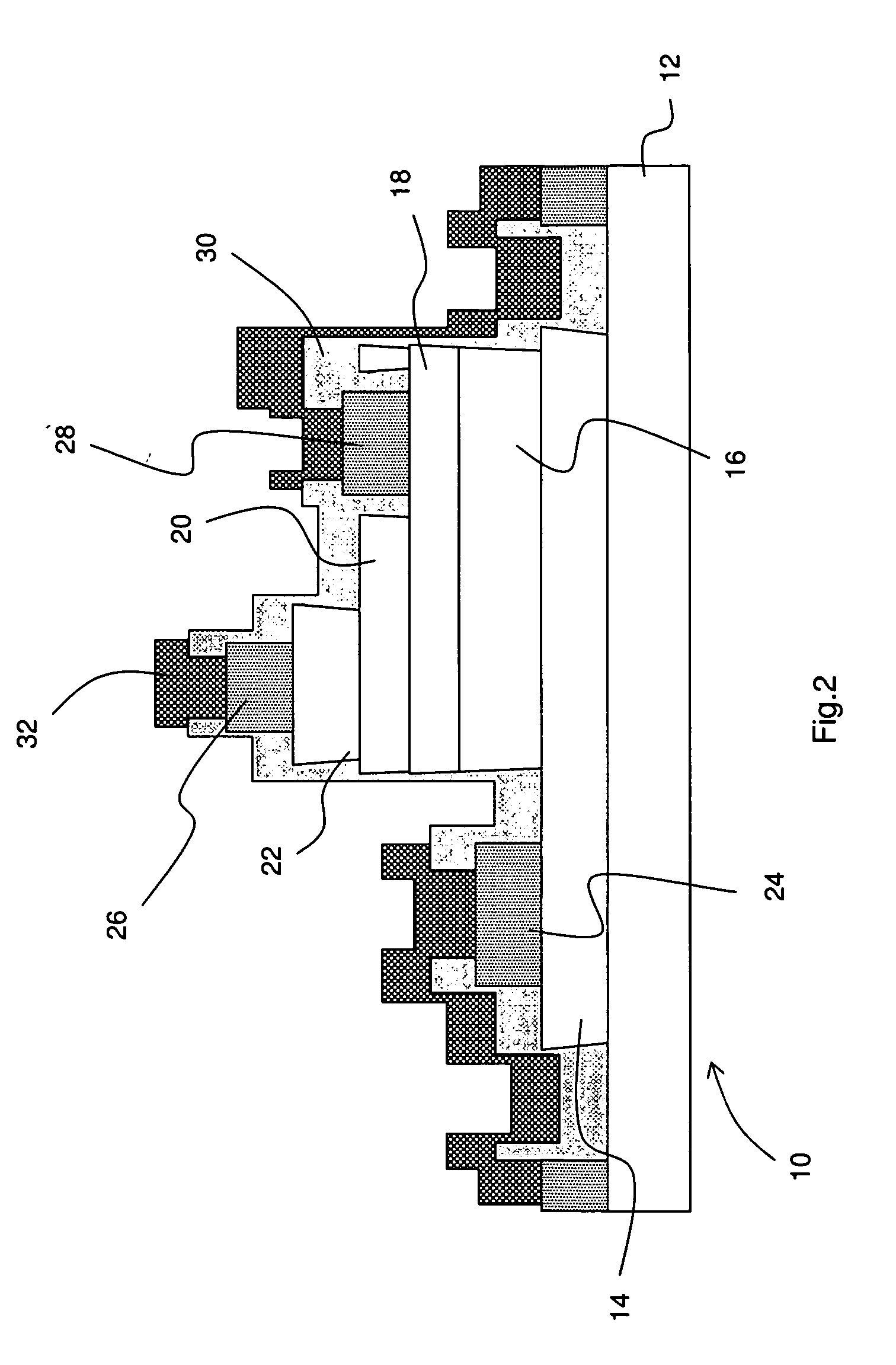
Integrated circuit package and method for fabricating same
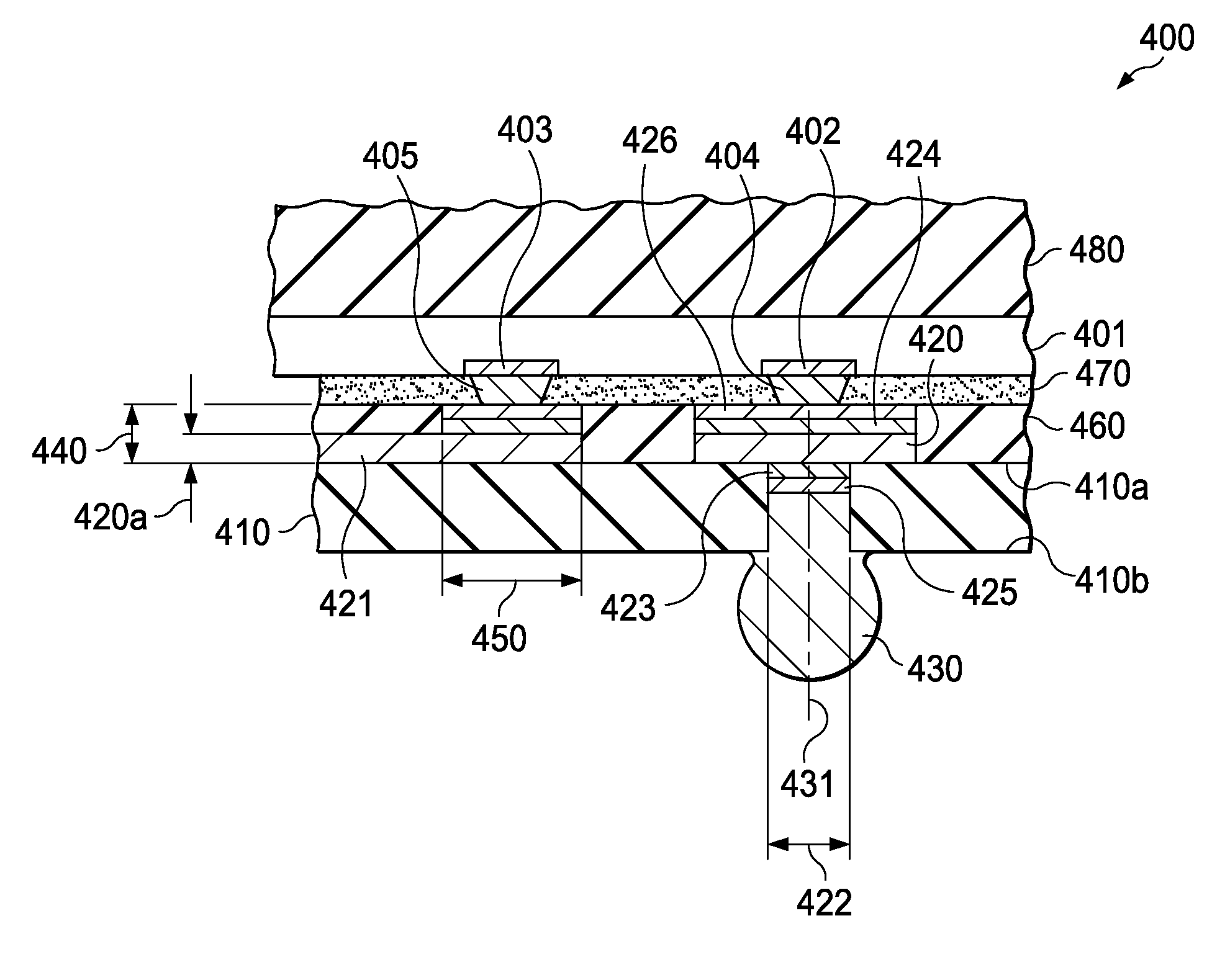
ActiveUS7348663B1Reduce electrical impedanceImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricContact pad
A process for fabricating an integrated circuit package includes: selectively etching a first side of a substrate thereby providing etched regions of the substrate to partially define at least a plurality of contact pads; adding a dielectric material to the etched regions of the substrate; selectively etching a second side of the substrate to further define at least the plurality of contact pads and thereby provide a package base of at least the contact pads and the dielectric; mounting a semiconductor die to the package base and connecting the semiconductor die to the contact pads; fixing a lid to the package base to cover the semiconductor die in a cavity between the lid and the package base; and singulating to provide the integrated circuit package.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Bioadhesive compositions and biomedical electrodes containing them
InactiveUS7076282B2Good bioadhesionHigh mechanical strengthElectrocardiographySurgical adhesivesWound dressingHydrophobic polymer
Owner:FIRST WATER
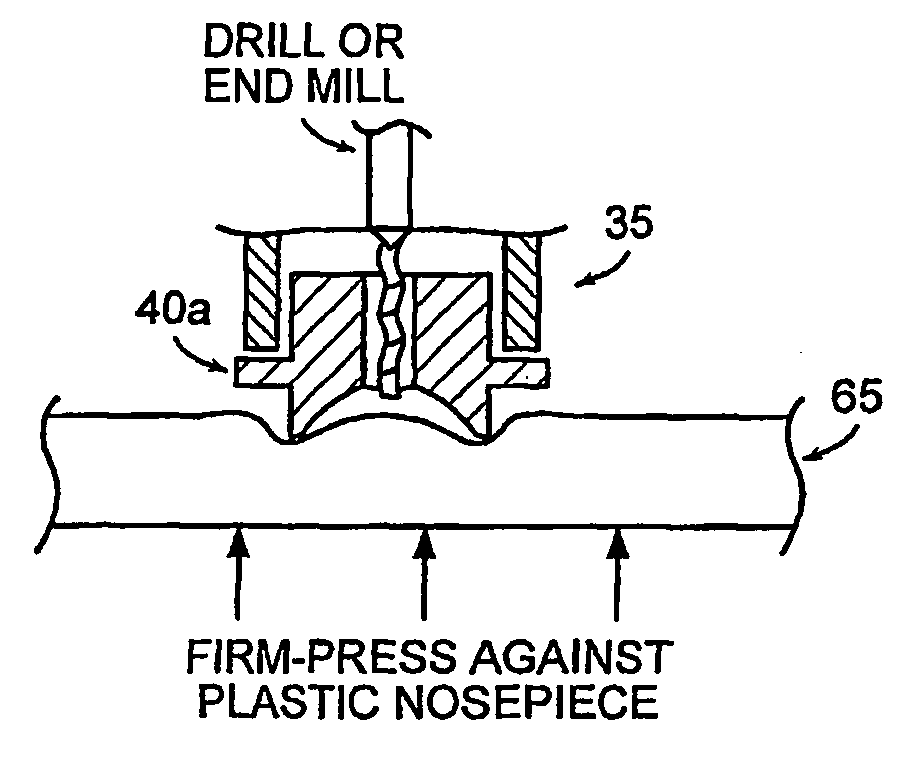
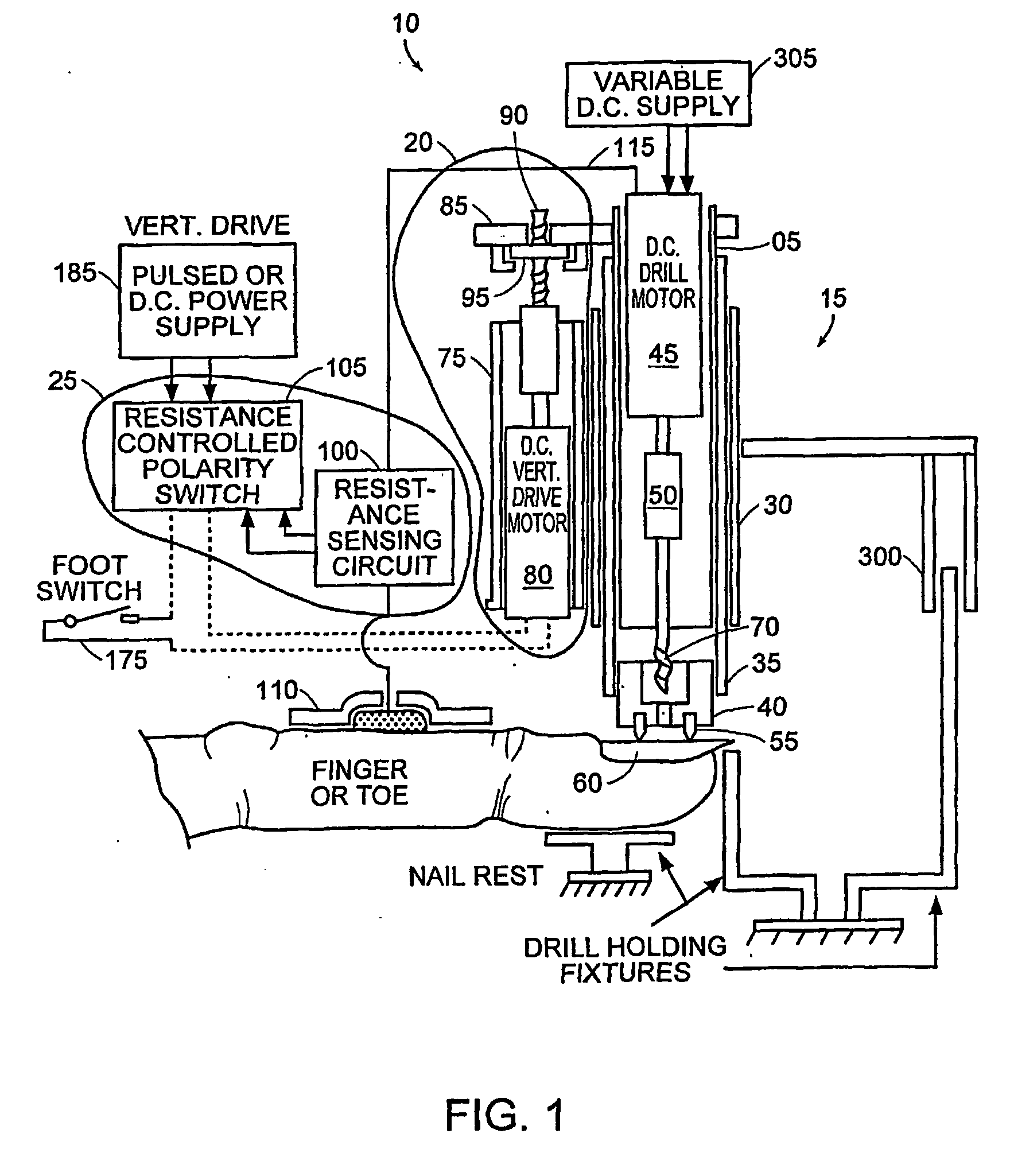
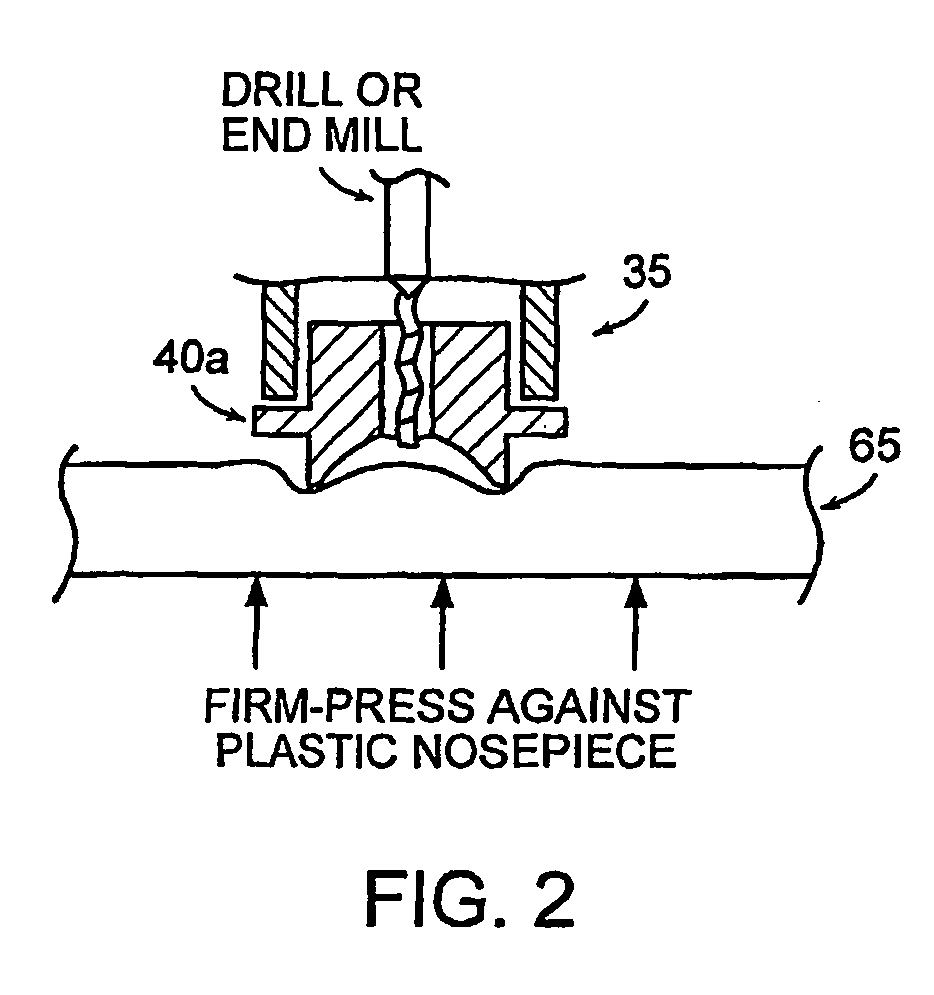
Drill device and method for forming microconduits
ActiveUS20060041241A1Facilitated DiffusionReduce electrical impedanceElectrotherapySurgeryElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention relates to methods and devices for formation of microconduits in tissue, particularly using an impedance sensing drill to form microconduits. One embodiment of the invention is an impedance sensing drill comprising a drilling assembly, a control module, mechanically connected to the drilling assembly for controlling the depth of drilling by the drilling assembly; and a sensor, electrically connected to the drilling assembly and control module for detecting a change in an electrical impedance of a material being drilled. Another embodiment is a method of forming a microconduit in a material, which comprises the steps of drilling into the material, monitoring an electrical impedance of the material, and stopping the drilling into the material when a change in the impedance is detected, thereby forming microconduit.
Owner:GALDERMA PHARMA
Thin leadless plastic chip carrier
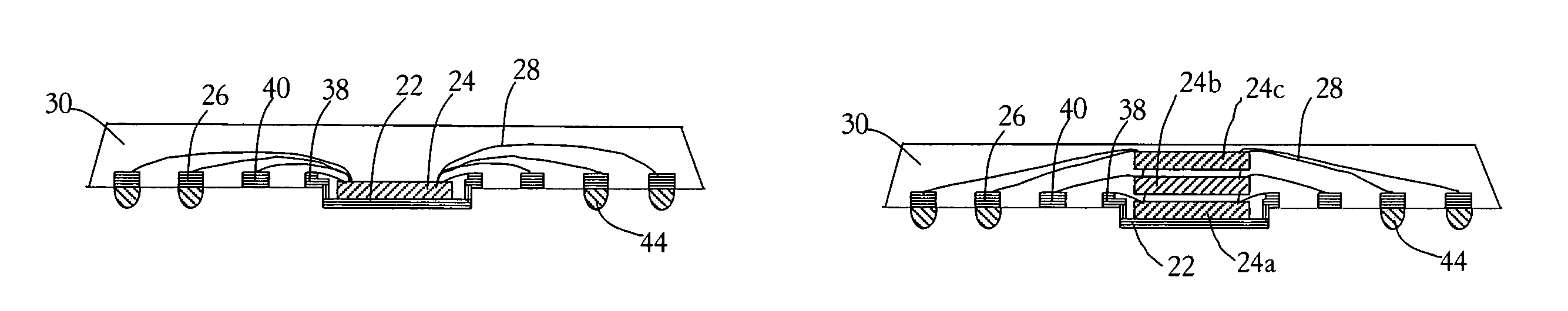
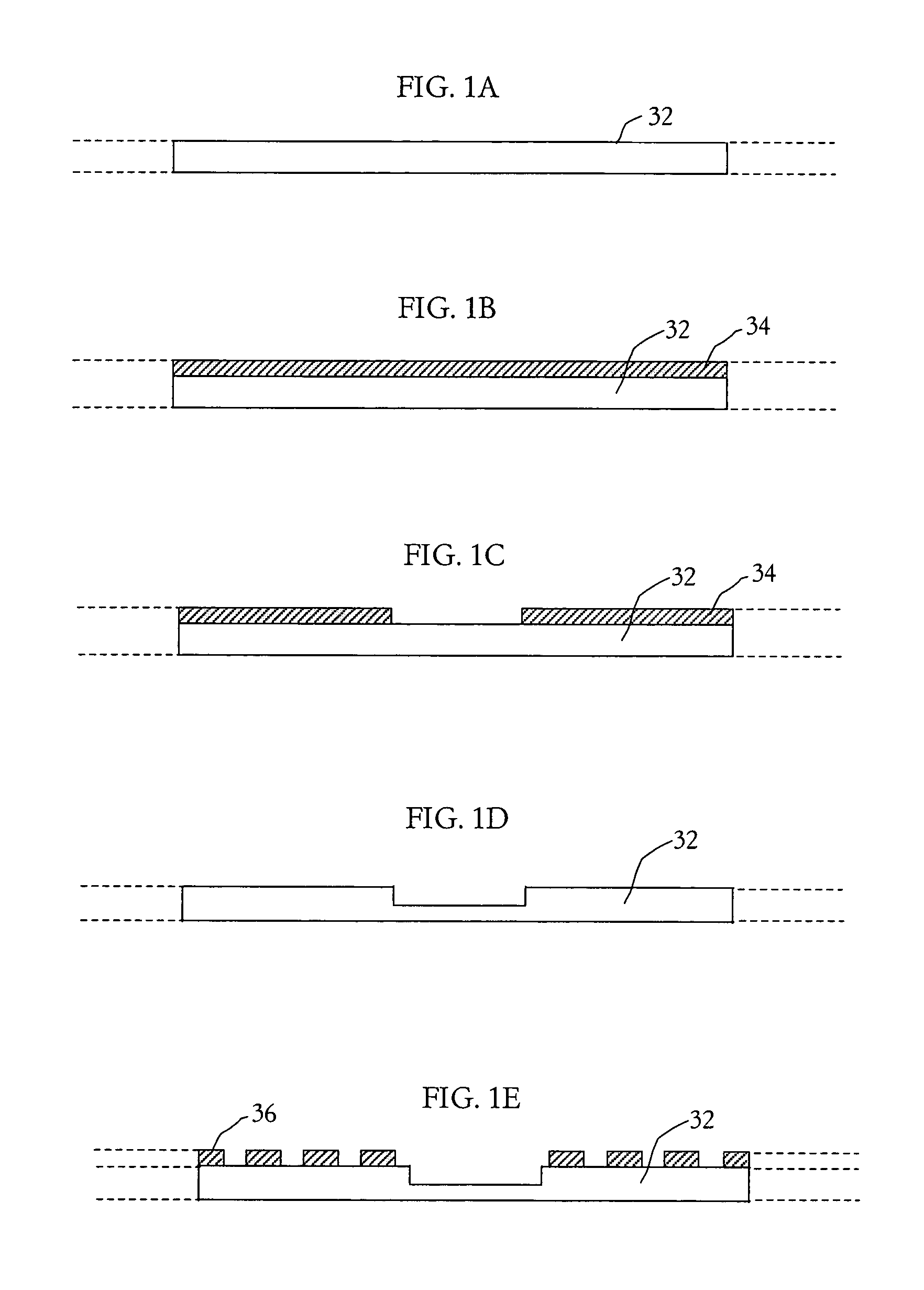
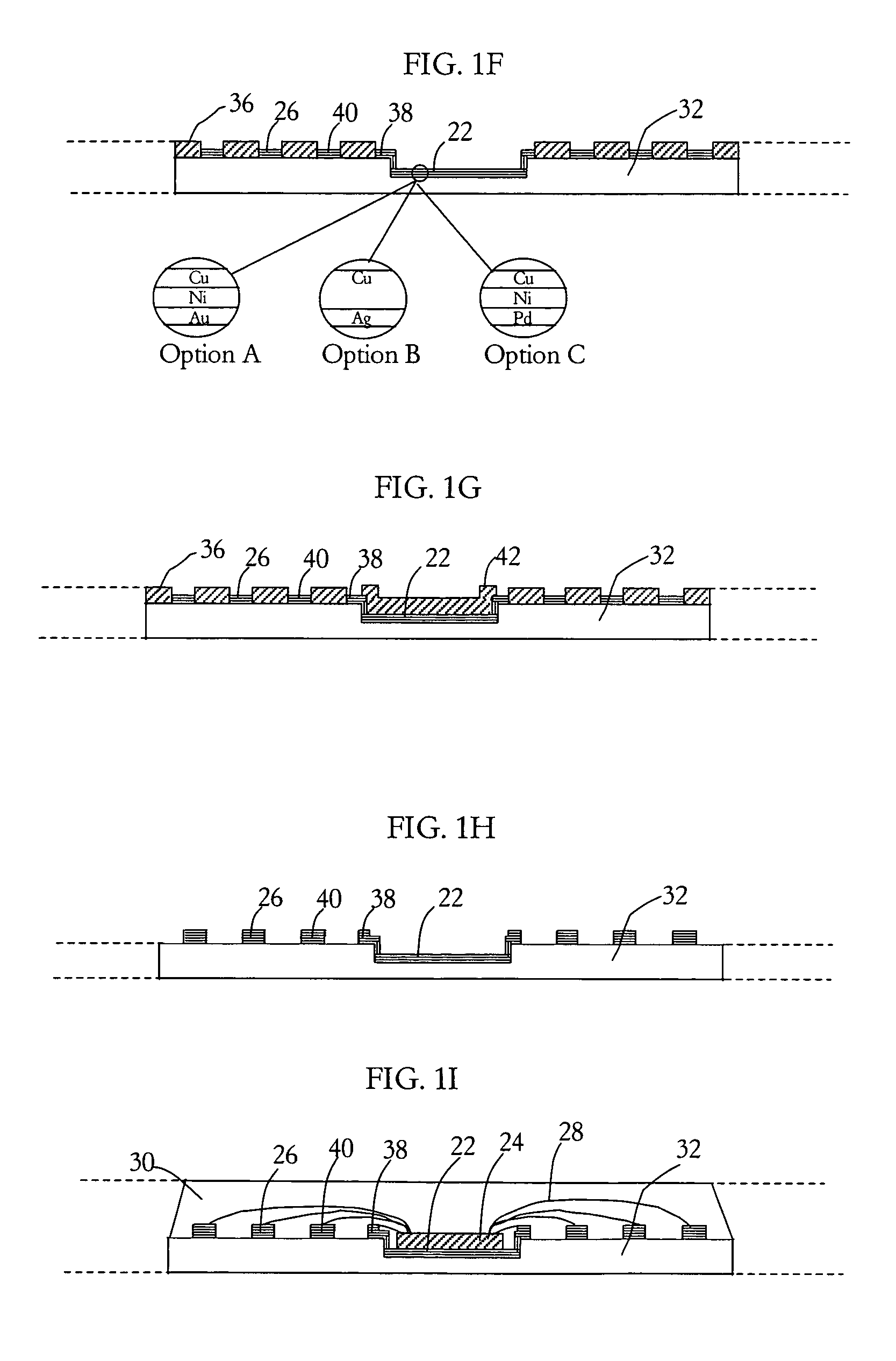
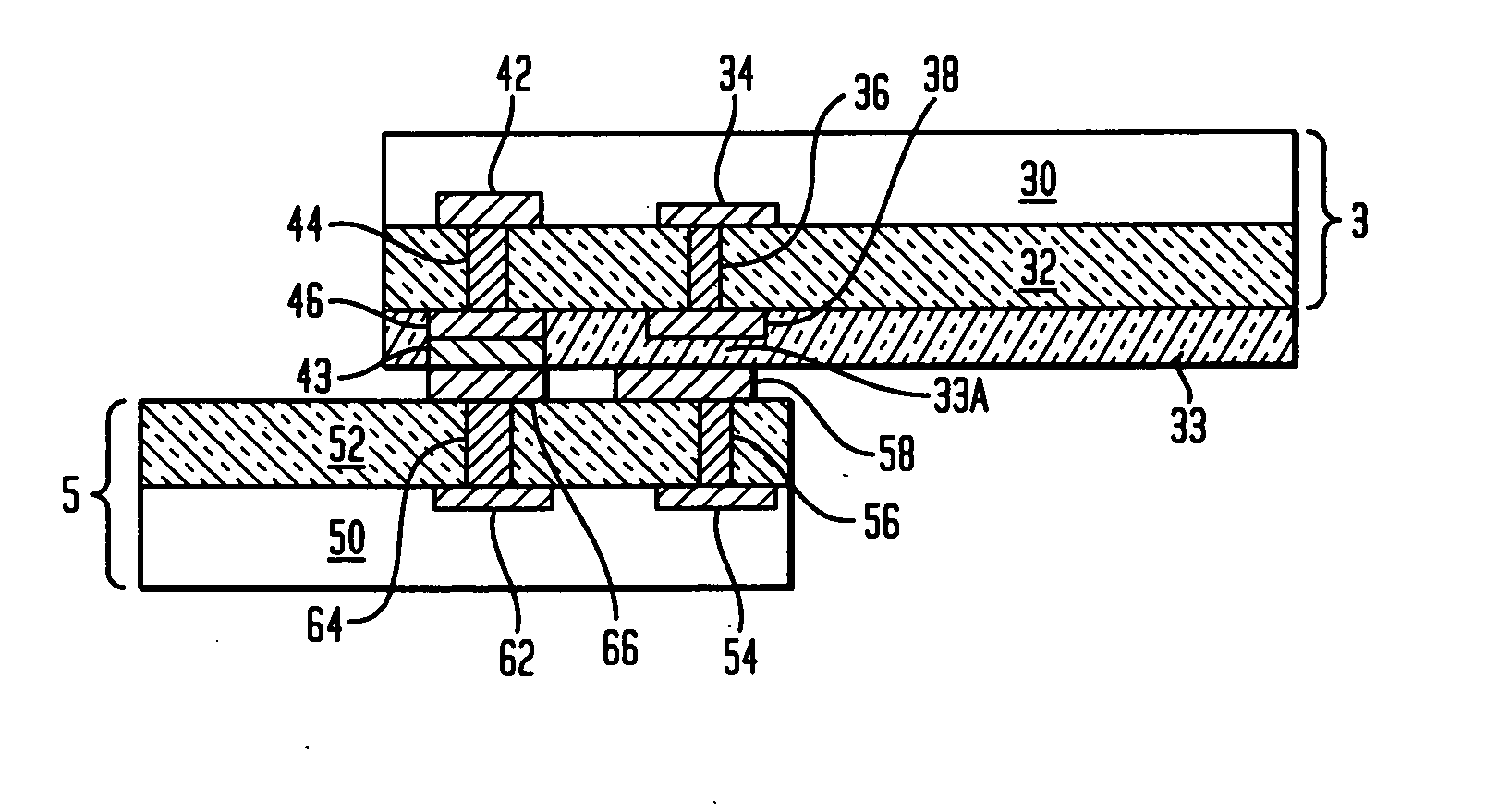
ActiveUS7009286B1Thin package profileReduce electrical impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
A leadless plastic chip carrier is fabricated by selectively etching a leadframe strip to reduce a thickness of the strip at a portion thereof. Selectively masking the surface of the leadframe strip using a mask, follows selectively etching, to provide exposed areas of the surface at the portion and contact pad areas on leadframe the strip. At least one layer of metal is deposited on the exposed areas to define a die attach pad on the portion of the leadframe strip with reduced thickness and to define contact pads on the surface of the strip. At least one semiconductor die is mounted to the die attach pad, followed by wire bonding the at least one semiconductor die to ones of the contact pads. The at least one semiconductor die, the wire bonds, and the contact pads are covered with an overmold material and the leadframe strip is etched to thereby remove the leadframe strip. The leadless plastic chip carrier is singulated from the leadframe strip.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Inter-chip ESD protection structure for high speed and high frequency devices
ActiveUS20070029646A1Reduce load capacitanceImprove system performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh velocity
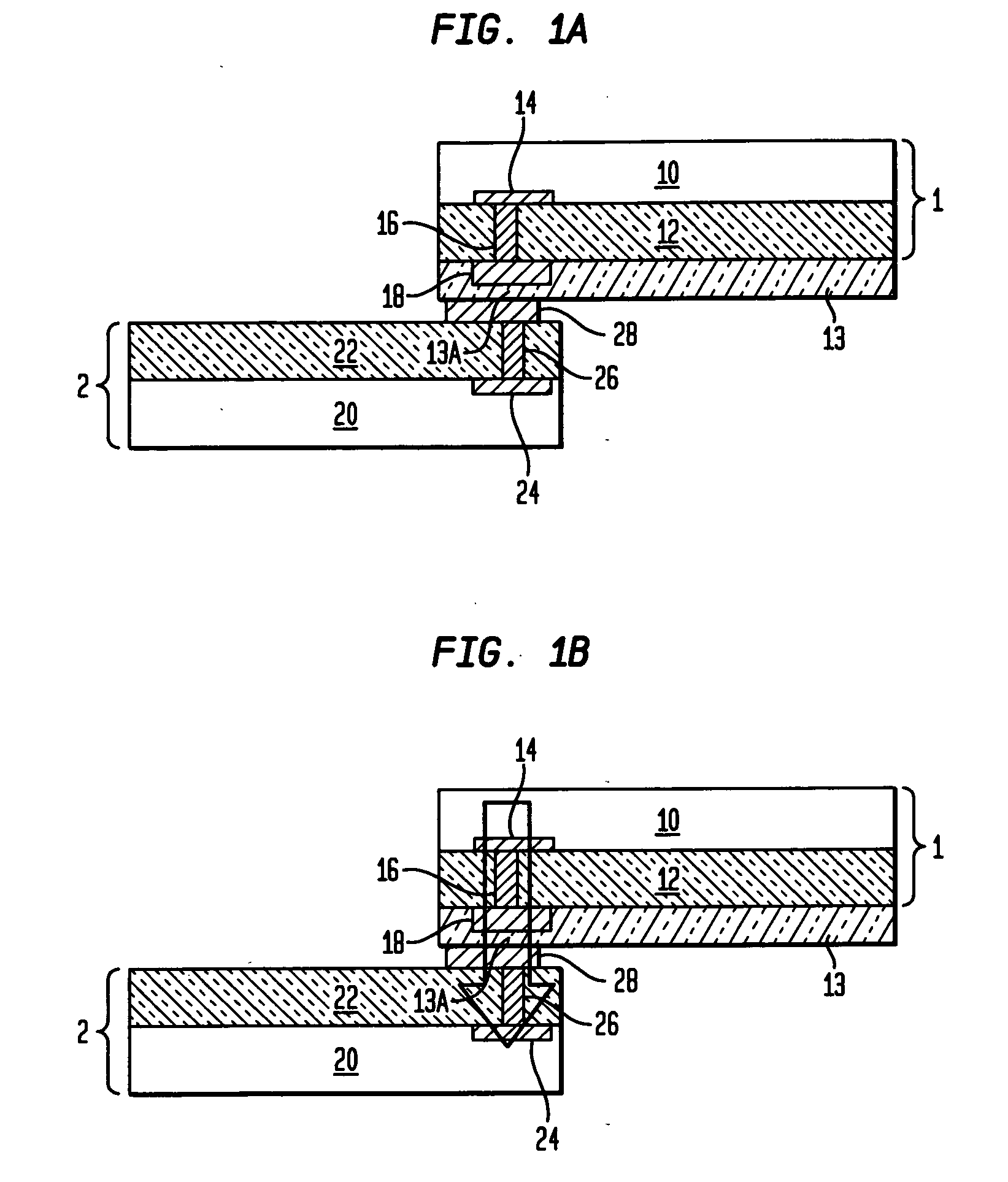
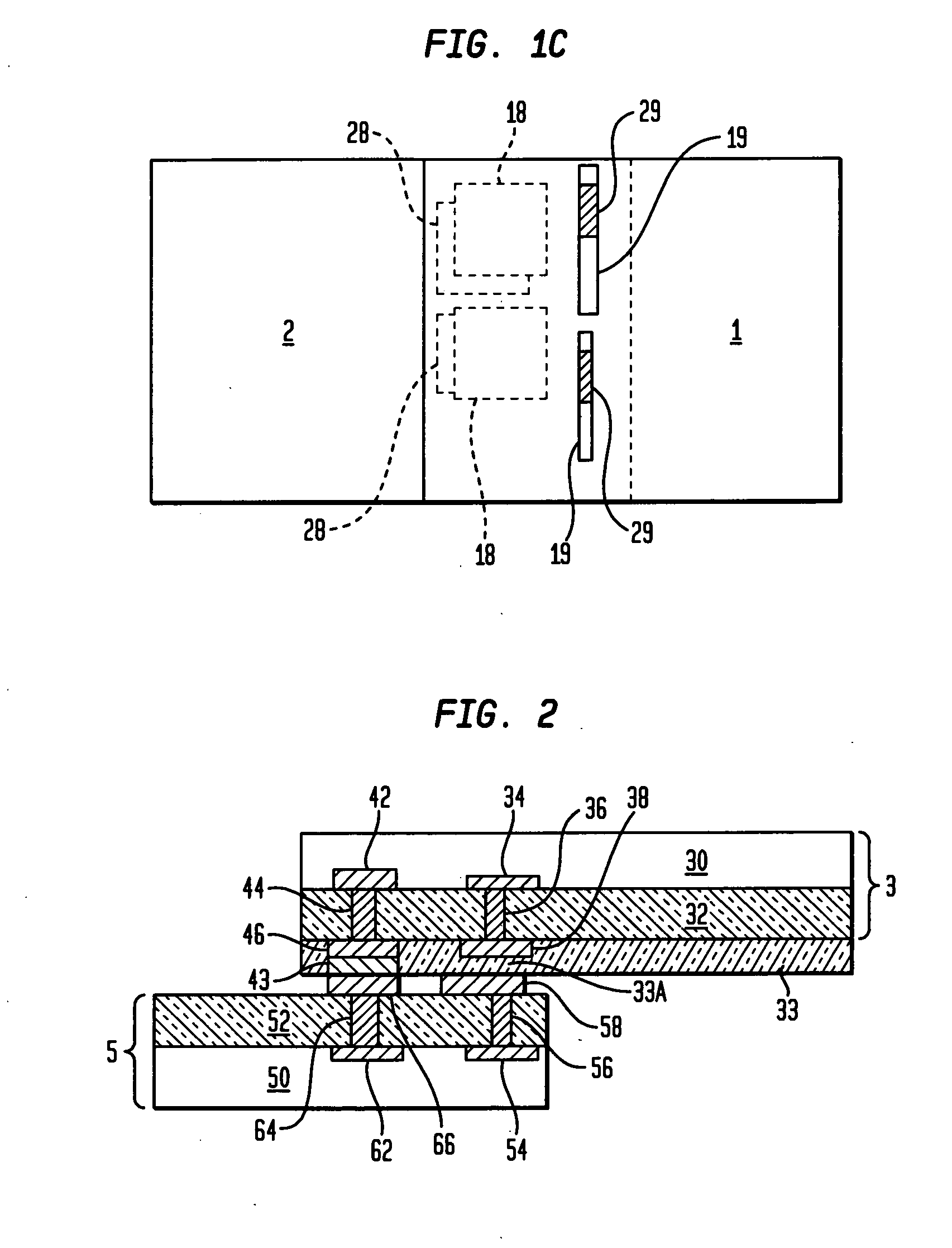
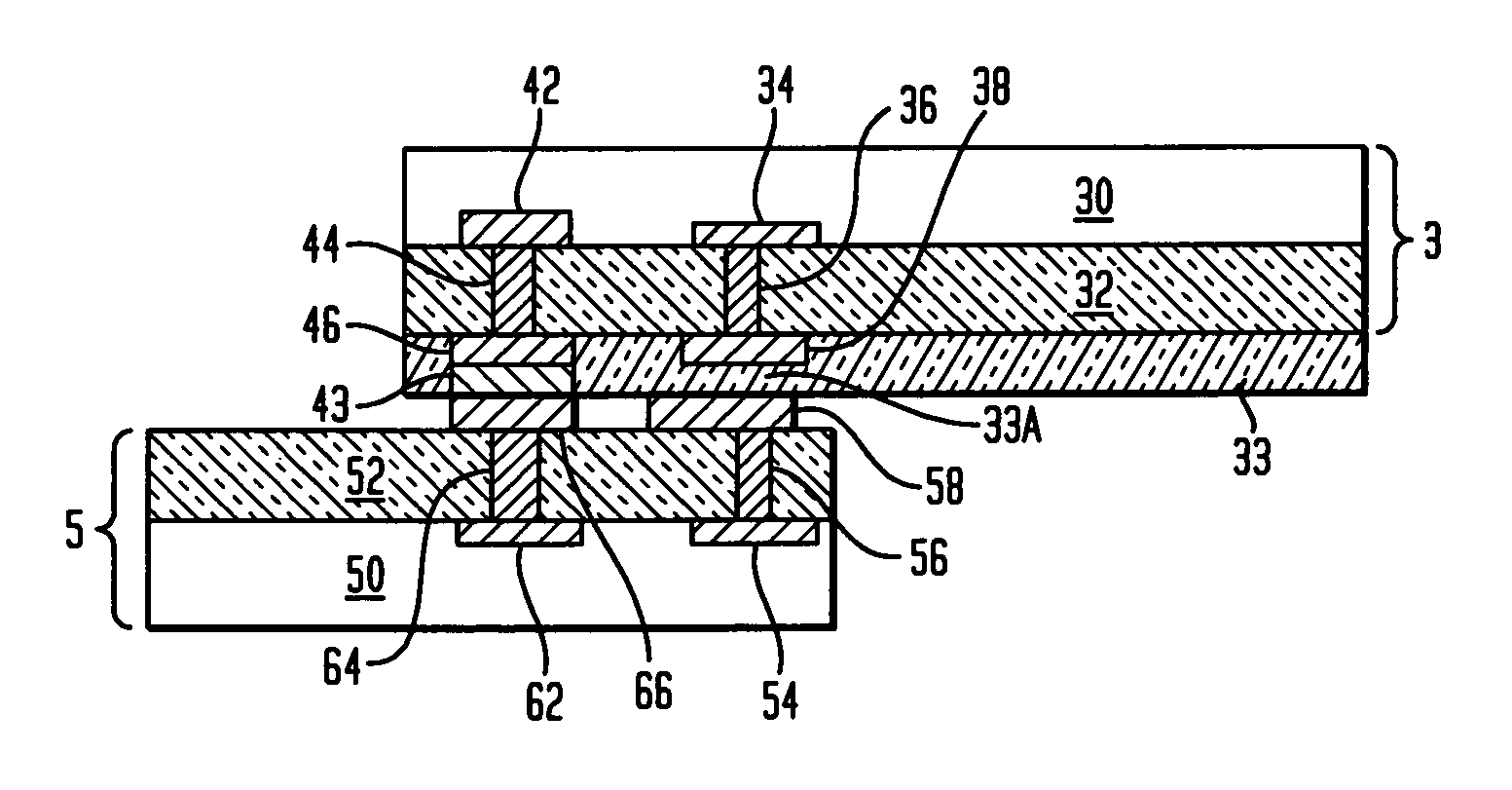
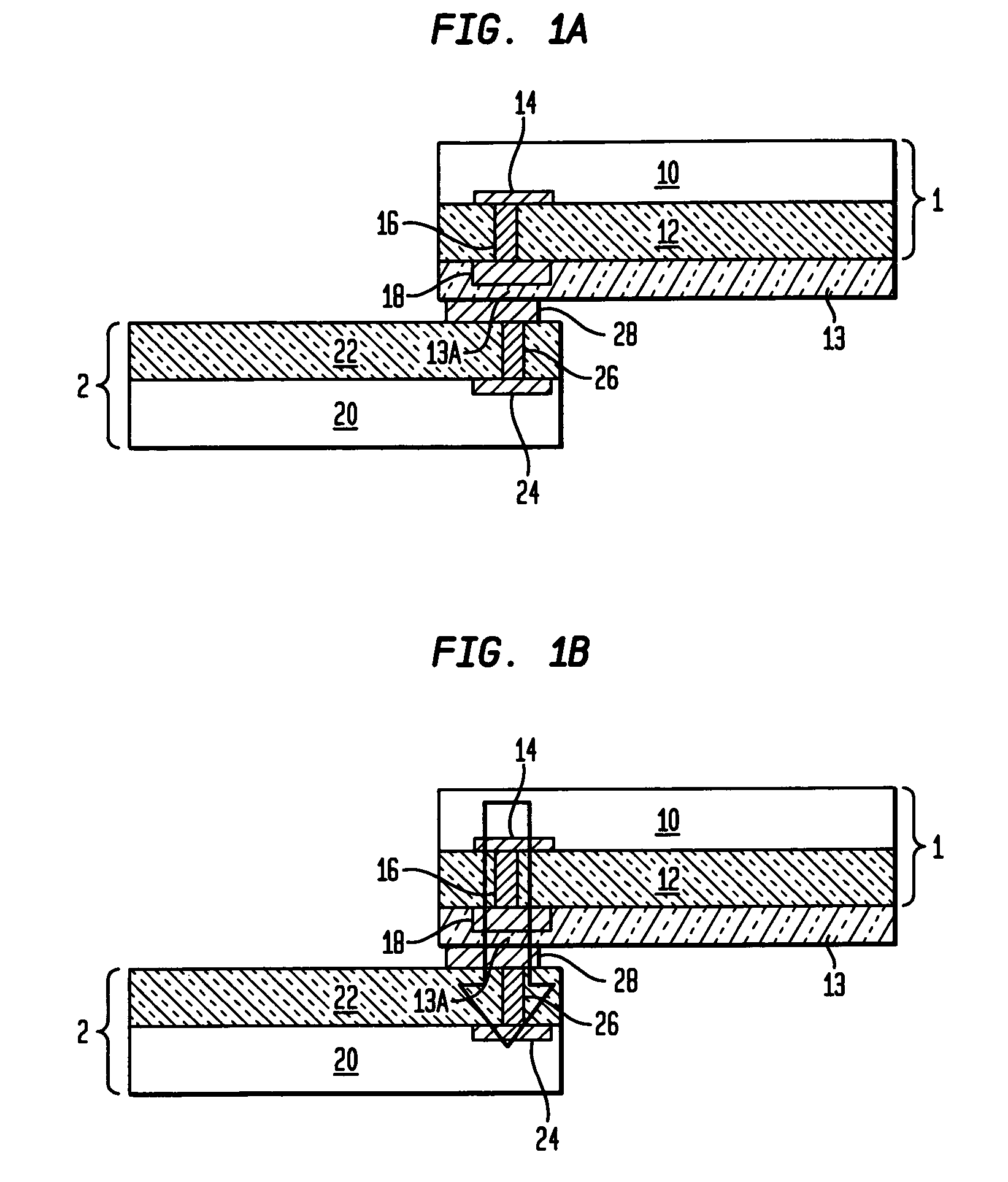
The present invention relates to inter-chip electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection structures for high speed, and high frequency devices that contain one or more direct, inter-chip signal transmission paths. Specifically, the present invention relates to a structure that contains: (1) a first chip including a first circuit, (2) a second chip including a second circuit, (3) an intermediate insulator layer located between the first and second chips, wherein the first and second circuits form a signal transmission path for transmitting signals through the intermediate insulator layer. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection path is provided in the structure between the first and the second chip through the intermediate insulator layer, to protect the signal transmission path from ESD damages.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Polyolefin and Ceramic Battery Separator for Non-Aqueous Battery Applications
InactiveUS20110171523A1Improve heat resistanceImprove carrying capacityCell component detailsVehicular energy storagePolyolefinPolymer science
A ceramic microporous polyolefin battery separator membrane, high in air permeability, low in shrinkage and improved temperature resistance addresses the safety requirements of lithium ion batteries. The separators made by the current invention consists of one or more polyolefin polymers and kaolin fillers comprised of aluminum oxide and silicon oxide. The membranes of current invention have a thickness of 5-200 microns, air permeability of 1-200 sec / 10 cc (Gurley seconds), and average pore diameter of less than 1 micron.
Owner:ADVANCED MEMBRANE SYST INC
Inter-chip ESD protection structure for high speed and high frequency devices
ActiveUS7535105B2Reduce electrical impedanceReduce load capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh velocity
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Flexible printed circuit board
InactiveUS20070102830A1Deterioration in transmission characteristicReduce electrical impedanceCoupling device connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInsulation layerEngineering
A flexible printed circuit board has an insulation layer, a first signal wiring layer including a microstrip line, a second signal wiring layer including a signal connection terminal for allowing the microstrip line to connect the exterior connector electrically, and a ground conductive section having a ground connection terminal for connecting the exterior connector. The microstrip line and the signal connection terminal are connected to each other by a wiring via hole. The wiring via hole passes through the insulation layer, the first signal wiring layer, and the second signal wiring layer. The microstrip line has a taper section which gradually enlarges a width of the microstrip line toward the wiring via hole in the vicinity of the wiring via hole. The ground conductive section that corresponds to the microstrip line has a taper section with a shape matching the taper section of the microstrip line.
Owner:SONY CORP
Low Inductance Ball Grid Array Device Having Chip Bumps on Substrate Vias
InactiveUS20090289362A1Eliminate couplingReduces bump-to-via current path inductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLow inductance
A high-frequency BGA device (500) with the chip (501) assembled by metal bumps (503) on an insulating substrate (502) with conductive vias (505) and metal traces (504). Chip bumps which serve the high frequency signal terminals are attached directly to the lands (510) on the vias in order to minimize parasitic electrical parameters such as inductance, resistance, and IR drops, thus achieving the required 0.1 nH inductance for each chip terminal. Chip bumps which serve the remaining chip terminals are attached to pads on certain substrate traces. In both cases, the bumps can be attached reliably because the lands on the vias and the pads on the traces are plated with additional metal layers (511, 512), which provide extra thickness as well as a metallurgically suitable surface.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for making multi-layer ceramic acoustic transducer
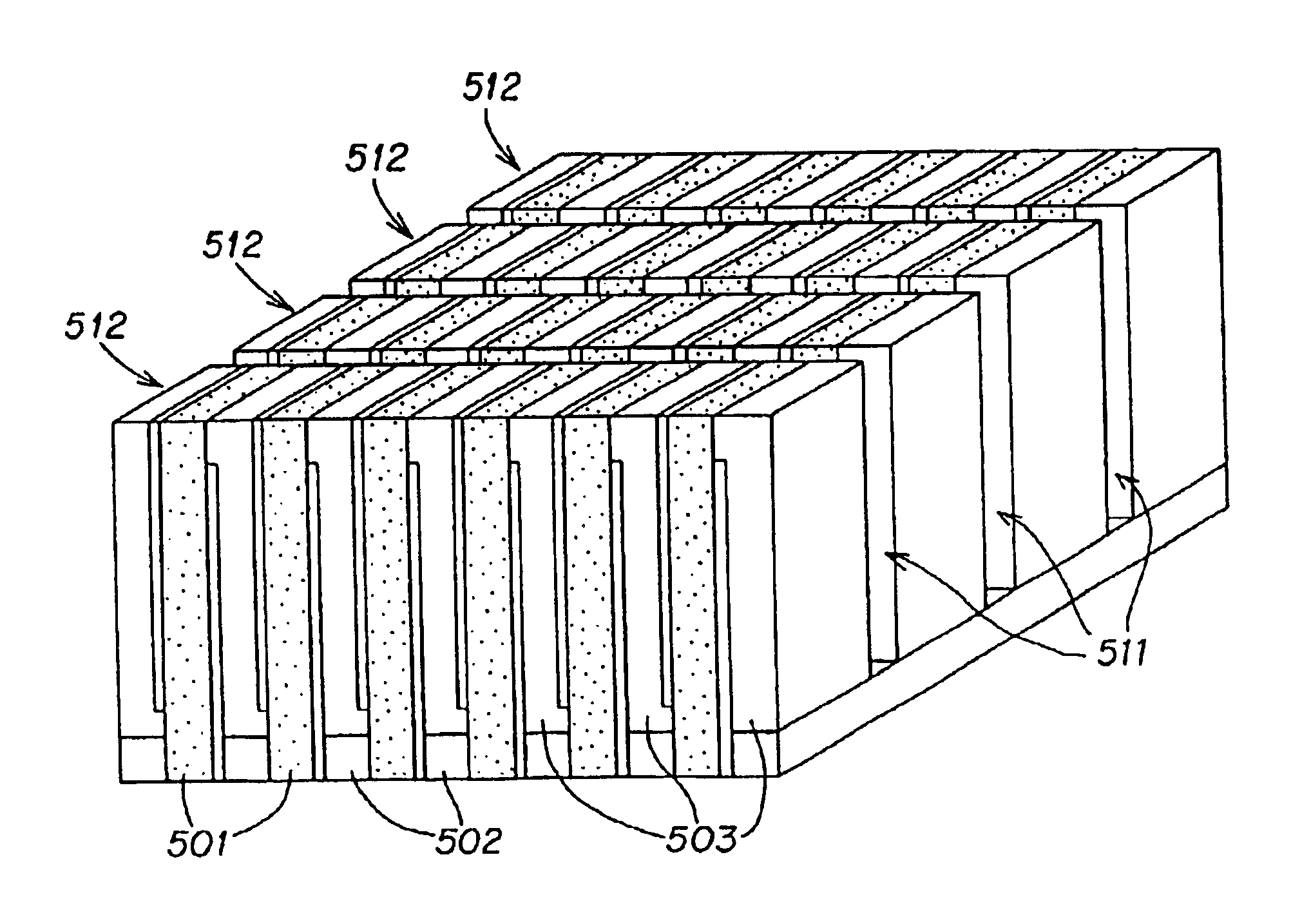
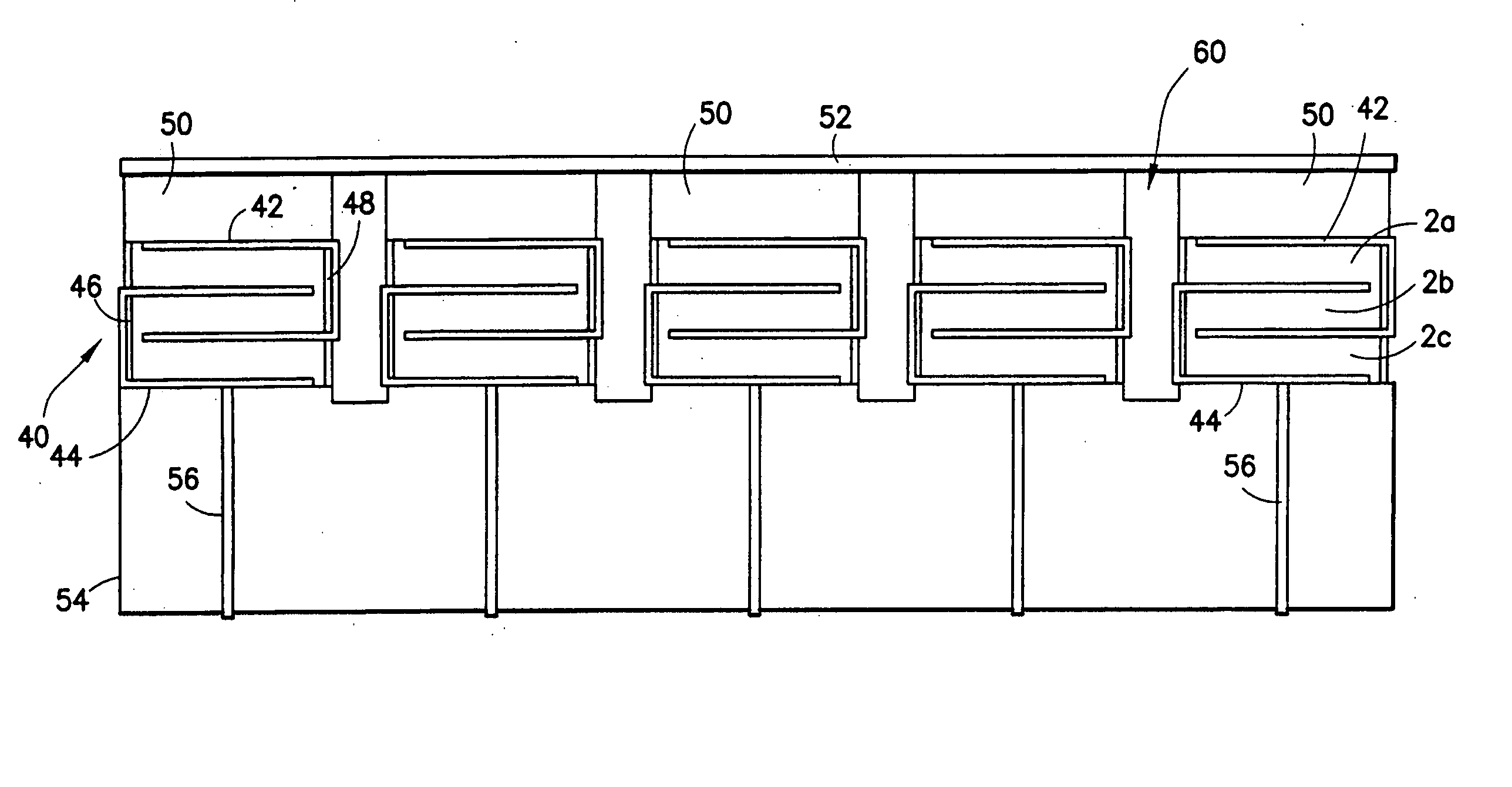
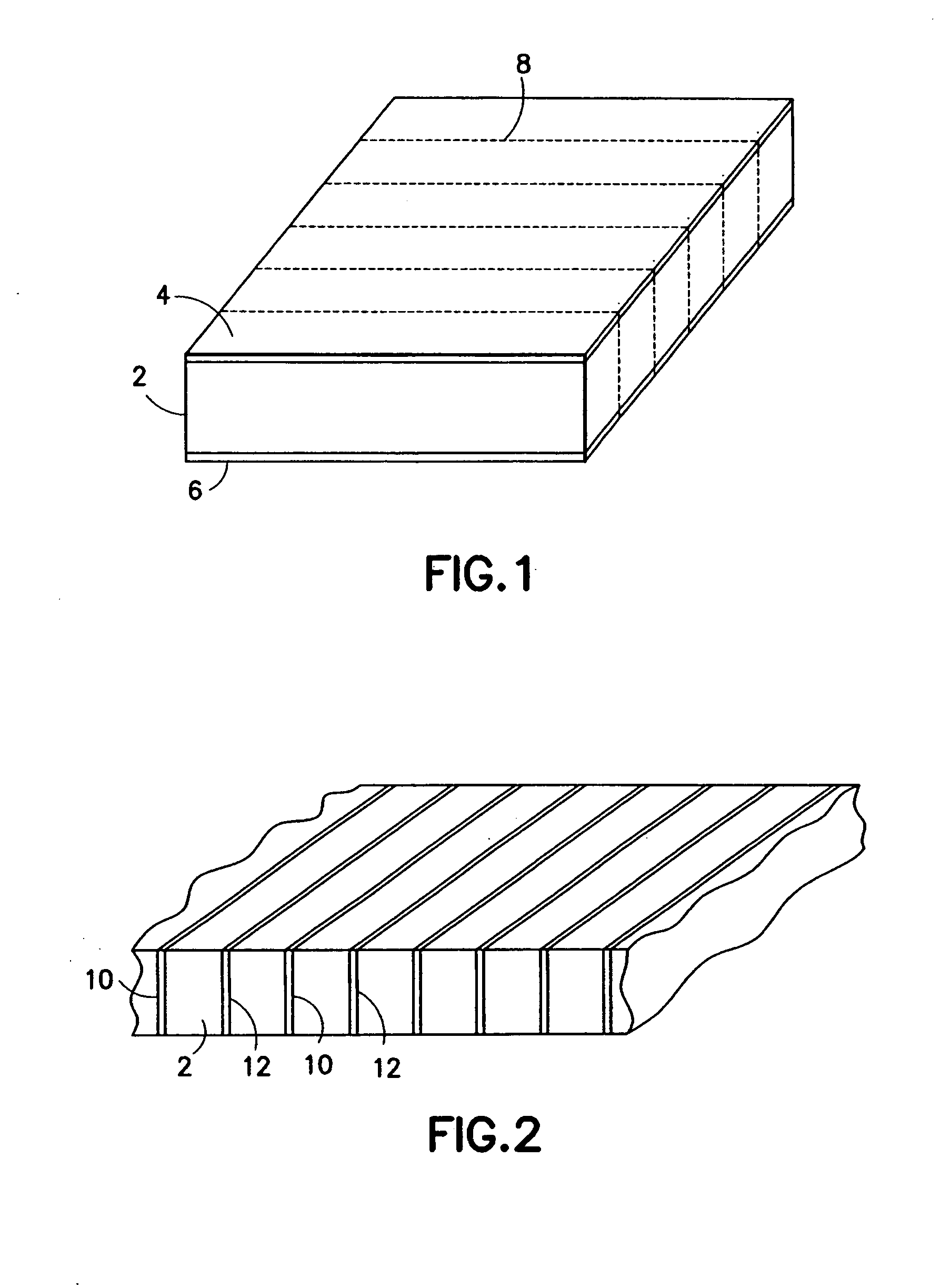
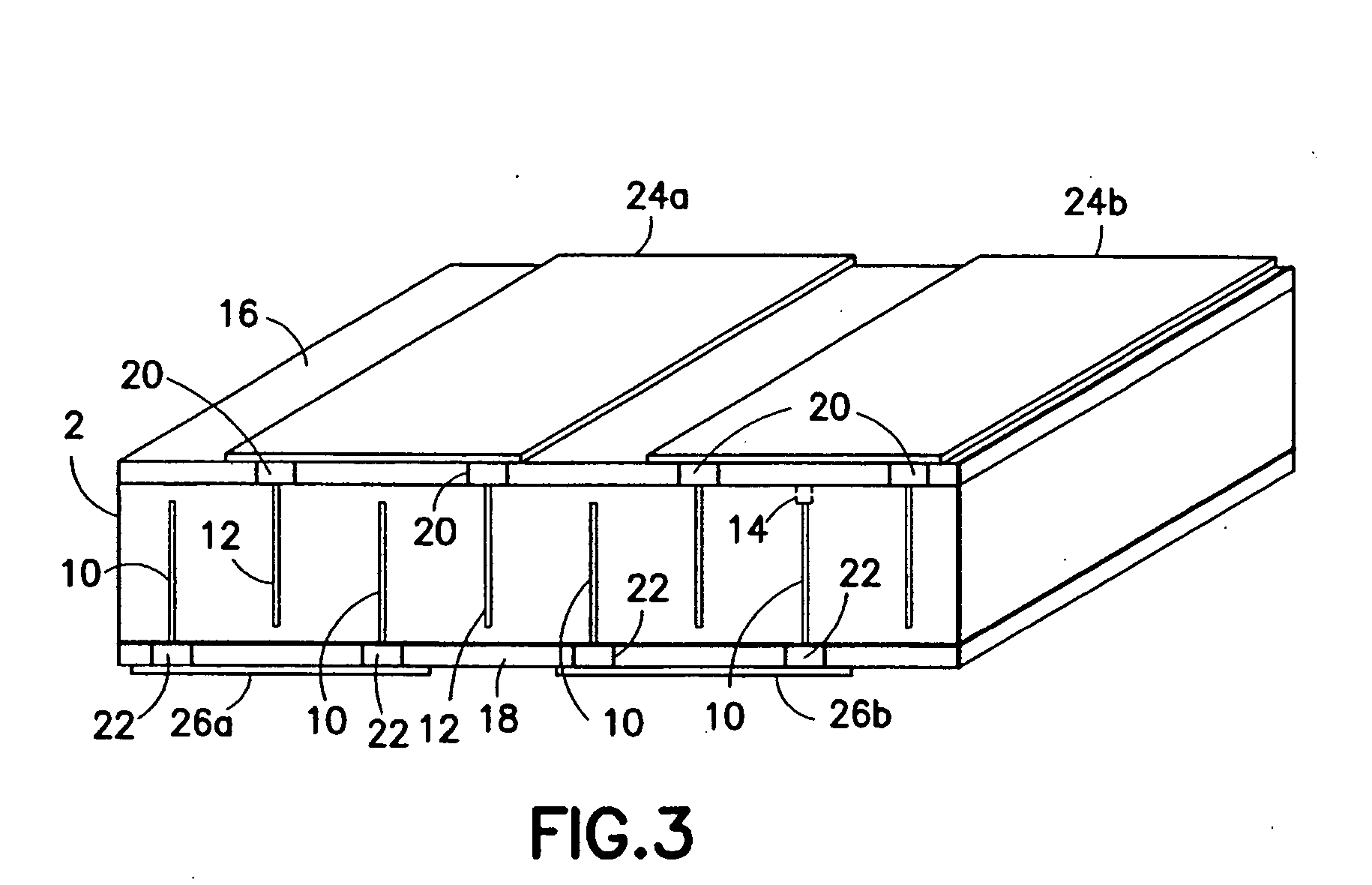
InactiveUS20050099096A1Reduce electrical impedanceGood acoustic matchingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
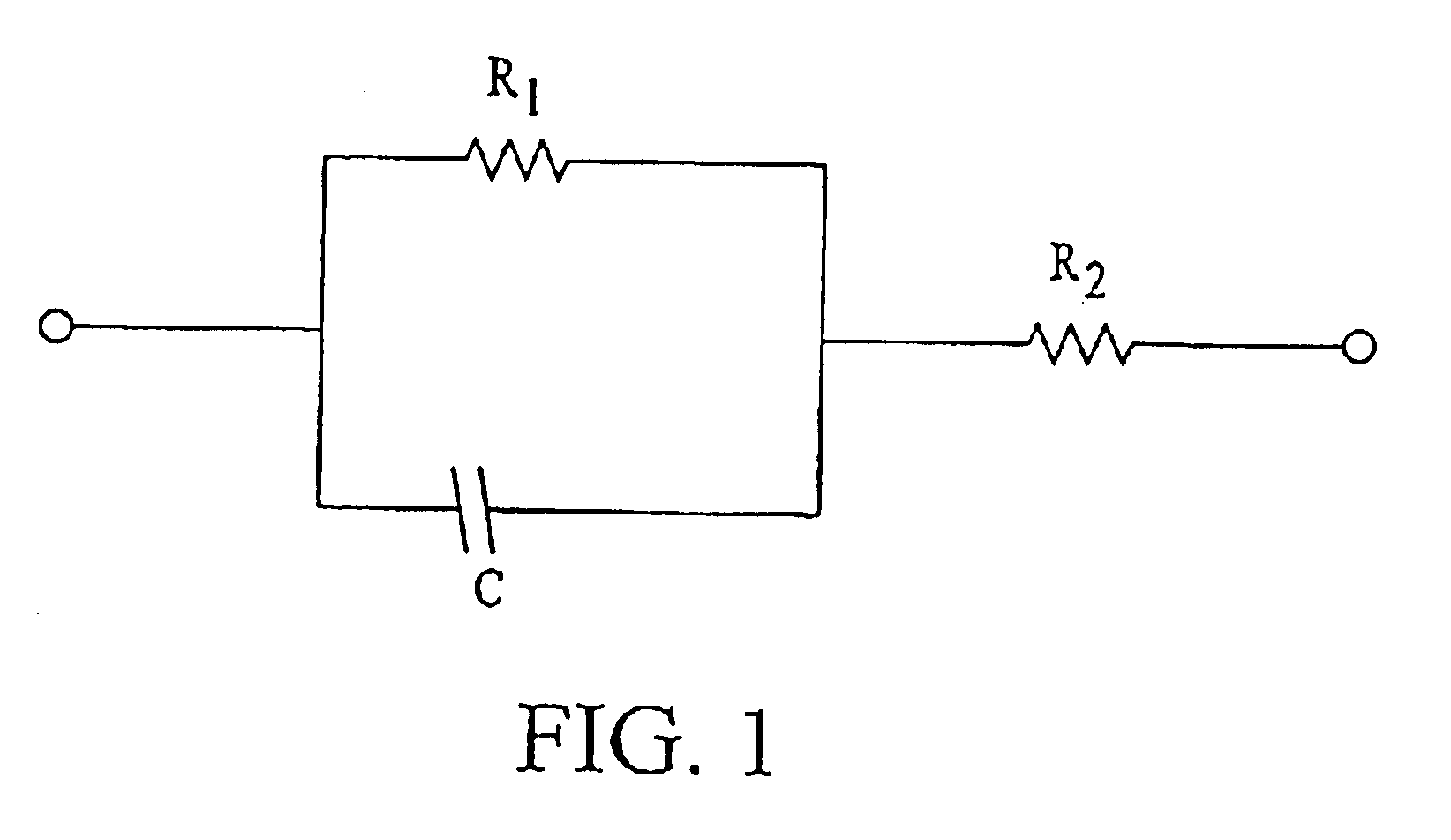
A method for manufacturing a multi-layer acoustic transducer with reduced total electrical impedance. The method is based on the bonding of two piezoelectric ceramic layers with confronting metallized surfaces to a thin electrical conductor, then electrically connecting the top and bottom surfaces to form a wrap-around electrode while a center conductor forms a second electrode. The total electrical impedance of a two-layer ceramic stack comprised of piezoelectric layers connected in this manner is one-fourth that of a solid ceramic element of the same size. This provides for better matching of the acoustic stack impedance to that of the electrical cable, increased penetration depth for imaging within the body, and improved acoustic element sensitivity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation for transmission and reception of electrical signals
InactiveUS20050049474A1Improve performanceImprove fidelityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricitySkin integrity
The invention provides a convenient and non-invasive means to prepare cells, tissues, and organs for electrical transmission and reception. In an embodiment of the invention, a control method comprises the use of at least one skin electrode, as a reference electrode, and an electrical sensor to measure periodically or continuously the skin's electrical conductance at the site of preparation. The dynamic change in the conductance through the skin is measured while the ultrasound is applied. Signal processing is performed on the measurement and the level of skin impedance change is controlled by performing a mathematical analysis and using the results of such analysis to control the application of ultrasonic energy. A desired level of skin impedance can be set at a predetermined value or based on a chosen level of skin integrity, subject's sensation of discomfort, or duration of the ultrasound application.
Owner:SONTRA MEDICAL
Method for making a transducer
InactiveUS6868594B2Decrease open-circuit sensitivityDecreased open-circuit sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerPolymer
A method for producing transducers having a 1-3 composite structure. The transducer element includes a plurality of thin piezoceramic wafers which are electroded on opposing major surfaces. The spaced wafers are separated by a passive polymer layer in a composite structure and the electrodes on the opposing major surfaces are connected to different ones of top and bottom electrode surfaces.
Owner:GUARDIAN IND CORP
Method for making multi-layer ceramic acoustic transducer
InactiveUS7156938B2Reduce electrical impedanceImprove matchPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyLamination ancillary operationsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Methods for preparing a multi-layer acoustic transducer with reduced total electrical impedance. The methods are based on the stacking of individual piezoelectric layers with metallized surfaces to form a plate in which the metal layers are electrically connected to form interdigitated electrodes. The total electrical impedance of a multi-layer stack comprised of piezoelectric layers connected in this manner is inversely related to the square of the number of layers in the stack. This provides for better matching of the acoustic stack impedance to that of the electrical cable and improved acoustic element sensitivity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
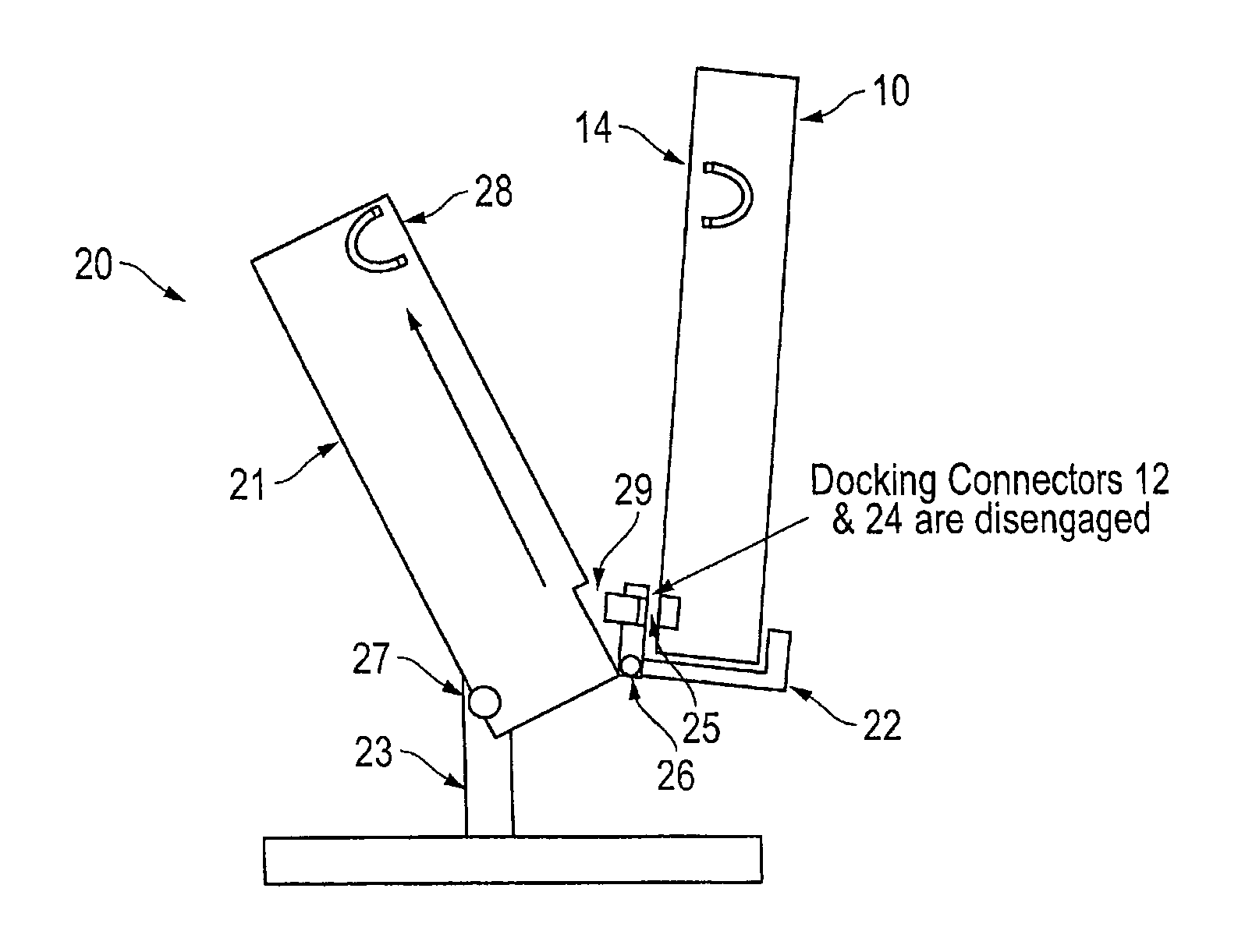
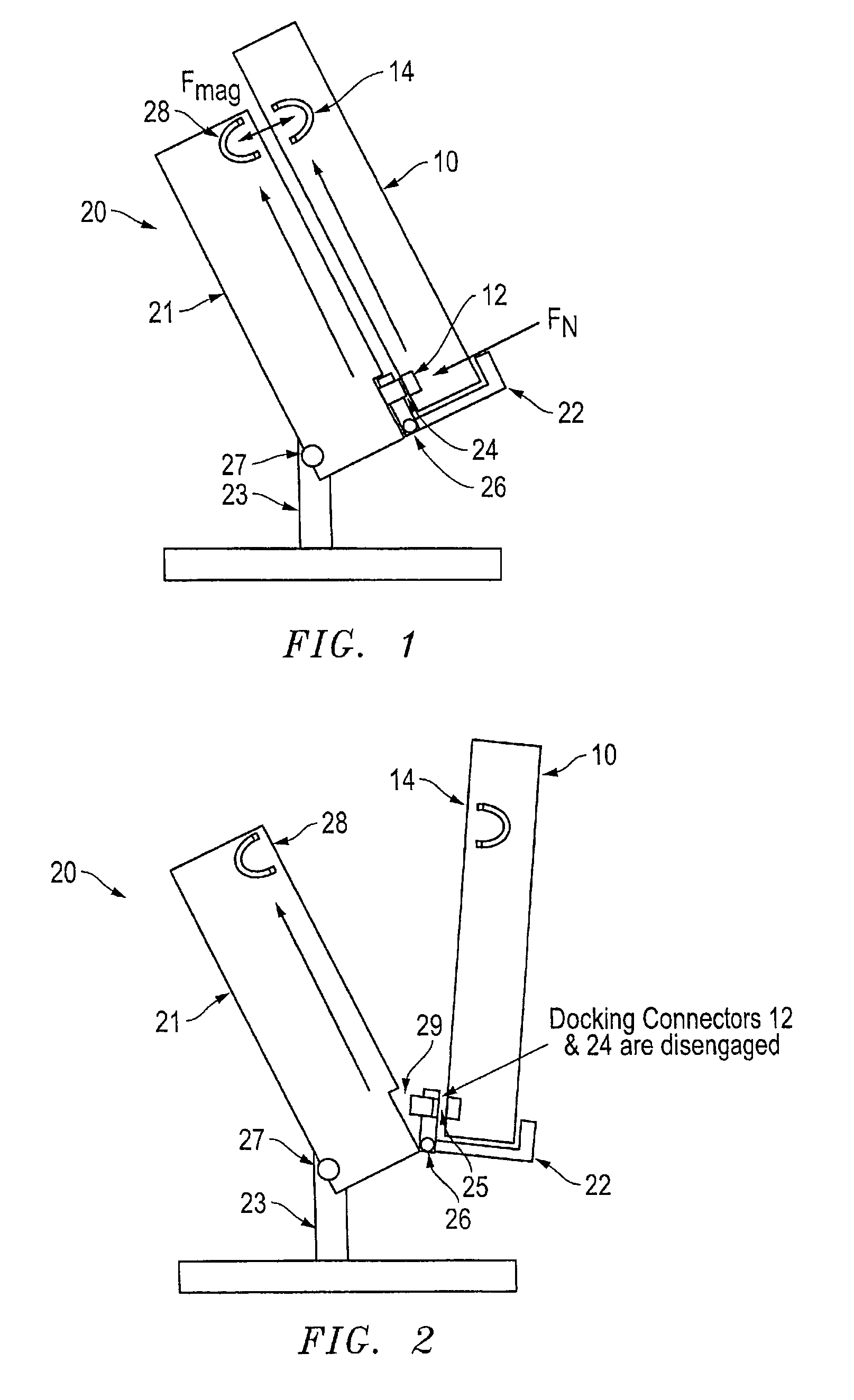
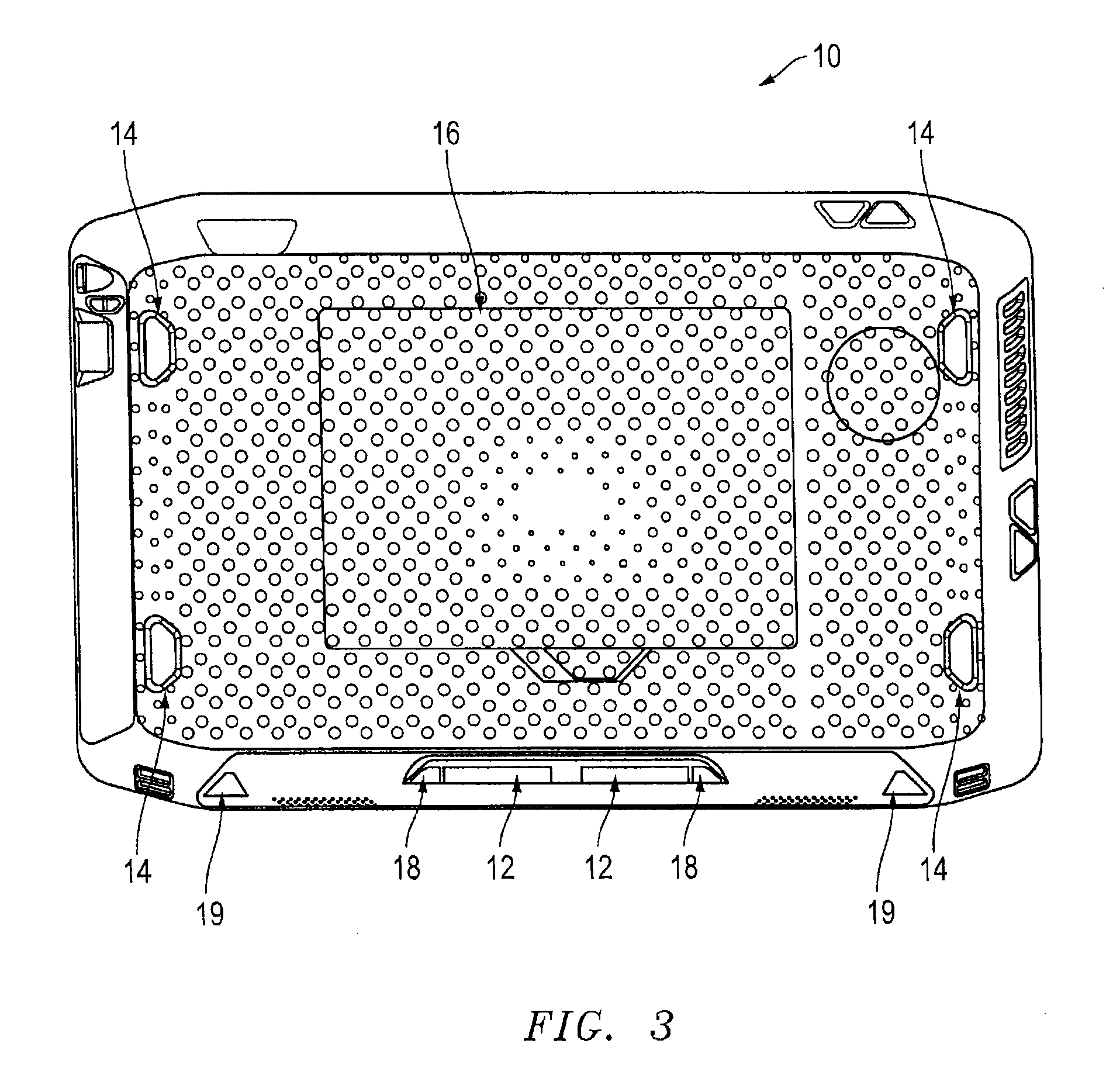
Portable electronic device to a docking station with improved docking and retention features
ActiveUS9429994B1Simple processReduce the number of stepsDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersDocking stationEmbedded system
According to one embodiment, a docking station is provided with a support surface configured for supporting a back surface of a portable electronic device, a rotating cradle configured for receiving a base of the portable electronic device, and a floating docking connector that extends out of a recess of the rotating cradle for connecting to a docking connector of the portable electronic device. According to one embodiment, the support surface of the docking station may include one or more magnetic structures, which are positioned to align with one or more magnetic structures on the back surface of the portable electronic device and configured to provide a magnetic force to retain the portable electronic device on the support surface.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Thin leadless plastic chip carrier
ActiveUS7081403B1Reduce attachmentShorten the lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Method for making multi-layer ceramic acoustic transducer
ActiveUS20050099097A1Reduce electrical impedanceImprove matchPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Methods for preparing a multi-layer acoustic transducer with reduced total electrical impedance. The methods are based on the stacking of individual piezoelectric layers with metallized surfaces to form a plate in which the metal layers are electrically connected to form interdigitated electrodes. The total electrical impedance of a multi-layer stack comprised of piezoelectric layers connected in this manner is inversely related to the square of the number of layers in the stack. This provides for better matching of the acoustic stack impedance to that of the electrical cable and improved acoustic element sensitivity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Microfluidic apparatus having an optimized electrowetting surface and related systems and methods
ActiveUS20170173580A1Reduce electrical impedanceLaboratory glasswaresMicroorganism fixing/supporting apparatusBiological cellAqueous droplet
Microfluidic devices having an electrowetting configuration and an optimized droplet actuation surface are provided. The devices include a conductive substrate having a dielectric layer, a hydrophobic layer covalently bonded to the dielectric layer, and a first electrode electrically coupled to the dielectric layer and configured to be connected to a voltage source. The microfluidic devices also include a second electrode, optionally included in a cover, configured to be connected to the voltage source. The hydrophobic layer features self-associating molecules covalently bonded to a surface of the dielectric layer in a manner that produces a densely-packed monolayer that resists intercalation and or penetration by polar molecules or species. Also provided are microfluidic devices having an electrowetting configuration that further include a section or module having a dielectrophoresis configuration; systems that include any of the microfluidic devices in combination with an aqueous droplet and a fluidic medium immiscible with the medium of the aqueous droplet; related kits; and methods of manipulating droplets, optionally containing micro-objects such as biological cells, within the microfluidic devices.
Owner:PHENOMEX INC
Method for making multi-layer ceramic acoustic transducer
InactiveUS7017245B2Reduce electrical impedanceImprove matchPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceSolid mass
A method for manufacturing a multi-layer acoustic transducer with reduced total electrical impedance. The method is based on the bonding of two piezoelectric ceramic layers with confronting metallized surfaces to a thin electrical conductor, then electrically connecting the top and bottom surfaces to form a wrap-around electrode while a center conductor forms a second electrode. The total electrical impedance of a two-layer ceramic stack comprised of piezoelectric layers connected in this manner is one-fourth that of a solid ceramic element of the same size. This provides for better matching of the acoustic stack impedance to that of the electrical cable, increased penetration depth for imaging within the body, and improved acoustic element sensitivity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
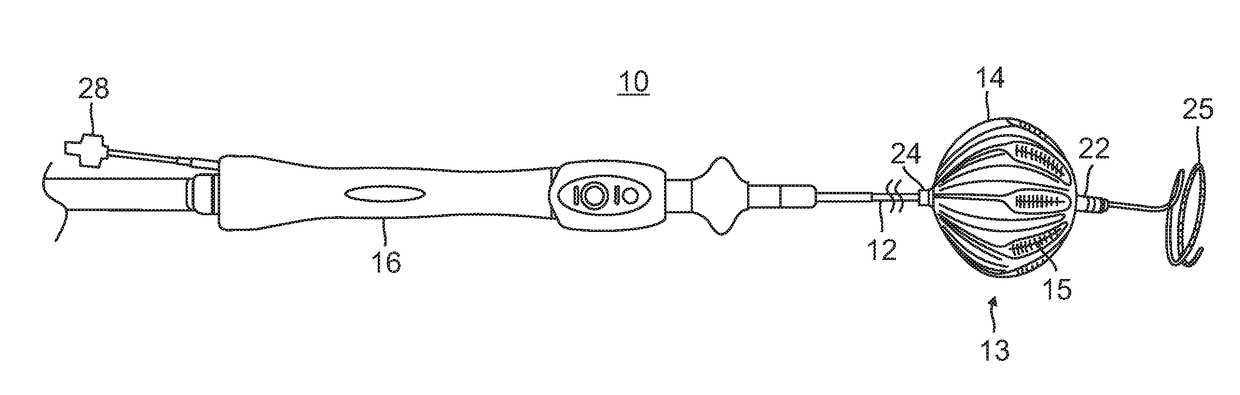
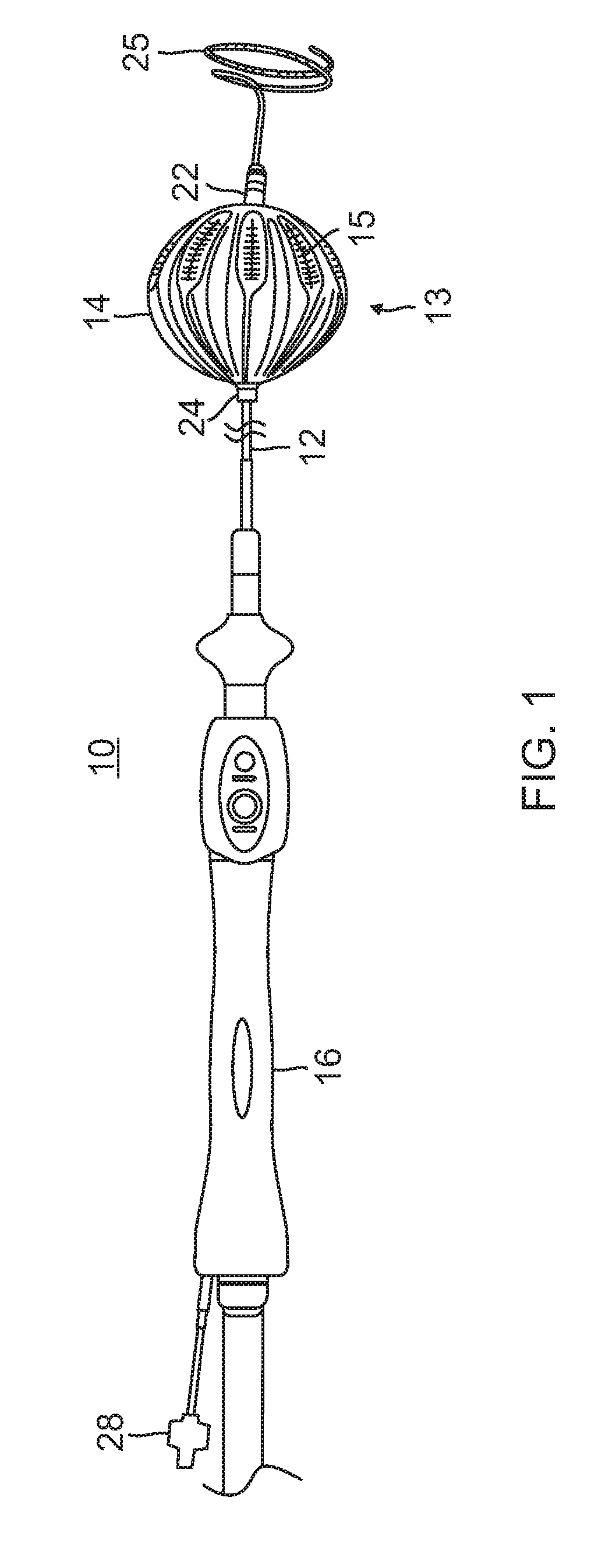
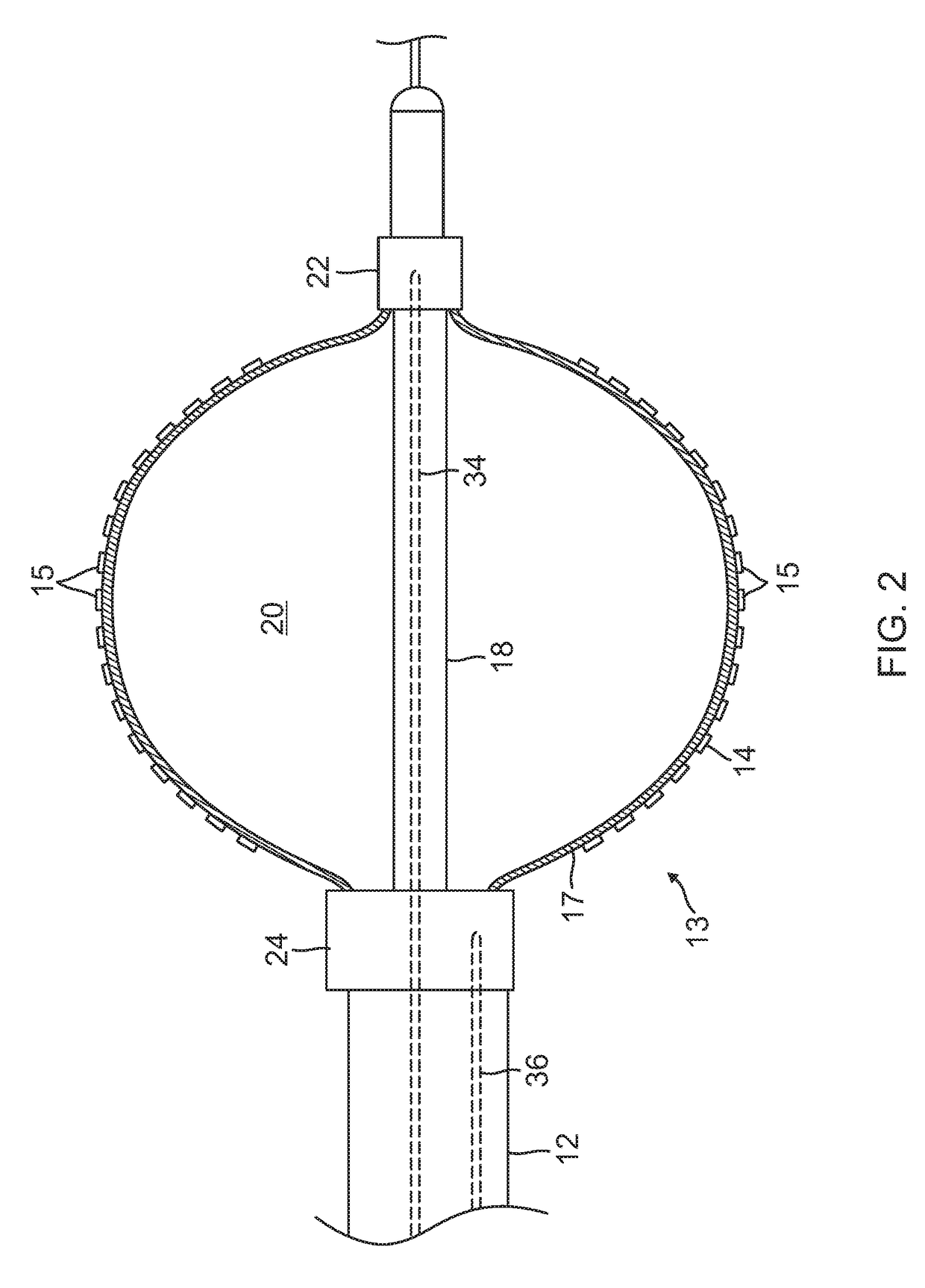
Balloon catheter and related impedance-based methods for detecting occlusion
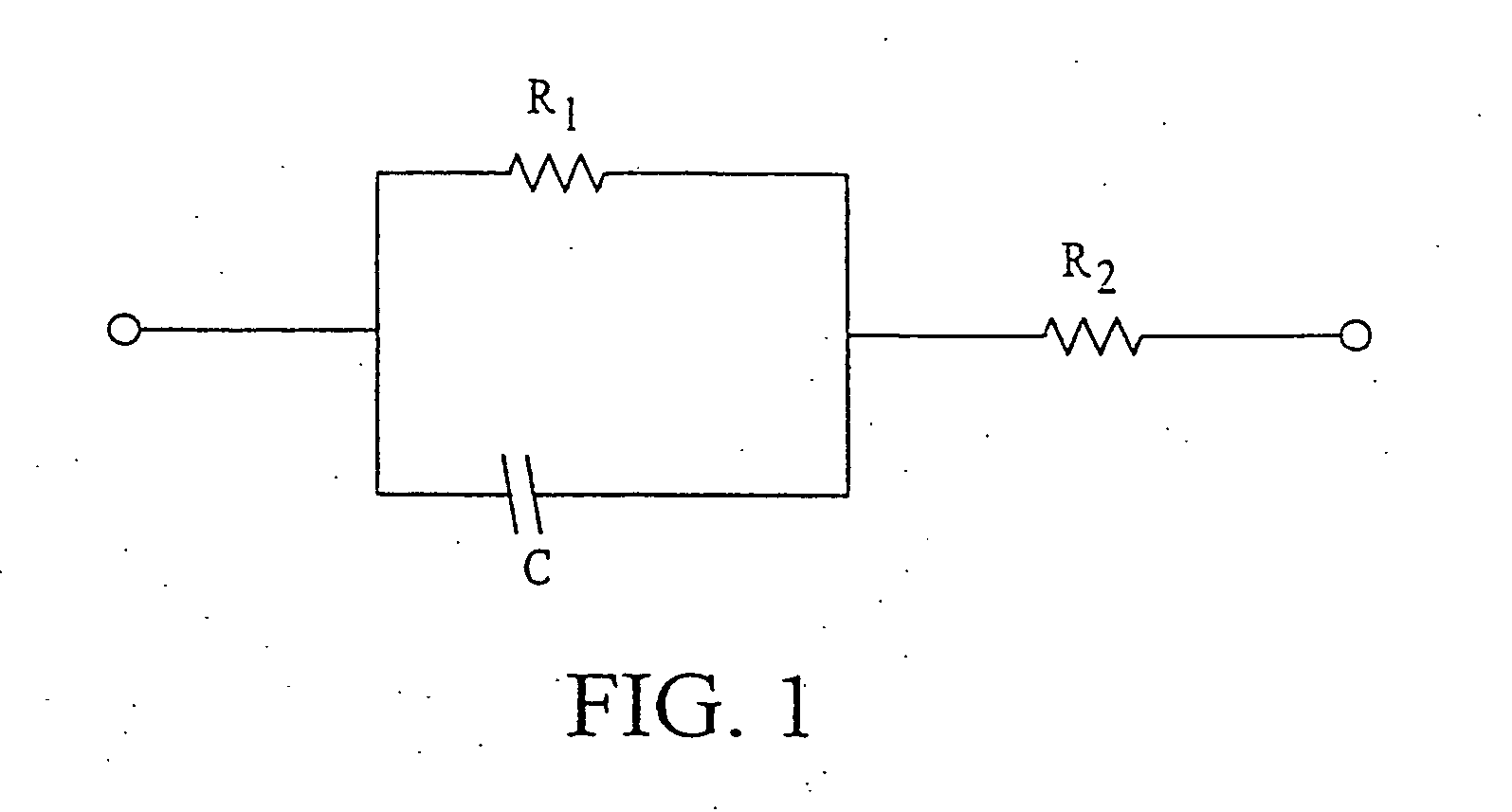
InactiveUS20170347896A1Reduce electrical impedanceHigh electrical impedanceBalloon catheterControlling energy of instrumentPower flowVoltmeter
A system for assessing occlusion of a region to blood flow includes a catheter with an inflatable member, a first electrode configured for placement upstream of the inflatable member and the second electrodes configured for placement downstream of the inflatable member, the inflatable member configured for inflation to occlude the blood flow through the region. The system further includes a current / voltage source, a resistor and a voltmeter, wherein these components along with the first and second electrodes are configured to form an impedance measuring circuit configured to detect a change in impedance for indicating occlusion of the region to the blood flow.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Leadless plastic chip carrier and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS7410830B1Shorten the lengthReduce electrical impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesShell moldingLead bonding
A process for fabricating a leadless plastic chip carrier includes providing a leadframe including a plurality of contacts circumscribing a void; fixing a heat sink to the contacts of the leadframe using an intermediate non-electrically conductive adhesive such that the heat sink spans the void; mounting a semiconductor die to the heat sink in the void; wire bonding ones of the contacts to the pads of the semiconductor die; encapsulating the semiconductor die and the wire bonds in a molding material and singulating the leadless plastic chip carrier.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
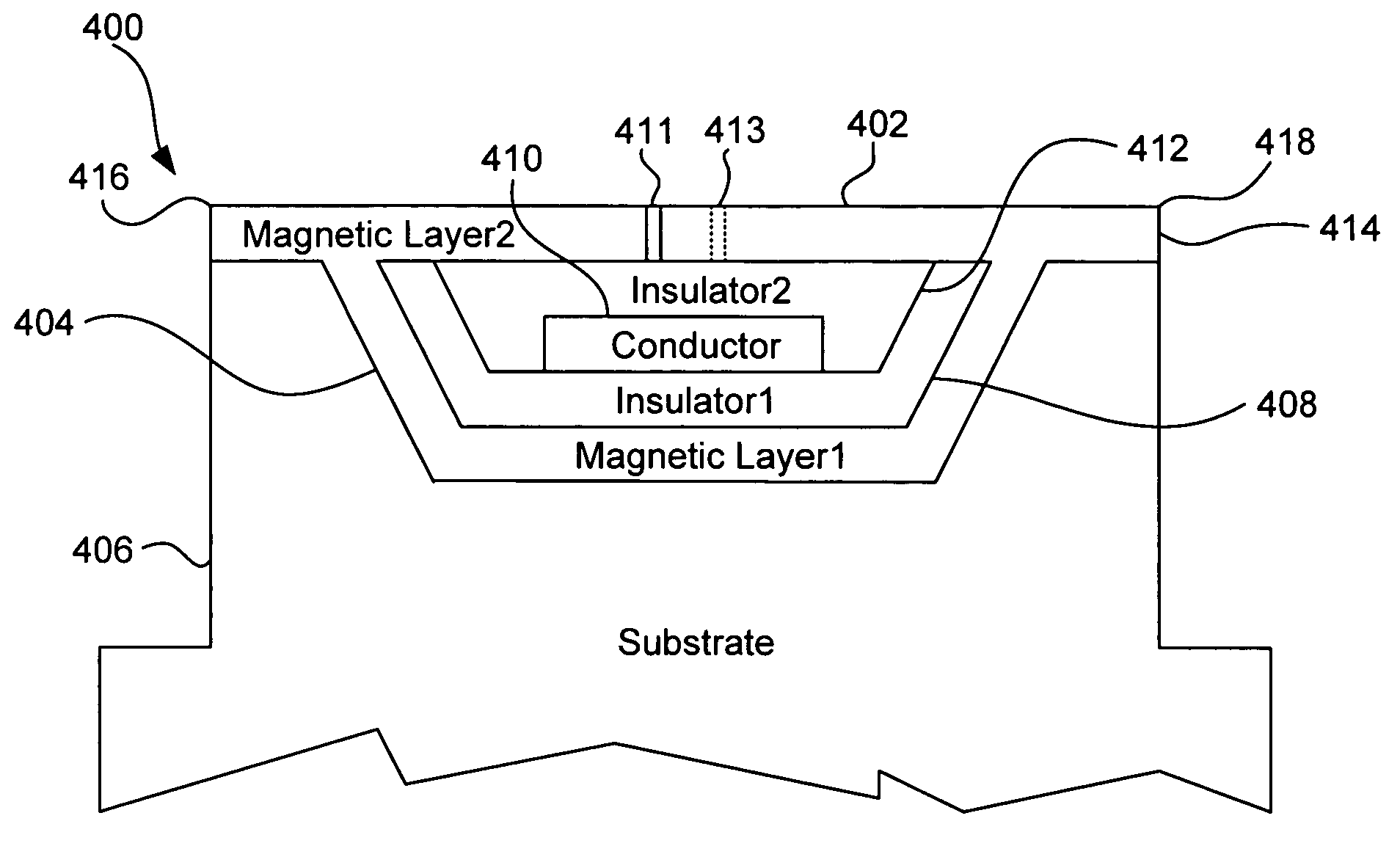
Method for fabricating magnetic write heads
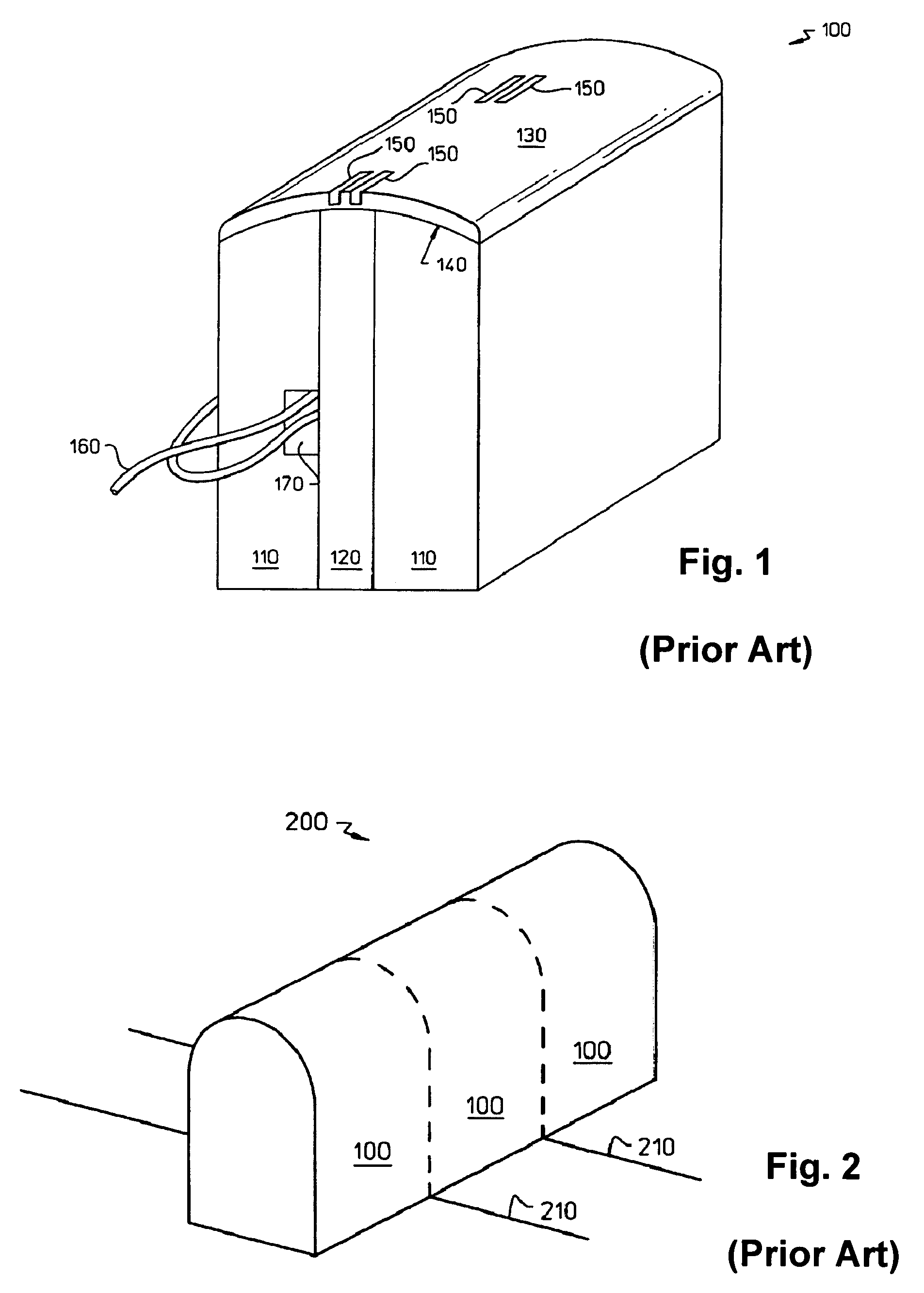
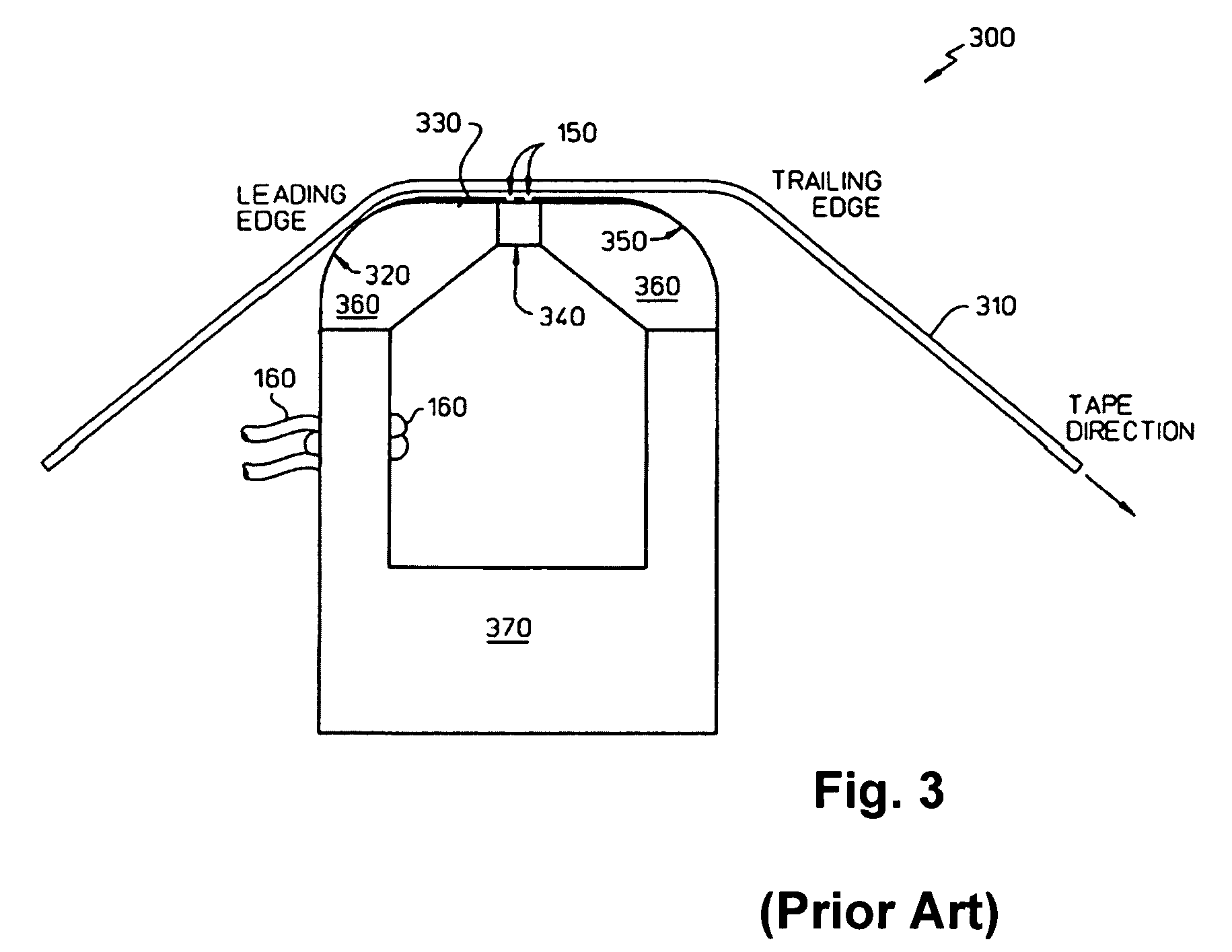
InactiveUS7322096B2Reduce spanImprove abilitiesManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersMagnetic fluxMagnetic layer
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
VCSEL fault location apparatus and method
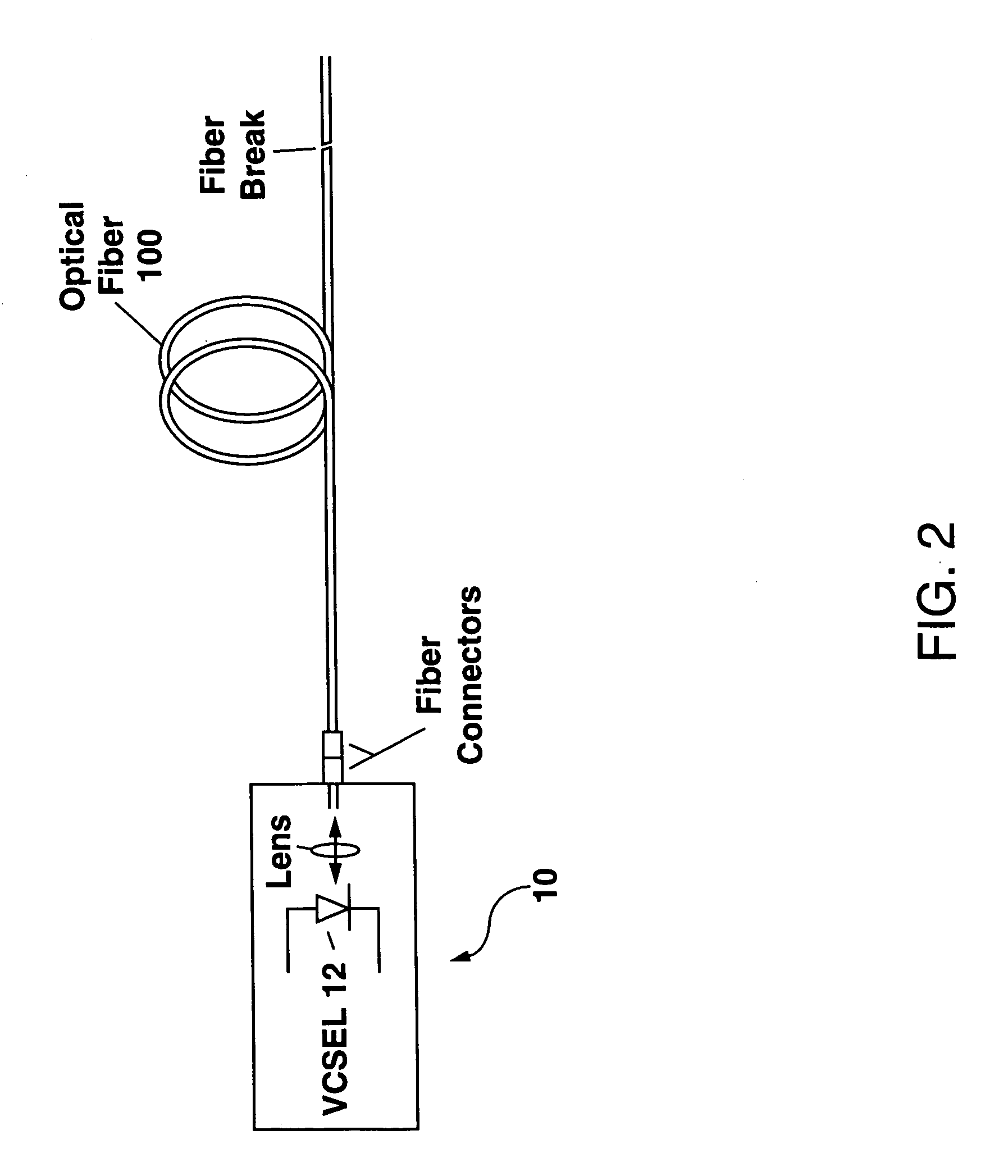
ActiveUS7218388B1Reduce electrical impedanceHigh impedanceMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainResonant cavityFiber
An apparatus for locating a fault within an optical fiber is disclosed. The apparatus, which can be formed as a part of a fiber-optic transmitter or as a stand-alone instrument, utilizes a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) to generate a test pulse of light which is coupled into an optical fiber under test. The VCSEL is subsequently reconfigured by changing a bias voltage thereto and is used as a resonant-cavity photodetector (RCPD) to detect a portion of the test light pulse which is reflected or scattered from any fault within the optical fiber. A time interval Δt between an instant in time when the test light pulse is generated and the time the reflected or scattered portion is detected can then be used to determine the location of the fault within the optical fiber.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Embedded wire planar write head system and method
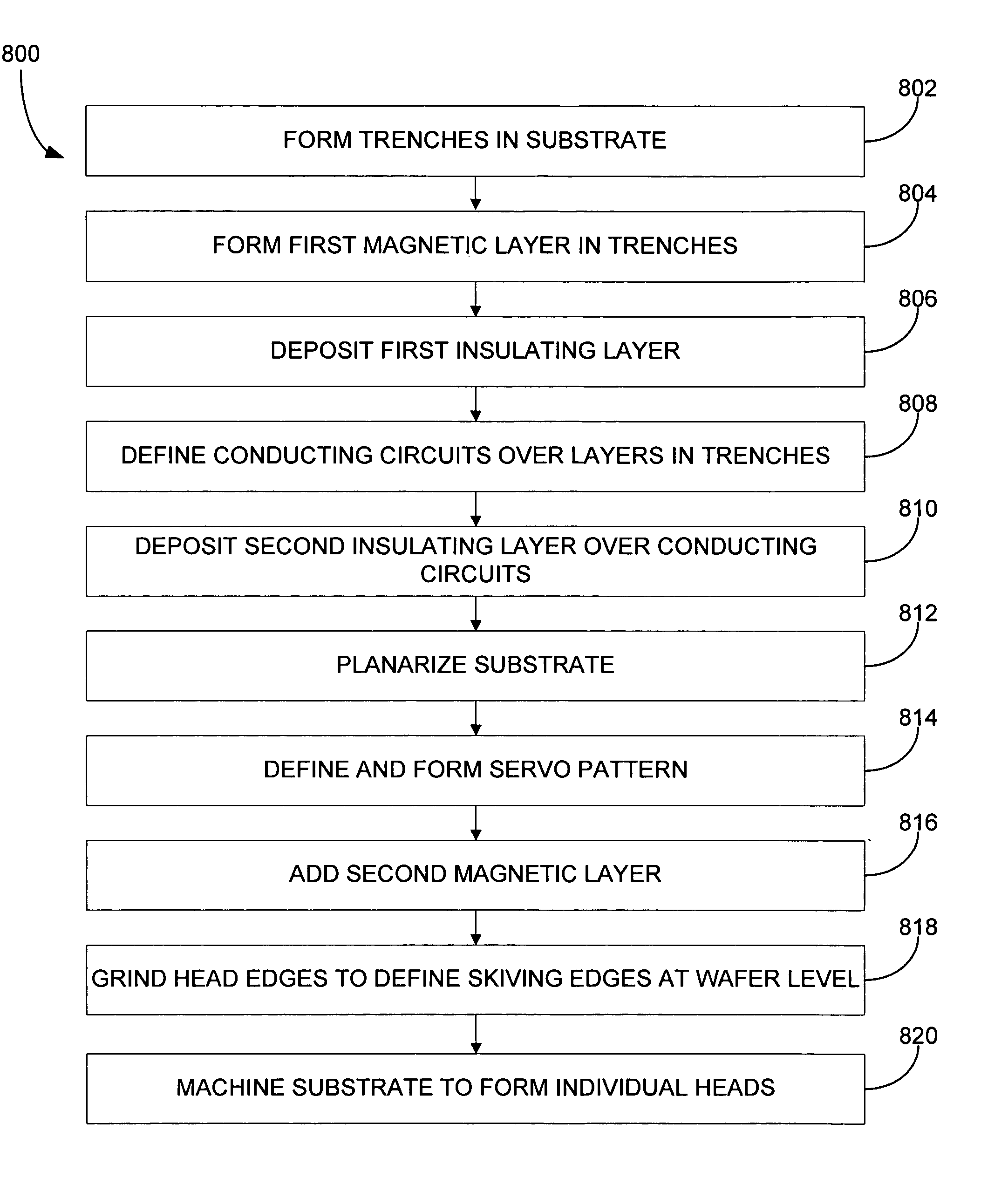
InactiveUS20050235483A1Reduce spanImprove abilitiesElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceHemt circuitsEngineering
A magnetic write head and method for bulk fabrication of the same are provided. A trench is formed in a nonmagnetic substrate. A first magnetically permeable layer is deposited in the trench of the substrate. An optional first insulating layer is deposited in the trench. A conducting circuit is defined in the trench. The conducting circuit creates the magnetic flux. An optional second insulating layer is deposited in the trench. Writer gaps are patterned and then a second magnetic layer is added over the second insulating layer. The substrate is divided to form individual write heads.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Coating metal with excellent heat diffusion character
InactiveCN1847337AUse effectivelyGood heat dissipationLiquid surface applicatorsMetal layered productsResin coatingPorous particle
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a coated metal material excellent in radiation properties and useful as the material of a casing for housing an electronic device having a heat source built therein (including an electric device or optical device having the heat source built therein) or the like, and an electronic device component using the coated metal material. SOLUTION: The coated metal material excellent in radiation properties is a coated metal member constituted by forming at least one resin coating film on one side or both sides of a metal base material and characterized in that the outermost layer of the coated metal member contains porous particles having pores with a pore size of 1-1,000 nm opened to their surfaces in a state at least partial exposed from the surface of the outermost layer and a coating film layer containing a radiant additive is preferably formed on the under layer side of the outermost layer. COPYRIGHT: (C)2007,JPO&INPIT
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN102122673AReduce the number of photomasksReduce manufacturing costTransistorOxide semiconductorElectricity
The invention discloses an oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and a preparing method thereof, the thin film transistor comprises a substrate, a gate electrode disposed on the substrate, a semiconductor insulation layer disposed on the substrate and the gate electrode, an oxide semiconductor layer disposed on the semiconductor insulation layer, a pattern semiconductor layer disposed on the oxide semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode respectively disposed on the pattern semiconductor layer and be a metal layer. The oxide semiconductor thin film transistor and a preparing method thereof are characterized in that, the pattern semiconductor layer is added between the oxide semiconductor layer and the metal layer, thereby protecting the oxide semiconductor layer from damage of etching liquid, obtaining lower electrical impedance to form ohmic contact and to obtain optimum electricity. Additionally, the number of photographic masks required by the technique is reduced, and effect of reducing production cost can be reached via matching of a wet etching technique and a dry etching technique.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Dry physiological recording device and method of manufacturing
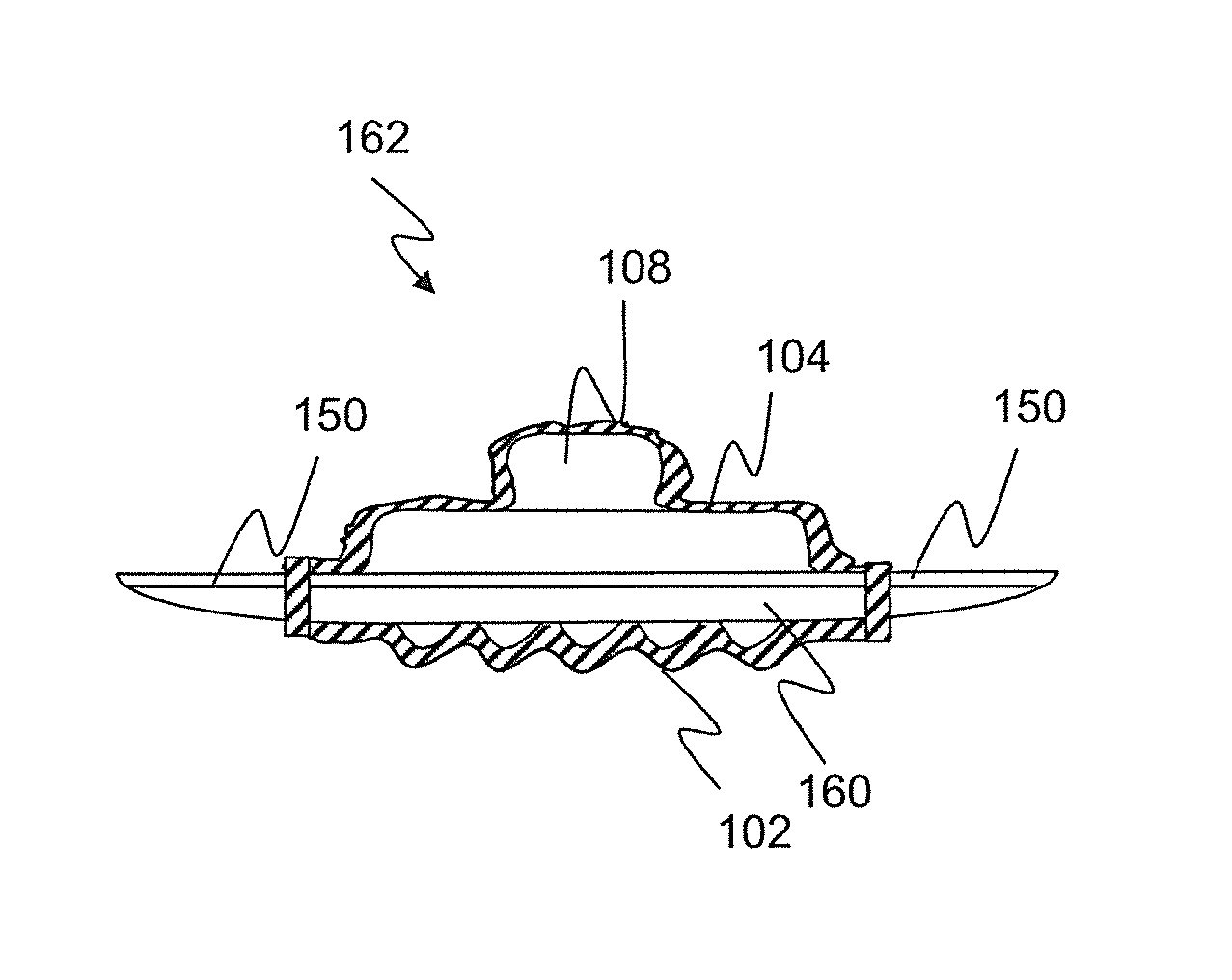
ActiveUS9192313B1Reduce material costsBetter electrical signalElectrocardiographyElectromyographyElectric signalBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed to a physiological recording device and, more particularly, to a physiological recording device that can be used without skin preparation or the use of electrolytic gels. The invention is further directed to an encouragement ring which stabilizes and helps situate the physiological recording device on a subject's skin to help provide a better electrical signal, increase surface area, and reduce and minimize noise and artifacts during the process of recording or monitoring a physiological signal. The invention is still further directed to surface features on a surface of the physiological recording device with a size and shape that will not substantially bend or break, which limits the depth of application of the recording device, and / or anchors the recording device during normal application. The invention is even further directed to a method for manufacturing a physiological recording device, and minimizing cost of manufacture.
Owner:ORBITAL RES
Voltage droop suppressing active interposer
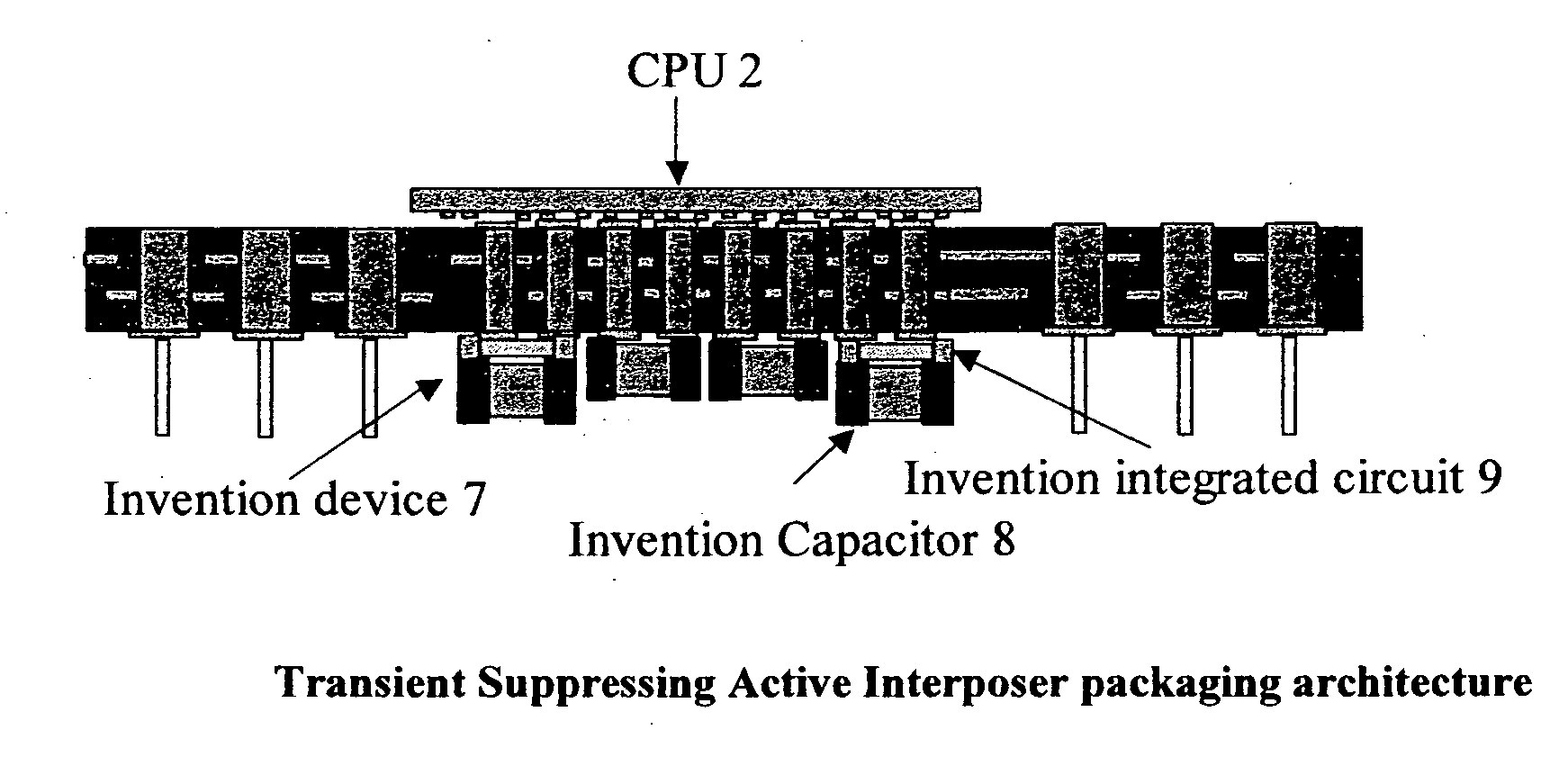
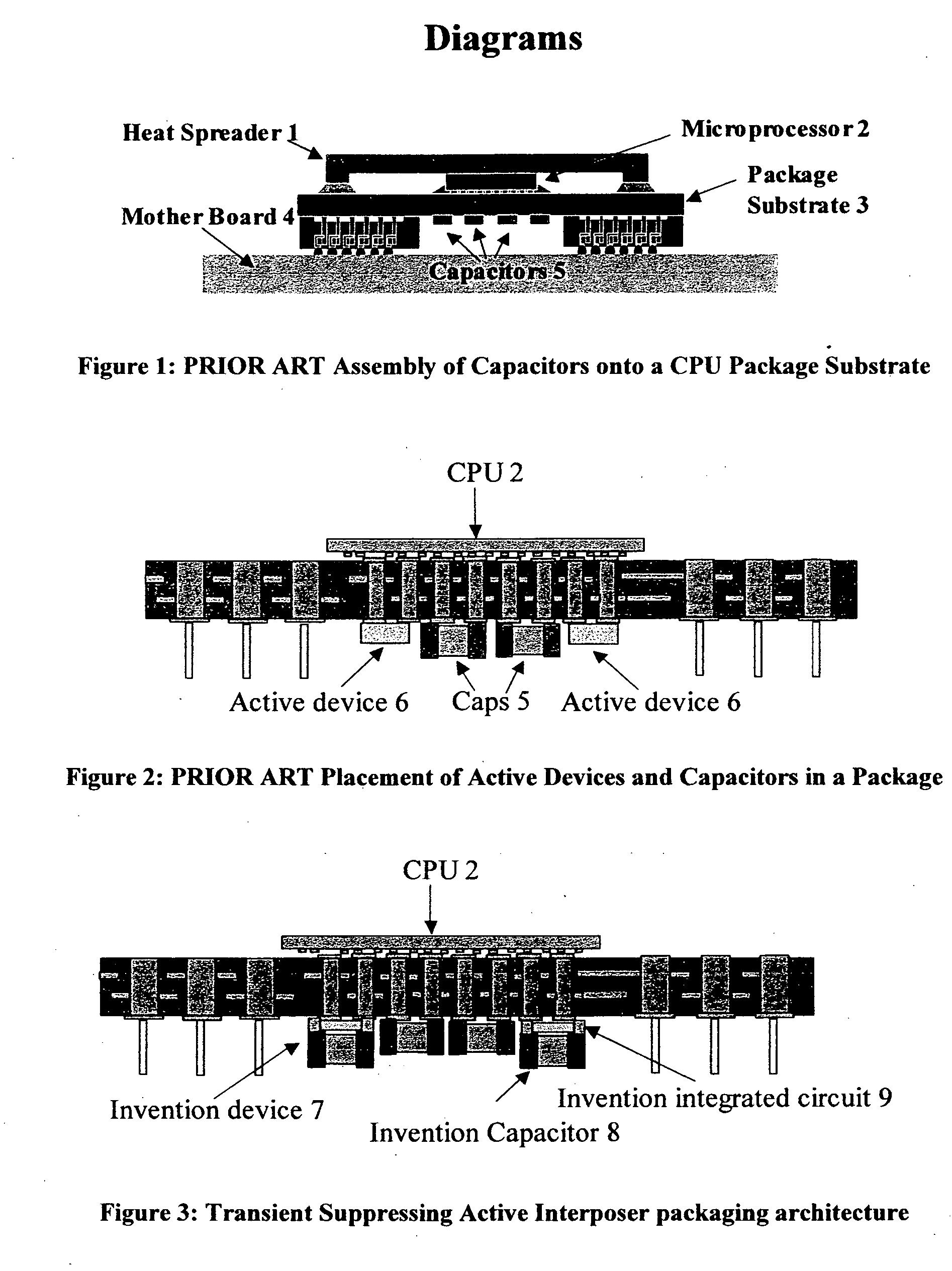
InactiveUS20050285252A1Reduction of electrical impedanceFast actionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVolume/mass flow measurementHigh frequencySemiconductor
The invention proposes an interposer assembly architecture for noise suppression circuits on the package of a CPU or high power, high frequency VLSI device. In this architecture, charge is stored on dedicated capacitors at a voltage substantially higher than the operating voltage of the VLSI device. These capacitors are mounted upon active circuits that are packaged to match the size and form factor of the capacitors and this assembly is then attached to the package substrate. Charge is conveyed from the capacitor terminals on the backside of the packaged active circuits chip. Depending upon the capacitor construction, these terminals may either be double-sided contact terminals along the edge of the active device's package, or may be feed-through contacts. The active device attaches to the package substrate through both edge terminals and terminals built-up on the surface of the chip, increasing it's number of electrical pathways into the package substrate, matching the package substrate interconnect and reducing the electrical impedance of the charge flow path. The circuits within the active device may be any combination of semiconductor switches and / or voltage regulators, and may also contain voltage and current sensing circuitry.
Owner:NAIR RAJENDRAN
Carbonaceous Nanocomposite Having Novel Structure And Fabrication Method Thereof
InactiveCN102482076AImprove adhesionGood heat dissipationMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationElectrical batteryCarbon nanotube
Disclosed is a carbonaceous nanocomposite, comprising: a substrate; a graphene sheet formed on a top surface of the substrate in parallel with the substrate; and a carbonaceous nano material provided at another surface of the graphene sheet, the material having an aspect ratio of 2 to 75,000 to make a predetermined angle with the graphene. The carbonaceous nanocomposite according to the present invention has excellent adhesion to the substrate and can be attached to the substrate without undergoing a pasting process. As a two-directional current flow is generated, the electrical resistance of the graphene and carbon nanotube is considerably reduced.; In addition, the carbon nanotube is configured to have a high current density through the graphene and a high specific surface area, thereby accelerating a redox reaction, and the excellent radiating property of the graphene sheet enables a speedy transfer of heat generated in the carbon nanotube to outside, thereby avoiding a degradation phenomenon of the carbon nanotube. Thus, when employed as an electrode for a battery or a field emission display, the present invention nanocomposite provides a higher current density and an extended life compared with the prior art.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Fully Cu-metallized III-V group compound semiconductor device with palladium/germanium/copper ohmic contact system
InactiveUS20090194846A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPlatinumOhmic contact
The present invention discloses a fully Cu-metallized III-V group compound semiconductor device, wherein the fully Cu-metallized of a III-V group compound semiconductor device is realized via using an N-type gallium arsenide ohmic contact metal layer formed of a palladium / germanium / copper composite metal layer, a P-type gallium arsenide ohmic contact metal layer formed of a platinum / titanium / platinum / copper composite metal layer, and interconnect metals formed of a titanium / platinum / copper composite metal layer. Thereby, the fabrication cost of III-V group compound semiconductor devices can be greatly reduced, and the performance of III-V group compound semiconductor devices can be greatly promoted. Besides, the heat-dissipation effect can also be increased, and the electric impedance can also be reduced.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com