Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146 results about "Memory refresh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
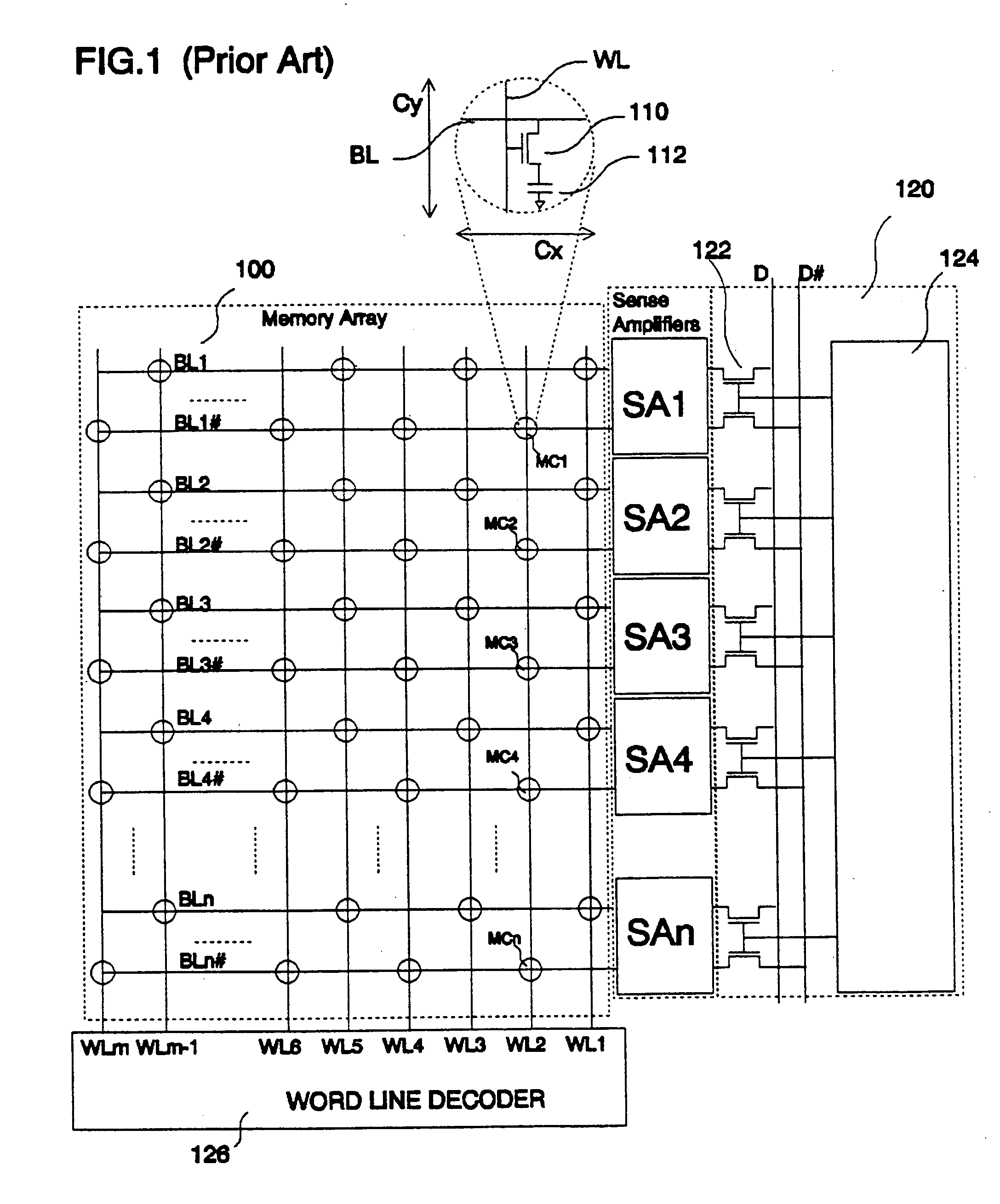
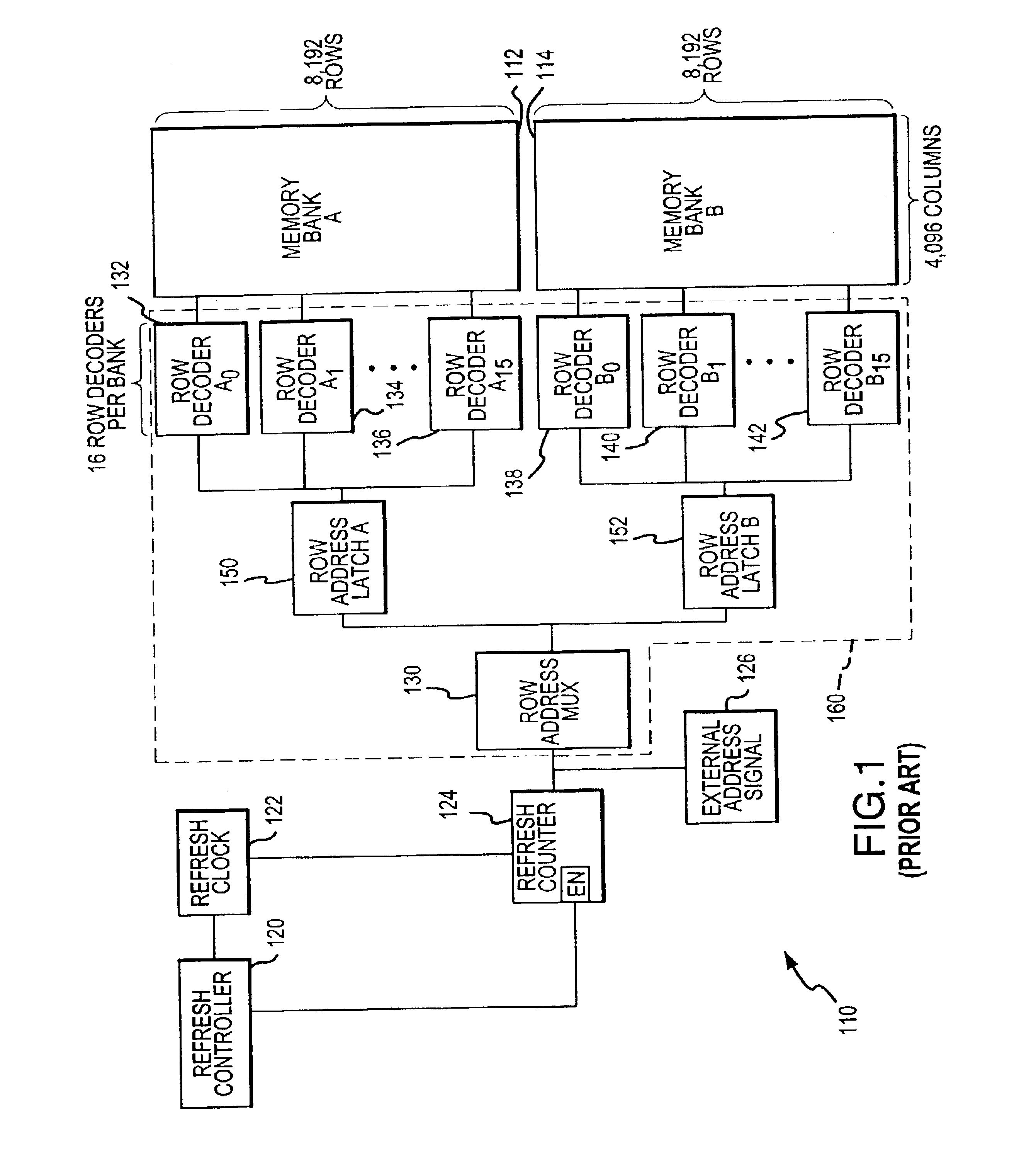
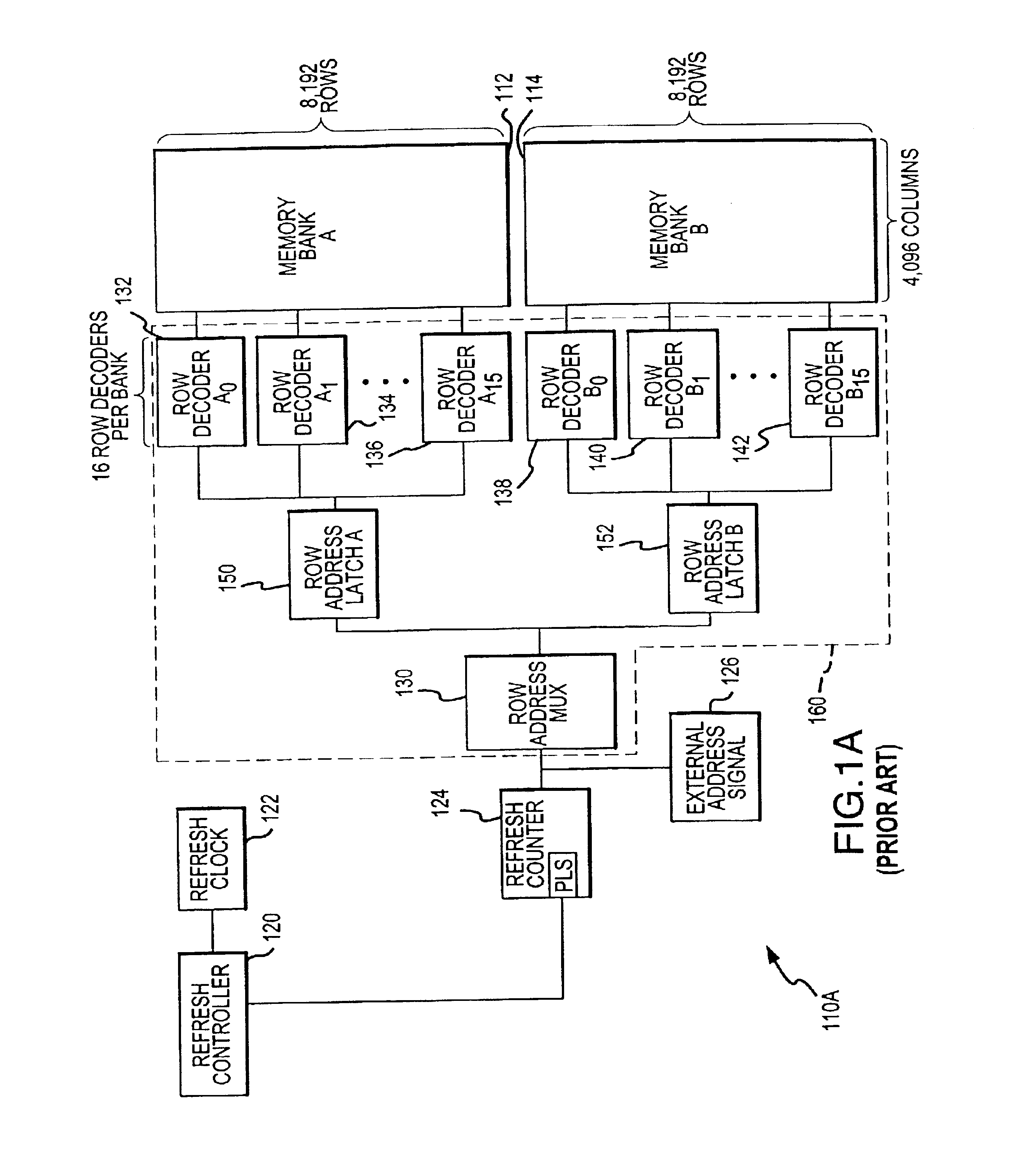
Memory refresh is the process of periodically reading information from an area of computer memory and immediately rewriting the read information to the same area without modification, for the purpose of preserving the information. Memory refresh is a background maintenance process required during the operation of semiconductor dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), the most widely used type of computer memory, and in fact is the defining characteristic of this class of memory.
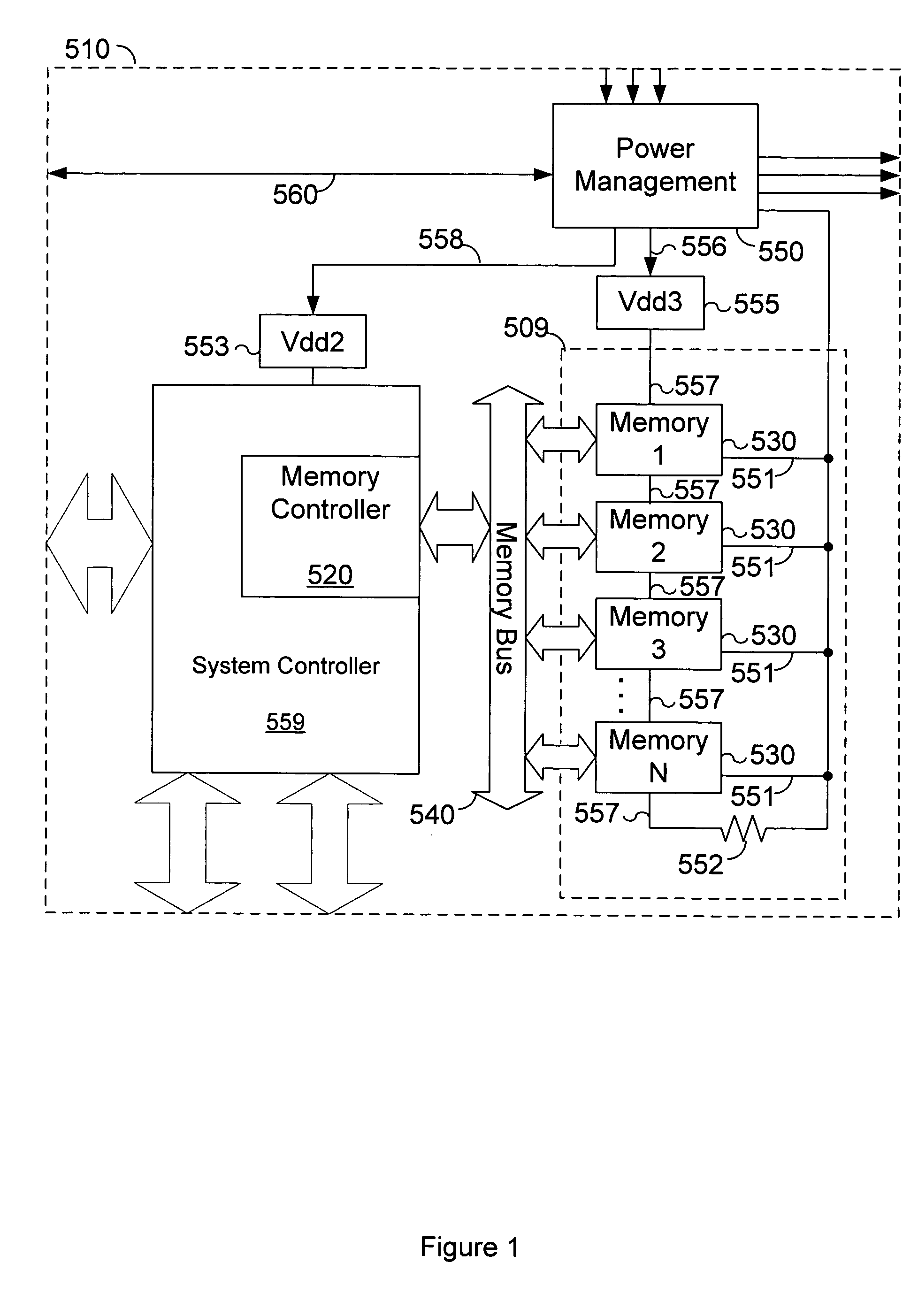
Power throttling in a memory system
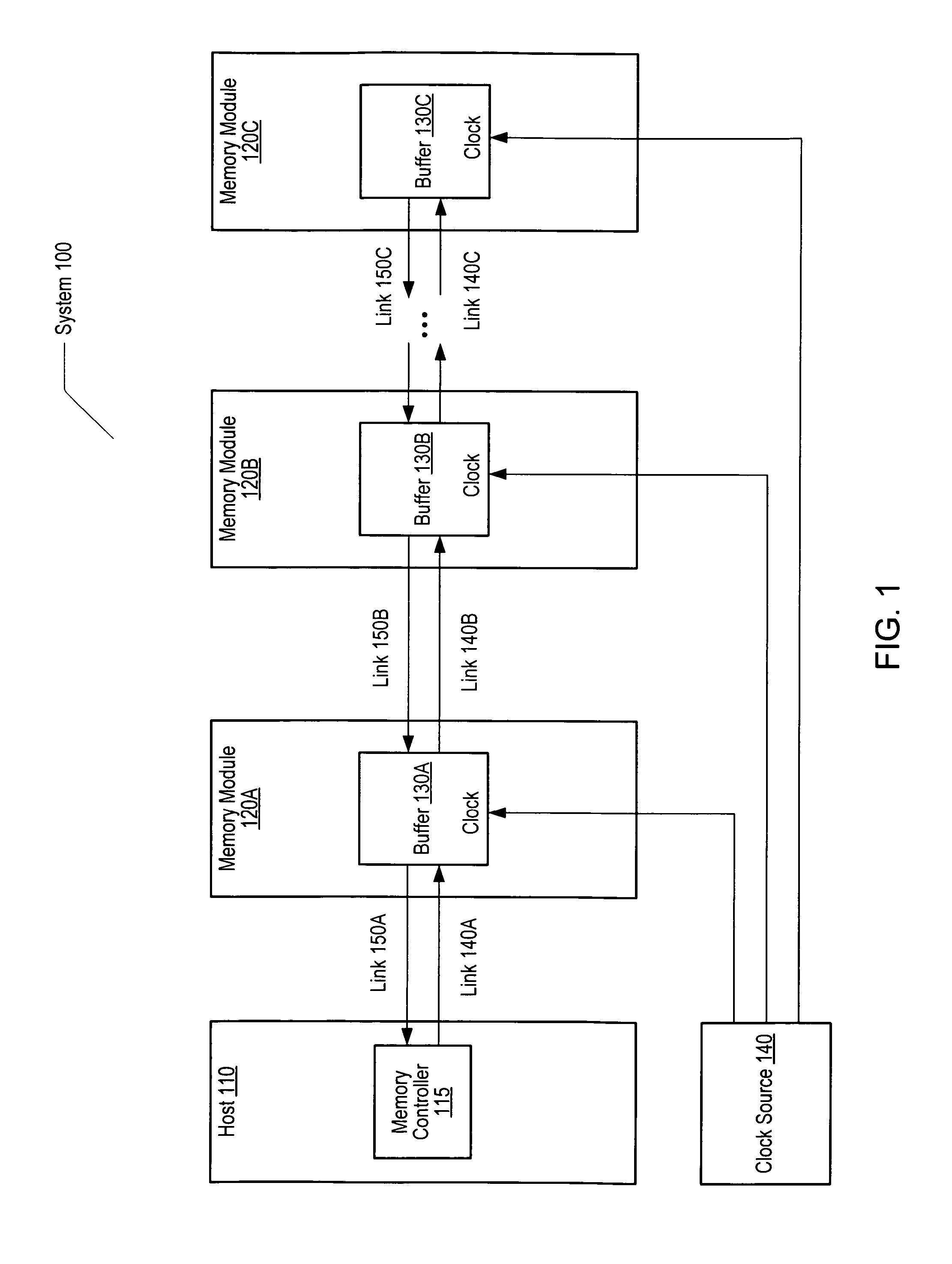
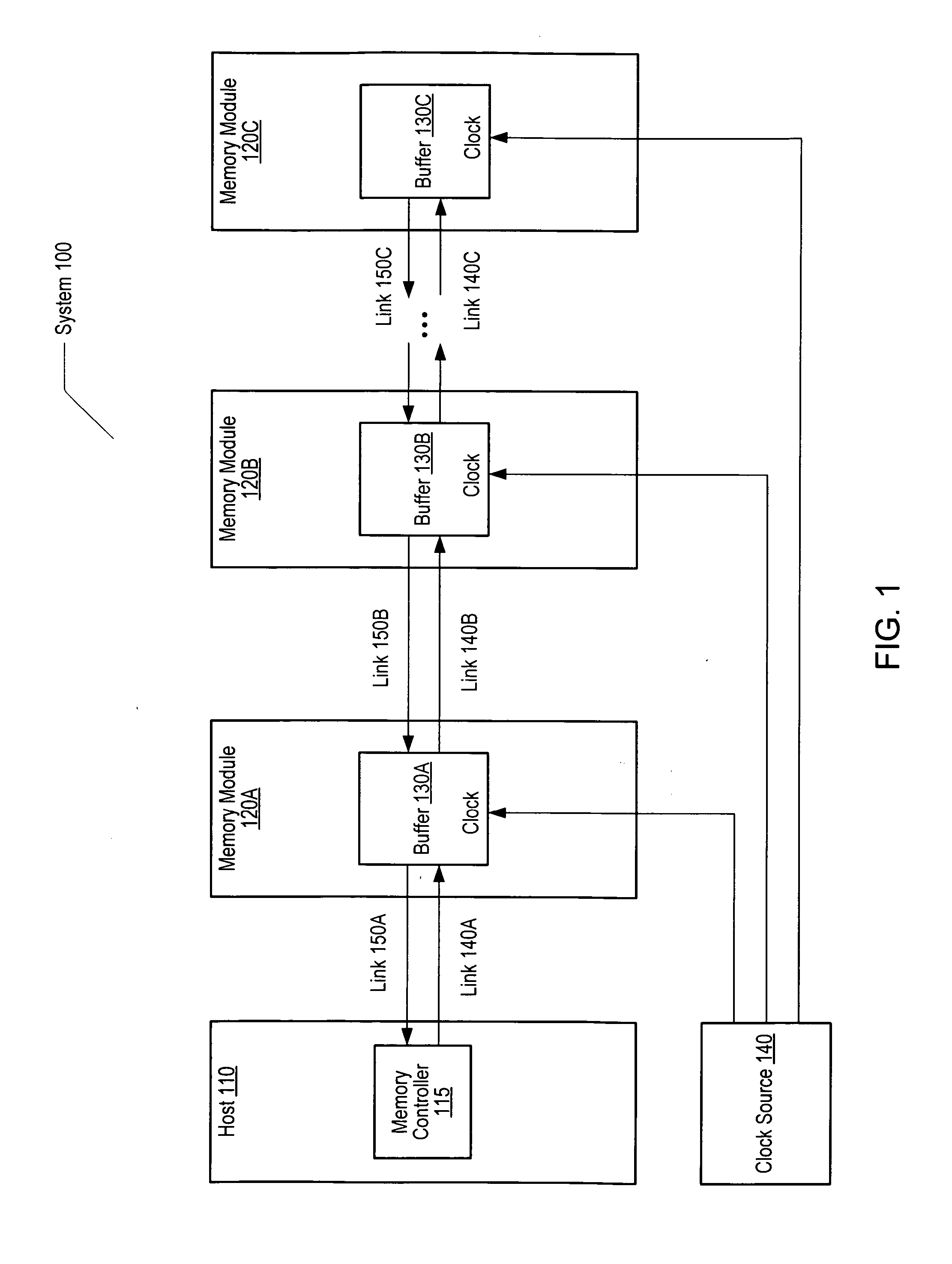
A memory system is disclosed. The memory system includes a memory controller coupled to one or more memory modules, at least one of the memory modules including a buffer. The memory controller is configured to convey a command to at least one of the memory modules in response to detecting that no memory requests addressed to the at least one of the memory modules have been received during a specified window of time. In response to the command, the buffer of the at least one of the memory modules is configured to enter a reduced power state. The specified window of time may be either a specified number of memory refresh intervals or buffer sync intervals. The memory controller maintains a count of memory refresh or buffer sync intervals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Power throttling in a memory system
ActiveUS20070083701A1Low power stateEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTerm memorySnubber
A memory system is disclosed. The memory system includes a memory controller coupled to one or more memory modules, at least one of the memory modules including a buffer. The memory controller is configured to convey a command to at least one of the memory modules in response to detecting that no memory requests addressed to the at least one of the memory modules have been received during a specified window of time. In response to the command, the buffer of the at least one of the memory modules is configured to enter a reduced power state. The specified window of time may be either a specified number of memory refresh intervals or buffer sync intervals. The memory controller maintains a count of memory refresh or buffer sync intervals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
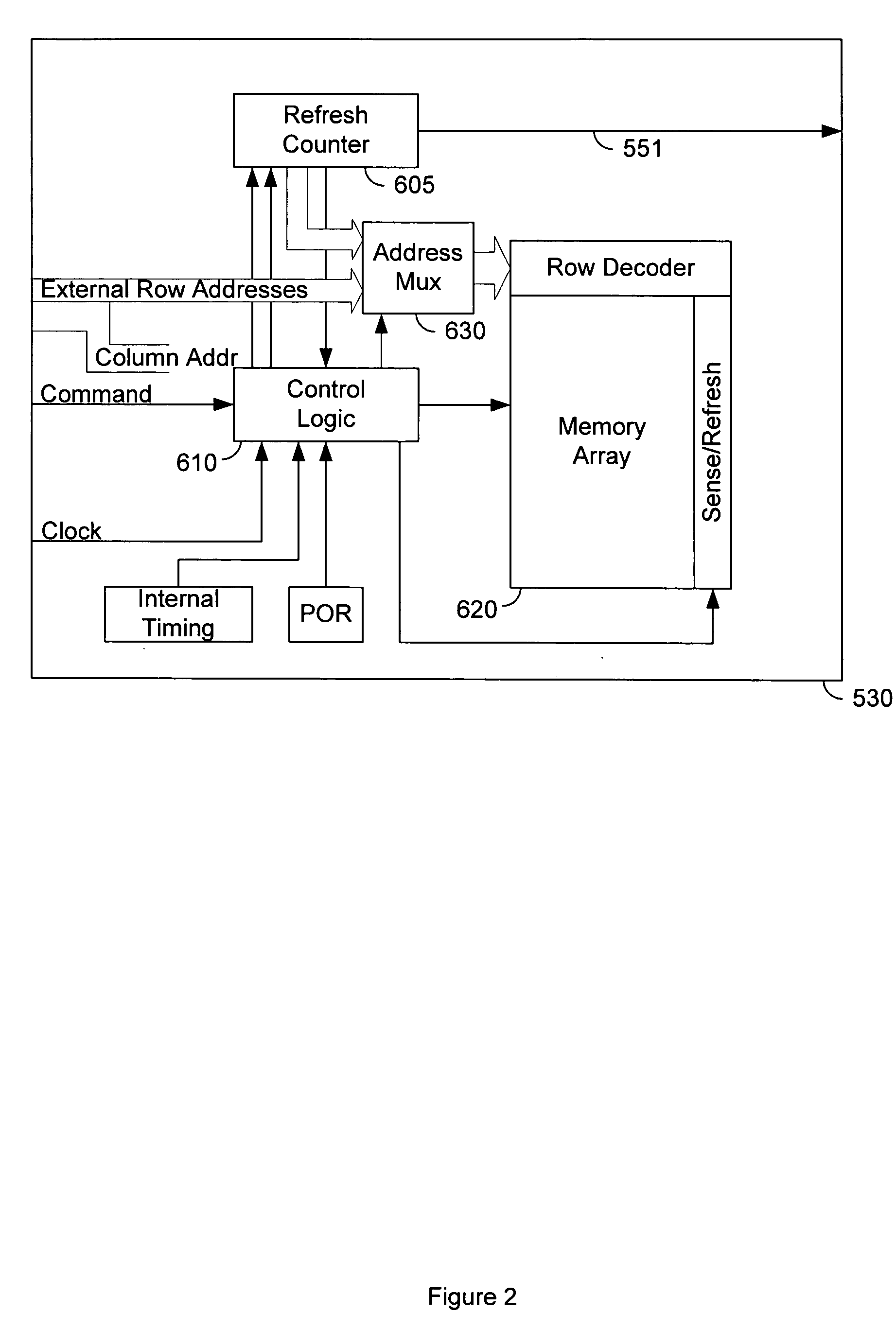
Method, apparatus and system for providing a memory refresh
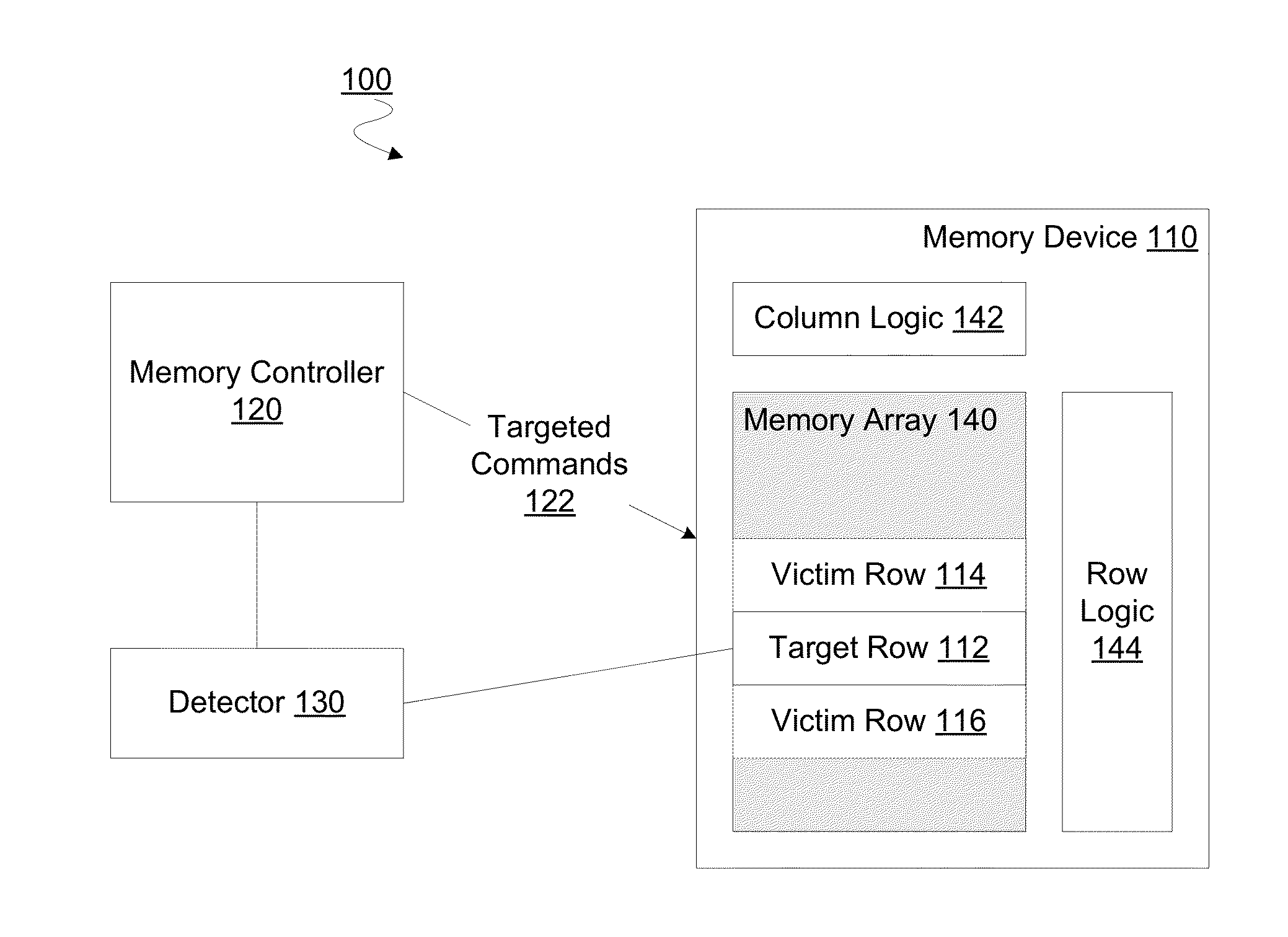
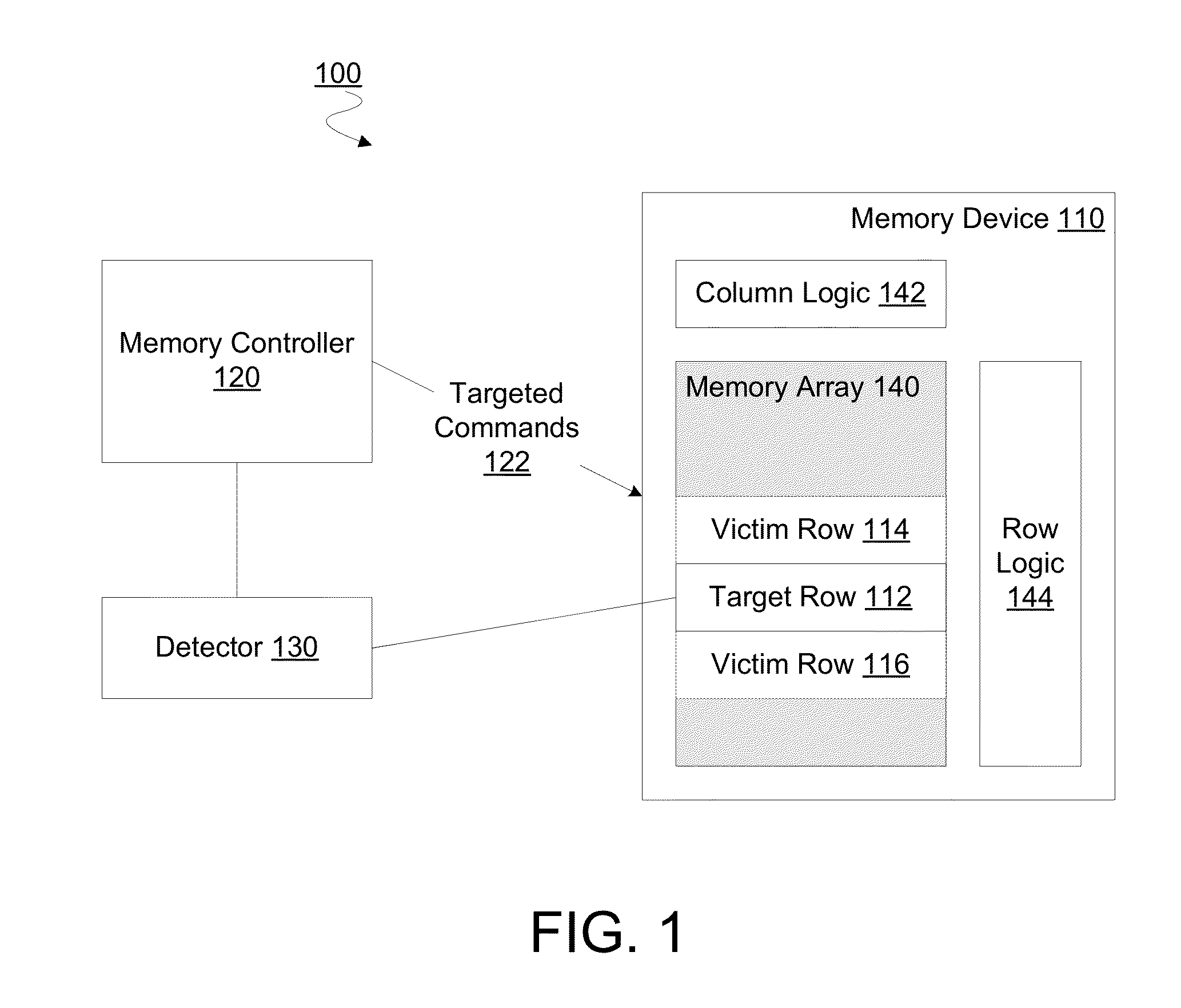
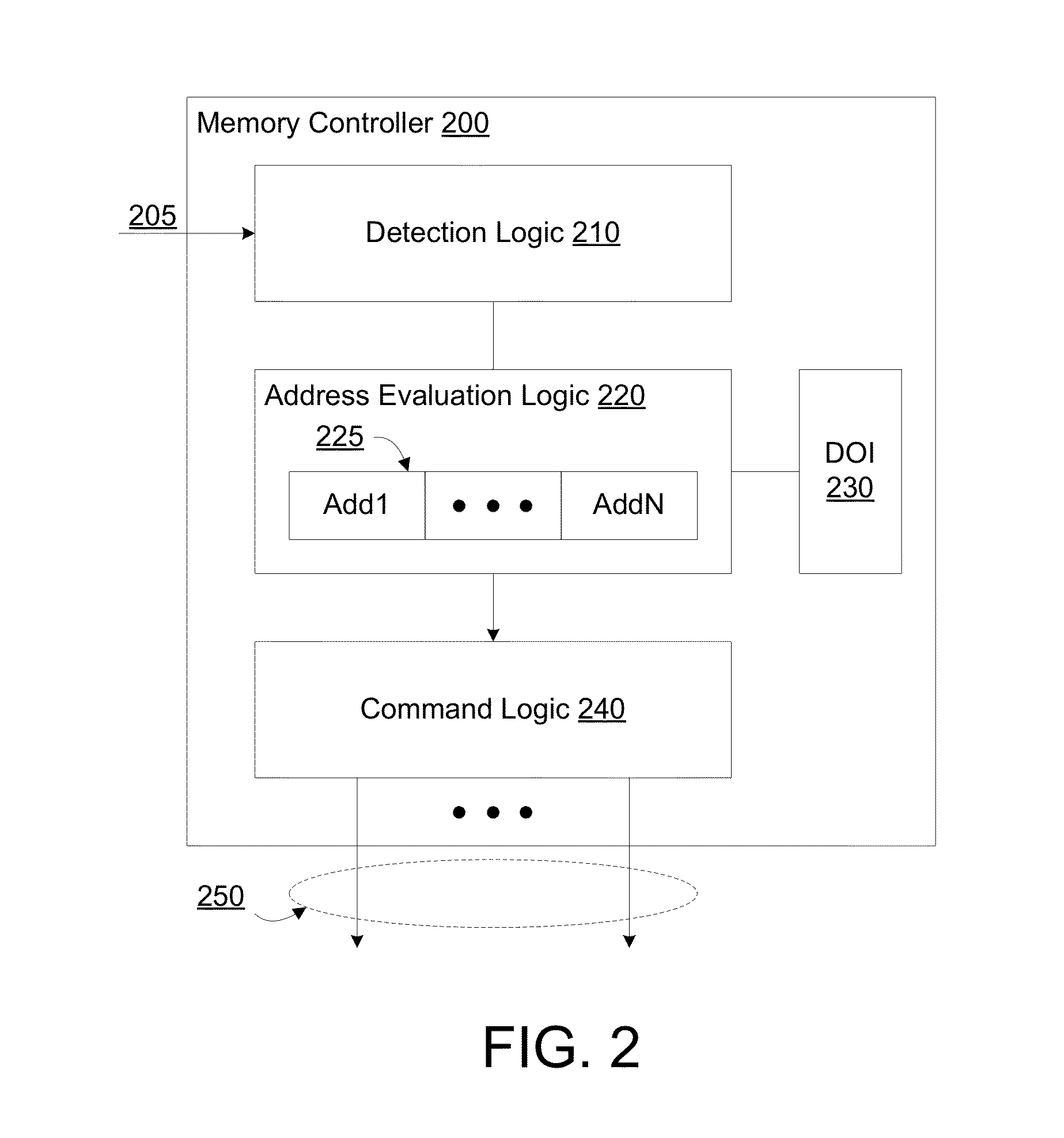
A memory controller to implement targeted refreshes of potential victim rows of a row hammer event. In an embodiment, the memory controller receives an indication that a specific row of a memory device is experiencing repeated accesses which threaten the integrity of data in one or more victim rows physically adjacent to the specific row. The memory controller accesses default offset information in the absence of address map information which specifies an offset between physically adjacent rows of the memory device. In another embodiment, the memory controller determines addresses for potential victim rows based on the default offset information. In response to the received indication of the row hammer event, the memory controller sends for each of the determined plurality of addresses a respective command to the memory device, where the commands are for the memory device to perform targeted refreshes of potential victim rows.
Owner:INTEL CORP
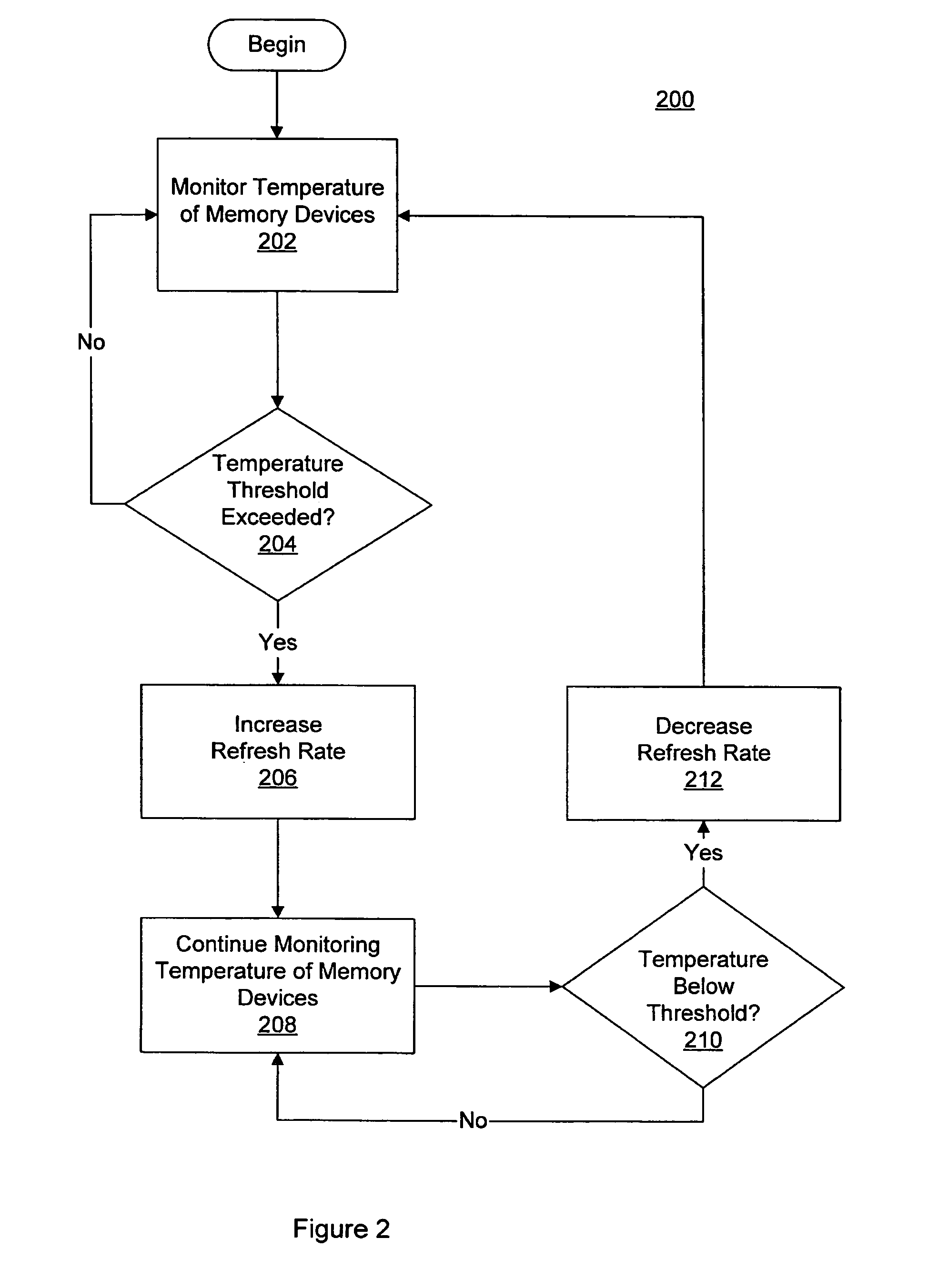
Variable memory refresh rate for DRAM
A method and apparatus for controlling a DRAM refresh rate. In one embodiment, a computer system includes a memory subsystem having a memory controller and one or more DRAM (dynamic random access memory) devices. The memory controller is configured to periodically initiate a refresh cycle to the one or more DRAM devices. The memory controller is also configured to monitor the temperature of the one or more DRAM devices. If the temperature exceeds a preset threshold, the memory controller is configured to increase the rate at which the periodic refresh cycle is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
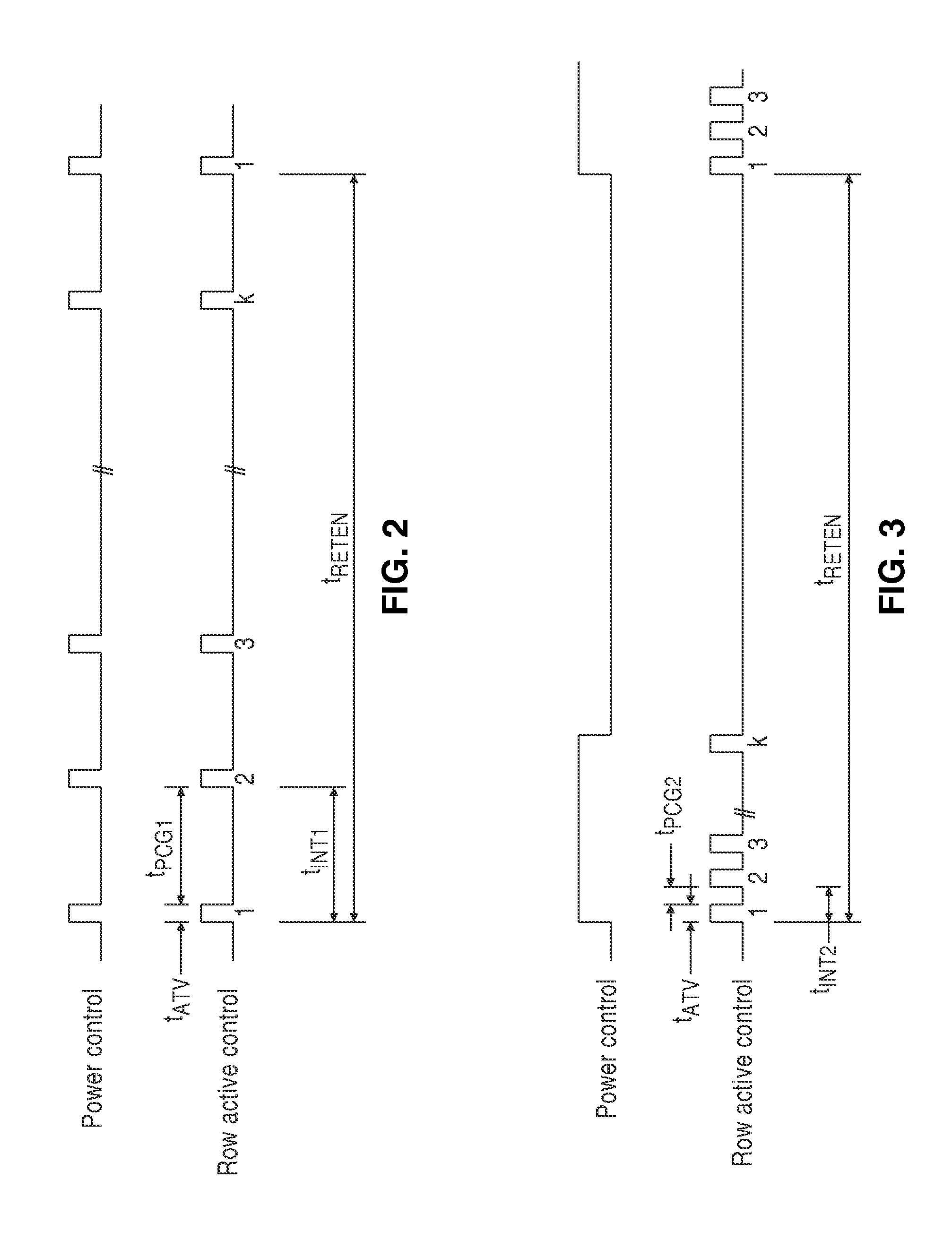
Dynamic memory refresh configurations and leakage control methods
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) circuits and methods are described for reducing leakage and increasing repaired yield. These objects are accomplished according to the invention by grouping refresh cycles within a single activation of power control, the use of limiting circuits or fuses to mitigate power losses associated with micro-bridging of bit-lines and word-lines, modulating the bit-line voltage at the end of precharge cycles, configuring refresh control circuits to use redundant word-lines in generating additional refresh cycles for redundant rows of memory cells, and combinations thereof. In one aspect, word-line fuses indicate modes of use as: unused, replacement, additional refresh, and replacement with additional refresh. The refresh control circuit utilizes these modes in combination with the X-address stored in the word-line fuses for controlling the generation of additional refresh cycles toward overcoming insufficient data retention intervals in select memory cell rows.
Owner:ZMOS TECH
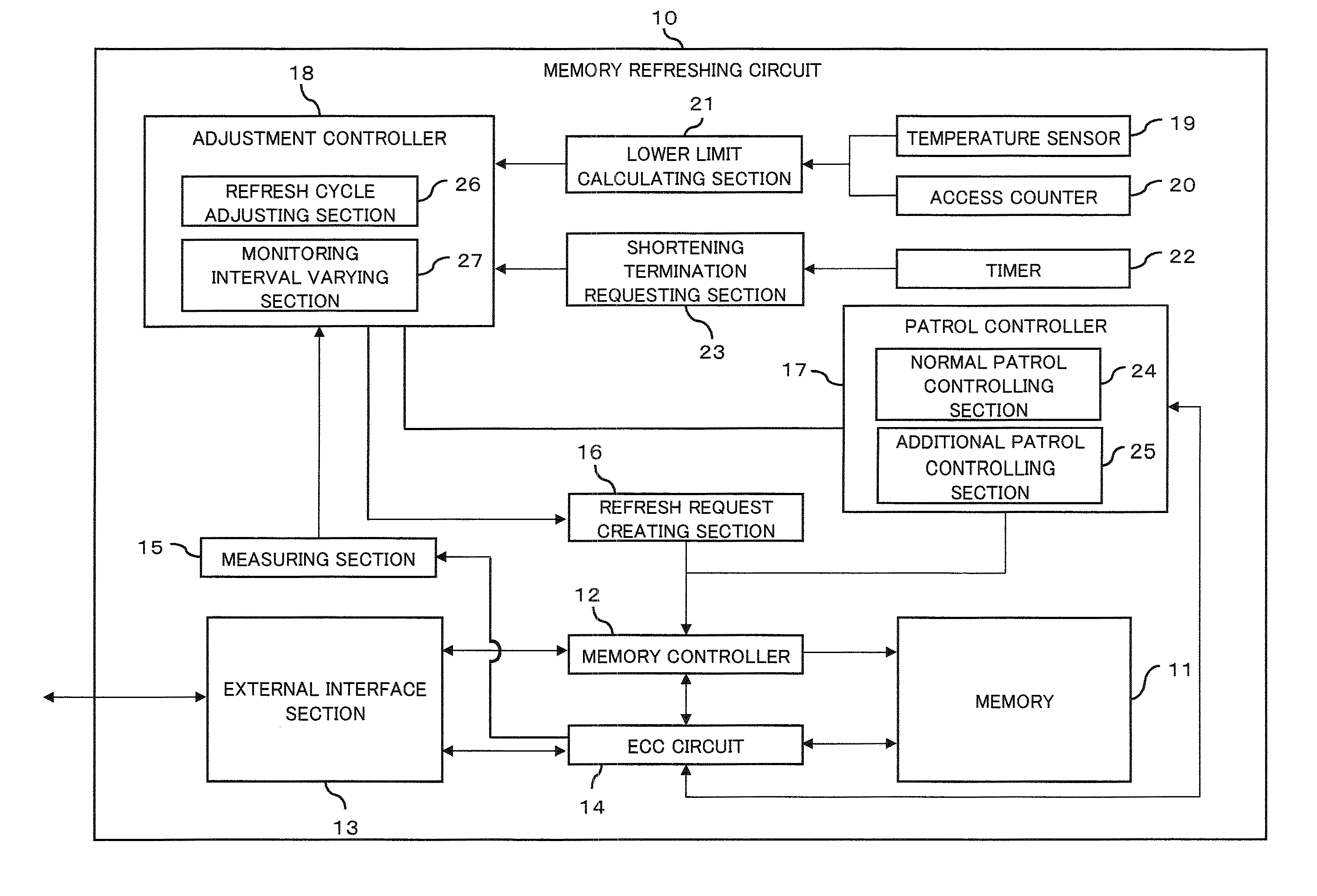
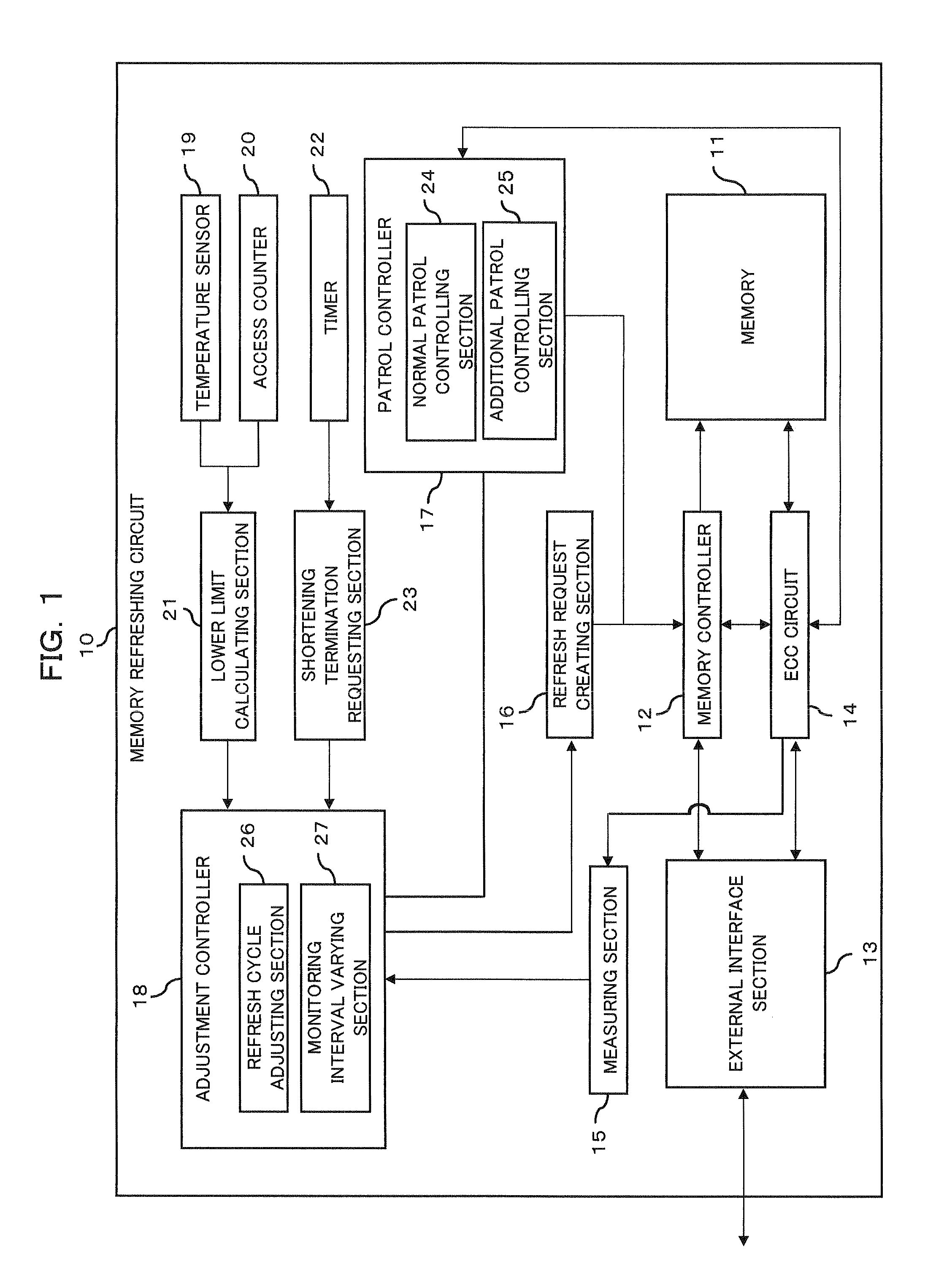
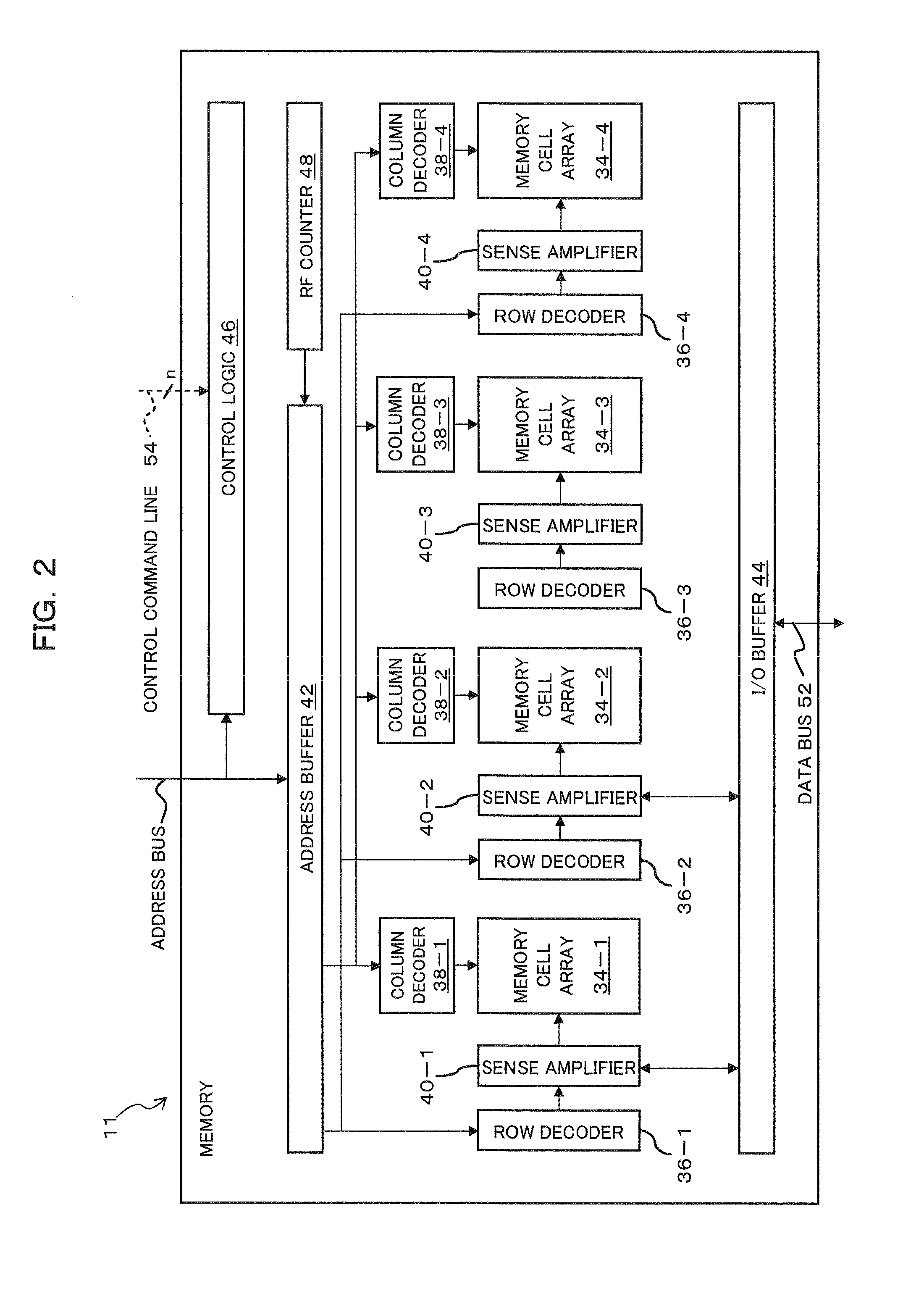
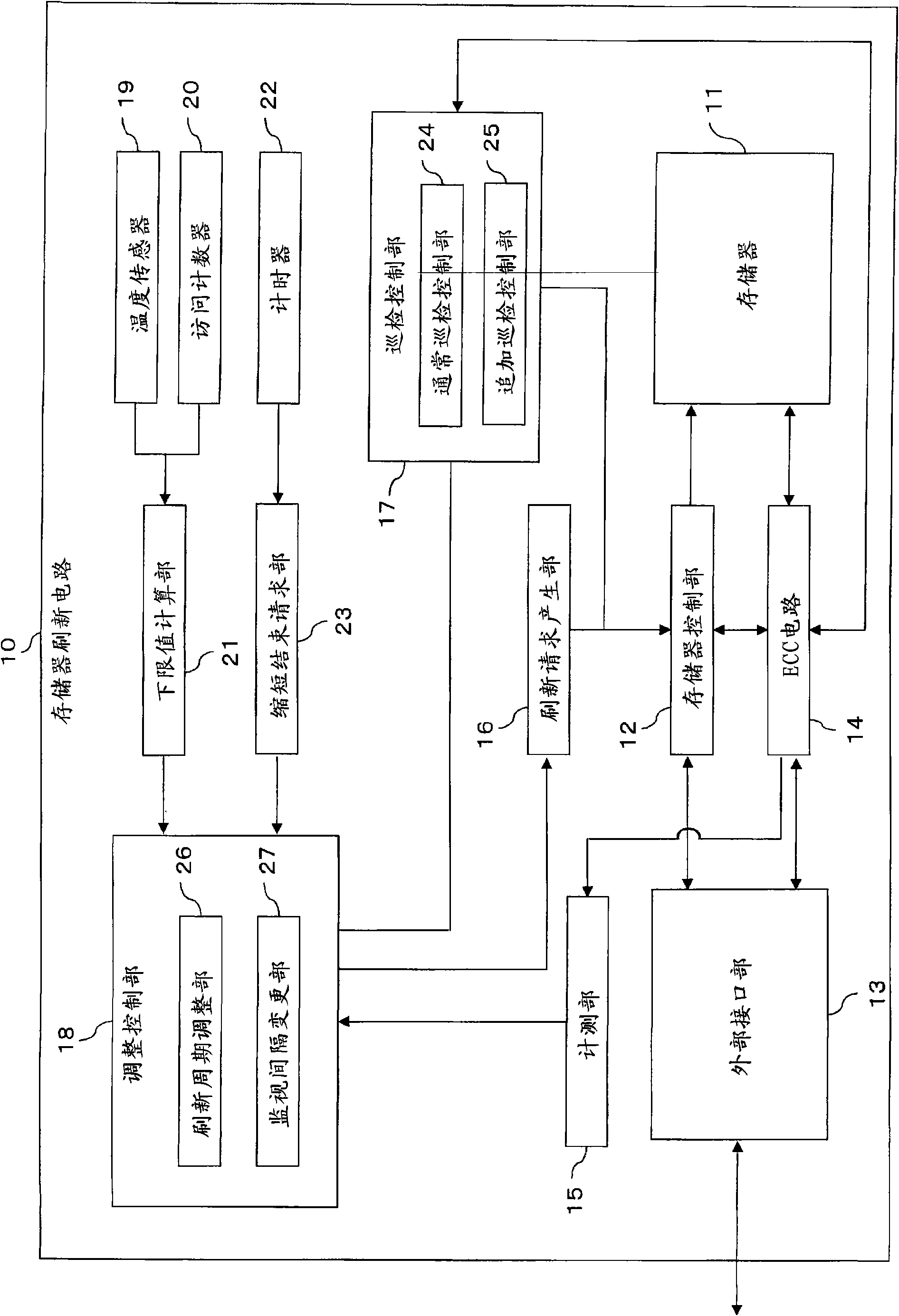
Memory refreshing apparatus and method for memory refresh
InactiveUS20100106901A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRefresh cycleComputer science
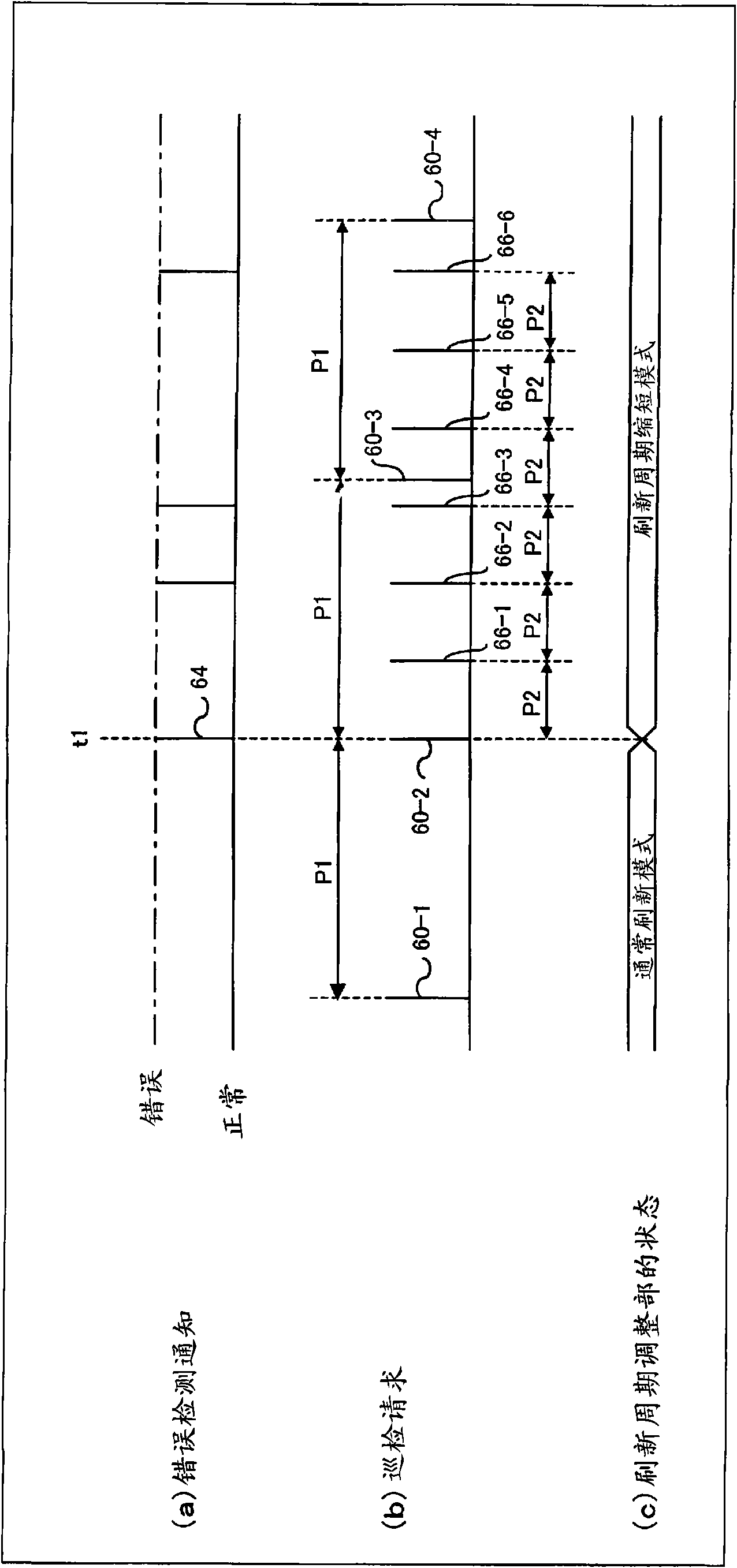
The optimization of a refresh cycle is carried out in harmony with the error occurrence state in the memory with the presence of a normal patrol controlling section controlling a normal patrol operation that patrols the memory; an additional patrol controlling section controlling an additional patrol operation that patrols, if a first error in the memory is detected during the normal patrol operation, an error occurring area in which the first error occurs and which is included in the memory; a measuring section (15) measuring, if a second error is detected in the error occurring area during the additional patrol operation, an error frequency representing information of error in the error occurring area; and a refresh cycle adjusting section adjusting the refresh cycle in accordance with the error frequency measured by the measuring section.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods and systems for arbitrating access to a disk controller buffer memory by allocating various amounts of times to different accessing units
A method and system for arbitrating access to a shared disk controller resource, including a buffer memory of a hard disk controller (HDC). An access cycle with a first cycle duration are disclosed and a first amount of time is allocated to a first accessing unit including an error correction code (ECC) engine, a microprocessor first-in-first-out (FIFO) unit, or a memory refresh / data format data fetch unit. The shared controller resource is accessed using the first accessing unit for a first duration, where the first duration is no greater than the first amount of time. A second amount of time and an unused portion of the first amount of time is allocated to a second accessing unit such as a disk formatter. Arbitration limit registers may be used to specify the number of HDC clock cycles per access cycle available to an accessing unit during which it can access the buffer memory. A global arbitration limit counter may be used to keep track of the duration of the accessing units.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
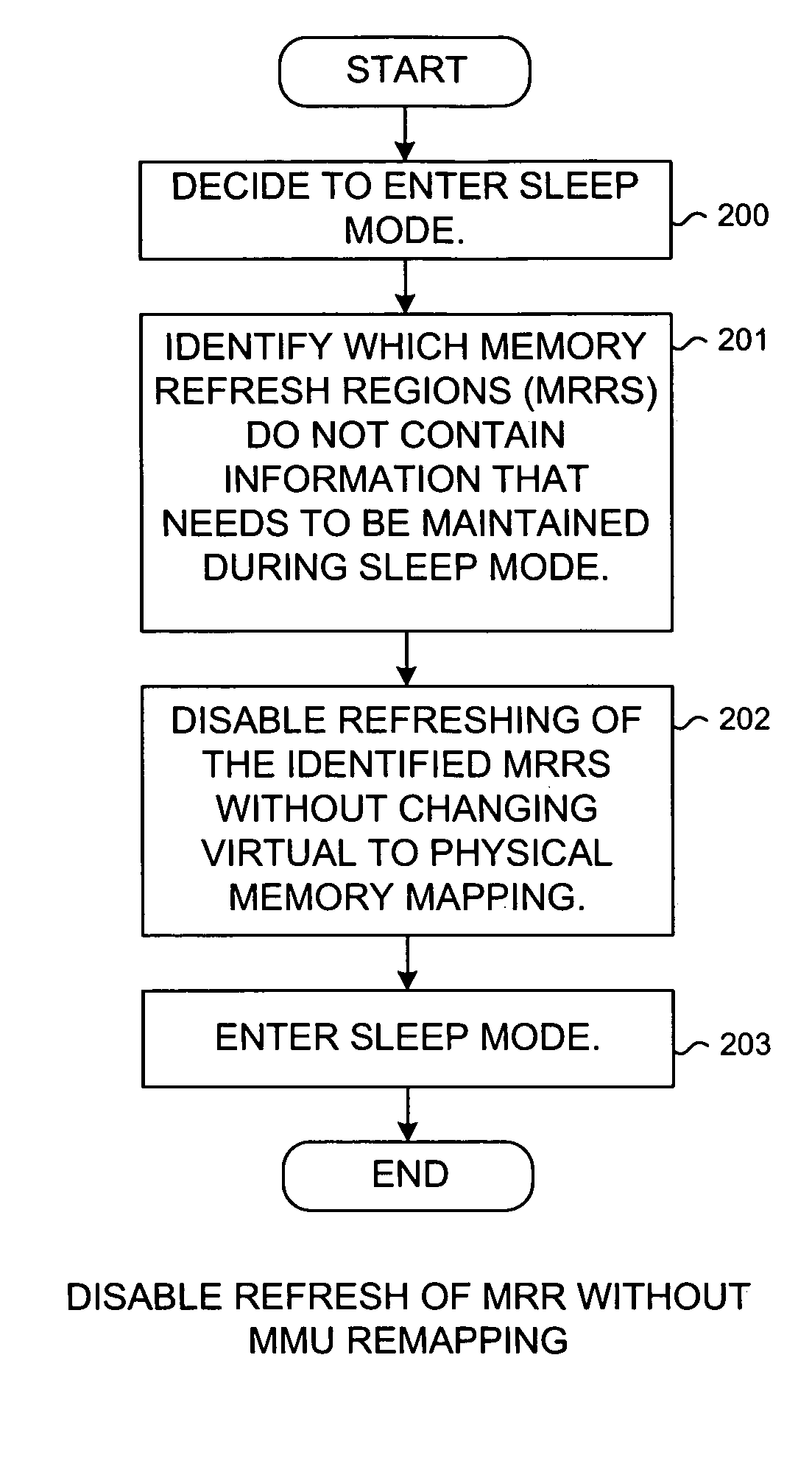
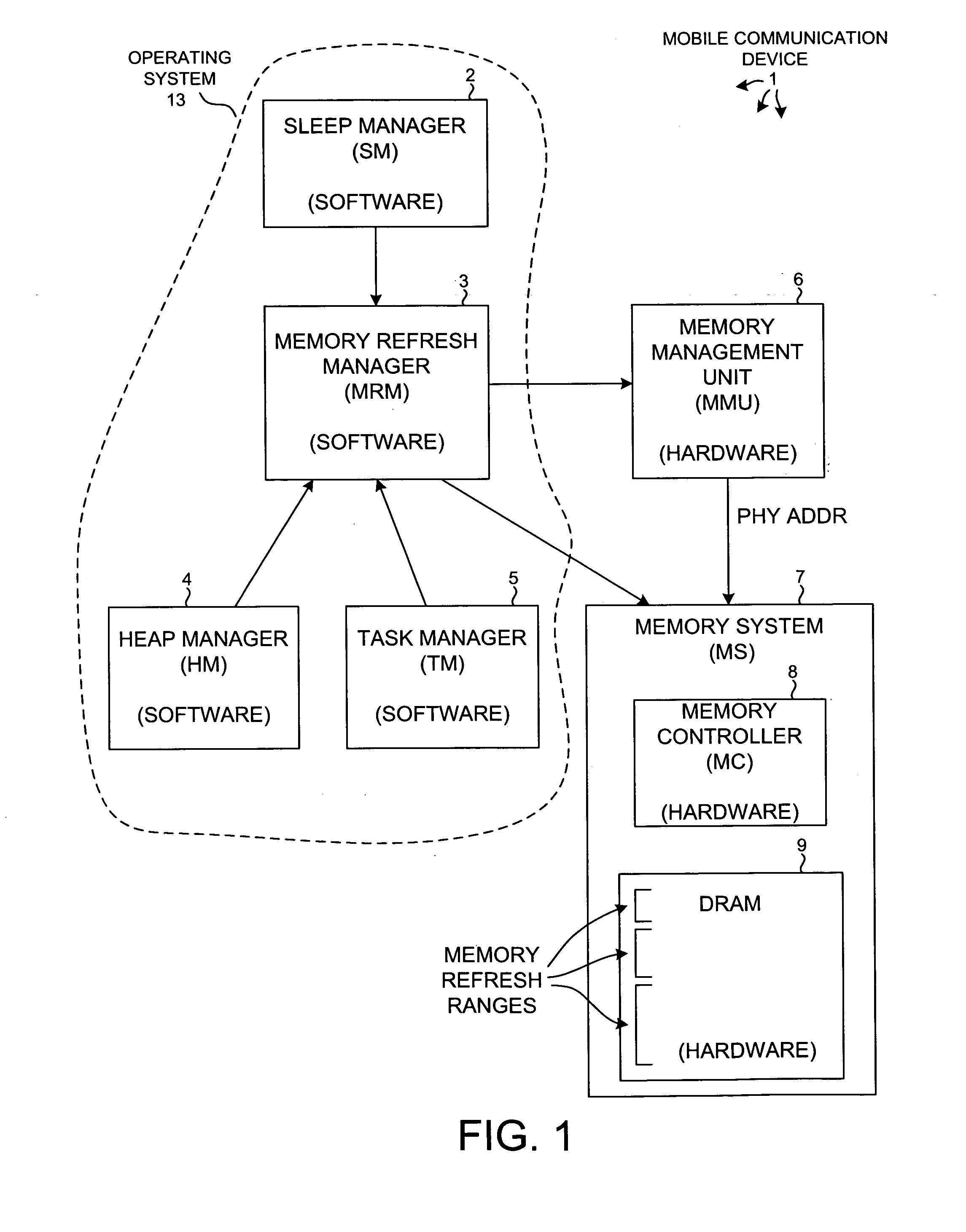
Reducing power consumption by disabling refresh of unused portions of DRAM during periods of device inactivity
InactiveUS20070180187A1Average power consumptionReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTVirtual memoryComputer architecture
Power consumption of a mobile communication device is reduced by disabling refreshing of unused portions of DRAM. DRAM includes multiple separately refreshable memory refresh ranges (MRRs). A memory refresh manager (MRM) within the device's operating system identifies ranges of virtual memory that will not be used during subsequent sleep mode operation. The MRM remaps virtual to physical memory space to conglomerate the physical memory pages (associated with virtual memory that will not be used) in certain MRRs such that the contents of entire MRRs need not be maintained in sleep mode. Information in any remapped physical page that needs to be maintained during sleep mode is copied so that it resides at the same virtual address after the remapping as before. Other software operates in virtual memory space and is not affected by the remapping. Refreshing of the certain MRRs is then disabled for sleep mode, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Programmable logic device (PLD) with memory refresh based on single event upset (SEU) occurrence to maintain soft error immunity
ActiveUS7764081B1Reduce memory cell densityMinimized circuitReliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsProgrammable logic deviceSingle event upset
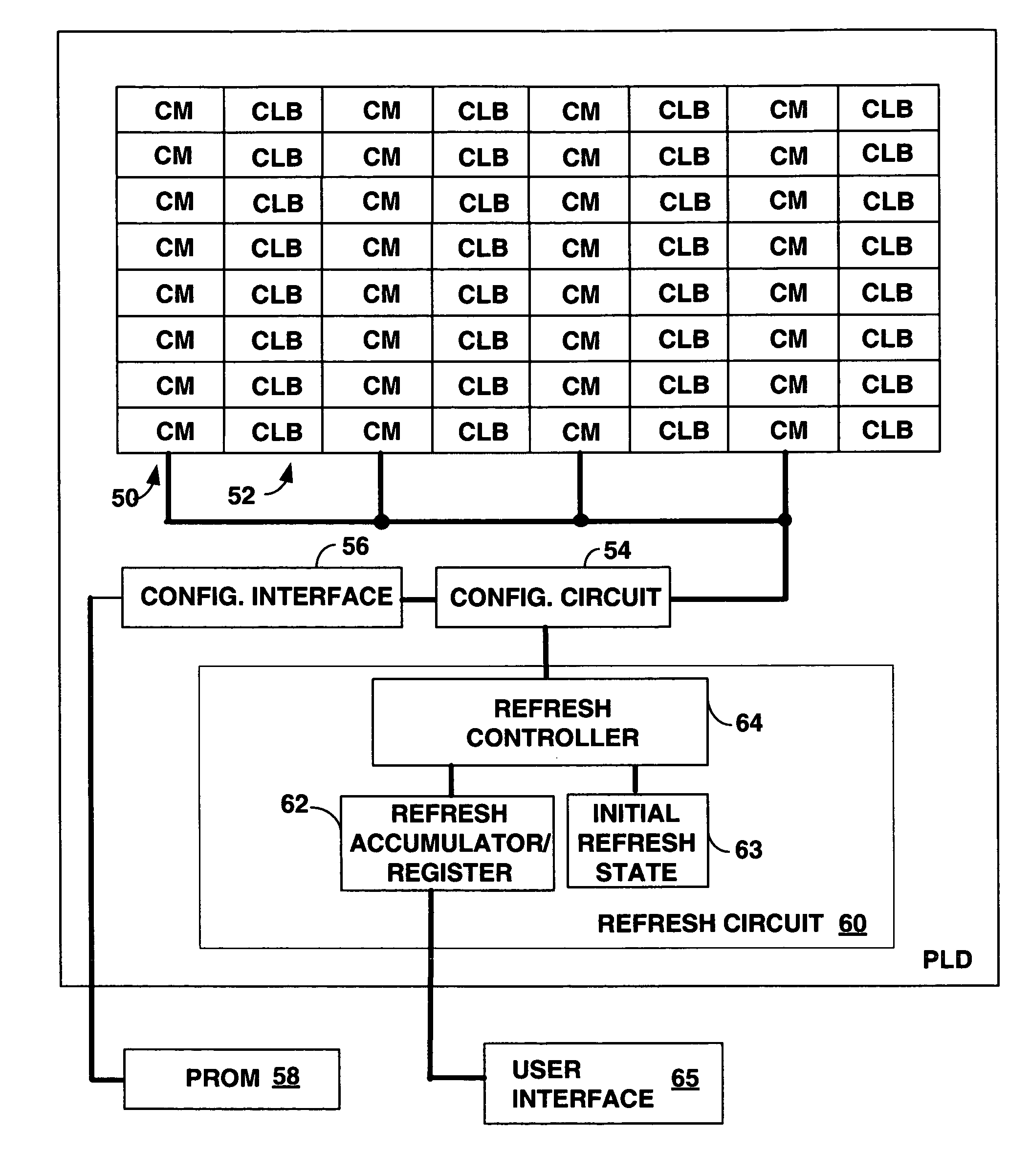
A Programmable Logic Device (PLD) is provided with configuration memory cells displaying a superior soft error immunity by combating single event upsets (SEUs) as the configuration memory cells are regularly refreshed from non-volatile storage depending on the rate SEUs may occur. Circuitry on the PLD uses a programmable timer to set a refresh rate for the configuration memory cells. Because an SEU which erases the state of a small sized memory cell due to collisions with cosmic particles may take some time to cause a functional failure, periodic refreshing will prevent the functional failure. The configuration cells can be DRAM cells which occupy significantly less space than the SRAM cells. Refresh circuitry typically provided for DRAM cells is reduced by using the programming circuitry of the PLD. Data in the configuration cells of the PLD are reloaded from either external or internal soft-error immune non-volatile memory.
Owner:XILINX INC
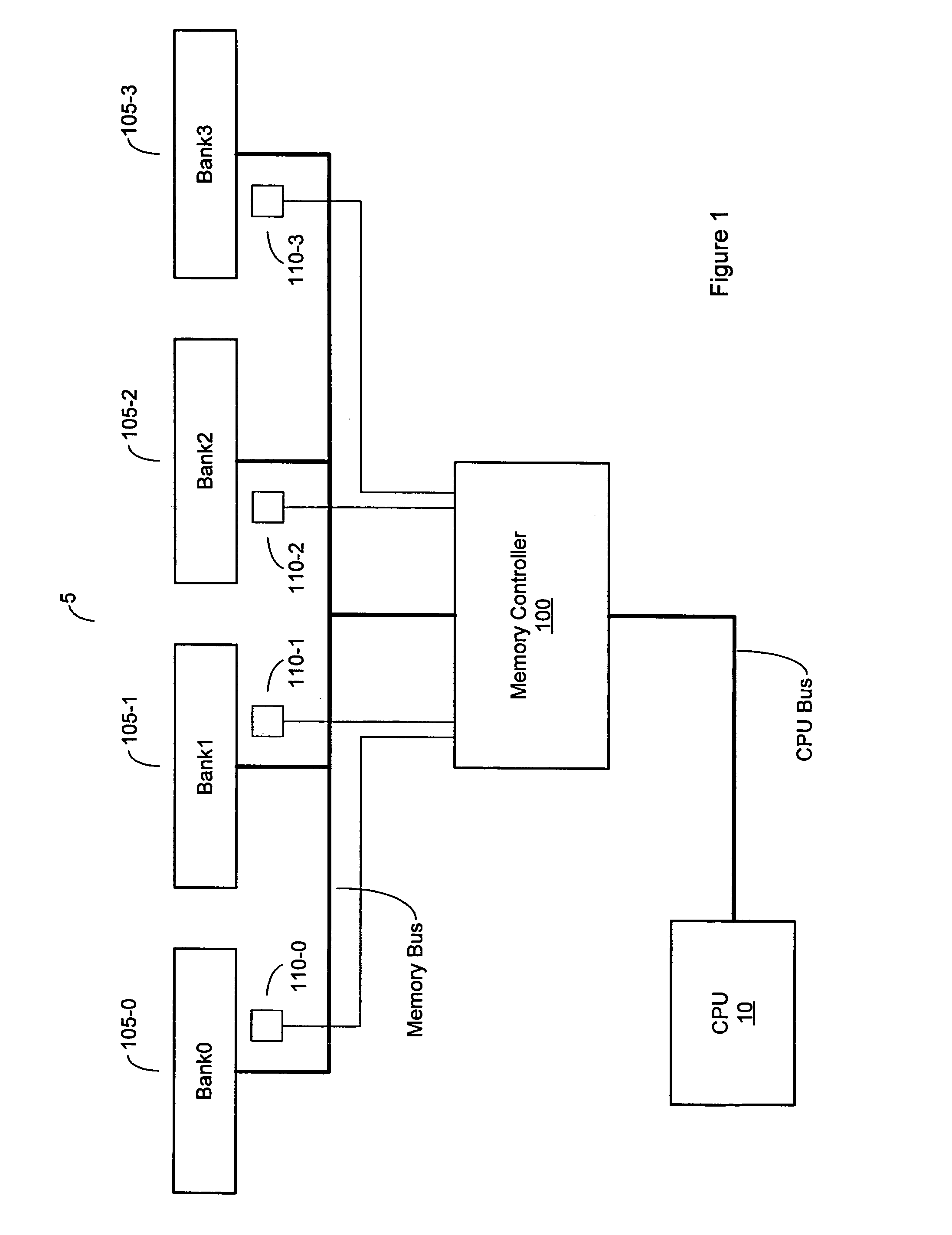
Memory interface for systems with multiple processors and one memory system
InactiveUS20050080999A1Resource allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionExternal storageMemory interface
Memory interface for multi-CPU system provides predefined time slots in which each CPU may access an external memory. The time slot assigned to each CPU may be defined according to the expected memory requirements of the CPU. In this way, each CPU is guaranteed to have a certain amount of dedicated bandwidth to the external memory. The predefined time slots also allow the latency of the system to be known, which is useful for real-time oriented applications. Moreover, each CPU may use its own clock during its allotted time slot to control the external memory, thus accommodating various clock domains in the system. Memory refresh and data protection functions are also provided. This Abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an Abstract that allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain subject matter of the technical disclosure. This Abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Memory persistence management control
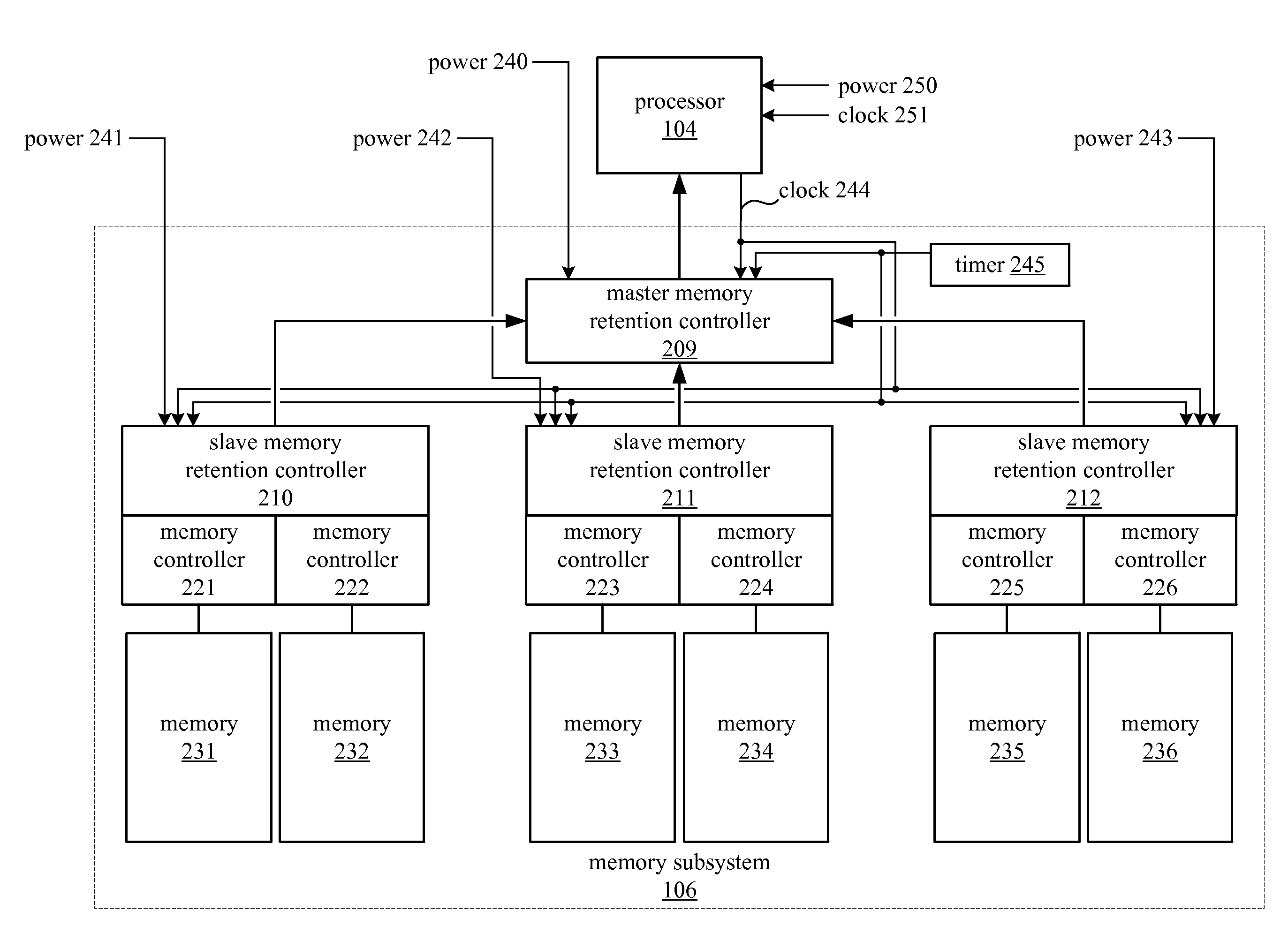
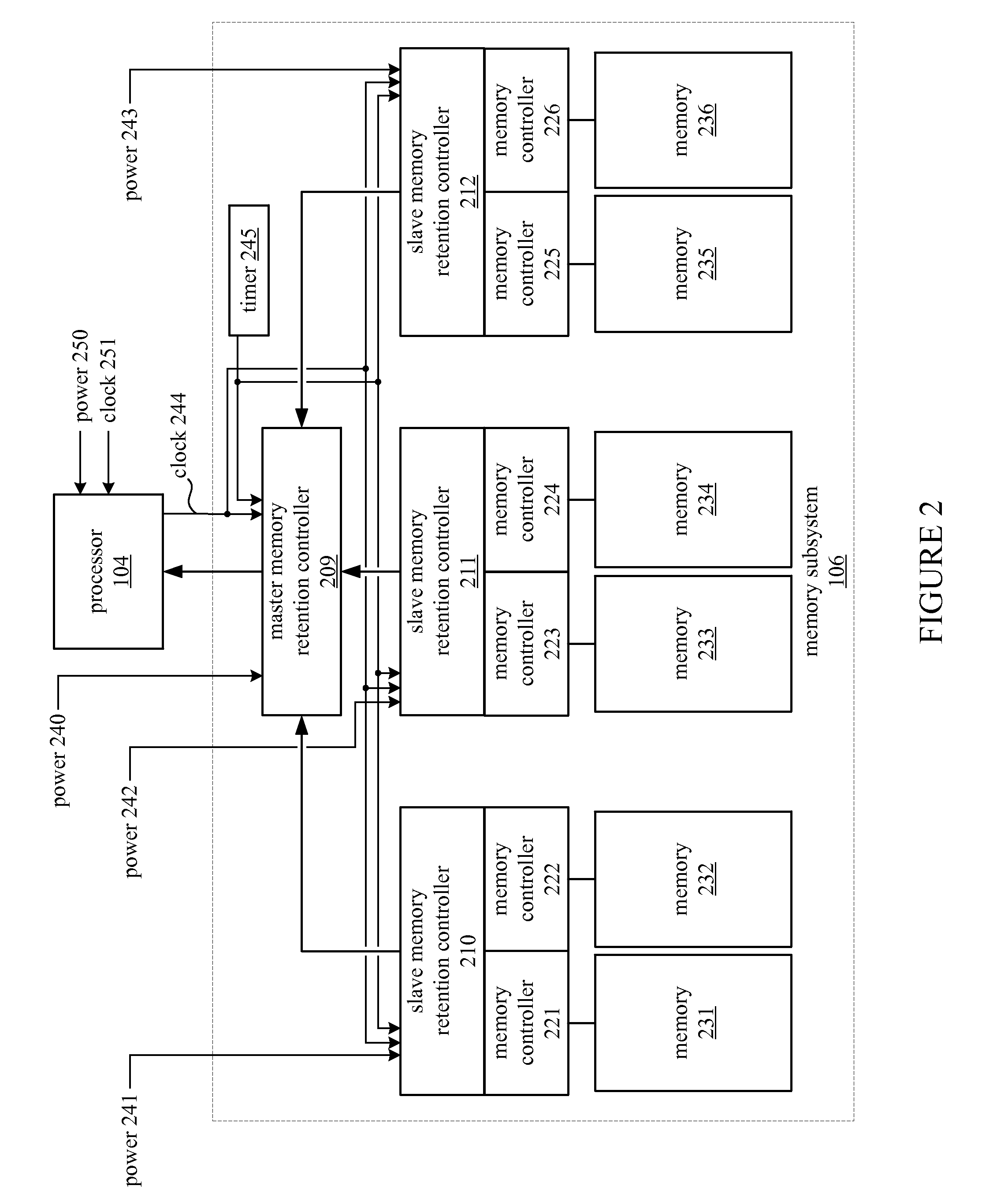
A memory retention controller may include a data structure configured to store a memory refresh interval corresponding to a memory region in a memory subsystem and control logic coupled with the data structure. The control logic is configured to perform a first refresh of the memory region prior to a power off transition of a host processor coupled with the memory subsystem, and to perform a second refresh of the memory region after the power off transition of the host processor, based on the memory refresh interval corresponding to the memory region, and in response to an elapsed time since the first refresh of the memory region.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
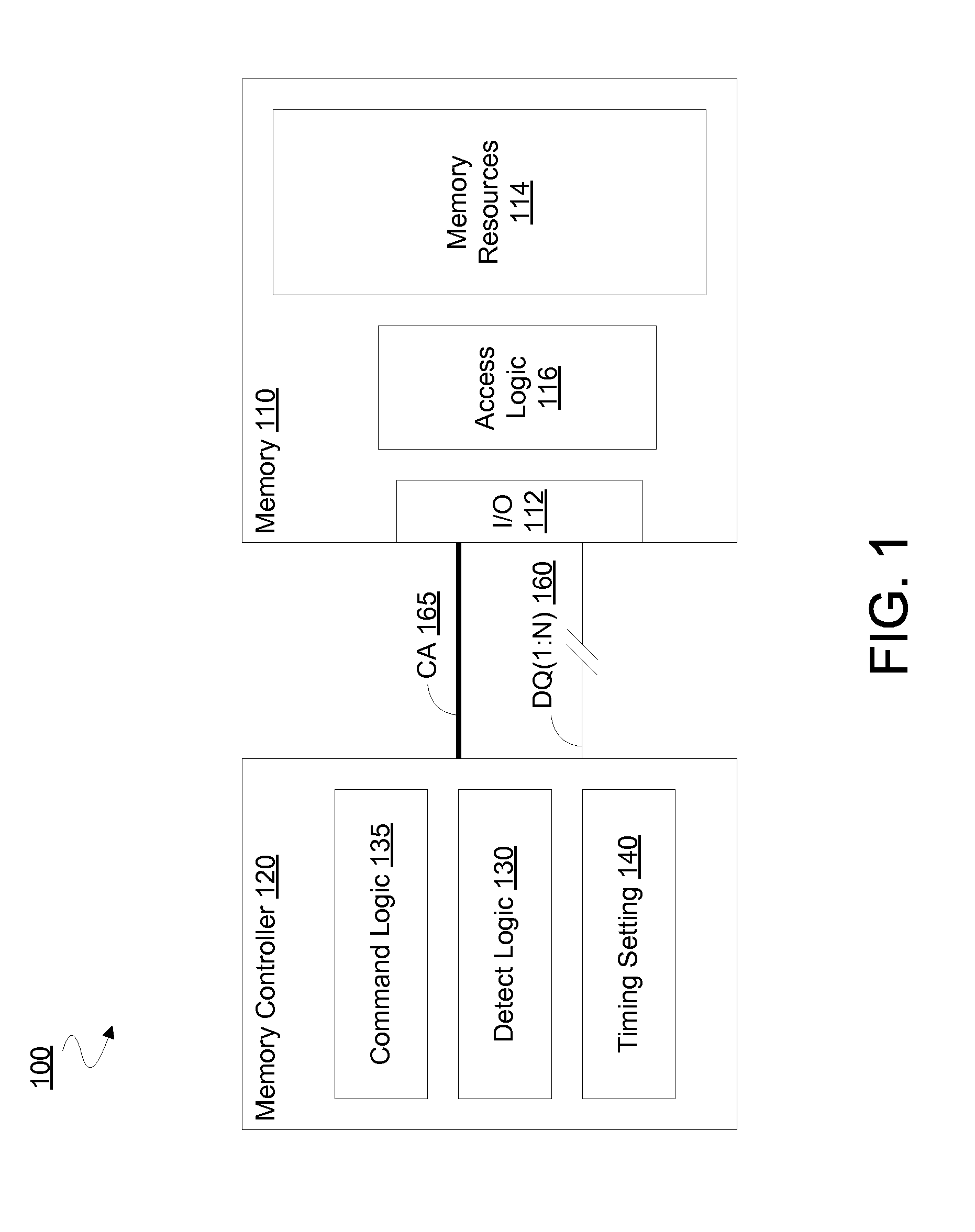
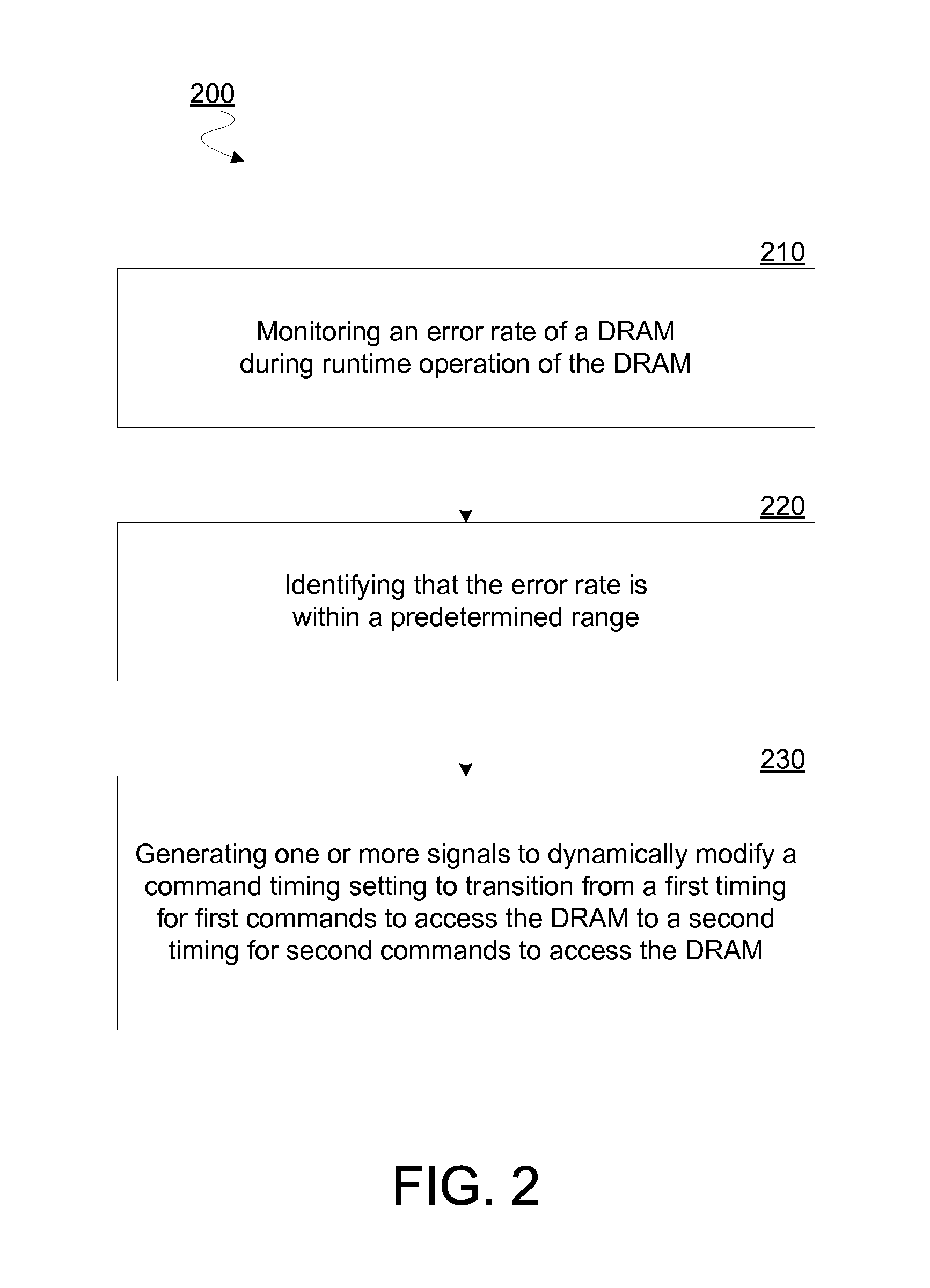
Apparatus, method and system to determine memory access command timing based on error detection
Techniques and mechanisms to dynamically adjustment a timing of commands to access a dynamic random access memory (DRAM). In an embodiment, a memory controller monitors an error rate of the DRAM and, based on such monitoring, identifies that the error rate is within a predetermined range. In response to the error rate being within the predetermined range, one or more signals are generated to dynamically modify a command timing setting. In another embodiment, modification of the command timing setting is to transition a memory controller from sending memory refresh commands successively at one rate to sending memory refresh commands successively at a different rate.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
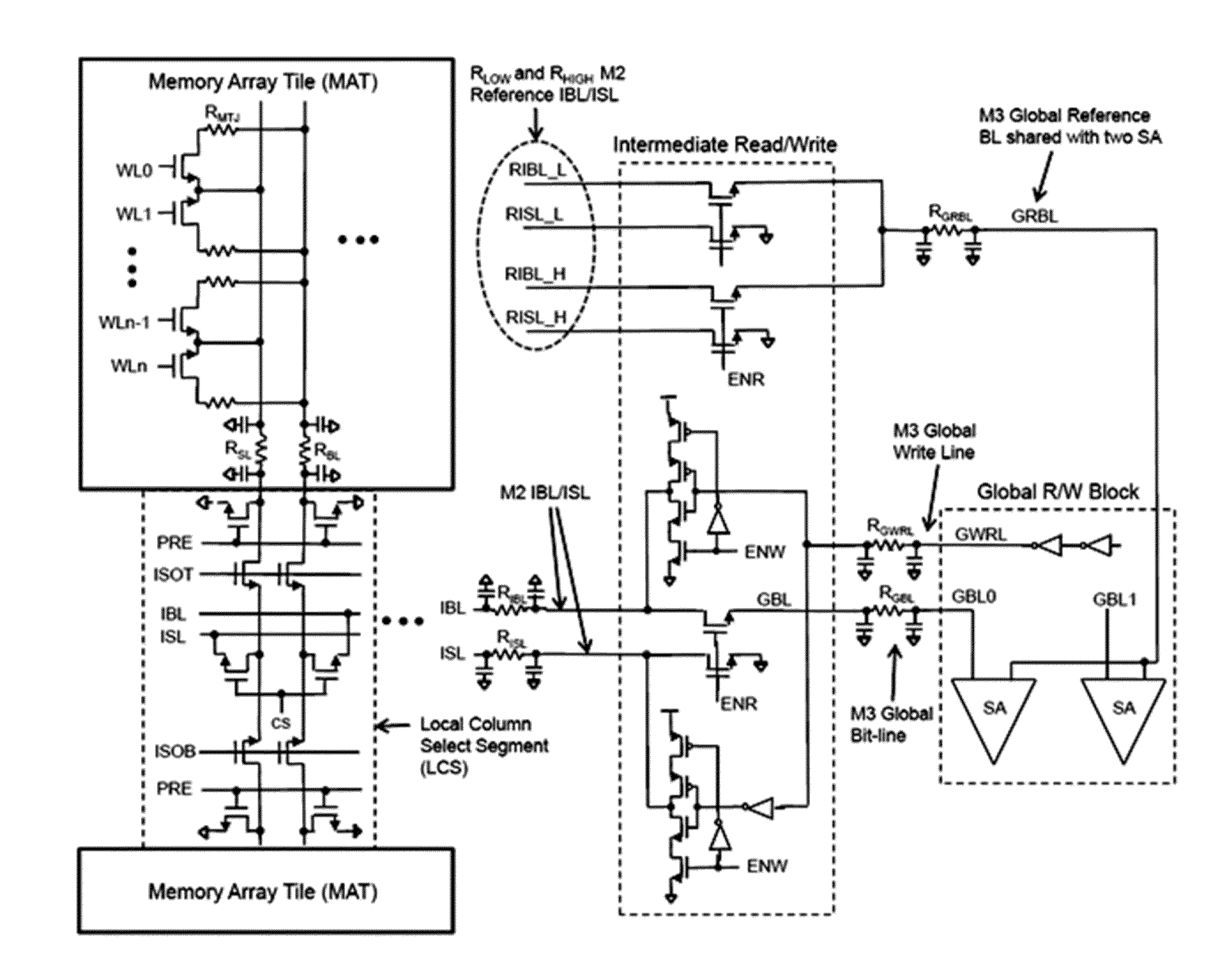
High performance embedded semiconductor memory devices with multiple dimension first-level bit-lines
InactiveUS20050133852A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineInternal memory
A dynamic random access memory solves long-existing tight pitch layout problems using a multiple-dimensional bit line structure. Improvement in decoder design further reduces total area of this memory. A novel memory access procedure provides the capability to make internal memory refresh completely invisible to external users. By use of such memory architecture, higher performance DRAM can be realized without degrading memory density. The requirements for system support are also simplified significantly.
Owner:UNIRAM TECH
Method and system for providing a smart memory architecture
ActiveUS20130212431A1High rateHigh error rateDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsMemory addressSmart memory
A smart memory system preferably includes a memory including one or more memory chips, and a processor including one or more memory processor chips. The processor may include a common address / data / control memory bus that is configured to provide an asynchronous handshaking interface between the memory array and the memory processor. The processor can offload error data from the memory chip for analysis, and can store poor retention bit address information for memory refreshing in a non-volatile error retention memory. Program logic can also be included for memory address re-configuration. Power management logic can also be included, which may have a process-voltage-temperature compensation voltage generator for providing stable and constant read currents. An asynchronous handshaking interface is provided between the memory array and the memory processor. Write error tagging and write verification circuits can also be included.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
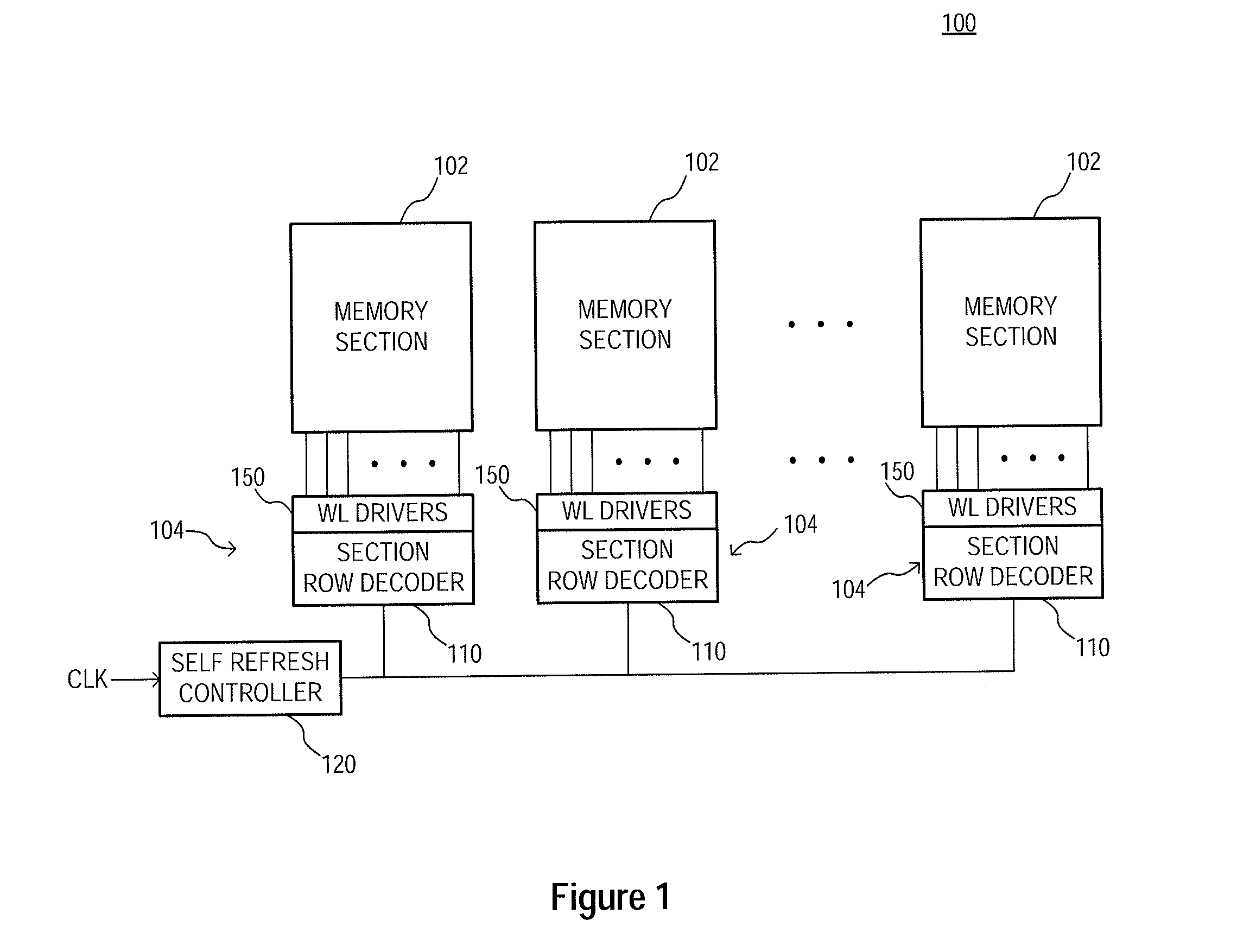
Memory refresh methods, memory section control circuits, and apparatuses
Apparatuses, memory section control circuits, and methods of refreshing memory are disclosed. An example apparatus includes a plurality of memory sections and a plurality of memory section control circuits. Each memory section control circuit is coupled to a respective one of the plurality of memory sections and includes a plurality of access line drivers, each of which includes a plurality of transistors having common coupled gates. During an operation of the apparatus a first voltage is provided to the commonly coupled gates of the transistors of at least some of the access line drivers of the memory section control circuit coupled to an active memory section and a second voltage is provided to the commonly coupled gates of the transistors of the access line drivers of the memory section control circuit coupled to an inactive memory section control circuit, wherein the first voltage is greater than the second voltage.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Power management control and controlling memory refresh operations
A memory devices provide signals indicating when refresh operations are complete. The signals from a number of memory devices can be combined, such as by Oring, to provide a refresh complete signal to a power management controller. Dynamic factors can affect the refresh operation and the memory may be refreshed without restoring the entire system to a high power state. The time required to perform a refresh operation can be determined dynamically, allowing the system to be returned to a low power state as soon as refresh is complete. Ambient temperatures can be monitored to dynamically determine when to perform a refresh operation.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
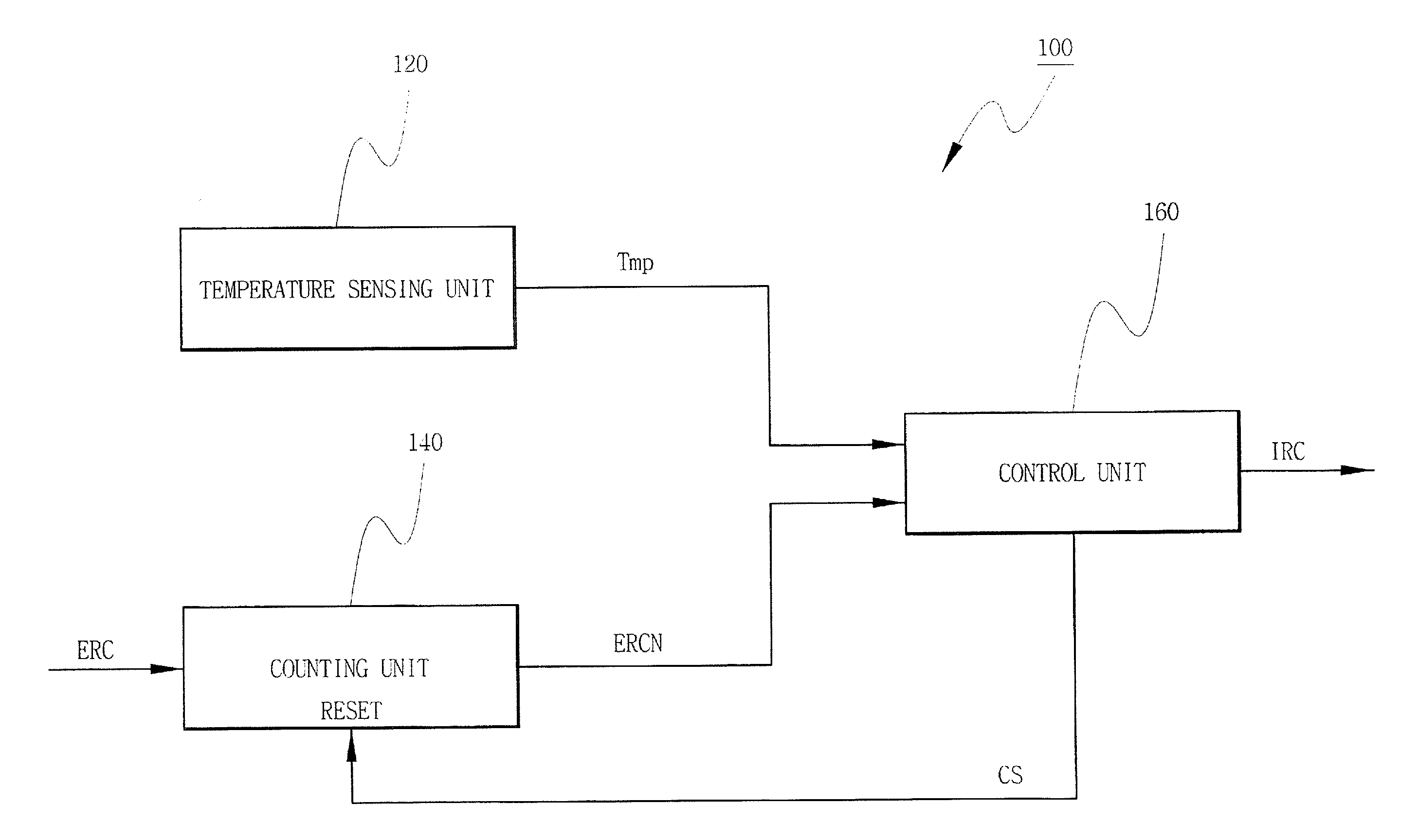
Memory refresh device and memory refresh method
InactiveCN101796497AImprove responsivenessShorten the refresh cycleMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareRefresh cycle
A memory refresh device comprises an ordinary patrol control unit (24) for controlling an ordinary patrol operation in which a memory (11) is patrolled, an additional patrol control unit (25) for, when an error of the memory (11) is detected in the ordinary patrol operation, controlling an additional patrol operation in which an error generating portion in the memory (11) is patrolled, a measuring unit (15) for, when an error is detected in the additional patrol operation, measuring information on the error in the error generating portion as error frequency, and a refresh period adjusting unit (26) for adjusting a refresh period according to the error frequency measured by the measuring unit (15). Thus, the optimization of the refresh period is efficiently performed according to the state of the generation of the error in the memory.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
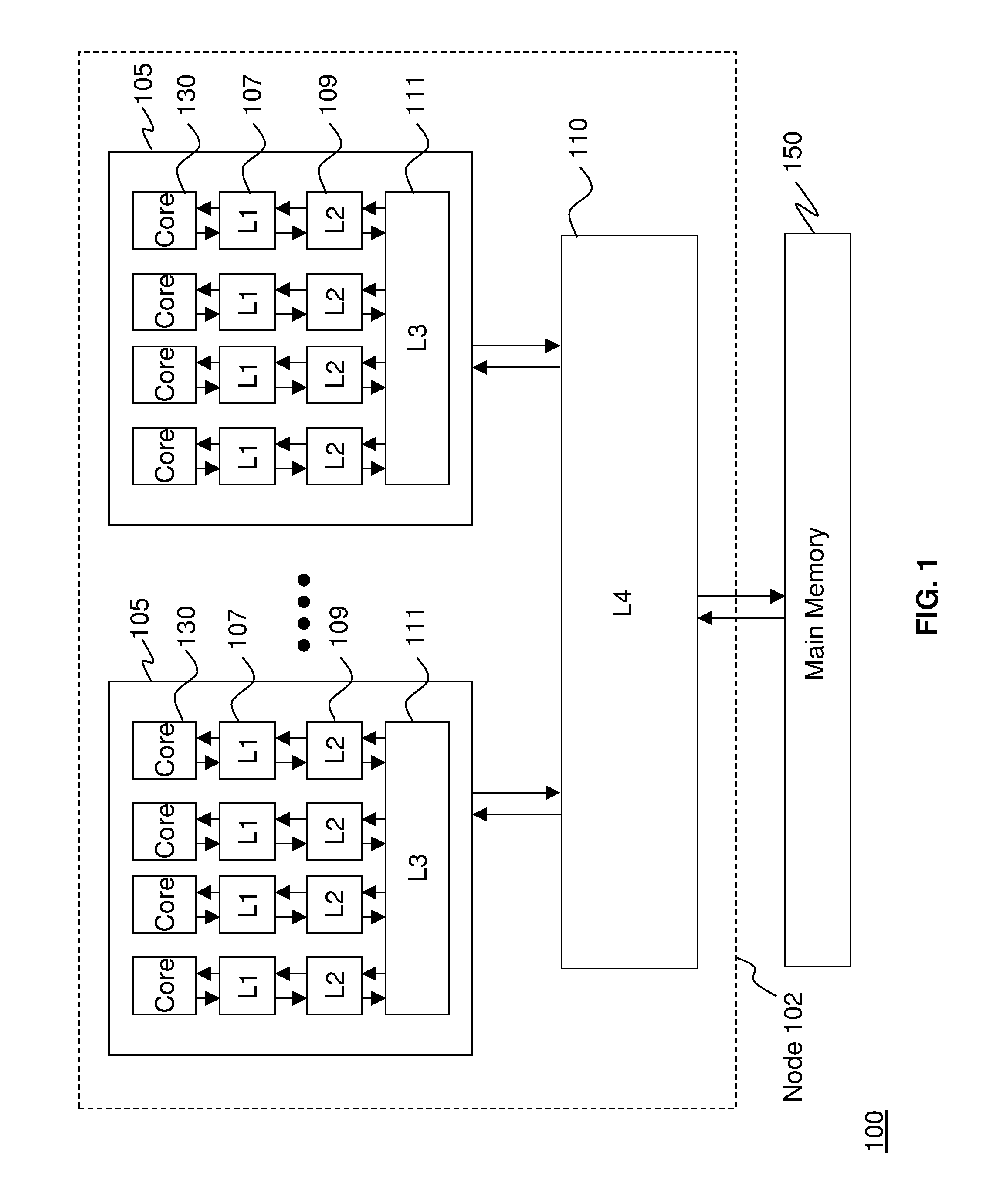
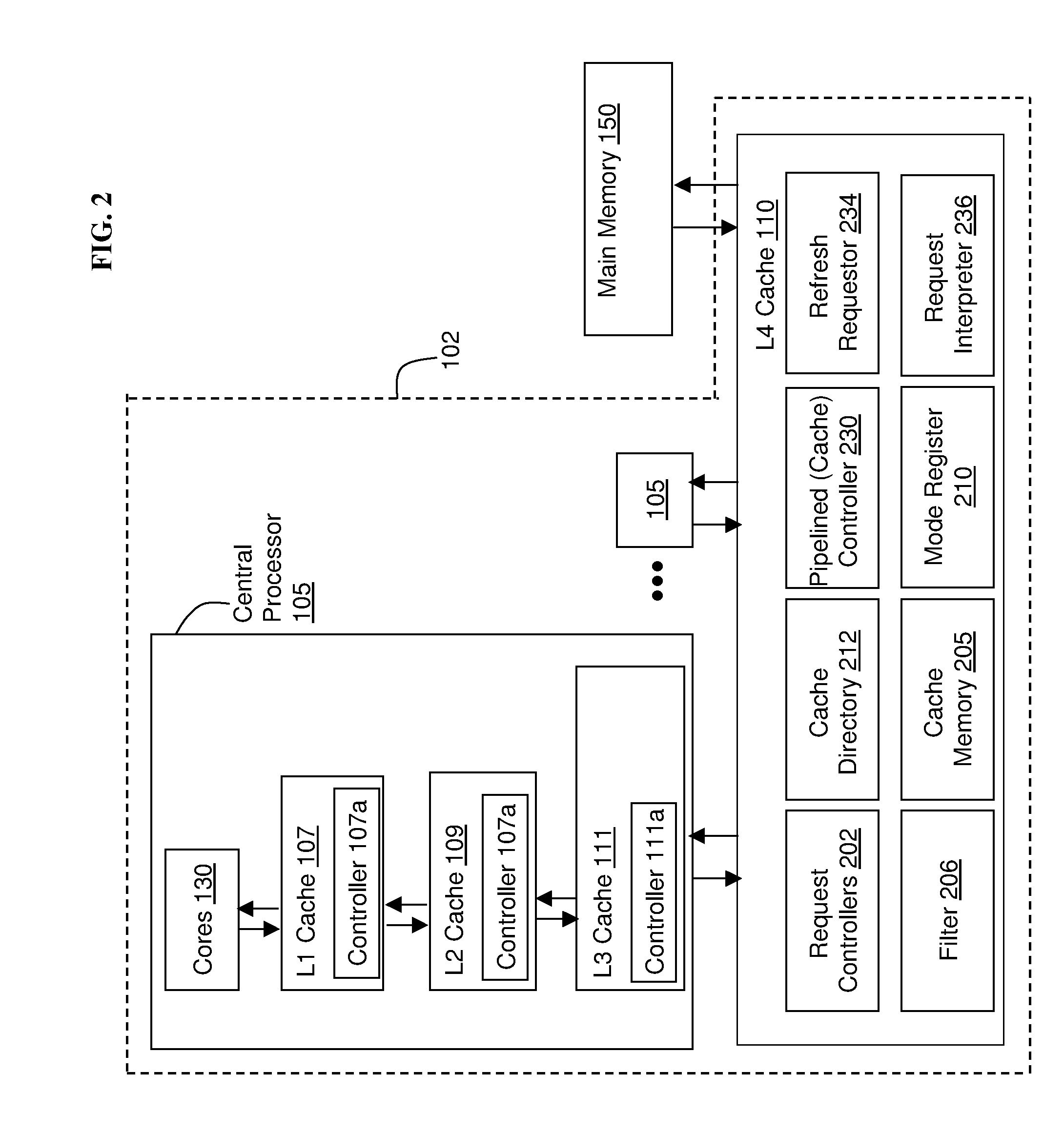
Edram refresh in a high performance cache architecture
ActiveUS20110320696A1High performance cacheMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory addressSingle chip
A memory refresh requestor, a memory request interpreter, a cache memory, and a cache controller on a single chip. The cache controller configured to receive a memory access request, the memory access request for a memory address range in the cache memory, detect that the cache memory located at the memory address range is available, and send the memory access request to the memory request interpreter when the memory address range is available. The memory request interpreter configured to receive the memory access request from the cache controller, determine if the memory access request is a request to refresh a contents of the memory address range, and refresh data in the memory address range when the memory access request is a request to refresh memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for isochronous arbitration to schedule memory refresh requests
InactiveUS7020741B1Minimizing memory access latencyDigital storageMemory systemsData signalMemory controller
For use with a memory controller in a data processor that is capable of executing memory refresh requests to refresh a memory of the data processor, an apparatus and method is disclosed for scheduling execution of the memory refresh requests. The apparatus comprises a periodic memory refresh hint unit that is capable of sending to the memory controller a data signal that comprises a periodic memory refresh hint. The periodic memory refresh hint informs the memory controller of an optimal time for a memory refresh to occur. The memory controller may immediately execute a memory refresh request when it arrives or delay the execution of the memory refresh request until a more opportune time. This feature enables the memory controller to reduce memory access latency in scheduling memory transactions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High performance embedded semiconductor memory devices with multiple dimension first-level bit-lines
InactiveUS20050036363A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesInternal memoryBit line
A dynamic random access memory solves long-existing tight pitch layout problems using a multiple-dimensional bit line structure. Improvement in decoder design further reduces total area of this memory. A novel memory access procedure provides the capability to make internal memory refresh completely invisible to external users. By use of such memory architecture, higher performance DRAM can be realized without degrading memory density. The requirements for system support are also simplified significantly.
Owner:UNIRAM TECH
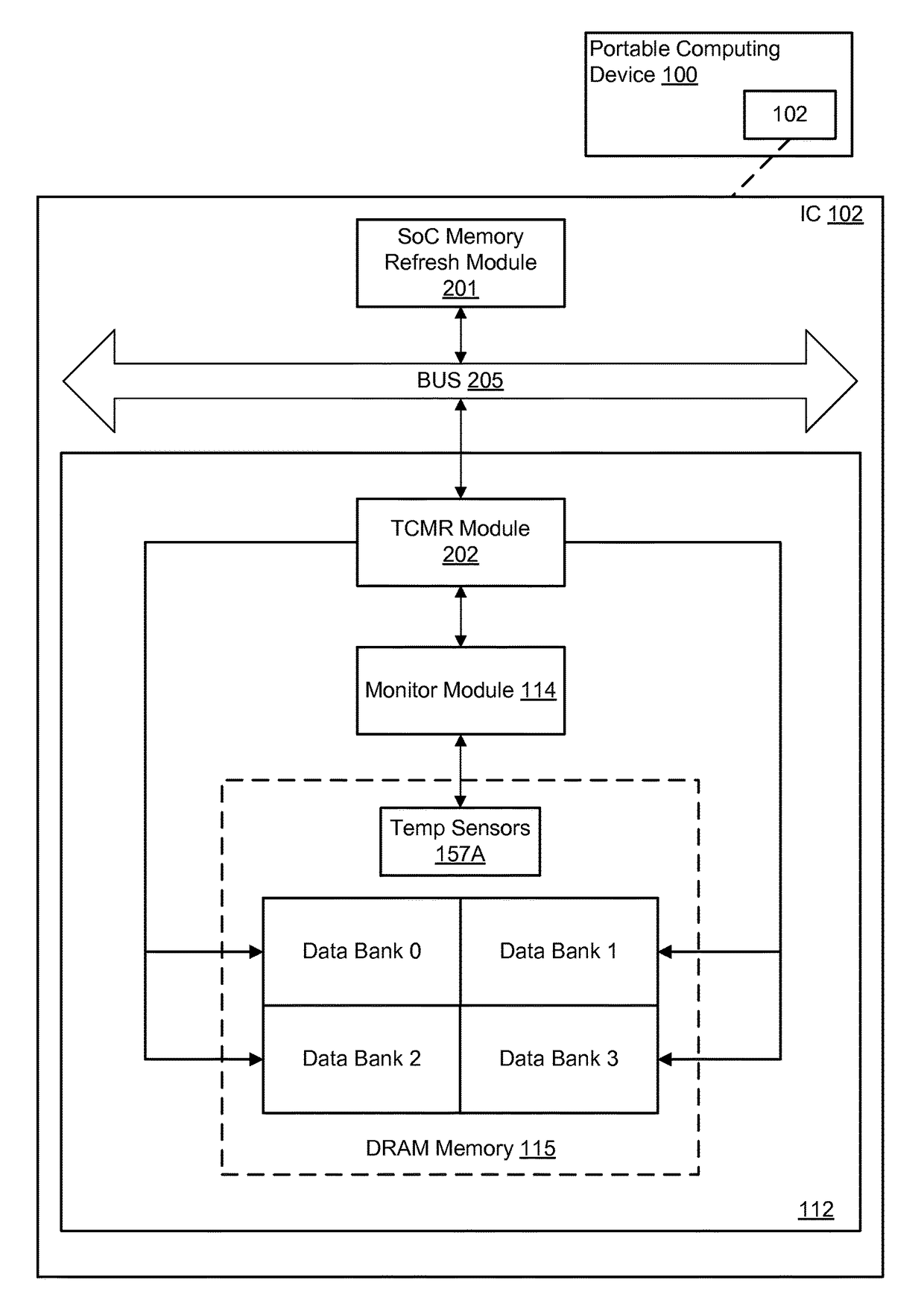
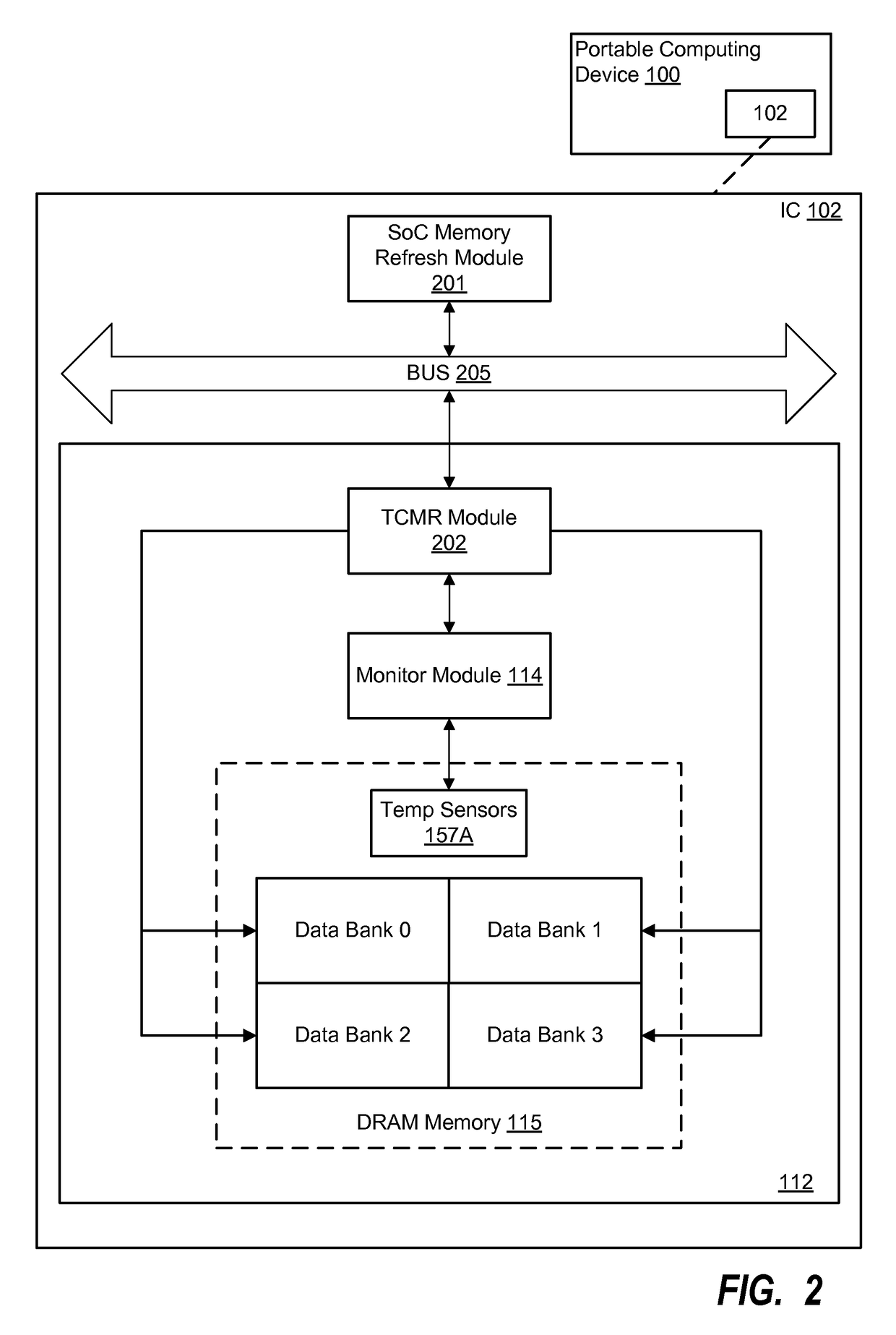
System and method for temperature compensated refresh of dynamic random access memory
InactiveUS9640242B1Digital data processing detailsDigital storageStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Various embodiments of methods and systems for temperature compensated memory refresh (“TCMR”) of a dynamic random access memory (“DRAM”) component are disclosed. Embodiments of the solution leverage a memory refresh module located within a memory subsystem to apply a refresh power supply received from a source on the SoC. Advantageously, even though the refresh power supply is received from a source on the SoC according to a certain delivery rate that may not be optimal for each and every bank in the DRAM component, embodiments of the solution are able to apply an effective refresh power supply rate to each bank according to its optimal cycle.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
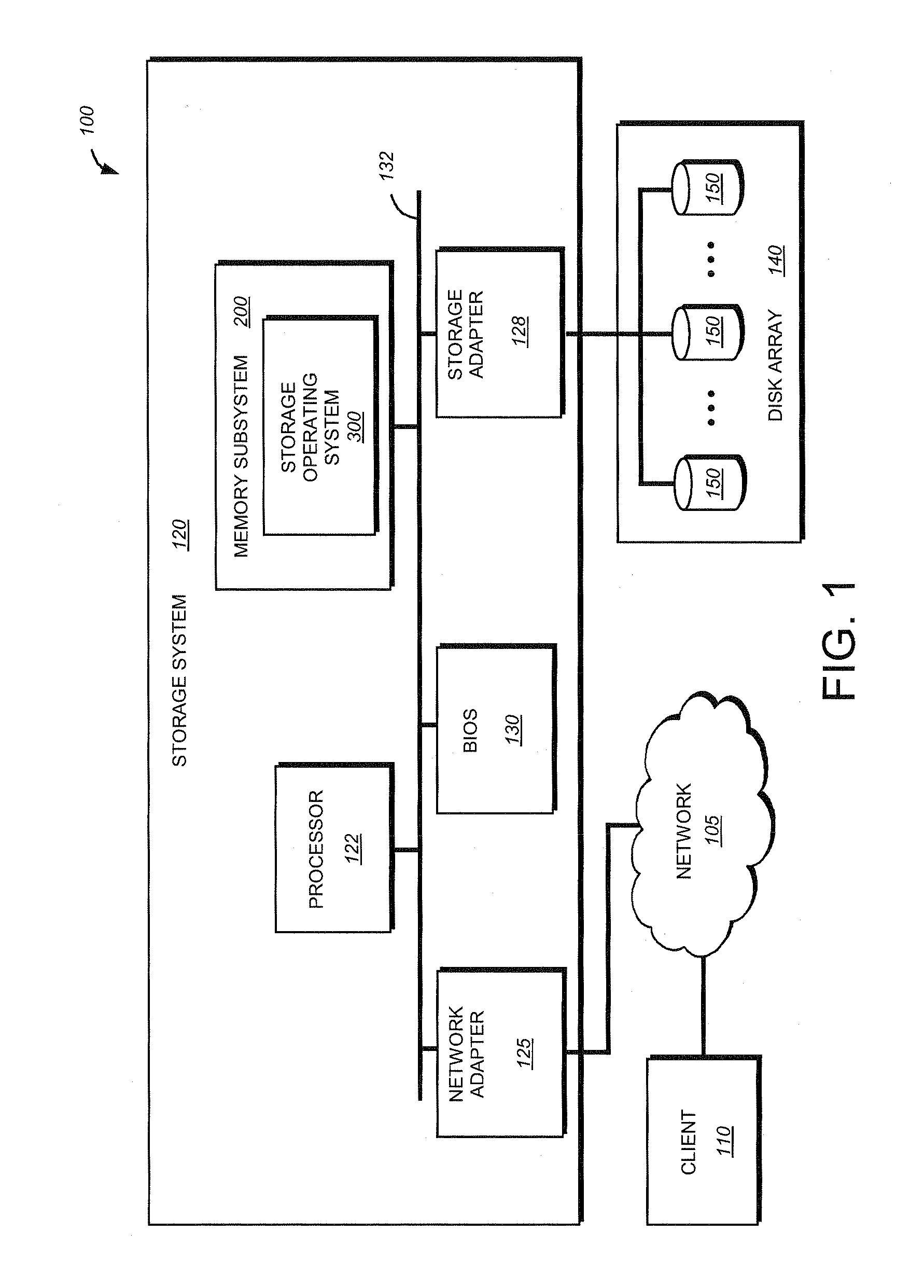
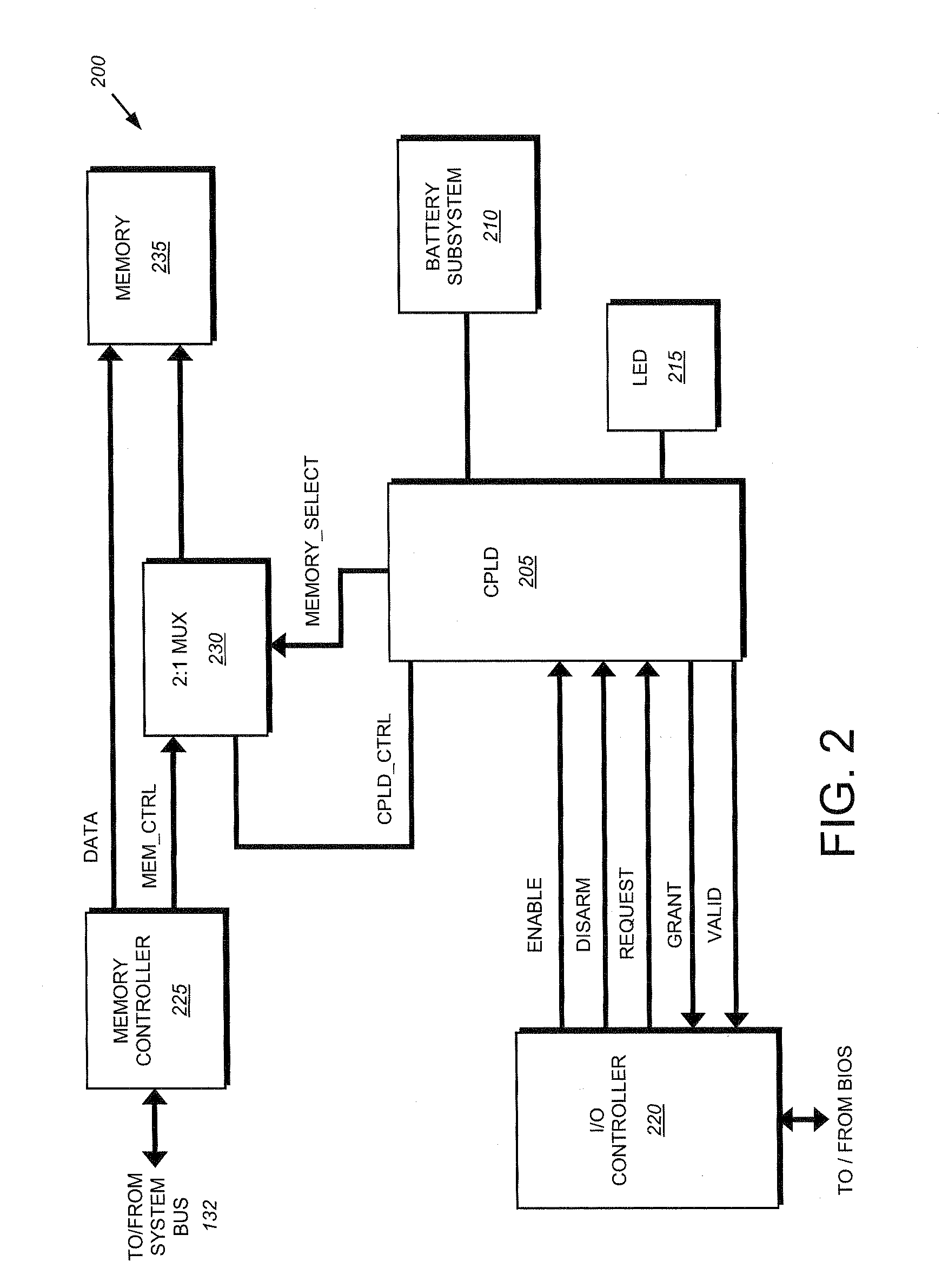
System and method for protecting memory during system initialization
ActiveUS20080270776A1Extend battery lifeOvercome disadvantagesError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsMultiplexerProgrammable logic device
A system and method for protecting memory during system initialization is provided. A complex programmable logic device (CPLD) is operatively interconnected with a multiplexer to enable control of a memory to be switched between a memory controller and the CPLD in response to error conditions. If an error condition is identified, the CPLD assumes control of the memory and activates a battery subsystem to provide memory refreshes until system re-initialization. Upon system bring-up, interactions between the BIOS and CPLD assure that protected memory is fully recovered by the system. The contents of memory will remain protected from any further faults that may occur during the bring-up sequence.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
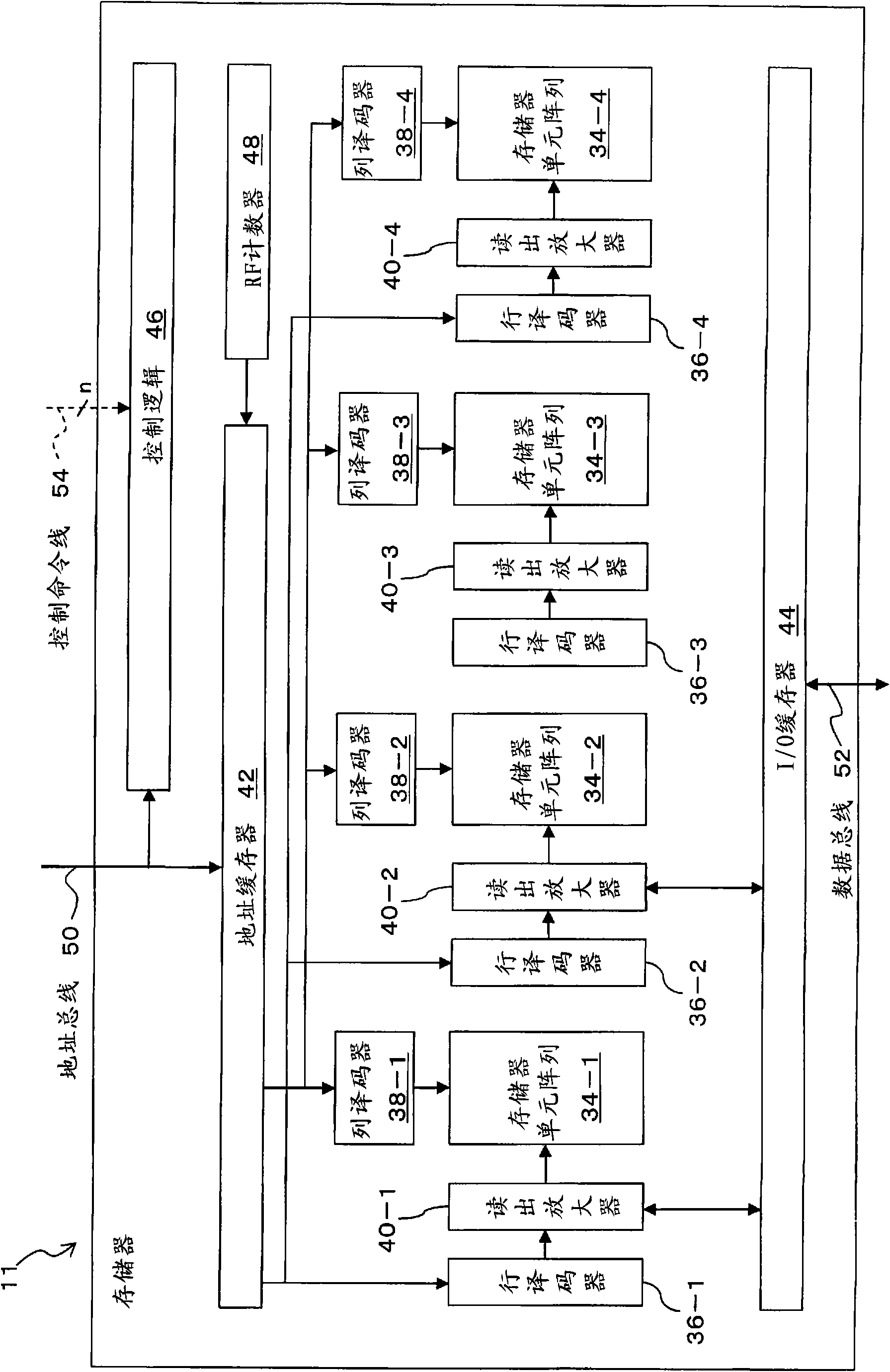
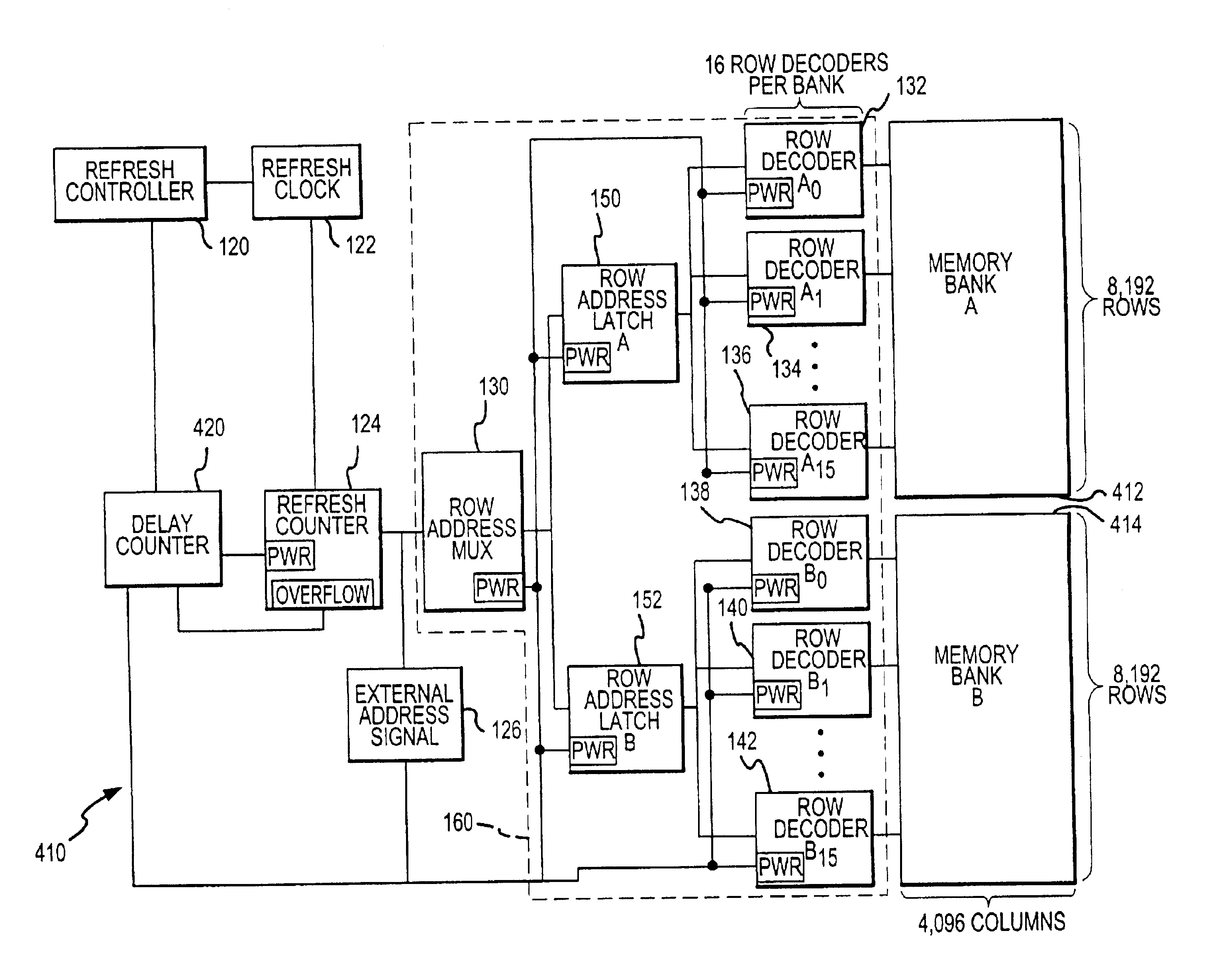
Dynamic memory refresh controller, memory system including the same and method of controlling refresh of dynamic memory
ActiveUS20070198771A1Maximize refresh trigger intervalMaximizing a refresh interval of dynamic memoryEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageComputer hardwareDynamic storage
A dynamic memory refresh controller includes a first in first out (FIFO) memory, a scheduler, a refresh control unit, and a signal generator. The FIFO memory stores and manages requests from a master device. The scheduler reorders the requests from the master device based on priorities assigned to the master device or provides information about following requests. The refresh control unit determines a refresh timing of the dynamic memory based on the existence of the following requests and an idle state of banks constituting the dynamic memory. Accordingly, the dynamic memory refresh controller may maximize a refresh trigger interval by changing the management order of the requests from the master device based on the priority of the response latency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
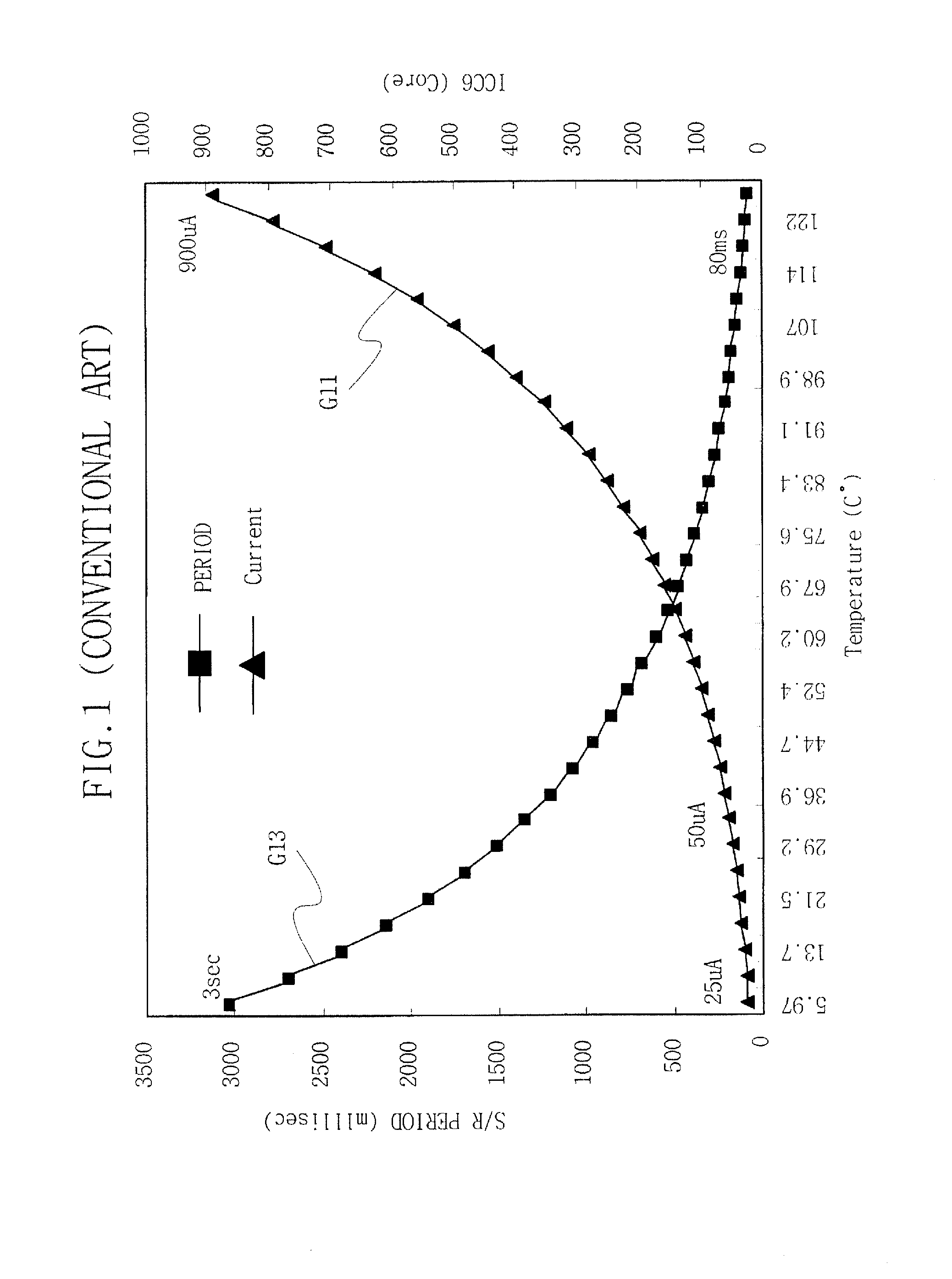
Circuit and method for controlling refresh periods in semiconductor memory devices
An integrated circuit memory device includes a refresh control circuit that generates an internal memory refresh command signal having a period that is changed relative to a period of an external memory refresh command signal received by the memory device. This change in the period of the internal memory refresh command may be in response to detecting a change in temperature of the memory device. In particular, the refresh control circuit is configured so that the period of the internal memory refresh command signal is increased in response to detecting a reduction in temperature of the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
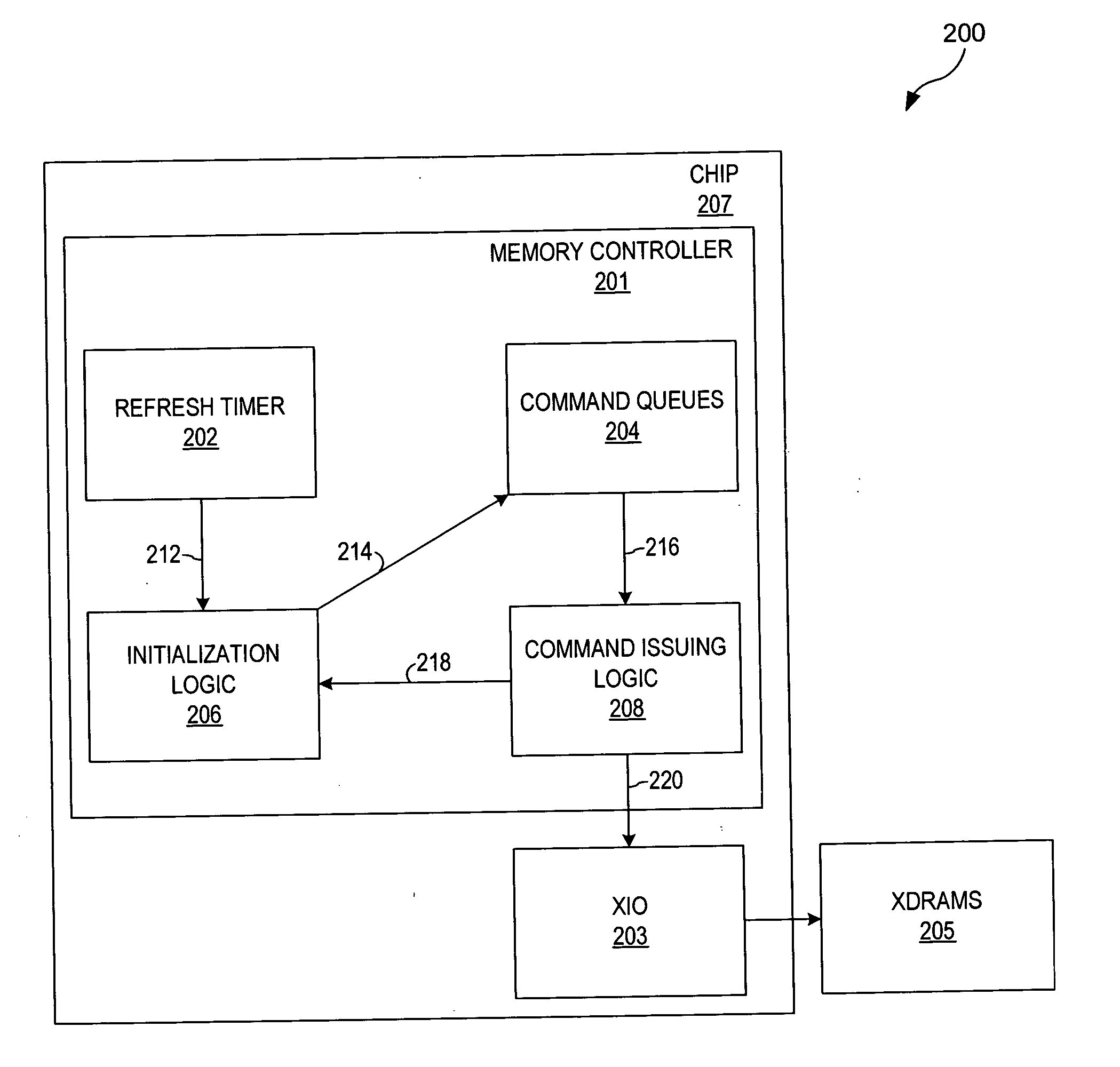
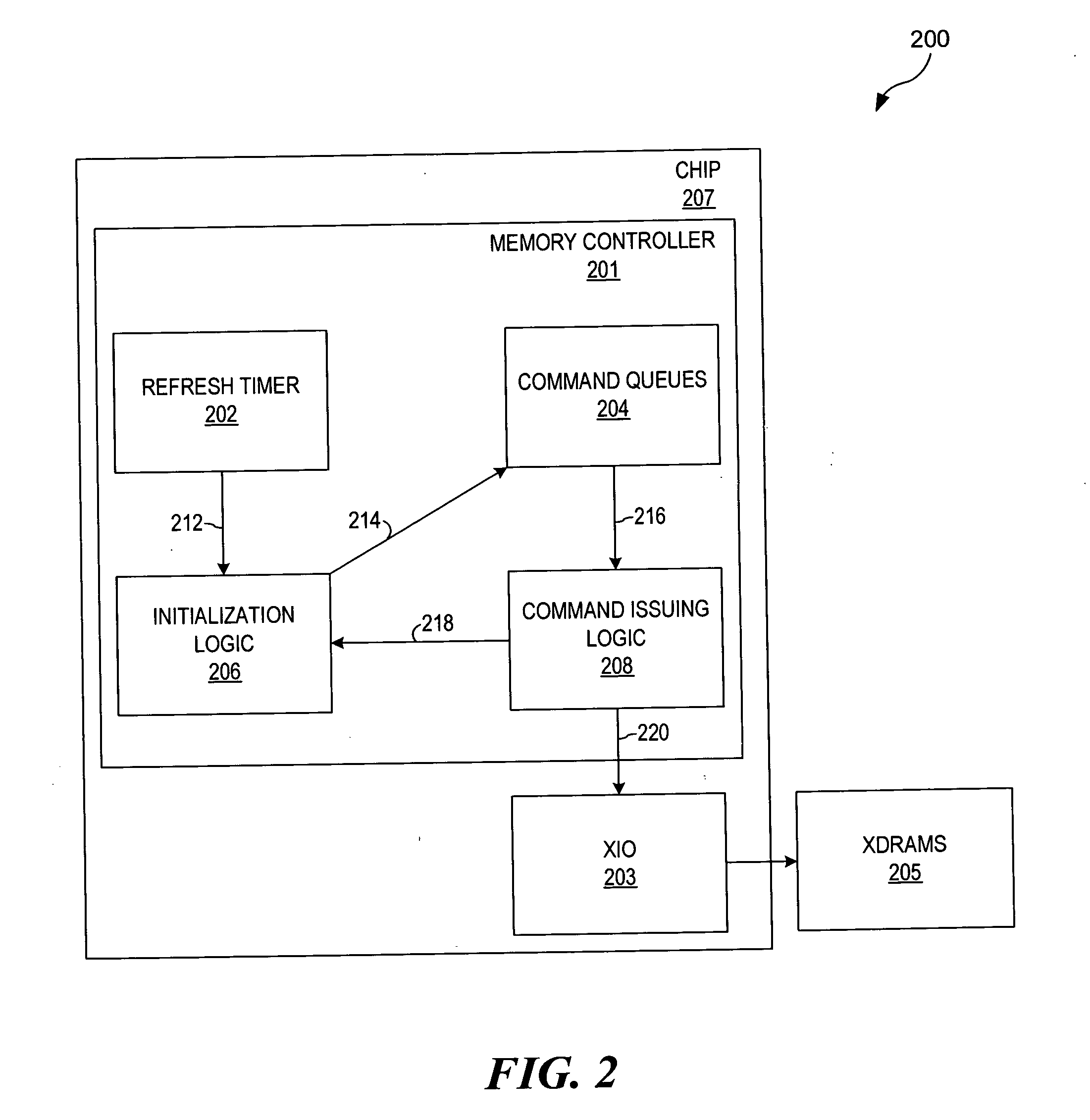
Deferring refreshes during calibrations in XDRTM memory systems
A method, an apparatus, and a computer program are provided to control refreshes in Extreme Data Rate (XDR™) memory systems. XDR™ memory systems employ calibrations to ensure the precise transmission of data. During calibrations, memory refreshes can occur; however, these refreshes can interfere with calibration streams. Therefore, to alleviate collisions and interferences, refreshes are deferred to periods where no calibrations are taking place. The number of deferred refreshes is also tracked such that the overall loss of refreshes is prevented.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for power saving memory refresh for dynamic random access memory devices after an extended interval
A delay device is added to the addressing and refreshing circuitry of a DRAM array including DRAM devices less volatile than conventional DRAM devices and, thus, need not be refreshed as often. The delay device is connected to intercept refresh signals generated by a conventional DRAM refresh controller and initiates a refresh cycle after disregarding a predetermined number of refresh signals generated by the refresh controller whose total duration equals the interval by which the less volatile DRAM devices must be refreshed. The delay device also is adapted to power off circuitry needed to address the DRAM devices when the DRAM devices are not being refreshed or otherwise accessed. Additional circuitry is added to selectively power on only specific addressing devices actually needed to address those certain portions of the array being refreshed at that time.
Dual inline memory module with temperature-sensing scenario mode
ActiveUS20170343198A1Accurate measurementEnsure proper implementationLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourceControl engineeringSource system
Disclosed is a dual inline memory module with temperature-sensing scenario modes. A plurality of volatile memory components and an EEPROM component are disposed on a module board. A plurality of LED components and a scenario-lighting controller are disposed at a radiant side of the module board. A light bar is located at the radiant side of the module board without direct installing relationship. A plurality of clamping-type heat spreaders are fastened to one another in a manner that the light bar is tightly clamped. Therein, the power of the scenario-lighting controller component is shared and linked with the power supply system of the LED components and the signals of the scenario-lighting controller component are shared and linked with the signal connection system of the EEPROM component. Accordingly, the lighting scenario performances controlled by the scenario-lighting controller accord with the sensing temperatures to adjust memory refreshing frequencies to avoid any incorrect performance caused by sensed temperature differences.
Owner:CORSAIR MEMORY INC
Semiconductor device including multi-bit memory cells and a temperature budget sensor
One embodiment provides a semiconductor device including a plurality of multi-bit memory cells, a first temperature balance sensor, and a circuit. Each of the plurality of multi-bit memory cells can be programmed to each of two or more states. The circuit compares the first signal from the first temperature budget sensor with the first reference signal to obtain a first comparison result. The circuit refreshes a plurality of multi-bit storage devices according to the first comparison result.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Using bit errors from memory to alter memory command stream
InactiveUS7631228B2Reduced activityIncrease ratingsCode conversionDigital storageComputer hardwareMemory controller
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
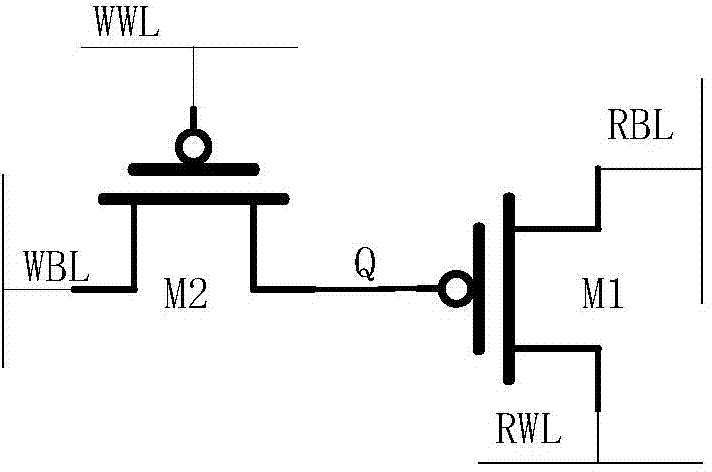
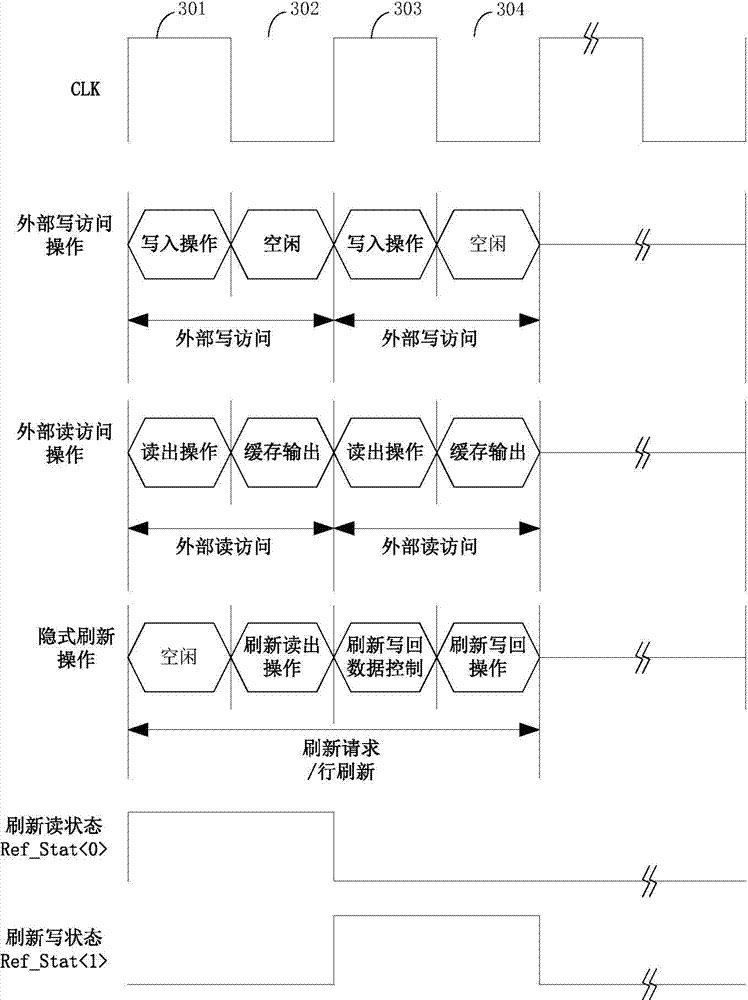
Dynamic memory refreshing method and refreshing controller
The invention discloses a dynamic memory refreshing method and a refreshing controller, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor memories. According to the dynamic memory refreshing method, based on a grain unit memory, by using a manner than the grain memory unit has two groups of mutually independent word lines and bit lines, read / write operation of external access is completed within an upper-half period of a clock, and refreshing read / refreshing write operation is completed within a lower-half period of the clock. According to the dynamic memory refreshing method, a refreshing request signal and a refreshing state signal are generated according to a refreshing period of the gain unit, a line number of a memory Bank and a clock period; control signals of corresponding refreshing read and refreshing write operations are generated according to a refreshing state to control refreshing read and refreshing write operations and external read / external write operation to be performed in parallel. According to the dynamic memory refreshing method, the confliction between a refreshing operation and the external access is eliminated, so that the memory can be accessed completely randomly in real time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com