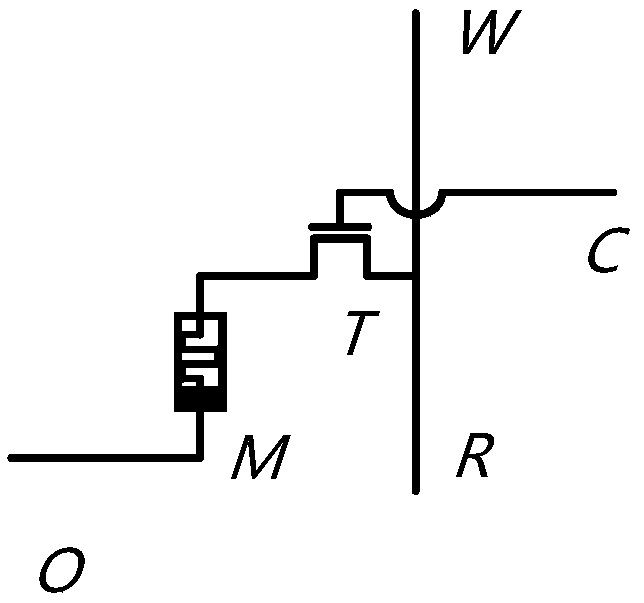
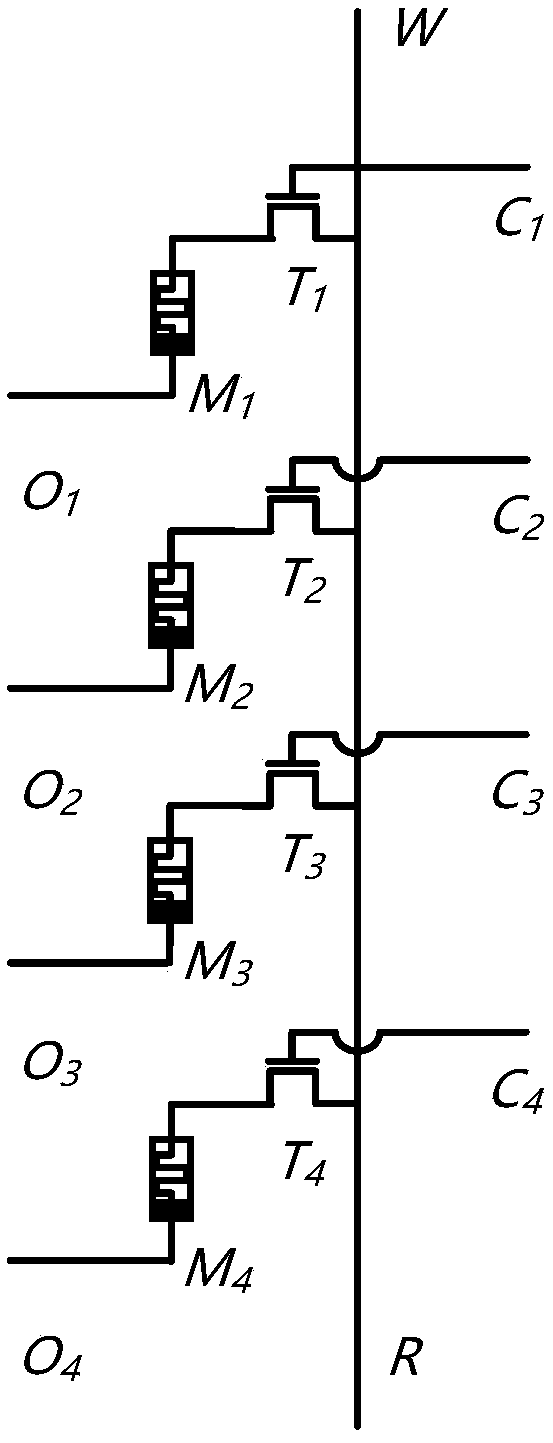
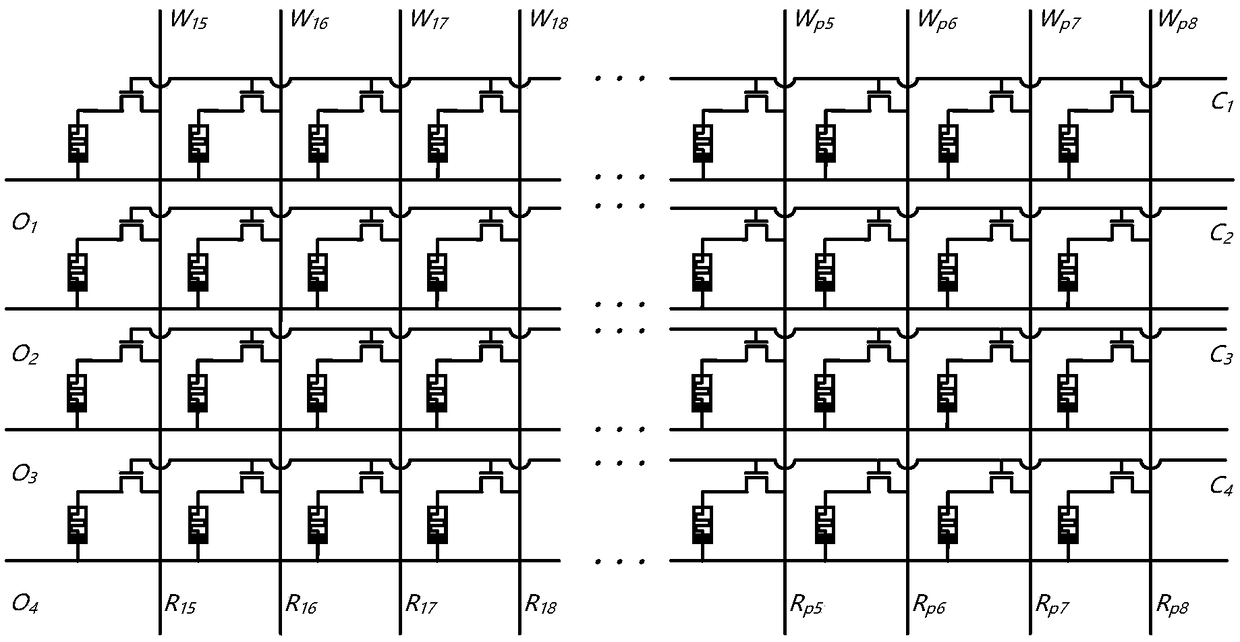
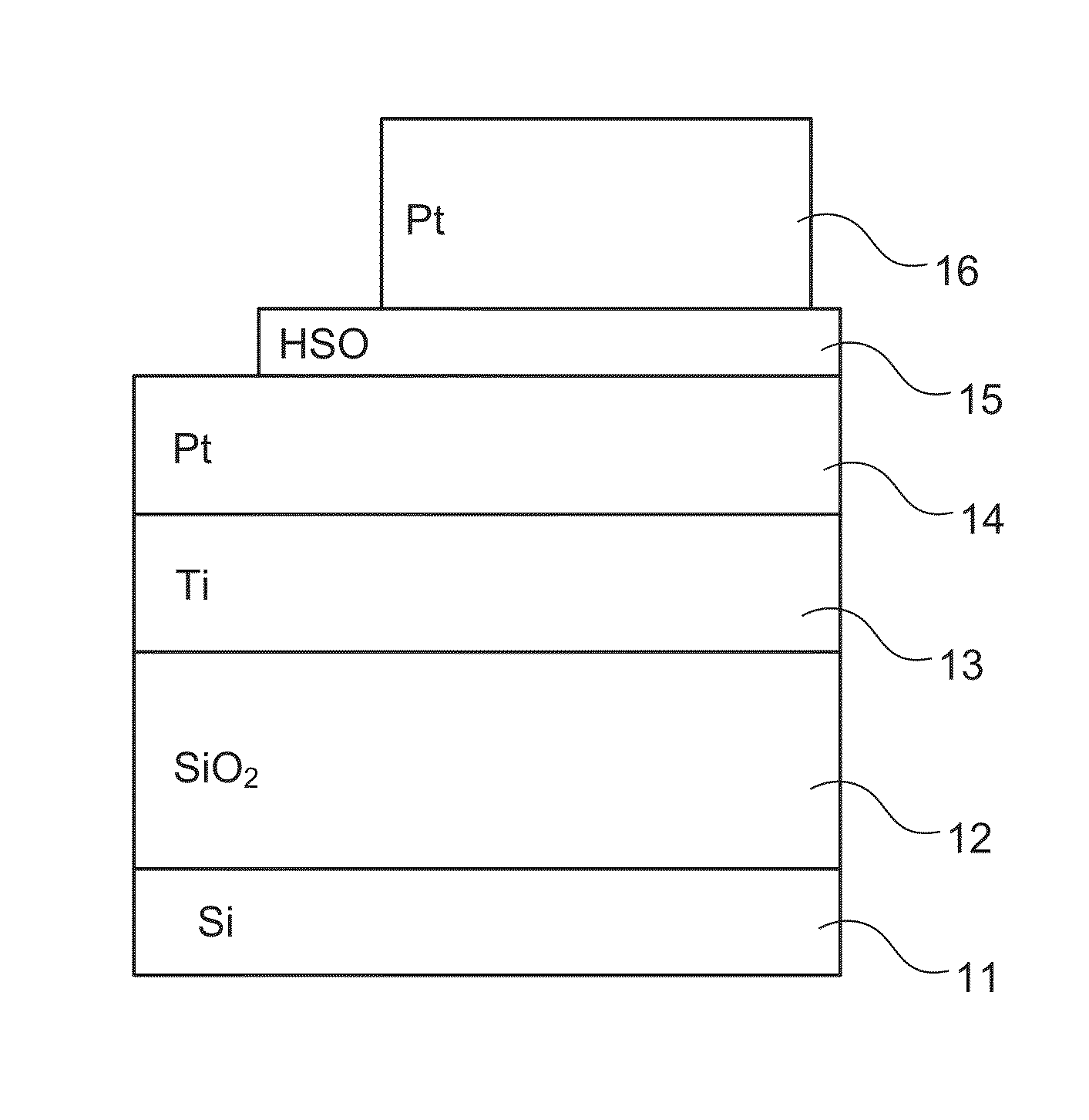
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "High resistance state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
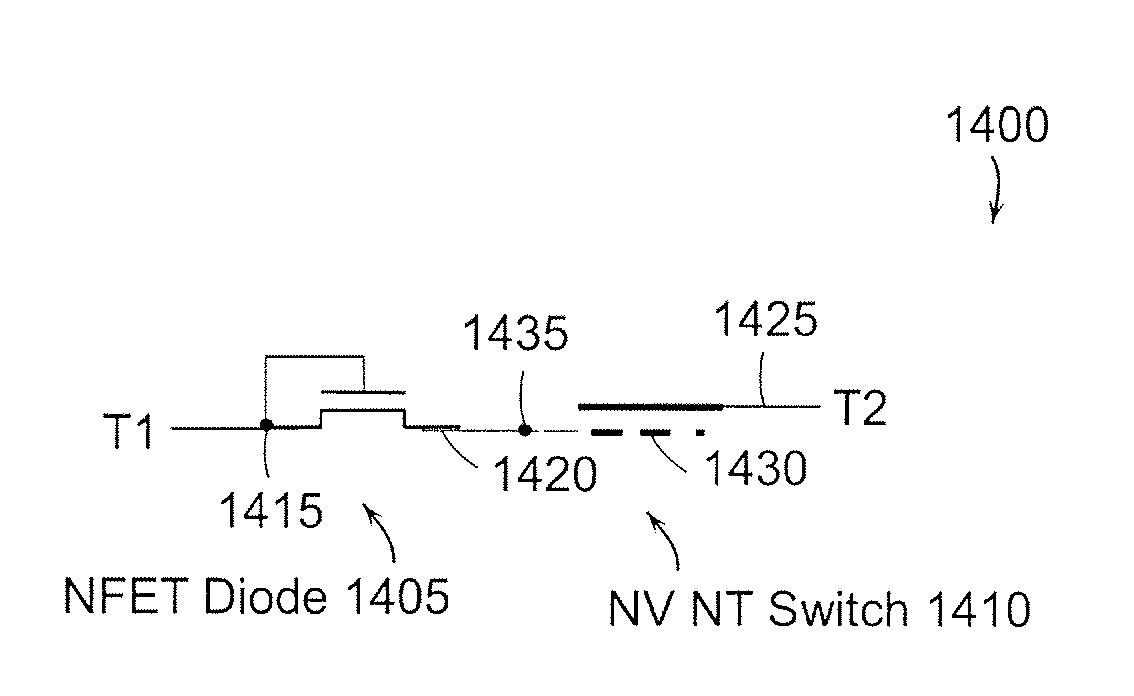
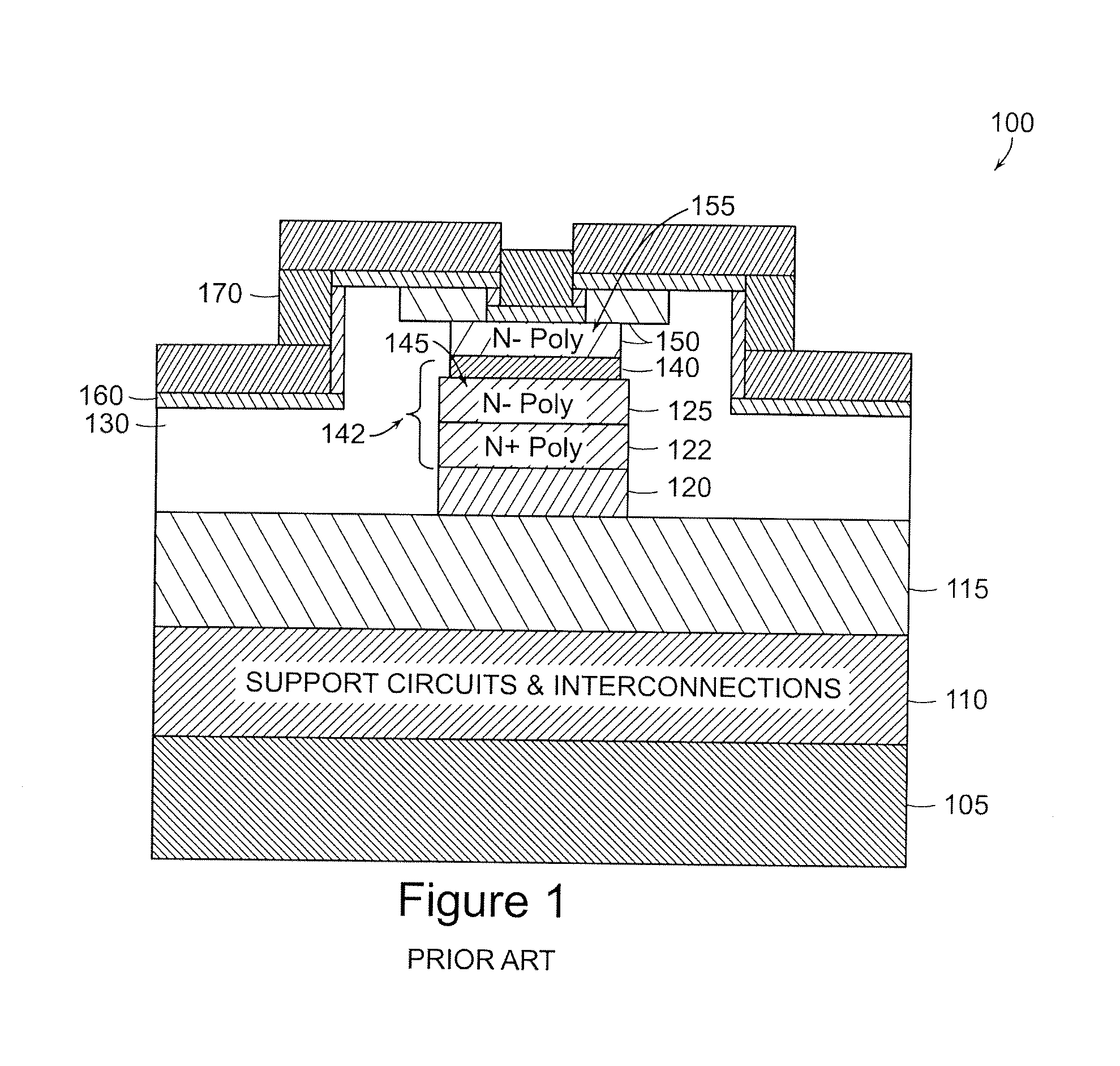
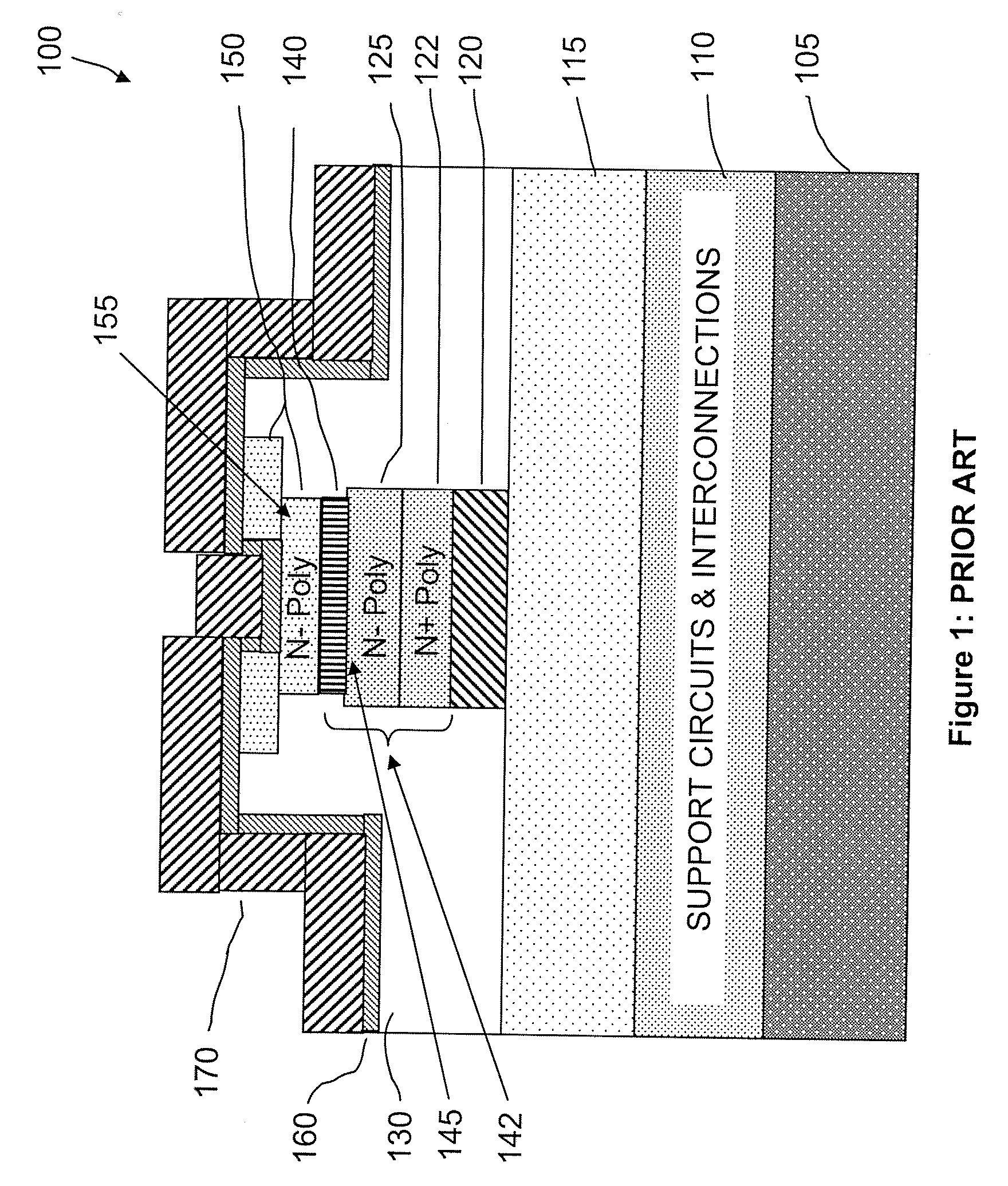
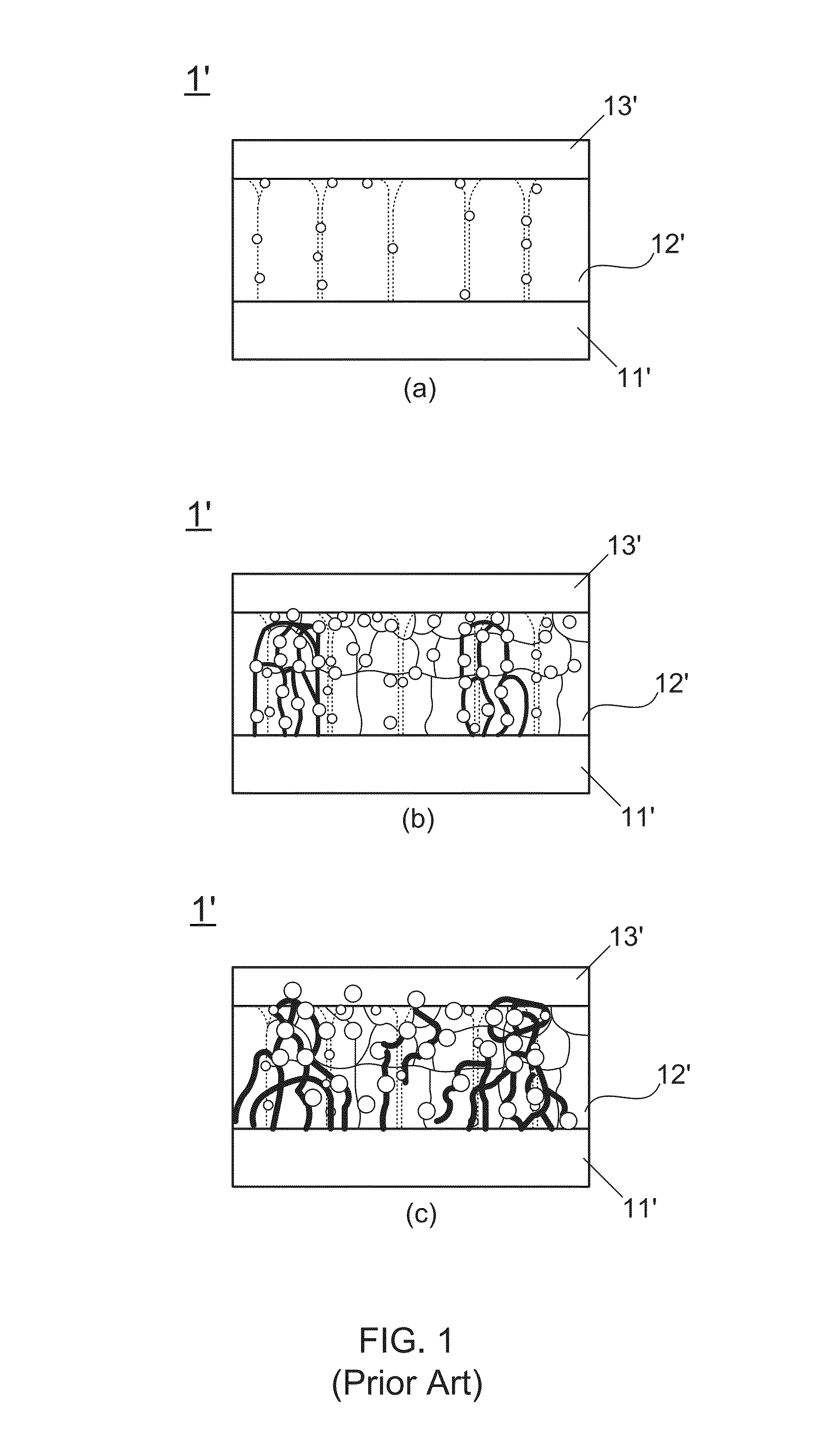
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080157126A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsEngineeringSemiconductor components
Under one aspect, a non-volatile nanotube diode device includes first and second terminals; a semiconductor element including a cathode and an anode, and capable of forming a conductive pathway between the cathode and anode in response to electrical stimulus applied to the first conductive terminal; and a nanotube switching element including a nanotube fabric article in electrical communication with the semiconductive element, the nanotube fabric article disposed between and capable of forming a conductive pathway between the semiconductor element and the second terminal, wherein electrical stimuli on the first and second terminals causes a plurality of logic states.
Owner:NANTERO
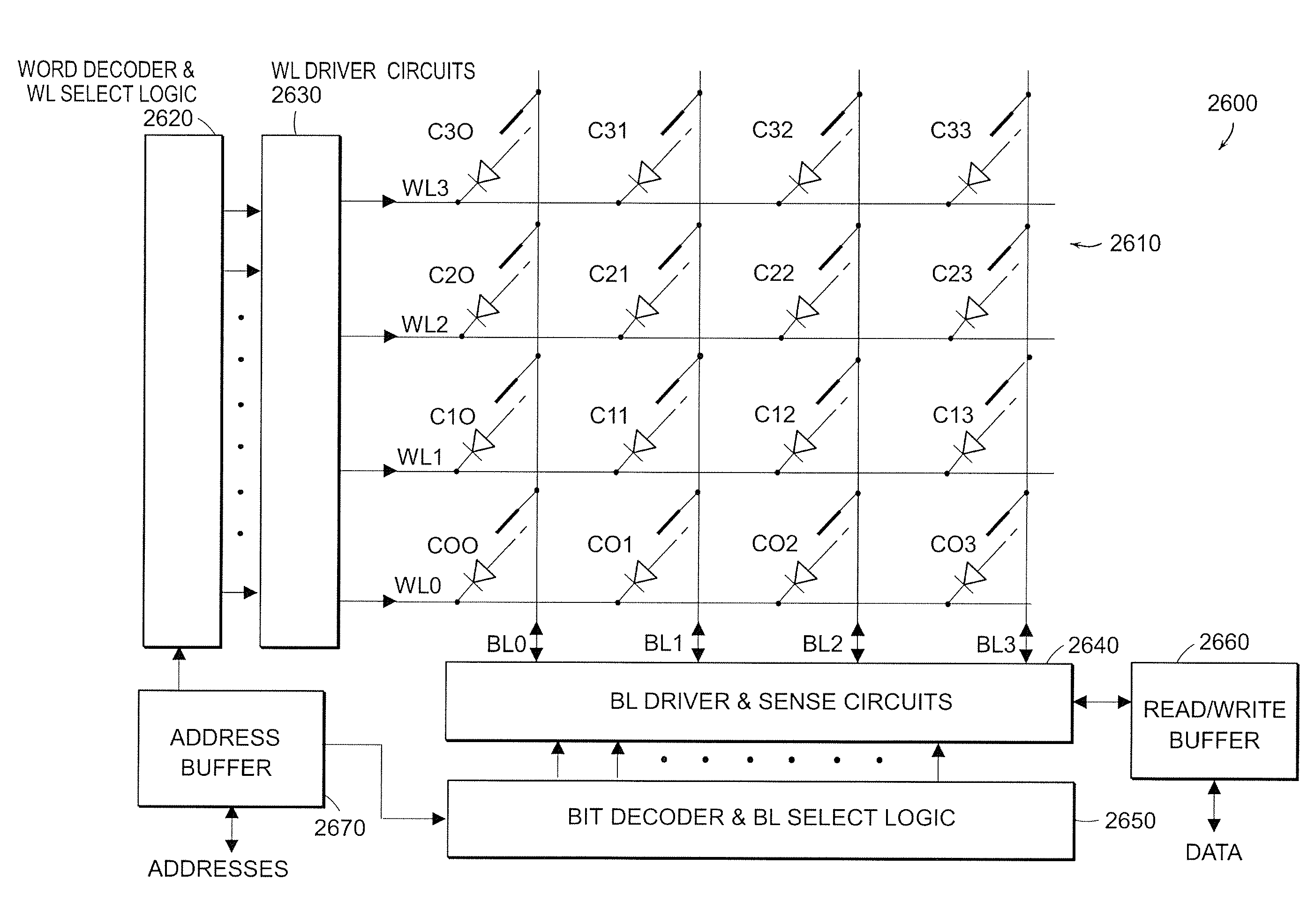
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080212361A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateNanotechSolid-state devicesBit lineElectricity
Under one aspect, a memory array includes word lines; bit lines; memory cells; and a memory operation circuit. Each memory cell responds to electrical stimulus on a word line and on a bit line and includes: a two-terminal non-volatile nanotube switching device having first and second terminals, a semiconductor diode element, and a nanotube fabric article capable of multiple resistance states. The semiconductor diode and nanotube article are between and in electrical communication with the first and second terminals, which are coupled to the word line bit line respectively. The operation circuit selects cells by activating bit and / or word lines, detects a resistance state of the nanotube fabric article of a selected memory cell, and adjusts electrical stimulus applied to the cell to controllably induce a selected resistance state in the nanotube fabric article. The selected resistance state corresponds to an informational state of the memory cell.
Owner:NANTERO
Nonvolatile Nanotube Diodes and Nonvolatile Nanotube Blocks and Systems Using Same and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20090184389A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsEngineeringElectronic states
A non-volatile nanotube switch and memory arrays constructed from these switches are disclosed. A non-volatile nanotube switch includes a conductive terminal and a nanoscopic element stack having a plurality of nanoscopic elements arranged in direct electrical contact, a first comprising a nanotube fabric and a second comprising a carbon material, a portion of the nanoscopic element stack in electrical contact with the conductive terminal. Control circuitry is provided in electrical communication with and for applying electrical stimulus to the conductive terminal and to at least a portion of the nanoscopic element stack. At least one of the nanoscopic elements is capable of switching among a plurality of electronic states in response to a corresponding electrical stimuli applied by the control circuitry to the conductive terminal and the portion of the nanoscopic element stack. For each electronic state, the nanoscopic element stack provides an electrical pathway of corresponding resistance.
Owner:NANTERO
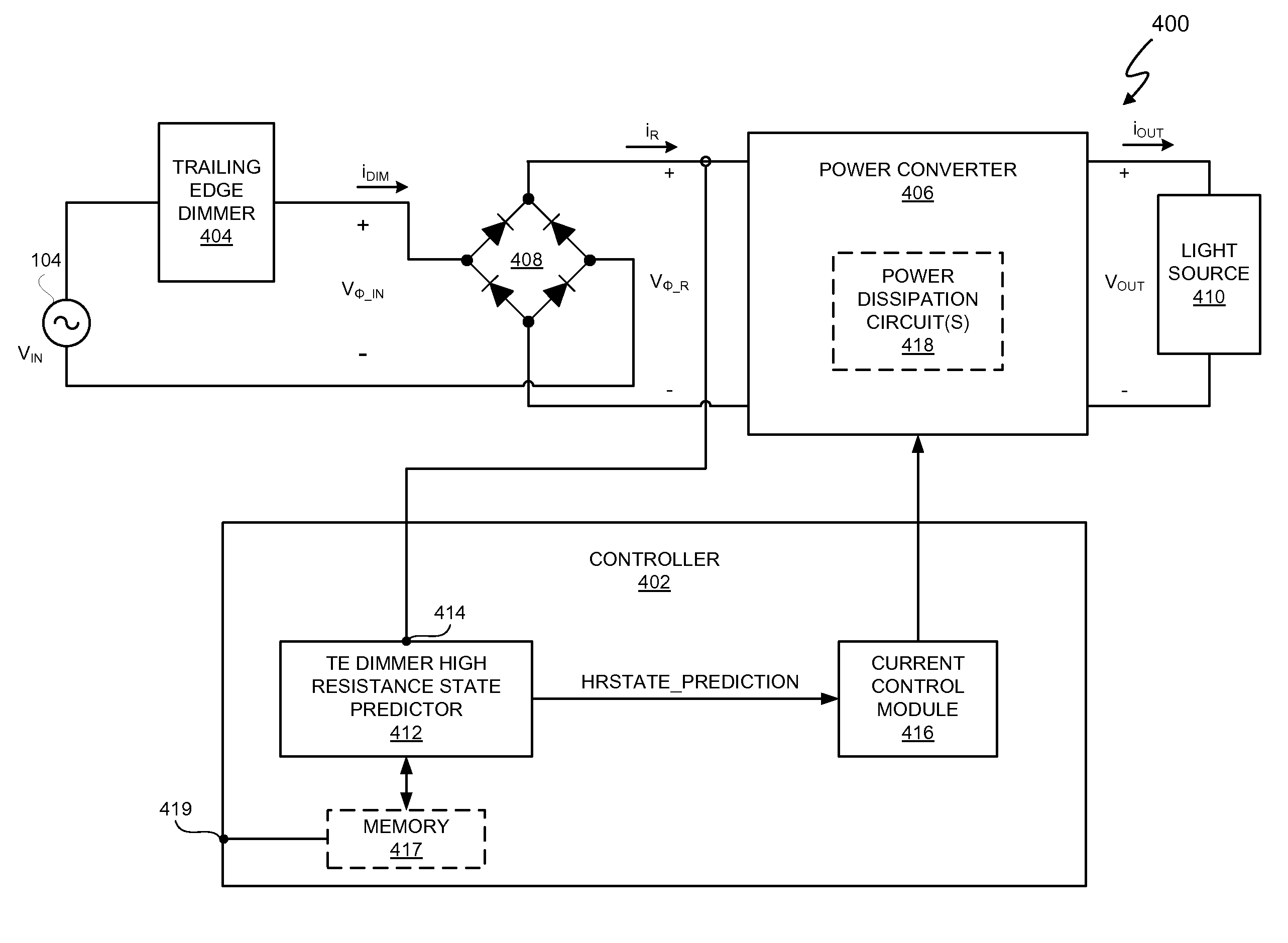
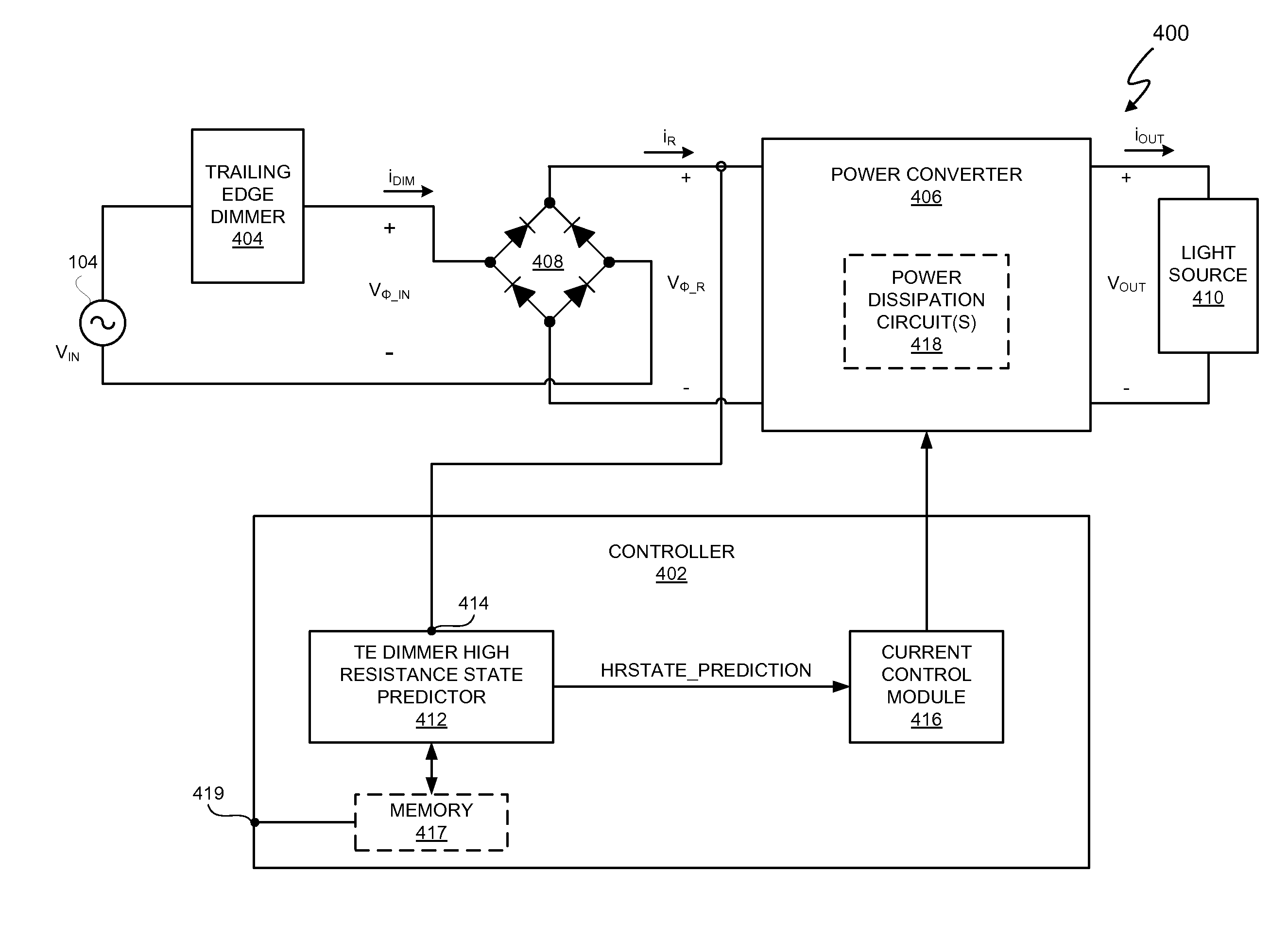
Trailing Edge Dimmer Compatibility With Dimmer High Resistance Prediction
ActiveUS20120119669A1Increase resistanceHigh occurrenceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh resistanceElectronic systems
In at least one embodiment, an electronic system includes a controller, and the controller provides compatibility between an electronic light source and a trailing edge dimmer. In at least one embodiment, the controller is capable of predicting an estimated occurrence of a trailing edge of a phase cut AC voltage and accelerating a transition of the phase cut AC voltage from the trailing edge to a predetermined voltage threshold. In at least one embodiment, the controller predicts an estimated occurrence of the trailing edge of the phase cut AC voltage on the basis of actual observations from one or more previous cycles of the phase cut AC voltage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
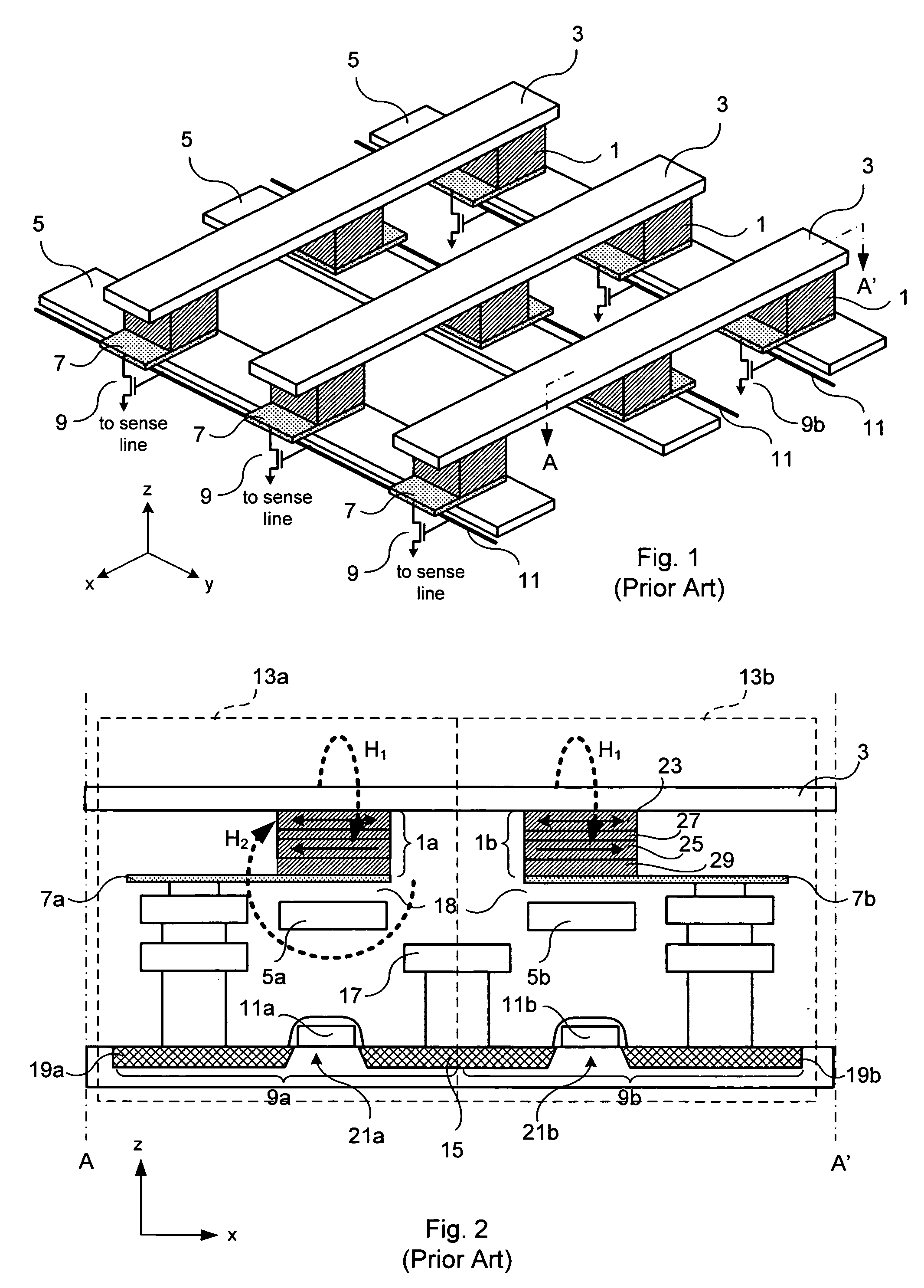
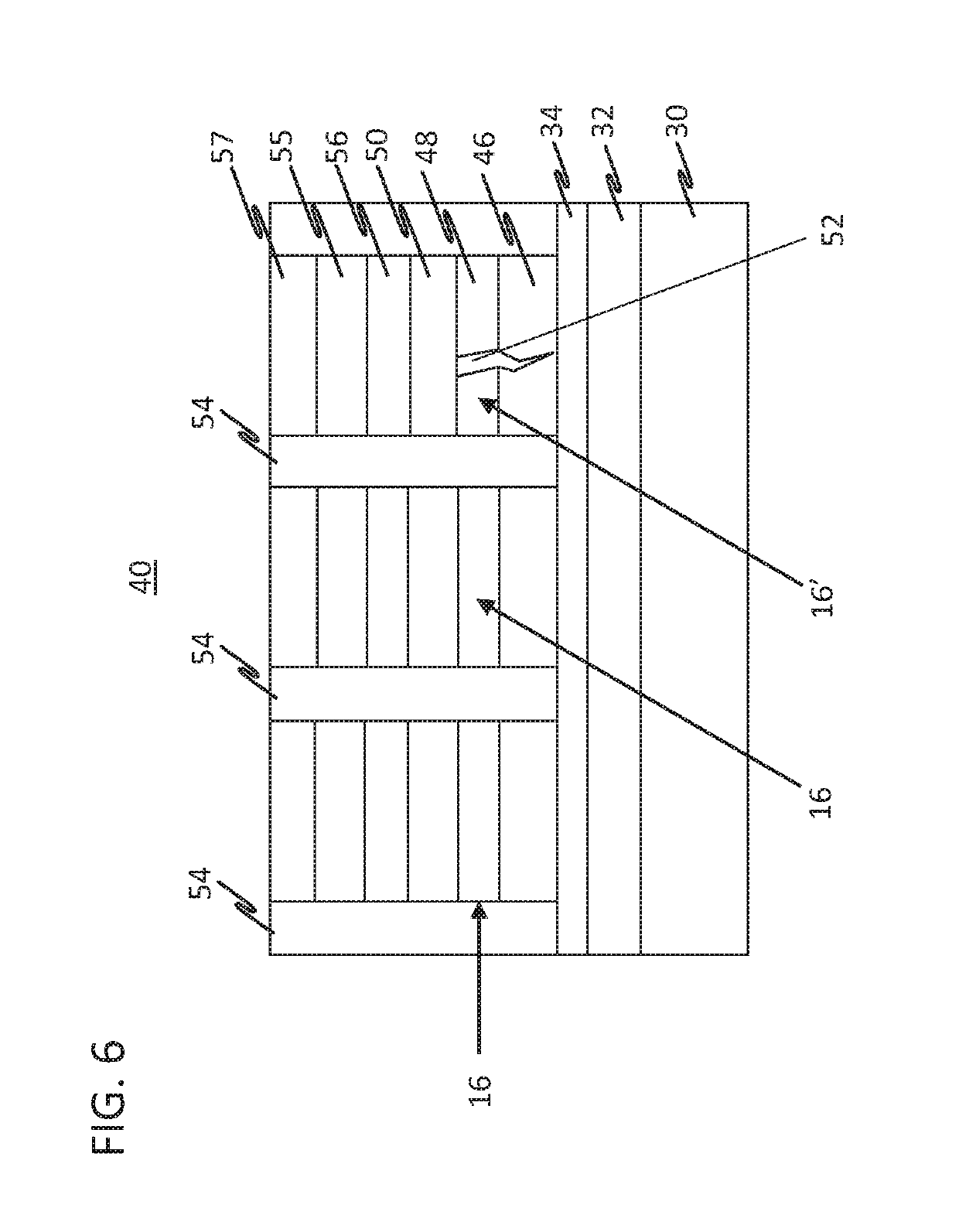
Magnetic memory device
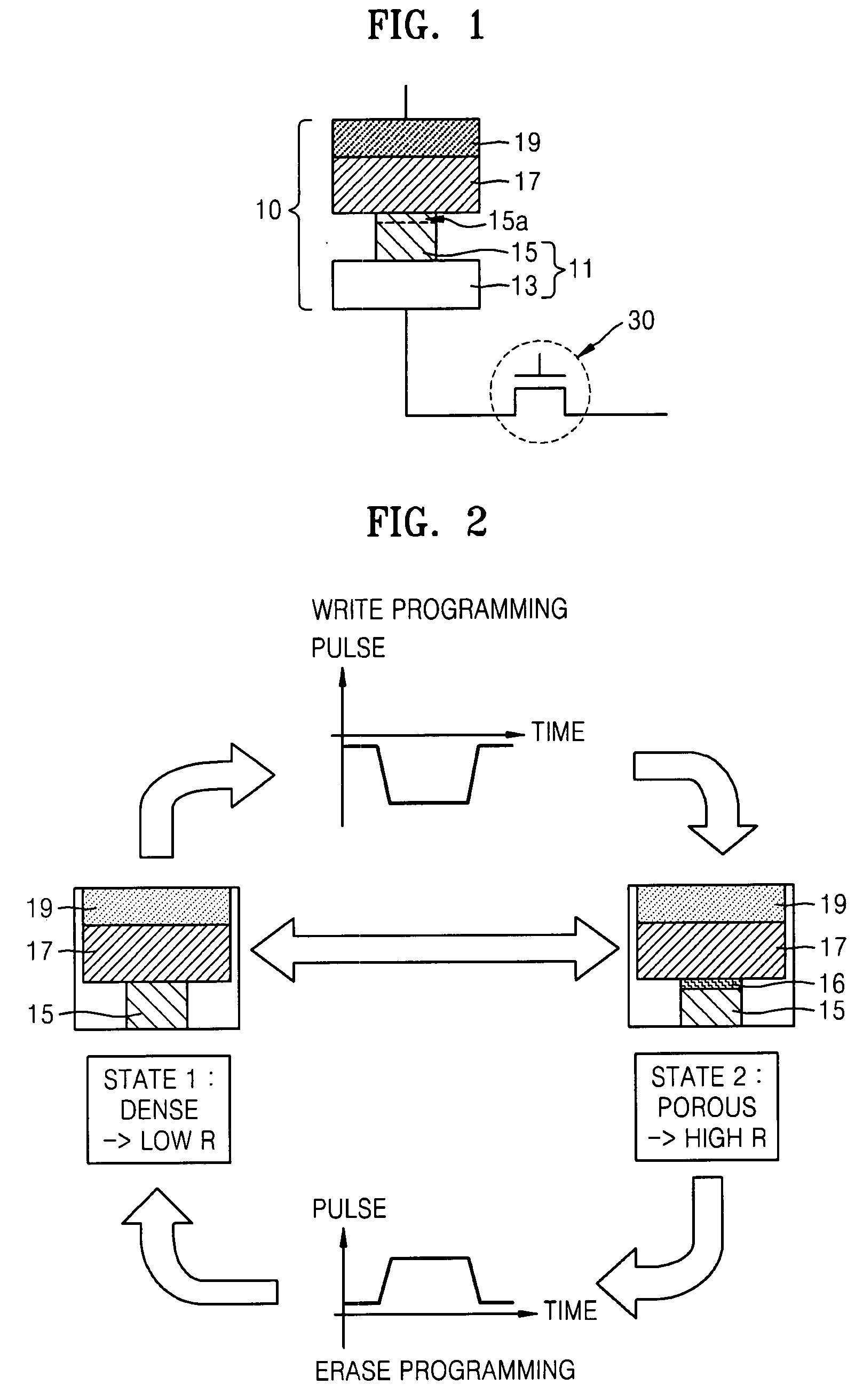
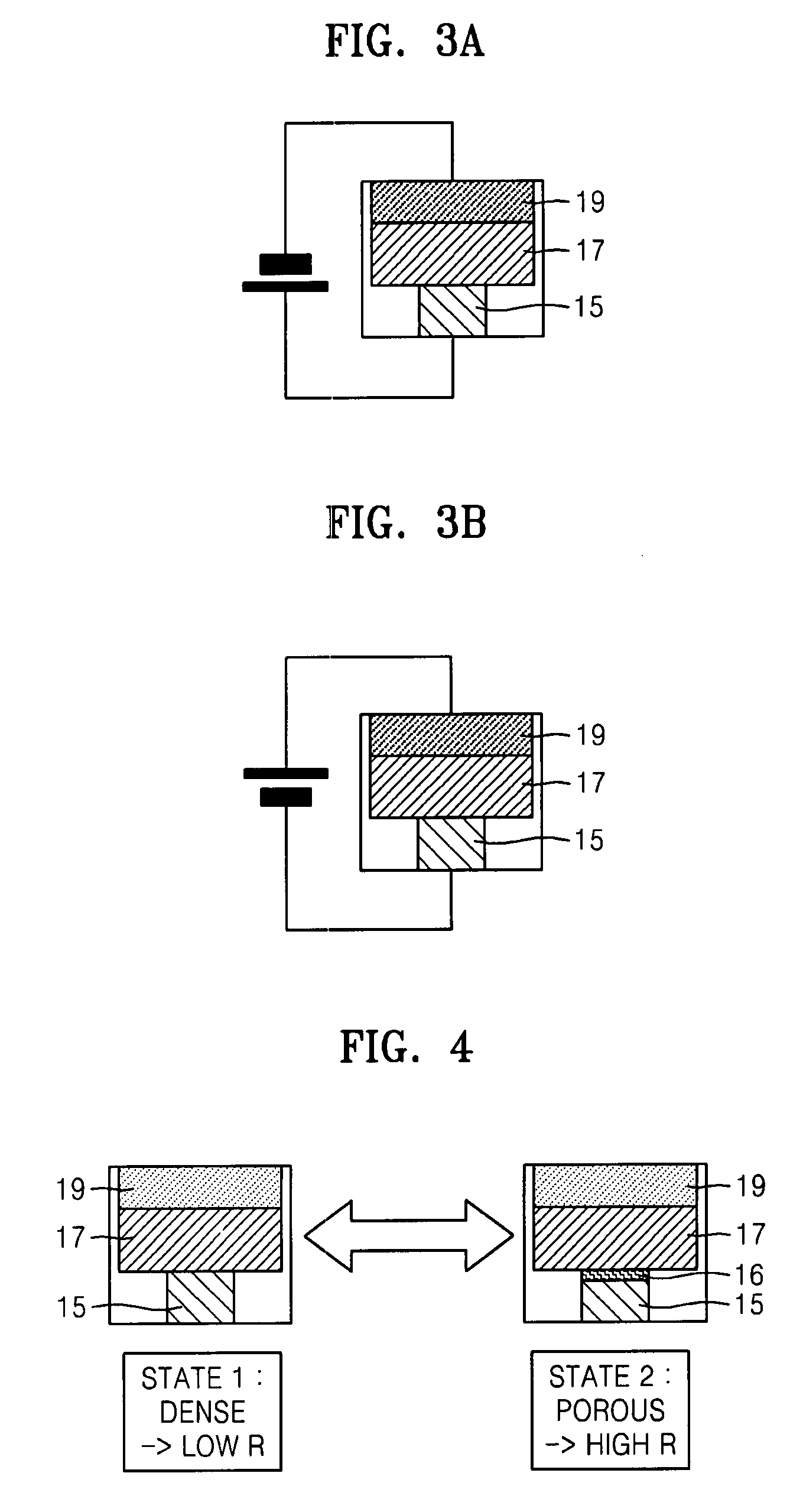
InactiveUS20080037179A1High resistance stateIncrease write speedNanotechRecord information storageHigh resistanceBit line
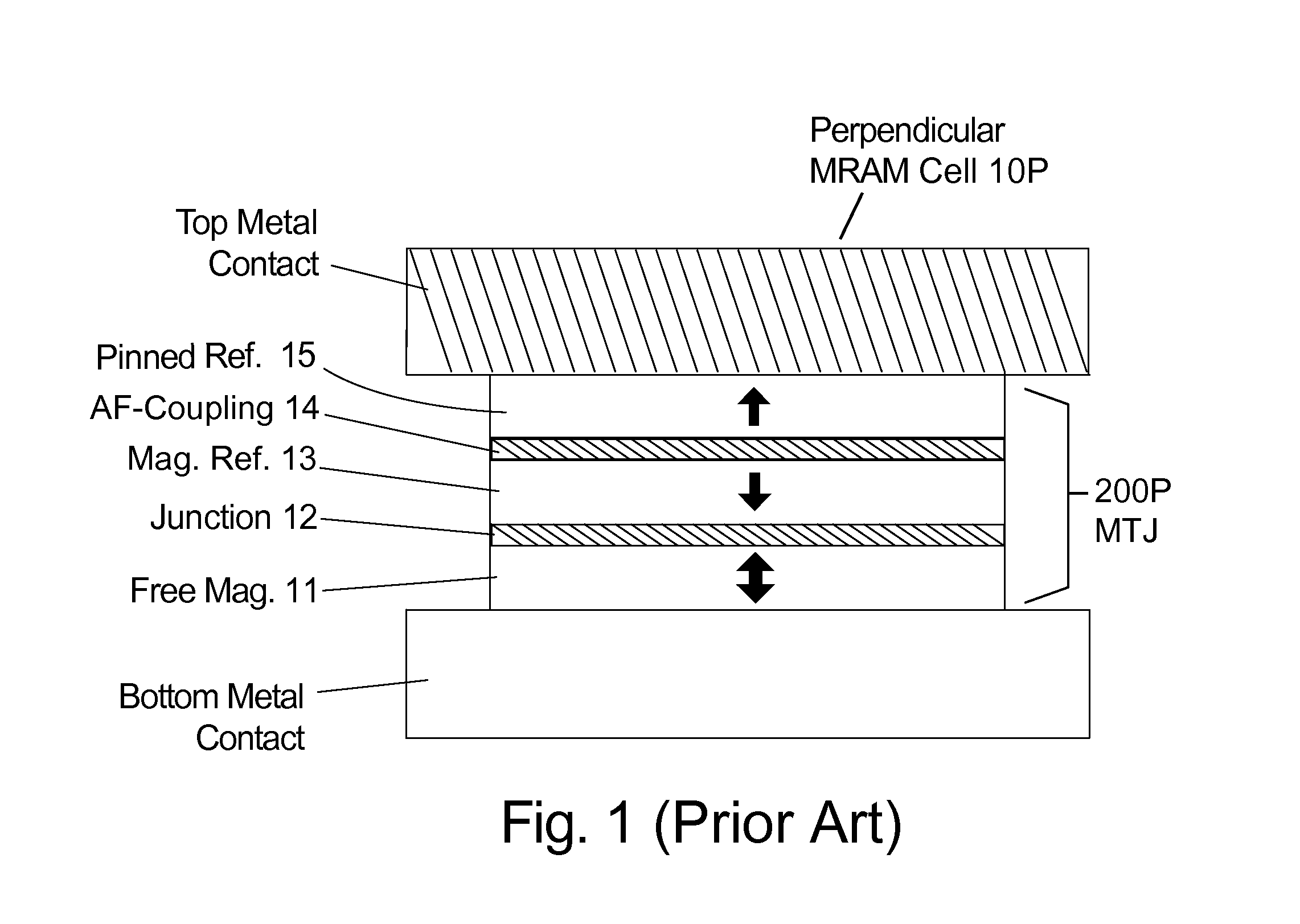
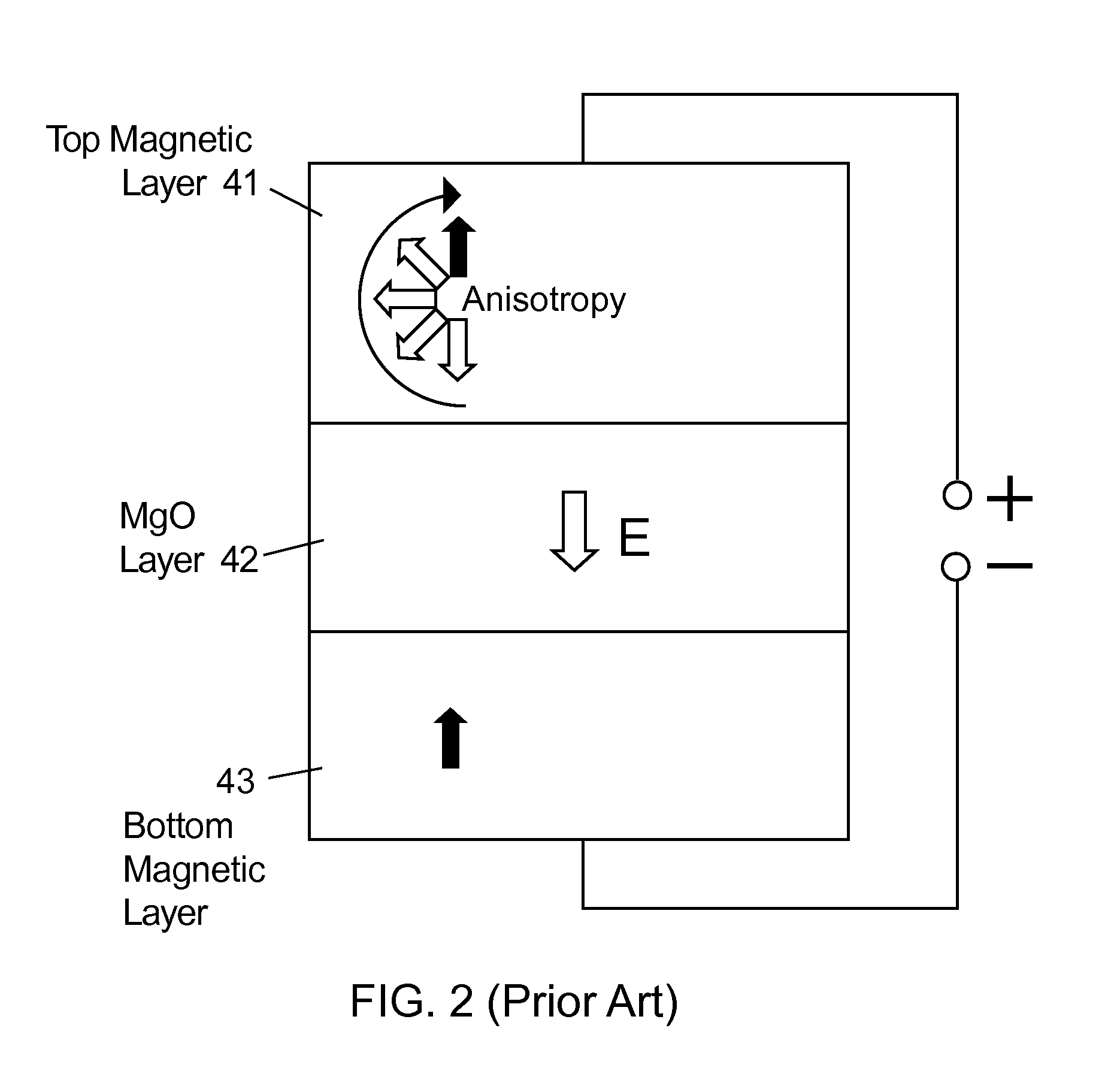
A magnetic memory device comprises a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) connecting to a bit line to a sense line through an isolation transistor. The MTJ includes a ferromagnetic layer having a magnetic hard axis. An assist current line overlies the bit line and is insulated from the bit line. The MTJ is switchable between a first, relatively high resistance state and a second, relatively low resistance state. The assist current line applies a magnetic field along the magnetic hard axis in the ferromagnetic layer, independently of current flow through the MTJ for assisting switching of the MTJ between the first and second states.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Trailing edge dimmer compatibility with dimmer high resistance prediction
ActiveUS8547034B2High resistance stateEasy transitionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh resistanceElectronic systems
In at least one embodiment, an electronic system includes a controller, and the controller provides compatibility between an electronic light source and a trailing edge dimmer. In at least one embodiment, the controller is capable of predicting an estimated occurrence of a trailing edge of a phase cut AC voltage and accelerating a transition of the phase cut AC voltage from the trailing edge to a predetermined voltage threshold. In at least one embodiment, the controller predicts an estimated occurrence of the trailing edge of the phase cut AC voltage on the basis of actual observations from one or more previous cycles of the phase cut AC voltage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Stabilized resistive switching memory
ActiveUS20080106927A1High resistance stateConductive materialSolid-state devicesOxygen vacancyEngineering
A non-volatile resistive switching memory that includes a material which changes between the insulative and conductive states. The material is stabilized against charge trapping by oxygen vacancies by an extrinsic ligand, such as carbon.
Owner:SYMETRIX MEMORY
Memory device and storage apparatus
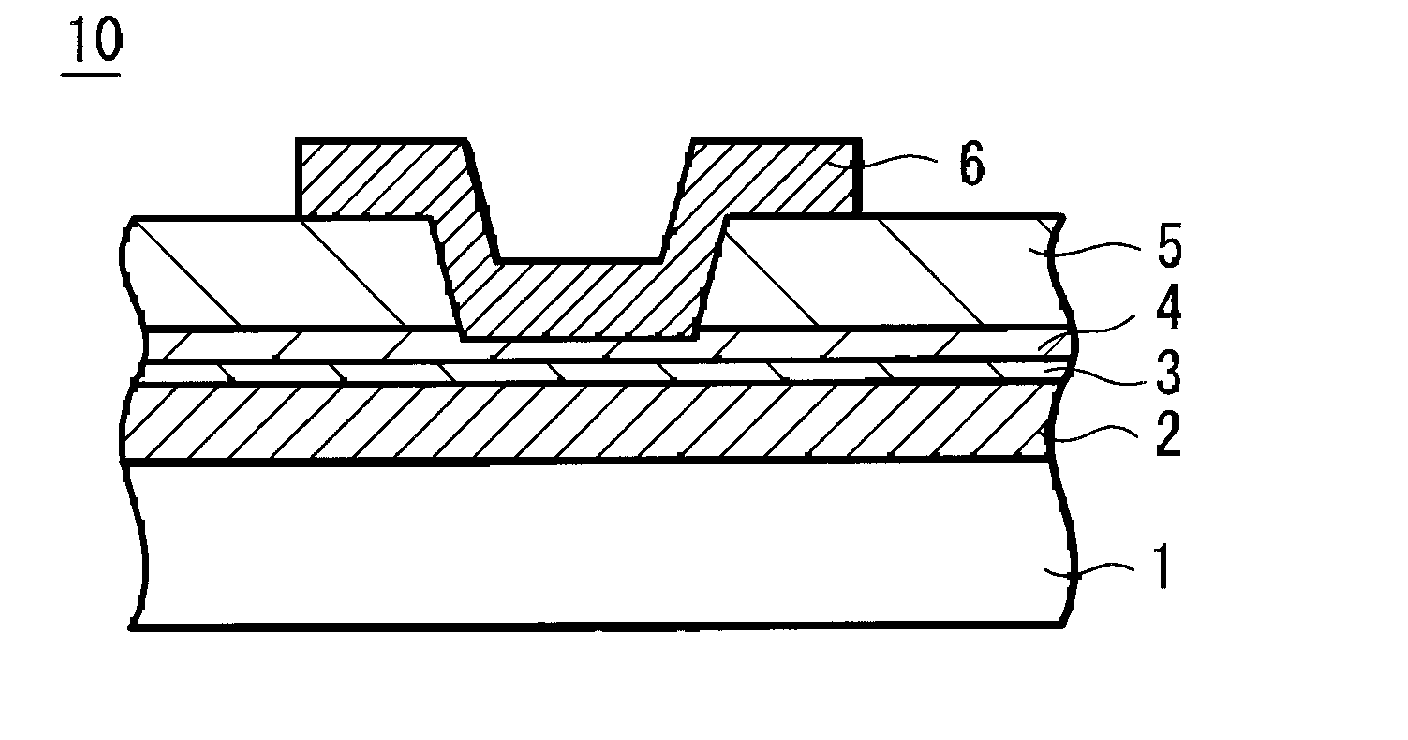
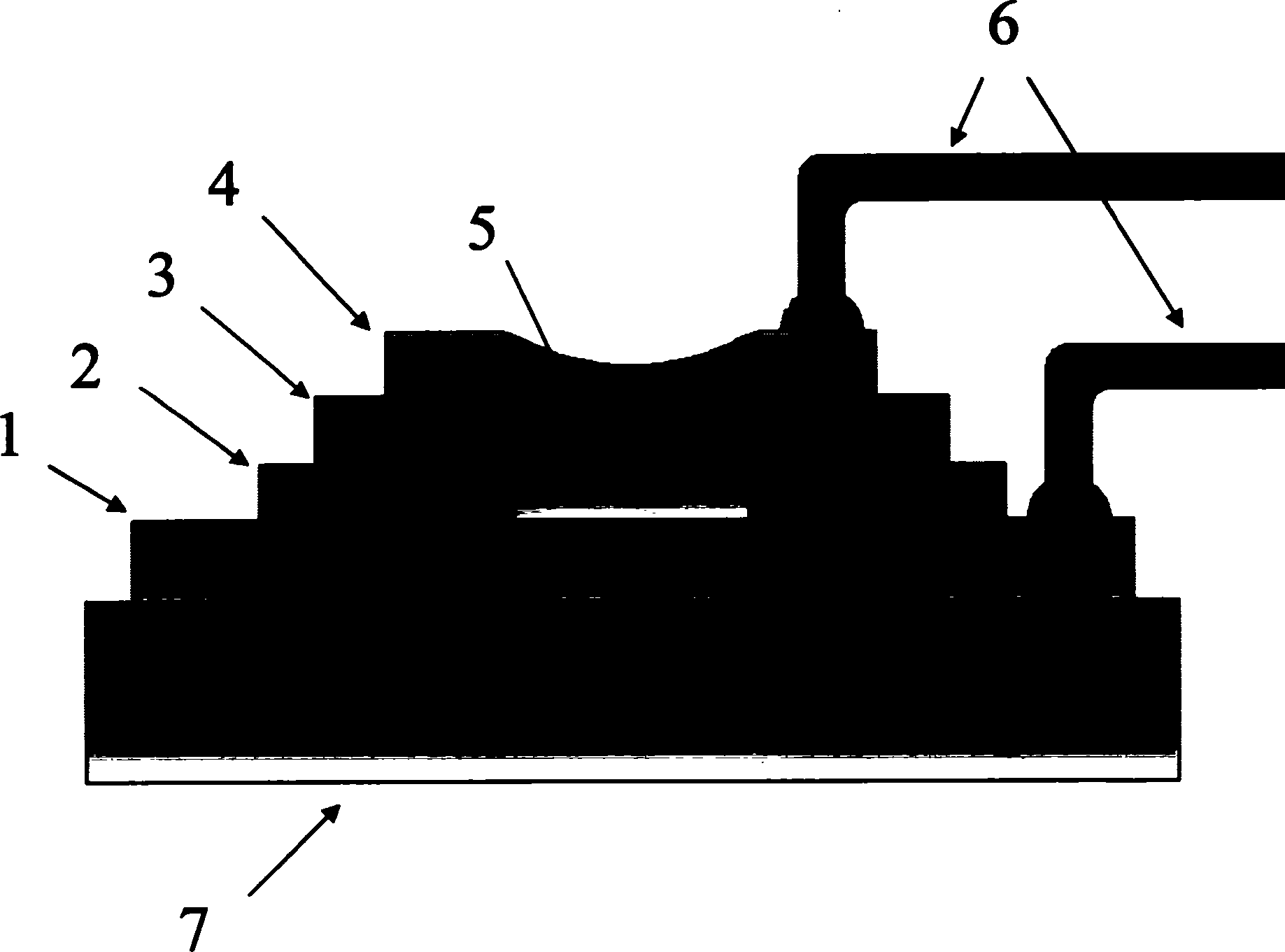
InactiveUS20050226036A1Easy to manufactureSimple manufacturing methodSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementOptoelectronics
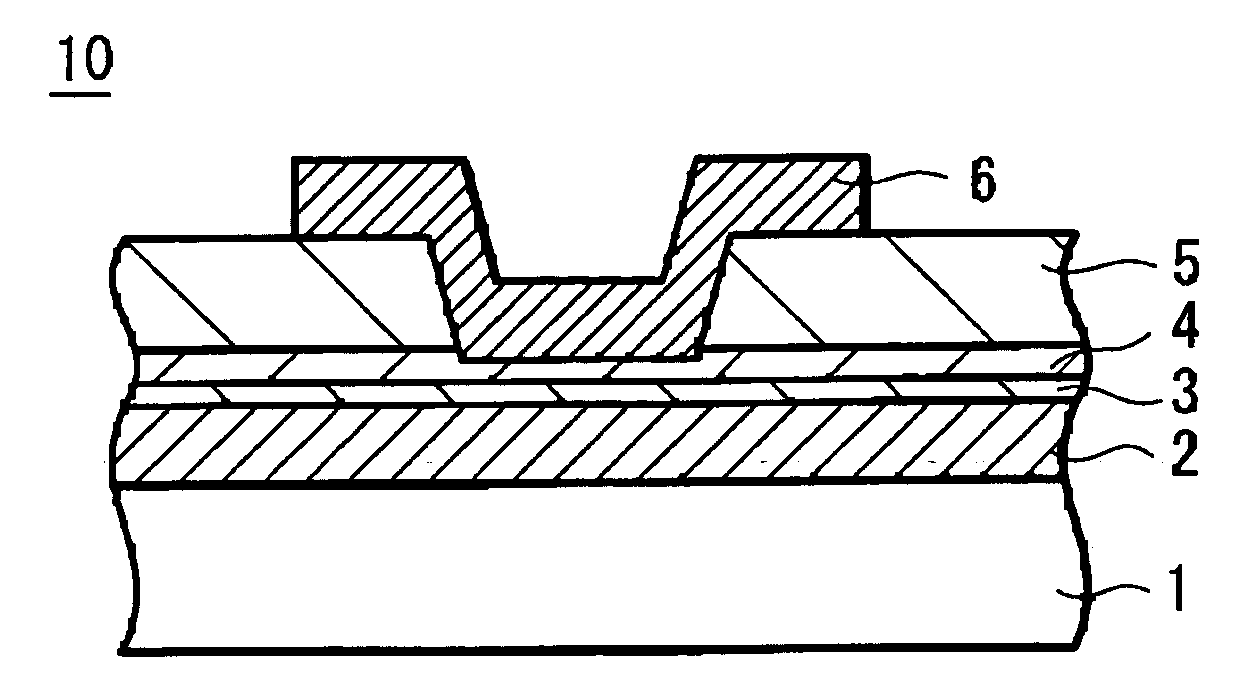
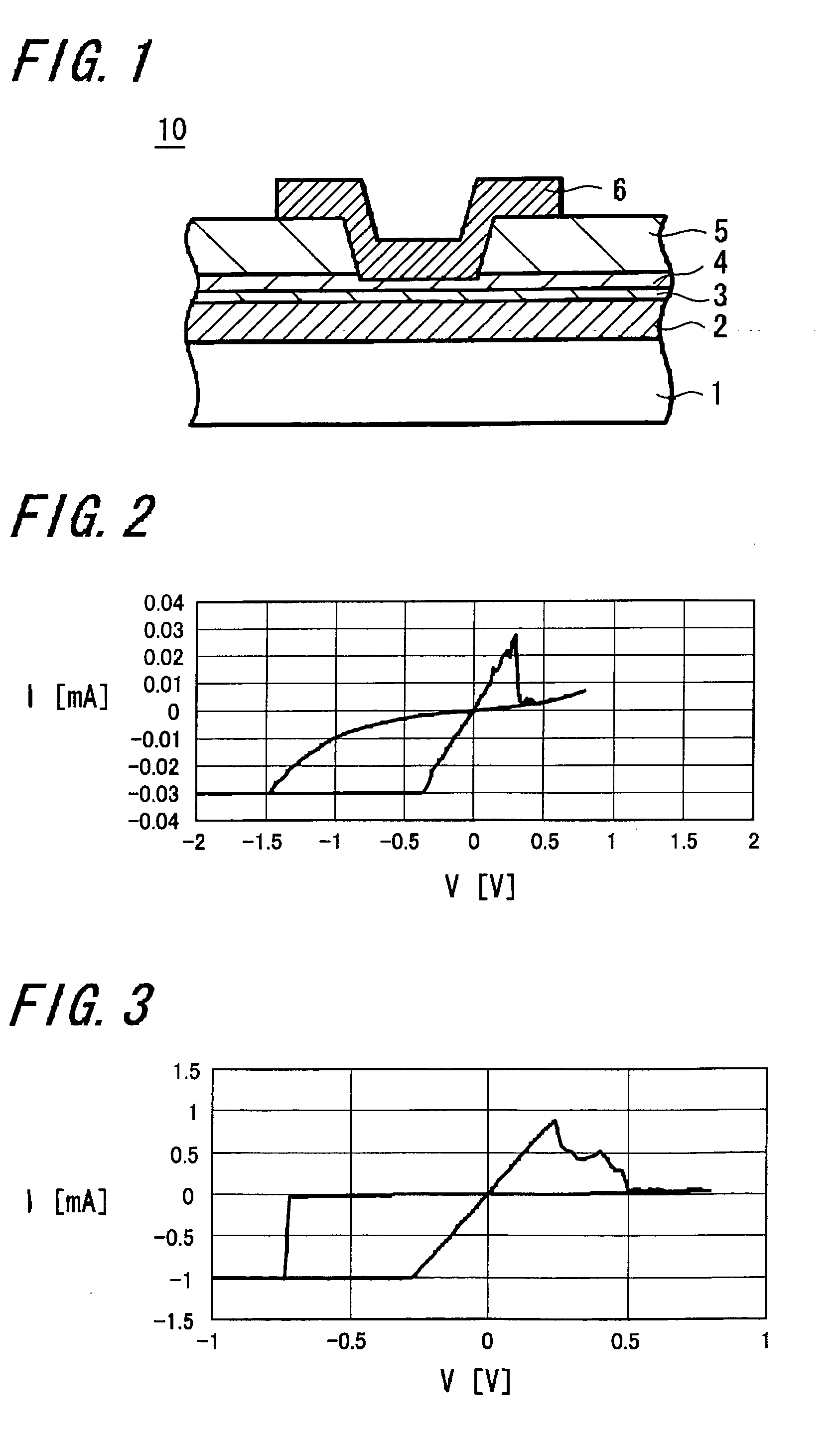
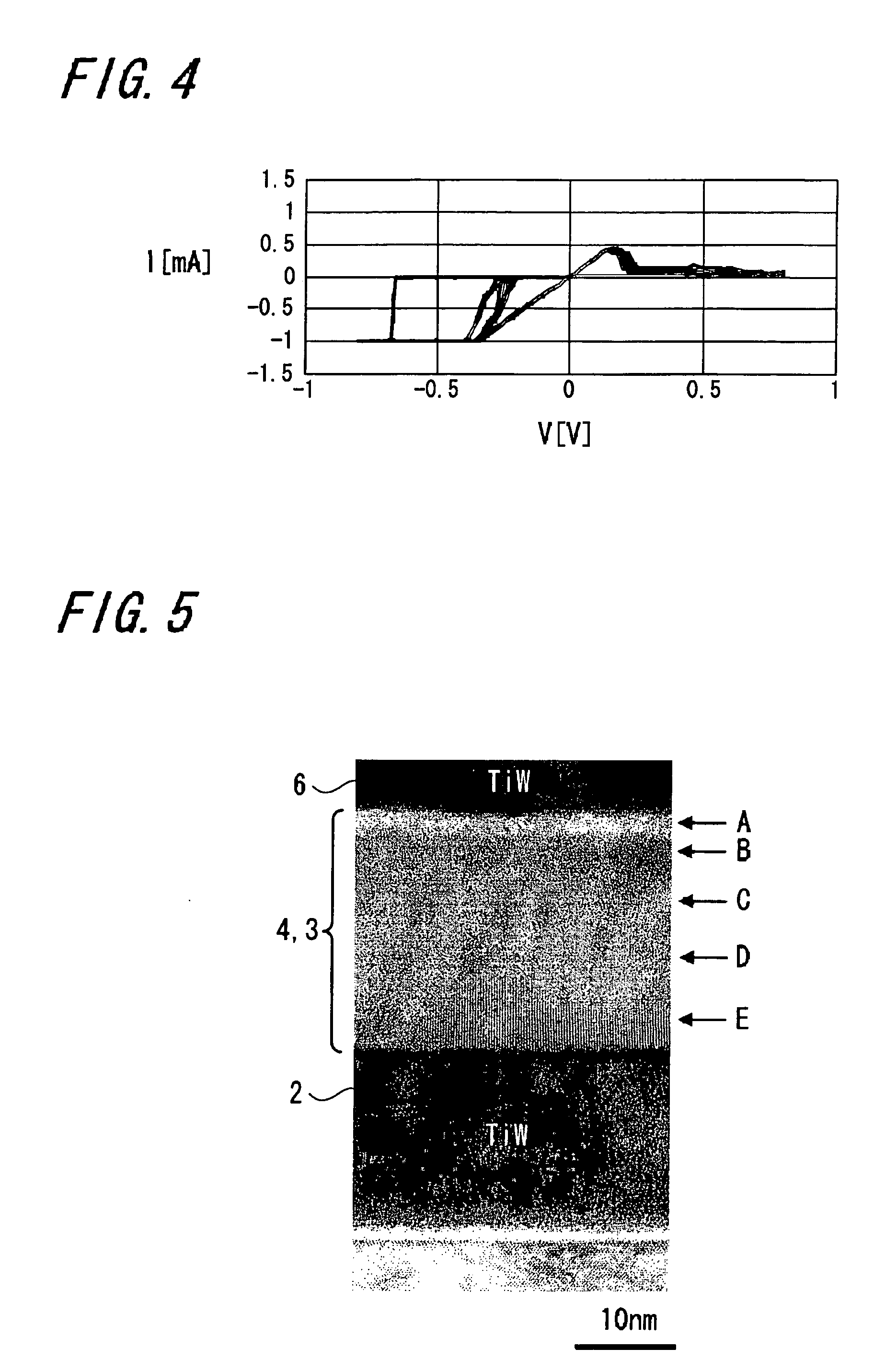
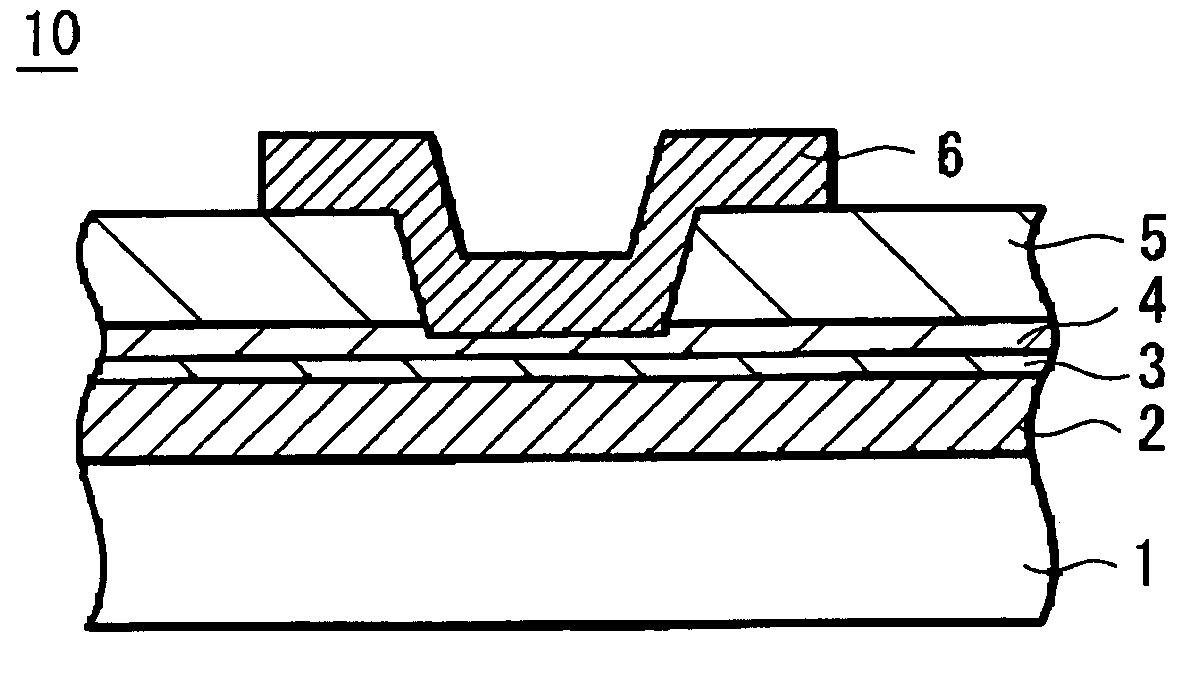
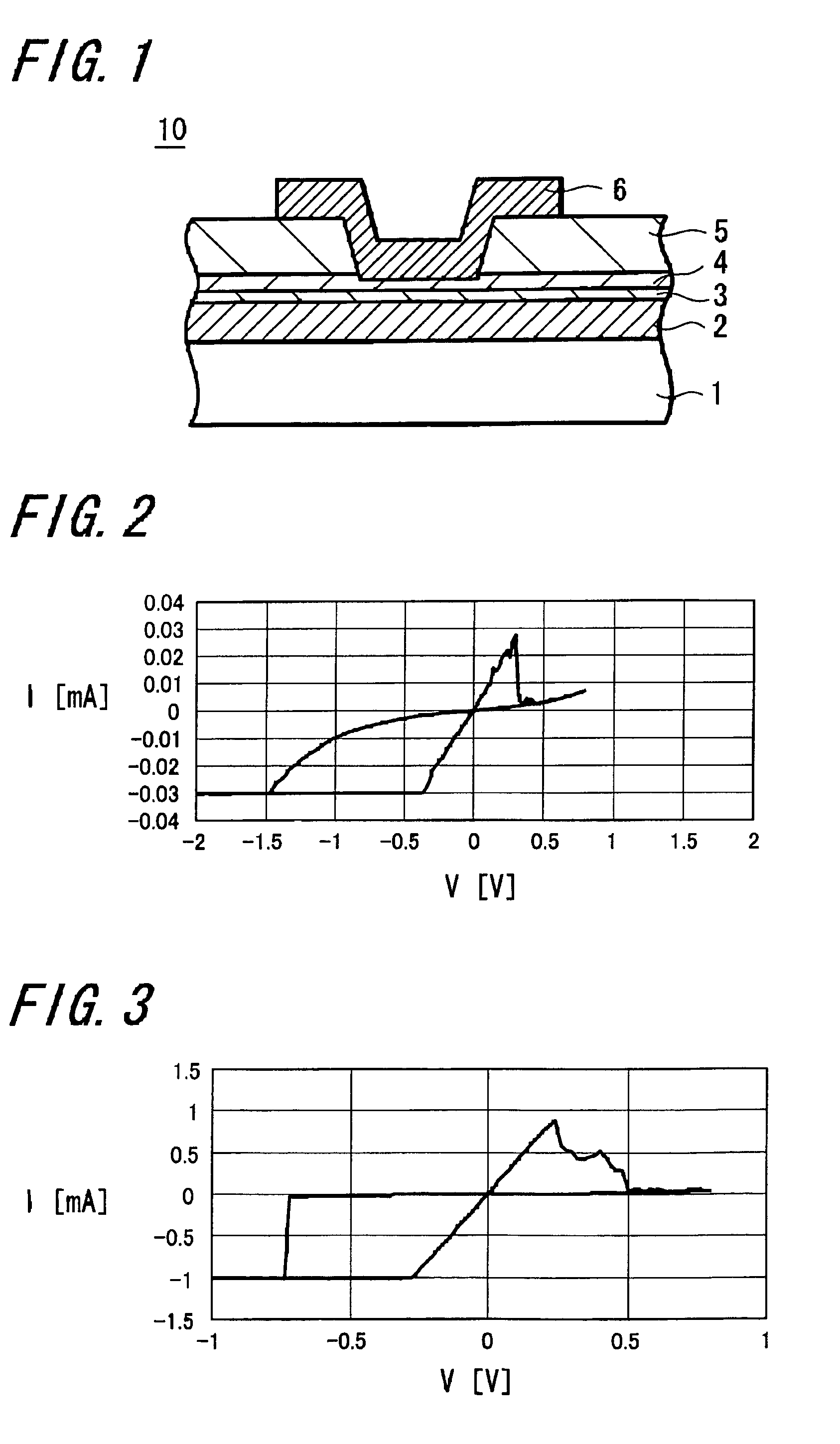
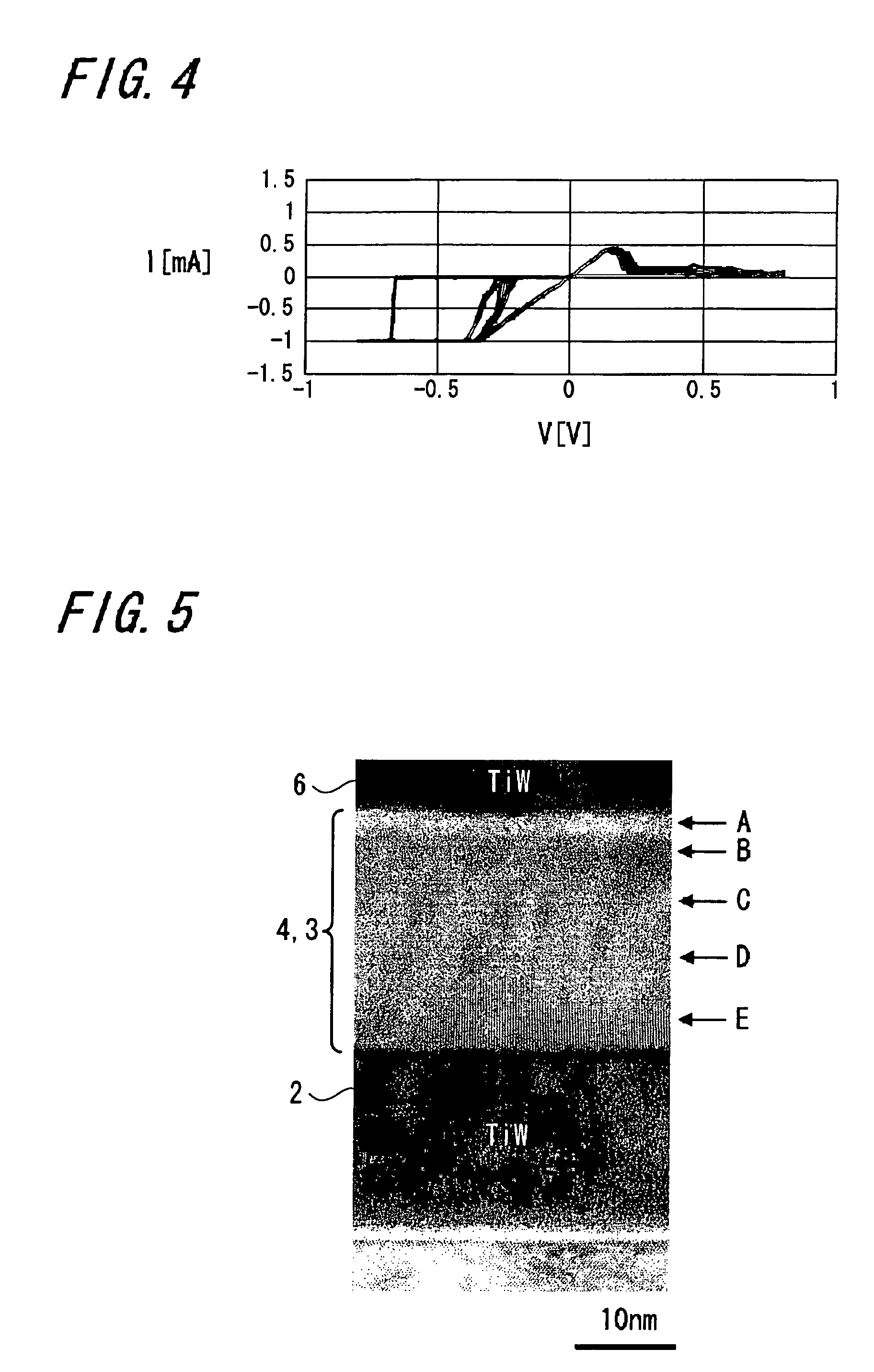
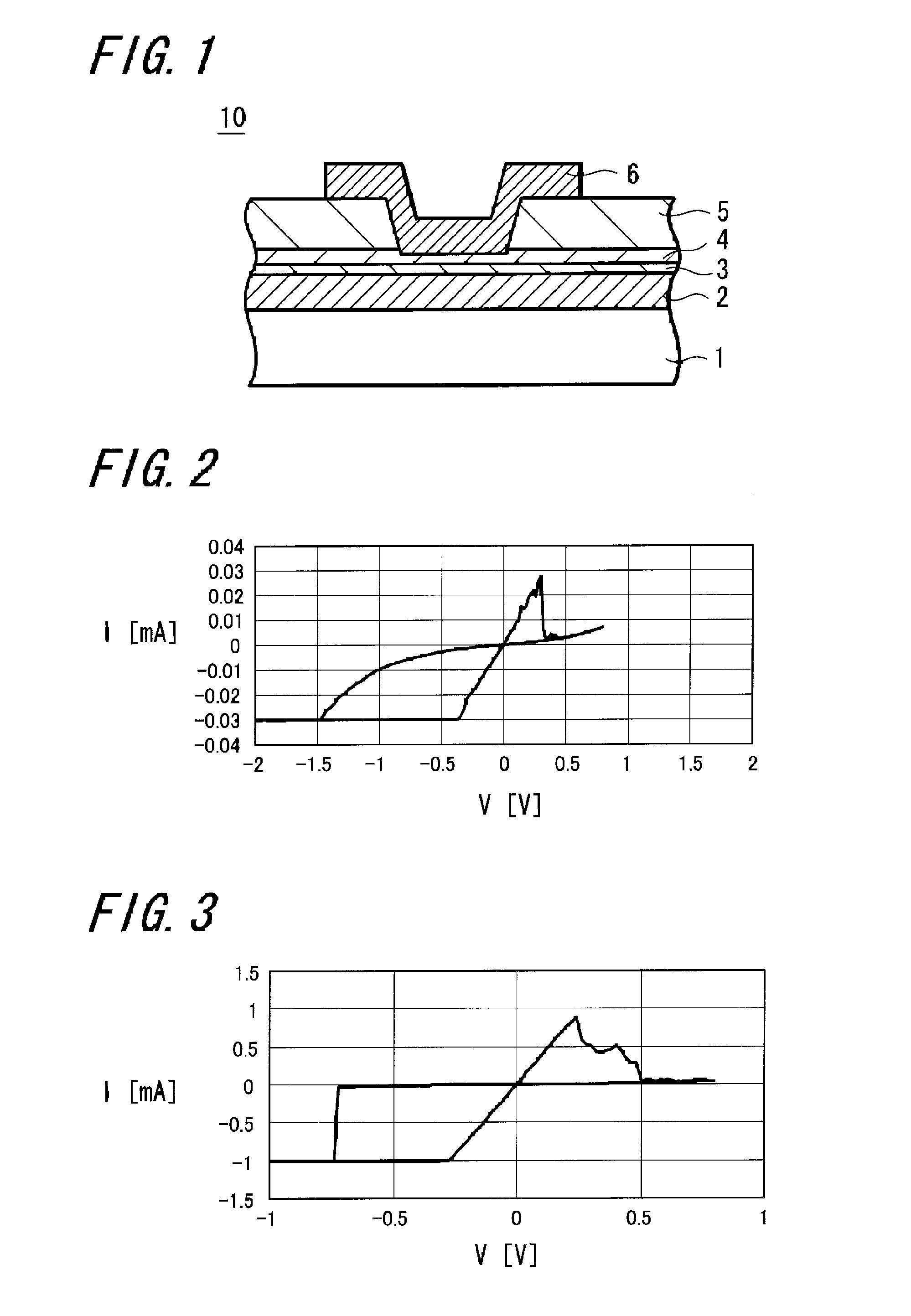
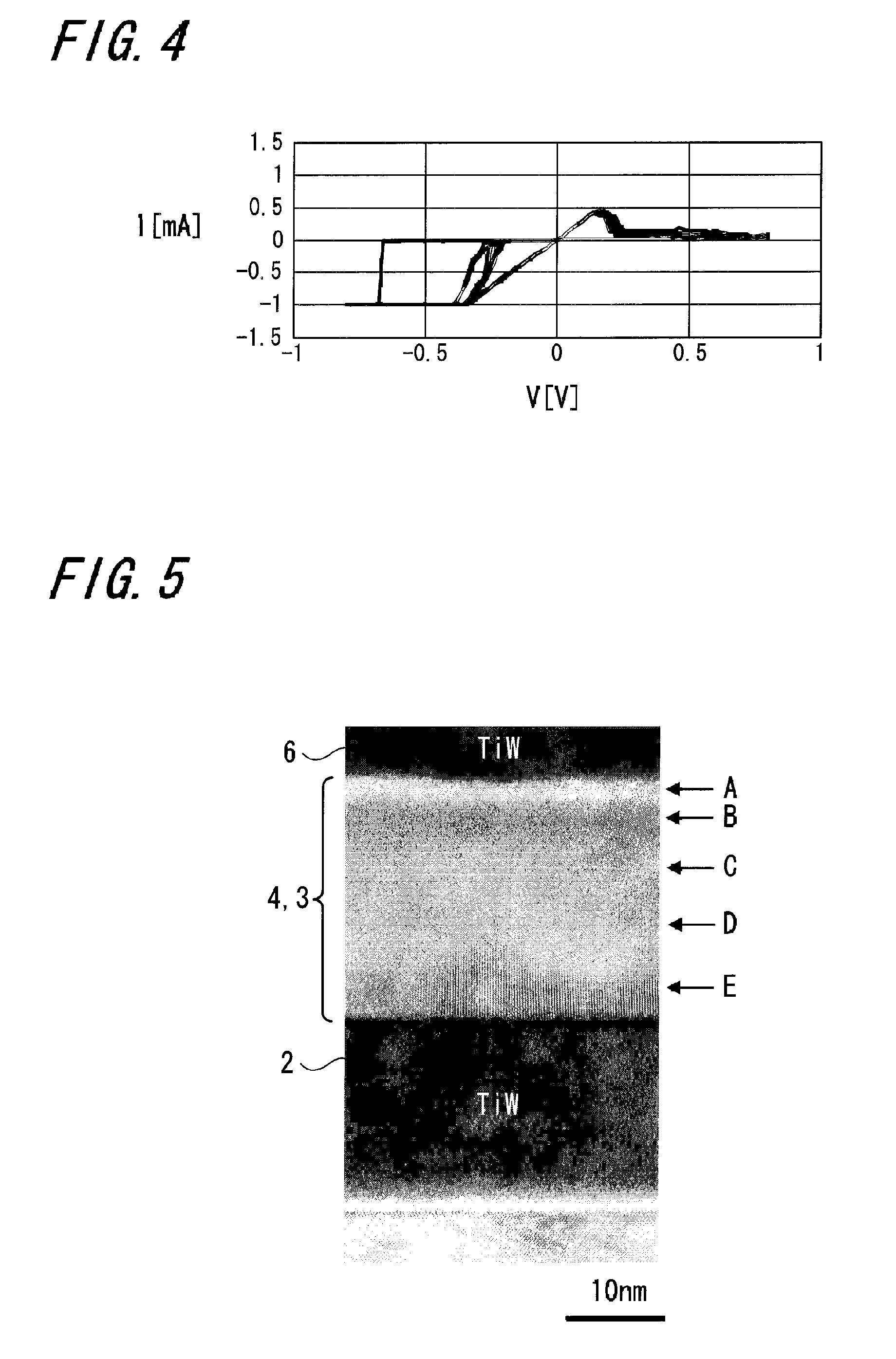
A memory device 10 has an arrangement in which a memory thin film 4 is sandwiched between first and second electrodes 2 and 6, the memory thin film 6 contains at least rare earth elements, the memory thin film 4 or a layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Cu, Ag, Zn and the memory thin film 4 or the layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Te, S, Se. The memory device can record and read information with ease stably, and this memory device can be manufactured easily by a relatively simple manufacturing method.
Owner:SONY CORP
Systems and methods for generating physically unclonable functions from non-volatile memory cells
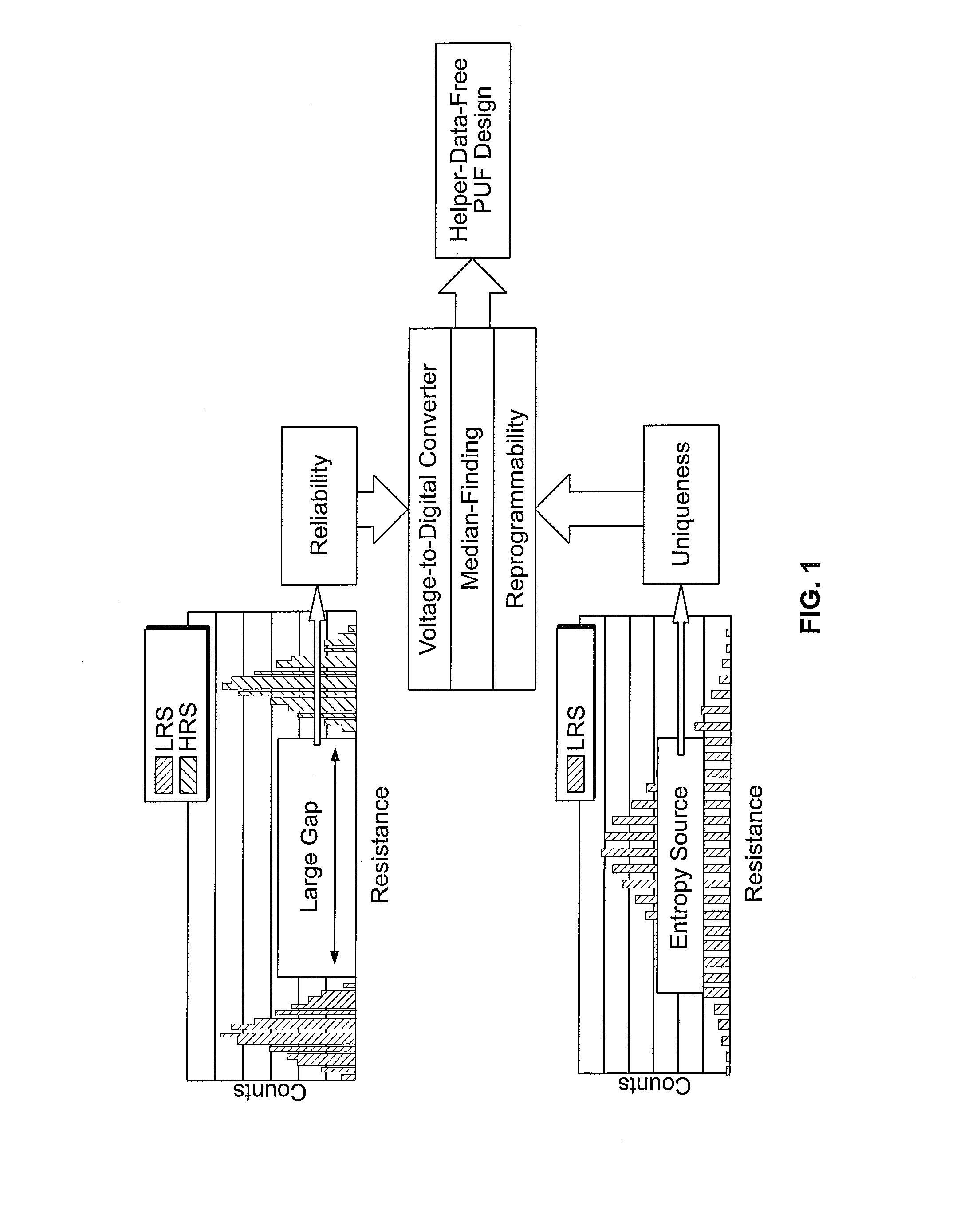
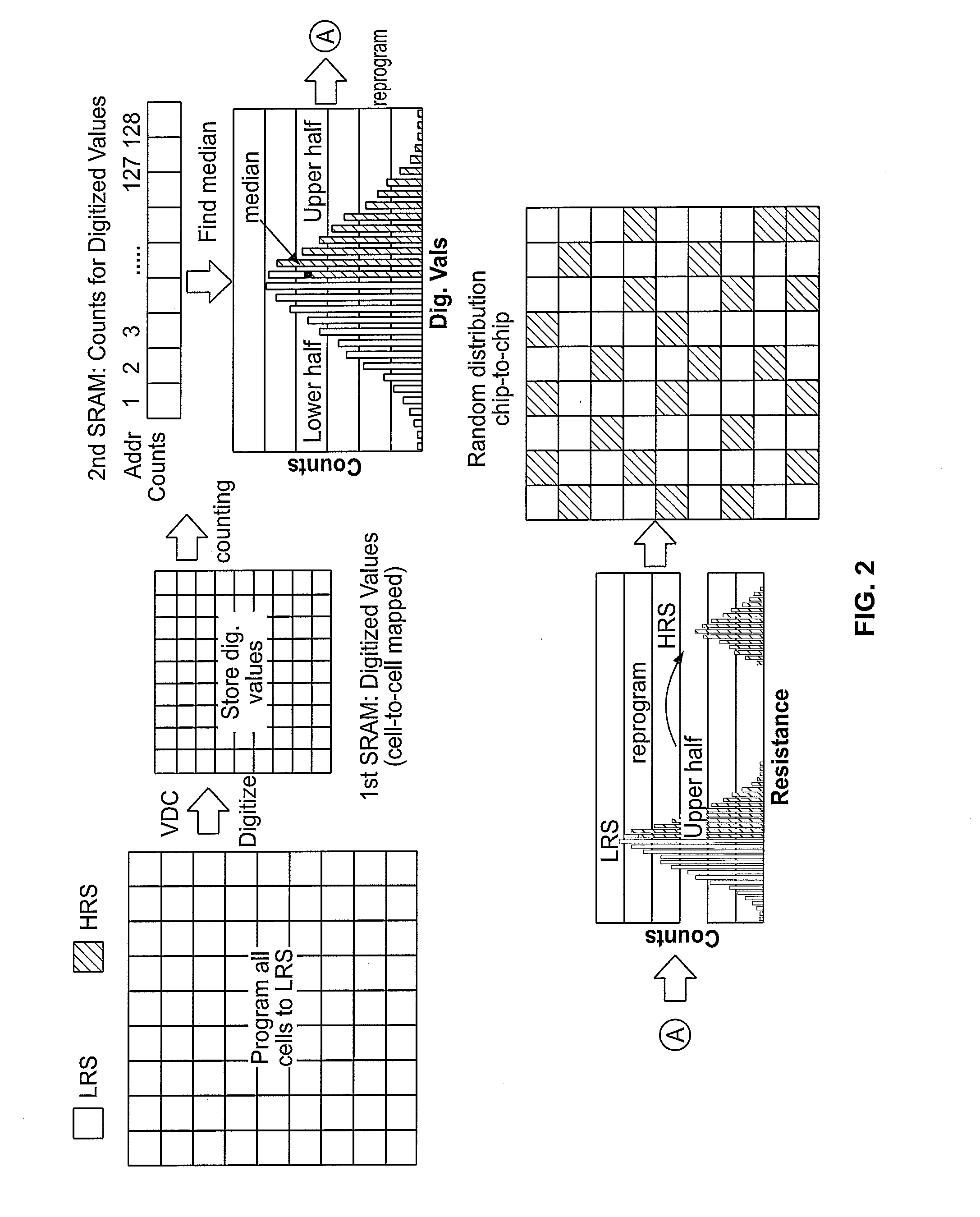
ActiveUS20160328578A1High resistance stateStable entropyDigital data processing detailsRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memory
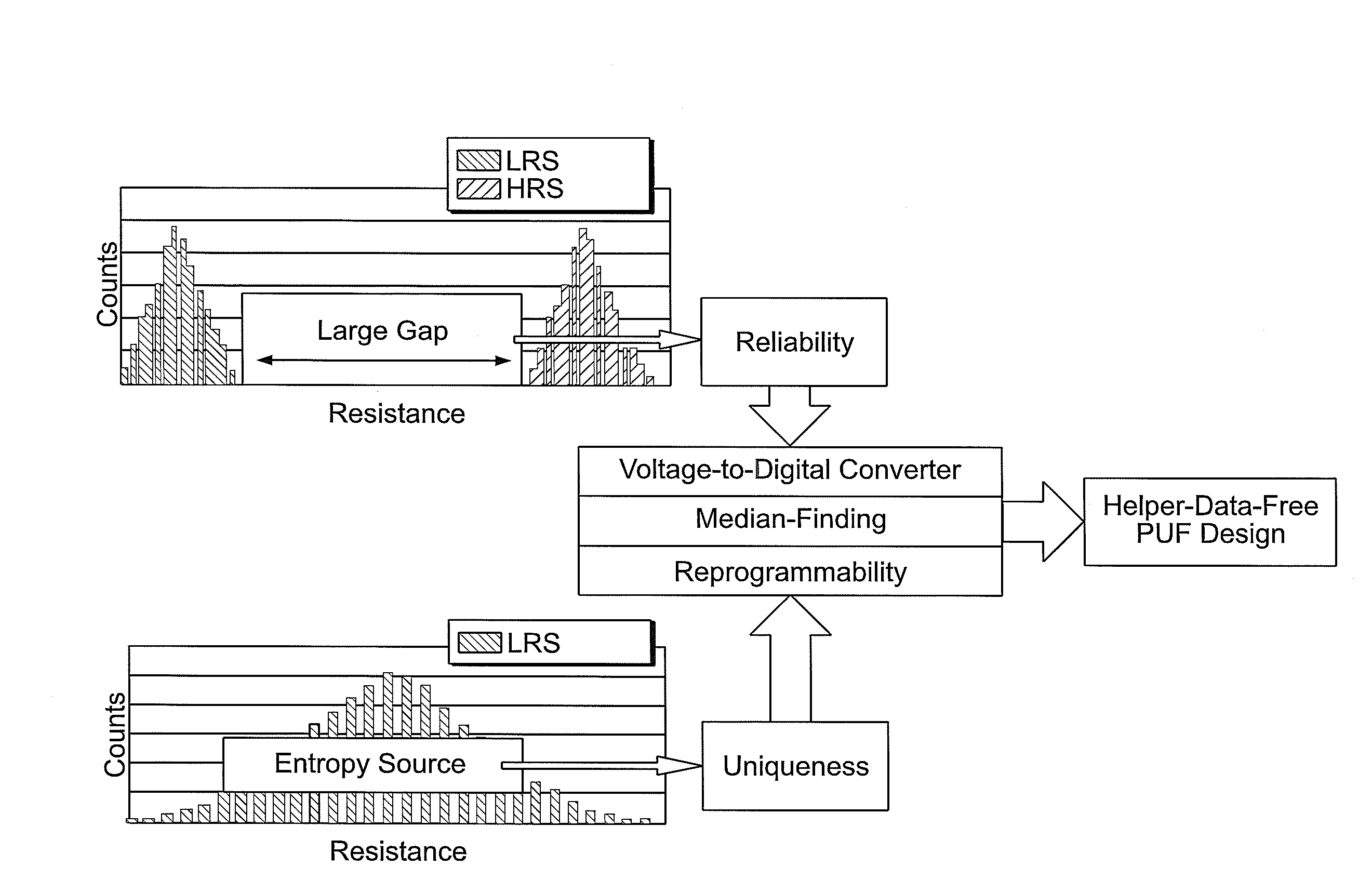
This disclosure describes techniques for generating physically unclonable functions (PUF) from non-volatile memory cells. The PUFs leverage resistance variations in non-volatile memory cells. Resistance variations in array of non-volatile memory cells may be produce a bitstring during an enrollment process. The bitstring may be stored in the non-volatile memory array. Regeneration may include retrieving the bitstring from the non-volatile memory array.
Owner:STC UNM
Non-volatile memory system with reset verification mechanism and method of operation thereof
InactiveUS9070441B2Increasing a read marginHigh resistance stateElectrical apparatusDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh resistance
A method of operation of a non-volatile memory system includes: providing a resistive storage element having a high resistance state and a low resistance state; coupling an analog multiplexer to the resistive storage element for applying a bias voltage; and switching between a verification bias and a read bias through the analog multiplexer for increasing a read margin between the high resistance state and the low resistance state.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Write-Time Based Memristive Physical Unclonable Function
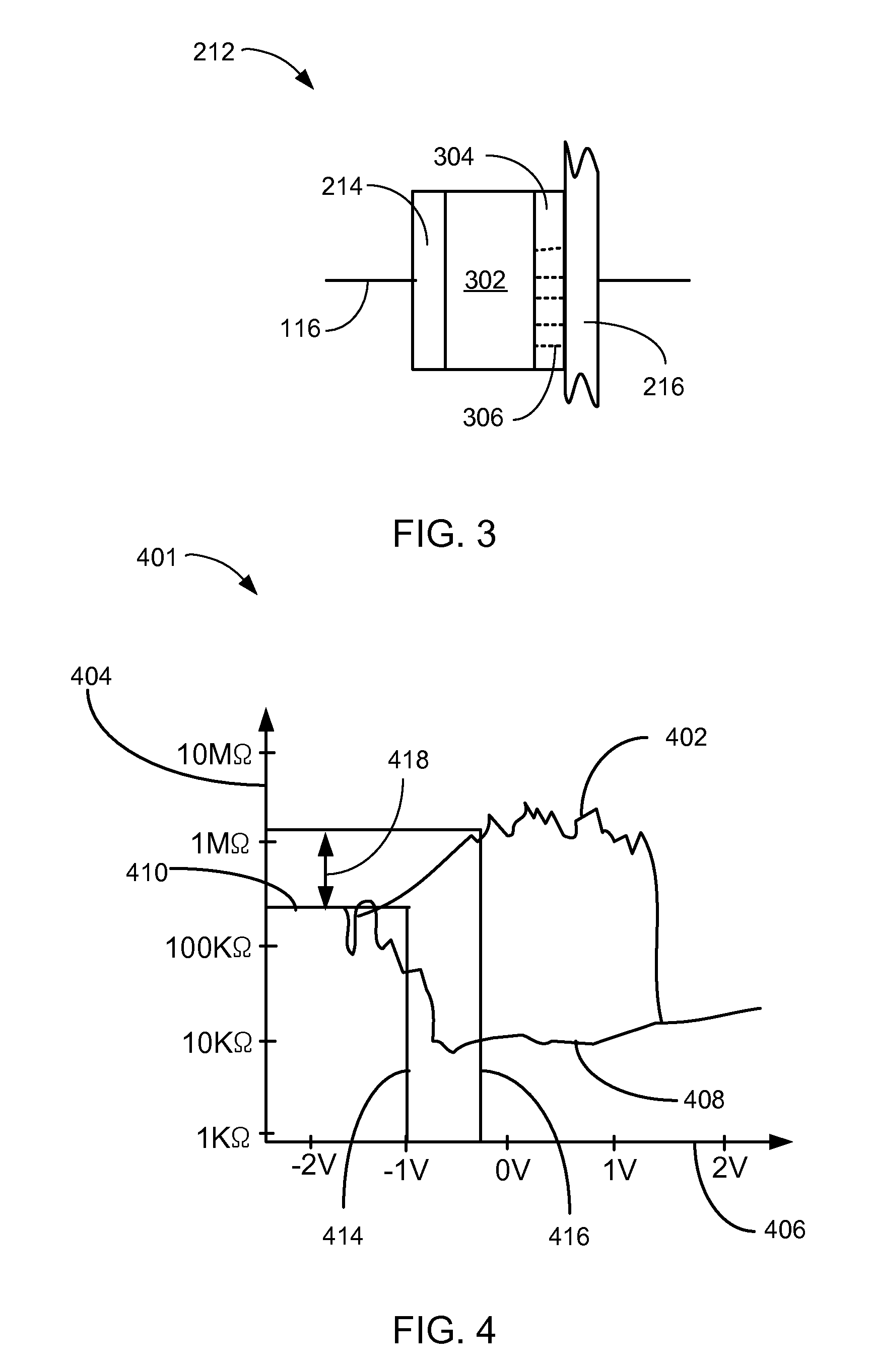
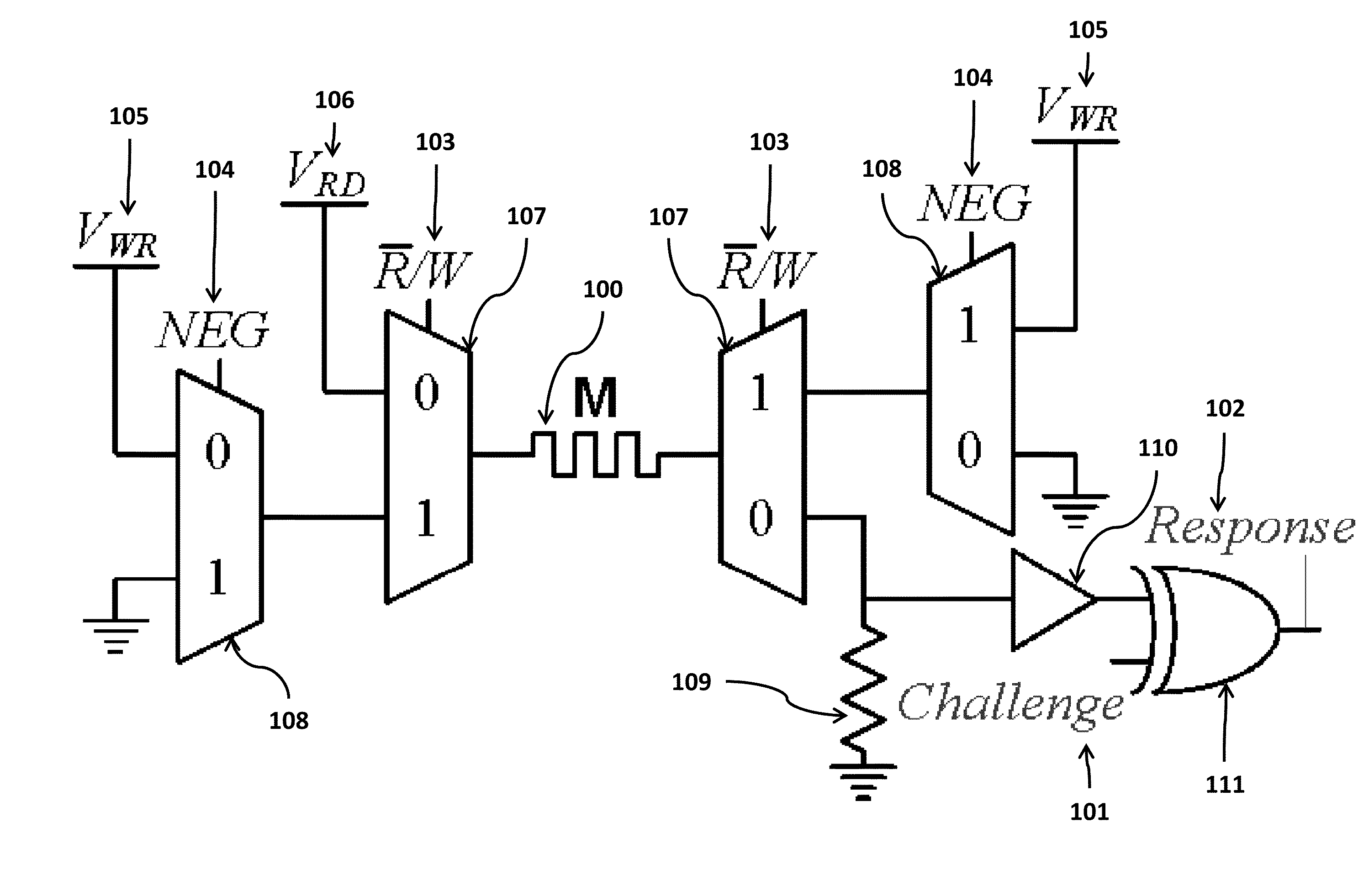
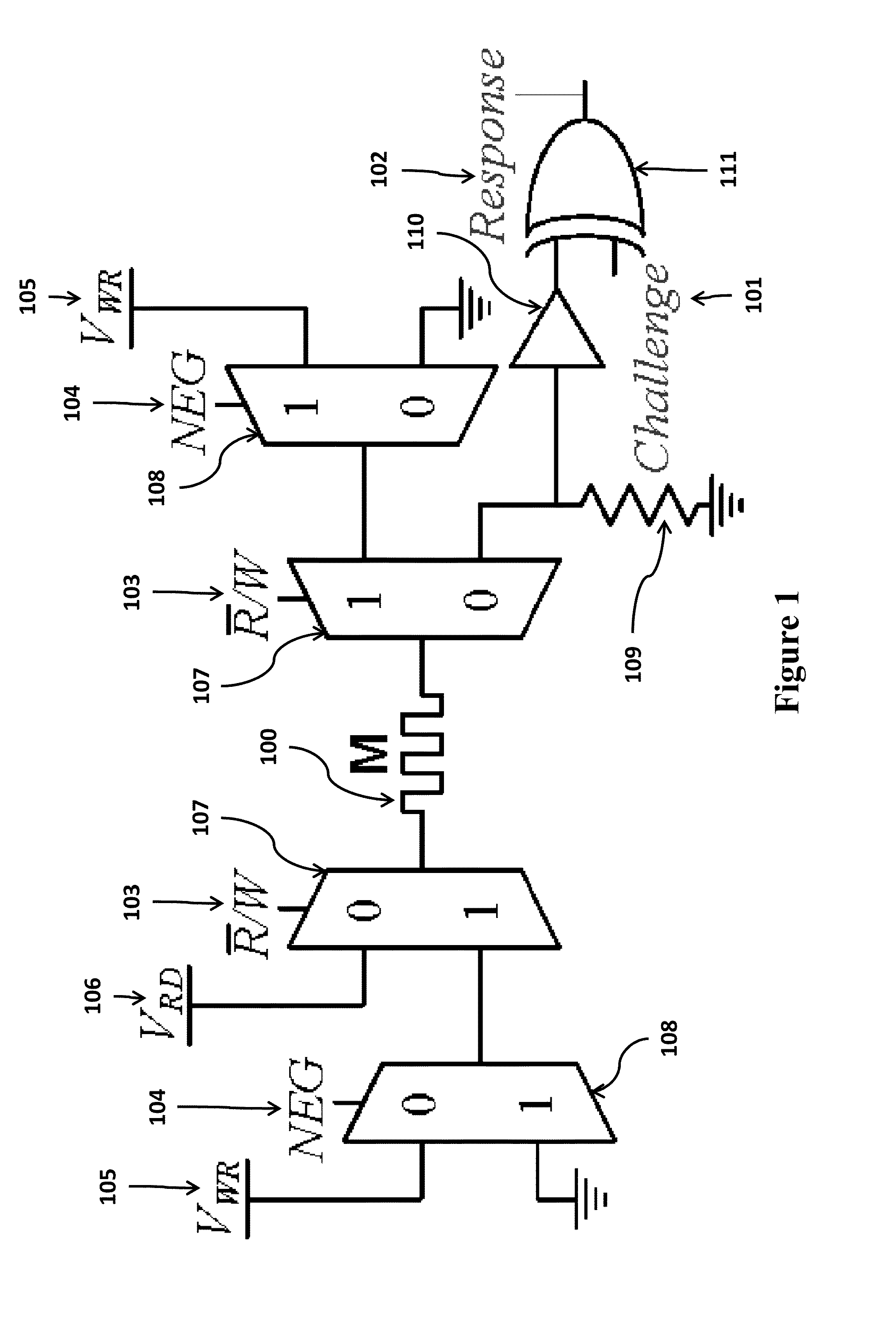
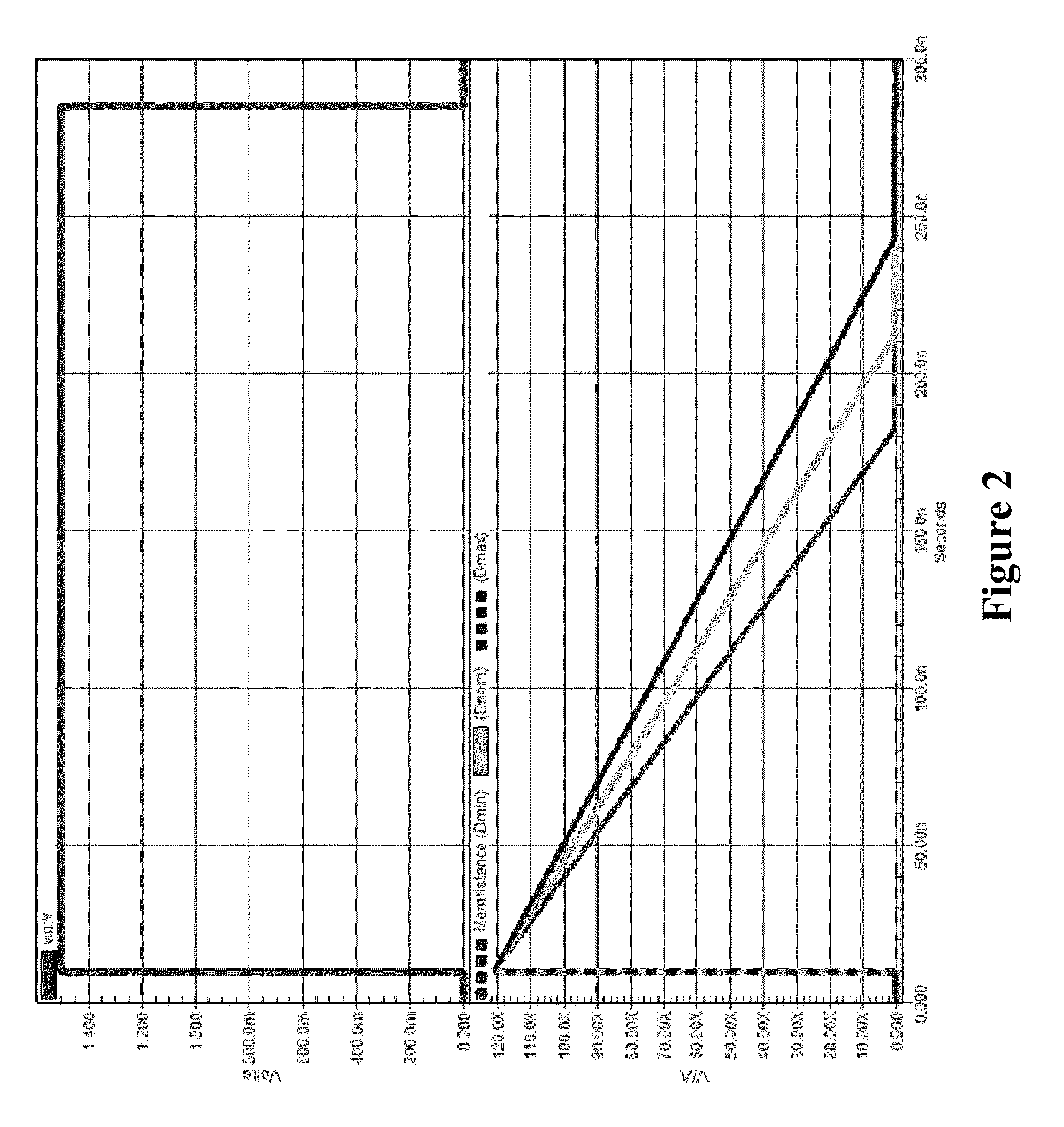
InactiveUS20140268994A1High resistance stateDigital storageInternal/peripheral component protectionHigh resistancePhysical unclonable function
A physical unclonable function (PUF) device consisting of a hybrid CMOS-memristor circuit that leverages variations in the required write-time of a memristor. Variations in the time required to write, or SET, a memristor from a high to low resistance state arise from variability in physical parameters such as the memristor thickness. When applying a SET voltage across the memristor for the nominal minimum SET time, variability leads to a situation where the memristor will actually SET to the low resistance state only 50% of the time. When the device does not SET it will remain in the high resistance state. Since the to resistance state of the memristor corresponds to reading either a logic 1 or logic 0 on the output of the circuit, the write-time based memristive PUF produces a digital signature directly corresponding to the fabrication process-induced physical variations of an integrated circuit.
Owner:BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED
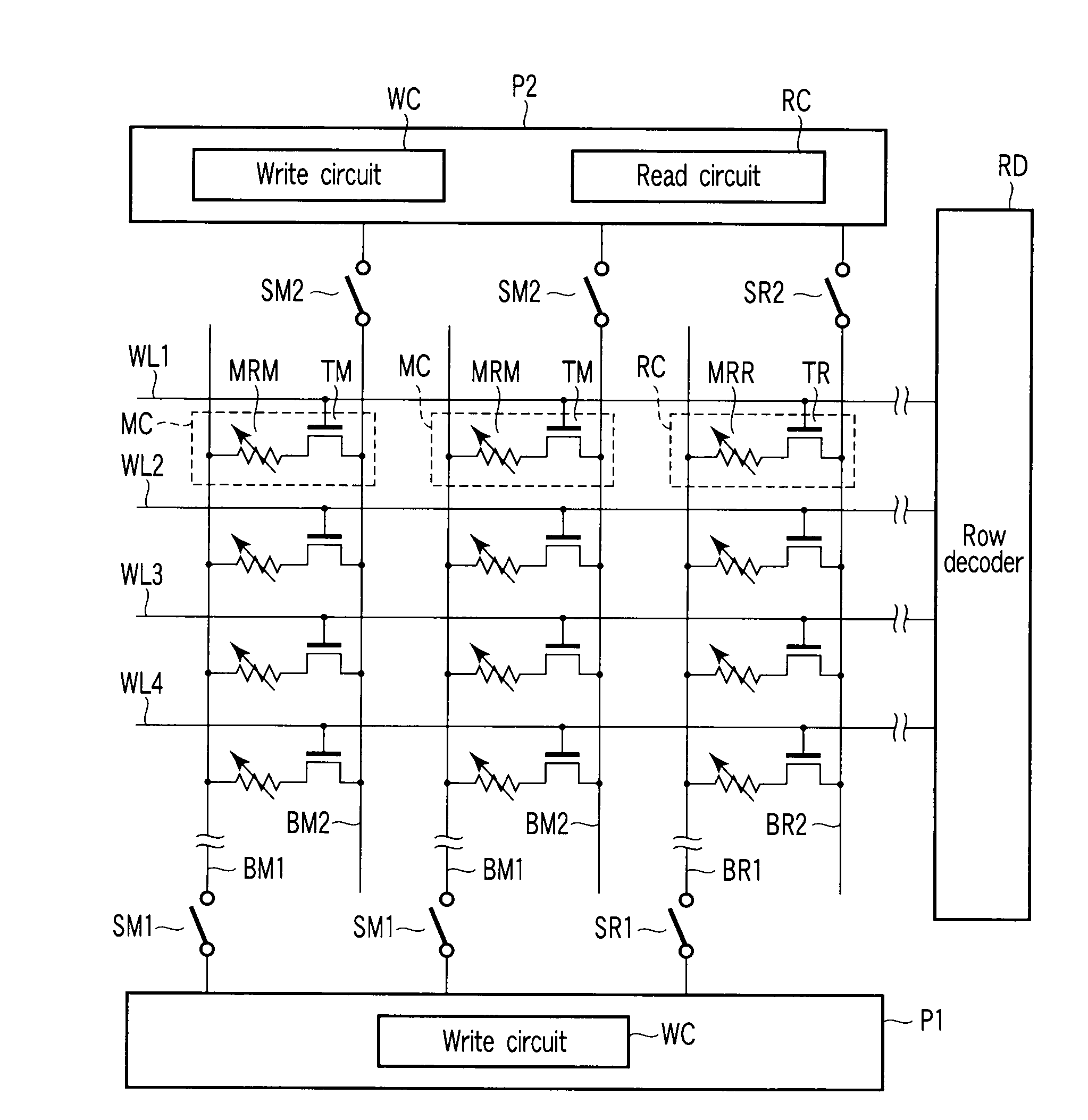
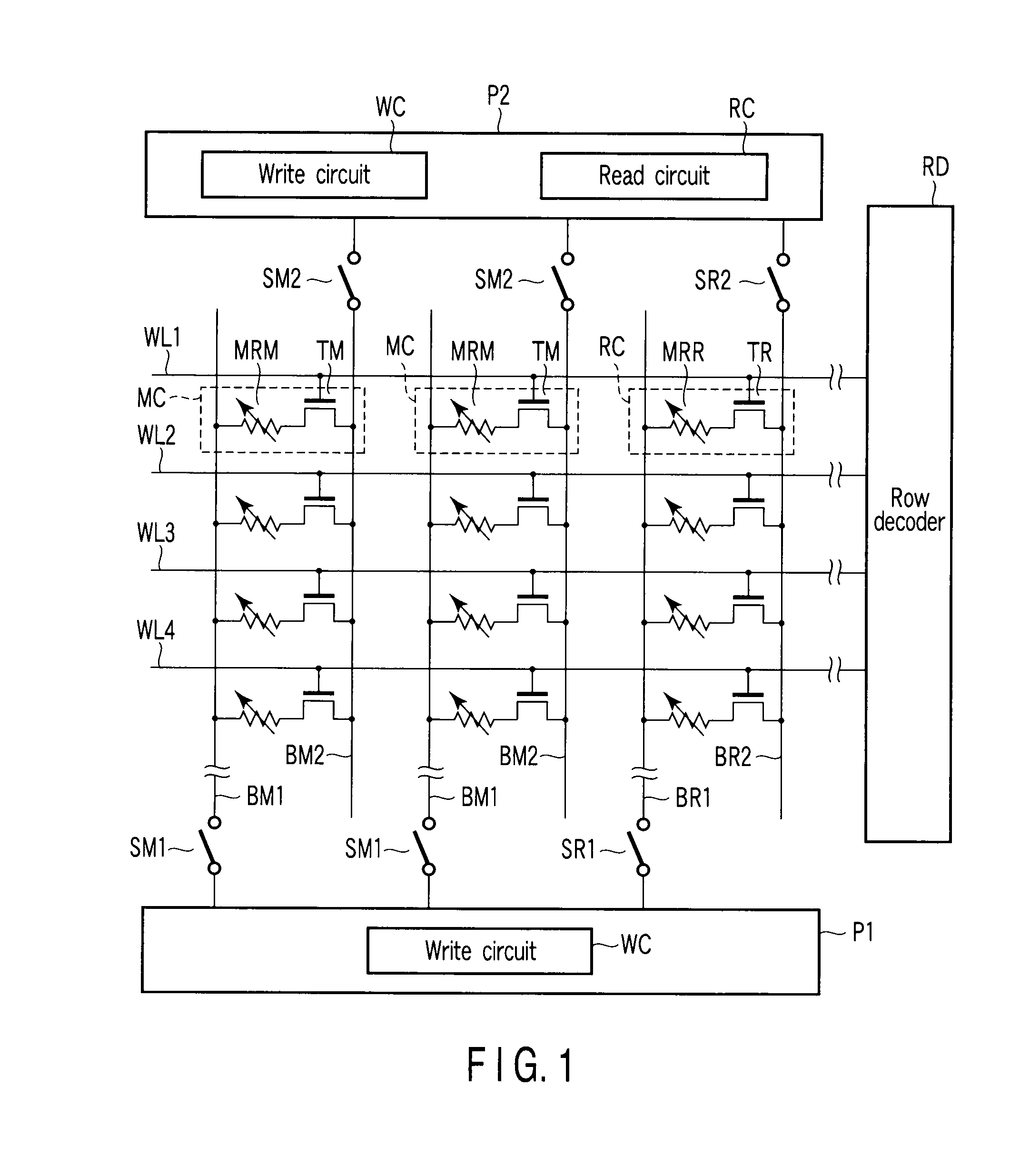
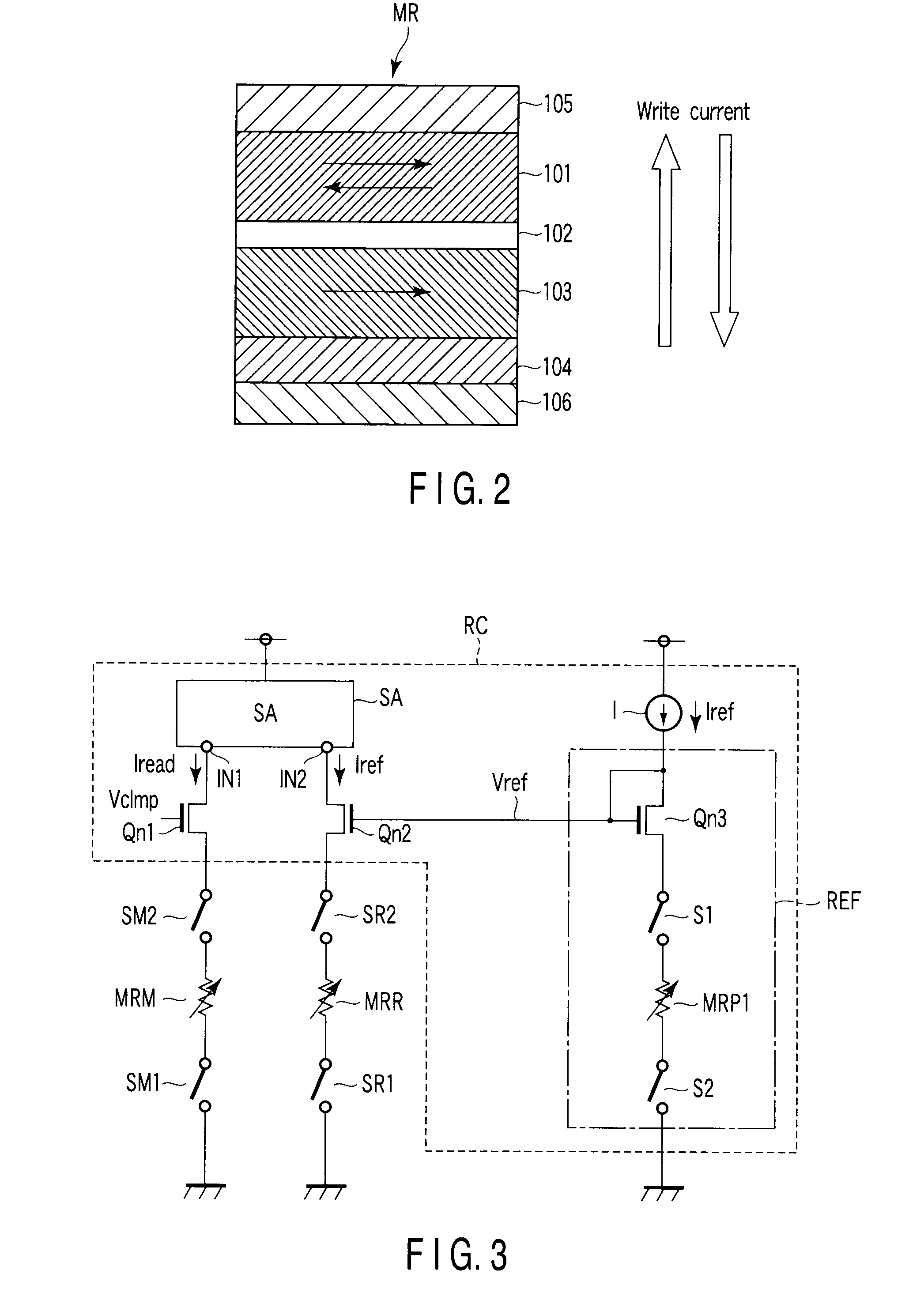
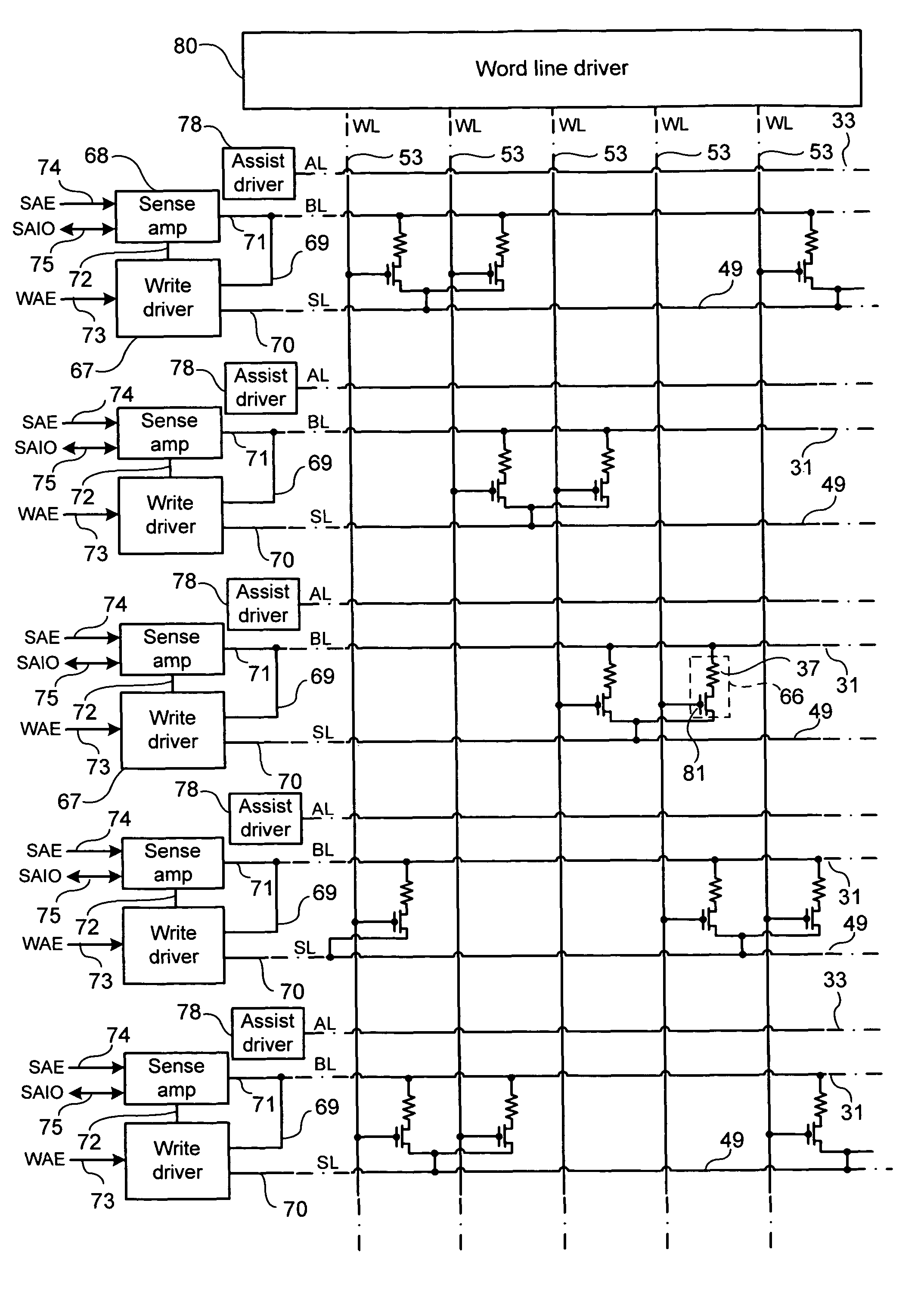
Magnetoresistive random access memory
A MRAM includes a first magnetoresistive effect (MR) element that takes a low and high resistance states. A second MR element is fixed to a low or high resistance state. First and second MOSFETs are connected to the first and second MR elements, respectively. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between values of current flowing through the first and second MOSFETs. A current circuit outputs reference current whose value lies between current flowing through the first MR element of the low and high resistance states. A third MOSFET has one end that receives the reference current and is connected to its own gate terminal. The gate terminal of the second MOSFET receives the same potential as the gate terminal of the third MOSFET. A first resistance element is connected to the others end of the third MOSFET and has the same resistance as the second magnetoresistive effect element.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
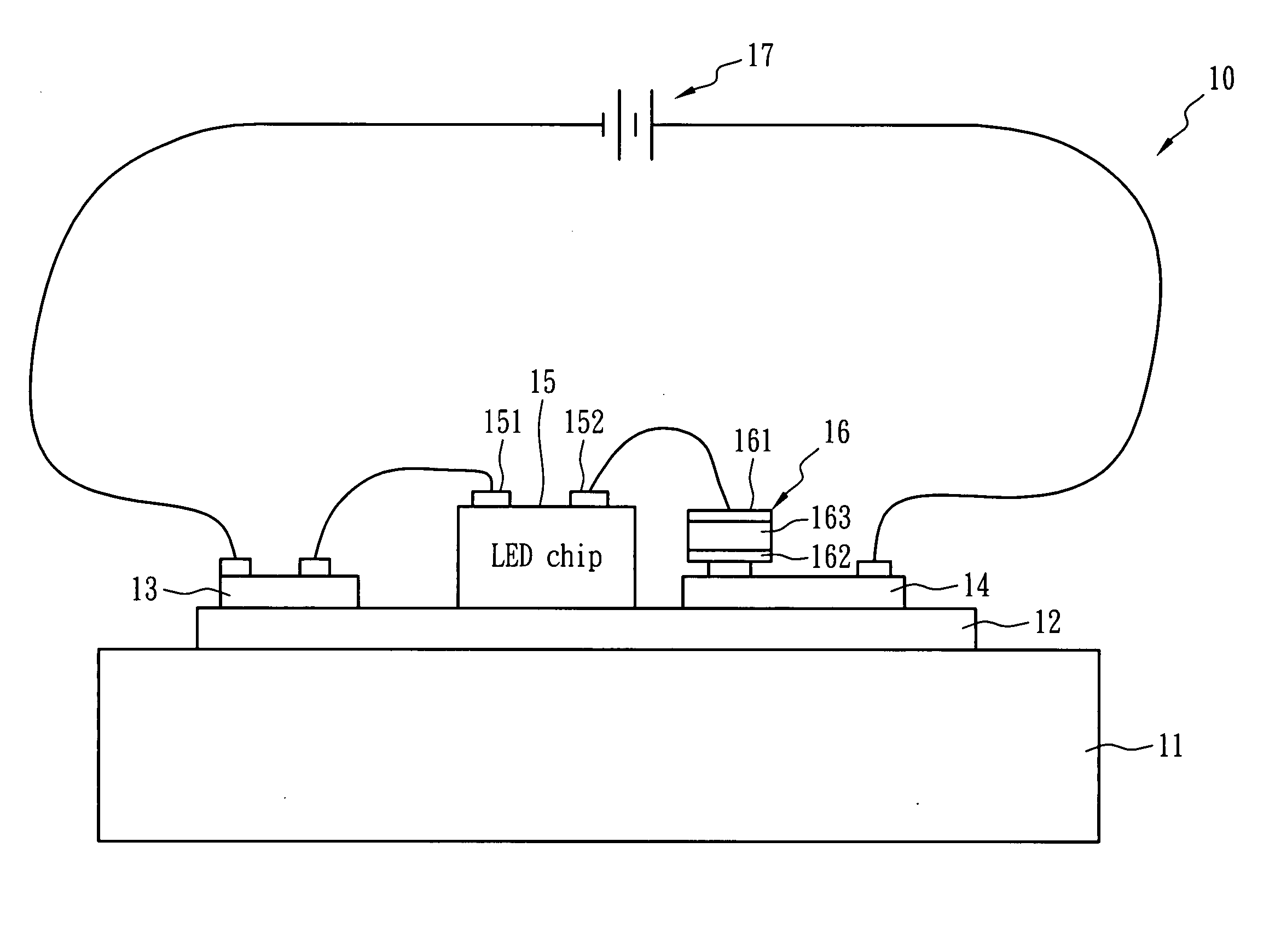
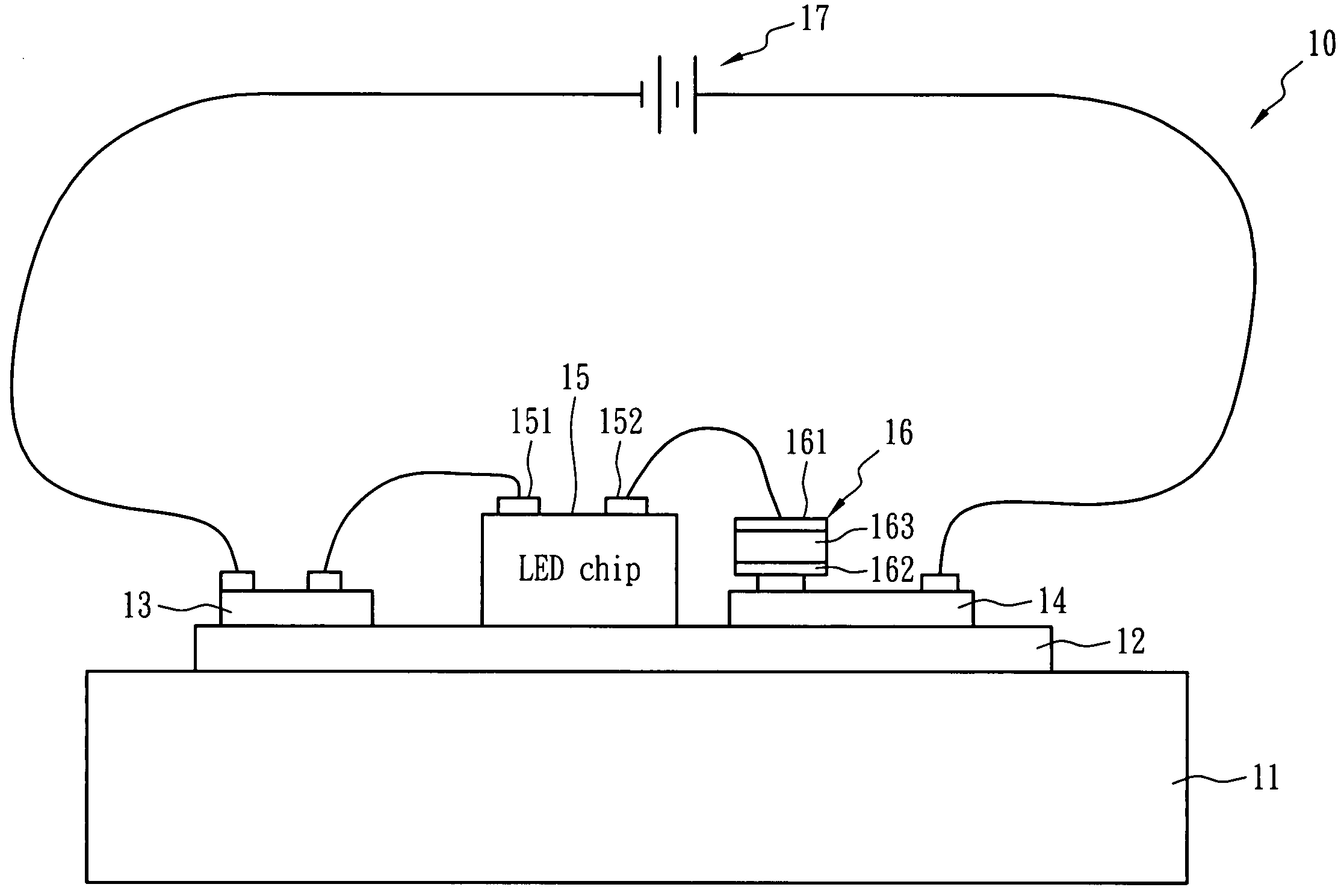
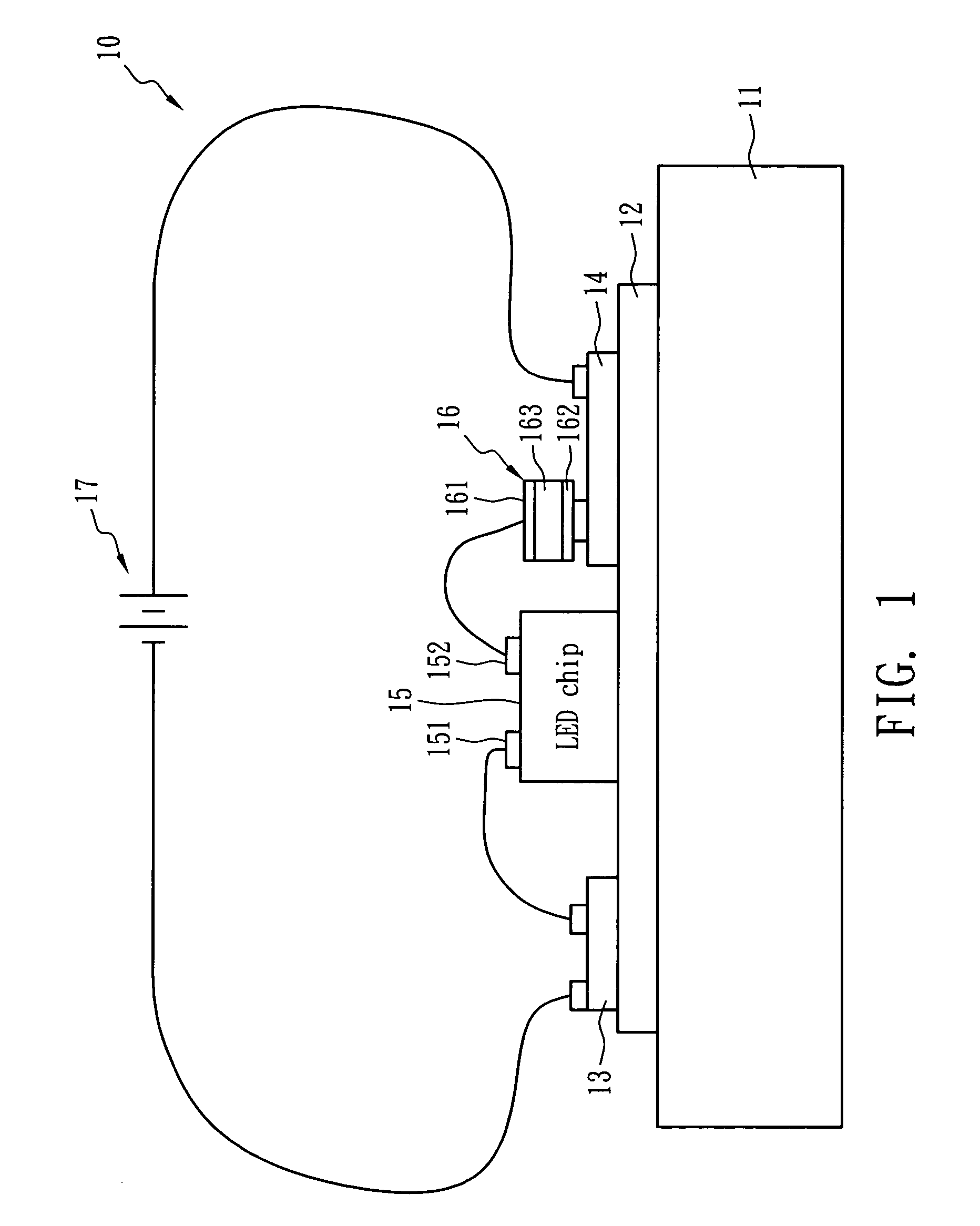
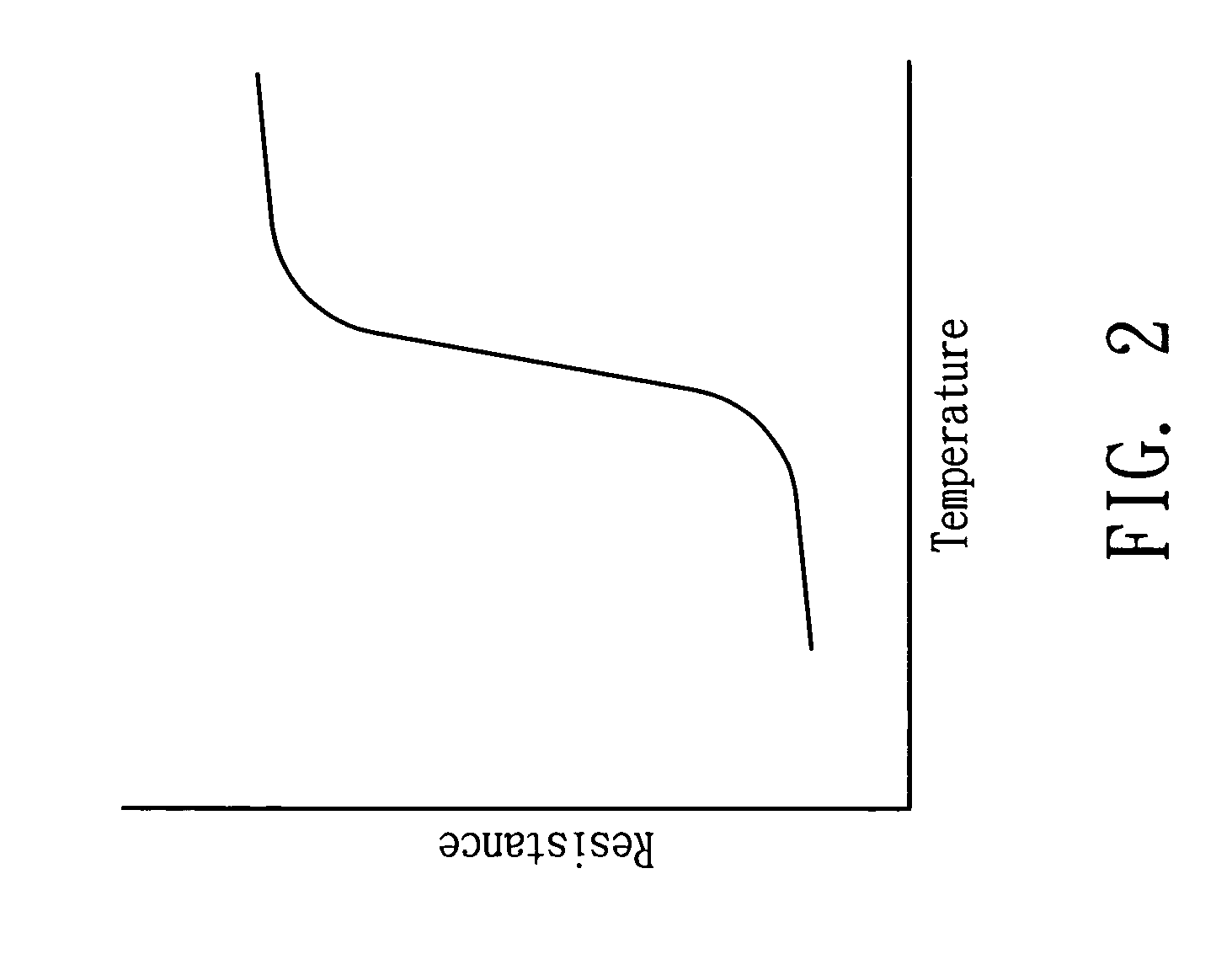
LED apparatus with temperature control function
InactiveUS20070139928A1Flexibly manufactureReduce trafficElectric circuit arrangementsLighting elementsElectricityDielectric
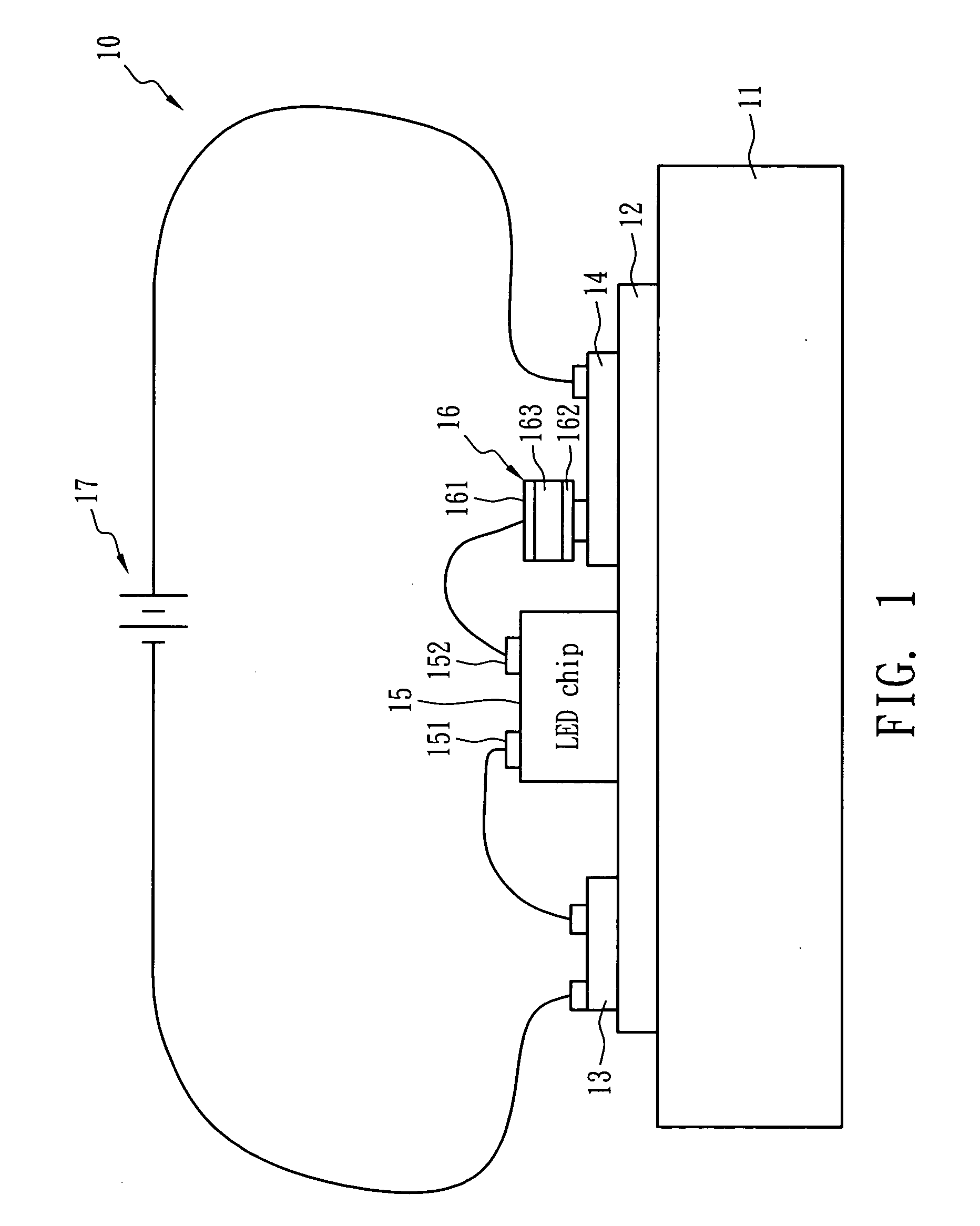
An LED apparatus with temperature self-regulating, over-temperature protection, and over-current protection function comprises an LED chip, a heat dissipation plate, a heat conductive layer and a temperature control device. The heat dissipation and the heat conductive layer disposed thereon carry the LED chip and dissipate the heat generated from the LED chip that is connected to an electric power source for luminance. The temperature control device exhibiting PTC behavior is electrically connected between the LED chip and the electric power source in series, and the distance between the LED chip and the temperature control device is less than 3 cm. The heat conductive layer can consist of polymeric dielectric material and has a heat conduction coefficient larger than 1.0 W / mK at 25° C.
Owner:POLYTRONICS TECH
Memory device and storage apparatus
InactiveUS7719082B2Easy to manufactureSimple manufacturing methodSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRare-earth elementOptoelectronics
A memory device 10 has an arrangement in which a memory thin film 4 is sandwiched between first and second electrodes 2 and 6, the memory thin film 6 contains at least rare earth elements, the memory thin film 4 or a layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Cu, Ag, Zn and the memory thin film 4 or the layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Te, S, Se. The memory device can record and read information with ease stably, and this memory device can be manufactured easily by a relatively simple manufacturing method.
Owner:SONY CORP
LED apparatus with temperature control function
InactiveUS7817009B2Reduce trafficLow heat generationElectric circuit arrangementsLighting elementsTemperature controlDielectric
An LED apparatus with temperature self-regulating, over-temperature protection, and over-current protection function comprises an LED chip, a heat dissipation plate, a heat conductive layer and a temperature control device. The heat dissipation and the heat conductive layer disposed thereon carry the LED chip and dissipate the heat generated from the LED chip that is connected to an electric power source for luminance. The temperature control device exhibiting PTC behavior is electrically connected between the LED chip and the electric power source in series, and the distance between the LED chip and the temperature control device is less than 3 cm. The heat conductive layer can consist of polymeric dielectric material and has a heat conduction coefficient larger than 1.0 W / mK at 25° C.
Owner:POLYTRONICS TECH
Memory device and storage apparatus
InactiveUS20100135060A1Easy to manufactureSimple manufacturing methodSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesRare-earth elementOptoelectronics
A memory device 10 has an arrangement in which a memory thin film 4 is sandwiched between first and second electrodes 2 and 6, the memory thin film 6 contains at least rare earth elements, the memory thin film 4 or a layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Cu, Ag, Zn and the memory thin film 4 or the layer 3 in contact with the memory thin film 4 contains any one of elements selected from Te, S, Se. The memory device can record and read information with ease stably, and this memory device can be manufactured easily by a relatively simple manufacturing method.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetoresistive logic cell and method of use
ActiveUS20130215673A1High resistance stateRA product MTJ junctionNanotechDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage pulse
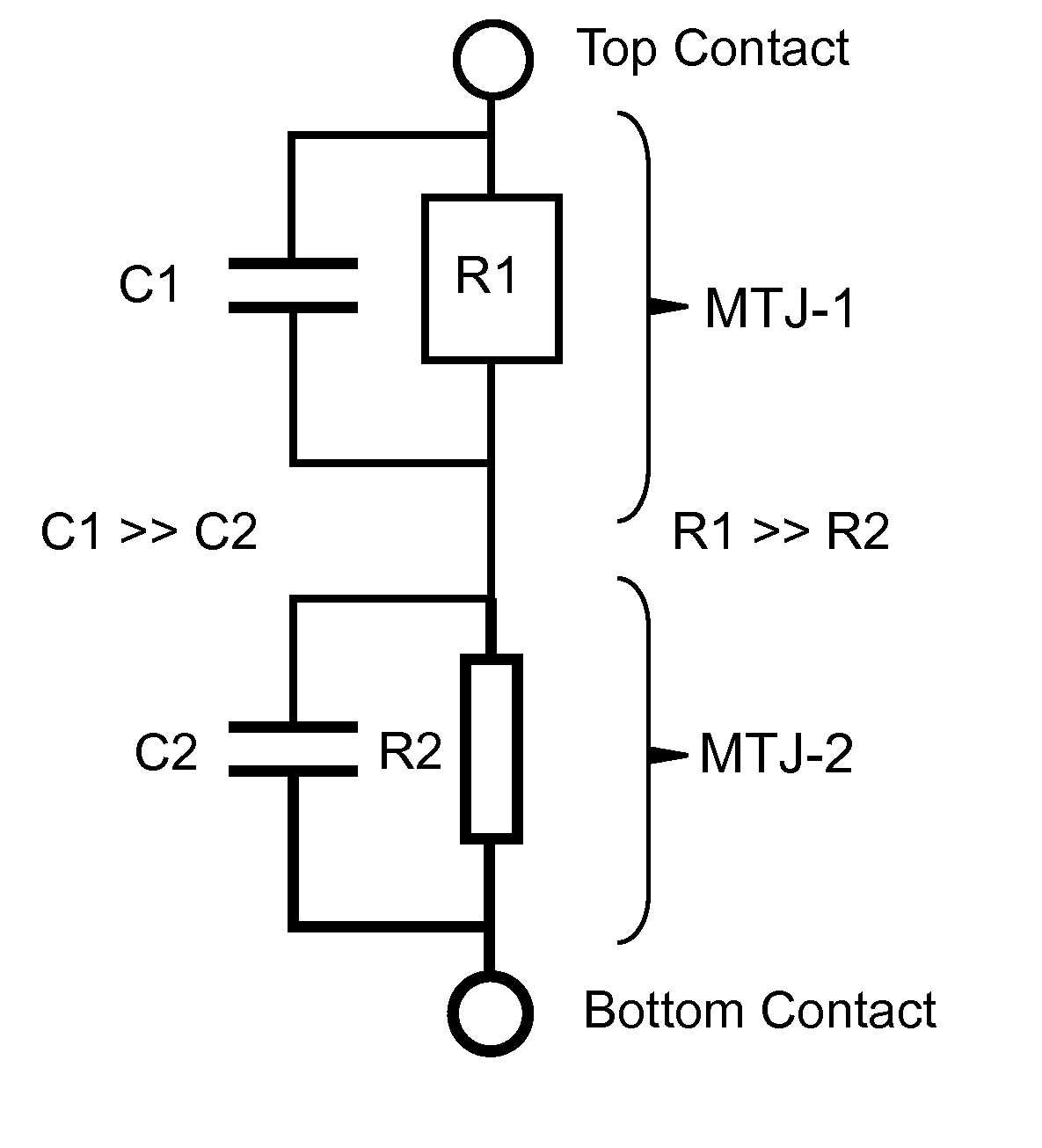
A magnetoresistive logic cell (MRLC) is described that includes two MTJs in series that share a common free layer (CFL). The relative magnetization orientations of the CFL and the switchable reference layer (SRL) in MTJ-1 dominate the overall resistance of the MRLC without regard to the fixed magnetization orientation of the nonswitchable reference layer in MTJ-2. High and low resistance states of the MRLC occurs based on the relative magnetization orientations of SRL and CFL. This behavior allows the MRLC to be used as a logical comparator. The CFL is switched by STT effect by application of selected relatively short voltage pulses that do not switch the SRL. A voltage-induced switching principle can be used with MRLC embodiments of the present invention to switch the SRL to parallel or anti-parallel with respect to the magnetization CFL in both perpendicular and in-plane anisotropy embodiments.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Inorganic flexible resistive memory and preparation method thereof
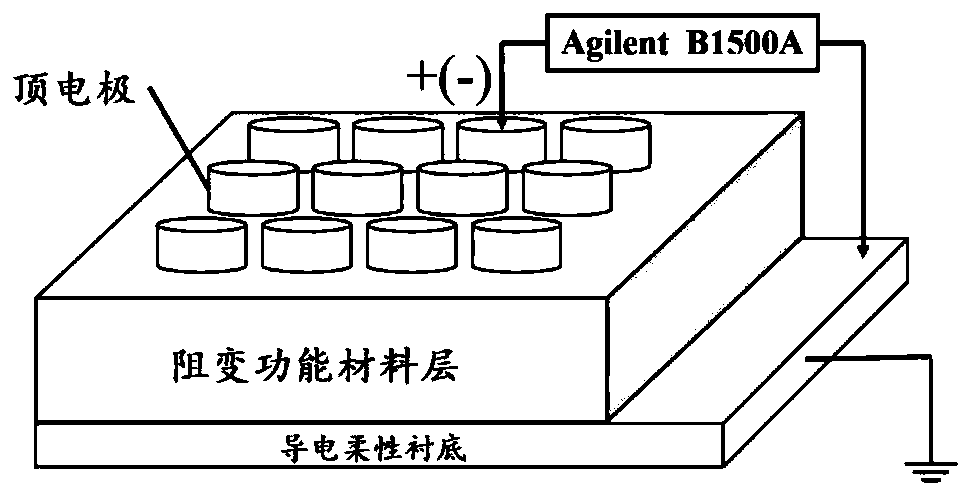
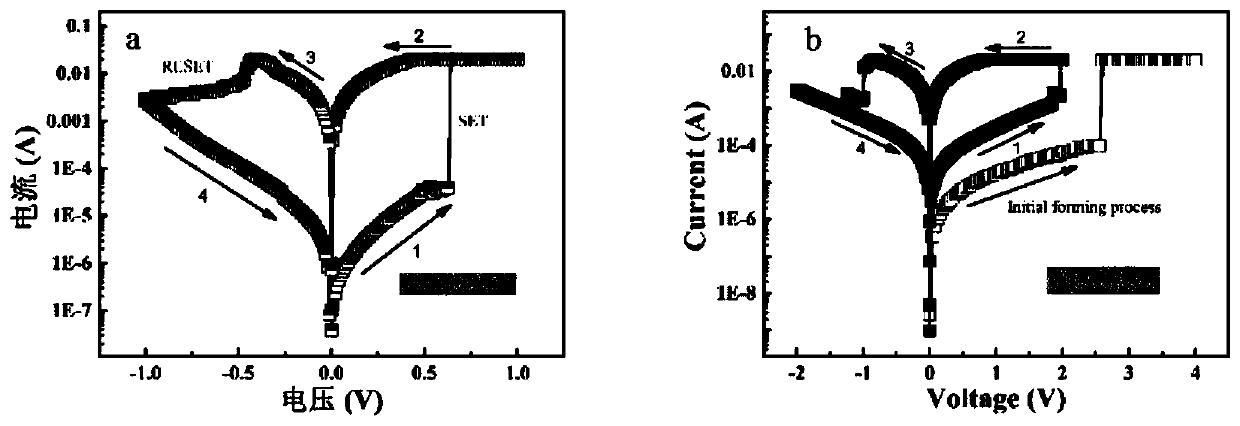
ActiveCN110165052AGood bending propertiesMitigate the impact of storage performanceElectrical apparatusNanotechnologyHigh resistancePulsed mode
The invention relates to the technical field of flexible electronic devices, in particular to an inorganic flexible resistive memory and a preparation method thereof. The inorganic flexible resistivememory has better bending characteristics, the high resistance state and low resistance state of the device are relatively stable under different bending radii and bending times, and the influence ofbending deformation on the storage performance of the functional layer material can be effectively alleviated. The inorganic flexible resistive memory has large switching ratio, low setting voltage and no Forming process and can ensure the normal operation of the device and meet the requirements of low power consumption. The inorganic flexible resistive memory has good thermal stability, the highand low resistance states of the device can be kept stable for about 105s under the condition of 85 DEG C, and the ratio of the high and low resistance states of the device is still above 102 after 107 consecutive switching operations in the pulse mode, which can ensure the normal operation of the device without misreading.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Non-volatile memory device and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20080158940A1Increase resistanceLower resistanceNanotechSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceElectrode Contact
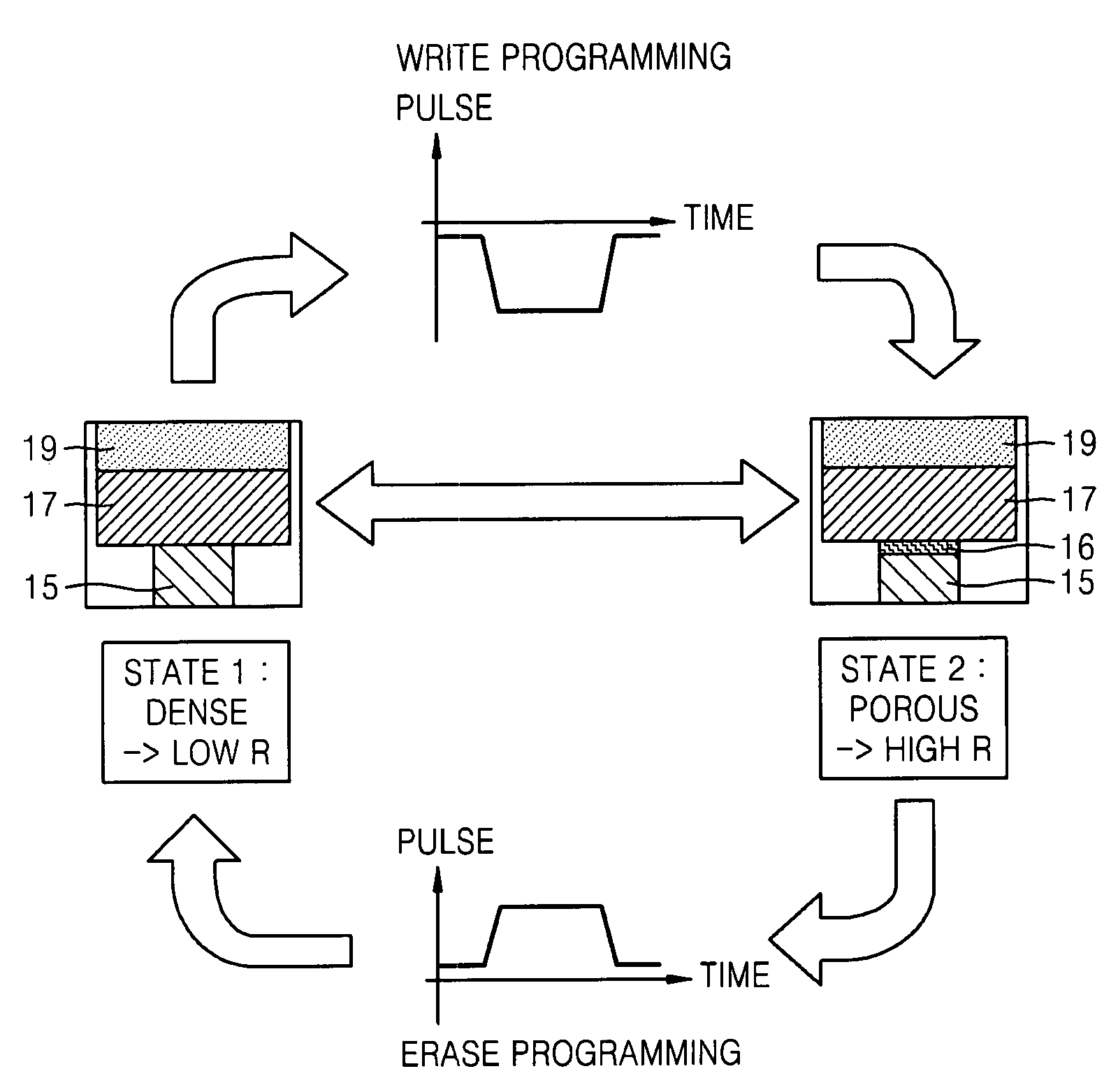
Provided are a non-volatile memory device and a method of operating the non-volatile memory device. The non-volatile memory device includes a switching device and a storage node connected to the switching device, wherein the storage node comprises: a first electrode connected to the switching device; a chalcogenide material layer formed on the first electrode; and a second electrode formed on the chalcogenide material layer, and one of the first and second electrodes comprises an electrode contact layer formed adjacent to a limited region of the chalcogenide material layer, and a property of the electrode region adjacent to the chalcogenide material layer is changed reversibly according to the direction in which a current is applied, thereby changing between a high resistance state and a low resistance state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic memory device
InactiveUS7738286B2High resistance stateIncrease write speedNanotechRecord information storageBit lineHigh resistance
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Non-volatile memory component based on RbAg4I5 film and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1889285AEasy to readGood switching effectElectrical apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The present invention discloses resistance switch effect based non-volatilisation phase transition memory element physical design preparation method. It contains setting solid electrolyte RbAg 4I5 film between reaction electrode and non - reaction electrode to construct one miniature sandwich structure of memory unit, said memory unit together with substrate and insulating layer all having five layers, depositing single-layer non - reaction electrode on substrate, depositing single-layer insulating layer on non - reaction electrode, and etching one micro pore in it to expose non - reaction electrode, depositing single-layer RbAg 4I5 film on insulating layer, thereon depositing single-layer reaction electrode, respectively leading out leading wire on non - reaction electrode and reaction electrode. Said memory element has advantages of compactness, simple structure, non-volatilisation, rapid read-write, low operating voltage and energy consumption, non - moving part, and nondestructive readout etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Moving target detection circuit based on memristor and CMOS
ActiveCN108712621AImprove compatibilityReduce dependenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExtensibilitySignal transition
The invention discloses a moving target detection circuit based on a memristor and a CMOS. The moving target detection circuit comprises an adjacent frame difference comparison module and a signal processing module connected in order; the adjacent frame difference comparison module receives external video data and is used for difference comparison of high 4-bit numerical values on various pixel points between adjacent two frame images; the signal processing module is used for acquiring binary output corresponding to various pixel points after orderly performing current-voltage signal conversion, weighted sum and threshold comparison on the difference comparison result output by adjacent frame difference comparison module, thereby generating a white-black image for describing the moving target contour. The difference comparison is performed on the signal from an image sensor through a mixed structure array of the memristor and the CMOS. The detection circuit has the advantages of beingsimple in structure, small in volume, strong in extensibility and low in power consumption, the contour detection on the moving target can be accomplished on a hardware circuit, and the data processing pressure of the computer can be shared, thereby laying the foundation for realizing higher-order image processing task.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resistive random access memory using rare earth scandate thin film as storage medium
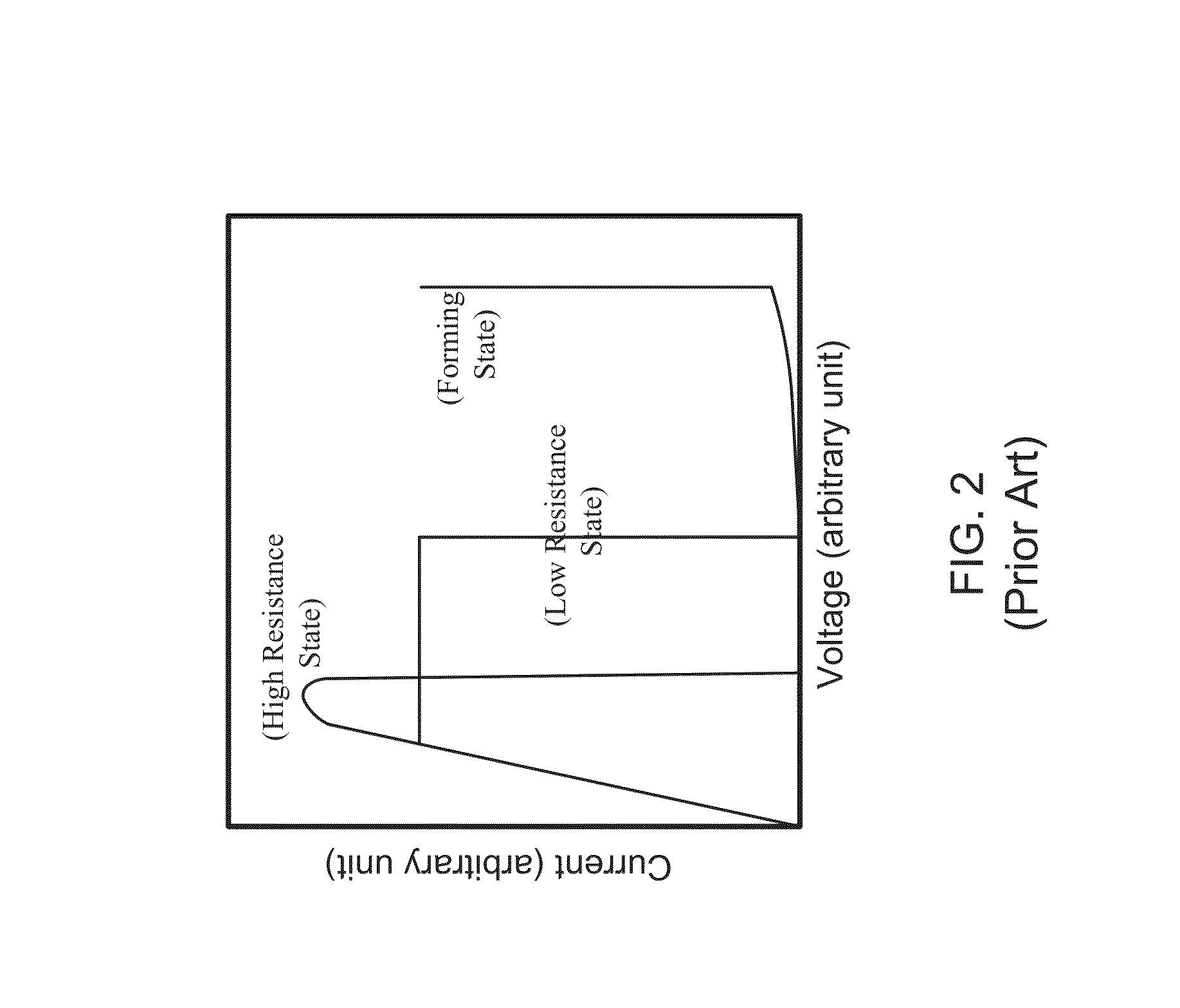
ActiveUS8445888B1Low operating voltageLow power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageHigh resistanceForming processes
The present invention relates to a resistive random access memory using the rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium, comprising a substrate, an insulation layer, a first electrode layer, a resistive memory layer, and a second electrode layer. In the present invention, it uses an amorphous rare earth scandate layer as the resistive memory layer of the resistive random access memory. Therefore, the resistive random access memory using the rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium having advantages of low operation voltage and low power consumption can easily be manufactured without using any forming process or thermal annealing process. Moreover, through the characteristics of unipolar resistance switching behavior revealed by the amorphous rare earth scandate layer, the resistive random access memory using rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium is able to perform a high resistance state and a low resistance state.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resistance variable oxide material Co3O4 thin film, preparation and use thereof
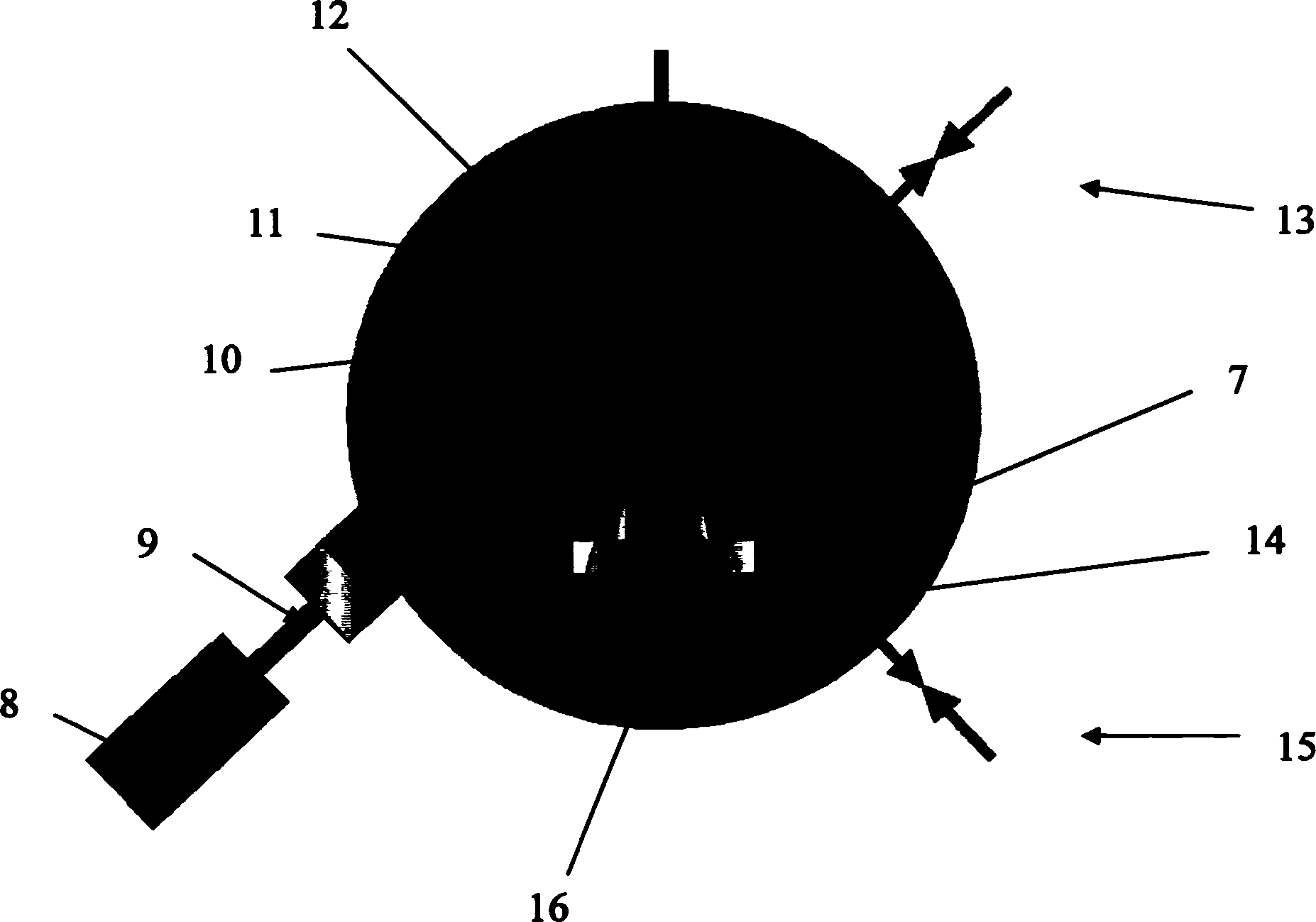
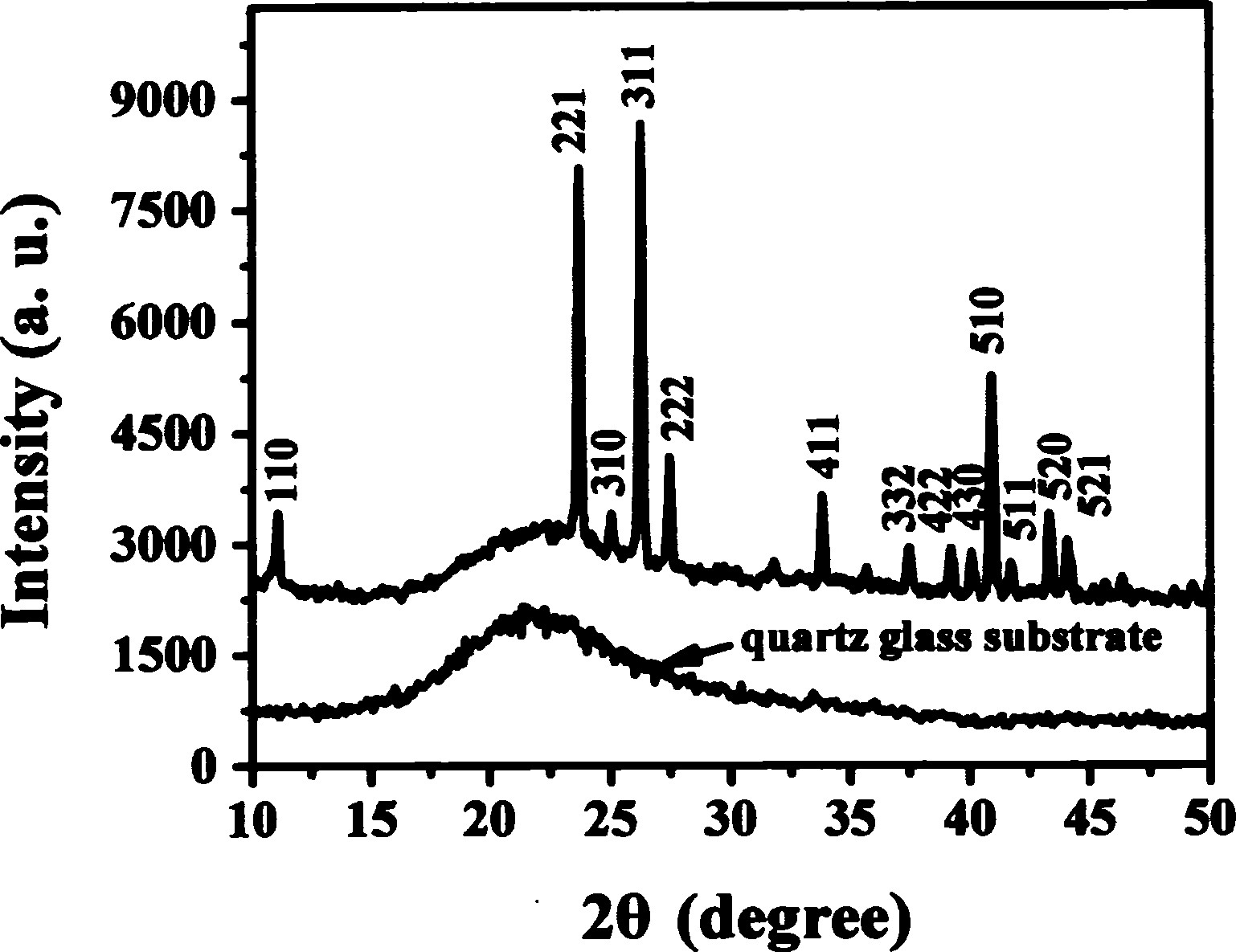
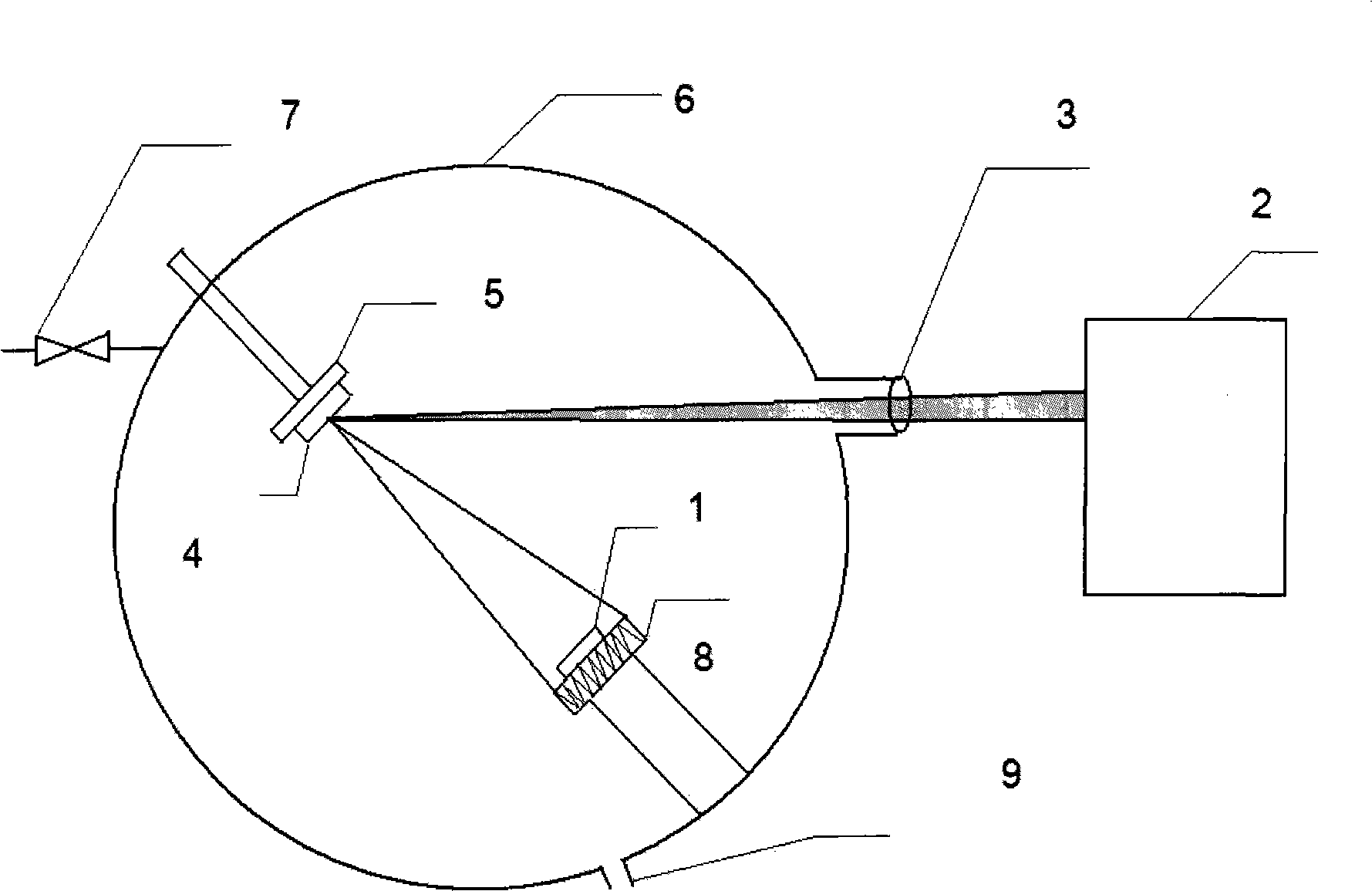
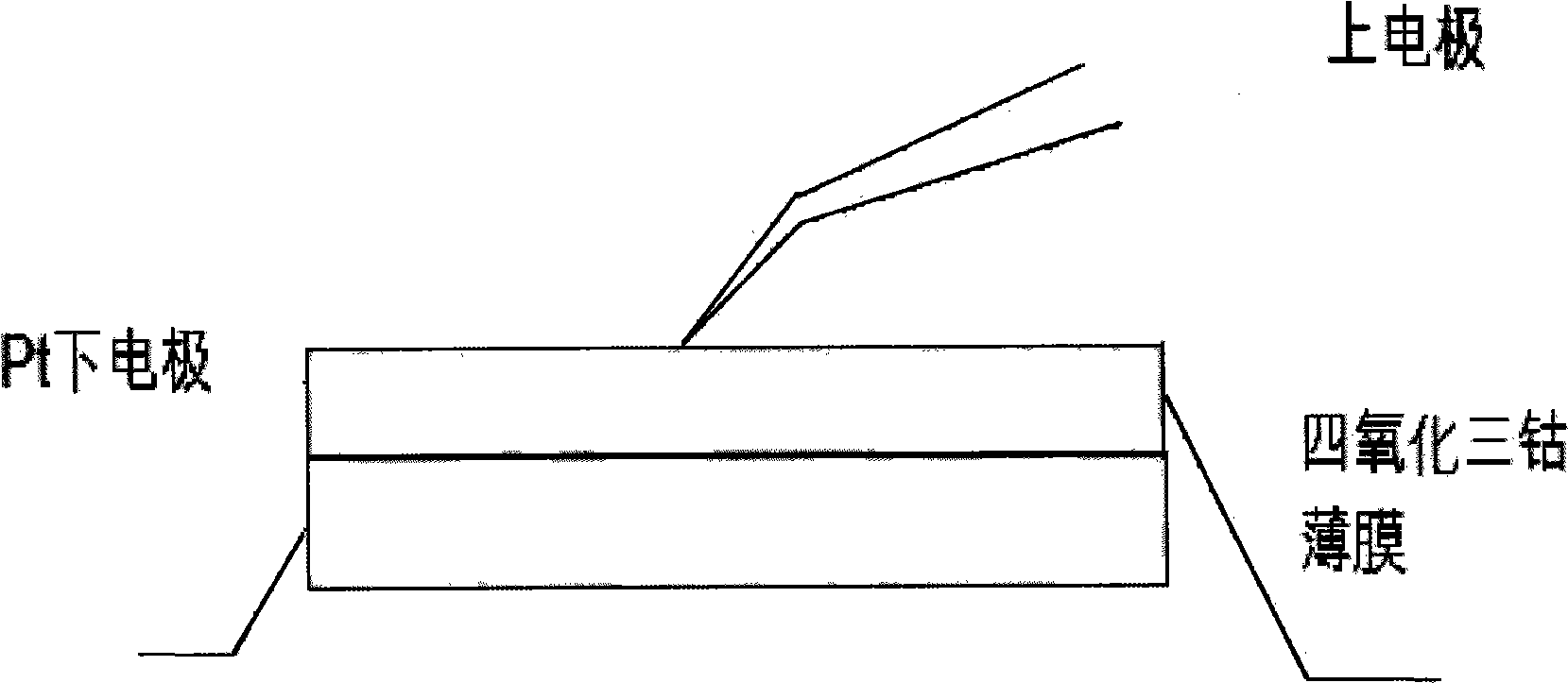
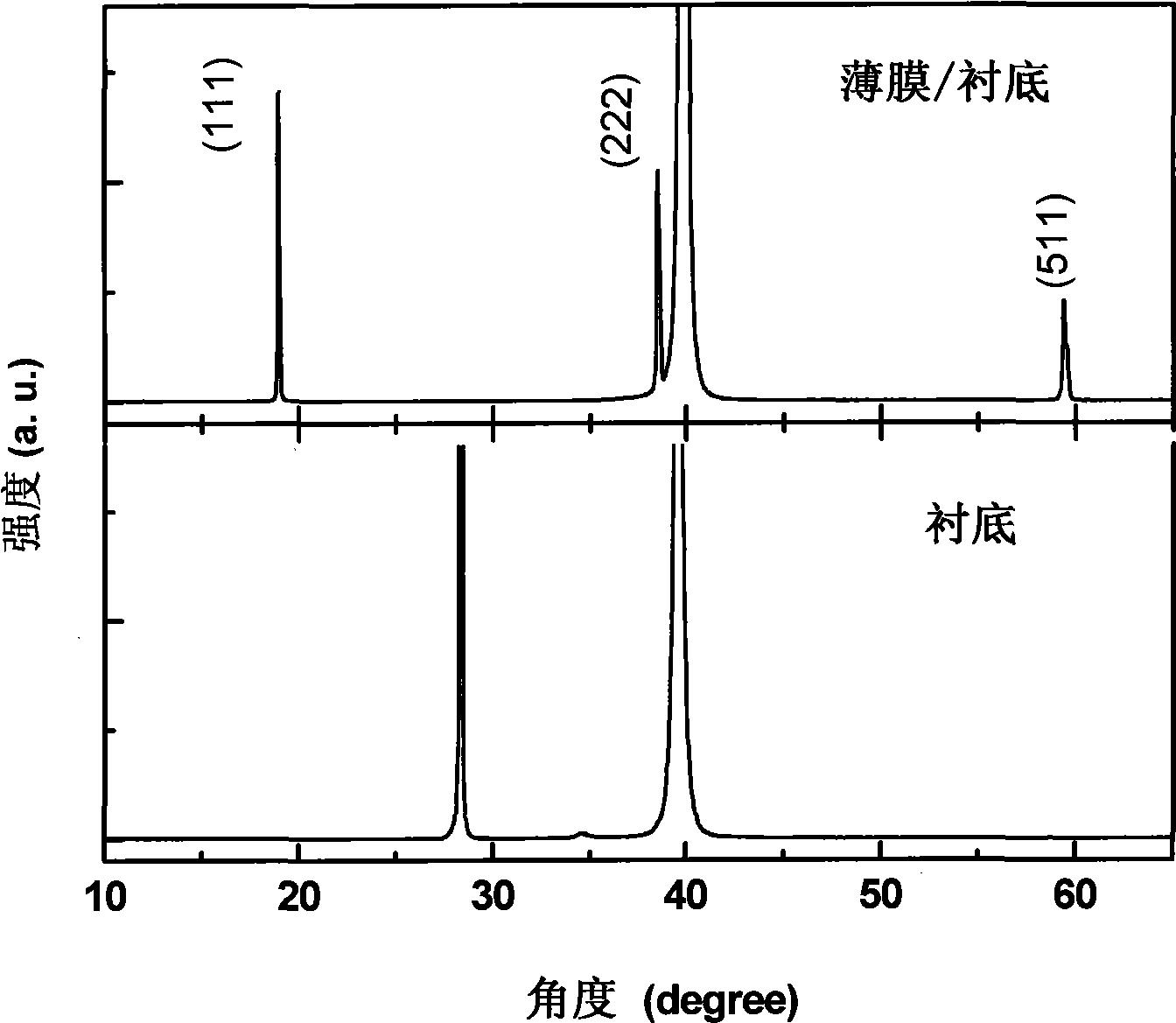
InactiveCN101498042AUniform thicknessClear interfacePolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingInlet valveLaser beams
The invention relates to a cobalt oxide film of interrupted oxide material, which is in a polycrystal state and has a chemical formula of Co3O4 and a thickness of 200nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing ceramic target material of CoOx (x is larger than 0 and less than 4 / 3); (2), fixing the target material of CoOx on a target, fixing a substrate on a substrate platform and arranging the target and the substrate platform in a growth chamber; (3), vacuumizing the growth chamber by a mechanical pump and a molecular pump, closing the mechanical pump, opening an inlet valve and pumping oxygen to the growth chamber until oxygen pressure is 20Pa; (4), focusing laser beams of a laser on the target material of CoOx by a lens; (5), heating the substrate platform by a resistance furnace so that the temperature of the substrate reaches a temperature of 660 DEG C; and (6), confirming sedimentation time according to single-pulse energy to sedimentate the film of Co3O4 with the thickness of 200nm on the substrate. The film is used to prepare a nonvolatile interrupted memory storage element which adopts a sandwich structure as a basic configuration, i.e., a polycrystal oxide film of Co3O4 is sedimentated on a Pt electrode film of a lower electrode, and a Pt probe is used as an upper electrode to form a memory unit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Trailing edge dimmer compatibility with dimmer high resistance prediction
ActiveUS20130342123A1High resistance stateEasy transitionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh resistanceElectronic systems
In at least one embodiment, an electronic system includes a controller, and the controller provides compatibility between an electronic light source and a trailing edge dimmer. In at least one embodiment, the controller is capable of predicting an estimated occurrence of a trailing edge of a phase cut AC voltage and accelerating a transition of the phase cut AC voltage from the trailing edge to a predetermined voltage threshold. In at least one embodiment, the controller predicts an estimated occurrence of the trailing edge of the phase cut AC voltage on the basis of actual observations from one or more previous cycles of the phase cut AC voltage.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Printing conductive patterns using LEP
ActiveUS7476603B2Reliably be printed into electrostatic patternHigh resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialEngineeringElectronic component
A method of printing an electrode component is disclosed. The method can include steps of electrostatically printing a polymer onto a substrate, where at least a portion of the printing occurs while the polymer is in a first conductive state, and altering the polymer to a second conductive state that is more conductive than the first conductive state, thereby forming the electronic component.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Printing conductive patterns using LEP
ActiveUS20060273305A1Reliably be printed into electrostatic patternHigh resistance statePrinted circuit aspectsConductive materialEngineeringElectronic component
A method of printing an electrode component is disclosed. The method can include steps of electrostatically printing a polymer onto a substrate, where at least a portion of the printing occurs while the polymer is in a first conductive state, and altering the polymer to a second conductive state that is more conductive than the first conductive state, thereby forming the electronic component.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Phase change memory array with integrated polycrystalline diodes
ActiveUS10256271B1High resistance stateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePhase-change memory
A method for deactivating memory cells affected by the presence of grain boundaries in polycrystalline selection devices includes crystallizing a semiconductor layer in a diode stack to form a polycrystalline layer for selection diodes formed in a crossbar array. To achieve a crystalline state in phase change memory elements coupled to corresponding selection diodes perform an anneal. Memory cells having shunted selection diodes due to grain boundaries are identified by scanning the array using sense voltages. A second voltage larger than the sense voltages is applied to the phase change memory elements gated by the shunted selection diodes such that the phase change memory elements gated by the shunted diodes achieve a permanently high resistive state.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pd-doped rGO/ZnO-SnO2 heterojunction quaternary composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113830753AHigh resistance stateHigh hydrogen responseMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesHeterojunctionHydrogen sensor
The invention relates to a Pd-doped rGO / ZnO-SnO2 heterojunction quaternary composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gas sensors. The composite material is secondary particles formed by agglomeration of primary particles, the primary particles take rGO of a two-dimensional net structure as a matrix, the surface of the matrix is coated with sheet nanometer materials ZnO and SnO2, ZnO and SnO2 are compounded to form n-n type heterojunctions, ZnO, SnO2 and rGO respectively form p-n type heterojunctions, and Pd nanoparticles are doped in ZnO, SnO2 and rGO. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing a flaky ZnO nano material and stannous chloride in water, sequentially adding DMF, sodium hydroxide and palladium chloride to obtain a mixed solution, then carrying out hydrothermal reaction on the mixed solution and a graphene oxide dissociation solution, and finally calcining. The composite material has the characteristics of high selectivity, quick response and low-concentration detection when being used in the hydrogen sensor.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
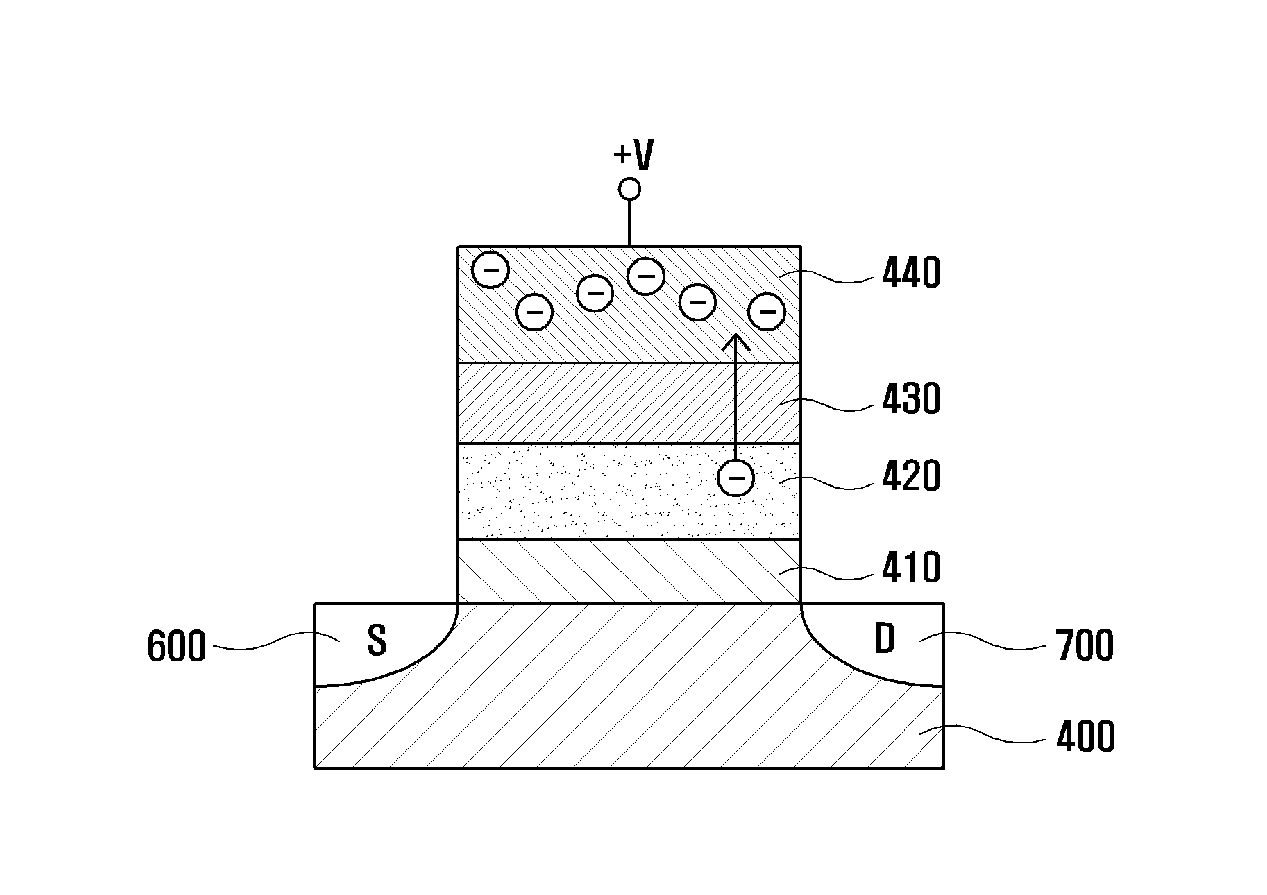
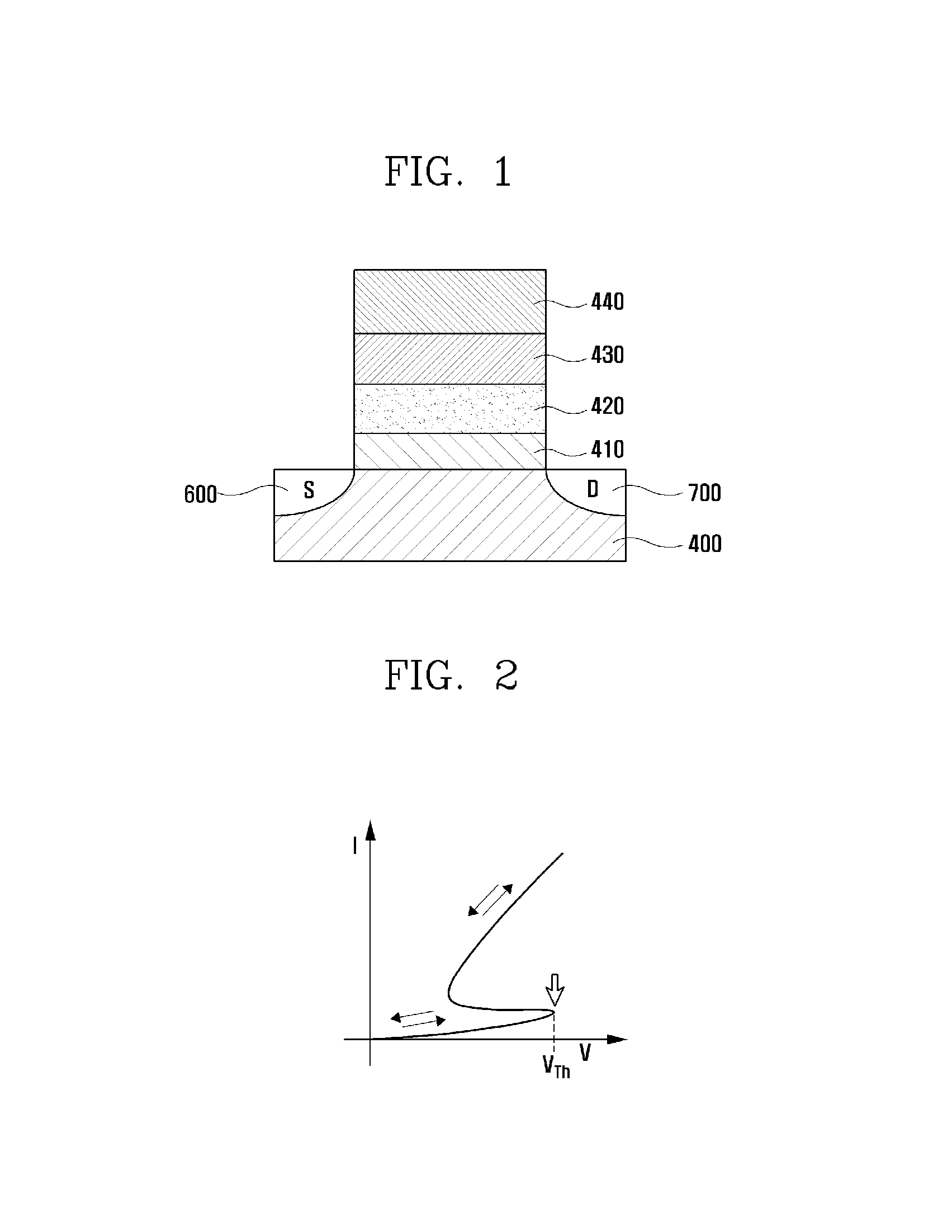
Nonvolatile memory device using a threshold voltage switching material and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20140036585A1Fast programmingImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention relates to a nonvolatile memory device and to a method for manufacturing same. According to the present invention, the blocking insulation layer of a nonvolatile memory device having a typical SONOS structure is replaced with a threshold voltage switching material, which changes to a low resistance state only while a voltage greater than a threshold voltage is applied while maintaining a high resistance state under normal conditions and returning to the high resistance state when the applied voltage is removed. The present invention performs a program operation by injecting charges from a gate electrode layer into a charge trap layer through an insulation layer formed of the threshold voltage switching material after applying a voltage pulse greater than the threshold voltage to the gate electrode layer.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com