Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Electronic states" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
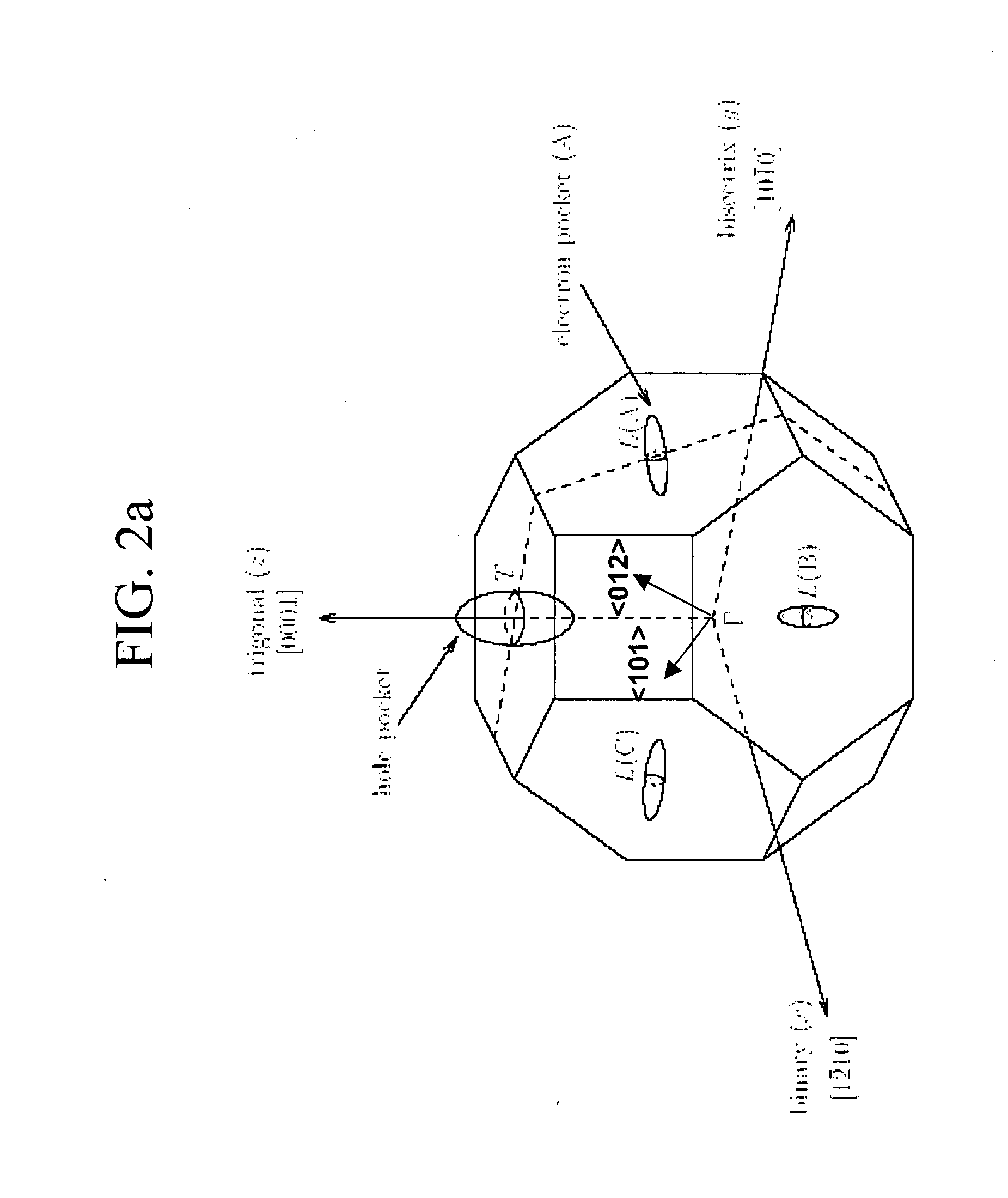
Super-resolution microscope system and method for illumination
InactiveUS6667830B1High resolutionReducing diffractive limitPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersElectronic statesExcited state
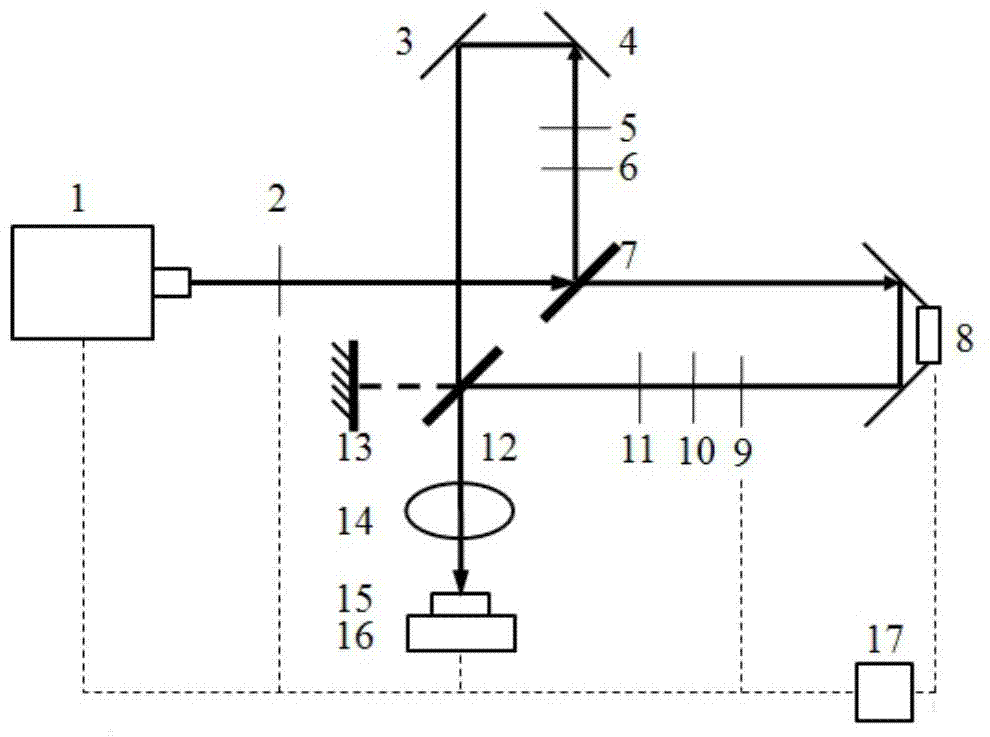
A microscope system comprising an adjusted specimen and a microscope body, wherein the adjusted specimen is dyed with molecule which has three electronic states including at least a ground state and in which an excited wavelength band from the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state overlaps a fluorescent wavelength band upon deexcitation through a fluorescence process from the first electron excited state to a vibrational level in the ground state. There is provided a novel microscope system which is enabled to condense an erase light for exciting a molecule in the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state in an excellent beam profile by using a simple, compact optical system and which has high stability and operability and an excellent super-resolution.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
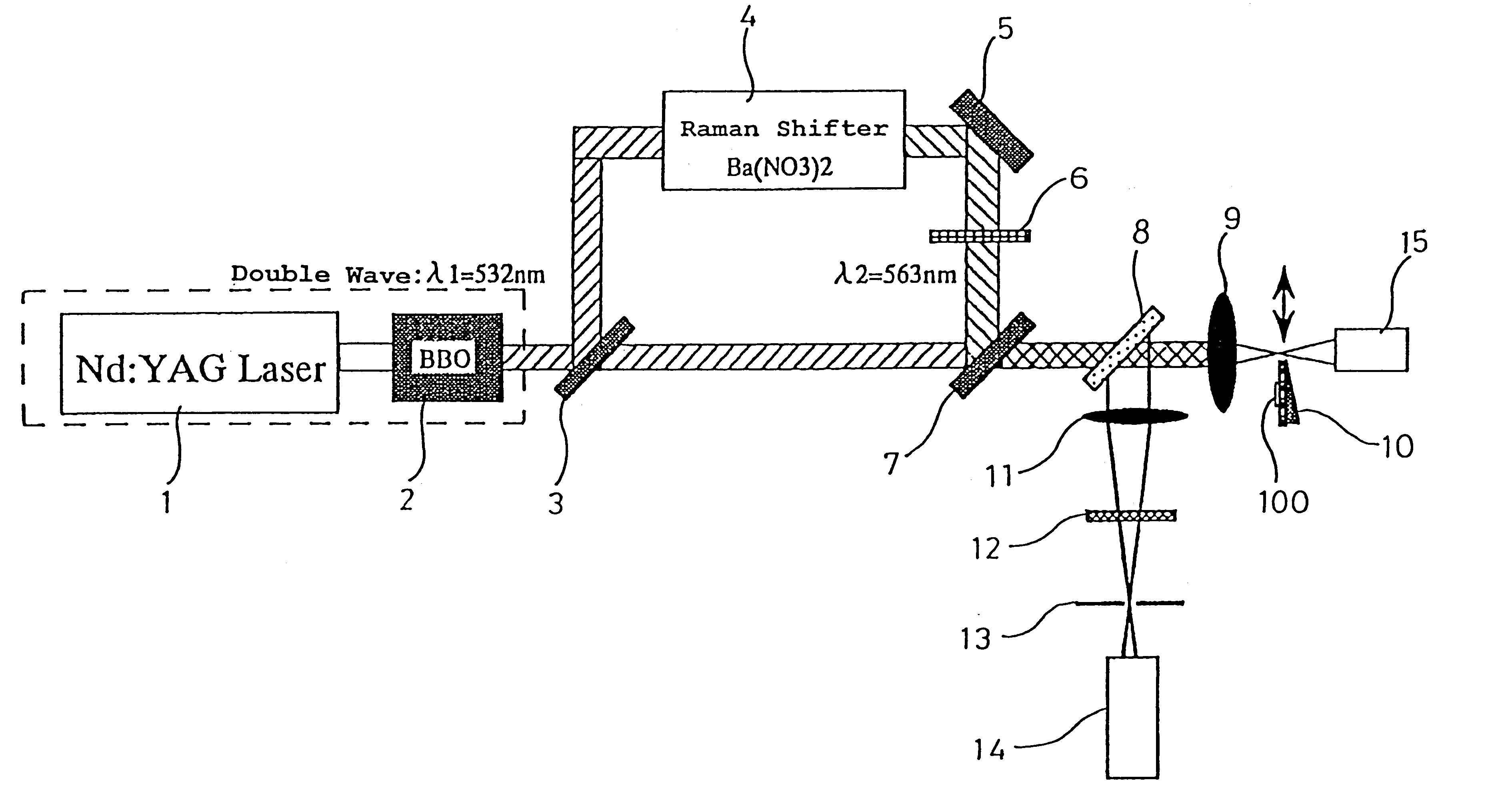
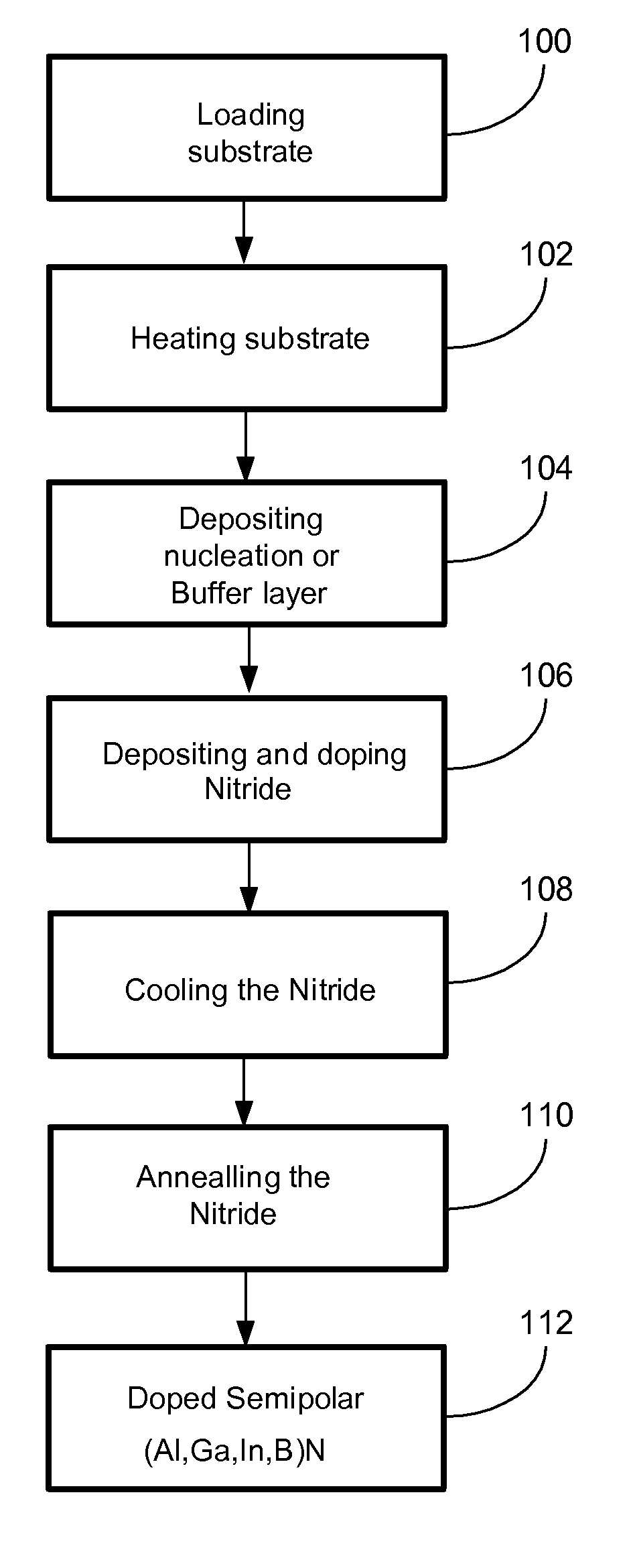
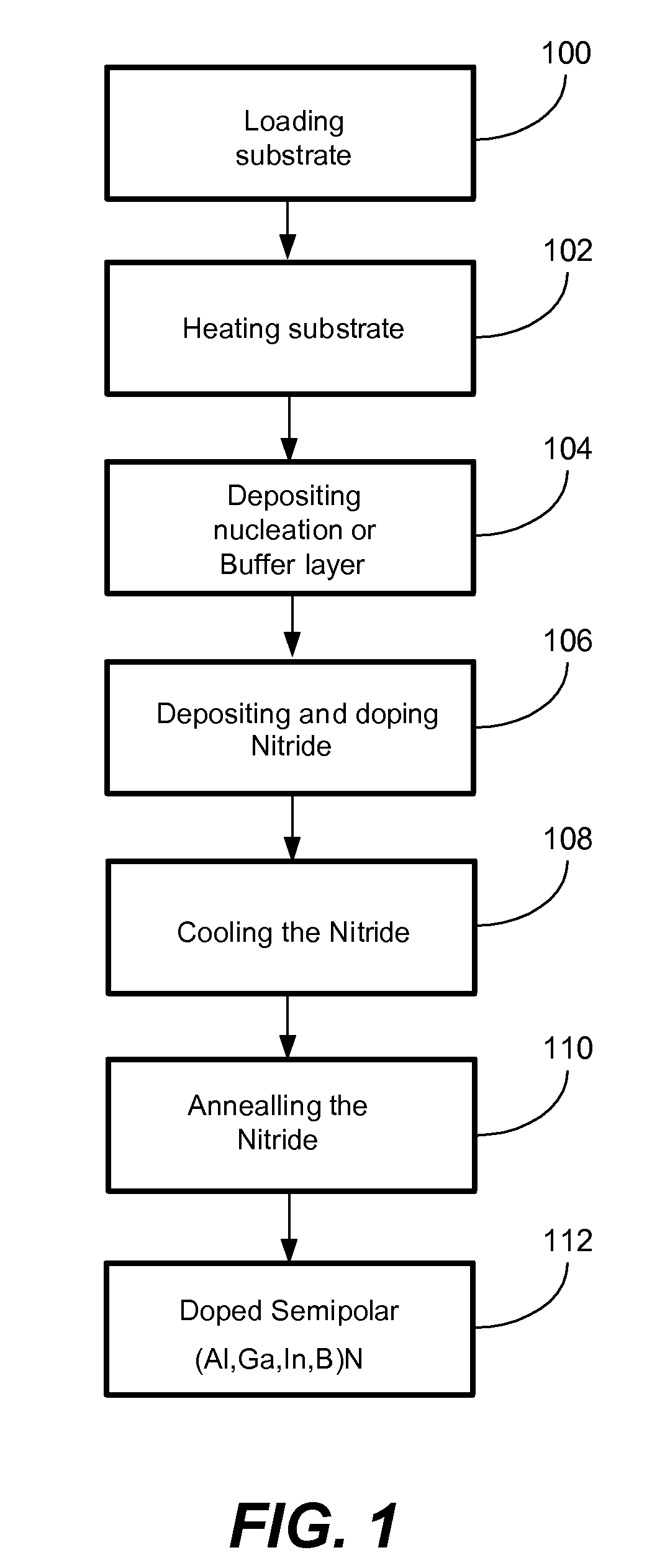
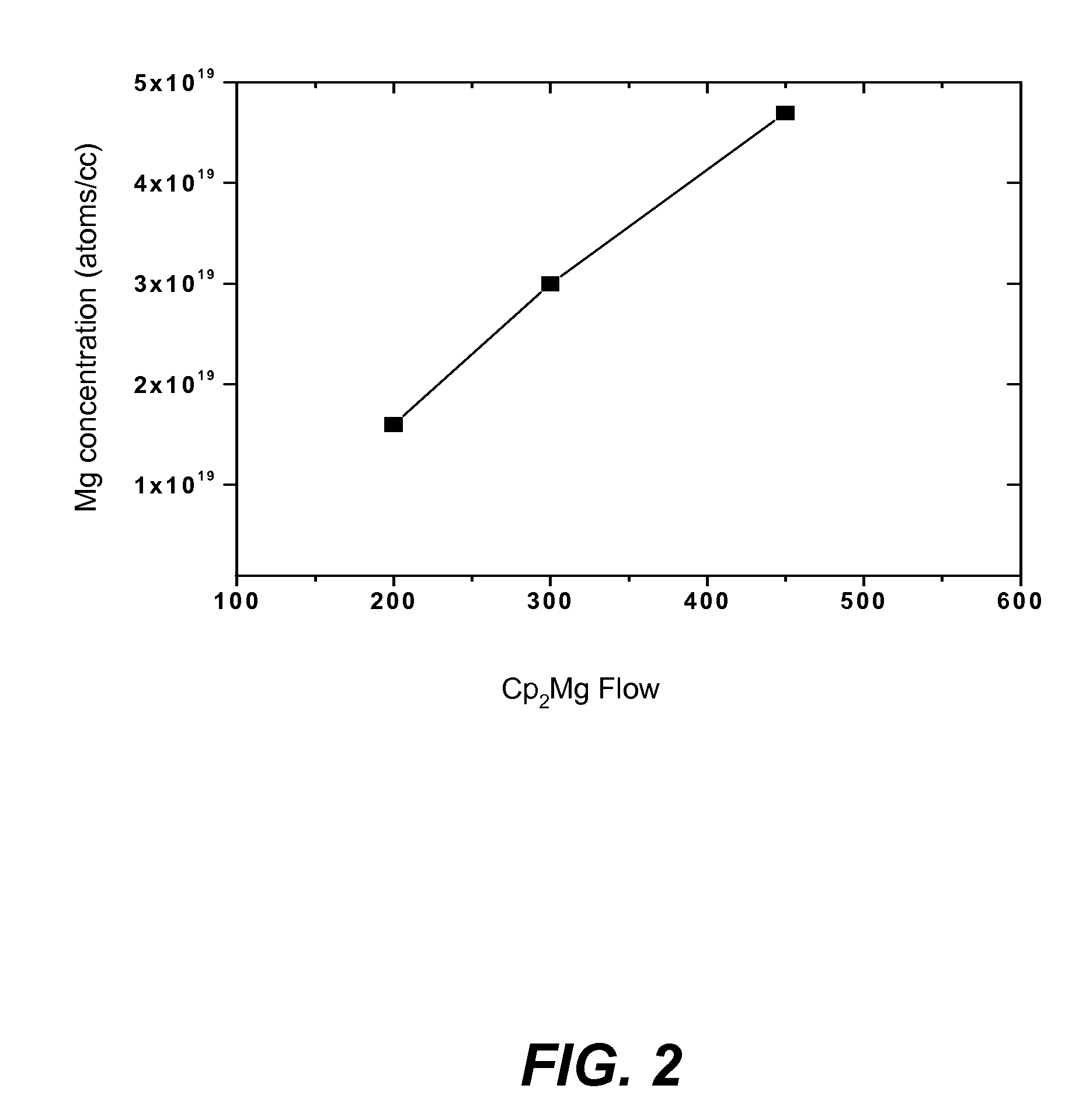
METHOD FOR CONDUCTIVITY CONTROL OF (Al,In,Ga,B)N
ActiveUS20070190758A1Improve conductivityEnhancing or tailoring conductivity propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectronic statesSpinel
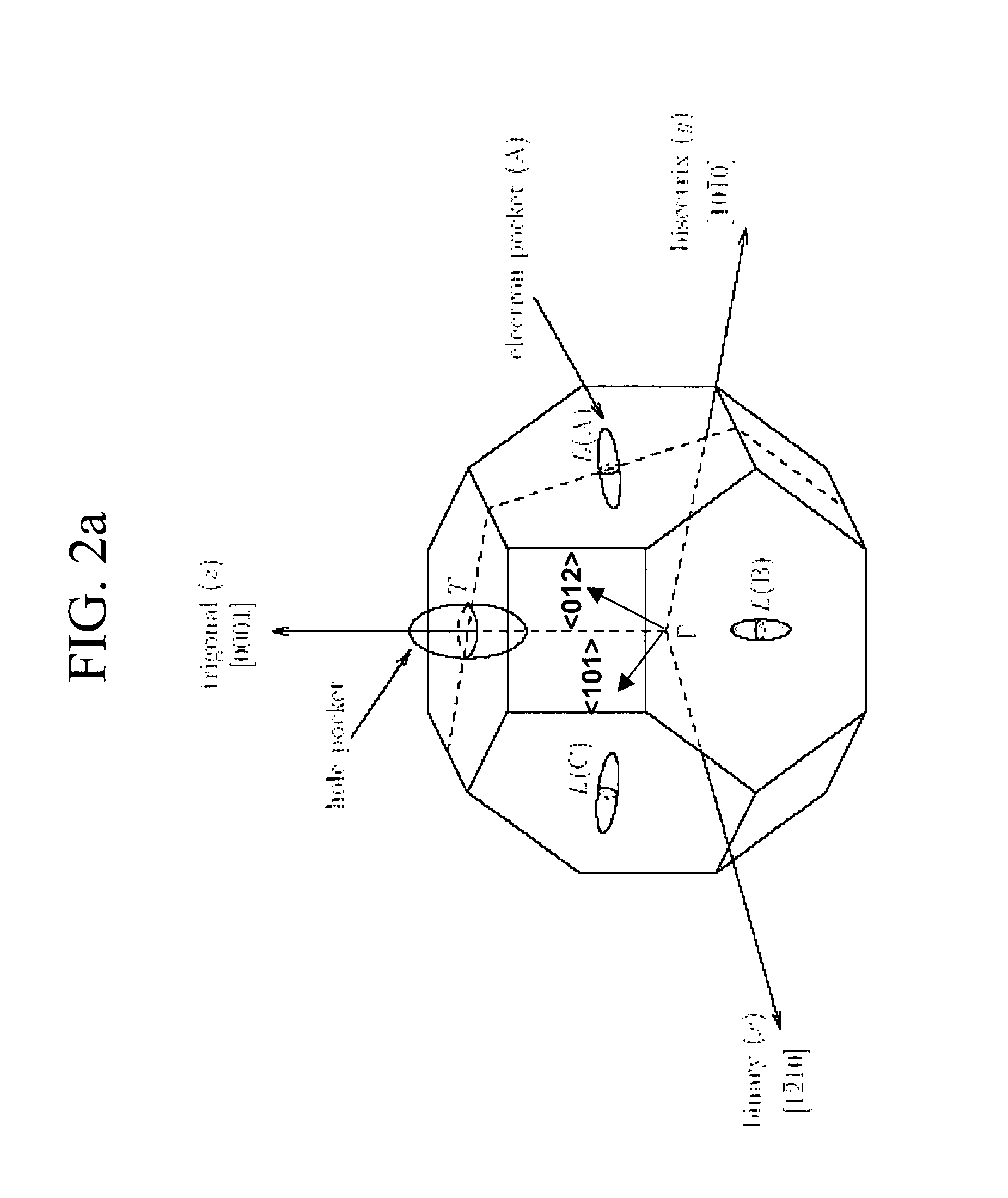
A method of controlled p-type conductivity in (Al,In,Ga,B)N semiconductor crystals. Examples include {10 11} GaN films deposited on {100} MgAl2O4 spinel substrate miscut in the <011> direction. Mg atoms may be intentionally incorporated in the growing semipolar nitride thin film to introduce available electronic states in the band structure of the semiconductor crystal, resulting in p-type conductivity. Other impurity atoms, such as Zn or C, which result in a similar introduction of suitable electronic states, may also be used.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
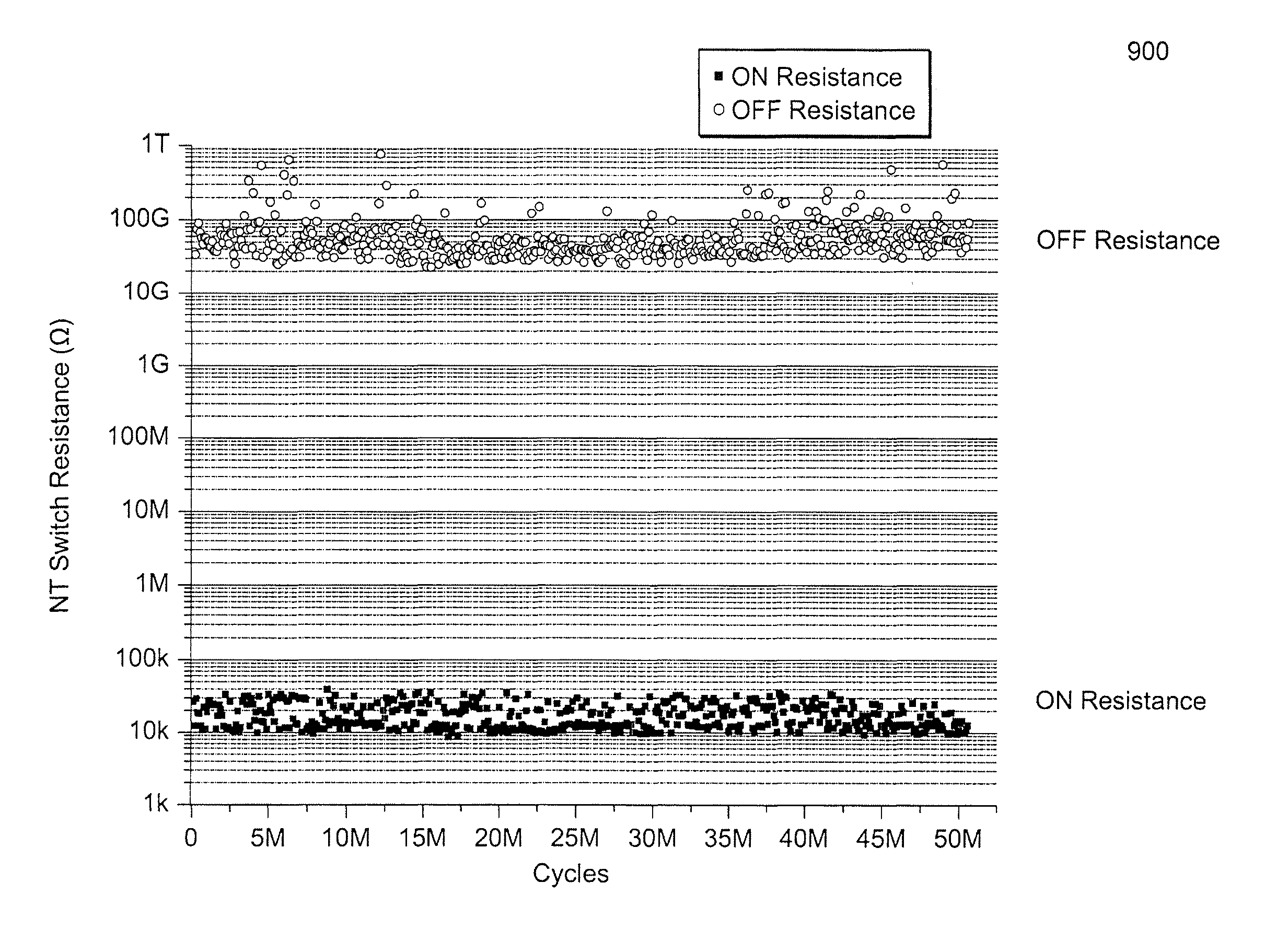
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS8217490B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsElectricityElectronic states
Under one aspect, a non-volatile nanotube switch includes a first terminal; a nanotube block including a multilayer nanotube fabric, at least a portion of which is positioned over and in contact with at least a portion of the first terminal; a second terminal, at least a portion of which is positioned over and in contact with at least a portion of the nanotube block, wherein the nanotube block is constructed and arranged to prevent direct physical and electrical contact between the first and second terminals; and control circuitry capable of applying electrical stimulus to the first and second terminals. The nanotube block can switch between a plurality of electronic states in response to a plurality of electrical stimuli applied by the control circuitry to the first and second terminals. For each different electronic state, the nanotube block provides an electrical pathway of different resistance between the first and second terminals.
Owner:NANTERO
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080170429A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsElectronic statesNanotube
Under one aspect, a non-volatile nanotube switch includes a first terminal; a nanotube block including a multilayer nanotube fabric, at least a portion of which is positioned over and in contact with at least a portion of the first terminal; a second terminal, at least a portion of which is positioned over and in contact with at least a portion of the nanotube block, wherein the nanotube block is constructed and arranged to prevent direct physical and electrical contact between the first and second terminals; and control circuitry capable of applying electrical stimulus to the first and second terminals. The nanotube block can switch between a plurality of electronic states in response to a plurality of electrical stimuli applied by the control circuitry to the first and second terminals. For each different electronic state, the nanotube block provides an electrical pathway of different resistance between the first and second terminals.
Owner:NANTERO
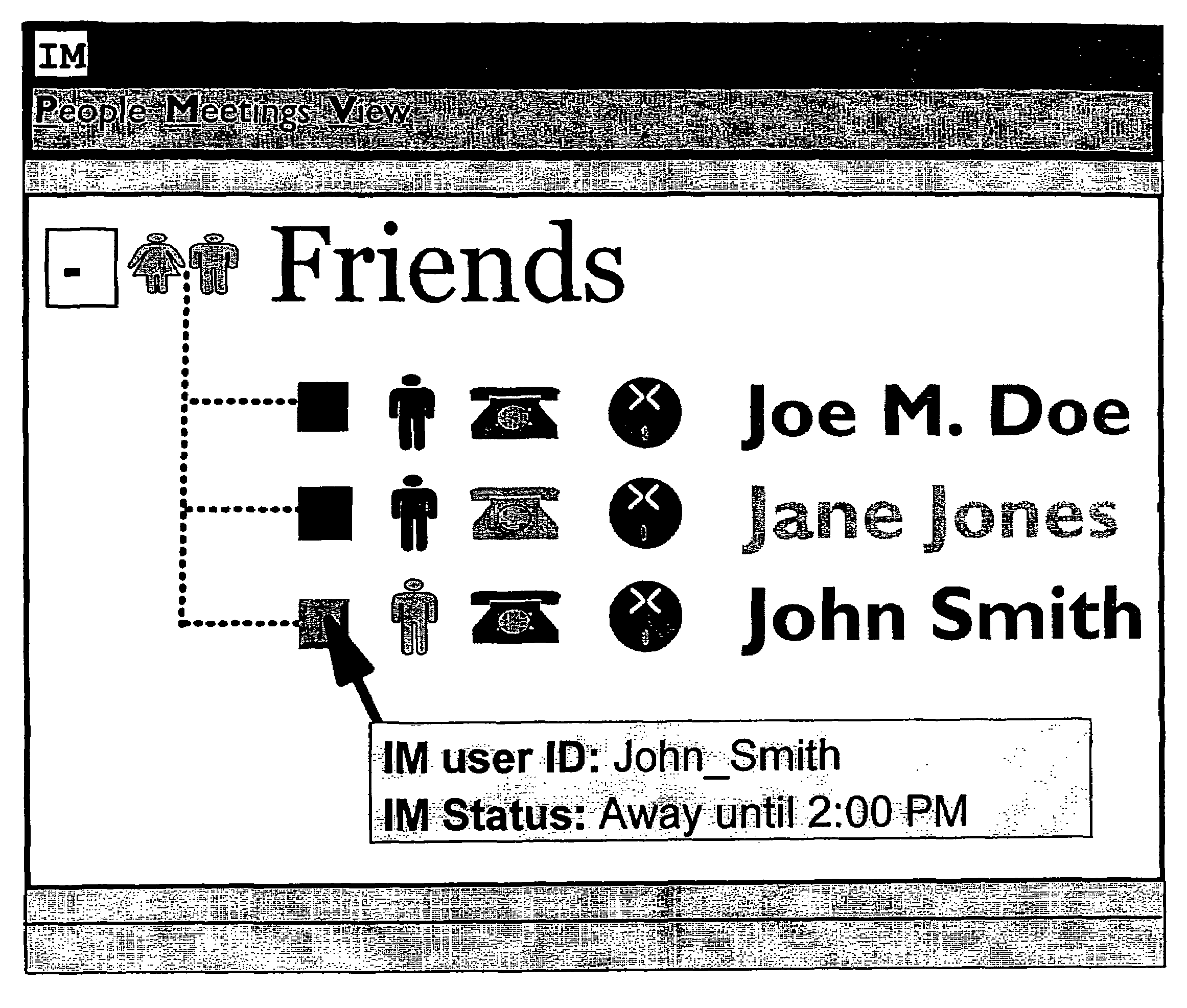
Calendar-enhanced awareness for instant messaging systems and electronic status boards
A method, system, and product are disclosed for providing calendar-enhanced awareness / presence information for instant messaging systems and electronic status boards. This invention automates status transitions, enhances and automates status messages, and automates and extends the IM “who can see me” function. Additionally, this invention extends awareness to dimensions other than IM status, to include availability in-person, via telephone, via wireless device or wireless messaging device (e.g., pager).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Memory elements and cross point switches and arrays of same using nonvolatile nanotube blocks
ActiveUS20080142850A1NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectronic states
Under one aspect, a covered nanotube switch includes: (a) a nanotube element including an unaligned plurality of nanotubes, the nanotube element having a top surface, a bottom surface, and side surfaces; (b) first and second terminals in contact with the nanotube element, wherein the first terminal is disposed on and substantially covers the entire top surface of the nanotube element, and wherein the second terminal contacts at least a portion of the bottom surface of the nanotube element; and (c) control circuitry capable of applying electrical stimulus to the first and second terminals. The nanotube element can switch between a plurality of electronic states in response to a corresponding plurality of electrical stimuli applied by the control circuitry to the first and second terminals. For each different electronic state, the nanotube element provides an electrical pathway of different resistance between the first and second terminals.
Owner:NANTERO
Optoelectronic devices utilizing materials having enhanced electronic transitions
An optoelectronic device that includes a material having enhanced electronic transitions. The electronic transitions are enhanced by mixing electronic states at an interface. The interface may be formed by a nano-well, a nano-dot, or a nano-wire.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
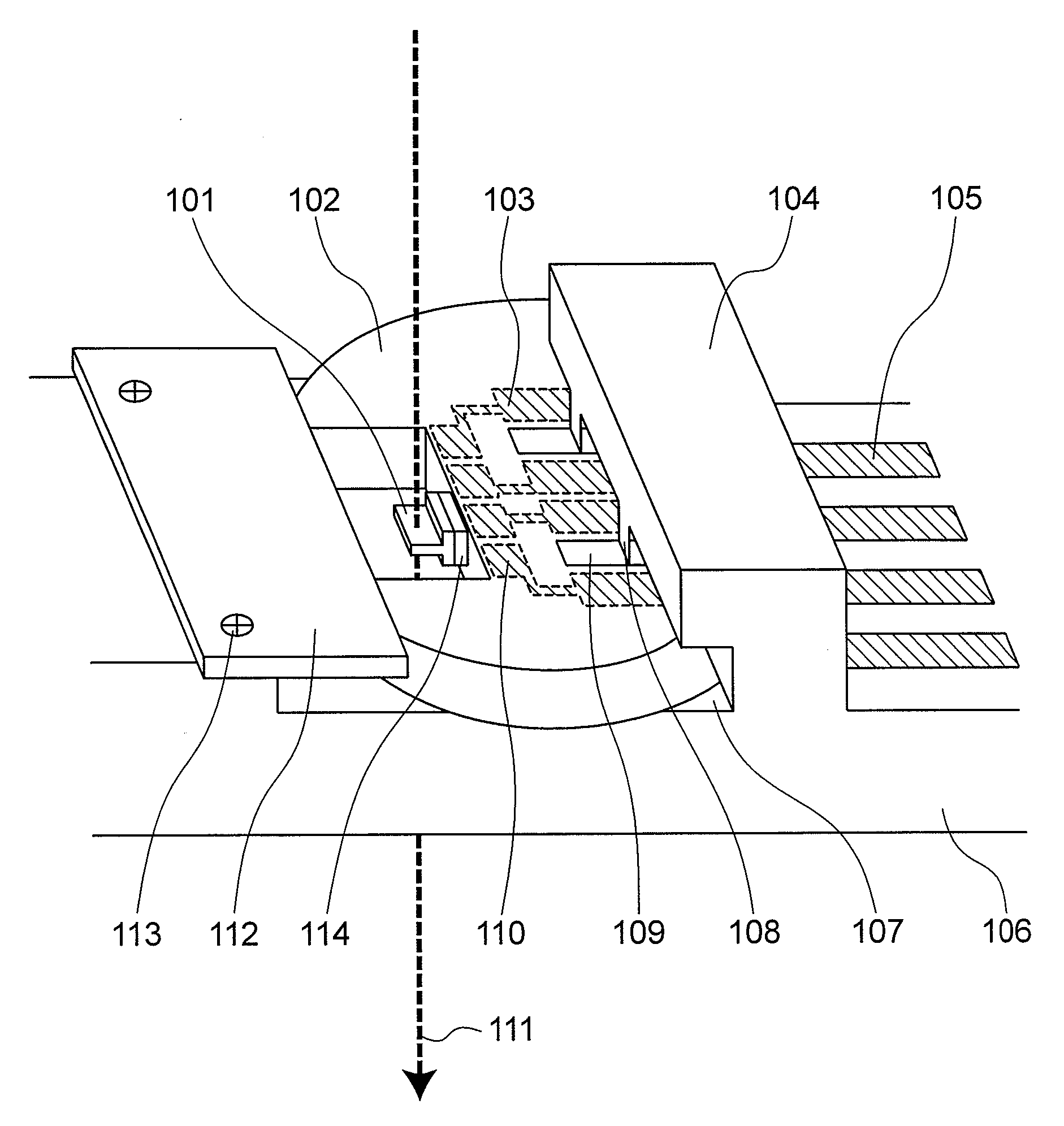
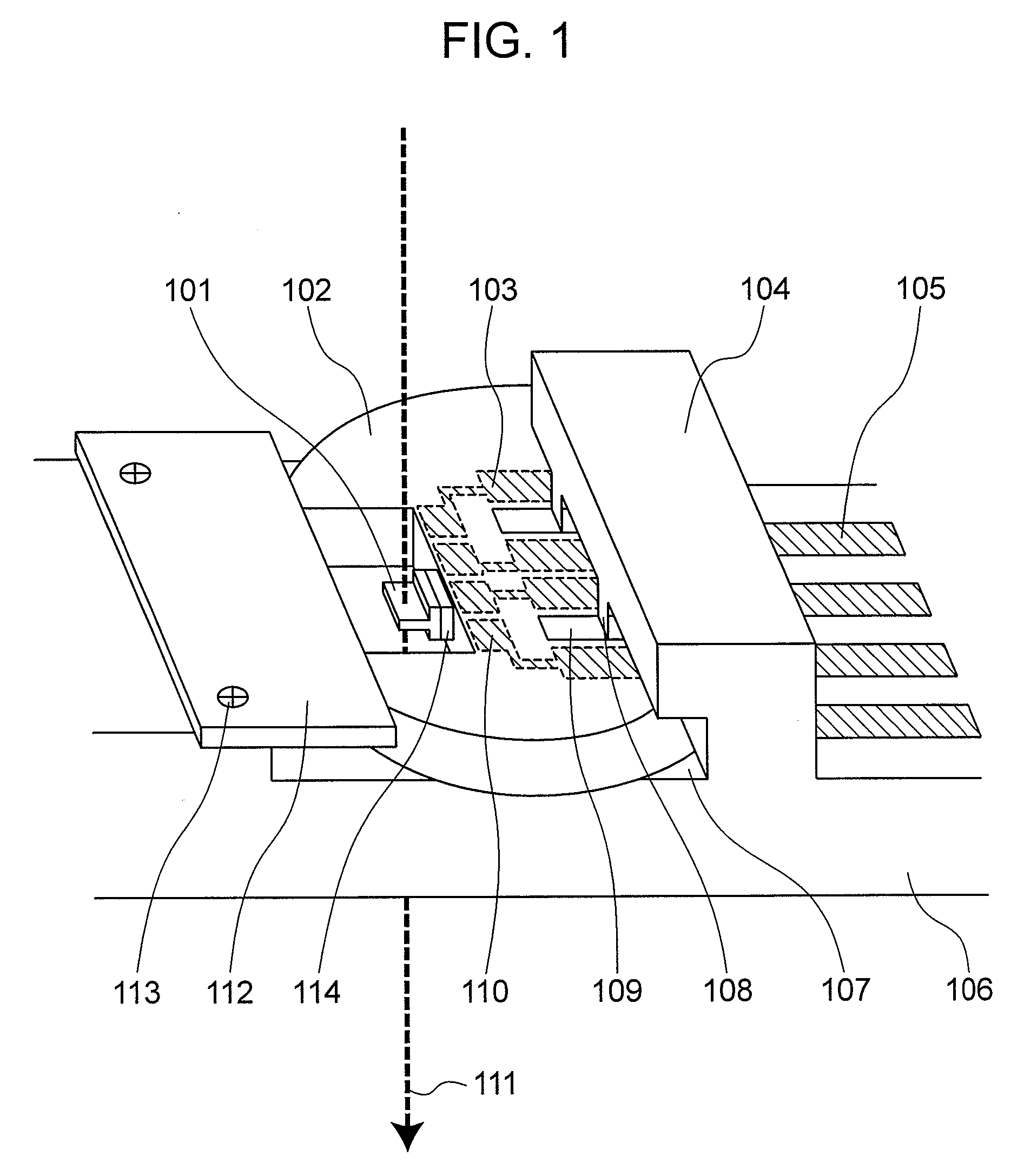
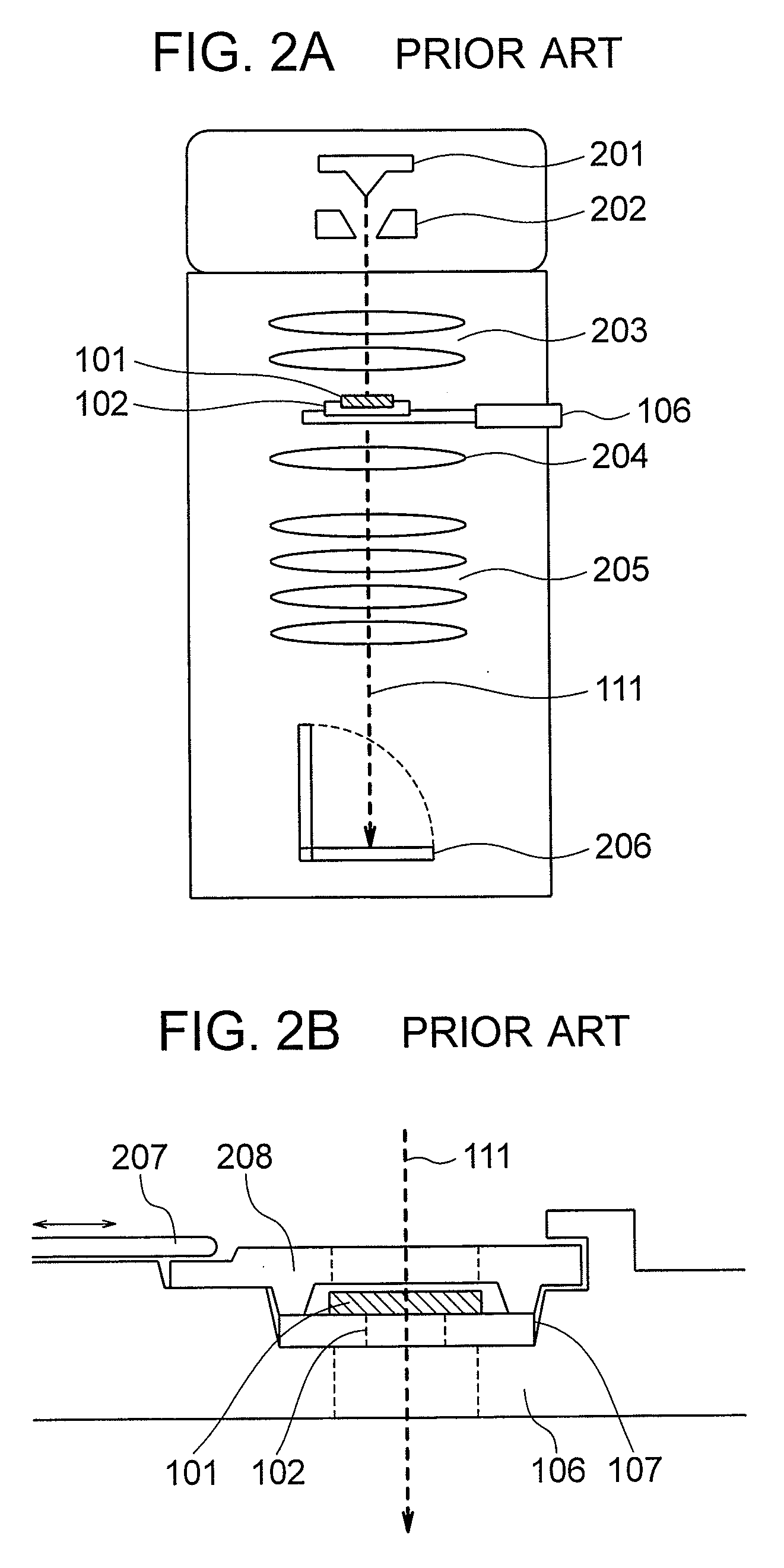
Specimen Analyzing Apparatus and Specimen Holder
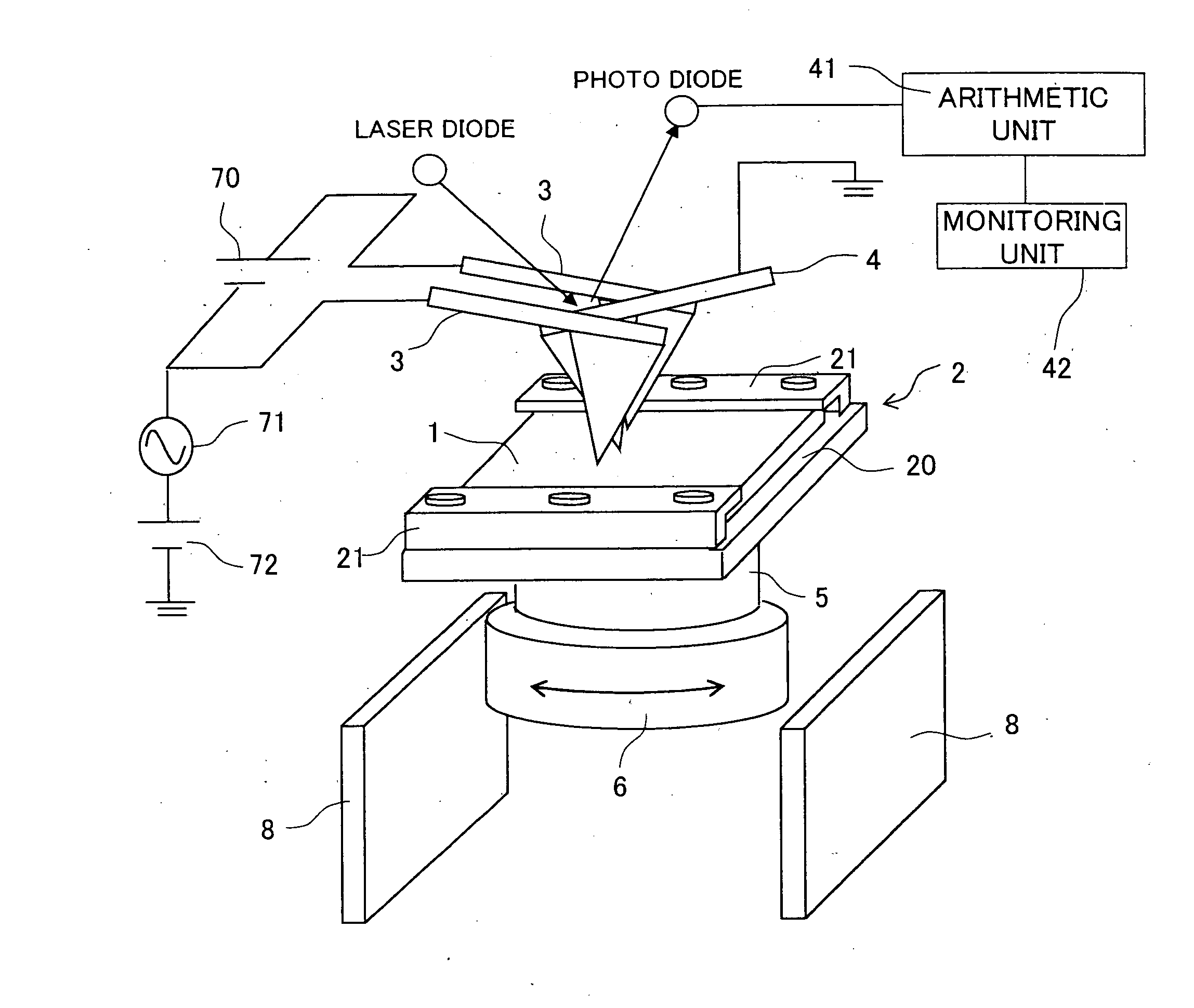
InactiveUS20080067374A1Slow exchangeIncrease freedomMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectronic statesElectron microscope
In a specimen analyzing apparatus such as a transmission electron microscope for analyzing the structure, composition and electron state of an observing specimen in operation by applying external voltage to the specimen to be observed, a specimen support (mesh) including a mesh electrode connectable to external voltage applying portions of the specimen and a specimen holder including a specimen holder electrode connectable to the mesh electrode and current inlet terminals as well are provided. Voltage is applied externally of the specimen analyzing apparatus to the external voltage applying portions of the specimen through the medium of the specimen holder electrode and mesh electrode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Quantum computation with quantum dots and terahertz cavity quantum electrodynamics
InactiveUS6988058B1Without significant qubit overheadQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCavity quantum electrodynamicsGate voltage
A quantum computer is proposed in which information is stored in the two lowest electronic states of doped quantum dots. Multiple quantum dots are located in a microcavity, and a pair of gates controls the energy levels in each quantum dot. A controlled NOT (CNOT) operations involving any pair of quantum dots can be effected by a sequence of gate voltage pulses which tune the quantum dot energy levels into resonance with frequencies of the cavity or a laser. The duration of a CNOT operation is estimated to be much shorter than the time for an electron to decohere by emitting an acoustic phonon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for calculating automobile condition by evaluating automobile condition indexes
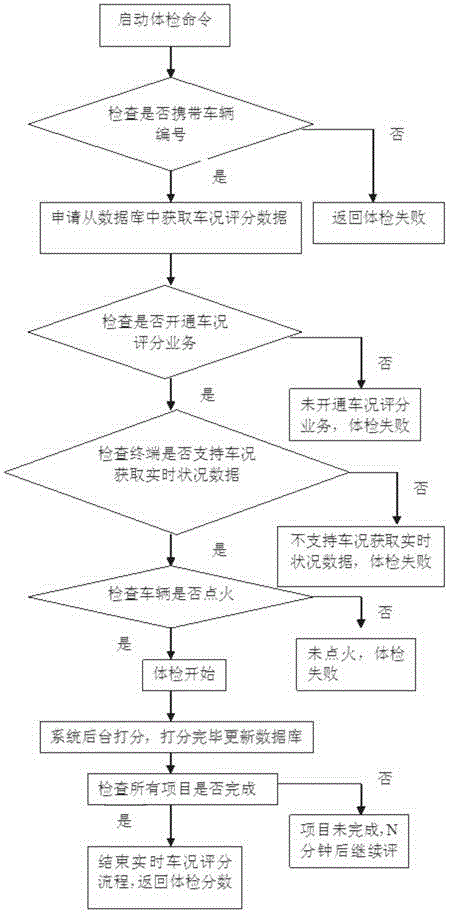
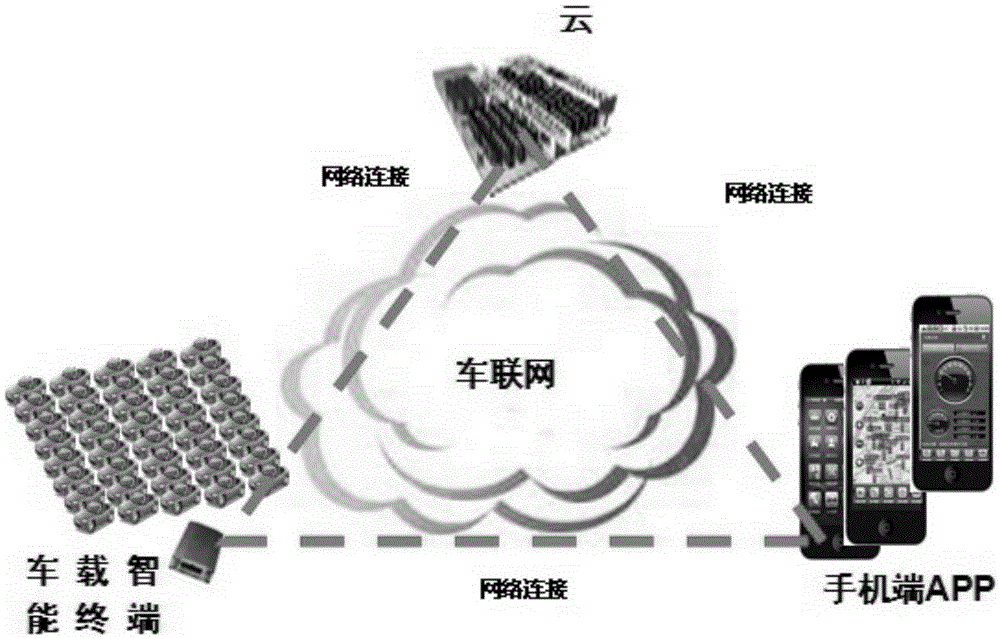
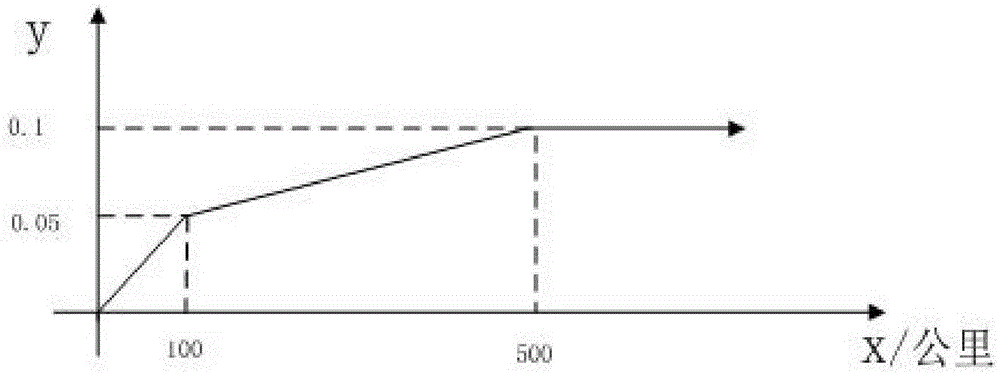
The invention discloses a method for calculating the automobile condition by evaluating the automobile condition indexes and belongs to the field of automobile management. According to the method, automobile intelligent terminal group identification (GID), a server cloud storage platform and a client terminal are included. According to the method, multiple indexes of the automobile performance are considered comprehensively, a specific formula is proposed, and the automobile condition is displayed on a cellphone client of an automobile networking terminal in a digital form. The method can be used for evaluating electronic states and conditions of automobiles so that a user can take corresponding improvement measures on account of automobile condition index scores and check the automobile health condition through a cellphone software APP. Fault information is displayed to the user, and the user can show the automobile condition scores on the cellphone platform of the automobile networking terminal and share the automobile condition with friends through the internet.
Owner:JIANGSU DIGITAL DNA TECH CO LTD
Method for femtosecond laser etching glass based on electronic dynamic regulation and control
The invention relates to a method for femtosecond laser etching glass based on electronic dynamic regulation and control and particularly relates to a method for scanning and modifying glass through femtosecond laser dipulse to improve the etching efficiency of a modified region, which belongs to the field of application technology of femtosecond laser. Traditional femtosecond laser is modulated to femtosecond laser dipulse to regulate and control the instant electronic state of a material so as to reinforce the modification degree and the modification uniformity of a femtosecond laser irradiation region to improve the etching efficiency of the irradiation region finally, and the etching efficiency of the modified region can be improved for multiple times compared with that of traditional femtosecond laser pulse.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Electronic status monitoring system for security containers
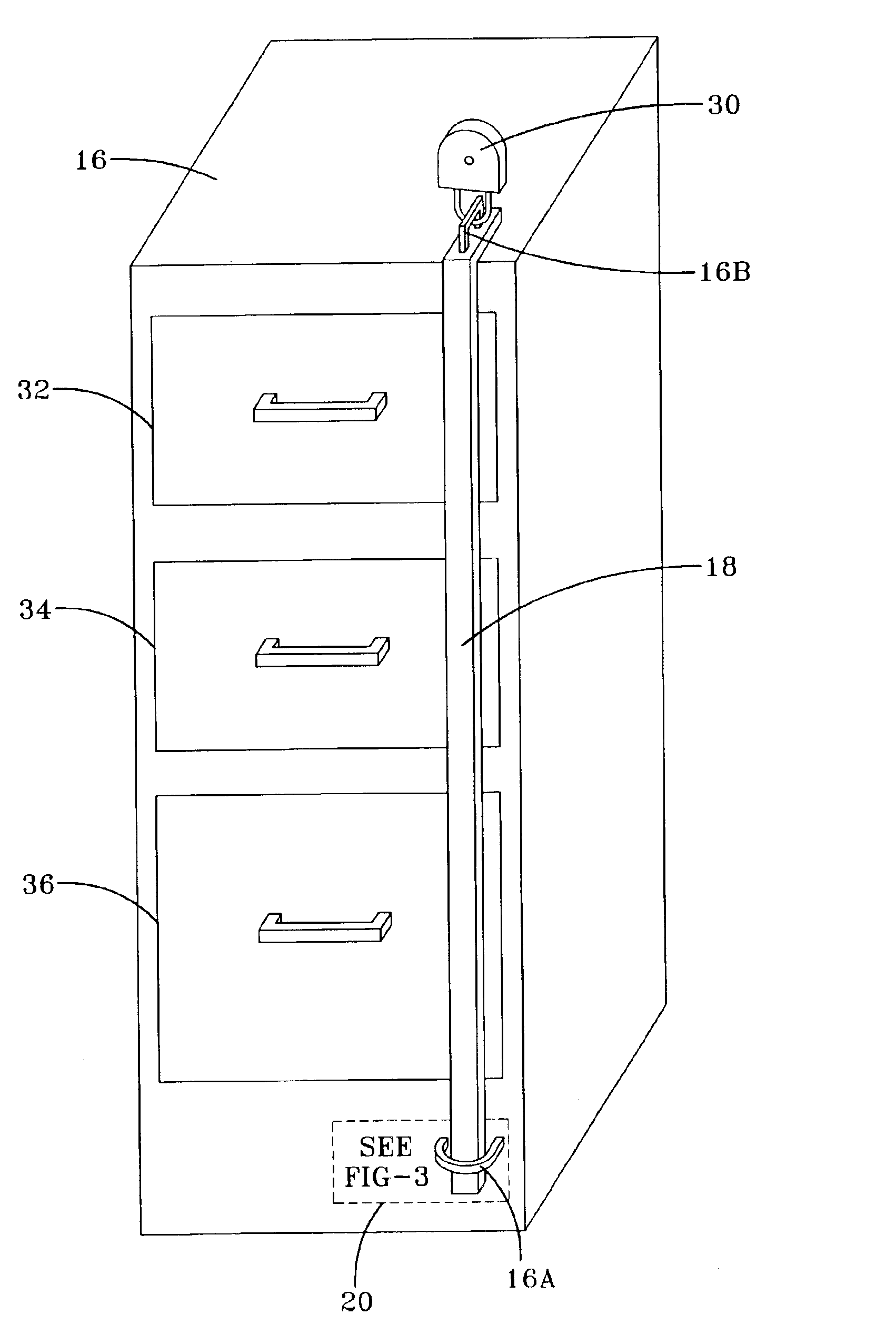
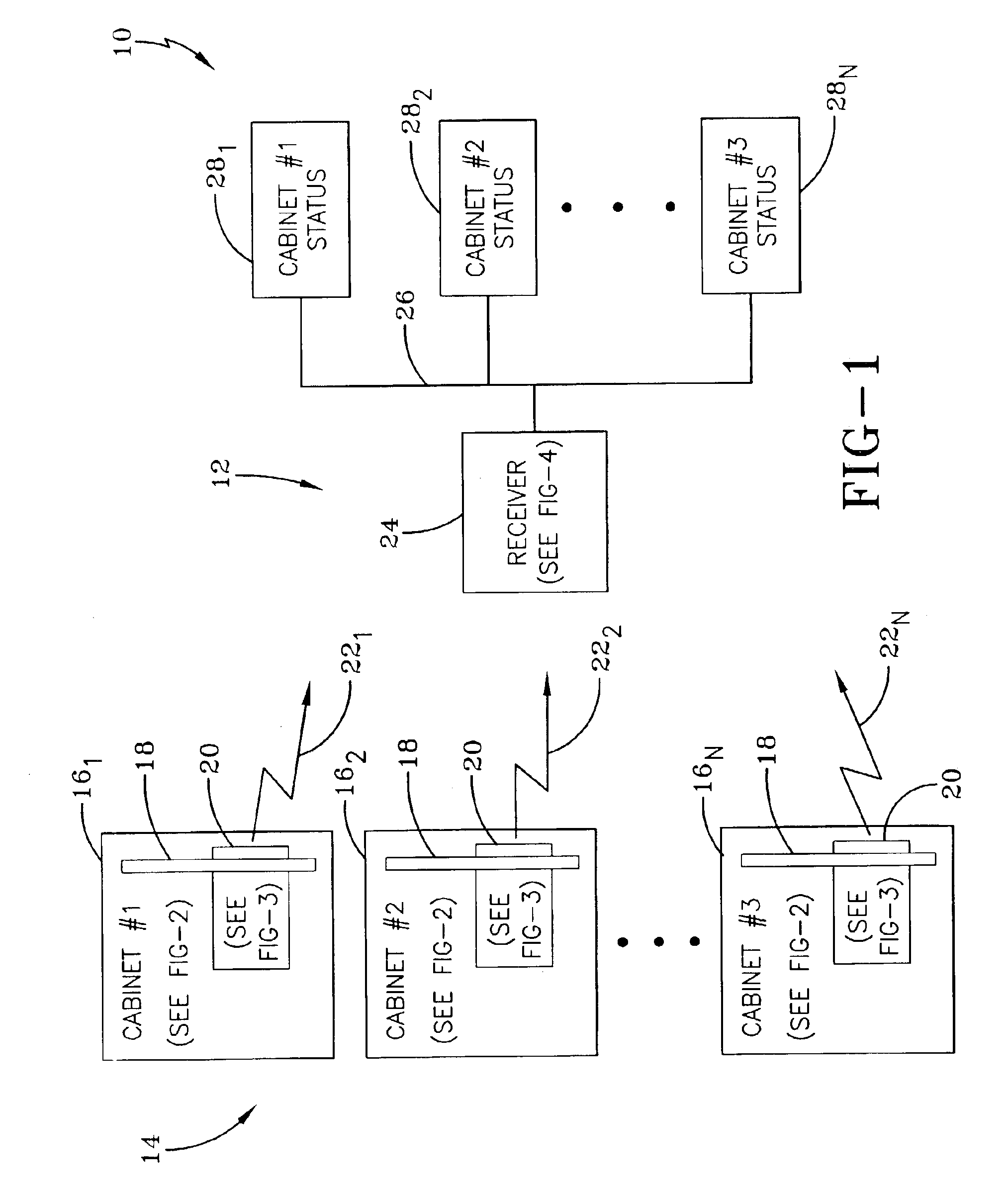
InactiveUS6921990B1High labor intensity costEnsure safetyBurglar alarm by openingBuilding locksClassified informationElectronic states
An electronic monitoring system is disclosed for detecting the open and closed conditions of containers or cabinets containing confidential or classified information. The electronic monitoring system includes a current sensor that detects the presence of a locking bar secured to the containers. A current sensor located on each cabinet operatively cooperates with the transmitter that transmits a signal to a central location, which provides an indicator of the secured or non-secured condition of the container.
Owner:NAVY THE US SEC
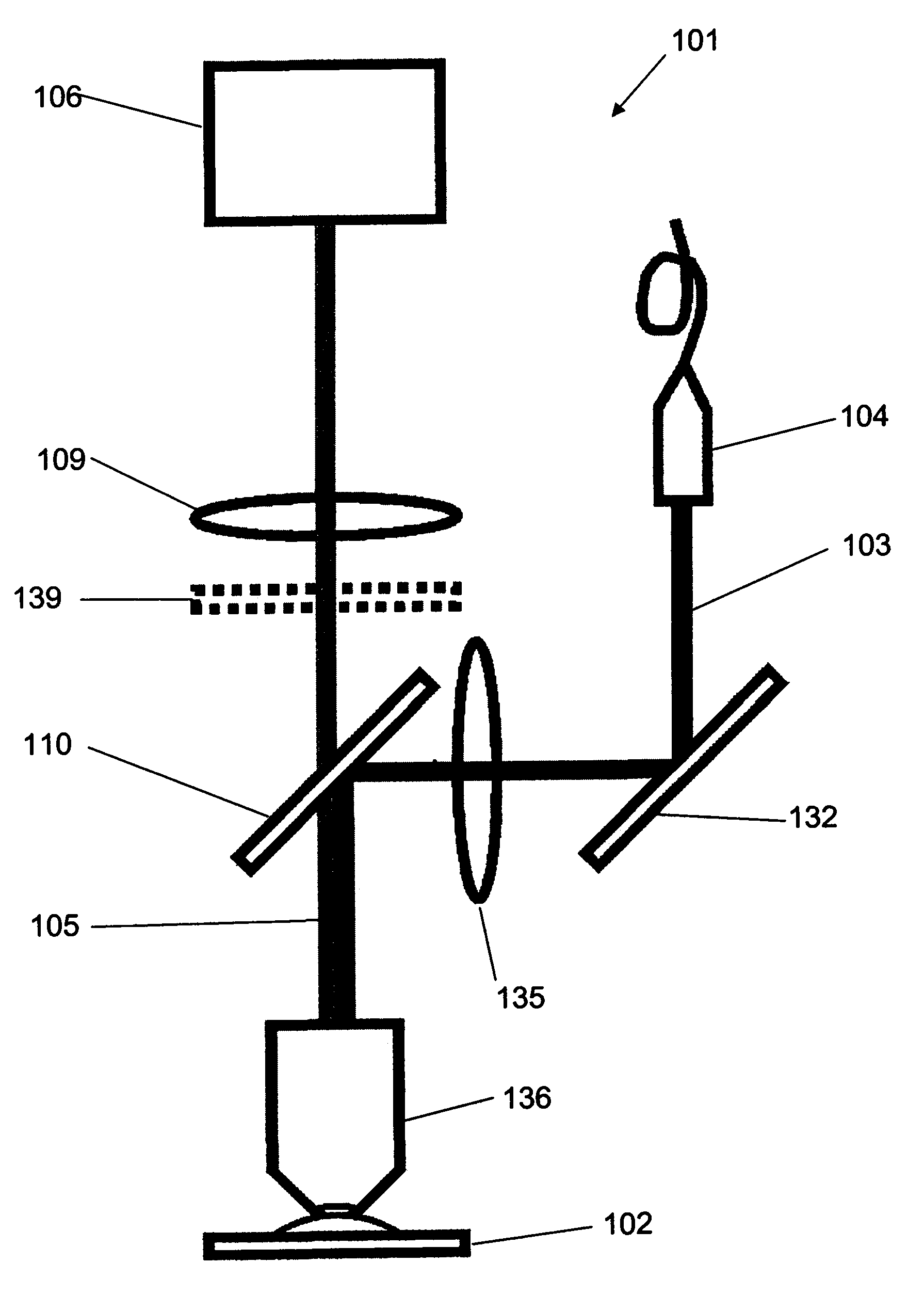
Method and device for optically measuring a sample
InactiveUS7719679B2High technical effortIncrease light intensityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElectronic statesOptical measurements
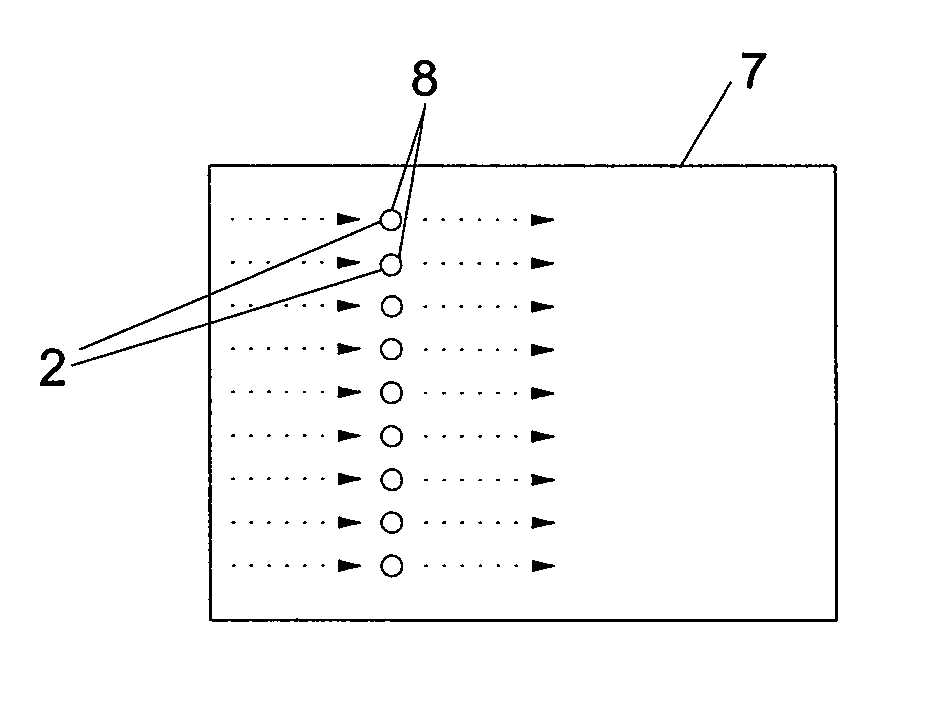
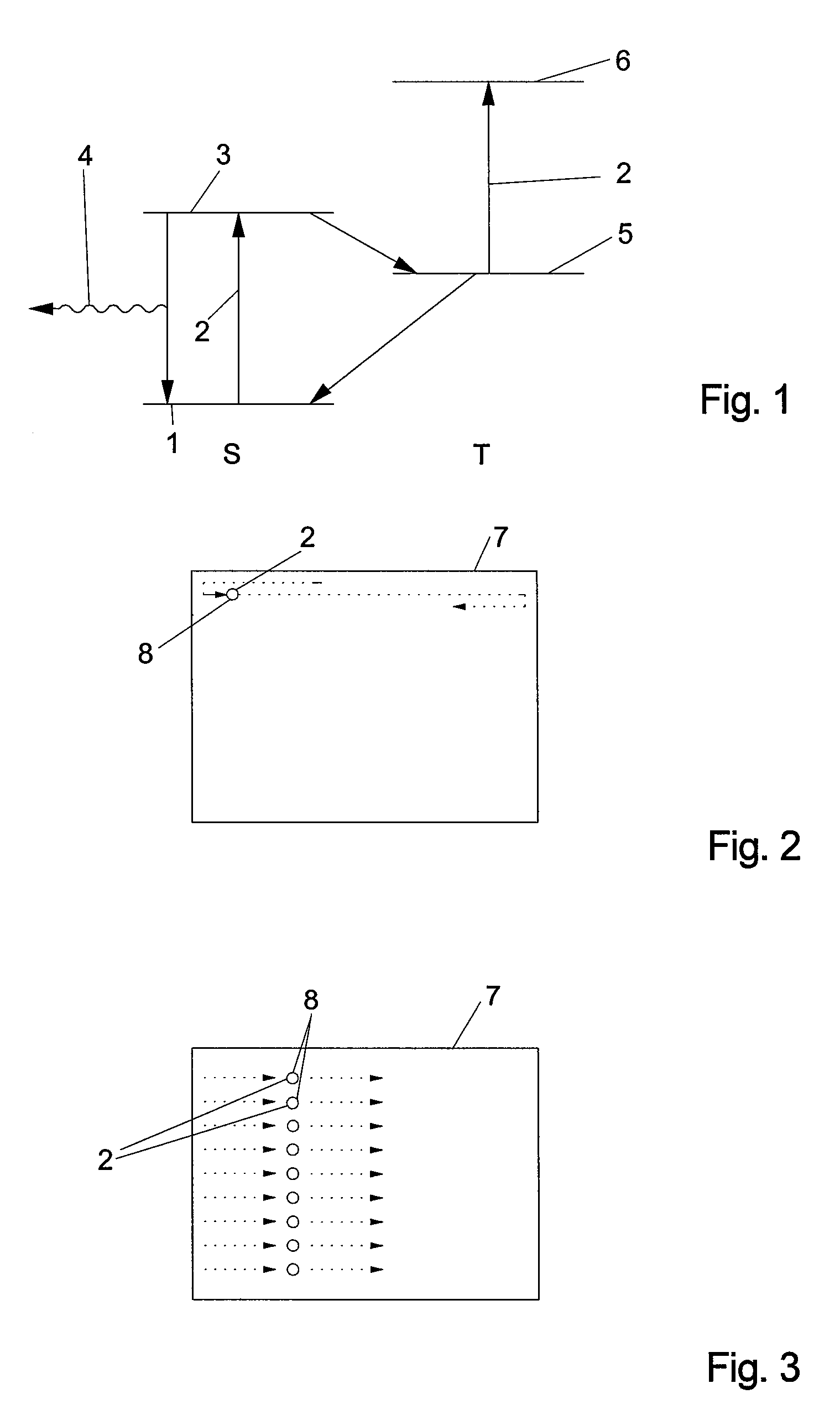
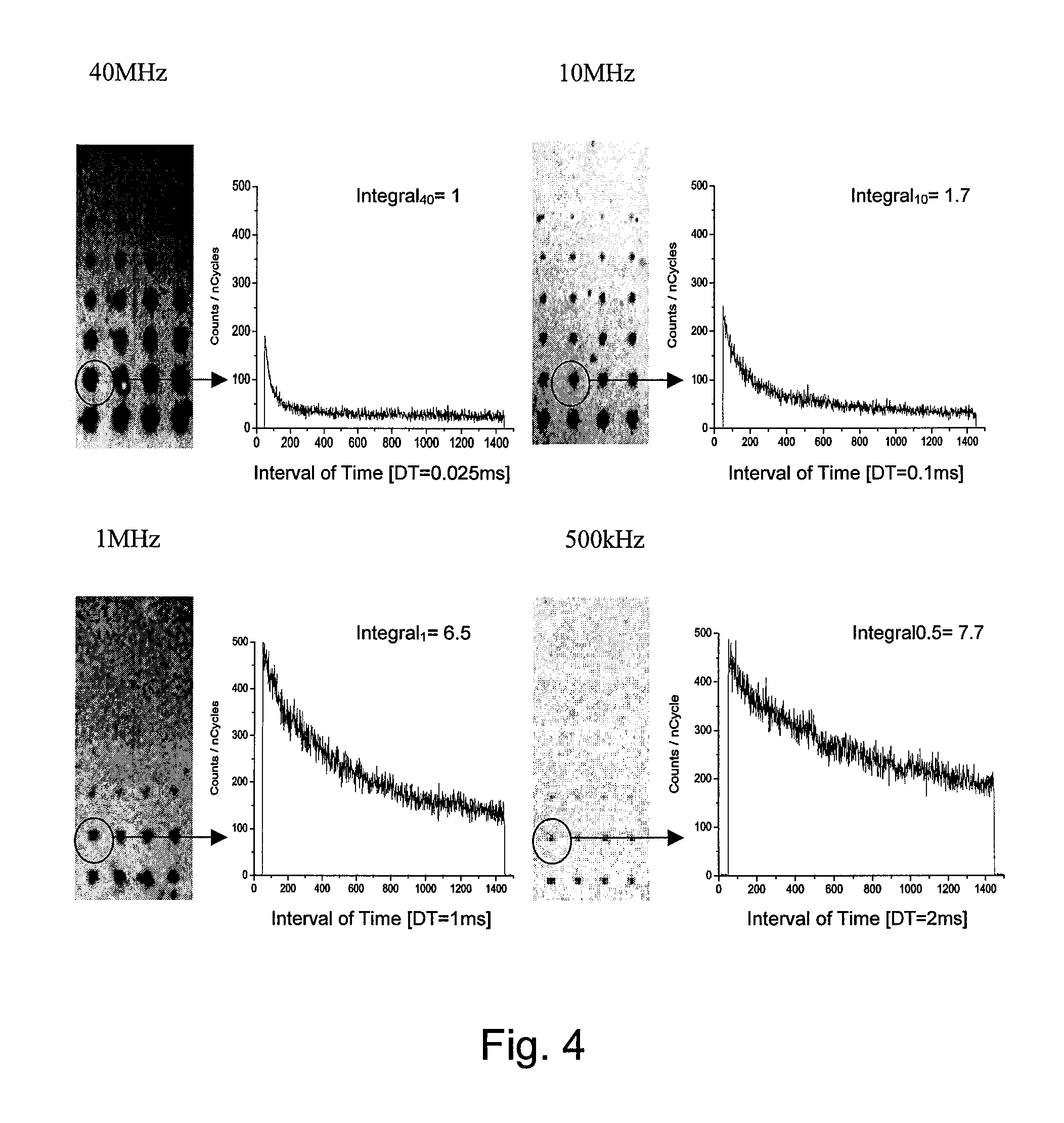
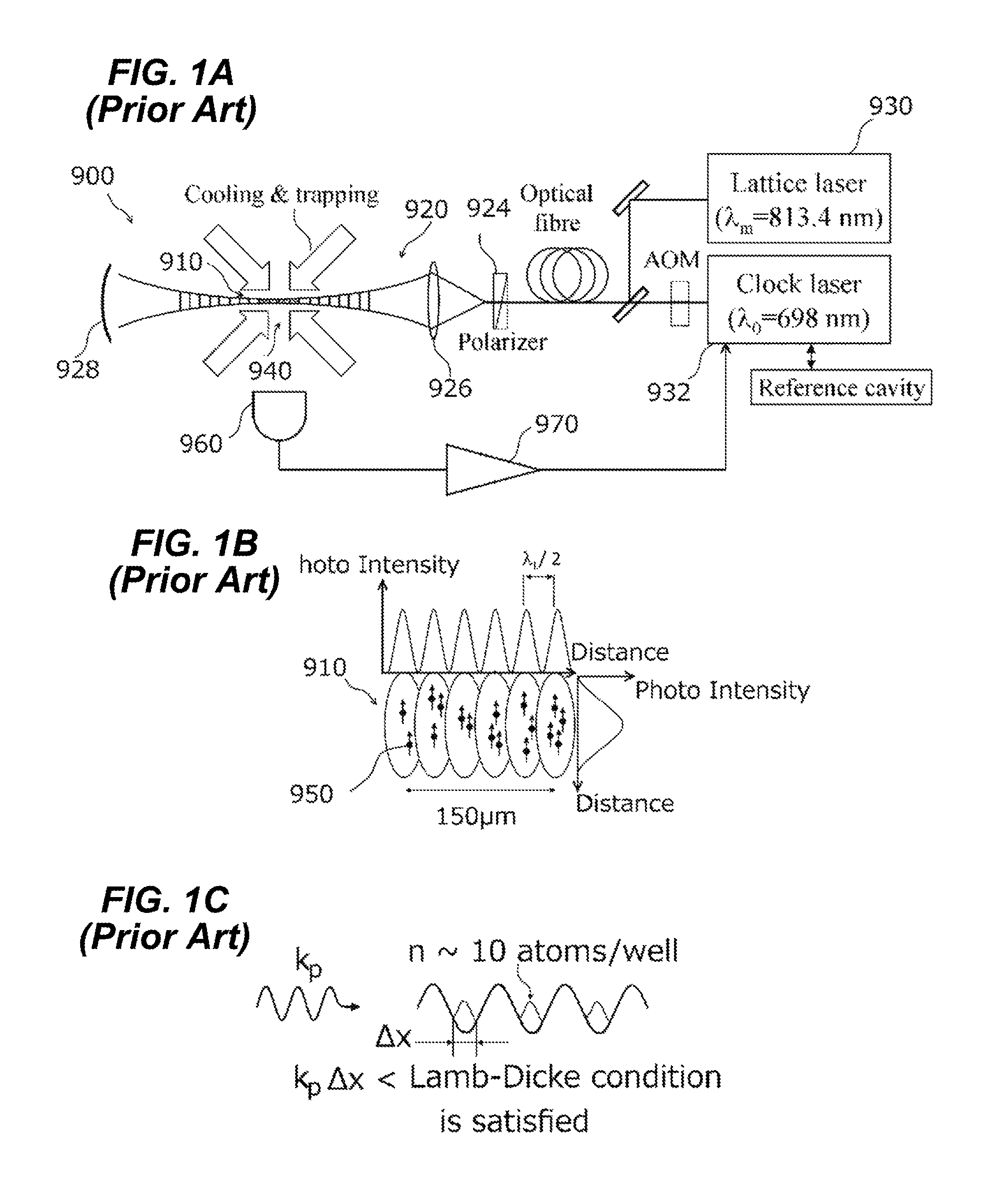
The inventive method for optically measuring a sample consists in temporarily repeatedly transmitting an electromagnetic signal (2) to the sample in such a way that a substance contained in the sample is transferred from a first electronic state (1) into a second electronic state (3), wherein at least one part of said substance in the second state (3) emits photons which are used for carrying out the optical measurement of the sample, the signal (2) is transmitted to the same sample area at a certain repetition interval and said repetition interval of the signal (2) is adjusted with a lifetime of the second state (3) of the substance having an order of magnitude of 1 ns on a value of at least 0.1 μs which is optimized with respect to photon yield from the substance.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
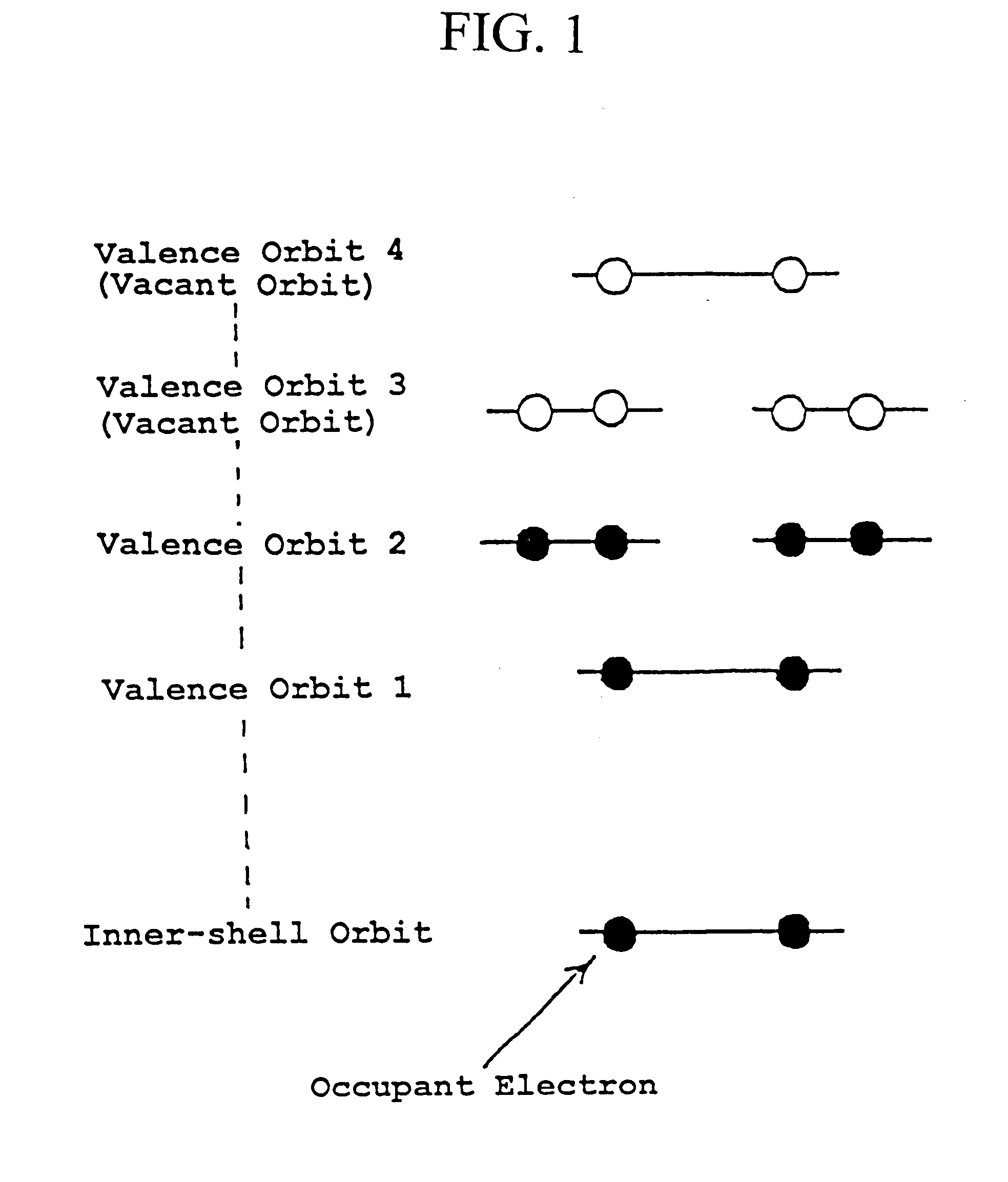
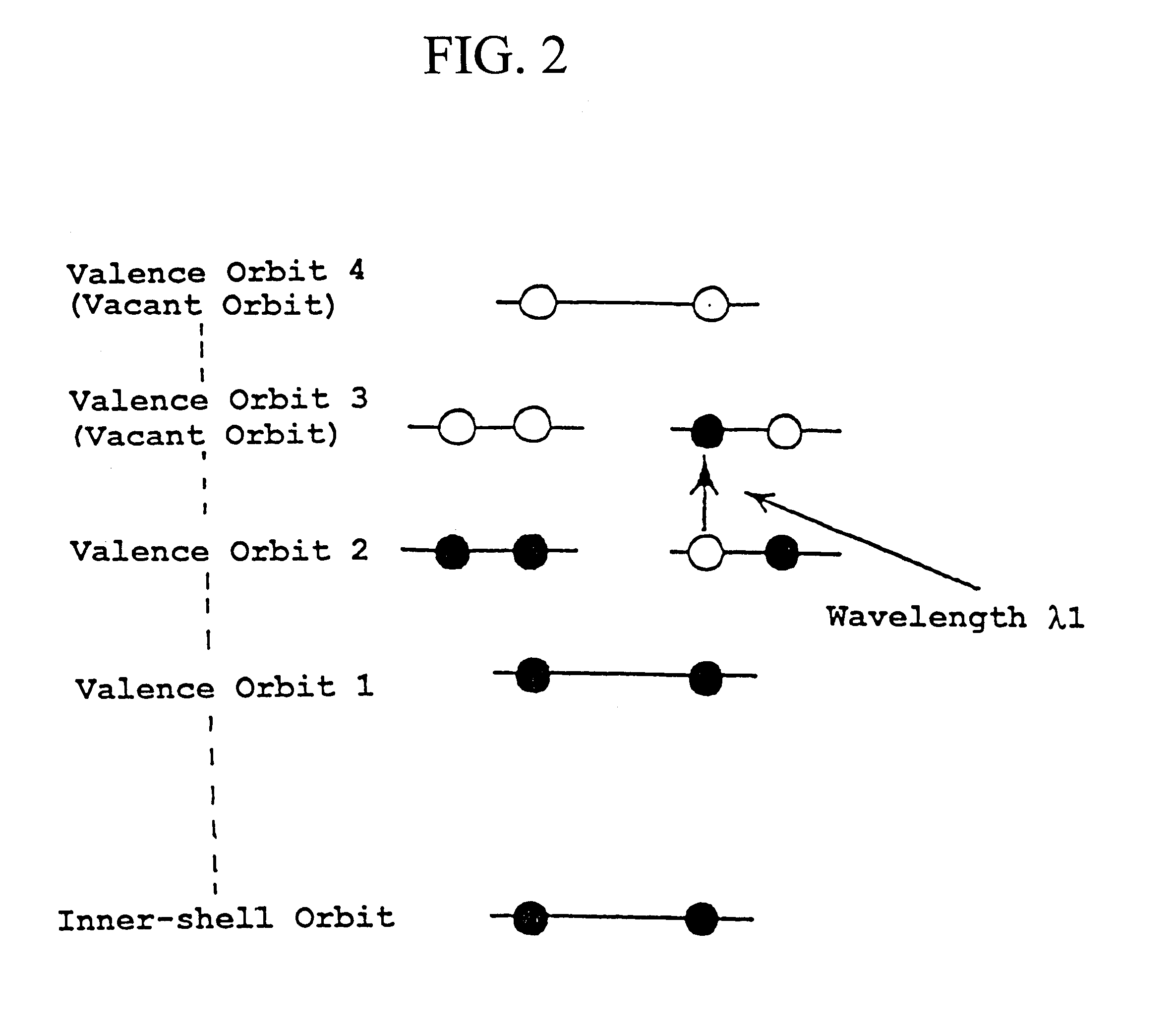
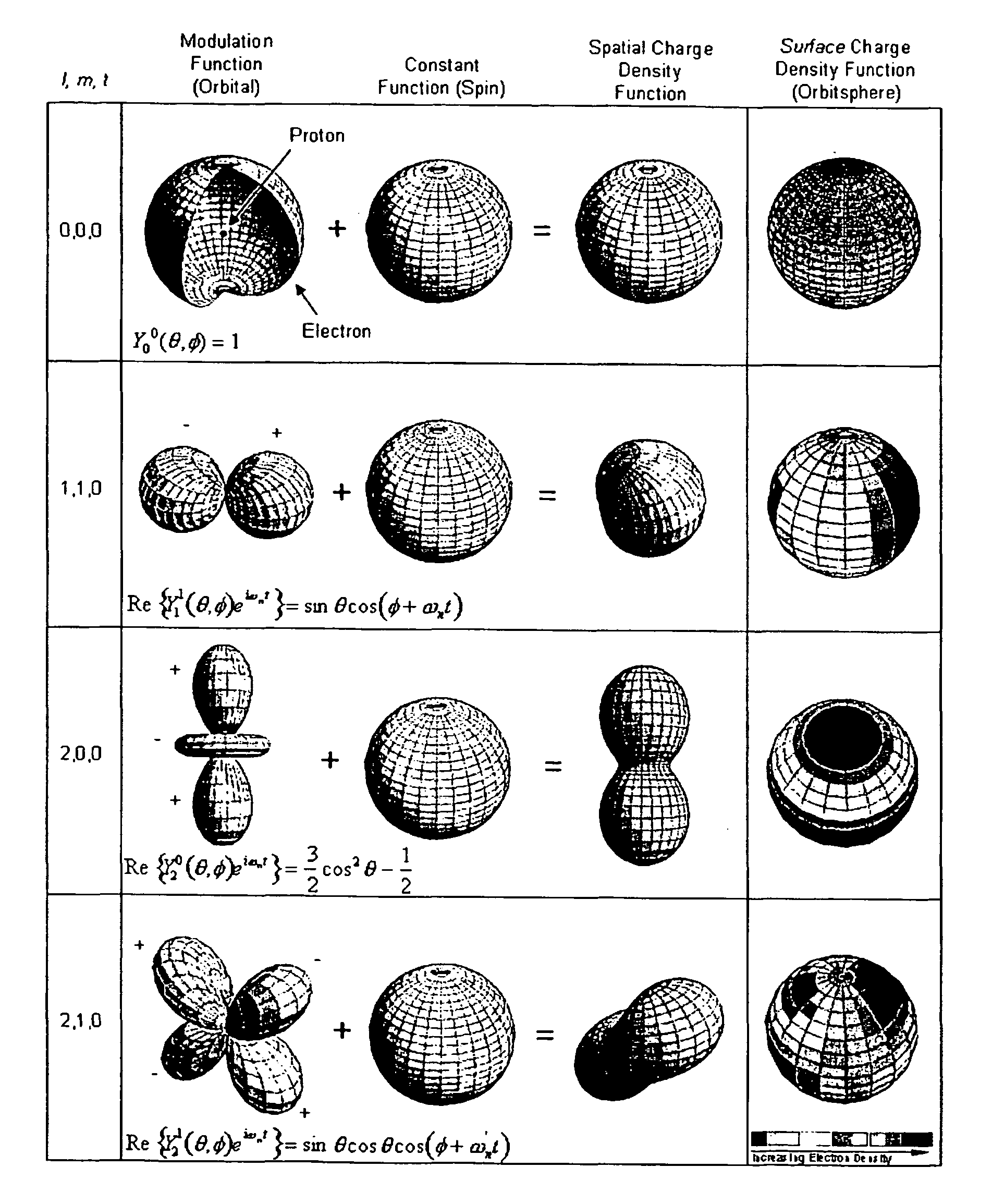
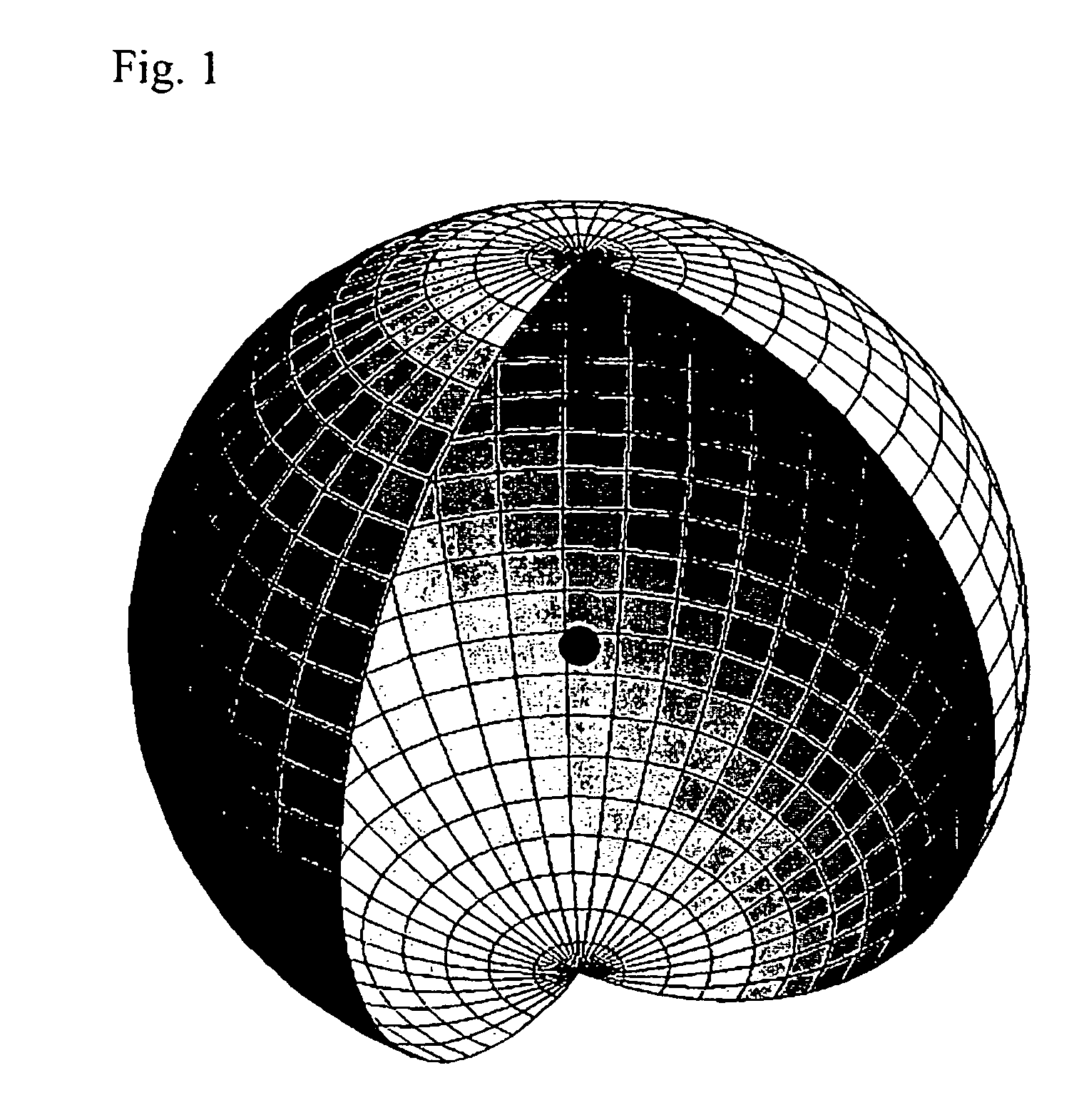
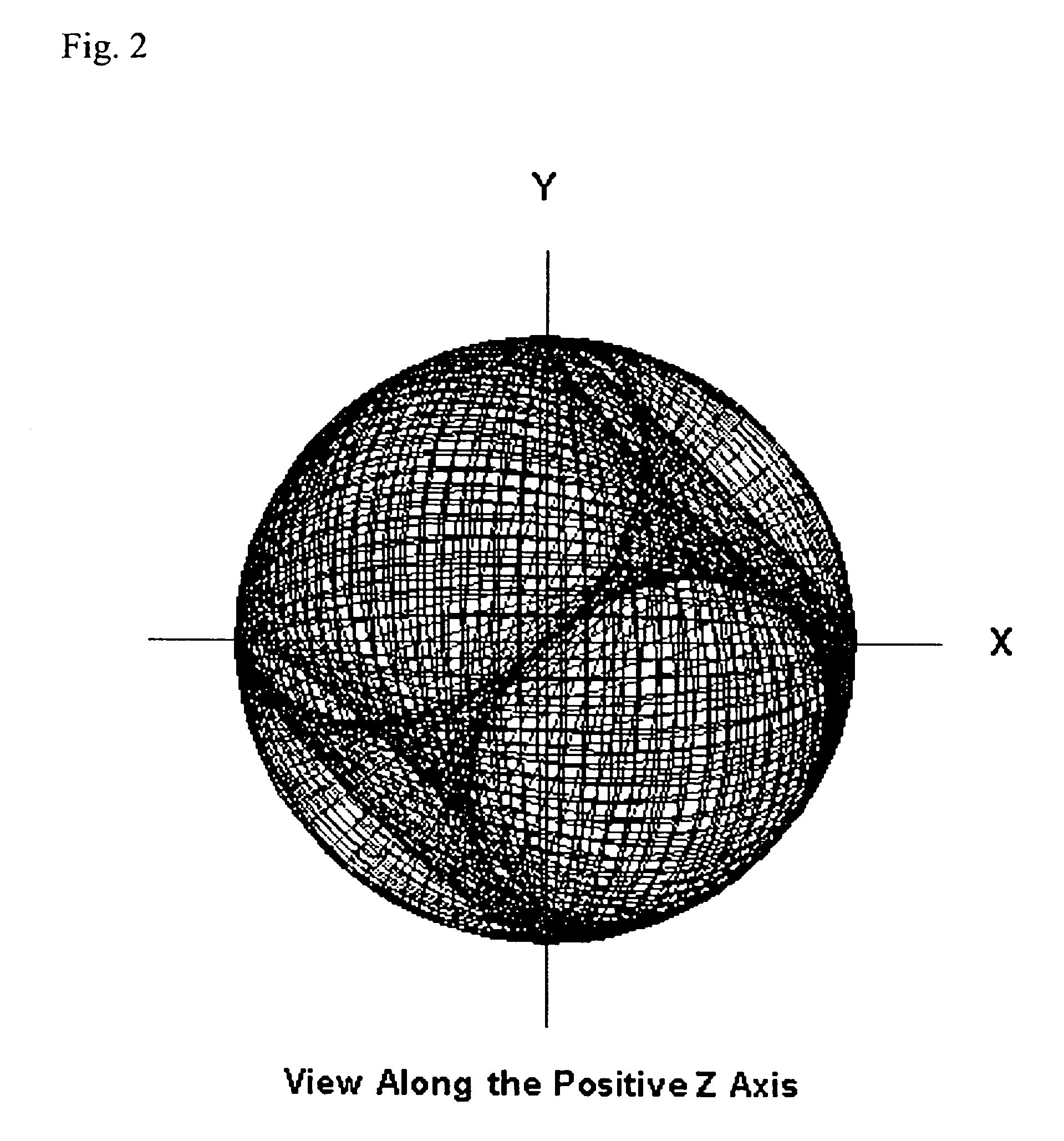
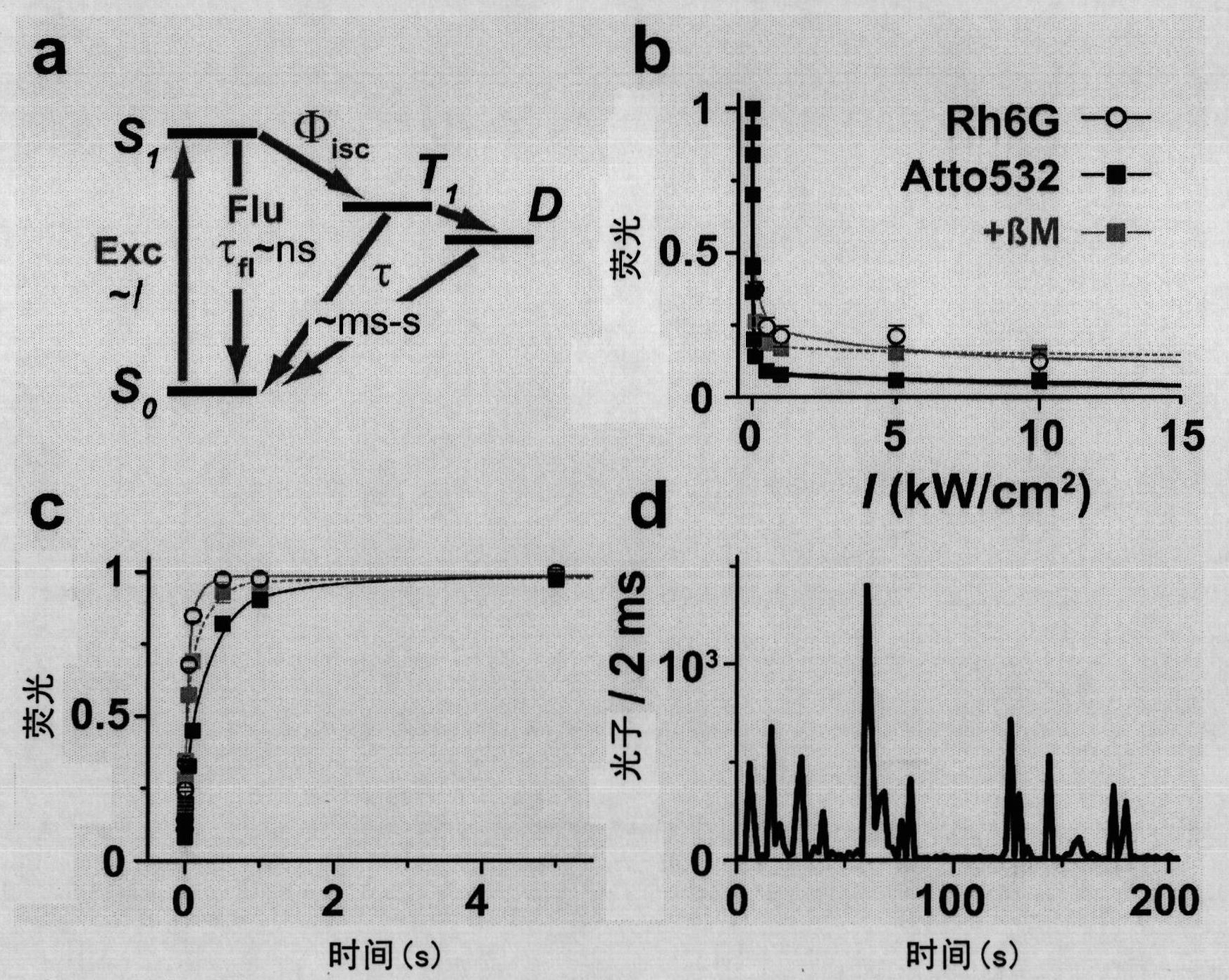
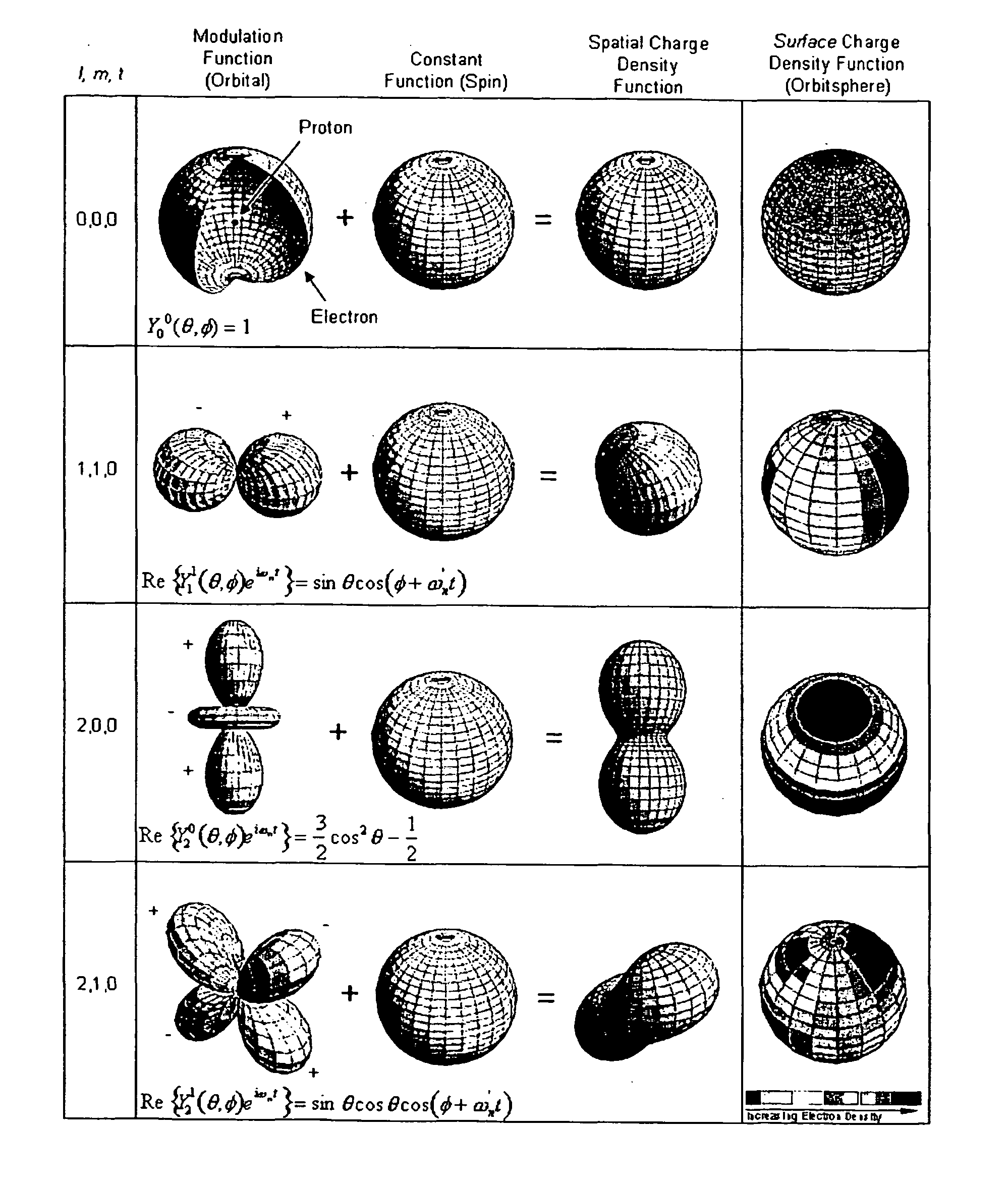
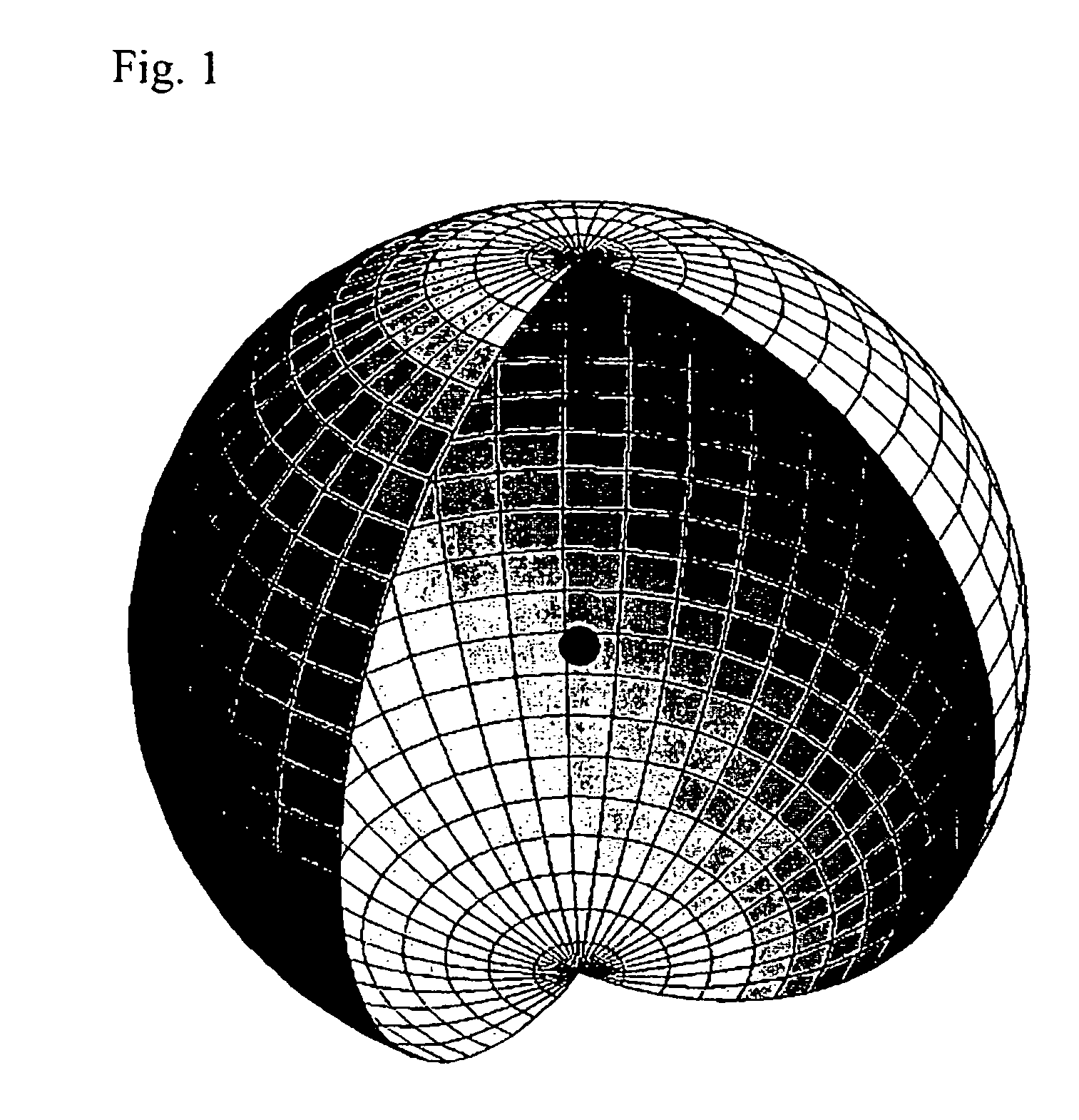
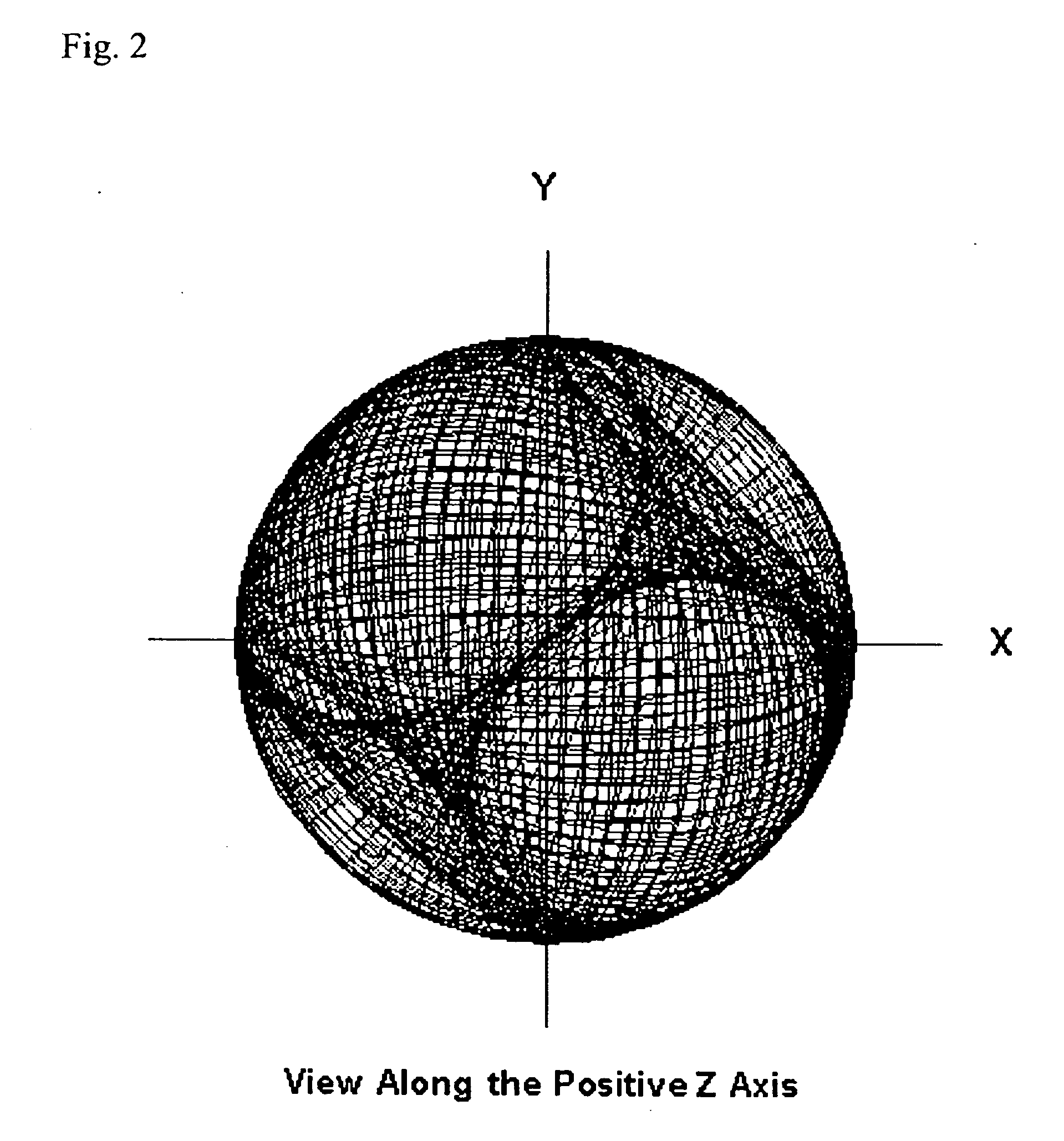
Method and system of computing and rendering the nature of the excited electronic states of atoms and atomic ions
InactiveUS7689367B2Chemical property predictionRadiation/particle handlingDisplay deviceMaxwell's equations
A method and system of physically solving the charge, mass, and current density functions of excited-state atoms and atomic ions using Maxwell's equations and computing and rendering the nature of excited-state electrons using the solutions. The results can be displayed on visual or graphical media. The display can be static or dynamic such that electron spin and rotation motion can be displayed in an embodiment. The displayed information is useful to anticipate reactivity and physical properties. The insight into the nature of excited-state electrons can permit the solution and display of those of other atoms and atomic ions and provide utility to anticipate their reactivity and physical properties as well as spectral absorption and emission to lead to new optical materials and light sources.
Owner:BRILLIANT LIGHT POWER
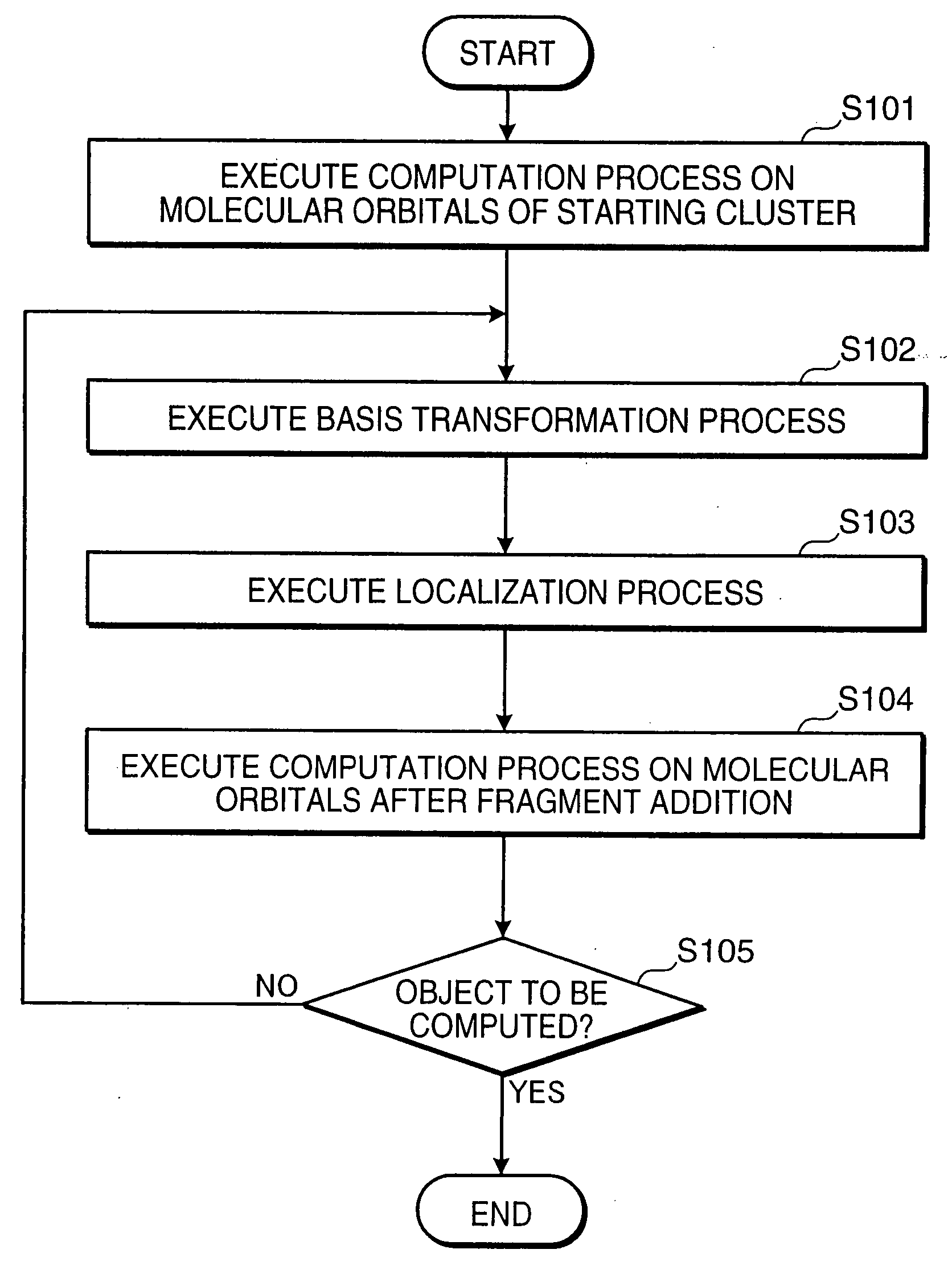
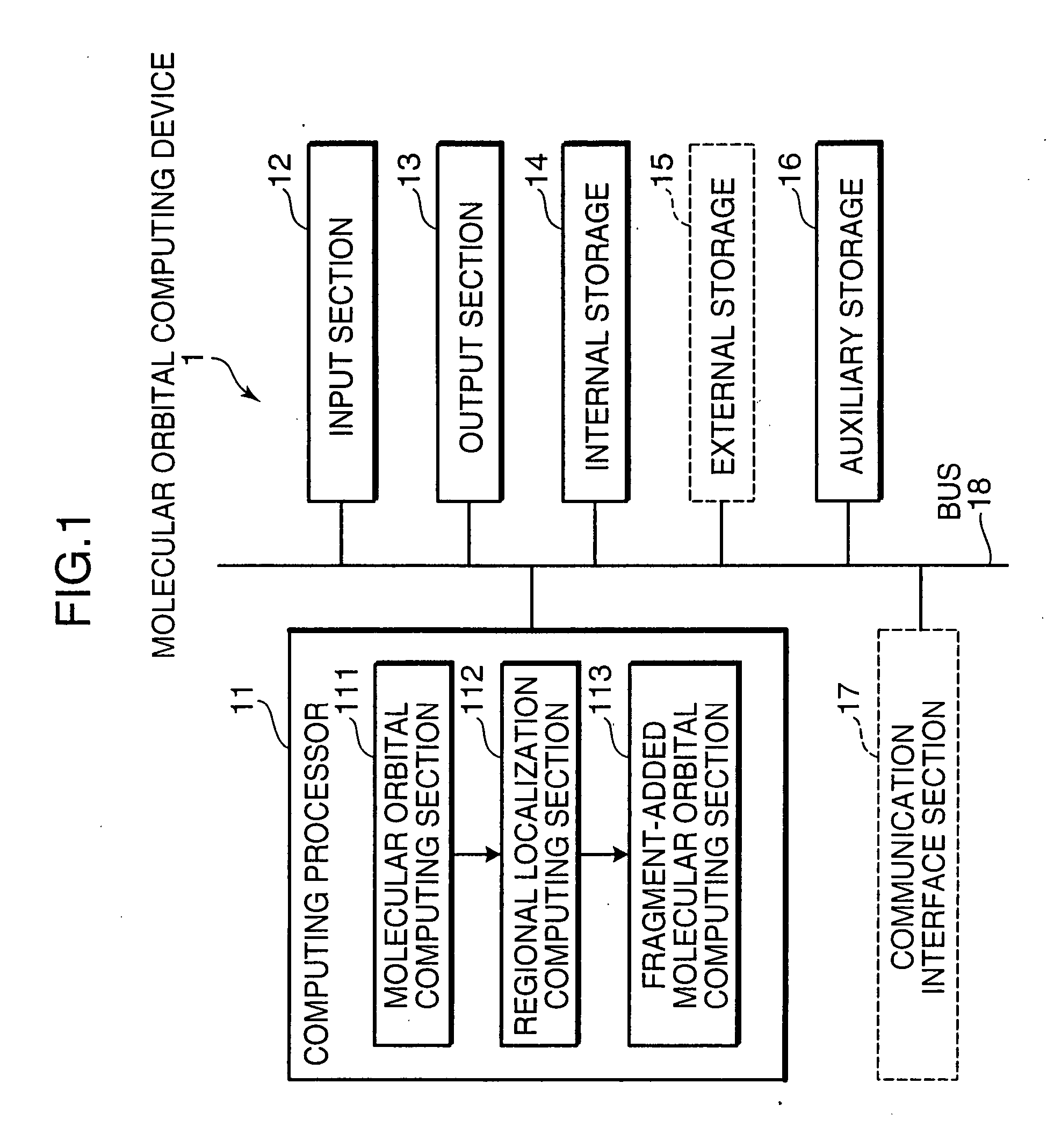
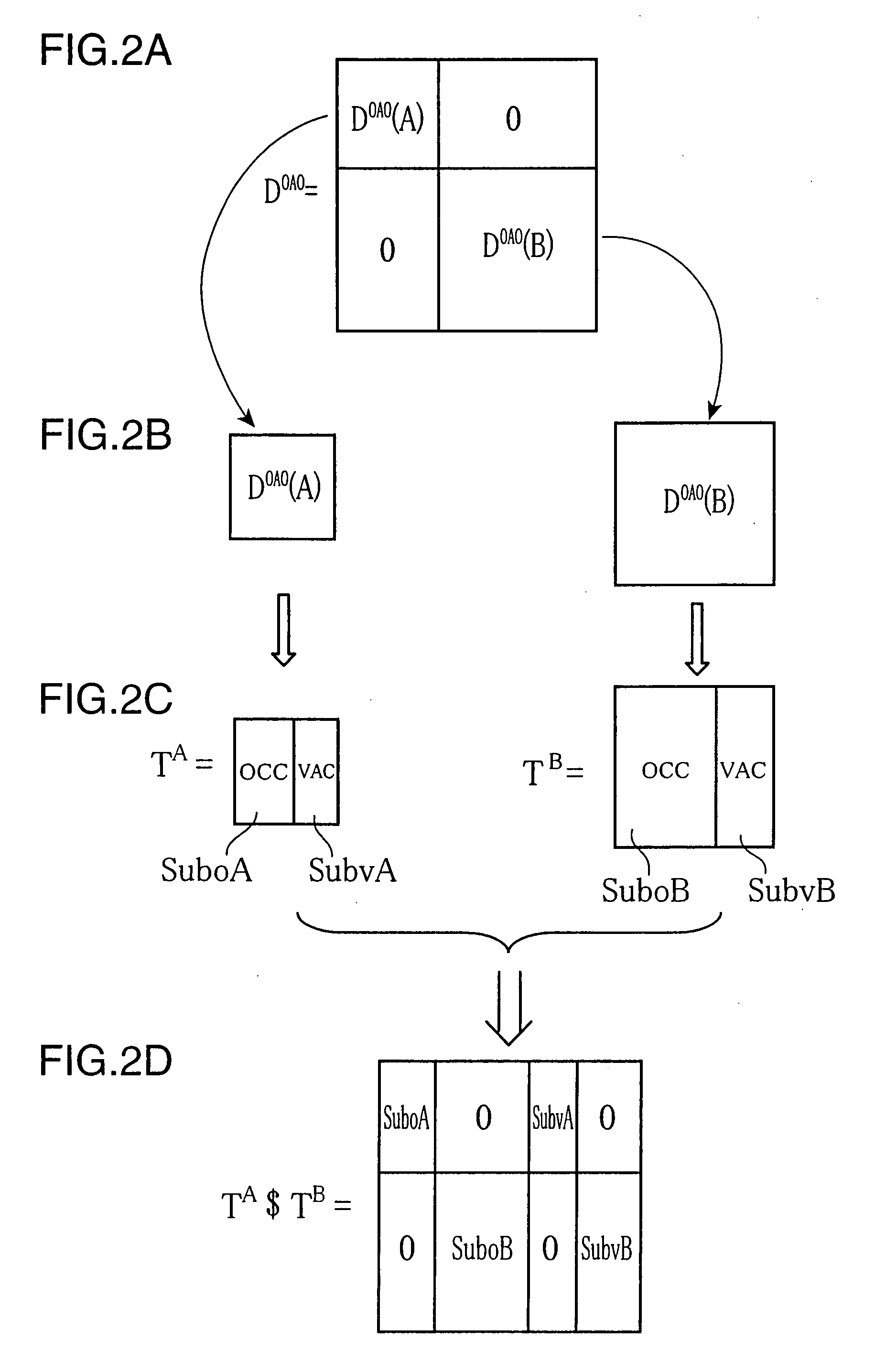
Molecular Orbital Computing Device for Elongation Method
InactiveUS20080059549A1Eliminate needHigh speed machiningAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational theoretical chemistryAtomic orbitalElectronic states
A molecular orbital computing device, method, program, and a recording medium recorded with the program, capable of computing electronic states at a high speed by an elongation method, are provided. A molecular orbital computing device (1) for determining molecular electronic states by the elongation method implements a localization process of transforming a canonical molecular orbital by an atomic orbital basis into a regional localized molecular orbital by using the formulas expressed by: YCMORLMO=CROCML+U CAORLMO=CAOCMOYCMORLMO where YCMORLMO is a transformation matrix for transforming into a regional localized molecular orbital by a canonical molecular orbital basis, CROCMO+ is a transpose matrix of a matrix representing a canonical molecular orbital by a regional atomic orbital basis, U is a transformation matrix for erasing elements in an off-diagonal block in a density matrix DRO by the regional atomic orbital basis by a Jacobi method, CAORLMO is a matrix representing a regional localized molecular orbital by the atomic orbital basis, and CAOCMO is a matrix representing the canonical molecular orbital by the atomic orbital basis.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
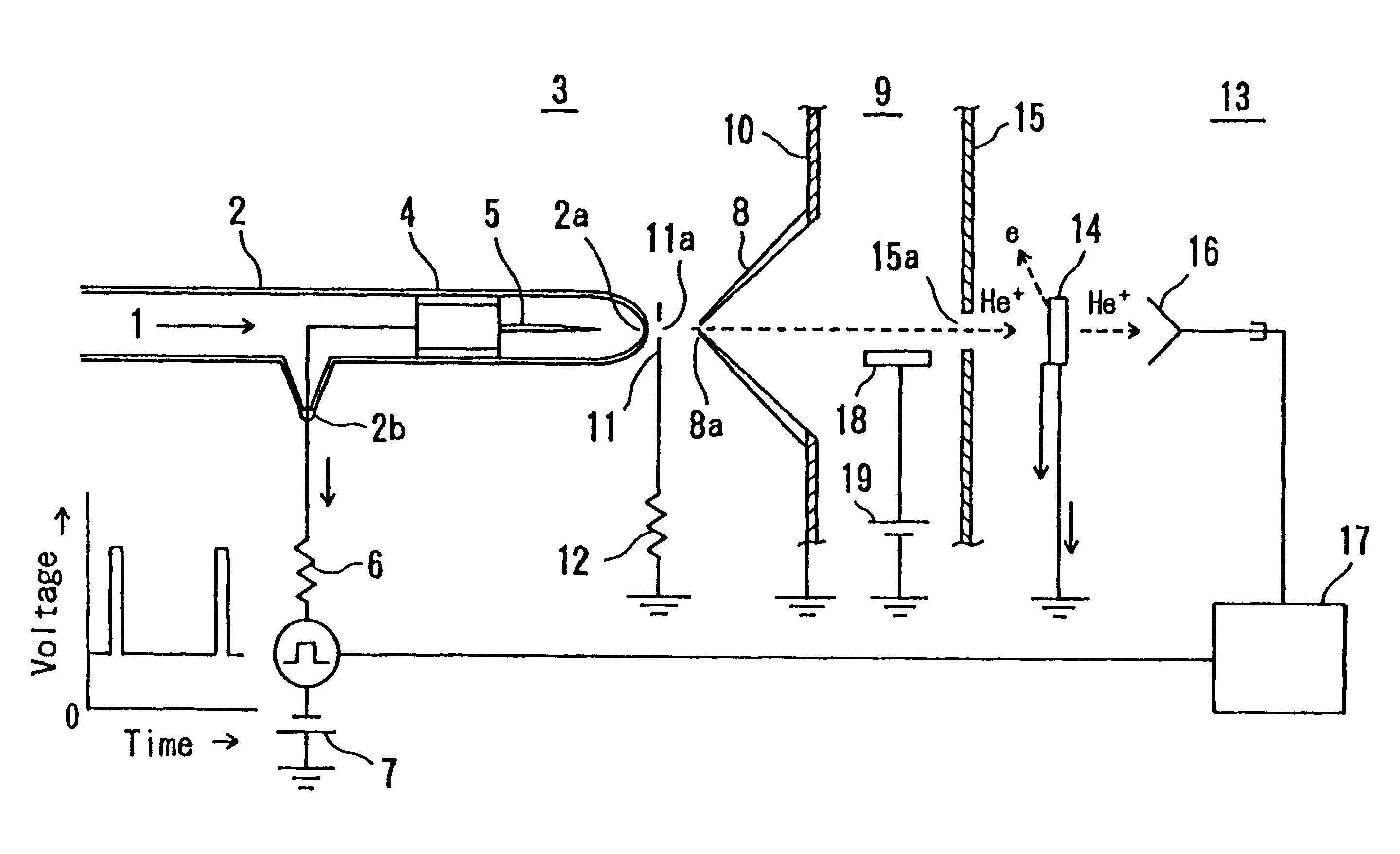
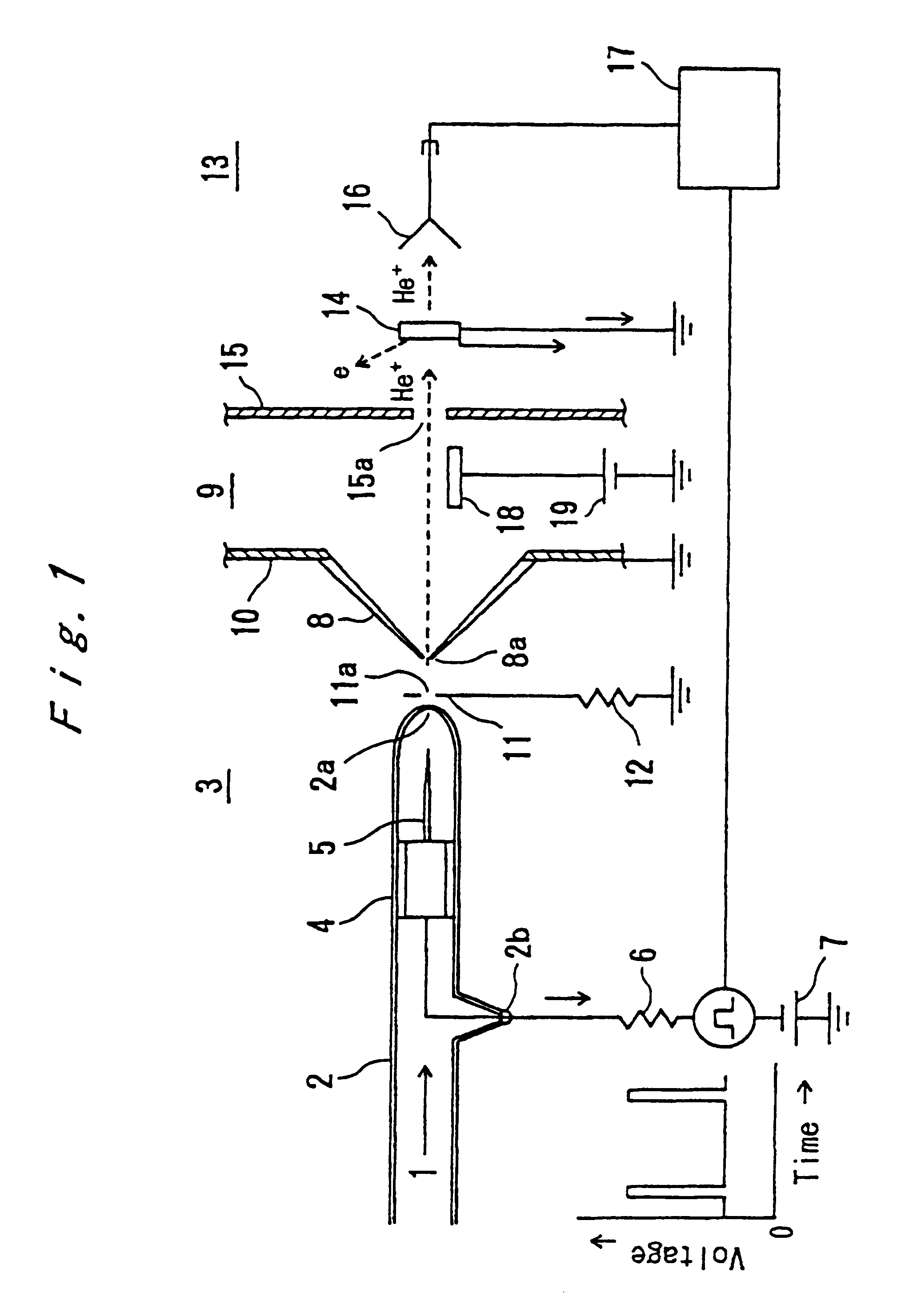
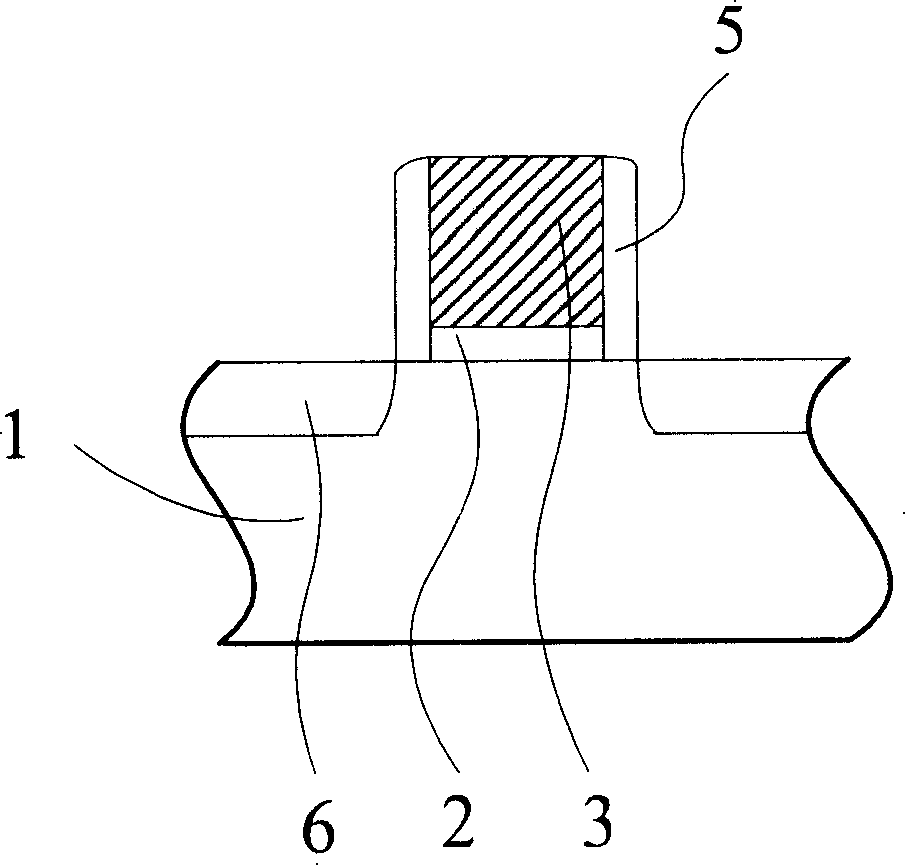
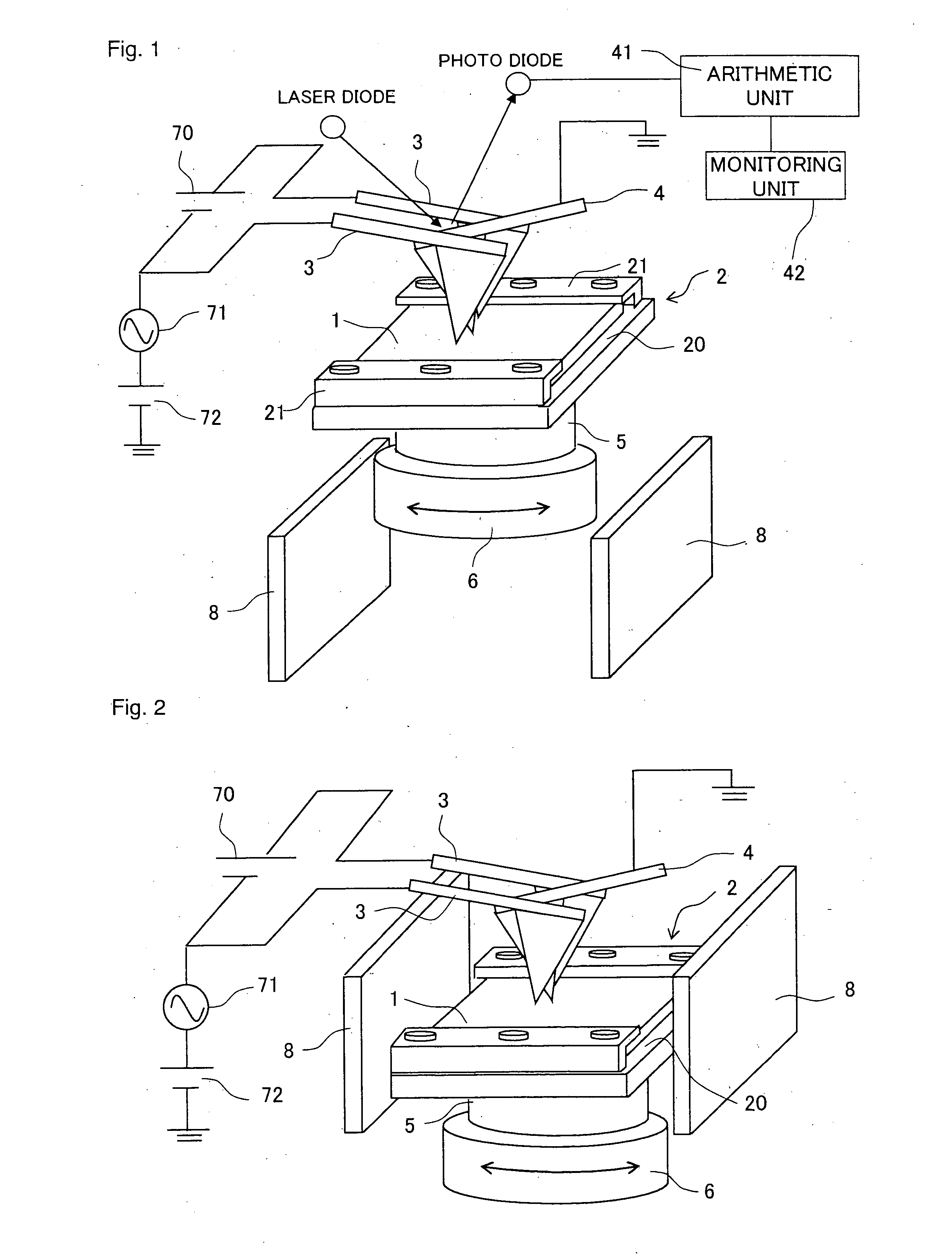
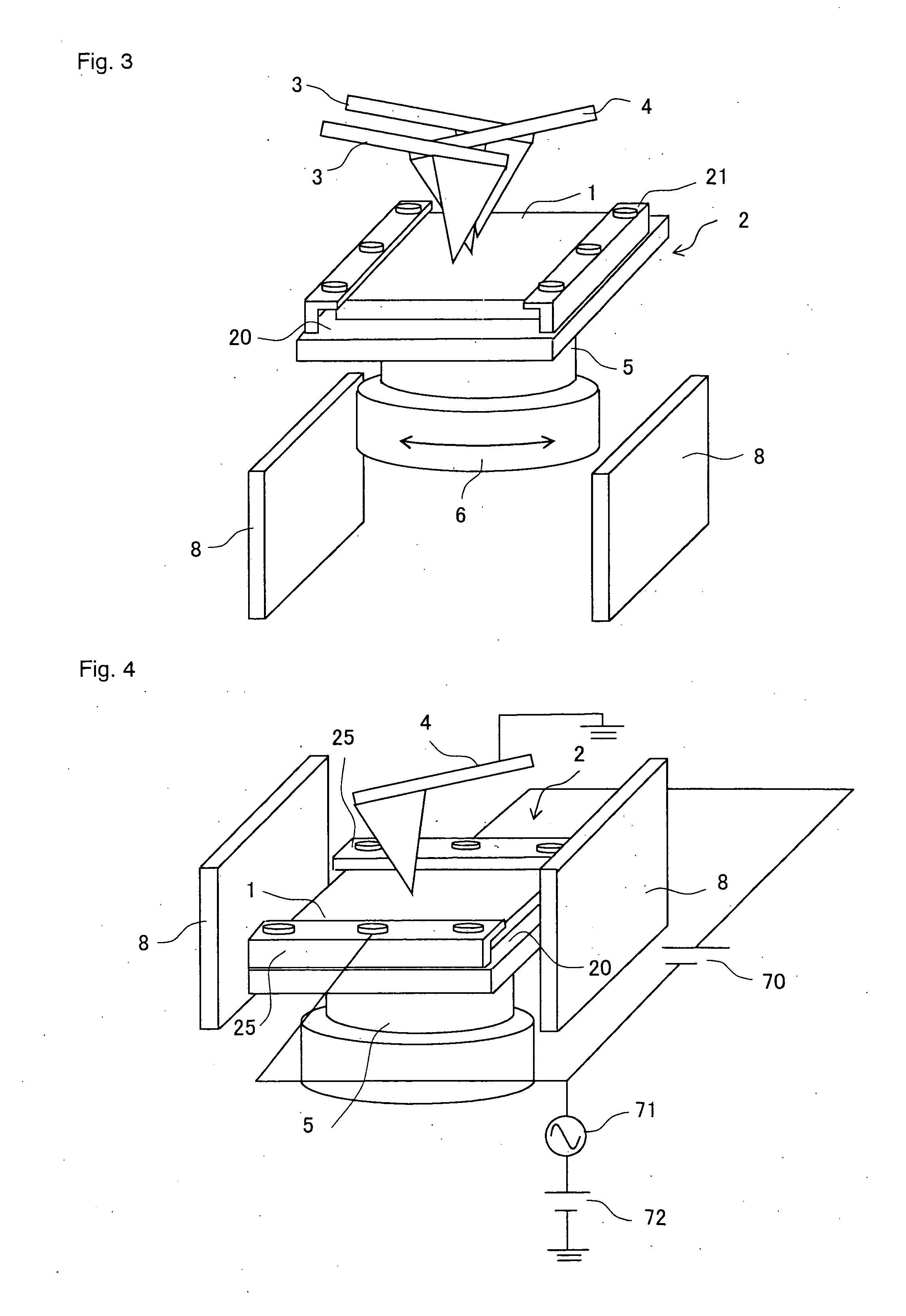
Method of generating a pulsed metastable atom beam and pulsed ultraviolet radiation and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6207951B1High strengthLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansChemical reactionElectronic states
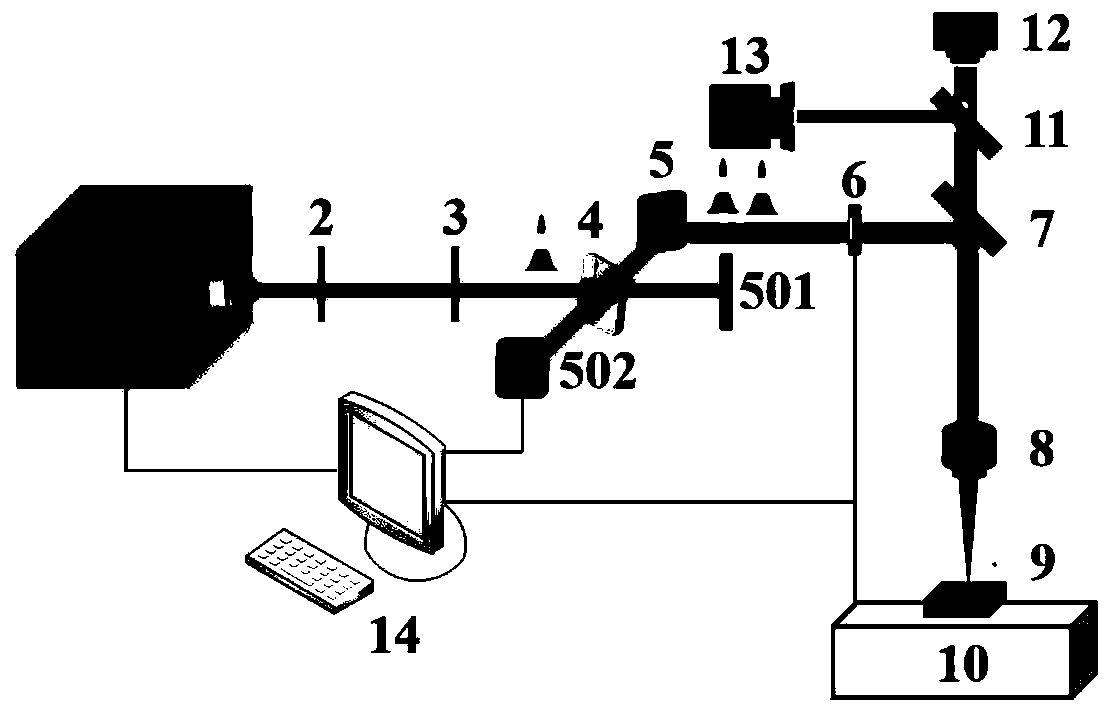
A pulse discharge is caused between an electrode in an insulating nozzle 2 jetting a gas in vacuum and a skimmer 8. An apparatus for performing the method includes an insulating nozzle 2 perforated with a gas jet hole 2a at a front end thereof and having a needle-like electrode 5 at an inside thereof, and includes a skimmer 8 formed in a funnel-like shape and having an opening portion 8a at a front end thereof. The opening 8a is arranged at a position remote from the gas jet hole 2a of the insulating nozzle 2 by a predetermined distance. The method and apparatus can be used in the field of measurement, material synthesis and the like with an object of surface science, and can form simultaneously and with high intensity both pulsed metastable atom beam and pulsed ultraviolet radiation which can be preferably used as a probe for investigating the electronic state at a surface of a substance and several layers on the inner side of the surface. It can also preferably be used for removing contamination or for depositing materials on the surface of a substrate by surface chemical reaction.
Owner:NATIONAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR METALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY AGENCY
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS9287356B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:NANTERO
Differential photochemical and photomechanical processing
The present invention relates to the process of selectively exposing matter to a specific wavelength of electromagnetic energy in sufficient flux density per wavelength to cause or promote a desired effect. The process includes, but is not limited to, destroying, disinfecting, denaturing, disinfesting, disrupting, or dehydration of one or more of the substances present. More specifically, present invention relates to subjecting matter, which may contain a mixture of substances, to electromagnetic energy, in concurrence with its spectral properties to exploit the spectral differences within the substance or within a mixture of substances. Energies are applied to cause wavelength-dependent reactions resulting from differential absorption; this additional applied energy manifests itself in changes, or quantum transitions, in the vibrational, rotational, magnetic, and electronic states of the molecules. Generally, the process utilizes wavelengths from about one light second to about ten electron volts, or wavelengths with energy levels less than that of ionization.
Owner:PHOTOMETICS
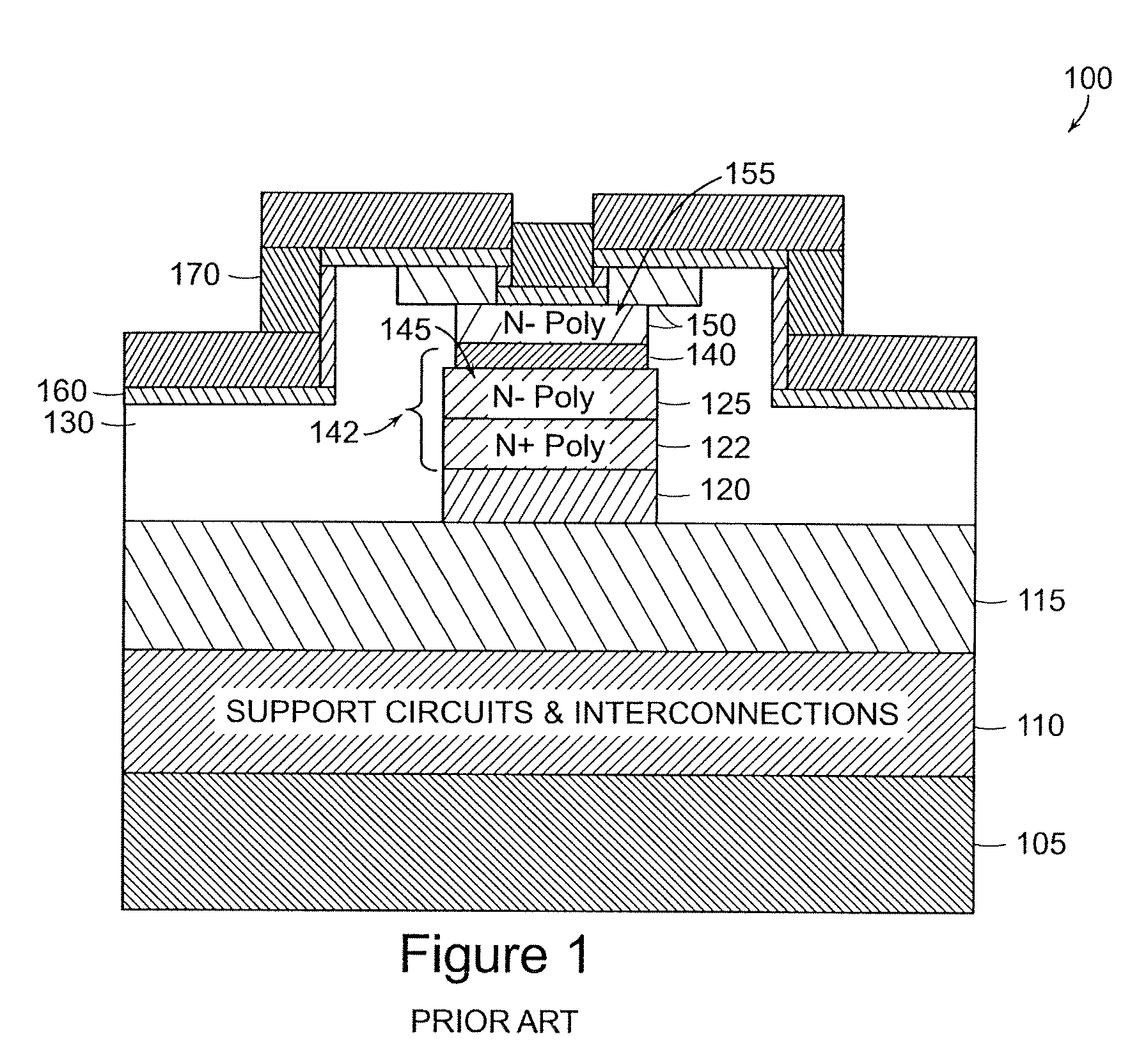
Semiconductor device and producing method thereof
ActiveCN101211970AReduce contact resistanceDopant ion concentration changesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGate dielectricEngineering
The invention relates to a semiconductor apparatus comprising a semiconductor substrate, a gate dielectric layer positioned on the semiconductor substrate, a gate positioned on the gate dielectric layer as well as a source cathode and a drain positioned between the two sides of the dielectric layer in the semiconductor layer. The semiconductor apparatus also comprises a joint interface layer extending along the surface of the source cathode and drain and the joint interface layer extending along the gate surface. The joint interface layers insulate and isolate with the gate dielectric layer. The joint interface layers of the semiconductor apparatus contain doping interface providing a continuous electronic states which can complete the electron transmission under low effect of a electric field, thus reducing the contact desistence between the semiconductor and the joint metal of the contact hole. The apparatus just needs the connection between the super thin doping interface layer and the metal layer so as to further reduce the size of the semiconductor apparatus and increase the density of the semiconductor apparatus.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
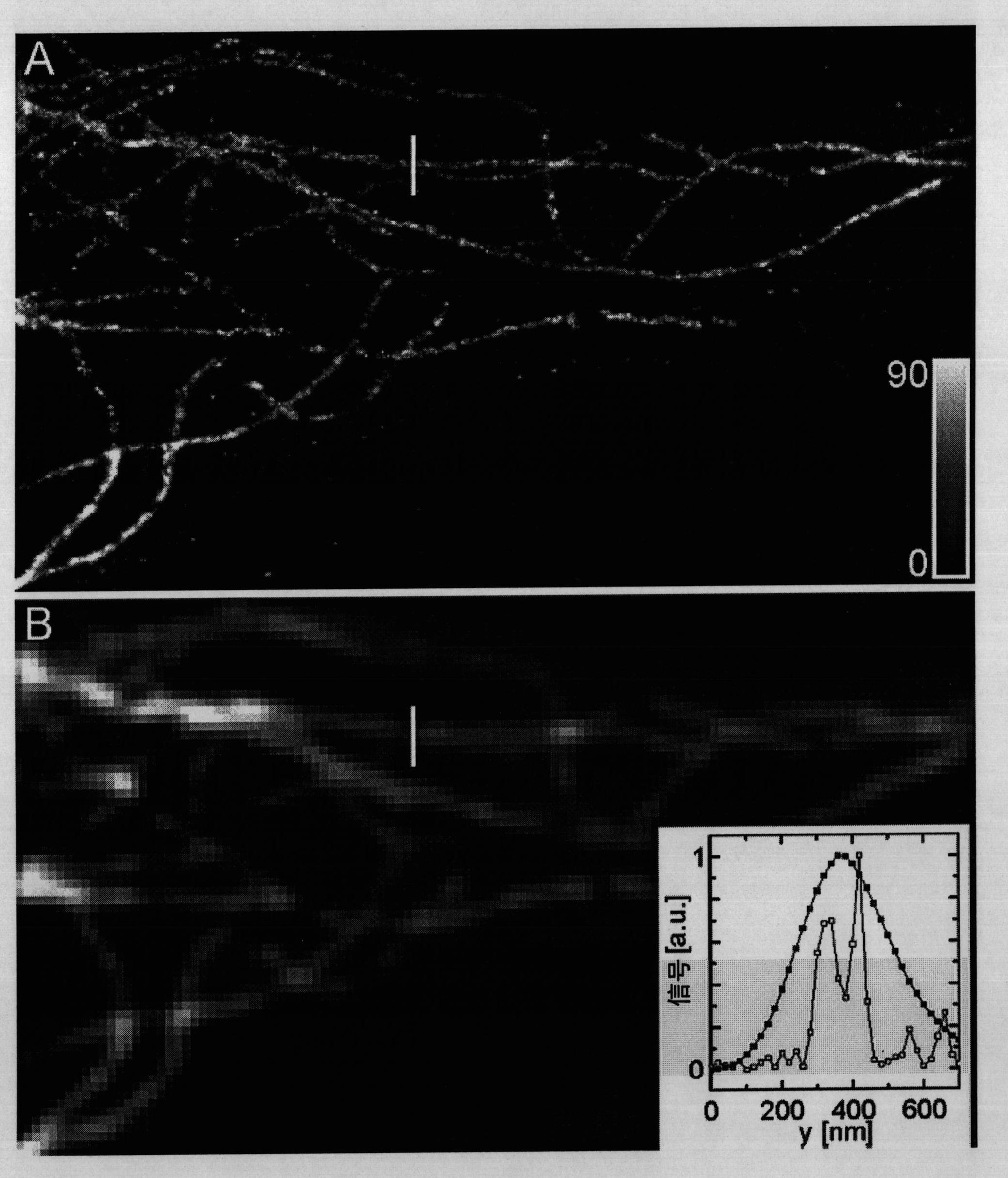
High spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen
ActiveCN102037347AFast readEasy to readMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceSensor arrayElectronic states
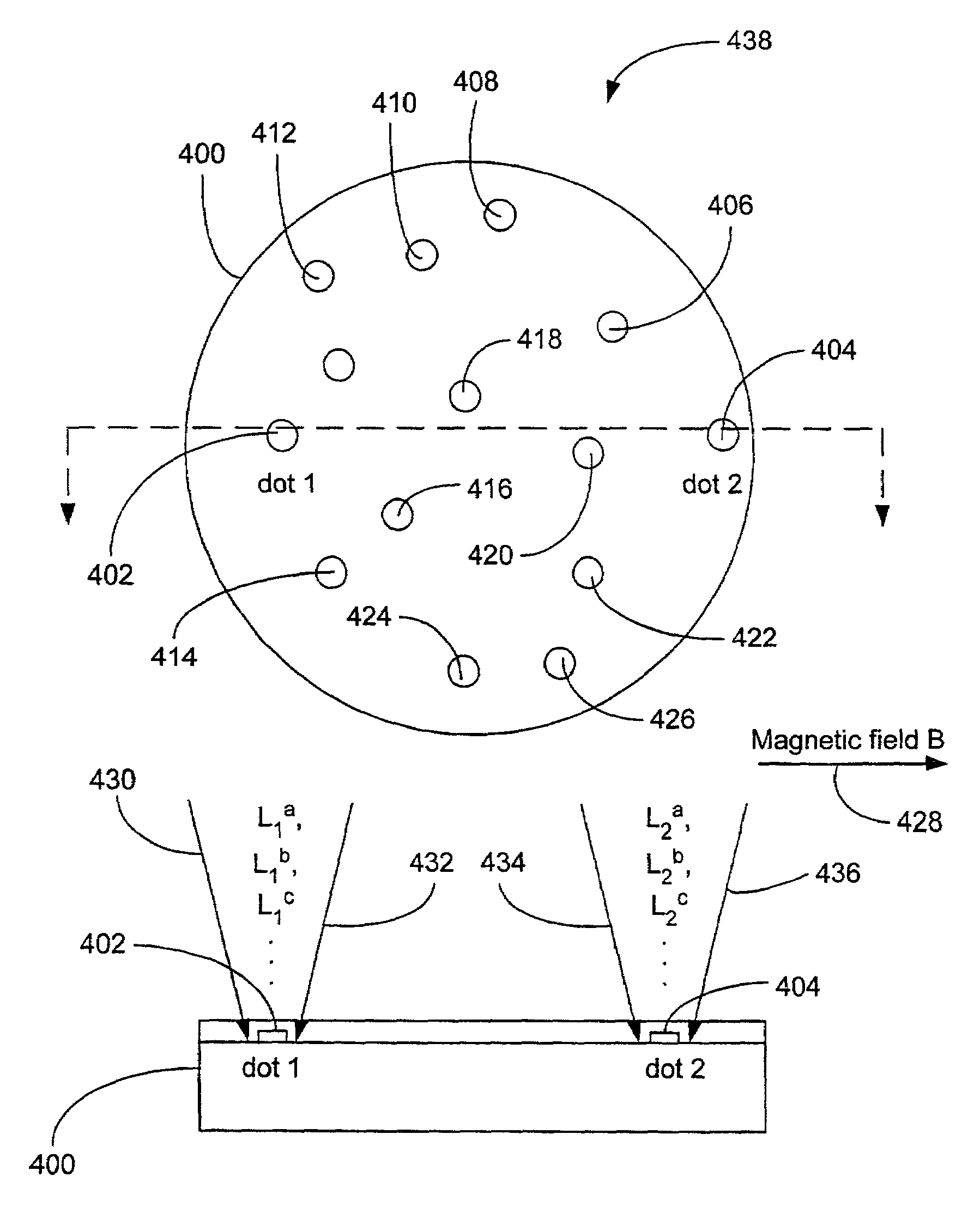
For high spatial resolution imaging of a structure of interest in a specimen, a substance is selected from a group of substances which have two different electronic states: a fluorescent first state and a nonfluorescent second state; which can be converted fractionally from their first state into their second state by light which excites them into fluorescence, and which return from their second state into their first state; the specimen's structure of interest is imaged onto a sensor array, a spatial resolution limit of the imaging being greater (i.e. worse) than an average spacing between closest neighboring molecules of the substance in the specimen; the specimen is exposed to light in a region which has dimensions larger than the spatial resolution limit, fractions of the substance alternately being excited by the light to emit fluorescent light and converted into their second state, and at least 10% of the molecules of the substance that are respectively in the first state lying at a distance from their closest neighboring molecules in the first state which is greater than the spatial resolution limit; and the fluorescent light, which is spontaneously emitted by the substance from the region, is registered in a plurality of images recorded by the sensor array during continued exposure of the specimen to the light.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and System of Computing and Rendering the Nature of the Excited Electronic States of Atoms and Atomic Ions
InactiveUS20080034287A1Chemical property predictionRadiation/particle handlingDisplay deviceMaxwell's equations
A method and system of physically solving the charge, mass, and current density functions of excited-state atoms and atomic ions using Maxwell's equations and computing and rendering the nature of excited-state electrons using the solutions. The results can be displayed on visual or graphical media. The display can be static or dynamic such that electron spin and rotation motion can be displayed in an embodiment. The displayed information is useful to anticipate reactivity and physical properties. The insight into the nature of excited-state electrons can permit the solution and display of those of other atoms and atomic ions and provide utility to anticipate their reactivity and physical properties as well as spectral absorption and emission to lead to new optical materials and light sources.
Owner:BRILLIANT LIGHT POWER
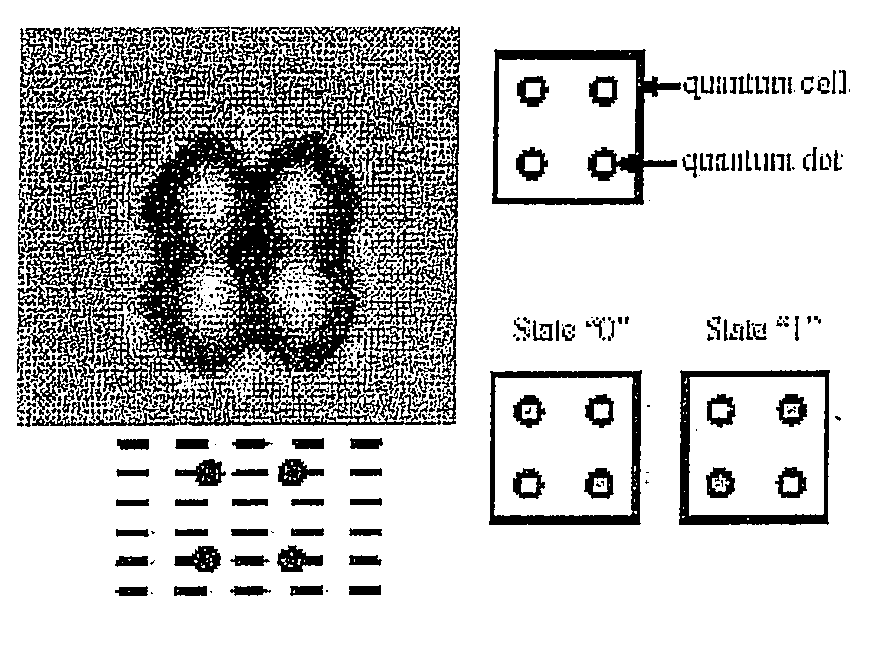
Atomistic quantum dot
A quantum device is provided that includes controllably quantum mechanically coupled dangling bonds extending from a surface of a semiconductor material. Each of the controllably quantum mechanically coupled dangling bonds has a separation of at least one atom of the semiconductor material. At least one electrode is provided for selectively modifying an electronic state of the controllably quantum mechanically coupled dangling bonds. By providing at least one additional electron within the controllably quantum mechanically coupled dangling bonds with the proviso that there exists at least one unoccupied dangling bond for each one additional electron present, the inventive device is operable at least to 293 degrees Kelvin and is largely immune to stray electrostatic perturbations. Room temperature operable quantum cellular automata and qubits are constructed therefrom.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
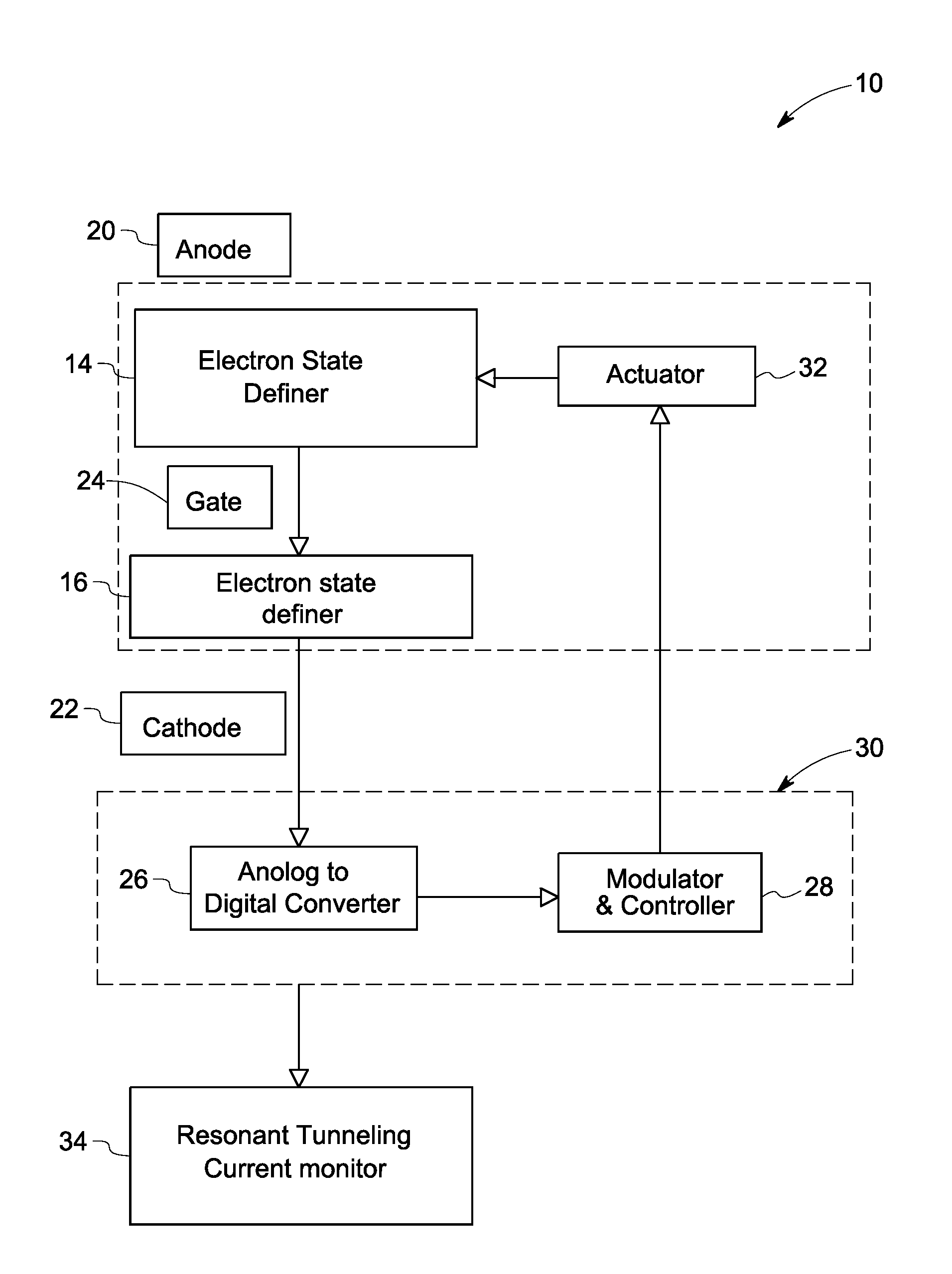
Devices and methods for electric field sensing
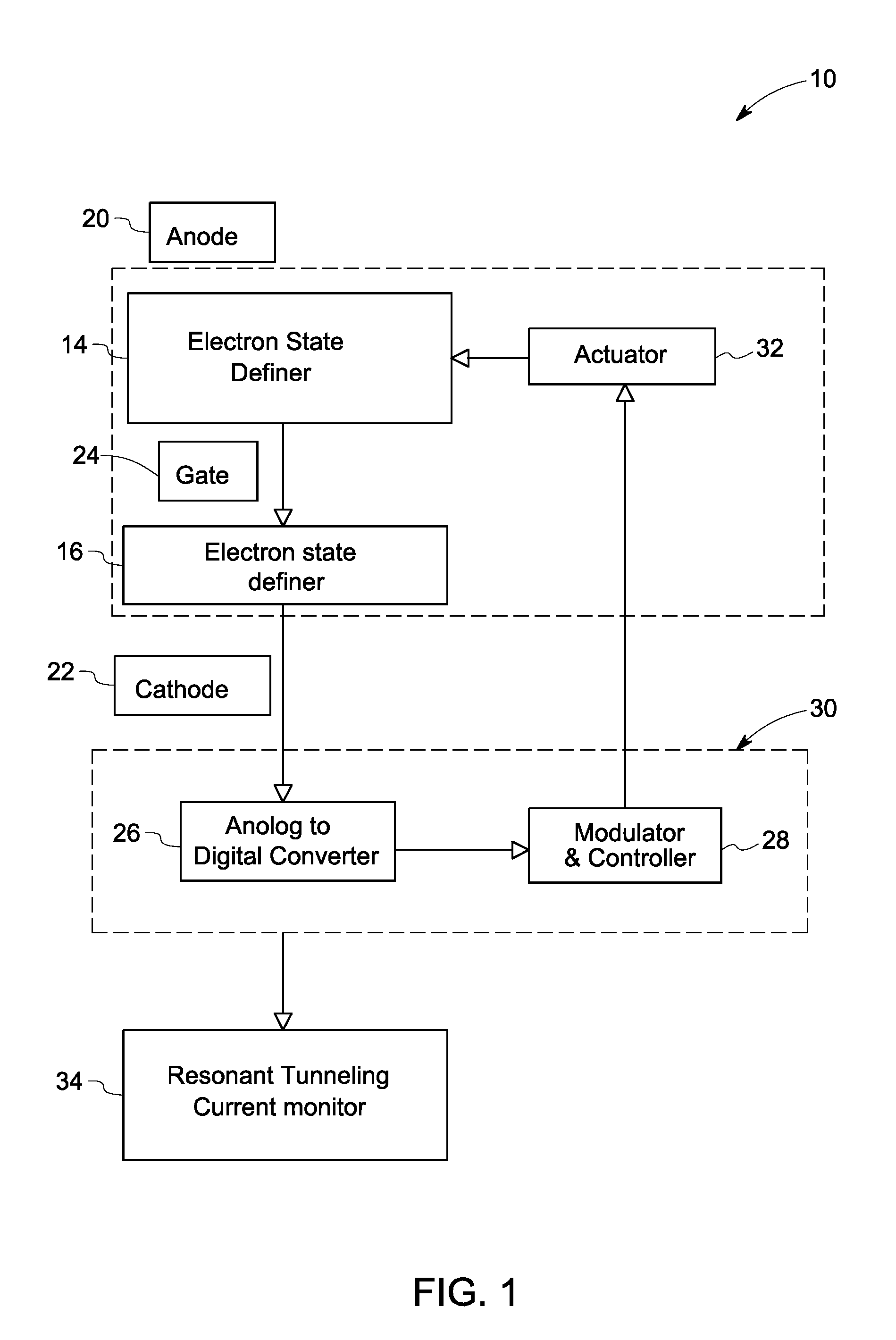
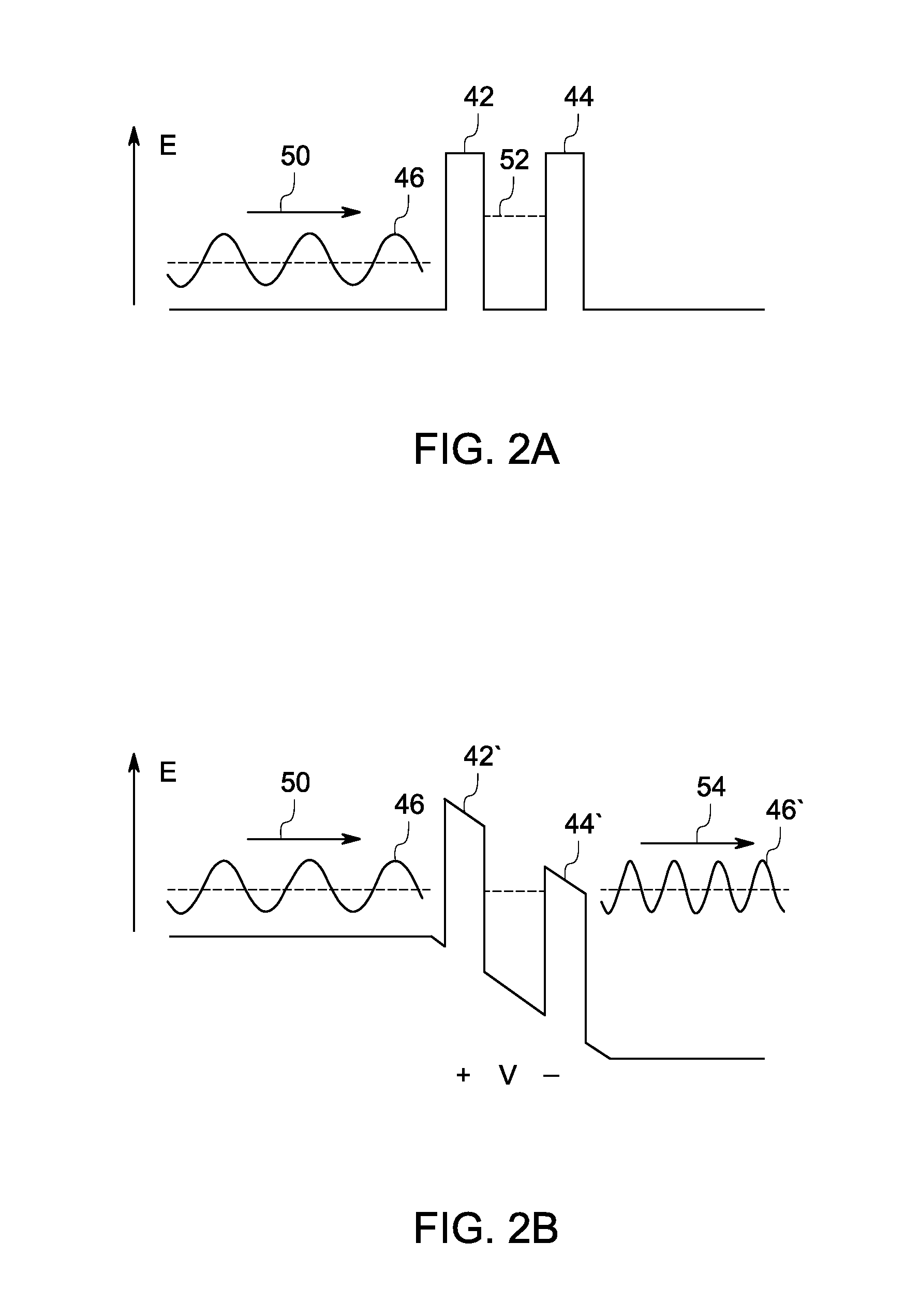
InactiveUS20110241648A1Electronic circuit testingCurrent/voltage measurementElectronic statesVariable Characteristic
A stand-off sensor assembly is provided. The sensor assembly includes a plurality of electron state definers for generating resonant tunneling current in response to the electric field, wherein the electron state definers include at least one variable characteristic such that a change in the variable characteristic affects the tunneling current, and a monitor for monitoring a change in the tunneling current exiting an electron state definer based on a change in the variable characteristic of the tunneling device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Devices and methods for assessing a sample's temperature exposure history
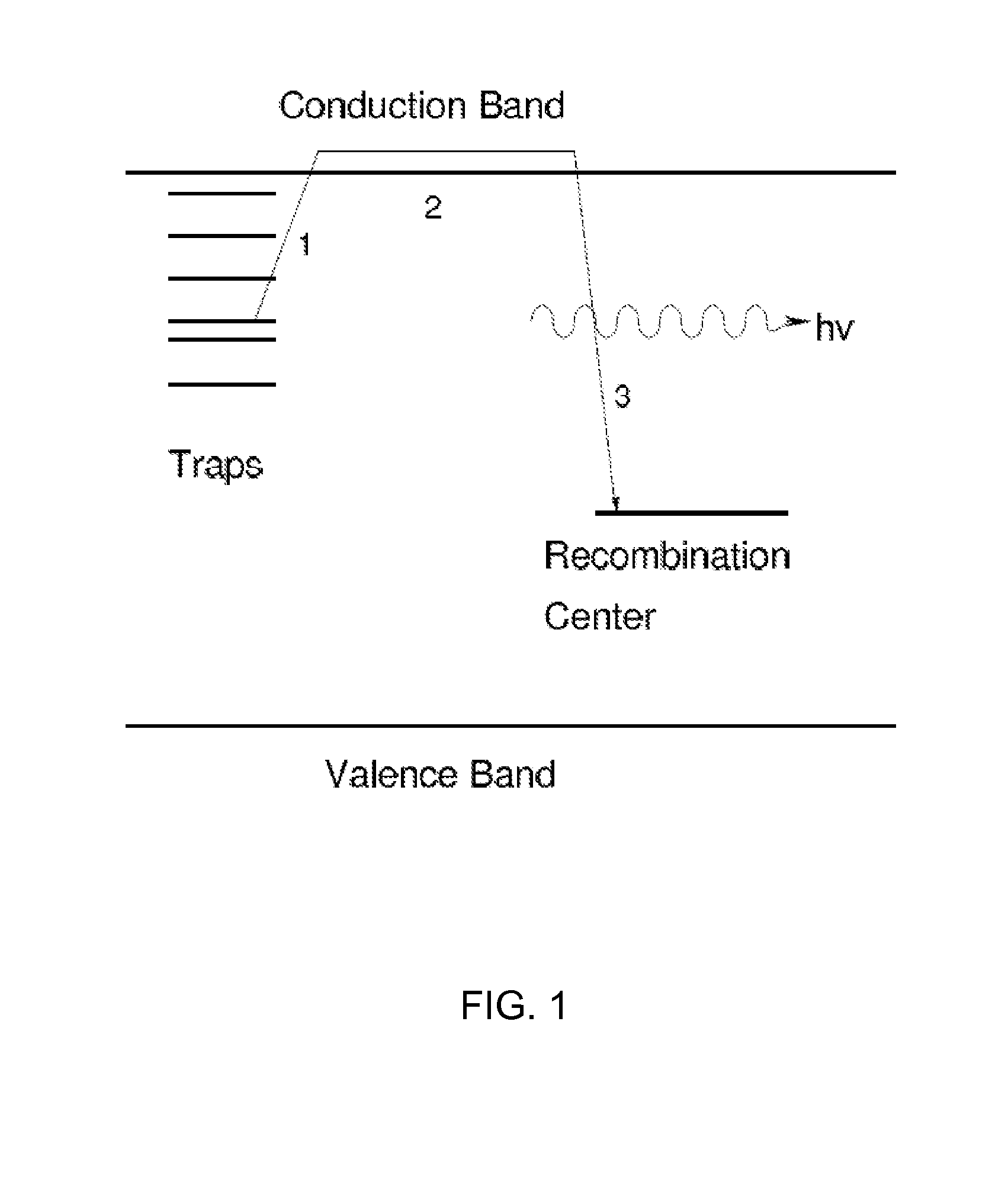
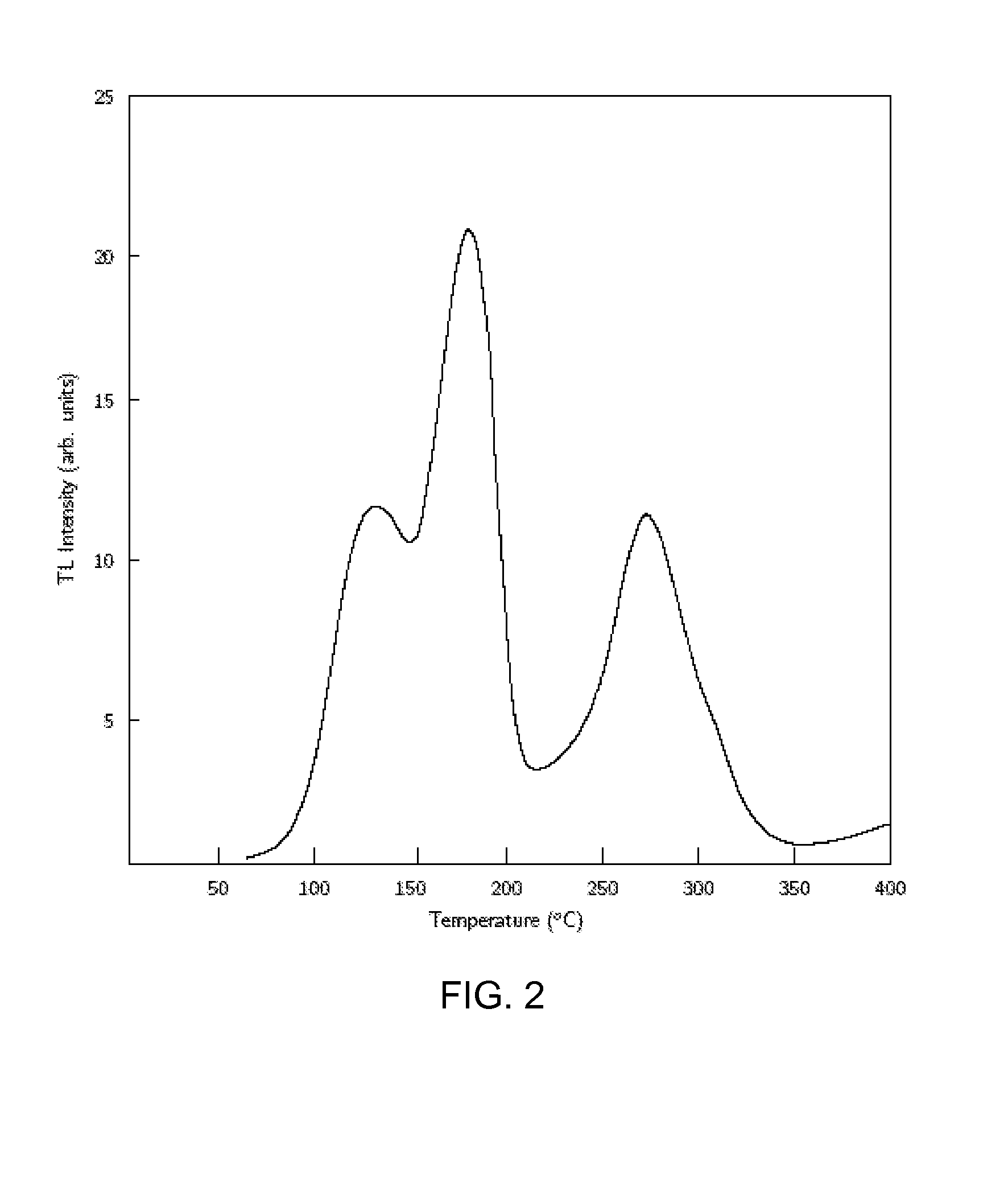
ActiveUS20100074297A1Thermometers using mean/integrated valuesThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectronic statesMetallic materials
Device and methods are provided for assessing a temperature exposure history of a sample that is comprised of a nonmetallic material. To assess the temperature exposure history, the pre-exposure and post-exposure electronic states of the sample are compared. Changes in the electronic state of the sample are indicative of the temperature exposure history.
Owner:LAWLESS JOHN L +1
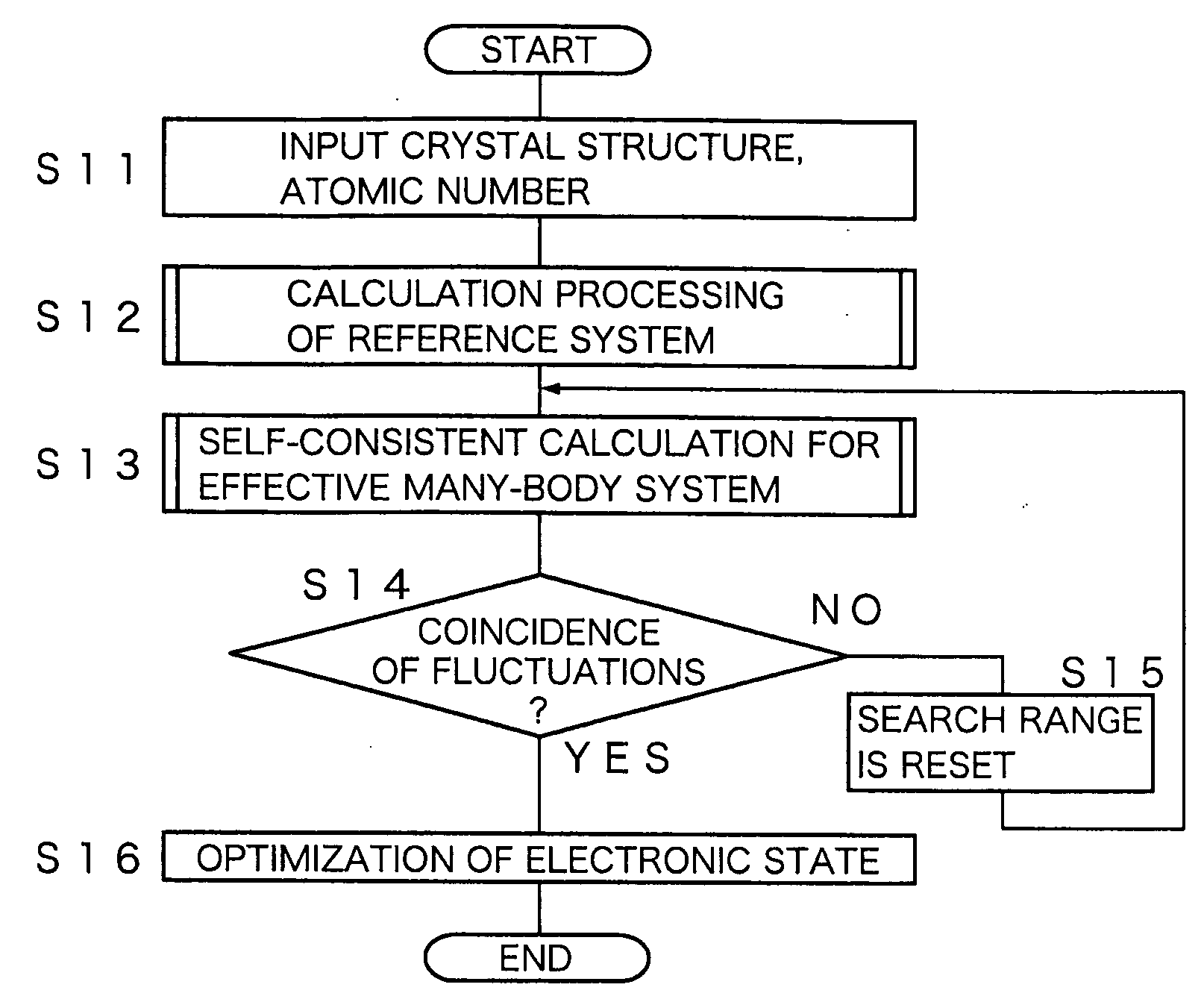
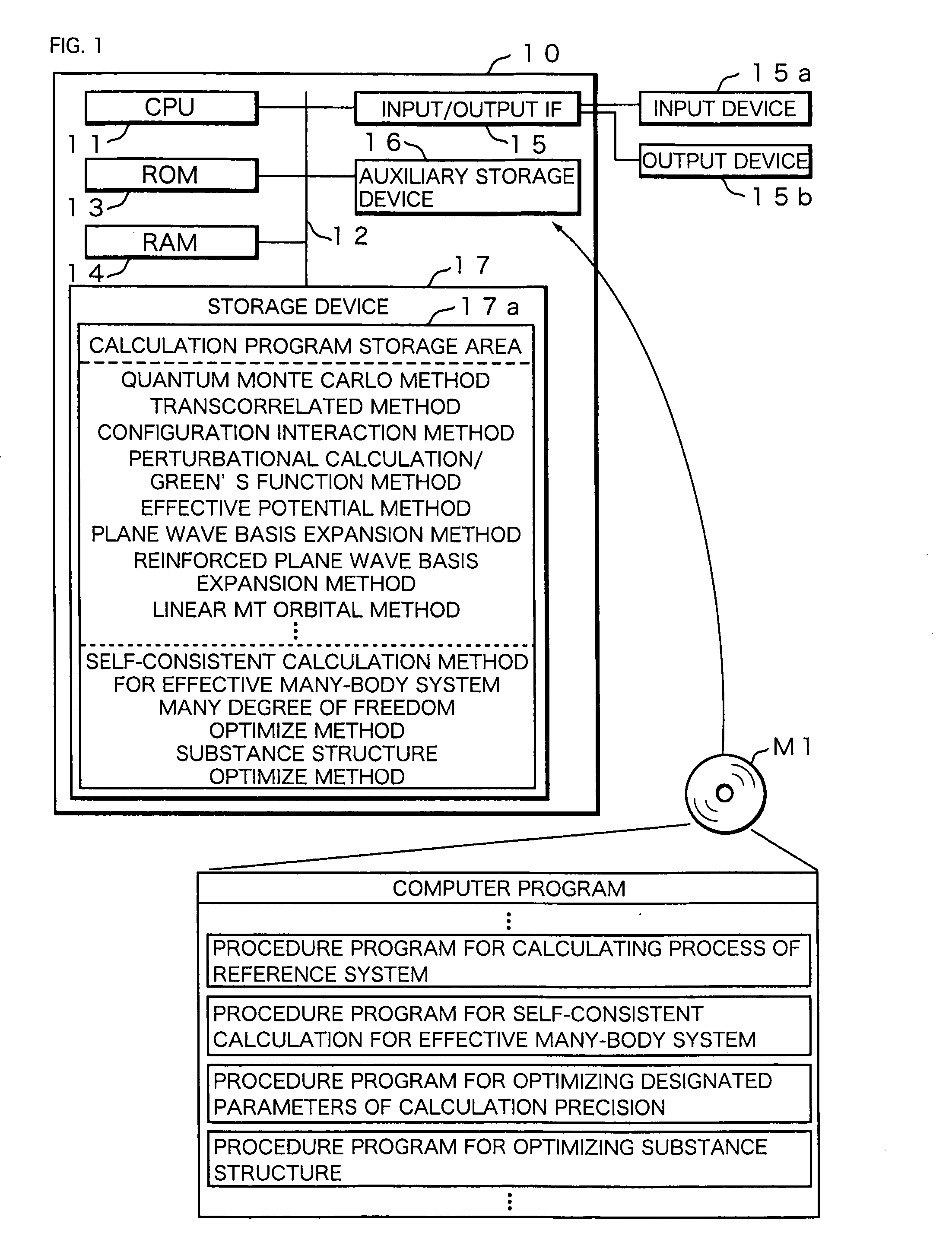
Electronic State Calculation Method, Electronic State Calculation Device, Computer Program, and Recording Medium
ActiveUS20090093973A1Guaranteed accuracyAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationElectronic statesMultibody system
By receiving input of a crystal structure and atom numbers, and specifying an atom group that can generate fluctuations from an electronic state calculation of a normal Kohn-Sham theory, an electronic state calculation device calculates a reference system. Next, based on an extended Kohn-Sham theory, the electronic state calculation device performs self-consistent calculation for an effective many-body system, then determines whether or not density fluctuations obtained for the reference system and density fluctuations obtained by the self-consistent calculation coincide with each other, and in a case of coincidence, acquires parameters of an exchange correlation energy and a local interaction. By the acquired parameters, an effective Hamiltonian is decided, and optimization of an electronic state is performed for a known crystal structure.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
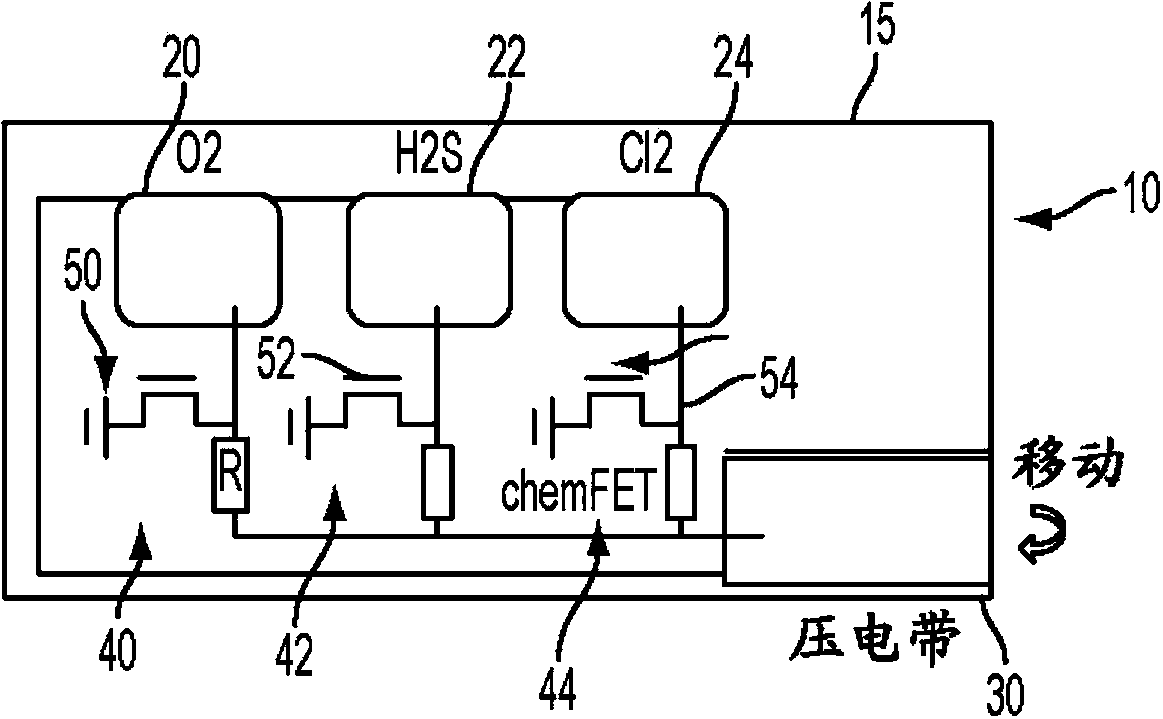
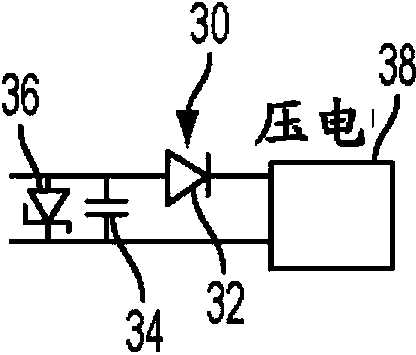
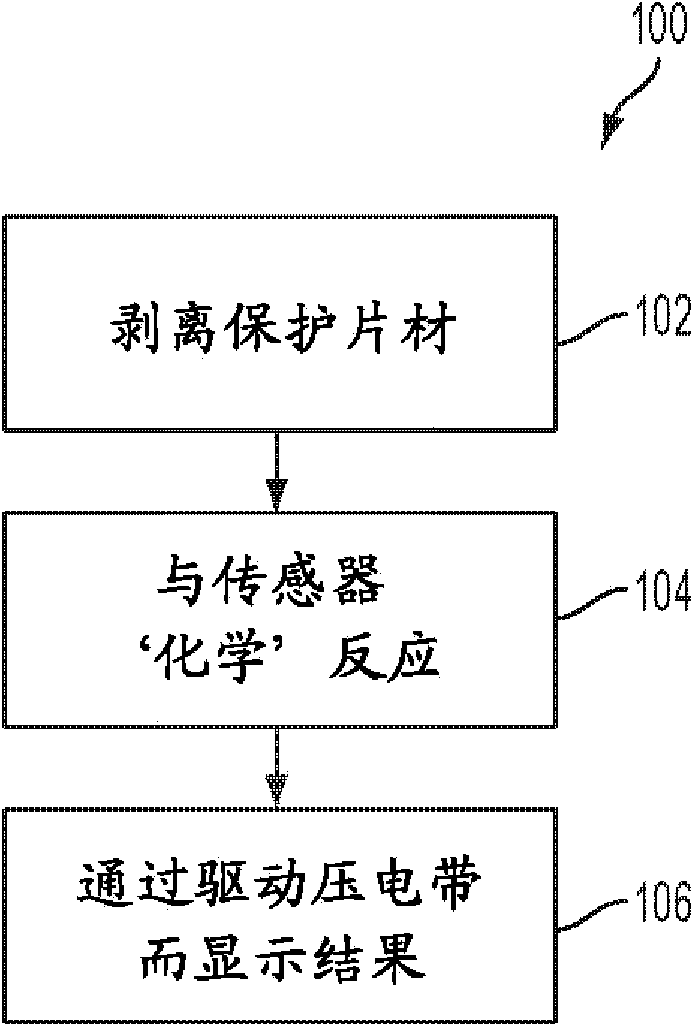
Piezo-powered sensor card and method therefor
InactiveCN103884744APiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMaterial resistanceElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An electronic sensor device, powered by a piezoelectric source and including an electronic element, is provided. The device may be used to test for the presence of substance such as a gas, a liquid, a chemical substance or a biological substance, etc. When the device is exposed to the substance, the electronic state (resistance / capacitance) of the electronic element (such as a transistor) changes (e.g. impacts the color of a connected display element) to allow for visual detection of the substance by a user.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Optoelectronic devices utilizing materials having enhanced electronic transitions
An optoelectronic device that includes a material having enhanced electronic transitions. The electronic transitions are enhanced by mixing electronic states at an interface. The interface may be formed by a nano-well, a nano-dot, or a nano-wire.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Anti-thrombosis and anti-infection titanium alloy implantation instrument with alveolate porous structure
ActiveCN109730802AExcellent super hemophobic performanceAvoid stickingStentsHeart valvesNiti alloyMicro nano
The invention relates to an anti-thrombosis and anti-infection titanium alloy implantation instrument with an alveolate porous structure and belongs to the technical field of surface modification of metal materials. According to the method, a traditional femtosecond laser shaping mode is replaced with a femtosecond laser dual-pulse mode, correspondingly a local instantaneous electronic state of amaterial is adjusted and controlled, and different micro-nano composite structures can be prepared. Through dynamic regulation and control of electrons, the unique alveolate porous structure is finally processed. According to the structure, the static contact angle between the structure and fresh rabbit blood is 143.4 degrees + / - 2.6 degrees, and the rolling angle is 8.5 degrees + / - 2 degrees. Because a fluorinated material has low surface energy, certain frictional resistance and excellent bactericidal and antithrombotic capability, by conducting fluorination treatment on a NiTi alloy surfaceof the alveolate porous structure, a super blood dispersing surface is obtained, wherein the static contact angle between the super blood dispersing surface and the fresh rabbit blood is 167.3 degrees + / -3.2 degrees, and the rolling angle of the super blood dispersing surface is 1.6 degrees + / - 0.3 degree; meanwhile, the obtained surface also has excellent antibacterial performance. The method isapplicable to the surfaces of titanium alloy materials different in size and shape.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical lattice clock, clock device and laser light source
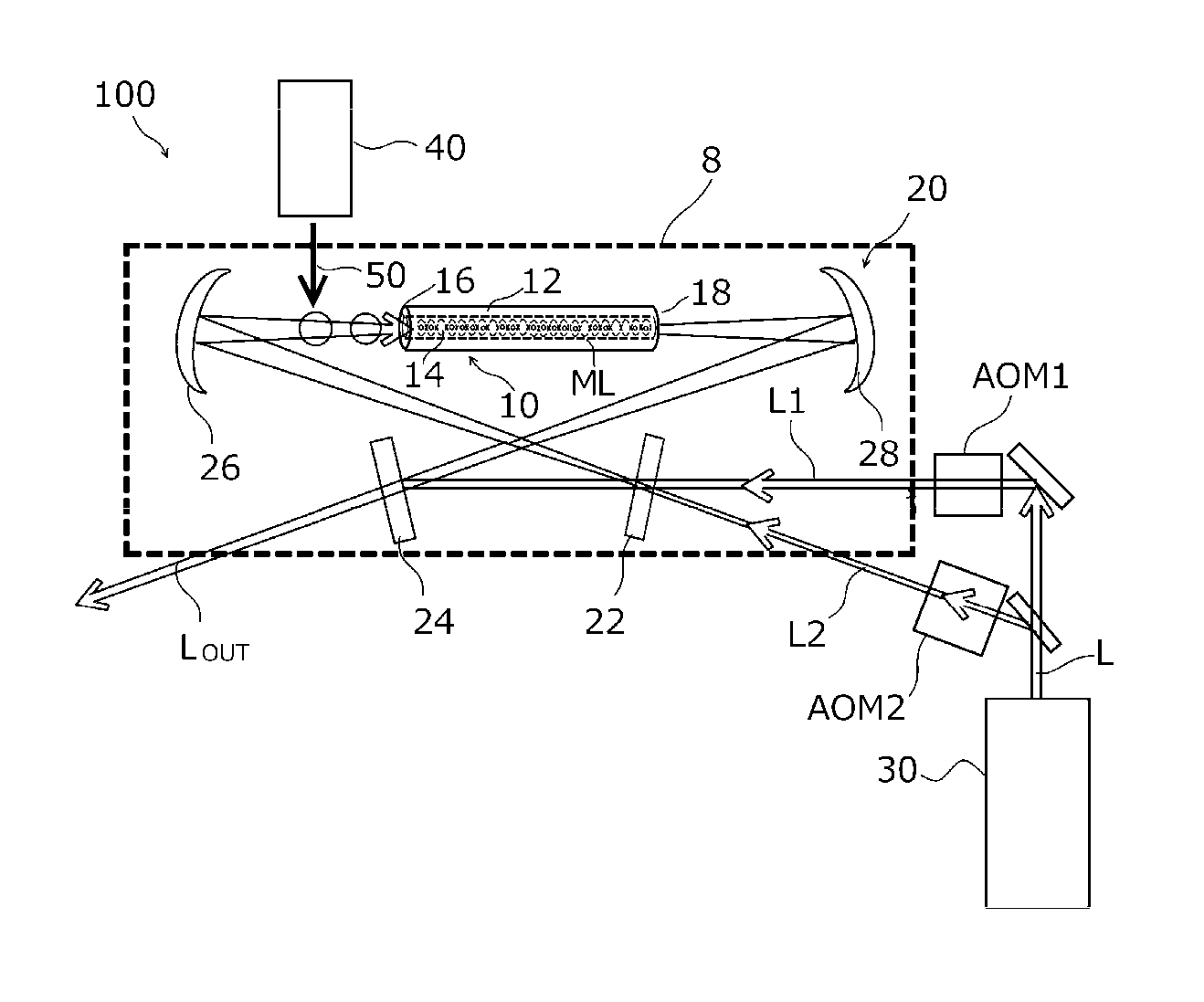
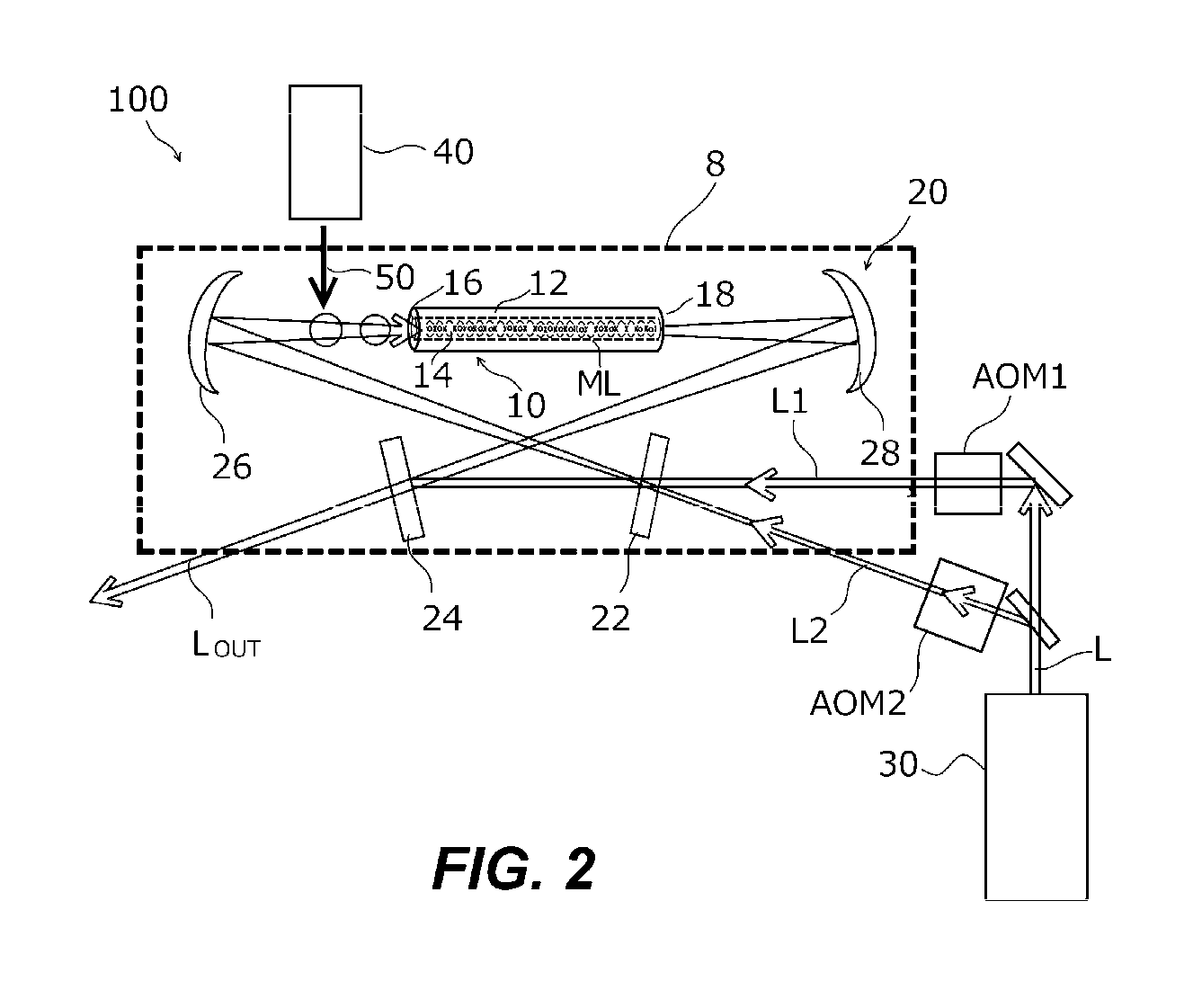
ActiveUS9553597B2Improve accuracyIncrease the number ofPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksOptical latticeElectronic states
Owner:RIKEN
Sample observation method and observation device
InactiveUS20070046285A1Solid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesElectronic statesElectron
A sample observation method and sample observation device of the present invention are for observing variation in surface potential of a sample due to variation in the Hall effect based on variation in an applied current or applied magnetic field to the sample, and allow the variation in the Hall effect generated in the sample to be locally observed. The Hall effect varies depending on internal structures, electronic states, etc. of the sample. The variation in surface potential due to variation in the Hall effect includes information on internal structures, electronic states, etc. of the sample.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com