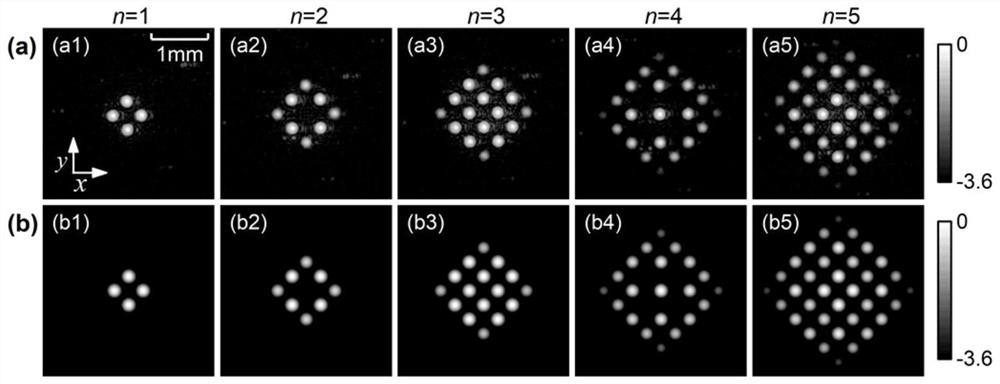
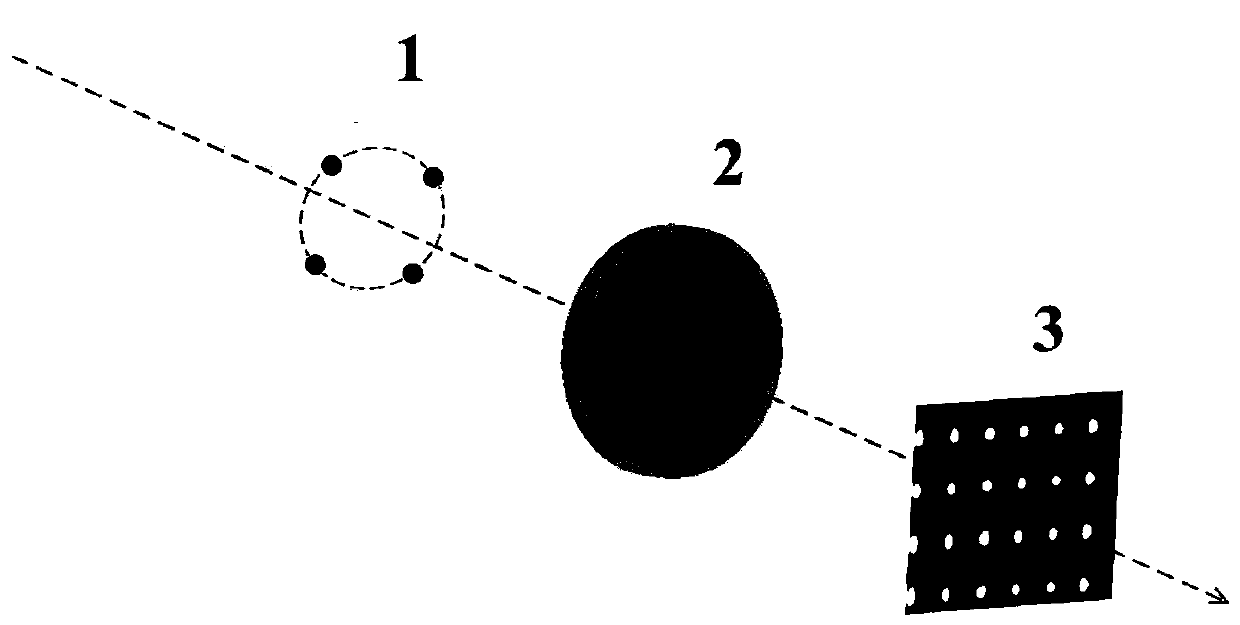
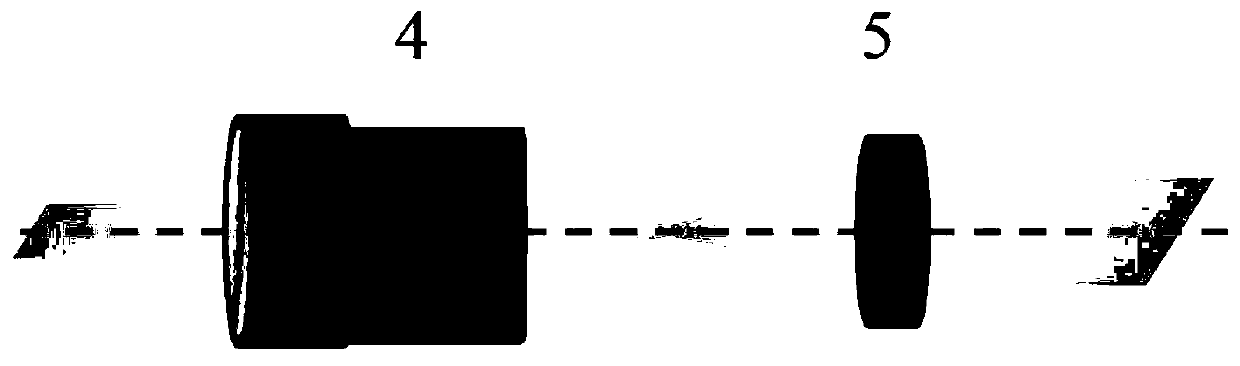
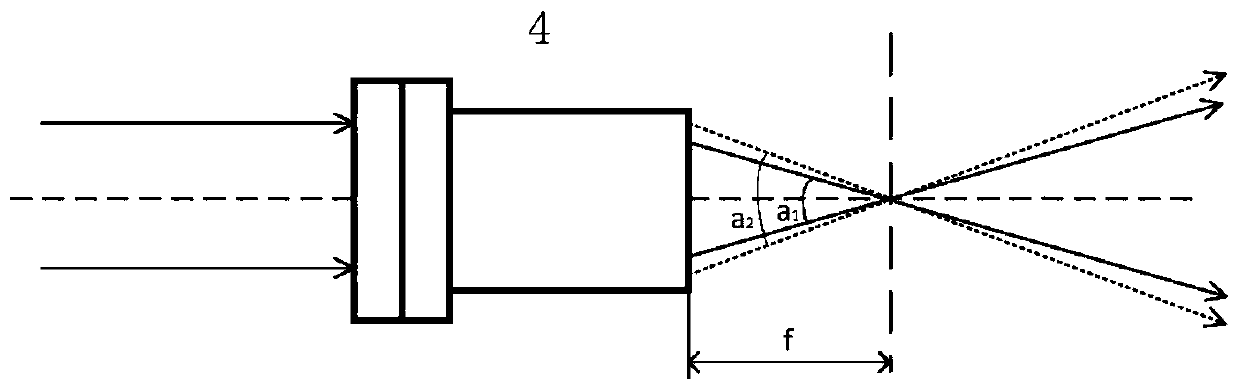
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Optical lattice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical lattice is formed by the interference of counter-propagating laser beams, creating a spatially periodic polarization pattern. The resulting periodic potential may trap neutral atoms via the Stark shift. Atoms are cooled and congregate in the locations of potential minima. The resulting arrangement of trapped atoms resembles a crystal lattice and can be used for quantum simulation.
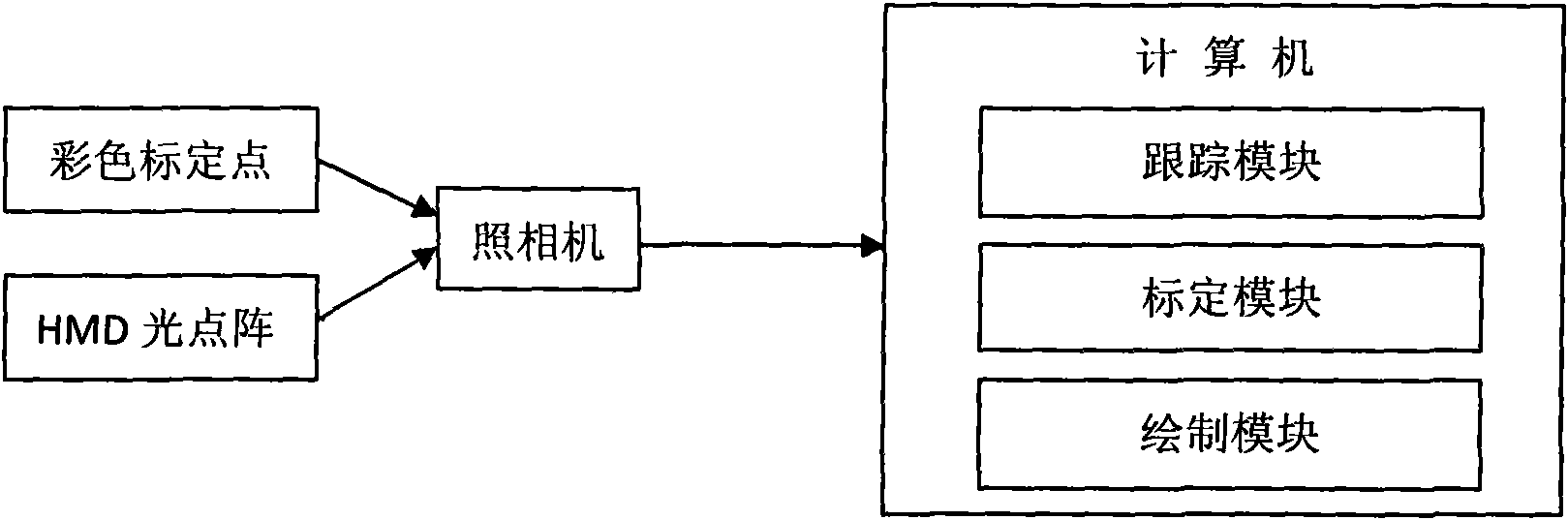
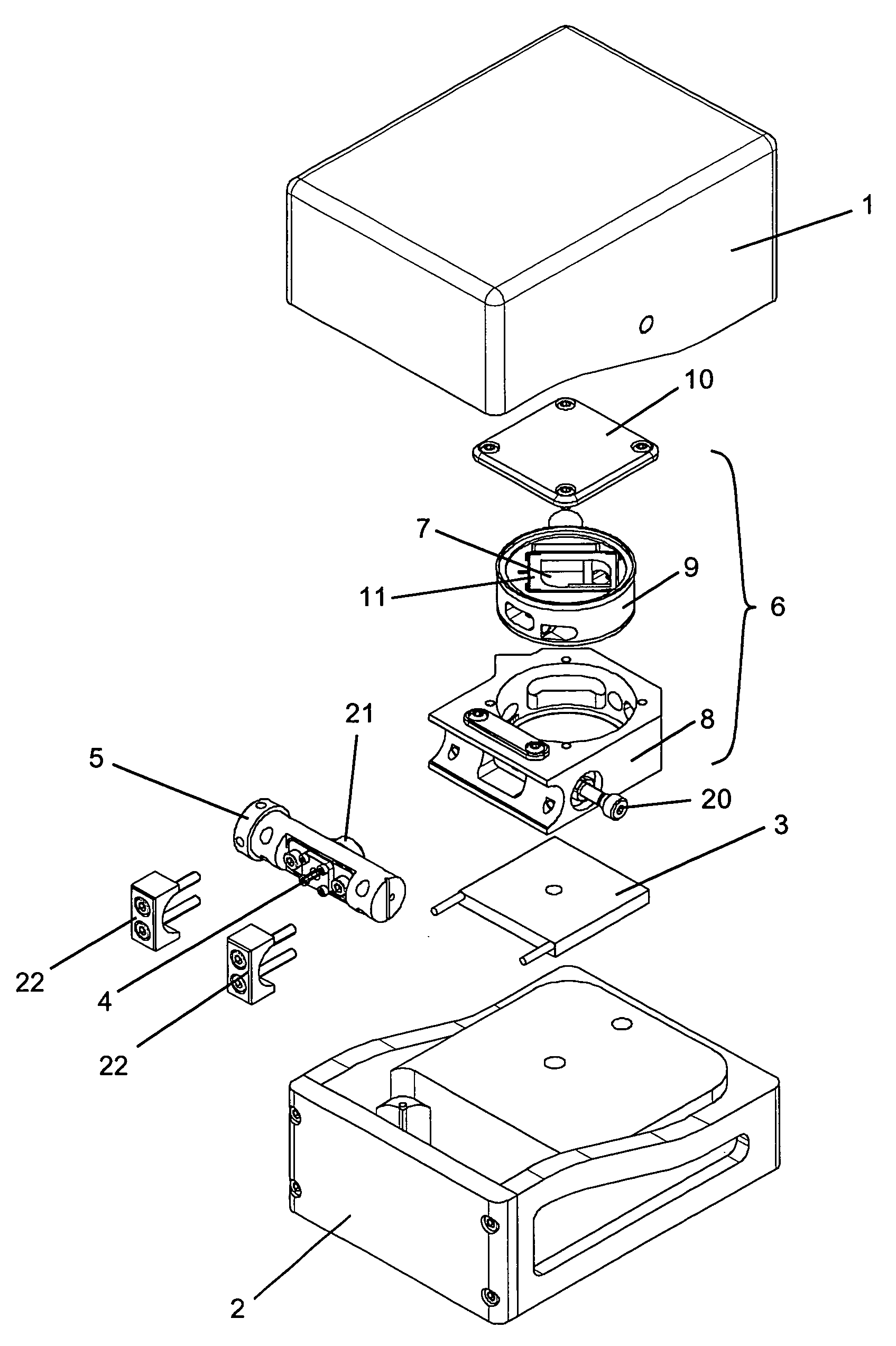
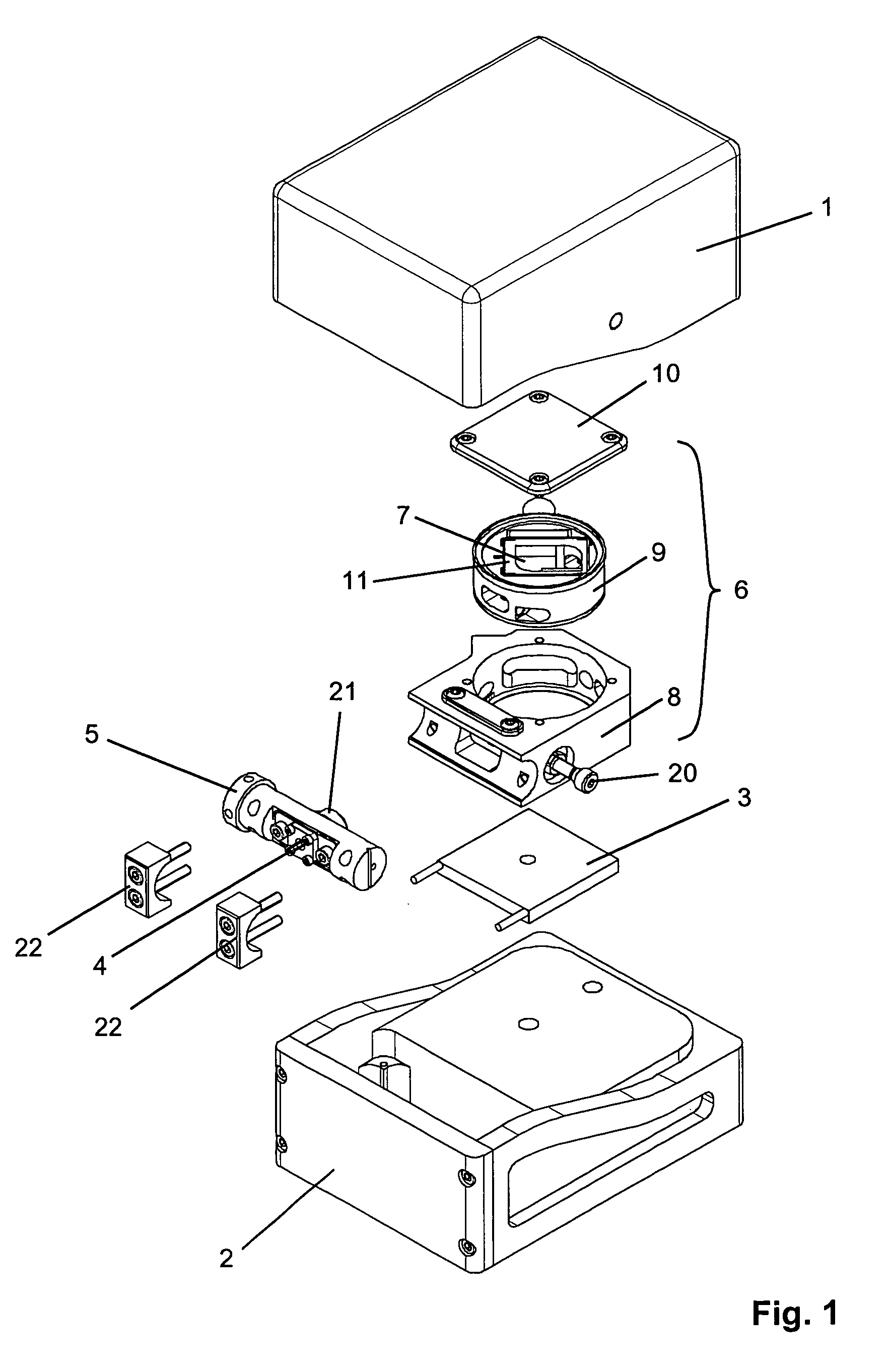
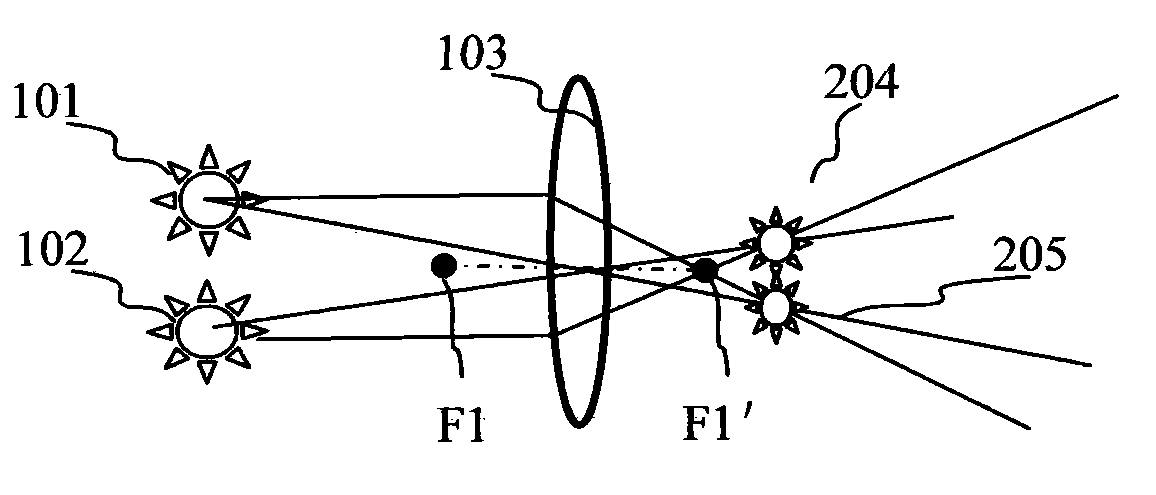
Operation guiding system and method based on optical enhancement reality technology
InactiveCN101904770ASurgical Field Enhanced DisplayThe display effect winsDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsOptical latticeMedical equipment
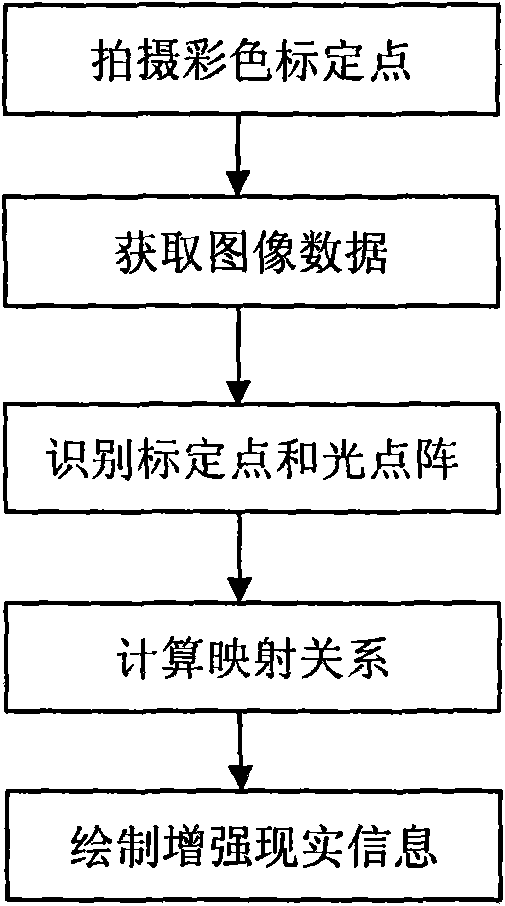
The invention belongs to the field of medical equipment, relating to an operation guiding system and method based on an optical enhancement reality technology. The method comprises the steps of: displaying optical lattice generated by a computer on a display screen of an optical helmet display; shooting a calibration plate and the optical lattice through the display screen by a camera; recognizing the optical lattice and colour calibration points in the shot digital image and acquiring two-dimension coordinates of the optical lattice and colour calibration points by the computer; calculating mapping of the three-dimensional space of the calibration points to the two-dimensional space of an imaging surface of the optical helmet display to complete the calibration; and drawing corresponding virtual information according to the required mapping, and displaying the information on the display screen of the optical helmet display to realize the enhancement of operation scene. The invention can well support the application of the enhancement reality technology to the operation guiding system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
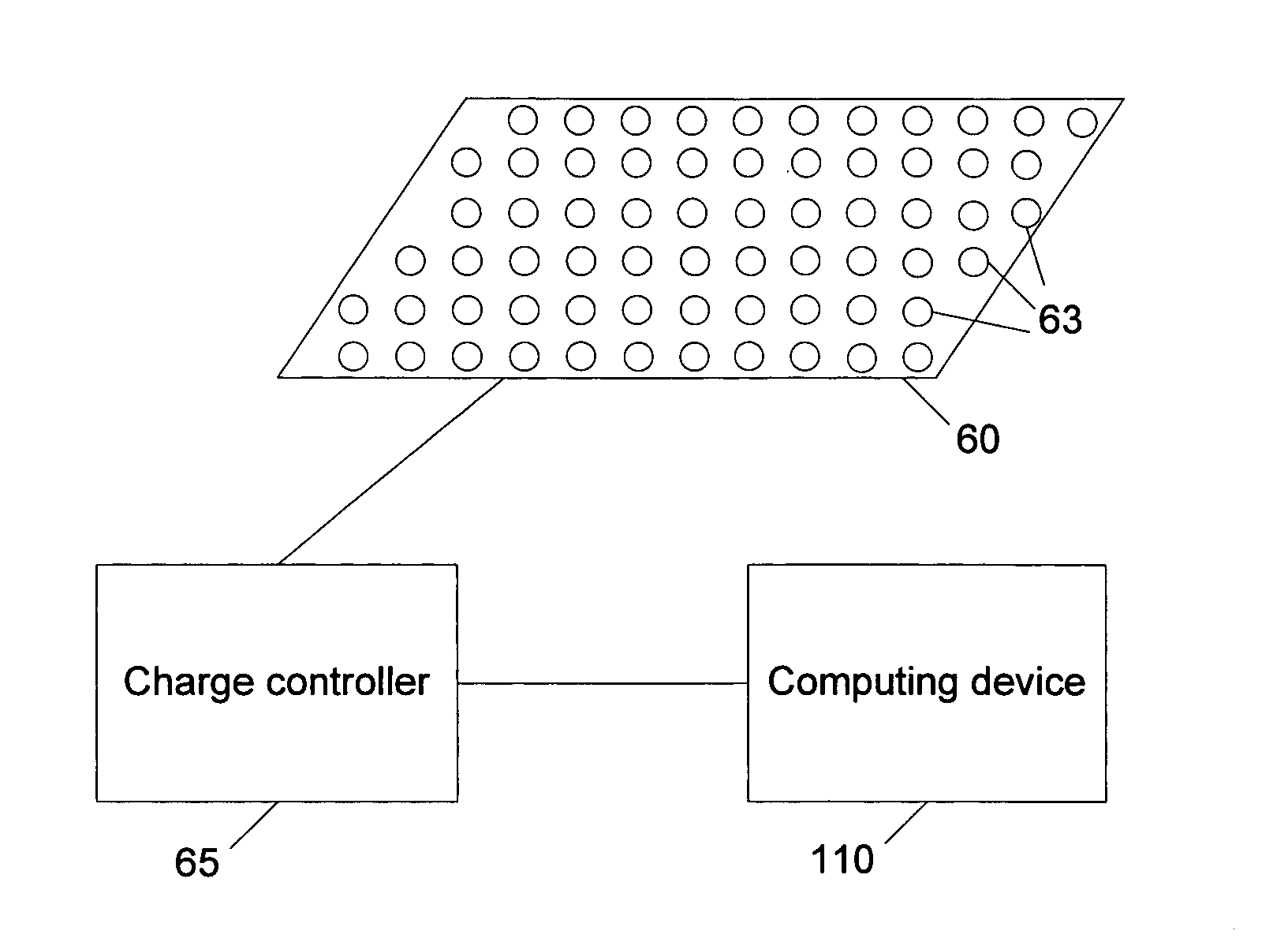
Lattice platforms for performing quantum computations
InactiveUS7566896B2Quantum computersSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptical latticeCrystal structure
Apparatus and methods for performing quantum computations are disclosed. Such apparatus and methods may include identifying a first quantum state of a lattice having a system of quasi-particles disposed thereon, moving the quasi-particles within the lattice according to at least one predefined rule, identifying a second quantum state of the lattice after the quasi-particles have been moved, and determining a computational result based on the second quantum state of the lattice. Various platforms can be used to physically implement such a quantum computer. Platforms include an optical lattice, a Josephson junction array, a quantum dot, and a crystal structure. Each platform comprises an appropriate array of associated sites that can be used to approximate a desired Kagome geometry. A charge controller is desirably electrically coupled to the platform so that the array may be manipulated as desired. A computing device may be coupled to the charge controller and / or the platform to provide instructions and support, record measurements, and make calculations, for example.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Fully reciprocal atomic interferometric gyroscope
A fully reciprocal atomic interferometric gyroscope is provided. The fully reciprocal atomic interferometric gyroscope includes an atomic chamber, a plurality of lasers, a controller and measurement sensor. The atomic chamber is used to hold an atom cloud. The plurality of lasers are selectively positioned to selectively direct laser beams into the atomic chamber. The controller is configured to control the plurality lasers to initially cool the atom cloud to a point where at least one optical lattice can be formed that is used to move wave function halves of atoms of the atom cloud along split wave function paths that form an interferometer cycle. The measurement sensor is configured to conduct a phase readout of a wave function upon the completion of at least one interferometer cycle around the split wave function paths.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Lattice platforms for performing quantum computations
InactiveUS20060043423A1Quantum computersSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptical latticeCrystal structure
Apparatus and methods for performing quantum computations are disclosed. Such apparatus and methods may include identifying a first quantum state of a lattice having a system of quasi-particles disposed thereon, moving the quasi-particles within the lattice according to at least one predefined rule, identifying a second quantum state of the lattice after the quasi-particles have been moved, and determining a computational result based on the second quantum state of the lattice. Various platforms can be used to physically implement such a quantum computer. Platforms include an optical lattice, a Josephson junction array, a quantum dot, and a crystal structure. Each platform comprises an appropriate array of associated sites that can be used to approximate a desired Kagome geometry. A charge controller is desirably electrically coupled to the platform so that the array may be manipulated as desired. A computing device may be coupled to the charge controller and / or the platform to provide instructions and support, record measurements, and make calculations, for example.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and equipment for realizes structured light in high performance based on uniqueness in field
InactiveCN1796933AEasy to determineEasy to installUsing optical meansOptical lattice3D reconstruction
The invention is a domain uniqueness-based method for realizing high efficiency structural light, producing a high efficiency coding phototemplate for a light projector in the structural light system and using the phototemplate for 3D reconstruction and comprising the steps of: (1) selecting different colors to compose a code set; (2) selecting elements from the code set, expressing each optical lattice by one color, making special code combination to produce the phototemplate and composing adjacent optical lattices into a coded word, which has the domain uniqueness; (3) corresponding the coded words to input and output beams of the light projector one to one; (4) corresponding the obtained image to the phototemplate to calculate the 3D coordinates. And a device for realizing the high efficiency structural light comprises light projector, vidicon and microprocessor, where the microprocessor comprises color set module, coding module, code word decoding module and 3D coordinates calculating module. The invention has high 3D sensing speed, high reconstructing efficiency and low use cost.
Owner:陈胜勇
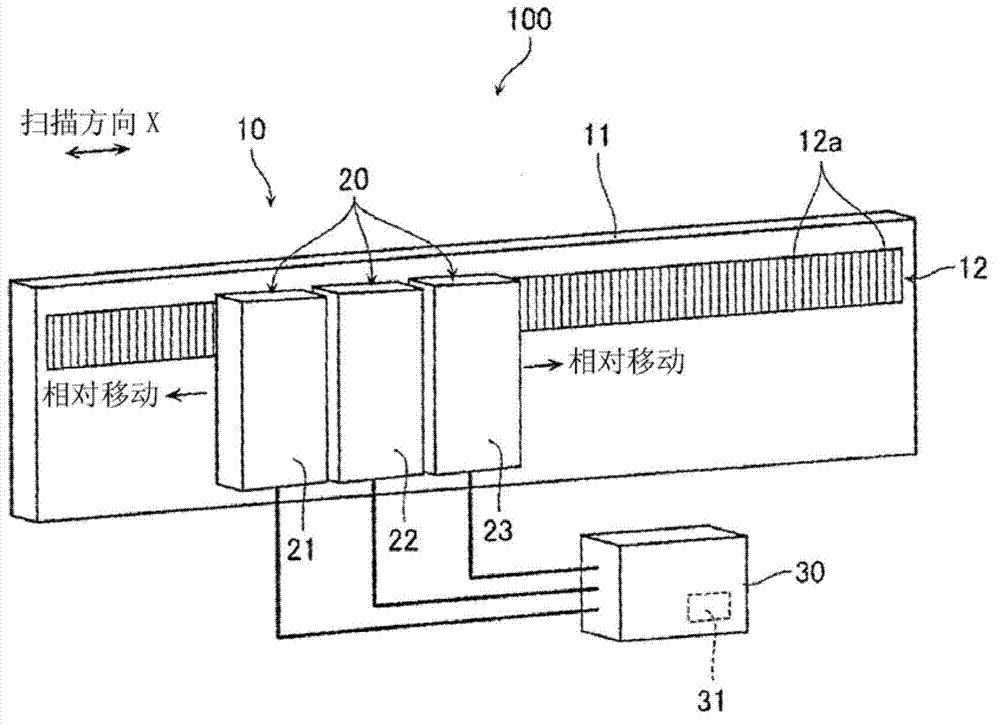
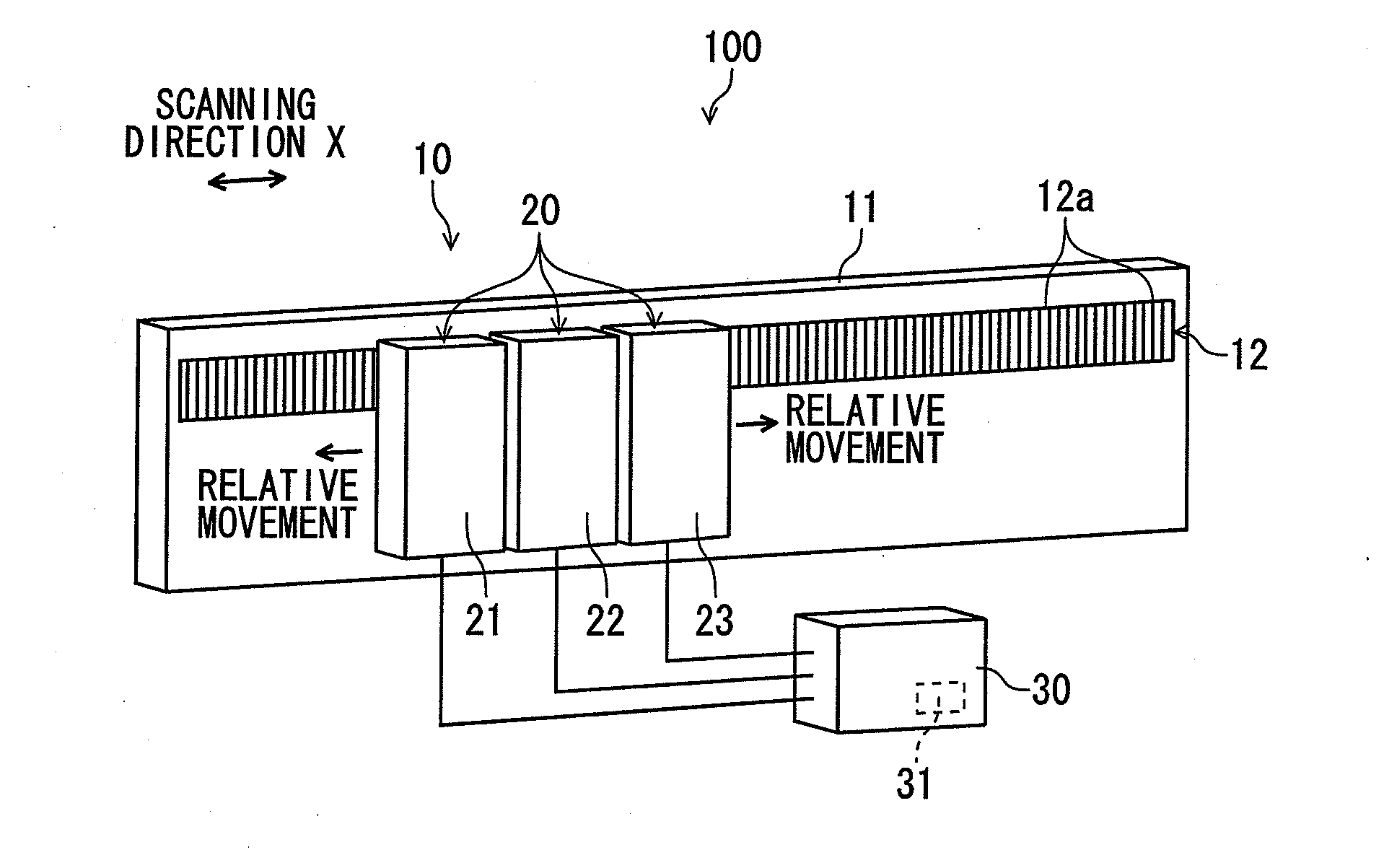
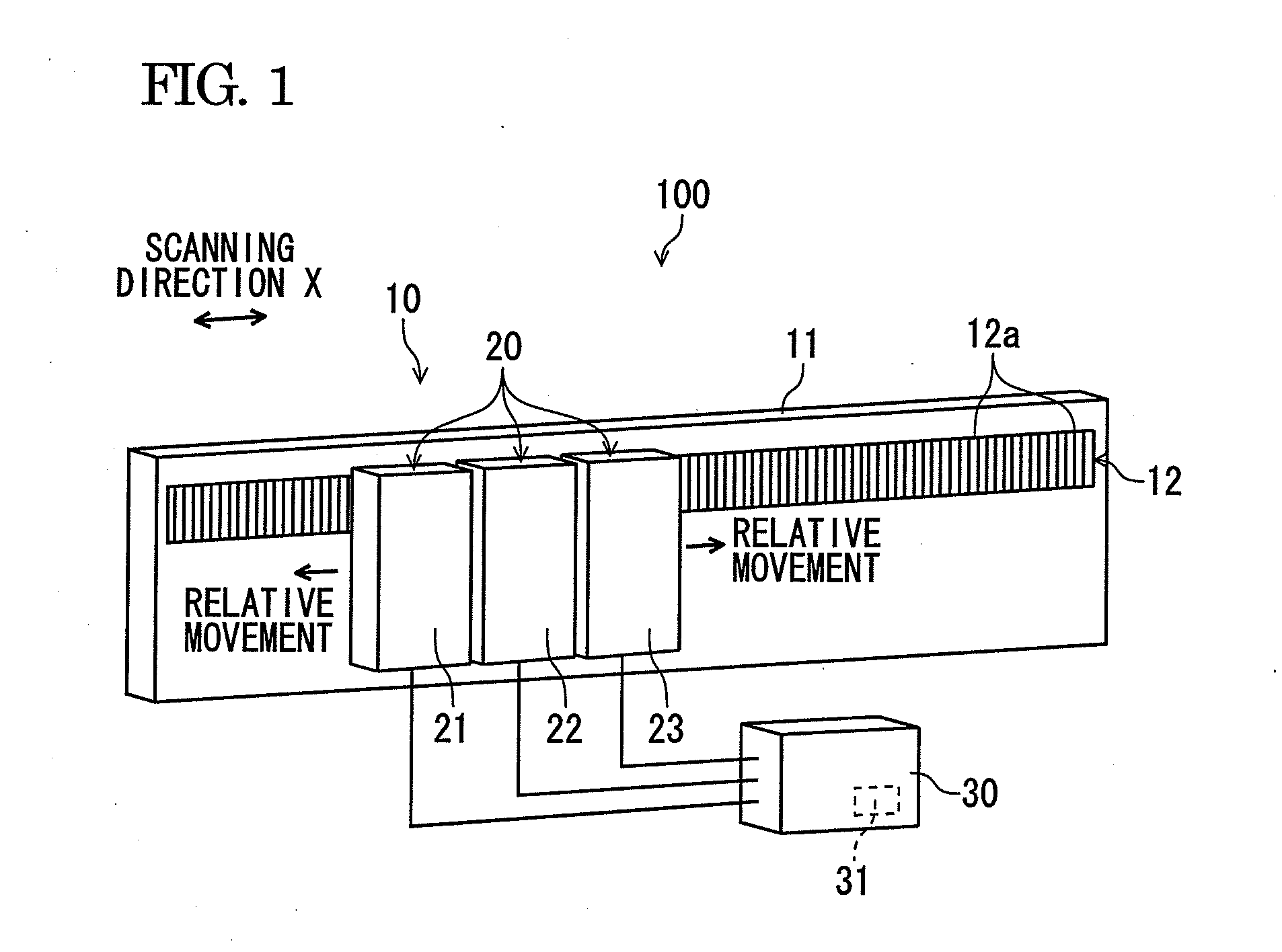
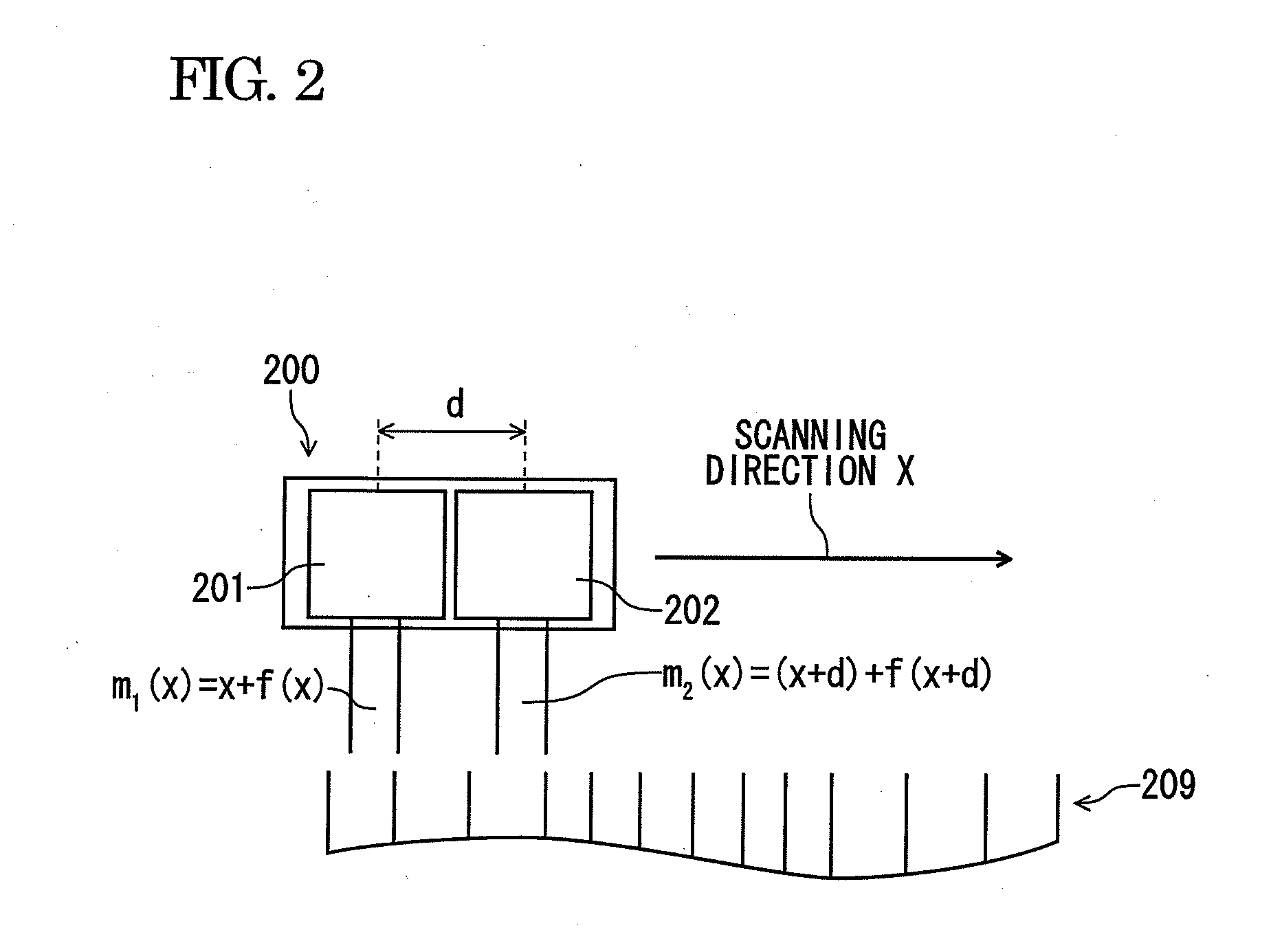
Displacement detecting device, scale calibrating method and scale calibrating program
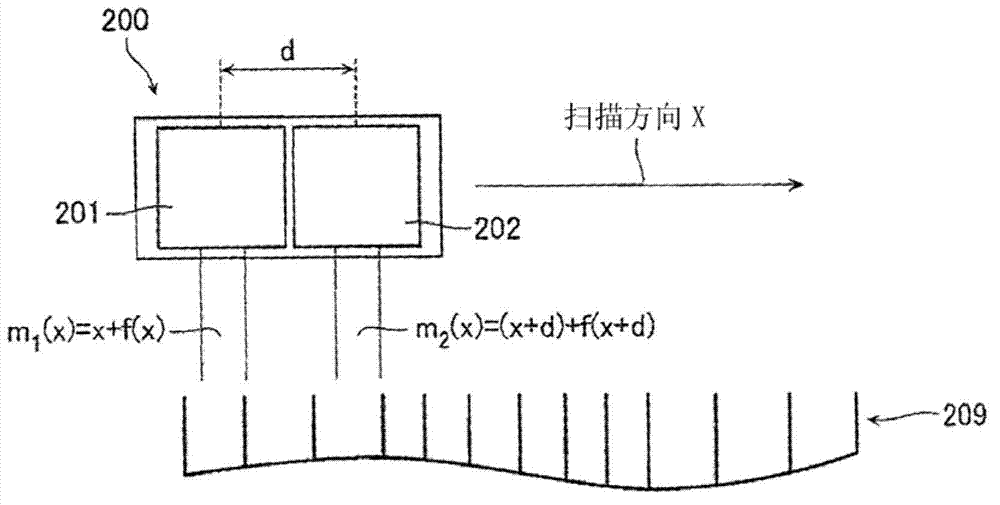
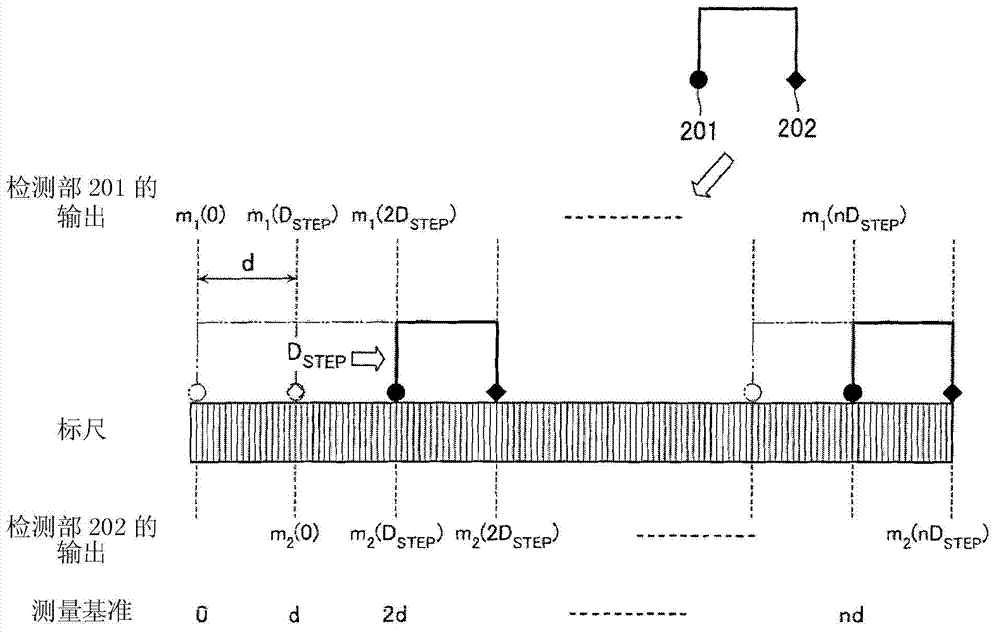
ActiveCN103075965AAccurately corrects for measurement errorsCalibration measurement errorUsing optical meansConverting sensor outputOptical latticeComputer vision
A displacement detecting device includes: a scale (10) which has an optical lattice; a detecting unit (20) which is disposed so as to be movable in a scanning direction relative to the scale, inclusive of at least a first detection portion (21), a second detection portion (22) and a third detection portion (23), arranged in the scanning direction for detecting position information from the optical lattice; and a calculating portion (30) configured to obtain a self-calibration curve on graduations of the scale by specifying positions of the detection portions and calculating measurement error based on the position information detected by the detecting unit, wherein: the detecting unit is provided so that a distance between the first detection portion (21) and the second detection portion (22) and a distance between the second detection portion (22) and the third detection portion (23) are different from each other and do not form an integral multiple.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Atom trapping and optical latticing method for chip surface
The invention discloses an atom trapping and optical latticing method for a chip surface, and relates to the field of neutral cold atom laser trapping and optical latticing. According to the method, the side surface of a coated inverted pyramid lens with an upward coated surface is irradiated by laser, evanescent waves generated by total reflection of the side surface of the lens are excited on the surface of a metal film to generate near-field surface plasmon polaritons, and loaded neutral cold atoms are subjected to effective trapping, one-dimensional atom surface optical latticing and two-dimensional atom surface optical latticing by the near-field surface plasmon polaritons and the interference light fields of the polaritons. The method can be used for achieving chip surface tom trapping and atom surface optical latticing of different types of neutral cold atoms, and is simple in principle, convenient to operate and wide in application range.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Tunable diode laser system with external resonator
ActiveUS7970024B2Reliable mode-hop-free tuningEasy and economical to realizeSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical latticeLight beam
A tunable diode laser system with external resonator in Littrow or Littman configuration has an optical lattice on which the light beam from a laser diode is diffracted, a support element to hold the lattice or to hold a mirror, which reflects the light diffracted by the lattice, and an actuator to change the position of the lattice or the mirror. The tunable diode laser system enables a reliable mode-hop-free tuning and furthermore is easy and economical to realize by having the support element include a carrier, on which the lattice or the mirror is arranged, and a base body, while the actuator acts on the carrier and rests against the base body. The carrier is connected to the base body via linkages, such that a linear deflection of the actuator is transformed into a rotation of the carrier in the plane of the light beam, while the center of rotation lies outside the base body.
Owner:TOPTICA PHOTONICS AG
Dual-path controllable one-dimensional optic crystal lattice device
InactiveCN102147536AShape stableSmall mechanical propertiesNon-linear opticsOptical elementsPotential wellBeam splitter
The invention relates to a dual-path controllable one-dimensional optic crystal lattice device which comprises a first single-mode fiber and a second single-mode fiber, a first output lens and a second output lens, a first precision five-dimensional fiber adjusting rack and a second precision five-dimensional fiber adjusting rack, a right-angle prism, a precision four-dimensional adjusting rack, a polarizing beam splitter prism, a first aberration-eliminating balsaming lens, an L-shaped transference part, a first three-dimensional manual linear regulating platform, a second aberration-eliminating balsaming lens, a second three-dimensional manual linear regulating platform, a first electro-optic crystal, a second electro-optic crystal, a plane reflective mirror, a precision two-dimensional angle adjusting rack and an optical flat. In the device disclosed by the invention, two symmetrical optical lattice optical paths are adopted, and one plane reflective mirror is used. The device disclosed by the invention has the features: the shape of the optical crystal lattice is stable, the position, the potential well depth and the polarization status are convenient to be controlled and regulated, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices by circular aperture array
The invention discloses a method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices by a circular aperture array and relates to the field of neutral cold atom laser imprison and cold atom optic lattices. The method is implemented by a laser source system, a focusing lens, a beam expanding lens, a sub-wavelength circular aperture array, two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices, magneto-optical trap atom optic viscose, an atom detector, a laser, a wave chopper, another focusing lens, an optical fiber and a computer system on the basis of near-field optic diffraction of the sub-wavelength circular aperture array. Laser light irradiates on the horizontally arranged sub-wavelength circular aperture and diffracts through the same, local reinforcing near optical fields distributed periodically are generated, and neutral cold atoms loaded can be effectively imprisoned, and two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices are realized. The method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices can realize surface optic lattices of neutral cold atoms of different types, lattice constant is adjustable, principle is simple, operation is convenient, and application range is wide.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Reflective surface shape measuring method and apparatus based on two-dimensional optical lattice
ActiveCN108303038AEasy to measureQuick measurementUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorMeasurement device
Provided are a reflective surface shape measuring method and apparatus based on a two-dimensional optical lattice. According to the method, emitting light that undergoes modulation of a spatial lightmodulator and that undergoes lens Fourier transform twice forms an optical lattice on a reflective to-be-measured surface and an optical lattice on a reference plane, the optical lattice on the to-be-measured surface shifts relative to the reference plane after undergoing surface shape modulation of the to-be-measured surface, and the surface shape of the to-be-measured surface is reconstructed onthe basis of the amount of shift and a mode reconstruction algorithm based on Zernike polynomials. The invention further provides the reflective surface shape measuring apparatus and applications ofthe method in shape changes of a measured object. According to the disclosure, measuring processes are simplified and quick measuring is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Optical touch panel
InactiveUS20120044212A1High resolutionCost containmentInput/output processes for data processingOptical latticeImage resolution
Light emitting optical waveguide cores are provided in one of opposite side portions located on opposite sides of a detection area, and light receiving optical waveguide cores are provided in the other side portion. Light beams are emitted from distal ends of the light emitting cores disposed along an inner edge of the one side portion, and received on distal ends of the light receiving cores disposed along an inner edge of the other side portion, whereby an optical lattice is defined on the detection area for detection of a touch position. The detection area includes a higher resolution detection portion defined by arranging distal ends of at least some of the light receiving cores at a pitch that is smaller than the pitch of distal ends of the other light receiving cores.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
High resolution imaging device used for cold atom system
ActiveCN102879915AEasy to operateCompact structureOptical elementsOptical latticeHigh resolution imaging
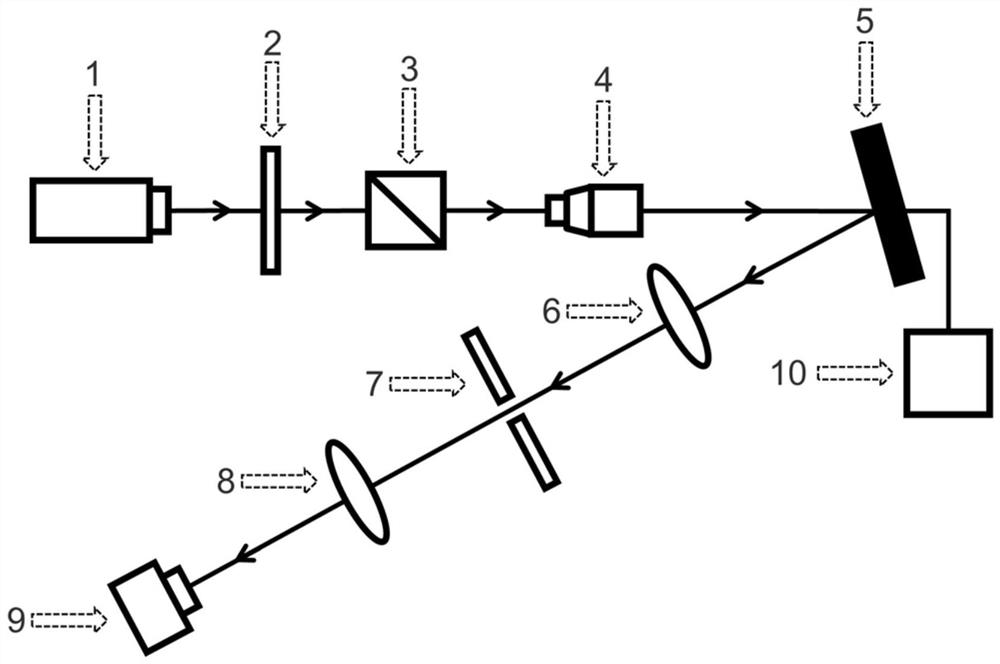
The invention discloses a high resolution imaging device used for a cold atom system. The device comprises a disordered optical lattice generation path and an imaging light path, and is characterized in that the disordered optical lattice generation path comprises a laser beam and is composed of a first lens, a second lens, a diffusion barrier, a reflection mirror and a dichroic mirror along the laser beam direction in sequence; the first lens and the second lens form a beam expanding system; the reflection mirror and the dichroic mirror are in 45 degrees with the beam direction; the imaging light path comprises an imaging lighting beam and is composed of a vacuum pool, a third lens, a dichroic mirror, a fourth lens and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) along the imaging lighting direction in sequence. According to the device, a laser speckle generation light path and an imaging light path are combined together, the purpose of loading disordered optical lattices to cold atom groups is realized by using an aberration elimination lens, the high resolution imaging of the atom groups is also realized, and the high resolution imaging device has the advantages of simple structure, high light path integration degree, less occupied space, adjustment convenience and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
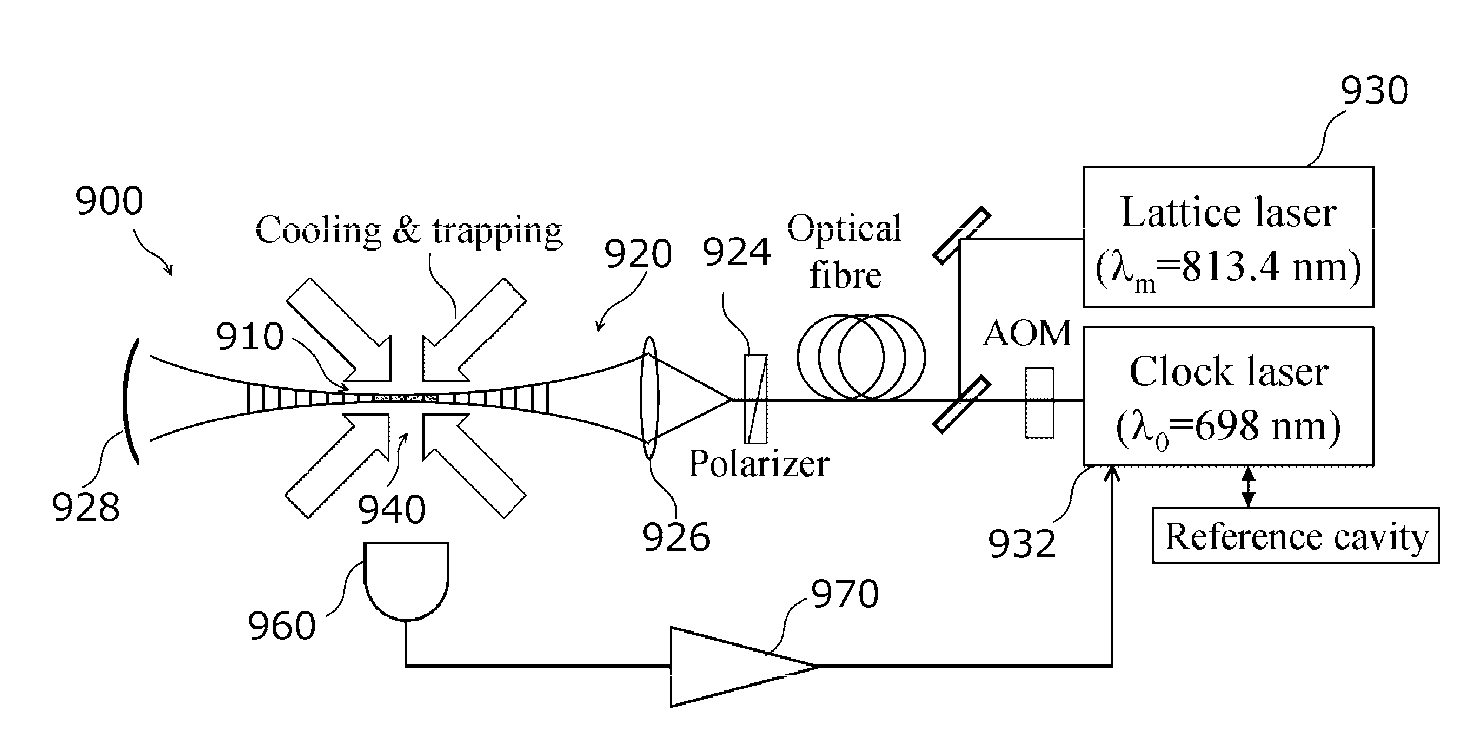
Optical lattice clock, clock device and laser light source
ActiveUS9553597B2Improve accuracyIncrease the number ofPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksOptical latticeElectronic states
Owner:RIKEN
Insurance policy based on optical lattice technology and information entering method and device
ActiveCN107369097AEliminate manual entrySave scanning and storage linksFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionHandwritingOptical lattice
The invention provides an insurance business system based on an optical lattice technology. The system includes an insurance policy, an insurance policy entering method and device, a medium and equipment. Lattice patterns are laid on the insurance policy, when a lattice digital pen is utilized to write on the insurance policy, a corresponding lattice pattern is detected as a user writes, and the detected lattice pattern is decoded into handwriting coordinate data which are then sent to terminal equipment. The terminal equipment receives the handwriting coordinate data, restores user handwriting characters on the electronic insurance policy according to the handwriting coordinate data, further converts the user handwriting characters into electronic text data, and uploads the electronic text data to the insurance business system, thereby completing handwritten insurance information entering work. The insurance business system omits many links such as scanning storage of an original form and manual entering on the basis of keeping a user handwriting habit, thereby greatly improving the entering efficiency of user information.
Owner:北京易教蓝天科技发展有限公司
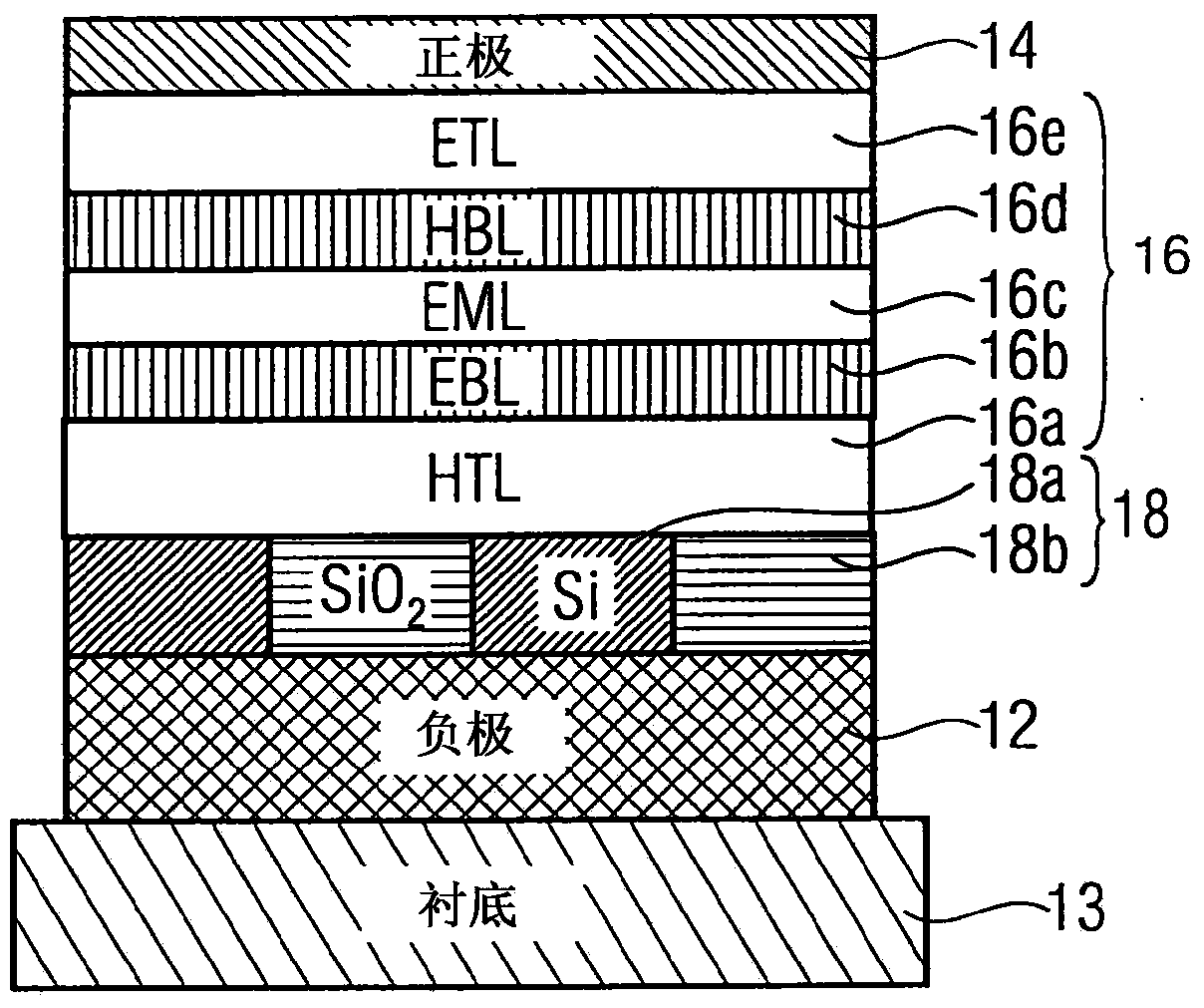
Electroluminescent light emission device comprising an optical lattice structure and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140103328A1Improve efficiencyImprove system efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerOptical lattice
A light emission device includes a substrate and a layer arrangement applied onto the substrate. The layer arrangement has a first electrode layer made of a conductive material and a second electrode layer made of a conductive material. At least one light-emitting layer made of an organic material is arranged between the first and second electrode layers. At least one intermediate layer having an optical lattice structure is provided between the light-emitting layer, a first main surface of the intermediate layer facing the light-emitting layer and the first main surface of the intermediate layer being formed to be planar within a tolerance range at least in the region of the optical lattice structure. The intermediate layer is conductive at least in regions between the first and a second main surface thereof.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Optical lattice imaging device
InactiveCN108872178ASmall distortionLarge axial magnificationFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical latticeImage resolution
The invention relates to an optical lattice imaging device. An atom source, a vacuum unit, a zero high-reflectivity mirror, a lens cone, a CCD imaging device, a detecting laser and a lattice light laser are arranged on a mounting plate; the vacuum unit is arranged on a light emitting direction of the atom source, the detecting laser and the lattice light laser; the zero high-reflectivity mirror isarranged on the front surface of the lattice light laser; the center lines of the lens cone and the CCD imaging device are coincided with each other and vertical to the propagation direction of lattice light; a lens assembly is arranged in the lens cone; the lens assembly comprises a convex lens, a plano-convex lens, a concave mirror, a first meniscus lens, a second meniscus lens and a plano-concave lens in turn from left to right. A larger caliber is adopted by the optical lattice imaging device, so that the collecting efficiency of fluorescent light can be increased, the spatial resolutionis larger, the CCD resolution ratio can be fully utilized, the distortion is smaller, the experimental error is reduced and the device can be popularized and applied to the field of optical lattice imaging devices.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
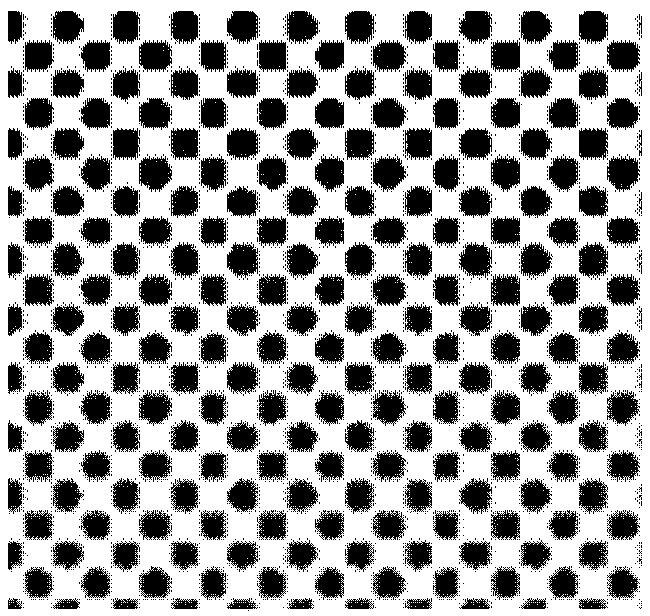
Method and system for improving display effect of optical lattice images
InactiveCN101546109AImprove the display effectQuality improvementPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceOptical latticeLight spot
The invention provides a method and a system for improving display effect of optical lattice images. Images consist of light spot arrays are reduced optically by a first optical element so as to generate a first optical image on a first imaging part with scattering effect, and until the space between light spots in the first optical image is less than or equal to the size of the light spot in an optical image, gaps do not exist between the light spots in the first optical image; and the first optical image is amplified optically by using a second optical element to form a second optical image of a light spot image on a second imaging part. By adopting the technique of the invention, the images after optical processing of the lattice images do not have lattice gaps when presented to people, thus, a smooth image feeling is provided to a viewer, the aim of improving the image display effect is achieved and further the image quality is improved. Simultaneously, the technique of the invention can also be used for designing new projection devices and illuminating systems.
Owner:BEIJING PAIRUIGEN SCI & TECH DEV
Filter for selectively processing optical and other signals
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
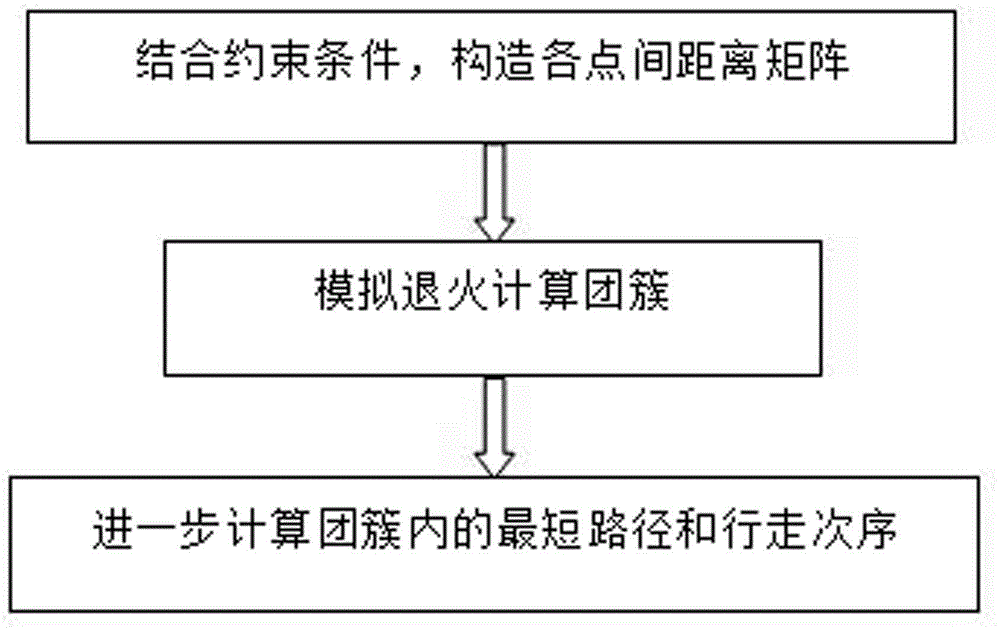
Path optimization method
InactiveCN104573880AReduce computing timeShort calculation timeForecastingThree levelOptical lattice
The invention discloses a path optimization method. The method is characterized in that the best and shortest path of large-scale destinations is calculated by a simulated annealing algorithm. According to the method and the system, the calculation time can be obviously shortened, and thus the method is relatively high in practicability and can be applied to cold atom dynamics and quantum phase transition calculation in an optical lattice, logistics distribution and other fields. The method can be applied to cold atom dynamics and quantum phase transition calculation in an optical lattice, logistics distribution and other fields, according to a three-level process algorithm, the calculation time can be obviously shortened, and thus the method is relatively high in practicability. In particular for calculation of large-scale destinations, the method is very short in calculation time and excellent in calculation effect, and thus the method is almost the unique feasible processing method.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Optical lattice clock, clock device and laser light source
ActiveUS20150194972A1Improve accuracyMiniaturizeApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlOptical latticeElectronic states
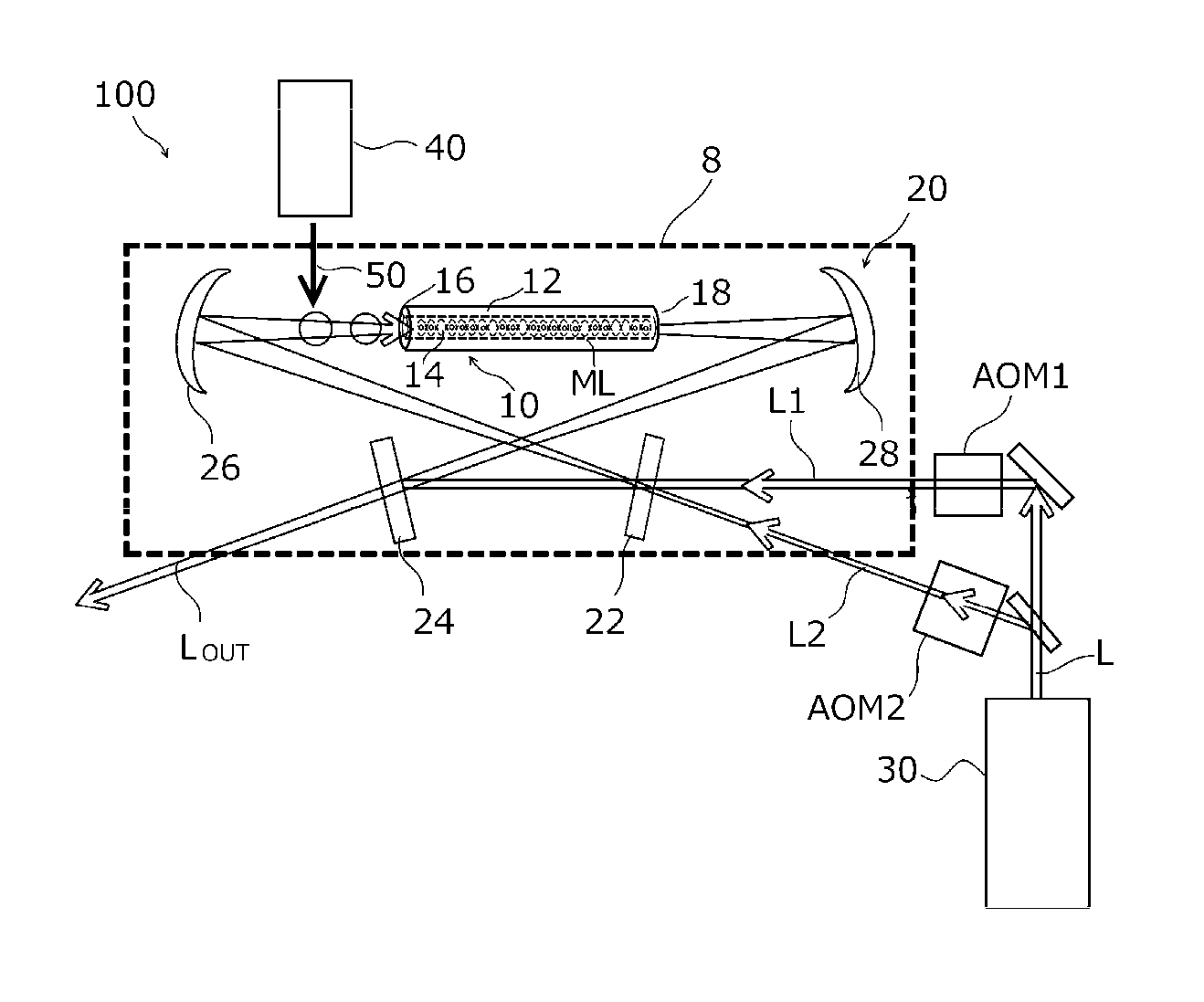
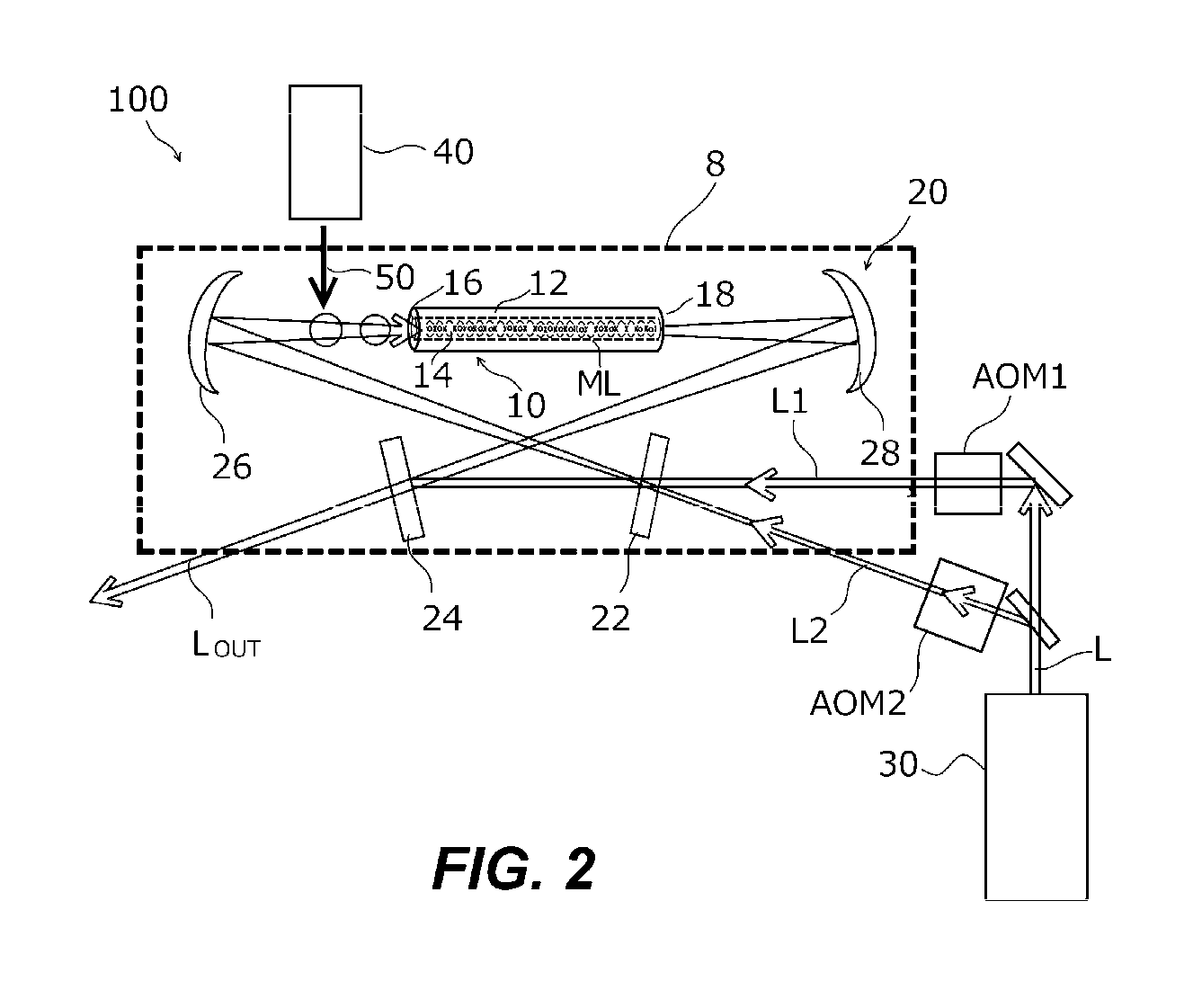
Various embodiments improve accuracy by increasing the number of atoms engaged in a clock transitions in an optical lattice clock. An exemplary optical lattice clock an embodiment comprises an optical waveguide, an optical path, a laser light source, and a laser cooler. The optical path has a hollow pathway that extends from a first end to a second end while being surrounded with a tubular wall, which is used as a waveguide path. The optical path passes between mirrors and through the pathway. The laser light source supplies to the optical path a pair of lattice lasers (L1 and L2) propagating in opposite directions with each other. The laser cooler supplies cooled atoms that have two levels of electronic states associated with a clock transition to the vicinity of the first end of the optical waveguide.
Owner:RIKEN
All-optical BEC preparation method based on three-dimensional Raman sideband cooling
ActiveCN111489846AShort timeThe principle is simpleRadiation/particle handlingOptical latticeMagneto-optical trap
The invention discloses an all-optical BEC preparation method based on three-dimensional Raman sideband cooling. The all-optical BEC preparation method comprises the steps: S1, preparing a cold atom group; S2, carrying out polarization gradient cooling; S3, carrying out three-dimensional Raman sideband cooling; cooling a group of atoms through a magneto-optical trap and preparing the atoms on a low hyperfine ground state; turning off the light and the magnetic field of the magneto-optical trap, opening an optical lattice, adiabatically loading each atom into each lattice point, and occupying agroup of vibration states according to the initial momentum; introducing a tiny magnetic field, enabling Zeeman splitting to be generated between different magneton energy level states, and cooling the atomic group to a dark state through pump light; S4, loading an optical dipole trap; S5, escaping, evaporating and cooling; and S6, achieving the escape evaporation cooling process by continuouslyreducing the depth of the optical trap, and finally preparing the BEC. The method has the advantages of being simple in principle, convenient to operate, capable of shortening preparation time and improving preparation efficiency and the like.
Owner:LOW SPEED AERODYNAMIC INST OF CHINESE AERODYNAMIC RES & DEV CENT
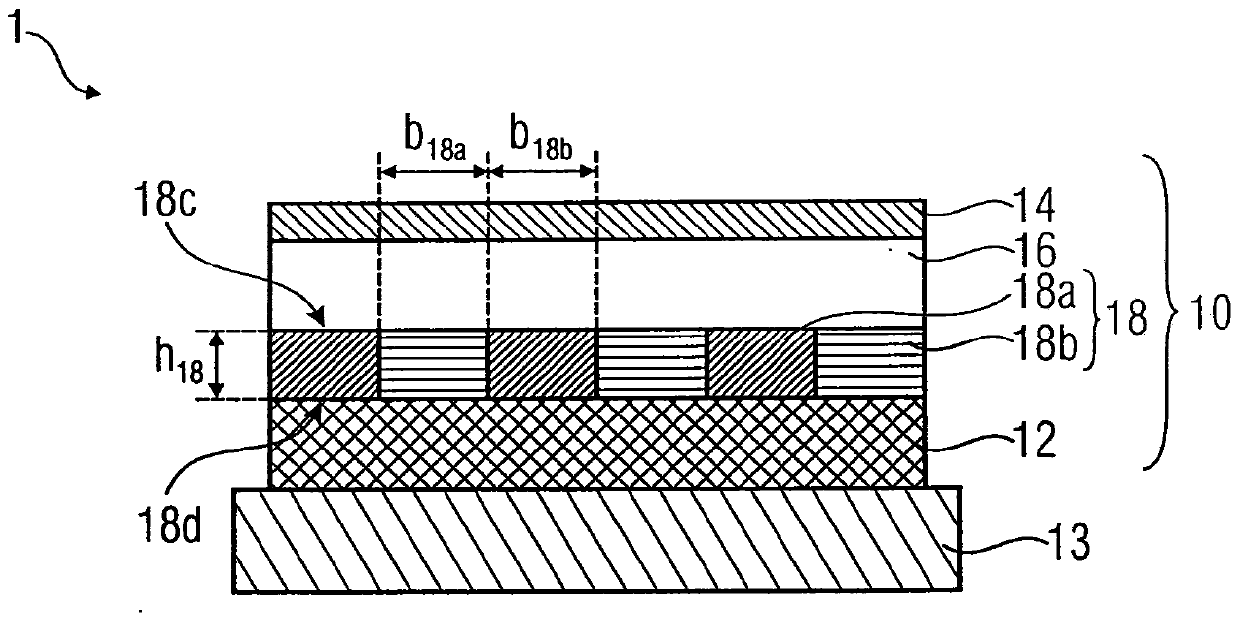
Electroluminescent light emission device having an optical grating structure, and method for production thereof
ActiveCN103636024ACoupling output efficiency improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical latticeGrating
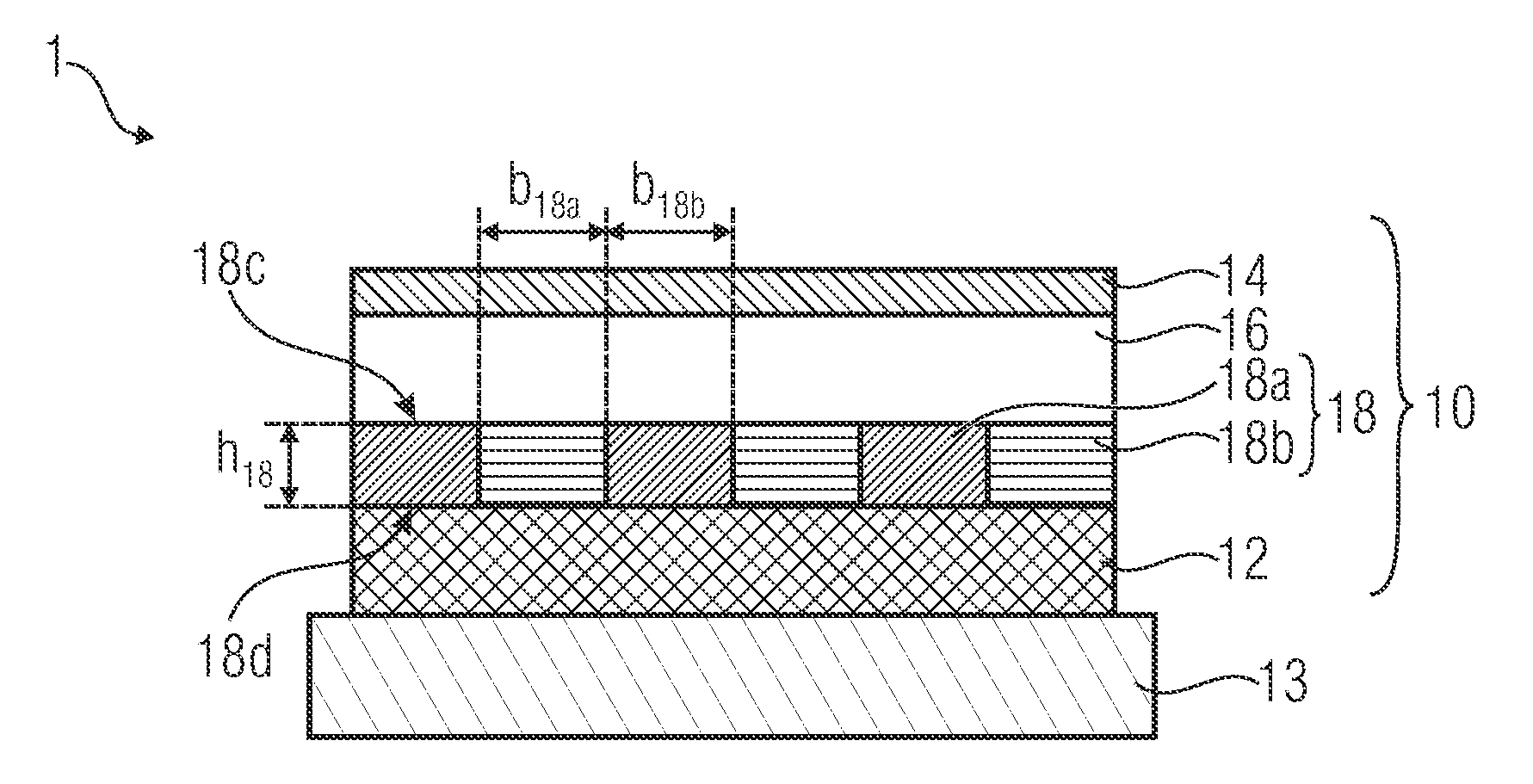
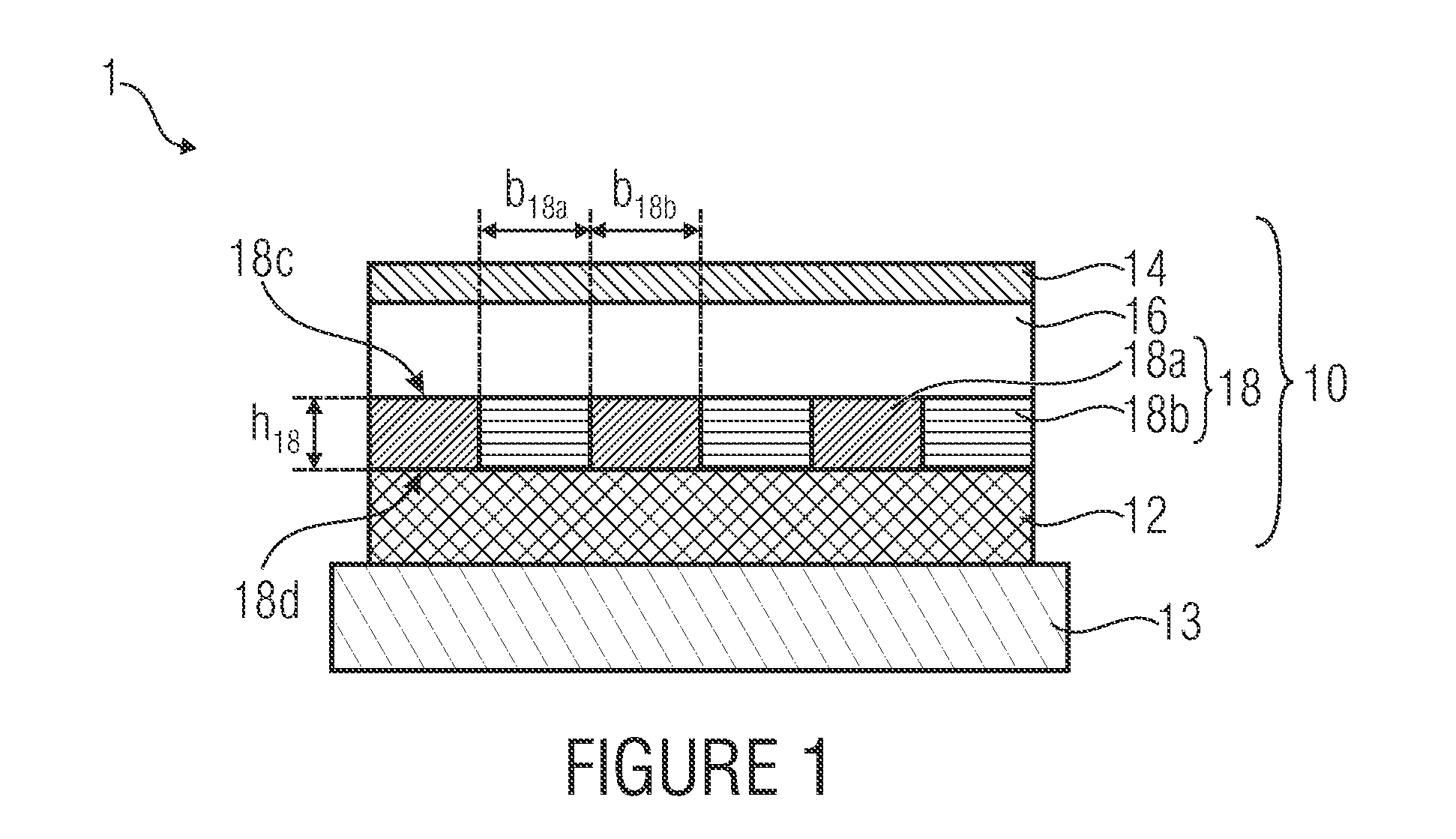
A light emission device 1 comprises a substrate 13 and a layer arrangement 10 that has been applied to the substrate 13. The layer arrangement 10 has a first electrode layer 12 consisting of a conductive material and a second electrode layer 14 consisting of a conductive material. At least one light-emitting layer 16 consisting of an organic material is arranged between the first and second electrode layers 12 and 14. At least one intermediate layer 18 having an optical grating structure is arranged between the light-emitting layer 16 and one of the two electrode layers. A first main surface 18c of the intermediate layer 18 faces the light-emitting layer 16, said first main surface 18c of the intermediate layer having a planar design at least in the region of the optical grating structure within a tolerance range. At least regions of the intermediate layer 18 between the first main surface and a second main surface 18c and 18d thereof are conductive.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Displacement detecting device, scale calibrating method and scale calibrating program
ActiveUS20130099106A1Configuration easily and inexpensivelyCorrect measurement errorMaterial analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyOptical latticeComputer vision
A displacement detecting device includes: a scale which has an optical lattice; a detecting unit which is disposed so as to be movable in a scanning direction relative to the scale, inclusive of at least a first detection portion, a second detection portion and a third detection portion, arranged in the scanning direction for detecting position information from the optical lattice; and a calculating portion configured to obtain a self-calibration curve on graduations of the scale by specifying positions of the detection portions and calculating measurement error based on the position information detected by the detecting unit, wherein: the detecting unit is provided so that a distance between the first detection portion and the second detection portion and a distance between the second detection portion and the third detection portion are different from each other and do not form an integral multiple.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Lattice light sheet microscope and method for tiling lattice light sheet in lattice light sheet microscope
ActiveCN111103678AEasy to tileHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesOptical latticeSpatial light modulator
The present disclosure relates to a lattice light sheet microscope and a method for tiling a lattice light sheet in the lattice light sheet microscope. The lattice light sheet microscope comprises: asingle spatial light modulator (SLM) of which the optical modulation plane conjugates to an image plane of an excitation objective lens and which is configured to: generate an optical lattice by loading a phase map obtained from a central cross section of a corresponding optical lattice of a desired lattice light sheet, and tile the optical lattice by loading a phase map obtained from an off-center cross section of the corresponding optical lattice; a transparent annular diaphragm, arranged at a plane conjugate to the entrance pupil of the excitation objective lens; and a first galvanometer, configured to: scan each optical lattice in the extending direction thereof so as to form a tiled lattice light sheet. Hence, an LLS may be easily tiled without changing the hardware structure of a conventional LLSM, and the high-resolution and high-speed imaging capabilities of an LLSM are maintained on an imaging field of view that is much greater than the size of the light sheet, which is convenient, low cost and may be easily applied.
Owner:WESTLAKE UNIV
Method and system for improving display effect of optical lattice images
InactiveCN101546109BImprove the display effectQuality improvementPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceOptical latticeImaging quality
The invention provides a method and a system for improving display effect of optical lattice images. Images consist of light spot arrays are reduced optically by a first optical element so as to generate a first optical image on a first imaging part with scattering effect, and until the space between light spots in the first optical image is less than or equal to the size of the light spot in an optical image, gaps do not exist between the light spots in the first optical image; and the first optical image is amplified optically by using a second optical element to form a second optical imageof a light spot image on a second imaging part. By adopting the technique of the invention, the images after optical processing of the lattice images do not have lattice gaps when presented to people, thus, a smooth image feeling is provided to a viewer, the aim of improving the image display effect is achieved and further the image quality is improved. Simultaneously, the technique of the invention can also be used for designing new projection devices and illuminating systems.
Owner:BEIJING PAIRUIGEN SCI & TECH DEV
Tunable diode laser system with external resonator
ActiveUS20090034563A1Reliable mode-hop-free tuningEasy and economical to realizeSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical latticeLight beam
A tunable diode laser system with external resonator in Littrow or Littman configuration has an optical lattice on which the light beam from a laser diode is diffracted, a support element to hold the lattice or to hold a mirror, which reflects the light diffracted by the lattice, and an actuator to change the position of the lattice or the mirror. The tunable diode laser system enables a reliable mode-hop-free tuning and furthermore is easy and economical to realize by having the support element include a carrier, on which the lattice or the mirror is arranged, and a base body, while the actuator acts on the carrier and rests against the base body. The carrier is connected to the base body via linkages, such that a linear deflection of the actuator is transformed into a rotation of the carrier in the plane of the light beam, while the center of rotation lies outside the base body.
Owner:TOPTICA PHOTONICS AG
Integrated general scientific cold atom experiment cavity
ActiveCN113161034ASimple structureEasy to installRadiation/particle handlingNuclear energy generationOptical latticeOptical mount
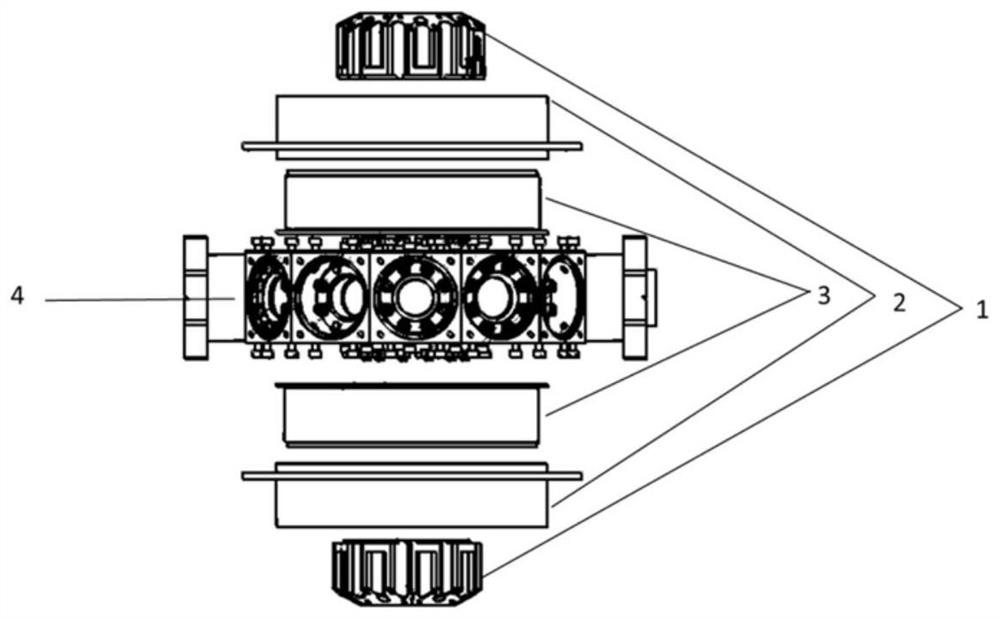
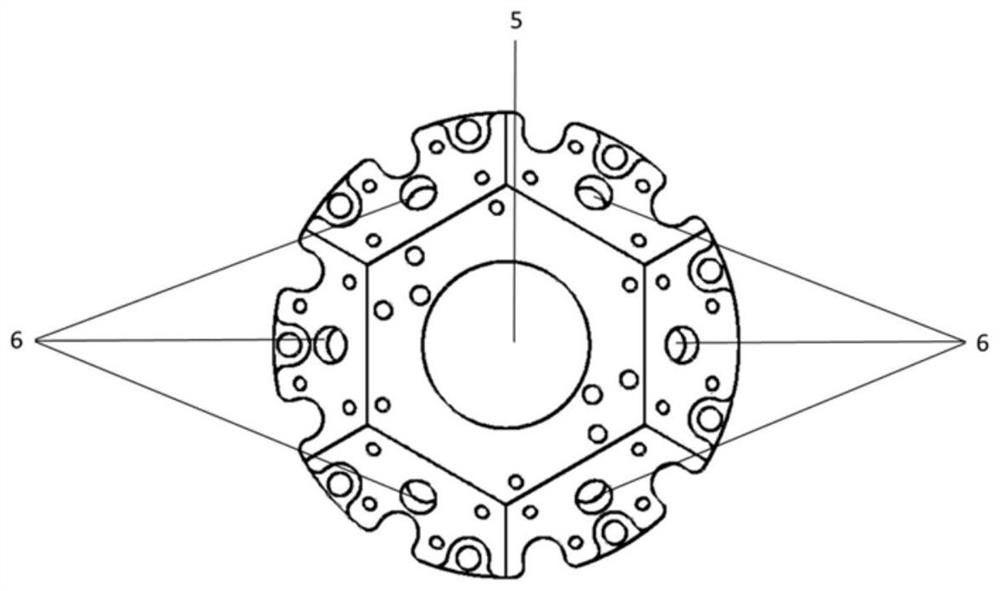
The invention discloses a brand-new integrated general scientific cold atom experiment cavity. The brand-new integrated general scientific cold atom experiment cavity comprises a vacuum cavity, an optical mounting disc and a magnetic field coil assembly. The integrated general scientific cold atom experiment cavity is comprehensive in function and provided with 24 optical windows; magnetic field coils of the experiment cavity are variable in direction, so a large gradient range, a large magnetic field coil with a one-way strong magnetic field and a fast-changing coil capable of achieving fast scanning can be provided, the requirements of cooling, detection and imaging during ultra-cold atom experiments and various scientific experiments on optical traps can be met, the light passing requirements of all the common optical lattice lasers of cold and ultra-cold atoms such as one-dimensional atoms, two-dimensional atoms, three-dimensional atoms, hexagonal atoms, triangular atoms and the like at present are met, and the requirements of corresponding magnetic fields are met. As a carrier for scientific experiments, the brand-new integrated general scientific cold atom experiment cavity of the invention provides a solution for a physical experiment engineering system of cold atoms.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
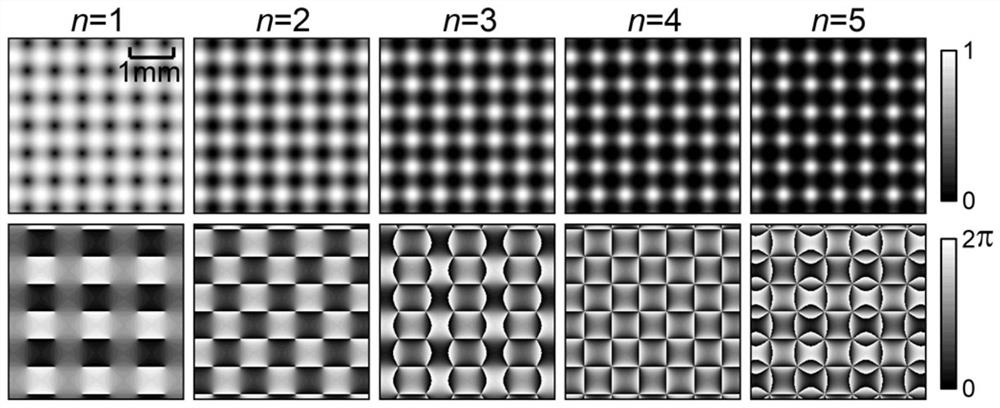
Optical system for generating any-order optical vortex array and limited optical lattice with defects
ActiveCN114019690AEasy to controlReduced accuracy requirementsPhotometryHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSpatial light modulatorOptical lattice
The invention discloses an optical system for generating an any-order optical vortex array and a limited optical lattice with defects. The optical system comprises a laser, a collimation and beam expansion system, a spatial light modulator, a 4-f system and an image detector which are arranged according to an optical path. Linear polarization Gaussian light emitted by the laser passes through the collimation and beam expansion system and then irradiates the spatial light modulator for complex amplitude modulation, first-order diffraction light of the emergent light generates an arbitrary-order alternating optical vortex array on the rear focal plane of the first 2-f system, and an adjustable limited optical lattice with defects is generated on the rear focal plane of the second 2-f system. The topological charge value of each vortex in the generated random-order alternating optical vortex array and the distance between the vortexes can be accurately controlled; light spots in the generated limited optical lattice are arranged according to a specific rule, the number of the light spots is limited and controllable, and optical lattice defects can be generated by controlling parameters; the generated controllable and adjustable limited space optical lattice with the optical lattice defects can be applied to optical control of various particles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Non-diffraction two-dimensional optical lattice period adjusting system based on zoom lens
ActiveCN110262044ARapid continuous adjustmentAchieve continuous adjustment effectOptical elementsCamera lensOptical lattice
The invention relates to a non-diffraction two-dimensional optical lattice period adjusting system based on a zoom lens. The system comprises a laser, a first half-wave plate, a lens group for expanding beams, a beam splitting prism, a second half-wave plate, a spatial light modulator, a first lens, a mask plate, a reflector, a second lens, a zoom lens, a third lens and a detector. After the light beam retaining the base level information is reflected by the reflector, the light beam is interfered behind the reflector through the second lens to form a non-diffraction two-dimensional optical lattice, then sequentially passes through the zoom lens and the third lens and is imaged on the detector, wherein the position of the back focal plane of the zoom lens is kept unchanged during focusing, and the distance between the zoom lens and the third lens is the sum of the back focal length of the zoom lens and the front focal length of the third lens; by adjusting the focal length of the zoom lens, the continuous change of the amplification factor of the beam expanding system is achieved, so that the rapid continuous adjustment of the diffraction-free two-dimensional optical lattice period can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com