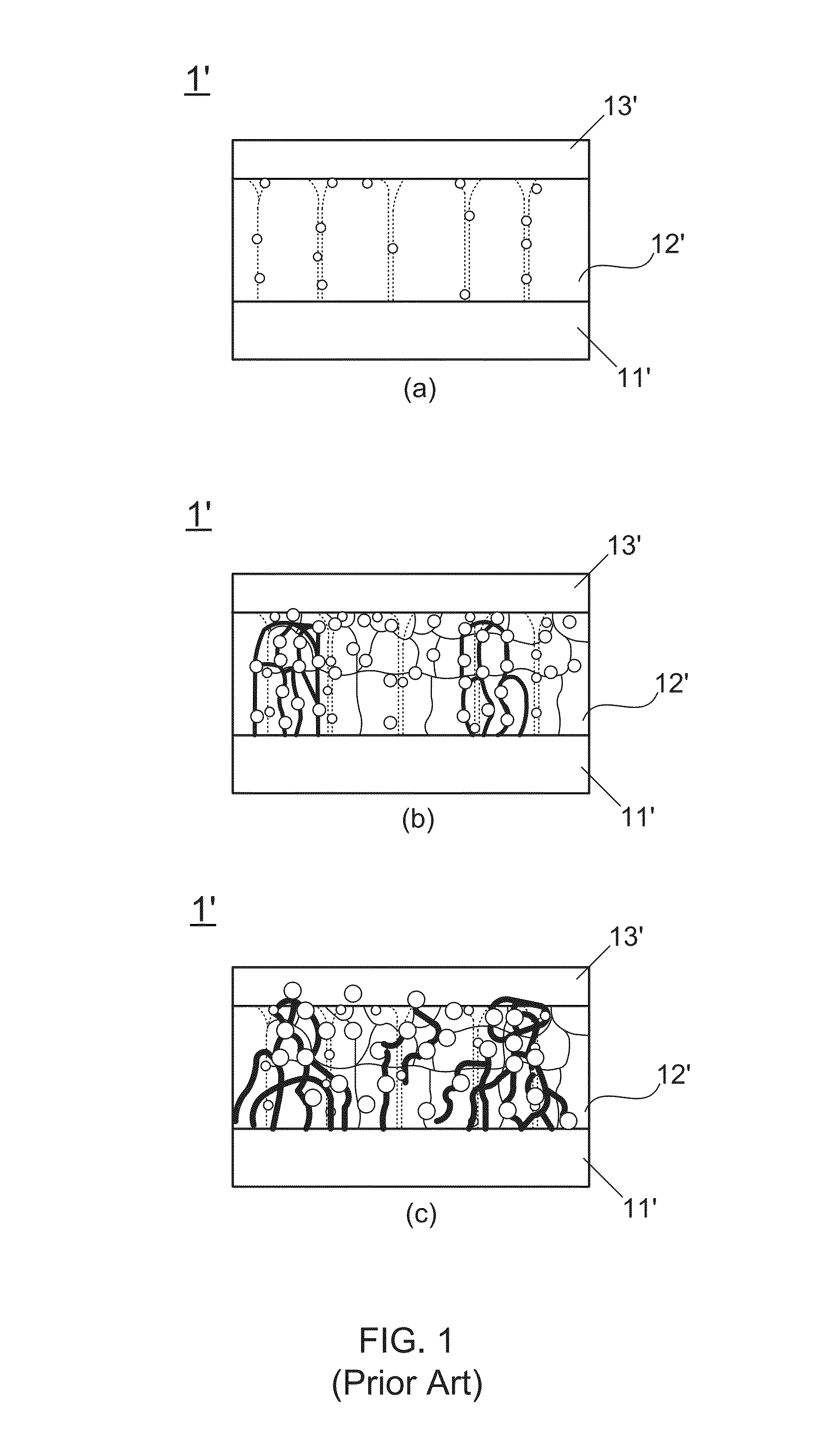
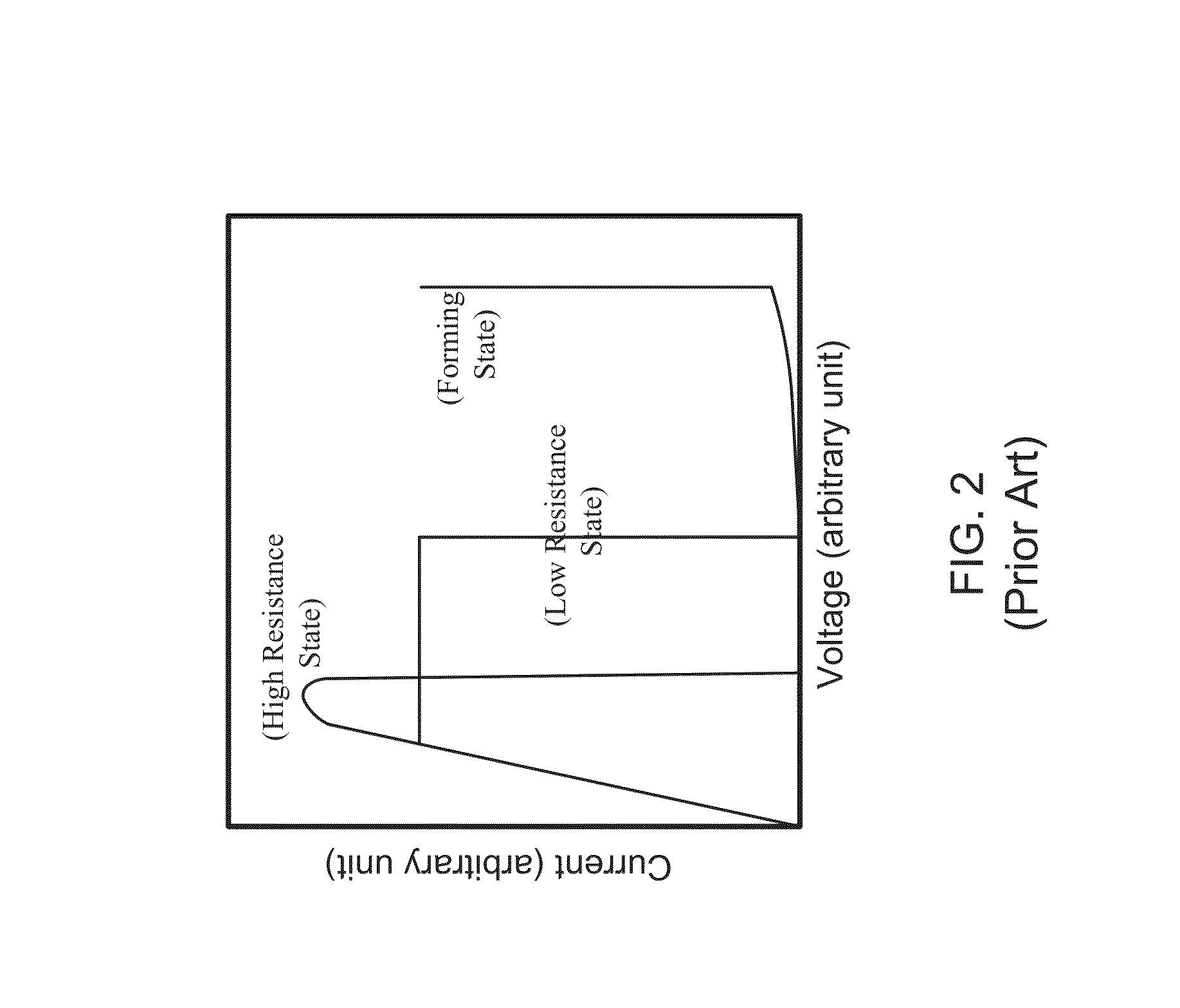
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Low resistance state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
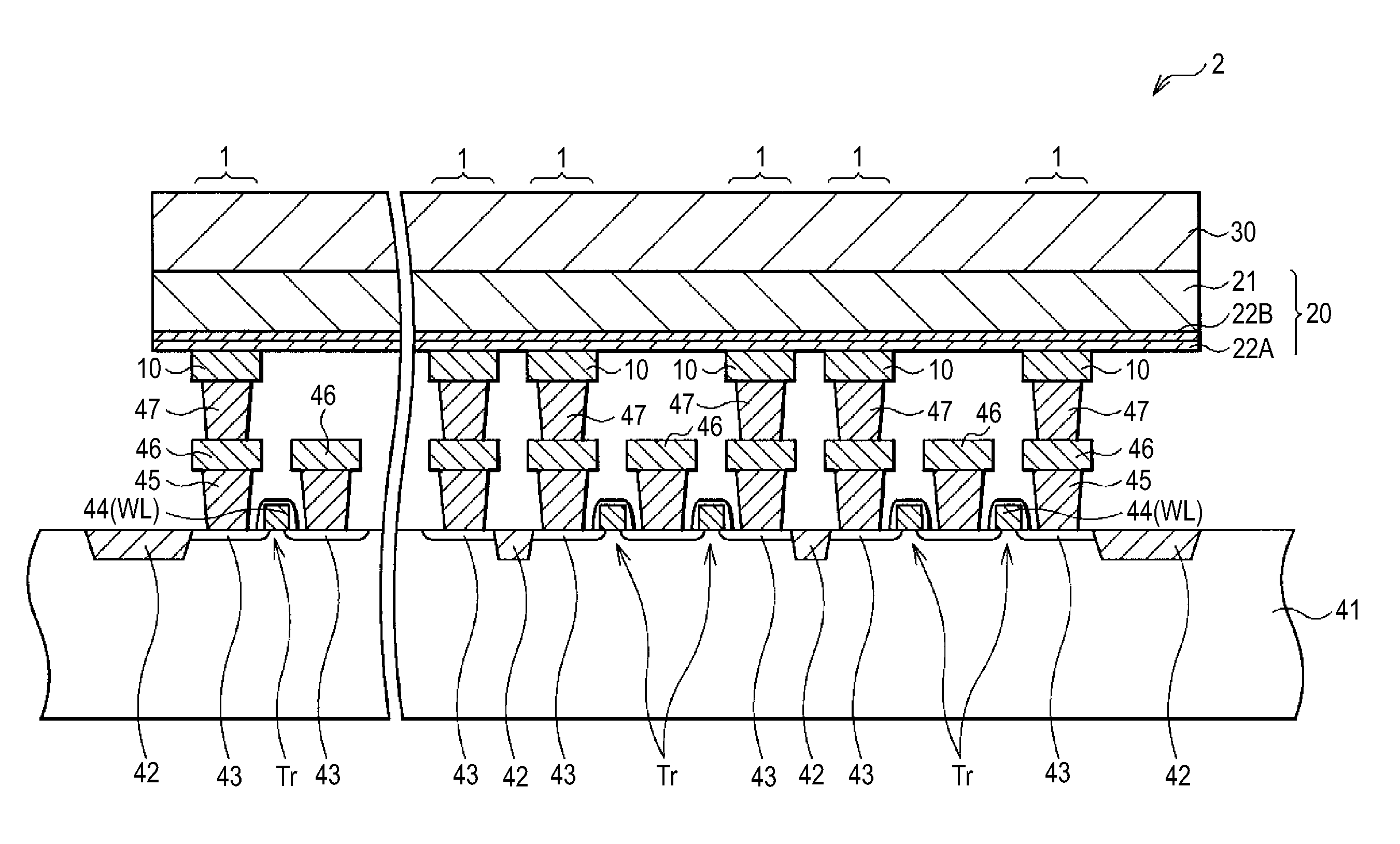
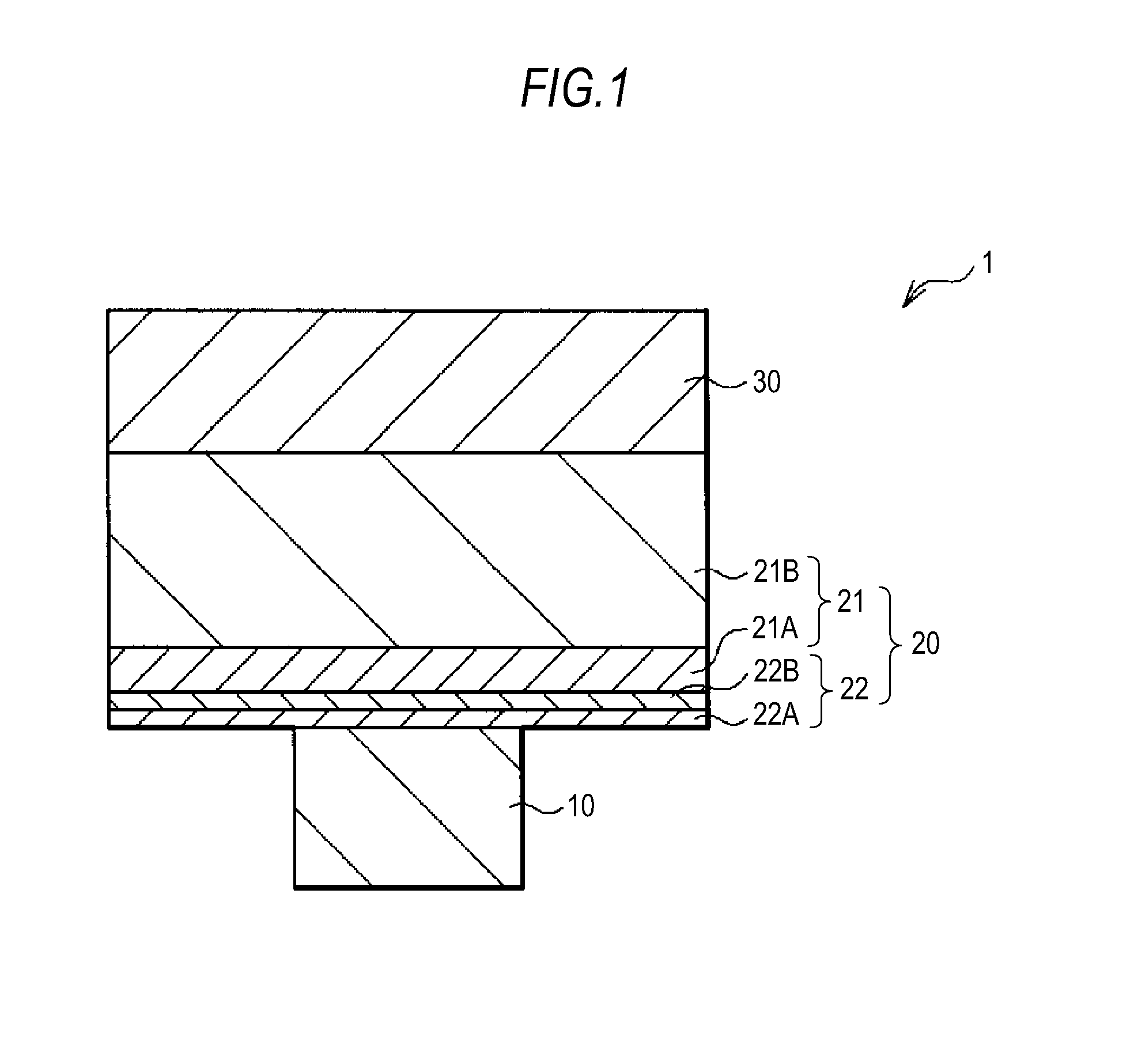
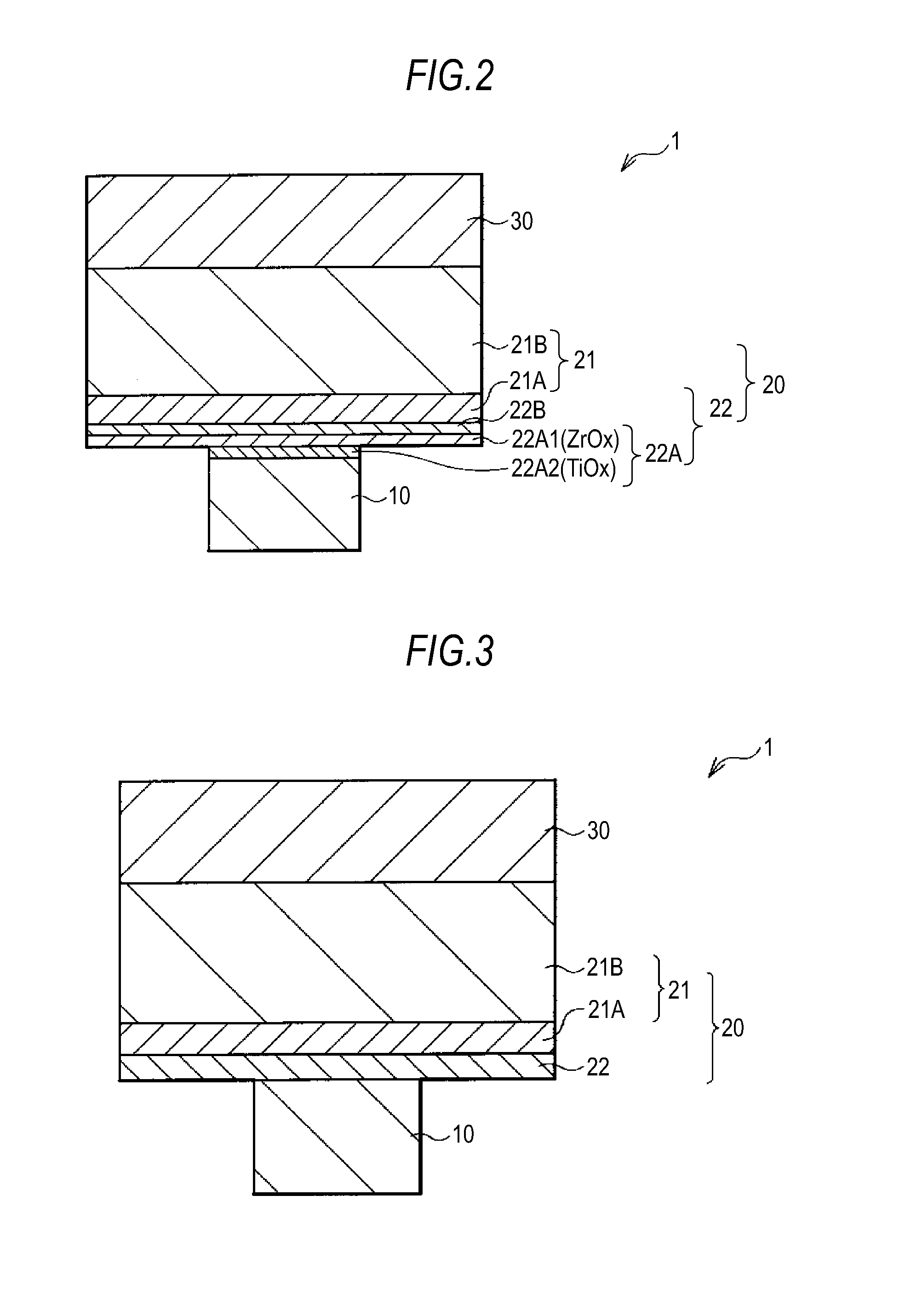
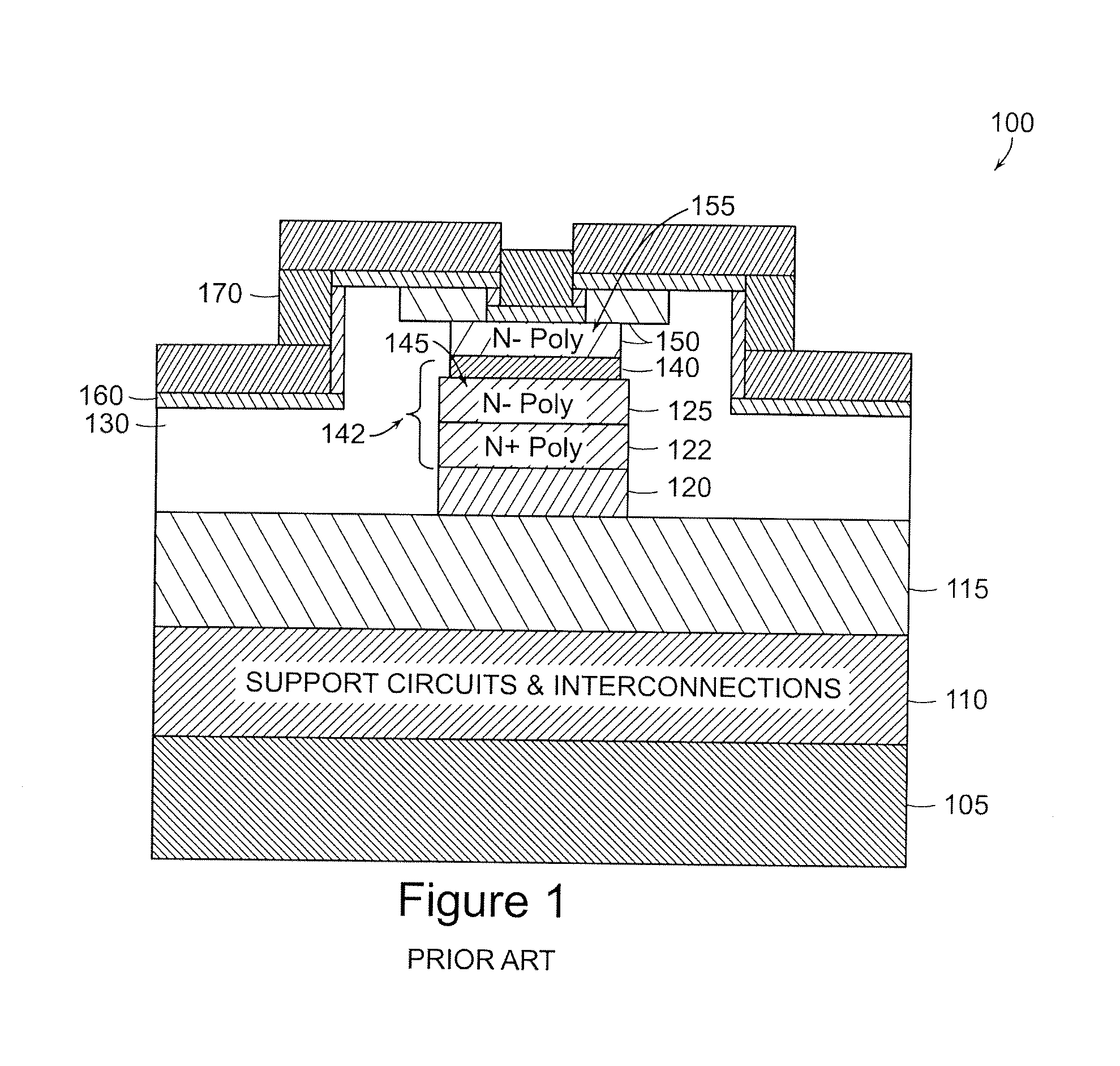
Memory component, memory device, and method of operating memory device
InactiveUS20110194329A1Avoid reactionImprove repetition durabilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageLow resistanceTellurium
A memory component includes: a first electrode; a memory layer; and a second electrode which are provided in that order, wherein the memory layer includes an ion source layer containing aluminum (Al) together with at least one chalcogen element selected from the group consisting of tellurium (Te), sulfur (S), and selenium (Se), and a resistance variable layer provided between the ion source layer and the first electrode and containing an aluminum oxide and at least one of a transition metal oxide and a transition metal oxynitride having a lower resistance than the aluminum oxide.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
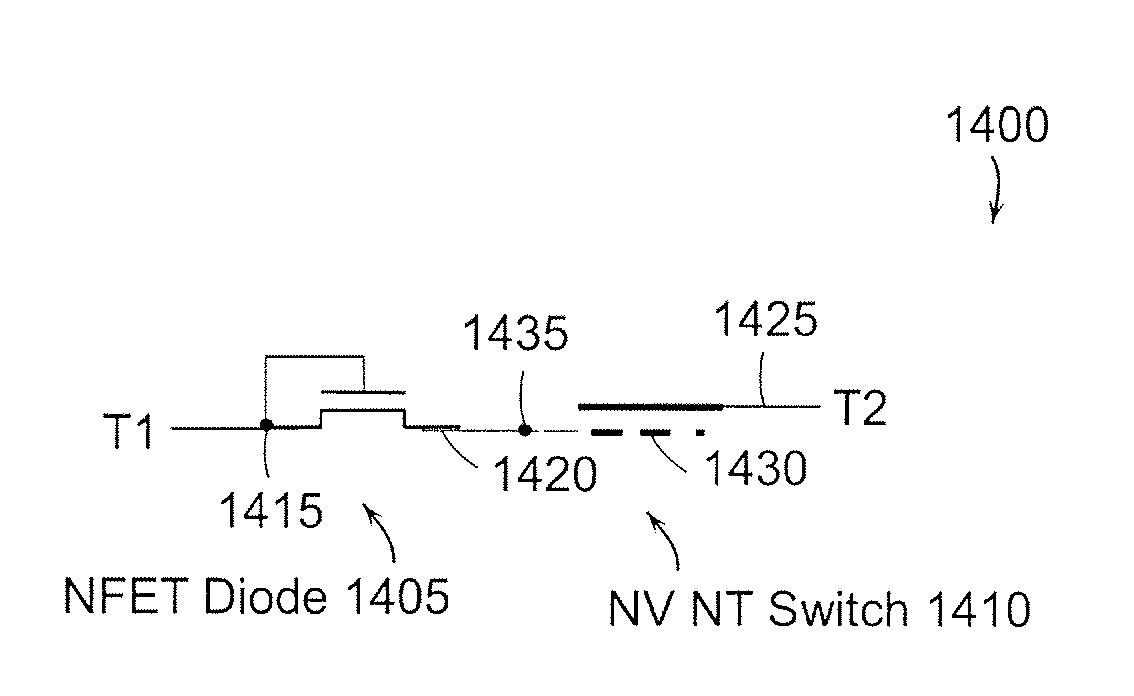
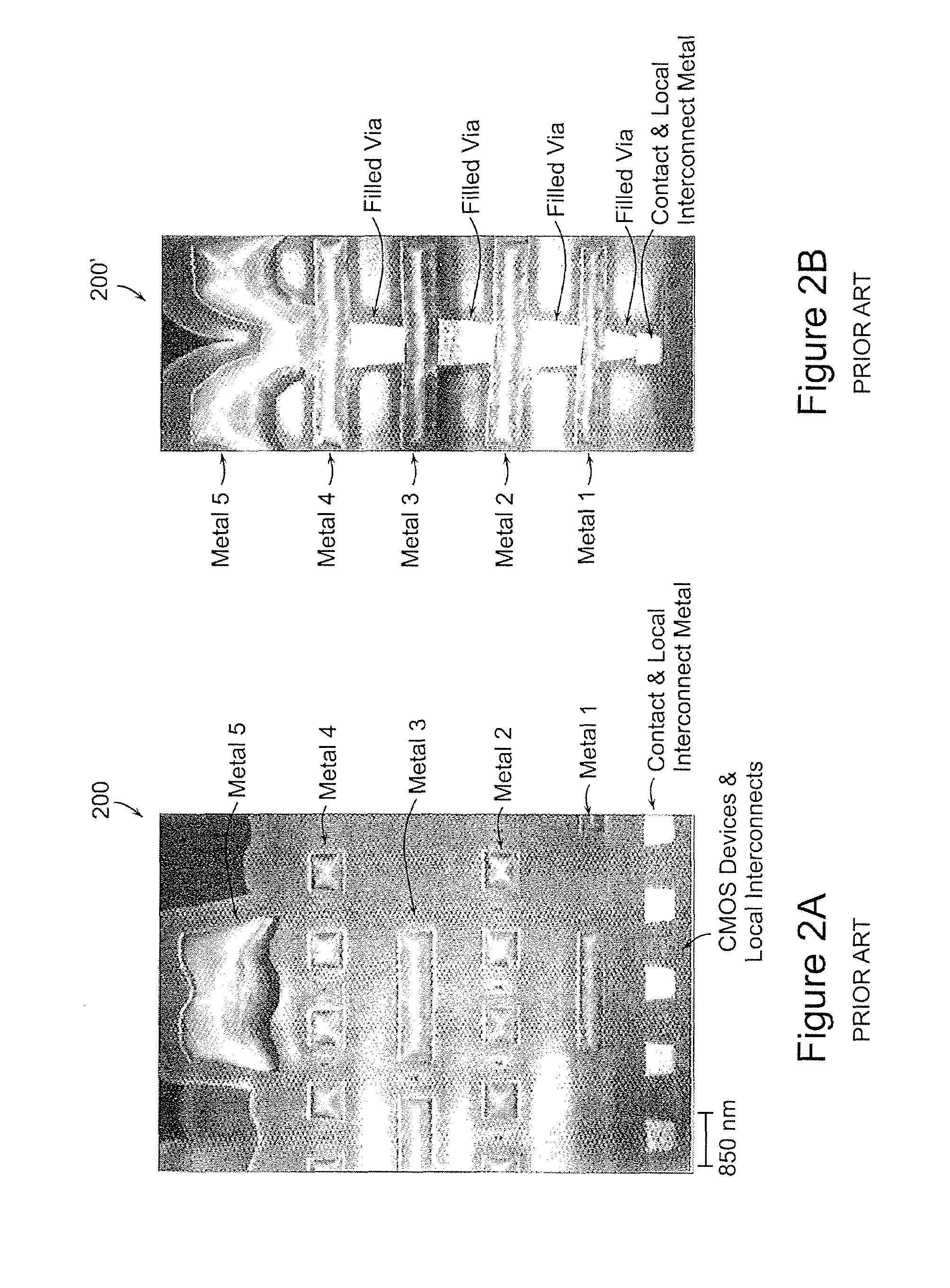
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080157126A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsEngineeringSemiconductor components
Under one aspect, a non-volatile nanotube diode device includes first and second terminals; a semiconductor element including a cathode and an anode, and capable of forming a conductive pathway between the cathode and anode in response to electrical stimulus applied to the first conductive terminal; and a nanotube switching element including a nanotube fabric article in electrical communication with the semiconductive element, the nanotube fabric article disposed between and capable of forming a conductive pathway between the semiconductor element and the second terminal, wherein electrical stimuli on the first and second terminals causes a plurality of logic states.
Owner:NANTERO
Programmable resistive memory cell with sacrificial metal
ActiveUS8097874B2Improve data retentionLow resistance stateBulk negative resistance effect devicesElectrical conductorStandard electrode potential
Programmable metallization memory cells include an electrochemically active electrode and an inert electrode and an ion conductor solid electrolyte material between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. A sacrificial metal is disposed between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. The sacrificial metal has a more negative standard electrode potential than the filament forming metal.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Power device
ActiveUS20060105624A1Inexpensively mass-producedHigh torqueCoupling device connectionsElectrically conductive connectionsEngineeringSurface plate
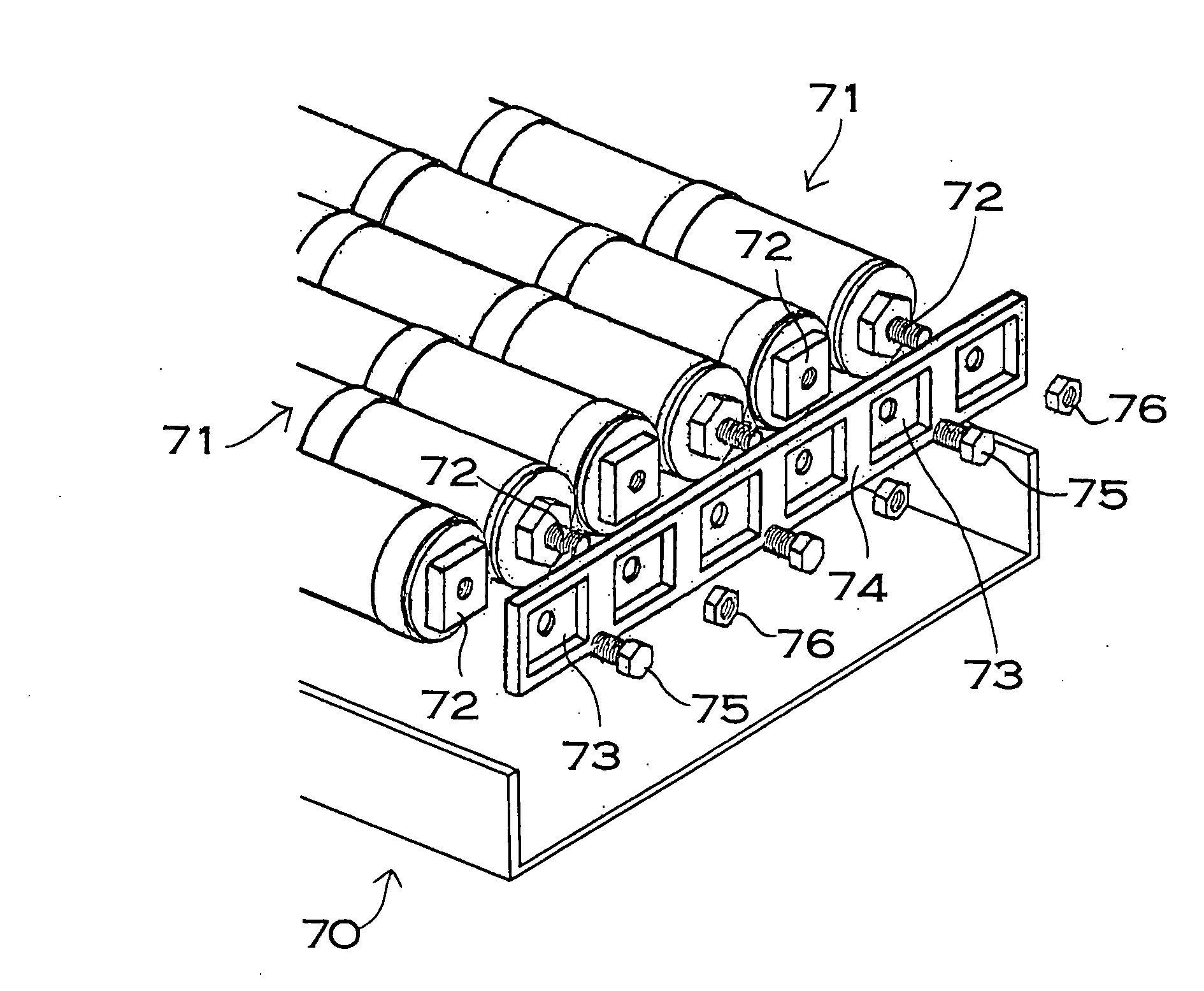
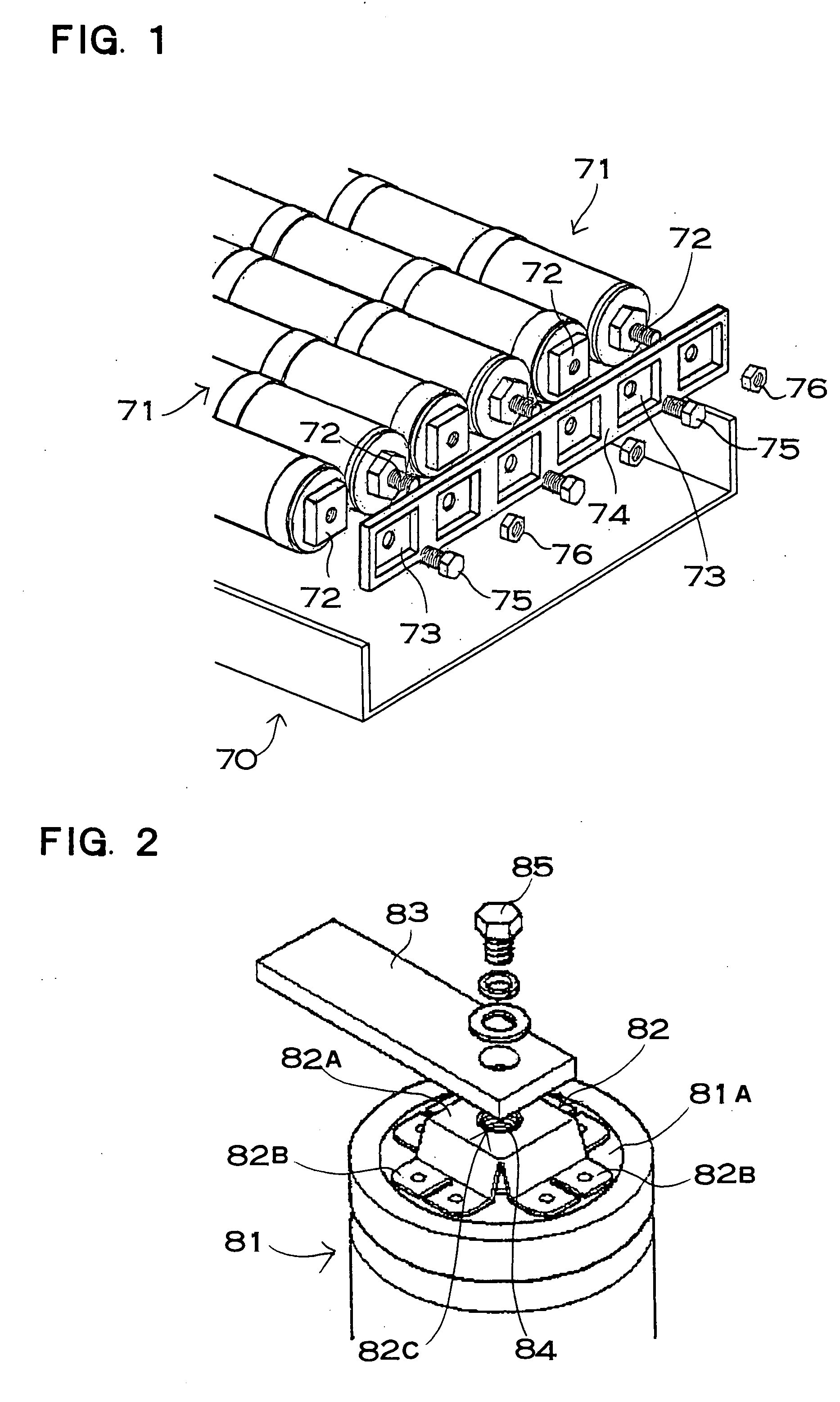
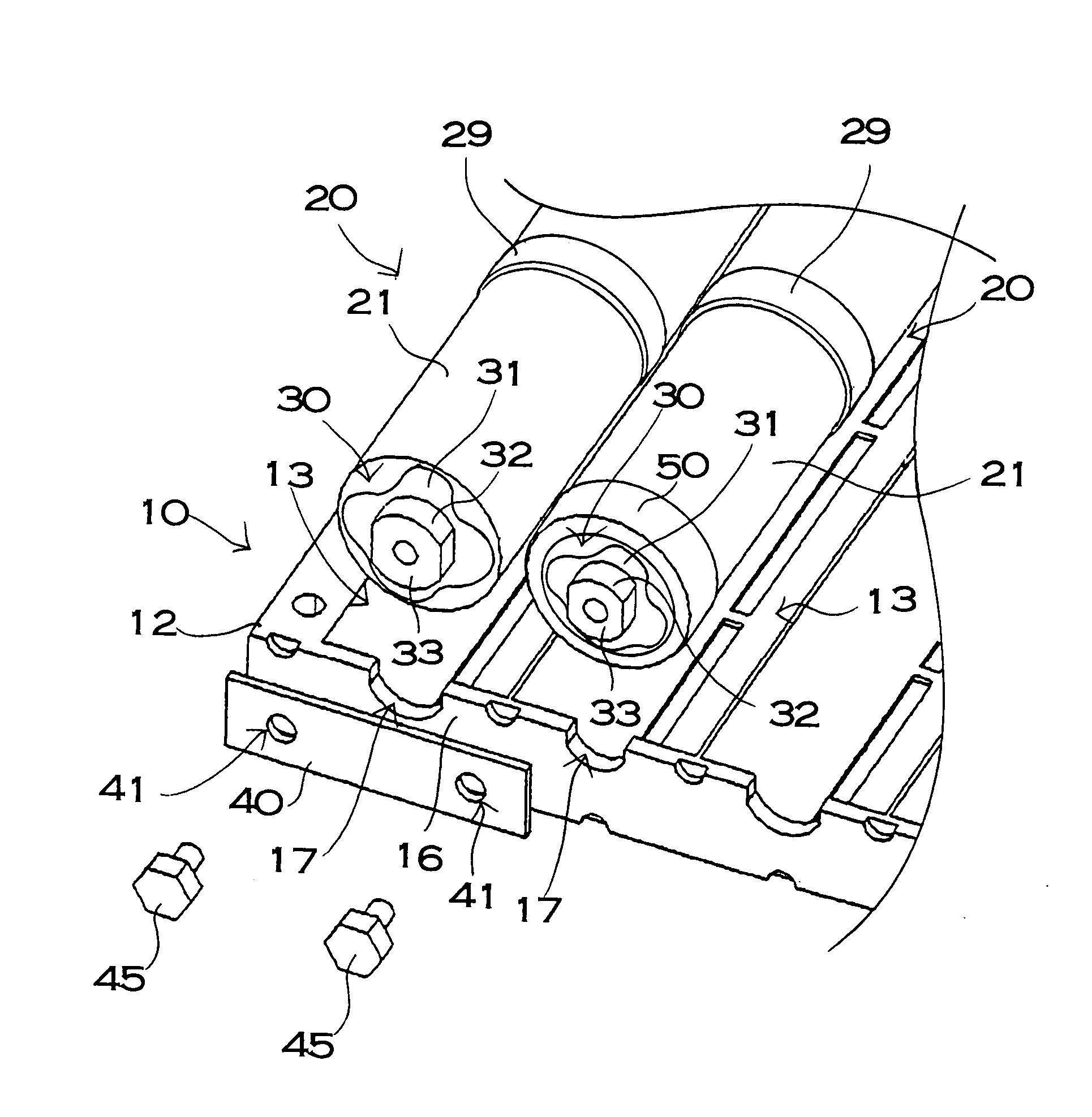
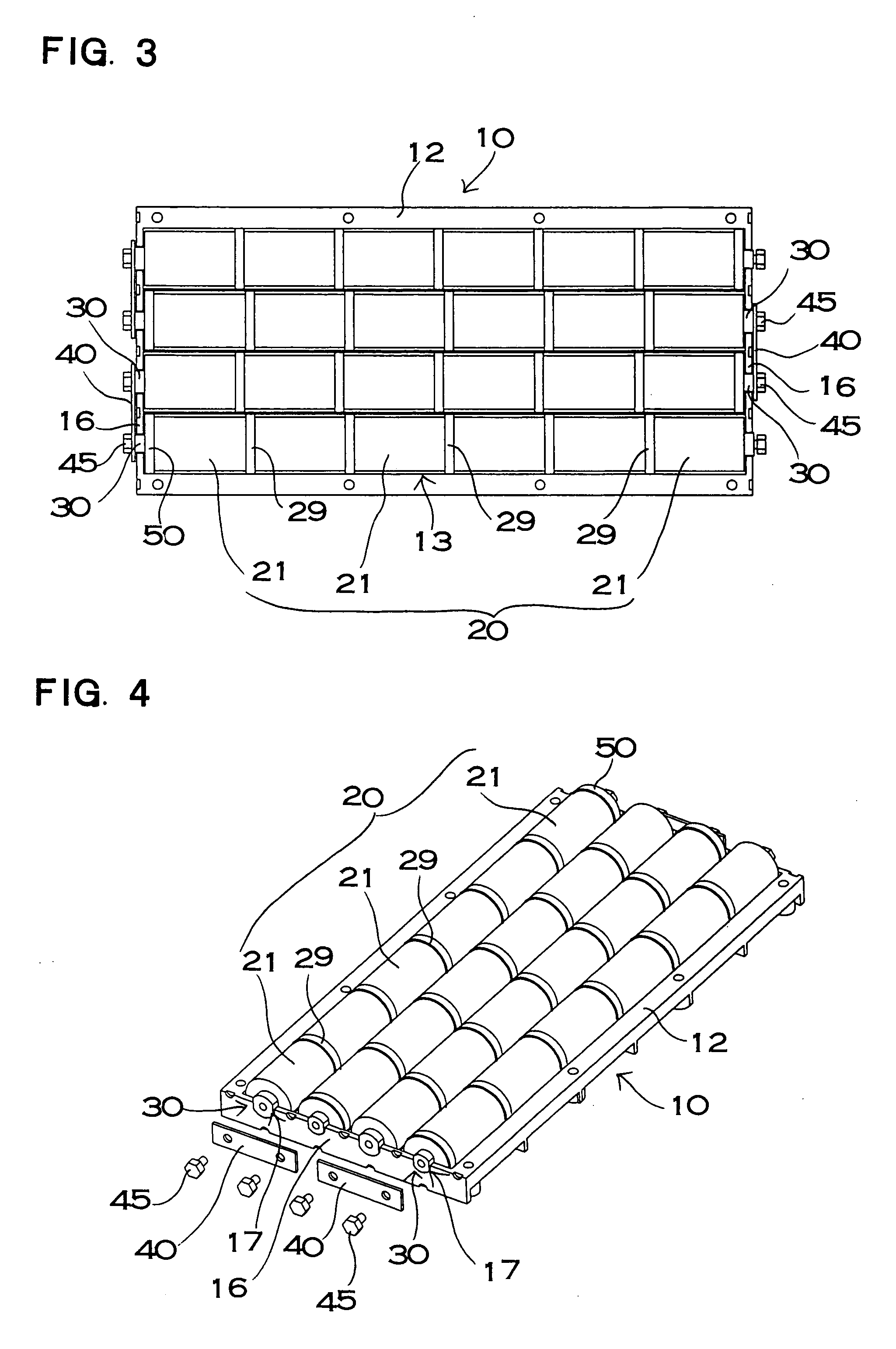
A power device includes a battery module for fixing a connecting terminal to an end and a bus bar connected to the connecting terminal of the battery module. The connecting terminal includes a fixing plate portion fixed to the end of the cell, an outer cylindrical portion protruded cylindrically from the fixing plate portion, an end face plate portion closing a tip surface of the outer cylindrical portion, and an inner cylindrical portion protruded from the end face plate portion toward the fixing plate portion. The connecting terminal is provided with a female screw on an internal surface of the inner cylindrical portion and a setscrew penetrating through the bus bar is screwed toward the female screw, and the bus bar is fixed to the connecting terminal through the setscrew.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Nonvolatile nanotube diodes and nonvolatile nanotube blocks and systems using same and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080212361A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateNanotechSolid-state devicesBit lineElectricity
Under one aspect, a memory array includes word lines; bit lines; memory cells; and a memory operation circuit. Each memory cell responds to electrical stimulus on a word line and on a bit line and includes: a two-terminal non-volatile nanotube switching device having first and second terminals, a semiconductor diode element, and a nanotube fabric article capable of multiple resistance states. The semiconductor diode and nanotube article are between and in electrical communication with the first and second terminals, which are coupled to the word line bit line respectively. The operation circuit selects cells by activating bit and / or word lines, detects a resistance state of the nanotube fabric article of a selected memory cell, and adjusts electrical stimulus applied to the cell to controllably induce a selected resistance state in the nanotube fabric article. The selected resistance state corresponds to an informational state of the memory cell.
Owner:NANTERO
Memory element and memory device
ActiveUS20090173930A1Low resistance stateGood controllabilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageVoltage pulsePhysics
A memory device of a resistance variation type, in which data retaining characteristic at the time of writing is improved, is provided. The memory device includes: a plurality of memory elements in which a memory layer is provided between a first electrode and a second electrode so that data is written or erased in accordance with a variation in electrical characteristics of the memory layer; and pulse applying means applying a voltage pulse or a current pulse selectively to the plurality of memory elements. The memory layer includes an ion source layer including an ionic-conduction material and at least one kind of metallic element, and the ion source layer further contains oxygen.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Nonvolatile Nanotube Diodes and Nonvolatile Nanotube Blocks and Systems Using Same and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20090184389A1High resistance stateLow resistance stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsEngineeringElectronic states
A non-volatile nanotube switch and memory arrays constructed from these switches are disclosed. A non-volatile nanotube switch includes a conductive terminal and a nanoscopic element stack having a plurality of nanoscopic elements arranged in direct electrical contact, a first comprising a nanotube fabric and a second comprising a carbon material, a portion of the nanoscopic element stack in electrical contact with the conductive terminal. Control circuitry is provided in electrical communication with and for applying electrical stimulus to the conductive terminal and to at least a portion of the nanoscopic element stack. At least one of the nanoscopic elements is capable of switching among a plurality of electronic states in response to a corresponding electrical stimuli applied by the control circuitry to the conductive terminal and the portion of the nanoscopic element stack. For each electronic state, the nanoscopic element stack provides an electrical pathway of corresponding resistance.
Owner:NANTERO
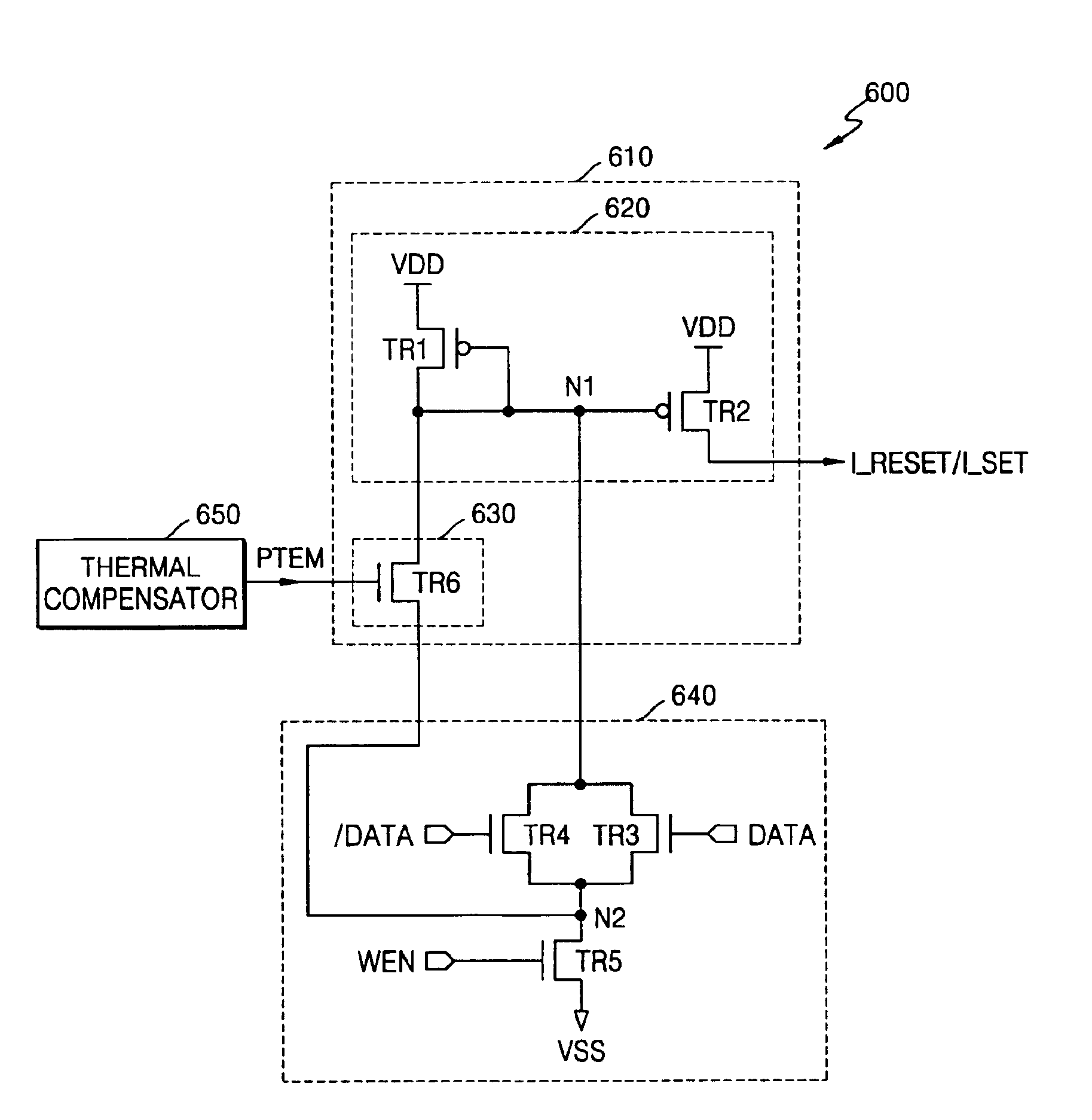
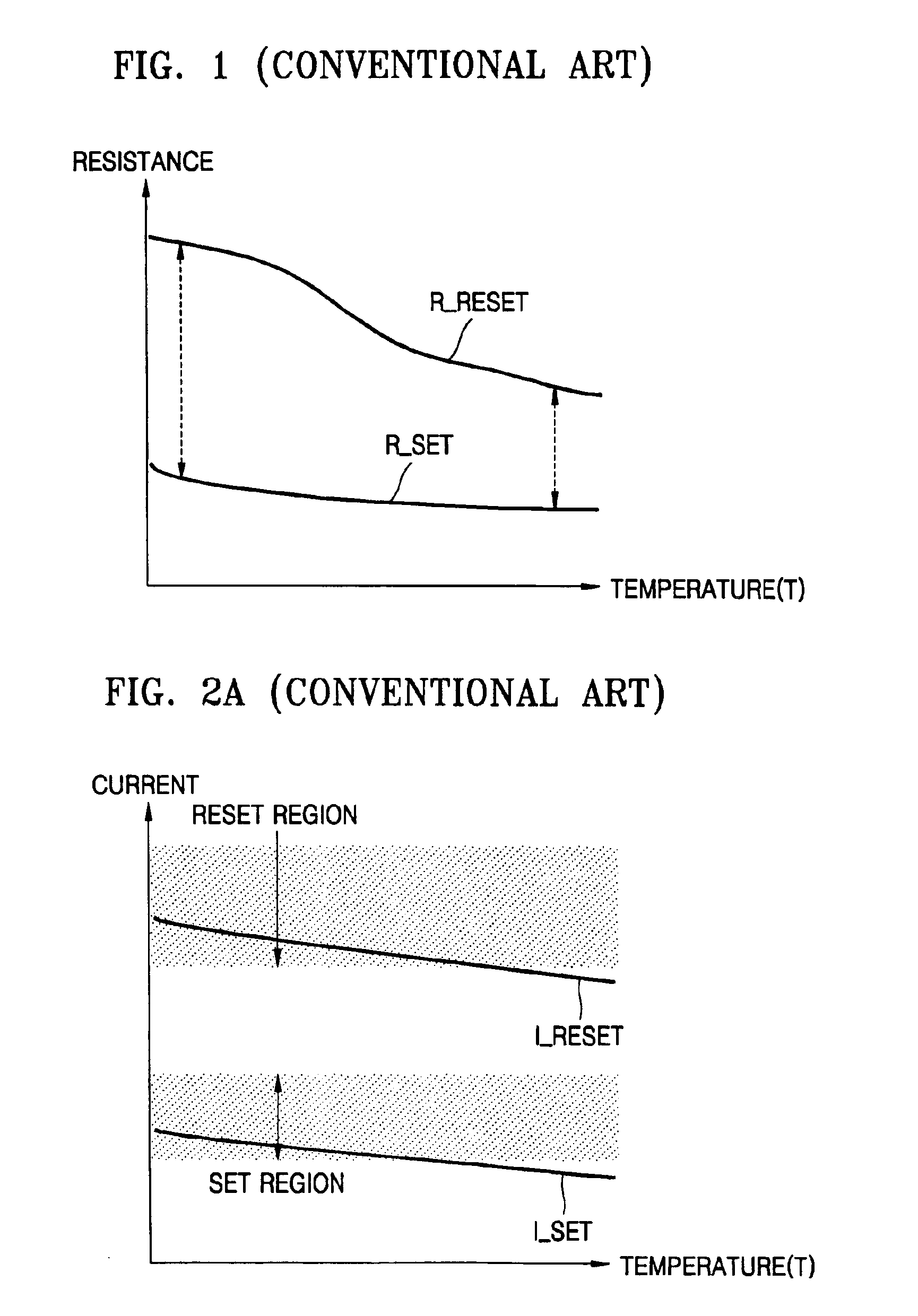
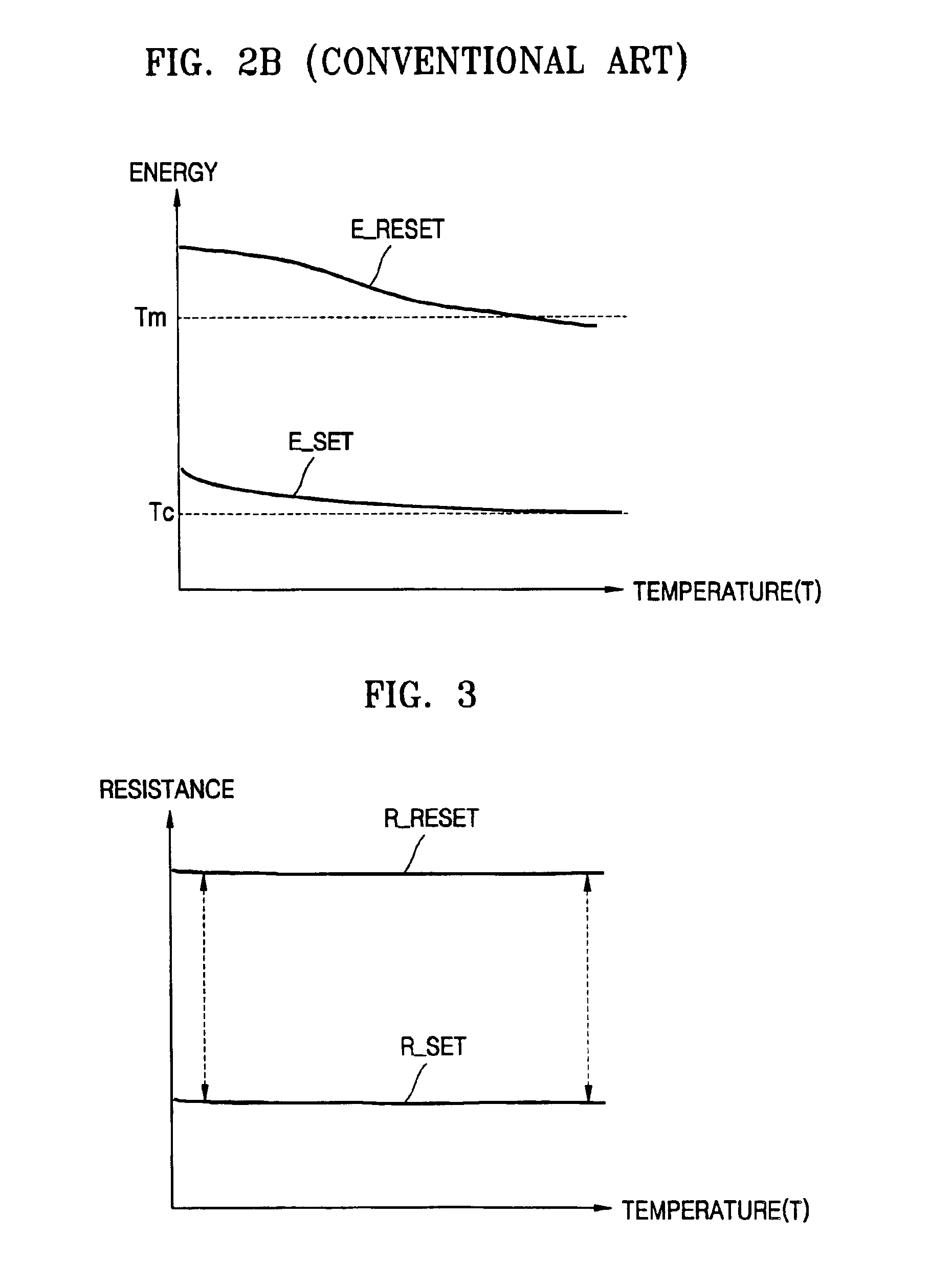
Programming method of controlling the amount of write current applied to phase change memory device and write driver circuit therefor
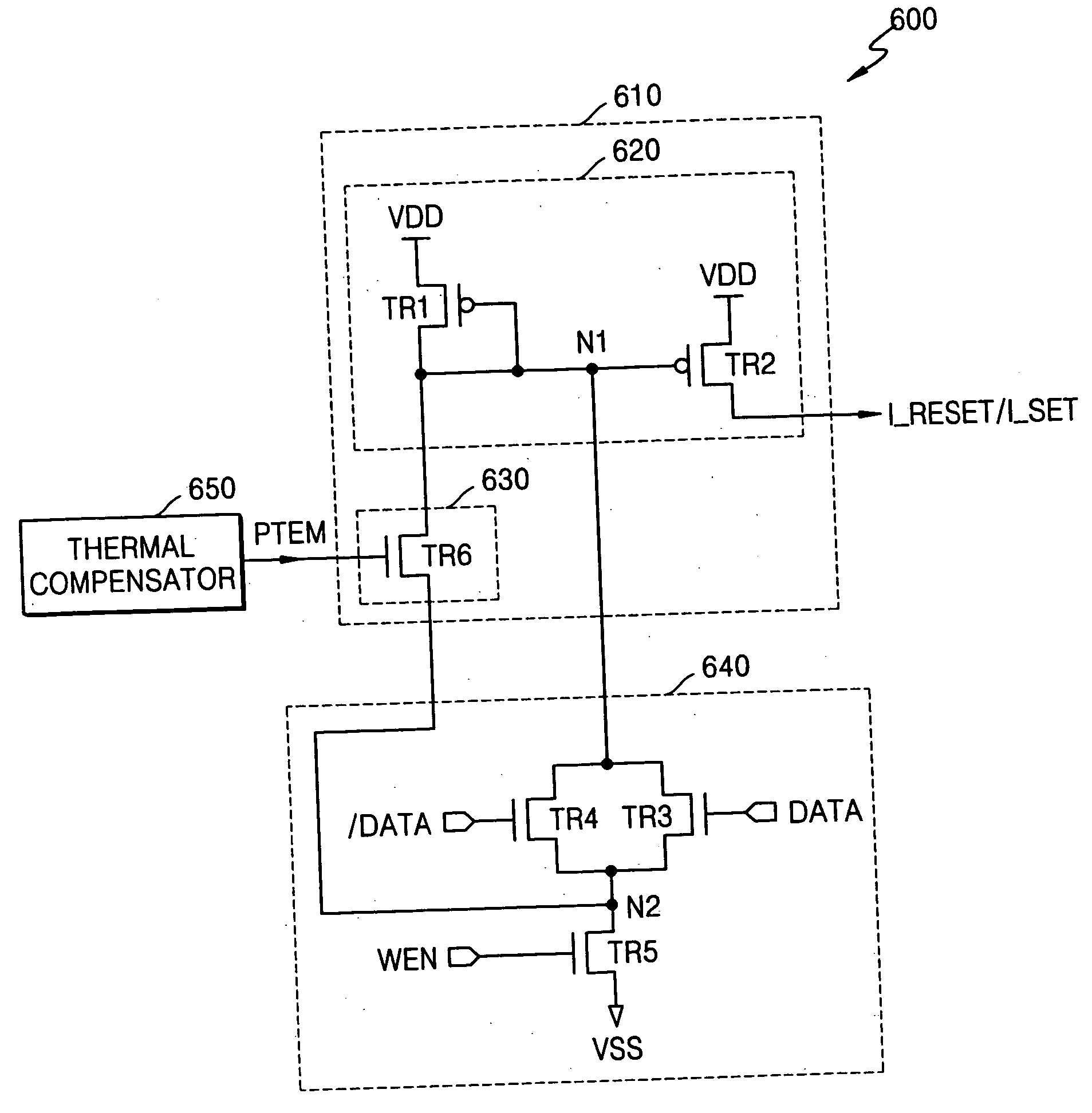
ActiveUS6885602B2Reduce the amount of settingsLow resistance stateSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDriver circuitHigh resistance
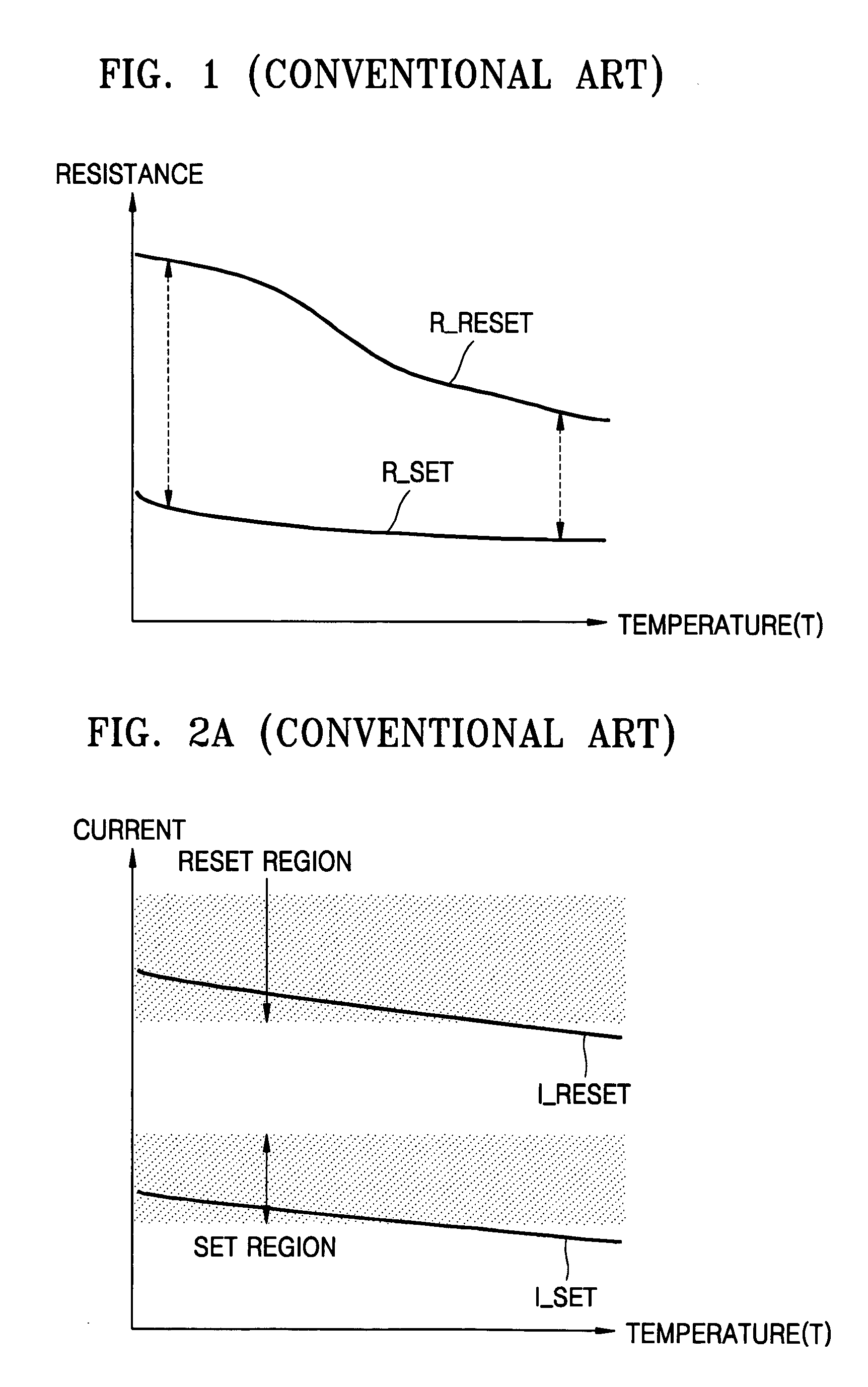
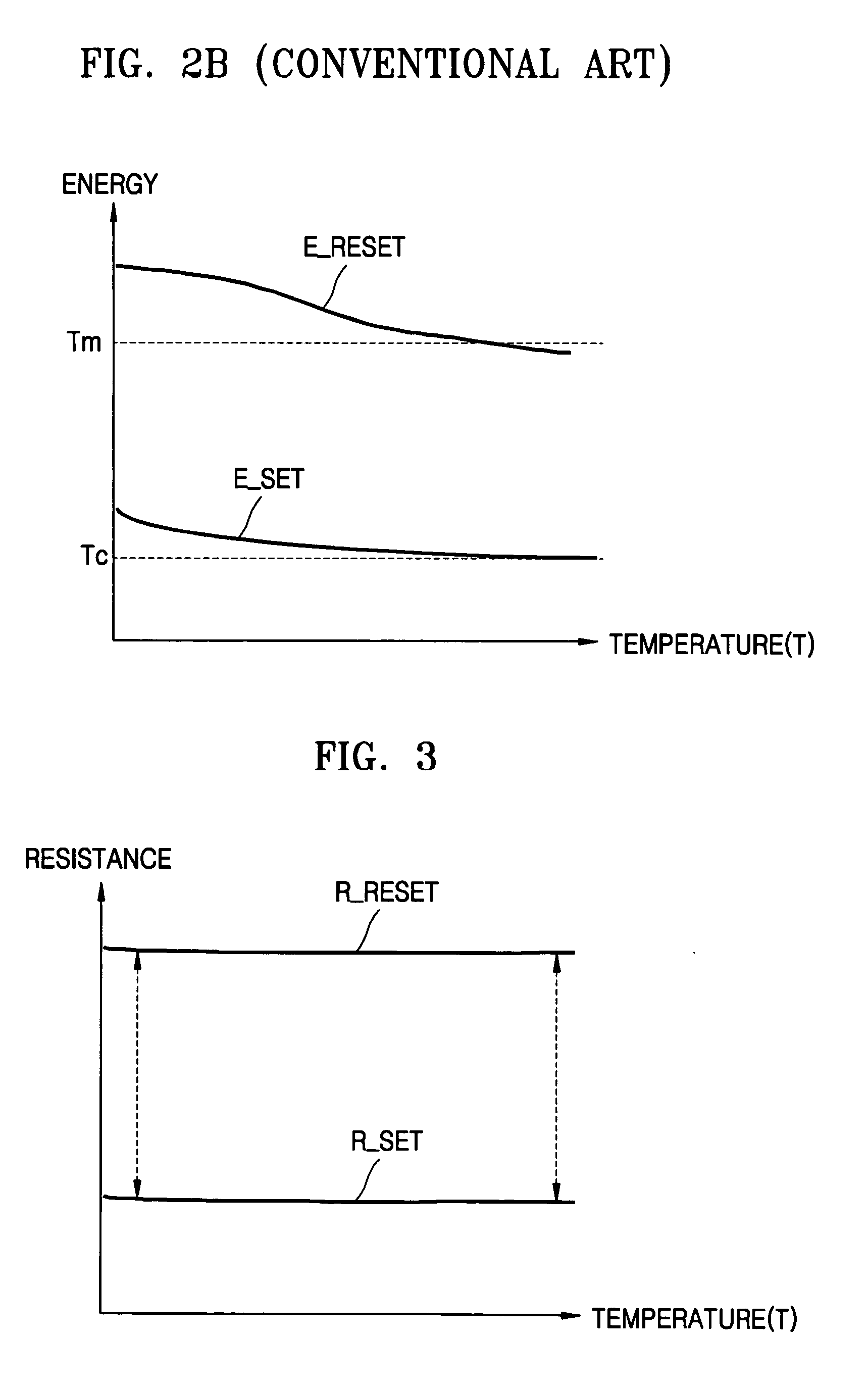
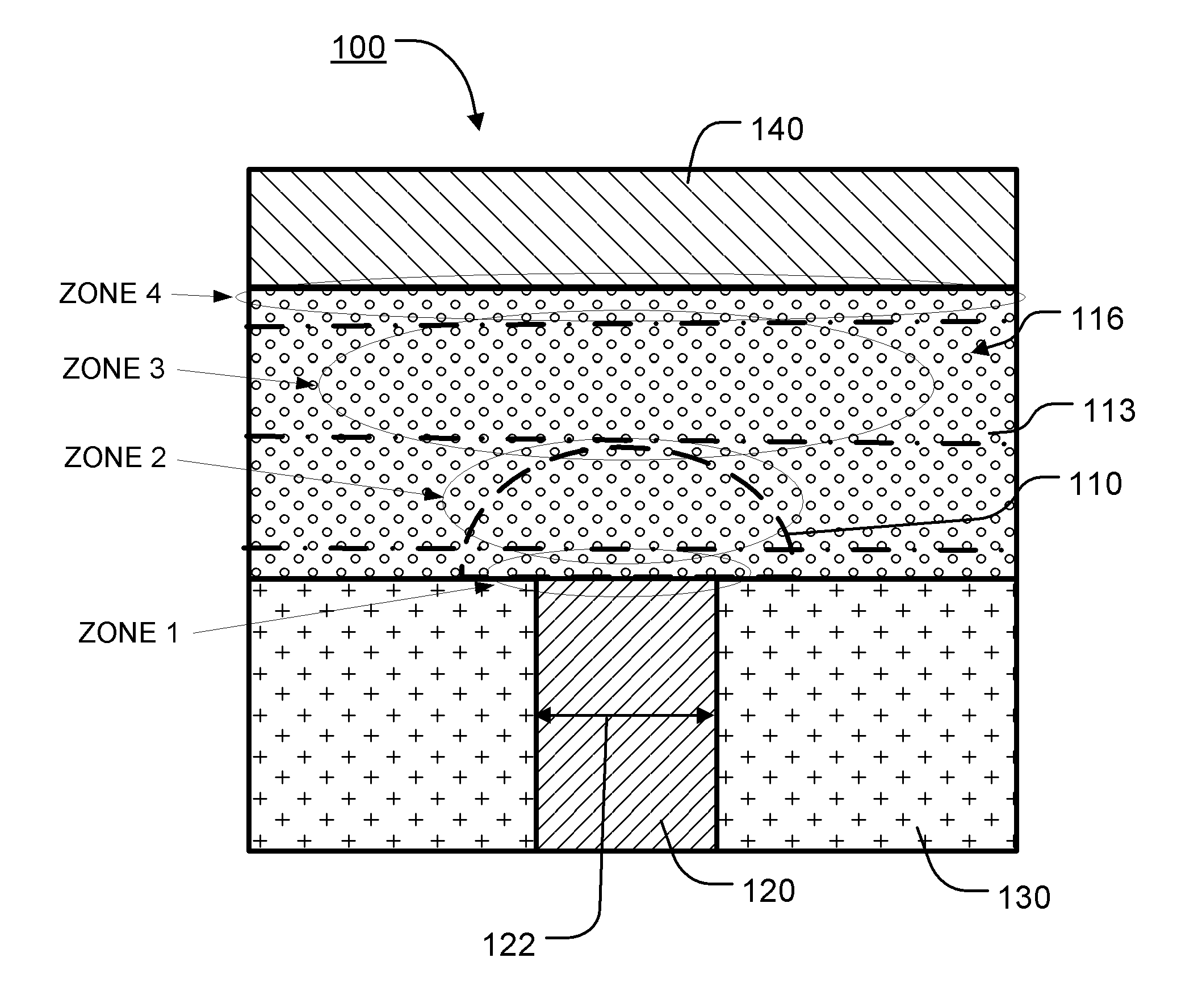
A programming method which controls the amount of a write current applied to a Phase-change Random Access Memory (PRAM), and a write driver circuit realizing the programming method. The programming method includes maintaining a ratio of a resistance of the PCM in the higher resistance state to a resistance of the Phase-change Memory (PCM) in the lower resistance state constant or substantially constant independent of an ambient temperature. The ratio may be maintained by increasing, decreasing, or keeping the same a reset current and / or a set current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
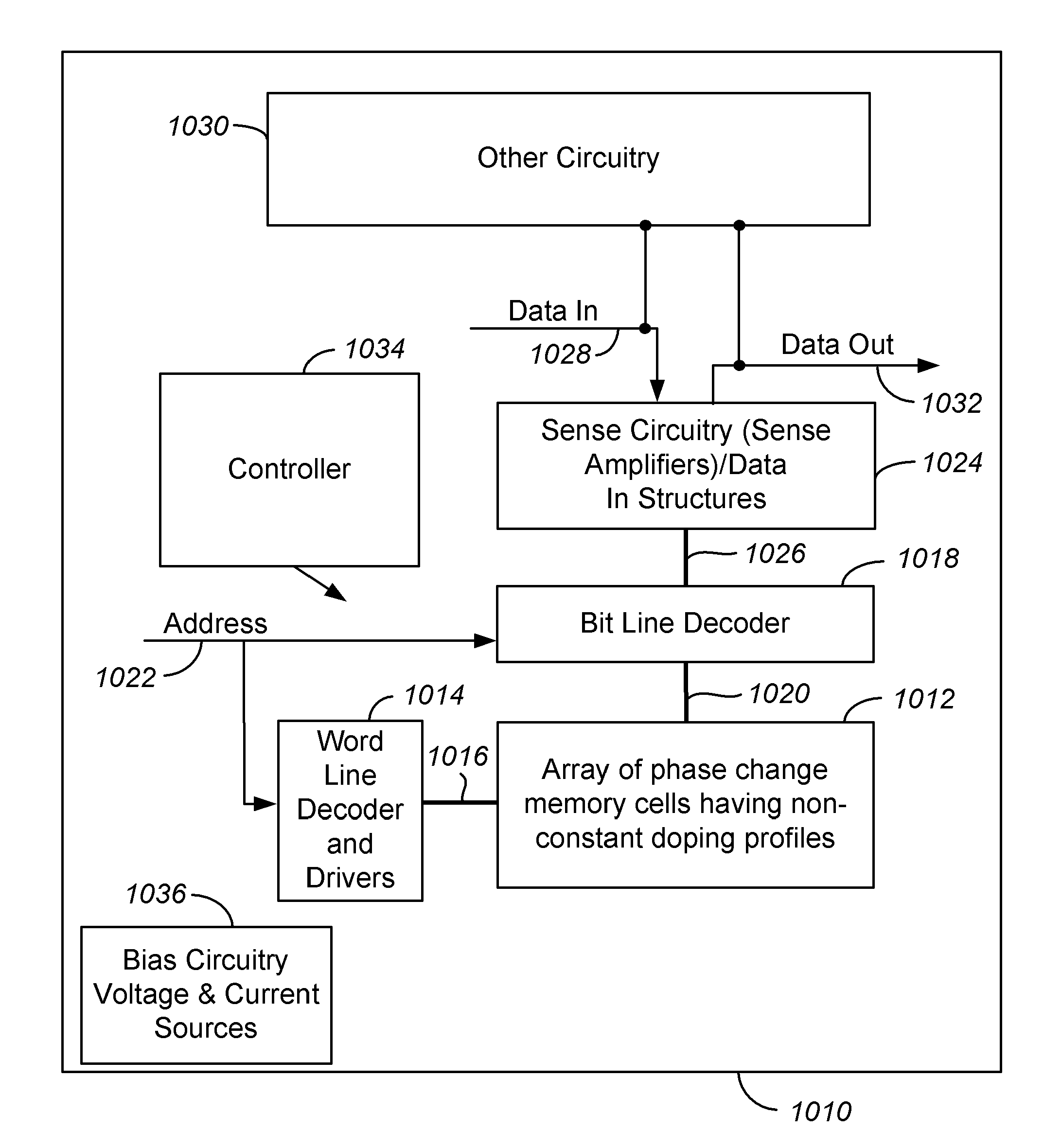
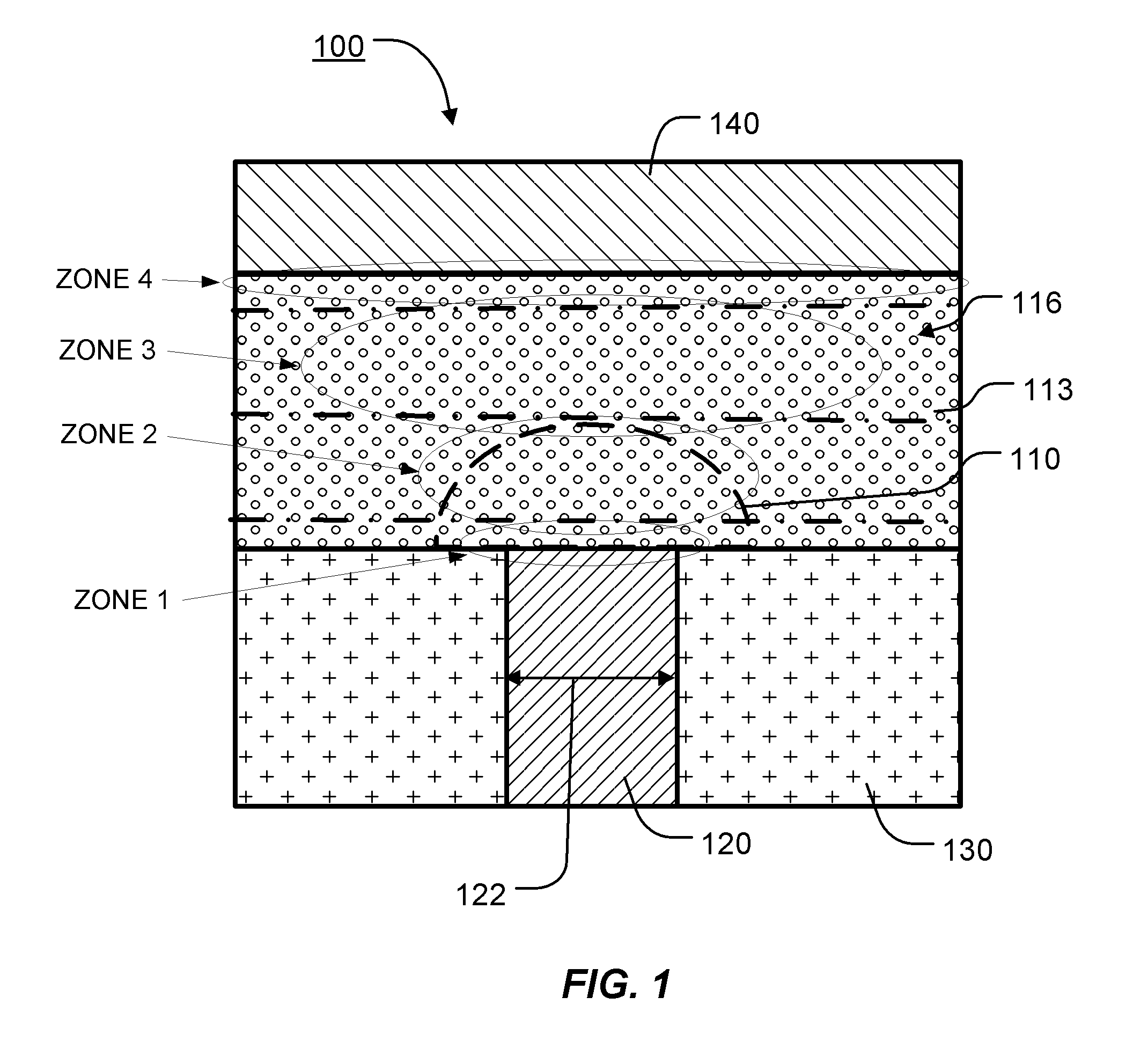
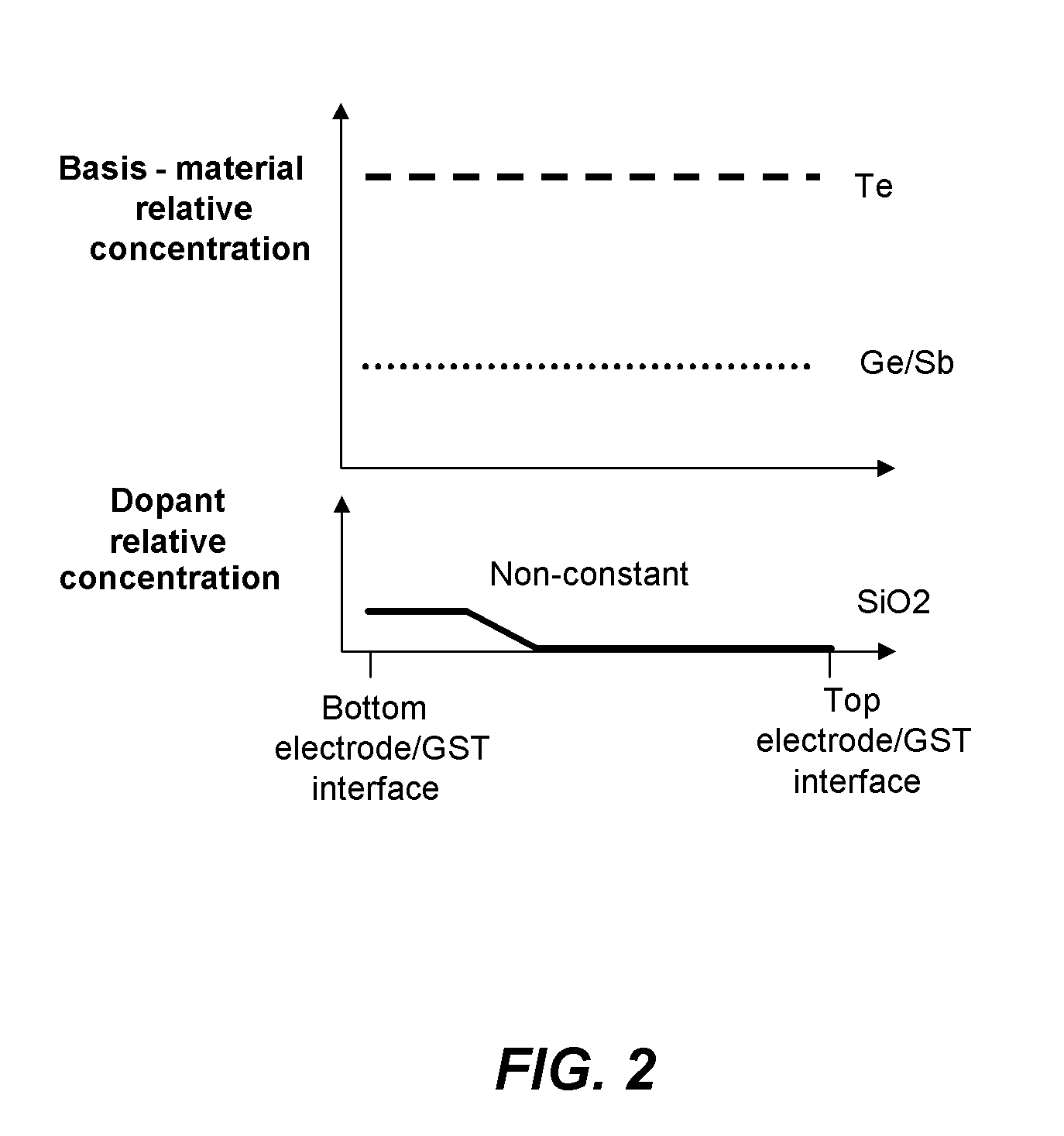
Phase change memory having one or more non-constant doping profiles
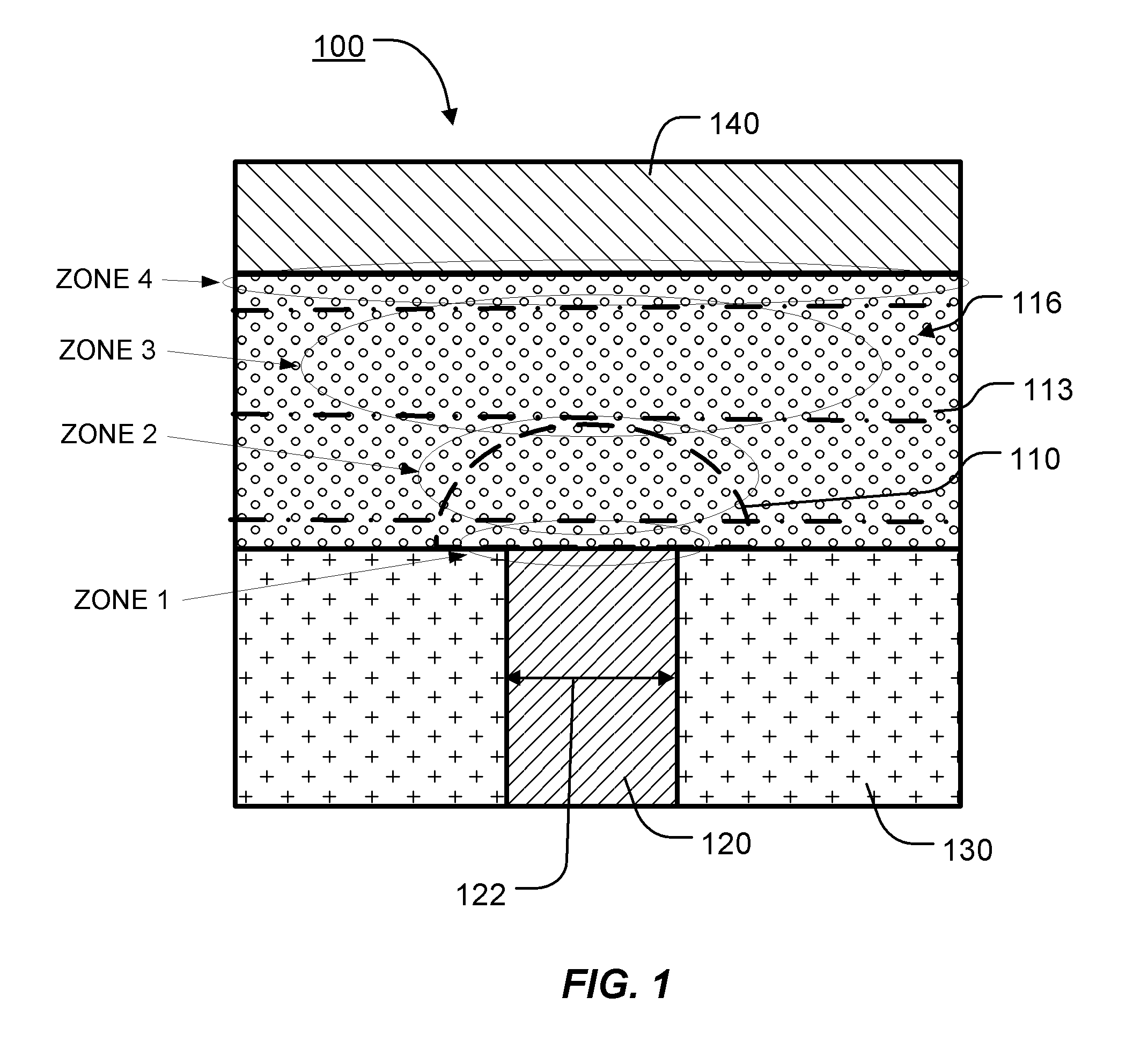
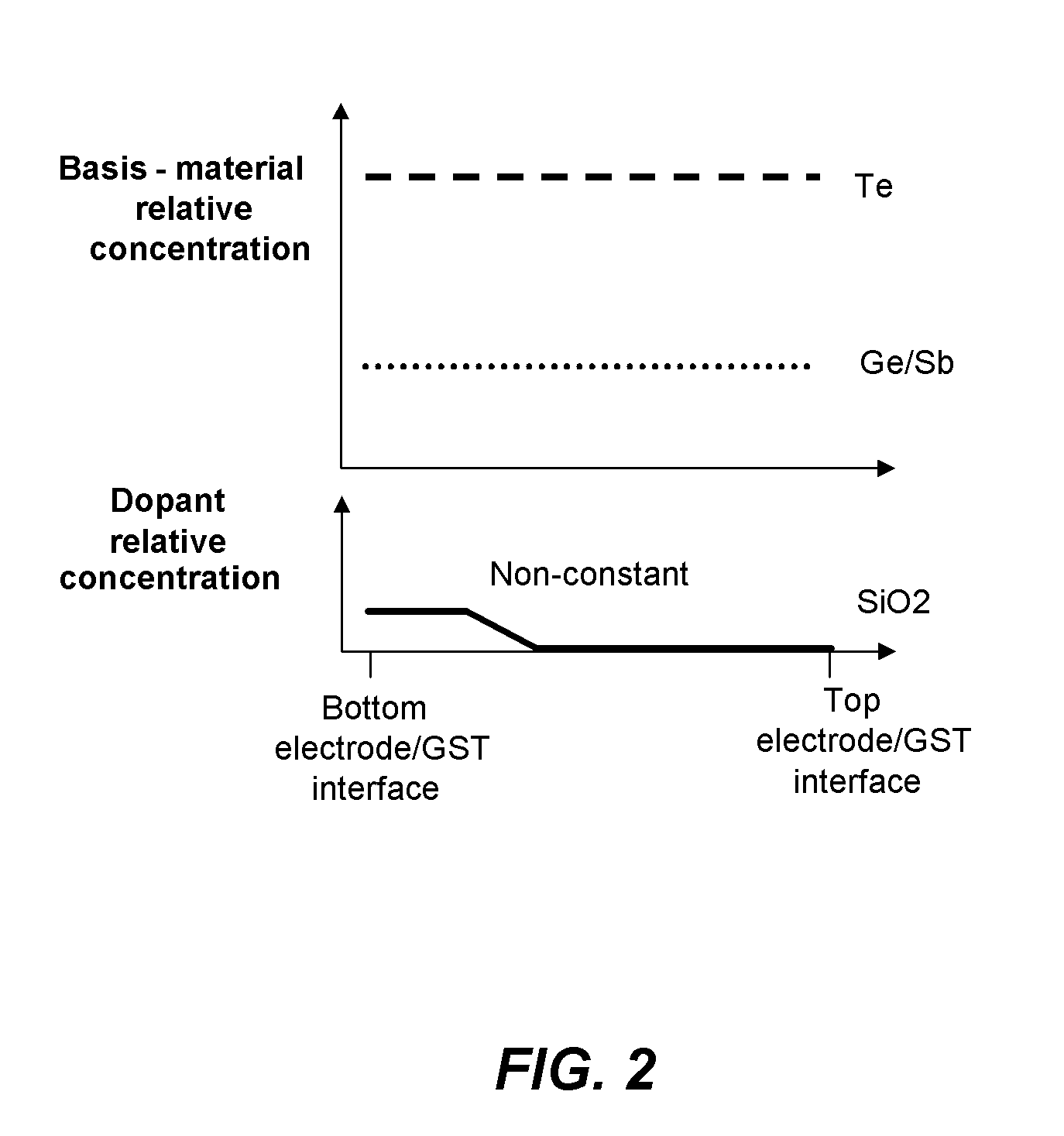
ActiveUS20100328996A1Improve stabilityImproved Impedance StabilityDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesPhase-change memoryPhase-change material
A phase change memory device with a memory element including a basis phase change material, such as a chalcogenide, and one or more additives, where the additive or additives have a non-constant concentration profile along an inter-electrode current path through a memory element. The use of “non-constant” concentration profiles for additives enables doping the different zones with different materials and concentrations, according to the different crystallographic, thermal and electrical conditions, and different phase transition conditions.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
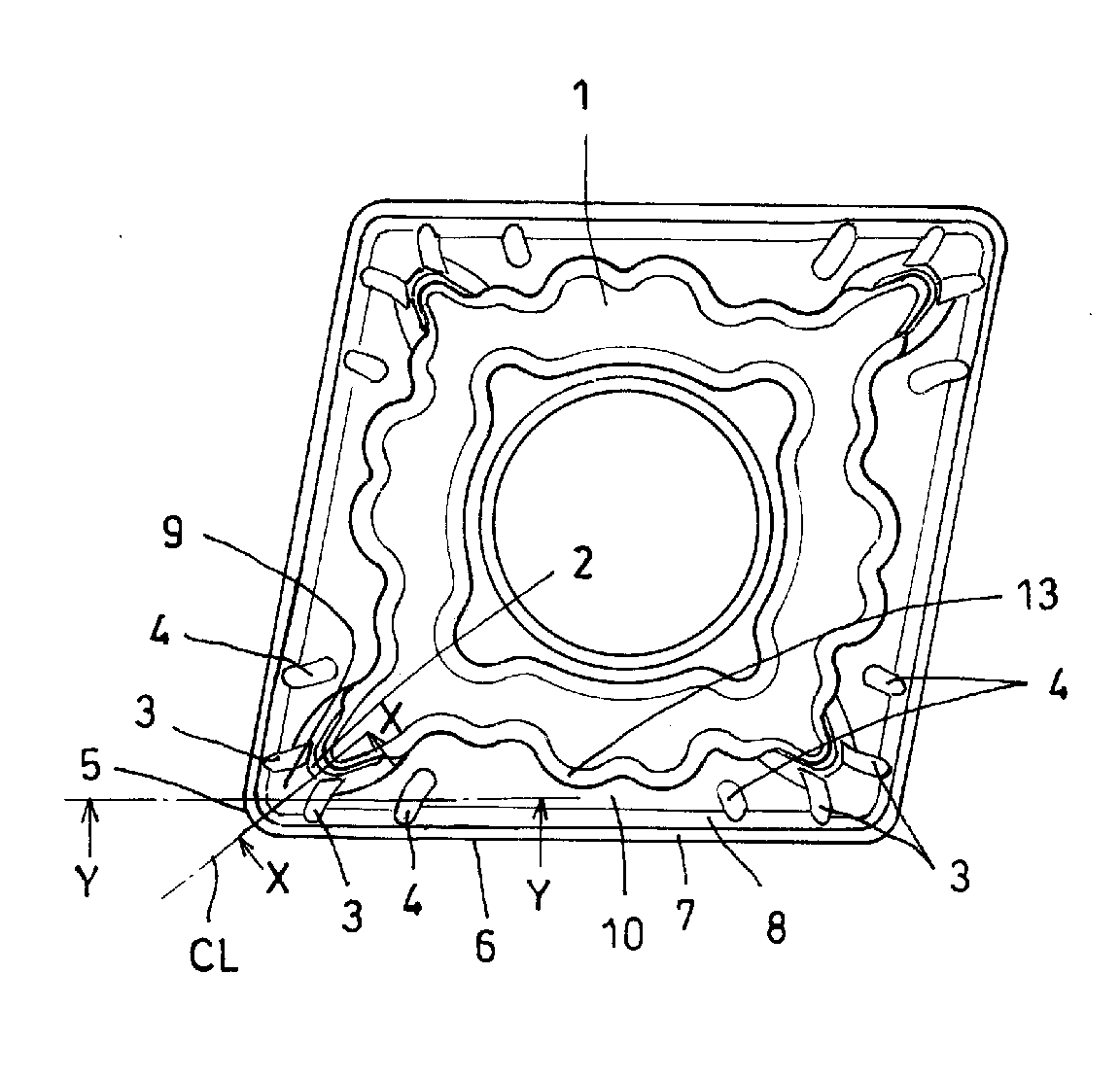
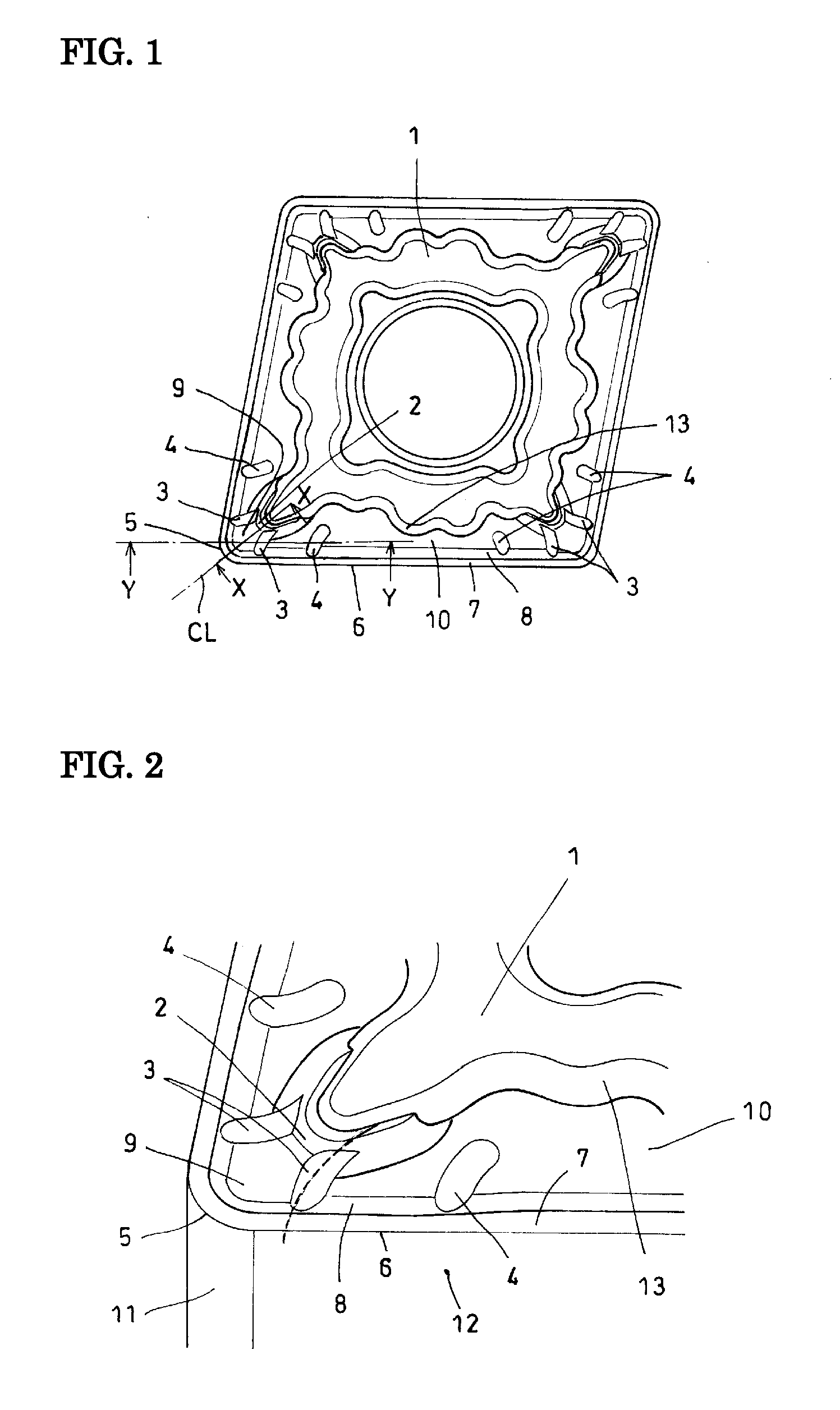
Indexable insert
ActiveUS20090226269A1Improve the protective effectReduce loadCutting insertsTurning toolsEngineeringKnife blades
An indexable insert has a rake face on which a first ridge (2) and a second ridge (3) are provided. The first ridge (2) protrudes from a boss surface (1) towards a nose, and the second ridge (3) extends continuously from the first ridge (2) to a slope (8) connected to a cutting-edge land (7) of a linear cutting edge (6). The second ridge (3) has a height lower than that of the first ridge (2) and is convex-curved towards a bisecting line (CL) of an apex angle of the nose in plan view, thereby achieving both enhanced chip processability and reduction of load received when raking a chip.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
Non-volatile memory system with reset verification mechanism and method of operation thereof
InactiveUS9070441B2Increasing a read marginHigh resistance stateElectrical apparatusDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh resistance
A method of operation of a non-volatile memory system includes: providing a resistive storage element having a high resistance state and a low resistance state; coupling an analog multiplexer to the resistive storage element for applying a bias voltage; and switching between a verification bias and a read bias through the analog multiplexer for increasing a read margin between the high resistance state and the low resistance state.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
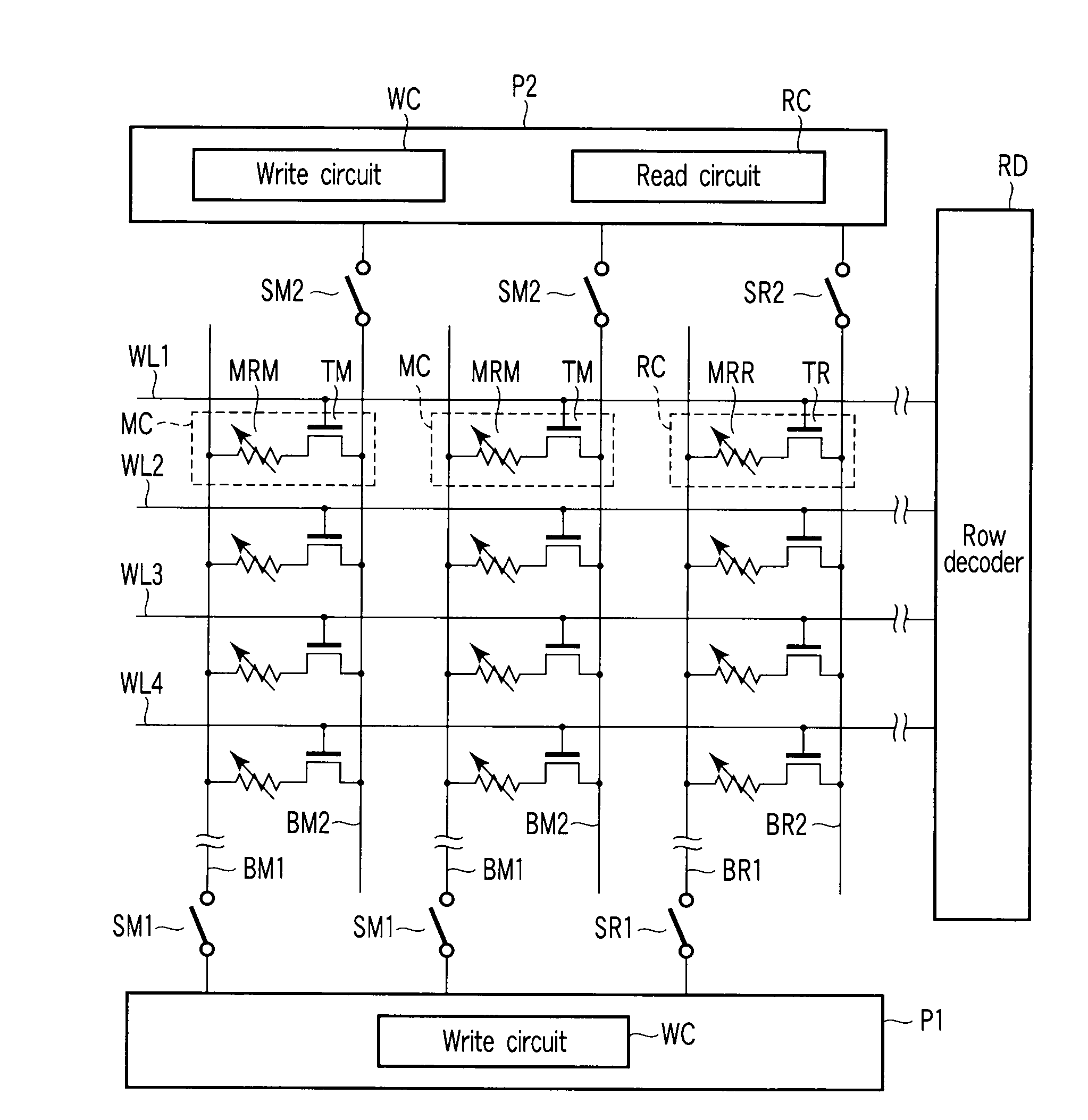
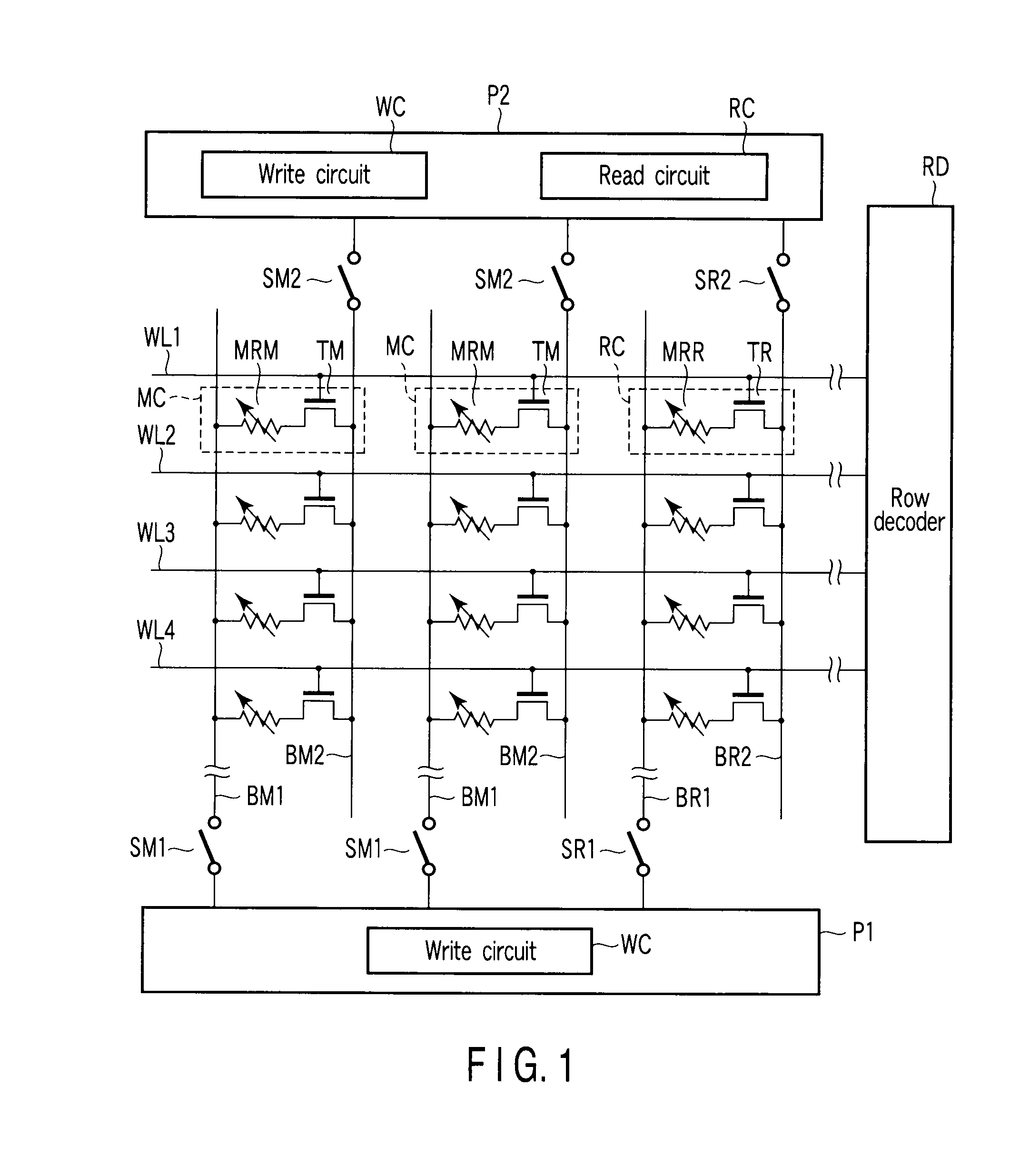
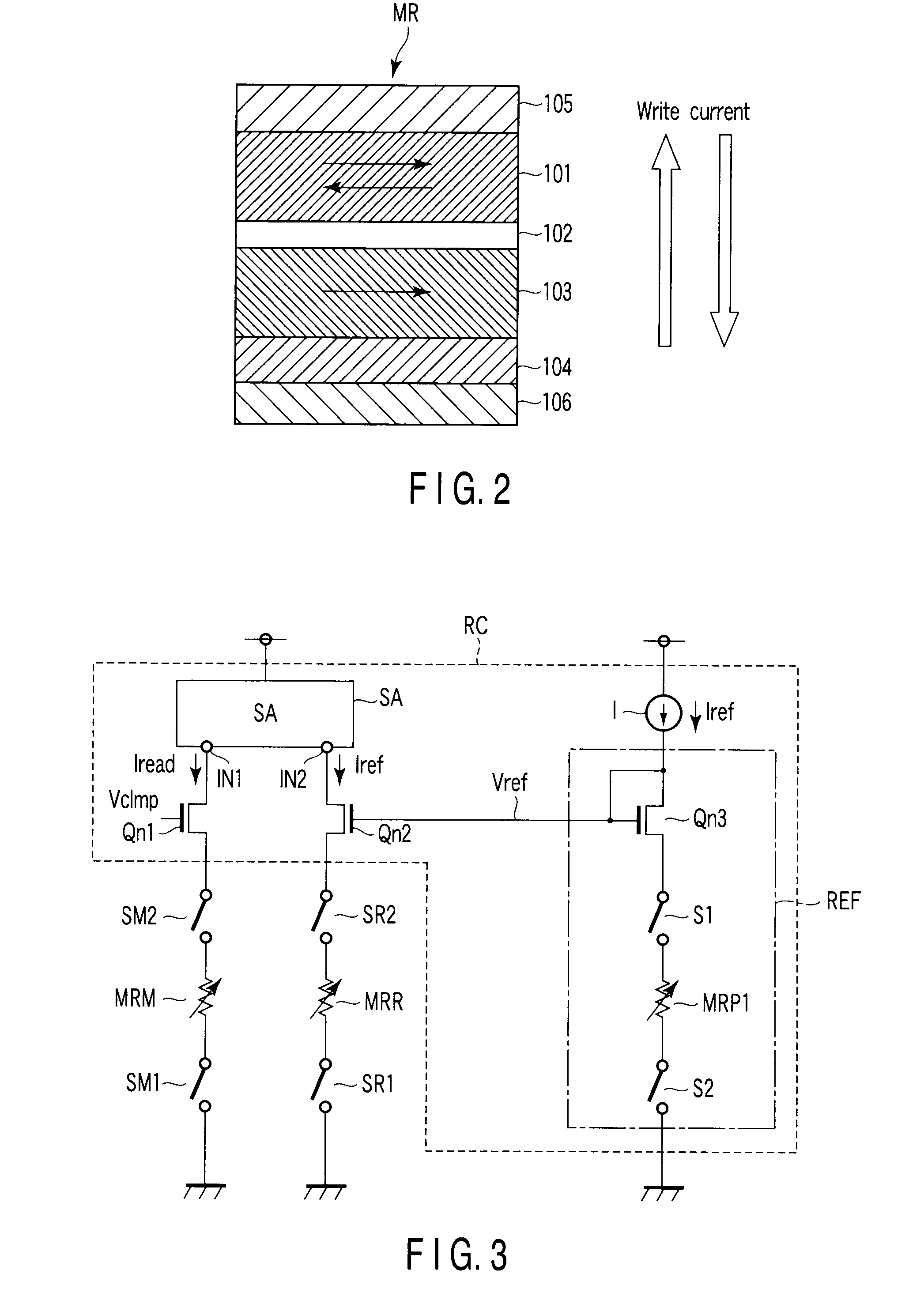
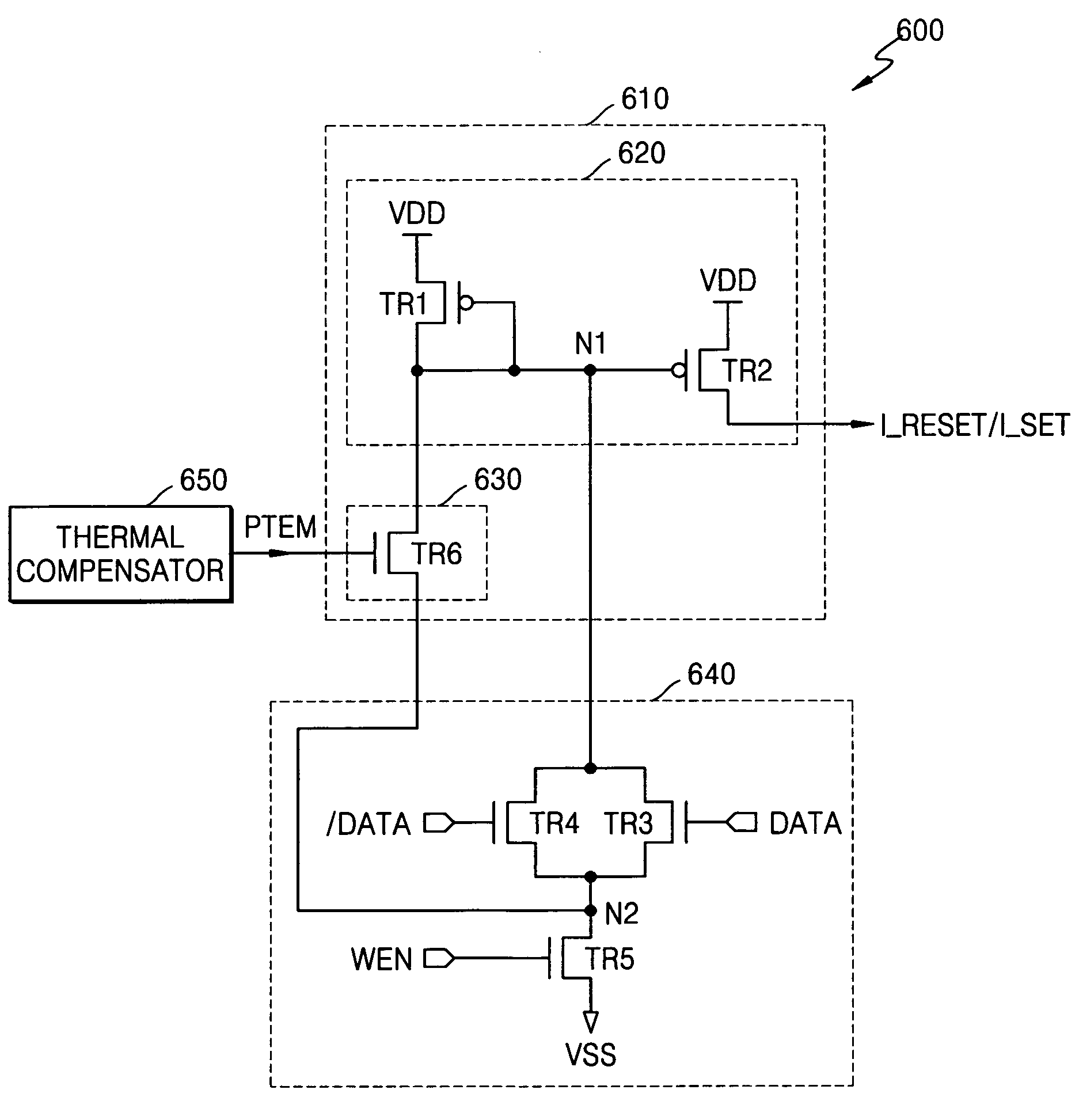
Magnetoresistive random access memory
A MRAM includes a first magnetoresistive effect (MR) element that takes a low and high resistance states. A second MR element is fixed to a low or high resistance state. First and second MOSFETs are connected to the first and second MR elements, respectively. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between values of current flowing through the first and second MOSFETs. A current circuit outputs reference current whose value lies between current flowing through the first MR element of the low and high resistance states. A third MOSFET has one end that receives the reference current and is connected to its own gate terminal. The gate terminal of the second MOSFET receives the same potential as the gate terminal of the third MOSFET. A first resistance element is connected to the others end of the third MOSFET and has the same resistance as the second magnetoresistive effect element.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Programming method of controlling the amount of write current applied to phase change memory device and write driver circuit therefor
ActiveUS20050041464A1Reduce the amount of settingsLow resistance stateSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDriver circuitHigh resistance
A programming method which controls the amount of a write current applied to a Phase-change Random Access Memory (PRAM), and a write driver circuit realizing the programming method. The programming method includes maintaining a ratio of a resistance of the PCM in the higher resistance state to a resistance of the PCM in the lower resistance state constant or substantially constant independent of an ambient temperature. The ratio may be maintained by increasing, decreasing, or keeping the same a reset current and / or a set current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phase change memory having one or more non-constant doping profiles
ActiveUS8363463B2Improve stabilityImproved Impedance StabilityDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesPhase-change memoryPhase-change material
A phase change memory device with a memory element including a basis phase change material, such as a chalcogenide, and one or more additives, where the additive or additives have a non-constant concentration profile along an inter-electrode current path through a memory element. The use of “non-constant” concentration profiles for additives enables doping the different zones with different materials and concentrations, according to the different crystallographic, thermal and electrical conditions, and different phase transition conditions.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
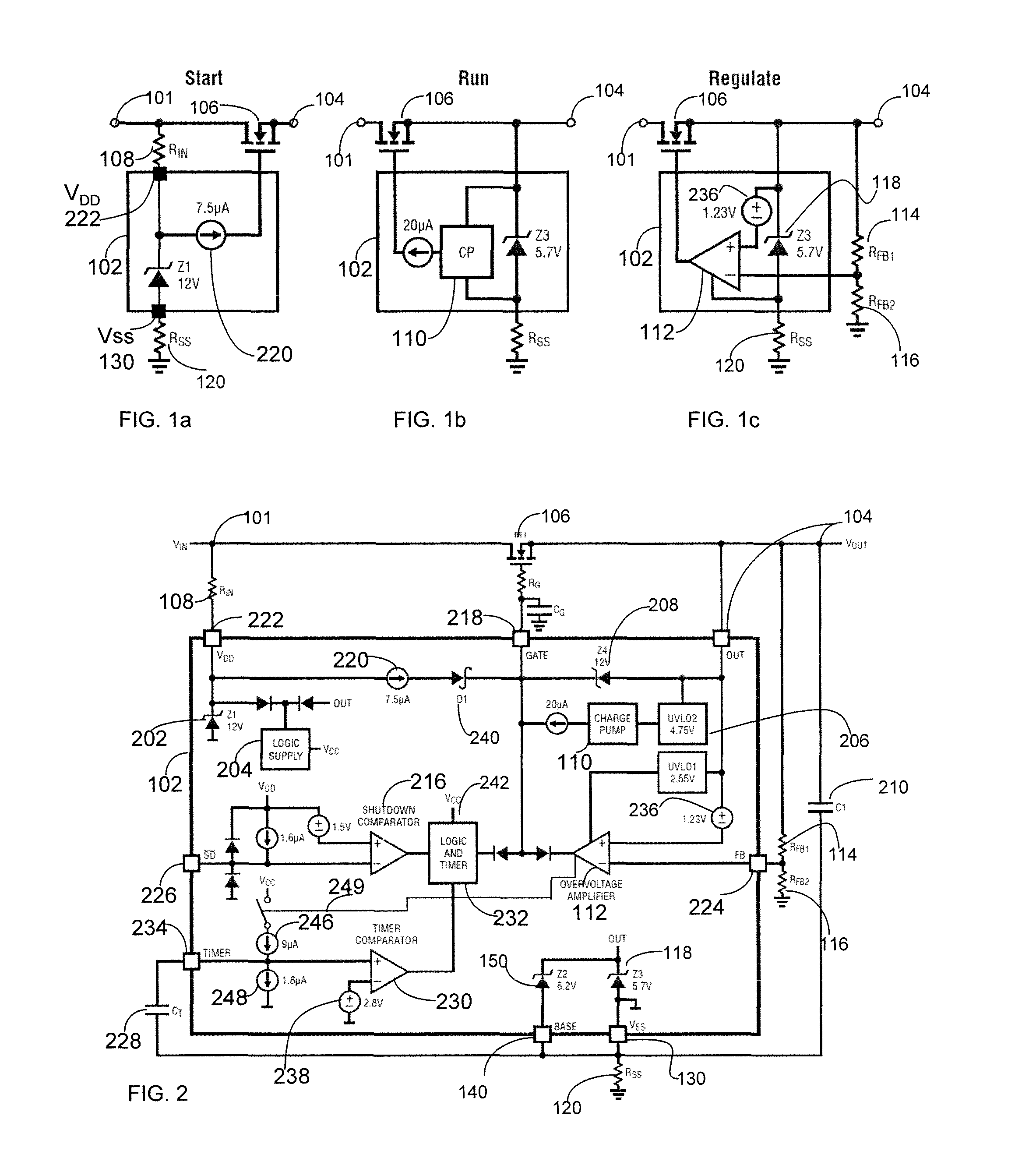
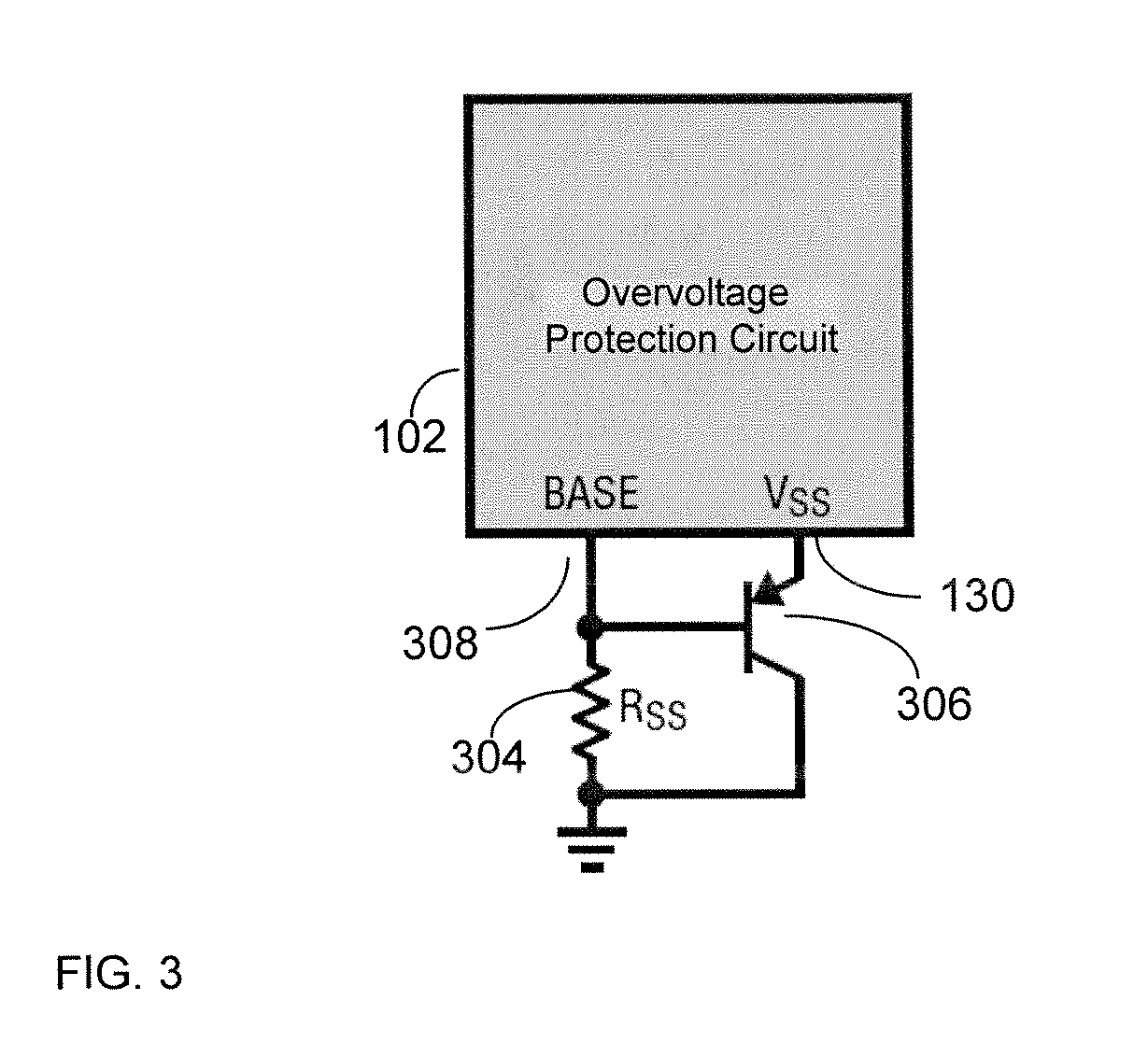
Circuitry to prevent overvoltage of circuit systems
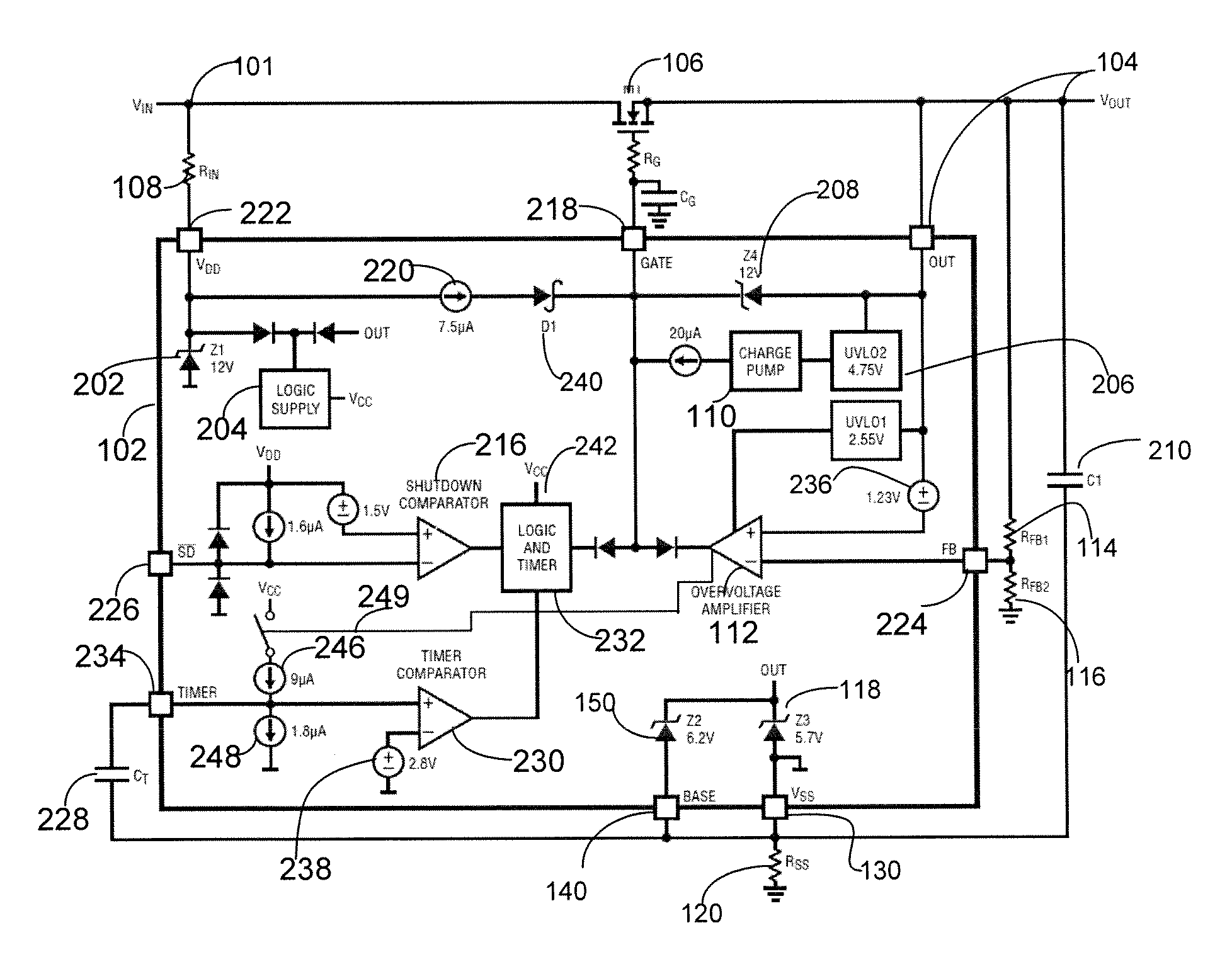
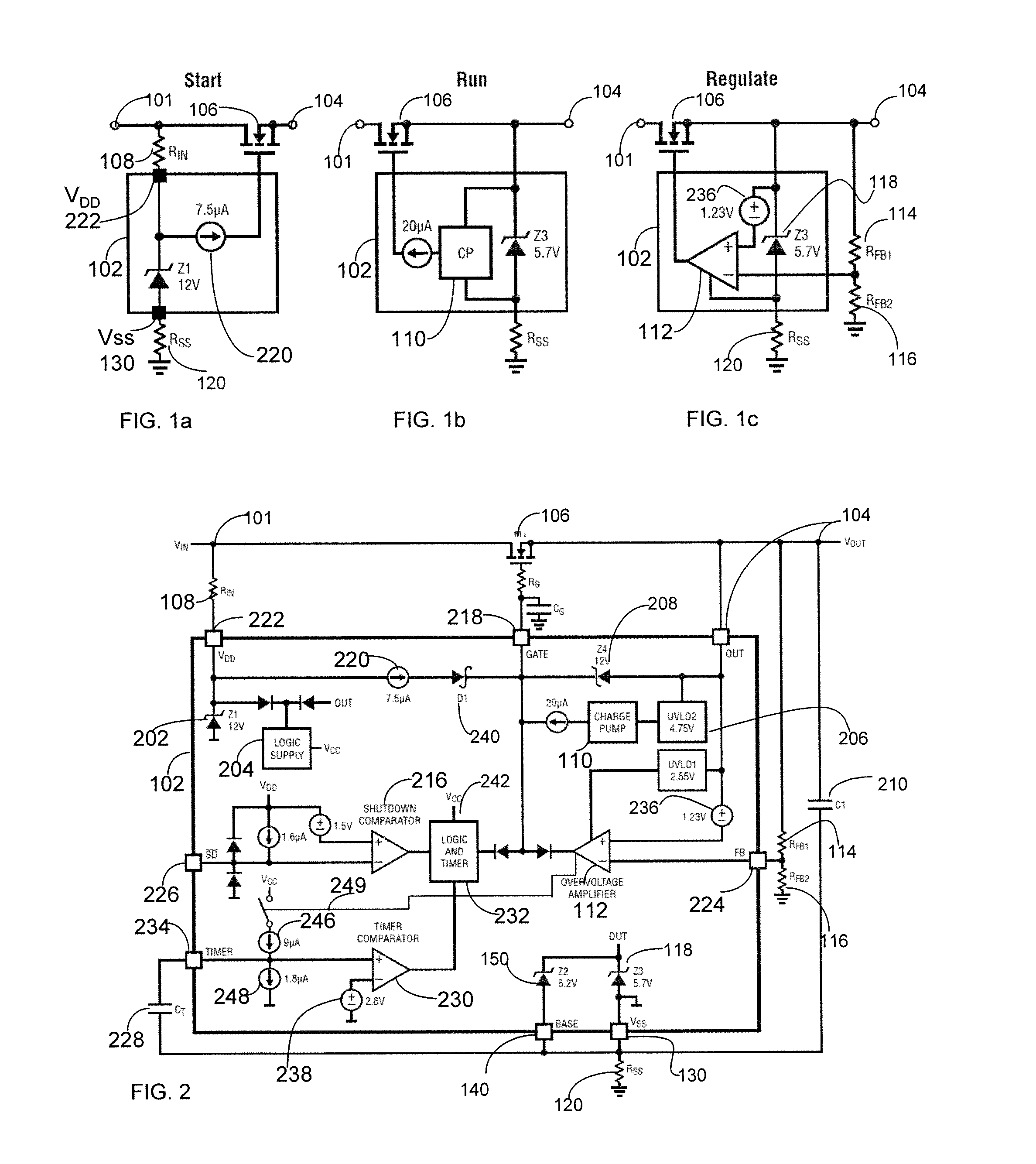
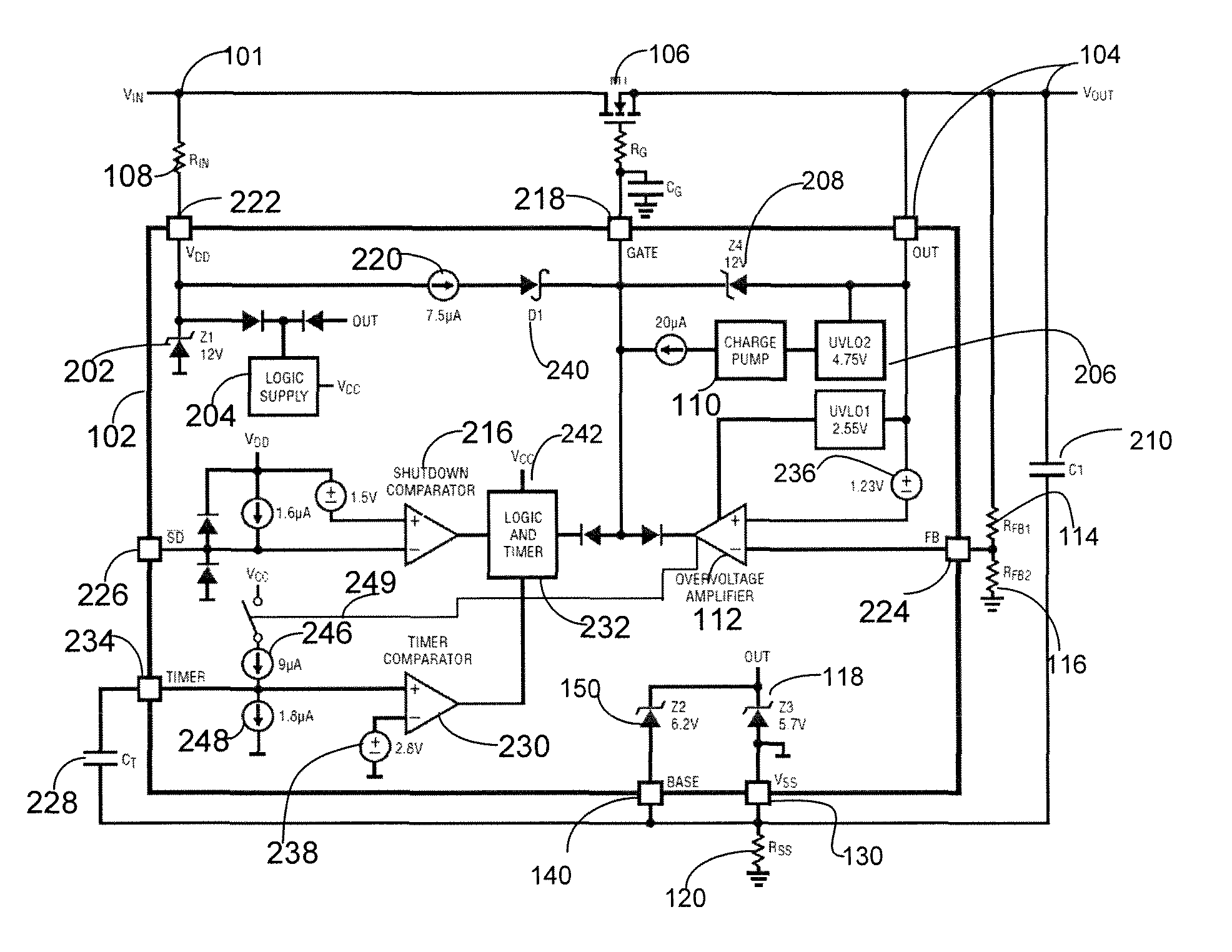
ActiveUS20120287540A1Low resistance stateAvoid overall overheatingEmergency protection for supplying operative powerEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMOSFETOvervoltage
An overvoltage protection method and circuit includes a positive supply input node, an output node, and a negative supply node. The overvoltage protection circuit further includes a first functional circuit configured to turn ON a MOSFET and maintain it in a low resistance state. A second functional circuit is configured to detect an overvoltage and control the gate of the MOSFET to regulate a voltage at the output node. A third functional circuit is configured to provide a startup wherein the overvoltage protection circuit is not damaged and / or to regulate an operating voltage such that an overvoltage does not appear on the overvoltage protection circuit. The external components include the MOSFET, which has a gate coupled to the output of the charge pump of the overvoltage protection circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Power device coupling a plurality of cells
ActiveUS7887943B2Lower resistanceMass-producing a connecting terminal inexpensivelyCoupling device connectionsFinal product manufactureElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
A power device includes a battery module for fixing a connecting terminal to an end and a bus bar connected to the connecting terminal of the battery module. The connecting terminal includes a fixing plate portion fixed to the end of the cell, an outer cylindrical portion protruded cylindrically from the fixing plate portion, an end face plate portion closing a tip surface of the outer cylindrical portion, and an inner cylindrical portion protruded from the end face plate portion toward the fixing plate portion. The connecting terminal is provided with a female screw on an internal surface of the inner cylindrical portion and a setscrew penetrating through the bus bar is screwed toward the female screw, and the bus bar is fixed to the connecting terminal through the setscrew.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Programming method of controlling the amount of write current applied to phase change memory device and write driver circuit therefor
ActiveUS20050162303A1Reduce the amount of settingsLow resistance stateAnalogue conversionSolid-state devicesDriver circuitHigh resistance
A programming method which controls the amount of a write current applied to a Phase-change Random Access Memory (PRAM), and a write driver circuit realizing the programming method. The programming method includes maintaining a ratio of a resistance of the PCM in the higher resistance state to a resistance of the PCM in the lower resistance state constant or substantially constant independent of an ambient temperature. The ratio may be maintained by increasing, decreasing, or keeping the same a reset current and / or a set current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
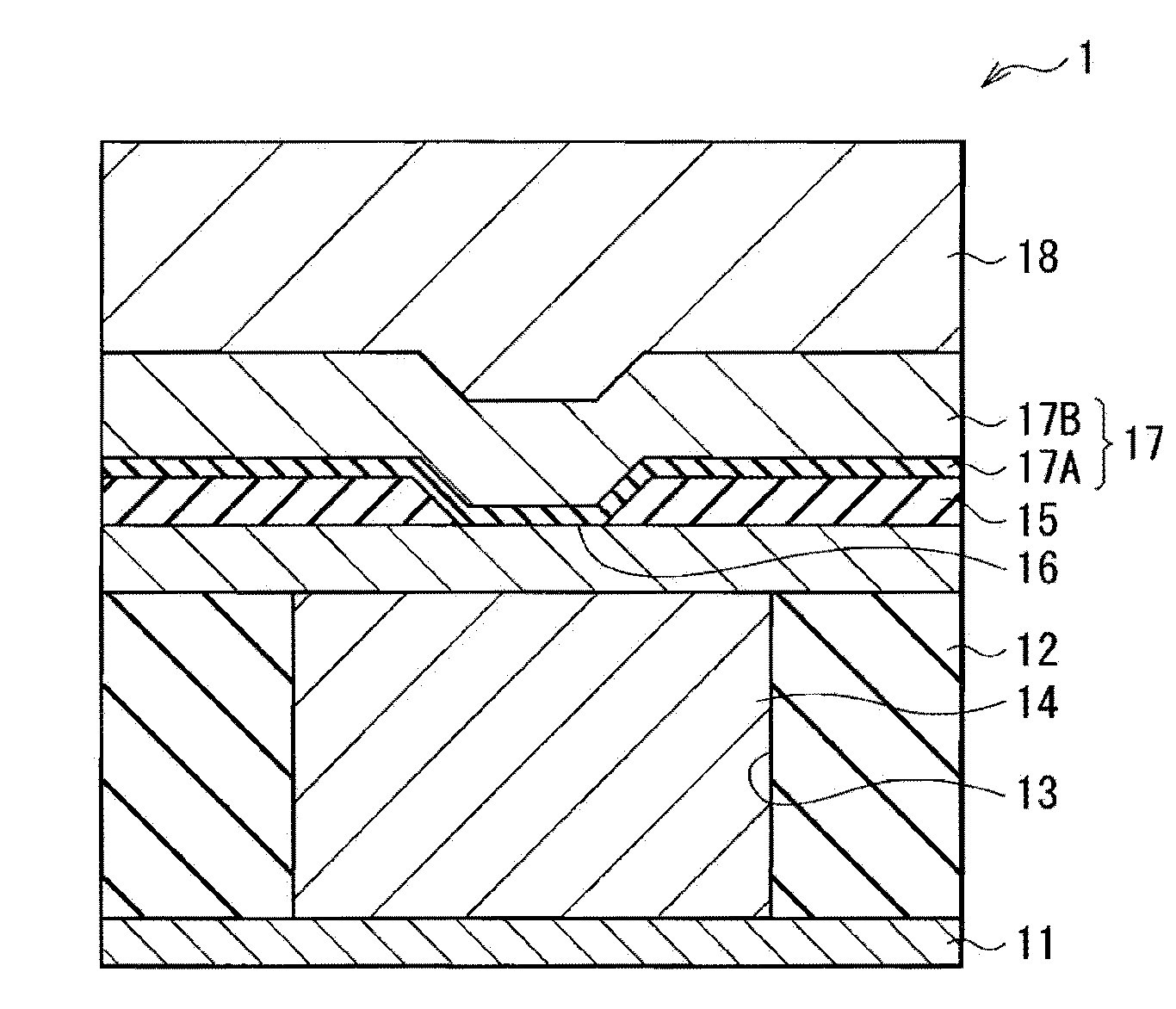
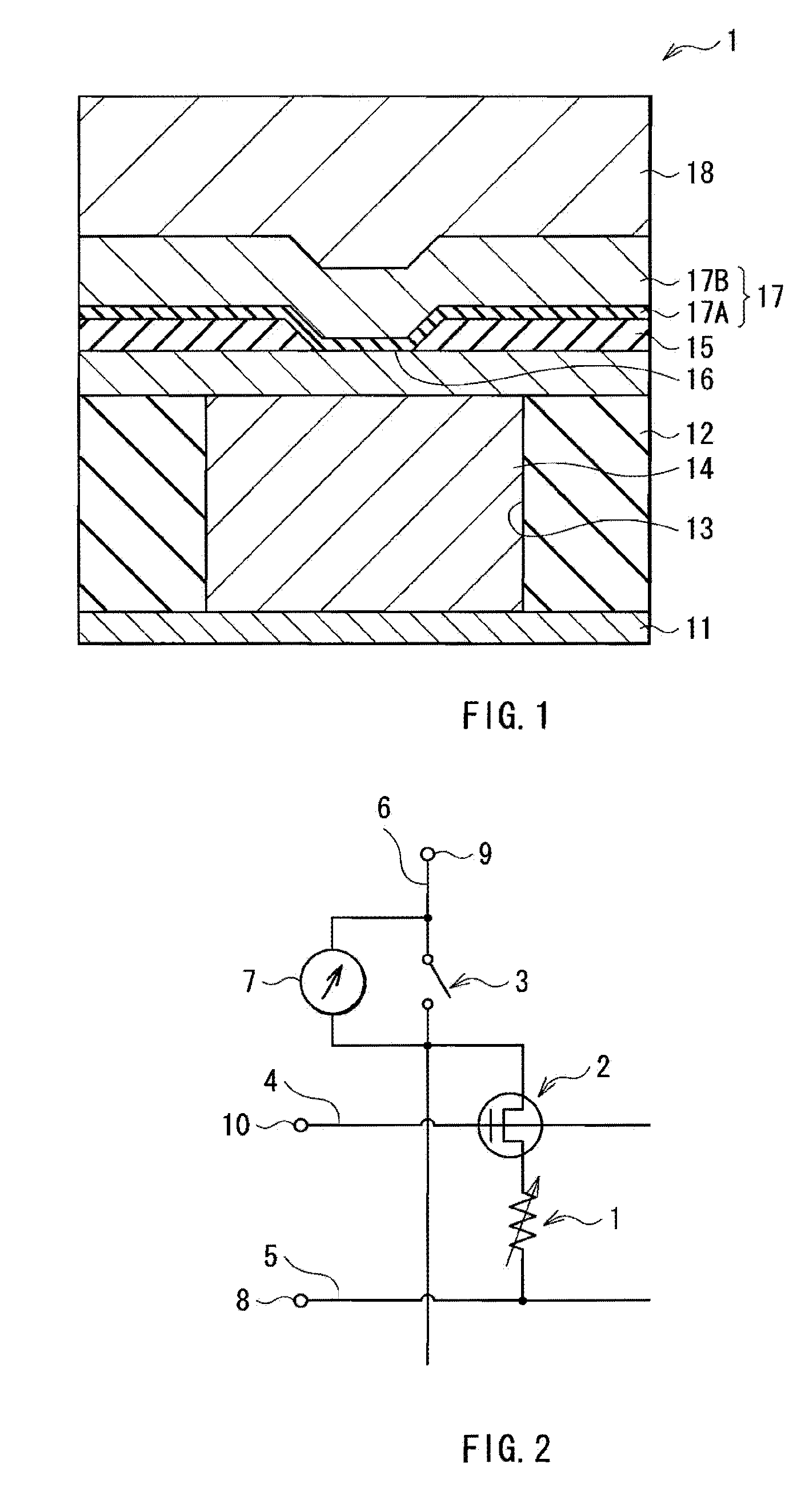
Memory component and memory device
InactiveUS20110175049A1Good maintenance characteristicsReduce the differenceSolid-state devicesDigital storageHigh resistanceSulfur
A memory component includes: a first electrode; a memory layer; and a second electrode in this order, wherein the memory layer includes a high resistance layer which includes tellurium (Te) as the chief component among anion components and is formed on the first electrode side; and an ion source layer which includes at least one kind of metal element and at least one kind of chalcogen element among tellurium (Te), sulfur (S) and selenium (Se) and is formed on the second electrode side.
Owner:SONY CORP
SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICES FOR USE IN ELECTRICALLY ALTERABLE READ ONLY MEMORY (ROM) AND SEMICONDUCTOR THIN FILM DEVICES (SPINTRONS and SPIN-ORBITRONS)
ActiveUS20170069839A1Improve stabilityLow resistance stateElectrical apparatusLayered structurePhysics
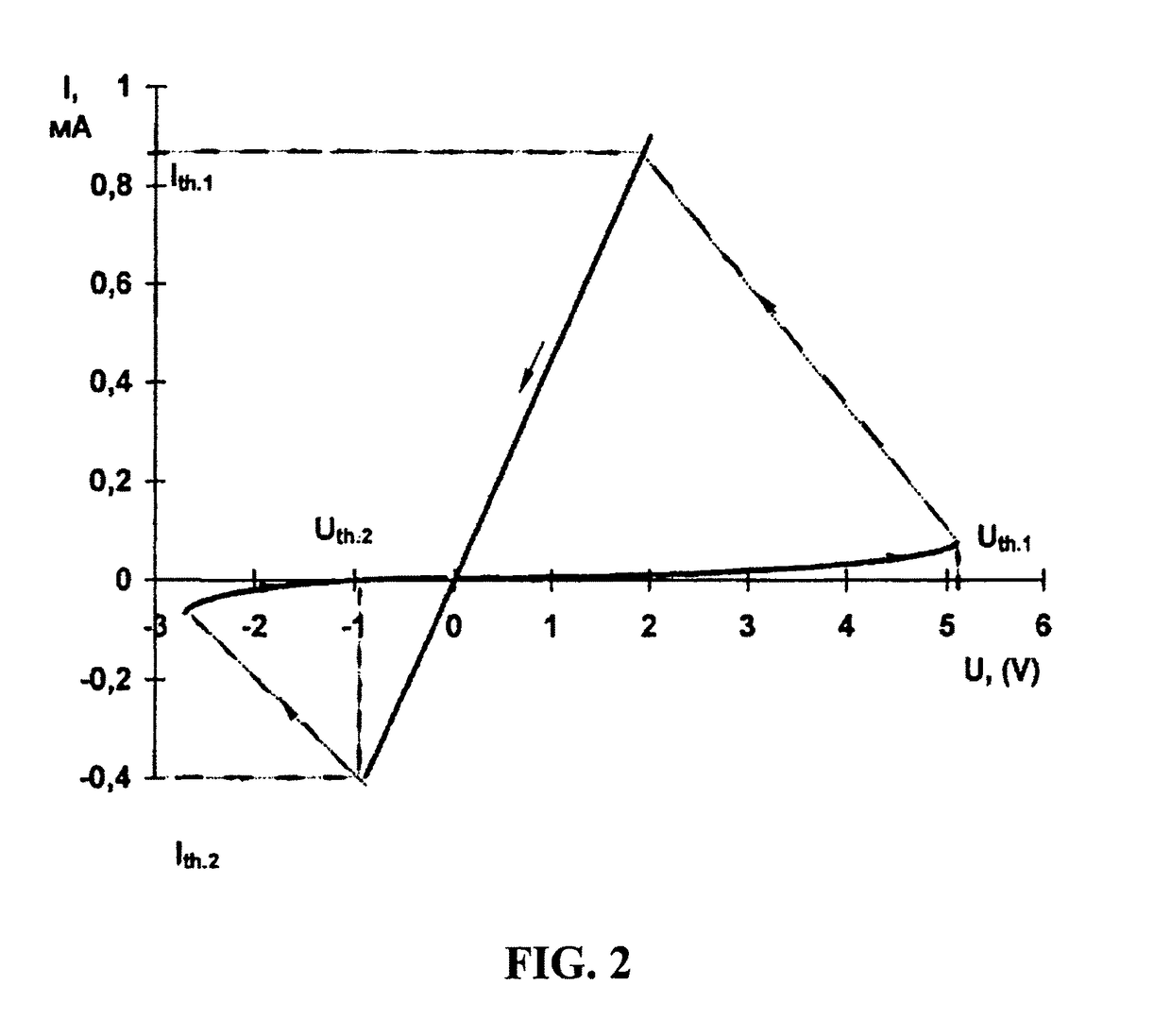
An electrically alterable thin film memory device or non-volatile trigger which can be switched from a high resistance state to a low resistance state. The device increases the concentration of electrically active impurities at correspondent electrodes to which respect impurities would electro migrate during a large number of set-reset cycles. The device comprises a layered structure with memory layers formed on an interface of two regions as the result of the mutual mixing and migration of their constituents. One region contains an electrically active donor impurity. A thin layer of dielectric is placed in the other region. Each of the memory layers includes an interface of chalcogenide films.
Owner:TROYAN EUGENIY
Methods for high speed reading operation of phase change memory and device employing same
ActiveUS20090323409A1Control speedIncrease speedDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesPhase-change memoryOperational approach
Phase change based memory devices and methods for operating described herein overcome the performance limitations of slow set speeds and long recovery times commonly associated with phase change memory devices, enabling high speed operation and extending their usefulness into high speed applications typically filled by DRAM and SRAM memory.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Inorganic flexible resistive memory and preparation method thereof
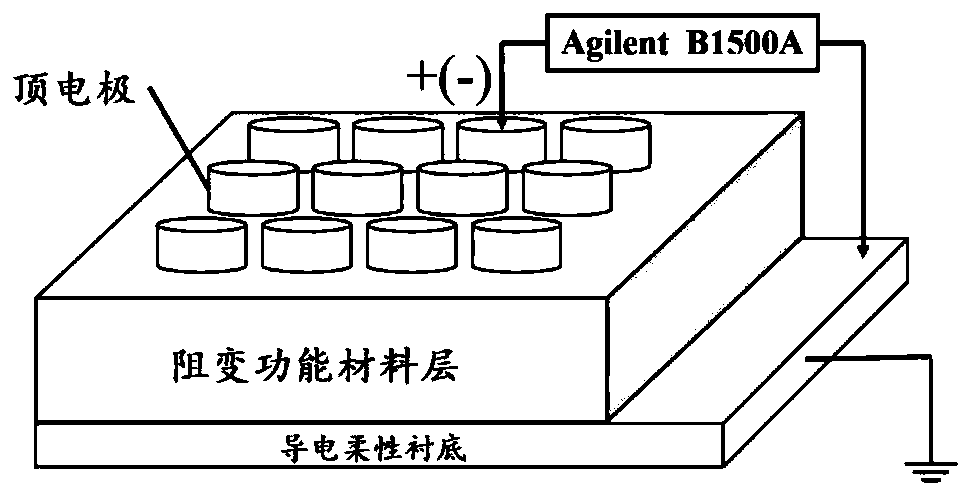
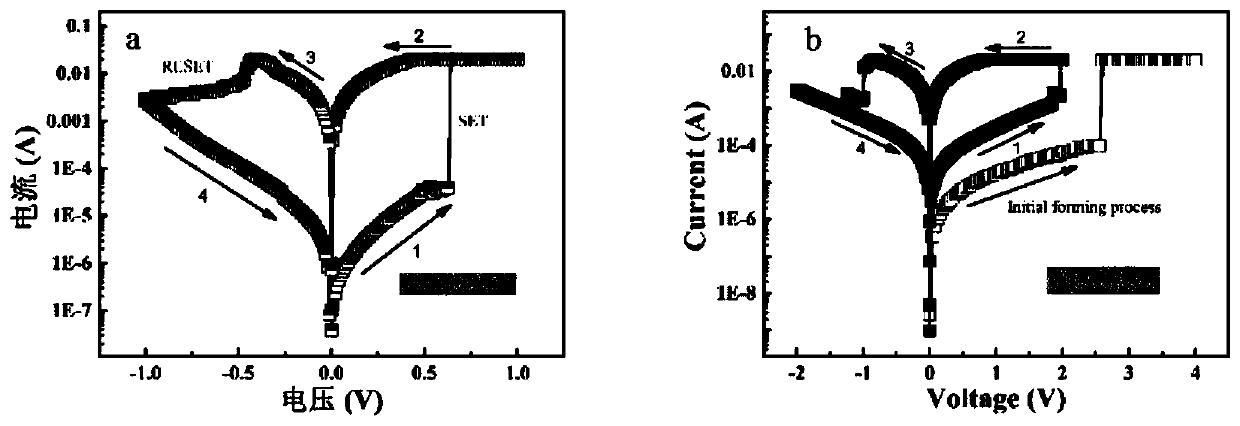
ActiveCN110165052AGood bending propertiesMitigate the impact of storage performanceElectrical apparatusNanotechnologyHigh resistancePulsed mode
The invention relates to the technical field of flexible electronic devices, in particular to an inorganic flexible resistive memory and a preparation method thereof. The inorganic flexible resistivememory has better bending characteristics, the high resistance state and low resistance state of the device are relatively stable under different bending radii and bending times, and the influence ofbending deformation on the storage performance of the functional layer material can be effectively alleviated. The inorganic flexible resistive memory has large switching ratio, low setting voltage and no Forming process and can ensure the normal operation of the device and meet the requirements of low power consumption. The inorganic flexible resistive memory has good thermal stability, the highand low resistance states of the device can be kept stable for about 105s under the condition of 85 DEG C, and the ratio of the high and low resistance states of the device is still above 102 after 107 consecutive switching operations in the pulse mode, which can ensure the normal operation of the device without misreading.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Circuitry to prevent overvoltage of circuit systems
ActiveUS8619400B2Low resistance stateAvoid overall overheatingEmergency protection for supplying operative powerEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMOSFETOvervoltage
An overvoltage protection method and circuit includes a positive supply input node, an output node, and a negative supply node. The overvoltage protection circuit further includes a first functional circuit configured to turn ON a MOSFET and maintain it in a low resistance state. A second functional circuit is configured to detect an overvoltage and control the gate of the MOSFET to regulate a voltage at the output node. A third functional circuit is configured to provide a startup wherein the overvoltage protection circuit is not damaged and / or to regulate an operating voltage such that an overvoltage does not appear on the overvoltage protection circuit. The external components include the MOSFET, which has a gate coupled to the output of the charge pump of the overvoltage protection circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Non-volatile memory component based on RbAg4I5 film and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1889285AEasy to readGood switching effectElectrical apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The present invention discloses resistance switch effect based non-volatilisation phase transition memory element physical design preparation method. It contains setting solid electrolyte RbAg 4I5 film between reaction electrode and non - reaction electrode to construct one miniature sandwich structure of memory unit, said memory unit together with substrate and insulating layer all having five layers, depositing single-layer non - reaction electrode on substrate, depositing single-layer insulating layer on non - reaction electrode, and etching one micro pore in it to expose non - reaction electrode, depositing single-layer RbAg 4I5 film on insulating layer, thereon depositing single-layer reaction electrode, respectively leading out leading wire on non - reaction electrode and reaction electrode. Said memory element has advantages of compactness, simple structure, non-volatilisation, rapid read-write, low operating voltage and energy consumption, non - moving part, and nondestructive readout etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
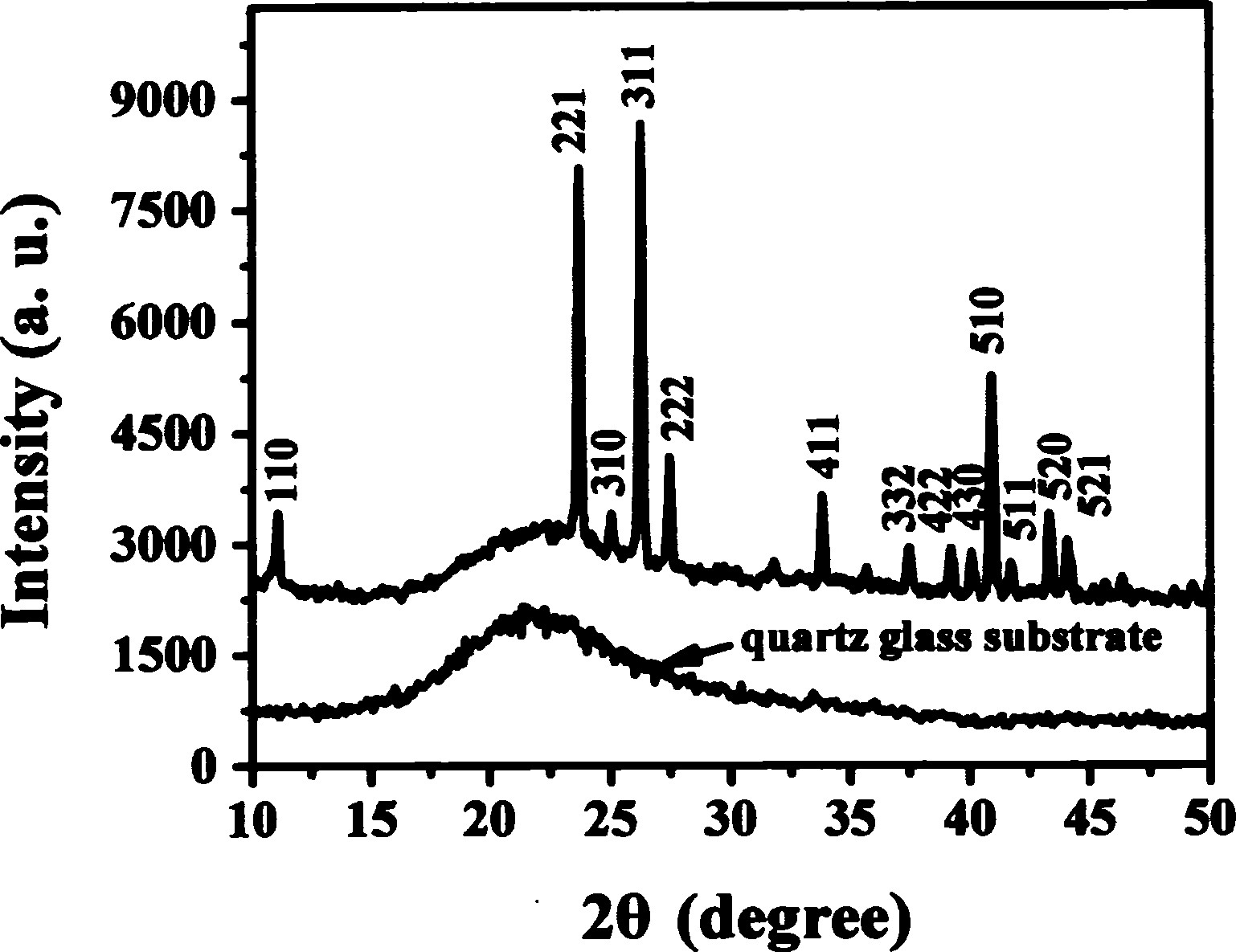
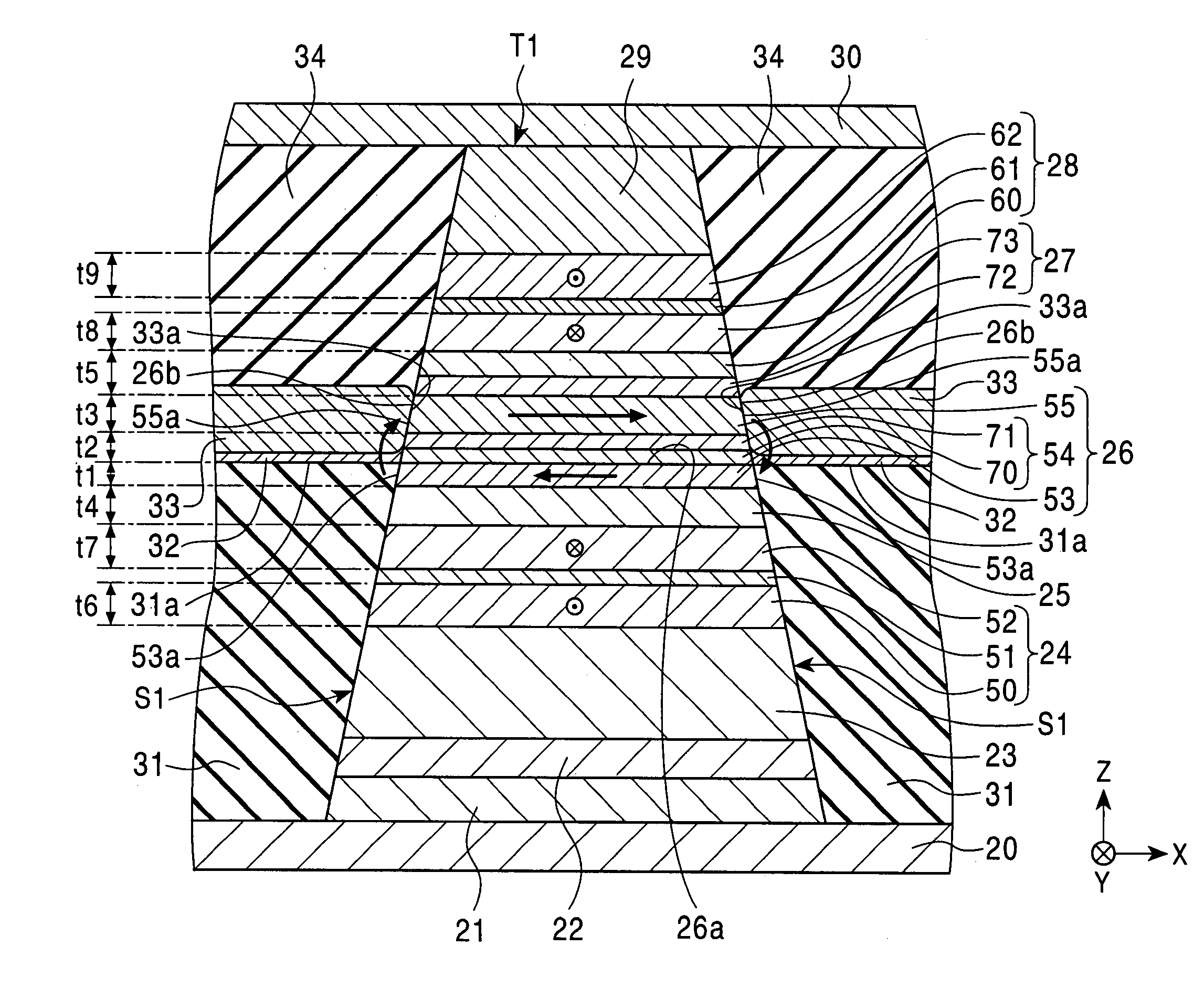
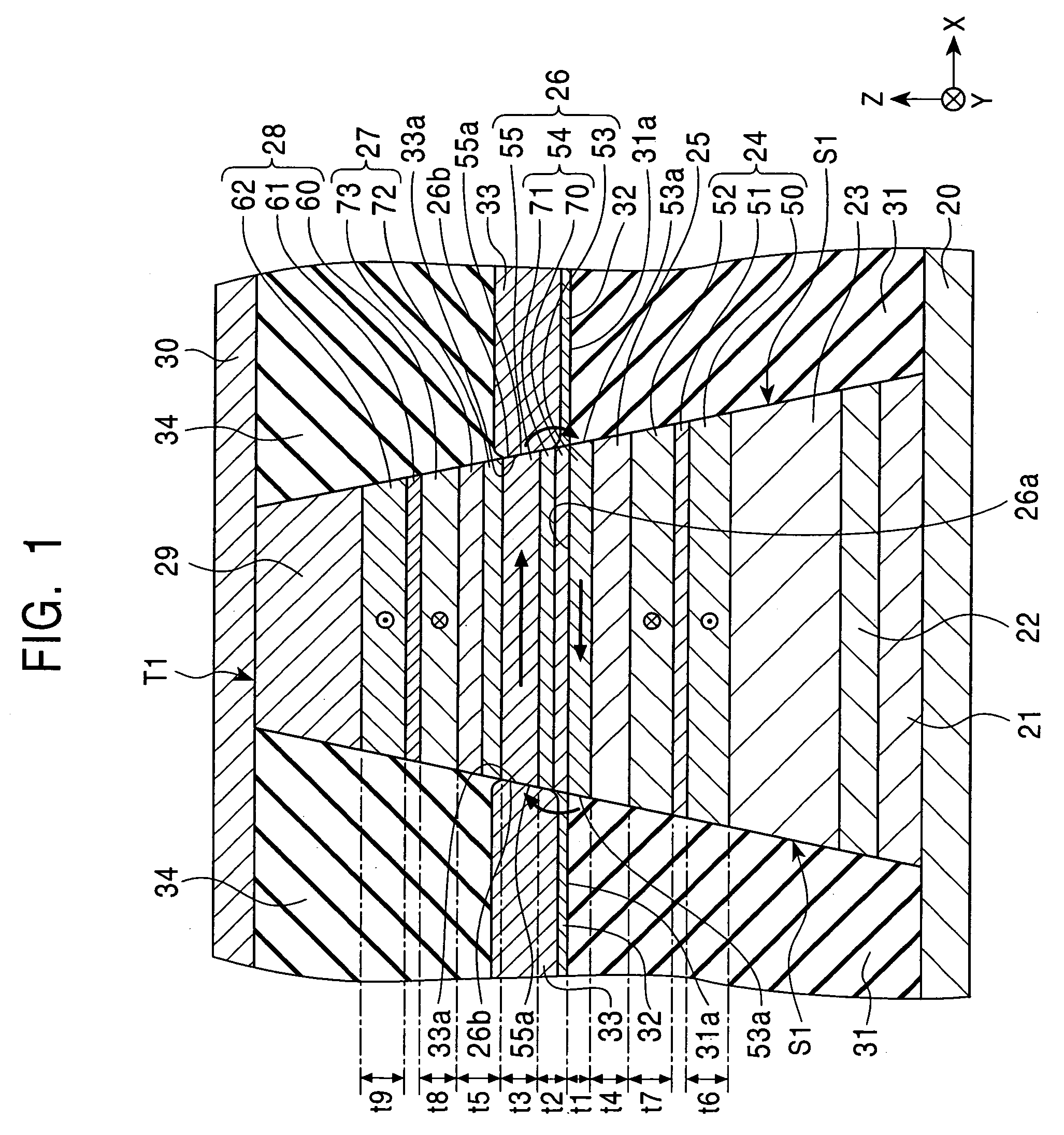
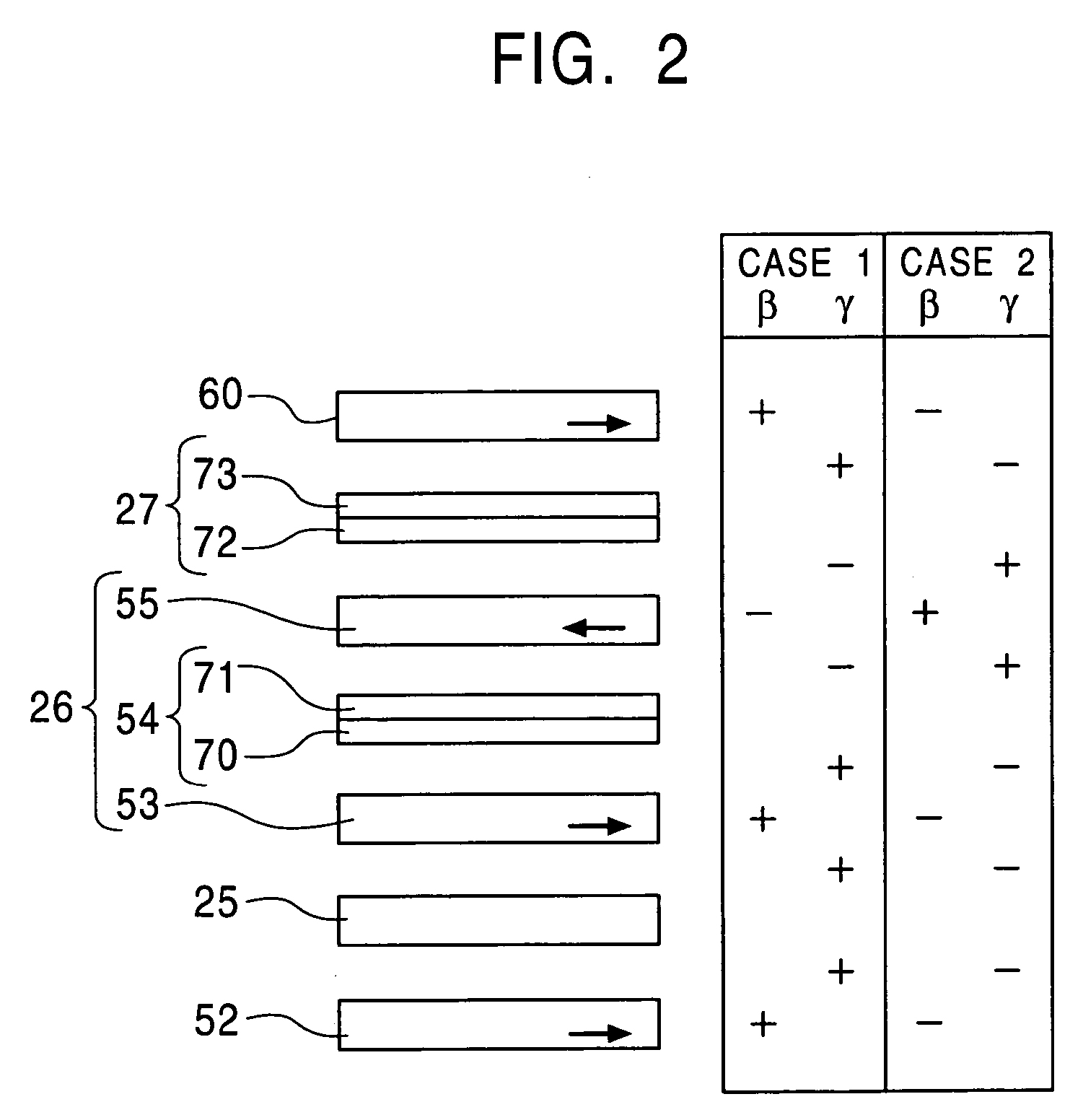
Dual-type magnetic detecting element in which free magnetic layer and pinned magnetic layer have suitably selected β values
ActiveUS7158354B2Increase changeIncrease differenceNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsConduction electronMagnetic layer
A first free magnetic layer, a second free magnetic layer, a lower pinned magnetic layer, and an upper pinned magnetic layer are formed of magnetic materials whose β values are suitably set so that the resistances for up-spin conduction electrons of all the magnetic layers become lower than those for down-spin conduction electrons when the magnetization of a free magnetic layer is changed to exhibit a lowest resistance. The magnetic detecting element exhibits an increased change in resistance per area.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Moving target detection circuit based on memristor and CMOS
ActiveCN108712621AImprove compatibilityReduce dependenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExtensibilitySignal transition
The invention discloses a moving target detection circuit based on a memristor and a CMOS. The moving target detection circuit comprises an adjacent frame difference comparison module and a signal processing module connected in order; the adjacent frame difference comparison module receives external video data and is used for difference comparison of high 4-bit numerical values on various pixel points between adjacent two frame images; the signal processing module is used for acquiring binary output corresponding to various pixel points after orderly performing current-voltage signal conversion, weighted sum and threshold comparison on the difference comparison result output by adjacent frame difference comparison module, thereby generating a white-black image for describing the moving target contour. The difference comparison is performed on the signal from an image sensor through a mixed structure array of the memristor and the CMOS. The detection circuit has the advantages of beingsimple in structure, small in volume, strong in extensibility and low in power consumption, the contour detection on the moving target can be accomplished on a hardware circuit, and the data processing pressure of the computer can be shared, thereby laying the foundation for realizing higher-order image processing task.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resistive random access memory using rare earth scandate thin film as storage medium
ActiveUS8445888B1Low operating voltageLow power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageHigh resistanceForming processes
The present invention relates to a resistive random access memory using the rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium, comprising a substrate, an insulation layer, a first electrode layer, a resistive memory layer, and a second electrode layer. In the present invention, it uses an amorphous rare earth scandate layer as the resistive memory layer of the resistive random access memory. Therefore, the resistive random access memory using the rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium having advantages of low operation voltage and low power consumption can easily be manufactured without using any forming process or thermal annealing process. Moreover, through the characteristics of unipolar resistance switching behavior revealed by the amorphous rare earth scandate layer, the resistive random access memory using rare earth scandate thin film as the storage medium is able to perform a high resistance state and a low resistance state.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resistance variable oxide material Co3O4 thin film, preparation and use thereof
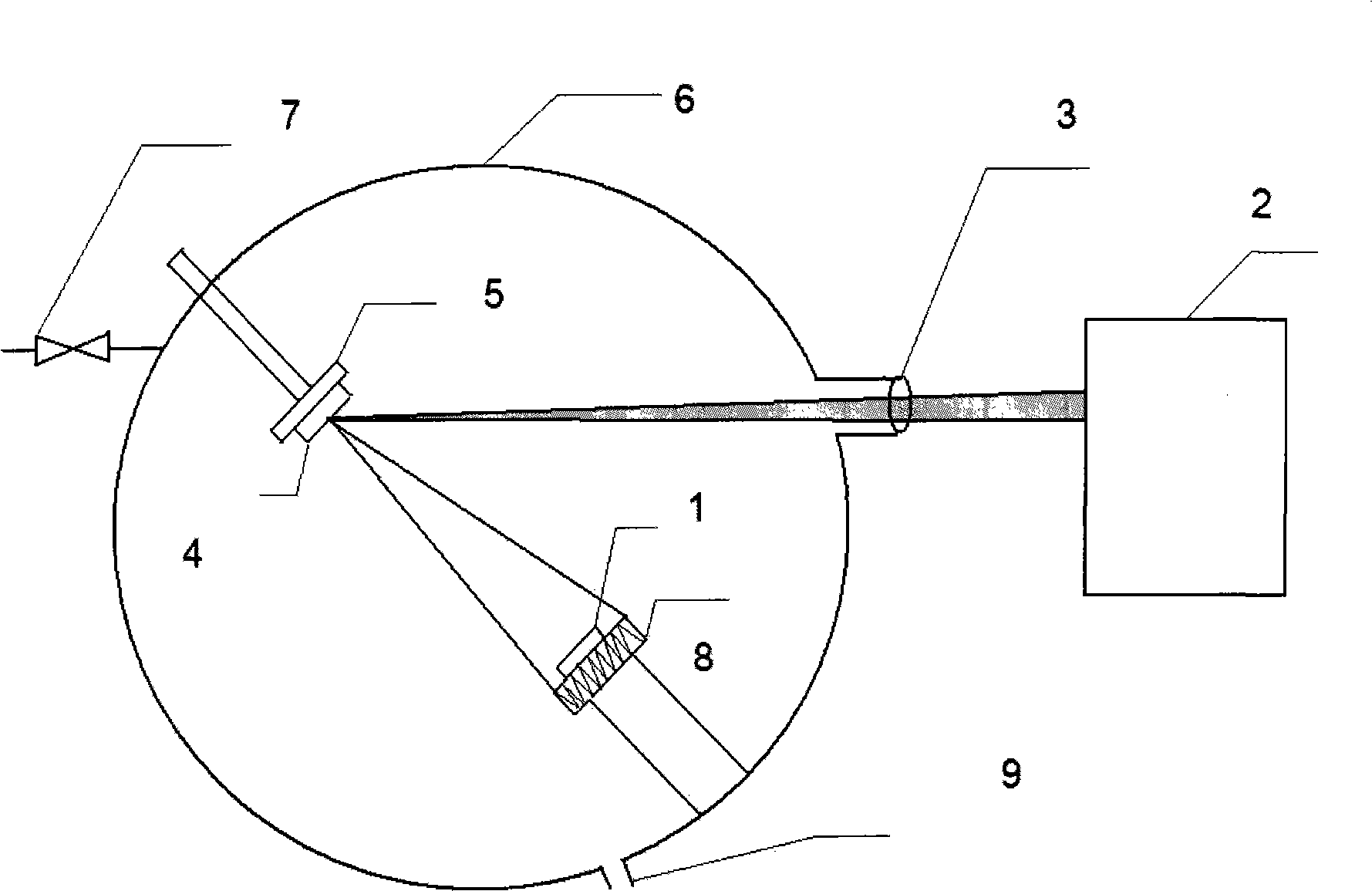
InactiveCN101498042AUniform thicknessClear interfacePolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingInlet valveLaser beams
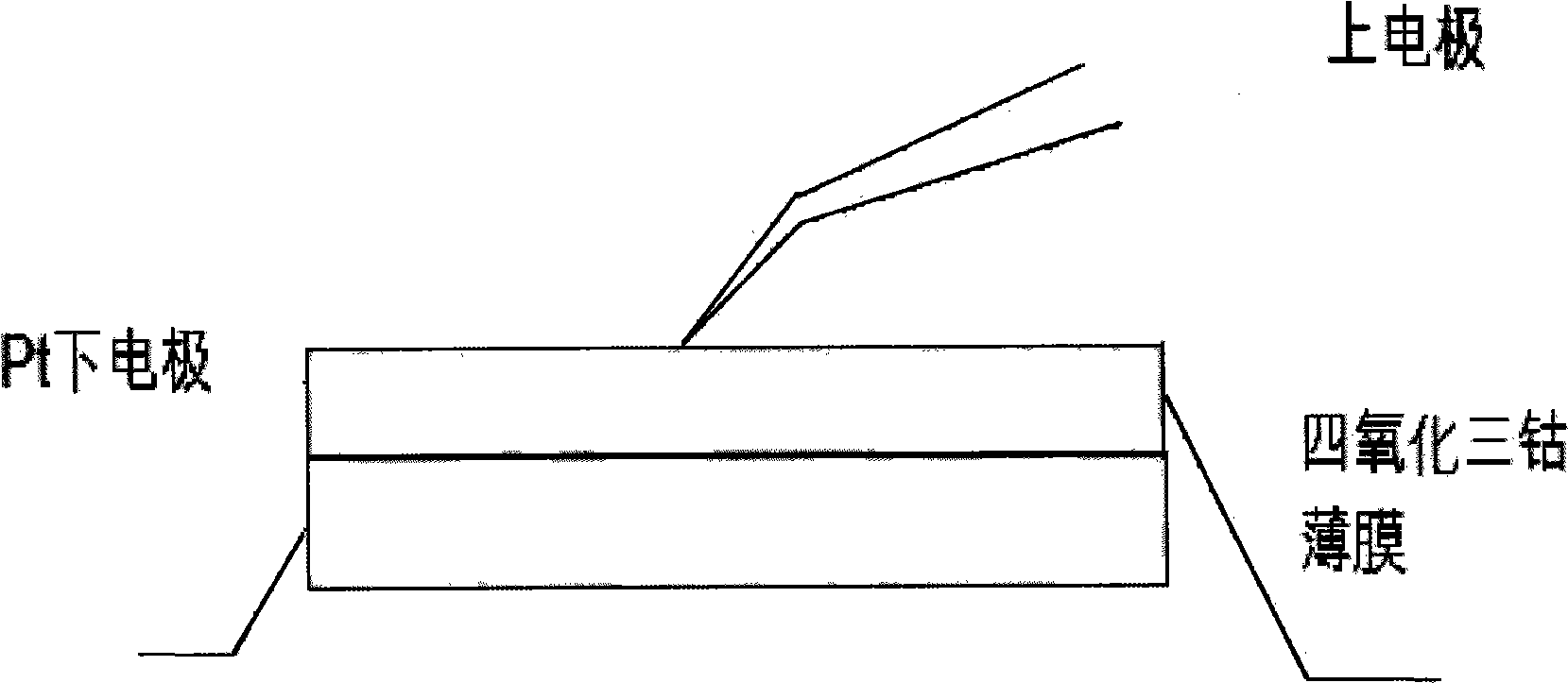
The invention relates to a cobalt oxide film of interrupted oxide material, which is in a polycrystal state and has a chemical formula of Co3O4 and a thickness of 200nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing ceramic target material of CoOx (x is larger than 0 and less than 4 / 3); (2), fixing the target material of CoOx on a target, fixing a substrate on a substrate platform and arranging the target and the substrate platform in a growth chamber; (3), vacuumizing the growth chamber by a mechanical pump and a molecular pump, closing the mechanical pump, opening an inlet valve and pumping oxygen to the growth chamber until oxygen pressure is 20Pa; (4), focusing laser beams of a laser on the target material of CoOx by a lens; (5), heating the substrate platform by a resistance furnace so that the temperature of the substrate reaches a temperature of 660 DEG C; and (6), confirming sedimentation time according to single-pulse energy to sedimentate the film of Co3O4 with the thickness of 200nm on the substrate. The film is used to prepare a nonvolatile interrupted memory storage element which adopts a sandwich structure as a basic configuration, i.e., a polycrystal oxide film of Co3O4 is sedimentated on a Pt electrode film of a lower electrode, and a Pt probe is used as an upper electrode to form a memory unit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Self-selection resistive random access memory suitable for intersected array, and reading method thereof
ActiveCN106169534AVolatileReduce volatilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCurrent limitingHigh density
The invention discloses a self-selection resistive random access memory suitable for an intersected array, and a reading method thereof. The self-selection resistive random access memory employs a quite thin active electrode, has a volatile low resistance state, through combination with a quite small current-limiting value and specific reading operation, when being applied to a cross intersected array, can inhibit leakage currents, and realizes selection-free high-density integration of a resistance variable unit.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Semiconductor memory devices for use in electrically alterable read only memory (ROM) and semiconductor thin film devices (spintrons and spin-orbitrons)
ActiveUS9865811B2Improve superconductivityImproved Impedance StabilityElectrical apparatusDielectricHigh resistance
An electrically alterable thin film memory device or non-volatile trigger which can be switched from a high resistance state to a low resistance state. The device increases the concentration of electrically active impurities at correspondent electrodes to which respect impurities would electro migrate during a large number of set-reset cycles. The device comprises a layered structure with memory layers formed on an interface of two regions as the result of the mutual mixing and migration of their constituents. One region contains an electrically active donor impurity. A thin layer of dielectric is placed in the other region. Each of the memory layers includes an interface of chalcogenide films.
Owner:TROYAN EUGENIY
Methods for high speed reading operation of phase change memory and device employing same
Phase change based memory devices and methods for operating described herein overcome the performance limitations of slow set speeds and long recovery times commonly associated with phase change memory devices, enabling high speed operation and extending their usefulness into high speed applications typically filled by DRAM and SRAM memory.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com