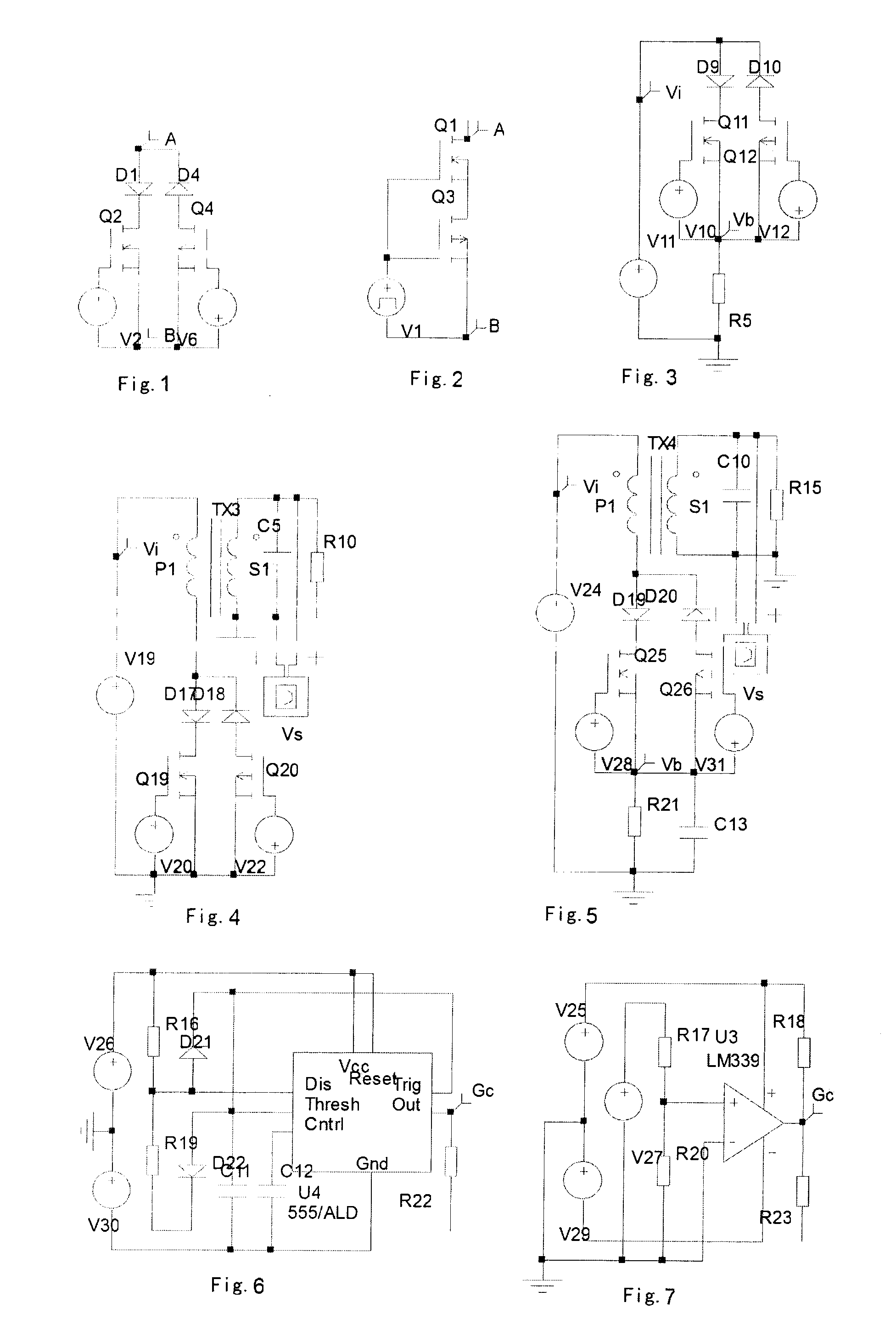Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
493 results about "Circuit complexity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In theoretical computer science, circuit complexity is a branch of computational complexity theory in which Boolean functions are classified according to the size or depth of Boolean circuits that compute them. One speaks of the circuit complexity of a Boolean circuit. A related notion is the circuit complexity of a recursive language that is decided by a uniform family of circuits C₁,C₂,… (see below).
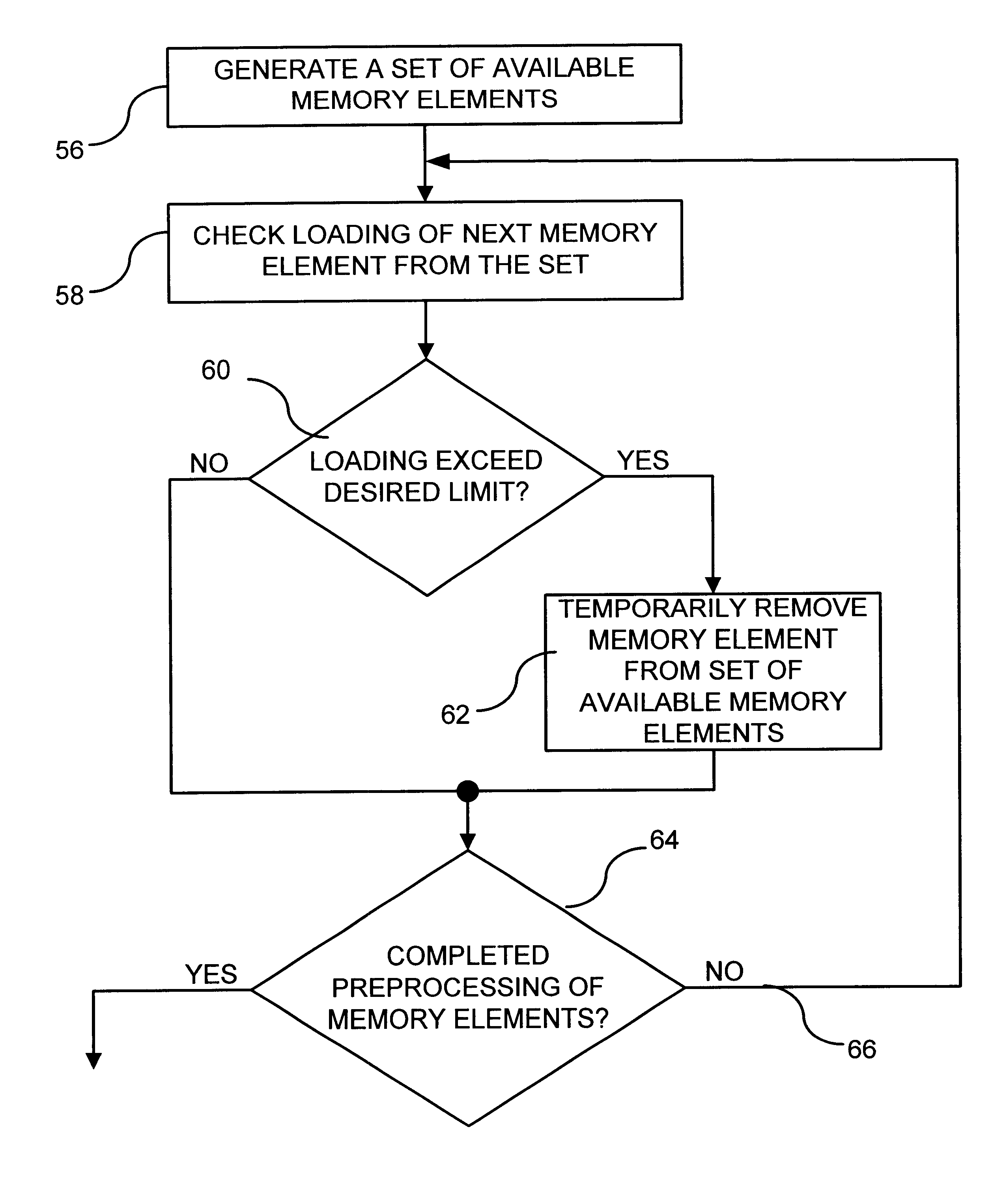
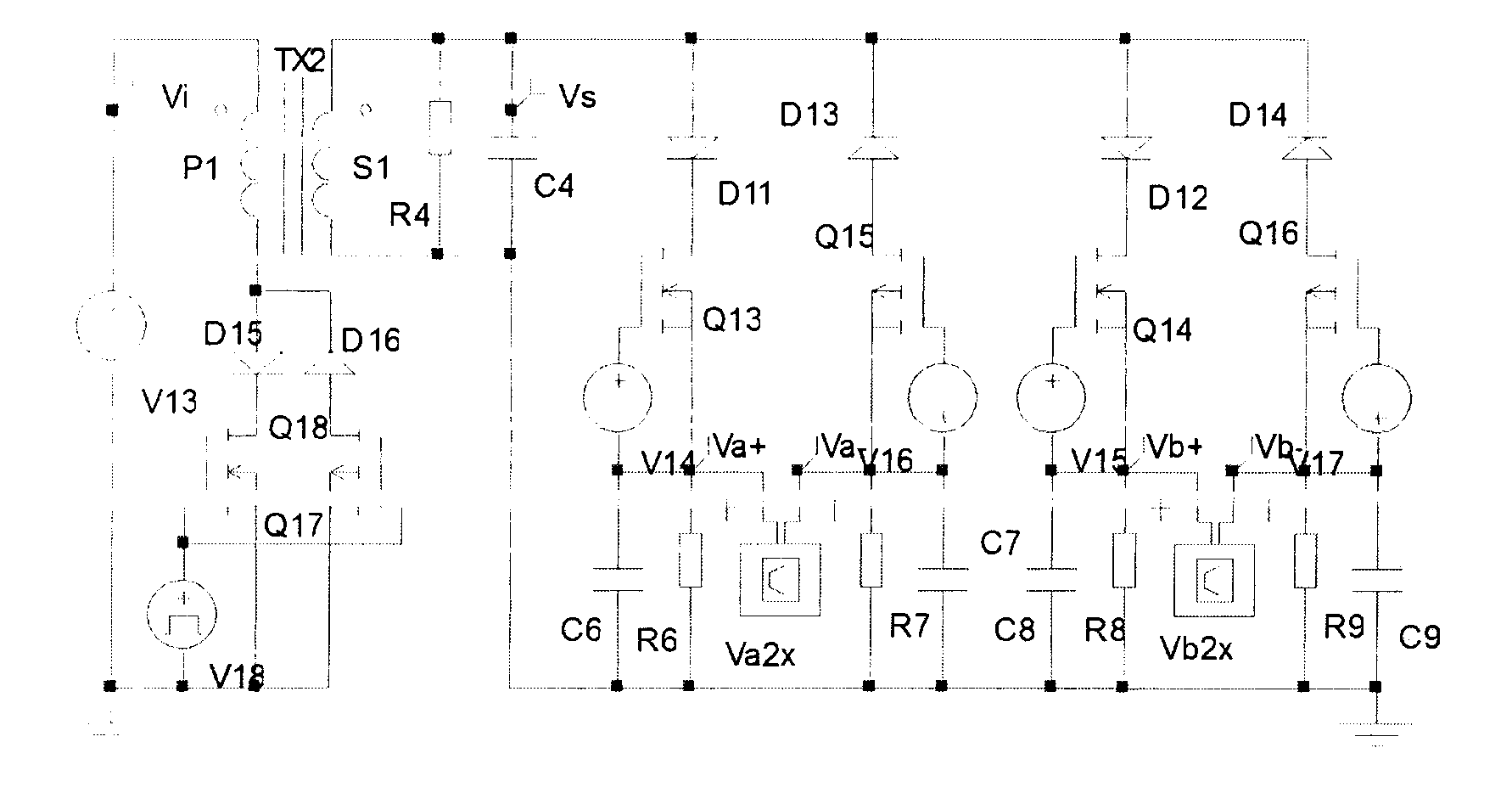
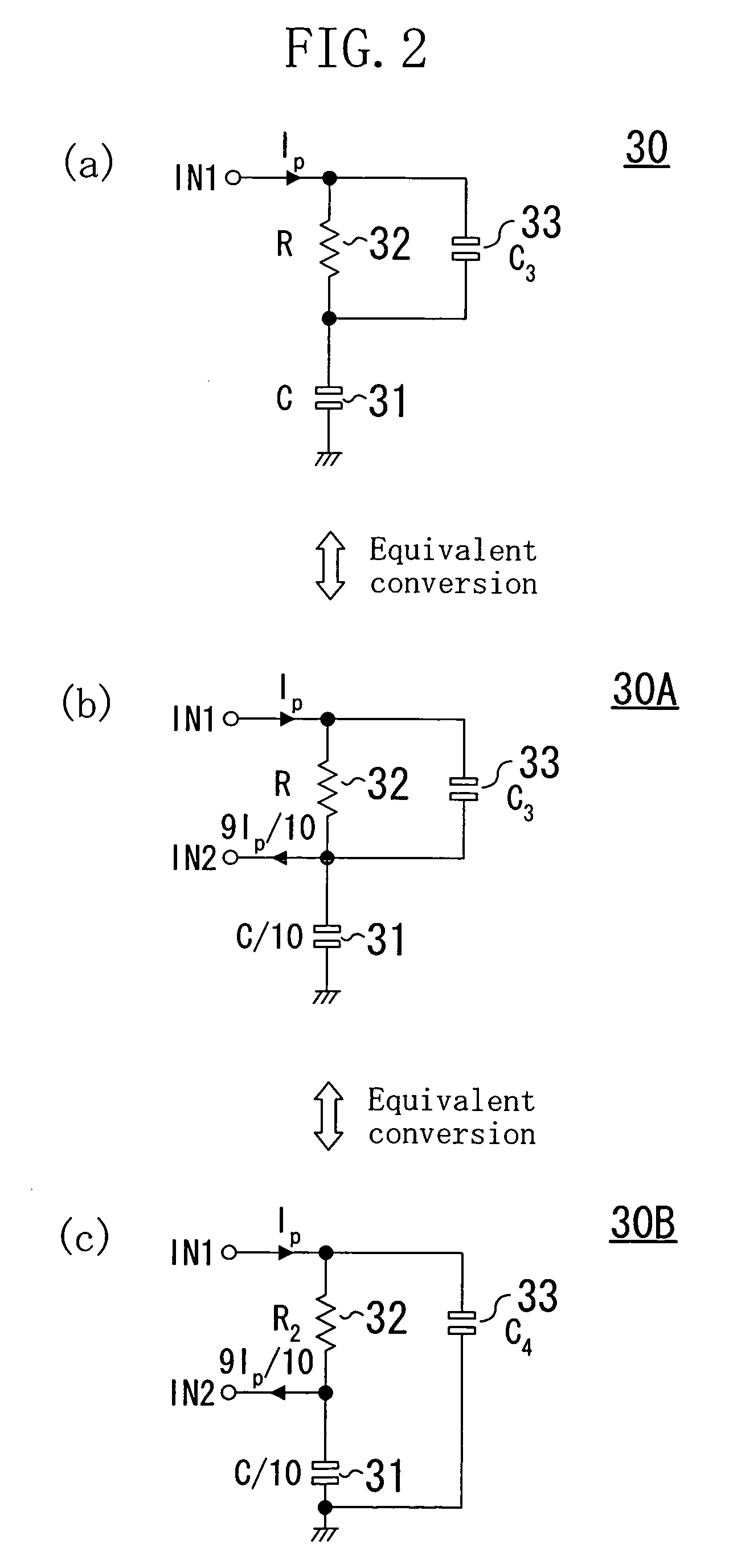
Phase shifter with reduced linear dependency
InactiveUS6874109B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionCircuit complexityLinear dependency
A method is disclosed for the automated synthesis of phase shifters. Phase shifters comprise circuits used to remove effects of structural dependencies featured by pseudo-random test pattern generators driving parallel scan chains. Using a concept of duality, the method relates the logical states of linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) and circuits spacing their inputs to each of the output channels. The method generates a phase shifter network balancing the loads of successive stages of LFSRs and satisfying criteria of reduced linear dependency, channel separation and circuit complexity.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
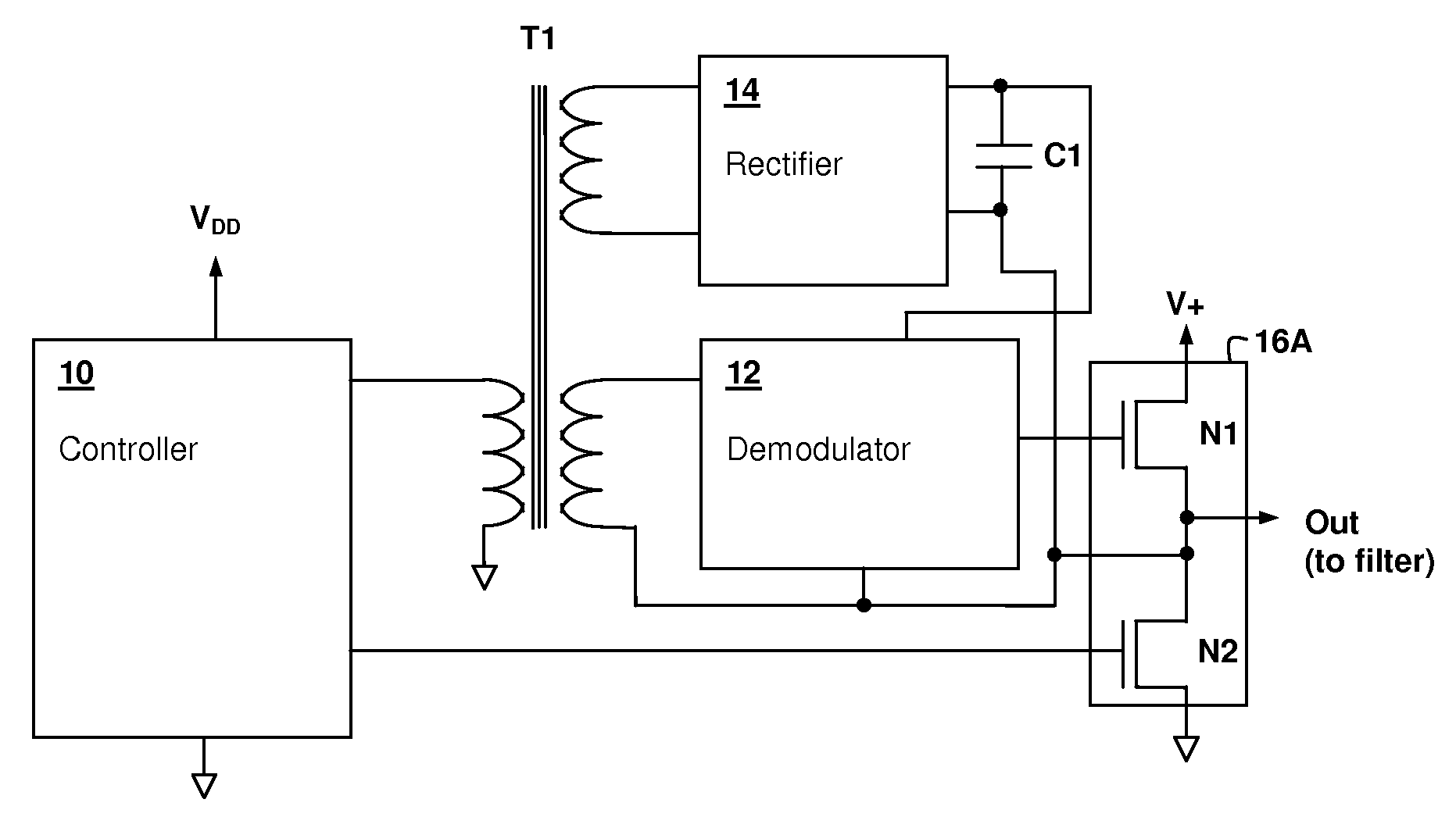
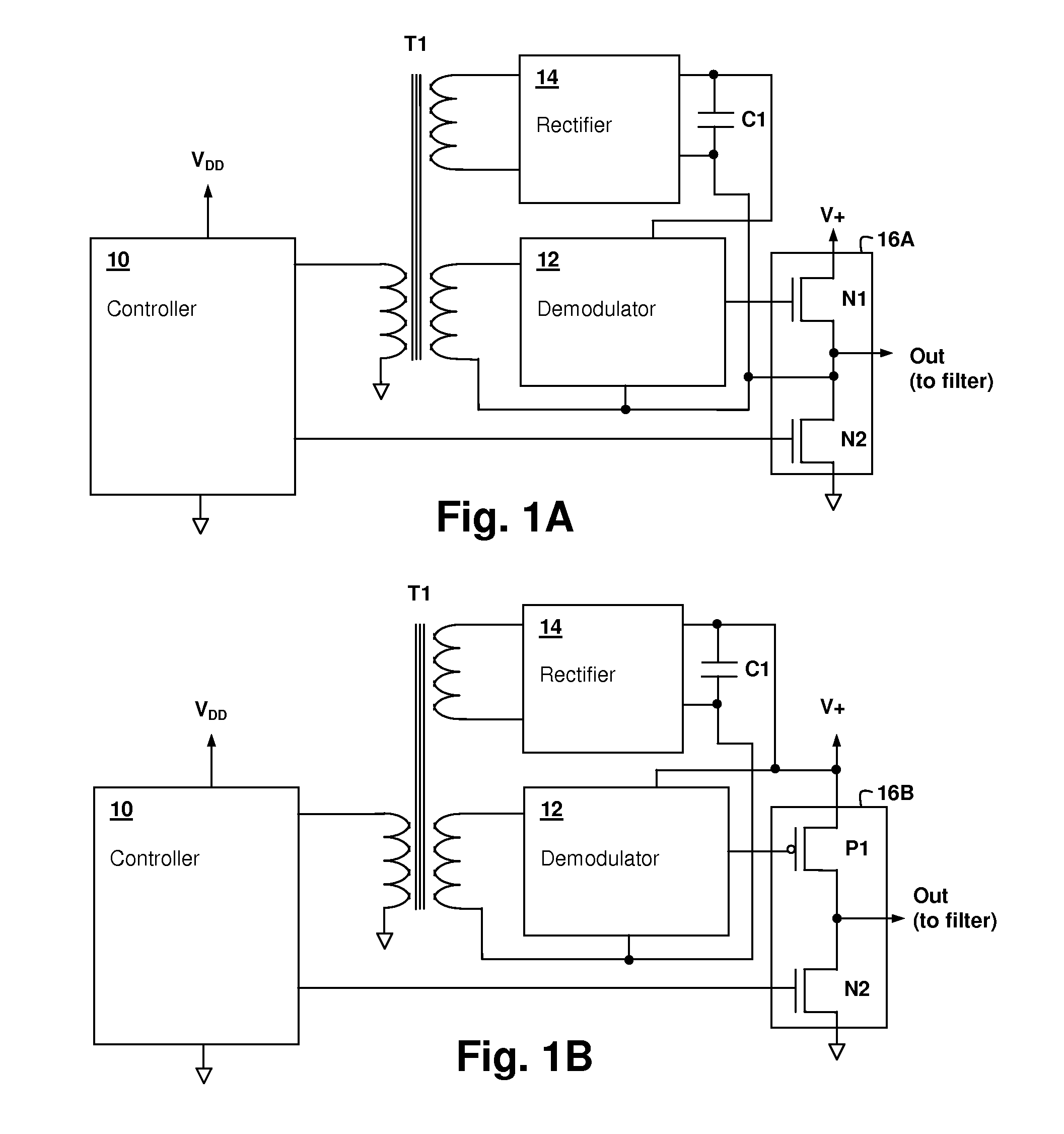
Modulated transformer-coupled gate control signaling method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090147544A1Wide range of pulse widthZero net magnetization currentDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalCircuit complexityControl signal
A modulated transformer-coupled gate control signaling method and apparatus provides reduction of circuit complexity and robust design characteristics in switching power circuits having a transformer-coupled gate drive. A modulated control signal at a rate substantially higher than the switching circuit gate control rate is provided from the controller circuit to a demodulator via transformer coupling. Power for the demodulator can be obtained by rectifying the modulated control signal at the demodulator, or from another transformer winding. The modulation scheme is chosen to have a DC average value of zero, eliminating any magnetization current management requirements. The modulated control signal may carry redundant control information and / or may encode additional information to provide a more sophisticated gate drive control, such as oversampled gate control information.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
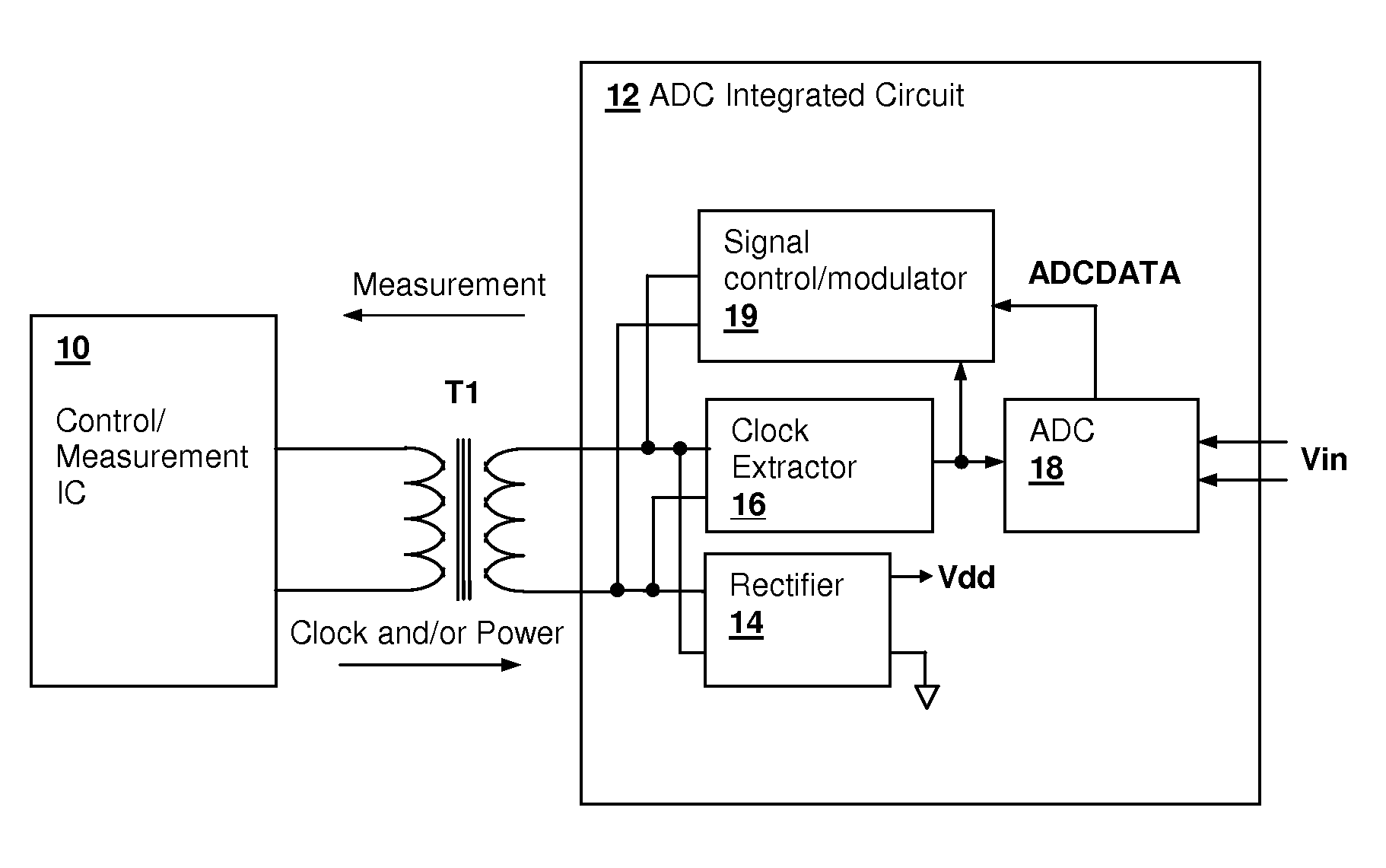
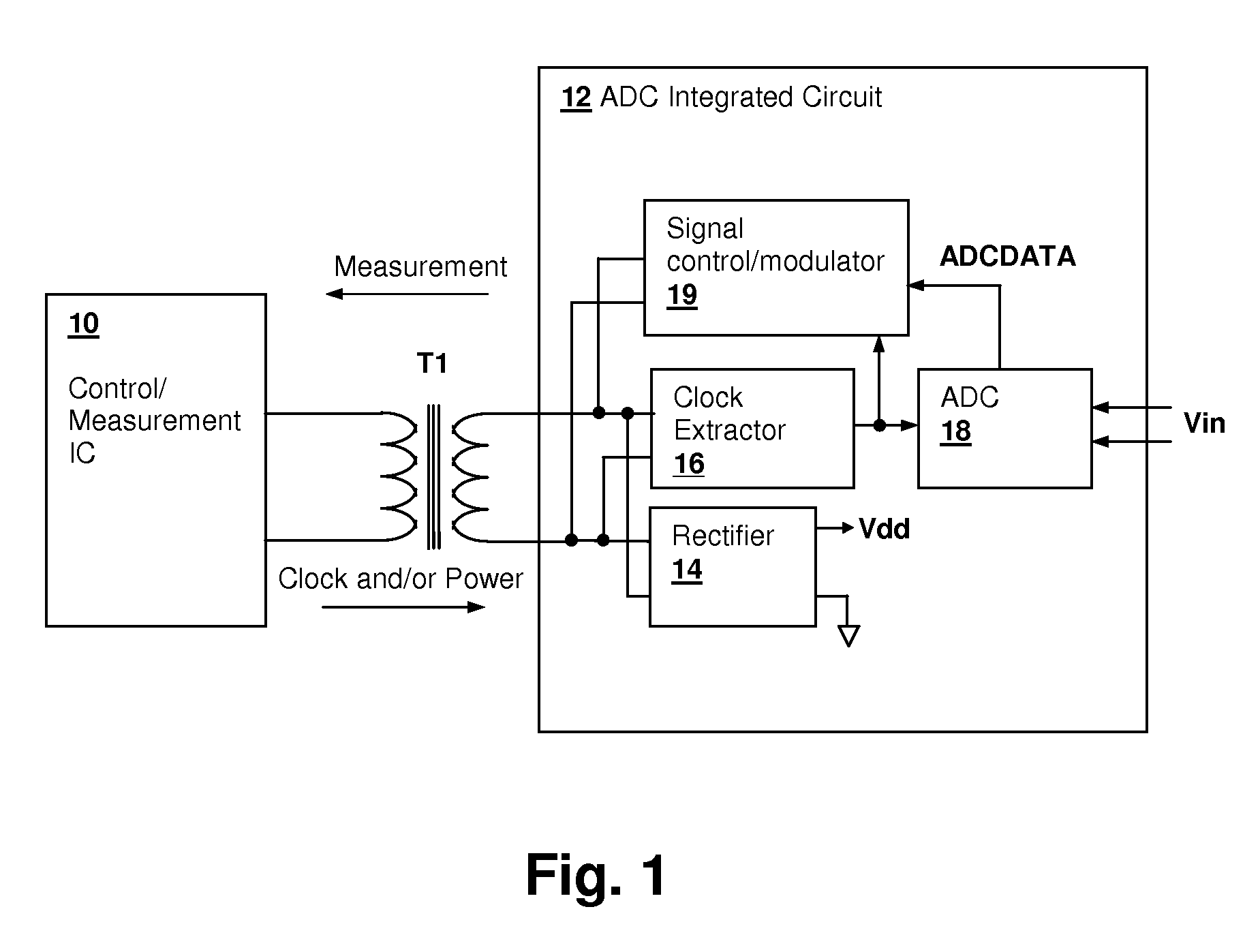
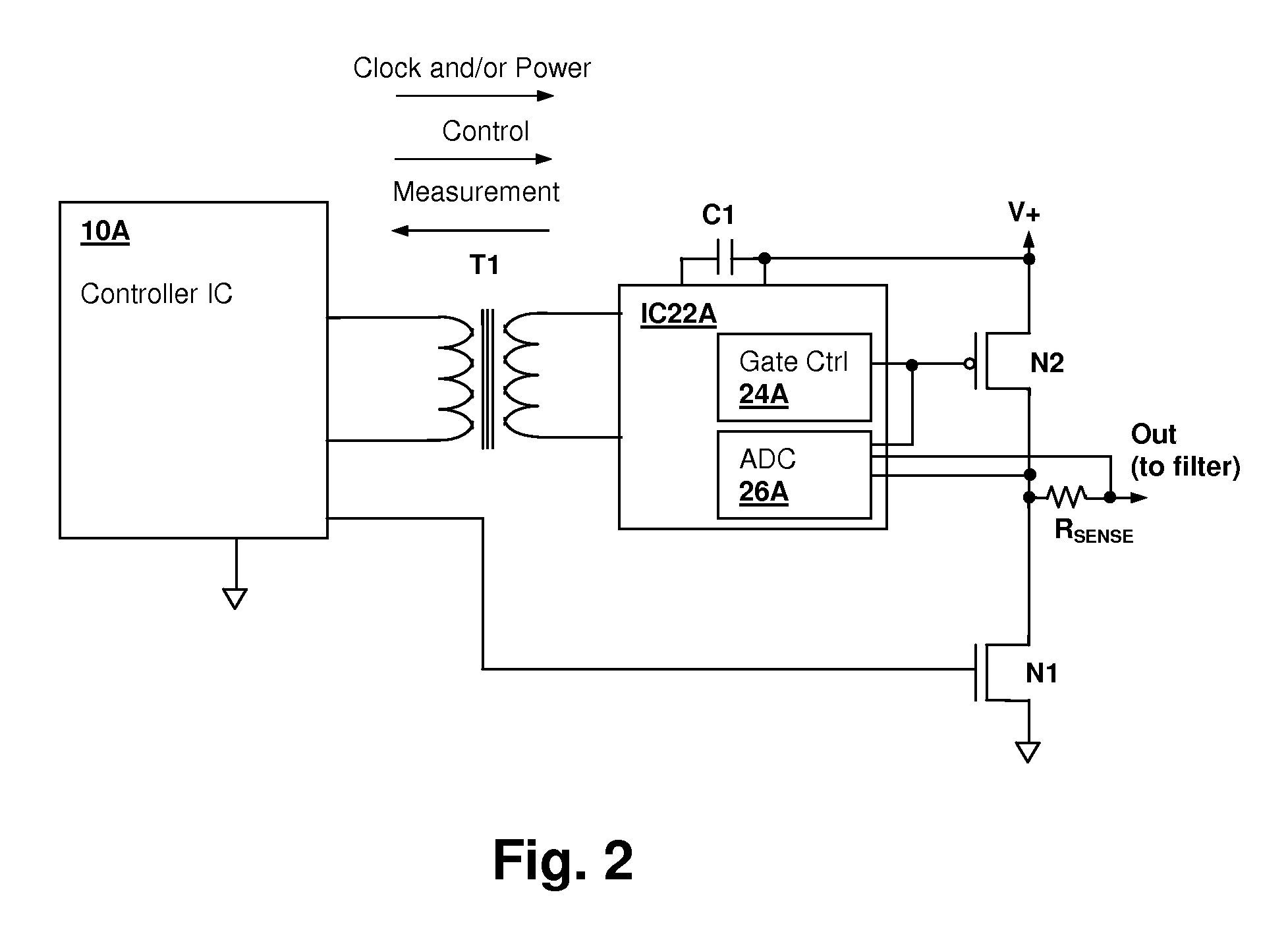
Transformer-isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) feedback apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090212759A1TransistorElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit complexityDigital down converter
A transformer-isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) feedback apparatus and method provides reduction of circuit complexity in high power / high voltage systems having a transformer-isolated sensing circuit. The feedback apparatus is a circuit including an ADC for receiving an analog input signal and a transformer having a first winding that receives a modulated output of the analog-to-digital converter. A second winding of the transformer provides an isolated data output of the ADC. A demodulator is coupled to the second winding of the transformer and demodulates the isolated output to generate a digital representation of the analog input signal. The ADC may be a delta-sigma converter and the demodulator may be the corresponding decimation filter. The circuit further includes an isolation circuit for introducing a clock signal and / or power supply waveform at the second winding of the transformer, so that the ADC circuit is supplied with an isolated clock and / or an isolated power supply.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Green Power Converter
InactiveUS20130009484A1Reduce complexityReduce consumptionDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionFailure rateCapacitance
The invention discloses a green power converter which omits the pulse width modulation (PWM) technique in the traditional power converter, does not have high-frequency power device, does not generate EMI interference, simultaneously adopts the symmetry basic primitive (SBP) technique, the amplitude high modulate (AHM) technique and the dynamic rectification (DR) technique, and only needs to perform traditional power conversion on a small part of the input power so as to acquire the whole output power, namely that a large part of the output power neither need traditional power conversion nor need to pass through a magnetic core transformer. The input AC voltage neither needs to be rectified and filtered nor has large inductance and large capacitance, thus the power factor is 1, and the total harmonic distortion (THD) is 0. A transformer secondary side adopts dynamic rectification, can acquire a DC circuit, and can also acquire an AC voltage. The circuit complexity, the power consumption and the failure rate of the whole green power converter are greatly lowered, and the power converter can be applied in all the fields to replace the traditional power converter.
Owner:YU BAICHOU
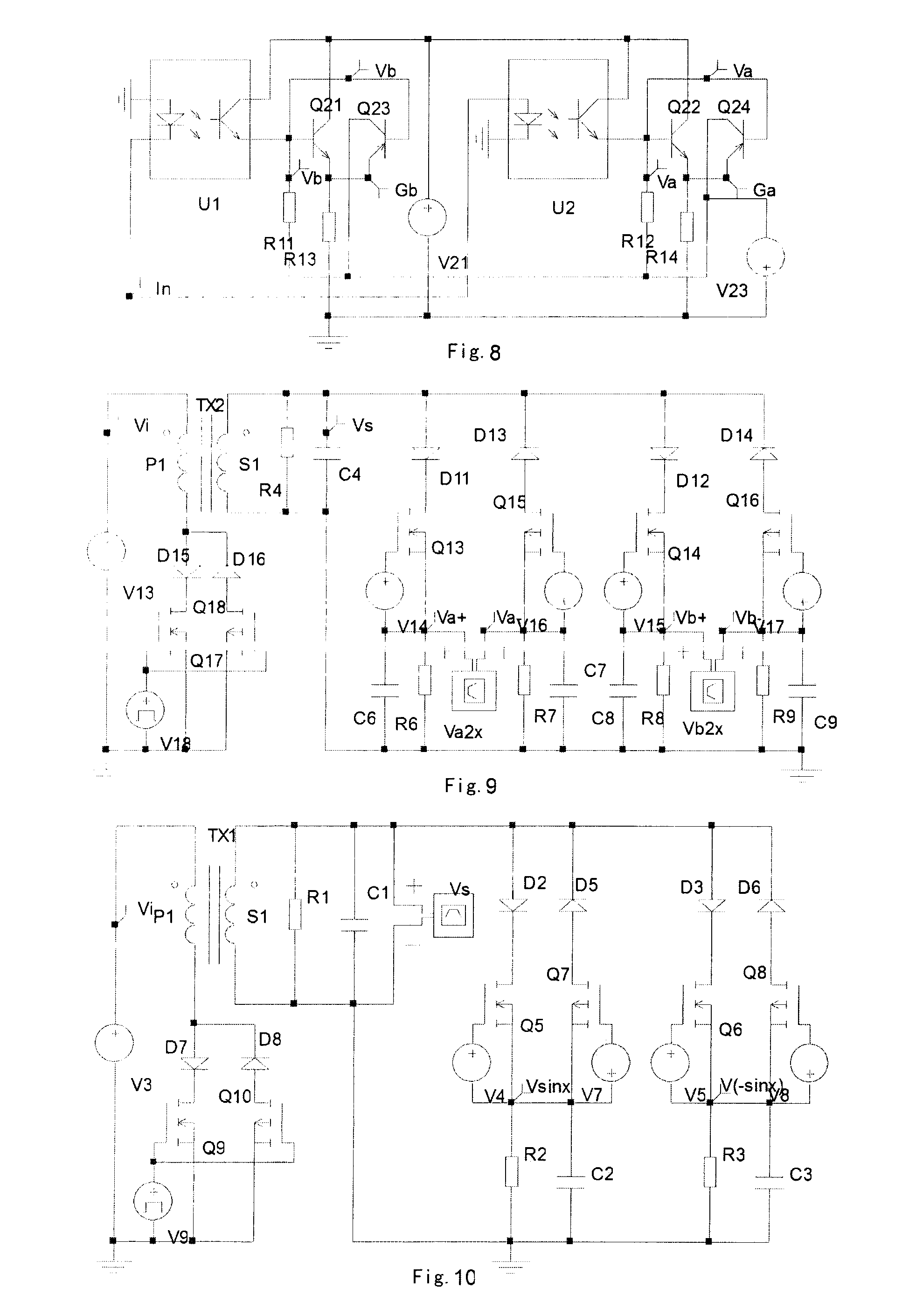
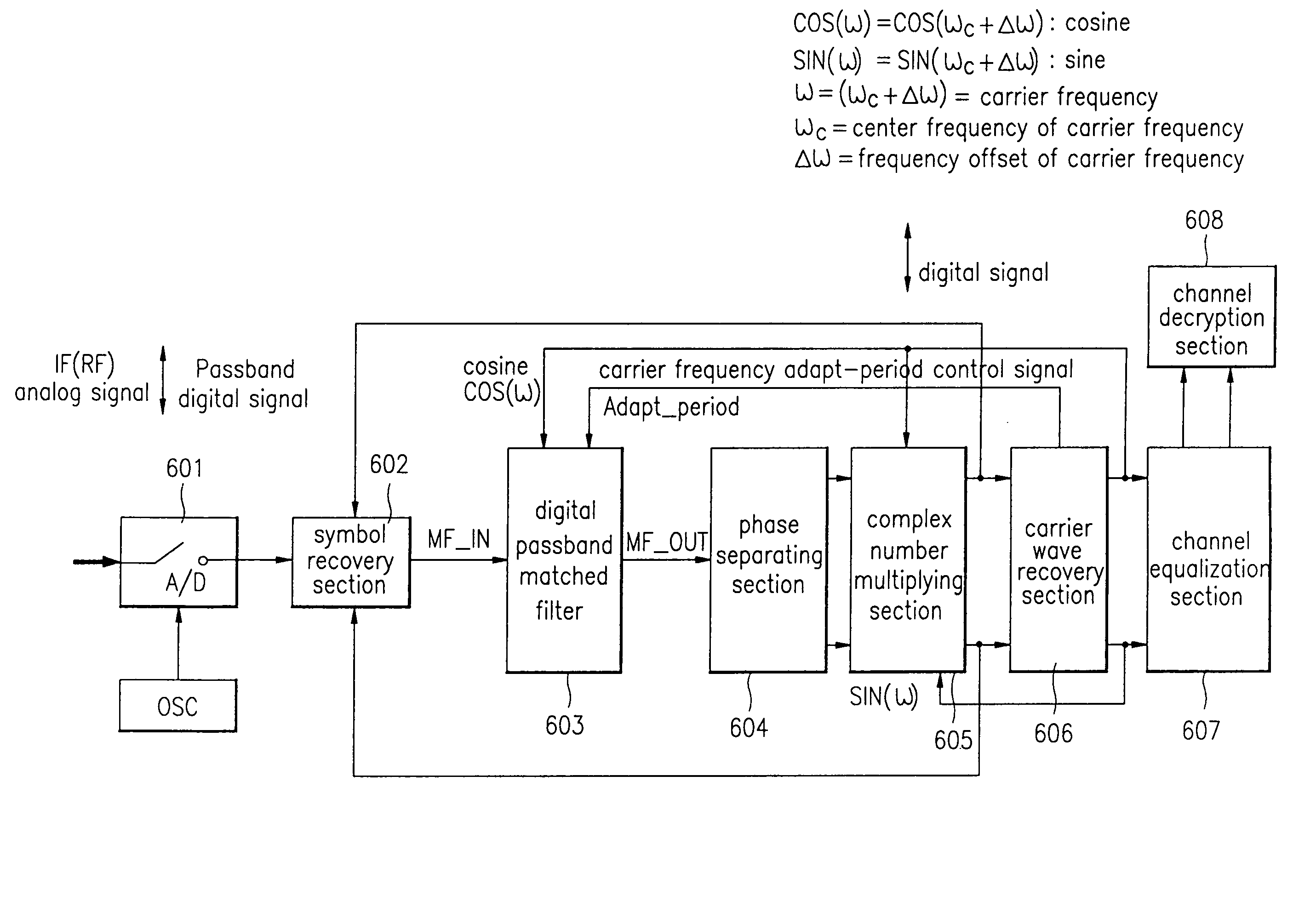
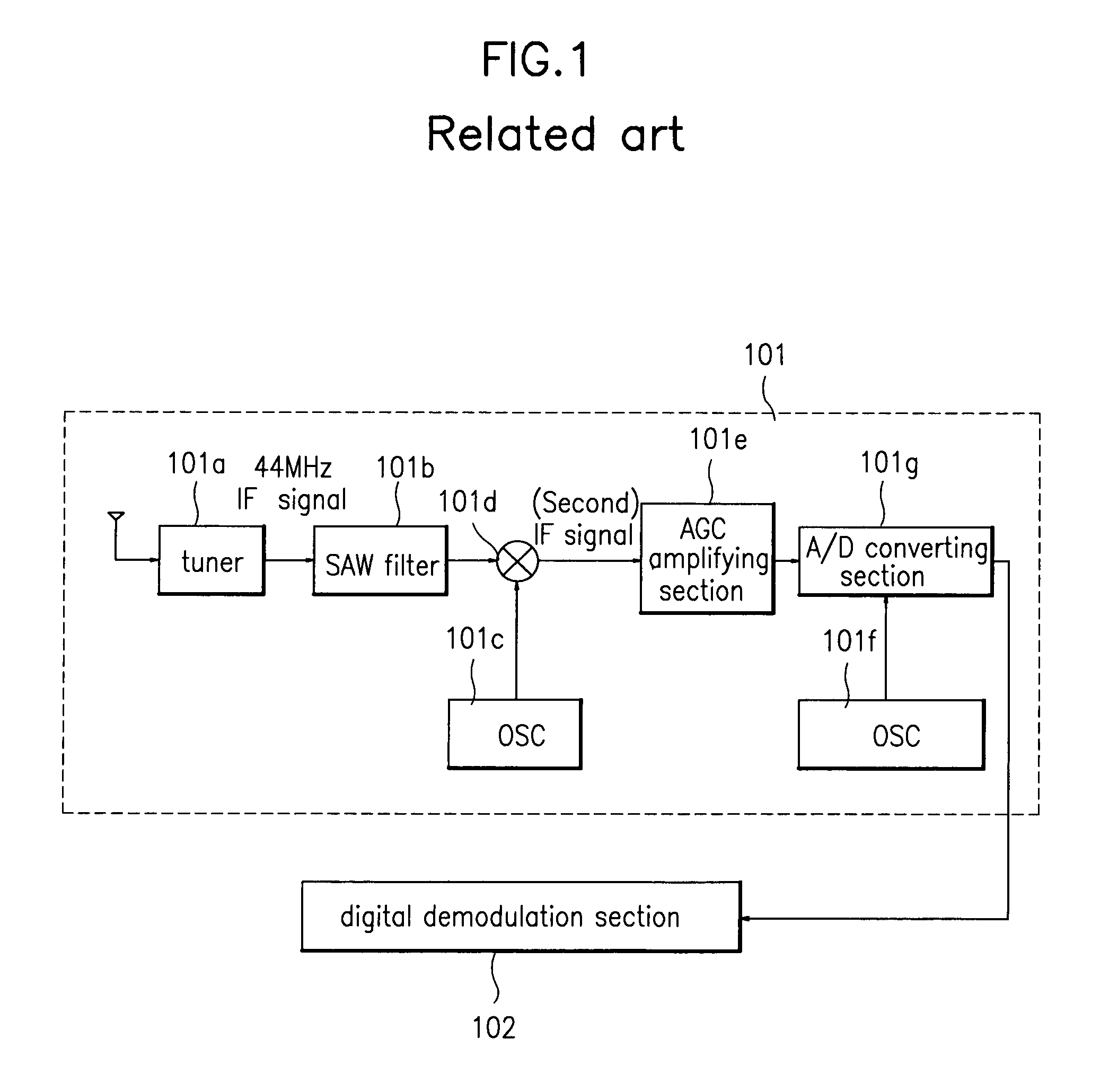
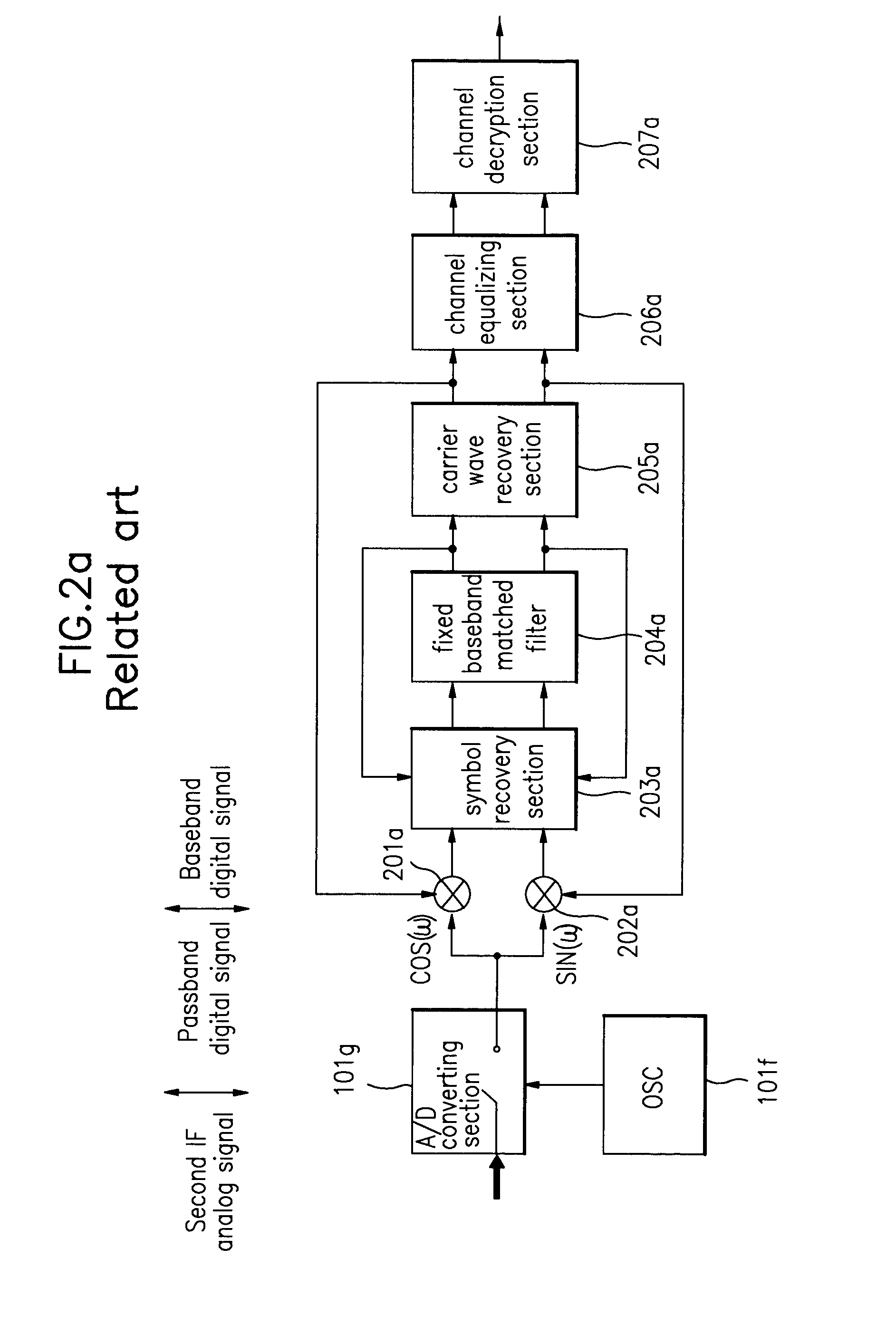
Matched filter, filtering method and digital broadcast receiver using the same
InactiveUS6980609B1Deterioration of SNR performanceIncreased circuit complexityCarrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCircuit complexityCarrier signal
A digital passband matched filter is automatically adapted to a carrier wave ω in accordance with a frequency offset of the carrier wave, to obtain a passband digital signal having no frequency distortion due to the frequency offset. Thus, a receiver in which drawbacks such as decrease of SNR and increase of circuit complexity caused by the fixed baseband / passband matched filter is obtained. Since a cosine wave generating section operates in a carrier wave frequency restoring mode and a carrier wave frequency adaptive mode, respectively, a single cosine wave ROM table can be used regardless of the respective operating modes, thereby reducing circuit complexity. Since the digital passband matched filter acts to renew the filter coefficients adapted to the carrier wave adaptive mode only, power consumption required to operate the filter can be minimized.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Low-pass filter, feedback system, and semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7078948B2Reduce circuit areaSmall sizeFluid heatersMultiple-port networksCircuit complexityCapacitance
In a low-pass filter which is preferably used as a loop filter in a PLL or DLL, filter characteristics which are the same as those of a conventional low-pass filter are realized without causing collateral problems, such as an increase in the circuit area, the circuit complexity, or the resistance value, which may be caused due to size reduction of a capacitive element in the conventional low-pass filter. Thus, in a loop filter including a capacitive element and a resistive element which are connected in series, the first input terminal is provided at the side including the resistive element, and the second input terminal is provided at a connection point of the capacitive element and the resistive element. The first input terminal is supplied with the first electric current. On the other hand, the second electric current, which is a part of the first electric current supplied to the first input terminal, is extracted from the second input terminal, so that the electric current flowing into the capacitive element is smaller than the electric current flowing through the resistive element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
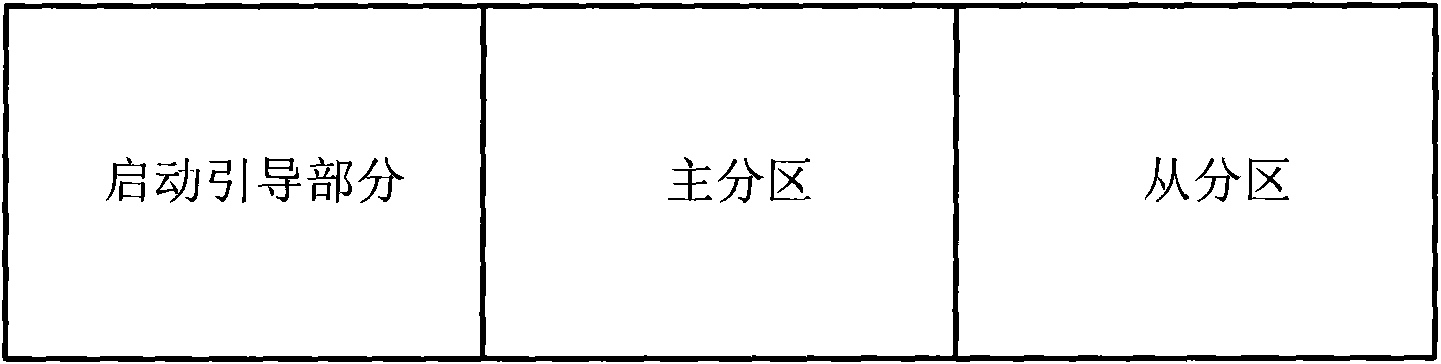
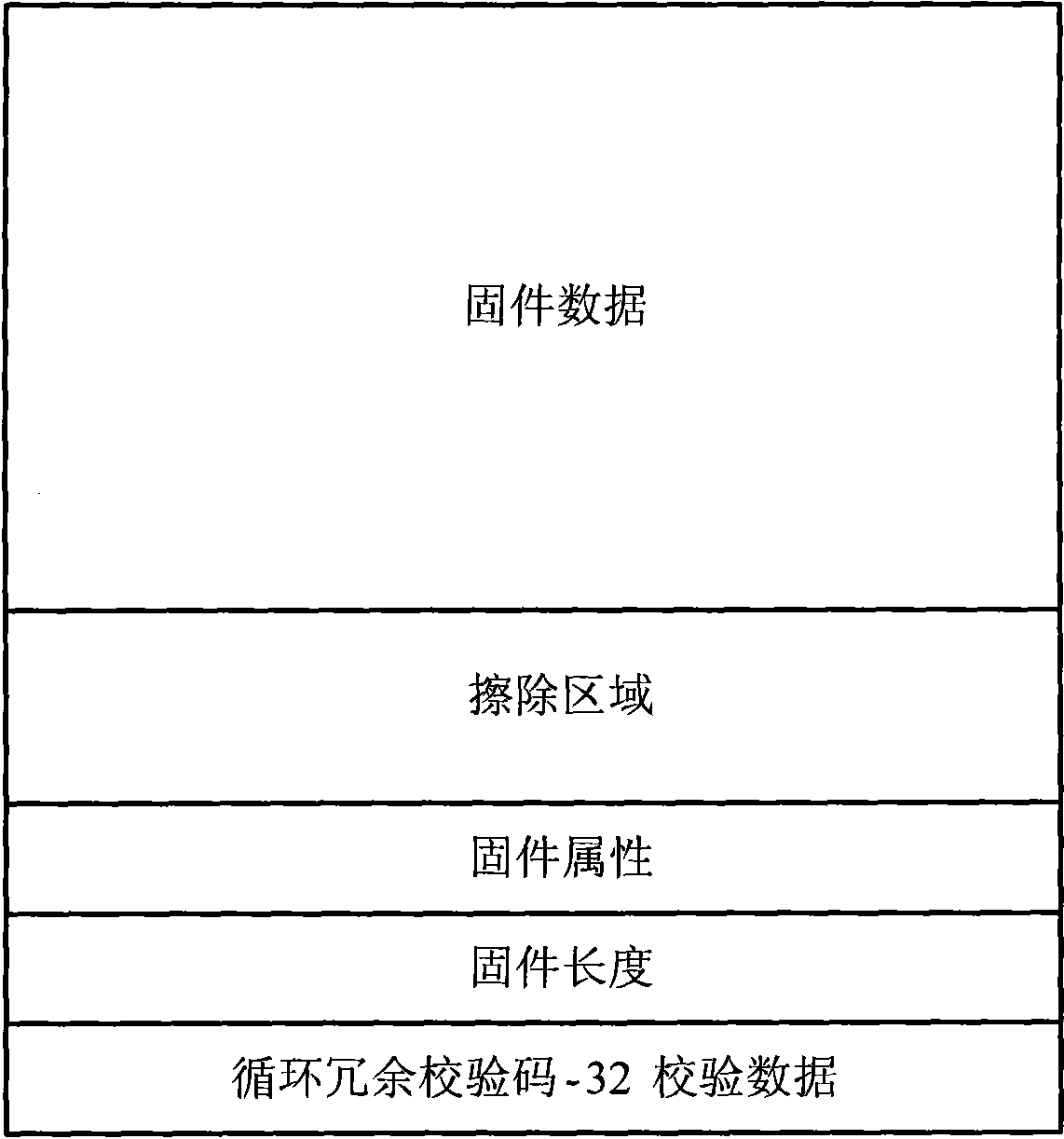
Memory device of embedded system and staring method and upgrading of firmware
ActiveCN101650662AAchieve normal startupReduce complexityProgram loading/initiatingCircuit complexityFirmware
The invention provides a memory device of an embedded system and a starting method and an upgrading method of a firmware, wherein the memory device is a read-write flash memory and at least comprises a first subregion used for storing a starting guide part of the embedded system as well as a main subregion and an auxiliary subregion which have consistent capacity and are used for storing parameters and data used for starting and upgrading the firmware; and the starting method based on the memory device comprises the following steps: starting a guide part and judging the firmware attributes oftwo subregions; verifying the validity of a cyclic redundancy check code of the current subregion, if so, erasing data of the main subregion, copying contents of the auxiliary subregion onto the mainsubregion, and then starting the auxiliary subregion; and if not, starting a program image from the main subregion. The flash memory is set in a partitioning way, the system functions can be realizedonly by utilizing one storage, therefore, the invention has the effects of reducing the circuit complexity and the cost of the system compared with the prior art. The starting method has better reliability.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Phase shifter with reduced linear dependency
InactiveUS20050015688A1Electronic circuit testingRecord information storageCircuit complexityLinear correlation
A method is disclosed for the automated synthesis of phase shifters. Phase shifters comprise circuits used to remove effects of structural dependencies featured by pseudo-random test pattern generators driving parallel scan chains. Using a concept of duality, the method relates the logical states of linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) and circuits spacing their inputs to each of the output channels. The method generates a phase shifter network balancing the loads of successive stages of LFSRs and satisfying criteria of reduced linear dependency, channel separation and circuit complexity.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
High intensity discharge lamp ballast
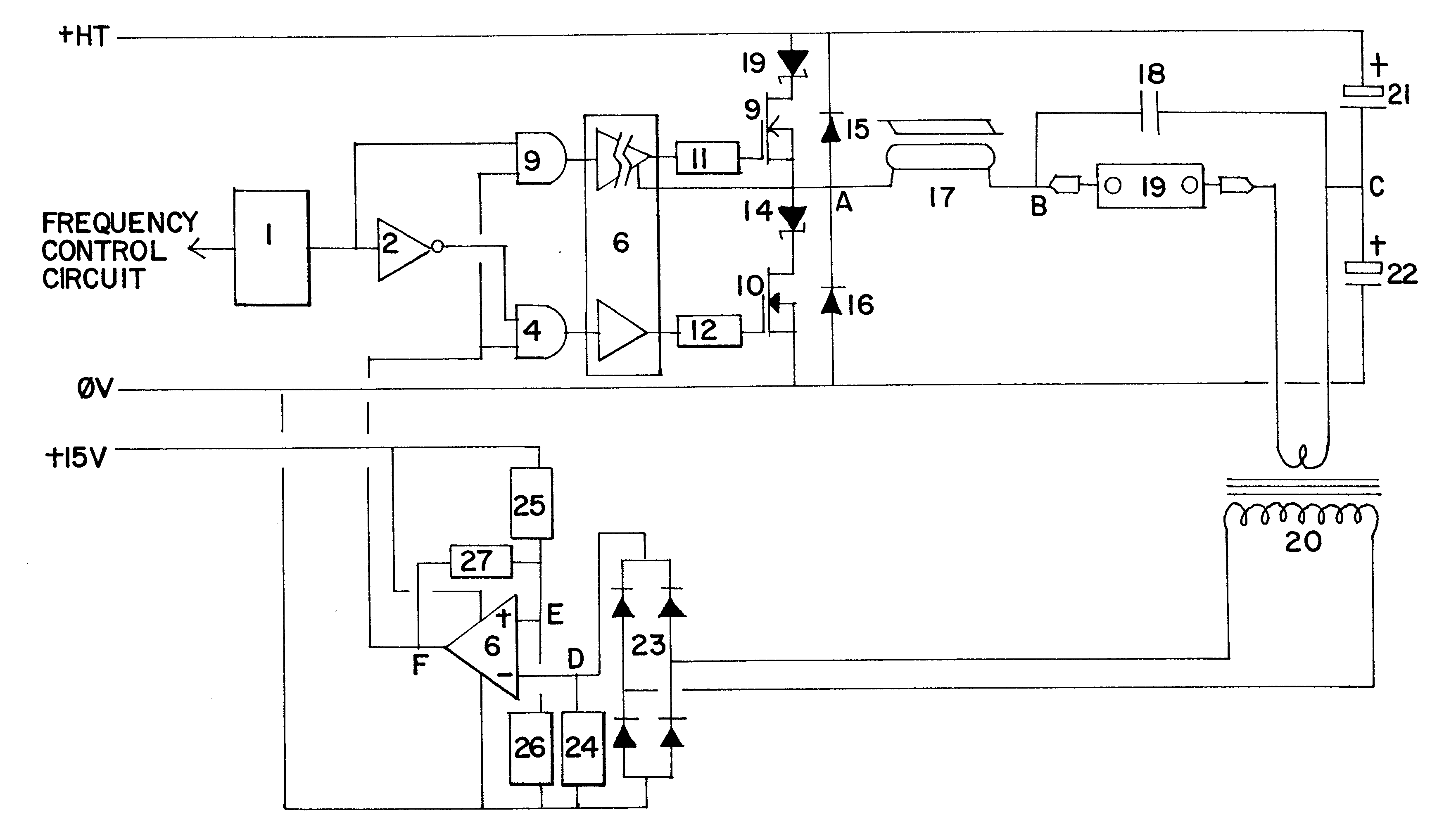
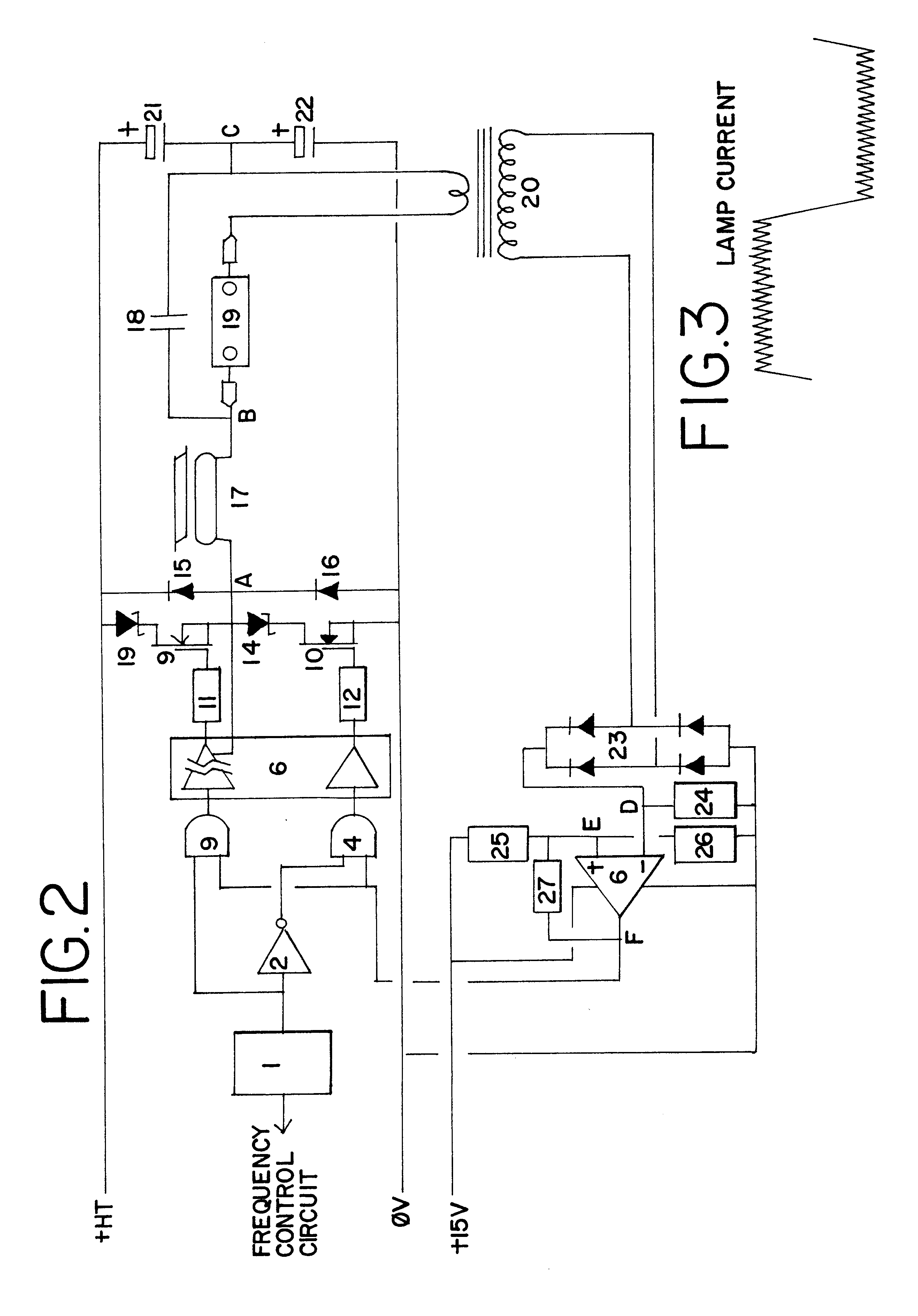
InactiveUS6188183B1Avoid spendingOvercome problemsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCircuit complexityPower switching
A means of ballasting for high intensity discharge (HID) lamps, wherein the necessary lamp striking voltage, warm-up current and steady state running current may all be controlled using only two power switching transistors 9,10 operating in two discrete modes. A further feature provides a means of lamp power control over a range of lamp voltages such that the lamp power input remains substantially constant throughout the ageing of the lamp 19. The use of this means of ballasting HID lamps can offer major cost benefits, lower circuit complexity, longer lamp life and colour maintenance and increased flexibility of the wiring installation and lamp position relative to the ballasting and striking means.
Owner:GREENWOOD SIMON RICHARD +1
Circuit for controlling light sources, method and display system
InactiveCN101772237ALow costImprove efficiencyElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCircuit complexityLinear regulator
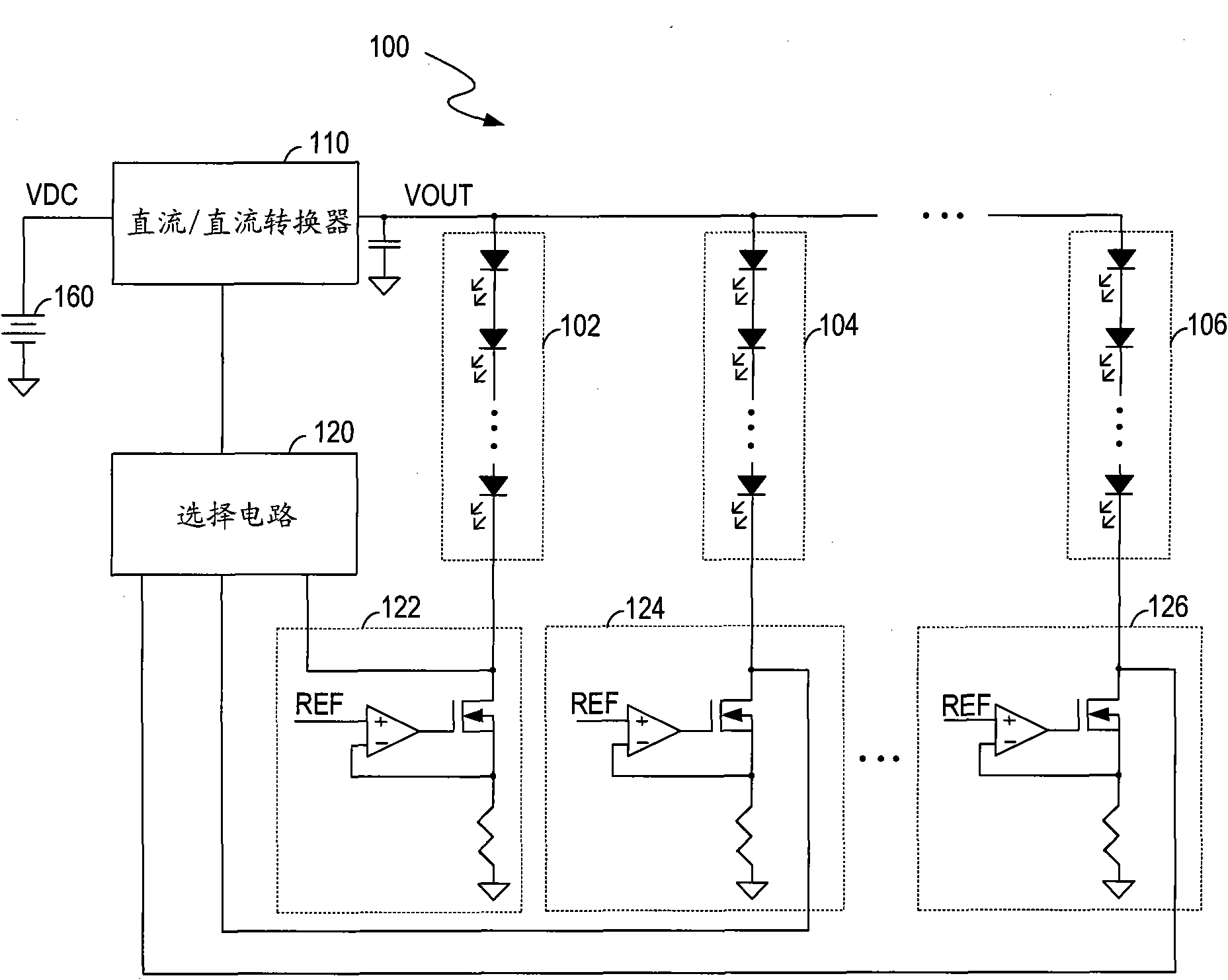
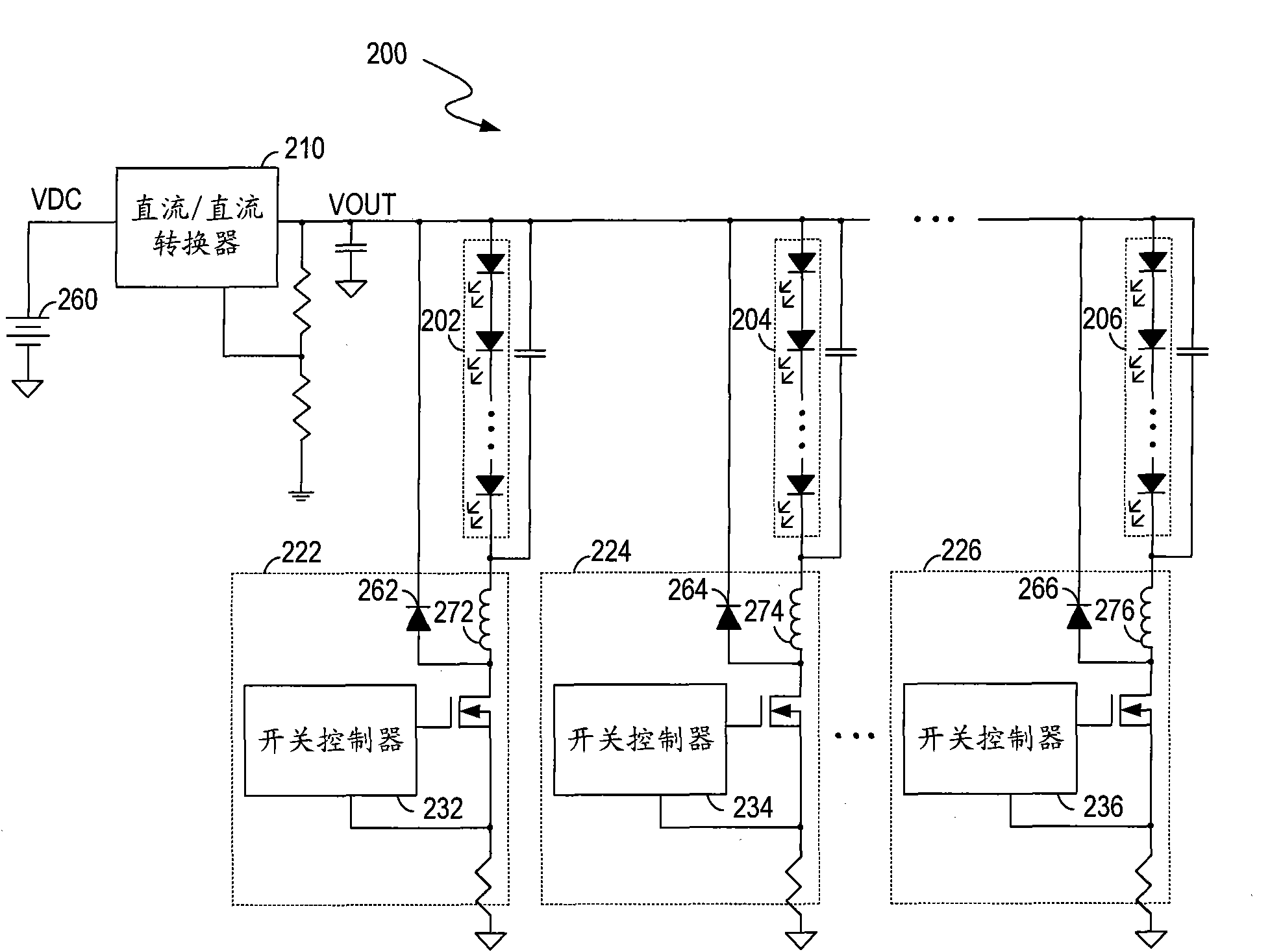
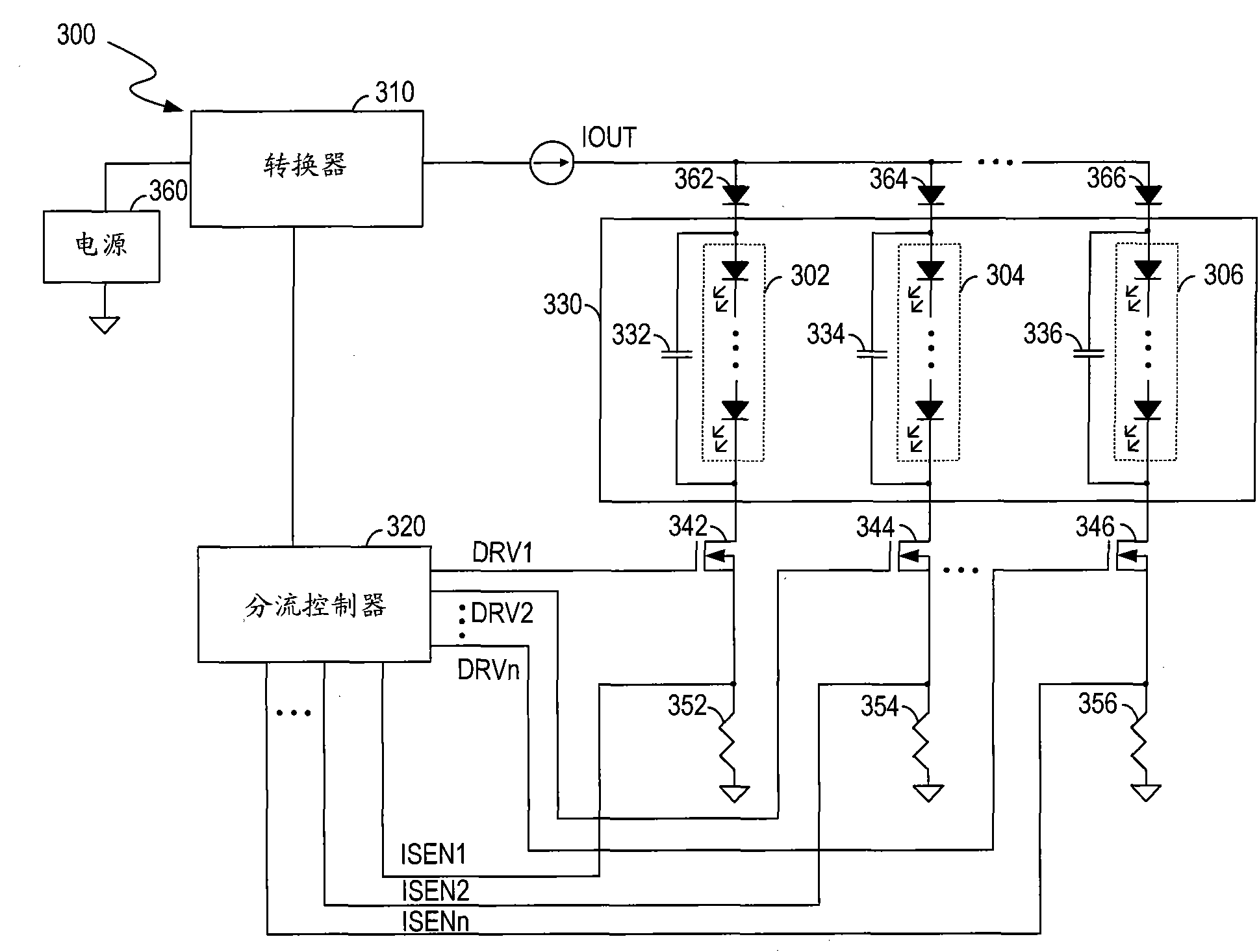
The invention discloses a circuit for controlling light sources, method and display system. The circuit for controlling light sources comprises a converter, a feedback circuit and a current distribution controller. The converter is operable for converting an input voltage to an output current and for providing the output current to the light sources. The feedback circuit is coupled to the light sources for generating feedback signals indicative of currents flowing through the light sources respectively. The current distribution controller is coupled to the feedback circuit for generating control signals based on the feedback signals respectively so as to regulate the currents of the light sources respectively, and for controlling the converter to regulate the output current based on the feedback signals. The circuit for controlling light sources without a plurality of linear regulators or switch controllers and switch regulators reduces the circuit cost, increases the circuit efficiency and reduces the circuit complexity.
Owner:AOTU ELECTRONICS WUHAN
Decompose method for arbitrarily quantum bit gate
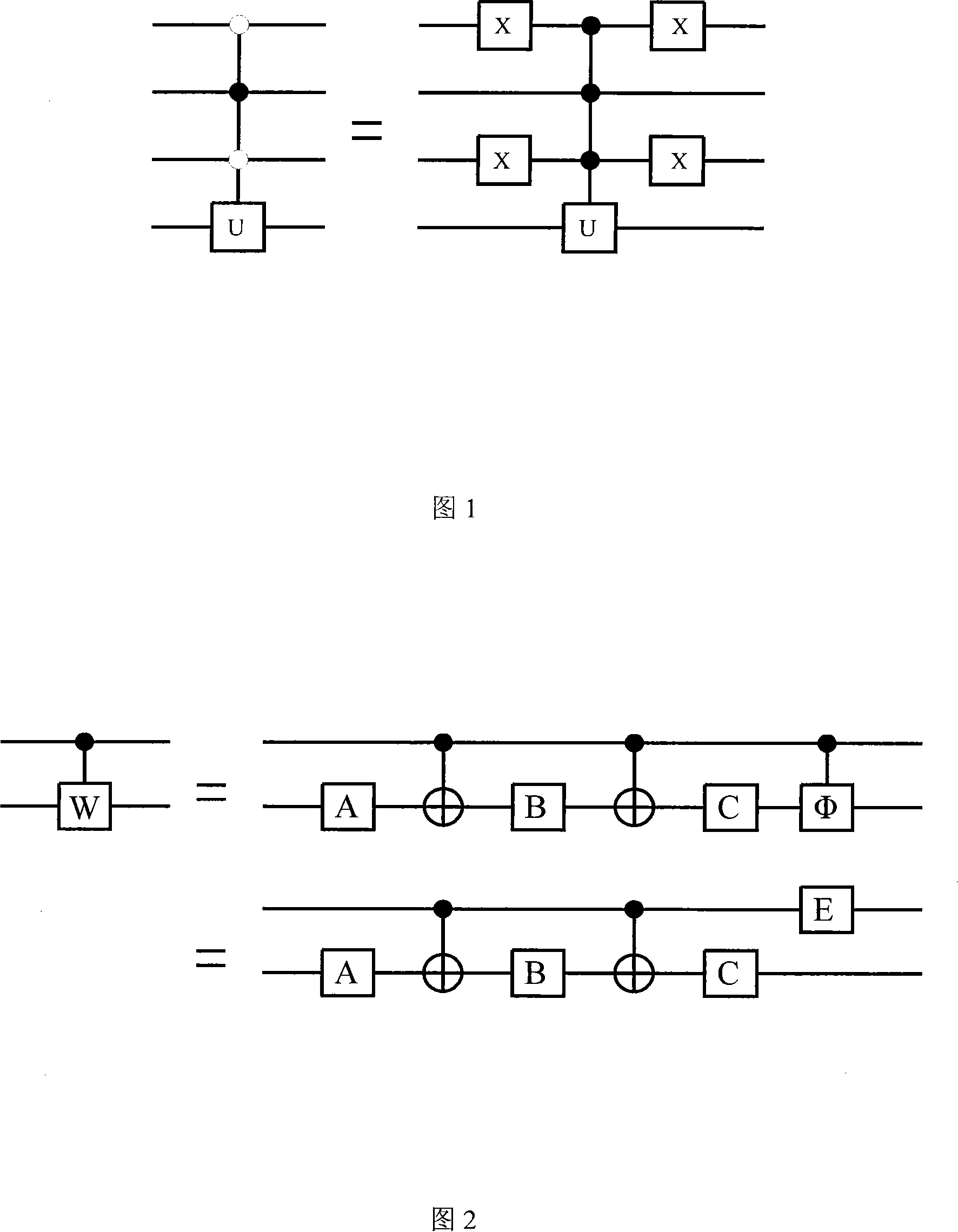
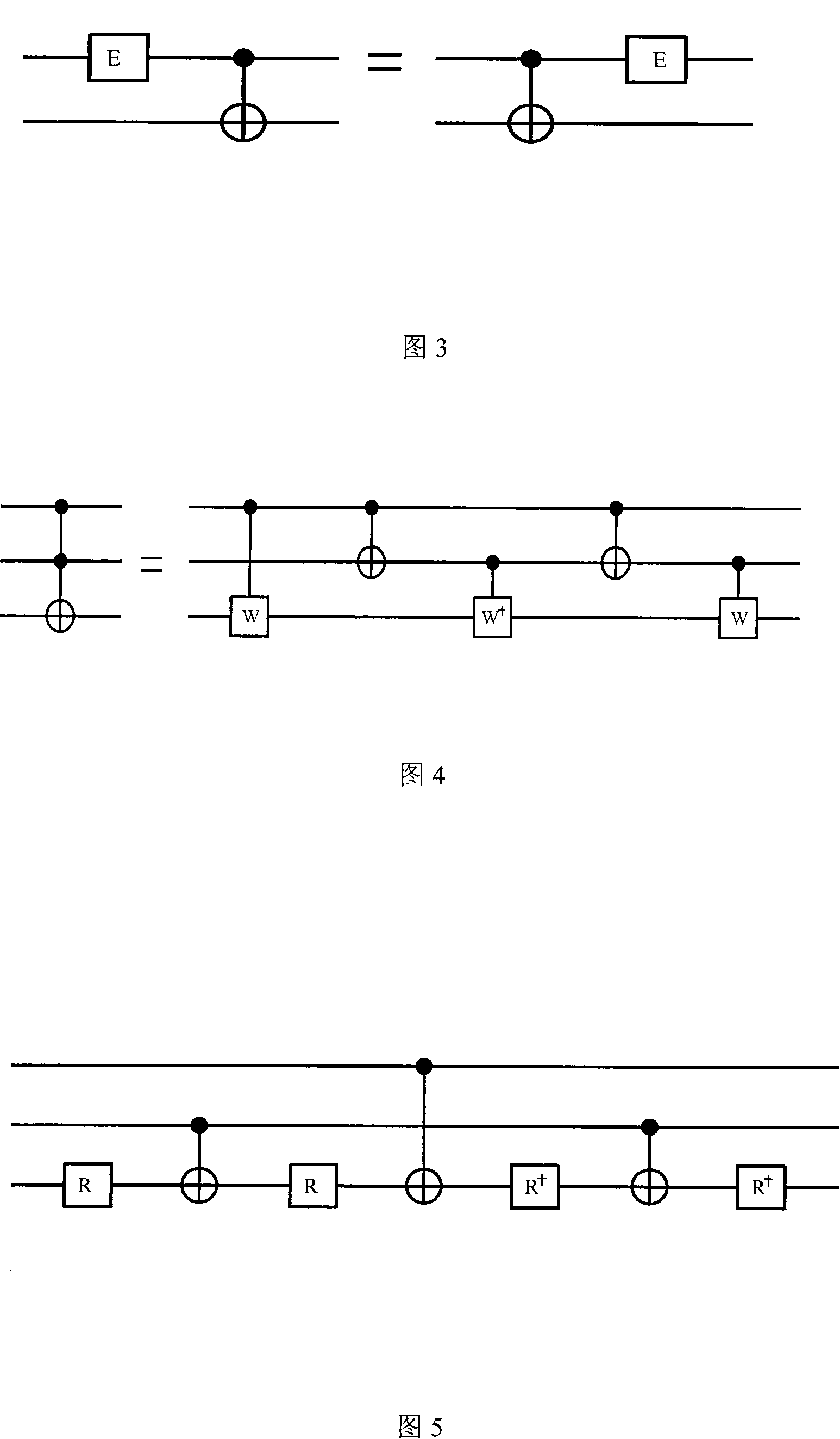
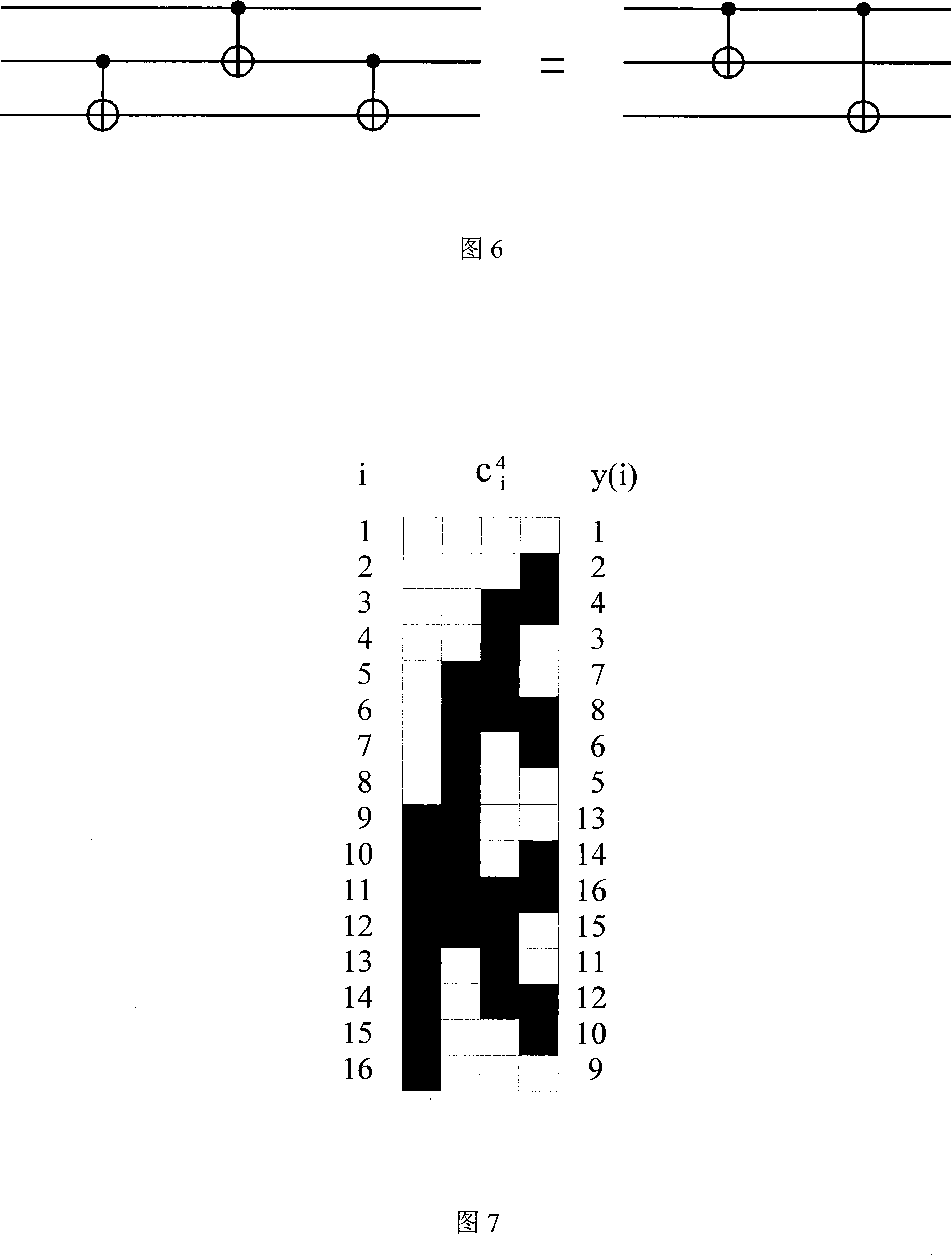
ActiveCN101118608AReduce complexityReduce the numberComputing modelsCircuit complexityQuantum circuit
The present invention discloses a decomposition method for a random quantum bit gate, and belongs to the field of the quantum state manipulating technology. The method includes: the bit gate U of a random quantum n is decomposed into a plurality of uninterrupted Cn (U) and the decomposition of a random quantum bit gate is achieved by adopting an index decomposition mode and a polynomial decomposition mode with circuit complexities of O (2n) and O (n2) respectively through the fundamental segment and the correcting segment of the structure and utilizing the mode of nested recursion. The present invention achieves that a random quantum bit gate is decomposed into a qubit index form and a polynomial form of complexities, gives the quantum circuit and the relevant analytical expression containing only two quantum bit CNOTs and a single quantum bit accurately, thereby achieving an arbitrary operation to a quantum state in the transmission process of the quantum state, figures out the number of a basic logic gate that the two decomposed forms need, uses a phaseshift approximate gate to replace the Toffolin gate and reduces the complexity of the circuit greatly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and circuit for dynamically equalizing battery management system
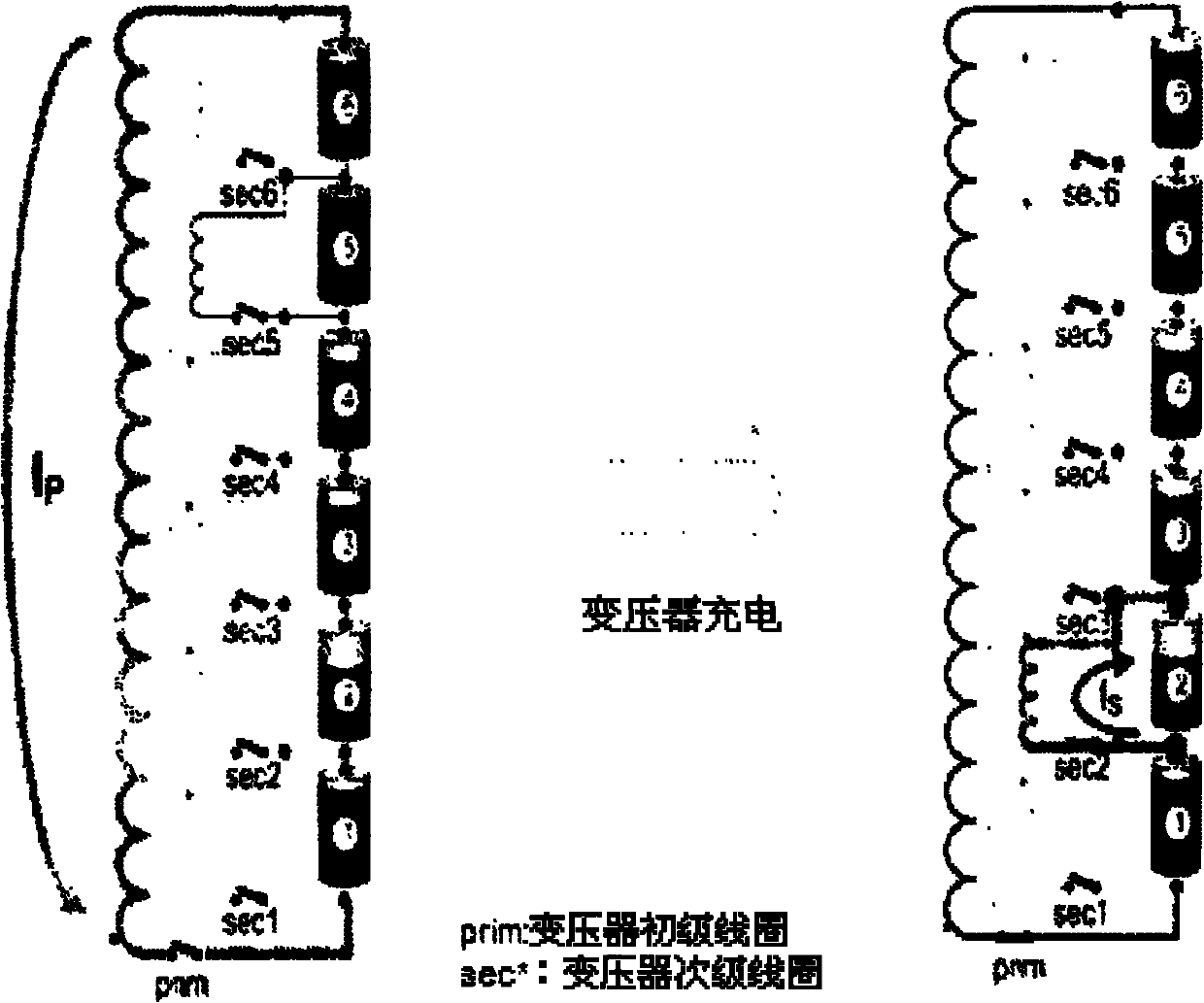
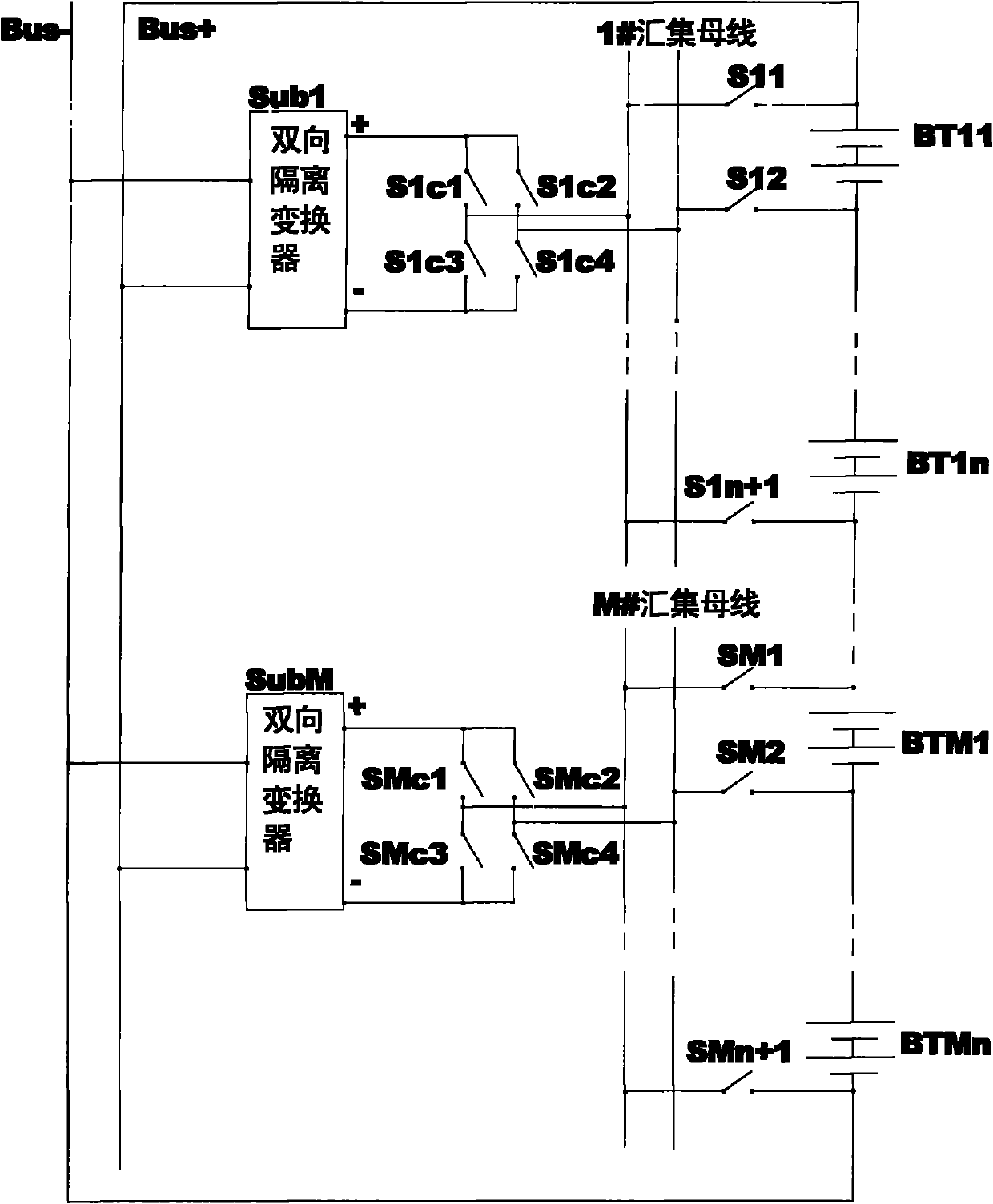
ActiveCN101917047AReduce in quantityReduce circuit complexityBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCircuit complexityEnergy transfer
The invention relates to a method and a circuit for dynamically equalizing a battery management system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) detecting the voltage of each single battery in each group of battery packs sequentially connected in series by using embedded control software; 2) judging the location number of the single battery which needs to be charged or discharged separately and has excessively low or high voltage by using a central processing unit (CPU); 3) giving a control command out by using the CPU, controllably gating a corresponding polarity selecting switch block to perform polarity inversion on a collection bus, controllably gating a corresponding battery selecting switch block to perform polarity matching at the same time, controlling the working direction of a bidirectional isolation transformer and connecting the single battery which needs to be charged or discharged separately and has the excessively low or high voltage to the connection bus for charging or discharging so as to realize energy transfer; and 4) repeating the steps 1) to 3) until the voltage of each single battery in each group of battery packs sequentially connected in series is in a set allowable error range so as to realize dynamic equilibrium. The number of charging and discharging devices and circuit complexity of the battery management system can be reduced remarkably.
Owner:SHENZHEN KELIE TECH
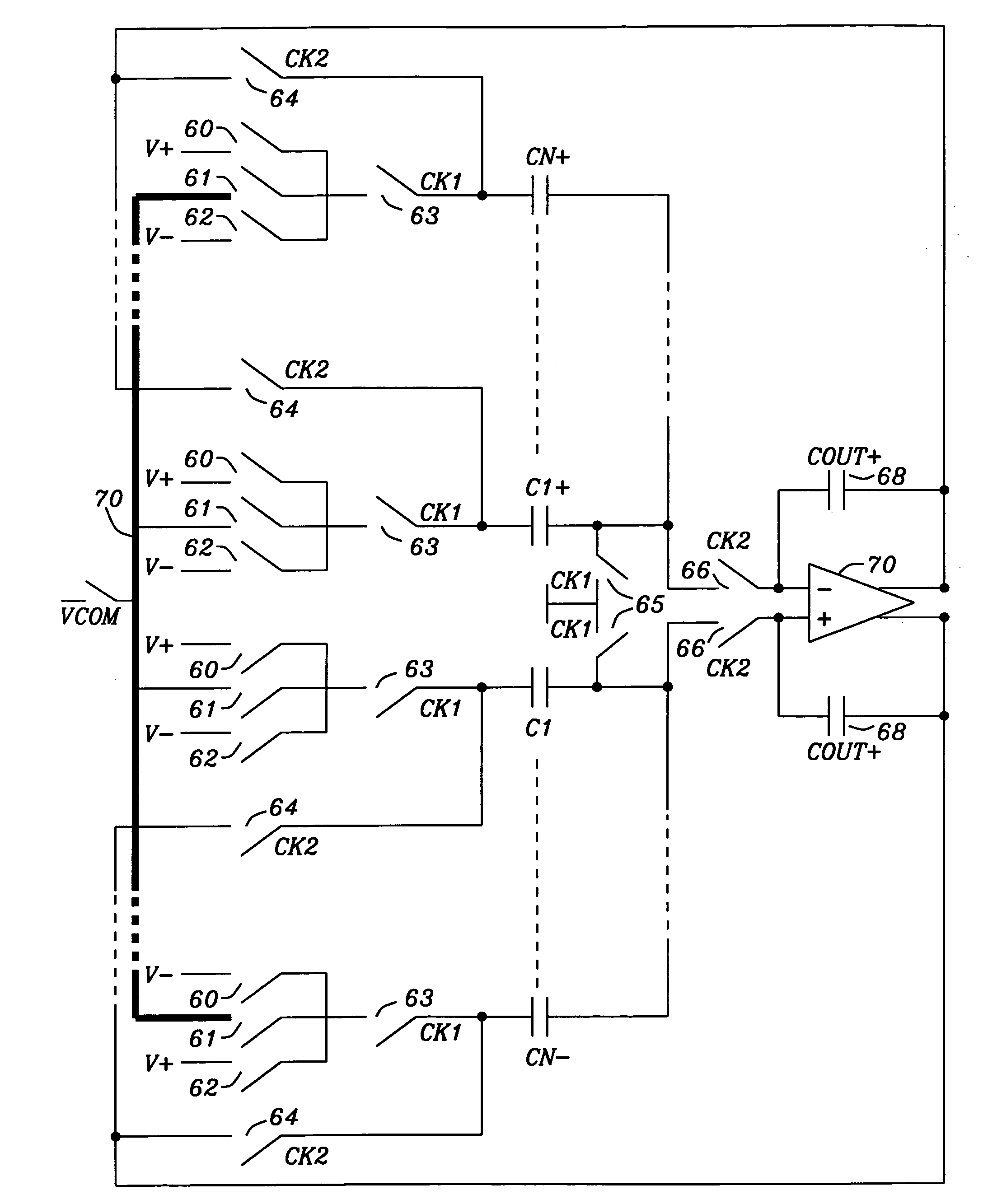
Tri-level dynamic element matcher allowing reduced reference loading and dac element reduction
ActiveUS20100245142A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionCircuit complexityNoise shaping
Systems and methods using the same to achieve a tri-level multi-bit delta-sigma DAC having reduced power consumption and voltage droop have been achieved. A new rotation-based first order noise-shaping Dynamic Element Matcher (DEM) technique for use with 3-level unit elements have been disclosed. Reduced reference loading has been achieved when the tri-level DEM scheme is applied to switched capacitor implementations in particular. Furthermore a differential switched-capacitor DAC implementation, which enables use of the DEM technique is disclosed. The invention allows reduced circuit complexity required to implement a N-bit DAC when constructed using 3-level unit elements.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
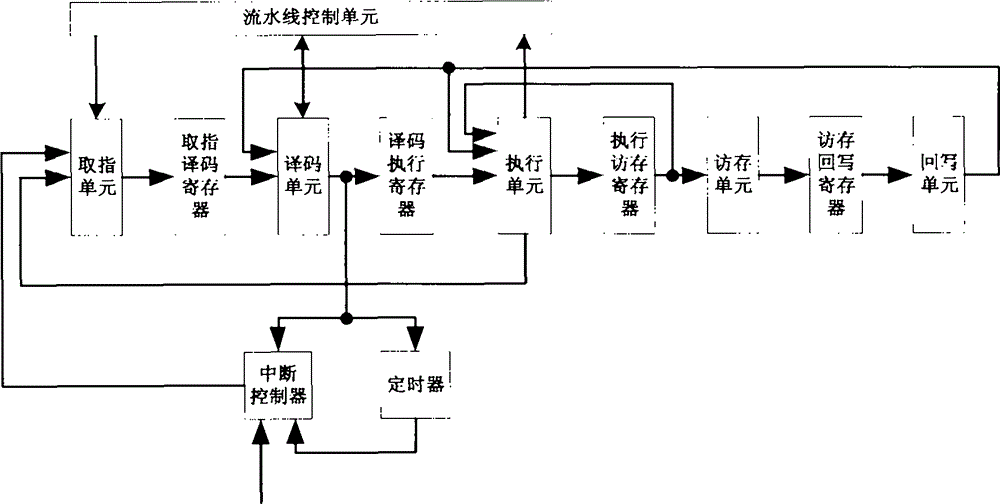
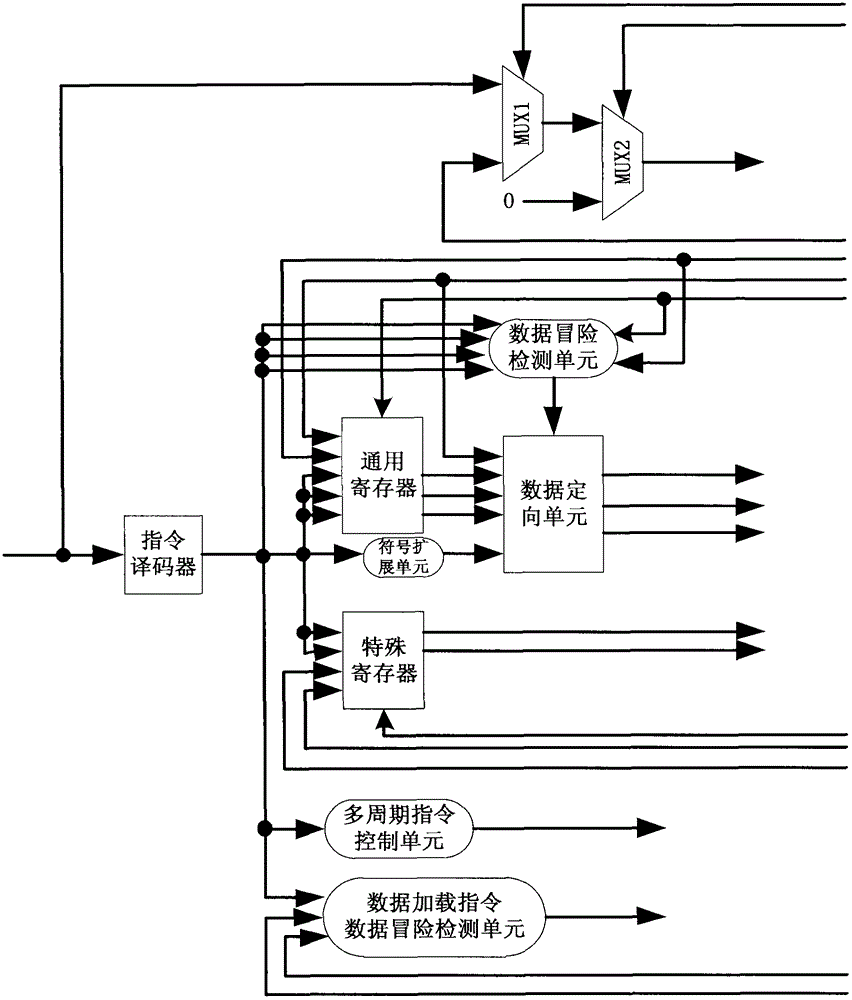
ASIP (application-specific instruction-set processor) based on extensible processor architecture and realizing method thereof
InactiveCN103150146AOvercoming complexityOvercome resourcesConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsCircuit complexityComputer architecture
The invention discloses an ASIP based on an extensible processor architecture and a realizing method thereof, which mainly solve the problem of high circuit complexity and large resource consumption in the prior art. Aiming at the extensible processor architecture after optimization, the invention adopts a five-level-pipeline realizing method, and adopts a data orientation technology and a branch non-execution strategy to solve data hazards and control hazards in pipeline treatment respectively. The ASIP comprises an instruction fetch unit, a decoding unit, an execution unit, a memory access unit, a write-back unit, a pipeline control unit, a timer and an interrupt controller. According to the ASIP and the method, the characteristics of a pipeline processor and an FPGA (field-programmable gate array) are considered sufficiently, the pipeline structure is partitioned reasonably, and the hardware resources of the FPGA are utilized to the utmost extent; and the ASIP and the method have the advantages of simple circuit design, low resource consumption, high processor performance and low power consumption, and are highly suitable for large-scale parallel processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
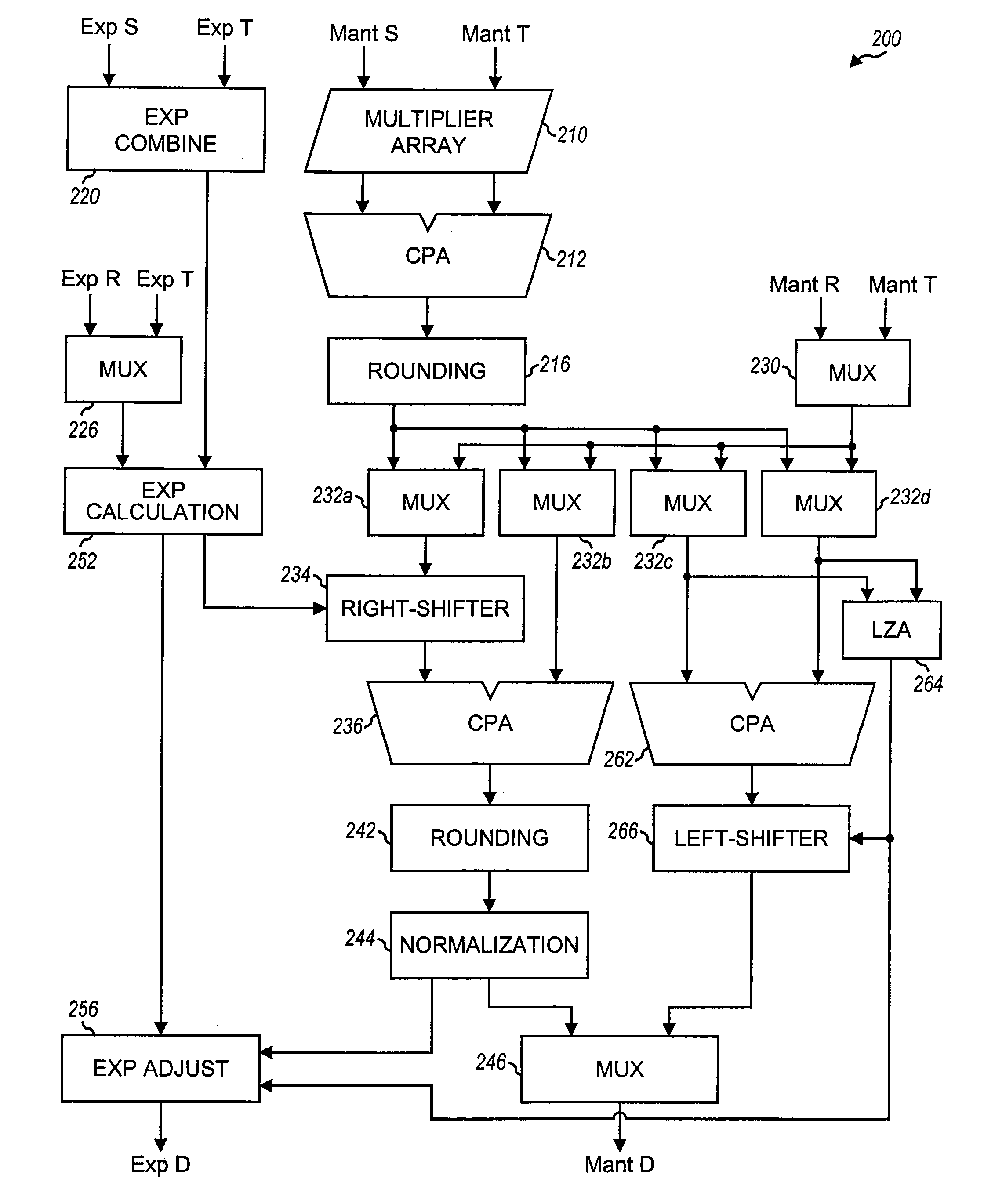
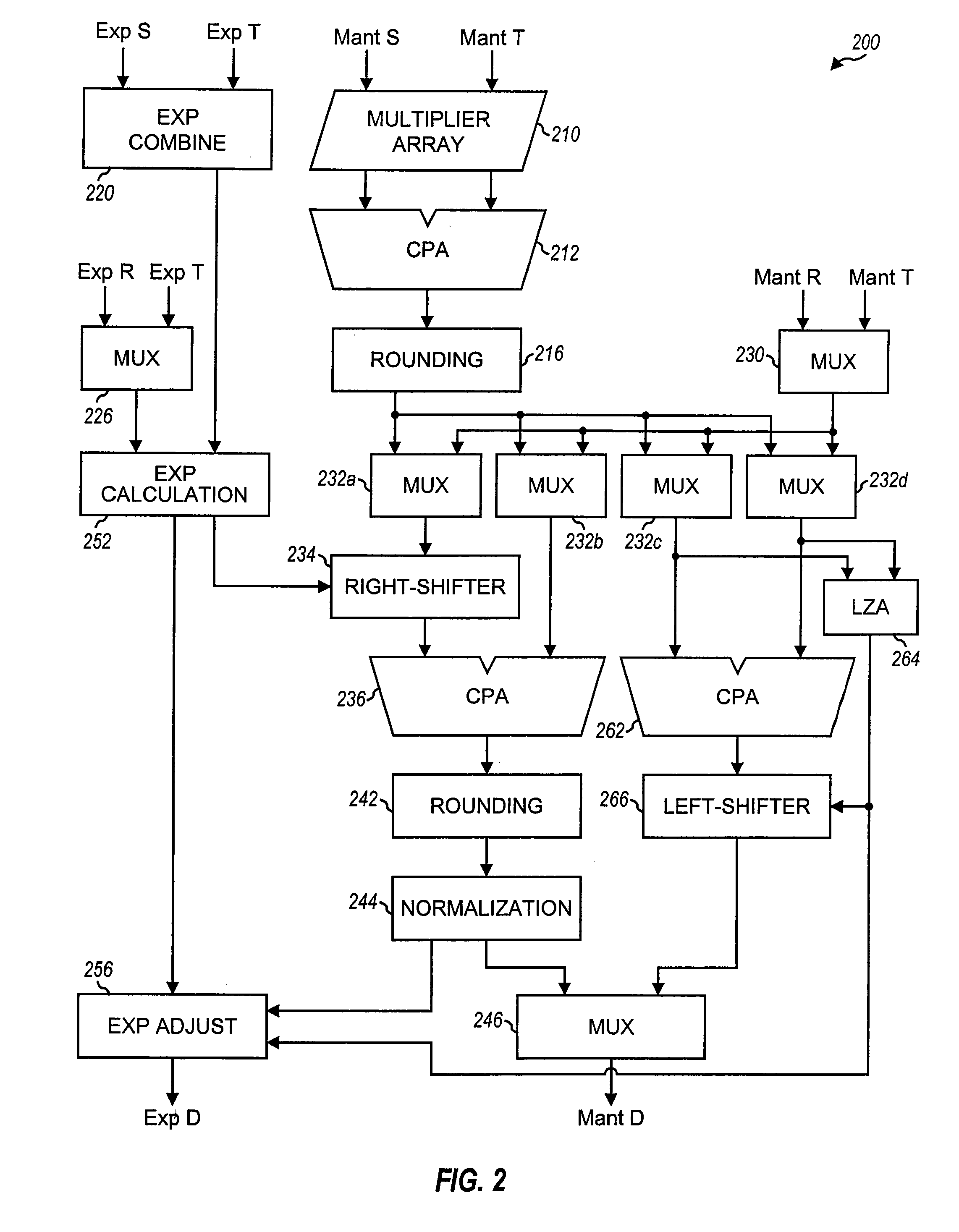
Processor With Improved Accuracy For Multiply-Add Operations
InactiveUS20080183791A1Improve accuracyReduce circuit complexityComplex mathematical operationsData conversionCircuit complexityBinary multiplier
Floating-point processors capable of performing multiply-add (Madd) operations and incorporating improved intermediate result handling capability. The floating-point processor includes a multiplier unit coupled to an adder unit. In a specific operating mode, the intermediate result from the multiplier unit is processed (i.e., rounded but not normalized or denormalized) into representations that are more accurate and easily managed in the adder unit. By processing the intermediate result in such manner, accuracy is improved, circuit complexity is reduced, operating speed may be increased.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Touch type induction device
ActiveCN1845045AReduce electromagnetic interferenceReduce leakage currentGraph readingMechanical pattern convertionCircuit complexityDifferential signaling
The invention discloses a touch sensor, which comprises: at least one sensing unit, one detector, one signal processing unit, and one reference signal circuit. Wherein, said sensing unit comprises a differential signal source for generating two signals with reversed polarities; two sensors while one is connected to the positive output of differential signal source and another sensor is connected to the negative output; said detector is connected to several sensing units to transform received signal into digital signal; the signal processing unit is connected to the output of detector, to find the sensor that contacted by object according to the frequency and phase of digital signal output by detector. The invention can reduce electromagnetic disturbance and current leakage, reduce the circuit complexity, and quick find touched position.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
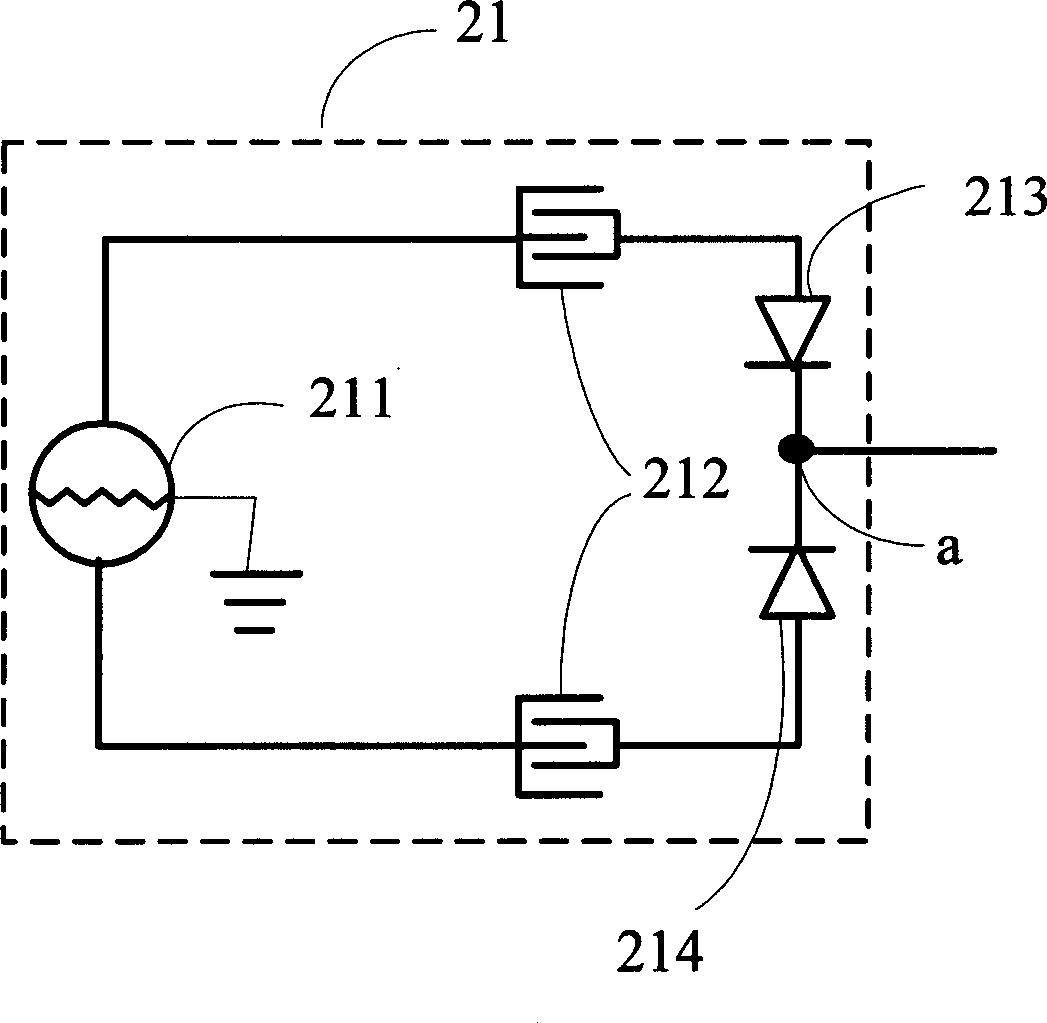
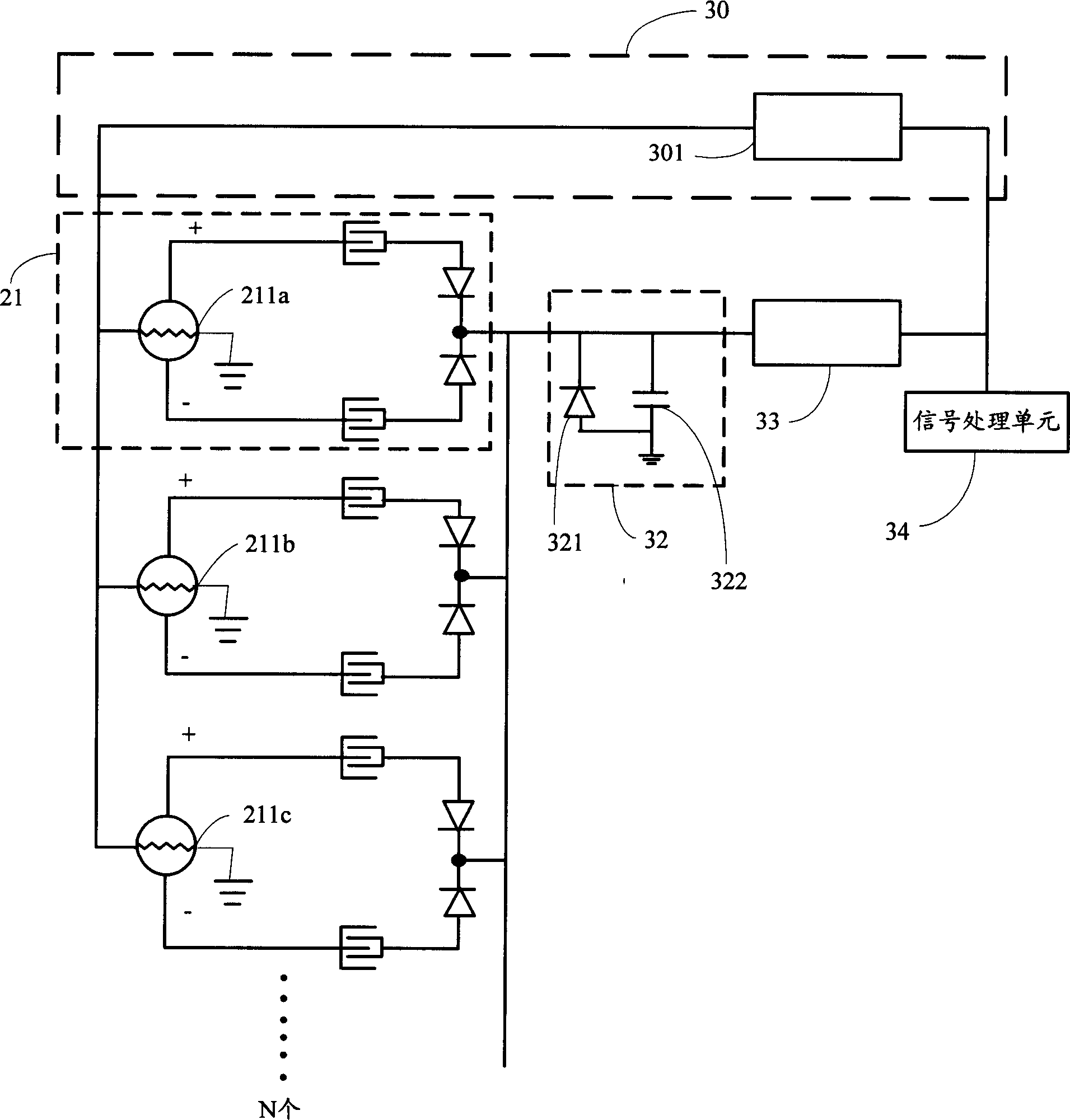
Current balance power supply circuit of multi-group light-emitting diode
ActiveCN101511136ALuminous brightness is the sameReduce power lossElectrical apparatusPoint-like light sourceCircuit complexityLuminosity
The invention relates to a current balance power supply circuit of a multi-group LBD for driving the multi-group LBD to has same luminosity. The current balance power supply circuit at least contains: a current power supply circuit for receiving the electrical power source and converting into a current with a special current size for providing to the multi-group LBD; a flow equalization circuit connected with the current power supply circuit and multi-group LBD which contains at least a coupling inductor for balancing the multi-group LBD current size; and a current control unit connected withthe current power supply circuit and at least one group LBD of the multi-group LBD for detecting current size of the multi-group LBD and controlling the output current of the current power circuit. The current balance power supply circuit can make each group LBD current balance and has same luminosity, low circuit power consumption, high operating efficiency, less element and low circuit complexity, and save cost greatly.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Successive approximation register analog to digital converter (SAR ADC) and switching method during analog-digital conversion thereof
ActiveCN105391451AReduce complexityReduce areaAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit complexityCapacitance
The invention discloses a successive approximation register analog to digital converter (SAR ADC) and a switching method during analog-digital conversion thereof. The SAR ADC comprises a multi-reference generating circuit, a capacitor array digital-to-analog converter (DAC), a comparator and successive approximation control logic. The capacitor array DAC may comprise couple capacitors with binary coding bits of N-3 which are 3 less than the binary coding bits of N outputted by the SAR ADC, the capacitors with N-3 bits can achieve excellent effects of resolution of N bits, the capacitor array area can be effectively reduced, the total number of unit capacitors can be reduced by 87.5%, therefore, the circuit complexity is reduced, the manufacturing cost is saved, and the small size is satisfied. With the switching method provided by the invention, in the switching process, no energy is consumed for the first two comparisons and afterwards, the amount of power consumption for each comparison is less than that of a traditional structure; and compared with the traditional structure, the invention can save up to 99.4% of an average amount of dynamic power consumption in the switching, thereby reducing the overall power consumption.
Owner:江苏芯力特电子科技有限公司
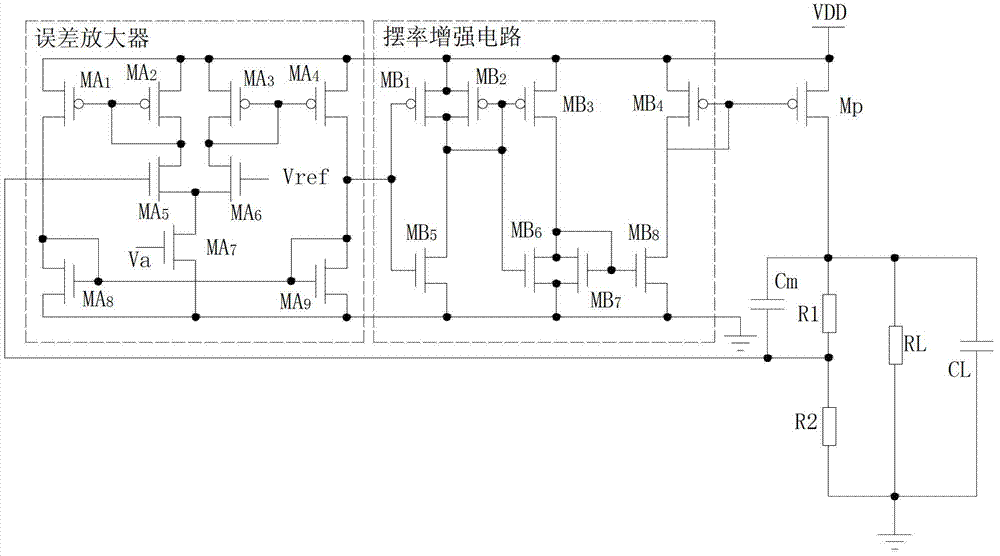
High-PSR (high power supply rejection) low-dropout regulator with slew rate enhancement circuit integrated thereto
ActiveCN103399607AIncrease slew rateImprove transient responseElectric variable regulationCircuit complexityCapacitance
The invention relates to power management technologies, solves the problem that generally voltage spike in output voltage is overcome for the existing low-dropout regulator at the costs of increased circuit complexity, decreased load capacity, increased output voltage noise and the like, and provides a High-PSR (high power supply rejection) low-dropout regulator with a slew rate enhancement circuit integrated thereto. According to the scheme, the regulator compared to the existing LDO regulators has the advantages that the slew rate enhancement circuit and a compensation capacitor are added, the positive phase input end of an error amplifier is connected with a reference voltage source, the negative phase input end of the error amplifier is connected with a resistance feedback circuit, the output end of the error amplifier is connected with the input end of the slew rate enhancement circuit, the output end of the slew rate enhancement circuit is connected with a gate of a pass transistor, one end of the compensation capacitor is connected with the negative phase input end of the error amplifier, and the other end of the compensation capacitor is connected with the output end of the error amplifier. The high-PSR low-dropout regulator has the advantages that transient response is enhanced and the scheme is applied to low-dropout regulators.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
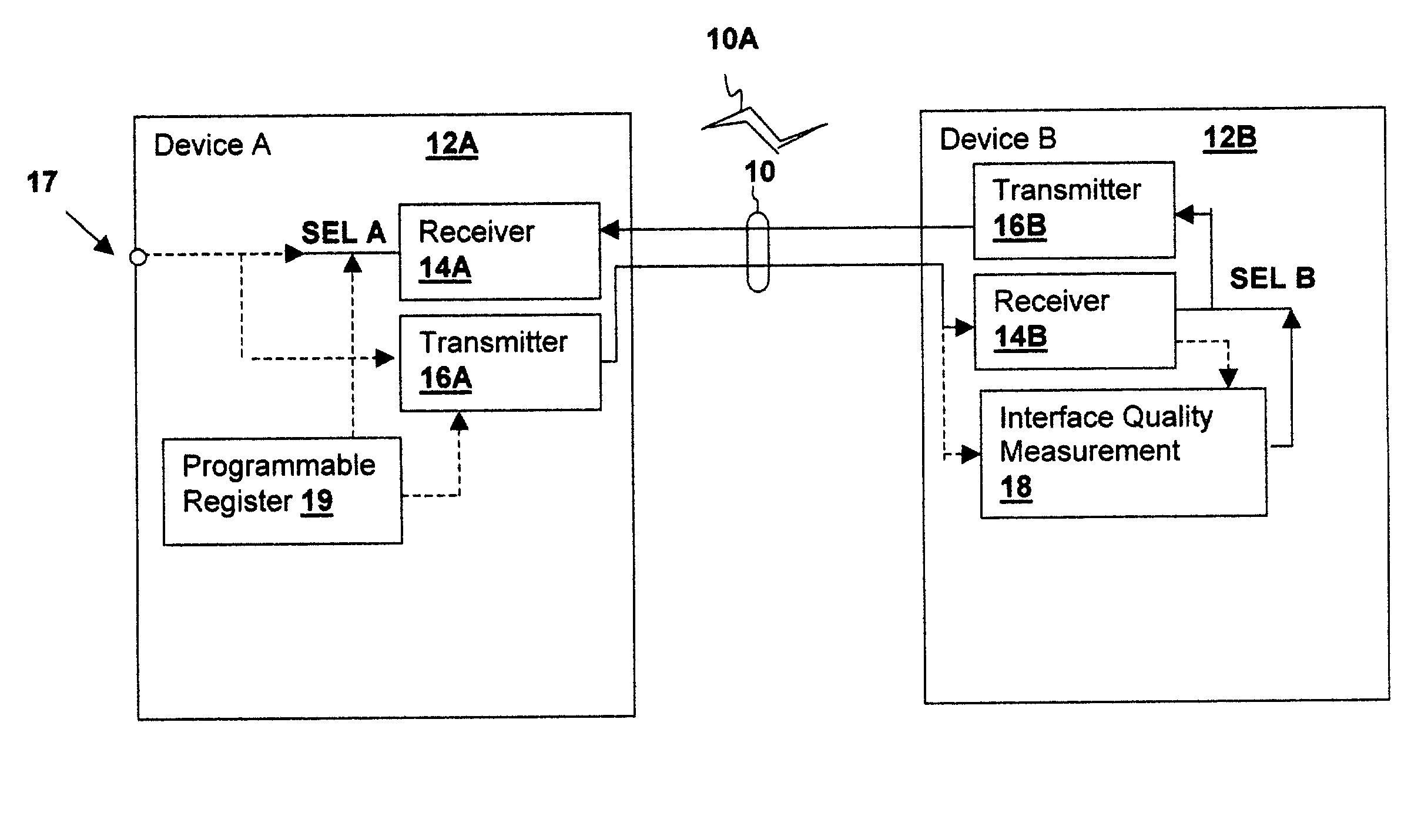
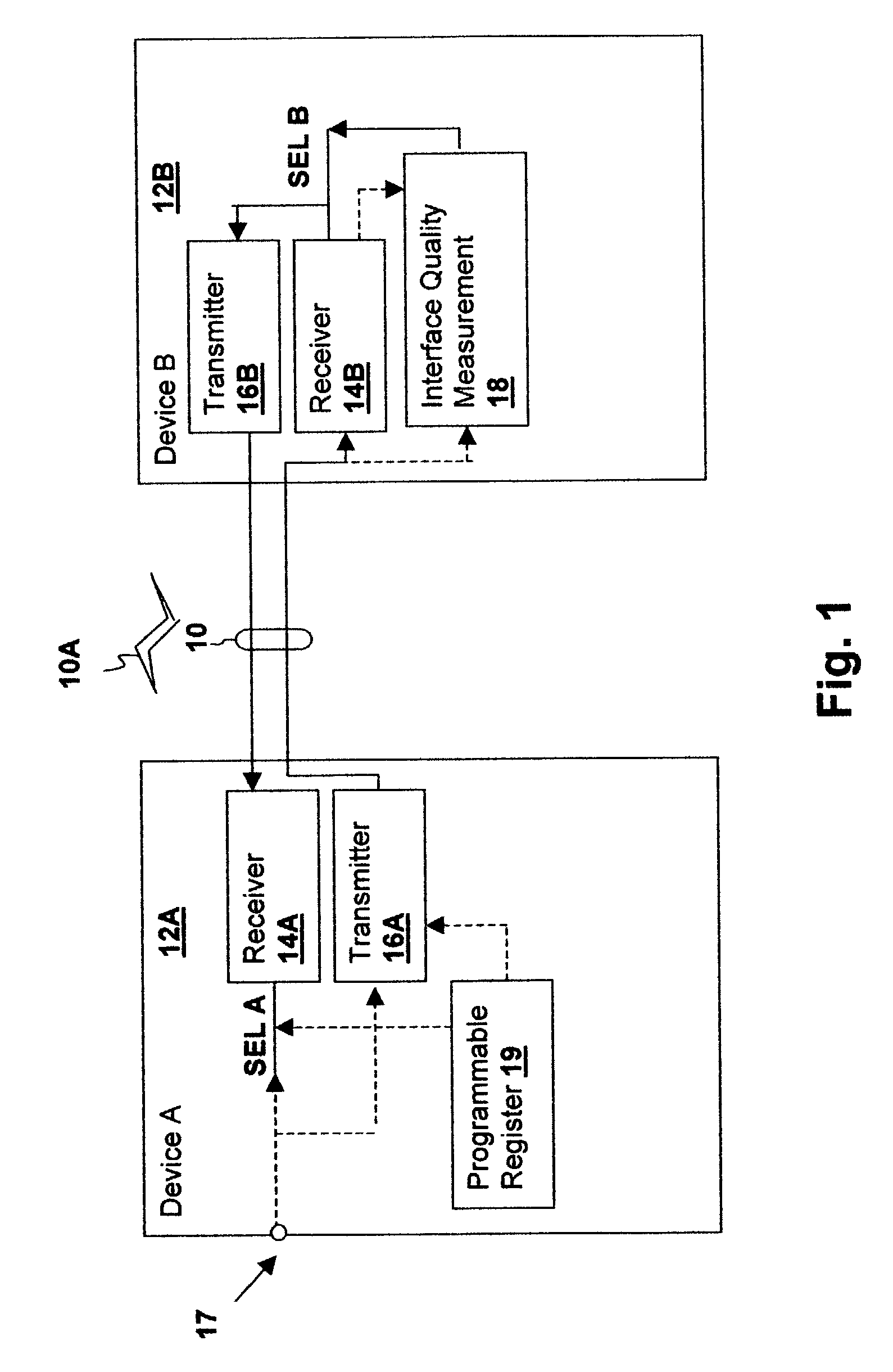
Interface transceiver power management method and apparatus including controlled circuit complexity and power supply voltage
An interface transceiver power management method and apparatus including controlled circuit complexity and power supply voltage reduces power consumption when interface conditions will support a transceiver having reduced complexity. The power supply voltage of the reduced complexity logic is then reduced if the lowered complexity will support a lower power supply voltage. The reduced complexity in combination with a reduced power supply voltage decreases power consumption to a greater degree than reducing transceiver complexity alone. The complexity of processing blocks within the receiver and / or transmitter are adjusted in conformity with one or more selection signals and an operating voltage level is selected in accordance with the requirements of the reduced complexity circuit. An interface quality measurement circuit may provide the selection signal, so that the transceiver complexity is adjusted in response to measured interface conditions or an external pin or register bit may be coupled to a select input.
Owner:IBM CORP
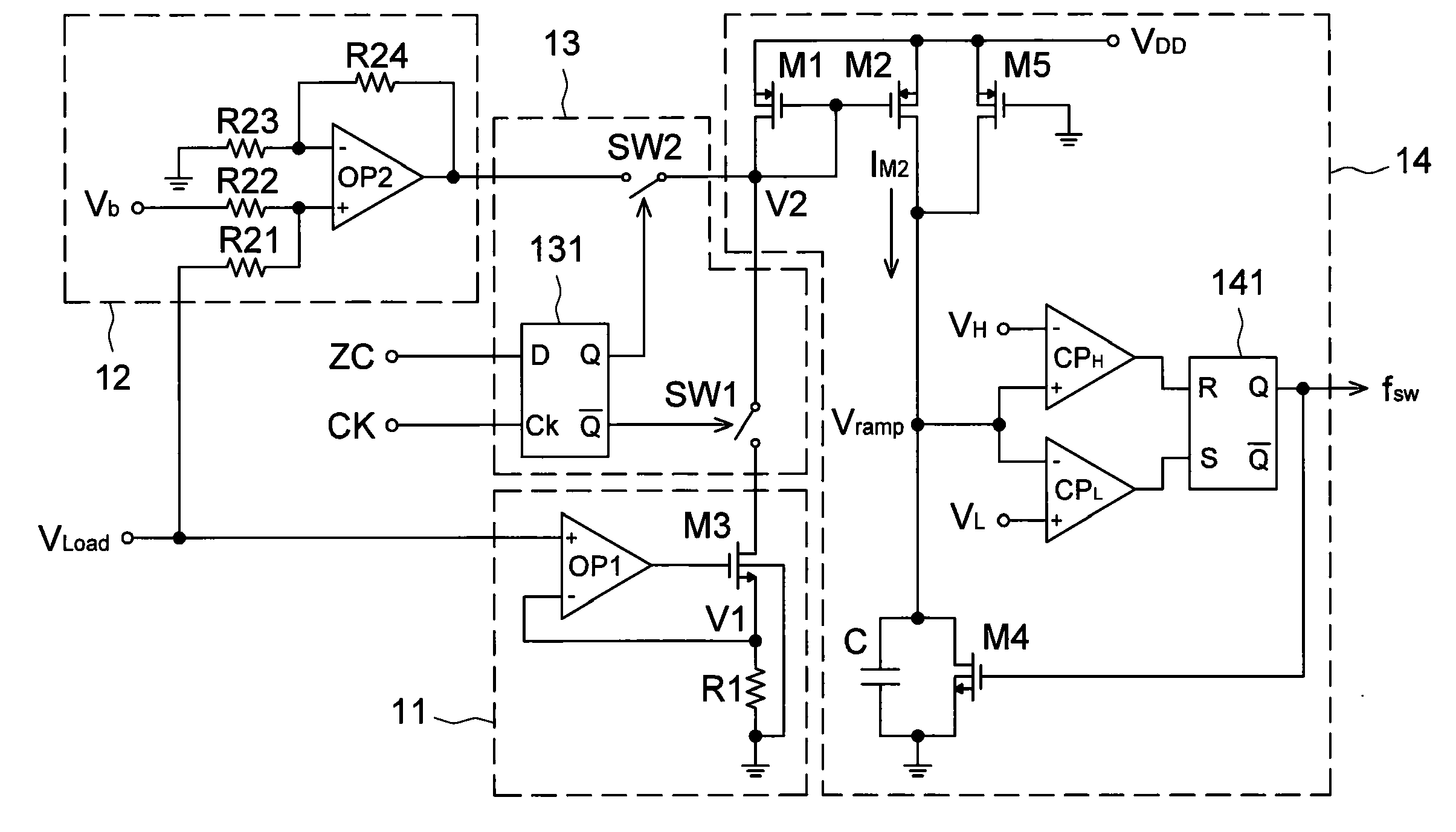
Analog variable-frequency controller and switching converter therewith
InactiveUS20100134079A1Optimized converter power efficiencyLess complexEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCircuit complexityControl signal
An analog variable-frequency controller includes a first current generator, a second current generator, a clock generator and a light / heavy load selector. The first and second current generator receive a load current signal and then output a first voltage signal and a second voltage signal, respectively. The clock generator generates a corresponding switching frequency according to the first voltage signal or the second voltage signal. The light / heavy load selector, connected with the first current generator, the second current generator and the clock generator, receives a control signal for controlling the clock generator to receive the first voltage signal or the second voltage signal. The abovementioned controller is implemented by an analog circuit, which has a lower circuit complexity, lower cost and is easy to be integrated into a switching converter.
Owner:MEGAWIN TECH +1
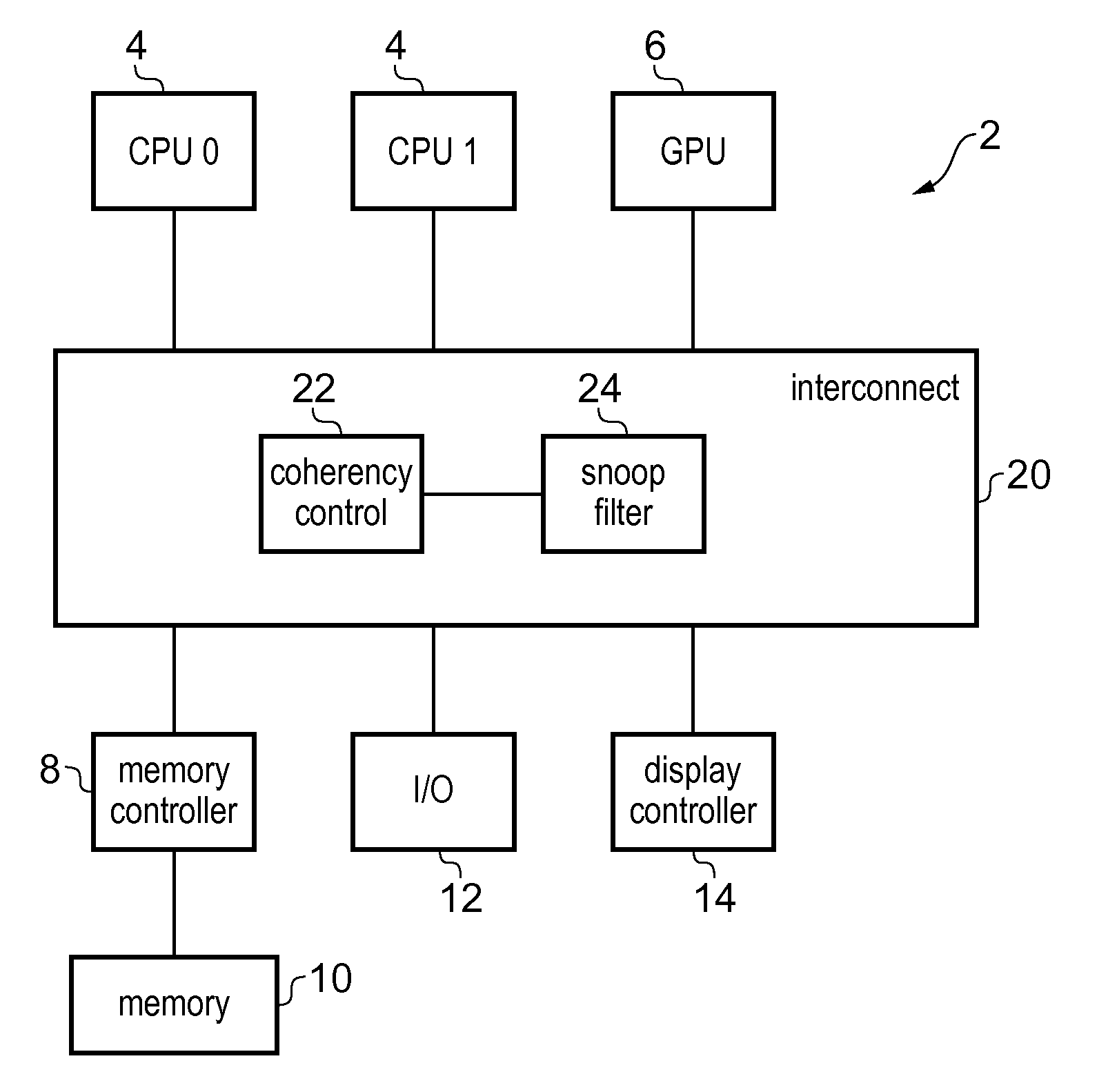
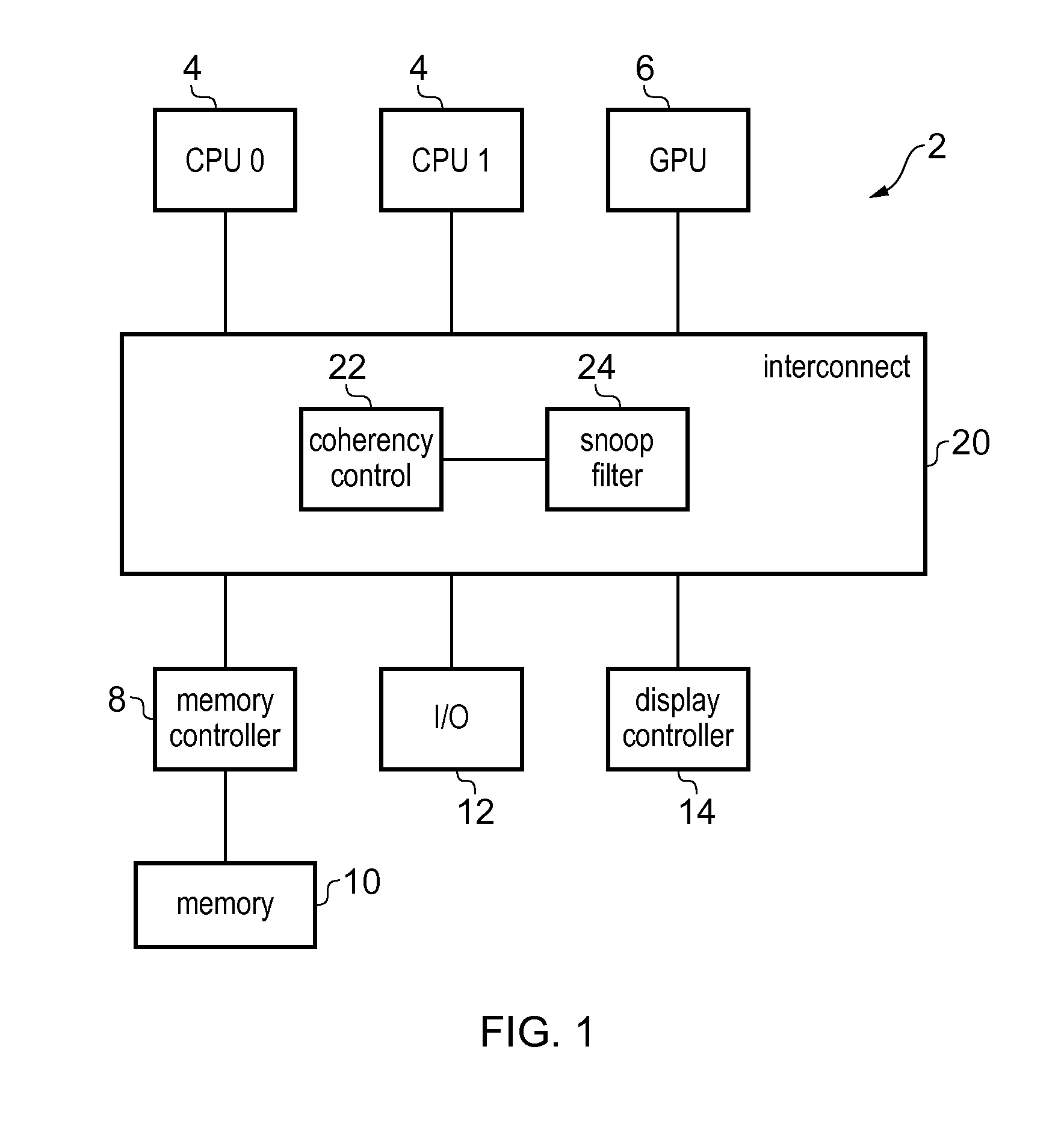
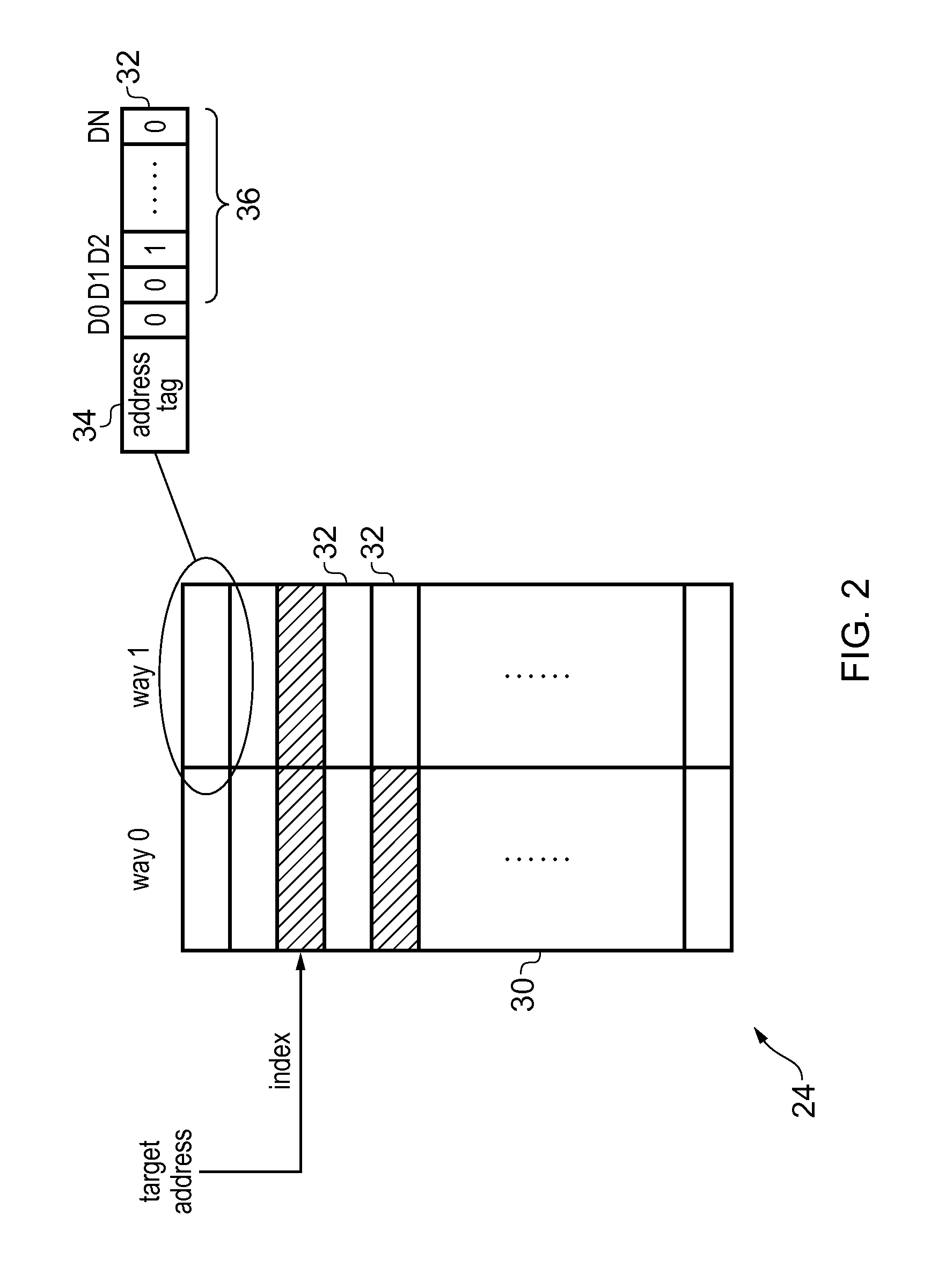
Coherency checking of invalidate transactions caused by snoop filter eviction in an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20160062890A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersCircuit complexityData access
An interconnect has coherency control circuitry for performing coherency control operations and a snoop filter for identifying which devices coupled to the interconnect have cached data from a given address. When an address is looked up in the snoop filter and misses, and there is no spare snoop filter entry available, then the snoop filter selects a victim entry corresponding to a victim address, and issues an invalidate transaction for invalidating locally cached copies of the data identified by the victim. The coherency control circuitry for performing coherency checking operations for data access transactions is reused for performing coherency control operations for the invalidate transaction issued by the snoop filter. This greatly reduces the circuitry complexity of the snoop filter.
Owner:ARM LTD
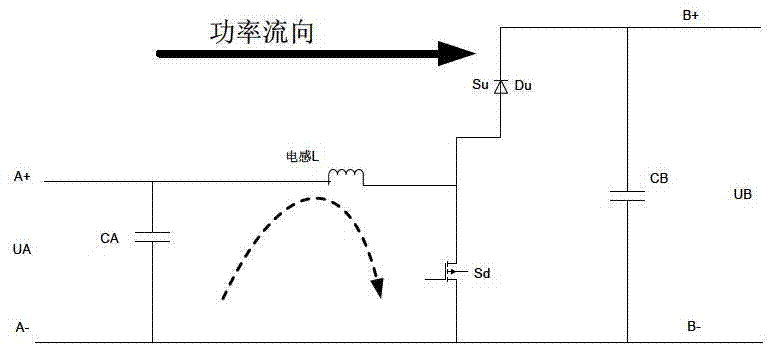
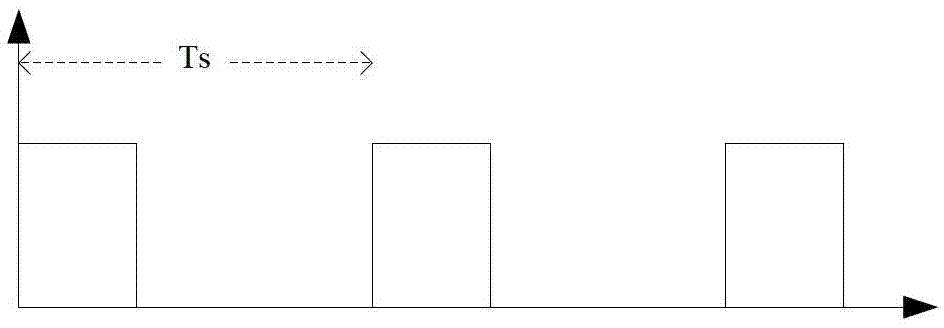
Control method of two-way direct current conversion device
InactiveCN103036433ASimple designGuaranteed continuityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCircuit complexityControl signal
The invention discloses a control method of a two-way direct current conversion device. The control method of the two-way direct current conversion device is suitable for high voltage and high power conversion sites, and can support frequent changing-over of power flow direction. Switching loss and circuit complexity can be balanced. At first an upper switch tube breakover time T 1 and a lower switch tube breakover time T 2 in a control cycle T s are calculated according to required pulse width modulation (PWM) control signal duty ratio D, and the ratio of T 1 to TS is D. In the process of practical control, one main circuit in the two-way direct current conversion device can be used as a reference subcircuit. The control on the reference subcircuit is that the upper switch tube and the lower switch tube in the reference subcircuit are controlled to be communicated in a complementary mode in each control circuit T s, and every time the upper switch tube and the lower switch tube are changed over, the dead time delta is added to carry out transition. Therefore the real breakover time of the upper switch tube is that T 1 subtracts the delta, and the real breakover time of the lower switch tube is that the T 2 subtracts the delta. The control on an un-referenced subcircuit is that control signals of all un-referenced subcircuits are the same, and differ by 180 degrees from the control signals of the reference circuit.
Owner:BEIJING POWER MACHINERY INST
Control and protection circuit for single-lithium battery electric tool and detection and control method for control and protection circuit
InactiveCN103166290AImprove cycle lifeReduce weightBatteries circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCircuit complexityMicrocontroller
The invention discloses a control and protection circuit for a single-lithium battery electric tool and a detection and control method for the control and protection circuit. The control and protection circuit comprises a singlechip power supply circuit, a battery charging and discharging voltage detection circuit, a battery charging and discharging temperature detection circuit, a battery charging control management circuit, a motor switching and commutation control circuit and a working state indication circuit. A singlechip is used as a master control integrated circuit (IC), and is matched with simple peripheral components to realize all functions of protecting and controlling the single-lithium battery electric tool, so that the functions are flexibly designed, circuit complexity is lowered, the number of electronic components is decreased, cost is lowered, and the circuit is high in safety and reliability, and is almost power consumption-free when not working, and has the advantages of environment friendliness, energy saving, lightweight, convenience for use, high operation efficiency, long cycle life of a battery, and the like.
Owner:SUNWODA ELECTRONICS
Slow clock crystal frequency compensation method and device for mobile communication terminal
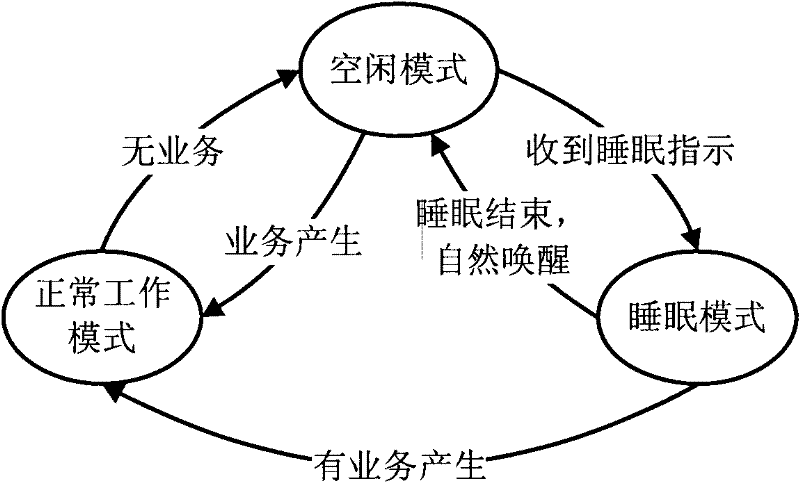
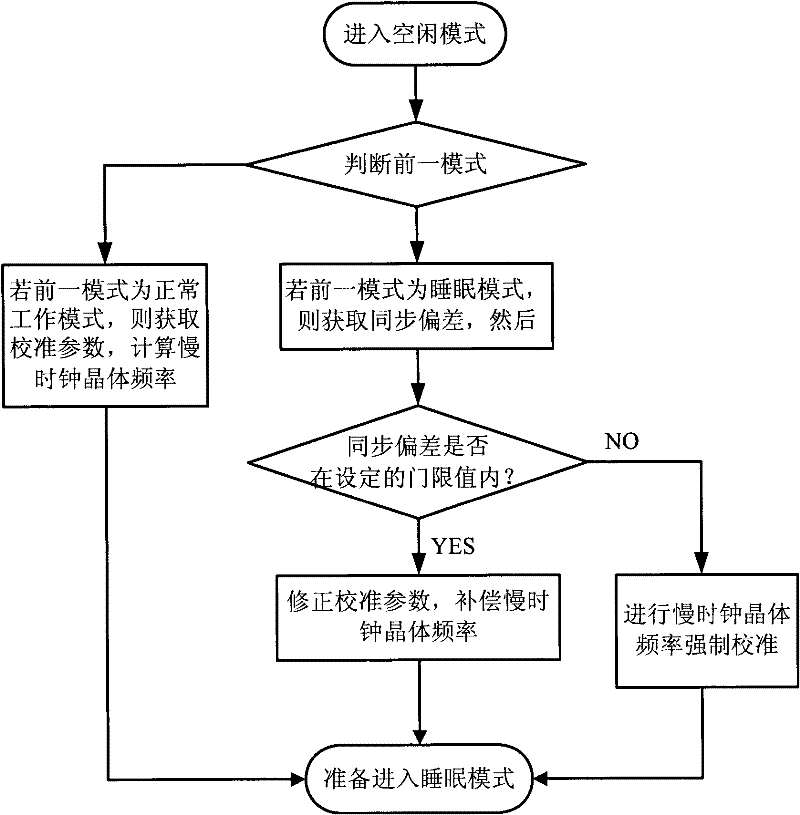
ActiveCN102540868AMaximize sleep timeAvoid Aging Rate ProblemsEnergy efficient ICTSynchronisation arrangementCircuit complexitySleep time
The invention relates to a slow clock crystal frequency compensation method and a slow clock crystal frequency compensation device for a mobile communication terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: entering an idle mode; judging a previous mode before entering the idle mode; acquiring a calibration parameter if the previous mode is a normal working mode; calculating slow clock crystal frequency; and if the previous mode is a sleep mode, firstly acquiring synchronism deviation, then judging whether the synchronism deviation is in a set threshold value, if the synchronism deviation is in the set threshold value, compensating the slow clock crystal frequency, and otherwise, forcibly calibrating the slow clock crystal frequency; the device comprises a forcible calibration unit, a synchronism deviation unit, a correction and calibration unit and a power-saving control unit; accurate sleep timing is guaranteed and a system does not fall out of step after being awakened without increasing the circuit complexity and terminal hardware cost, and starting of a clock calibration unit to the minimum extent is also guaranteed, so that the sleep time is maximized when the mobile communication terminal is in the idle mode, and the power consumption of the mobile communication terminal is reduced.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method for repairing establishing timing sequence
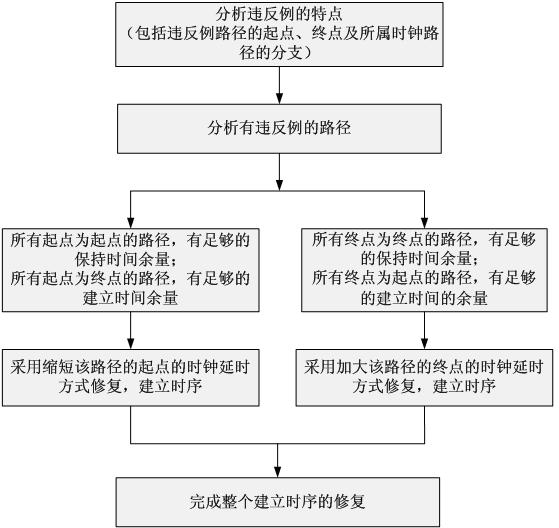
InactiveCN102456087AReduce complexitySmall design areaSpecial data processing applicationsCircuit complexityRetention time
The invention discloses a method for repairing an establishing timing sequence, wherein with intervention to a clock channel, the design problems of a data channel are partially transferred to the clock channel; and the problems of the reduction of the working frequency of a chip and the increase of the designed area of the chip due to the repairing of the establishing timing sequence are solved. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing the characteristics of a timing sequence violation and analyzing a path having a violation; when all paths with the starting points thereof as the starting points have sufficient retention time surplus and all paths with the starting points thereof as the terminal points have sufficient establishing time surplus, entering the mode of repairing the establishing timing sequence by shortening the clock delay of the path starting points; and when all paths with the terminal points thereof as the terminal points have sufficient retention time surplus and all paths with the terminal points thereof as the starting points have sufficient establishing time surplus, entering the mode of repairing the establishing timing sequence by extending the clock delay of the path terminal points. The method provided in the invention is capable of effectively reducing the circuit complexity of the design of an integrated circuit chip, increasing the working frequency of the chip and reducing the designed area of the chip in such a design manner of selecting different clock delays.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Liquid crystal display device
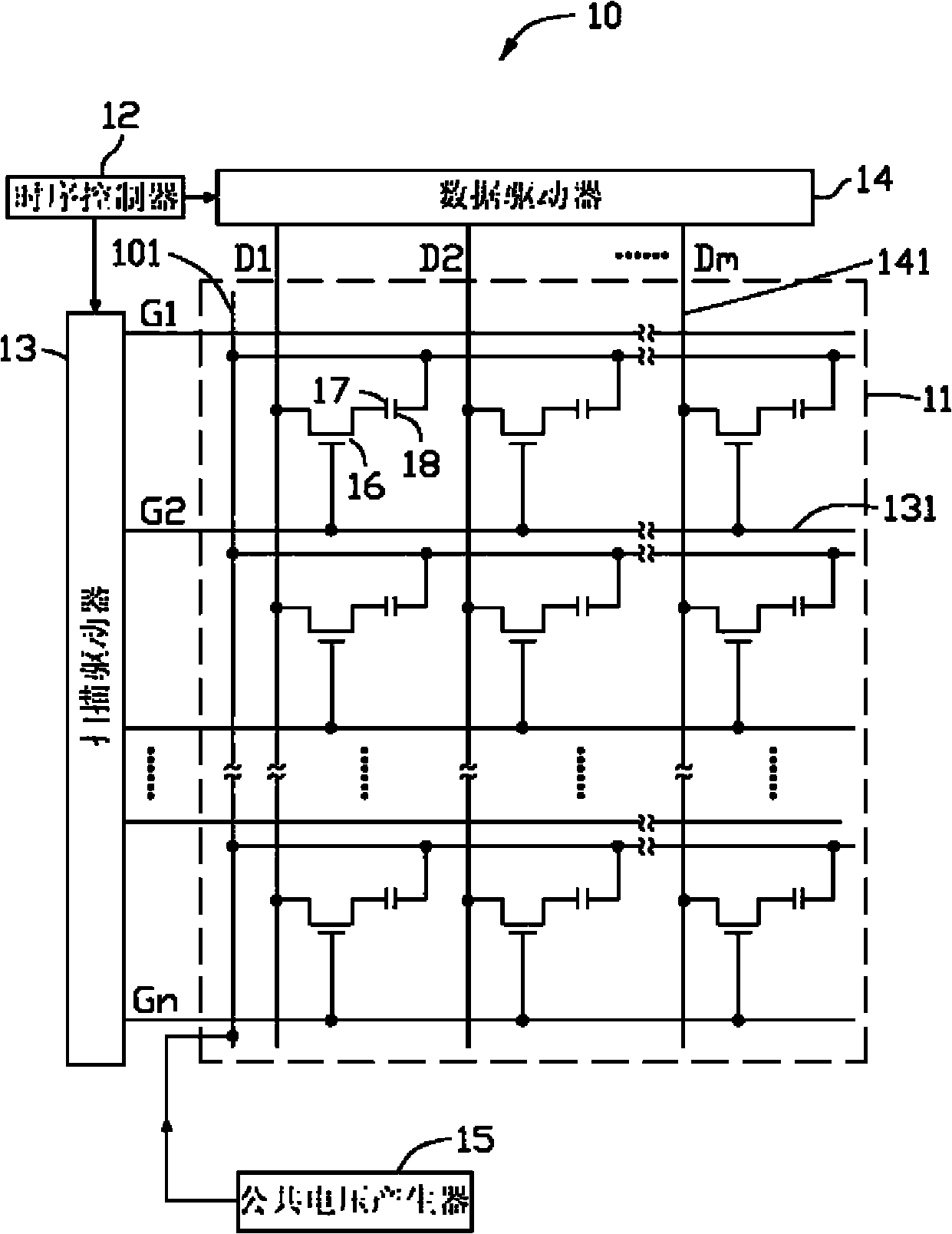
InactiveCN102081245AReduce complexityLow costStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCircuit complexityLiquid-crystal display
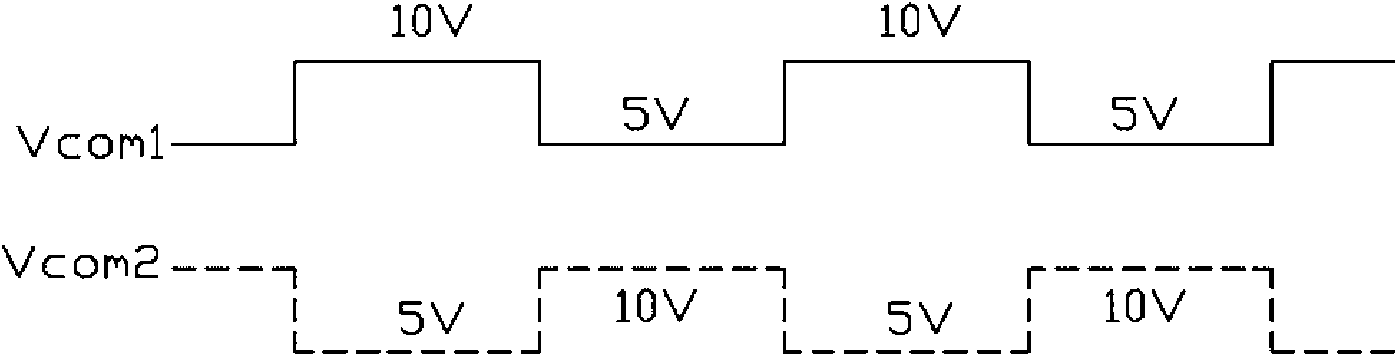
The invention provides a liquid crystal display device. In the liquid crystal display device, a first public voltage and a second public voltage which are constantly changed are used, public electrodes of different pixel units at the same row are respectively connected with the first public voltage and the second public voltage, thus a data driver dose not need to provide twice public voltage, thereby relatively reducing the production process and circuit complexity of the driving circuit of the liquid crystal display device so as to reduce cost.
Owner:INNOCOM TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Double-input operational amplifier shared margin gain amplifying circuit
InactiveCN101860335AHigh precisionReduce power consumptionGain controlDifferential amplifiersCircuit complexityCapacitance
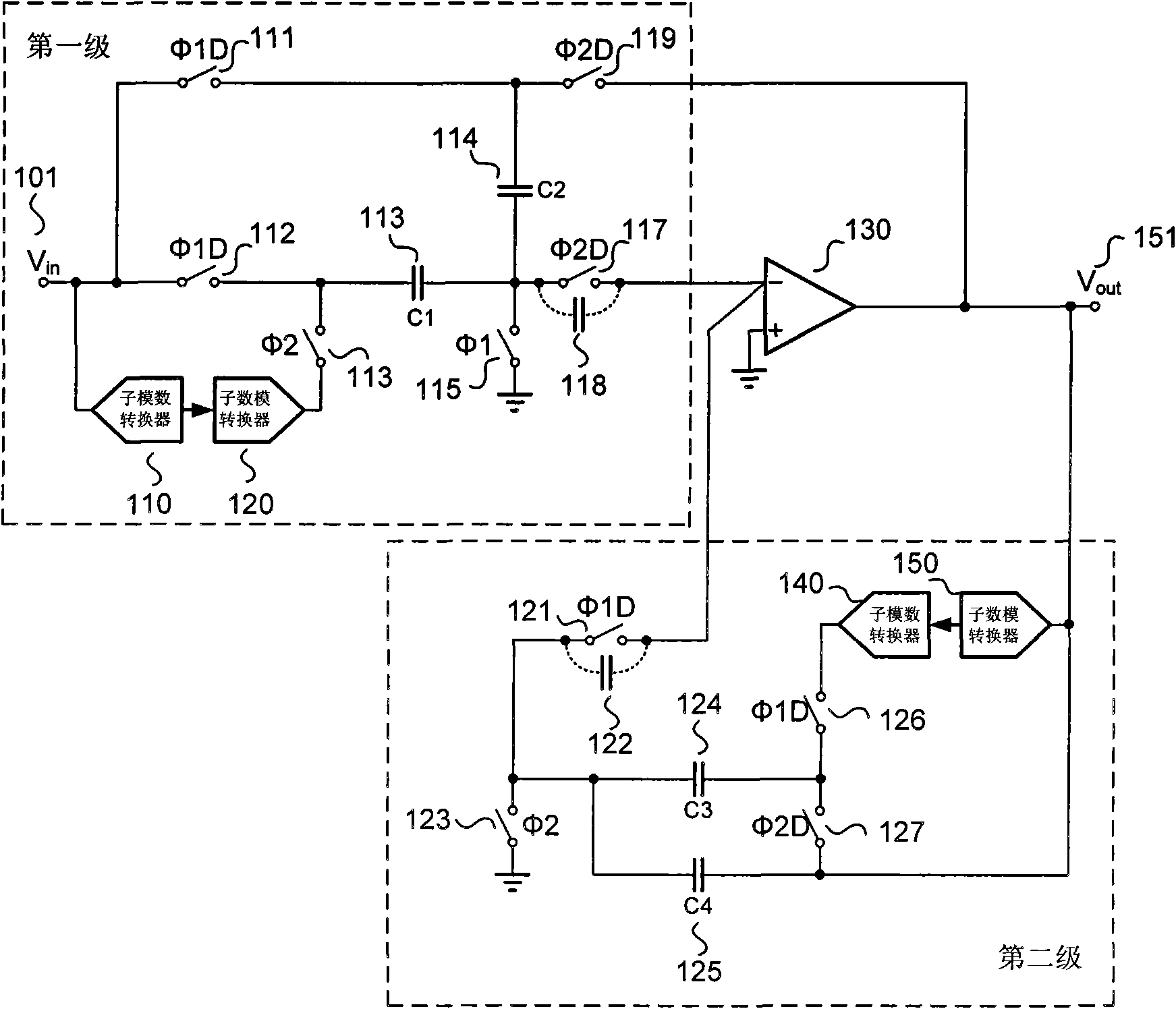
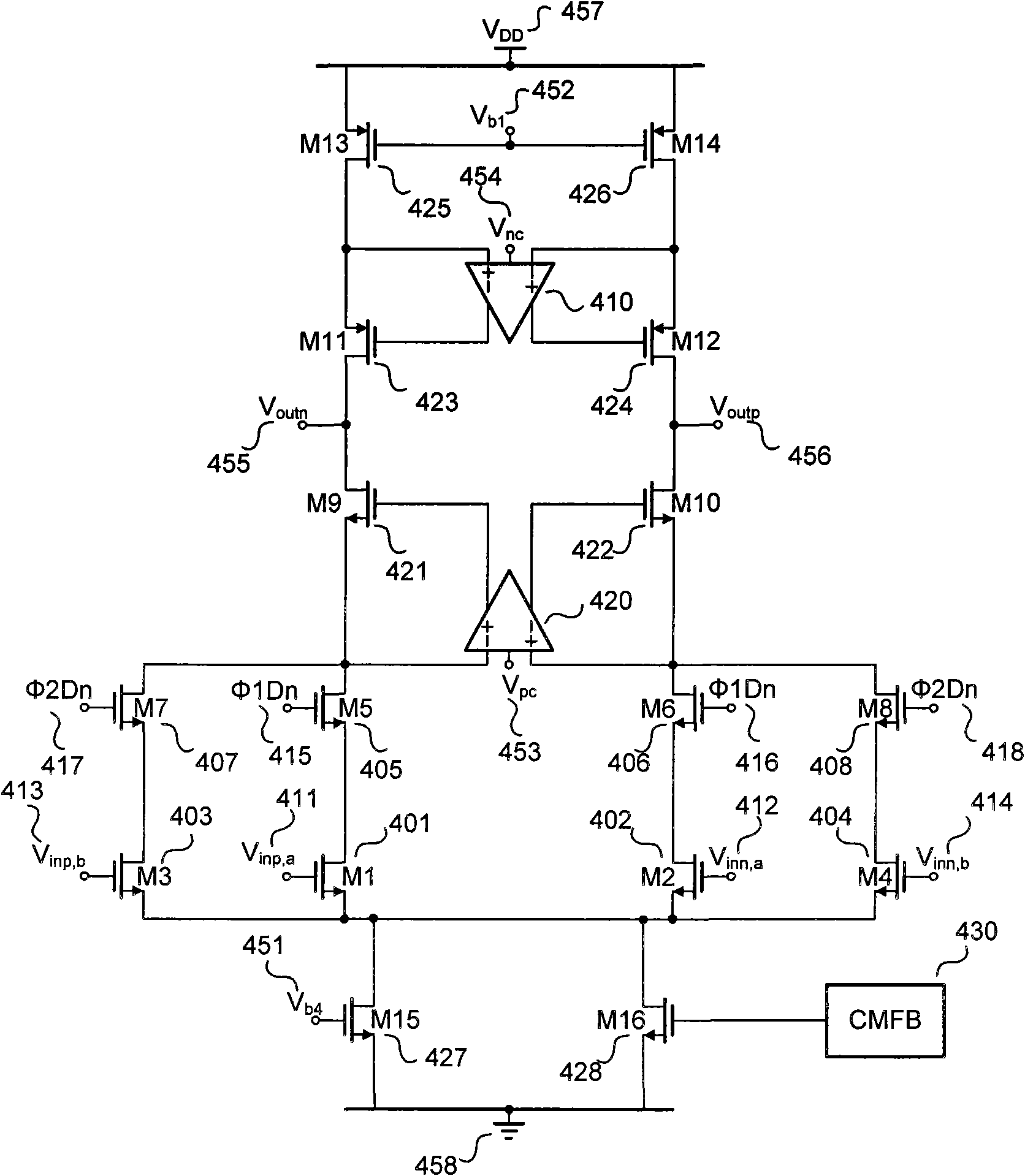
The invention belongs to the technical field of data converters in integrated circuit design, and discloses a double-input operational amplifier shared margin gain amplifying circuit. The amplifying circuit comprises a double-input operational amplifier, a clock generating circuit, a sub digital-to-analog converter, a sub analog-to-digital converter, a capacitor, a switch and the like. Two groups of differential input pair tubes are controlled through the switch controlled by bidirectional overlapped clocks and embedded inside the operational amplifier by adopting the operational amplifier of two groups of input differential pairs and are alternately used at two phases of the clocks, and meanwhile the input differential pairs are alternately reset to a common-mode input voltage so as to fully eliminate the influence of memory effect and inter-stage feed-through in the traditional circuit, improve the signal establishing precision under the condition of keeping the same area, power consumption and circuit complexity and further improve the precision of analog-to-digital conversion.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Structure for a Phase Locked Loop with Adjustable Voltage Based on Temperature
InactiveUS20090021314A1Reduce usageImprove device yieldThermometer detailsTemperatue controlCircuit complexitySilicon
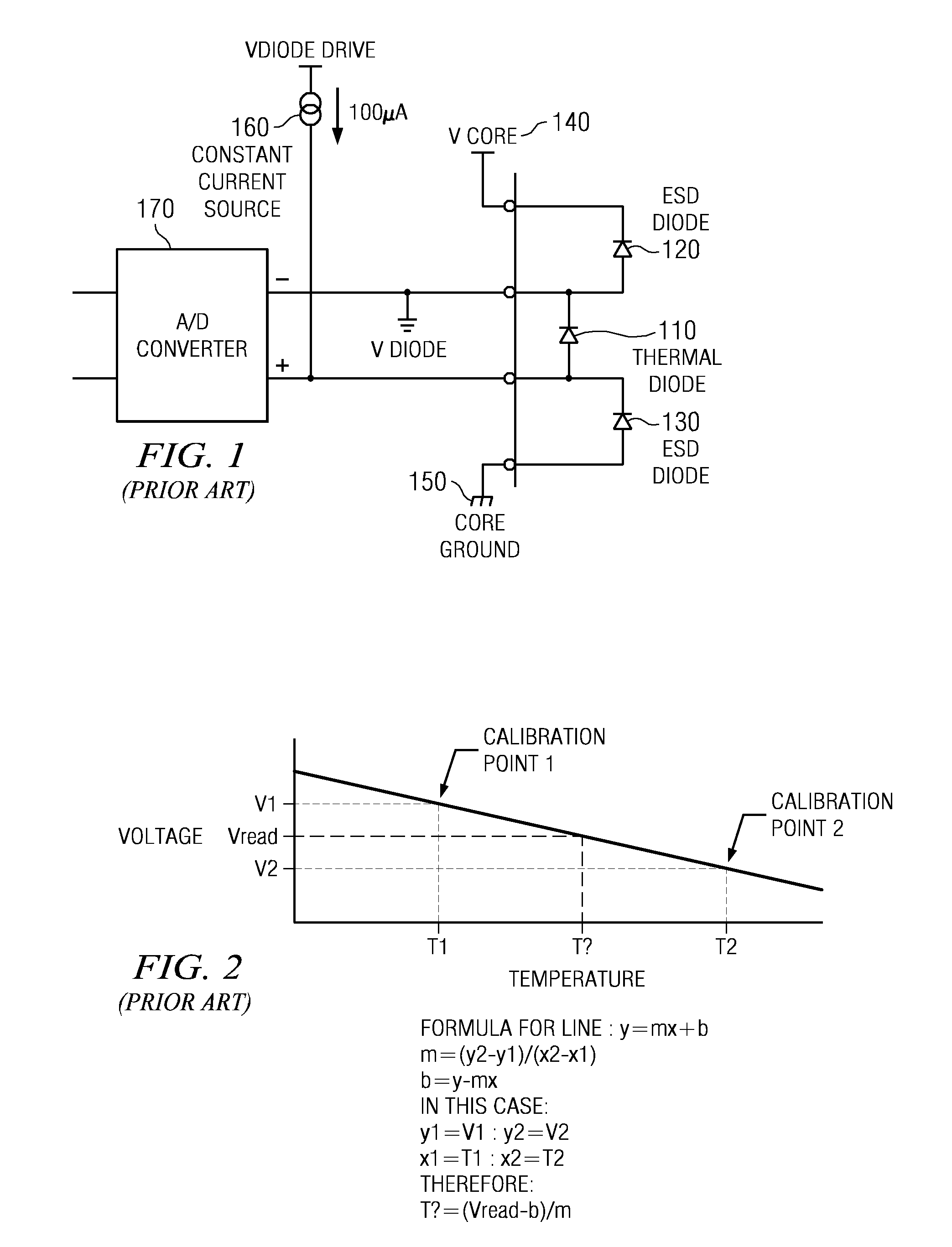
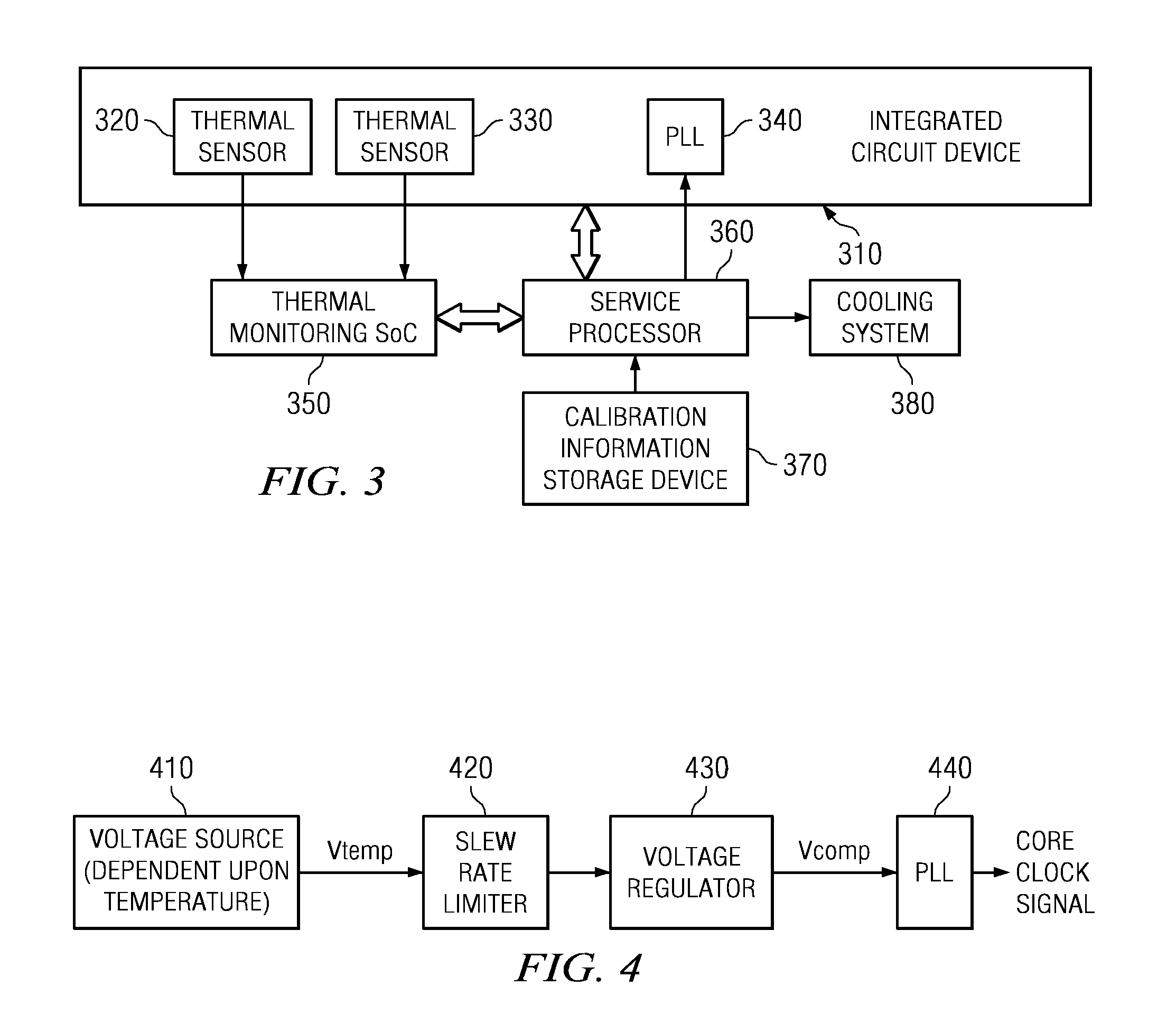
A design structure for an apparatus for utilizing a single set of one or more thermal sensors, e.g., thermal diodes, provided on the integrated circuit device, chip, etc., to control the operation of the integrated circuit device, associated cooling system, and high-frequency PLLs, is provided. By utilizing a single set of thermal sensors to provide multiple functions, e.g., controlling the operation of the integrated circuit device, the cooling system, and the PLLs, silicon real-estate usage is reduced through combining circuitry functionality. Moreover, the integrated circuit device yield is improved by reducing circuitry complexity and increasing PLL robustness to temperature. Furthermore, the PLL circuitry operating range is improved by compensating for temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com