Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Pump wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
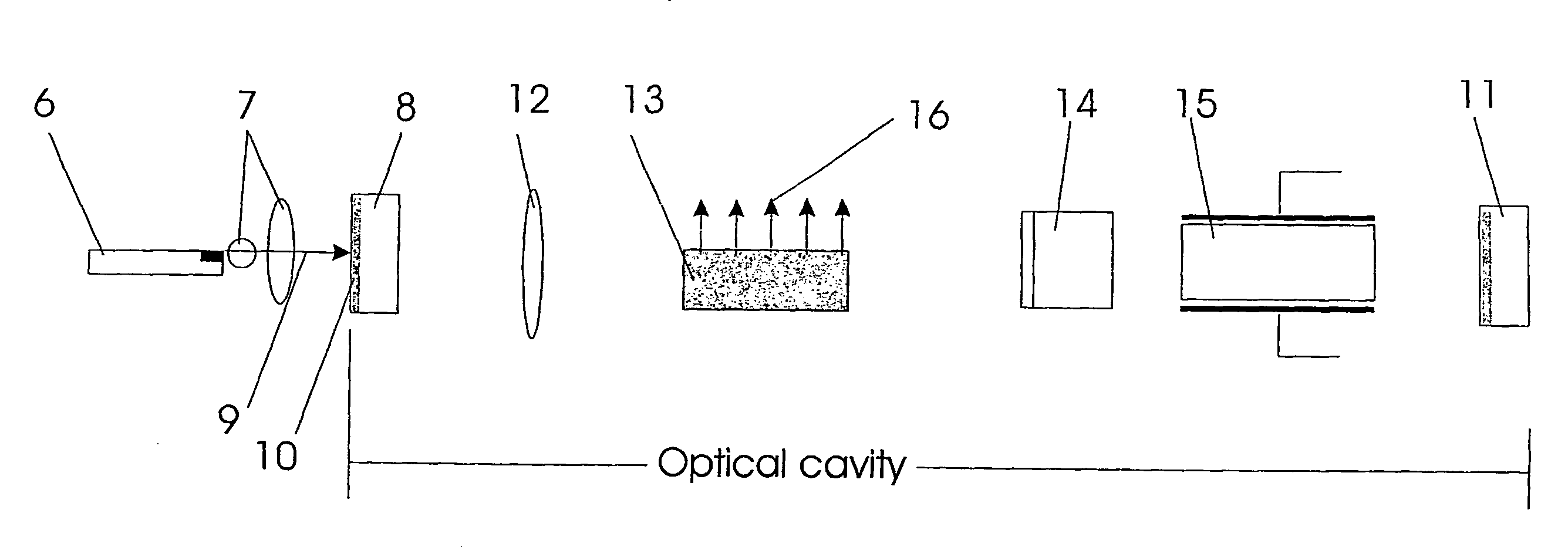
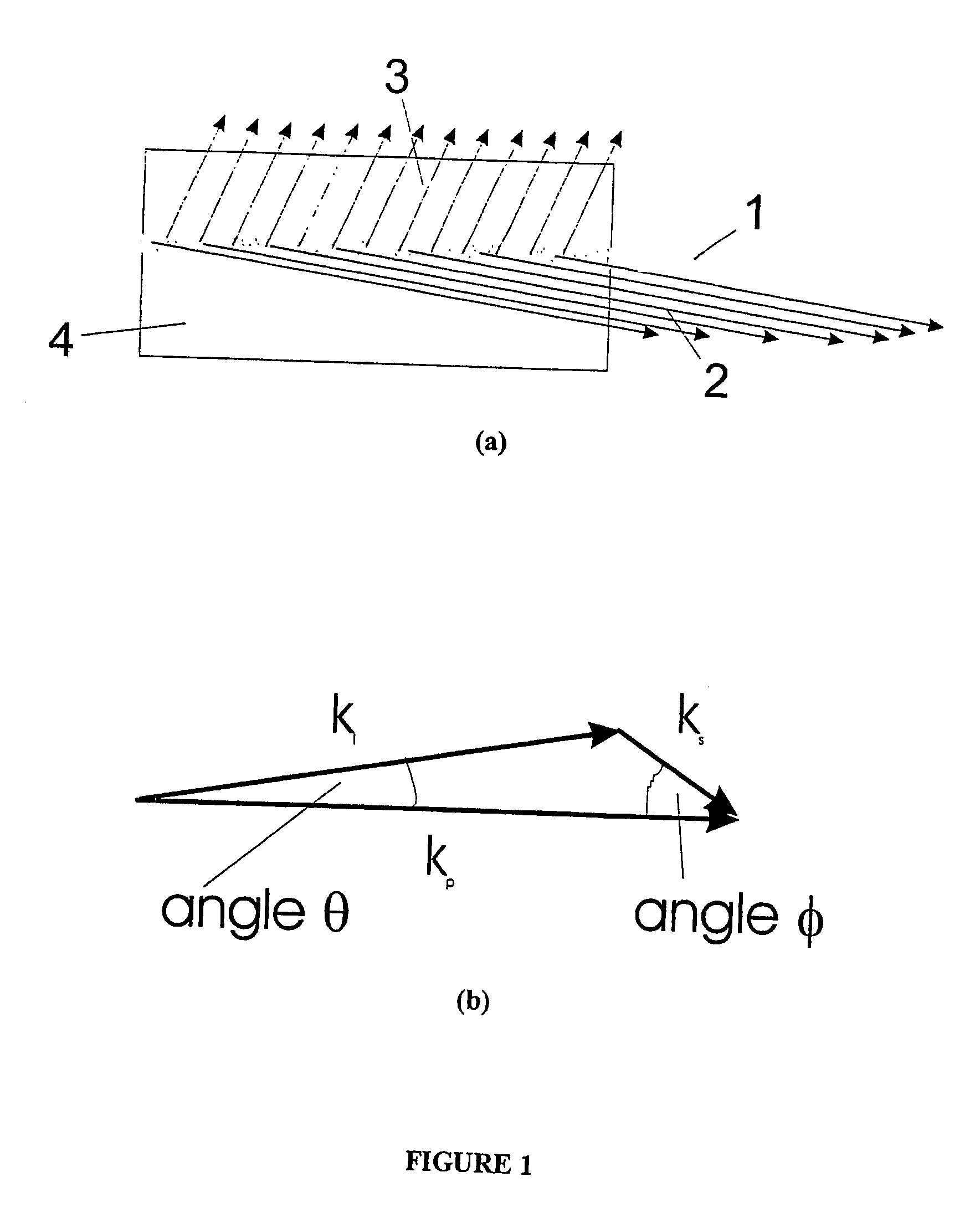
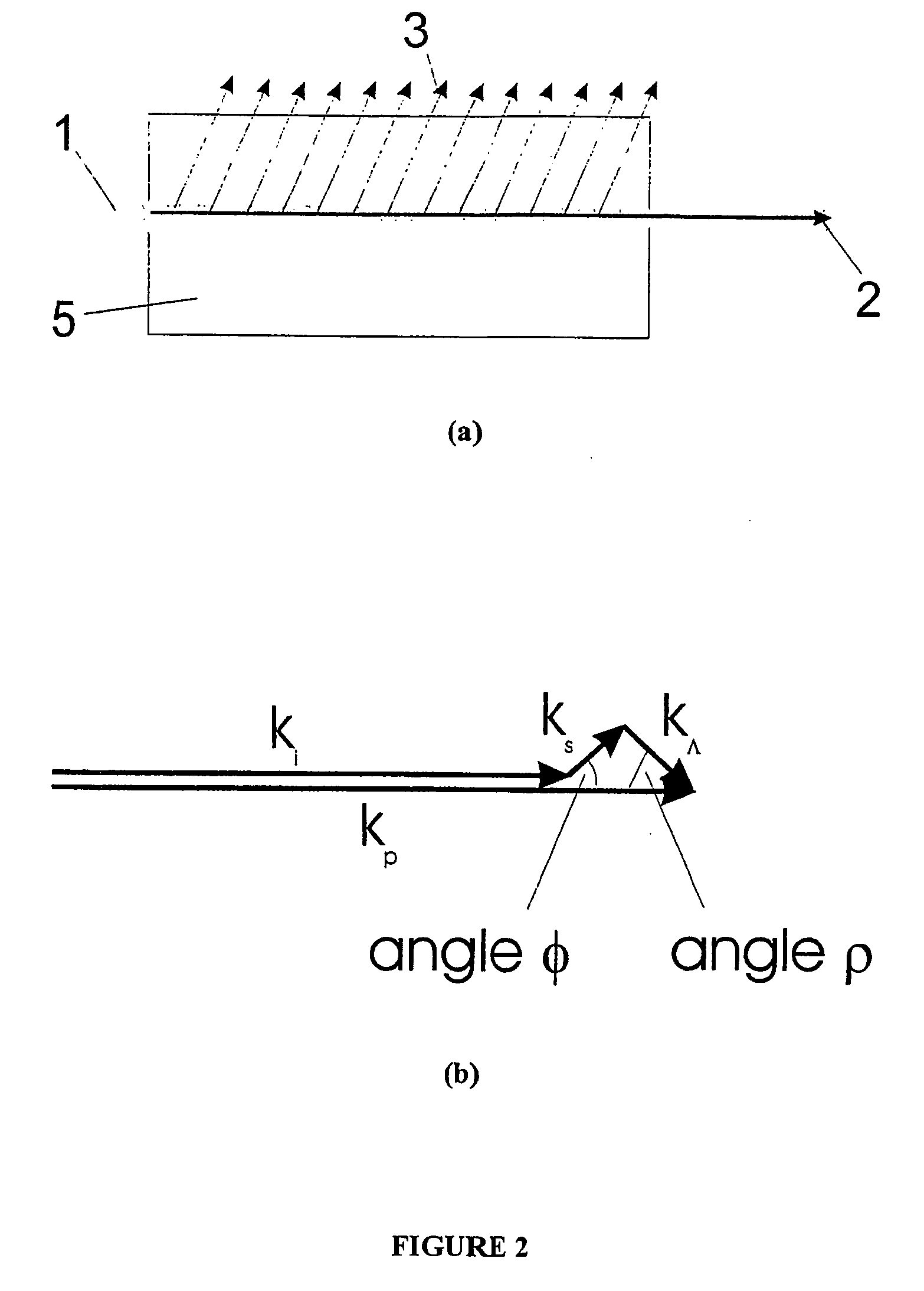
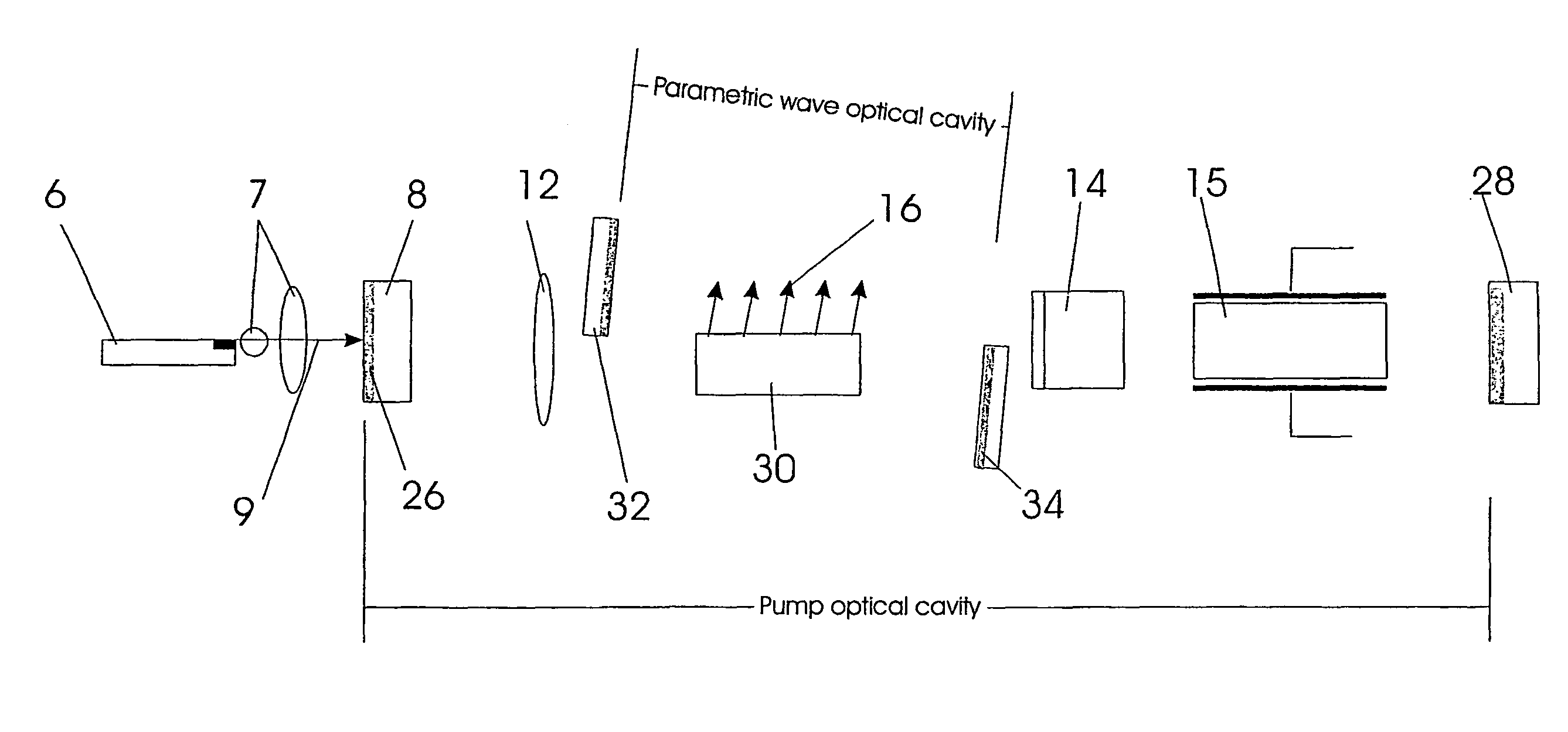
Laser device
InactiveUS6320886B1Scattering properties measurementsOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierOptical axis
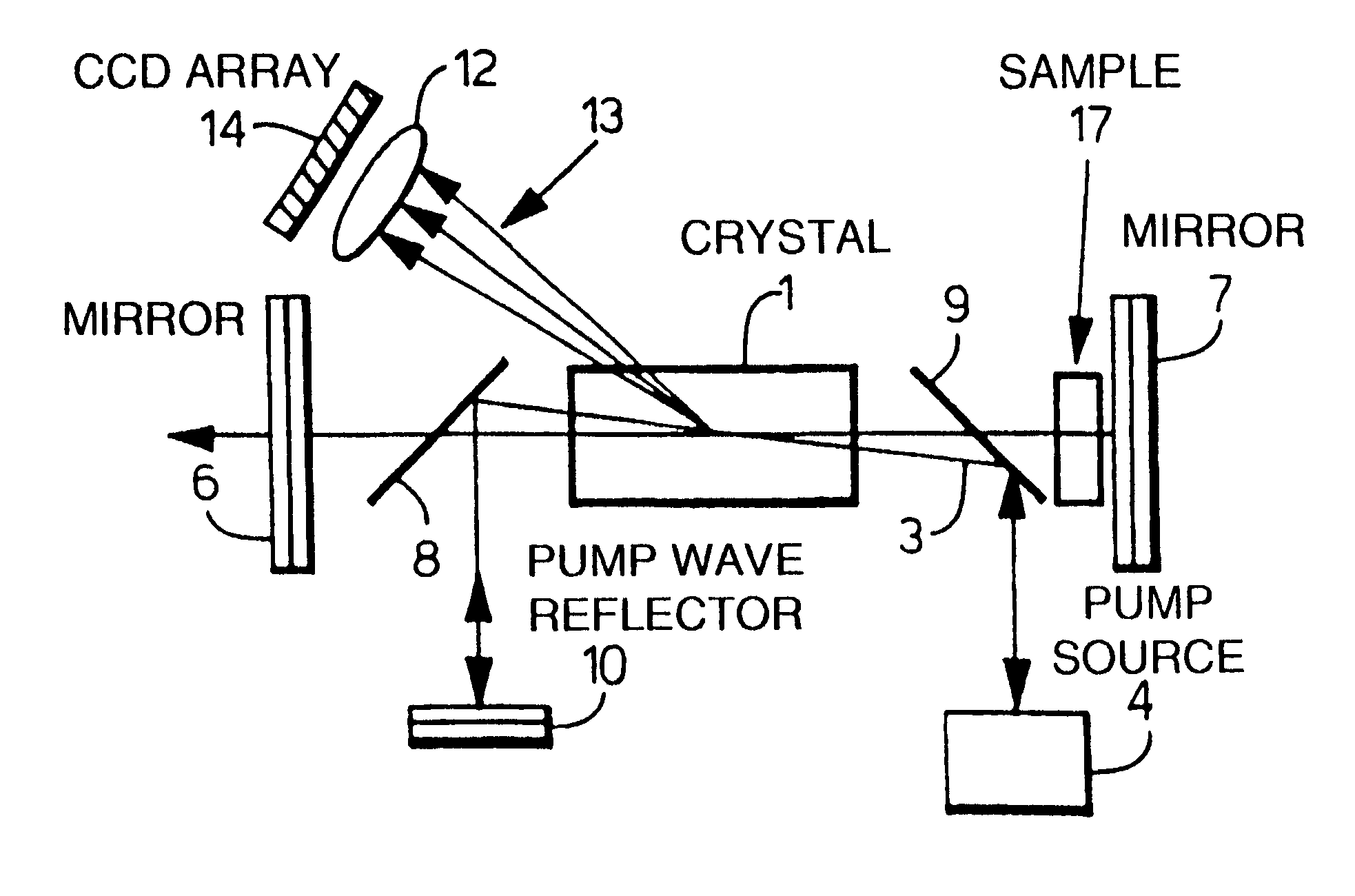
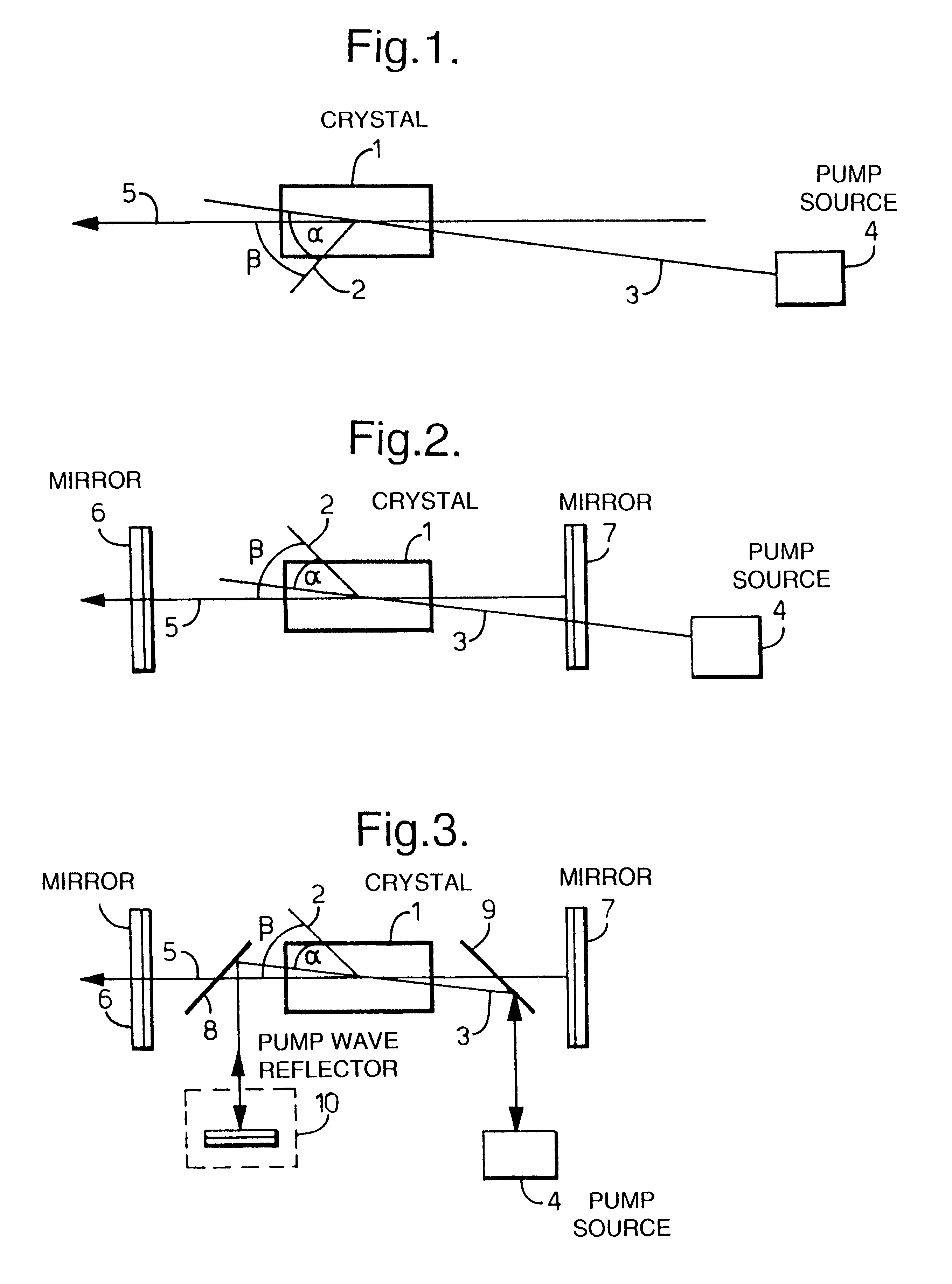
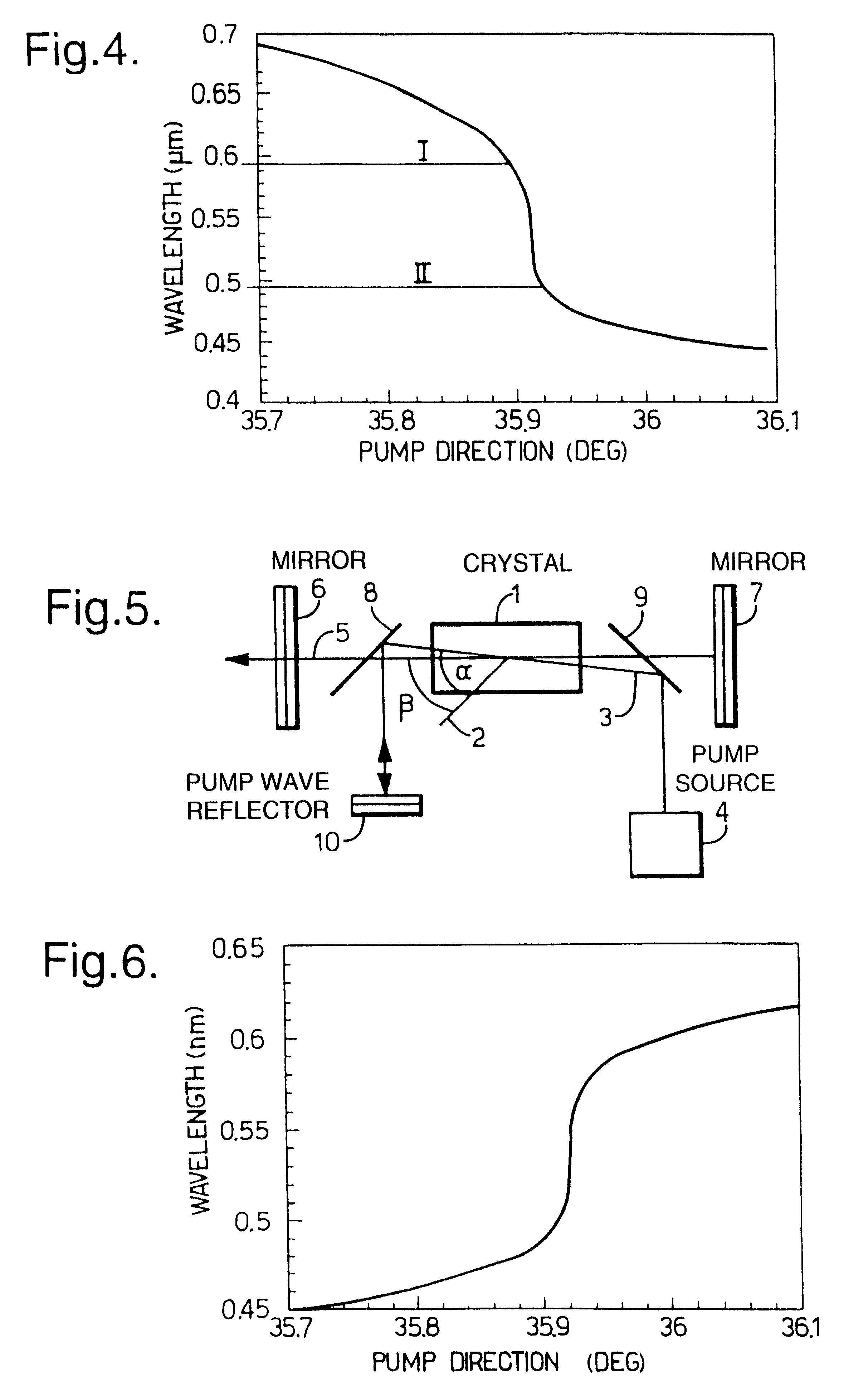
A laser device comprises a non-collinear optical parametric generator (OPG) and a pump wave source (4). The OFG comprises a non-linear crystal (1) fixedly mounted within the generator wherein the relative orientations of the pump wave (3) and each generated wave (5) to an optic axis (2) of the non-linear crystal (1) are substantially such that a point of inflexion is produced in a tuning curve of wavelength versus pump wave orientation of one of the generated waves, such that a broadband spectral output is obtained. This device has many applications including an amplifier for an input seed wave in which the crystal dose not have to be rotated to match the wavelength of the seed wave; or as part of a continuously tuneable narrowband source.
Owner:SEC OF DEFENCE IN HER BRITANNIC MAJESTYS GOVERNMENT OF THE UK OF GREAT BRITAIN & NORTHERN IRELAND THE +1
System and method for resolution enhancement of a distributed sensor
ActiveUS20050213869A1Reduce resolutionForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLine width
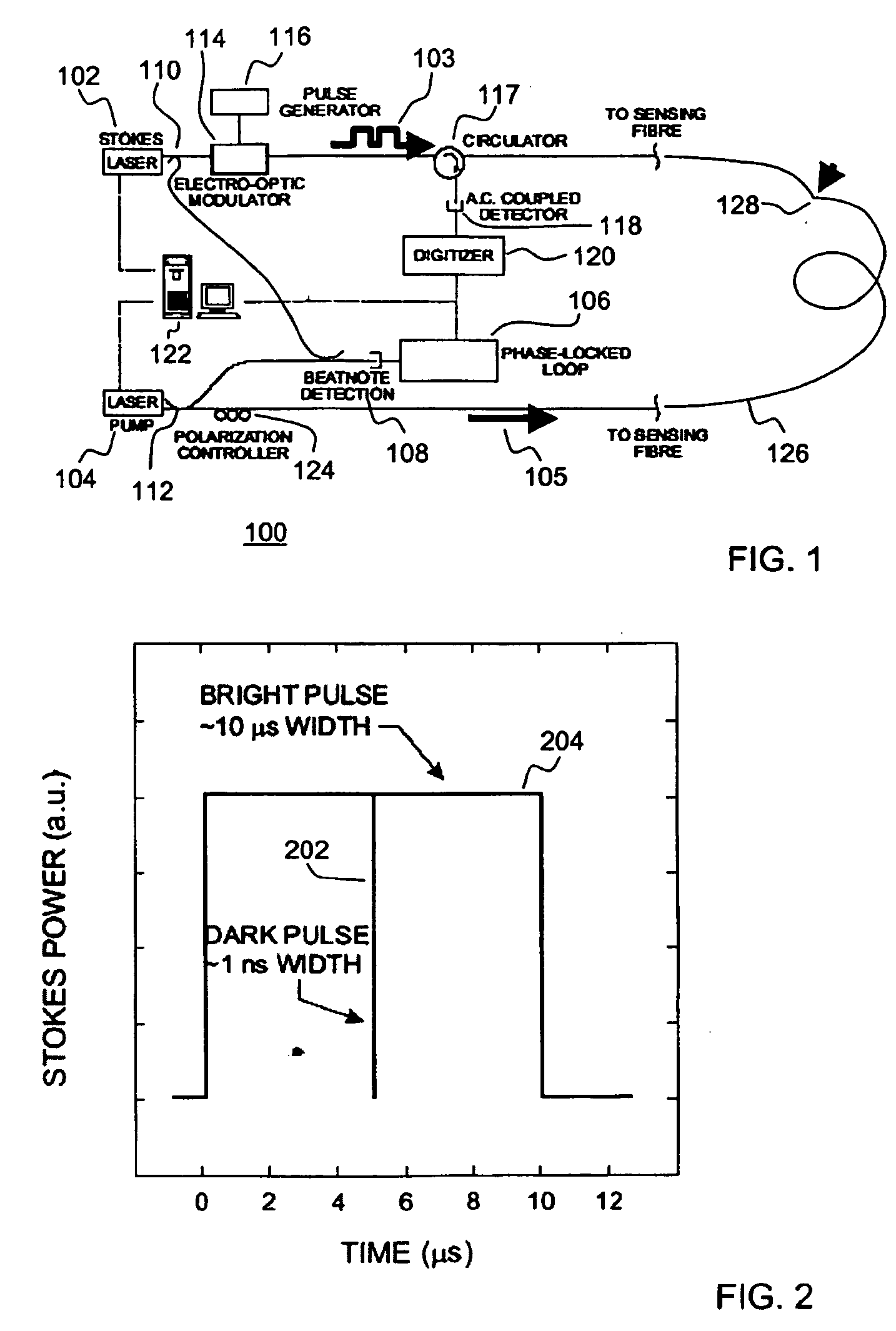
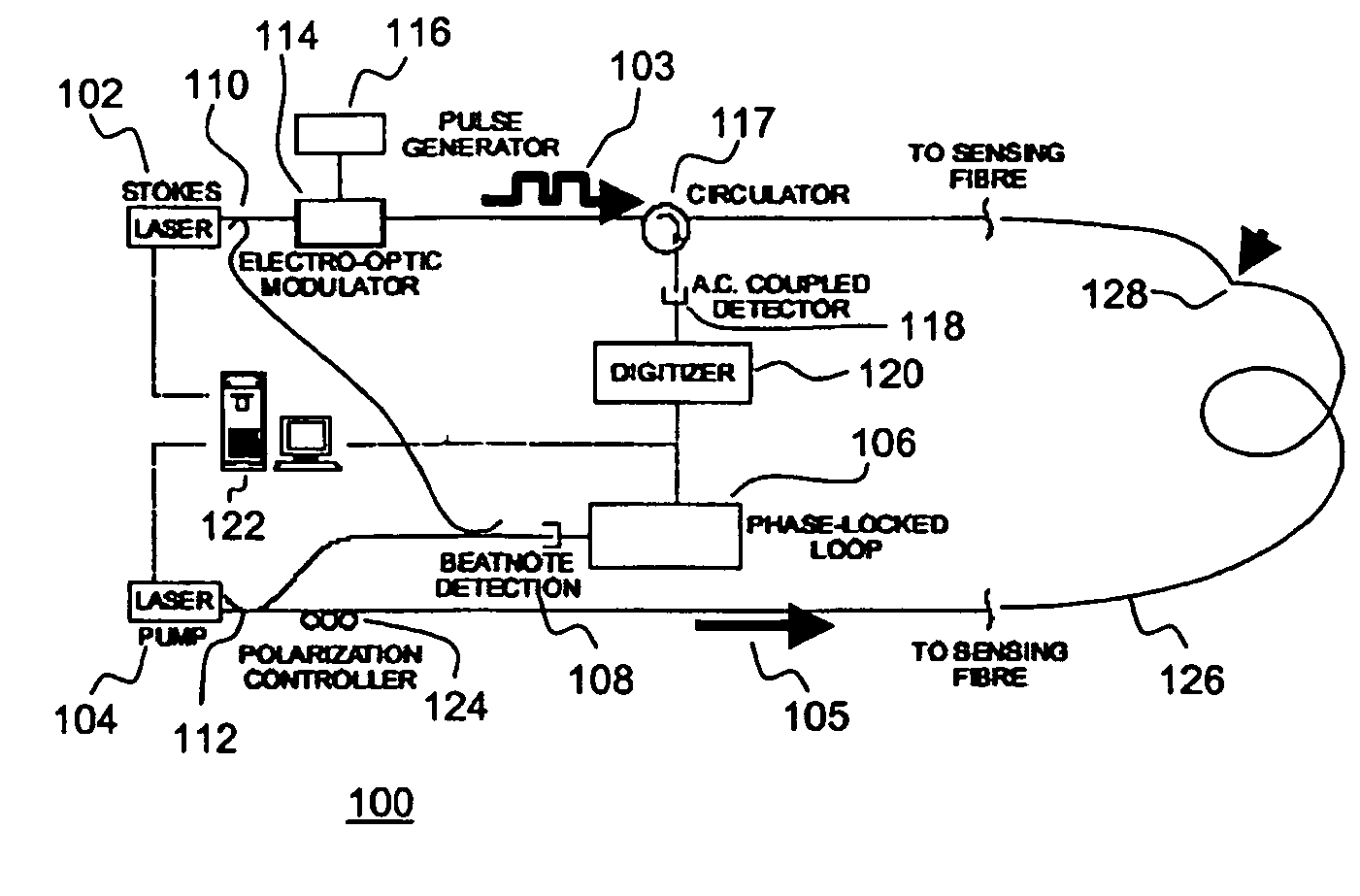
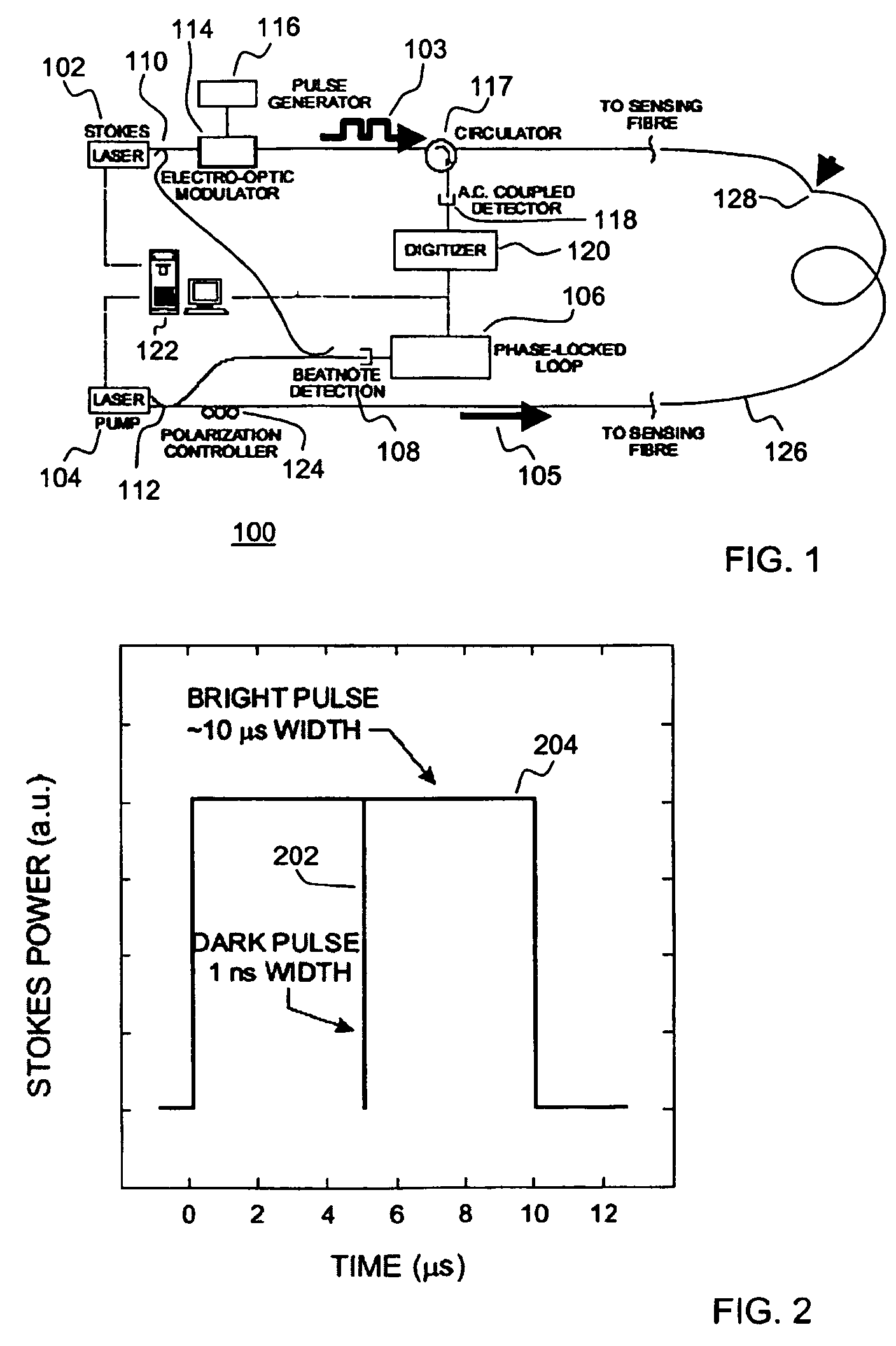
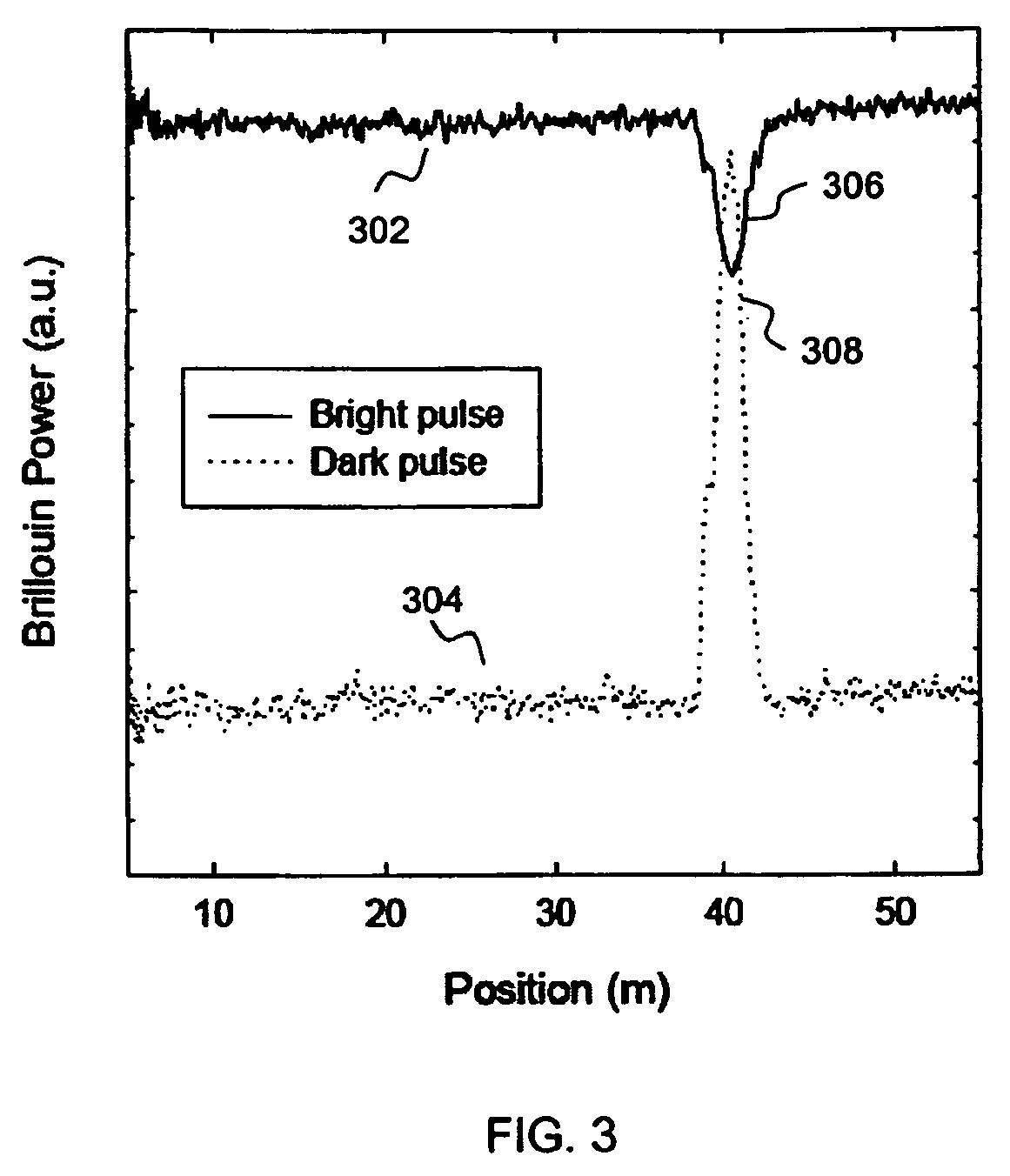
A Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis (BOTDA) distributed sensor system and method use a continuous wave (cw) Stokes wave interrupted with a dark pulse for improved spatial resolution. The cw Stokes wave causes a continuous depletion of the pump wave. The dark pulse causes the depletion to stop for the duration of the pulse. Brillouin interactions are measured during the dark pulse. Very narrow dark pulses can be used because sufficient Stokes wave energy is maintained. The system produces a stronger time-domain signal and narrower linewidth Brillouin spectra than traditional techniques using a bright Stokes pulse. Narrower measurement pulses can be used leading to improved spatial resolution. A quasi-cw Stokes wave can be used to reduce the effect of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in long measurement fibers. The system can be used for distributed strain or temperature measurements.
Owner:DARKPULSE TECH INC
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
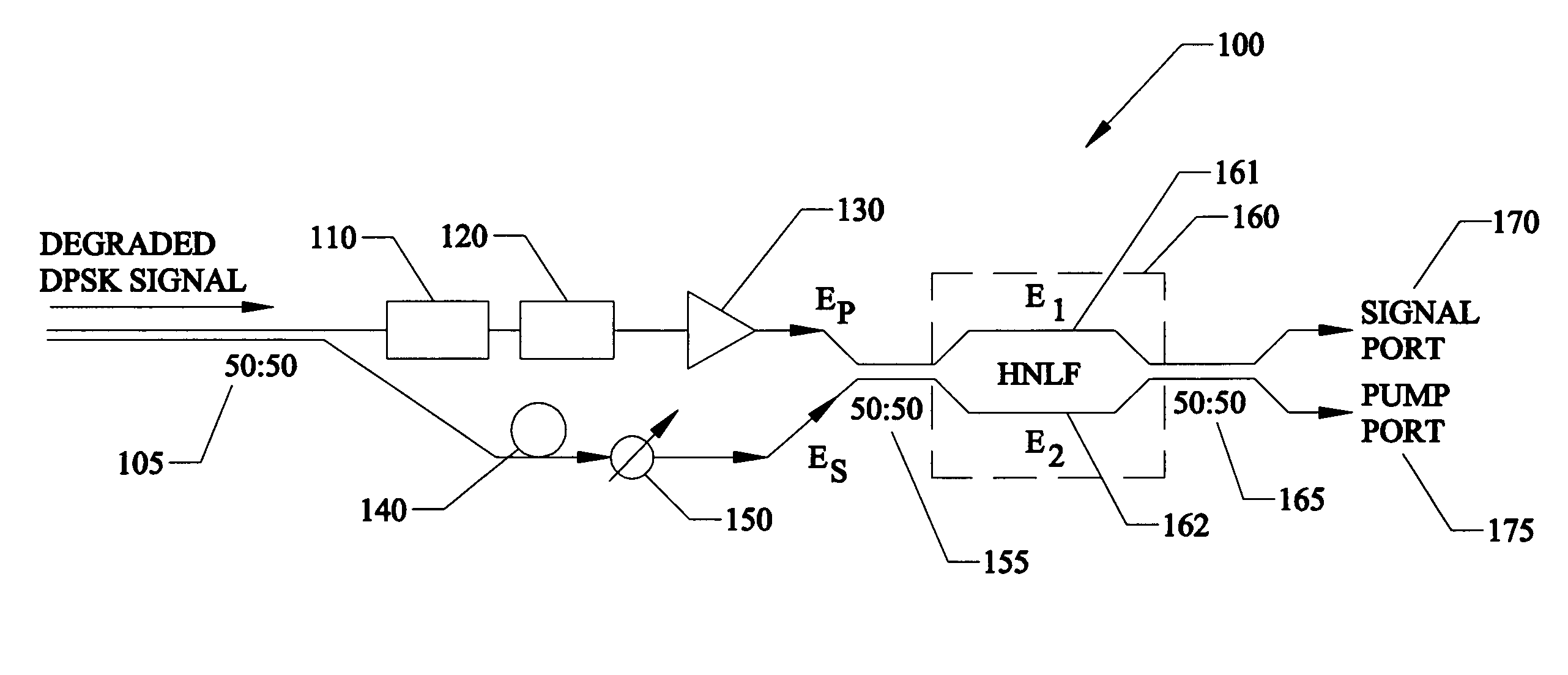
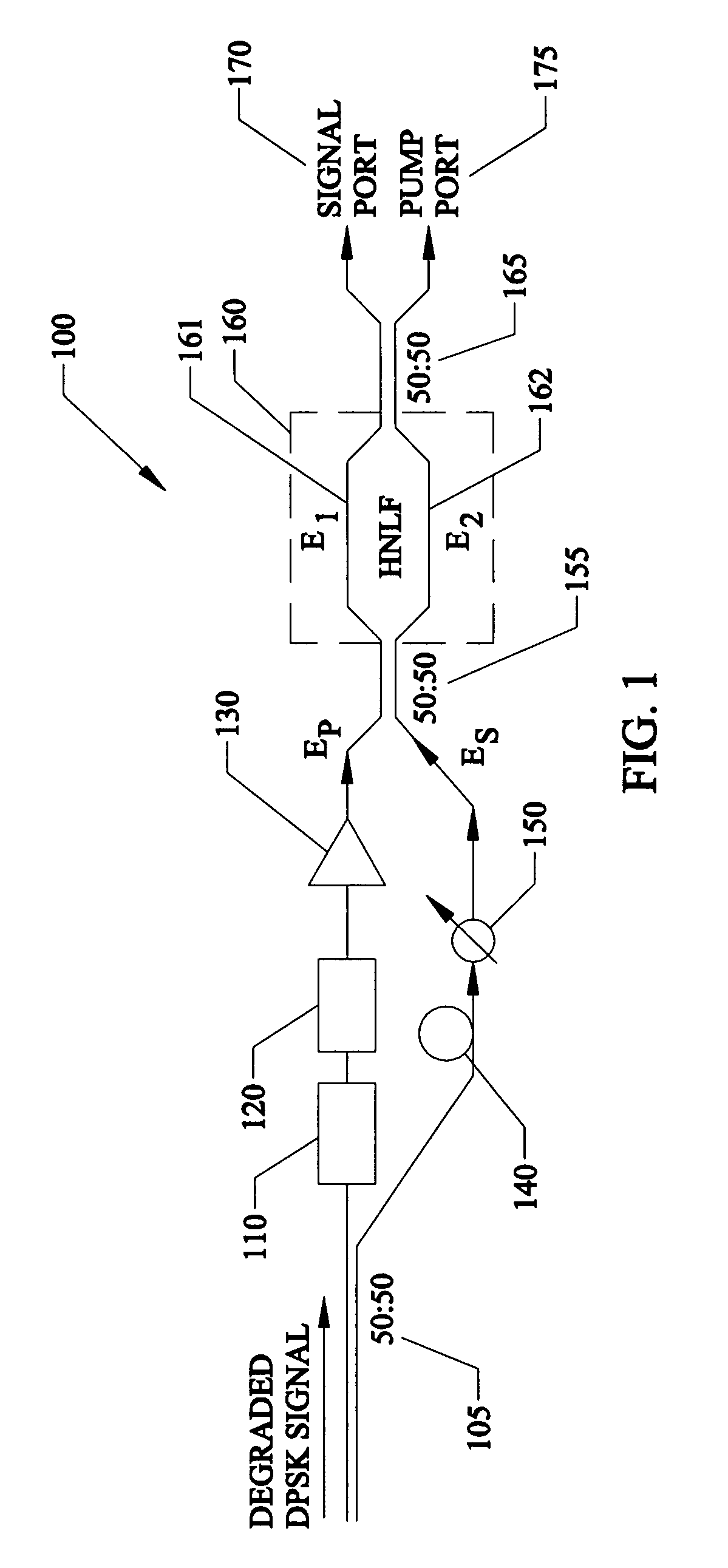
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
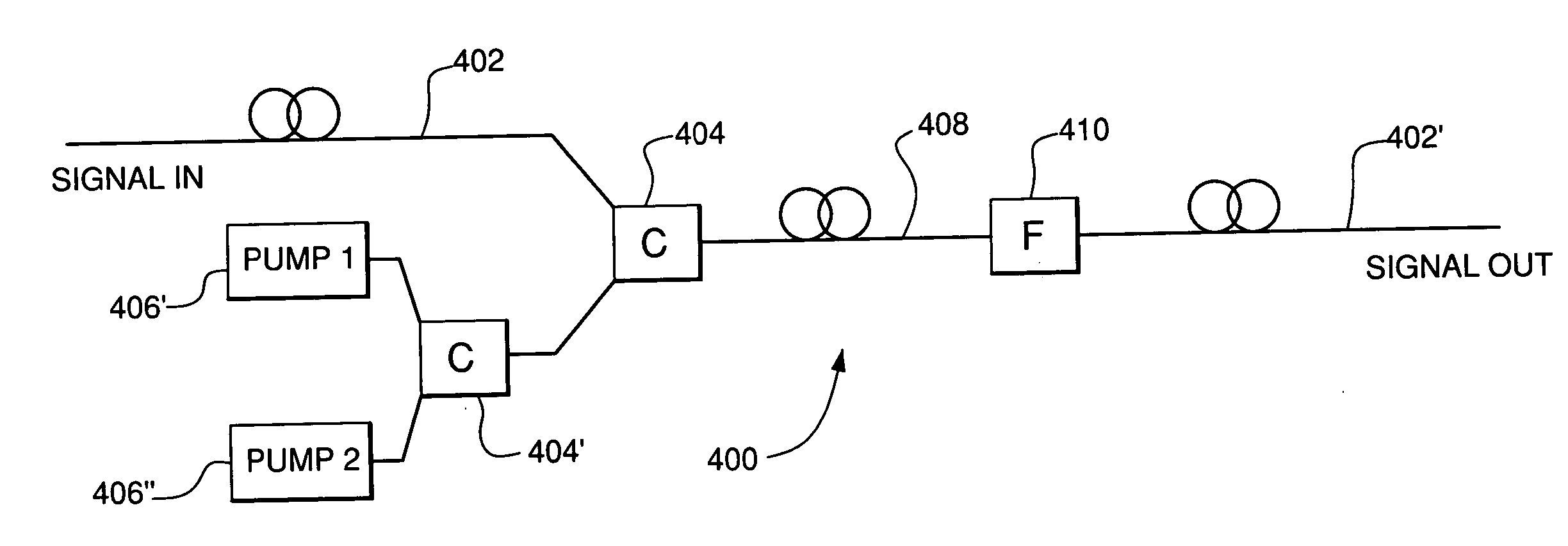
Optical amplifiers, optical fiber raman amplifiers and optical systems
An object of the present invention is to prevent an interruption circuit of an optical amplifier from malfunctioning due to Raman pump wave. A typical mode of the present invention is characterized in that an pump wave elimination filter is inserted before an input-light detector and a reflected-light detector which constitute the optical amplifier. This permits only a signal component to be detected, enabling interruption operation, while eliminating a remaining component of Raman pump wave transmitted from for example a downstream of an optical fiber transmission line. In addition, a judgment threshold value for the interruption operation is changed according to ON / OFF condition of the pump wave. Or the Raman pump wave itself is used for detecting output's open.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Parametric amplification using two pump waves
InactiveUS7164526B2Parametric amplifiersLight demodulationCommunications systemOptical parametric amplifier
An optical parametric amplifier (OPA) driven with at least two pump waves. The pump waves may be configured such that the OPA produces uniform exponential gain over a range of wavelengths that extends, for example, at least 30 nm on either side of the average pump-wave wavelength. In addition, since the Brillouin scattering limit applies to each pump wave independently, substantially twice the amount of energy may be pumped into an OPA of the present invention compared to that in the corresponding single pump-wave OPA of the prior art. An OPA of the present invention may be used in a WDM communication system and configured for simultaneous signal amplification and wavelength conversion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Regeneration of optical phase modulated signals
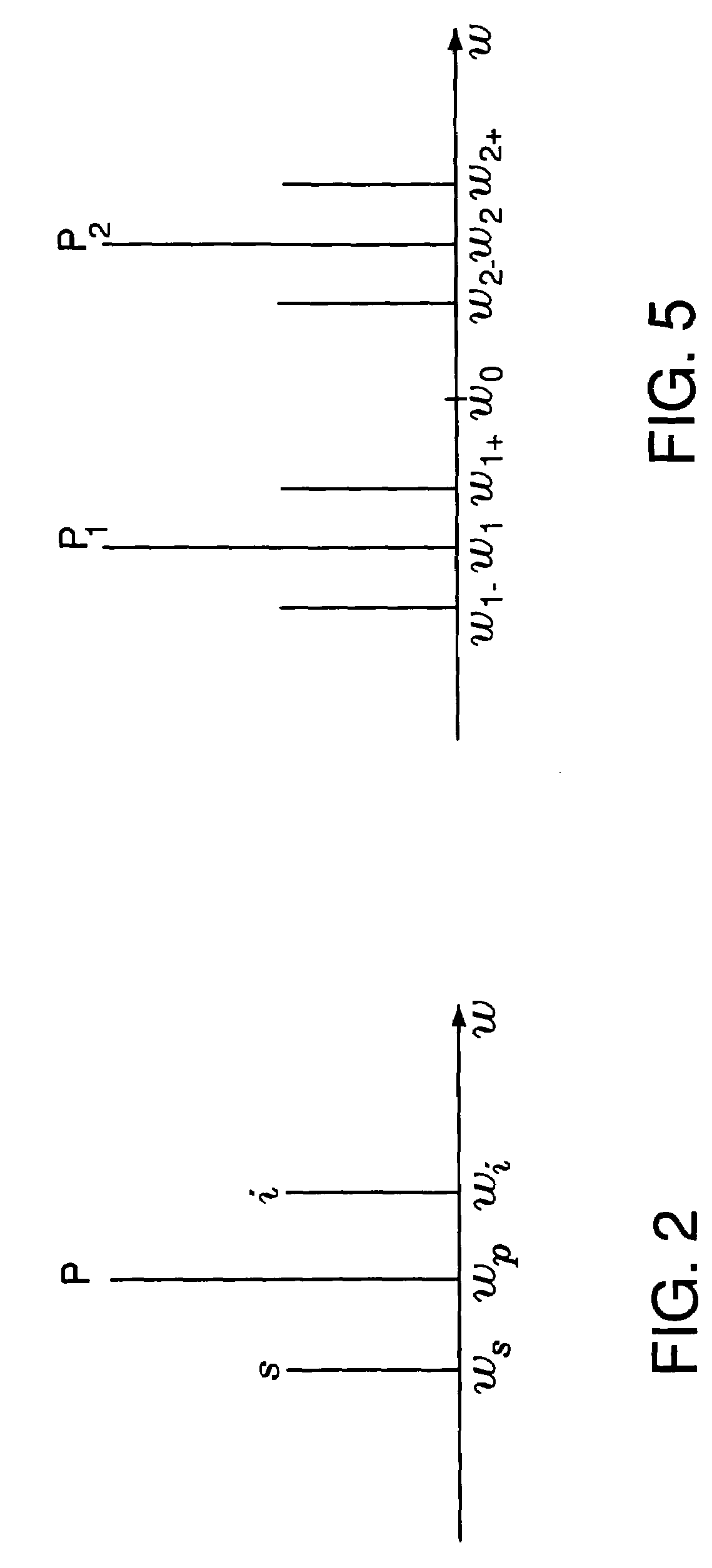
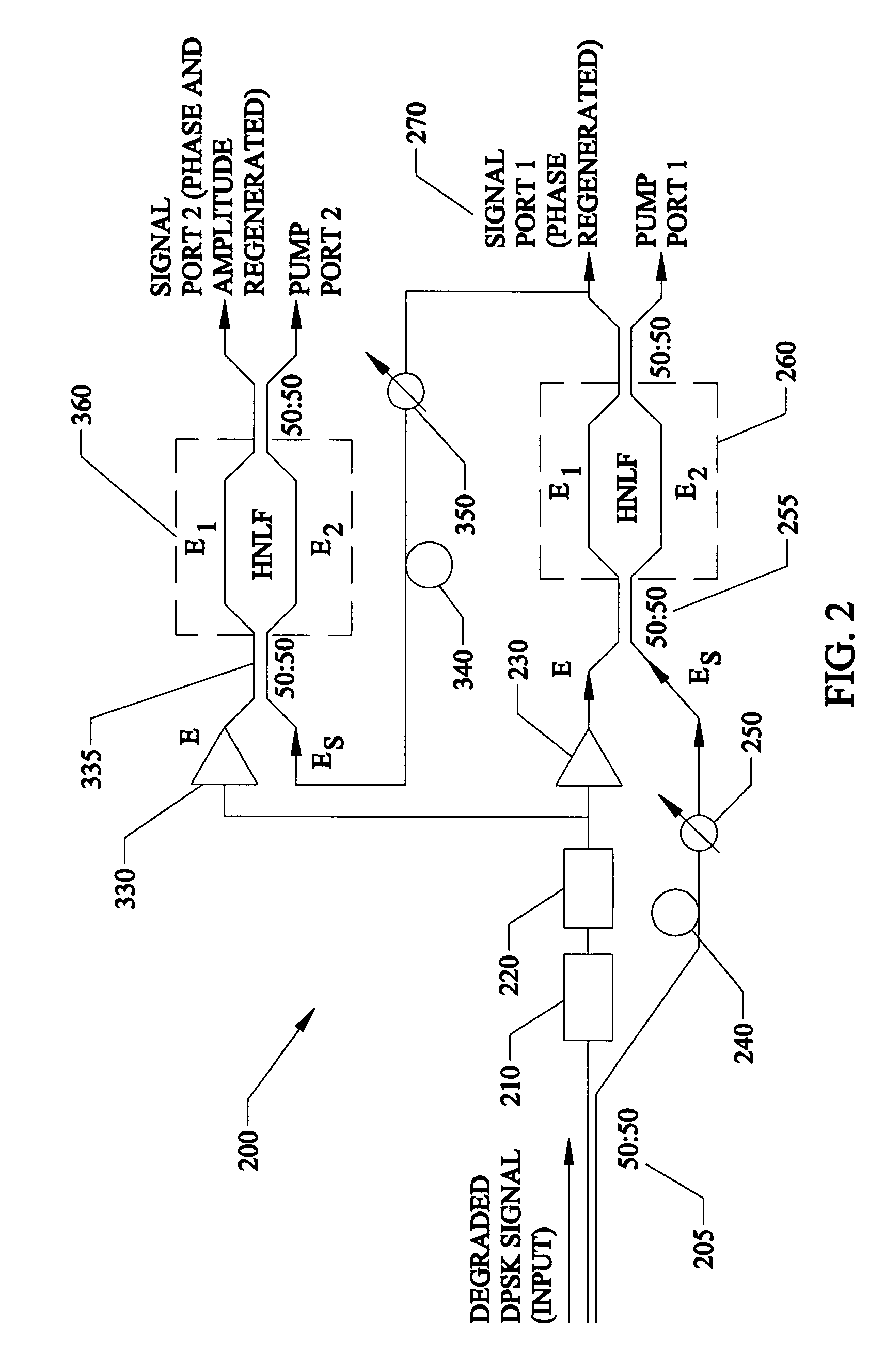
InactiveUS7369779B1Minimized amplitudeNoise minimizationLaser detailsCladded optical fibrePhase differencePhase sensitive
A regenerator for restoring the originally encoded optical phase of a differential-phase-shift-keyed signal. In an embodiment, the regenerator simultaneously provides limiting amplification and reduces amplitude noise based on a phase-sensitive optical amplifier that combines a weak signal field of a degraded input data with a strong pump field supplied by a local oscillator in a nonlinear interferometer. The two fields interact through degenerate four-wave mixing, and optical energy is transferred from the pump to the signal and vice versa. The phase sensitive nature of the optical gain leads to amplification of a specific phase component of the signal, determined by the input pump-signal phase difference and the incident signal phase is restored to two distinct states, separated by 180° according to the original encoding. Simultaneously, gain saturation of the pump wave by the signal wave results in limiting amplification of the signal wave for removing signal amplitude noise.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
System and method for resolution enhancement of a distributed sensor
ActiveUS7245790B2Reduce resolutionForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLine width
Owner:DARKPULSE TECH INC
Parametric amplification using two pump waves
InactiveUS20050146780A1Parametric amplifiersLight demodulationCommunications systemOptical parametric amplifier
An optical parametric amplifier (OPA) driven with at least two pump waves. The pump waves may be configured such that the OPA produces uniform exponential gain over a range of wavelengths that extends, for example, at least 30 nm on either side of the average pump-wave wavelength. In addition, since the Brillouin scattering limit applies to each pump wave independently, substantially twice the amount of energy may be pumped into an OPA of the present invention compared to that in the corresponding single pump-wave OPA of the prior art. An OPA of the present invention may be used in a WDM communication system and configured for simultaneous signal amplification and wavelength conversion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Reman optical fibre amplifier with dynamic gain wave control
InactiveCN1472585AReduce the change of signal optical powerAvoid Large Nonlinear EffectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNon-linear opticsLaser arrayOptoelectronics
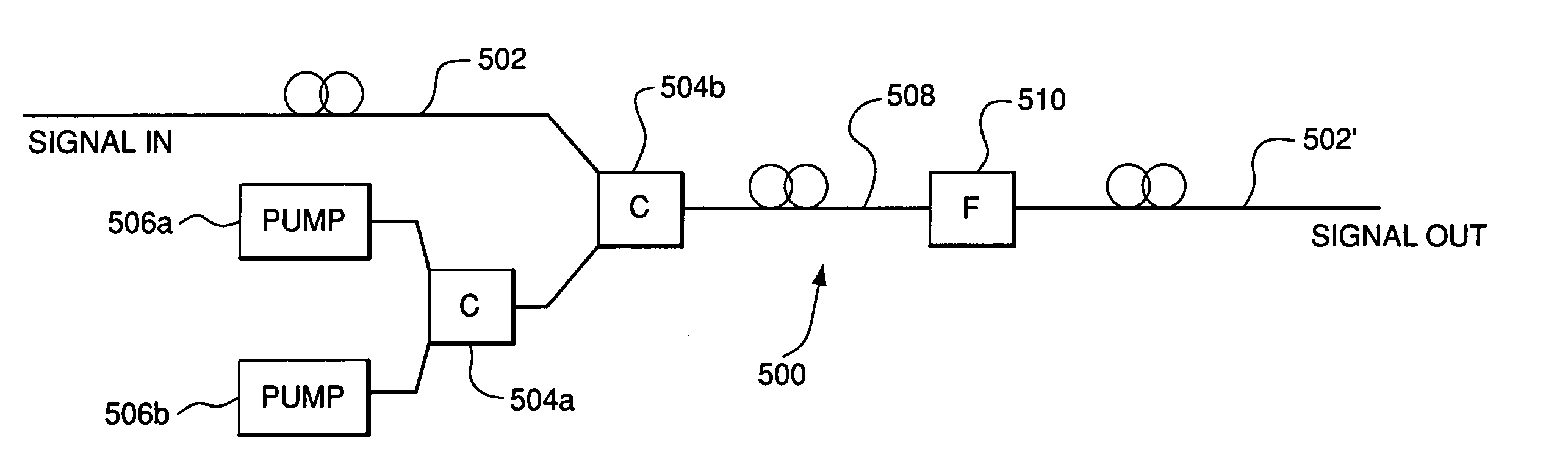
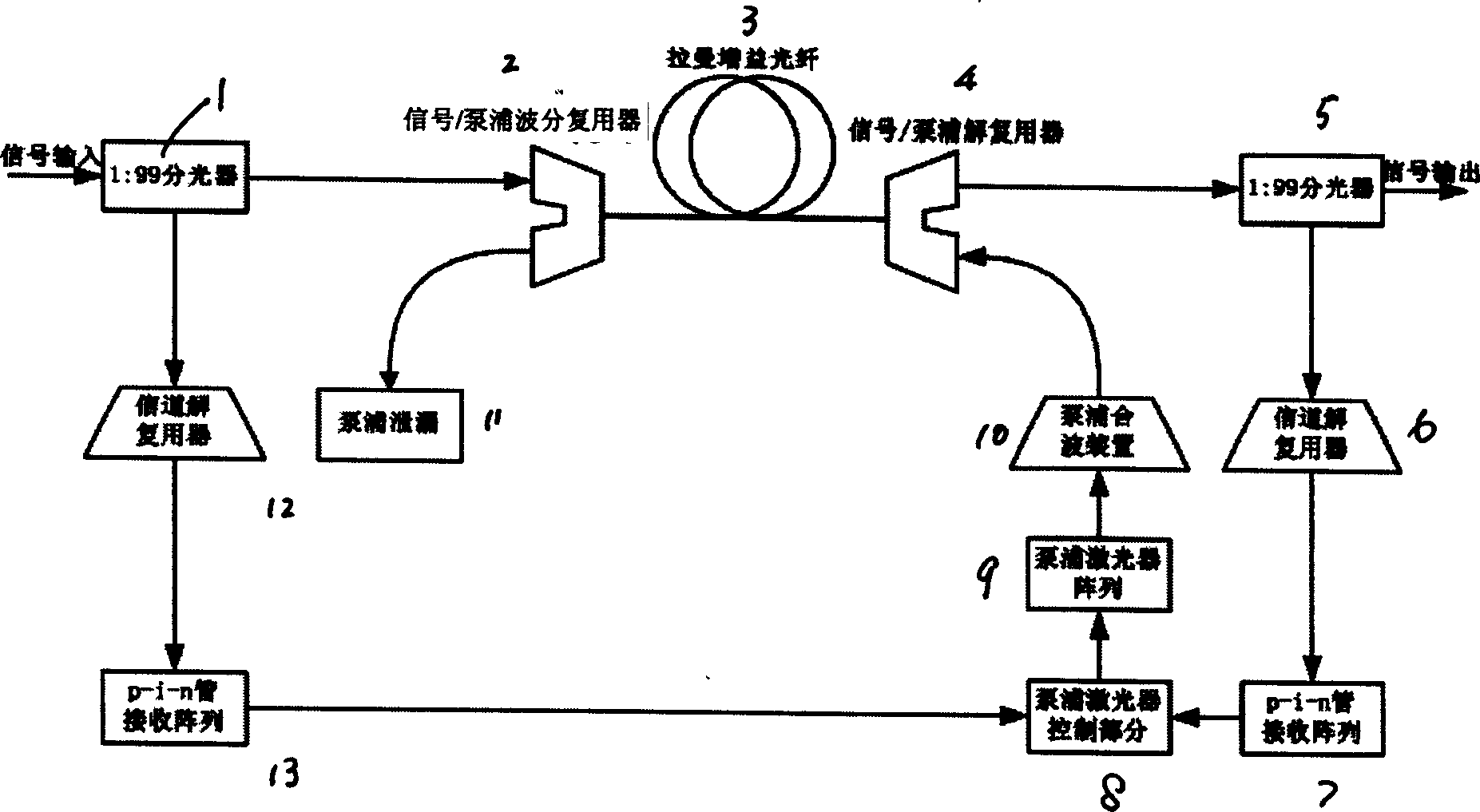
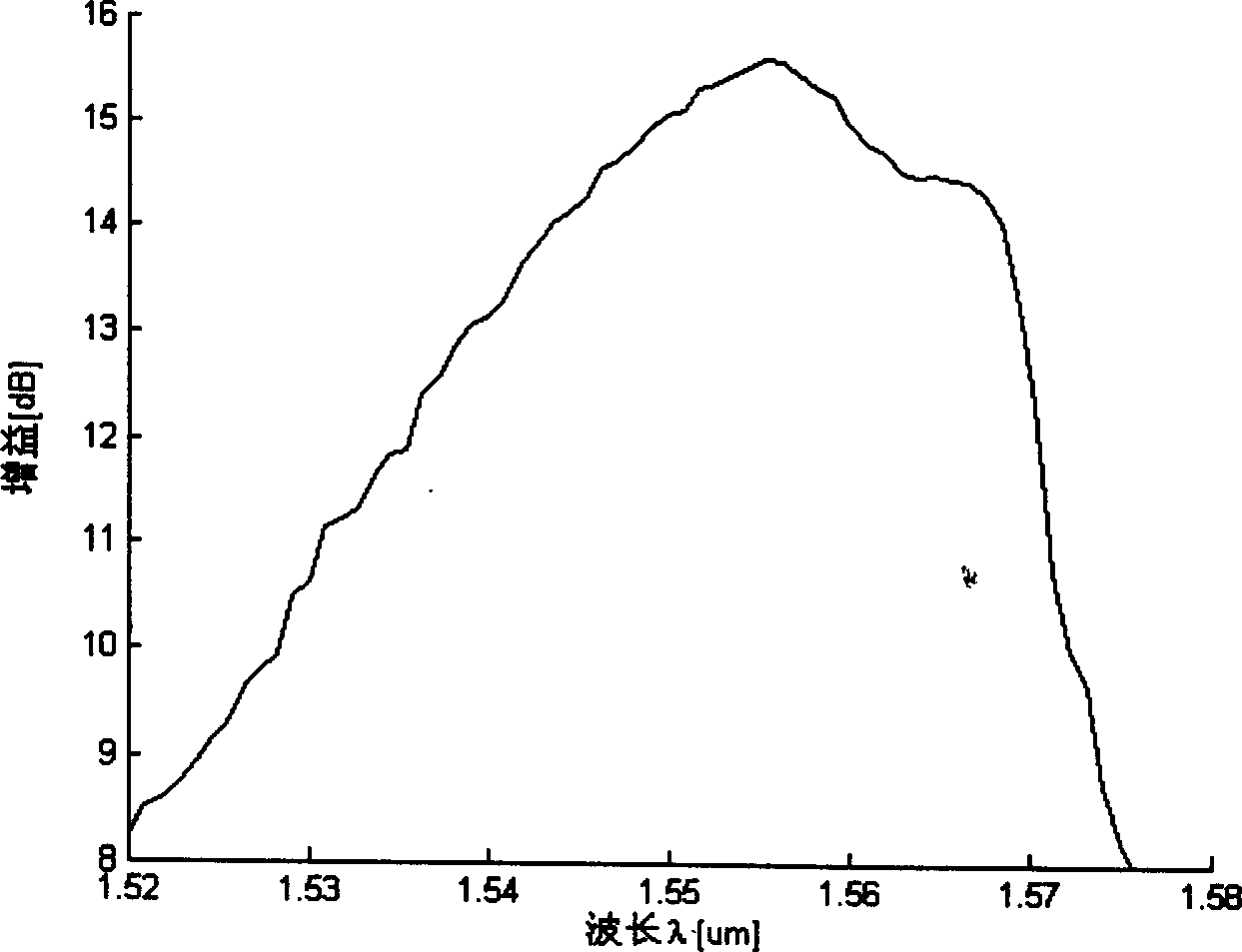
An amplifier includes two parts as Raman amplifying part consists of a set of pumping laser array, pumping wave combining device, a section of Raman gain optical fibre, signal / pumping multiplexer and demultiplexer and signal demultiplexer; gain feedback control device consists of signal input-output power measurement and pumping laser controller. As discrete Raman optical fibre amplifier, it can realize C+L waveband 1428-1604 nm dispersion compensation by applying dispersion compensating fibre as Raman gain media and realize gain spectrum smooth and fluctuation control for optical signal waveband by controlling output power of N number of pumping lasers in 14xxnm.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Electromagnetic wave oscillating devices
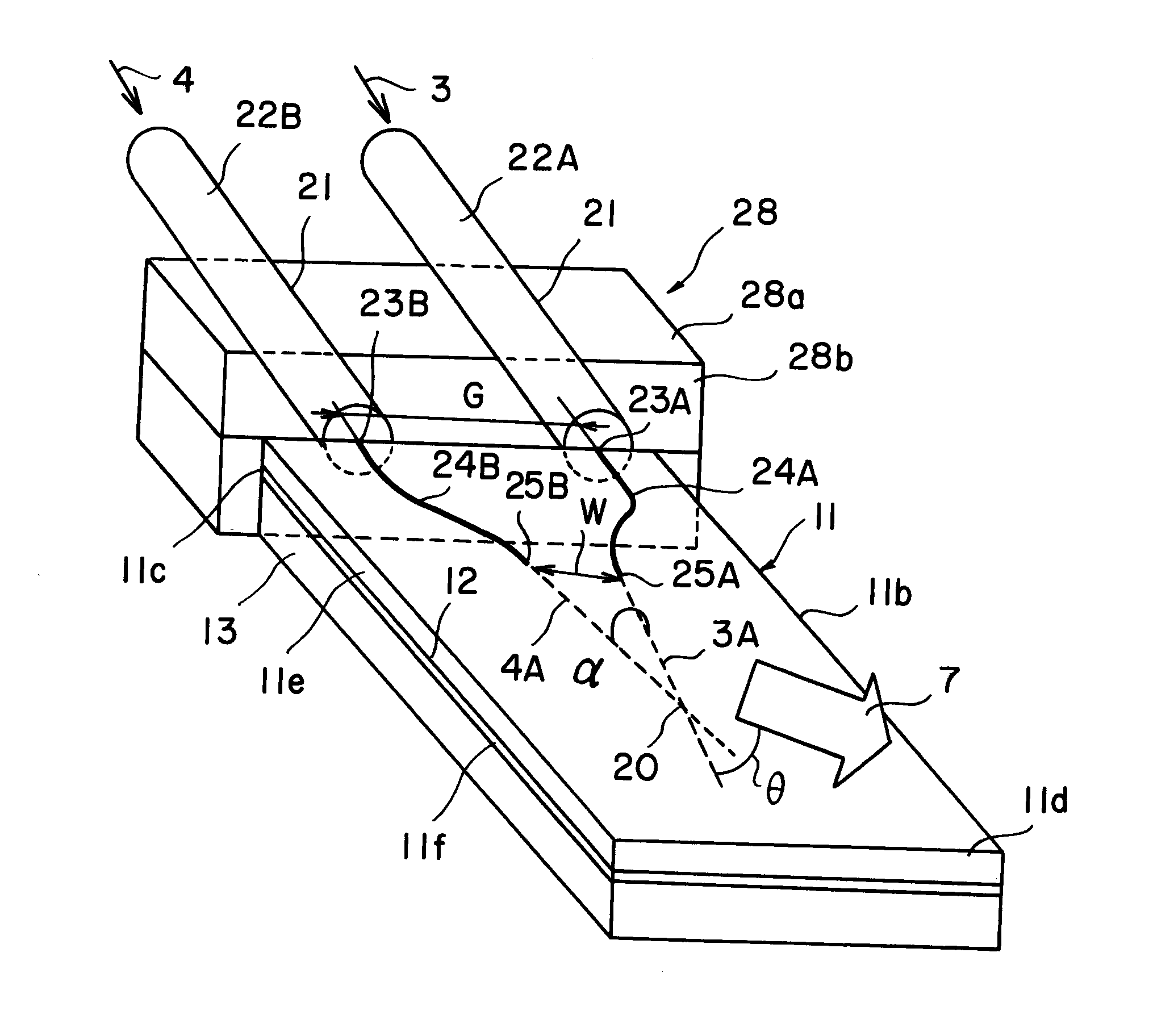
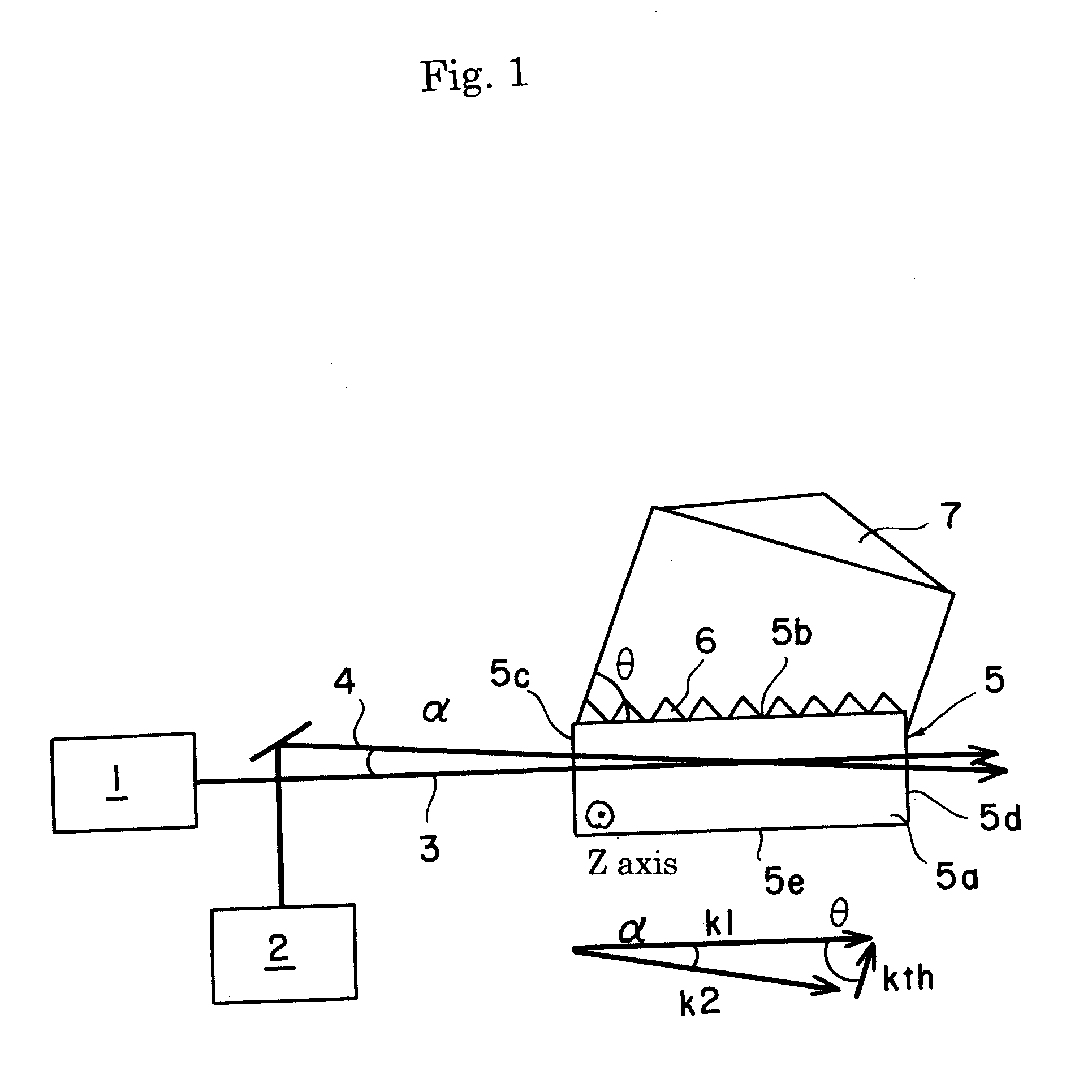
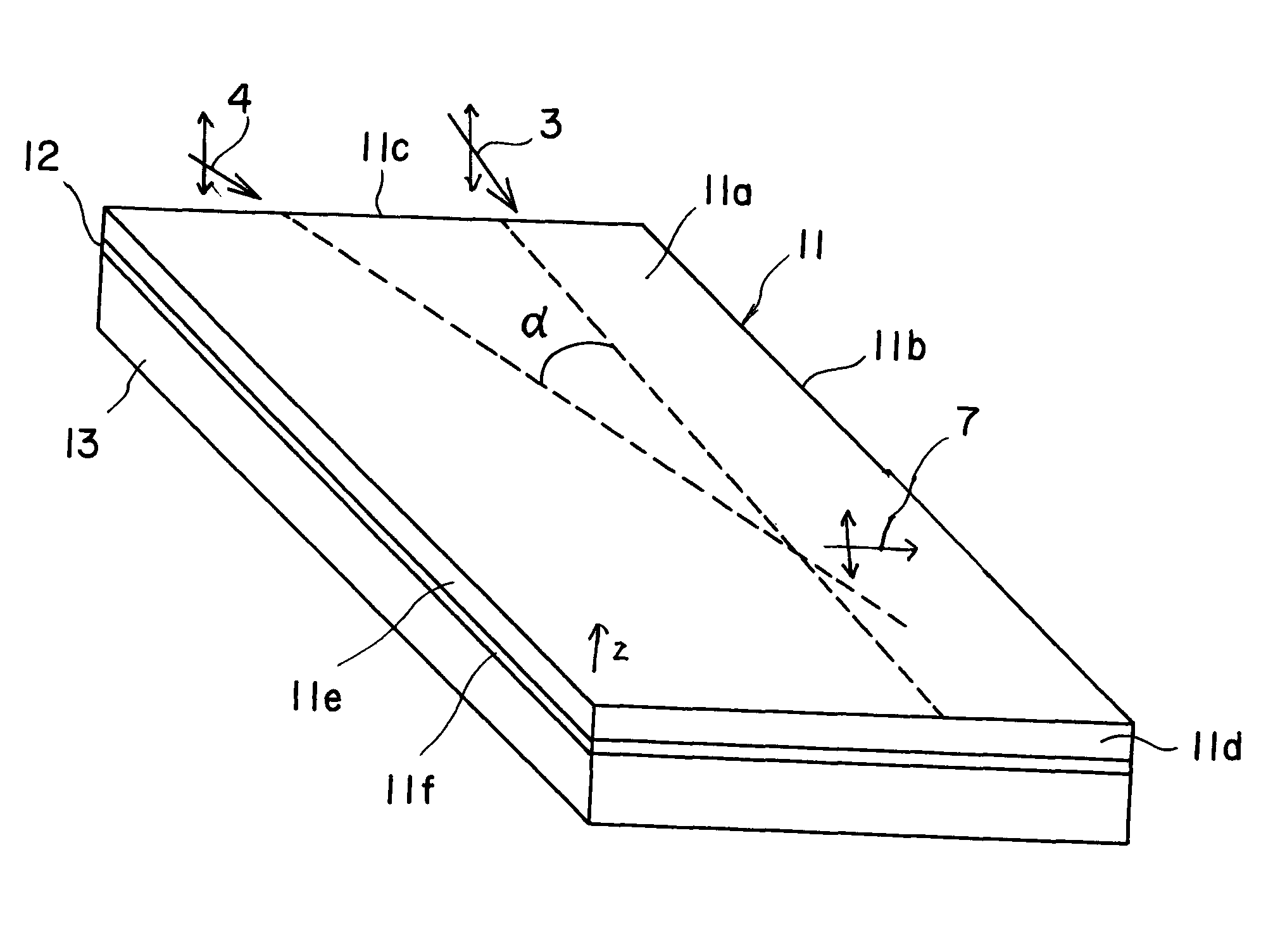
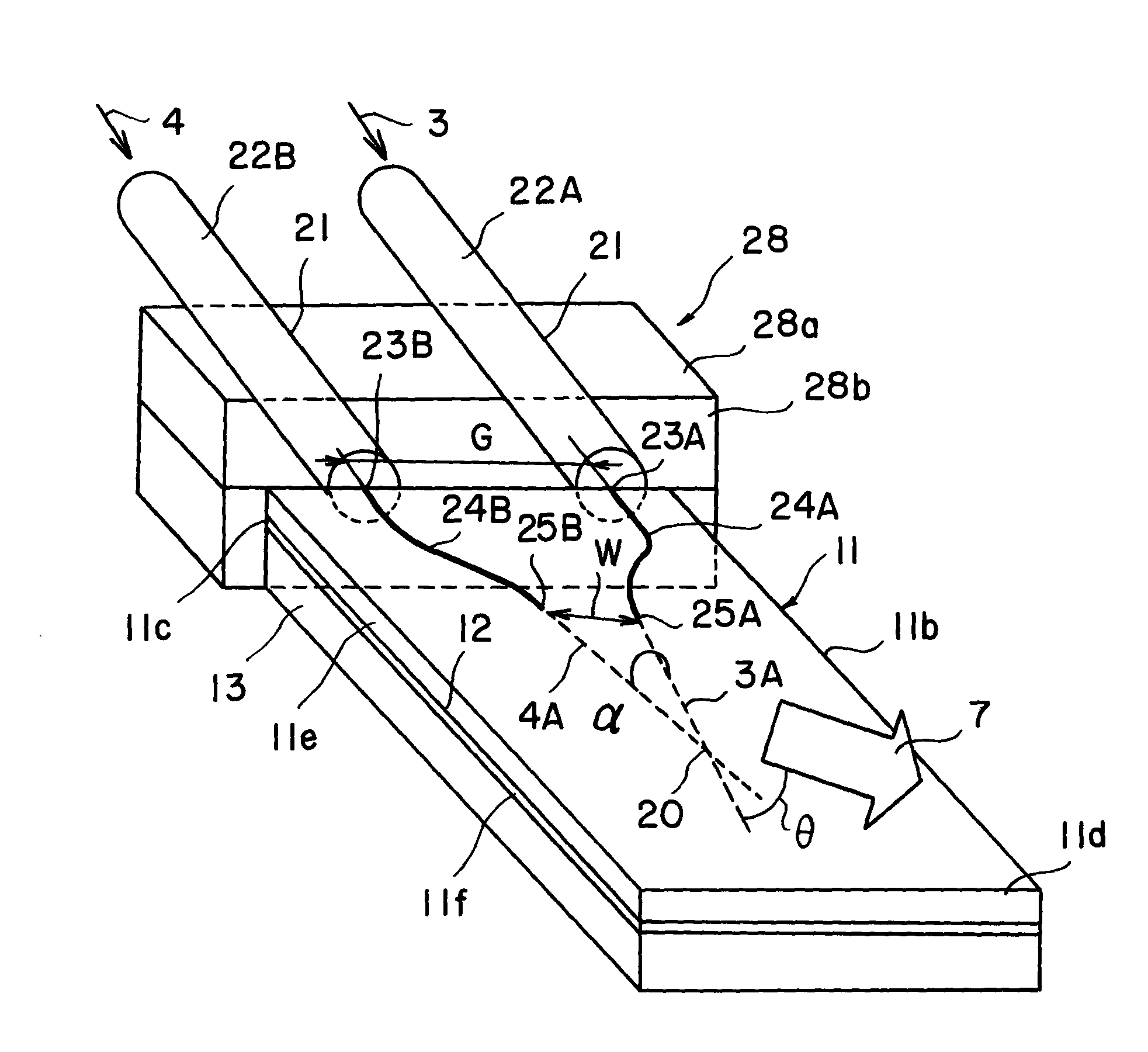
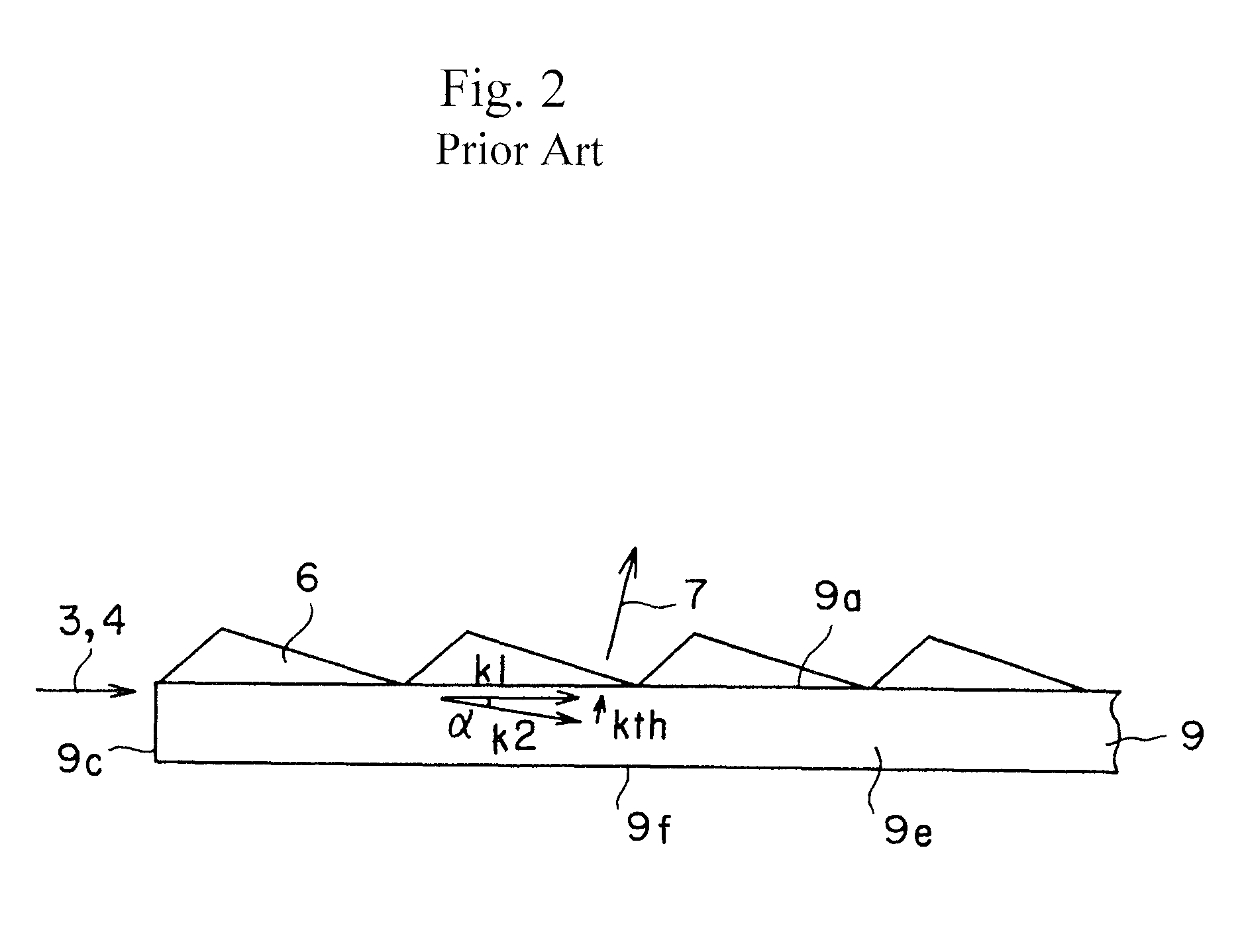
ActiveUS20110032600A1Increase output powerSufficient distanceLight demodulationNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalPump wave
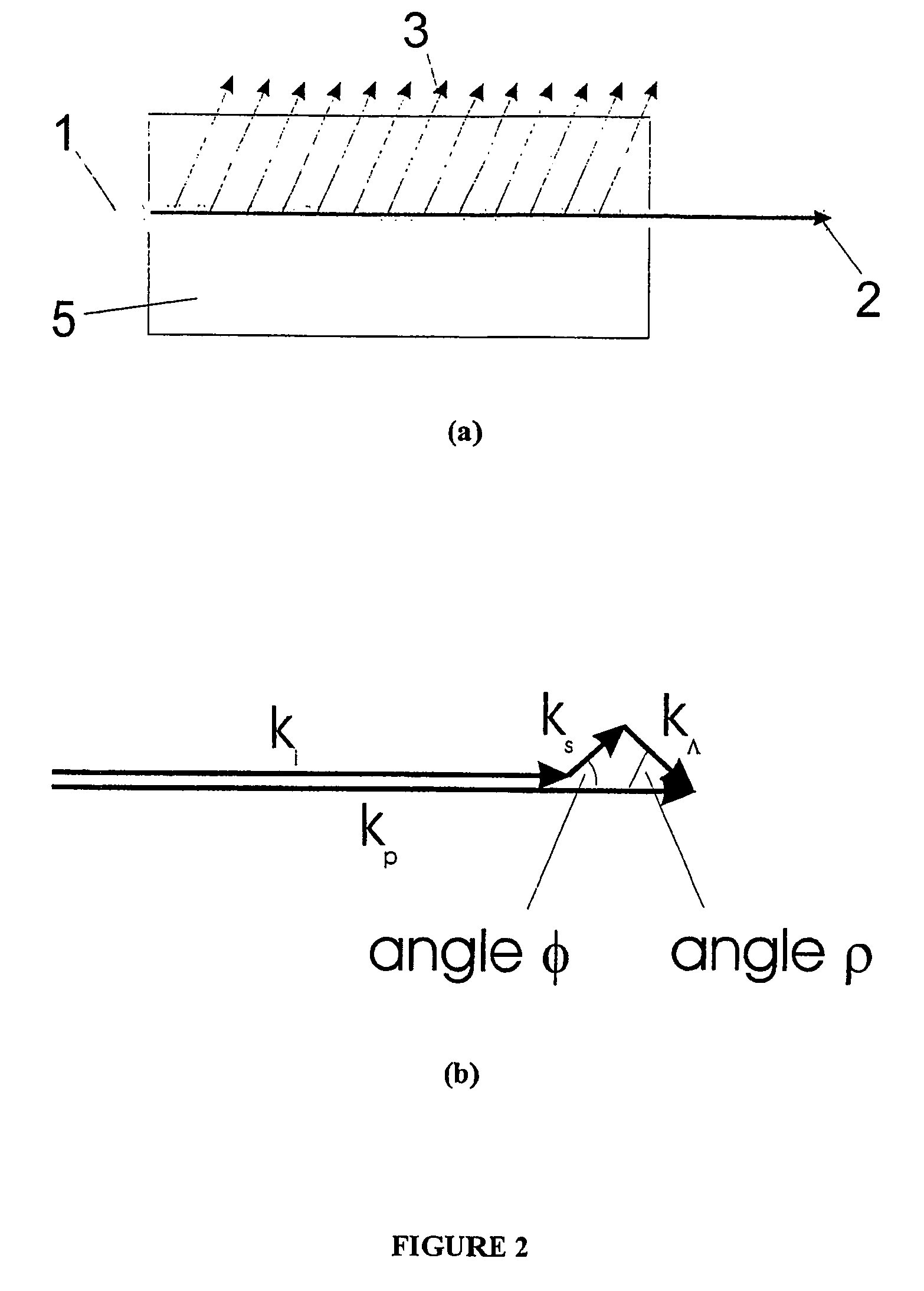
An oscillating device includes an oscillating substrate 11 of a non-linear optical crystal and having an incident face 11c where a pump wave 3 and an idler wave 4 are made incident; a first waveguide 24A provided in the oscillating substrate 11 and between the incident face 11c and an interacting part 20 of the pump wave 3 and idler waves 4; and a second waveguide 24B provided in the oscillating substrate 11 and between the incident face 11c and the interacting part 20. The first waveguide 24A guides the pump wave 3 and the second waveguide 24B guides the idler wave 4.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electromagnetic wave oscillating devices
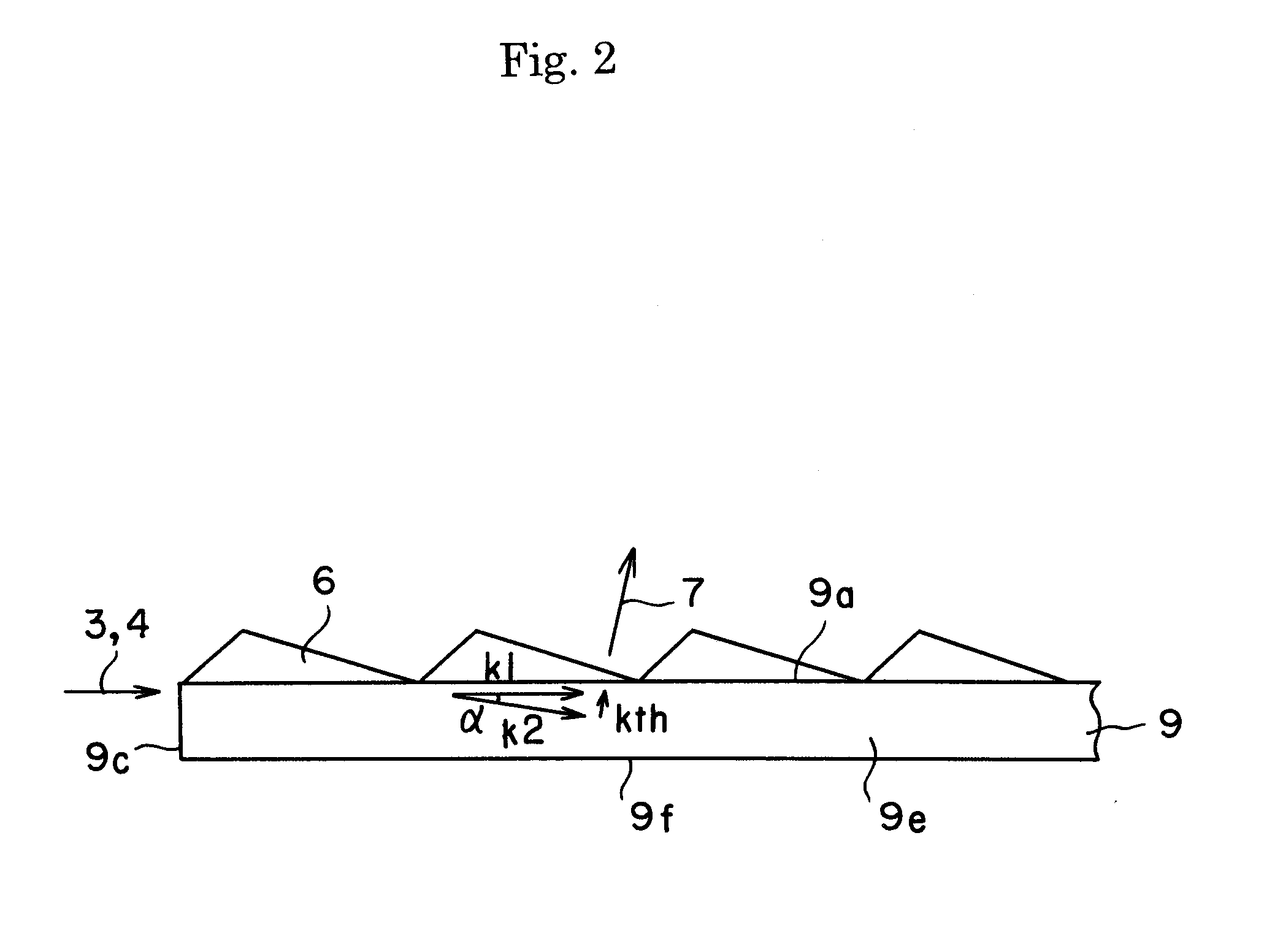
ActiveUS8305679B2Increase absorbanceEfficient emissionsLight demodulationOptical light guidesNonlinear optical crystalElectromagnetic electron wave
A device for oscillating an electromagnetic wave having a frequency of 0.1 THz to 3 THz from pump and idler waves by a parametric effect. The device includes a supporting body, an oscillating substrate made of a non-linear optical crystal, and an adhesive layer adhering the supporting body and oscillating substrate. The oscillating substrate includes an upper face, a bottom face and an incident face on which the pump wave is made incident. The oscillating substrate provides cut-off with respect to the electromagnetic wave oscillated by the parametric effect when the pump and idler waves propagate in parallel with the bottom face.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method and installation for acousto-optic imaging
InactiveUS7733742B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsSignal waveAcousto-optics
This invention concerns an acousto-optic imaging method comprising a step which consists in engraving in a dynamic holographic material a complex index array resulting from the interference of the acousto-optic component of the signal wave and a pump wave of frequency equal to the frequency of the acousto-optic component.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Cascaded raman pump for raman amplification in optical systems
InactiveUS20050259315A1Enhanced signalLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesNonlinear parametersPump wave
A pumping module having a cascaded Raman laser for Raman amplified optical transmission systems. Non-linear parametric phenomena, such as Raman-assisted three-wave mixing, in Raman amplified signals from a cascaded Raman pump are strongly reduced by substantially suppressing from the output spectrum of the Raman pump the emission peaks at wavelengths shorter than that of the desired pumping wave on a specific wavelength λn, and within a given spacing from λn. The pumping non-zero dispersion fibres have zero dispersion between the wavelength range of the transmission signal and the wavelength range of the pump signal.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Signal processor and detector
ActiveUS20160359569A1Electromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsNon-linear opticsAudio power amplifierPump wave
A system and method for processing an input signal includes a non-linear material component for receiving the signal. The non-linear material component is selected to mix the input signal with an optical pump wave to output an optical signal. The system also includes a parametric amplifier coupled to the non-linear material to obtain the optical signal and to amplify the optical signal to generate an amplified signal and an amplified idler which is a conjugate image of the amplified signal. The system also includes a frequency converter, to obtain the amplified signal and the amplified idler from the parametric amplifier and to convert the amplified signal and the amplified idler into a first output and a second output. The system also includes a first spectral sampling and processing apparatus to obtain and process the first output.
Owner:PERSPECTA LABS INC
Output adjustment method for sound energy obtained by sound wave interaction in nonlinear medium
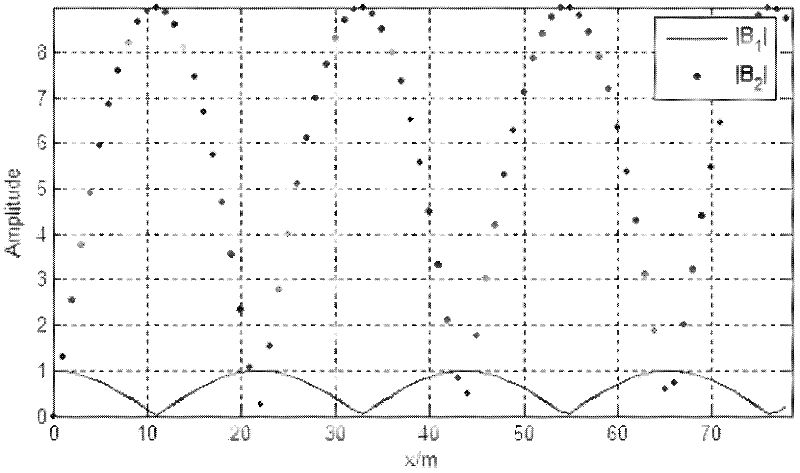
The invention provides an output adjustment method for sound energy obtained by sound wave interaction in a nonlinear medium. The output adjustment method comprises the following steps of: (a) performing nonlinear interaction on a pump wave with the frequency of w3 and a weak signal wave with the frequency of omega1, and generating a resonance wave with the frequency of omega2; (b) respectively calculating amplitude values B1(x), B2(x) and B3(x) of the three waves at the displacement x after interaction according to the frequencies omega3, omega1 and omega2 of the pump wave, the weak signal wave and the resonance wave; and (c) adjusting the output energy of the three waves according to the change characteristics of the amplitude values B1(x), B2(x) and B3(x) of the pump wave, the weak signal wave and the resonance wave. According to the output adjustment method, the energy of the generated sound wave is changed according to a pulse rule on the basis of a basic theory of interaction of sound waves in optics and hydroacoustics; therefore, the output energy of each wave can be adjusted according to actual requirements.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and system for an ultimately fast frequency-scanning brillouin optical time domain analyzer
ActiveUS20160273998A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainComputational physics
A method and a system for ultimately fast frequency-scanning Brillouin optical time domain analysis are provided herein. The method may include: simultaneously launching two pairs each having a pulsed pump wave and a counter-propagating constant wave (CW) probe wave, into an optical fiber, wherein the pulsed pumps have orthogonal States of Polarization (SOPs), and wherein the two CW probe waves have a same SOP; scanning common pump-probe frequency difference, over a frequency range that encompasses a respective Brillouin Gain Spectrum (BGS) and current and expected spectral shifts of the BGS along the optical fiber; deriving, a local Brillouin Frequency Shift (BFS), in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, which is defined as the pump-probe frequency difference which maximizes the Brillouin gain on the BGS; and determining strain and / or temperature in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, based on the respective local BFS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Parametric Generation with Lateral Beam Coupling
ActiveUS20090040597A1Improve pumping capacityGeneration process is improvedLight demodulationNon-linear opticsSignal waveAudio power amplifier
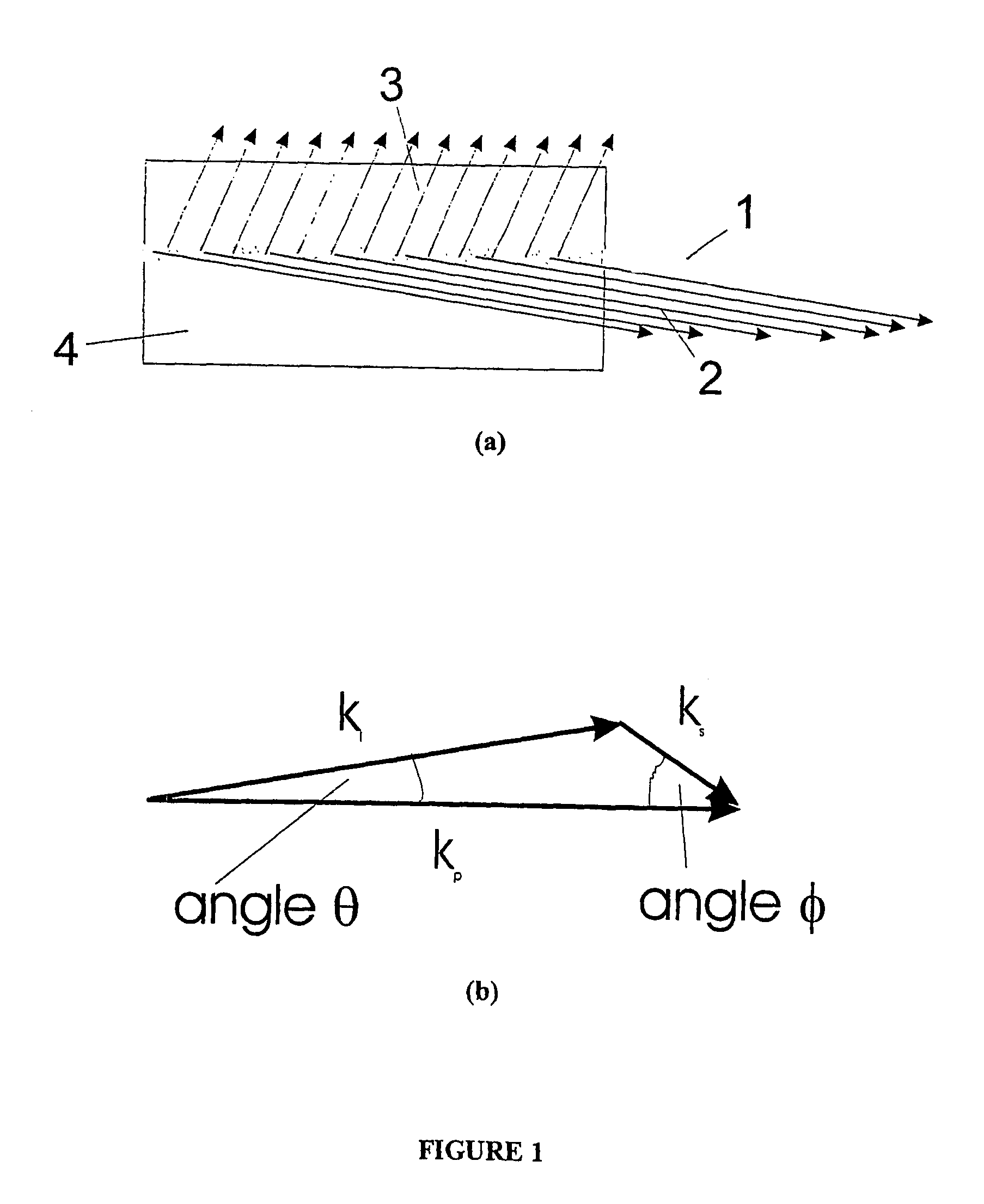
An optical parametric device, for example an optical parametric generator or amplifier or oscillator, comprising a non-linear material (13) that is operable to generate a signal and an idler wave in response to being stimulated with a pump wave. The non-linear medium is such that the pump and idler waves are substantially collinear and the signal wave is non-collinear.
Owner:M SQUARED LASERS
Parametric generation with lateral beam coupling
ActiveUS7706054B2Reduce absorptionIncrease in sizeLight demodulationNon-linear opticsSignal waveAudio power amplifier
An optical parametric device, for example an optical parametric generator or amplifier or oscillator, comprising a non-linear material (13) that is operable to generate a signal and an idler wave in response to being stimulated with a pump wave. The non-linear medium is such that the pump and idler waves are substantially collinear and the signal wave is non-collinear.
Owner:M SQUARED LASERS
Optical amplifiers, optical fiber raman amplifiers and optical systems
InactiveUS6891659B2Laser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionPump waveOptical fiber transmission
An object of the present invention is to prevent an interruption circuit of an optical amplifier from malfunctioning due to Raman pump wave. A typical mode of the present invention is characterized in that an pump wave elimination filter is inserted before an input-light detector and a reflected-light detector which constitute the optical amplifier. This permits only a signal component to be detected, enabling interruption operation, while eliminating a remaining component of Raman pump wave transmitted from for example a downstream of an optical fiber transmission line. In addition, a judgment threshold value for the interruption operation is changed according to ON / OFF condition of the pump wave. Or the Raman pump wave itself is used for detecting output's open.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical amplification structure with an integrated optical system and amplification housing integrating one such structure
InactiveUS20040076372A1Avoid reflectionsIntroduce noiseCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionMultiplexingMicrowave
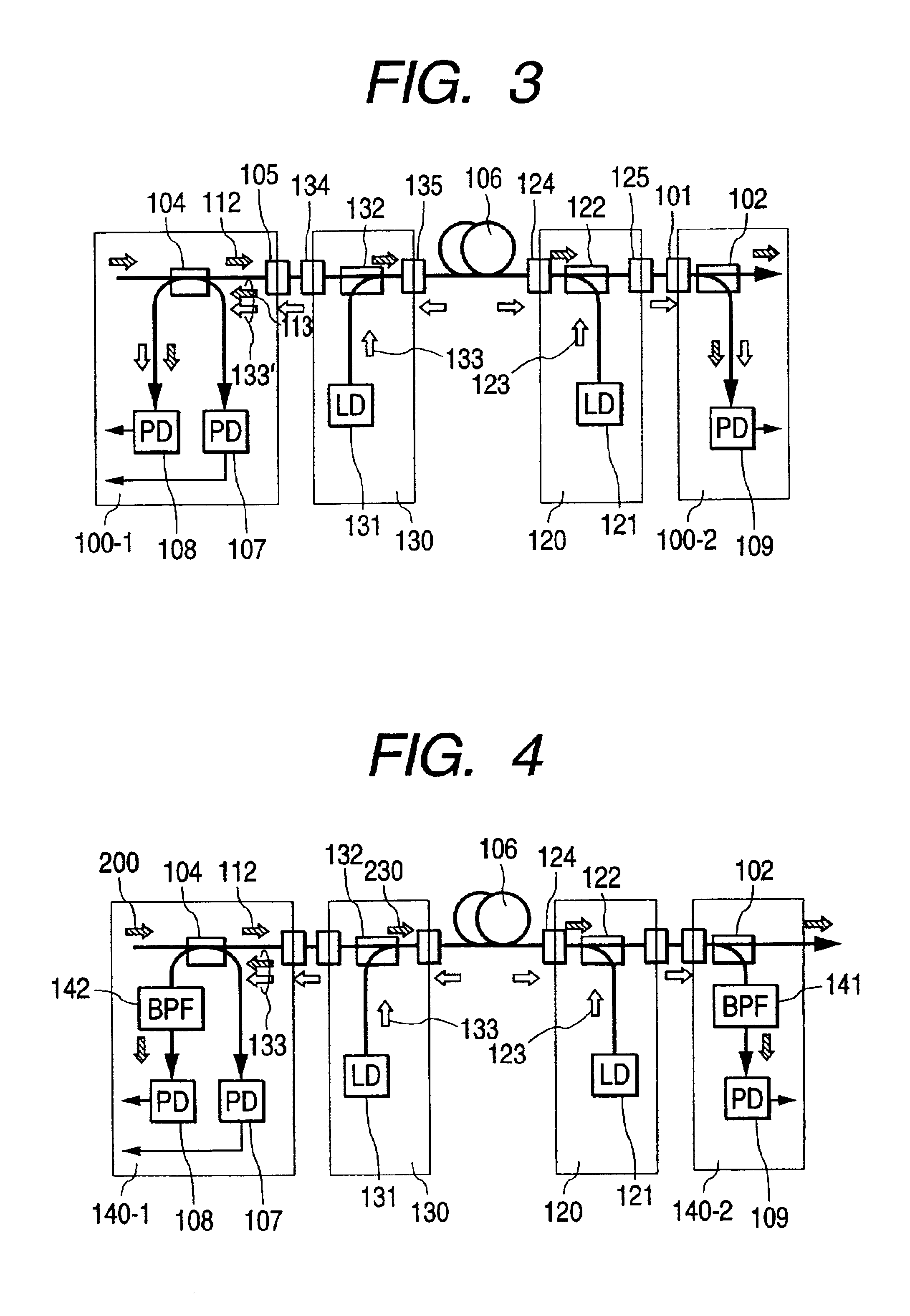
The invention relates to an optical amplifying structure capable of amplifying at least one light wave S, comprising in a substrate, for each wave to be amplified, an amplifying assembly composed of: a first micro-waveguide (7) capable of receiving the light wave S to be amplified, a second micro-waveguide (9) capable of receiving a pumping wave L, a multiplexing device (11) associated with the first and second micro-waveguides, and capable of providing a coupled light wave composed of the wave S and the wave L, an amplifying device (13) connected to an output of the multiplexing device and capable of amplifying the light wave S by at least partial absorption of the pumping wave L, the amplifying device being capable of providing at one output the amplified light wave S. a third micro-waveguide (15) connected to the output of the amplifying device and capable of carrying the amplified light wave S, and a demultiplexing device (19) associated with the third micro-waveguide and capable of demultiplexing the pumping wave L from the amplified wave S, and of providing on a fourth micro-waveguide (17) an amplified light wave S, purged of the pumping wave. The structure of the invention is applied to all fields necessitating an amplification of a light wave and in particular in the field of optical telecommunications by optical fibres.
Owner:TEEM PHOTONICS
Automatic raman gain control
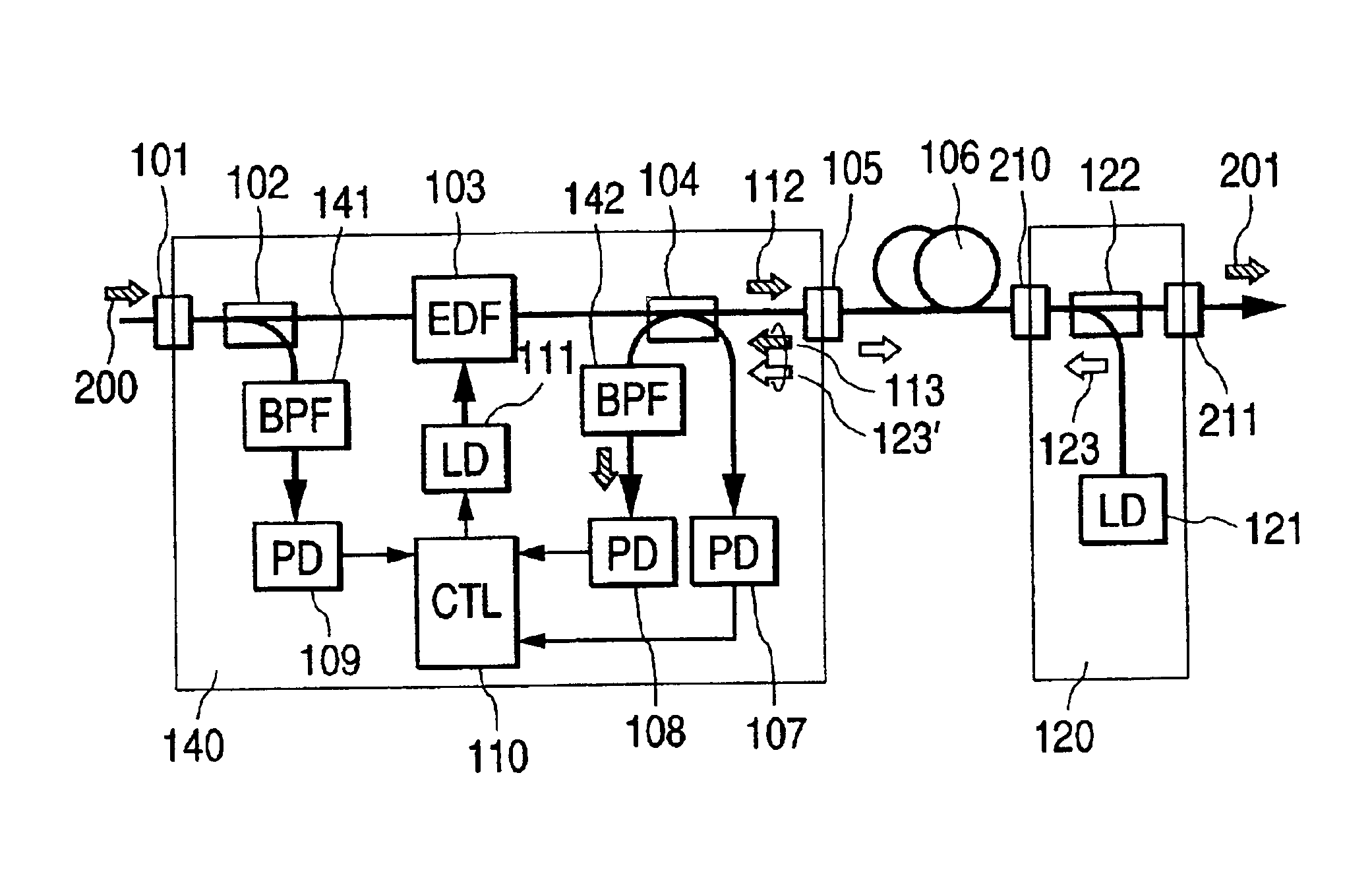
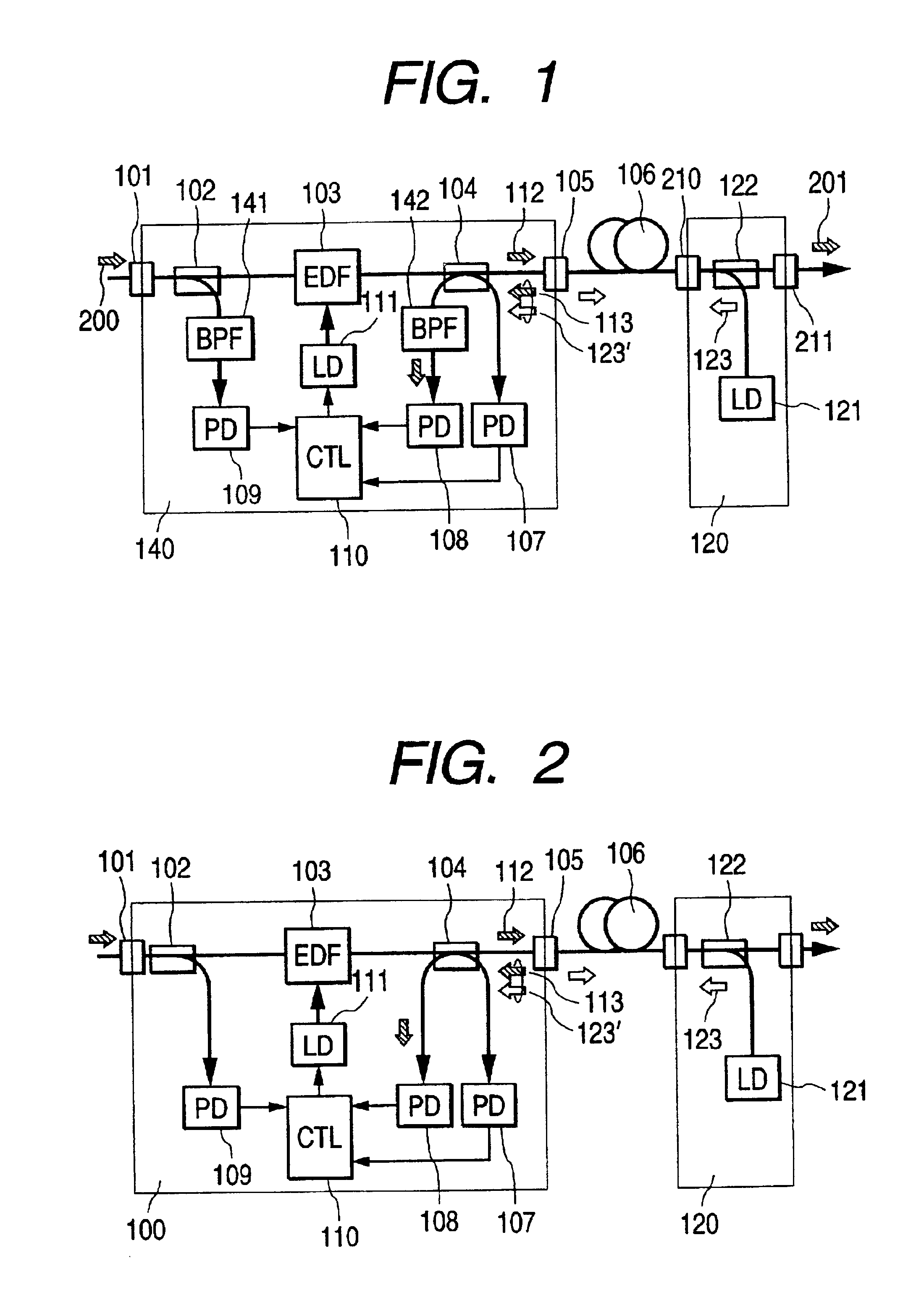
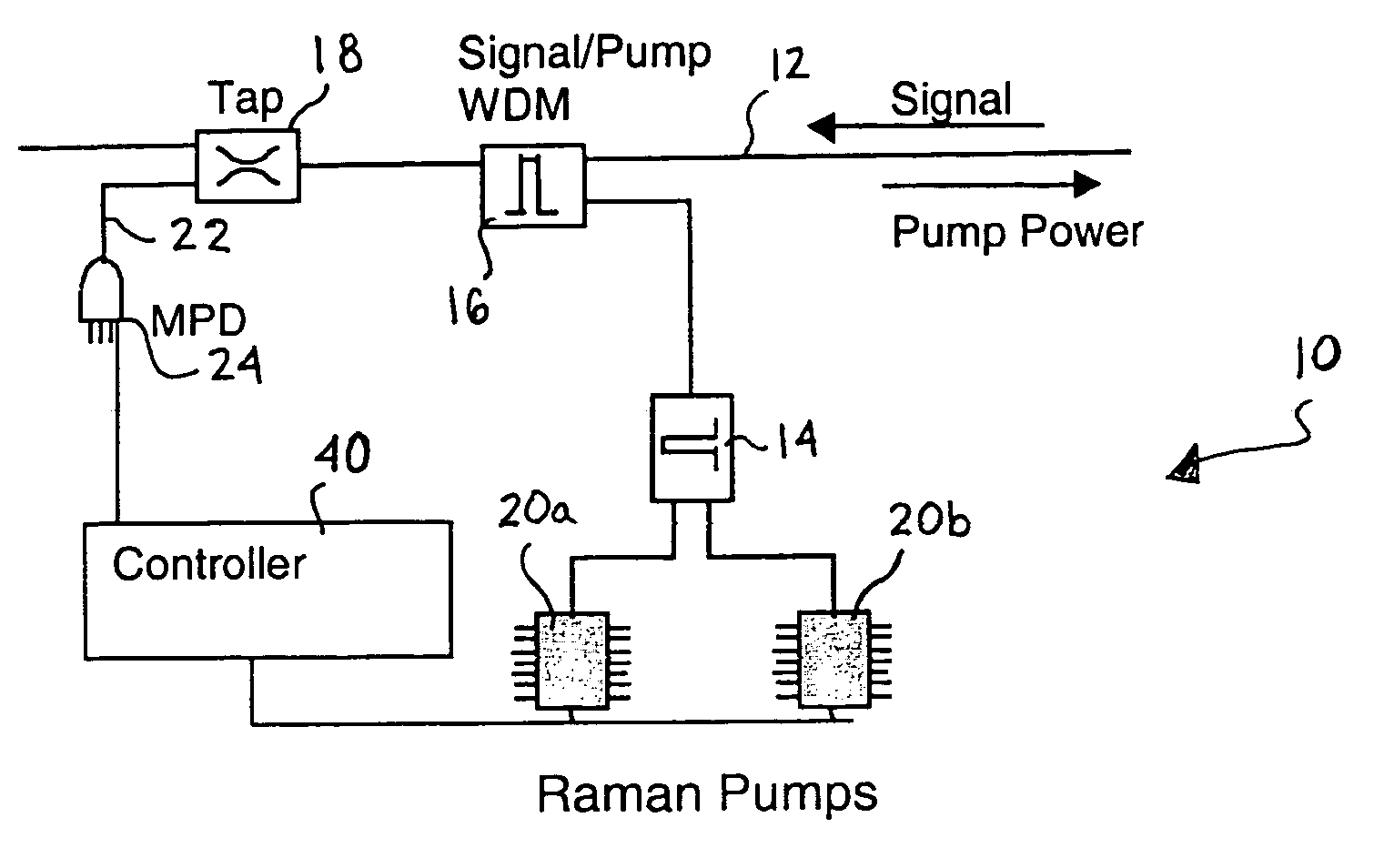
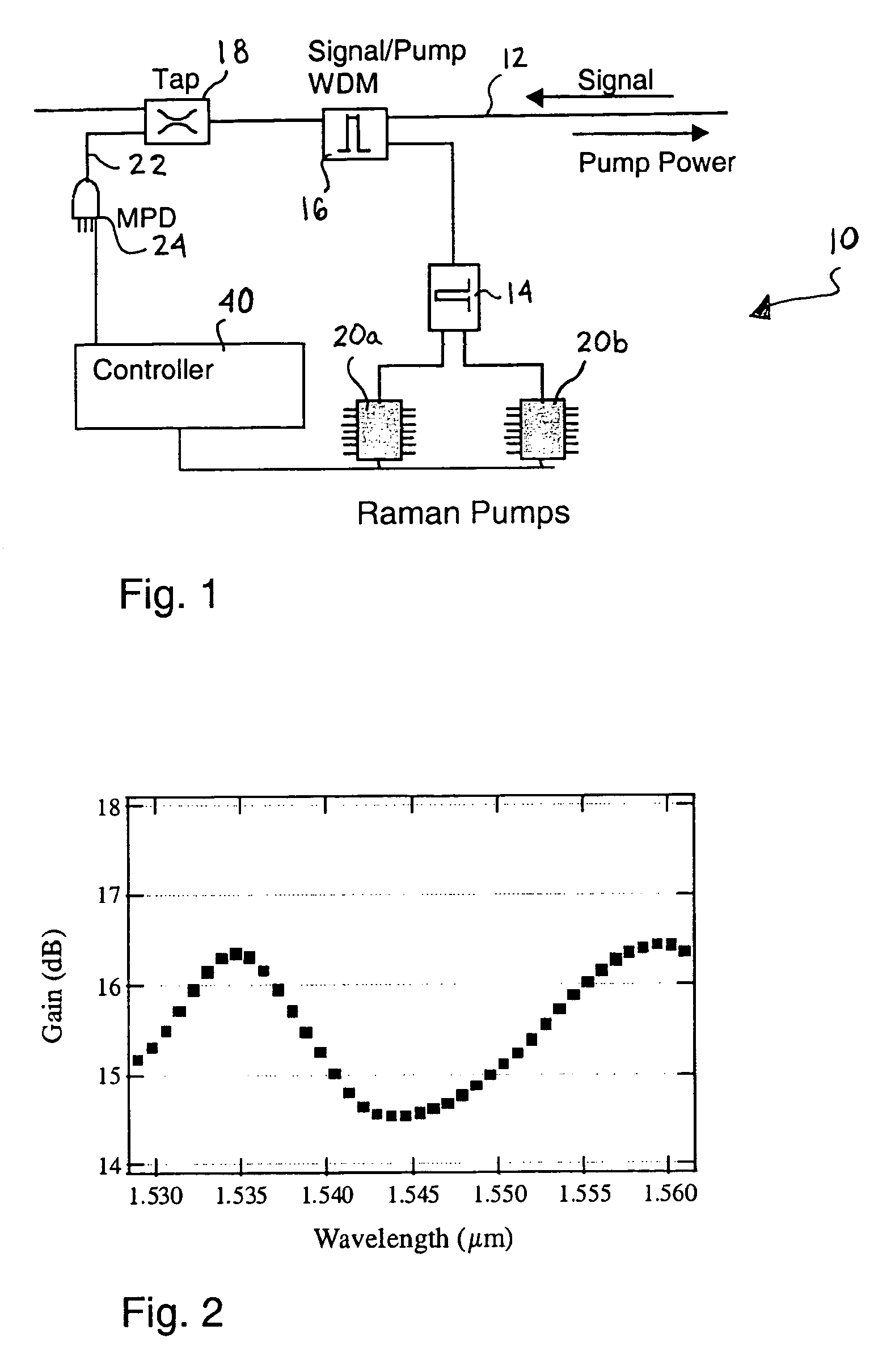
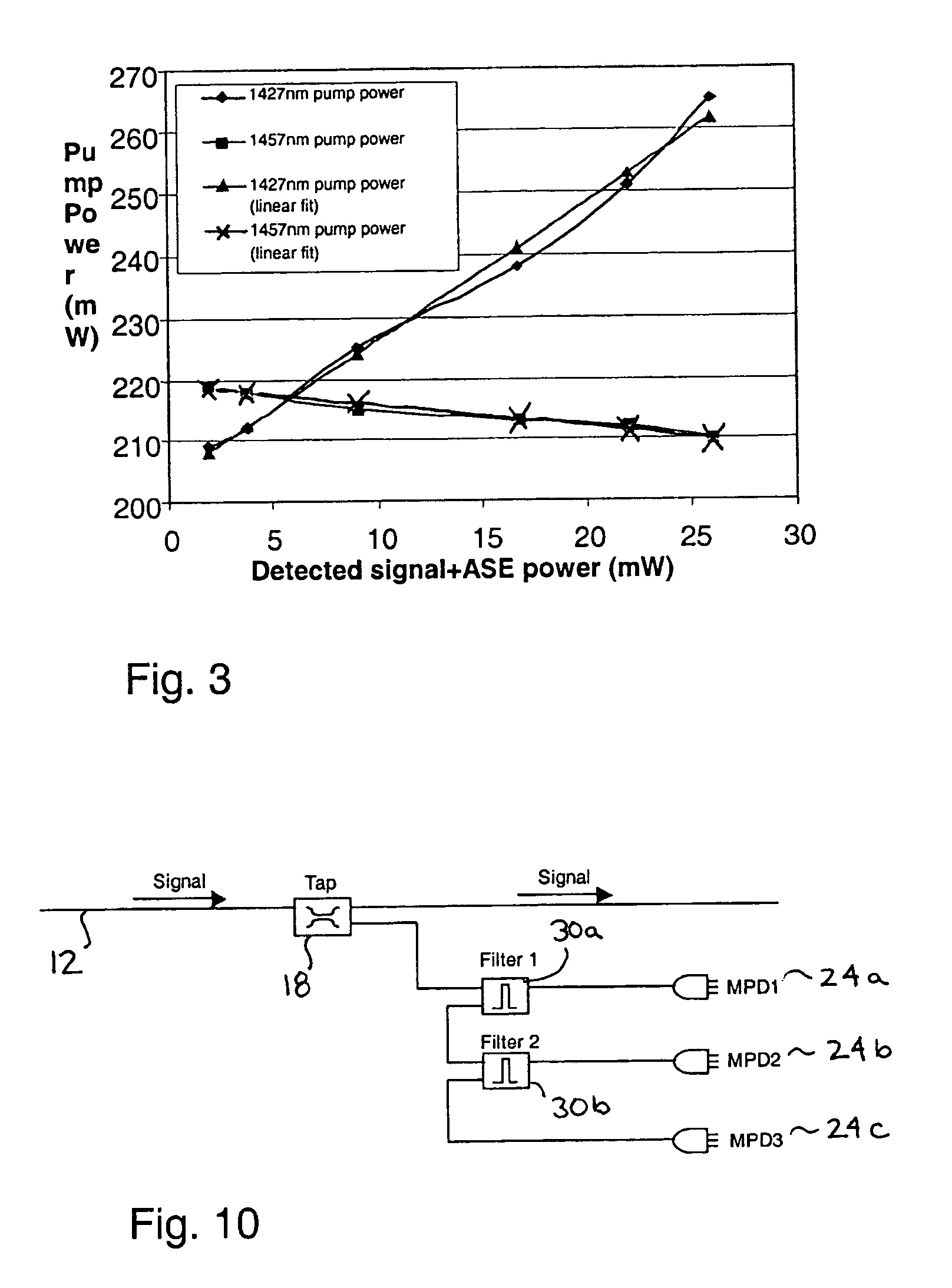
ActiveUS6963681B2Laser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierRaman amplifiers
The invention relates to a method for automatic dynamic gain control in optical Raman amplifiers and an optical Raman amplifier adapted for the same. The present invention has found that in multiple pump Raman amplifiers a substantially linear relationship exists between total amplified signal power and pump power for each of different wavelength pumps, in order to maintain an original gain profile and gain levels for an optical link with a fully loaded channel configuration, in response to dropped channels. In accordance with the method, and an amplifier programmed to practice the method, a set of pump power values and signal level values required to maintain the characterized gain profile and gain levels for a plurality of channel loading configurations are pre-established for the each pump wavelength. A linear function from each set of pre-established values is derived for each pump wavelength. Advantageously, a single photodiode can replace a costly and complex channel monitor for providing signal responsive pump control.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Laser device triggered by a photonic fiber
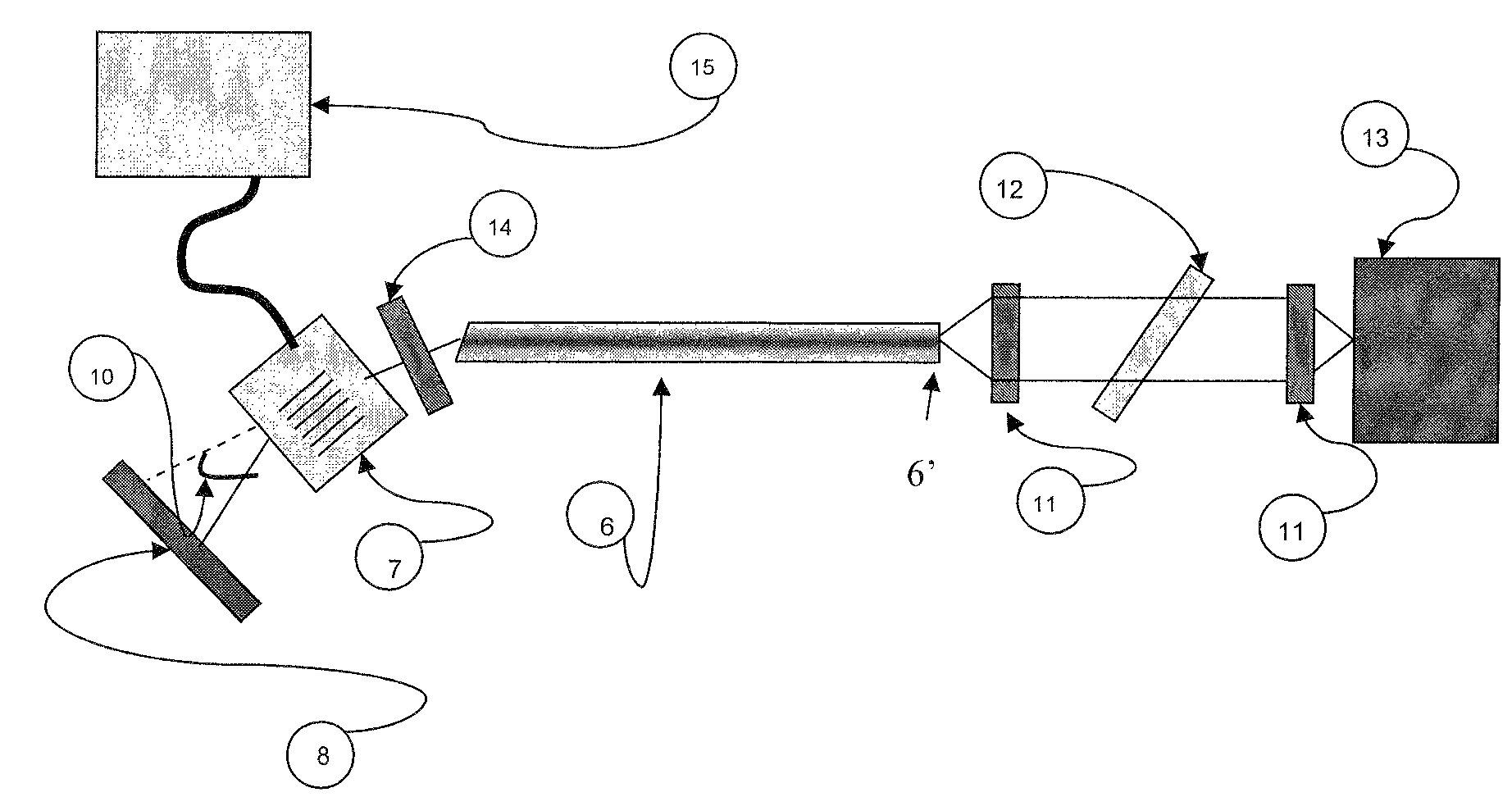
InactiveUS7558298B2High gainShort pulse durationLaser using scattering effectsLaser constructional detailsFiberOptical axis
A device producing laser pulses of durations smaller than 30 ns, and including along its internal optical axis: a laser resonator of optical length smaller than 2 m including two reflecting ends and incorporating an MPF photonic fiber pumped continuously by at least one pump wave with laser diodes, the laser medium being a medium where the laser wave is guided and has a gain with very weak signal greater than 10 per passage, the resonator also incorporating an optical modulator. The optical modulator may deflect the internal laser axis via an electric control along two stable directions, the first direction corresponding to an axis along which the internal laser beam undergoes sufficient losses to prevent the laser effect, the second direction corresponding to an axis along which the laser beam is reflected towards itself at least partially by an optical return element.
Owner:EOLITE SYST
Hybrid multiplexing passive optical communication method and hybrid multiplexing passive optical communication network
InactiveCN101635869AGuaranteed "colorless"Guaranteed Passive CharacteristicsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhotonic crystalMultiplexer
The invention relates to a hybrid multiplexing passive optical network and a communication method thereof, which are characterized in that a pumping wave which can be used for four-wave mixing frequency is injected into an optical communication line; after carrying out wavelength division multiplexing (FWM), the pumping wave and a user terminal uplink optical signal are injected into a high non-linear optical fiber or a high non-linear photonic crystal optical fiber; the high non-linear optical fiber or the high non-linear photonic crystal optical fiber realizes the FWM between the pumping wave and the user terminal uplink optical signal and generates a wavelength conversion optical signal; and after passing through a wavelength division multiplexer, the wavelength conversion optical signal is transmitted to an optical line terminal, thereby realizing optical signal uplink communication and supporting the transmission of a plurality of time division multiplexing optical networks in a single optical fiber. The hybrid multiplexing passive optical communication network utilizes the FWM effect in the high non-linear optical fiber and the high non-linear photonic crystal optical fiber, has favorable compatibility with original ONU equipment and the passive characteristics of ODN, can realize the upgrading of the network without changing the ONU equipment and greatly reduce the reforming cost of the network.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parametrical generation laser
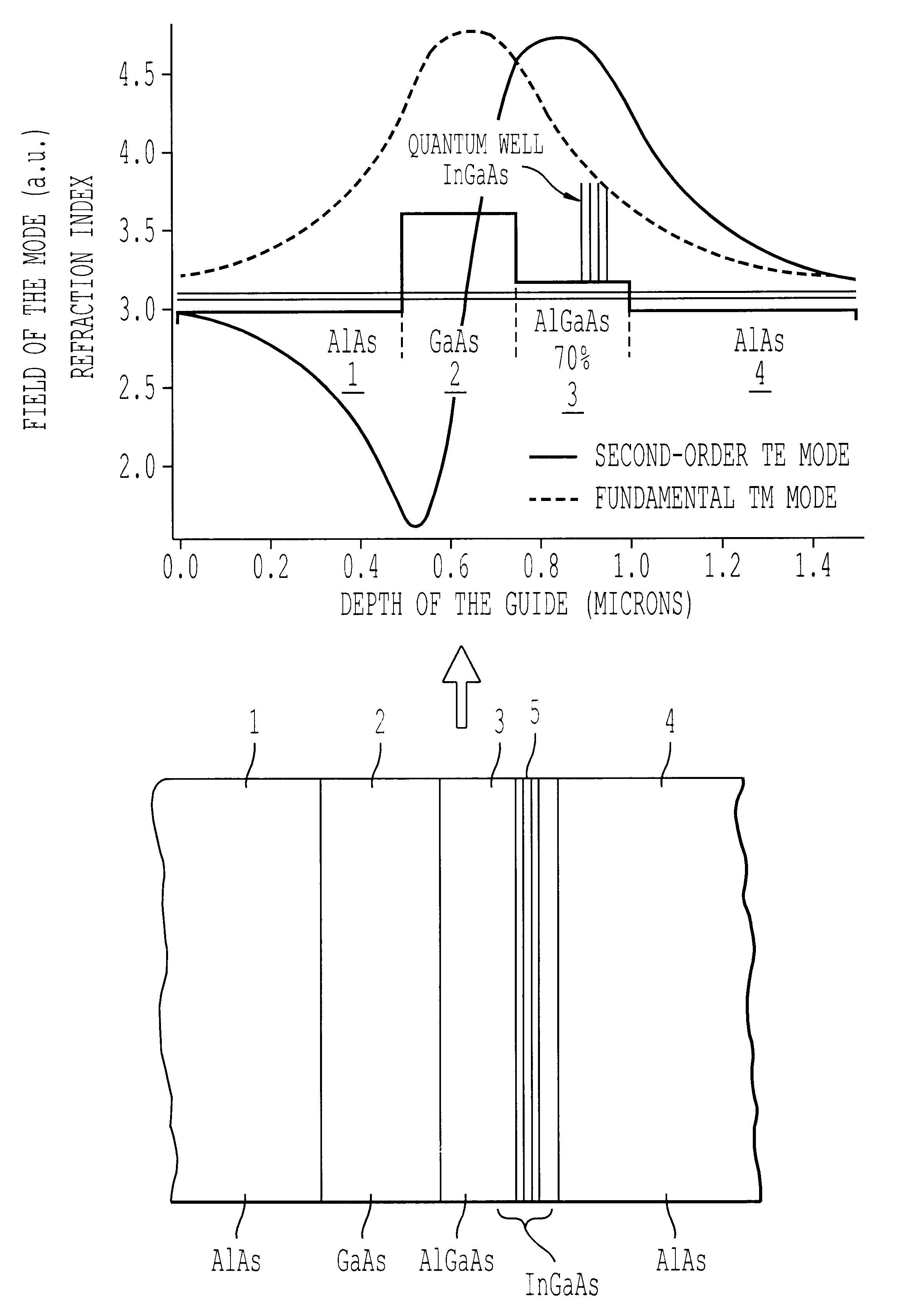
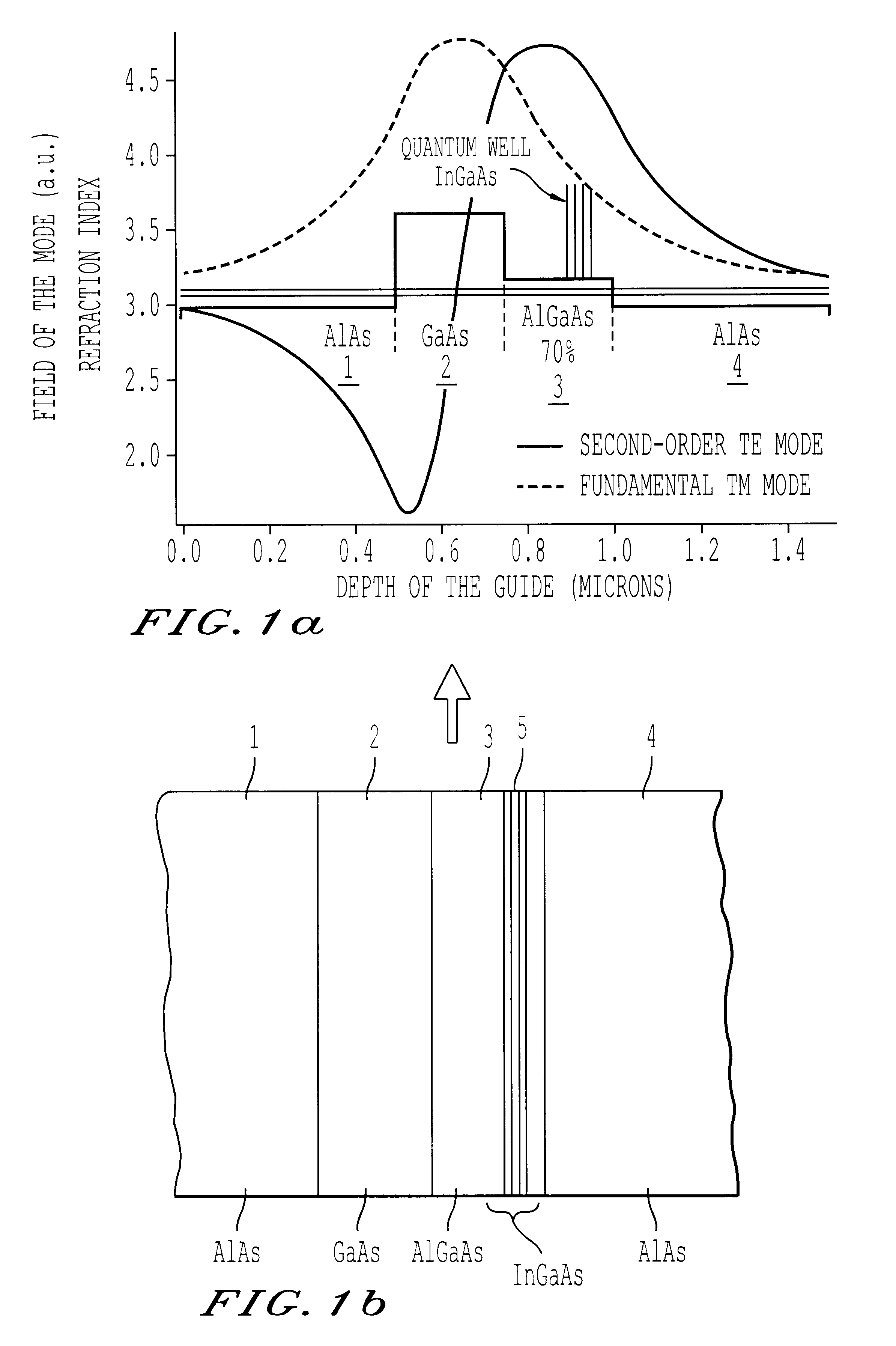
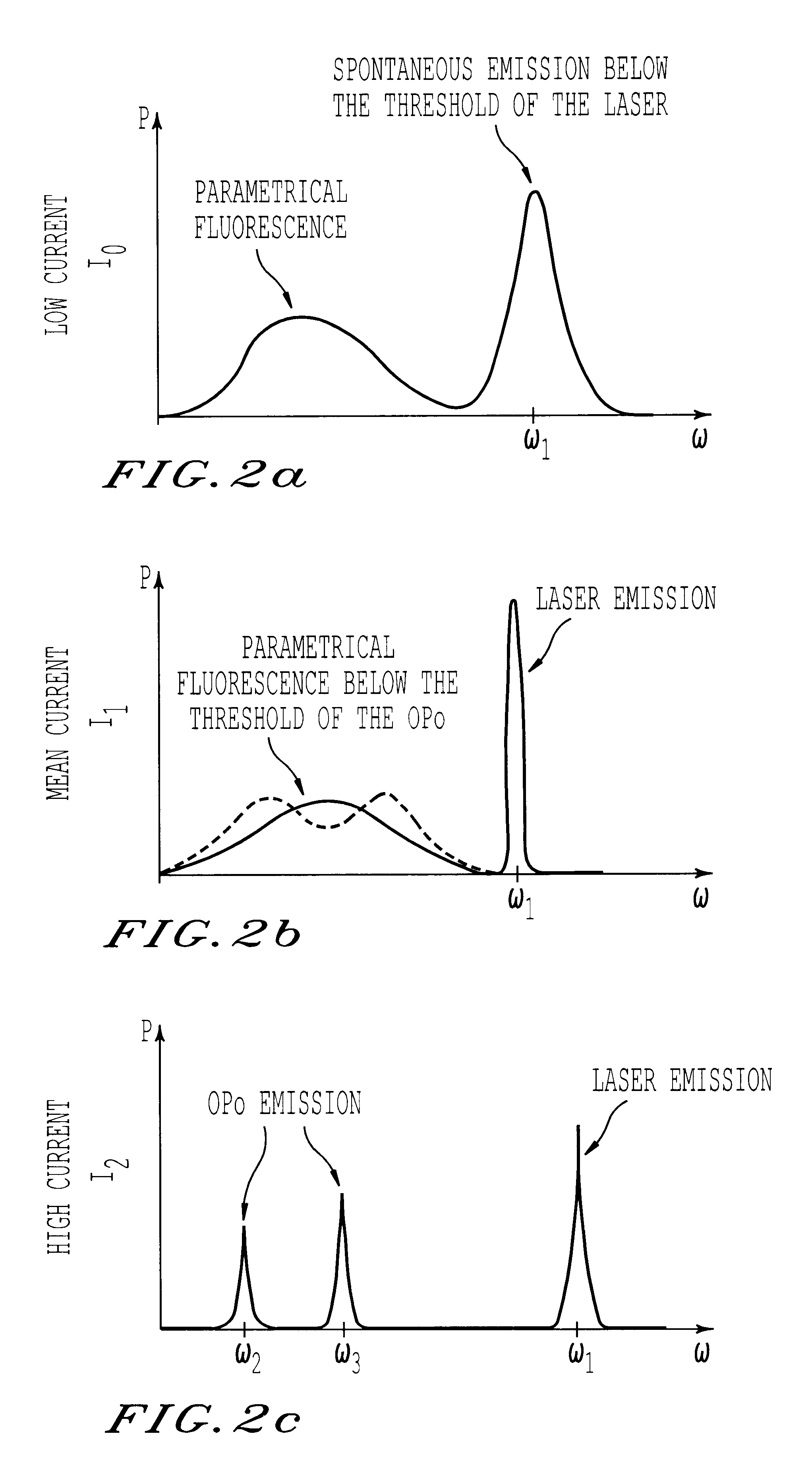
InactiveUS6631151B1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusQuantum wellFluorescence
This semiconductor laser comprises at least two layers of optically non-linear material as well as a quantum well at least located within one of the layers of optically non-linear material. The thicknesses and optical indices of these two layers are such that the waveguide constituted by these two layers has a modal phase matching condition for the process of parametrical fluorescence between the pump wave emitted by the quantum well and the parametrical conversion waves.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Free-space optical communication links with improved sensitivity
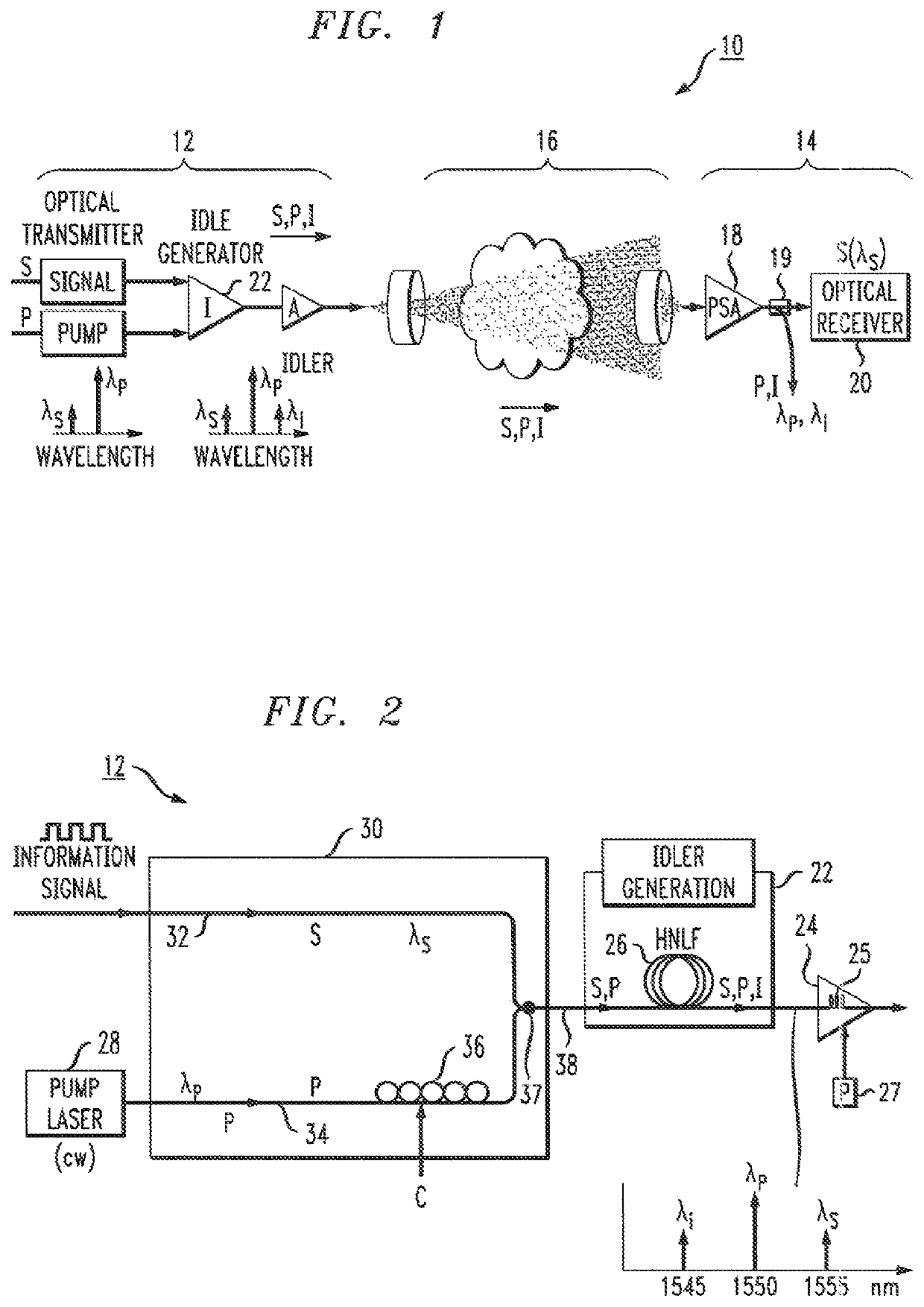
ActiveUS10536218B2Material analysis by optical meansLine-of-sight transmissionTelecommunications linkOriginal data
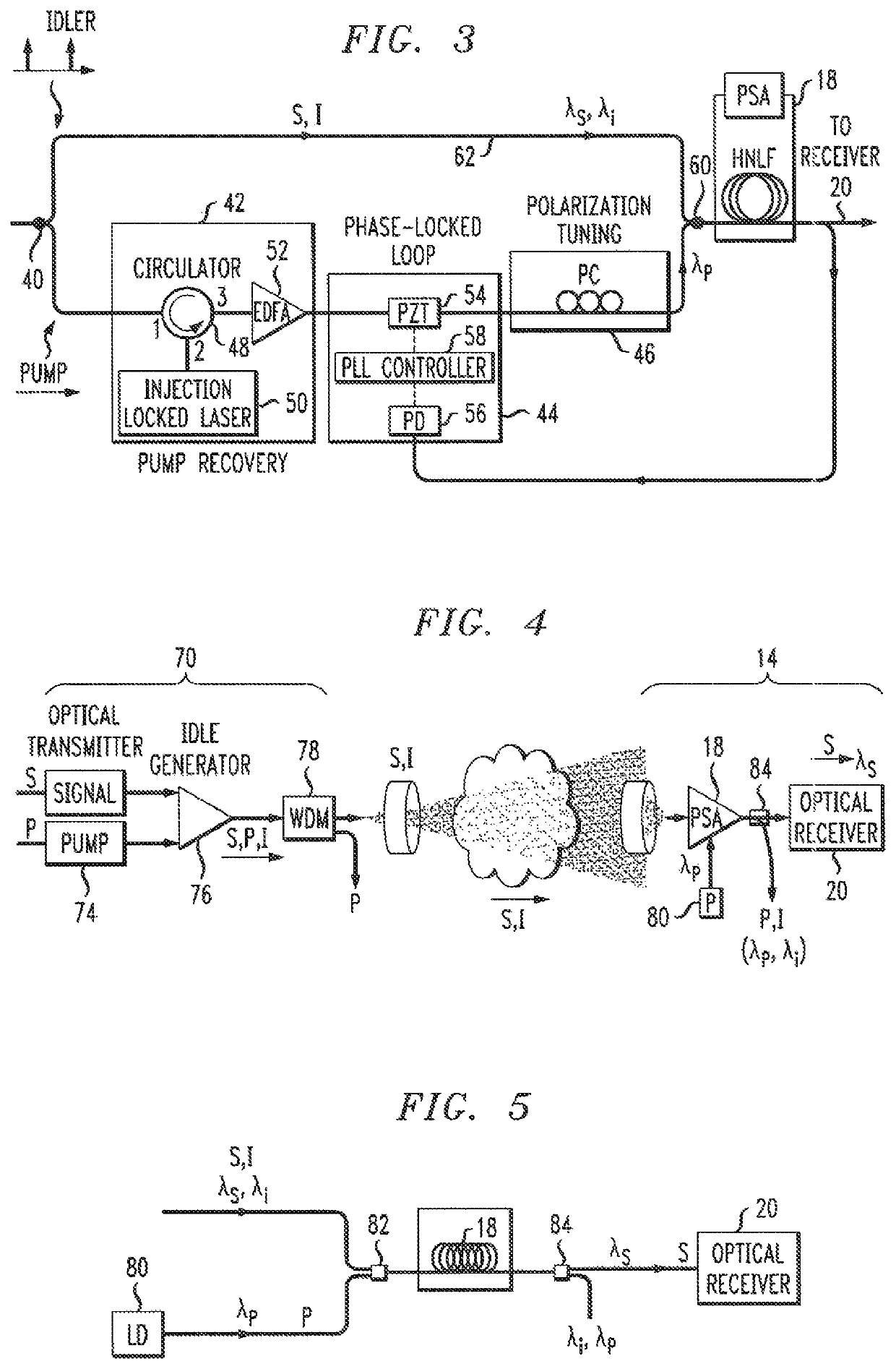
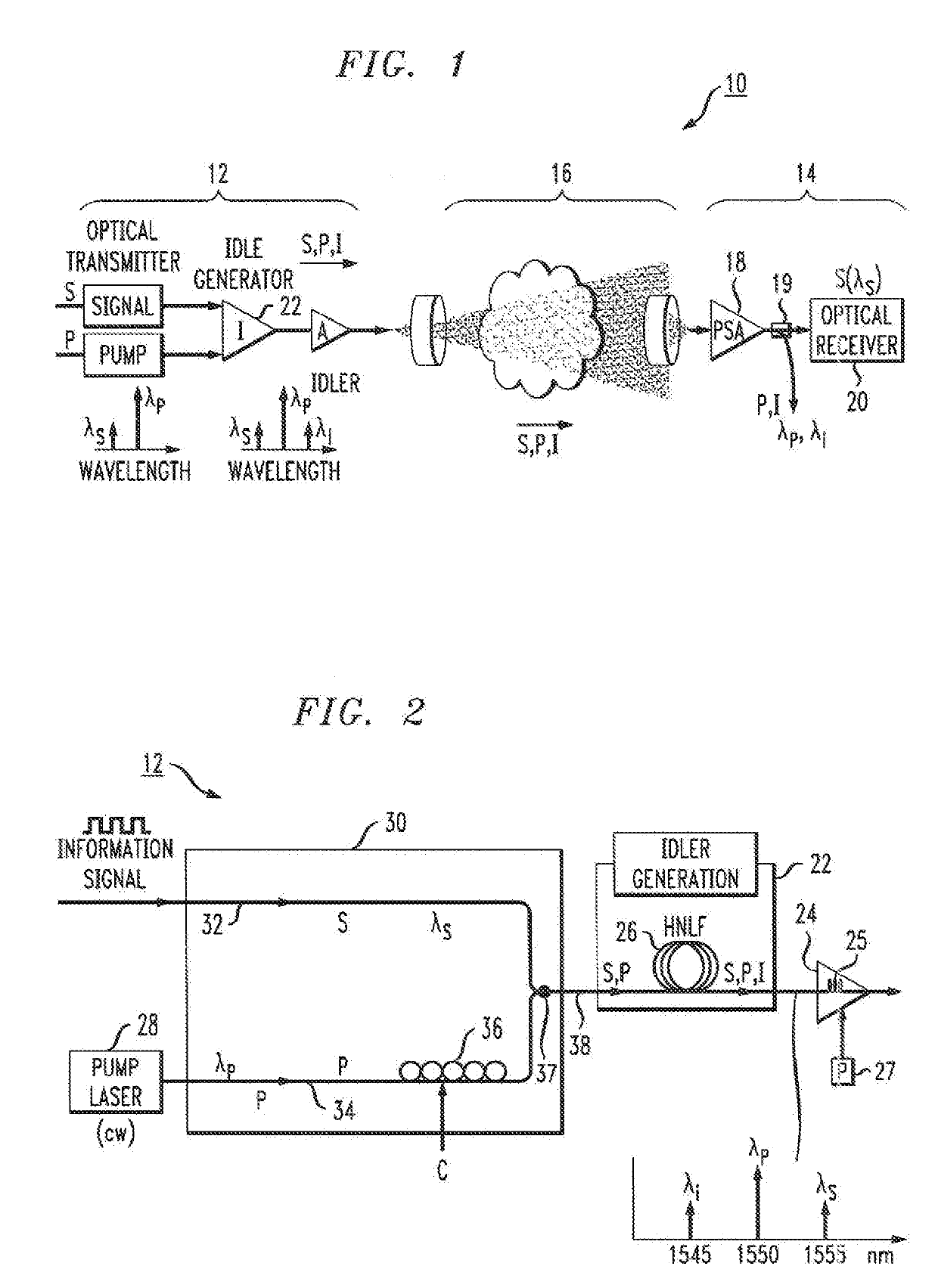
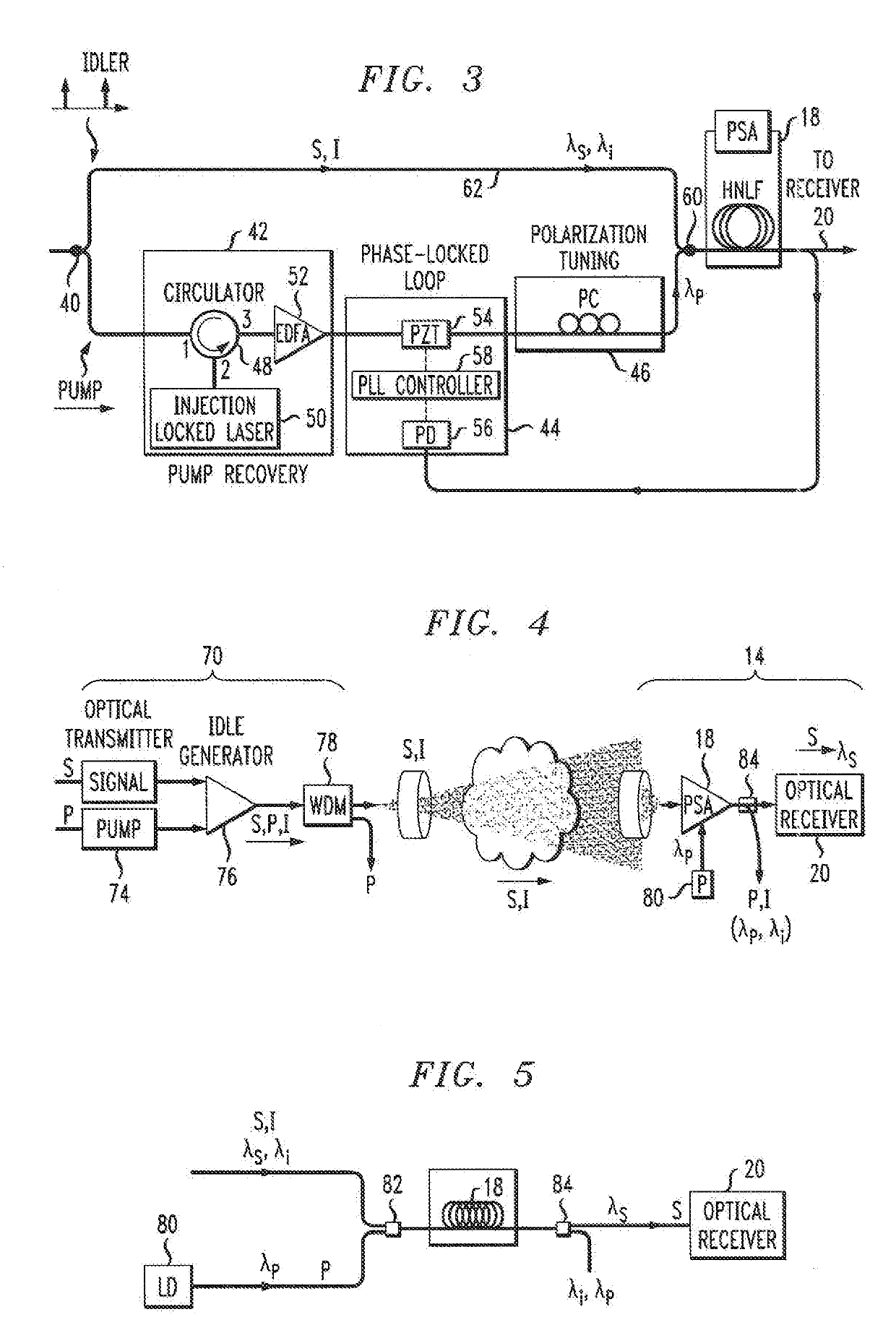
A free-space optical communication link is proposed that utilizes phase-sensitive amplification of the received optical signal at the input to the receiver portion of the link. The transmitter component of the FSO link generates an idler signal that is transmitted through free space with the original data signal and used at the PSA in conjunction with a pump wave to impart gain onto the received information signal. The PSA performs four-wave mixing (FWM) of the data, idler and pump to create the amplified data signal. In one embodiment, the pump wave used to generate the idler at the transmitter is sent through free space with the information and idler signals and used by the PSA to perform amplification. Alternatively, the PSA may use a co-located pump laser, in combination with the received idler signal, to perform the phase-sensitive amplification process.
Owner:ANDREKSON PETER AVO +1
Free-space optical communication links with improved sensitivity
A free-space optical communication link is proposed that utilizes phase-sensitive amplification of the received optical signal at the input to the receiver portion of the link. The transmitter component of the FSO link generates an idler signal that is transmitted through free space with the original data signal and used at the PSA in conjunction with a pump wave to impart gain onto the received information signal. The PSA performs four-wave mixing (FWM) of the data, idler and pump to create the amplified data signal. In one embodiment, the pump wave used to generate the idler at the transmitter is sent through free space with the information and idler signals and used by the PSA to perform amplification. Alternatively, the PSA may use a co-located pump laser, in combination with the received idler signal, to perform the phase-sensitive amplification process.
Owner:ANDREKSON PETER AVO +1
Ultrasonic detection scanning imaging device for inside coating interface defect of cylindrical shell and application method thereof
ActiveCN107255674AThe detection process is fastThe test data is accurateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNonlinear ultrasoundEngineering
The invention discloses an ultrasonic detection scanning imaging device for an inside coating interface defect of a cylindrical shell and an application method thereof. Two step motors are used for driving a cylindrical shell part to be rotated and driving a ultrasonic transducer to be translated, so the complete imaging of the interface adhesion situation of the inside coating is realized. In the scanning process, the vibration is added to the cylindrical shell part by a low frequency pump wave, the purpose of the added vibration is to open and close tiny cracks of the coating interface continuously, and the nonlinear effect is generated; in addition, the high frequency ultrasonic transducer continuously transmits / receives an ultrasonic signal, the received ultrasonic wave generates the nonlinear ultrasonic phenomenon under the effect of the low frequency pump wave, and the shape and position of the tiny defect of the coating interface are detected by extracting the nonlinear ultrasonic characteristic parameters. The device has the advantages of rapid detection speed, accurate test data, simple device operation and strong practicability, and has the extensive application prospect.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
Electromagnetic wave oscillating devices
ActiveUS8355197B2Improve accuracyIncrease output powerLight demodulationNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalPump wave
An oscillating device includes an oscillating substrate of a non-linear optical crystal and having an incident face where a pump wave and an idler wave are made incident; a first waveguide provided in the oscillating substrate and between the incident face and an interacting part of the pump wave and idler waves; and a second waveguide provided in the oscillating substrate and between the incident face and the interacting part. The first waveguide guides the pump wave and the second waveguide guides the idler wave.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method and device for generating transmittable high-power pulse string
The invention belongs to the field of nonlinear optical research, and in particular relates to a method and a device for generating a transmittable high-power pulse string. The technical problem that the current high-power pulse string with continuous wave background cannot transmit stably is solved. The device for generating the transmittable high-power pulse string comprises the following steps: a, generating a beam of high-power pulse string with continuous wave background; b, separating the beam of high-power pulse string with continuous wave background into at least two beams, wherein the first beam is input into an optical spectrum analyzer, and the second beam is input into an optical adjustable band-strop filter; c, according to the wave length of pump wave, represented by the center frequency of the high-power pulse string with continuous wave background, analyzed by the optical spectrum analyzer, filtering the back ground waves of the center frequency part of the high-power pulse string with continuous wave background to obtain the transmittable high-power pulse string with zero background. The method and the device for generating the transmittable high-power pulse string are simple, convenient and efficient, and have important application value in high-power pulse transmission in optical fiber communication.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com