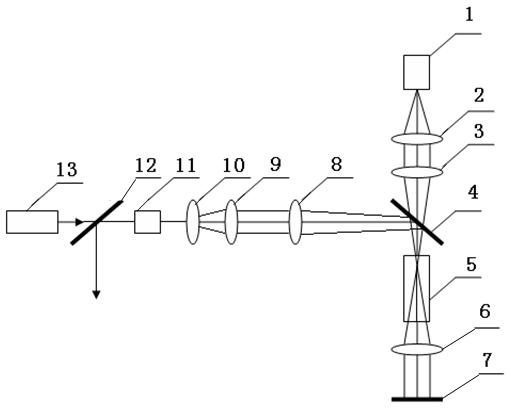
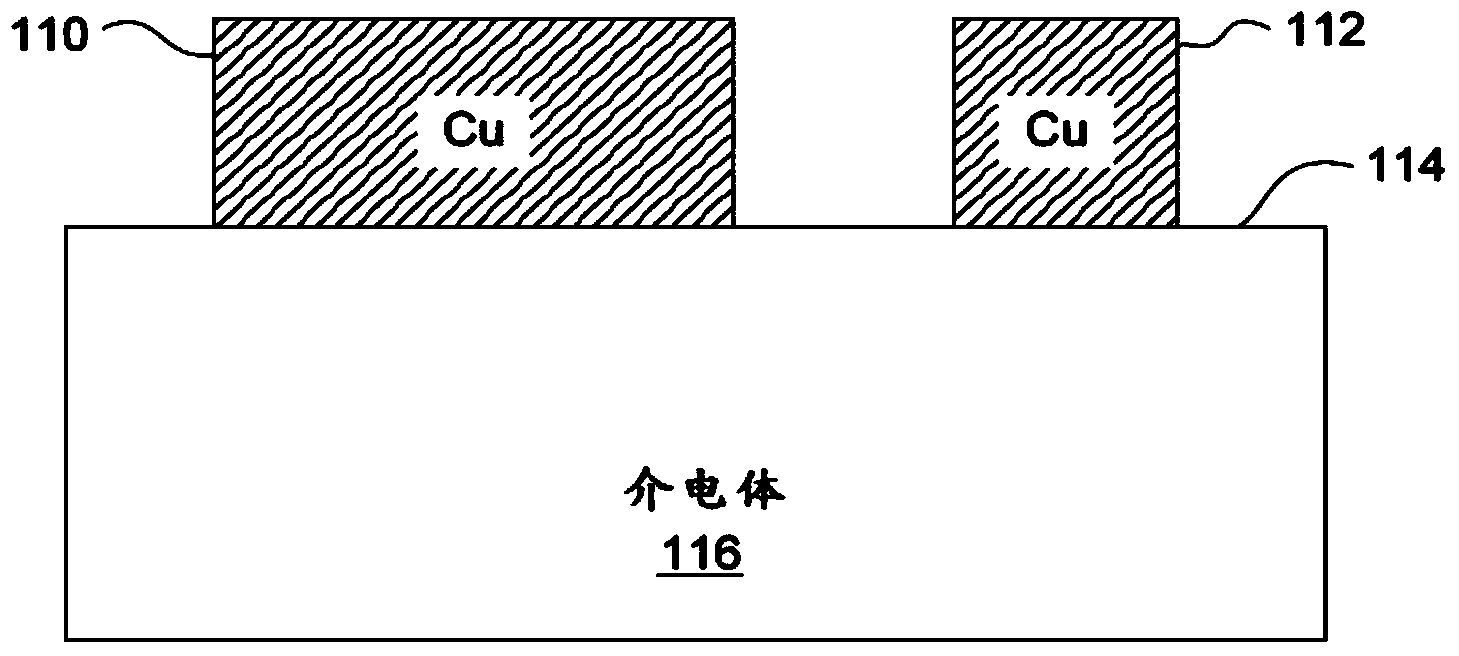
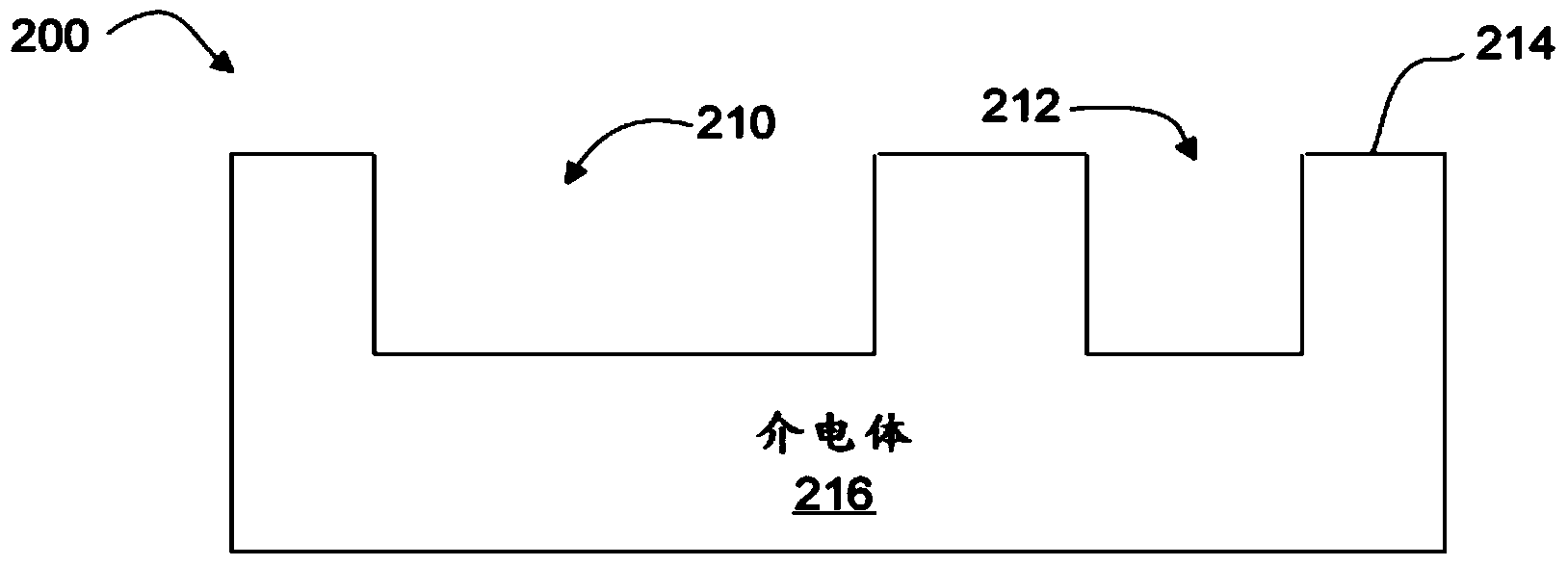
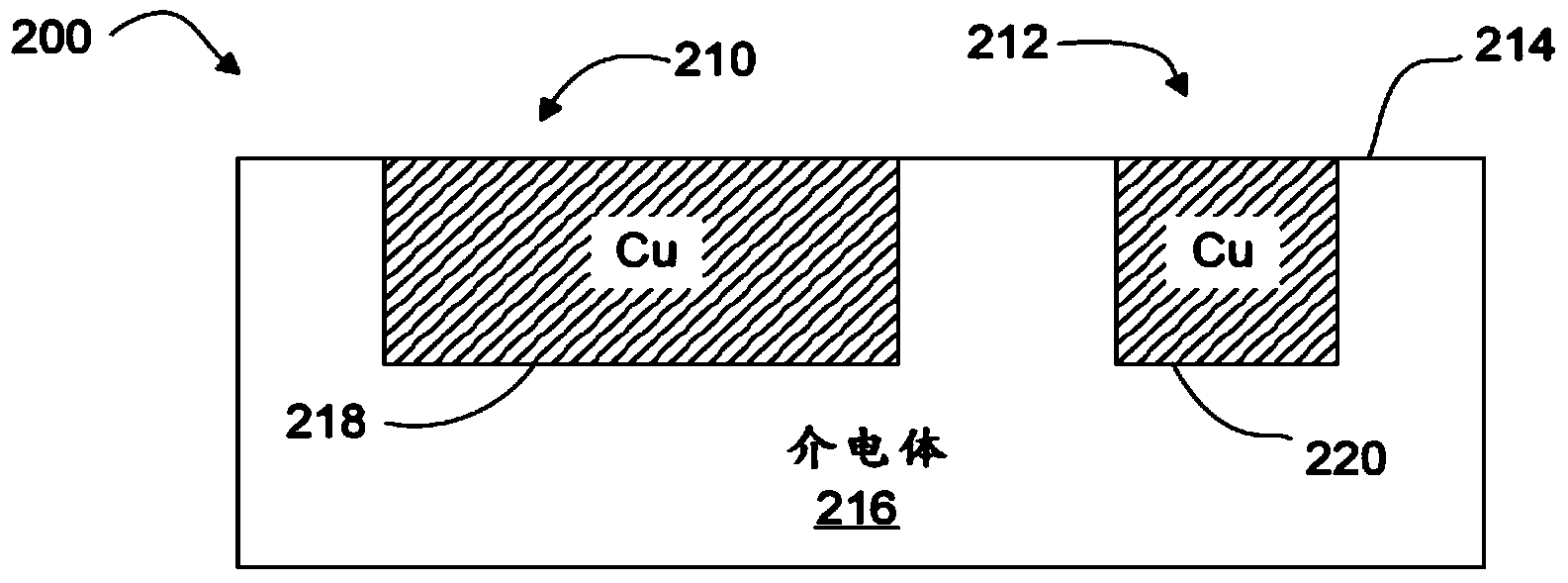
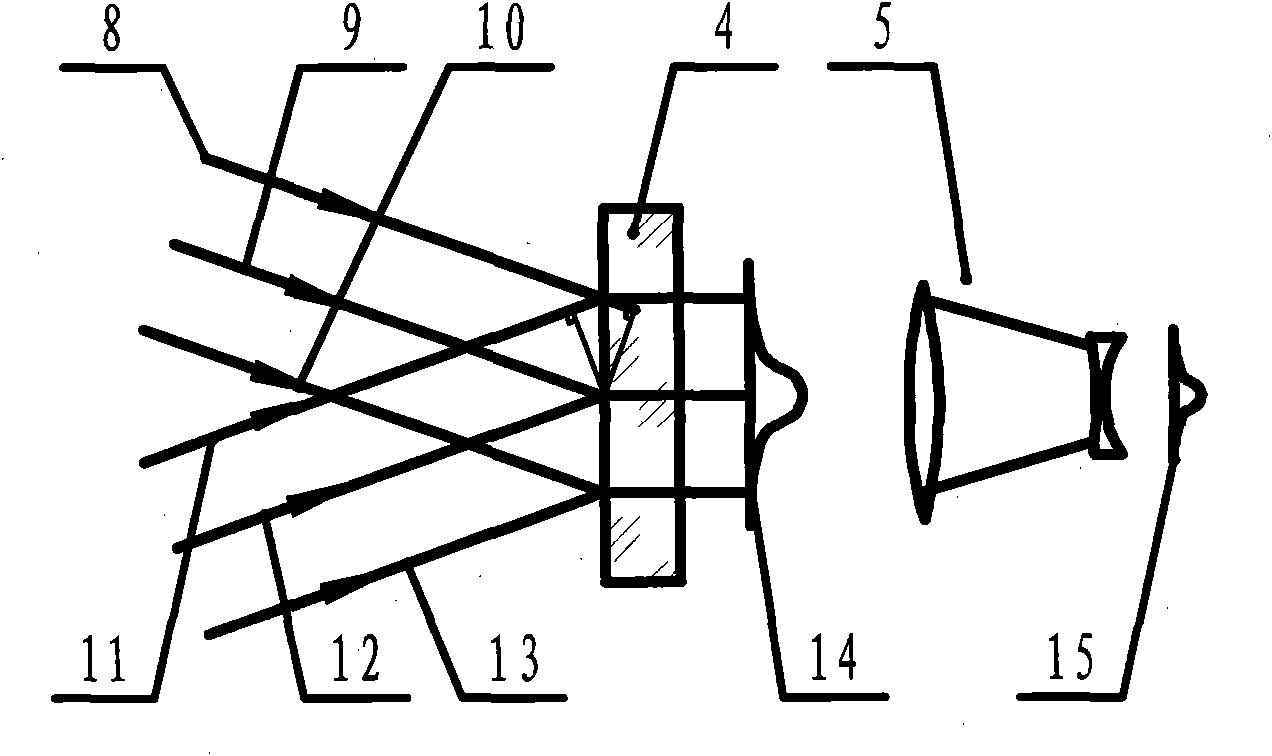
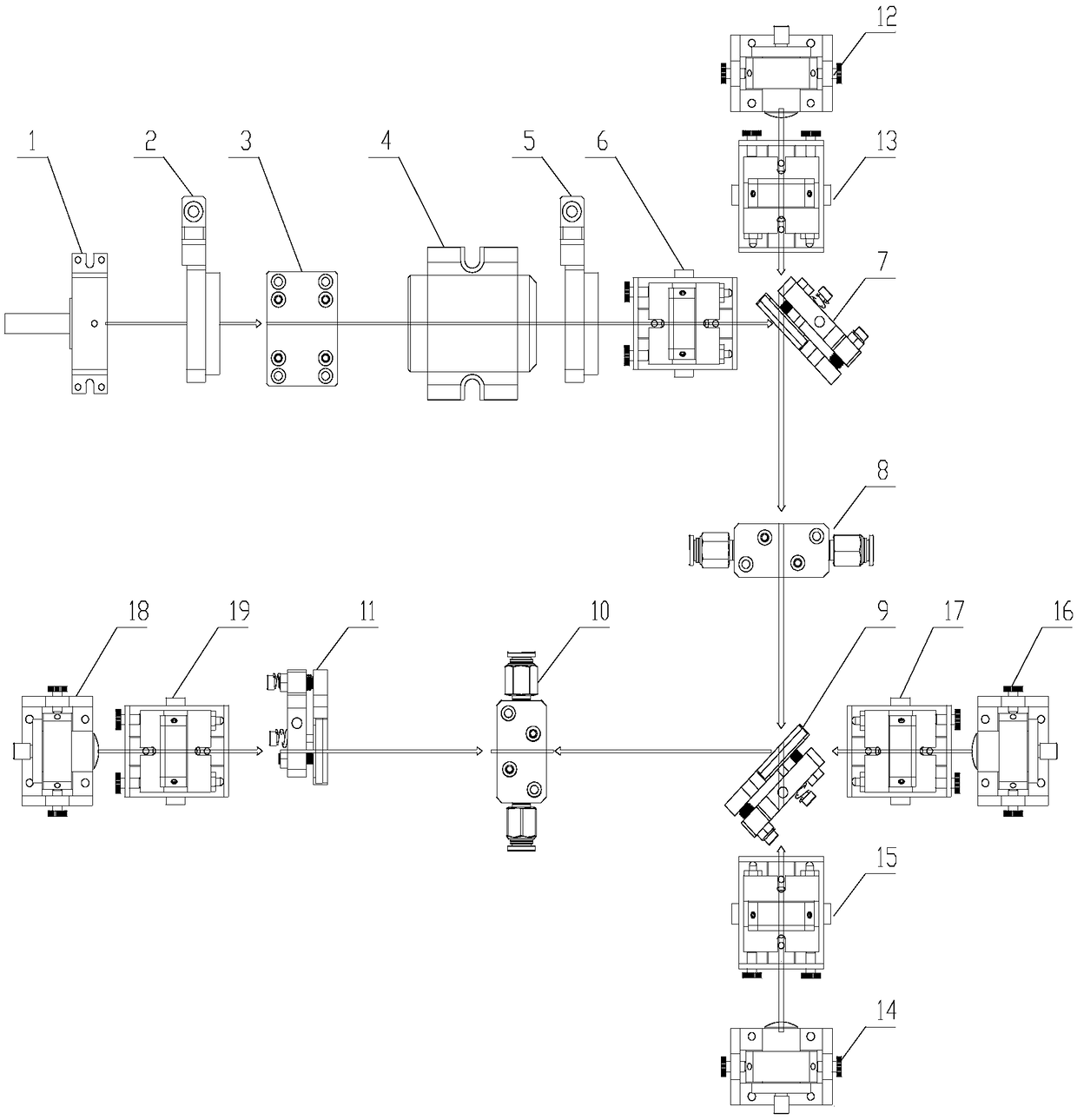
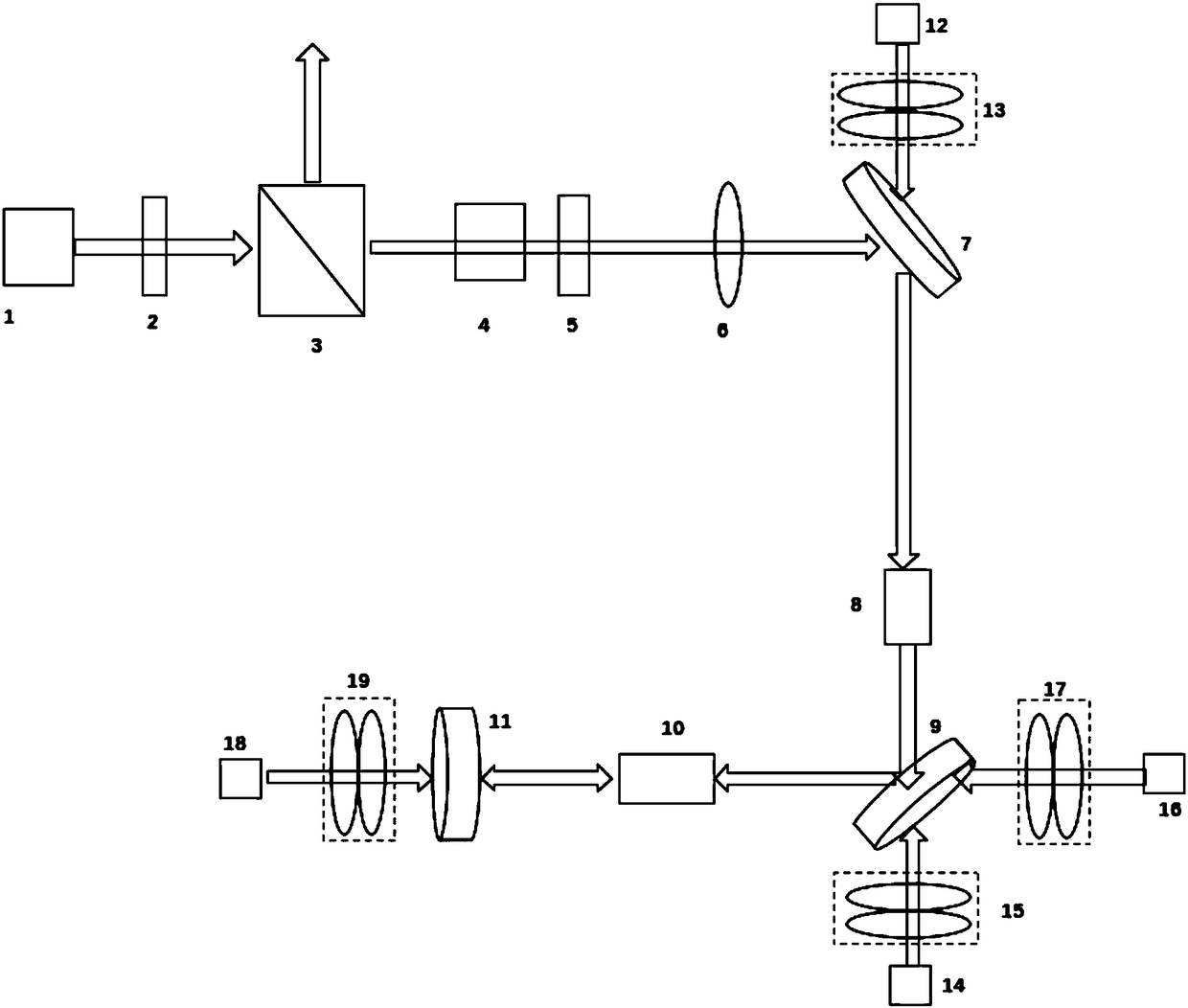
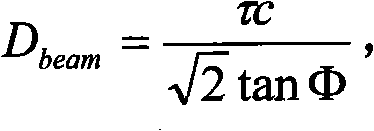Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Picosecond laser pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
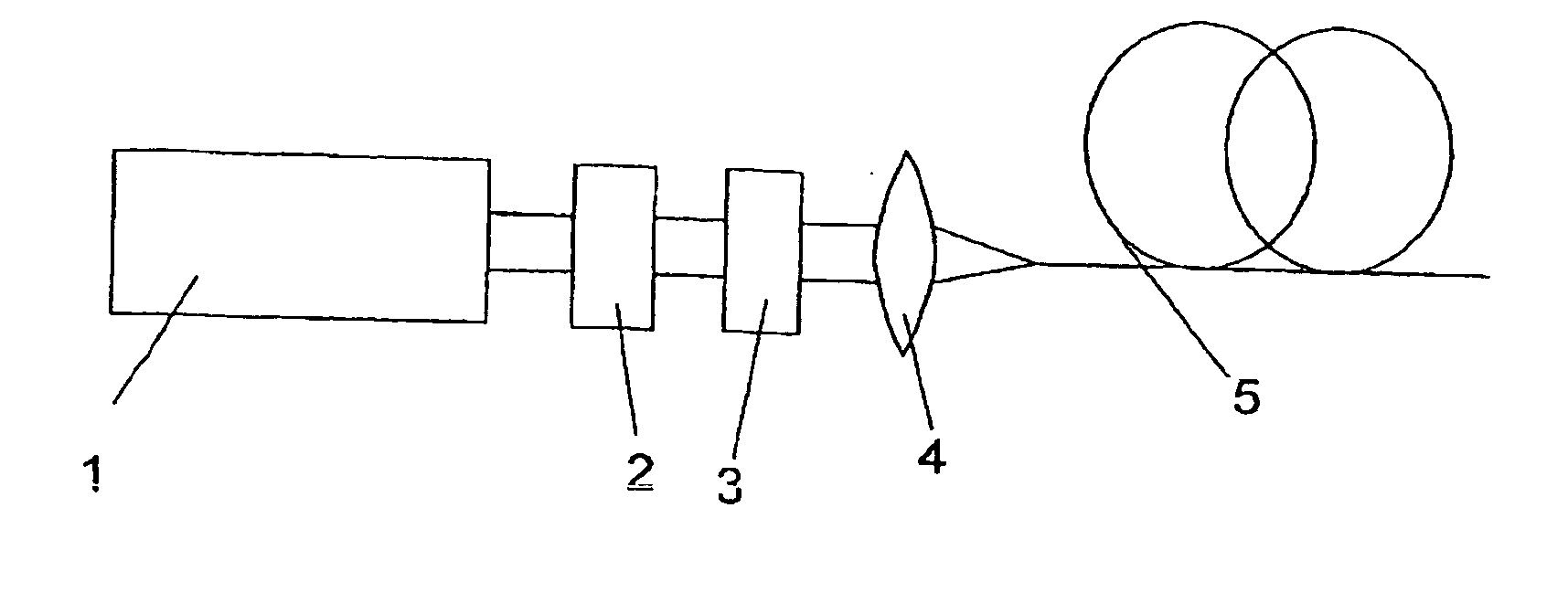
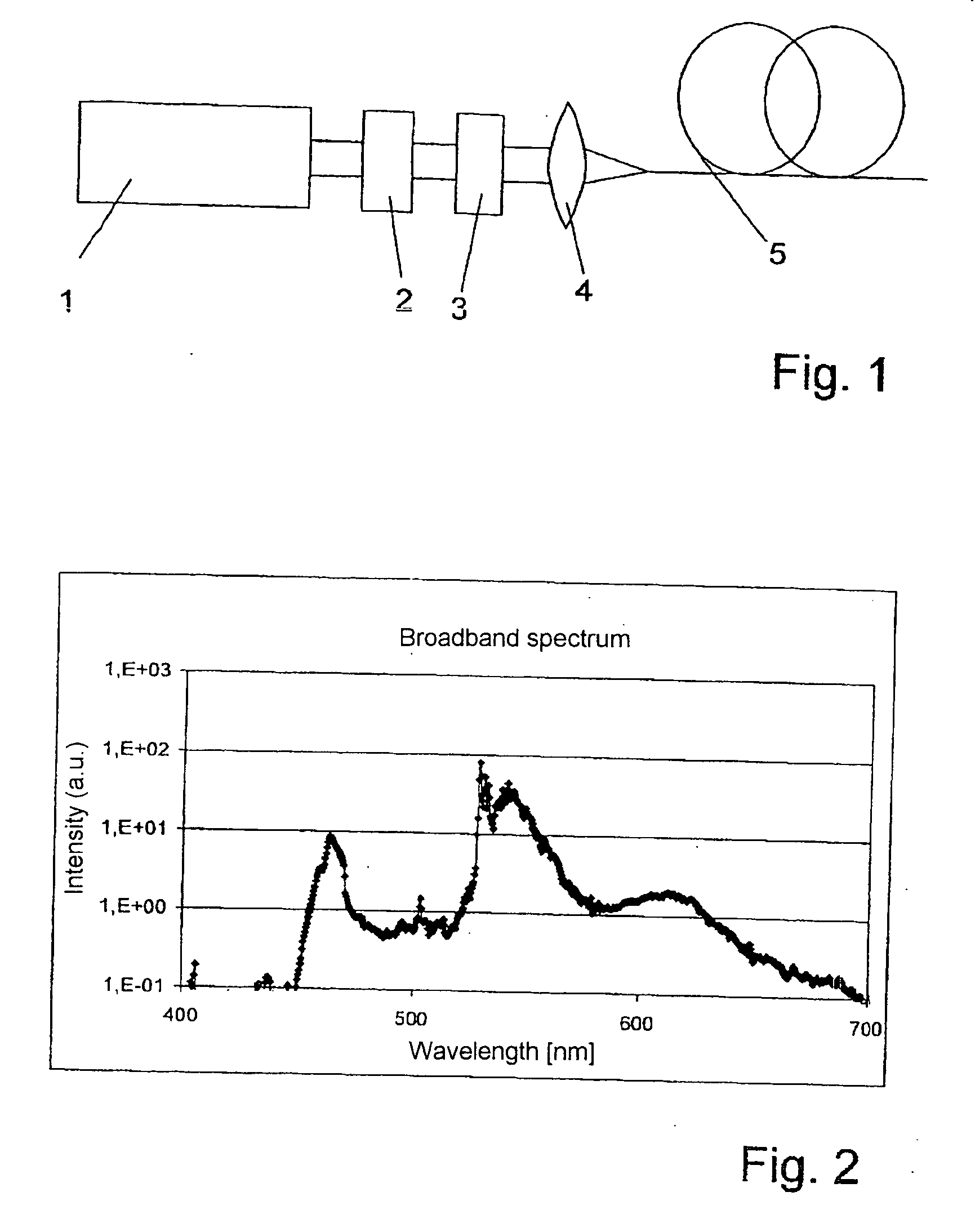
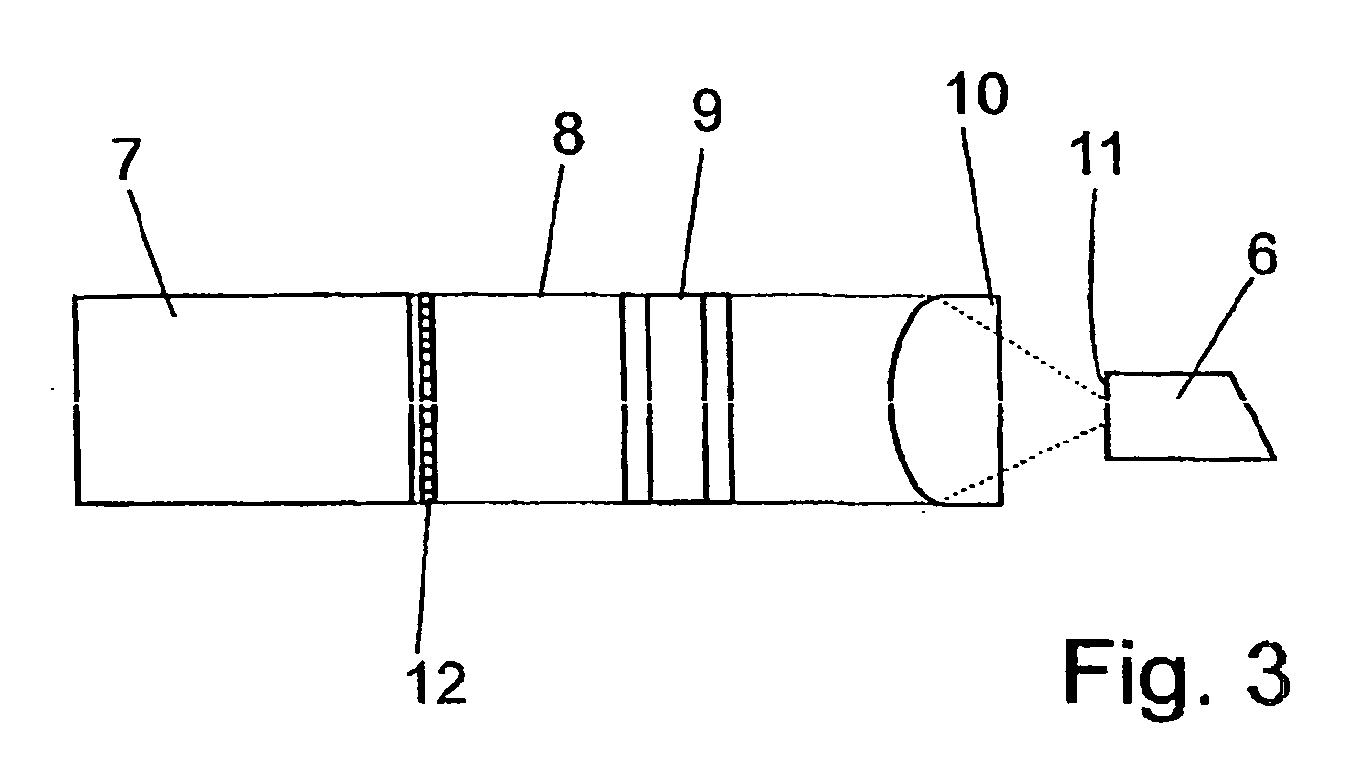
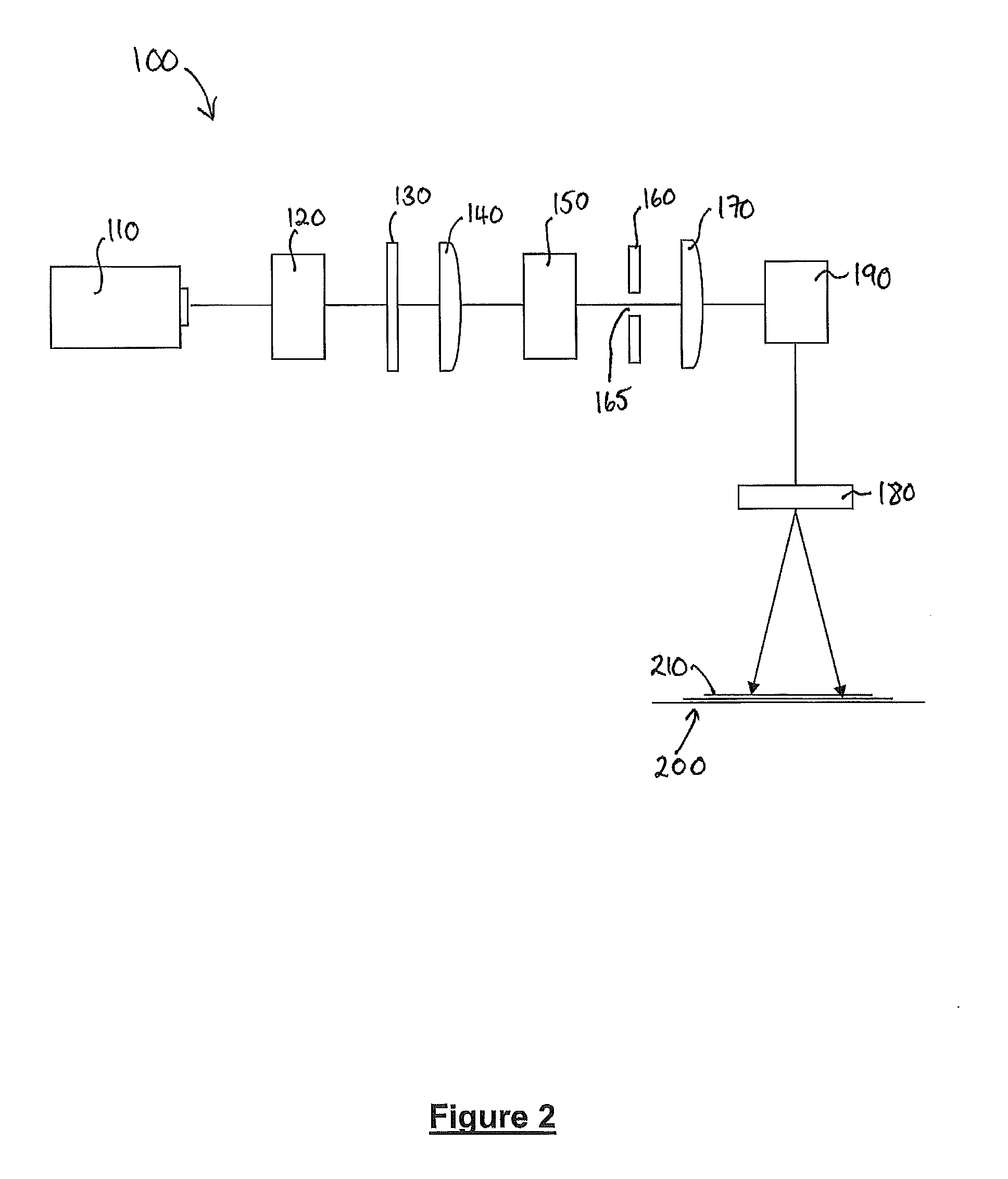
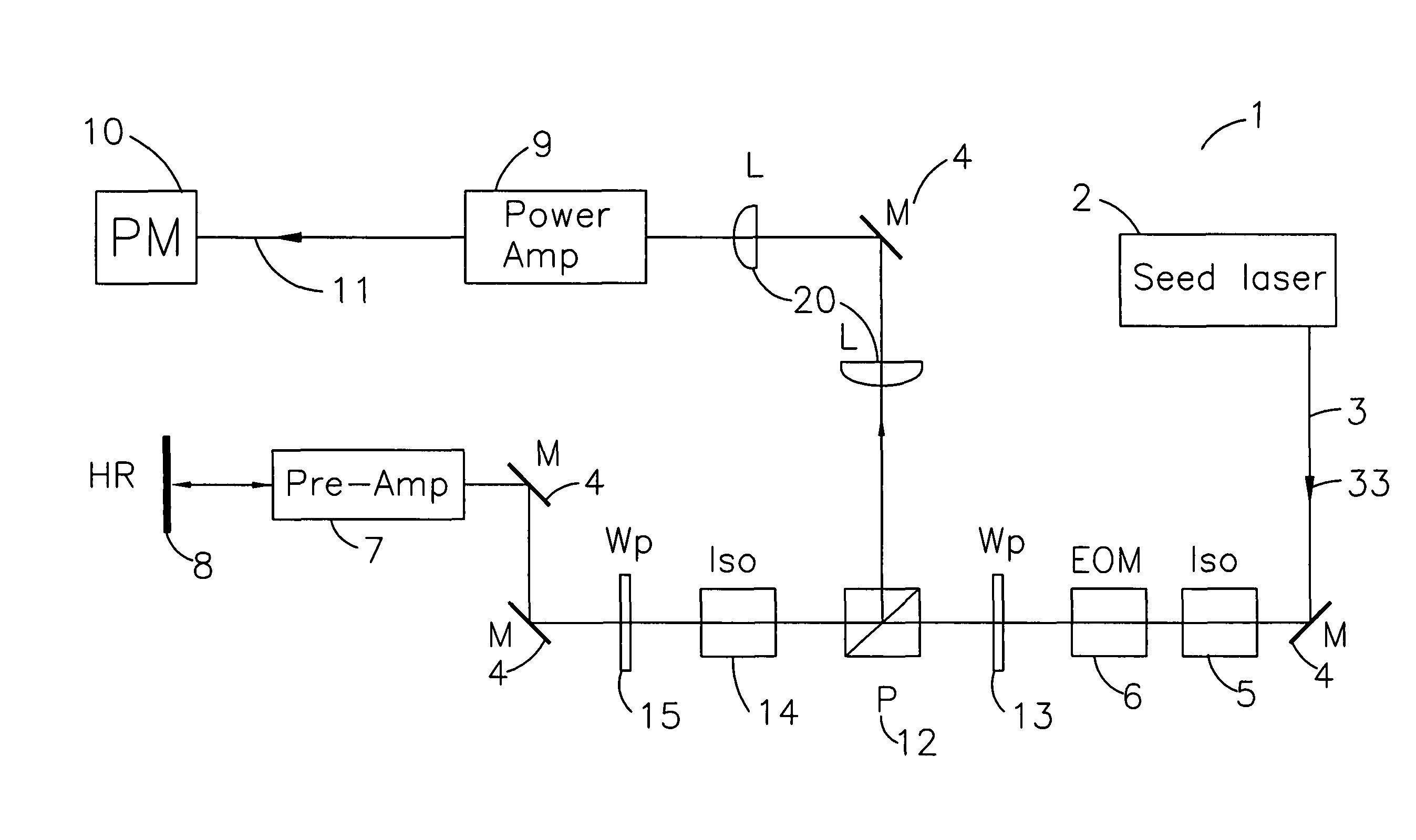
Method and optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum
InactiveUS20060002437A1Easy to operateEasy constructionLaser detailsNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention is directed to a method and an optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum in which wavelength regions are selected in an application-oriented manner already during spectrum generation in order to provide increased laser power. A passively mode-coupled solid-state laser provides picosecond laser pulses with an infrared output wavelength which is transformed to a secondary wavelength in the visible spectral range by nonlinear optical processes. The picosecond laser pulses are coupled into a nonlinear optical fiber which is optically adapted to the secondary wavelength with respect to dispersion and nonlinear characteristics, so that a radiation output interval comprising a visible wavelength region is selectively generated. The broadband spectrum has high brilliance and can be used, for example, in spectroscopy, microscopy, cytometry or for array readers.
Owner:JENOPTIK OPTICAL SYST
Laser direct ablation with picosecond laser pulses at high pulse repetition frequencies
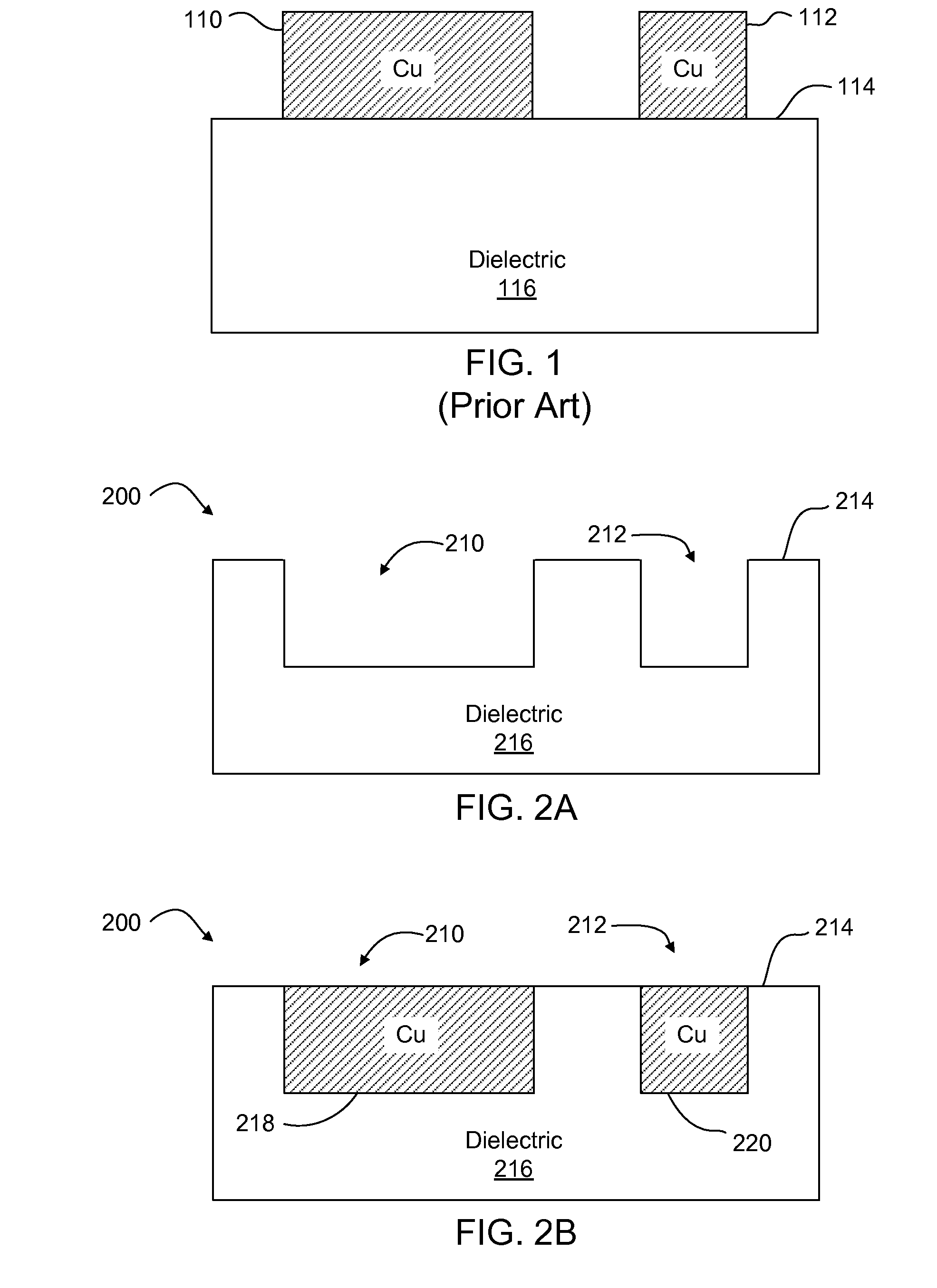
ActiveUS8648277B2Efficient processingSufficient pulse overlapSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuitsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
Laser direct ablation (LDA) produces patterns cut into a dielectric layer for the formation of electrically conductive traces with controlled signal propagation characteristics. LDA processing includes selecting a dose fluence for removing a desired depth of material along a scribe line on a surface of a workpiece, selecting a temporal pulsewidth for each laser pulse in a series of laser pulses, and selecting a pulse repetition frequency for the series of laser pulse. The pulse repetition frequency is based at least in part on the selected temporal pulsewidth to maintain the selected dose fluence along the scribe line. The selected pulse repetition frequency provides a predetermined minimum overlap of laser spots along the scribe line. The LDA process further includes generating a laser beam including the series of laser pulses according to the selected dose fluence, temporal pulsewidth, and pulse repetition frequency.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method of making at least one hole in a transparent body and devices made by this method
InactiveUS20050025445A1Improved micromachining speedCoupling light guidesGlass reforming apparatusPicosecond laser pulseErbium lasers
A method of making an at least one hole in an optically transparent body comprises the following steps: (i) providing an ultrashort pulse laser for producing a laser output with a wavelength λ, the laser output having a subpicosecond laser pulse duration; (ii) providing a laser output focusing lens for focusing the laser output, the focusing lens having a numerical aperture NA; (iii) providing an optically transparent body, the optically transparent body having a transparency at λ of at least 90% / cm; (iv) providing a liquid filled container situated proximate to the optically transparent body, such that the optically transparent body is in direct contact with the liquid; and (v) directing the laser output through the focusing lens to produce a focused laser output with a subpicosecond laser pulse duration proximate the optically transparent body, wherein the focused laser output traces at least one hole track pattern through the transparent glass body while the optically transparent body and said focused laser output move relative to one another in X-Y-Z directions. The at least one hole track pattern is in contact with the liquid and the focused laser output, in conjunction with the liquid, creates at least one hole in the optically transparent body.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of making at least one hole in a transparent body and devices made by this method
InactiveUS6990285B2Improved micromachining speedCoupling light guidesGlass reforming apparatusPicosecond laser pulseErbium lasers
A method of making an at least one hole in an optically transparent body comprises the following steps: (i) providing an ultrashort pulse laser for producing a laser output with a wavelength λ, the laser output having a subpicosecond laser pulse duration; (ii) providing a laser output focusing lens for focusing the laser output, the focusing lens having a numerical aperture NA; (iii) providing an optically transparent body, the optically transparent body having a transparency at λ of at least 90% / cm; (iv) providing a liquid filled container situated proximate to the optically transparent body, such that the optically transparent body is in direct contact with the liquid; and (v) directing the laser output through the focusing lens to produce a focused laser output with a subpicosecond laser pulse duration proximate the optically transparent body, wherein the focused laser output traces at least one hole track pattern through the transparent glass body while the optically transparent body and said focused laser output move relative to one another in X-Y-Z directions. The at least one hole track pattern is in contact with the liquid and the focused laser output, in conjunction with the liquid, creates at least one hole in the optically transparent body.
Owner:CORNING INC
Whole-solid kHz picosecond laser pulse regeneration amplifier
InactiveCN101055401AEfficient amplificationImprove stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPicosecond laser pulseOperating frequency
A solid condition kHz pico-second laser burst regenerative amplifier belongs to a omni-solid condition regenerative amplifier, which is characterized in that: the two lumen mirror of the magnifying resonant cavity are consisted of an average lumen formed by a first omni-opposite lumen mirror (7) and a second omni-opposite lumen mirror (14), the inner of the resonant cavity is arranged with a minus lens (12) and a second lambada / 4wave plate (13) arranged between the laser crystal (9) which is a Nd:YAG bar and the second omni-opposite lumen mirror. The fast axis of the wave plate is parallel with the light vector of the inputting linearly-polarized light. The minus lens is arranged between the laser crystal and the second lambada / 4 wave plate or the second lambada / 4 wave plate and the second omni-opposite lumen mirror. The pump source is a continuously worked semiconductor laser diode array (10) and the working frequency is 1kHz. The laser crystal can also be a Nd:YLF bar, here the second lambada / 4 wave plate is needless. The invention reduces the volume and the costs of the system, effectively solves the problem of Nd:YAD regenerative amplifier domino offect, and effectively ensures the magnification and the beam quality.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods and Apparatus Pertaining to Picosecond Pulsed Fiber Based Lasers
ActiveUS20140168755A1Good dispersionReduce the compression ratioOptical resonator shape and constructionFibre transmissionPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
A pulsed fiber laser apparatus for outputting picosecond laser pulses can comprise a fiber delivered pulsed seed laser for providing picosecond optical seed pulses, and at least one optical fiber amplifier in optical communication with the fiber delivered pulsed seed laser. The optical fiber amplifier can comprise a gain optical fiber that receives and optically amplifies picosecond optical pulses by operating in a nonlinear regime wherein the picosecond optical pulses can be spectrally broadened by a factor of at least 8 during amplification thereof. The apparatus can further comprise a pulse compressor apparatus in optical communication with the optical fiber amplifier for providing compressed picosecond optical pulses. The pulse compressor apparatus can provide a dispersion of at least 50 ps / nm and can provide a compression ratio of the time duration of the picoseconds optical pulses received by the pulse compressor apparatus to the time duration of the compressed picosecond optical pulses of no greater than about 50.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Preparation method for metal nano-particle ordered microstructure
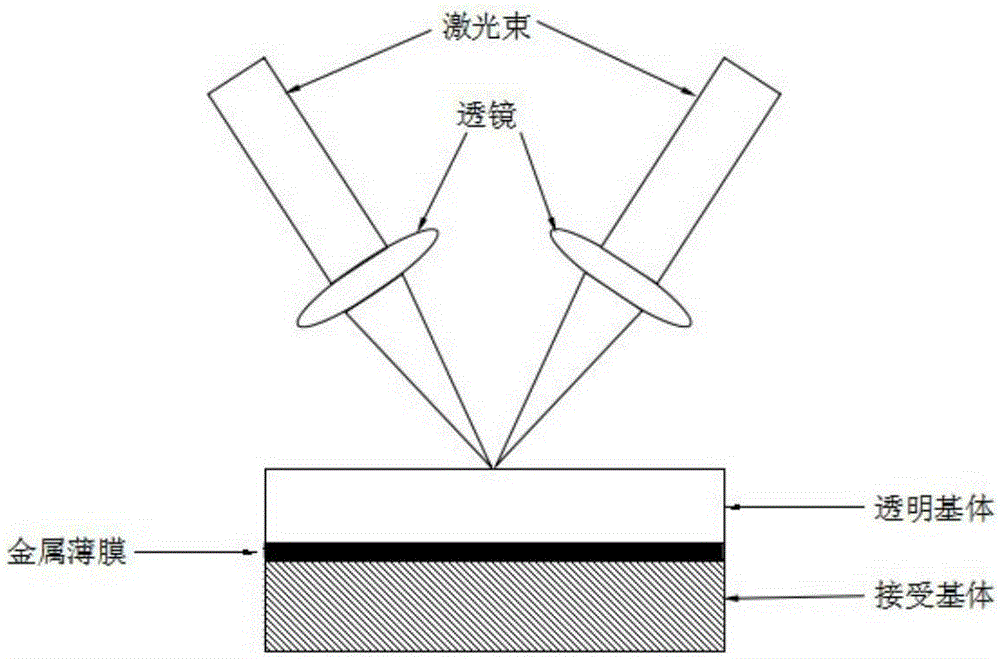
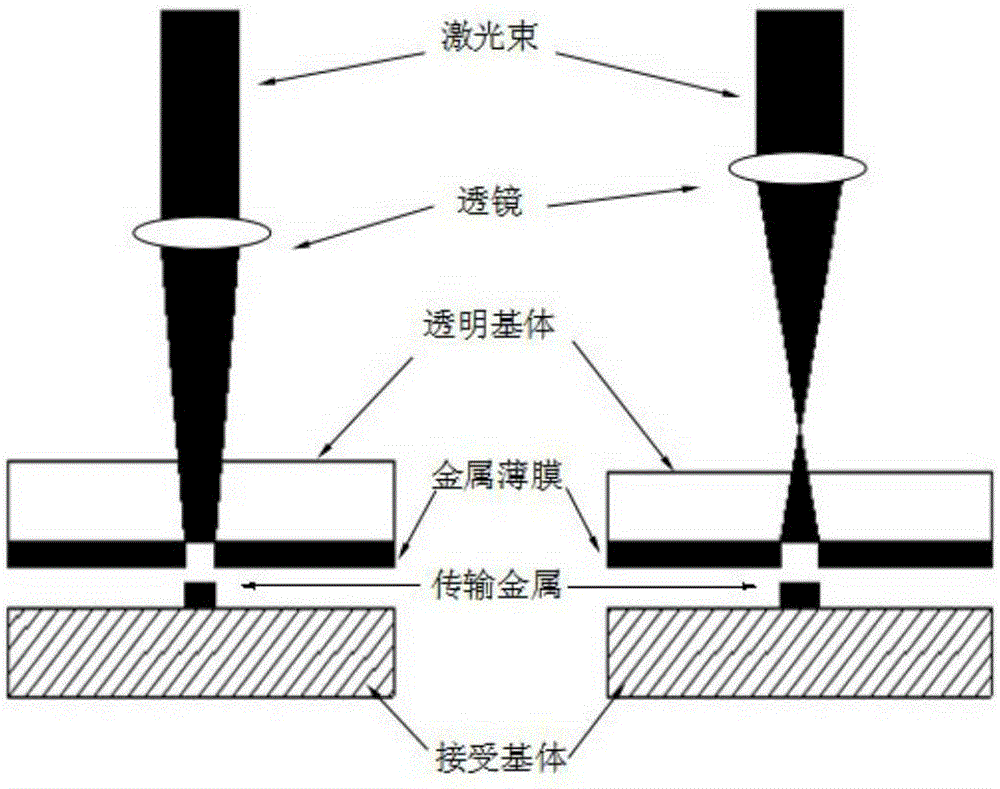
ActiveCN105220117AReduce usageThere is no problem that it cannot be effectively usedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention discloses a preparation method for a metal nano-particle ordered microstructure. The preparation method comprises the following steps that (1) a transparent substrate is cleaned up; (2) a layer of metal thin film is prepared on the surface of the transparent substrate by adopting a film coating process; (3) a reception substrate is taken and placed on a three-dimensional mobile platform controlled by a computer, the side, deposited with the metal thin film, of the transparent substrate makes contact with the reception substrate, irradiation is conducted from the side without the thin film with picosecond laser, and the ordered microstructure is deposited on the reception substrate; and (4) the reception substrate deposited with the ordered microstructure is added to a chemical compound solution containing AuCl-4 or PtCl2-6, mixing is conducted, a reaction is stopped when the color of the solution changes, and in this way, the gold or platinum nano-particle ordered microstructure is obtained on the surface of the reception substrate. According to the preparation method, the theories of picosecond laser pulses and metal replacement reactions are adopted, and metal with high reduction potential is replaced by metal with low reduction potential; the metal nano-particle ordered microstructure with the line width below 500 nm can be obtained. The preparation process is simple, high in efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:胡万谦
Method and apparatus for enhancing plasmon polariton and phonon polariton resonance
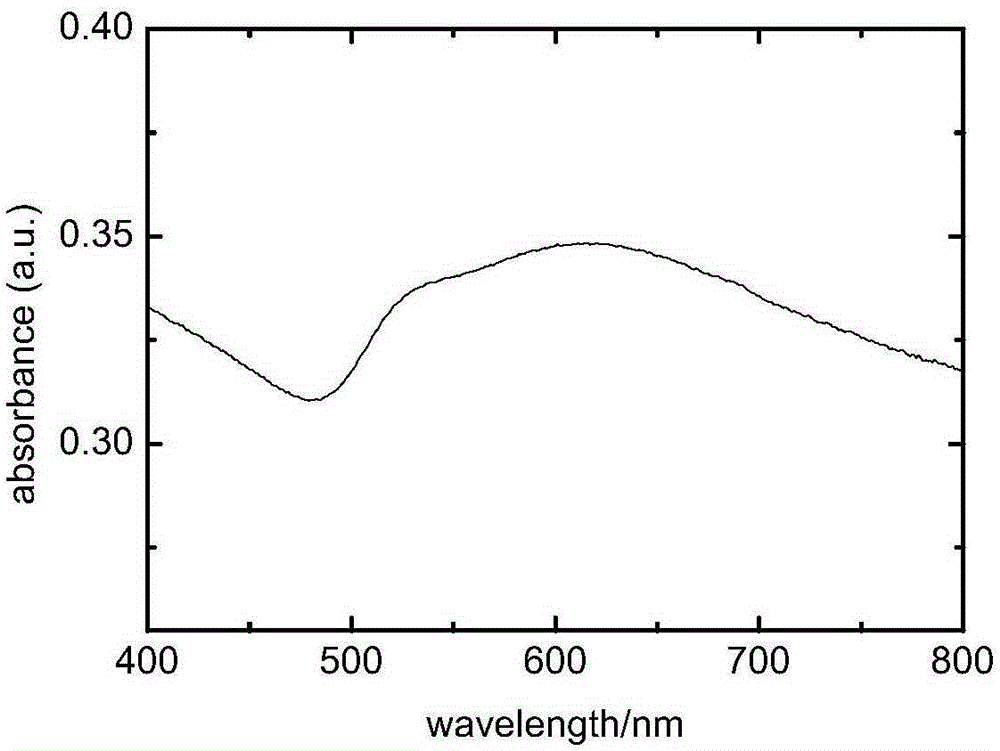
ActiveUS20070273959A1Laser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPicosecond laser pulsePhoton emission
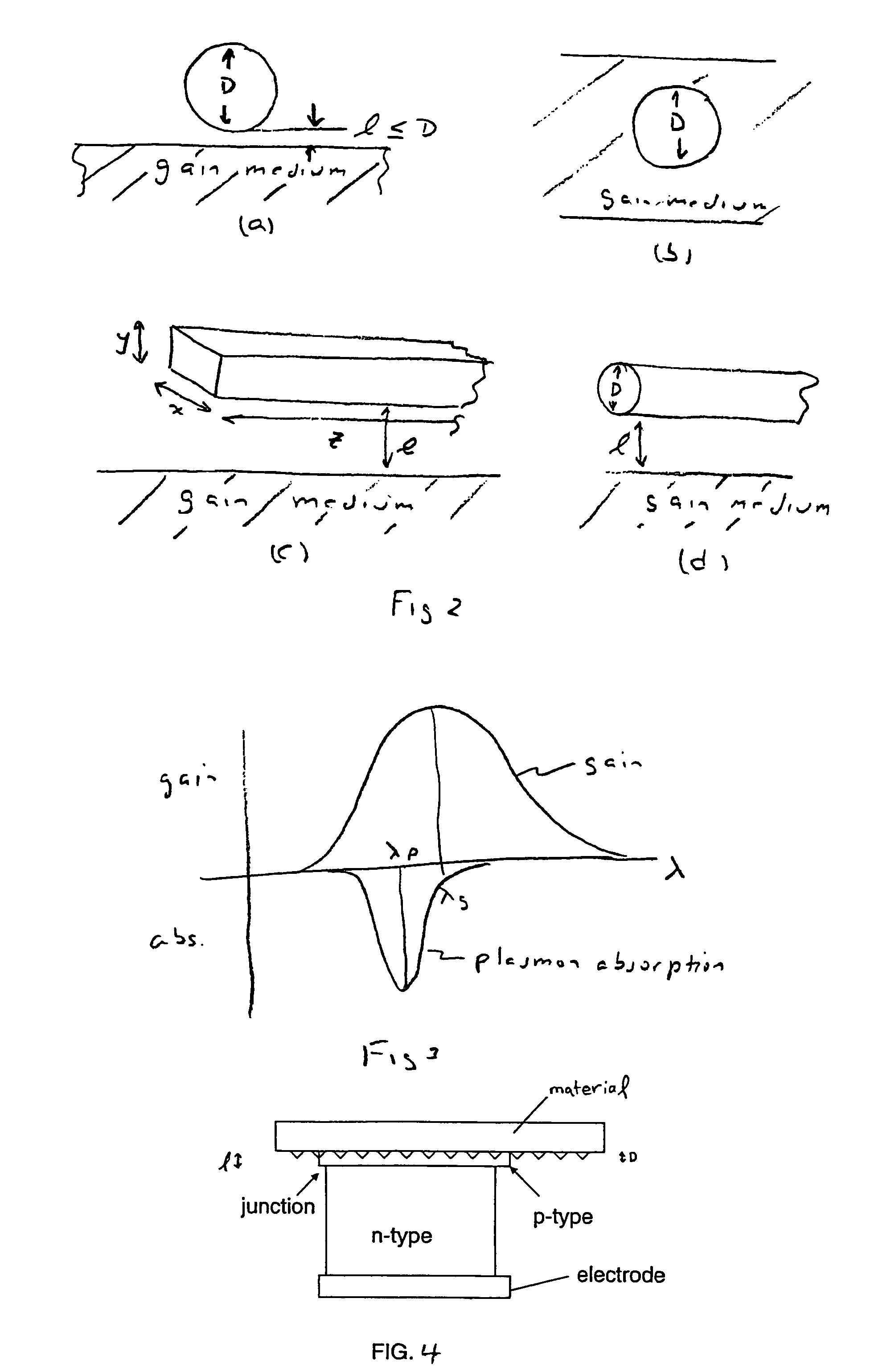
A metallic nano-particle surrounded by an amplifying medium results in a boundary condition that creates a singularity in the particle's dynamic polarizability at the localized surface plasmon resonance and at a critical value of the gain is disclosed. The boundary condition may be time dependent due to excitation by a sub-picosecond laser pulse and couples to the electromagnetic vacuum resulting in photon emission in an analogue of the Unruh Effect. The vacuum emission from 2-D nanostructures embedded in high gain laser dyes predicts energies nearly two orders of magnitude larger than the spontaneous emission background. The vacuum radiation is may have a unique dependence on the excitation.
Owner:SOLARIS NANOSCI
Methods and Apparatus For Patterning Photovoltaic Devices and Materials For Use With Such Devices
ActiveUS20130244449A1Simple materialImprove matchSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPicosecond laser pulsePicosecond laser
A picosecond laser beam shaping assembly is disclosed for shaping a picosecond laser beam for use in patterning (e.g., scribing) semiconductor devices. The assembly comprises a pulsed fibre laser source of picosecond laser pulses, a harmonic conversion element for converting laser pulses at a first laser wavelength having a first spectral bandwidth to laser pulses at a second laser wavelength having a second spectral bandwidth, and a beam shaping apparatus for shaping the laser beam at the second laser wavelength, the beam shaping apparatus having a spectral bandwidth that substantially corresponds to the second spectral bandwidth so as to produce a laser beam having a substantially rectangular cross-sectional profile.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
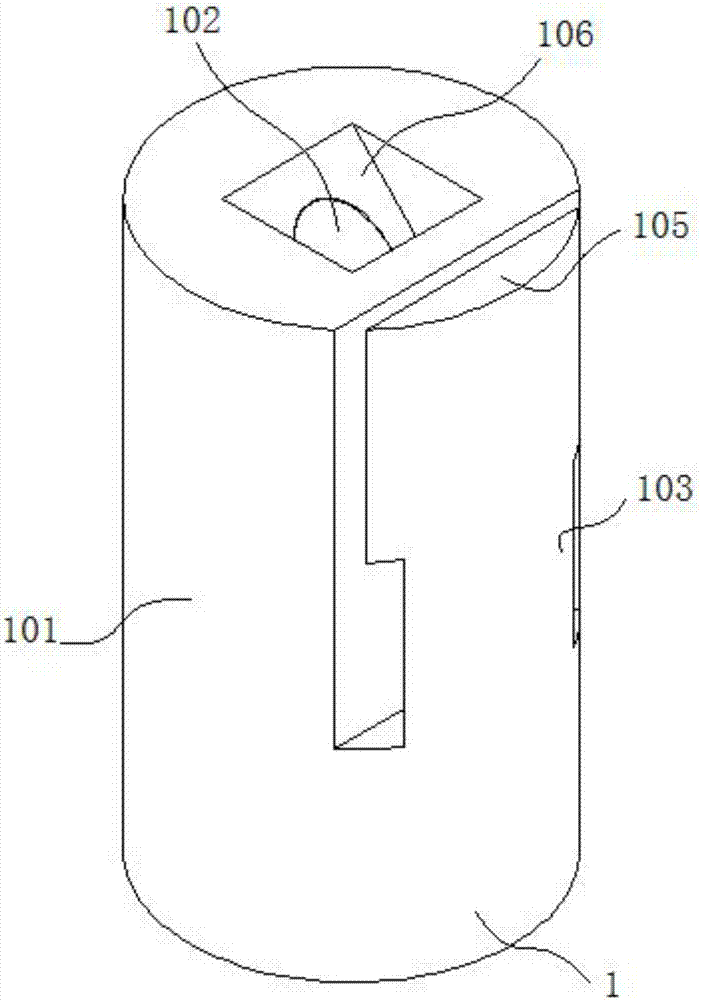
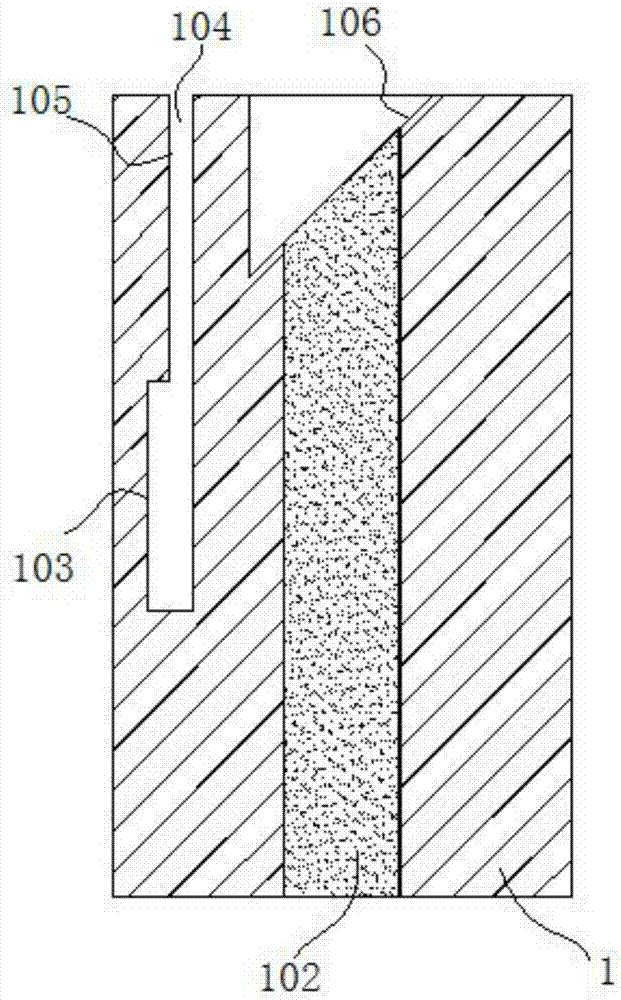
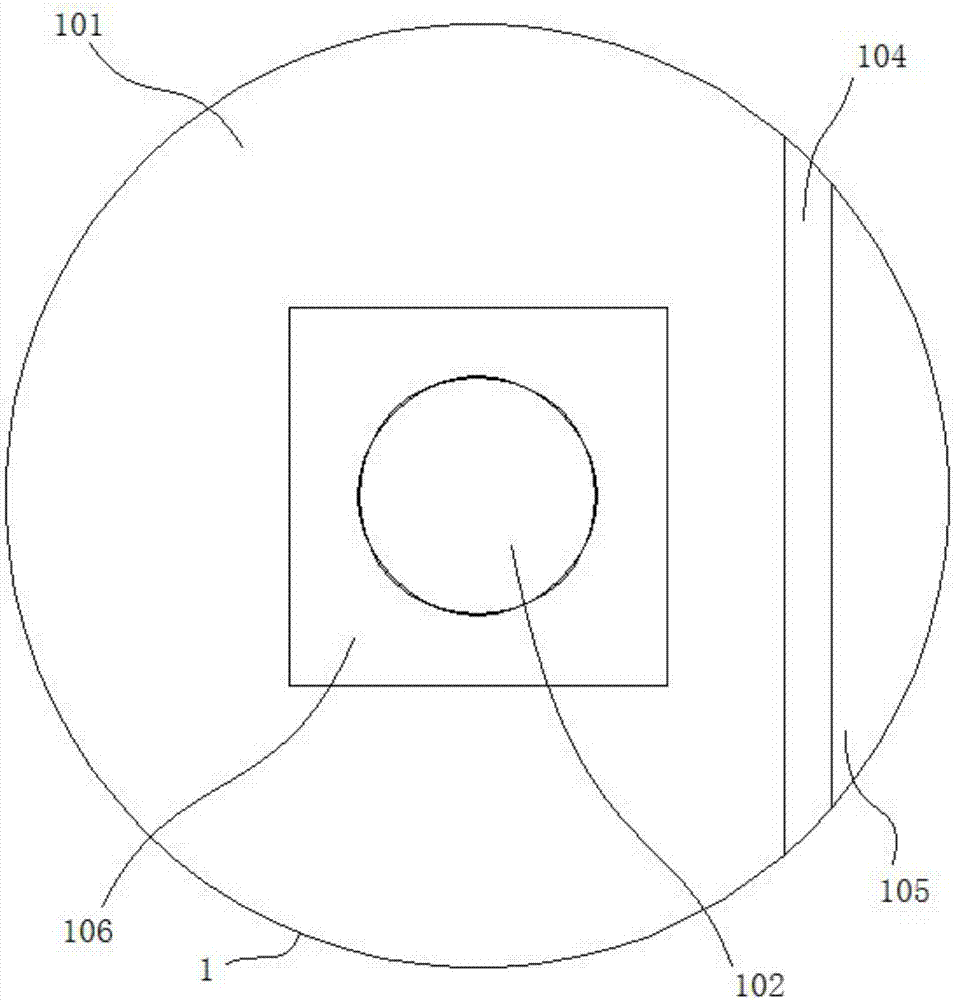
High-sensitivity optical fiber micro cantilever sensor for detecting acceleration and machining method
InactiveCN107015024ARealize acceleration signal detectionRealize remote real-time monitoringAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPicosecond laser pulseManufacturing cost reduction
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity optical fiber micro cantilever sensor for detecting acceleration. The sensor comprises an optical fiber, and one end face of the optical fiber is equipped with a mirror. A Fabry-Perot cavity is arranged in a coating layer of the optical fiber. The coating layer of the optical fiber is machined and etched with picoseconds laser pulse to get an optical fiber micro cantilever and an acceleration sensitive mass block. An optical fiber micro cantilever is arranged at one side of the Fabry-Perot cavity. An acceleration sensitive mass block is formed on a surface of the optical fiber micro cantilever. The acceleration sensitive mass block and the mirror constitute an interferometric optical fiber sensor. By using one communication optical fiber to integrate sensing and transmission, acceleration signal detection and transmission are realized, and remote real-time monitoring is realized. The sensor is small and light, and is suitable for acceleration monitoring in a limited space environment. The optical fiber cantilever is manufactured using the laser machining technology, manufacturing is quick and can be carried out on a large scale, and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
Owner:李俊
Method for generating high-energy and high repetition rate laser pulses from CW amplifiers
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
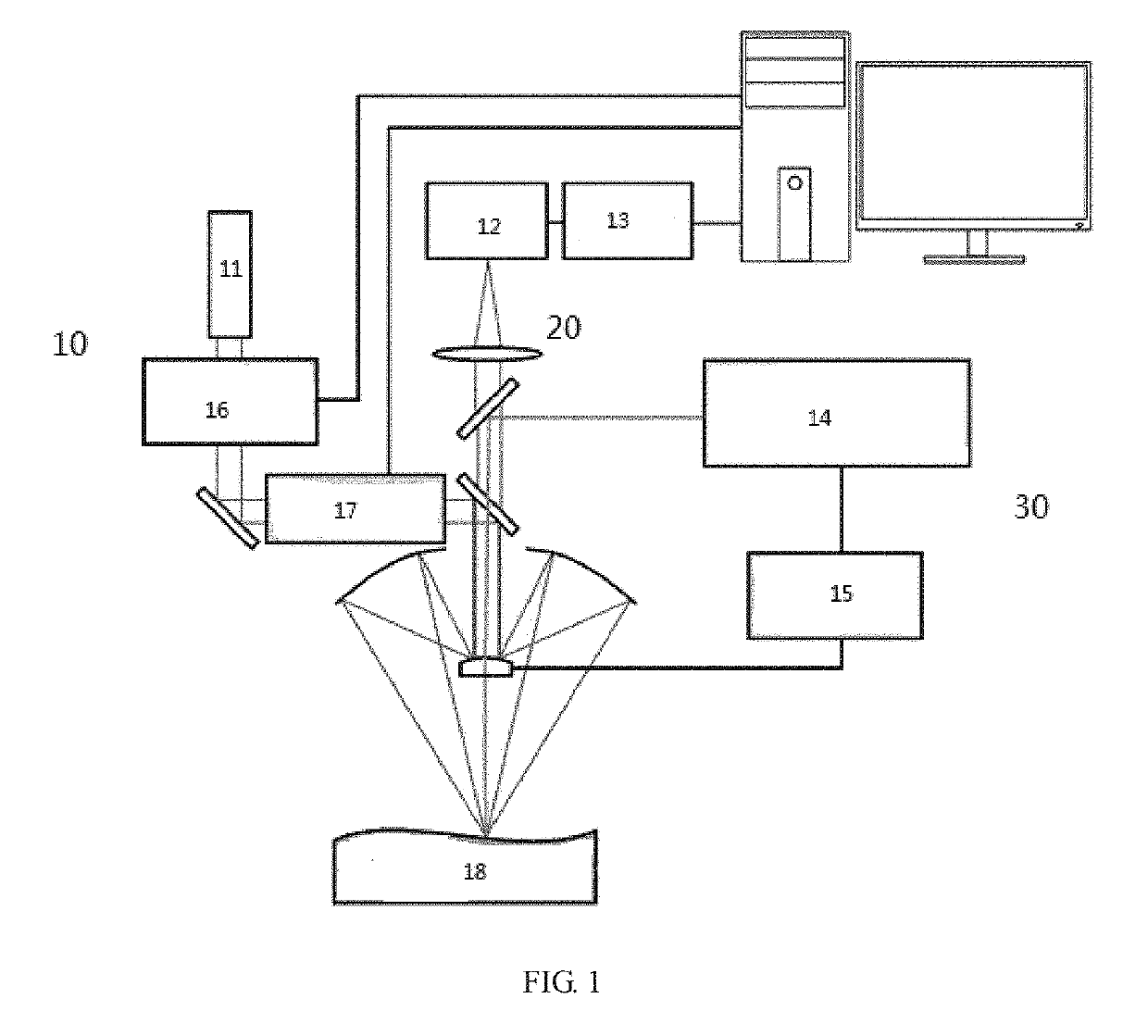
Method for Detecting Composition of Steel Sample by Using Multi-Pulse Laser-Induced Plasma Spectrometer
ActiveUS20190219511A1Enhance emission of spectralSignal-to-noise ratioAnalysis by thermal excitationFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond laserNanosecond laser pulse
The present invention relates to a method for detecting steel sample components by using a multi-pulse laser induced plasma spectral analysis device, and in particular, to a method for detecting steel sample components by using a multi-pulse laser induced plasma spectral analysis device that includes picosecond and nanosecond laser pulse widths. A laser induced light source is a laser light source that includes nanosecond and picosecond ultrashort pulses, and one pulse laser device can be used to generate two pulse lasers, namely, a nanosecond and a picosecond laser; the two pulse lasers pass through a same output and focusing light path, so as to ensure that the two pulse lasers are focused on a same position of a sample to be detected; a surface of the sample is irradiated by using a first beam of nanosecond laser pulse to generate plasmas; subsequently, the plasmas are irradiated by using a second beam of picosecond laser pulse to enhance spectral line emission.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
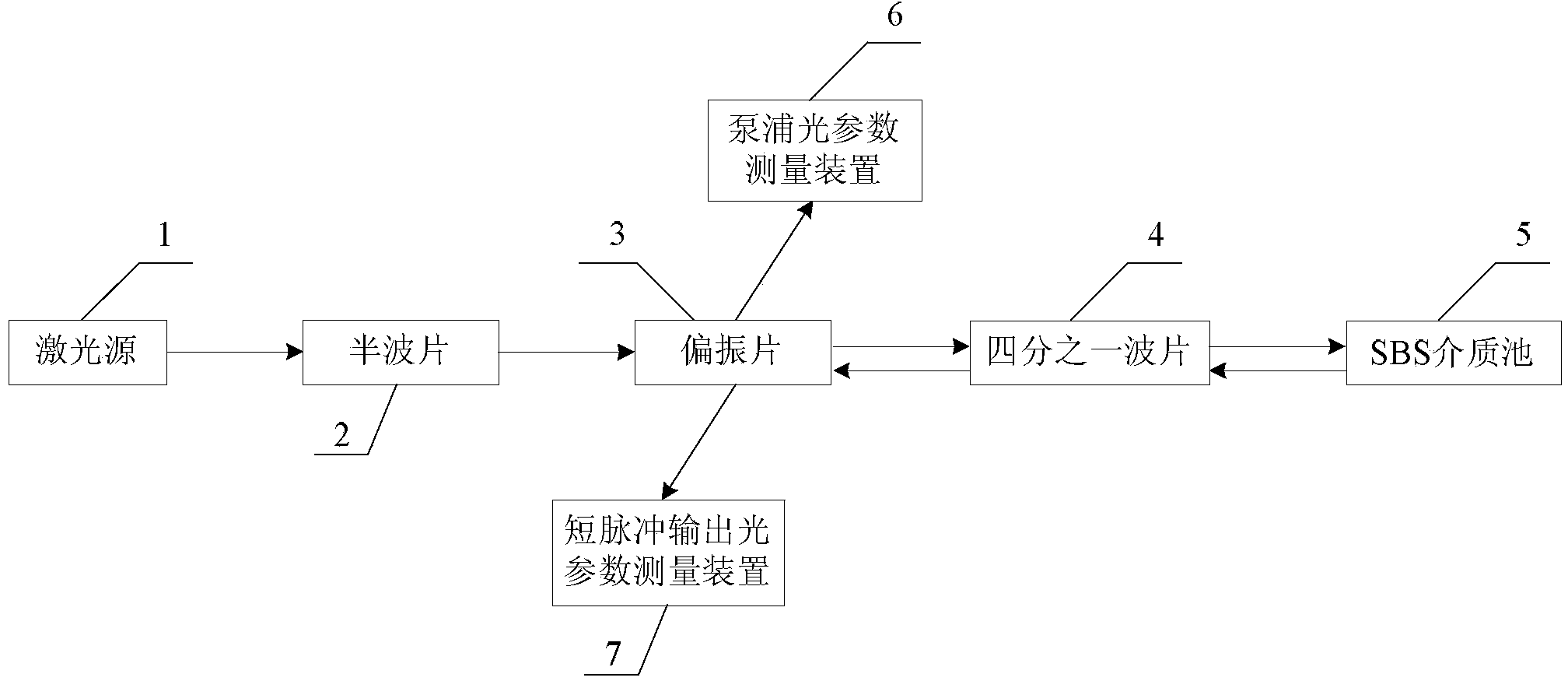
High-energy hundred-picosecond laser pulse generation device highly stable in time
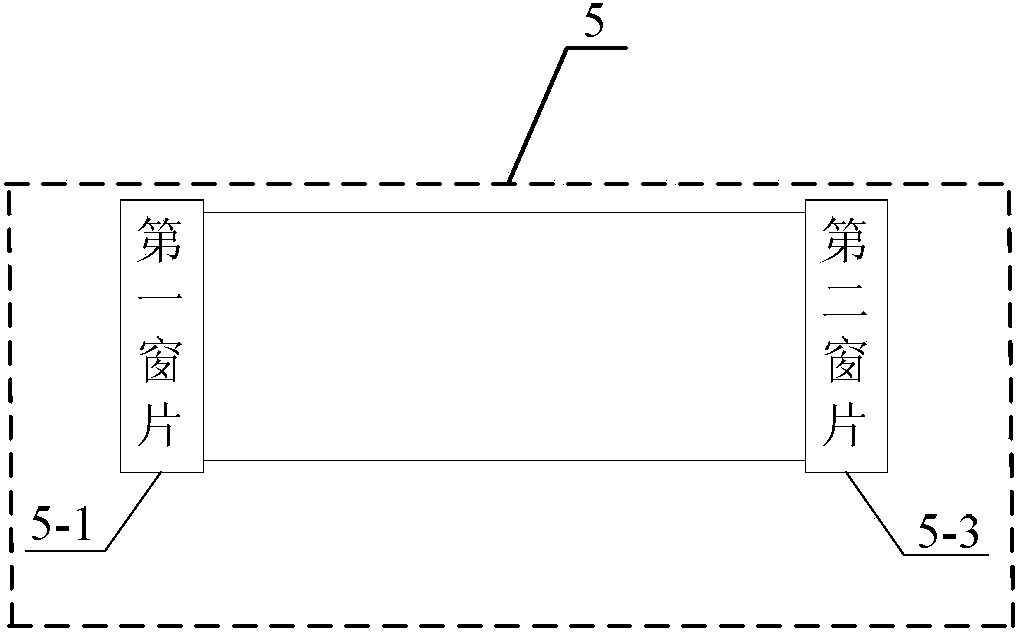
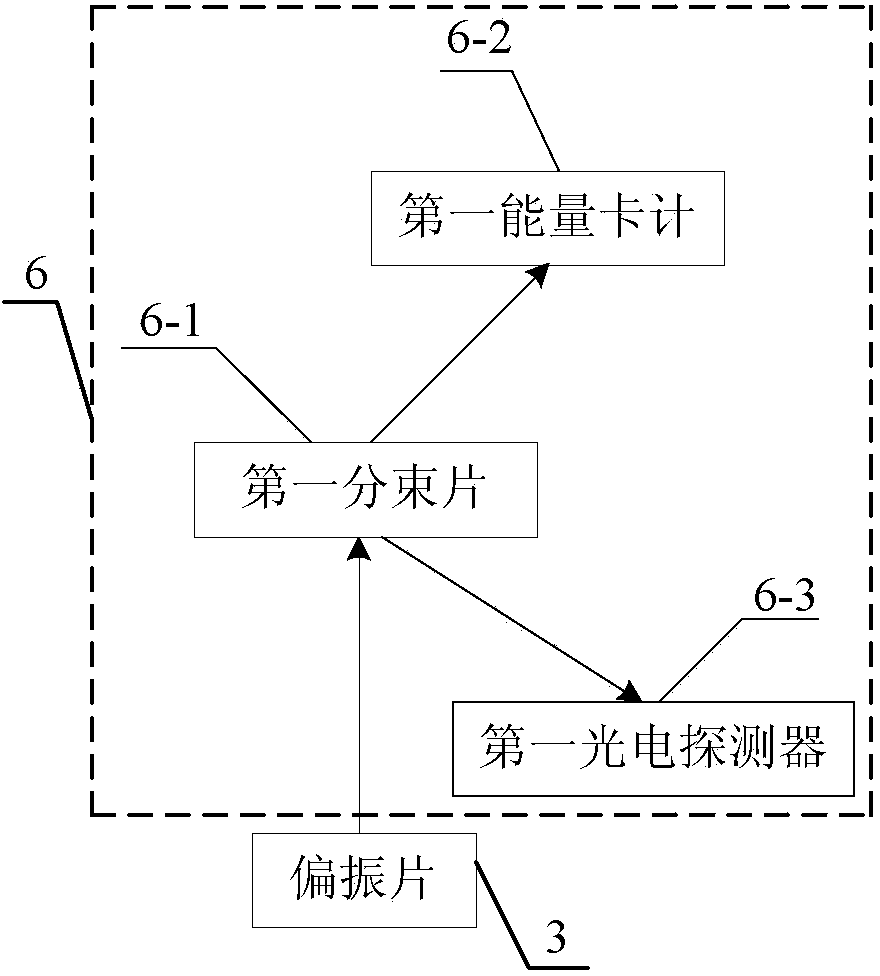
The invention relates to a high-energy hundred-picosecond laser pulse generation device highly stable in time and belongs to the field of nonlinear optics. The high-energy hundred-picosecond laser pulse generation device highly stable in time solves the problems that the laser pulse energy generated by an existing laser pulse generation device is low, the optical structure of an amplification system is complex, the amplification efficiency is low, the spectrum of the generated laser pulse is wide, the pulse compression mode is poor in stability, and the device is limited in application. The high-energy hundred-picosecond laser pulse generation device highly stable in time comprises a laser source, a half-wave plate, a polarizer, a quarter-wave plate, an SBS medium pool, a pump light parameter measurement device and a short pulse output light parameter measurement device. The pump light parameter measurement device comprises a first beam splitting plate, a first energy card meter and a first photoelectric detector. The SBS medium pool is a hollow cylindrical container, and the two ends of the SBS medium pool are sealed by a first window sheet and a second window sheet respectively. The short pulse output light parameter measurement device comprises a second beam splitting plate, a second energy card meter and a second photoelectric detector. The high-energy hundred-picosecond laser pulse generation device highly stable in time is used for generating high-energy pulse lasers and particularly applicable to large-caliber laser pumps.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
High-energy picosecond laser pulse POD control system and method
ActiveCN107069411ARealize the POD functionSolve the problem of low frequency limited outputLaser detailsPicosecond laser pulsePicosecond laser
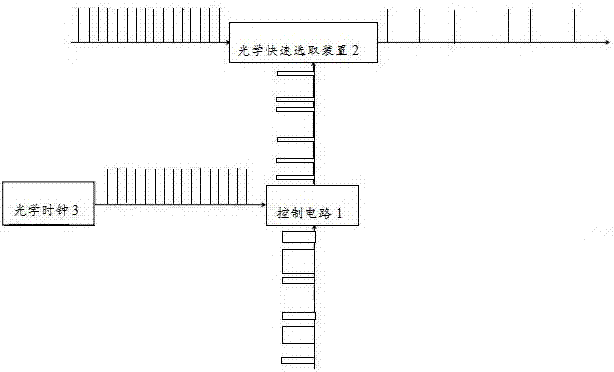
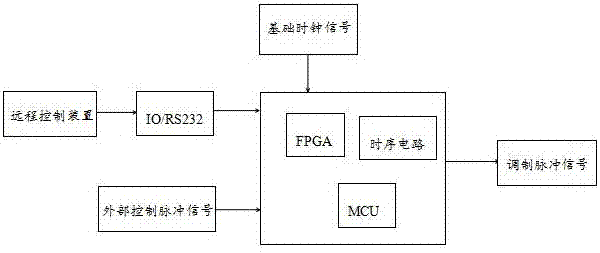
The invention provides a high-energy picosecond laser pulse POD (Pulse on Demand) control system and a method. The system comprises a control circuit, an optical fast selection device, and a main optical clock. The main optical clock is connected with the control circuit. The control circuit is connected with the optical fast selection device. The main optical clock is used for emitting a base clock laser pulse signal and transmitting the base clock laser pulse signal to the control circuit. The control circuit is used for outputting a modulated pulse signal to the optical fast selection device according to the base clock laser pulse signal and a received external control pulse signal. The optical fast selection device is used for screening laser pulses emitted by a picosecond laser according to the modulated pulse signal. Every picosecond laser pulse required can be selected precisely from high-energy picosecond laser pulses as high as 1MHz. The POD function of the picosecond laser can be achieved. The laser output frequency can be modulated and changed in real time with external control signals.
Owner:WUHAN HUARAY PRECISION LASER
Synchronized pulsed lada for the simultaneous acquisition of timing diagrams and laser-induced upsets
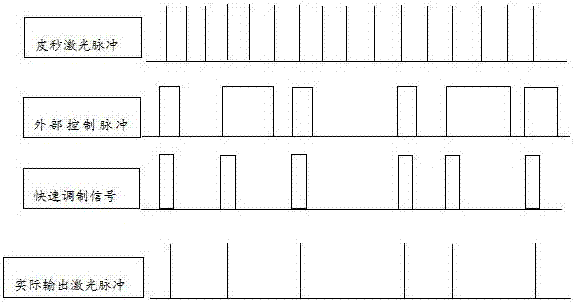
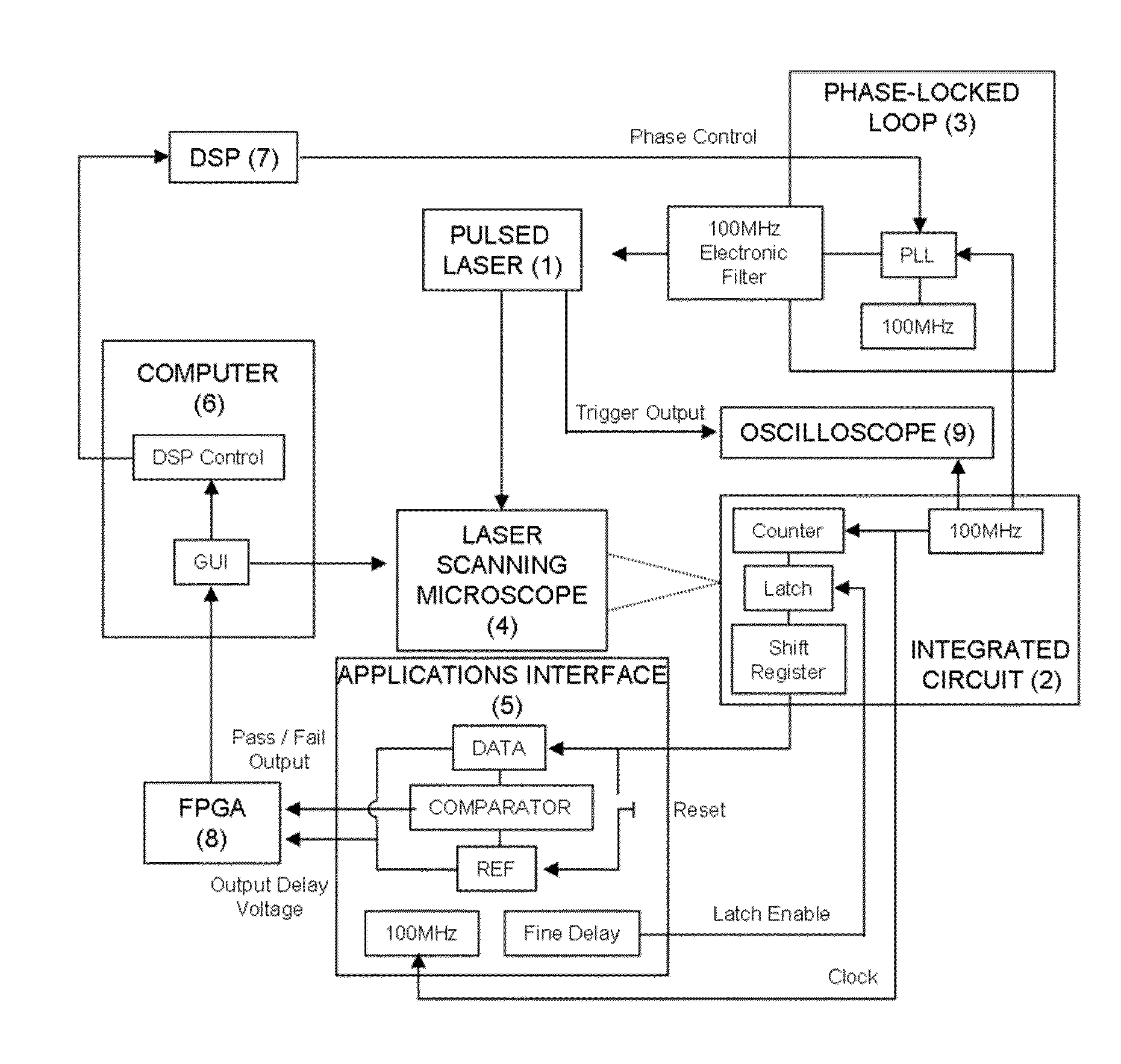
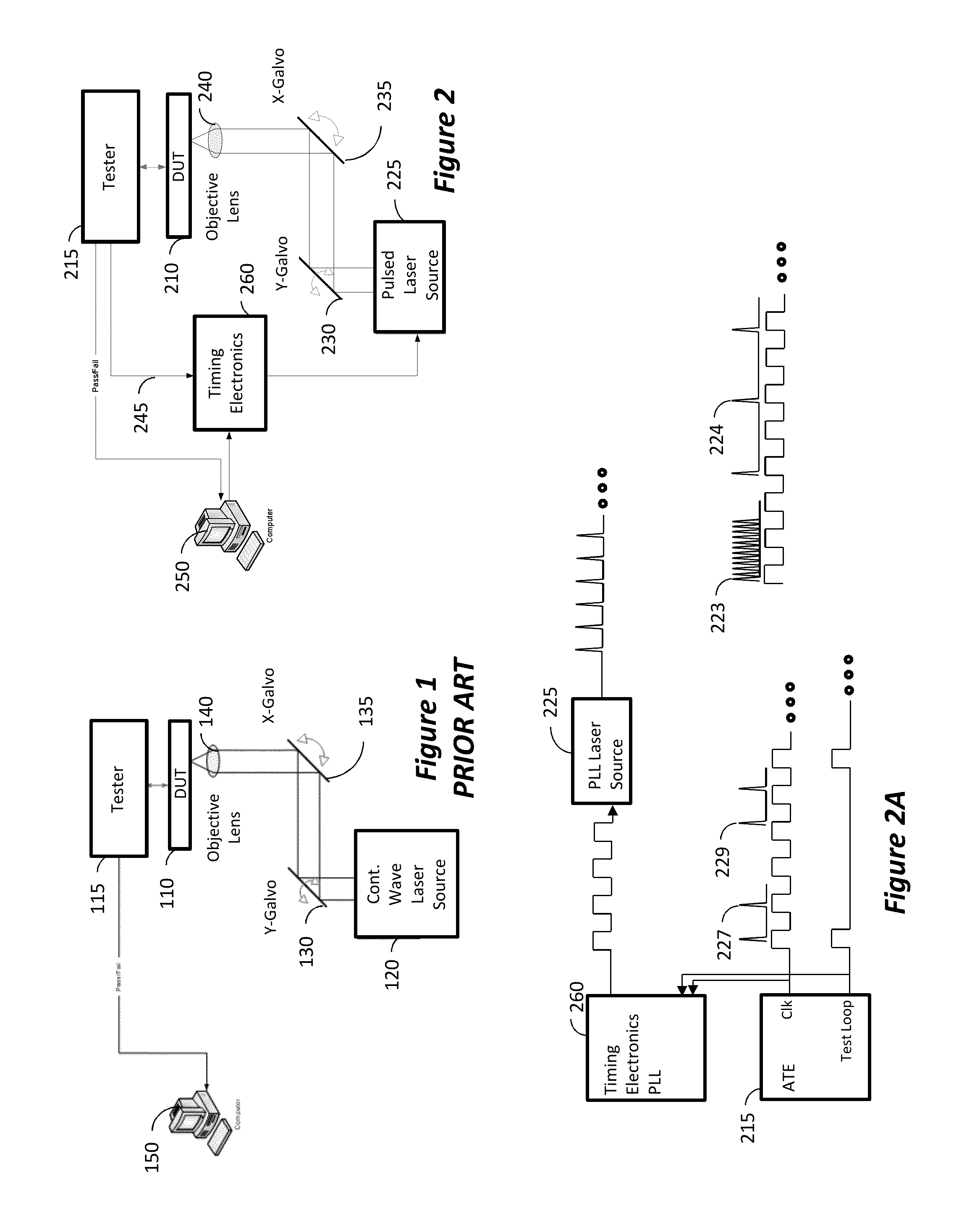
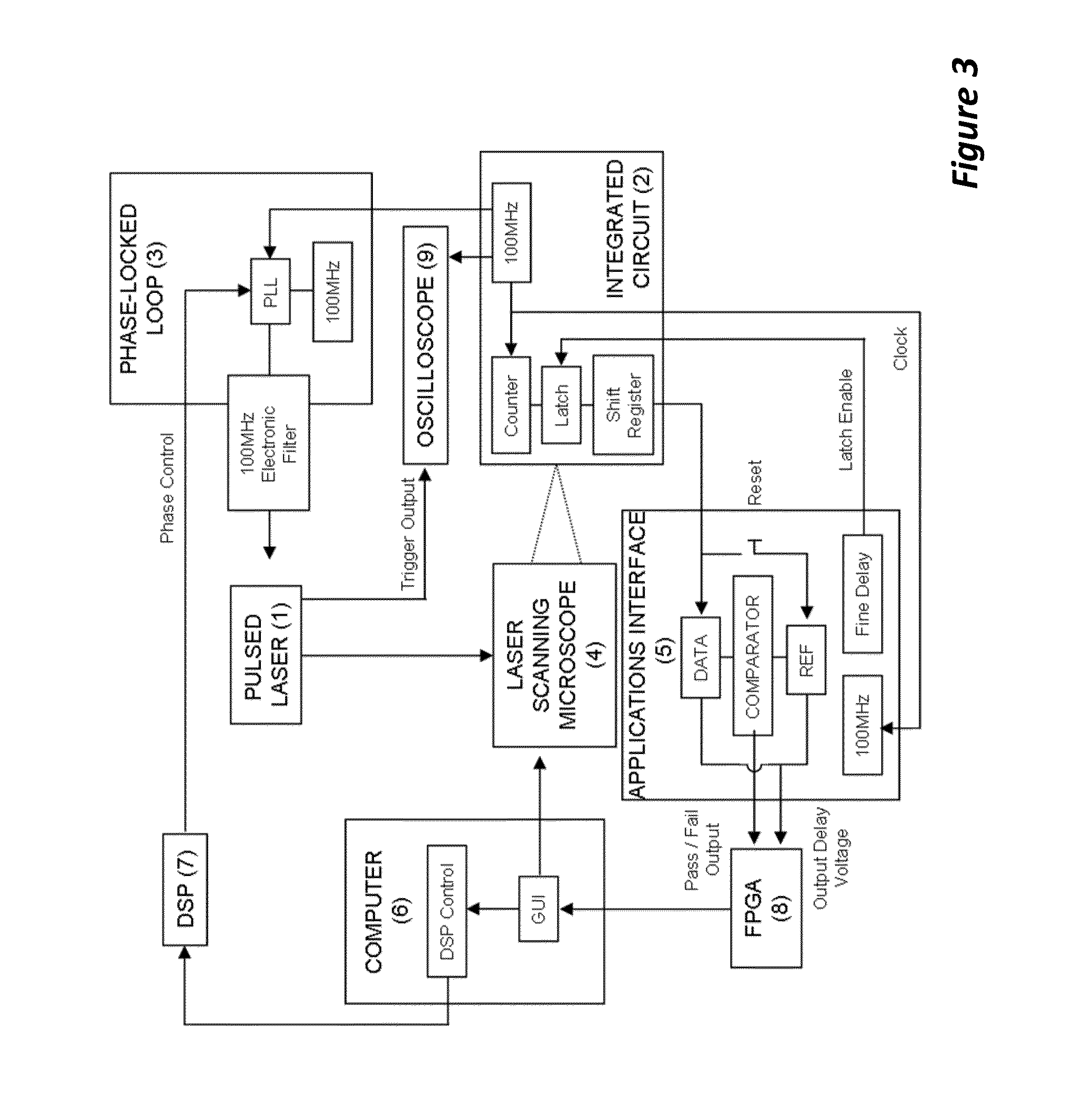
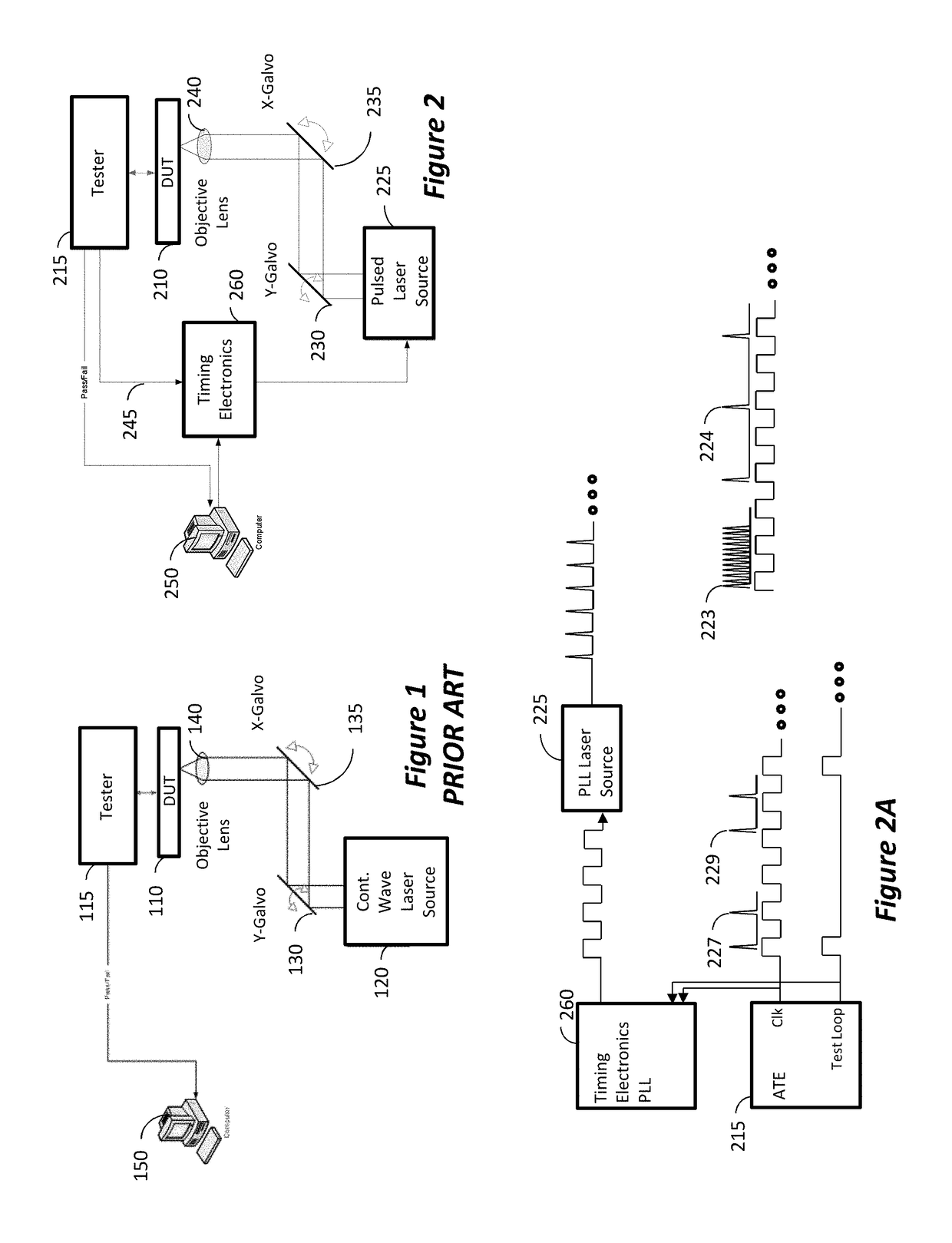
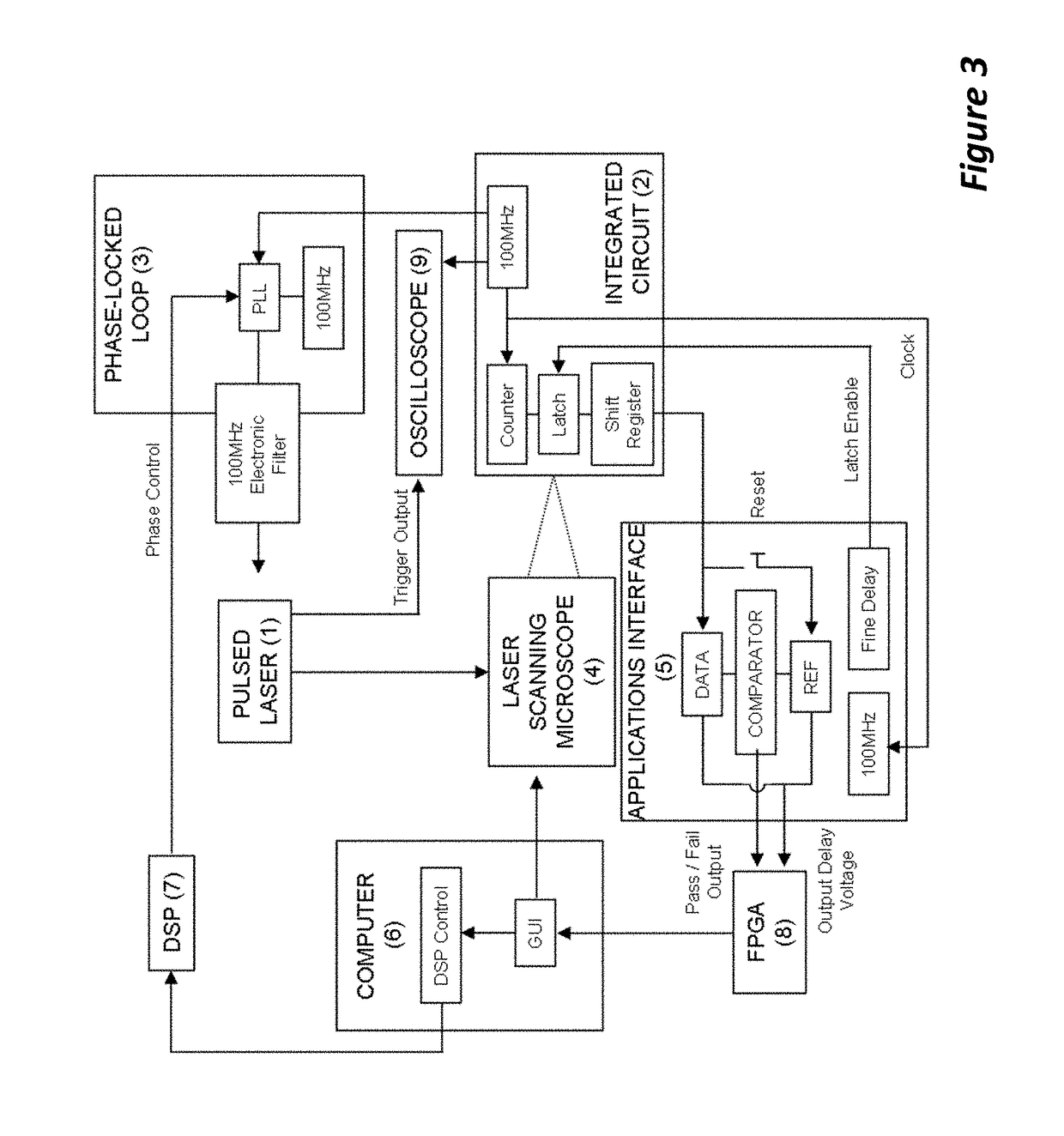
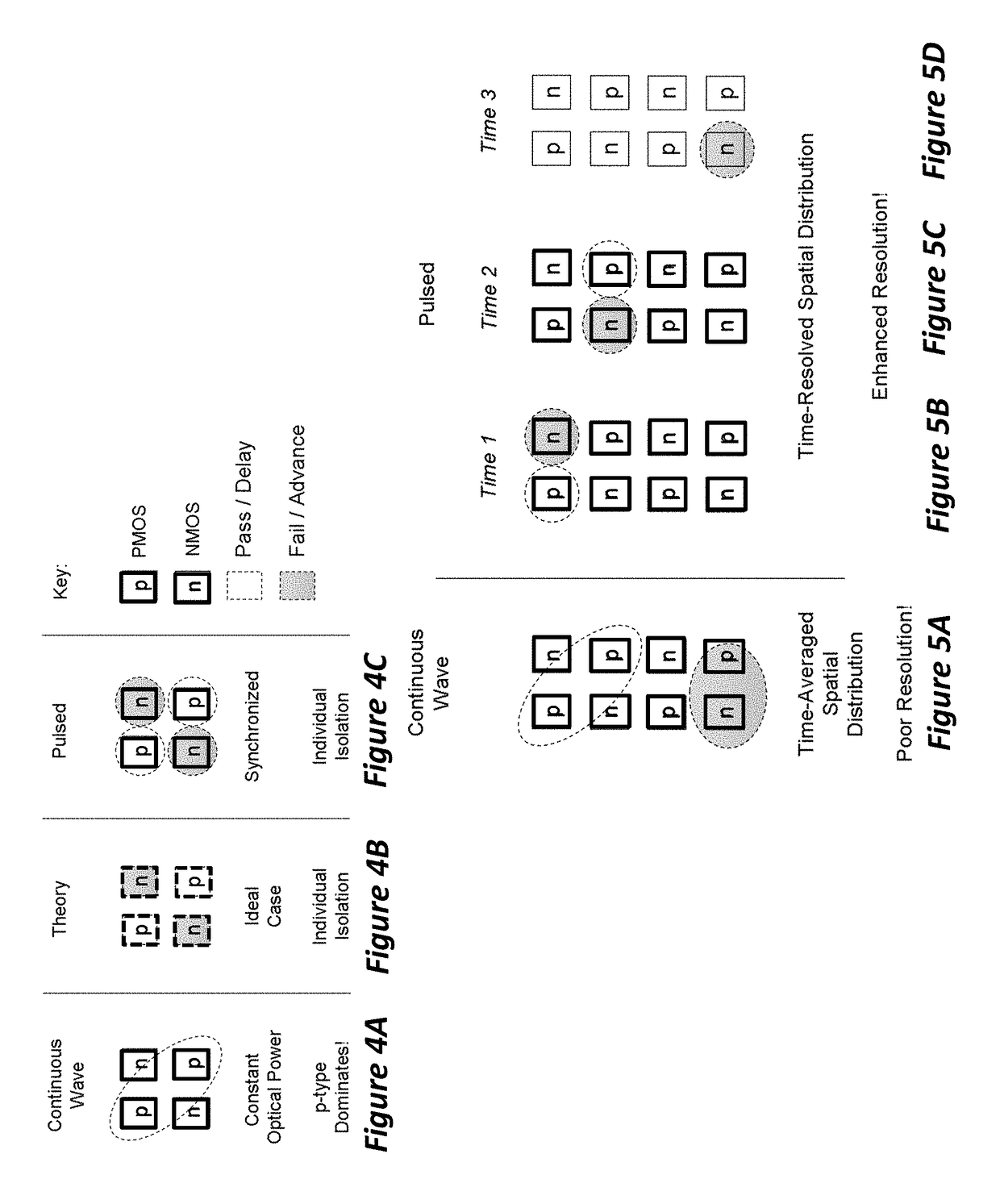
ActiveUS20140285227A1Improve spatial resolutionSufficient energyContactless circuit testingLaser-assisted device alterationPicosecond laser
Method to extract timing diagrams from synchronized single- or two-photon pulsed LADA by spatially positioning the incident laser beam on circuit feature of interest, temporally scanning the arrival time of the laser pulse with respect to the tester clock or the loop length trigger signal, then recording the magnitude and sign of the resulting fail rate signature per laser pulse arrival time. A Single-Photon Laser-Assisted Device Alteration apparatus applies picosecond laser pulses of wavelength having photon energy equal to or greater than the silicon band-gap. A Two-Photon Laser-Assisted Device Alteration apparatus applies femtosecond laser pulses of wavelength having photon energy equal to or greater than half the silicon band-gap at the area of interest. The laser pulses are synchronized with test vectors so that pass / fail ratios can be altered using either the single-photon or the two-photon absorption effect. A sequence of synthetic images with error data illustrates timing sensitive locations.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
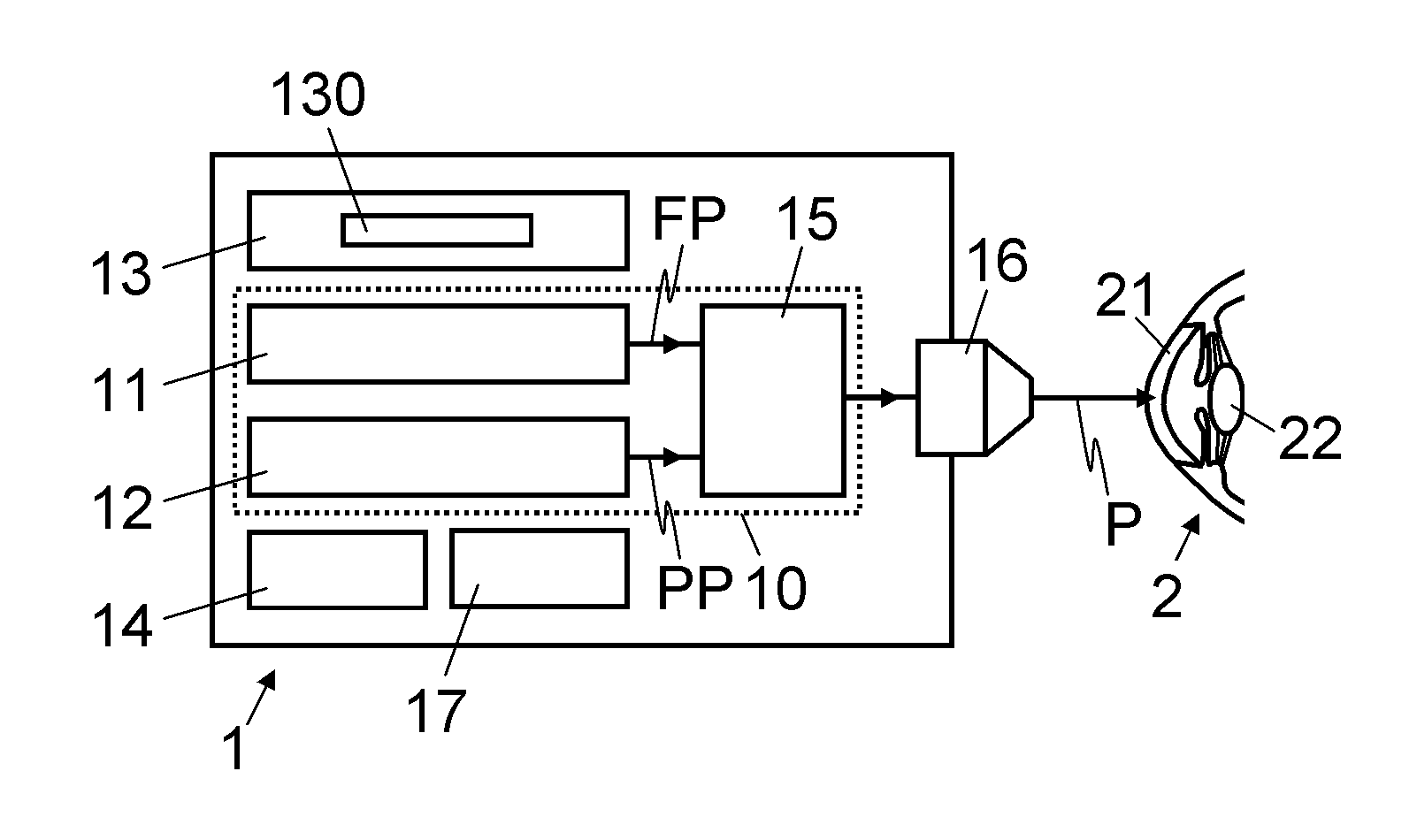
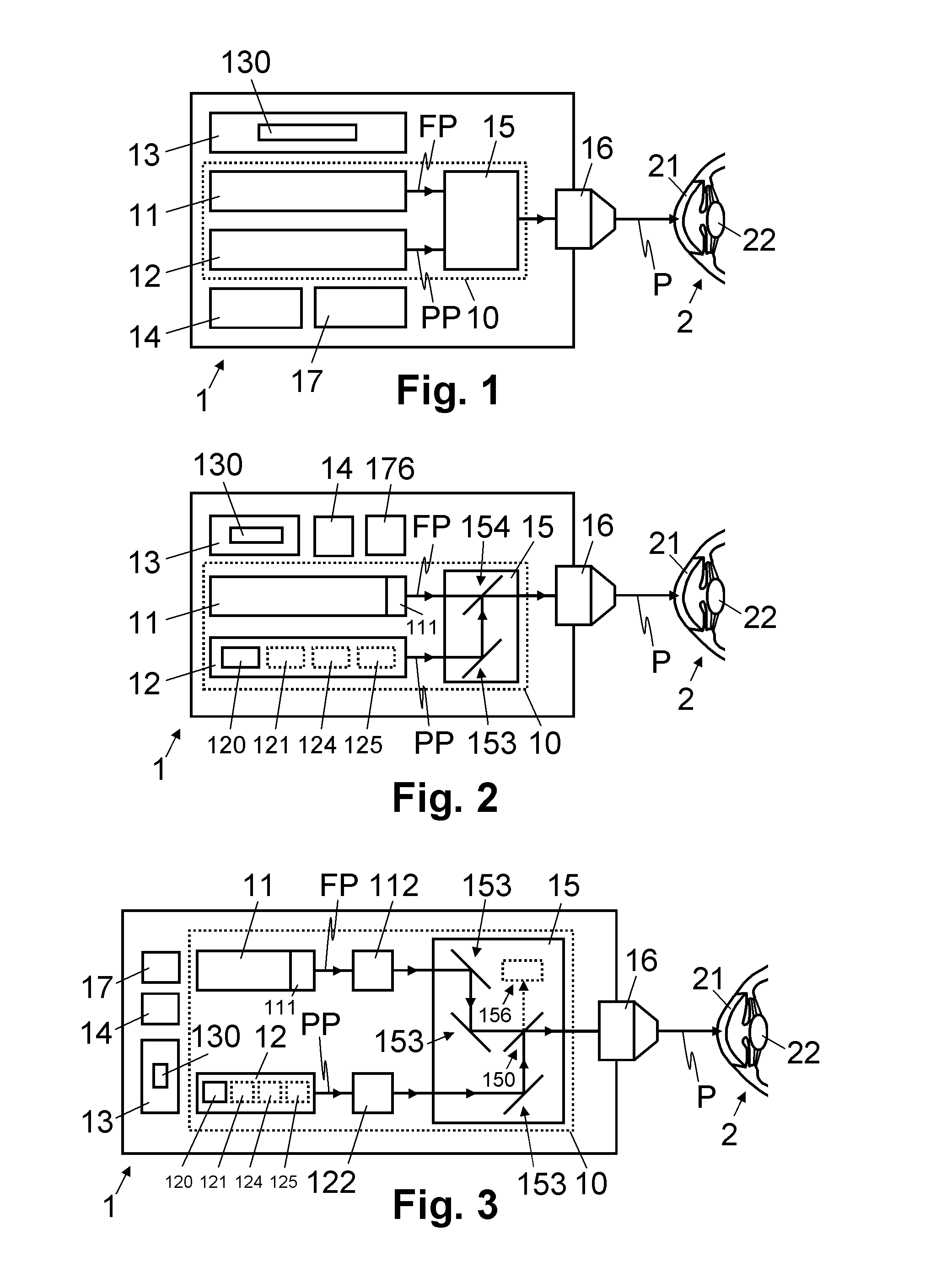
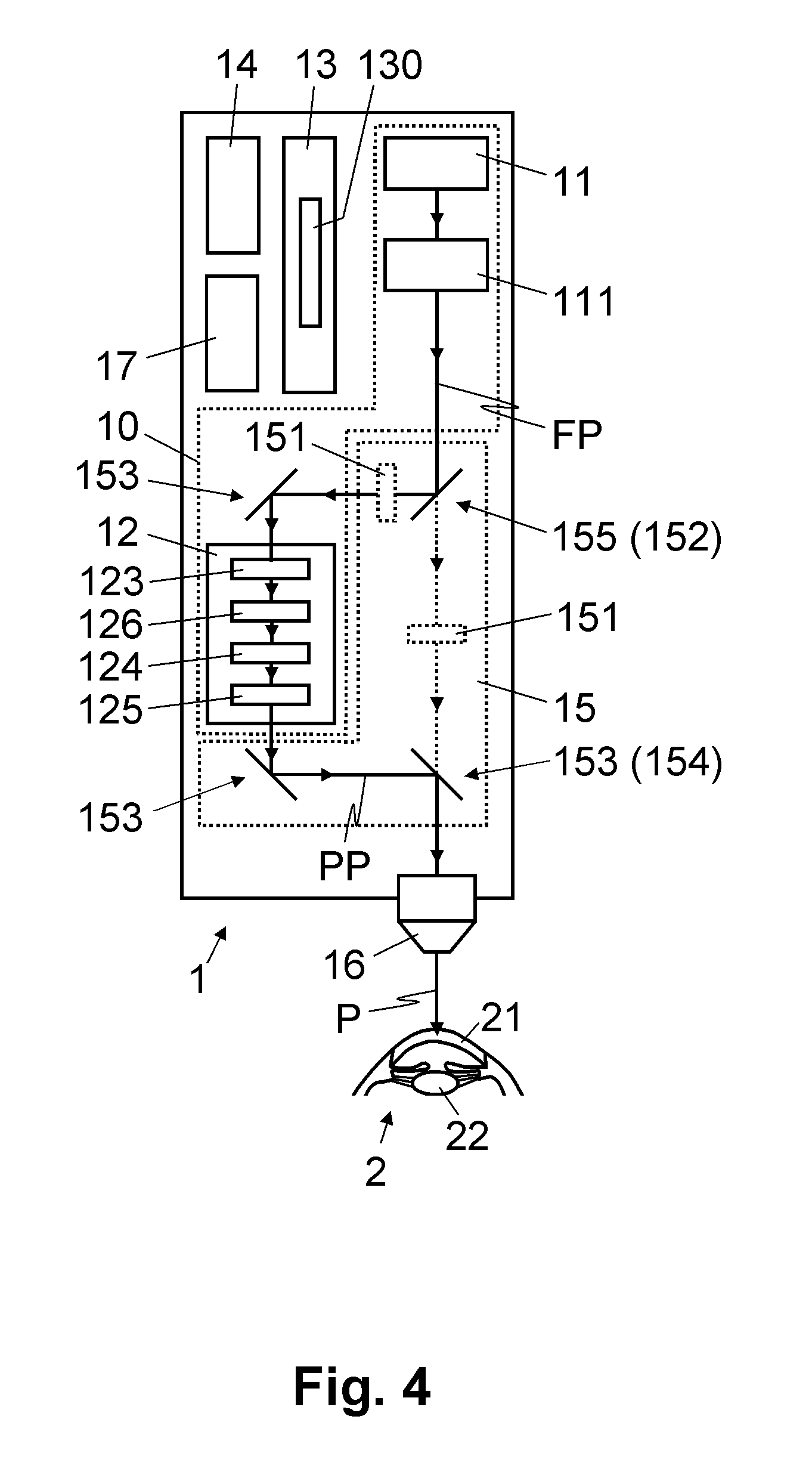
Device for treating eye tissue
InactiveUS20120165798A1Complicate and expensiveHigh pulse energyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
An ophthalmological device for treating eye tissue, with a femtosecond laser oscillator for generating femtosecond laser pulses and with a light projector for projecting the laser pulses onto or into the eye tissue in a focused fashion is moreover provided with a picosecond laser module for generating picosecond laser pulses. In the process, femtosecond laser pulses and / or picosecond laser pulses can selectively be fed to the light projector for treating the eye tissue. Hence, the ophthalmological device can selectively be used for performing precise cuts in the eye tissue by means of the femtosecond laser pulses and for fragmenting eye tissue by tissue fragmentation by means of the picosecond laser pulses.
Owner:RATHJEN CHRISTIAN
High-gain double-stroke traveling-wave amplifier for picosecond laser pulse amplification
ActiveCN102510000AAchieve maximum overlapImprove extraction efficiencyLaser detailsPicosecond laser pulseAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a high-gain double-stroke traveling-wave amplifier for picosecond laser pulse amplification. A semiconductor diode pumping source is joined with a first lens; the first lens is joined with a second lens; the second lens is joined with a first plane mirror; the first plane mirror is joined with a laser crystal; the laser crystal is joined with a third lens; the third lens is joined with a second plane mirror; a picosecond seed source is joined with a thin film polaroid; the thin film polaroid is joined with a Faraday optical rotator; the Faraday optical rotator is joined with a sixth lens; the sixth lens is joined with a fifth lens; the fifth lens is joined with a fourth lens; and the fourth lens is joined with the first plane mirror. According to the invention, the seed laser is subjected to beam expansion and focusing by utilizing the lens combination, the overlapping of seed optical pumping lights in a crystal is realized; at the same time, the surplus pumping lights are reflected to the inner part of the crystal for reuse by utilizing the combination of the lenses and reflection mirrors; and the high-gain double-stroke traveling-wave amplifier has the advantages of high amplification gain, outstanding output facula quality, good stability and the like.
Owner:苏州贝林激光有限公司
Laser direct ablation with picosecond laser pulses at high pulse repetition frequencies
ActiveCN103493182ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuitsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Real-time in situ picosecond laser pulse auto-correlation meter
InactiveCN107505054AReduce structural complexityLow costInstrumentsPicosecond laser pulseBeam splitter
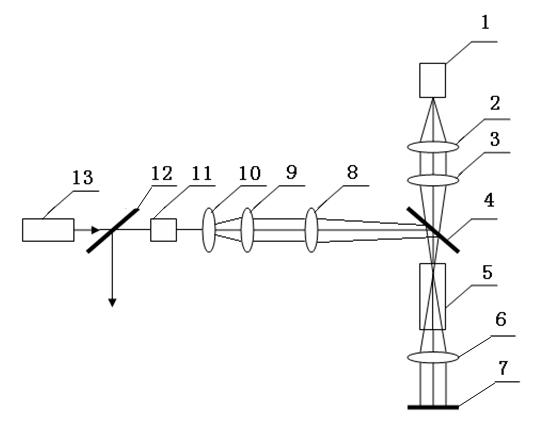
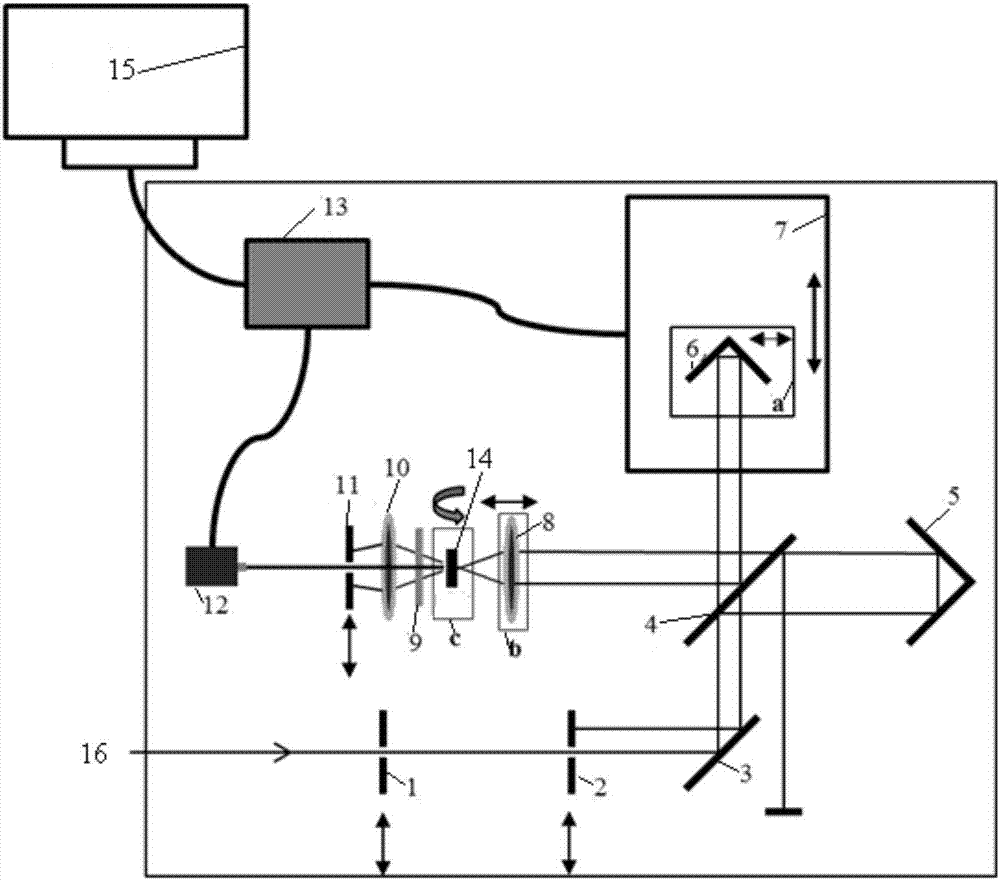
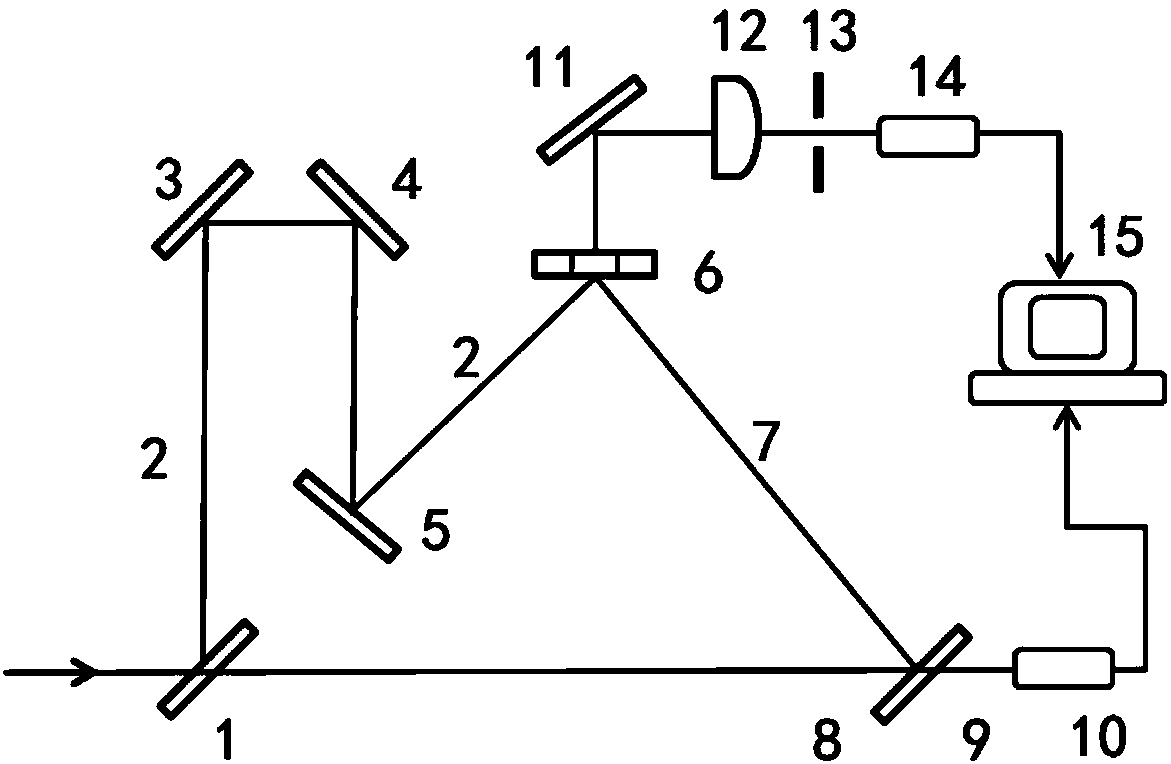
The invention relates to a real-time in situ picosecond laser pulse auto-correlation meter. An incident light diaphragm component, a reflection mirror and a beam splitter are sequentially fixed along the advancing direction of incident pulse laser. The incident pulse laser is split into a first beam of light and a second beam of light through the beam splitter. The first beam of light is reflected to a right angle prism through the beam splitter, is reflected to the beam splitter through the right angle prism, and finally is transmitted to a first lens through the beam splitter. The second beam of light is transmitted to a retroreflector through the beam splitter, is reflected to the beam splitter through the retroreflector, and finally is reflected to the first lens through the beam splitter. The first beam of light and the second beam of light converge at a frequency doubling crystal through the first lens to produce a second harmonic signal. The second harmonic signal sequentially passes through a filter, a second lens, a diaphragm and a photodiode detector to generate an electrical signal, and the electrical signal is collected by a master control system. The real-time in situ picosecond laser pulse auto-correlation meter provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, easy operation, easy setting up, easy debugging, wide application range, and can continuously change the time range of the measured laser pulse.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for enhancing plasmon polariton and phonon polariton resonance
ActiveUS7760421B2Laser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPicosecond laser pulsePhoton emission
A metallic nano-particle surrounded by an amplifying medium results in a boundary condition that creates a singularity in the particle's dynamic polarizability at the localized surface plasmon resonance and at a critical value of the gain is disclosed. The boundary condition may be time dependent due to excitation by a sub-picosecond laser pulse and couples to the electromagnetic vacuum resulting in photon emission in an analogue of the Unruh Effect. The vacuum emission from 2-D nanostructures embedded in high gain laser dyes predicts energies nearly two orders of magnitude larger than the spontaneous emission background. The vacuum radiation is may have a unique dependence on the excitation.
Owner:SOLARIS NANOSCI
Large-range picosecond laser pulse width measuring device
InactiveCN108254088ALow error measurementEliminate measurement errorsInstrumentsPicosecond laser pulseImaging processing
The invention relates to a large-range picosecond laser pulse width measuring device. The device includes a first spectroscope, a second spectroscope, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a third reflecting mirror, a fourth reflecting mirror, a nonlinear crystal, a cylindrical mirror, a slit diaphragm, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector and image processing unit. The device can realize the pulse width measurement of the measuring range of 0.3-50 ps.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-level amplification picosecond laser for removing freckles
ActiveCN106169691AShort widthHigh peak functionLaser detailsLight therapyPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention discloses a three-level amplification picosecond laser for removing freckles. The three-level amplification picosecond laser comprises a metal plate rack and a laser power supply. A water tank is mounted at the lower layer of the metal plate rack. A filter pot is mounted on the water tank. A water pump is mounted on one side face of the water tank. The laser power supply is mounted at the upper layer of the metal plate rack. A laser is mounted above the laser power supply. A heat dissipation frame is arranged on one side face of the laser. The three-level amplification picosecond laser has the advantages that through three-level amplification, a pulse width of an output picosecond laser is low, a peak function is high, the time acting on skin is short, the contact range with the skin is small, and shattered melanin is liable to be discharged from a body through skin lymph.
Owner:广州桦洋电子科技有限公司
Hundred picosecond pulse width measuring instrument
InactiveCN101871819APulse Width Measurement ImplementationInstrumentsPicosecond laser pulseMeasuring instrument
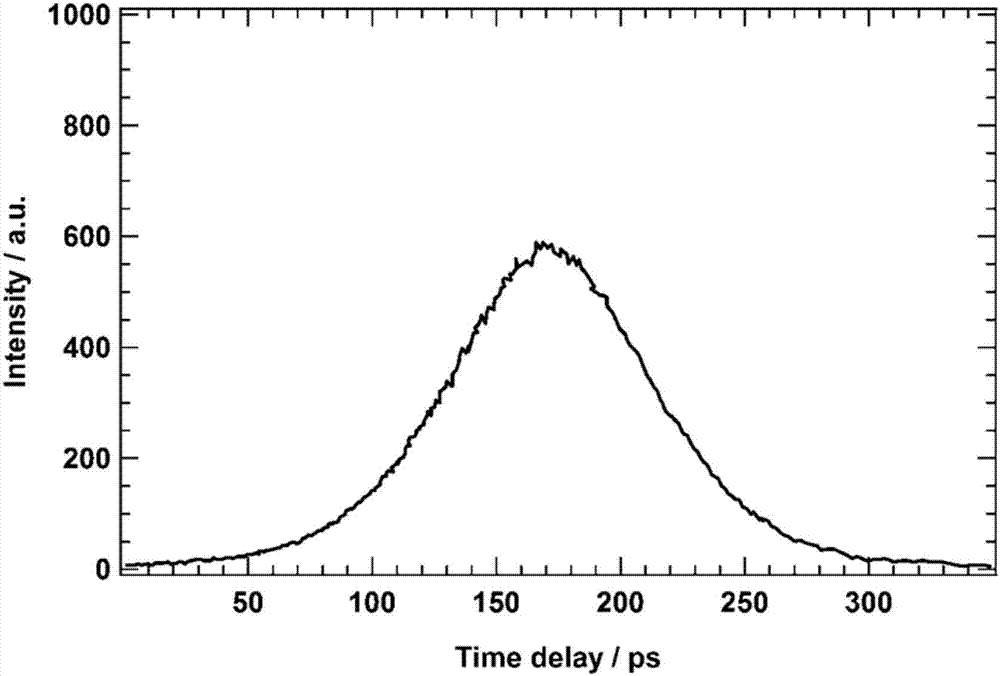
The invention relates to a hundred picosecond pulse width measuring instrument which comprises a spectroscope, a first light guide reflector, a second light guide reflector, a non-linear frequency doubling crystal, an optical imaging system, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector and a data acquisition and processing system, wherein the position relation of all components is shown as follow: an incident picosecond laser pulse to be measured divides a pulse to be measured into transmitted light and reflected light through the spectroscope; the transmitted light and the reflected light respectively pass through the first light guide reflector and the second light guide reflector and simultaneously enter into the non-linear frequency doubling crystal to generate a frequency doubling signal; and the frequency doubling signal is imaged on the CCD detector through the optical imaging system, and the data acquisition and processing system is used for finishing acquisition and data processing. The measuring instrument has the maximum measurable pulse time range of 150ps and the resolution ratio of 0.2ps.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Picosecond laser two-way two-stage amplification device
PendingCN108598860AHigh amplification gainHigh output spot qualityLaser arrangementsICT adaptationPicosecond laser pulsePicosecond laser
The invention relates to a picosecond laser two-way two-stage amplification device. The device comprises a picosecond seed source, a polarizing beam splitter, a first dichronic mirror, a second dichronic mirror, and a third dichronic mirror, wherein the picosecond seed source is at an injection end of the polarizing beam splitter and is used for generating seed light and injecting the seed light into the polarizing beam splitter, the polarizing beam splitter is used for transmitting seed light parallel to the polarizing direction so as to filter seed light vertical to polarization, the first dichronic mirror is on an optical axis transmitting the seed light of the polarizing beam splitter, the mirror surface of the first dichronic mirror and the optical axis has a certain angle, the seconddichronic mirror is on an optical axis reflecting the seed light of the first dichronic mirror, and the mirror surface of the second dichronic mirror and the optical axis has a certain angle. The picosecond laser two-way two-stage amplification device uses a first laser crystal and a second laser crystal so as to perform two-stage amplification; the amplification gain can be increased by two orders of magnitude to 10<5>, so that the picosecond laser two-way two-stage amplification device has the advantages of high amplification gain, stable output power, and high-quality output spot, and theamplified picosecond laser pulse can be widely used in the field of micro-processing.
Owner:SHENZHEN HYMSON LASER INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
A picosecond pulsed fiber laser
InactiveCN105186270BFrequency stabilitySimple structureActive medium shape and constructionPicosecond laser pulsePicosecond laser
Owner:深圳市欧凌镭射科技有限公司 +1
On-chip photon multi-stage switch based on Si-Ge2Sb2Te5 mixed waveguide
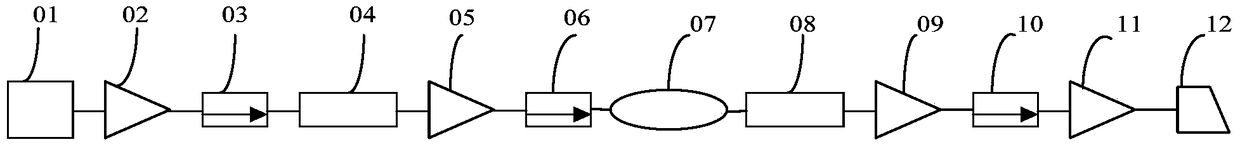
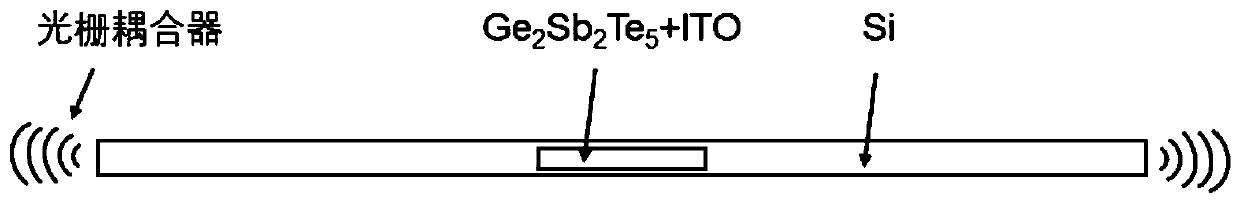
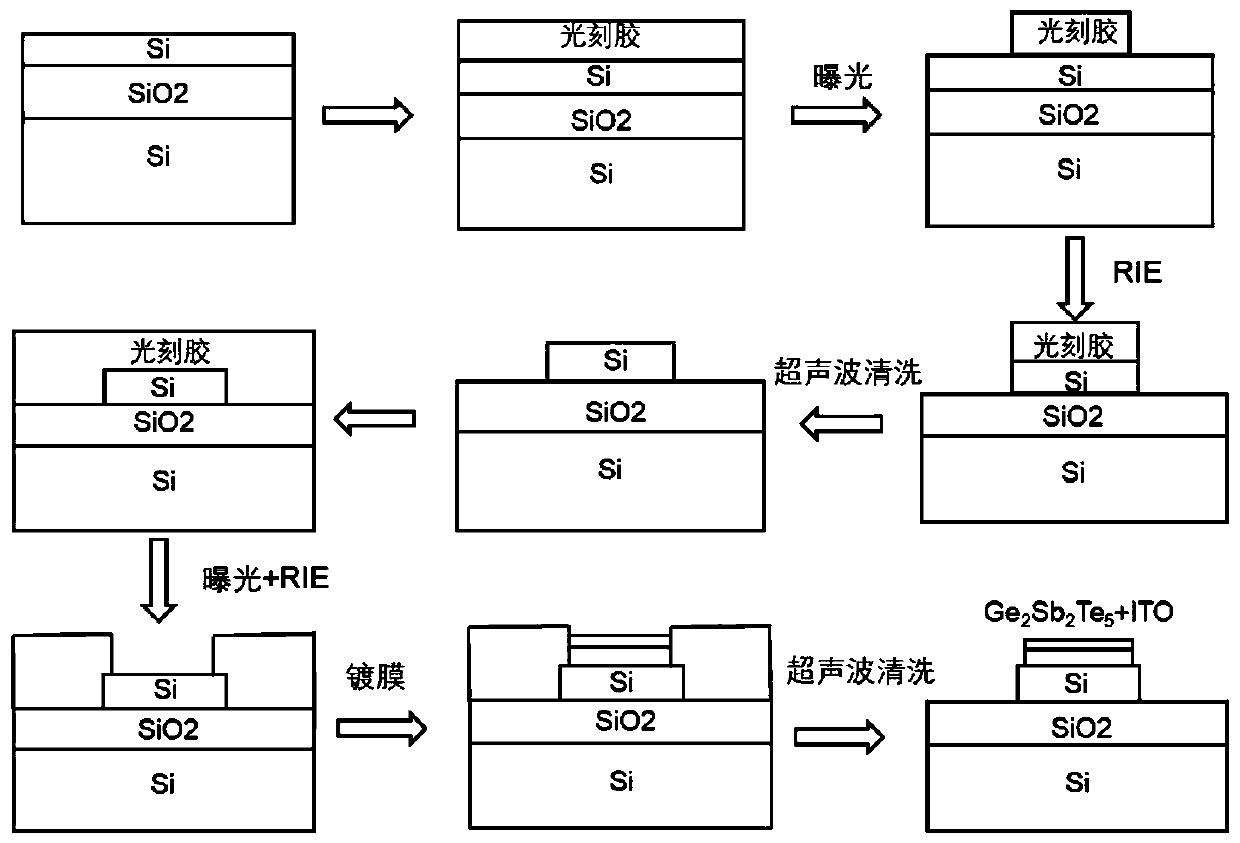
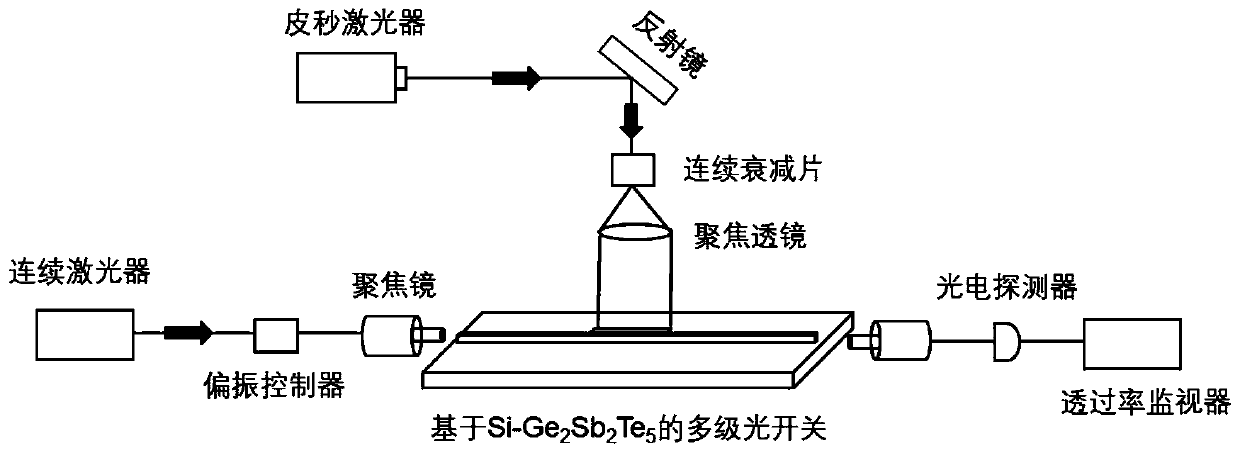
InactiveCN111258001AImplement multi-level operationsImprove conversion efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention discloses an on-chip photon multi-stage switch based on a Si-Ge2Sb2Te5 mixed waveguide, and belongs to the technical field of picosecond laser and continuous laser application. The on-chip photon multi-stage switch is based on a laser multi-pulse effect and an evanescent wave coupling theory. Amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5 is directly coupled with a single-mode Si waveguide, a Ge2Sb2Te5 thin film is deposited through a magnetron sputtering method, and different crystalline states of the Ge2Sb2Te5 are adjusted by adjusting the picosecond laser pulse number and pulse energy to achieve multi-stage switching operation. The on-chip photon multi-stage switch does not need to maintain the energy consumption of a traditional optical switch caused by the thermo-optic effect and the electro-opticeffect, and is a green device. In addition, the Ge2Sb2Te5 has different optical constants in different crystalline states, and the crystalline refractive index and extinction coefficient of the Ge2Sb2Te5 are higher than those of the Ge2Sb2Te5 in an amorphous state, so that the coupling capacity of a material to light and the absorption capacity of the material to the light are different, and multi-stage operation is further realized. The on-chip photon multi-stage switch can be widely applied to optical communication systems.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Synchronized pulsed LADA for the simultaneous acquisition of timing diagrams and laser-induced upsets
ActiveUS10191111B2Improve spatial resolutionSufficient energyContactless circuit testingLaser-assisted device alterationPicosecond laser
Method to extract timing diagrams from synchronized single- or two-photon pulsed LADA by spatially positioning the incident laser beam on circuit feature of interest, temporally scanning the arrival time of the laser pulse with respect to the tester clock or the loop length trigger signal, then recording the magnitude and sign of the resulting fail rate signature per laser pulse arrival time. A Single-Photon Laser-Assisted Device Alteration apparatus applies picosecond laser pulses of wavelength having photon energy equal to or greater than the silicon band-gap. A Two-Photon Laser-Assisted Device Alteration apparatus applies femtosecond laser pulses of wavelength having photon energy equal to or greater than half the silicon band-gap at the area of interest. The laser pulses are synchronized with test vectors so that pass / fail ratios can be altered using either the single-photon or the two-photon absorption effect. A sequence of synthetic images with error data illustrates timing sensitive locations.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
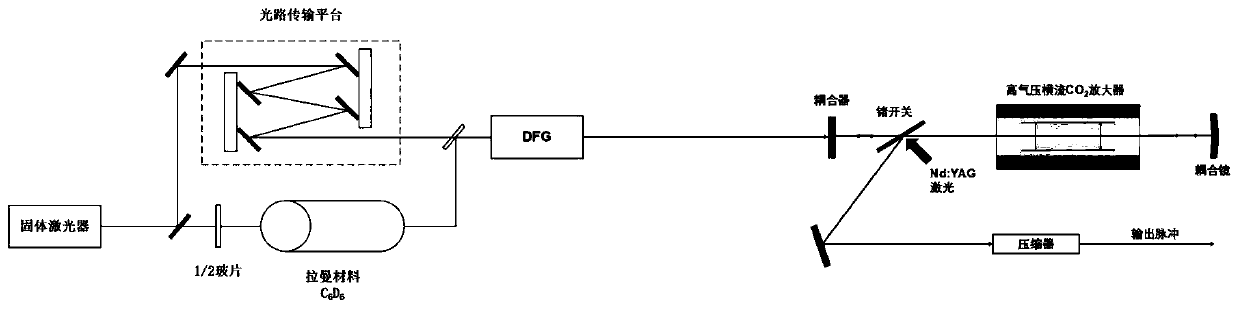
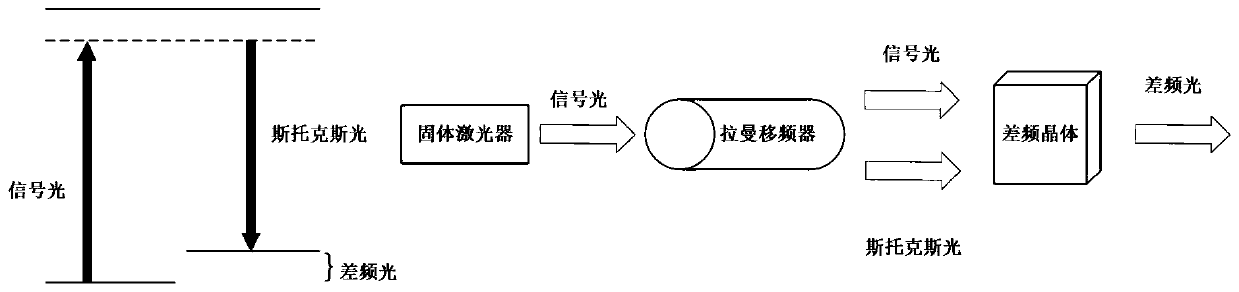
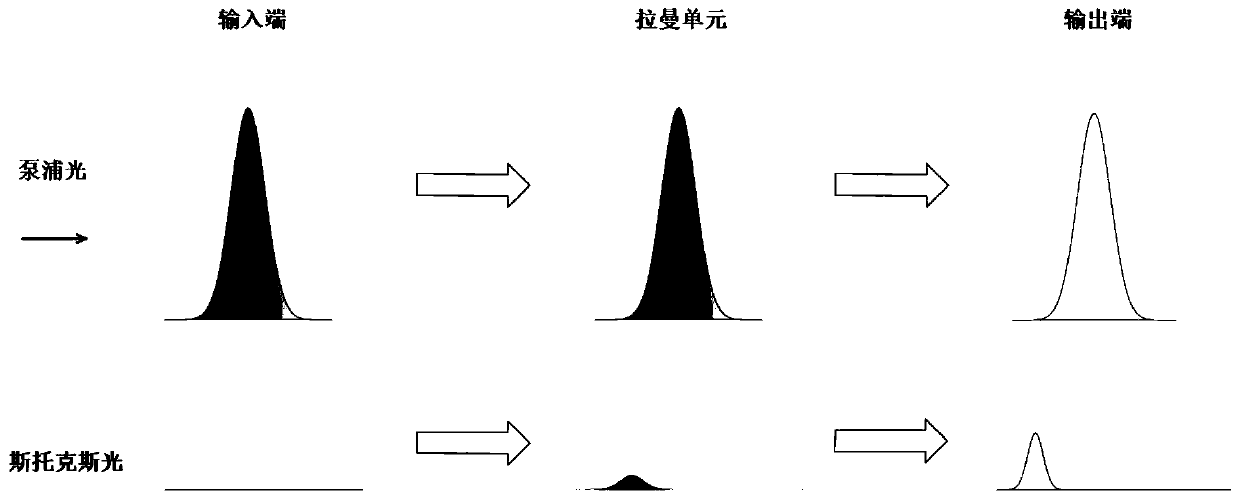
Picosecond Terawatt CO2 laser amplification system and method based on Raman frequency shift difference frequency
InactiveCN110676685ASolve discrete and discontinuous technical problemsOvercoming the Fundamental Problem of Difficult Gain AmplificationLaser using scattering effectsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention discloses a picosecond Terawatt CO2 laser amplification system and method based on Raman frequency shift difference frequency. The system comprises a solid picosecond laser generator, aRaman frequency shifter, a difference frequency crystal and a cross-flow CO2 laser amplifier. One part of picosecond laser pulses generated by the solid picosecond laser generator enter the Raman frequency shifter, the other part of the picosecond laser pulses is injected into the difference frequency crystal together with output light pulses of the Raman frequency shifter to generate seed light,and the seed light is amplified through the cross-flow CO2 laser amplifier. The method comprises the following steps: picosecond laser pulses generated by a solid picosecond laser generator generate Raman frequency shift, and light pulses of a first Stocks sideband are obtained; the obtained light pulses and a reference picosecond pulse are injected into a difference frequency crystal to obtain seed light; and the obtained seed light is injected into a cross-flow CO2 amplifier and amplified in the cross-flow CO2 amplifier. The technical problem that picosecond Terawatt CO2 laser seed light isextremely difficult to amplify and the spectral lines are discrete and discontinuous in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods and apparatus pertaining to picosecond pulsed fiber based lasers
ActiveUS9300105B2Good dispersionReduce intensityOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrangementsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
A pulsed fiber laser apparatus for outputting picosecond laser pulses can comprise a fiber delivered pulsed seed laser for providing picosecond optical seed pulses, and at least one optical fiber amplifier in optical communication with the fiber delivered pulsed seed laser. The optical fiber amplifier can comprise a gain optical fiber that receives and optically amplifies picosecond optical pulses by operating in a nonlinear regime wherein the picosecond optical pulses can be spectrally broadened by a factor of at least 8 during amplification thereof. The apparatus can further comprise a pulse compressor apparatus in optical communication with the optical fiber amplifier for providing compressed picosecond optical pulses. The pulse compressor apparatus can provide a dispersion of at least 50 ps / nm and can provide a compression ratio of the time duration of the picoseconds optical pulses received by the pulse compressor apparatus to the time duration of the compressed picosecond optical pulses of no greater than about 50.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Methods and apparatus for patterning photovoltaic devices and materials for use with such devices
ActiveUS9425334B2Simple materialImprove matchSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
A picosecond laser beam shaping assembly is disclosed for shaping a picosecond laser beam for use in patterning (e.g., scribing) semiconductor devices. The assembly comprises a pulsed fibre laser source of picosecond laser pulses, a harmonic conversion element for converting laser pulses at a first laser wavelength having a first spectral bandwidth to laser pulses at a second laser wavelength having a second spectral bandwidth, and a beam shaping apparatus for shaping the laser beam at the second laser wavelength, the beam shaping apparatus having a spectral bandwidth that substantially corresponds to the second spectral bandwidth so as to produce a laser beam having a substantially rectangular cross-sectional profile.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com