Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
364 results about "Optical beam deflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
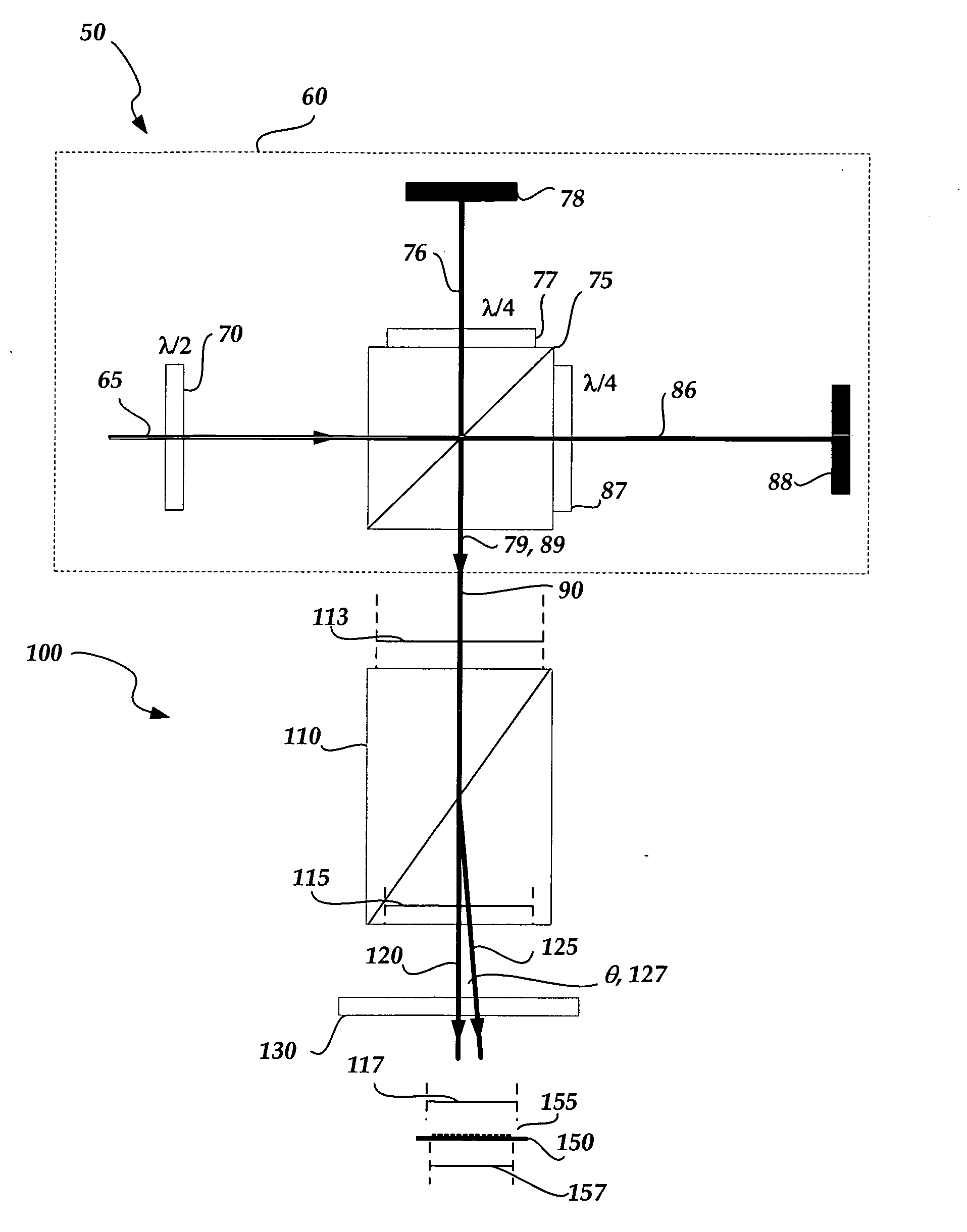
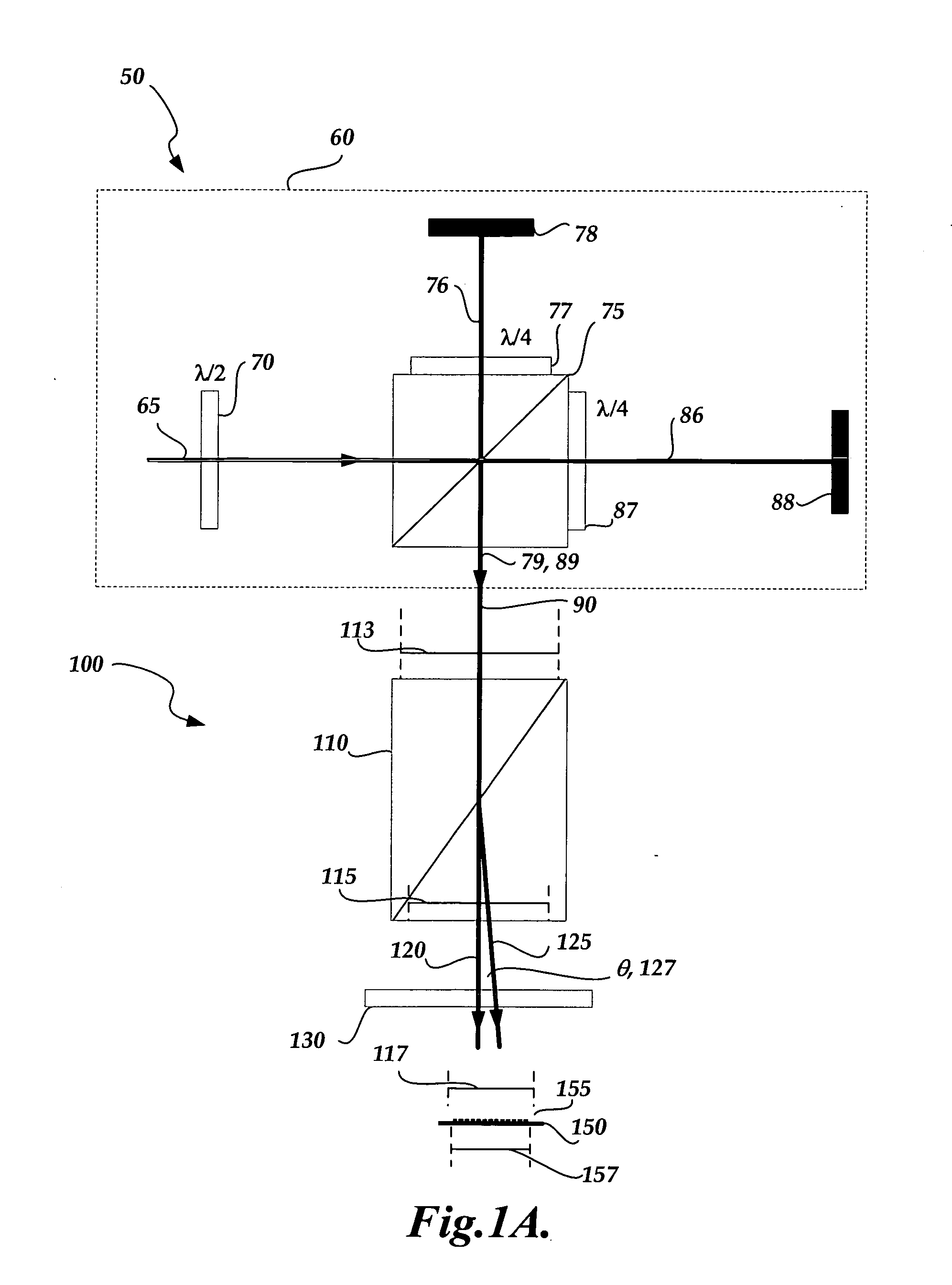
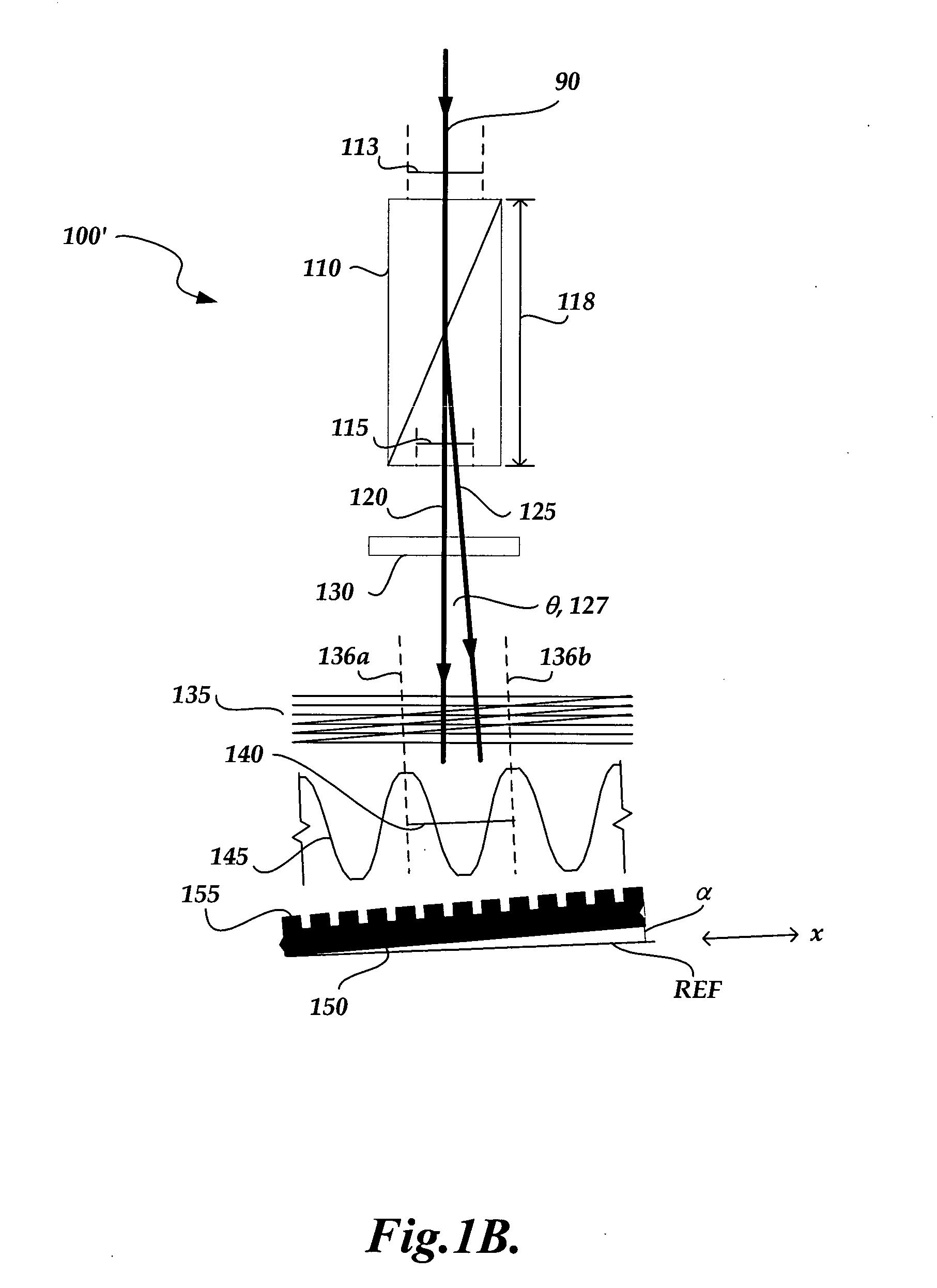
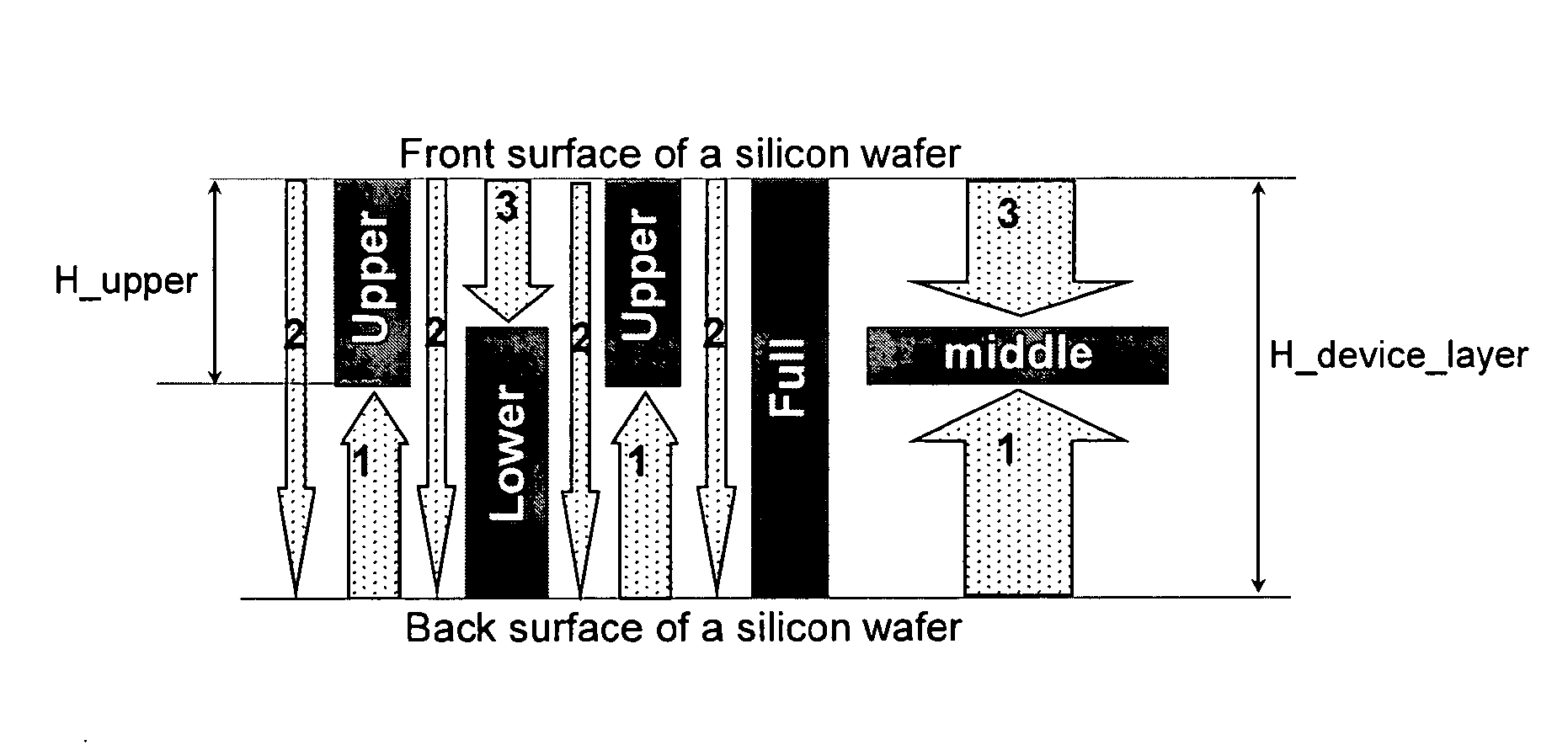
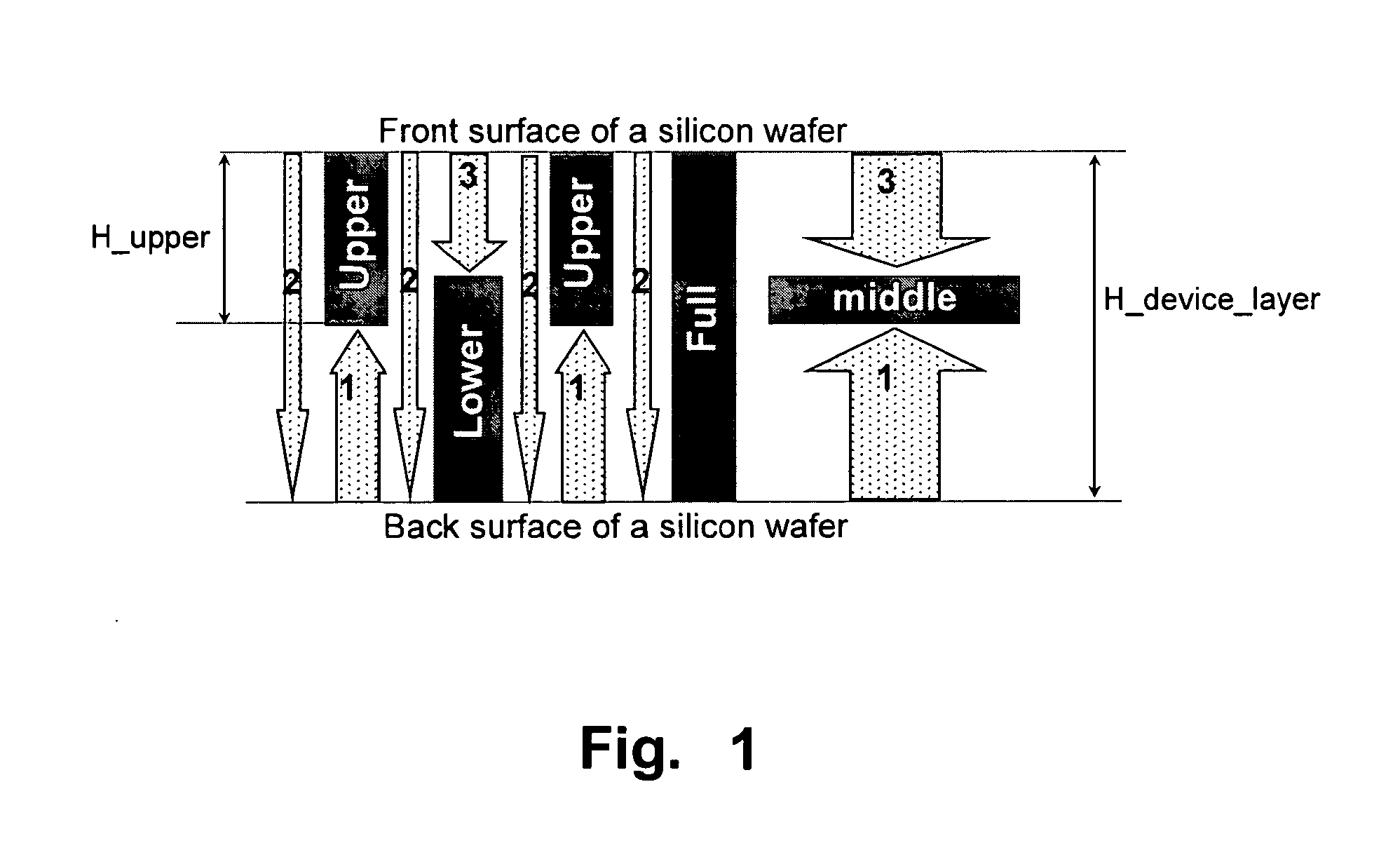
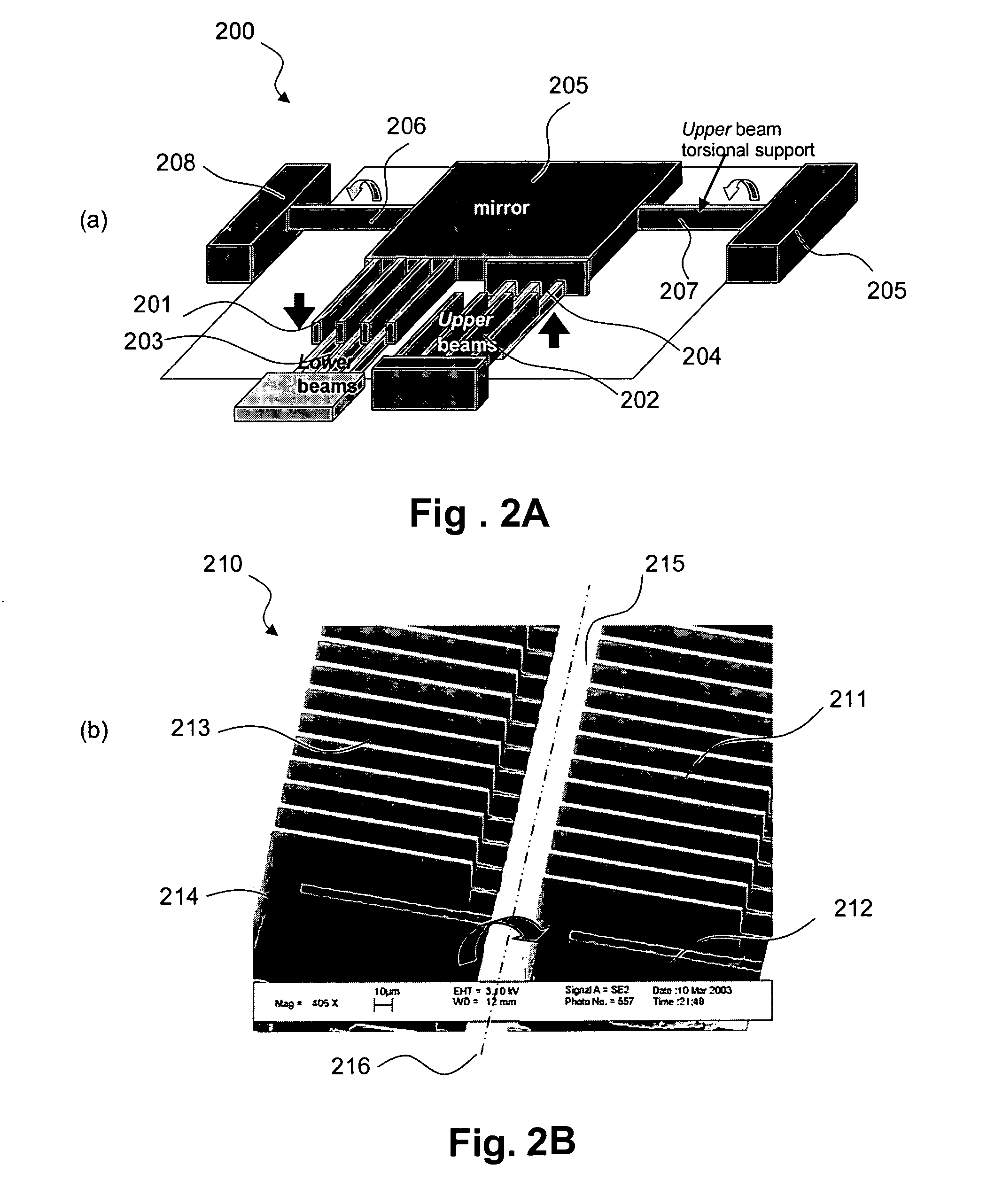
Gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system tip-tilt and tip-tilt-piston actuators and a method for forming the same
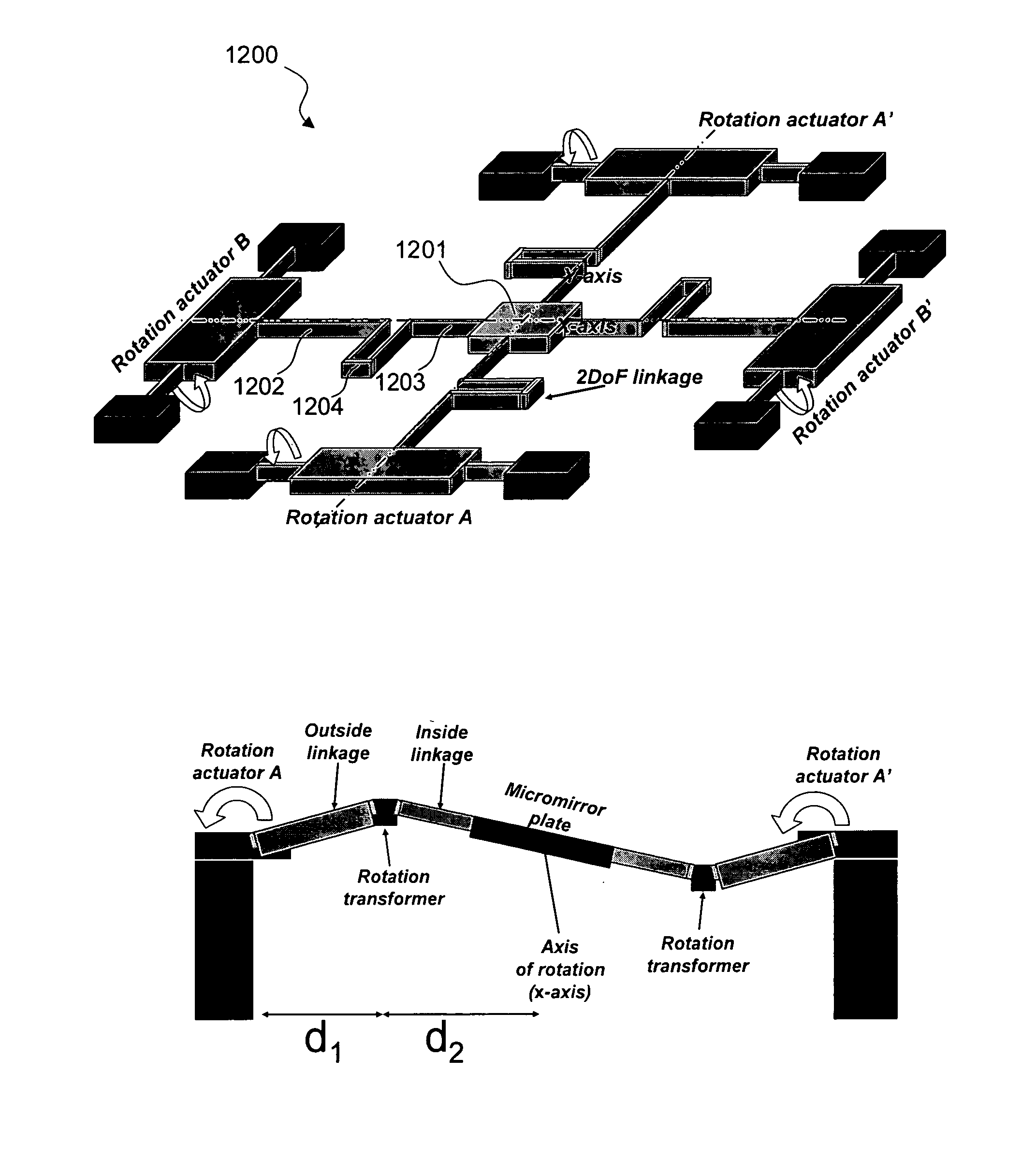
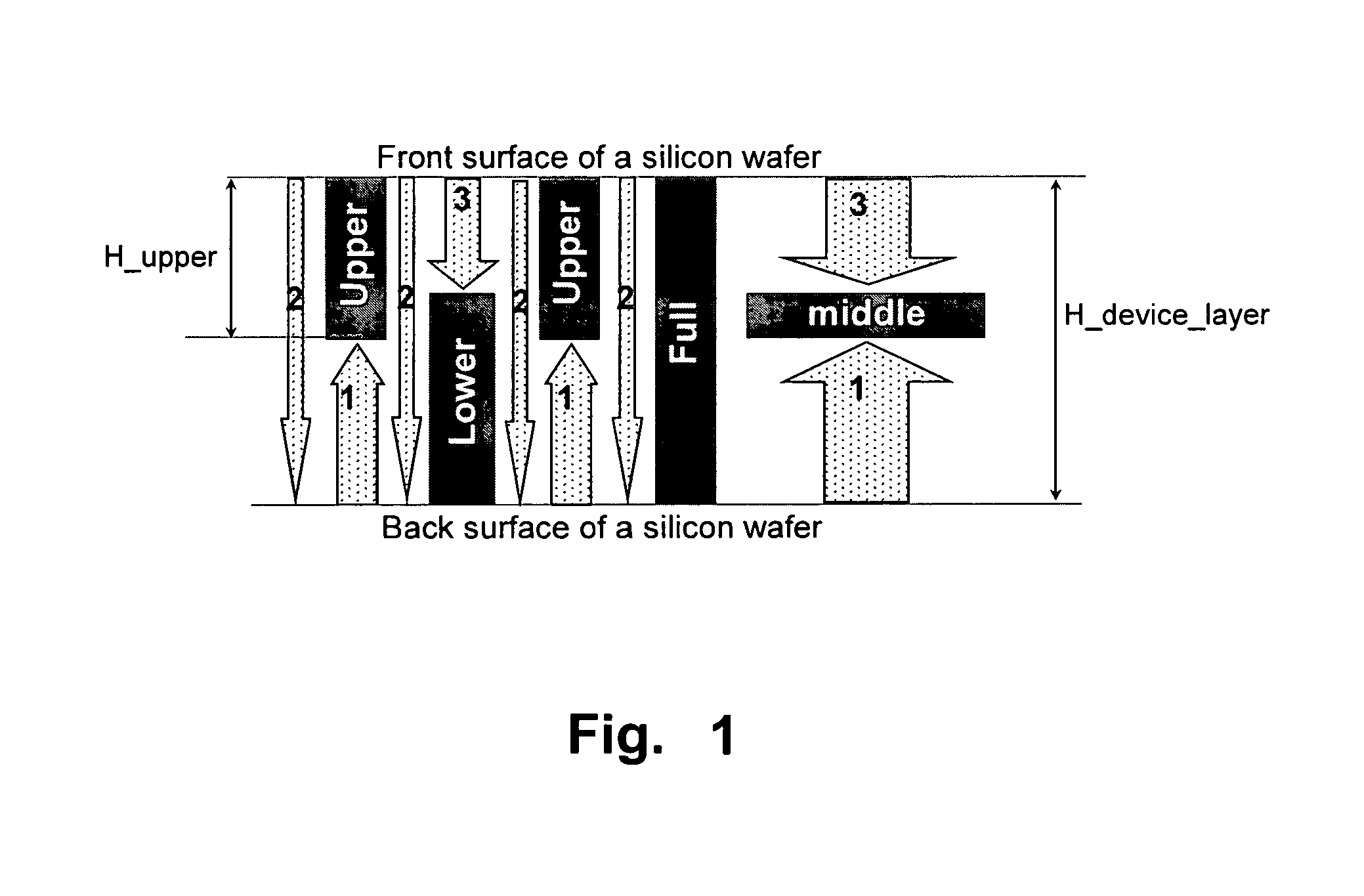
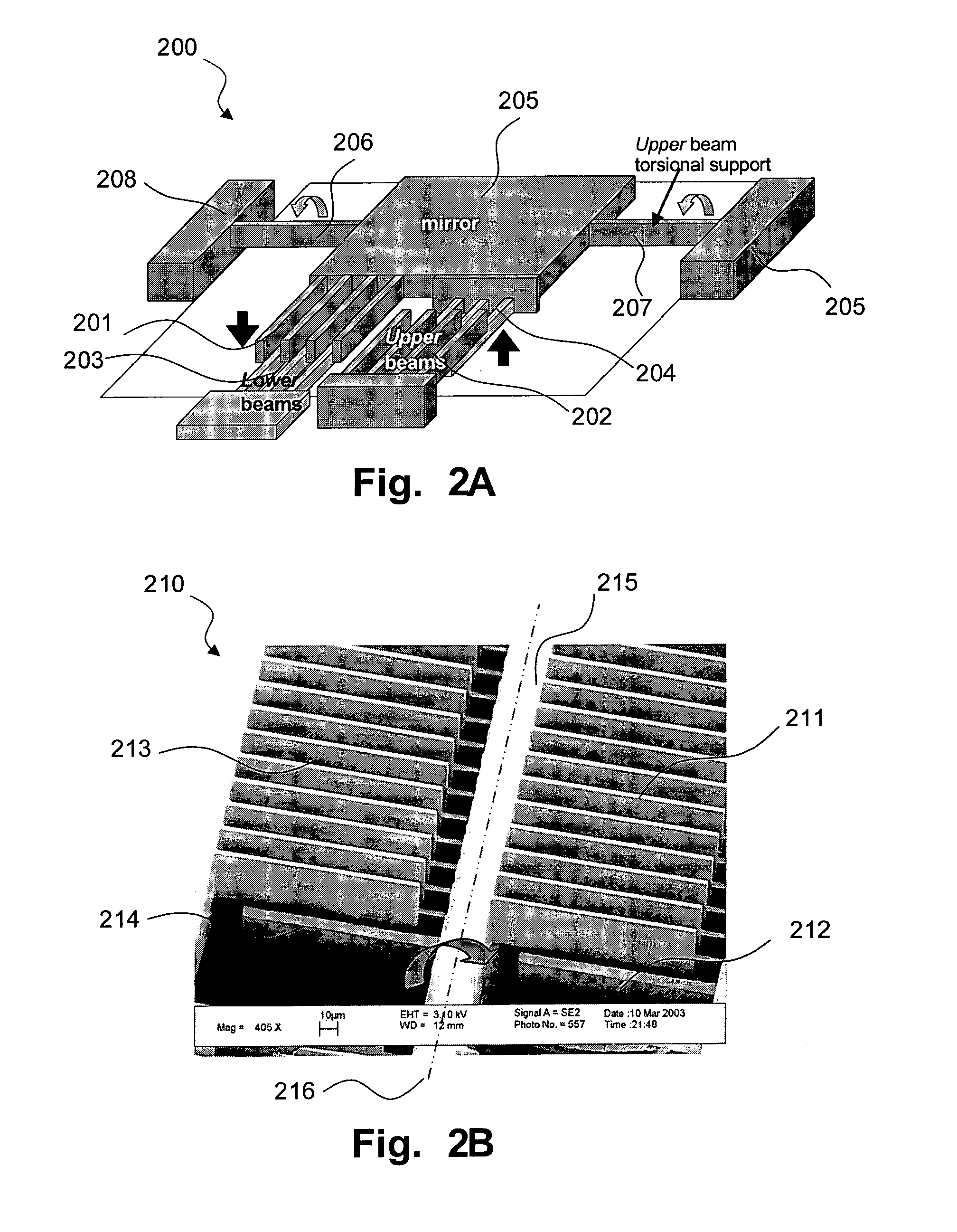
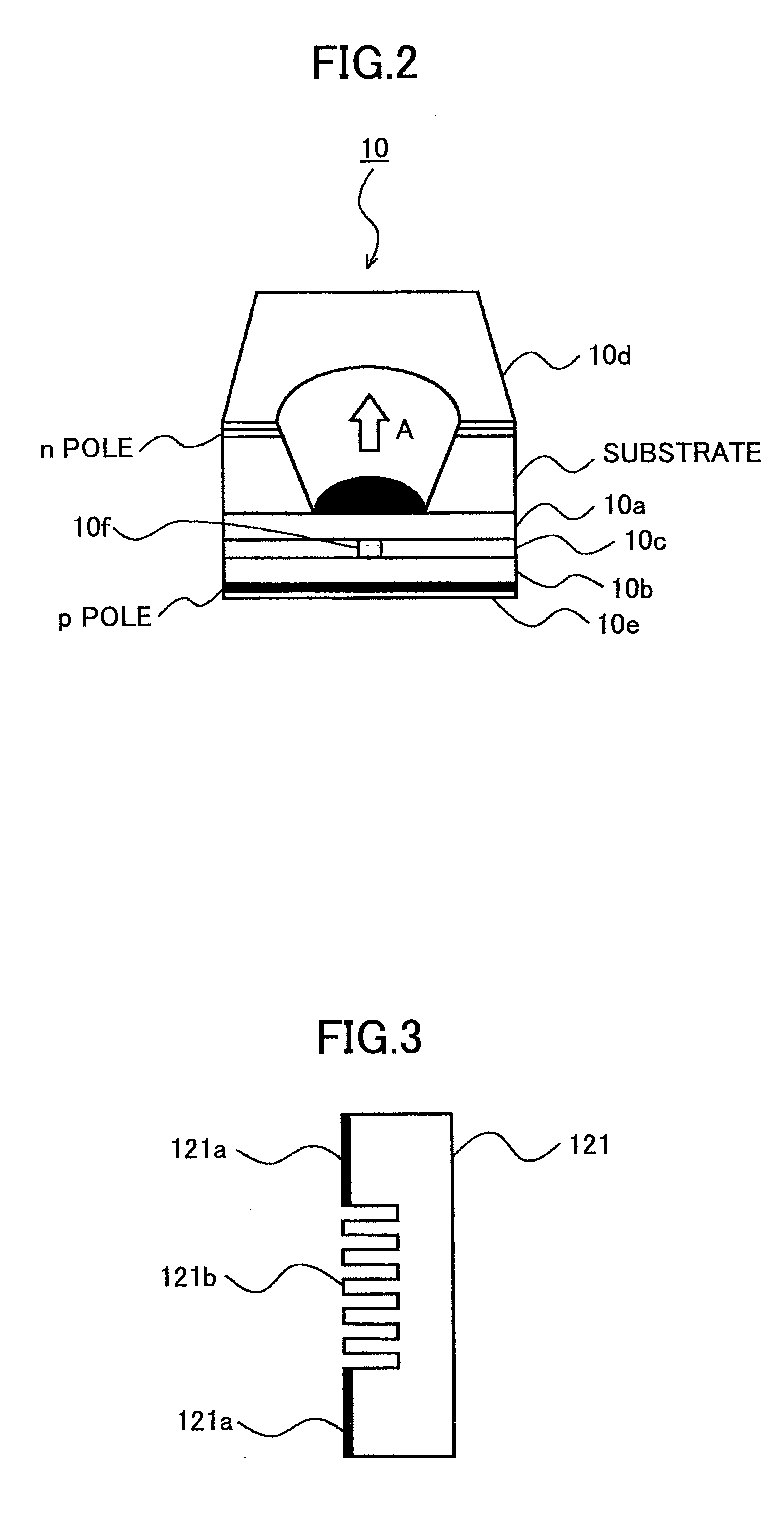
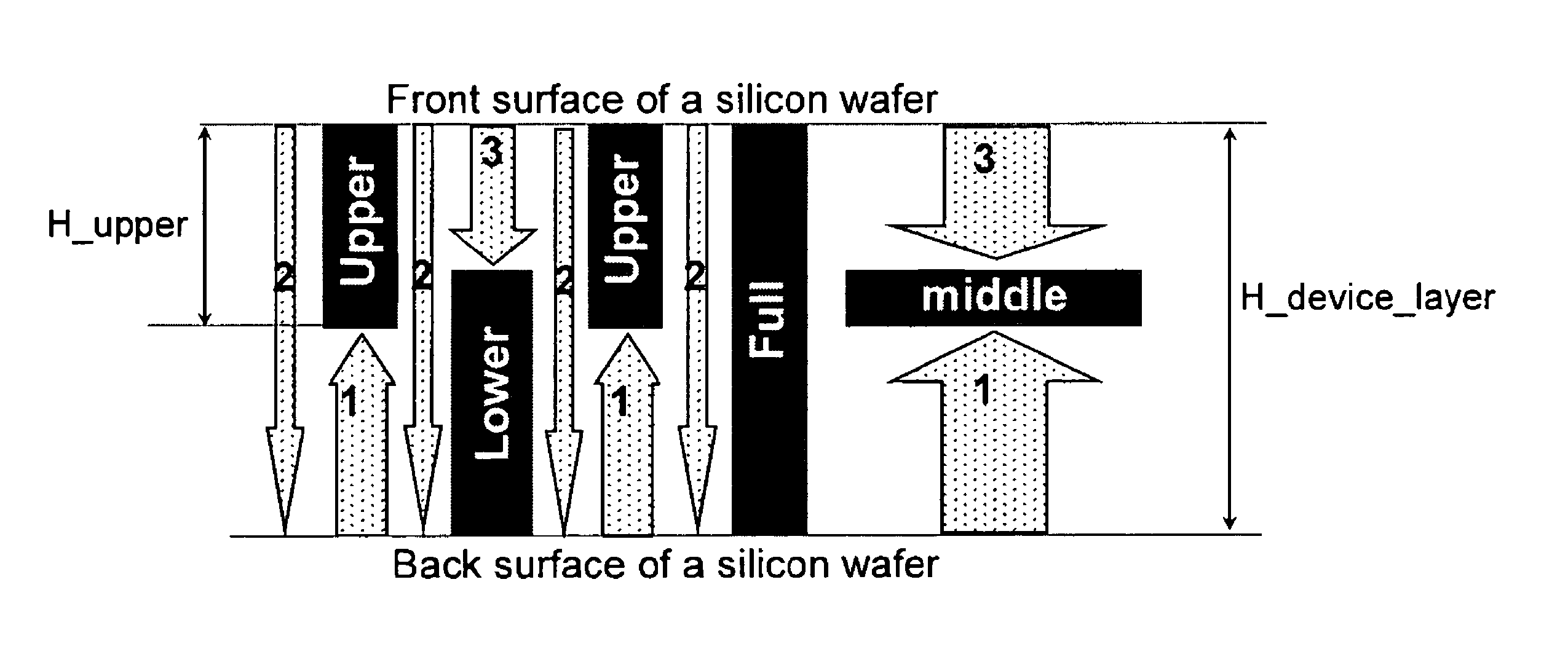
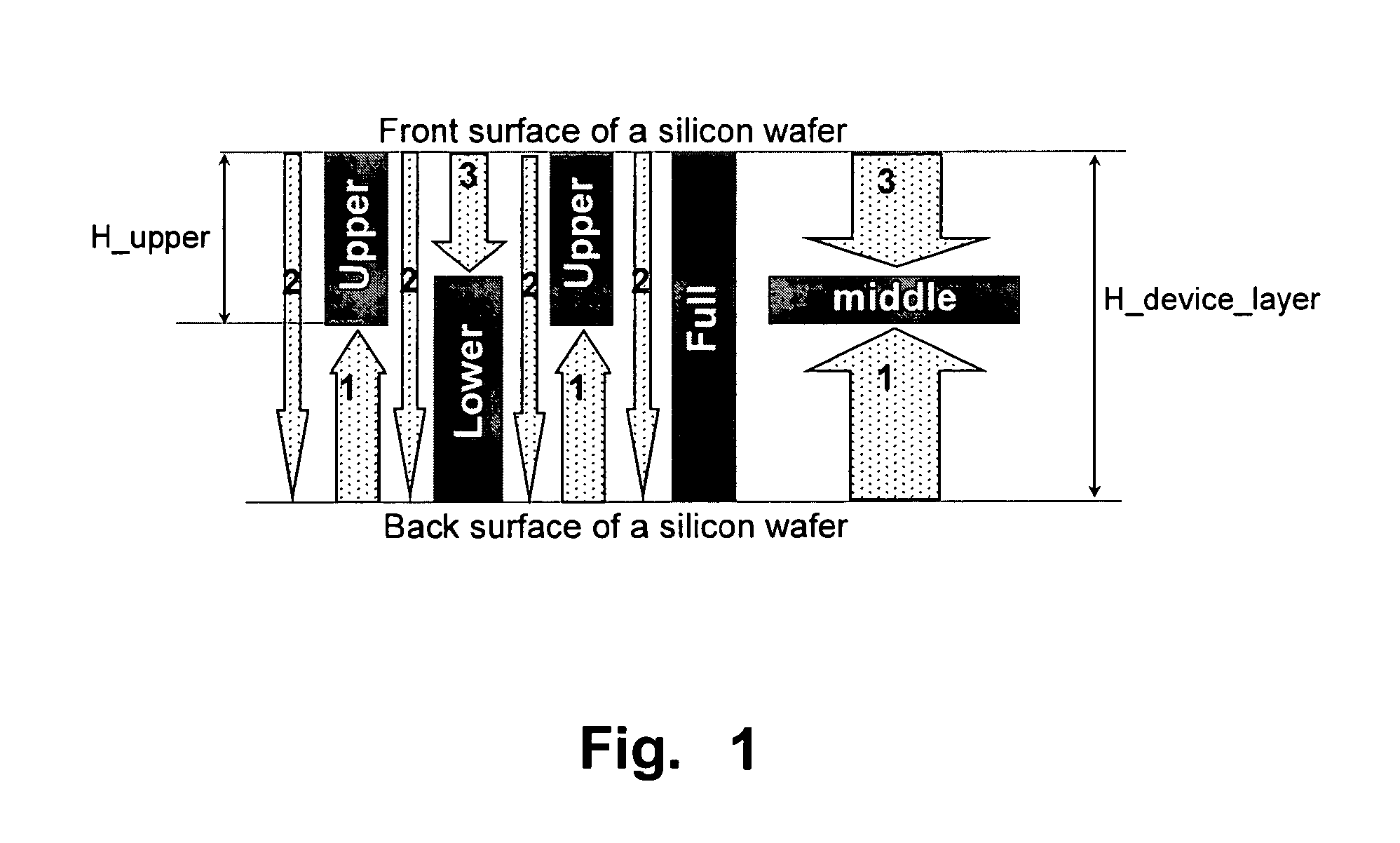
Fully monolithic gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system (MEMS) devices with large static optical beam deflection and fabrications methods are disclosed. The devices can achieve high speed of operation for both axes. Actuators are connected to a device, or device mount by linkages that allow static two-axis rotation in addition to pistoning without the need for gimbals, or specialized isolation technologies. The device may be actuated by vertical comb-drive actuators, which are coupled by bi-axial flexures to a central micromirror or device mount. Devices may be fabricated by etching an upper layer both from the top side and from the bottom side to form beams at different levels, The beams include a plurality of lower beams, a plurality of full-thickness beams, and a plurality of upper beams, the lower, full-thickness and upper beams That form vertical combdrive actuators, suspension beams, flexures, and a device mount.
Owner:ADRIATIC RES INST
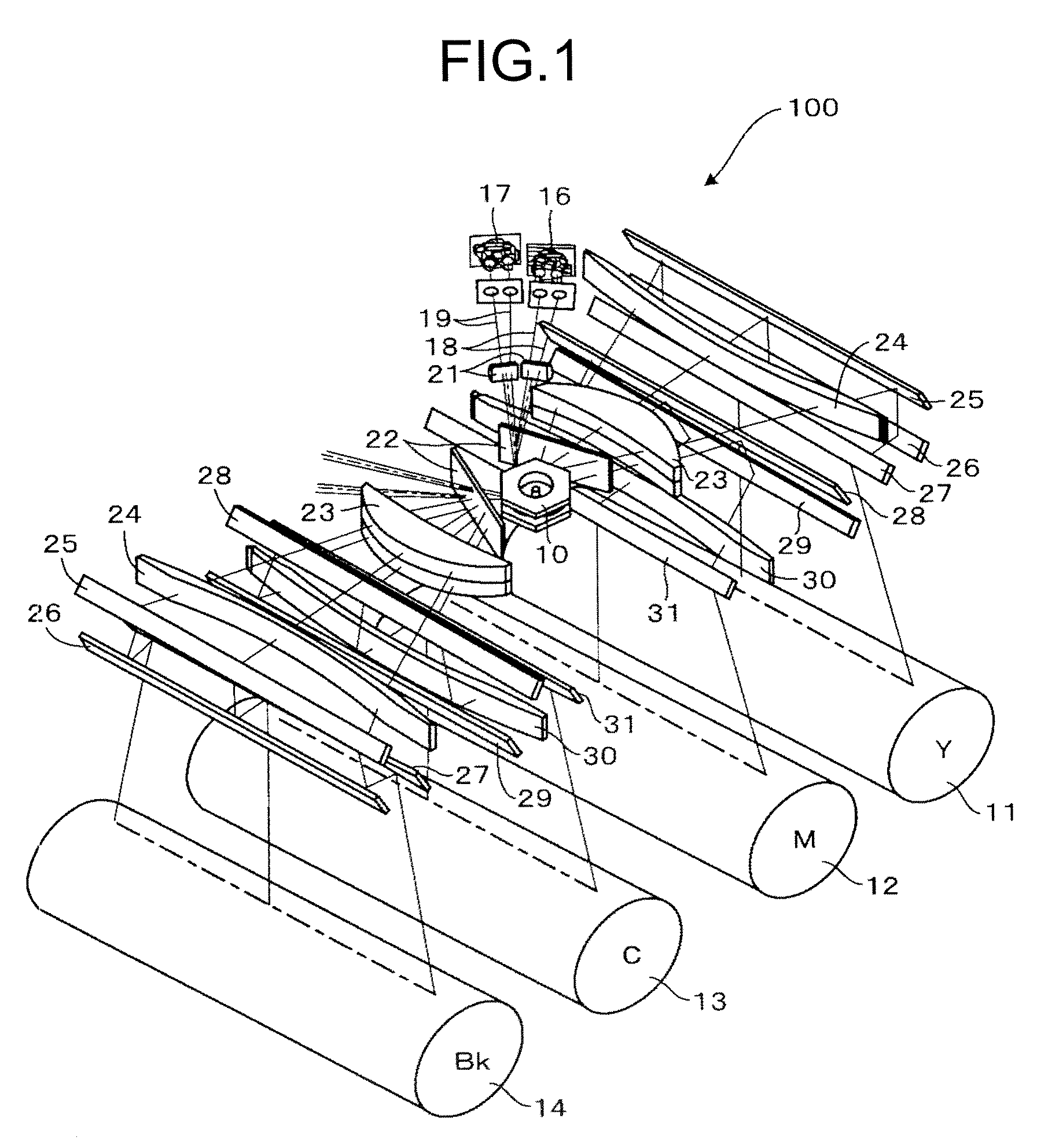
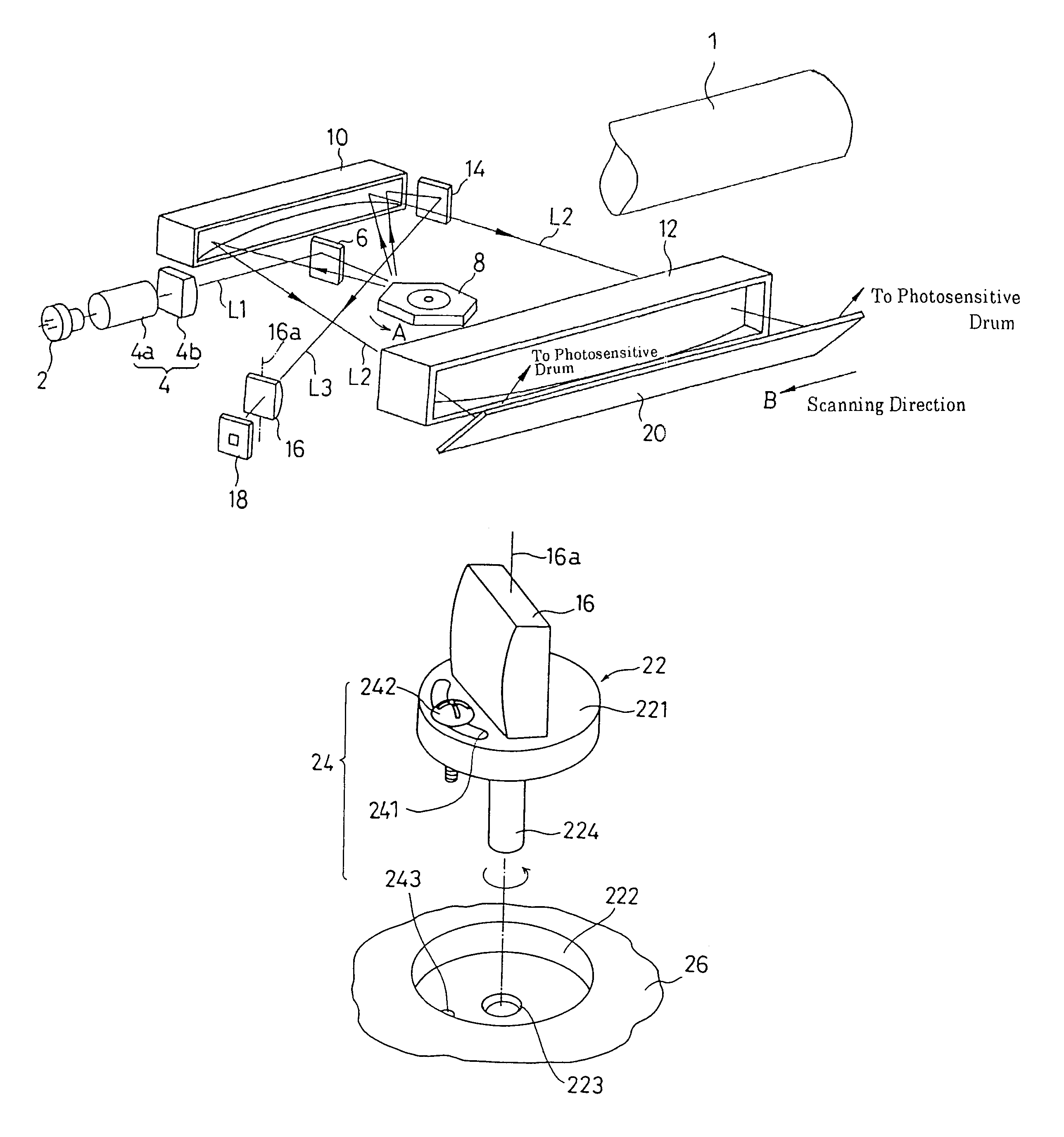
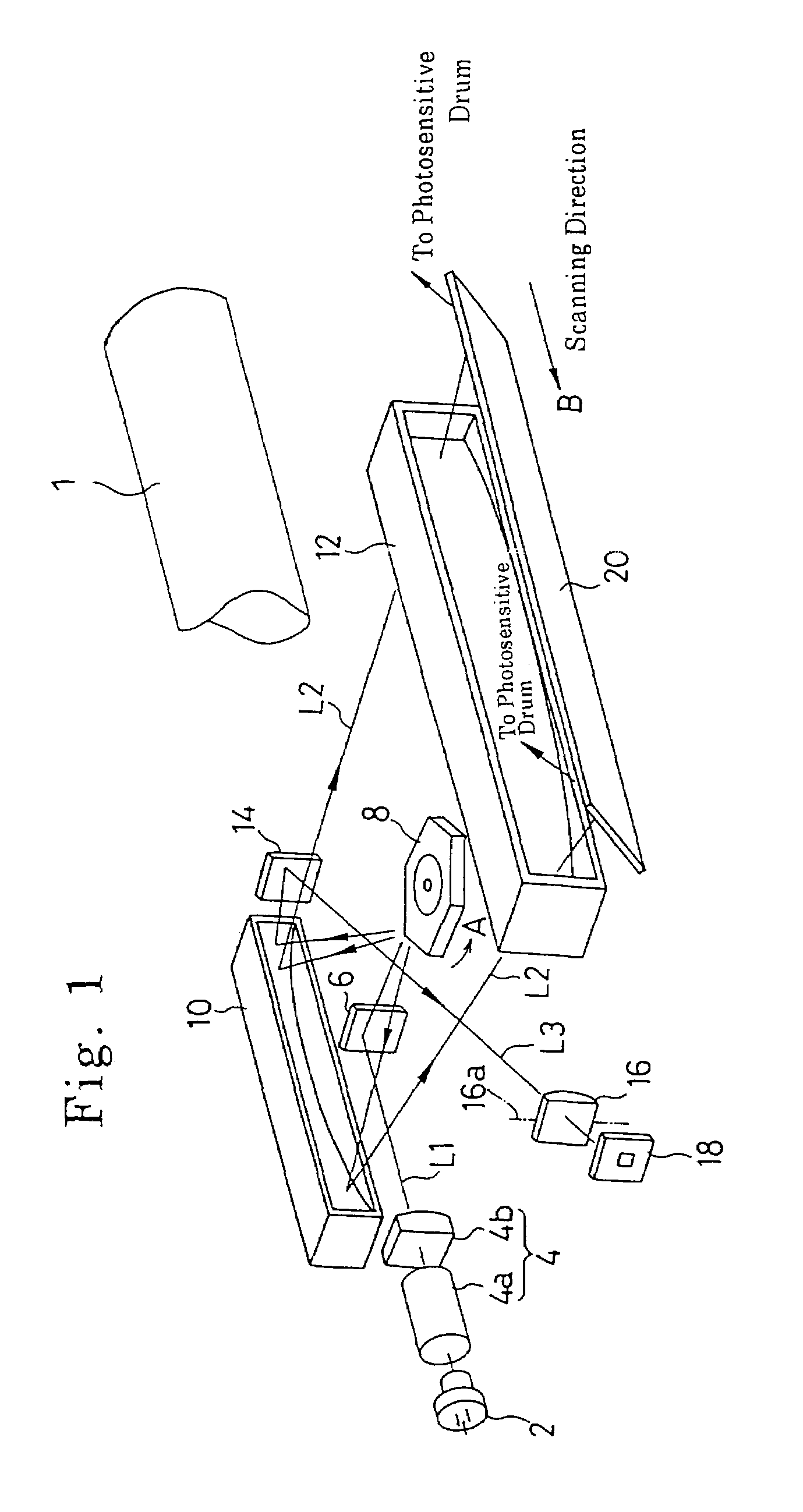
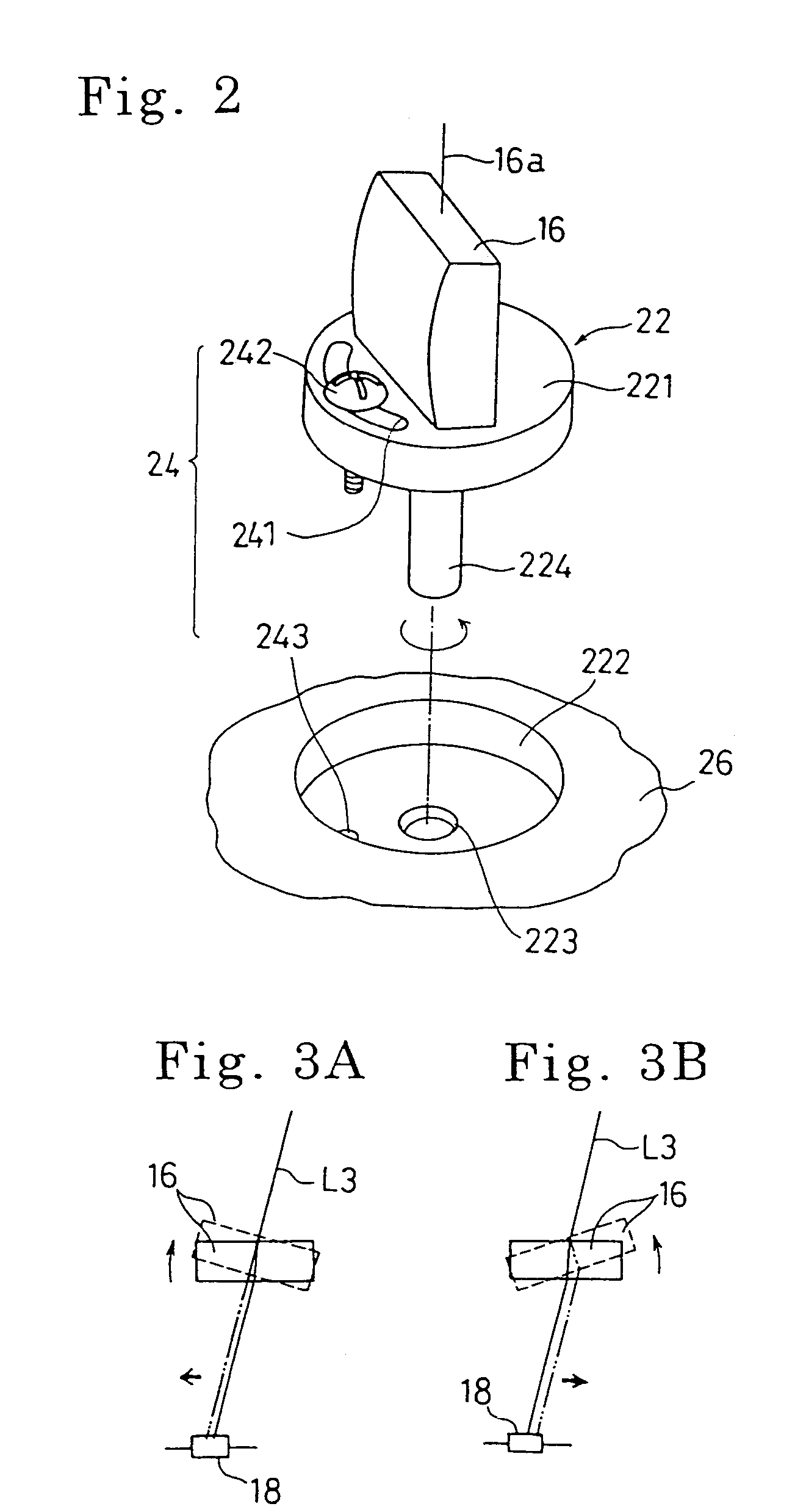
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
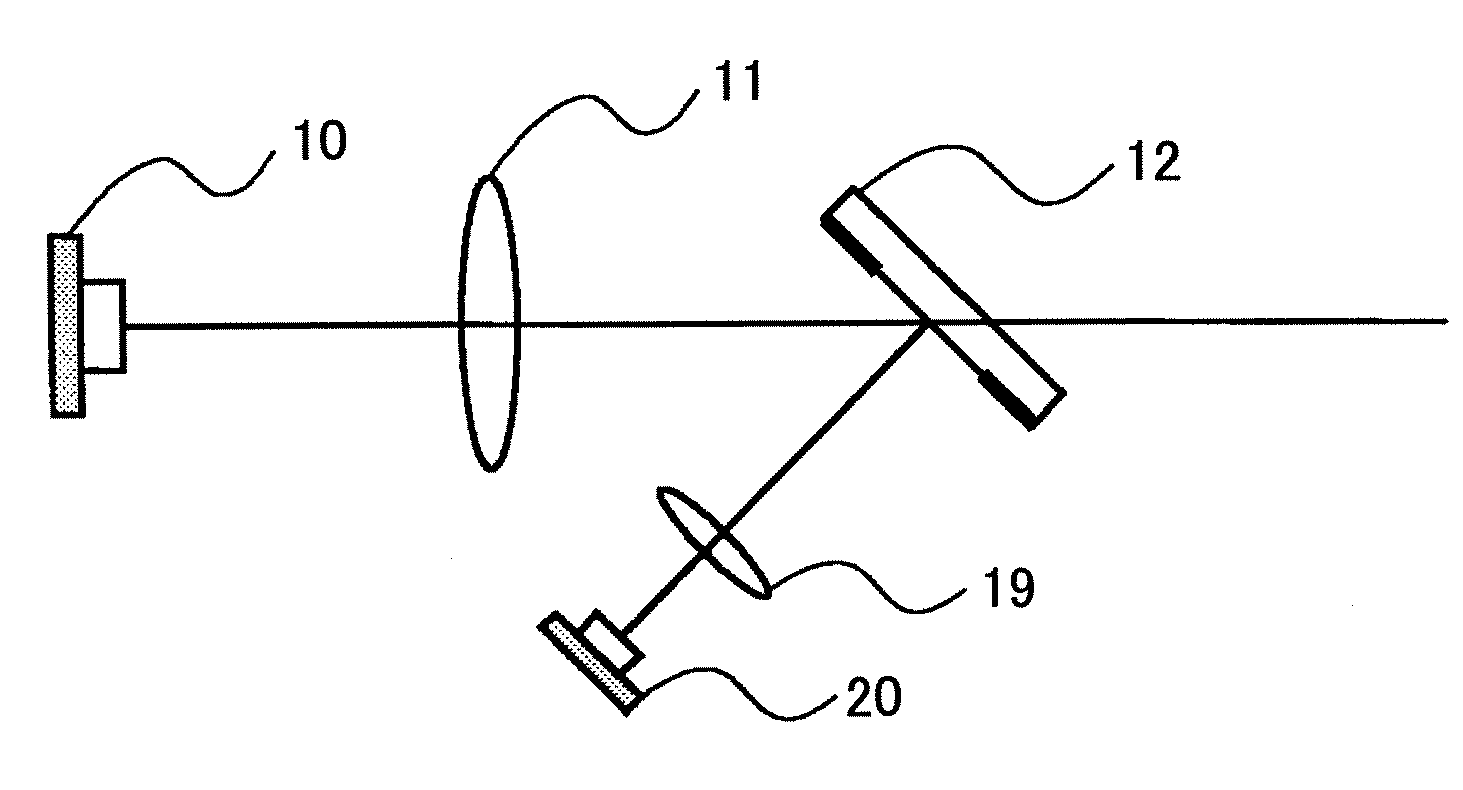
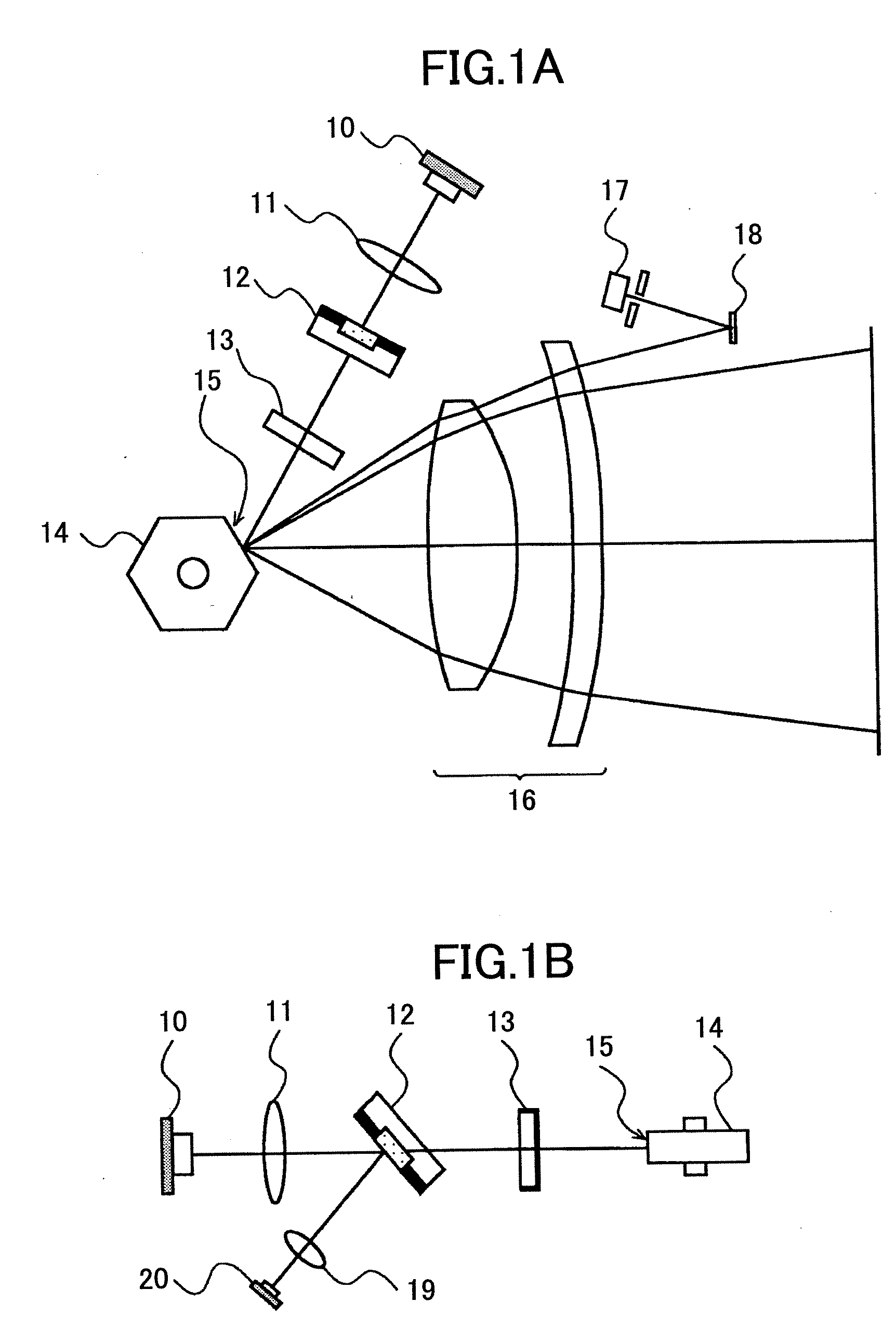
An optical scanning device includes a light source, a deflector that deflects a light beam from the light source, a first optical system that guides the light beam to the deflector, a second optical system that guides the light beam from the deflector to a surface to be scanned, and a housing that holds the light source and the deflector. At least one optical element included in the first optical system or the second optical system is attached to the housing via an intermediate member. The optical element is adjustable with respect to the intermediate member. The number of directions in which the optical element can be adjusted is two or more.
Owner:RICOH KK
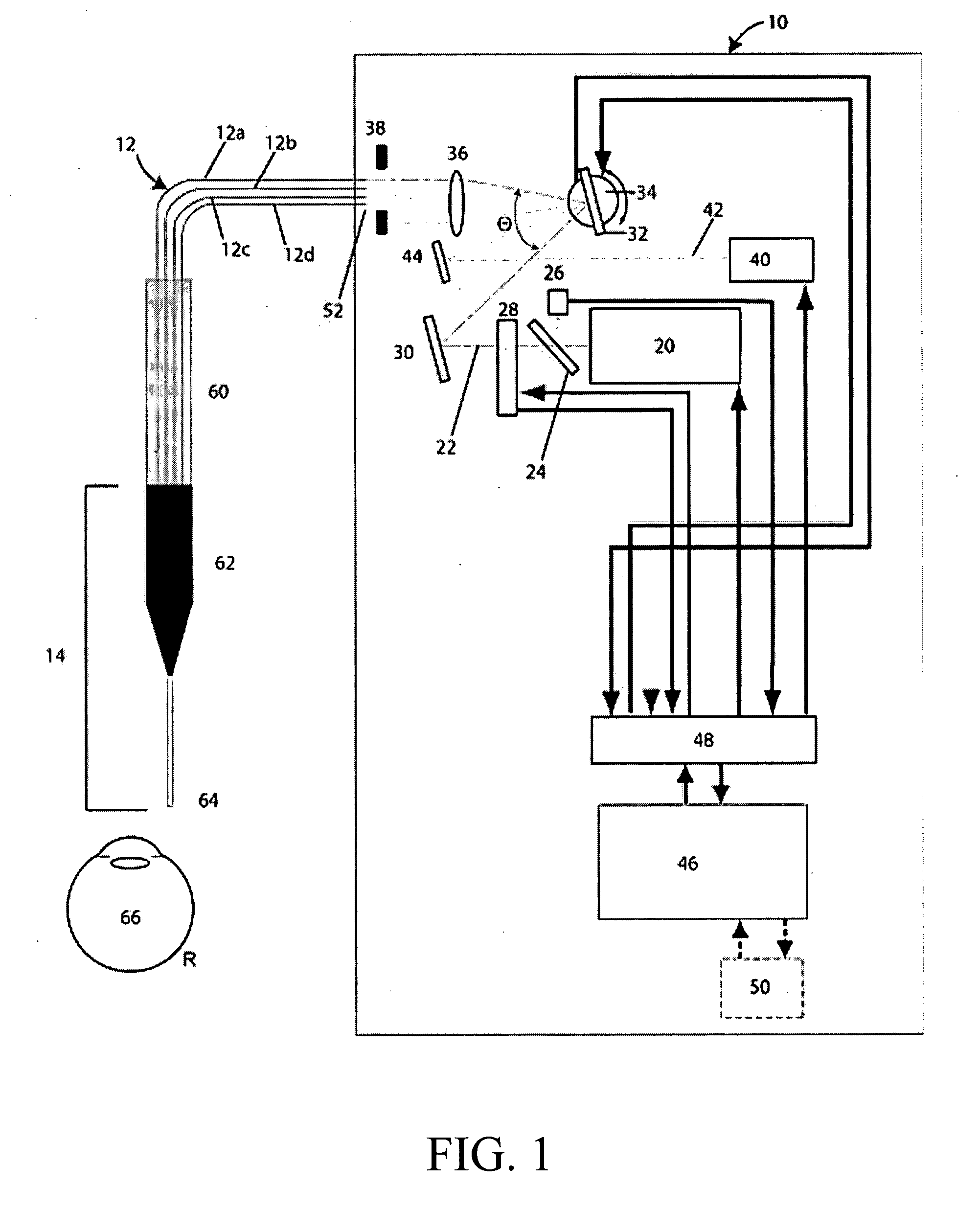
Multi-spot optical fiber endophotocoagulation probe
A system and method for treating target tissue including a light source for generating a beam of light, a plurality of optical fibers, a deflection device configured to selectively deflect the light beam into the input ends of the optical fibers, one optical fiber input end at a time, and a probe having a tip with the output ends of the optical fibers and configured for insertion into target tissue. The probe tip is configured to sequentially project spaced apart spots of the light beam from the output ends as the deflection device deflects the light beam into the optical fibers. One or more moving or static deflecting optics at the probe tip can be used to statically or dynamically deflect the beam exiting the optical fibers.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
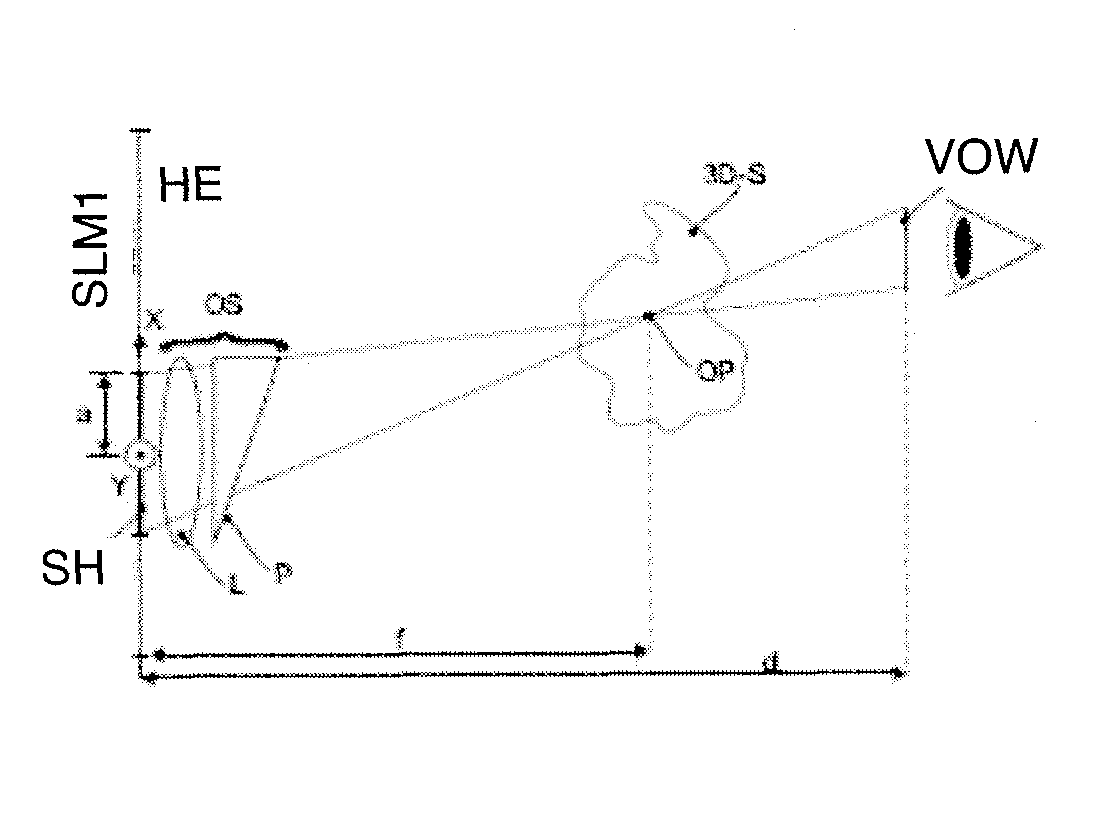
Holographic display with a variable beam deflection
ActiveUS8218211B2Reduce optical effectsHolographic optical componentsDigital holography electronic componentSpatial light modulatorLight beam
A holographic display including a spatial light modulator, and including a position detection and tracking system, such that a viewer's eye positions are tracked, with variable beam deflection to the viewer's eye positions being performed using a microprism array which enables controllable deflection of optical beams.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Image forming method, image forming apparatus, optical scan device, and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7256815B2Correct position shiftSave energyPrintingOptical elementsOptical beam deflectionLight beam
An optical scan device having an optical deflector reflecting a light beam from a light beam source so as to deflect the light beam and having a surface to be scanned on which information is written such that the light beam deflected by the deflector scans the surface is disclosed. Optical detectors are arranged at least in two locations, a start side of writing and an end side of writing, which locations are outside an effective writing area. A measuring part measures a scan time required by the light beam deflected by the optical deflector to scan a range between the optical detectors. A correcting part corrects each dot position of image data in the effective writing area to an arbitrary position based on a variation amount of the measured scan time.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for optically scanning a scene
InactiveUS20040212863A1Reduce sensitivityLarge luminous surfaceOptical signallingElectromagnetic wave reradiationContinuous scanningPhotodetector
A light beam is deflected by refraction and total internal reflection through a first prism, and projected through a first lens onto a scene that is to be scanned. The prism rotates, which varies the deflection angle and scans the beam across the scene along a scan line. Preferably, the successive side surfaces of the prism have different tilt angles relative to the rotation axis, so as to respectively deflect the beam in different deflection planes which cause successive scan lines of the beam across the scene. The emitted beam gives rise to a reflected beam from the scene, which is received through a second lens and deflected onto a photodetector through a second prism congruent to and rotating synchronously with the first prism. This apparatus is suitable as a laser scanning device for an object recognition system or a spacing distance regulation system of a motor vehicle.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE DISTANCE CONTROL SYST +1
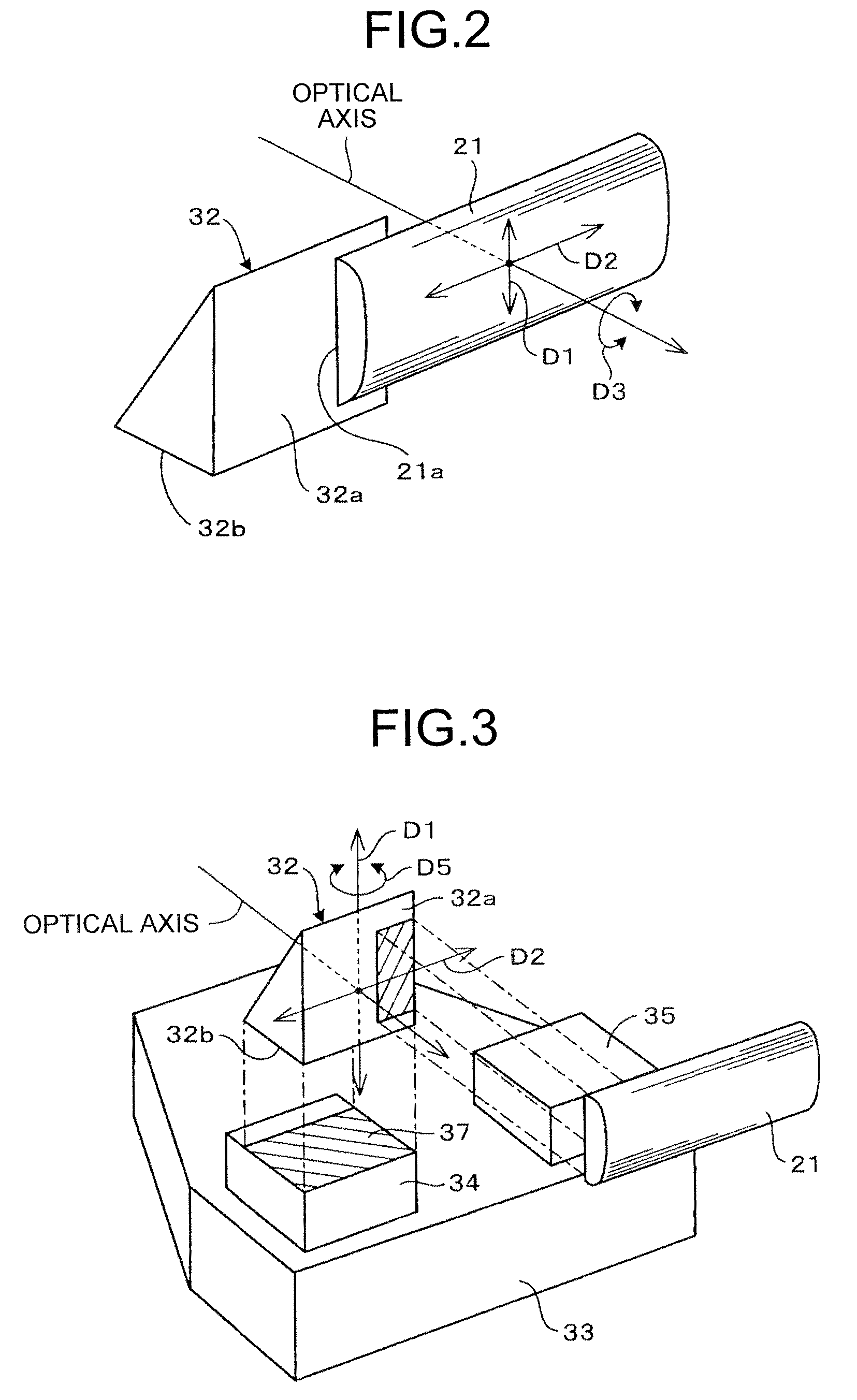
Light source device, optical scanning device, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20070146473A1Quality improvementLow costInking apparatusDiffraction gratingsTarget surfaceBeam splitting
A disclosed device for optically scanning a target surface includes a light source unit configured to emit a light beam; a light intensity detecting unit; a coupling unit configured to substantially collimate the emitted light beam; a beam limiting unit configured to limit the amount of the collimated light beam; a beam splitting unit configured to split the beam limited light beam and thereby to cause a first portion of the beam limited light beam to enter the light intensity detecting unit, wherein the light intensity detecting unit is configured to detect the intensity of the first portion of the beam limited light beam; and a beam deflecting unit configured to deflect a second portion of the split light beam toward the target surface. In the disclosed device, the beam limiting unit and the beam splitting unit are integrated as a single unitary structure and positioned between the coupling unit and the light deflecting unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
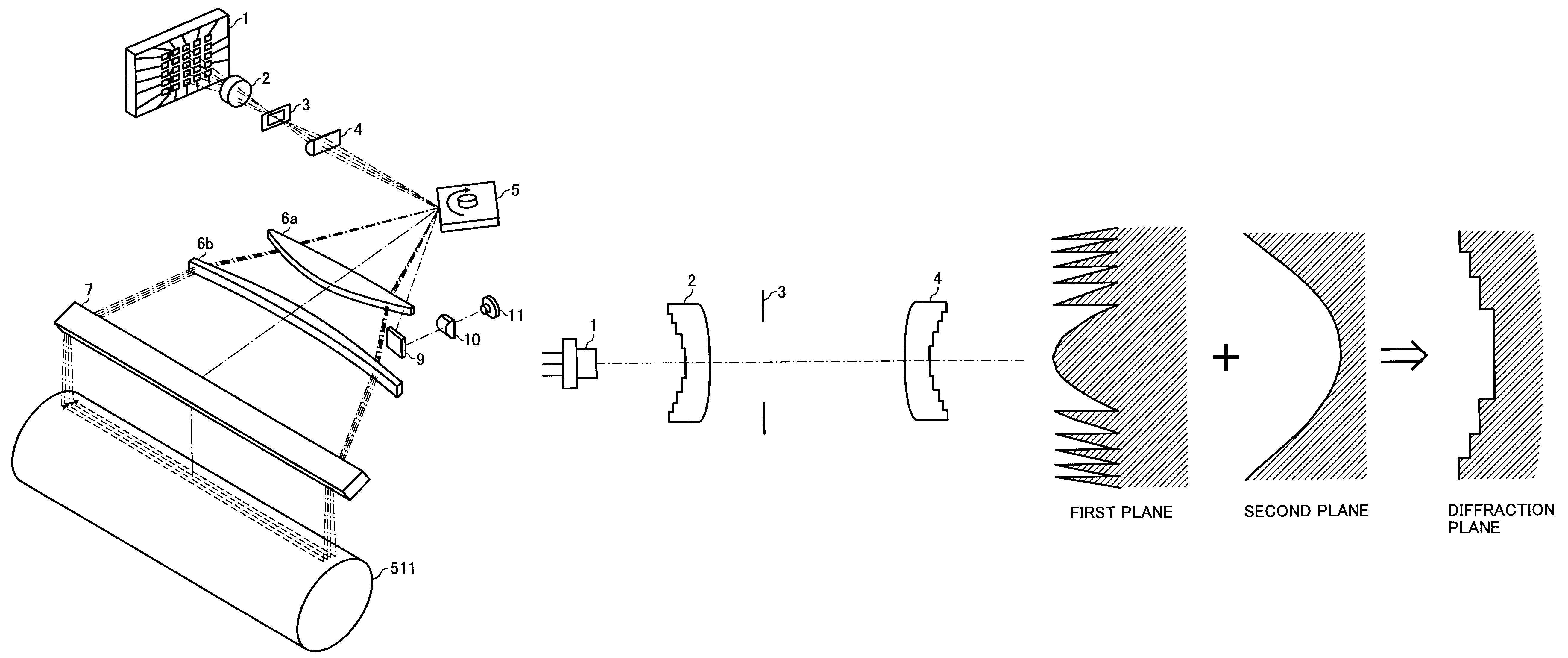
A coupling lens arranged on an optical path of an optical beam from a VCSEL, which has a refraction plane and a diffraction plane that respectively change a power according to a temperature change and suppresses a beam-waist position change in a main-scanning direction and a sub-scanning directions on the scanning surface caused by the temperature change, by a wavelength change of the optical beam caused by power changes of the refraction plane and the diffraction plane and the temperature change. A deflecting unit deflects the optical beam that passed through the coupling lens. A scanning optical system condenses a deflected optical beam on the scanning surface.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical beam deflector modifying phases of respective portions of optical beam by two arrays of optical phase modulators
InactiveUS6341136B1Agile and stable and reliable scanningIncrease deflectionSemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical beam deflectionOptical modulator
An optical beam deflector in which a crosssection of an incident optical (e.g., laser) beam is divided into a first plurality of portions (micro crosssections) by an array of first lenses, a plurality of phases of the optical beam in the first micro crosssections are respectively modified by an array of first optical phase modulators so that a desired phase distribution is realized over the crosssection of the optical beam, and thereafter the crosssection of the optical beam is further divided into a plurality of second micro crosssections, and a plurality of phases of the optical beam in the second micro crosssections are respectively modified by an array of second optical phase modulators. An array of second lenses is provided corresponding to the second optical phase modulators to collect a plurality of portions of the optical beam output from the second optical phase modulators. The first and second optical phase modulators are driven by a driving unit so that the optical beam output from the array of second lenses as a whole is finally directed in a desired direction of deflection or to a desired point.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Detector for interferometric distance measurement
ActiveUS20070229843A1Improve reliabilityReduce sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhase difference
A detector for interferometric distance or displacement measurement. The detector may receive orthogonally polarized object and reference path output beams, which are directed to a polarization-sensitive beam deflecting element. The beam deflecting element deflects one or both orthogonally polarized beams to provide a desired divergence angle between the beams. The diverging beams are input to a mixing polarizer. The beams exiting the mixing polarizer are similarly polarized and therefore interfere. The interfering diverging beams form interference fringes. The spatial phase of the fringes relative to a photodetector array characterizes the phase difference between the object and reference beams of the interferometer.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system tip-tilt and tip-tilt-piston actuators and a method for forming the same
ActiveUS20080061026A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical beam deflectionLight beam
Fully monolithic gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system (MEMS) devices with large static optical beam deflection and fabrications methods are disclosed. The devices can achieve high speed of operation for both axes. Actuators are connected to a device, or device mount by linkages that allow static two-axis rotation in addition to pistoning without the need for gimbals, or specialized isolation technologies. The device may be actuated by vertical comb-drive actuators, which are coupled by bi-axial flexures to a central micromirror or device mount. Devices may be fabricated by etching an upper layer both from the top side and from the bottom side to form beams at different levels. The beams include a plurality of lower beams, a plurality of full-thickness beams, and a plurality of upper beams, the lower, full-thickness and upper beams That form vertical combdrive actuators, suspension beams, flexures, and a device mount.
Owner:ADRIATIC RES INST
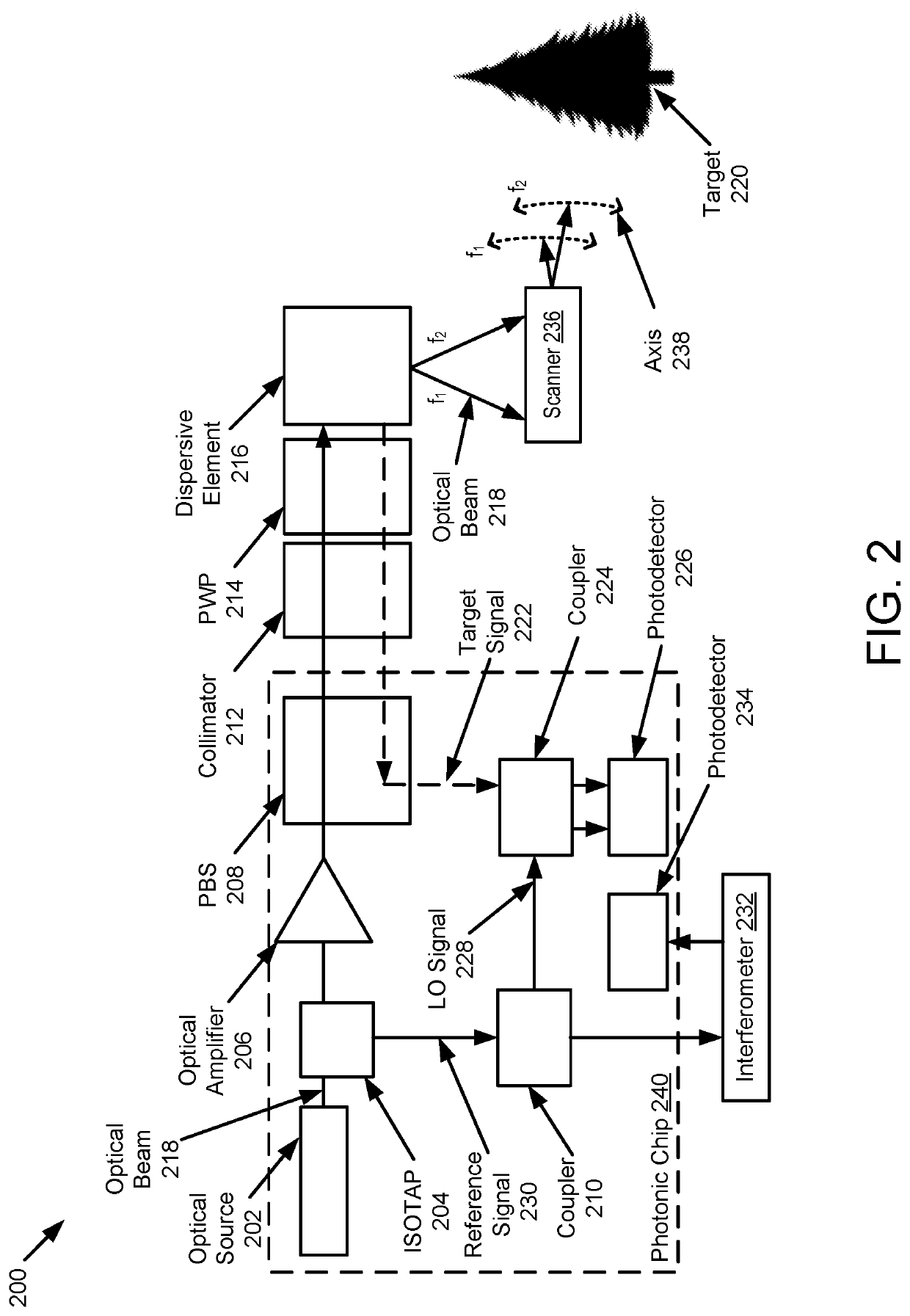
Lidar system with solid state spectral scanning
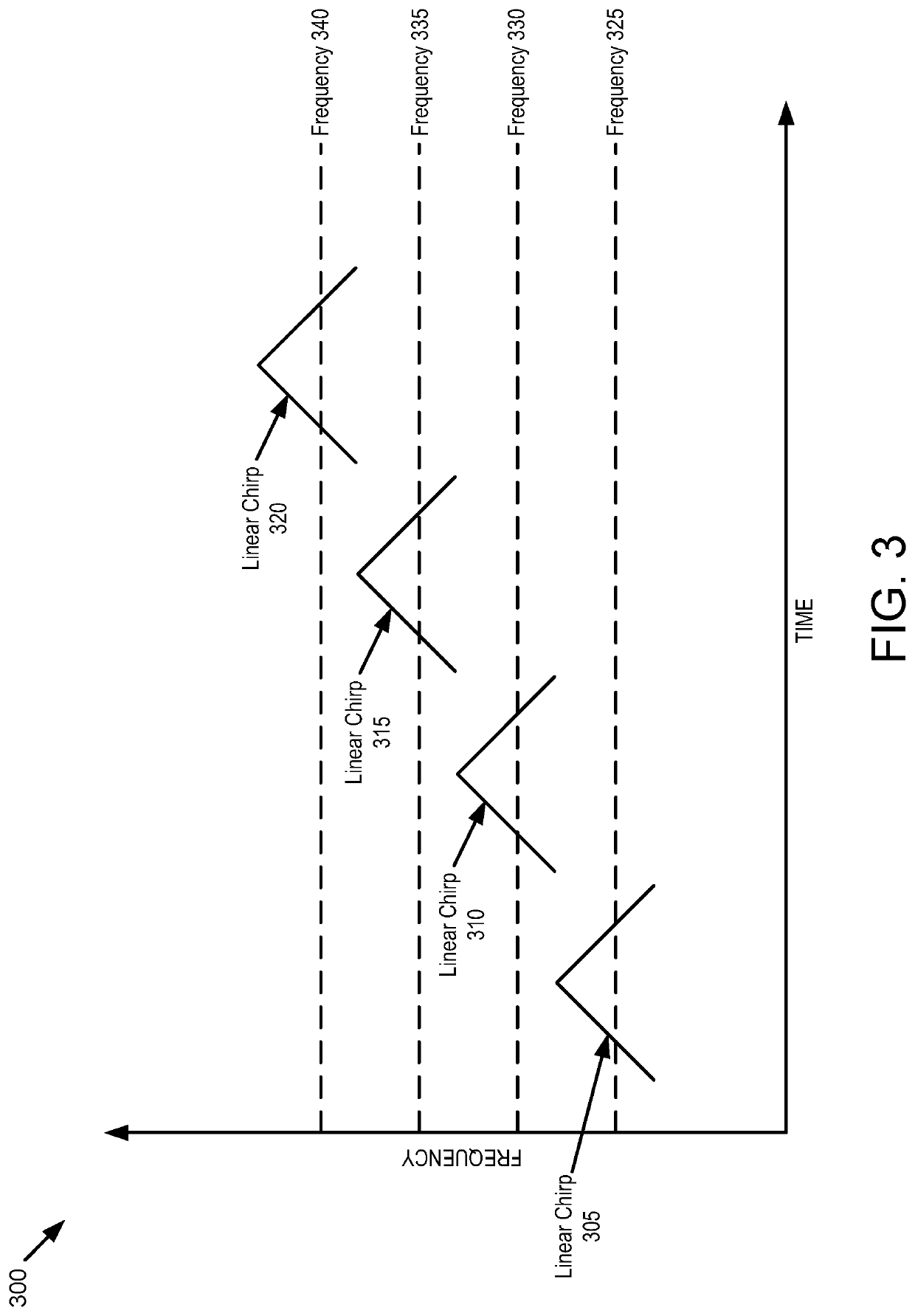
A light detection and ranging (LIDAR) apparatus is provided that includes an optical source to emit a first optical beam having a first frequency and a second optical beam having a second frequency and a dispersive element to deflect the first optical beam having the first frequency at a first angle and the second optical beam having the second frequency at a second angle.
Owner:AEVA INC
Optical fiber array phase array deflection transmission system based on SPGD algorithm
ActiveCN108196244ARealize far-field coherent combiningGuaranteed stabilityWave based measurement systemsPulse beamClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to an optical fiber array phase array deflection transmission system based on SPGD algorithm, belonging to the technical field of photoelectric detection. The system includes a driving and temperature control circuitry, an optical wave phase control system based on SPGD algorithm, a continuous fiber laser, an optical fiber, an electro-optic modulator, a phase modulator, an optical isolator, a continuous fiber amplifier, a collimating beam expander and a sampler. In the invention, the power of N continuous optical fiber lasers can be amplified by using a feedback fine stable driving and temperature control circuit, the N ways of the synthesized light beams can be increased without limit according to the requirement of detection power, At the same time, by using SPGD algorithm , the closed-loop feedback regulation and phase real-time compensation of the phase of the power amplified pulse light changes of N-way can be realized, It can realize the phase locking of theN-way pulsed beam while meeting the beam coherent synthetic deflection under a certain angle. And it can solve the problem of great inertia of traditional mechanical scanning, low sensitivity, closedetection distance and its traditional SPGD method not realizing the deflection of scanning beam.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical beam scanning device
InactiveUS6888655B2Ensuring control timeReduce variationPrintingPictoral communicationOptical beam deflectionLight beam
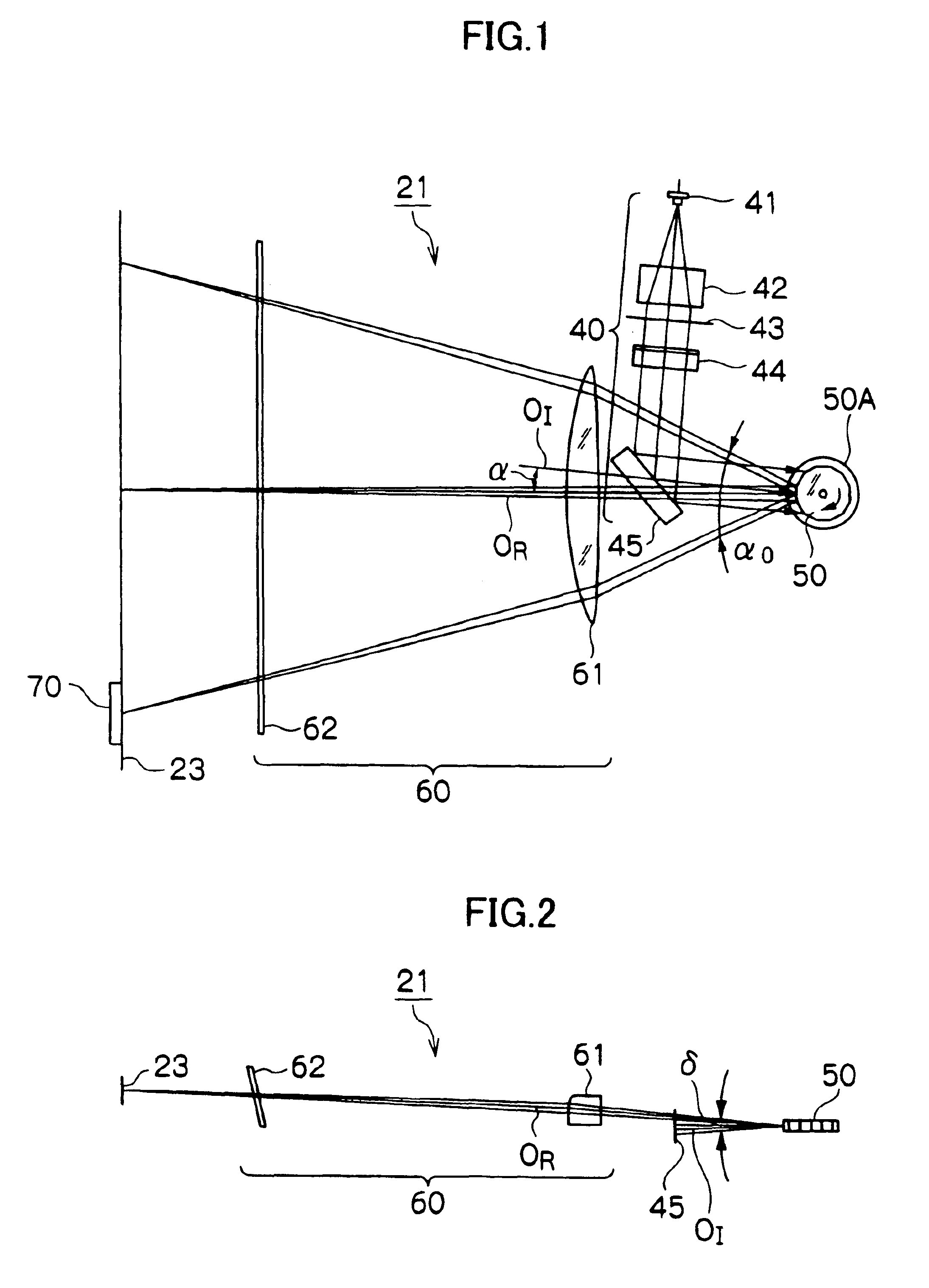
An optical beam scanning device comprises optical beam scanning means for rotational polygonal mirror to deflect entering luminous flux and scan an object to be scanned with the luminous flux; pre-deflection optical system which shapes a luminous flux emitted from light source means to image the resultant luminous flux onto the optical beam scanning means; and imaging optical system which images the luminous flux from the optical beam scanning means onto the object to be scanned. In the optical beam scanning device, the imaging optical system comprises an imaging optical element that in the entire main scanning area for luminous flux from the optical beam scanning means, the central scanning position has a main scanning direction curvature different from that of the scanning position of the scanning end, and a scanning angle α0 [rad] at which the optical beam scanning means scans the object to be scanned with the luminous flux is defined by the following expression,α0≦π{(2 / N)−(Vr / 3)×10−7}wherein N indicates the number of surfaces of the rotational polygonal mirror and Vr [r.p.m.] indicates the revolution of the rotational polygonal mirror.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
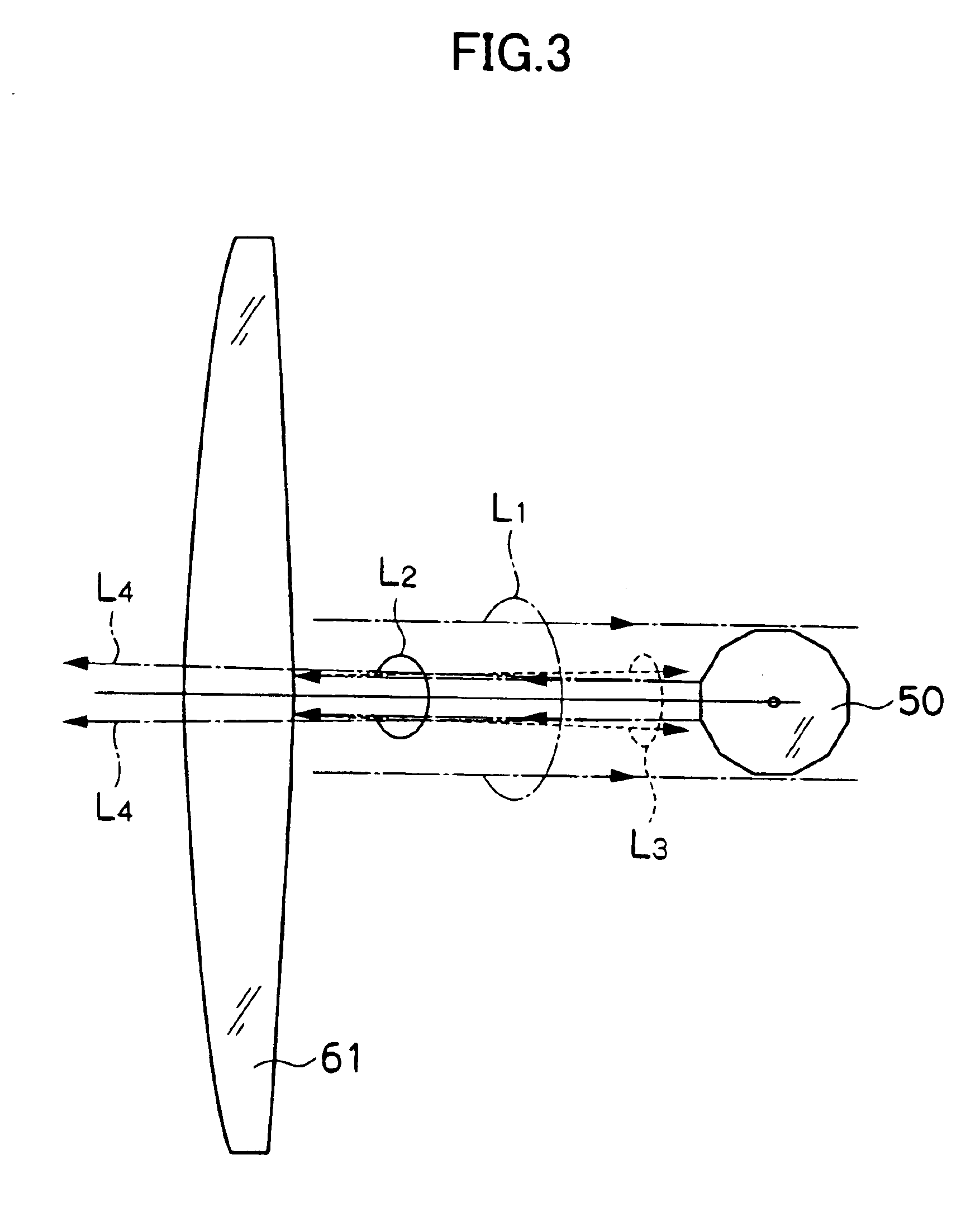
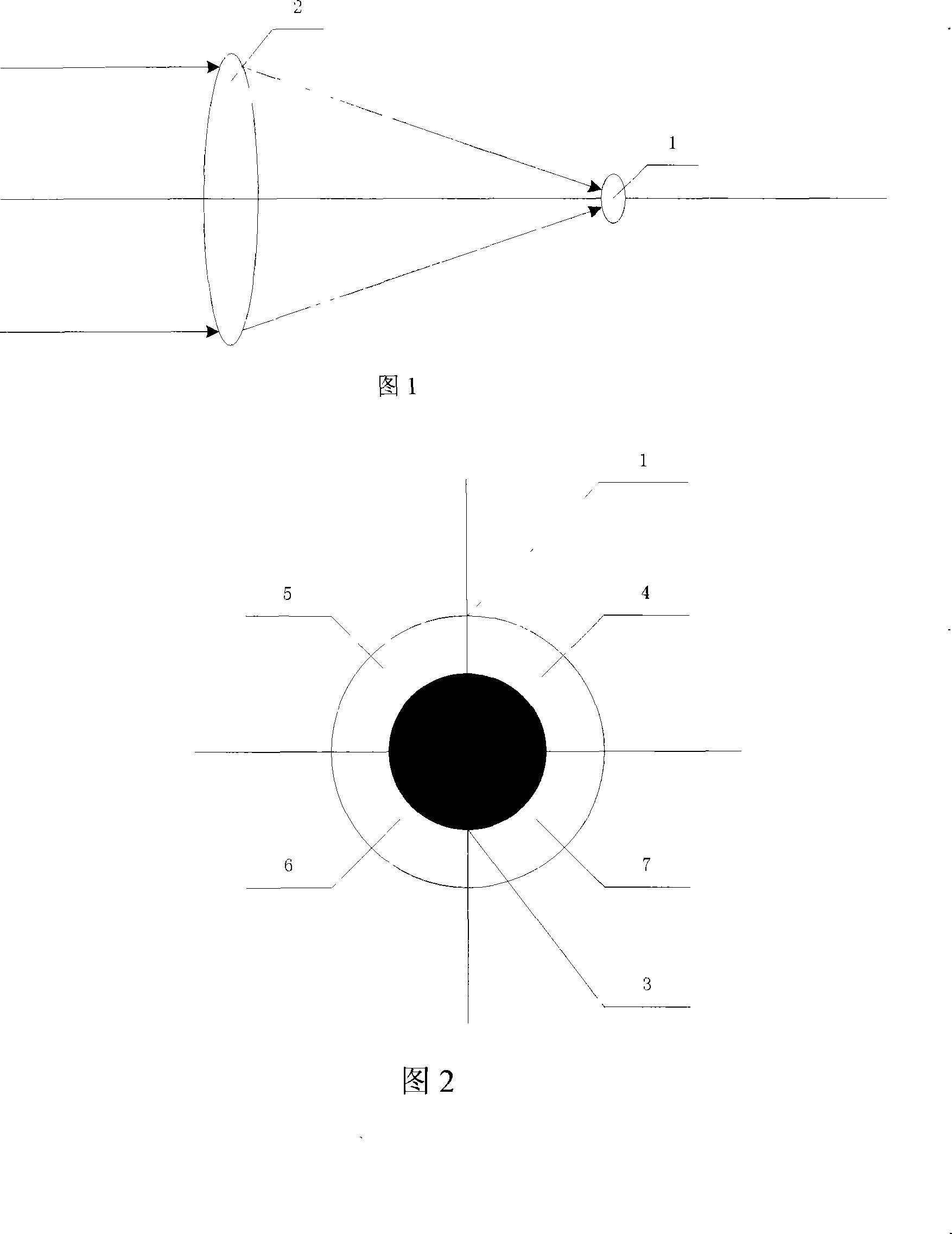
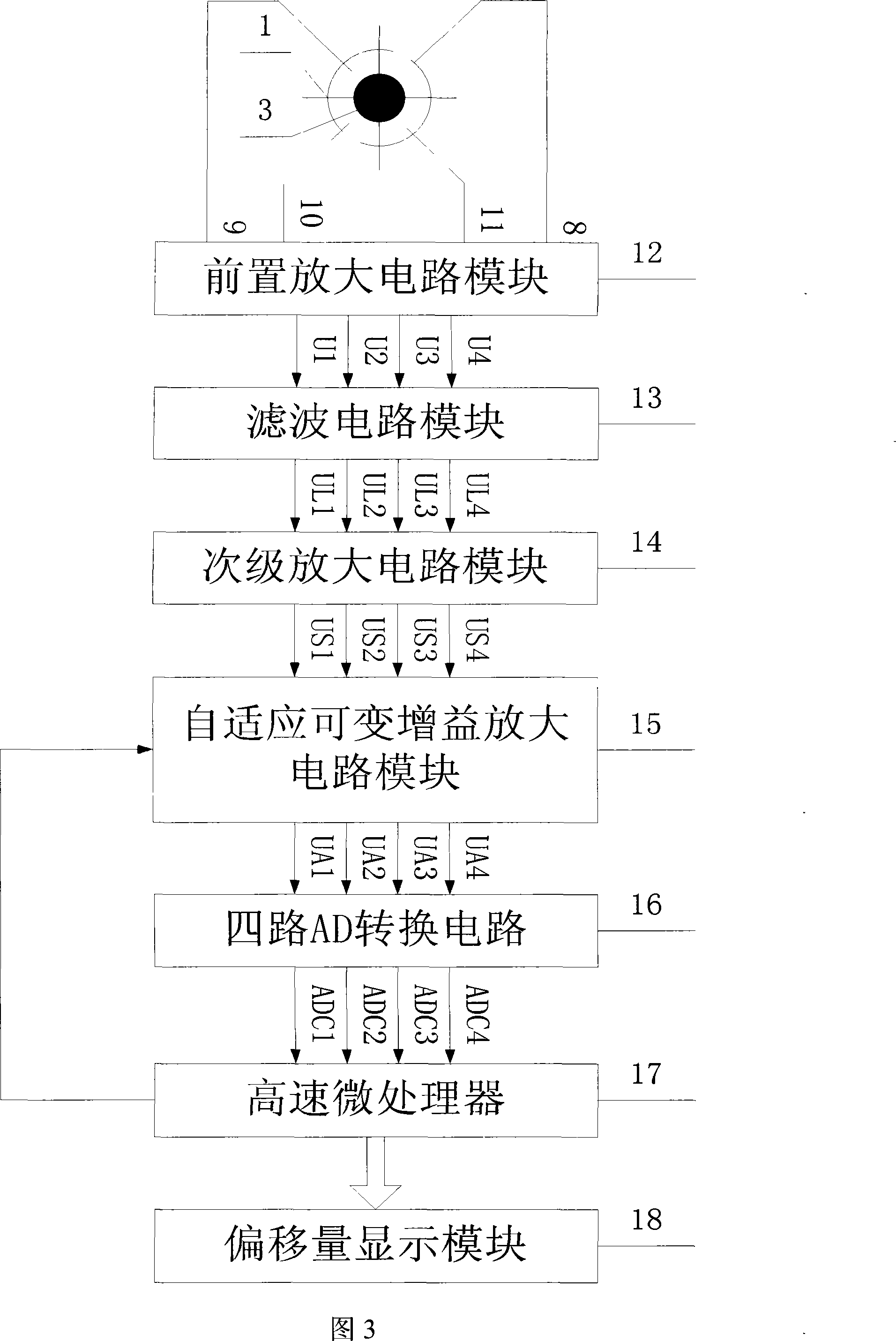
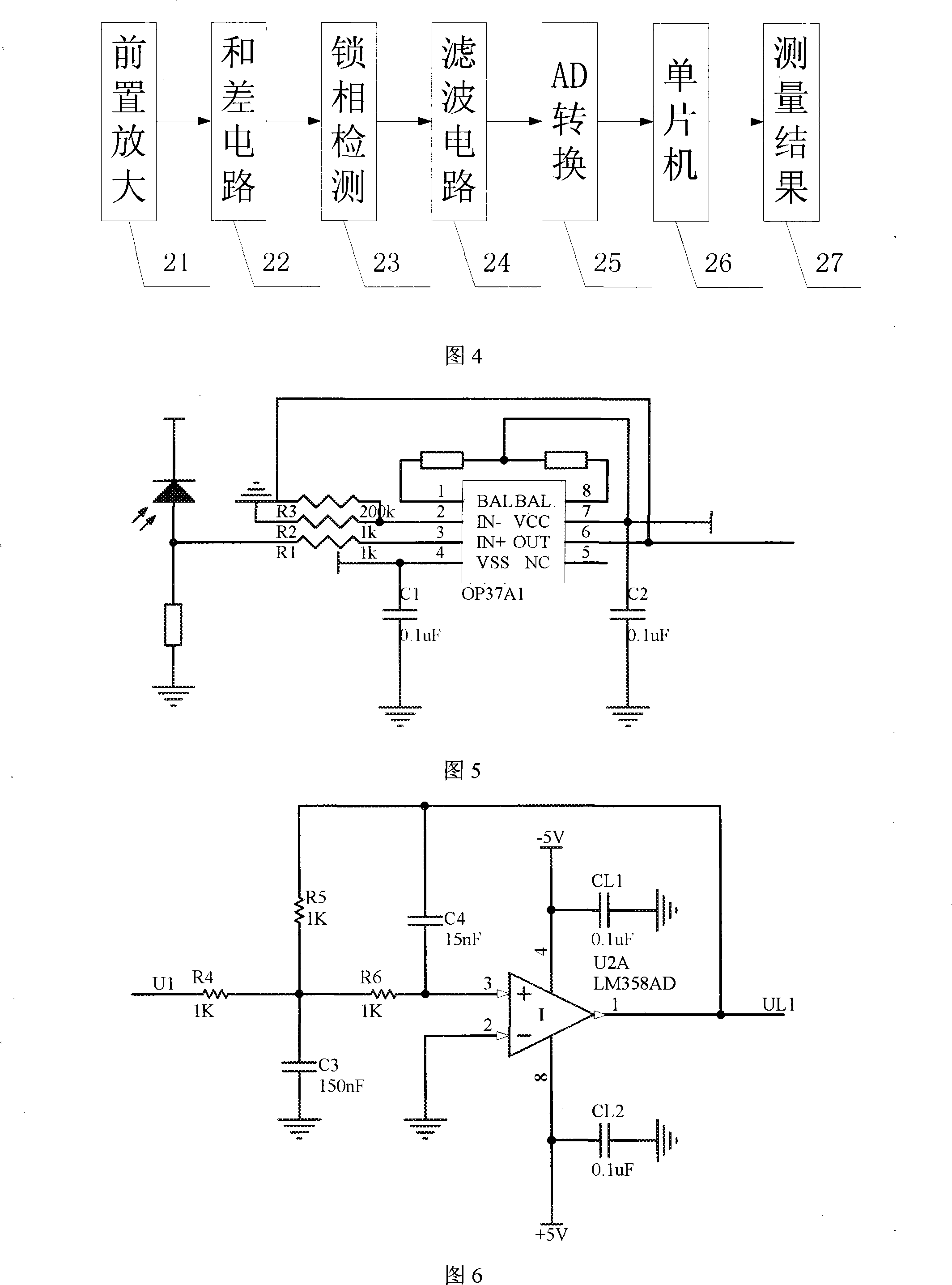
Complete digitisation 4 quadrant detector detecting laser beam deflection angle device and method
InactiveCN101158590AHigh solution accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing electrical meansUsing optical meansMicrocontrollerSignal to noise ratio degradation
The invention relates to a device and a method of the detection of a laser-beam deflection angle by a full digital four quadrant detector, and comprises a preposed amplifying electric circuit (12), a filtering electric circuit(13), an AD switching electric circuit(16), an offset display module(18), a four quadrant detector(1), a secondary amplifying electric circuit module(14), a variable gain amplifying electric circuit module(15) and a high speed micro processor module(17). The invention solves the problem of reduced measurement precision by using a full digital processing method; the model adopts the auto adaptation and the variable gain amplifying electric circuit to maintain the strength of signals entering an AD collecting unit by the automatic variation of the gain according to strengths of input signals; the model overcomes a reduced resolving precision caused by a reduced signal to noise ratio resulting from the variation of input light intensity. The invention overcomes the defect of a slow resolving speed caused by using a single chip for resolving by using the high speed micro processor to resolve the beam reflection angles.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Scanner having a light beam incident position adjusting device
InactiveUS7158269B2Finely and easily adjustBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansRotational axisOptical beam deflection
A scanner is provided that has a light-beam emitter for emitting a light beam, a light-beam deflector for deflecting the light beam to scan a scanning surface, a photo-detector provided at a position outside an image-forming scanning range of the scanning surface to detect a scanning light beam before the scanning light beam starts generating a scanning line in the image-forming scanning range, a rotatable member located in front of an incident surface of the photo-detector and positioned in a recess formed on an outer surface of a housing. The rotatable member is rotatable about a rotational axis perpendicular to a plane defined by the scanning light beam by said deflector. The scanner also has an optical member provided on the rotatable member that allows the scanning light beam to pass therethrough to be incident upon the incident surface of the photo-detector, and a device for adjusting rotational position of said rotatable member about said rotational axis. A through hole through which the optical member is inserted in the housing is formed at the bottom of the recess, and the optical member is inserted into the housing through the through hole.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20090195636A1Solve problemsInking apparatusOther printing apparatusPhase differenceOptical beam deflection
A pre-deflector optical system includes an isolator arranged on an optical path of a light beam from a light source. The isolator has a first surface with different light transmittances depending on a polarization state of an incident light beam on a first side close to the light source and a second surface imparting an optical phase difference of a ¼ wavelength to the incident light beam on a second side. A deflector deflects the light beam passed through the pre-deflector optical system. A rotation mechanism rotates the isolator around its optical axis. A holding member holds the light source and the isolator in a predetermined positional relationship.
Owner:RICOH KK
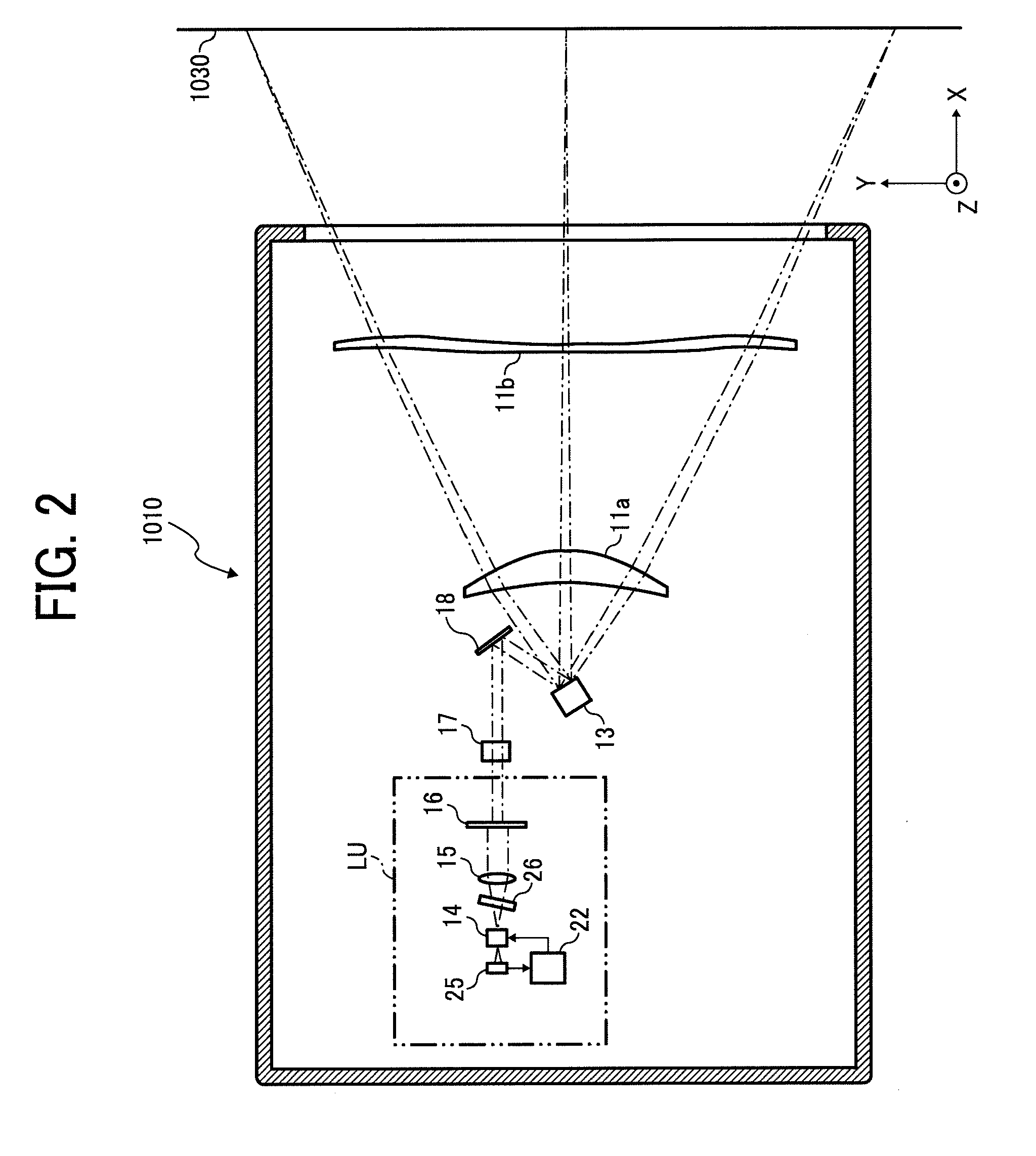
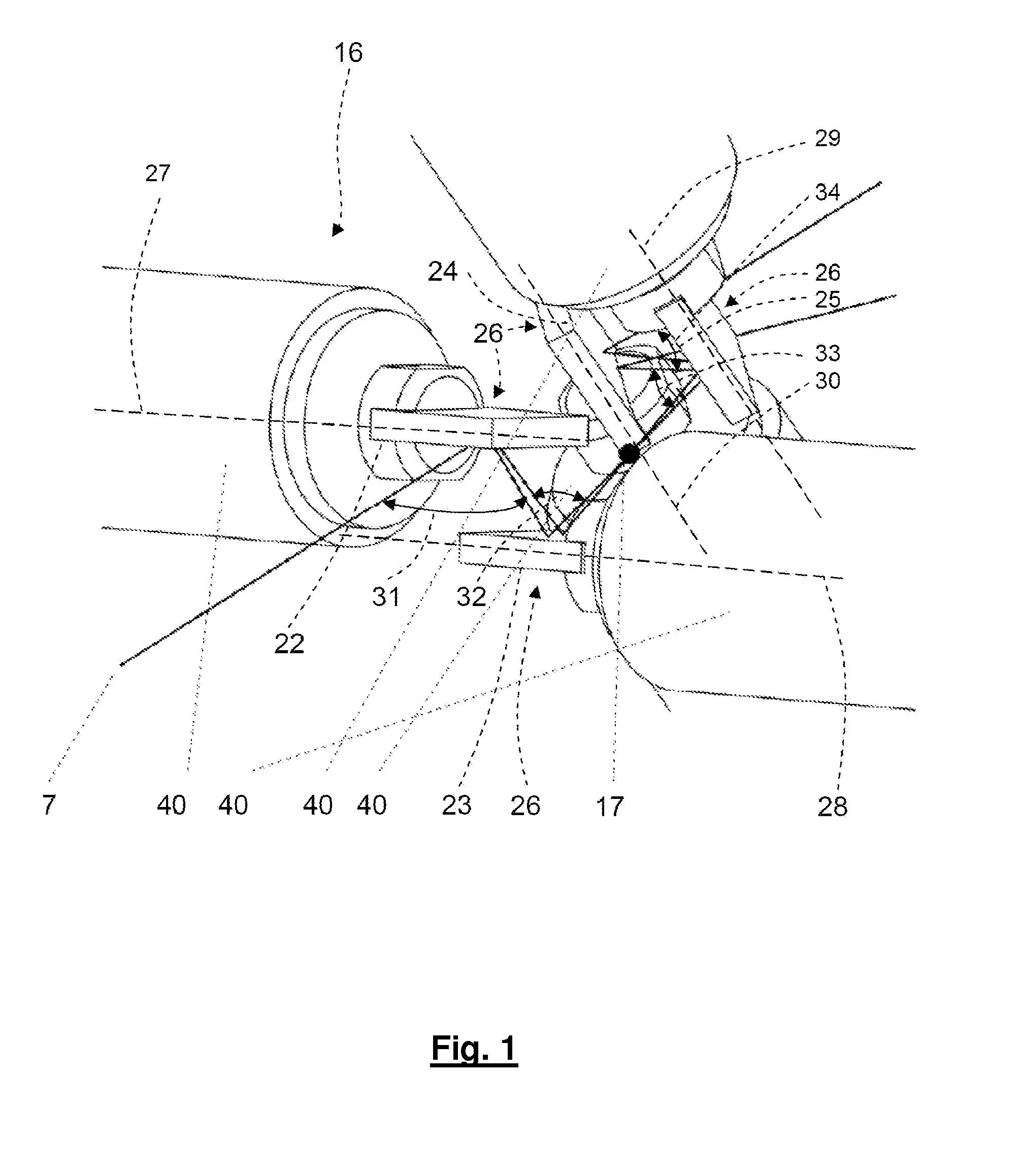
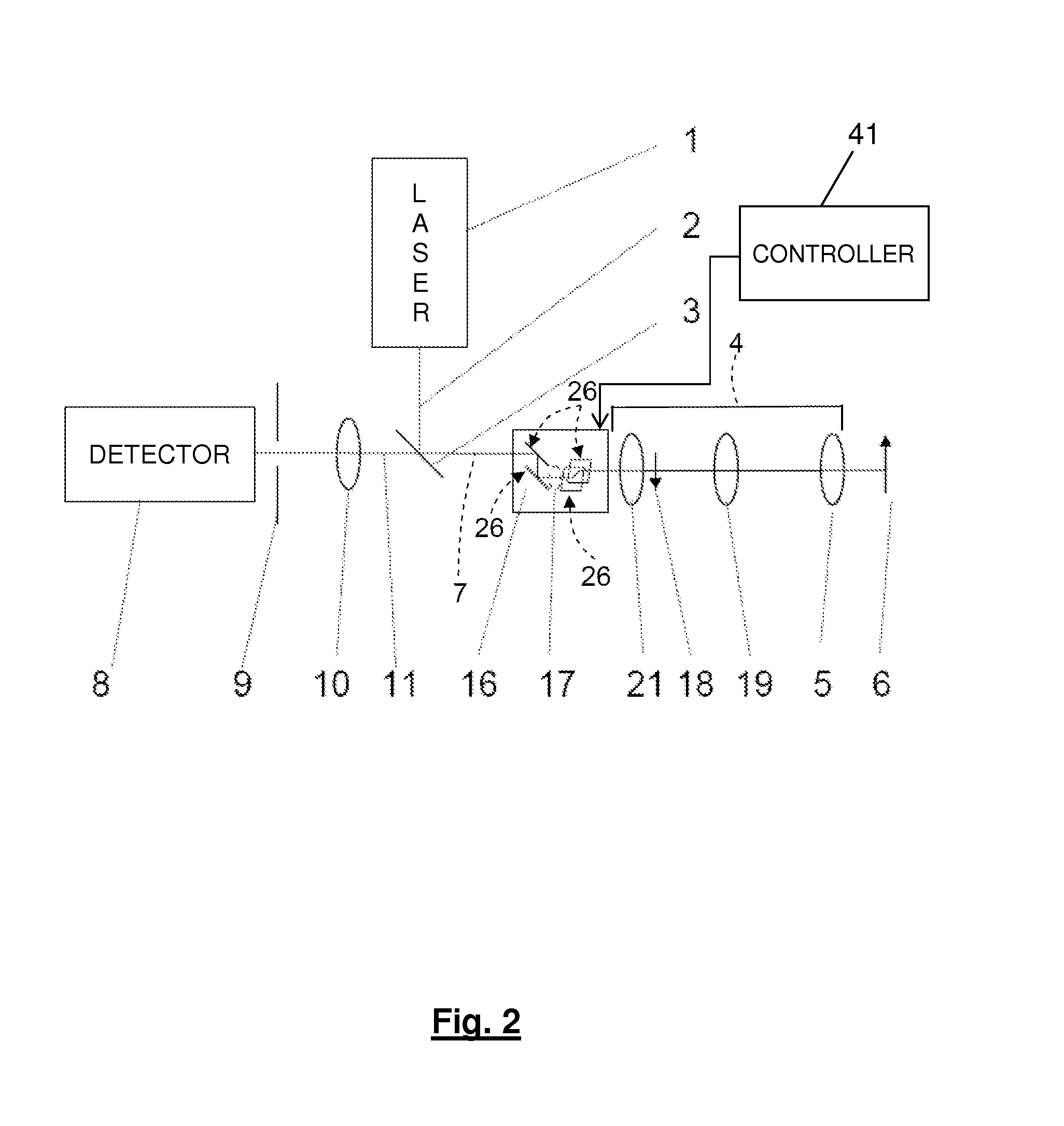
Method and Device for Dynamically Shifting a Light Beam with Regard to an Optic Focussing the Light Beam
For dynamically shifting a light beam (7) with regard to an optic focussing the light beam to scan an object in a two-dimensional scanning range with the focussed light beam, at least two beam deflectors (26) are connected in series per each direction in which the light beam is to be deflected with regard to the optical axis of the focussing optic. The two beam deflectors deflect the light beam by two deflection angles (31, 32 and 33, 34, respectively) which are dynamically variable independently on each other. The deflection angles (31 to 34) of all beam deflectors (26) are predetermined for each point of the scanning range (35) in such a way that the light beam (7), in scanning the whole two-dimensional scanning range, always runs through the pupil of the optic (4) at essentially the same point.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
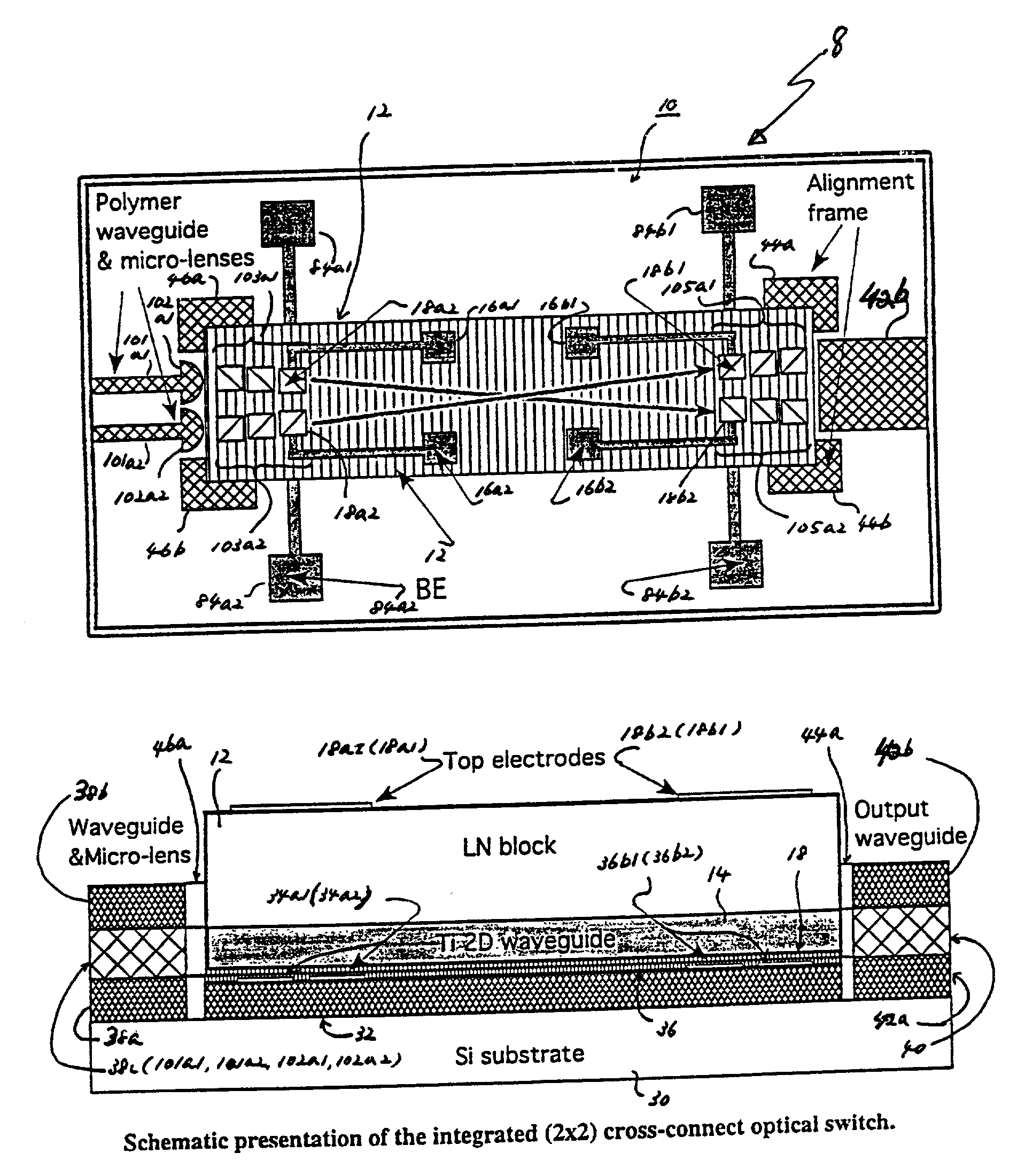
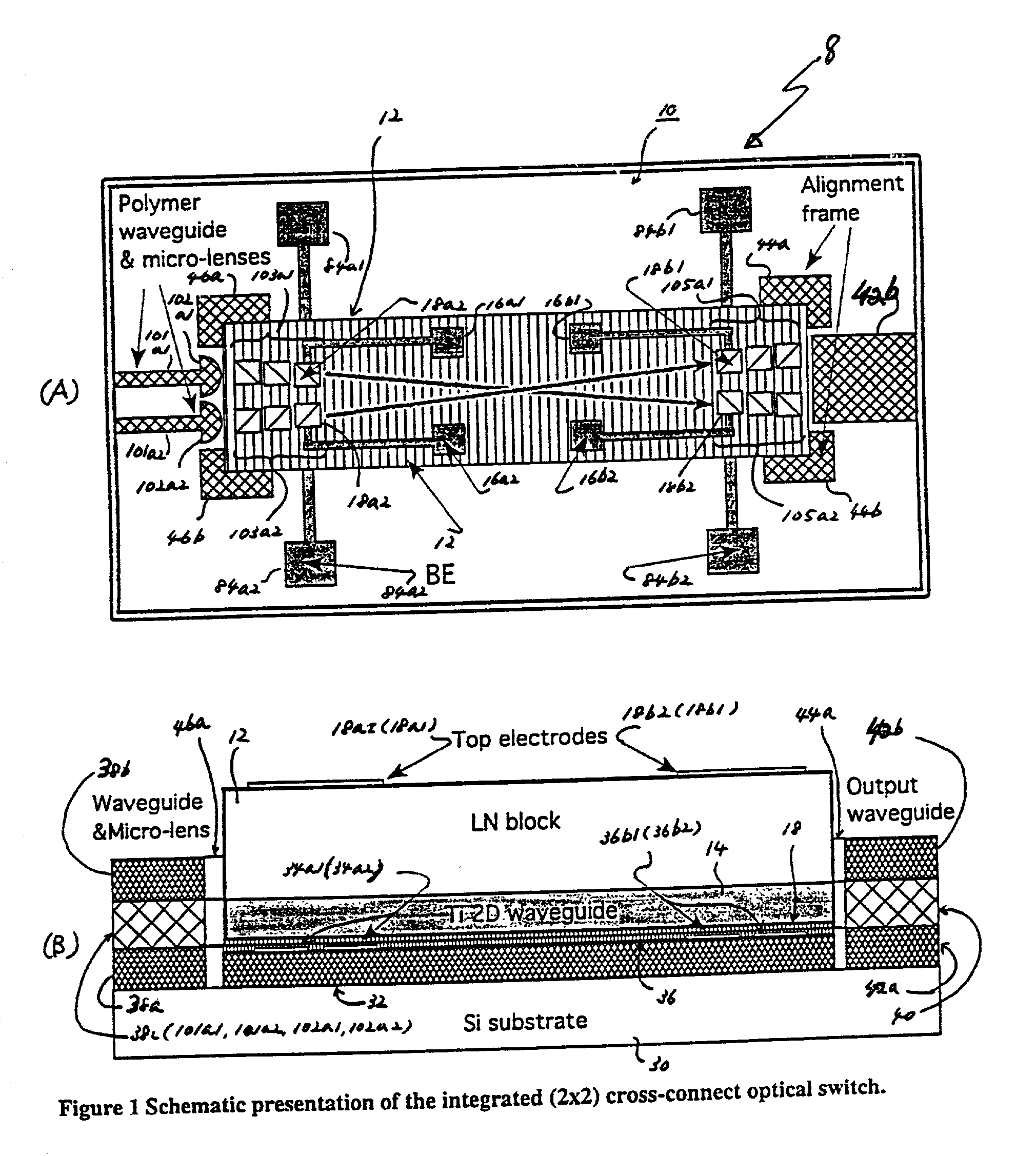
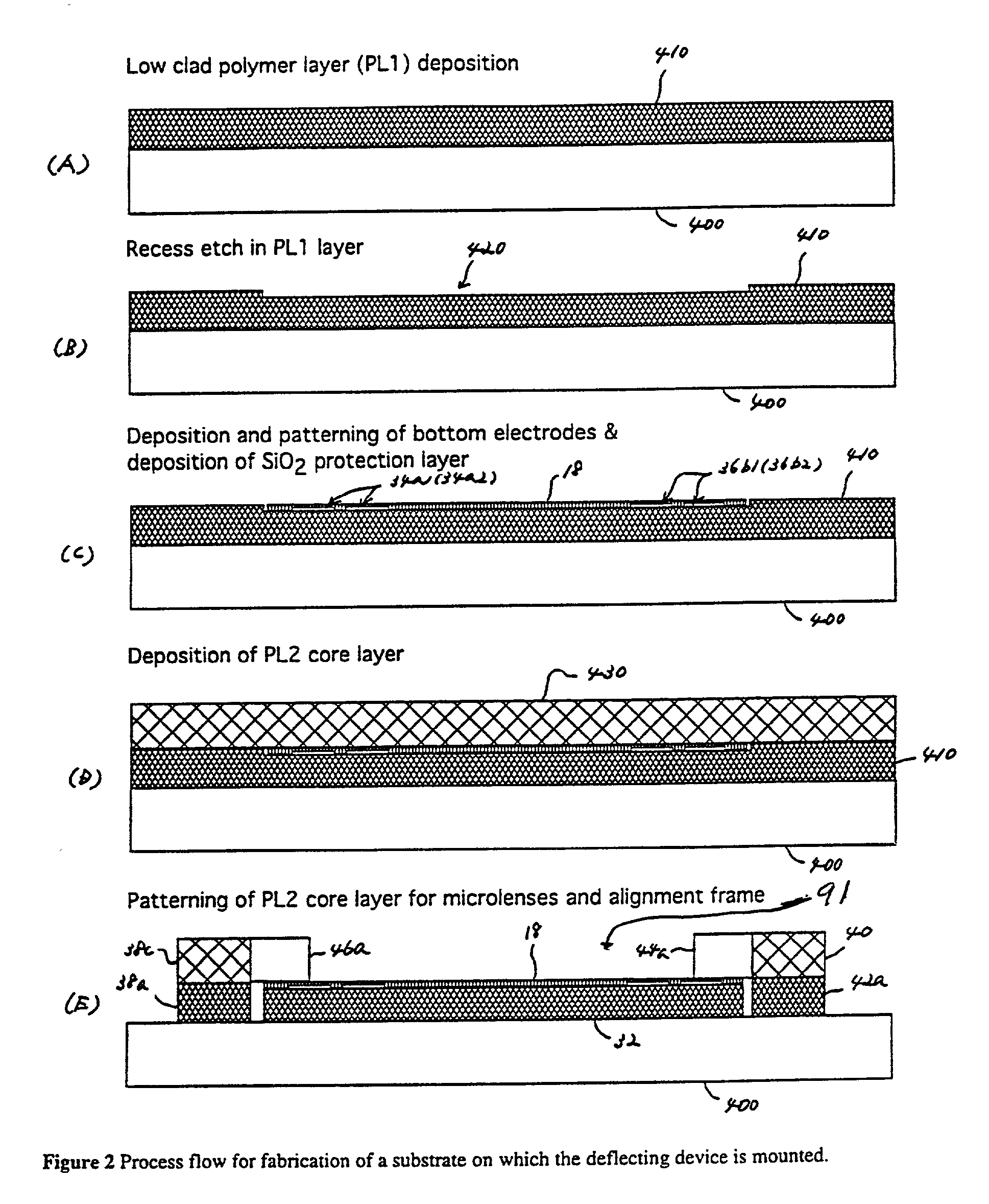
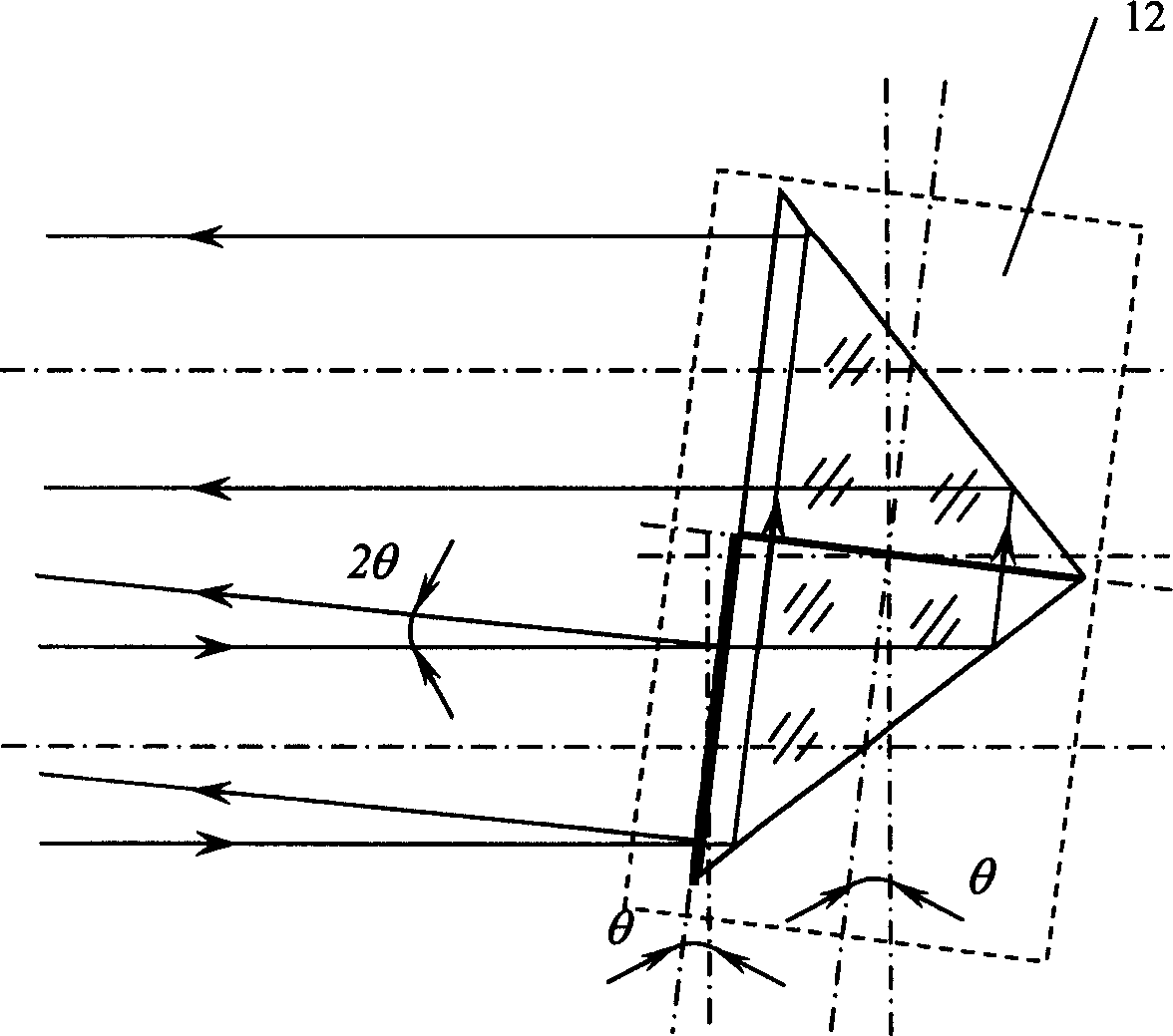
Optical switching apparatus and method for fabricating
InactiveUS20030035614A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCross connectionOptical beam deflection
A hybrid integration process for fabrication of an optical cross-connect switching apparatus. The switching element is based on the deflection of light beam in electro-optic materials by applying electric field across electrodes of an appropriate configuration. The integration process includes fabrication of a substrate (e.g. silicon substrate) with 2D imaging optics from polymeric materials (or silica), fabrication of the light deflecting element, and assembly of the deflecting element on the substrate with imaging optics. The fabrication of the light deflecting element includes fabrication of a LN (lithium niobate) block. The LN block assembled in an optical switching apparatus includes a two-dimensional waveguide formed on a surface of the LN block and an electrode on a surface of the LN block.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Long-distance 2D polarized photoelectric autocollimation device and method for drift quantity returned from feedback of target drone
Combination of polarized laser source, polarized beam splitter mirror and quarter Lambda wave plate is adopted in the 2D photoelectric autocollimation tube, which uses characteristic of polarization to avoid that measuring light beam feeds back laser source so as to prevent further angle drift of the measuring light. Obtaining measurement signal of 2D variance in small angle, beam splitter type target detector also obtains angle drift component of separated and fed back light beam. The said component is identical to inherent component of laser source. Monitoring device monitors quantity of angle drift. Based on quantity of angle drift obtained, computer control 2D optical beam deflection device in real time to adjust the measuring light beam according to direction opposite to quantity of angle drift. The invention restrains and eliminates quantity of angle drift coupled in measuring light beam in propagation path of the measuring light beam.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
Light scanning apparatus
InactiveUS9086645B2Reduce distortionSimple configurationElectrographic process apparatusMountingsOptical beam deflectionLight beam
A light scanning apparatus, including: a light source; a deflector having a rotary polygon mirror configured to deflect the light beam emitted from the light source, and a motor configured to rotate the polygon mirror; a plurality of reflecting mirrors configured to reflect the light beam to the photosensitive member; and an optical box on which the light source is mounted, wherein the optical box has an installation wall on which the deflector is installed and a support wall positioned on a side of the photosensitive member with respect to the polygon mirror, the support wall being provided with a support portion configured to support at least one reflecting mirror, a stepped portion having a plurality of steps is formed between the installation wall and the support wall, and a back surface of the stepped portion has a shape following an inside surface of the stepped portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Two-dimensional beam deflector
A two dimensional beam deflector is disclosed which deflects beams from multiple optical assemblies. The input of beams of the multiple optical assemblies follow parallel optical paths until deflection to a wafer. An ellipsometer using a two-dimensional beam deflector is also disclosed.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTR LTD
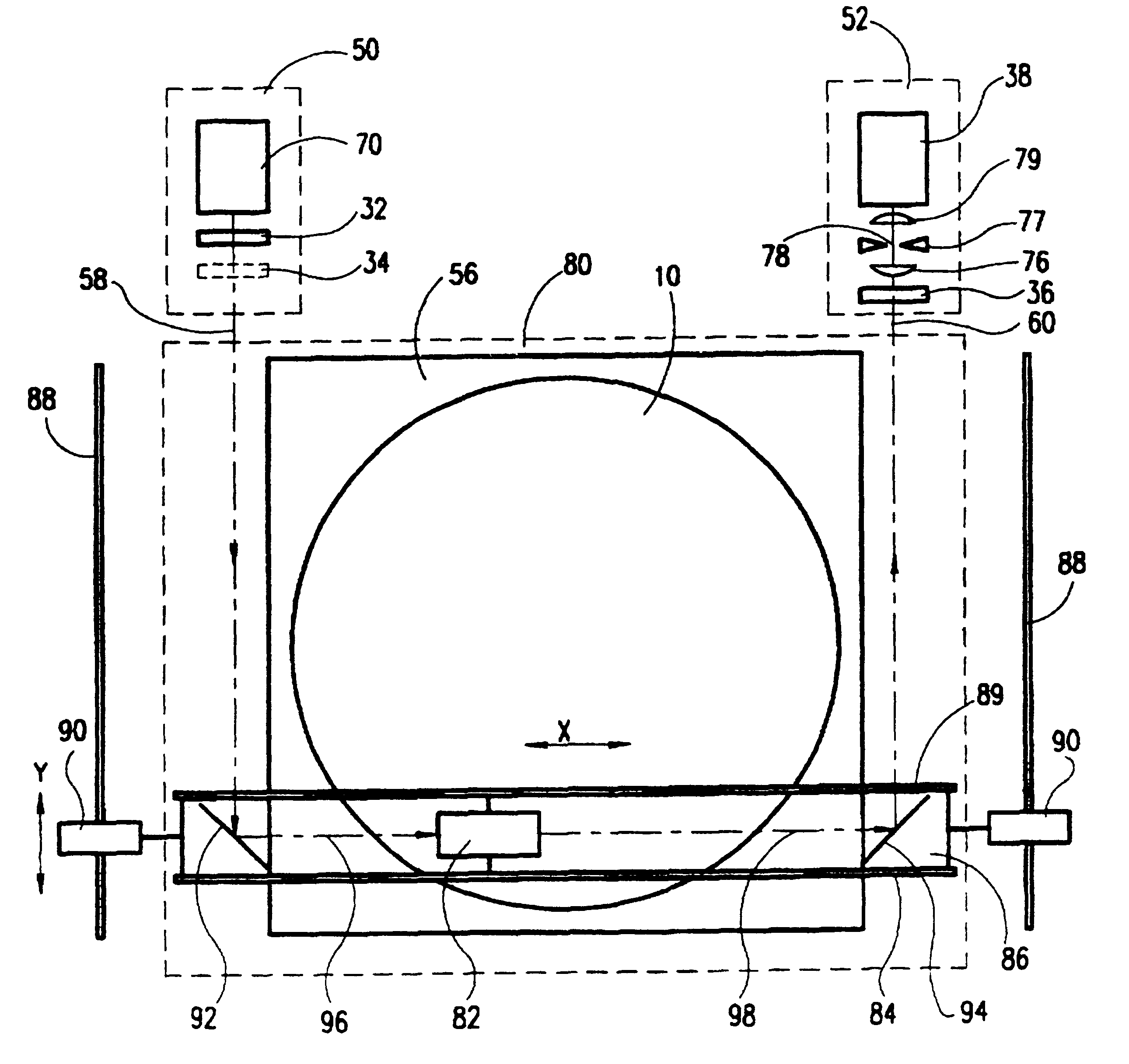
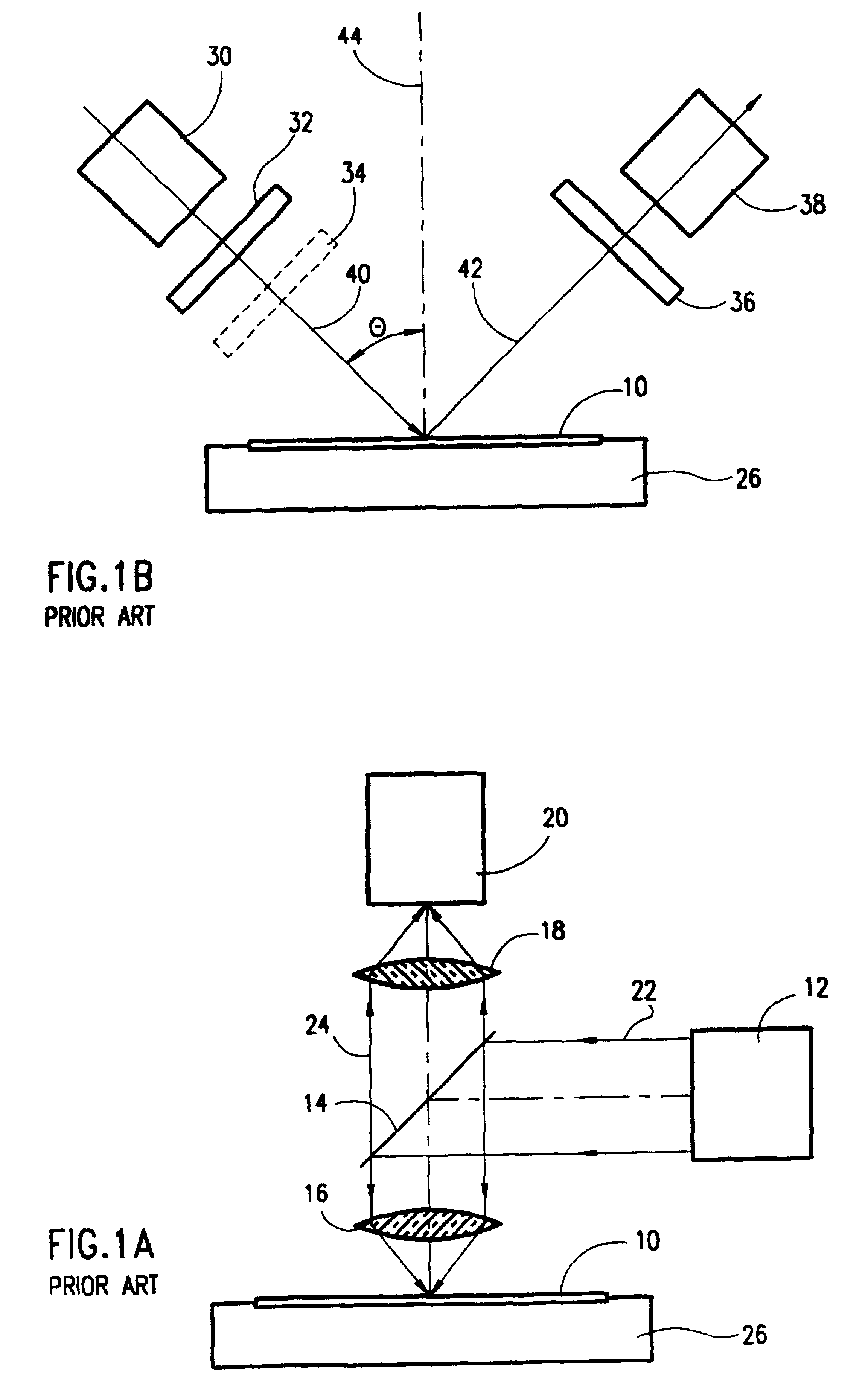
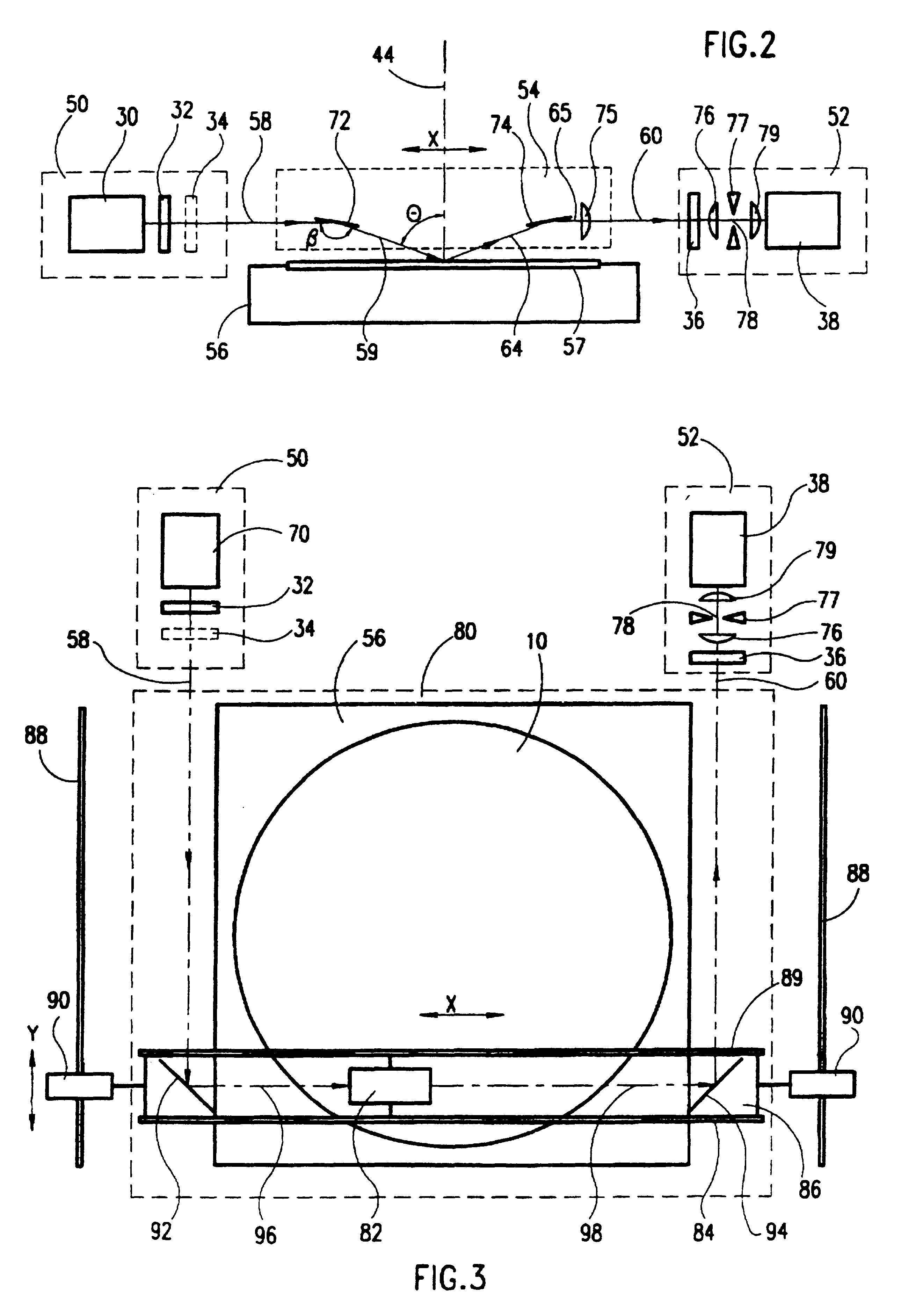
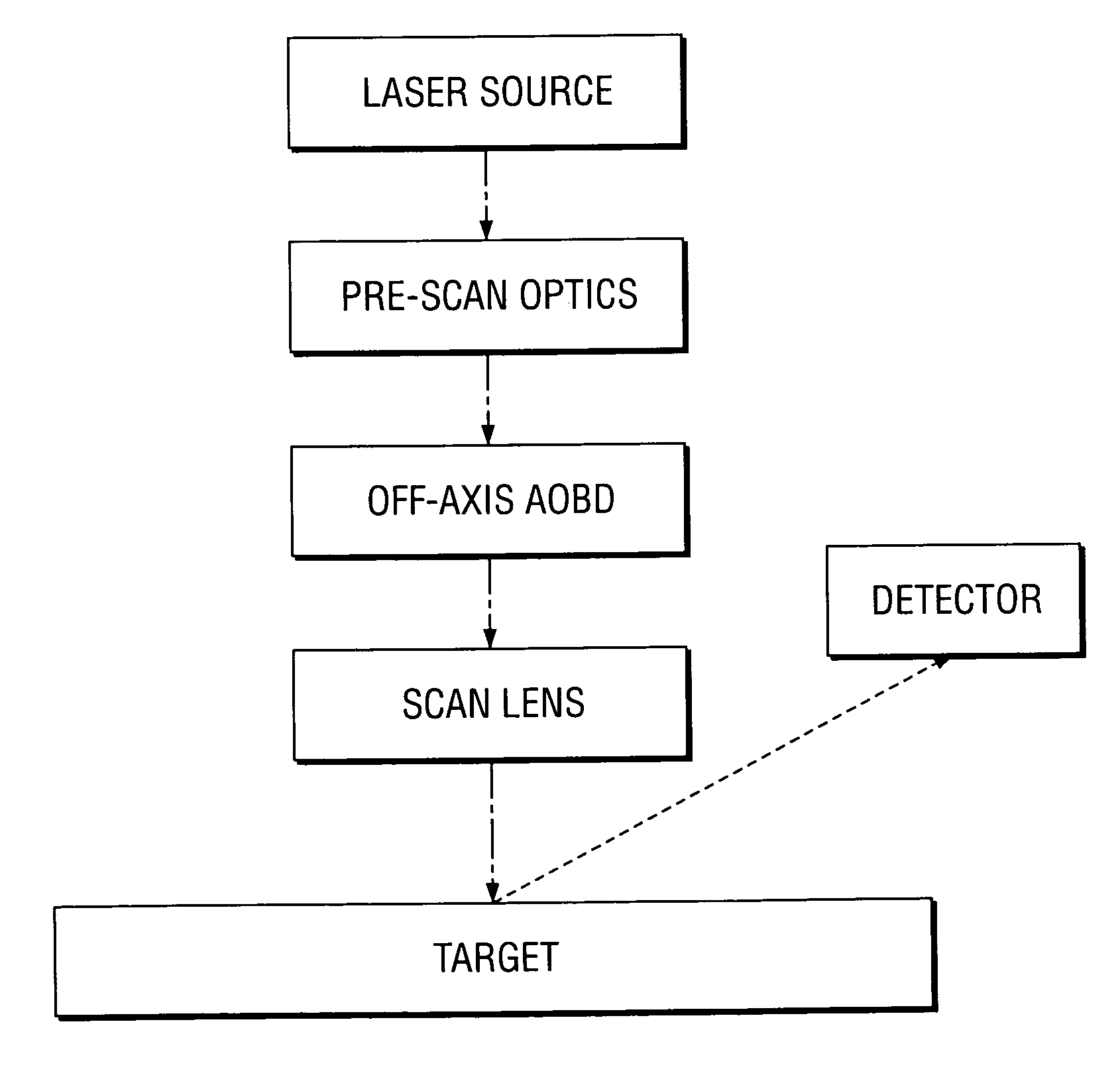
Optical scanning method and system and method for correcting optical aberrations introduced into the system by a beam deflector
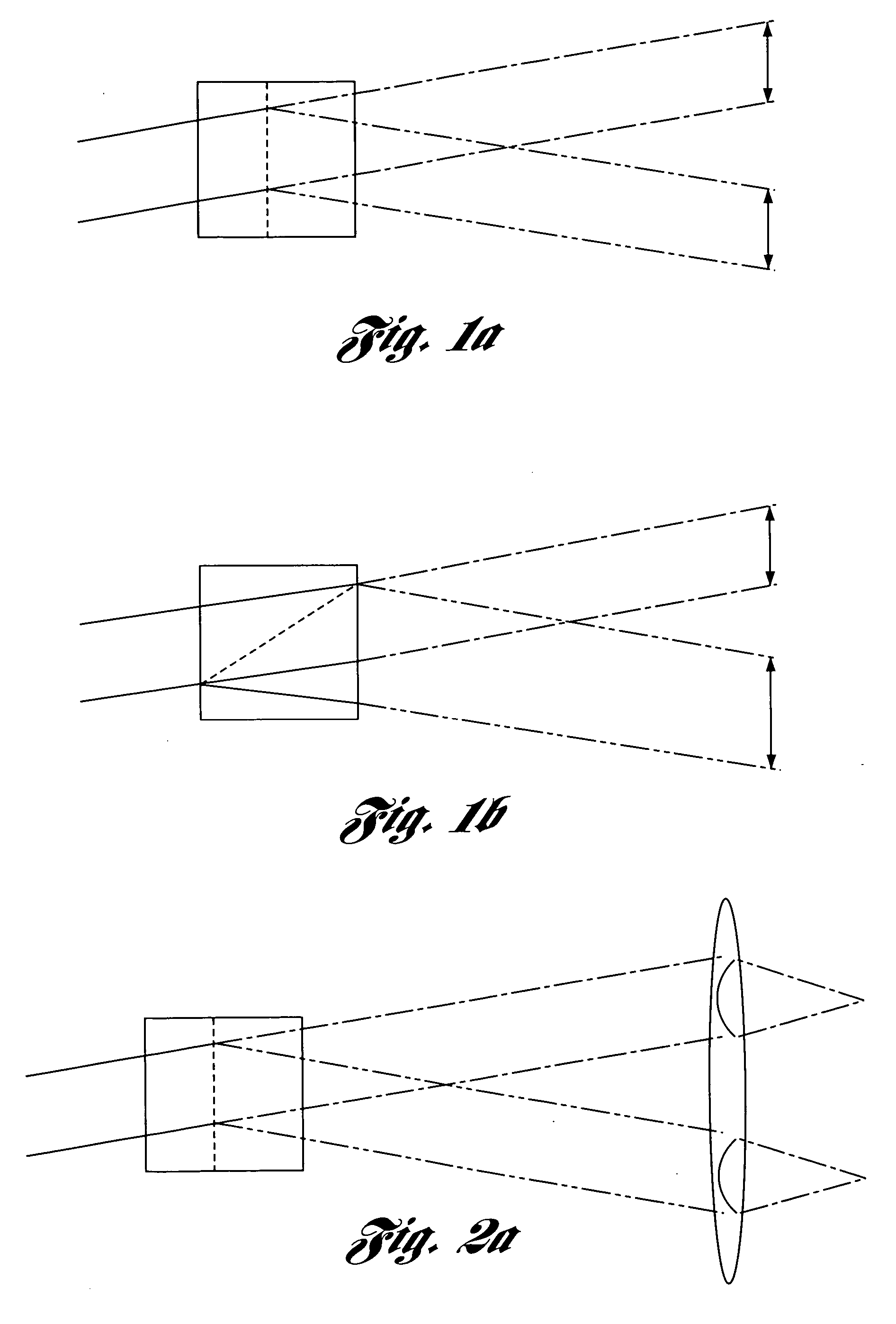
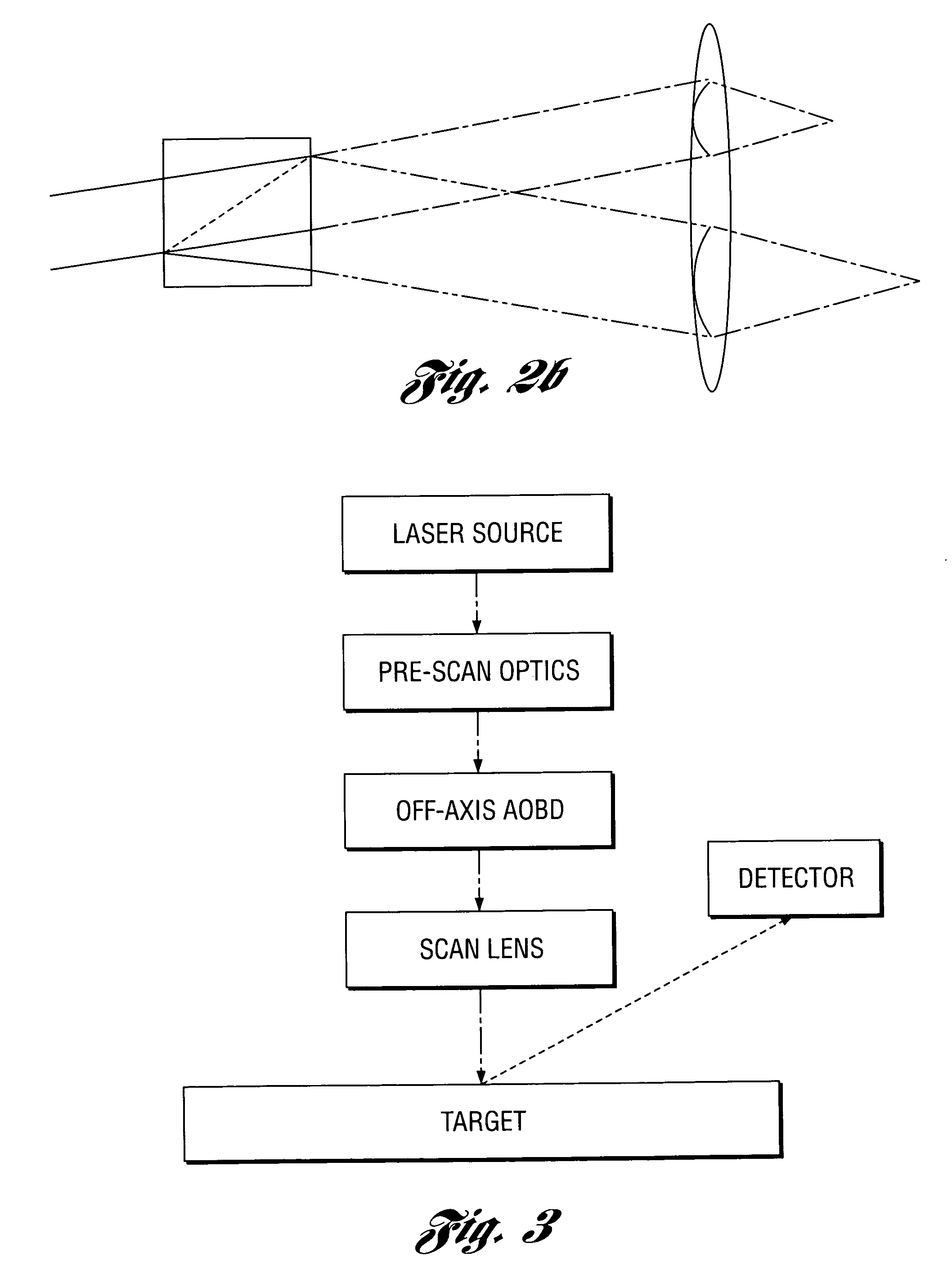
ActiveUS20060256181A1Enhance the imageCorrect optical aberrationElectrographic processes using charge patternPrintingOptical beam deflectionLight beam
An optical scanning method and system and method for correcting optical aberrations introduced into the system by a beam deflector are provided. The optical scanning method and system utilize a tilt-corrected, off-axis beam deflector. The scanning system includes an off-axis acousto-optic beam deflector with a walk-off angle operated at high speed and post-scan optics used to focus the scanned beam. A tilted in-scan focus plane resulting from beam width variation through the scan and the cylindrical lens effect is corrected with one or more tilted lens elements within the post-scan optical train.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system tip-tilt and tip-tilt-piston actuators and a method for forming the same
Fully monolithic gimbal-less micro-electro-mechanical-system (MEMS) devices with large static optical beam deflection and fabrications methods are disclosed. The devices can achieve high speed of operation for both axes. Actuators are connected to a device, or device mount by linkages that allow static two-axis rotation in addition to pistoning without the need for gimbals, or specialized isolation technologies. The device may be actuated by vertical comb-drive actuators, which are coupled by bi-axial flexures to a central micromirror or device mount. Devices may be fabricated by etching an upper layer both from the top side and from the bottom side to form beams at different levels. The beams include a plurality of lower beams, a plurality of full-thickness beams, and a plurality of upper beams, the lower, full-thickness and upper beams That form vertical combdrive actuators, suspension beams, flexures, and a device mount.
Owner:ADRIATIC RES INST
Optical alignment method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050024649A1Shorten the timeOpportunities decreaseUsing optical meansOptical beam deflectionLight beam
A method establishing a reference point for a machine tool with X-, Y-, and Z-stages. A YZ-plane is established by reflecting a light beam off an X-stage reflector to sense at a detector. The X-stage is moved while repositioning the head and reflector and maintaining sensing. An optical alignment module (OAM) is mounted optically perpendicular to the beam, with a bending mirror centered at the Z-axis. The Z-axis is established bending mirror deflecting the beam to the Z-axis, reflecting it off of a Z-stage reflector so it is sensed, and moving the Z-stage while repositioning the OAM relative to the X- and Y-axes to maintain sensing. An XY-plane is established by bending mirror deflecting the beam to the Y-axis, reflecting it off of a Y-stage reflector so it is sensed, and moving the Y-stage while repositioning the Y-reflector relative to the X- and Z-axes to maintain sensing.
Owner:EXCEL PRECISION
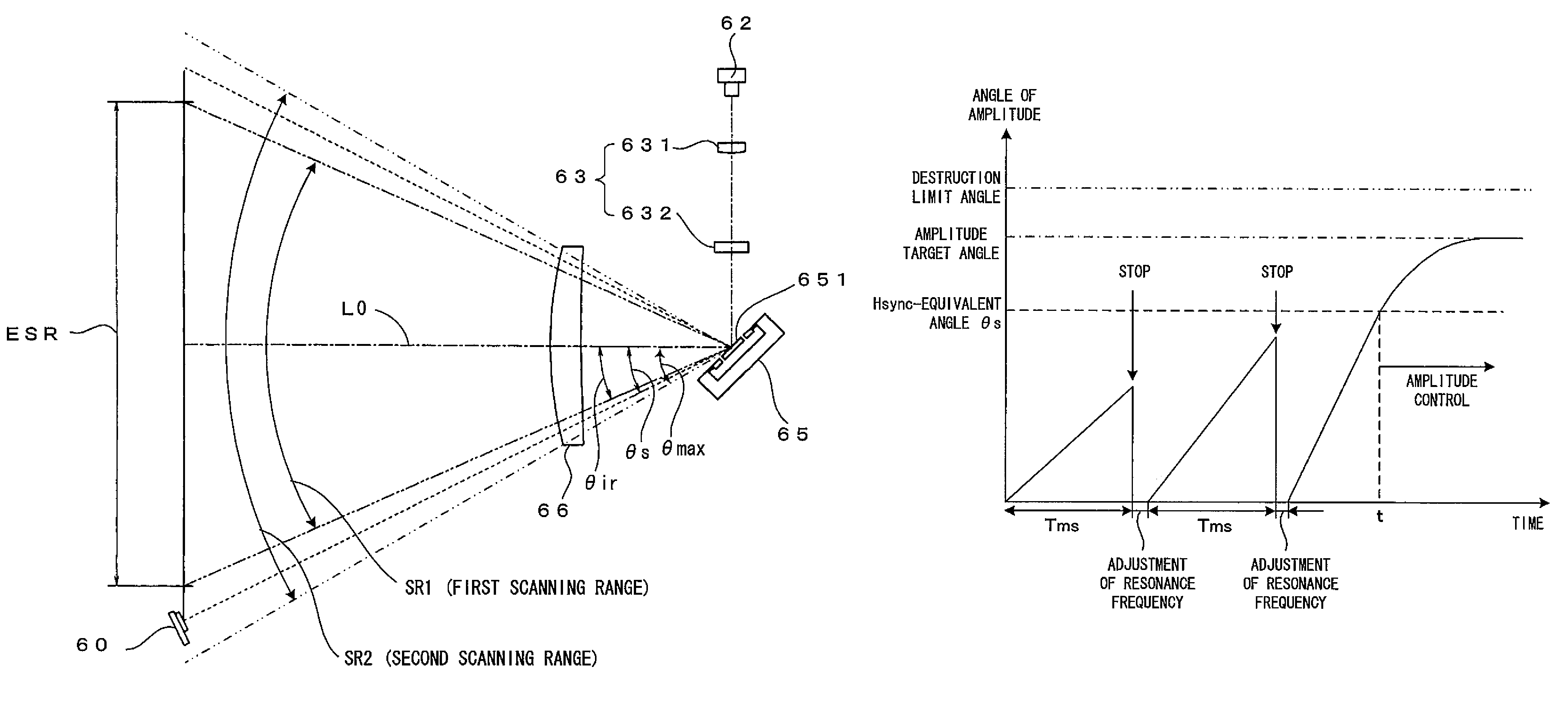
Light scanning apparatus and method to prevent damage to an oscillation mirror in an abnormal control condition via a detection signal outputted to a controller even though the source still emits light
InactiveUS7436564B2Avoid vibrationAvoid destructionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical beam deflectionLight beam
A light scanning apparatus makes a light beam scan along a main scanning direction on an effective scanning region having a predetermined width. A deflector includes an oscillation mirror which deflects the light beam and makes the light beam scan a second scanning range which contains but extends beyond a first scanning range corresponding to the effective scanning region A detector detects the scanning light beam which moves through a position outside the first scanning range but within the second scanning range, and outputs a detection signal A controller drives the oscillation mirror based on the detection signal and accordingly adjusts the amplitude of the oscillation mirror, and stops driving the oscillation mirror when the detection signal is not outputted from the detector even though a light source is turned on to emit the light beam.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Laser beam scanning device employing a scanning element having a flexible photo-etched gap region disposed between an anchored base portion and a light beam deflecting portion having a natural frequency of oscillation tuned by the physical dimensions of said flexible photo-etched gap region and forcibly oscillated about a fixed pivot point at an electronically-controlled frequency of oscillation substantially different from said natural resonant frequency of oscillation
InactiveUS6874689B2Avoids shortcoming and drawbackUltra low power consumptionDigital data information retrievalMirrorsLow speedLaser scanning
Disclosed is laser beam scanning apparatus in the form of an electronically-controlled mechanically-damped off-resonant laser beam scanning mechanism. The scanning mechanism comprises an etched scanning element having a small flexible gap region of closely-controlled dimensions disposed between an anchored base portion and a laser beam deflection portion The light beam deflection portion supports a permanent magnet and a light beam deflecting element (e.g., mirror or hologram). A reversible magnetic force field producing device (e.g., an electromagnet) is placed in close proximity with the permanent magnet so that it may be forcibly driven into oscillation in response to electrical current flowing through the electromagnet. The resonant frequency of oscillation of the laser beam deflecting portion relative to the anchored base portion is determined by the closely controlled dimensions of the flexible gap region set during manufacture. The steady-state frequency of oscillation of the laser beam deflecting portion is determined by the frequency of polarity reversal of the electromagnet, which is electronically controlled by the polarity of electrical current supplied thereto. In the illustrative embodiments, the forcing frequency of the electromagnet is selected to be at least ten percent off (i.e. greater or less than) the natural resonant frequency of the laser beam deflecting portion of manufacture to be any one of a very large range of values (e.g., 25-127 Hz) for use in both low-speed and high-speed laser scanning systems.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
System and process for measuring strain in materials at high spatial resolution
ActiveUS20150076346A1Reduce dynamical diffraction effectEliminate relative motionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesDiffraction effectHigh spatial resolution
A process for measuring strain is provided that includes placing a sample of a material into a TEM as a sample. The TEM is energized to create a small electron beam with an incident angle to the sample. Electrical signals are generated that control multiple beam deflection coils and image deflection coils of the TEM. The beam deflection control signals cause the angle of the incident beam to change in a cyclic time-dependent manner. A first diffraction pattern from the sample material that shows dynamical diffraction effects is observed and then one or more of the beam deflection coil control signals are adjusted to reduce the dynamical diffraction effects. One or more of the image deflection coil control signals are then adjusted to remove any motion of the diffraction pattern. A diffraction pattern is then collected from a strained area of the material after the adjusting step, and the strain is then determined from a numerical analysis of the strained diffraction pattern compared to a reference diffraction pattern from an unstained area of the material.
Owner:APPFIVE
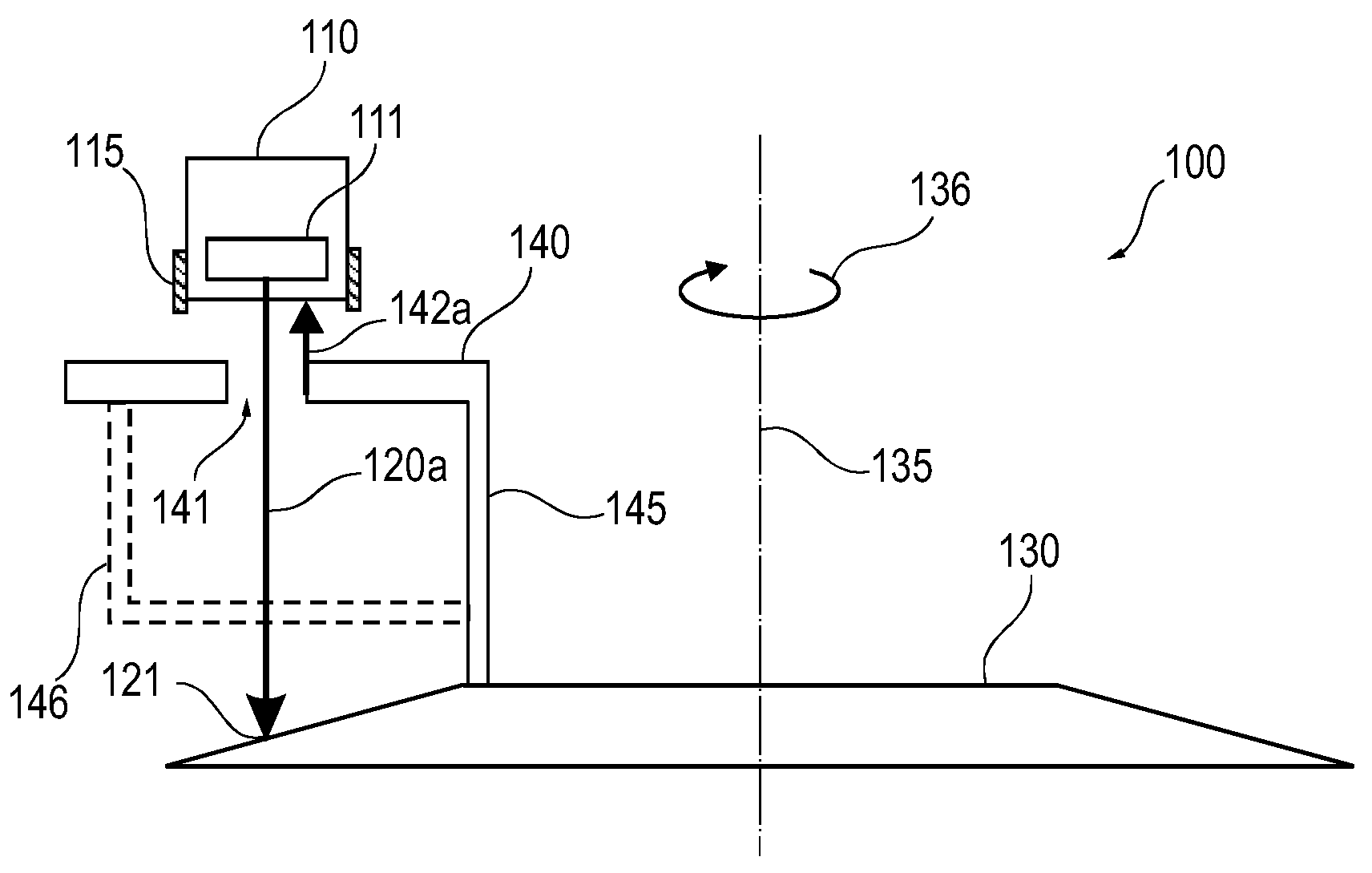
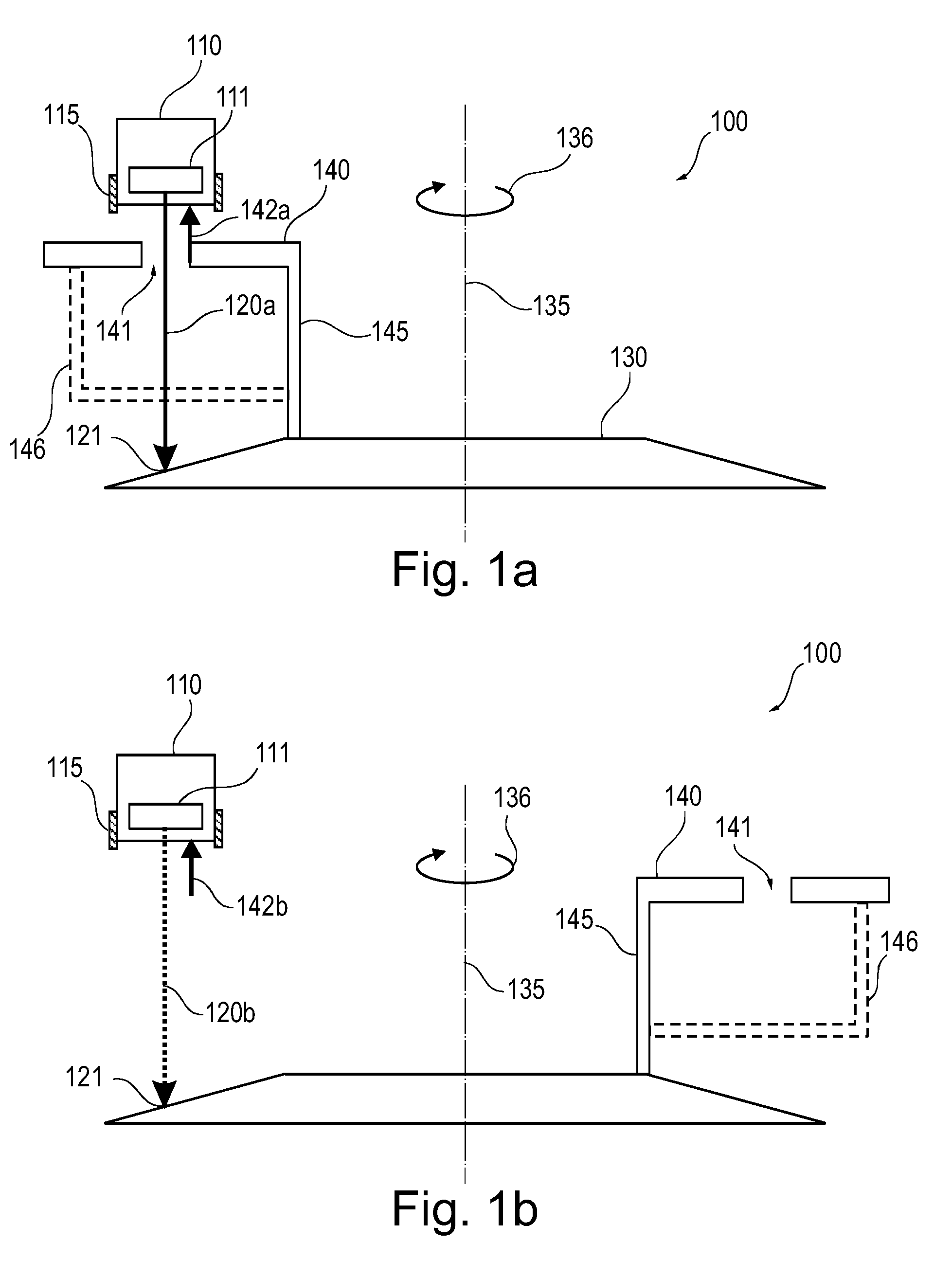
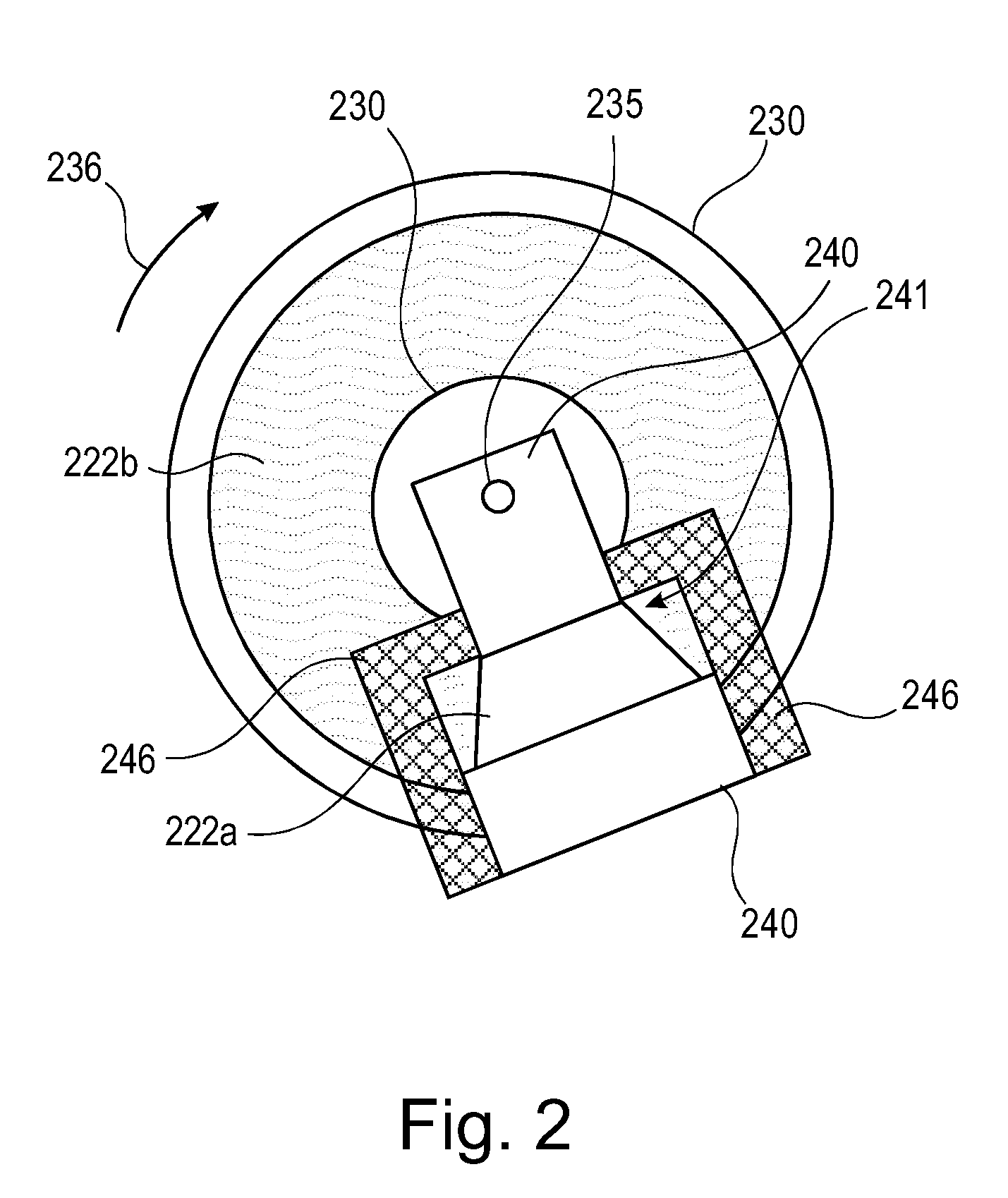
X-ray tube whose electron beam is manipulated synchronously with the rotational anode movement
InactiveUS20090154649A1Easy to adjustImprove spatial resolutionX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingElectron sourceOptical beam deflection
It is described an X-ray tube (100) comprising a rotating anode (130), which is provided with a pull electrode (140). The pull electrode (140) interacts with a fixed electron source (110) in order to generate a modulated electron beam (120a, 120b). The beam modulation may be an intensity variation and / or a spatial deflection. The pull electrode (140) is mounted in a fixed position with respect to the anode (130) and rotates together therewith. The pull electrode (140) may have a hole (141) for passing the electron beam (120a). When being in front of the electron source (110), the pull electrode (140) causes a high electric field (142a) such that a strong electron beam (120a) is generated. When being not in front of the electron source (110) only a low current or a zero current electron beam (120b) is generated. However, the pull electrode (740) may also cause a radial beam deflection such that depending on the angular position of the anode (730) the position of a focal spot (721a, 721b) of the electron beam (720) is varied.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Illumination system for illuminating a mask in a microlithographic exposure apparatus
ActiveCN101669071APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingControl signal
An illumination system for illuminating a mask in a microlithographic exposure apparatus has an optical axis and a pupil surface. The system can include an array of reflective or transparent beam deflection elements such as mirrors. Each deflection element can be adapted to deflect an impinging light ray by a deflection angle that is variable in response to a control signal. The beam deflection elements can be arranged in a first plane. The system can further include an optical raster element, which includes a plurality of microlenses and / or diffractive structures. The beam deflection elements), which can be arranged in a first plane, and the optical raster element, which can be arranged in a second plane, can commonly produce a two-dimensional far field intensity distribution. An opticalimaging system can optically conjugate the first plane to the second plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com