Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Volumetric imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Volumetric Imaging. Volumetric imaging is a 3D technique where all the MRI signals are collected from the entire tissue sample and imaged as a whole entity, therefore providing a high signal to noise ratio.
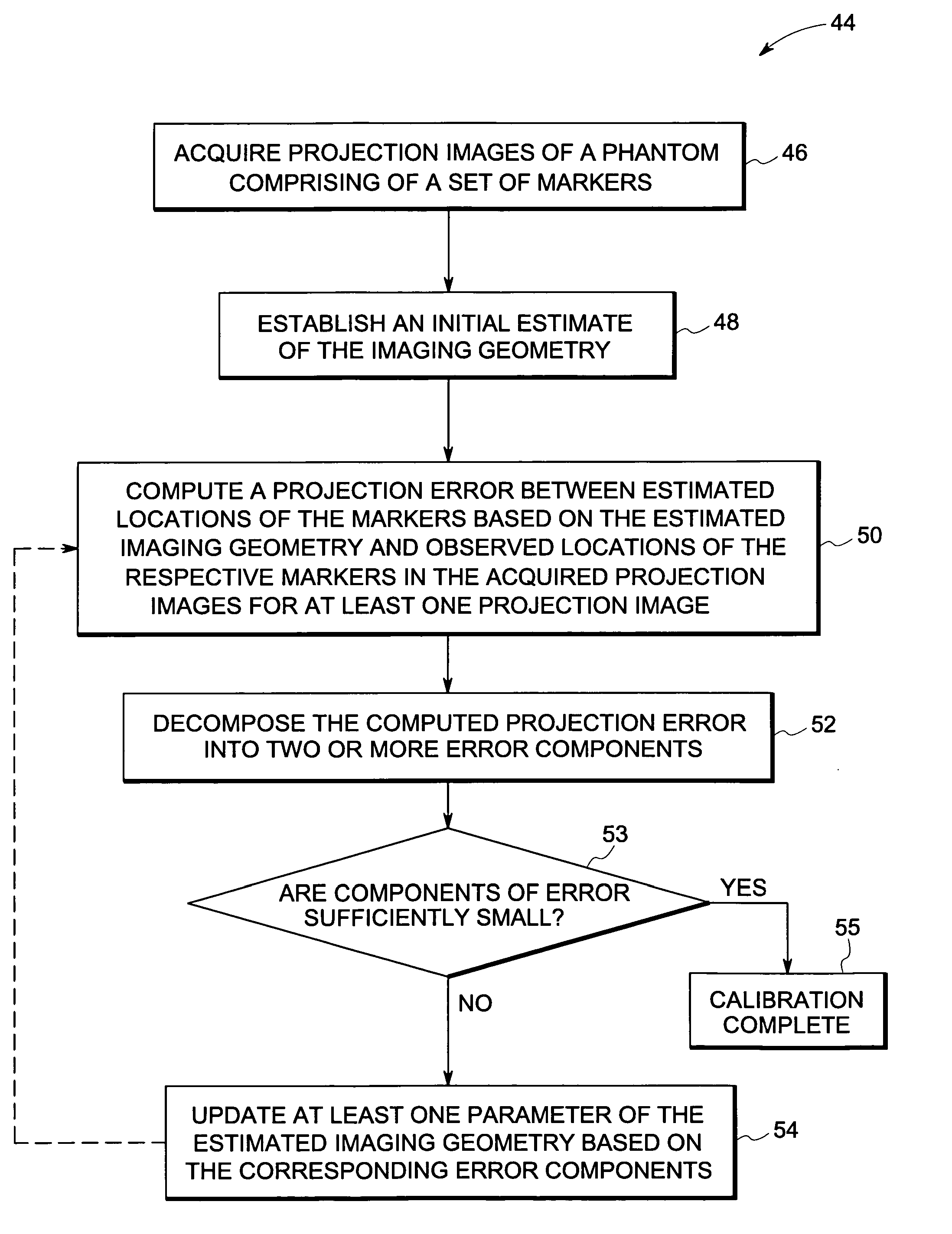
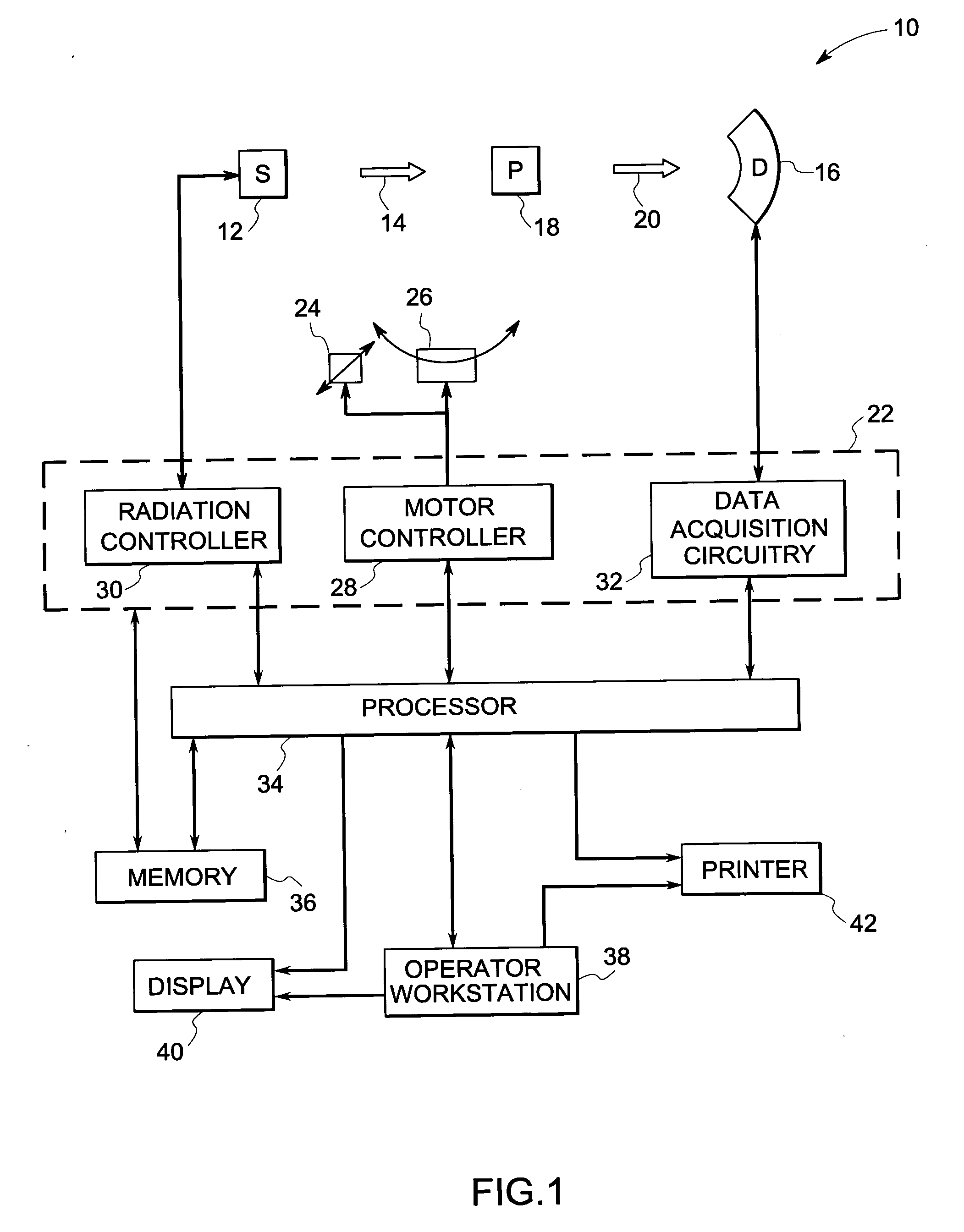
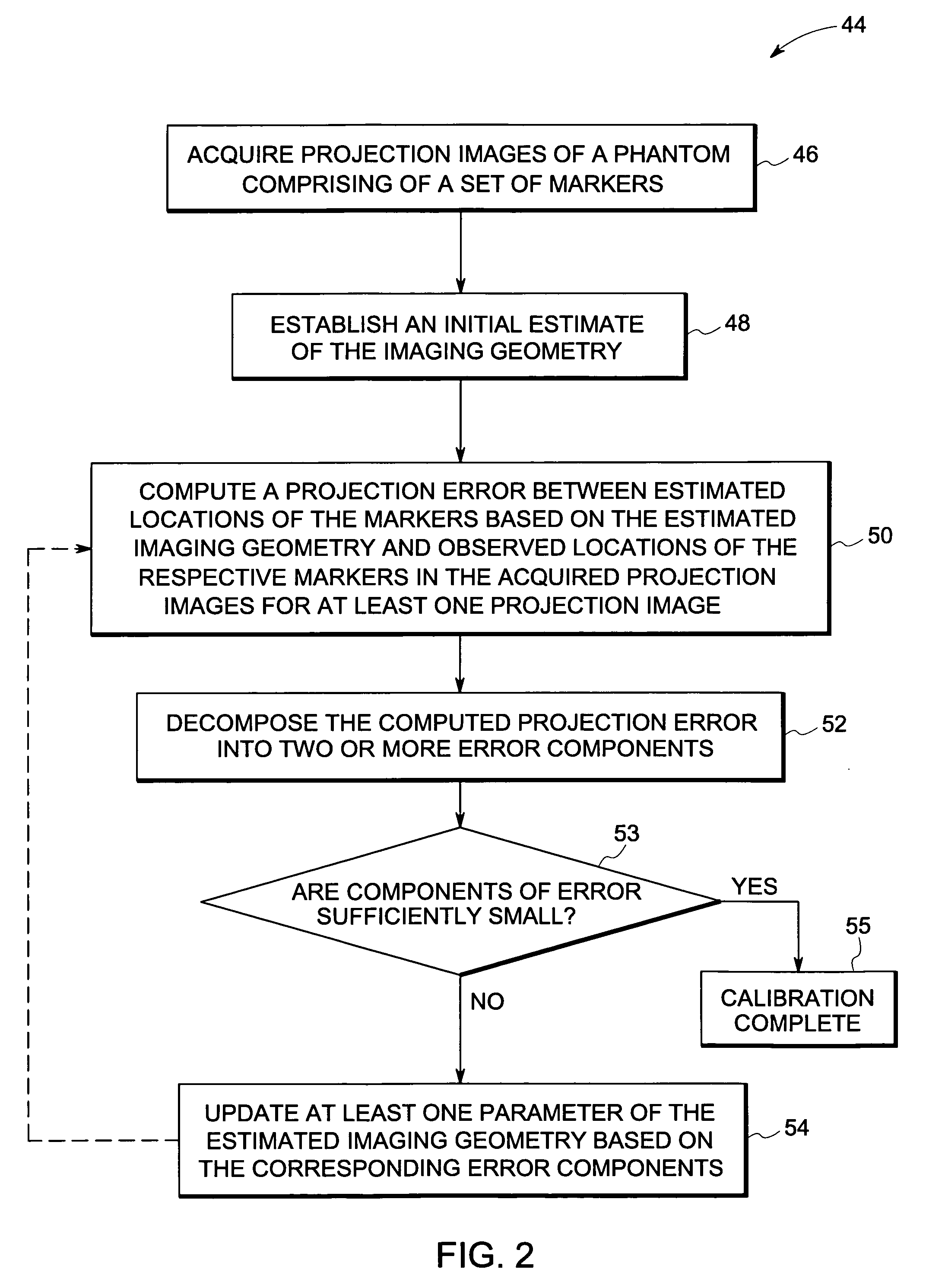
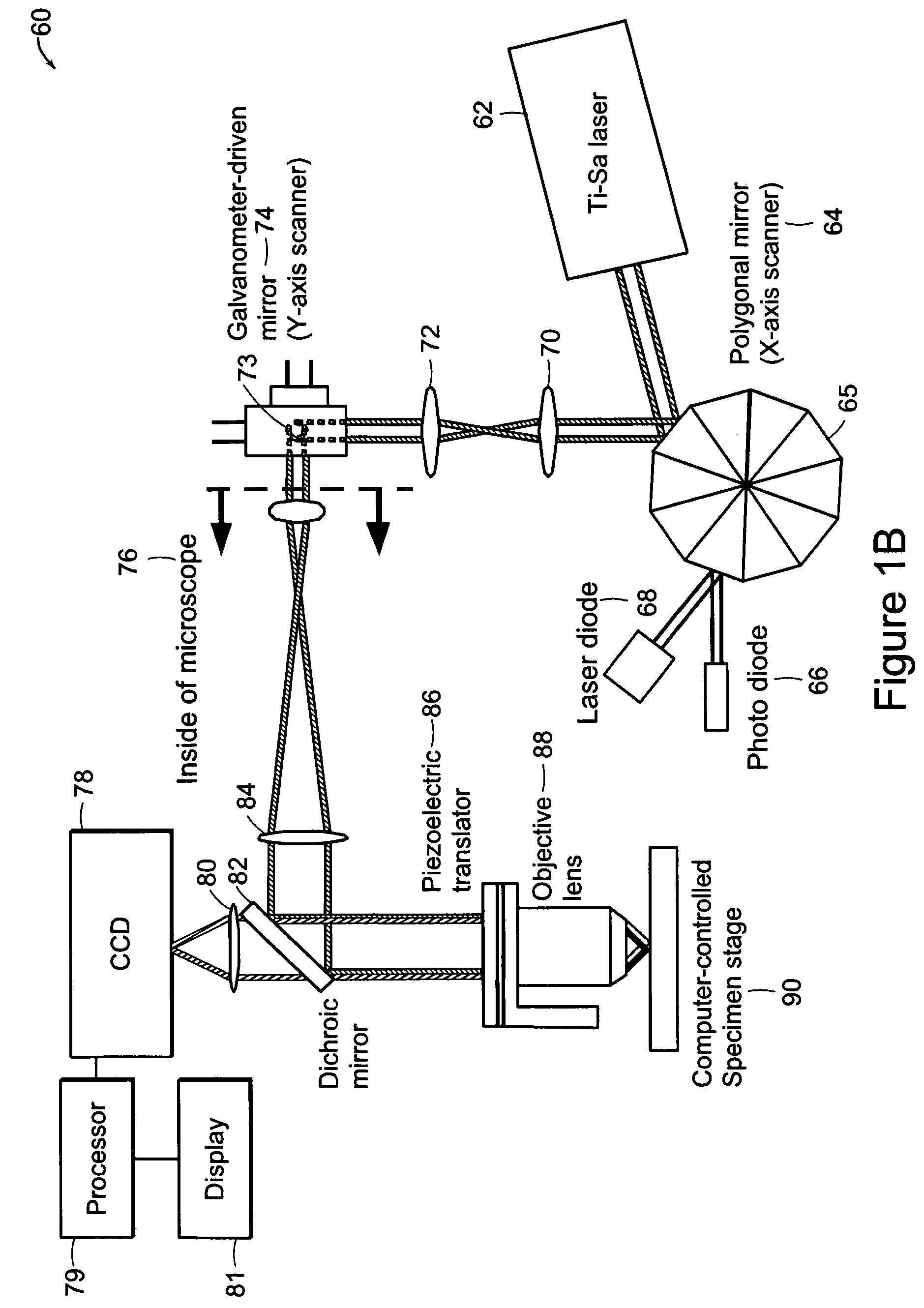
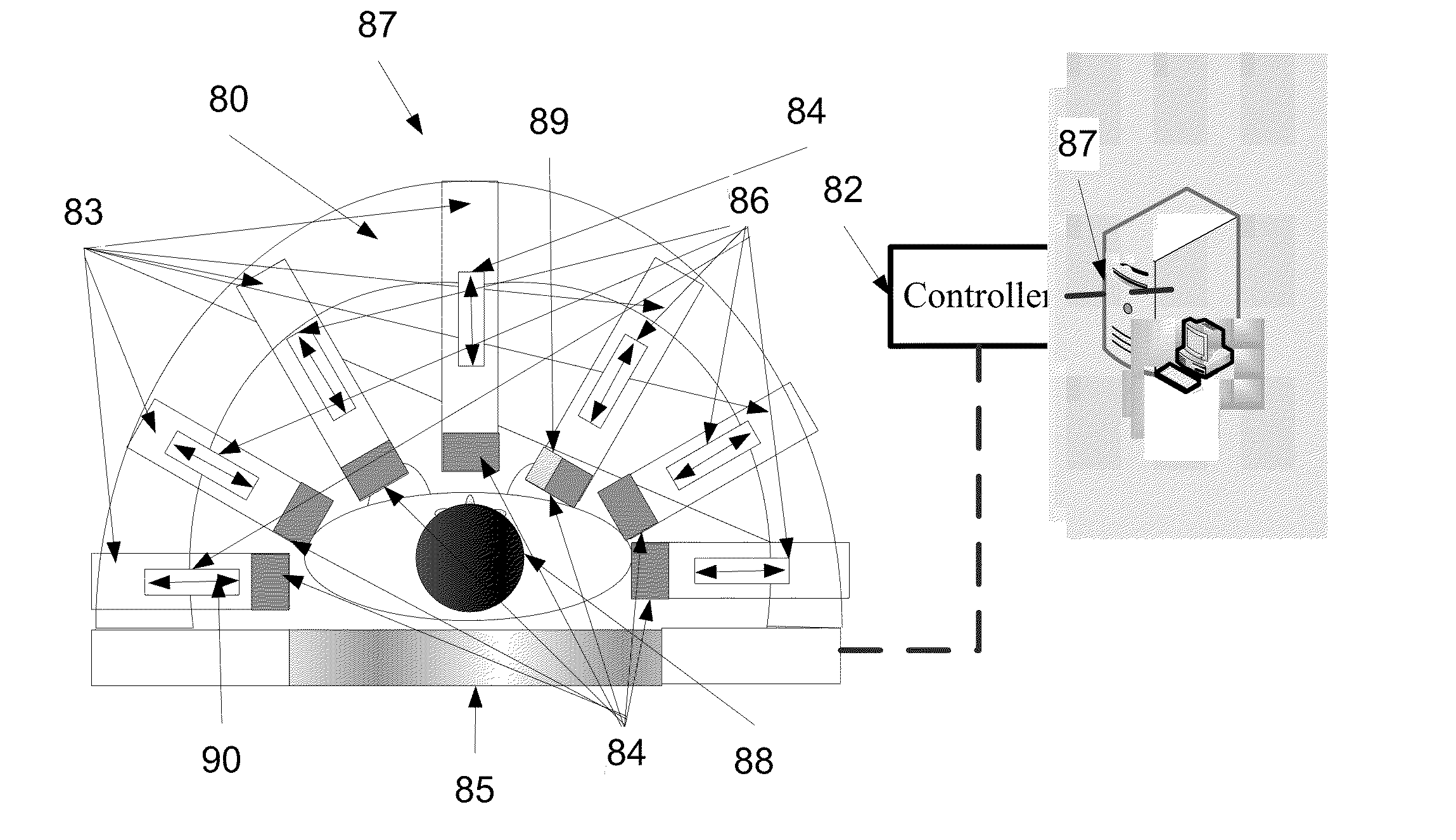
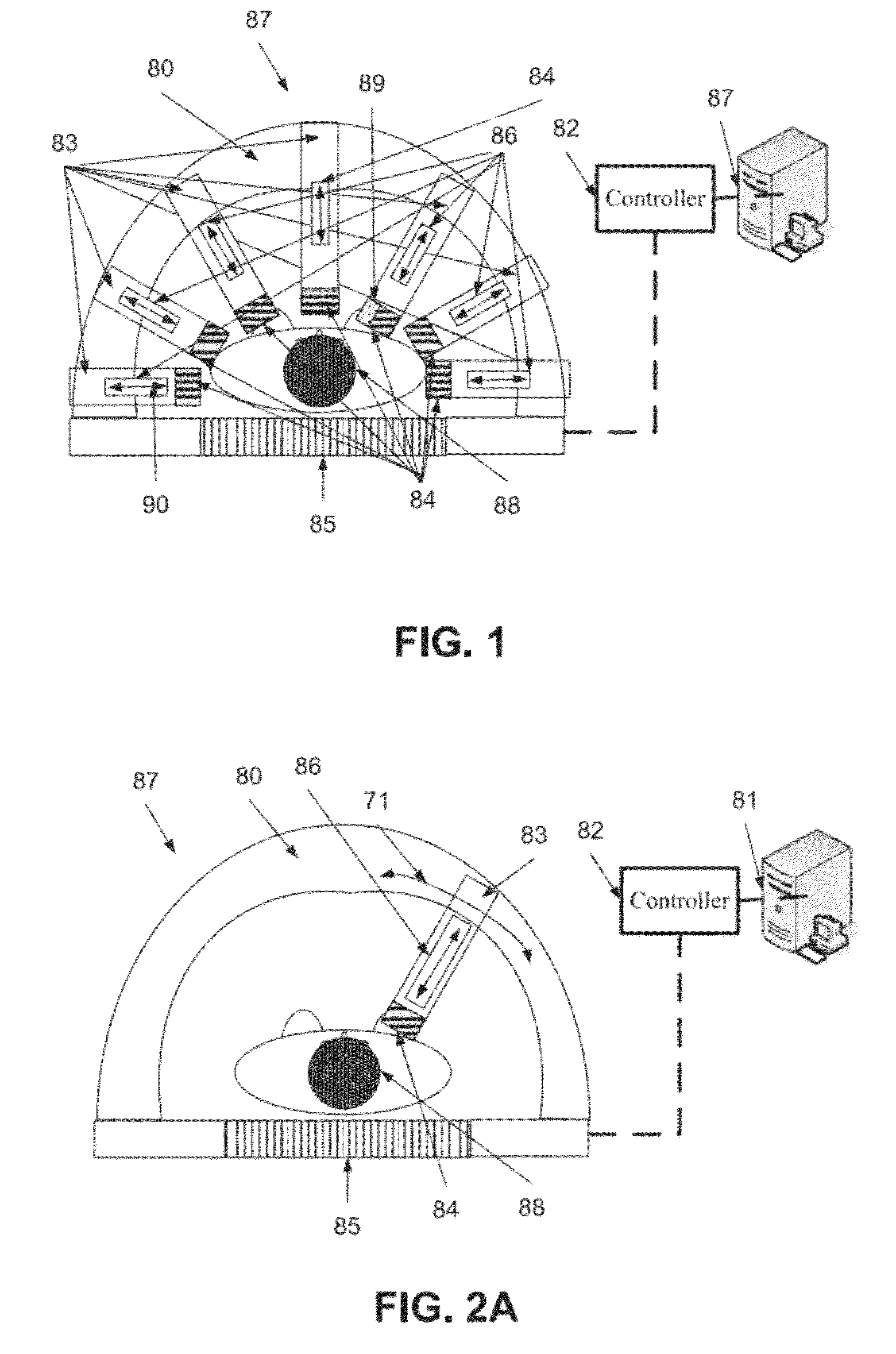
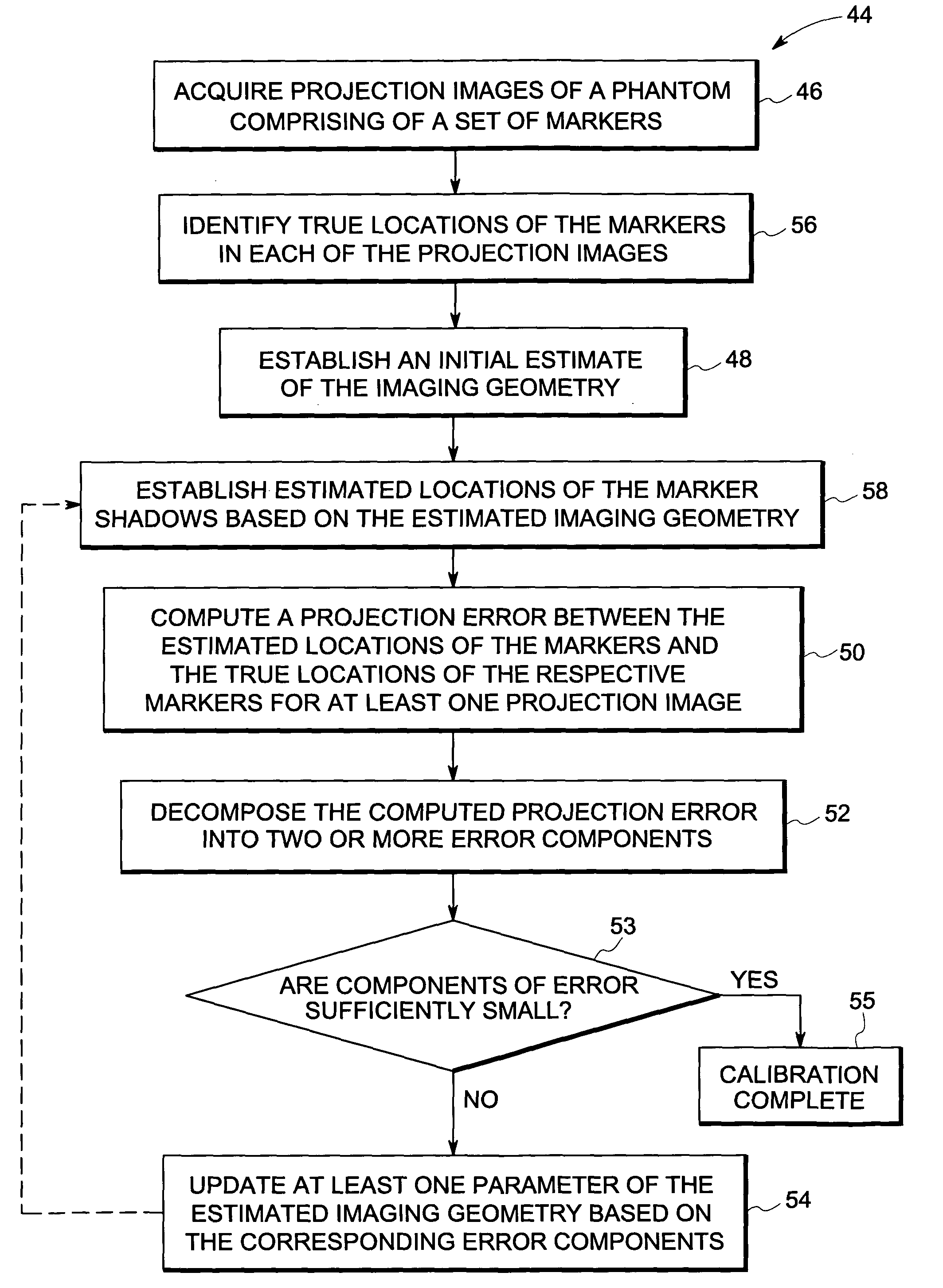
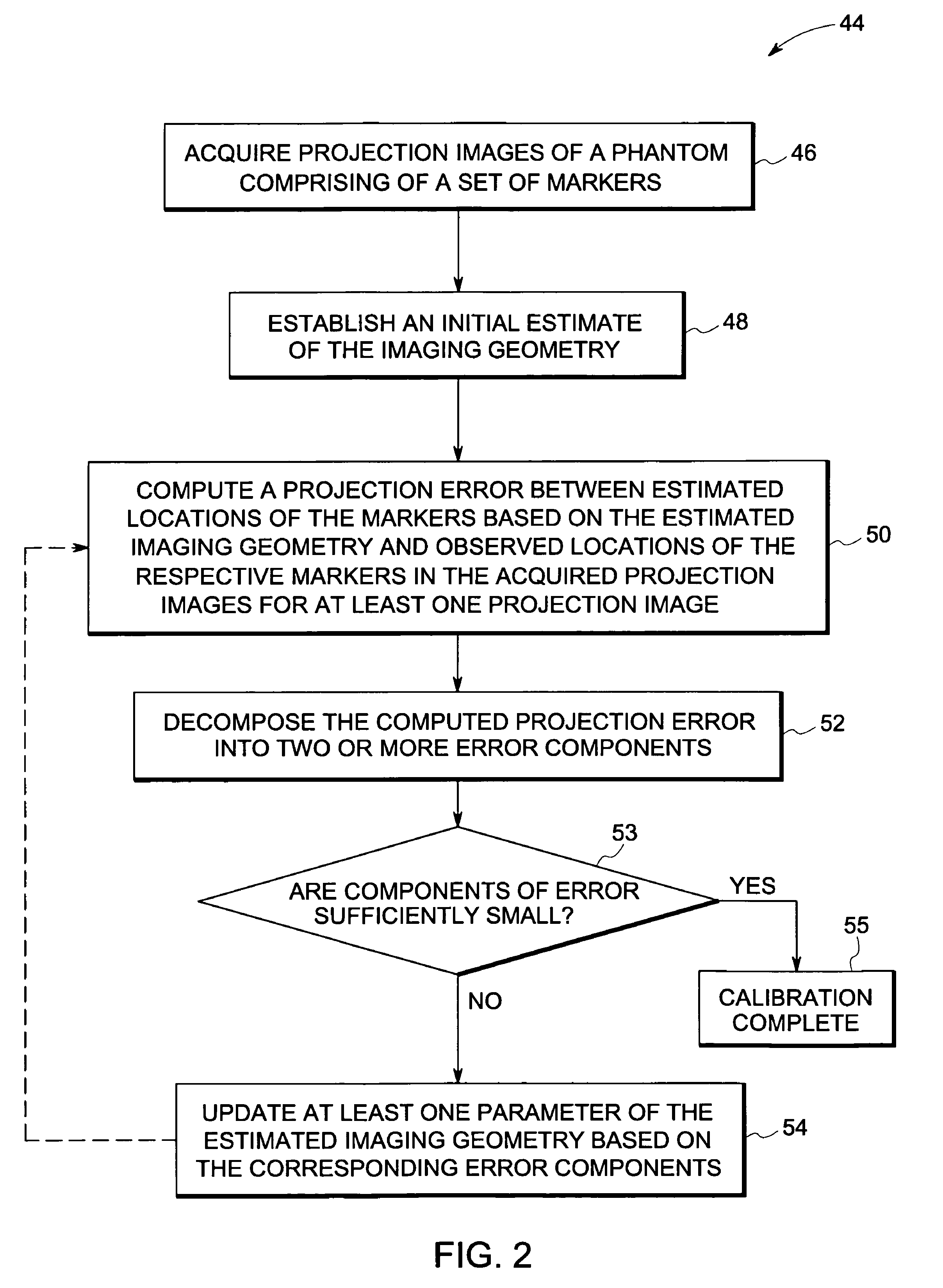
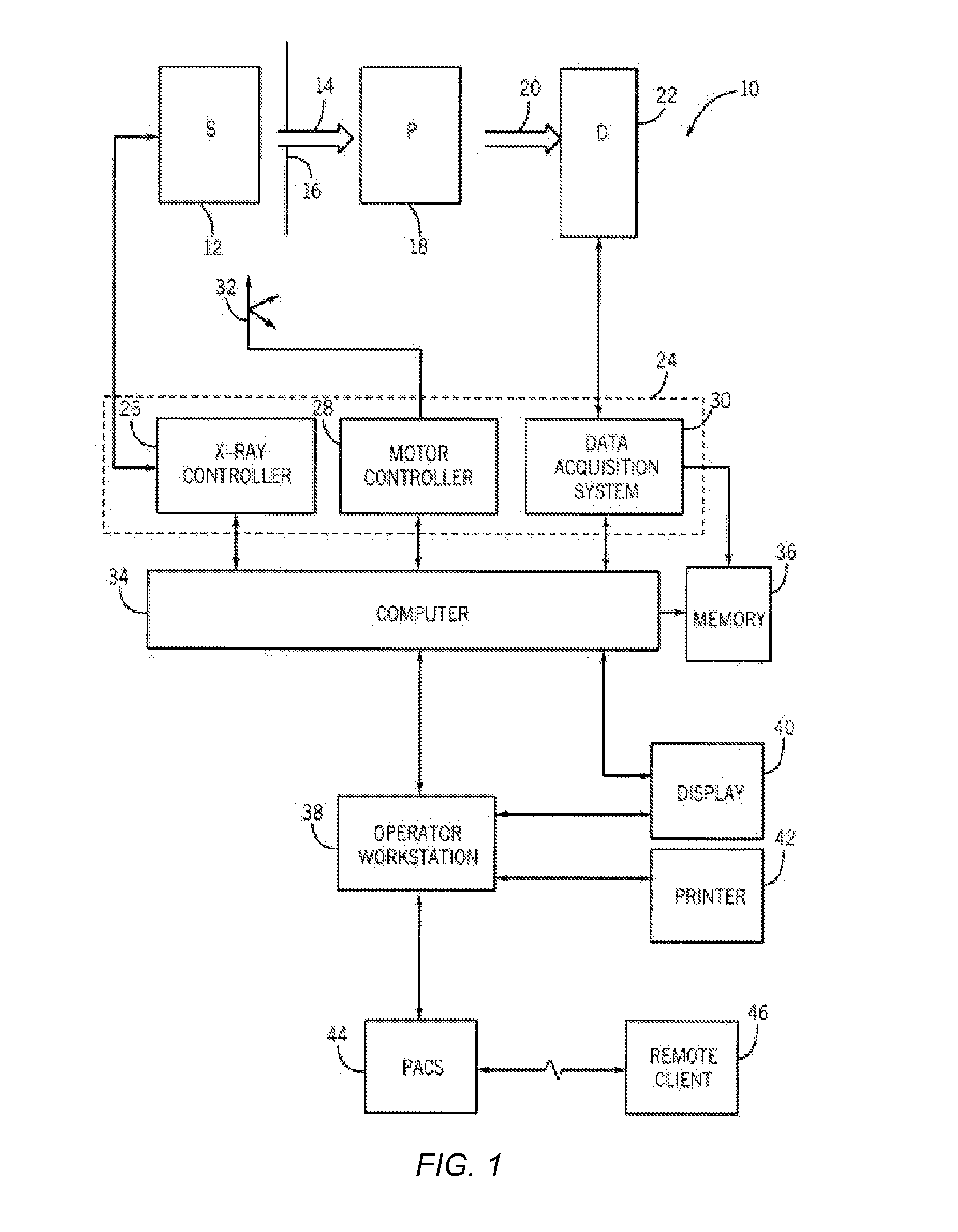
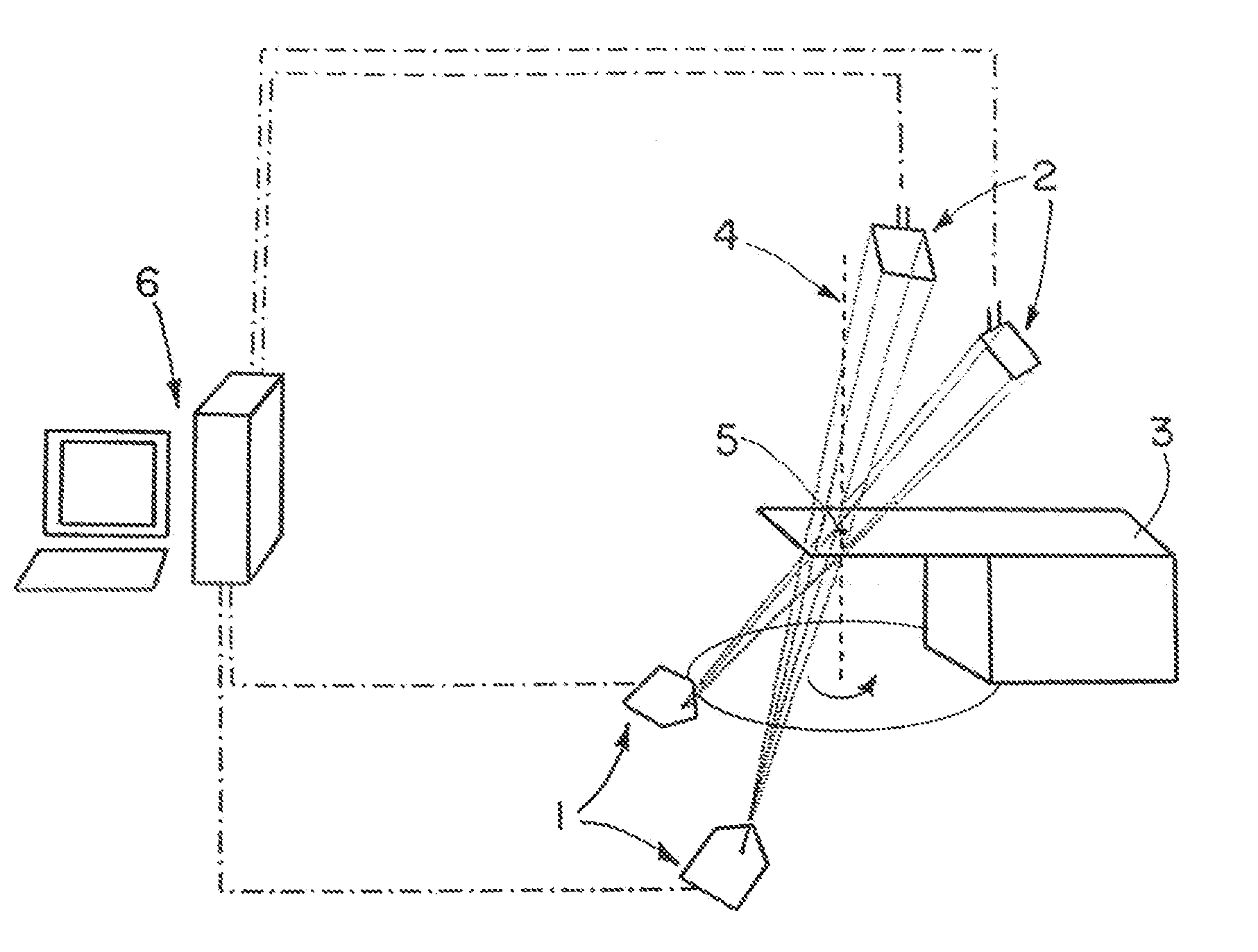
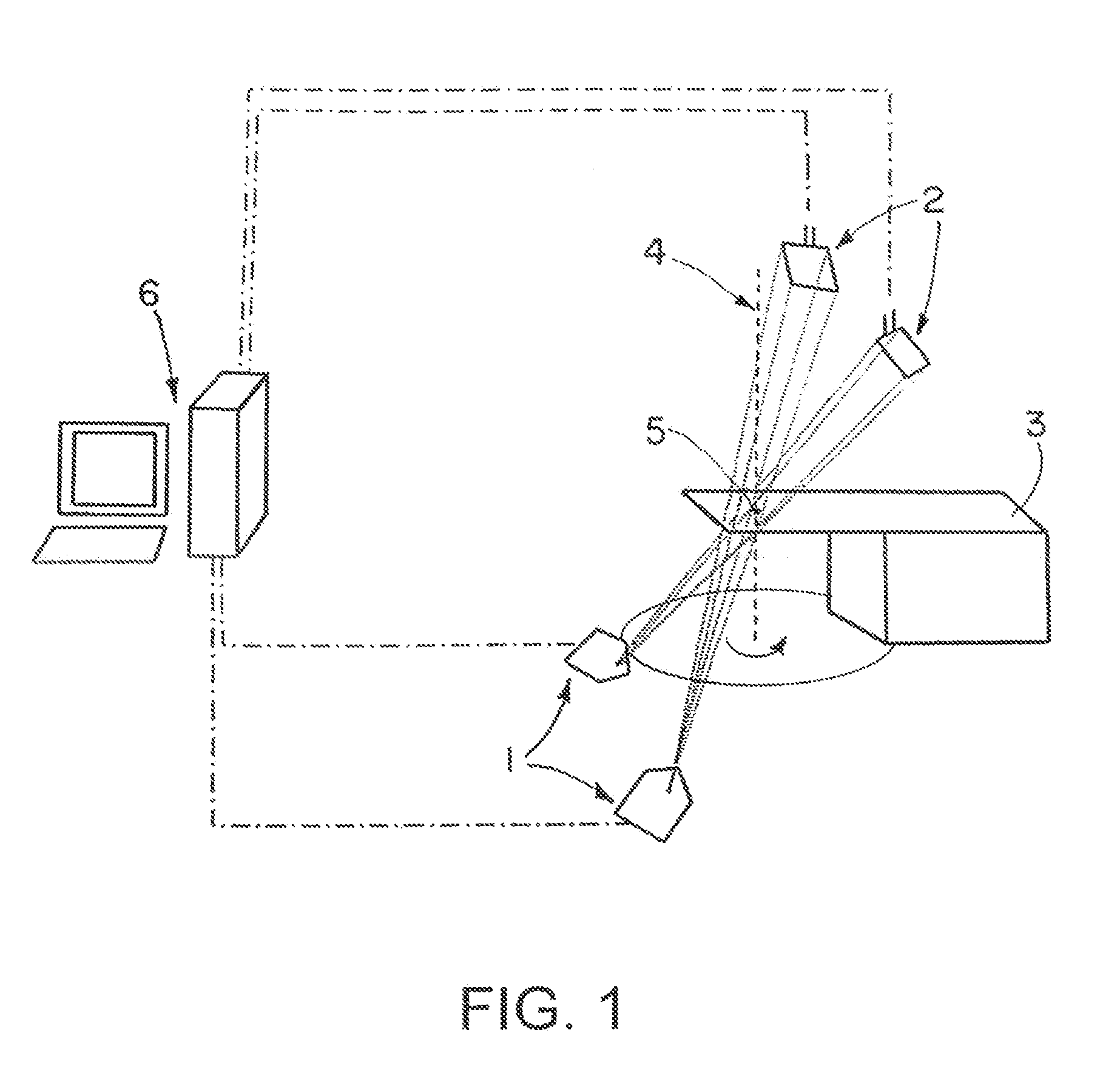
Method and device for geometry analysis and calibration of volumetric imaging systems
ActiveUS20070122020A1Enhance the imageImprove accuracyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVolumetric imagingProjection image
A technique is provided for geometrical analysis and calibration of a volumetric imaging system. The technique includes computing a projection error between estimated locations of a set of markers of a phantom based on a estimated imaging geometry and observed locations of the respective markers for at least one projection image, decomposing the computed projection error into one or more error components corresponding to respective geometric parameters of the imaging geometry, and updating at least one parameter of the estimated imaging geometry based on the one or more error components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Volumetric imaging on a radiotherapy apparatus
InactiveUS20060050848A1Accurate operationSmooth rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVolumetric imagingImaging processing
Volumetric imaging on a radiotherapy apparatus, wherein a body, of which a volumetric image data set is to be produced, is positioned on a couch of the radiotherapy apparatus, and the couch or a bearing area of the couch or the body itself is rotated about a spatially fixed axis. During rotation, multiple x-ray images of the body or of a part of the body are produced and stored by at least one radiation source / image recorder system which is separate from the radiotherapy apparatus and whose radiation path is substantially not parallel to the spatially fixed axis. The rotational position of the couch or the bearing area of the couch or the body itself is detected while the images are produced, and the rotational position is assigned to the corresponding image, wherein a volumetric image data set of the body is reconstructed from the x-ray images by image processing and assignment by a computer system.
Owner:BRAINLAB
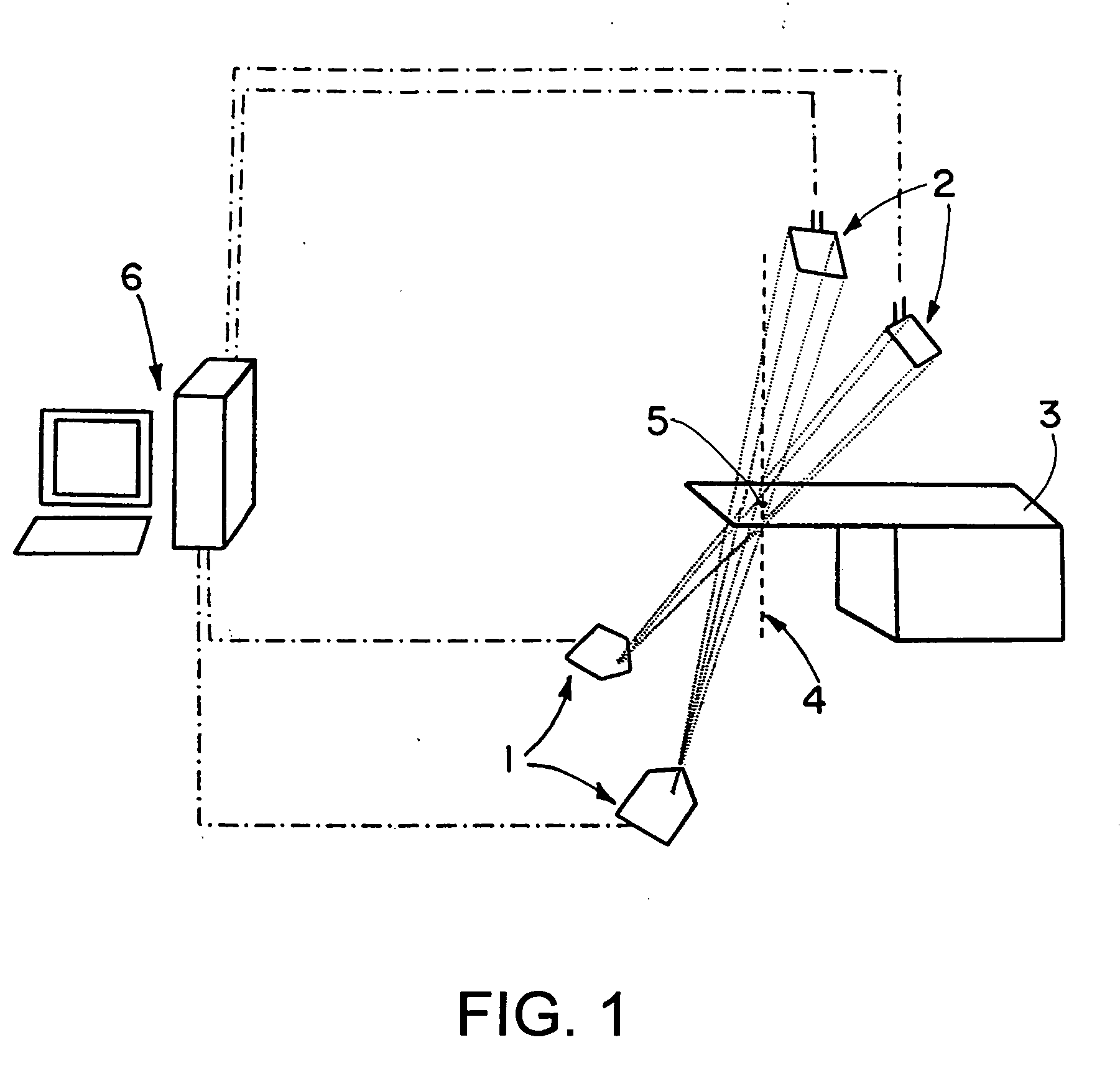
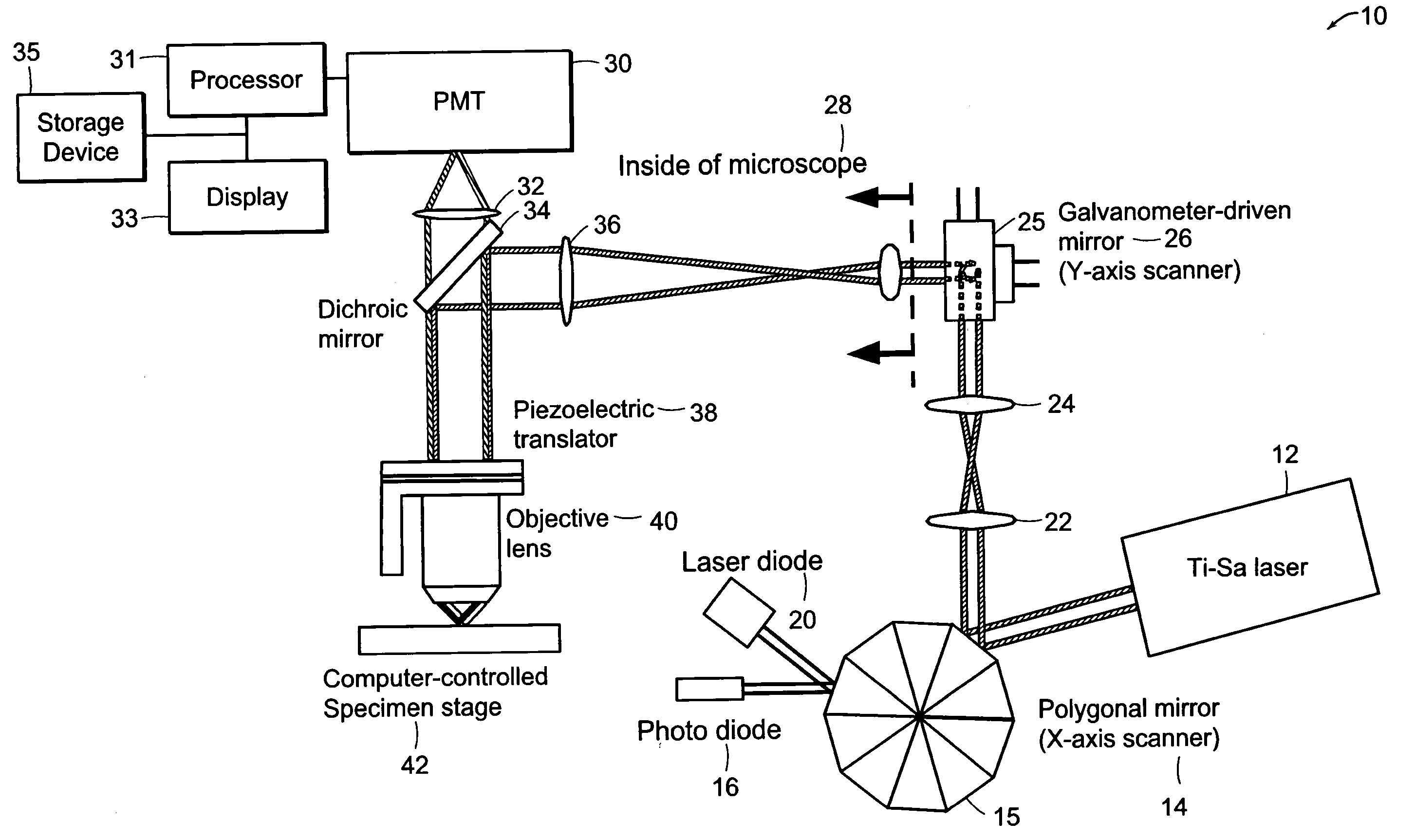
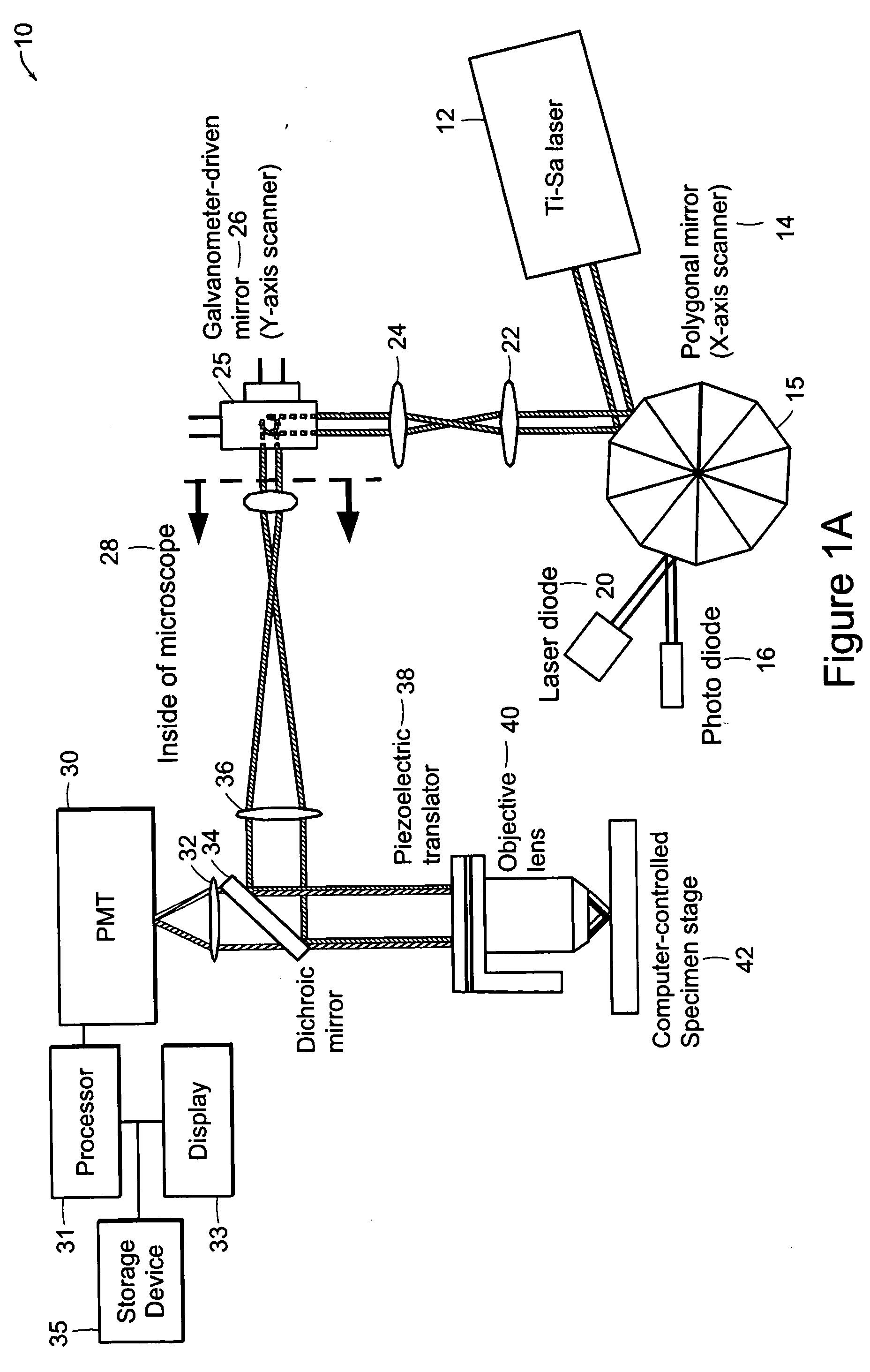
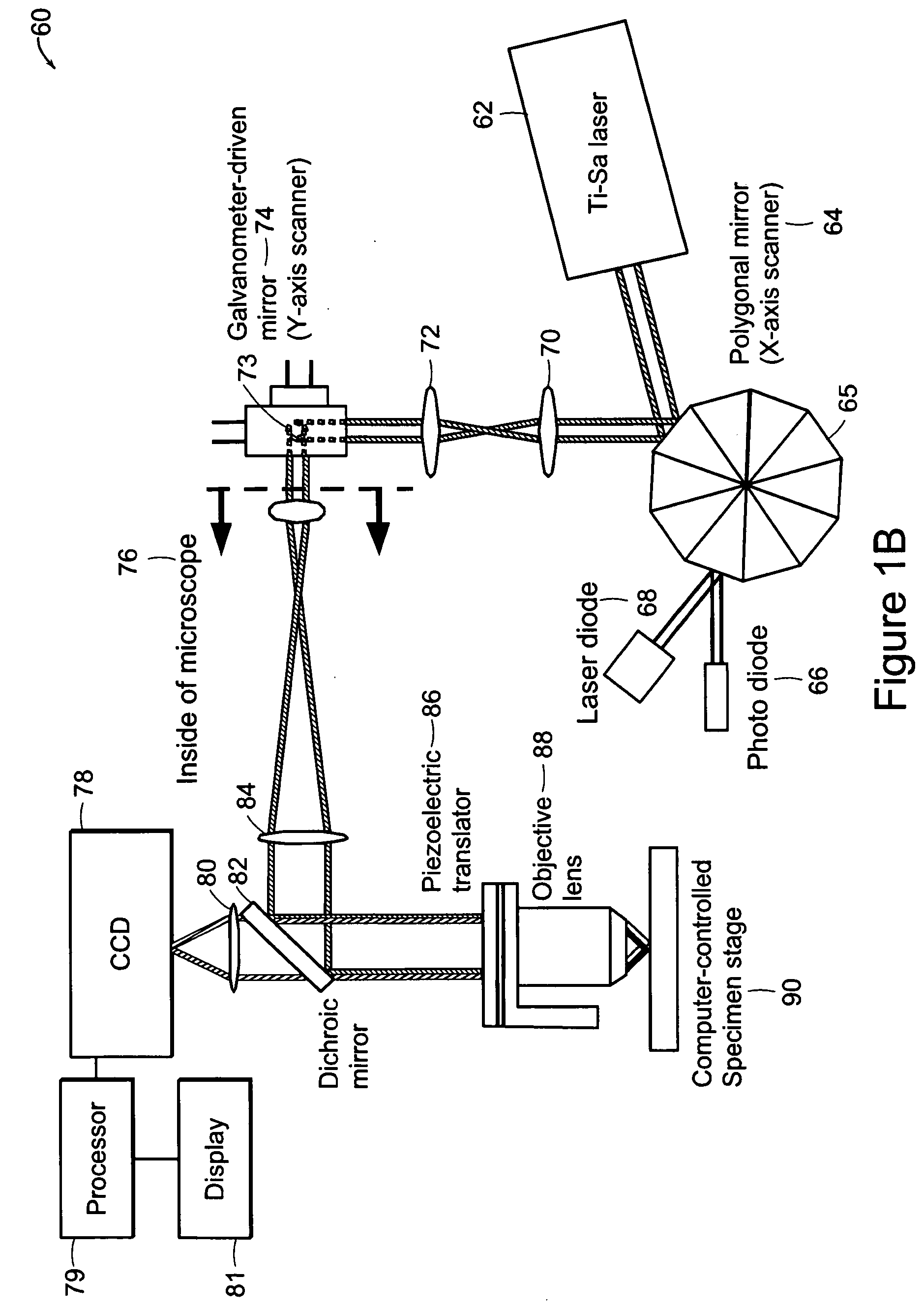
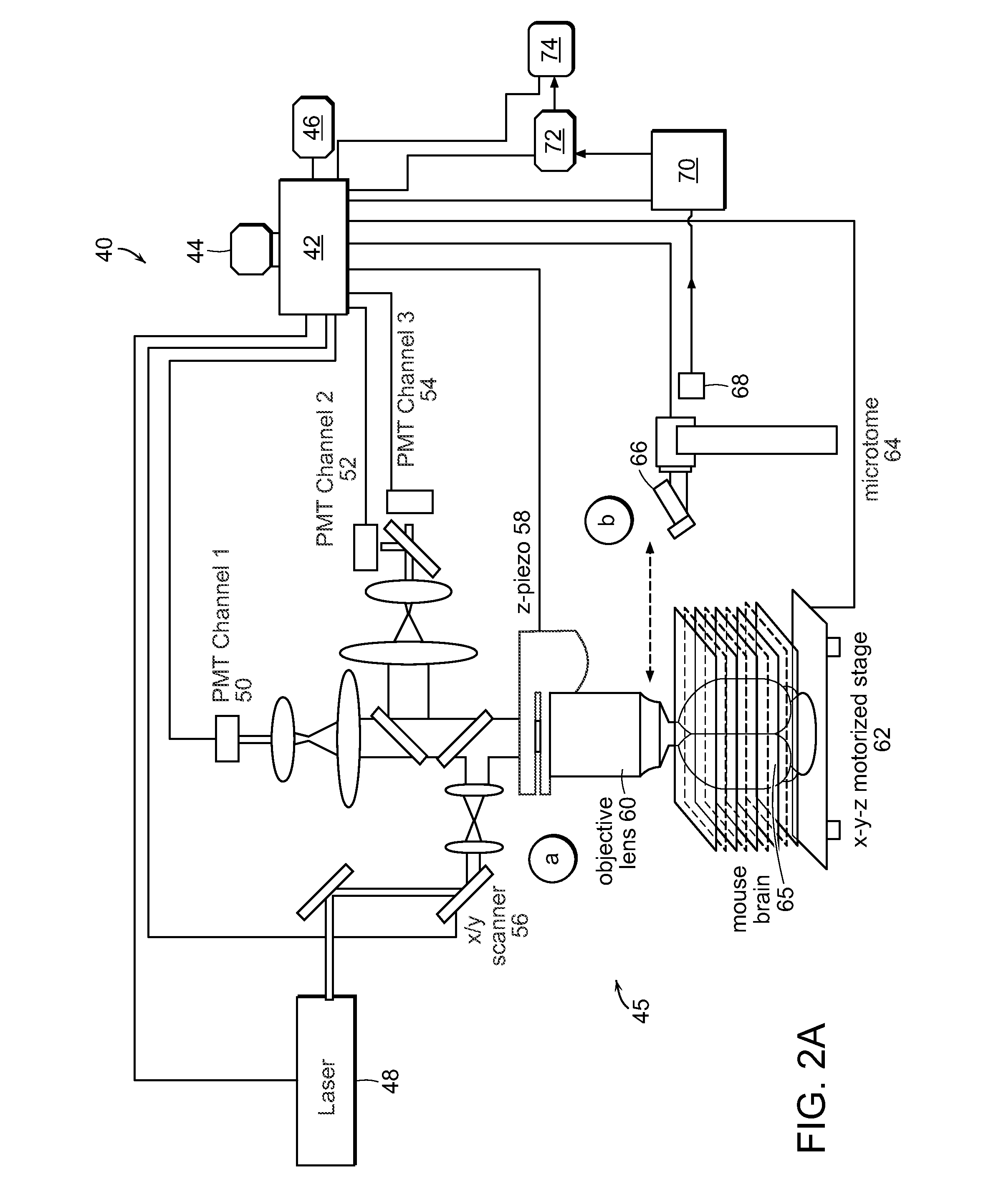
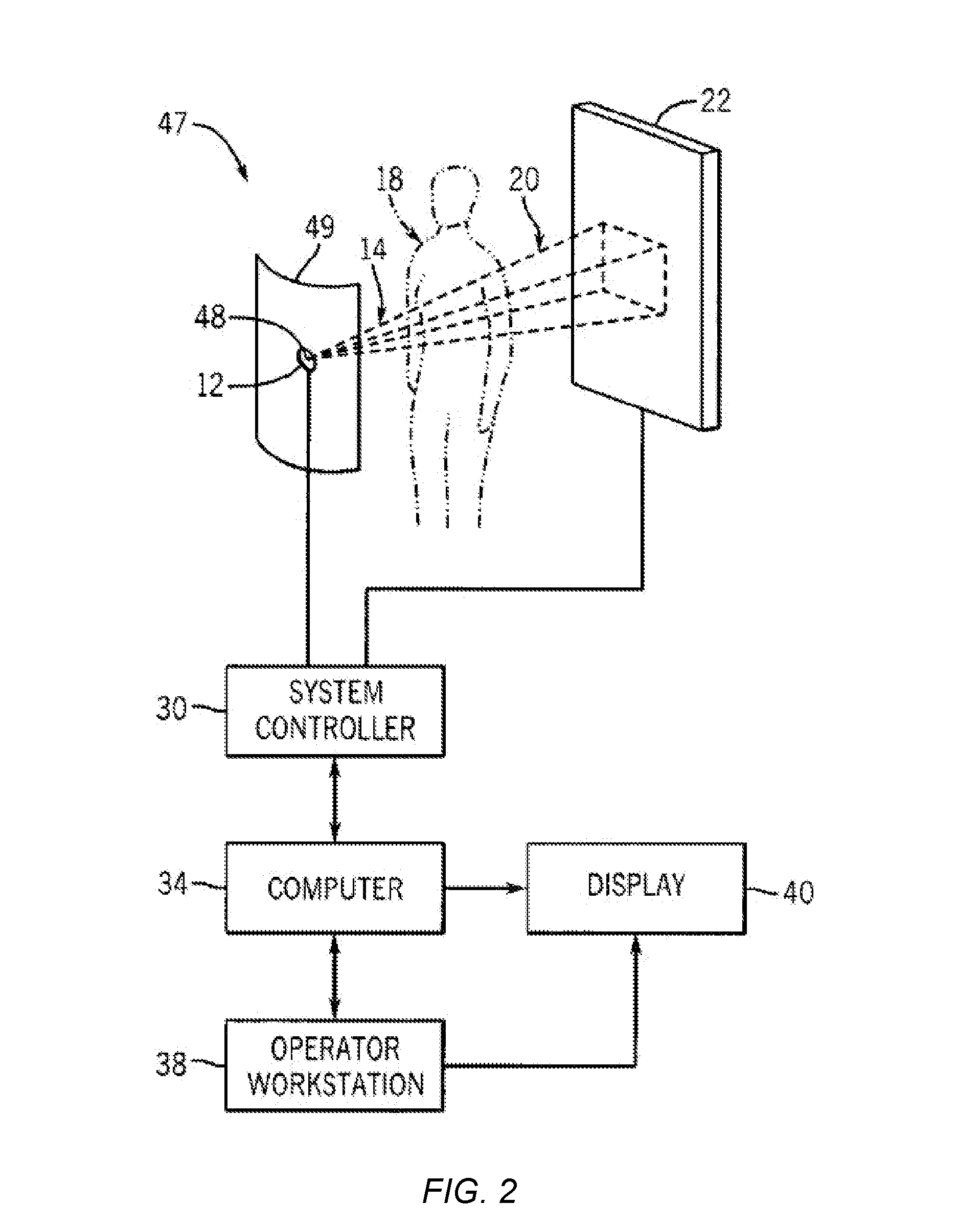
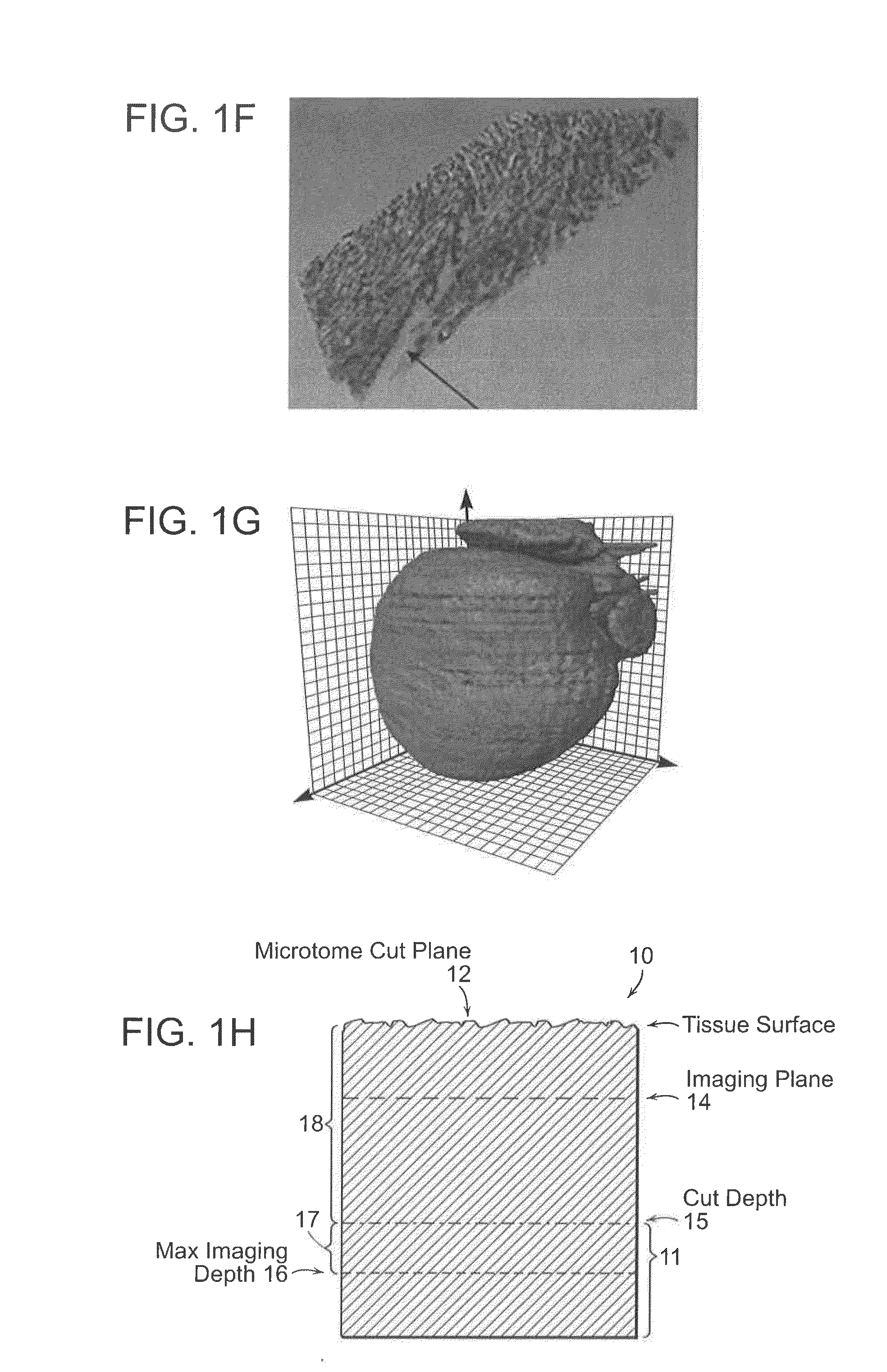
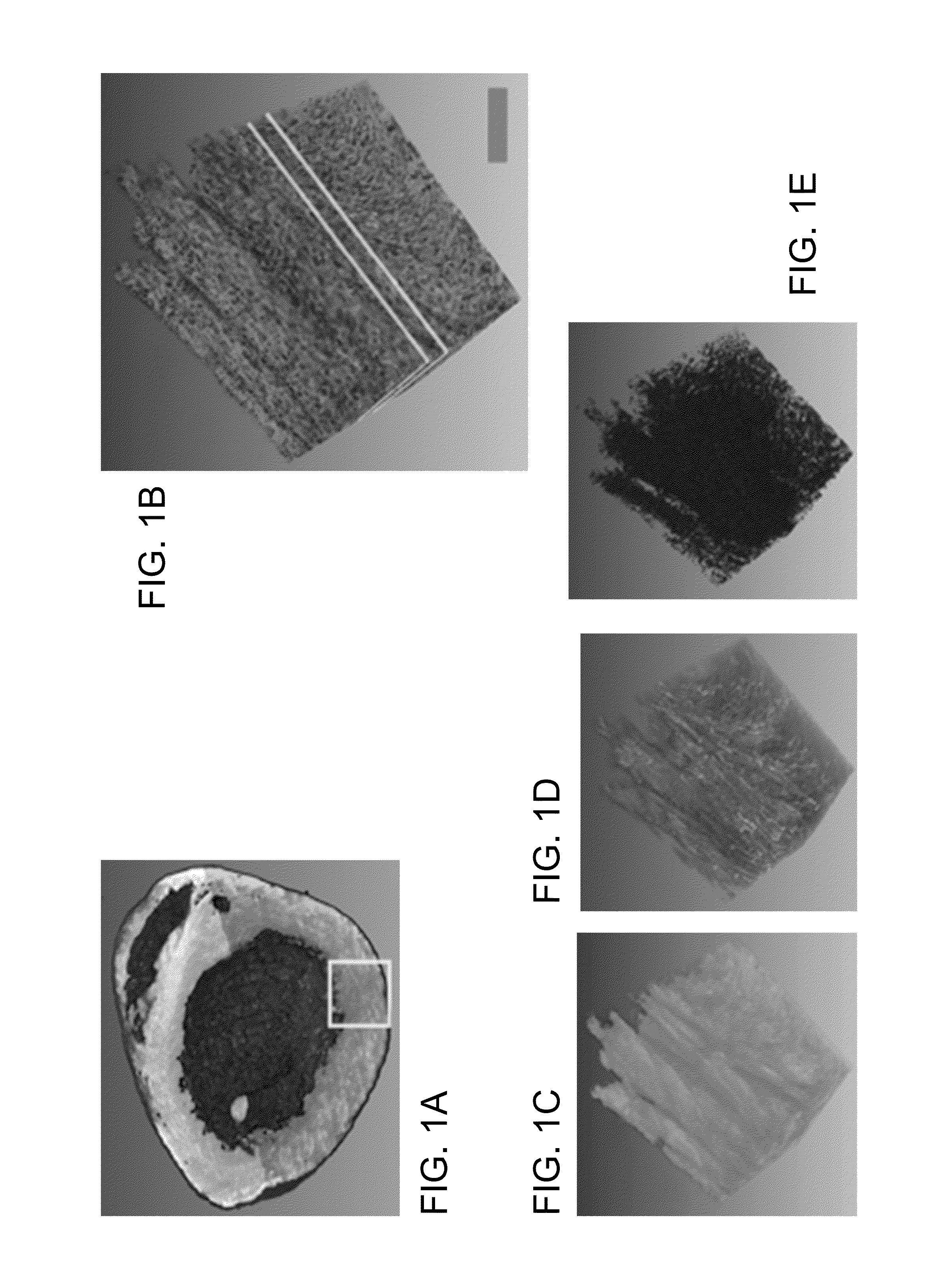
Systems and methods for volumetric tissue scanning microscopy
ActiveUS20050036667A1Minimal photodamageReduce phototoxicitySamplingAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsVolumetric imagingFluorescence
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
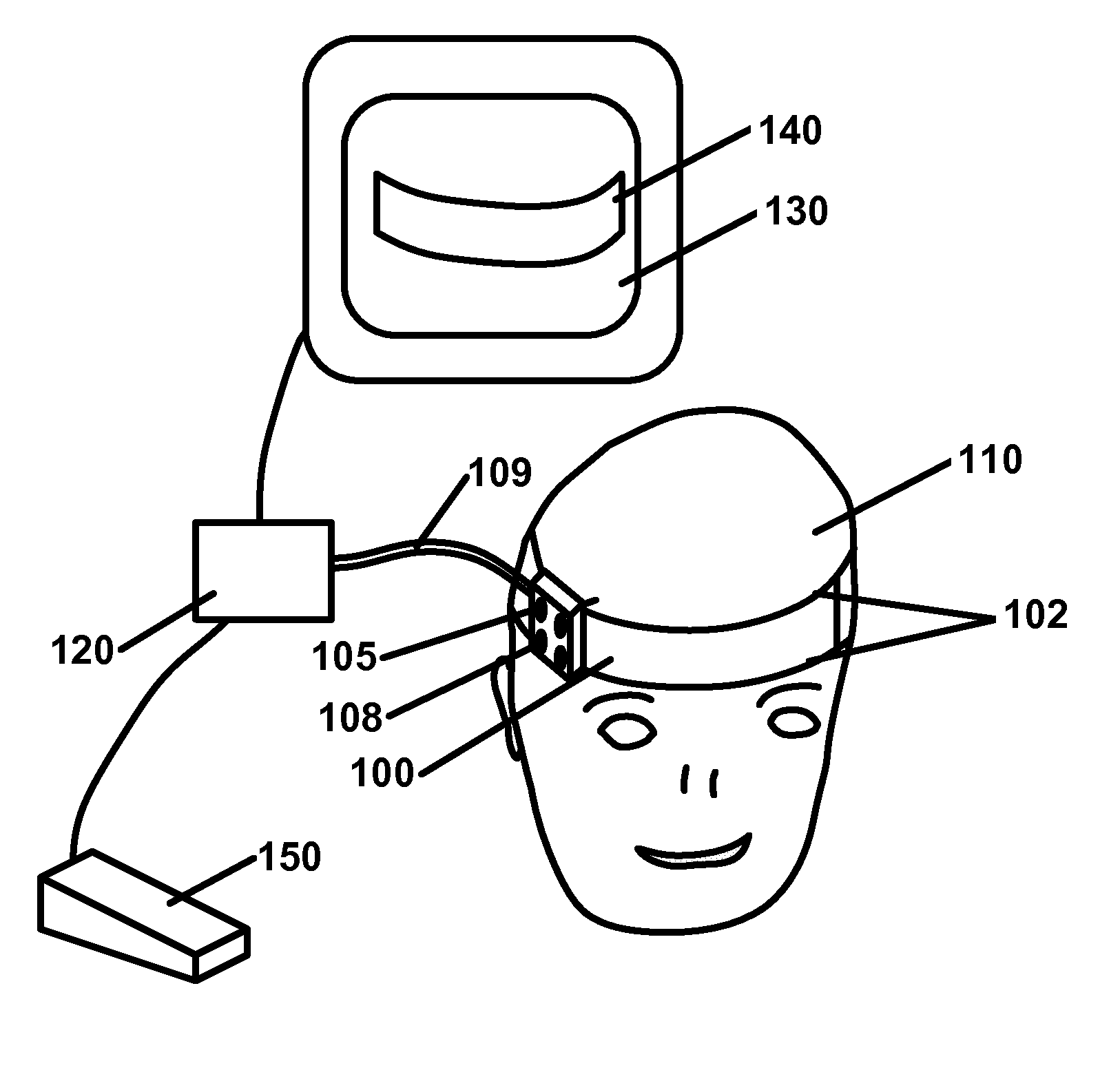
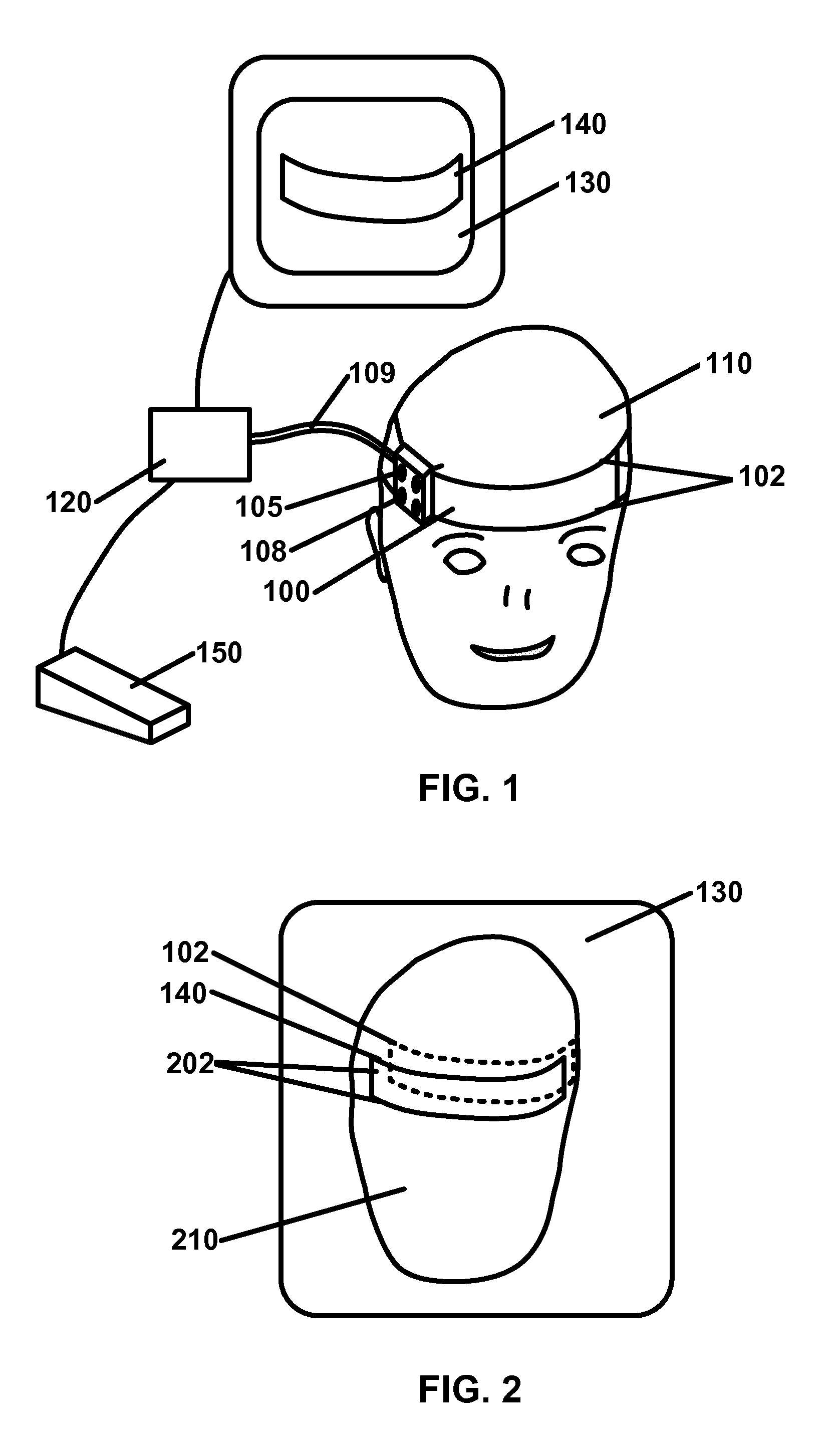
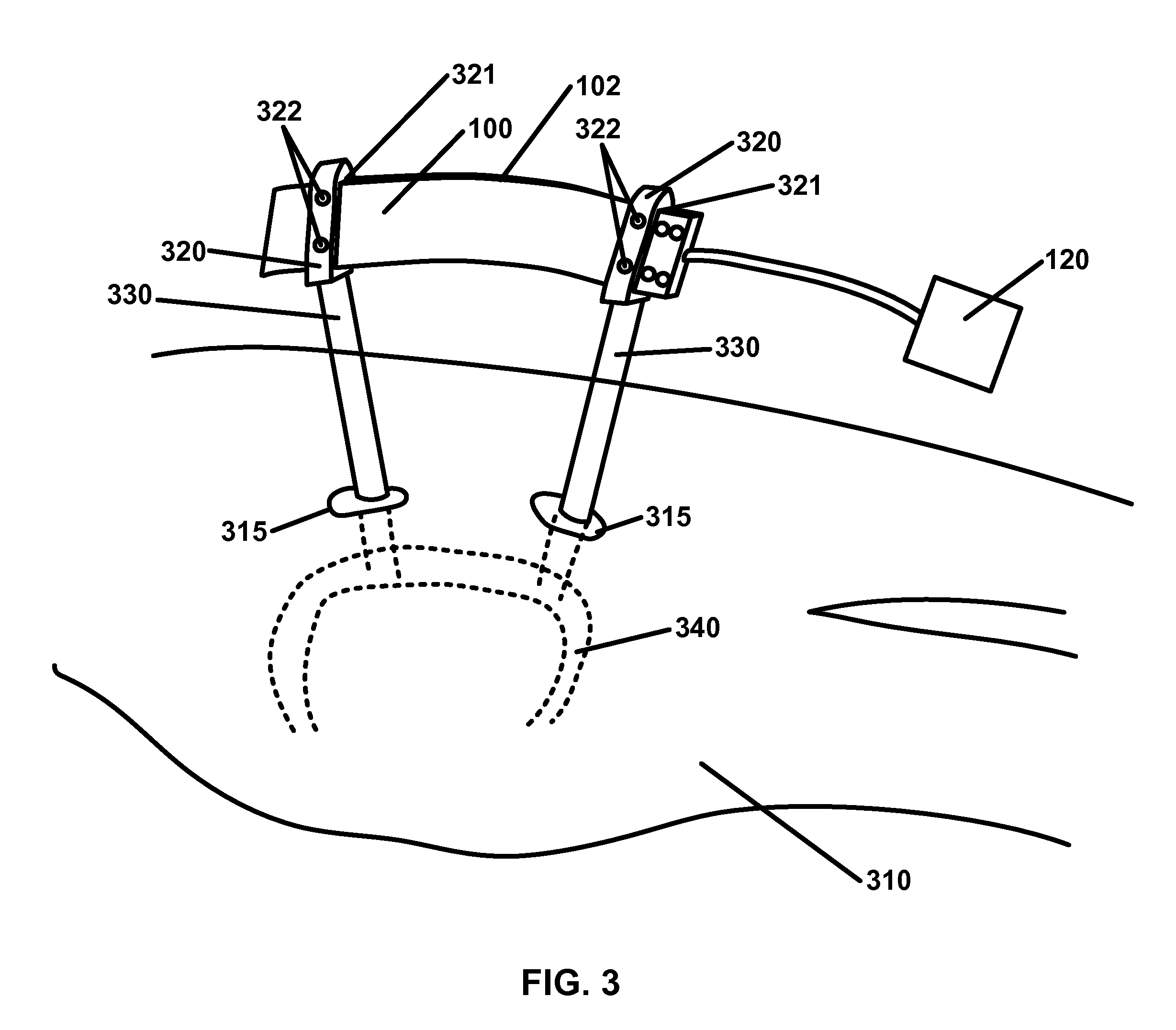
Apparatus for registering and tracking an instrument
InactiveUS20110054303A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setComputer-assisted surgery
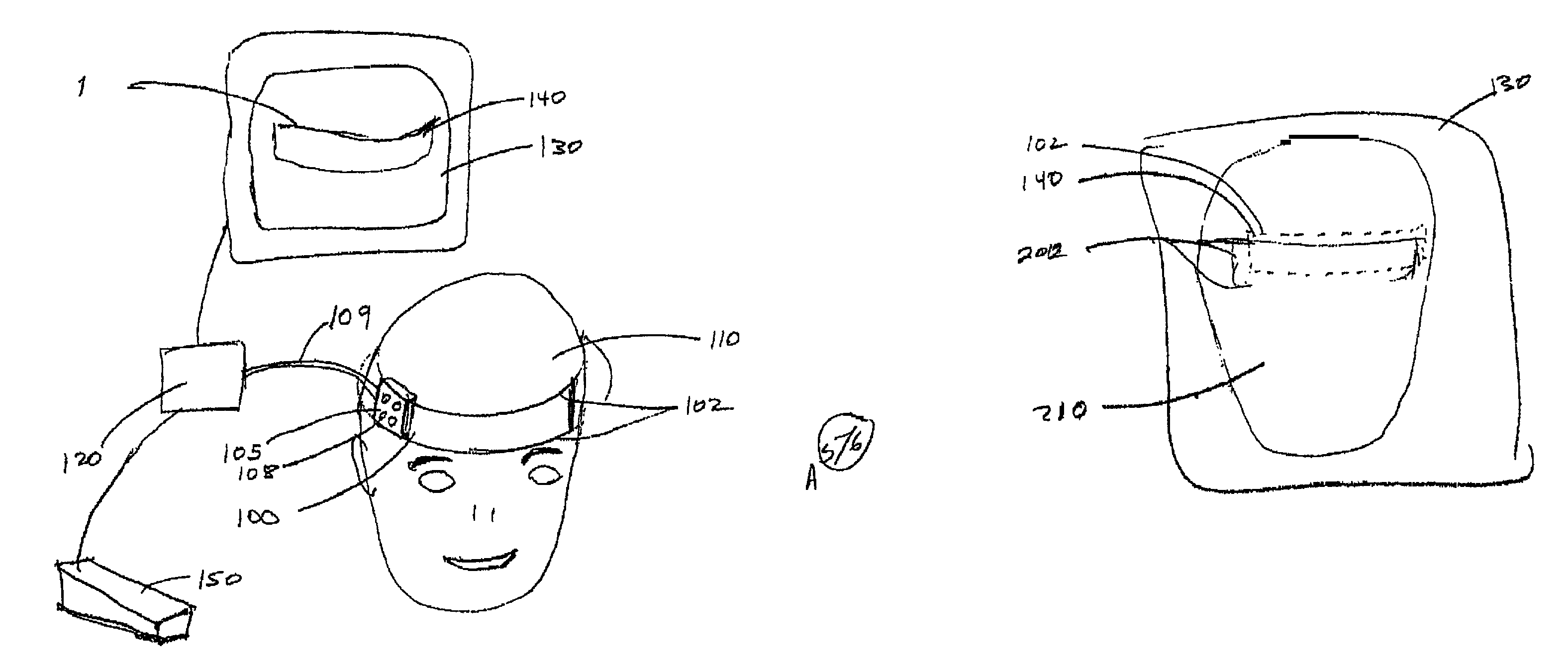
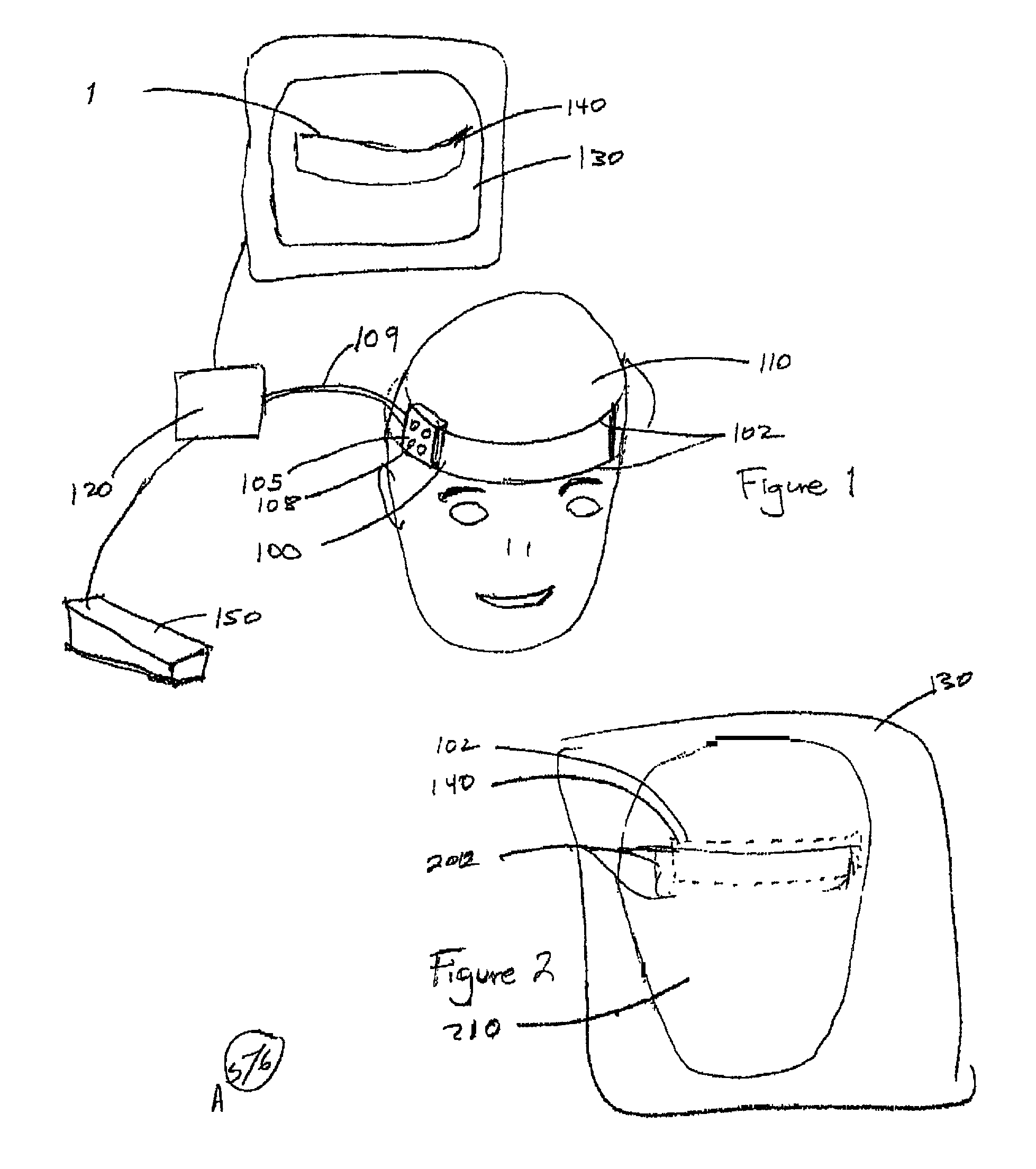
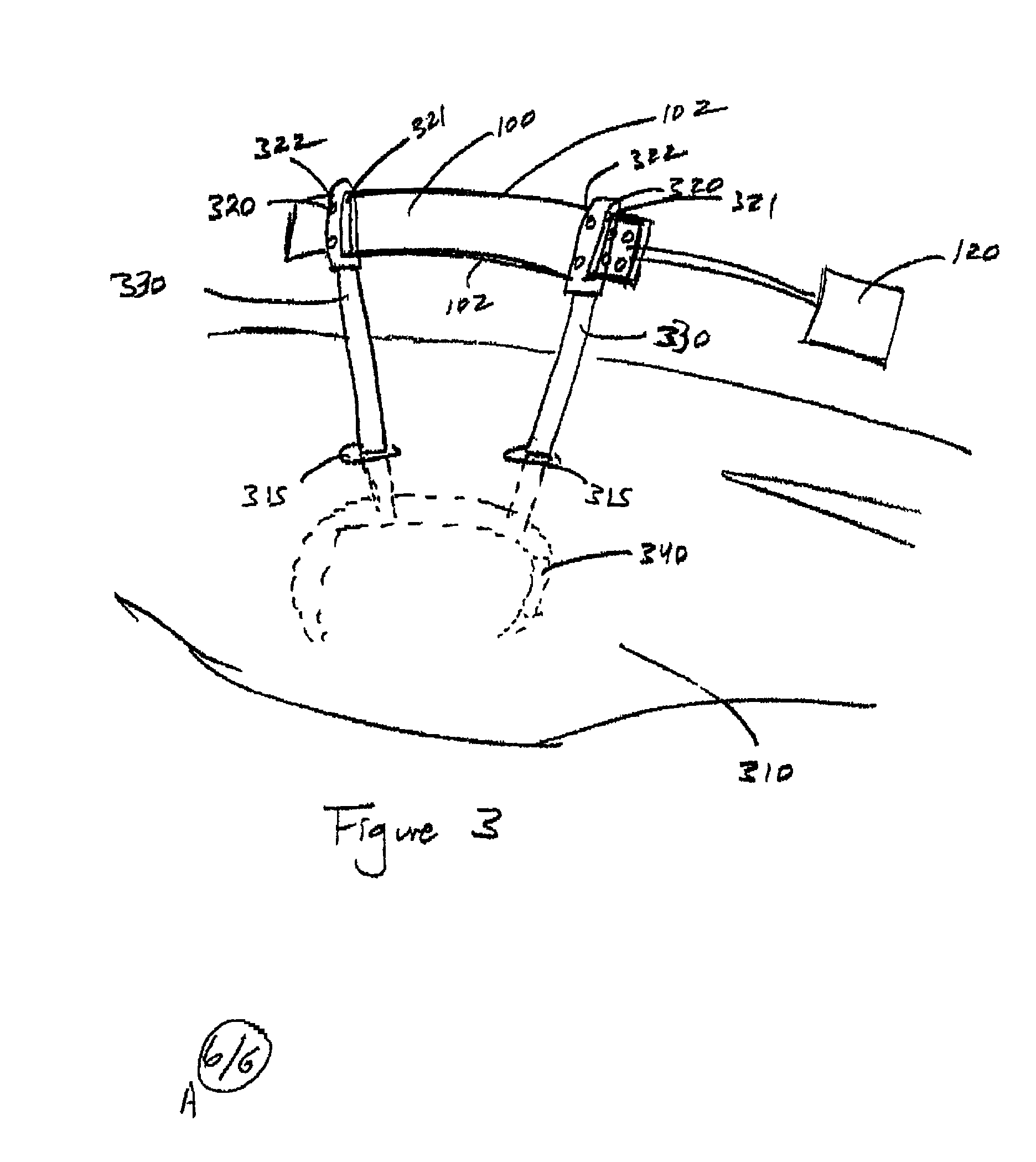
There is provided a device for generating a frame of reference and tracking the position and orientation of a tool in computer-assisted image guided surgery or therapy system. A first curvature sensor including fiducial markers is provided for positioning on a patient prior to volumetric imaging, and sensing the patient's body position during surgery. A second curvature sensor is coupled to the first curvature sensor at one end and to a tool at the other end to inform the computer-assisted image guided surgery or therapy system of the position and orientation of the tool with respect to the patient's body. A system is provided that incorporates curvature sensors, a garment for sensing the body position of a person, and a method for registering a patient's body to a volumetric image data set in preparation for computer-assisted surgery or other therapeutic interventions. This system can be adapted for remote applications as well.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
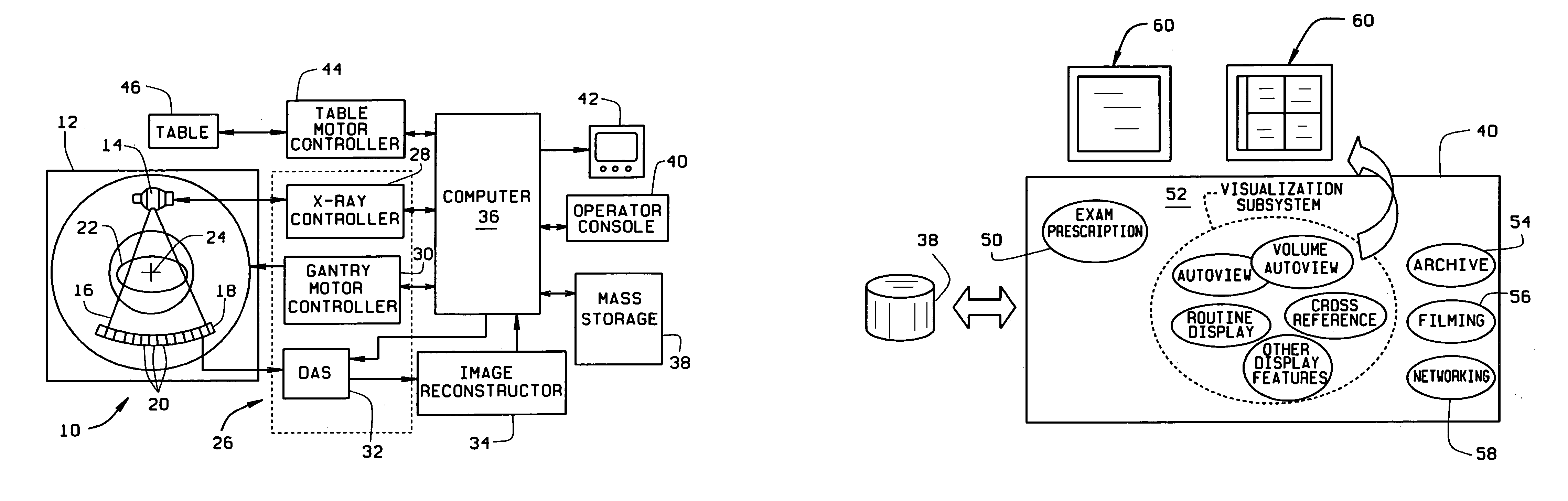
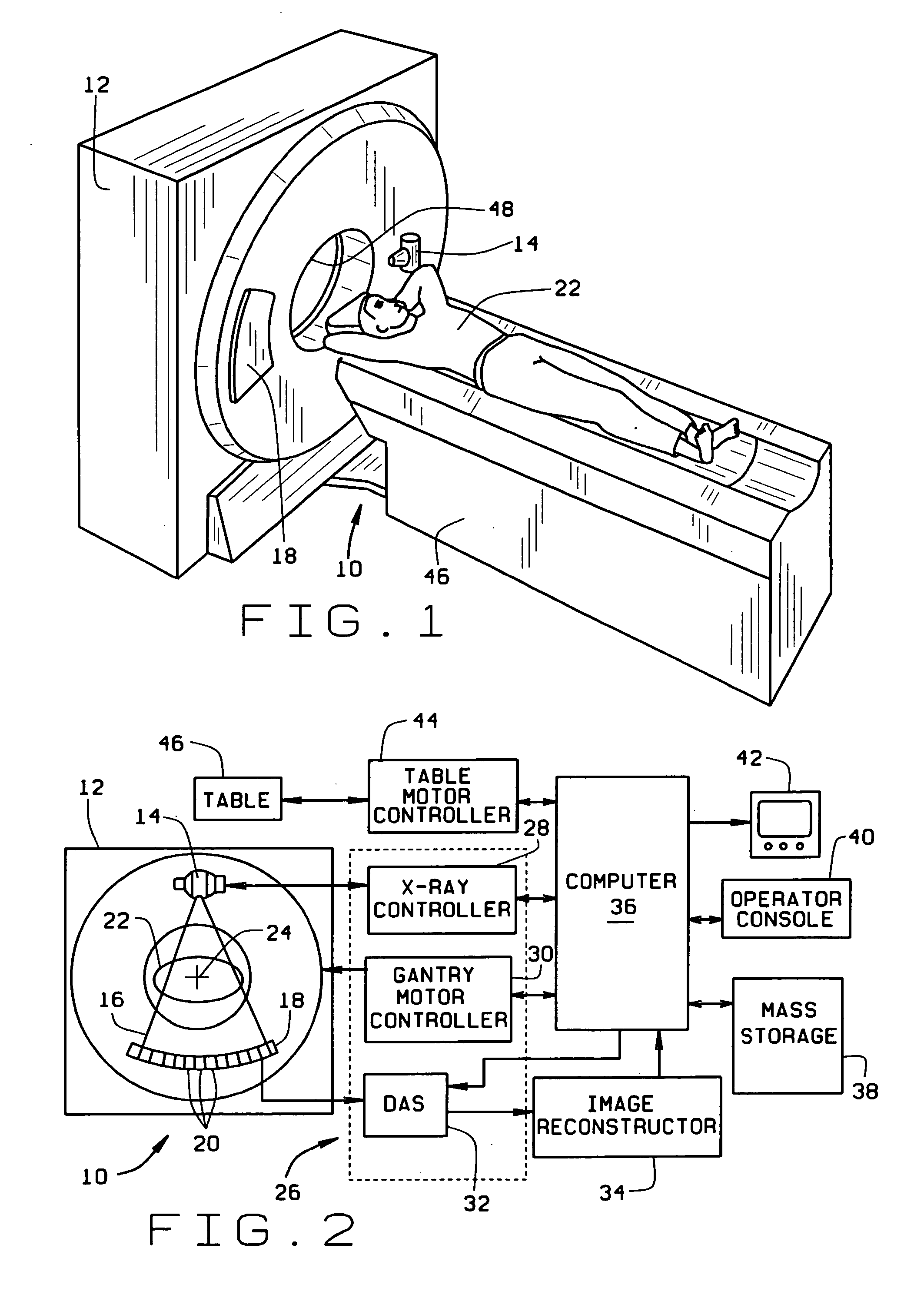
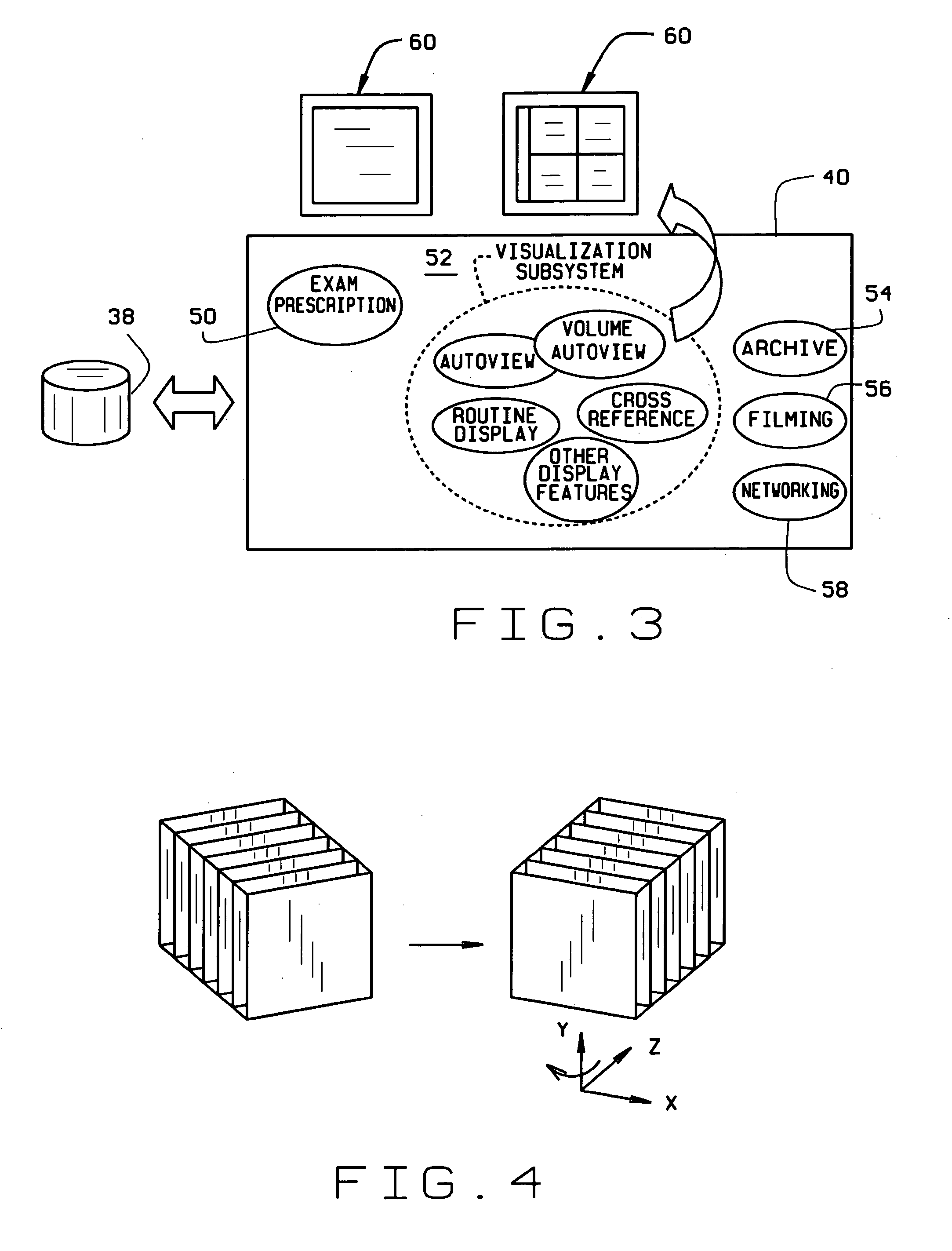
Volume imaging system
A volume imaging system which progressively constructs, analyzes, and updates three dimensional models while acquiring cross-sectional data is described. The system constructs and displays three-dimensional renderings, and performs quantitative calculations in real time during the imaging system data collection process, displays interactive three-dimensional renderings in a traditional post-data collection process, as well as prescribes, archives, films, and transmits rendering procedures, parameters, renderings, measurements, and processed data, during data collection and post-acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
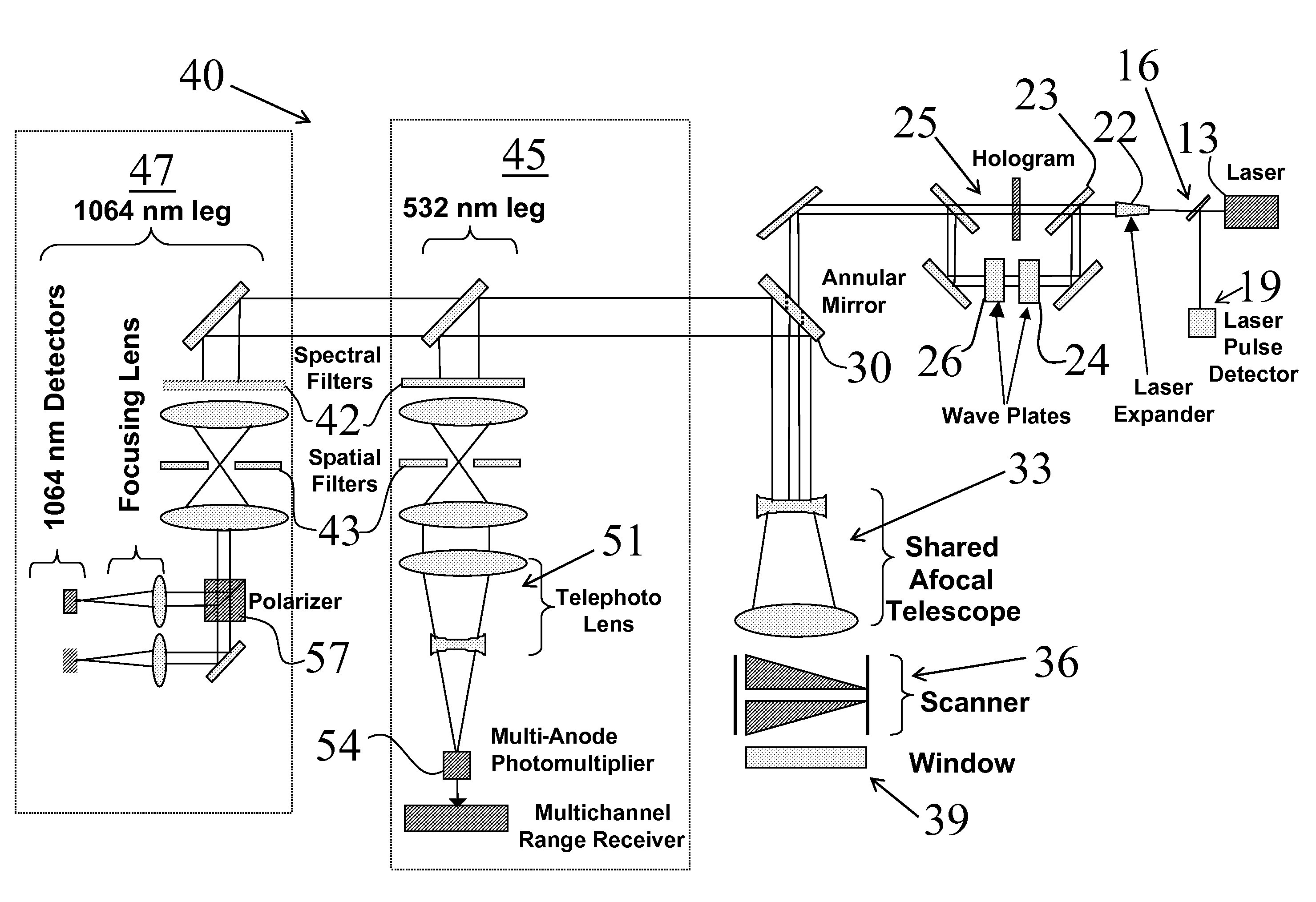
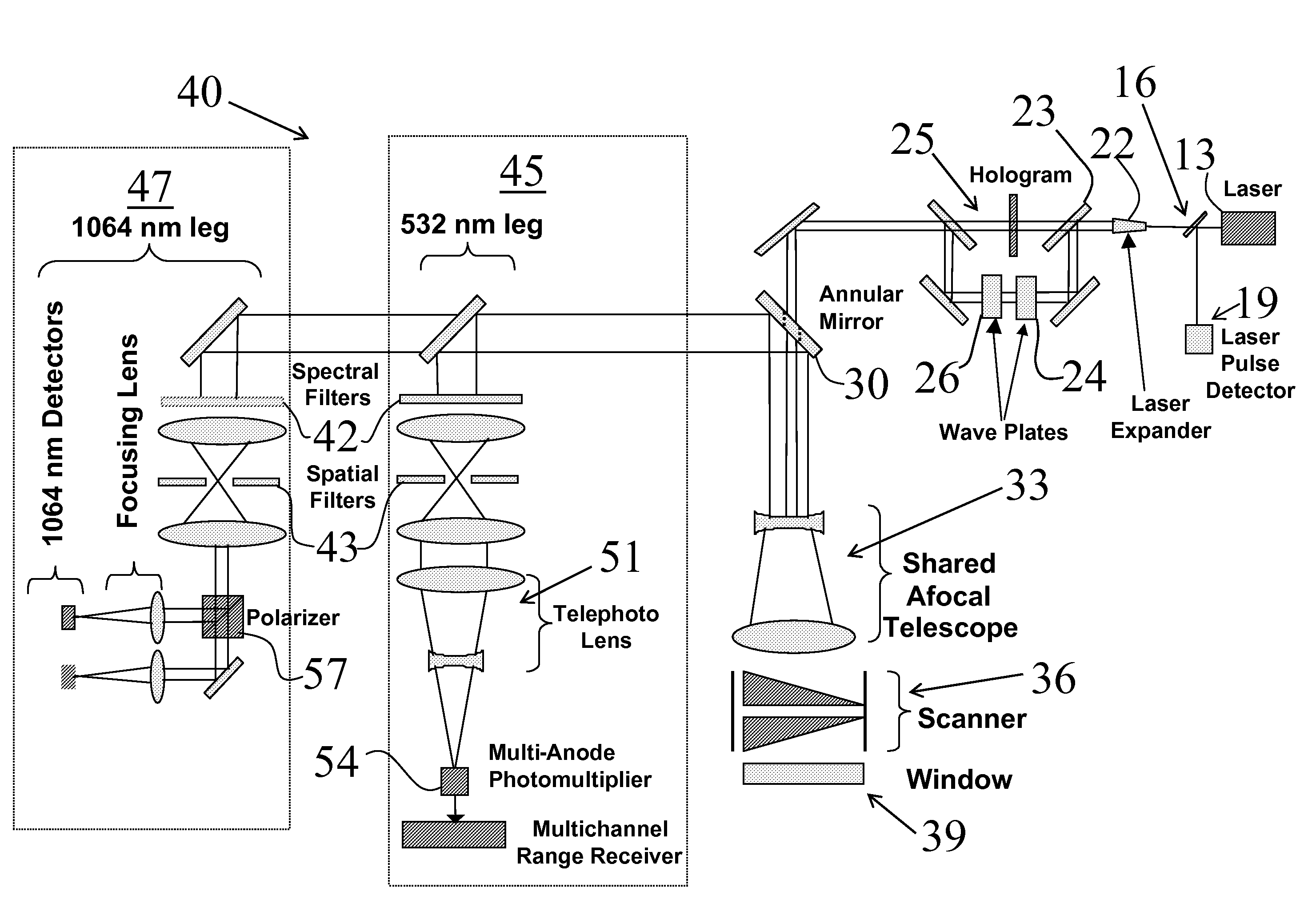
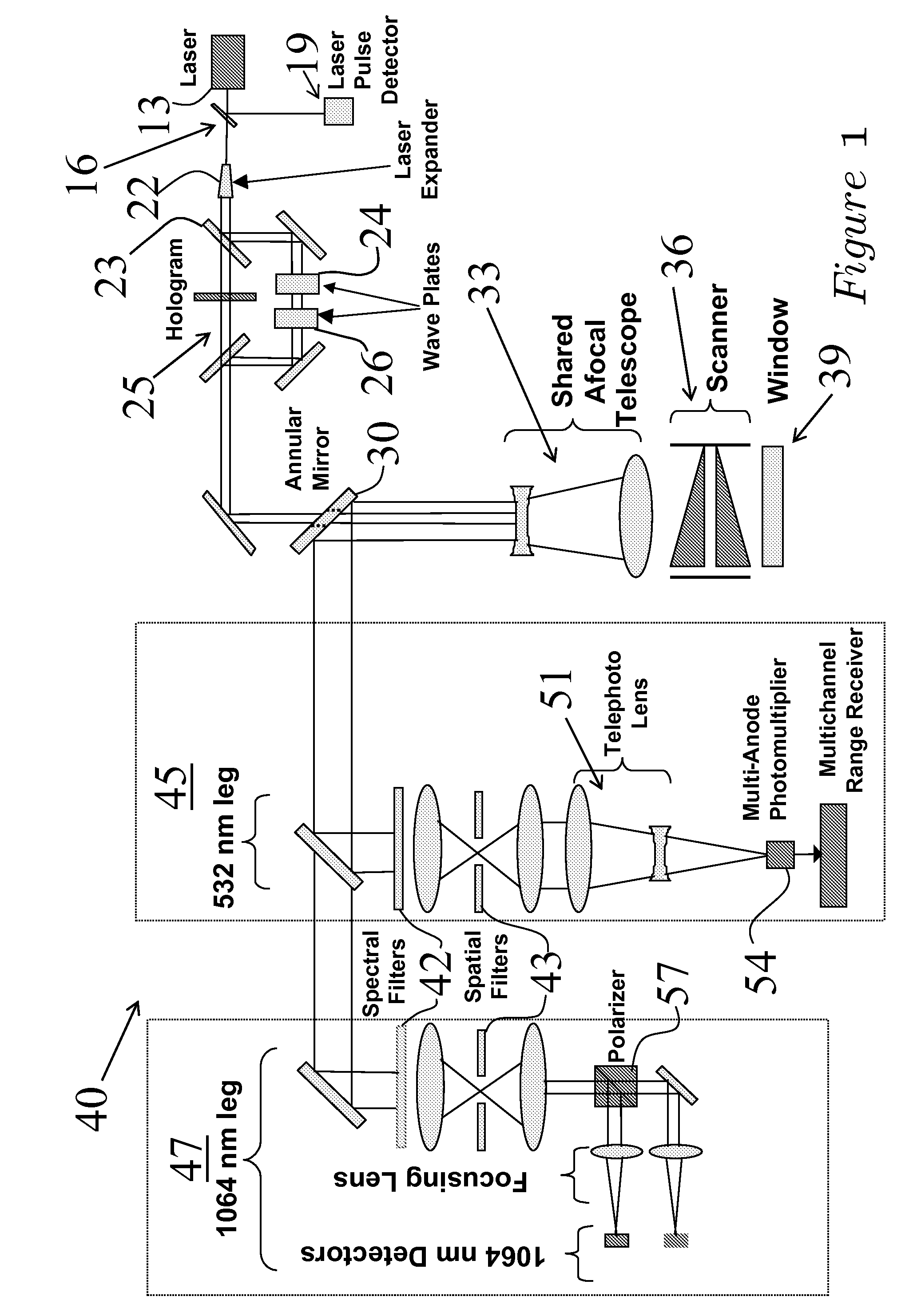
Scanner/optical system for three-dimensional lidar imaging and polarimetry
ActiveUS20070279615A1High repetition rateReduce solar background noiseOptical rangefindersColor television detailsOptical scannersLaser beams
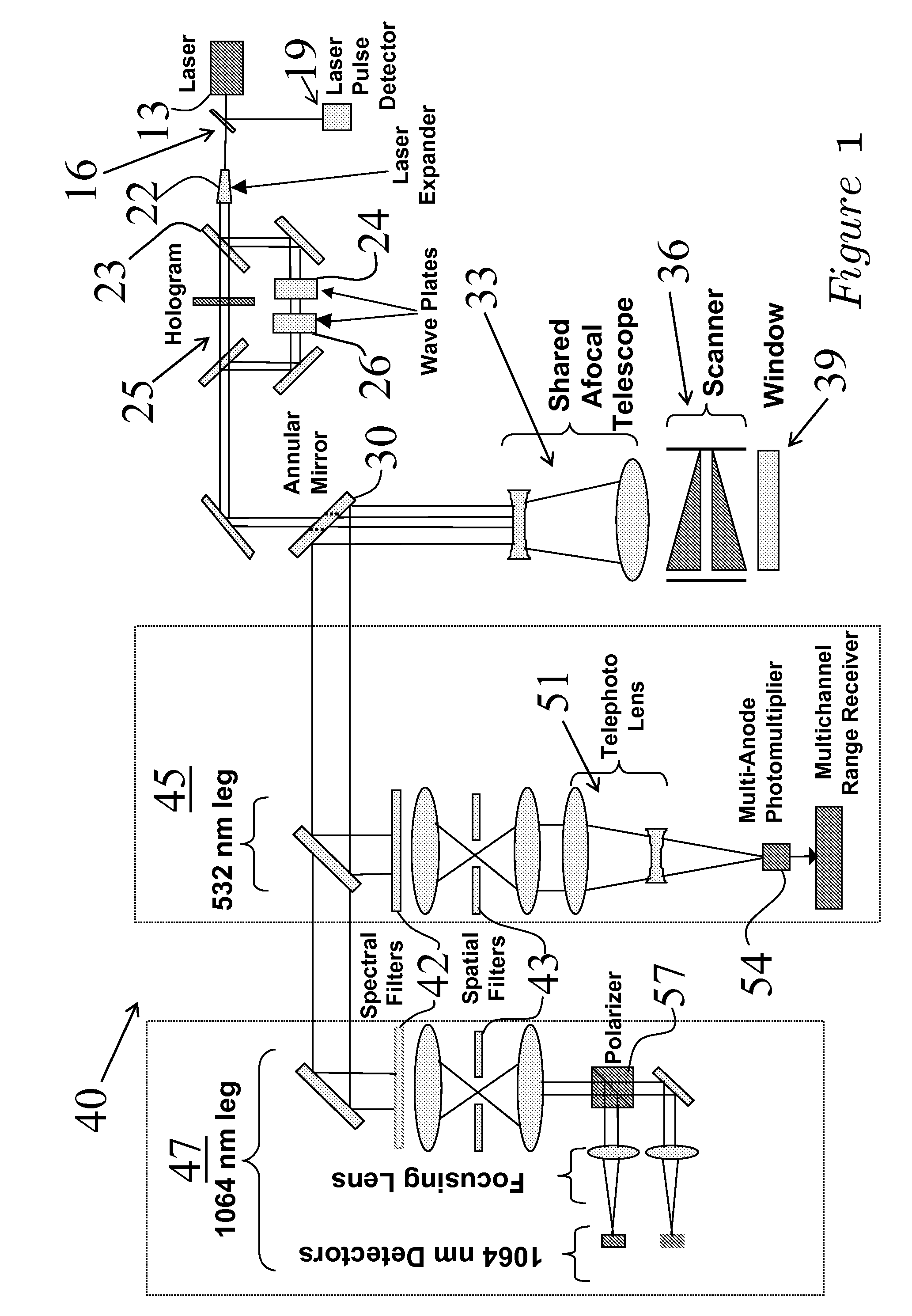
An optical scanner system for contiguous three-dimensional topographic or volumetric imaging of a surface from an aircraft or spacecraft is disclosed. A servo controller synchronizes the rotation rates of a pair of wedge scanners with high precision to the multi-kilohertz laser fire rate producing an infinite variety of well-controlled scan patterns. This causes the beam pattern to be laid down in precisely the same way on each scan cycle, eliminating the need to record the orientations of the wedges accurately on every laser fire, thereby reducing ancillary data storage or transmission requirements by two to three orders of magnitude and greatly simplifying data preprocessing and analysis. The described system also uses a holographic element to split the laser beam into an array that is then scanned in an arbitrary pattern. This provides more uniform signal strength to the various imaging detector channels and reduces the level of optical crosstalk between channels, resulting in a higher fidelity three-dimensional image.
Owner:INTERGRAPH
Systems and methods for volumetric tissue scanning microscopy
ActiveUS7372985B2Minimal photodamageReduce phototoxicitySamplingAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsVolumetric imagingFluorescence
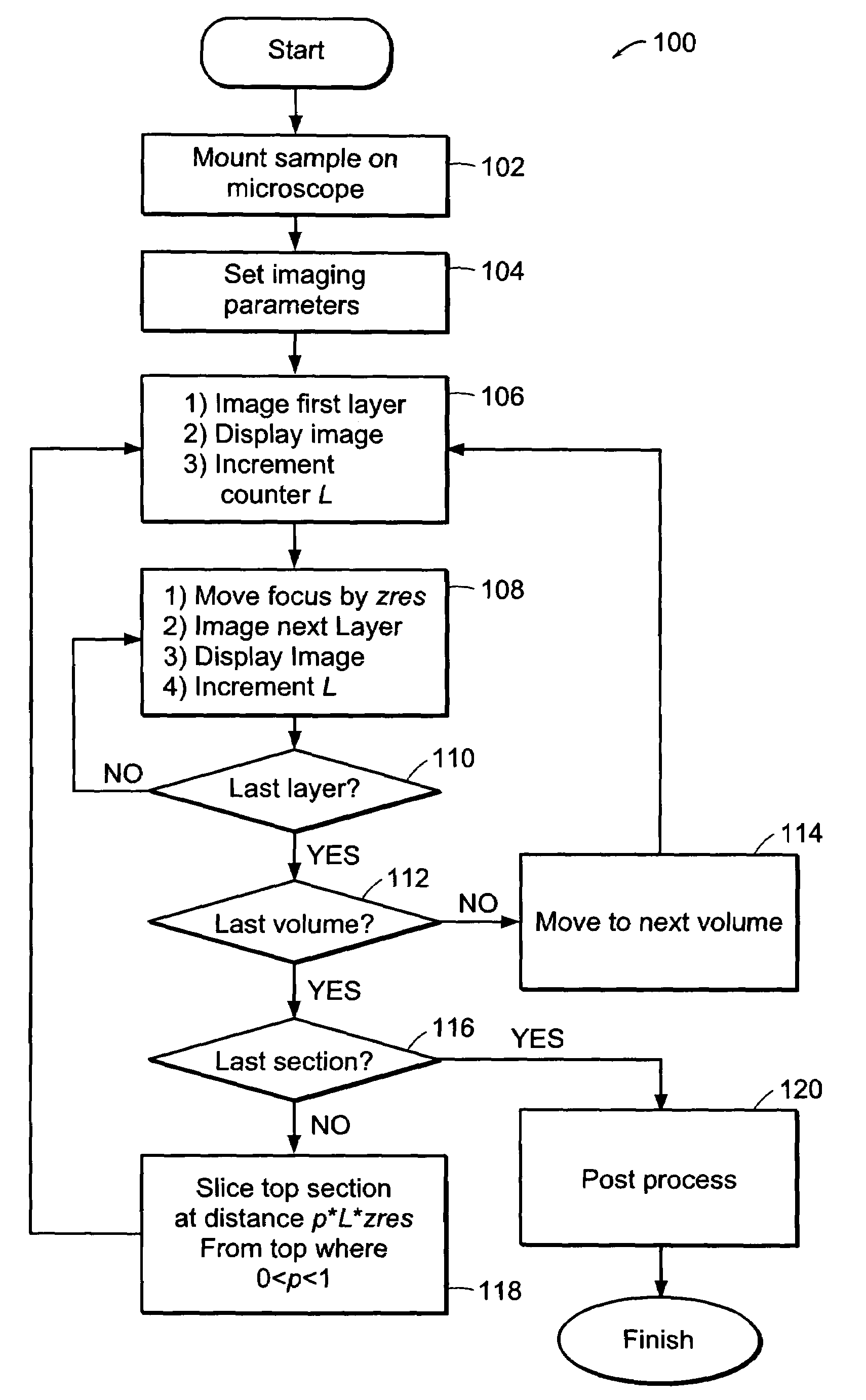
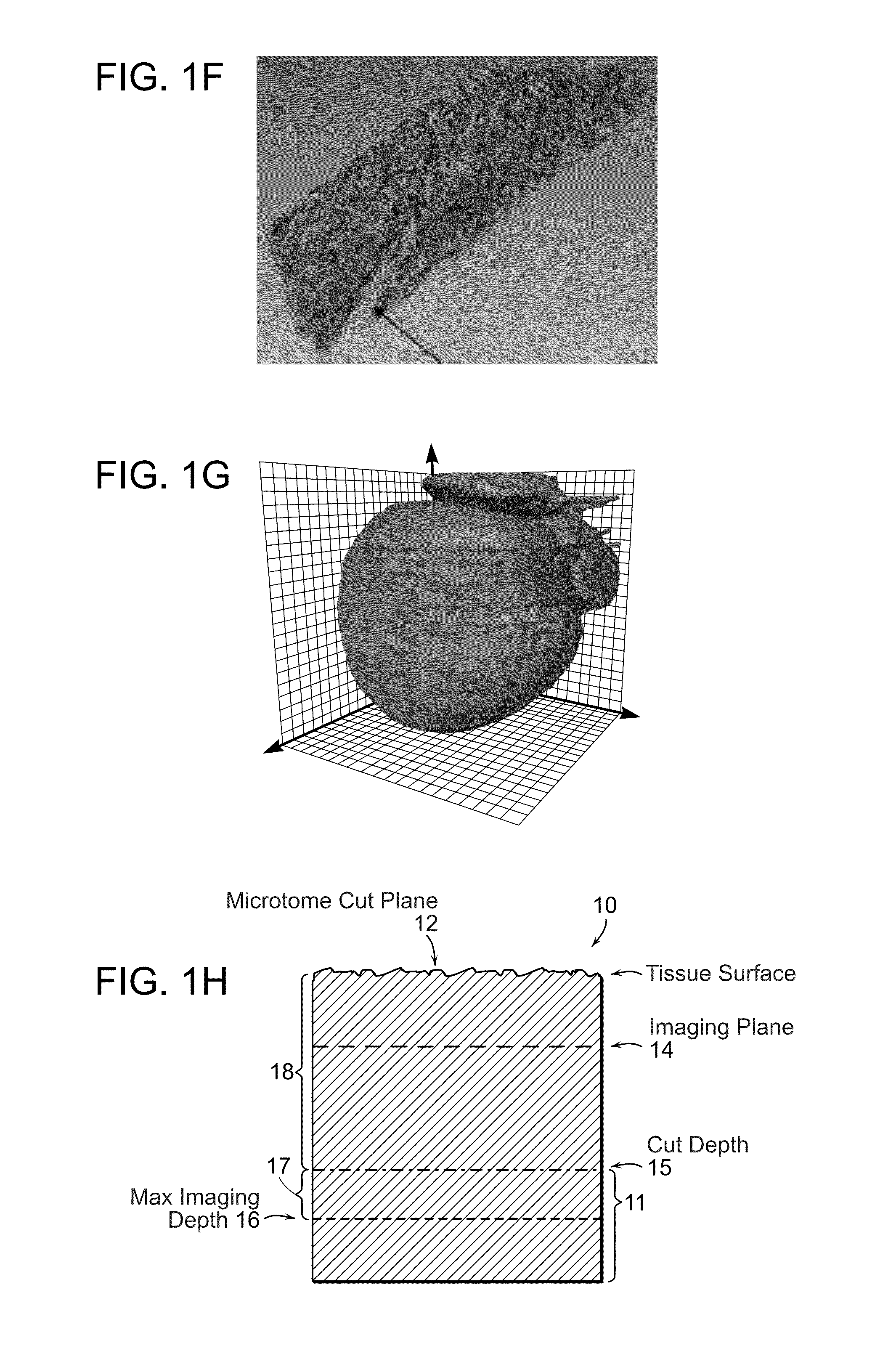
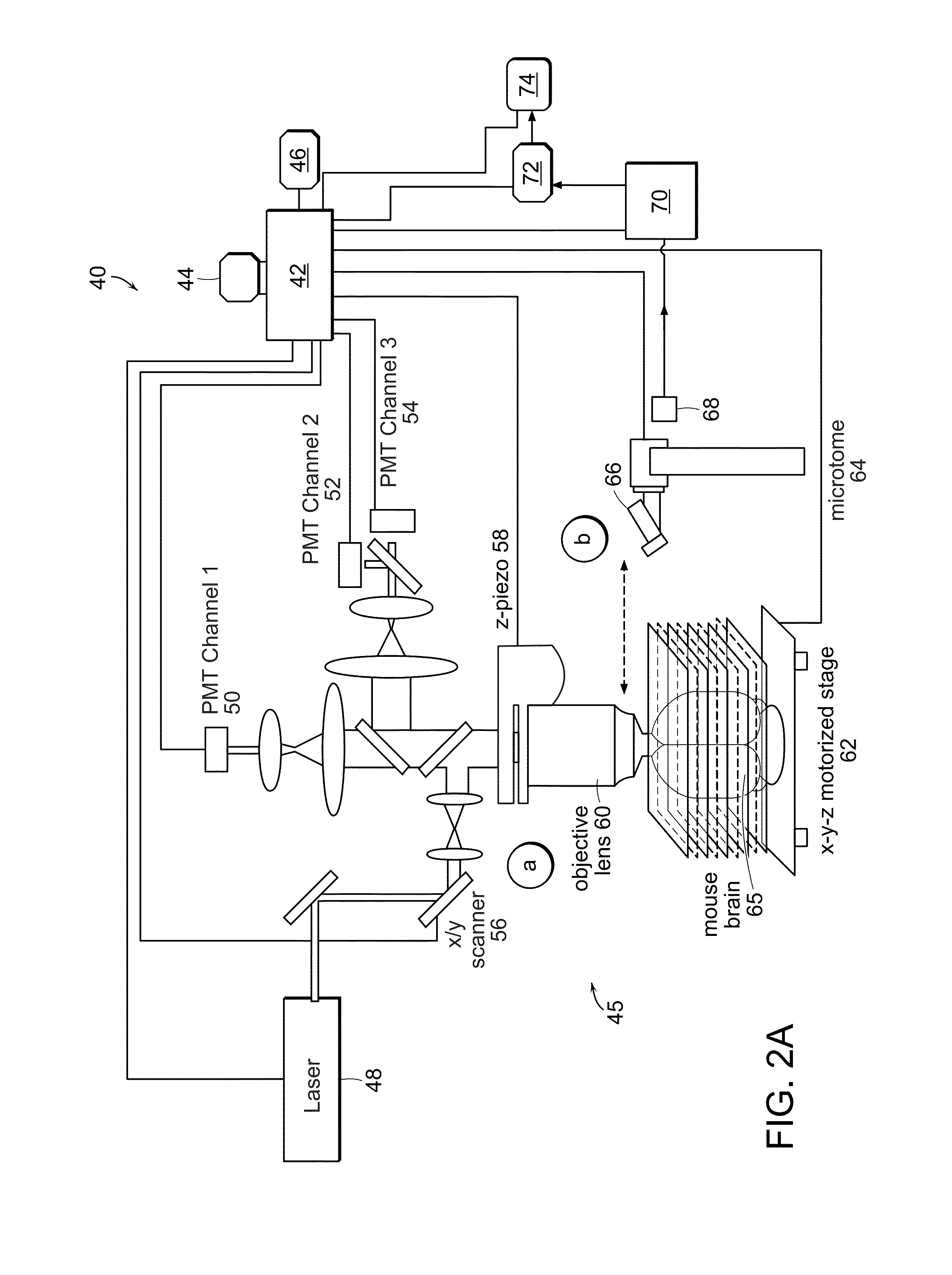
In accordance with preferred embodiments of the present invention, a method for imaging tissue, for example, includes the steps of mounting the tissue on a computer controlled stage of a microscope, determining volumetric imaging parameters, directing at least two photons into a region of interest, scanning the region of interest across a portion of the tissue, imaging a plurality of layers of the tissue in a plurality of volumes of the tissue in the region of interest, sectioning the portion of the tissue and imaging a second plurality of layers of the tissue in a second plurality of volumes of the tissue in the region of interest, detecting a fluorescence image of the tissue due to said excitation light; and processing three-dimensional data that is collected to create a three-dimensional image of the region of interest.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
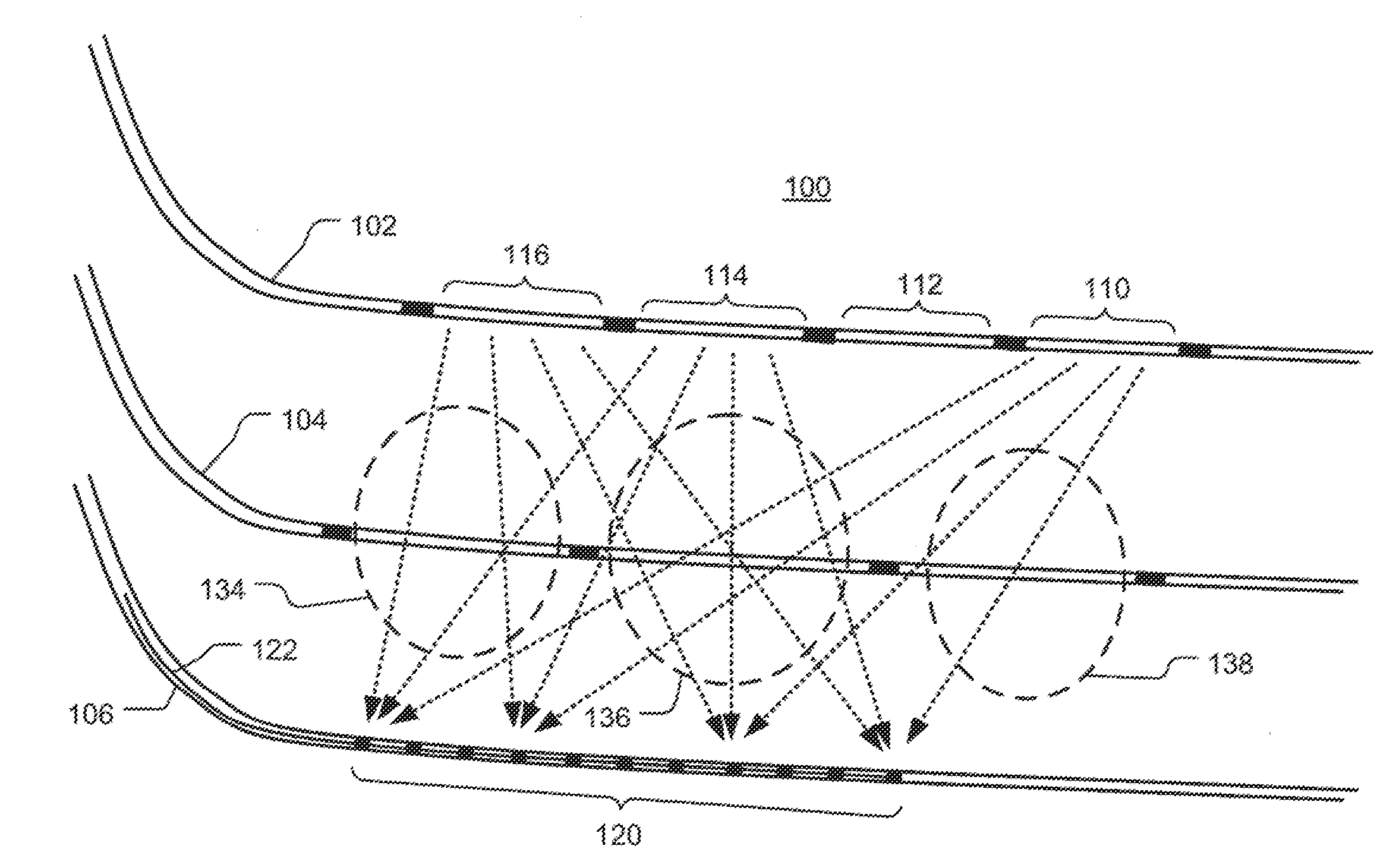
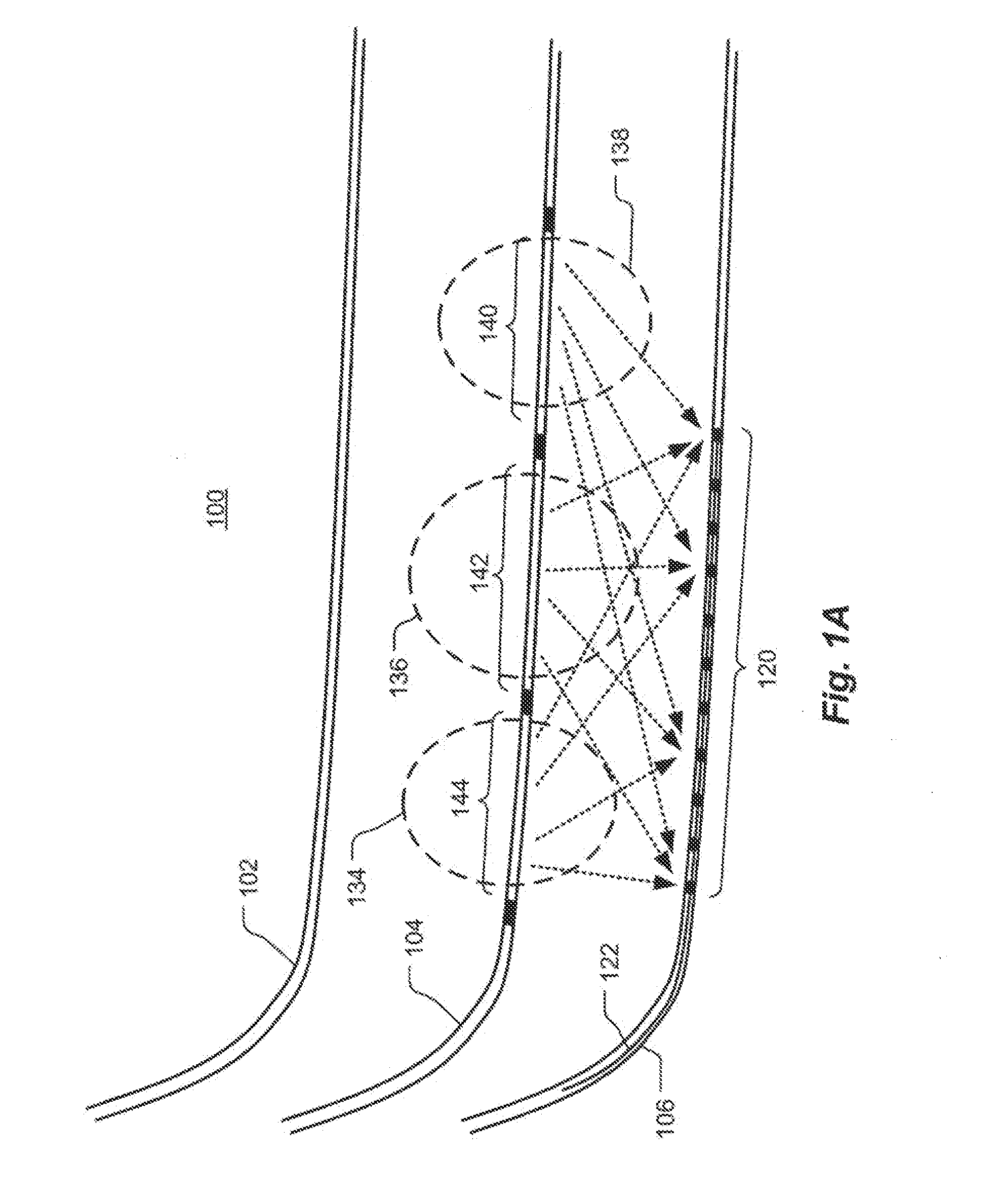
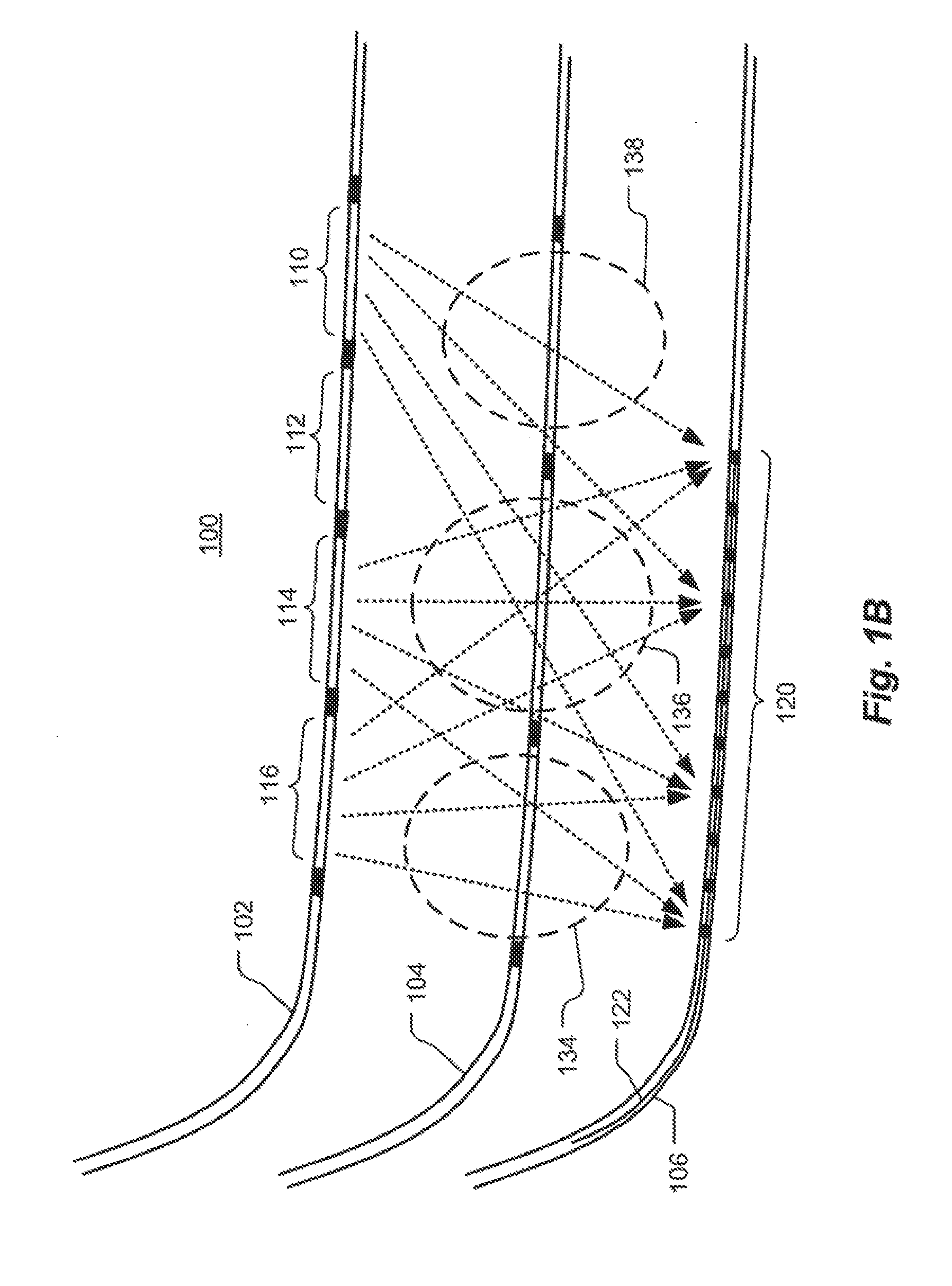
Volume imaging for hydraulic fracture characterization
InactiveUS20110188347A1Fluid removalSeismology for water-loggingVolumetric imagingHydraulic fracturing
Methods and systems are described for measuring effects of a hydraulic fracturing process. The techniques can utilizes cross-well seismic technology, such as used in Schlumberger's DeepLook-CS tools and service, or in some case surface to borehole or borehole to surface seismic technology. The downhole seismic sources at known locations can be conventional sources or can be other types of equipment operating at known locations such as perforation guns. The source is activated or swept creating energy which is transmitted through the formation. The energy is recorded at the receiver array and processed to yield a tomographic image indicating changes in the subterranean formation resulting from the hydraulic fracturing process. The process can be performed pre and post hydraulic fracture stimulation to generate a difference image of propped fractures in the reservoir.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
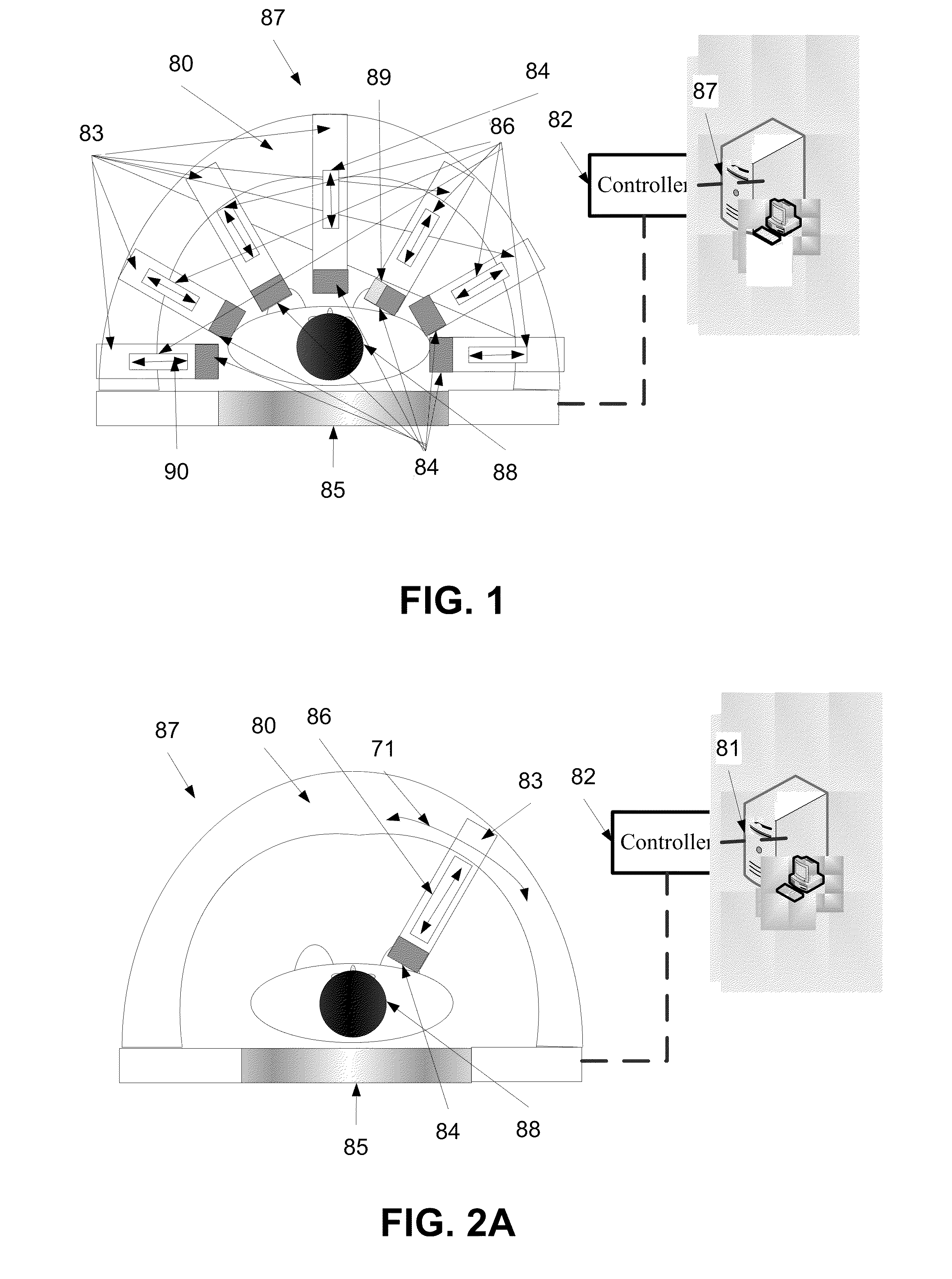
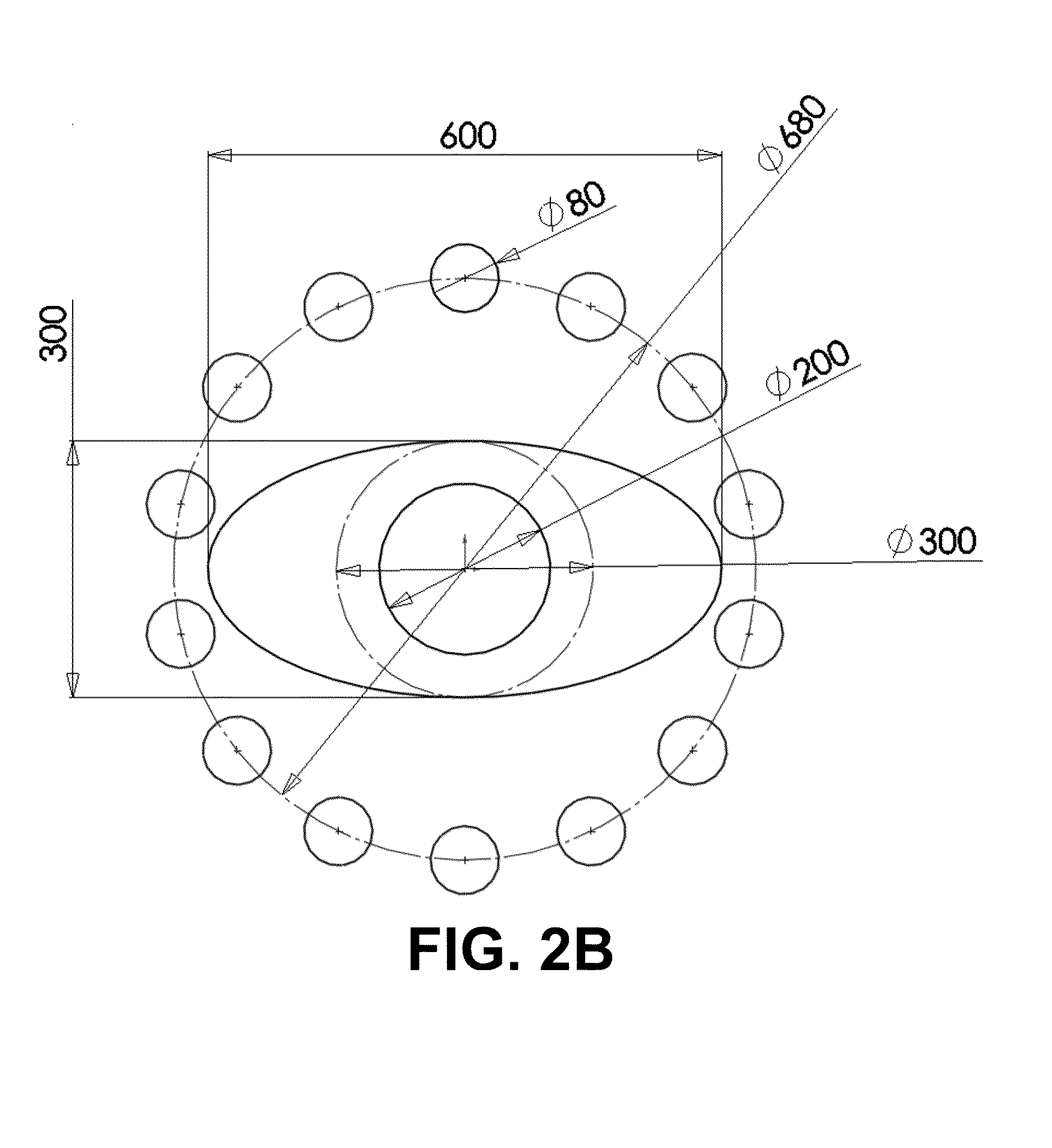
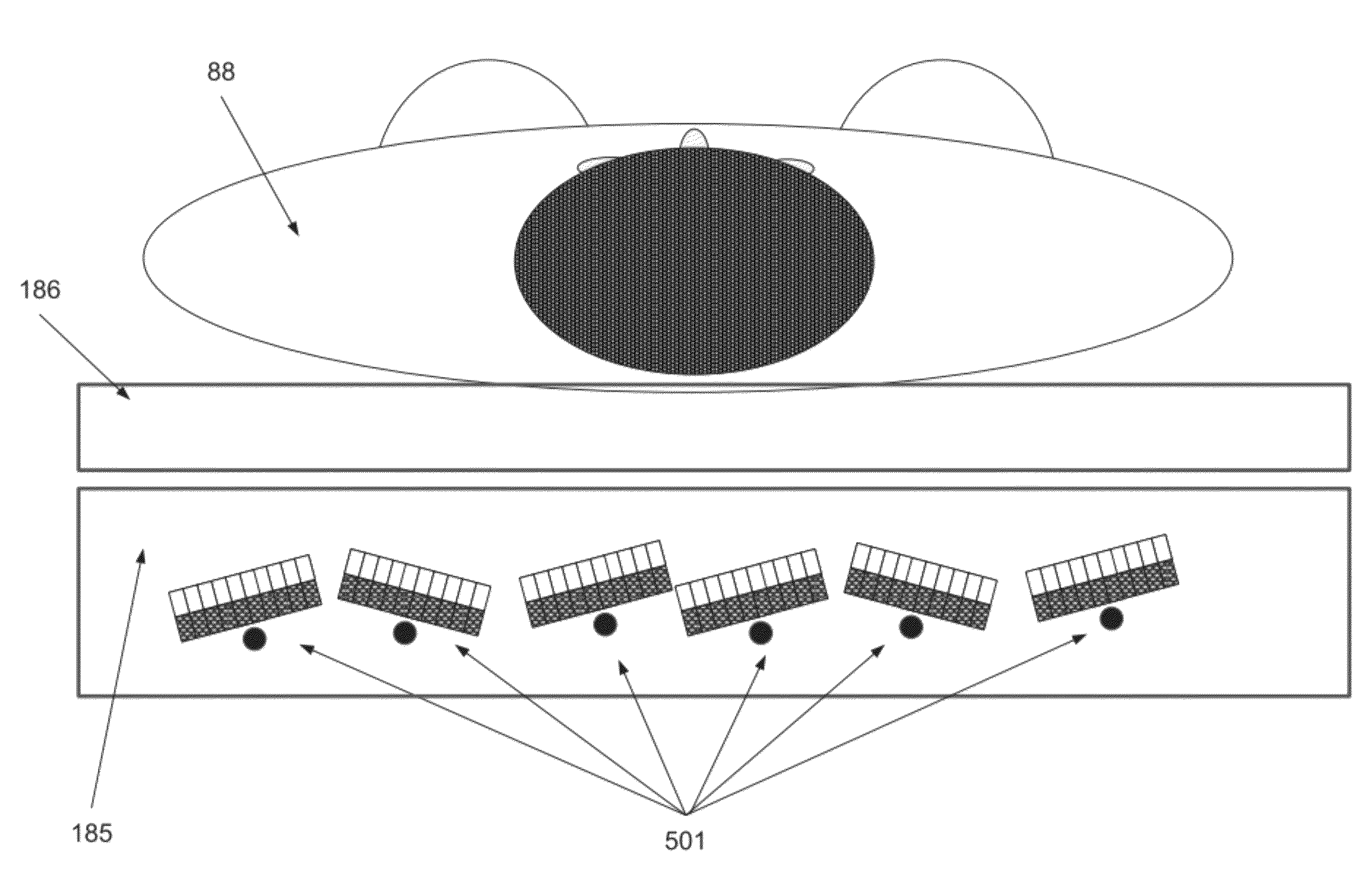
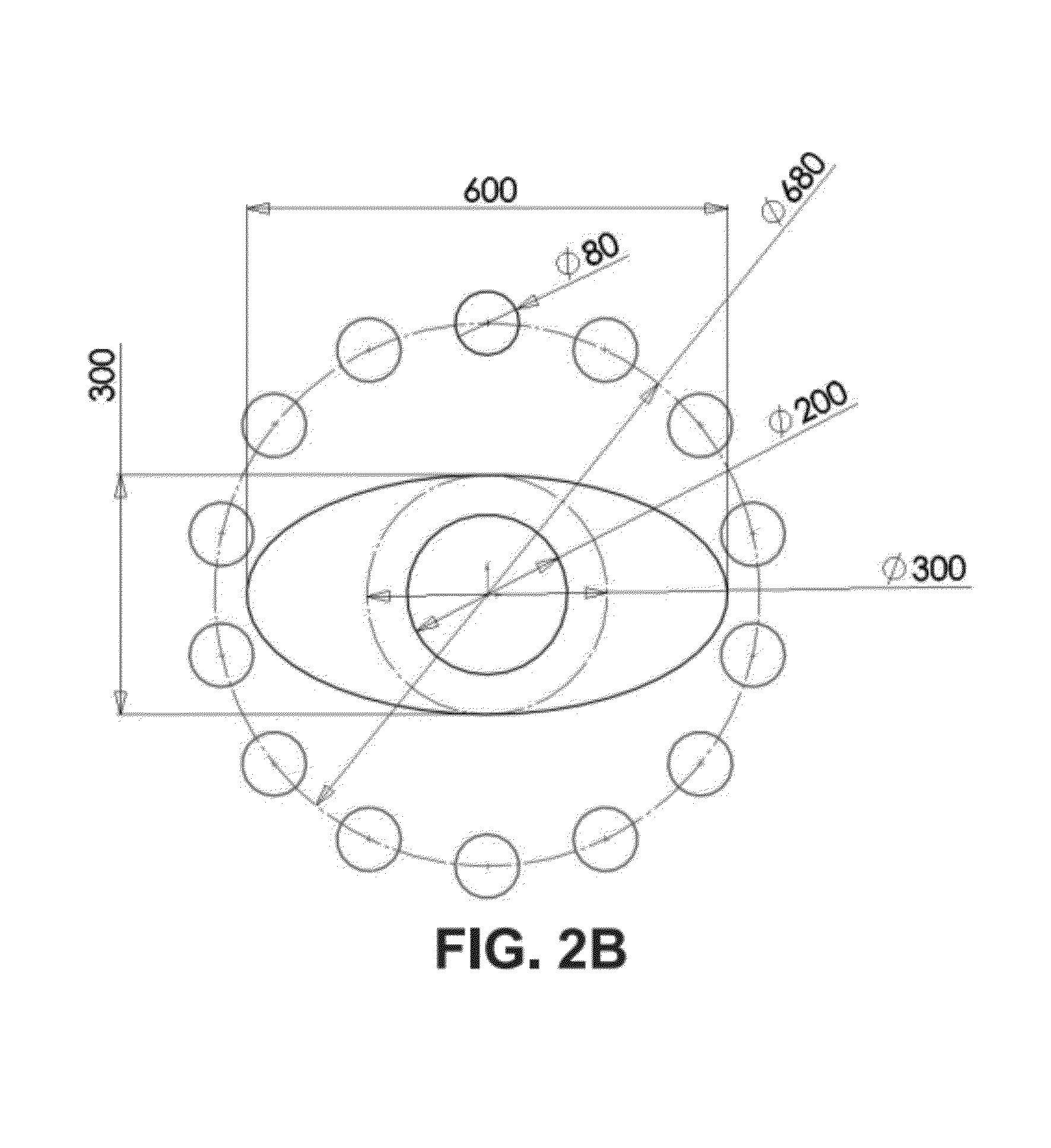
Method and system of optimized volumetric imaging
ActiveUS20110026685A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersVolumetric imagingActuator
A system of performing a volumetric scan. The system comprises a surface of positioning a patient in a space parallel thereto, a plurality of extendable detector arms each the detector arm having a detection unit having at least one radiation detector, and an actuator which moves the detection unit along a linear path, and a gantry which supports the plurality of extendable detector arms around the surface so that each the linear path of each respective the extendable detector arm being directed toward the space.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Method and system of optimized volumetric imaging
ActiveUS8338788B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansVolumetric imagingActuator
A system of performing a volumetric scan. The system comprises a surface of positioning a patient in a space parallel thereto, a plurality of extendable detector arms each the detector arm having a detection unit having at least one radiation detector, and an actuator which moves the detection unit along a linear path, and a gantry which supports the plurality of extendable detector arms around the surface so that each the linear path of each respective the extendable detector arm being directed toward the space.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
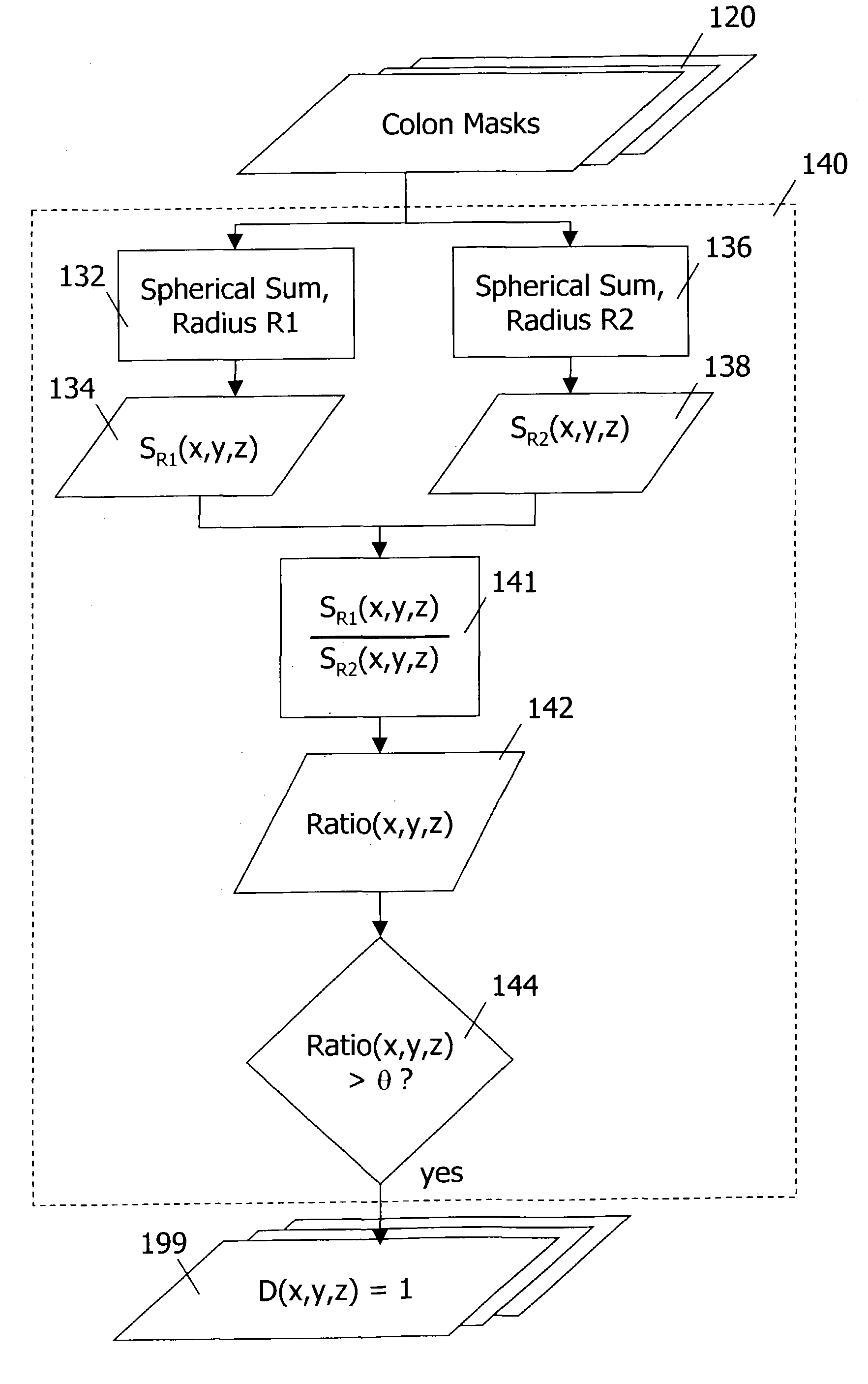
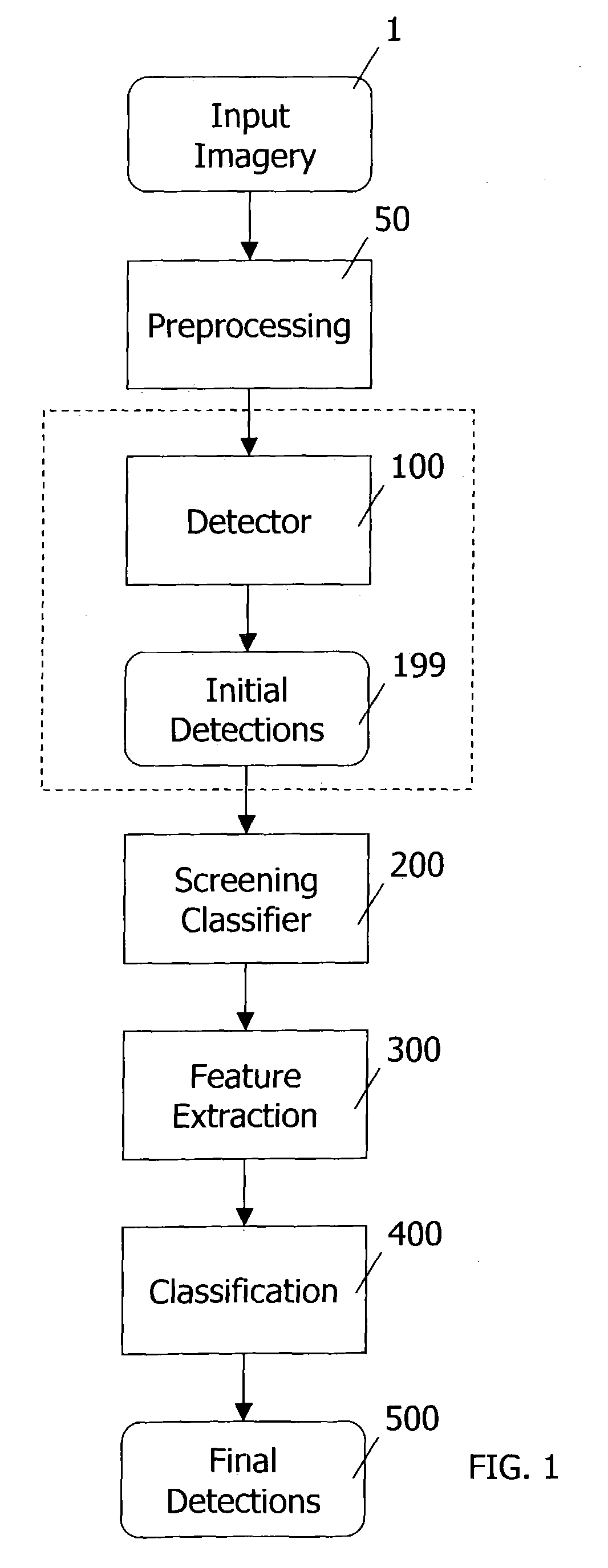
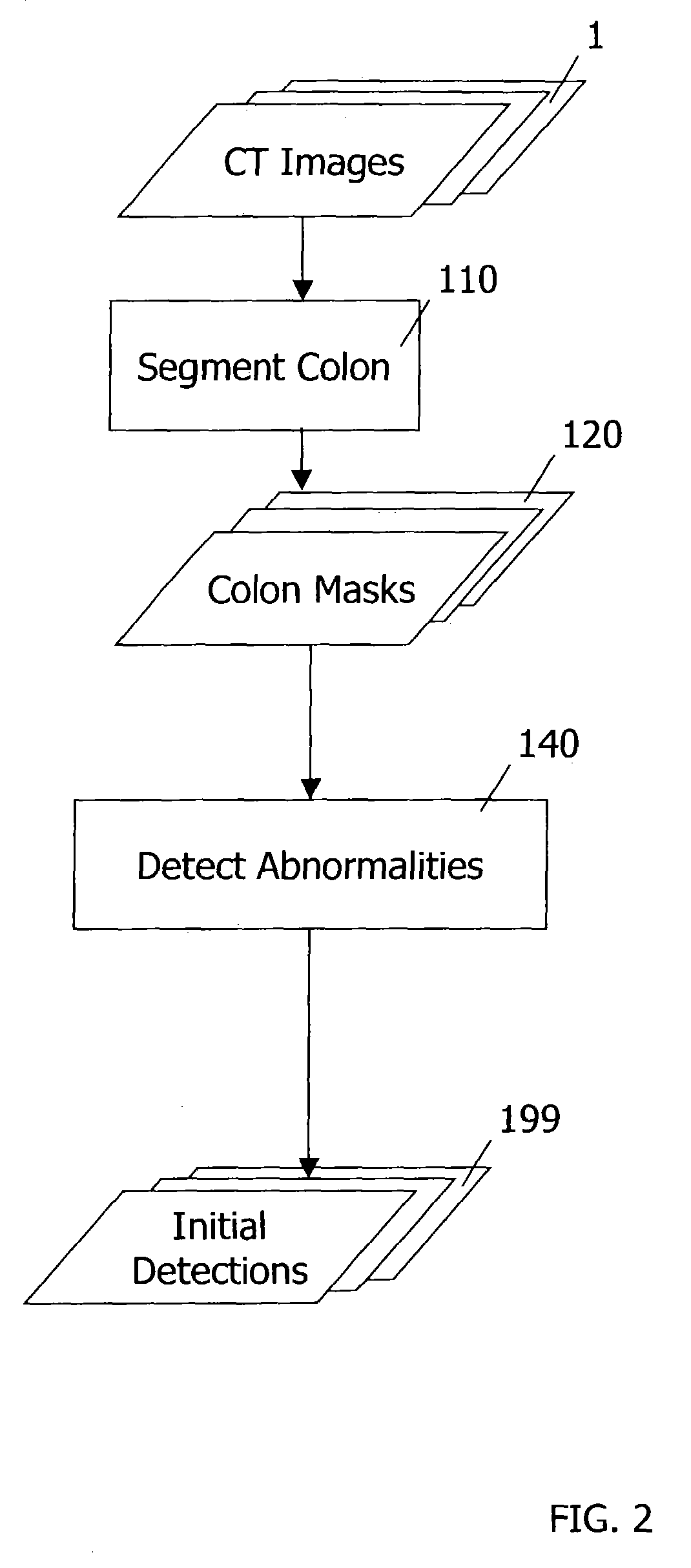
Computer-aided detection methods in volumetric imagery
This invention provides a method for detecting abnormalities in medical images, particularly for the detection of polyps in the colon from computed tomography imagery. Specifically a set of colon masks is input to a detector where summations over spherical volumes with two different radii are computed. Abnormalities are detected based on the ratio of spherical summation values computed for every pixel location.
Owner:ICAD INC
System and method for automatic shape registration and instrument tracking
InactiveUS7747312B2Surgical navigation systemsPerson identificationComputer-assisted surgeryVolumetric imaging
There is provided a device for generating a frame of reference and tracking the position and orientation of a tool in computer-assisted image guided surgery or therapy system. A first curvature sensor including fiducial markers is provided for positioning on a patient prior to volumetric imaging, and sensing the patient's body position during surgery. A second curvature sensor is coupled to the first curvature sensor at one end and to a tool at the other end to inform the computer-assisted image guided surgery or therapy system of the position and orientation of the tool with respect to the patient's body. A system is provided that incorporates curvature sensors, a garment for sensing the body position of a person, and a method for registering a patient's body to a volumetric image data set in preparation for computer-assisted surgery or other therapeutic interventions. This system can be adapted for remote applications as well.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Method and device for geometry analysis and calibration of volumetric imaging systems
ActiveUS7950849B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVolumetric imagingProjection image
A technique is provided for geometrical analysis and calibration of a volumetric imaging system. The technique includes computing a projection error between estimated locations of a set of markers of a phantom based on a estimated imaging geometry and observed locations of the respective markers for at least one projection image, decomposing the computed projection error into one or more error components corresponding to respective geometric parameters of the imaging geometry, and updating at least one parameter of the estimated imaging geometry based on the one or more error components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
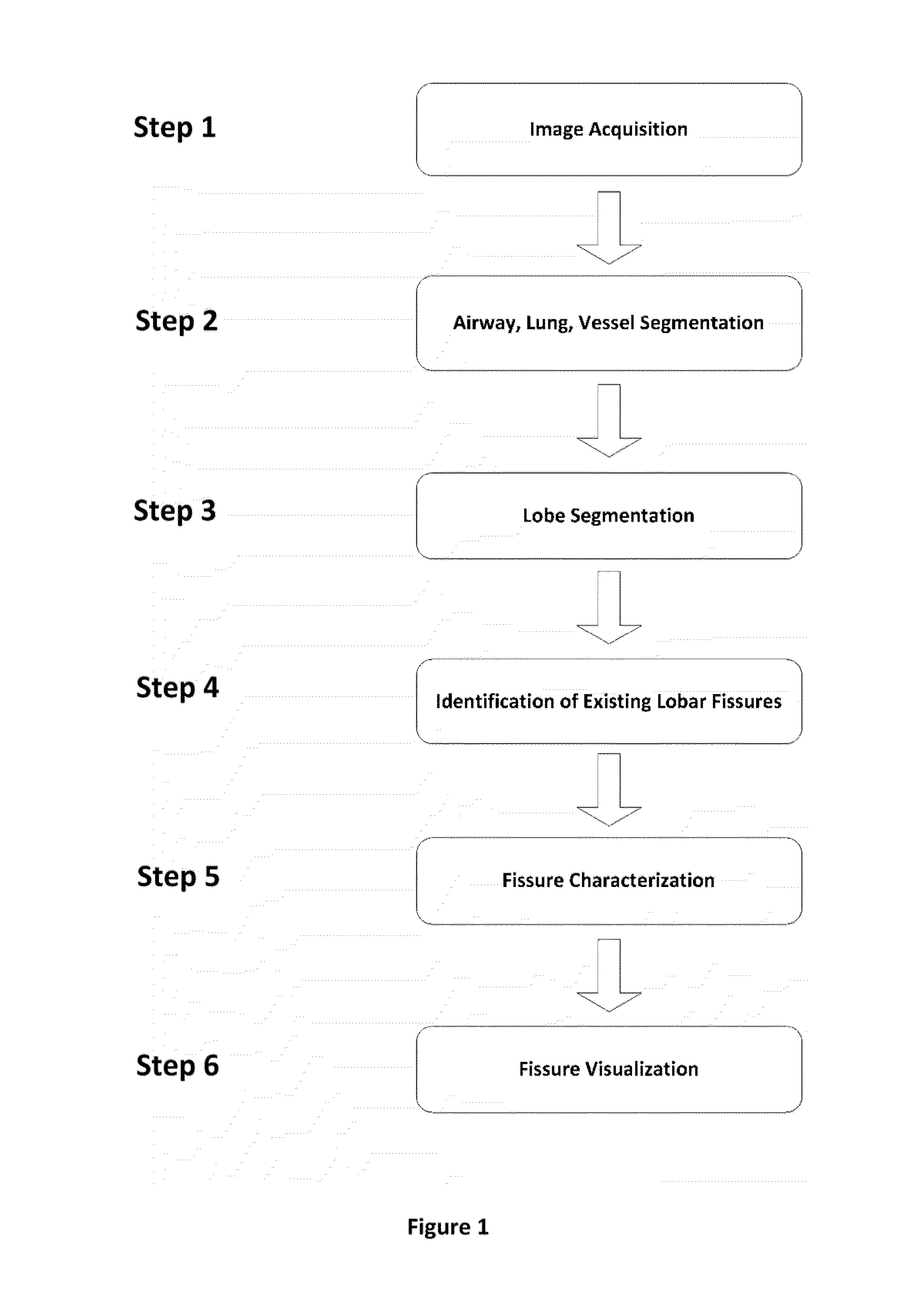
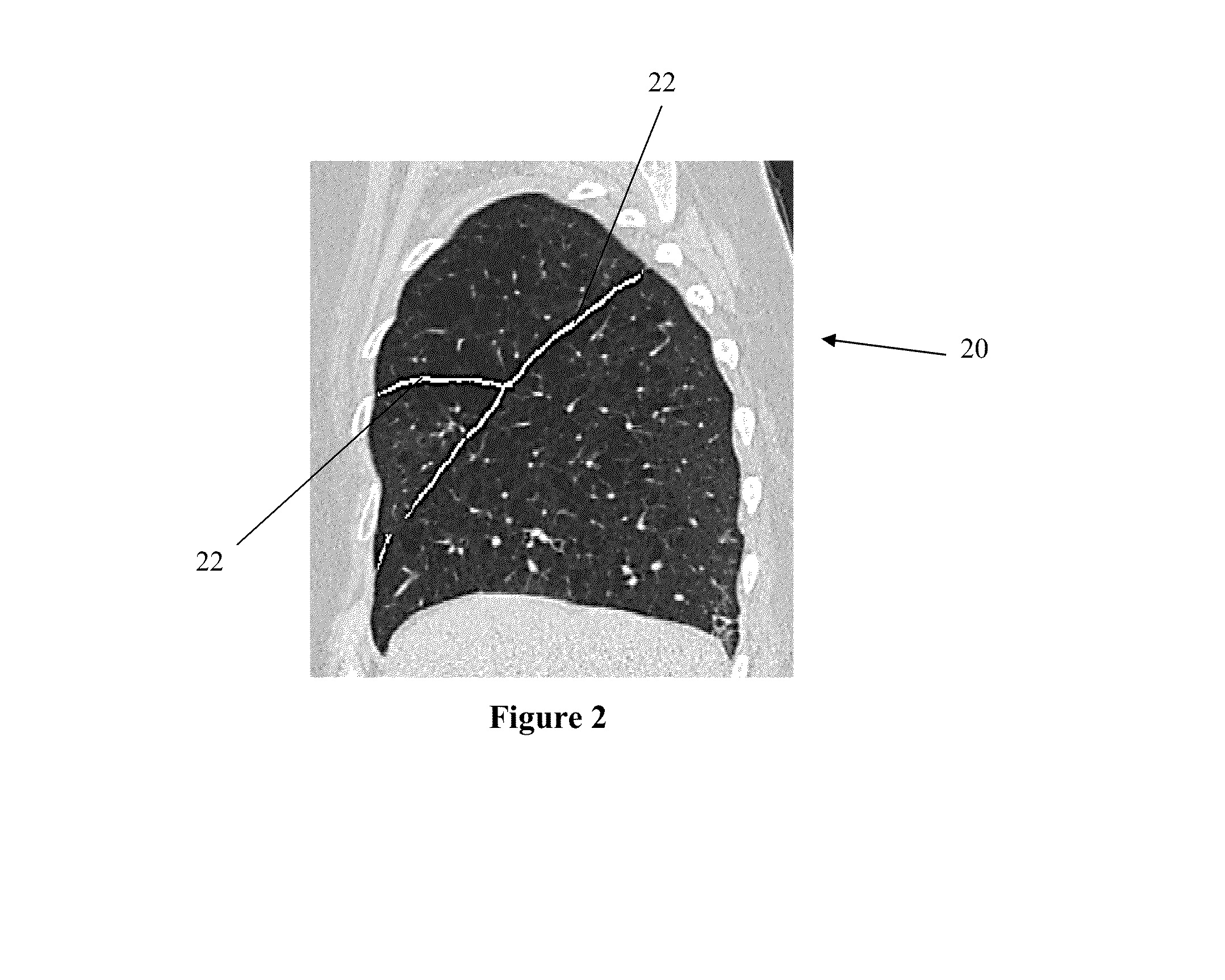
Visualization and characterization of pulmonary lobar fissures
ActiveUS20140105472A1Easy to understandReduce consumptionImage enhancementImage analysisVolumetric imagingLung lobe
Systems and methods for visualizing pulmonary fissures including a processor and software instructions for creating a 3 dimensional model of the fissures. Creating the 3 dimensional model includes accessing volumetric imaging data of the patient's lungs, analyzing the volumetric imaging data to segment the lungs into lobes, using the segmented lobes to identify locations at which pulmonary fissures should be present where the lobes abut each other, analyzing the volumetric images to identify locations at which pulmonary fissures actually are present as existing fissure, comparing the locations at which pulmonary fissures should be present to the locations at which pulmonary fissures are present to identify locations of missing fissure, and creating a visual display comprising a 3 dimensional model of the pulmonary fissures including existing fissure portions and missing fissure portions, with the existing fissure portion visually distinct from the missing fissure portions.
Owner:VIDA DIAGNOSTICS
Systems and methods for adaptive volume imaging
ActiveUS20100260398A1Improve image qualityIncrease ratingsImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging processingVolumetric imaging
Systems and methods which provide volume imaging by implementing survey and target imaging modes are shown. According to embodiments, a survey imaging mode is implemented to provide a volume image of a relatively large survey area. A target of interest is preferably identified within the survey area for use in a target imaging mode. Embodiments implement a target imaging mode to provide a volume image of a relatively small target area corresponding to the identified target of interest. The target imaging mode preferably adapts the beamforming, volume field of view, and / or other signal and image processing algorithms to the target area. In operation according to embodiments, the target imaging mode provides a volume image of a target area with improved volume rate and image quality.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
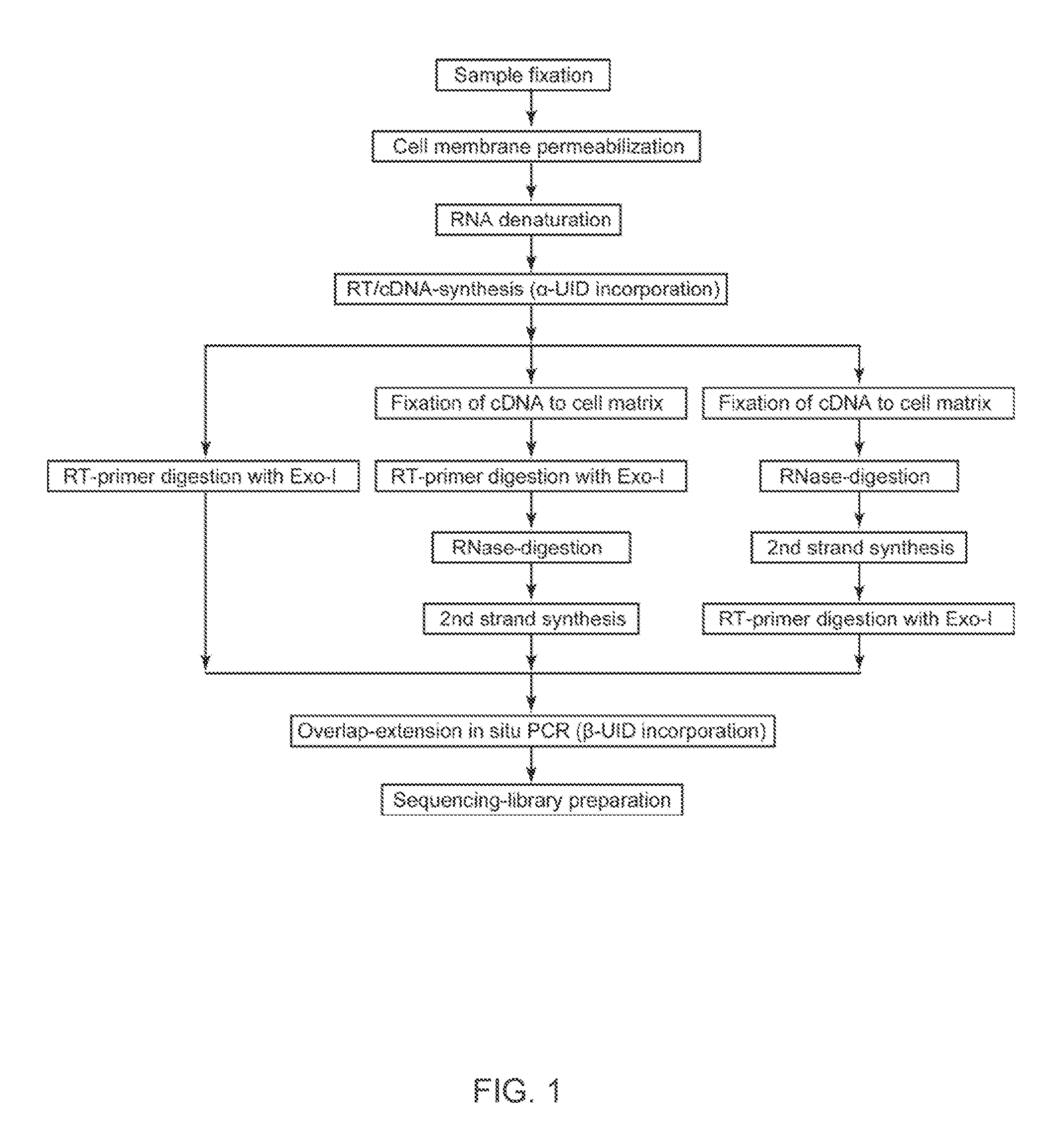
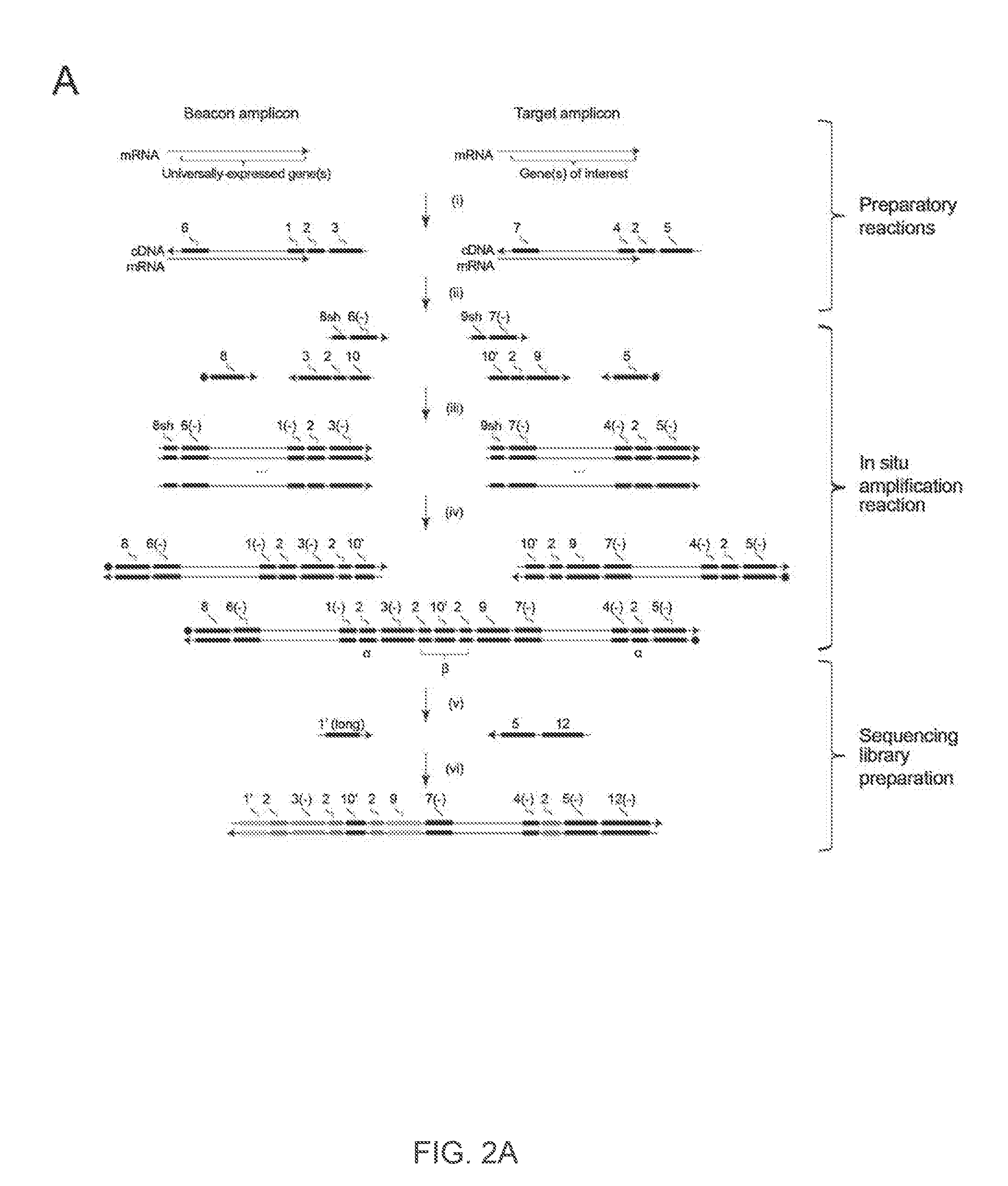
Spatial and cellular mapping of biomolecules in situ by high-throughput sequencing
The present invention relates to molecular microscopy or volumetric imaging by proximal unique molecular identifiers (“UID”) reaction (“VIPUR”) microscopy methods to record the cellular co-localization and / or spatial distributions of arbitrary nucleic acid sequences, or other biomolecules tagged with nucleic sequences. The method involves one or both of two DNA sequence-components such as an α-UID, which may identify the targeted sequences-of-interest themselves and / or spatial beacons relative to which their distances are measured, and a −β-UID, which labels α-UID association events.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
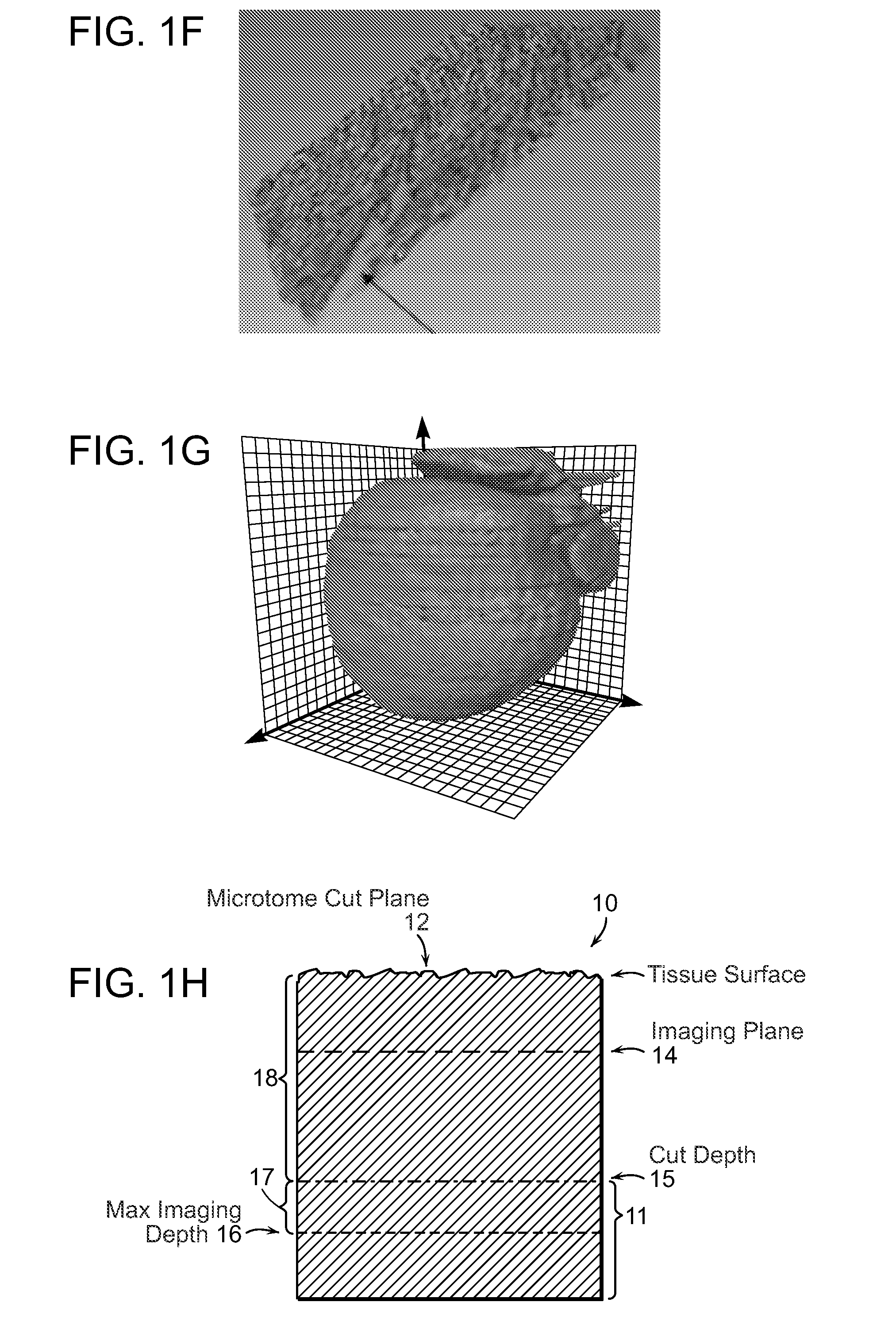
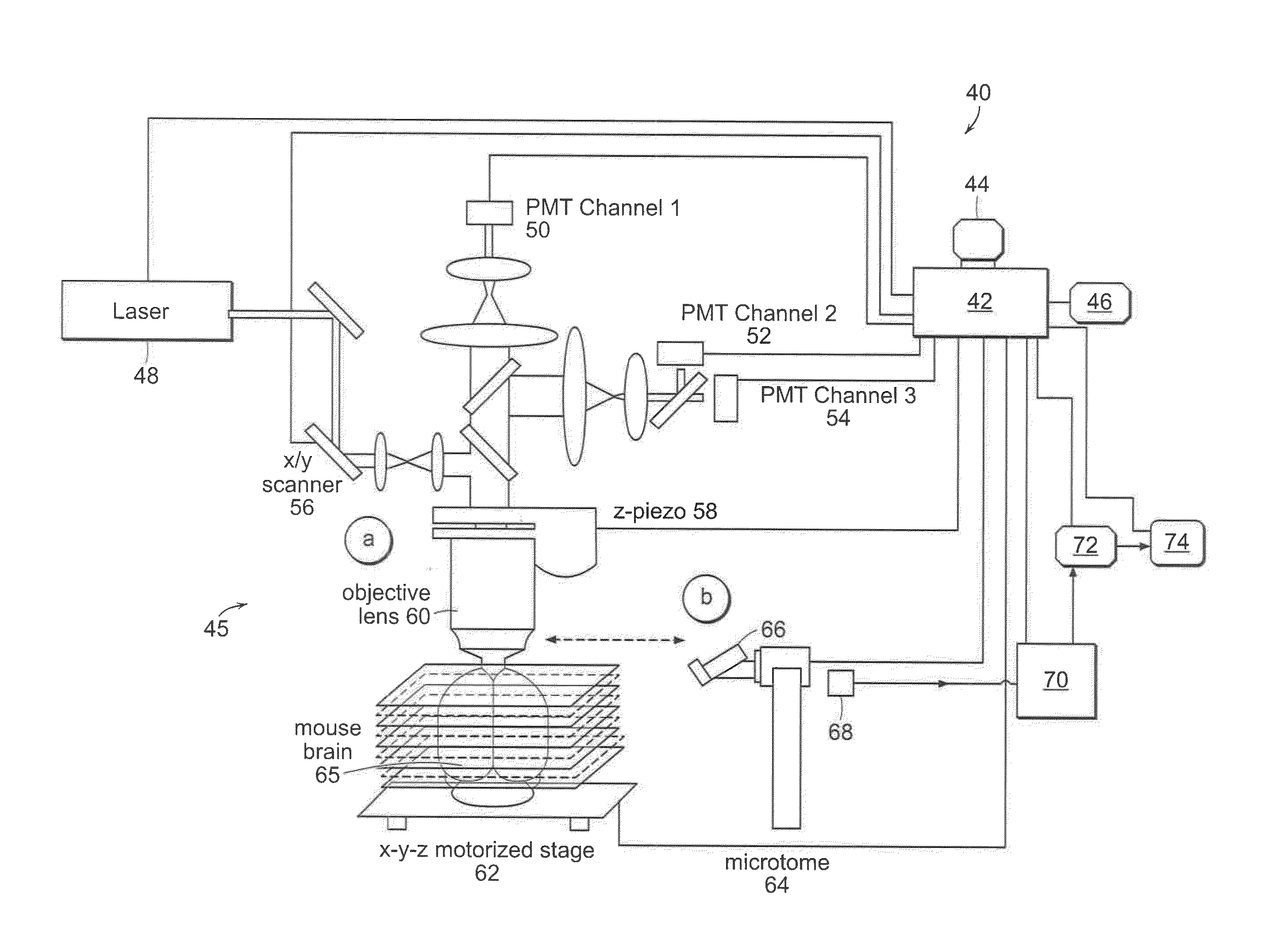
Systems and methods for imaging and processing tissue
ActiveUS20120208184A1Limited depth penetrationPrecise positioningOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsVolumetric imagingTissue imaging
In accordance with preferred embodiments of the present invention, a method for imaging tissue, for example, includes the steps of mounting the tissue on a computer controlled stage of a microscope, determining volumetric imaging parameters, directing at least two photons into a region of interest, scanning the region of interest across a portion of the tissue, imaging layers of the tissue, sectioning a portion of the tissue, capturing the sectioned tissue, and imaging additional layers of the tissue in a second volume of the tissue, and capturing each portion of sectioned tissue, and processing three-dimensional data that is collected to create a three-dimensional image of the region of interest. Further, captured tissue sections can be processed, re-imaged, and indexed to their original location in the three dimensional image.
Owner:TISSUEVISION
Gradient bore cooling providing RF shield in an MRI system
InactiveUS7397244B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceVolumetric imagingRadio frequency
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device for imaging a volume includes a main magnet for generating a magnetic field, an insulator sheet formed into a tube extending along an axis, a gradient coil disposed on an outside surface defining the tube for manipulating the magnetic field generated by the main magnet to image the volume, and a cooling circuit disposed between the gradient coil and a RF coil. The cooling circuit is disposed on an opposite inside surface defining the tube, wherein the cooling circuit shields the gradient coil from the RF coil while cooling the gradient coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and Methods for Imaging a Volume-of-Interest
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Scanner/optical system for three-dimensional lidar imaging and polarimetry
ActiveUS8493445B2Reduce complexityMeet cutting requirementsOptical rangefindersColor television detailsOptical scannersLaser beams
An optical scanner system for contiguous three-dimensional topographic or volumetric imaging of a surface from an aircraft or spacecraft is disclosed. A servo controller synchronizes the rotation rates of a pair of wedge scanners with high precision to the multi-kilohertz laser fire rate producing an infinite variety of well-controlled scan patterns. This causes the beam pattern to be laid down in precisely the same way on each scan cycle, eliminating the need to record the orientations of the wedges accurately on every laser fire, thereby reducing ancillary data storage or transmission requirements by two to three orders of magnitude and greatly simplifying data preprocessing and analysis. The described system also uses a holographic element to split the laser beam into an array that is then scanned in an arbitrary pattern. This provides more uniform signal strength to the various imaging detector channels and reduces the level of optical crosstalk between channels, resulting in a higher fidelity three-dimensional image.
Owner:INTERGRAPH
Digital breast tomosynthesis reconstruction using adaptive voxel grid
Some embodiments are associated with generation of a volumetric image representing an imaged object associated with a patient. According to some embodiments, tomosynthesis projection data may be acquired. A computer processor may then automatically generate the volumetric image based on the acquired tomosynthesis projection data. Moreover, distances between voxels in the volumetric image may be spatially varied.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for imaging and processing tissue
ActiveUS20140356876A1Fast imagingControl depthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVolumetric imagingFluorescence
In accordance with preferred embodiments of the present invention, a method for imaging tissue, for example, includes the steps of mounting the tissue on a computer controlled stage of a microscope, determining volumetric imaging parameters, directing at least two photons into a region of interest, scanning the region of interest across a portion of the tissue, imaging a plurality of layers of the tissue in a plurality of volumes of the tissue in the region of interest, sectioning the portion of the tissue, capturing the sectioned tissue, and imaging a second plurality of layers of the tissue in a second plurality of volumes of the tissue in the region of interest, and capturing each sectioned tissue, detecting a fluorescence image of the tissue due to said excitation light; and processing three-dimensional data that is collected to create a three-dimensional image of the region of interest. Further, captured tissue sections can be processed, re-imaged, and indexed to their original location in the three dimensional image.
Owner:TISSUEVISION
Systems and methods for imaging and processing tissue
ActiveUS8771978B2Improve reliabilityPrecise positioningOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsVolumetric imagingTissue imaging
Owner:TISSUEVISION
Ultrasound imaging with sparse array probes
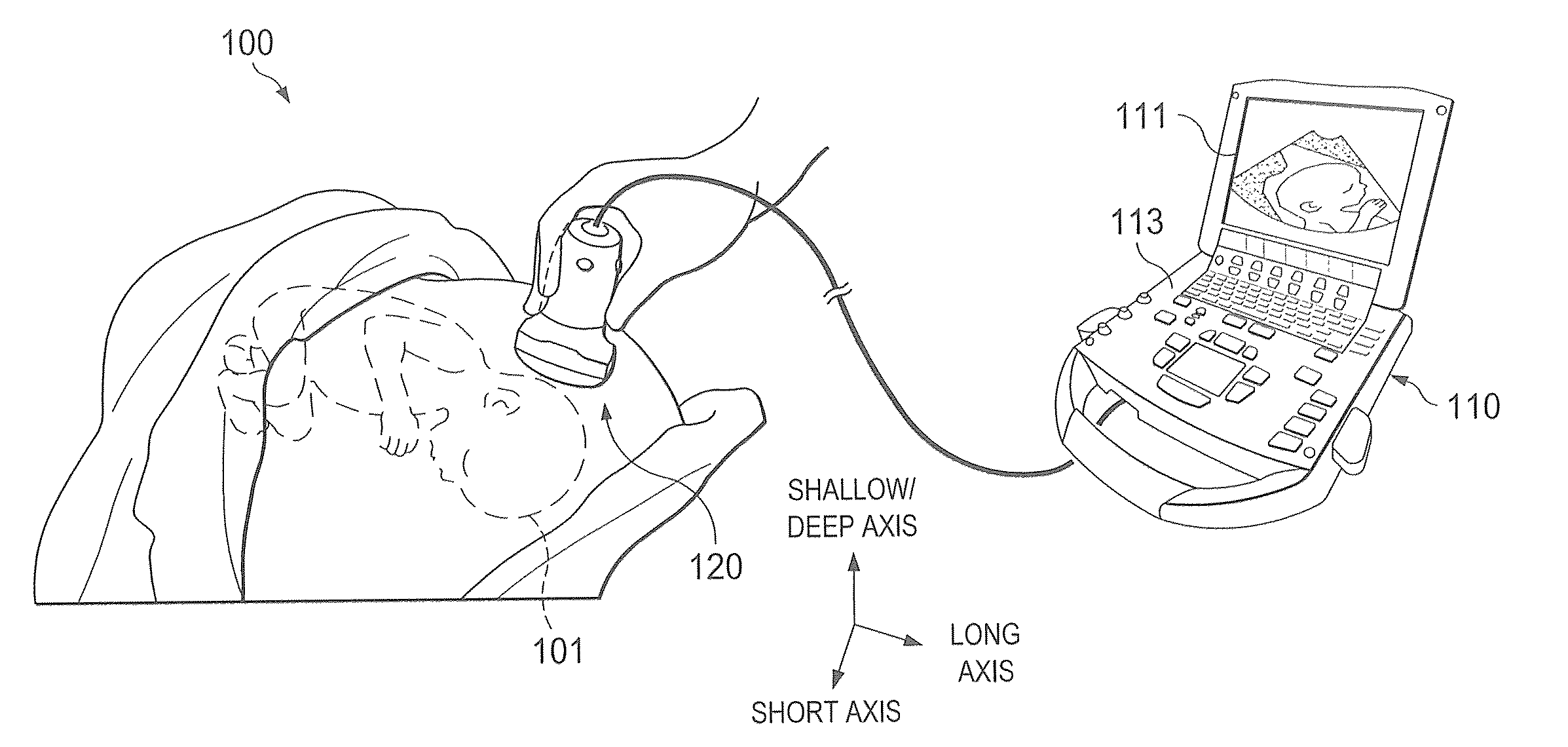
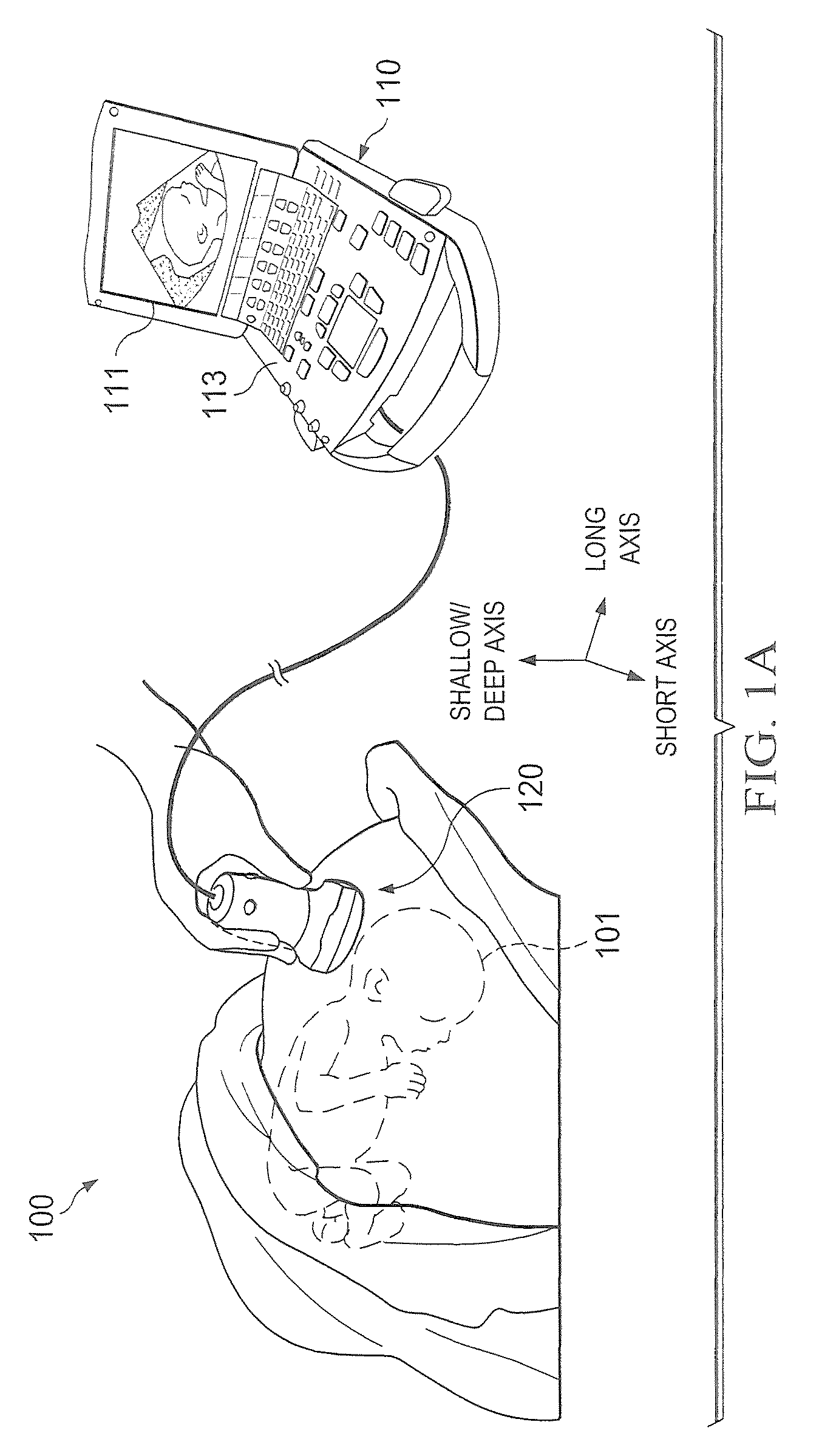
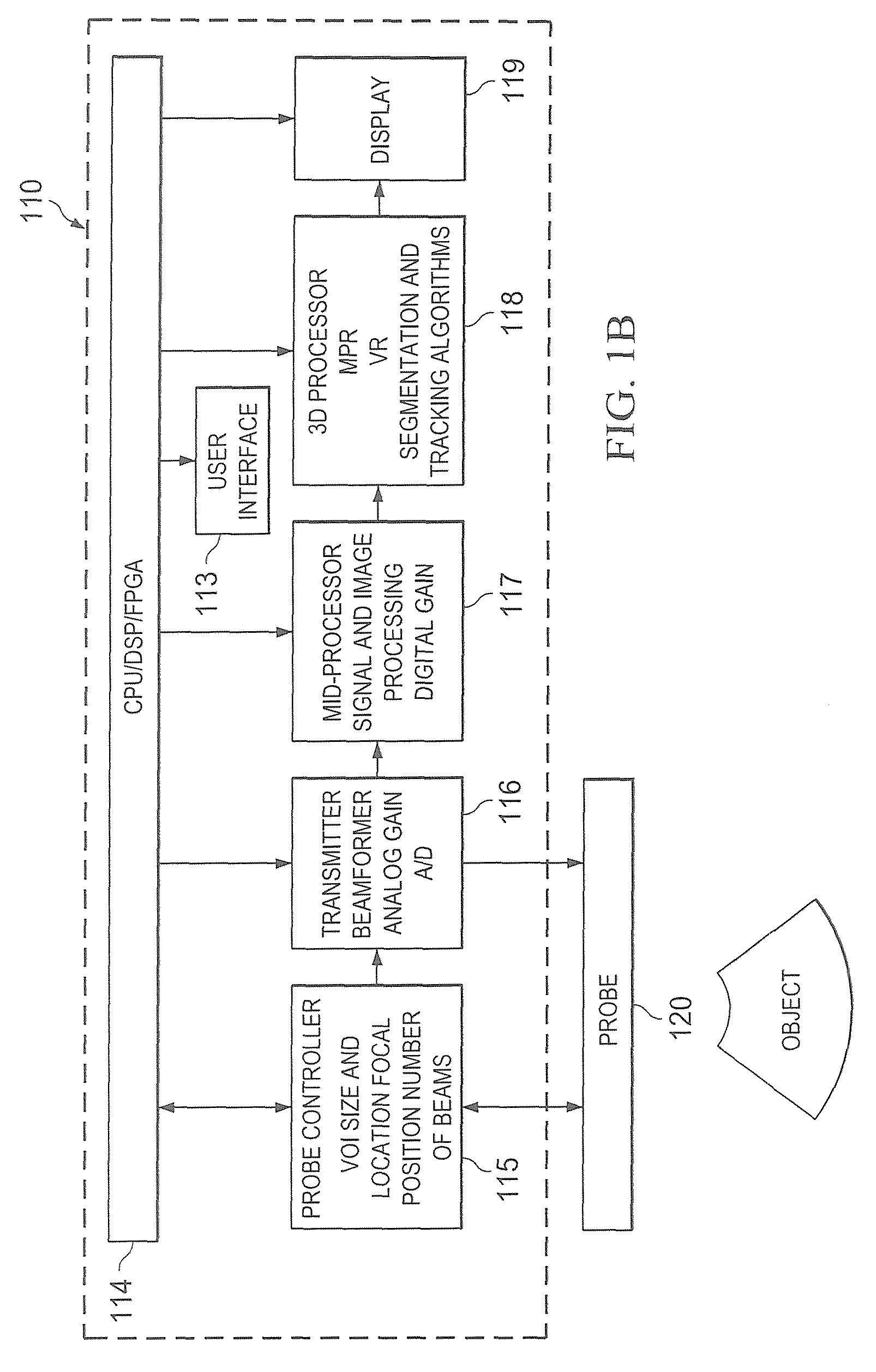
ActiveUS20170209121A1Slow frame rateSufficient capturingOrgan movement/changes detectionMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound imagingVolumetric imaging
Sparse arrays of transducer elements may be beneficial in providing ultrasound transducer probes with a wide total aperture while containing a manageable number of transducer elements. Sparse arrays made with bulk piezoelectric materials or with arrays of micro-elements can be effectively with ping-based multiple aperture ultrasound imaging techniques to perform real-time volumetric imaging.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
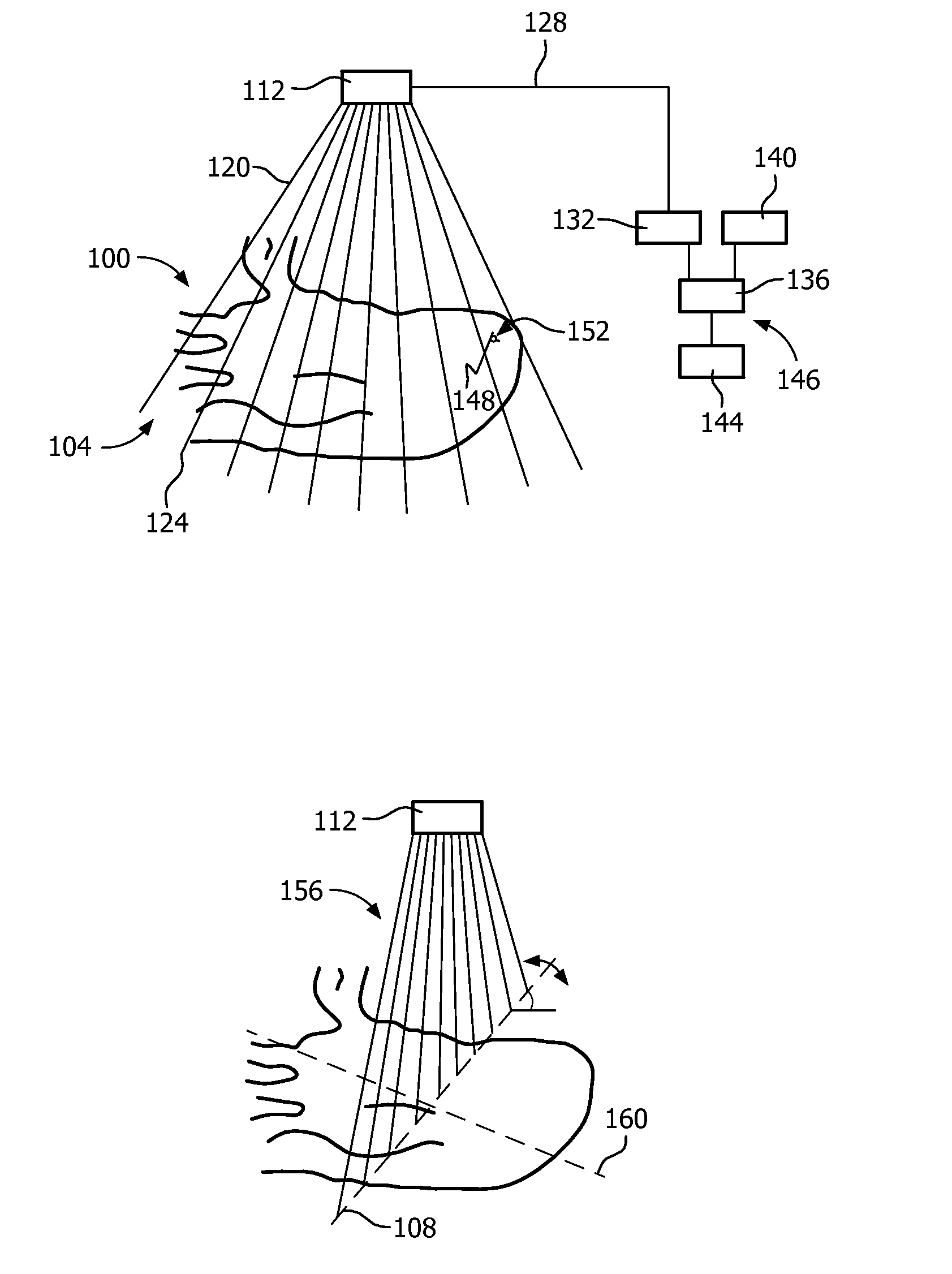
System and method for fast retinal imaging
An optical system and measurement method for imaging three-dimensional objects with low light scatter comprising at least one source of radiation; a radiation projection means for creating a set of foci through a volume of an object; and a means for imaging the returned light from the set of foci on at least one camera, wherein the imaging of the volume of the object is at a different angle from the projection, allowing for detection of the returned light on separate camera pixels. The measurement method further comprises projecting a longitudinal grid of elongated foci through the volume of an object; imaging returned light from the object at a different angle on at least one camera, so as to avoid overlapping the elongated images; and analyzing the imaged, returned light to yield depth information of the object at a multiplicity of points.
Owner:SLITLED LTD
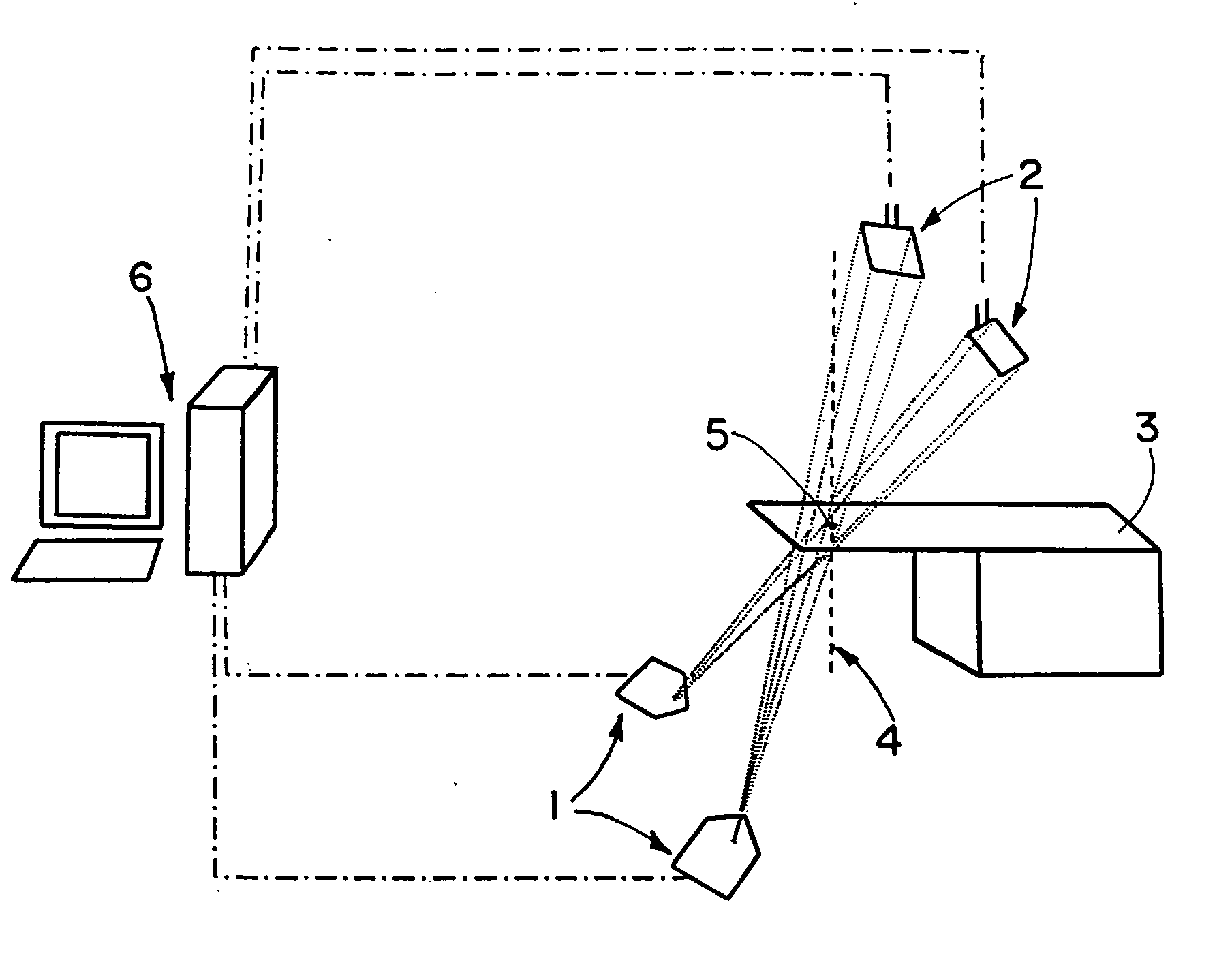
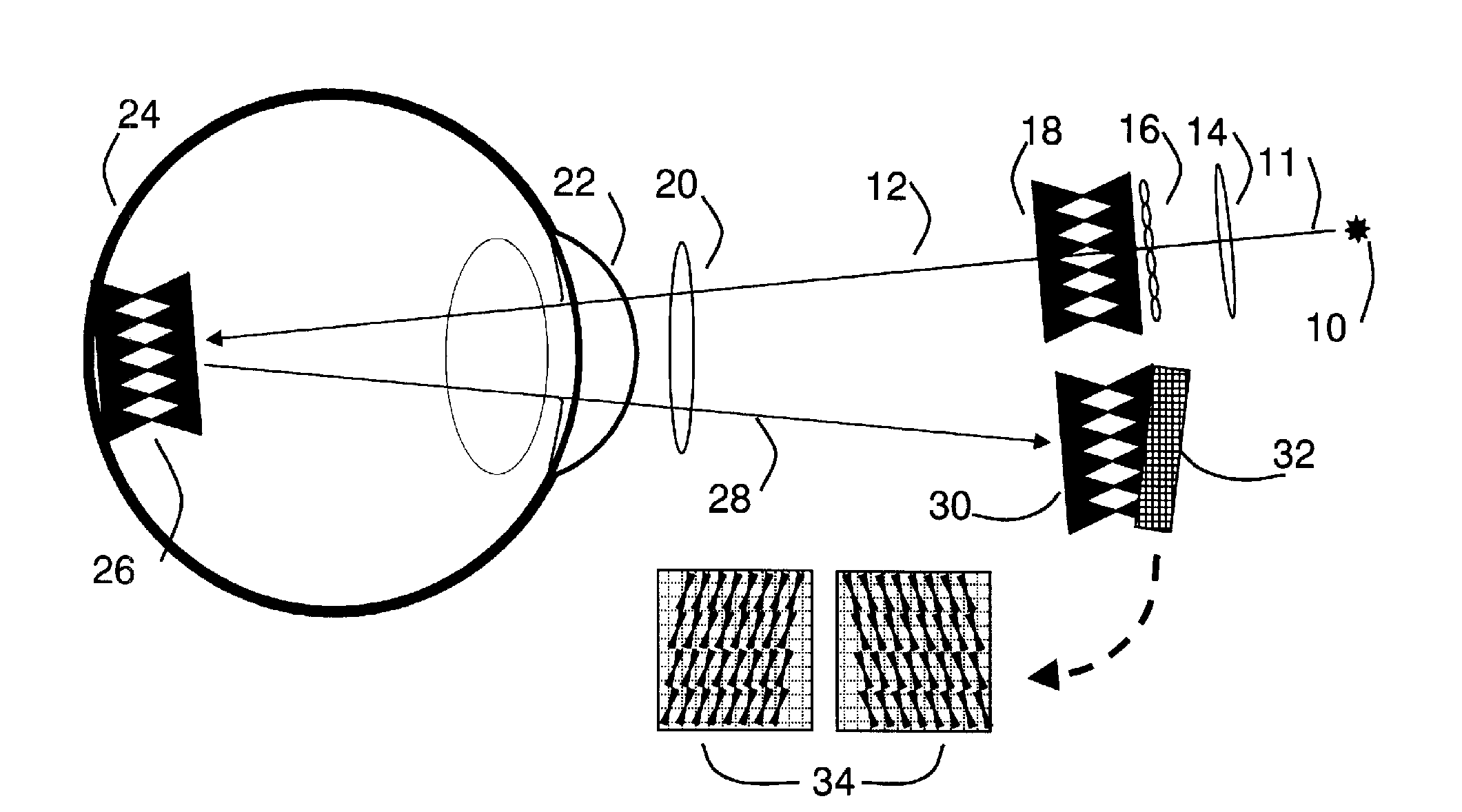
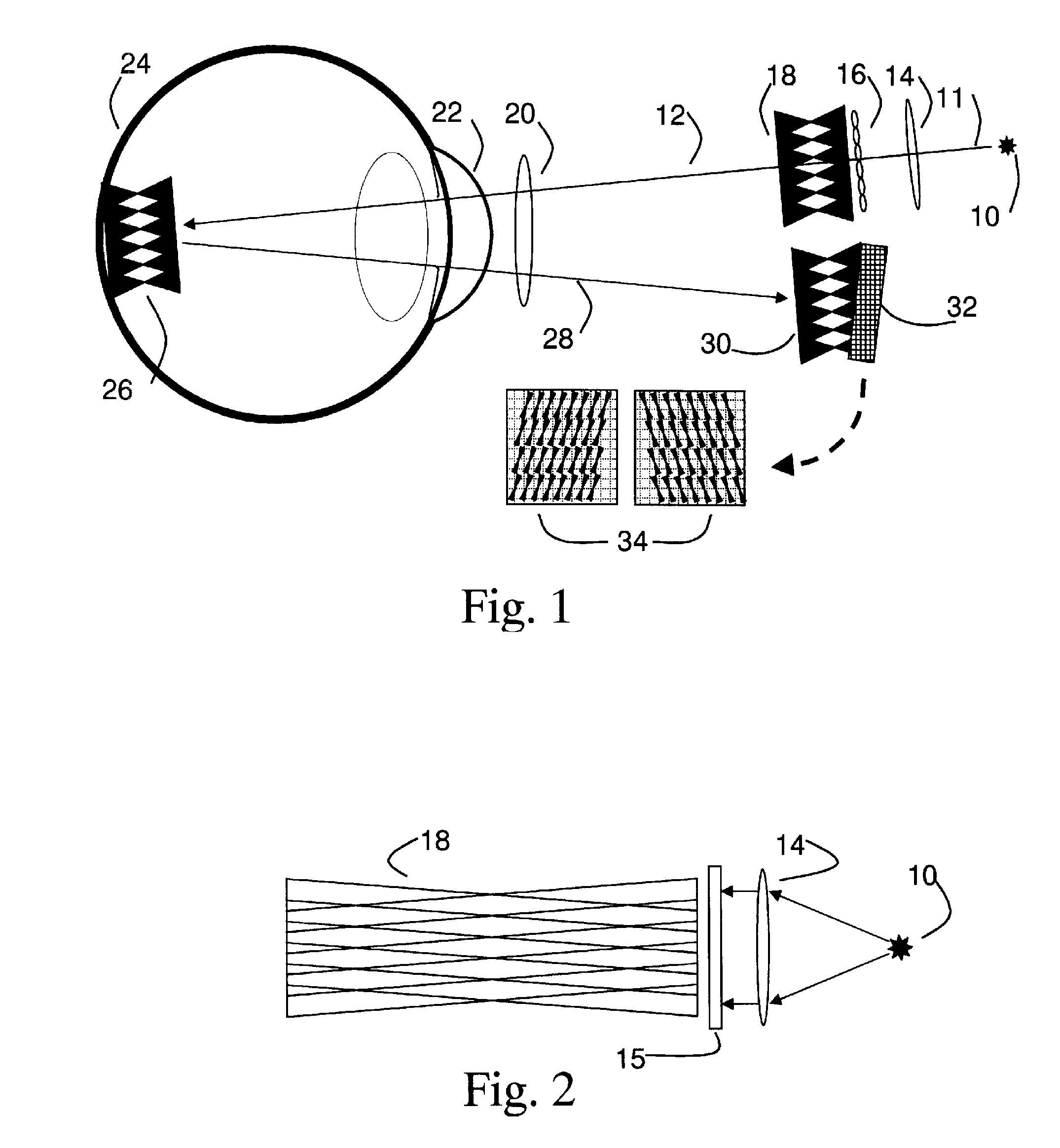
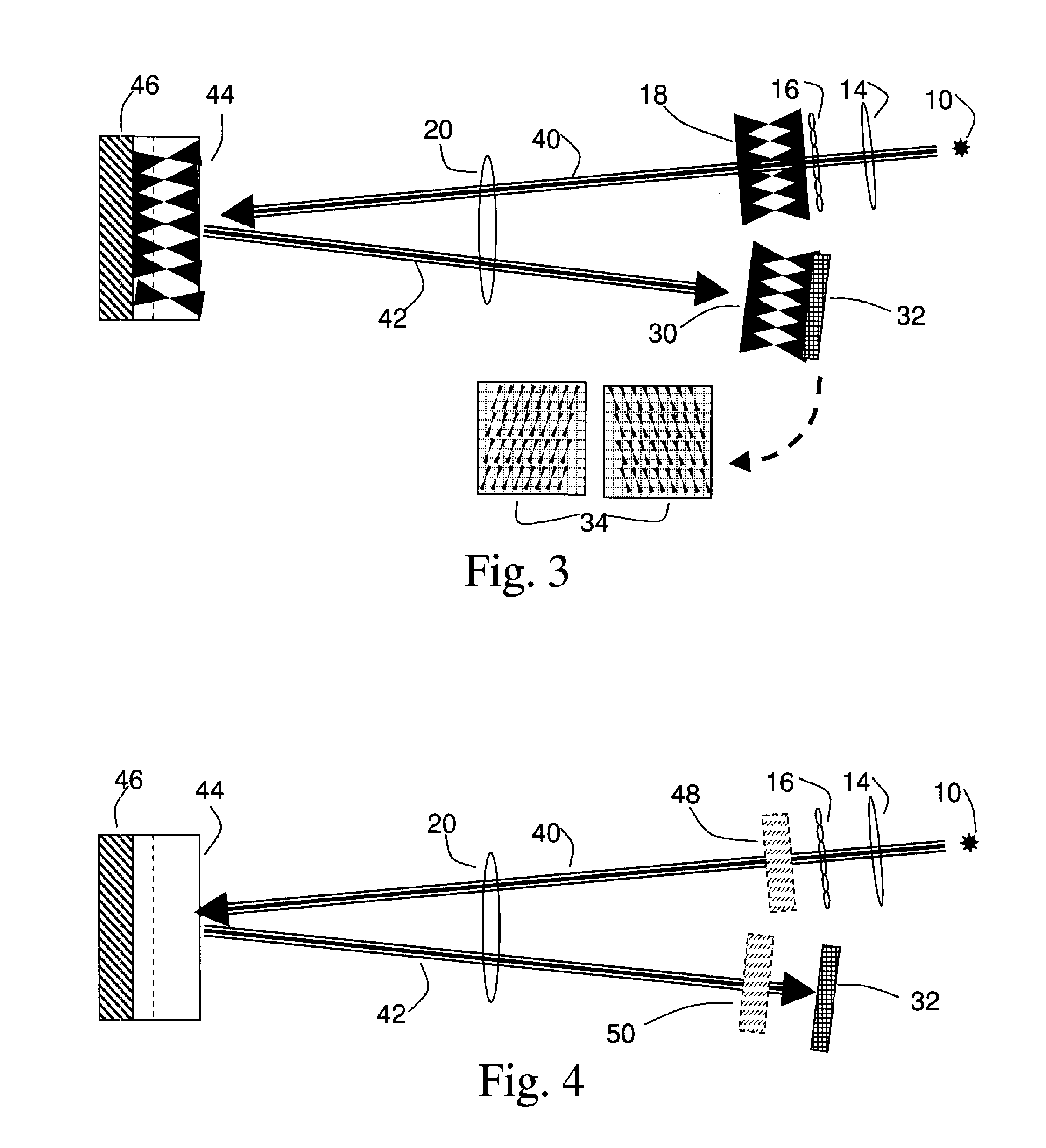
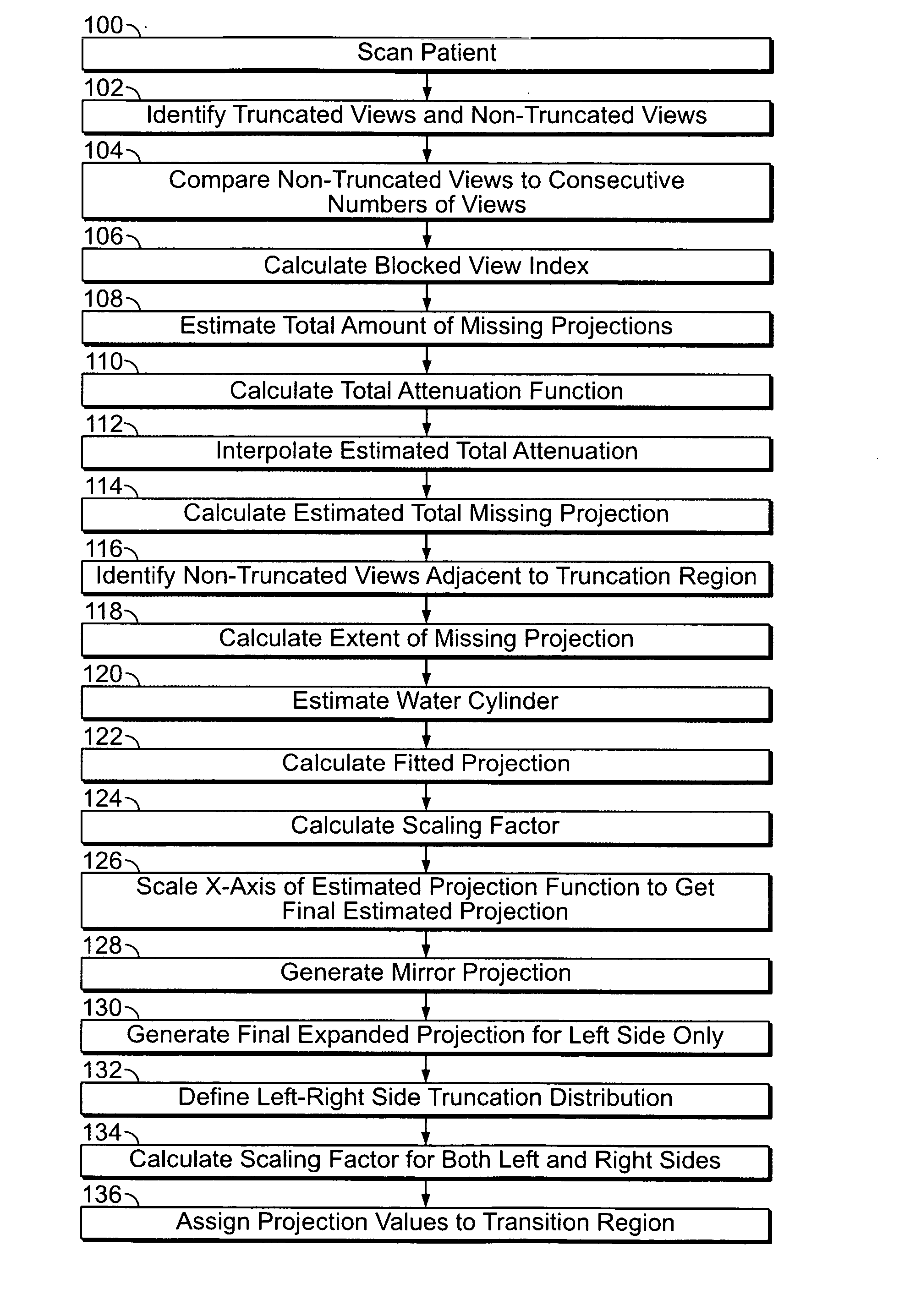
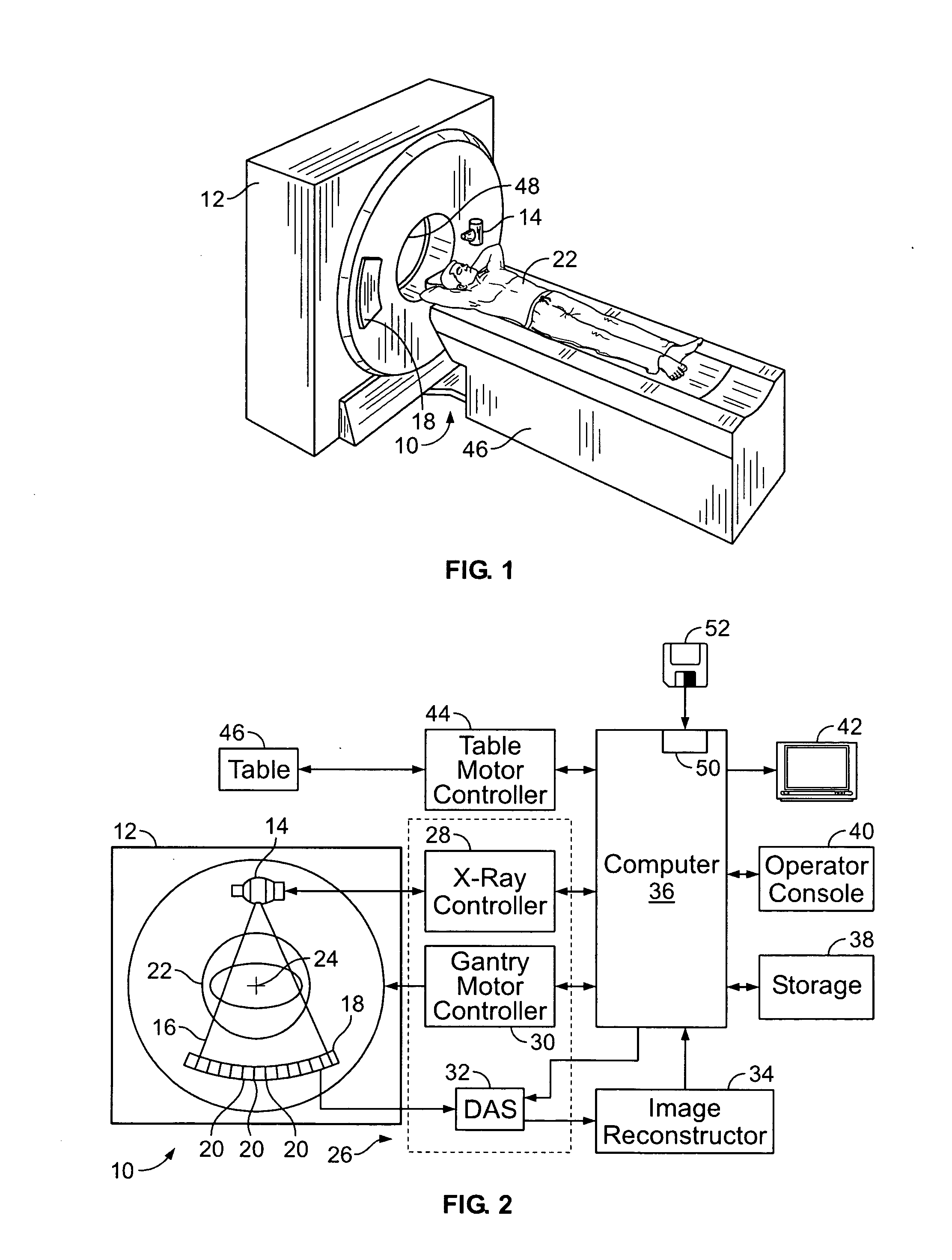
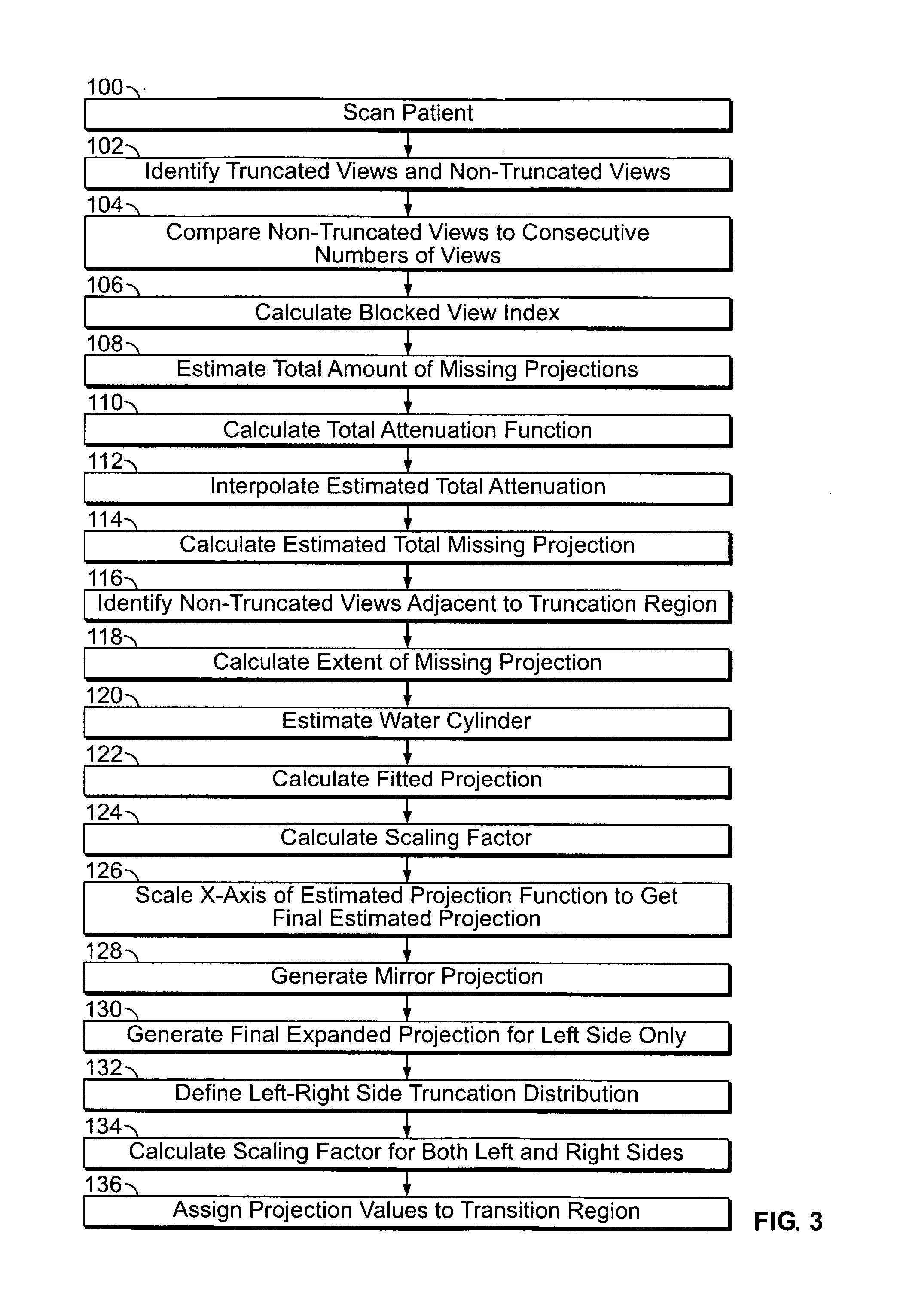
Method and apparatus for field-of-view expansion of volumetric CT imaging
ActiveUS20070116344A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound attenuationView based
A method for expanding a field-of-view of a volumetric computed tomography scan comprises identifying truncated views having projection truncation and non-truncated views without projection truncation based on an average value of one or more edge channels. An estimated missing projection is calculated for each of the truncated views based on at least one neighboring non-truncated view. A projection profile is calculated for each of the truncated views based on the estimated missing projection, and the projection profile provides at least one of attenuation data and projection data for an area outside a field-of-view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Excitation schemes for low-cost transducer arrays
InactiveUS20140243673A1High riskBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationVolumetric imagingLight beam
A device images time-wise in parallel using transducer elements of a group (428, 432, 436, 440). In some embodiments, the elements are of a current group and imaging is time-wise sequential by group. The groups may be spatially disposed (408, 412) with respect to each other so as to mutually intermesh element-wise. The imaging may include volumetric imaging. The device can be configured for not collectively using any of the elements to focus, nor to steer, a beam used in the imaging. The device might be operable to transition between spacing states (404, 408, 412) at least one of which is characterized by a respective minimum, nonzero, degree of intra-group, element-to-element non-adjacency (470), or may be fixed at one spacing state. The transitioning may be automatic, in response to input indicative of blood vessel size and / or depth.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Systems and methods for adaptive volume imaging
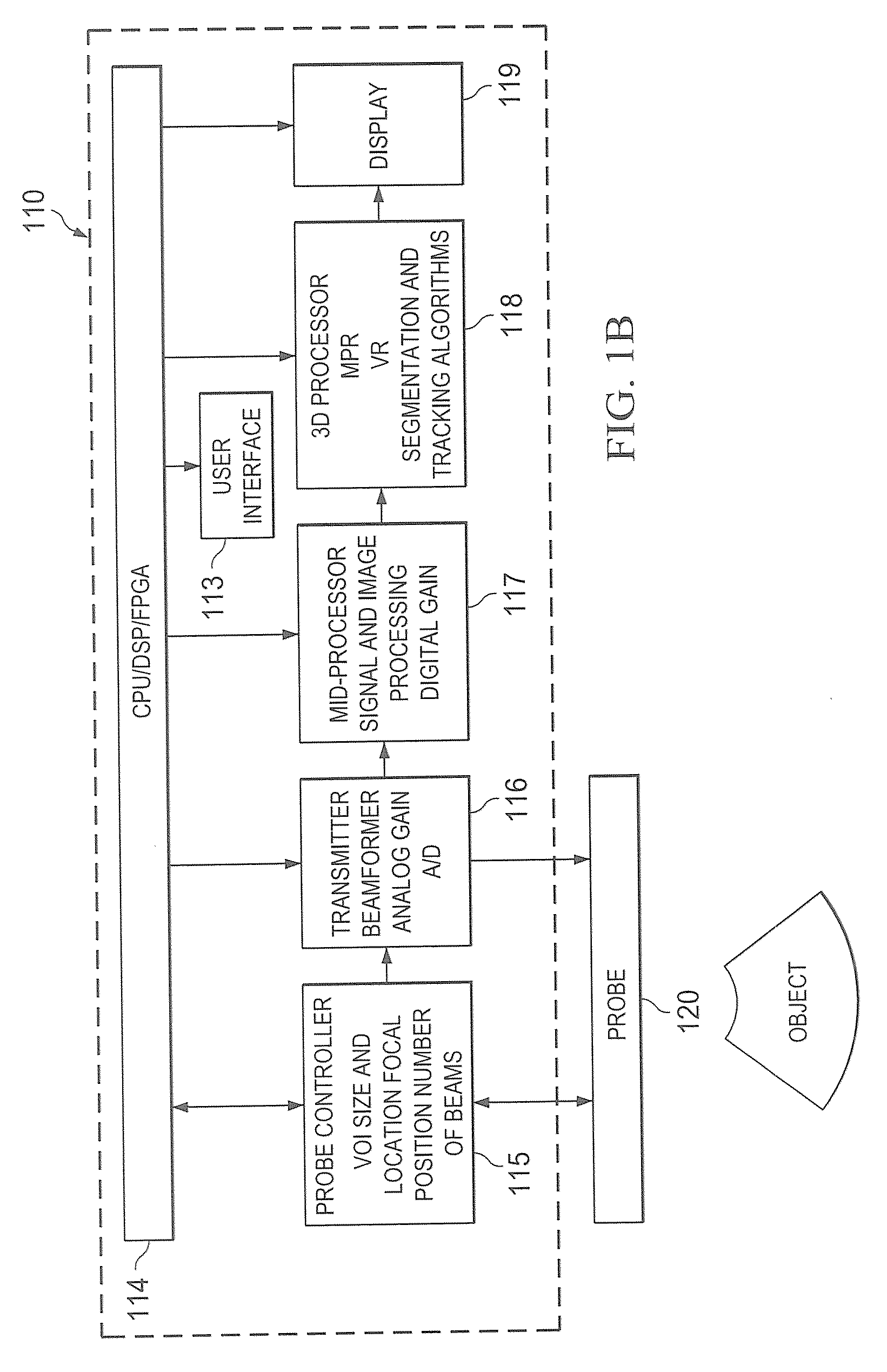
ActiveUS8355554B2Quality improvementIncrease ratingsImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging processingVolumetric imaging
Systems and methods which provide volume imaging by implementing survey and target imaging modes are shown. According to embodiments, a survey imaging mode is implemented to provide a volume image of a relatively large survey area. A target of interest is preferably identified within the survey area for use in a target imaging mode. Embodiments implement a target imaging mode to provide a volume image of a relatively small target area corresponding to the identified target of interest. The target imaging mode preferably adapts the beamforming, volume field of view, and / or other signal and image processing algorithms to the target area. In operation according to embodiments, the target imaging mode provides a volume image of a target area with improved volume rate and image quality.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Volumetric imaging on a radiotherapy apparatus
InactiveUS7324626B2Accurate operationSmooth rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVolumetric imagingImaging processing
Owner:BRAINLAB
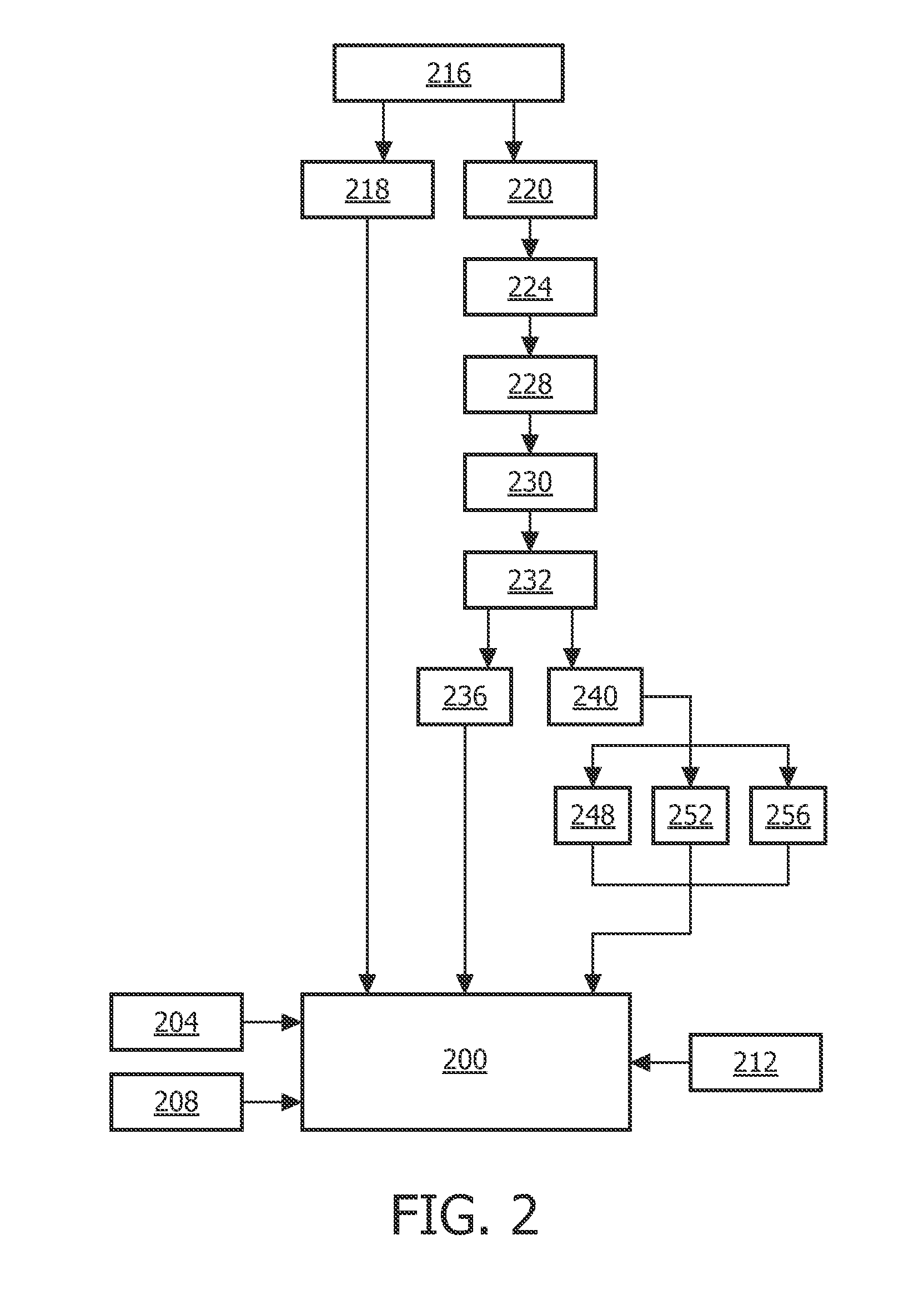
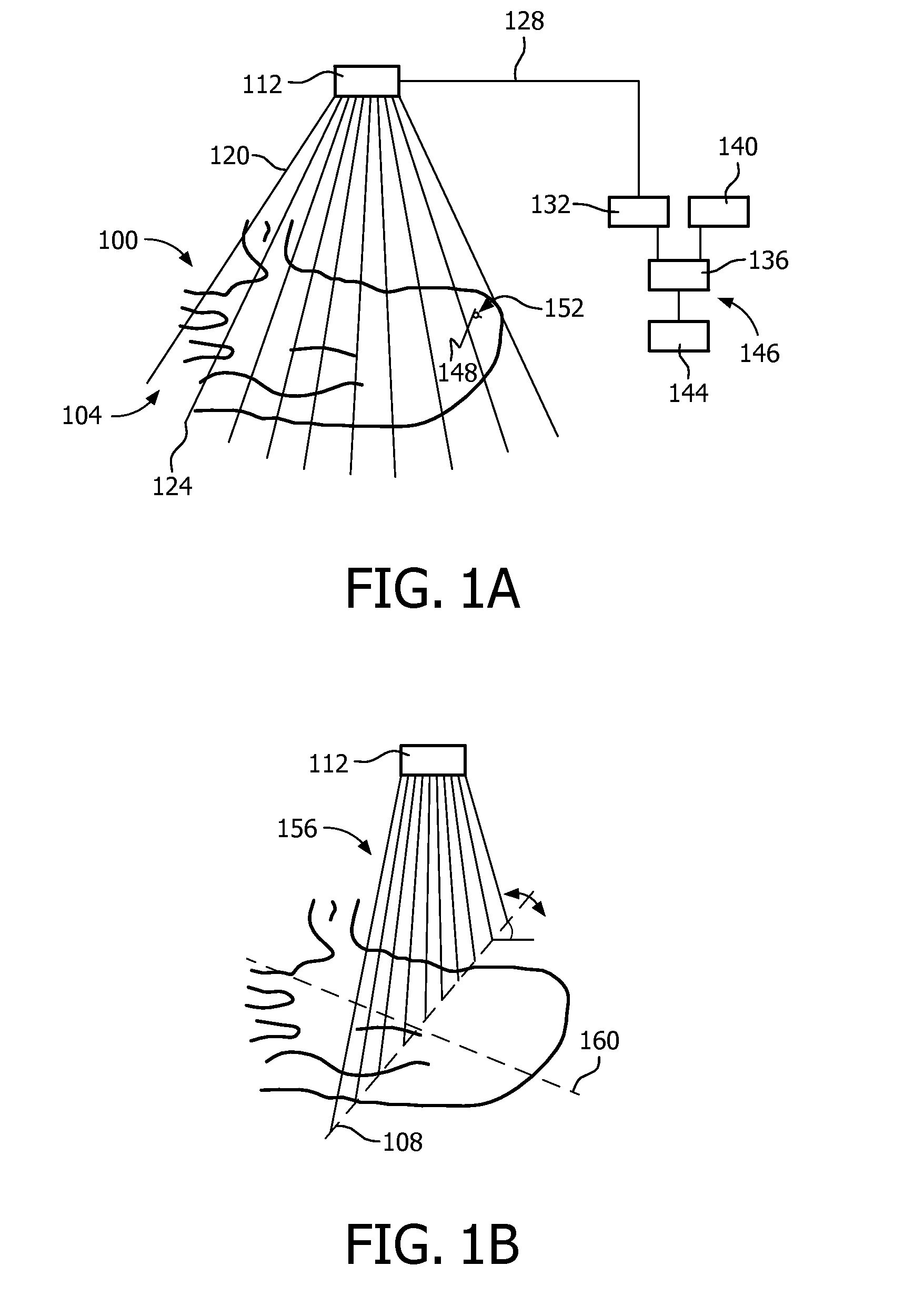
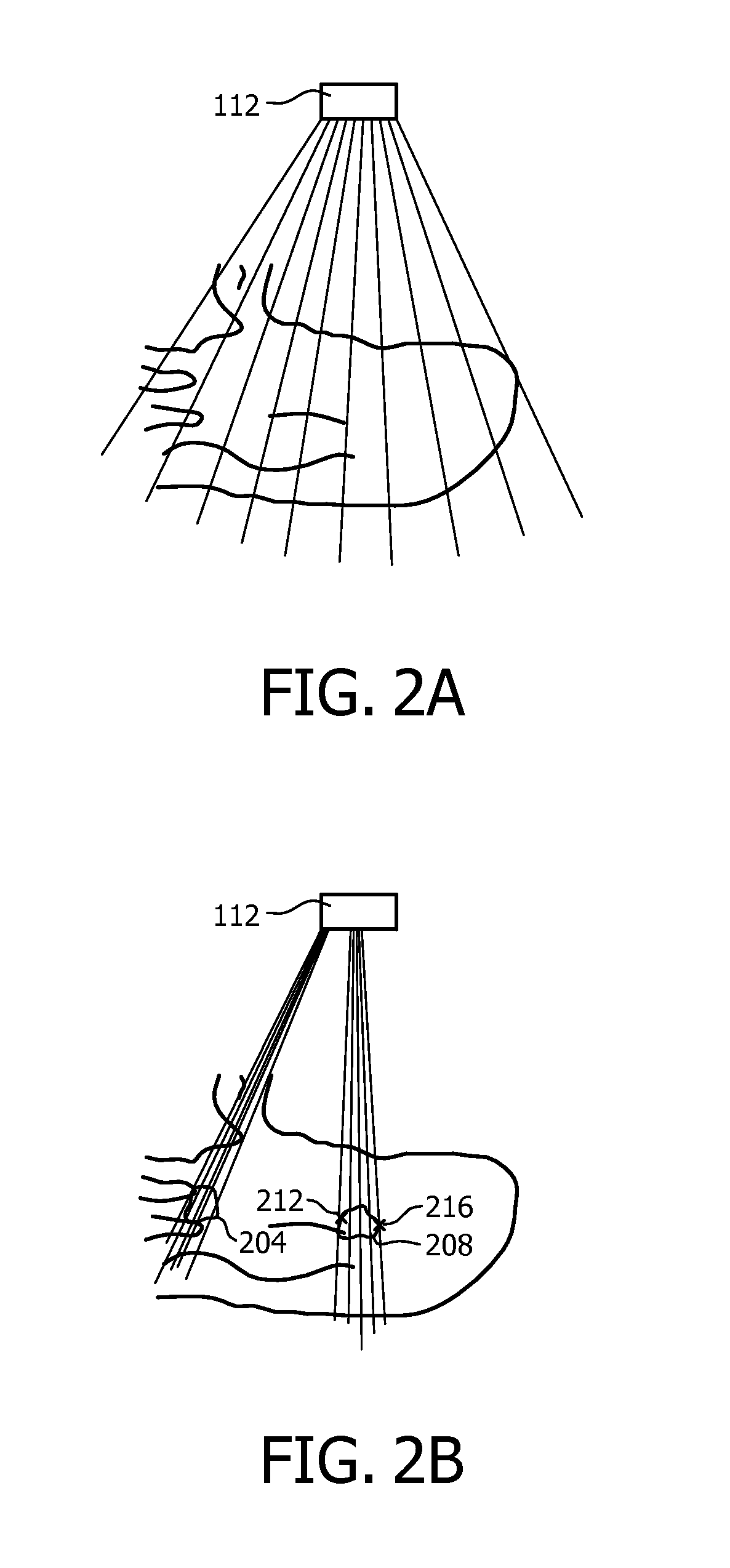
Automatic imaging plane selection for echocardiography
InactiveUS20150011886A1High resolutionRapid diagnosisWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical structuresTime response
Based on anatomy recognition from three-dimensional live imaging of a volume, one or more portions (204, 208) of the volume are selected in real time. In further real time response, live imaging or the portion(s) is performed with a beam density (156) higher than that used in the volume imaging. The one or more portion may be one or more imaging plane selected for optimal orientation in making an anatomical measurement (424) or display. The recognition can be based on an anatomical model, such as a cardiac mesh model. The model may be pre-encoded with information that can be associated with image locations to provide the basis for portion selection, and for placement of indicia (416, 420, 432, 436) displayable for initiating measurement within an image provided by the live portion imaging. A single TEE or TTE imaging probe (112) may be used throughout. On request, periodically or based on detected motion of the probe with respect to the anatomy, the whole process can be re-executed, starting back from volume acquisition (S508).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com