Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "High-speed imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
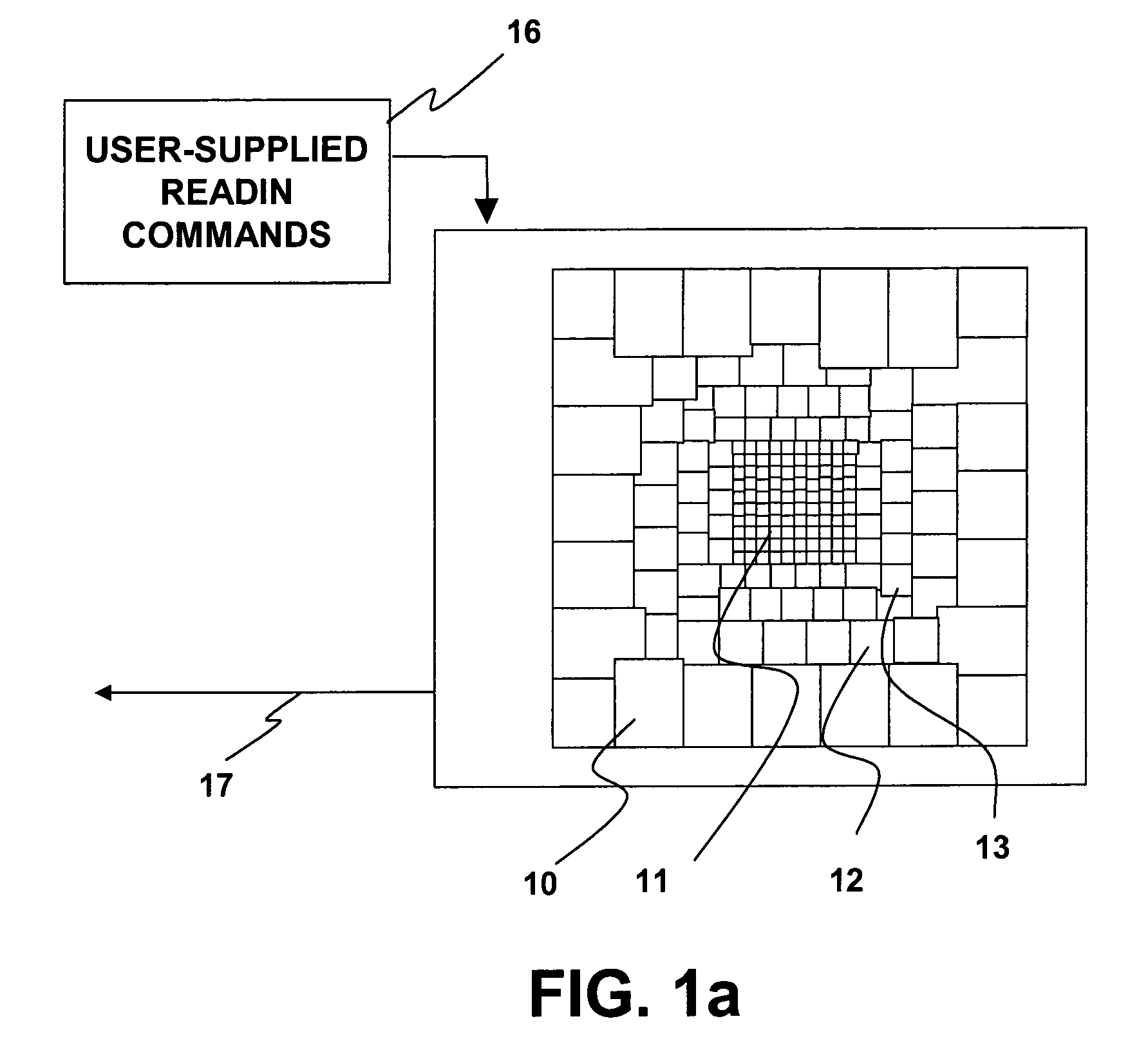
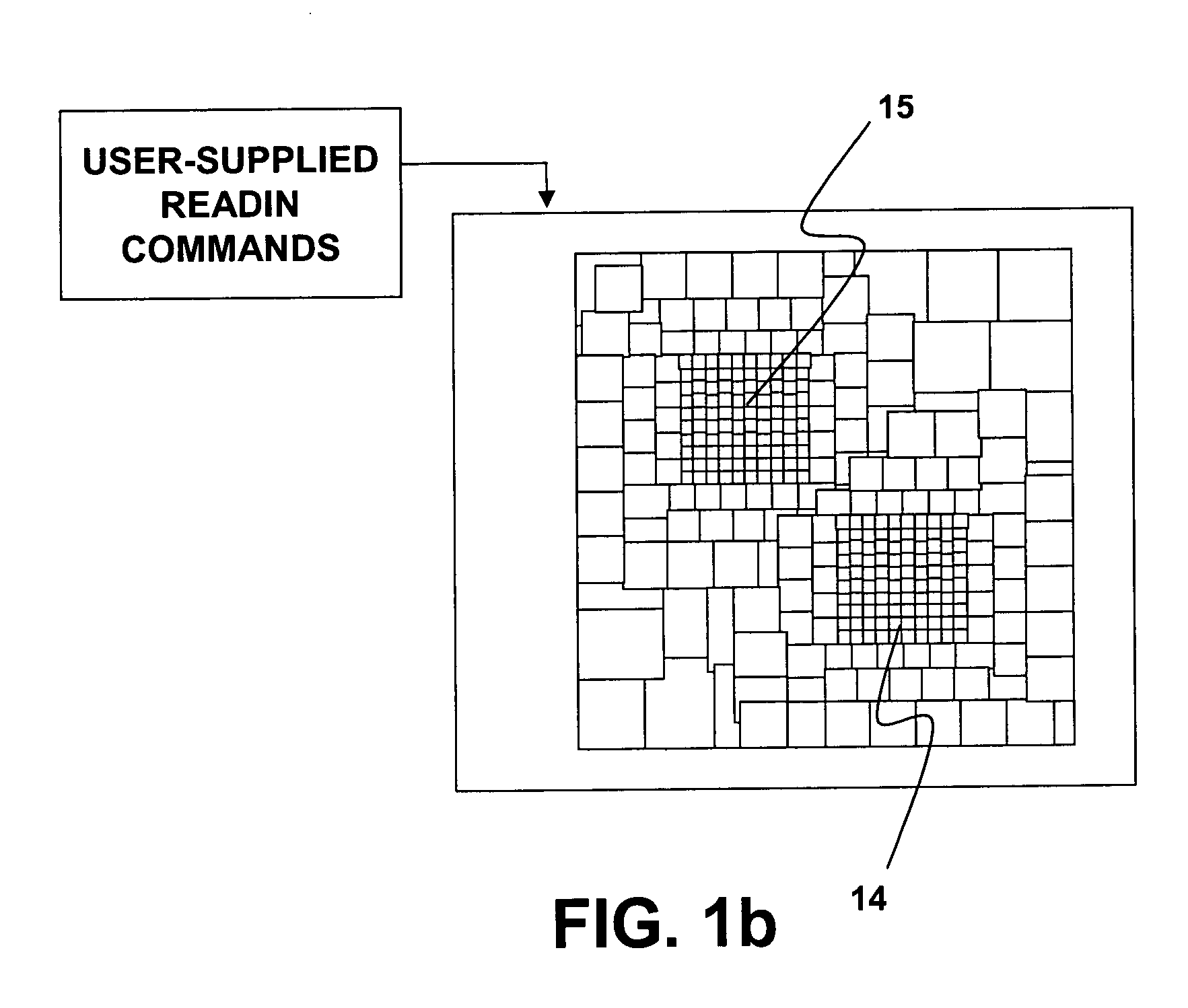
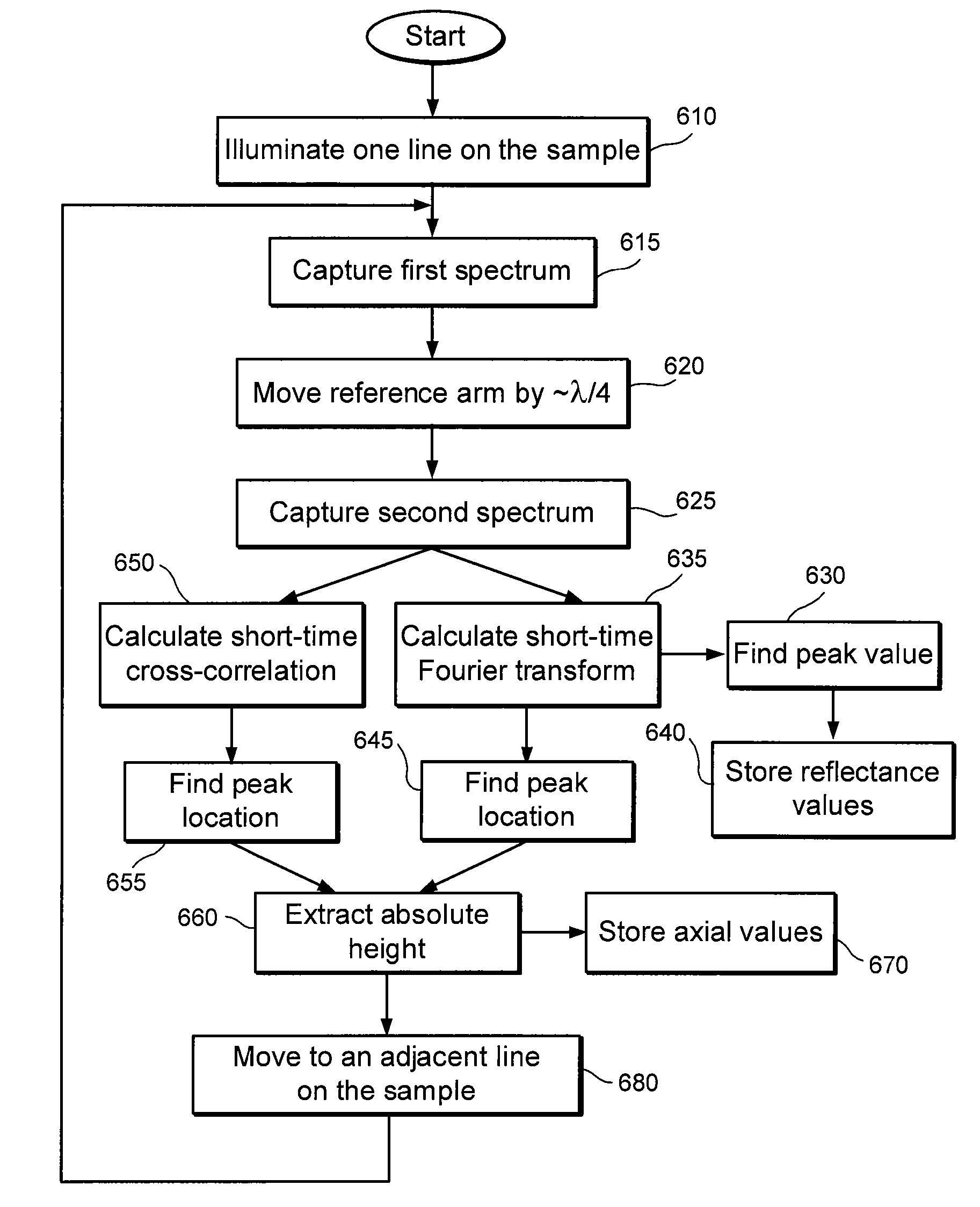
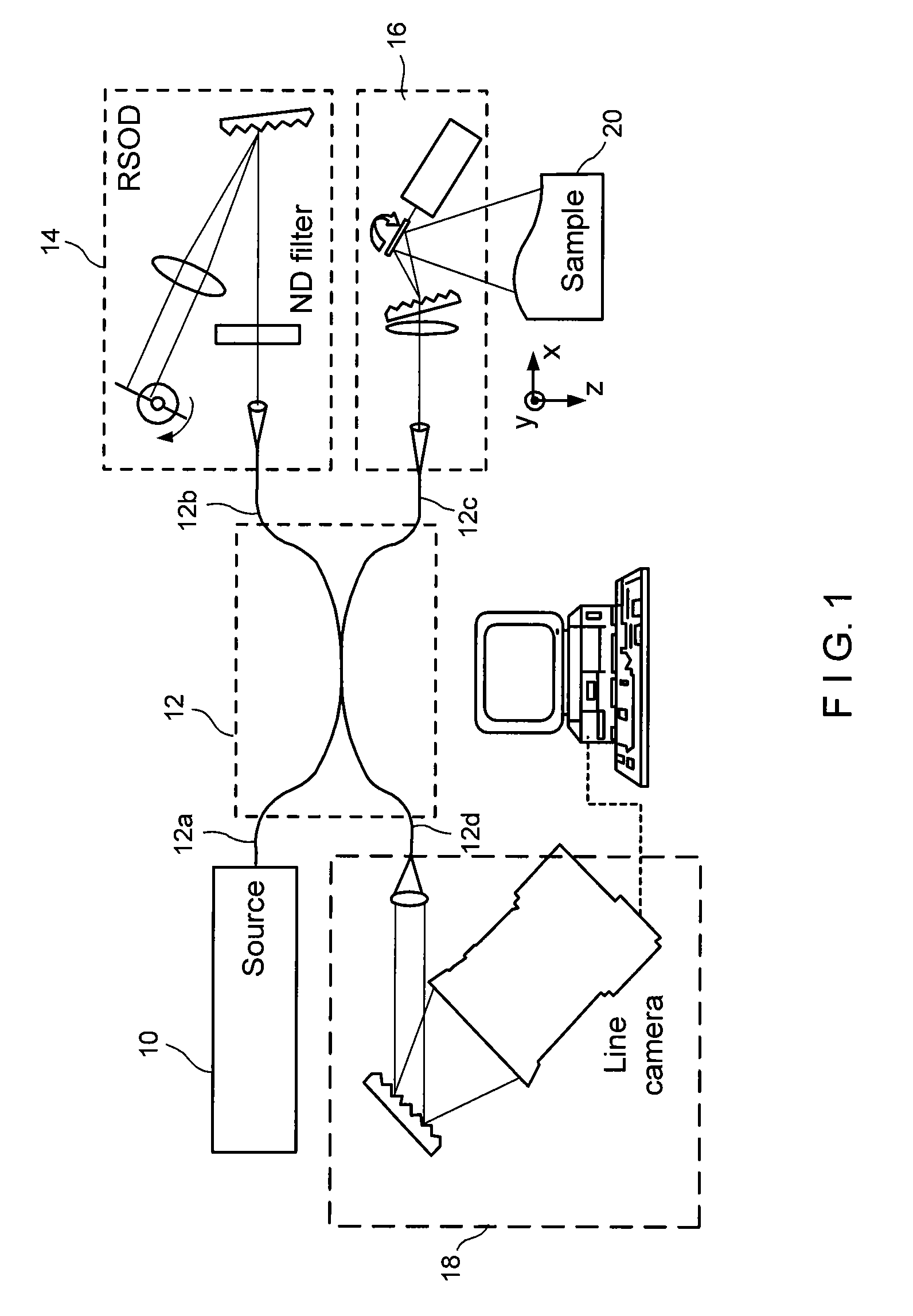
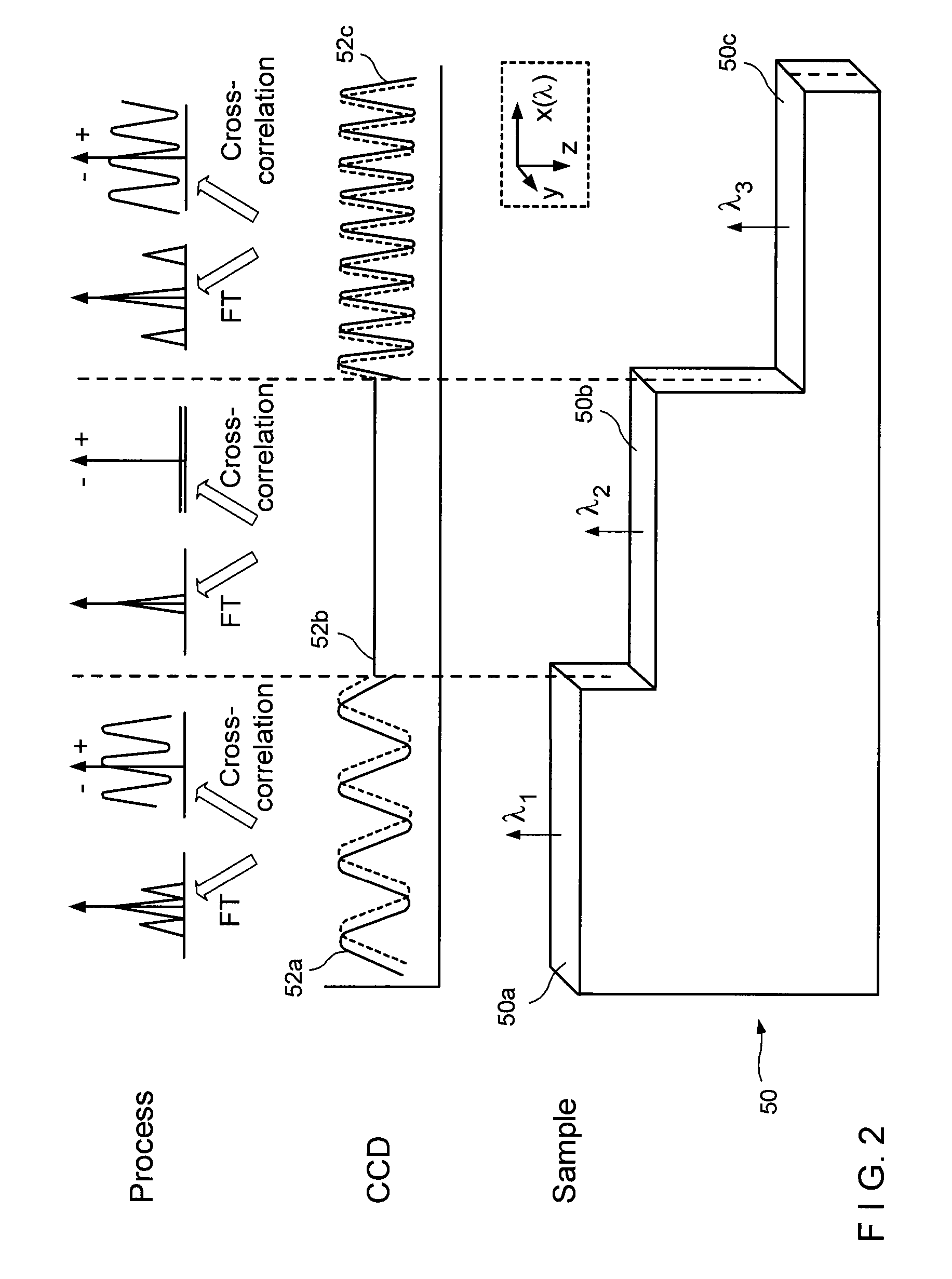
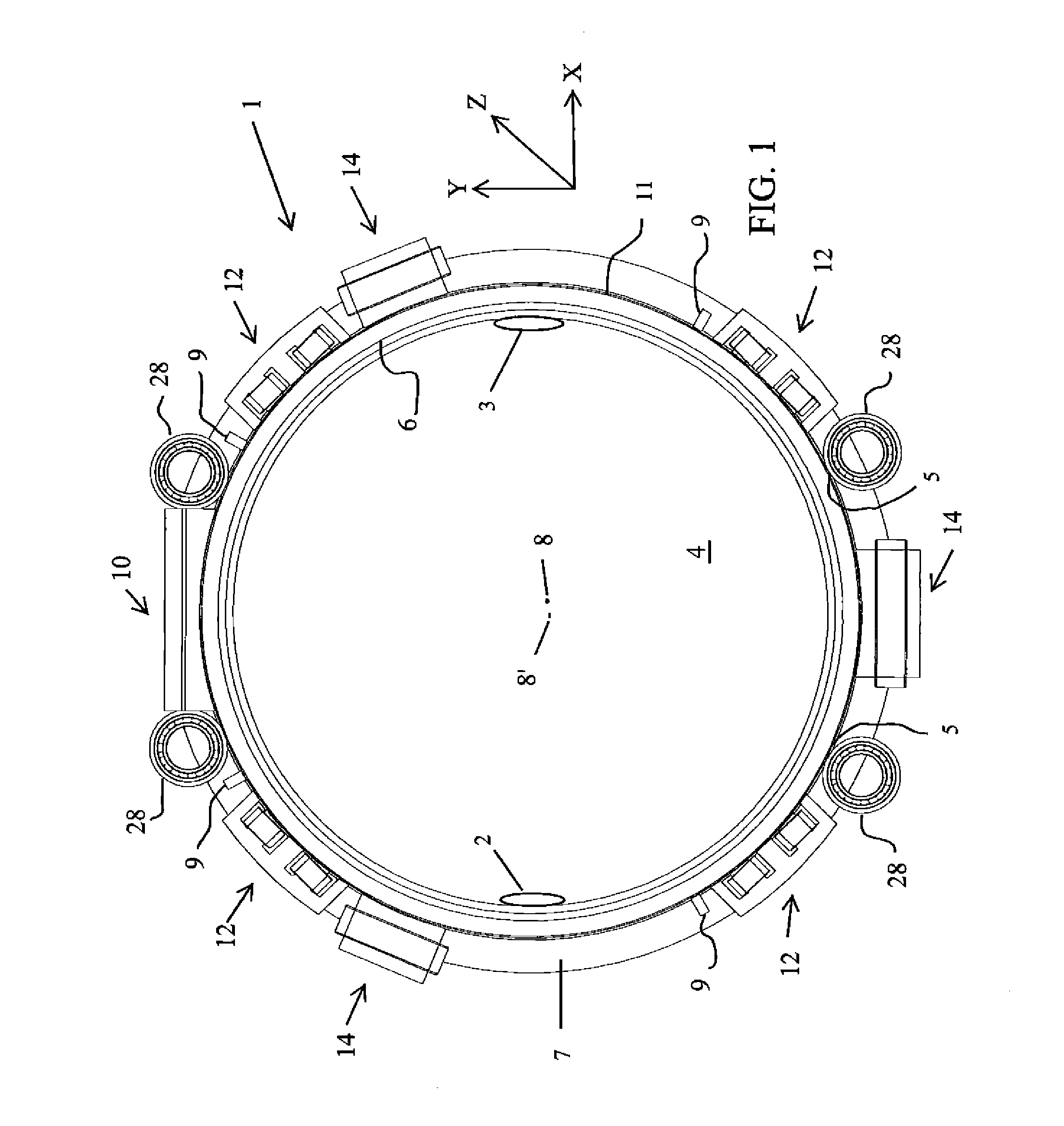
Dental Optical Coherence Tomograph
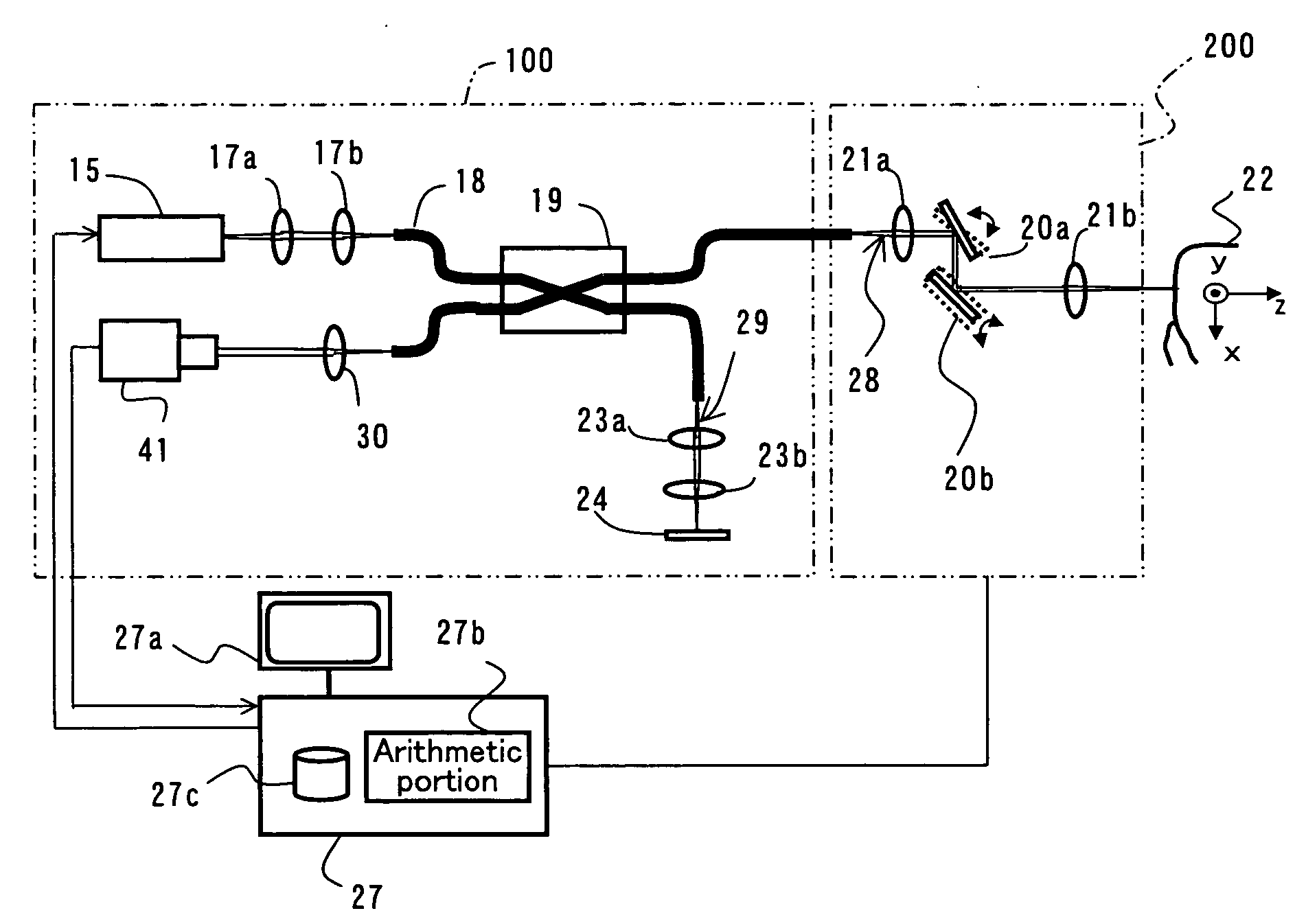
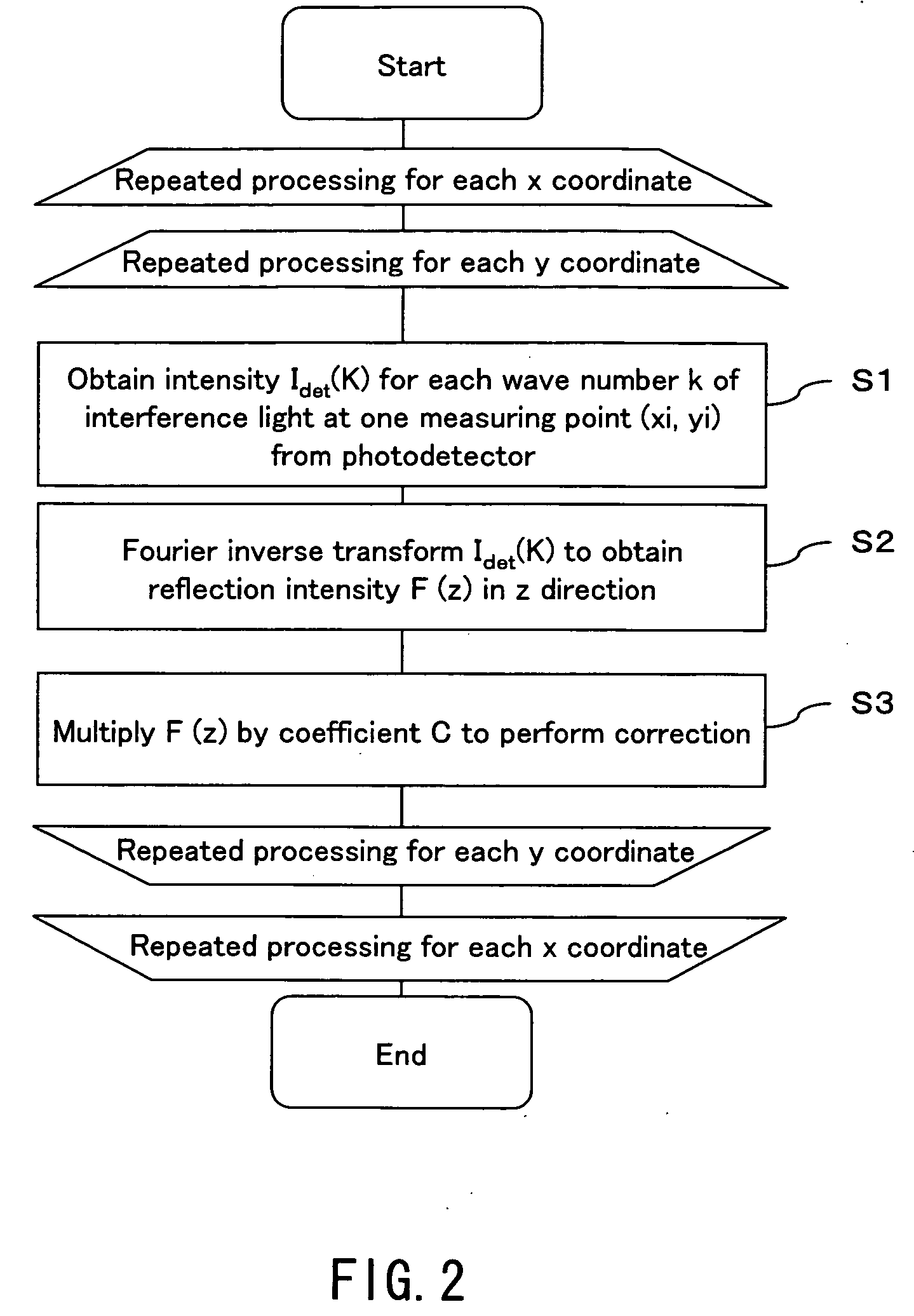
InactiveUS20090079993A1Simple structureHigh imagingInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological bodyFourier transform on finite groups
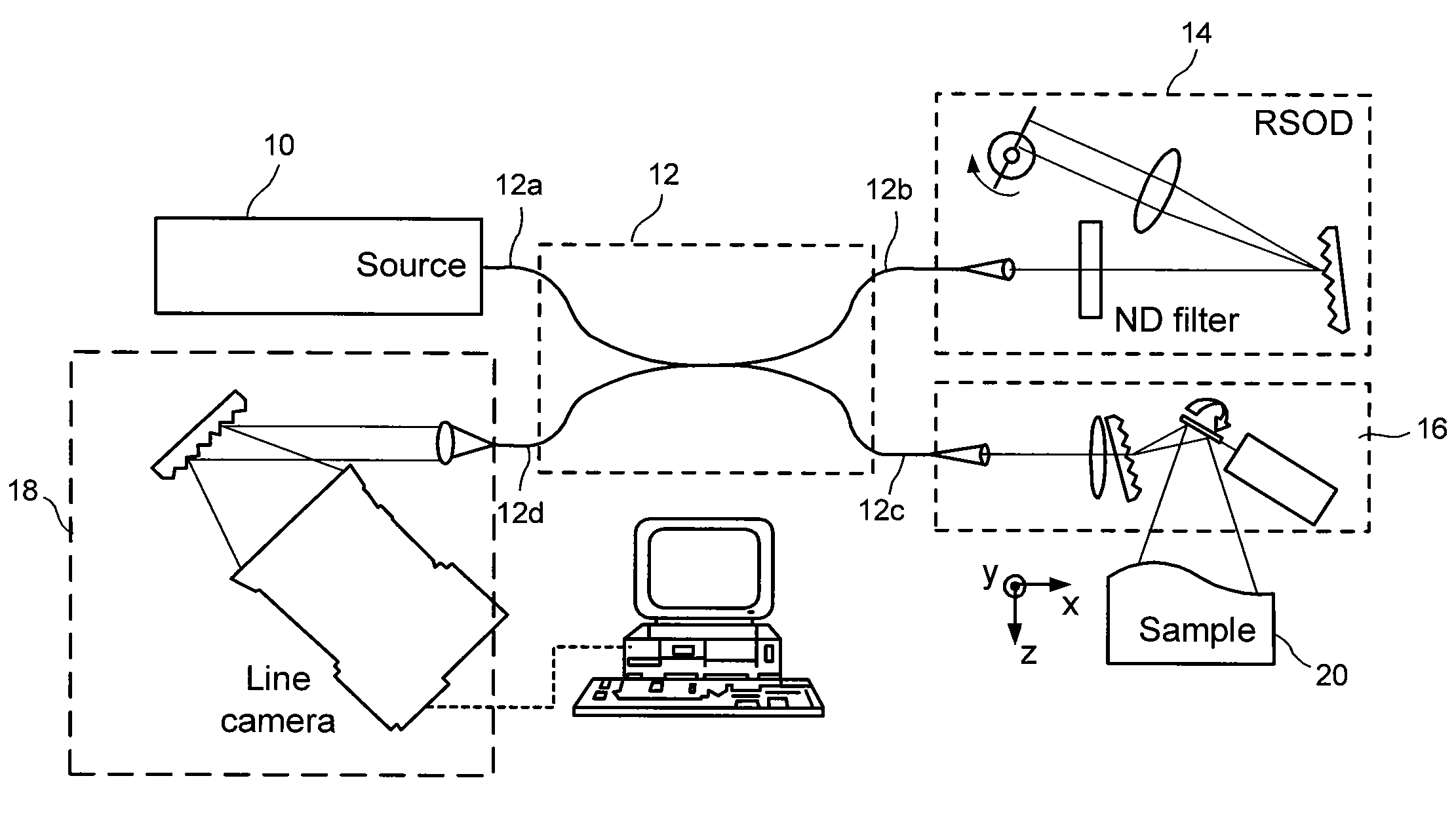
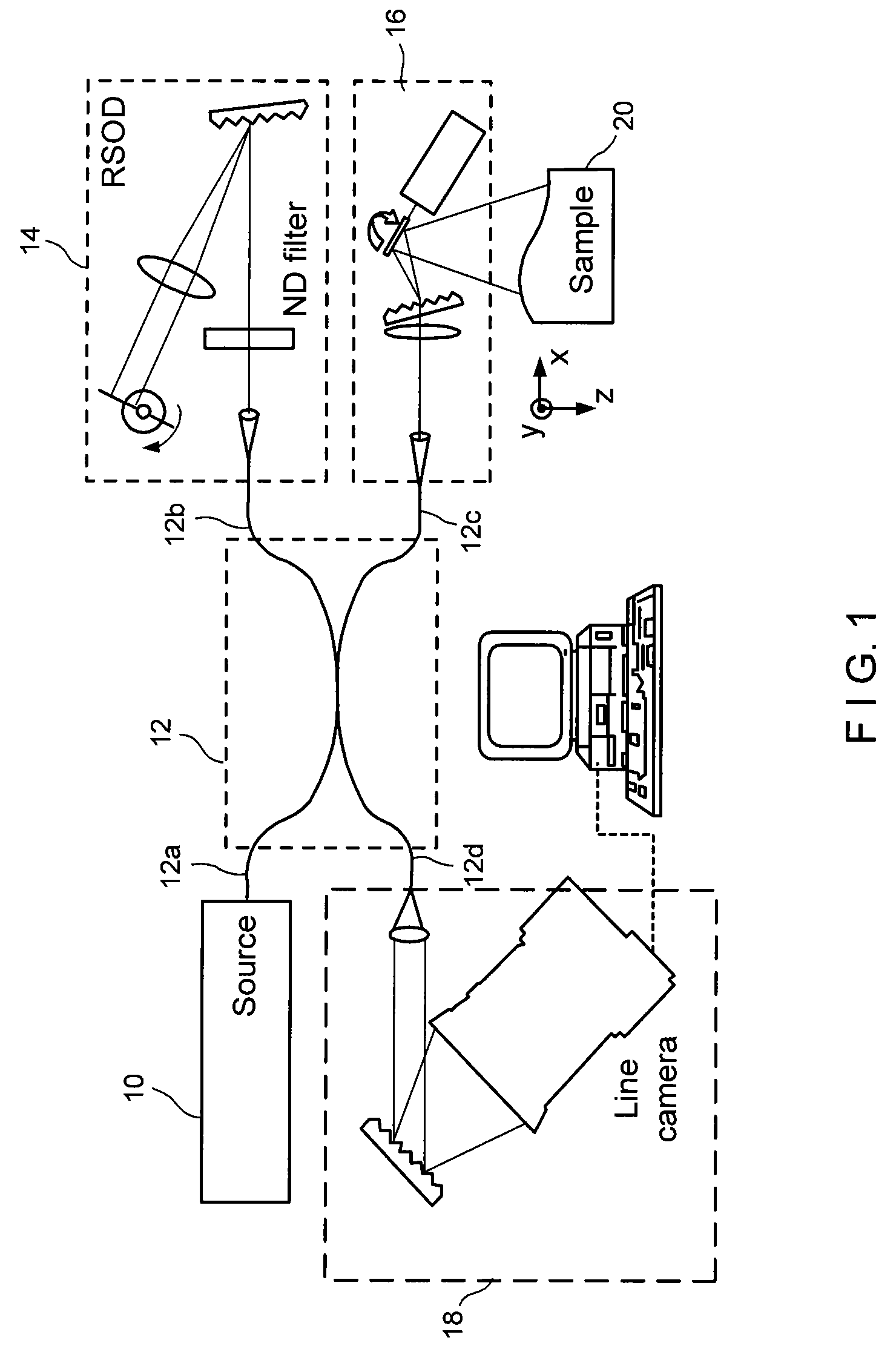
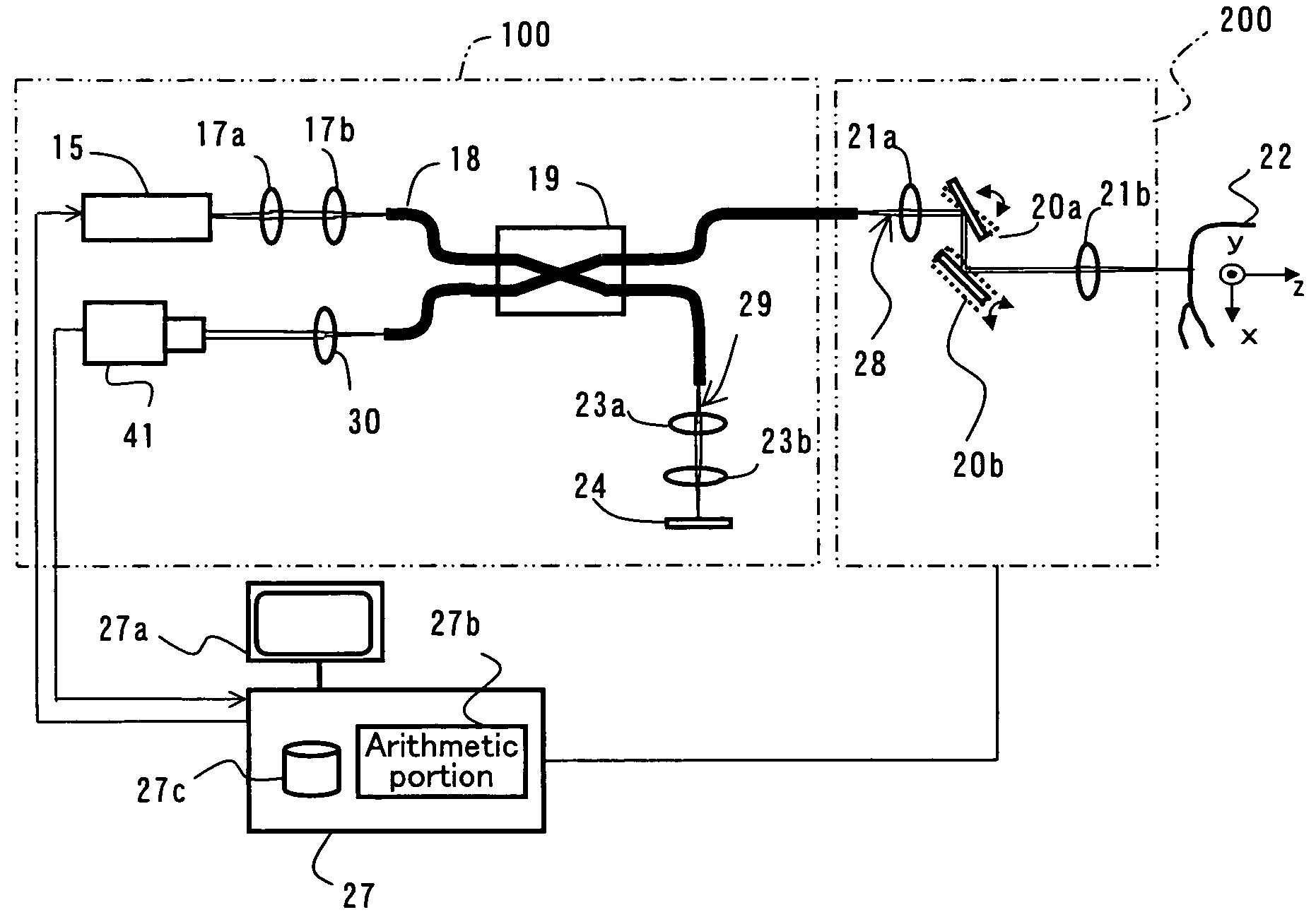
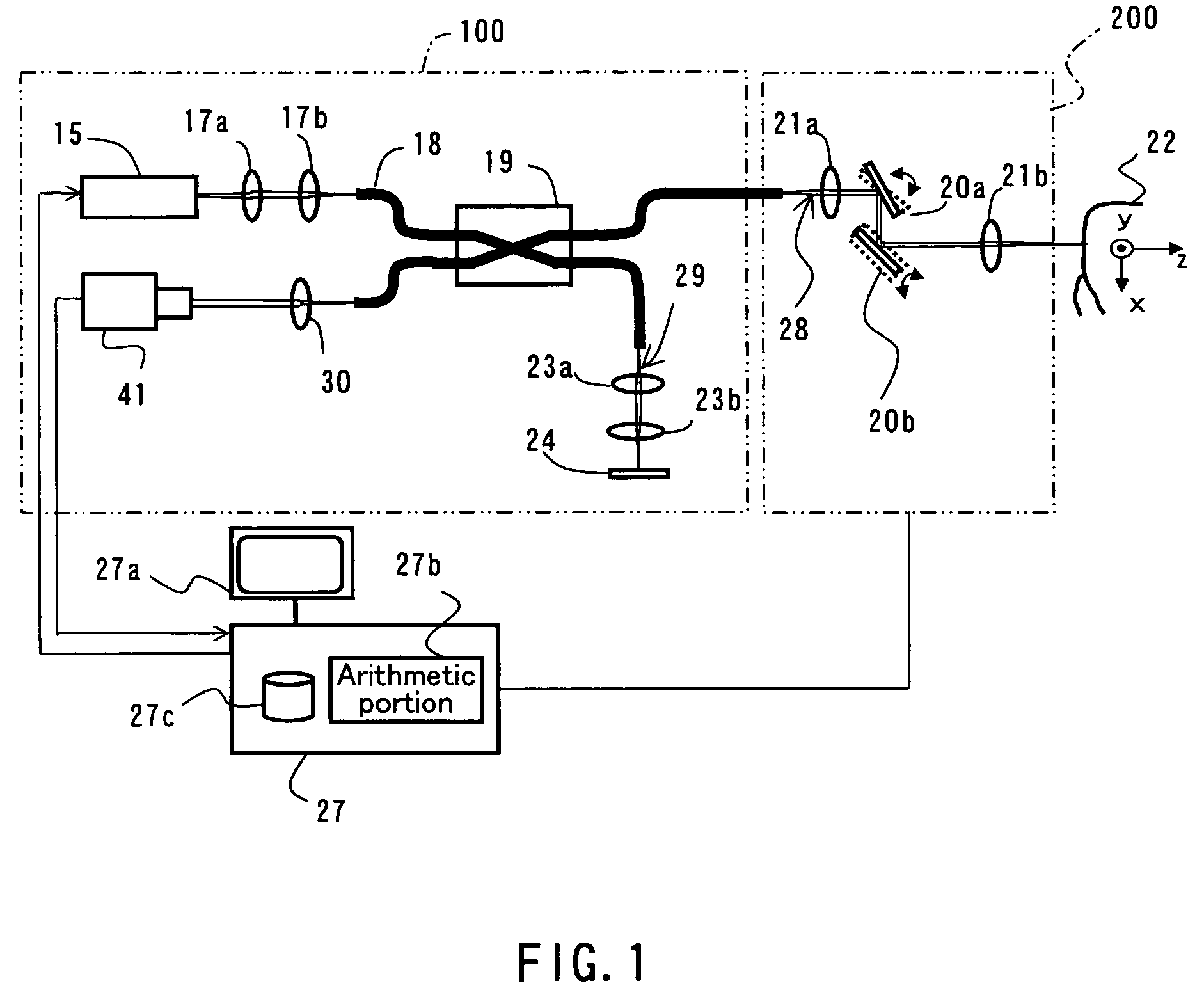
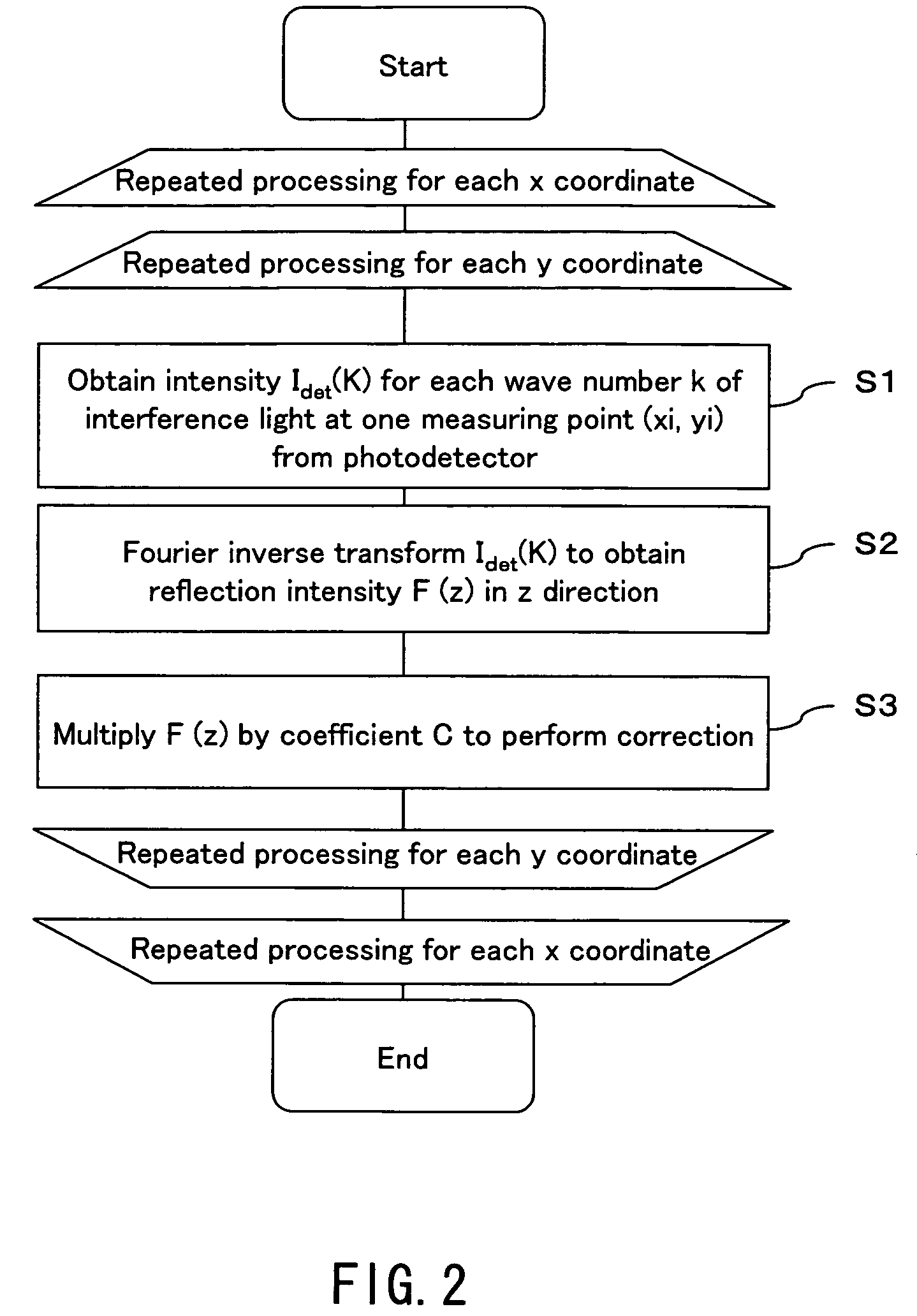
A dental optical coherence tomography apparatus for measuring tissue in a stomatognathic region of a living body or an artificial composition in the stomatognathic region as a measured object includes: a variable wavelength light source (15); a light splitting portion (19) that splits light-source light emitted from the variable wavelength light source (15) into reference light (29) and measuring light (28); an interference portion (19) that causes the measuring light (28) and the reference light (29) to interfere with each other, thereby generating interference light; a photodetection portion (41) that measures the interference light; and an arithmetic portion (27b) that generates an image of a measured object (22) by Fourier transforming or inverse Fourier transforming the intensity of the interference light, whose wavelength changes with time, that has been detected by the photodetection portion for each of the wavelengths. Accordingly, an optical coherence tomography apparatus applicable to dental measurement can be provided.
Owner:SHOFU INC
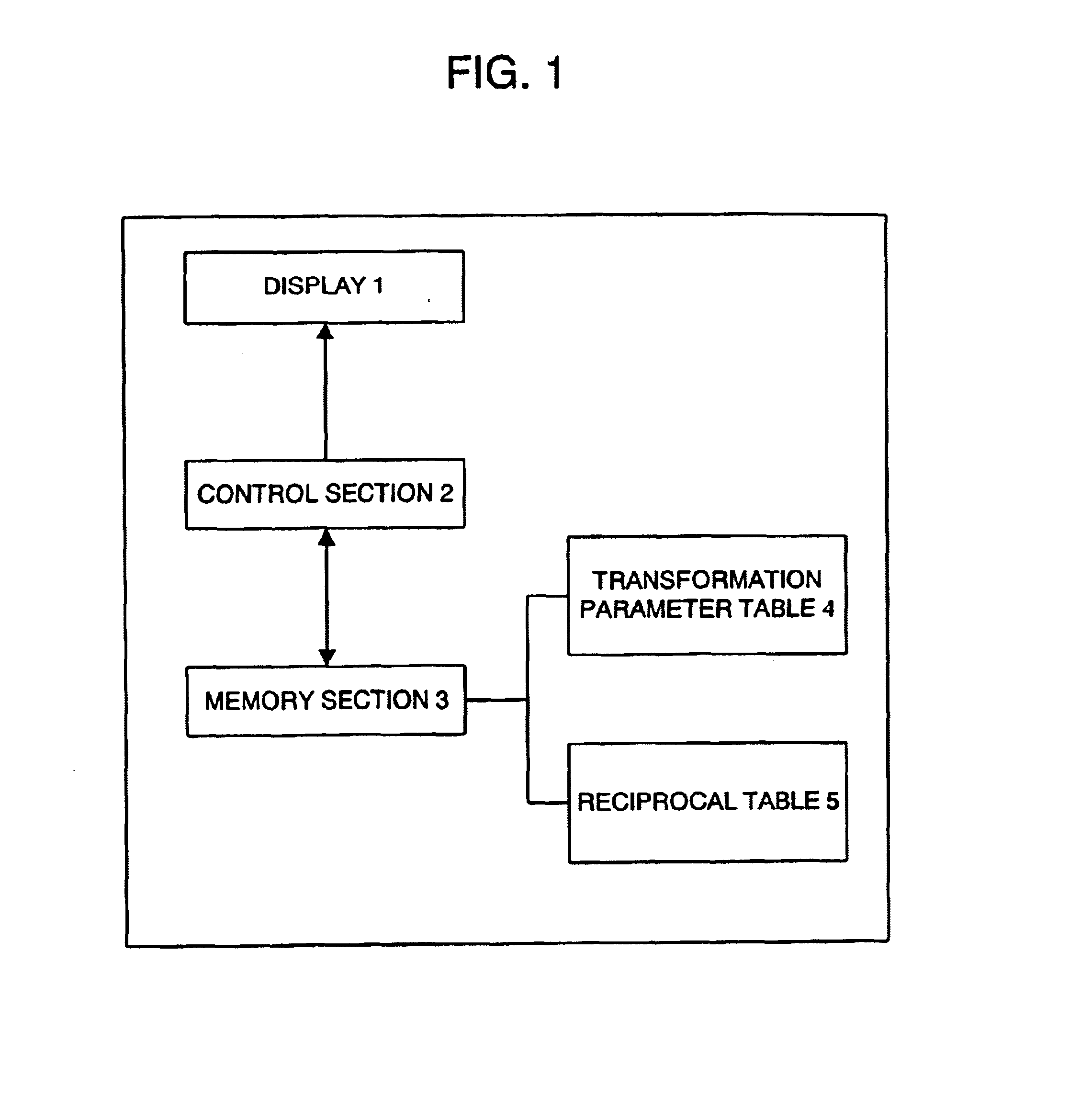
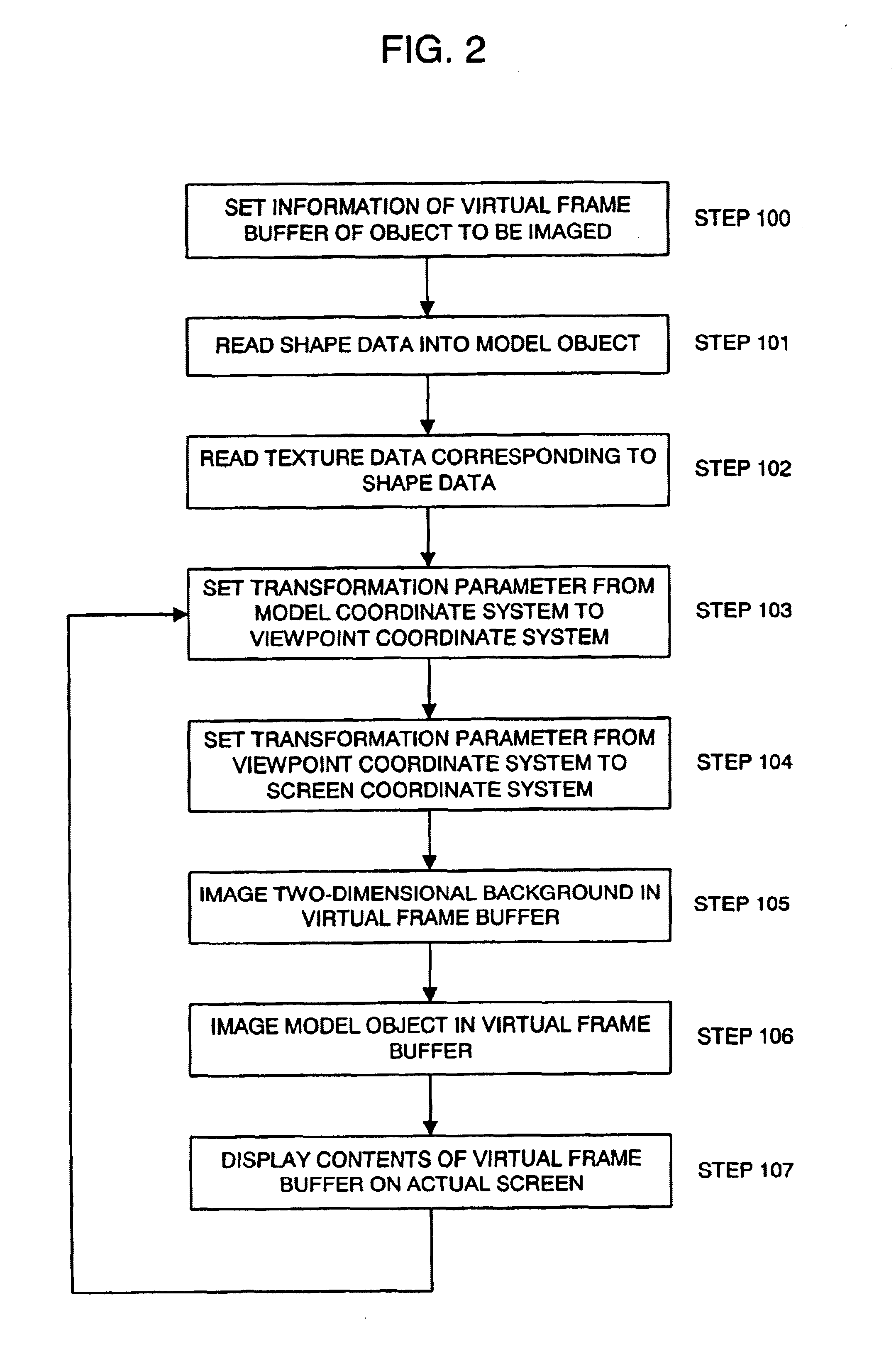
Information processing apparatus
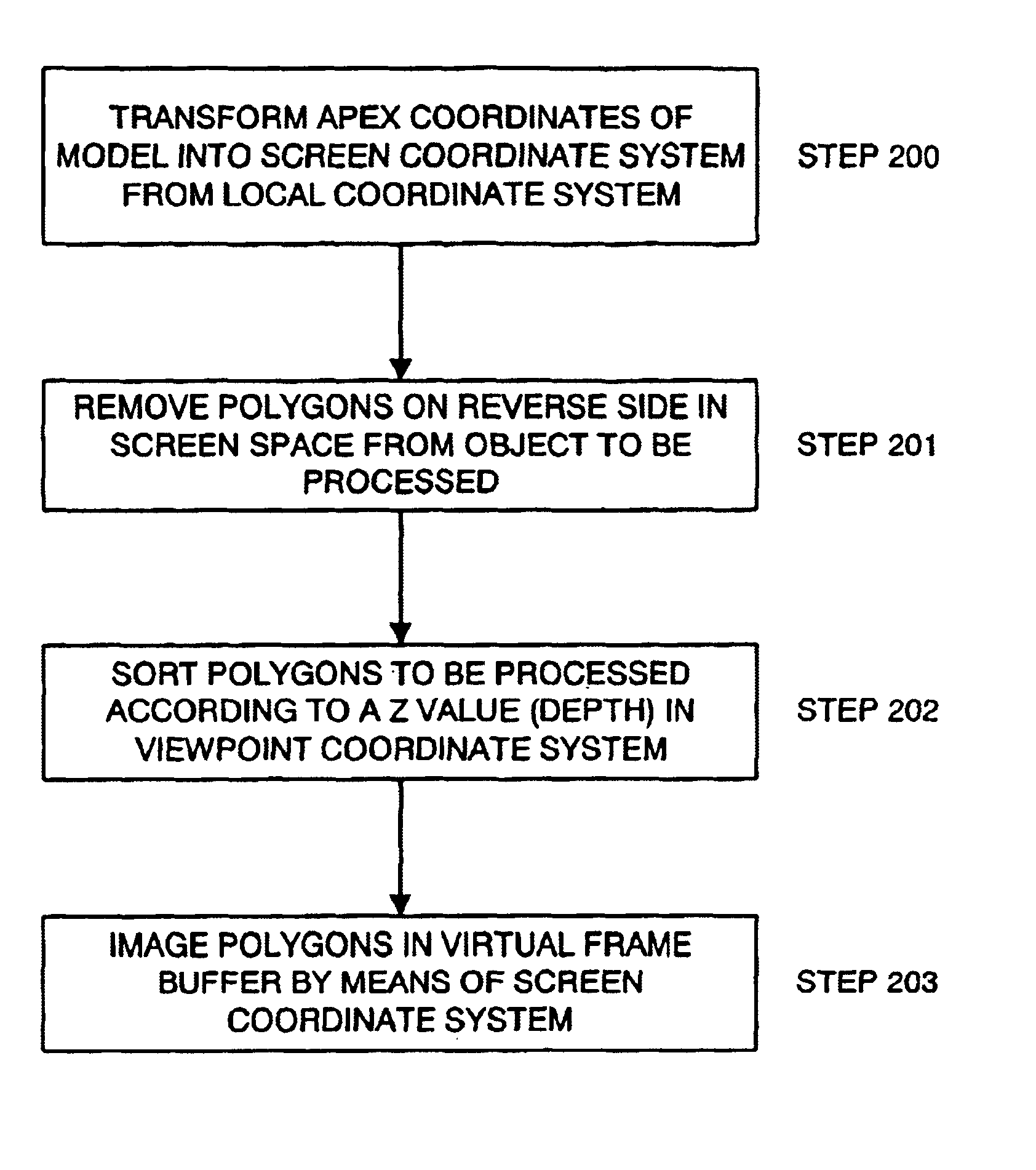
InactiveUS6970178B2Increase speedReduce capacityGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInformation processingSoftware engineering
In an information processing apparatus for conducting an affine transformation representative of (x′y′z′)=A(xyz)+(t1t2t3),a matrix A′=(a11′a12′a13′a21′a22′a23′a31′a32′a33′)=λ A=(λ a11λ a12λ a13λ a21λ a22λ a23λ a31λ a32λ a33)obtained by multiplying a matrix A for the affine transformation by λ(≠0) is stored in a memory section in advance. In case of conducting calculation processing for transforming coordinates (x,y,z)t into coordinates (x′,y′,z′)t by means of the affine transformation, A′ and a matrix (t1,t2,t3)t are read from the memory section,x′=(a′11*x+a′12*y+a′13*z) / λ+t1;y′=(a′21*x+a′22*y+a′23*z) / λ+t2;z′=(a′31*x+a′32*y+a′33*z) / λ+t3;are calculated, and the coordinates (x′,y′,z′)t are obtained.
Owner:HI CORP (JP)
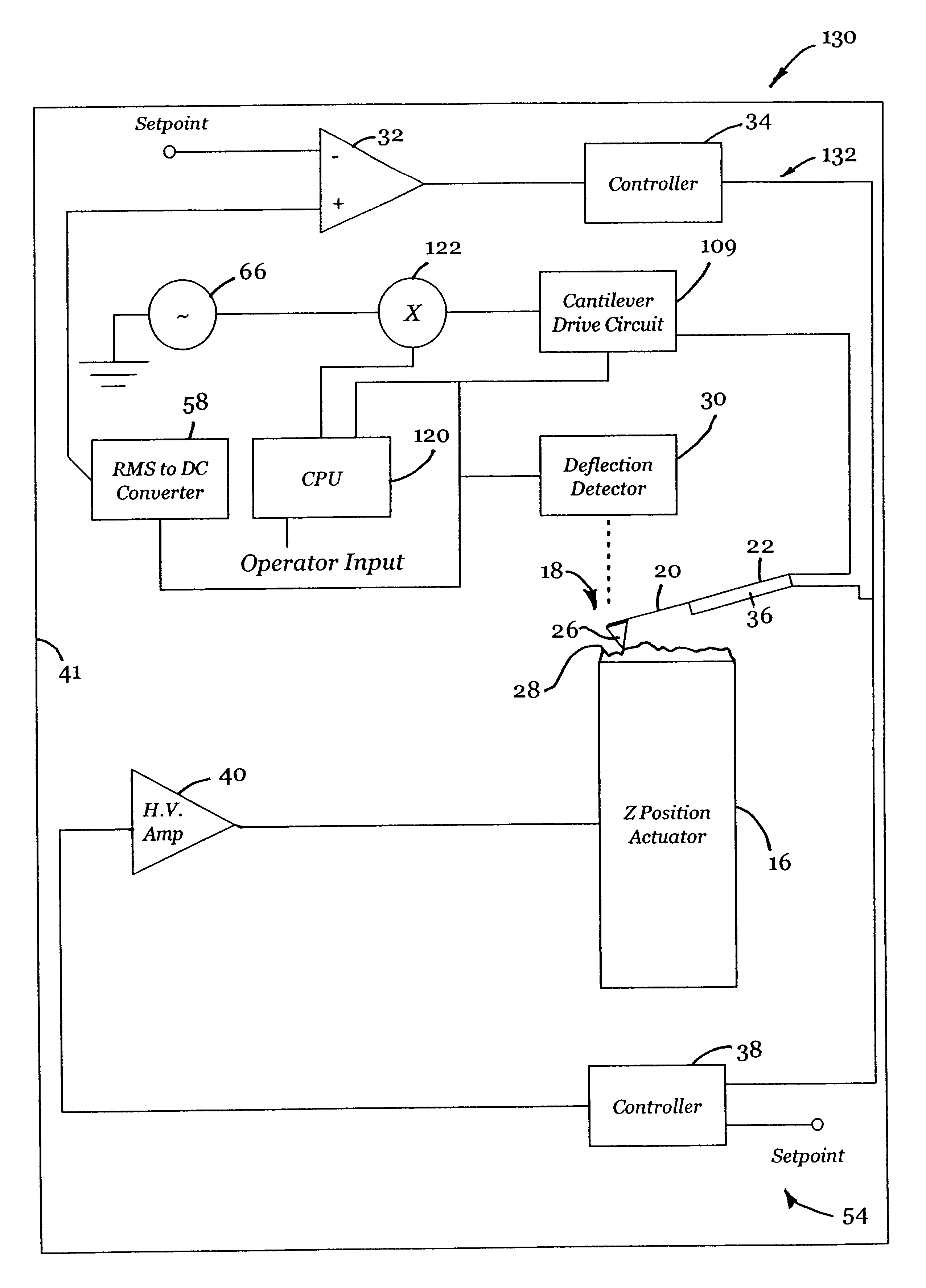
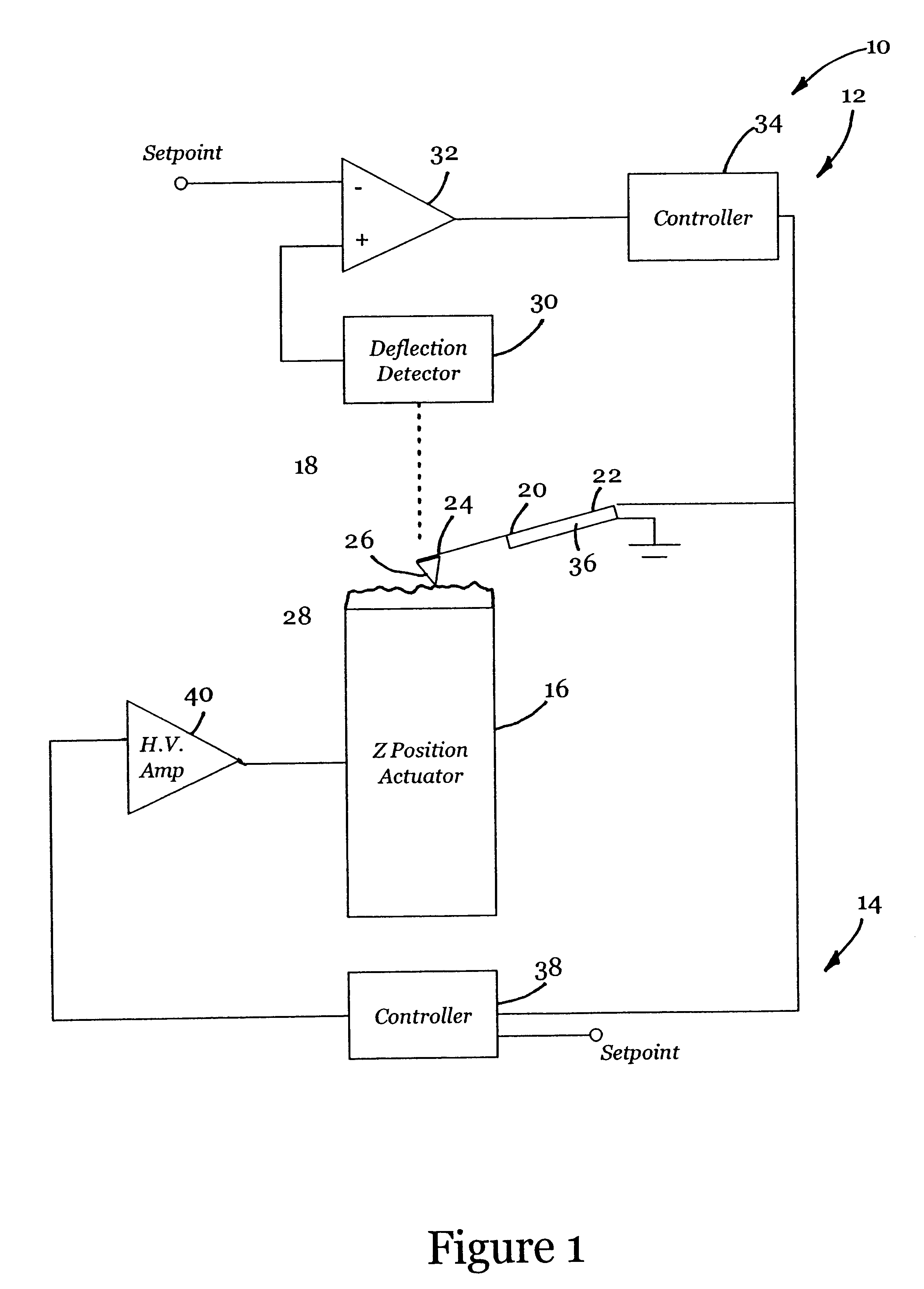
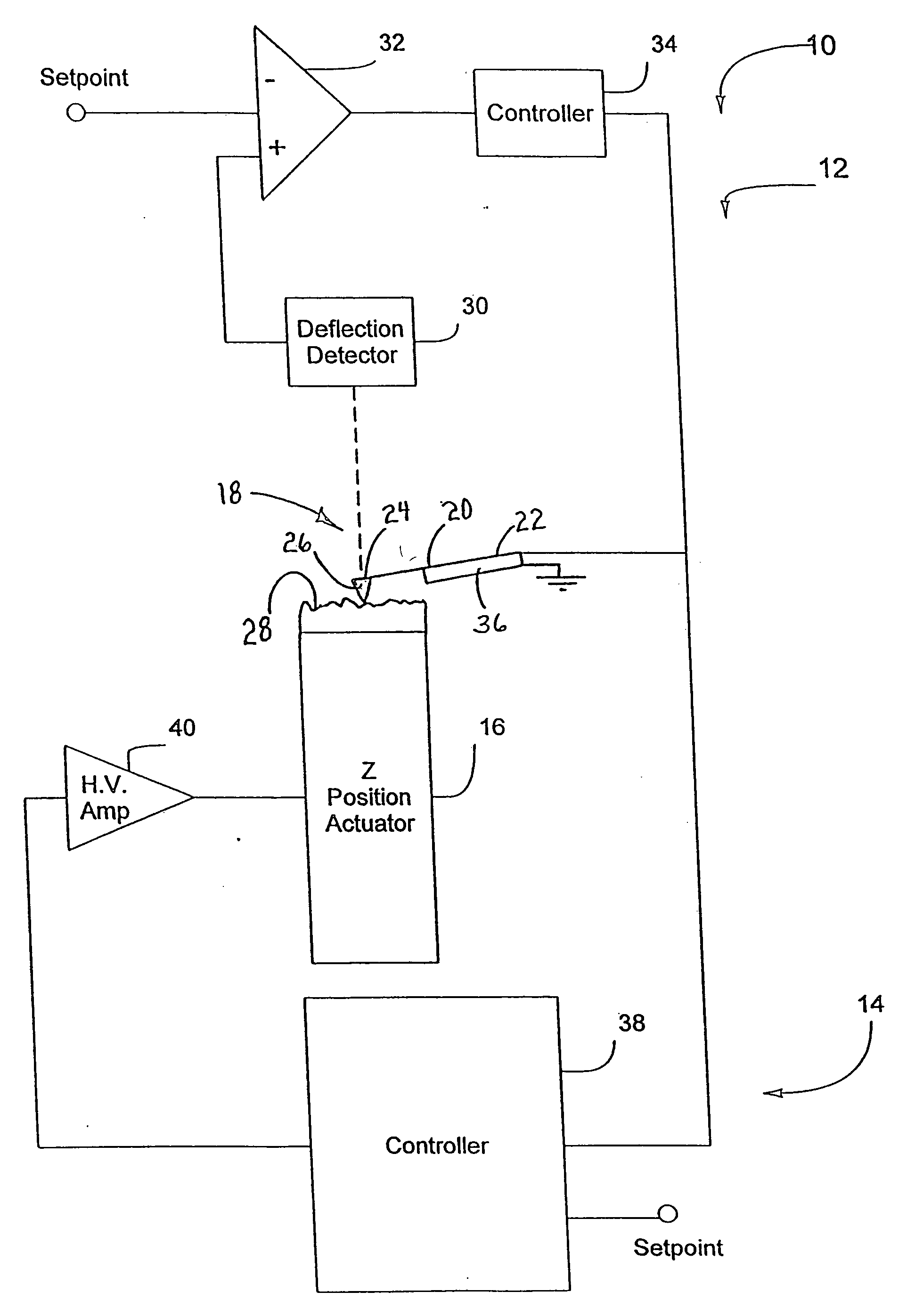
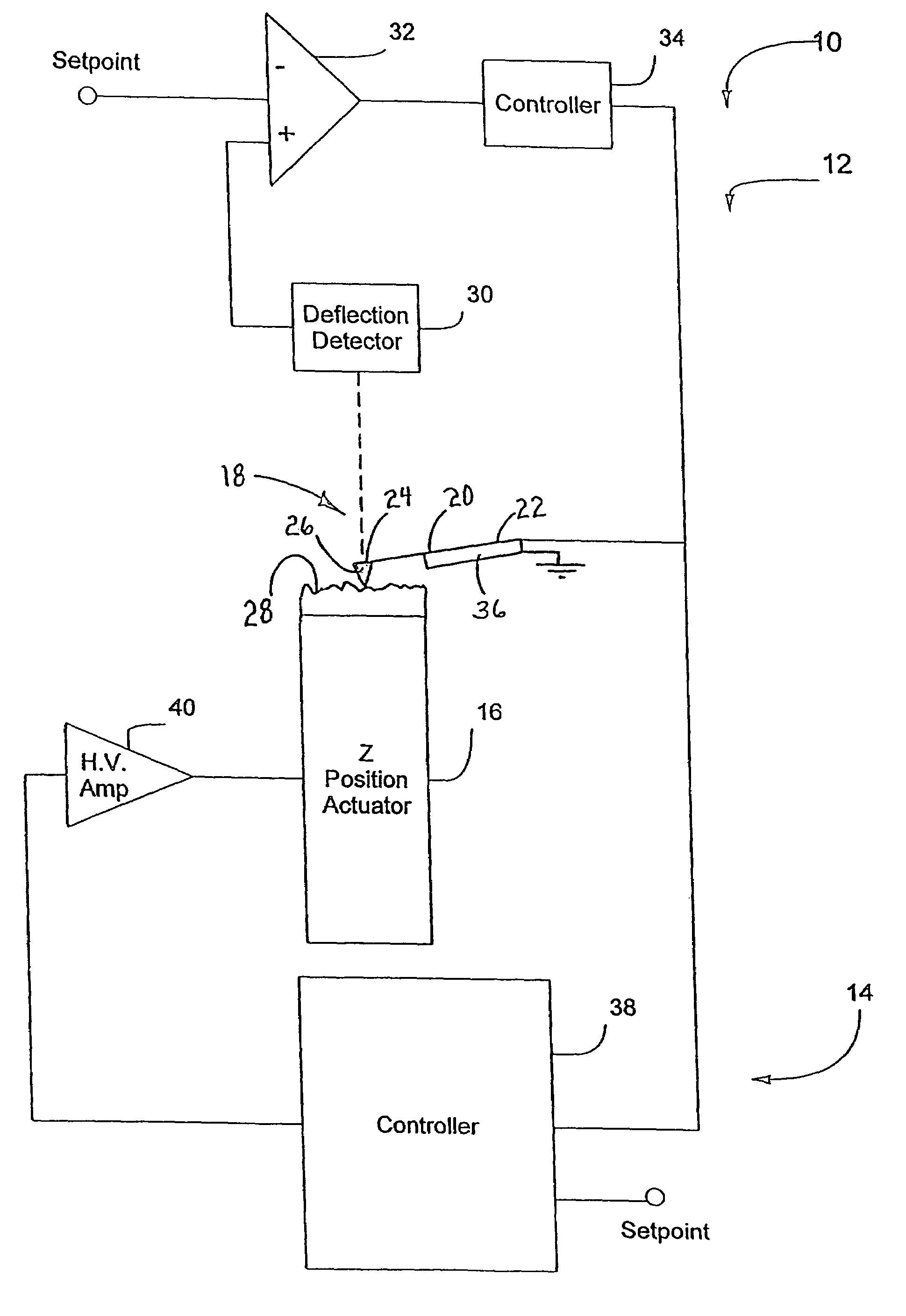
Active probe for an atomic force microscope and method of use thereof
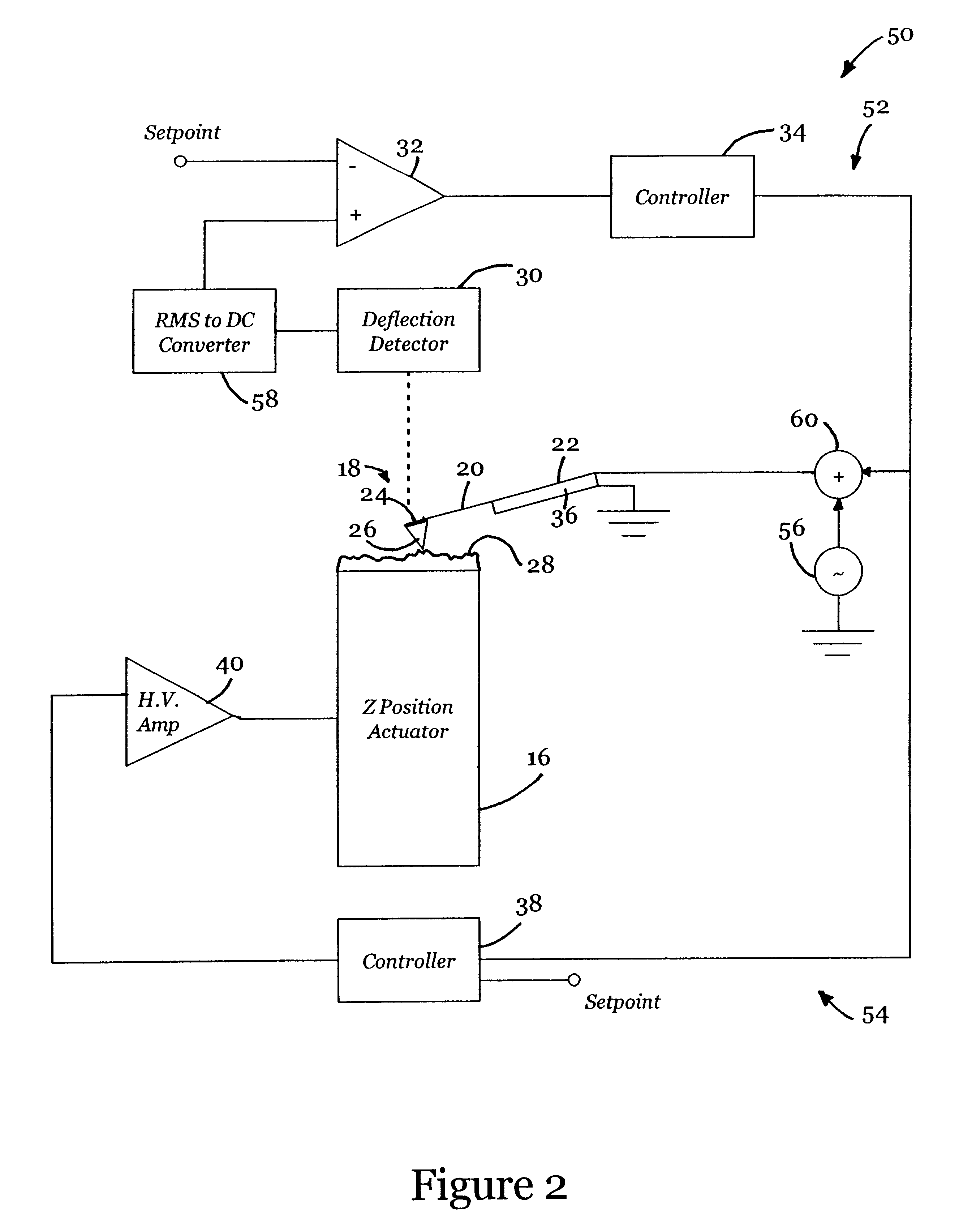
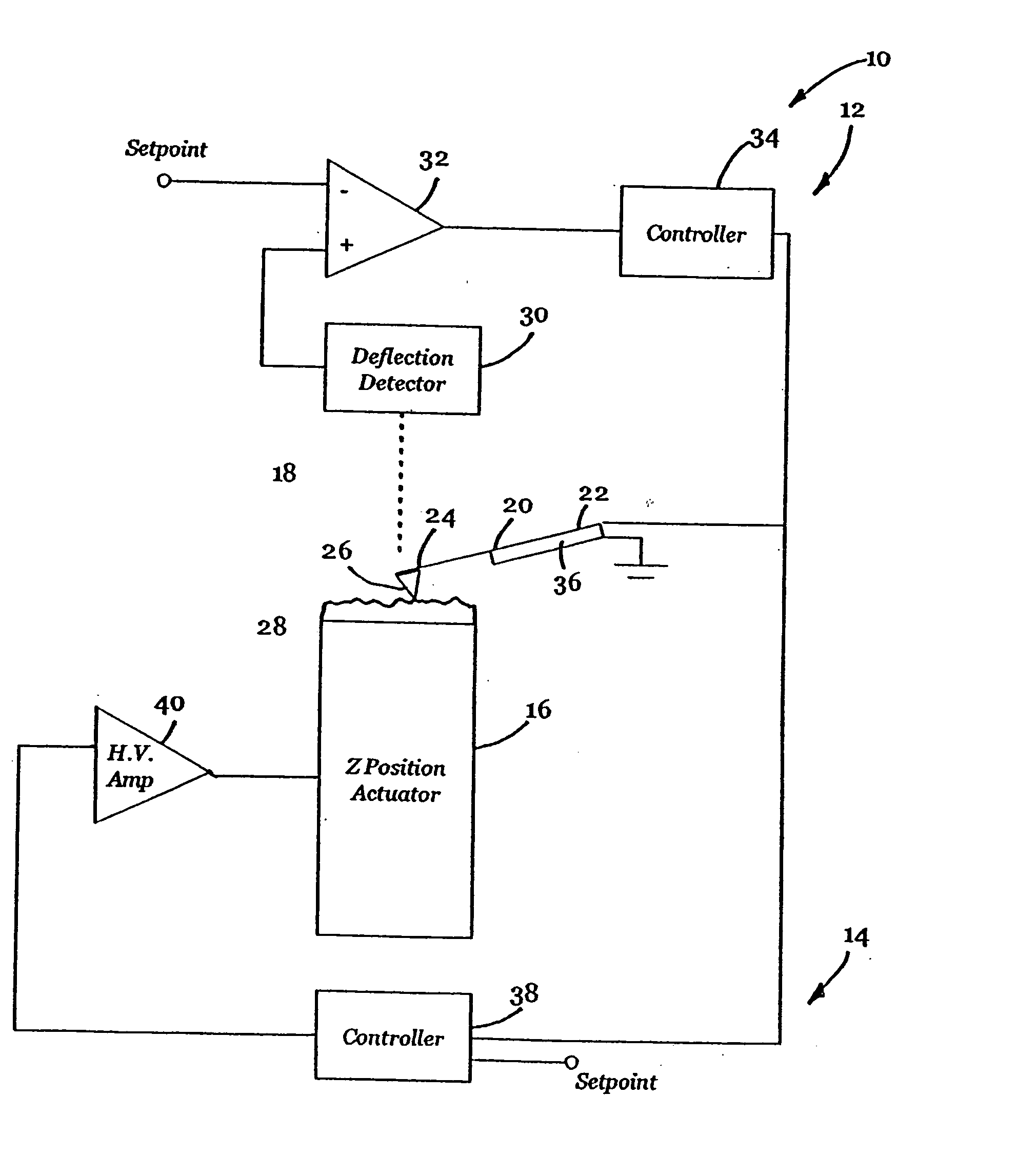
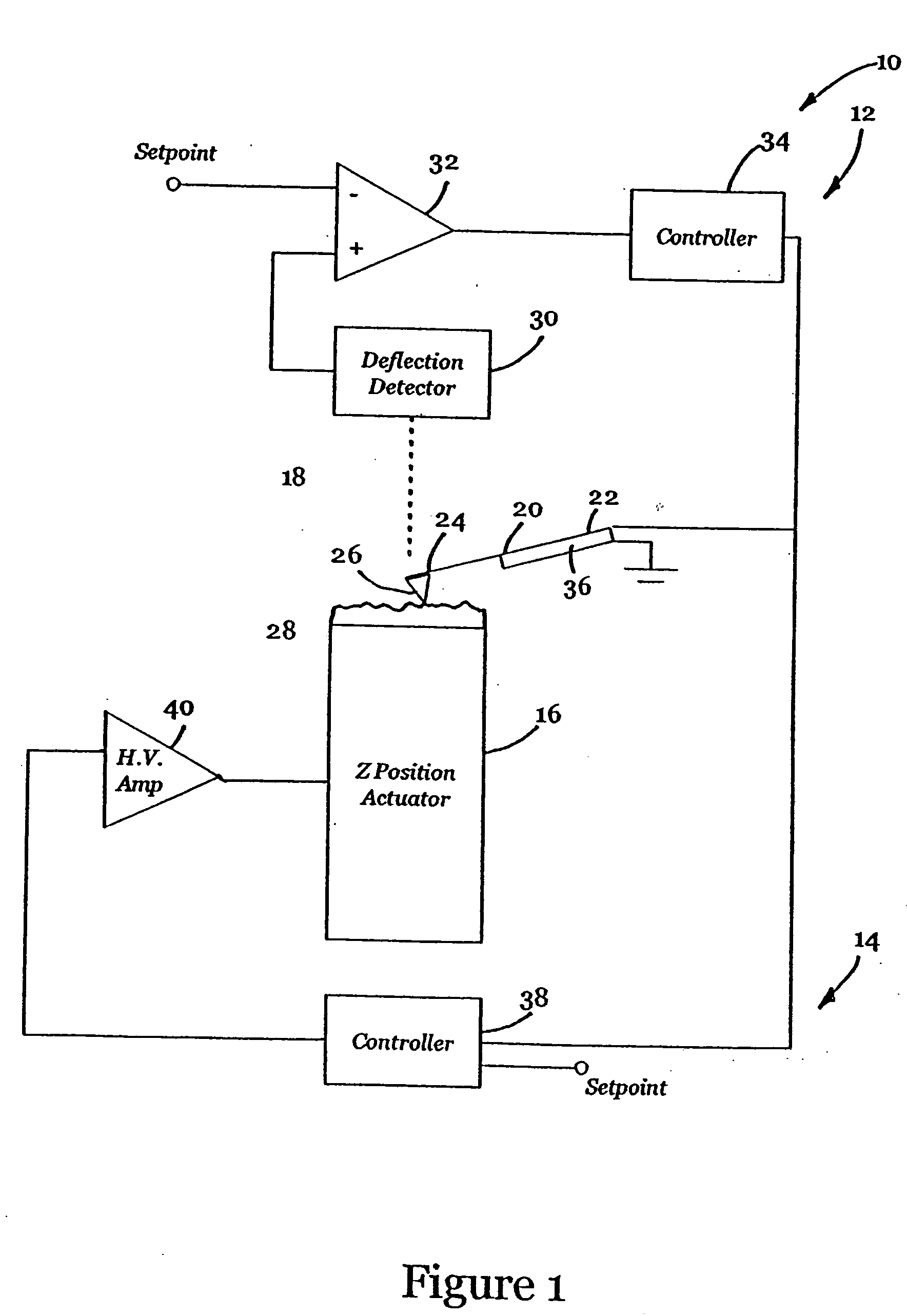
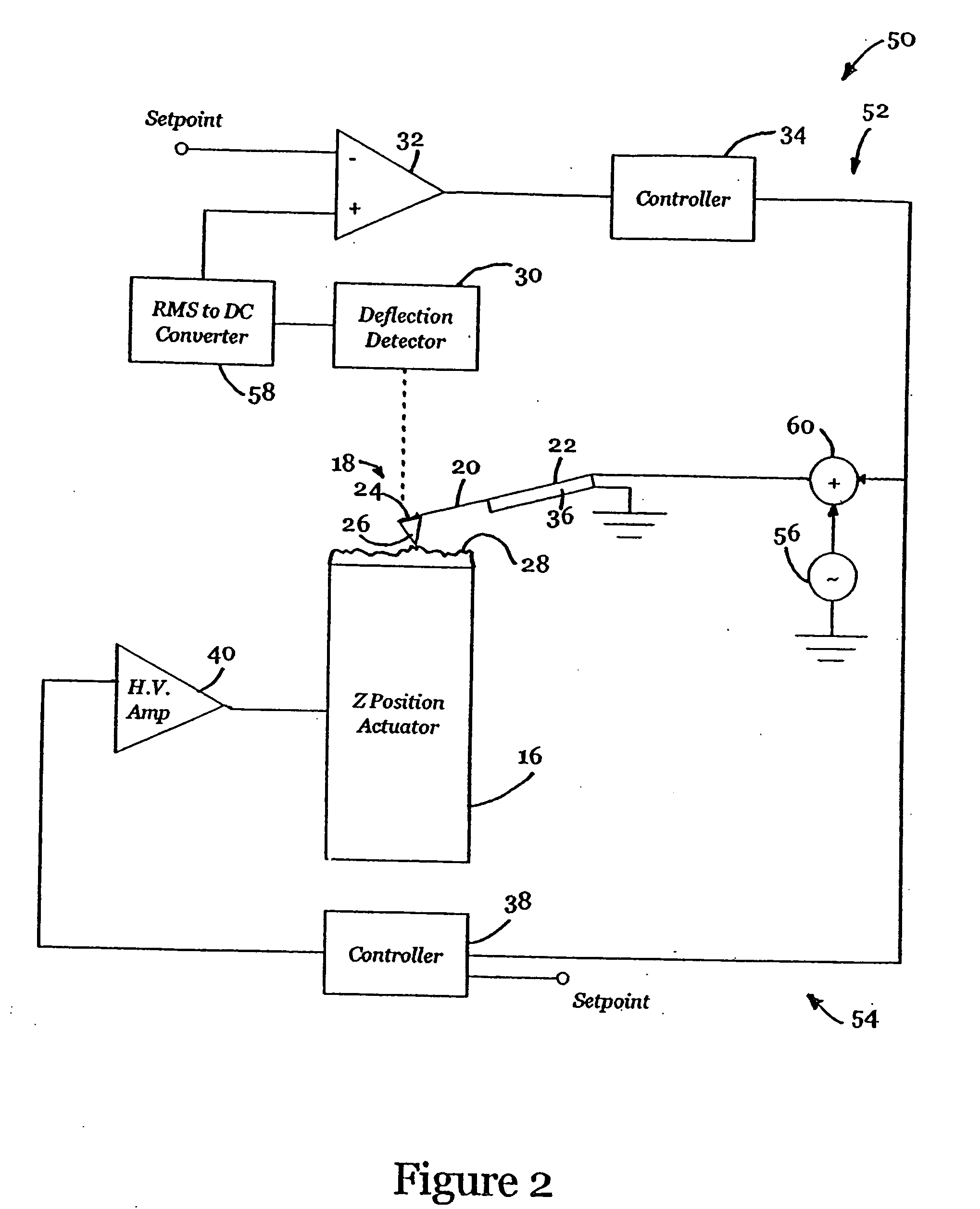
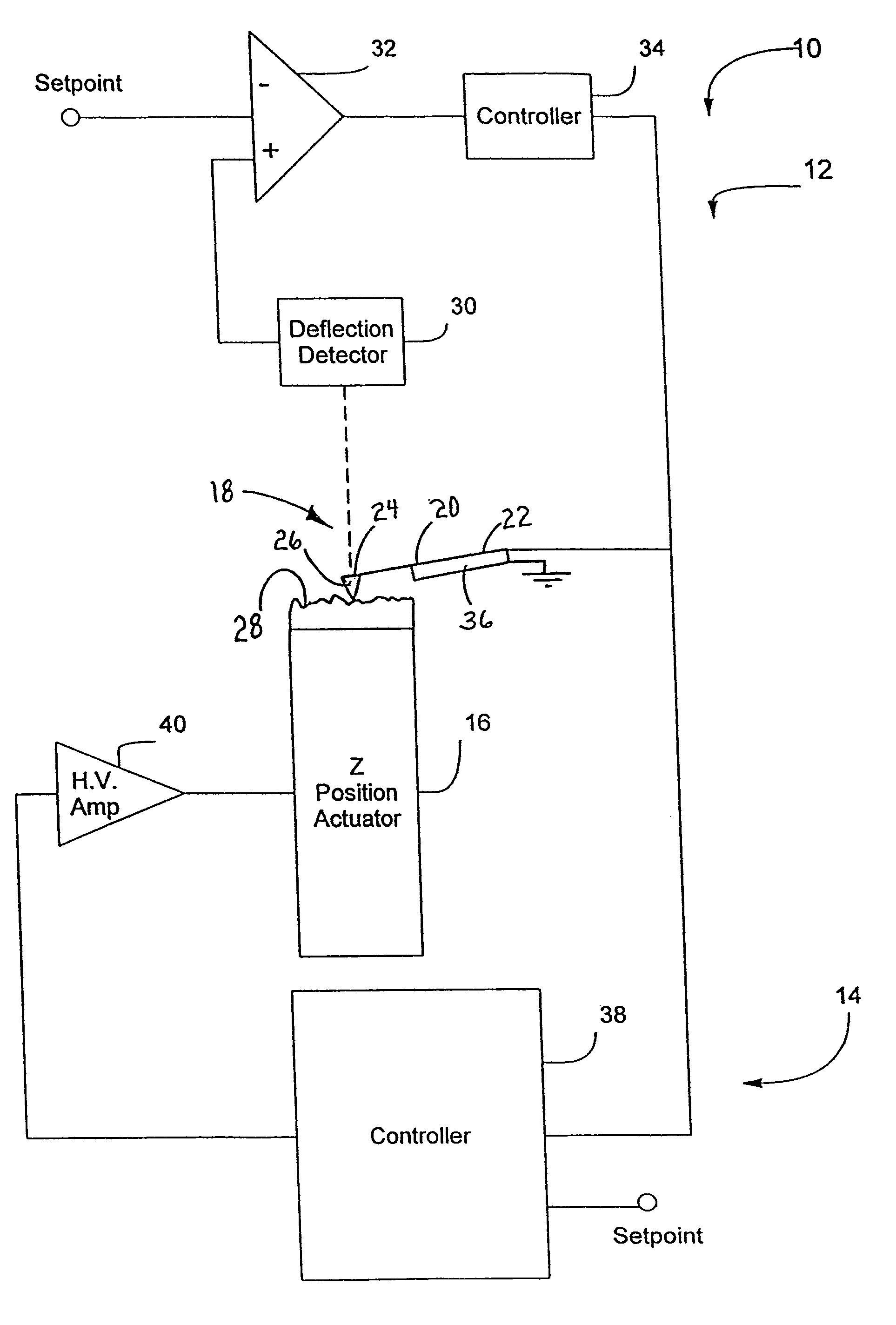
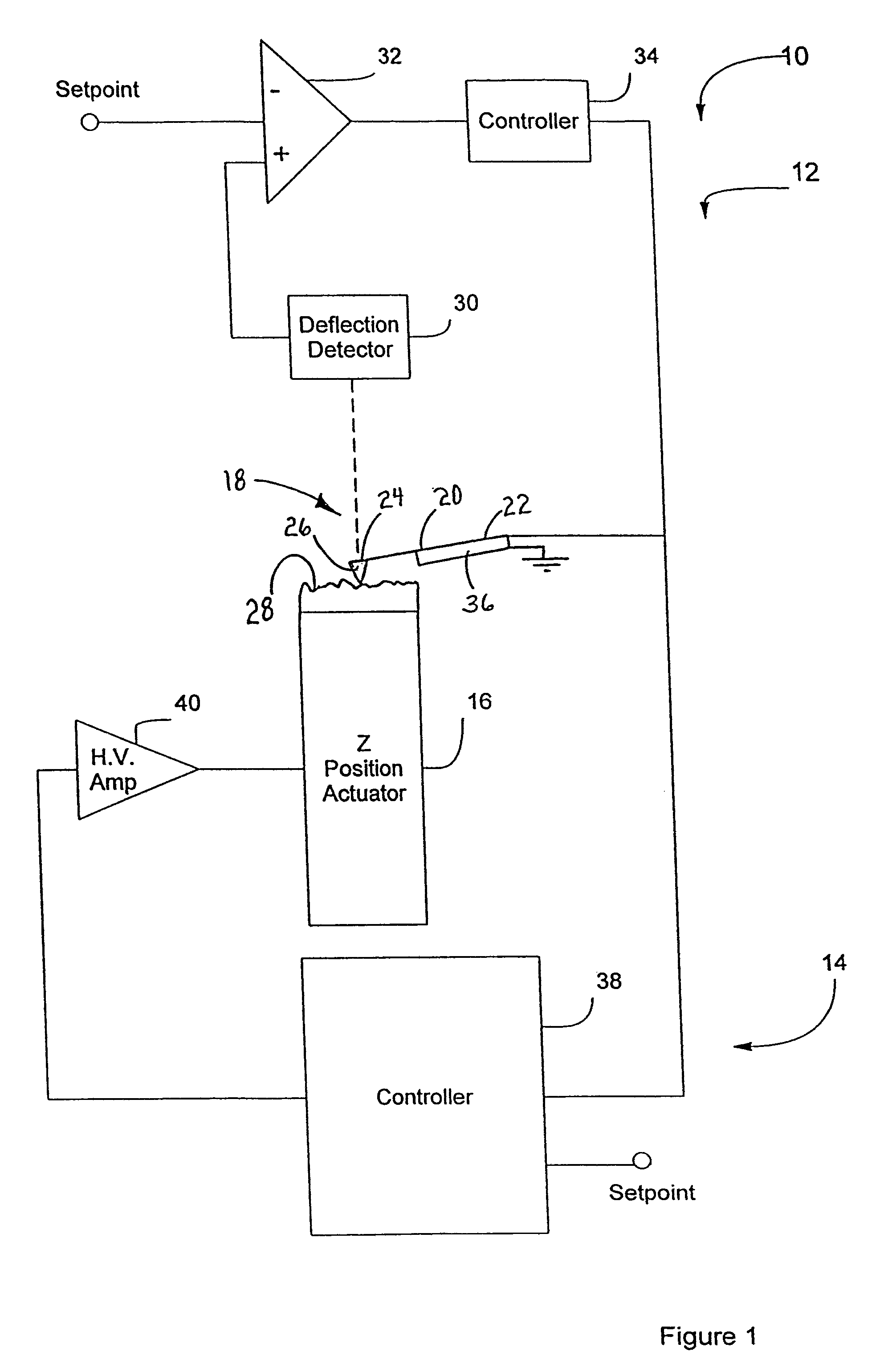
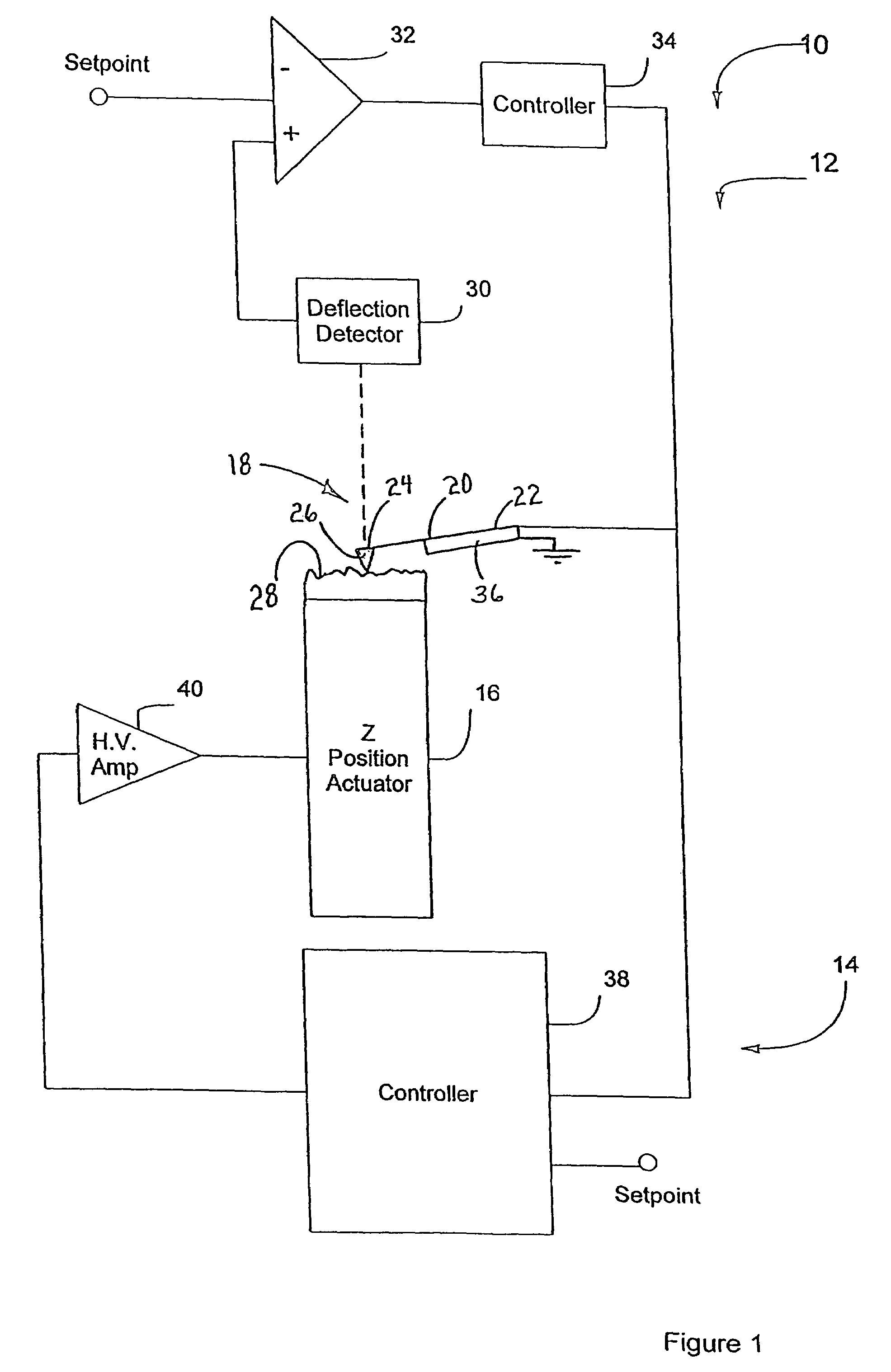
InactiveUS6530266B1High-speed imagingAccurate Z position measurementNanotechElectric discharge tubesFrequency oscillationCantilever
An AFM that combines an AFM Z position actuator and a self-actuated Z position cantilever (both operable in cyclical mode and contact mode), with appropriate nested feedback control circuitry to achieve high-speed imaging and accurate Z position measurements. A preferred embodiment of an AFM for analyzing a surface of a sample in either ambient air or fluid includes a self-actuated cantilever having a Z-positioning element integrated therewith and an oscillator that oscillates the self-actuated cantilever at a frequency generally equal to a resonant frequency of the self-actuated cantilever and at an oscillation amplitude generally equal to a setpoint value. The AFM includes a first feedback circuit nested within a second feedback circuit, wherein the first feedback circuit generates a cantilever control signal in response to vertical displacement of the self-actuated cantilever during a scanning operation, and the second feedback circuit is responsive to the cantilever control signal to generate a position control signal. A Z position actuator is also included within the second feedback circuit and is responsive to the position control signal to position the sample. In operation, preferably, the cantilever control signal alone is indicative of the topography of the sample surface. In a further embodiment, the first feedback circuit includes an active damping circuit for modifying the quality factor ("Q") of the cantilever resonance to optimize the bandwidth of the cantilever response.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
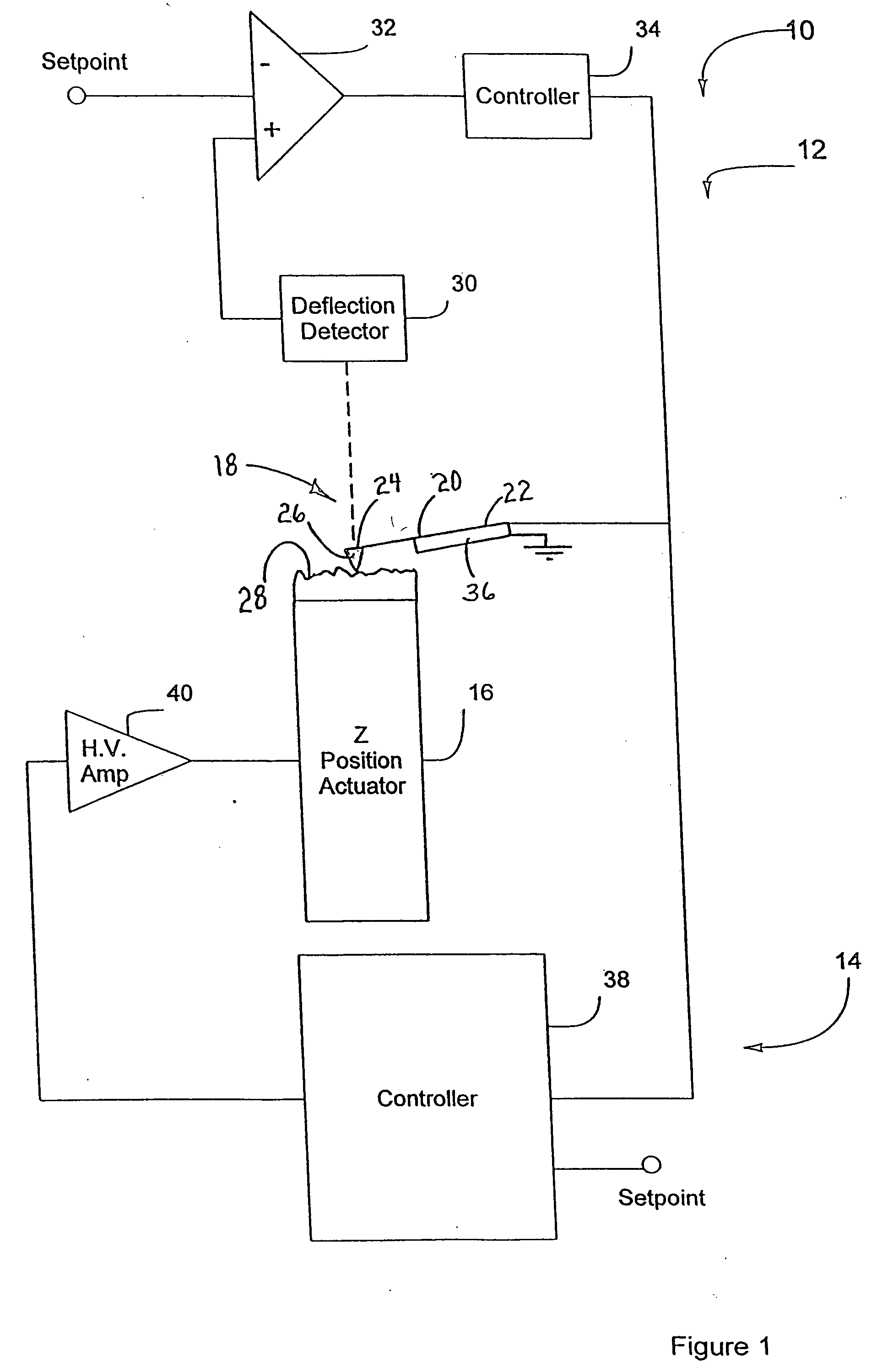
Active probe for an atomic force microscope and method for use thereof
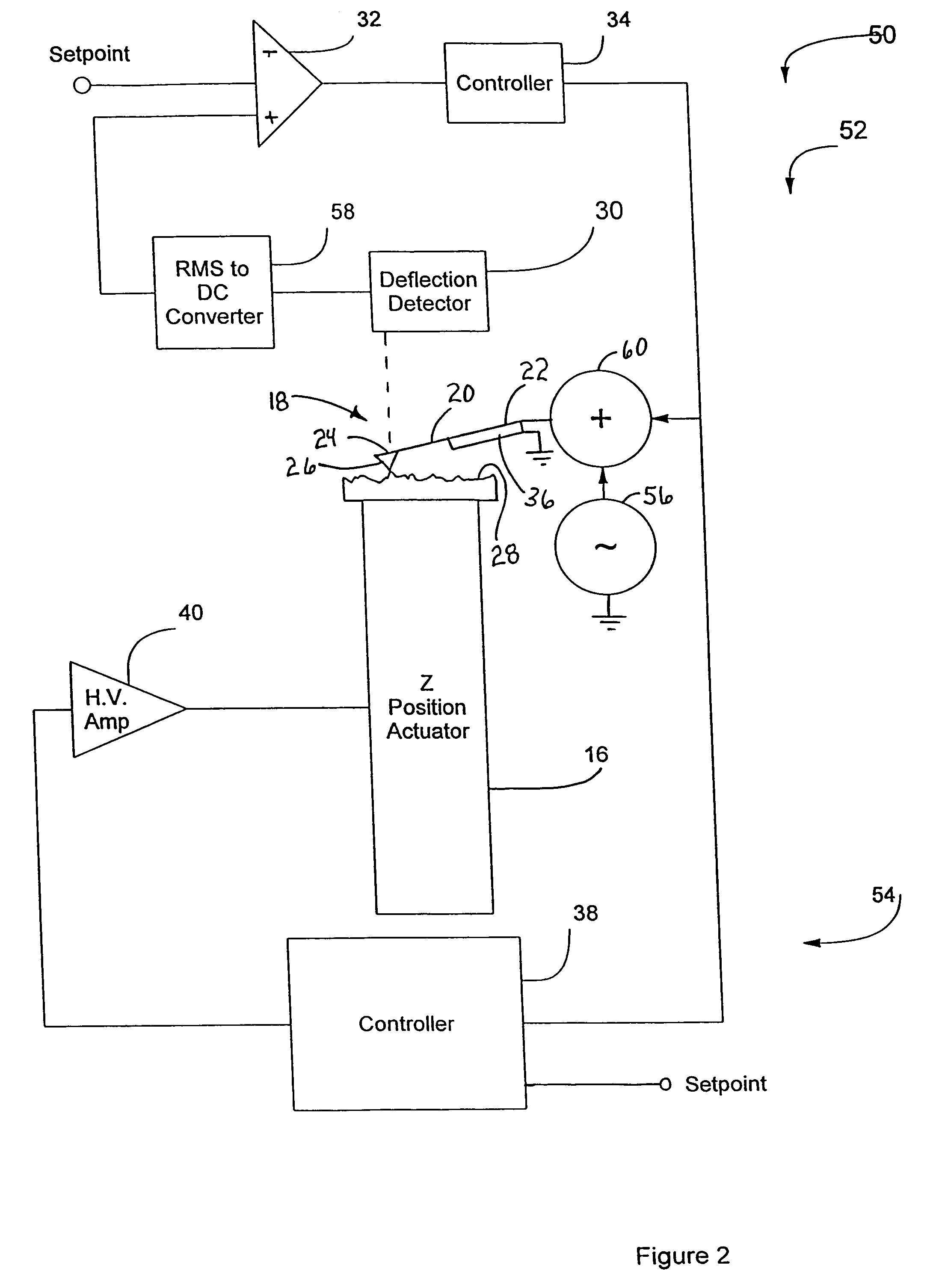
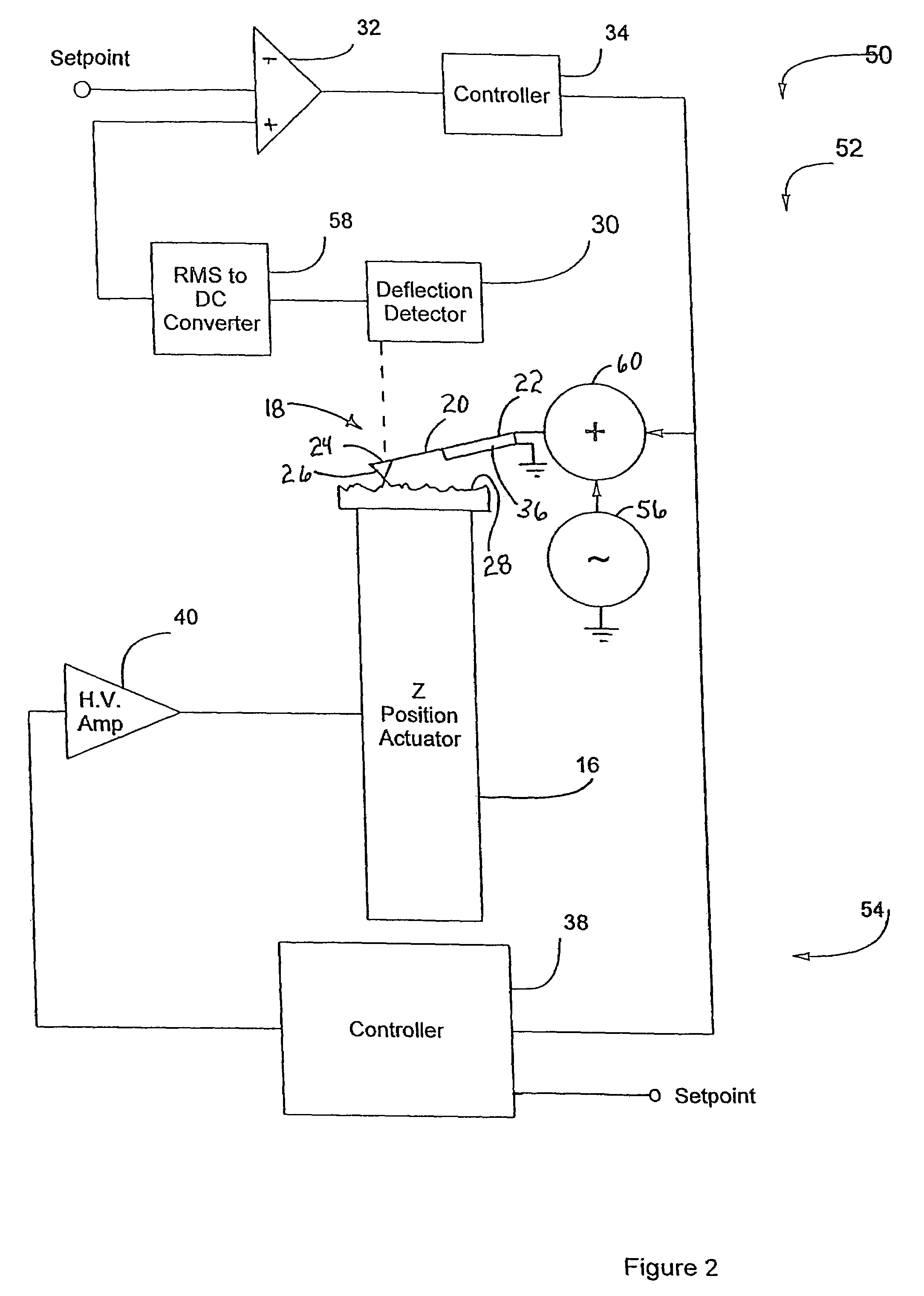
InactiveUS20050066714A1High-speed imagingAccurate measurementNanotechElectric discharge tubesControl signalFeedback circuits
An AFM that combines an AFM Z position actuator and a self-actuated Z position cantilever (both operable in cyclical mode and contact mode), with appropriate nested feedback control circuitry to achieve high-speed imaging and accurate Z position measurements. A preferred embodiment of an AFM for analyzing a surface of a sample in either ambient air or fluid includes a self-actuated cantilever having a Z-positioning element integrated therewith and an oscillator that oscillates the self-actuated cantilever at a frequency generally equal to a resonant frequency of the self-actuated cantilever and at an oscillation amplitude generally equal to a setpoint value. The AFM includes a first feedback circuit nested within a second feedback circuit, wherein the first feedback circuit generates a cantilever control signal in response to vertical displacement of the self-actuated cantilever during a scanning operation, and the second feedback circuit is responsive to the cantilever control signal to generate a position control signal. A Z position actuator is also included within the second feedback circuit and is responsive to the position control signal to position the sample. In operation, preferably, the cantilever control signal alone is indicative of the topography of the sample surface. In a further embodiment, the first feedback circuit includes an active damping circuit for modifying the quality factor (“Q”) of the cantilever resonance to optimize the bandwidth of the cantilever response.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Systems and methods for generating data based on one or more spectrally-encoded endoscopy techniques
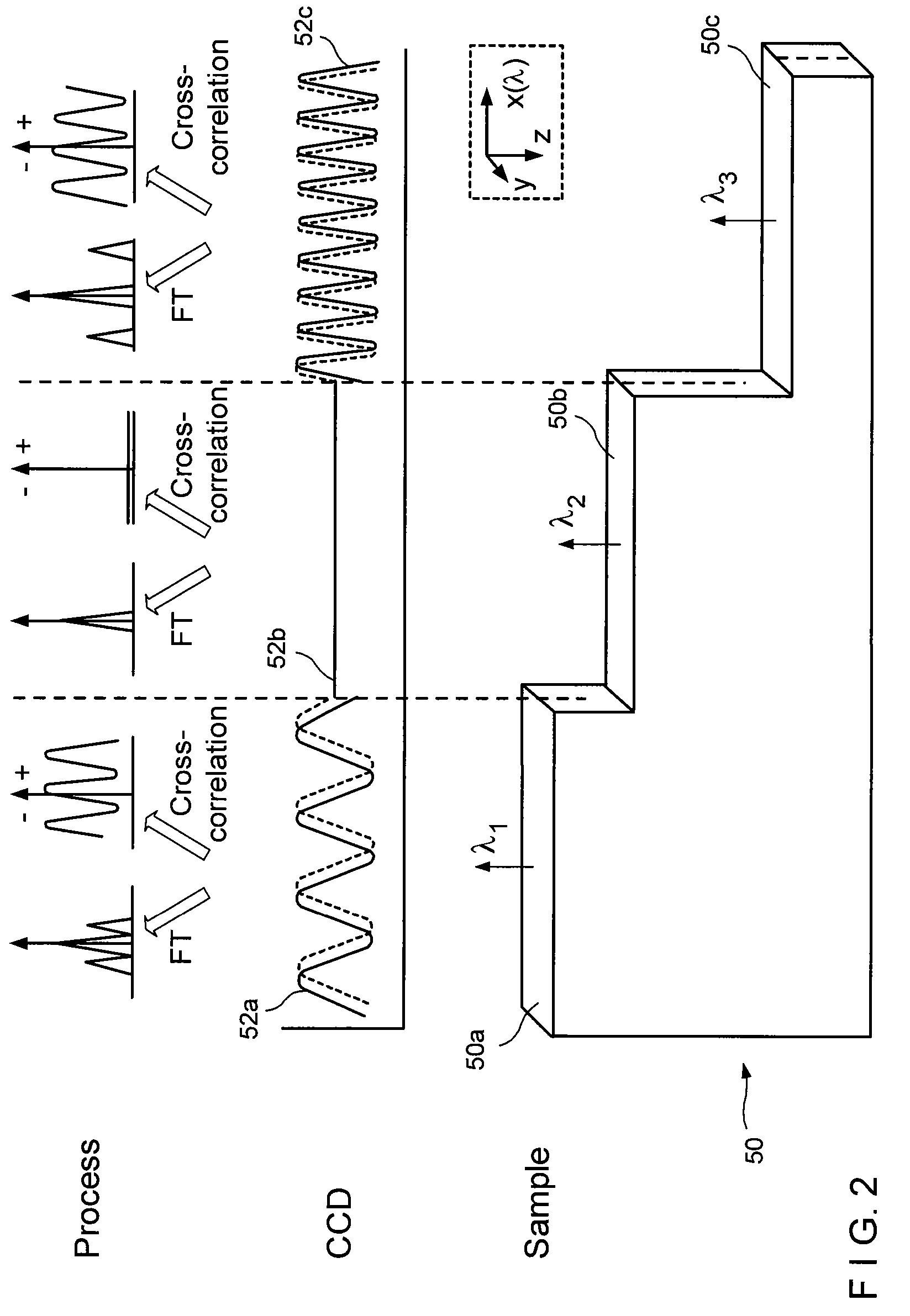
ActiveUS7796270B2High-speed imagingImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLength waveElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for an on-chip variable acuity imager array incorporating roll, pitch and yaw angle rates measurement
InactiveUS7408572B2Improve spatial resolutionHigh-speed imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRolling angleRate measurement
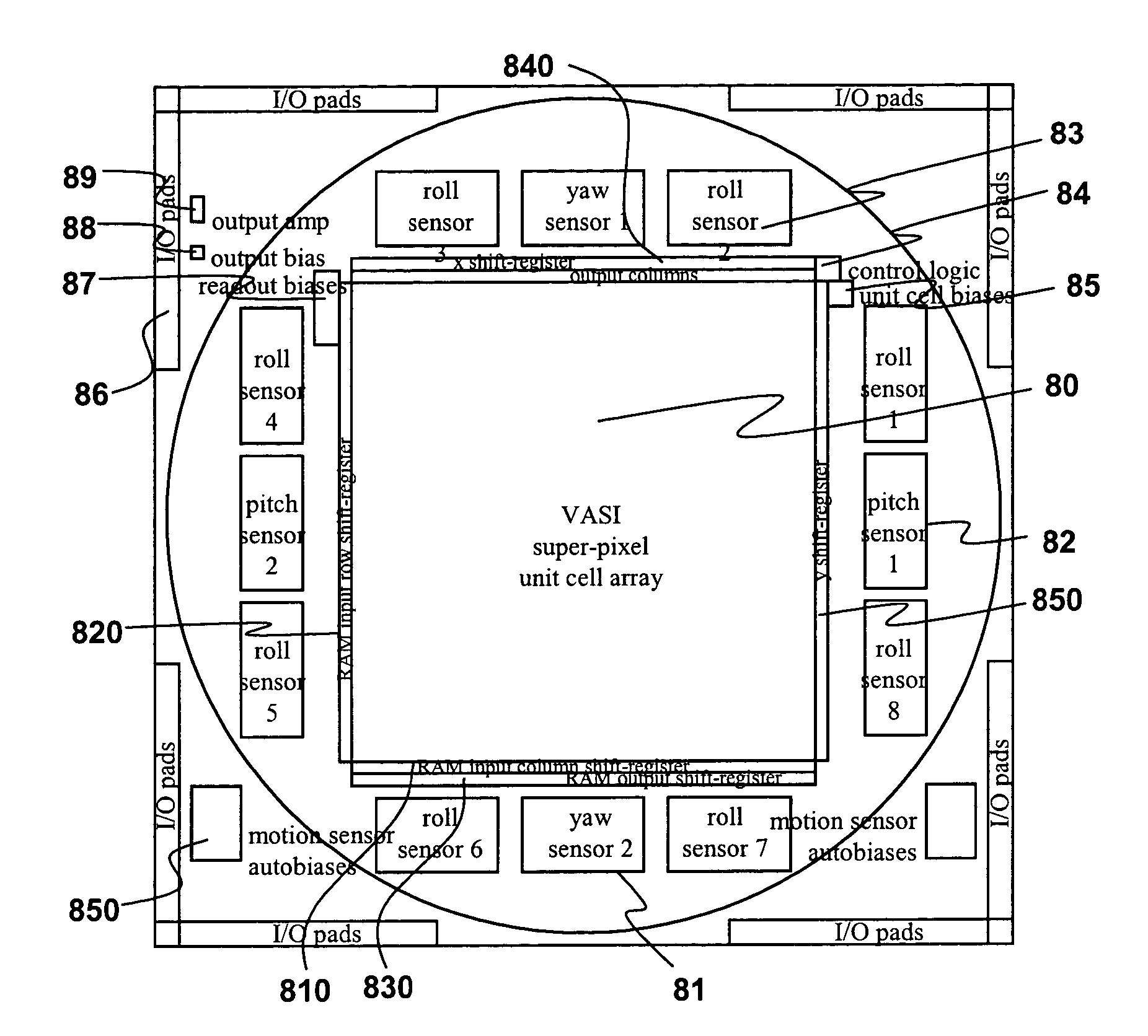
A variable acuity imager incorporates an array of detection elements for light energy, in the visible, infrared, ultraviolet, or light energy in another region of the electromagnetic spectrum with a means to change the spatial configuration of the array to include “superpixels” by combining energy detected by adjacent elements, thus permitting any number of high-resolution “foveal” regions to be placed within the confines of the focal plane array and moved around at the frame rate of the imaging device. Detectors to measure the pitch, yaw and roll angle rates of background imagery using velocity-sensing circuitry are employed for variation of the foveal regions to accommodate motion of the array.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Systems and methods for generating data based on one or more spectrally-encoded endoscopy techniques
ActiveUS20070263208A1High-speed imagingImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Exemplary systems and methods for generating data associated with at least one portion of a sample can be provided. For example, according to one exemplary embodiment of such systems and methods, it is possible to provide a particular radiation using at least one first arrangement. The particular radiation can include at least one first electro-magnetic radiation directed to at least one sample and at least one second electro-magnetic radiation directed to a reference arrangement. The first radiation and / or the second radiation can comprise a plurality of wavelengths. The first electro-magnetic radiation can be spectrally dispersed along at least one portion of the sample. The second electro-magnetic radiation measured at two or more different lengths of the reference arrangement with respect to the first arrangement. Data can be generated which is associated with the first and second electro-magnetic radiations obtained at the two different lengths using at least one second arrangement which comprises a spectrometer arrangement.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
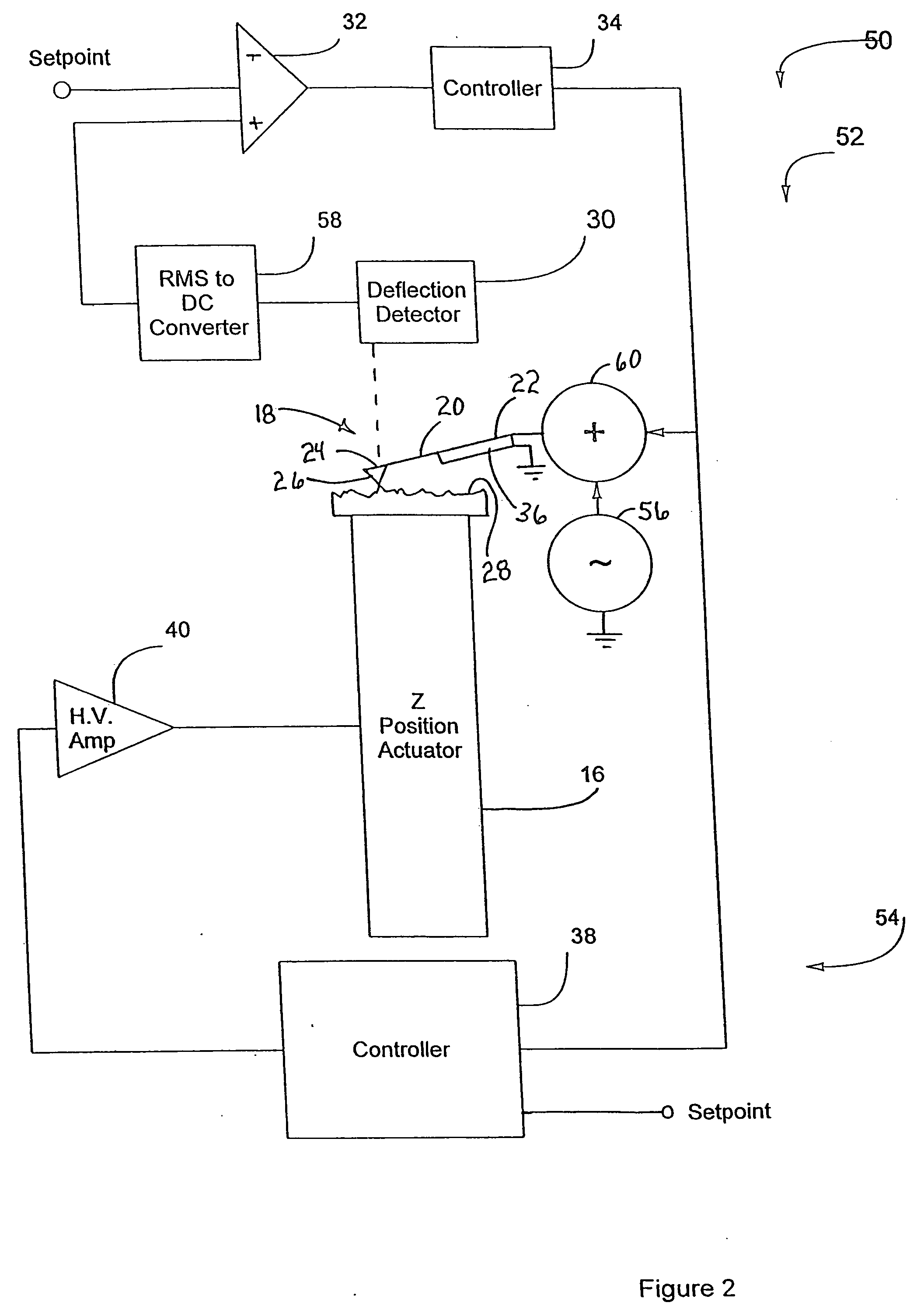
Dynamic activation for an atomic force microscope and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20060191329A1Increase speedIncrease usageNanotechScanning probe microscopyPhotodetectorLight beam
A scanning probe microscope method and apparatus that modifies imaging dynamics using an active drive technique to optimize the bandwidth of amplitude detection. The deflection is preferably measured by an optical detection system including a laser and a photodetector, which measures cantilever deflection by an optical beam bounce technique or another conventional technique. The detected deflection of the cantilever is subsequently demodulated to give a signal proportional to the amplitude of oscillation of the cantilever, which is thereafter used to drive the cantilever.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
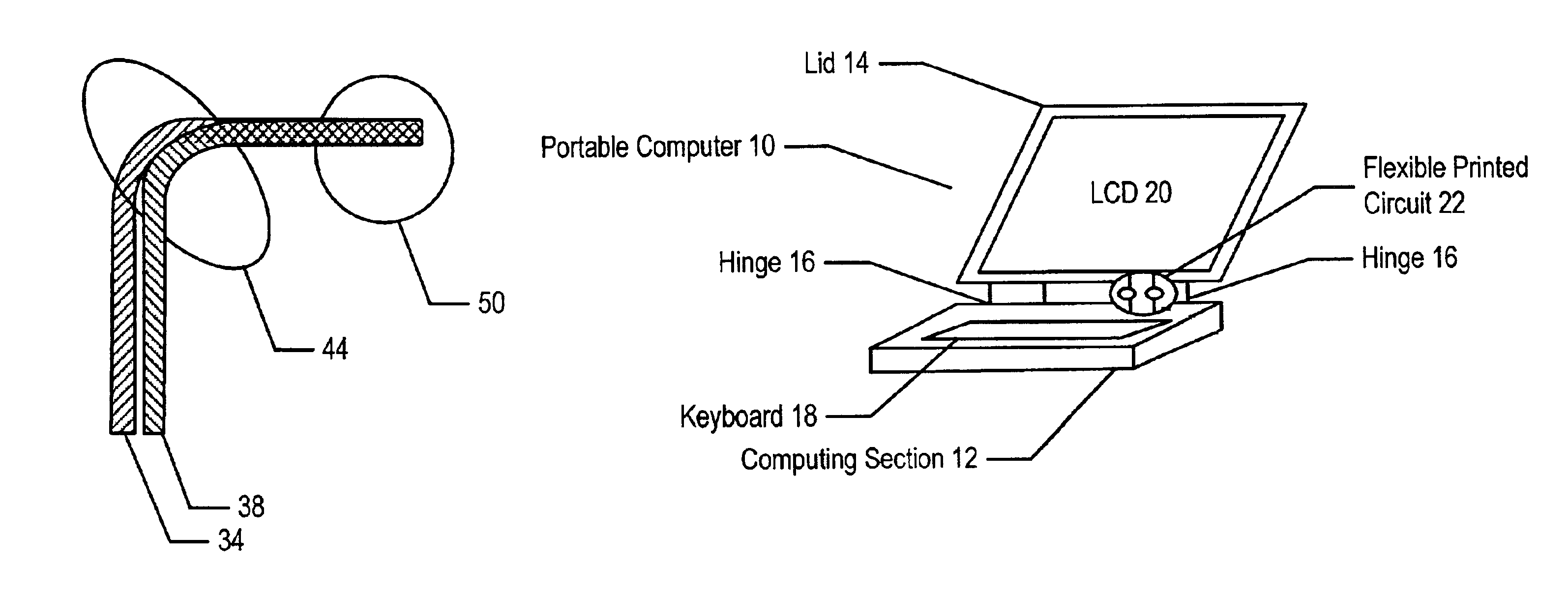
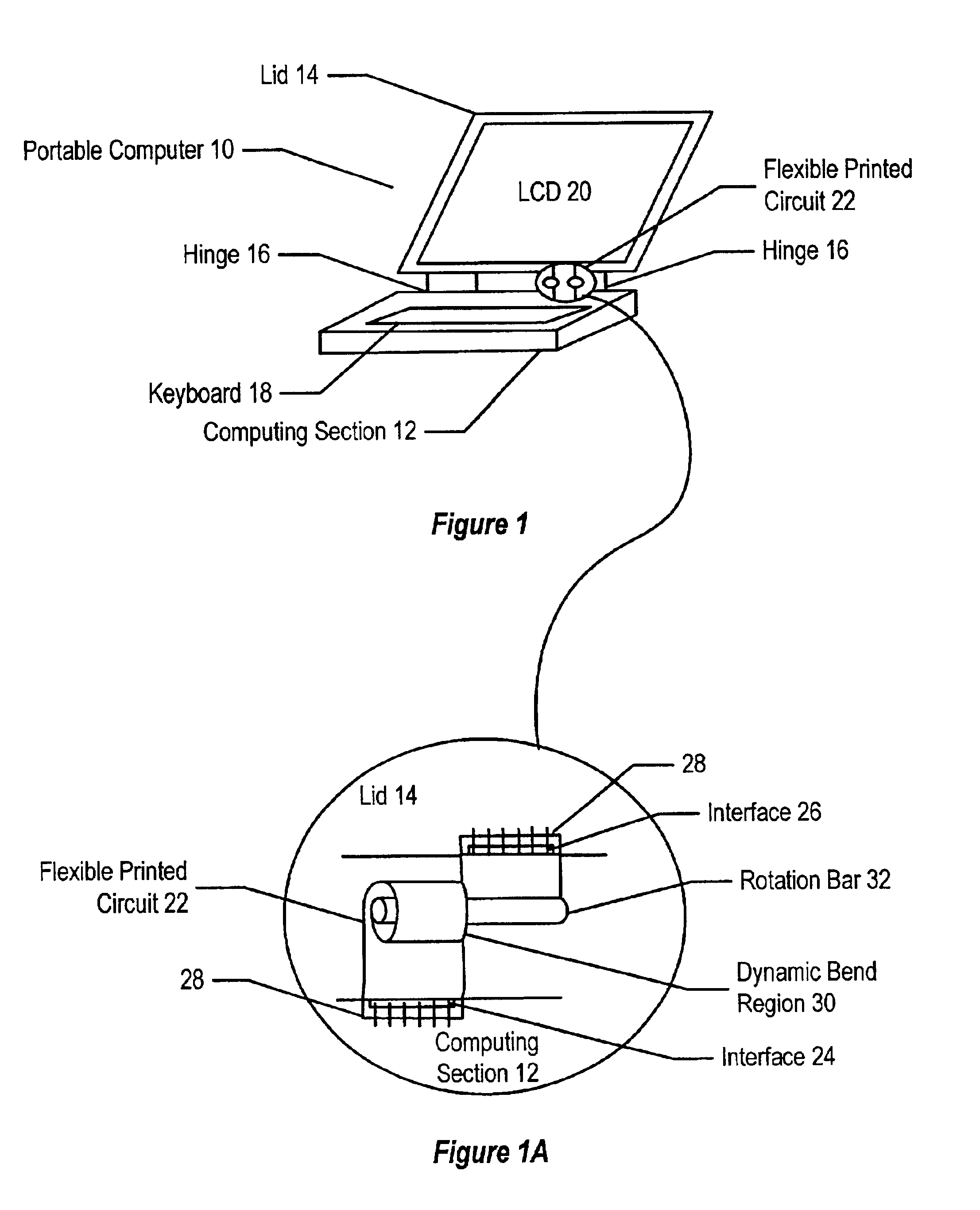
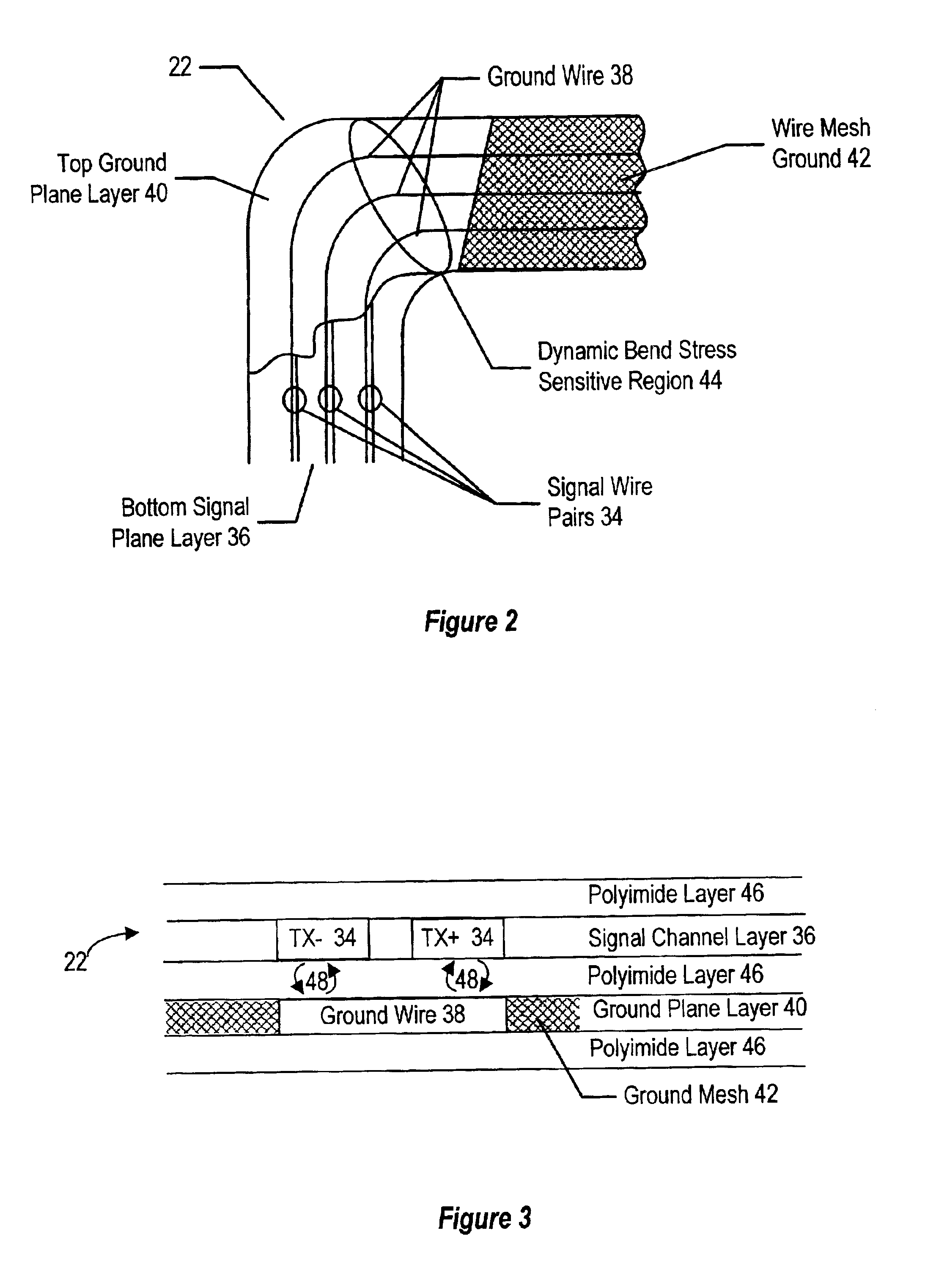
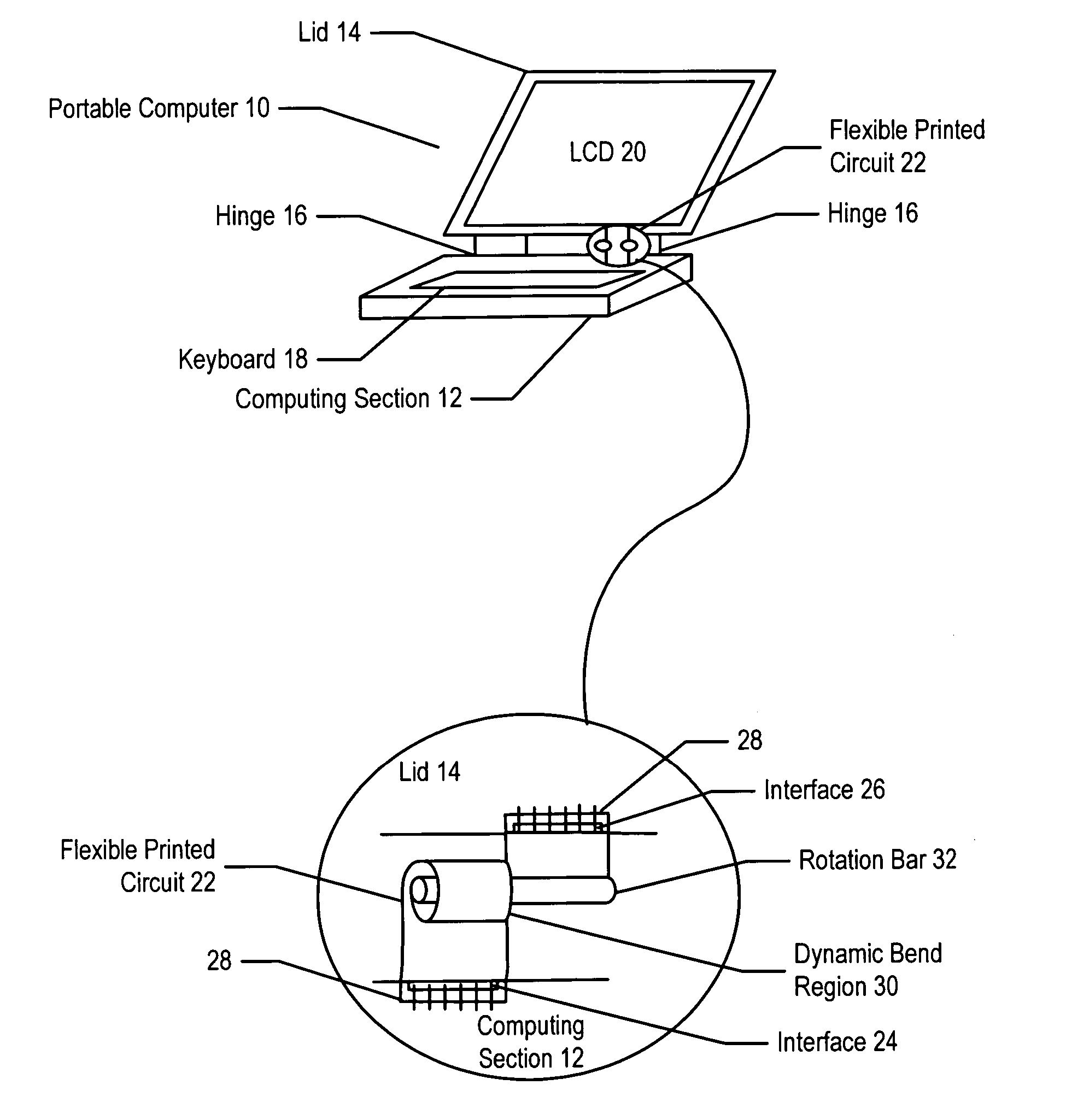
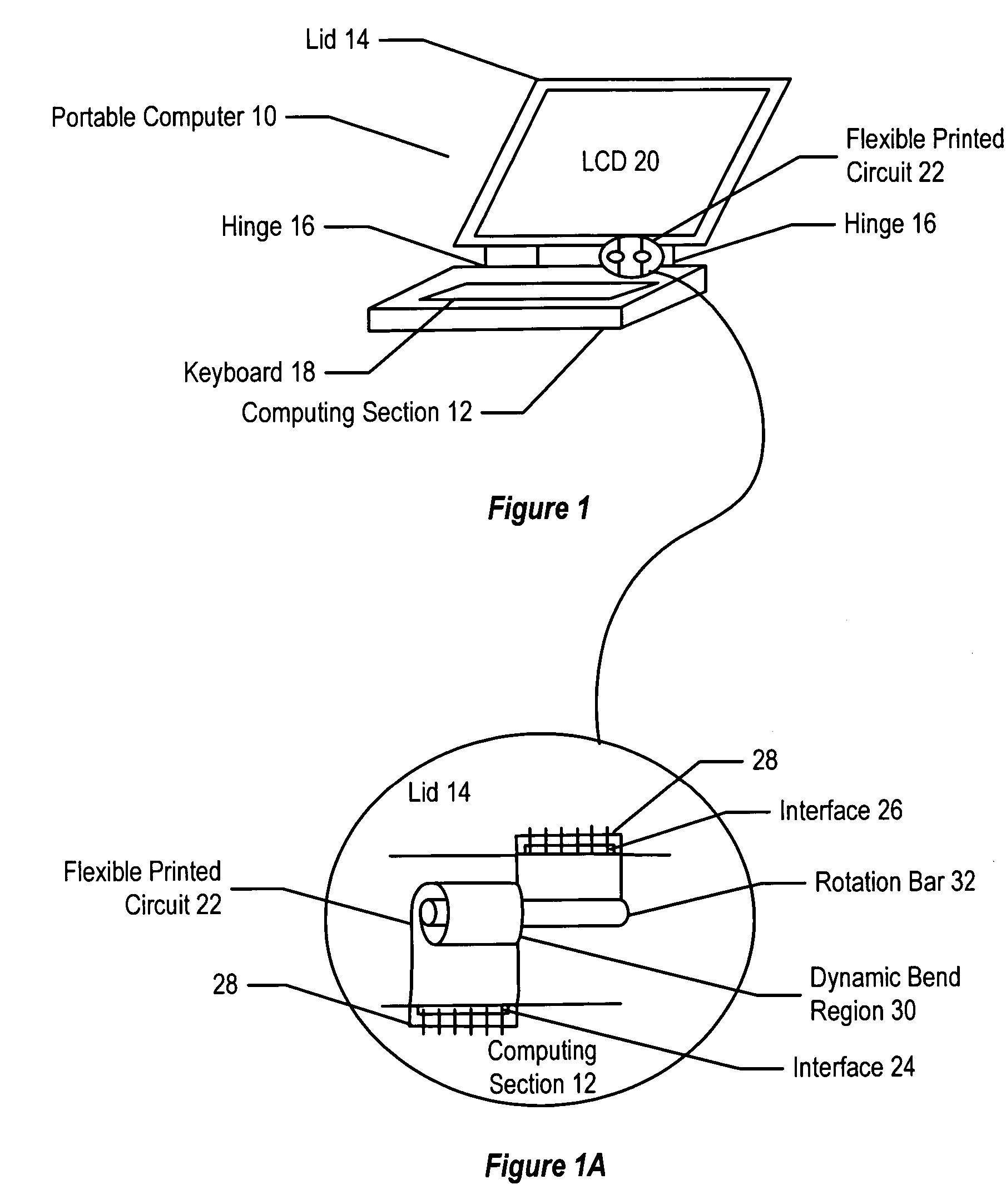
System and method for flexible circuits
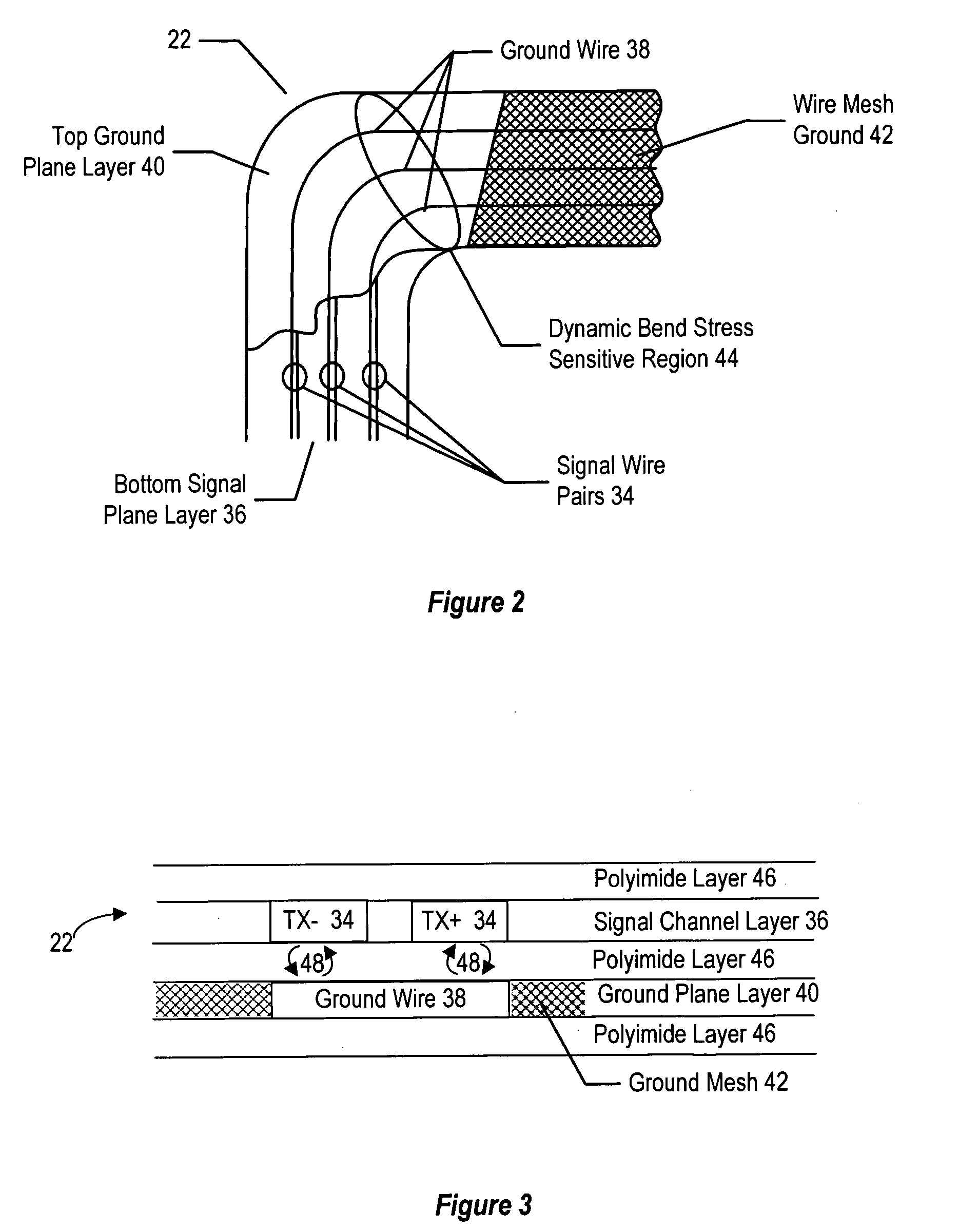
InactiveUS6885549B2Reduce problem and difficulty associateReduce resistanceWing accessoriesPrinted circuit aspectsData transmissionGround plane
A flexible printed circuit improves data transfer rates by disposing ground wires in a ground plane proximate to signal wires disposed in a signal channel plane. One or more ground wires is associated with each signal wire pair or each signal wire for imaging of the return currents of the signal pairs. An overlapping alignment minimizes loop area between a ground wire and its associated signal wire. An offset alignment provides a reduced loop area and reduced breakage risk since movement of the flexible circuit does result in compression of the signal wire and its associated ground wire. A combination of overlapping and offset alignment balances signal transfer effectiveness with breakage risk by offsetting ground and signal wires is stress sensitive regions and overlapping ground and signal wires in stress tolerant regions. In one embodiment, the flexible circuit interfaces a portable computer with a display lid to support high-speed display signals with reduced breakage risk from cycling the display lid between an open and closed position.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
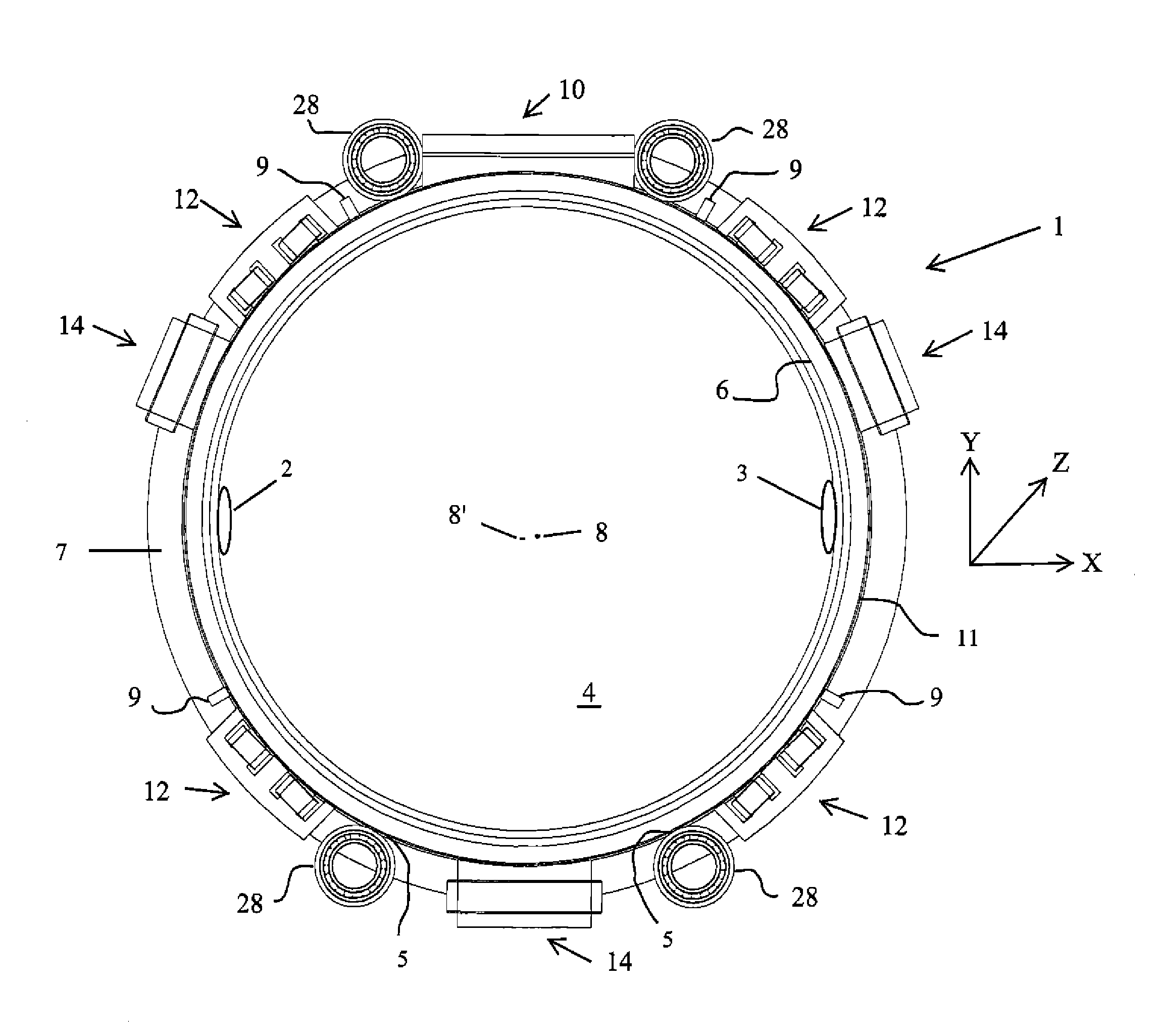
Diagnostic Scanning Apparatus
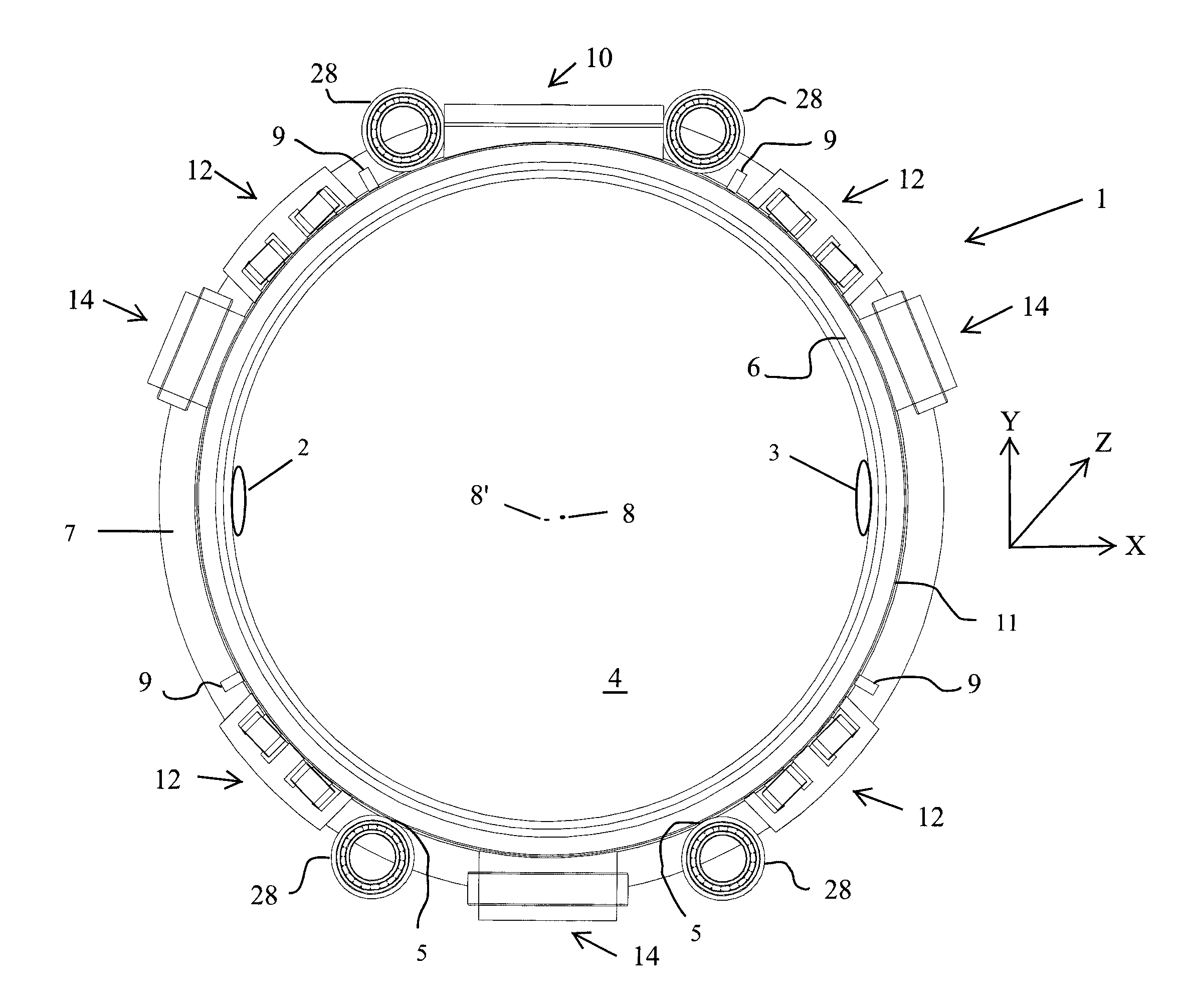
ActiveUS20110194669A1Reduced and no lubrication requirementMinimizing and eliminating amountMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLinear bearingsRotational axisMagnetic bearing
An apparatus includes an annular rotor that rotates about a rotational axis. A magnetic bearing system influences the position of the annular rotor in three-dimensional space and includes at least three actuators, wherein at least one actuator generates a force for lifting the annular rotor in a vertical direction, at least one actuator influences the position of the annular rotor in the radial direction of the annular rotor and at least assists in maintaining an annular gap between at least one non-magnetic bearing and the annular rotor during operation and at least one actuator influences the position of the annular rotor in an axial direction of the annular rotor. At least one radiation source may be fixedly mounted on the annular rotor.
Owner:AB SKF
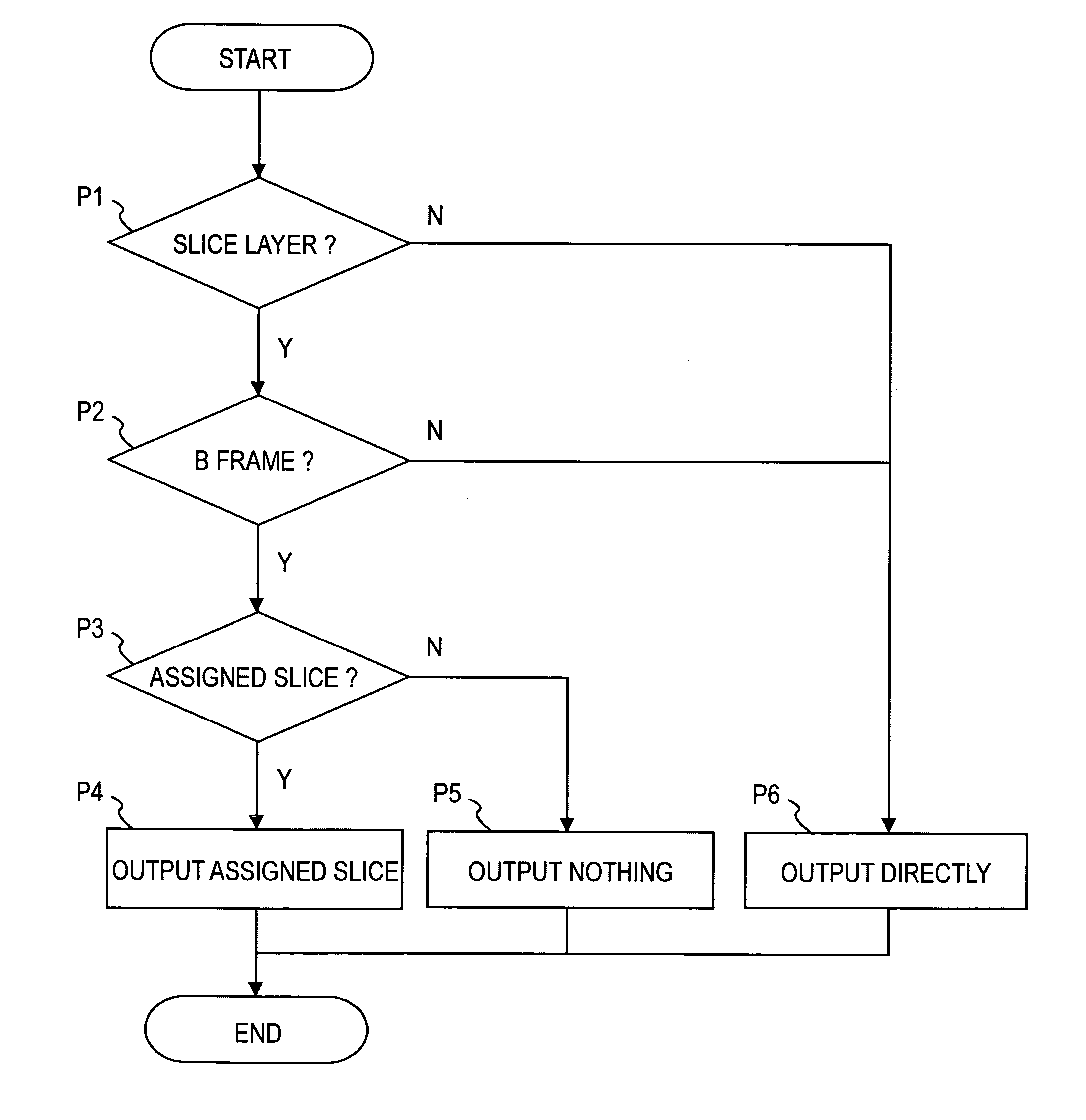
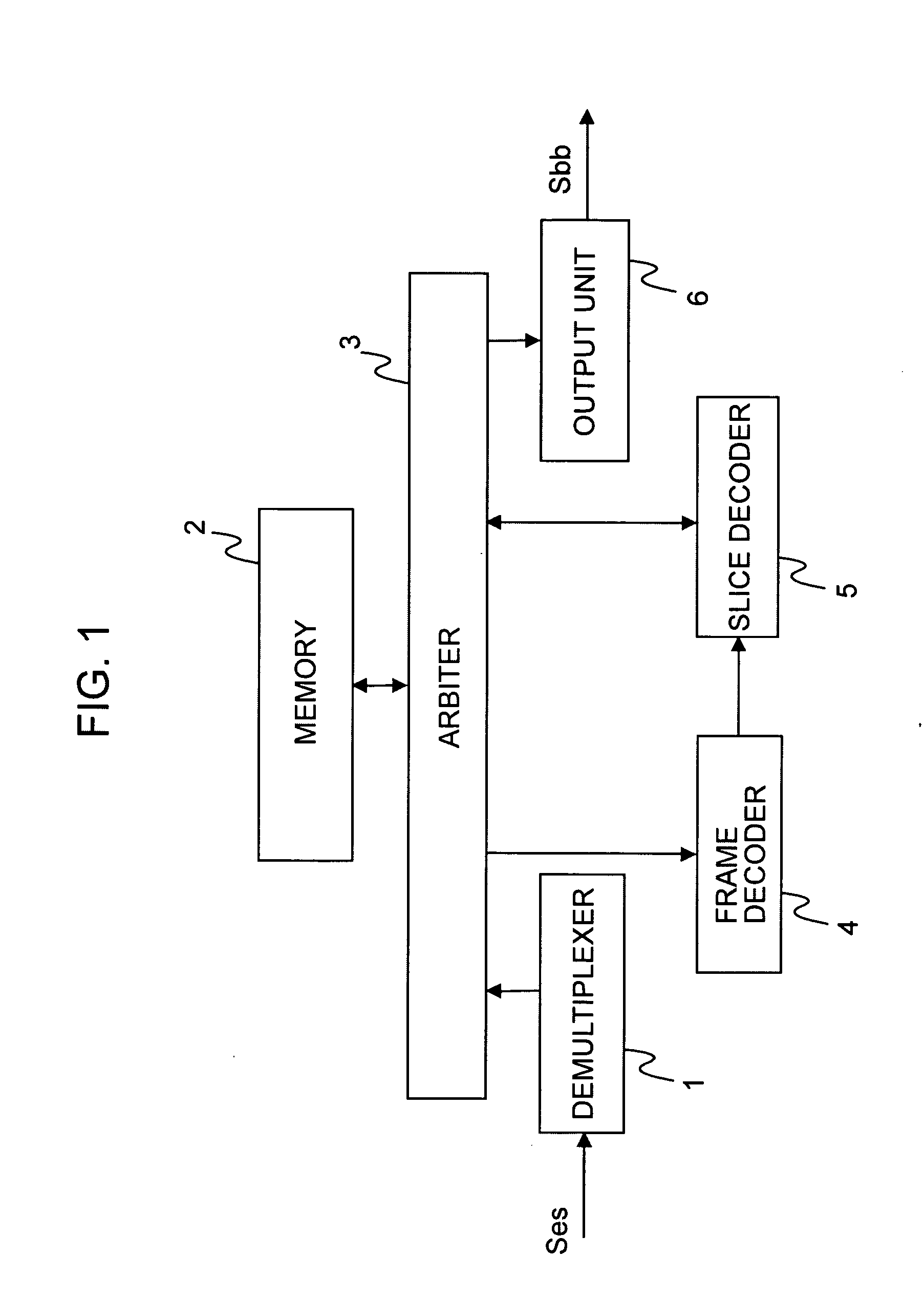
Decoding device, electronic apparatus, computer, decoding method, program, and recording medium
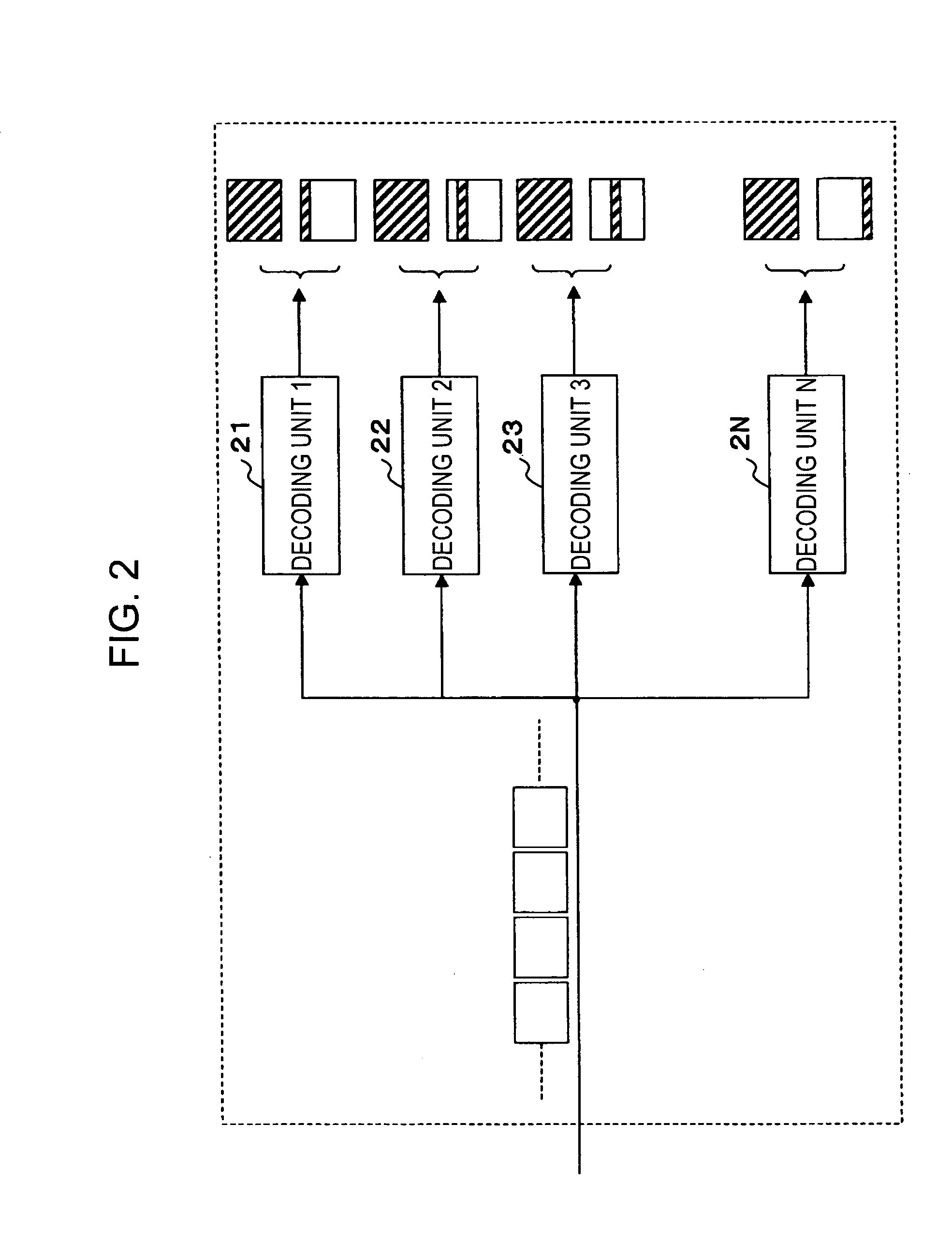
InactiveUS20050147166A1Increase speedHigh-speed imagingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsImaging data
A decoding device for decoding an image stream containing bi-directionally predictive-coded image data includes “N” number of decoding units for decoding the image stream in a parallel manner, wherein “N” is a natural number greater than or equal to 2. Each of the decoding units decodes a partial image being assigned to the decoding unit out of “N” number of partial images forming a frame when the bi-directionally predictive-coded image data is input, and decodes an entire frame when image data coded by using a method other than the bi-directionally predictive-coding method is input.
Owner:SONY CORP
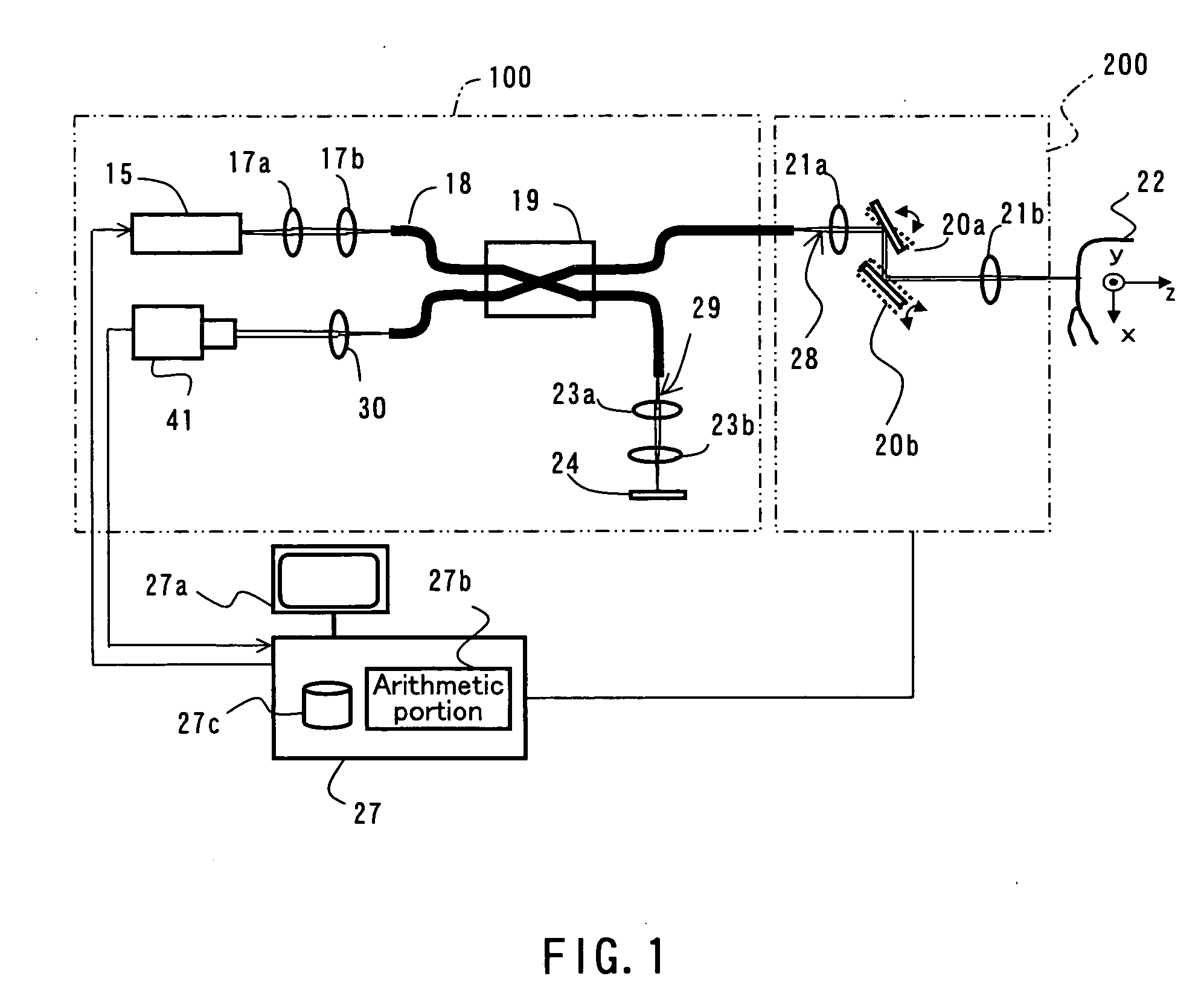
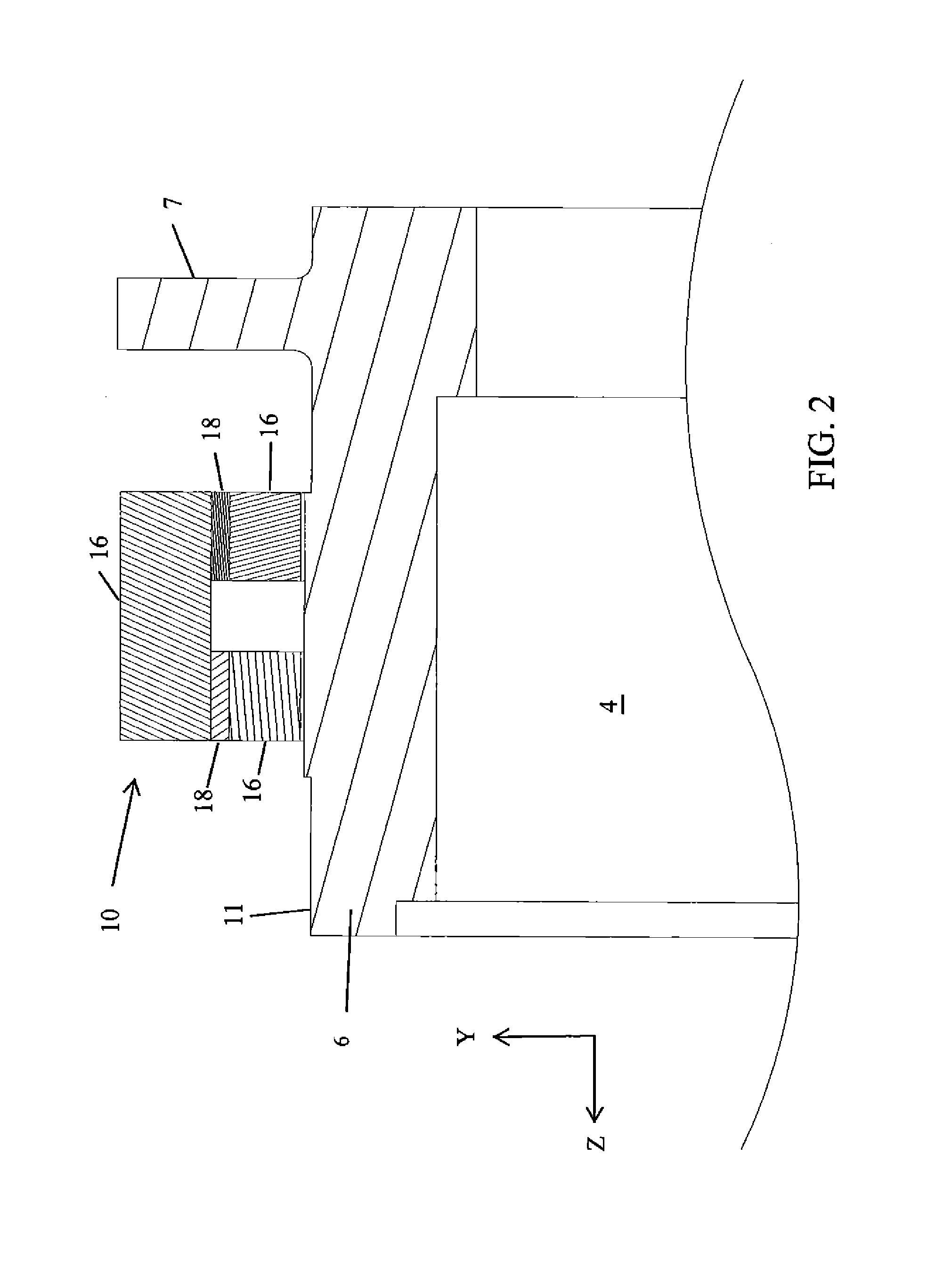
Dental optical coherence tomograph
InactiveUS7823782B2Simple structureHigh-speed imagingInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological bodyFourier transform on finite groups
A dental optical coherence tomography apparatus for measuring tissue in a stomatognathic region of a living body or an artificial composition in the stomatognathic region as a measured object includes: a variable wavelength light source (15); a light splitting portion (19) that splits light-source light emitted from the variable wavelength light source (15) into reference light (29) and measuring light (28); an interference portion (19) that causes the measuring light (28) and the reference light (29) to interfere with each other, thereby generating interference light; a photodetection portion (41) that measures the interference light; and an arithmetic portion (27b) that generates an image of a measured object (22) by Fourier transforming or inverse Fourier transforming the intensity of the interference light, whose wavelength changes with time, that has been detected by the photodetection portion for each of the wavelengths. Accordingly, an optical coherence tomography apparatus applicable to dental measurement can be provided.
Owner:SHOFU INC
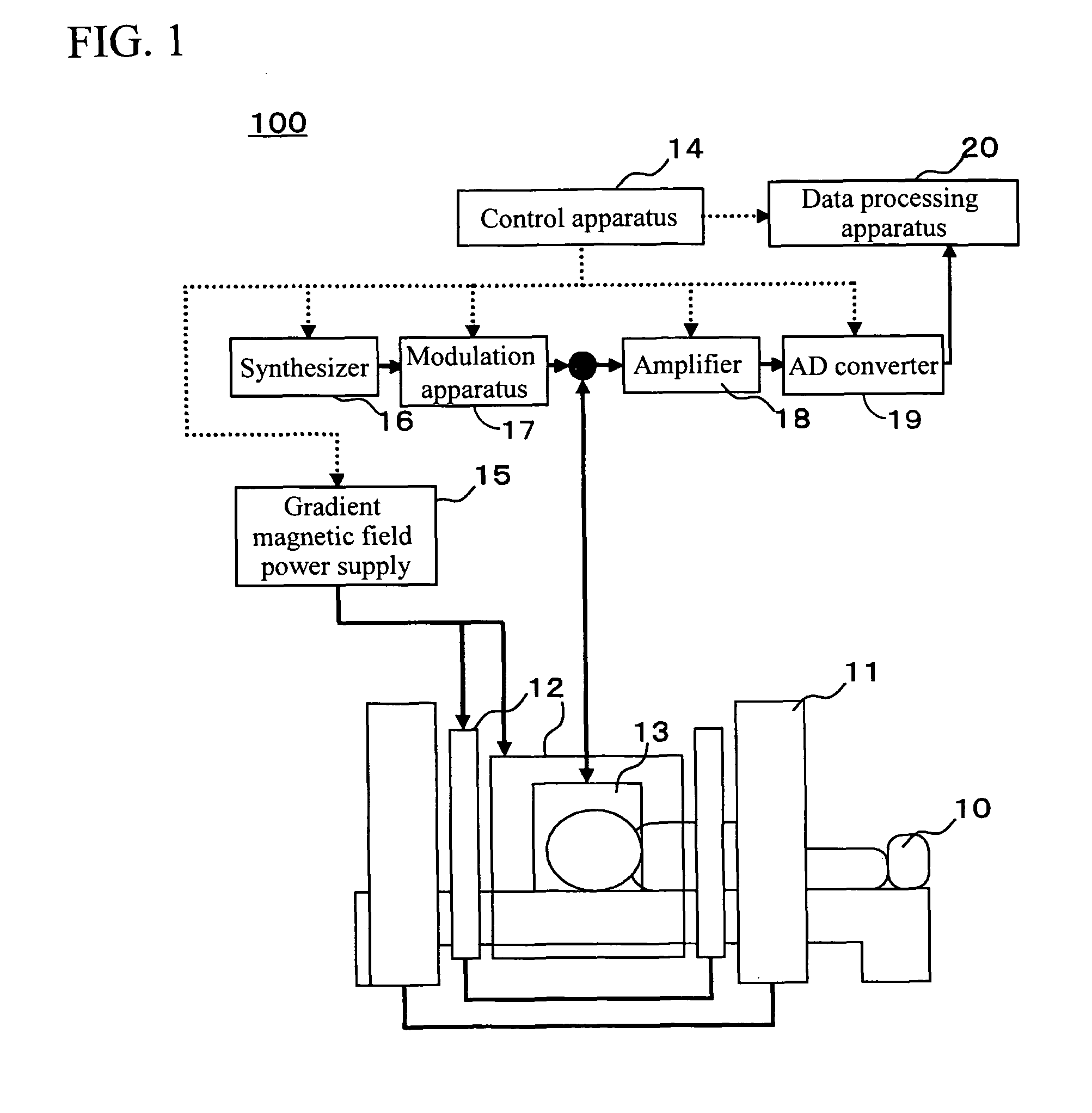
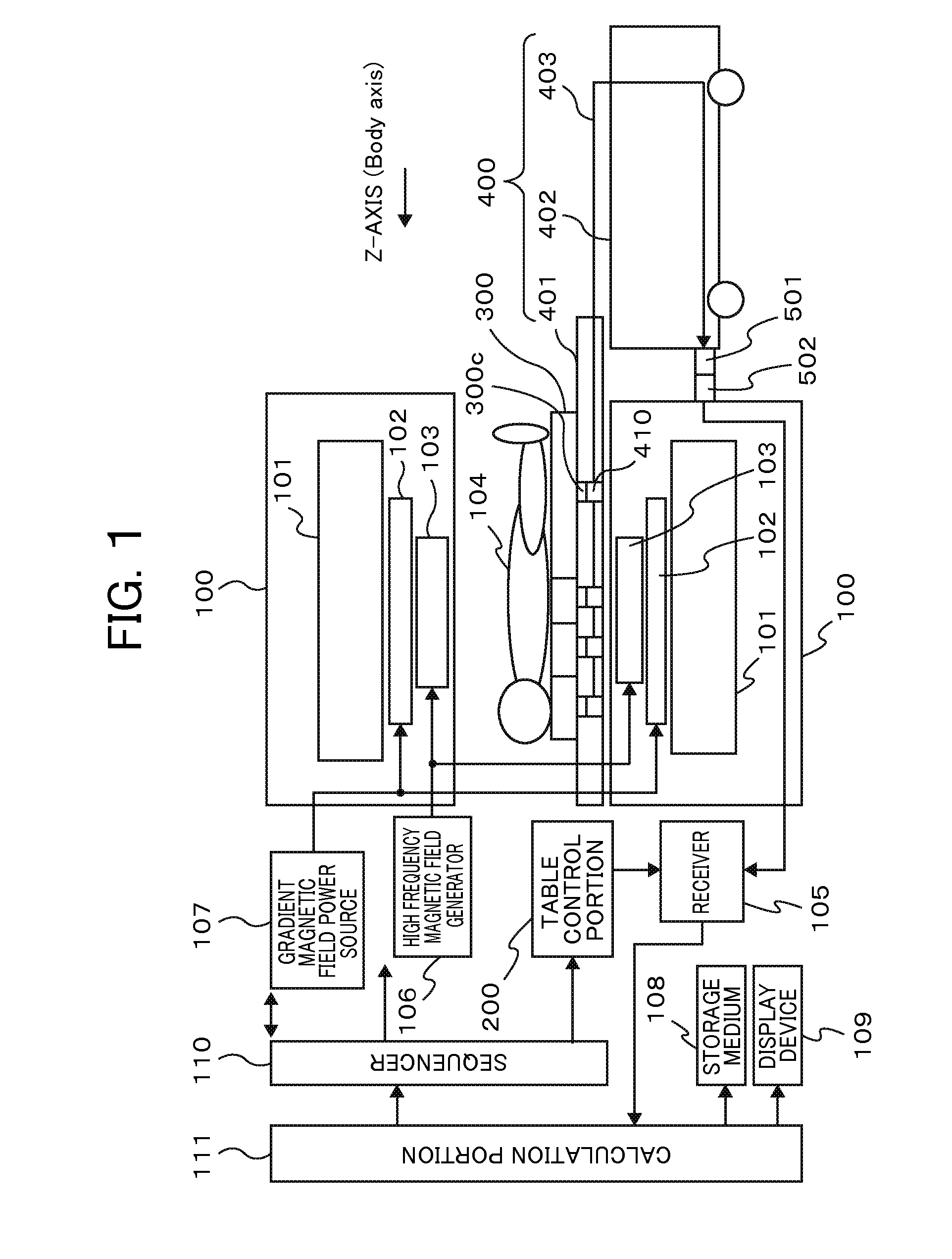
Magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveUS7723987B2Reduced measurement timeSuppress artifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementBody movement
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for driving touch panel
ActiveUS20110043488A1High-speed imagingStable operationInput/output processes for data processingPhysicsTouch panel
A touch panel includes a plurality of pixels each of which is provided with a photo sensor including a photodiode, a first transistor, and a second transistor. Each pixel performs first operation in which a potential of a photodiode reset signal line which is electrically connected to the photodiode is set so that a forward bias is applied to the photodiode, second operation in which a potential of a gate of the first transistor is changed by a photocurrent of the photodiode, and third operation in which a potential of a gate of the second transistor is changed and the photo sensor output signal line and a photo sensor reference signal line are brought into conduction through the first transistor and the second transistor so that the potential of the photo sensor output signal line is changed in accordance with the photocurrent.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
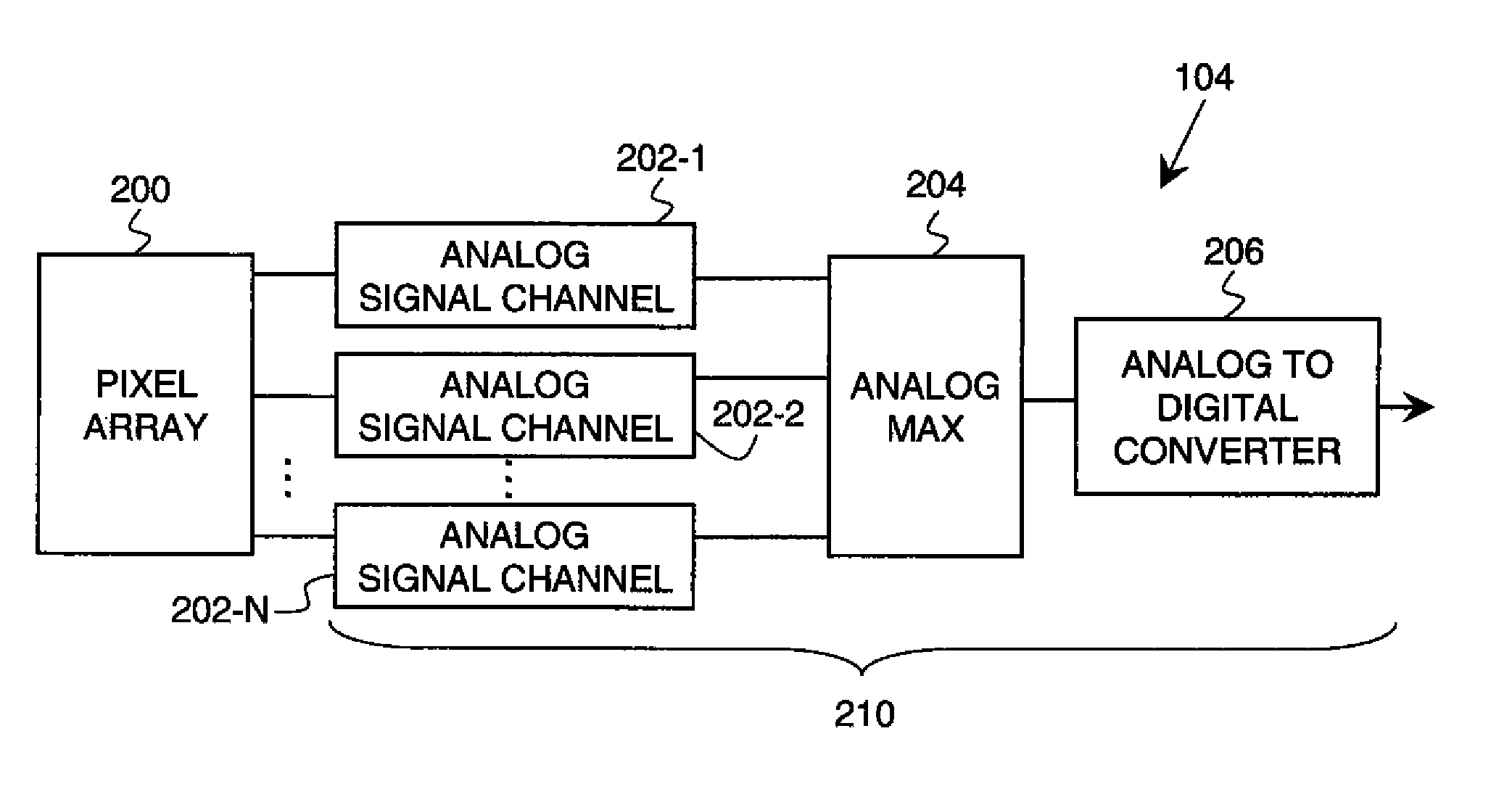
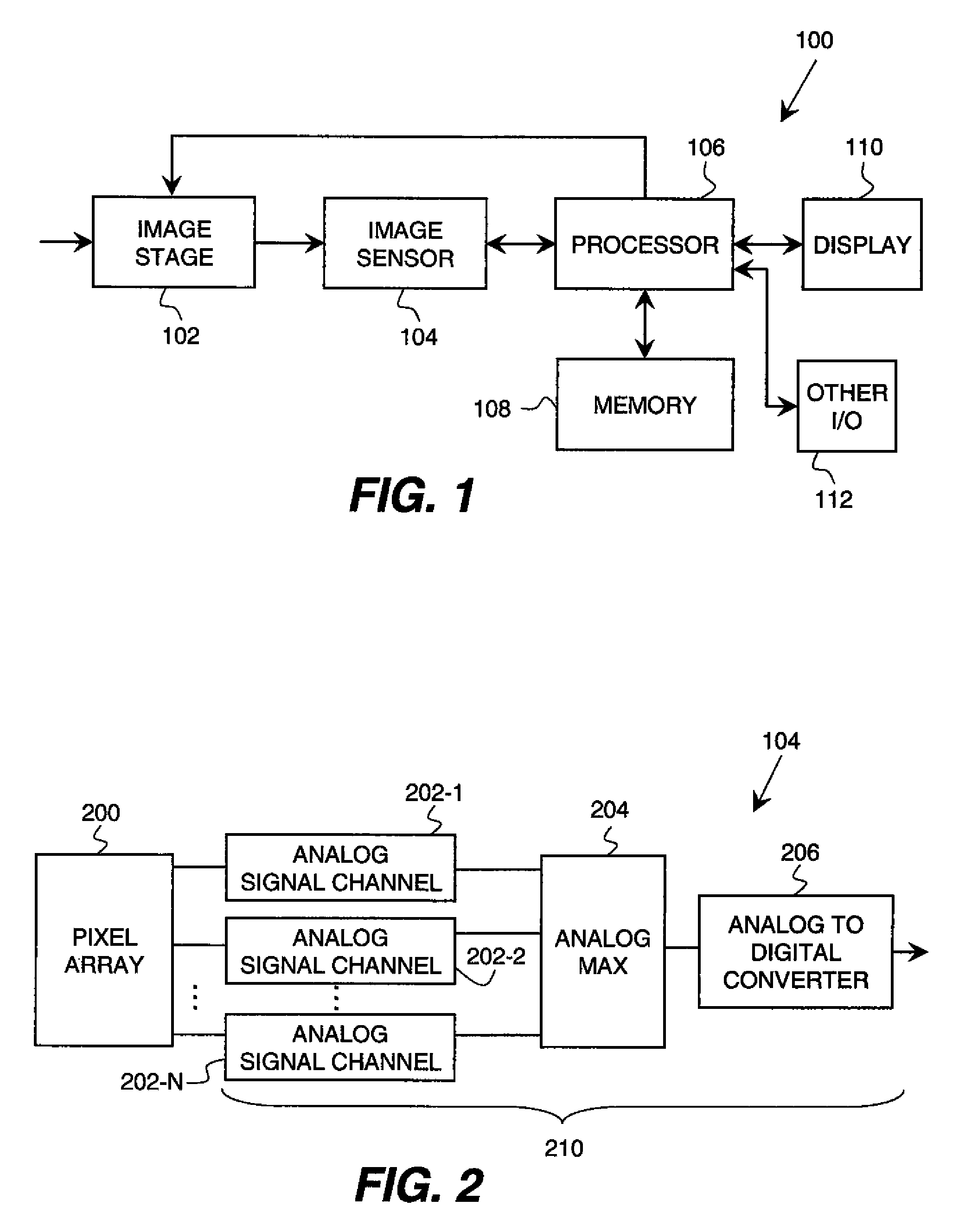
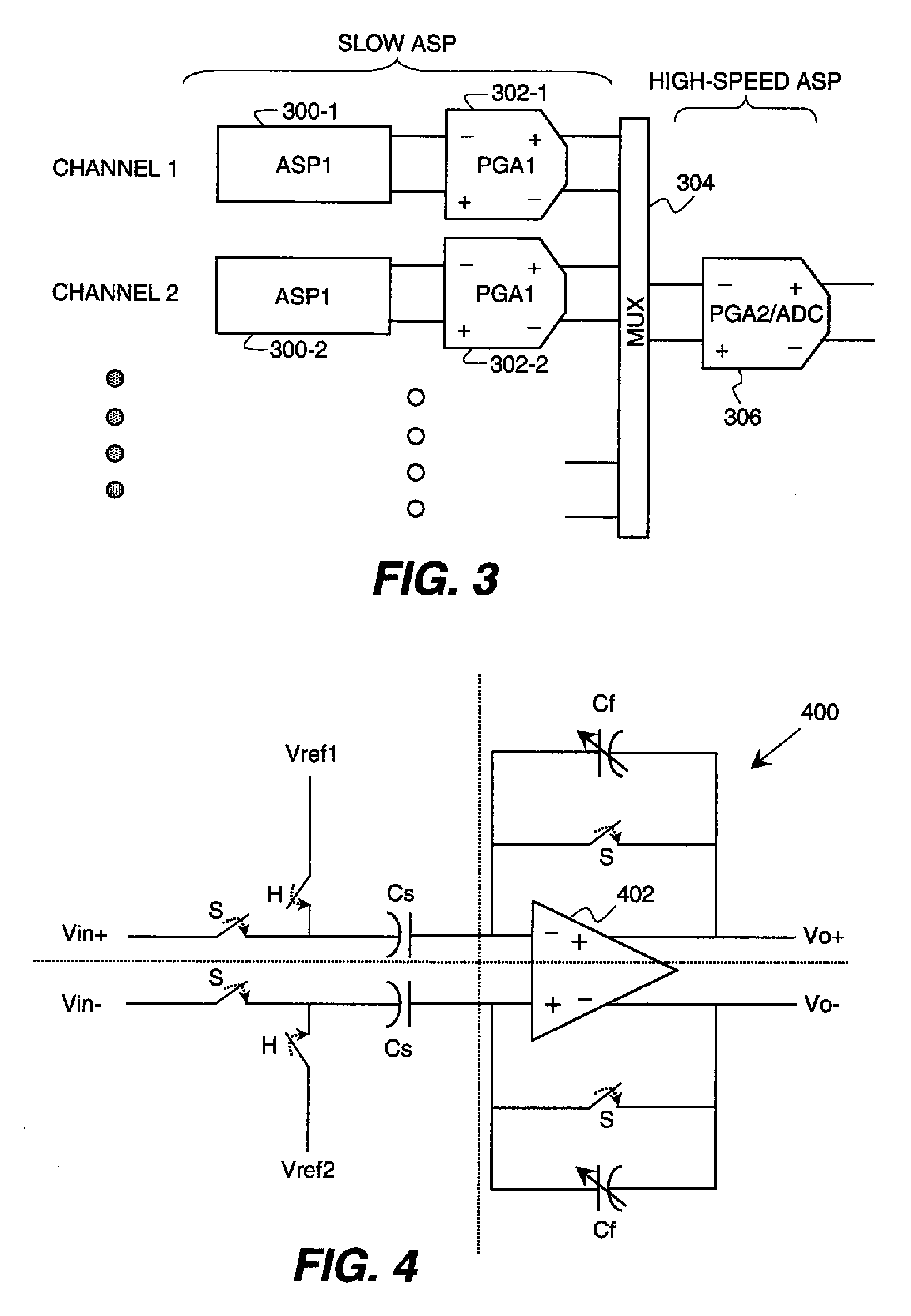
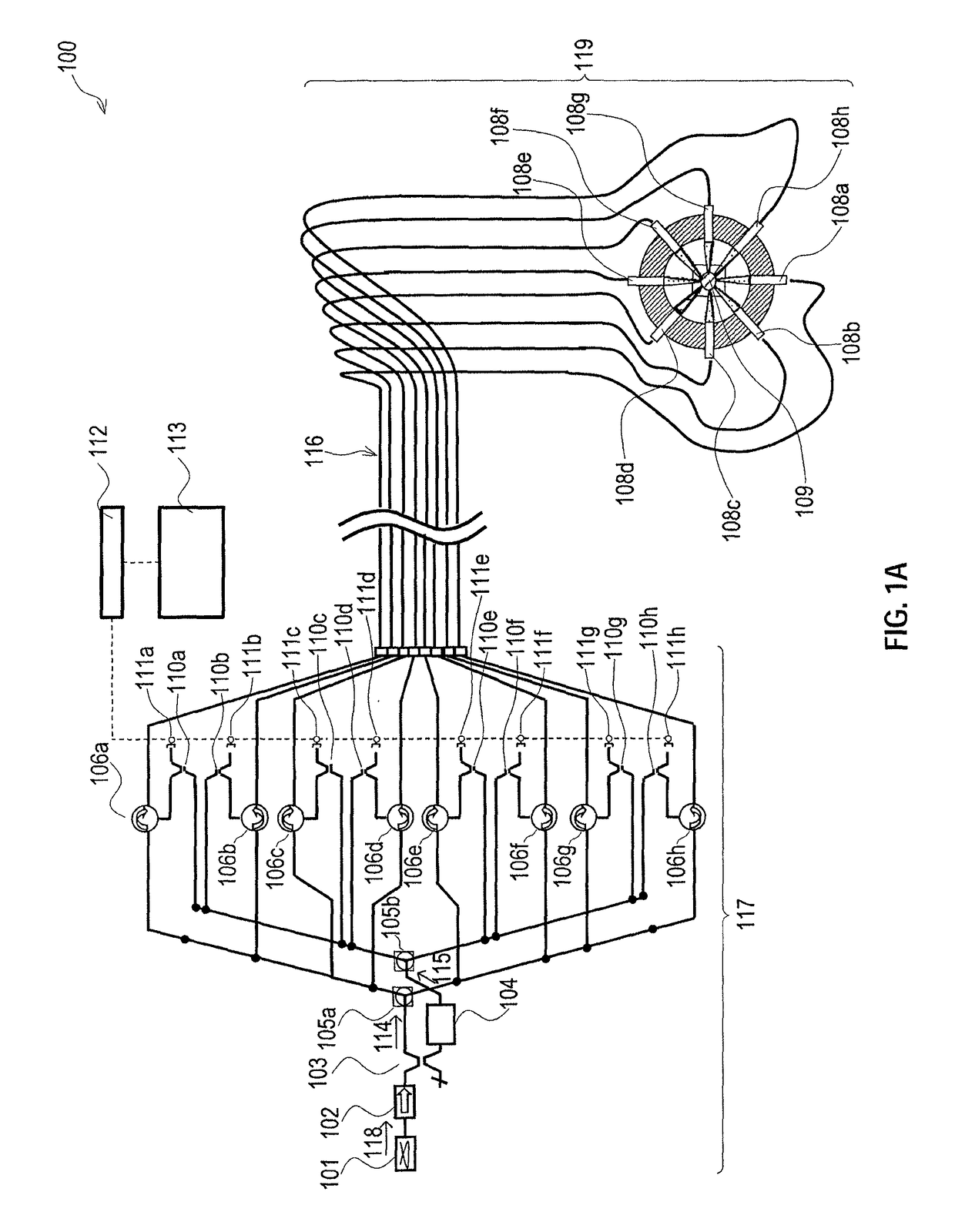
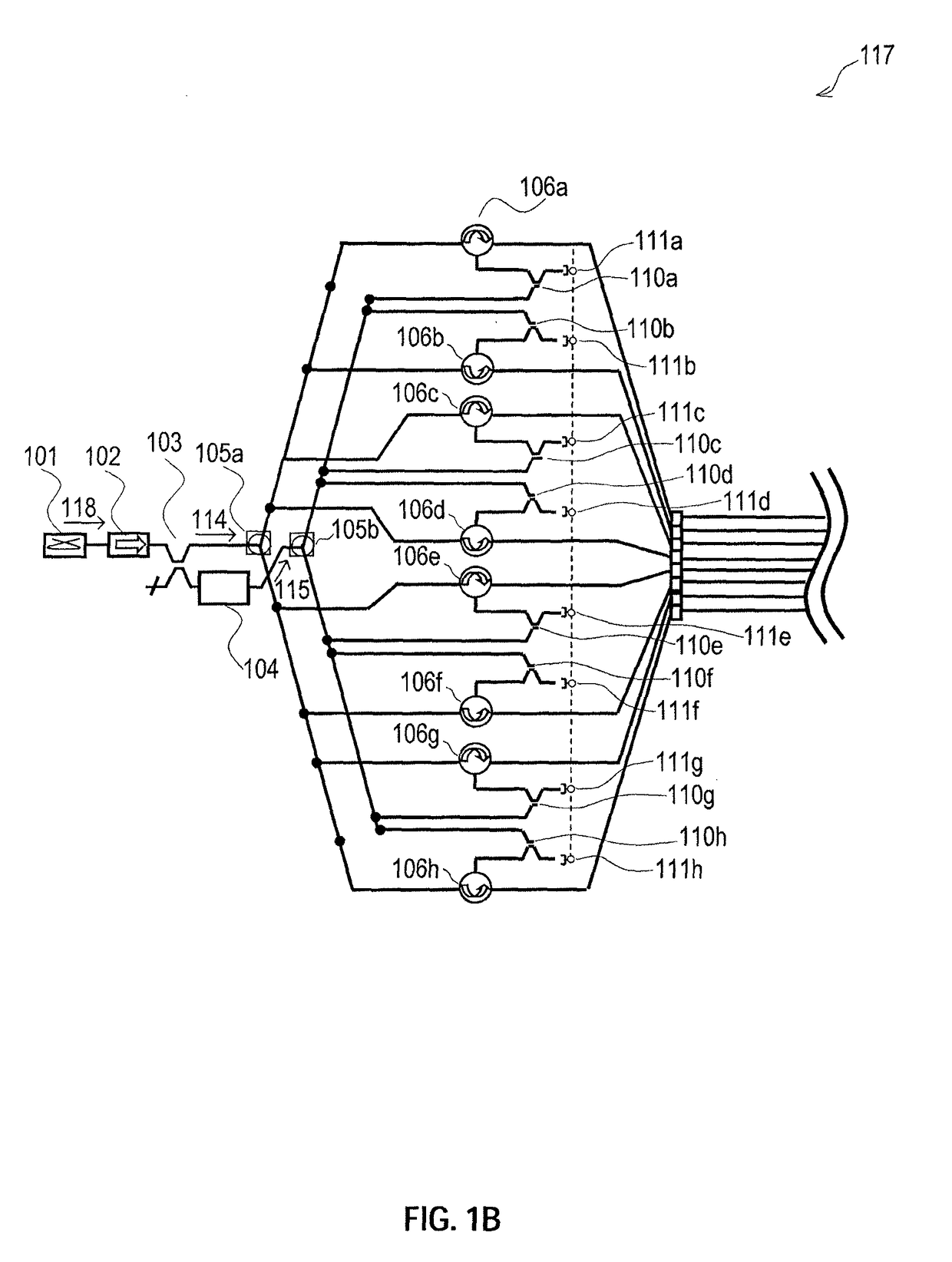
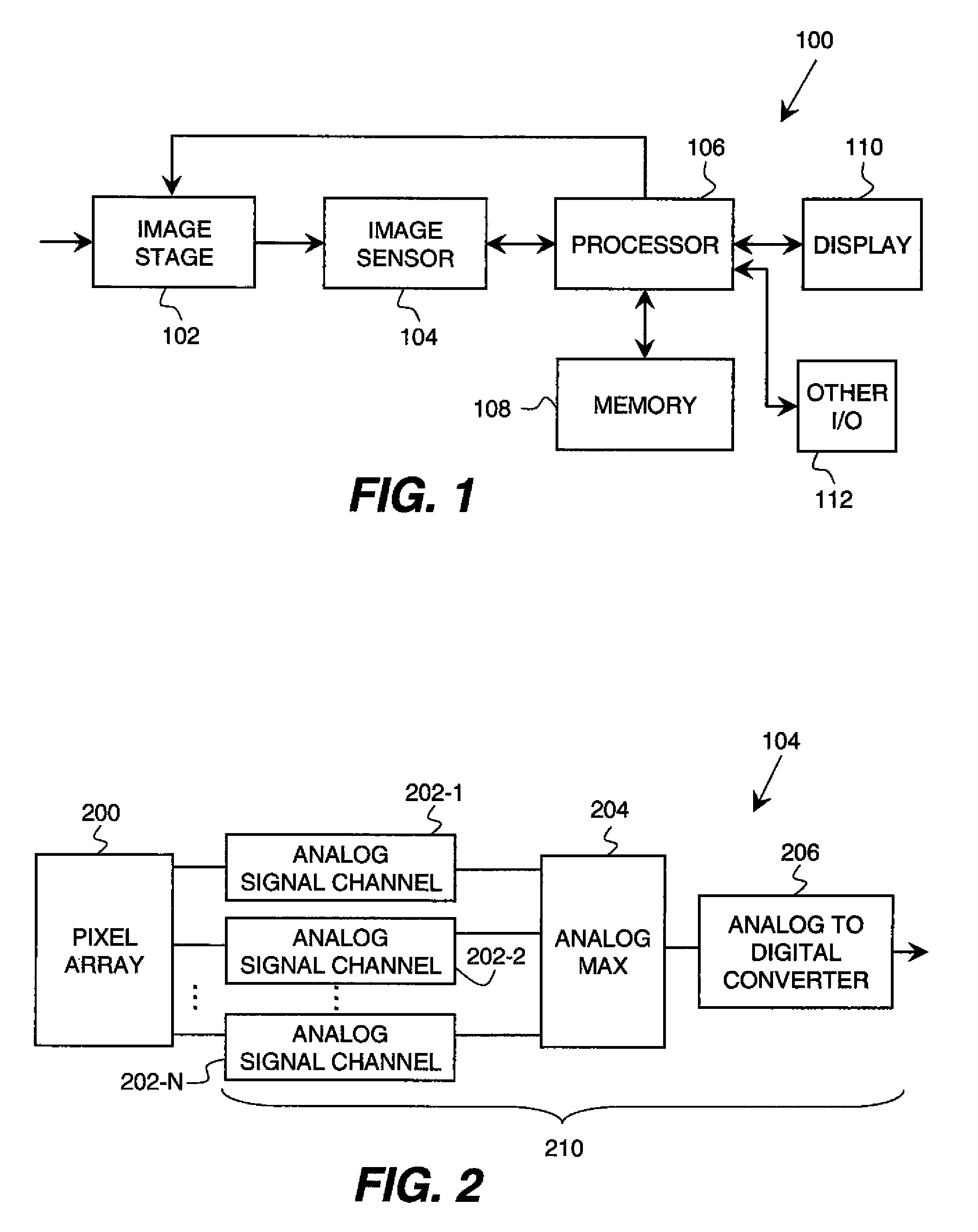
Analog multiplexer configured to reduce kickback perturbation in image sensor readout
ActiveUS20100141822A1High-speed imagingReduce and eliminate perturbationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingAudio power amplifier
An analog multiplexer is configured to multiplex a plurality of input analog signal channels into a single output analog signal channel. The analog multiplexer comprises a plurality of input sampling circuits associated with respective ones of the input analog signal channels and an amplifier having an input controllably connectable in turn to each of the input sampling circuits. The analog multiplexer is further configured to connect at least a given one of the input analog signal channels to a sampling element of its corresponding input sampling circuit at a predetermined time prior to connecting the sampling element of that input sampling circuit to the input of the amplifier. The predetermined time is less than a full clock cycle of a sampling clock of the amplifier. The analog multiplexer may be implemented in readout circuitry coupled to a pixel array in an image sensor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Dynamic activation for an atomic force microscope and method of use thereof
InactiveUS7036357B2Improve ease of useIncrease speedNanotechSurface/boundary effectPhotodetectorLight beam
A scanning probe microscope method and apparatus that modifies imaging dynamics using an active drive technique to optimize the bandwidth of amplitude detection. The deflection is preferably measured by an optical detection system including a laser and a photodetector, which measures cantilever deflection by an optical beam bounce technique or another conventional technique. The detected deflection of the cantilever is subsequently demodulated to give a signal proportional to the amplitude of oscillation of the cantilever, which is thereafter used to drive the cantilever.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
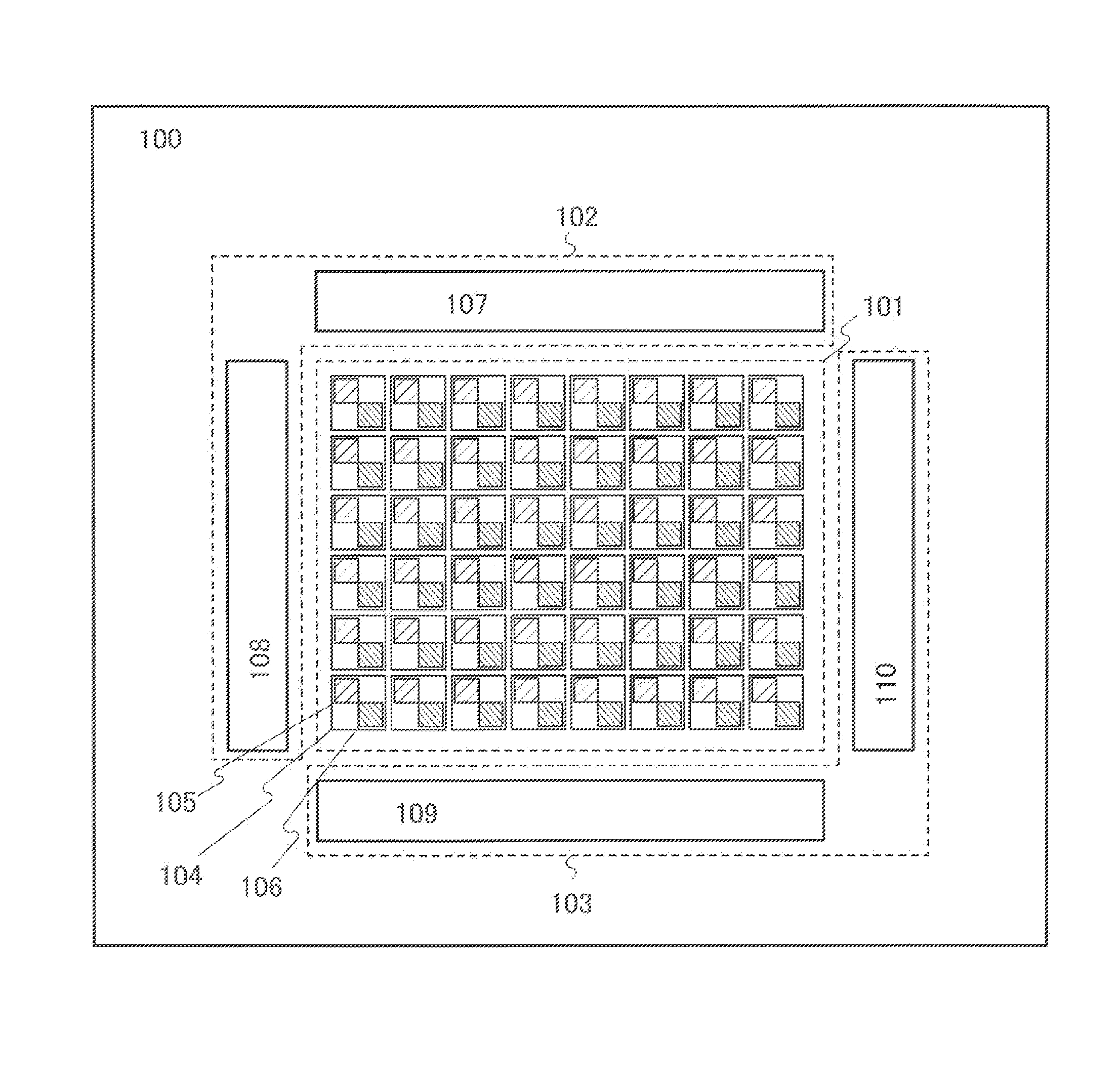
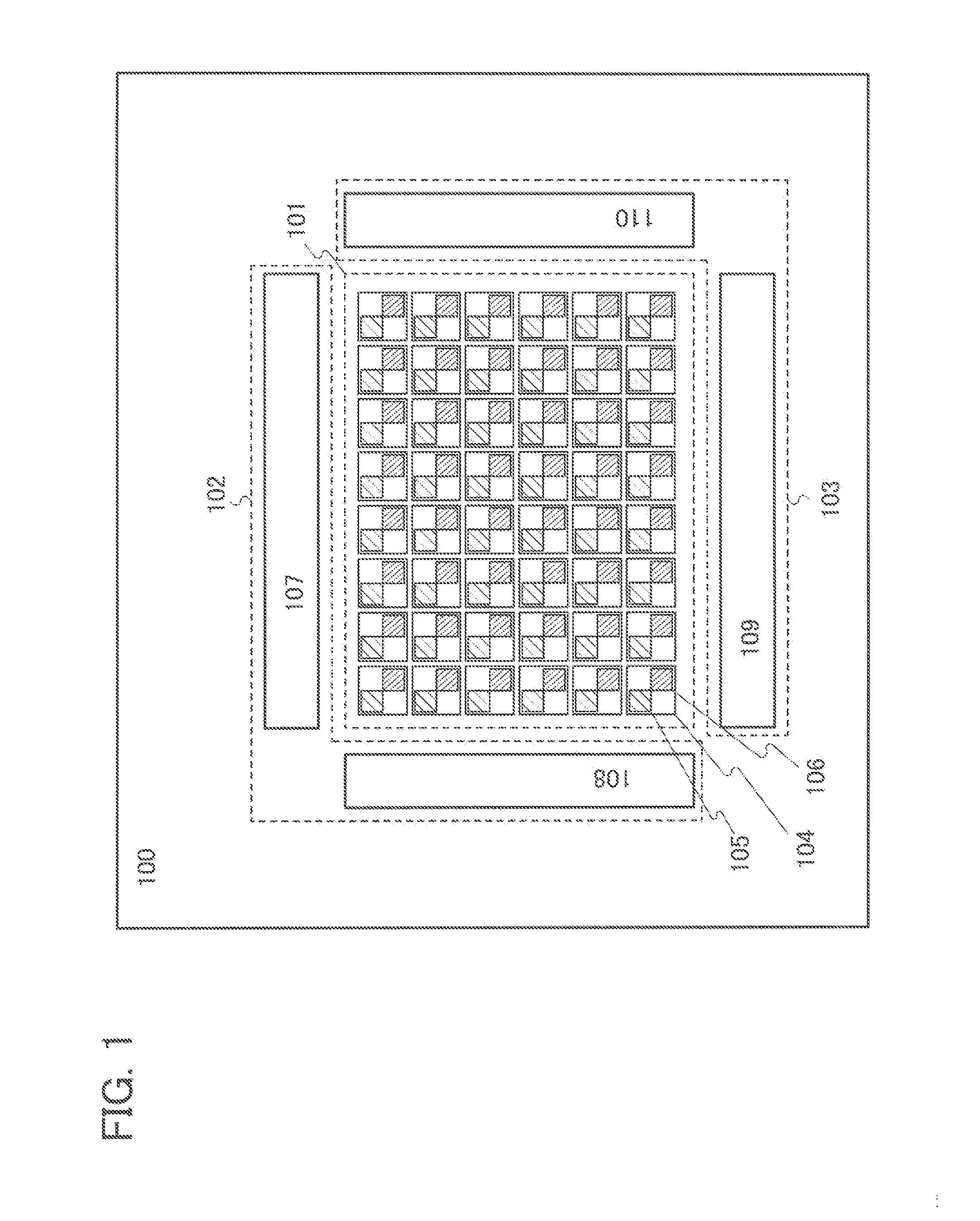
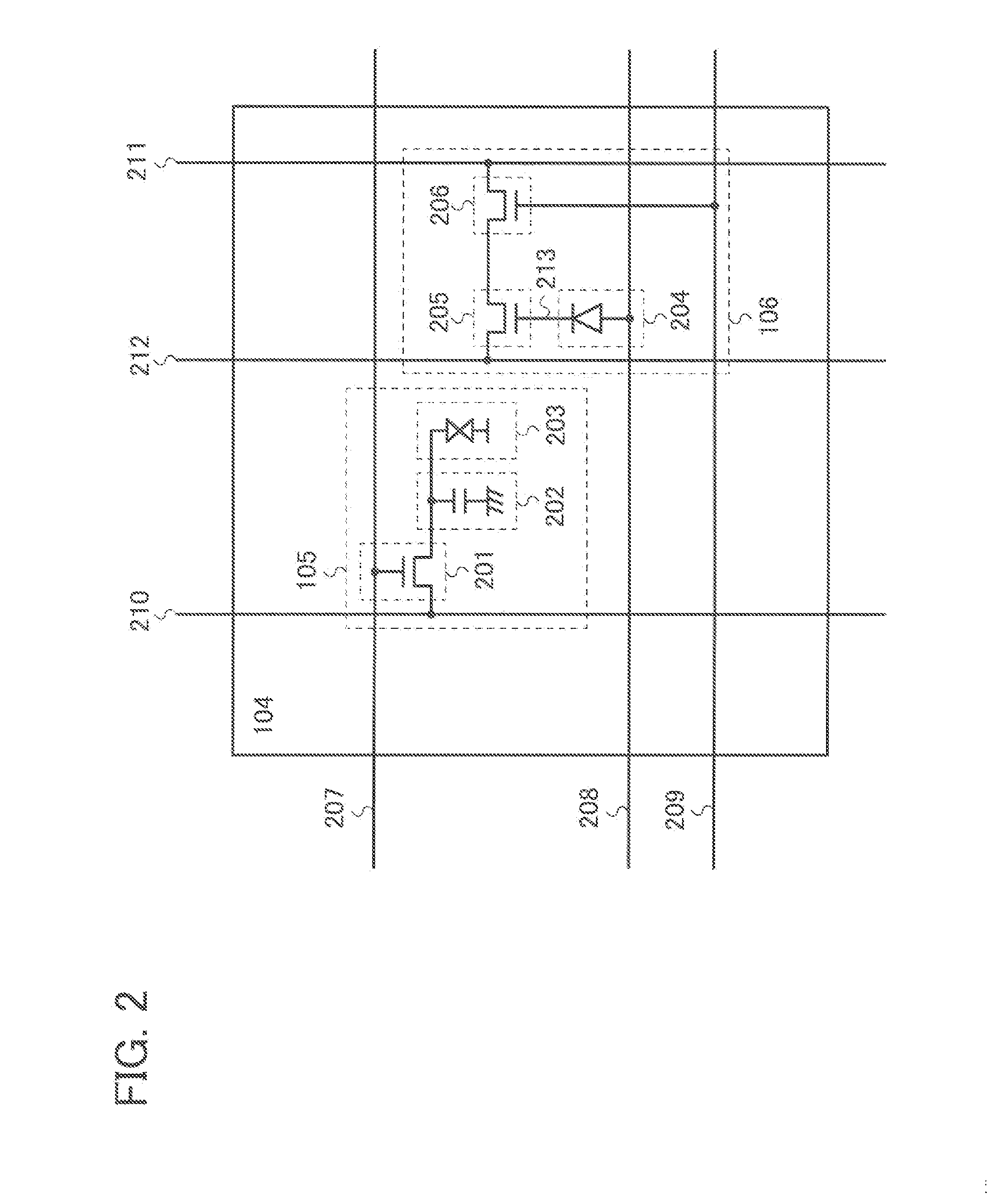
Semiconductor device, imaging device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20160126283A1Reduce areaReduce power consumptionTransistorTelevision system detailsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
Provided is a novel semiconductor device, a semiconductor device with reduced area, or a versatile semiconductor device. The semiconductor device includes a pixel portion including a first pixel, a second pixel, a third pixel, and a fourth pixel; a first switch and a second switch located outside the first to fourth pixels; a first wiring located outside the first to fourth pixels; a second wiring electrically connected to the first and second pixels; and a third wiring electrically connected to the third and fourth pixels. A first terminal of the first switch is electrically connected to the first wiring. A second terminal of the first switch is electrically connected to the second wiring. A first terminal of the second switch is electrically connected to the first wiring. A second terminal of the second switch is electrically connected to the third wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Hybrid design of an anode disk structure for high prower X-ray tube configurations of the rotary-anode type
ActiveUS8553844B2Increase speedHigh-speed imagingX-ray tube laminated targetsReflex klystronsX-rayPeak value
This invention relates to high power X-ray sources, in particular to those equipped with a rotating X-ray anode capable of delivering a higher short time peak power than conventional rotating x-ray anodes. This invention can overcome the thermal limitation of peak power by allowing fast rotation of the anode and by introducing a lightweight material with high thermal conductivity in the region adjacent to the focal track material. The fast rotation can be provided by using sections of the rotating anode disk made of anisotropic high specific strength materials with high thermal stability that can be specifically adapted to the high stresses of anode operation. Uses include high speed image acquisition for X-ray imaging, for example, of moving objects in real-time such as in medical radiography.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Omnidirectional Camera
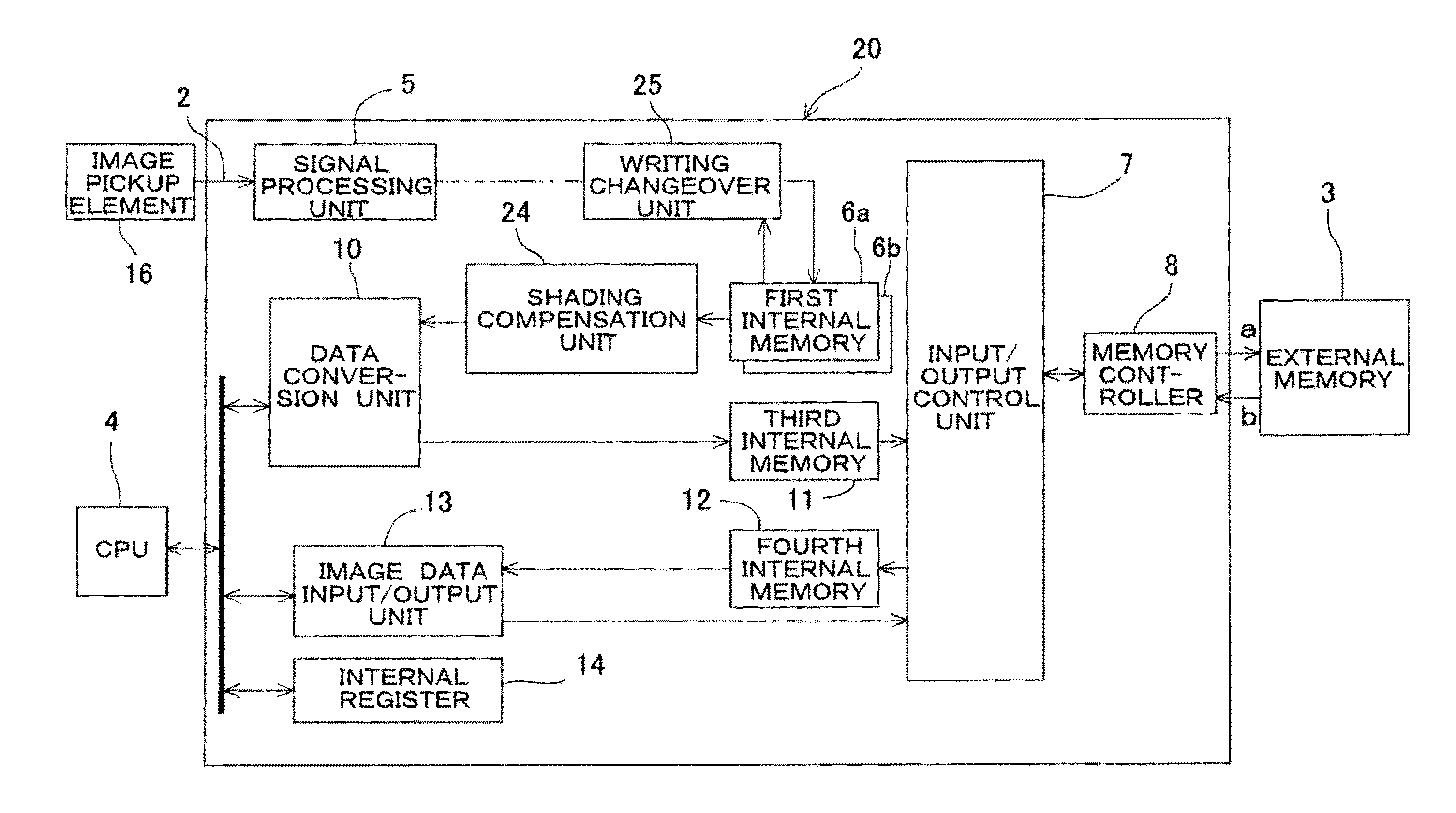
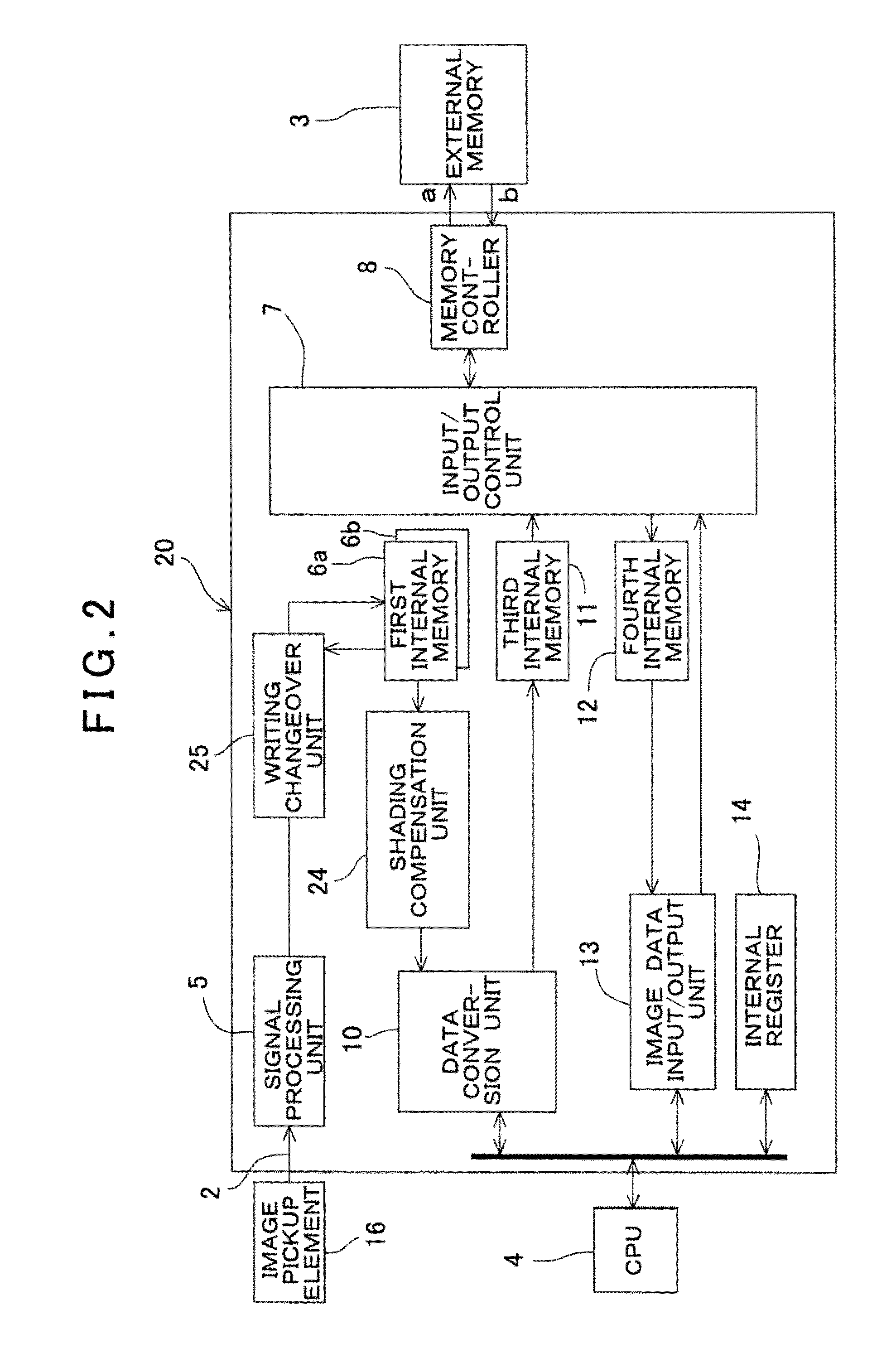
ActiveUS20140092207A1Improve brightness uniformityIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInternal memoryTime signal
An omnidirectional camera comprises a camera having an image pickup element for acquiring a digital image, an image data processing device for compressing signals from the camera and for converting the signal to an image signal, and an external memory. The image data processing device has a signal processing unit, a writing changeover unit, a set of two first internal memories, a signal compensation unit, a data conversion unit, a third internal memory for temporarily storing the outputted data, and an input / output control unit for controlling the input / output of the data between the third internal memory and the external memory. The writing changeover unit accumulates signals outputted from the signal processing unit in one of the first internal memories until the signals are accumulated to a predetermined amount, and then, the writing changeover unit changes the destination of accumulation and repeatedly accumulates in the other first internal memory.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Dynamic activation for an atomic force microscope and method of use thereof
InactiveUS7204131B2Increase speedIncrease usageNanotechSurface/boundary effectPhotodetectorLight beam
A scanning probe microscope method and apparatus that modifies imaging dynamics using an active drive technique to optimize the bandwidth of amplitude detection. The deflection is preferably measured by an optical detection system including a laser and a photodetector, which measures cantilever deflection by an optical beam bounce technique or another conventional technique. The detected deflection of the cantilever is subsequently demodulated to give a signal proportional to the amplitude of oscillation of the cantilever, which is thereafter used to drive the cantilever.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Diagnostic scanning apparatus
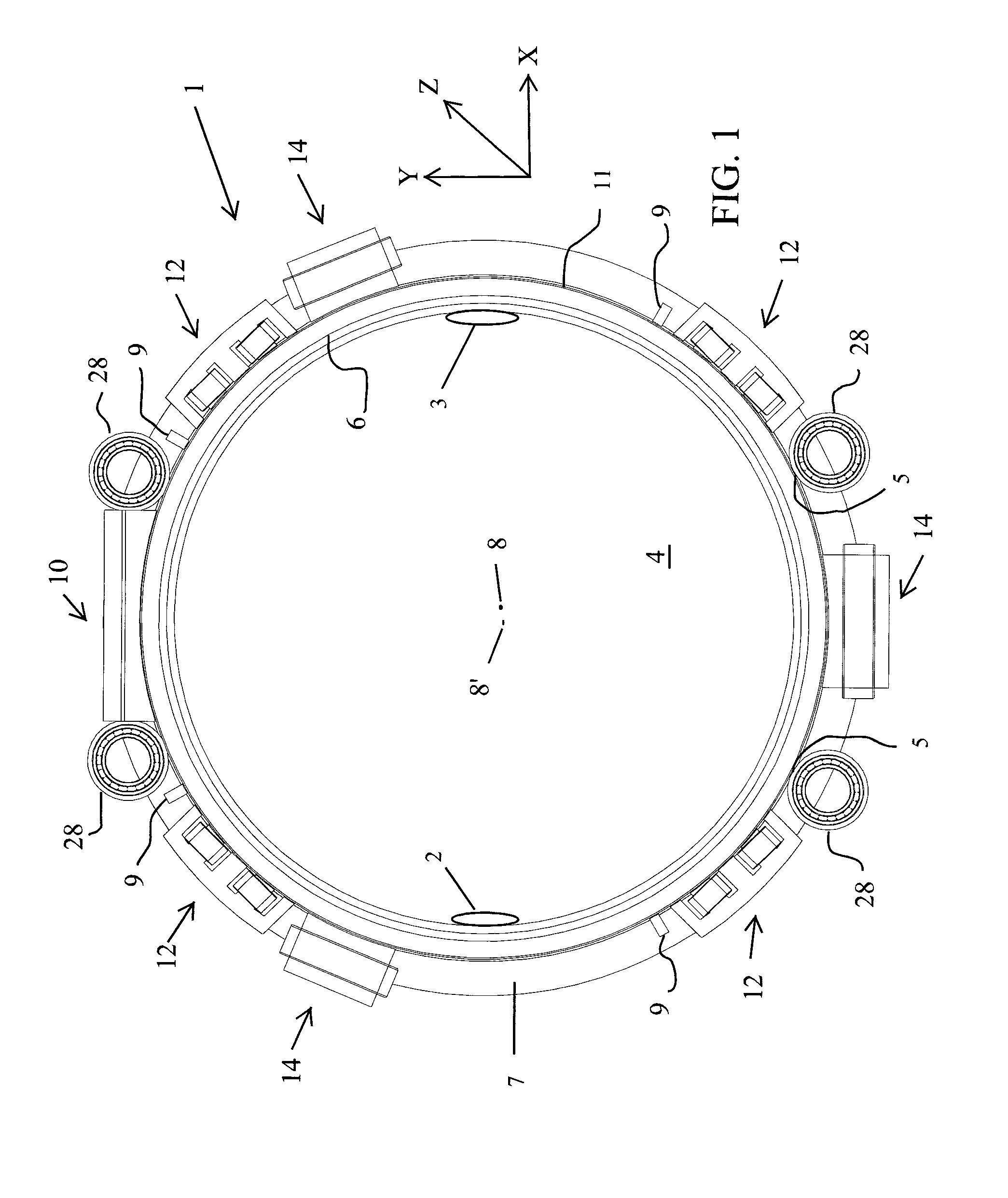
ActiveUS20140270051A1Reduced and no lubrication requirementMinimizing and eliminating amountMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRolling contact bearingsEngineeringActuator
A diagnostic scanning apparatus includes a hollow rotor sized to receive a patient. First and second flanges are connected to and extend radially outward from the rotor in a spaced-apart relationship, each of the first and second flanges including, at least in part, a magnetically-permeable material. A radiation source is affixed to the first flange and / or the rotor. A first axial actuator generates a variable magnetic field, is fixedly disposed adjacent to the first flange and can magnetically pull the first flange in a first axial direction of the rotor. A second axial actuator generates a variable magnetic field, is fixedly disposed adjacent to the second flange and can magnetically pull the second flange in a second axial direction of the rotor that is opposite of the first axial direction. The first and second axial actuators are both at least substantially disposed between the first and second flanges.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +2
Single-pixel multispectral calculation imaging system and imaging method based on bundled optical fibers
ActiveCN110793633AHigh speed imagingRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyVIT signalsImage sensor
The invention provides a single-pixel multispectral calculation imaging system and imaging method based on the bundled optical fibers, thereby realizing the high anti-interference capacity, reducing hardware consumption resources, and reducing the requirements for texts. The invention provides a novel method for observing matrix changes by replacing a DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) with bundledoptical fibers and an image sensor (CCD). One of the bundled optical fibers is connected with a sensor to collect signals, and the other branches are connected with a modulatable light source. Different light intensity distribution is formed on an irradiated target in different on-off states of the light sources; according to the light intensity distribution, the observation matrix is able to realize modulation of 10 to 100KHz simply by the light source and thus the change frequency of the observation matrix can also reach the rate. After the system is built, he observation matrix is collectedand recorded frame by frame through a CCD and a recovery model is built; and no collection is performed in the follow-up actual observation process. With the provided method, the high-speed single-pixel imaging can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and system for conformal imaging vibrometry
ActiveUS20150285613A1Fully characterizedHigh-speed imagingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansMultiplexingStructural dynamics
Systems and methods for conformal imaging vibrometry capable of real-time measurements of the dynamic motions of any arbitrary two-dimensional or three-dimensional structure. The disclosed systems and methods are able to fully characterize the dynamic behavior of an object of any arbitrary geometry. The test object is illuminated with multiple laser beams whose directions conform to the local normal axis of the surface. The approach enables high-speed vibration imaging of whole-body dynamics of arbitrarily shaped structures in real-time, with no multiplexed data capture or synthesized motion reconstruction, as is currently practiced. By measuring the object's vibrations simultaneously at multiple points, the disclosed systems and methods are able to reproduce the structural behavior under operational conditions, which can then be spectrally decomposed to determine the modal, complex modal and transient nature of the true structural dynamics.
Owner:ADVANCED SYST & TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging device and RF coil
ActiveUS20150028873A1Improve installabilityEasy to operateMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical connectionEngineering
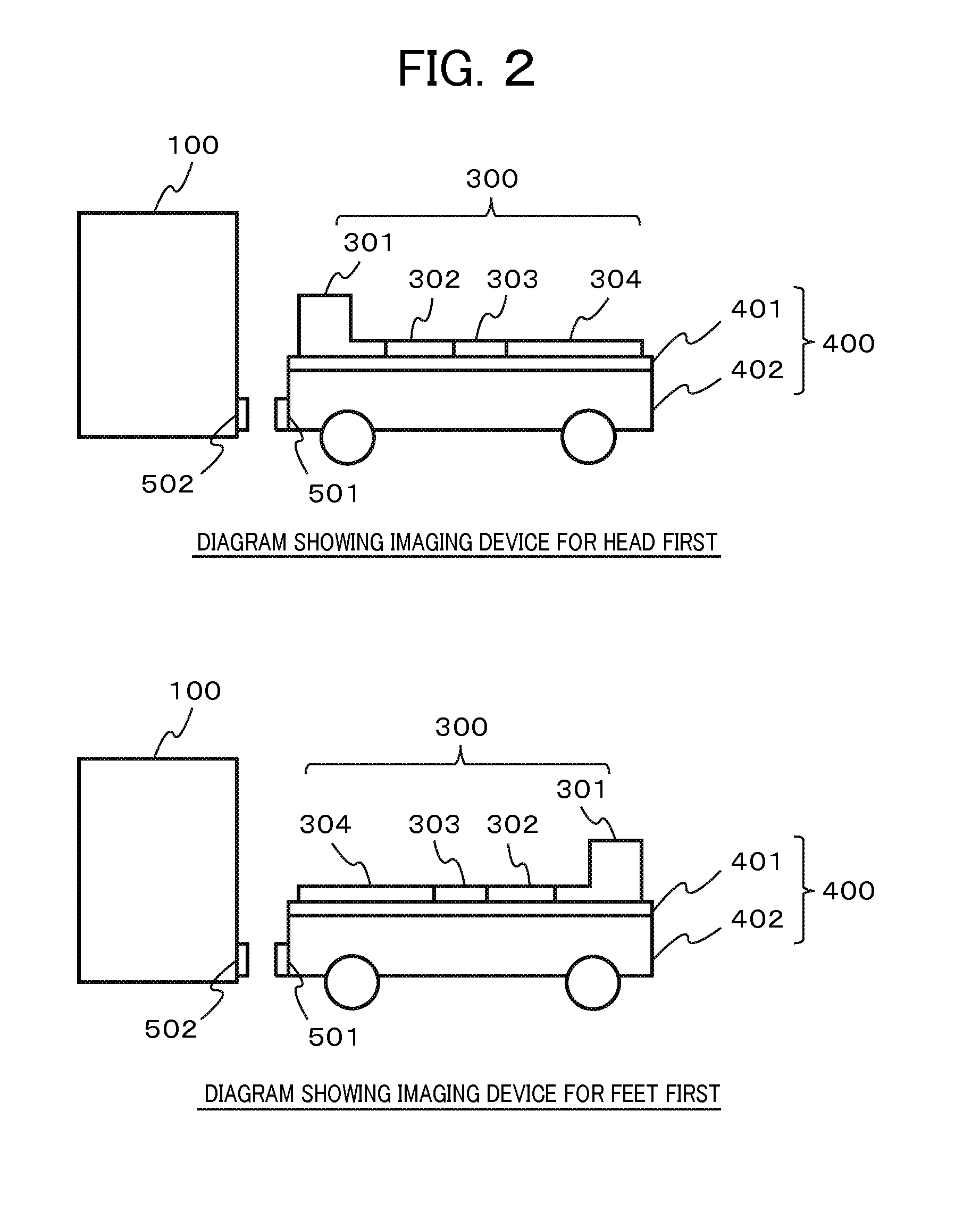
A lower cost MRI device with a portable table detachable from the gantry is provided along with a lower cost table equipped with an easy-to-use and easy-to-install RF coil system able to perform high-resolution head and neck imaging and high-speed whole body imaging in both head-first and feet-first modes. This magnetic resonance imaging device has a portable table detachable from the gantry, and the portable table has a docking connector that can be connected to the gantry and a ceiling panel on which an RF coil can be installed to receive nuclear magnetic resonance signals generated by the examinee and to irradiate the examinee with a high-frequency magnetic field. The RF coil is divided into two or more RF coil units, the ceiling panel has a plurality of ceiling panel connectors enabling each RF coil unit to be connected, and each RF coil unit has a connector. Each RF coil unit is arranged in overlapping fashion on the ceiling plate and the ceiling panel connectors and coil connectors are connected without having to establish an electrical connection between RF coil units.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
System and method for flexible circuits
InactiveUS20050180100A1Reduce inductanceHigh-speed imagingInsulated cablesElectrical apparatus contructional detailsFlexible circuitsReturn current
A flexible printed circuit improves data transfer rates by disposing ground wires in a ground plane proximate to signal wires disposed in a signal channel plane. One or more ground wires is associated with each signal wire pair or each signal wire for imaging of the return currents of the signal pairs. An overlapping alignment minimizes loop area between a ground wire and its associated signal wire. An offset alignment provides a reduced loop area and reduced breakage risk since movement of the flexible-circuit does result in compression of the signal wire and its associated ground wire. A combination of overlapping and offset alignment balances signal transfer effectiveness with breakage risk by offsetting ground and signal wires is stress sensitive regions and overlapping ground and signal wires in stress tolerant regions. In one embodiment, the flexible circuit interfaces a portable computer with a display lid to support high-speed display signals with reduced breakage risk from cycling the display lid between an open and closed position.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Wiring structure for display device
ActiveUS20140227462A1Improve heat resistanceLower resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrofluoric acidRare-earth element
Provided is a wiring structure for display device which does not generate hillocks even when exposed to high temperatures at levels around 450 to 600° C., has excellent high-temperature heat resistance, keeps electrical resistance (wiring resistance) of the entire wiring structure low, and further has excellent resistance to hydrofluoric acid. This wiring structure for a display device comprises a structure in which are laminated, in order from the substrate side, a first layer of an Al alloy that contains at least one chemical element selected from the group (group X) consisting of Ta, Nb, Re, Zr, W, Mo, V, Hf, Ti, Cr, and Pt and contains at least one rare earth element, and a second layer of an Al alloy nitride, or a nitride of at least one chemical element selected from the group Y consisted of Ti, Mo, Al, Ta, Nb, Re, Zr, W, V, Hf, and Cr.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
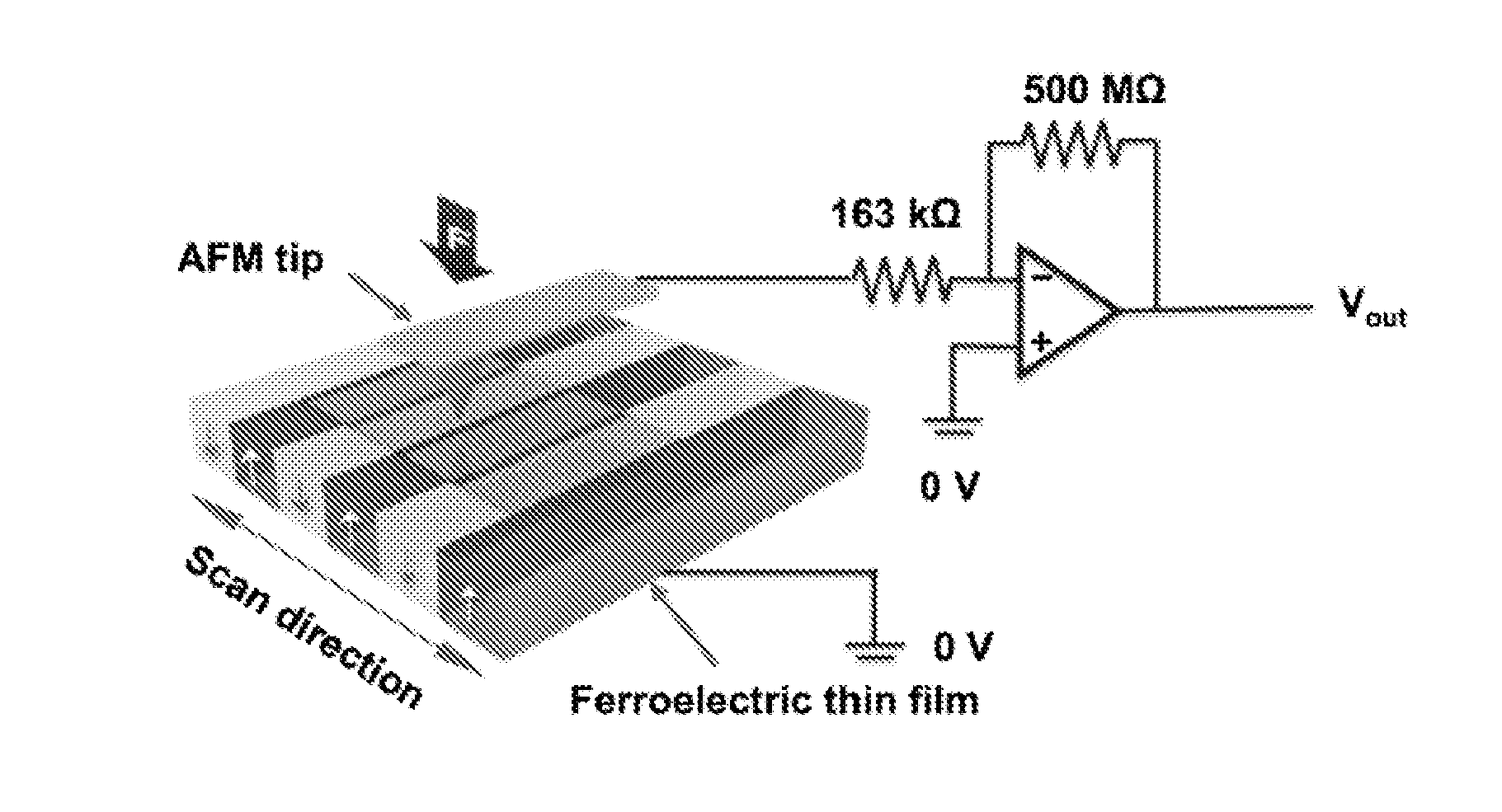
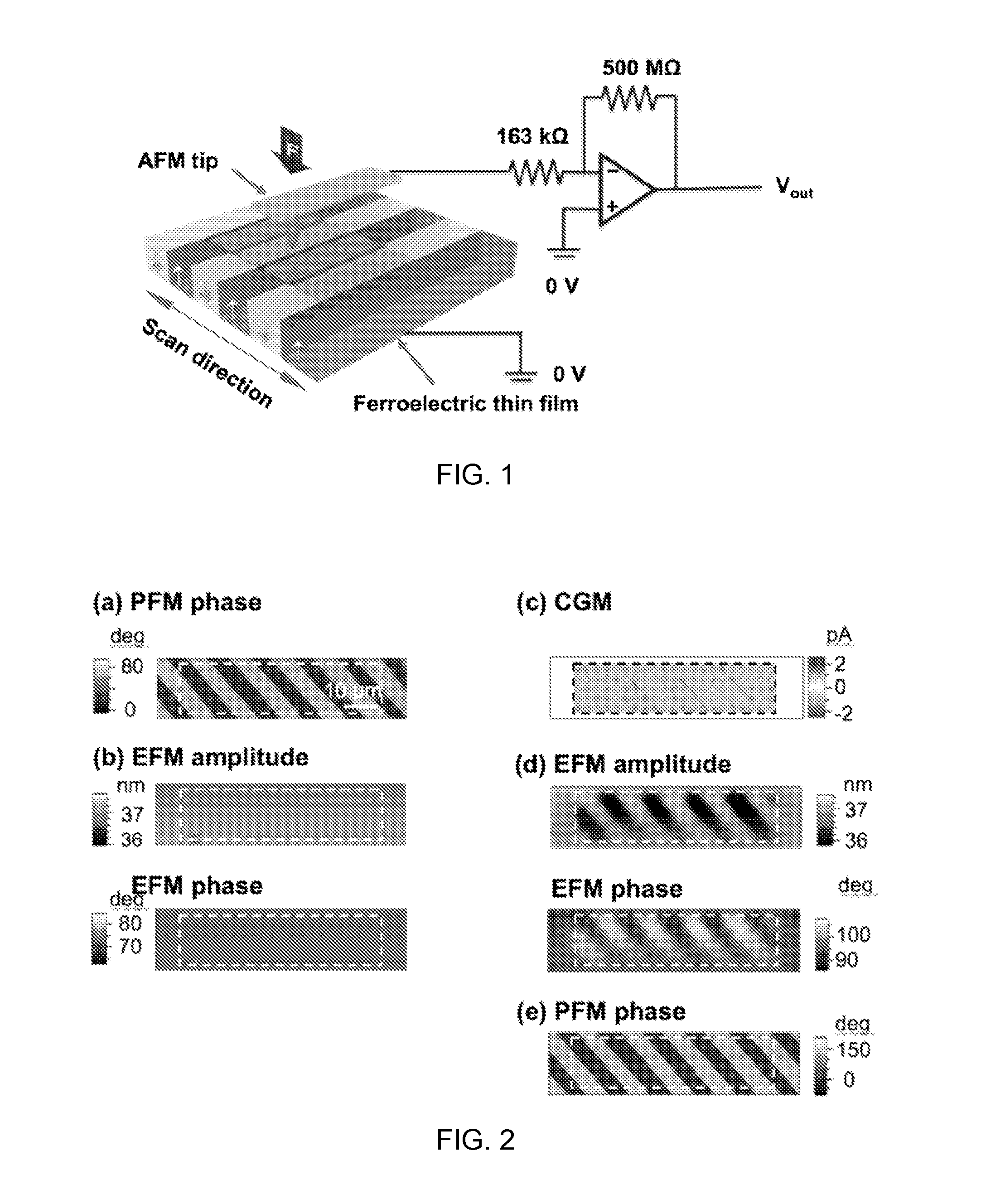
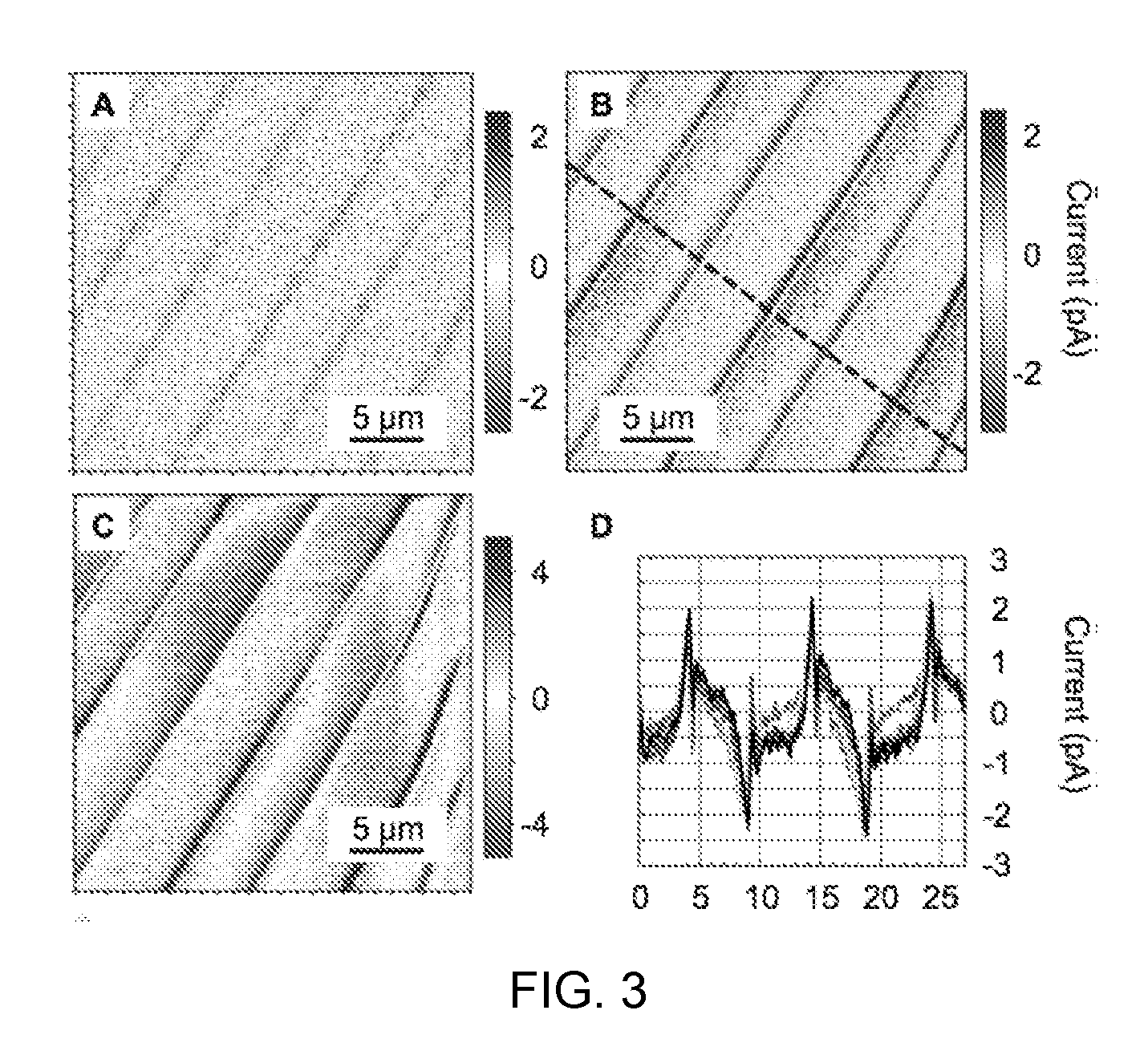
Charge gradient microscopy
ActiveUS20150301324A1Effective approachHigh-speed imagingColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsRapid imagingData detection
A method for rapid imaging of a material specimen includes positioning a tip to contact the material specimen, and applying a force to a surface of the material specimen via the tip. In addition, the method includes moving the tip across the surface of the material specimen while removing electrical charge therefrom, generating a signal produced by contact between the tip and the surface, and detecting, based on the data, the removed electrical charge induced through the tip during movement of the tip across the surface. The method further includes measuring the detected electrical charge.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method and system for conformal imaging vibrometry
InactiveUS9829374B2Fully characterizedHigh-speed imagingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansMultiplexingStructural dynamics
Systems and methods for conformal imaging vibrometry capable of real-time measurements of the dynamic motions of any arbitrary two-dimensional or three-dimensional structure. The systems and methods are able to fully characterize the dynamic behavior of an object of any arbitrary geometry. The test object is illuminated with multiple laser beams whose directions conform to the local normal axis of the surface. The approach enables high-speed vibration imaging of whole-body dynamics of arbitrarily shaped structures in real-time, with no multiplexed data capture or synthesized motion reconstruction, as is currently practiced. By measuring the object's vibrations simultaneously at multiple points, the disclosed systems and methods are able to reproduce the structural behavior under operational conditions, which can then be spectrally decomposed to determine the modal, complex modal and transient nature of the true structural dynamics.
Owner:ADVANCED SYST & TECH
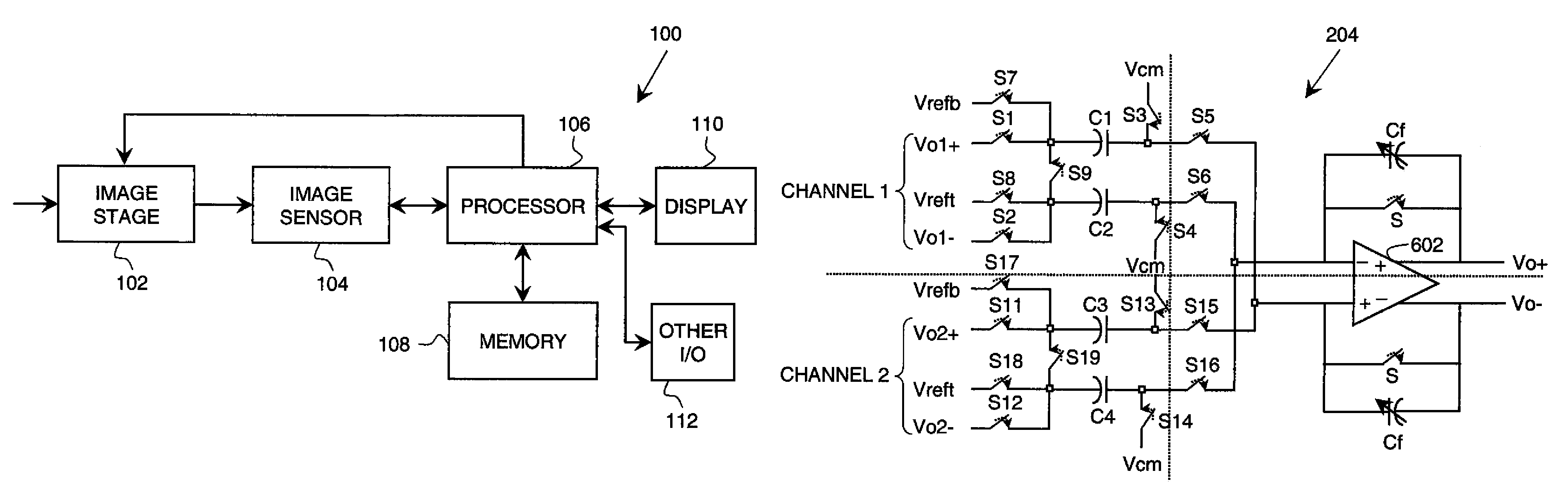
Analog multiplexer configured to reduce kickback perturbation in image sensor readout
ActiveUS8184184B2High-speed imagingReduce and eliminate perturbationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingAudio power amplifier
An analog multiplexer is configured to multiplex a plurality of input analog signal channels into a single output analog signal channel. The analog multiplexer comprises a plurality of input sampling circuits associated with respective ones of the input analog signal channels and an amplifier having an input controllably connectable in turn to each of the input sampling circuits. The analog multiplexer is further configured to connect at least a given one of the input analog signal channels to a sampling element of its corresponding input sampling circuit at a predetermined time prior to connecting the sampling element of that input sampling circuit to the input of the amplifier. The predetermined time is less than a full clock cycle of a sampling clock of the amplifier. The analog multiplexer may be implemented in readout circuitry coupled to a pixel array in an image sensor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
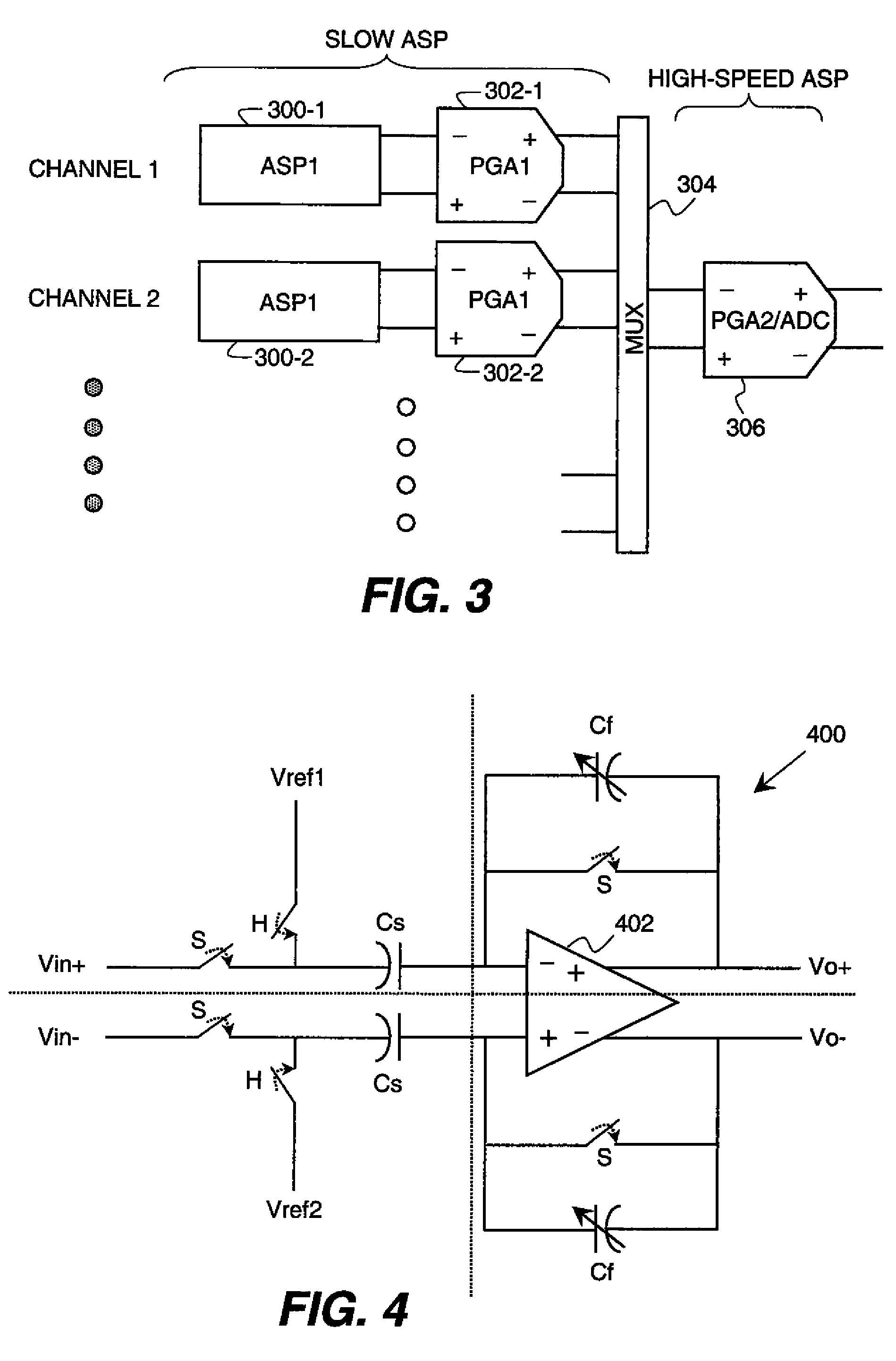
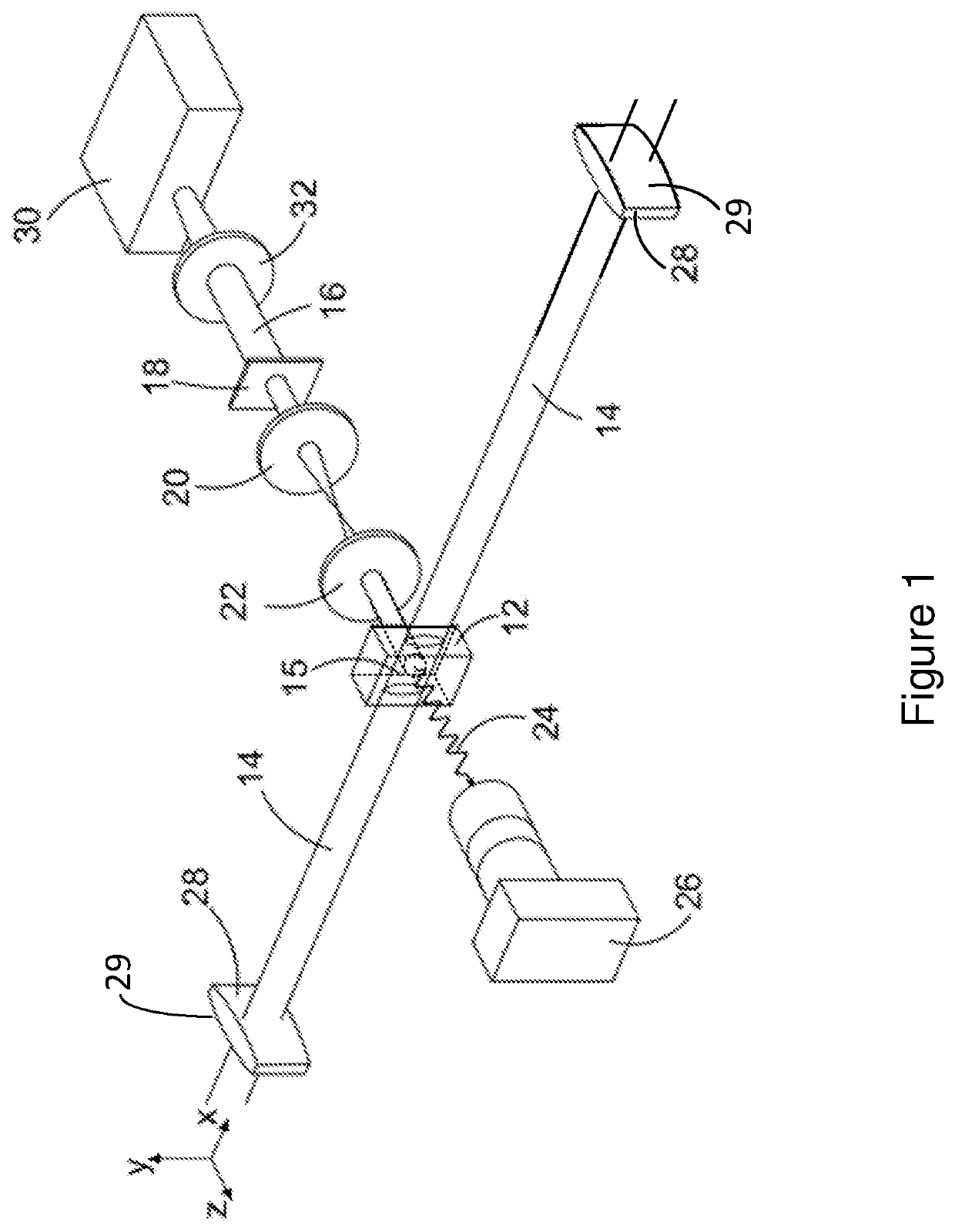
Method and Apparatus for Terahertz or Microwave Imaging
PendingUS20210389248A1Reduce image blurIncrease field strengthMaterial analysis using microwave meansFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical fluorescenceMicrowave imaging
An apparatus and method for imaging using microwave or terahertz radiation are described. The apparatus (10) comprises: a cell (12) comprising a vapour of atoms; one or more laser beams (14) propagating through said cell (12), said one or more laser beams (14) defining a sensing region (15) in said cell (12); an imaging beam (16) for illuminating an object receiving area for receiving an object (18) to be imaged, said imaging beam (16) comprising microwave or terahertz radiation; an imaging system (20, 22) for focussing the imaging beam (16) to form, in use, an image of said object (18) at said sensing region (15) in said cell (12); wherein respective frequencies of said one or more laser beams (14) and said imaging beam (16) are such that at least some of said atoms, when subjected to radiation of both said one or more laser beams (14) and said imaging beam (16), are excited to a final excited state which decays to a lower energy state by emission of optical fluorescence (24).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DURHAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com