Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2381 results about "Subnetwork" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
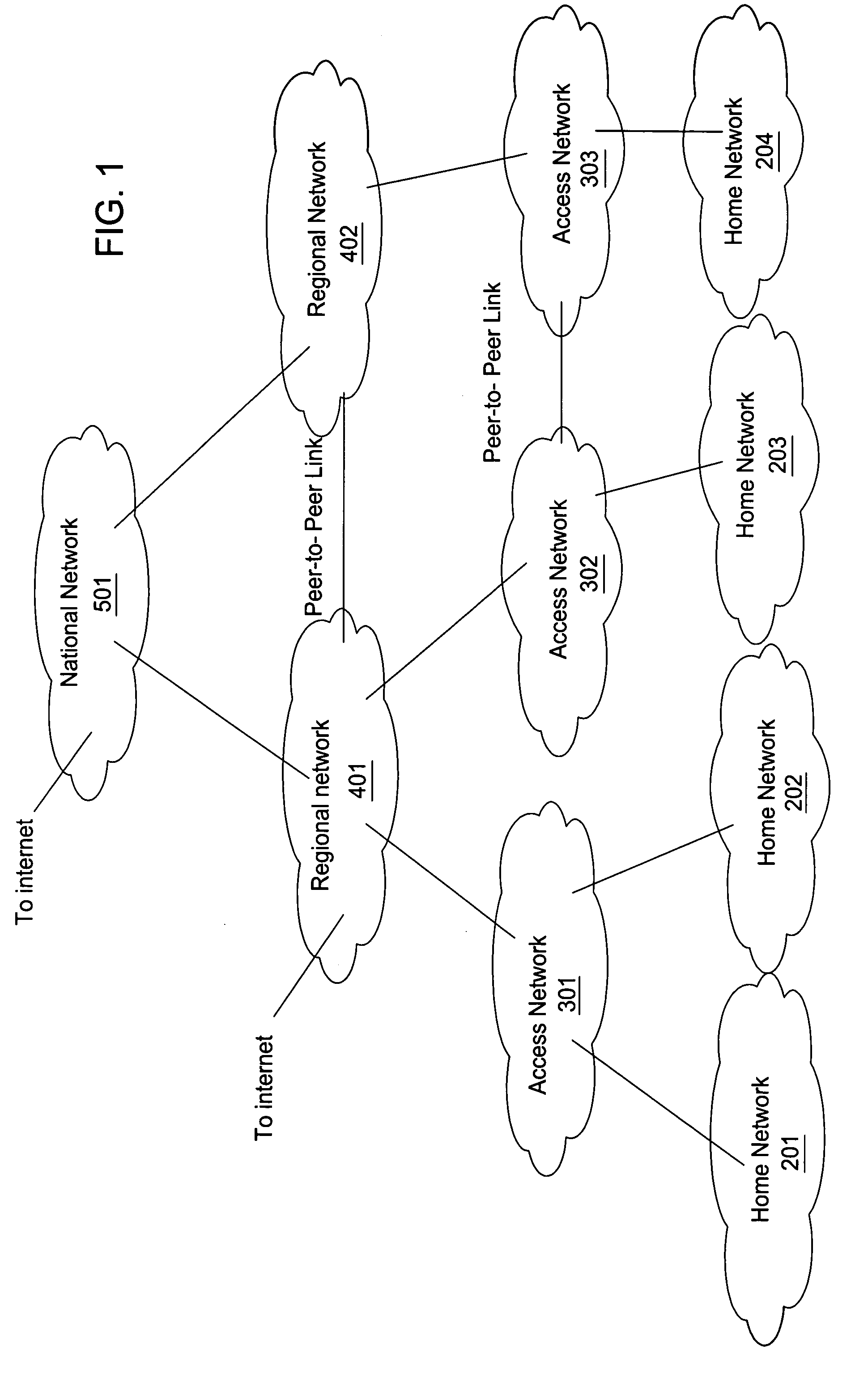
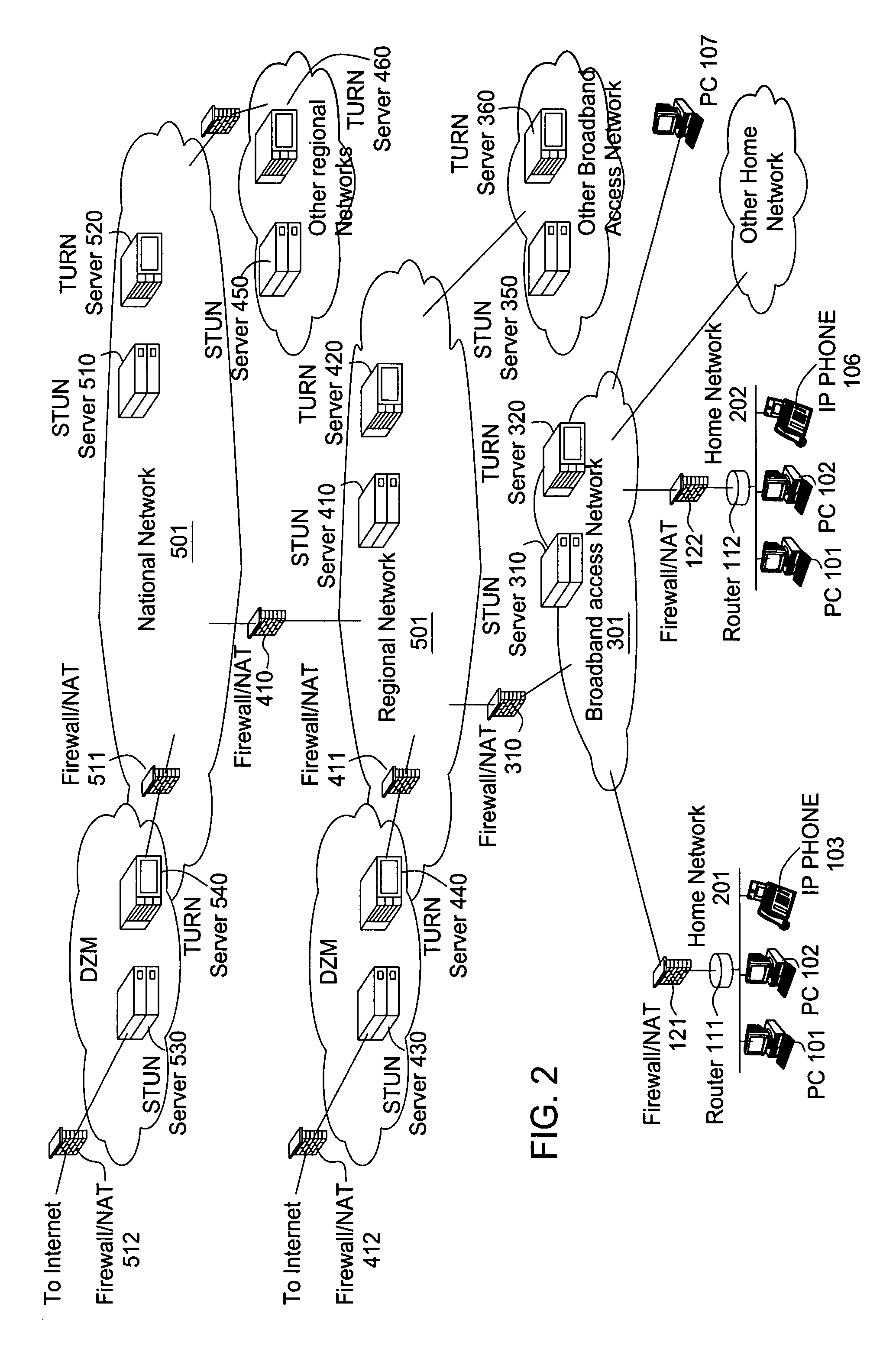
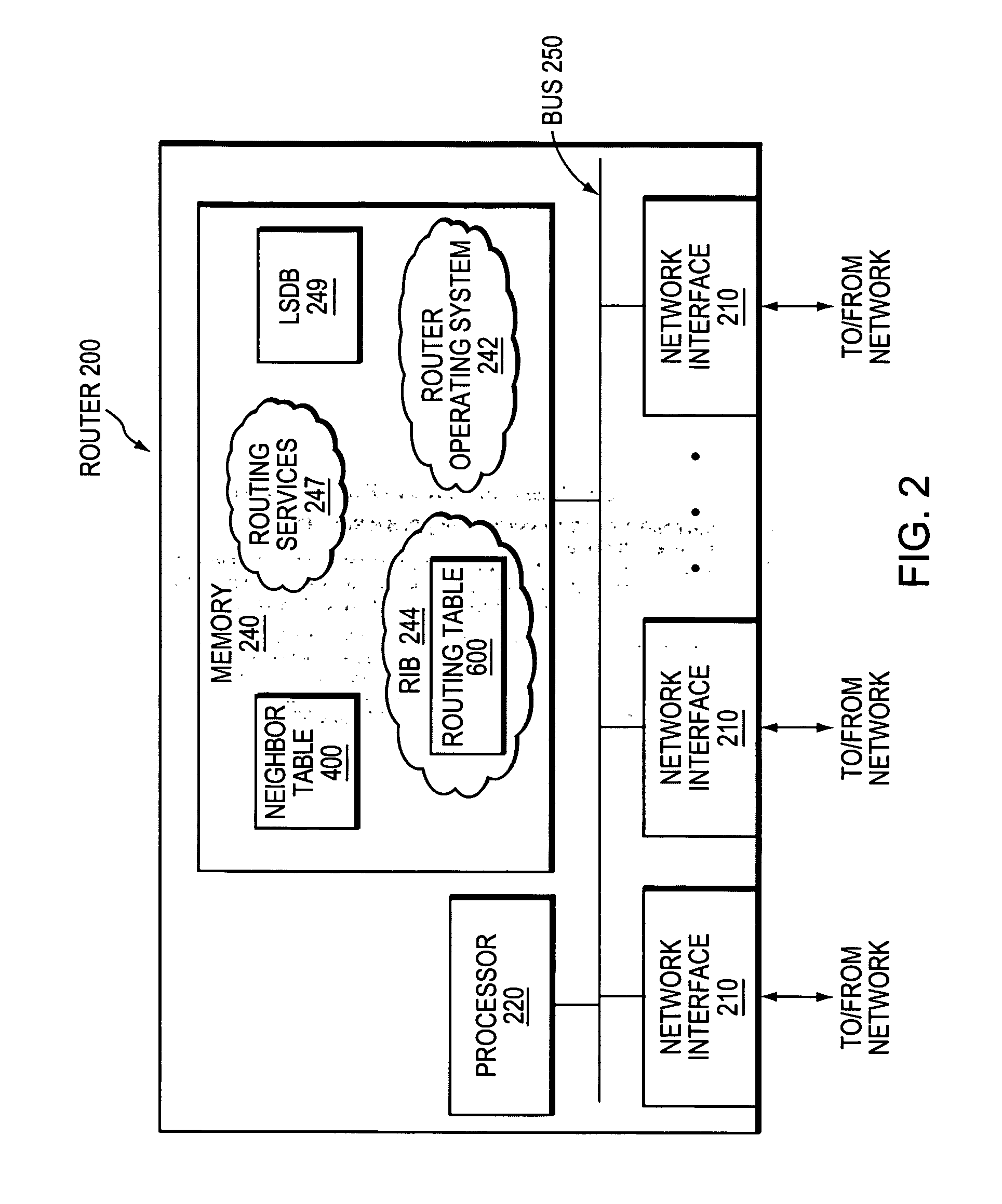
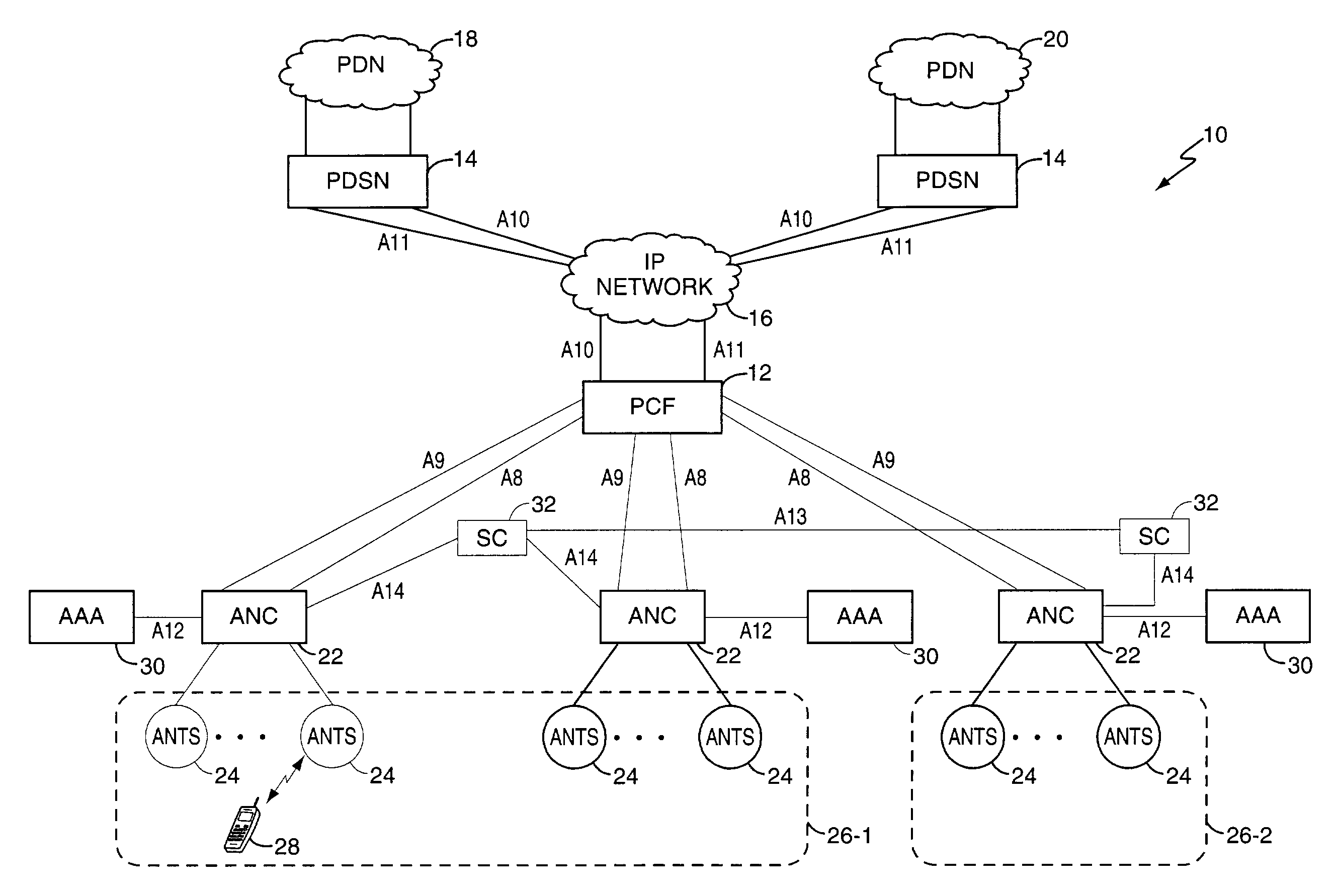
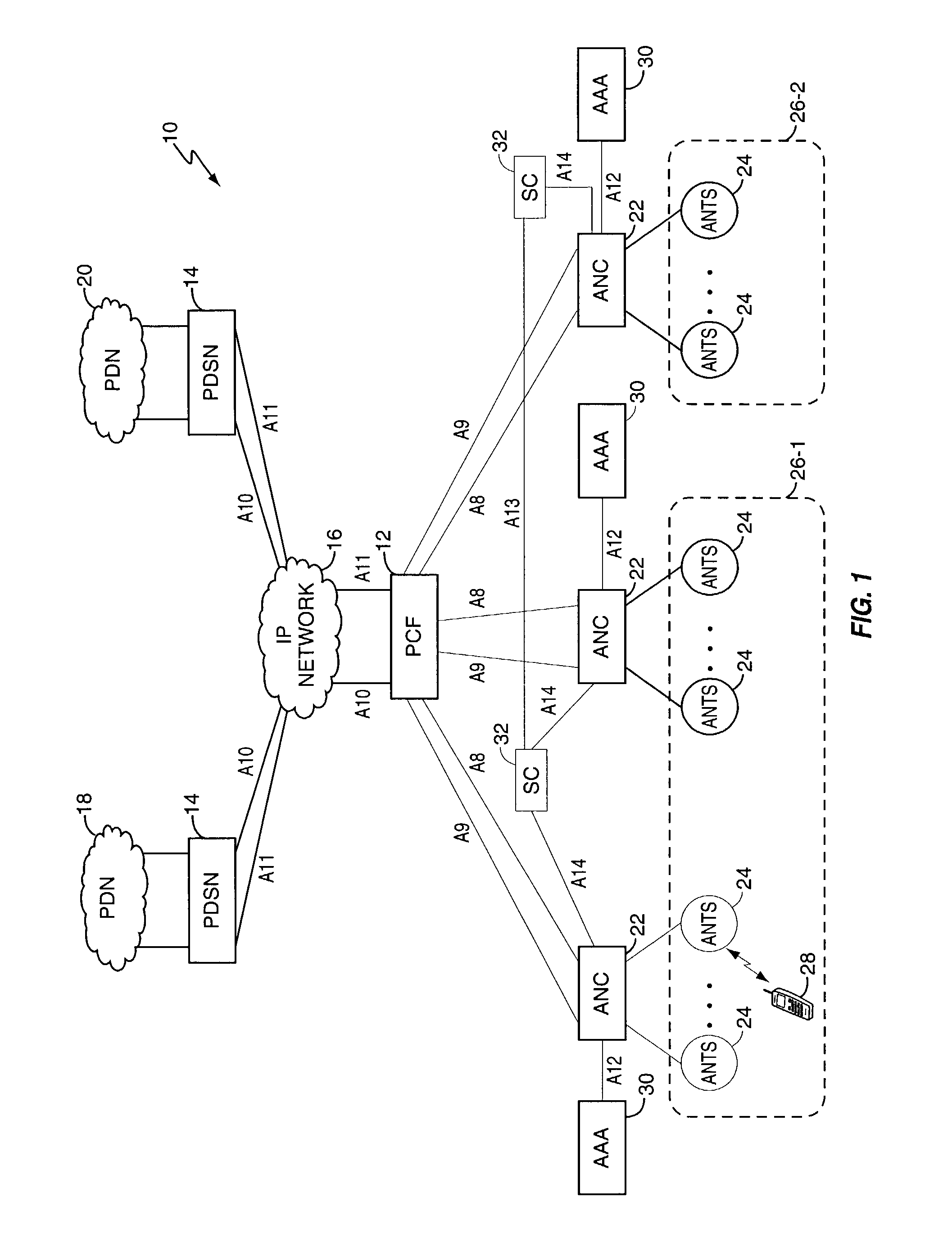
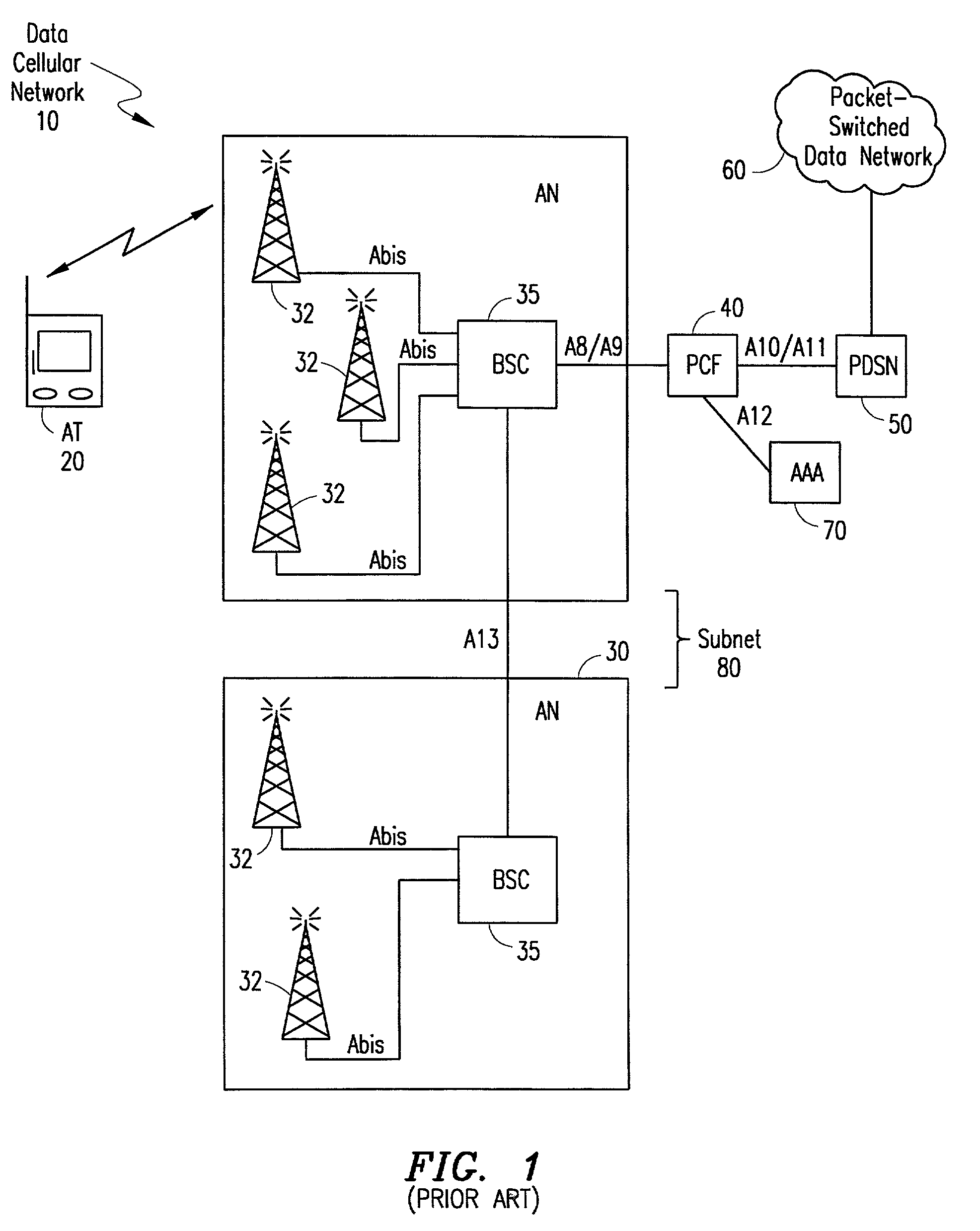
A subnetwork or subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting. Computers that belong to a subnet are addressed with an identical most-significant bit-group in their IP addresses. This results in the logical division of an IP address into two fields, the network number or routing prefix and the rest field or host identifier. The rest field is an identifier for a specific host or network interface.
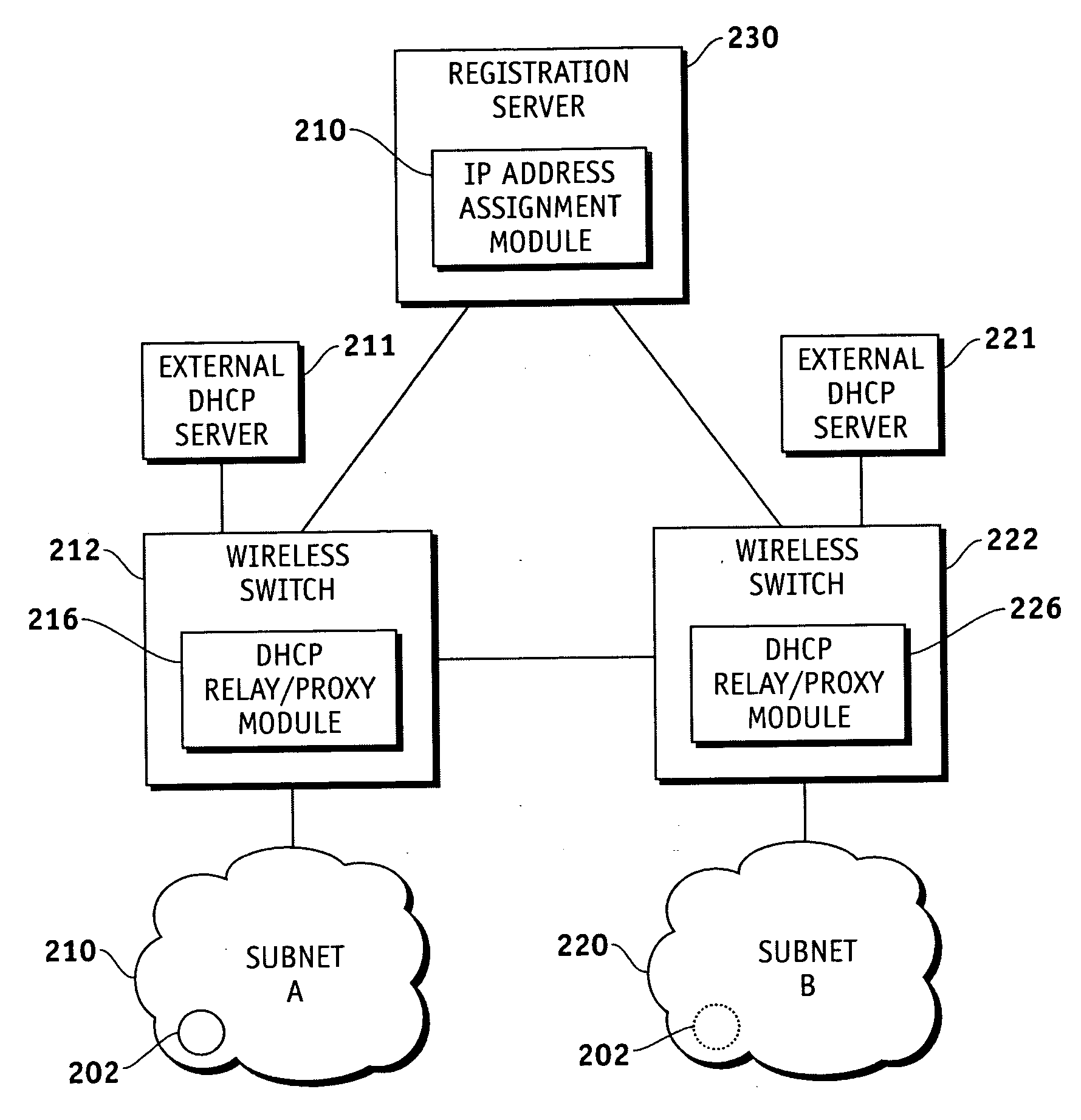
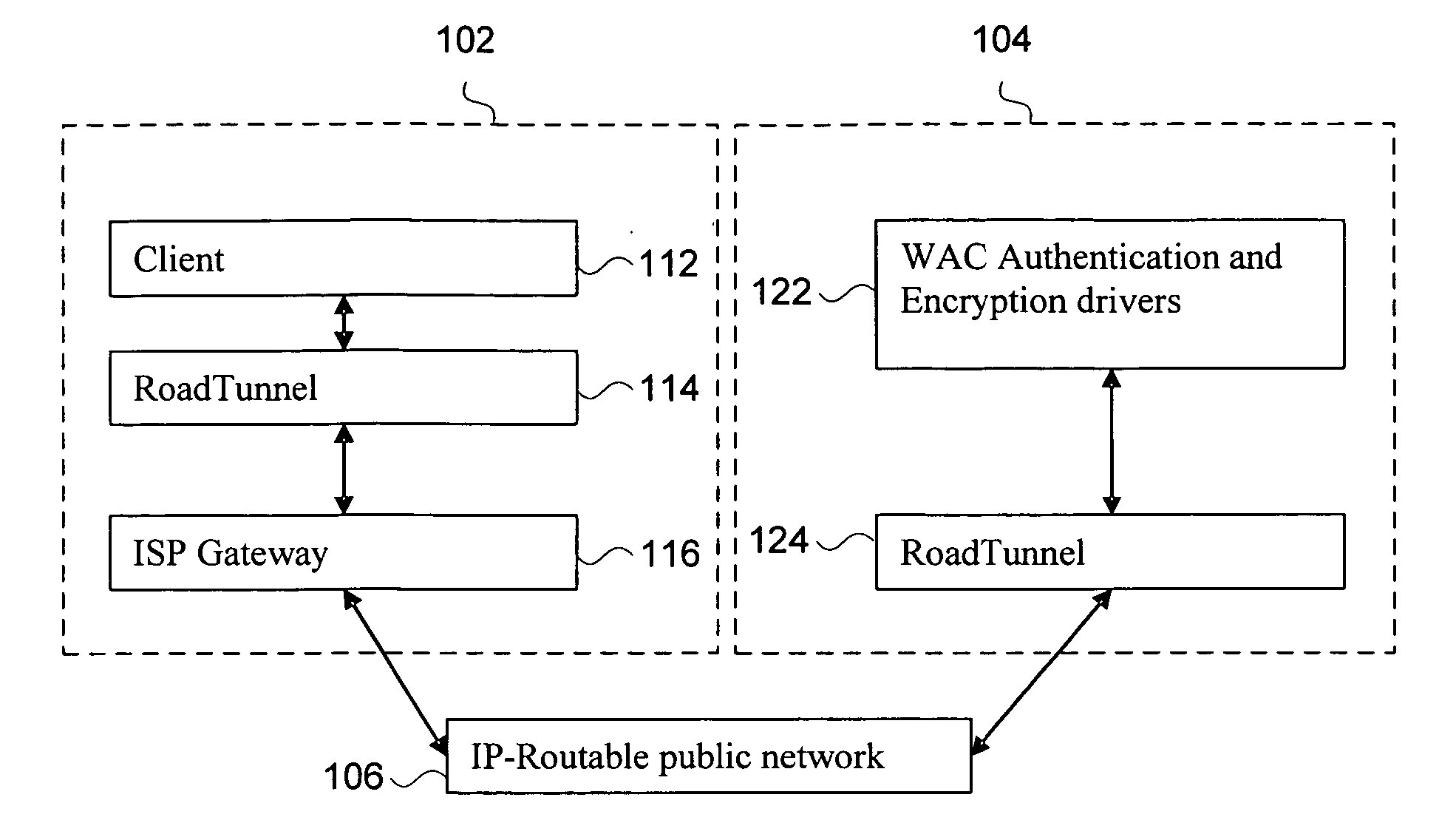
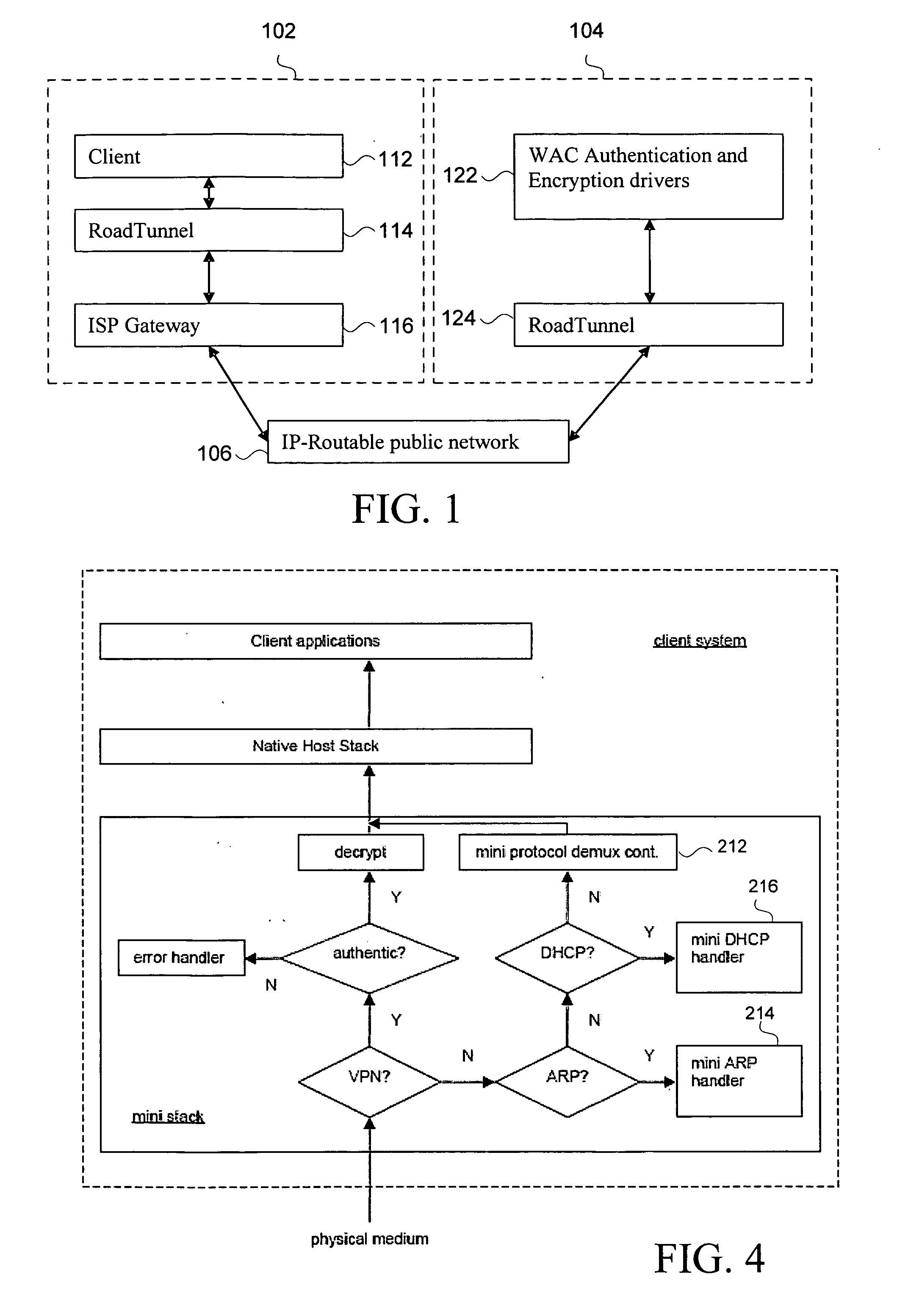
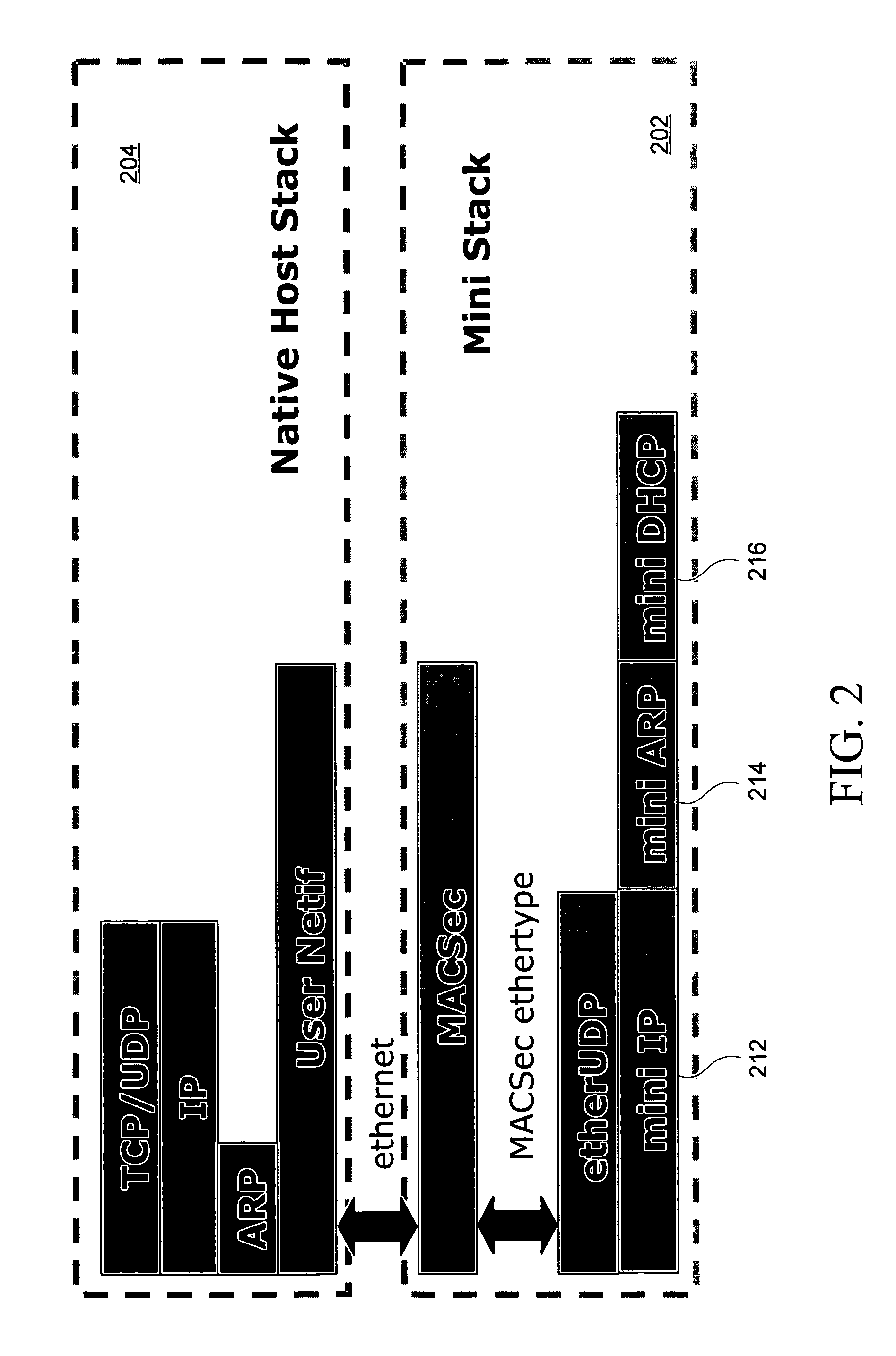
Method, system and apparatus for assigning and managing IP addresses for wireless clients in wireless local area networks (WLANs)
Techniques are provided IP address assignment and management in a wireless network. Such a wireless network can comprise a plurality of wireless clients, a registration server, a plurality of wireless switches each being configured to support a particular subnet. Each wireless client can generate a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request for an Internet Protocol (IP) address when the client either powers up in of moves to a new subnet, 802.11 authenticates and associates and 802.1x authenticates. The wireless switches can communicate with the registration server over an IP tunnel. For example, each wireless switch can receive the DHCP requests from wireless clients associated with the subnet of the wireless switch, and forward the DHCP requests to the registration server. The registration server can receive the forwarded DHCP requests, and assign IP addresses to the wireless clients based on the forwarded DHCP requests.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Method for optimal path selection in traversal of packets through network address translators
InactiveUS20050259637A1Reduce administrative overheadFast convergenceMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork addressNetwork address translation
Reduction of administrative overhead in maintaining network information, rapid convergence on an optimal routing path through the data network, and utilization of only required network resources are realized by a novel method for establishing a call path between network users. The method is based upon deployment of a network information server that stores network topology information and that is addressable by each end user. In this method, the network information server receives a request to establish a call path. The request identifies at least the calling party. In response to the request, the network information server determines a network traversal between the calling party and a root network wherein the network traversal includes call path information about the sub-networks between the calling party and the root network. The request for establishing a call path can also identify the called party. Based on the calling and called party identification, the network information server also determines a second network traversal between the called party and the root network. The second network traversal is sent to either the calling party or the called party or to both the calling and called parties. The server can determine an intersection of the traversals and send the intersection information to the parties. The intersection information is known as a merge point and represents an optimal call path between the parties.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
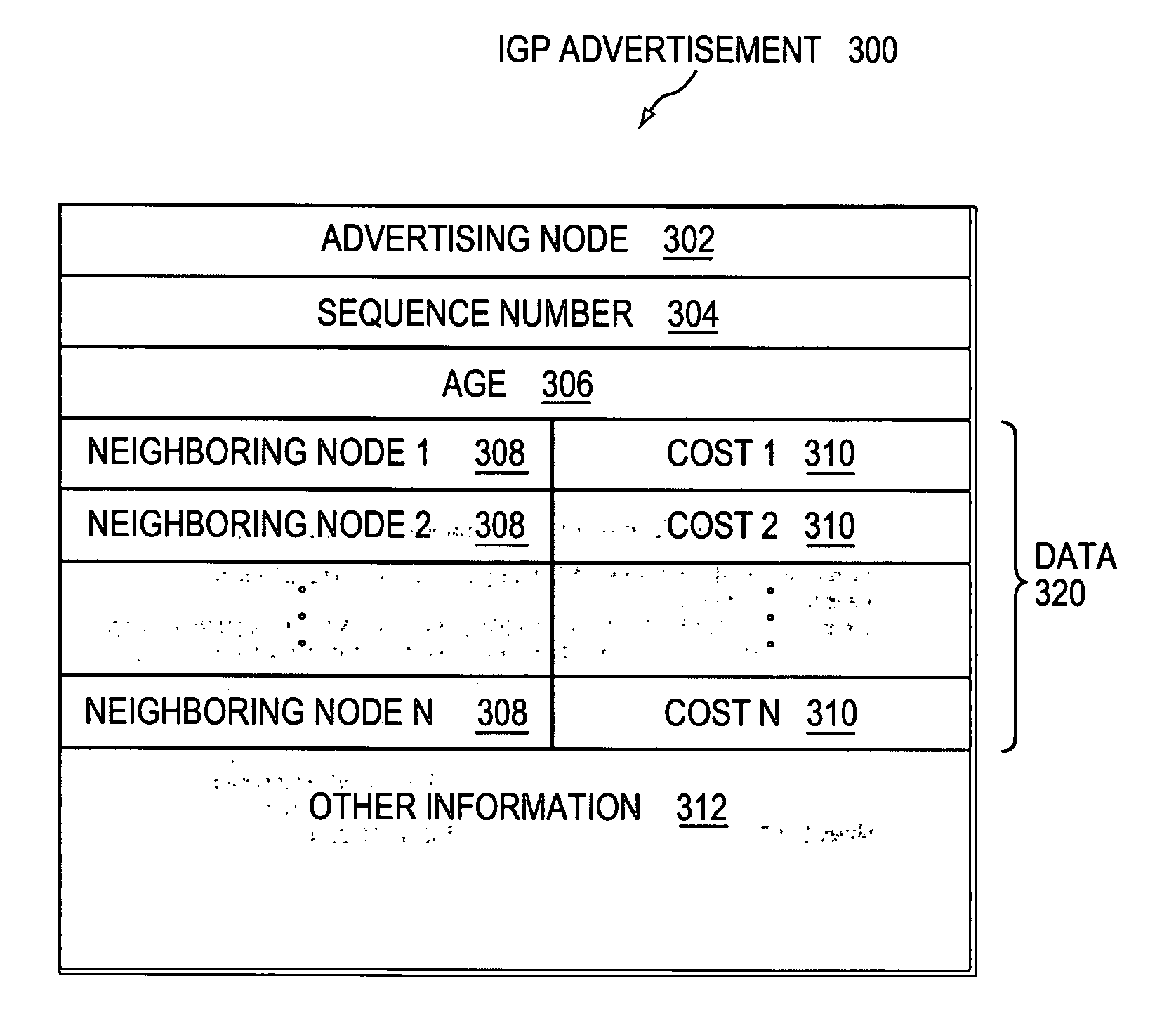
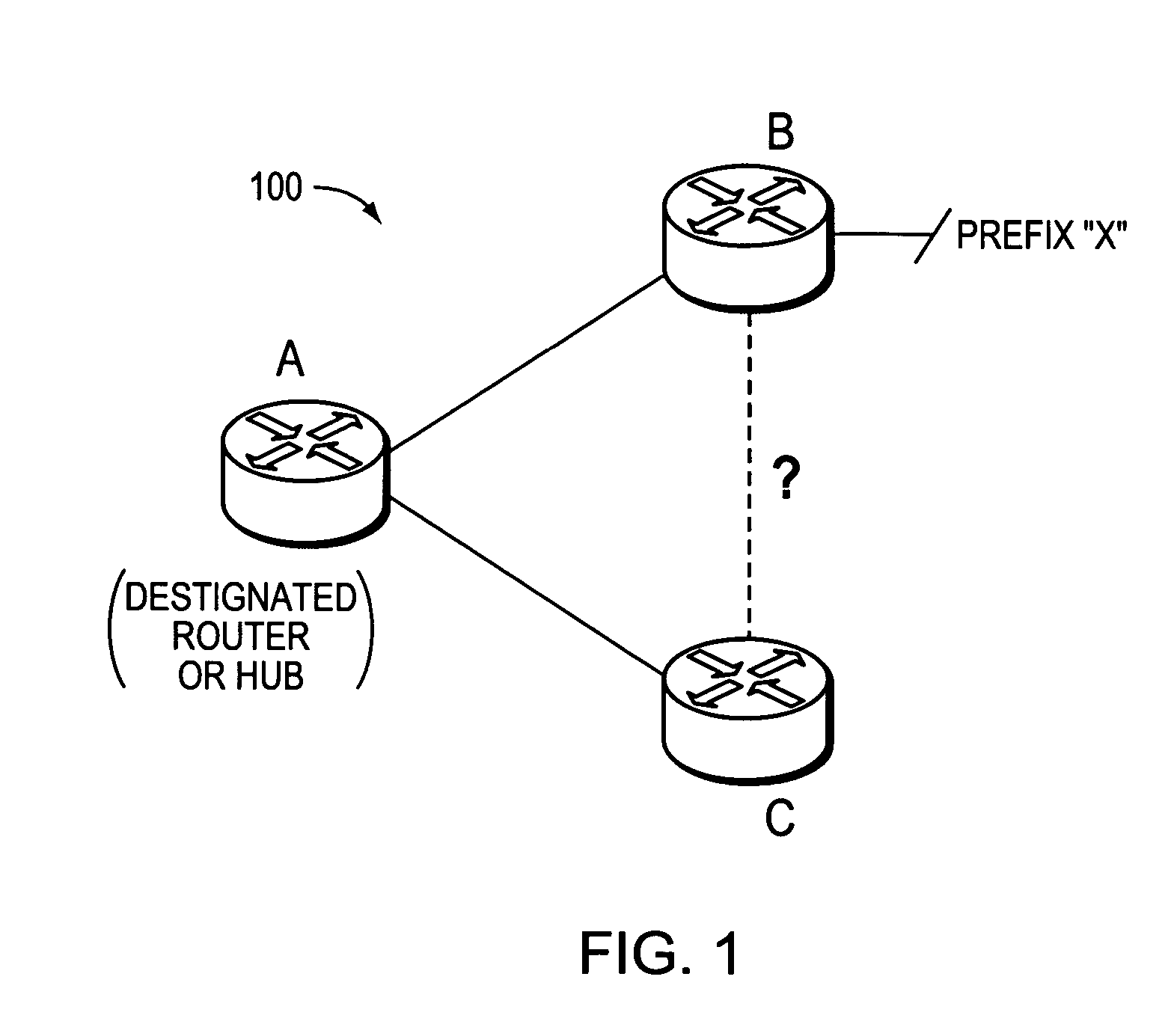
Dynamically configuring and verifying routing information of broadcast networks using link state protocols in a computer network
ActiveUS20070245034A1Reduce needAvoid installationDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationBroadcastingComputer science
A technique dynamically configures and verifies routing information of broadcast networks using link state protocols in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a router within the broadcast network receives a link state protocol routing information advertisement from an advertising router, e.g., a designated router or other adjacent neighbor. The router learns of a next-hop router (“next-hop”) to reach a particular destination from the advertisement, and determines whether the next-hop is located within the same broadcast network (e.g., subnet) as the designated router. If so, the router further determines whether the next-hop is directly addressable (i.e., reachable), such as, e.g., by checking for link adjacencies to the next-hop or by sending request / reply messages (e.g., echo messages or “ping” messages) to the next-hop. In the event the next-hop for the destination is not directly addressable by the router (e.g., no adjacency or reply), the router installs a route to the destination via the designated router. Otherwise, the router installs a route to the destination via the next-hop.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
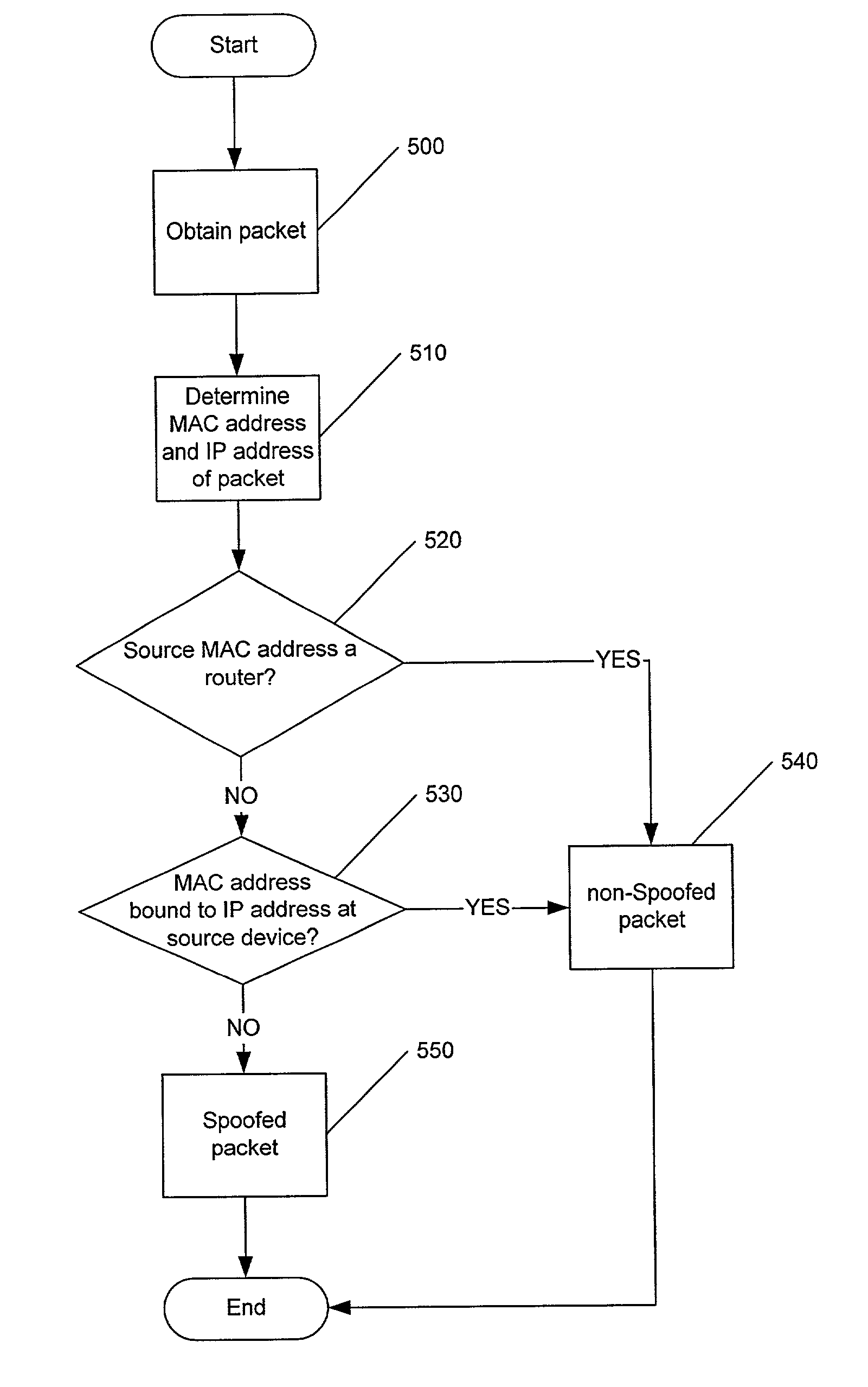
Methods, systems and computer program products for detecting a spoofed source address in IP datagrams
InactiveUS7134012B2Improve usabilityFrequency-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIp addressMedia access control
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for determining if a packet has a spoofed source Internet Protocol (IP) address. A source media access control (MAC) address of the packet and the source IP address are evaluated to determine if the source IP address of the packet has been bound to the source MAC address at a source device of the packet. The packet is determined to have a spoofed source IP address if the evaluation indicates that the source IP address is not bound to the source MAC address. Such an evaluation may be made for packets having a subnet of the source IP address which matches a subnet from which the packet originated.
Owner:IBM CORP
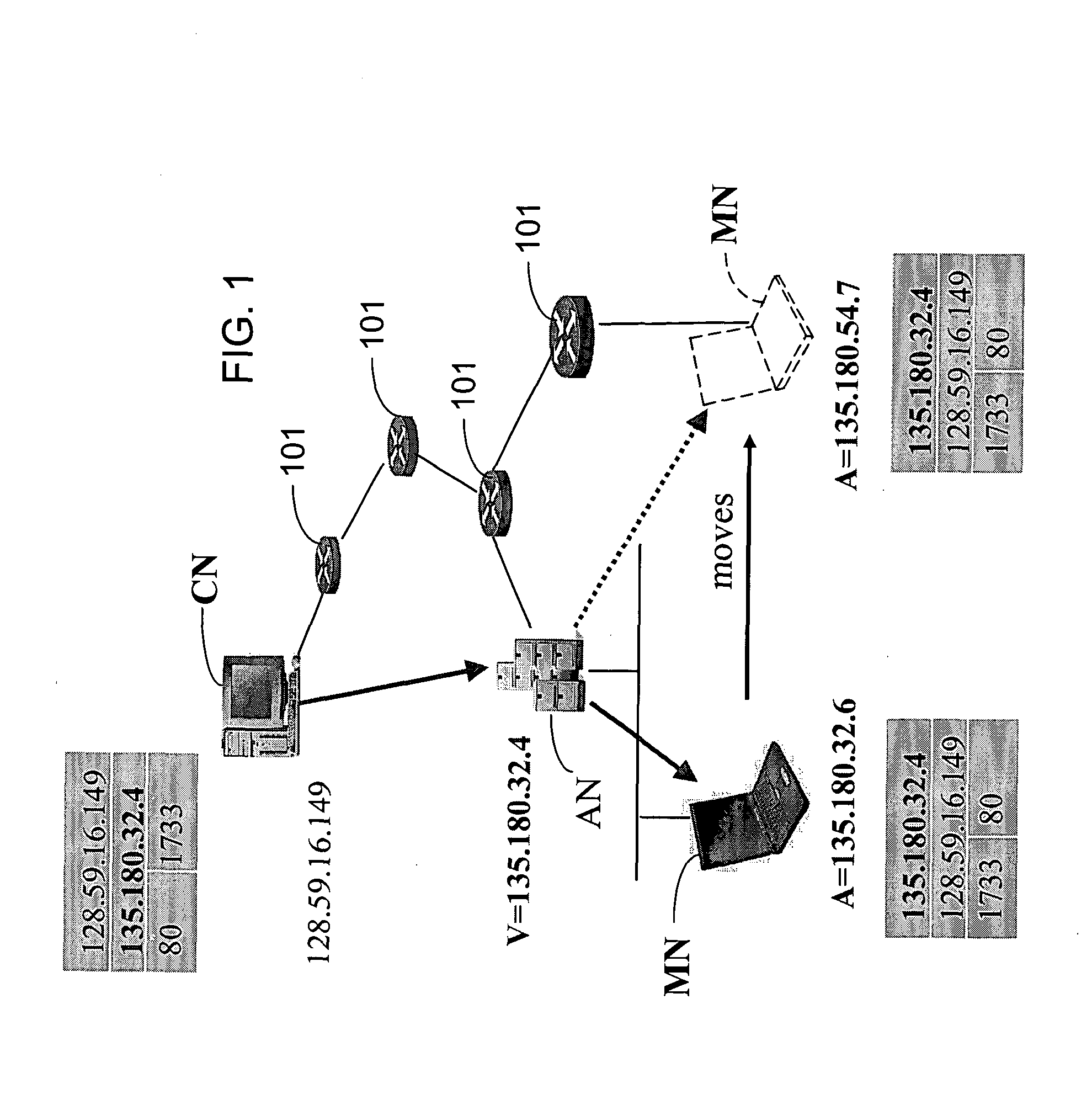
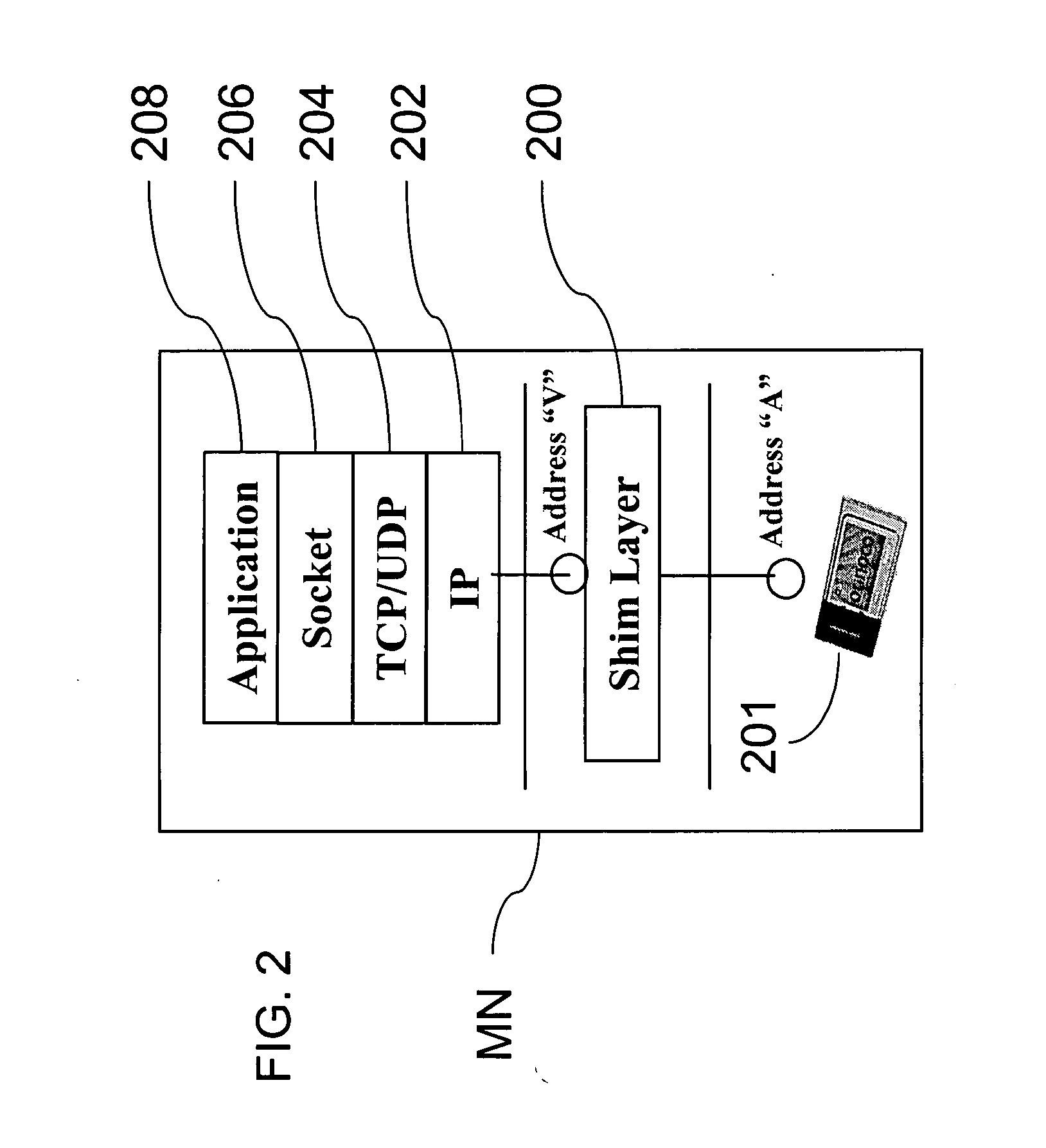
Method and system for mobility across heterogeneous address spaces
ActiveUS20050013280A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAddress spaceInternet Protocol
A mobile node includes a processor, a network interface, and a storage device having computer program code for execution by the processor. The computer program code includes a network layer for transmitting and receiving packets and an intermediate driver that transmits packets to the network layer and receives packets from the network layer using a virtual internet protocol (IP) address to identify the mobile node. The intermediate driver transmits packets to the network interface and receives packets from the network interface using a routable actual IP address to identify the mobile node. The intermediate driver permits the actual IP address to change when the mobile node moves from a first subnet to a second subnet without a corresponding change in the virtual IP address. A corresponding NAT associates the virtual IP address with a second actual IP address when the NAT is notified that the mobile node is in the second subnet.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Mobility architecture using pre-authentication, pre-configuration and/or virtual soft-handoff
ActiveUS20050163078A1Higher-layer handoffMinimizing interruptionData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsMobile architectureDistributed computing
In some illustrative embodiments, a novel system and method is provided that can, for example, extend concepts of pre-authentication (such as, e.g., IEEE 802.11i pre-authentication) so as to operate across networks or subnetworks (such as, e.g., IP subnets). In preferred embodiments, a novel architecture includes one or both of two new mechanisms that substantially improve, e.g., higher-layer handoff performance. A first mechanism is referred to as “pre-configuration,” which allows a mobile to pre-configure higher-layer information effective in candidate IP subnets to handoff. A second mechanism is referred to as “virtual soft-handoff,” which allows a mobile to send or receive packets through the candidate IP subnets even before it is actually perform a handoff to any of the candidate IP subnets.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +1
Method, apparatus and system for sharing multimedia content within a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20090094317A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication softwareMiddleware
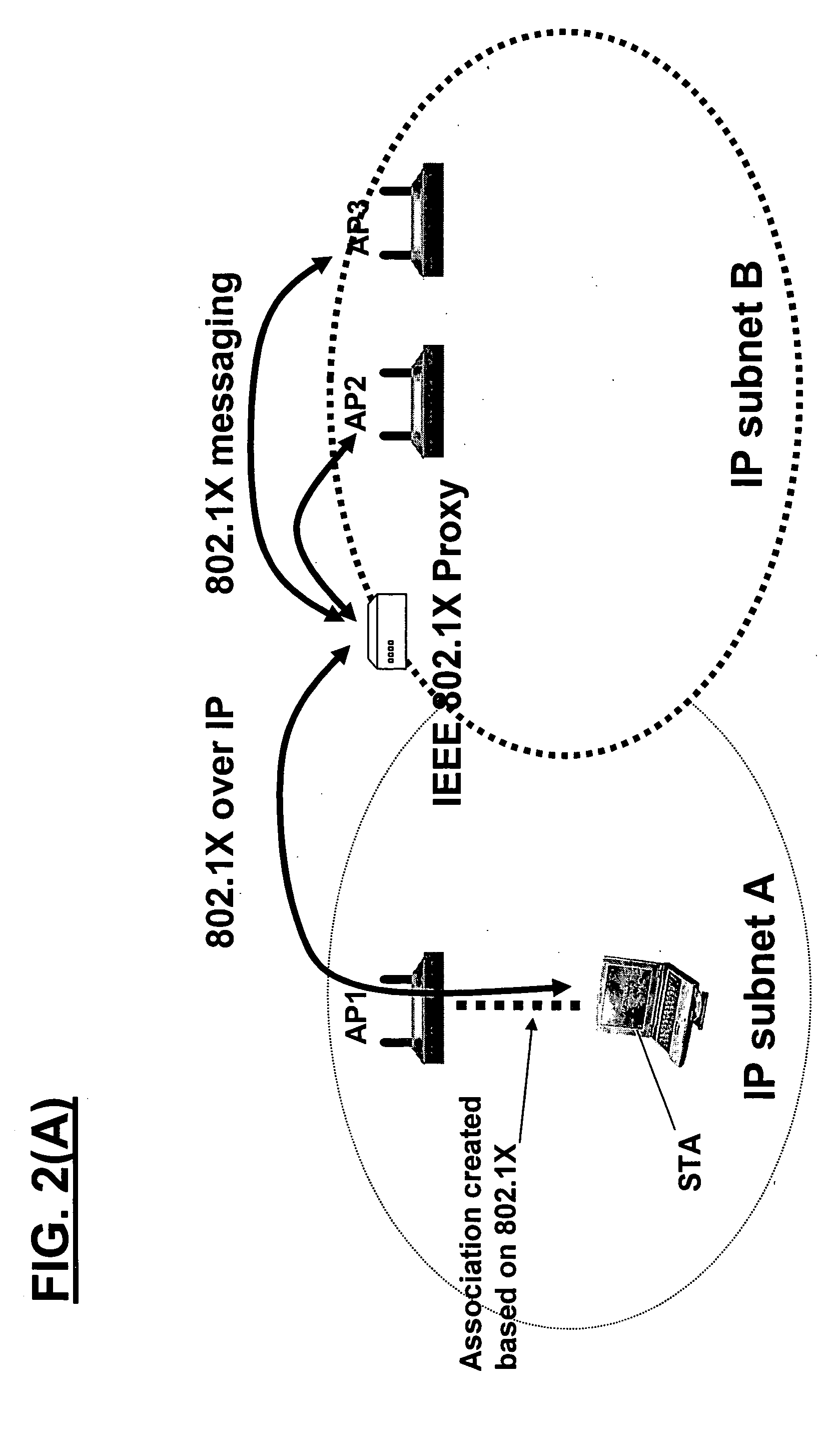
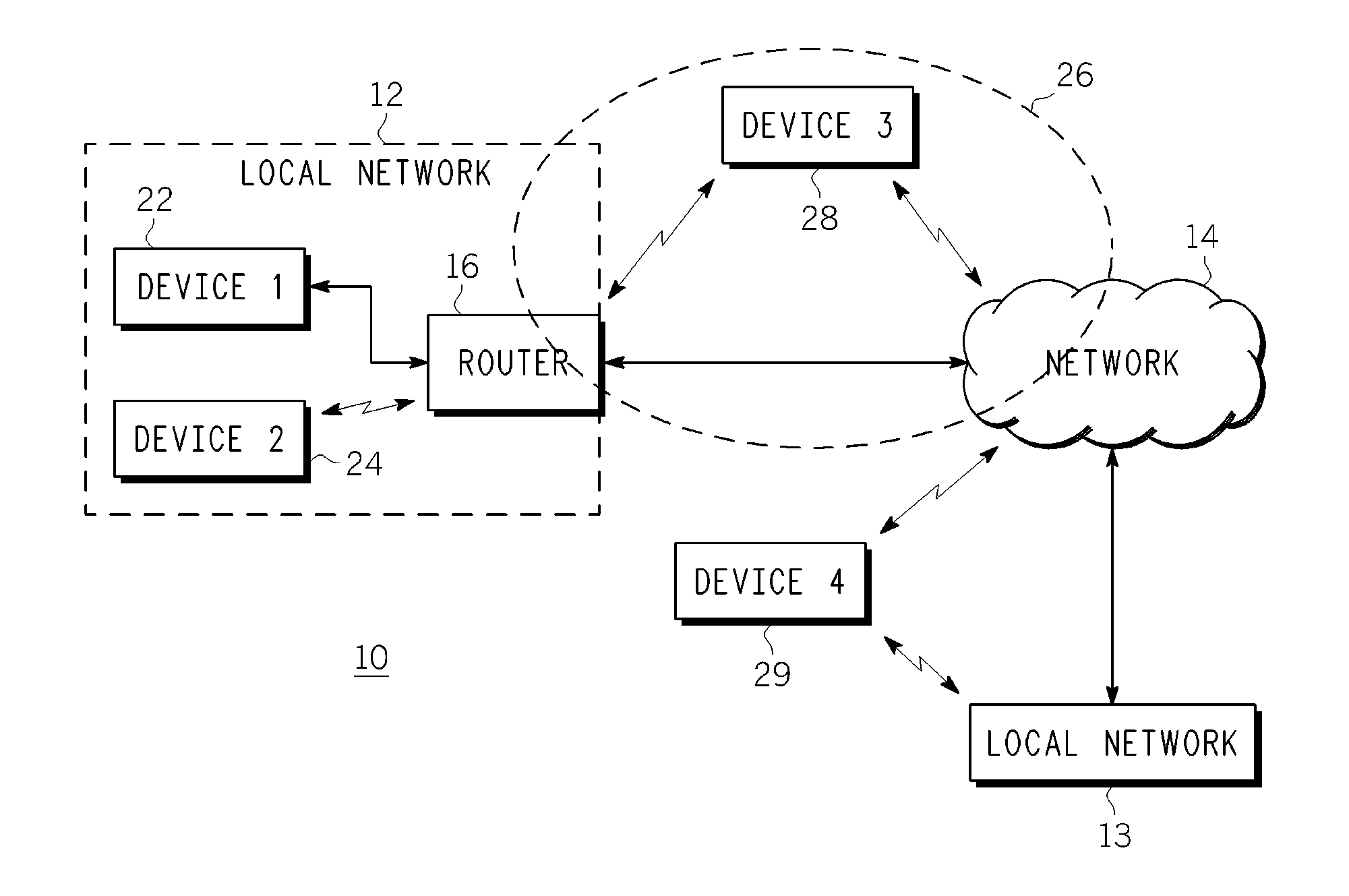
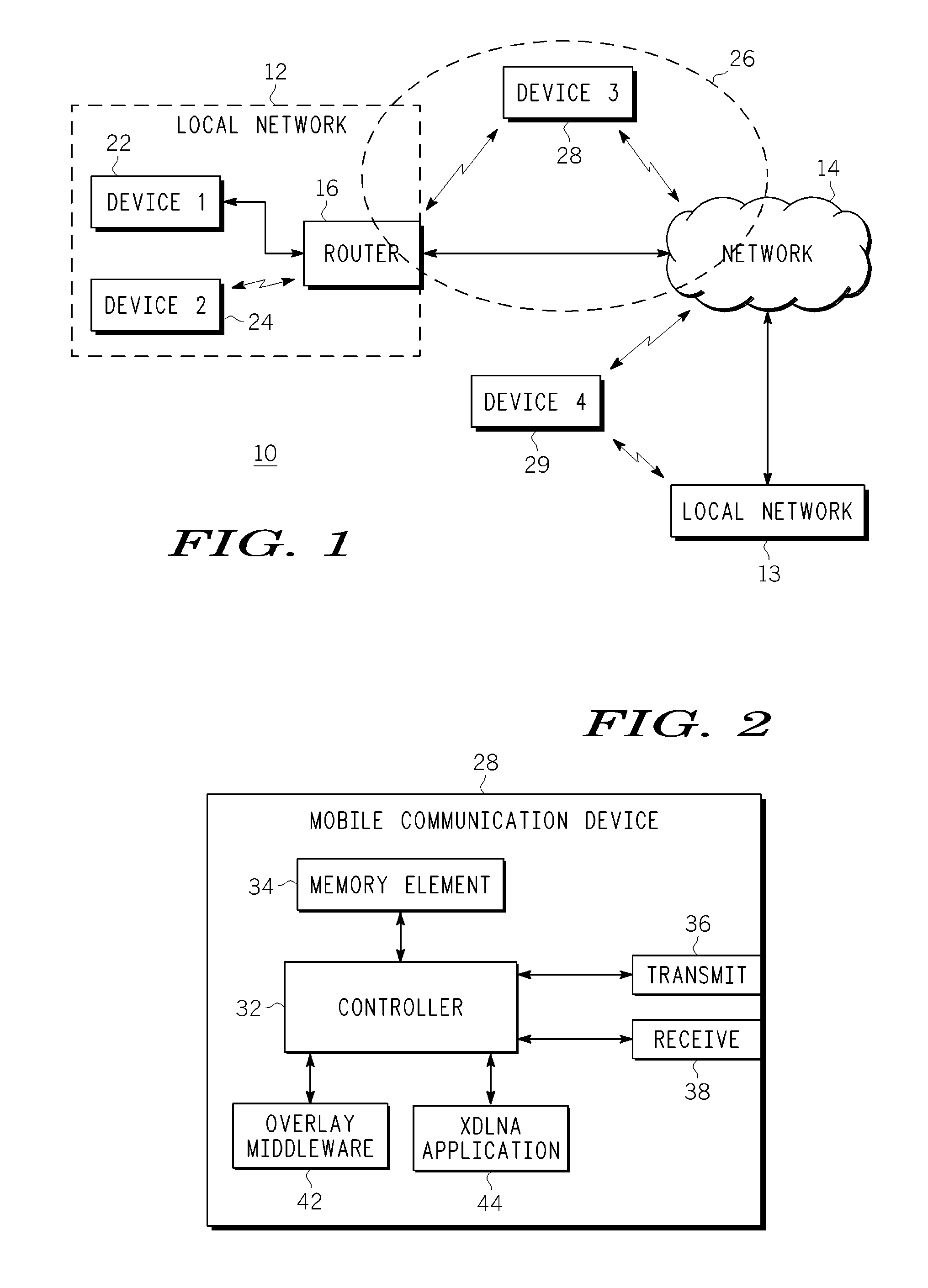
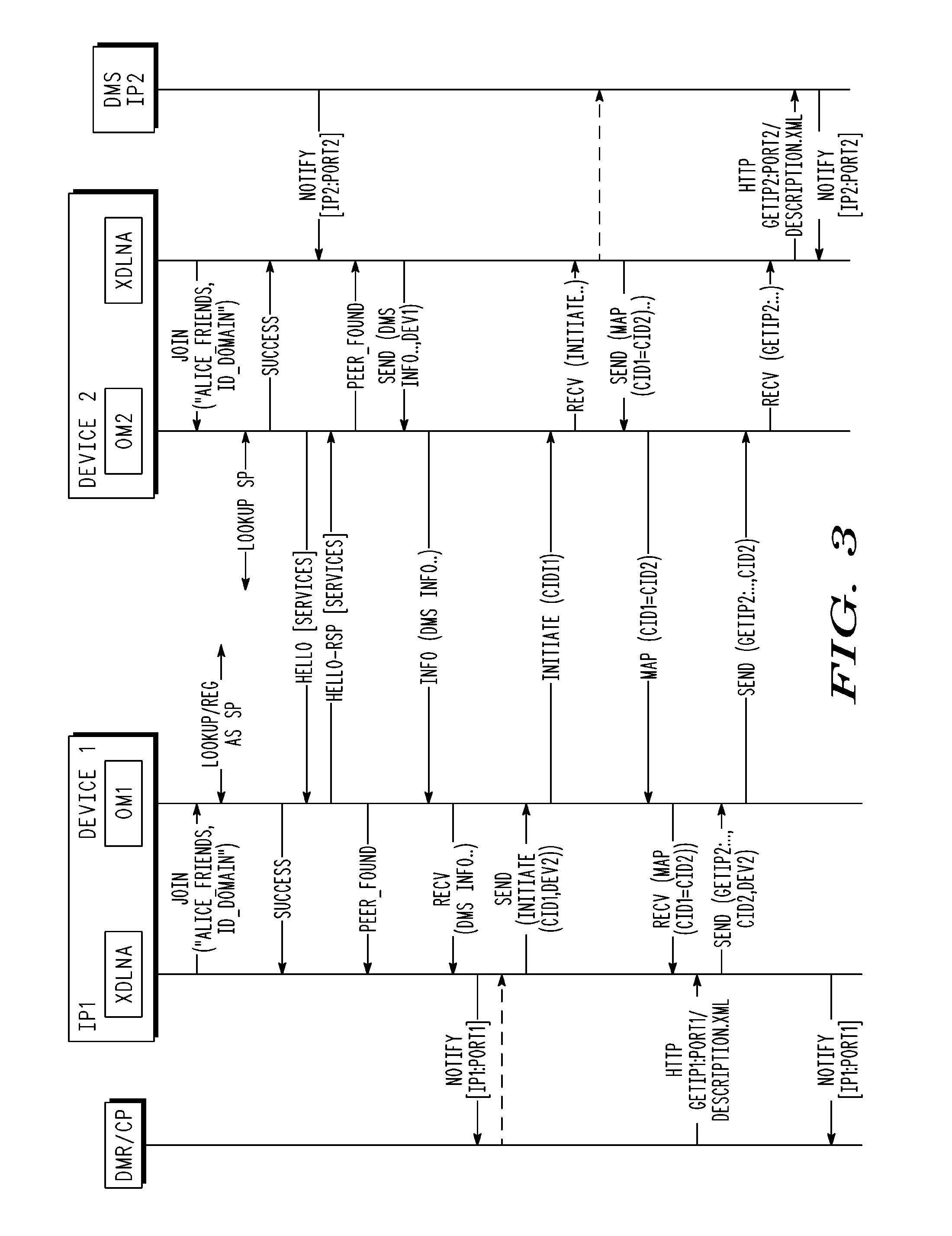
A system, method and communication device configuration for sharing multimedia content between network devices, such as UPnP or UPnP / DLNA devices and mobile communication devices, across different local networks or subnets. One possible system arrangement or architecture is based on the communication devices forming groups and then sharing UPnP control messages across the groups. The system arrangement supports enabling group member access to UPnP devices that are in other group devices or reachable via other group devices. By enabling devices to form groups across wide-area networks and distribute UPnP messages within the group members, the system effectively extends the range of a UPnP network. Devices include an overlay middleware and an xDLNA application to provide the functionality to form or join a device group and communicate multimedia content with other devices in the group as if the devices are within the same local network.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Mobility management entity for high data rate wireless communication networks
ActiveUS7457265B2Reduce amountEasy to manageTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSession controlGranularity
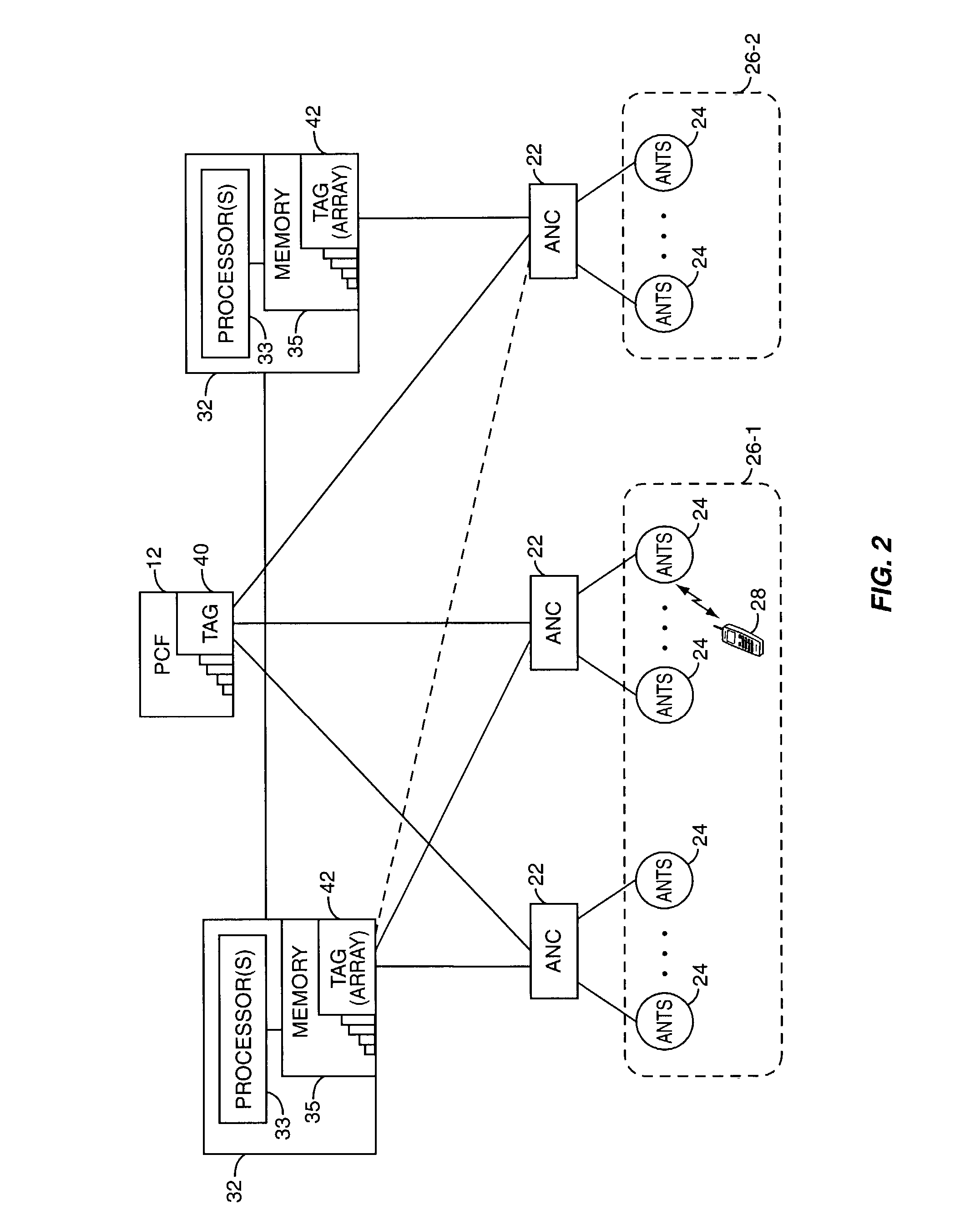
A session controller provides mobility management support in a 1xEVDO wireless communication network, such as one configured in accordance with the TIA / EIA / IS-856 standard. Operating as a logical network entity, the SC maintains location (e.g., a pointing tag) and session information at an access network controller (ANC) granularity, thus allowing it to track access terminal (AT) transfer between ANCs but within subnet boundaries, where a network subnet comprises one or more ANCs. This allows a packet control function (PCF) to maintain location information at a packet zone granularity, thereby reducing mobility management overhead at the PCF. The SC provides updated tag and session information to PCFs, ANCs, and other SCs as needed. Information exchange with other SCs arises, for example, when two or more SCs cooperate to maintain or transfer routing and session information across subnets.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Secure cloud fabric to connect subnets in different network domains
ActiveUS20140337500A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksStructure of Management InformationNetwork topology
A secure virtual network platform connects two or more subnets in different or separate network domains. The secure virtual network can use the under layer physical networks in various domains as an IP forwarding fabric without changing any existing firewalls, security settings, or network topology. A first type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting server groups. A second type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting a server group to a physical network. A third type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting a physical network to another physical network.
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Method of subnet roaming within a network
Disclosed is an apparatus and method of client device roaming from a home subnet to a foreign subnet of a network. The method includes the client device accessing the network through a first access node of the home subnet, and the client device roaming to a second access node of the foreign subnet, the client device accessing the network through the second access node, the client device maintaining a fixed client IP address, default gateway IP address and IP subnet attachment as the client device roams from the first access node to the second access node.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
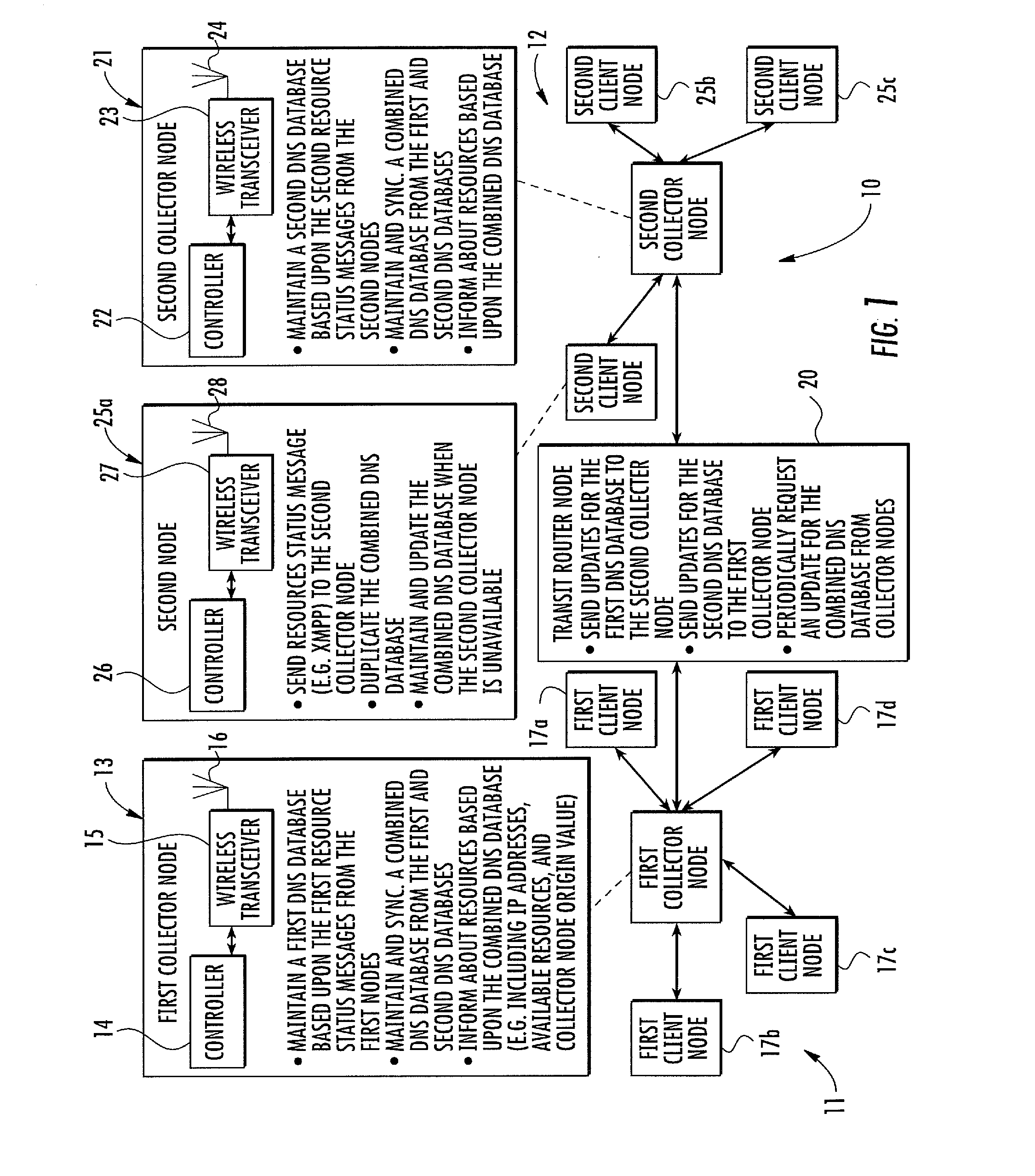
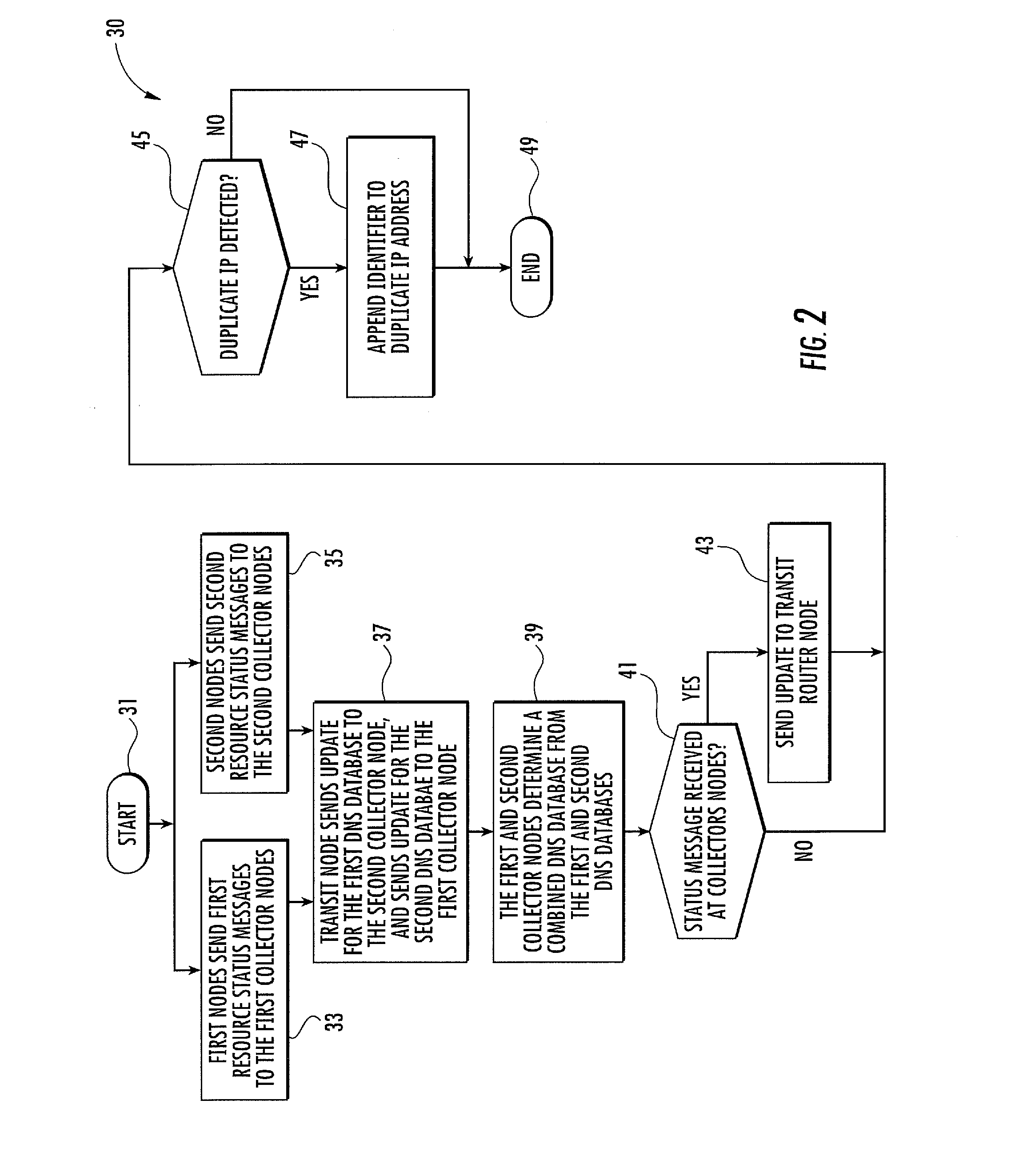
Manet with DNS database resource management and related methods
ActiveUS20130311661A1Effective resourcesEffective redirectingDigital computer detailsTransmissionEngineeringResource management
A network includes a first MANET subnet including a first collector node and first client nodes sending first resource status messages to the first collector node. The first collector node maintains a first DNS database based upon the first resource status messages. The network includes a second MANET subnet including a second collector node and second client nodes sending second resource status messages to the second collector node. The second collector node maintains a second DNS database based upon the second resource status messages. The network includes a transit router node sending updates from the first DNS database to the second collector node, and sending updates from the second DNS database to the first collector node. The first and second collector nodes each maintain and synchronize a combined DNS database from the first and second DNS databases, providing resource availability and status throughout the combined network to their respective clients.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Isolation of hosts connected to an access network
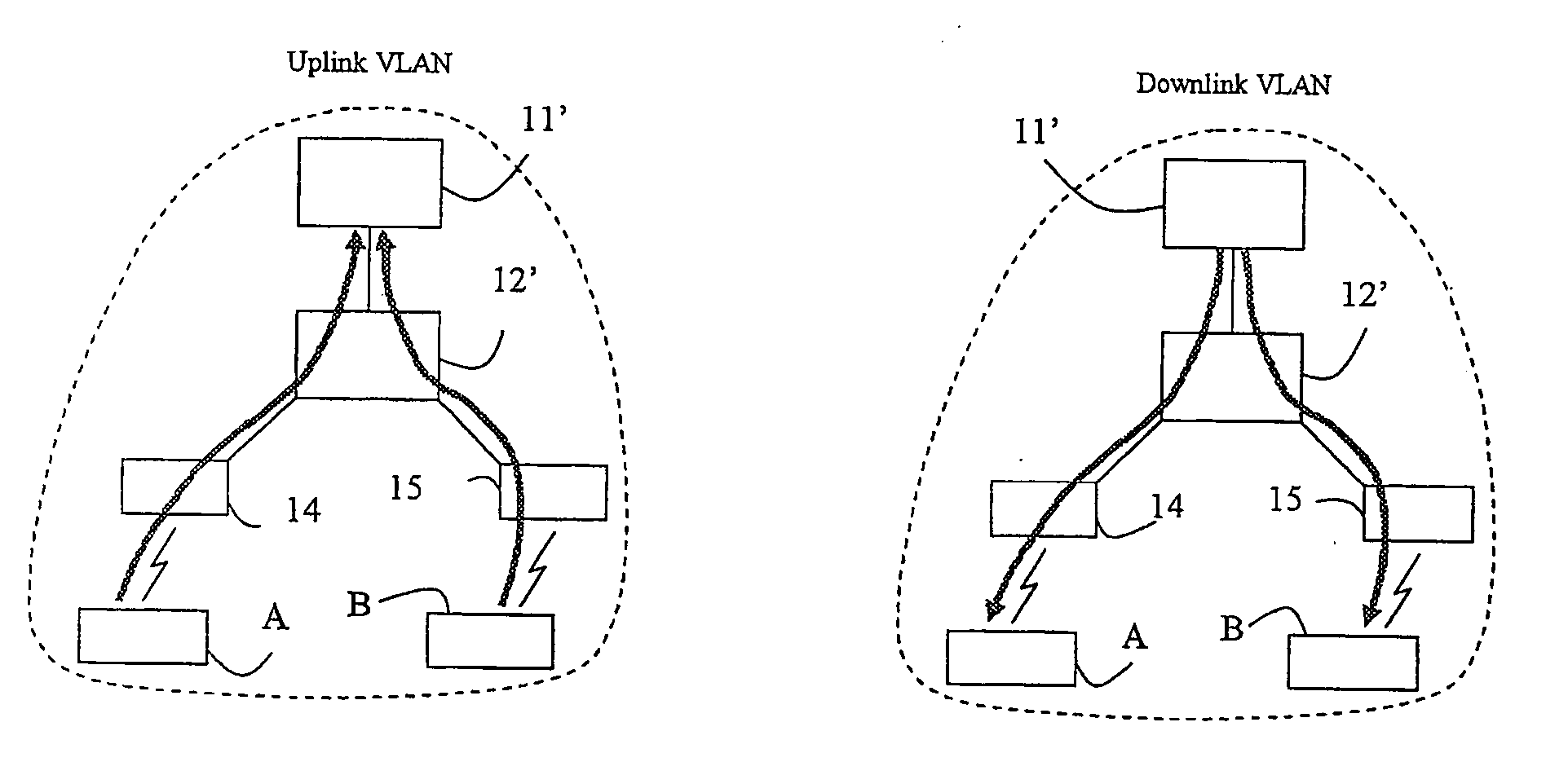
InactiveUS20060062187A1Effective trafficEfficiently broadcastedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkAddress Resolution Protocol
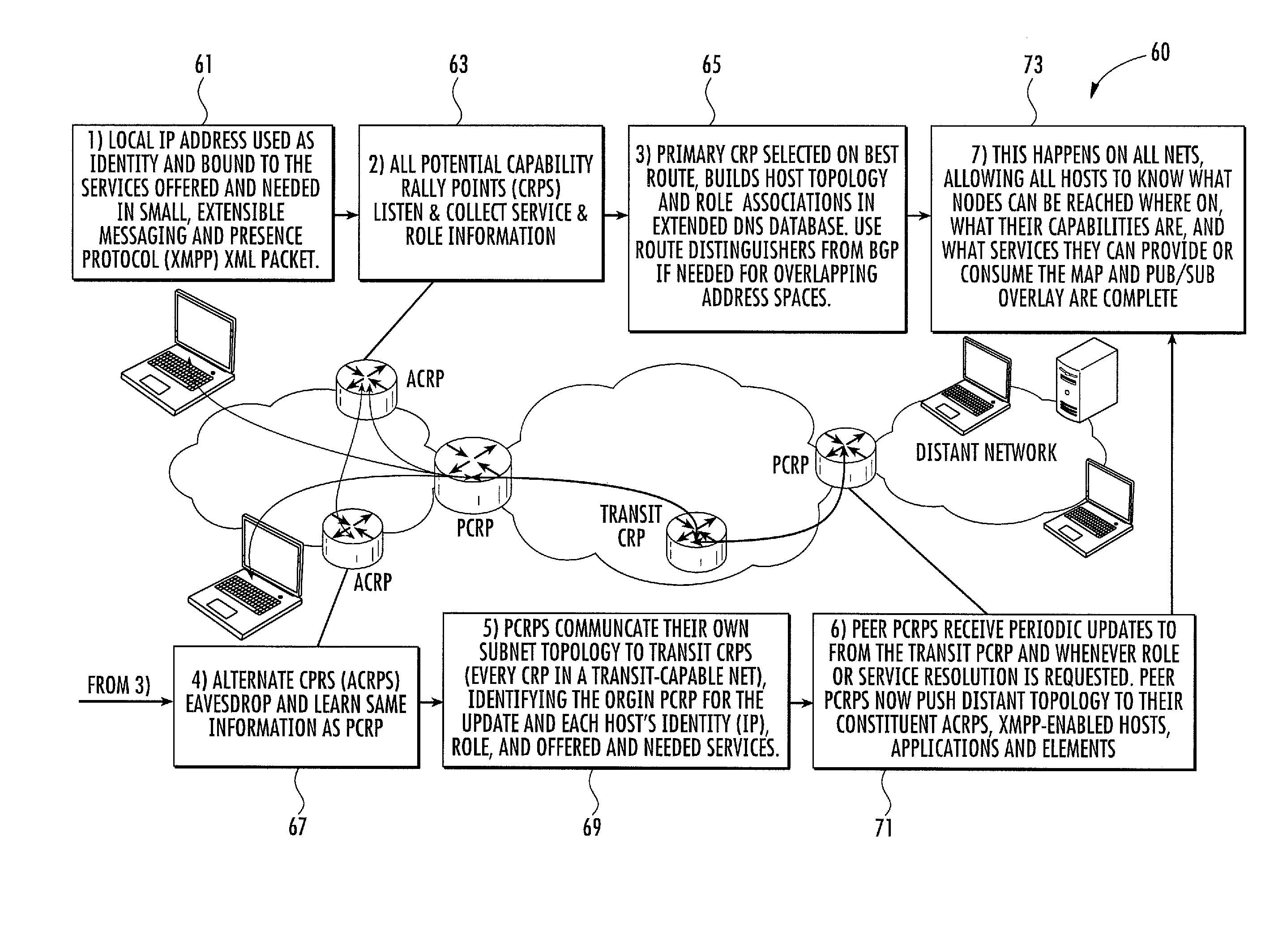
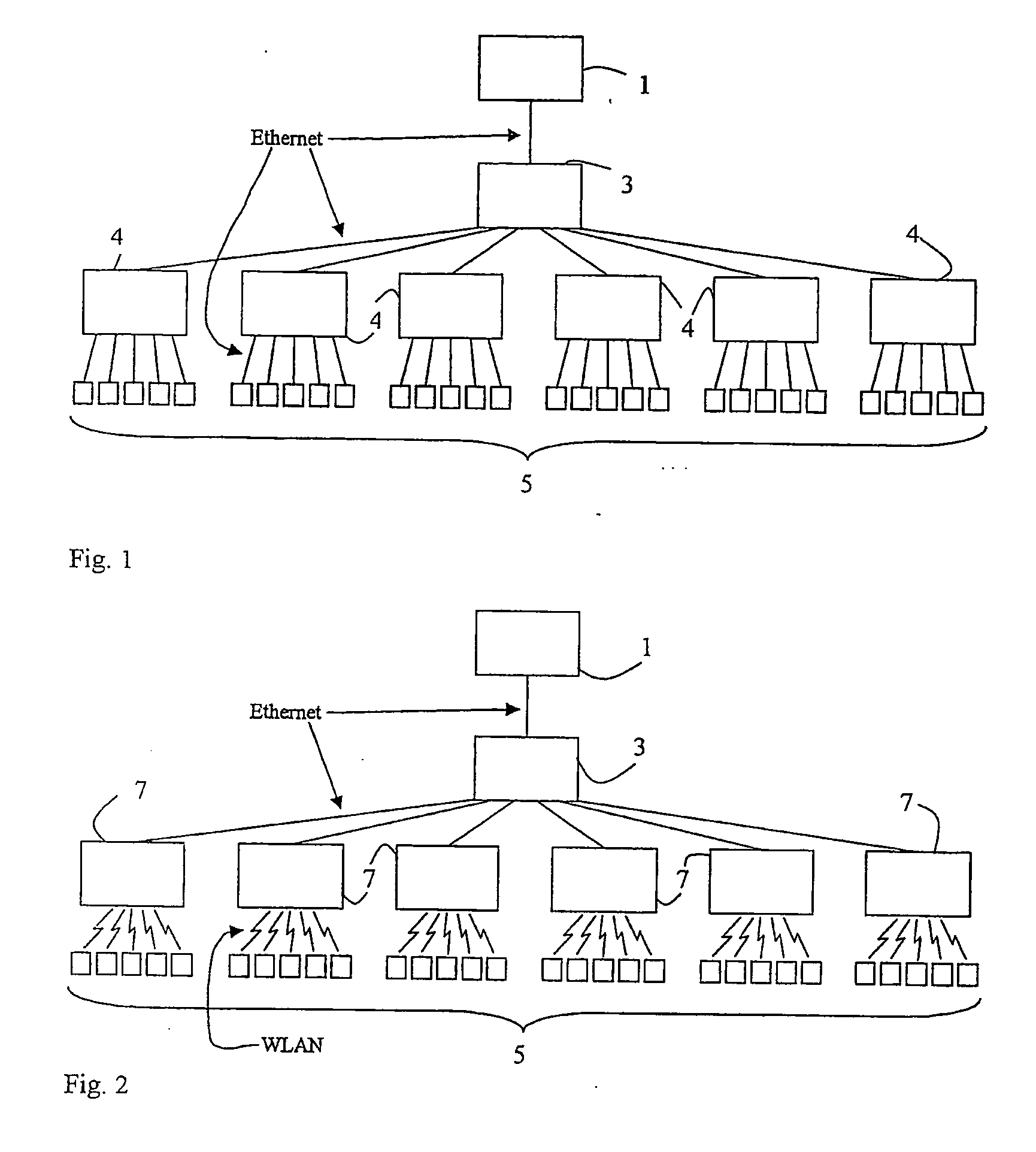
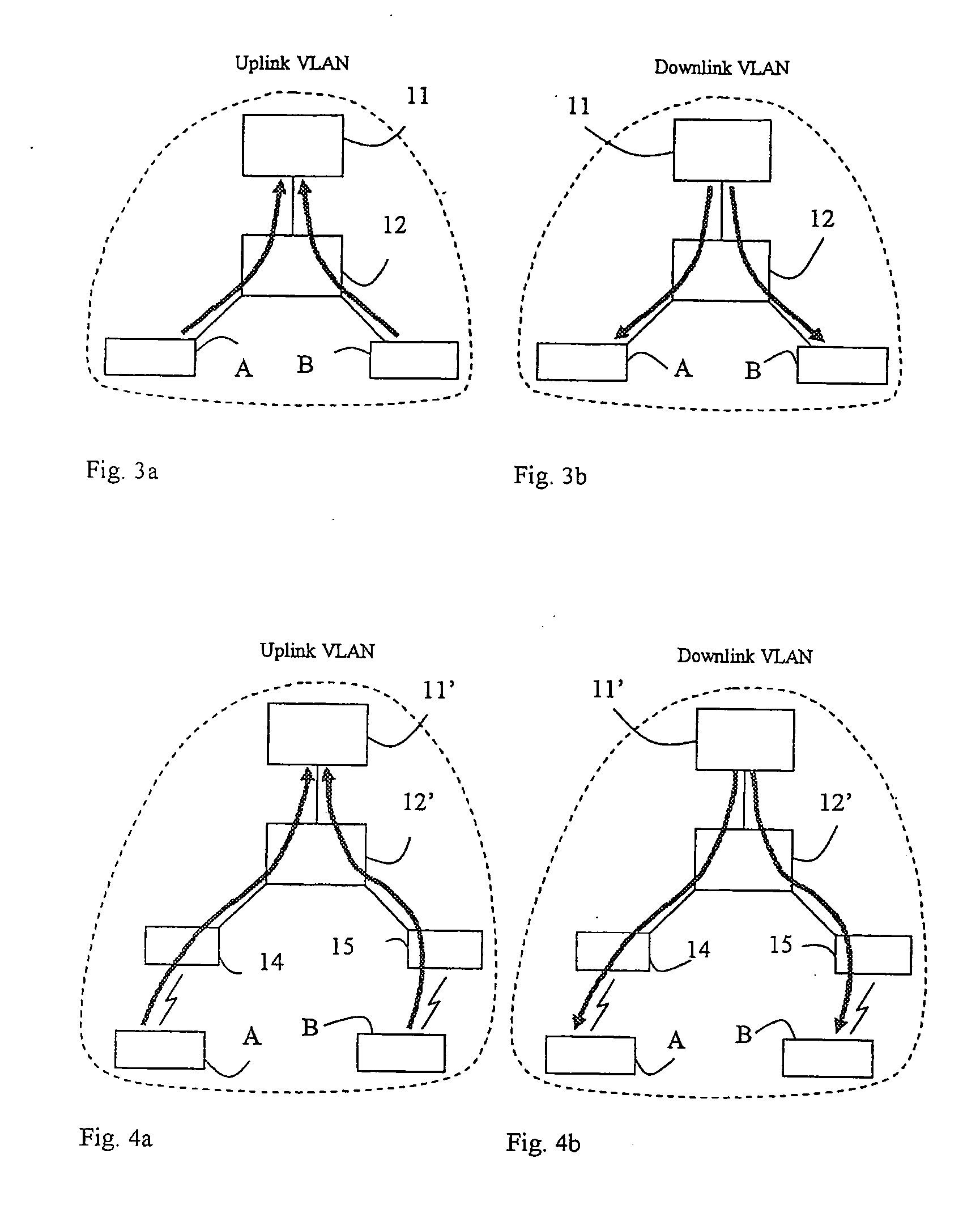
A method and an arrangement in an access network for preventing hosts (5;A,B) connected to the access network from communicating directly with each other. Said method comprises the steps of defining Virtual Local Area Networks, VLANs, in switches (3;12;12′;35,36,37;83) such that traffic arriving in the switches from said hosts is forced to an access router (1;11;11′;11″;81) and defining in the switches one asymmetrical downlink VLAN for downlink traffic from the access router to the hosts, said downlink VLAN being common to said hosts. According to the invention the method comprises the further steps of configuring the VLANs such that said hosts connected to the access network belong to the same IP subnet and configuring the access router to perform intra-subnet routing and to be an Address Resolution Protocol proxy.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for improved session management in a data cellular network
InactiveUS20030135626A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementSession managementAccess network
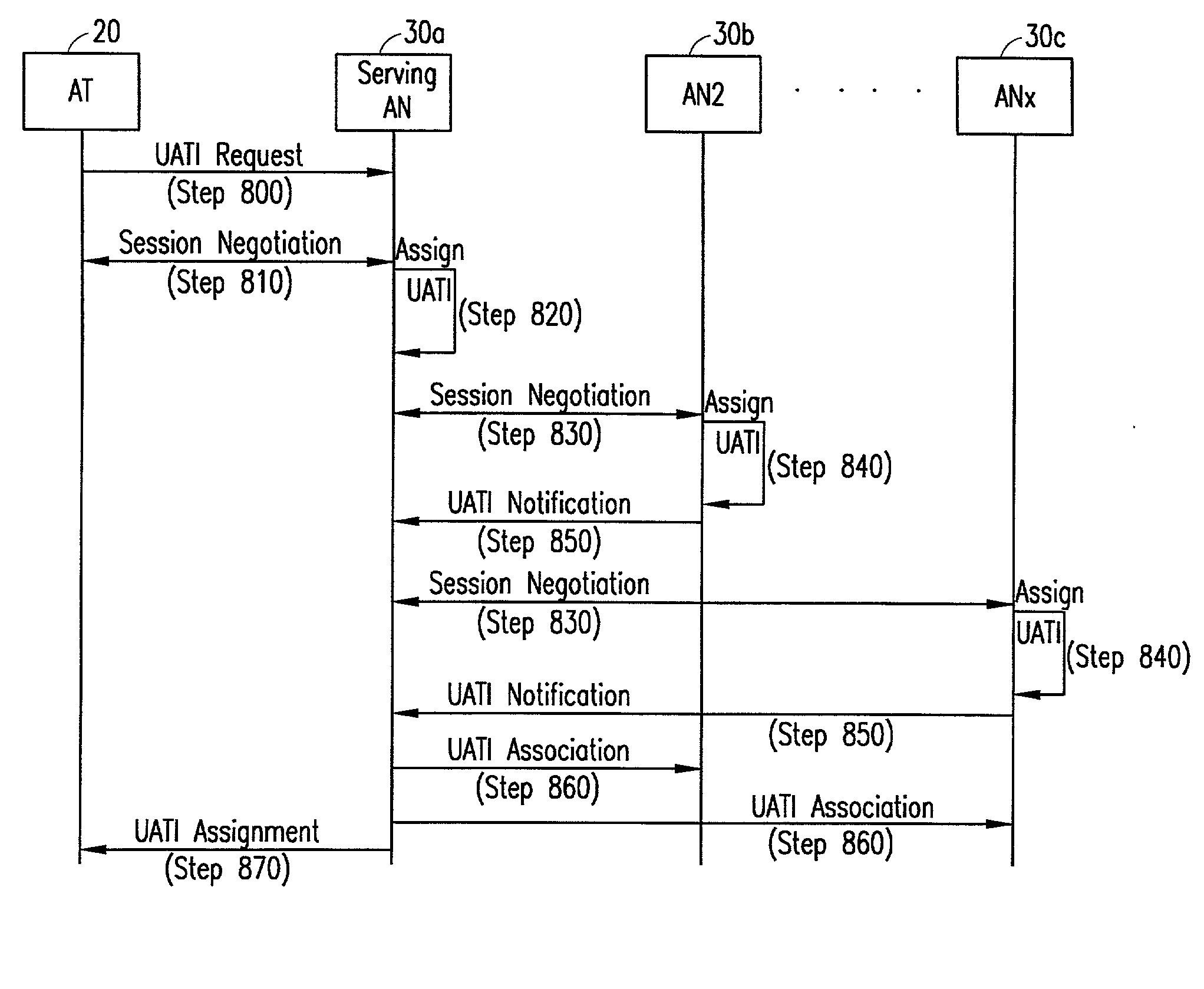
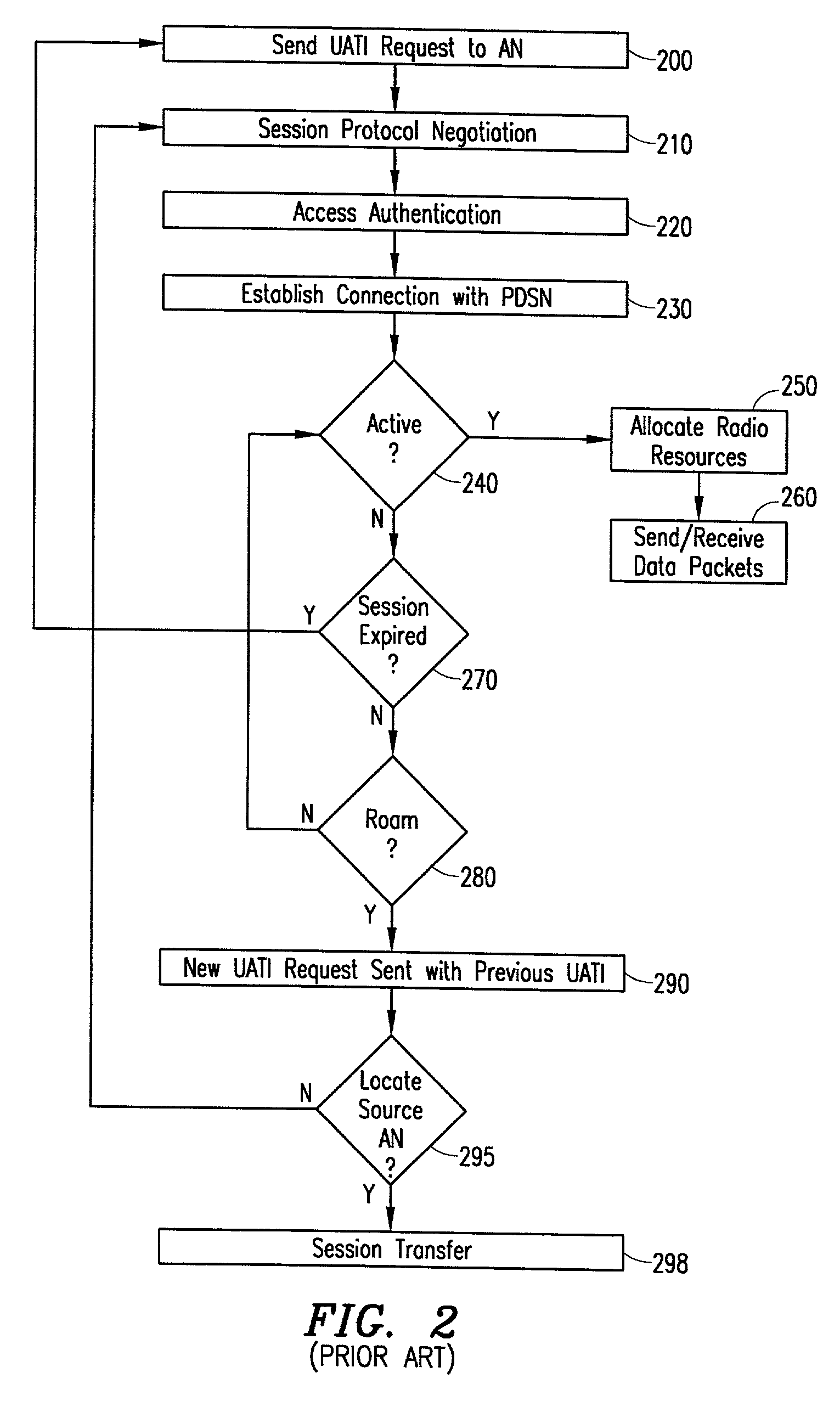
A system and method is disclosed for improved session management when roaming between access networks (AN) within a data cellular network. In one embodiment, gateway functionality is added to one AN in each subnet. The Gateway AN (GAN) provides session transfer capabilities during a dormant handoff with a source AN located in a different subnet. The GAN is responsible for receiving session information request messages from target AN's within the local subnet, querying other GANs within other subnets to locate the subnet that contains the source AN for the session and routing the session information back to the target ANs. In another embodiment, an extended session is established across several ANs within a subnet. When an Access Terminal (AT) initiates a new extended session, the responsible AN negotiates a common session across the ANs covered by the extended session area. During the session negotiation, each AN establishes a new session and allocates a new Unicast Access Terminal Identifier (UATI). Each AN is notified of each UATI allocated for the extended session. Once the negotiation between ANs is completed, the AT can roam anywhere within the extended session area without re-negotiating the session or transferring session information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
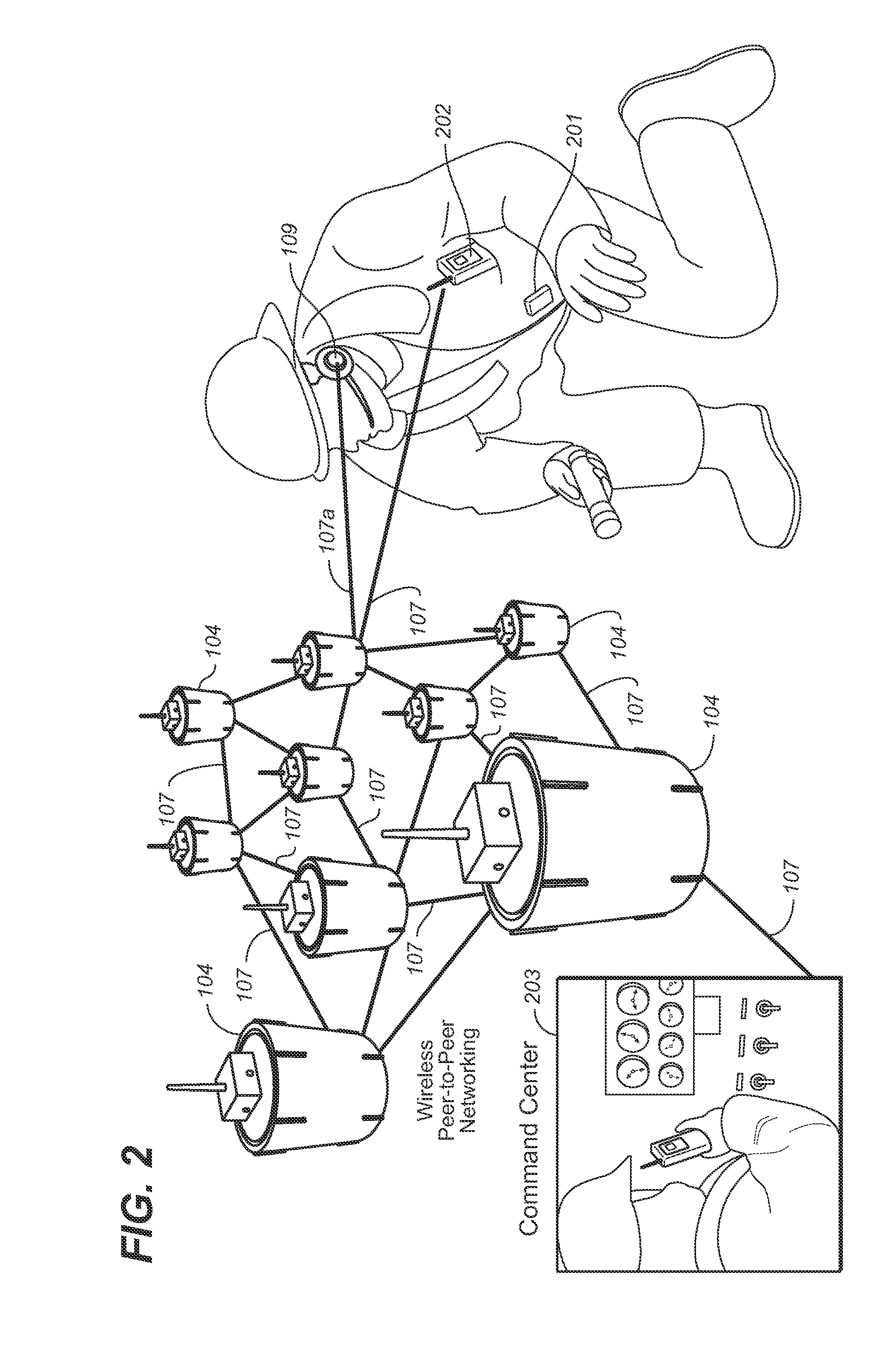
Subnetwork synchronization and variable transmit synchronization techniques for a wireless medical device network
ActiveUS20070251835A1Efficient routingWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDrug and medicationsWireless Application ProtocolFluid infusion
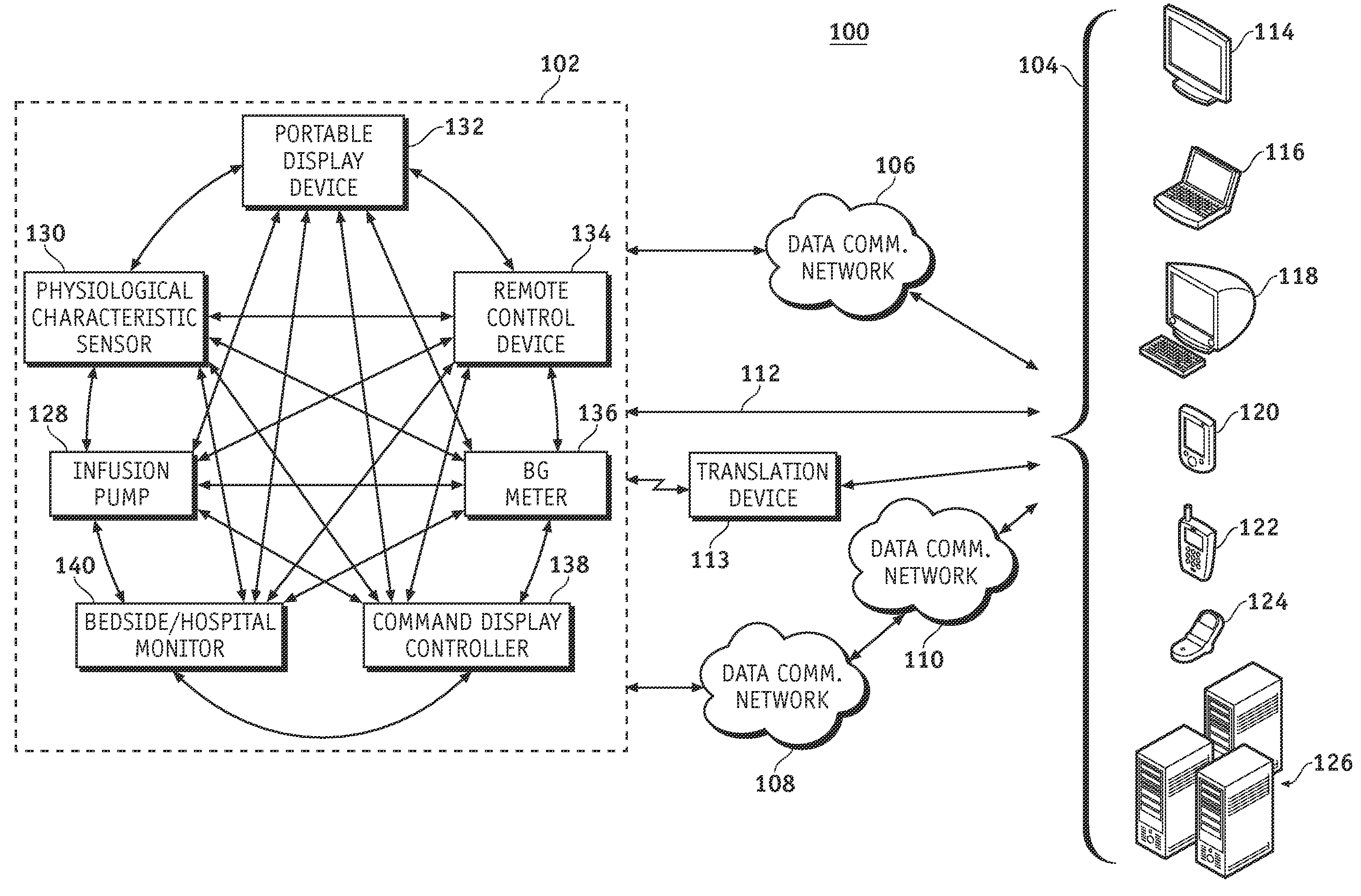
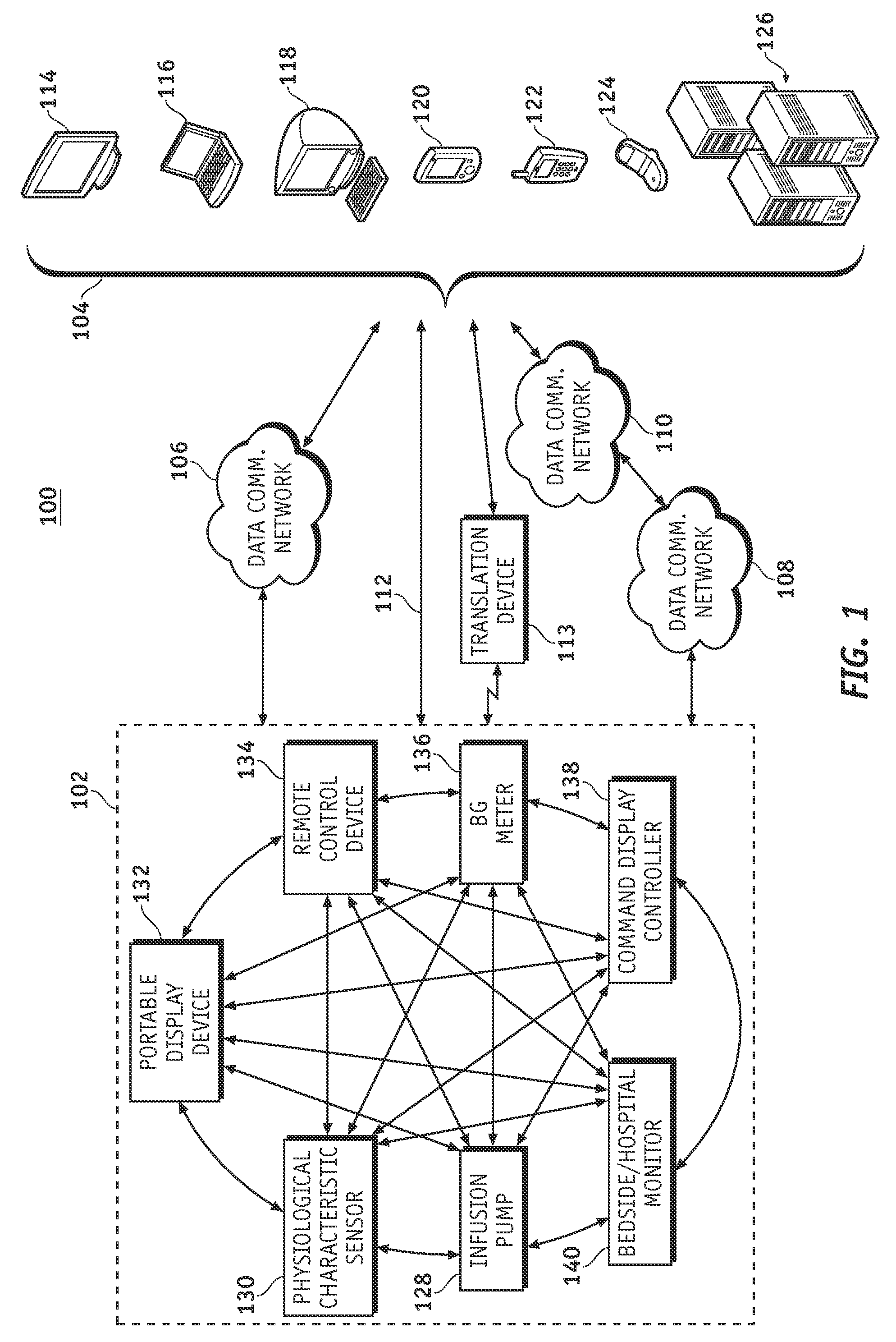
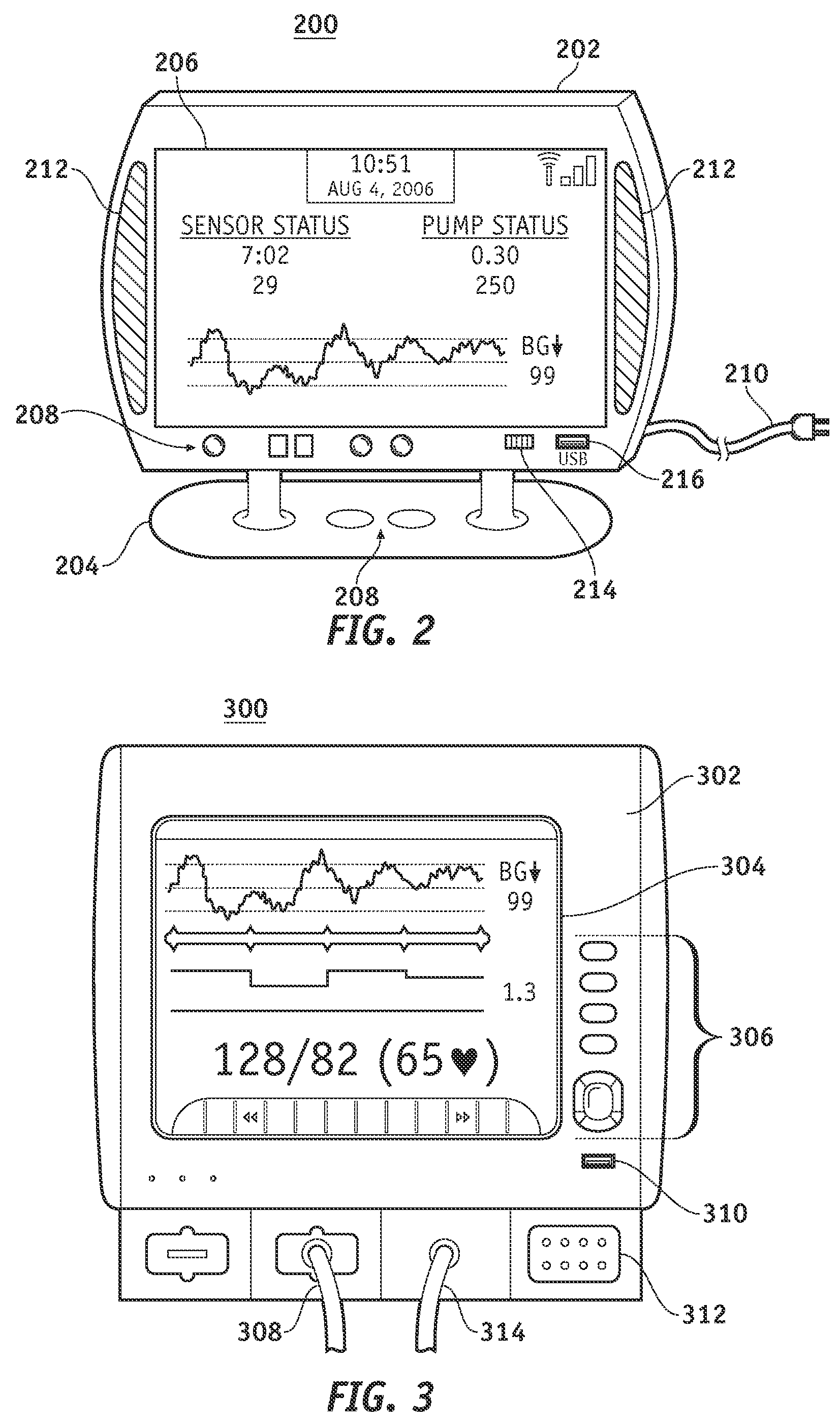
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Mobility architecture using pre-authentication, pre-configuration and/or virtual soft-handoff
ActiveUS7046647B2Higher-layer handoffMinimizing interruptionData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsMobile architectureDistributed computing
In some illustrative embodiments, a novel system and method is provided that can, for example, extend concepts of pre-authentication (such as, e.g., IEEE 802.11i pre-authentication) so as to operate across networks or subnetworks (such as, e.g., IP subnets). In preferred embodiments, a novel architecture includes one or both of two new mechanisms that substantially improve, e.g., higher-layer handoff performance. A first mechanism is referred to as “pre-configuration,” which allows a mobile to pre-configure higher-layer information effective in candidate IP subnets to handoff. A second mechanism is referred to as “virtual soft-handoff,” which allows a mobile to send or receive packets through the candidate IP subnets even before it is actually perform a handoff to any of the candidate IP subnets.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +1
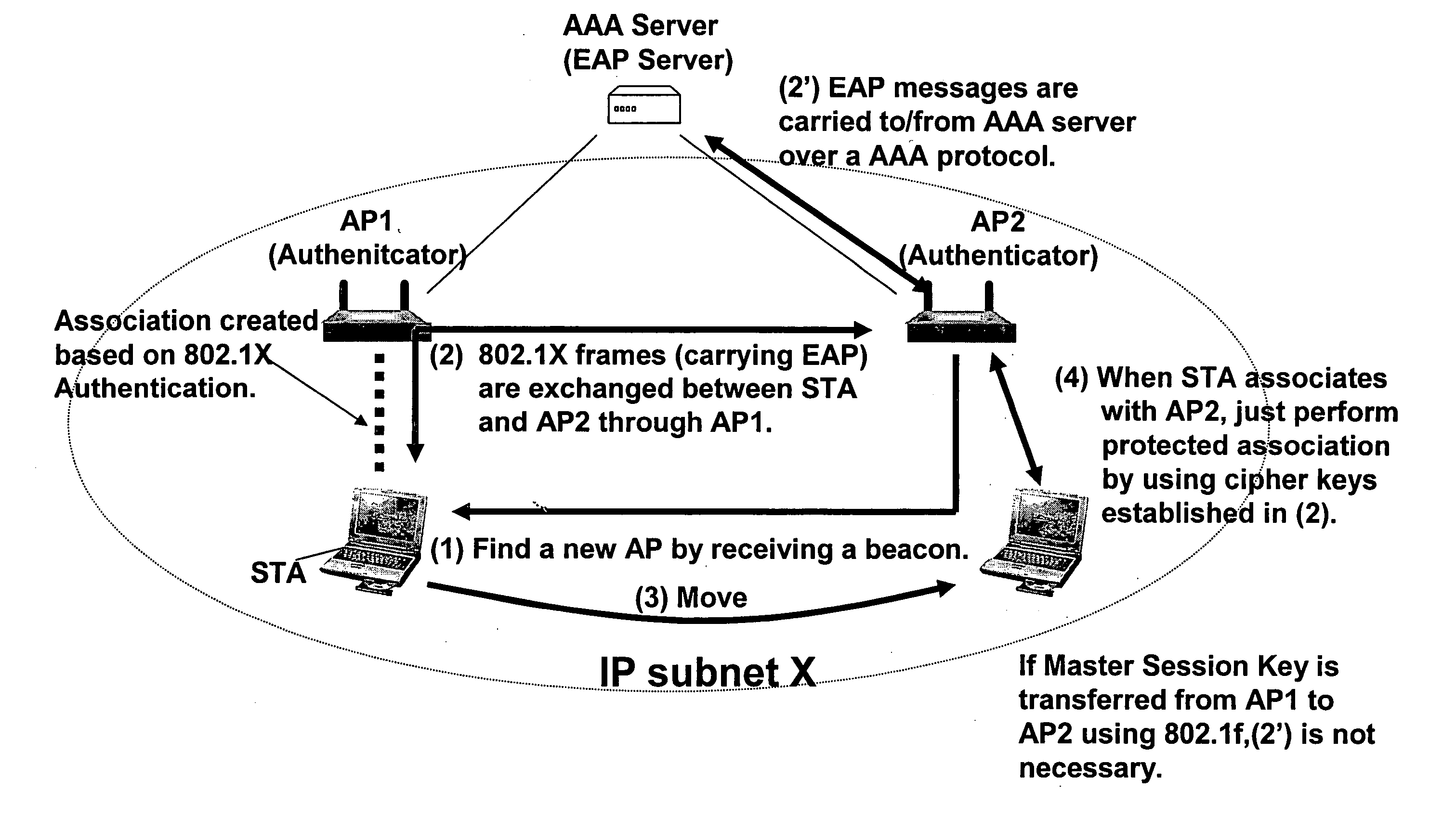
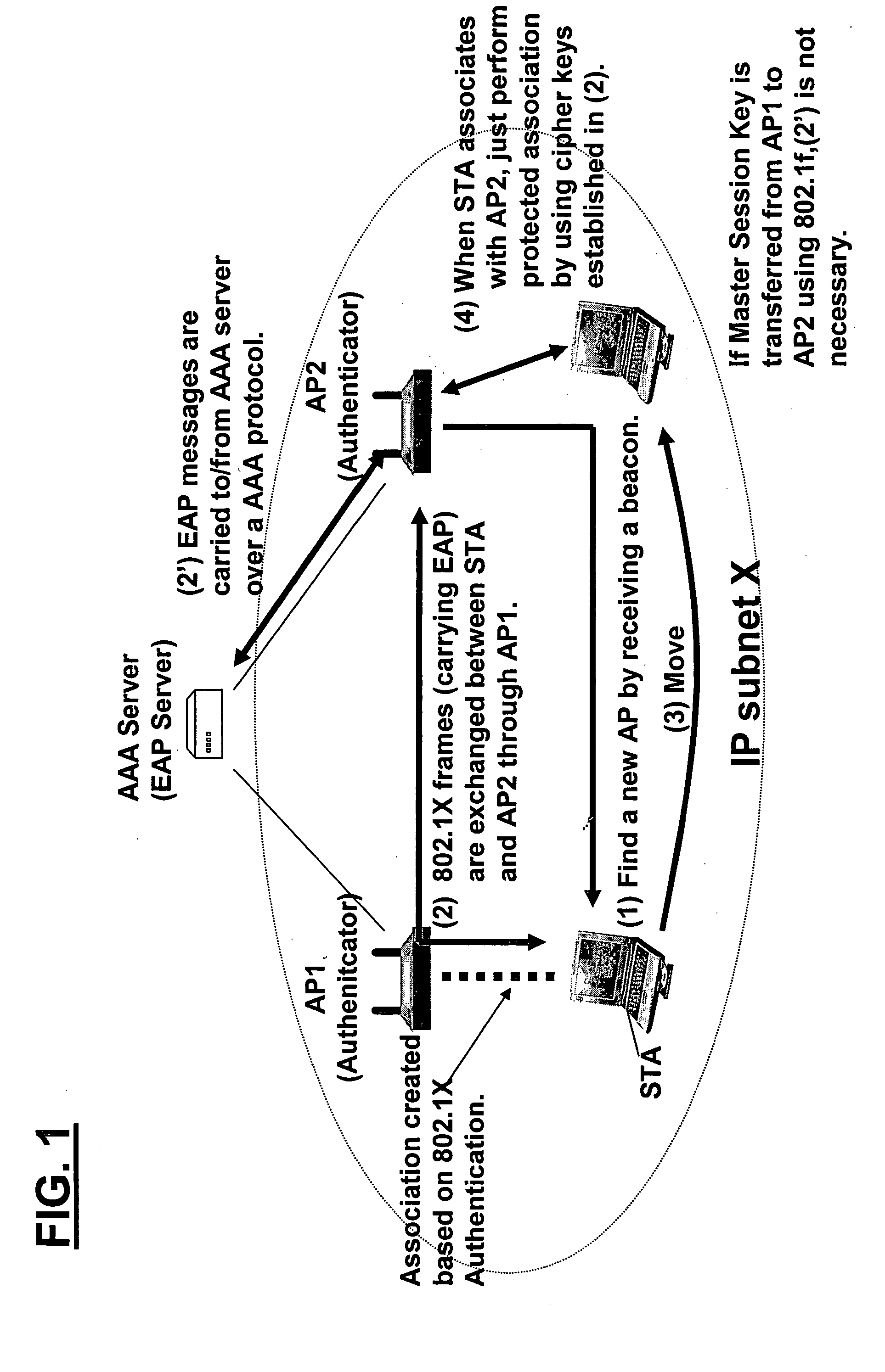
802.11 using a compressed reassociation exchange to facilitate fast handoff
ActiveUS7350077B2Reduce the burden onUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesComputer networkRogue access point
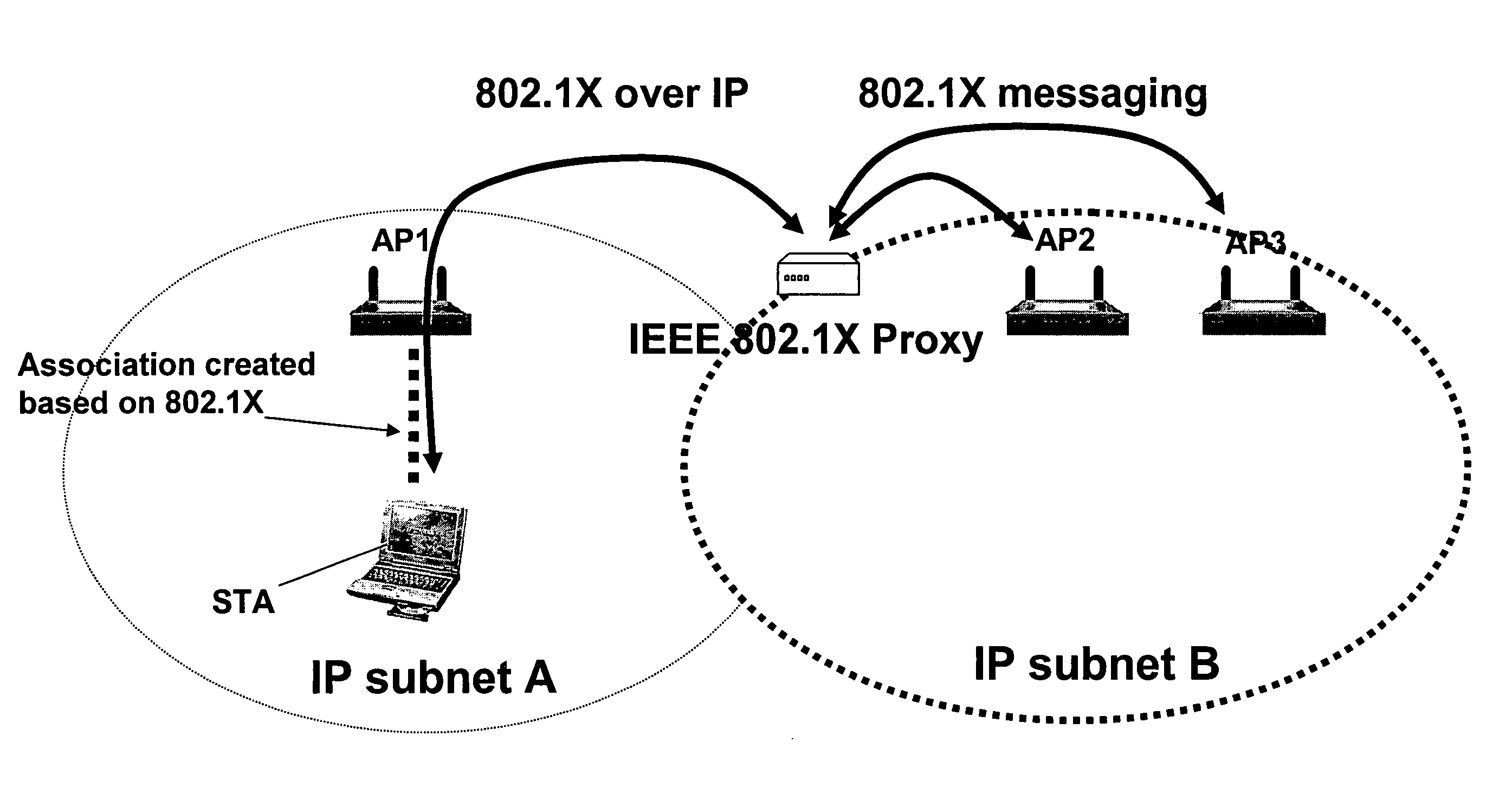
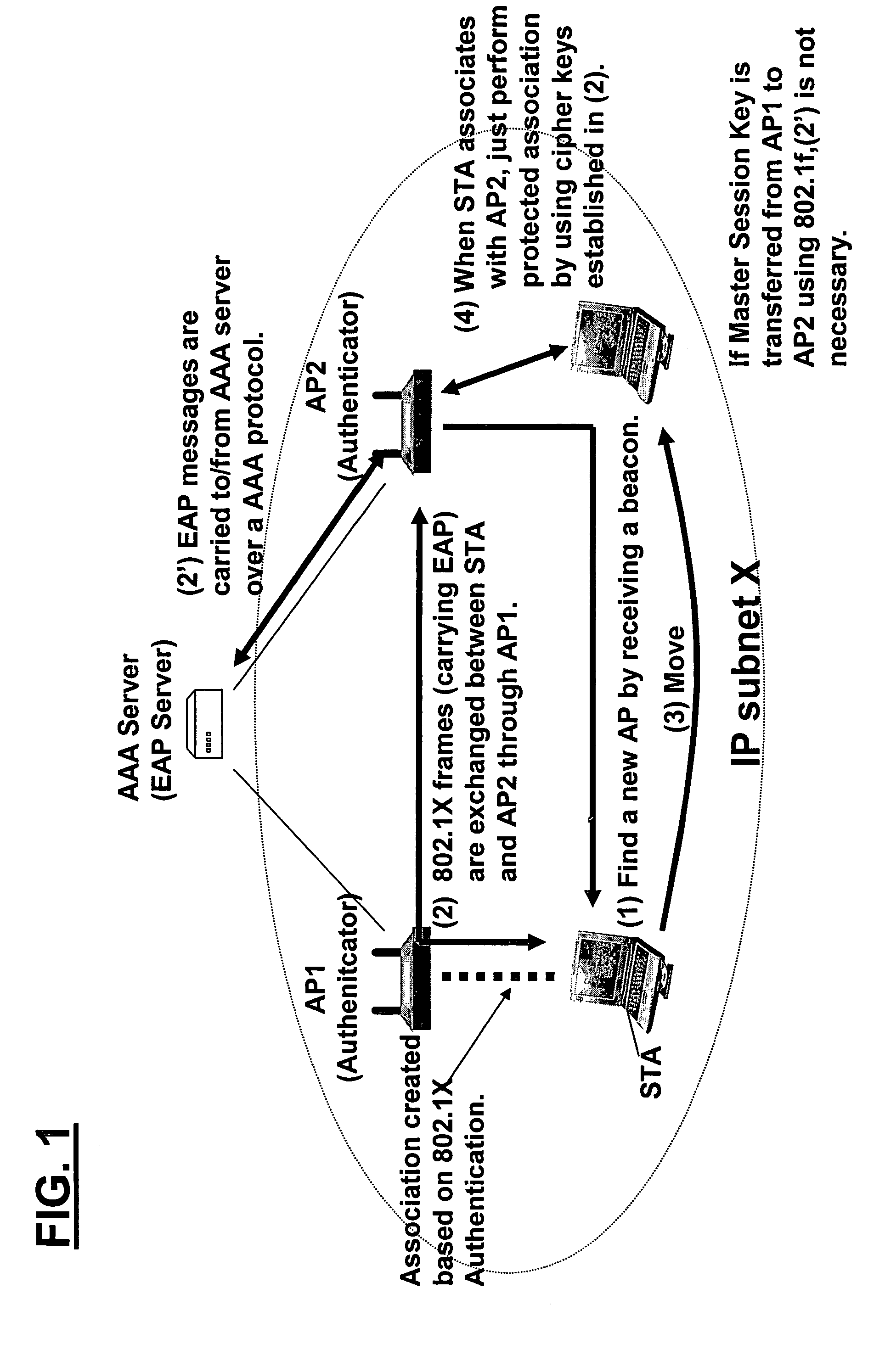
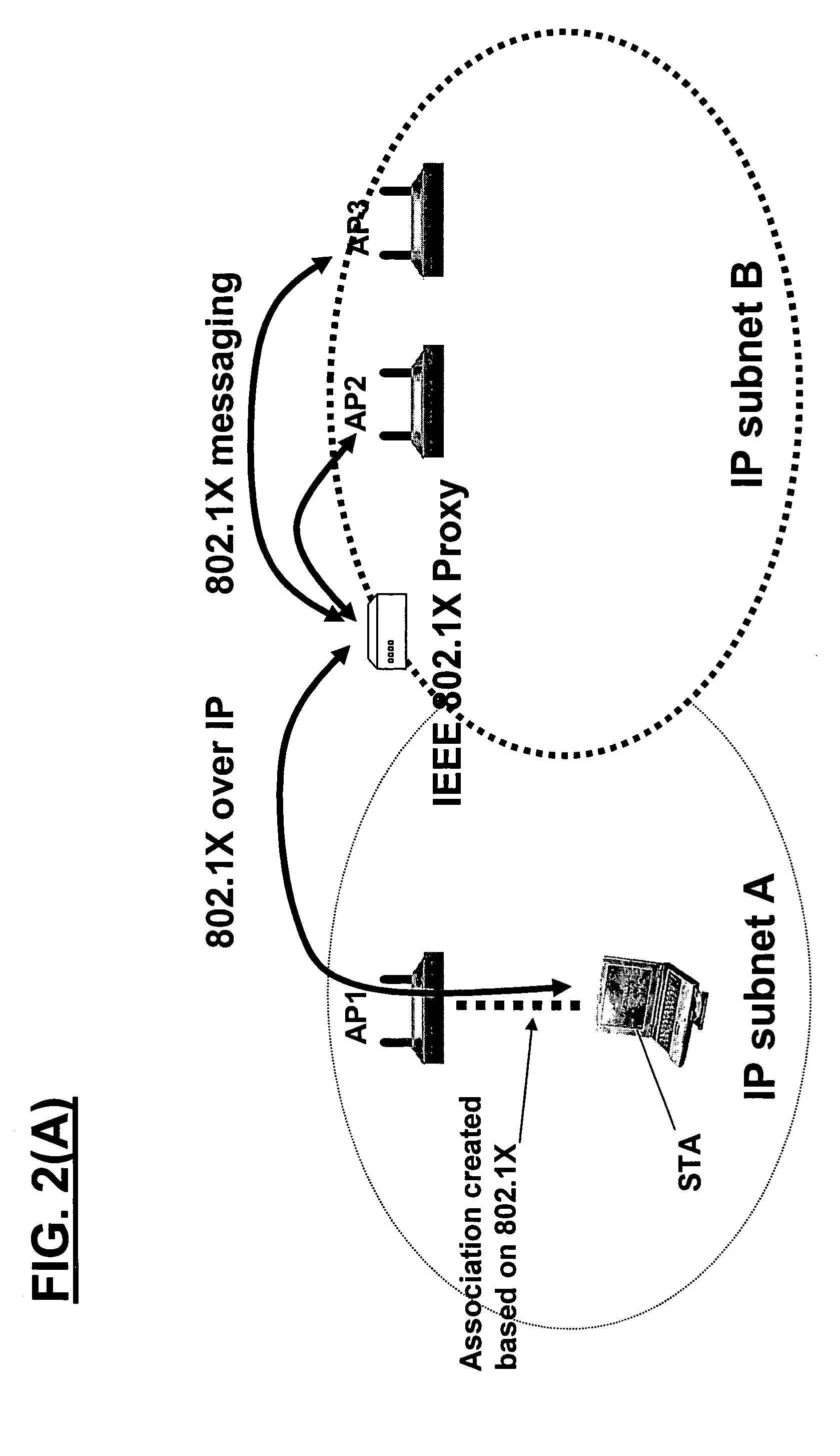
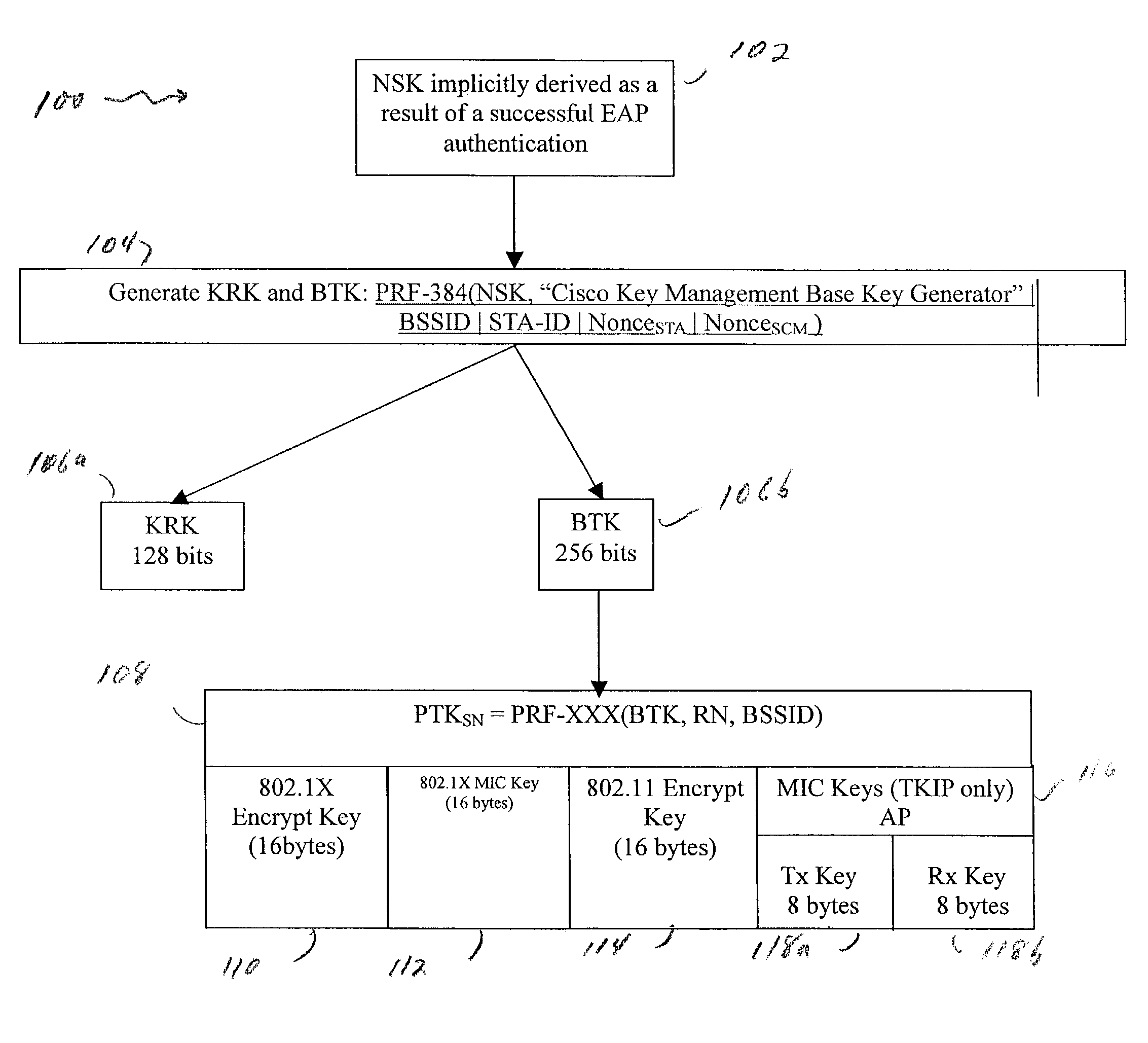
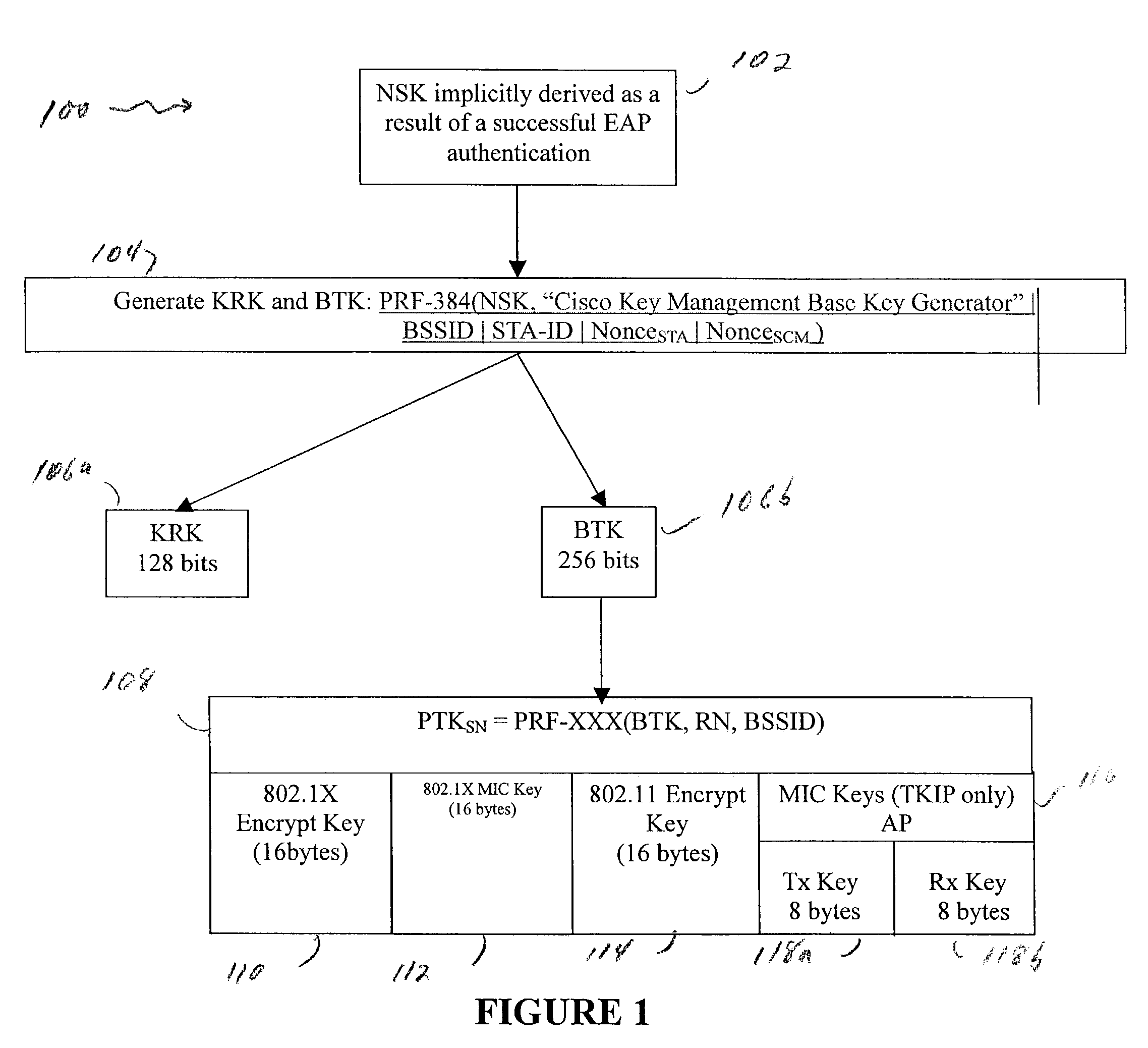
A method and system for handling roaming mobile nodes in a wireless network. The system uses a Subnet Context Manager to store current Network session keys, security policy and duration of the session (e.g. session timeout) for mobile nodes, which is established when the mobile node is initially authenticated. Pairwise transit keys are derived from the network session key. The Subnet Context Manager handles subsequent reassociation requests. When a mobile node roams to a new access point, the access point obtains the network session key from the Subnet Context Manager and validates the mobile node by computing a new pairwise transient key from the network session key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Wireless mine tracking, monitoring, and rescue communications system
InactiveUS20080137589A1Emergency connection handlingParticular environment based servicesRelevant informationCommunications system
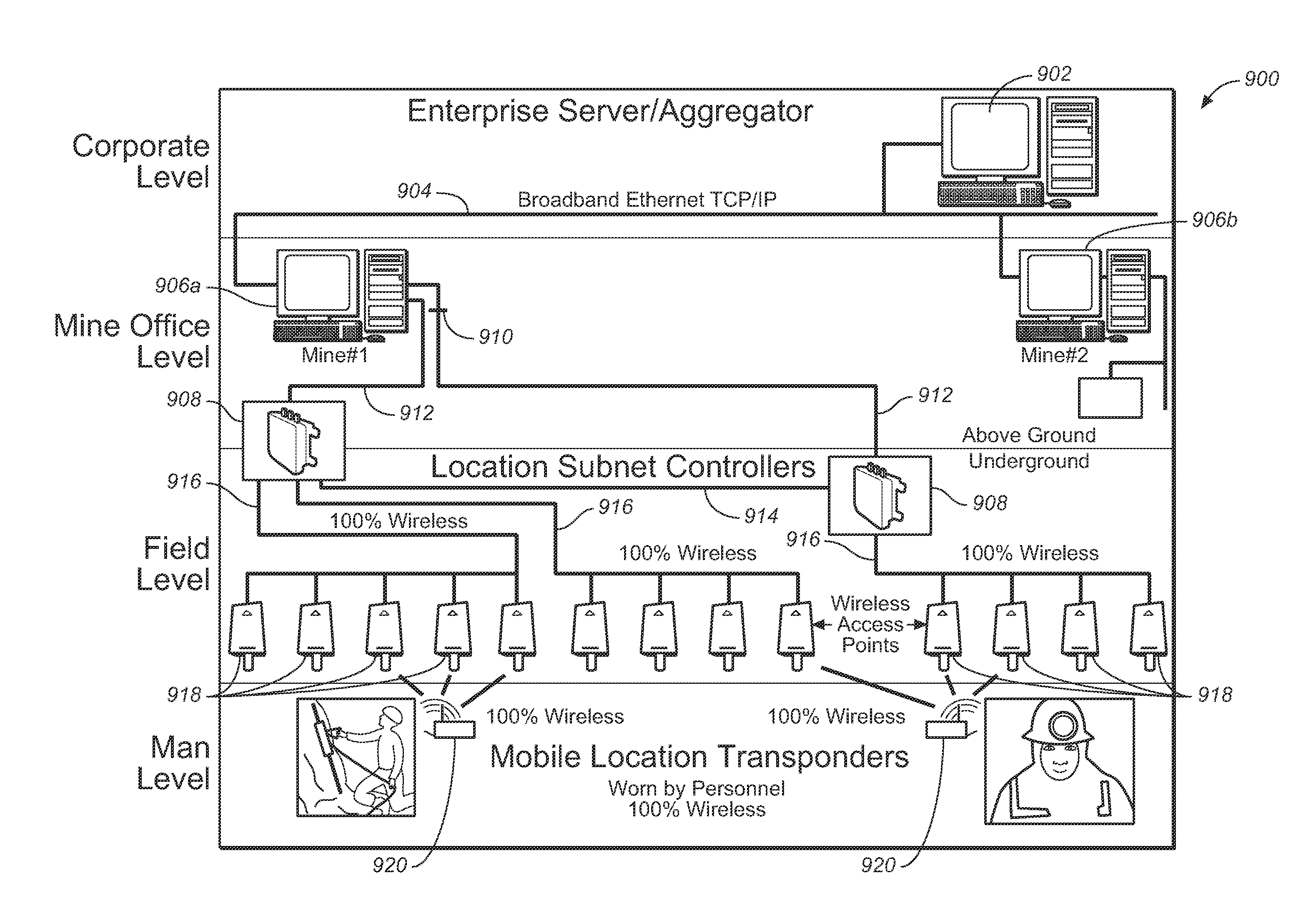
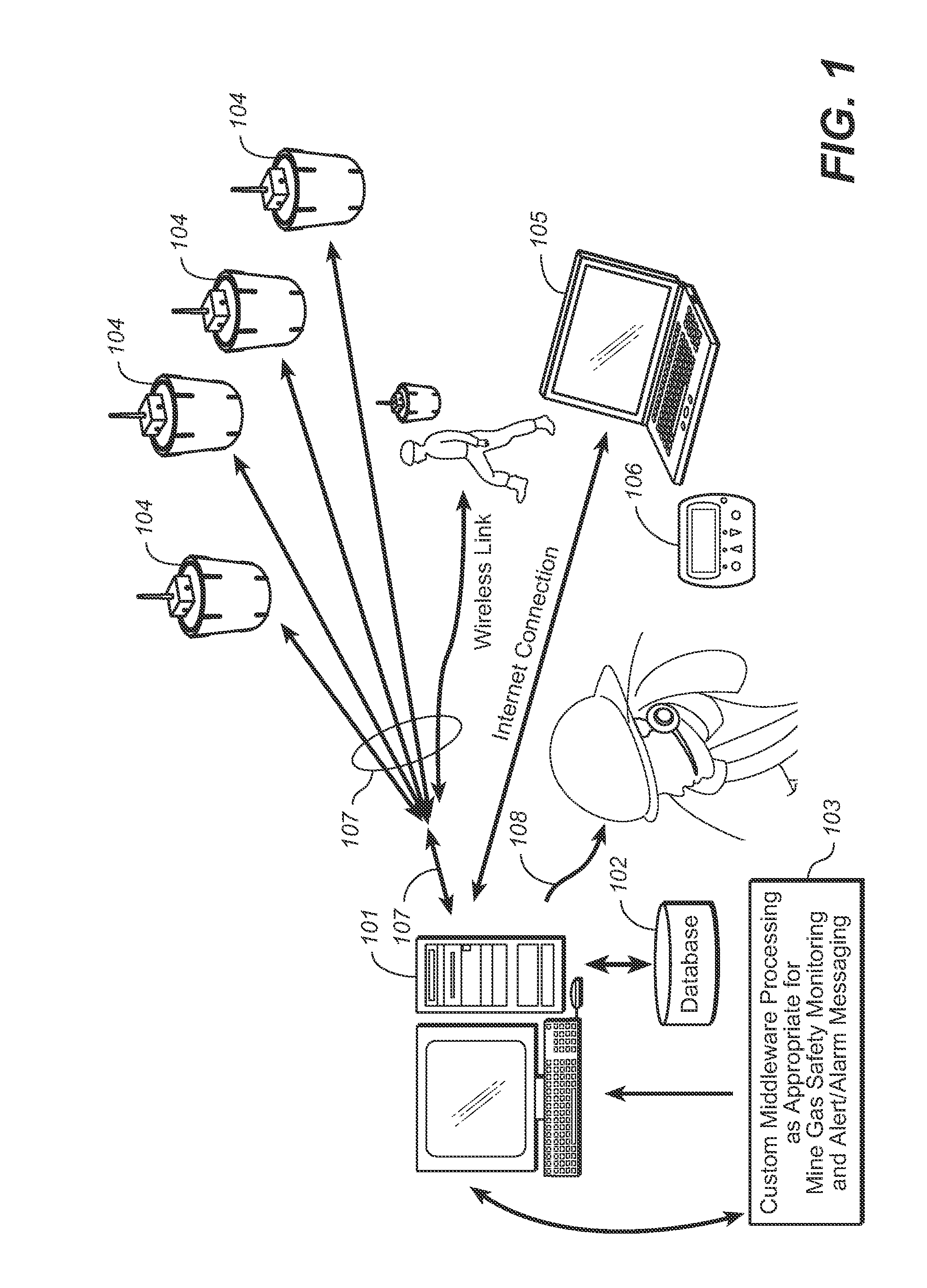
An intrinsically safe accurate location information network for personnel and assets in underground mines, including wireless access points and subnetwork controllers, active wireless locator / messenger tags, network controller(s), and enterprise servers running application control software. The wireless access points are installed in mine entries and crosscuts and track the active wireless locator / messenger tags. The active tags may be worn by mine personnel or installed in mining equipment. The network subsystems form relay networks that wirelessly carry telemetry and control data without the need to penetrate the earth. The subsystems determine the location of persons and assets underground and monitor safety-related information, which can be used for disaster avoidance, early warning of impending disaster, and improved rescue effectiveness. .
Owner:VENTURE CORP LTD
Method and apparatus for managing hardware address resolution
InactiveUS20070248085A1Data switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
Disclosed herein is a network device, such as a host computer, that simultaneously has two IP identities: a local IP identity on a local network (e.g., a non-virtual private network) to which the host computer is connected; and a remote IP identity on a second network (e.g., virtual private network) that is remote to the host. Only the remote IP identity is visible to the host operating system's network stack. Each IP identity has its own ARP cache and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). The local ARP cache is managed with respect to a connection of the host to a local subnet (e.g., an Internet Service Provider (ISP) subnet) and the remote ARP cache is managed with respect to a remote subnet reachable through a gateway on the local subnet.
Owner:E COLT SYST INC
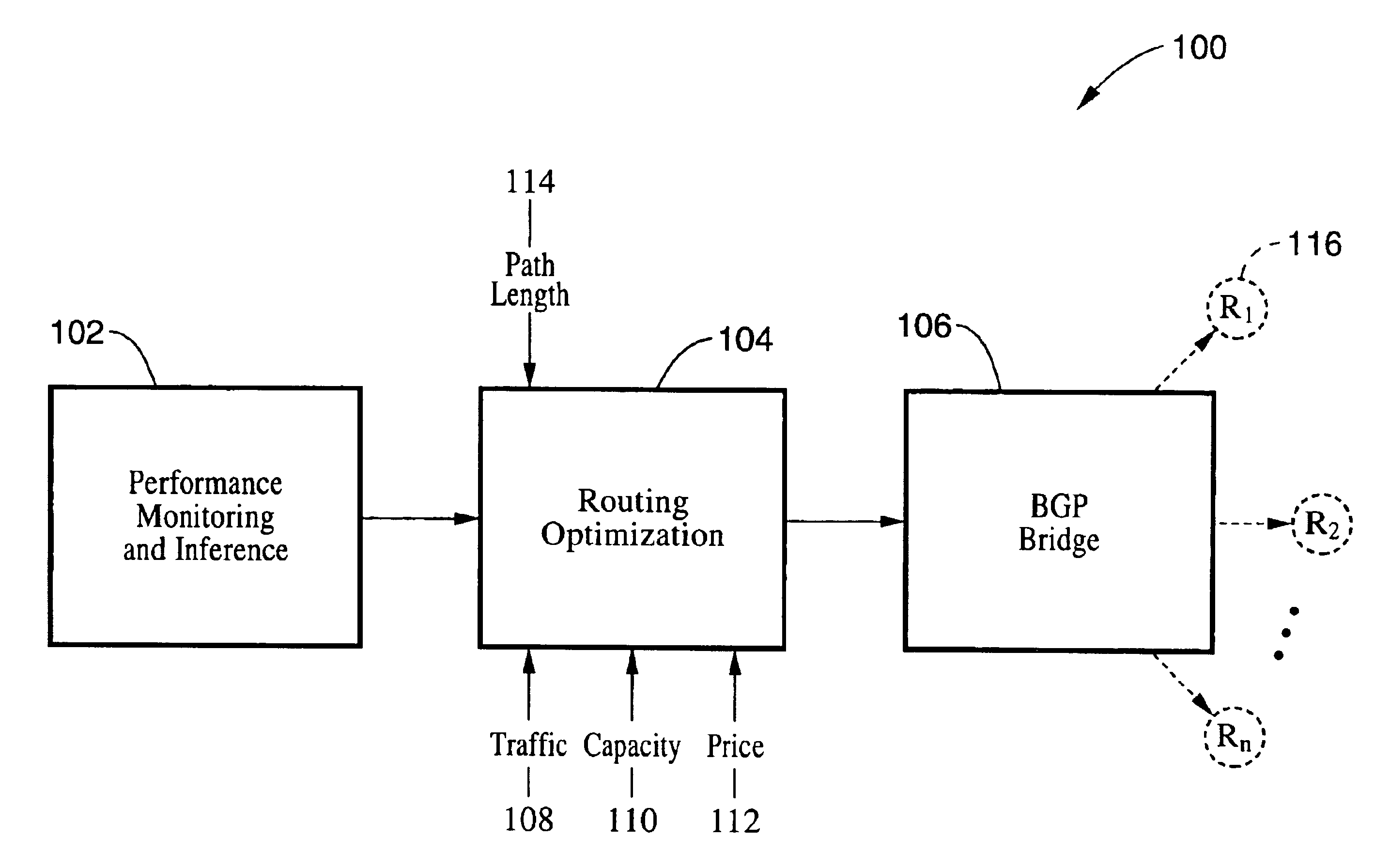
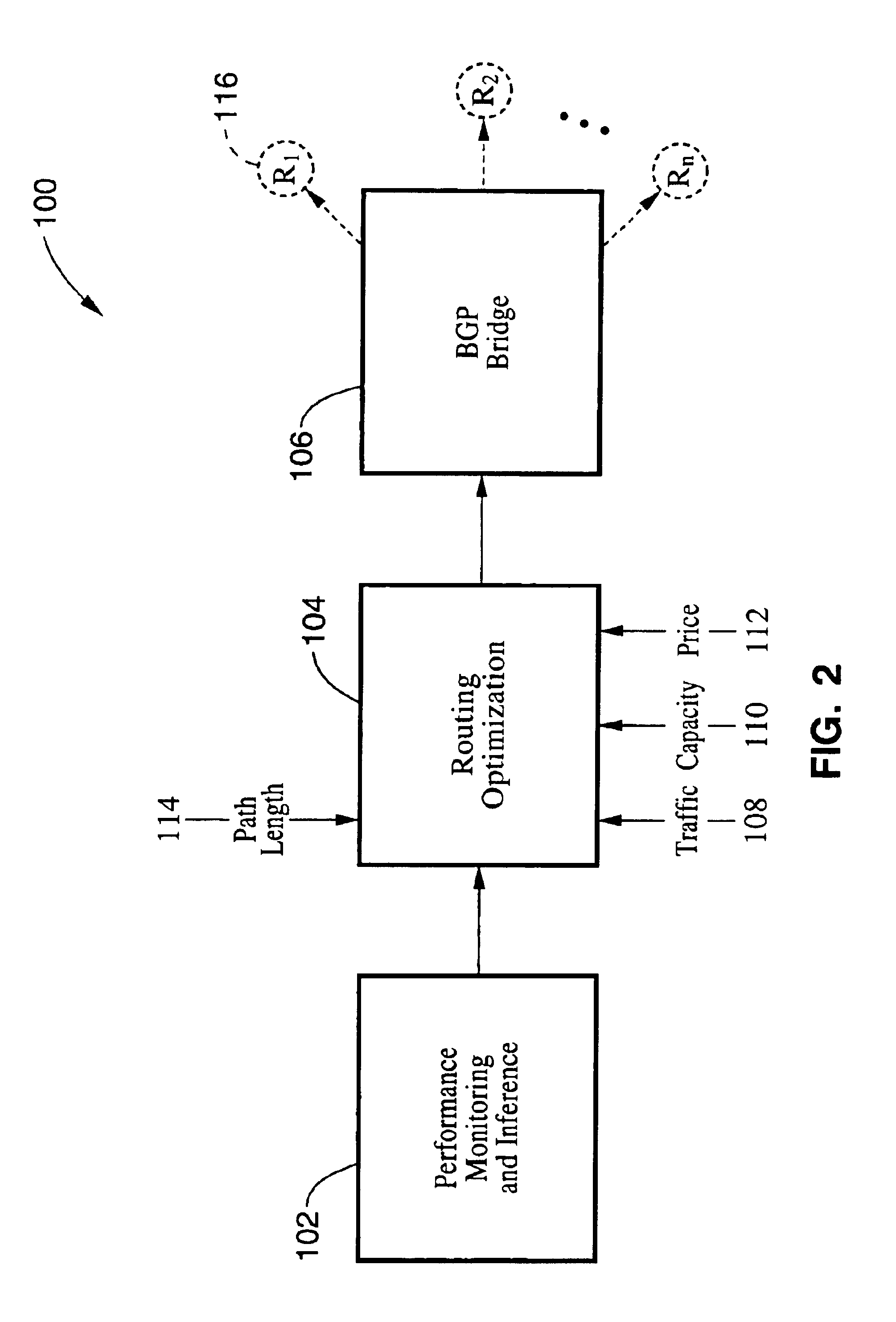
Method and system for optimizing routing through multiple available internet route providers
InactiveUS6981055B1Optimize route selectionInability to overcomeDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityRouting table
A method and system for optimizing routing traffic to a destination when multiple routes are available. A performance monitoring and inference component measures the performance of the available paths to a large set of subnetworks, and uses those measurements to infer the performance of all available paths to an even larger set of subnetworks. A routing optimization component uses a cost function that assigns a cost to a routing table based on information from the performance monitoring and inference component, as well as other path characteristics, and further uses a minimization methodology to find a routing table with a very low cost, as defined by the cost function. A BGP bridge takes the routing table generated by the routing optimization component and communicates that information to the routers using BGP, thereby ensuring that the routers will route traffic in accordance with the routing table.
Owner:INTERNAP HLDG LLC
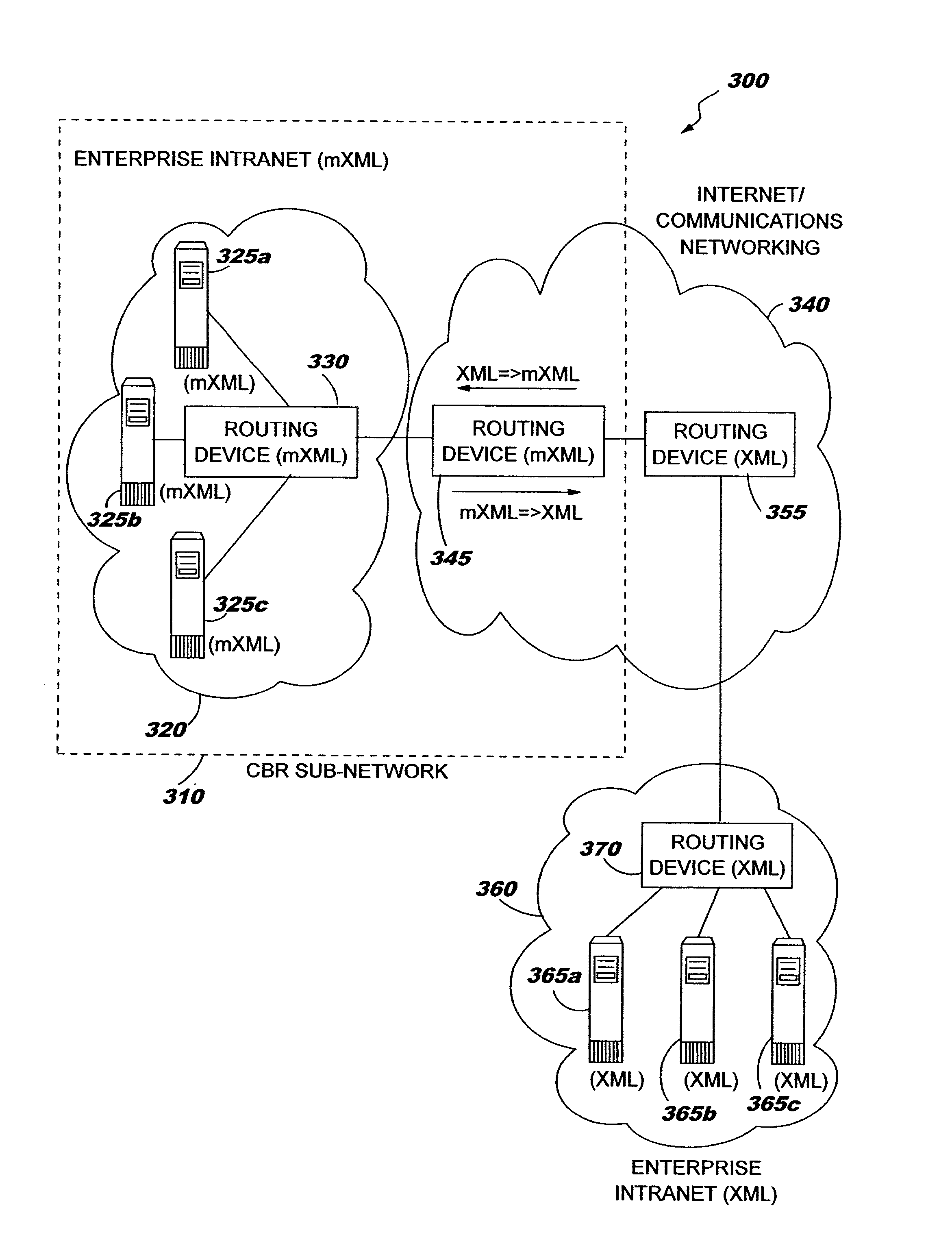
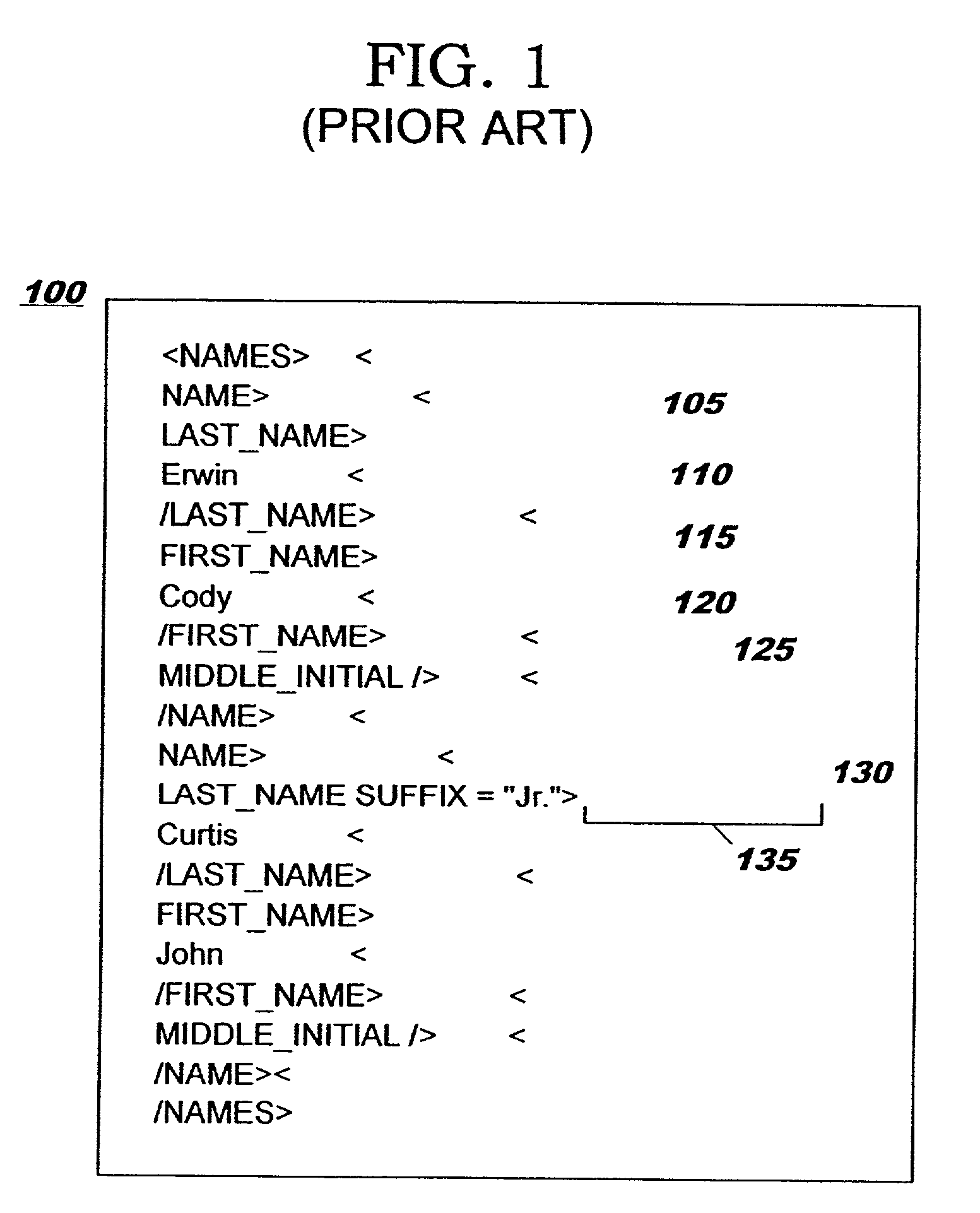
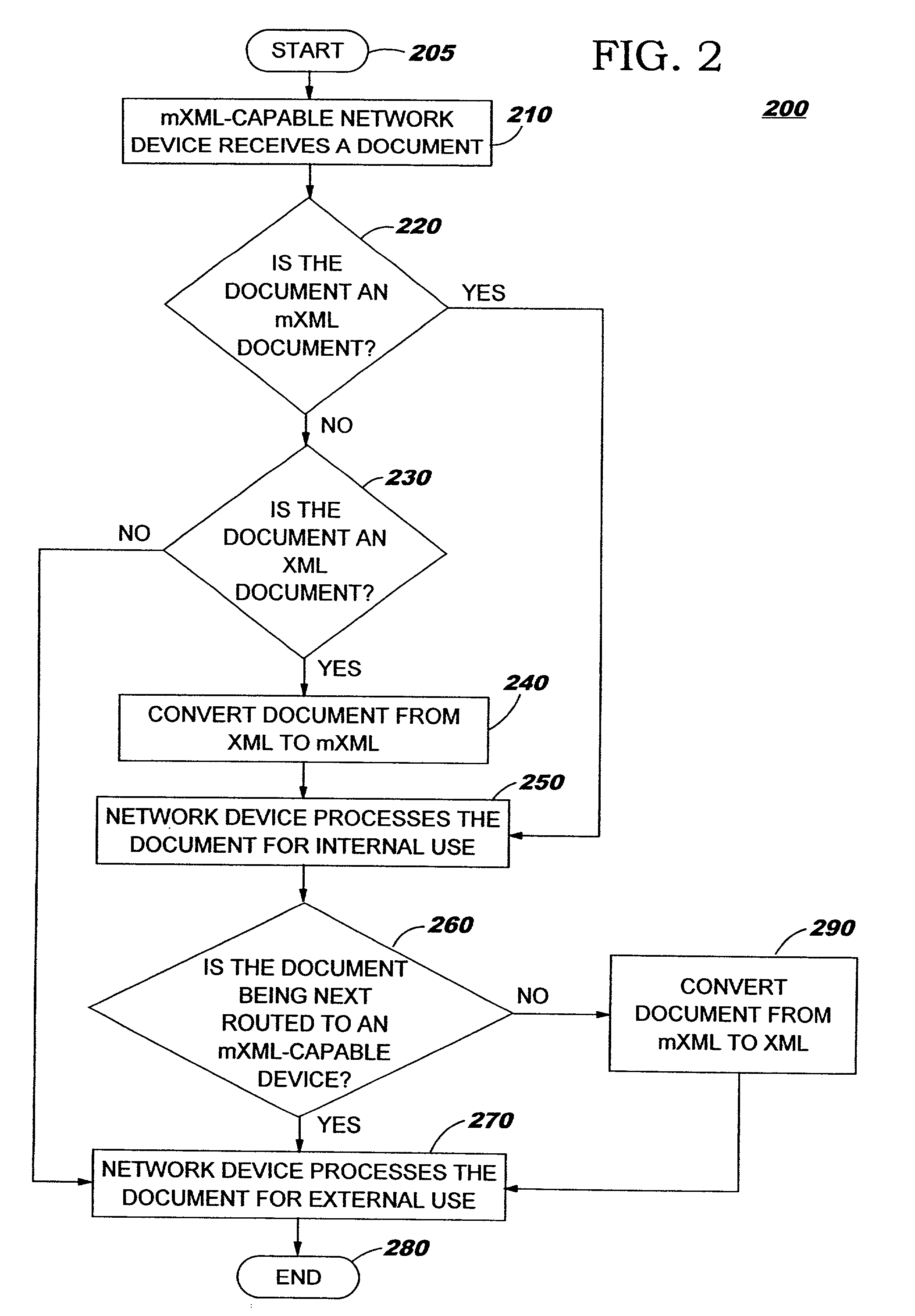
Conversion of documents between XML and processor efficient MXML in content based routing networks
InactiveUS7134075B2Efficient processingImprove performanceNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsSemanticsExtensible markup
A method, system, and computer program product for efficient processing of Extensible Markup Language (XML) documents in Content Based Routing (“CBR”) networks. Specifically, the method involves converting existing XML documents to a machine-oriented notation (“mXML”) which is significantly more compact than XML, while still conveying the content and semantics of the data and the structure of the document. Documents are converted from XML to mXML upon entering a CBR subnetwork and / or upon receipt by an mXML-capable device. The documents are then processed in mXML format. Devices within the inventive system are provided with an awareness of whether target devices or processes are mXML-capable. Documents being routed to a target which is mXML-capable are passed in mXML format while documents being routed to a target which is not mXML-capable are converted to XML before they are passed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for self-organizing node groups on a network
Method and apparatus for the self-organization of nodes into groups in network computing environments. Embodiments may provide the ability to deploy nodes on a network, and to allow the nodes to organize into groups without human intervention. In one embodiment, a node may broadcast a query looking for a master node for the group. If the query produces no responses, the node may self-elect as the master node for the group and the node may broadcast its presence as the master node. If two or more nodes self-elect as master nodes, the nodes may negotiate to determine which node will be the master node. If the master node becomes unavailable, the remaining nodes in the group may elect a new master node. Some embodiments may be implemented on a peer-to-peer platform, such as the JXTA peer-to-peer platform, which may allow the scope of the group to span subnetworks and networks.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
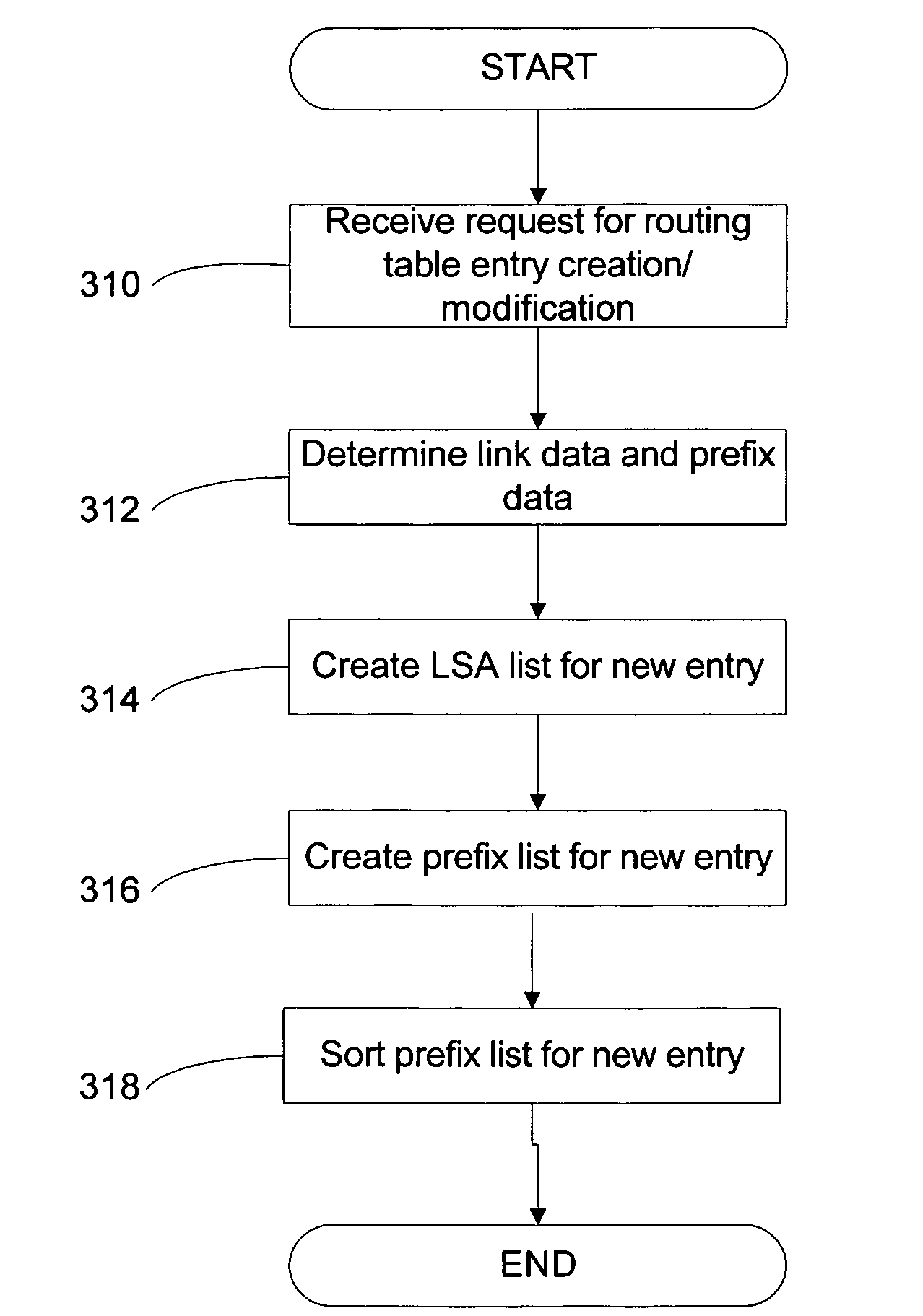
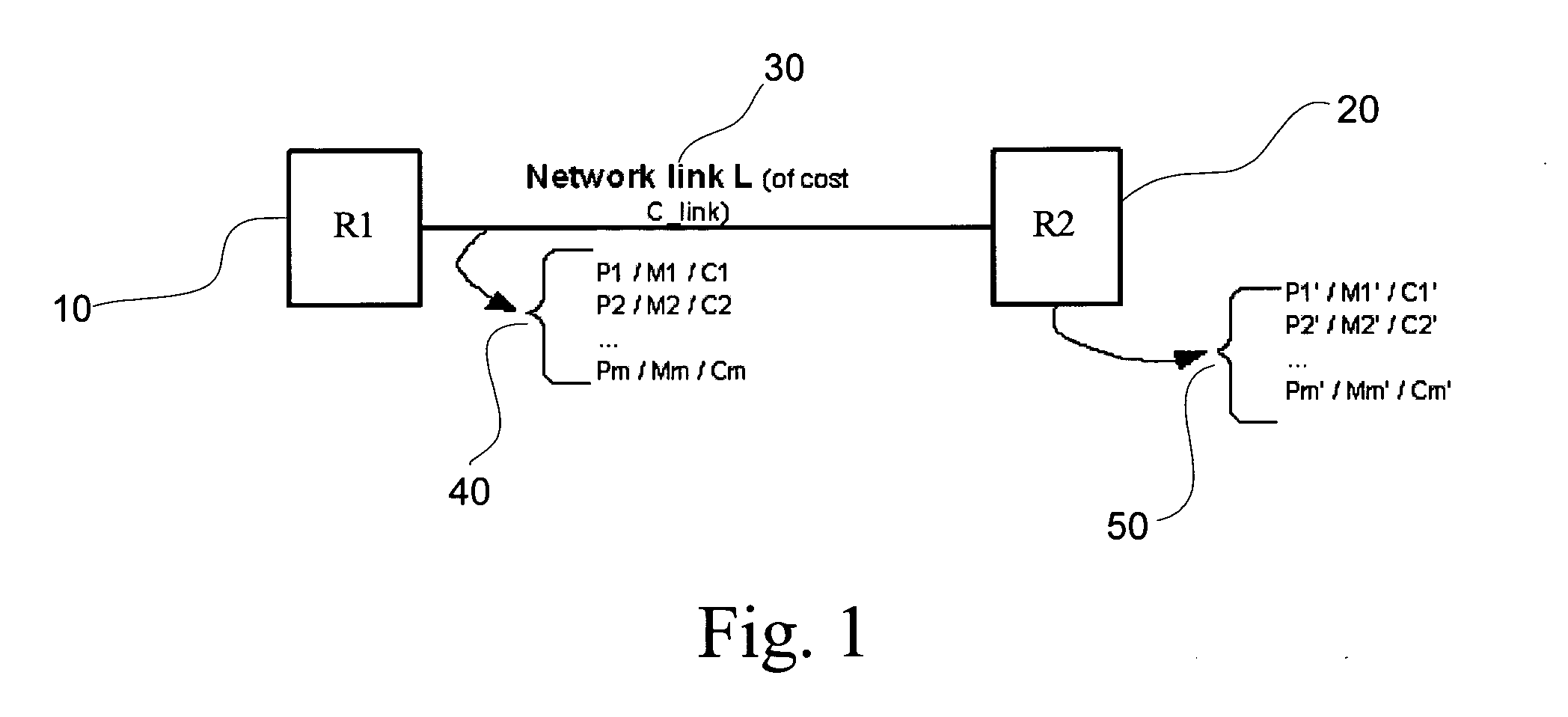
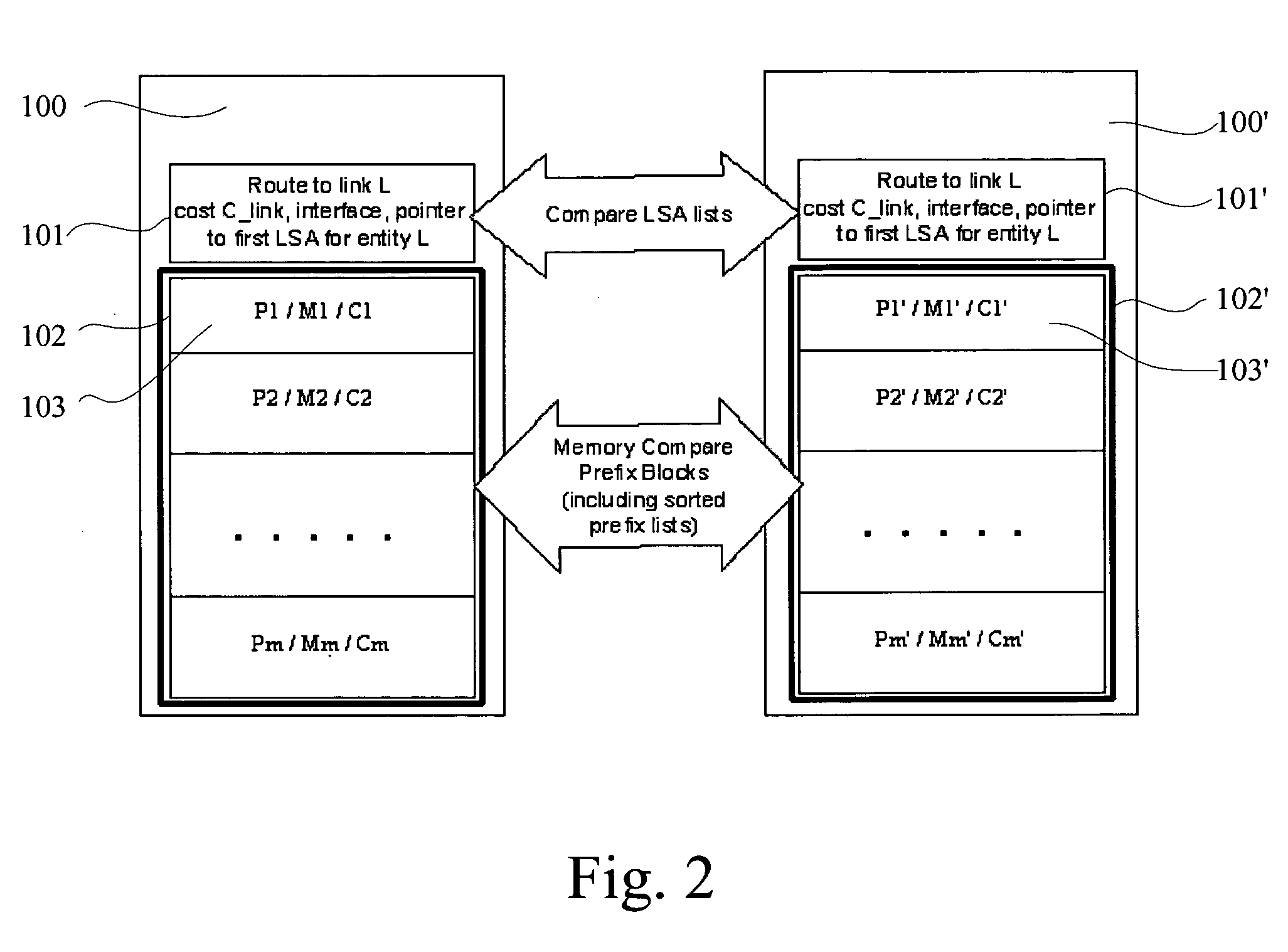
System and method for routing table computation and analysis
InactiveUS20070189284A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting tableNetwork link
Described is a system and method for determining routing information for a network link, the network link including a plurality of subnets, each subnet having the same routing information as the network link, storing the routing information as an entry in a routing table, determining subnet information for each of the plurality of subnets and storing the subnet information for each of the plurality of subnets in the entry. Methods of comparing and searching the subnet information are also described.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
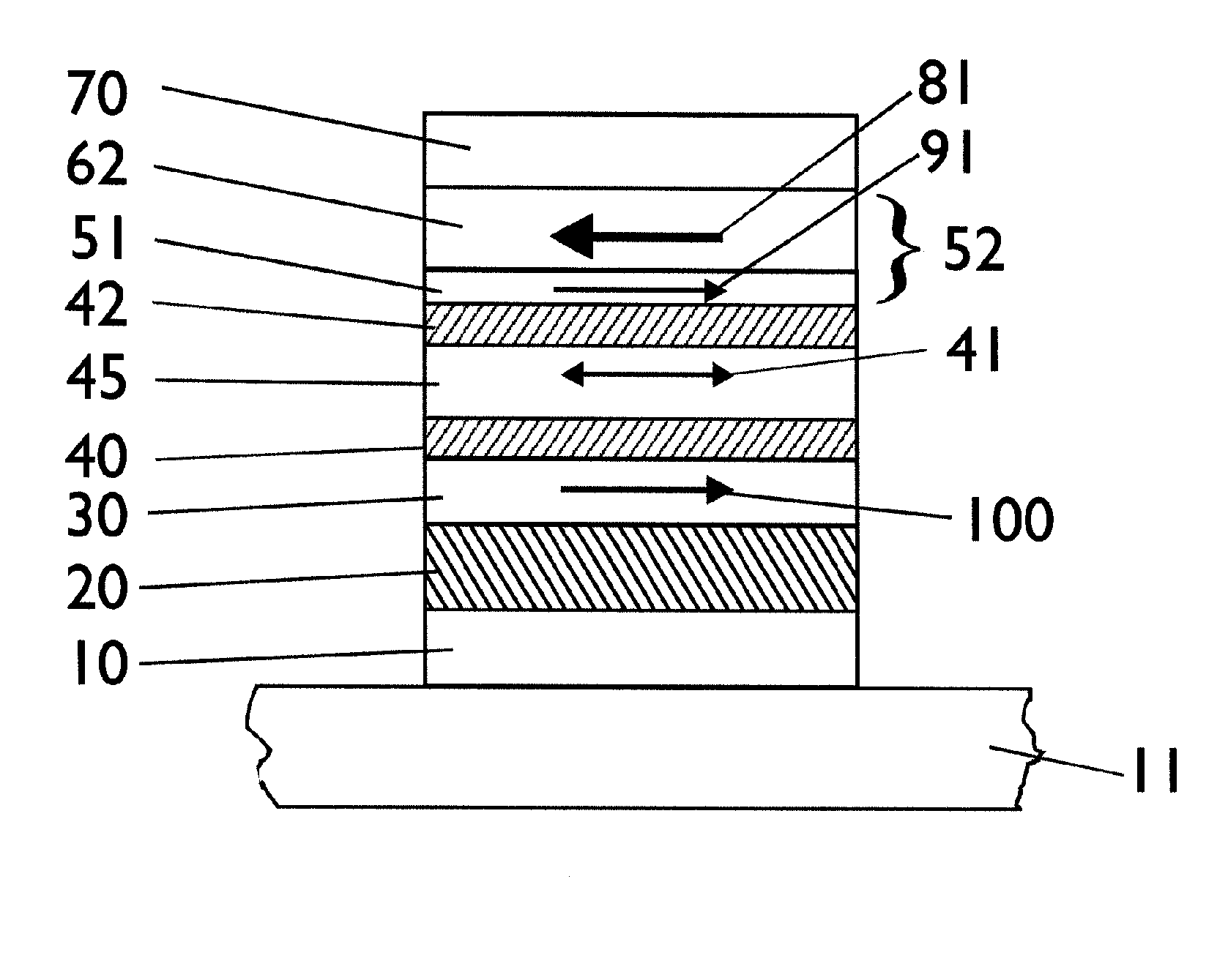
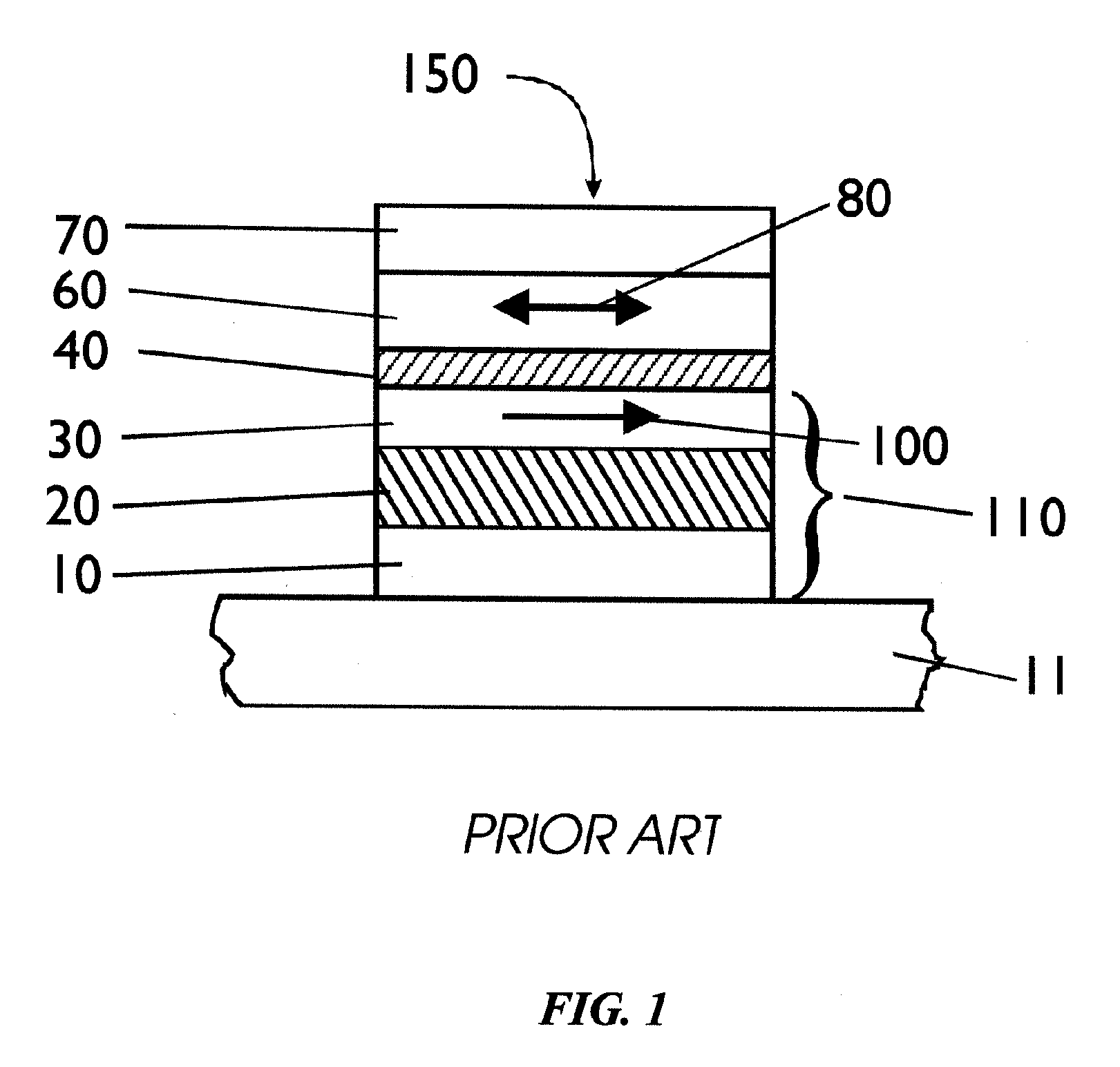
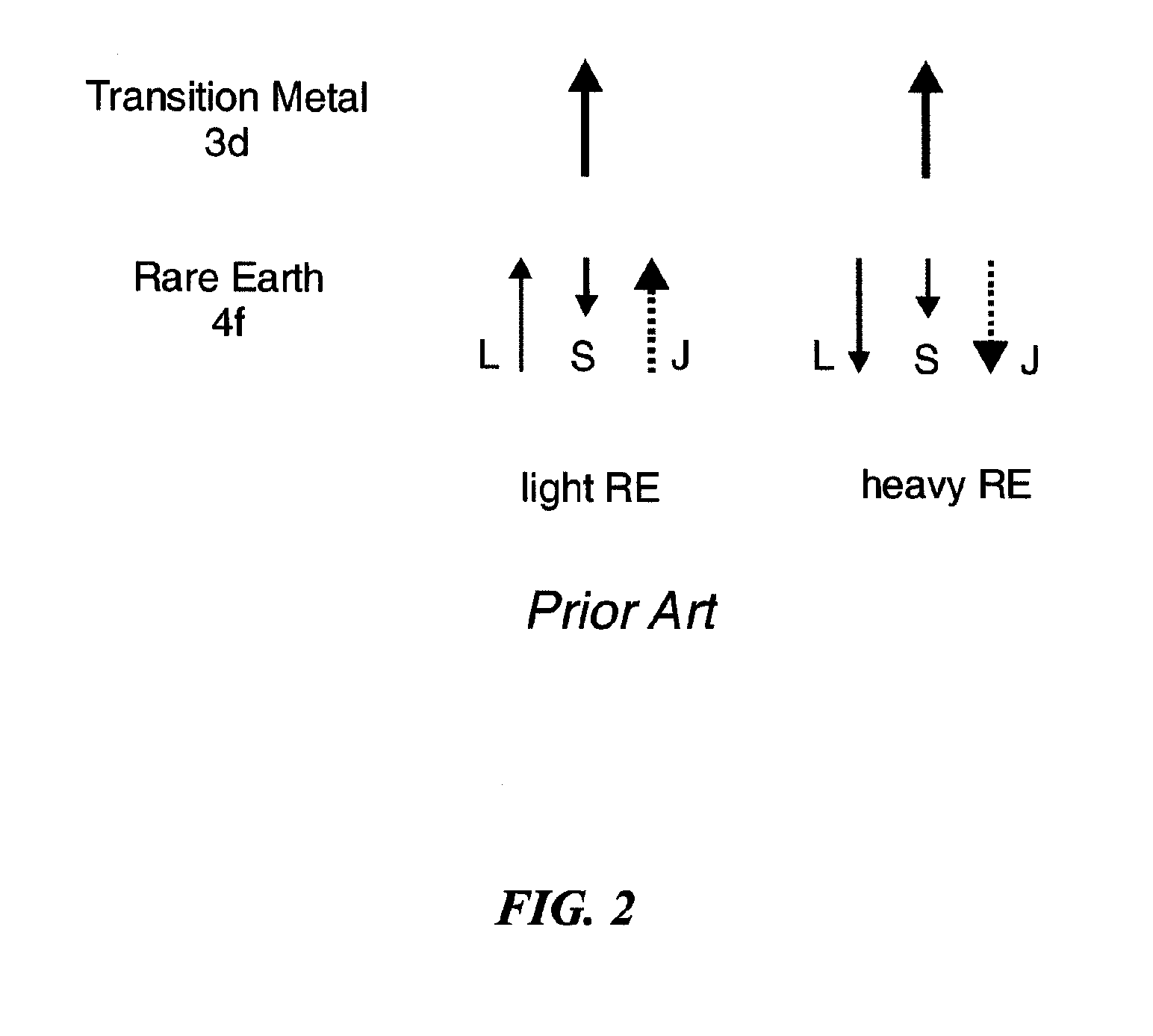
Spin-polarization devices using rare earth-transition metal alloys
ActiveUS7230265B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionRare-earth elementMetal alloy
A tunnel barrier in proximity with a layer of a rare earth element-transition metal (RE—TM) alloy forms a device that passes negatively spin-polarized current. The rare earth element includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb. The RE and TM have respective sub-network moments such that the absolute magnitude of the RE sub-network moment is greater than the absolute magnitude of the TM sub-network moment. An additional layer of magnetic material may be used in combination with the tunnel barrier and the RE—TM alloy layer to form a magnetic tunnel junction. Still other layers of tunnel barrier and magnetic material may be used in combination with the foregoing to form a flux-closed double tunnel junction device.
Owner:IBM CORP
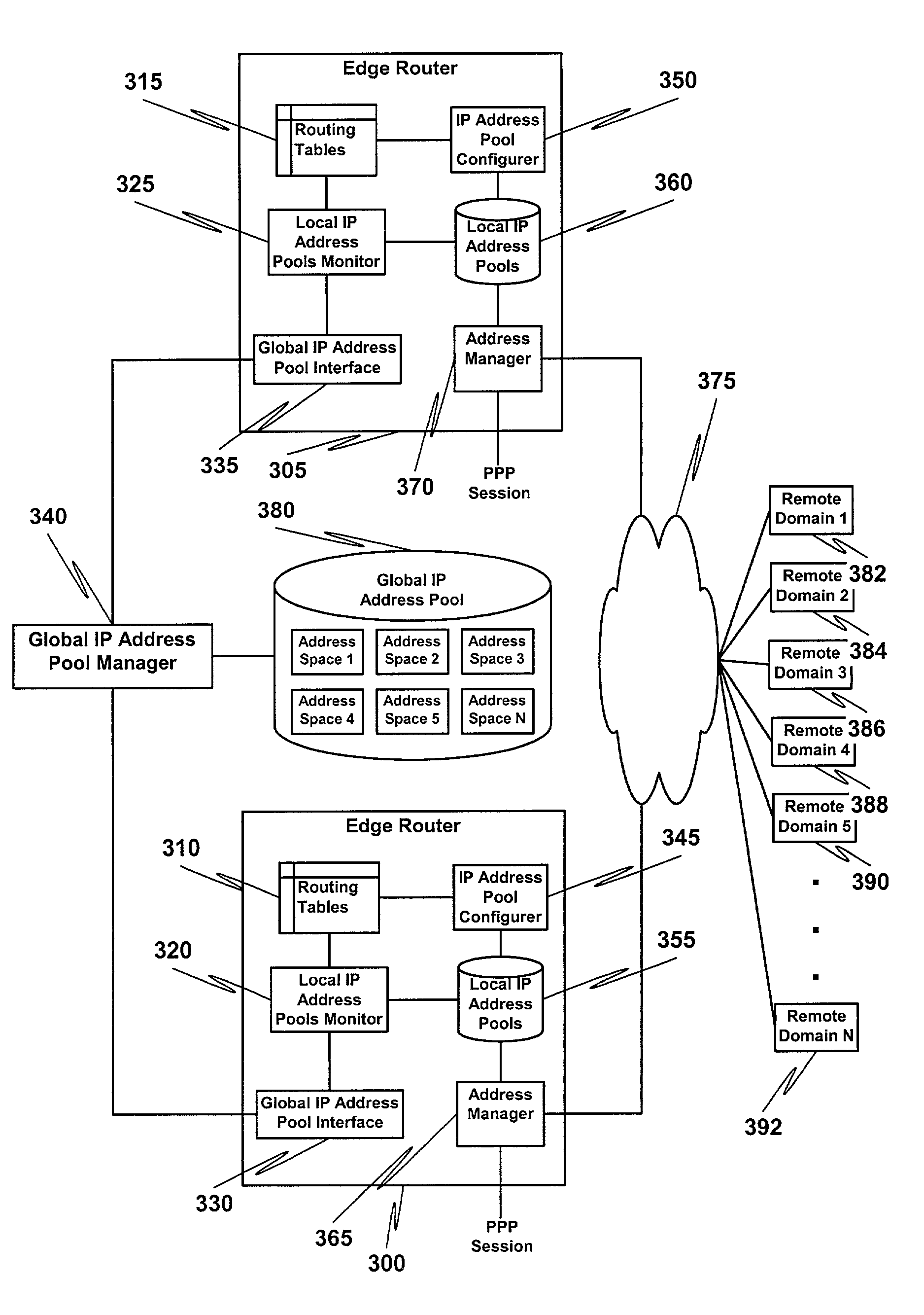
On-demand address pools
InactiveUS7197549B1Effective distributionDigital computer detailsTransmissionProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessDistributed computing
A method for on-demand management of Internet Protocol (IP) address pools includes allocating an unused IP address from a local IP address pool designated for a remote domain if a request to connect to the remote domain is received and deallocating an IP address back to the local IP address pool if the IP address is unused. The method also includes apportioning one or more of the at least one subnet between the global IP address pool and the local IP address pool based upon utilization of the local IP address pool. The local IP address pool includes one or more of at least one subnet obtained from a global IP address pool and each subnet specifies a contiguous set of one or more IP addresses.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
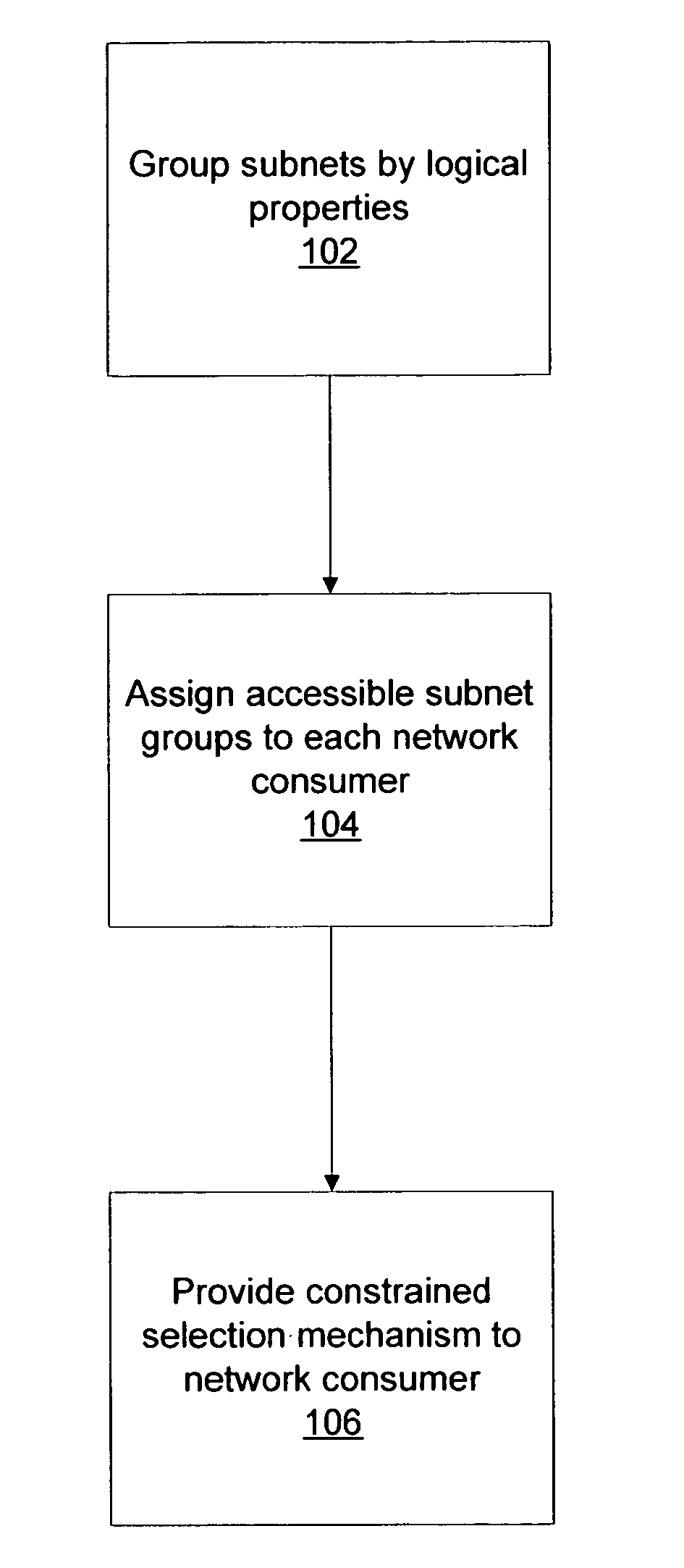
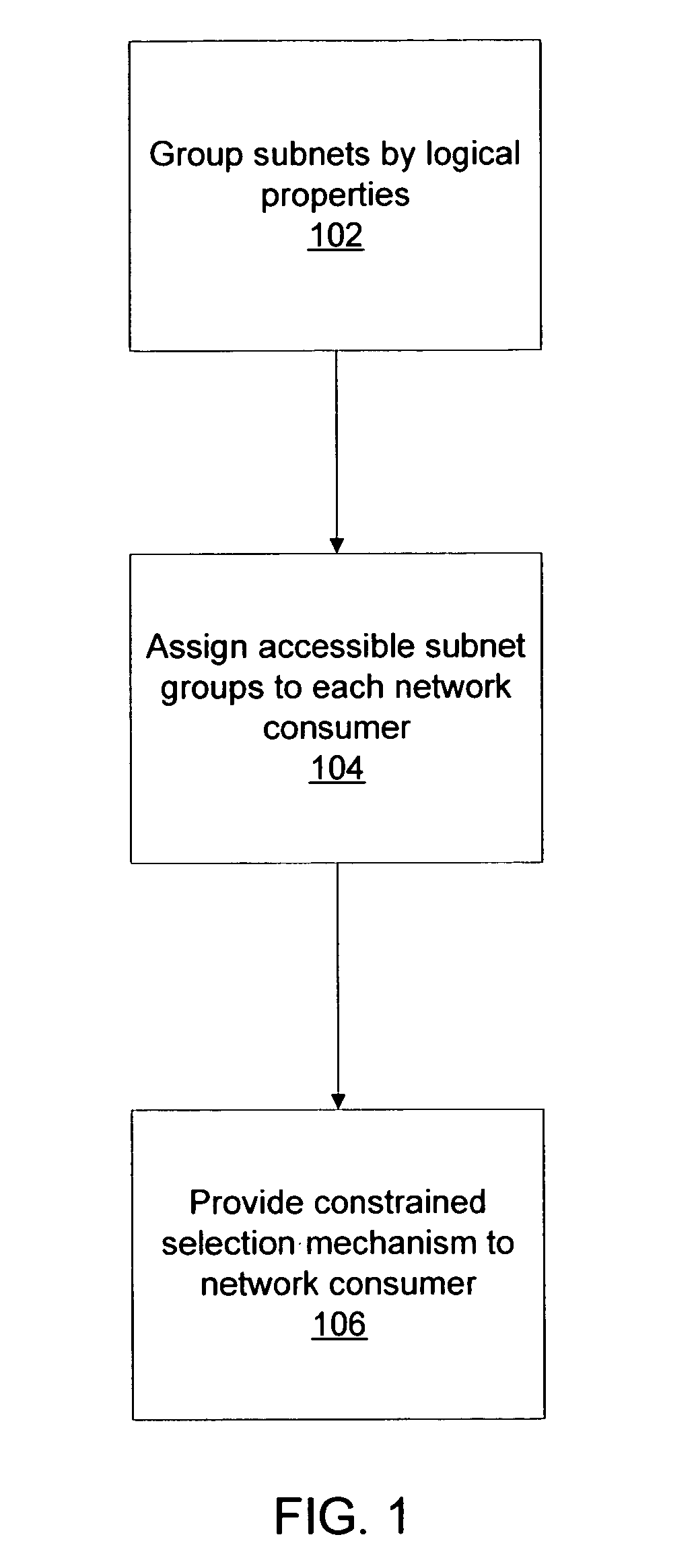
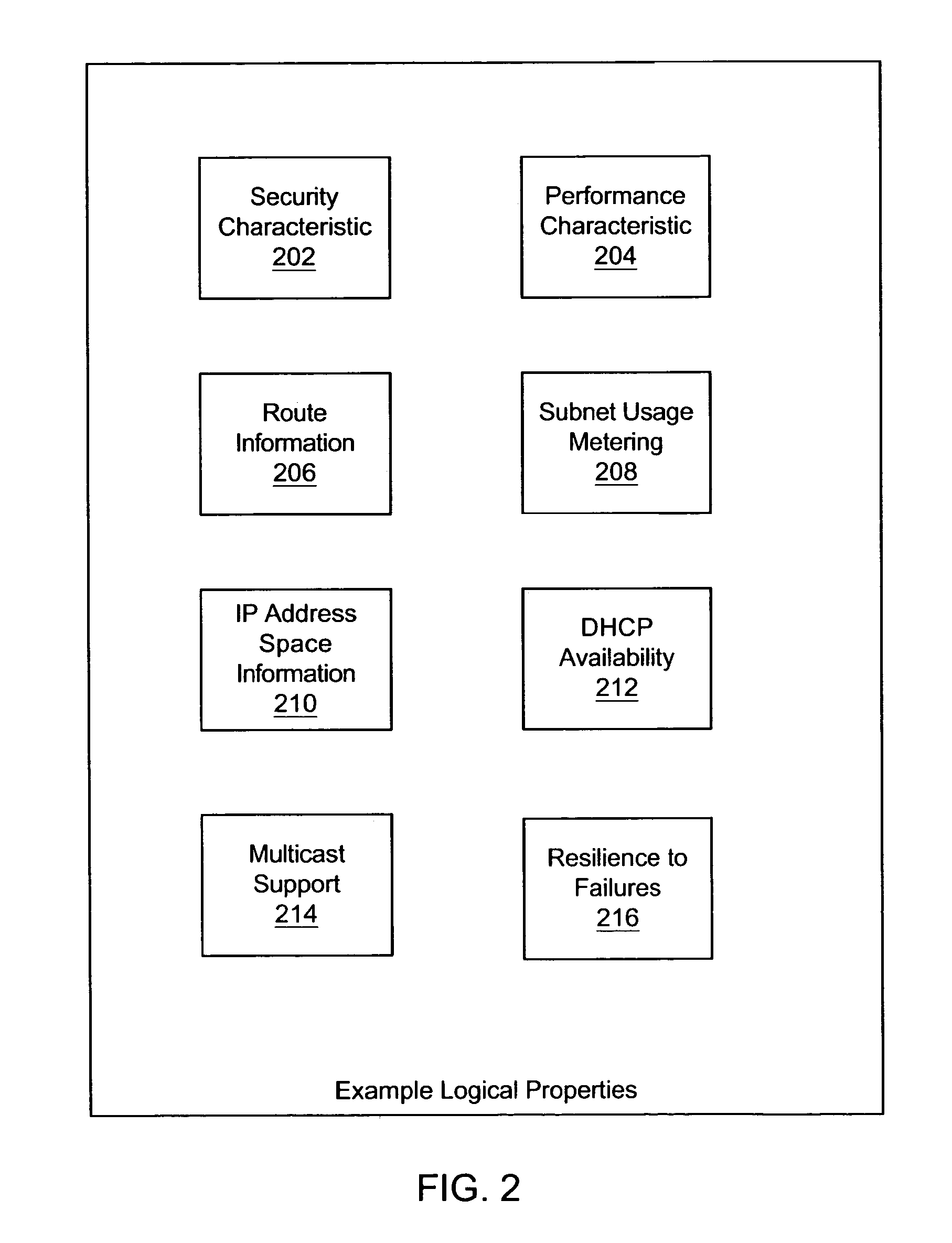
System and method for subnet configuration and selection
One embodiment disclosed relates to a method for provisioning subnets. The subnets are grouped into subnet groups based on logical properties of the subnets. Each network consumer is assigned those subnet groups that are accessible to that network consumer. The network consumer is then provided with an interface for constrained selection of a particular subnet.
Owner:REGIONAL RESOURCES LTD
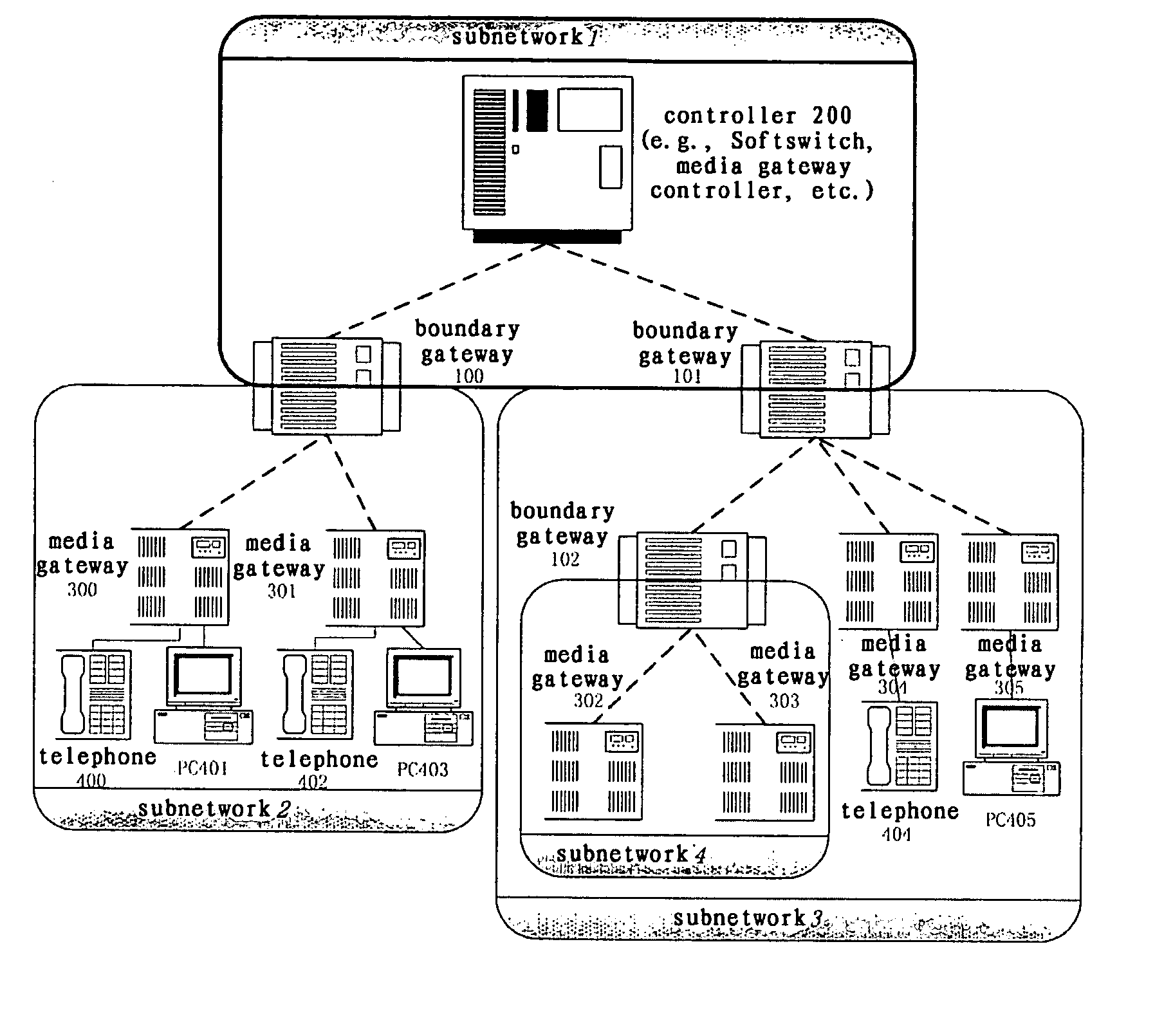
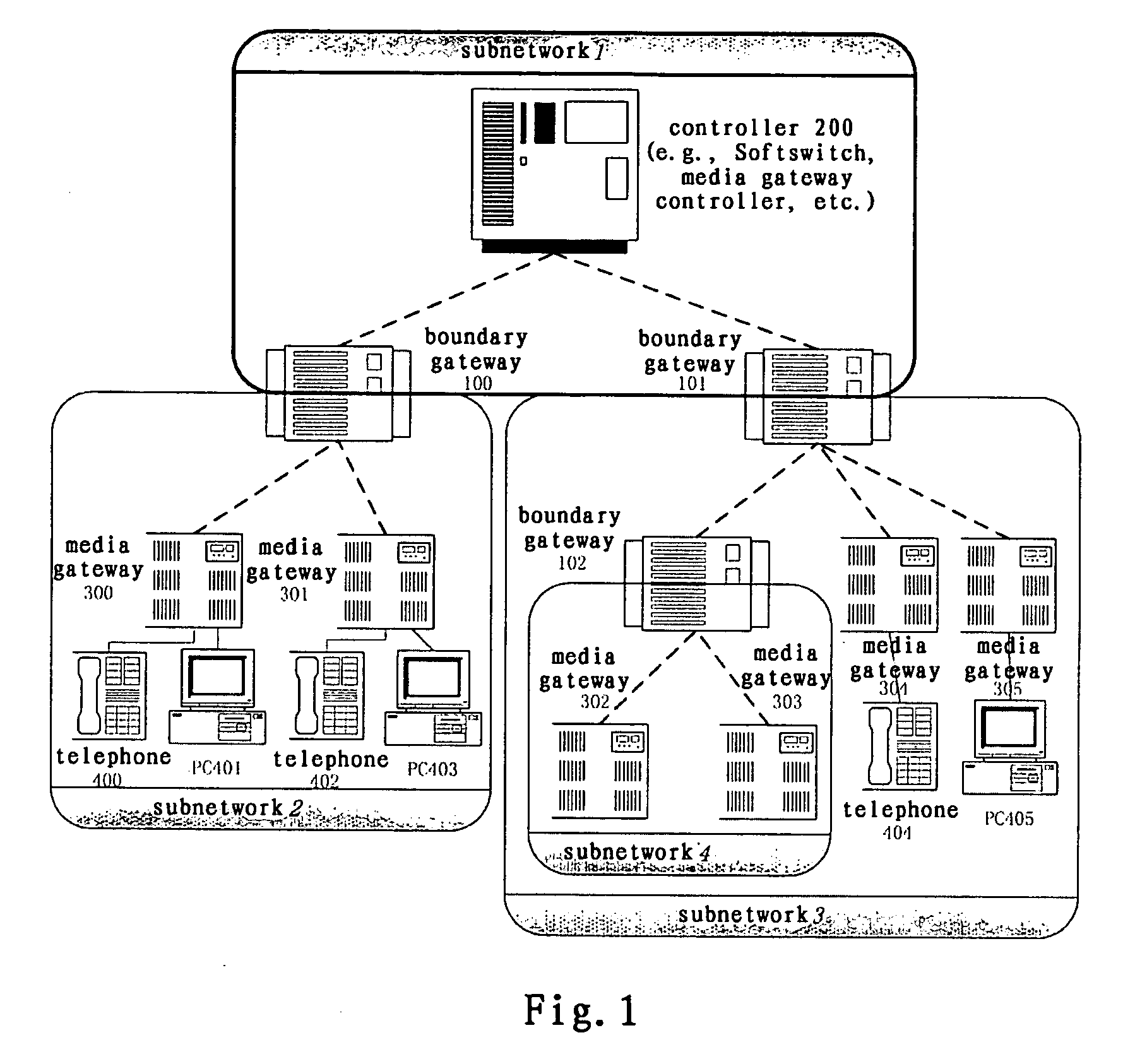
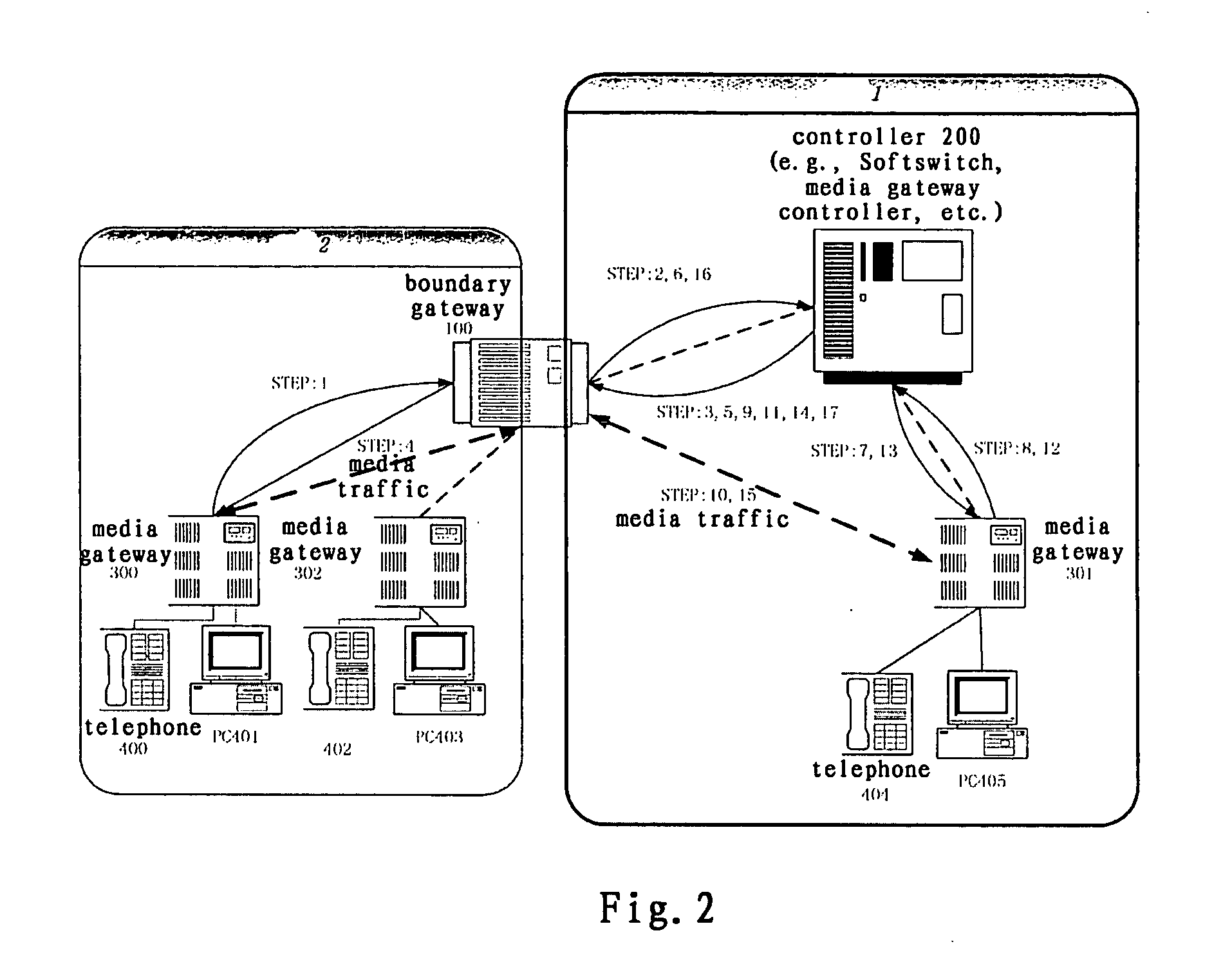
System and method for implementing multimedia calls across a private network boundary
ActiveUS20070140267A1Integrity guaranteedData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesInformation processingPrivate network
A system and method of the present invention for implementing multimedia calls across a private network boundary is provided, the system comprising a public network and at least one private network, and at least the following hardware components: at least one media gateway for connecting with multimedia terminals of various protocols; at least one boundary gateway for connecting the private network and the public network and performing the translation of a private network address and a public network address between each other, wherein each boundary gateway is provide with an unique subnetwork ID to correspond to the private network connected therewith; a call controller for establishing calls and controlling service logics, in which is recorded the correspondence relationship information of all said boundary gateways and the subnetwork IDs; wherein, the call controller processes a call concerning a private network according to the subnetwork ID information. The system and method of the present invention is simple to implement, has high efficiency and wide application range; saves the boundary gateway resources, does not modify the signaling content and retain its integrity; is applicable to the media gateways of various protocols, and has a high adaptability.
Owner:ZTE CORP
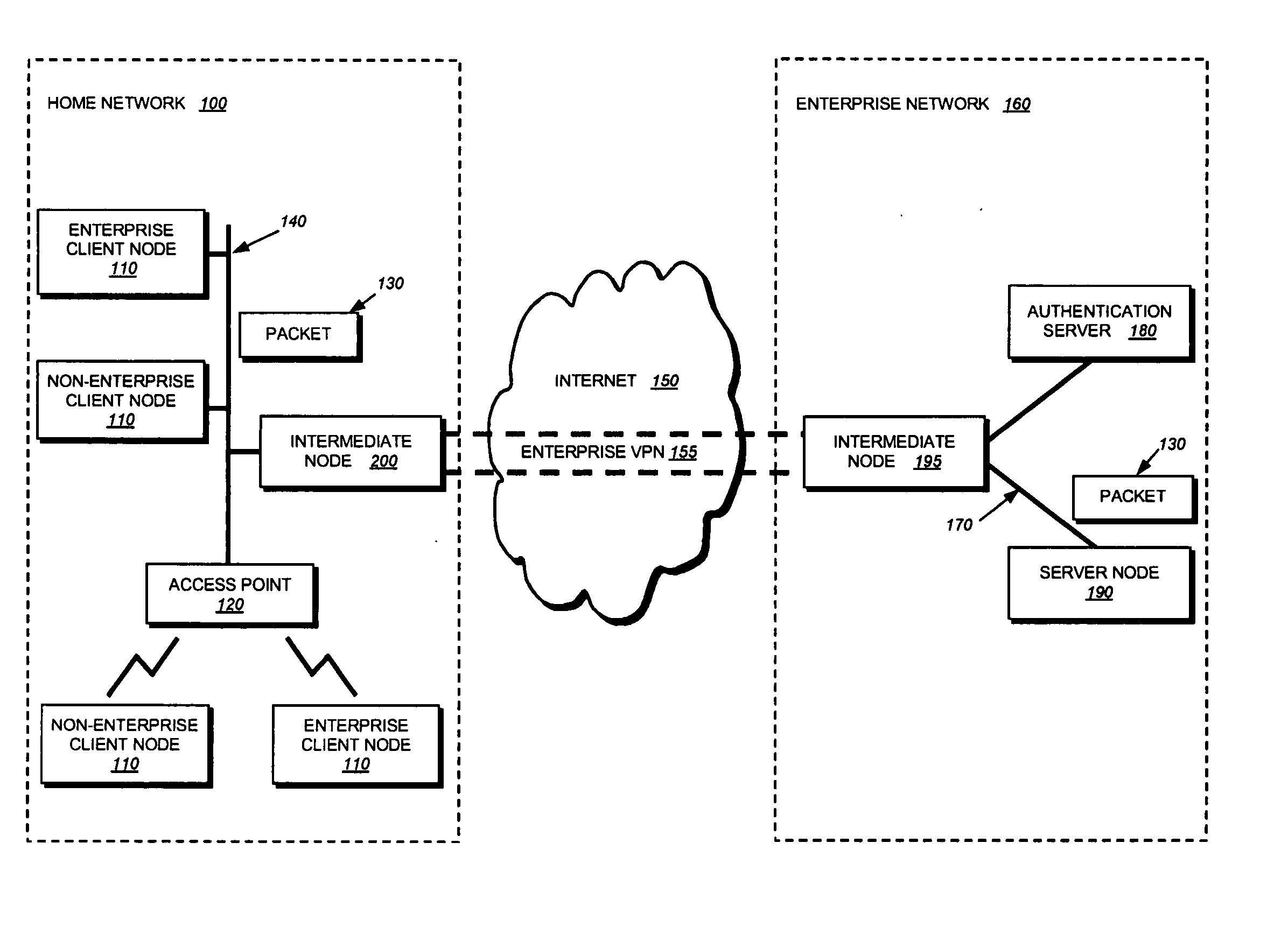
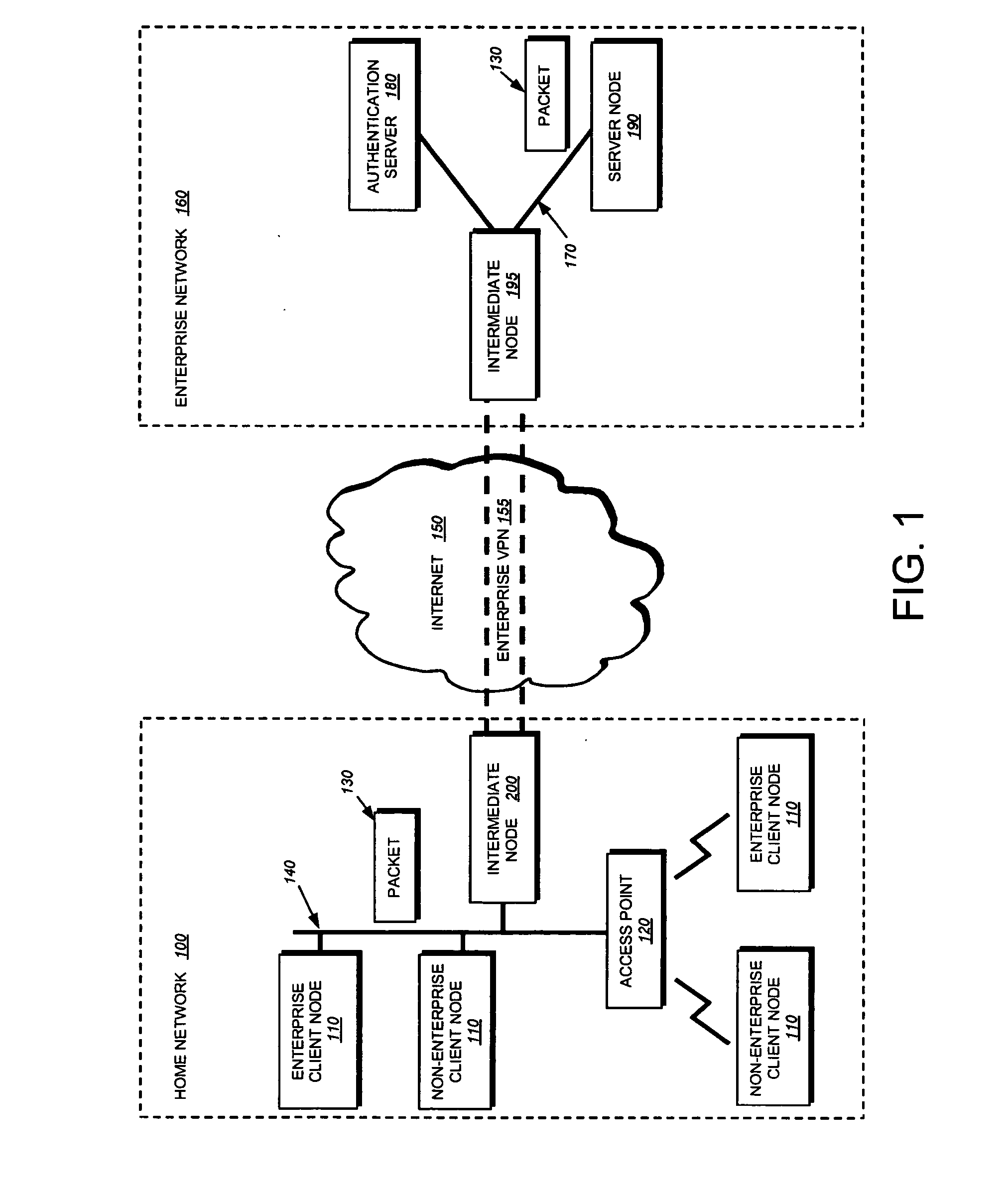
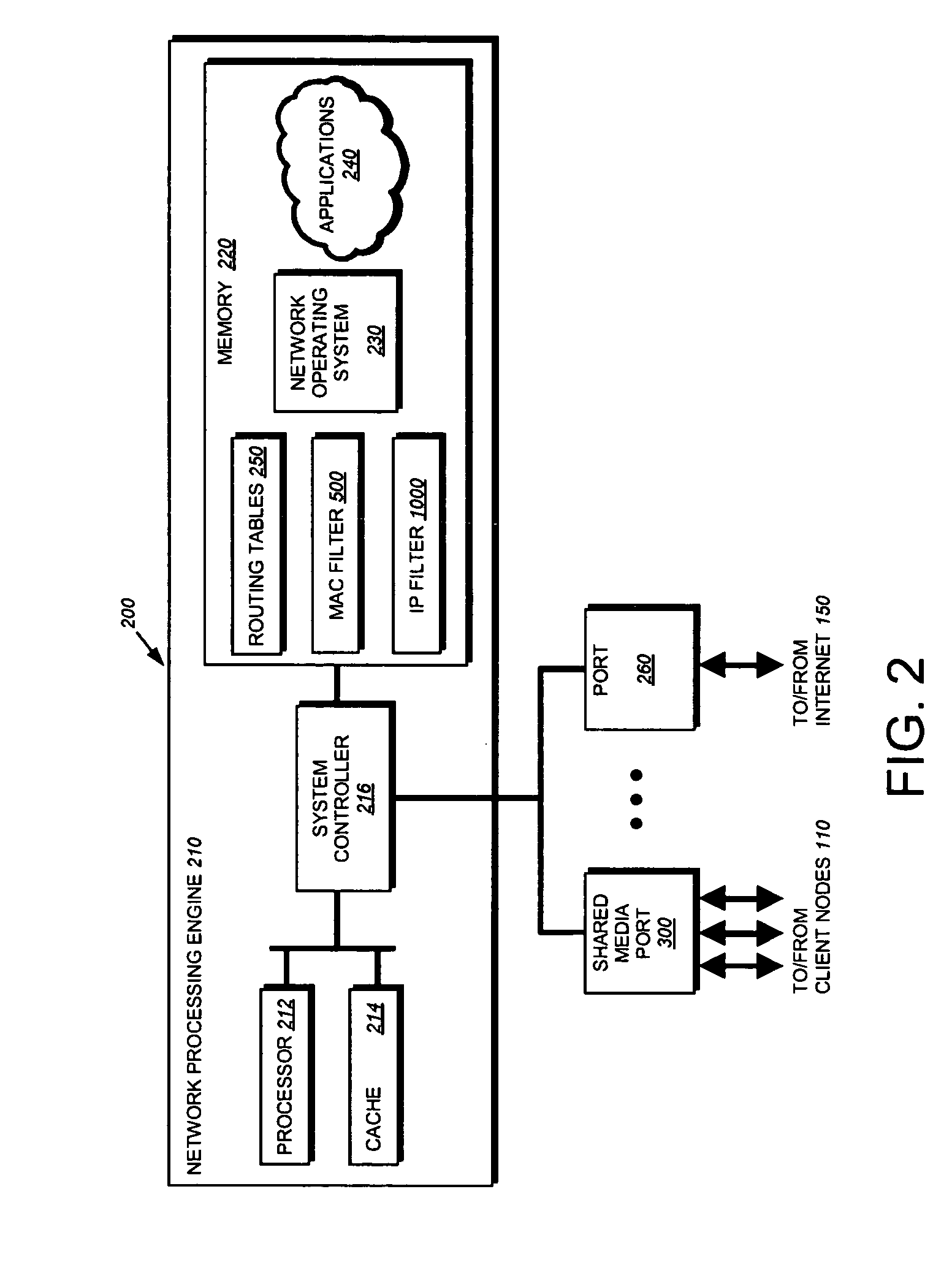
802.1X authentication technique for shared media
ActiveUS20050125692A1Increase network-access securityConvenient access controlDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideNetwork Access Control
The present invention provides a technique for securely implementing port-based authentication on a shared media port in an intermediate node, such as a router. To that end, the invention provides enhanced port-based network access control that includes client-based control at the shared media port. Unlike previous implementations, the port does not permit multiple client nodes to access a trusted subnetwork as soon as a user at any one of those nodes is authenticated by the subnetwork. Instead, port-based authentication is performed for every client node that attempts to access the trusted subnetwork through the shared media port. As such, access to the trusted subnetwork is not compromised by unauthenticated client nodes that “piggy-back” over the shared media port after a user at another client node has been authenticated by the trusted subnetwork.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
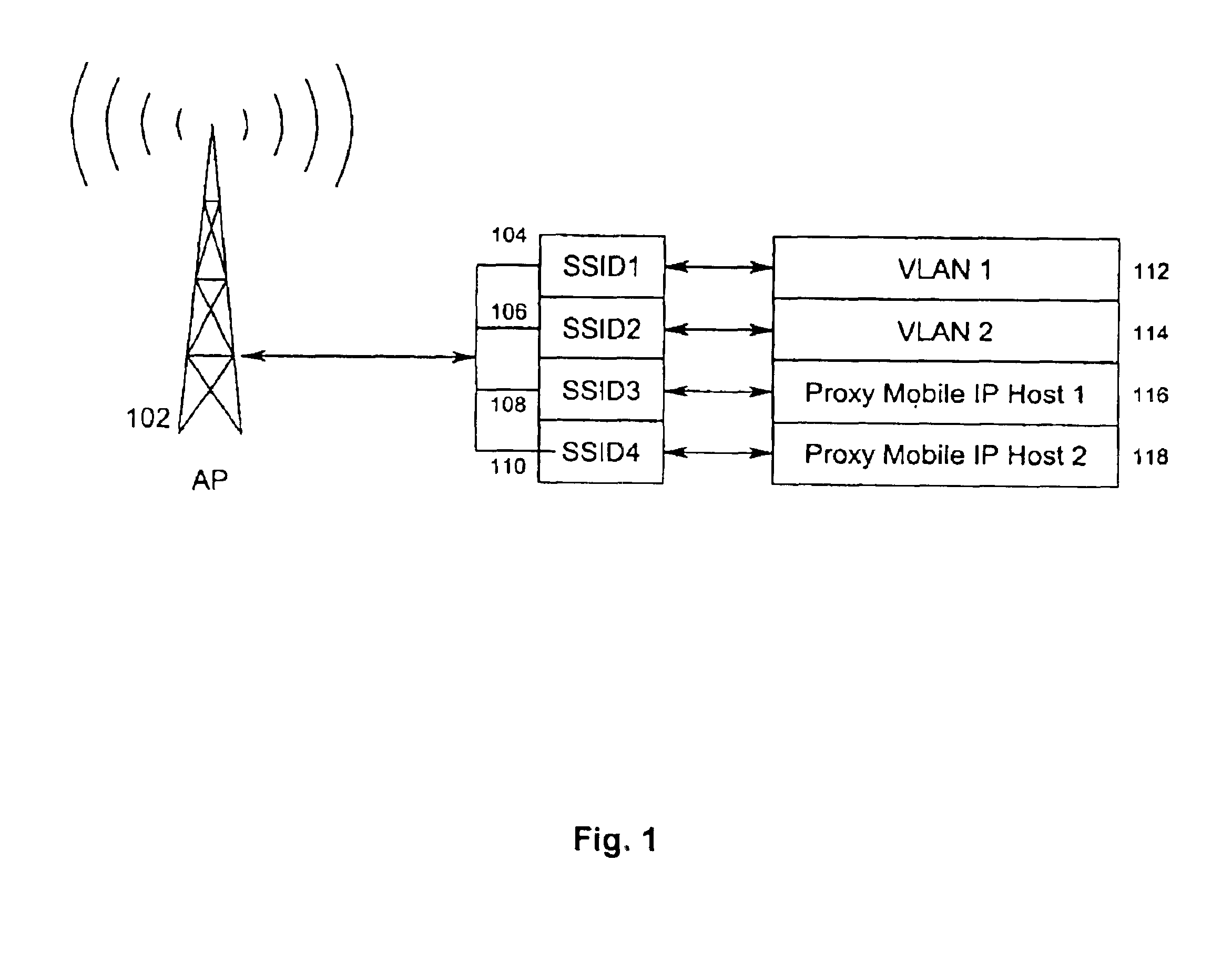
Method for grouping 802.11 stations into authorized service sets to differentiate network access and services
InactiveUS6950628B1Near-field transmissionElectric signal transmission systemsTelecommunicationsNetwork service
A method for associating a WSTA to a service set, wherein the service set is configurable at the AP. Each service set is an arbitrary grouping of one or more network service parameters, and is typically configured for either VLAN or proxy mobile IP host. When a wireless station desires to associate with an access point, the wireless station sends a message to the access point, the message containing a SSID. The access point then matches the SSID to a service set and associates the WSTA to either a home subnet or a VLAN based on the SSID. By locally configuring the service set, the default VLAN and home subnet for a WSTA may be different at each AP the WSTA encounters. A security server is configured with a list of allowed SSIDs for each wireless station to prevent unauthorized access to a VLAN or home subnet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
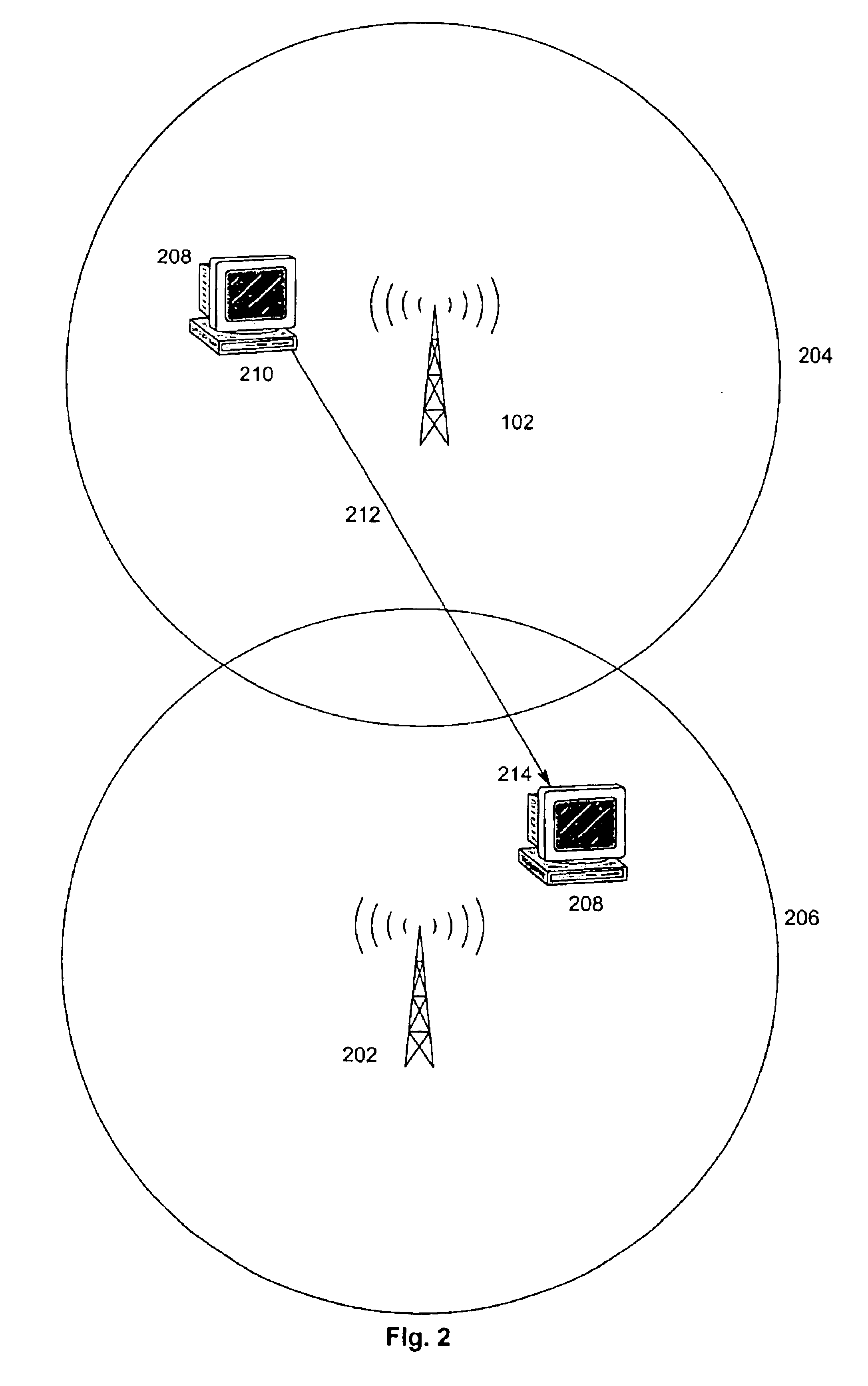
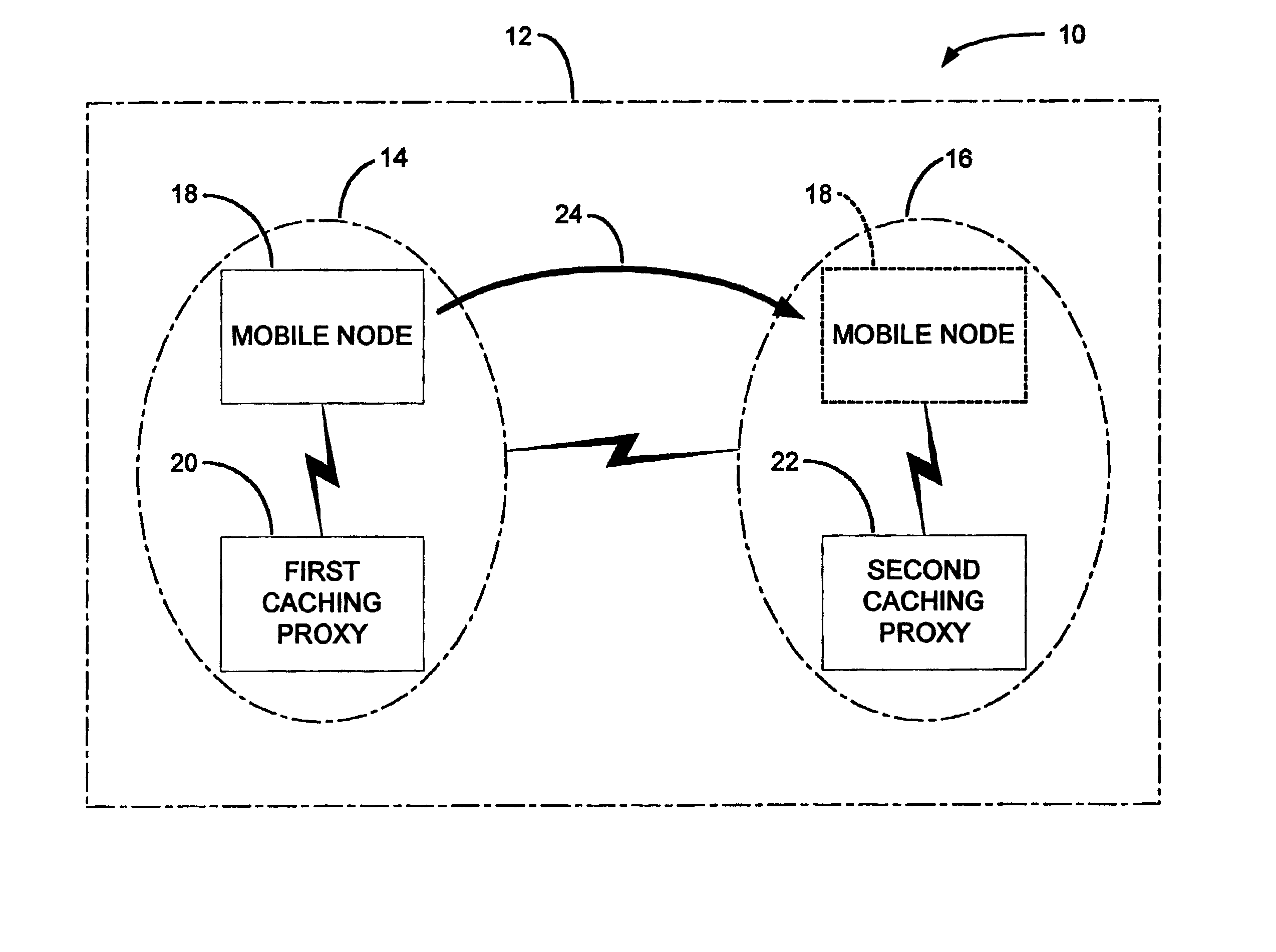
System for management of cacheable streaming content in a packet based communication network with mobile hosts
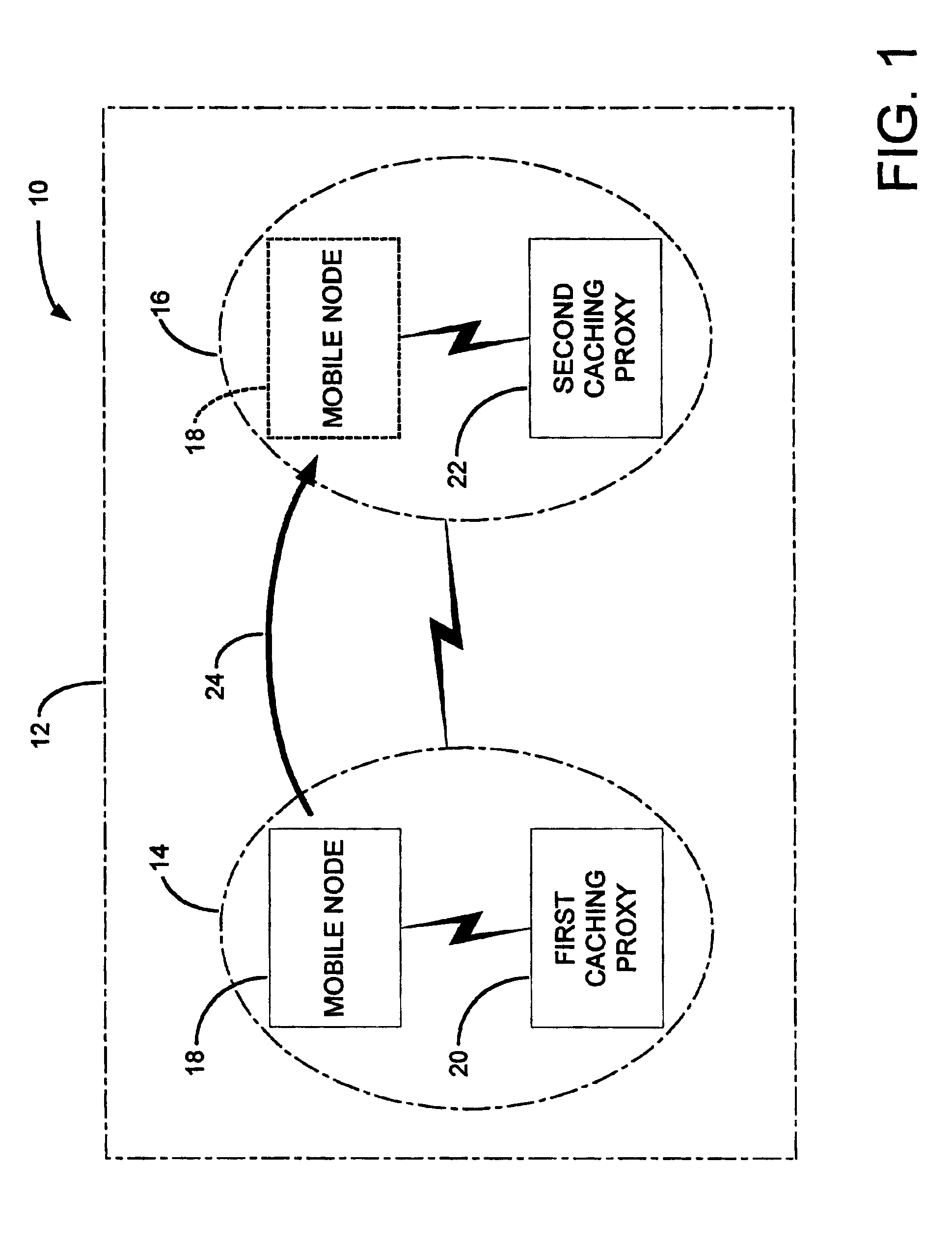
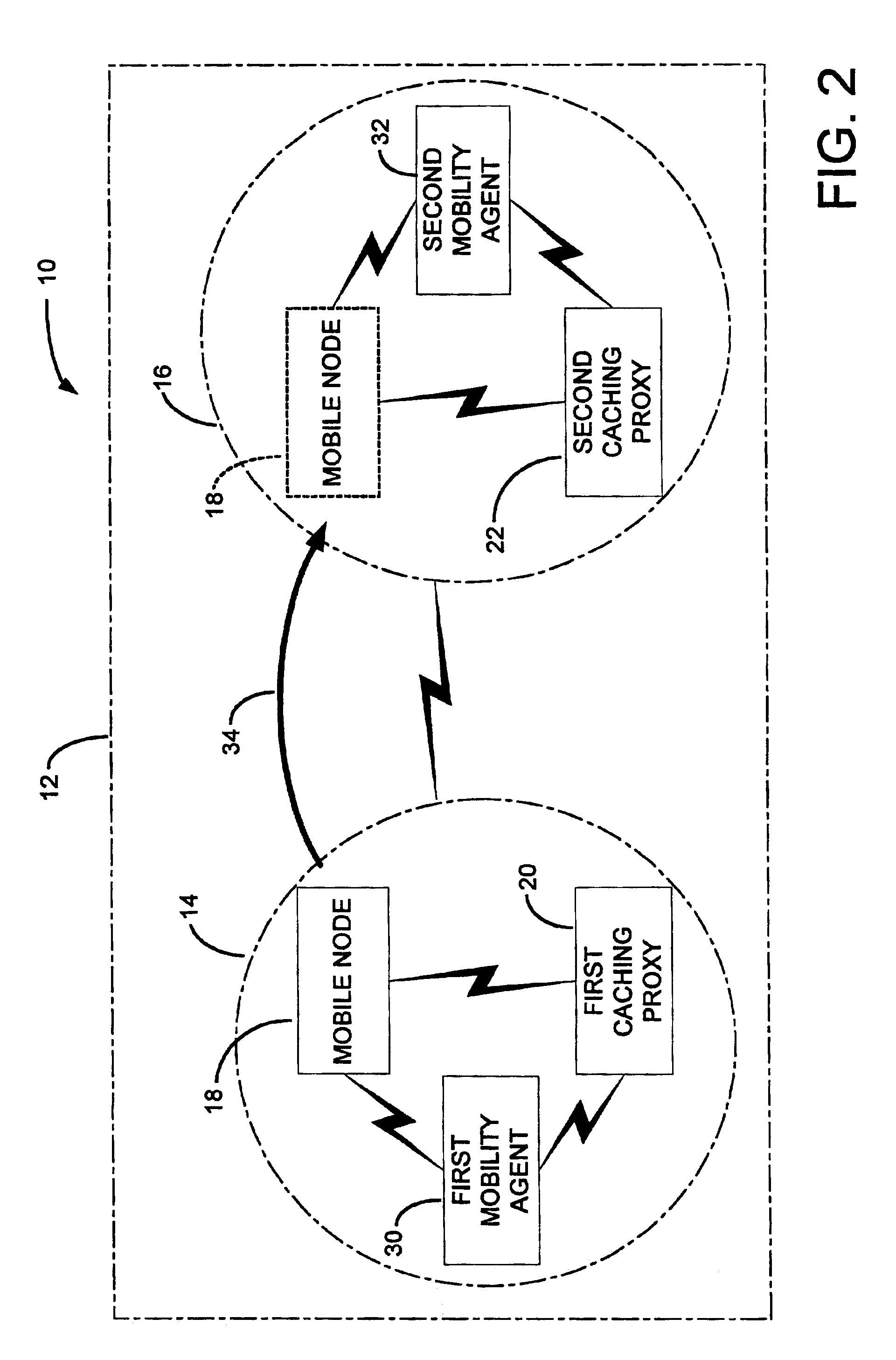
InactiveUS6907501B2Quantity minimizationEffectively and efficient fulfillData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork architectureBroadcast communication network
A cache handoff system for managing cacheable streaming content requested by a mobile node within a network architecture is disclosed. The network architecture includes a first subnet and a second subnet. The cache handoff system includes a first caching proxy operable in the first subnet to supply a content stream in response to a request of the mobile node operable in the first subnet. In addition, the cache handoff system includes a second caching proxy operable in the second subnet. The first caching proxy may initiate a cache handoff of the request to the second caching proxy when the mobile node relocates to the second subnet. The second caching proxy may seamlessly continue to supply the requested content stream as a function of the cache handoff.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Data center topology with transparent layer 4 and layer 7 services
InactiveUS20060095960A1Expensive to operateExpensive to setMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlData centerDistributed computing
A data center topology routes traffic between internal sub-nets and between a sub-net and an outside network through a common chain of services. The data center topology employs transparent layer 7 and layer 4 services on a common chassis or platform to provide routing, load balancing and firewall services while reducing the number of devices necessary to implement the data center and simplifying configuration.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com